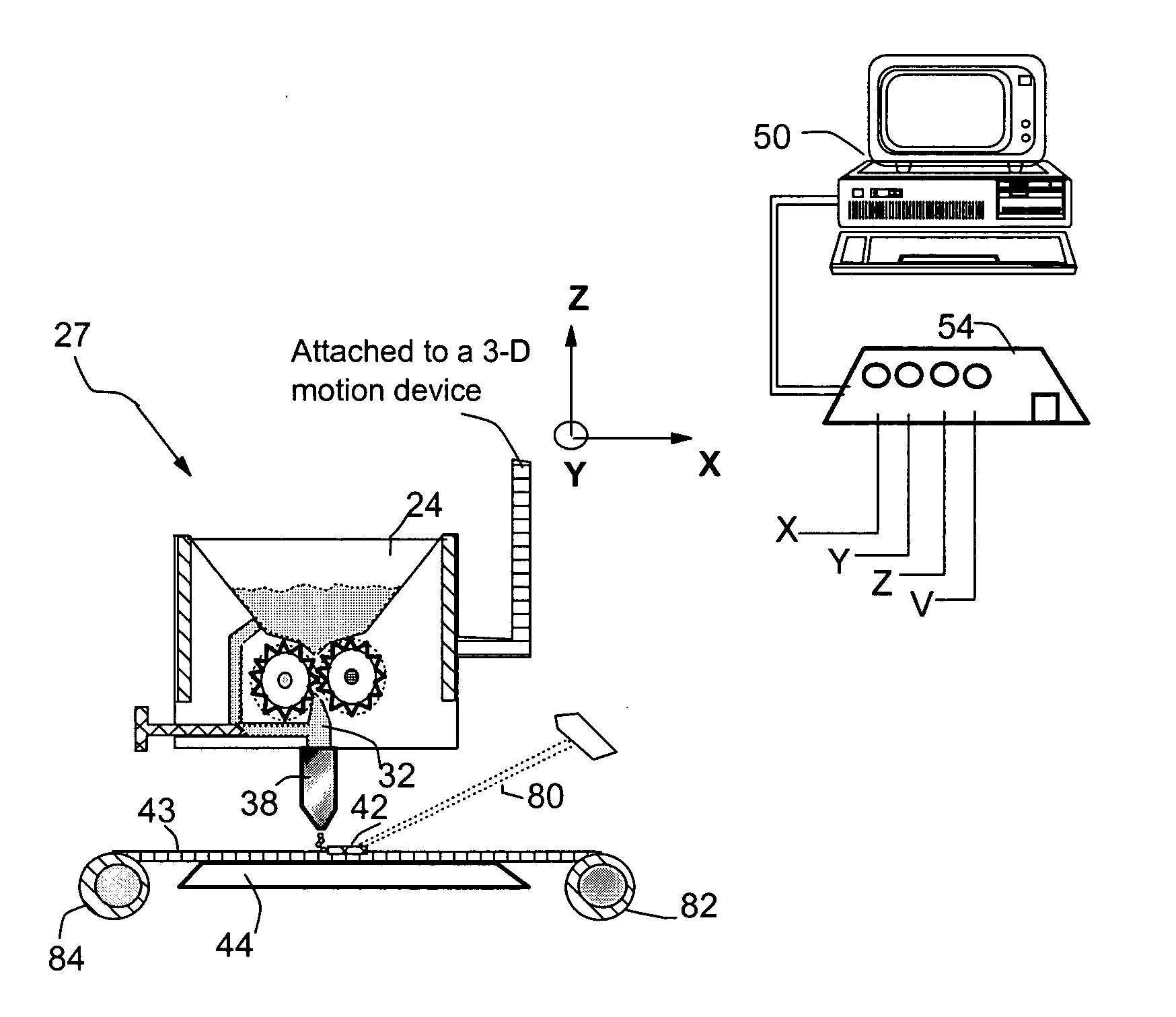
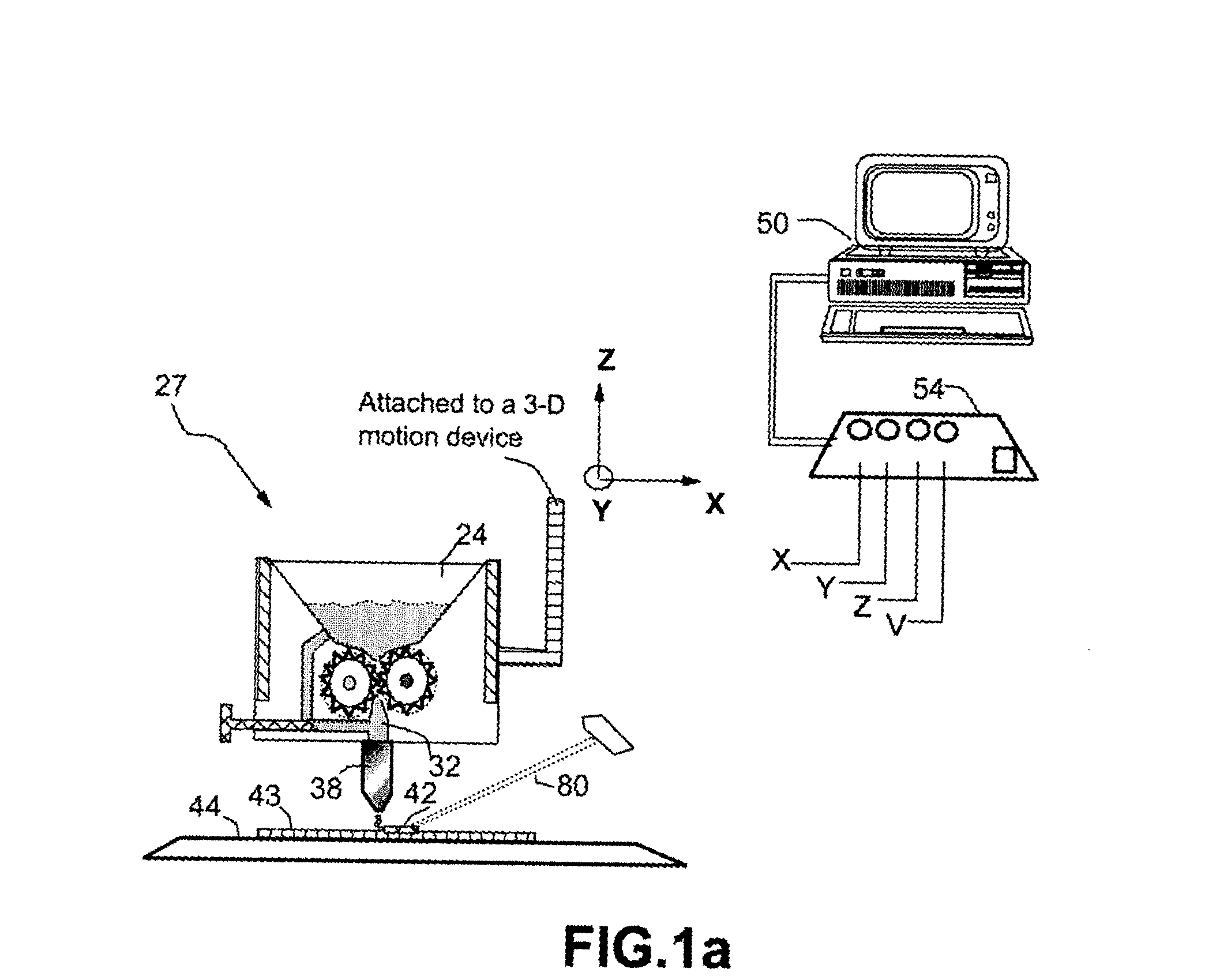
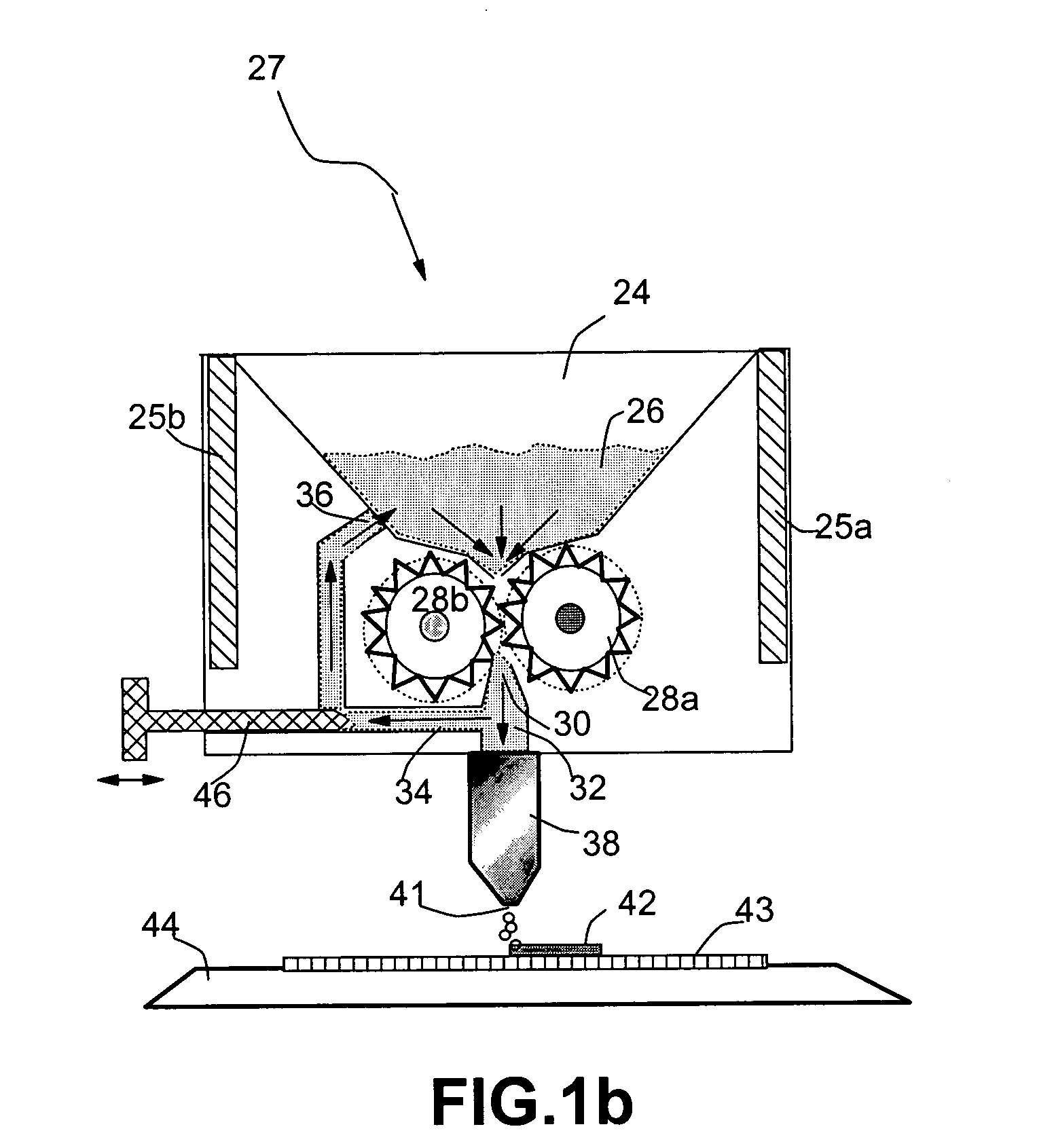
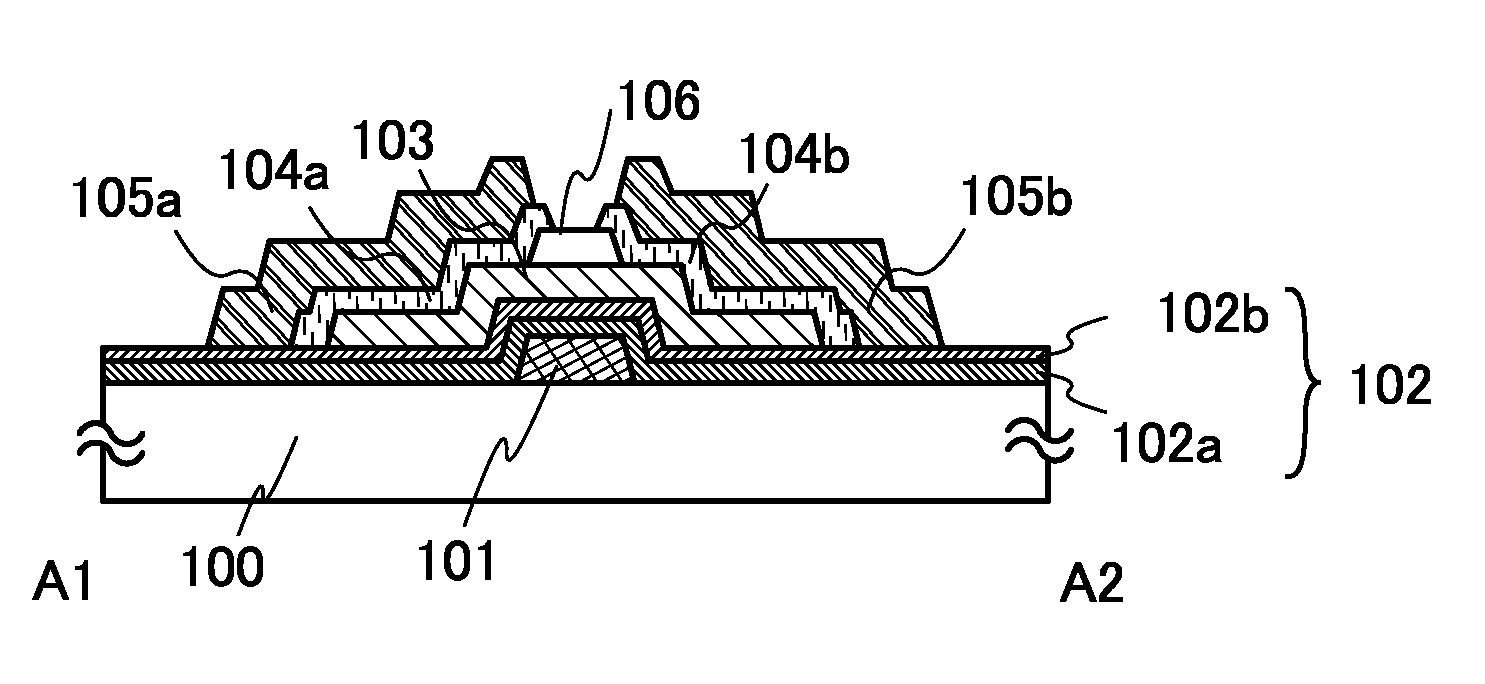
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2006results about How to "Small amount" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
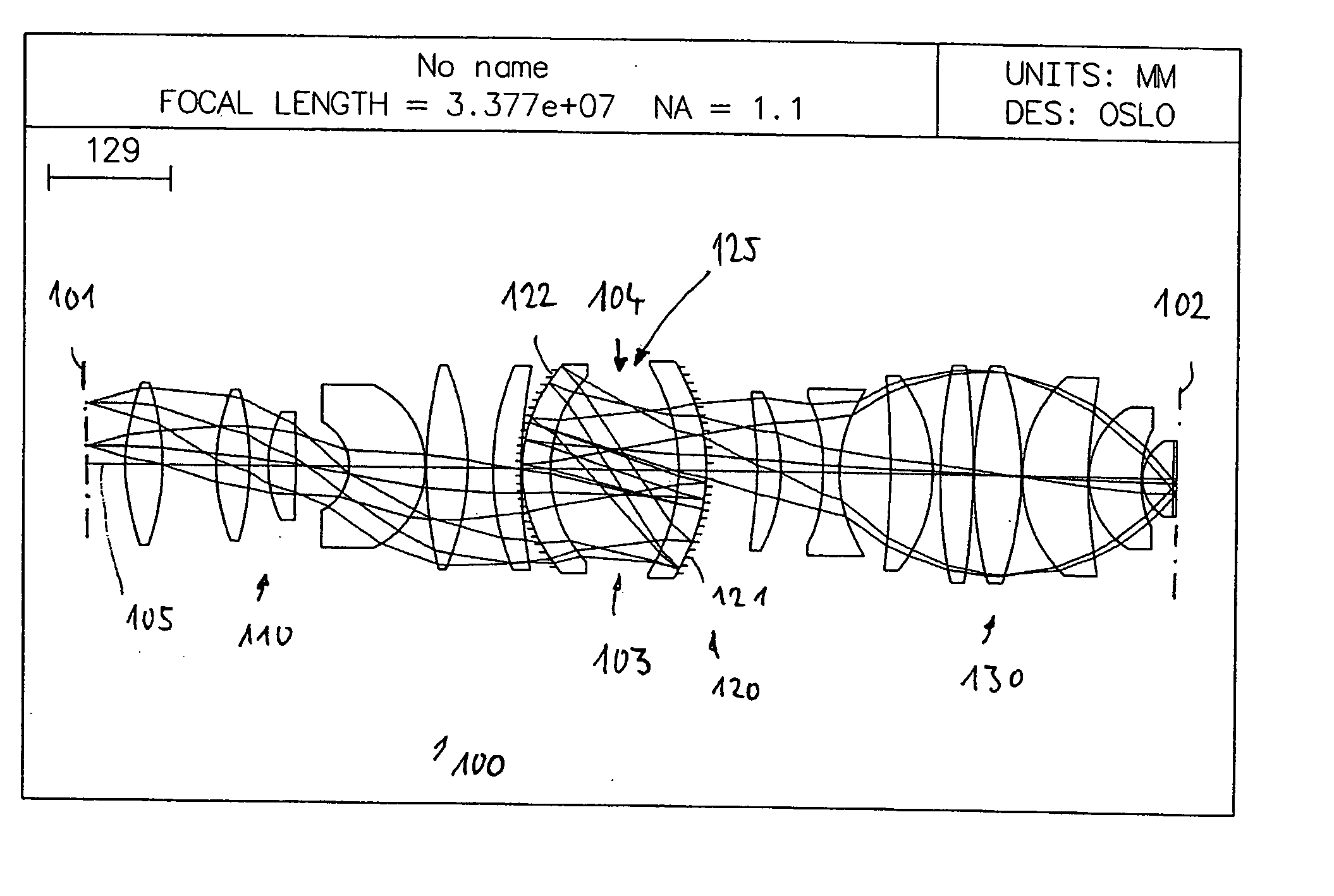
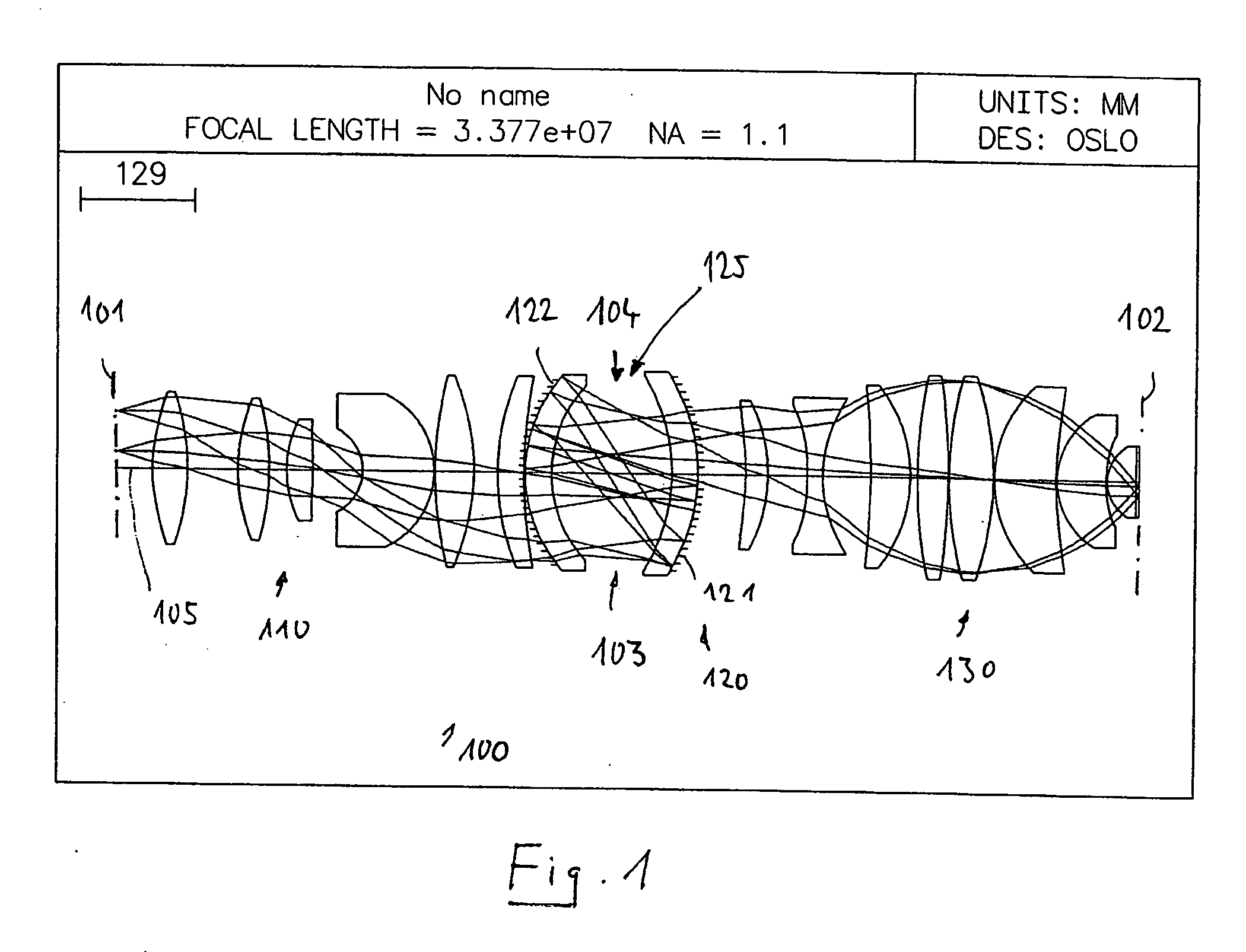
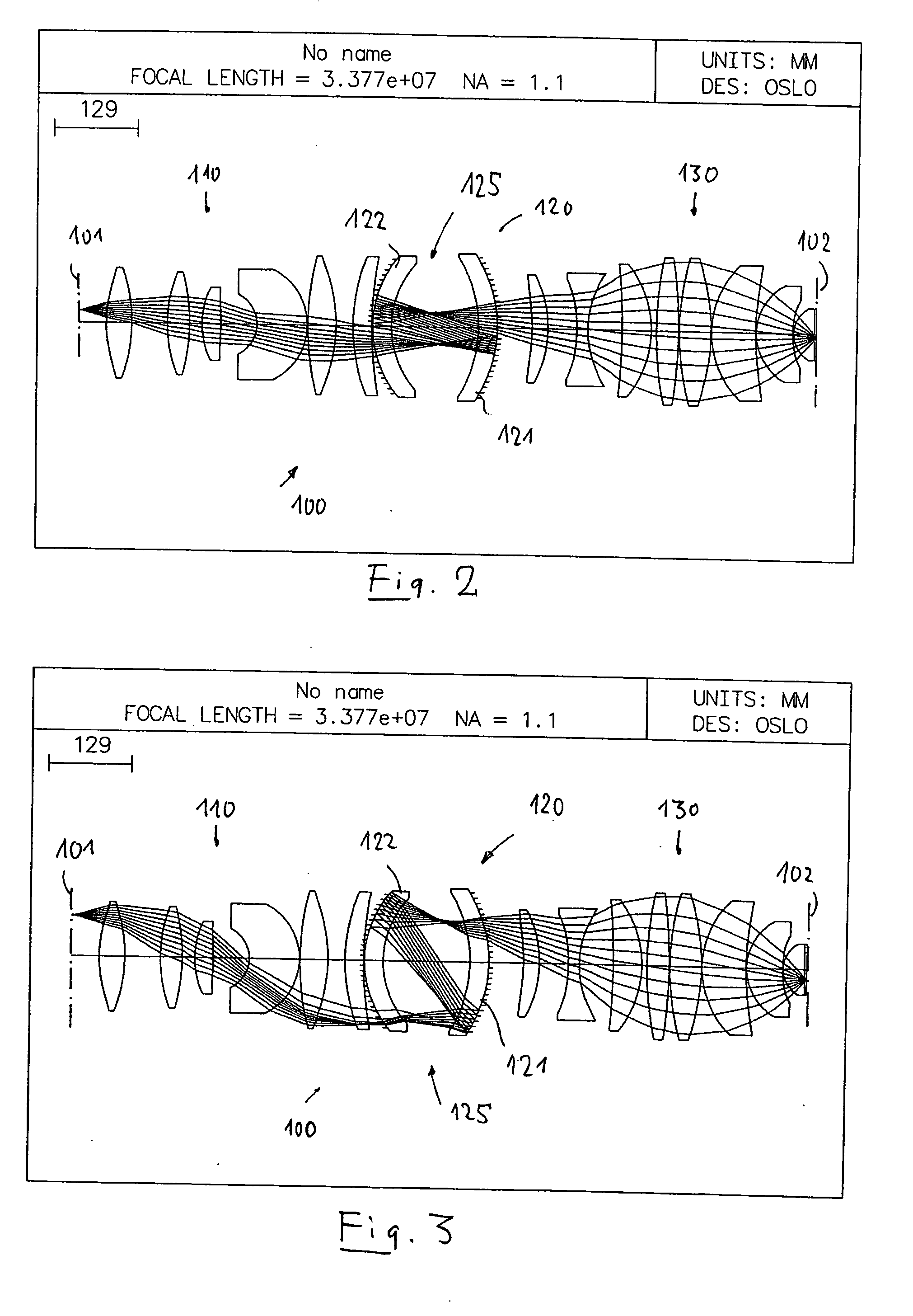
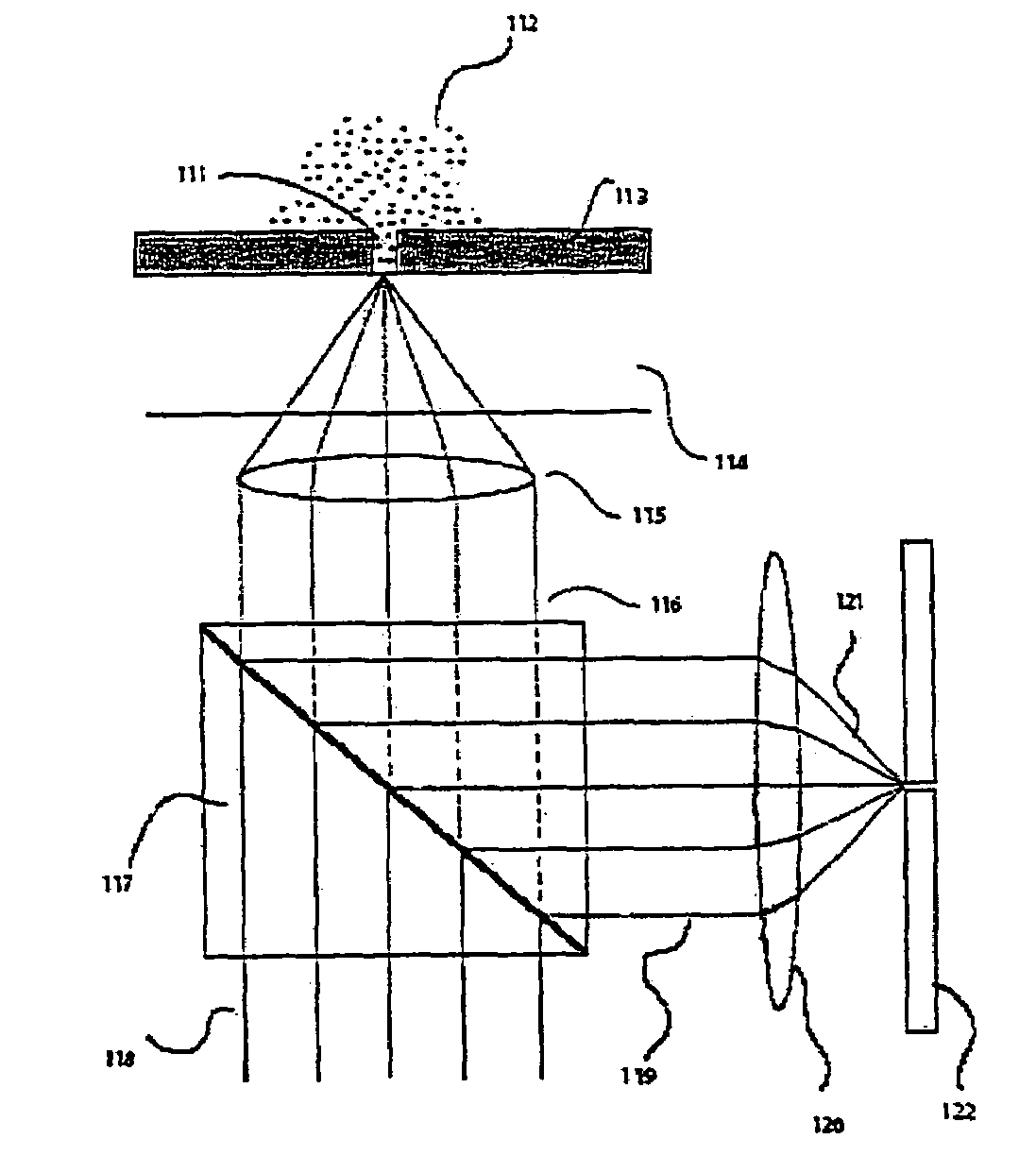
Catadioptric projection objective
ActiveUS20050190435A1High image side numerical apertureSmall amountSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesIntermediate imageHigh numerical aperture
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern provided in an object plane of the projection objective onto an image plane of the projection objective comprises: a first objective part for imaging the pattern provided in the object plane into a first intermediate image; a second objective part for imaging the first intermediate imaging into a second intermediate image; a third objective part for imaging the second intermediate imaging directly onto the image plane; wherein a first concave mirror having a first continuous mirror surface and at least one second concave mirror having a second continuous mirror surface are arranged upstream of the second intermediate image; pupil surfaces are formed between the object plane and the first intermediate image, between the first and the second intermediate image and between the second intermediate image and the image plane; and all concave mirrors are arranged optically remote from a pupil surface. The system has potential for very high numerical apertures at moderate lens material mass consumption.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Apparatus and method for analysis of molecules
ActiveUS7302146B2Improve accuracyEasy to implementMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreMolecular analysisChemical reaction
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
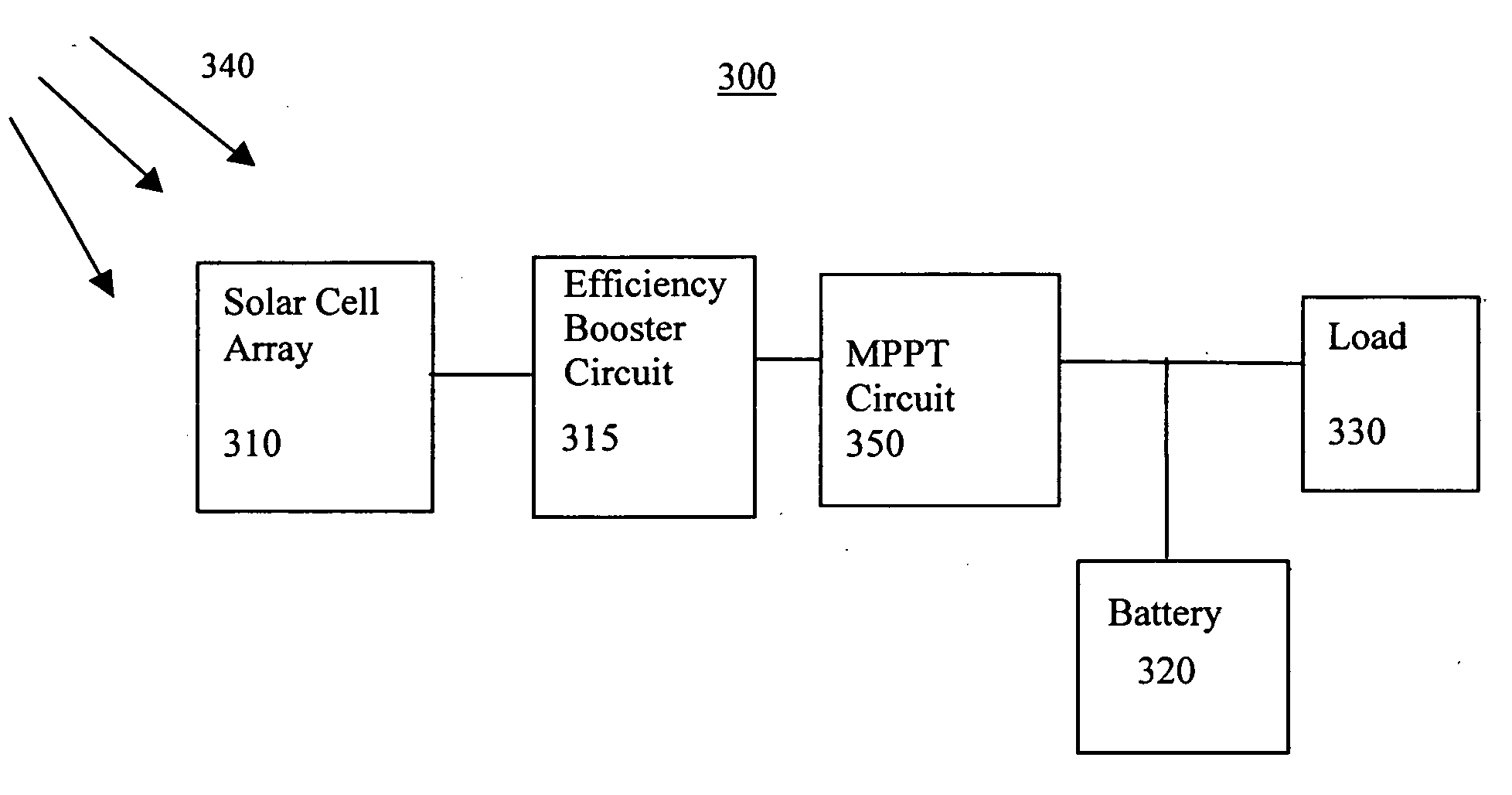
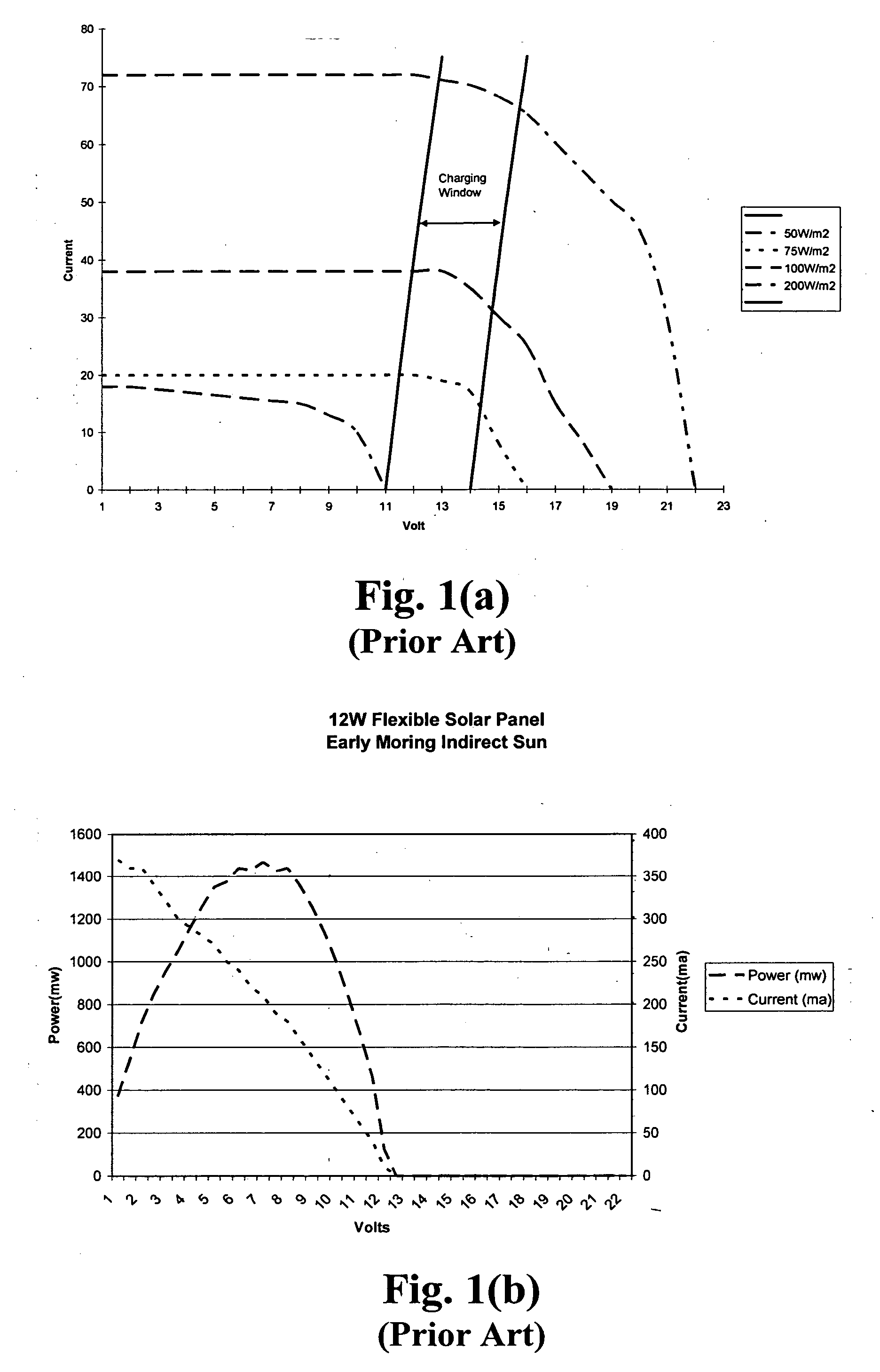
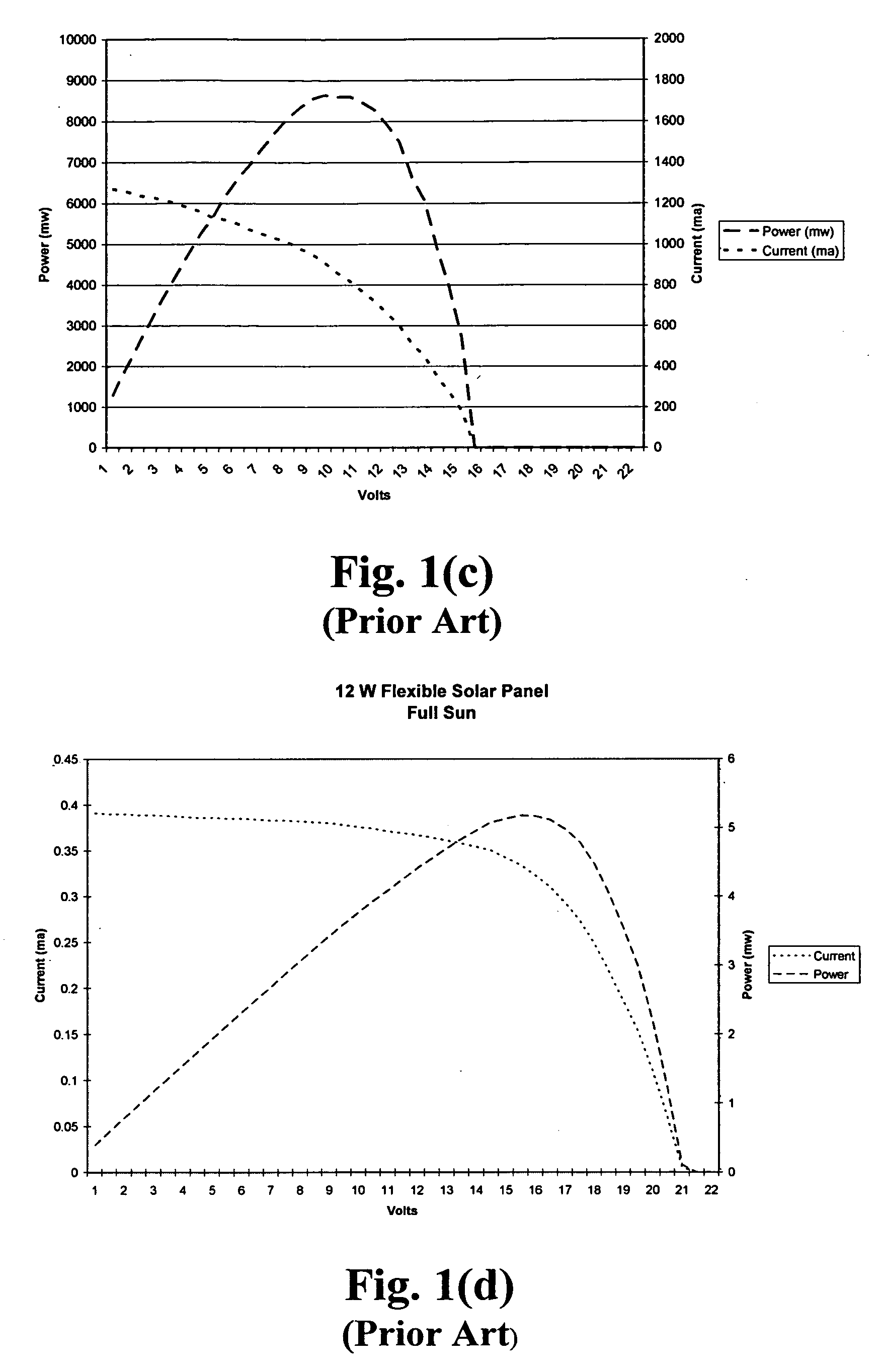
Efficiency booster circuit and technique for maximizing power point tracking
InactiveUS20060174939A1Reduce voltageConsiderable amount of energyBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsSolar cellPoint tracking
The present invention provides an efficiency booster circuit and accompanying switch mode power conversion technique to efficiently capture the power generated from a solar cell array that would normally have been lost, for example, under reduced incident solar radiation. In an embodiment of the invention, the efficiency booster circuit generates an output current from the solar cell power source using a switch mode power converter. A control loop is closed around the input voltage to the converter circuit and not around the output voltage. The output voltage is allowed to float, being clamped by the loading conditions. If the outputs from multiple units are tied together, the currents will sum. If the output(s) are connected to a battery, the battery's potential will clamp the voltage during charge. This technique allows all solar cells in an array that are producing power and connected in parallel to work at their peak efficiency.
Owner:ISG TECH
Deformable tools and implants
InactiveUS20060271061A1Add dimensionReduce riskDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringGreatest Diameter
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
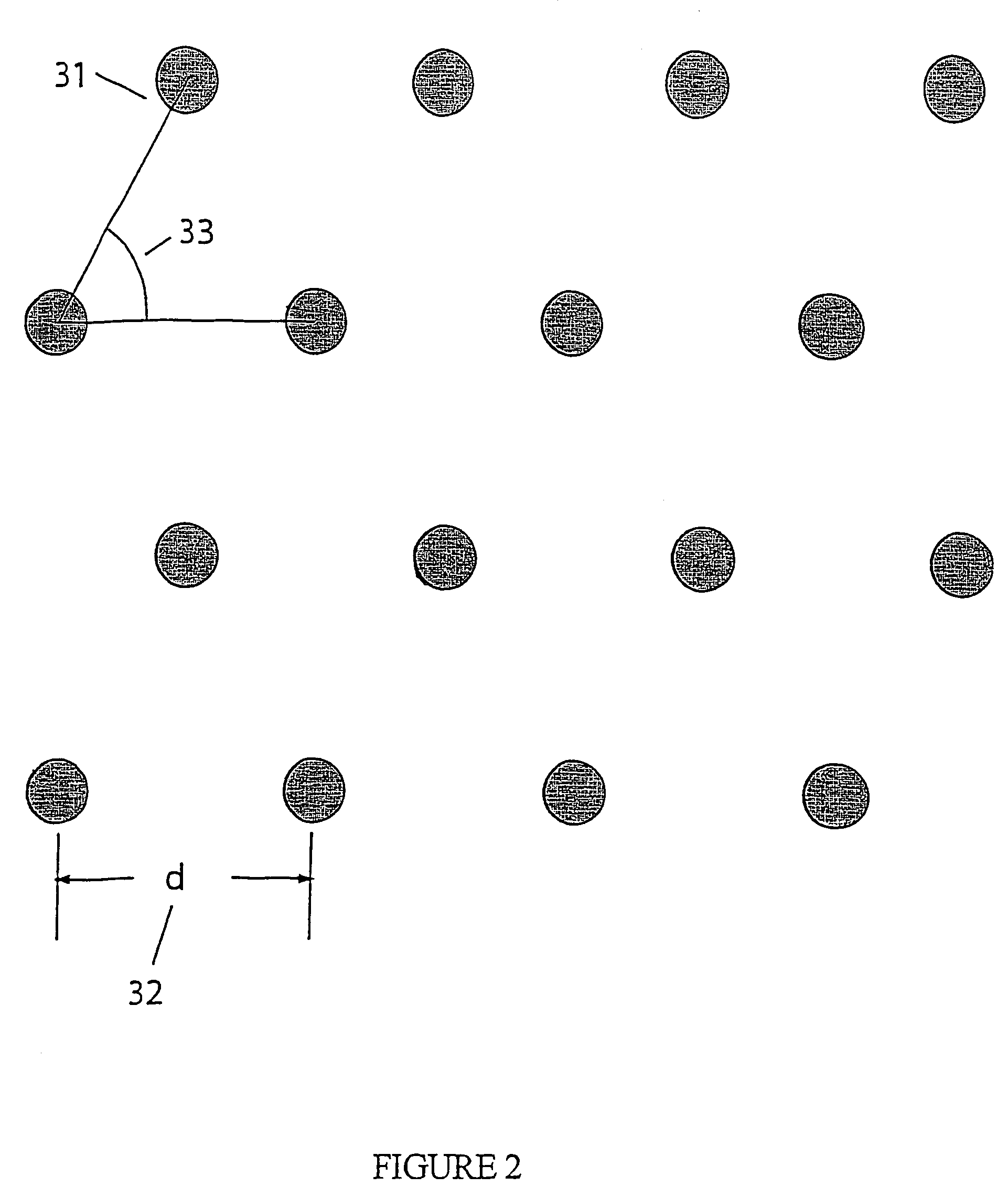
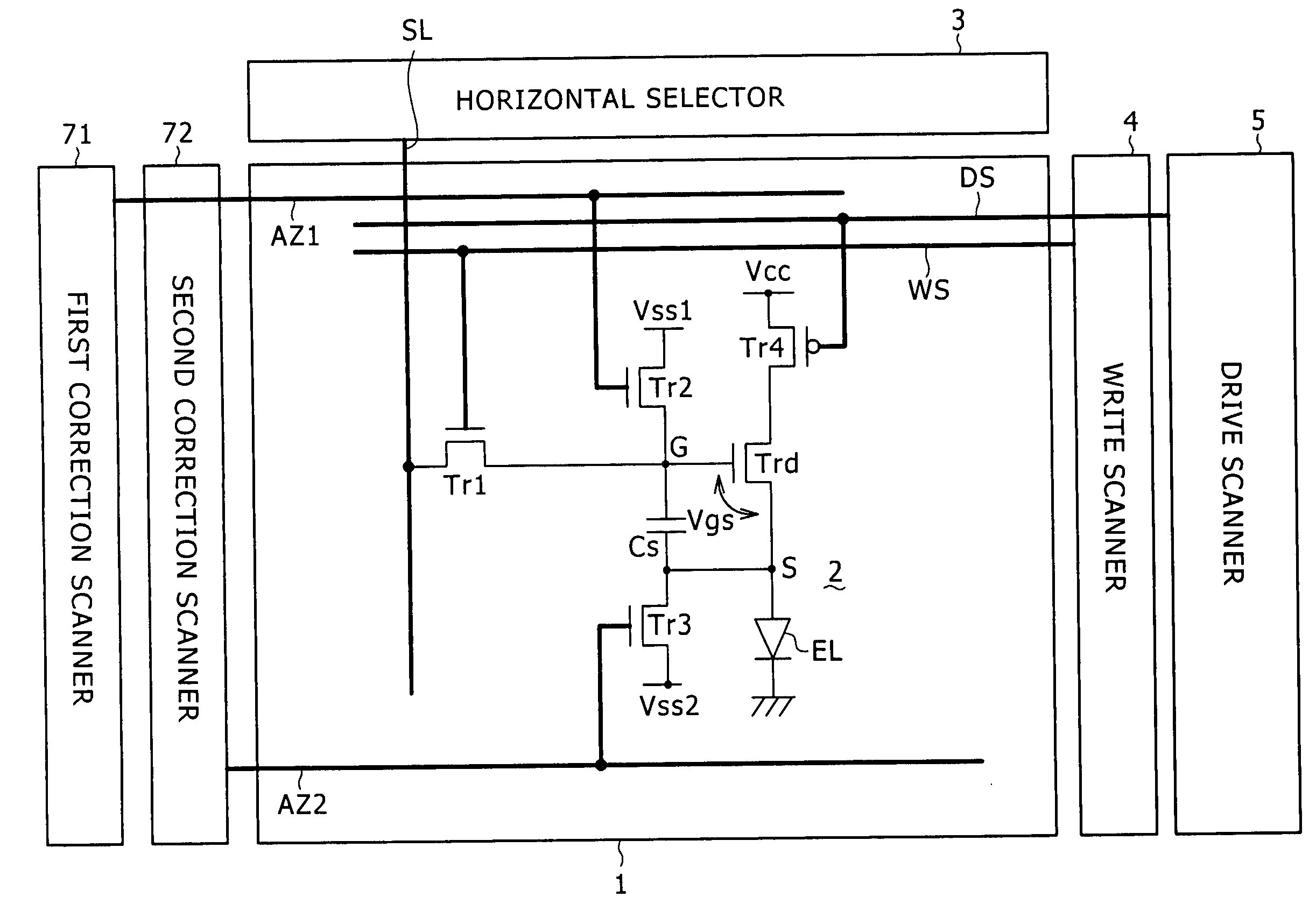
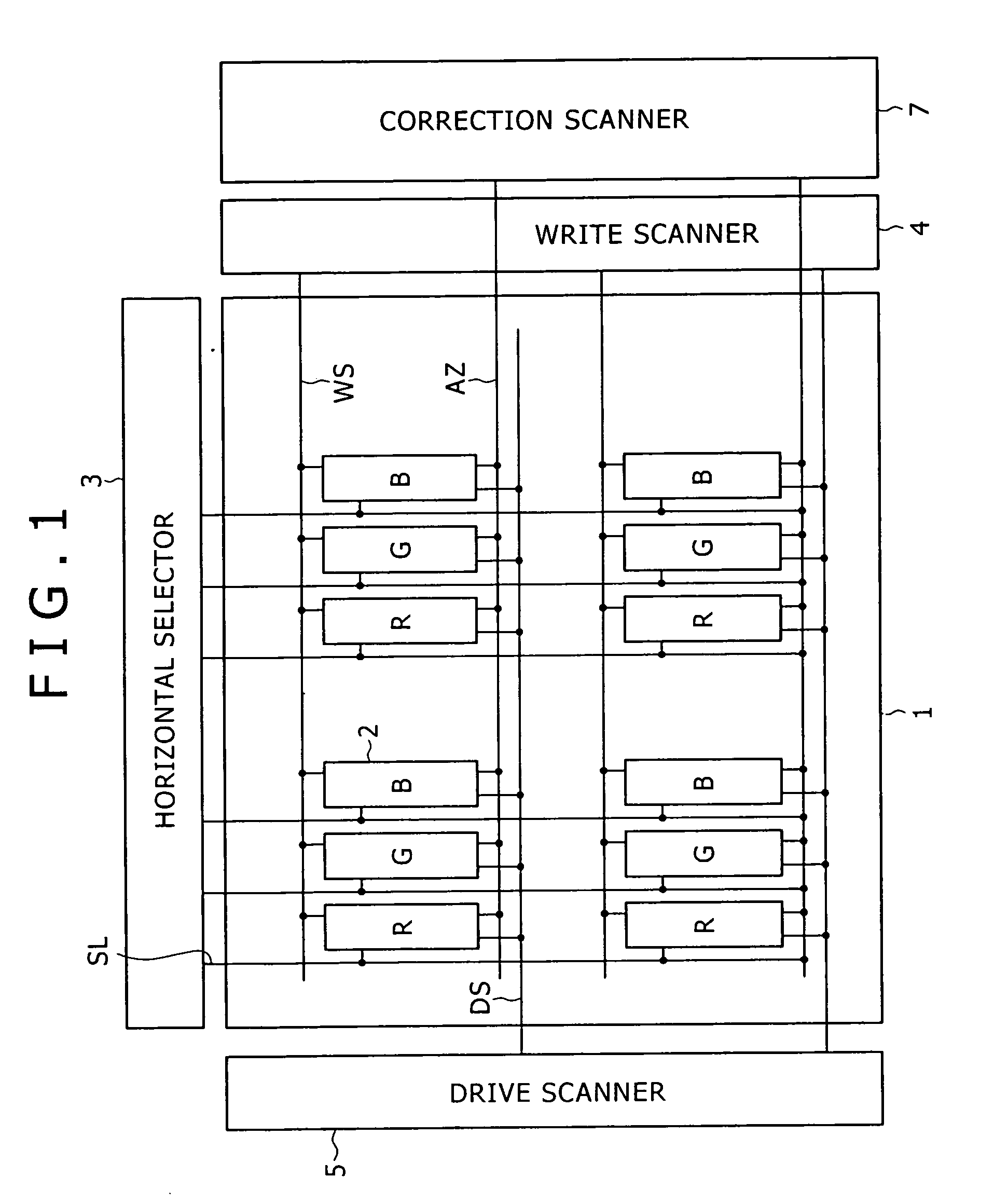
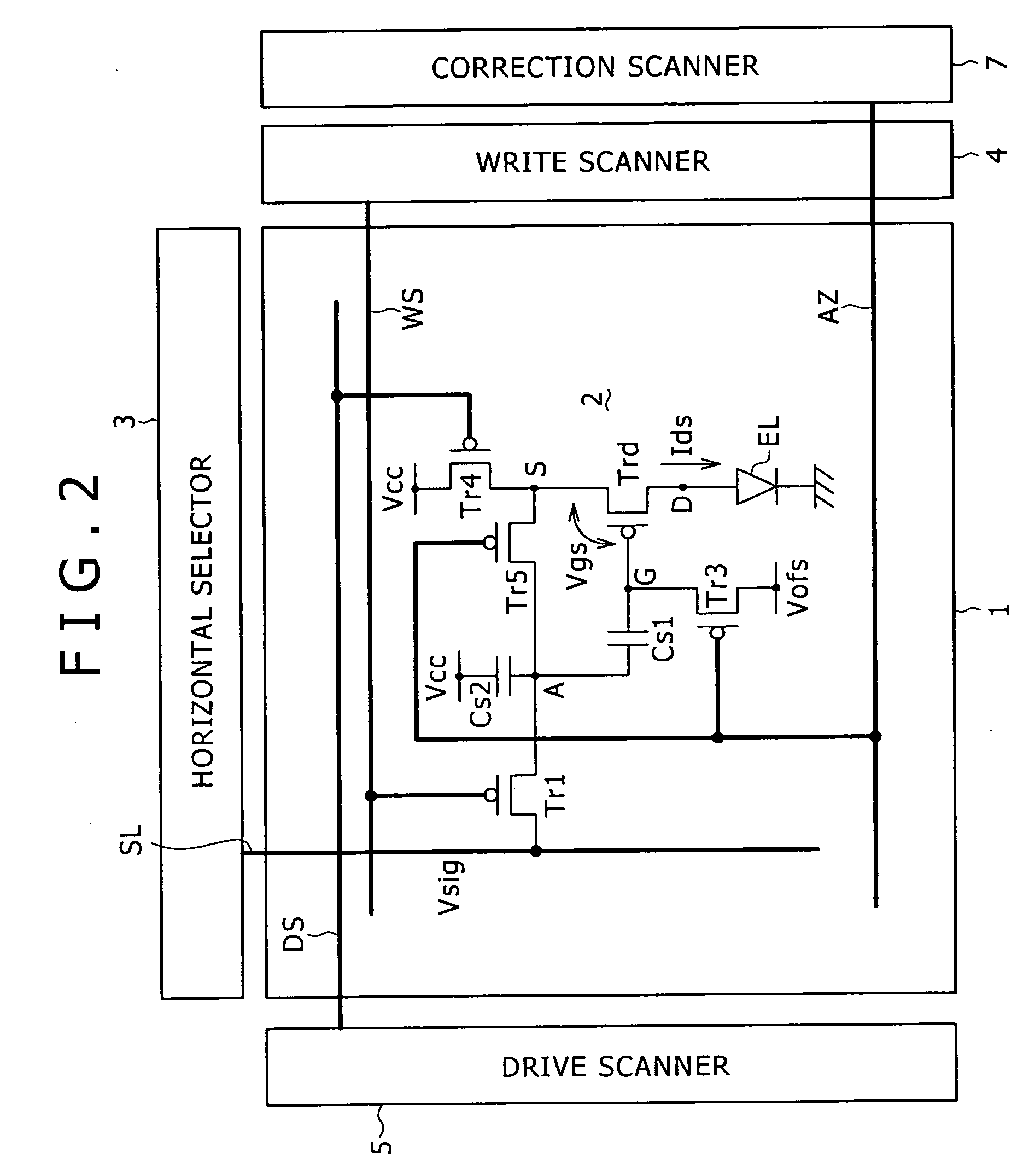
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060170628A1Eliminate dependenciesImprove mobilityElectroluminescent light sourcesHeater elementsCapacitanceScan line
The invention provides a pixel circuit that can cancel the influence of the mobility of a drive transistor. A drive transistor supplies to a light-emitting element, an output current dependent upon an input voltage during a certain emission period. The light-emitting element emits light with a luminance dependent upon a video signal in response to the output current supplied from the drive transistor. The pixel circuit includes a correction unit that corrects the input voltage held by a capacitive part before the emission period or at the beginning of the emission period, in order to cancel the dependence of the output current on the carrier mobility. The correction unit operates during part of a sampling period in response to control signals supplied from scan lines. Specifically, the correction unit extracts the output current from the drive transistor while the video signal is sampled, and negatively feeds back the output current to the capacitive part to thereby correct the input voltage.
Owner:SONY CORP
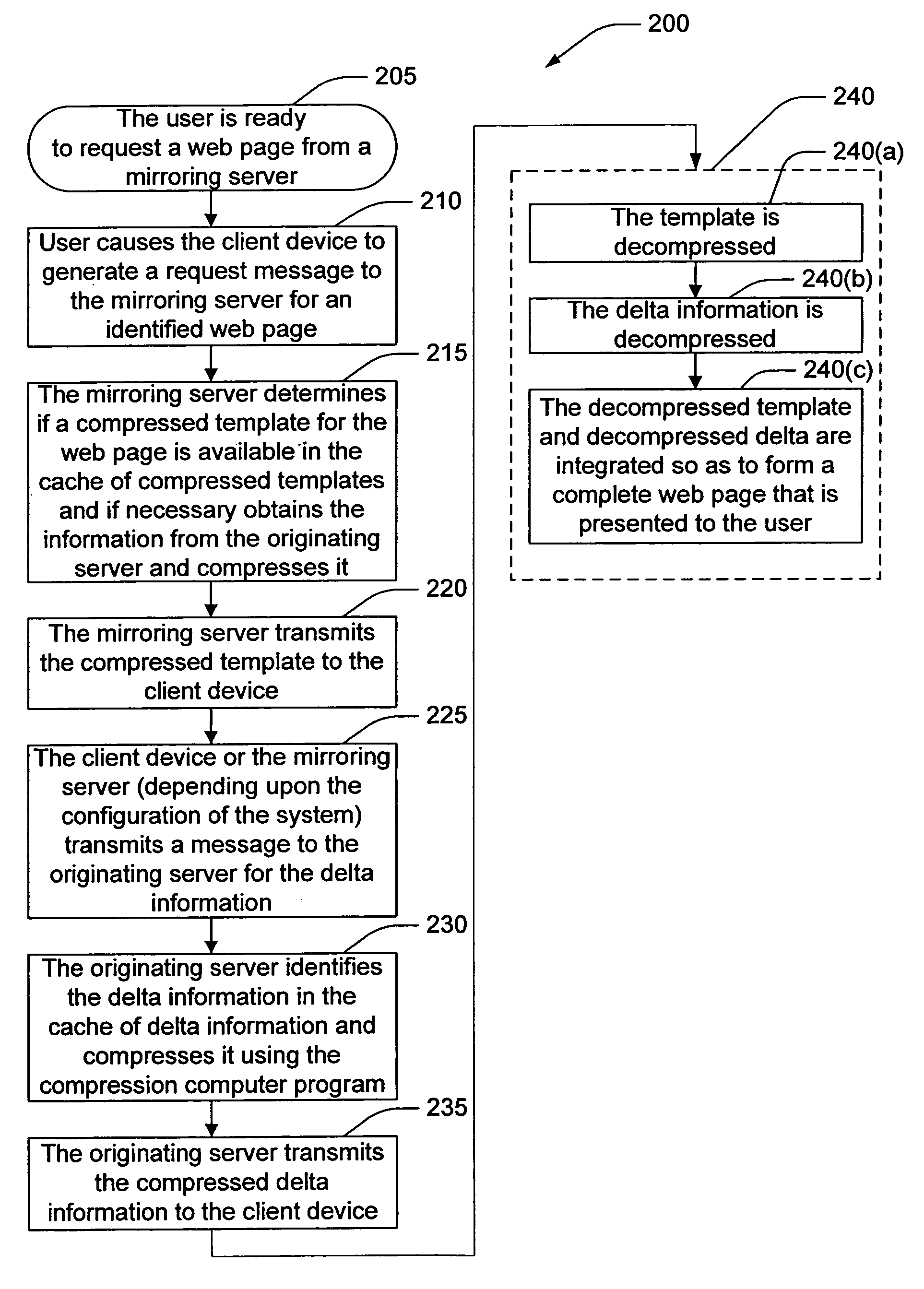
Efficient compression using differential caching
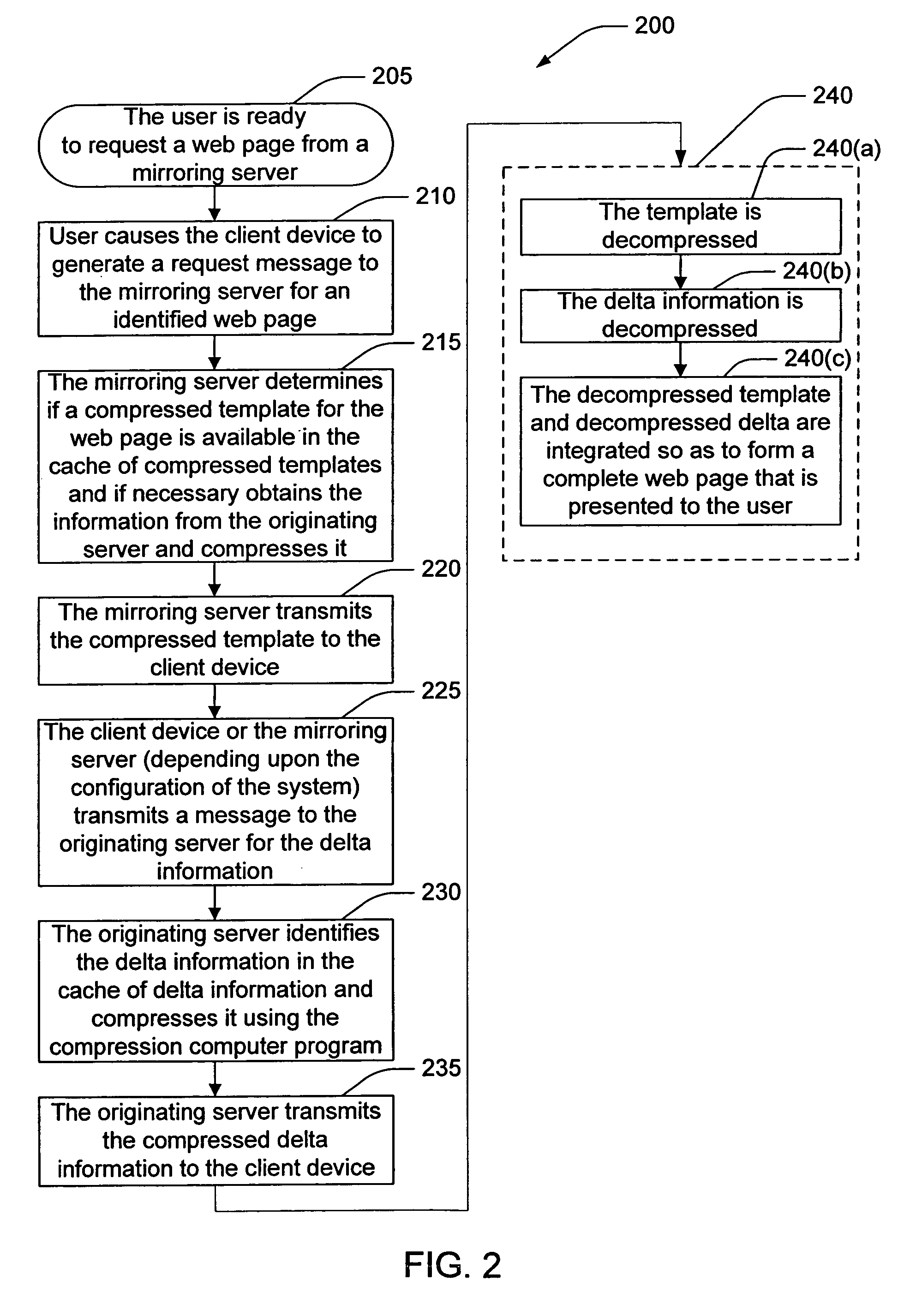
InactiveUS7188214B1Less resourcesSmall amount of calculationDigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWeb pageBand width
A technique for increased efficiency of content delivery over a network is described. Instances of web pages are divided into (1) templates including those elements of a web page that are relatively unchanging and (2) delta information including those elements that are ephemeral or customized. Each template is compressed and cached at an originating server. Transmission of the delta information is decoupled from transmission of the template. When a user requests a page, the compressed template is sent (either from an originating server or a mirror thereof). The delta information is compressed and sent separately. Since the template is only compressed once and is cached locally, it requires less bandwidth and allocation of other computing resources to transmit than transmission of a compressed web page.
Owner:DIGITAL RIVER INC
Laparoscopic Laser Device and Method
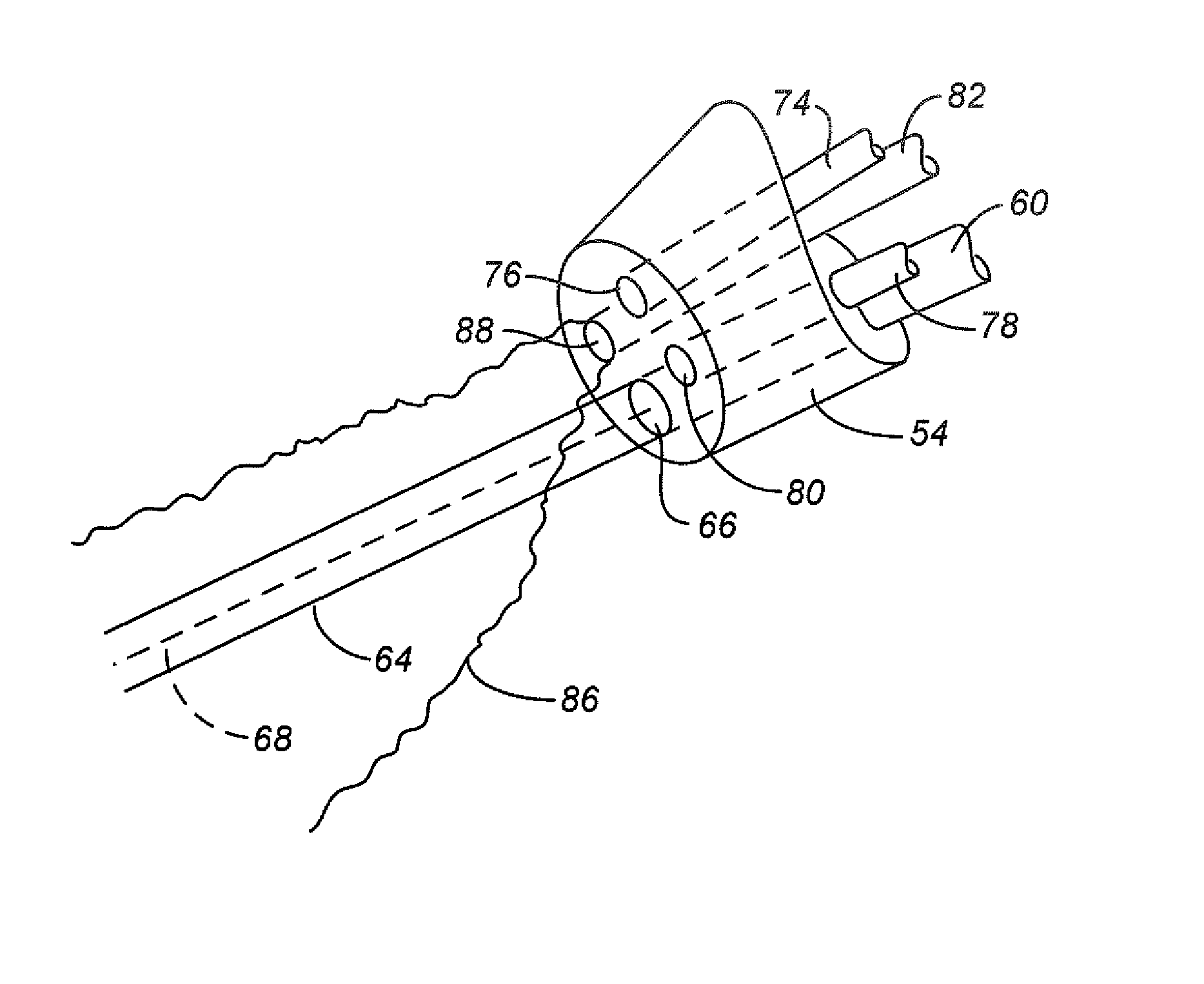
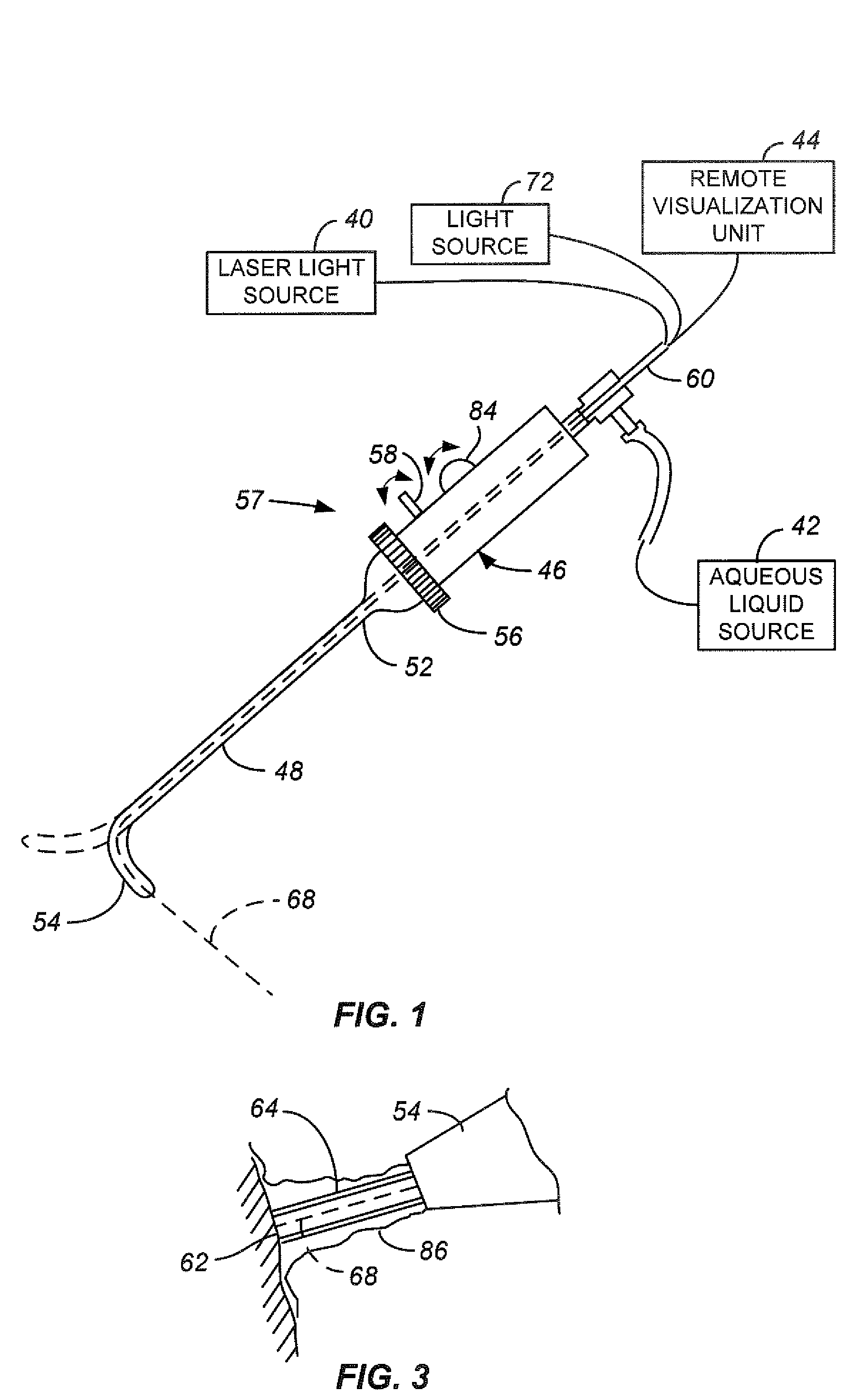
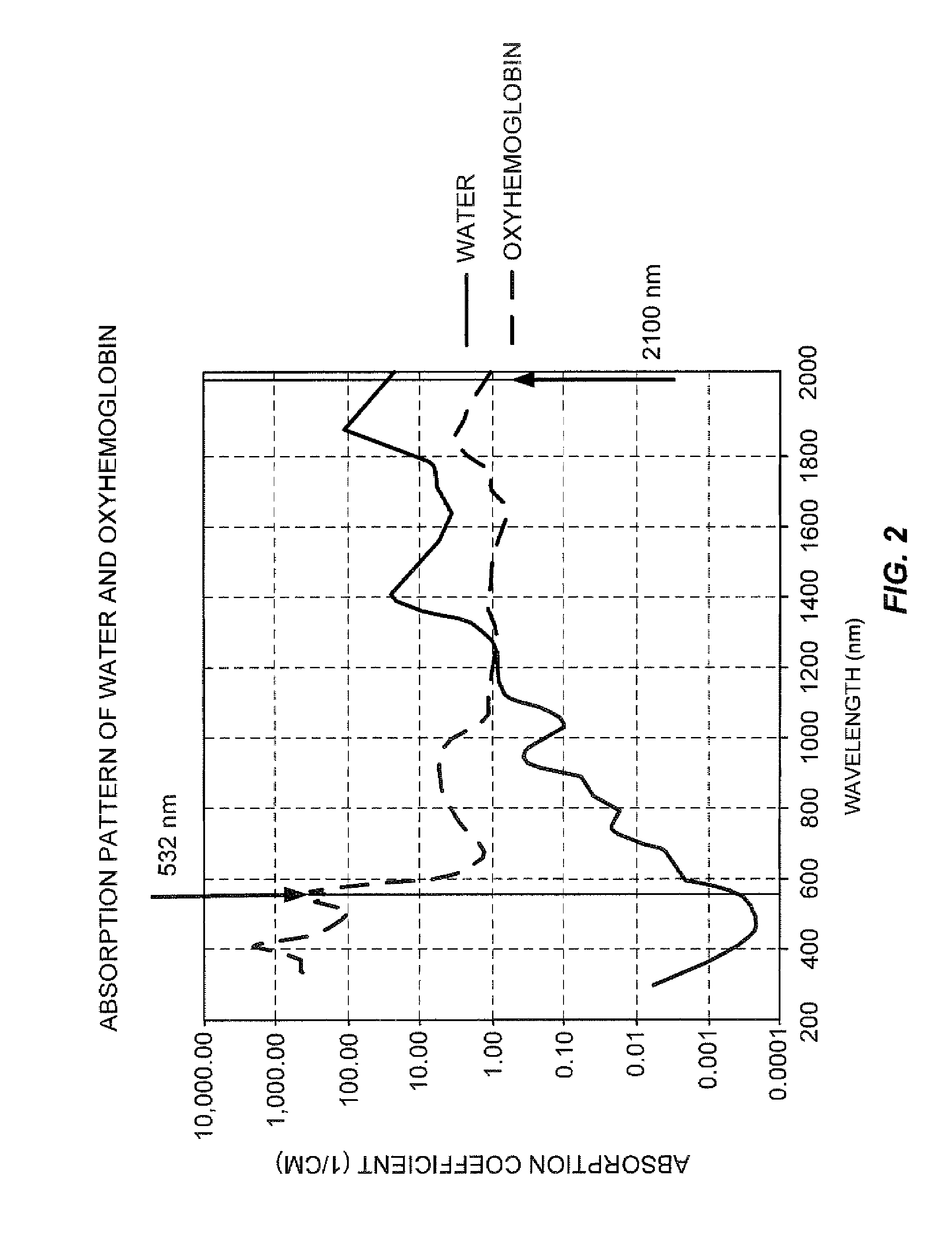
InactiveUS20070185474A1Reduce heatProtect from preventable damageLaser detailsEndoscopesMedicineVaporization
Laser radiation delivered to a treatment area causes vaporization of a substantially greater volume of tissue than the volume of residual coagulated tissue. The laser radiation may have a wavelength of about 300 nm to about 700 nm, may be used with a smoke suppressing irrigant, may have an average irradiance greater than about 5 kilowatts / cm2, and may have a spot size of at least 0.05 mm2. A laparoscopic laser device, for use with an insufflated bodily cavity, may include an elongate body adapted for insertion into an insufflated bodily cavity. A laser energy delivery element, at the distal end of the elongate body, may be coupleable to a source of tissue-vaporization-capable laser energy and capable of delivering laser energy along a laser energy path extending away from the laser energy delivery element. A smoke-suppressing liquid pathway, extending along the elongate body to an exit opening at the distal end, may be coupleable to a source of a smoke-suppressing liquid. The smoke-suppressing liquid is directed generally along the laser energy path. A remote visualization device may be used to view along the laser energy path.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
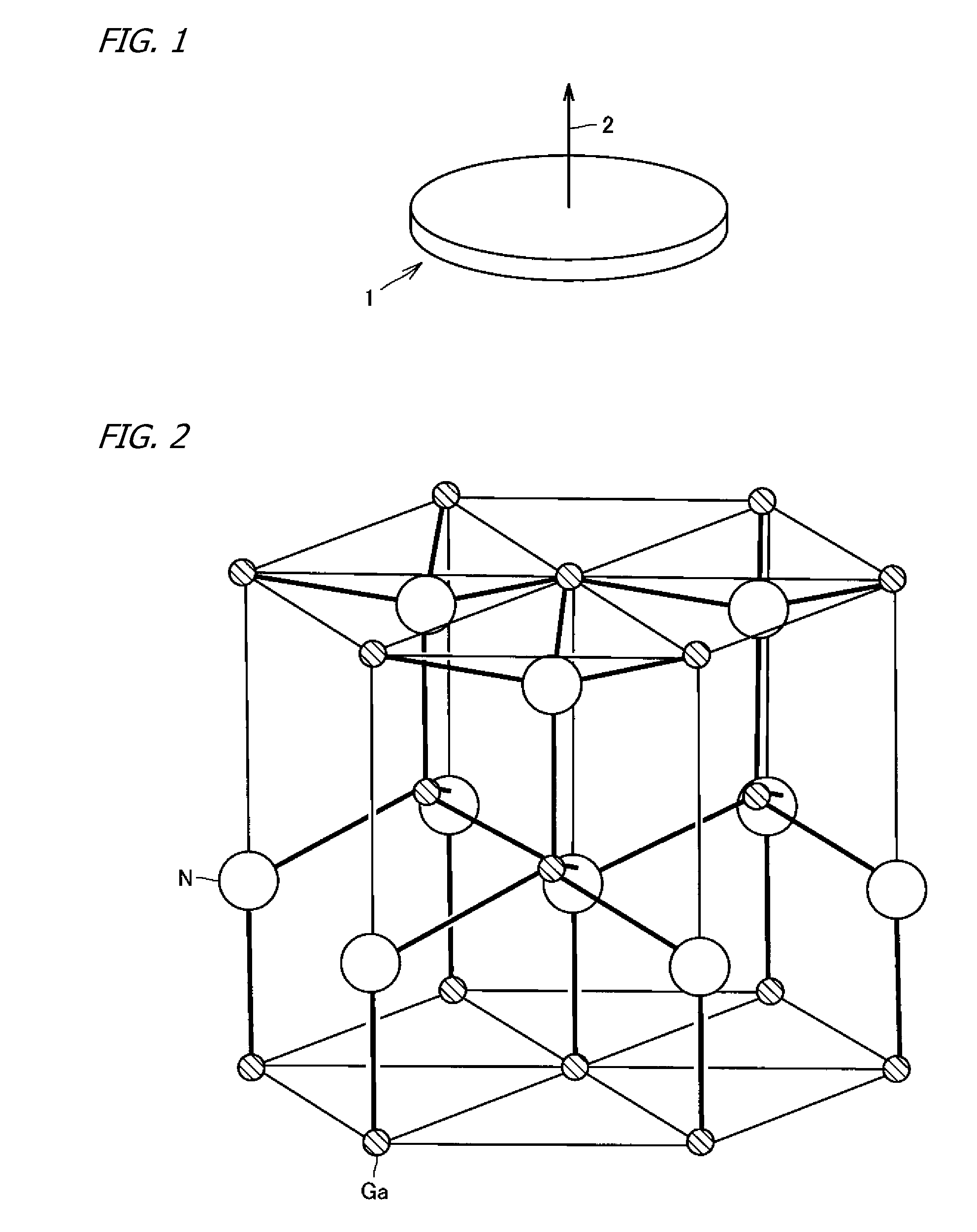
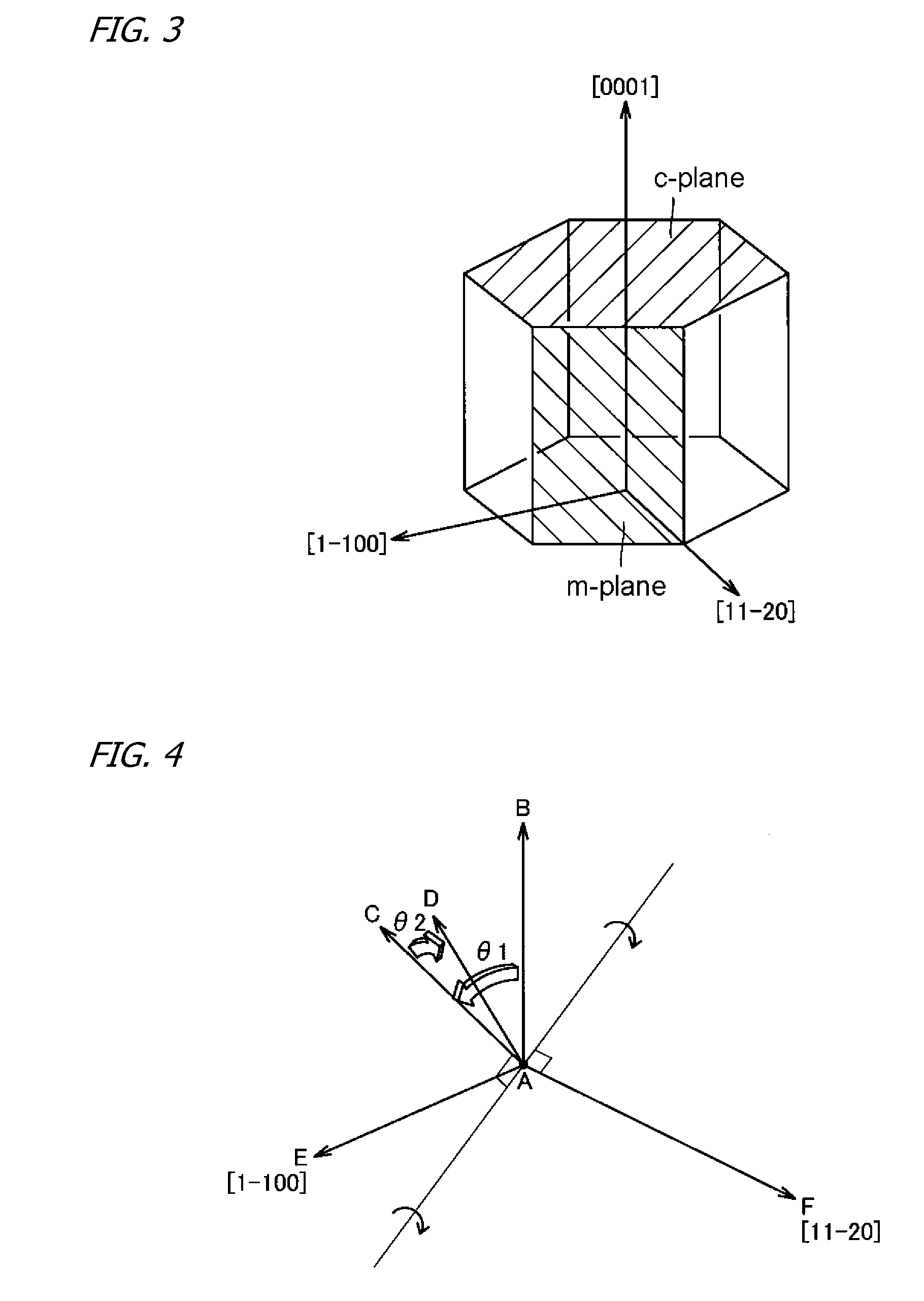
GaN Substrate, Substrate with an Epitaxial Layer, Semiconductor Device, and GaN Substrate Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20080308815A1Control fluctuationsImprove emission efficiencyAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesPolycrystalline material growthDevice materialPlane orientation
Affords a GaN substrate from which enhanced-emission-efficiency light-emitting and like semiconductor devices can be produced, an epi-substrate in which an epitaxial layer has been formed on the GaN substrate principal surface, a semiconductor device, and a method of manufacturing the GaN substrate. The GaN substrate is a substrate having a principal surface with respect to whose normal vector the [0001] plane orientation is inclined in two different off-axis directions.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
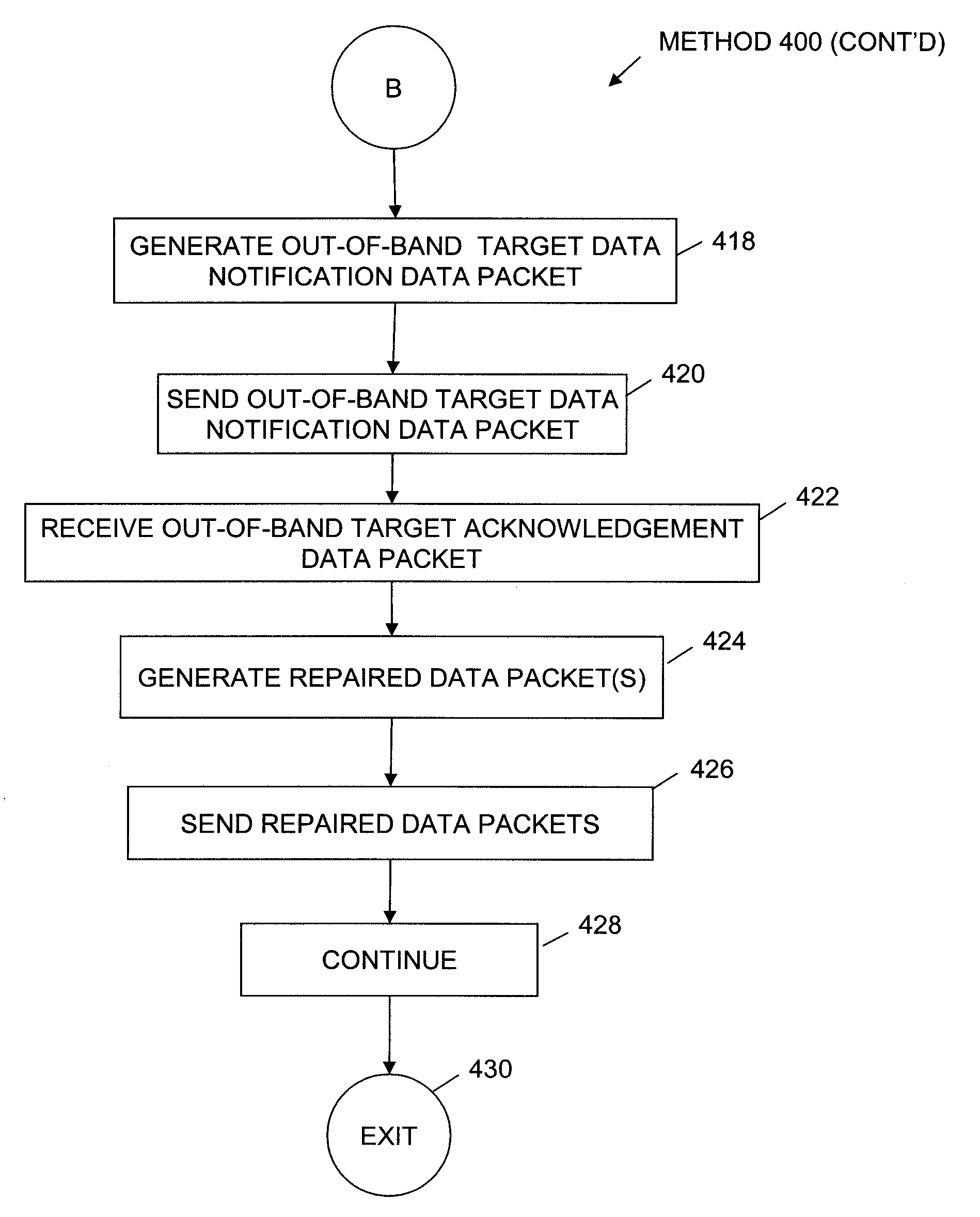
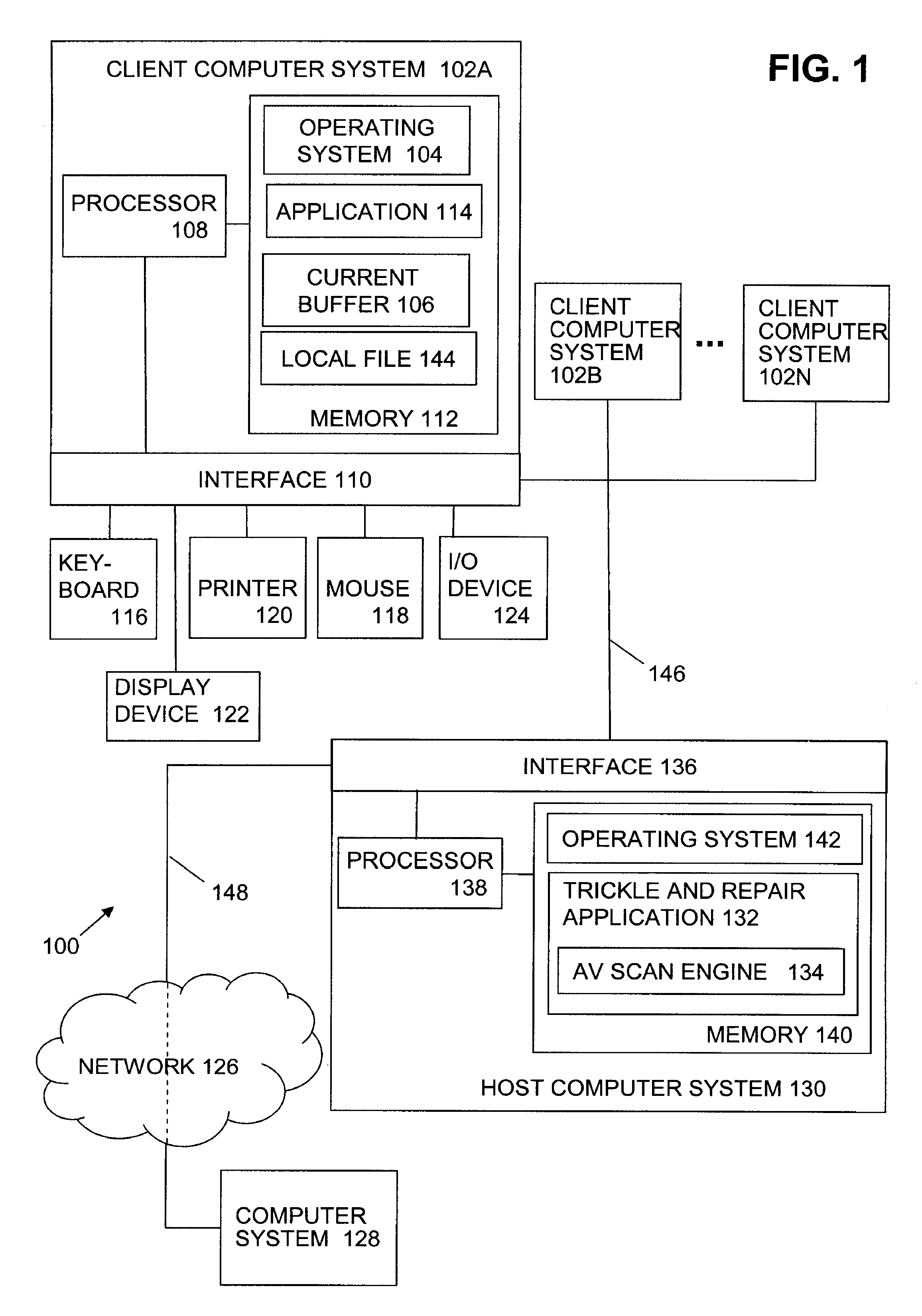
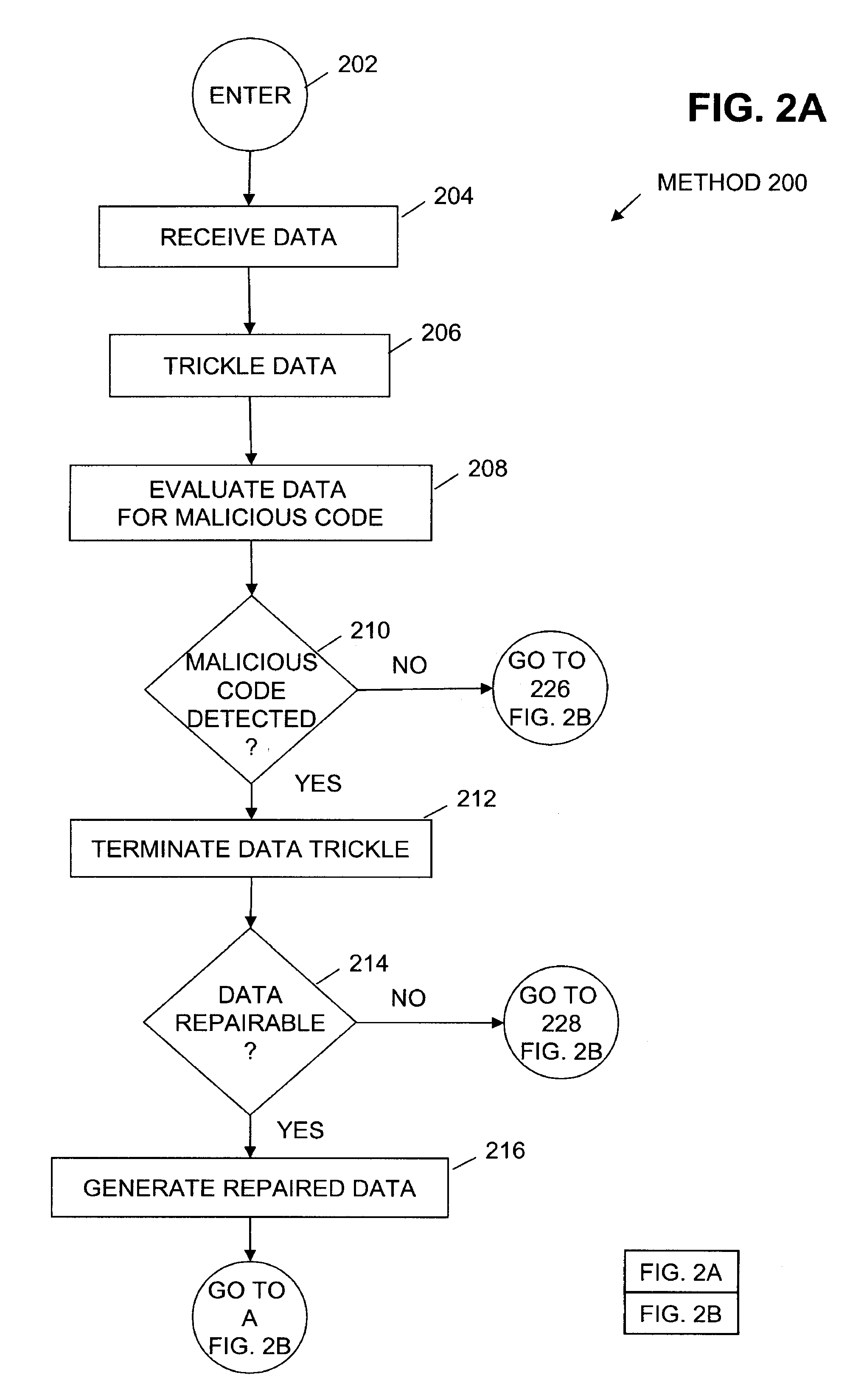
Method to trickle and repair resources scanned using anti-virus technologies on a security gateway
ActiveUS7930750B1Small amountMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnti virusComputer hardware
In one embodiment, a trickle and repair application receives data from a sending computer system and trickles the data to a target computer system over an in-band communication channel. The received data is evaluated for the presence of malicious code. When malicious code is detected in the data, trickling of the data is terminated. If the infected data is repairable, the data is repaired and an out-of-band target data notification is generated and sent to the target computer system. In one embodiment, receipt of the out-of-band target data notification causes the target computer system to flush the current buffer and any local files containing the trickled data. The target computer system returns an out-of-band target acknowledgement to the trickle and repair application and the repaired data is sent to the target computer system.
Owner:CA TECH INC
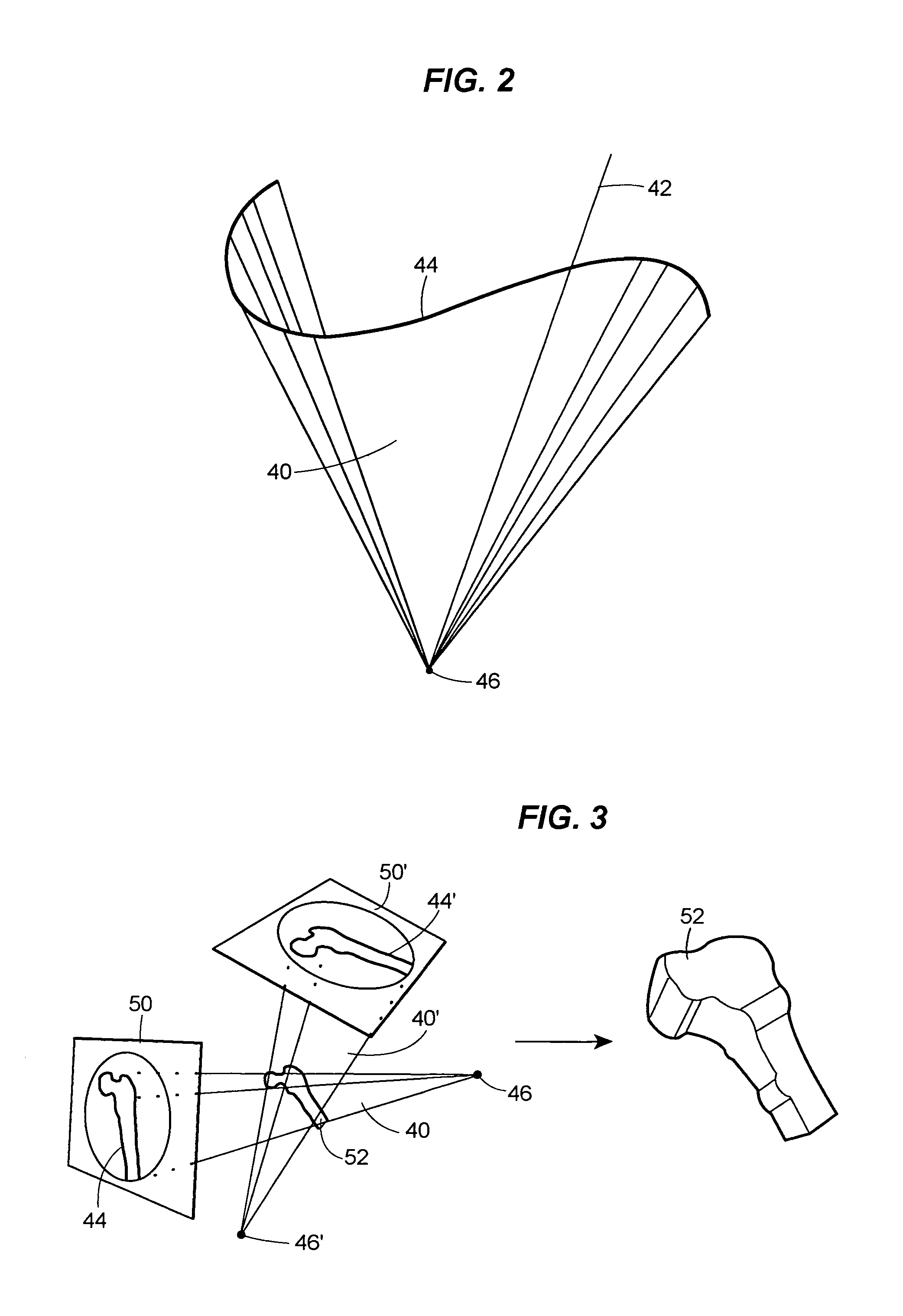
Method for navigating in the interior of the body using three-dimensionally visualized structures
ActiveUS7167738B2Easy alignmentIncrease exposureImage enhancementImage analysisAngle of viewMarine navigation
A method is described for navigating in the interior of the body using three-dimensionally visualized structures. In a first step of the method, at least two two-dimensional images of the same anatomical object are provided from different perspectives, and also items of information that make it possible to draw conclusions about the respective spatial position of an imaging system relative to the anatomical object. The projections of a geometrical structure to be visualized are then created in every two-dimensional image, wherein a geometrical structure to be visualized is created in each two-dimensional image, wherein the geometrical structure to be visualized is different from the anatomical object. A cone surface is then generated in space for each image wherein the spatial positions of the cone vertex and cone directrix are determined from the respective spatial position of the imaging system and the shape of the cone directrix is determined from the shape of the projection of the geometrical structure to be visualized on the image. Finally, a spatial intersection of the individual cone surfaces is formed to determine the geometrical structure and the geometrical structure determined and / or an intersection of a plurality of geometrical structures determined are / is represented and the representation is used for navigation.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
System and method for measuring an analyte in a sample
ActiveUS20090184004A1Interference minimizationLess of concentration profileImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Methods of determining a corrected analyte concentration in view of some error source are provided herein. The methods can be utilized for the determination of various analytes and / or various sources of error. In one example, the method can be configured to determine a corrected glucose concentration in view of an extreme level of hematocrit found within the sample. In other embodiments, methods are provided for identifying various system errors and / or defects. For example, such errors can include partial-fill or double-fill situations, high track resistance, and / or sample leakage. Systems are also provided for determining a corrected analyte concentration and / or detecting some system error.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
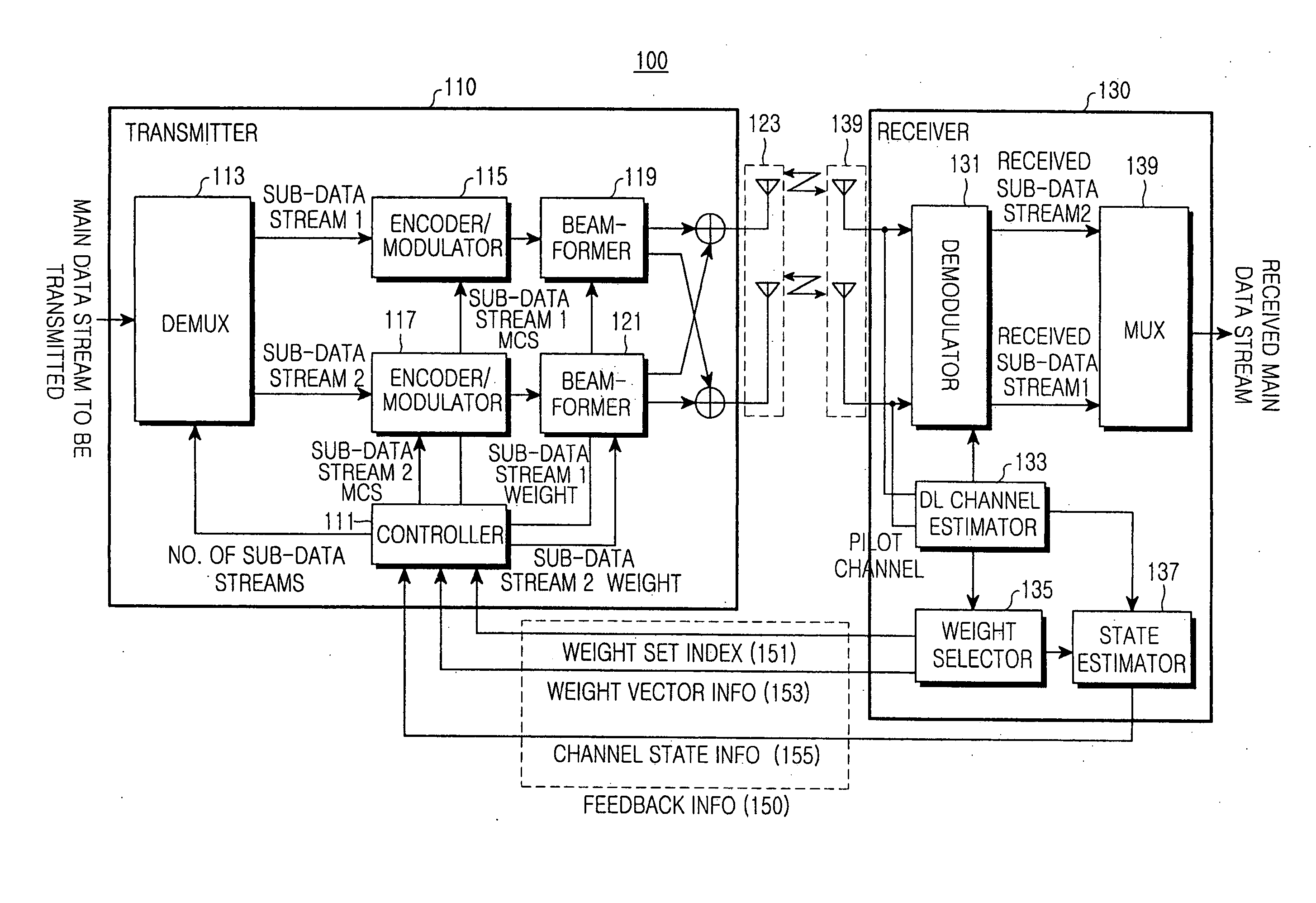
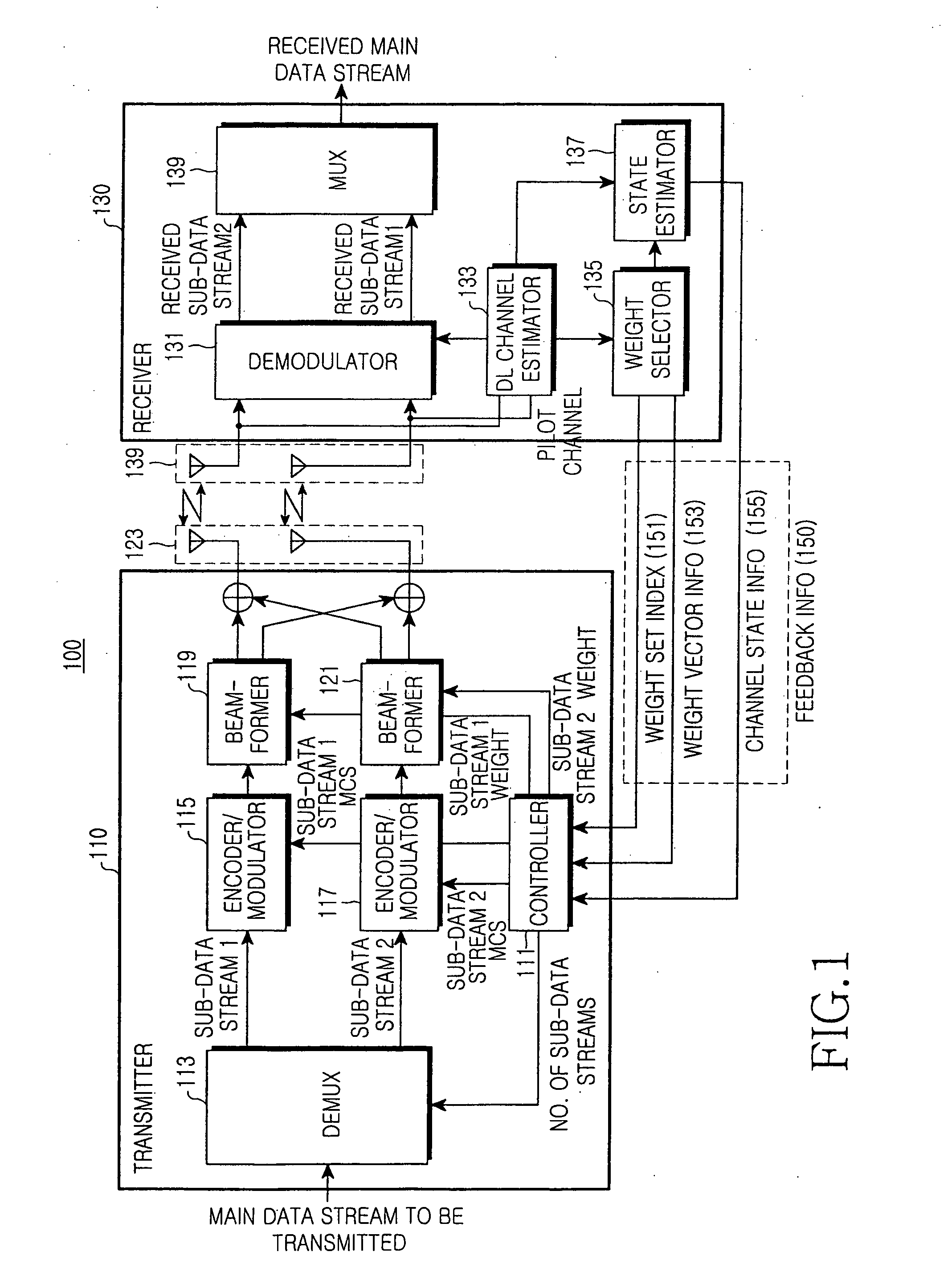
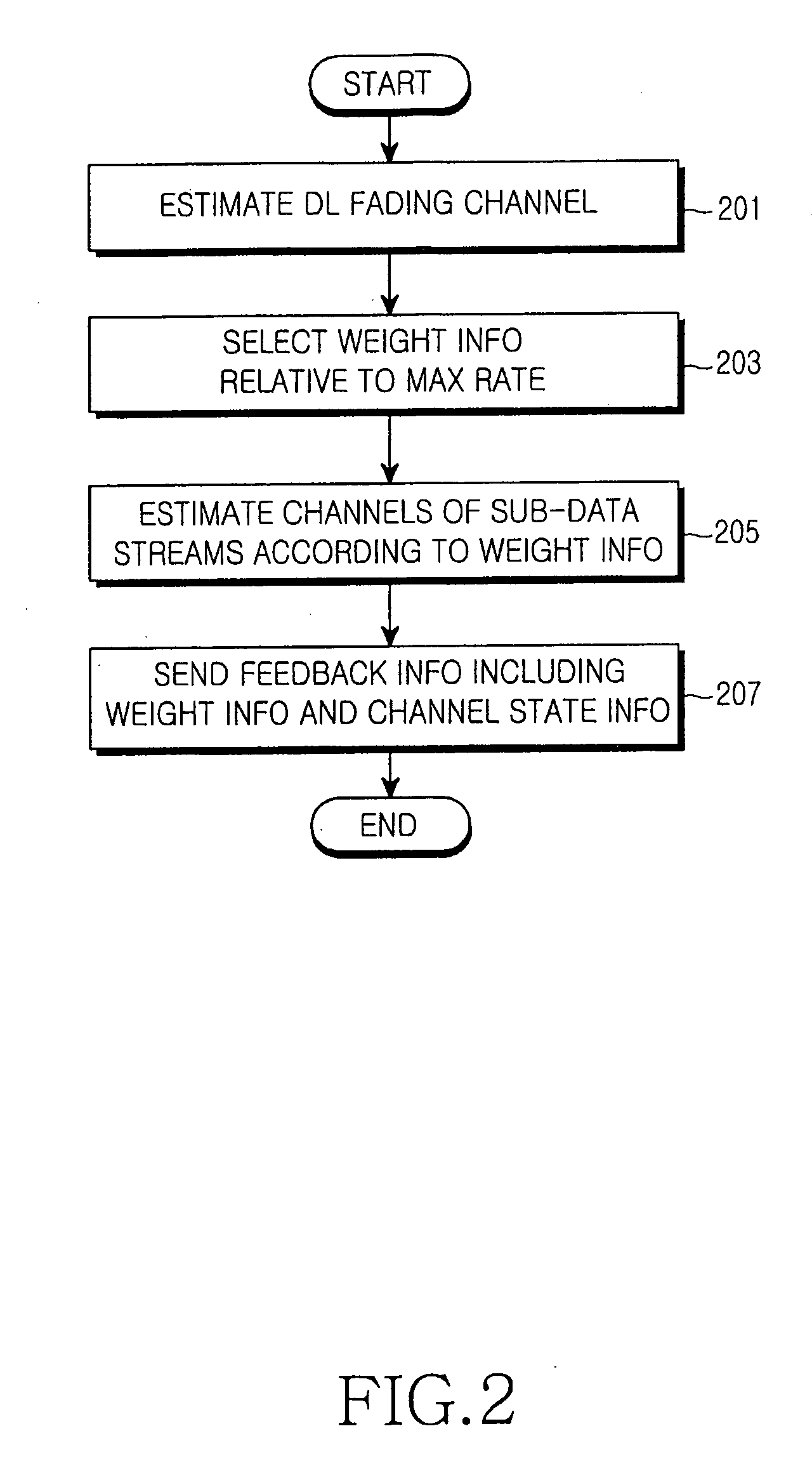
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving data in a mobile communication system using multiple antennas
ActiveUS20060270360A1Provide data transmission rateImprove data transfer rateFrequency-division multiplex detailsPolarisation/directional diversityChannel state informationData stream
An apparatus and method for transmitting / receiving data in a mobile communication system using multiple antennas are provided. A receiver estimates a fading channel of received data, selects a weight set relative to a maximum data transmission rate from at least one weight set with elements of a plurality of orthogonal weight vectors, and transmits feedback information including the selected weight set and channel-by-channel state information to a transmitter. The transmitter demultiplexes data to be transmitted on a basis of the feedback information into at least one sub-data stream, multiplies each sub-data stream by an associated weight, and transmits the data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
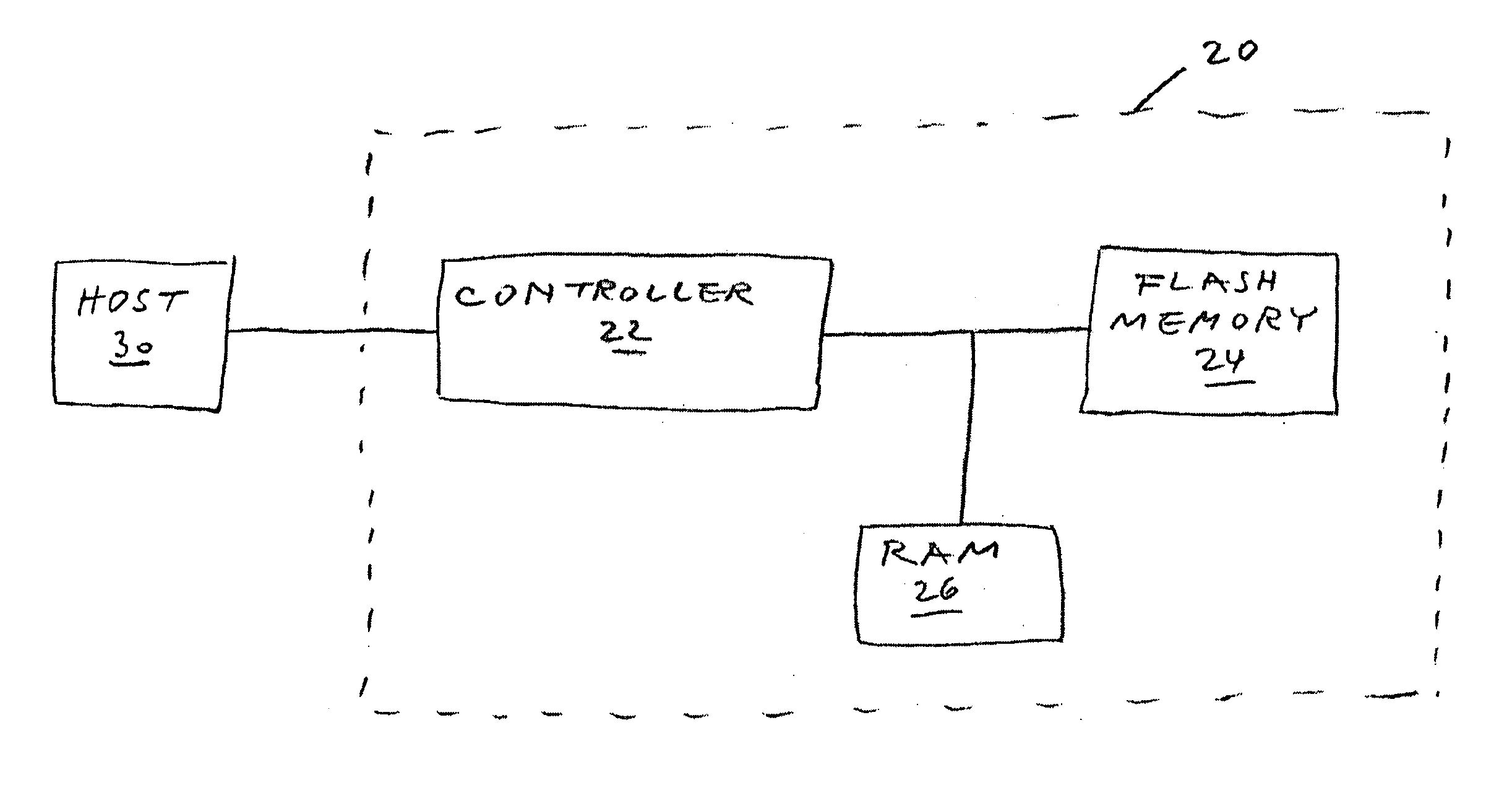
Method of error correction in MBC flash memory
InactiveUS20070089034A1Reduce wasteHigh bit error rateStatic storageRedundant data error correctionData bitsFlash memory
A plurality of logical pages is stored in a MBC flash memory along with corresponding ECC bits, with at least one of the MBC cells storing bits from more than one logical page, and with at least one of the ECC bits applying to two or more of the logical pages. When the pages are read from the memory, the data bits as read are corrected using the ECC bits as read. Alternatively, a joint, systematic or non-systematic ECC codeword is computed for two or more of the logical pages and is stored instead of those logical pages. When the joint codeword is read, the logical bits are recovered from the codeword as read. The scope of the invention also includes corresponding memory devices, the controllers of such memory devices, and also computer-readable storage media bearing computer-readable code for implementing the methods.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
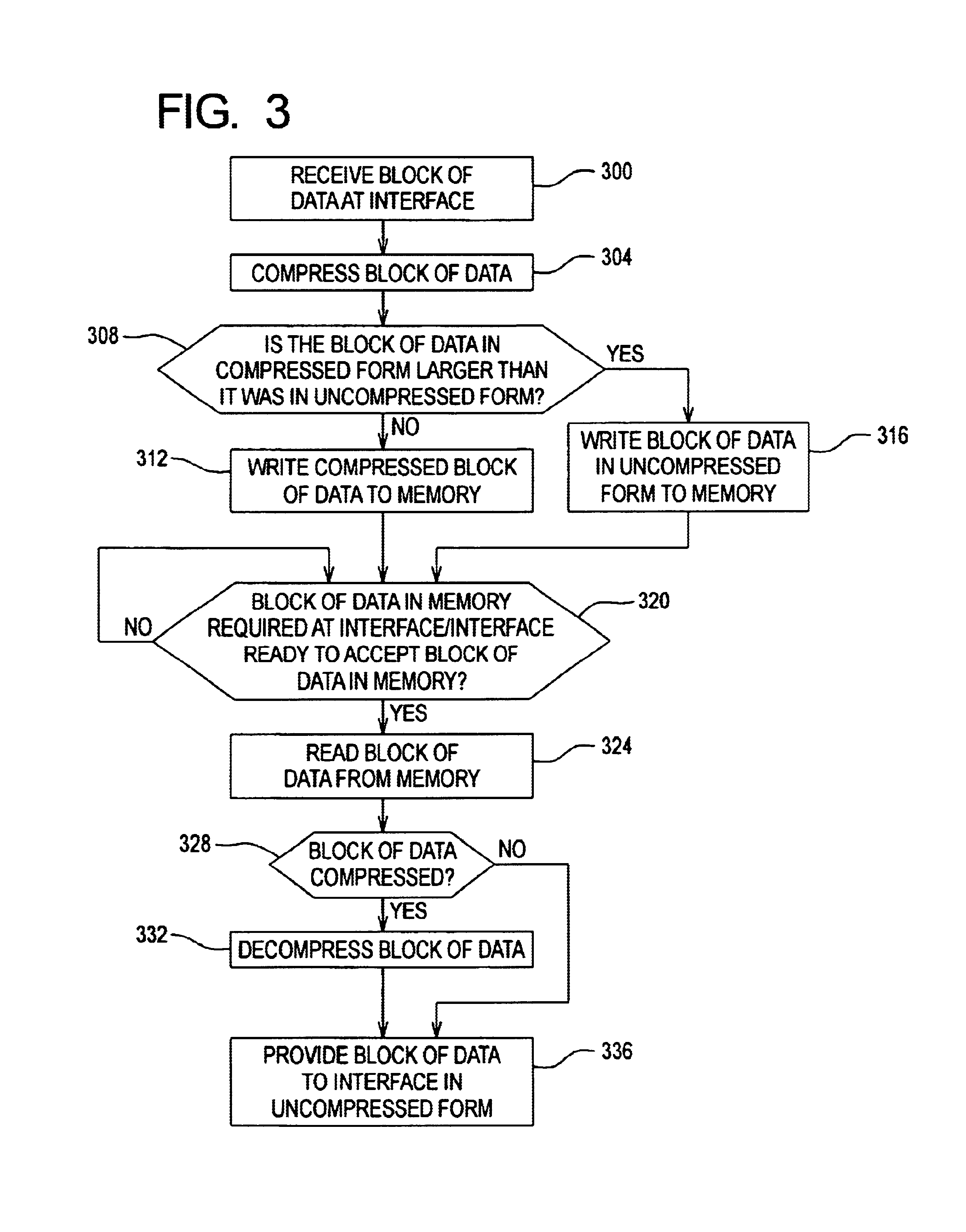
Method and apparatus for using data compression as a means of increasing buffer bandwidth
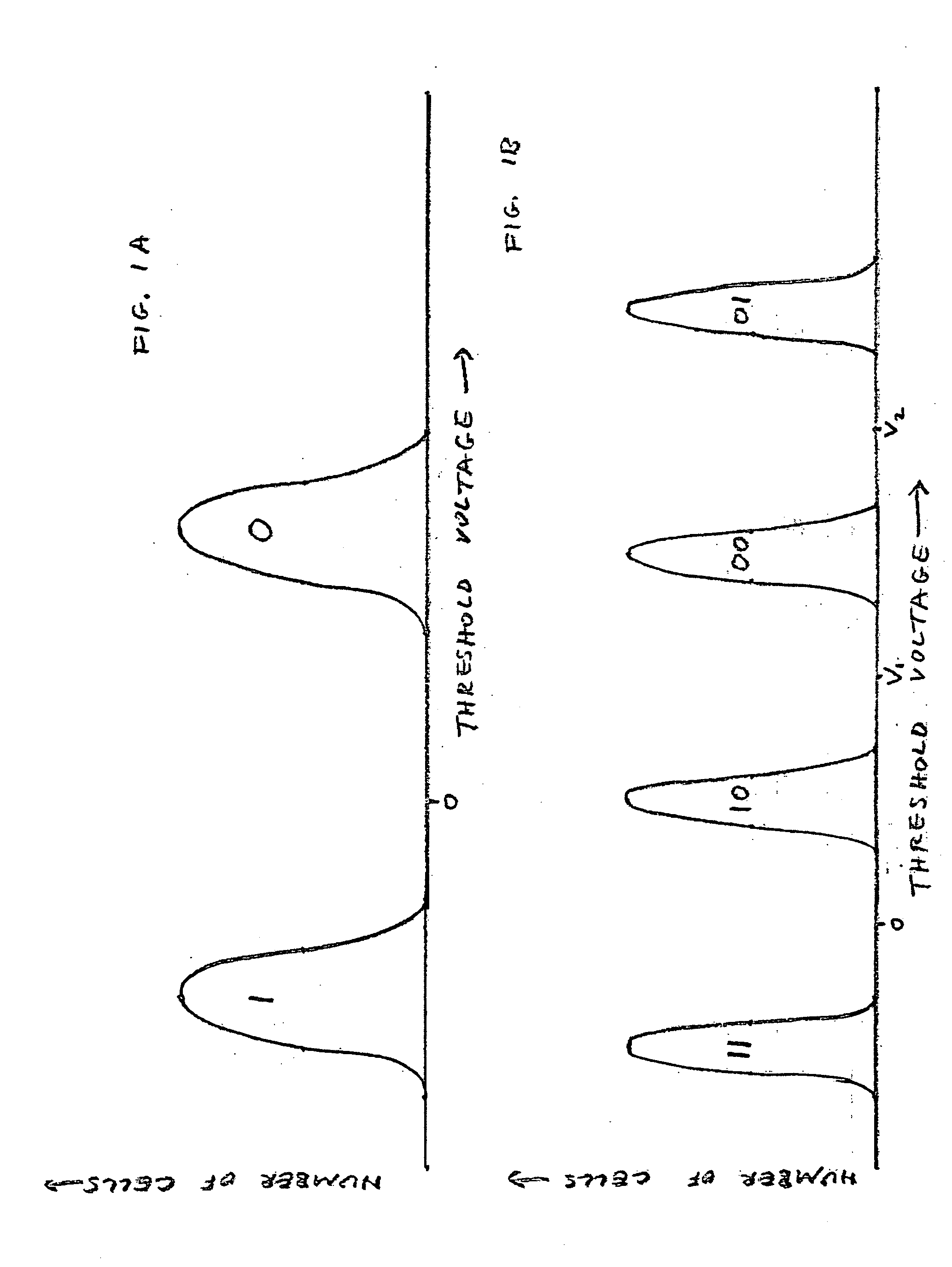
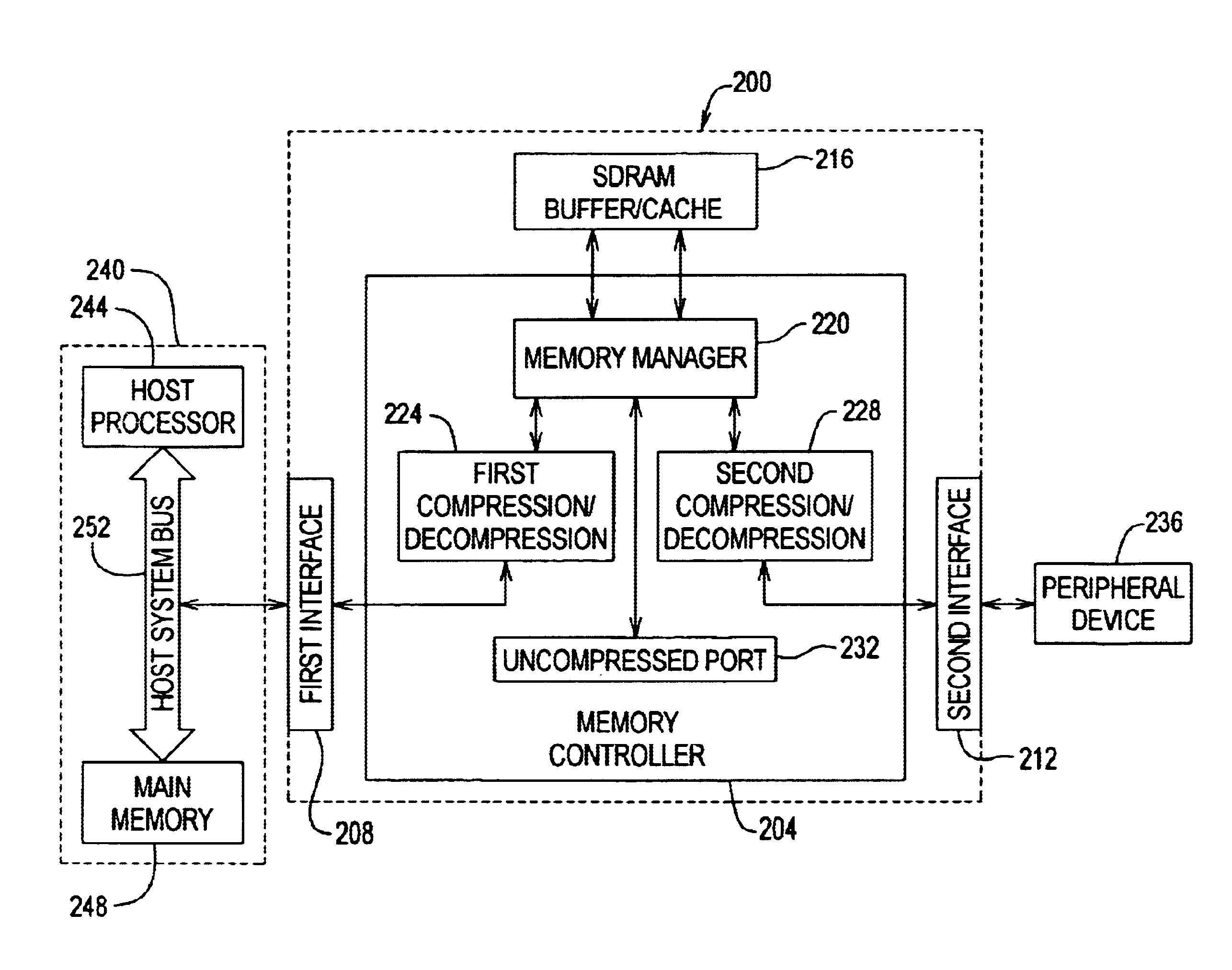
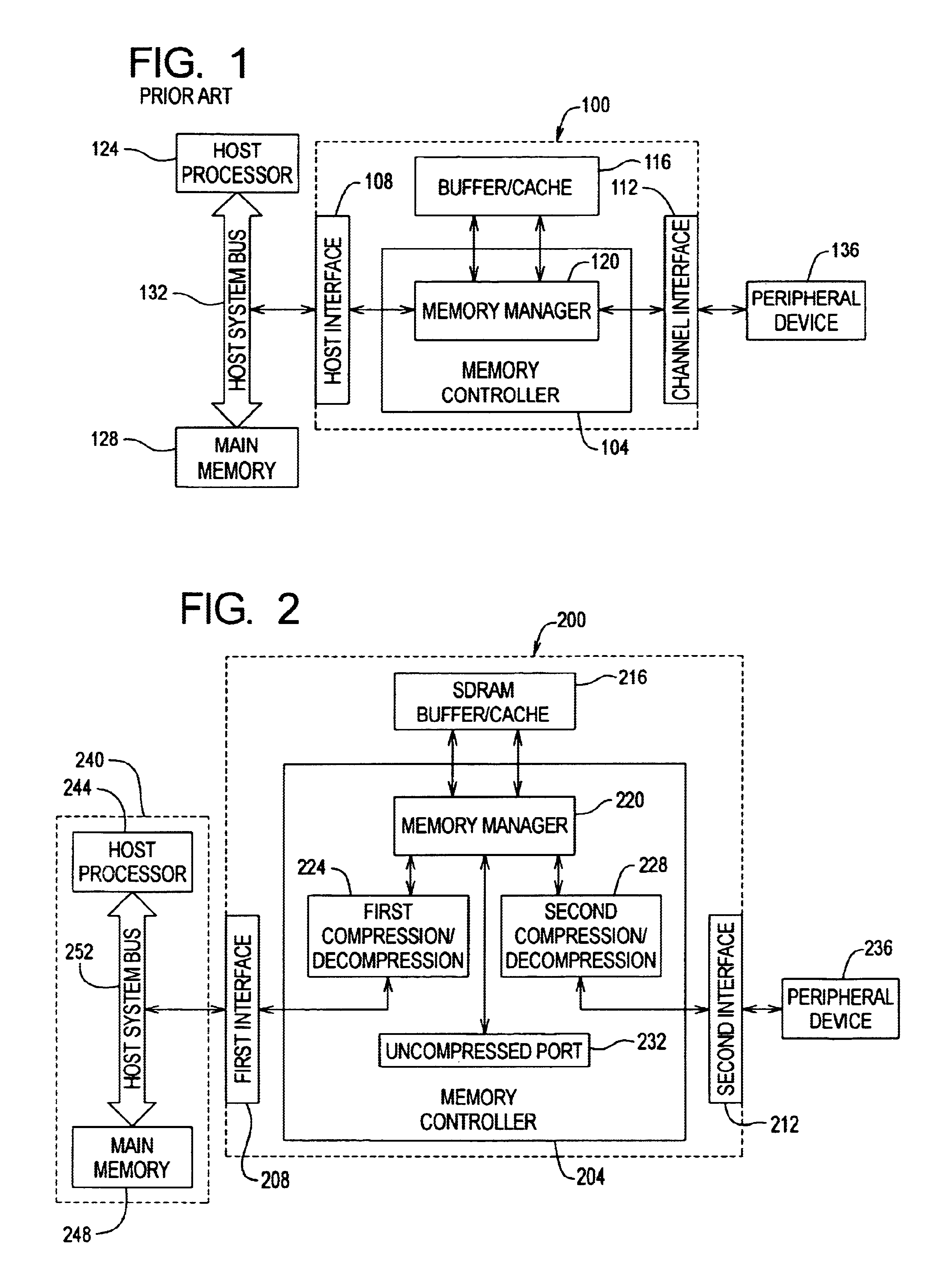
InactiveUS6883079B1Increase effective bandwidthEffective bandwidth of memoryMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData compressionMemory controller
A method and apparatus for increasing the bandwidth of a memory controller system are provided. According to the invention, data received at an interface of a memory controller system is compressed in the memory controller by a compression engine for storage in associated memory. The address of the data written to memory is maintained in a memory controller. When data is read from the memory for provision to an interface of the memory controller, the memory manager retrieves the data from memory and provides it to a decompression engine. The decompression engine restores the data to its original, uncompressed form. The data is then provided to the appropriate interface.
Owner:MAXTOR
Process for the electrolytic deposition of metal layers
InactiveUS6099711AOptimize allocationImpairing propertyCellsElectrolysisHigh current densityMetal coating
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 05140 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 21, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 19206 PCT Pub. Date May 29, 1997The invention relates to a method for the electrolytic deposition of metal coatings, in particular of copper coatings with certain physical-mechanical and optical properties and uniform coating thickness. According to known methods using soluble anodes and applying direct current, only uneven metal distribution can be attained on complex shaped workpieces. By using a pulse current or pulse voltage method, the problem of the coatings being of varying thickness at various places on the workpiece surfaces can indeed be reduced. However, the further problem of the geometric ratios being changed continuously during the depositing process by dissolving of the anodes is not resolved thus. This can be avoided by using insoluble anodes. In order to guarantee sufficient stability of the anodes and a bright coating even at those points on the workpiece surfaces, onto which the metal is deposited with high current density, it is essential to add compounds of an electrochemically reversible redox system to the depositing solution.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Direct write process and apparatus
ActiveUS20050015175A1Fast preparationIncrease back pressureRecording apparatusAdditive manufacturing apparatusDielectricControl signal
A direct write process and apparatus for fabricating a desired circuit component onto a substrate surface of a microelectronic device according to a computer-aided design (CAD). The process includes (a) providing a support member by which the device is supported while being fabricated; (b) providing a chamber for containing a precursor fluid material under a substantially constant pressure differential relative to the ambient pressure, with the precursor fluid material having a viscosity no less than 10 cps; (c) operating an inkjet-based dispensing head with a control valve or actuator for dispensing and depositing minute droplets of the precursor fluid material onto the substrate surface; (d) energy- or heat-treat the deposited precursor fluid material for converting it to the desired active or passive component; and (e) operating a machine controller for generating control signals in response to the CAD coordinates for controlling the position of the dispensing head relative to the support member in response to the control signals to control dispensing and depositing of the precursor material to form the desired component. The process is useful for depositing a wide range of component materials onto an electronic device, including conductor, resistor, capacitor, dielectric, inductor, antenna, solar cell electrode, battery electrode, interconnect, superconductor, sensor, and actuator element materials.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100025676A1Small amount of photocurrentReduce parasitic capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge carrierOhmic contact
To offer a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor having excellent characteristics and high reliability and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device without variation. The summary is to include an inverted-staggered (bottom-gate structure) thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor film containing In, Ga, and Zn is used for a semiconductor layer and a buffer layer is provided between the semiconductor layer and source and drain electrode layers. An ohmic contact is formed by intentionally providing a buffer layer containing In, Ga, and Zn and having a higher carrier concentration than the semiconductor layer between the semiconductor layer and the source and drain electrode layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Pharmaceutical composition and method for transdermal drug delivery
InactiveUS20050042268A1Improves transdermal penetrationSmall amountOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHormones regulationTransdermal medication
A pharmaceutical composition for transdermal administration of a hormone (e.g., testosterone), which includes urea and / or a derivative thereof as a penetration enhancer, and methods utilizing same for treating medical conditions in which elevating a hormone serum level is beneficial are disclosed.
Owner:AGIS INDUSTRIES (1983) LTD
Diagnostic sanitary test strip
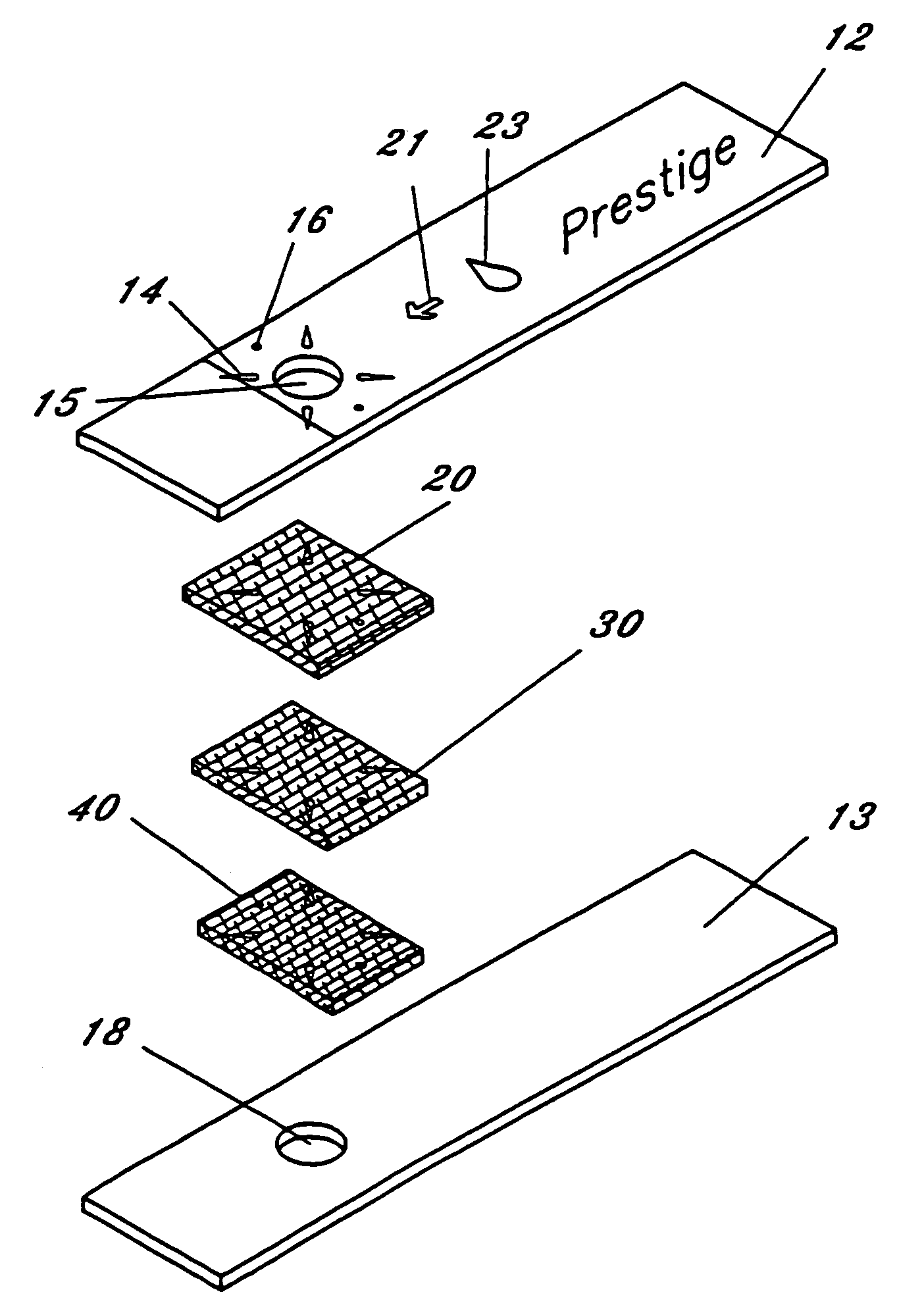
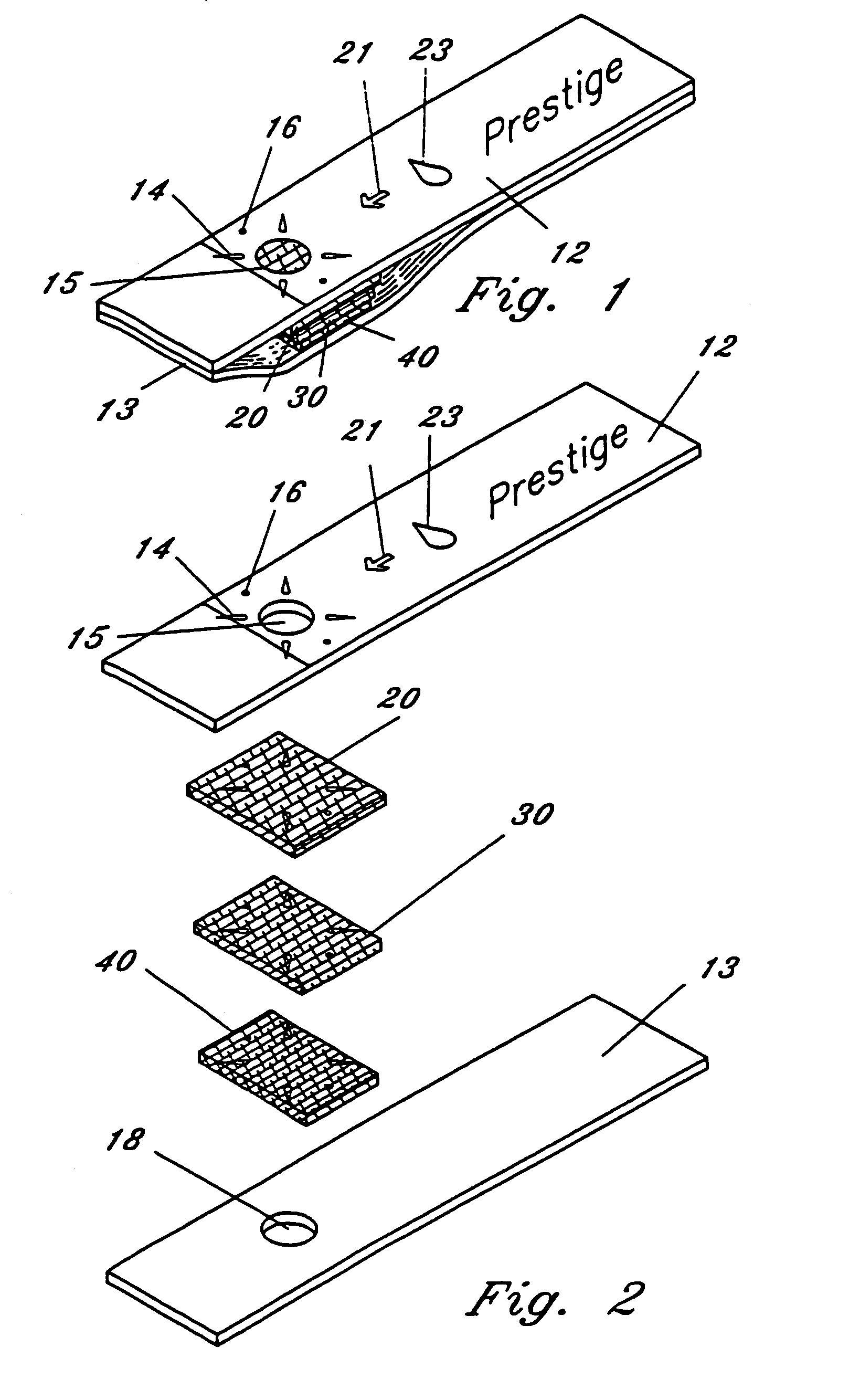
InactiveUS6991940B2Easy to useBroaden applicationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor changesFluid specimen
An improved multi-layered diagnostic sanitary test strip for receiving a heterogenous fluid, such as whole blood, to test for presence and / or amount of a suspected analyte in the fluid by facilitating a color change in the strip corresponding to the amount of the analyte in the fluid, wherein the test strip includes fluid volume control dams to prevent spillage of the fluid from the strip and a chemical reagent solution that facilitates end-point testing. The improved test strip comprises no more than two operative layers and: (a) a reaction membrane containing a reagent capable of reacting with the analyte of interest to produce a measurable change in said membrane; (b) an upper support layer defining a sample receiving port for receiving the fluid sample thereat; (c) one or more structures for directing the sample containing the analyte of interest through at least a portion of said reaction membrane; and (d) a lower support layer having a reaction viewing port in vertical alignment with said membrane for displaying said measurable change, said lower support being associated with said upper support to secure said reaction membrane in said test strip.
Owner:NIPRO DIAGNOSTICS INC
Pharmaceutical composition and method for transdermal drug delivery
InactiveUS20050020552A1Increase concentrationImproves transdermal penetrationOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryIsostearic acidHormones regulation
A pharmaceutical composition for transdermal administration of a hormone (e.g., testosterone), which includes isostearic acid as a penetration enhancer, and methods utilizing same for treating medical conditions in which elevating a hormone serum level is beneficial are disclosed.
Owner:AGIS INDUSTRIES (1983) LTD
Inflator system
InactiveUS20070228703A1Efficient use ofSmall amountVehicle seatsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTraffic volumeMixing chamber
Method for inflating an airbag in a vehicle to protect an occupant in the event of a crash involving the vehicle in which an inflator having a propellant is arranged in the vehicle, the propellant is ignited after determination of a crash involving the vehicle to generate gas therefrom, the gas is directed into an airbag and pressure in the airbag is controlled based on the occupant by varying the flow of gas into the airbag. Variation in the flow of gas into the airbag may be obtained by varying a flow of aspirating gas into a mixing chamber in which the aspirating gas mixes with gas generated from the propellant.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE TECH INT
Charging system
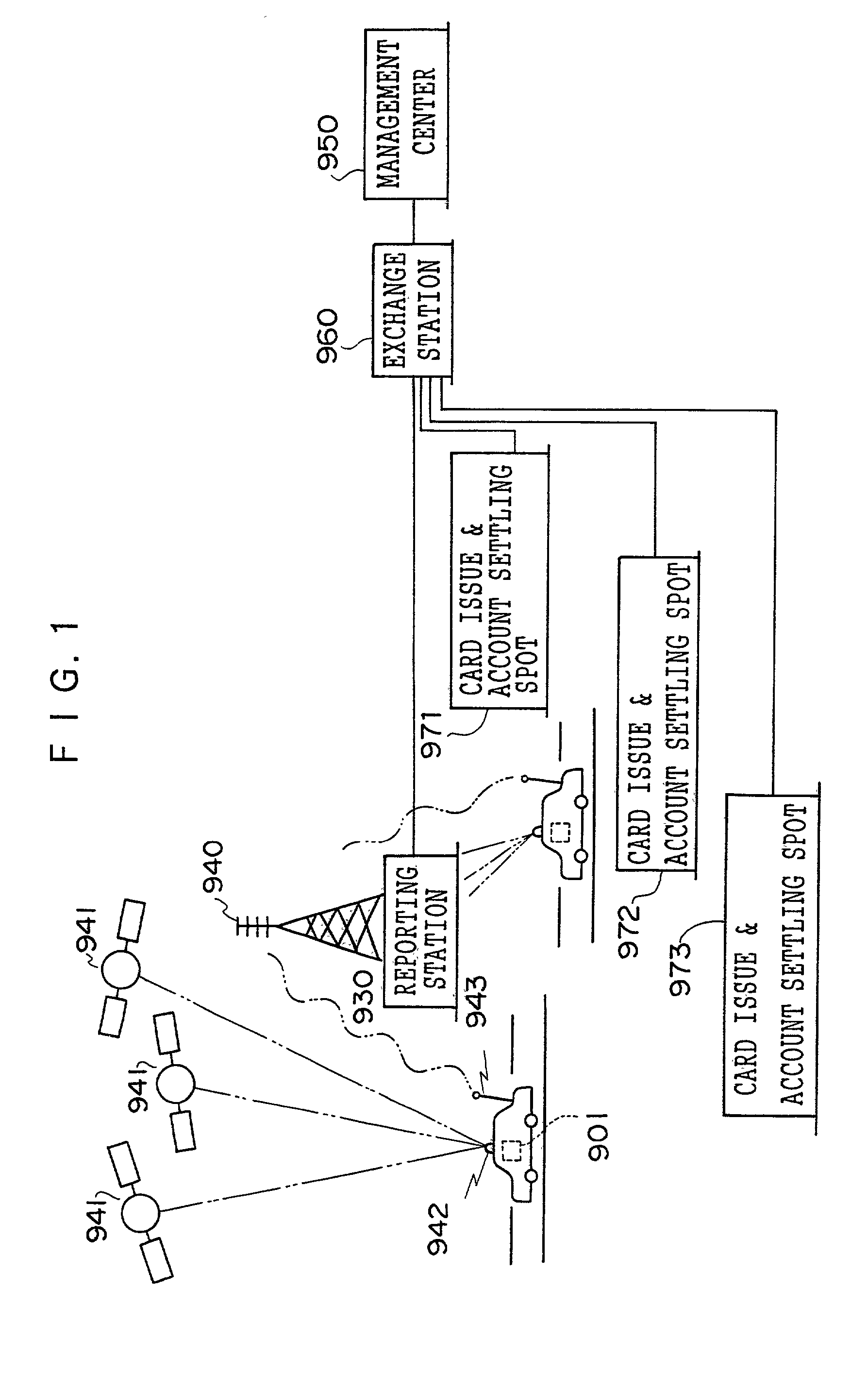
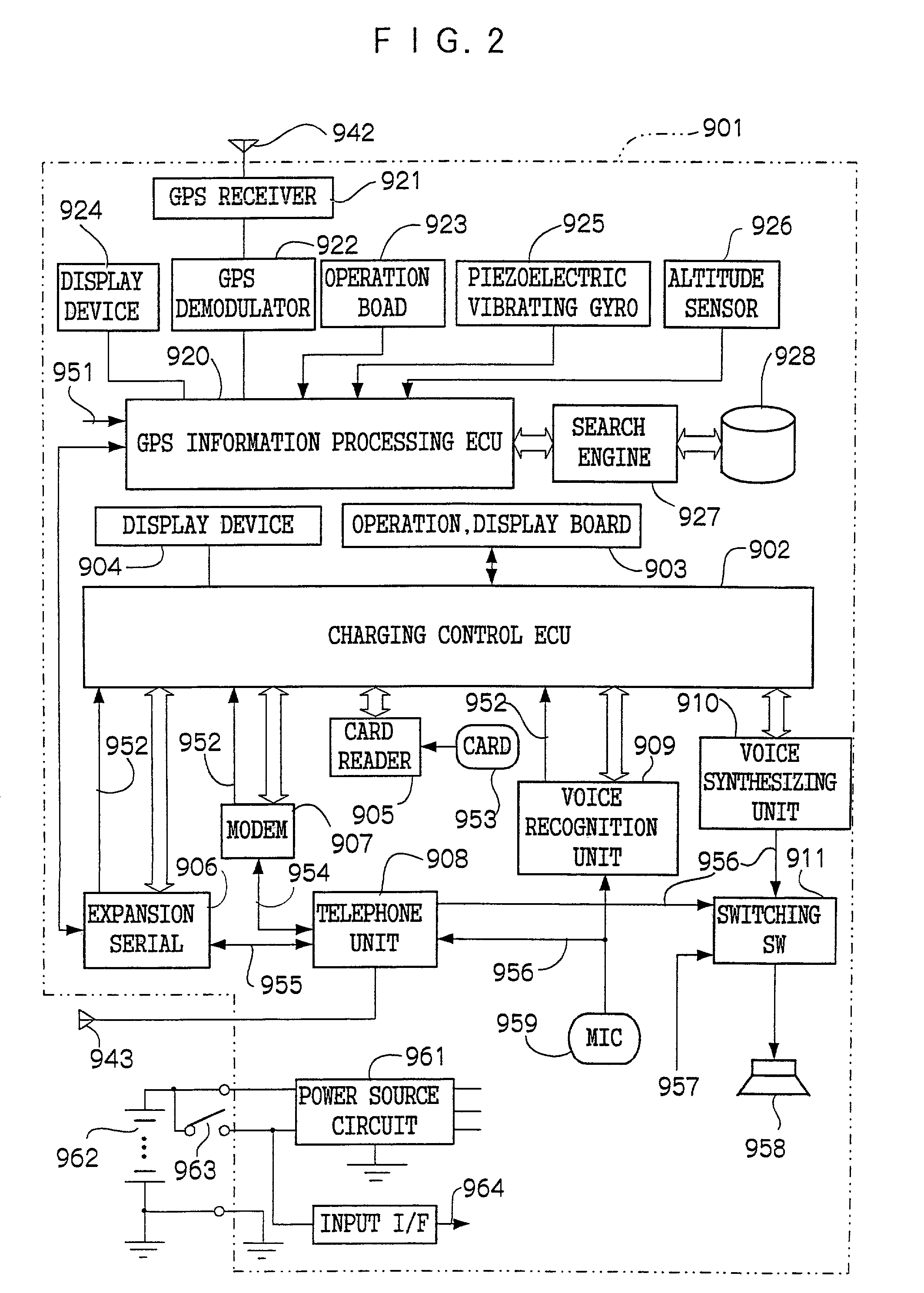
InactiveUS20020049630A1Small data amountLow accuracyInstruments for road network navigationTicket-issuing apparatusGeographical featureEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a charging system which carries out position confirmation of a moving body at a place where there is a radio wave blocked facility, and which carries out automatic detection of GPS antenna blockage for avoiding charging. In a charging system including a GPS positioning device 921 for recognizing a vehicle position, a vehicle speed pulse measuring device 920 for dead reckoning navigating, a monitor device 920, 927, 928 which generates information expressing a current position by using these, and a charging processing 902 which judges whether or not a recognized current position is within a charge area and which carries out data processing for charging, the monitor 920 includes a simple map database 928 which includes positions of facilities or geographical features at which GPS positioning is impossible, and when GPS positioning is impossible, the facility or geographical feature corresponding to the current position is detected, and that position is made to be a current position.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Diagnostic sanitary test strip
InactiveUS7049130B2Easy to testPrevent spill and overflowBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteVertical alignment
An improved multi-layered diagnostic sanitary test strip for receiving a heterogenous fluid, such as whole blood, to test for presence and / or amount of a suspected analyte in the fluid by facilitating a color change in the strip corresponding to the amount of the analyte in the fluid, wherein the test strip includes fluid volume control dams to prevent spillage of the fluid from the strip and a chemical reagent solution that facilitates end-point testing. The improved test strip comprises no more than two operative layers and: (a) a reaction membrane containing a reagent capable of reacting with the analyte of interest to produce a measurable change in said membrane; (b) an upper support layer defining a sample receiving port for receiving the fluid sample thereat; (c) one or more structures for directing the sample containing the analyte of interest through at least a portion of said reaction membrane; and (d) a lower support layer having a reaction viewing port in vertical alignment with said membrane for displaying said measurable change, said lower support being associated with said upper support to secure said reaction membrane in said test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Low complexity high-speed communications transceiver
InactiveUS7590168B2Improve data transfer rateReduce interferenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationTransceiverCommunications system
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
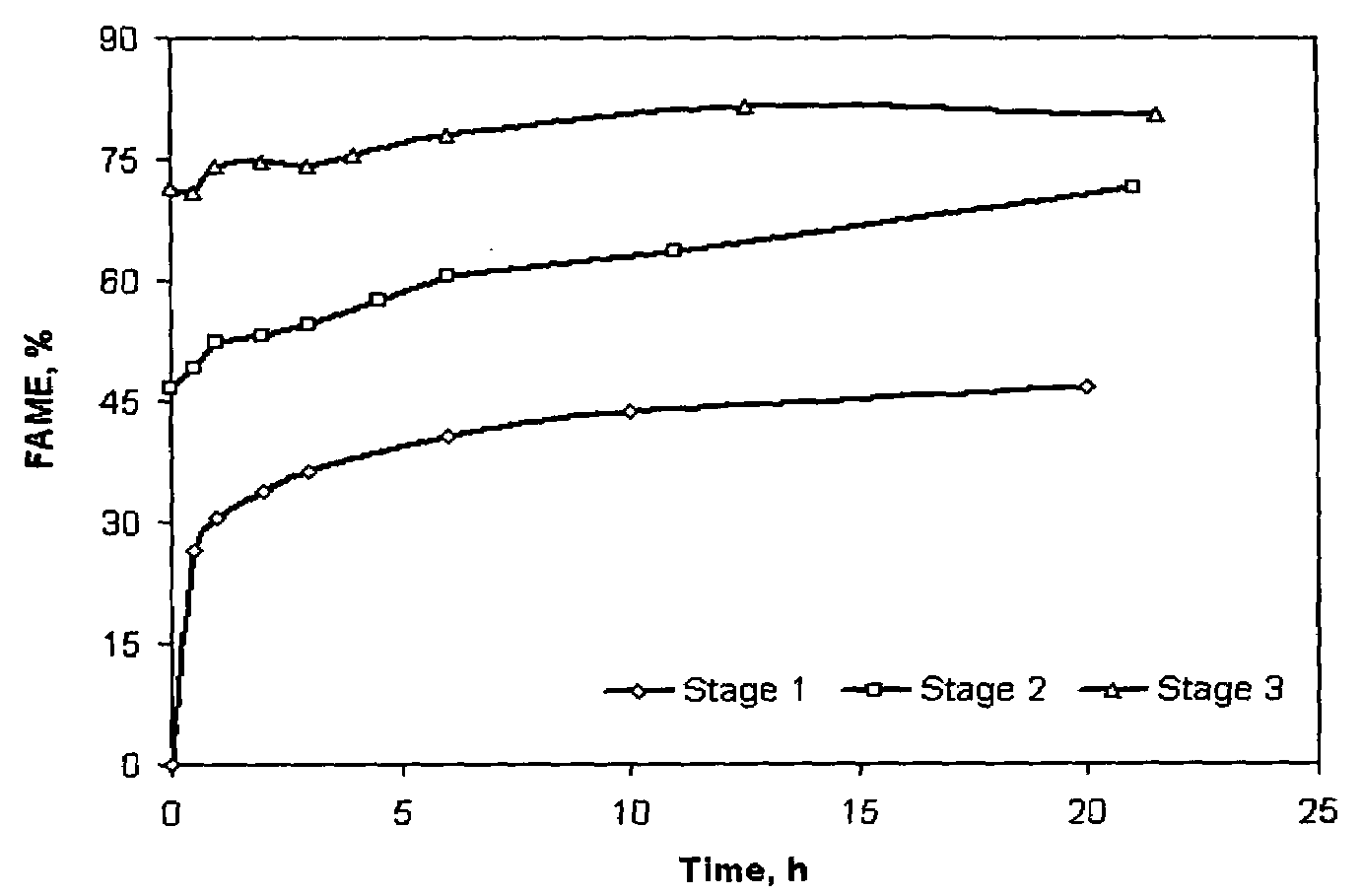
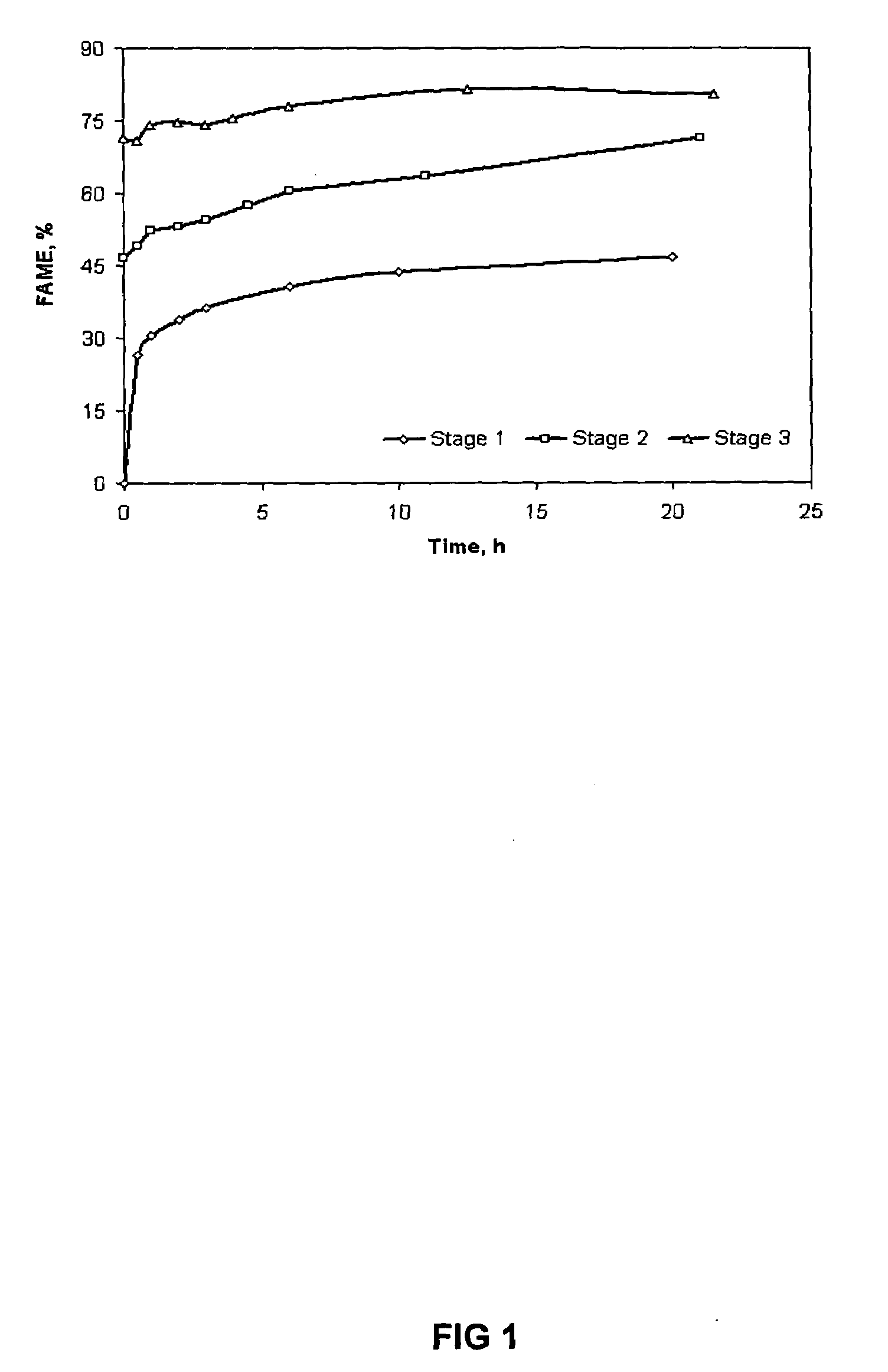
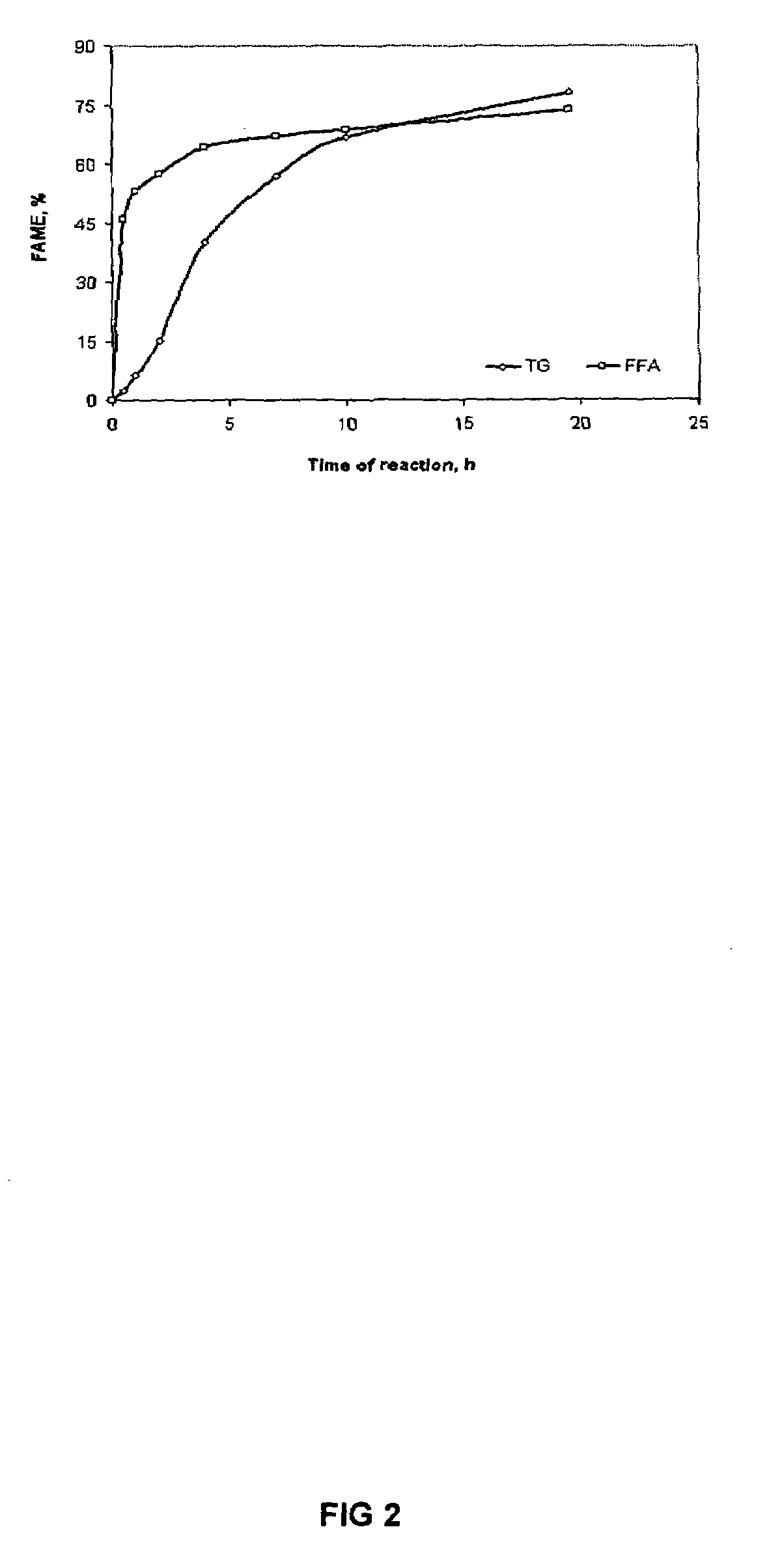
Method of converting free fatty acids to fatty acid methyl esters with small excess of methanol
InactiveUS6965044B1Cost efficientEasily separateFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningFatty acid esterFatty acid methyl ester
A method for converting free fatty acids in acid oil or acid fat into fatty acid methyl esters is disclosed. The method involves adding a small amount of methanol and an acid catalyst to the acid oil or acid fat and subjecting the mixture to conditions that allow the fatty acid methyl esters to form. A lipid phase containing the fatty acid methyl esters and triglycerides can from and be separated from the rest of the reaction mixture. The lipid phase can then be subjected to conditions suitable for converting the triglycerides into fatty acid methyl esters. The method of present invention is especially useful for a process of generating biodiesel using a starting material of vegetable and animal oils and fats that contain a relatively high level of free fatty acids.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
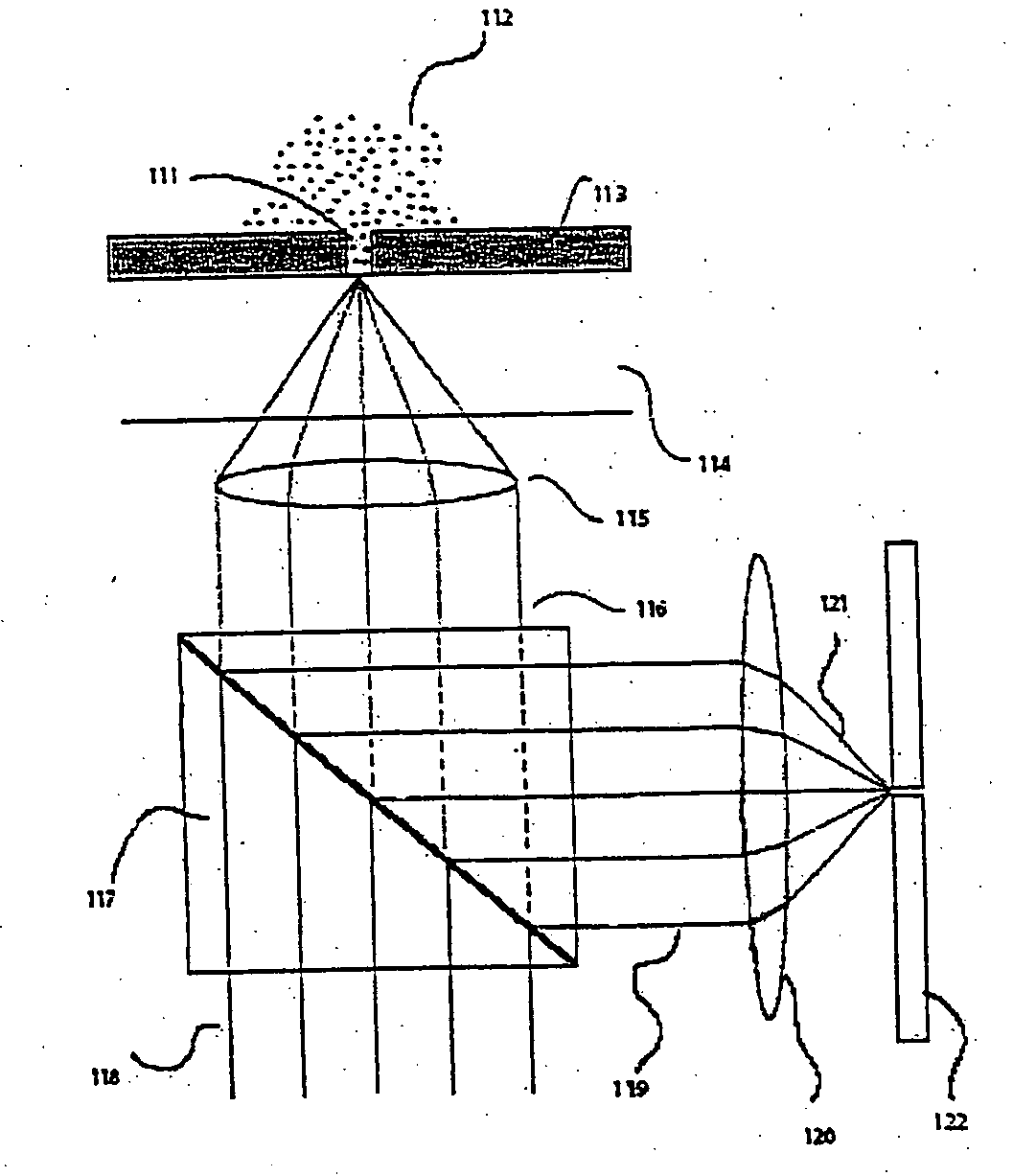
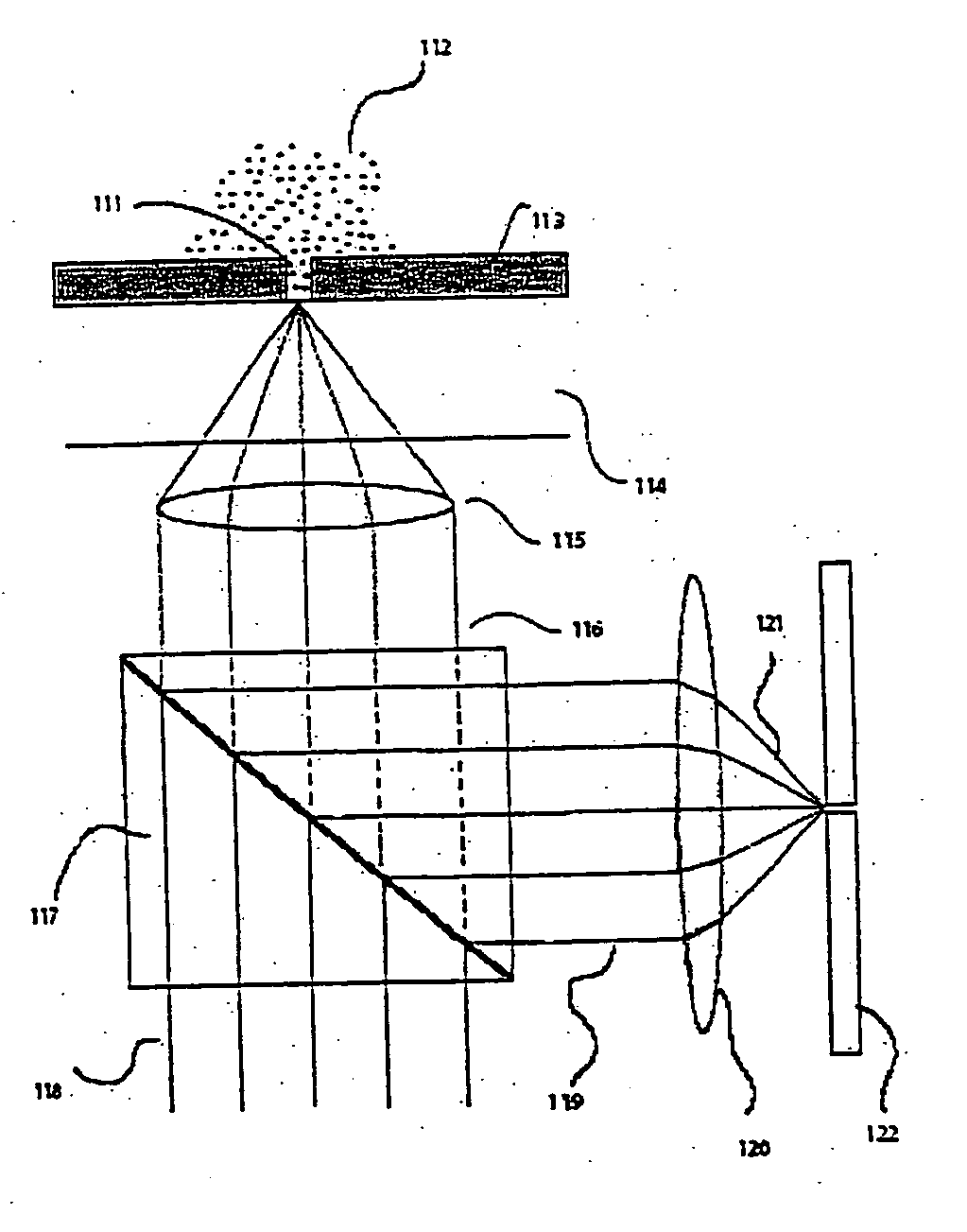
Apparatus and method for performing nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS20060063264A1Effective volumeHigh fill fraction arrayMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reactionMolecular analysis
The present invention relates to optical confinements, methods of preparing and methods of using them for analyzing molecules and / or monitoring chemical reactions. The apparatus and methods embodied in the present invention are particularly useful for high-throughput and low-cost single-molecular analysis.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
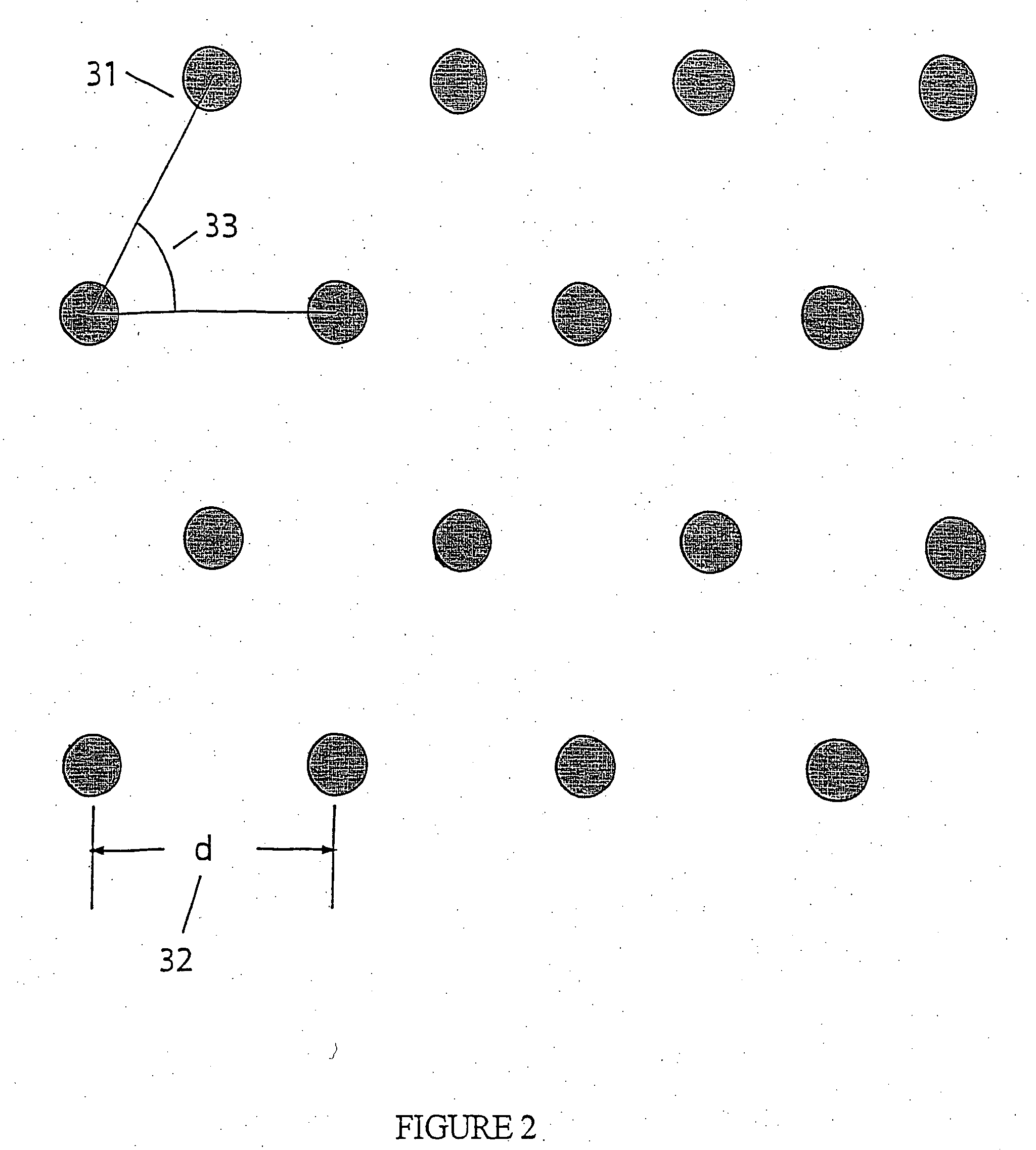
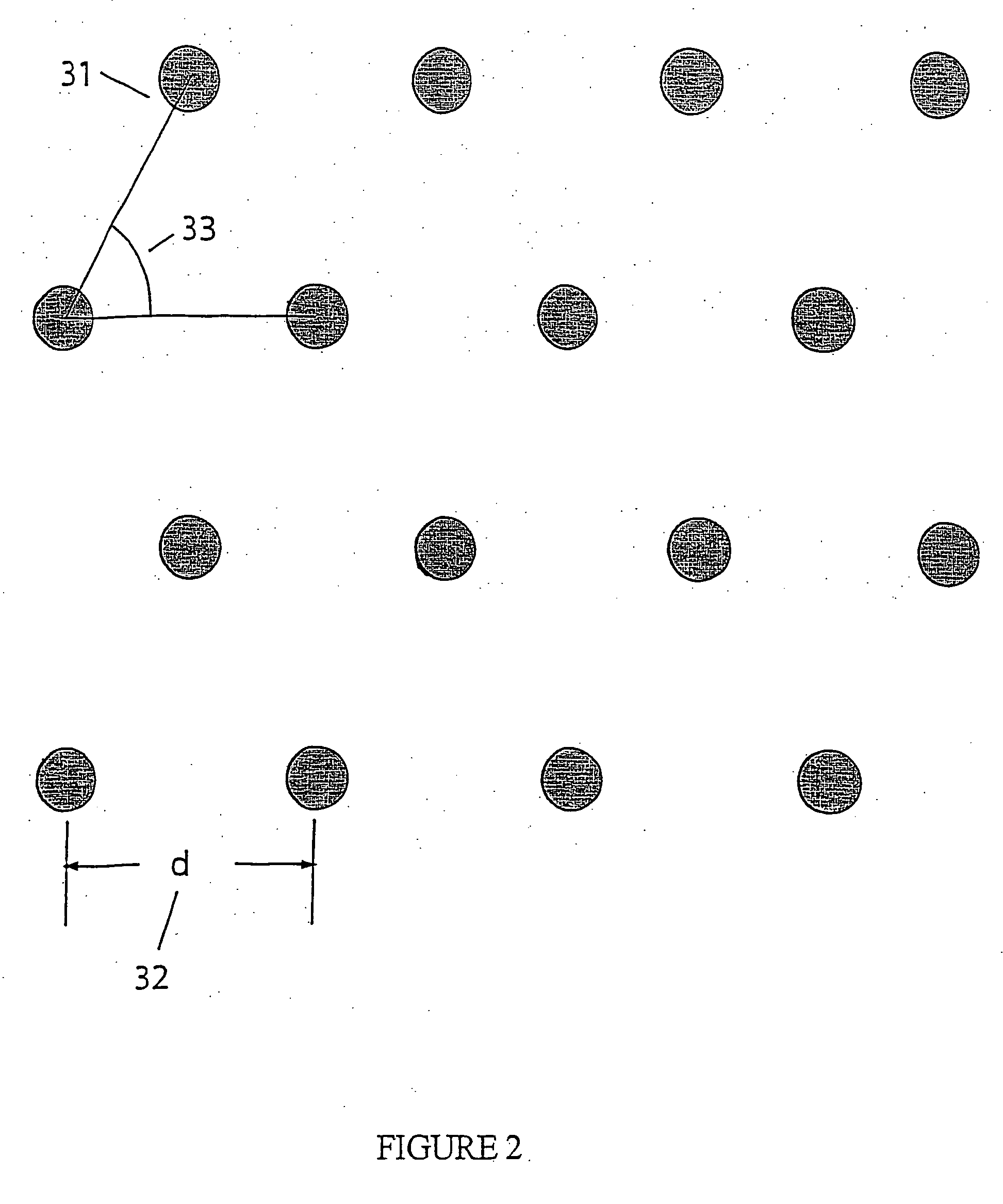
Arrays of optical confinements and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060061754A1Effective volumeHigh fill fraction arrayMaterial nanotechnologyLaser detailsMolecular analysisChemical reaction
The present invention relates to optical confinements, methods of preparing and methods of using them for analyzing molecules and / or monitoring chemical reactions. The apparatus and methods embodied in the present invention are particularly useful for high-throughput and low-cost single-molecular analysis.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
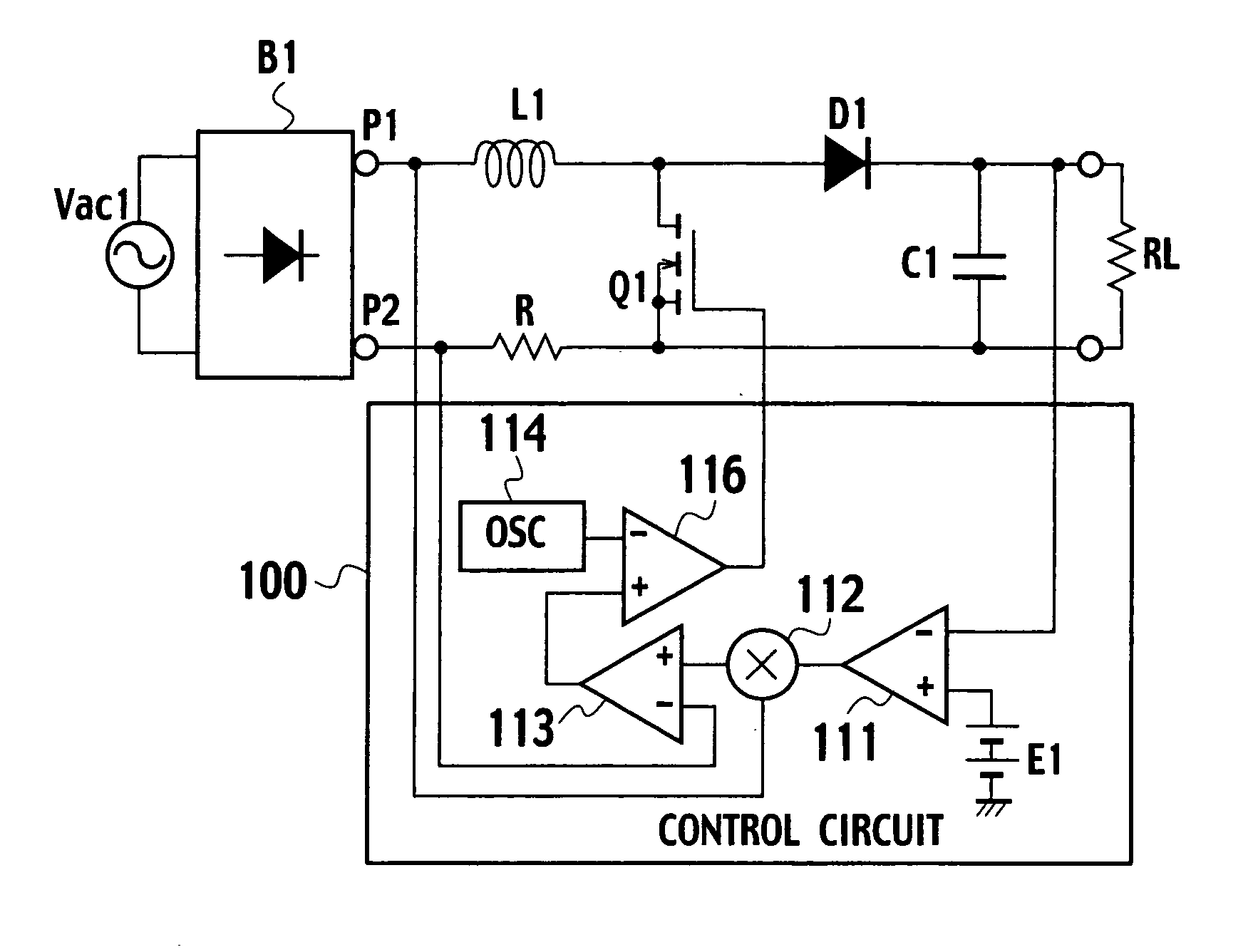
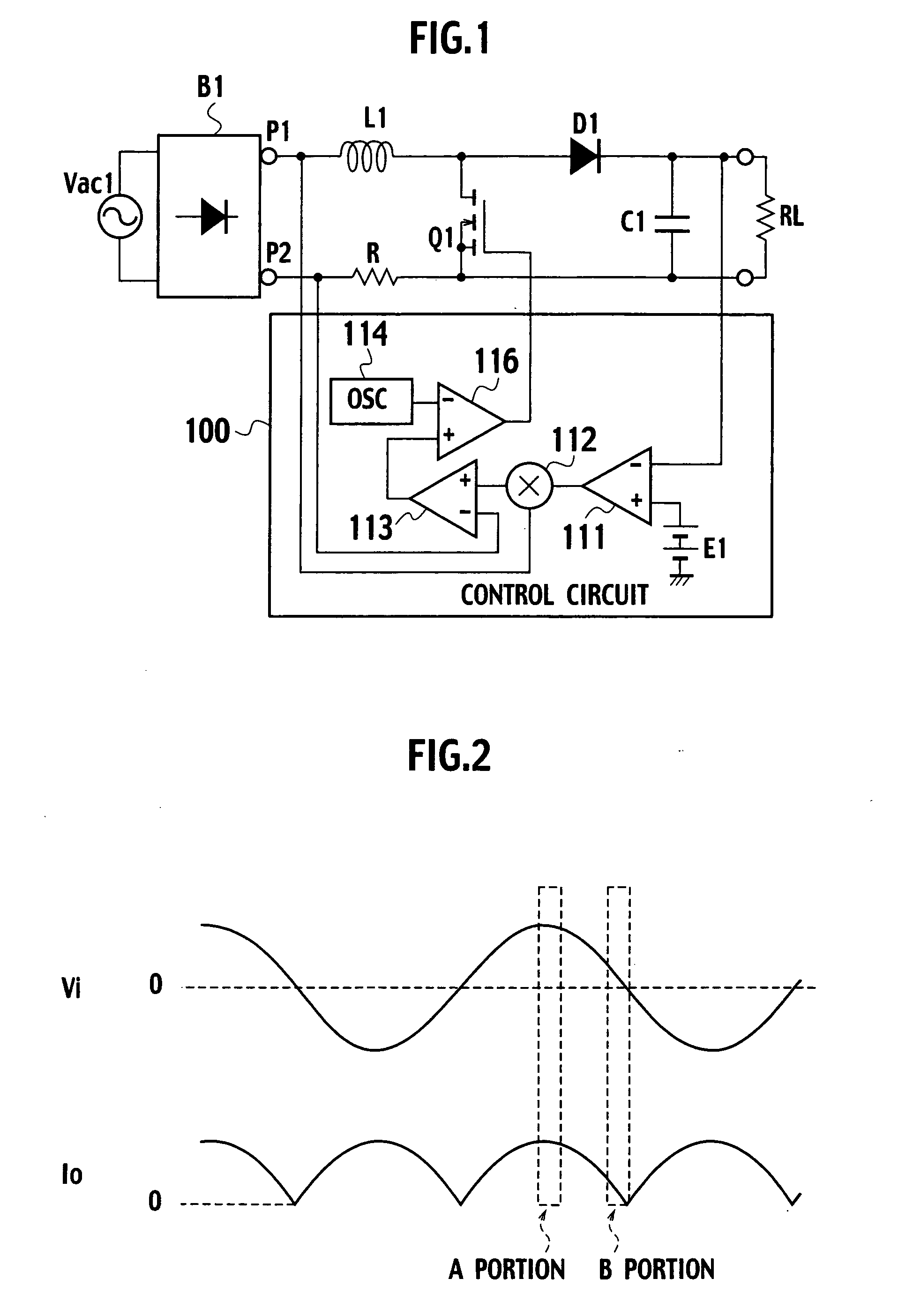
Power factor improving circuit
InactiveUS20070103949A1Power loss increaseReduce efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSine waveAC power
A power factor improving circuit including: a boost reactor that inputs a rectified voltage obtained by rectifying an AC power supply voltage of an AC power supply by a rectifier circuit; a main switch that inputs the rectified voltage through the boost reactor and is turned on / off; a converting section that converts a voltage obtained when the main switch is turned on / off into a DC output voltage; and a control section that controls turn-on / off of the main switch to shape an AC power supply current to a sine wave form, controls an output voltage of the converting section to a predetermined voltage, and controls a switching frequency of the main switch according to a value of current flowing into the AC power supply, or that of current flowing into the rectifier, or that of current flowing into the main switch.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
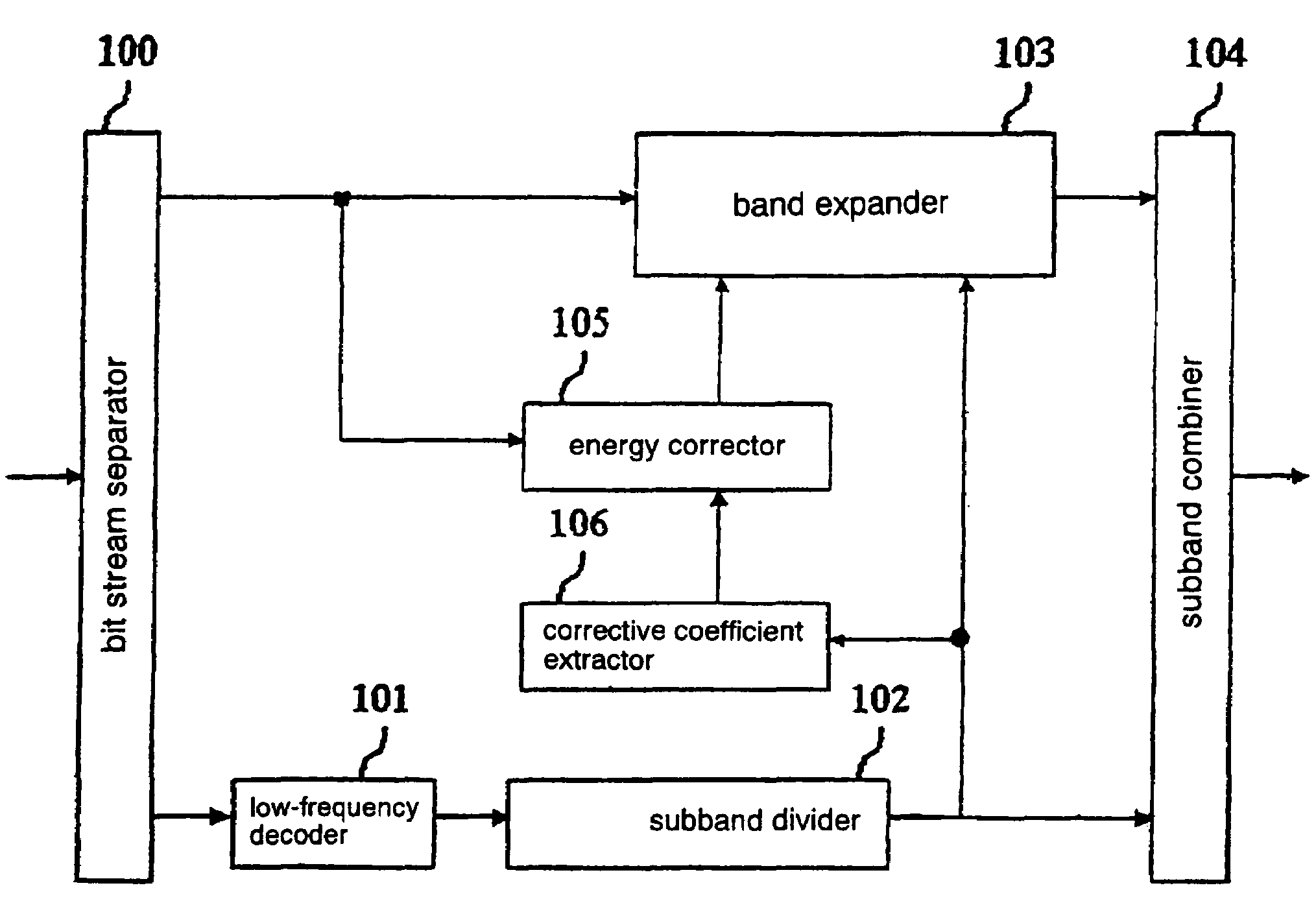
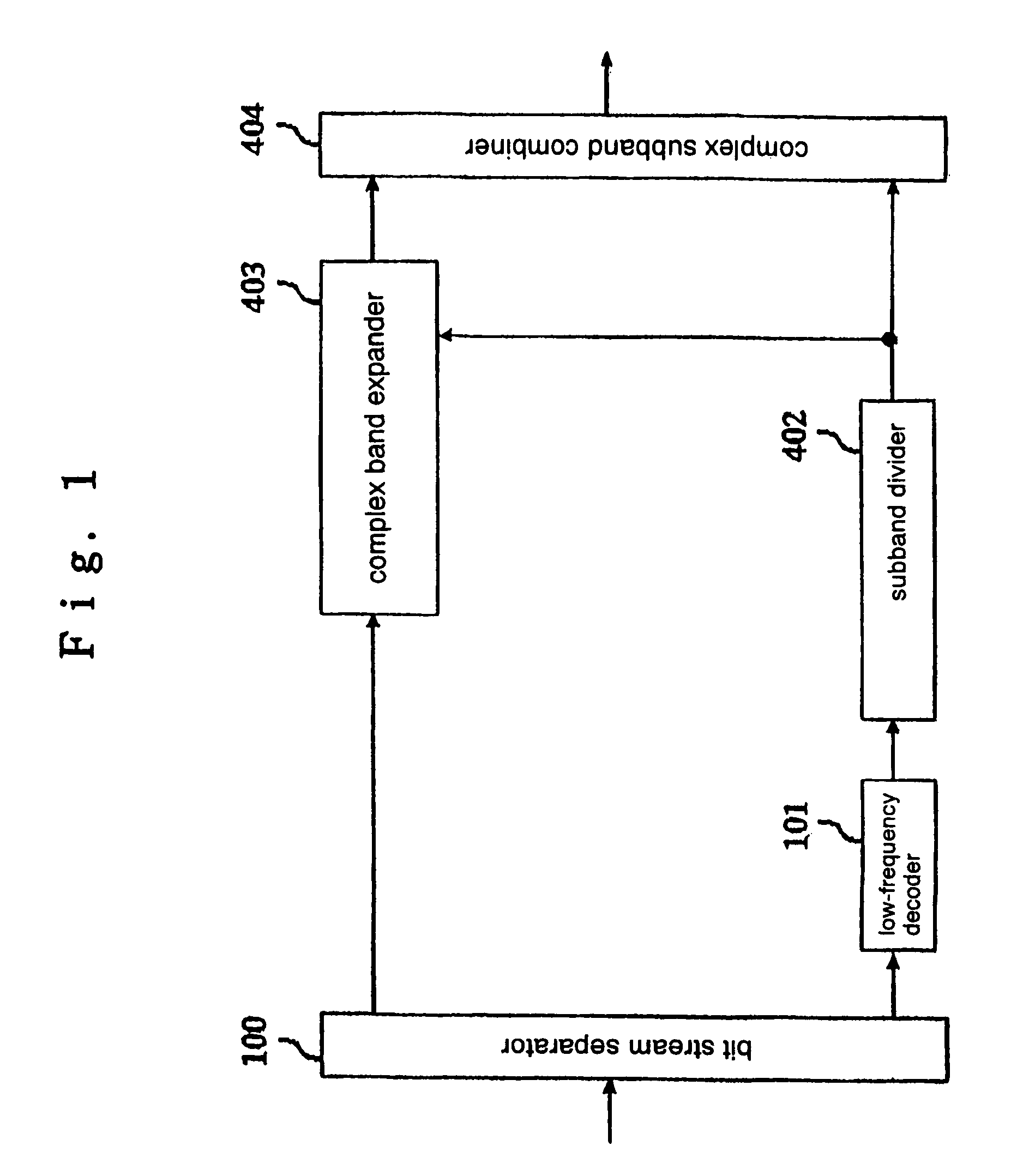
Audio decoding device, decoding method, and program
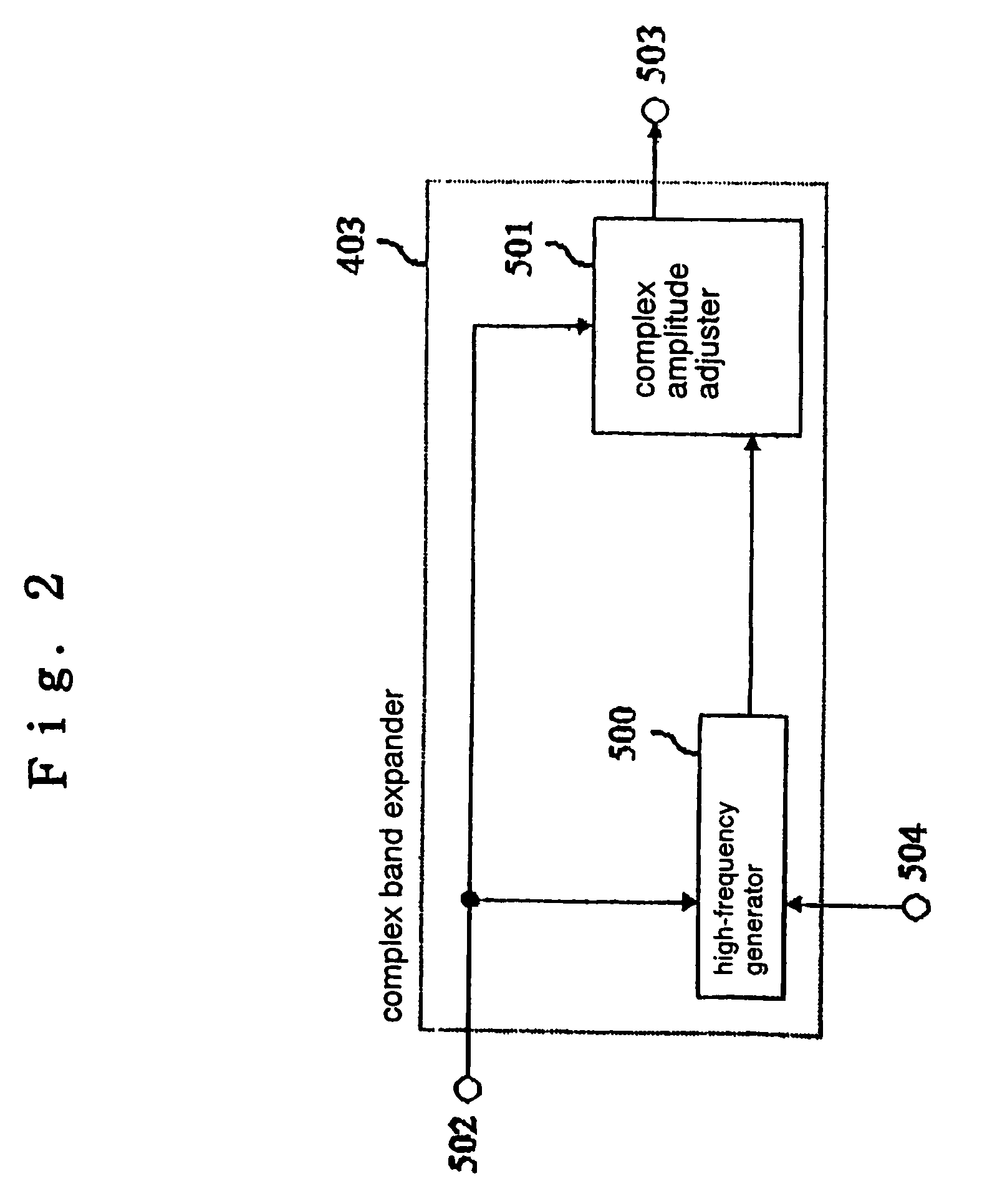
ActiveUS7555434B2Reduce the amount of calculationImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsSound quality
An energy corrector (105) for correcting a target energy for high-frequency components and a corrective coefficient calculator (106) for calculating an energy corrective coefficient from low-frequency subband signals are newly provided. These processors perform a process for correcting a target energy that is required when a band expanding process is performed on a real number only. Thus, a real subband combining filter and a real band expander which require a smaller amount of calculations can be used instead of a complex subband combining filter and a complex band expander, while maintaining a high sound-quality level, and the required amount of calculations and the apparatus scale can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Scalable motion control system
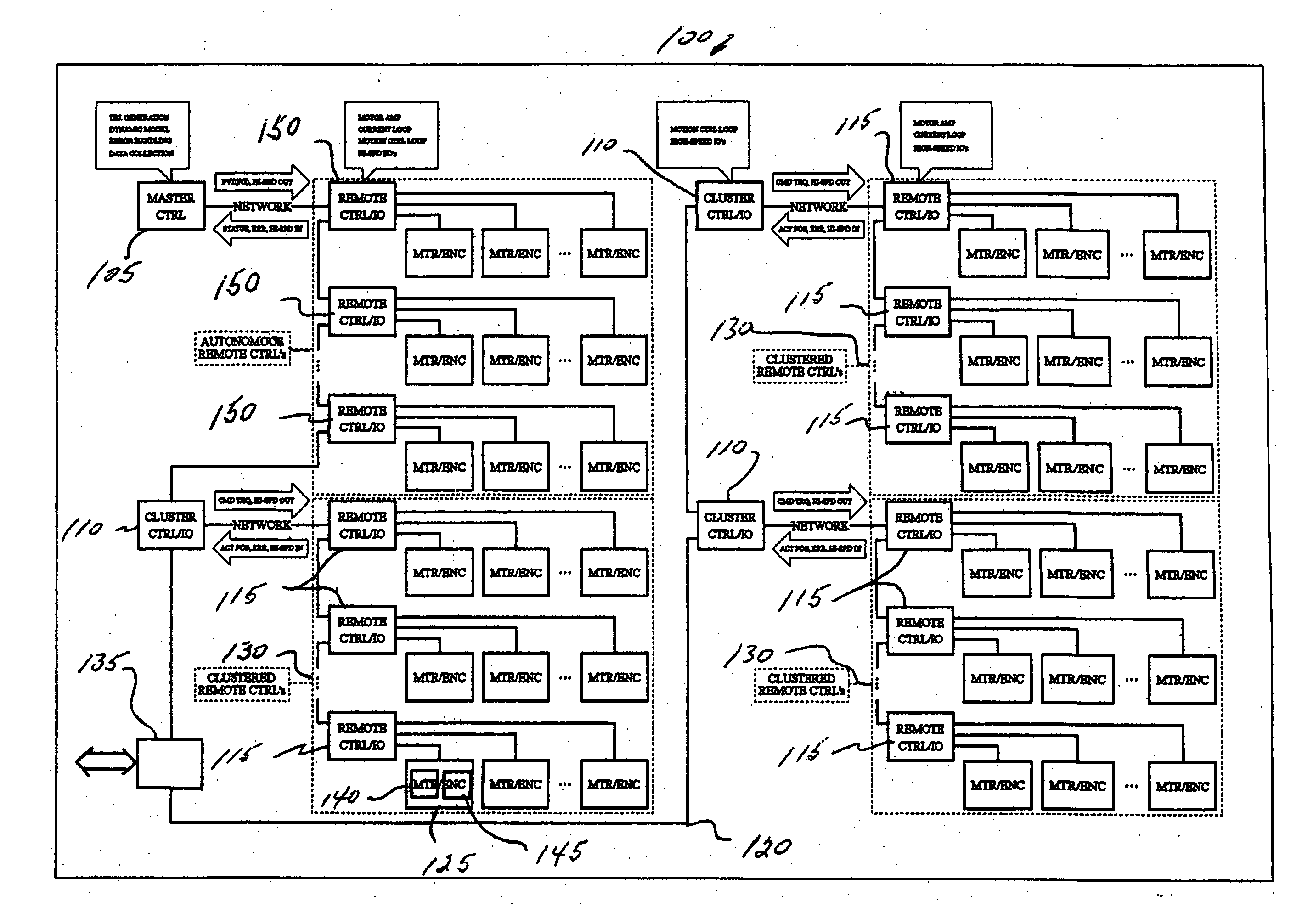
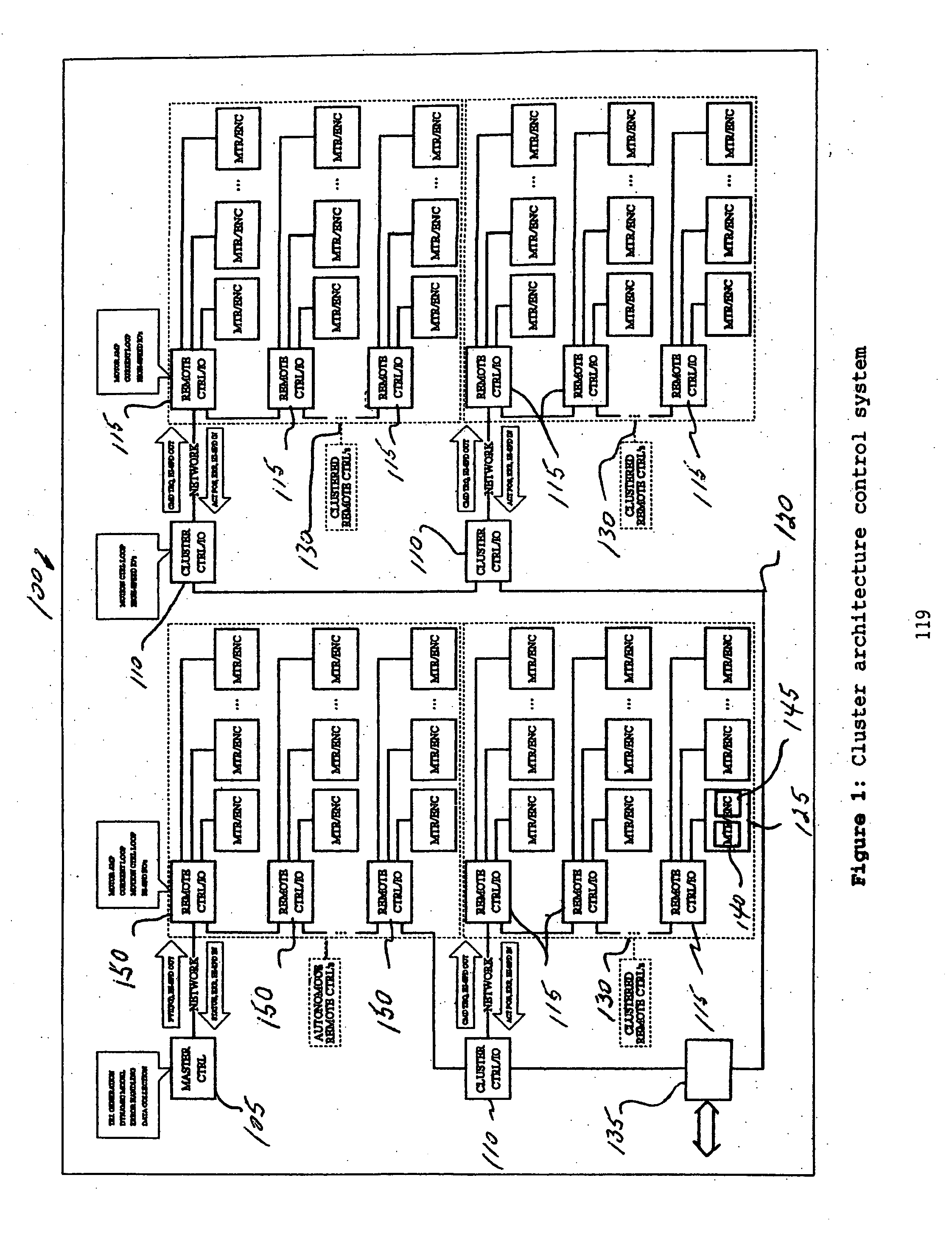
ActiveUS20070010898A1Maintain integrityEasy to implementLiquid surface applicatorsComputer controlDirect controlMaster controller
A control system includes a clustered architecture having a master controller, a central control section including one or more first remote controllers under direct control of the master controller, and a distributed control section including a cluster controller controlled by the master controller. The cluster controller controls the activities of one or more second remote controllers. Each of the first and second remote controllers are utilized to drive one or more axes.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com