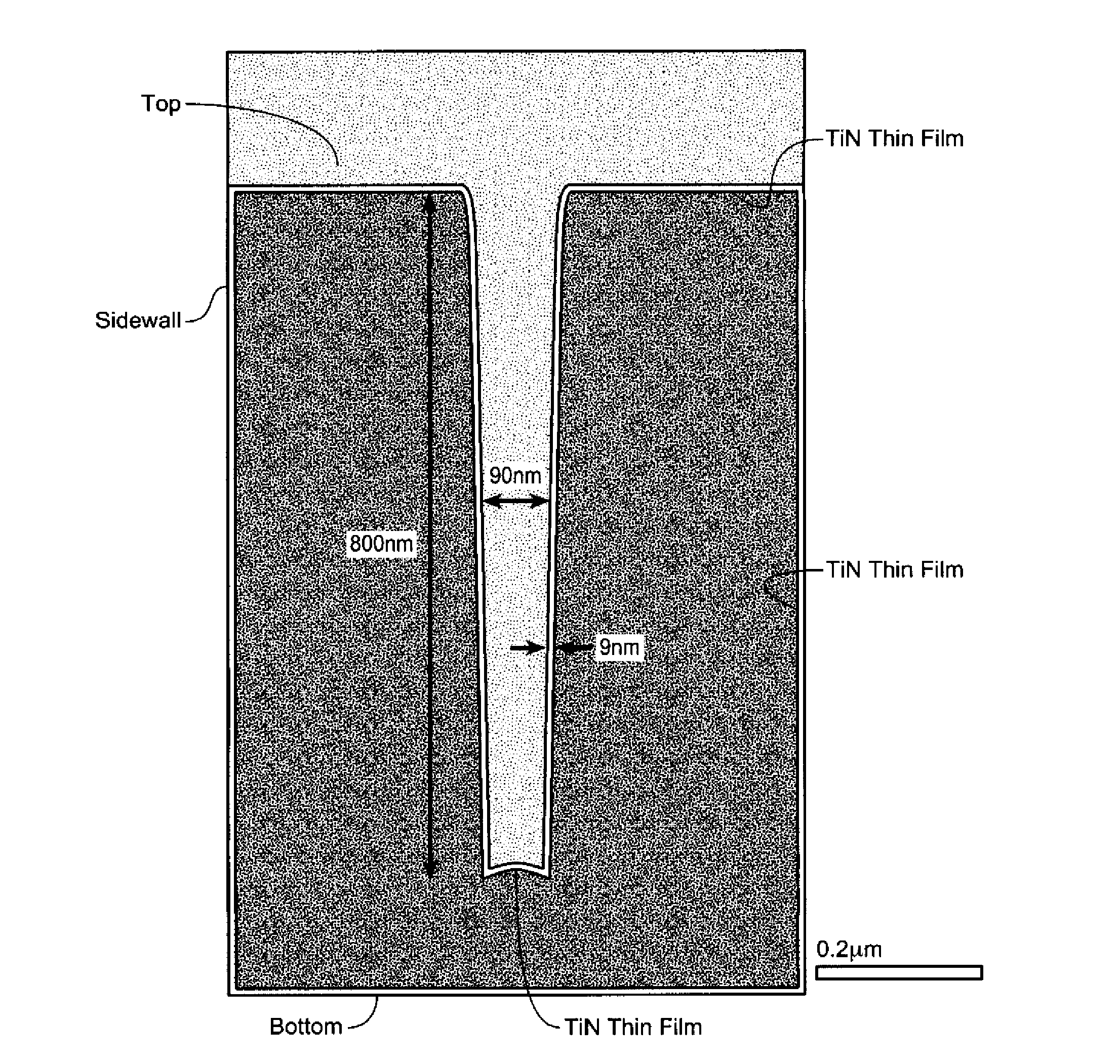
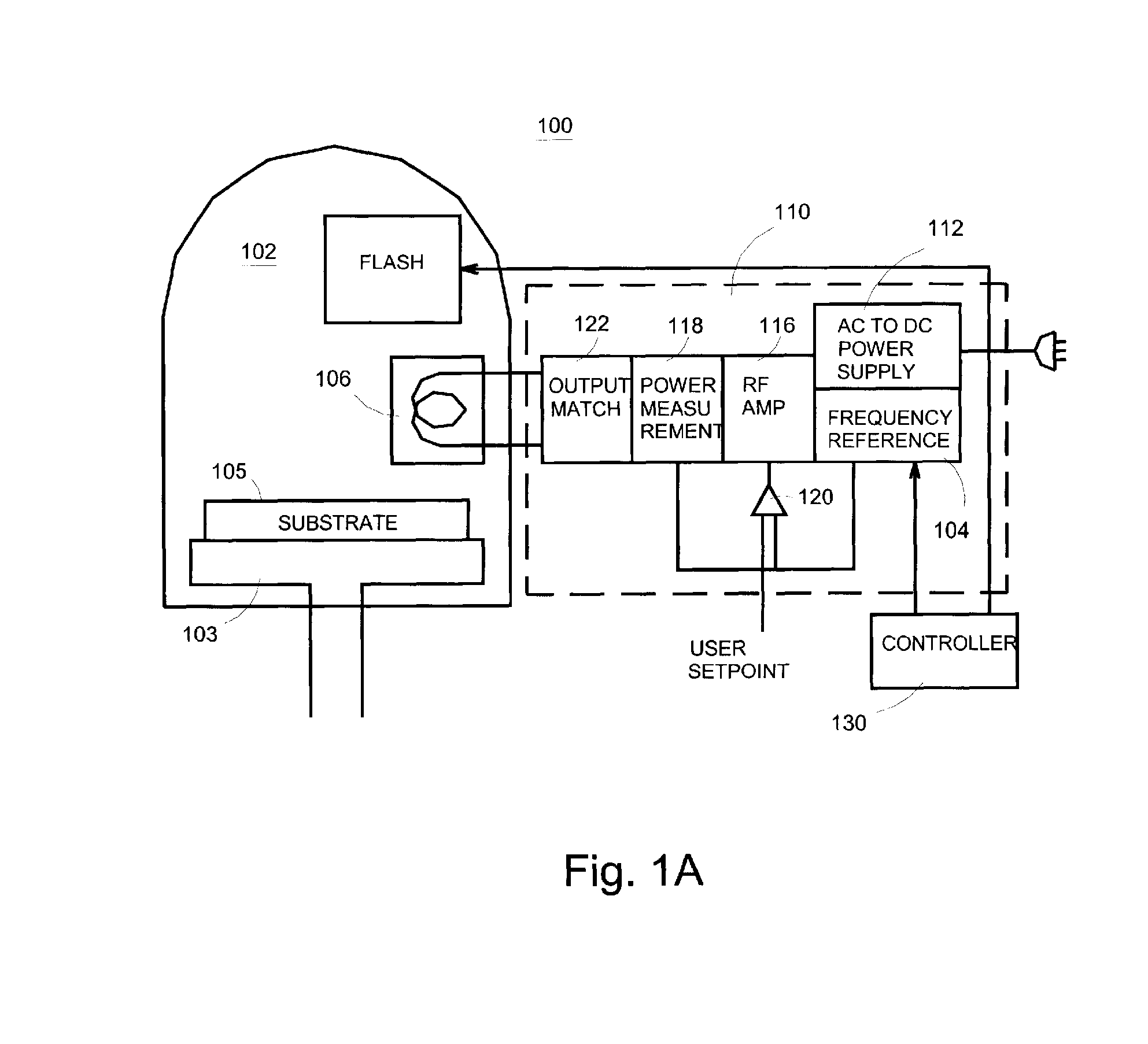
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "High deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
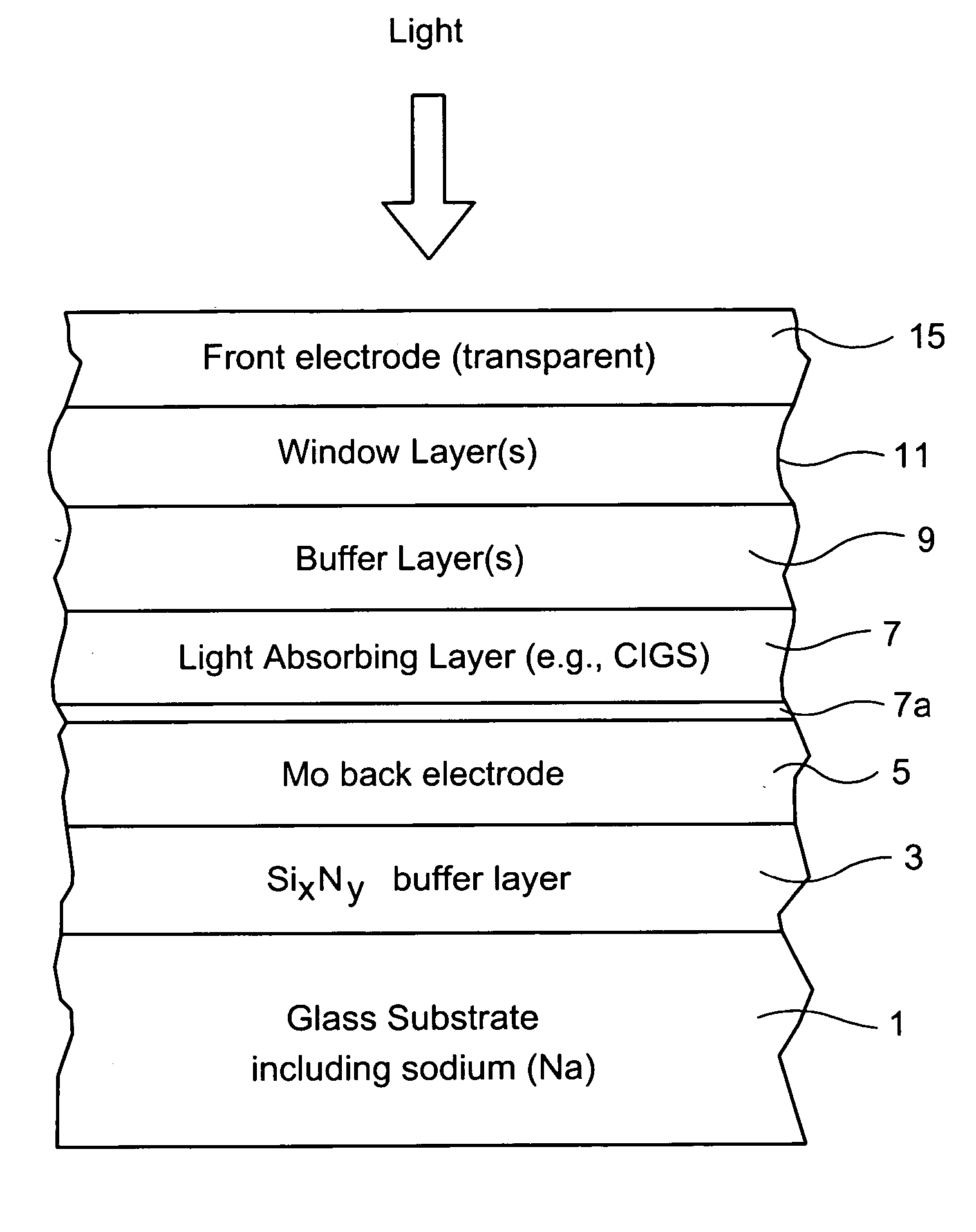
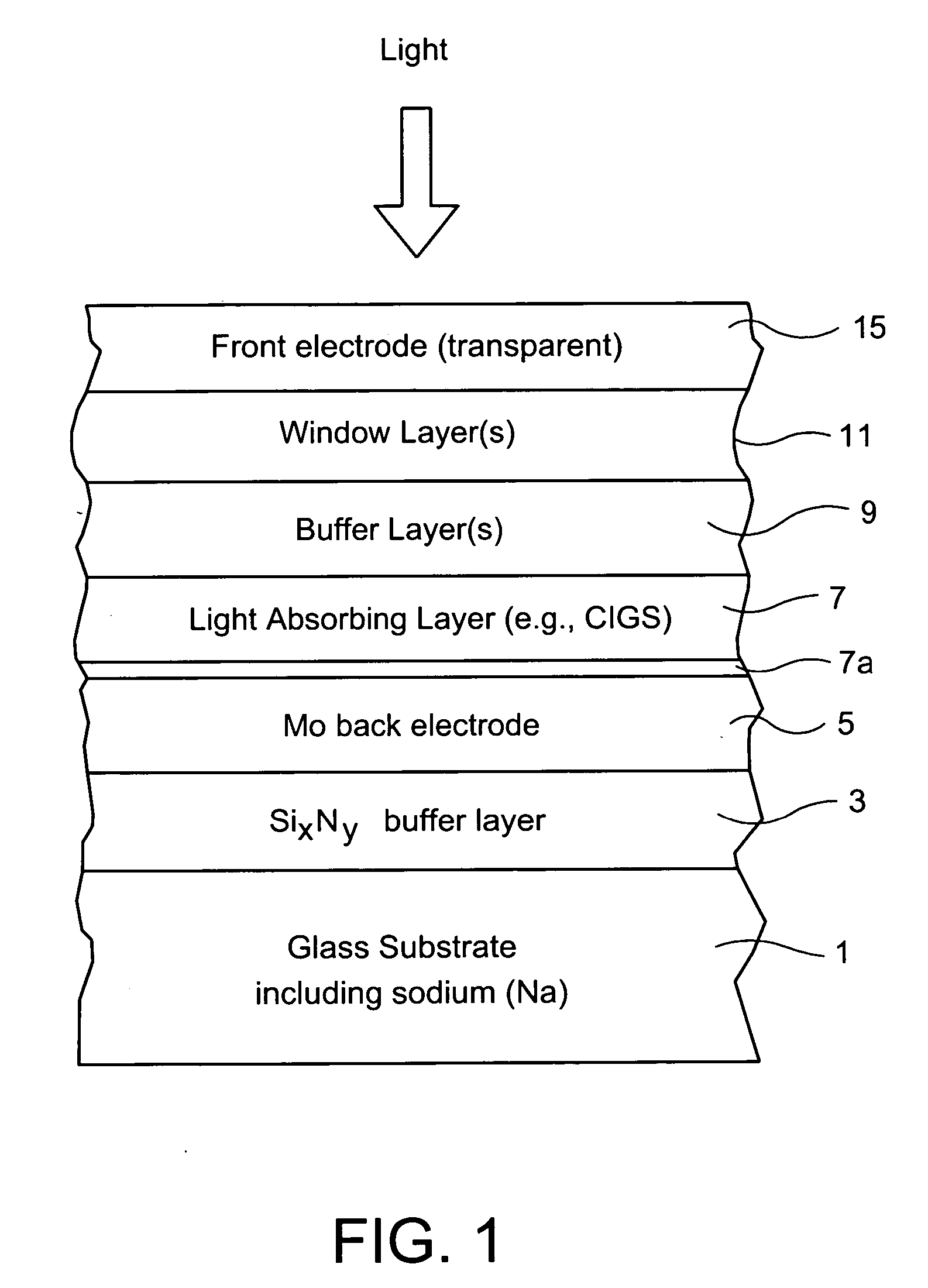
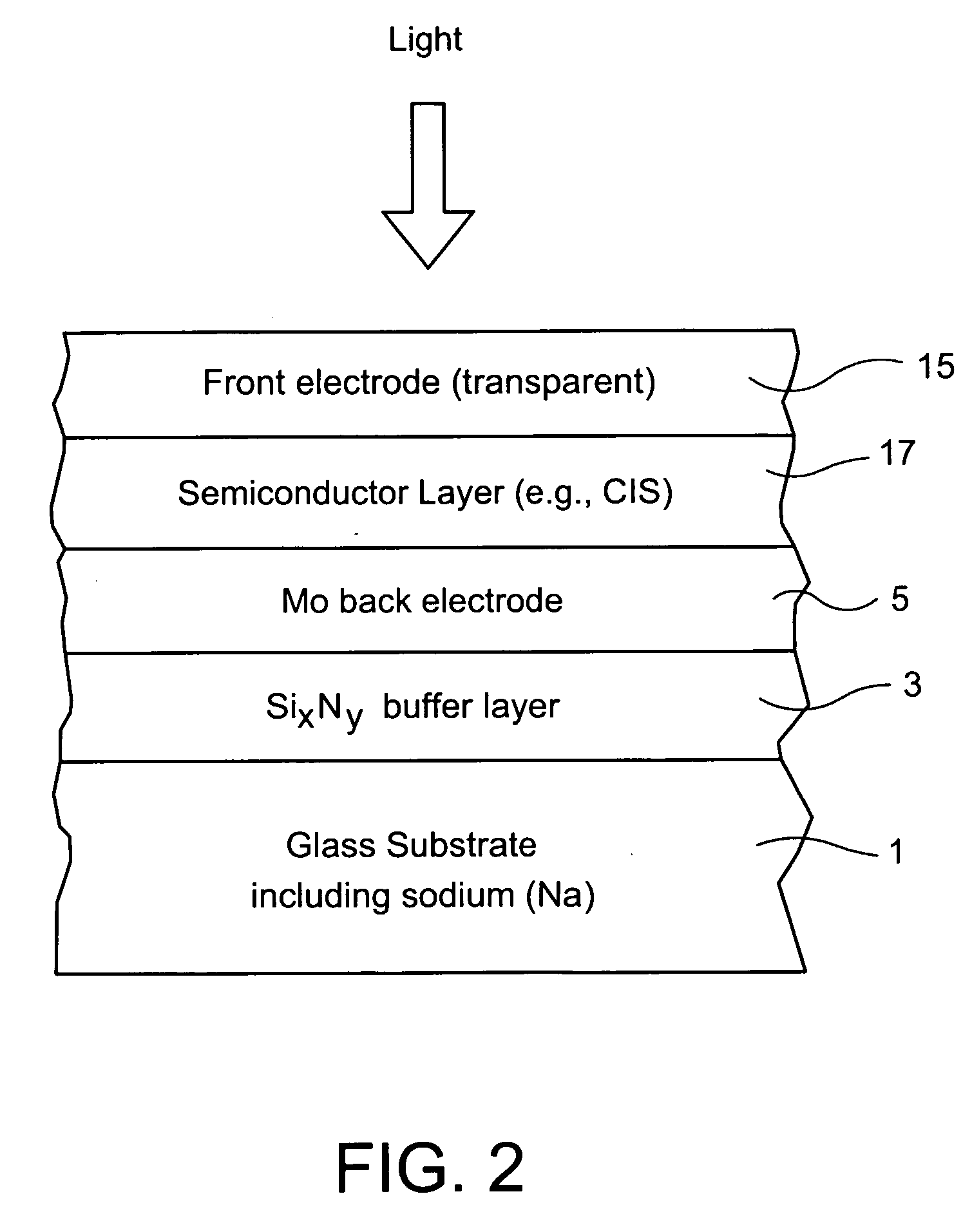
Electrode structure for use in electronic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20070193623A1Reduce and prevent migrationControl of mechanical and efficiency propertyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOptoelectronicsSoda lime
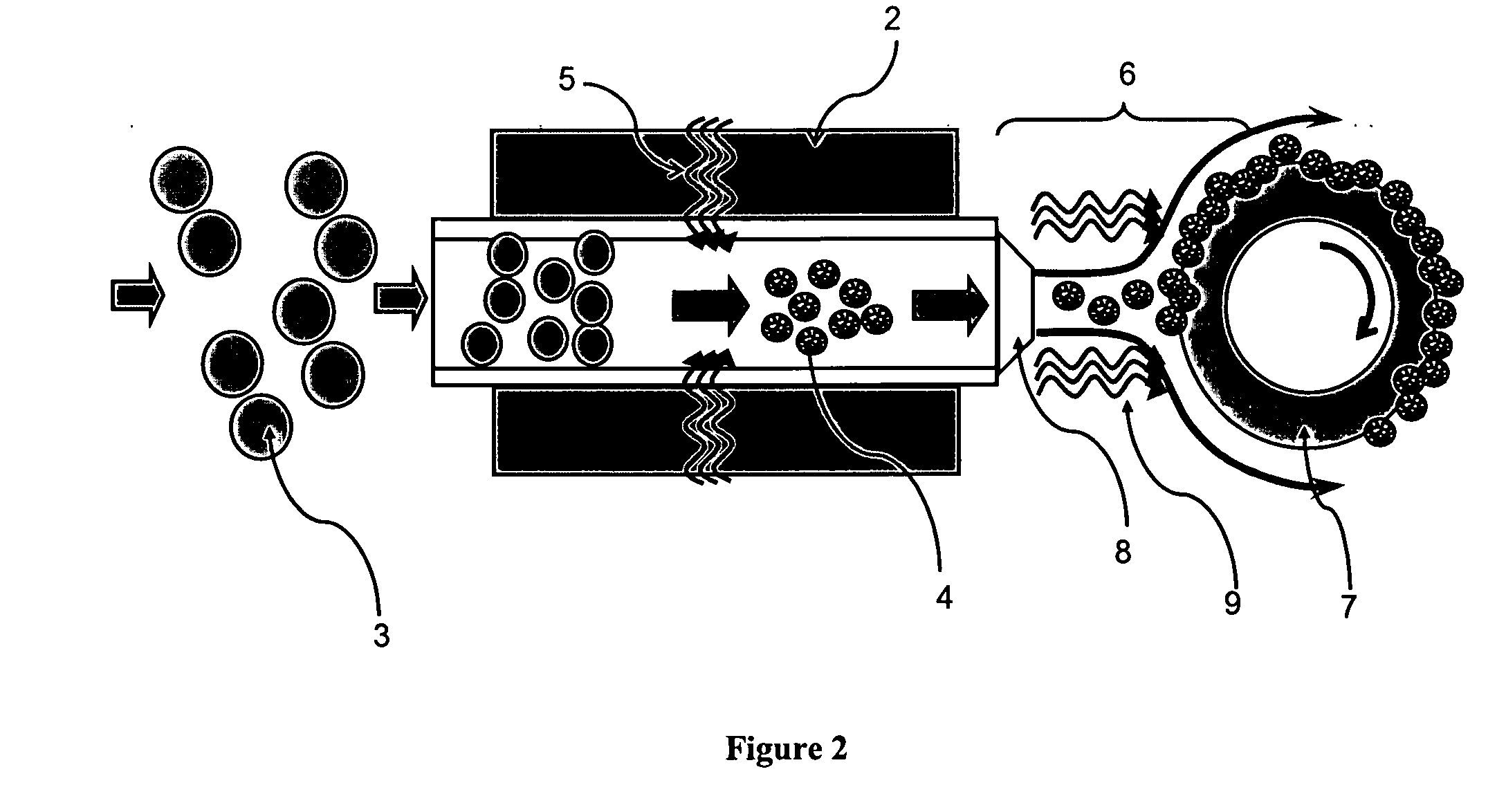
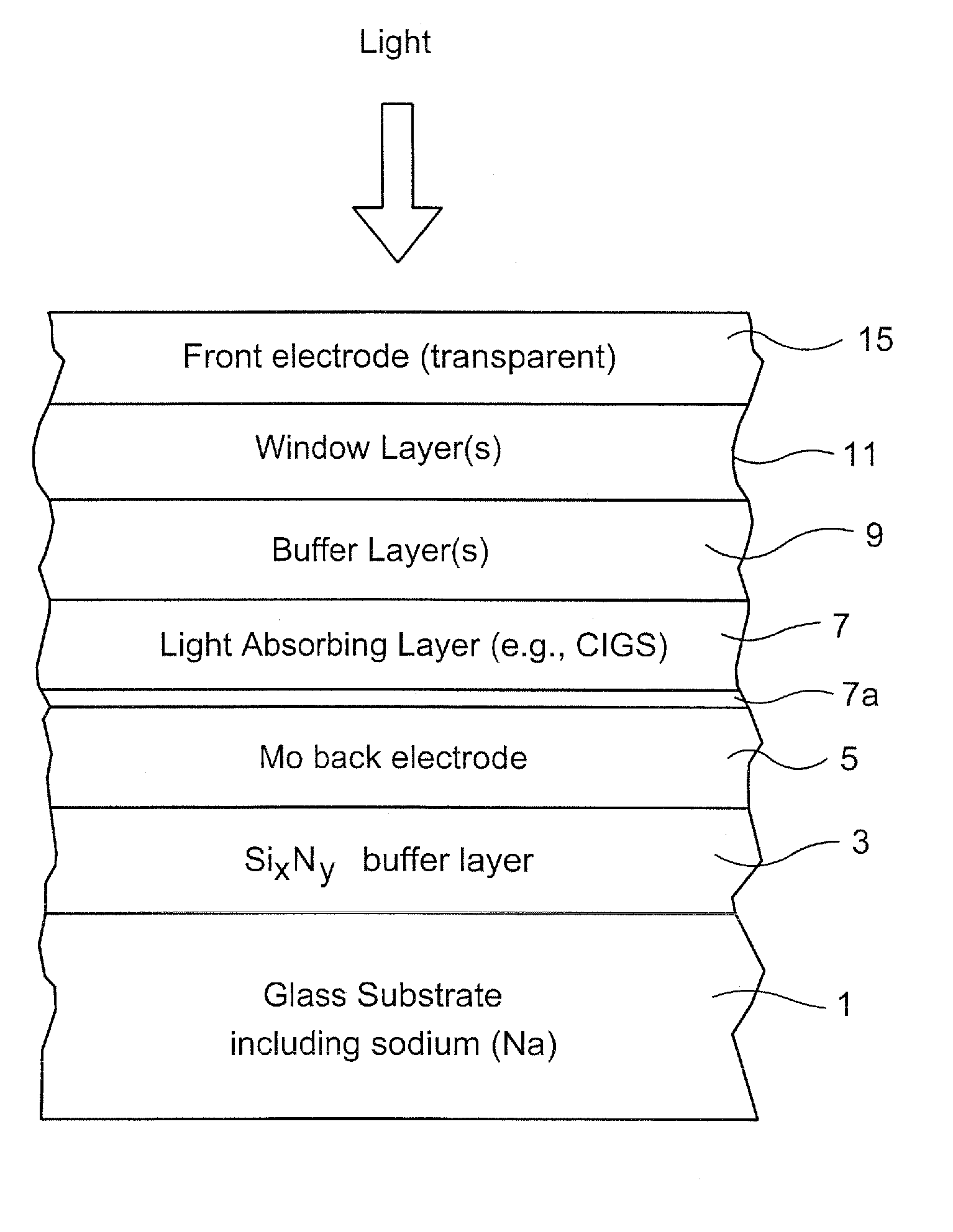
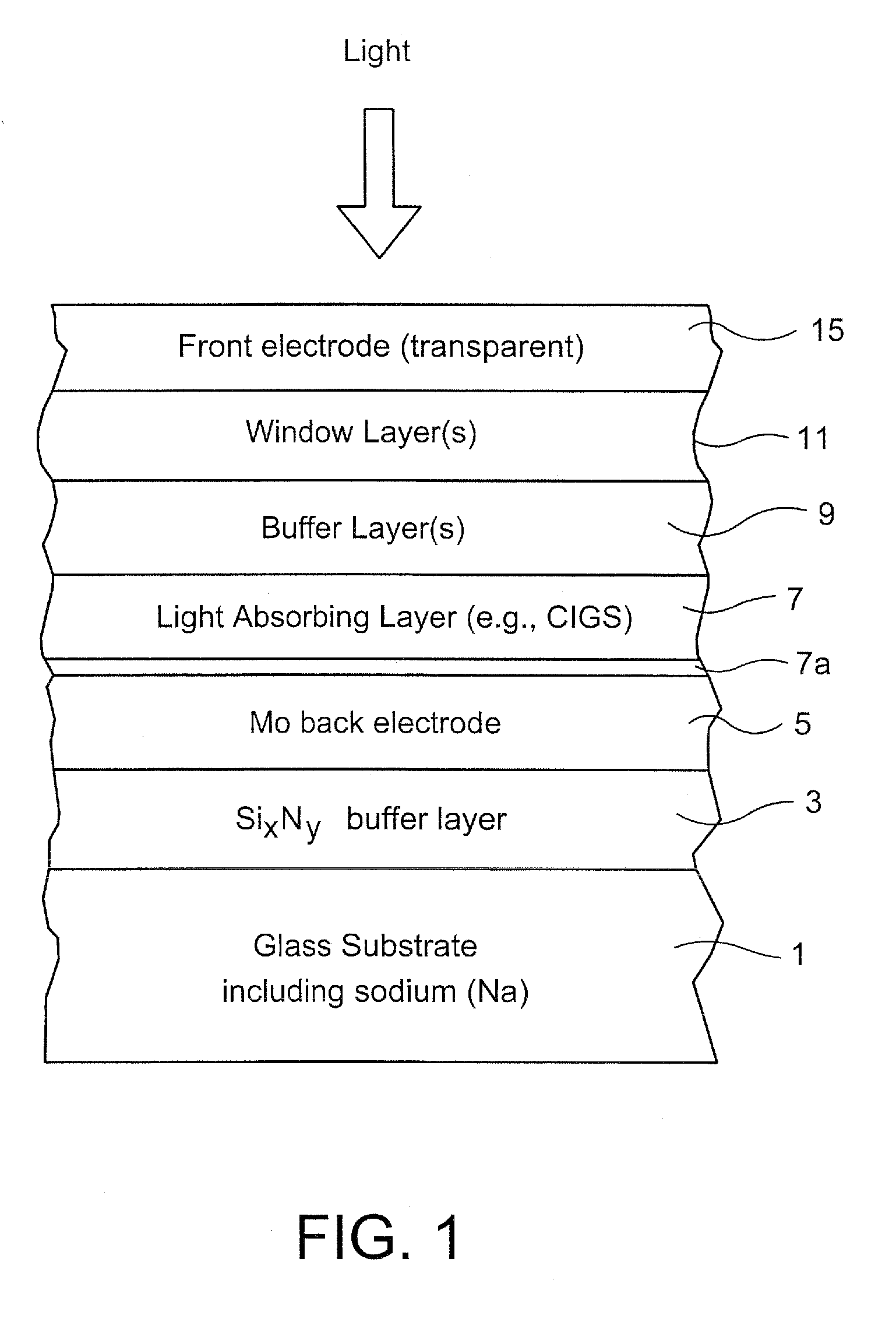
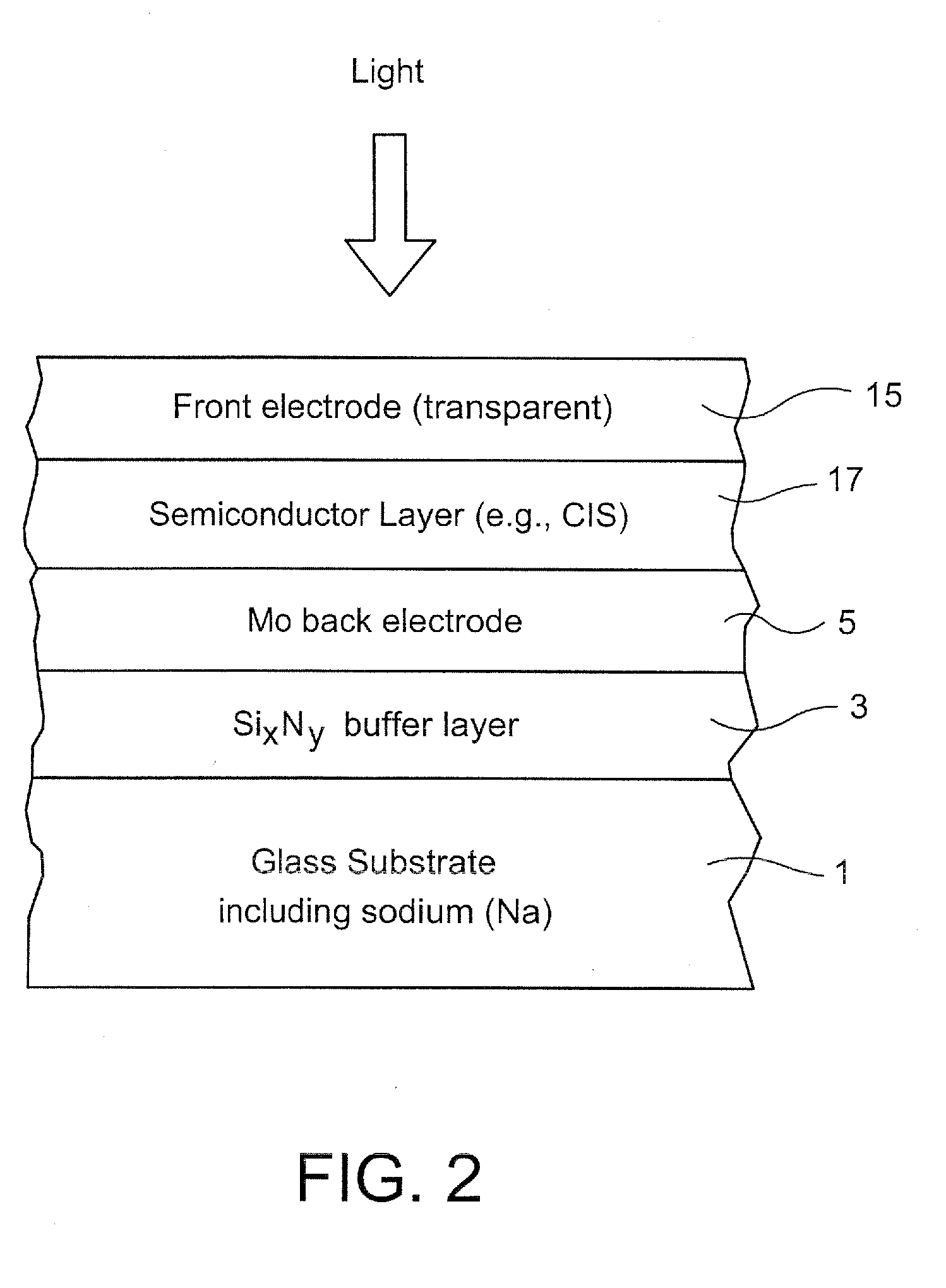
An electrode structure is provided for use in an electronic device. In certain example embodiments, an electrode structure includes a supporting glass substrate (e.g., soda-lime silica based float glass), a buffer layer (e.g., SixNy), and a conductive electrode (e.g., Mo) provided in this order. The buffer layer is advantageous in that it prevents or reduces sodium (Na) migration from the glass substrate into semiconductor layer(s) of the electronic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Spray ejector device and methods of use
InactiveUS20130299607A1High depositionEasy to useMedical devicesSpray nozzlesSymmetric configurationFluid loading
An ejector device for ejecting droplets of fluid onto a surface includes an ejector mechanism attached to a fluid reservoir through a fluid loading plate that is configured to pierce the reservoir and channel the fluid to a rear surface of the ejector mechanism by capillary action. The ejector mechanism may have a centro-symmetric configuration with a lead free piezo actuator and may be covered by an auto-closing cover.
Owner:EYENOVIA
Flux-cored welding wire and method for arc overlay welding using the same
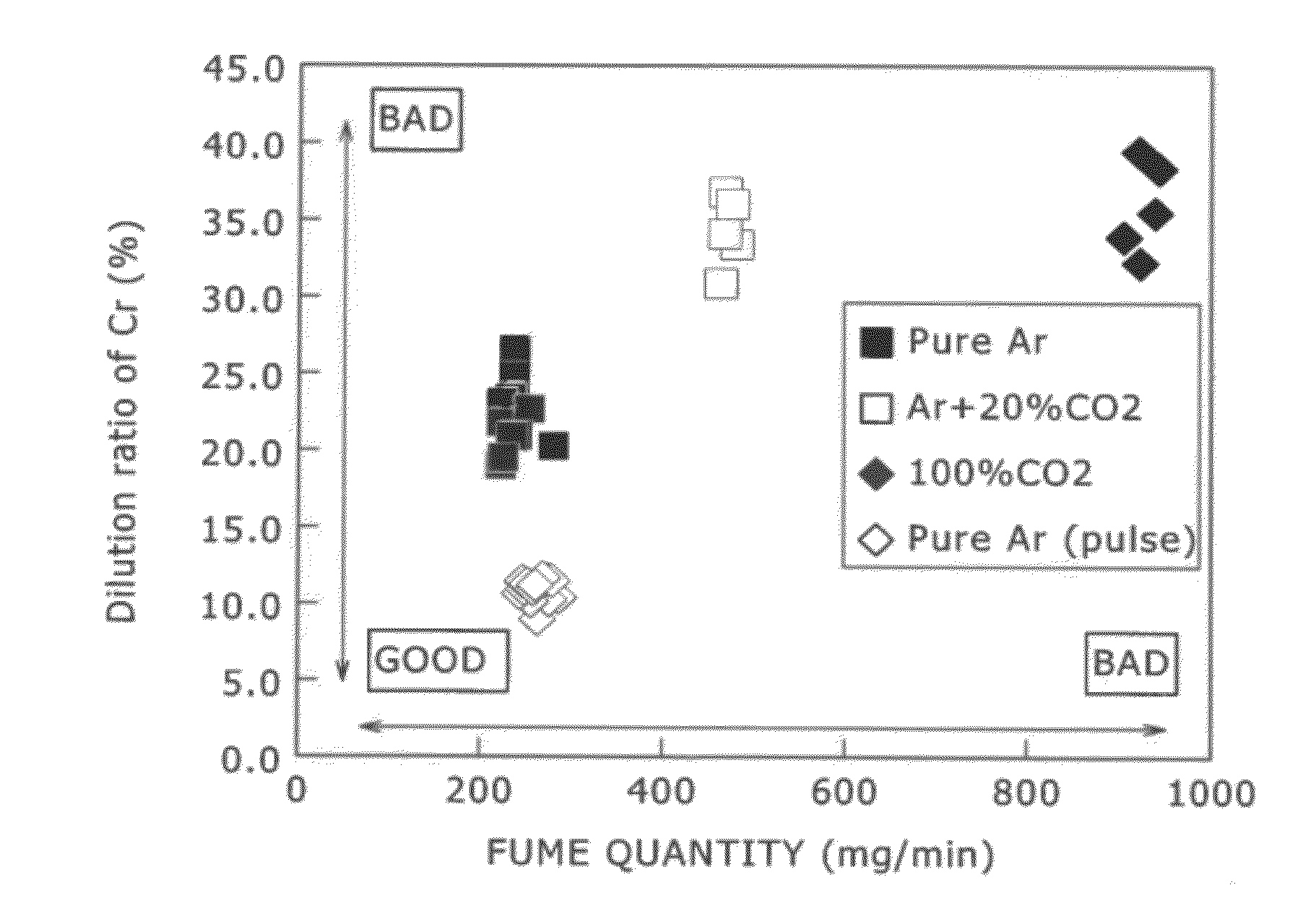
InactiveUS20120055903A1Improve solderabilityLow dilution ratioArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsShielding gasCorrosion resistant
To provide a flux-cored welding wire and a method for arc overlay welding attaining excellent weldability and low dilution ratio and obtaining a weld bead excellent in corrosion resistance in overlay welding using the flux-cored welding wire having an advantage of high deposition rate and deposition efficiency. The flux-cored welding wire for gas shielded arc welding including flux filled up in an outer sheath and using pure Ar as a shielding gas contains, as percentage to the total mass of the flux-cored welding wire, C: 0.20 mass % or below, Si: 15.00 mass % or below, Mn: 20.00 mass % or below, P: 0.0500 mass % or below, S: 0.0500 mass % or below, and Cr: 15.0-50.0 mass %, with the remainder being Fe and inevitable impurities.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Coated silica particles and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20030118824A1High depositionAdvantageous physicalMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSilica particleCerium oxide
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
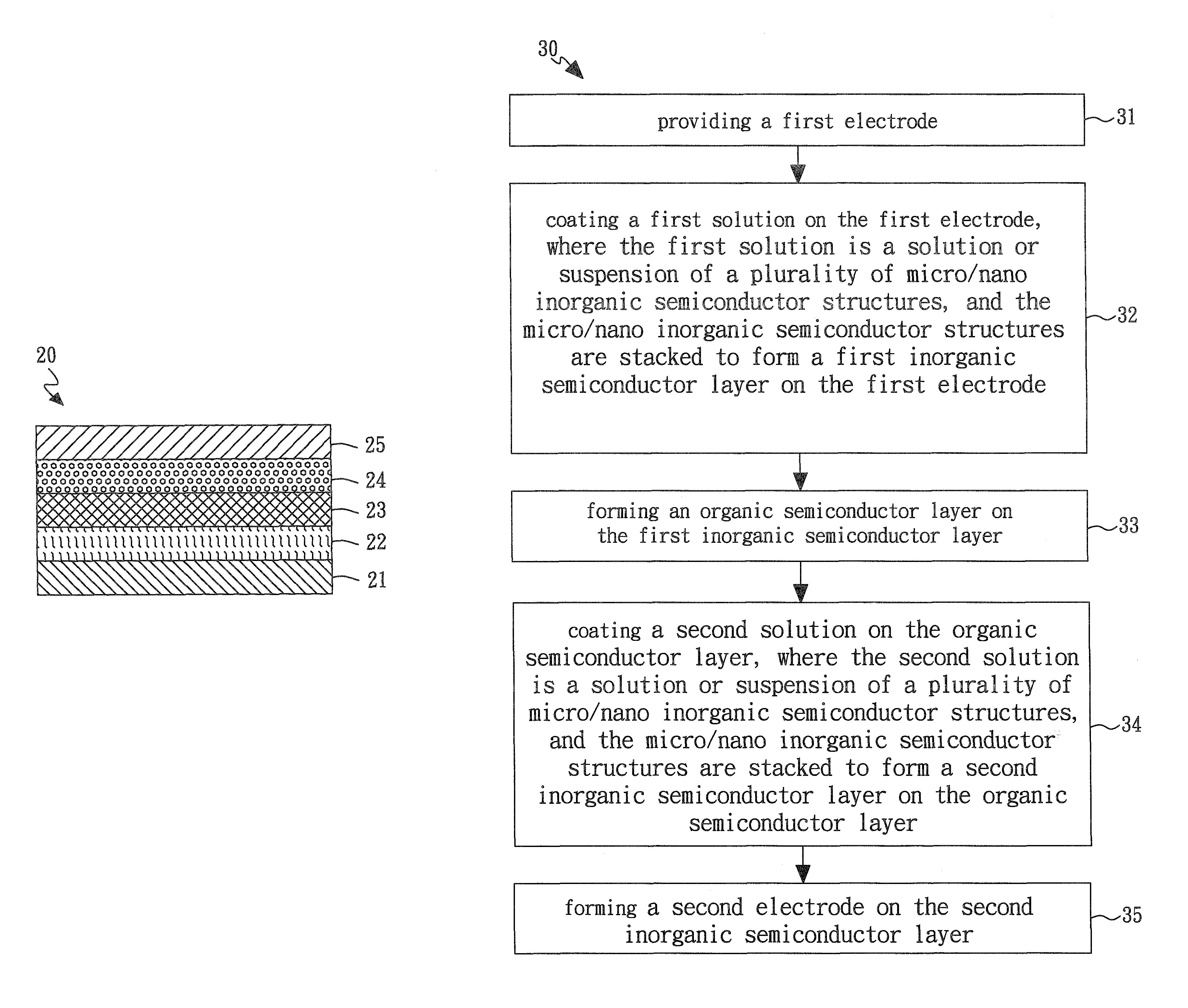
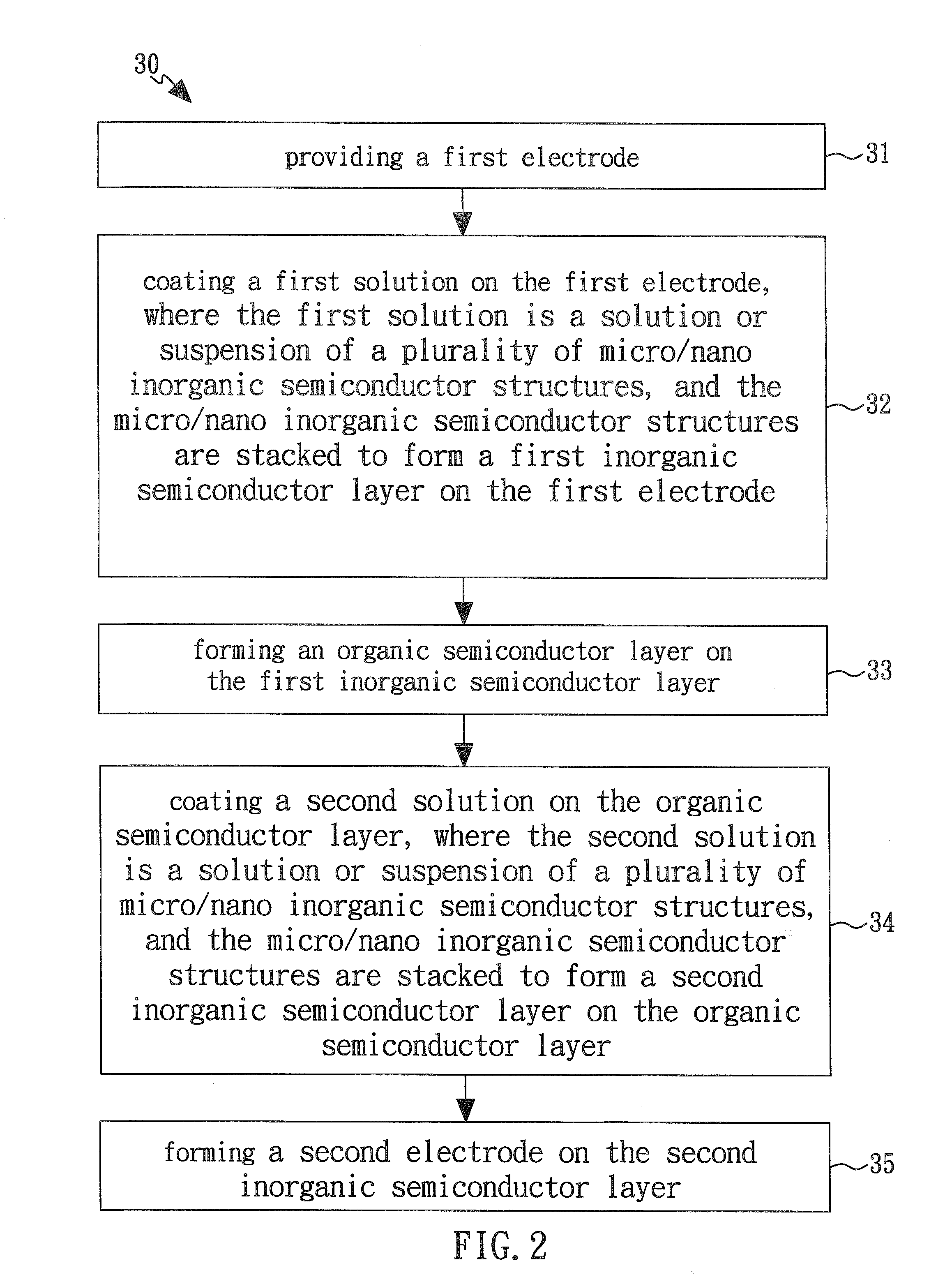
Methods for tailoring the surface topography of a nanocrystalline or amorphous metal or alloy and articles formed by such methods
InactiveUS20100282613A1Reducing width and depthHigh depositionElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNumber densityTopography
Electrochemical etching tailors topography of a nanocrystalline or amorphous metal or alloy, which may be produced by any method including, by electrochemical deposition. Common etching methods can be used. Topography can be controlled by varying parameters that produce the item or the etching parameters or both. The nanocrystalline article has a surface comprising at least two elements, at least one of which is metal, and one of which is more electrochemically active than the others. The active element has a definite spatial distribution in the workpiece, which bears a predecessor spatial relationship to the specified topography. Etching removes a portion of the active element preferentially, to achieve the specified topography. Control is possible regarding: roughness, color, particularly along a spectrum from silver through grey to black, reflectivity and the presence, distribution and number density of pits and channels, as well as their depth, width, size. Processing parameters that have been correlated in the Ni—W system to topography features include, for both the deposition phase and the etching phase of a nanocrystalline surface: duty cycle, current density, deposition duration, plating chemistry, polarity ratio. The relative influence of the processing parameters can be noted and correlated to establish a relationship between values for processing parameters and degree of topography feature. Control can be established over the topography features. Correlation can be made for any such system that exhibits a definite spatial distribution of an active element that bears a predecessor spatial relationship to a desired topography feature.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Process for the deposition of uniform layer of particulate material
InactiveUS20050221018A1High speedImprove capacityElectric shock equipmentsPretreated surfacesSolventSolubility
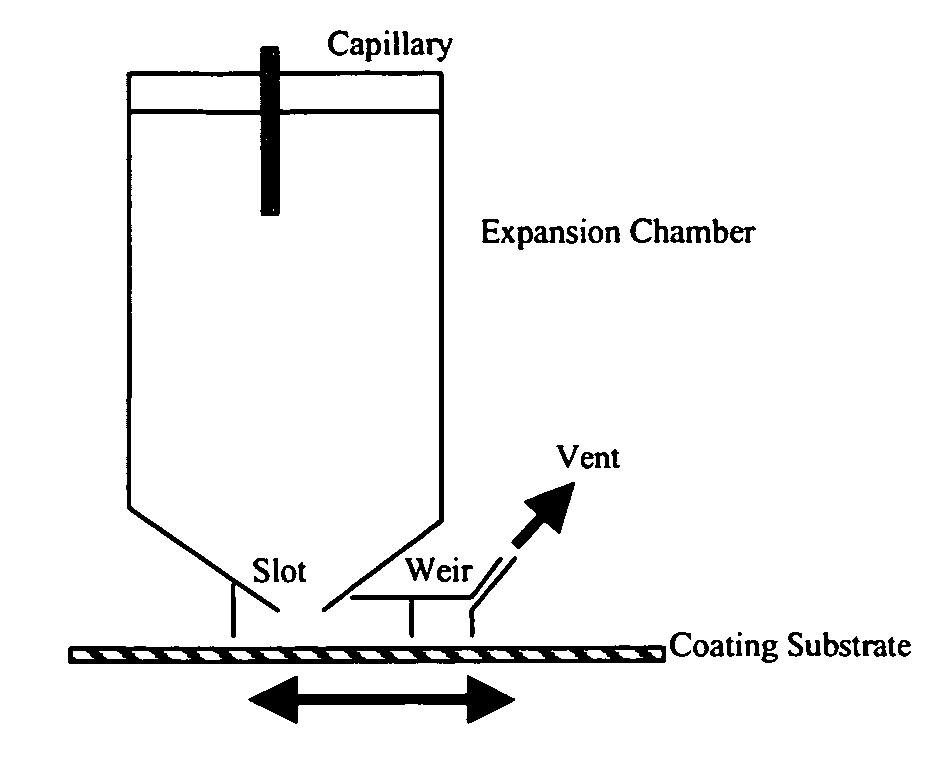
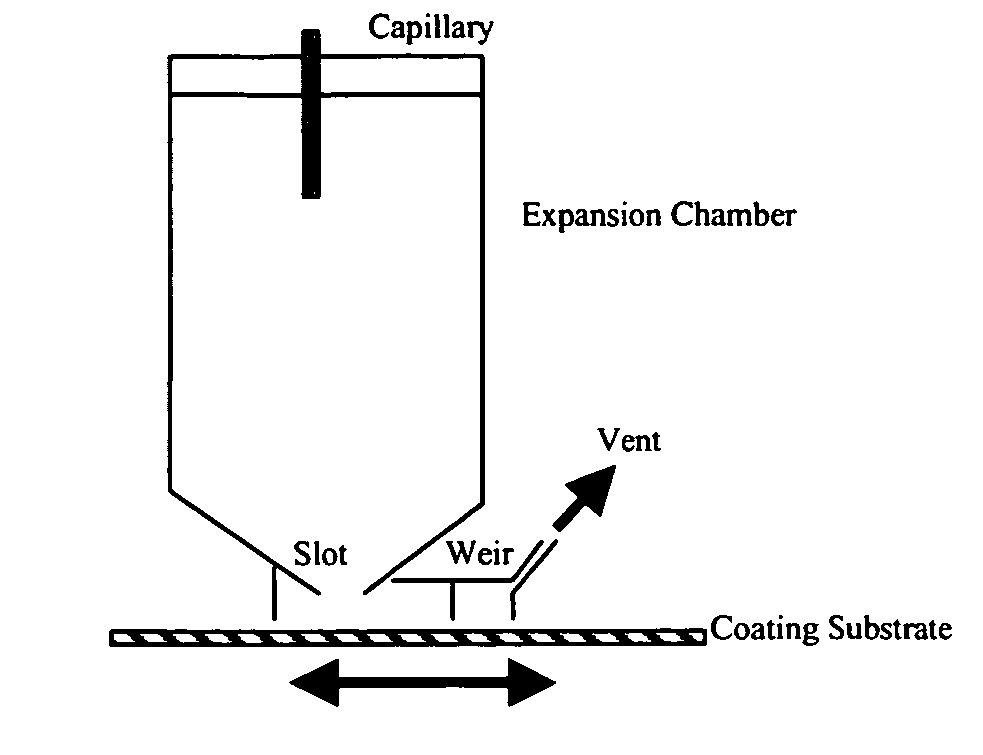
A process for the deposition of particulate material of a desired substance on a surface includes: (i) charging a particle formation vessel with a compressed fluid; (ii) introducing into the particle formation vessel a first feed stream comprising a solvent and the desired substance dissolved therein and a second feed stream comprising the compressed fluid, wherein the desired substance is less soluble in the compressed fluid relative to its solubility in the solvent and the solvent is soluble in the compressed fluid, and wherein the first feed stream is dispersed in the compressed fluid, allowing extraction of the solvent into the compressed fluid and precipitation of particles of the desired substance; (iii) exhausting compressed fluid, solvent and the desired substance from the particle formation vessel at a rate substantially equal to the rate of addition of such components to the vessel in step (ii) through a restrictive passage to a lower pressure whereby the compressed fluid is transformed to a gaseous state and a flow of particles of the desired substance is formed; and (iv) exposing a receiver surface to the exhausted flow of particles of the desired substance and depositing a uniform layer of particles on the receiver surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Guar hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride and uses thereof in hair treatment compositions
ActiveUS20140154200A1Improve deposition efficiencyPleasant dry hair feel attributeCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsChlorideDegree of substitution
The present invention relates to a non-cellulosic polysaccharide derivative:i) having a mean average molecular weight (Mw) from about 100,000 g / mol, preferably from about 150,000 g / mol and more preferably from about 200,000 g / mole to about 2,000,000 g / mol, preferably to about 1,800,000 g / mol and more preferably to about 1,400,000 g / mole; andii) containing at least one cationic group, with a cationic degree of substitution (DScat.)extraction, from about 0.20 to about 0.30.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Resin composition for laser welding and molded article
A polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) resin composition for laser welding which can be evenly welded to attain high weld strength although it contains PBT as the base. The laser-weldable resin composition comprises 100 parts by weight of a polybutylene terephthalate resin (homopolyester or copolyester) (A), 1 to 50 parts by weight of an elastomer (B) such as a thermoplastic polystyrene elastomer or thermoplastic polyester elastomer, 5 to 100 parts by weight of a polycarbonate resin (C), 1 to 10 parts by weight of a plasticizer (D) (e.g., an aromatic polycarboxylic ester or acrylic plasticizer), and 0 to 100 parts by weight of a filler or reinforcement (E) such as glass fibers. This resin composition gives a molded article in which the light transmittance fluctuates little from part to part. This molded article can hence be evenly laser-welded to a mating material.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
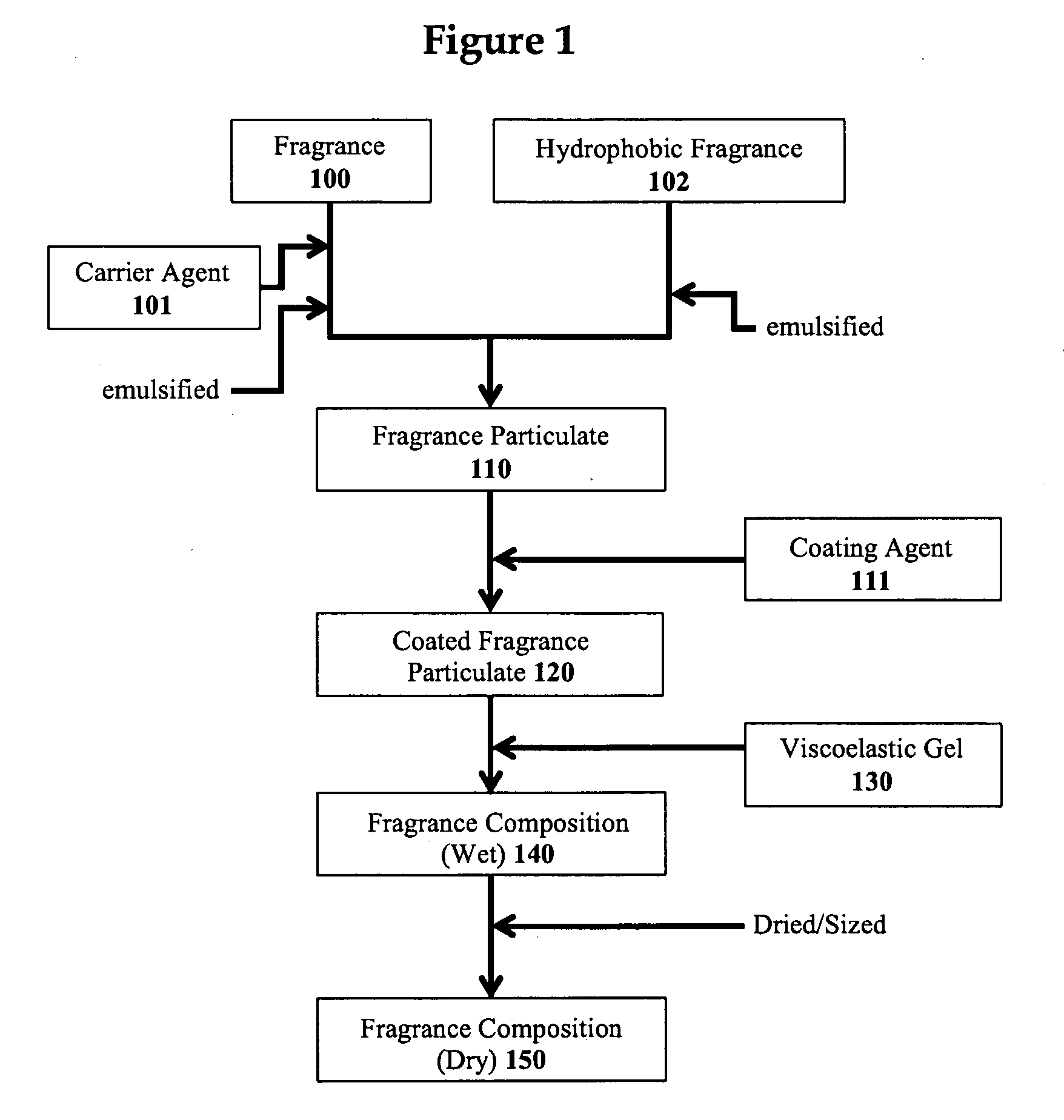
Multilayer fragrance encapsulation comprising kappa carrageenan
InactiveUS8188022B2Facilitate and improve adherenceHigh depositionCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsParticulatesKappa-Carrageenan
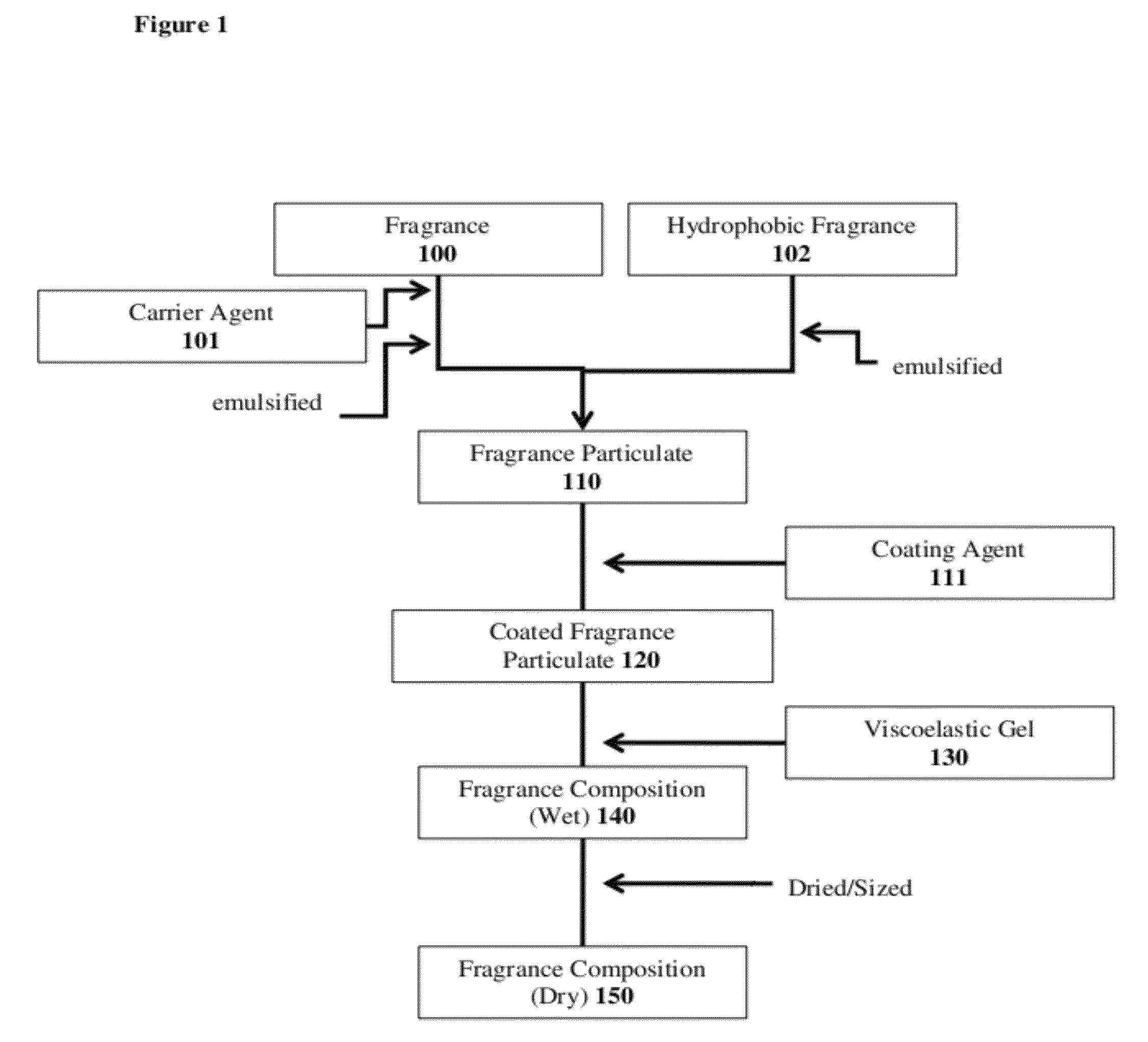
Disclosed herein is a fragrance composition and a method for making the same having a fragrance particulate and a viscoelastic gel; where the composition has enhanced fragrance retention throughout the processing of the composition.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Nasal nebulizer
InactiveUS20110303218A1Increase surface areaIncrease blood flowRespiratorsMedical devicesNasal cavityNebulizer
A nasal delivery system for and a method of delivering aerosolized medication to the nasal passageway of a patient for treating an ailment in the upper respiratory tract above the trachea, comprising: contacting a nosepiece to a patient's nose, the nosepiece being coupled to a directly to the mesh of the vibrating mist nebulizer via a connecting portion, activating the nebulizer to create aerosolized medication from liquid medication in the chamber, directing the aerosolized medication through the connecting portion to the nosepiece; and dispensing, from apertures in the nosepiece, the aerosolized medication directly through the patient's nose.
Owner:SINUTOPIC INC
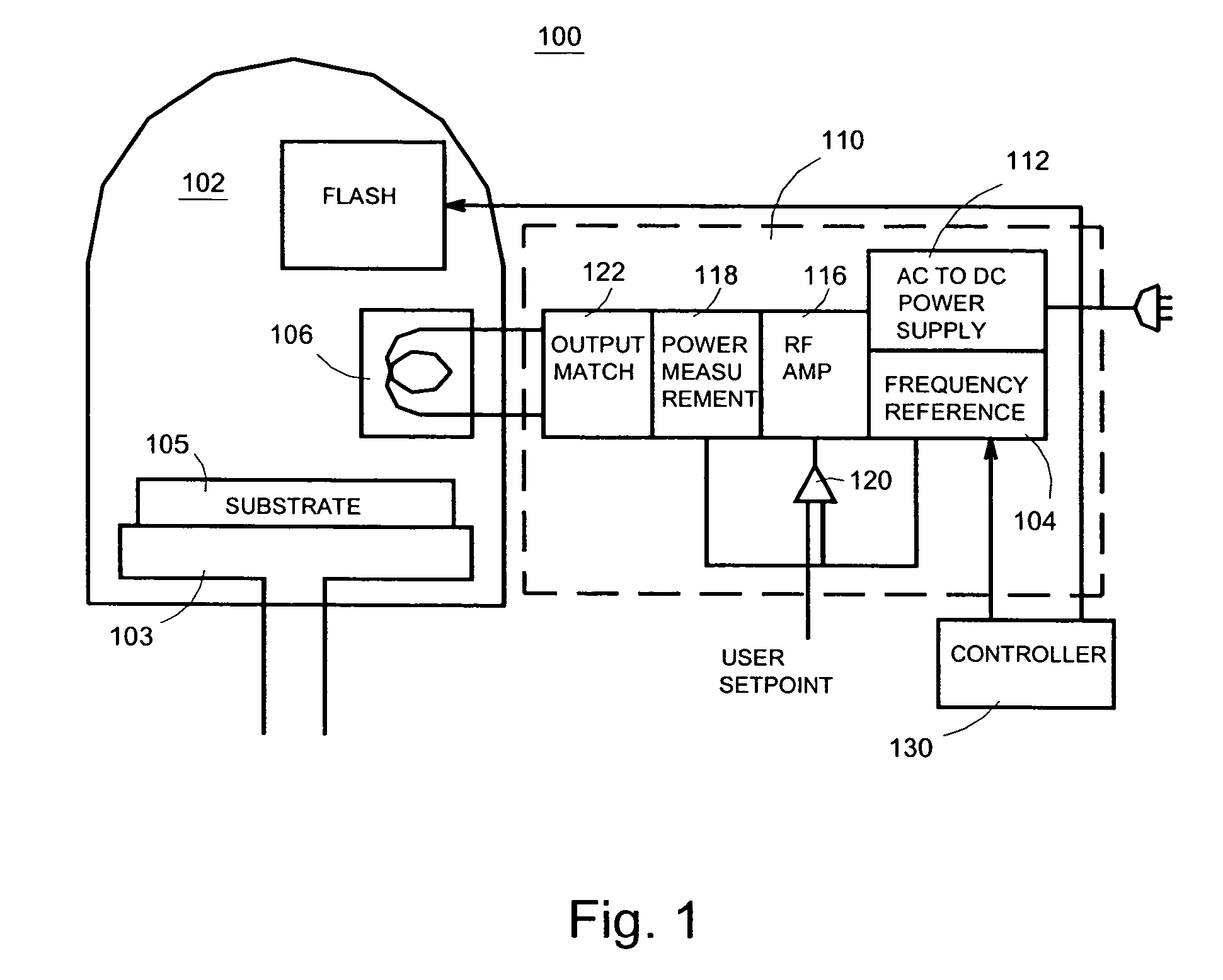
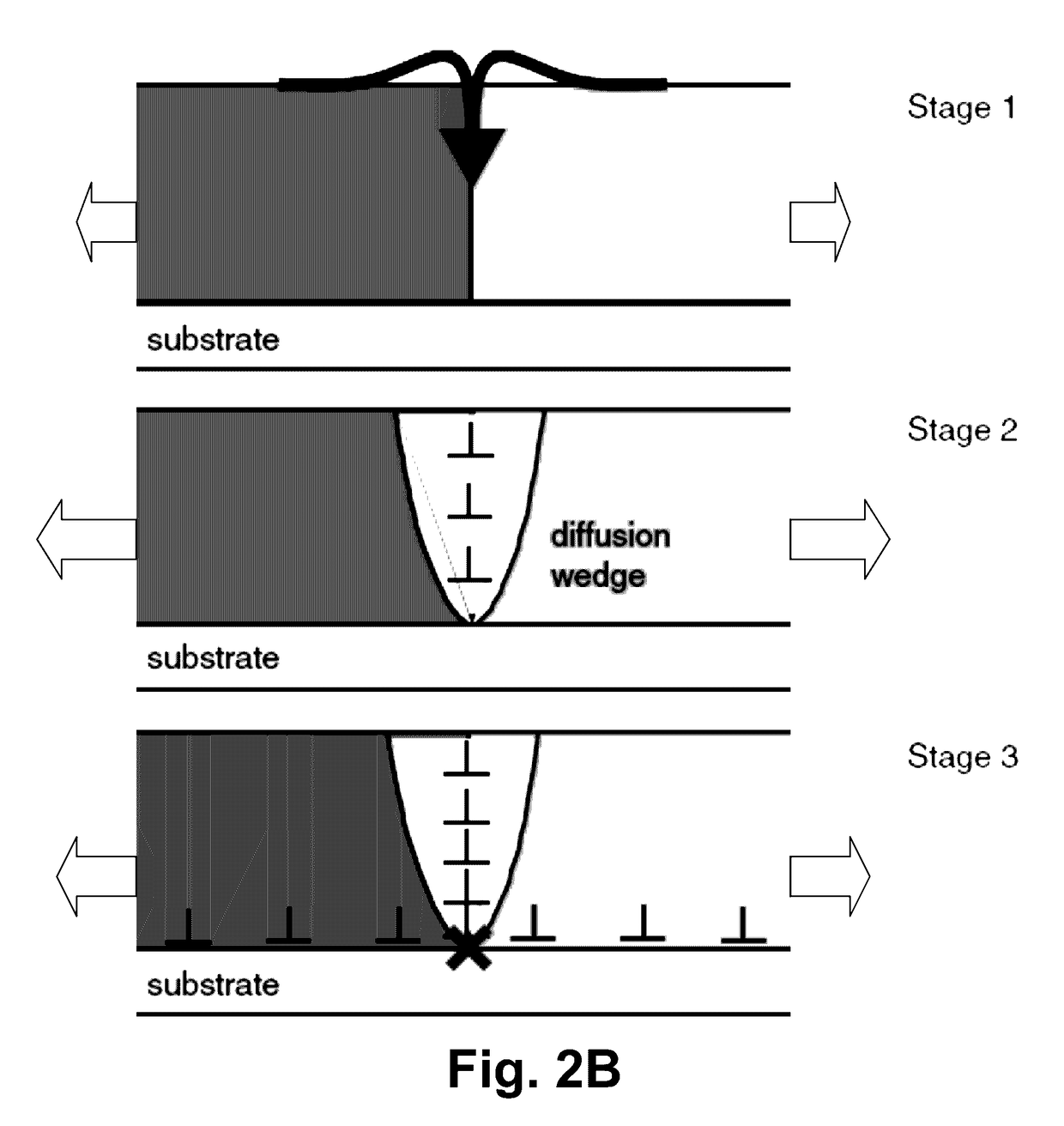
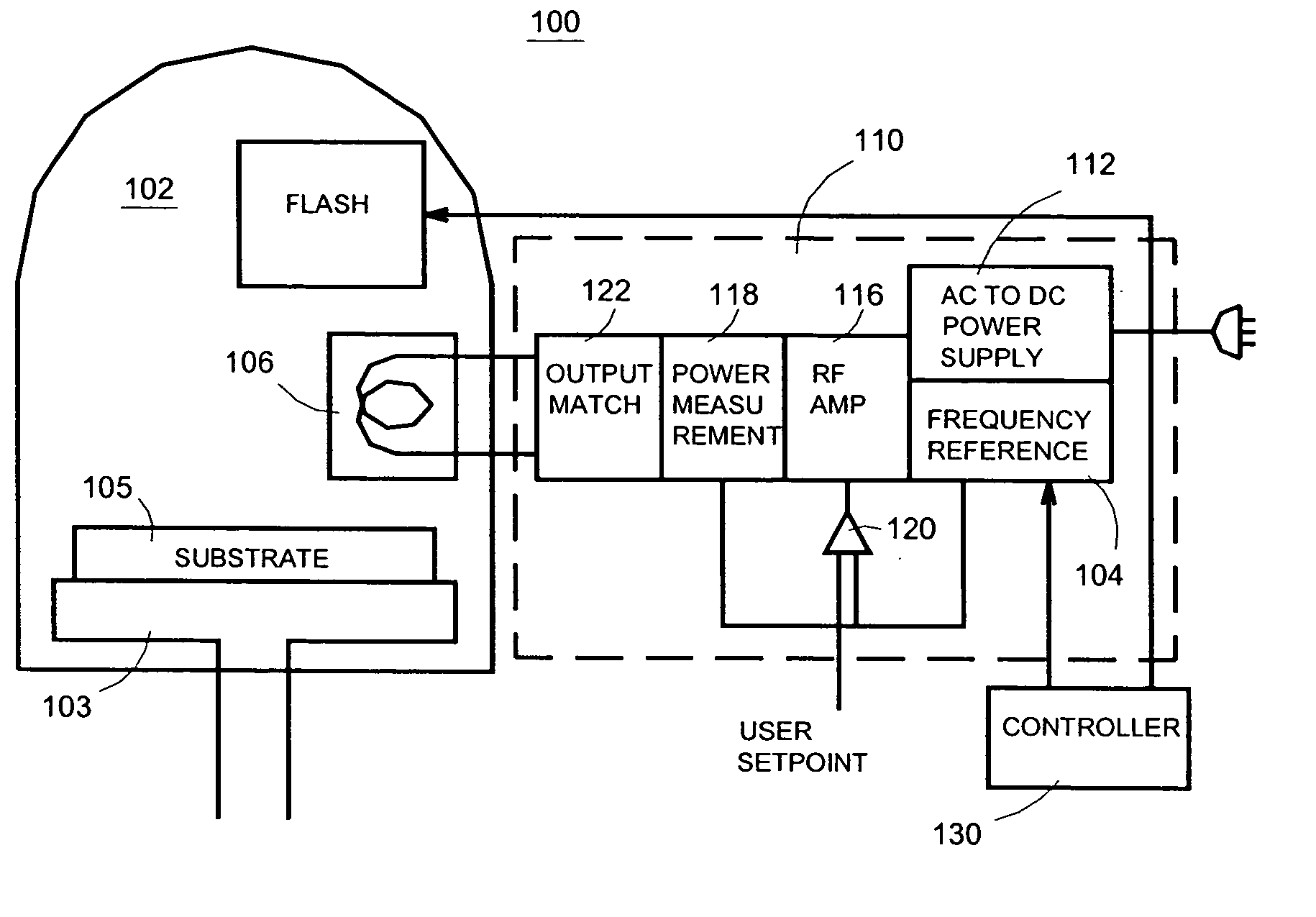
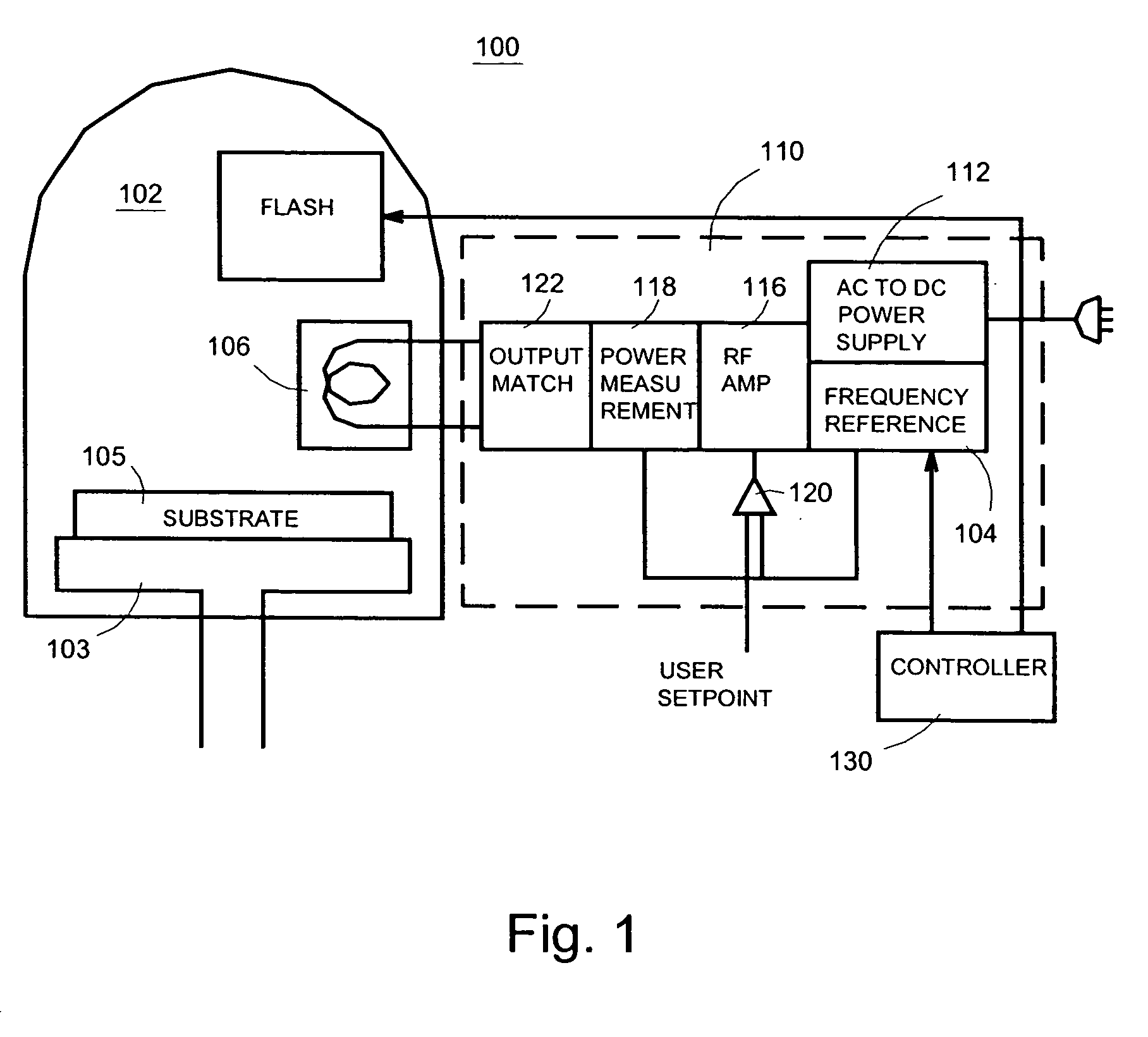
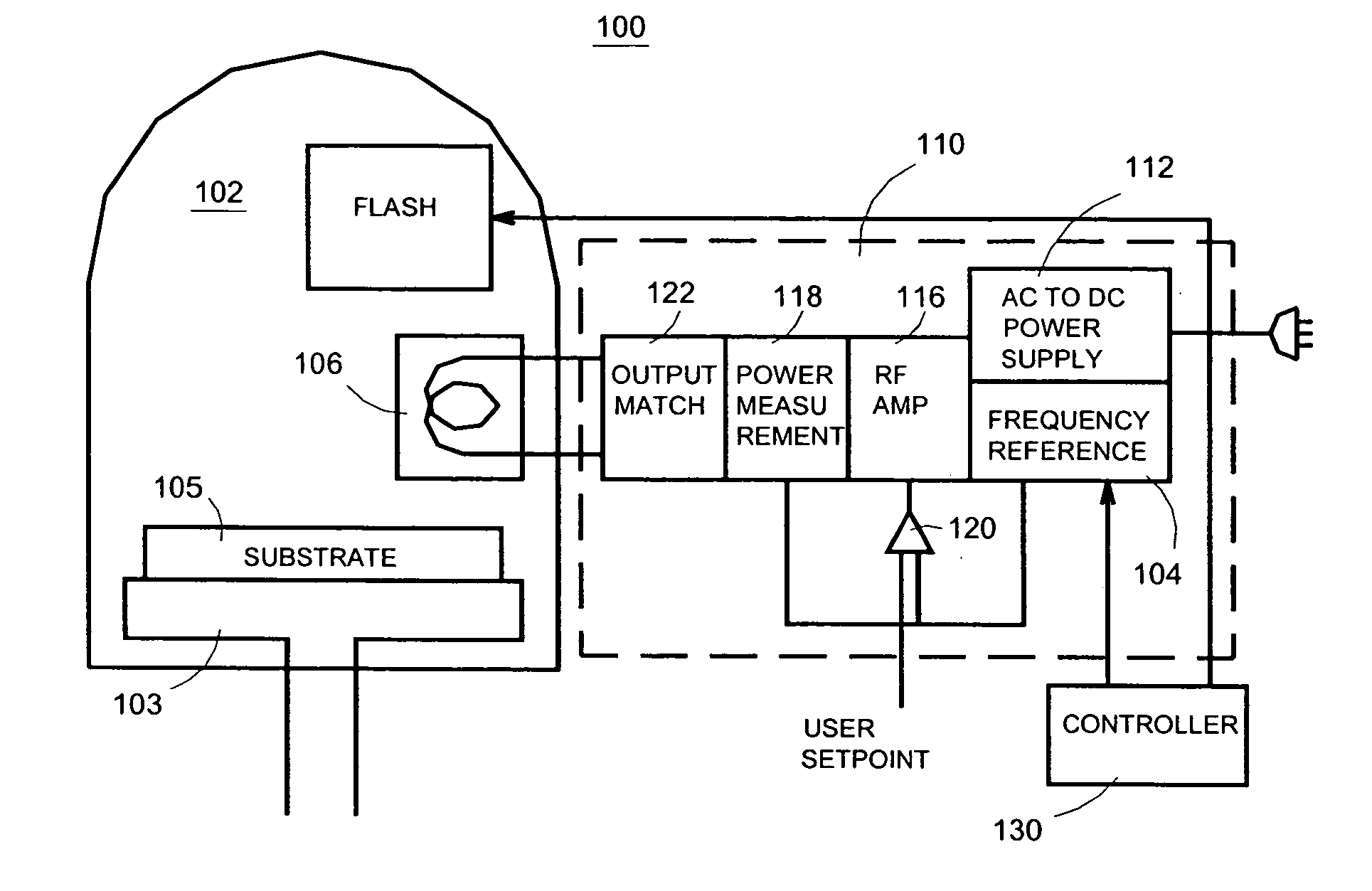
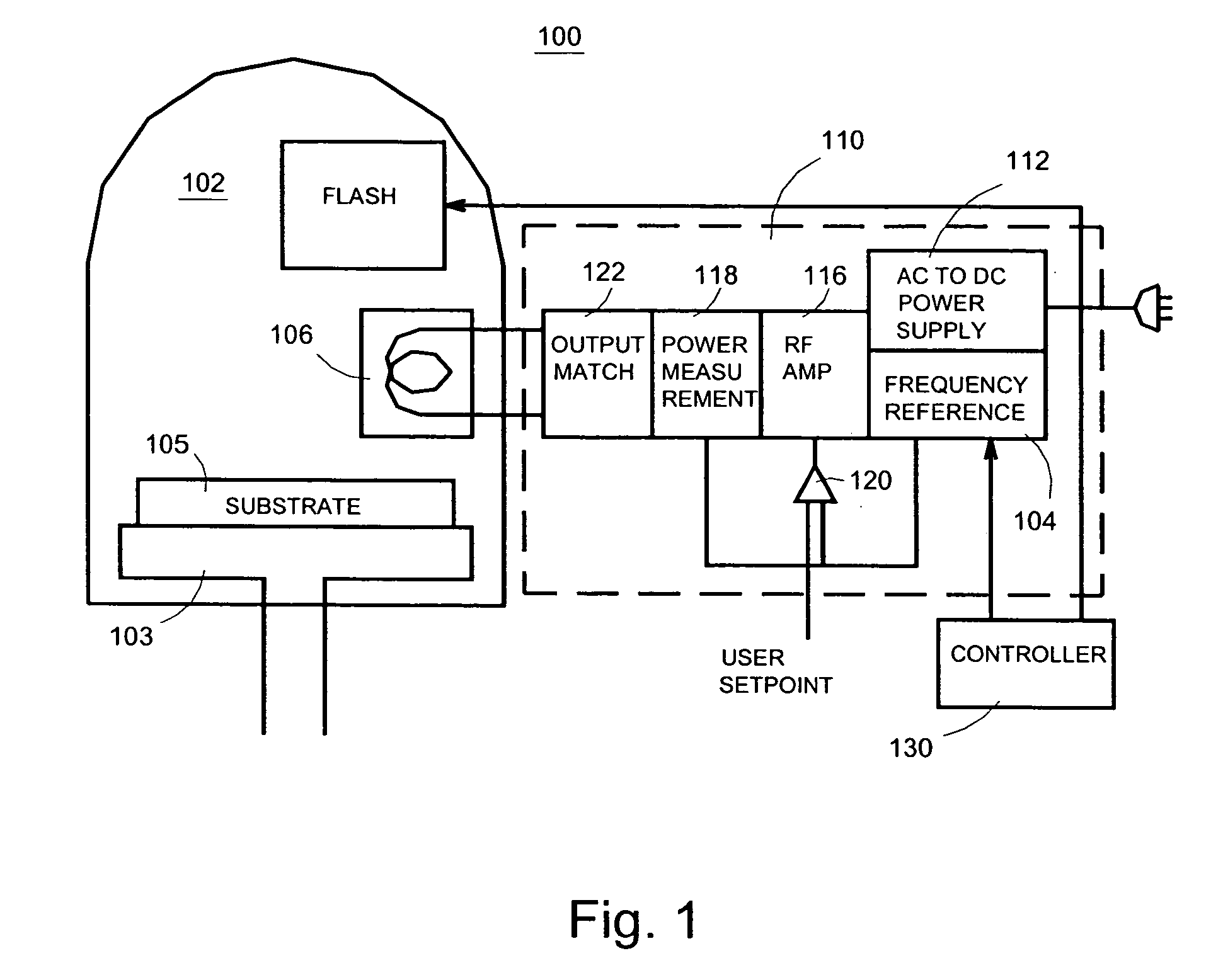
Semiconductor processing system and method
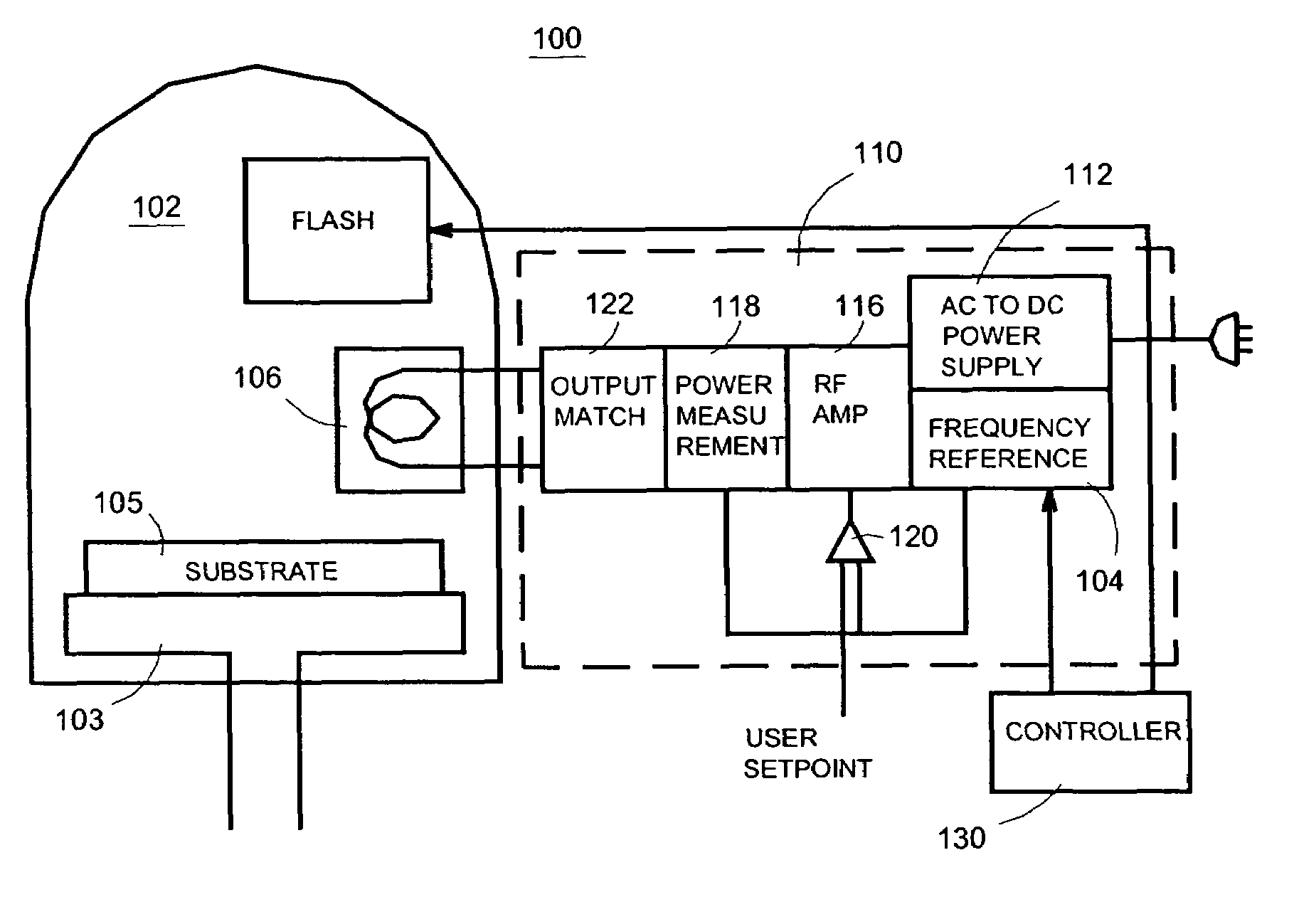
InactiveUS7442615B2Excellent propertyStrict controlLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesComputer hardwareWafer
Systems and methods are disclosed to perform semiconductor processing with a process chamber; a flash lamp adapted to be repetitively triggered; and a controller coupled to the control input of the flash lamp to trigger the flash lamp. The system can deploy a solid state plasma source in parallel with the flash lamp in wafer processing.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Deposition of uniform layer of desired material
InactiveUS20060275542A1High depositionIncrease speedMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsVitrificationChemical transformation
A process for the deposition of a thin film of a desired material on a surface comprising: (i) providing a continuous stream of amorphous solid particles of desired material suspended in at least one carrier gas, the solid particles having a volume-weighted mean particle diameter of less than 500 nm, at an average stream temperature below the glass transition temperature of the solid particles of desired material, (ii) passing the stream provided in (i) into a heating zone, and heating the stream in the heating zone to elevate the average stream temperature to above the glass transition temperature of the solid particles of desired material, wherein no substantial chemical transformation of the desired material occurs due to heating of the desired material, (iii) exhausting the heated stream from the heating zone through at least one distributing passage, at a rate substantially equal to its rate of addition to the heating zone in step (ii), wherein the carrier gas does not undergo a thermodynamic phase change upon passage through heating zone and distribution passage, and (iv) exposing a receiver surface that is at a temperature below the temperature of the heated stream to the exhausted flow of the heated stream, and depositing particles of the desired material to form a thin uniform layer of the desired material on the receiver surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
System and method for semiconductor processing
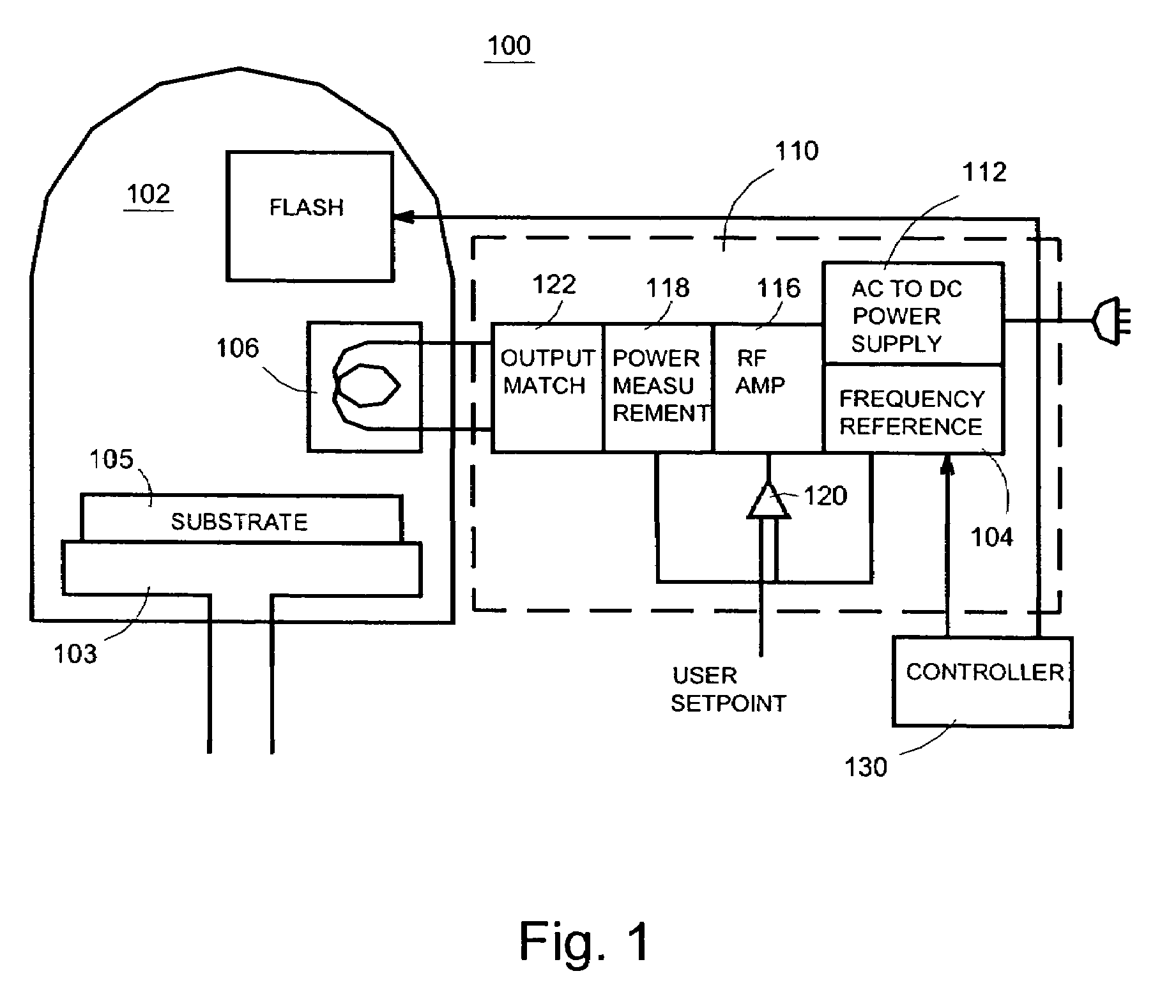
InactiveUS7867905B2Excellent propertyStrict controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Systems and methods are disclosed to perform semiconductor processing with a process chamber; a flash lamp adapted to be repetitively triggered; and a controller coupled to the control input of the flash lamp to trigger the flash lamp. The system can deploy a solid state plasma source in parallel with the flash lamp in wafer processing.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Multilayer fragrance encapsulation
InactiveUS20090258812A1Facilitate and improve adherenceHigh depositionCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsChemistryFlavor
Disclosed herein is a fragrance composition and a method for making the same having a fragrance particulate and a viscoelastic gel; where the composition has enhanced fragrance retention throughout the processing of the composition.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
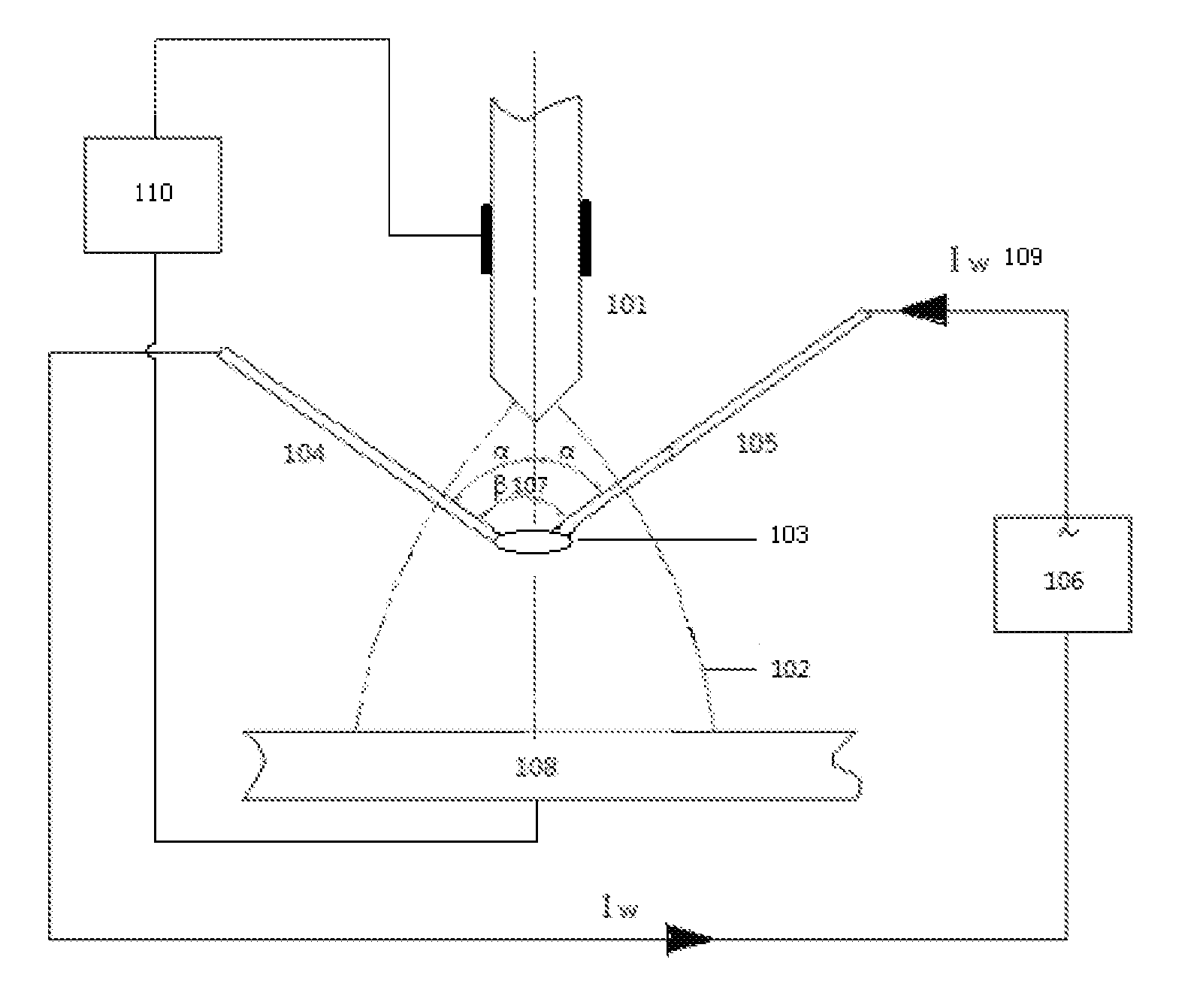
Gas tungsten arc welding with cross ac arcing twin wires
ActiveUS20140291297A1High depositionLow heat inputArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusSide effectGas tungsten arc welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) is a widely used process for joining metals. Its main advantage over its competition gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) is its high productivity in depositing metals. However, to melt metal from the wire to deposit into the work-piece, additional heat is consumed and applied to the work-piece with an uncontrolled fixed proportion to the effective heat that melts the wire. Such additional heat is often in excess of the needed heat input for the work-piece. The side-effects include a waste of the energy, an increased distortion, and possible materials property degradation. This invention is to device a method to transfer this part of heat to melt the wire by adding two wires, which form a pair of arc spots, under a tungsten arc. It also devices a method to assure the arc between the two wires be maintained stable such that the transfer be successfully continuous. The successful continuous transfer improves the energy efficiency, eliminates the adverse effects on the distortion and materials property, and decouples the controls on mass input and heat input on the work-piece.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
System and method for reducing attractive forces between a deposition mask and substrate and a deposition system and method utilizing the same
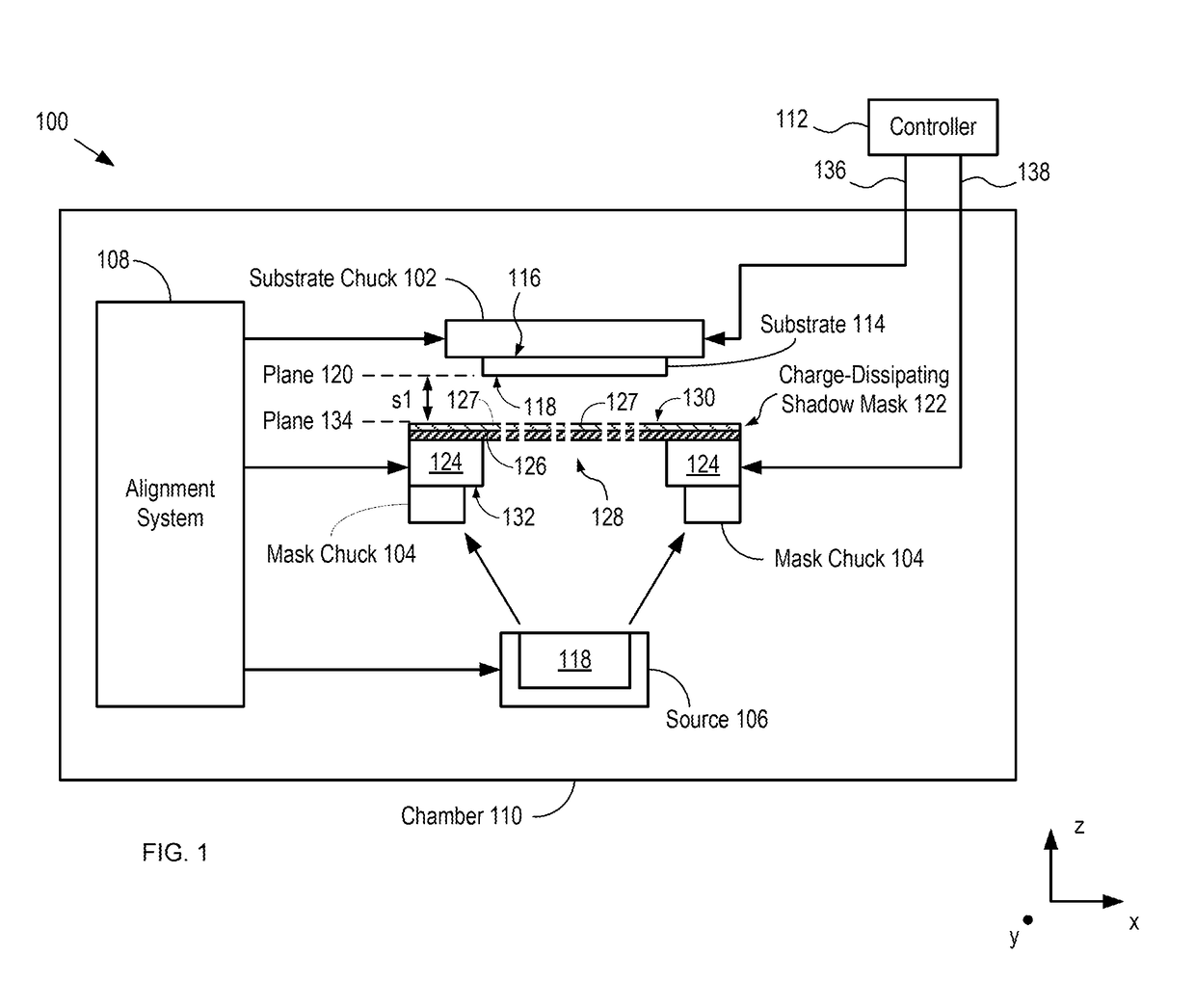
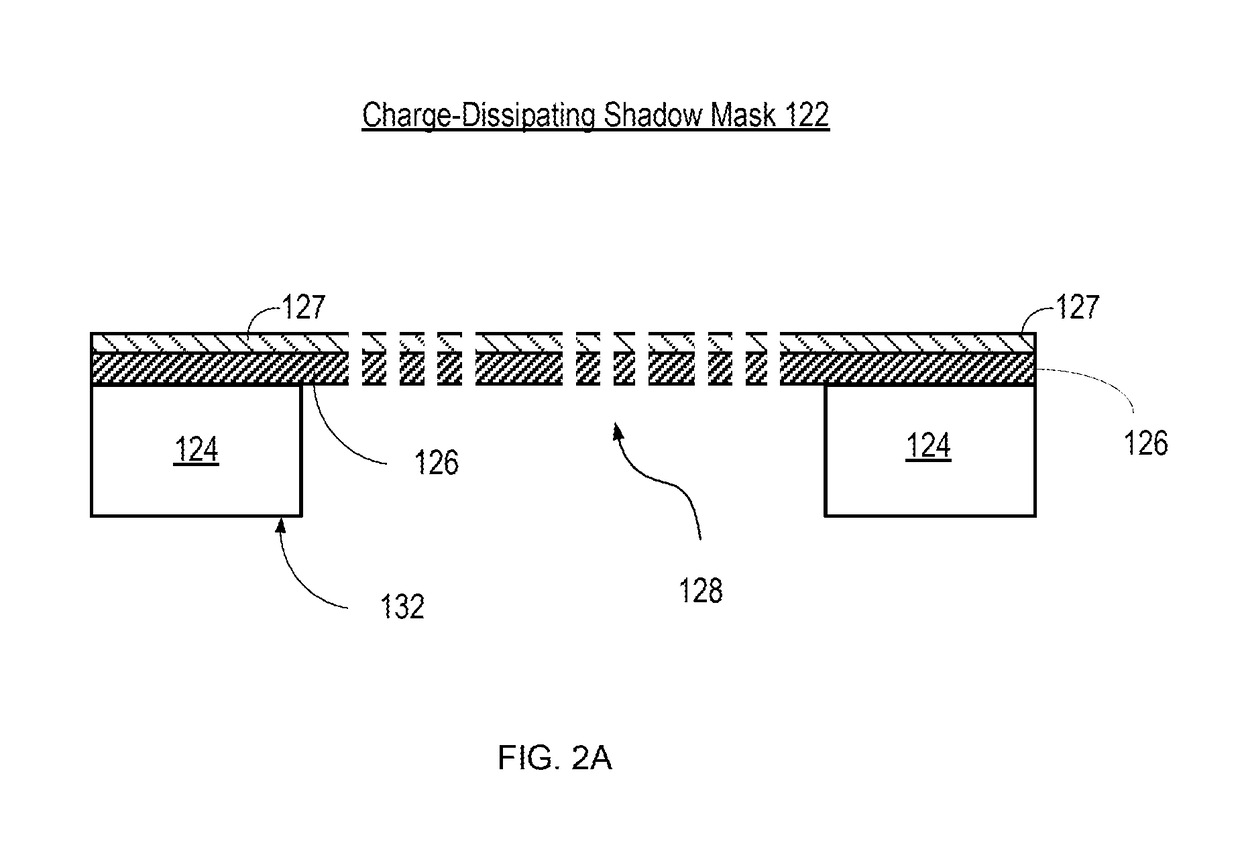
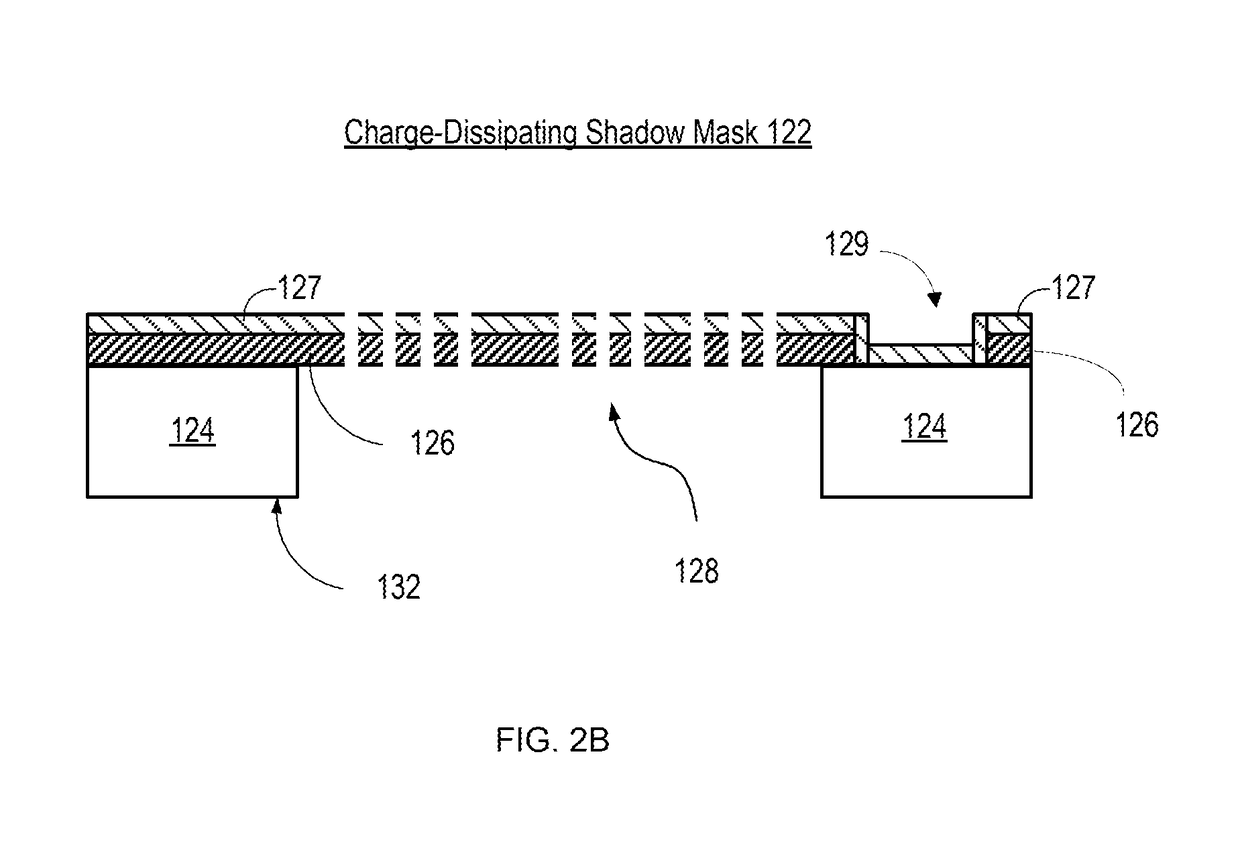
InactiveUS20180340252A1Less attractiveDissipate chargeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingImage resolutionEngineering
A system and method for reducing attractive forces between a deposition mask and a substrate is provided that enables high-resolution direct deposition of a patterned layer of material on a substrate using electrostatic chucks for holding the substrate and the shadow mask. A charge-dissipating shadow mask is utilized that comprises a thin conductive layer on the surface of the membrane of the shadow mask. The conductive layer helps to dissipate the charge that accumulates on the membrane of the shadow mask, thereby reducing the attractive forces between the substrate and the shadow mask. As a result, the shadow mask and substrate can be placed in closer proximity to each other than would be possible without the charge-dissipating shadow mask, thereby reducing feathering effects and enabling higher resolution direct deposition.
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
Method for electrodeposition of bronzes
InactiveUS20050263403A1Bath stabilityAdvantageous solubility of metalSurface reaction electrolytic coatingCopperAcid electrolyte
A method for electrodeposition of bronzes, with which the substrate to be coated is plated in an acid electrolyte that contains at least tin and copper ions, an alkylsulfonic acid and a wetting agent, and the preparation of such an electrolyte.
Owner:ENTHONE INC
Method and apparatus for continuous or batch optical fiber preform and optical fiber production
InactiveUS20070240454A1Reduce lossesImprove deposition efficiencyGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberLength wave
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for fiber and / or fiber perform production and in particular, optical fiber and optical fiber preform production in which a fiber substrate and a multilayered preform can be continuously produced. The layered preform is constructed from particles deposited from one or more aerosol streams containing multicomponent particles wherein individual particles have the ratio of components as desired in the perform layer. Preferably, the components of the aerosol particles have a sub-particle structure in which the subparticle structure dimensions are smaller than the particle diameter and more preferably smaller than the wavelength of light and more preferably on the molecular scale. Preferably, the particles are deposited on the perform substrate via one or more deposition units. Multiple deposition units can be operated simultaneously and / or in series. As the preform is synthesized, it can be simultaneously fed into a drawing furnace for continuous production of fiber. The method can also be used for batch production of fiber preforms and fiber.
Owner:BROWN DAVID P
Electrode structure for use in electronic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20130019940A1Reduce and prevent migrationControl of mechanical and efficiency propertyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOptoelectronicsSoda lime
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
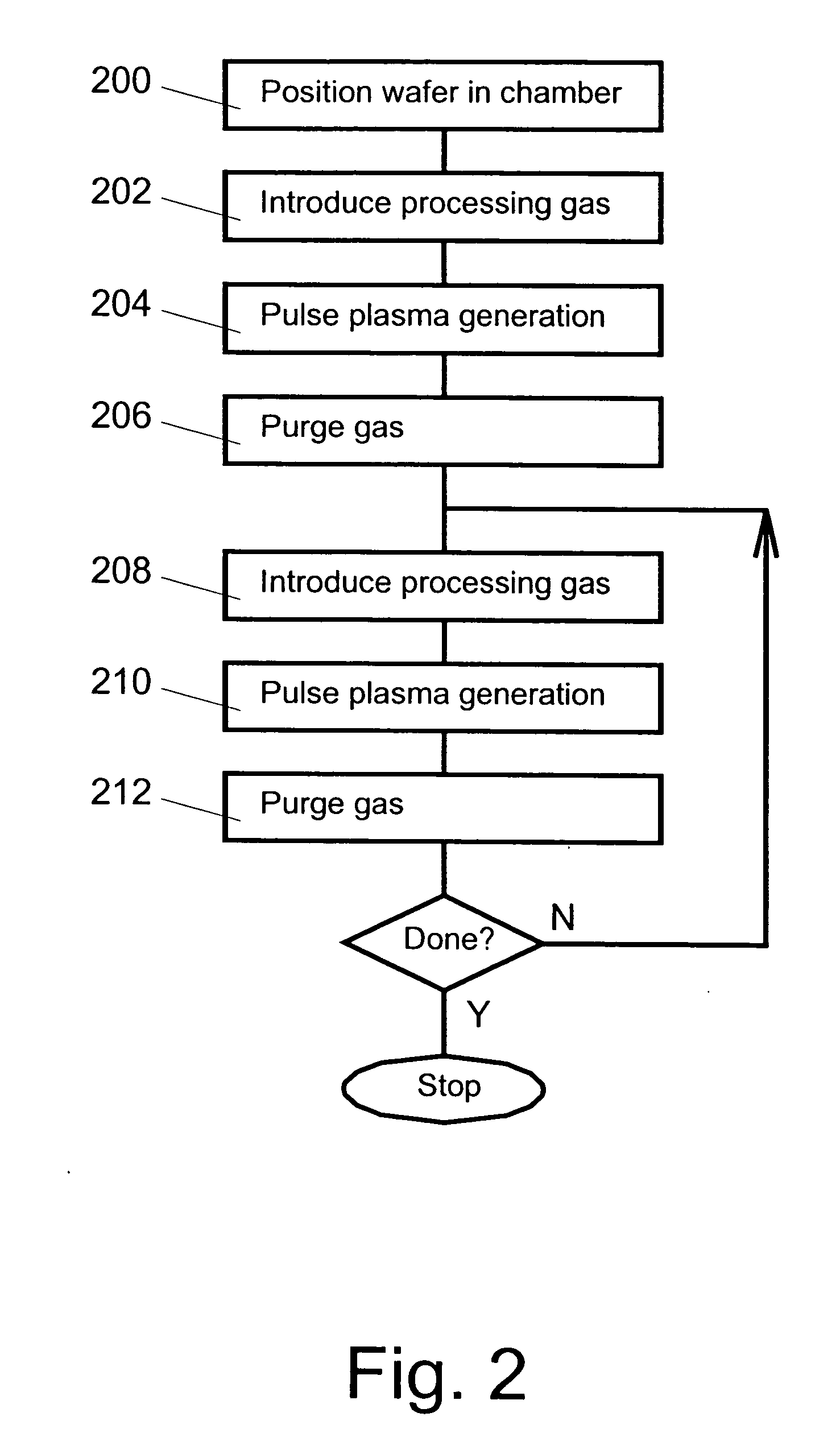
Nanolayer deposition using plasma treatment
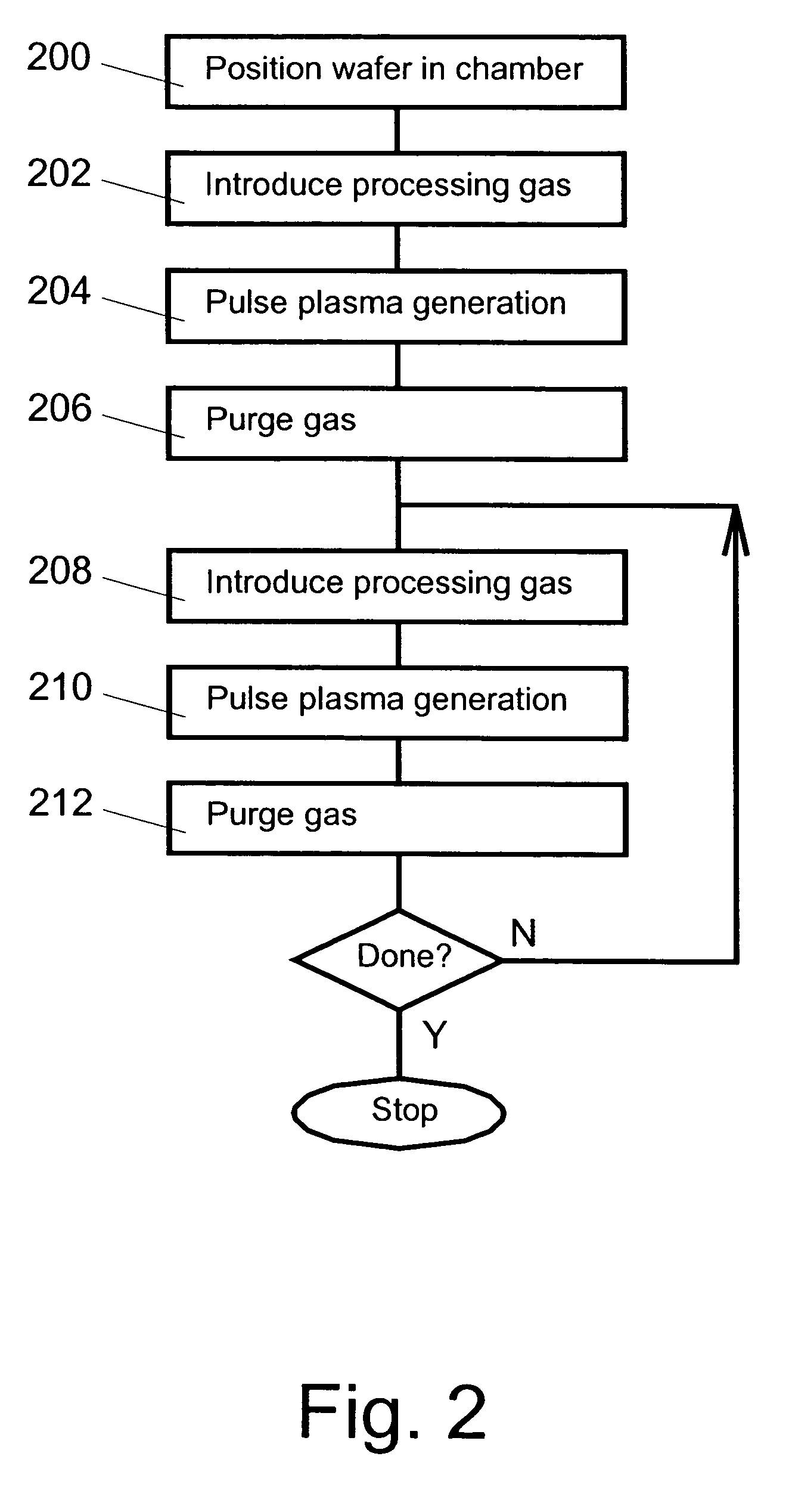
InactiveUS20120202353A1Improve throughputHighly conformalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
A process to deposit a thin film by chemical vapor deposition includes evacuating a chamber of gases; exposing a device to a gaseous first reactant, wherein the first reactant deposits on the device to form the thin film having a plurality of monolayers in thickness; evacuating the chamber of gases; exposing the device, coated with the first reactant, to a gaseous second reactant under a plasma treatment, wherein the thin film is treated by the first reactant; and repeating the previous steps.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Sulfonic group-containing, maleic acid-based, water-soluble copolymer aqueous solution and powder obtained by drying the aqueous solution
ActiveUS20100292122A1High depositionGood storage stabilityOrganic detergent compounding agentsTransportation and packagingWater solubleDicarboxylic acid
Provided is a copolymer aqueous solution which exerts a high calcium carbonate-deposition suppressing ability even under high hardness condition, has excellent storage stability, and suppresses coloring of a detergent to yellow even when used as a detergent raw material. The water-soluble copolymer aqueous solution includes a water-soluble copolymer and hydrogen peroxide as essential components, in which: the water-soluble copolymer at least includes, as its structure, a structural unit originating from a monoethylenic unsaturated dicarboxylic acid (or dicarboxylate) monomer having 4 to 6 carbon atoms or its anhydride (a) at 30 to 60 mol %, a structural unit originating from a monoethylenic unsaturated monocarboxylic acid (or monocarboxylate) monomer having 3 to 8 carbon atoms (b), and a structural unit originating from a monoethylenic unsaturated monomer having a sulfonic (or sulfonate) group (c); the water-soluble copolymer has a weight average molecular weight of 1,000 or more and 50,000 or less; the water-soluble copolymer aqueous solution has a weight ratio of the hydrogen peroxide of 10 ppm to 50,000 ppm with respect to a solid content of the water-soluble copolymer aqueous solution; and the water-soluble copolymer aqueous solution has a weight ratio of water of 33% to 99%.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
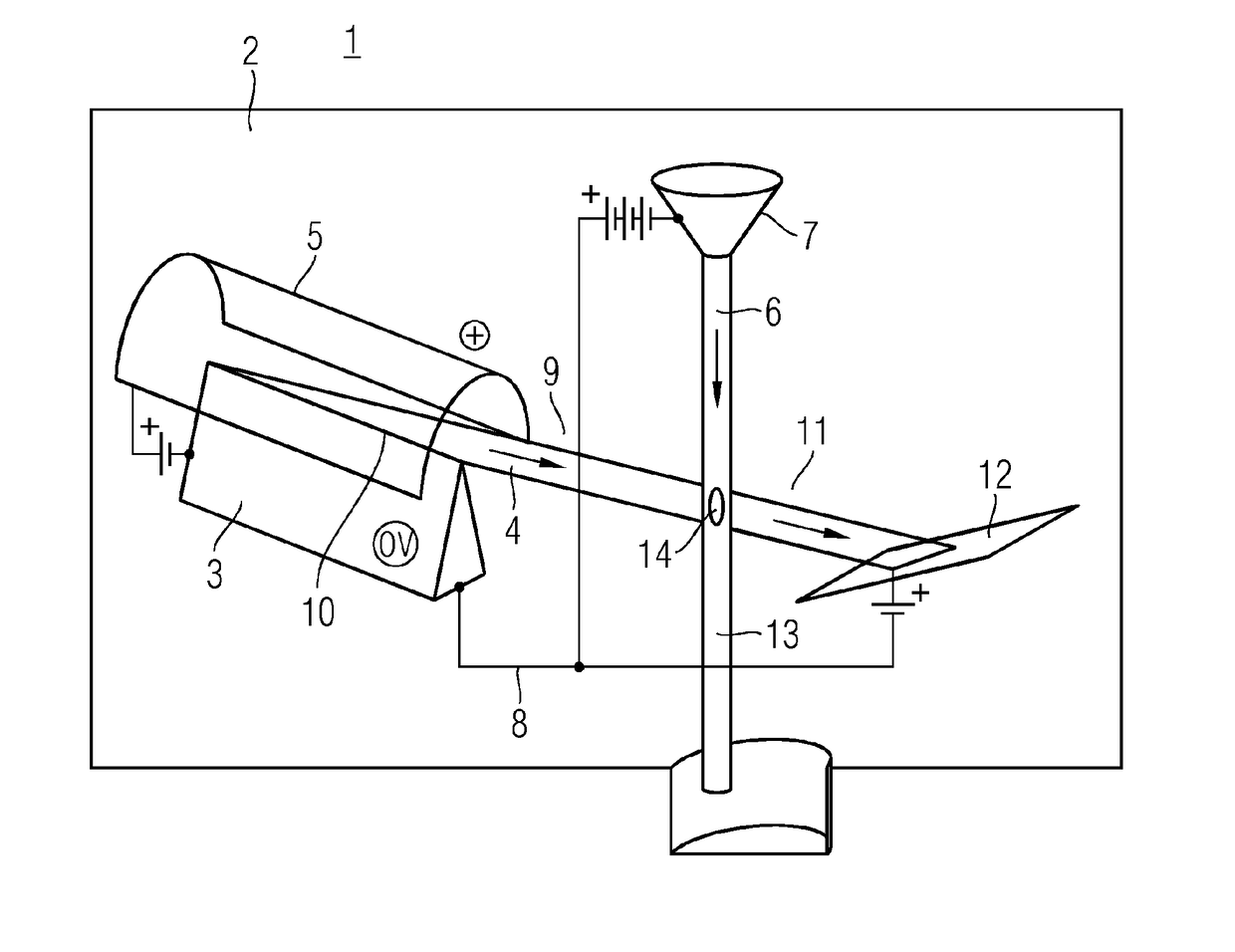
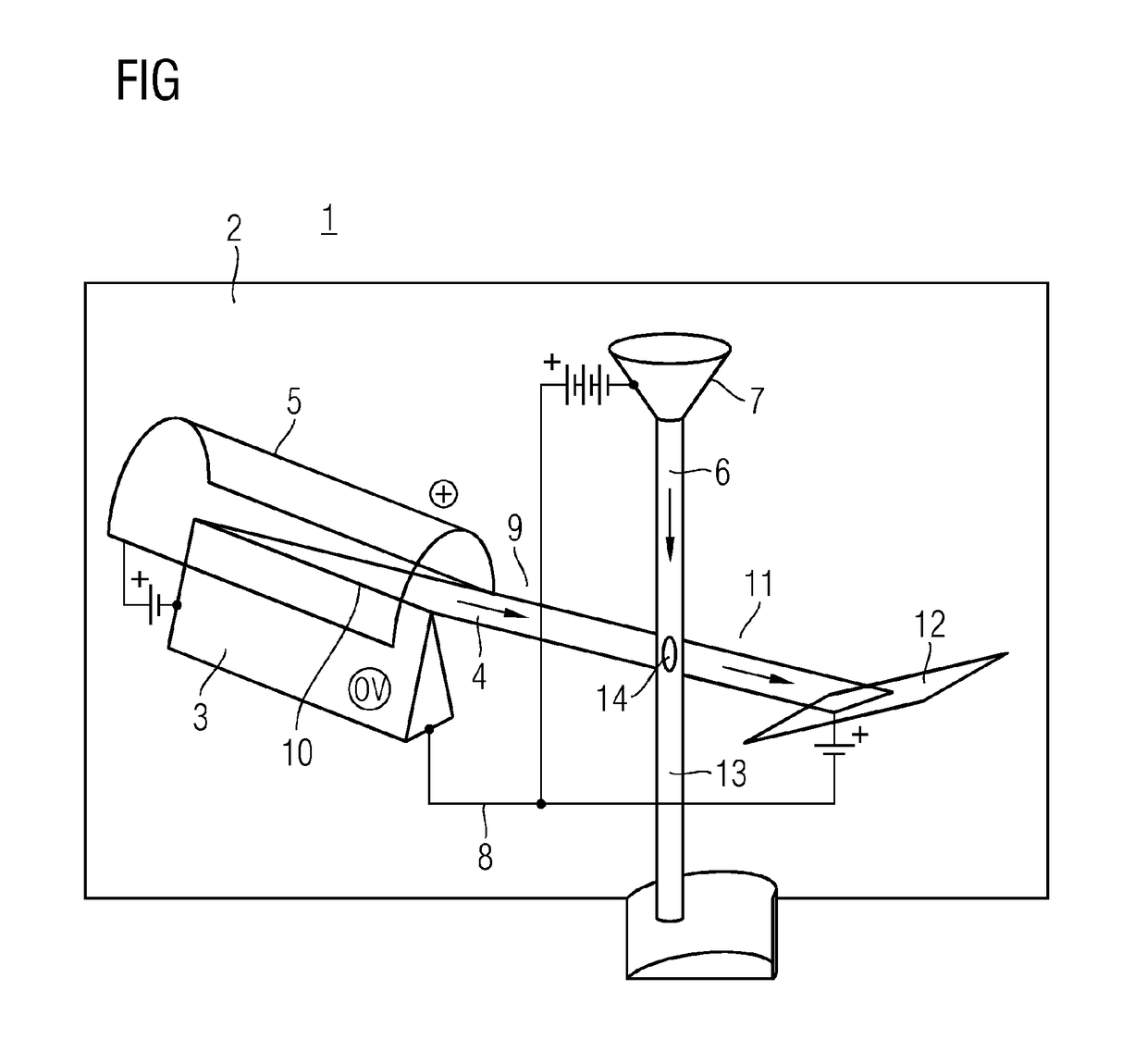
Metal jet x-ray tube
ActiveUS20170345611A1Light production efficiencyImprove efficiencyX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube cold cathodesCold cathodeX-ray
The invention relates to a metal jet x-ray tube which is less affected by the problem of the power density at the point of impact of the electron beam on the anode component than conventional tubes. For this purpose the metal jet x-ray tube has a metal jet (6) as anode component (7), which metal jet is so thin that an electron beam (4) impinging on the metal jet (6) is only partially decelerated by the metal jet. Furthermore a blade cathode is provided as a cathode component (3), which blade cathode comprises a cathode blade (10) directed with a slight inclination downwards in the direction of the liquid metal jet (6) of the anode component (7).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Non-ozone depleting medicinal formulations with low greenhouse effect
InactiveUS20120207685A1Satisfactory uniformity of doseStable suspension formulationsDispersion deliveryAntipyreticMedicineAtmospheric ozone
Pharmaceutical pressurized metered dose inhalers are disclosed having a composition free of CFCs and totally or partially free of HFAs, thus allowing the manufacture of medicinal aerosols without damaging the atmospheric ozone layer and with low or negligible greenhouse effect.
Owner:LAB PABLO CASSARA
Meg recovery apparatus and meg recovery method
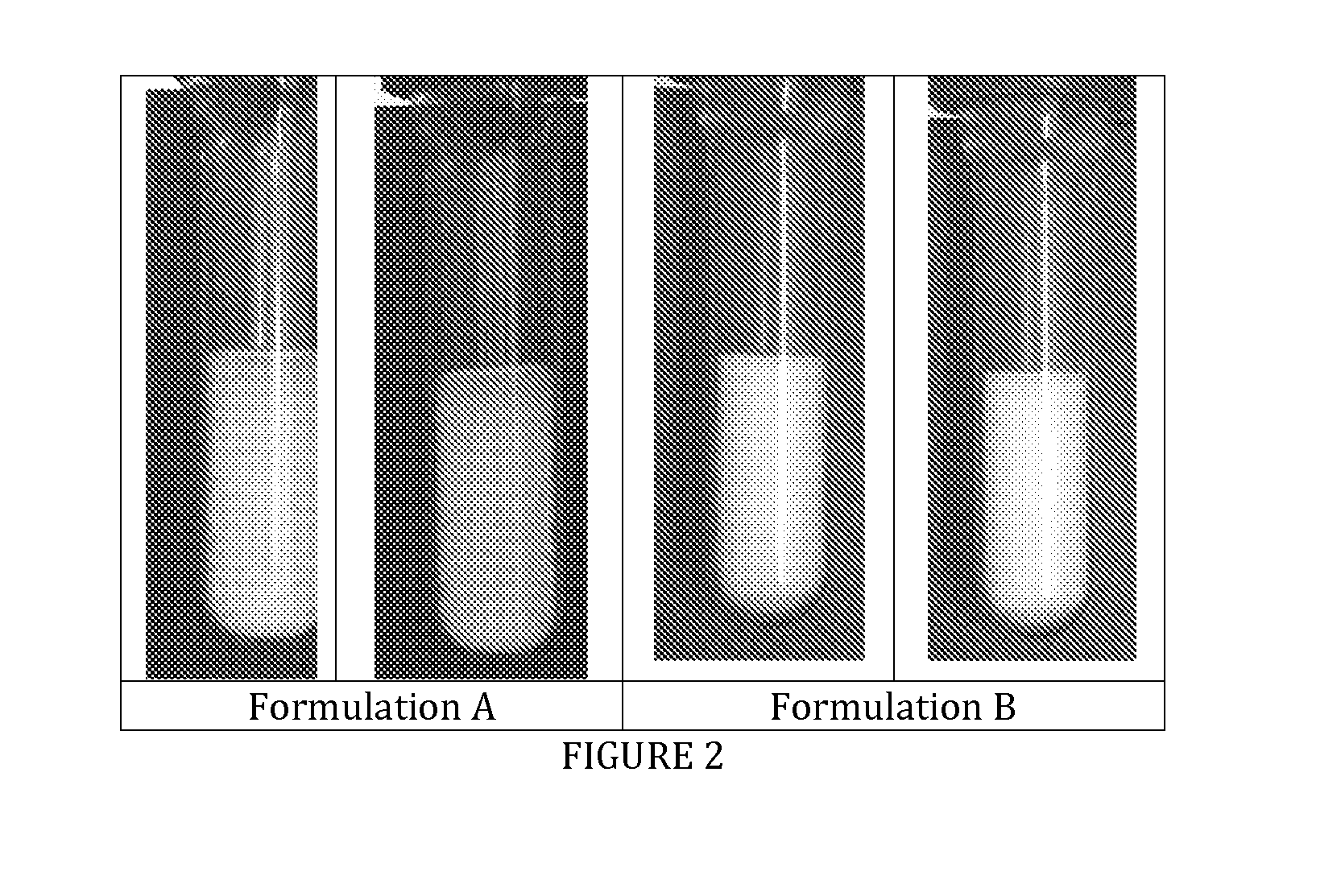
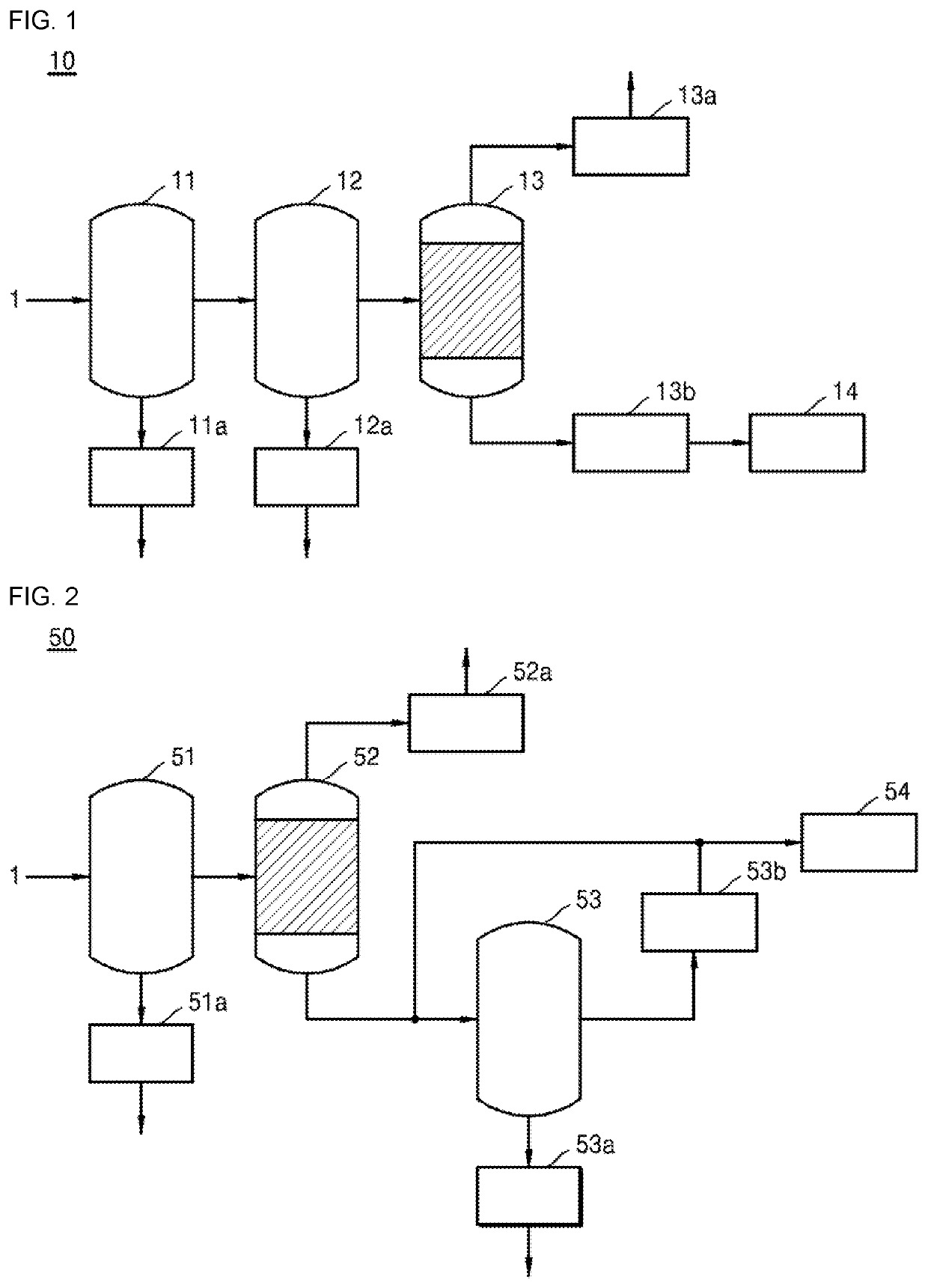
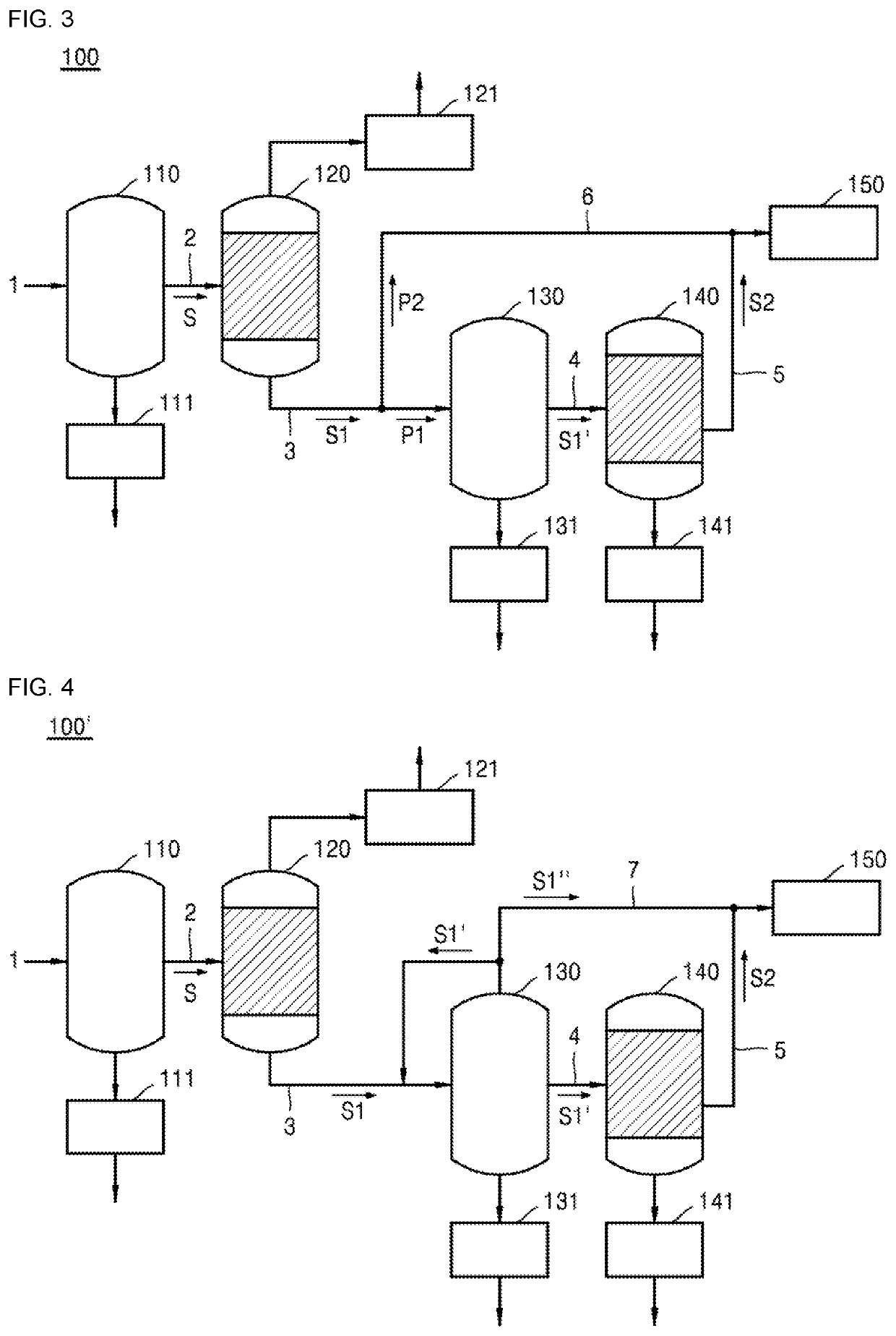
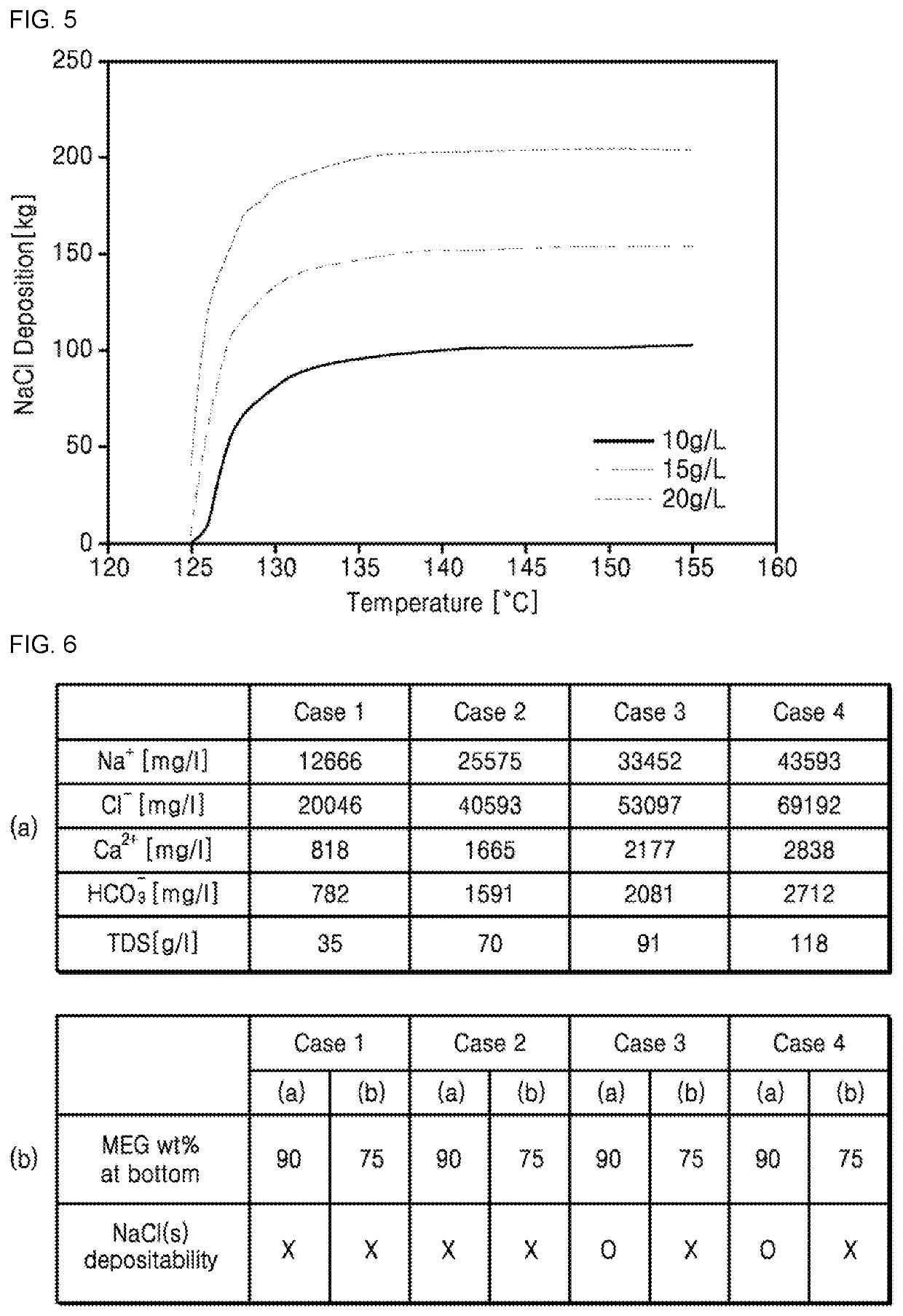
ActiveUS20200078702A1High depositionAvoid depositionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationEnvironmental engineeringGlycol synthesis
Provided are a mono-ethylene glycol (MEG) recovery apparatus and a MEG recovery method. The MEG recovery apparatus includes a pretreater receiving the raw material from a raw material supplier to remove the low soluble salts, a first distiller connected to the pretreater to receive the raw material from which the low soluble salts are removed, and to form a first treated solution by vaporizing a certain amount of the water, a high soluble salt remover connected to the first distiller to remove the high soluble salts from the first treated solution, a second distiller connected to the high soluble salt remover to form a second treated solution by vaporizing the water from the first treated solution from which the high soluble salts are removed, and a recovery unit connected to the second distiller to recover the second treated solution.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Optoelectronic device having a sandwich structure and method for forming the same
ActiveUS8623684B2Improve performanceAvoid damageElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic semiconductorSemiconductor
An optoelectronic device is formed having a sandwich structure, which consists of an inorganic semiconductor layer, an organic semiconductor layer, and another inorganic semiconductor layer, where both of the two inorganic semiconductor layers are produced by a solution process.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
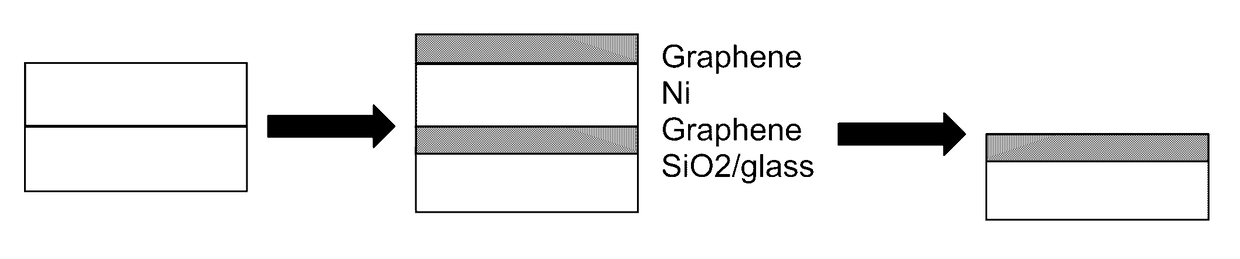
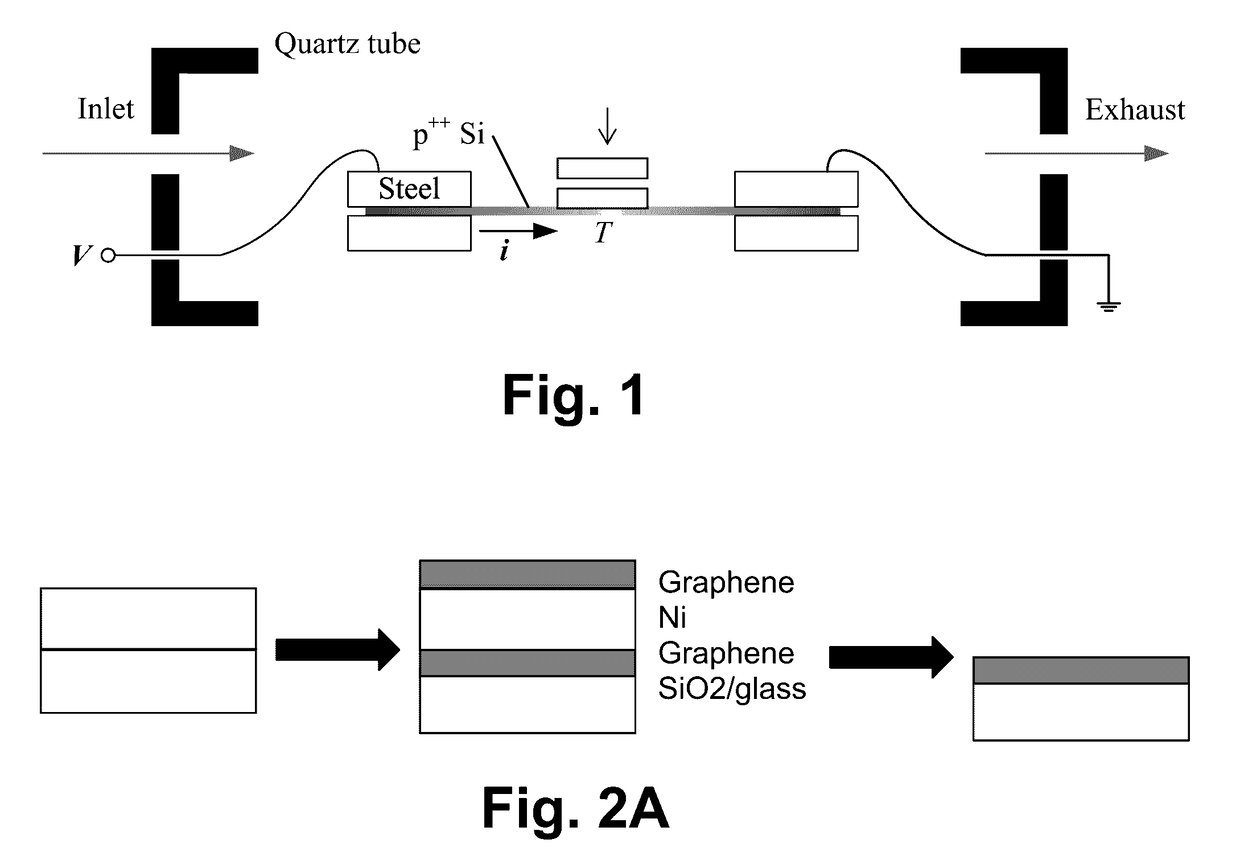
Methods for low-temperature graphene precipitation onto glass, and associated articles/devices
InactiveUS9593019B2Susceptibility to ion diffusionLimited transparencyMaterial nanotechnologyLamination ancillary operationsCvd graphenePrecipitation
Certain example embodiments relate to methods for large area graphene precipitation onto glass, and associated articles / devices. For example, coated articles including graphene-inclusive films on substrates, and / or methods of making the same, are provided. A metal-inclusive catalyst layer (e.g., of or including Ni and / or the like) is disposed on the substrate. The substrate with the catalyst layer thereon is exposed to a precursor gas and a strain-inducing gas at a temperature of no more than 350-600 degrees C. for 10s or 100s of minutes. Graphene is formed and / or allowed to form both over and contacting the catalyst layer, and between the substrate and the catalyst layer, in making the coated article. The catalyst layer, together with graphene formed thereon, is removed, e.g., through excessive strain introduced into the catalyst layer as associated with the graphene formation. Products including such articles, and / or methods of making the same, also are contemplated.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Semiconductor processing system and method
InactiveUS20070020945A1Well controlled thicknessMaintain good propertiesLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringSemiconductor
Systems and methods are disclosed to perform semiconductor processing with a process chamber; a flash lamp adapted to be repetitively triggered; and a controller coupled to the control input of the flash lamp to trigger the flash lamp. The system can deploy a solid state plasma source in parallel with the flash lamp in wafer processing.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
System and method for semiconductor processing
ActiveUS20070020898A1Well control thicknessHigh precisionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlash-lampEngineering
Systems and methods are disclosed to perform semiconductor processing with a process chamber; a flash lamp adapted to be repetitively triggered; and a controller coupled to the control input of the flash lamp to trigger the flash lamp. The system can deploy a solid state plasma source in parallel with the flash lamp in wafer processing.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Optoelectronic device having a sandwich structure and method for forming the same
ActiveUS20110127494A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove performanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic semiconductorSemiconductor
An optoelectronic device is formed having a sandwich structure, which consists of an inorganic semiconductor layer, an organic semiconductor layer, and another inorganic semiconductor layer, where both of the two inorganic semiconductor layers are produced by a solution process.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Process for the deposition of uniform layer of particulate material
InactiveUS7223445B2High depositionIncrease speedElectric shock equipmentsPretreated surfacesSolubilityChemical physics
A process for the deposition of particulate material of a desired substance on a surface includes: (i) charging a particle formation vessel with a compressed fluid; (ii) introducing into the particle formation vessel a first feed stream comprising a solvent and the desired substance dissolved therein and a second feed stream comprising the compressed fluid, wherein the desired substance is less soluble in the compressed fluid relative to its solubility in the solvent and the solvent is soluble in the compressed fluid, and wherein the first feed stream is dispersed in the compressed fluid, allowing extraction of the solvent into the compressed fluid and precipitation of particles of the desired substance; (iii) exhausting compressed fluid, solvent and the desired substance from the particle formation vessel at a rate substantially equal to the rate of addition of such components to the vessel in step (ii) through a restrictive passage to a lower pressure whereby the compressed fluid is transformed to a gaseous state and a flow of particles of the desired substance is formed; and (iv) exposing a receiver surface to the exhausted flow of particles of the desired substance and depositing a uniform layer of particles on the receiver surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com