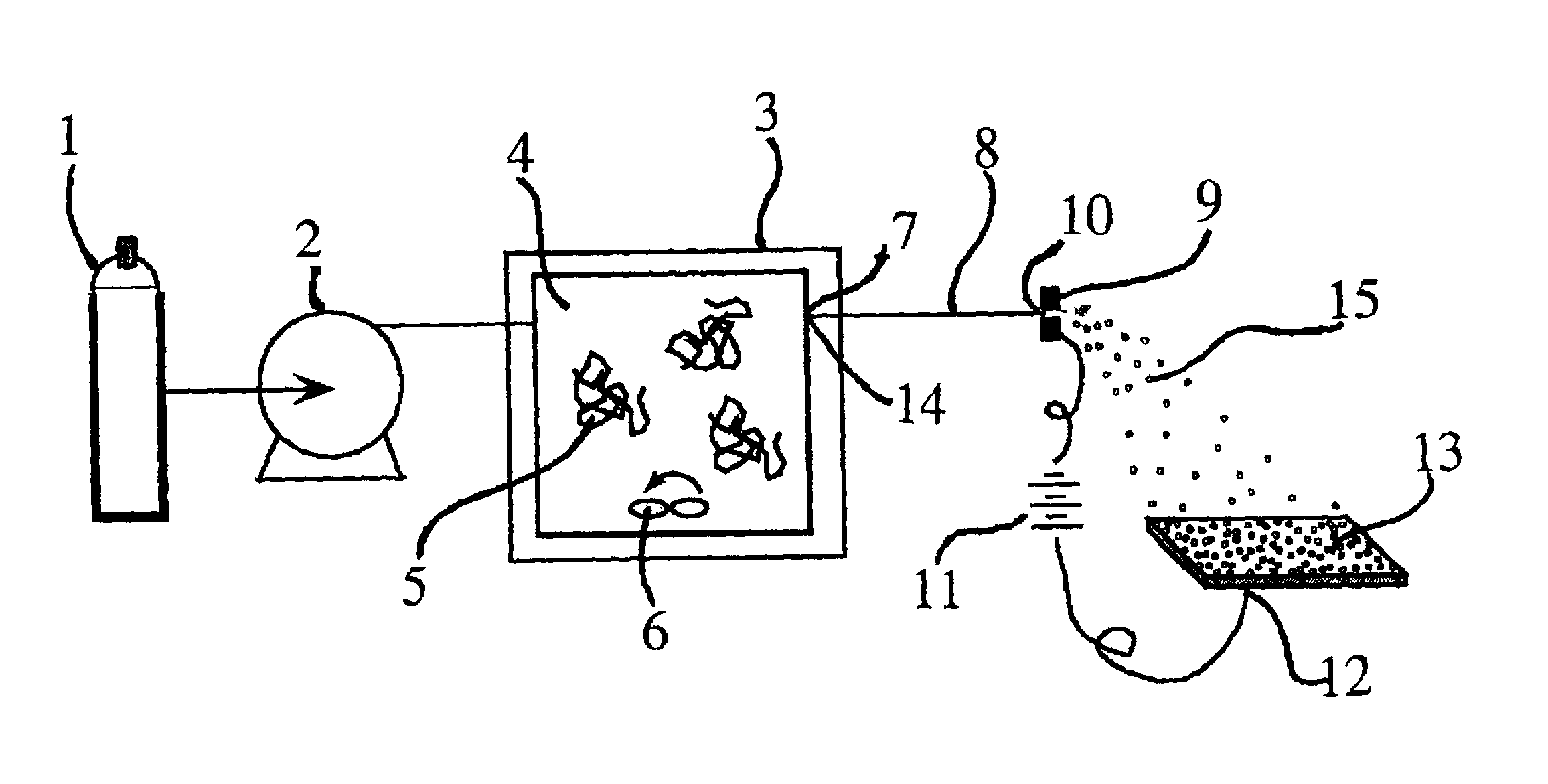
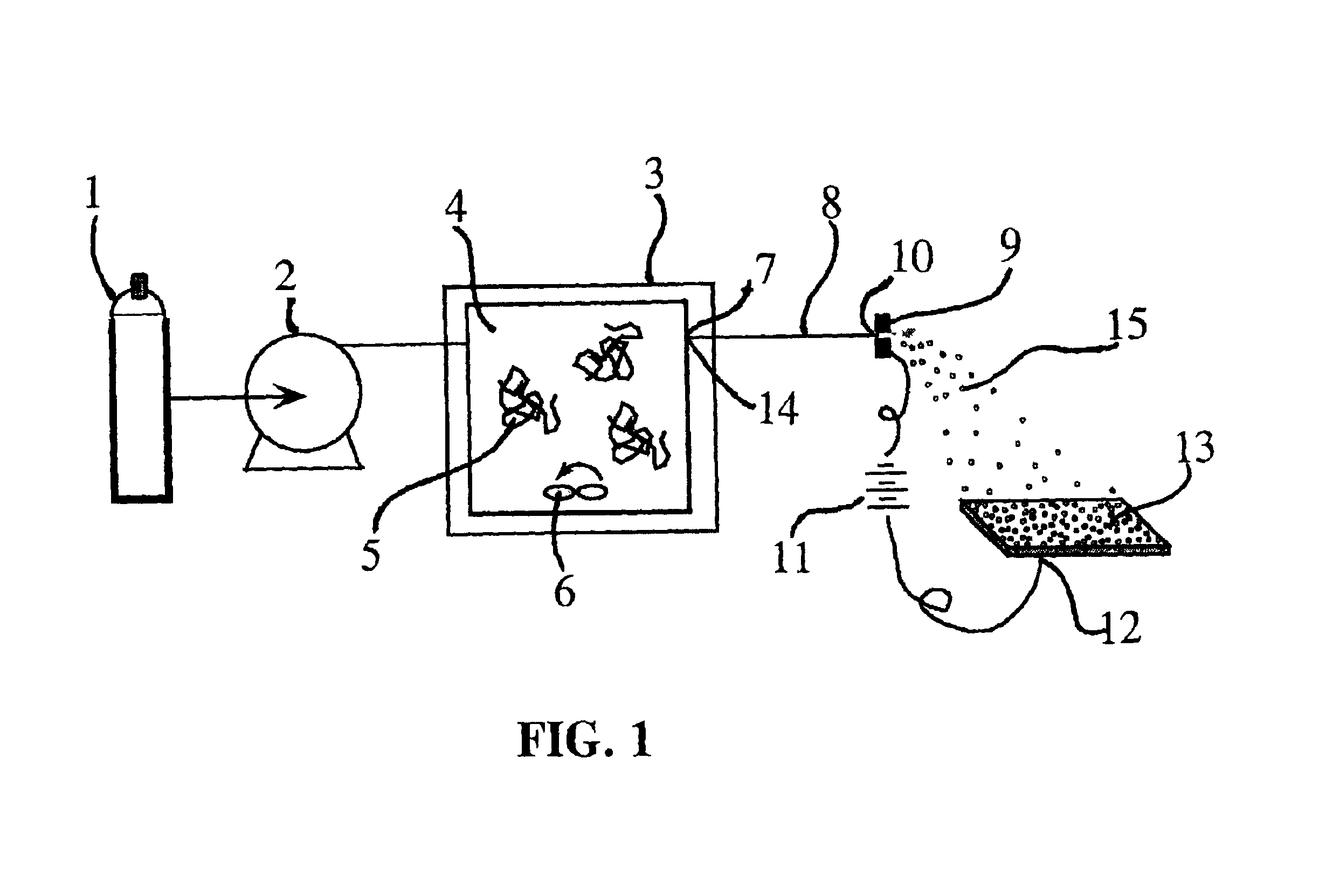
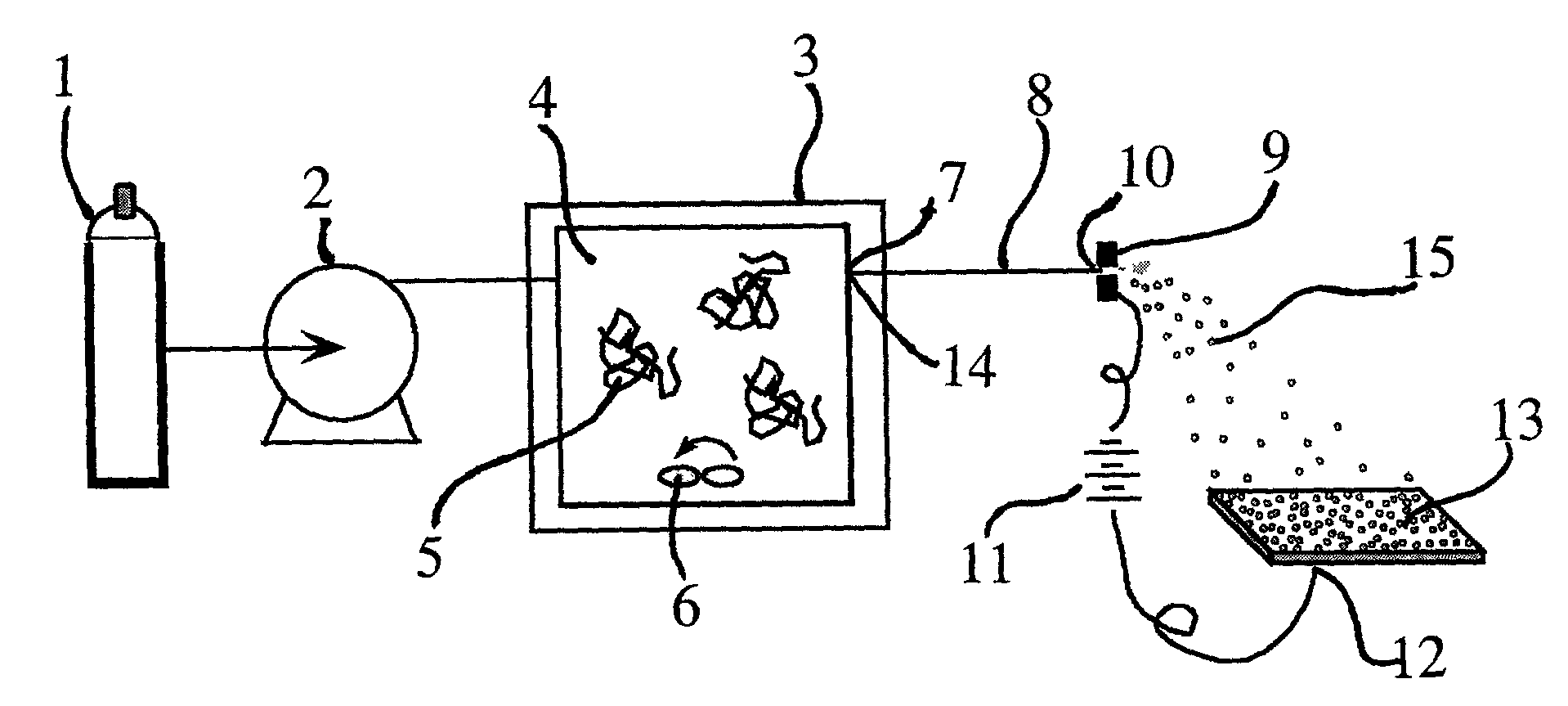
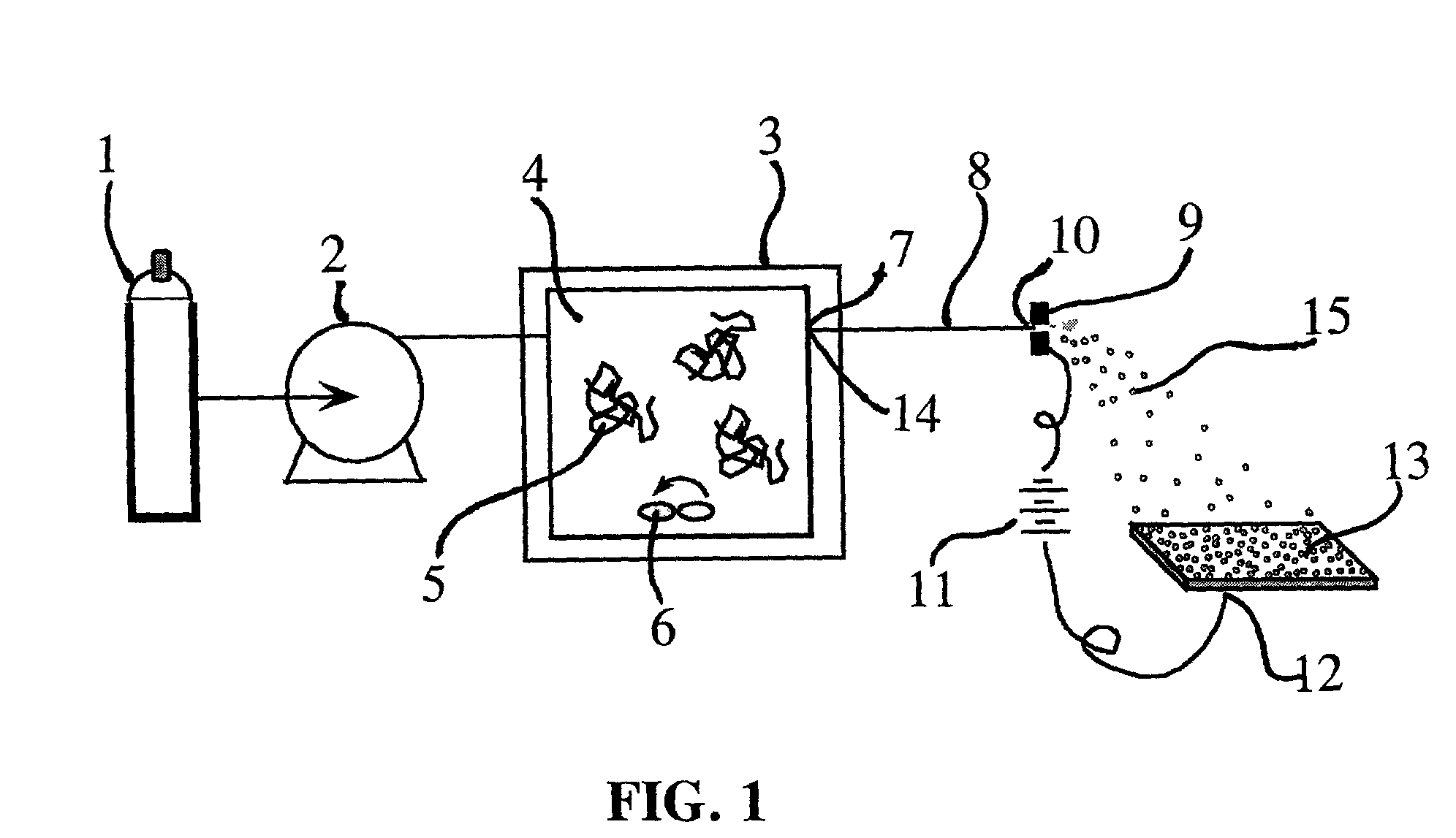
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
529 results about "Compressed fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A compressed fluid (also called a compressed or unsaturated liquid, subcooled fluid or liquid) is a fluid under mechanical or thermodynamic conditions that force it to be a liquid. At a given pressure, a fluid is a compressed fluid if it is at a temperature lower than the saturation temperature. This is the case, for example, for liquid water at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. In a plot that compares pressure and specific volume (commonly called a p-v diagram), compressed fluid is the state to the left of the saturation curve.
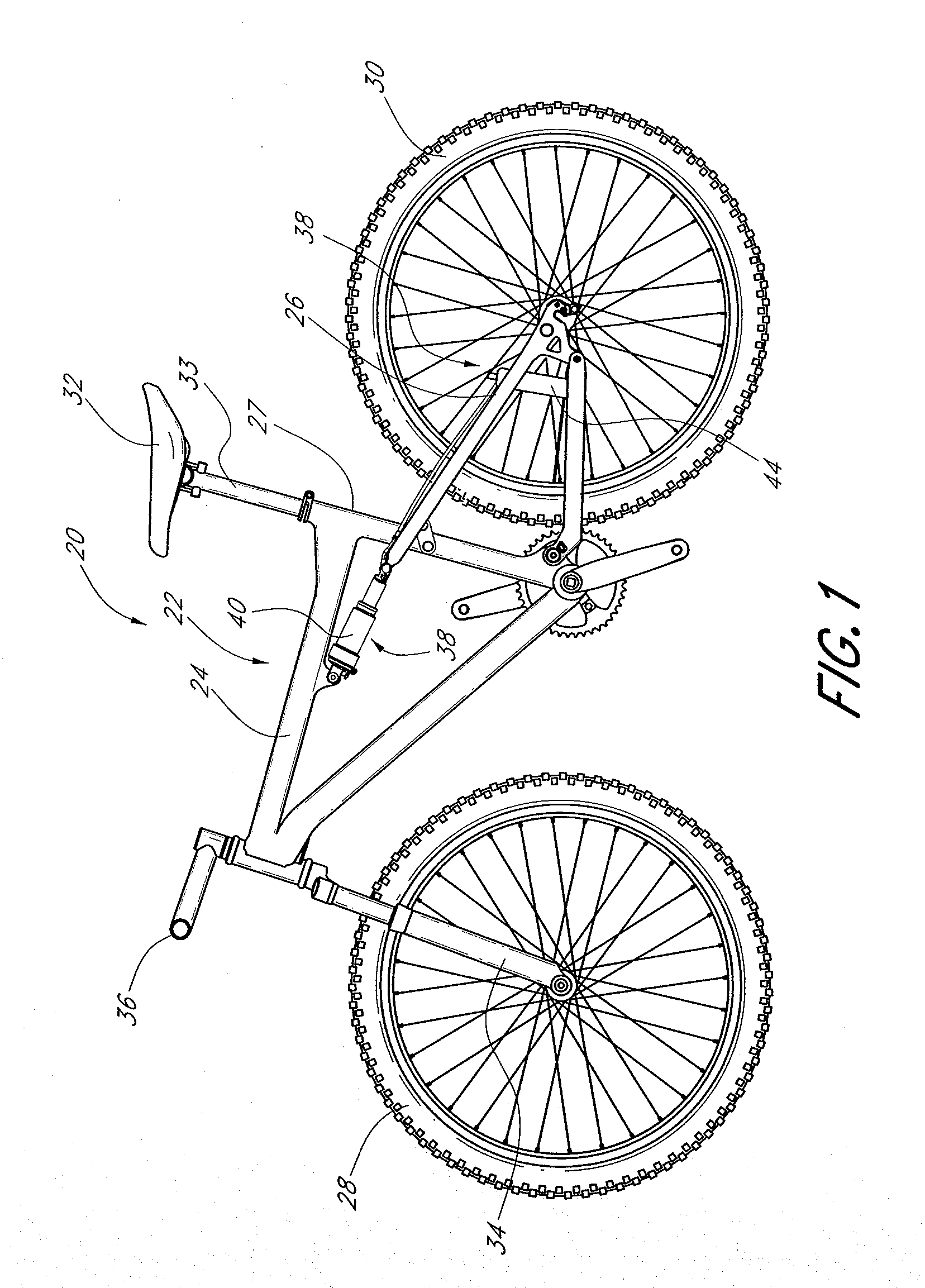
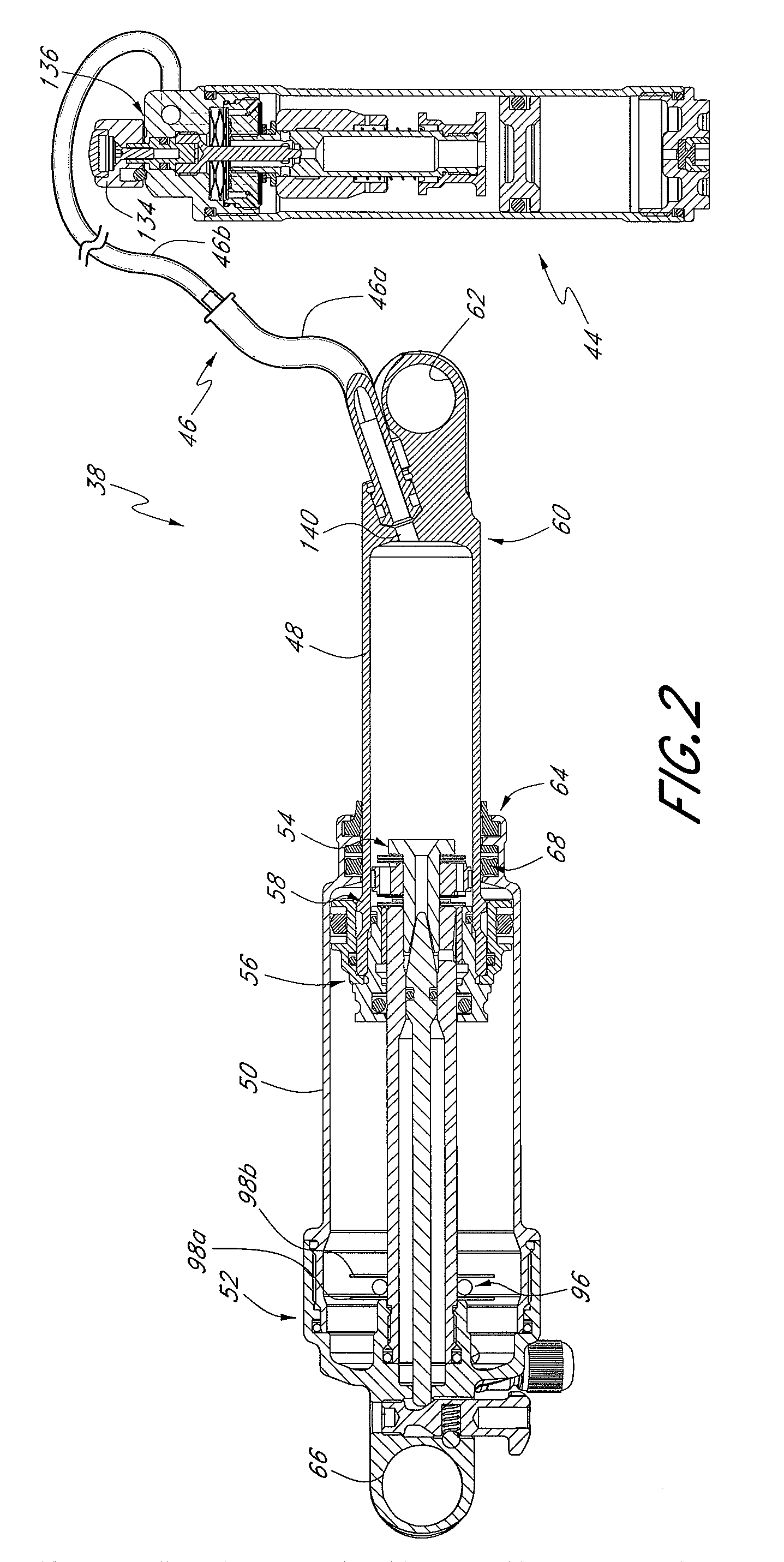
Bicycle damping enhancement system
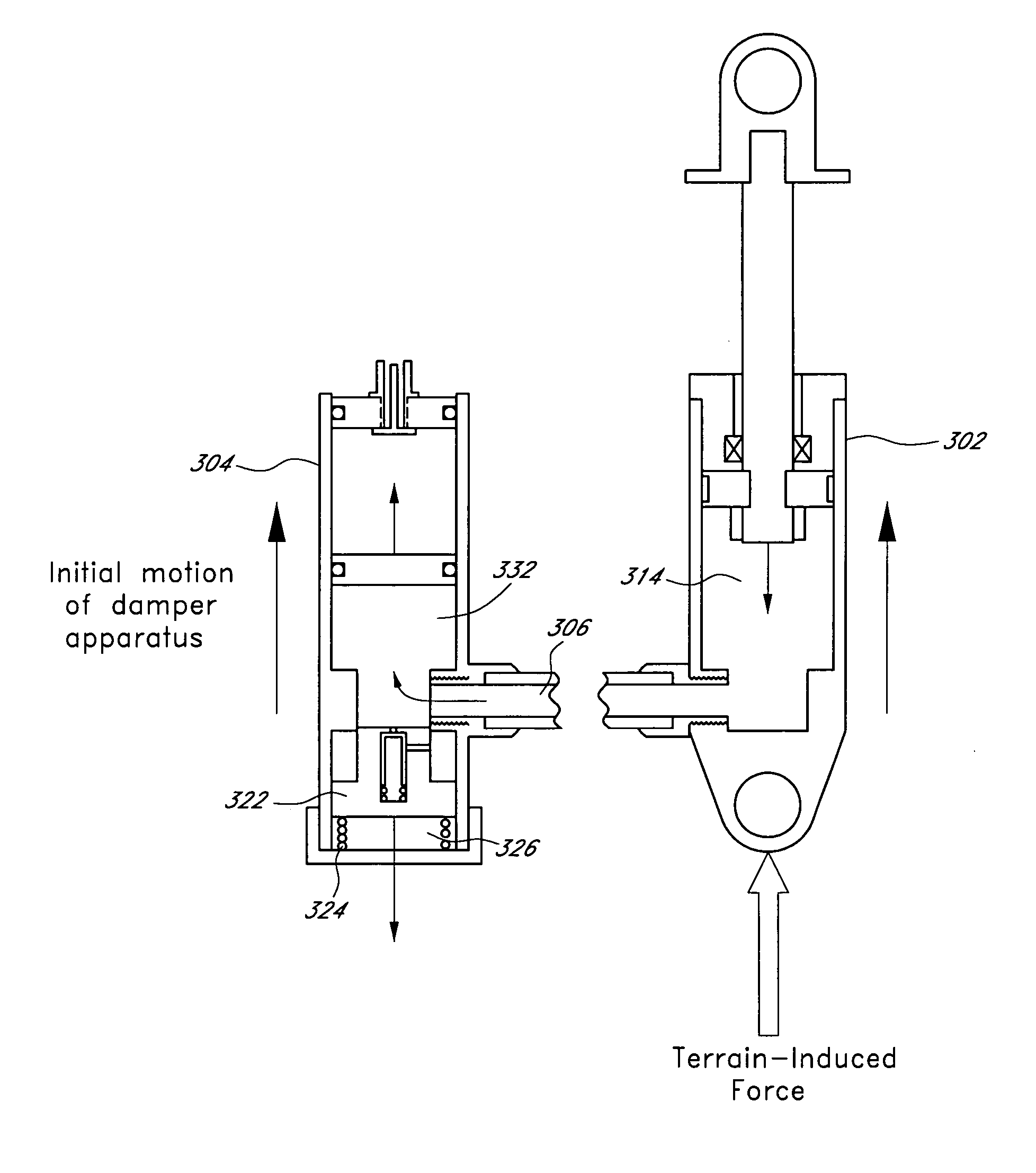
A bicycle shock absorber for differentiating between rider-induced forces and terrain-induced forces includes a first fluid chamber having fluid contained therein, a piston for compressing the fluid within the fluid chamber, a second fluid chamber coupled to the first fluid chamber by a fluid communication hose, and an inertial valve disposed within the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve opens in response to terrain-induced forces and provides communication of fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve does not open in response to rider-induced forces and prevents communication of the fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
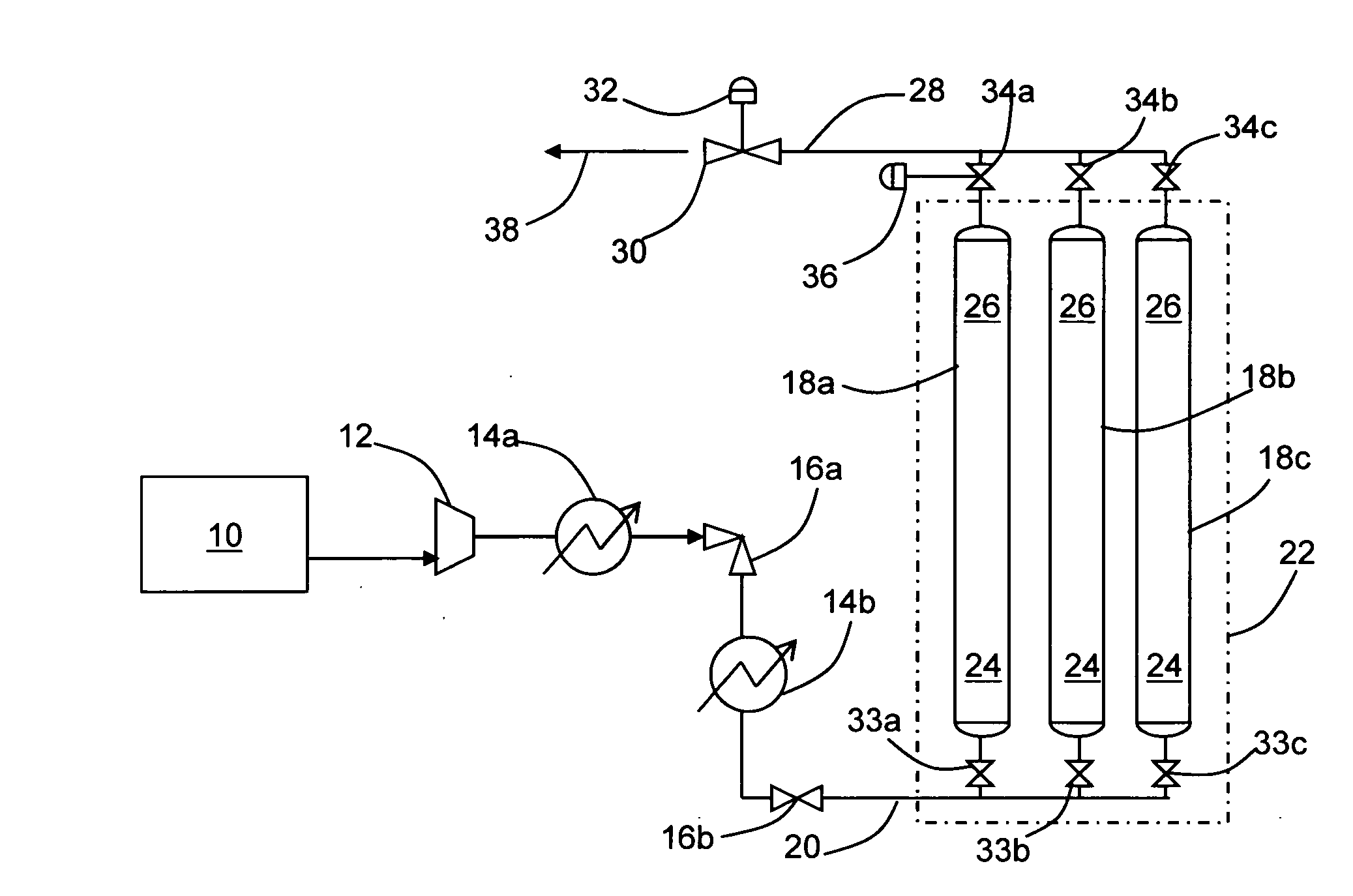
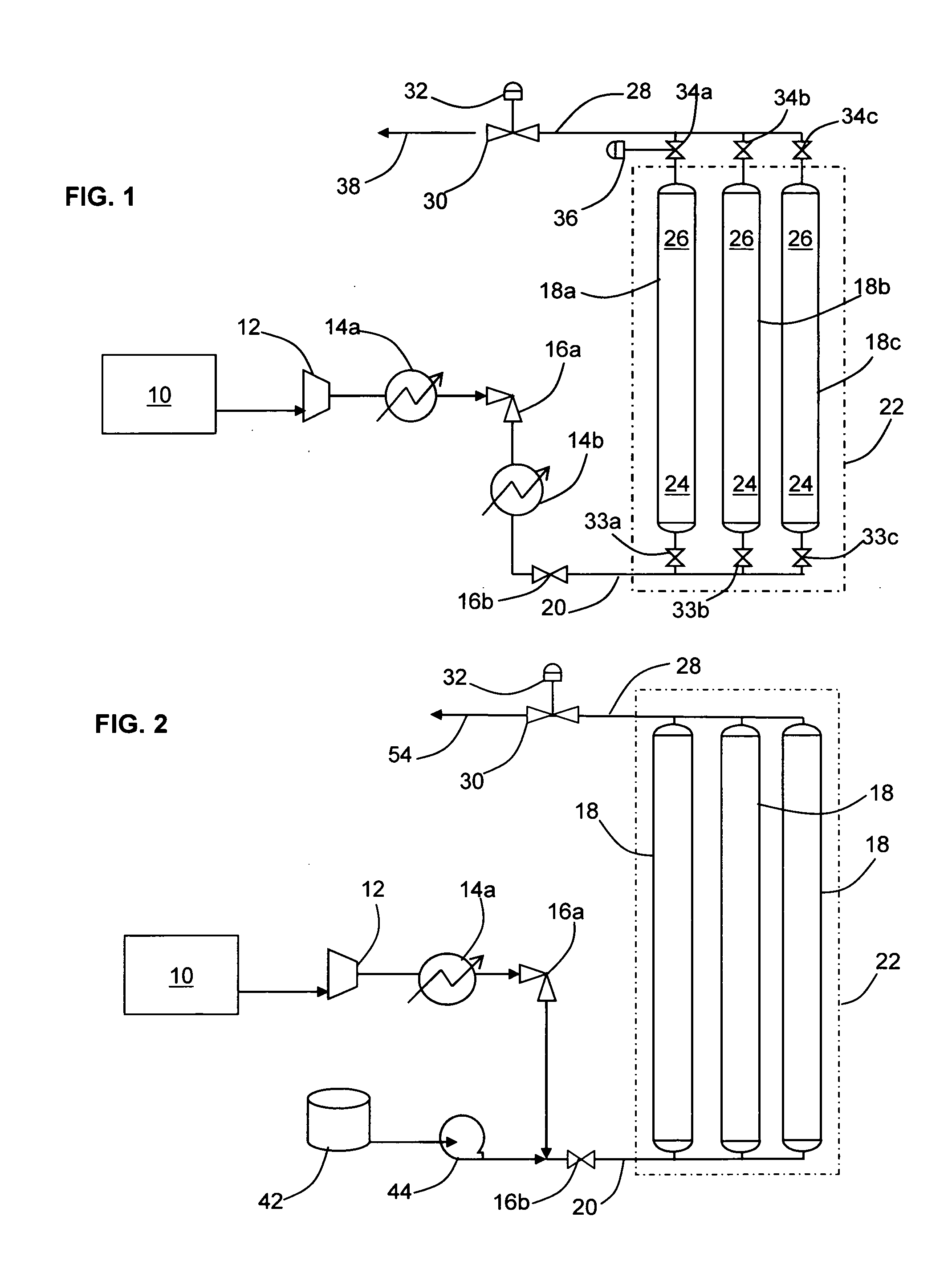
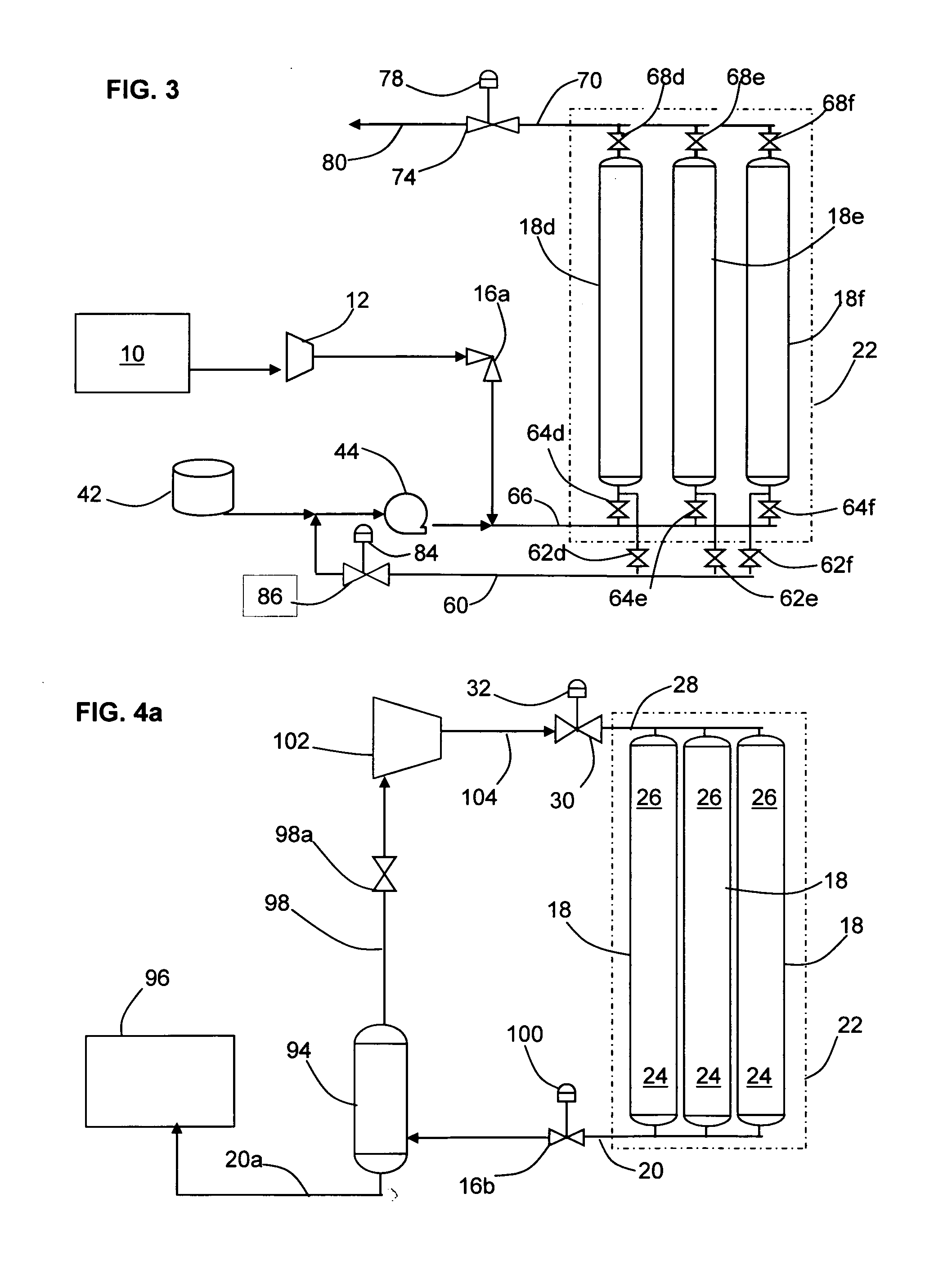
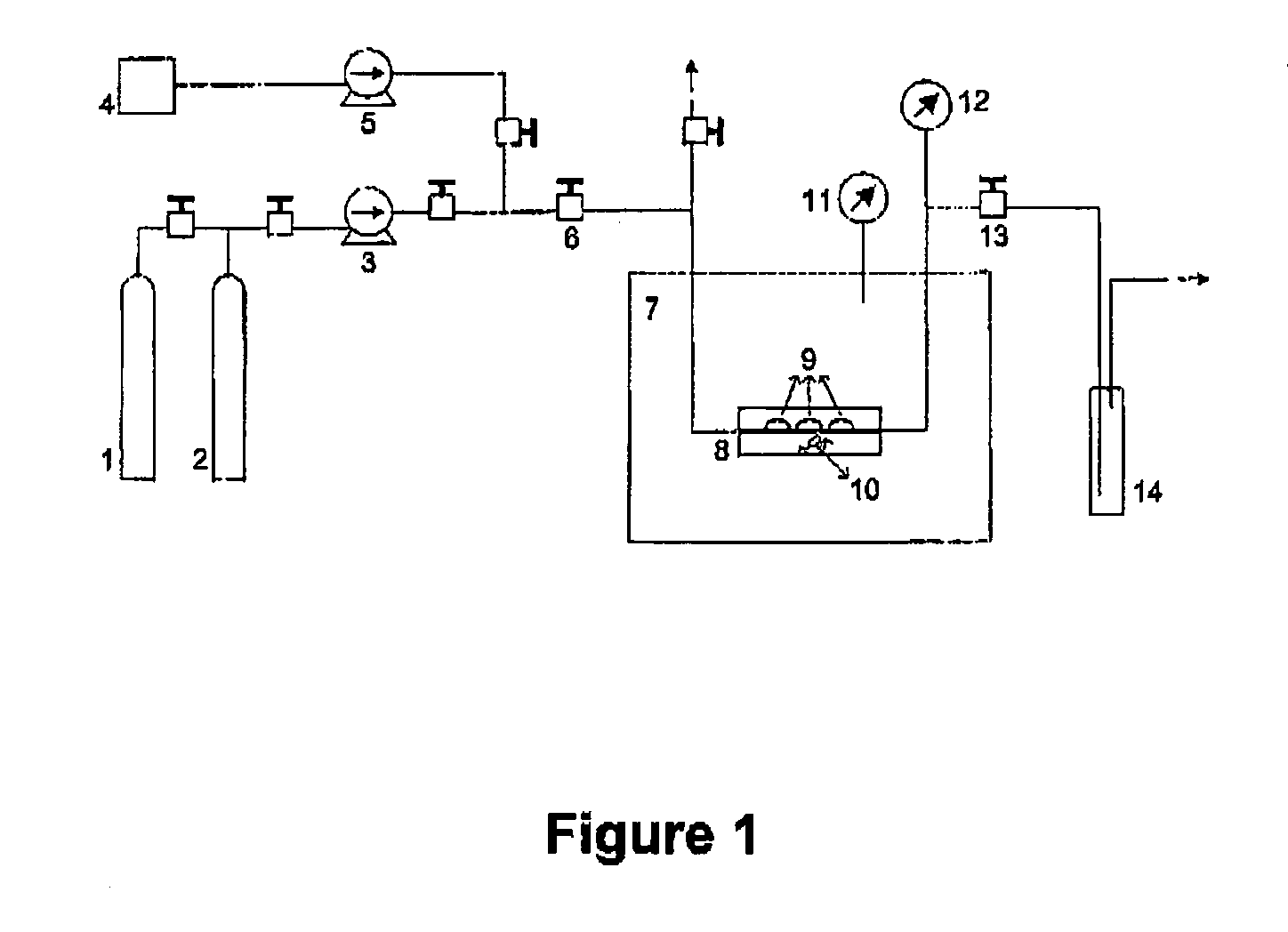
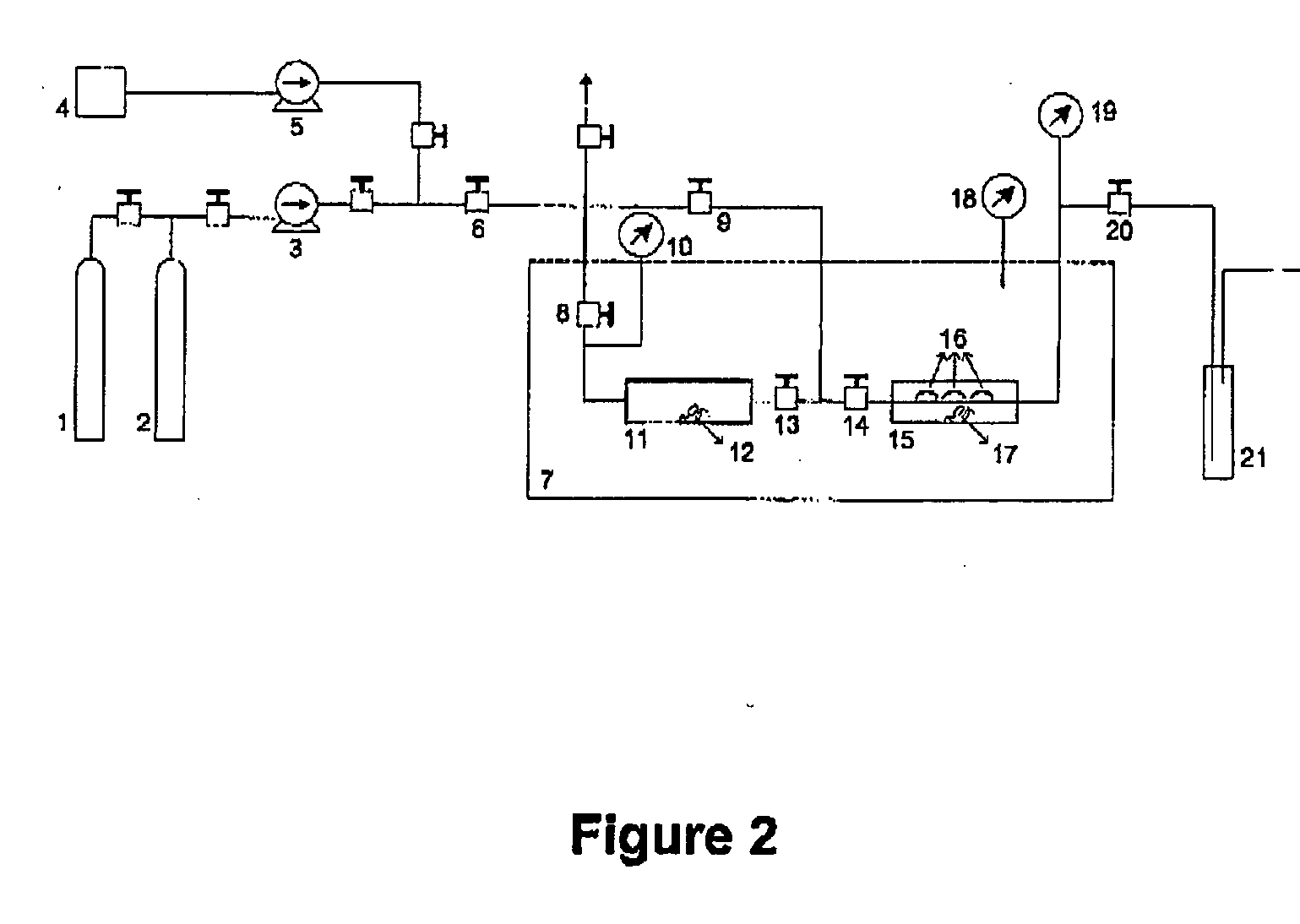
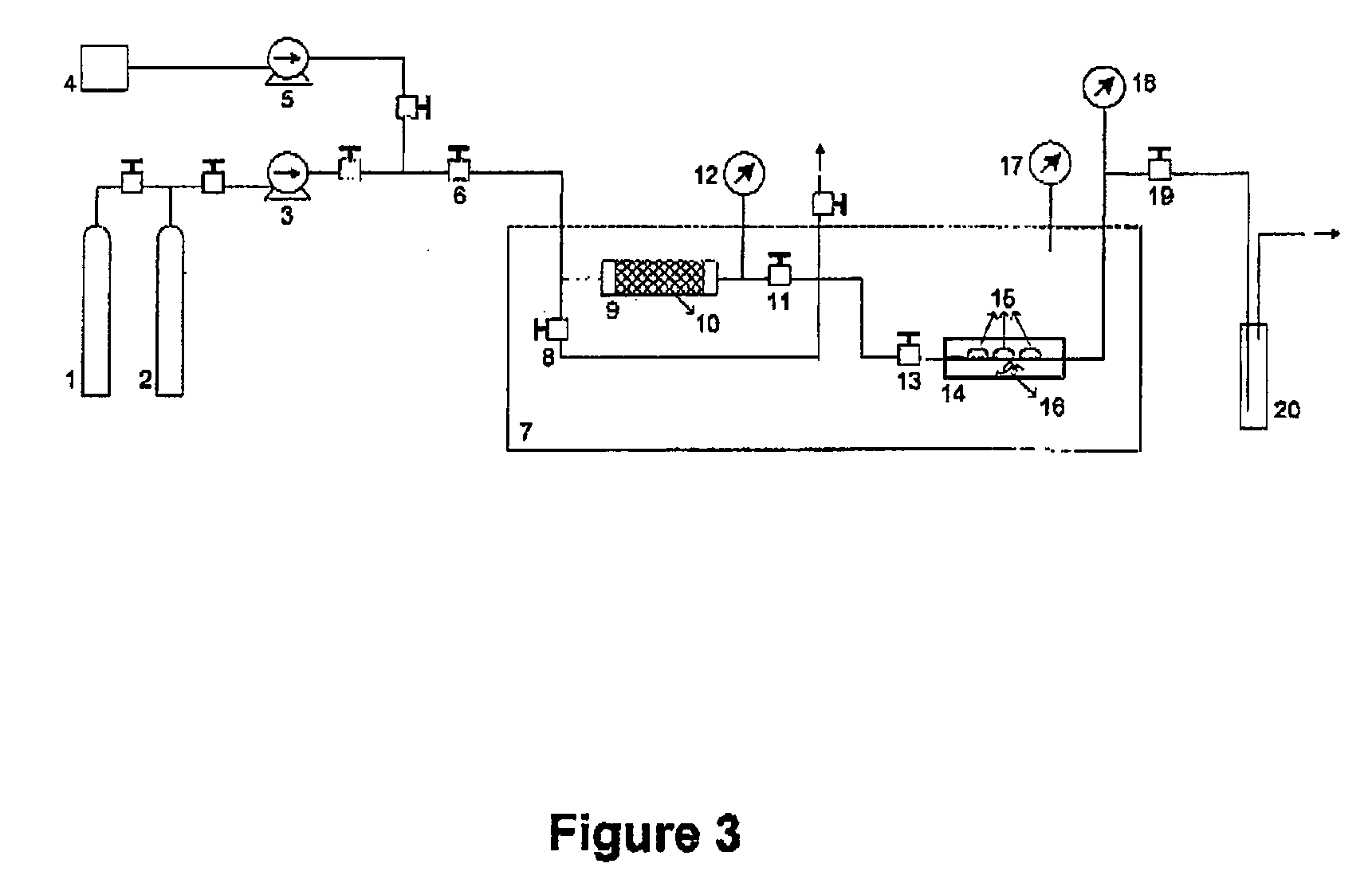
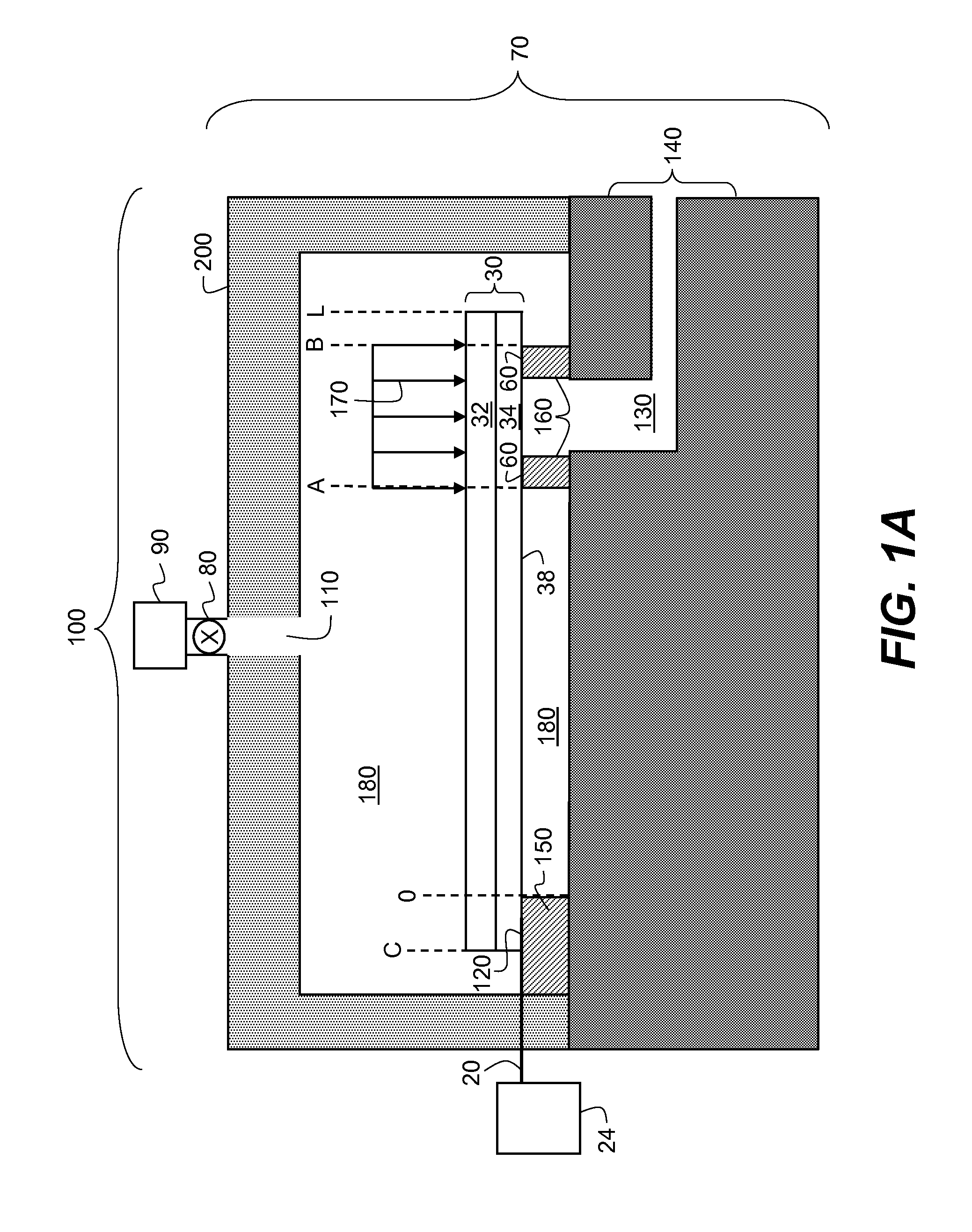
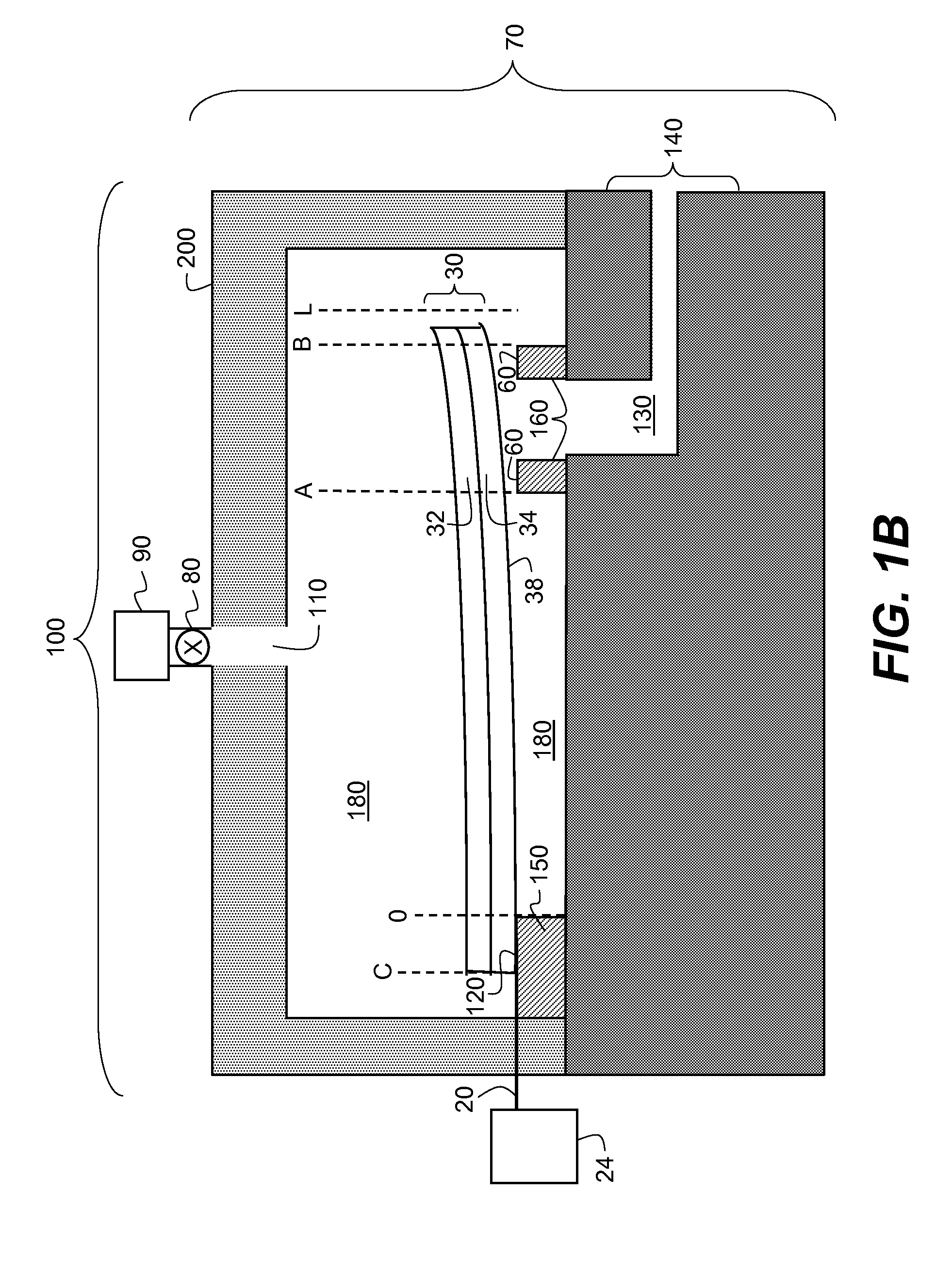
Apparatus and method for flowing compressed fluids into and out of containment
ActiveUS20080209916A1Adjustable temperatureGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsChemical compositionCompressed fluid
Methods for loading a compressed fluid, such as natural gas, into and discharging the compressed fluid out of containment are provided. The compressed fluid is injected into a bottom portion of a container system for storage and / or transport until a target pressure is reached after which gas is withdrawn from an upper portion of the container system at a rate to maintain the target pressure while the compressed fluid is injected in the bottom portion. The compressed fluid is cooled through an expansion valve and by refrigerated chillers or by injecting a cold liquid of the same chemical composition as the compressed fluid, such as liquid natural gas, into the compressed fluid prior to injection into the container system. Withdrawal or discharge from the container system to a receiving facility begins with blow down from the bottom portion of the container system without a displacement fluid and continues until pressure falls below an acceptable differential pressure. The discharge stream is passed through a separator and a light gas from the separator is pressurized and injected into an upper portion of the container system to drive the compressed fluid out the bottom. The light gas is pressurized using either a compressor or a heated tank system, where two vessels operate in parallel, trapping and heating the light gas and then discharging to the container system from one while filling the other and alternating the operation between the two.
Owner:WHITE CHARLES N +1
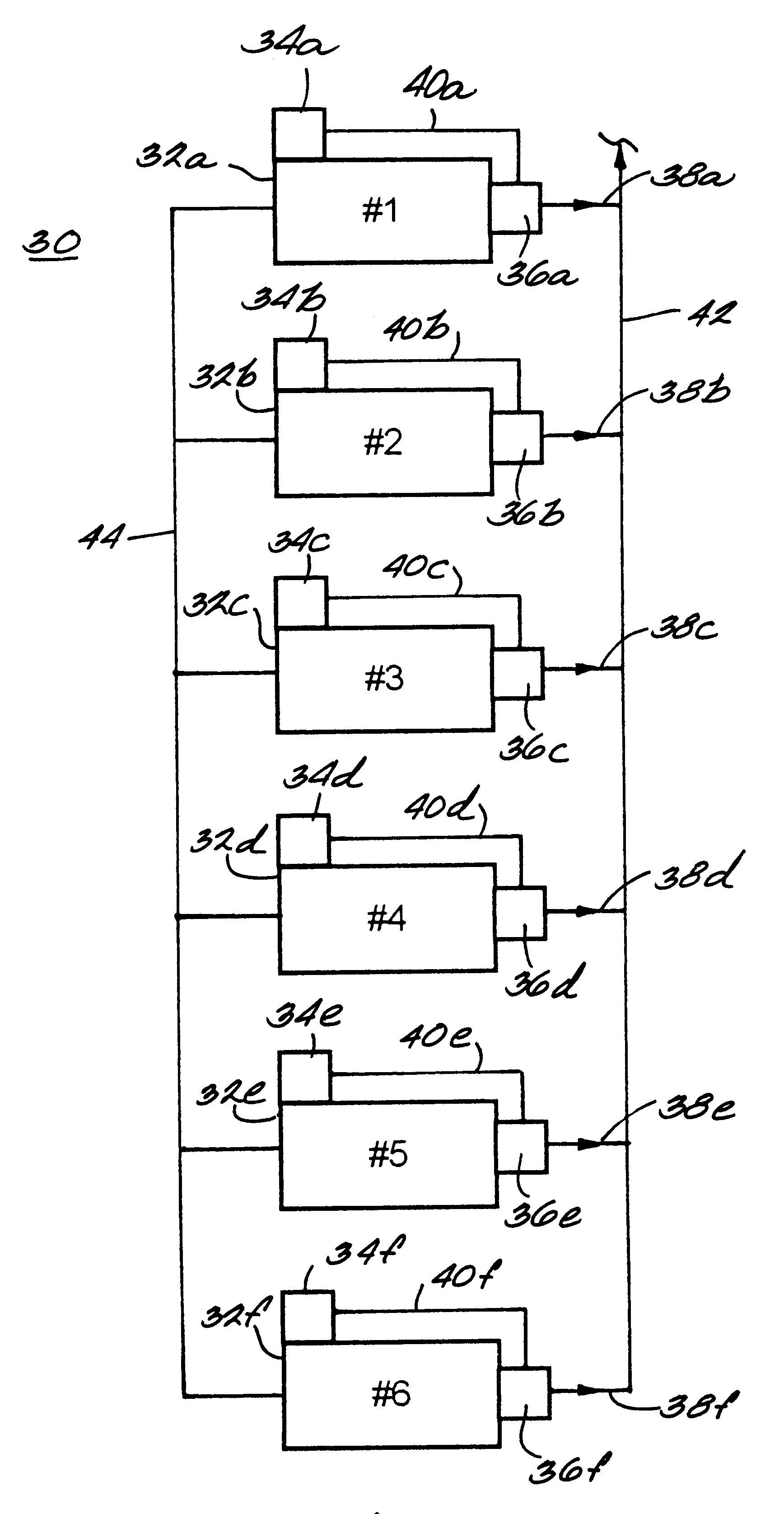
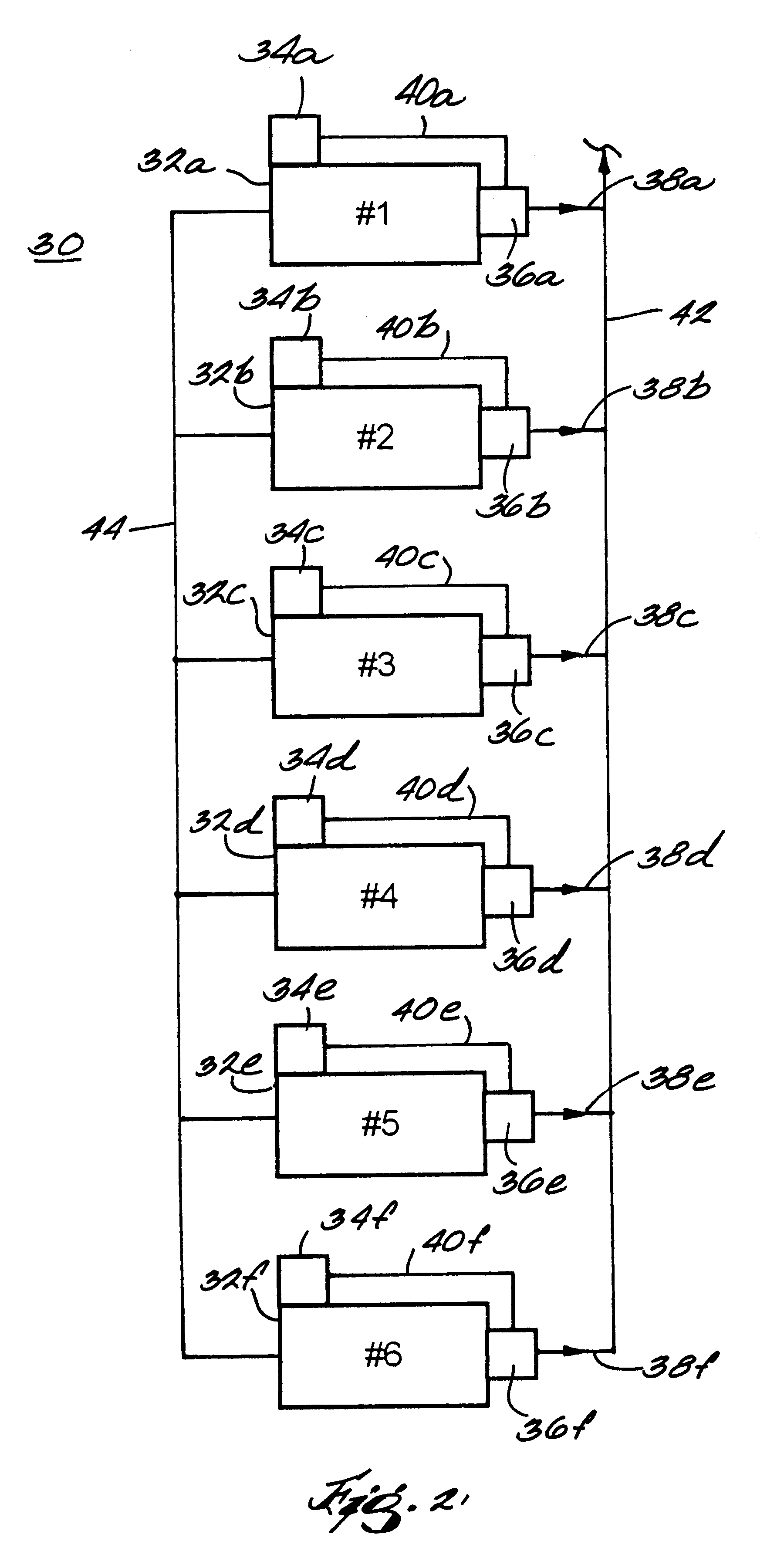
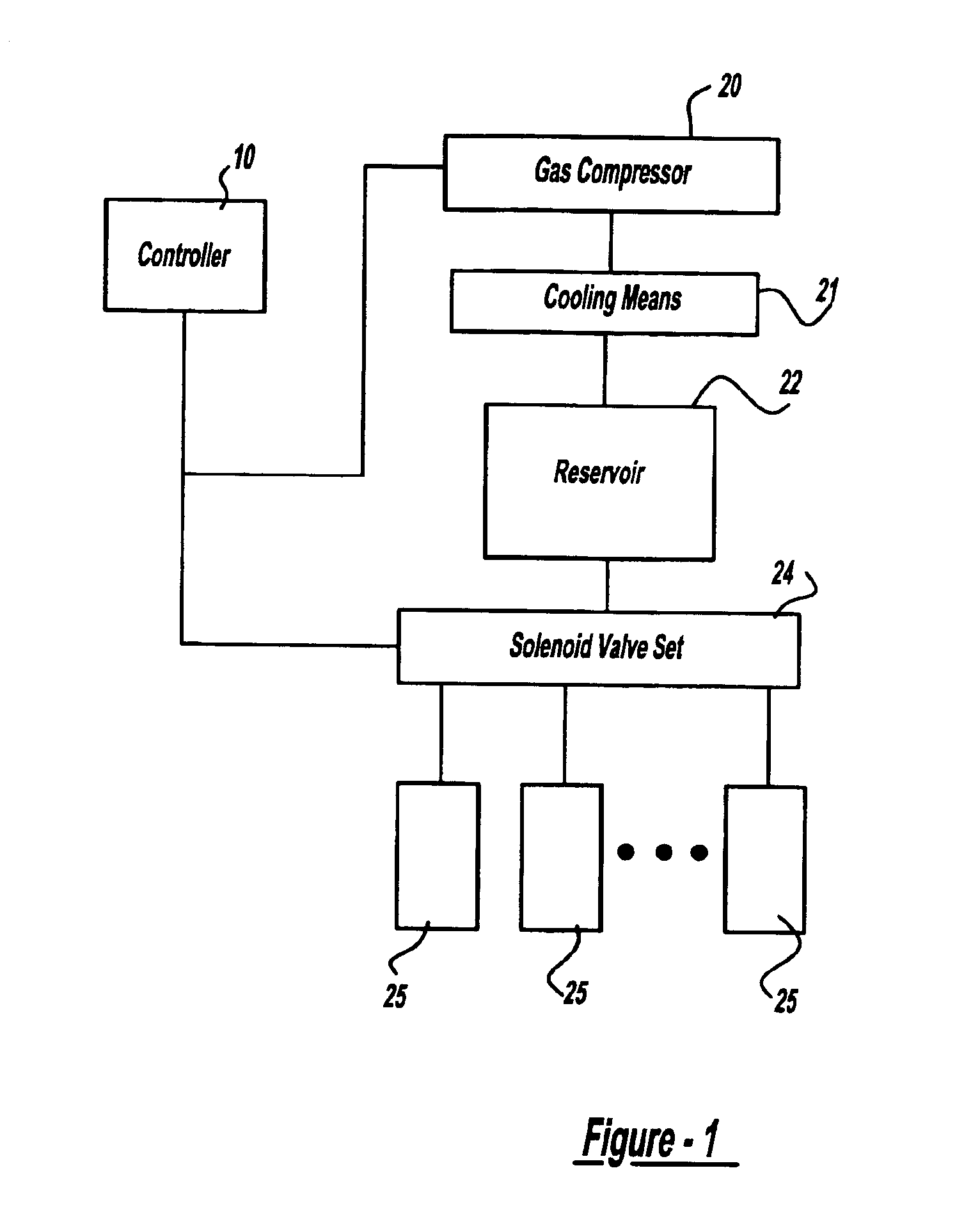
Method for controlling the operation of a compression system having a plurality of compressors
InactiveUS6233954B1Space heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsCompressed fluidRanking
A fluid compression system includes a plurality of compressors, each compressor having a local controller for controlling operation thereof and a sensor for sensing the pressure of compressed fluid discharged therefrom. A method for controlling operation of the fluid compression system includes establishing a set point pressure threshold for loading and unloading each compressor, and assigning a ranking to each compressor for identifying a highest ranked compressor and a lowest ranked compressor, whereby the highest ranked compressor for the compression system initiates all commands for controlling all of the lower ranked compressors in the compression system. The method also includes commencing a loading subroutine including loading the highest ranked unloaded compressor, setting a load delay timer, sensing the pressure of the compressed fluid discharged from the highest ranked compressor, comparing the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and transmitting a load command from the controller of the highest ranked compressor to the controller of the next highest ranked unloaded compressor if the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor remains less than or equal to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and the load delay timer equals zero. The loading subroutine is repeated until the discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor is greater than the set point pressure threshold established therefor.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND CO
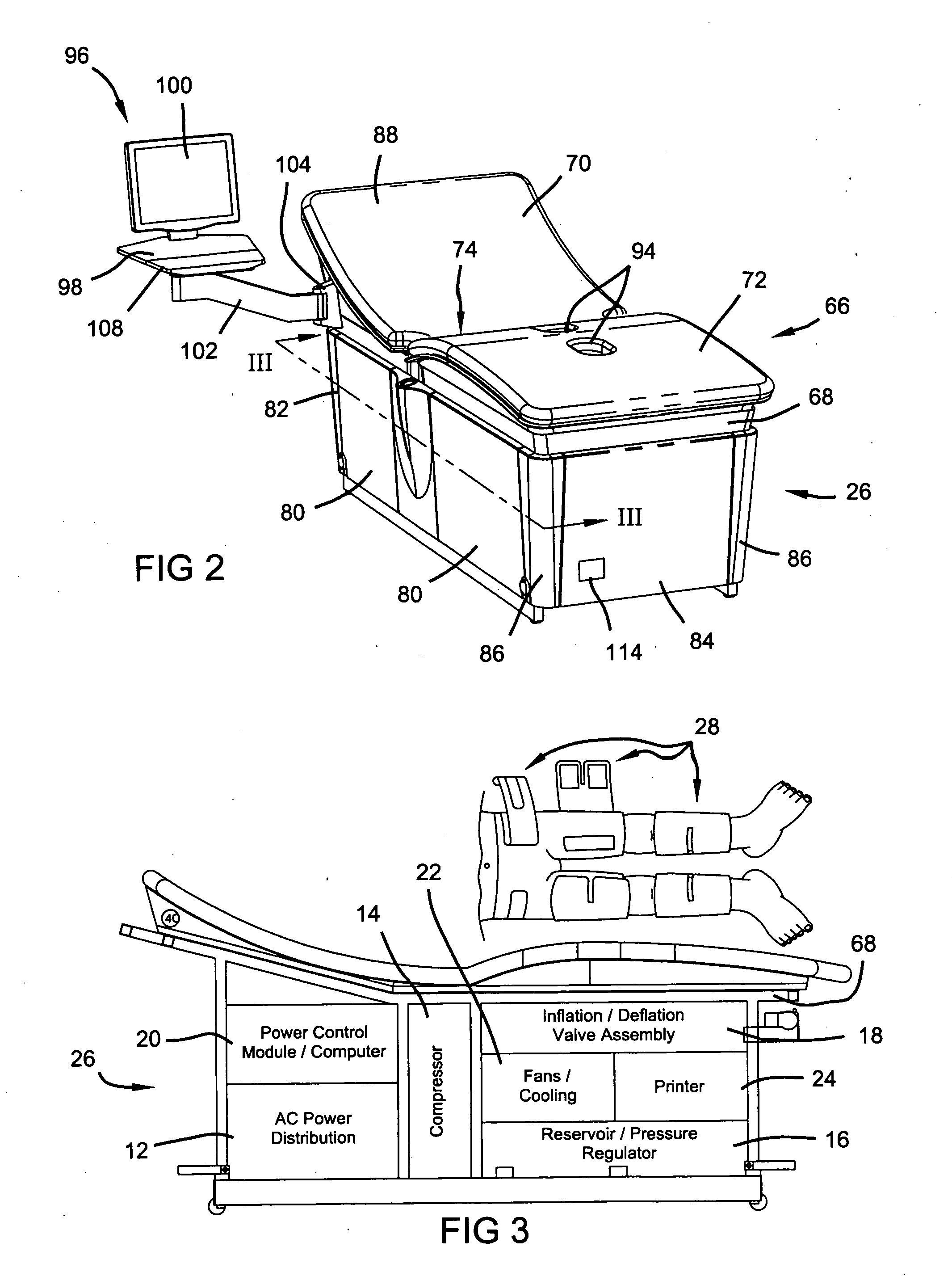
External counterpulsation device having a curvilinear bed
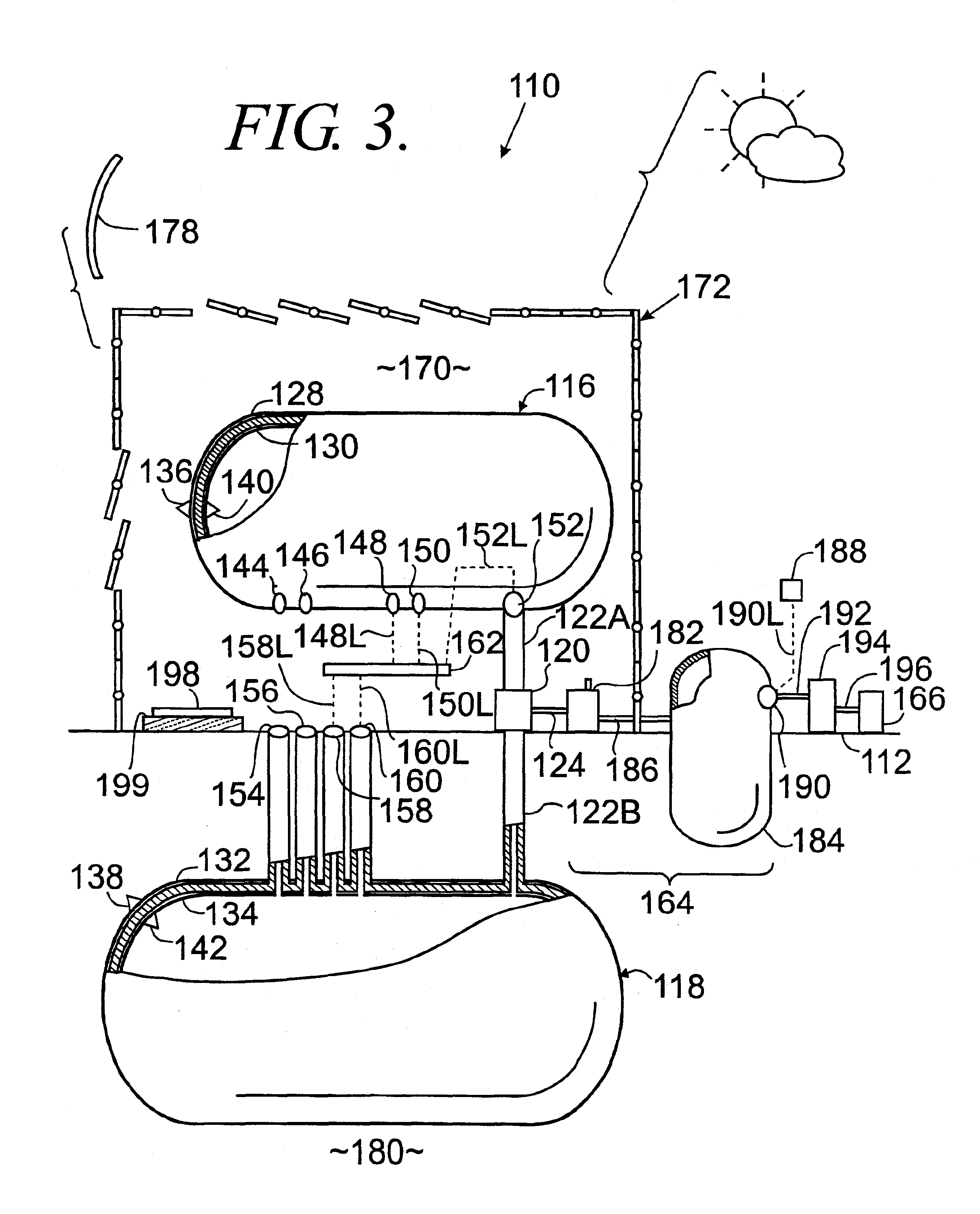
InactiveUS20060058717A1Augmented diastolic central aortic pressureIncreased venous returnPneumatic massageDiagnosticsCompressed fluidComputer module
A unitary external counterpulsation apparatus includes a curvilinear bed supported by a frame housing and fluid distribution assembly and control module. The bed includes a concave upper portion, a convex lower portion, and a saddle point therebetween. The fluid distribution assembly interconnects a plurality of inflatable devices adapted to be received about the lower extremities of a patient and a compressed fluid source. The control module controls distribution of compressed fluid from the source to the inflatable devices. Variable flow-rate valves optimize distribution of the compressed fluid.
Owner:HUI JOHN C K +3
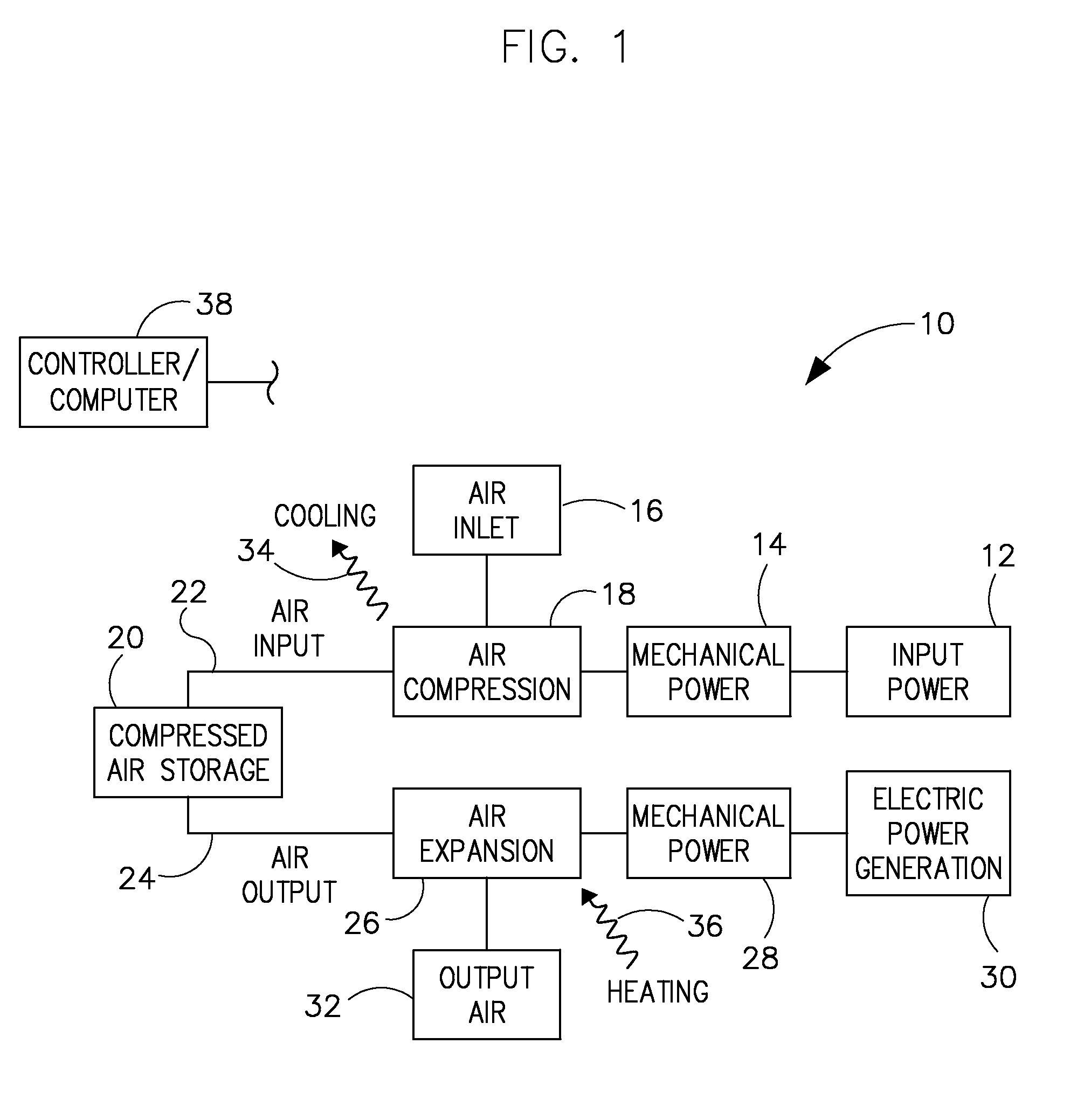
Method and apparatus for energy generation utilizing temperature fluctuation-induced fluid pressure differentials
A method and apparatus for producing energy is provided for generating renewable energy. Captive compressed fluid cycles between two coupled containers through a motive power source. The captive compressed fluid flows between the containers in response to a difference in the pressure of the compressed fluid within the first container compared to the pressure of the compressed fluid within the second container. This pressure differential develops as the compressed fluid within the first container experiences a temperature change of a differing percentage magnitude or direction than the compressed fluid within the second container over the same period of time. The differing percentage temperature fluctuations result as the containers are provided dissimilar exposure to natural renewable or man-made energy sources or are insulated therefrom. A continuous supply of additional compressed fluid is not required, nor is fluid routinely vented to the atmosphere.
Owner:CORCORAN CRAIG C
External counterpulsation and method for minimizing end diastolic pressure
InactiveUS7048702B2Increase loopAugmented diastolic central aortic pressurePneumatic massageDiagnosticsCompressed fluidEngineering
An external counterpulsation apparatus and method for minimizing end diastolic pressure includes a fluid distribution assembly interconnecting a plurality of inflatable devices adapted to be received about the lower extremities of the patient and a source of compressed fluid to be distributed by the fluid distribution assembly to the inflatable devices. The controller in communication with the fluid distribution assembly controls inflation and deflation of the inflatable devices to minimize end diastolic pressure. The controller controls deflation of the inflatable devices without reducing venous return and then minimizes energy spent in ventricular isovolumetric contraction. Further, the controller controls inflation of the inflatable devices to inflate a distal inflatable device prior to inflating a proximal inflatable device. Further, the controller controls a plurality of inflation functions including rate of pressure applied, the magnitude of pressure applied, the duration of time that external pressure is applied, and the duration of time to deflate the inflatable devices.
Owner:VASOMEDICAL
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method for preparing therapeutic ophthalmic articles using compressed fluids
The present invention describes a method for the impregnation of a drug or a drug composition into ophthalmic articles, in order to prepare drug sustained release systems mainly for the treatment of glaucoma and other eye diseases. Ophthalmic articles can be for example contact lenses. The drug or drug composition is dissolved in a compressed fluid, or mixture of compressed fluids, in a liquid, sub-critical liquid, gaseous or supercritical state. Co-solvents can be added to increase drug solubility in the compressed fluids. The mixture is subsequently contacted with the ophthalmic article. This process can be done in a single step or in a double step manner. The impregnation can be carried out in finished or semi-finished ophthalmic articles.
Owner:UNIVE DE COIMBRA +1
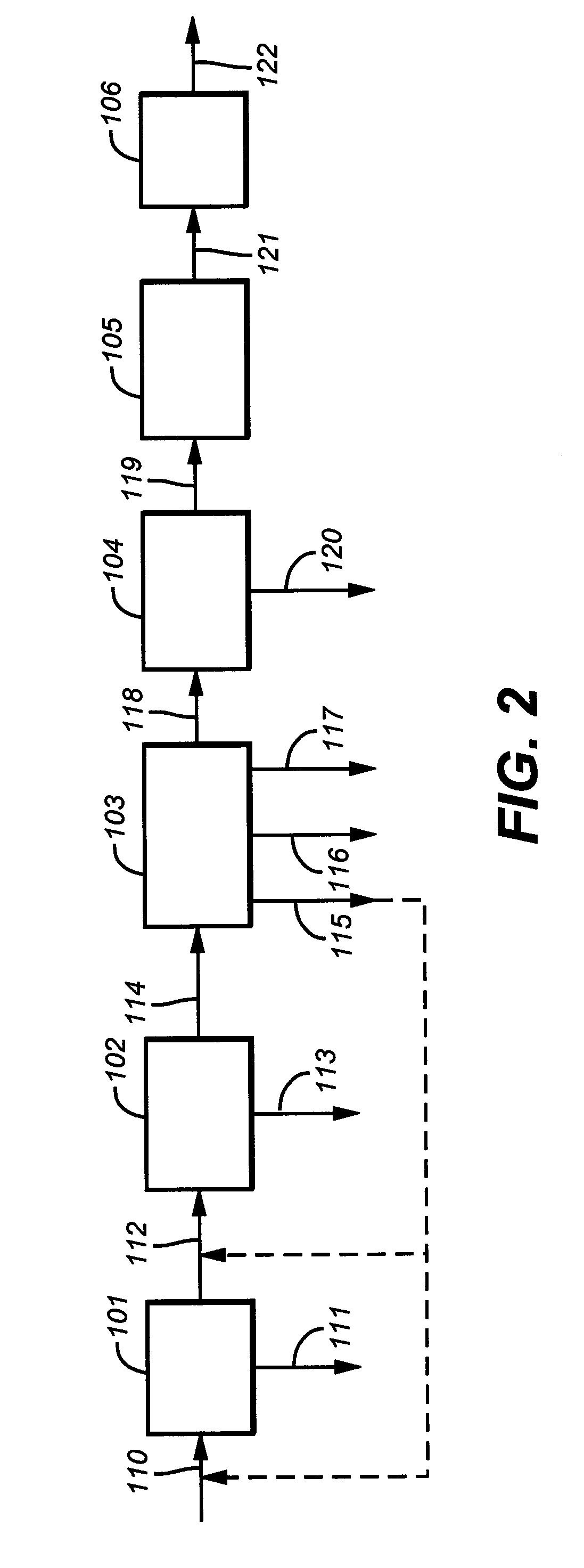
Process and apparatus for the separation of a gaseous mixture
A process for separating carbon dioxide from a carbon dioxide containing fluid comprises the steps of: compressing the fluid in a compressor to form a compressed fluid, drying at least part of the compressed fluid to form a compressed and dried fluid, cooling at least part of the compressed and dried fluid to form a compressed, dried and cooled fluid, separating the compressed, dried and cooled fluid at a temperature lower than 0° C. into a carbon dioxide rich stream, a carbon dioxide lean stream and at least one intermediate purity liquid stream having a carbon dioxide purity lower than that of the carbon dioxide rich stream and higher than that of the carbon dioxide lean stream, expanding at least one intermediate purity liquid stream to produce at least one expanded stream using at least one expanded stream to cool the compressed and dried fluid and recycling at least part of the expanded stream.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
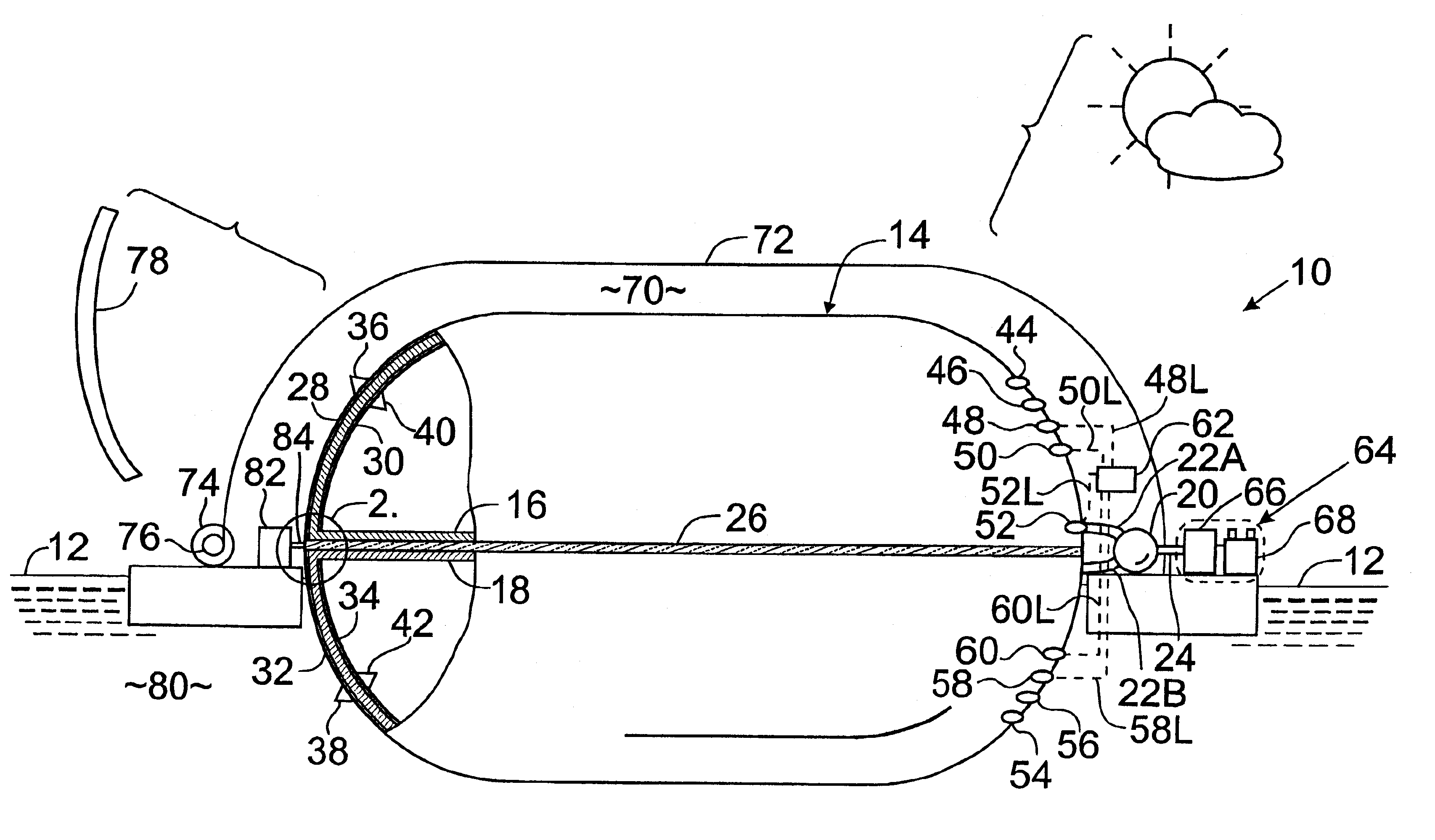
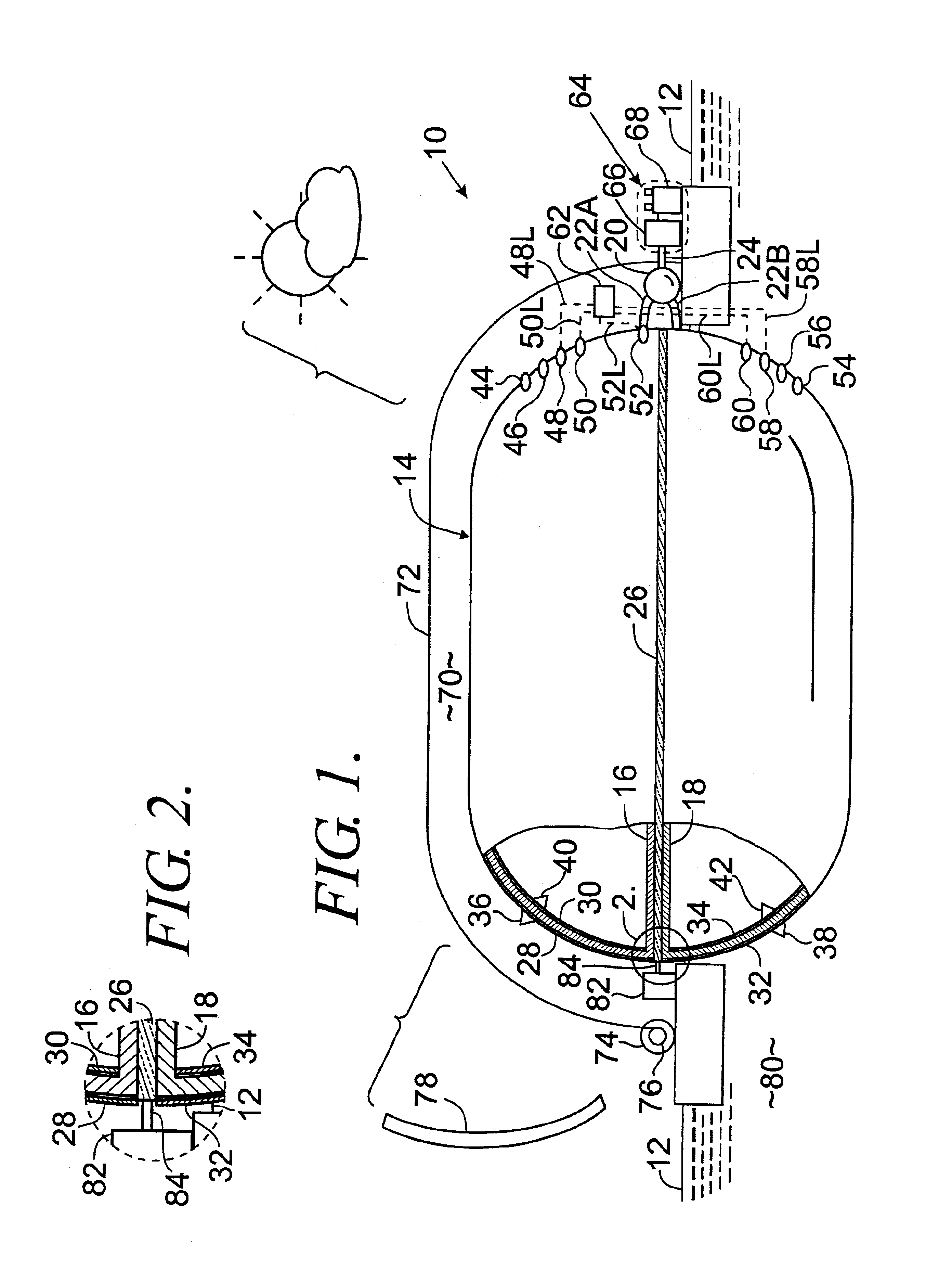
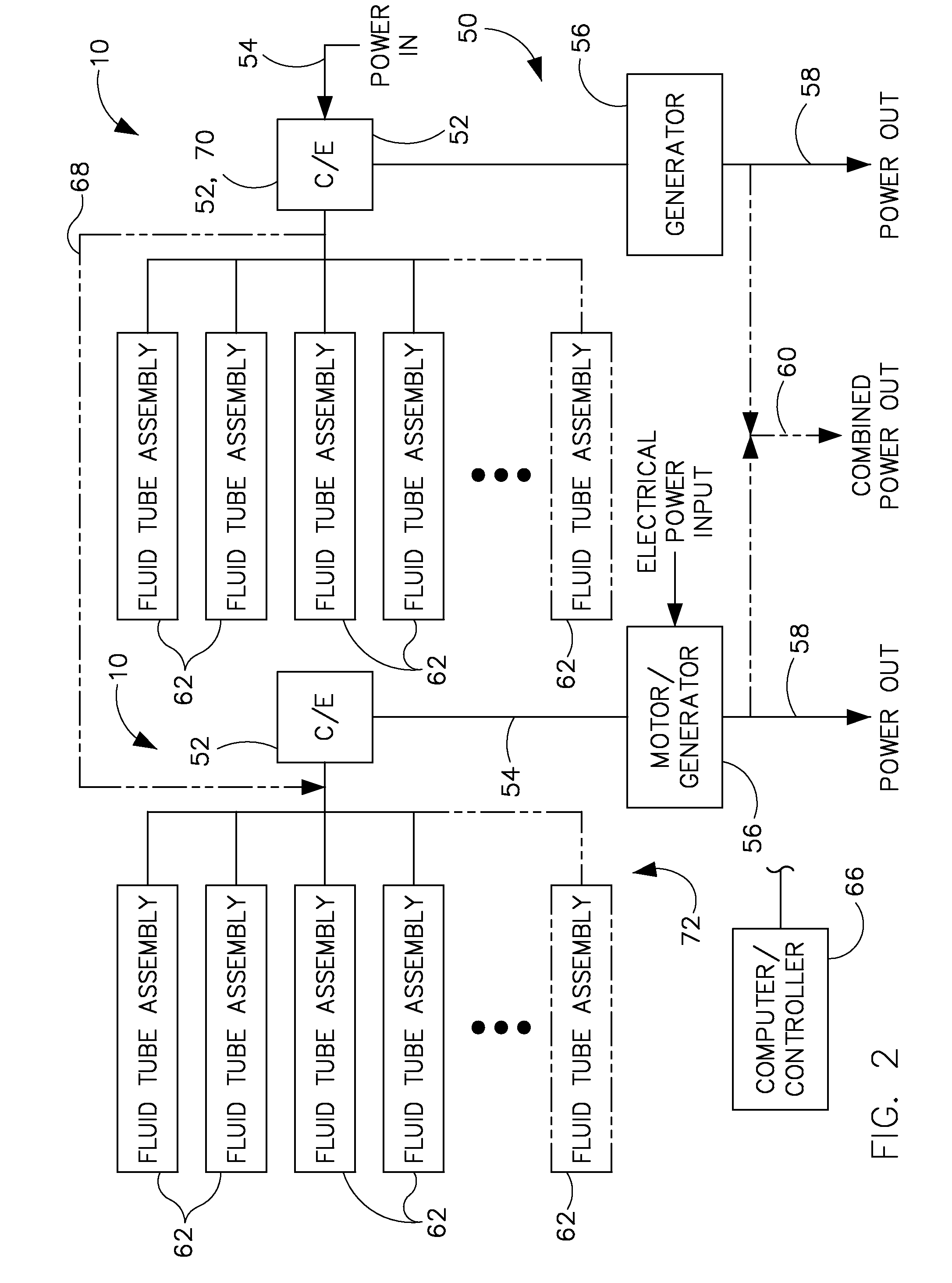
System for underwater compressed fluid energy storage and method of deploying same
InactiveUS20110070031A1Efficient and cost-effectiveArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresCompressed fluidEngineering
A system and method for underwater compressed fluid energy storage include a compressed fluid storage system that comprises a fluid containment vessel positioned on a floor of a body of water, wherein the fluid containment vessel comprises sediment positioned therein to ballast the vessel on the floor.
Owner:BRIGHT ENERGY STORAGE TECHNOLOGIES LLP
Bicycle damping enhancement system
A bicycle shock absorber for differentiating between rider-induced forces and terrain-induced forces includes a first fluid chamber having fluid contained therein, a piston for compressing the fluid within the fluid chamber, a second fluid chamber coupled to the first fluid chamber by a fluid communication hose, and an inertial valve disposed within the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve opens in response to terrain-induced forces and provides communication of fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber. The inertial valve does not open in response to rider-induced forces and prevents communication of the fluid compressed by the piston from the first fluid chamber to the second fluid chamber.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Protective athletic equipment
ActiveUS20150101899A1More commercial practicalityAvoid less flexibilityLiquid resistance brakesBufferCompressed fluidCustom fitting
Custom fitting protective athletic equipment composed of larger compressive chambers to generally surround a body part as well a plurality of smaller compressive chambers, which can be shaped to absorb rotational impact forces, outside the larger compressive chambers. A hard or yielding shell positioned either outside the chambers or between them can provide additional impact dampening and protection. Both the larger and smaller compressible chambers preferably contain compressible fluid, such as air, another gas, gel or liquid. Valves are preferably provided in the chambers so that the fluid can be controlled when an impact is received. A method is also disclosed to use three-dimensional scanning techniques and three-dimensional 3D printer manufacturing techniques to produce the protective athletic equipment of the present invention.
Owner:ROUSSEAU RES INC
Storing, transporting and handling compressed fluids
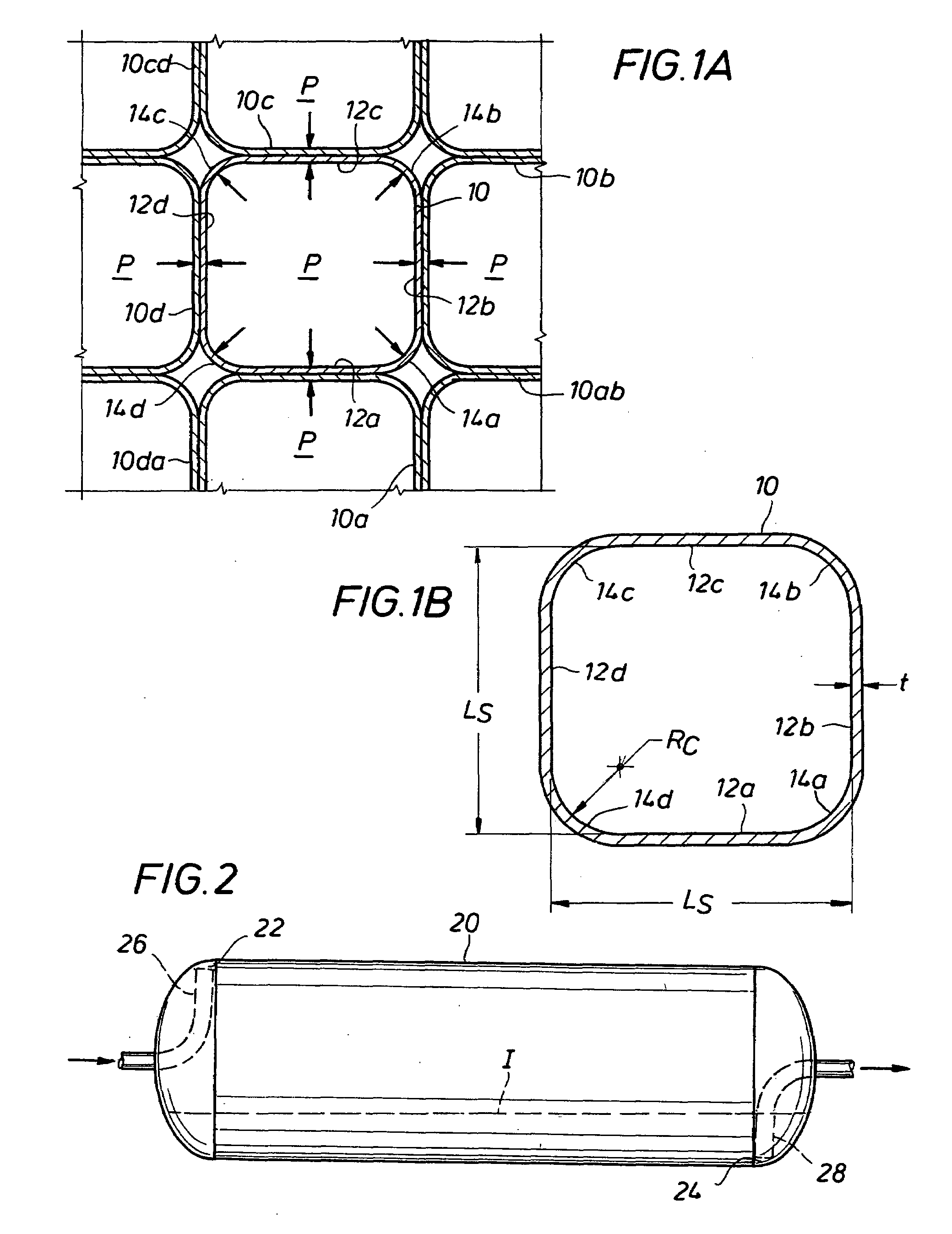
ActiveUS20080209918A1Reduce the amount requiredDesired rangeGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsSupporting systemSquare cross section
A container and a method for storage and / or transport of a compressed fluid such as compressed natural gas are provided. The container has a pair of opposing heads and a wall section between the heads, the wall section defining a square cross-section comprising substantially planar sides joined together by rounded corners. The container is designed for the side walls to deflect outwardly while under pressure, but to be supported externally by a support system that restricts outward expansion of the side walls. The support system can be provided as the walls of a cargo hold in a marine or land transport vessel, an ISO shipping container or an underground shaft. Multiple containers can be located side by side in the external support system so that the sides of adjacent containers rest against each other for support while under pressure. In one embodiment, a container comprises an outside tank and a flexible membrane tank inside the outside tank, an annular space being defined in between, where a first fluid is charged into the membrane tank and a second fluid is charged into the annular space in order to discharge the first fluid. In another embodiment, a long tube having a square cross-section is coiled in a support structure and made gas-tight for holding a compressed fluid. The walls of the tube would tend to expand while under pressure, but adjacent coils and the support structure limit the expansion.
Owner:WHITE CHARLES N +1
Wankel and similar rotary engines
InactiveUS8312859B2High power outputGuaranteed uptimeInternal combustion piston enginesEngine of arcuate-engagement typeCombustion chamberCompressed fluid
Owner:ROM HAIM +1
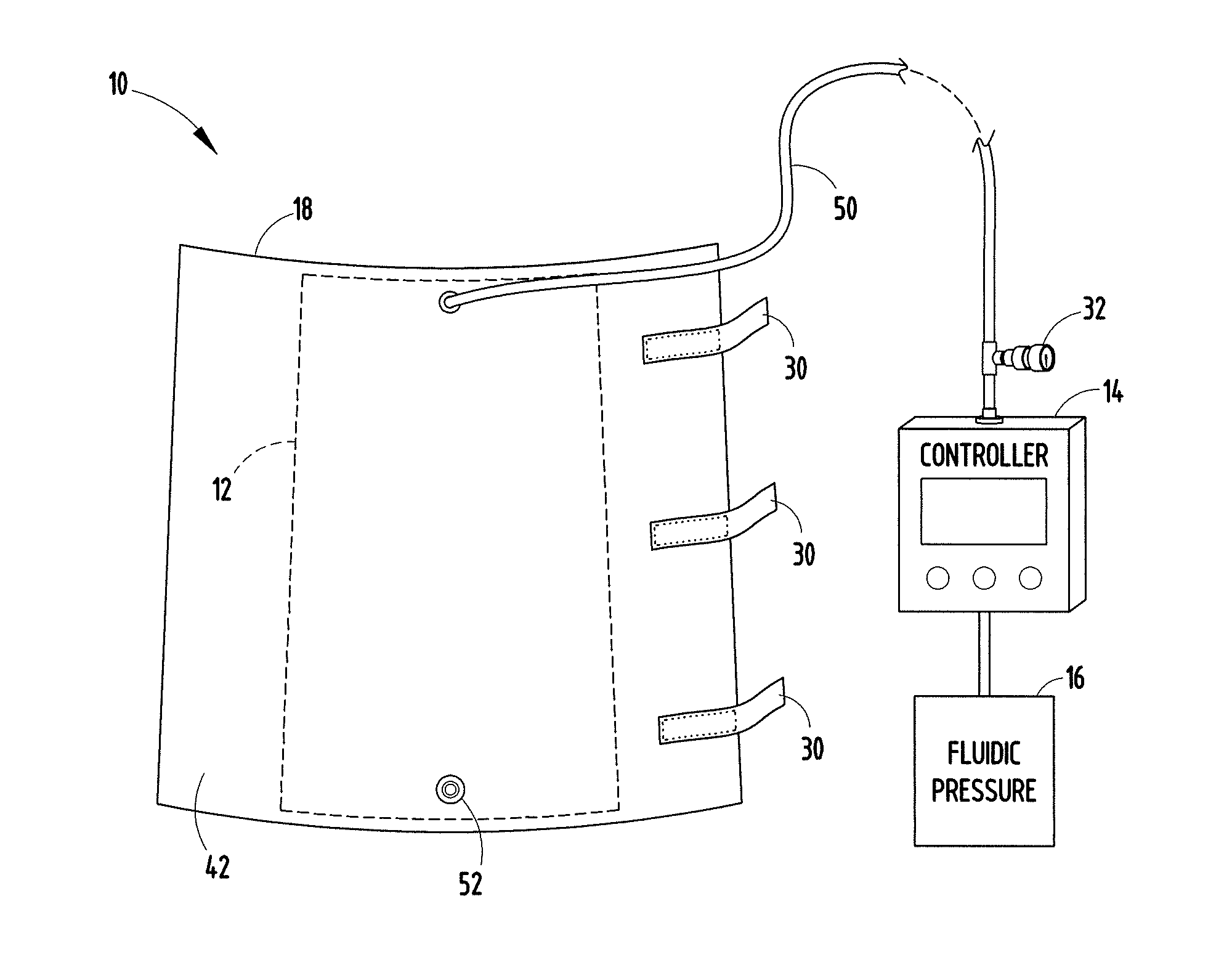
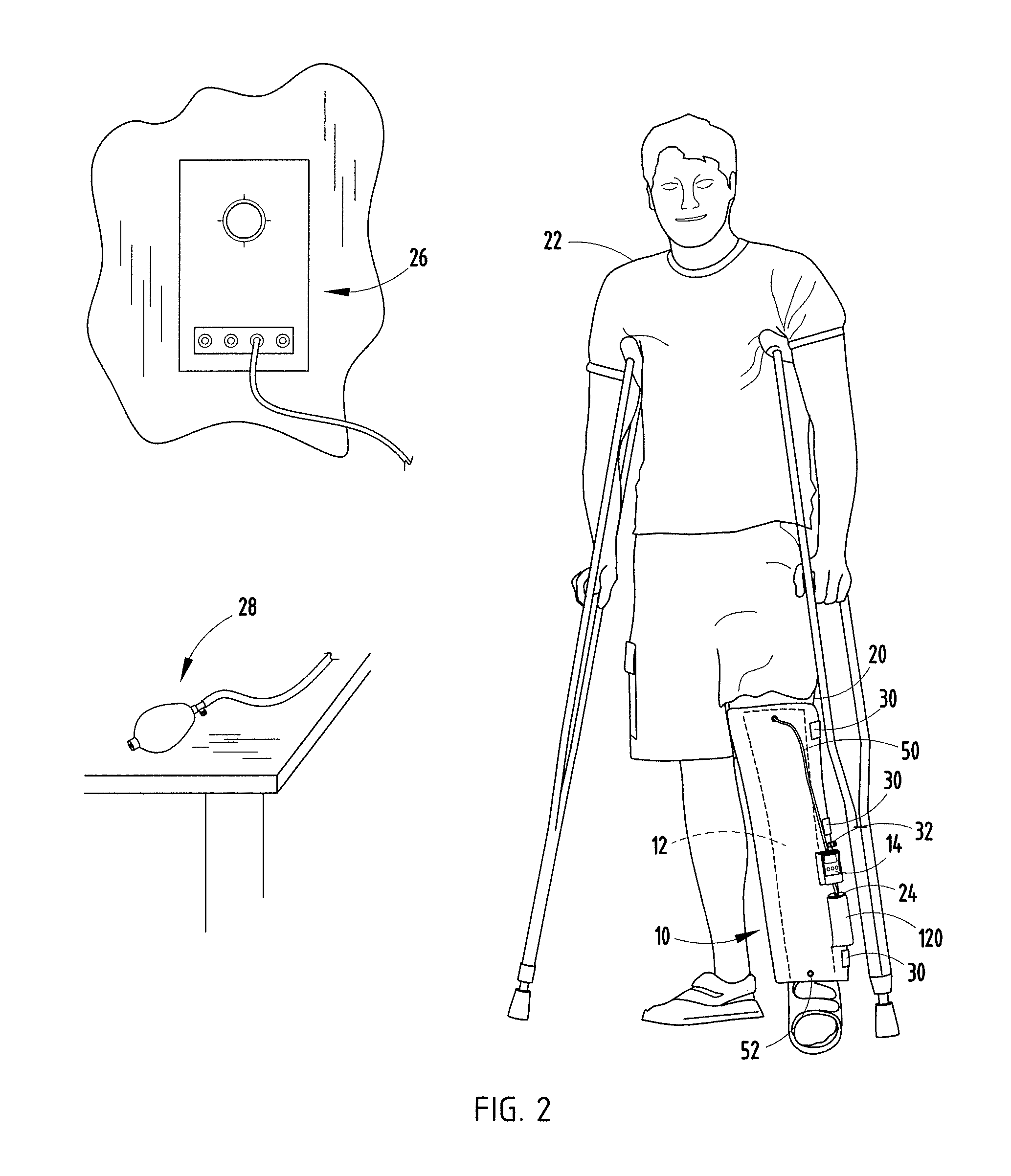
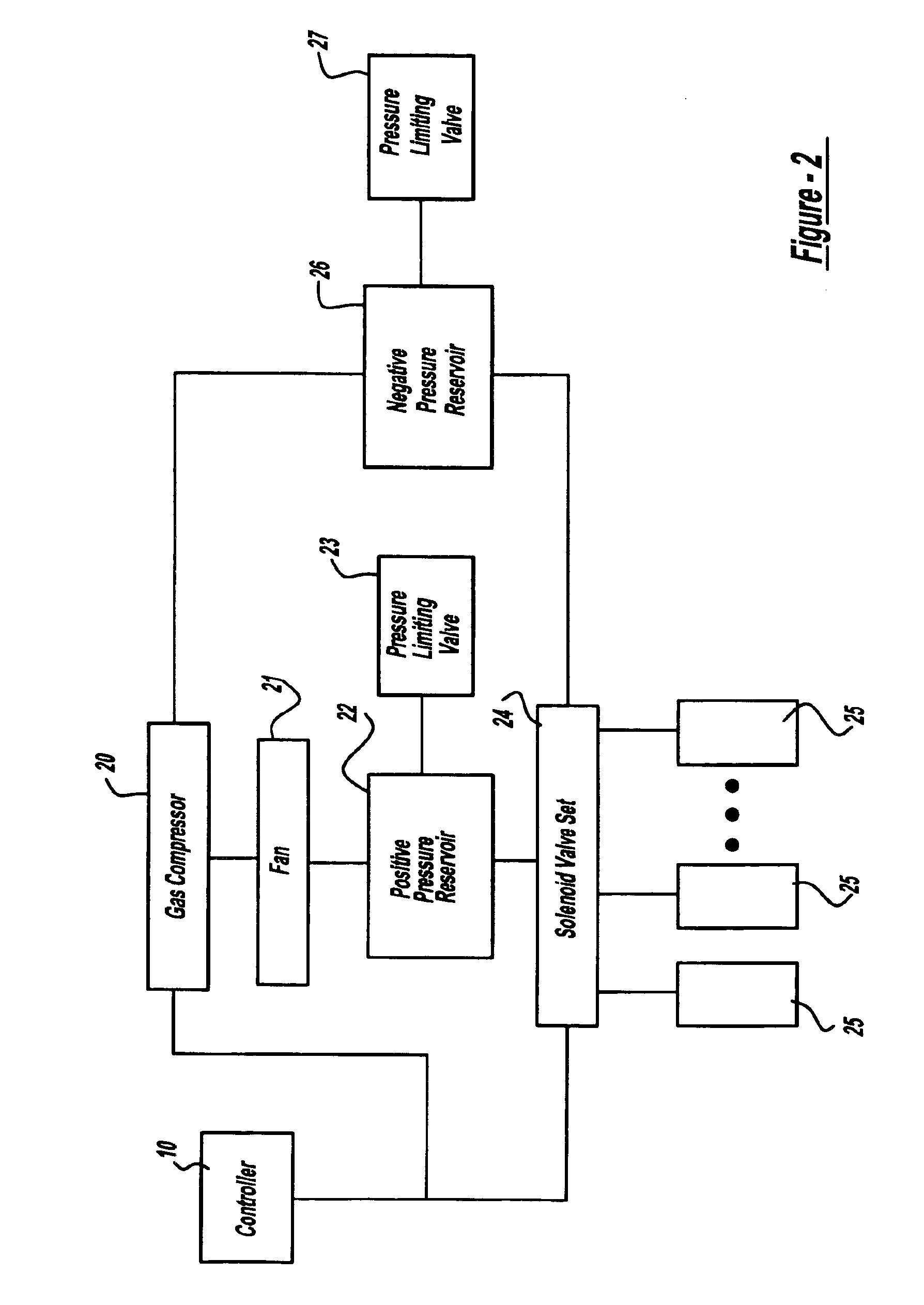
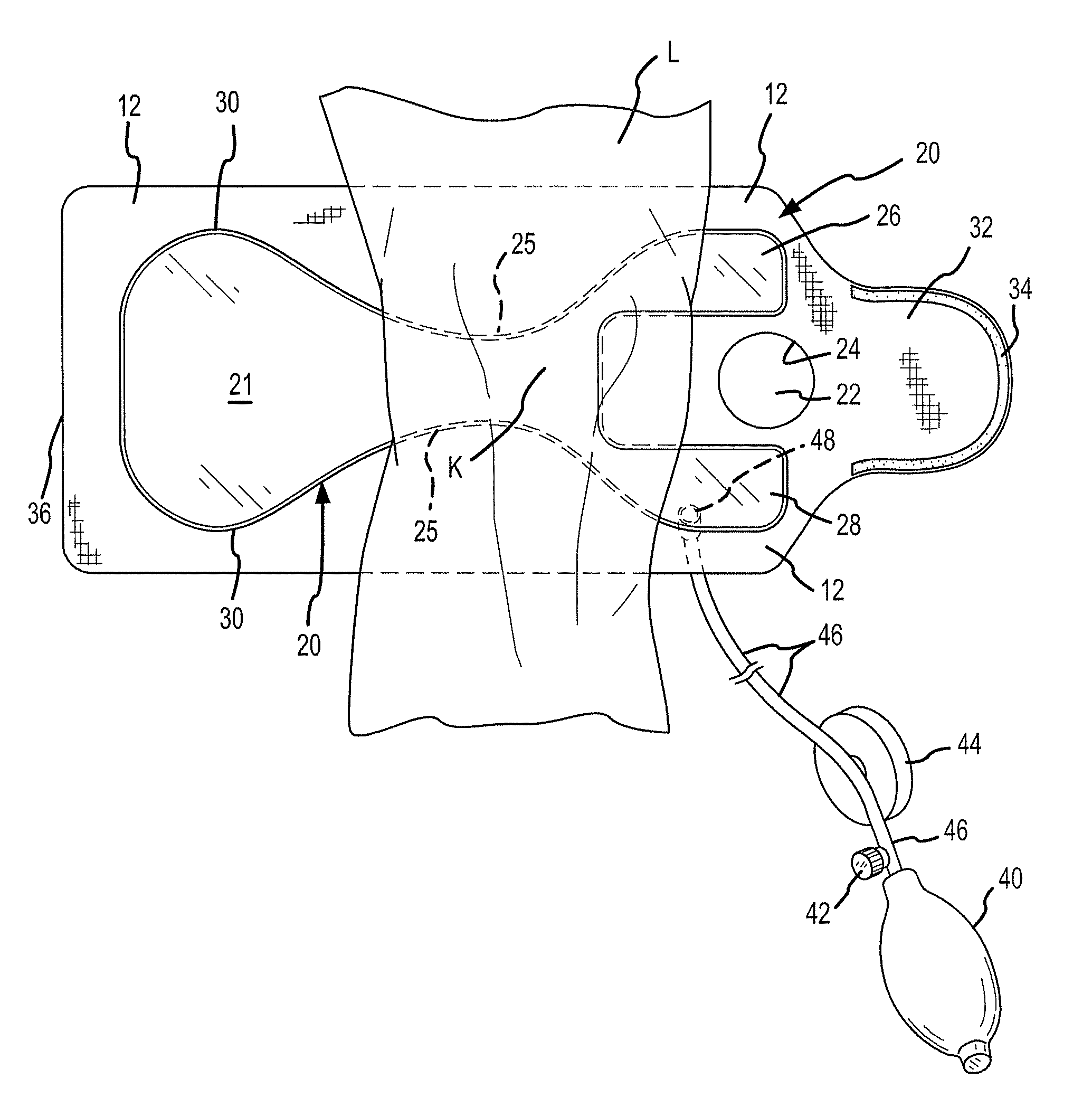
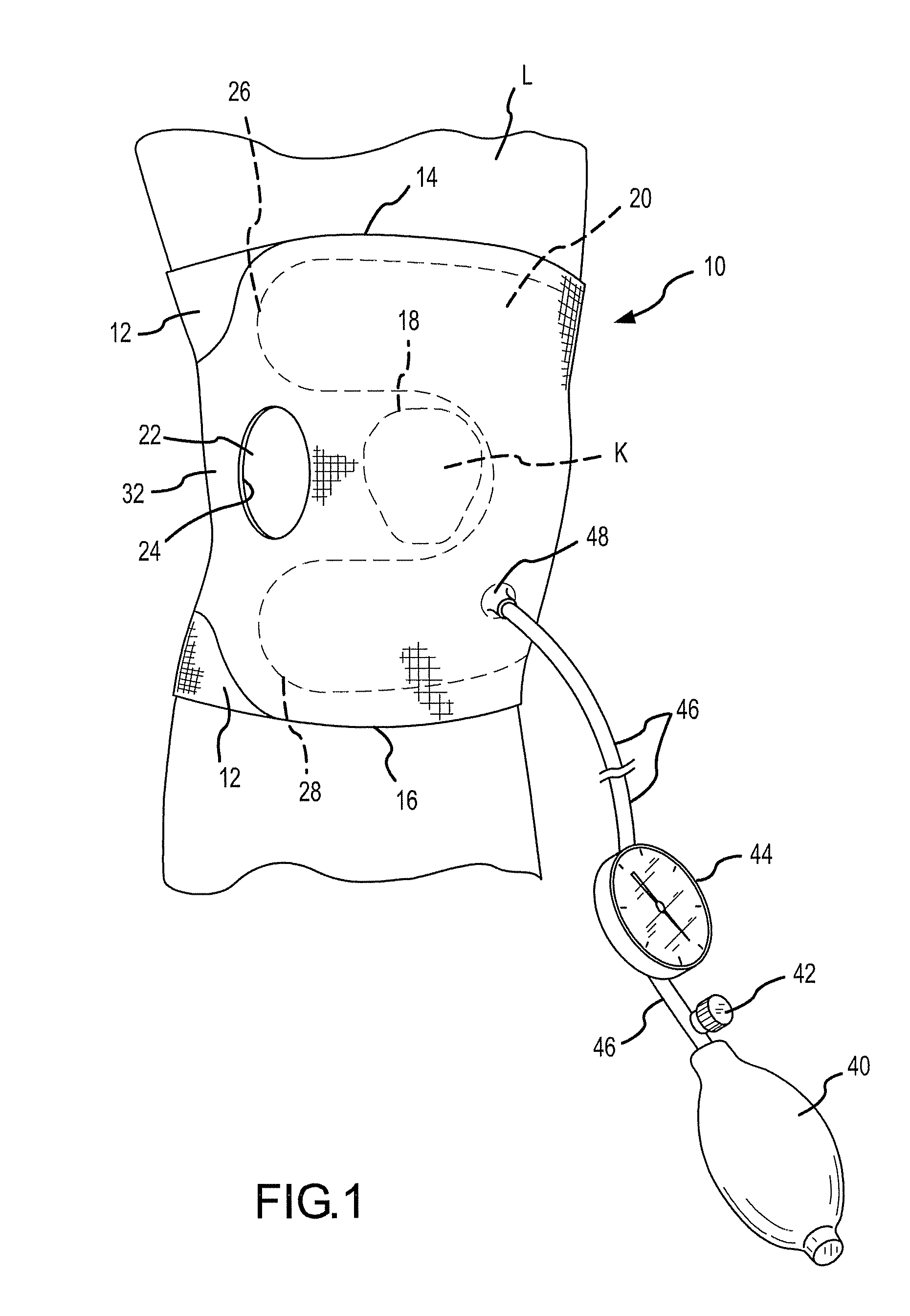
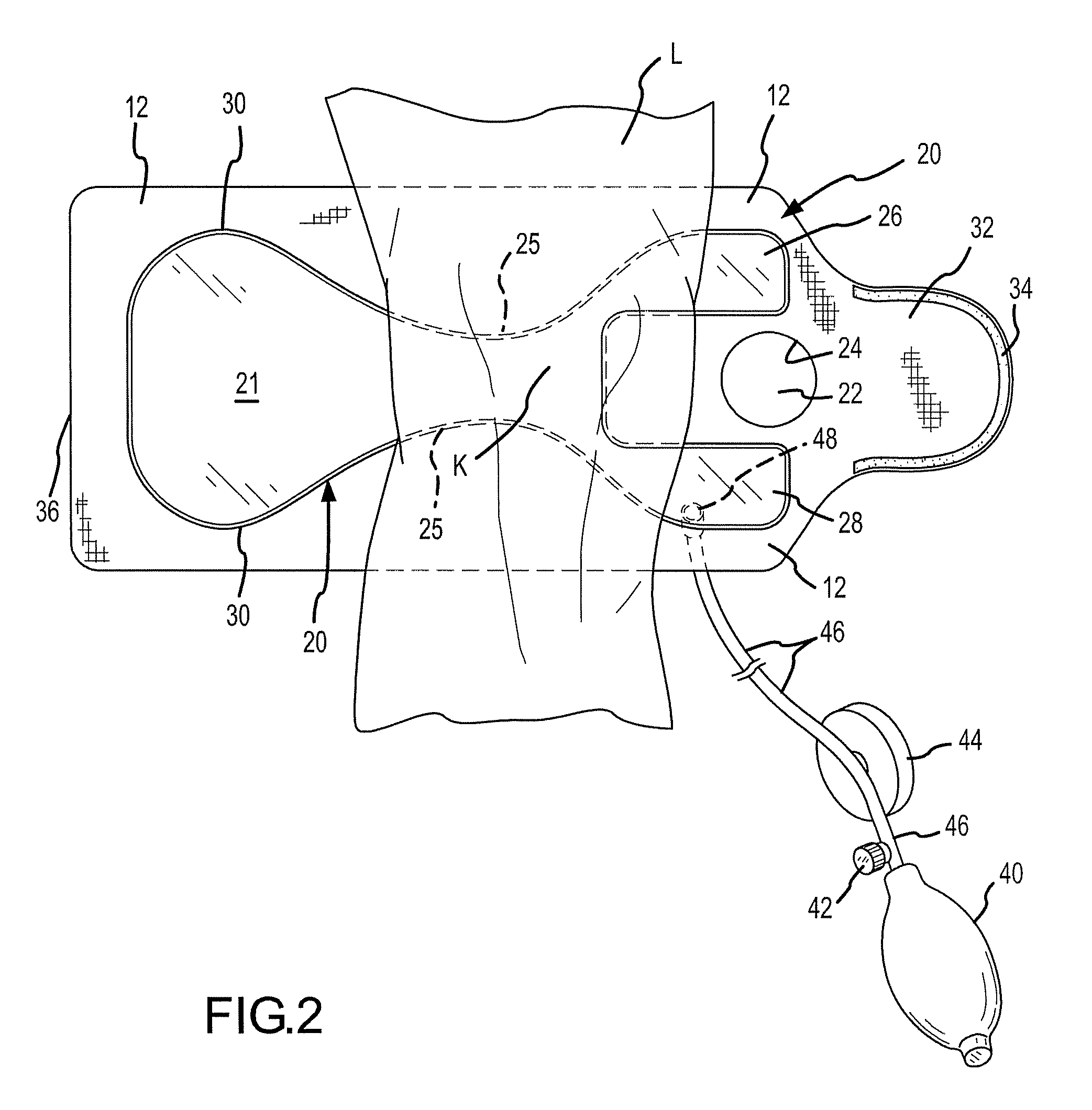
Compression device and control system for applying pressure to a limb of a living being
InactiveUS20110245743A1Constant pressurePneumatic massageChiropractic devicesCompressed fluidControl system
A compression device (10) comprising an inflatable bladder (12), an optional controller (14), a source of fluidic pressure (16), and a cuff (18) at least partially housing the inflatable bladder and capable of being attached to a body part (20) of a living being. The controller is in fluid communication with the source of fluidic pressure and the inflatable bladder. The controller is capable of maintaining the fluid pressure that the source of fluidic pressure supplies to the inflatable bladder at a constant fluid pressure, even if the body part to which the device is attached decreases in volume. The source of fluidic pressure can be container of compressed fluid, like carbon dioxide. The source of fluidic pressure and the controller can be removably attachable to the cuff. A method of using the device to maintain constant pressure to decrease the volume of a limb or to lessen lymphedema.
Owner:MEDICAL MINDS
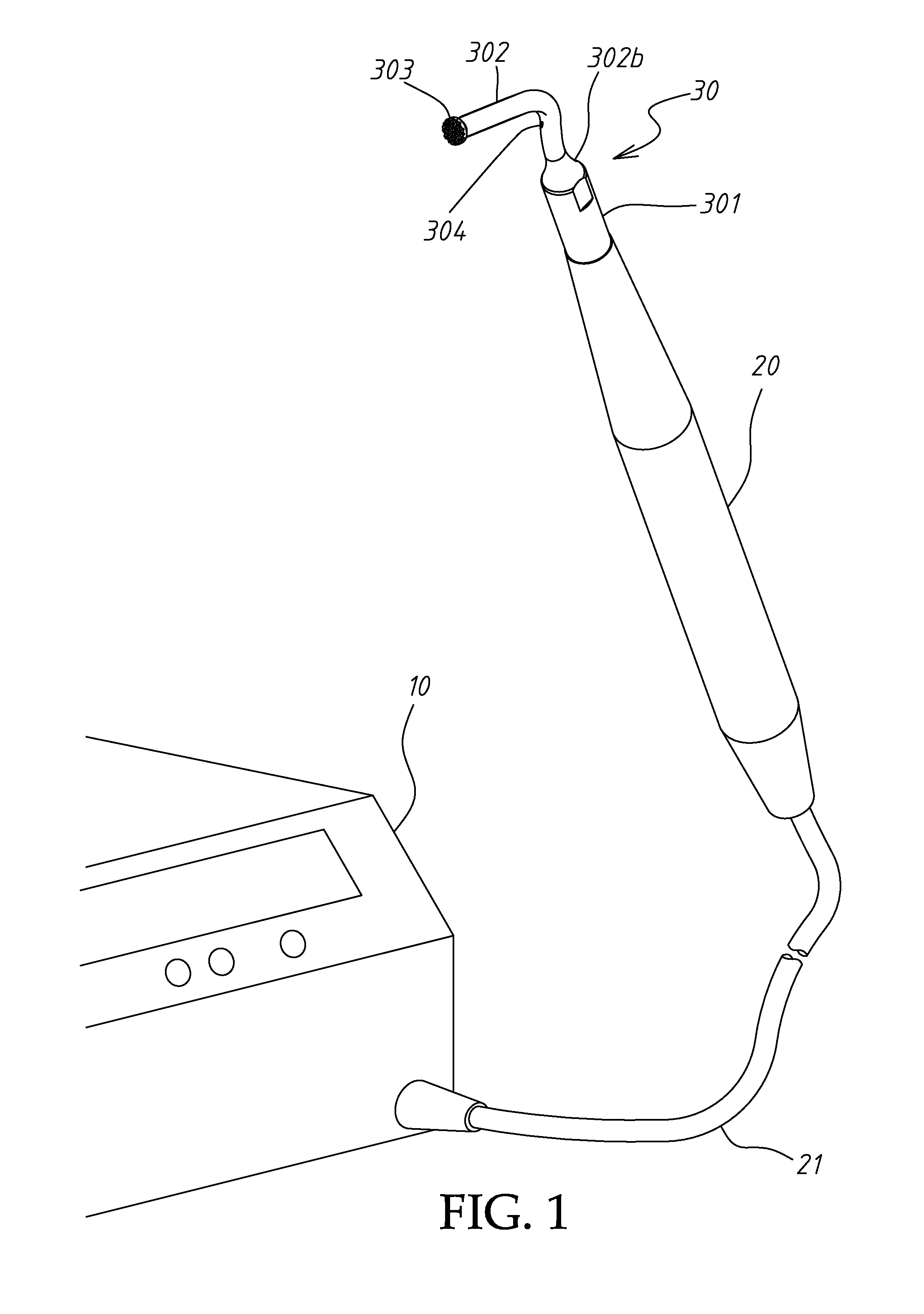
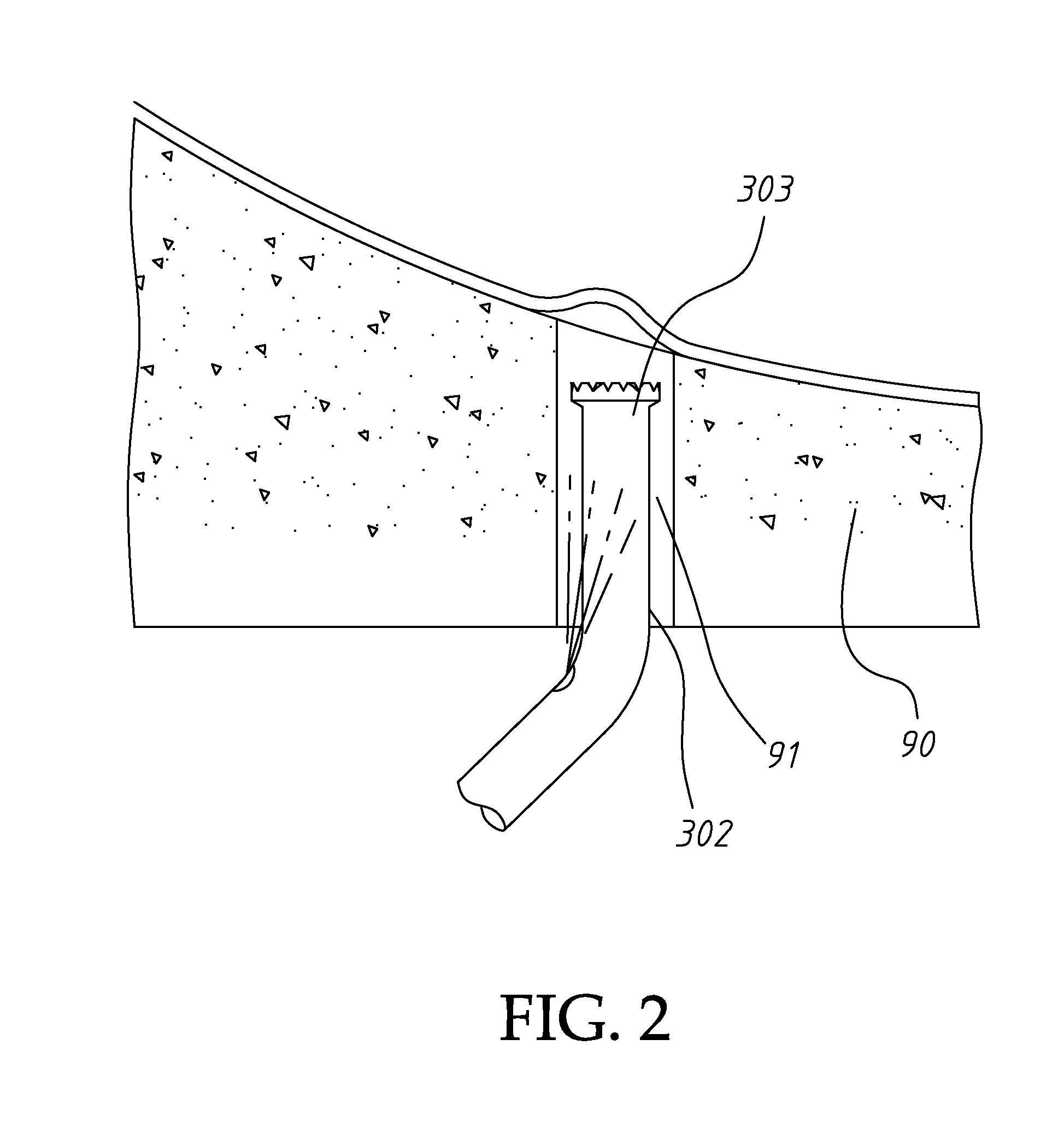
Ultrasonic dental implant tool set
An ultrasonic dental implant tool set includes an ultrasonic machine, a hand piece connected to the ultrasonic machine and tool members selectively mounted on the hand piece for providing vibrations and a compressed fluid. Each tool member has a connection base, a pole and a cutter tip. The spray nozzle has a connection base, a pole extends from the connection base and having a longitudinal fluid passage for the passing of a fluid and a fluid injection hole for injecting a fluid into a vertical hole made on the alveolar ridge of the patient to be treated, and an operating tip located on one end of the pole remote from the connection base and for insertion into the vertical hole made on the alveolar bone of the patient to transfer ultrasonic vibrations to the fluid applied to the inside of the vertical hole on the alveolar bone of the patient.
Owner:CHEN CHUN LEON
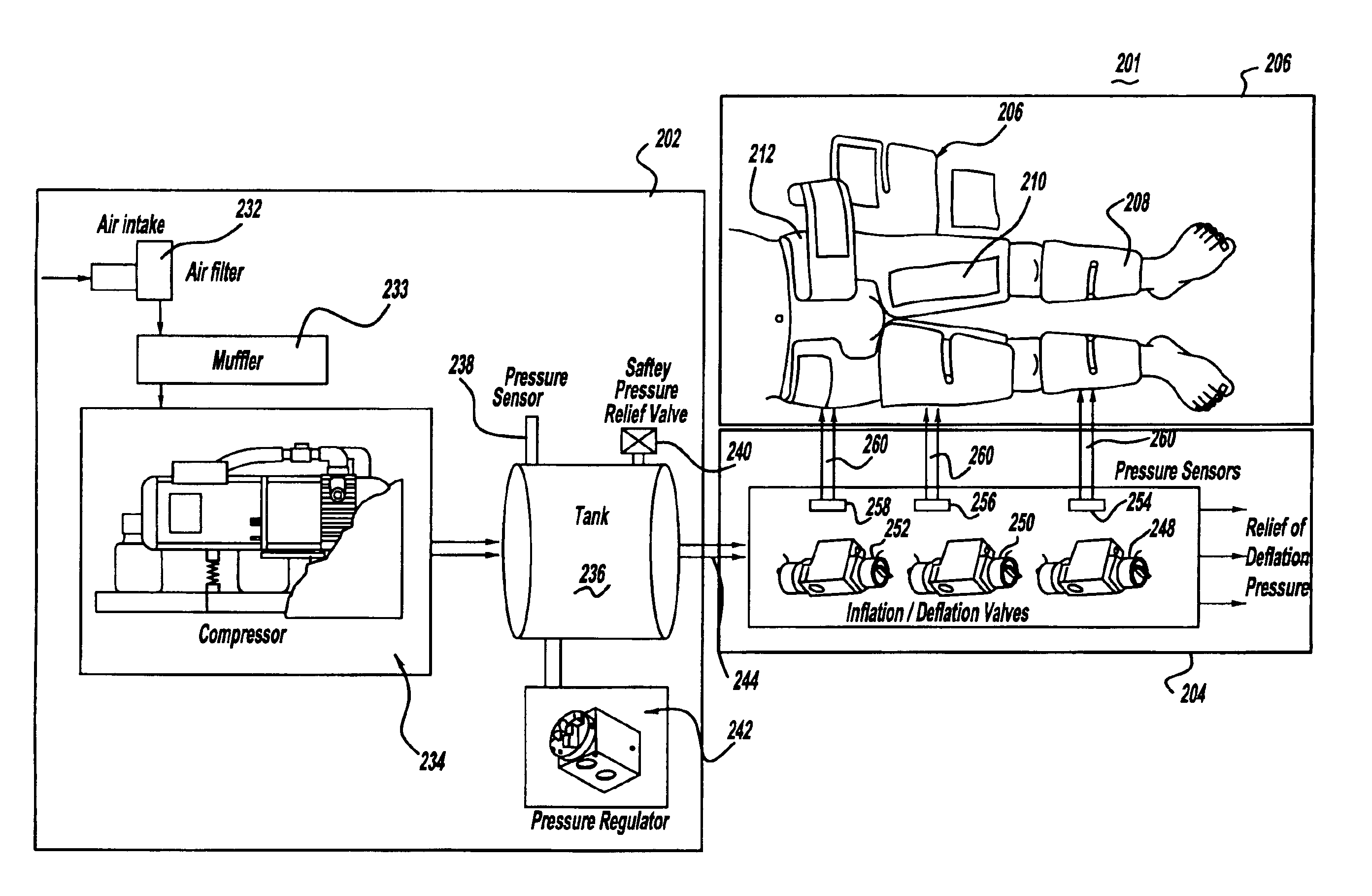
High efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus and method for controlling same
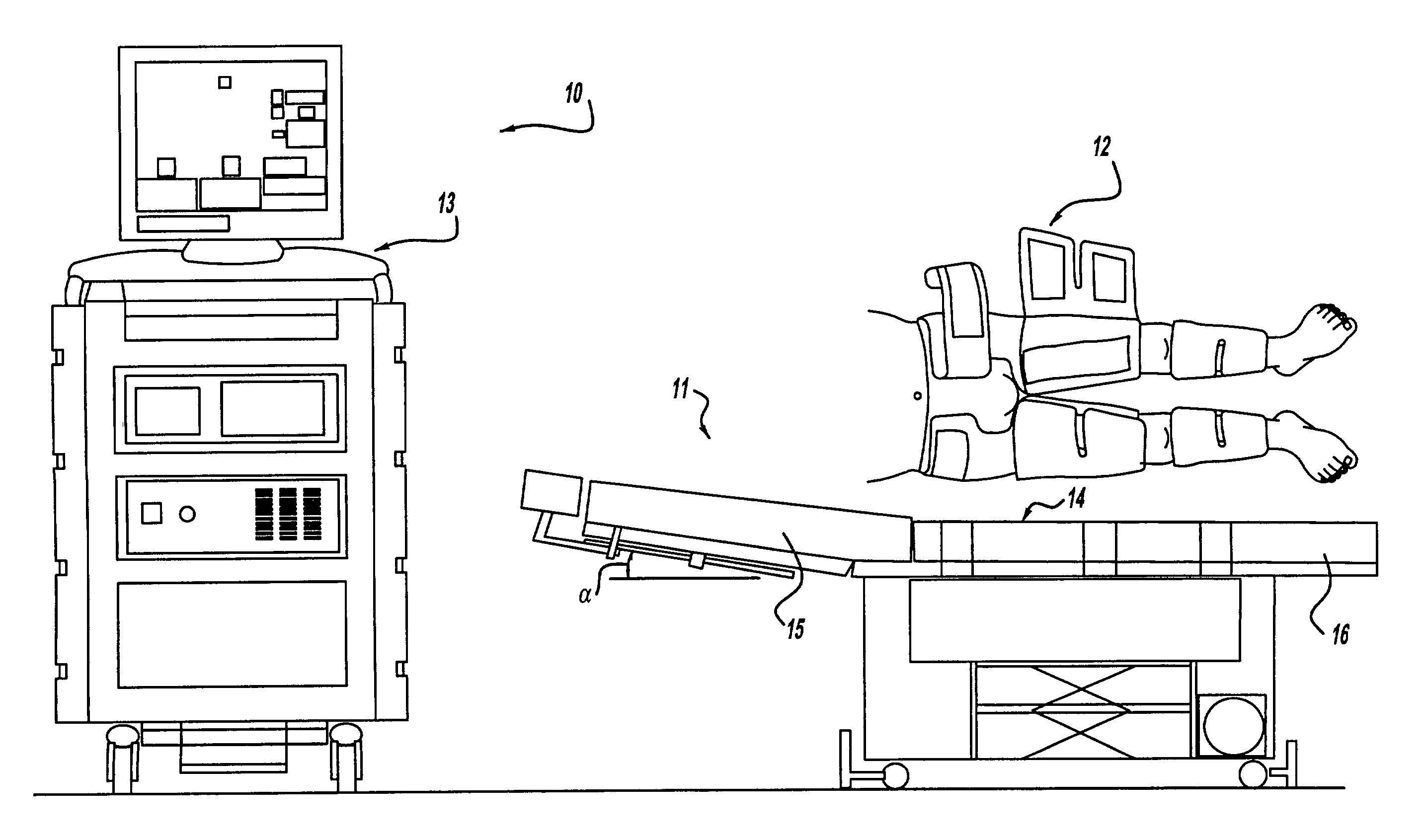
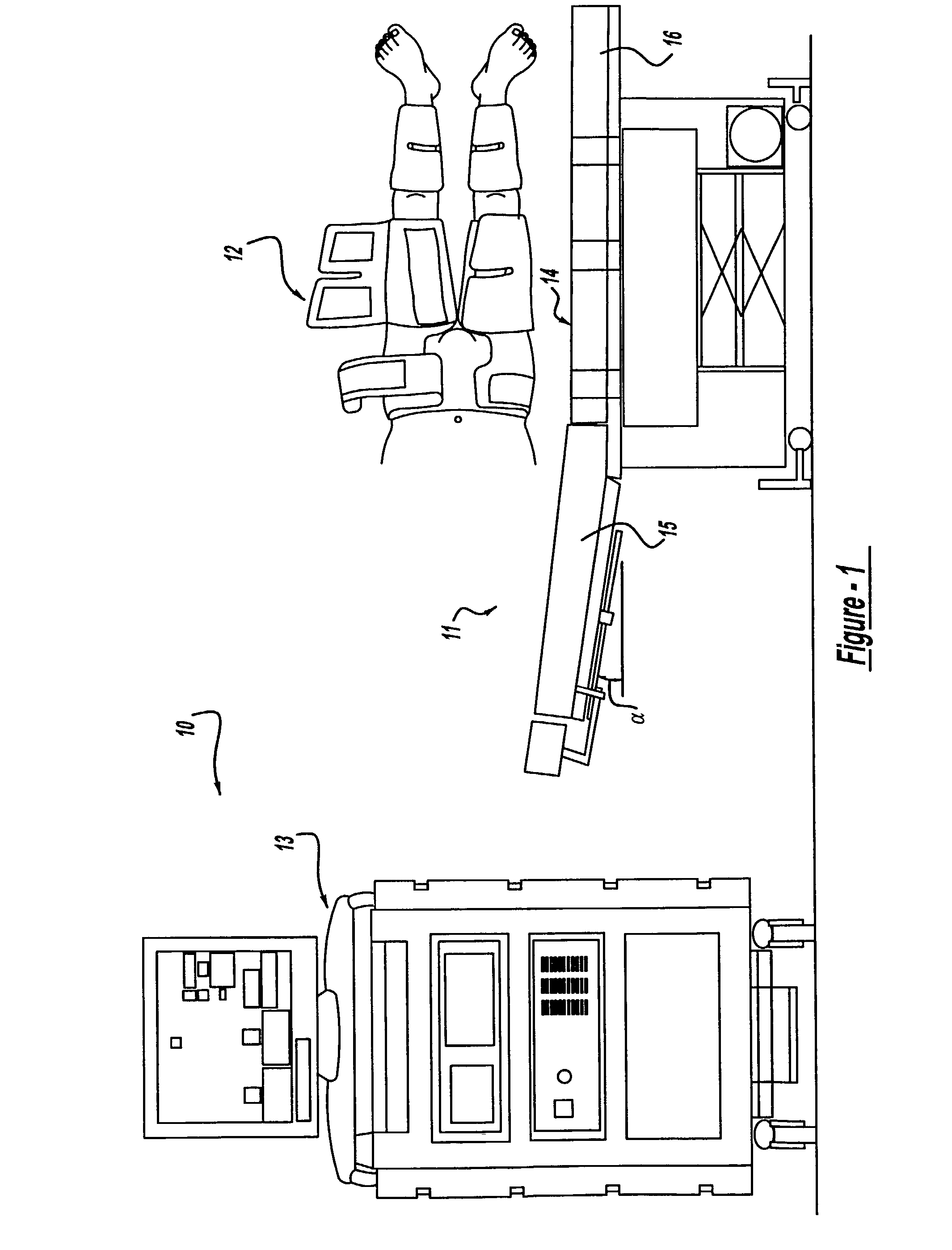
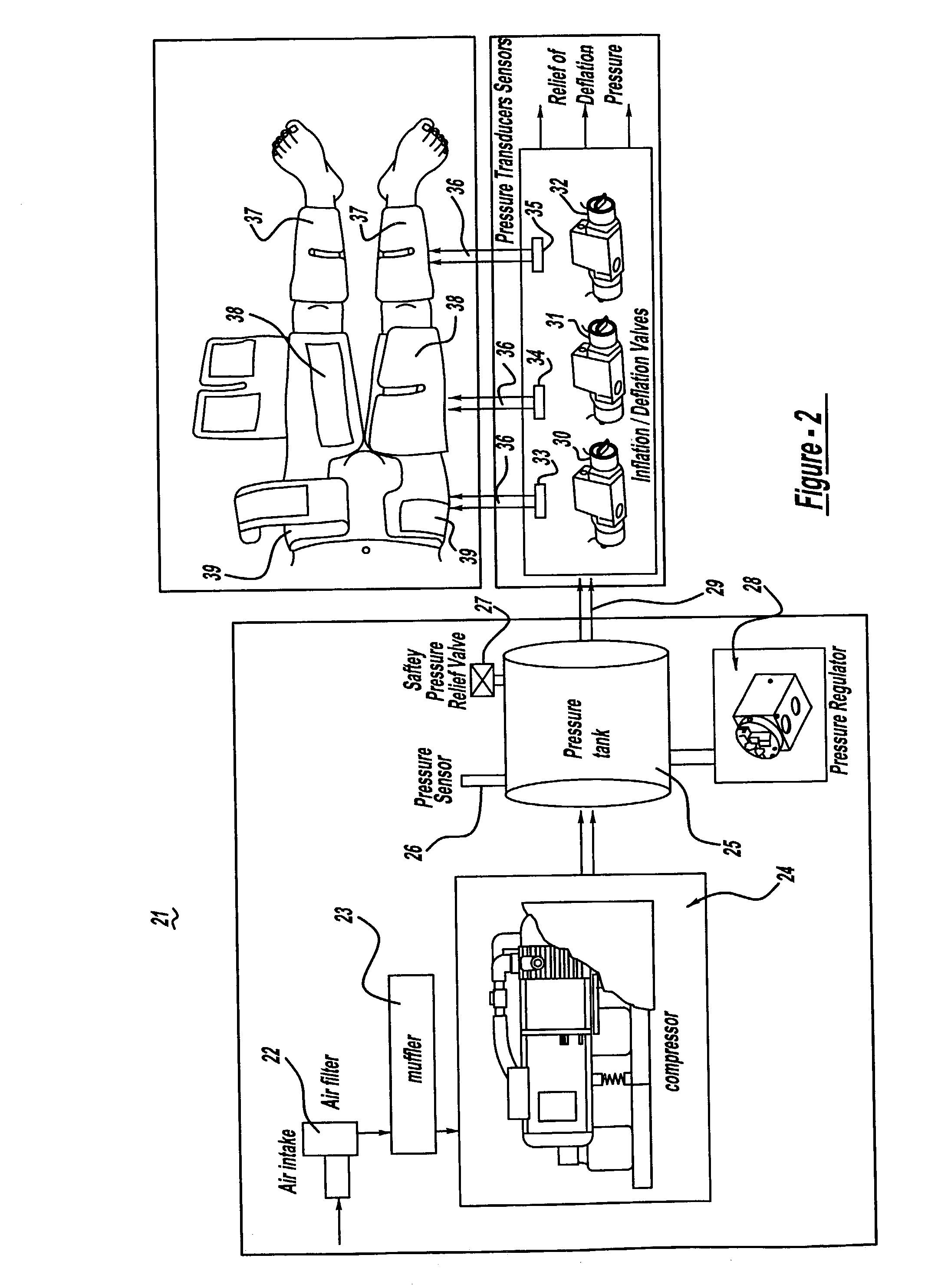
InactiveUS6962599B2Improve Utilization and EfficiencyIncrease loopElectrotherapyPneumatic massageCompressed fluidRoom temperature
The present invention provides a high efficiency external counterpulsation apparatus having accurate and reliable timing of inflation and deflation and reduced temperature of the pressurized gas, such that the gas flow temperature of the inflatable devices is near to room temperature, as well as faster and more responsive inflation / deflation equipment. The external counterpulsation apparatus includes a plurality of inflatable devices received about the lower extremities of the patient, a source of compressed fluid in communication with said plurality of inflatable devices, and a fluid distribution assembly interconnecting said source of compressed fluid and said inflatable devices. The fluid distribution assembly includes a selectively operable inflation / deflation valve interconnected between each of said inflatable devices and said source of compressed fluid. The fluid distribution assembly separately operates each inflation / deflation valve to sequentially inflate and deflate each inflatable devices.
Owner:VASOMEDICAL
Joint aspirate facilitating device
ActiveUS7468048B2Improve abilitiesIncreasing size and pressureNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCompressed fluidEngineering
A joint aspirate-facilitating device is provided including a flexible main panel that is secured to the joint to be aspirated. An inflatable bladder is secured to the main panel and is placed in contact with the soft tissues overlying and surrounding the joint space. The bladder is used to apply pressure to selected areas of the joint to compress the fluid sacs in the joint. An access opening is formed in the main panel designating the location where joint fluid is to be aspirated. The joint fluid is directed to flow to the area of the joint exposed at the access opening based on the shape of the bladder that compresses surrounding areas of the fluid sacs. A conventional hand pump may pressurize the bladder or the bladder may be filled with a viscous gel material to generate pressure. Multiple access openings may be formed on the main panel designating locations where aspiration is to be conducted. For multiple access openings, plugs may be used to fill those openings where aspiration is not conducted, thereby maximizing joint fluid flow only to the selected location where aspiration is to be conducted. An ultrasound probe may be attached and incorporated into the device to confirm joint fluid displacement into the targeted location prior to need aspiration. A disposable molded sterile dressing may applied to the access opening to reduce the risk of infections. The device can be used on any joint of the body, and the particular shape of the main panel and bladder accommodates maximum joint fluid flow to the point where aspiration is desired.
Owner:NAT JEWISH MEDICAL & RES CENT
Microvalve for control of compressed fluids
InactiveUS20110073788A1Avoid flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCompressed fluidElectrical connection
A micro-electromechanical device for controlling compressed fluid flow is provided. A chamber includes a fluid flow inlet port, a high pressure region exceeding 30 bar, and a fluid flow outlet port. A moveable micro-electromechanical valve is positioned to contact the fluid flow outlet port when the moveable micro-electromechanical valve is in a first position. An electrical connection to the moveable micro-electromechanical valve provides an electrical pulse train to the moveable micro-electromechanical valve to actuate the valve at a rate of 10 KHz or more to move the valve in order to control fluid communication between the high pressure region and a low pressure region downstream from the fluid flow outlet port.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
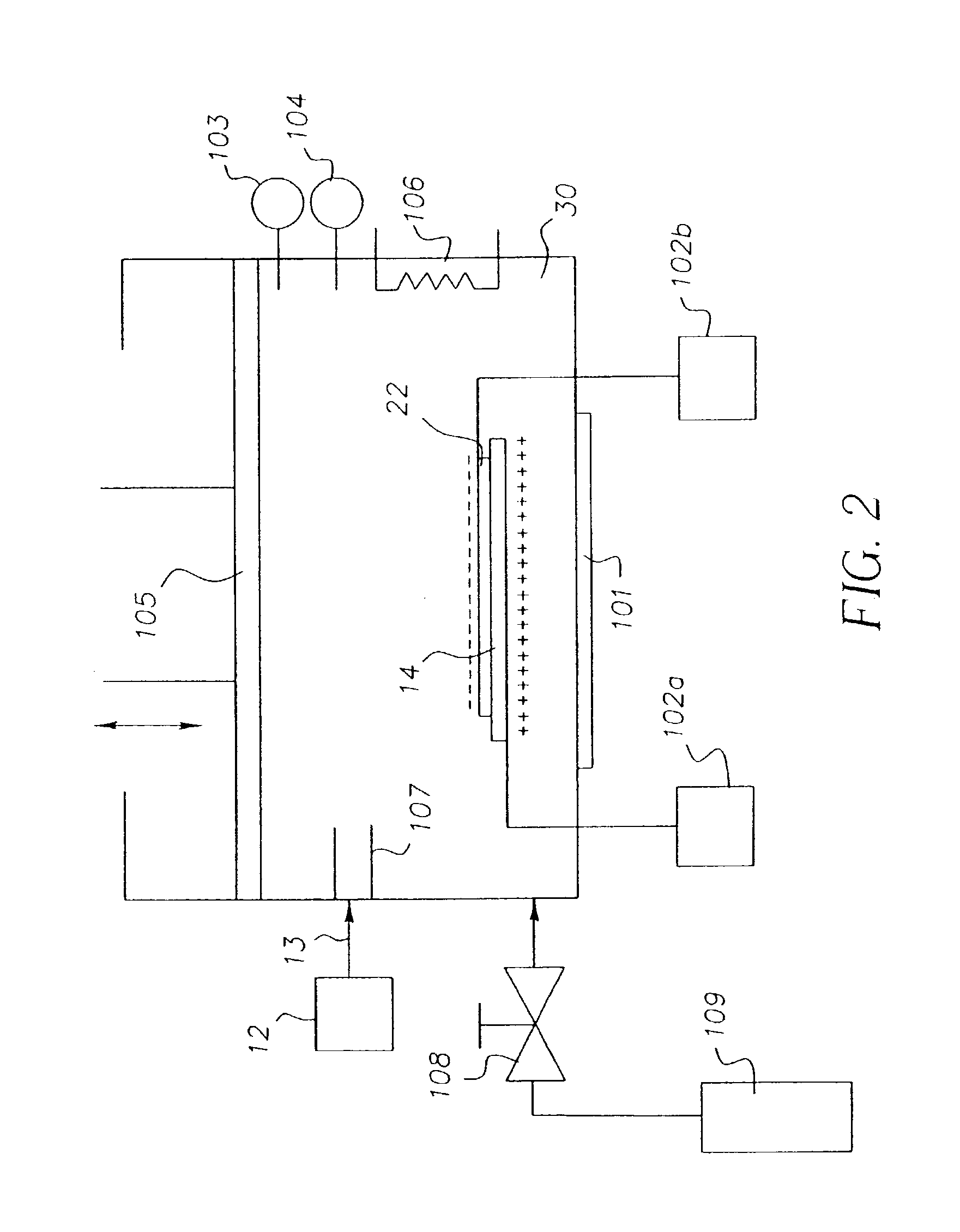
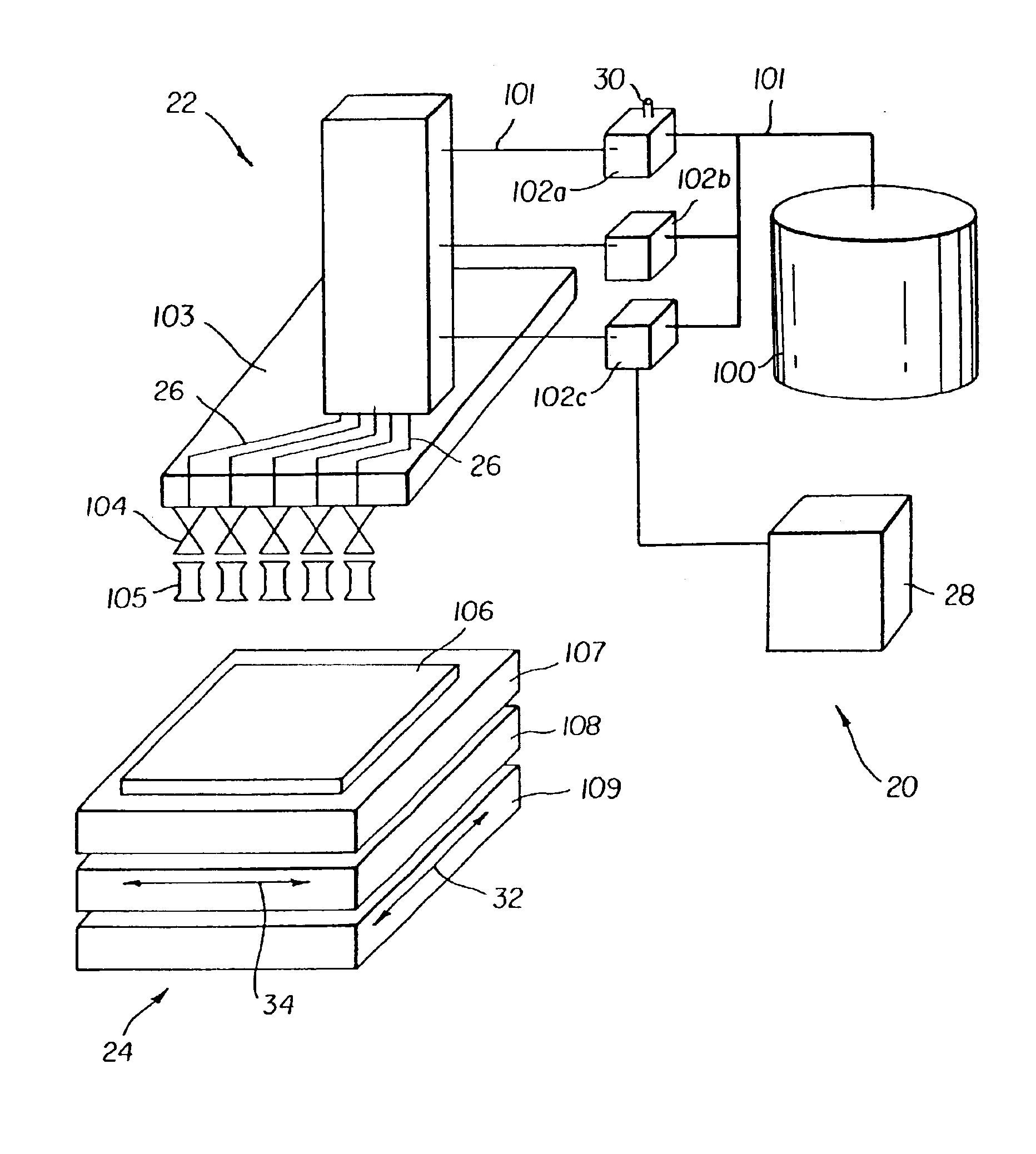
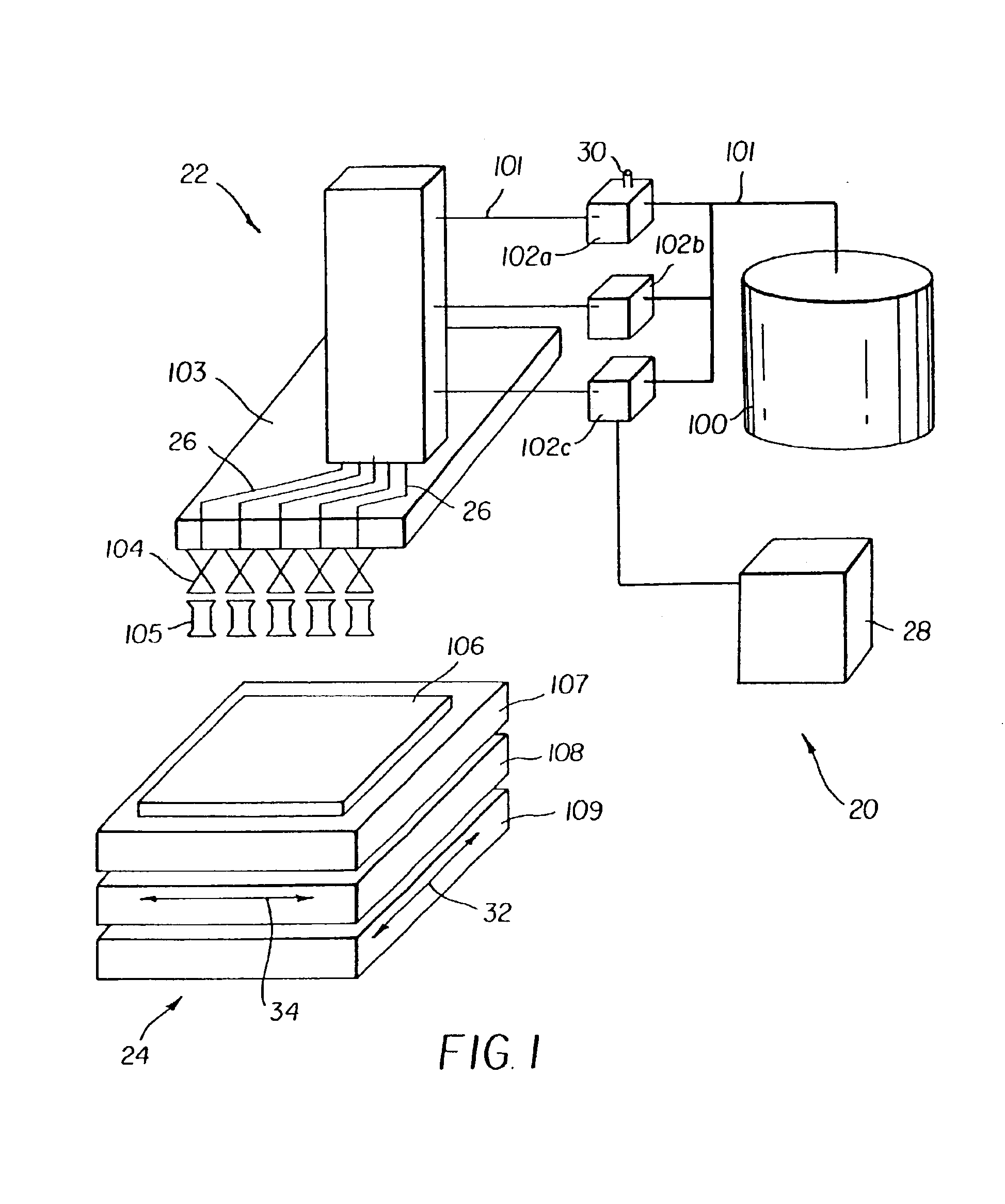
Method of manufacturing a color filter
A method of forming a color filter is provided. The method includes providing a mixture of a color filter material and a compressed fluid; providing at least a partially controlled environment for retaining a substrate, the at least partially controlled environment being in fluid communication with the mixture of the color filter material and the compressed fluid; providing a shadow mask in close proximity to the substrate retained in the at least partially controlled environment; and chargably releasing the mixture of the color filter material and the compressed fluid into the at least partially controlled environment, wherein the color filter material becomes free of the compressed fluid prior to contacting the substrate at locations defined by the shadow mask thereby forming a patterned deposition on the substrate.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method of forming a color filter
A method of forming a color filter and a color filter are provided. The method includes providing a mixture of a color filter material and a compressed fluid; providing a substrate; providing a printhead adapted to deliver the mixture of the color filter material and the compressed fluid toward the substrate; positioning the printhead in a predetermined location relative to the substrate; and ejecting the mixture of the color filter material and the compressed fluid through the printhead toward the substrate, wherein the color filter material becomes free of the compressed fluid prior to the color filter material contacting the substrate at the predetermined location.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
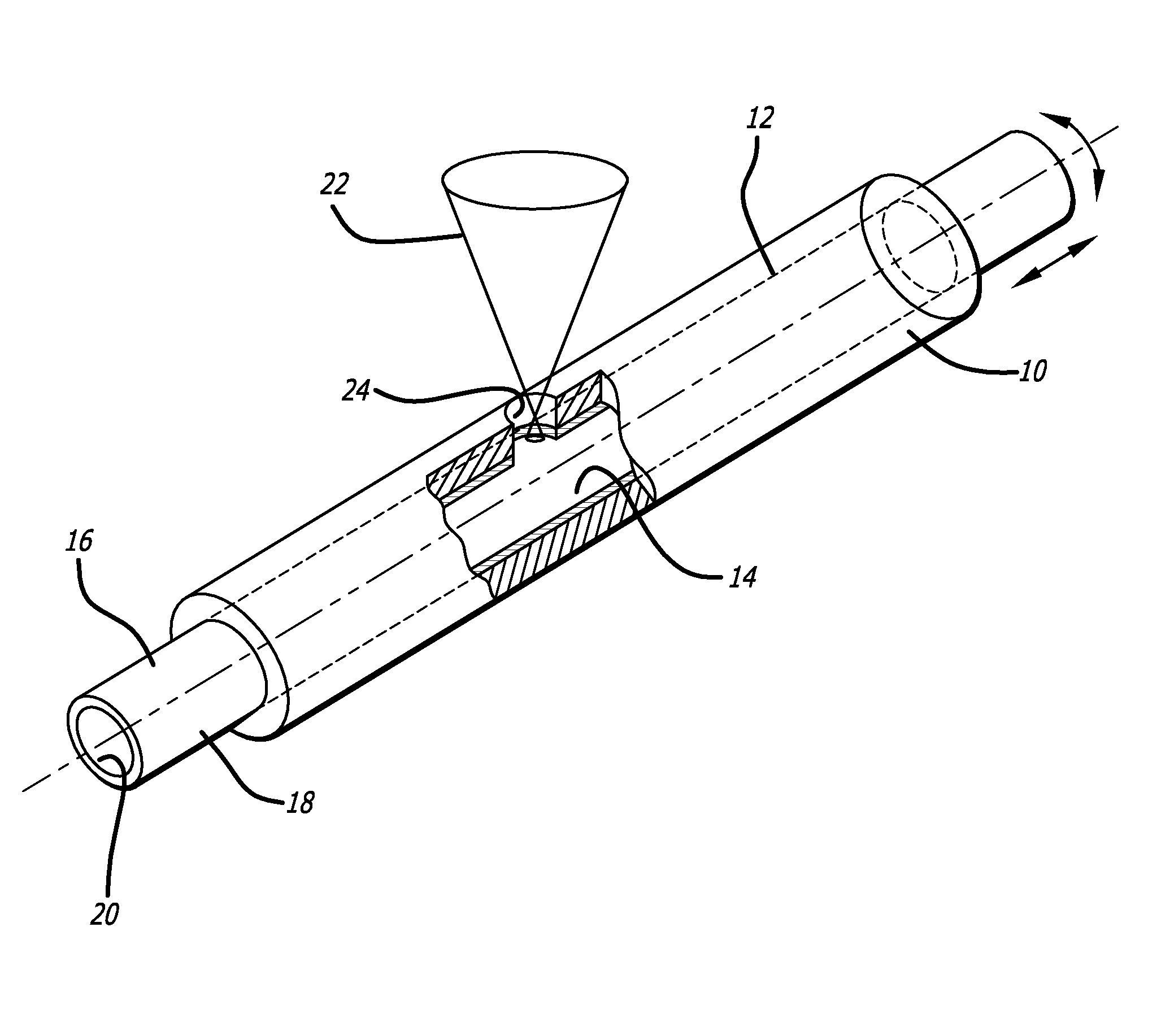
Methods for laser cutting and processing tubing to make medical devices
A method for making a device includes providing a tubular member which will be formed into the device, masking at least a portion of the inner surface of the tubular member with a removable sacrificial material, selectively removing a portion of the tubular member and sacrificial material using a laser device, and mechanically removing the sacrificial material from the inner surface of the tubular member. Ultrasonic energy could be applied to a workpiece which is being laser cut to prevent any generated slag from welding itself to an exposed surface of the workpiece. A compressed fluid or gas, such as air, could be used to clean the surface of the laser-cut workpiece to remove slag formation which adheres to the surface of the cut workpiece.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Valve method for drilling with casing using pressurized drilling fluid
A valve (30), a drill string valve assembly (10) and a method of drilling using compressed fluid as a drill drilling fluid are described. The valve and valve assembly (10) may be used in order to prevent escape of compressed fluid during the time that a connection is being made into the drill string. The valve (10) can be insertable into a drill string inner diameter to seal against fluid passage past the body except through the valve (30) and can be selected to maintain fluid pressure in the drill string when the upper end of the drill string is open to atmosphere. The valve can also be capable of being releasably engaged to a drive mechanism, such as a top drive (40) which is handling the drill string (12) to be slidably moved within the drill string, as driven by the drive mechanism, but releasable from the drive mechanism, when the drive mechanism is removed from the drill string.
Owner:TESCO CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for flowing compressed fluids into and out of containment
ActiveUS8281820B2Adjustable temperatureGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsChemical compositionDifferential pressure
Methods for loading a compressed fluid, such as natural gas, into and discharging the compressed fluid out of containment are provided. The compressed fluid is injected into a bottom portion of a container system for storage and / or transport until a target pressure is reached after which gas is withdrawn from an upper portion of the container system at a rate to maintain the target pressure while the compressed fluid is injected in the bottom portion. The compressed fluid is cooled through an expansion valve and by refrigerated chillers or by injecting a cold liquid of the same chemical composition as the compressed fluid, such as liquid natural gas, into the compressed fluid prior to injection into the container system. Withdrawal or discharge from the container system to a receiving facility begins with blow down from the bottom portion of the container system without a displacement fluid and continues until pressure falls below an acceptable differential pressure. The discharge stream is passed through a separator and a light gas from the separator is pressurized and injected into an upper portion of the container system to drive the compressed fluid out the bottom. The light gas is pressurized using either a compressor or a heated tank system, where two vessels operate in parallel, trapping and heating the light gas and then discharging to the container system from one while filling the other and alternating the operation between the two.
Owner:WHITE CHARLES N +1
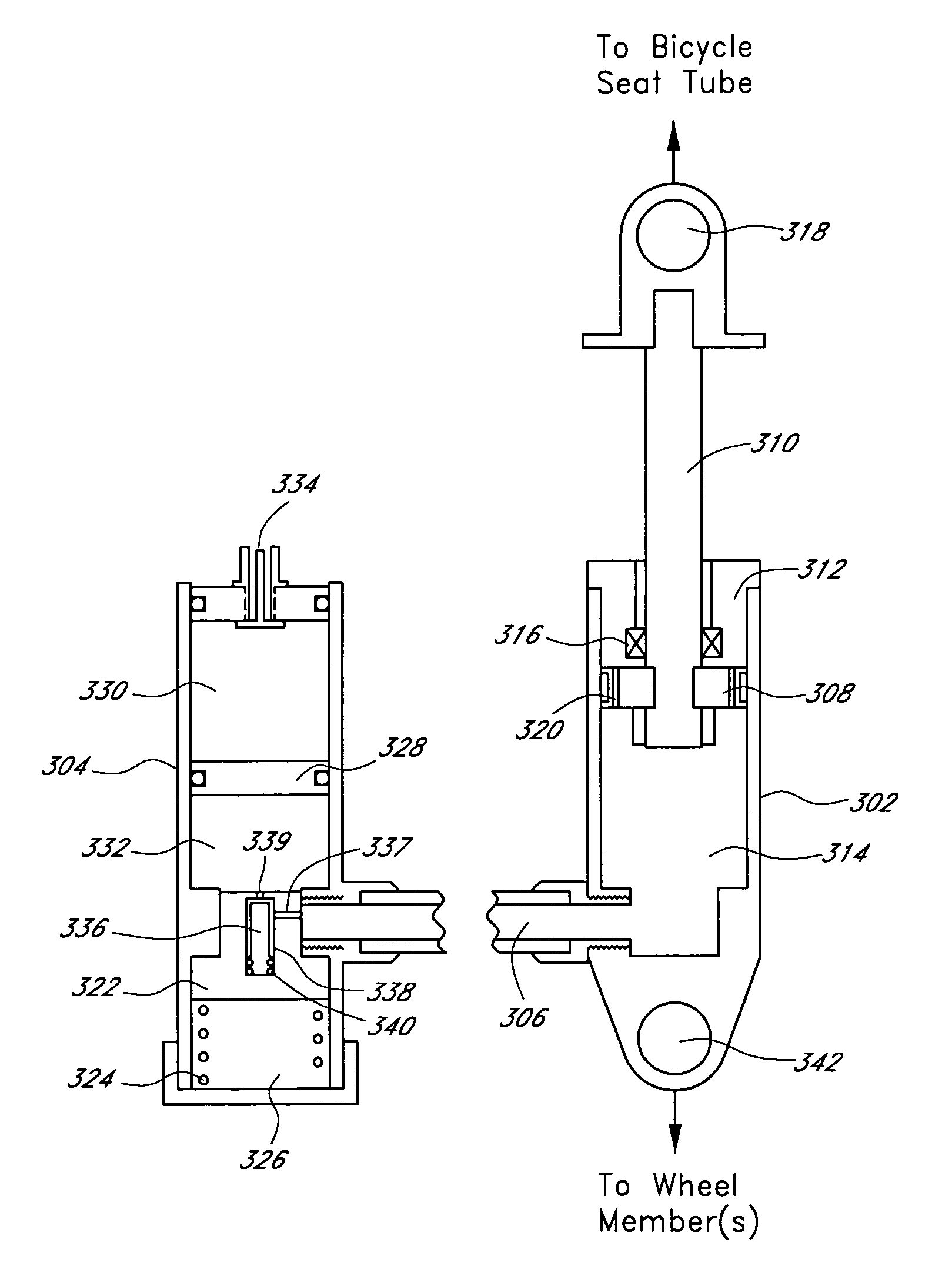
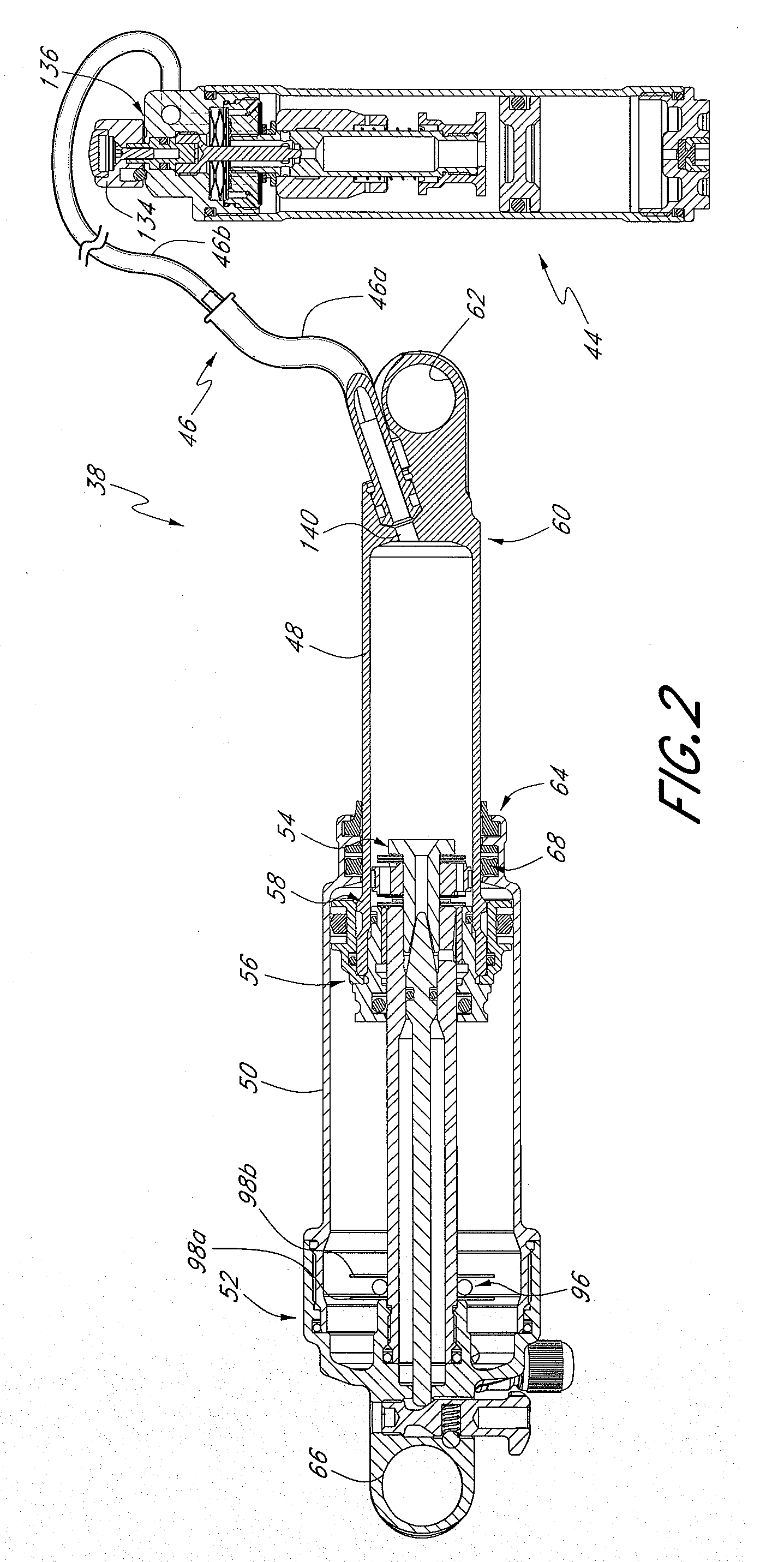
Bicycle damper
A damper for a bicycle having, in one arrangement, a primary unit and a remote unit. The primary unit includes a damper tube, a spring chamber, and a piston rod that supports a main piston. The main piston is movable within the damper chamber of the primary unit. The main piston and the damper tube at least partially define a compression chamber. The remote unit comprises a remote fluid chamber and an inertial valve within the remote unit. The inertial valve is preferably responsive to terrain-induced forces and preferably not responsive to rider-induced forces when the shock absorber is assembled to the bicycle. A fluid flow control arrangement within the remote unit utilizes compression fluid flow to delay closing of the inertia valve after acceleration forces acting on the inertia valve diminish. In some arrangements, the inertia valve and fluid flow control arrangement may reside in the primary unit.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Tire pressure monitoring method
A method of monitoring the fluid pressure of, with a sensor of a tire pressure management system disposed without, a tire that prevents overinflation of same. The method of monitoring a fluid pressure of a tire with a sensor, disposed in conduit assemblies for conducting fluid to or from the tire, of a tire pressure management system includes providing a pulse of compressed fluid to the conduit assemblies, unless a counter exceeds a count, the fluid in the conduit assemblies thereafter having a conduit pressure. The pulse has a duration that corresponds to a ratio defined by a first predetermined amount divided by a second predetermined amount.
Owner:DANA HEAVY VEHICLE SYSTEMS GROUP LLC
Authentication method and apparatus for use with compressed fluid printed swatches
InactiveUS20050018013A1Digital marking by photographic/thermographic registrationPrintingCompressed fluidEngineering
Authentication systems, apparatus, and methods authenticate an identification marking including a nanocrystalline material. One or more properties of the marking are ascertained to provide a measured profile. The measured profile is compared to at least one member of a closed set of reference profiles. Each reference profile has predetermined values of one or more properties. Each reference profile is unique within the set. At least one reference profile is characteristic of an indicator material in a nanocrystalline morphology and non-characteristic of the same indicator material in a bulk morphology.
Owner:EAPEIRON SOLUTIONS INC
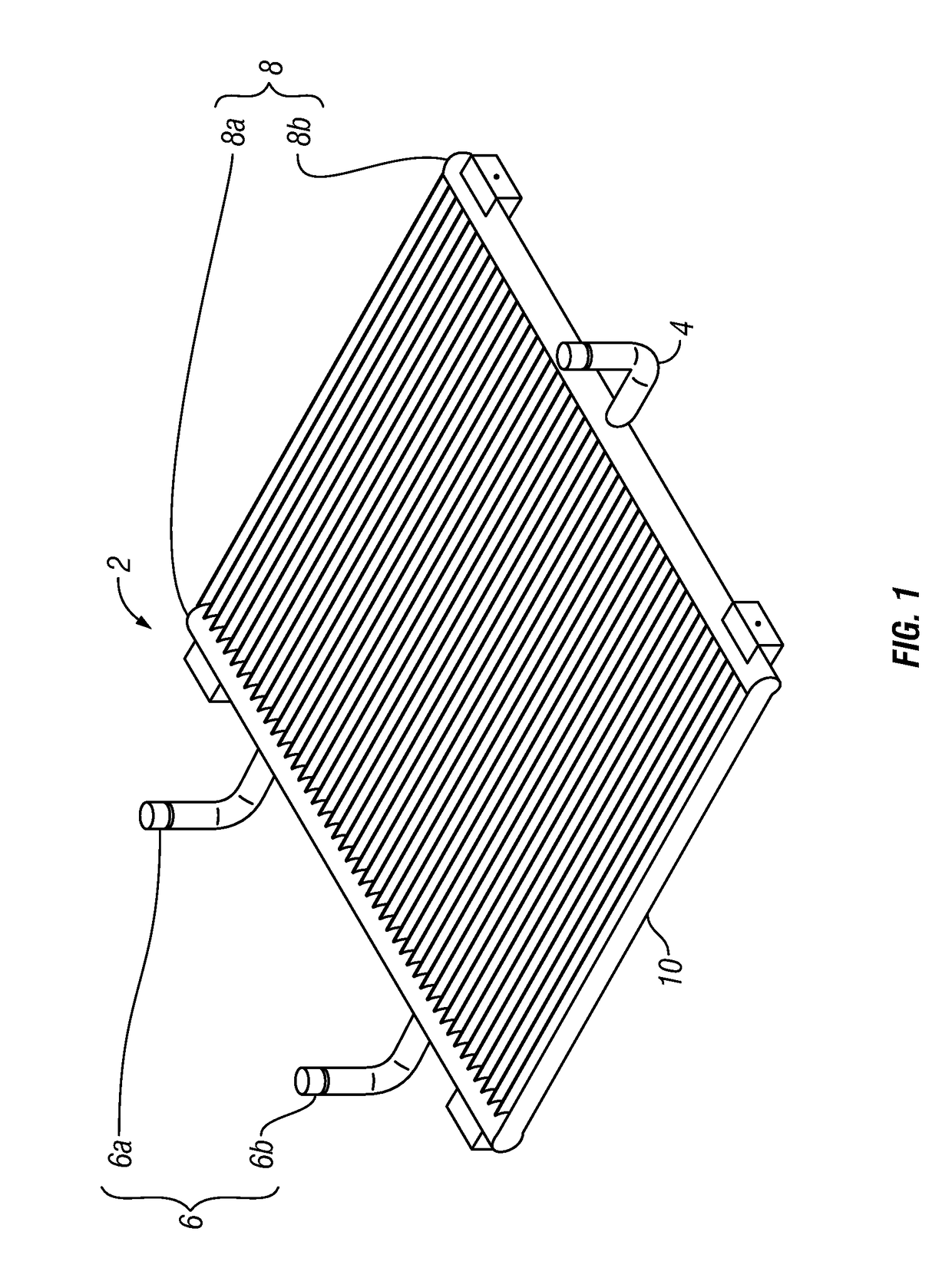
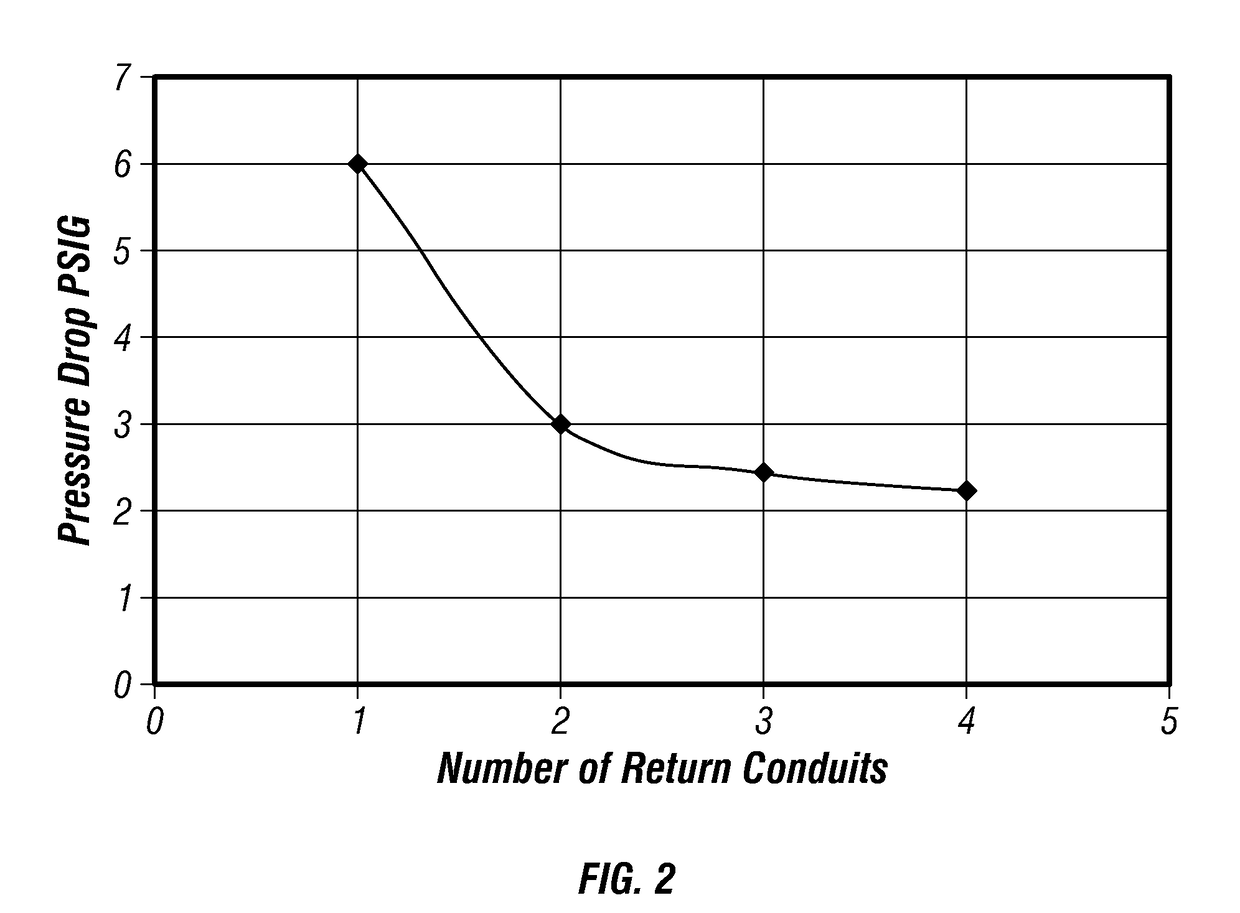
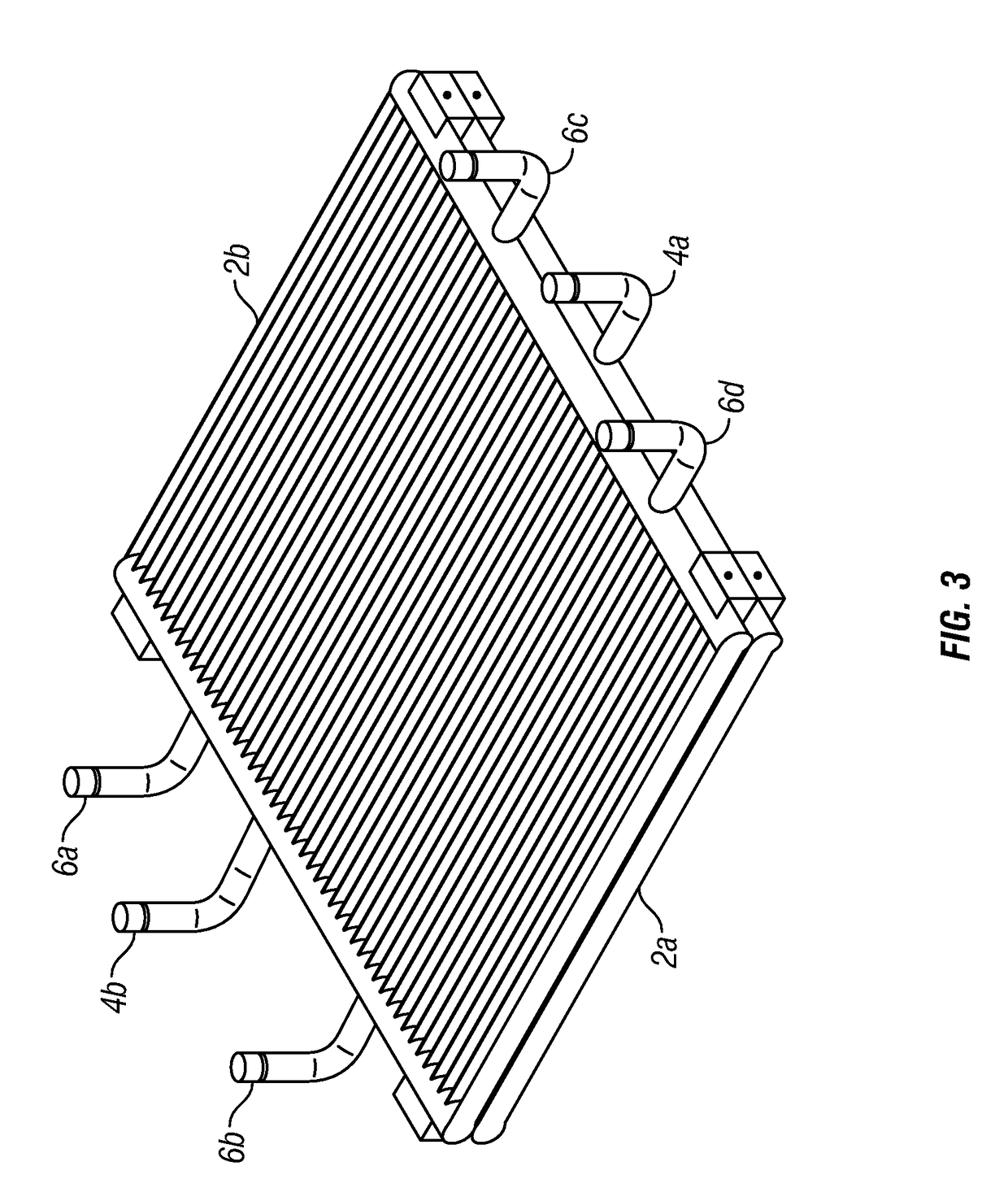
Heat exchanger and method for use in precision cooling systems
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Bicycle damper
A damper for a bicycle having, in one arrangement, a primary unit and a remote unit. The primary unit includes a damper tube, a spring chamber, and a piston rod that supports a main piston. The main piston is movable within the damper chamber of the primary unit. The main piston and the damper tube at least partially define a compression chamber. The remote unit comprises a remote fluid chamber and an inertial valve within the remote unit. The inertial valve is preferably responsive to terrain-induced forces and preferably not responsive to rider-induced forces when the shock absorber is assembled to the bicycle. A fluid flow control arrangement within the remote unit utilizes compression fluid flow to delay closing of the inertial valve after acceleration forces acting on the inertial valve diminish. In some arrangements, the inertial valve and fluid flow control arrangement may reside in the primary unit.
Owner:SPECIALIZED BICYCLE COMPONENTS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com