Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10531results about "Stationary conduit assemblies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
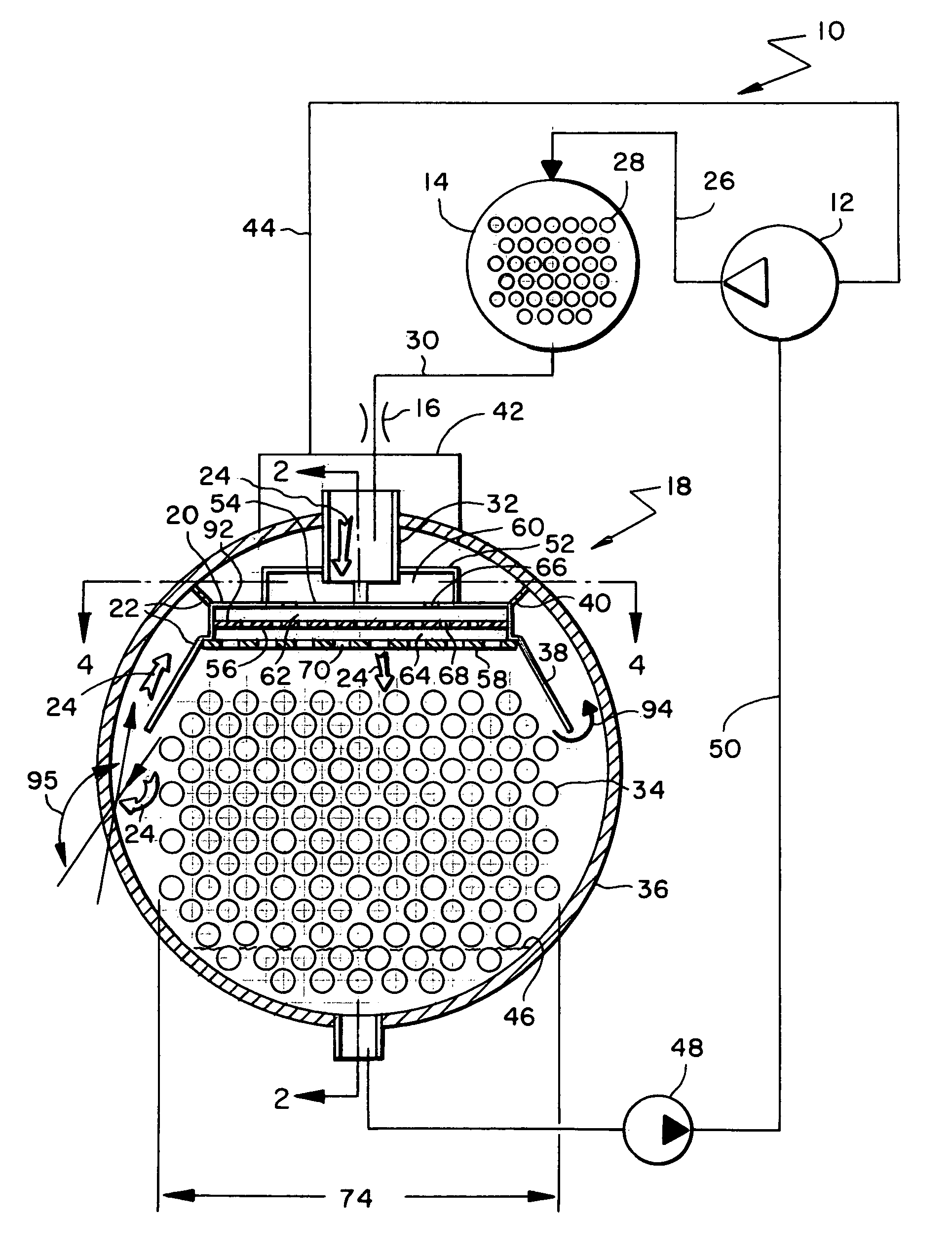
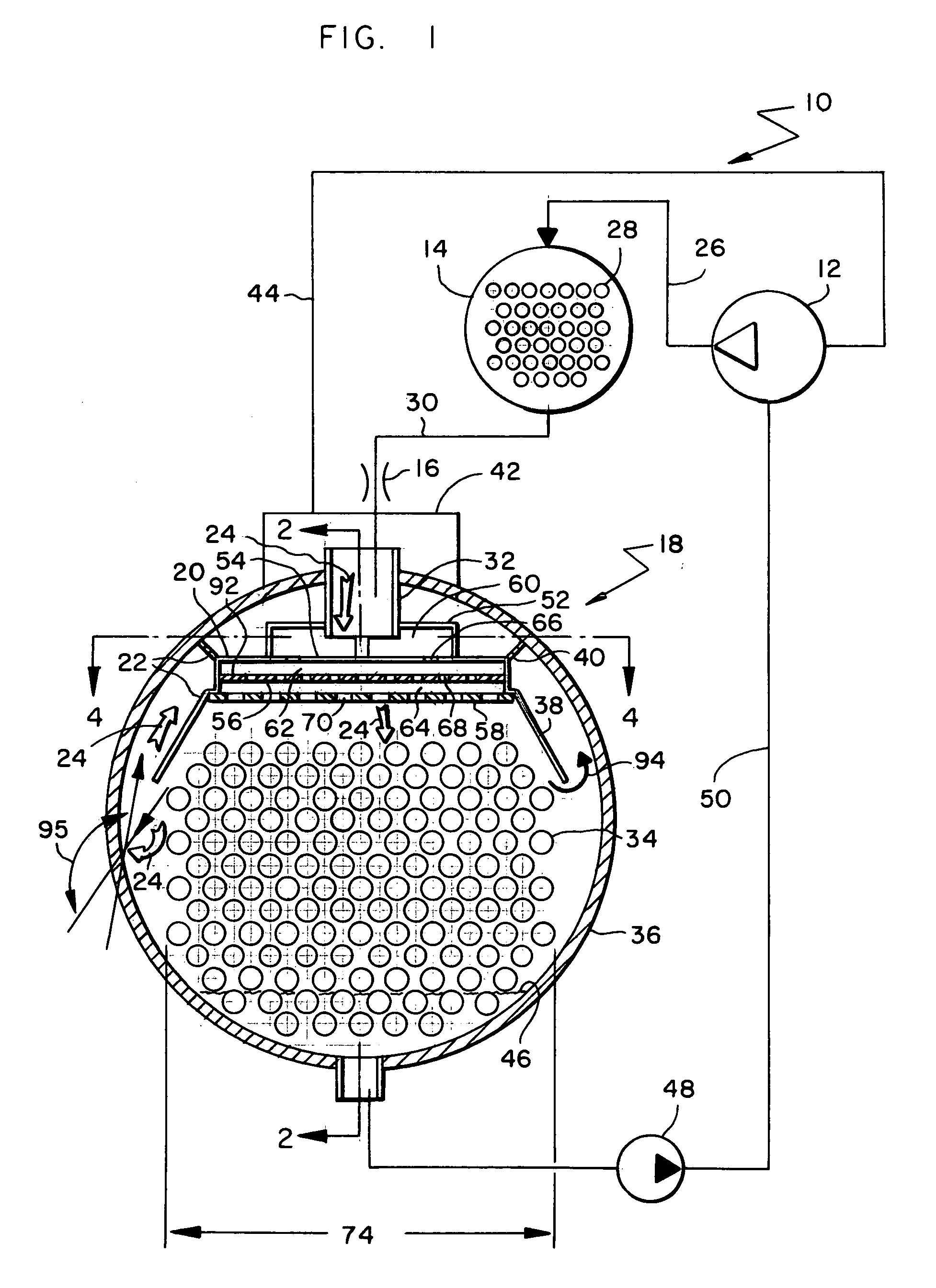
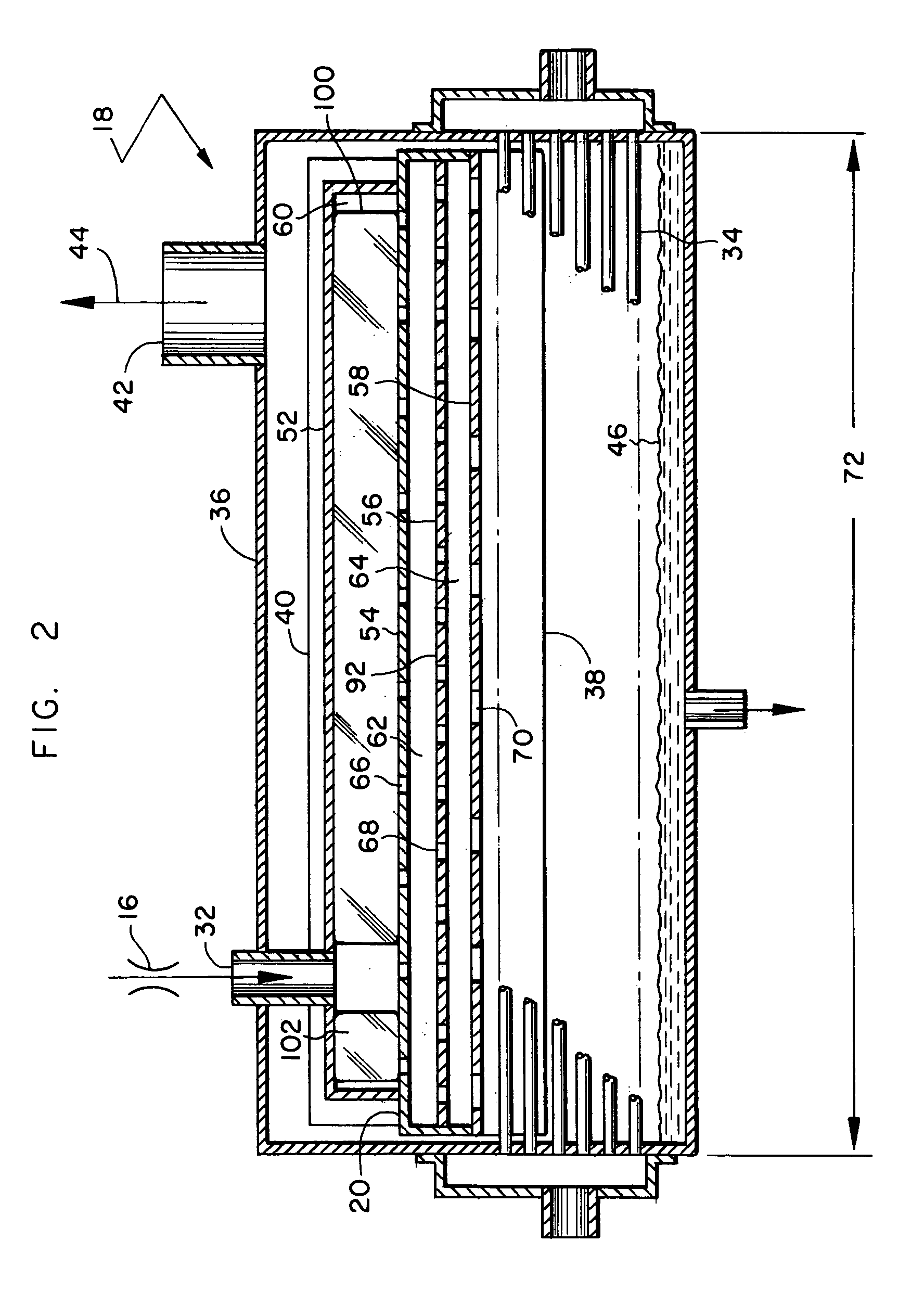
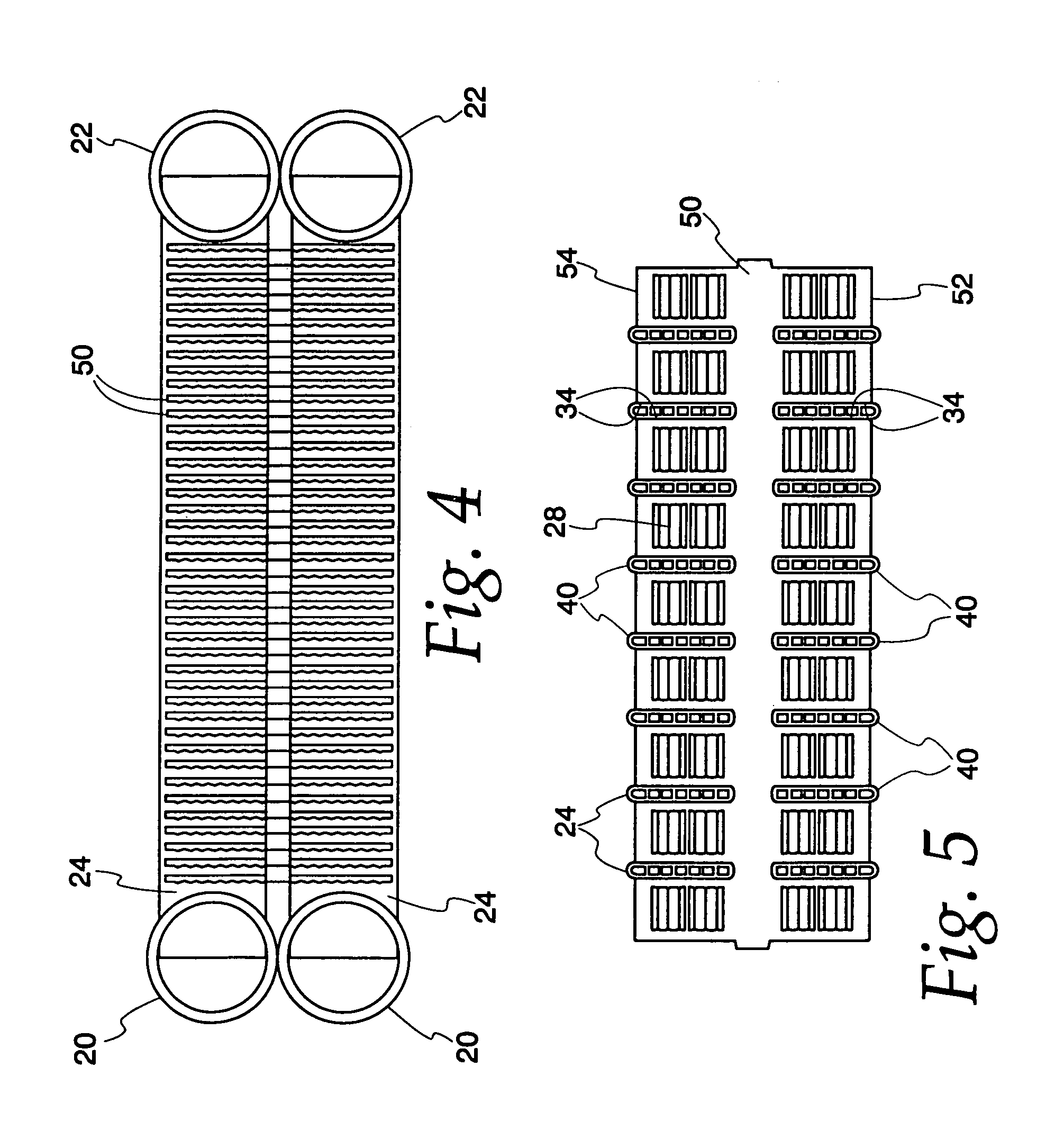
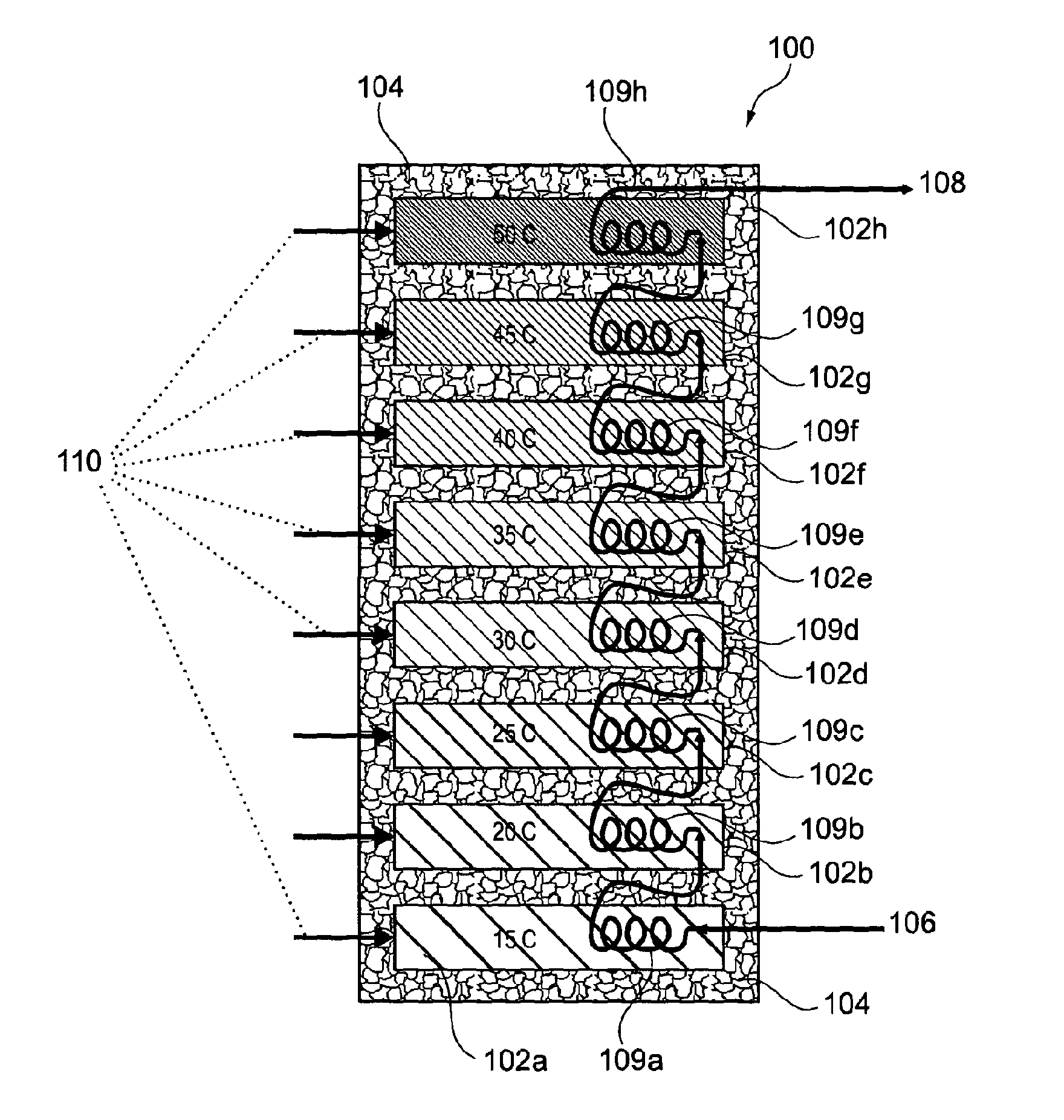
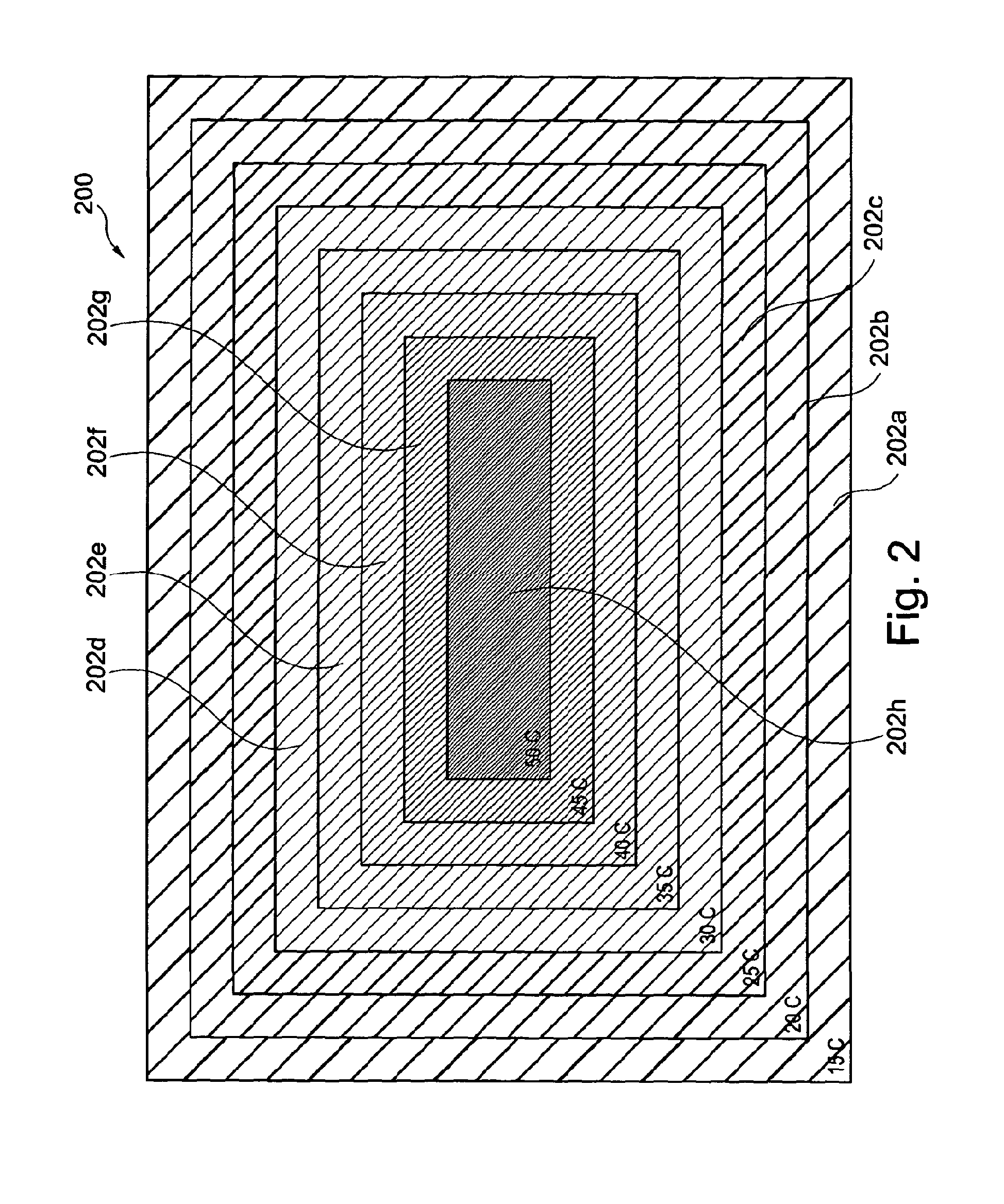
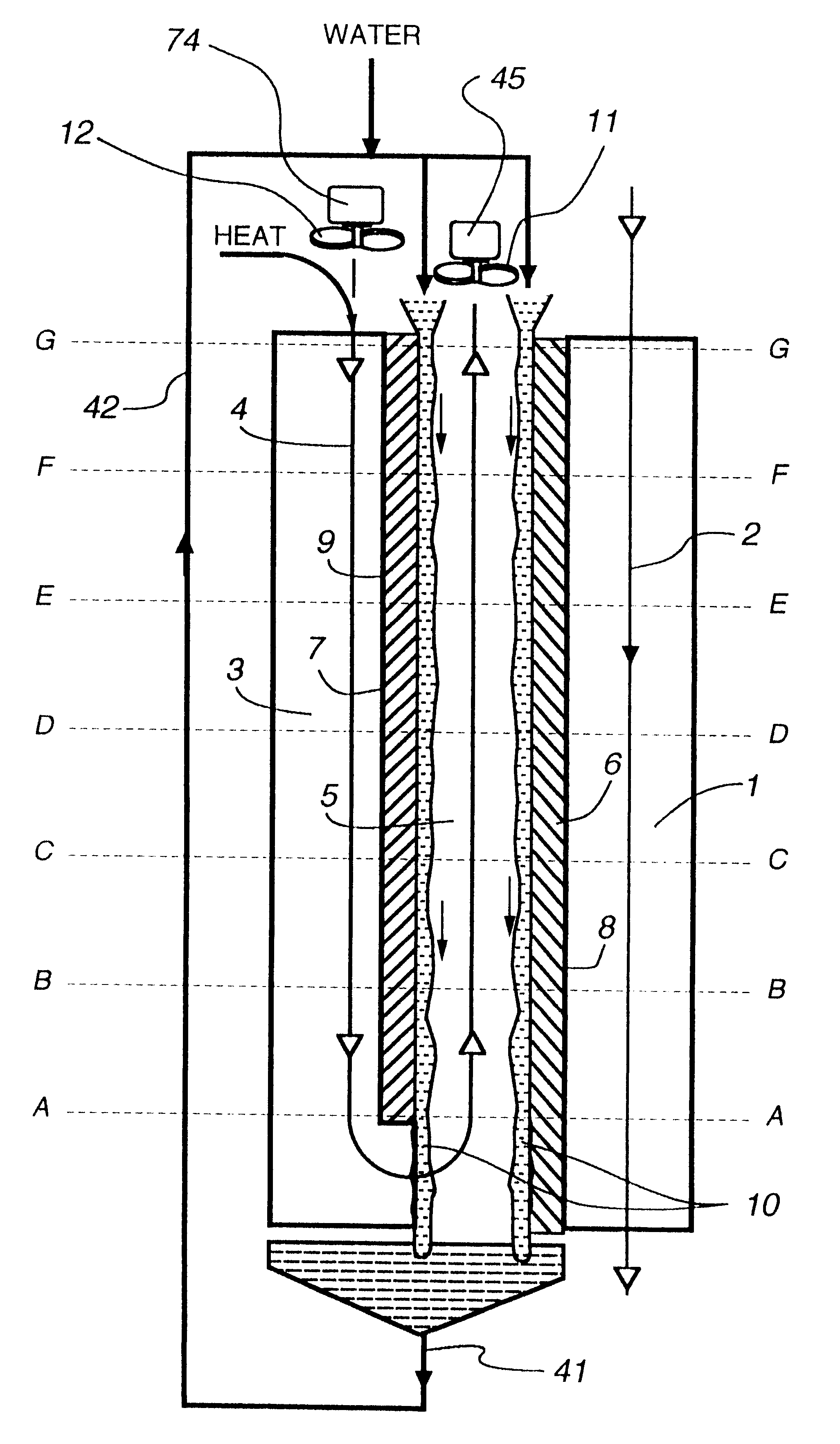
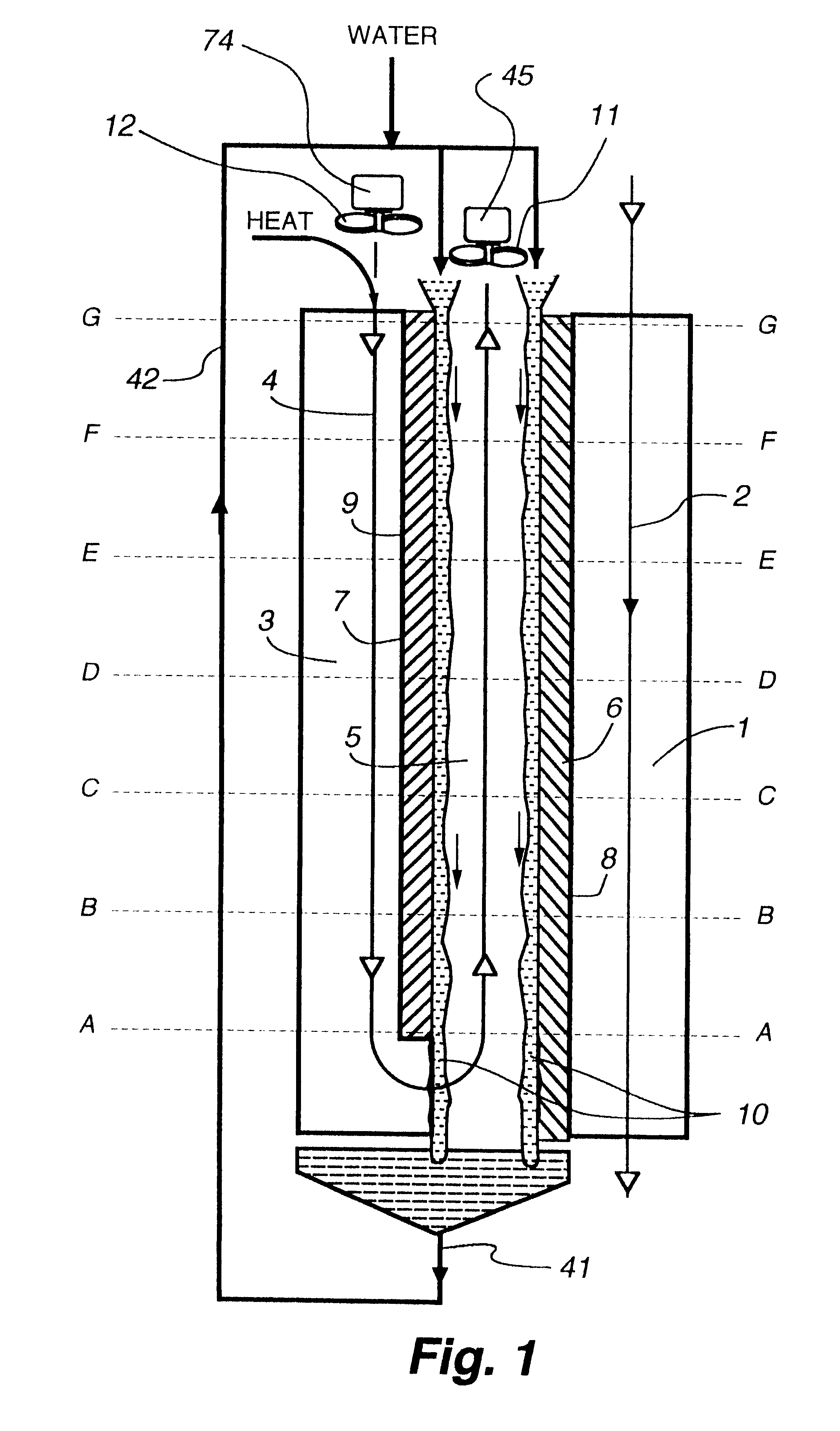
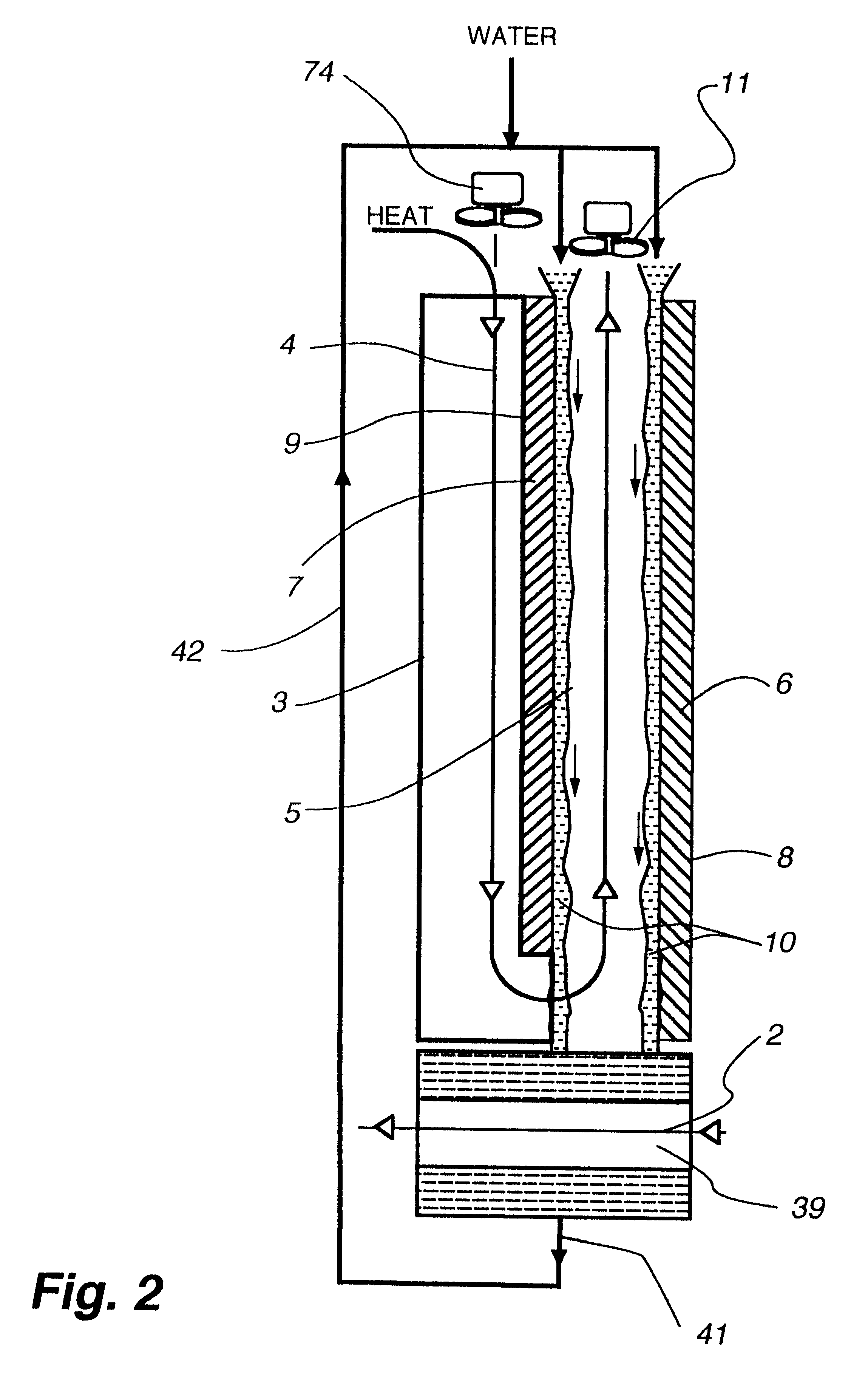
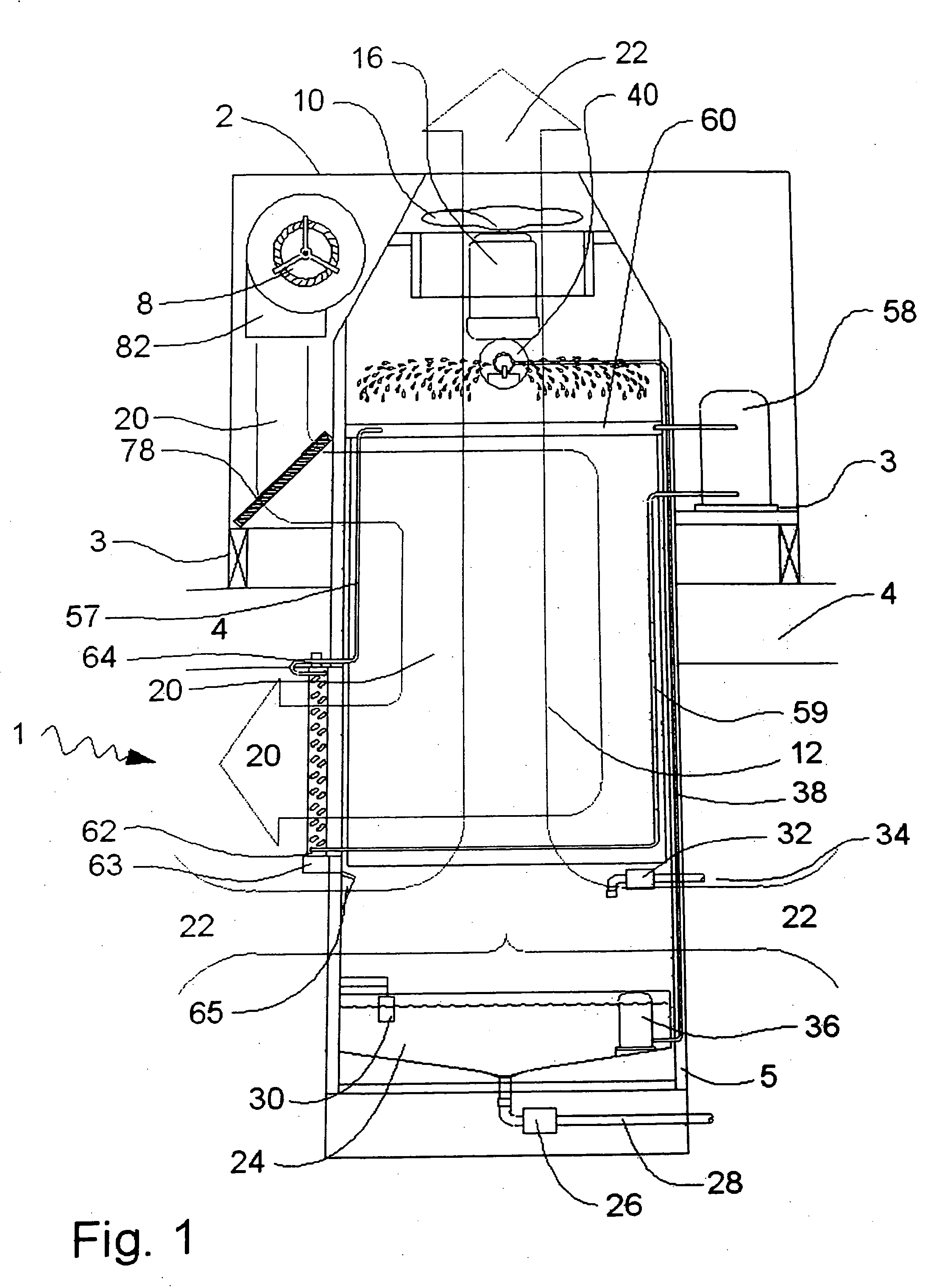
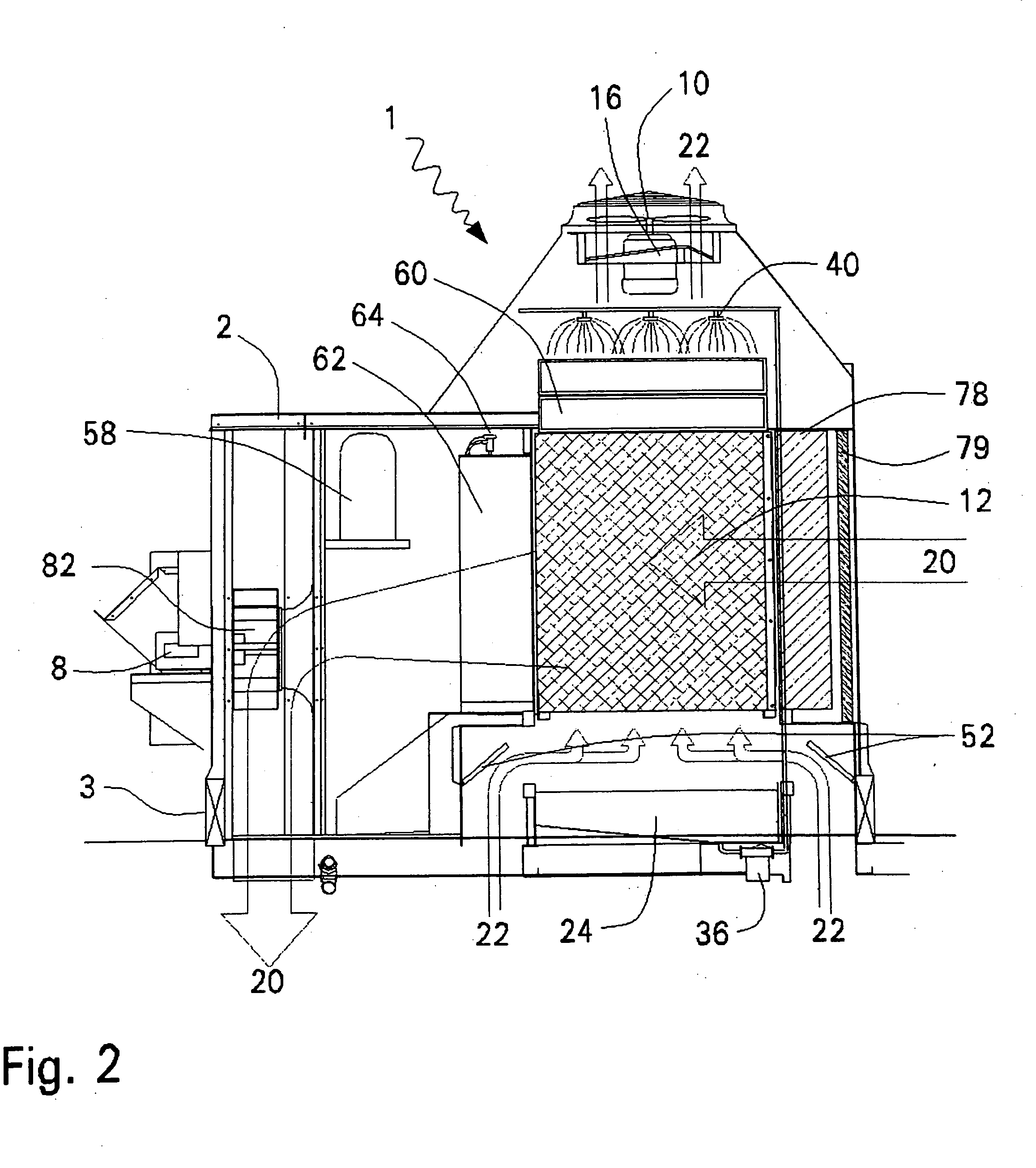
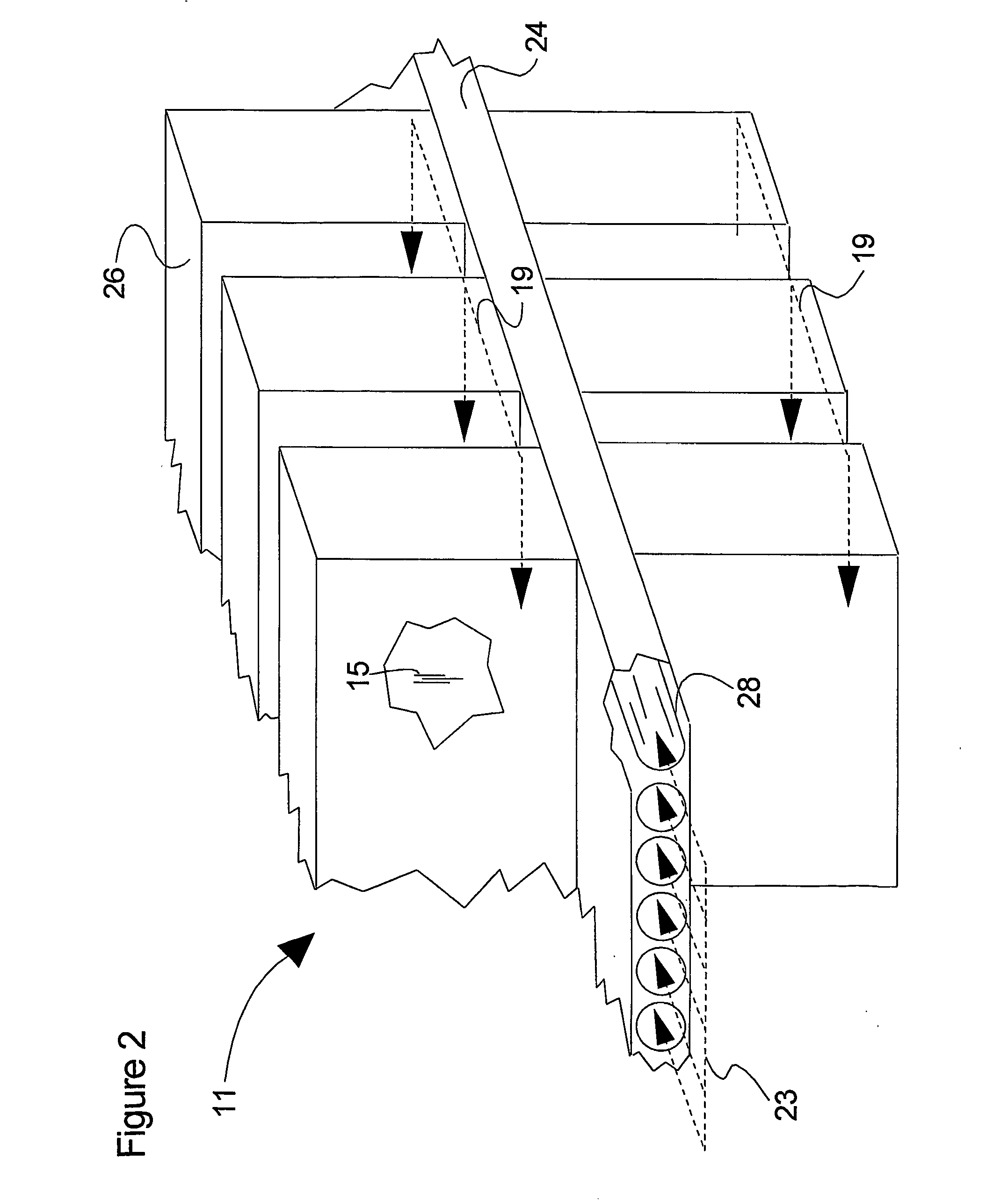
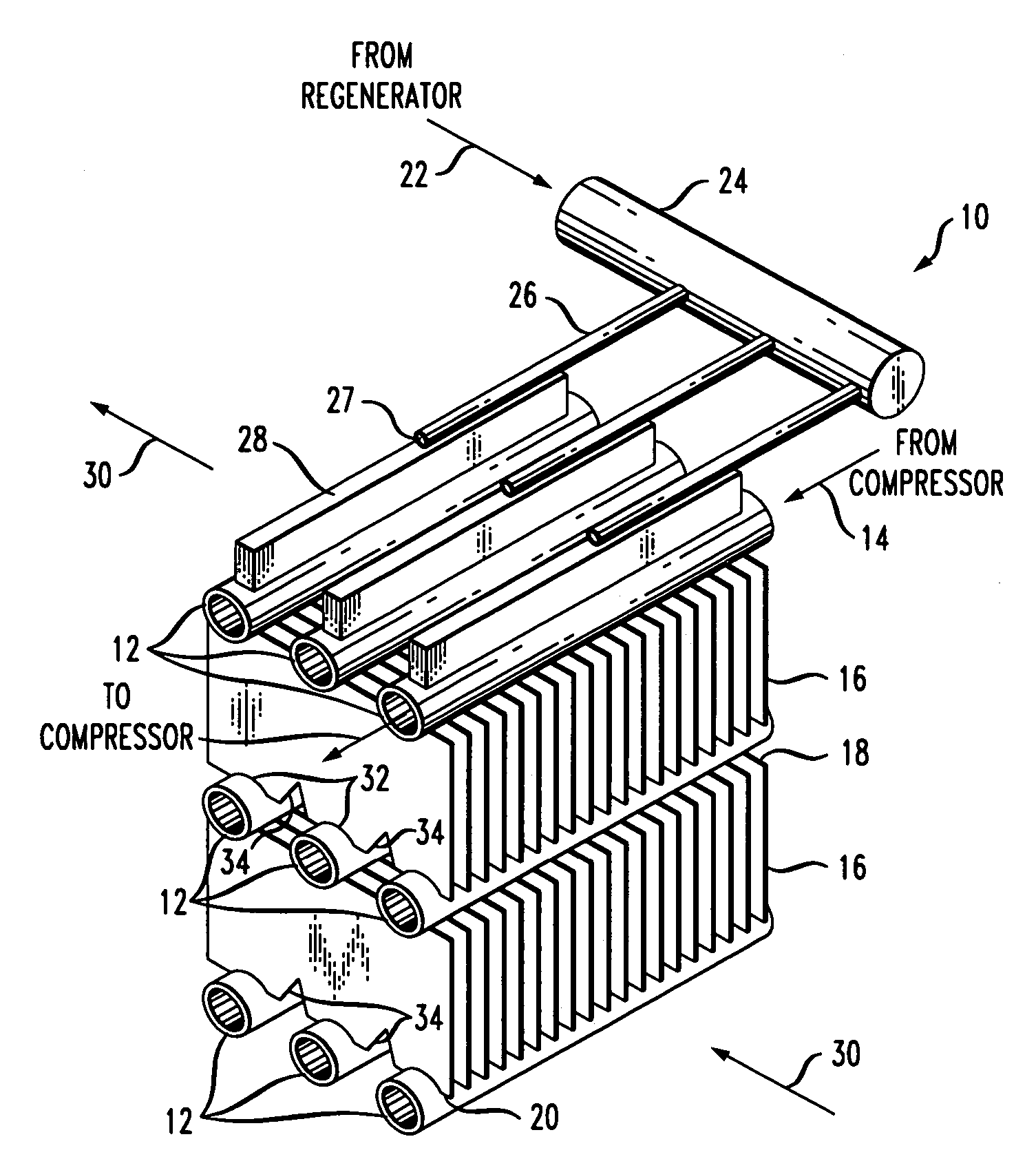
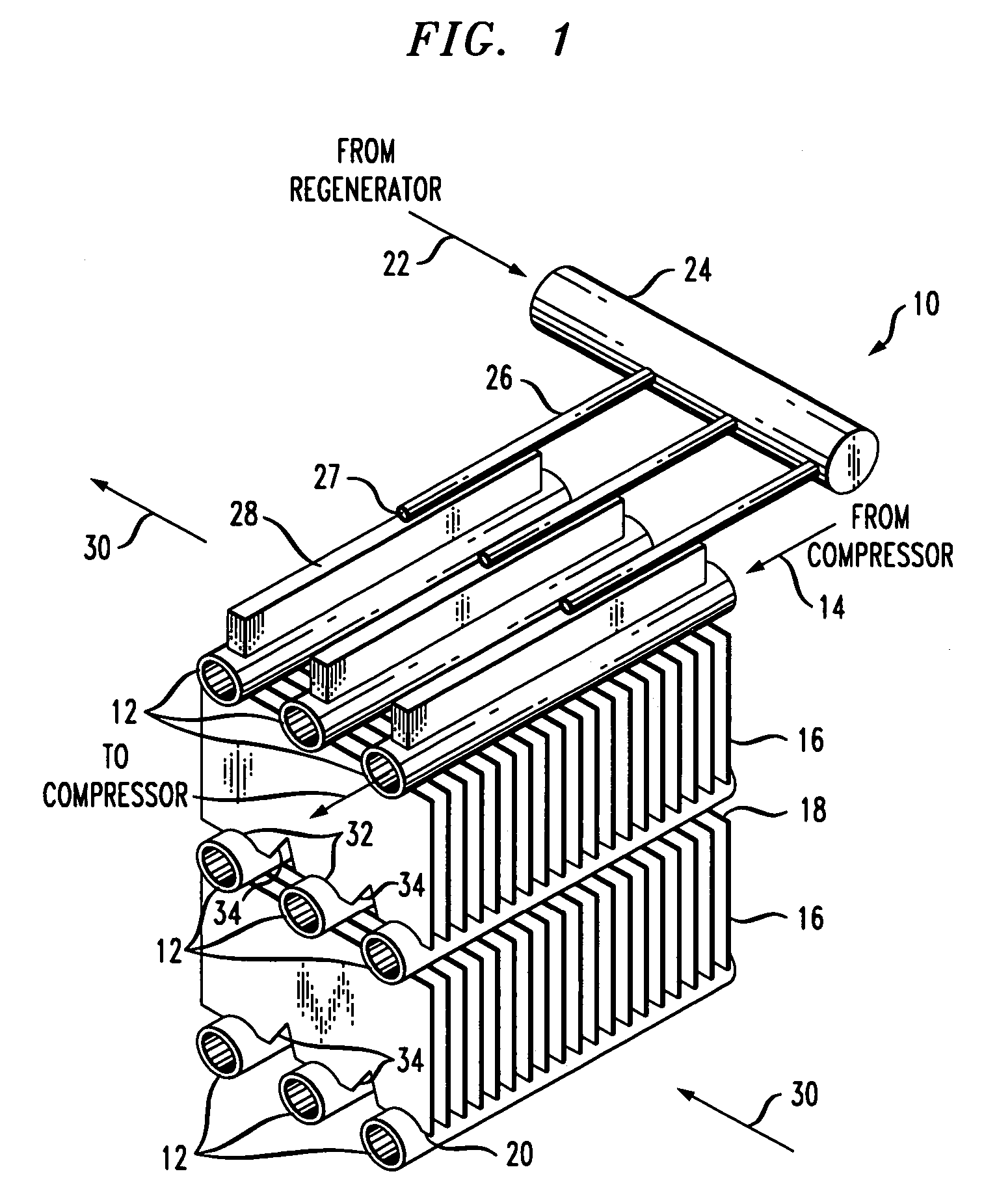
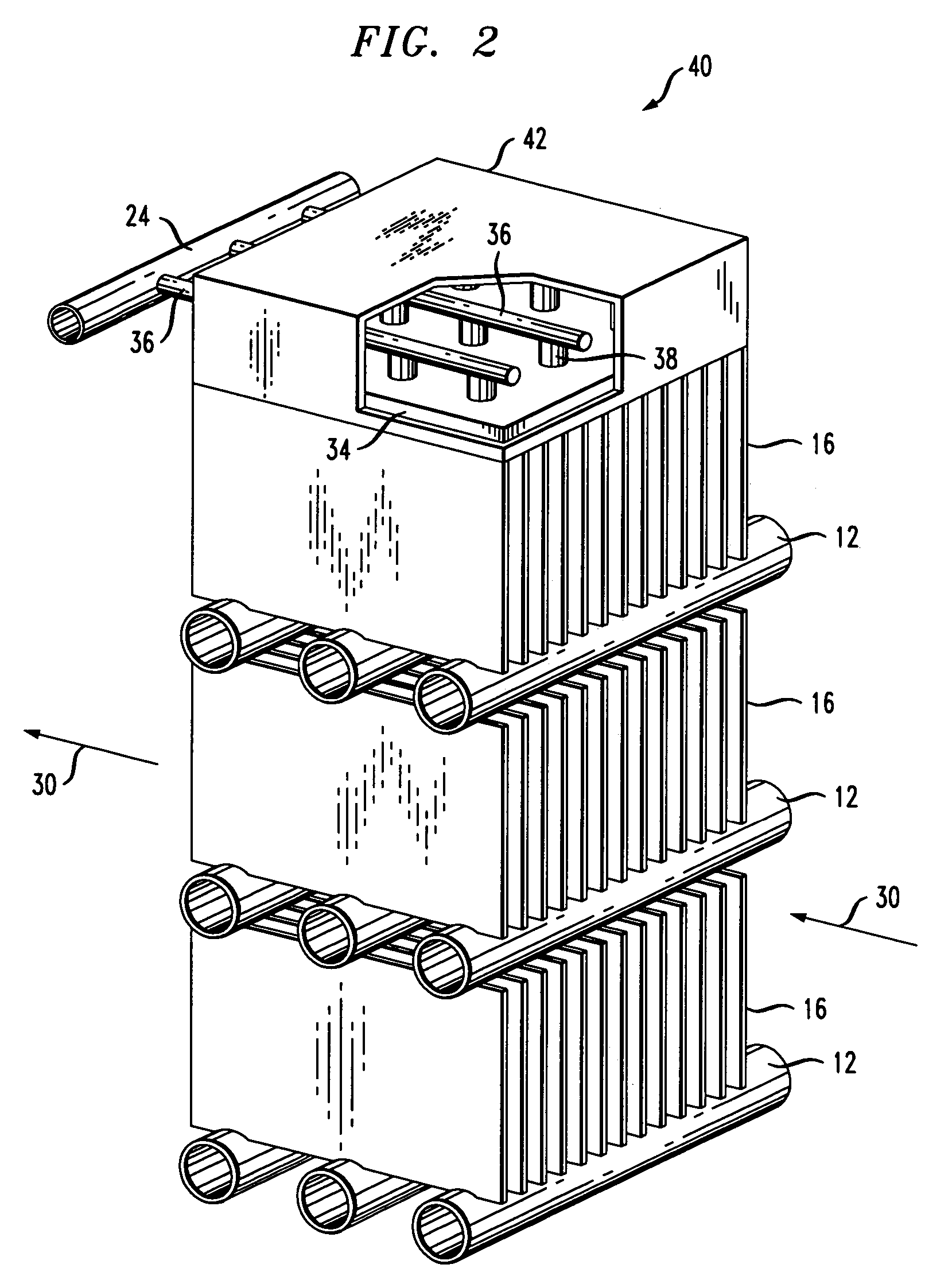
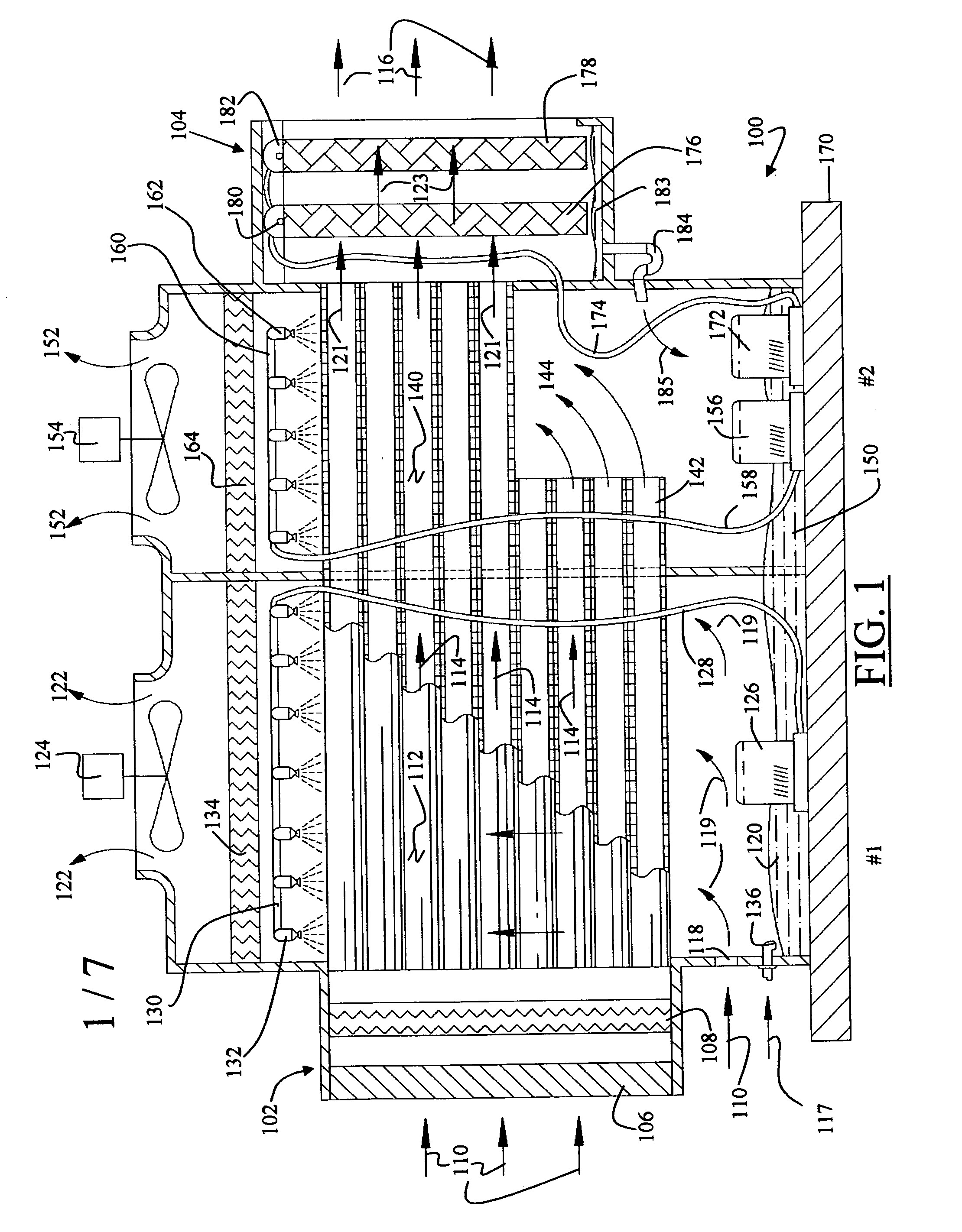
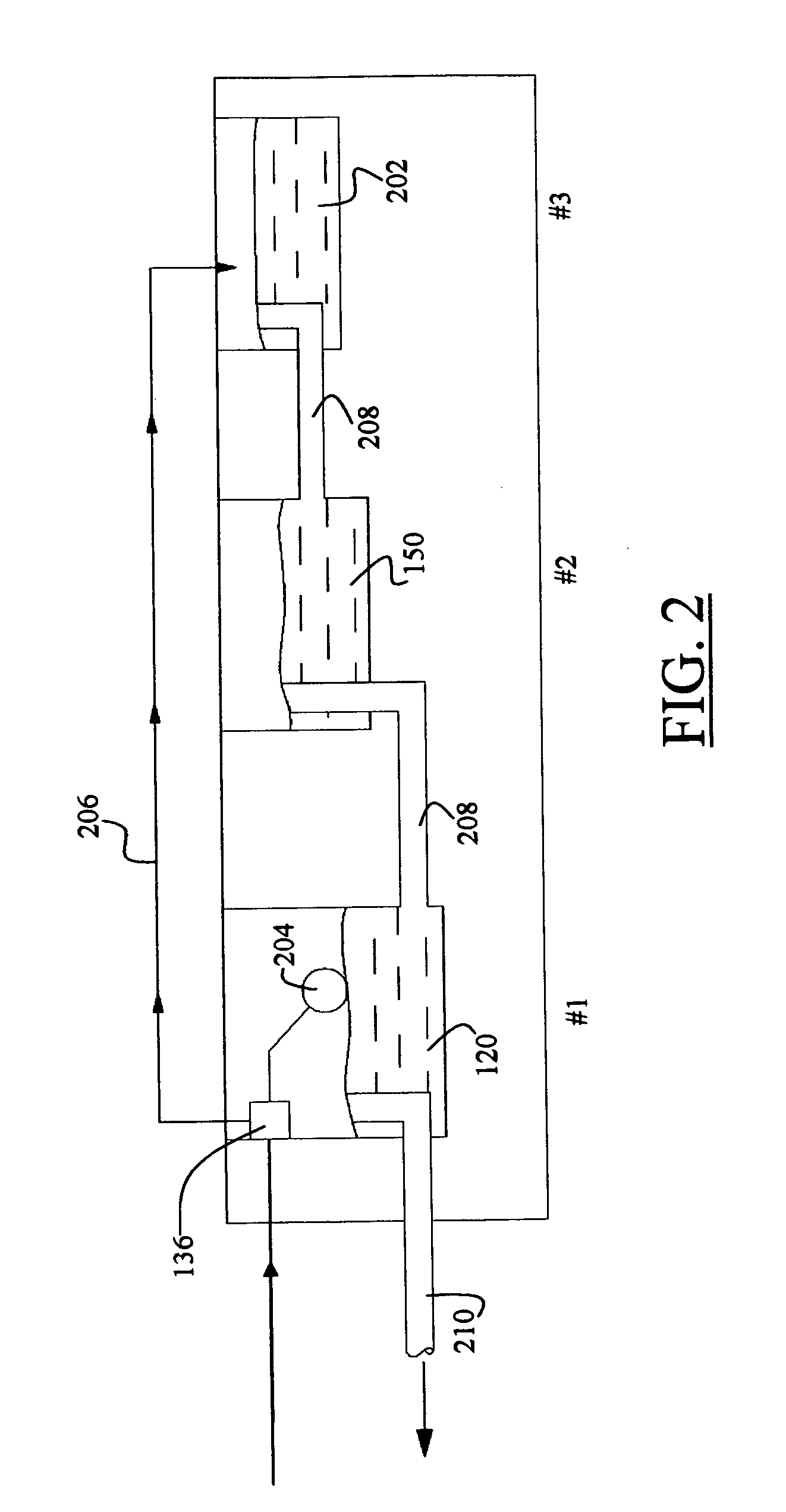
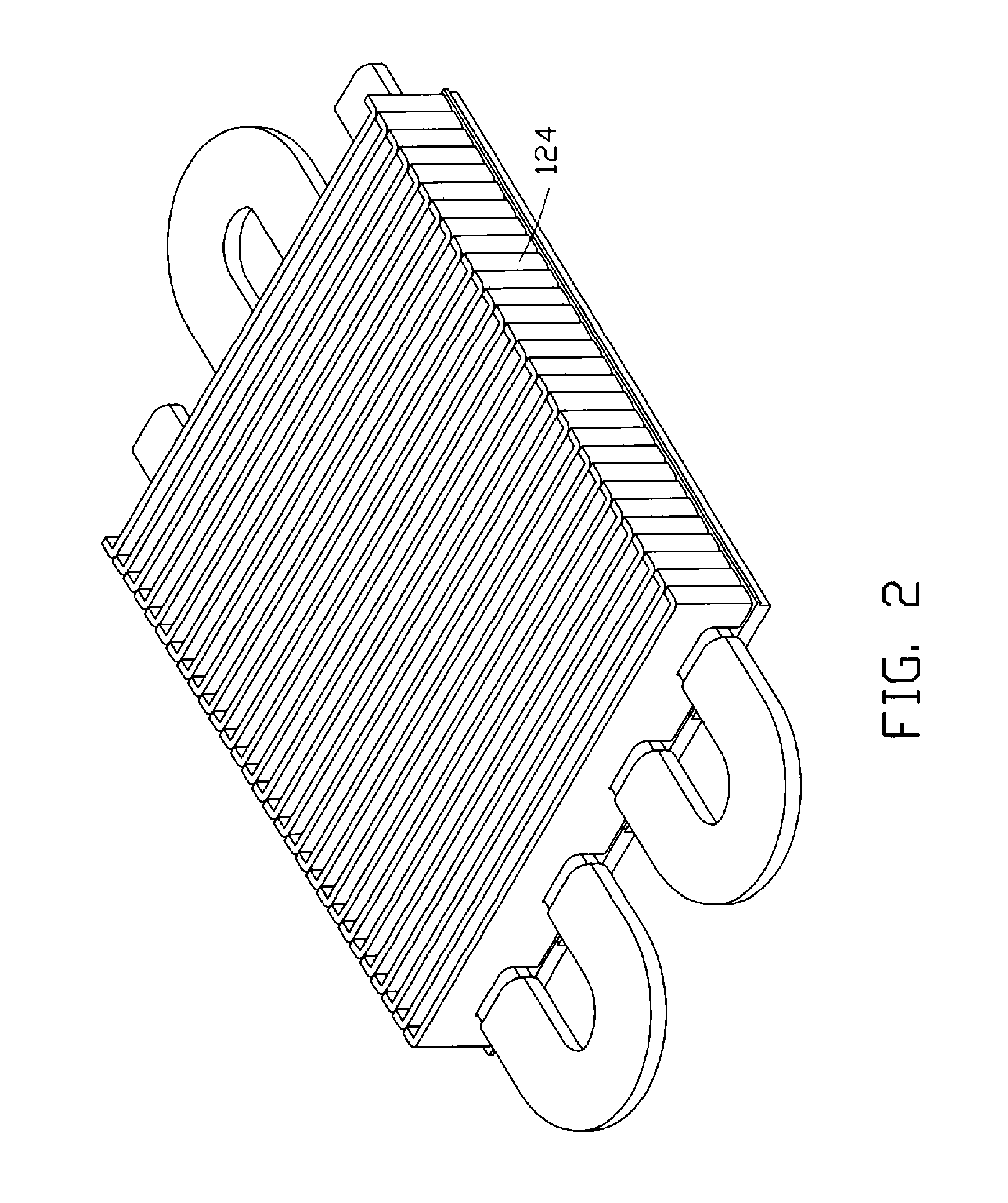
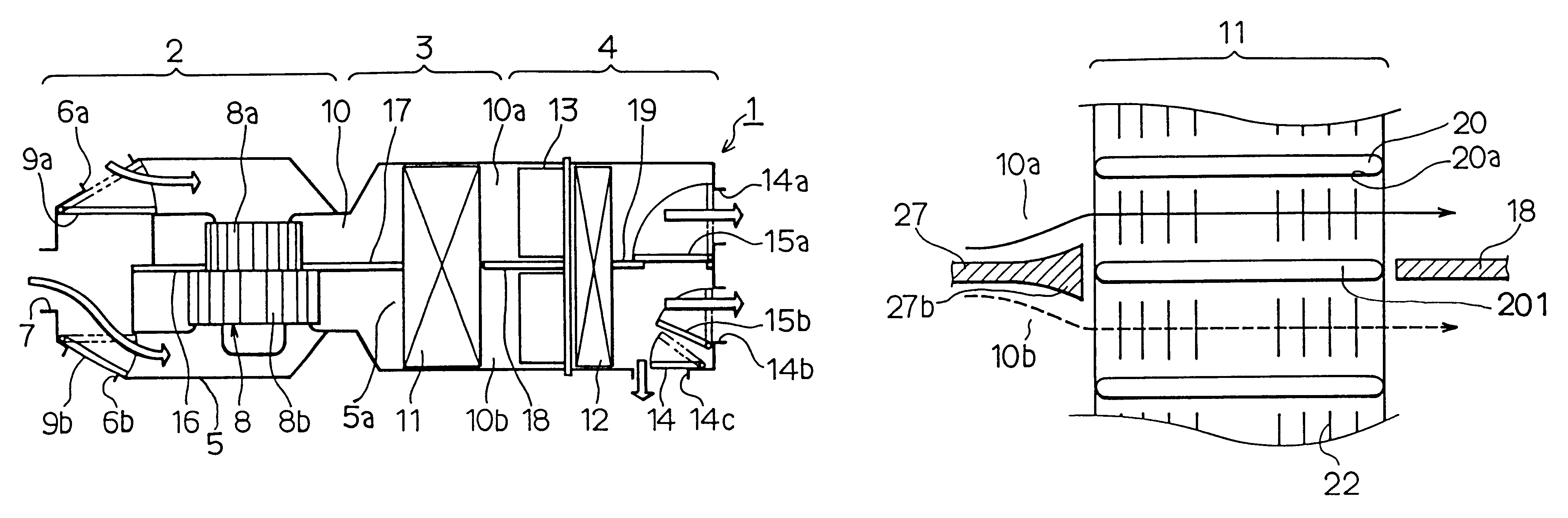
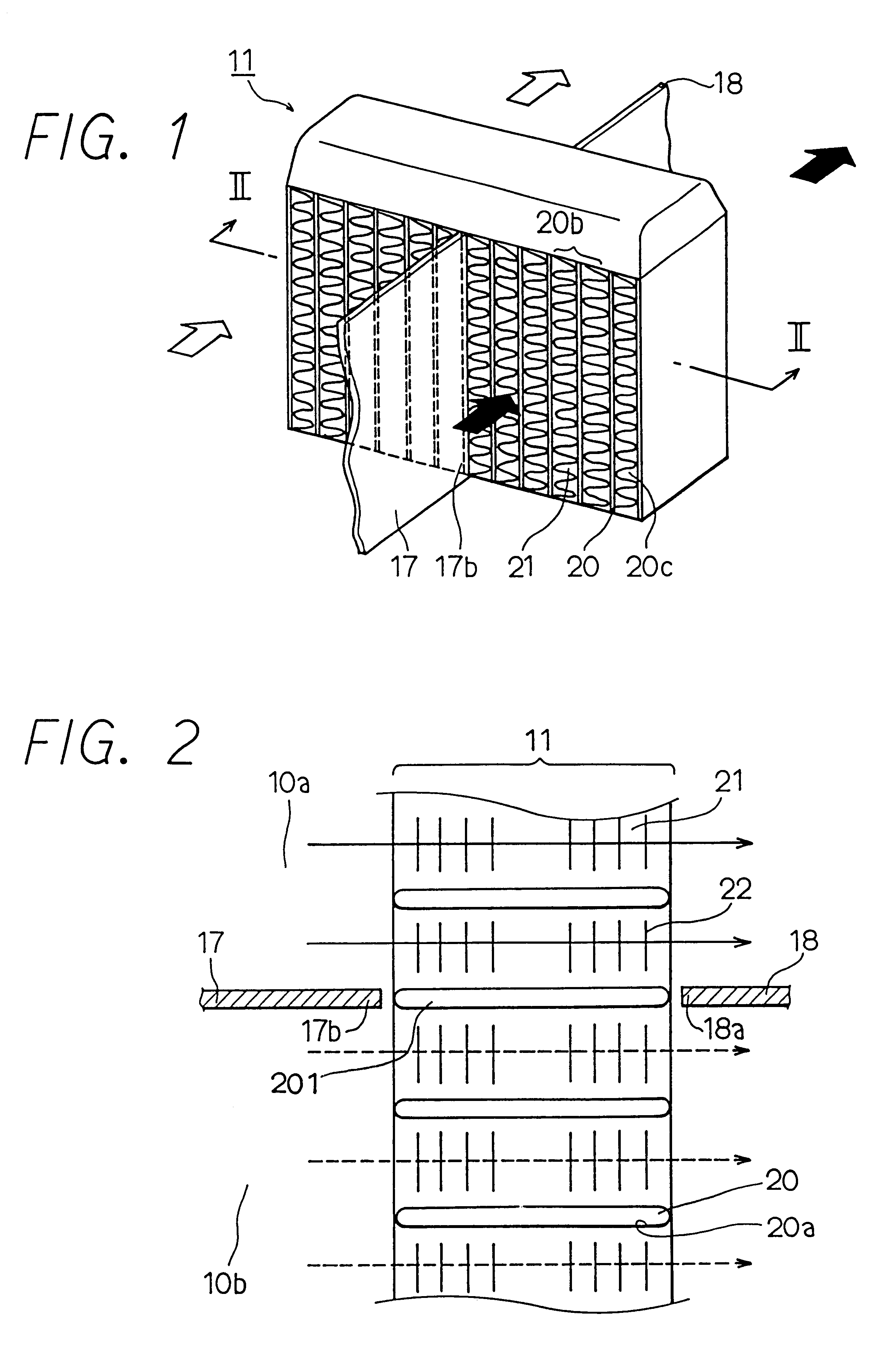
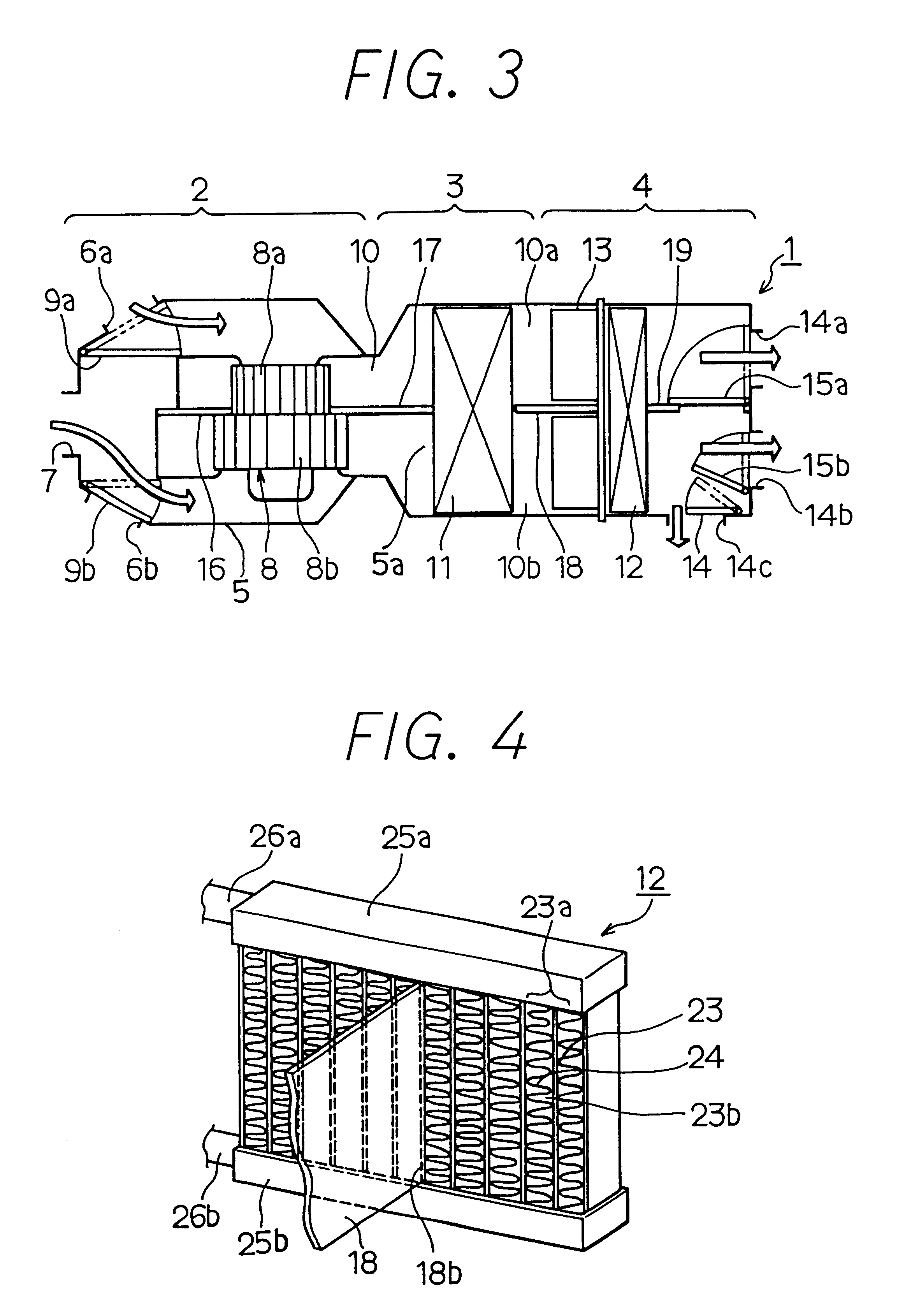
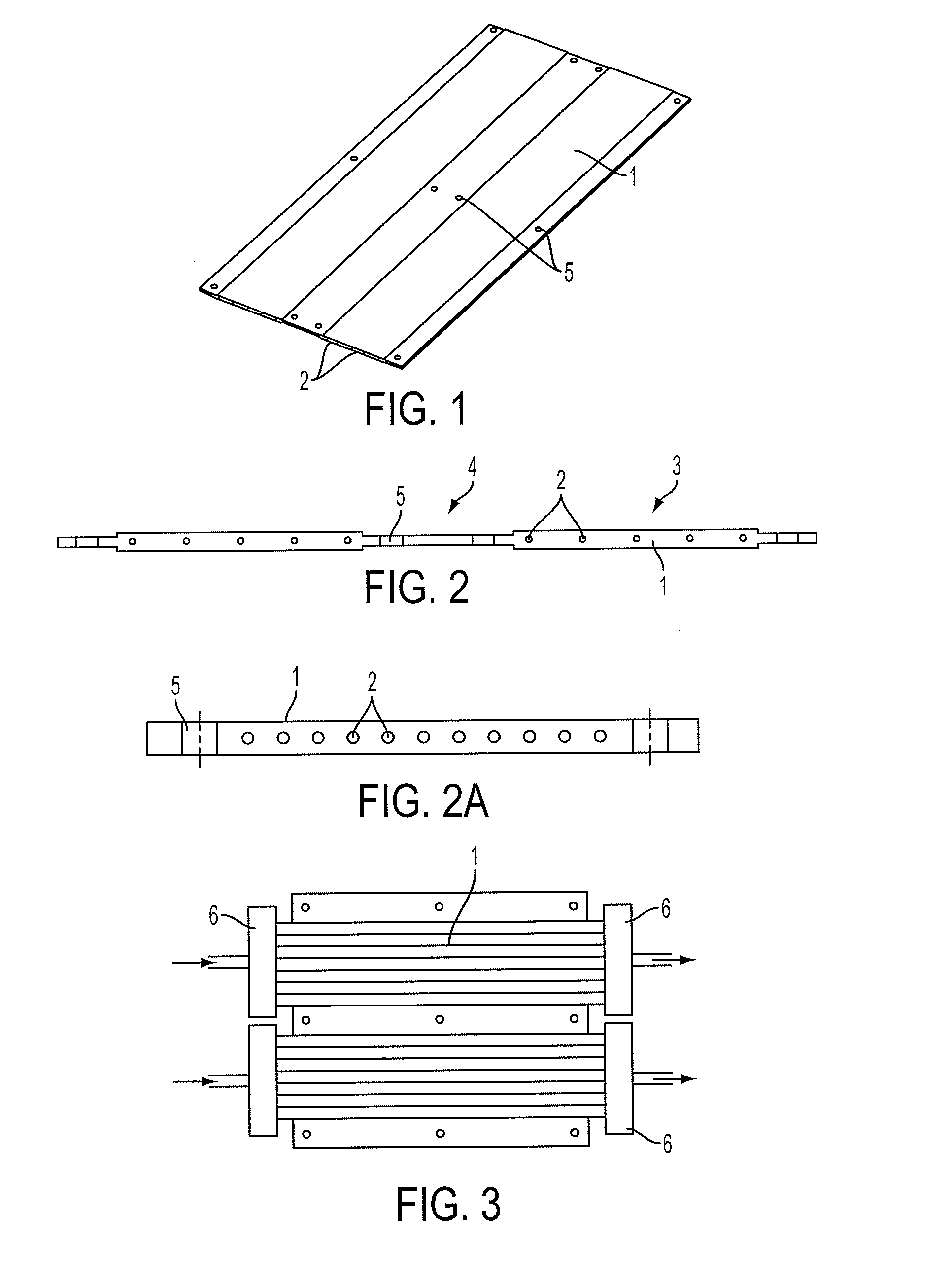
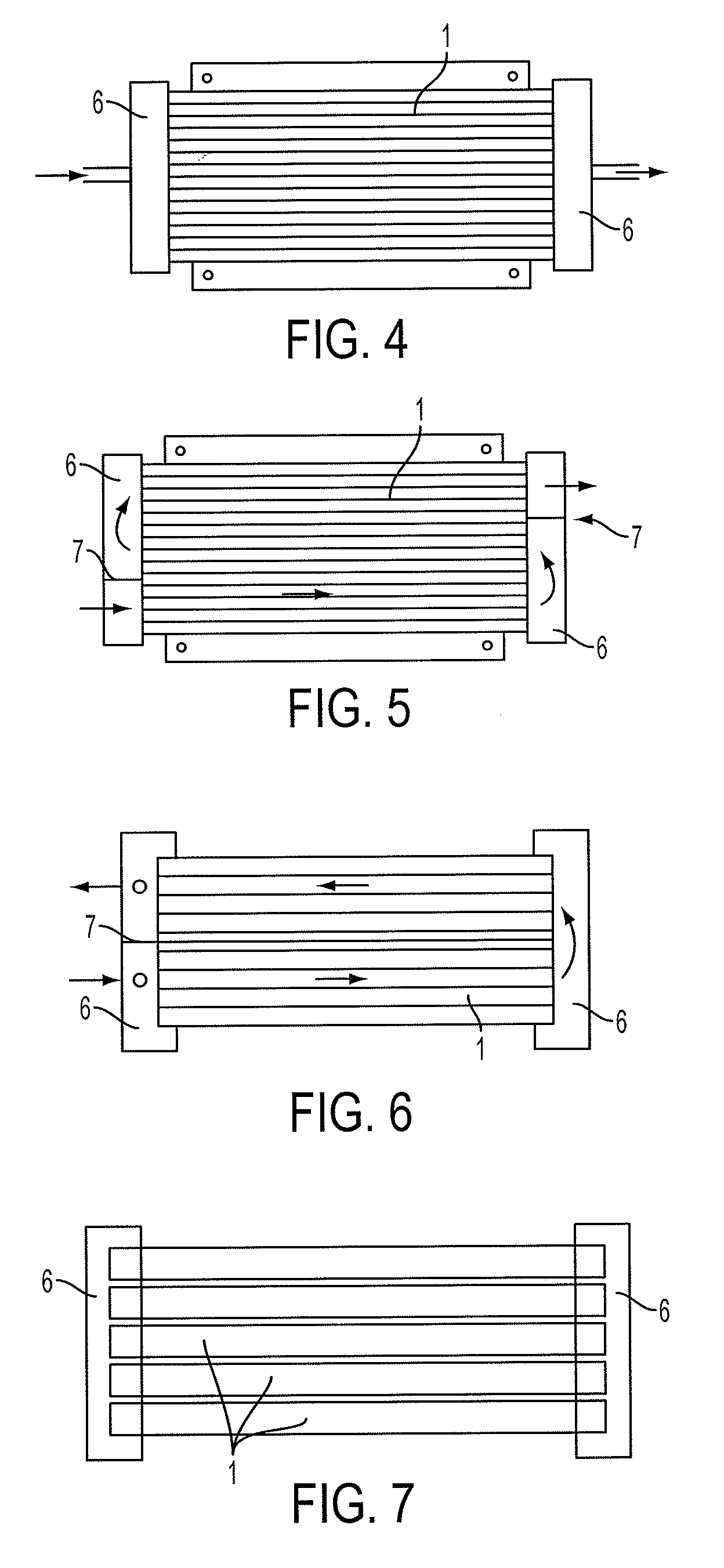
Flow distributor and baffle system for a falling film evaporator
ActiveUS6868695B1Even flow distributionEasy to separateMilk preservationEvaporators/condensersEngineeringRefrigerant
A falling film evaporator includes a flow distributor for uniformly distributing a two-phase refrigerant mixture across a tube bundle. The flow distributor includes a stack of at least three perforated plates each of which are separated by nearly full-width, full-length gaps or chambers. The flow distributor may also include a suction baffle and / or a distributor baffle. The distributor baffle extends downward to provide a hairpin turn past which refrigerant travels before exiting the evaporator. This directional change helps separate liquid from a primarily gaseous refrigerant stream. The suction baffle has various size openings to ensure that the flow rate of refrigerant through the hairpin turn is generally uniform and is maintained low enough to ensure liquid disentrainment over and along the length of the tube bundle within the evaporator.
Owner:TRANE INT INC
Method and apparatus for using light emitting diodes
InactiveUS20050231983A1Milk preservationLighting heating/cooling arrangementsThermal energyEngineering
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for using light emitting diodes for curing and various solid state lighting applications. The method includes a novel method for cooling the light emitting diodes and mounting the same on heat pipe in a manner which delivers ultra high power in UV, visible and IR regions. Furthermore, the unique LED packaging technology of the present invention utilizes heat pipes that perform very efficiently in very compact space. Much more closely spaced LEDs operating at higher power levels and brightness are possible because the thermal energy is transported in an axial direction down the heat pipe and away from the light-emitting direction rather than a radial direction in nearly the same plane as the “p-n” junction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
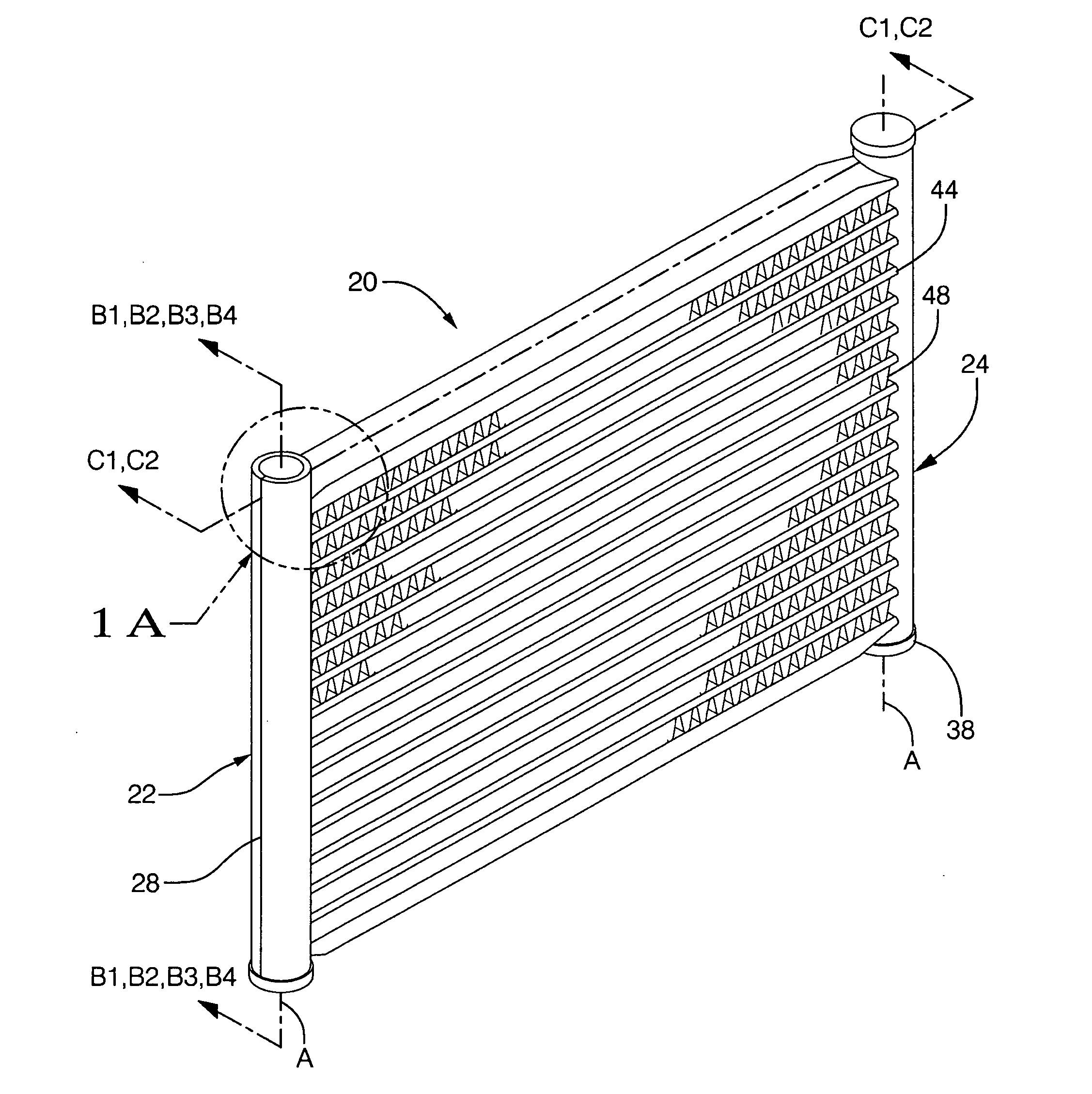
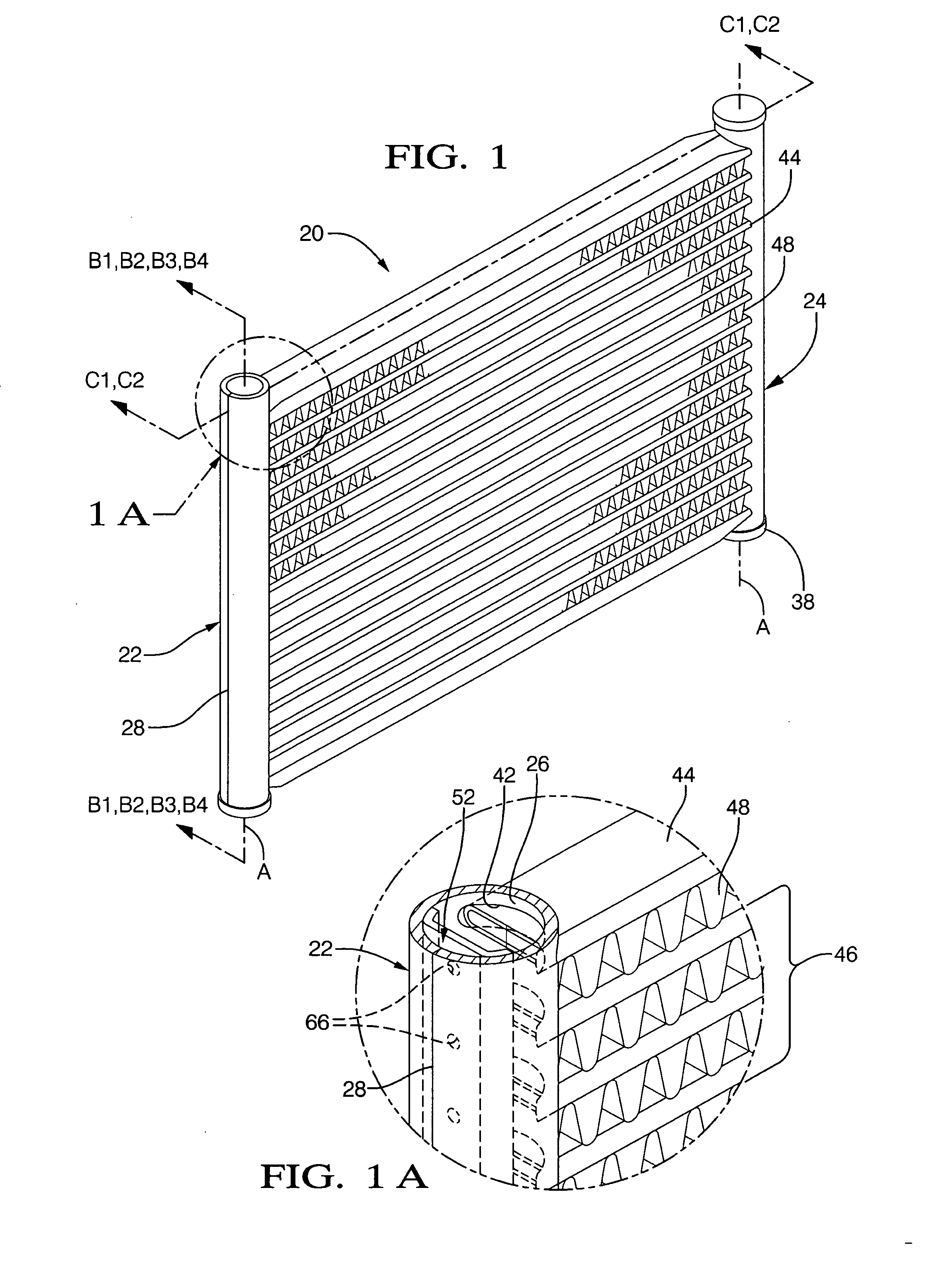
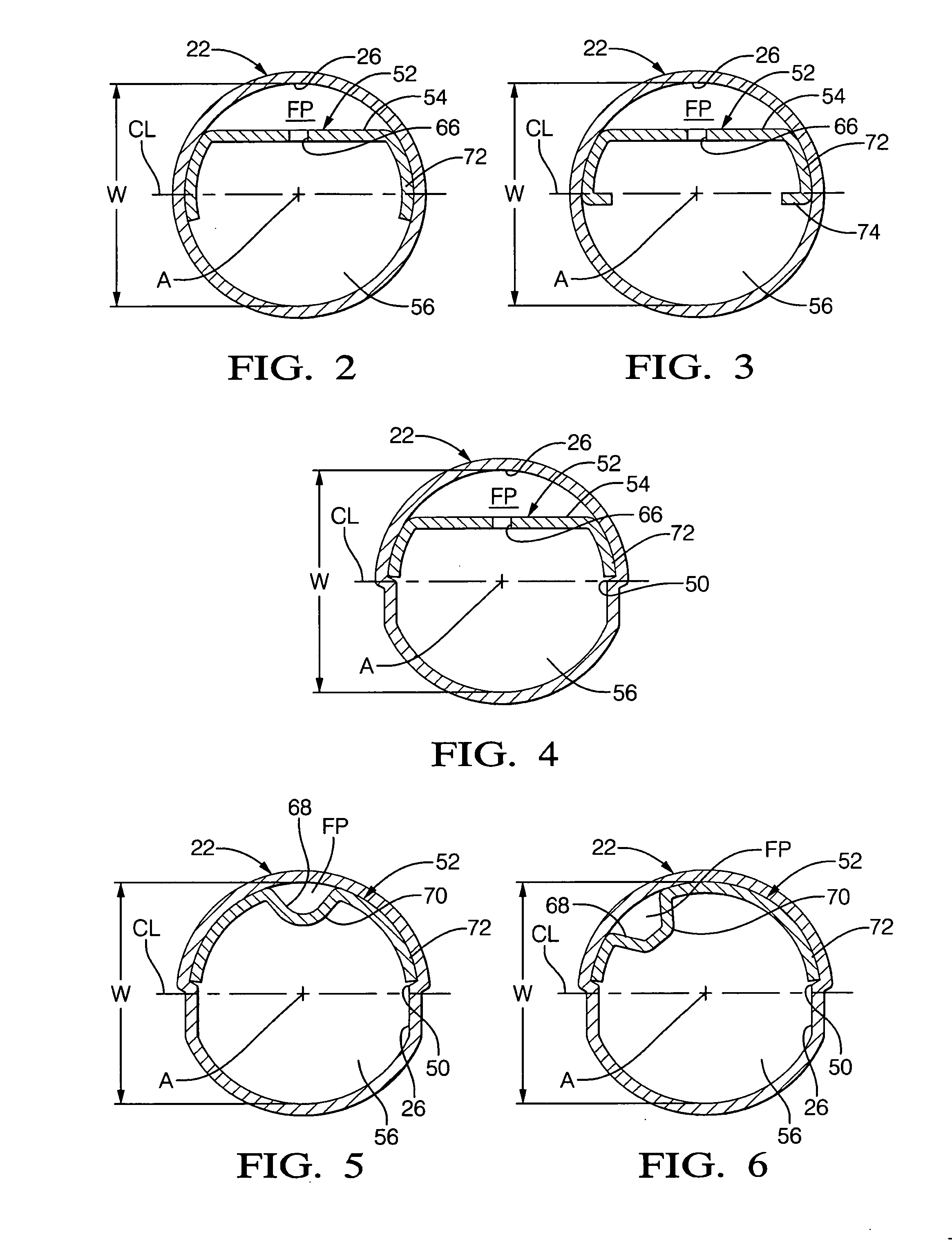
Heat exchanger
InactiveUS6964296B2Eliminate requirementsImprove relationshipSoldering apparatusHeat exhanger finsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Heat exchange inefficiencies found in round tube plate fin heat exchangers are eliminated in an aluminum heat exchanger that includes first and second headers (20), (22) and at least one flattened tube (24), (70) extending between the headers (20), (22). A plurality of generally parallel tube runs are defined and each has opposite edges. A plurality of plate fins (26), (50) are arranged in a stack and each has a plurality of open ended slots (34), one for each run of the tubes (24), (70). Each of the tube runs (24), (70) is nested within corresponding slots (26) and the fins (26), (50) with one of the edges (40) of the tube runs extending outwardly of the corresponding fin (34). The assembly is brazed together.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
Reaction apparatus for producing silicon
ActiveUS20050201908A1Reduce spacingReduce distanceAfter-treatment apparatusSiliconProcess engineeringSilicon
A silicon production reactor comprising a reaction vessel and heating means, said reaction vessel comprising a vertically extending wall and a space surrounded by the wall, said heating means being capable of heating at least a part, including lower end portion, of the wall's surface facing the space to a temperature of not lower than the melting point of silicon, said silicon production reactor being adapted to flow raw gas for silicon deposition from an upper part of the space of the reaction vessel toward a lower part thereof, characterized in that the space of the reaction vessel is of slit form in cross-sectional view. This silicon production reactor is capable of attaining improvement with respect to problems encountered at apparatus scaleup, such as decrease of reactivity of raw gas and generation of by-products, thereby accomplishing a striking enhancement of production efficiency.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Energy storage systems
InactiveUS20120227926A1Low costReduce usageSolar heating energySolar heat devicesThermal energyThermal energy storage
There is herein described energy storage systems. More particularly, there is herein described thermal energy storage systems and use of energy storable material such as phase change material in the provision of heating and / or cooling systems in, for example, domestic dwellings.
Owner:SUNAMP
Light emitting apparatus
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for using light emitting diodes for curing and various solid state lighting applications. The method includes a novel method for cooling the light emitting diodes and mounting the same on heat pipe in a manner which delivers ultra high power in UV, visible and IR regions. Furthermore, the unique LED packaging technology of the present invention utilizes heat pipes that perform very efficiently in very compact space. Much more closely spaced LEDs operating at higher power levels and brightness are possible because the thermal energy is transported in an axial direction down the heat pipe and away from the light-emitting direction rather than a radial direction in nearly the same plane as the “p-n” junction.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
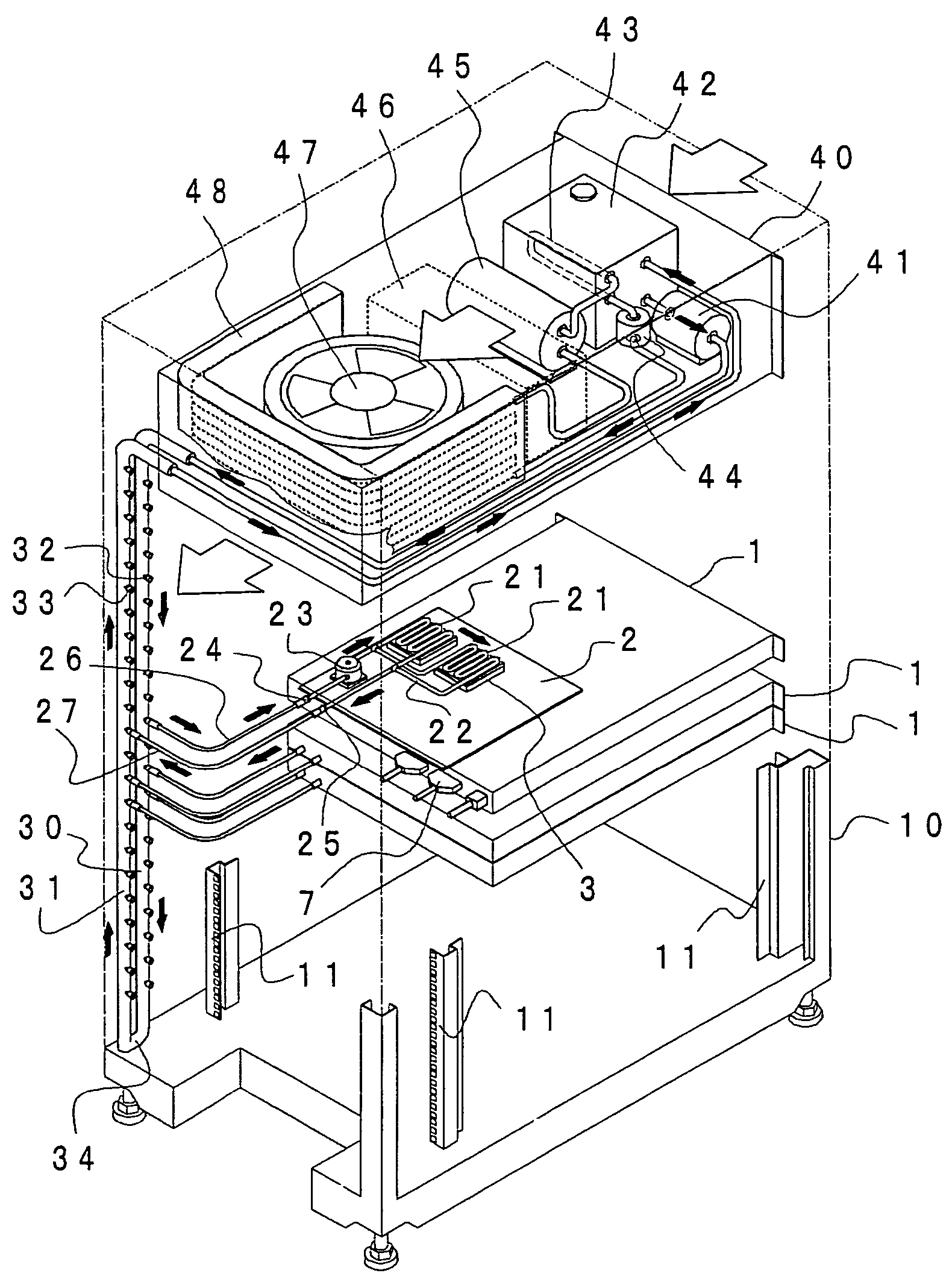
Battery pack thermal management system
InactiveUS20090023056A1Increase thermal massReduce temperature riseAir-treating devicesCell temperature controlElectrical resistance and conductanceThermal management system
A battery pack thermal management system for use in an electric car. The battery pack thermal management system includes a plurality of thermistors connected to a plurality of cells of a battery pack. A battery monitor board is connected to the thermistors. The system also includes a manifold and a plurality of cooling tubes connected to the manifold. A tube seal plug is arranged over an end of the cooling tube and an end fitting is arranged on an end of the cooling tube. The thermal management system will cool the battery pack to predetermined temperatures to increase the longevity of the battery pack within the electric vehicle.
Owner:TESLA INC
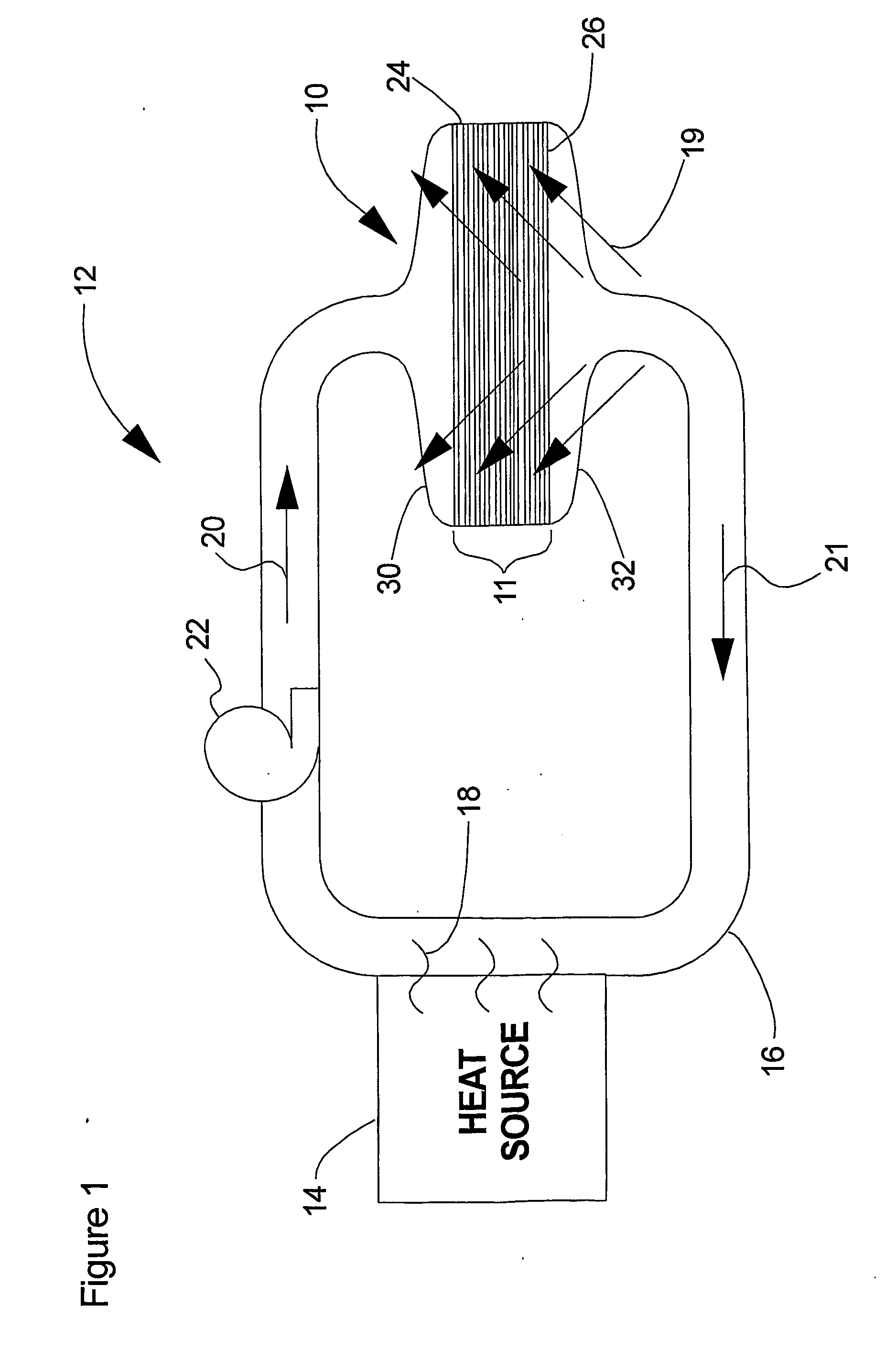
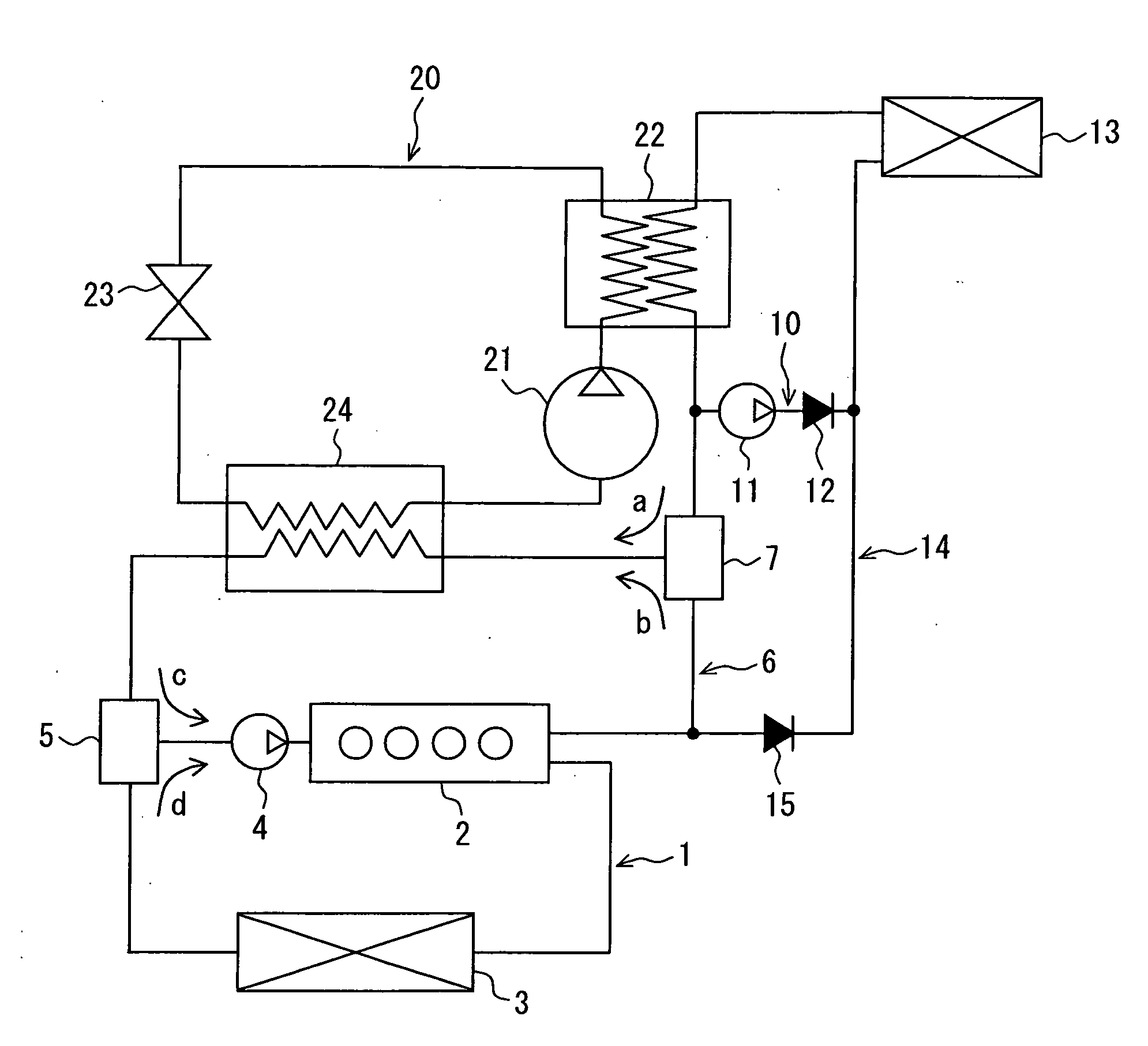
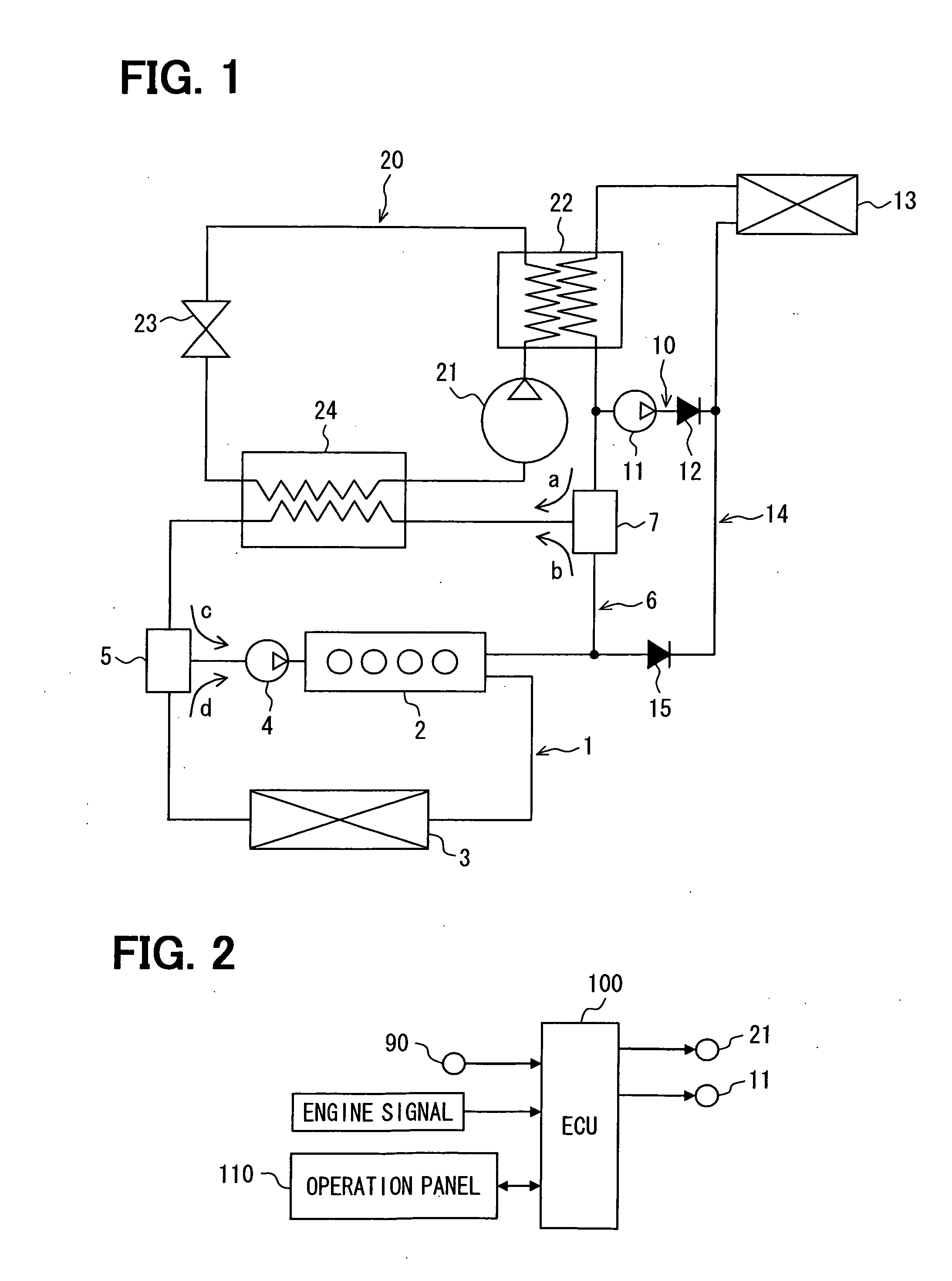
Method and apparatus of indirect-evaporation cooling
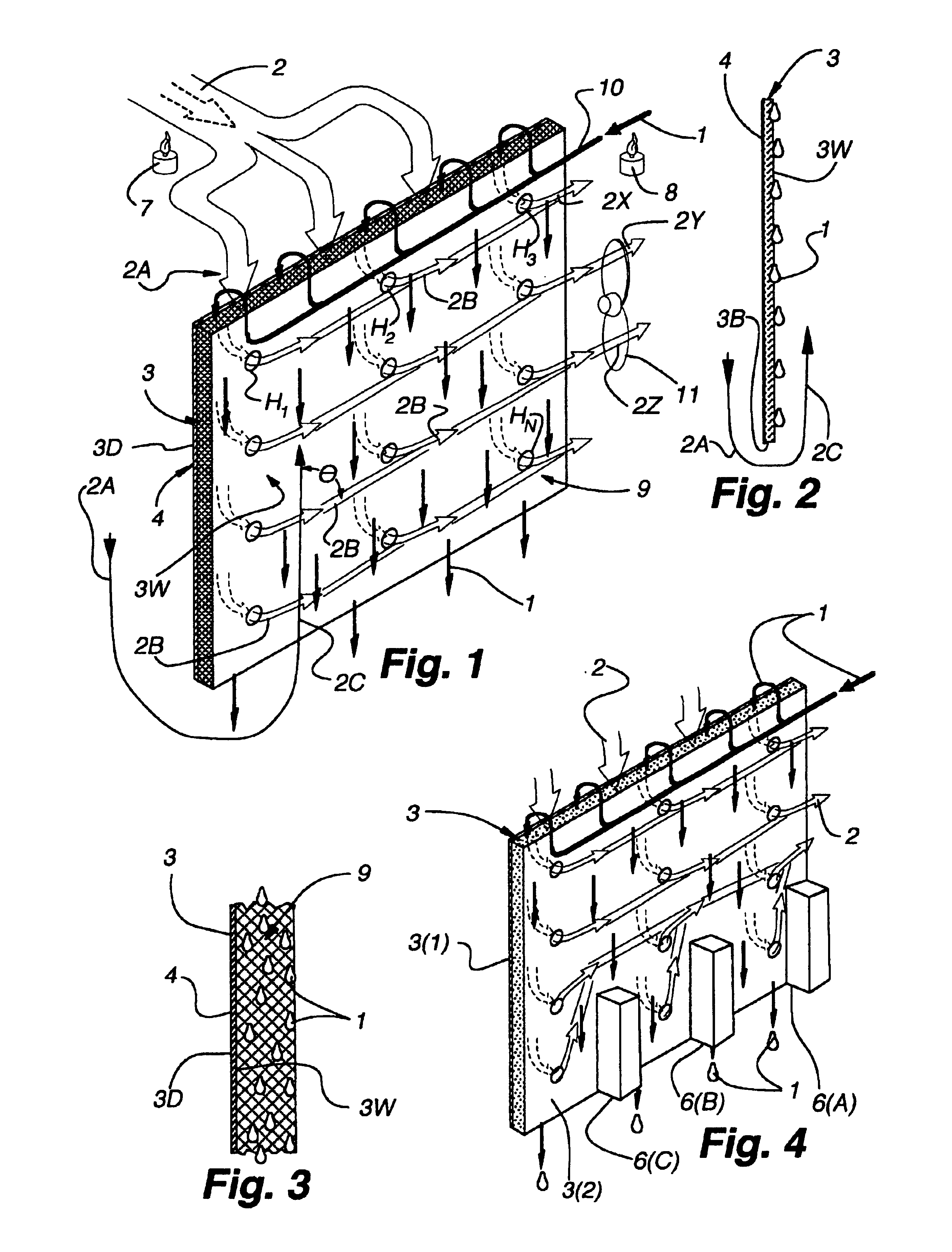
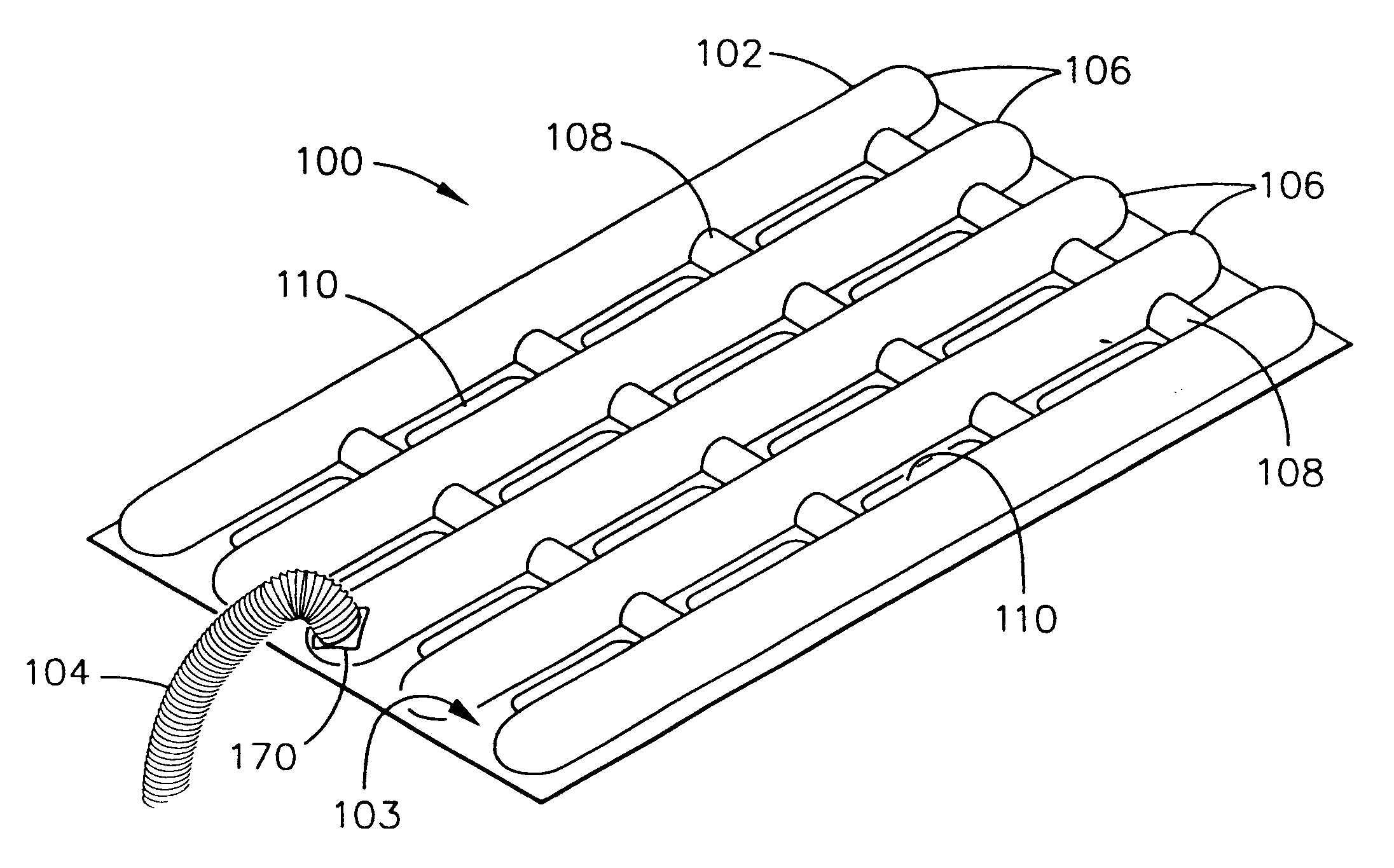
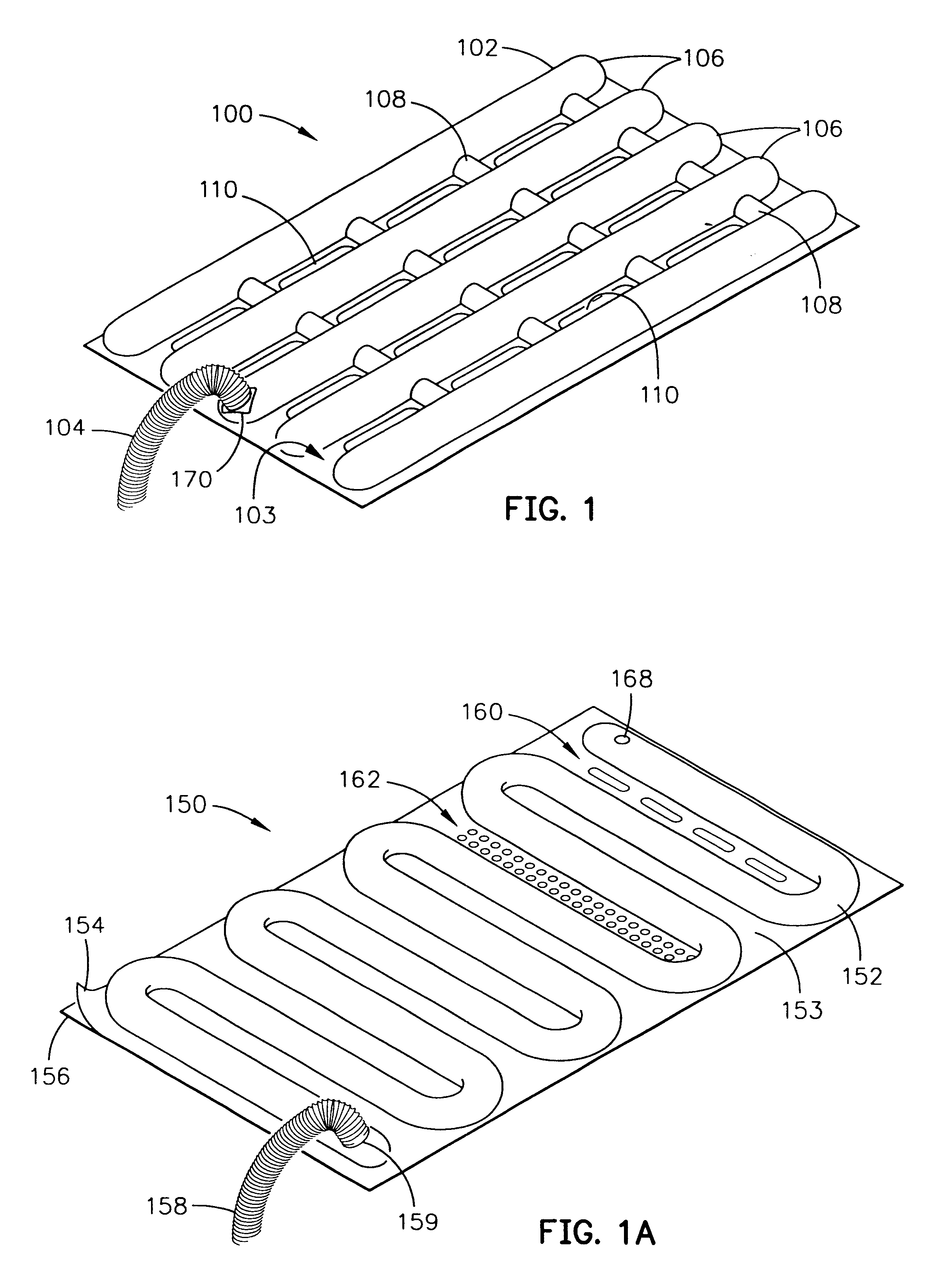
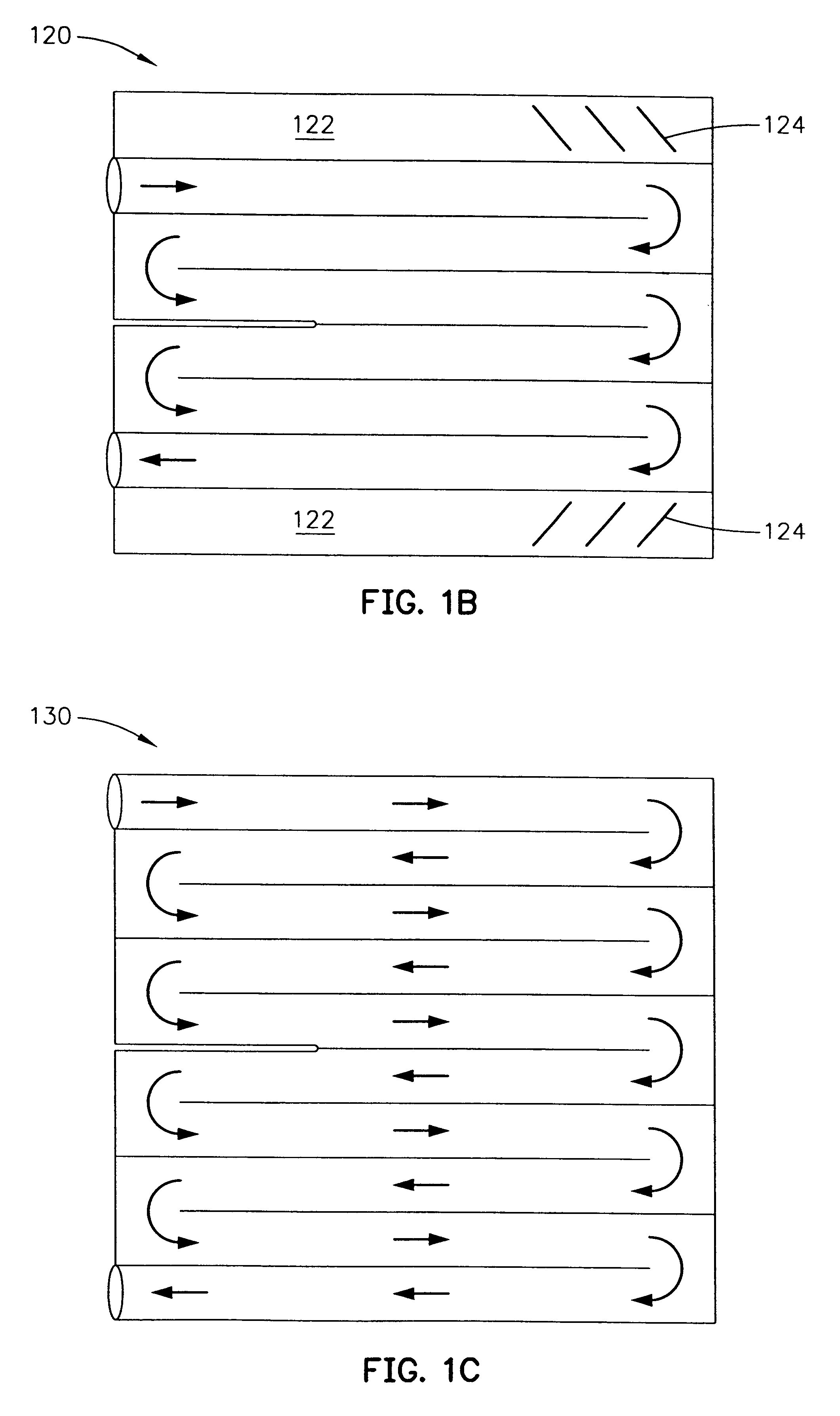
InactiveUS6497107B2Less energyHigh energy costFree-cooling systemsStationary conduit assembliesWorking fluidEvaporation
The within invention improves on the indirect evaporative cooling method and apparatus by making use of a working fluid that is pre-cooled with and without desiccants before it is passed through a Wet Channel where evaporative fluid is on the walls to take heat and store it in the working fluid as increased latent heat. The heat transfer across the membrane between the Dry Channel and the Wet Channel may have dry, solid desiccant or liquid desiccant and may have perforations, pores or capillary pathways. The evaporative fluid may be water, fuel, or any substance that has the capacity to take heat as latent heat. The Wet Channel or excess cooled fluid is in heat transfer contact with a Product Channel where Product Fluid is cooled without adding any humidity. An alternative embodiment for heat transfer between adjacent channels is with heat pipes.
Owner:F F SEELEY NOMINEES
Hydronic rooftop cooling systems
InactiveUS20050056042A1Improve RTU efficiencyEnhanced evaporative cooling effectEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsAir filterEngineering
A roof top cooling unit has an evaporative cooling section that includes at least one evaporative module that pre-cools ventilation air and water; a condenser; a water reservoir and pump that captures and re-circulates water within the evaporative modules; a fan that exhausts air from the building and the evaporative modules and systems that refill and drain the water reservoir. The cooling unit also has a refrigerant section that includes a compressor, an expansion device, evaporator and condenser heat exchangers, and connecting refrigerant piping. Supply air components include a blower, an air filter, a cooling and / or heating coil to condition air for supply to the building, and optional dampers that, in designs that supply less than 100% outdoor air to the building, control the mixture of return and ventilation air.
Owner:DAVIS ENERGY GROUP
Carbon nanotube heat-exchange systems
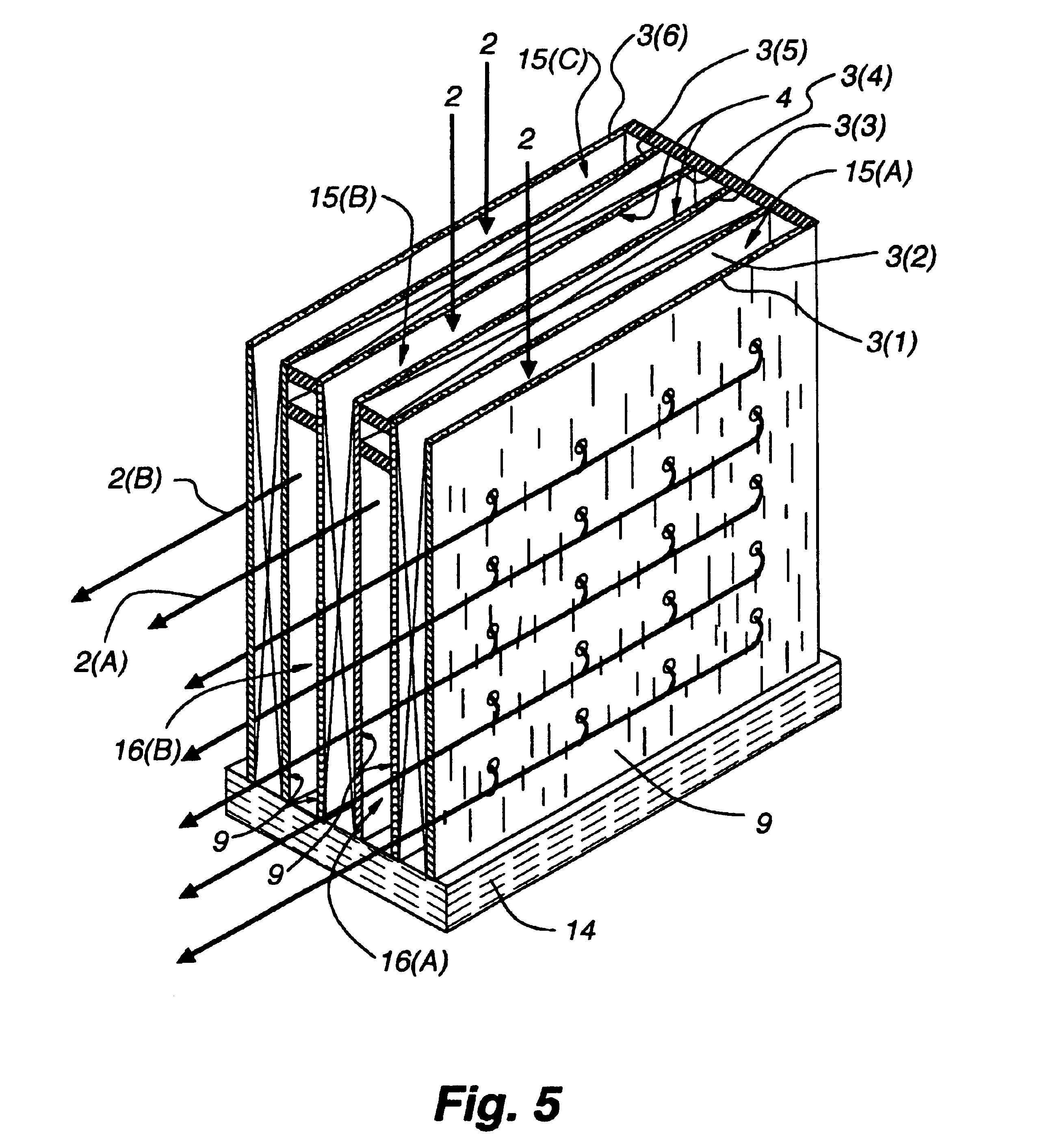
InactiveUS20040194944A1Stationary conduit assembliesHeat transfer modificationCarbon nanotubeCooling fluid
A carbon nanotube heat-exchange system (10) and method for producing the same. One embodiment of the carbon nanotube heat-exchange system (10) comprises a microchannel structure (24) having an inlet end (30) and an outlet end (32), the inlet end (30) providing a cooling fluid into the microchannel structure (24) and the outlet end (32) discharging the cooling fluid from the microchannel structure (24). At least one flow path (28) is defined in the microchannel structure (24), fluidically connecting the inlet end (30) to the outlet end (32) of the microchannel structure (24). A carbon nanotube structure (26) is provided in thermal contact with the microchannel structure (24), the carbon nanotube structure (26) receiving heat from the cooling fluid in the microchannel structure (24) and dissipating the heat into an external medium (19).
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
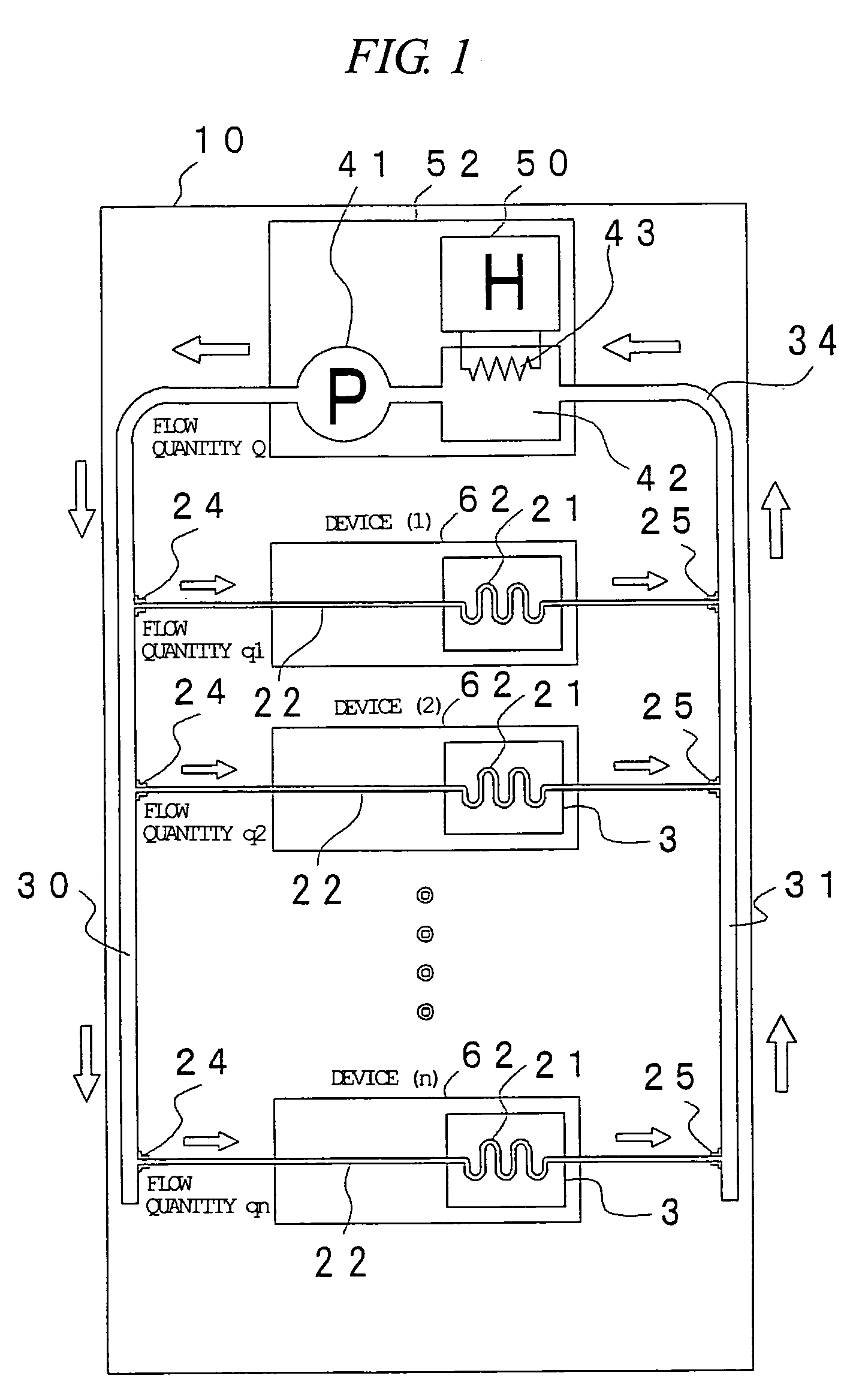
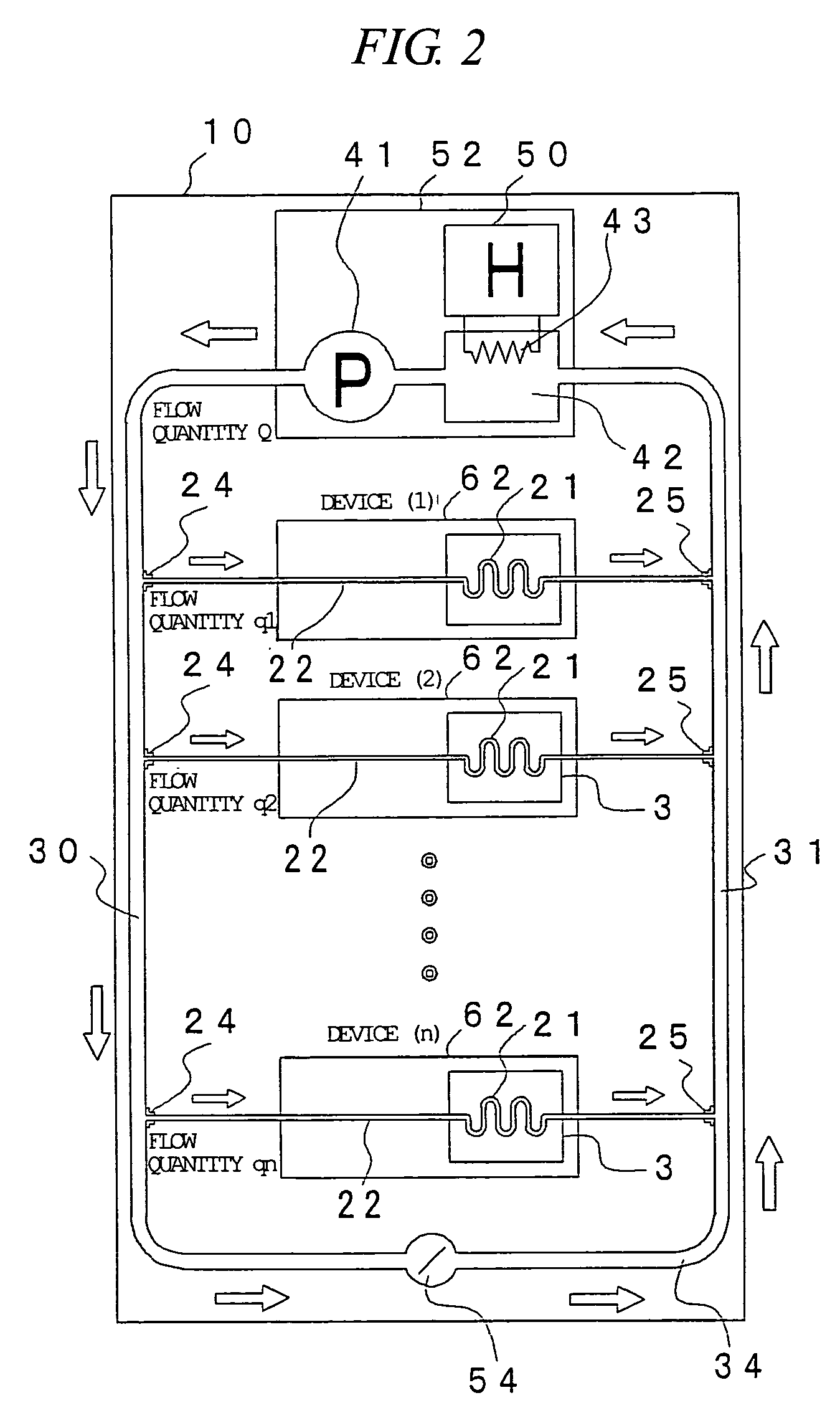
Liquid cooling system for a rack-mount server system
ActiveUS7318322B2Suppress mutationImprove cooling effectDomestic cooling apparatusDigital data processing detailsNuclear engineeringComputer module
A rack-mount server system of a liquid cooling system, in which a heat-generating component such as a CPU is cooled by a coolant has a plurality of server modules with heat-generating components which are cooled by the circulating coolant. The server modules are connected in parallel to a circulation coolant path through which the coolant to cool the server modules is circulated. In the middle of the coolant circulation path is a cooling unit that cools the coolant by radiating its heat to the outside air. Furthermore, a bypass route parallel to the server modules and going around the server modules is provided in the coolant circulation path, and the circulation quantity of the coolant is controlled in the bypass route. Alternatively, the flow quantity of the coolant is controlled in each of the server modules.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
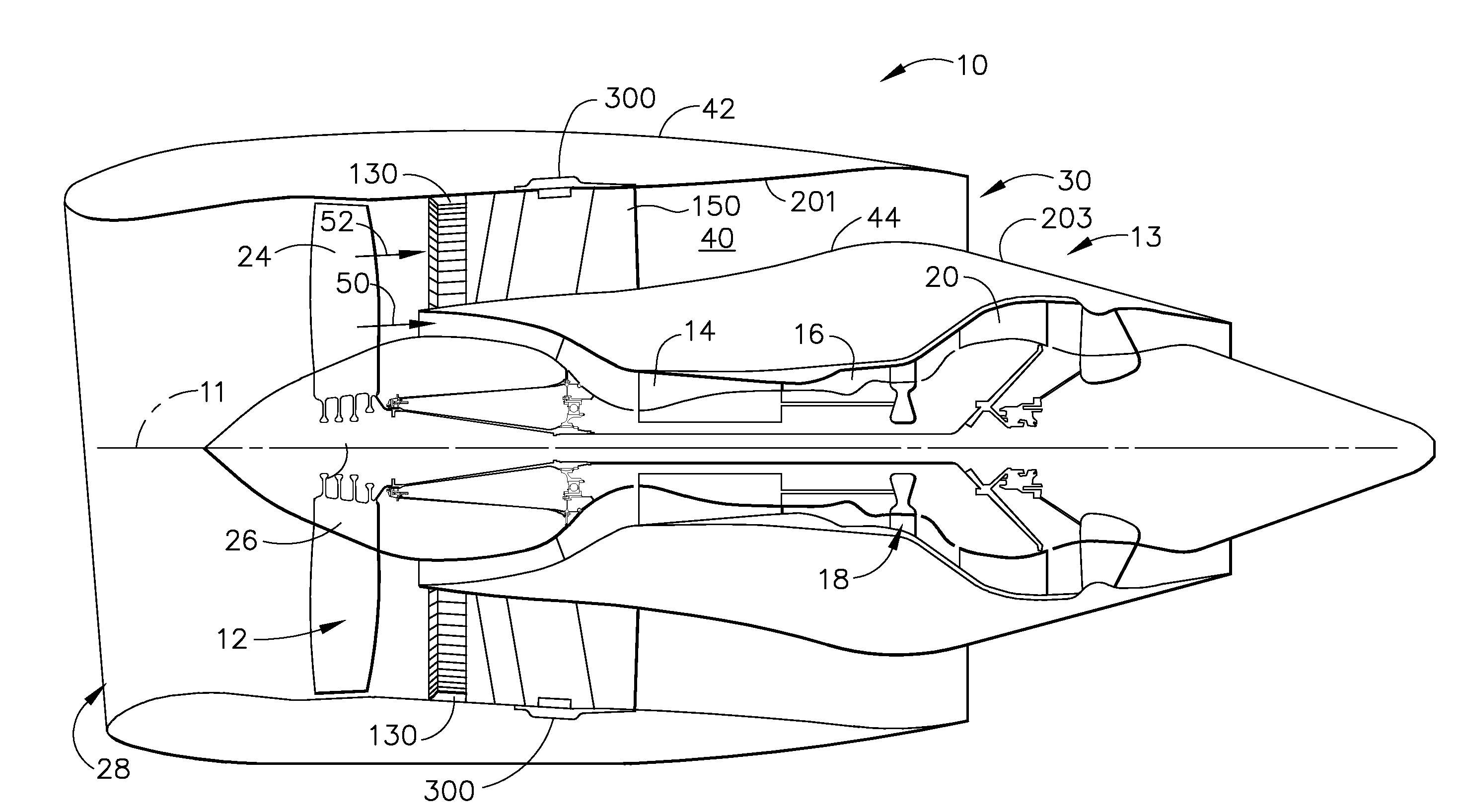
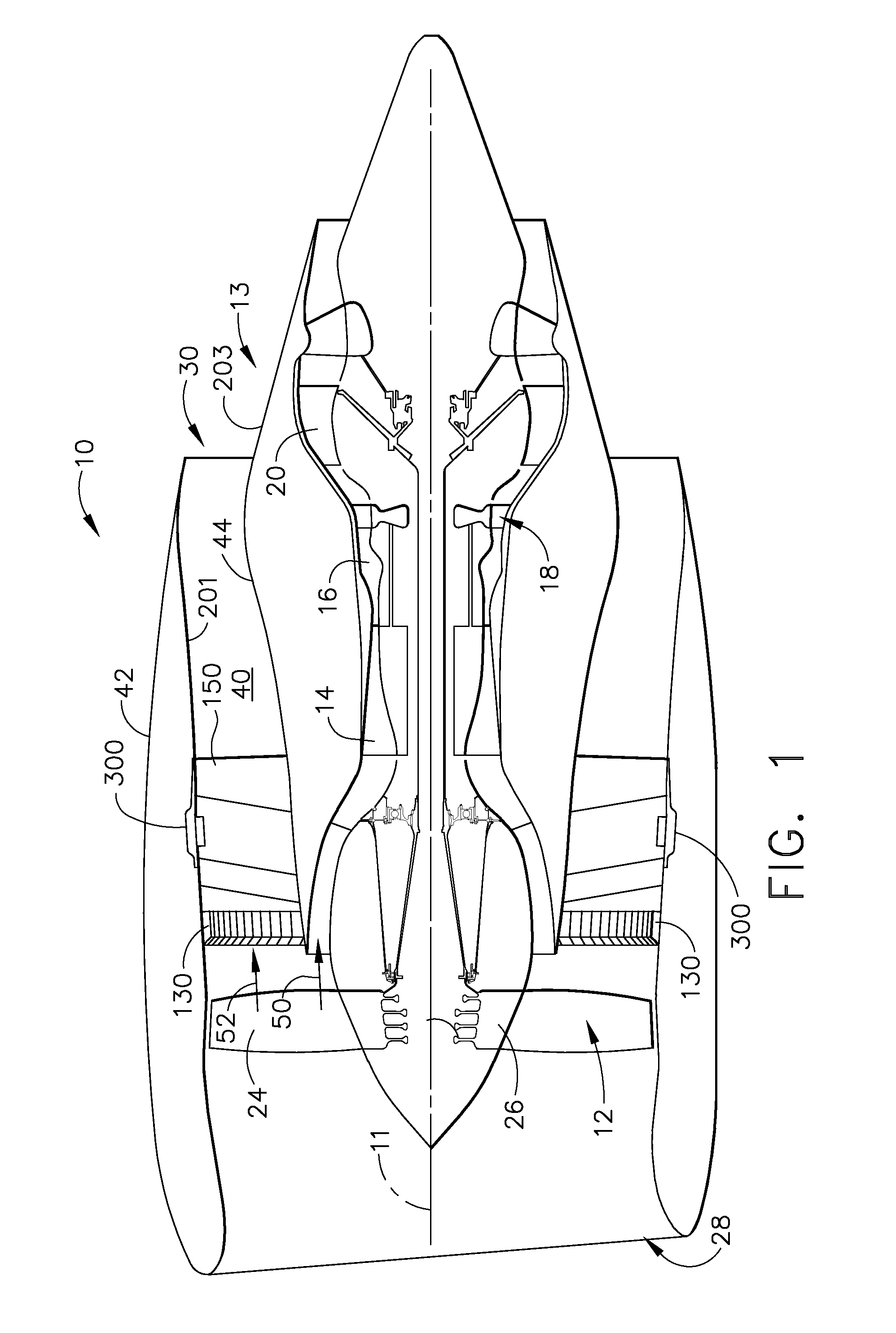
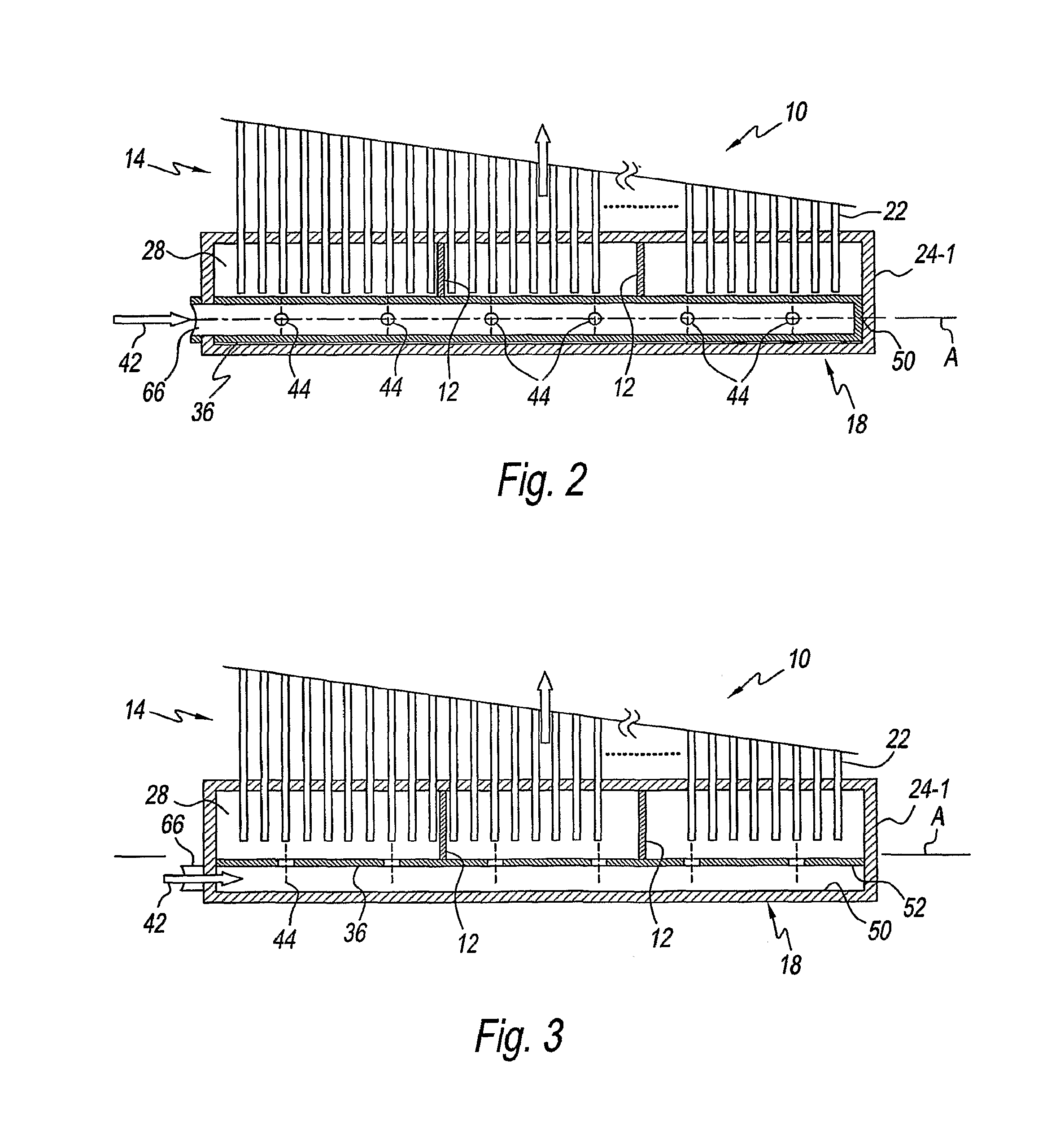
Method and apparatus for operating gas turbine engine heat exchangers
ActiveUS20080095611A1Turbine/propulsion engine coolingEfficient propulsion technologiesEngineeringTurbine
A method for assembling a turbine engine includes assembling a heat exchanger assembly that includes at least a radially inner plate, a radially outer plate, and a heat exchanger coupled between the radially inner and outer plates, forming the heat exchanger assembly such that the heat exchanger assembly has a substantially arcuate shape, and coupling the heat exchanger to a fan casing such that the heat exchanger is positioned upstream or downstream from the fan assembly.
Owner:UNISON INDUSTRIES +1
Method of evaporative cooling of a fluid and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6854278B2Reduce the temperatureLess pressure dropMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsDesiccantMechanical engineering
The operating efficiency of indirect evaporative cooling processes and indirect evaporative cooling apparatus employing a dry side channel and a wet side channel separated by a heat exchange plate are improved by placement of holes in the heat exchange plate. Further improvements are obtained when the flow direction in the wet side channel is cross-current to the flow direction in the dry side channel. Placement of desiccant materials in the dry side channel also serve to improve the operating efficiencies of these processes and apparatus.
Owner:IDALEX TECH INC
Heat exchanger tube having integrated thermoelectric devices
InactiveUS20080028769A1Maximize heating efficiencyMaximize efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectVehicle heating/cooling devicesEngineeringThermoelectric effect
A heat exchanger for a vehicle is shown, wherein the heat exchanger includes a plurality of tubes having integrated thermoelectric devices disposed thereon to facilitate heat transfer between the tubes and an atmosphere surrounding the tubes.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
Vehicle air conditioning system with seat air conditioning unit
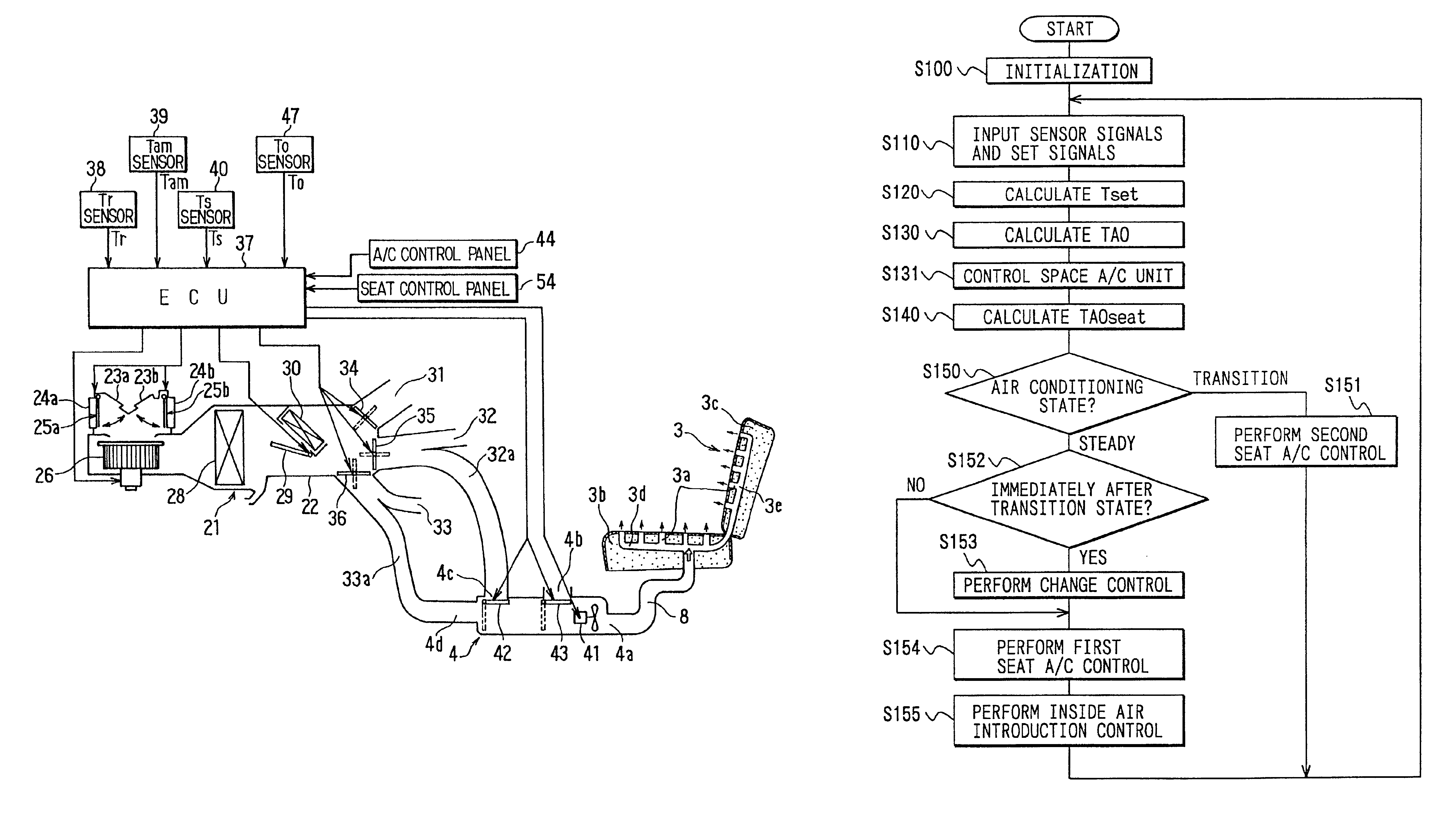
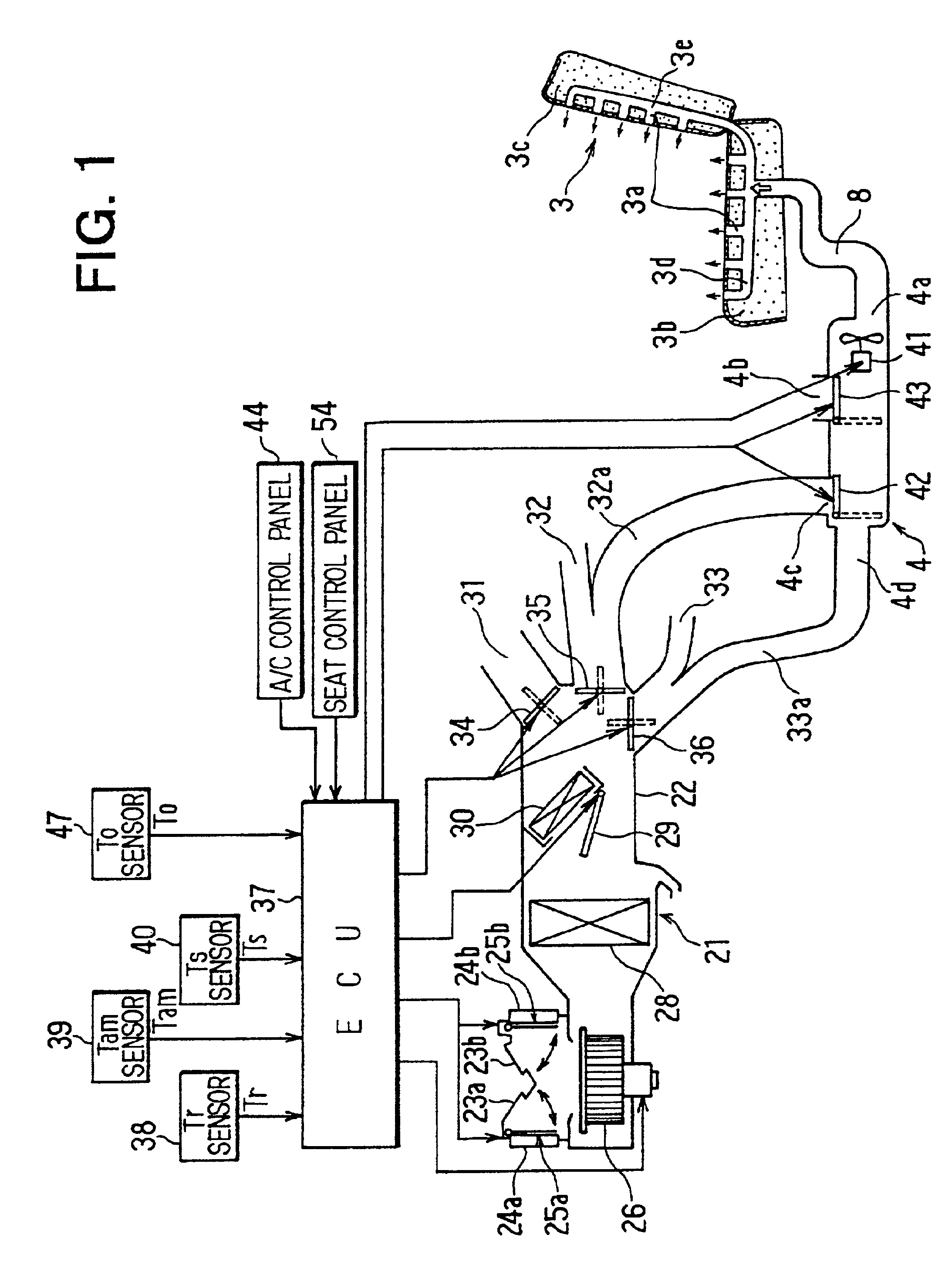
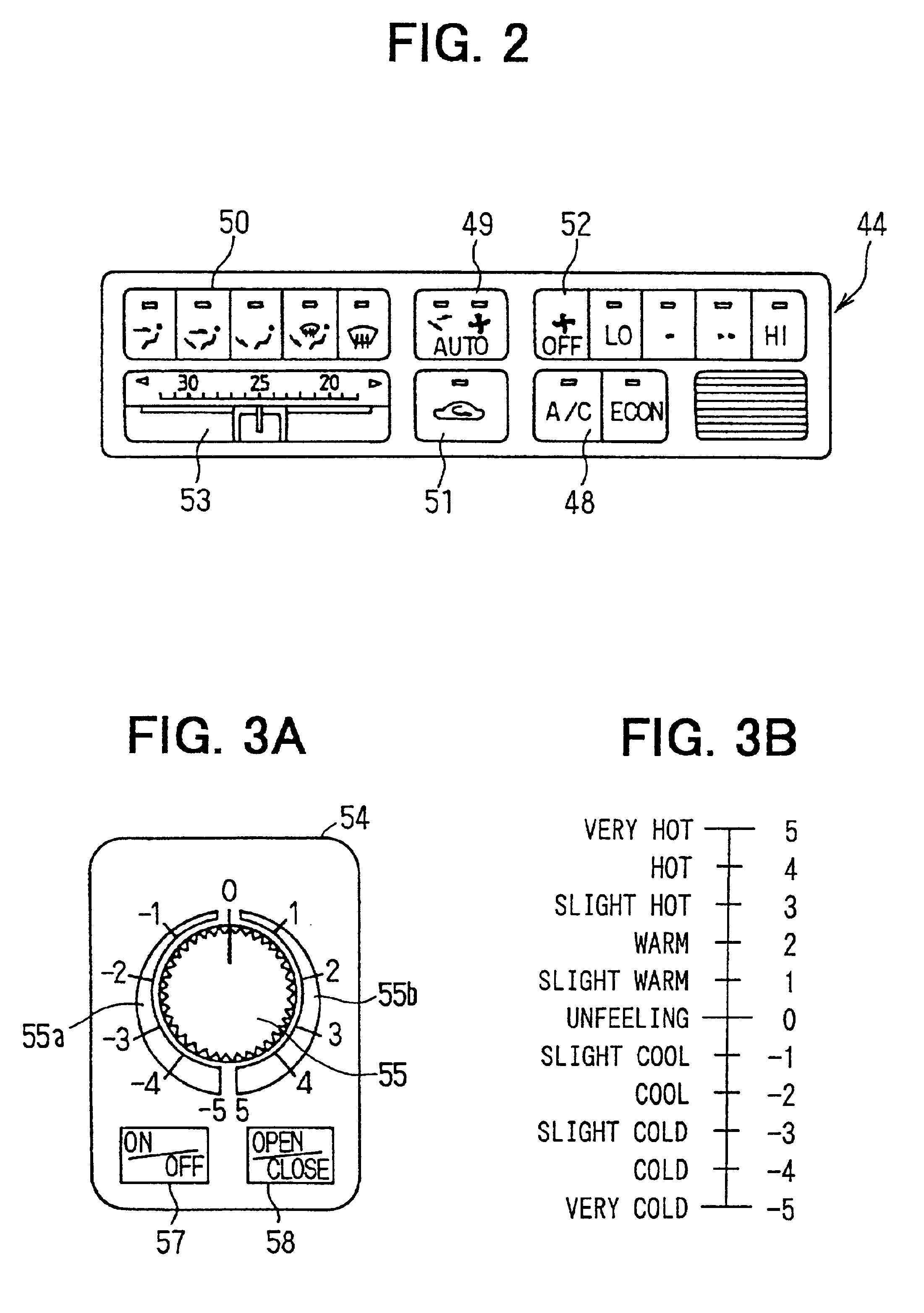
InactiveUS6793016B2Set thermal sensation level of a seat surfaceSmall amountAir-treating devicesSeat heating/ventillating devicesEngineeringAir conditioning
A vehicle air conditioning system includes a space air conditioning unit for blowing conditioned air into a passenger compartment, a seat air conditioning unit for blowing air into a vehicle seat, and a control unit for controlling the space air conditioning unit and the seat air conditioning unit. The control unit includes space controlling means for controlling the space air conditioning unit in accordance with a space control value calculated based on a space target air temperature, and seat controlling means for controlling the seat air conditioning unit in accordance with a seat control value calculated based on the space target air temperature. Further, the seat controlling means includes a first seat air conditioning means which determines the seat control value in a steady air conditioning state of the passenger compartment, and a second seat air-conditioning means which determines the seat control value in a transition air-conditioning state of the passenger compartment.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Heat and mass exchanger
ActiveUS7269966B2Additional exchangeEfficient exchangeSpacing meansDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringContinuous flow
Owner:AIL RES
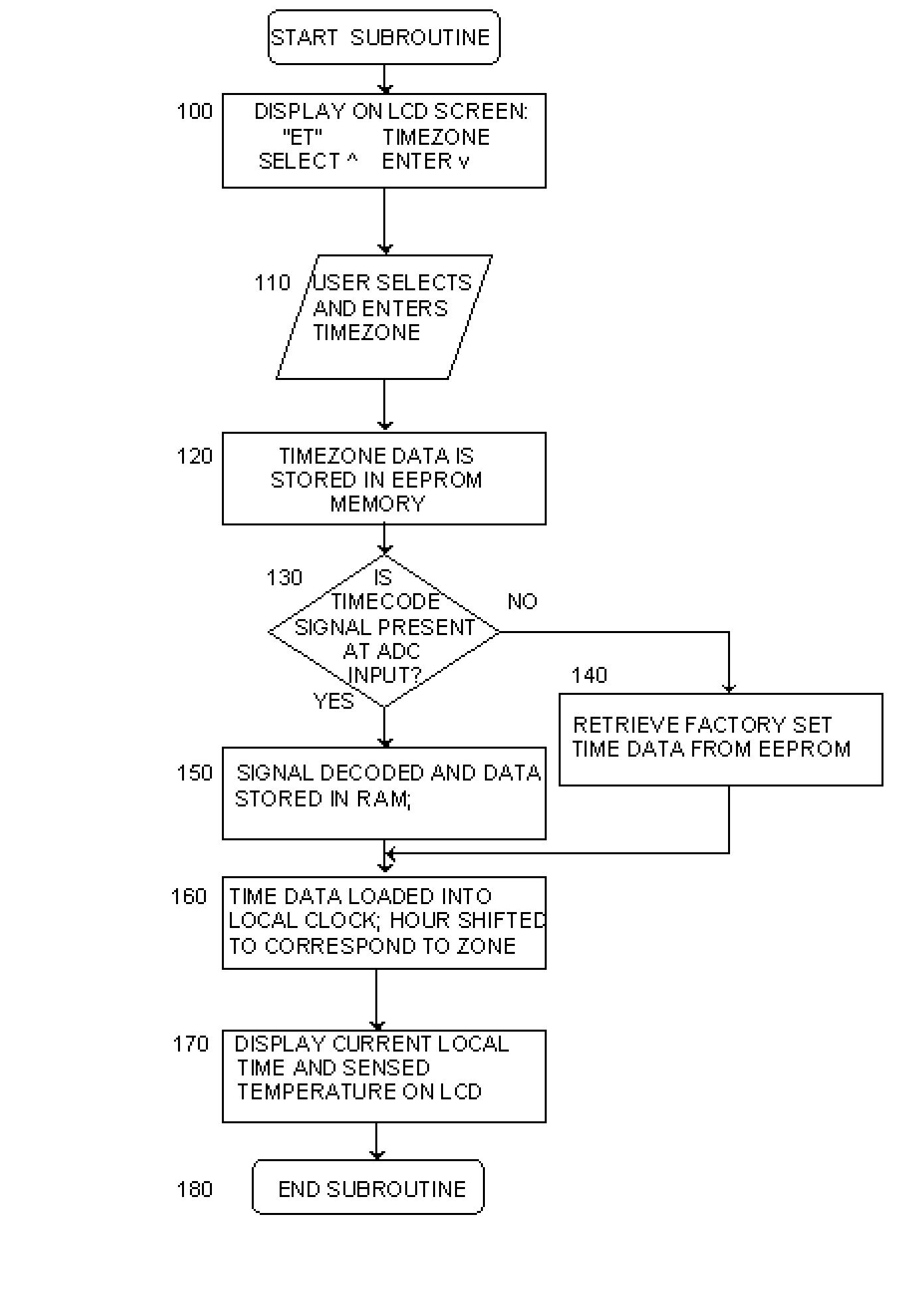
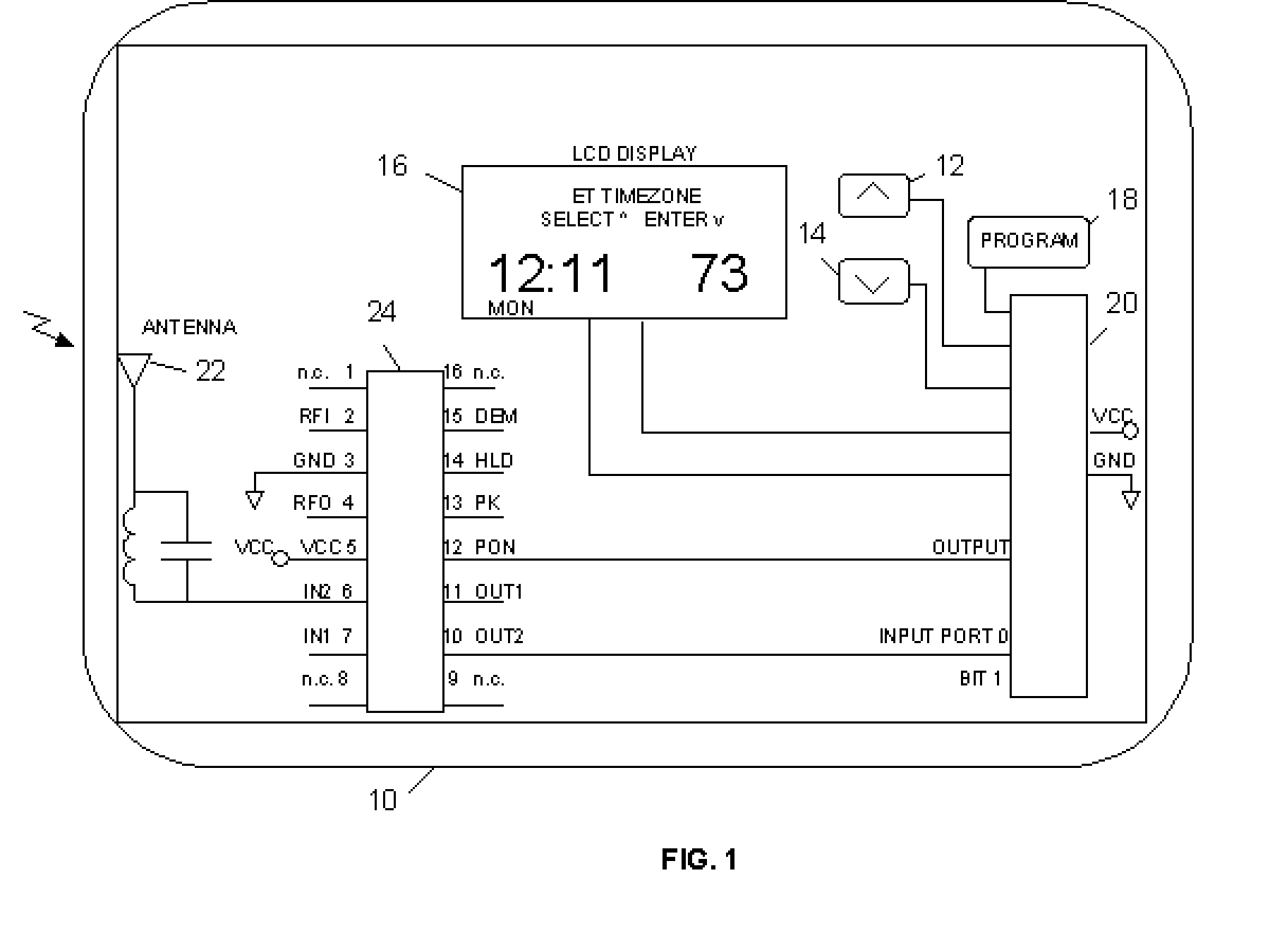
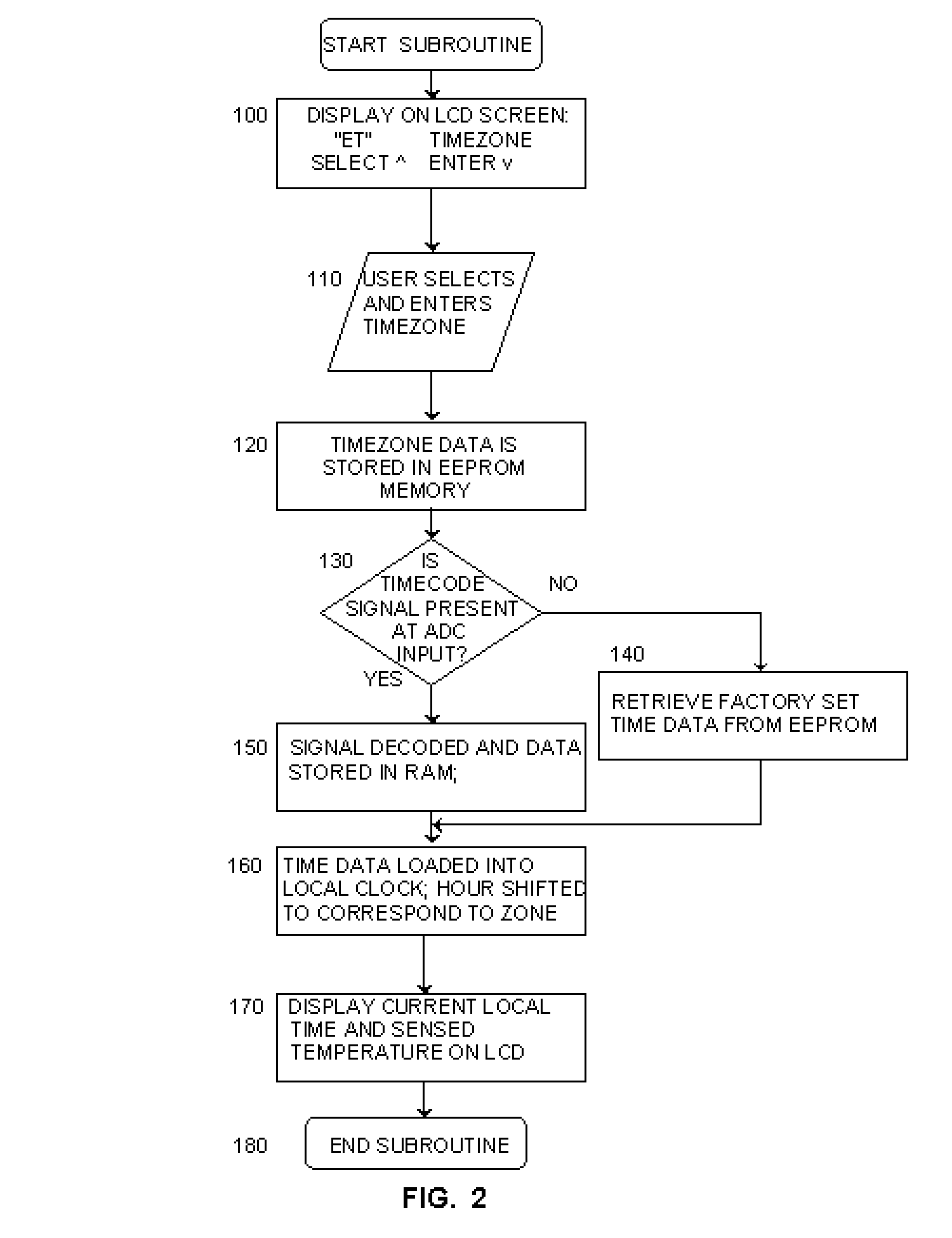
Thermostat With One Button Programming Feature
InactiveUS20030121652A1Easy programmingEasy to startMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsTime segmentEngineering
Abstract of Disclosure A digital programmable thermostat comprising up and down temperature adjustment buttons, an LCD display, and a Program button, which a user can simply press once to initiate a single setback program that sets back the last user selected temperature setting during a predetermined setback time period. The thermostat can also automatically set the current time and date, to allow the user to initiate the program without having to set the current time and date.
Owner:COPELAND COMFORT CONTROL LP
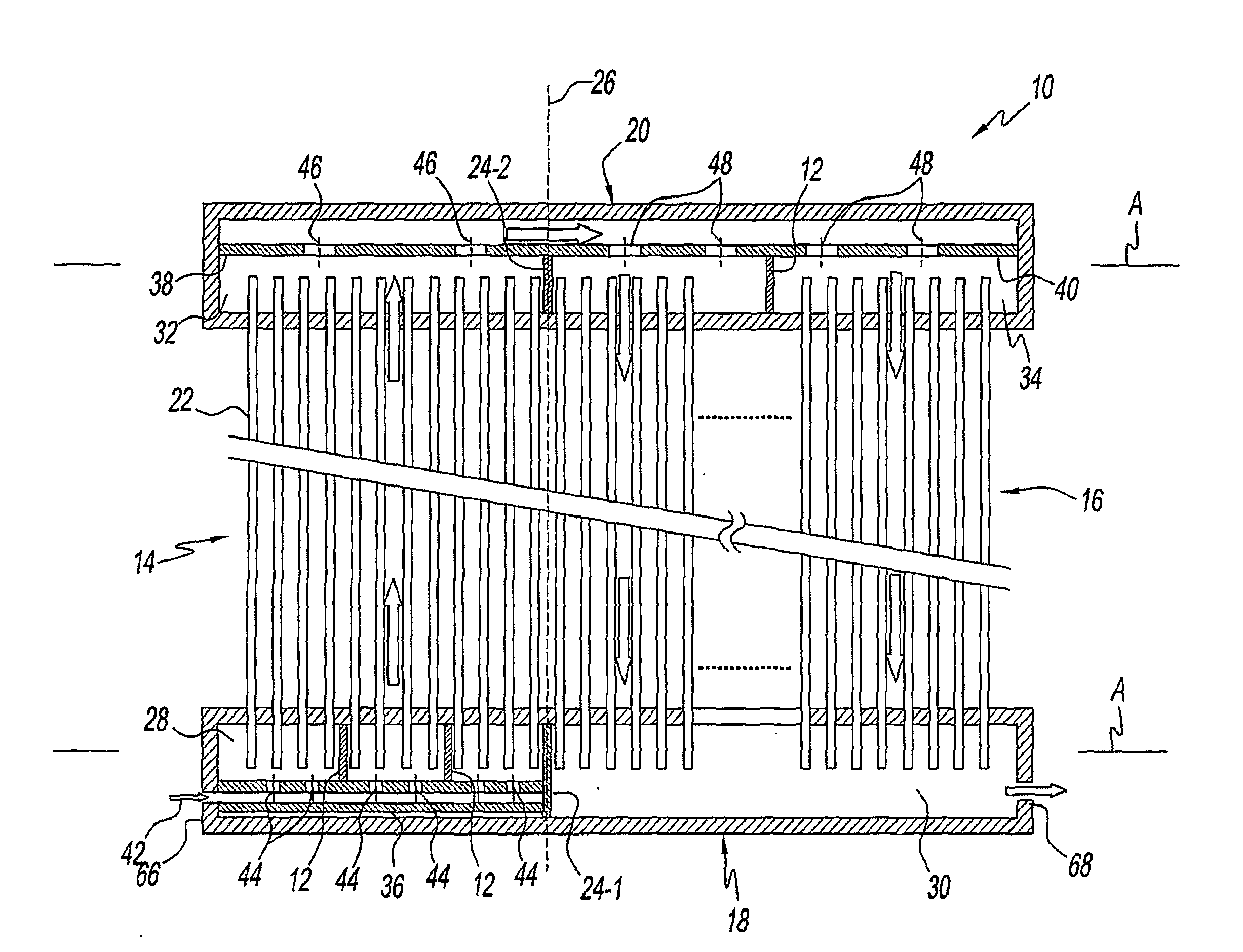
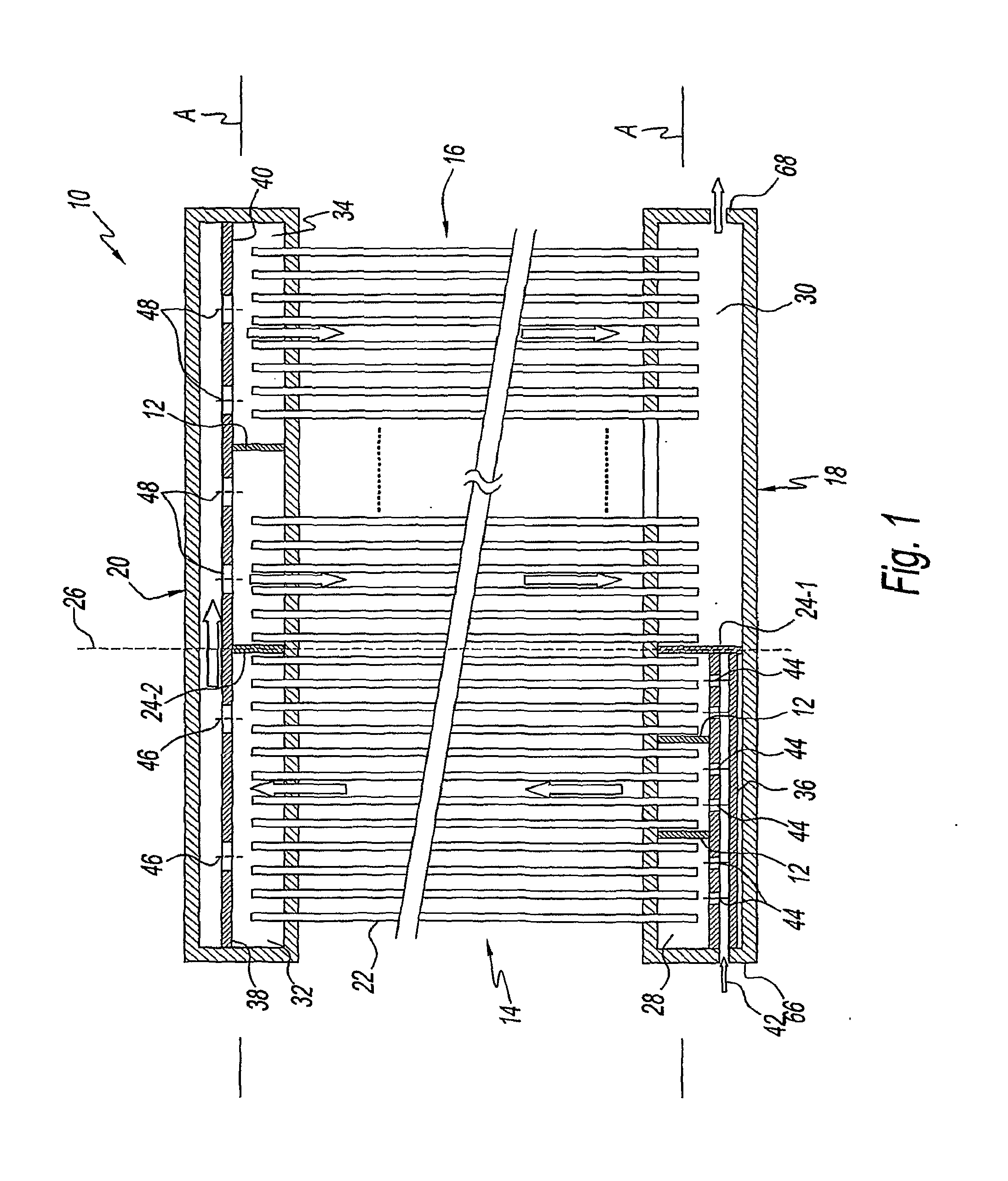
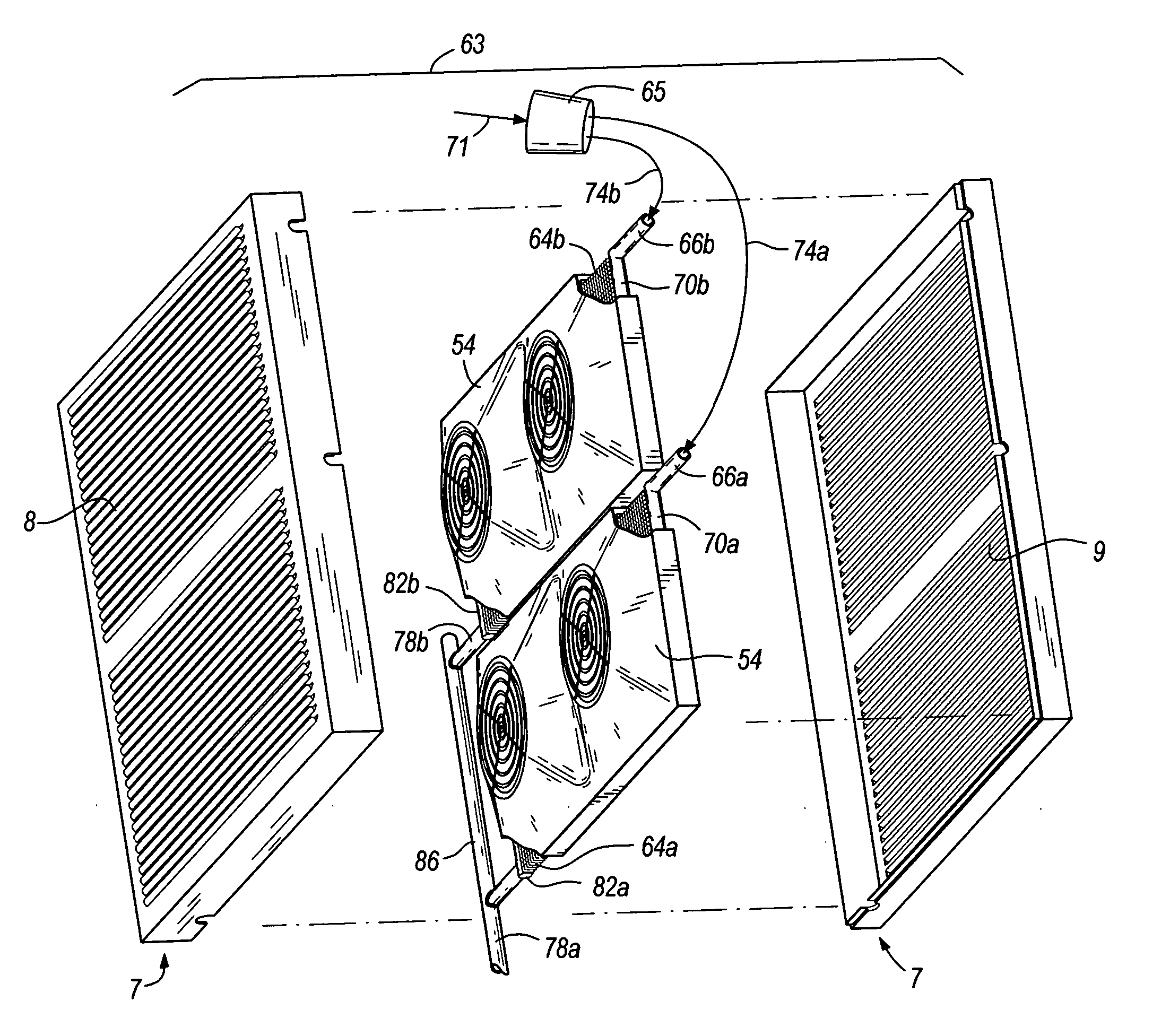
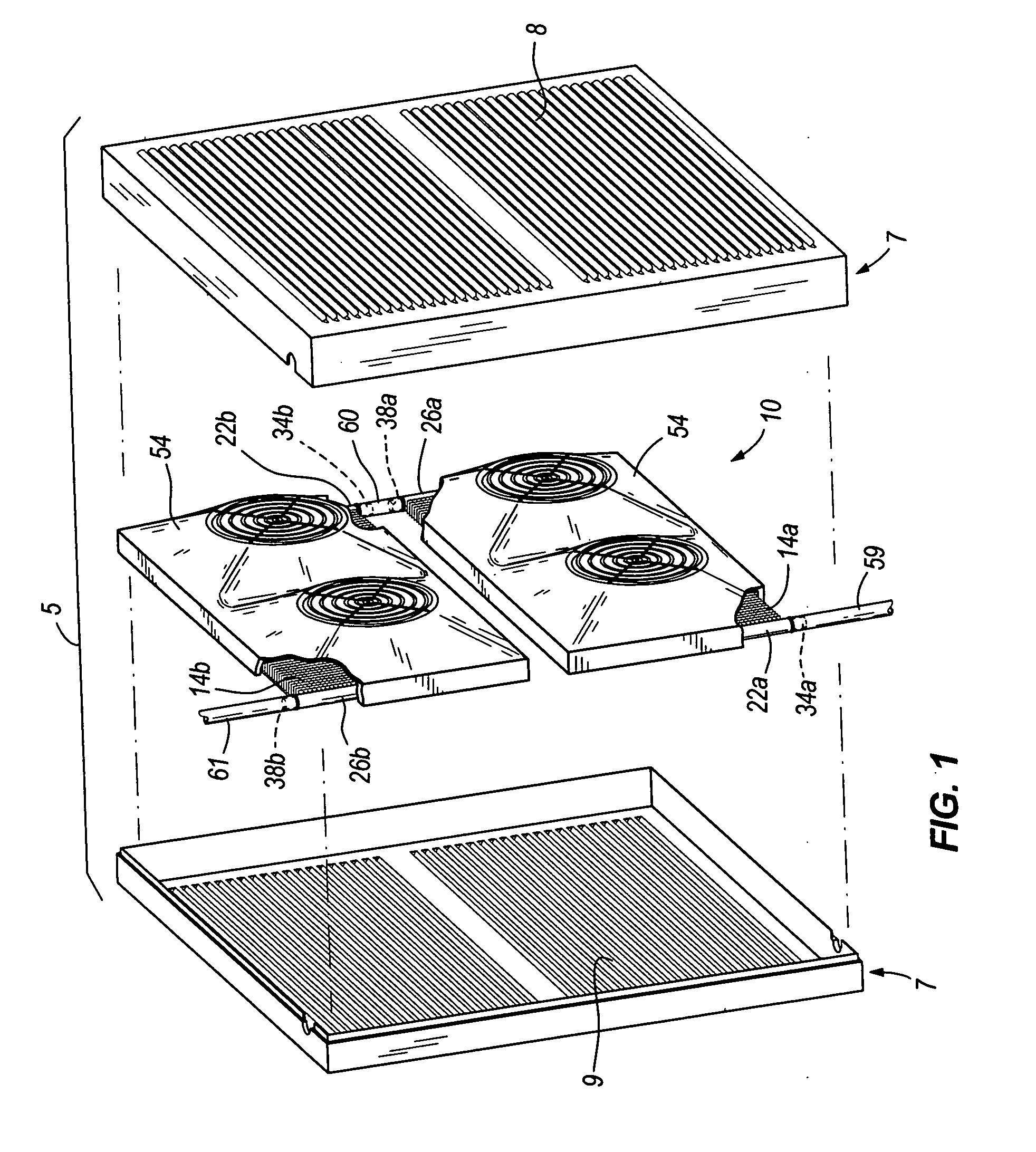
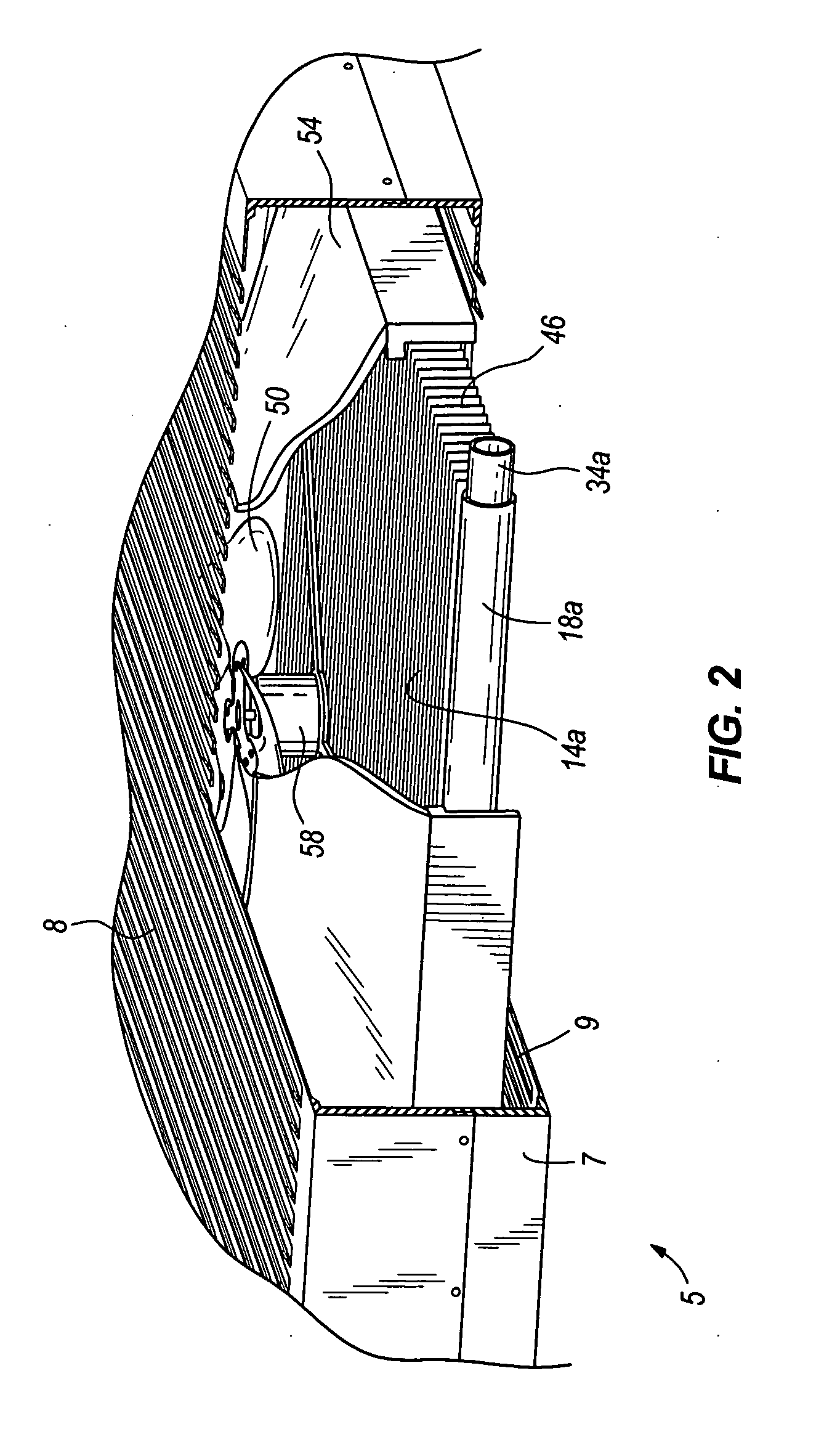
Heat exchangers having baffled manifolds
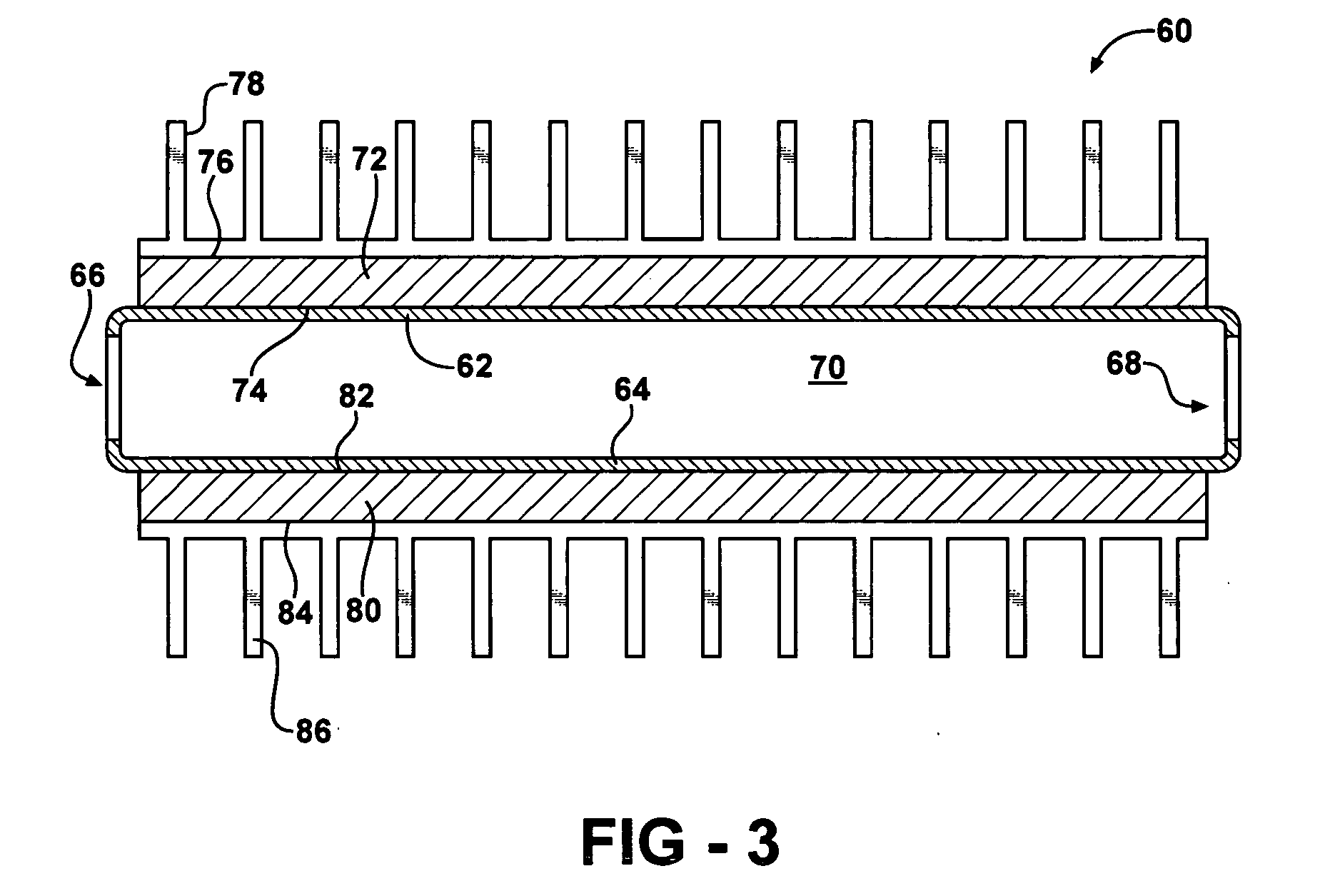
InactiveUS20100206535A1Prevent maldistributionEvaporators/condensersStationary conduit assembliesGas phaseEngineering
A heat exchanger for a fluid having a vapor-phase and a liquid-phase is provided. The heat exchanger includes a first manifold, a second manifold, a plurality of parallel channels, a mixing device, and one or more baffles. The parallel channels are in fluid communication with the first and second manifolds. The mixing device mixes the fluid flowing into the first manifold so that the fluid is a substantially homogeneous two-phase mixture of the vapor and liquid phases. The baffles are within the first manifold and ensure that the fluid enters the parallel channels as the substantially homogeneous two-phase mixture.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
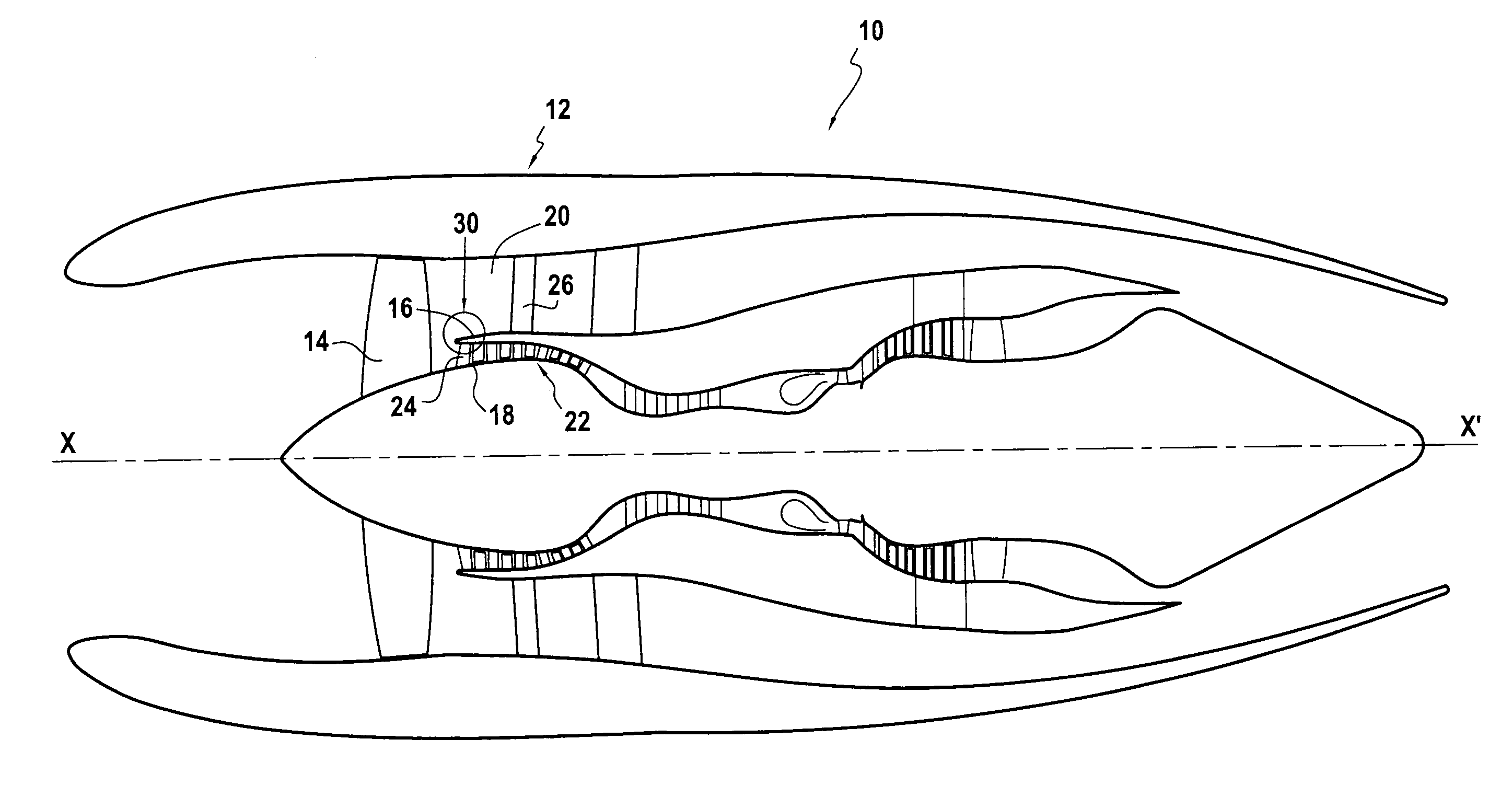
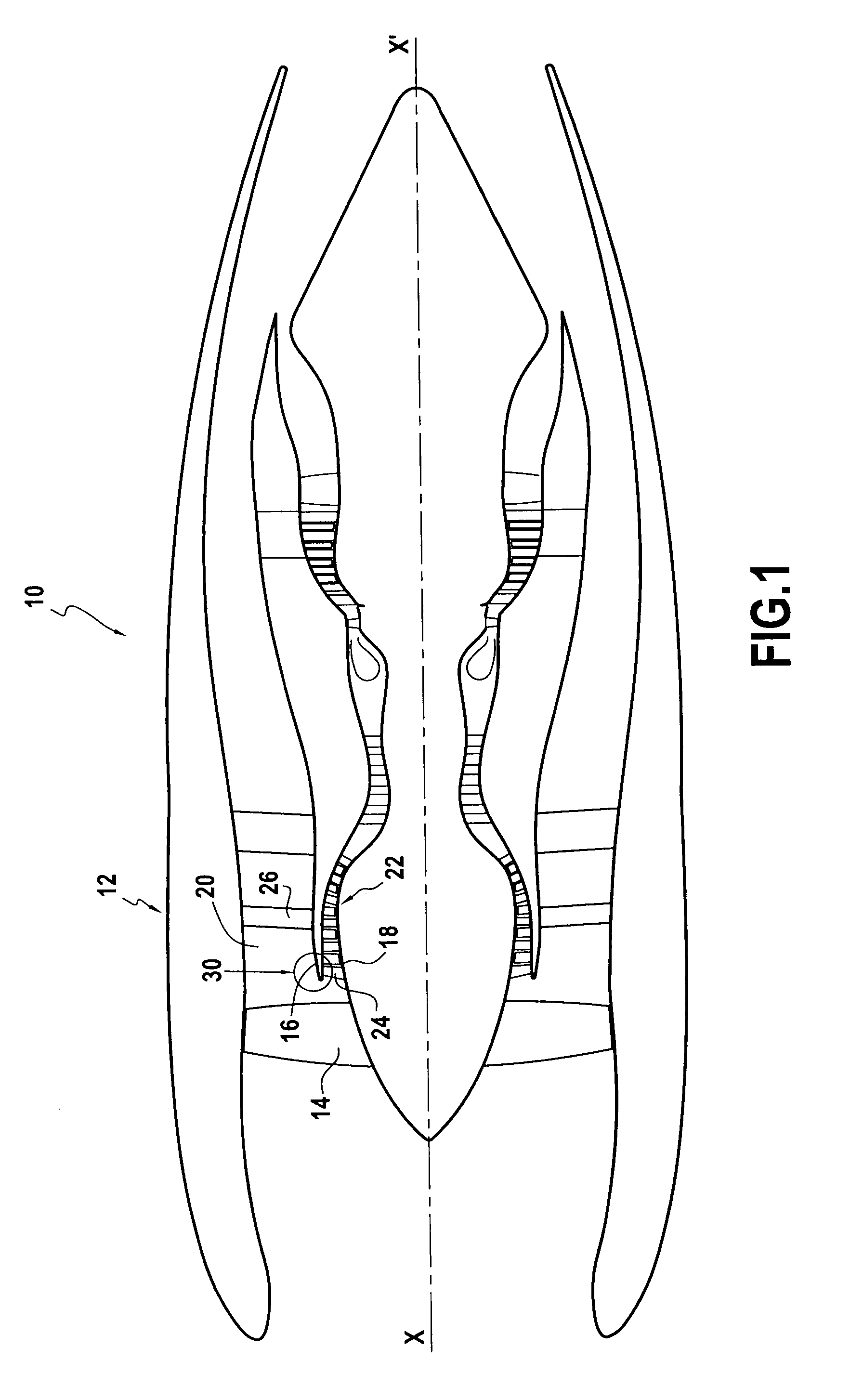
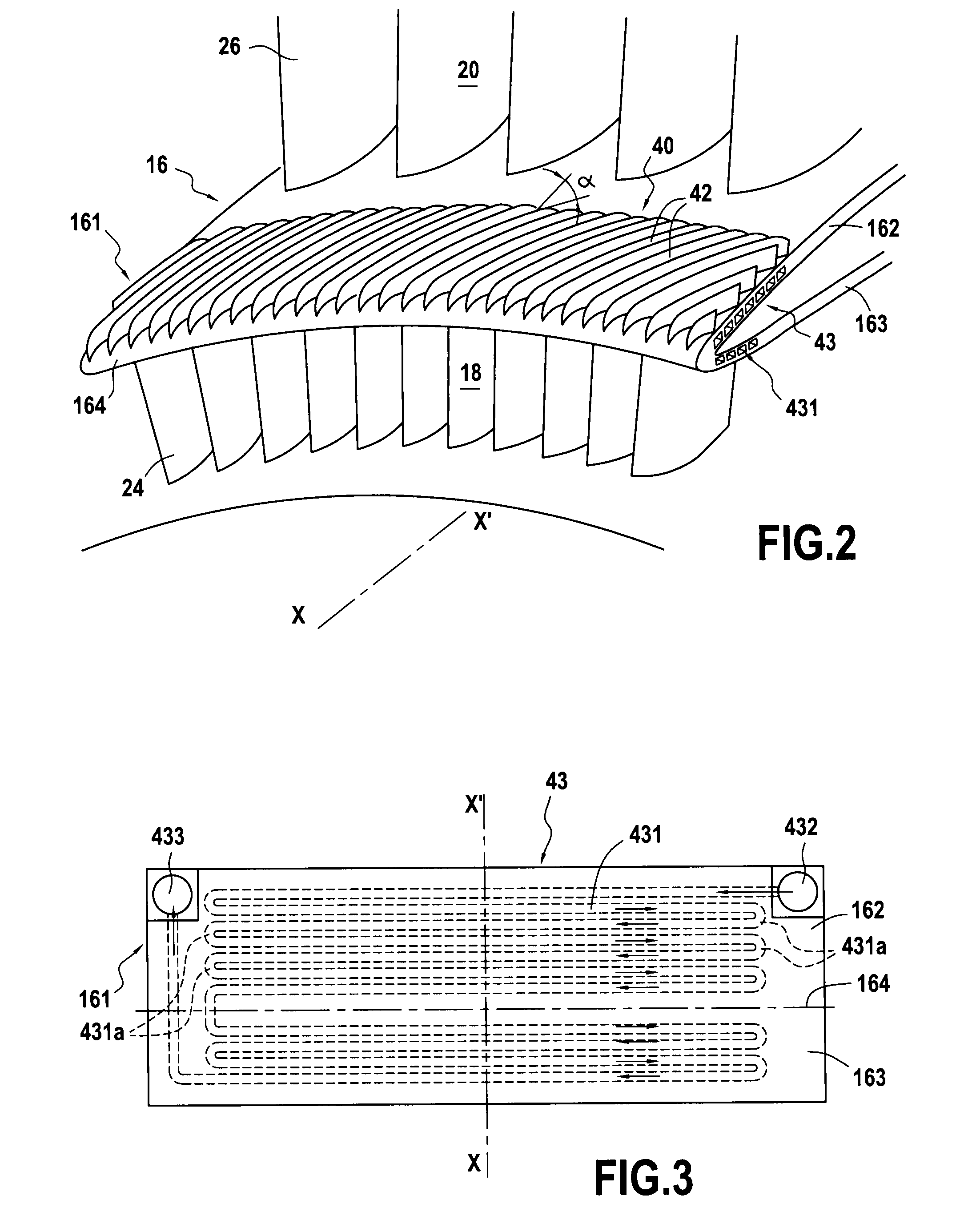
Air-oil heat exchanger placed at the location of the air separator nose of a turbojet, and a turbojet including such an air-oil heat exchanger
InactiveUS20090165995A1Prevent freezingWithout significantly disturbing the air streamExhaust apparatusTurbine/propulsion engine coolingLeading edgeJet engine
The invention relates to an air-oil heat exchanger located at the inner shroud of the secondary duct of a turbojet. In characteristic manner, it comprises an oil circuit placed inside the separator nose and fins placed outside the top wall of the separator nose, between the leading edge of the separator nose and the outlet guide vanes.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
Heat exchanger assembly
InactiveUS20080023185A1Avoid separationImprove heat transfer effectStationary conduit assembliesHeat exchanger casingsEngineeringHeat exchanger
A heat exchanger assembly includes a first single-piece manifold and a second single-piece manifold spaced from and parallel to the first single-piece manifold. Each of the first and second single-piece manifolds has a tubular wall defining a flow path. A plurality of flow tubes extend in parallel between the first and second single-piece manifolds and are in fluid communication with the flow paths. An insert having a distribution surface is slidably disposed in the flow path of the first single-piece manifold to establish a distribution chamber within the first single-piece manifold. A series of orifices defined in the distribution surface of the insert are in fluid communication with the flow path and the distribution chamber for uniformly distributing a heat exchange fluid between the flow path and the flow tubes.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
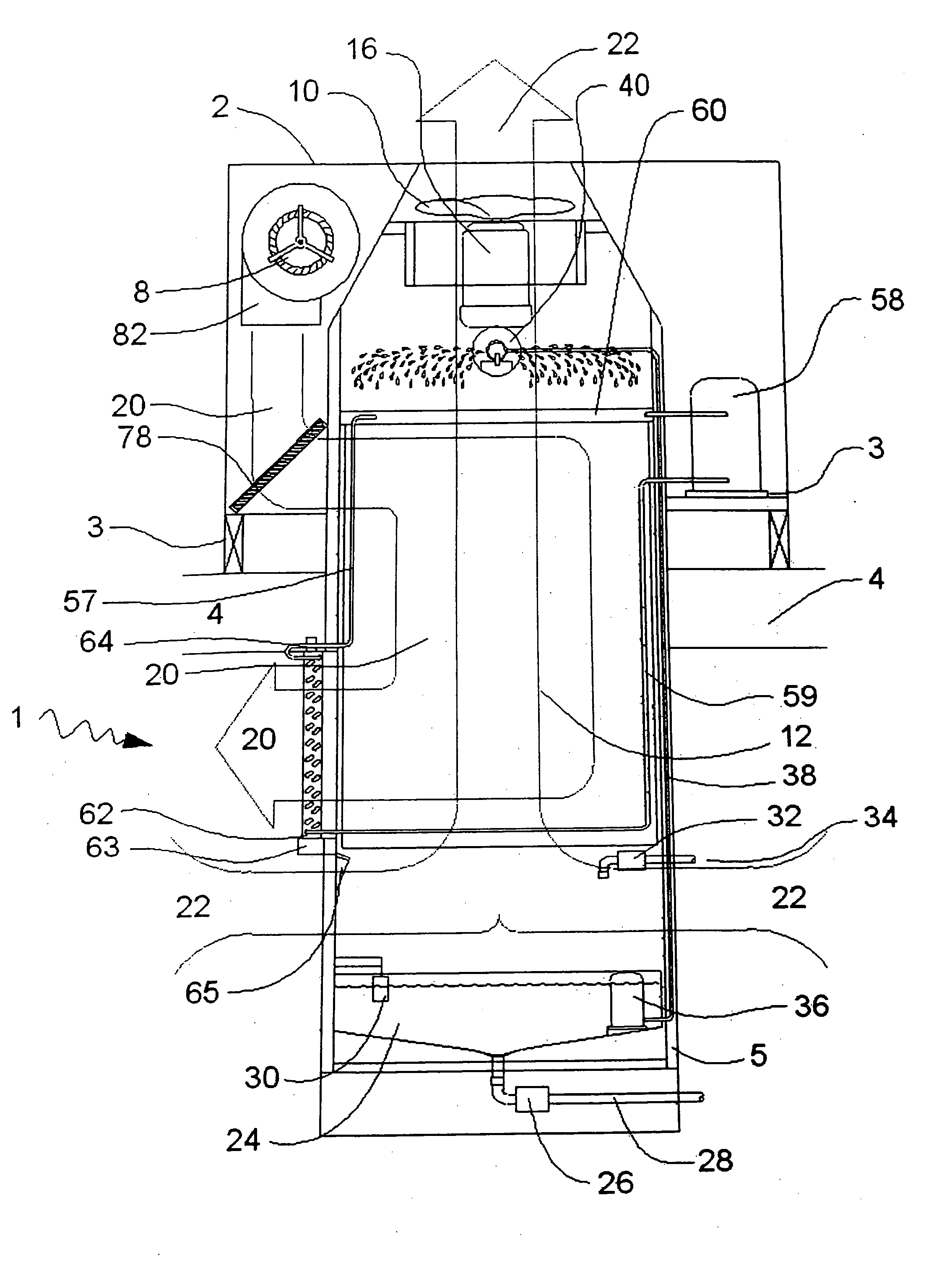
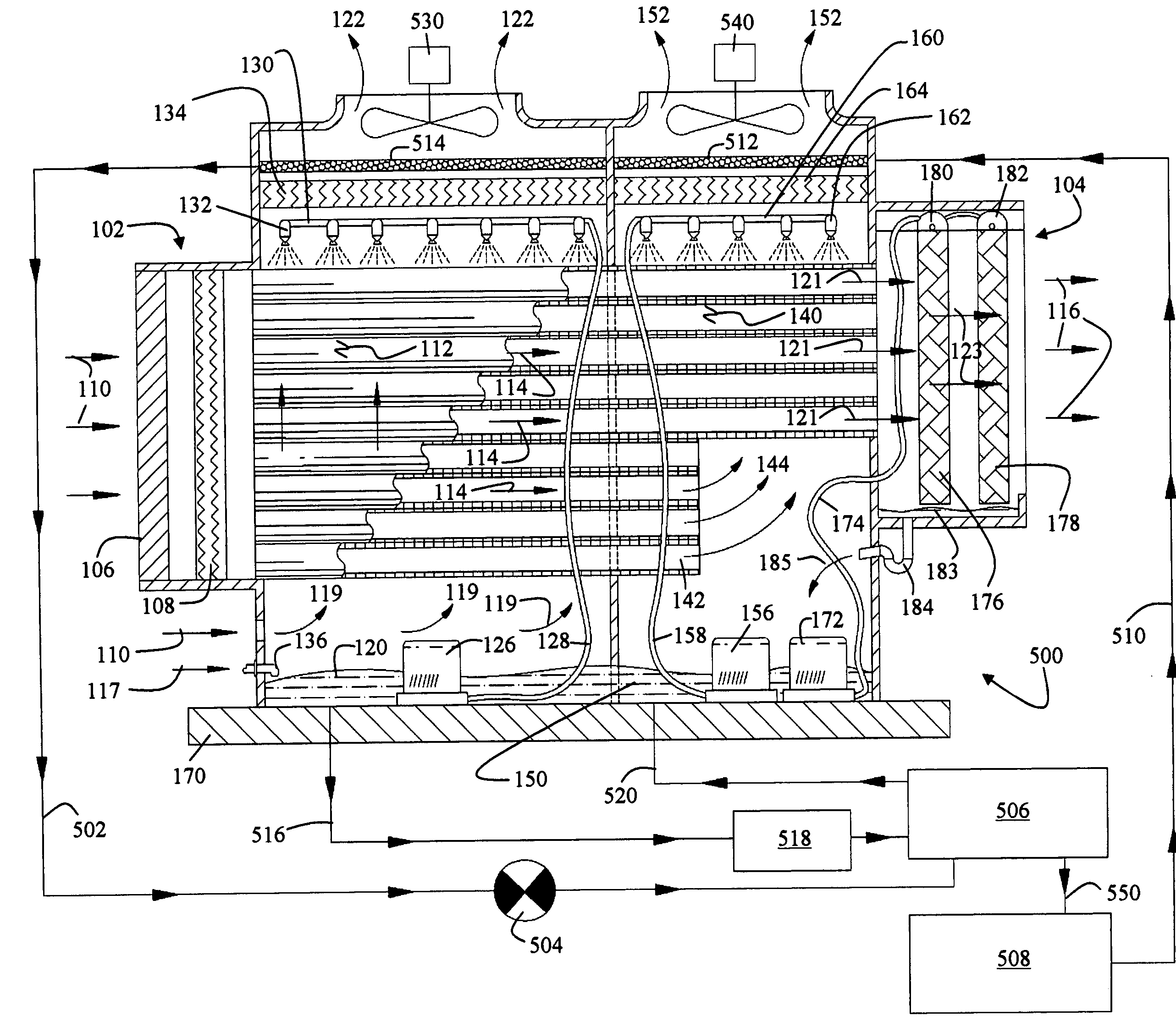
Multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system
InactiveUS20070101746A1Improve efficiencyFree-cooling systemsEfficient regulation technologiesEngineeringRefrigeration
A multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system is described as having a direct evaporative cooling subsystem and an indirect evaporative cooling subsystem having one of a horizontal and a vertical set of heat exchanger channels. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system with a horizontal set of heat exchanger channels has a portion of the horizontal heat exchanger channels partially extended into a next stage of the multi-stage system. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system with the vertical set of heat exchanger channels includes a first set of vertical set of heat exchanger channels spanning a substantial vertical height of the stage of the hybrid evaporative cooling system, and a second set spanning approximately half the height of the stage. The multi-stage hybrid evaporative cooling system further includes a refrigeration system for lowering the temperature of the indirect evaporative cooling subsystem air without affecting its pressure flow.
Owner:S&T MFG CO
Heat dissipation device for light emitting diode module
InactiveUS20080062694A1Point-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLiquid cooling systemEngineering
A heat dissipation device for a light emitting diode (LED) module includes a liquid cooling system. The liquid cooling system includes a heat-absorbing member, which includes an inlet, an outlet and at least one pipe extending between the inlet and the outlet. The inlet and the outlet are provided for permitting liquid to flow through the at least one pipe, which is in thermal contact with at least one LED of the LED module.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Microchannnel evaporator assembly
The present invention provides a unit cooler adapted for use in a refrigerated environment. The unit cooler includes a housing adapted to be positioned within the refrigerated environment and at least one microchannel evaporator coil supported by the housing. The at least one microchannel evaporator coil includes an inlet manifold and an outlet manifold. The inlet manifold has an inlet port for receiving refrigerant, and the outlet manifold has an outlet port for discharging the refrigerant.
Owner:HUSNN
Air conditioning apparatus
According to the present invention, an air conditioning apparatus include a case partitioned into a first air passage and a second air passage by partition plates (16-19), a heat exchanger such as a heater core. The heater exchanger is sandwiched between the partition plates. Further, the heat exchanger is formed by laminating tubes and a fin while the fin is disposed in each main air passage formed between tube walls of the tubes. Each end of the partition plates is opposite to each end of the tubes so that the partition plates are parallel to the tubes. In this way, airflows which respectively have passed from the air first and second passages pass through the heat exchanger without being mixed with each other therein. As a result, the separation characteristics of airflows can be improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
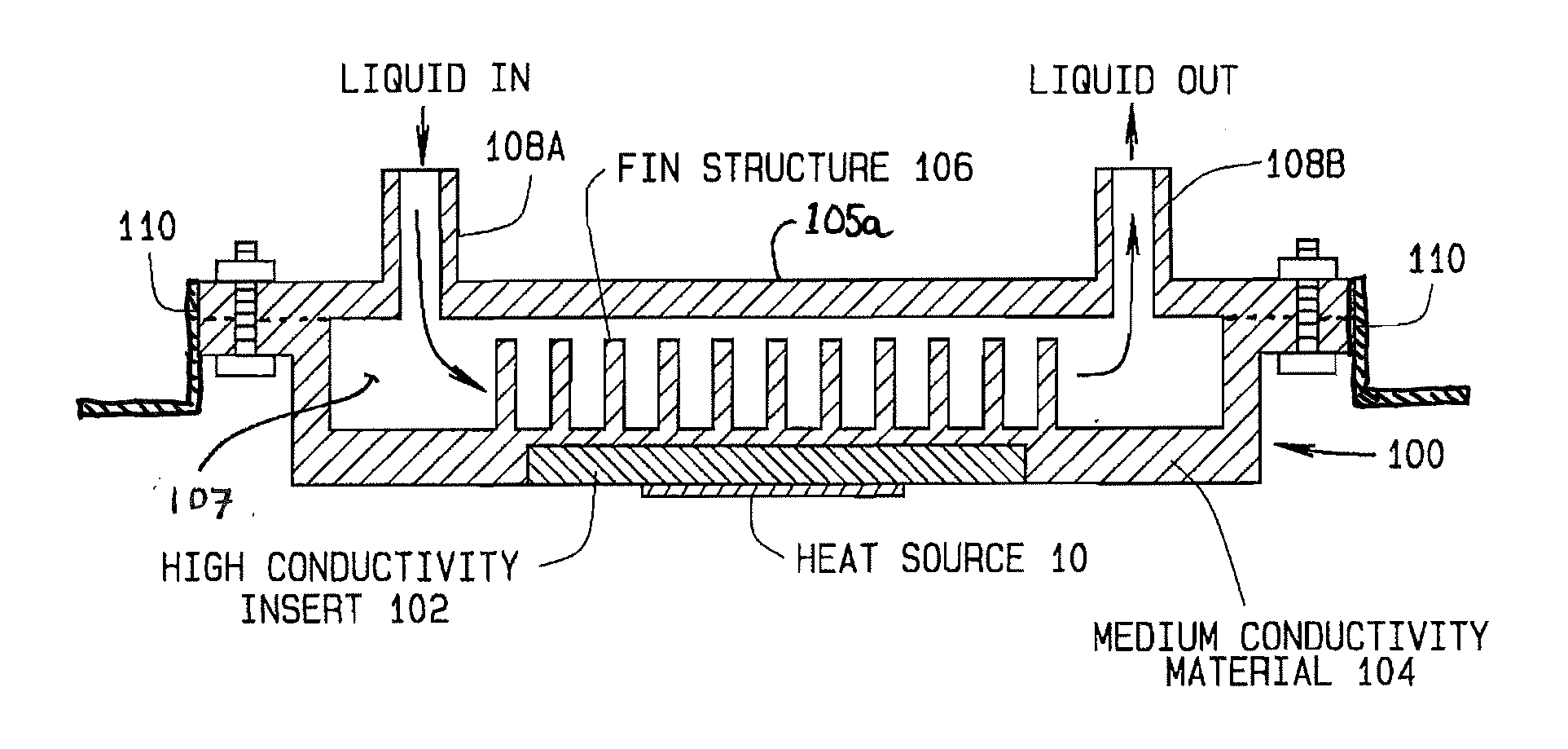
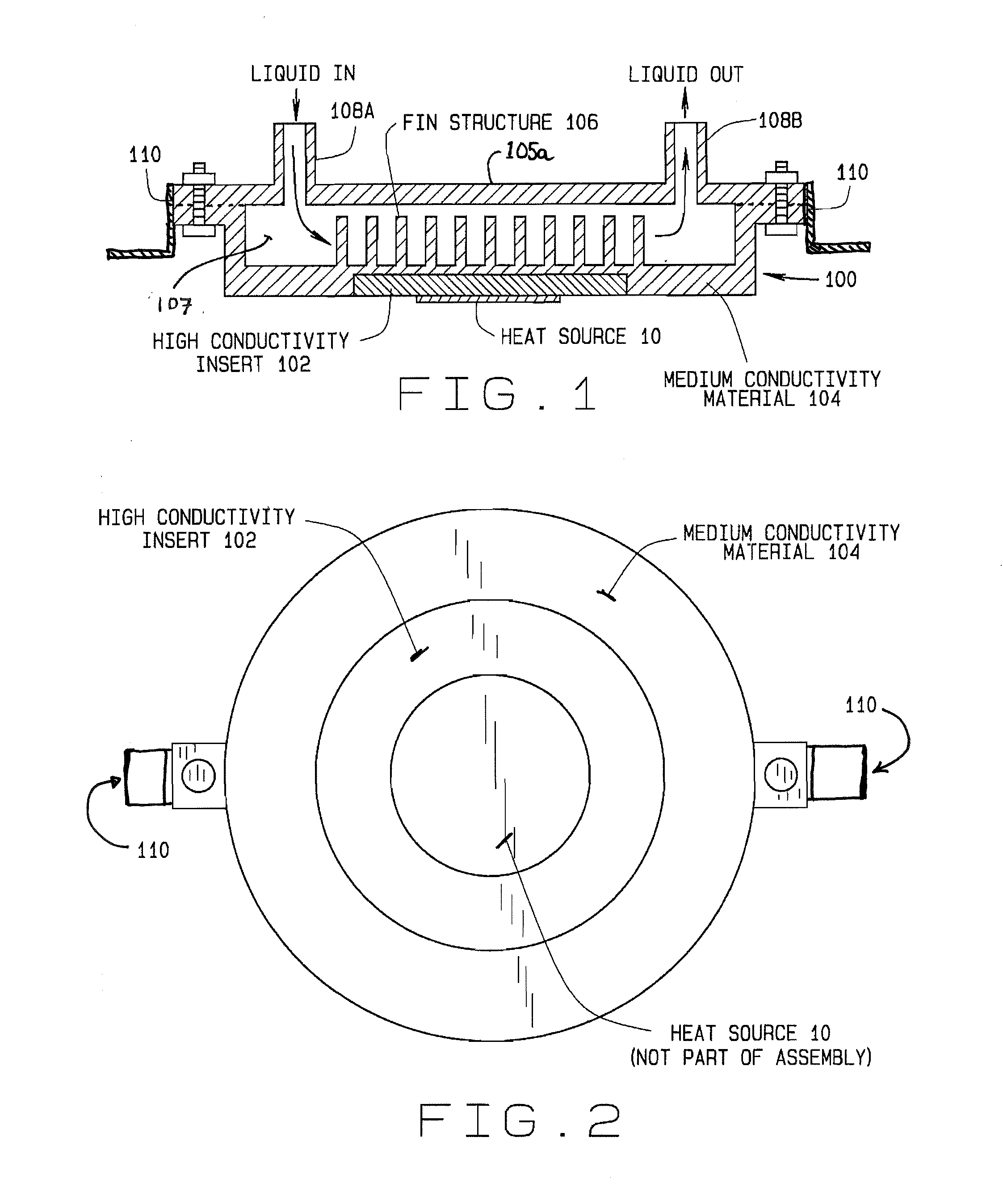
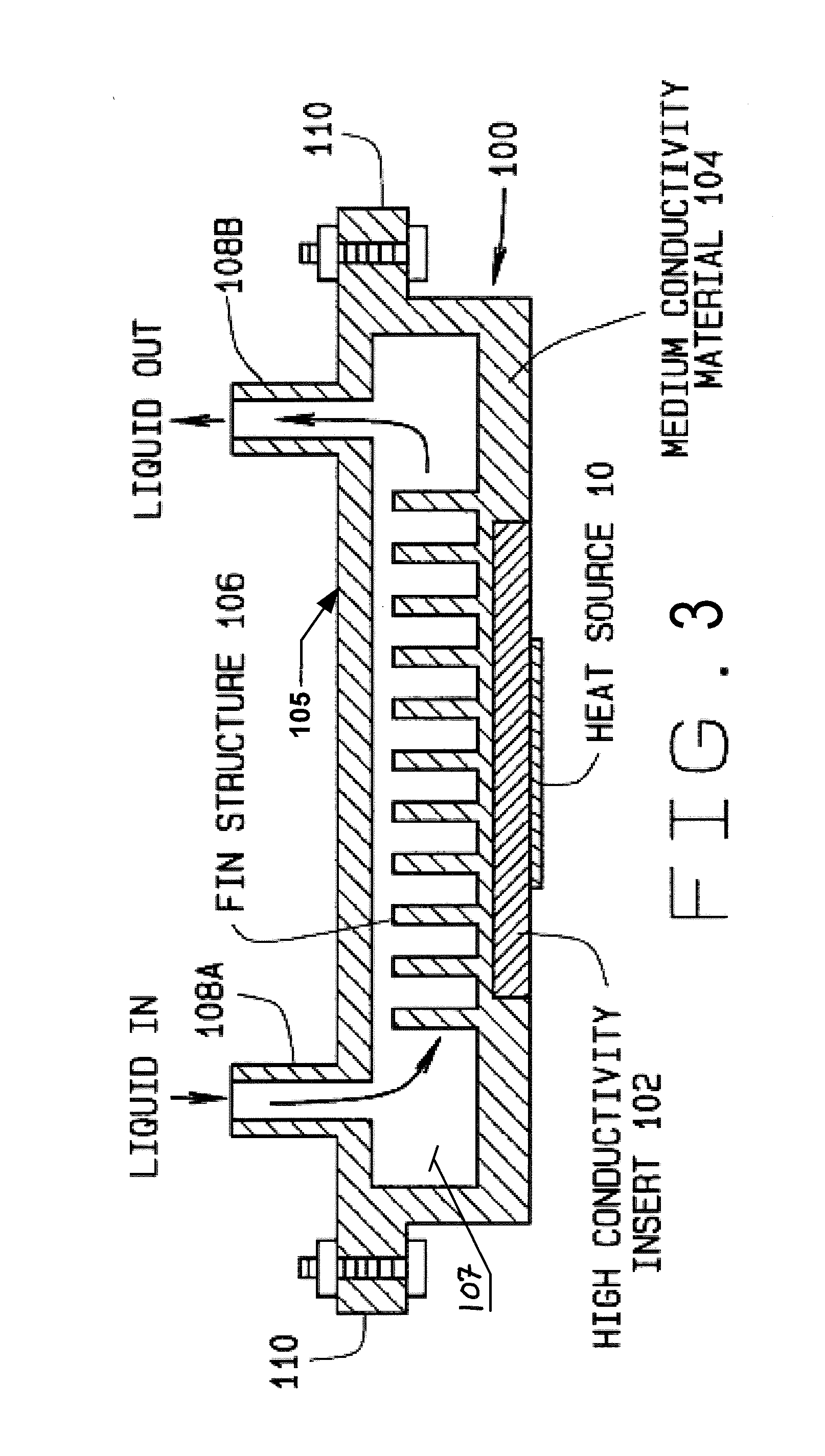
Liquid Cooling System Cold Plate Assembly
InactiveUS20120175094A1Convenient and efficient transferSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal energyLiquid cooling system
A cold plate assembly consisting of a thermally conductive base component with an insert having a high thermal transfer characteristic adapted for contacting the surface of a heat source on one side. The surface of the base component opposite from the insert is surrounding by a housing defining an enclosed volume through with a flow of liquid coolant is directed. Inlet baffles adjacent to a fluid inlet in the housing direct the incoming flow of liquid coolant towards the surface of the base component in proximity to the insert, facilitating an efficient transfer of thermal energy from the heat source to the liquid coolant through the insert and base component. Optional extensions or fins extending into the liquid coolant contained in the enclosed volume from the surface of the base component further facilitate the transfer of thermal energy from the heat source.
Owner:ASETEK DANMARK
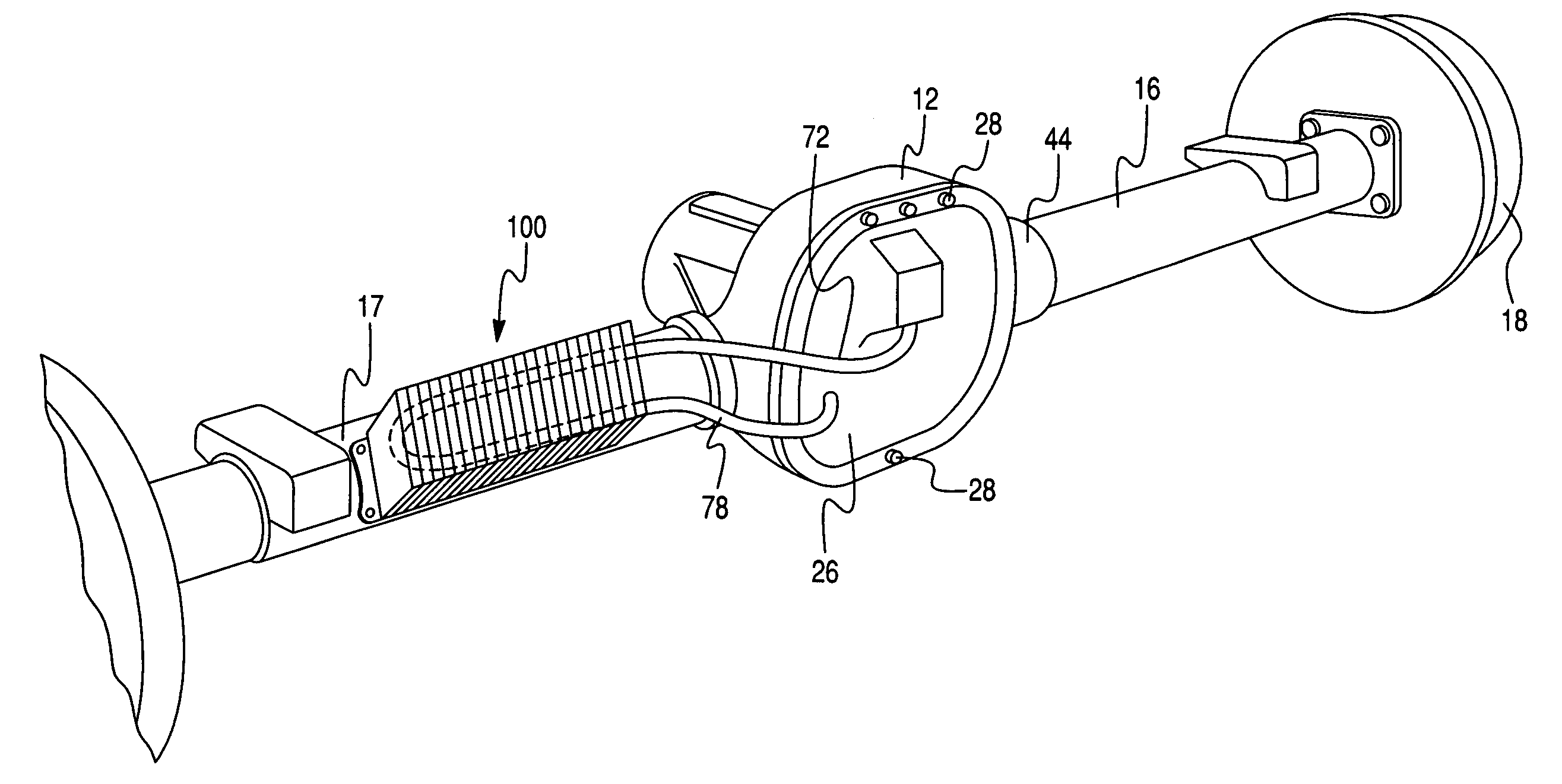
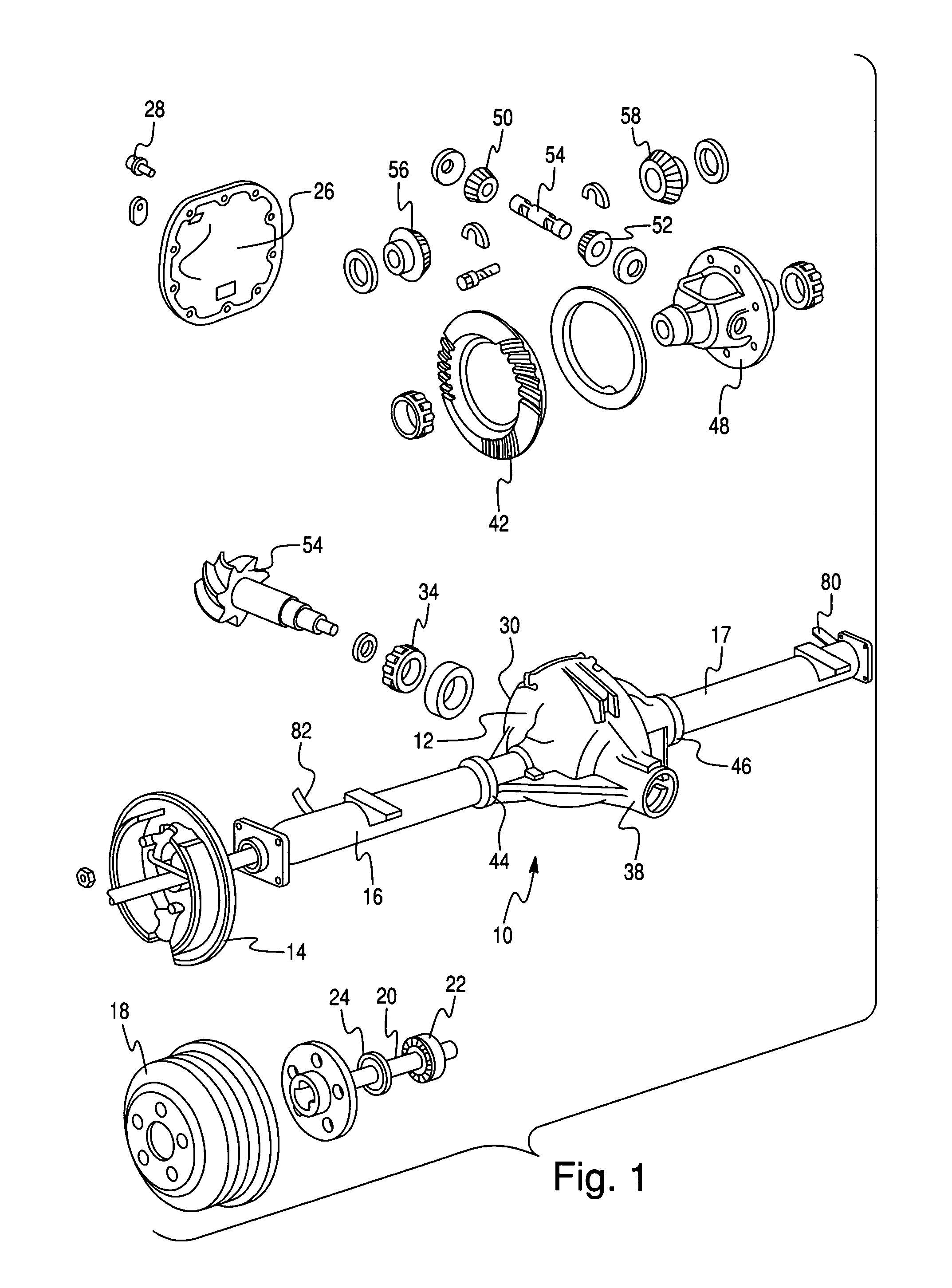
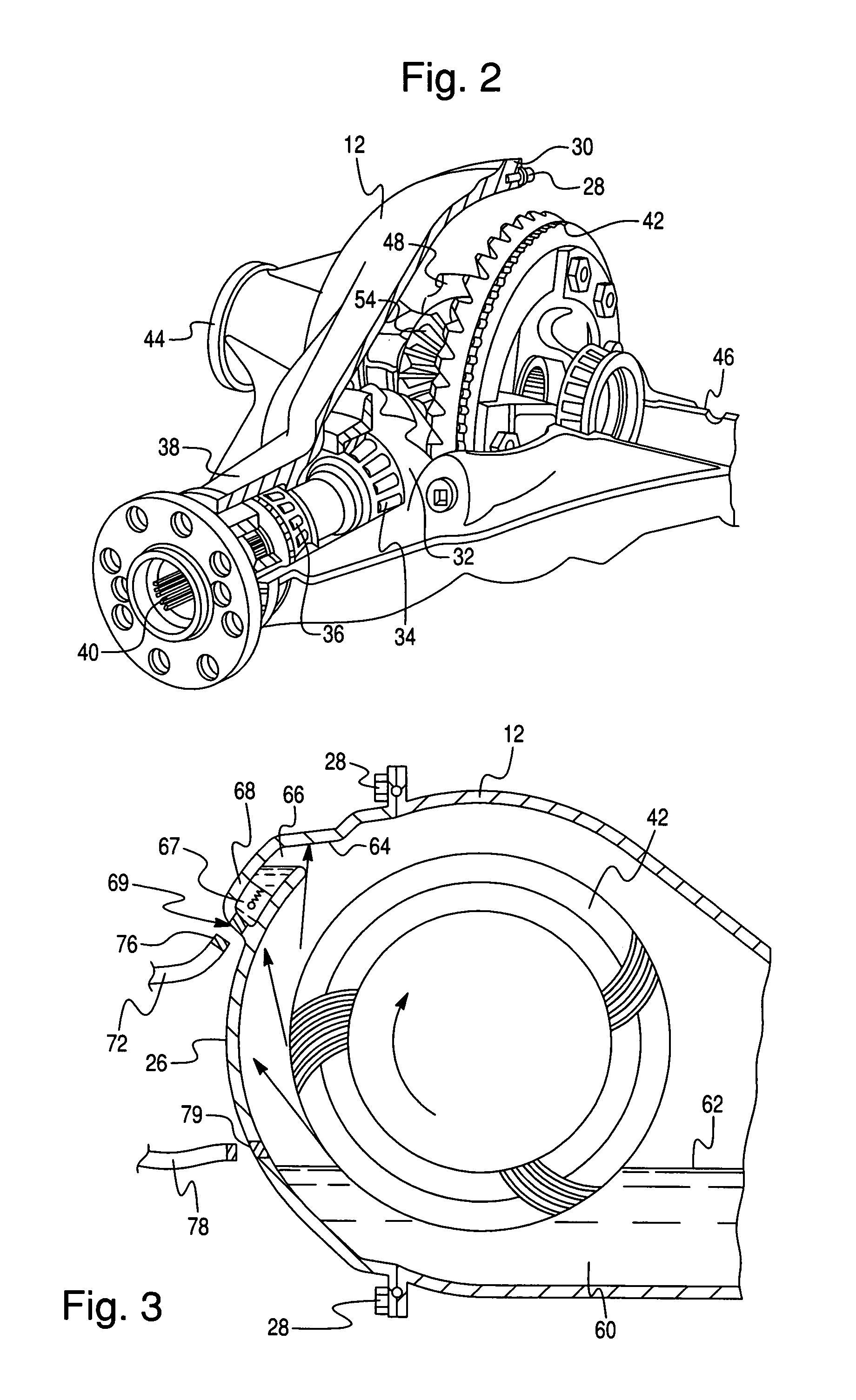
Lubricant cooling system for a motor vehicle axle
In a driven axle assembly (12) for a motor vehicle that includes a differential housing located substantially in the center of the axle and tubes (16, 17) extending laterally from the differential, surrounding axle shafts (20) and opening into a lubricant reservoir (60) in the differential housing, a system for circulating and cooling axle lubricant includes a cover (26) for closing and sealing the housing having a first aperture into the housing where a ring gear rotates through the lubricant reservoir. The aperture in the cover opens to a chamber that holds lubricant carried through the aperture by the rotating ring gear. Conduit (72) connected by a hydraulic fitting to the chamber has its opposite end connected to an oil cooler mounted on the axle tube. Conduit (78) returns the lubricant to the reservoir in the differential housing. Lubricant flows via a gravity feed through the first conduit into the cooler and back to the housing reservoir via the second conduit, effectively cooling the lubricant without the addition of a pump.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
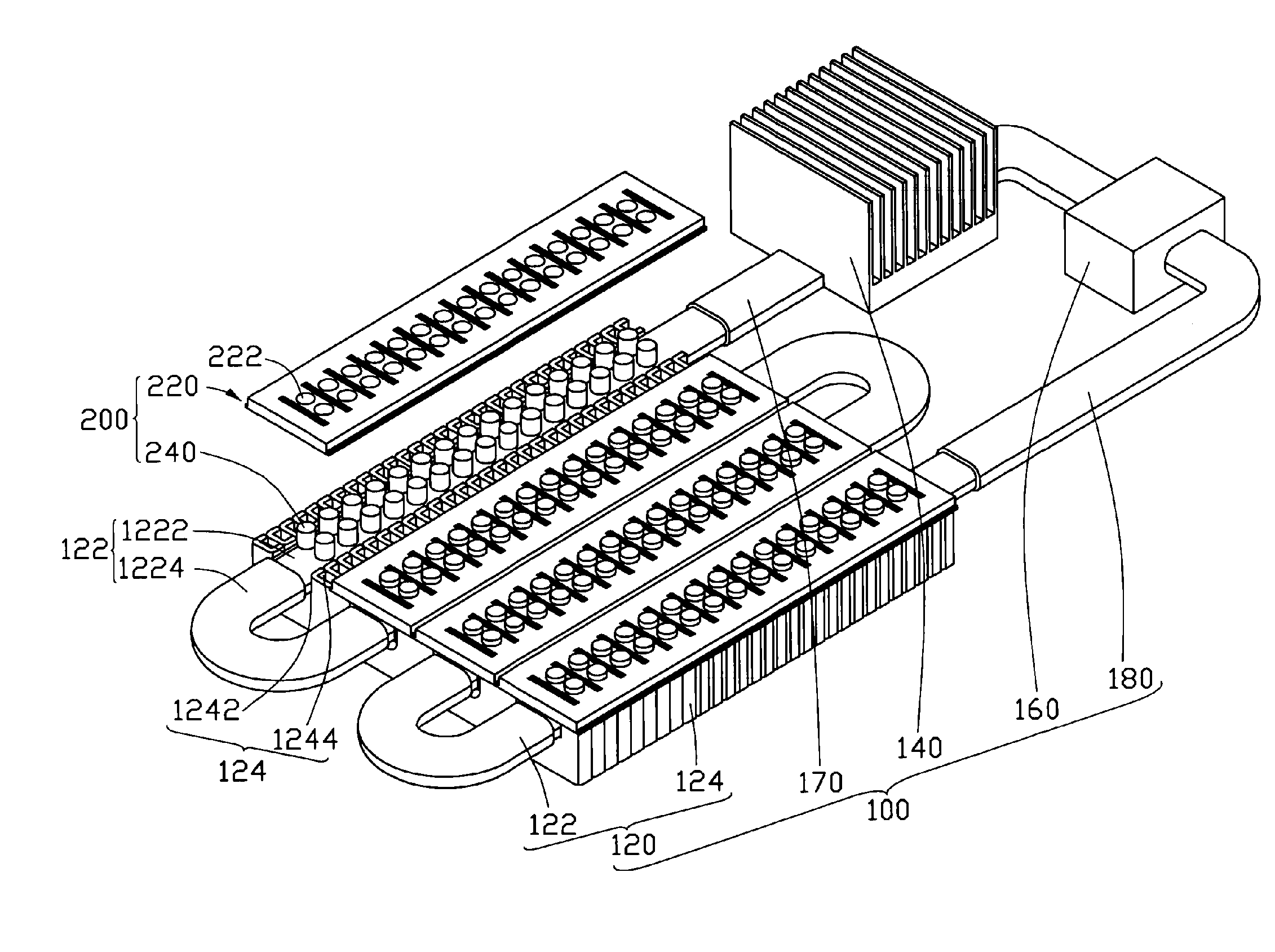
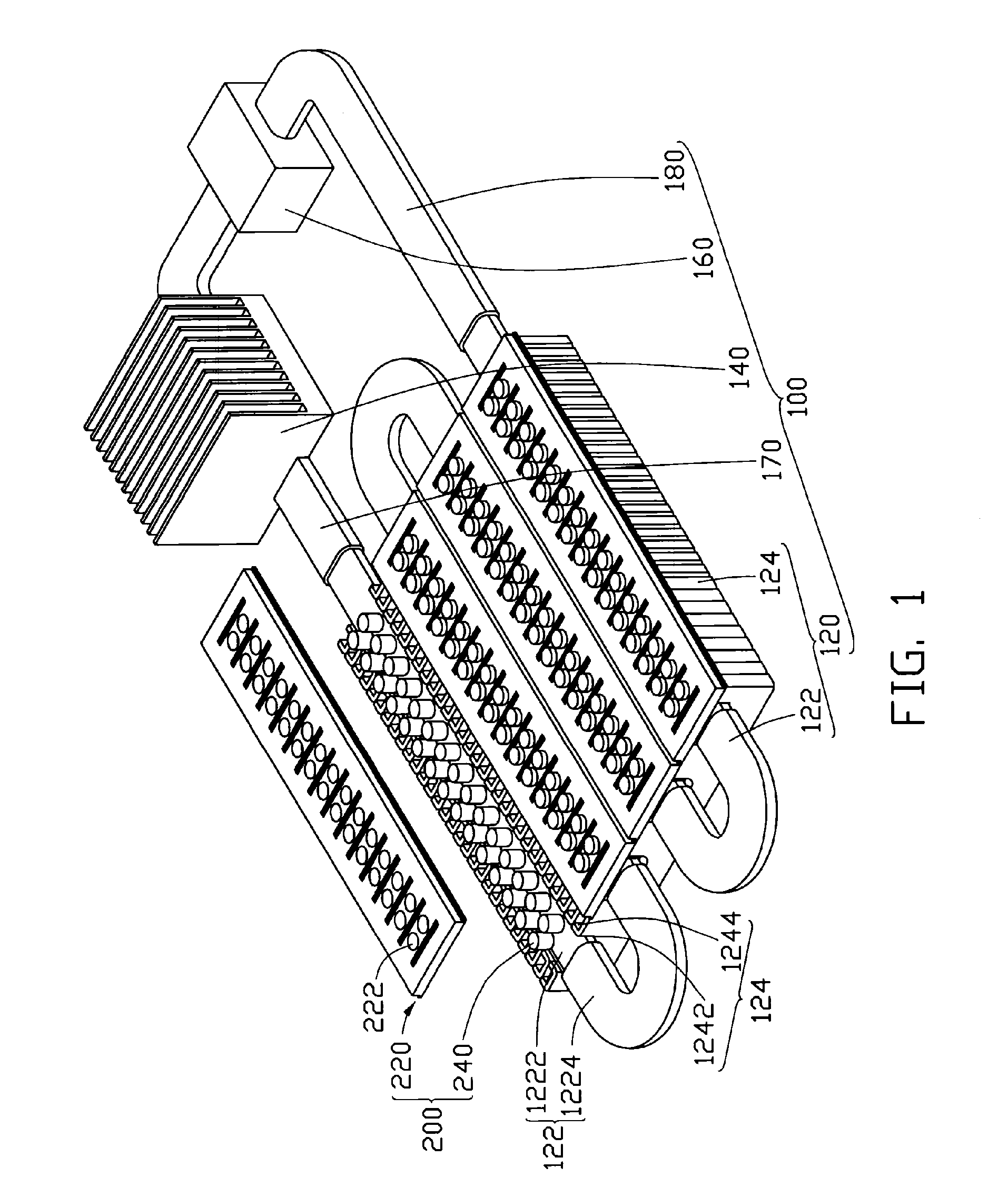
Cooling devices with high-efficiency cooling features
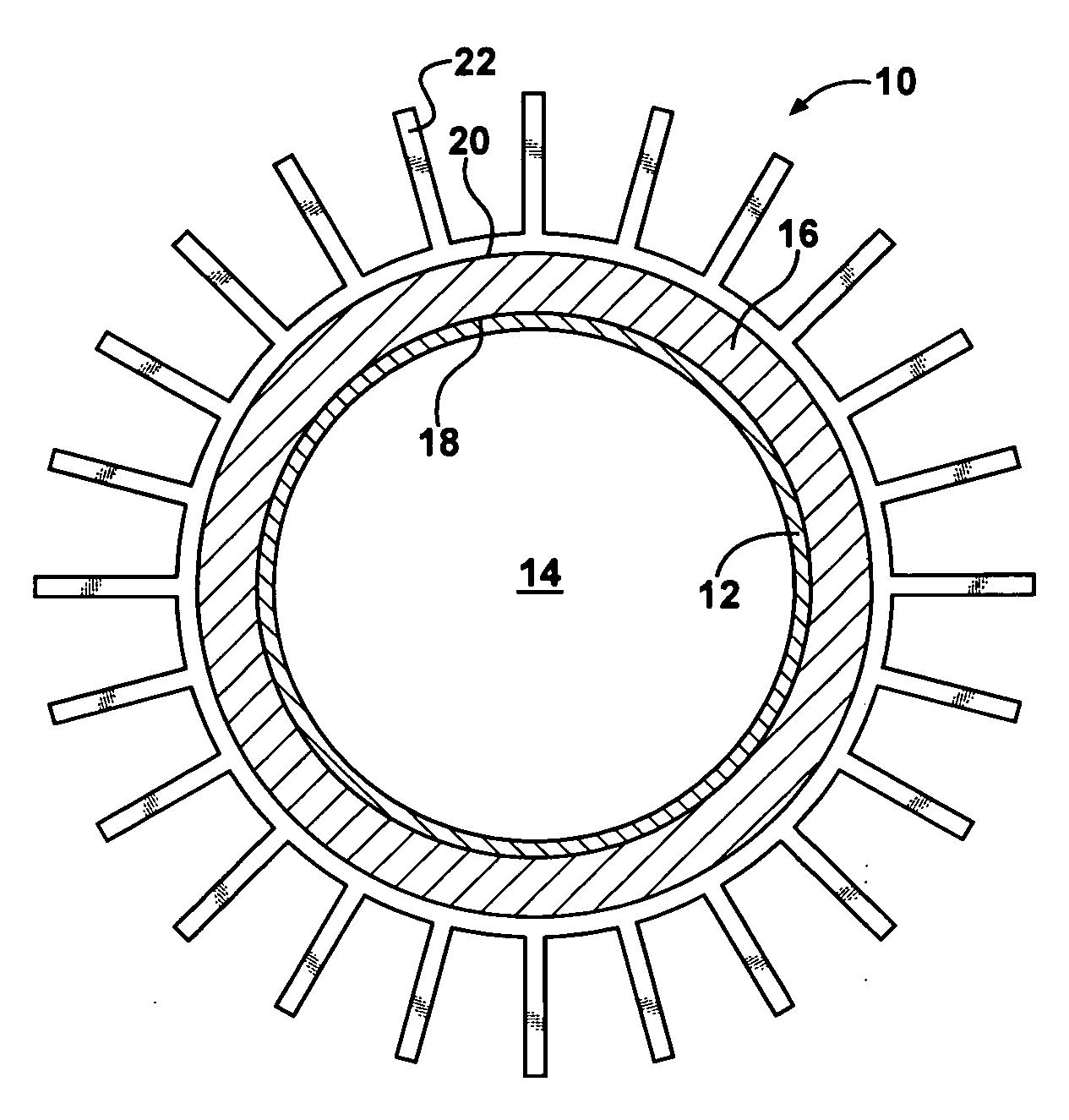
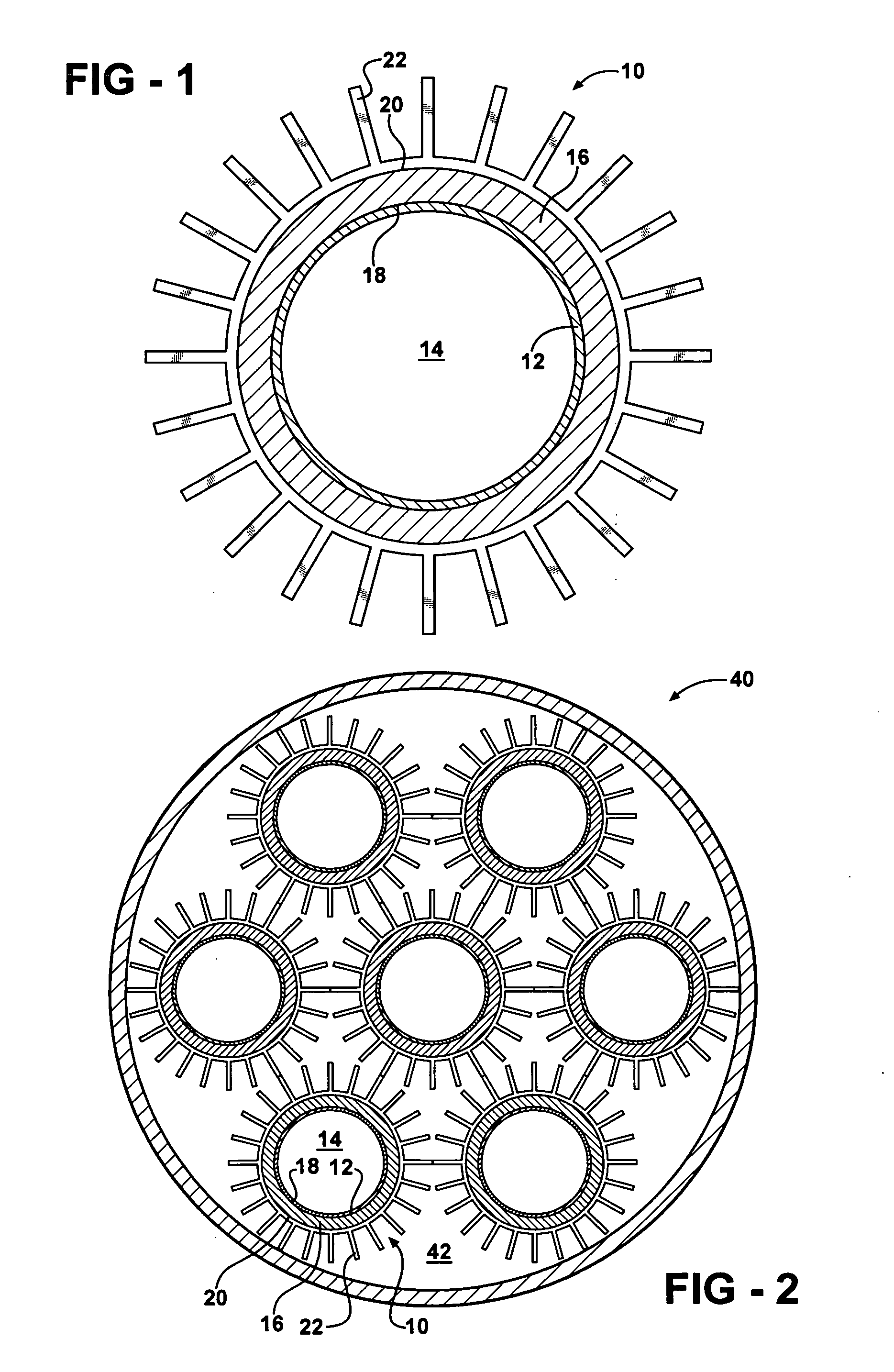
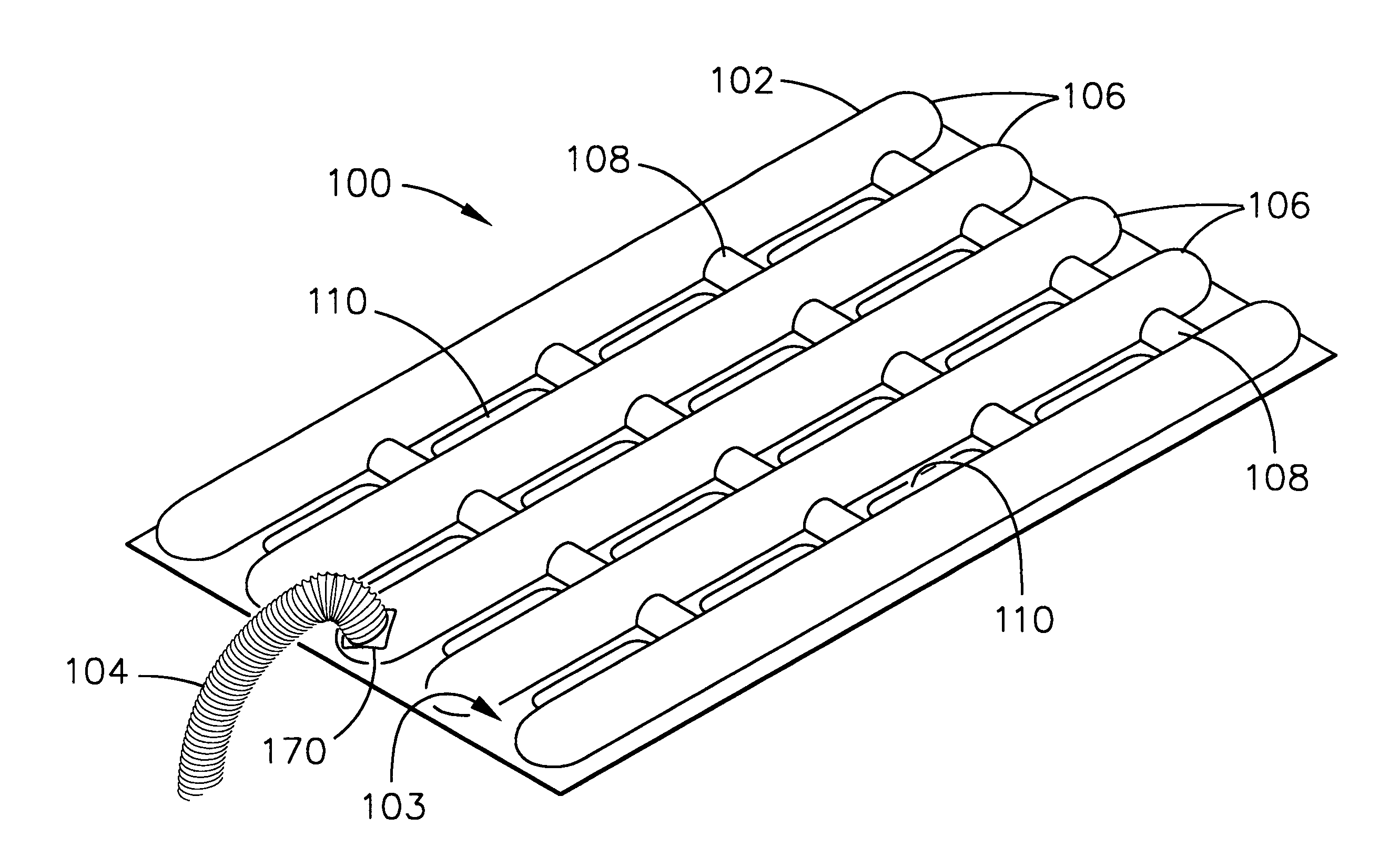
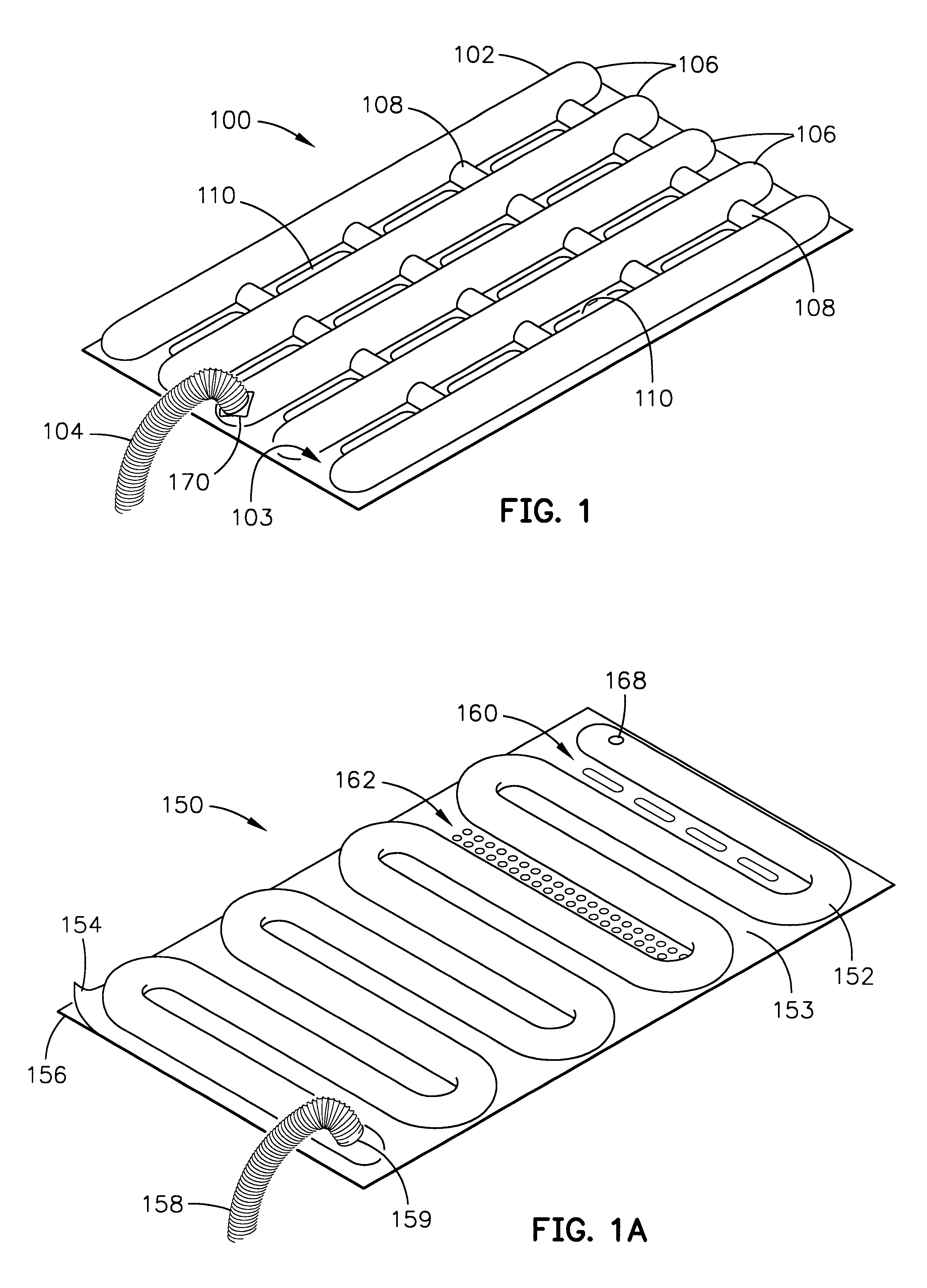
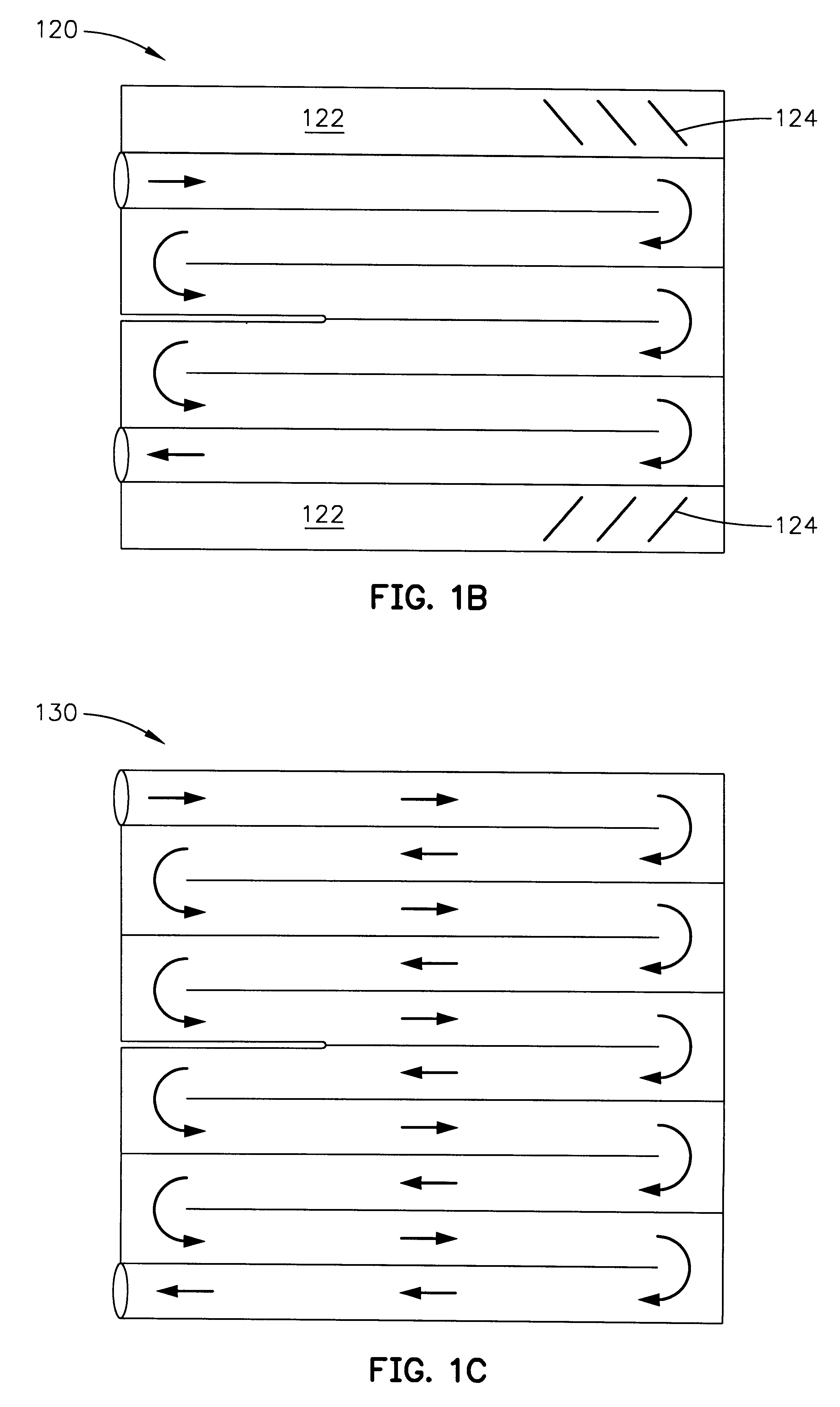
InactiveUS6354099B1Domestic cooling apparatusStationary conduit assembliesEvaporationCooling chamber
Cooling devices are provided to reduce a person's temperature by evaporative, convective, and / or conductive cooling. One such device maximizes evaporative cooling by aiding the flow of air to the person and the removal of vapor-laden air from the person. An upper sheet and a base sheet are adhered to define numerous elongated, parallel, inflatable cooling chambers separated by flat connecting membranes. Ventilating cross-members interconnect the cooling chambers. Air enters the chambers through an inlet, exits the chambers toward the person through air permeable regions of the base sheet. Air heated by the person's body exits the device upward through evaporation openings in the connecting membranes. The foregoing device, or different variations thereof, may be modified for use in conductive cooling by adding an absorbent sheet beneath the base sheet, or substituting the absorbent sheet for the base sheet itself This device directs air upon the wetted absorbent sheet to cool this layer, and thereby conductively cool the patient's skin in thermal contact with the absorbent sheet. As one example, this device may be configured in serpentine shape, with multiple winding segments. The device may include body-contour slits extending inward from the perimeter, permitting the device to conform to a person's legs and outstretched arms. Cooling devices may also include optional features to enhance thermal contact between the absorbent sheet and the person's skin, and / or to prevent water runoff from the cooling field.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL
Cooling devices with high-efficiency cooling features
InactiveUS6519964B2Domestic cooling apparatusStationary conduit assembliesEvaporationCooling chamber
Cooling devices are provided to reduce a person's temperature by evaporative, convective, and / or conductive cooling. One such device maximizes evaporative cooling by aiding the flow of air to the person and the removal of vapor-laden air from the person. An upper sheet and a base sheet are adhered to define numerous elongated, parallel, inflatable cooling chambers separated by flat connecting membranes. Ventilating cross-members interconnect the cooling chambers. Air enters the chambers through an inlet, exits the chambers toward the person through air permeable regions of the base sheet. Air heated by the person's body exits the device upward through evaporation openings in the connecting membranes. The foregoing device, or different variations thereof, may be modified for use in conductive cooling by adding an absorbent sheet beneath the base sheet, or substituting the absorbent sheet for the base sheet itself. This device directs air upon the wetted absorbent sheet to cool this layer, and thereby conductively cool the patient's skin in thermal contact with the absorbent sheet. As one example, this device may be configured in serpentine shape, with multiple winding segments. The device may include body-contour slits extending inward from the perimeter, permitting the device to conform to a person's legs and outstretched arms. Cooling devices may also include optional features to enhance thermal contact between the absorbent sheet and the person's skin, and / or to prevent water runoff from the cooling field.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL
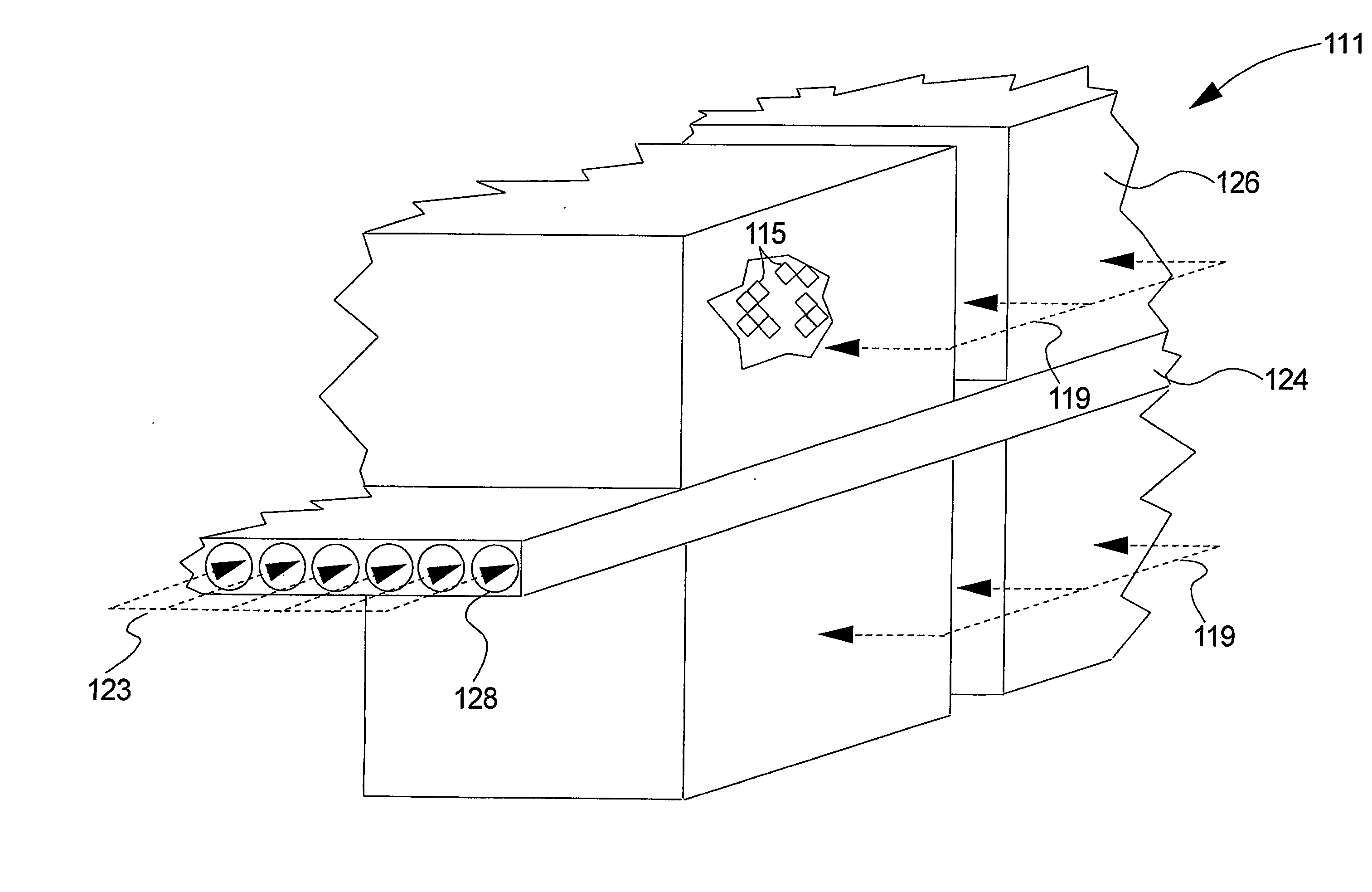
Device for cooling a vehicle battery
InactiveUS20110132580A1Effective and reliable coolingImprove pressure resistanceFuel cell heat exchangeThermal insulationElectricityElectrical battery
A device for cooling a vehicle battery is provided that includes a plurality of electrical storage elements, and a cooling element having ducts for a fluid to flow through, wherein the electrical storage elements are in thermal contact with the cooling elements and heat can be transmitted from the storage elements to the fluid, and wherein the cooling element which comprises the ducts is embodied as at least one extruded profile.
Owner:BEHR GMBH & CO KG
Air conditioner for vehicle
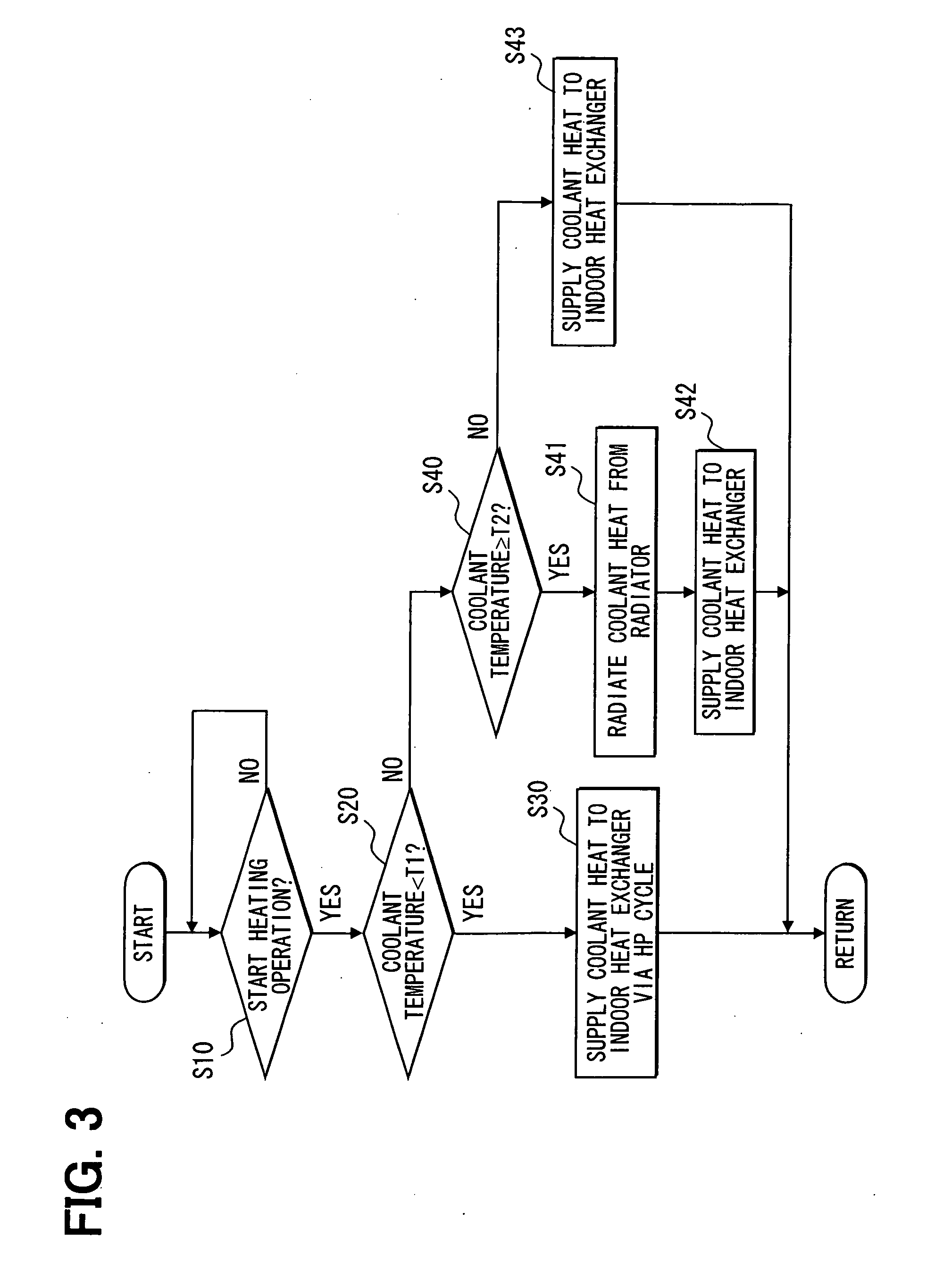
InactiveUS20100281901A1Solve insufficient heating capacityReduce energy lossAir-treating devicesRailway heating/coolingCoolant flowEngineering
In an air conditioner for a vehicle, in a heating operation for heating a vehicle compartment, when heating capacity is obtained by flowing a coolant through an inside of an indoor heat exchanger, the coolant flows directly in the inside of the indoor heat exchanger to heat air to be supplied to the vehicle compartment. In contrast, when the heating capacity is not obtained by flowing the coolant through the inside of the indoor heat exchanger, the coolant flows through a first water-refrigerant heat exchanger and a refrigerant in a heat pump cycle circulates so that heat of the coolant is absorbed by the refrigerant in the first water-refrigerant heat exchanger, and the air is heated in the indoor heat exchanger by using heat of the refrigerant that has absorbed the heat of the coolant.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com