Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3710results about "Fatty acid esterification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
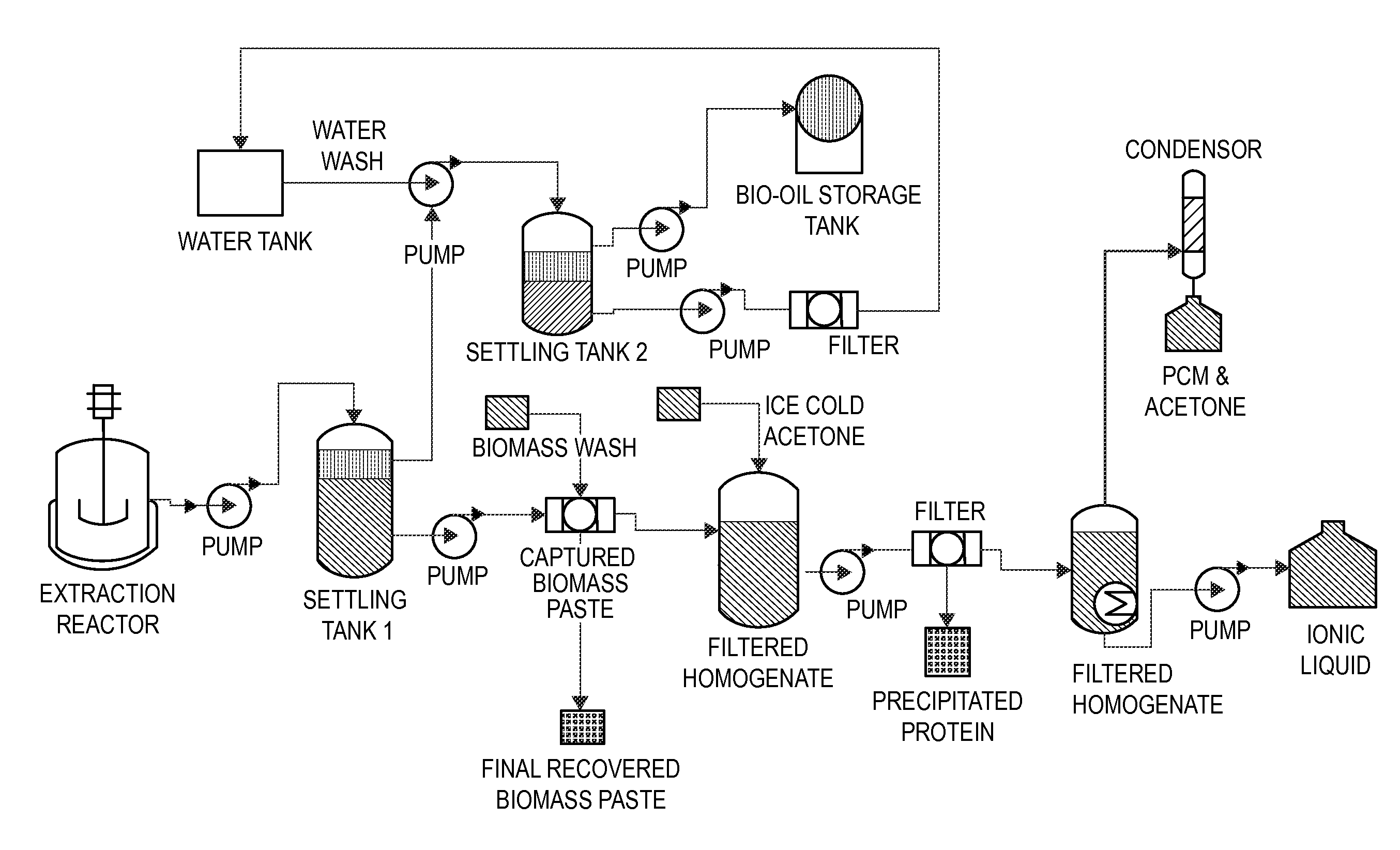
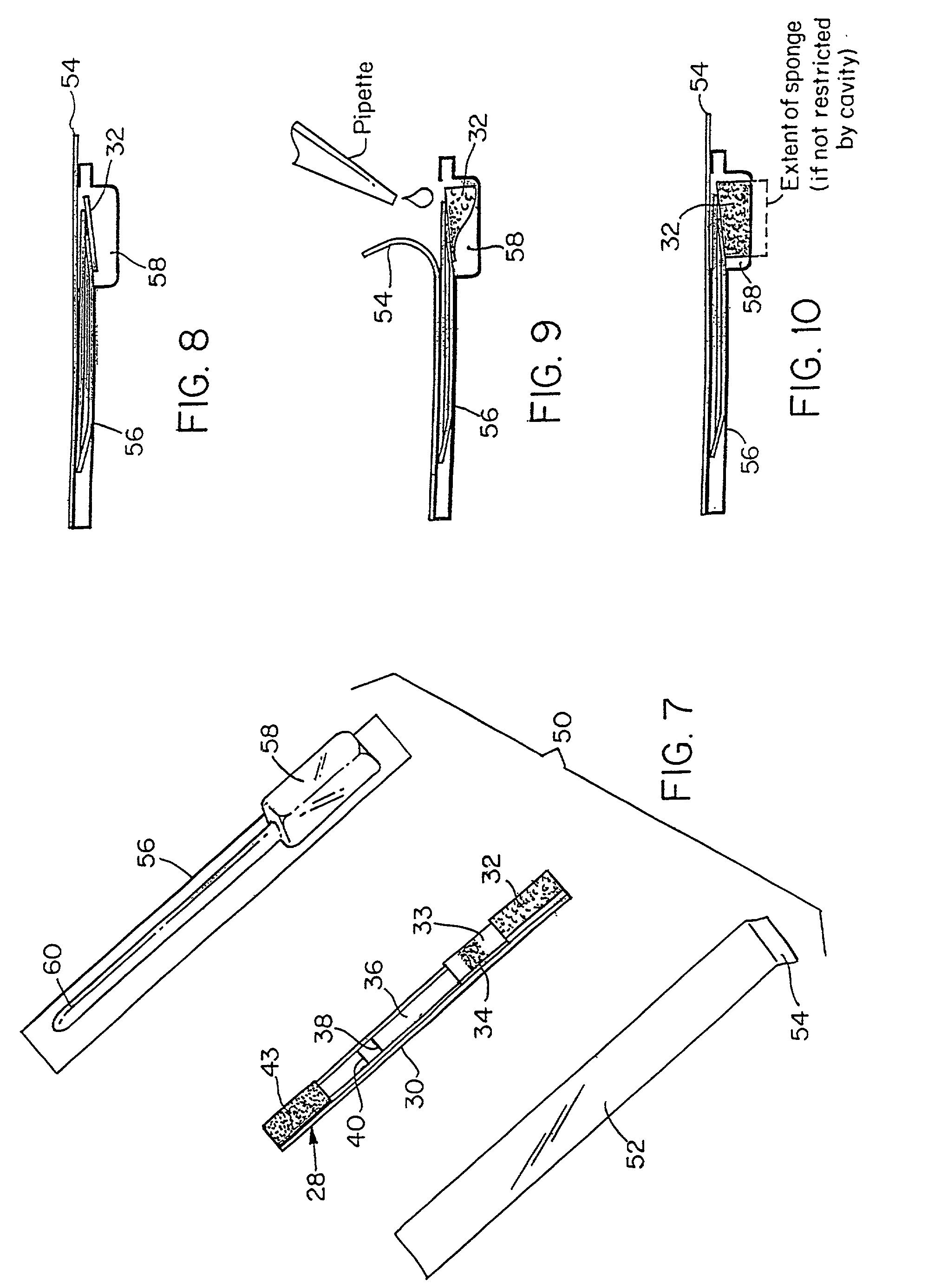
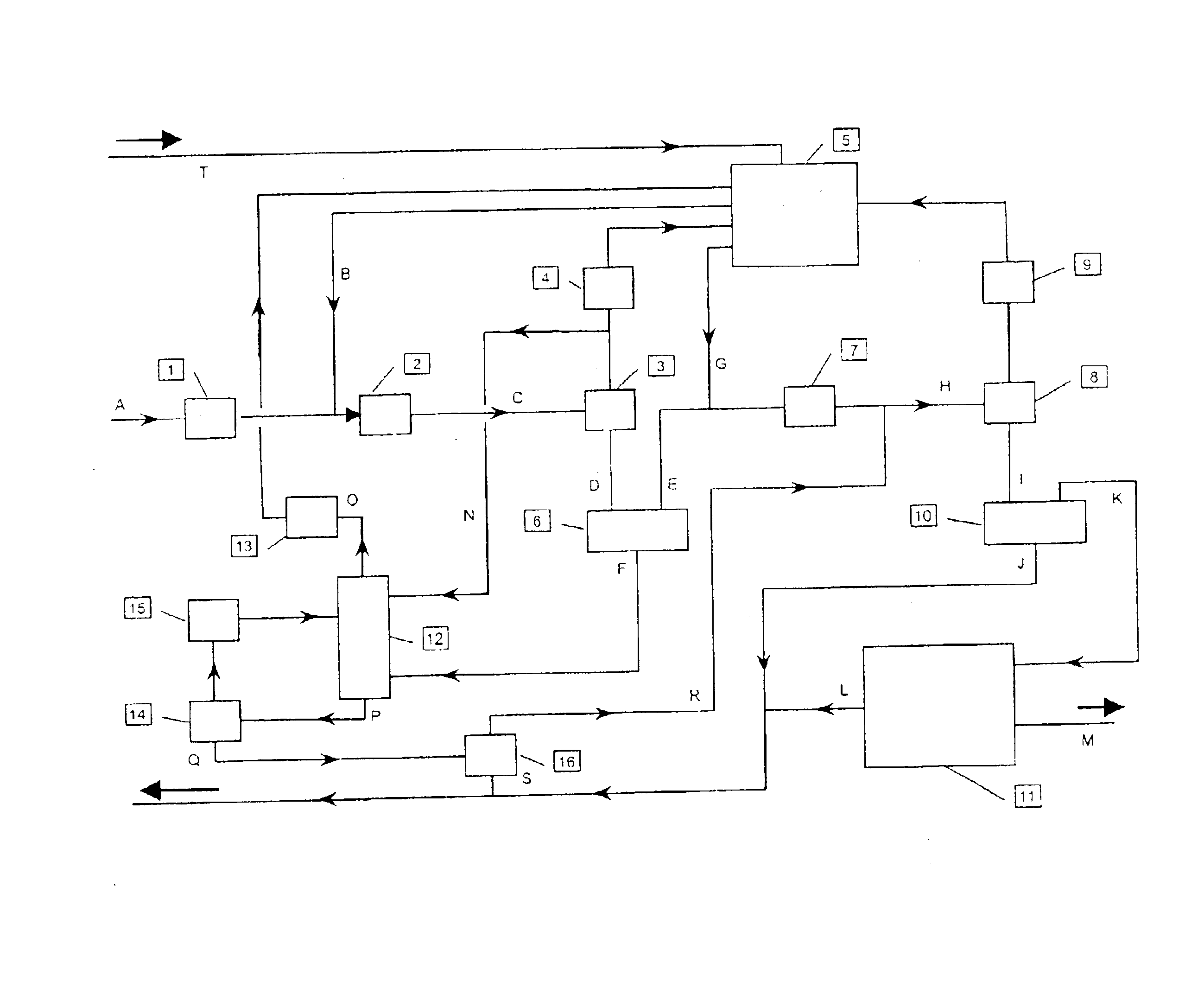
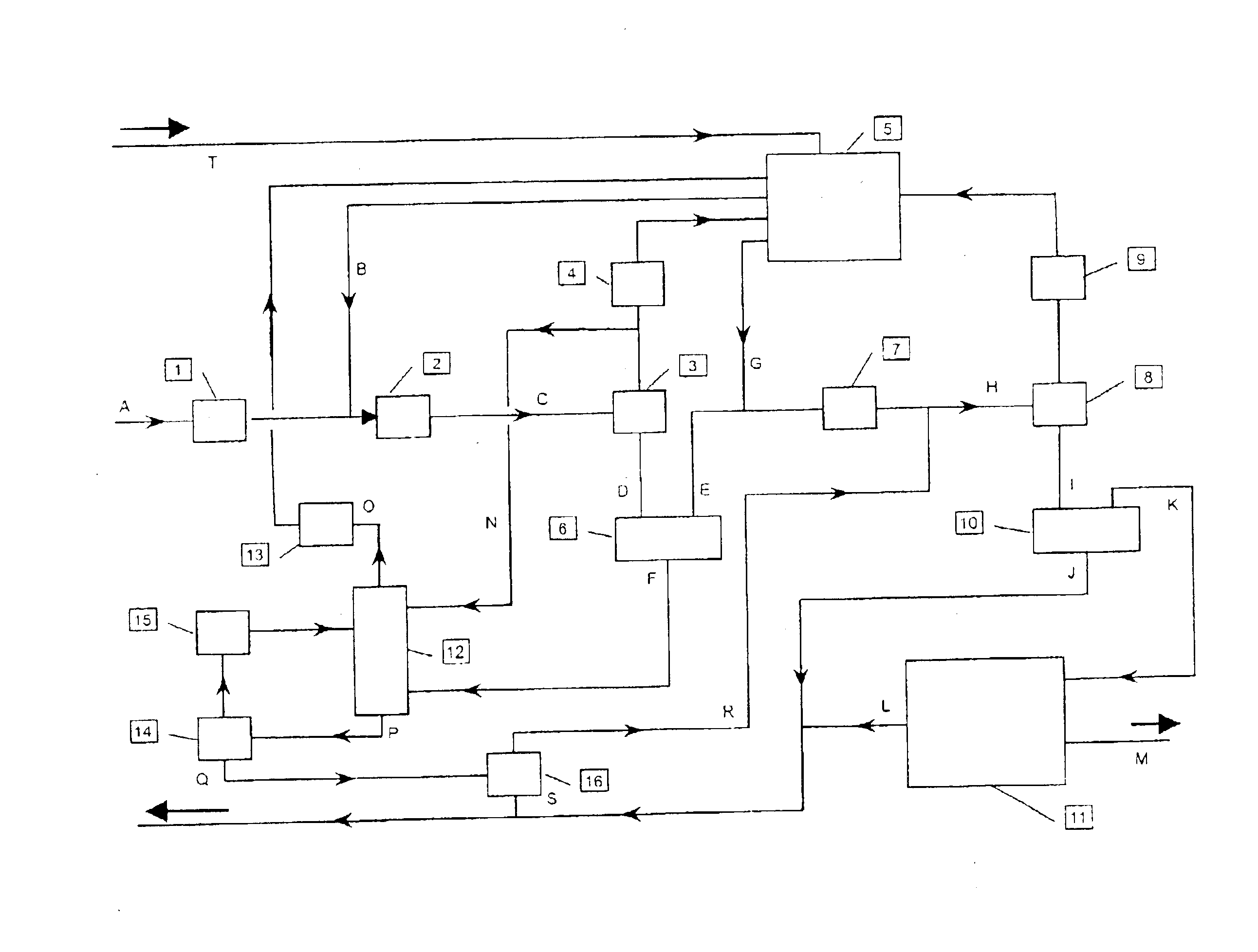
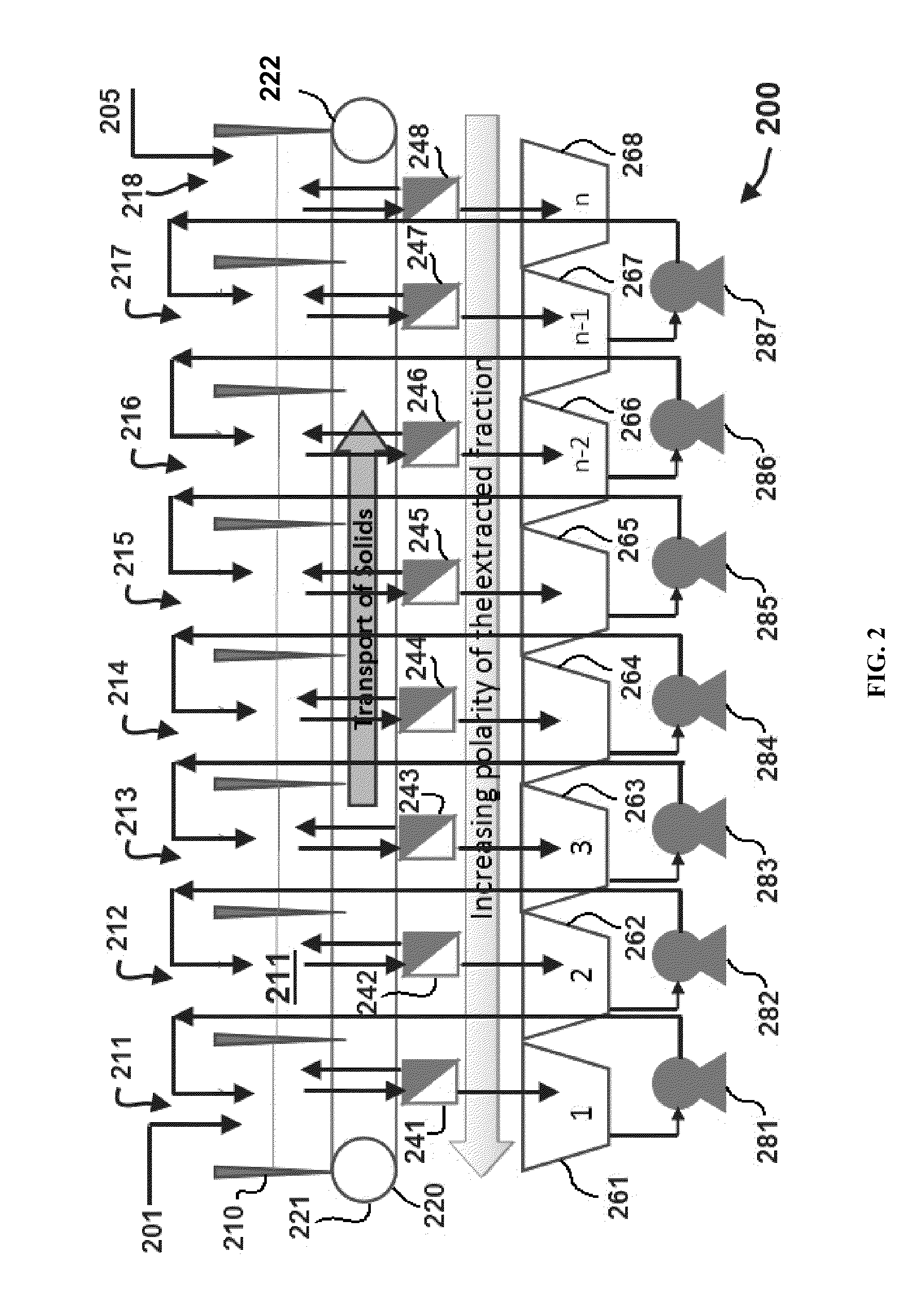
Methods and compositions for extraction and transesterification of biomass components
InactiveUS20090234146A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationBiofuel
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the direct transesterification and extraction of bio-lipids and bio-oils in the production of biofuel, particularly fatty acid methyl ester products.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Methods for producing biodiesel
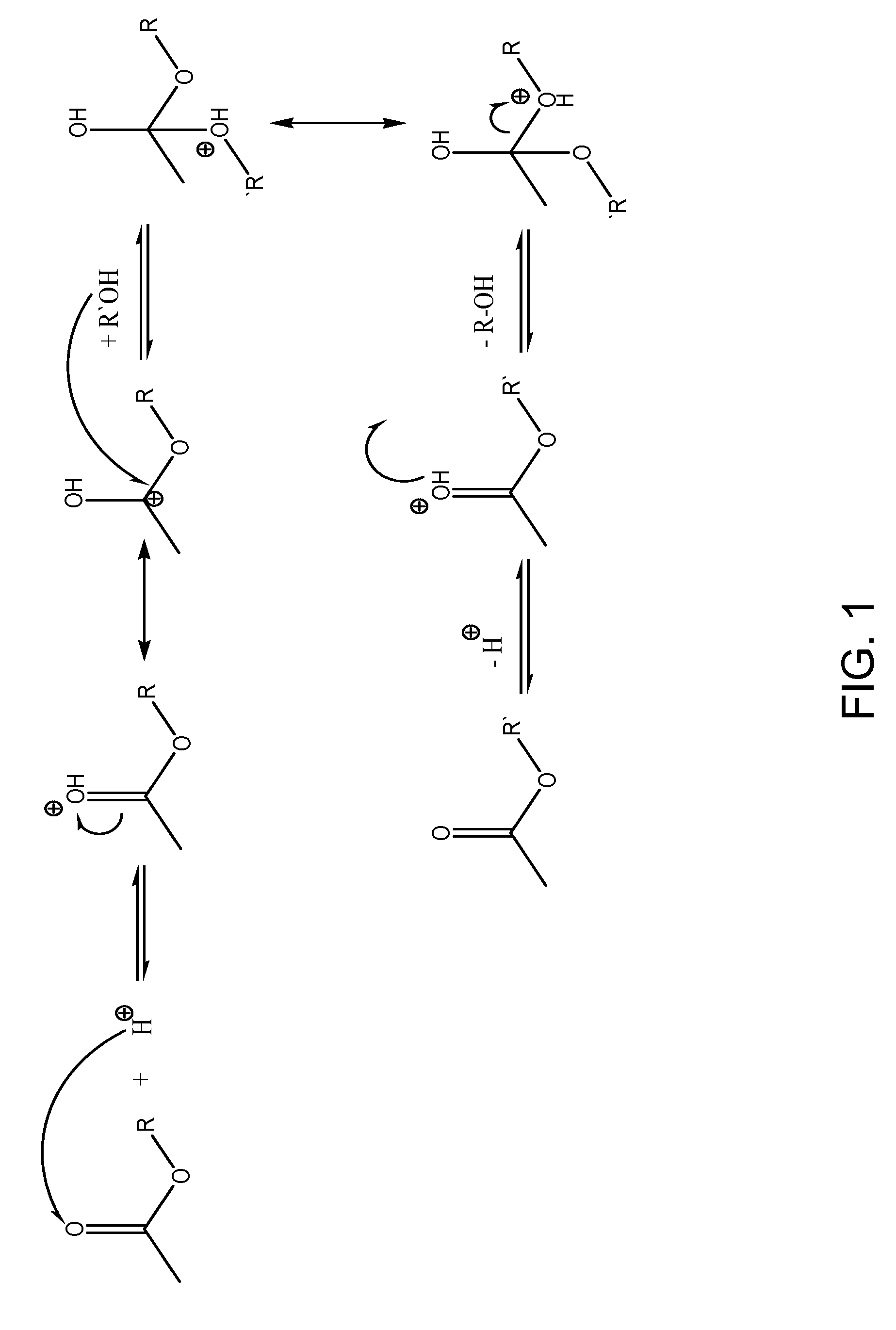
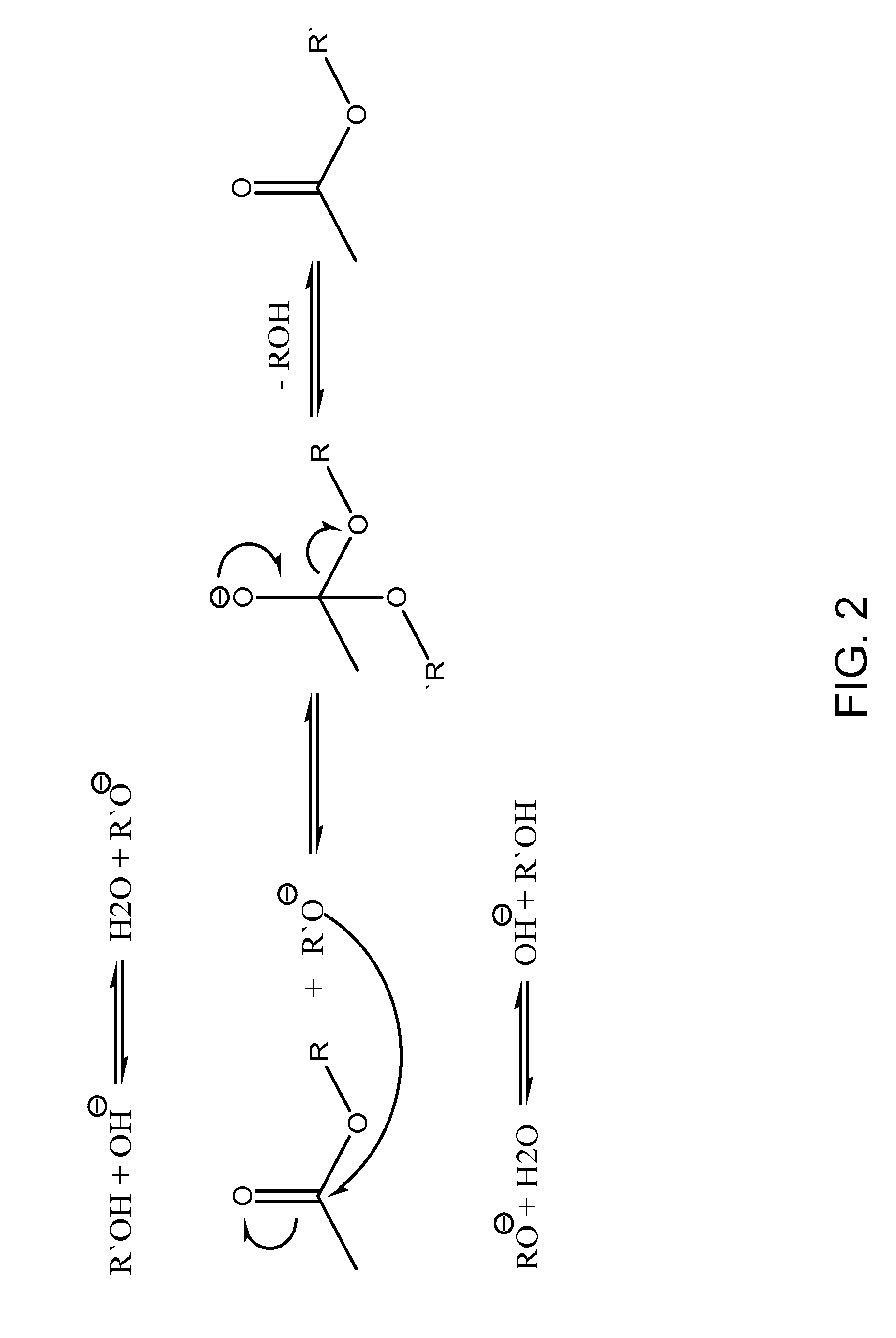
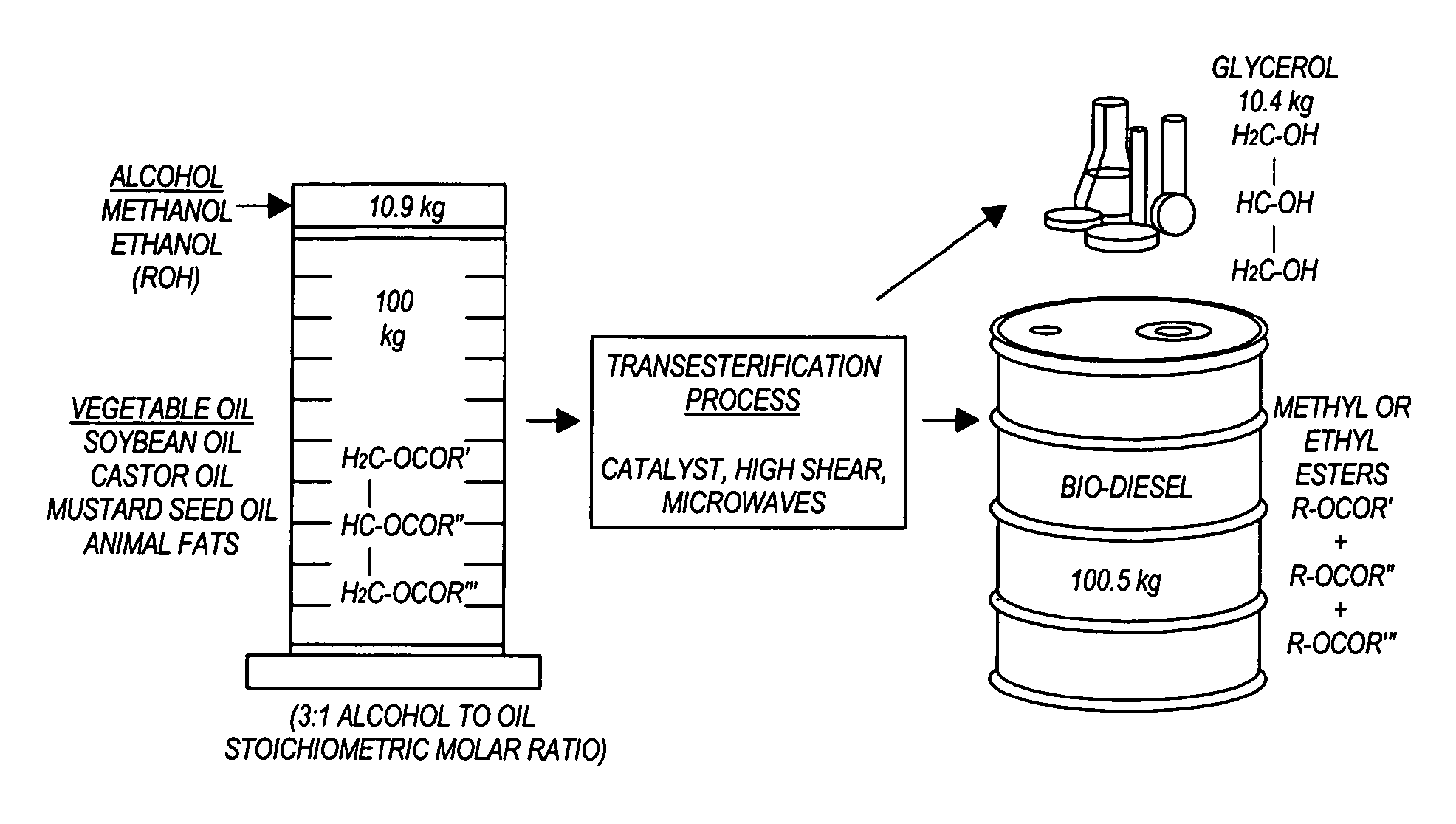
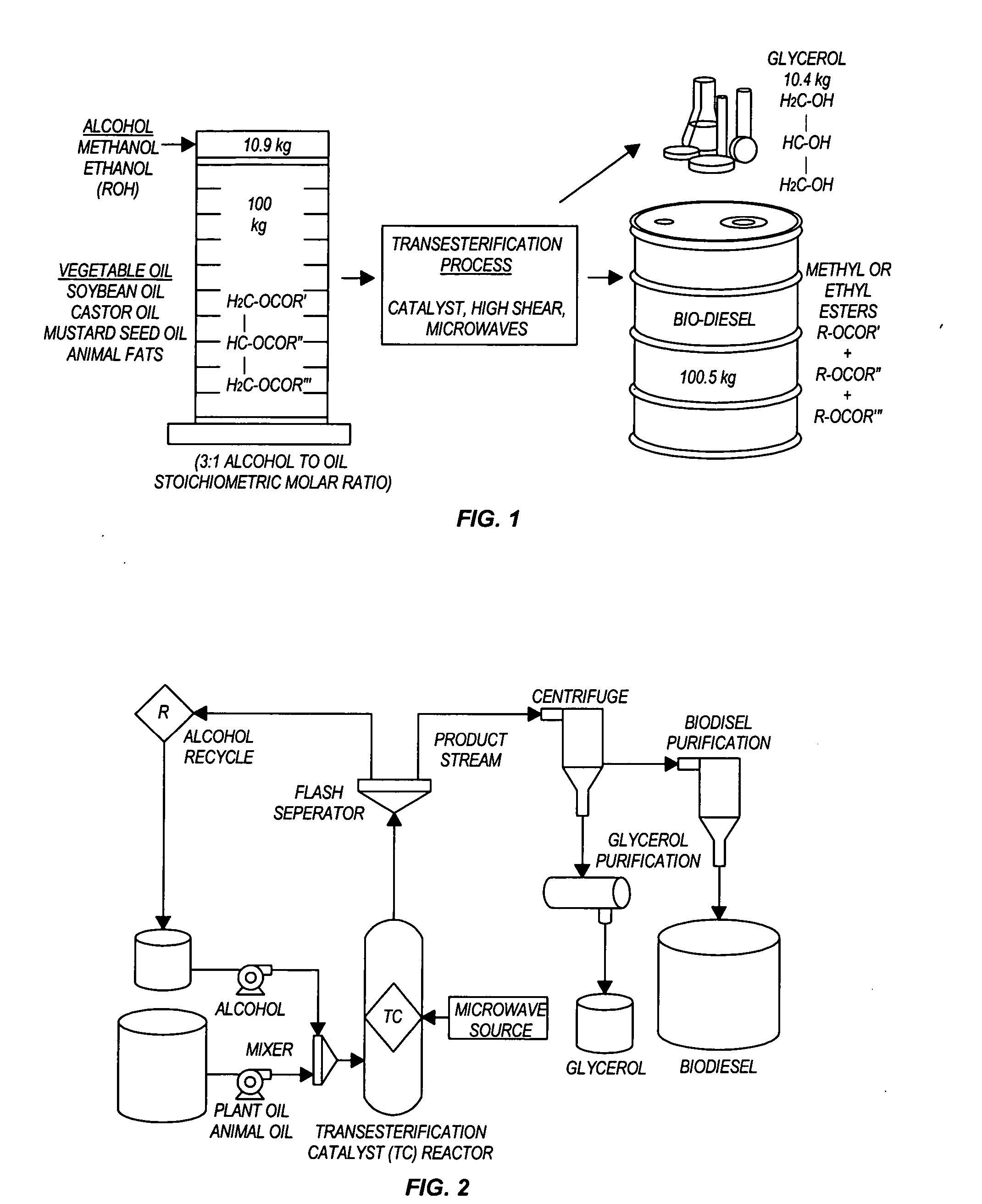
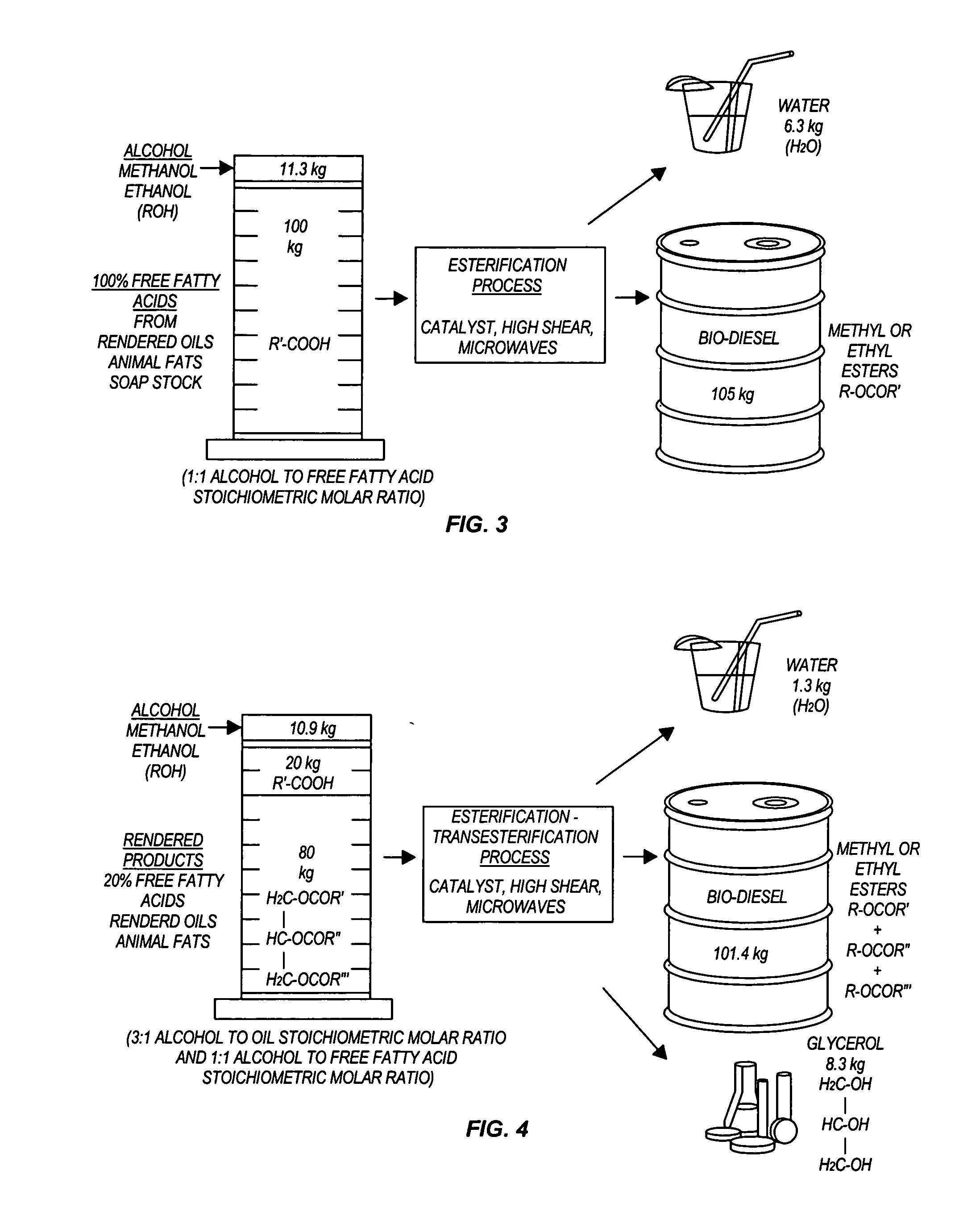
InactiveUS20050274065A1Fatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMicrowaveTransesterification
Transesterification, esterification, and esterification-transesterification (both one-step and two-step) for producing biofuels. The process may be enhanced by one or more of the following: 1) applying microwave or RF energy; 2) passing reactants over a heterogeneous catalyst at sufficiently high velocity to achieve high shear conditions; 3) emulsifying reactants with a homogeneous catalyst; or 4) maintaining the reaction at a pressure at or above autogeneous pressure. Enhanced processes using one or more of these steps can result in higher process rates, higher conversion levels, or both.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
System and process for producing biodiesel
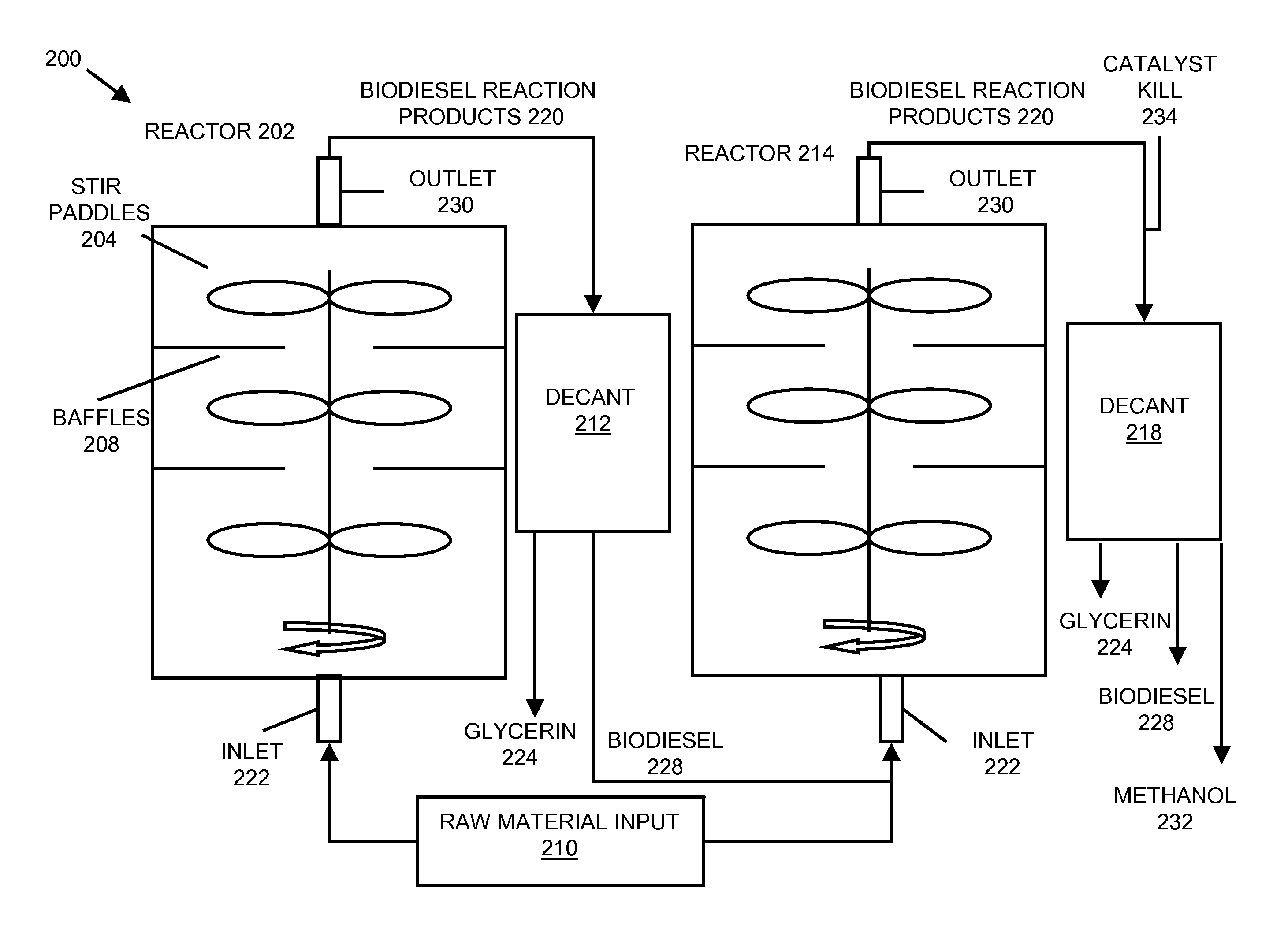
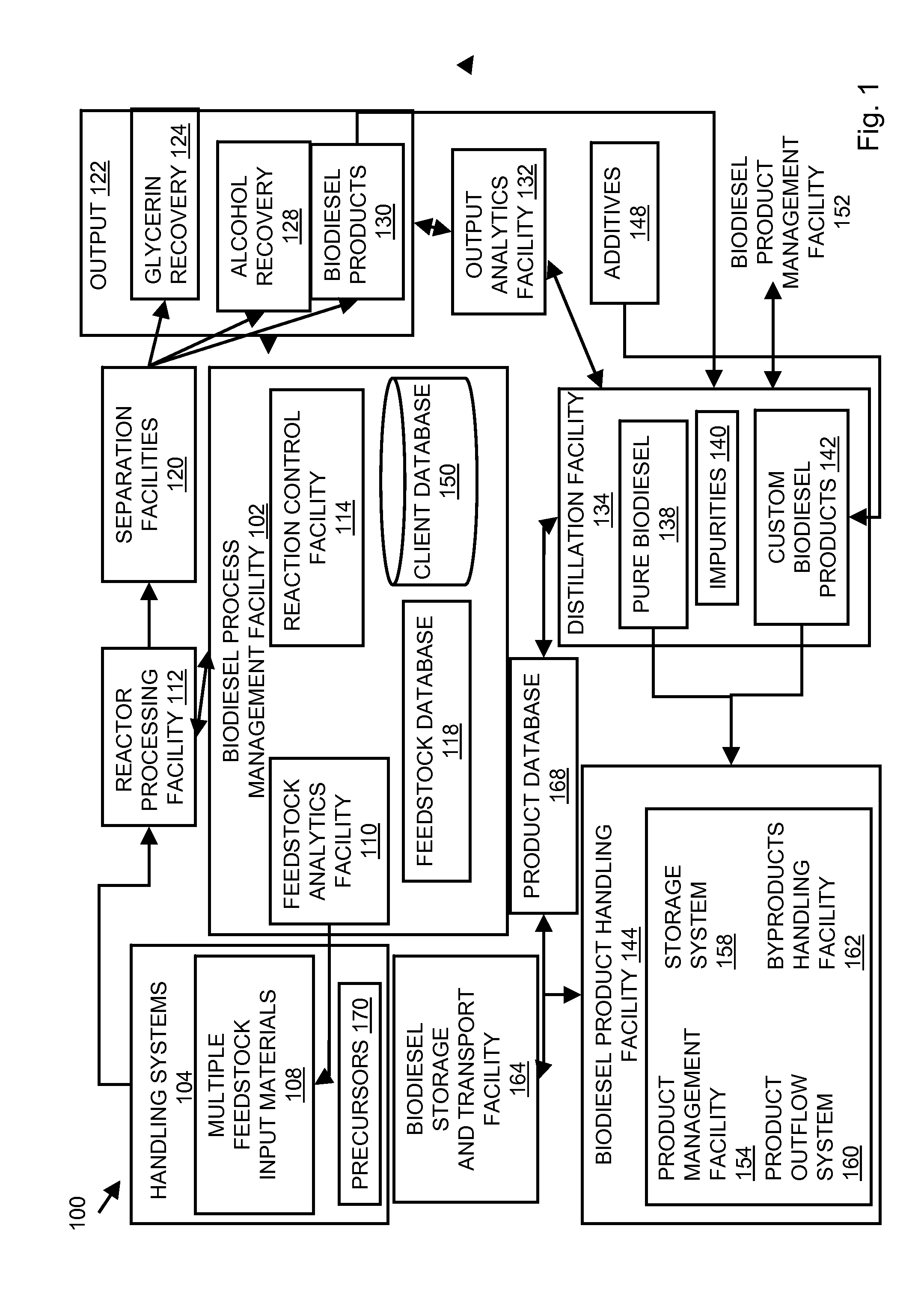
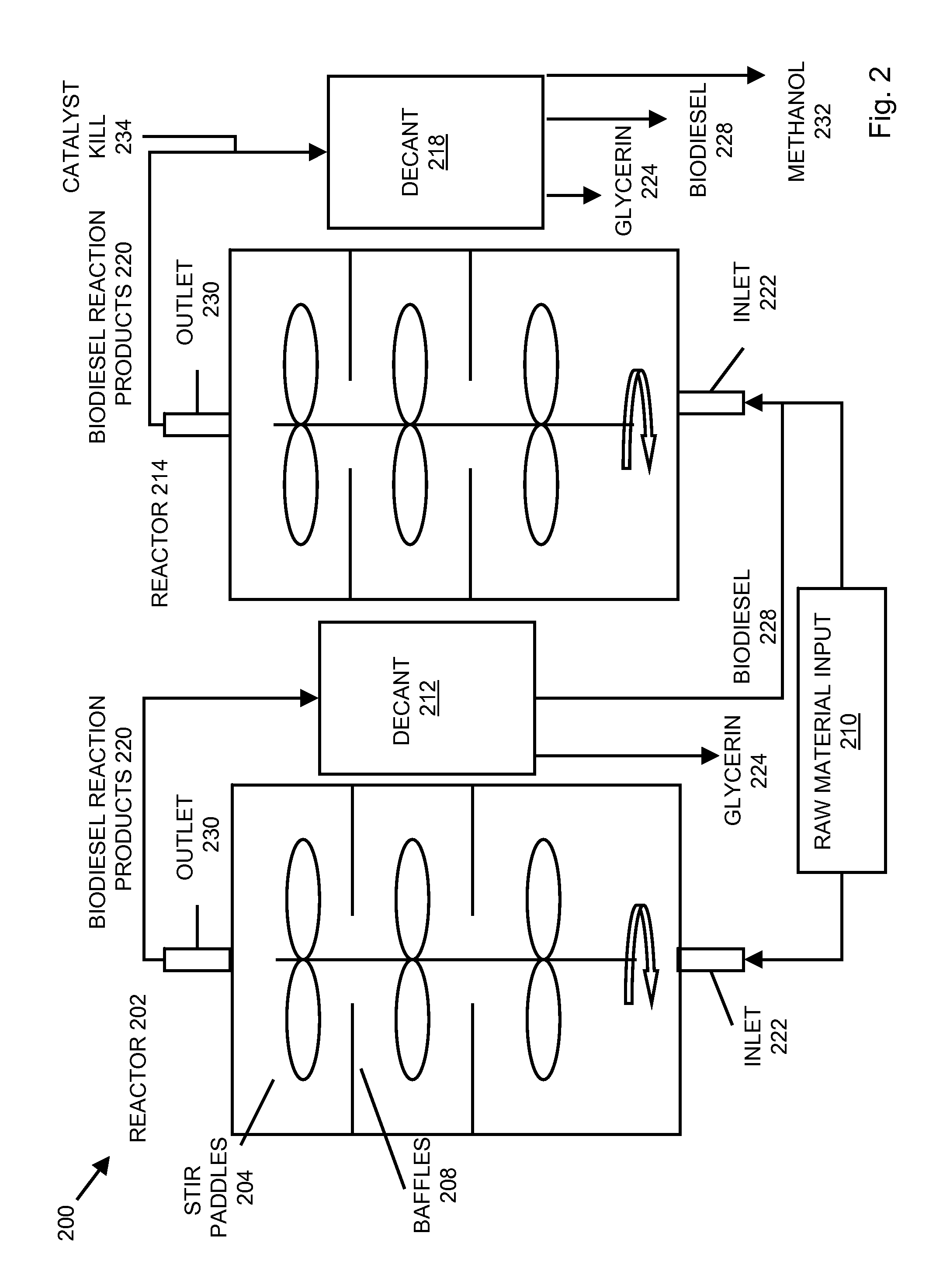
InactiveUS20080282606A1Reducing filter blocking tendencyEnhance biodiesel stabilityFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningBiodieselDistillation
In embodiments of the present invention, systems for producing a biodiesel product from multiple feedstocks may include a biodiesel reactor, a decanter, a flash evaporator and a distillation column. In other embodiments of the present invention, a process for producing a biodiesel comprises distilling a biodiesel reaction product to remove tocopherols and sterol glucosides and, optionally, adding biodiesel stabilizers to the resultant biodiesel to enhance thermal stability. The components of the system are interrelated so that parameters may be regulated to allow production of a custom biodiesel product.
Owner:IMPERIUM PROCESS TECH
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component
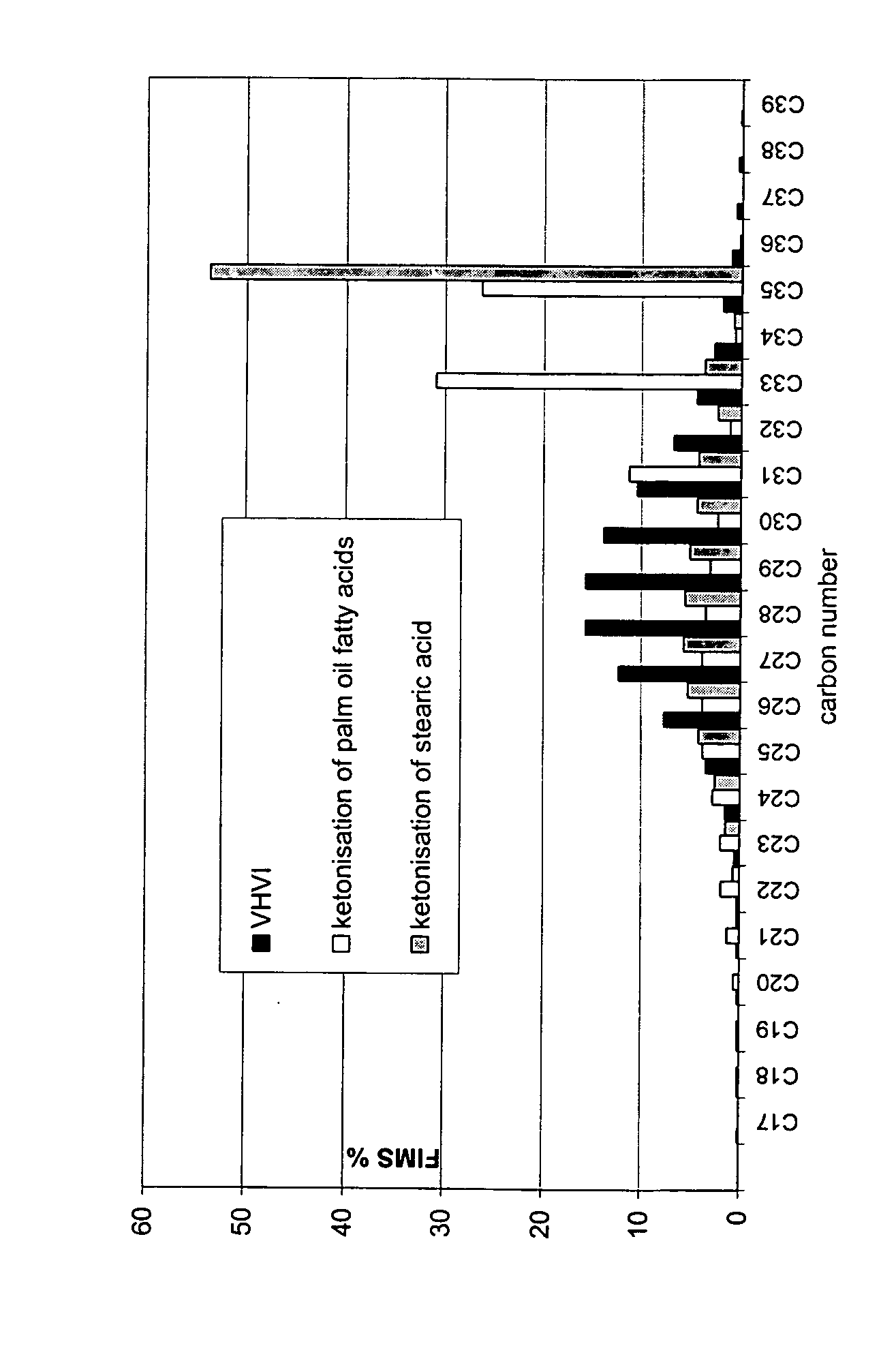
ActiveUS20070161832A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove low temperature performanceFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid hydrogenationIsomerizationHydrodeoxygenation
The invention relates to a process for producing a new type of high-quality hydrocarbon base oil of biological origin. The process of the invention comprises ketonisation, hydrodeoxygenation, and isomerization steps. Fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters based on a biological raw material are preferably used as the feedstock.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS7816570B2Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Method for Obtaining Biodiesel, Alternative Fuels and Renewable Fuels Tax Credits and Treatment
InactiveUS20090076913A1Improve responseReduce sulfur contentFatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationAlternative fuelsTax credit
Owner:ENDICOTT BIOFUELS II
Production of Ester-based Fuels Such As Biodiesel From Renewable Starting Materials
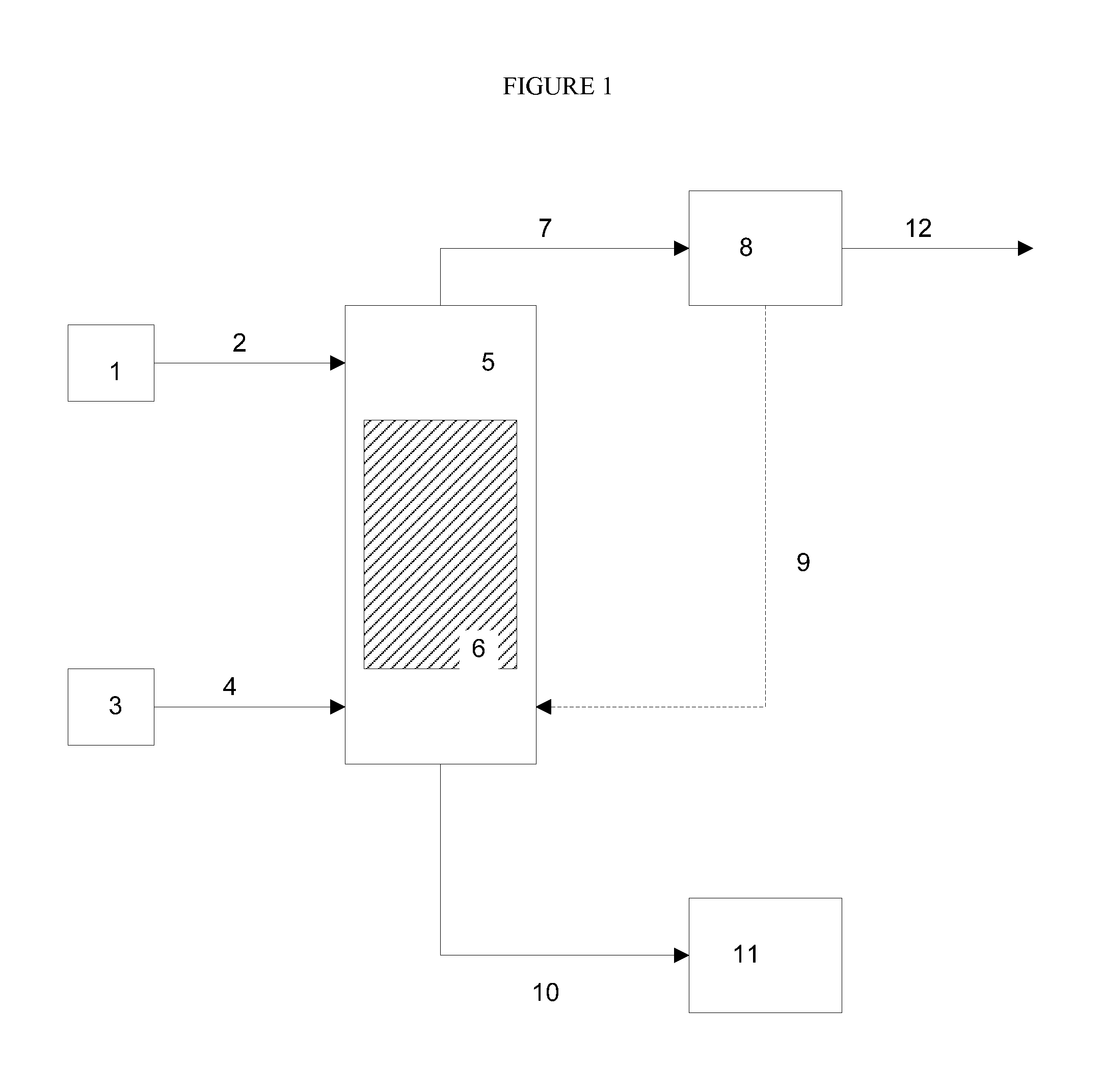
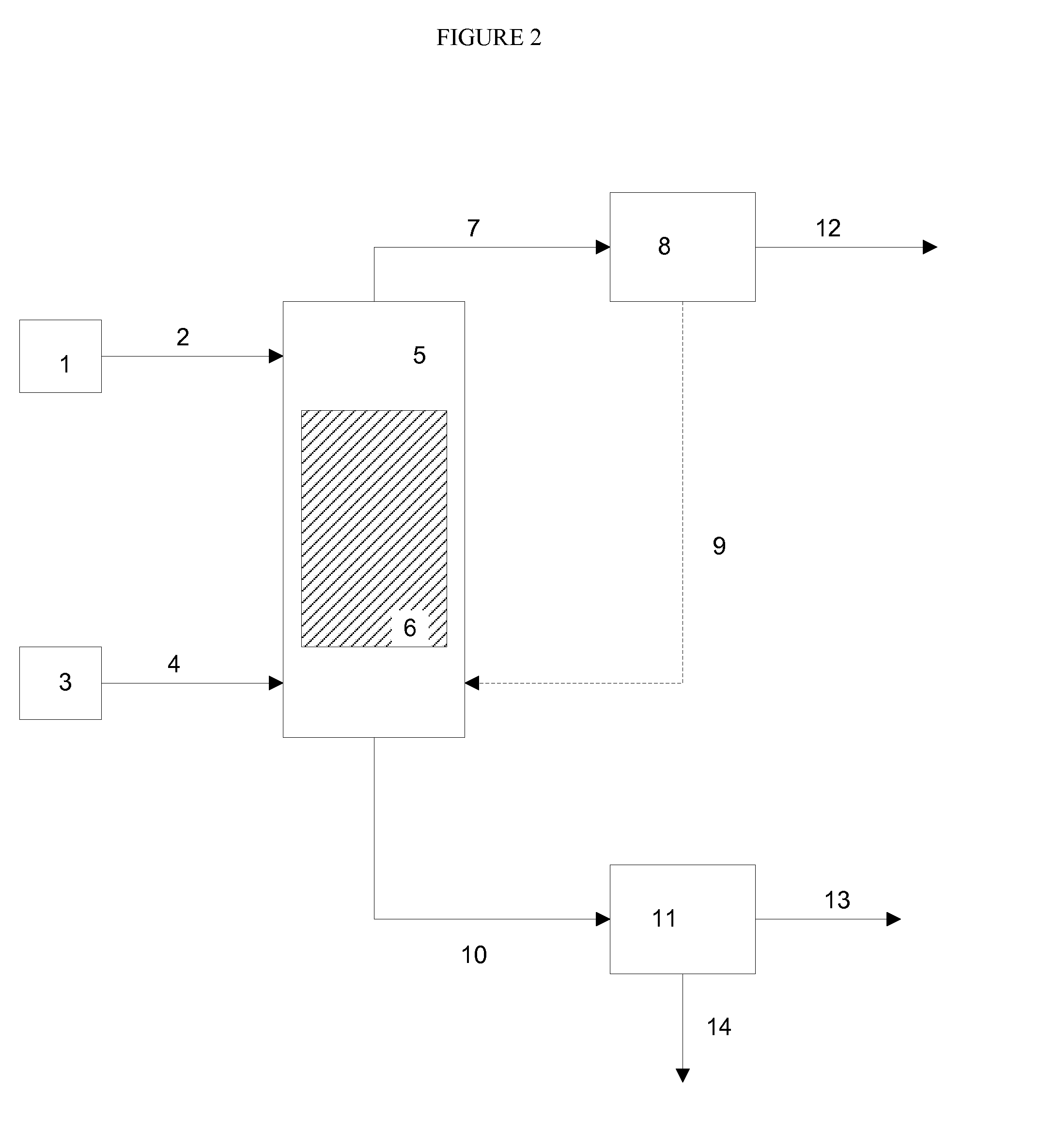
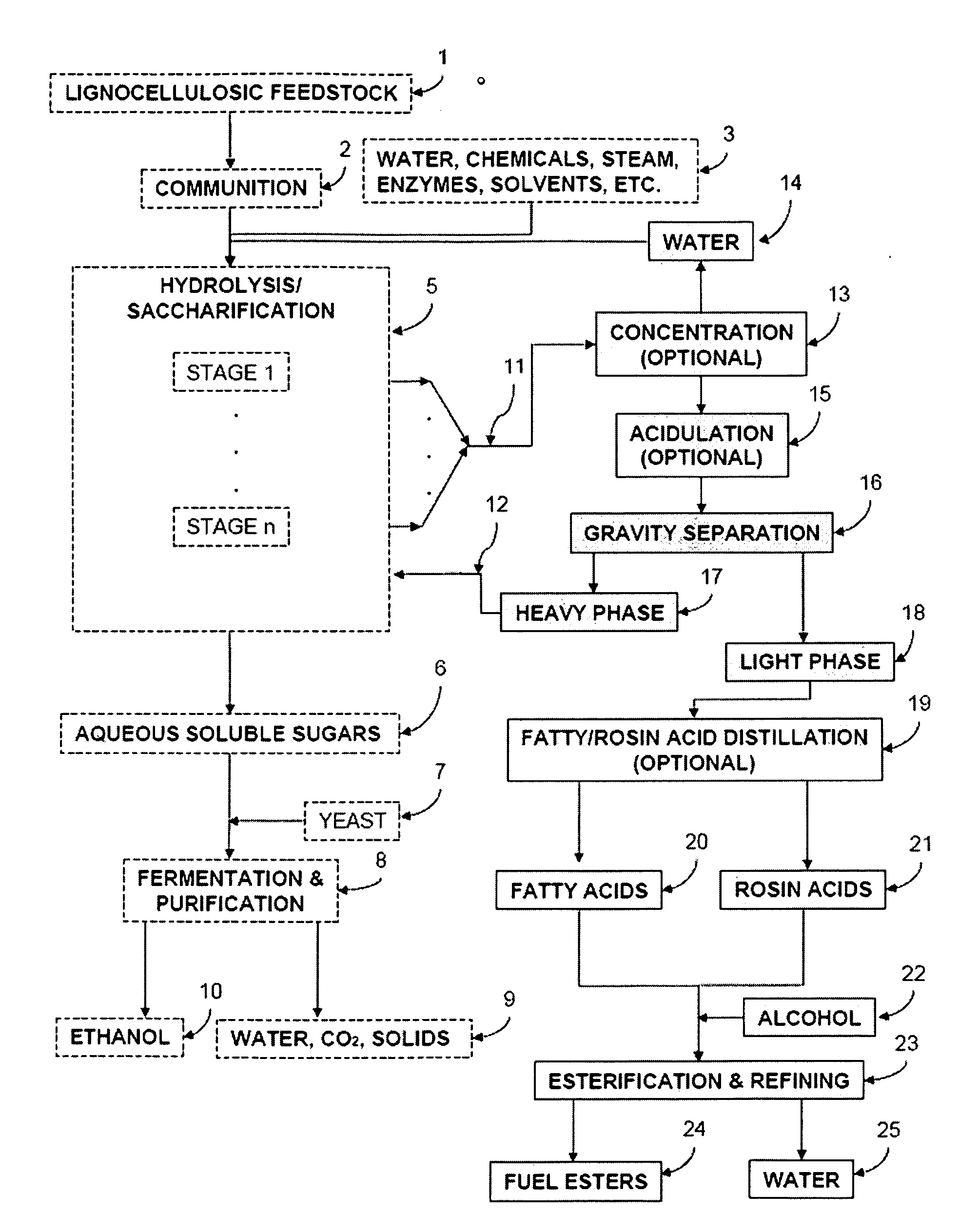
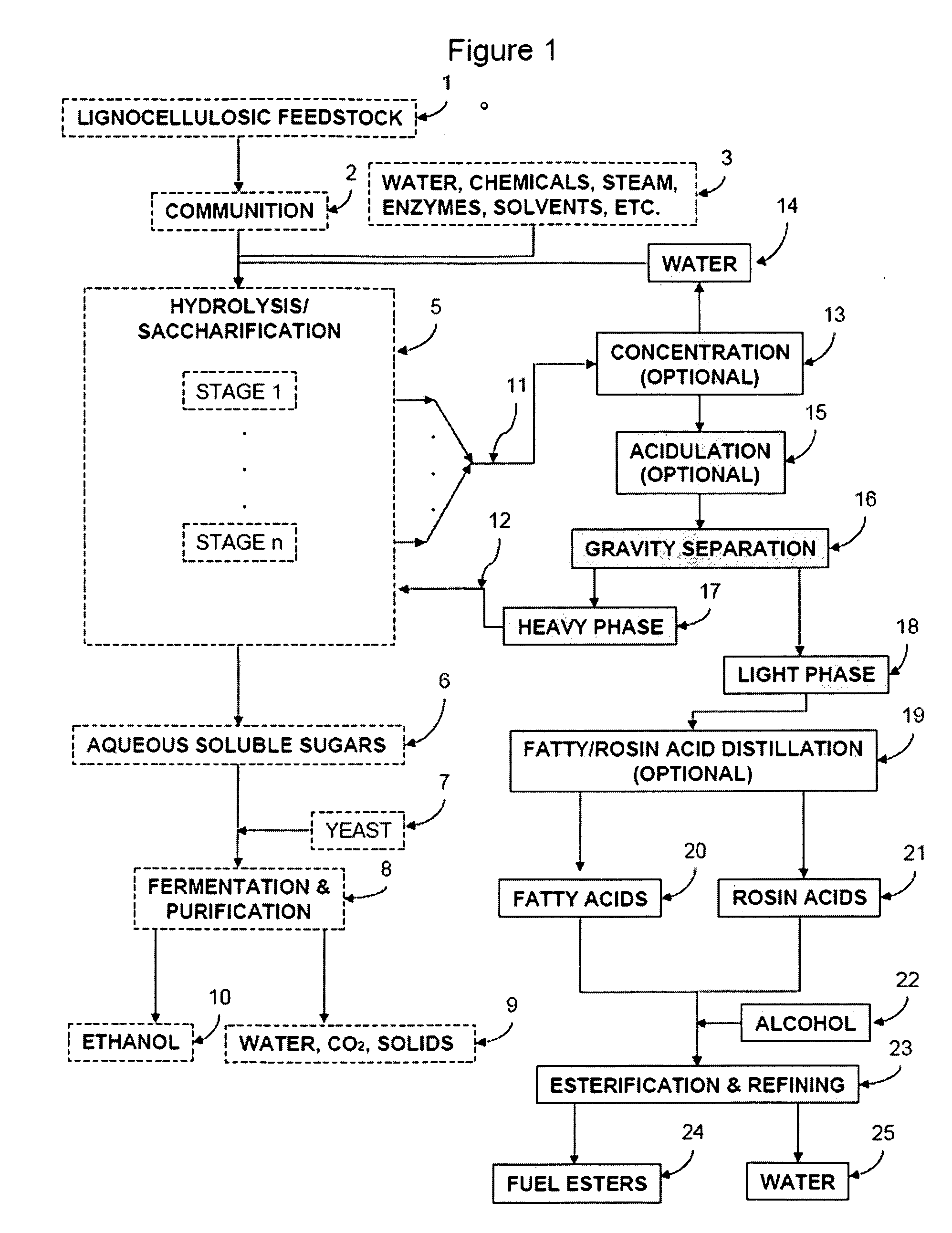
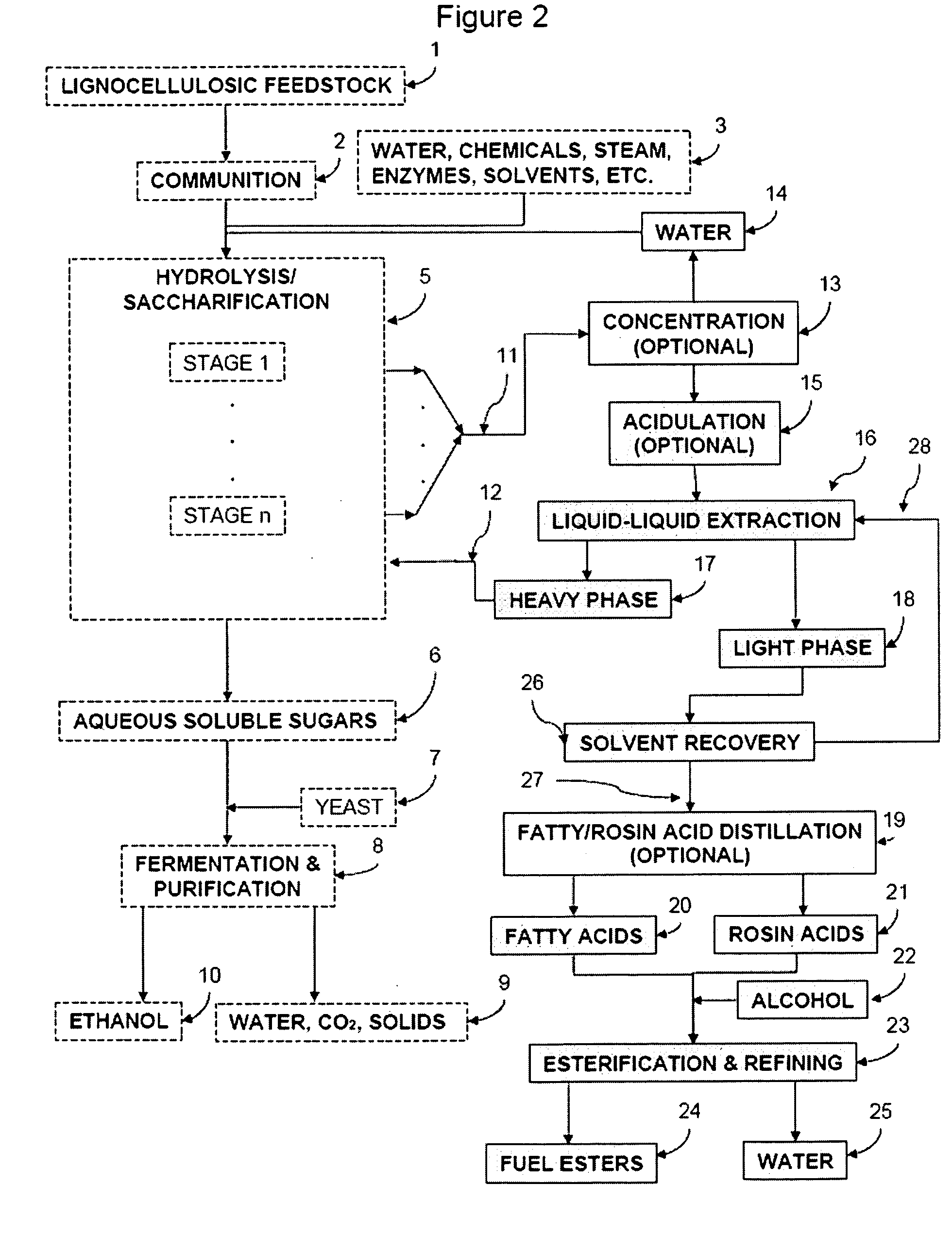
ActiveUS20090056201A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationCelluloseBiodiesel
Production of ester-based fuels such as biodiesel or jet fuel from renewable starting materials such as lignocellulosic material or algae is disclosed. Pulping and saccharification of the renewable starting materials produces carboxylic acids such as fatty acids or rosin acids, which are esterified via a gas sparged, slurry form of heterogeneous reactive distillation to yield ester-based fuels.
Owner:ENDICOTT BIOFUELS II
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
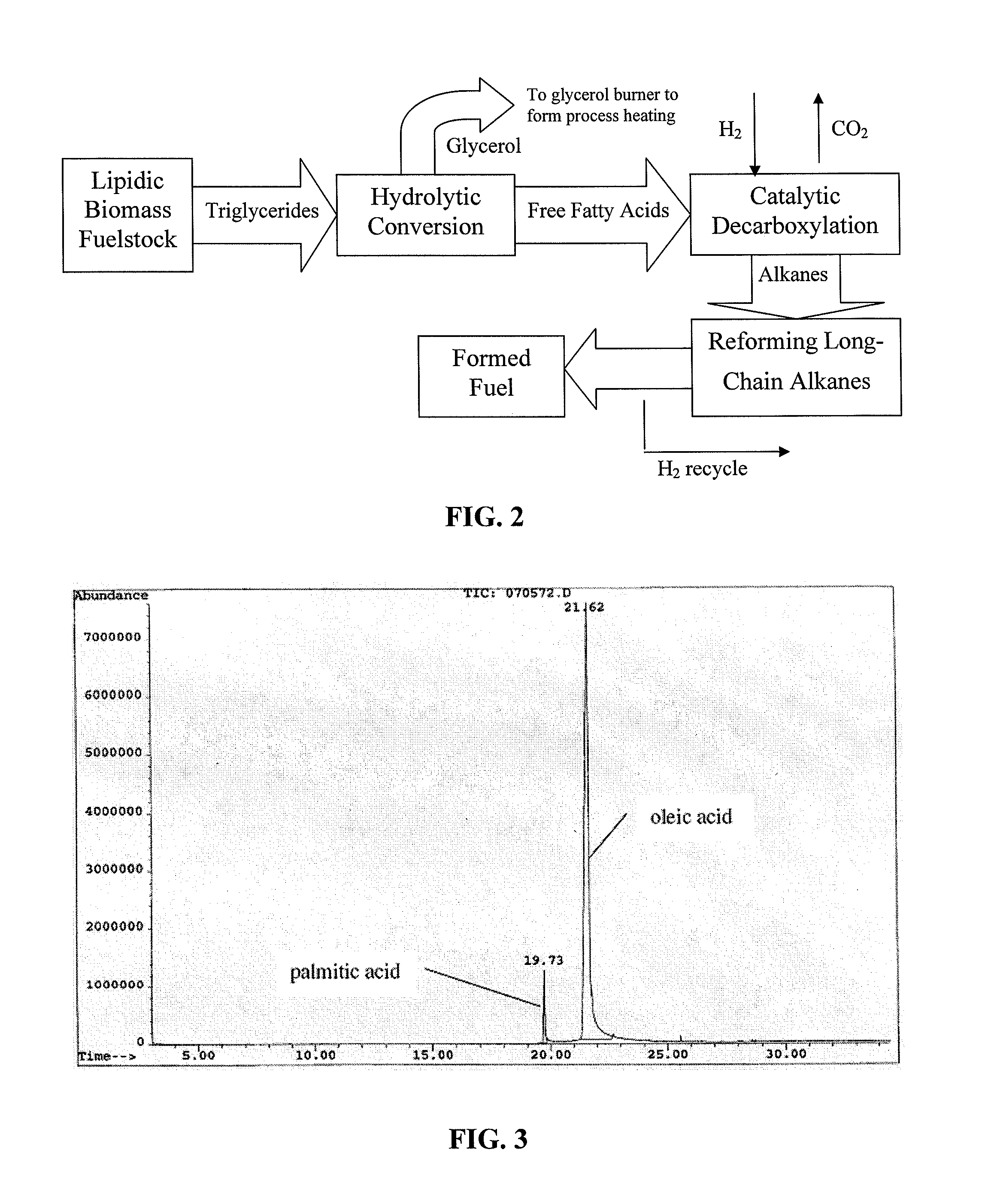
ActiveUS20090069610A1Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
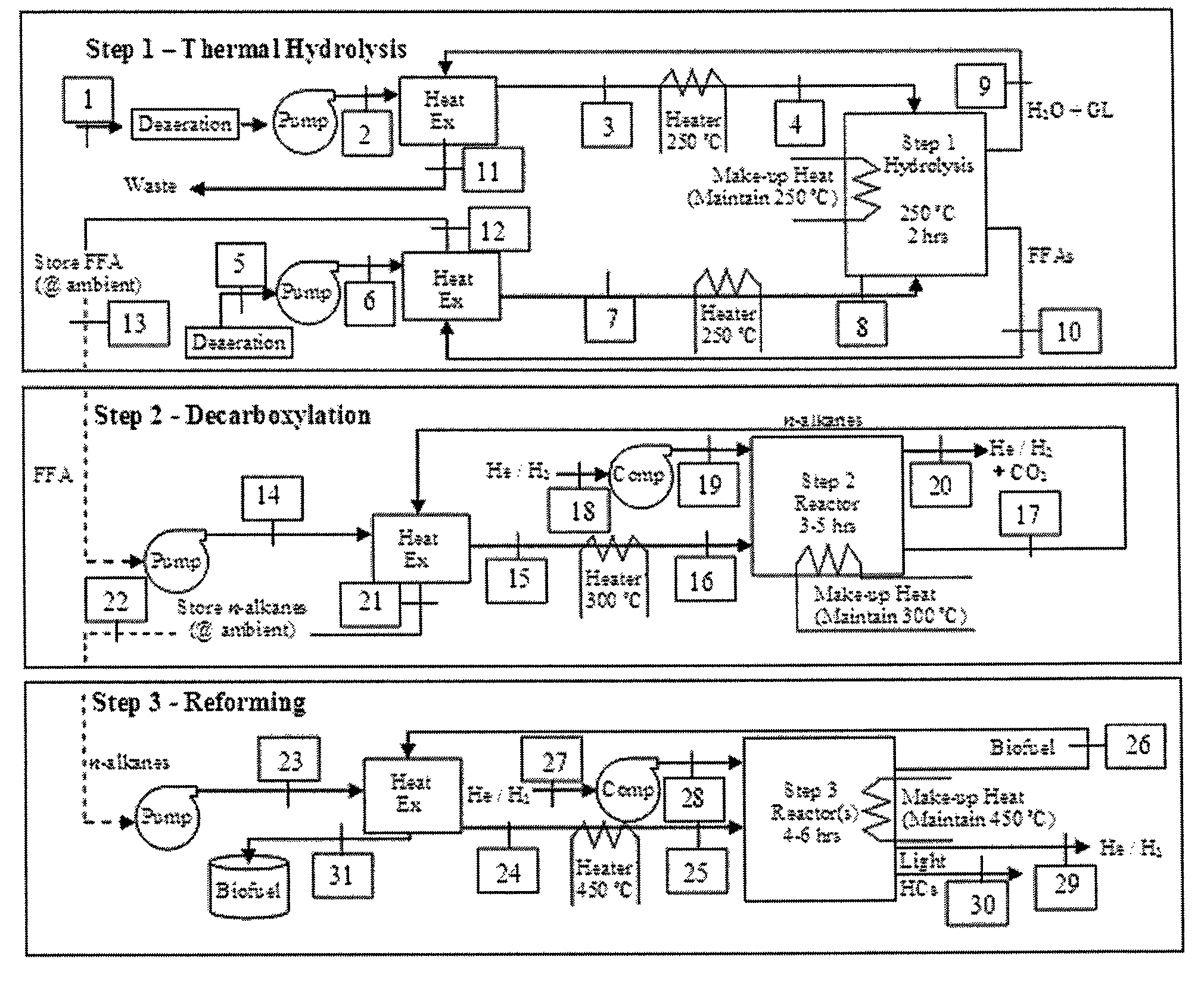
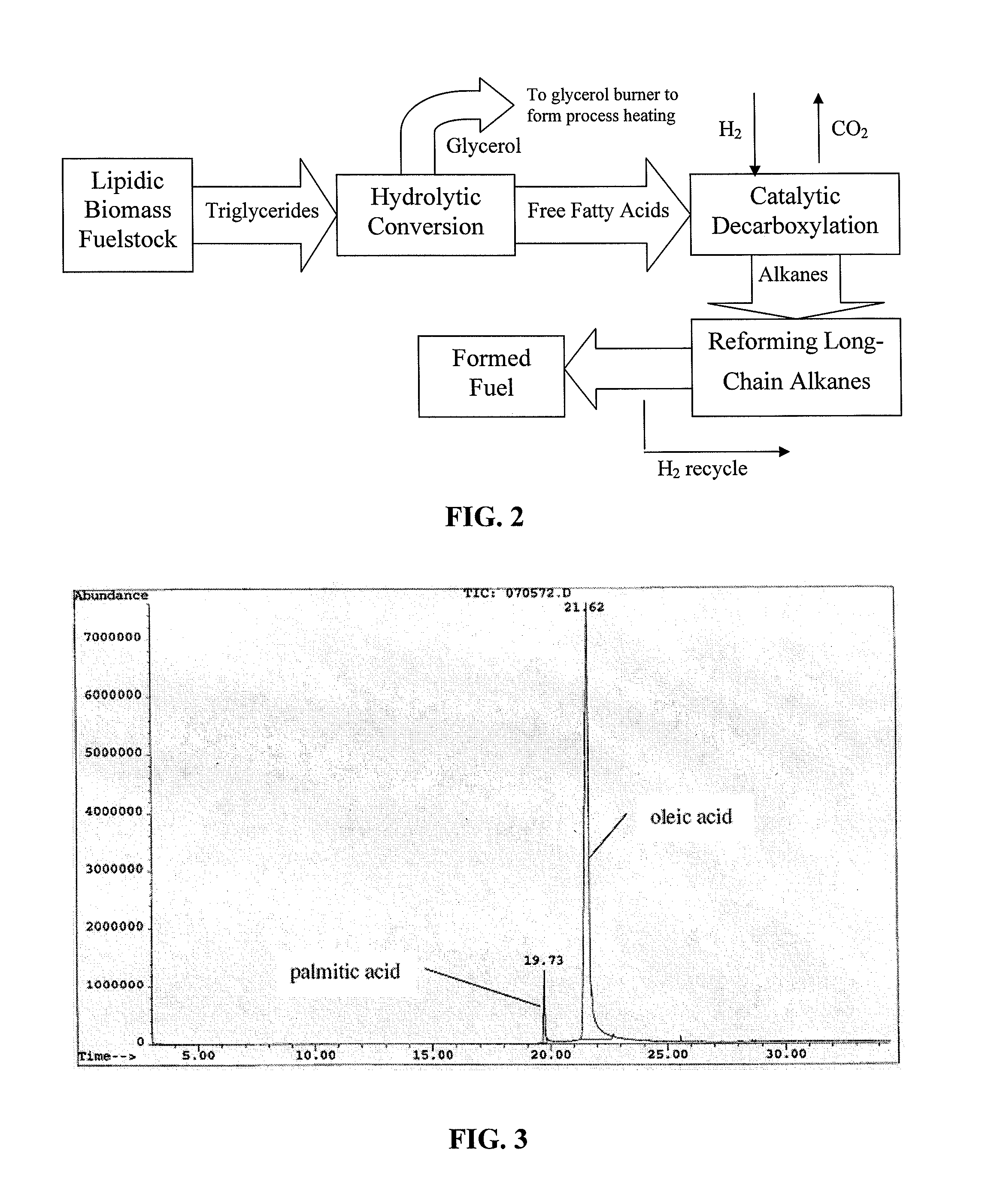
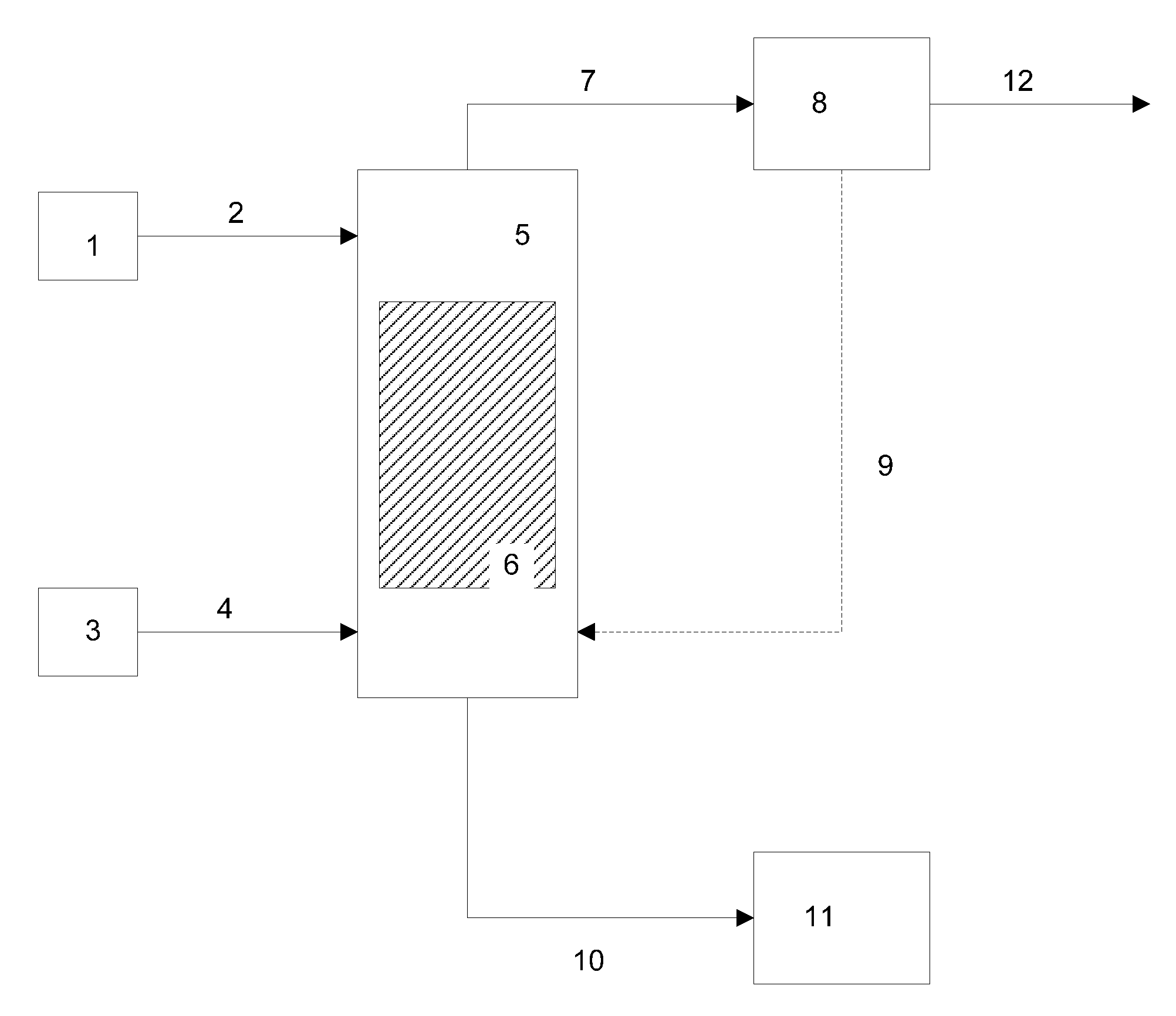
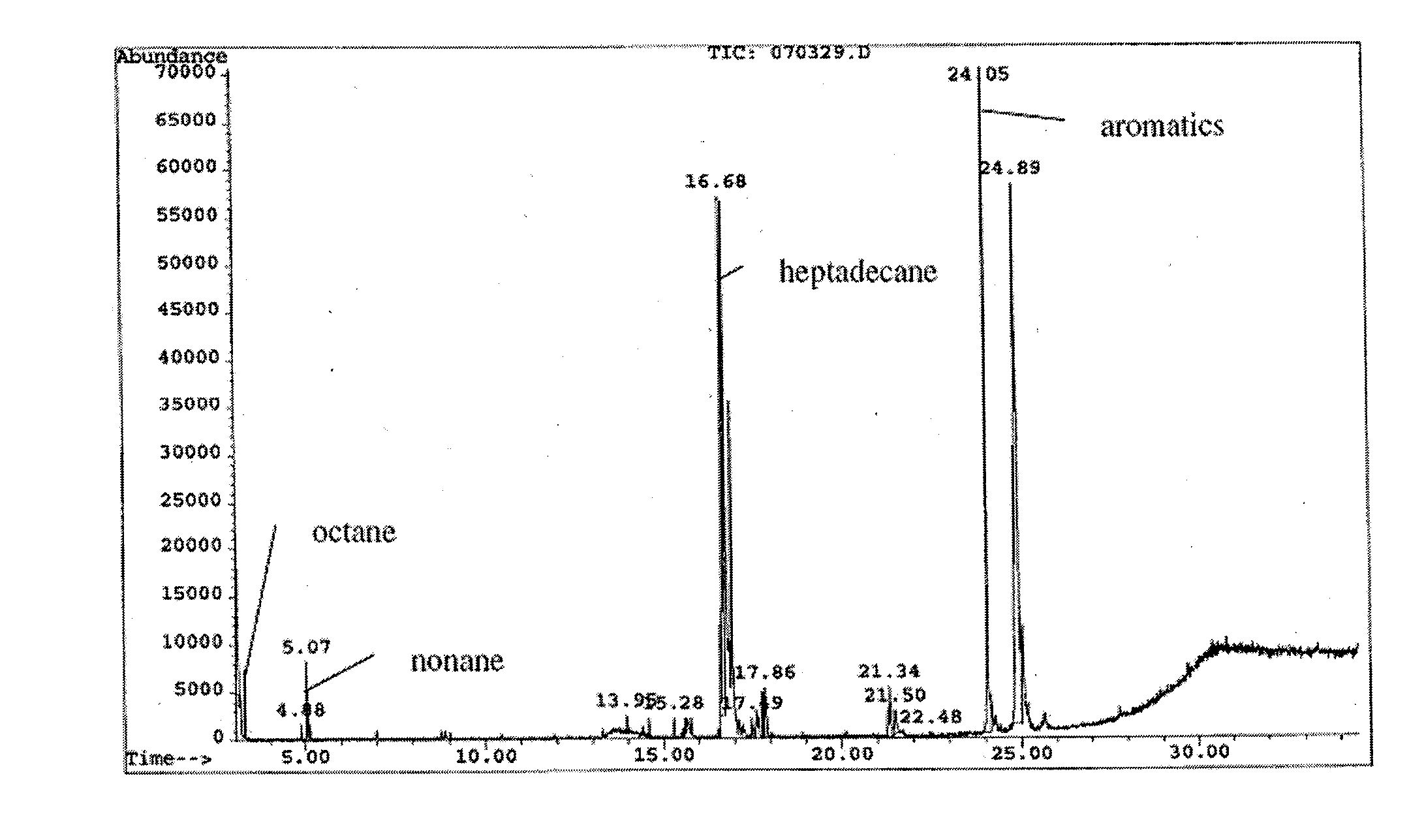
The present invention is directed to processes for the direct conversion of lipidic biomass fuelstock to combustible fuels. In particular, the invention provides a process for the direct conversion of animal fats to transportations fuels suitable as replacement for petroleum-derived transportation fuels. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of hydrolyzing a lipidic biomass to form free fatty acids, catalytically deoxygenating the free fatty acids to form n-alkanes, and reforming at least a portion of the n-alkanes into a mixture of compounds in the correct chain length, conformations, and ratio to be useful transportation fuels. Particularly, the product prepared according to the invention comprises mixtures of hydrocarbon compounds selected from the group consisting of n-alkanes, isoalkanes, aromatics, cycloalkanes, and combinations thereof.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Method for producing biodiesel from an alga
InactiveUS20090298159A1Avoid Microbial ContaminationOrganic chemistryFatty acid esterificationMembrane lipid metabolismOrganism
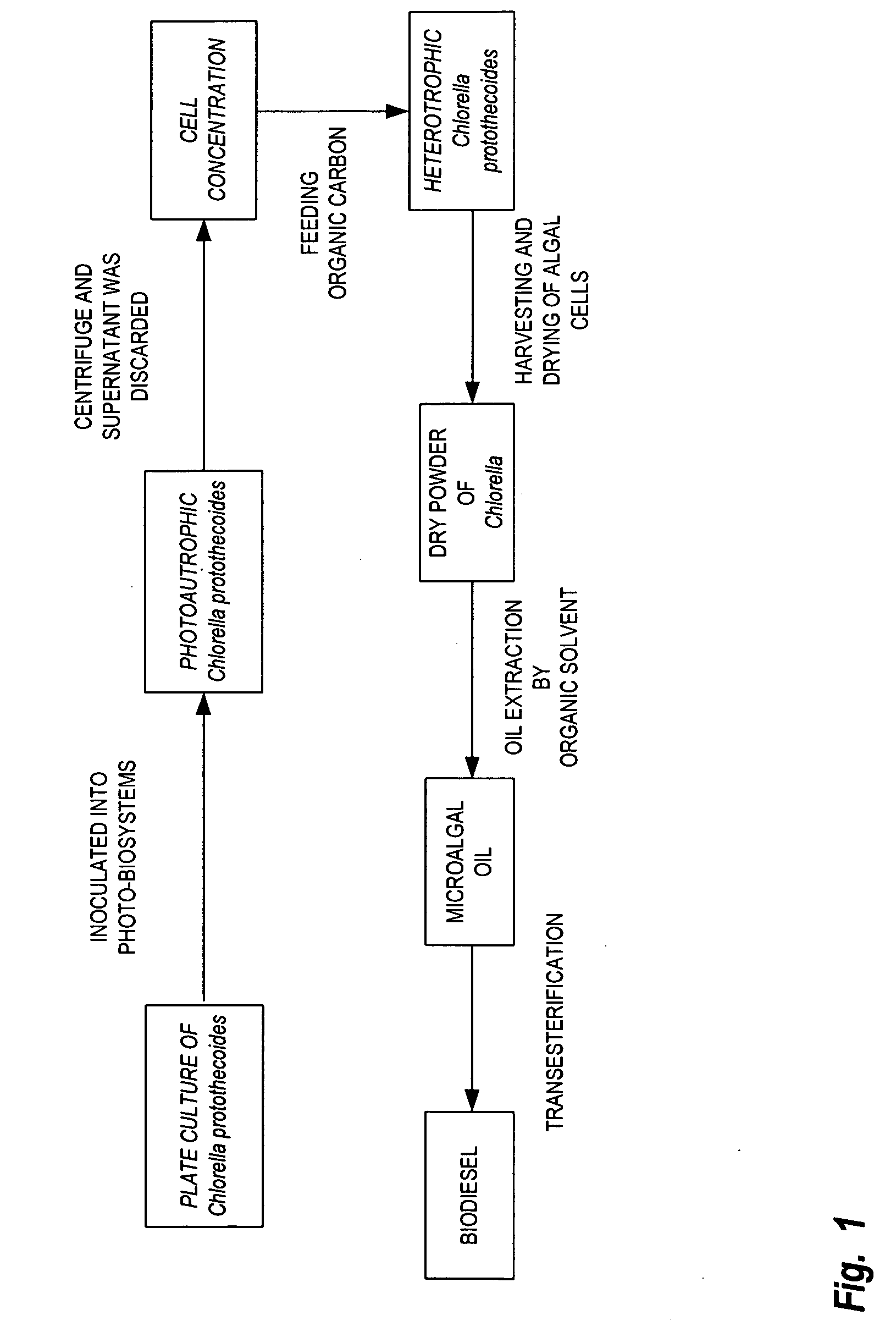
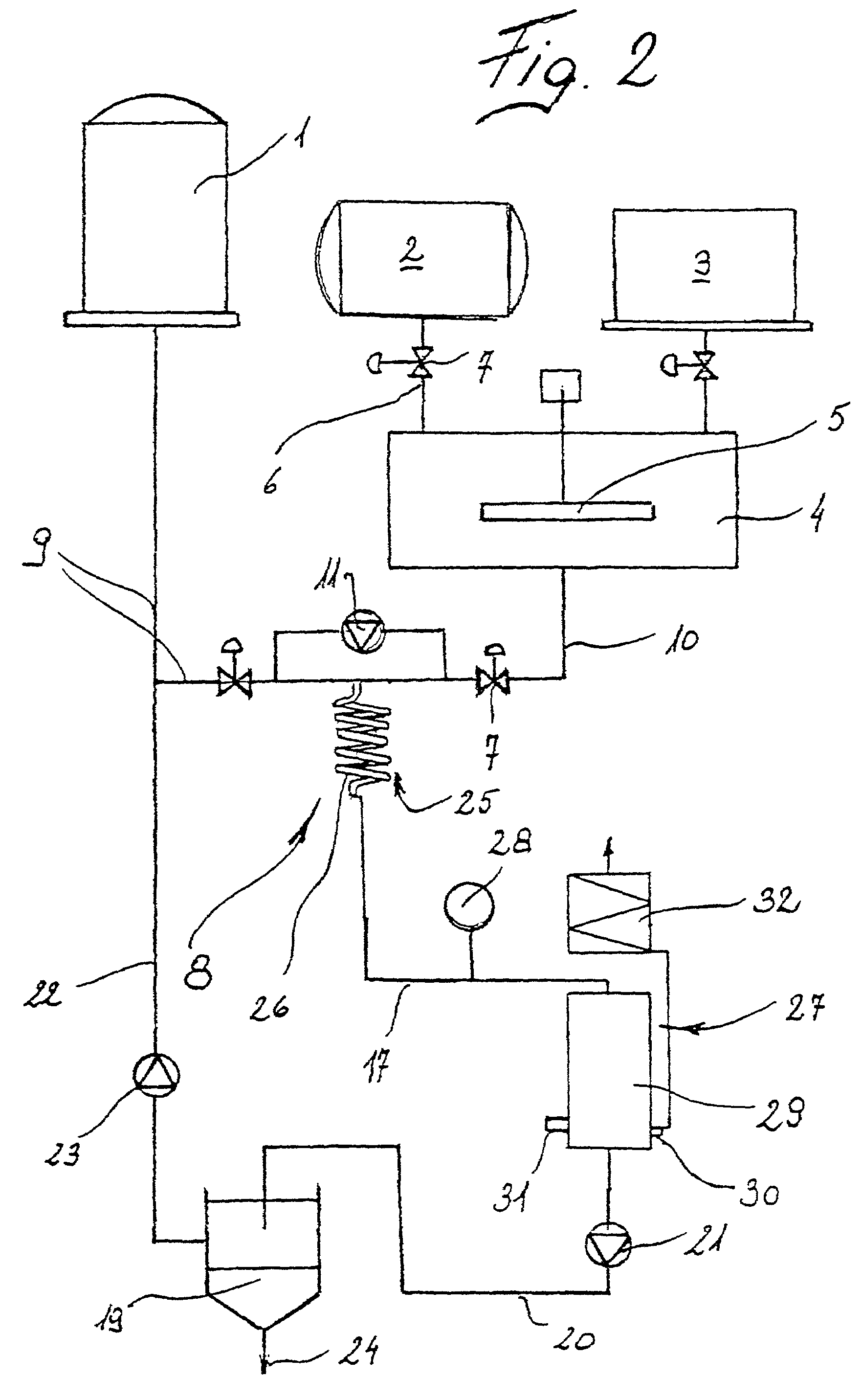
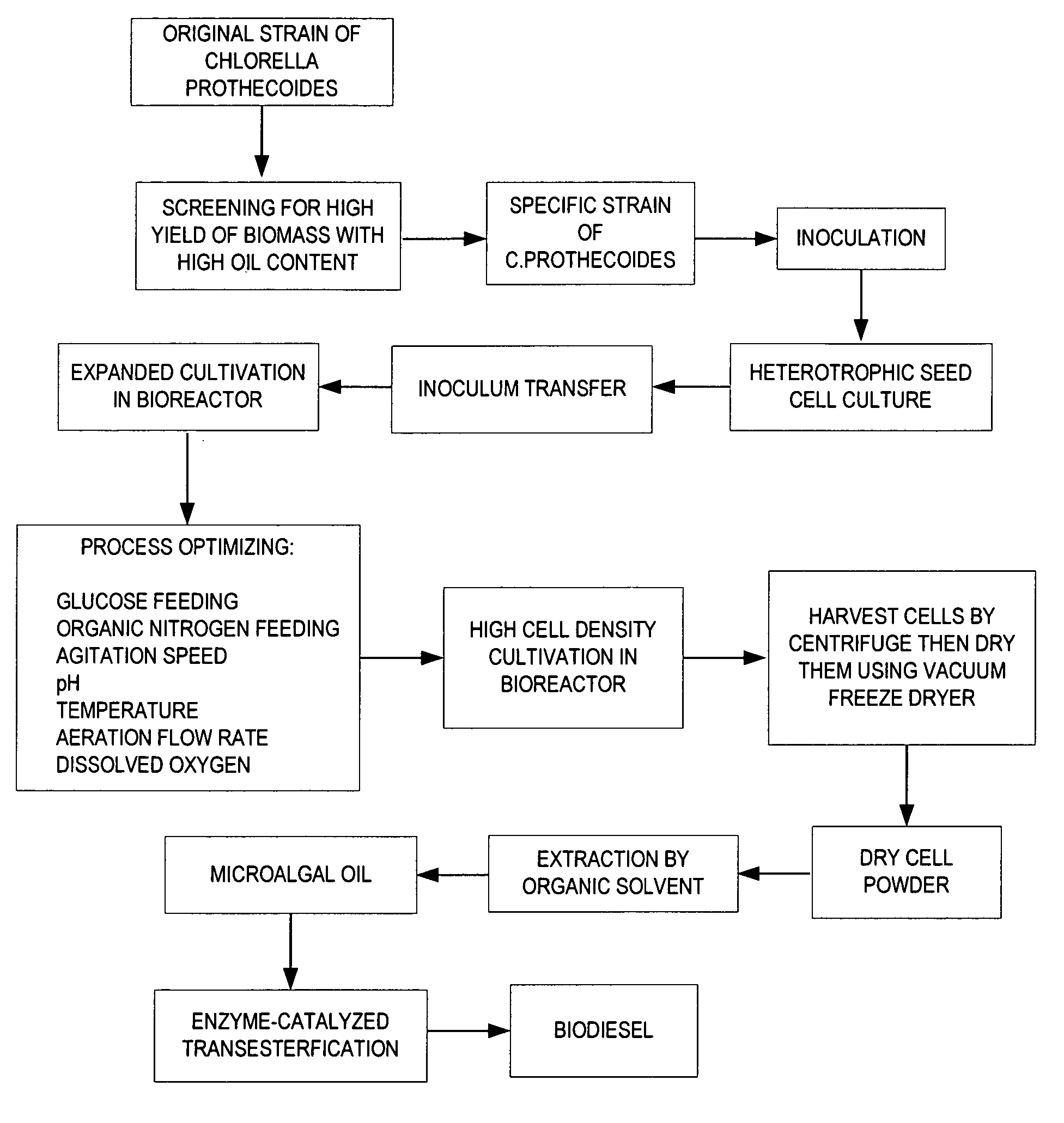
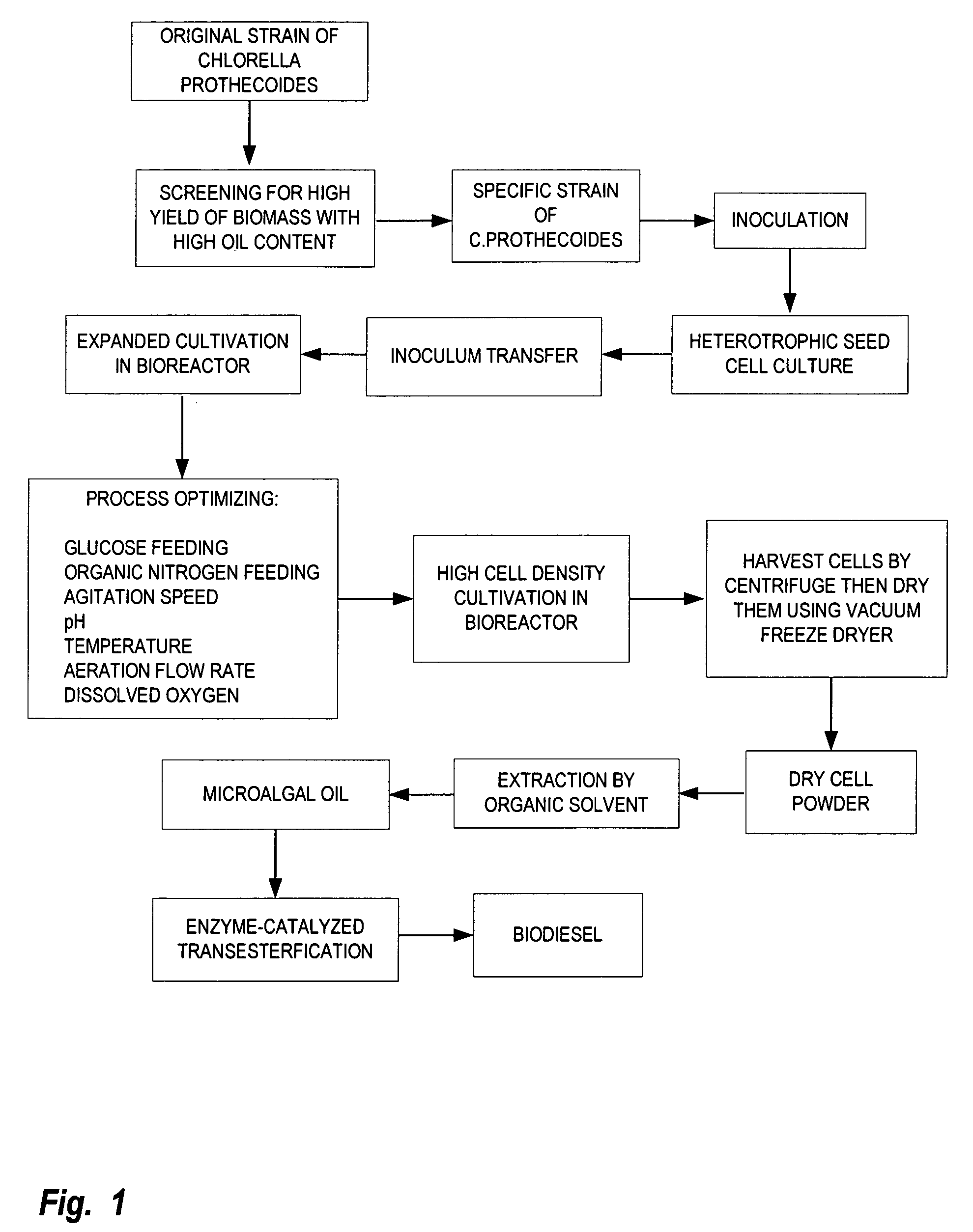
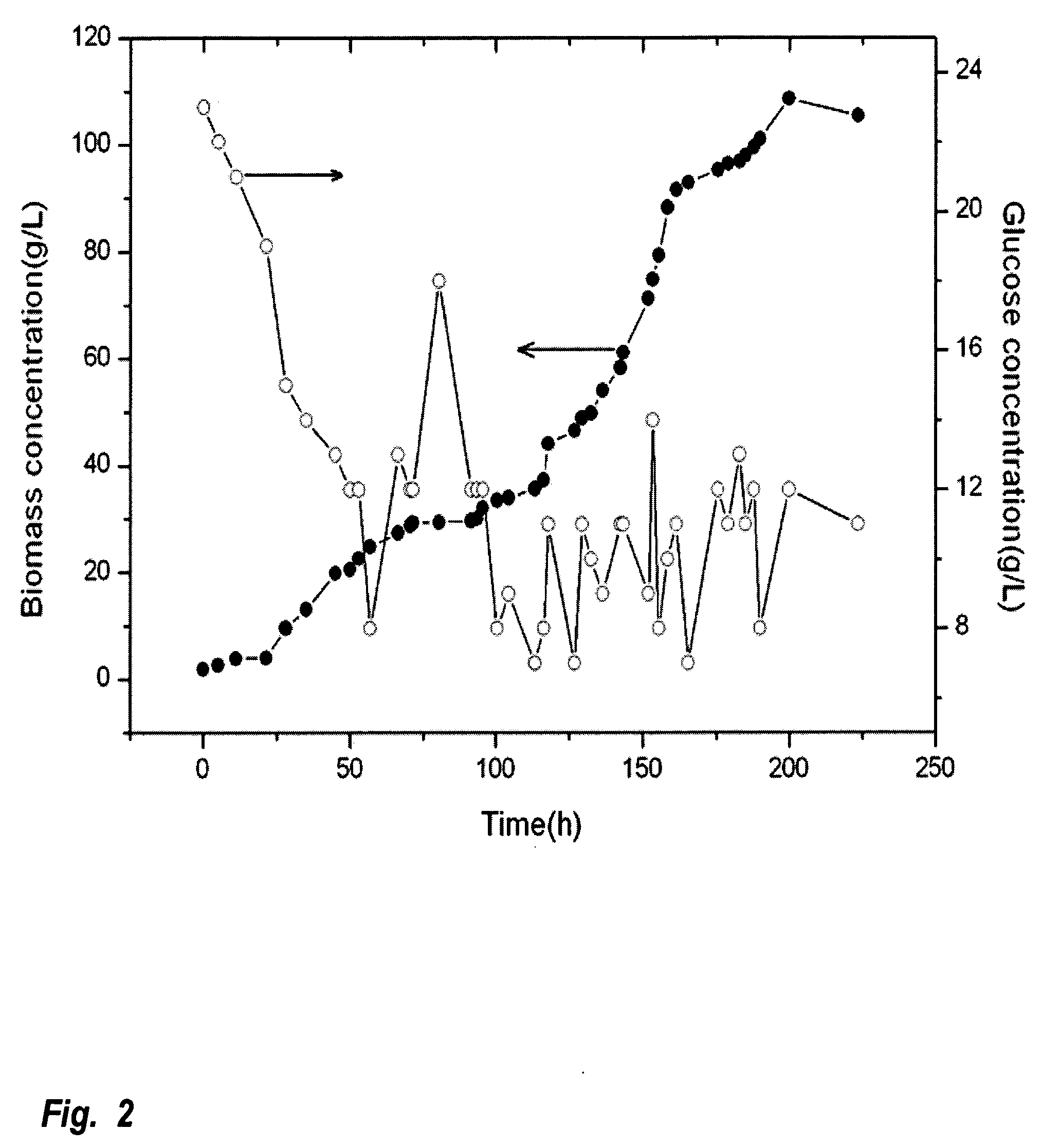
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a two-stage, autotrophic and heterotrophic cultivations of chlorella for biodiesel production. This method includes a sequence of procedures: cultivating photoautotrophic algae, concentrating cells and then transferring them to a fermentor for heterotrophic cultivation. During the photoautotrophic cultivation stage, the culture is exposed to a light source, such as sunlight with carbon dioxide obtained from a carbon dioxide source or from air. antibacterial agents may be added to prevent contamination from undesired microorganisms. Organic carbons are added during heterotrophic cultivation stage. Fermentation conditions are optimized for maximizing lipid synthesis. High biomass is achieved to about 108 g / L with lipid content reaching about 52% of dry cell weight. After cultivation, biodiesel is made through extraction and transesterification of algae lipids.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Lipid rich compositions, production of lipid rich compositions, production of fatty acid alkyl esters from heterogeneous lipid mixtures
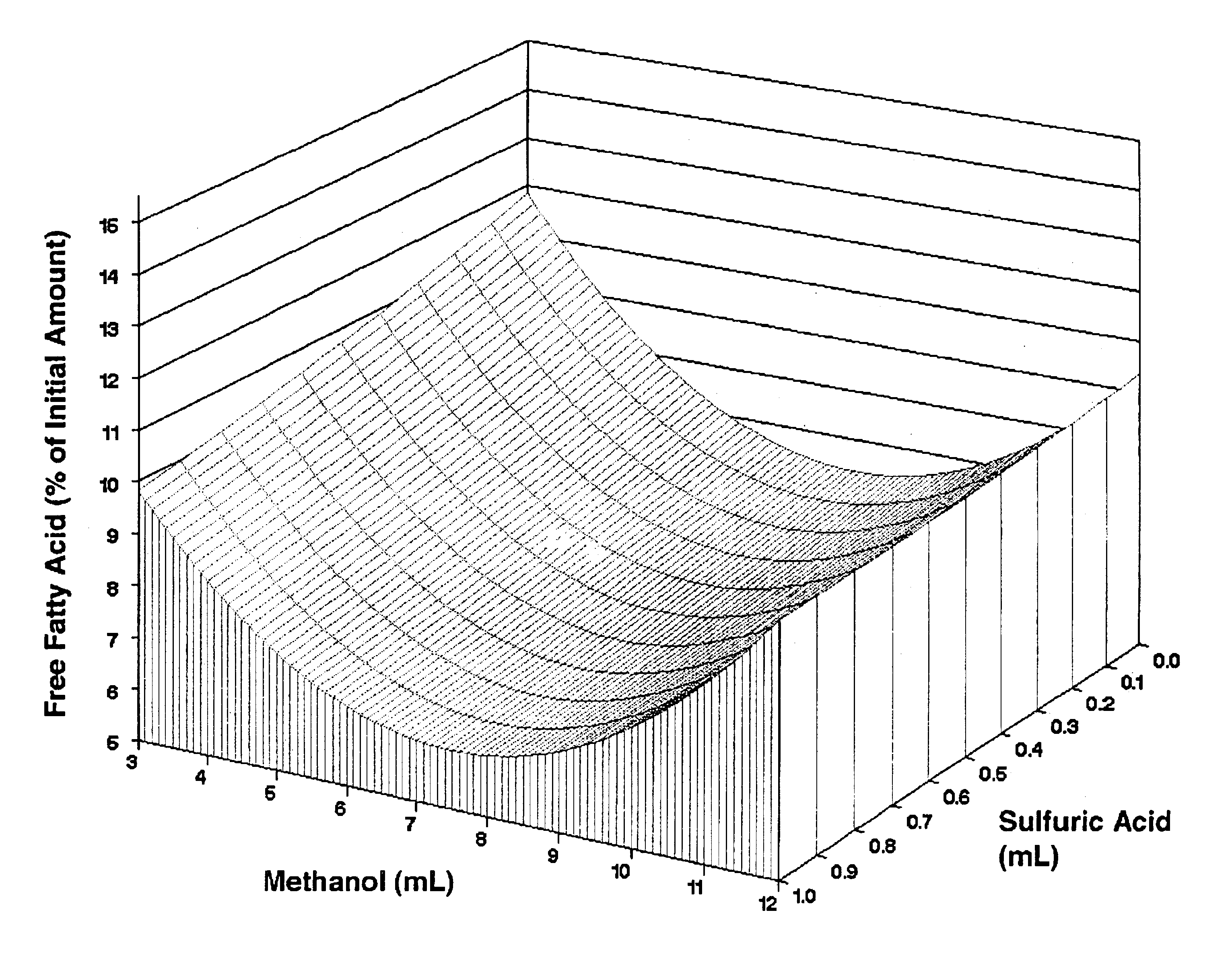
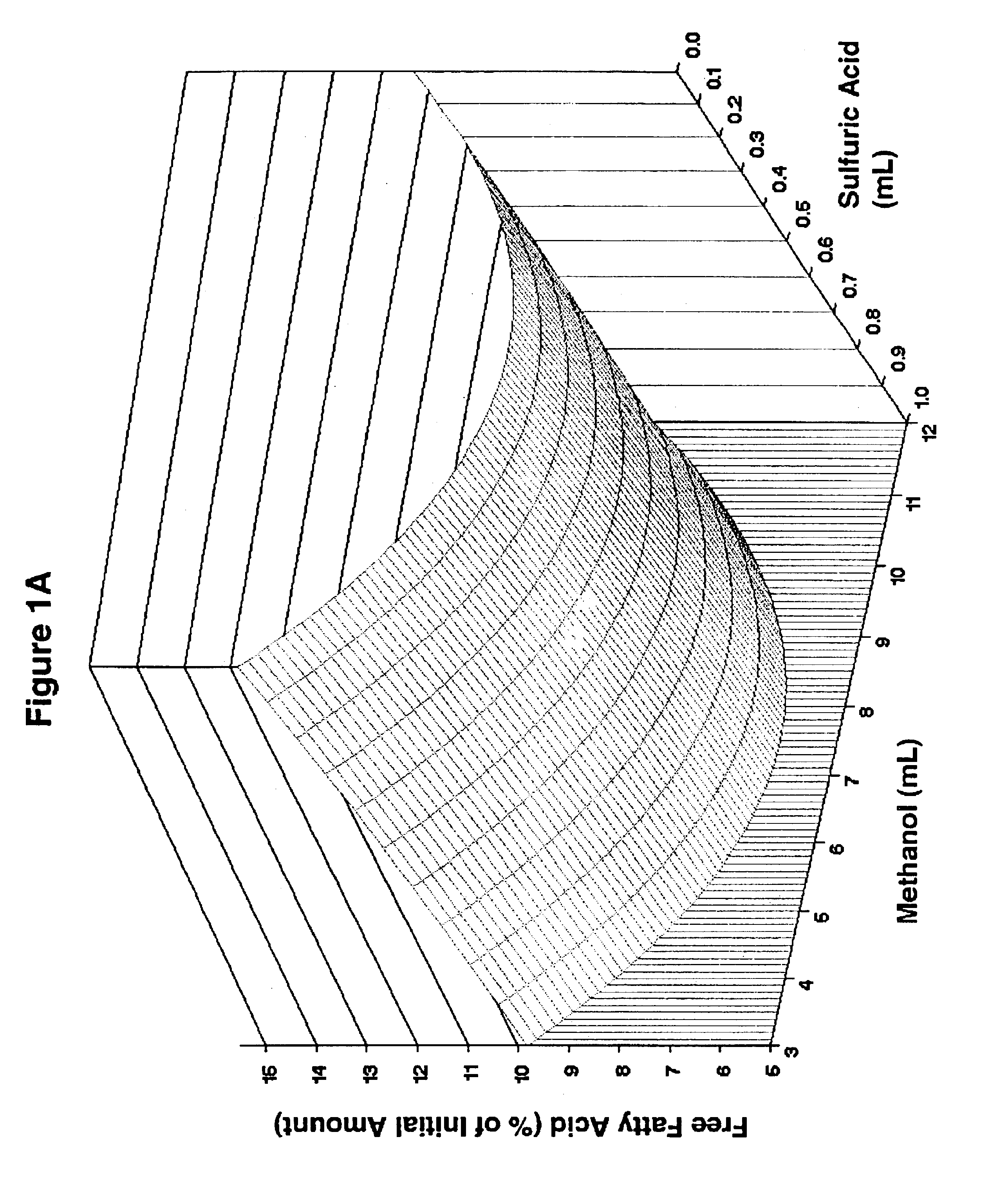
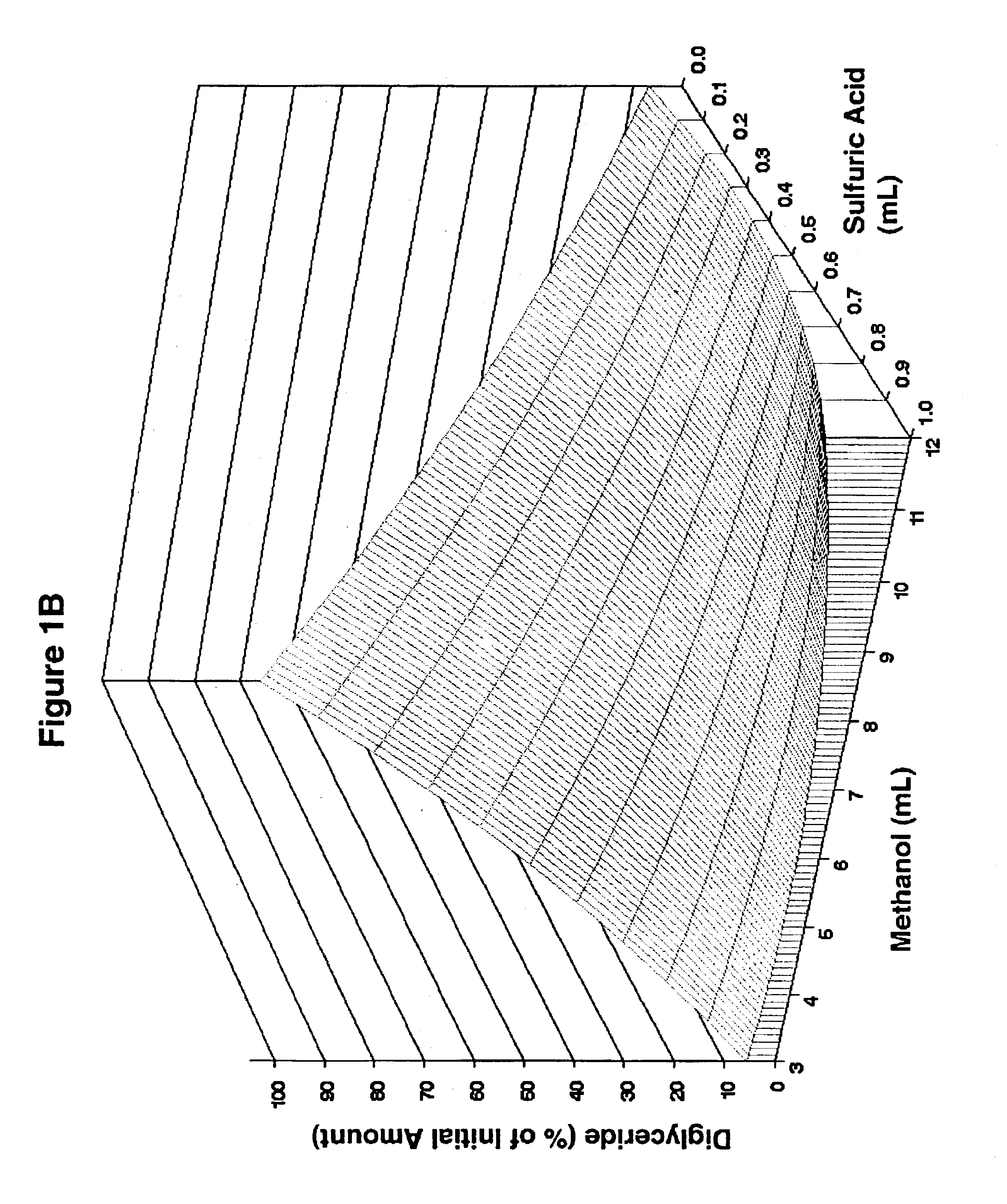
InactiveUS6855838B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationFatty acid esterSulfuric acid
The present invention relates to a method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters, involving esterifying a material containing free fatty acids (FFA) with an alcohol and an inorganic acid catalyst to form a product containing fatty acid alkyl esters, wherein (i) the material contains at least about 40% FFA and is produced by reacting a feedstock with steam and sulfuric acid at a pH of about 1-about 2 or (ii) the material contains at least about 80% FFA and is produced by reacting a feedstock with steam and alkali at a pH of about 11-about 13 and further reacting the feedstock with steam and sulfuric acid at a pH of about 1-about 2. The feedstock may be selected from the oils or soapstocks of soy, coconut, corn, cotton, flax, palm, rapeseed / canola, safflower, sunflower; animal fats; waste greases; and mixtures thereof; or other fully or partially hydrolyzed preparations of such feedstocks. The present invention also relates to a method for producing a lipid rich composition containing at least about 80% FFA, the method involving reacting a feedstock with steam and alkali at a pH of about 11-about 13 and further reacting the feedstock with steam and sulfuric acid at a pH of about 1-about 2. The feedstock may be selected from soy, coconut, corn, cotton, flax, palm, rapeseed / canola, safflower, sunflower, animal fats, waste greases, and mixtures thereof. The feedstock may be selected from the oils or soapstocks of soy, coconut, corn, cotton, flax, palm, rapeseed / canola, safflower, sunflower; animal fats; waste greases; and mixtures thereof; or other fully or partially hydrolyzed preparations of such feedstocks. Furthermore, the present invention concerns a lipid rich composition containing at least about 80% FFA.
Owner:RUNYON IND +1
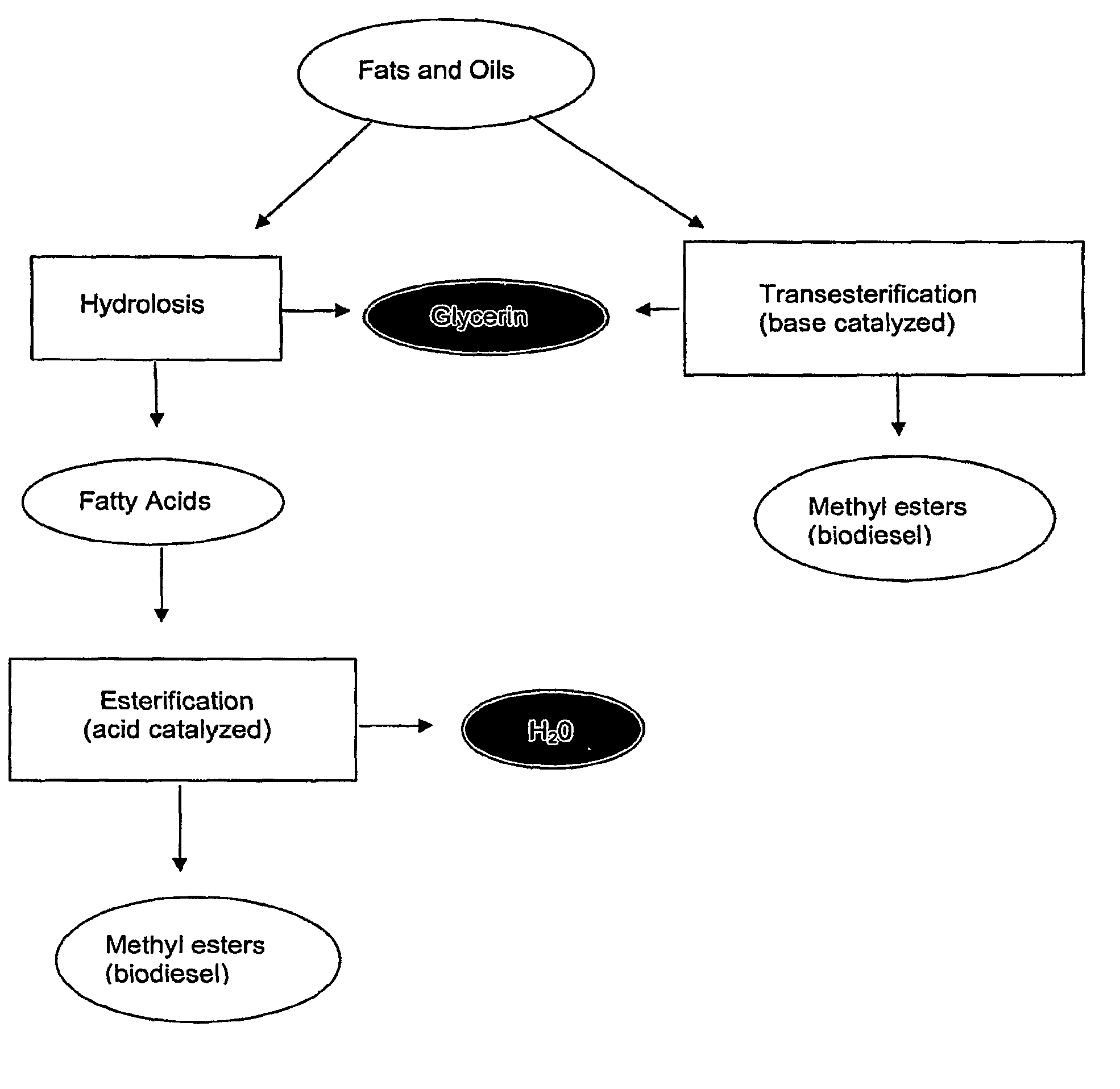
Process for producing biodiesel, lubricants, and fuel and lubricant additives in a critical fluid medium
InactiveUS6887283B1Limited mass transferImprove reaction speedFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselVegetable oil
A process for producing alkyl esters useful in biofuels and lubricants by transesterifying glyceride- or esterifying free fatty acid-containing substances in a single critical phase medium is disclosed. The critical phase medium provides increased reaction rates, decreases the loss of catalyst or catalyst activity and improves the overall yield of desired product. The process involves the steps of dissolving an input glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with an alcohol or water into a critical fluid medium; reacting the glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with the alcohol or water input over either a solid or liquid acidic or basic catalyst and sequentially separating the products from each other and from the critical fluid medium, which critical fluid medium can then be recycled back in the process. The process significantly reduces the cost of producing additives or alternatives to automotive fuels and lubricants utilizing inexpensive glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substances, such as animal fats, vegetable oils, rendered fats, and restaurant grease.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Novel Process for Separating Lipids From a Biomass
InactiveUS20100261918A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofuelAlgae
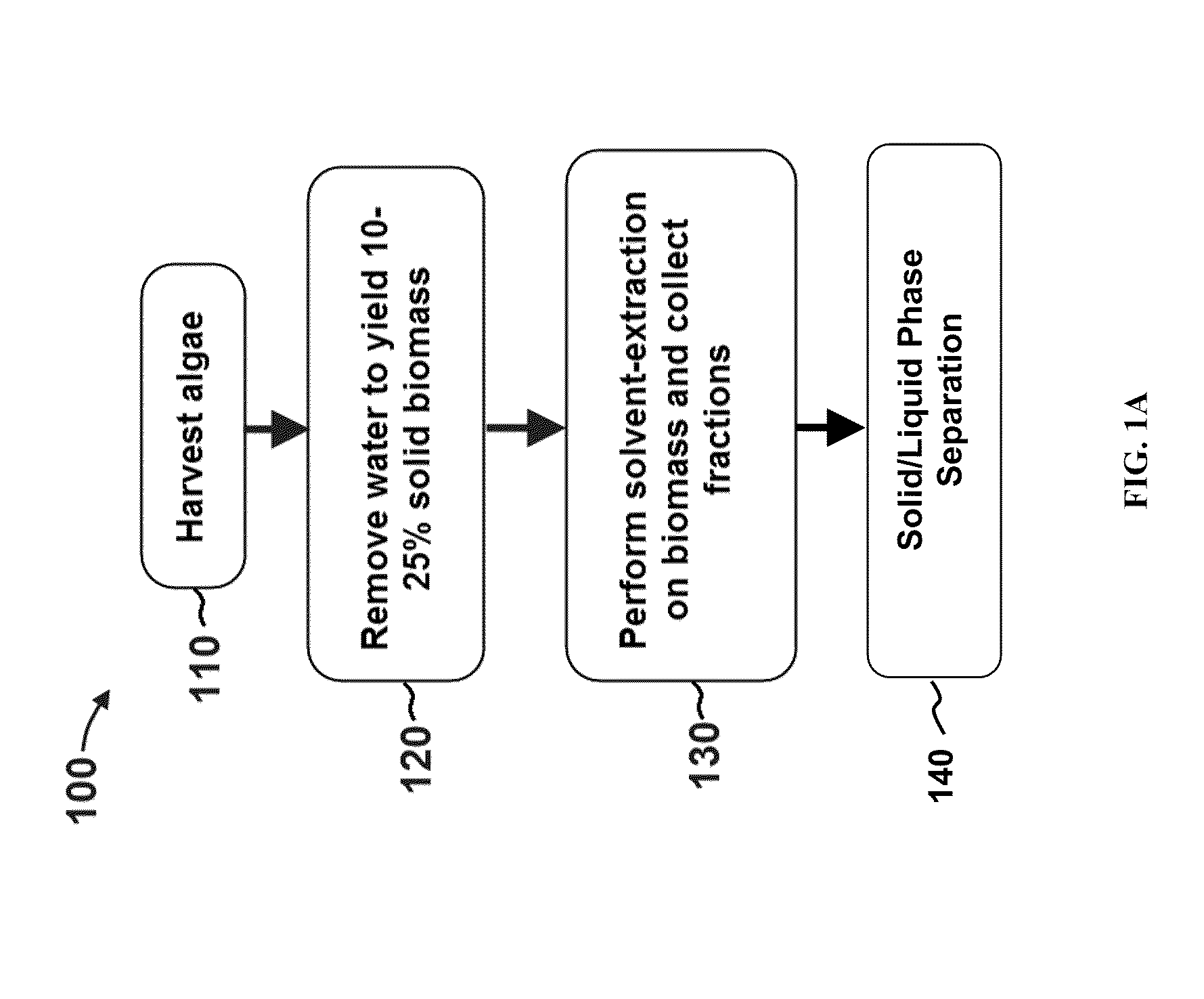
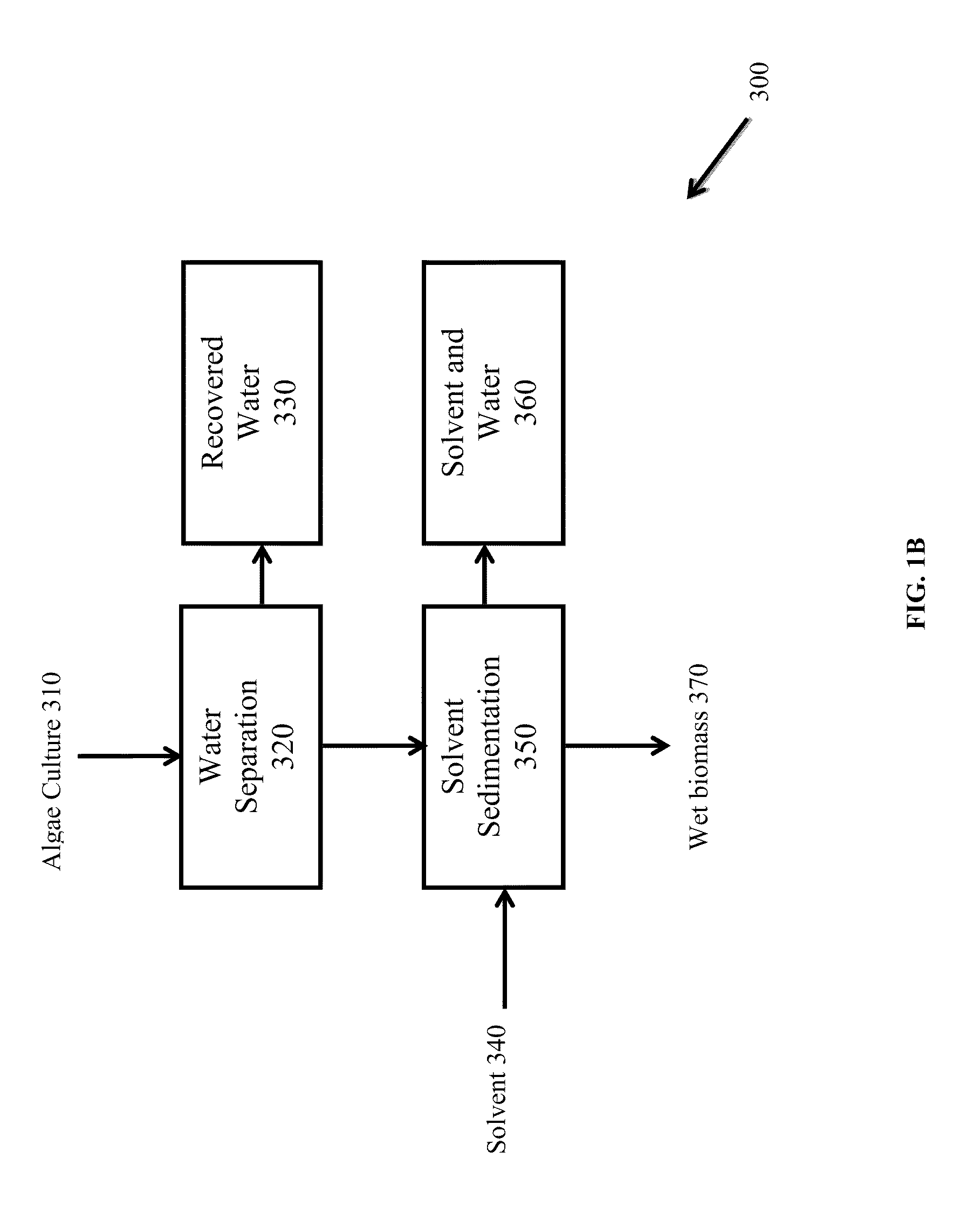
A novel low cost separation process for separating lipid oil from an algal biomass for biofuel production is described herein. The process of the present invention comprises of two steps: (i) breaking the algae cells and (ii) separation of the lipid oils from the broken cells. The separated lipids are extracted by conventional techniques followed by conversion to a biofuel.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
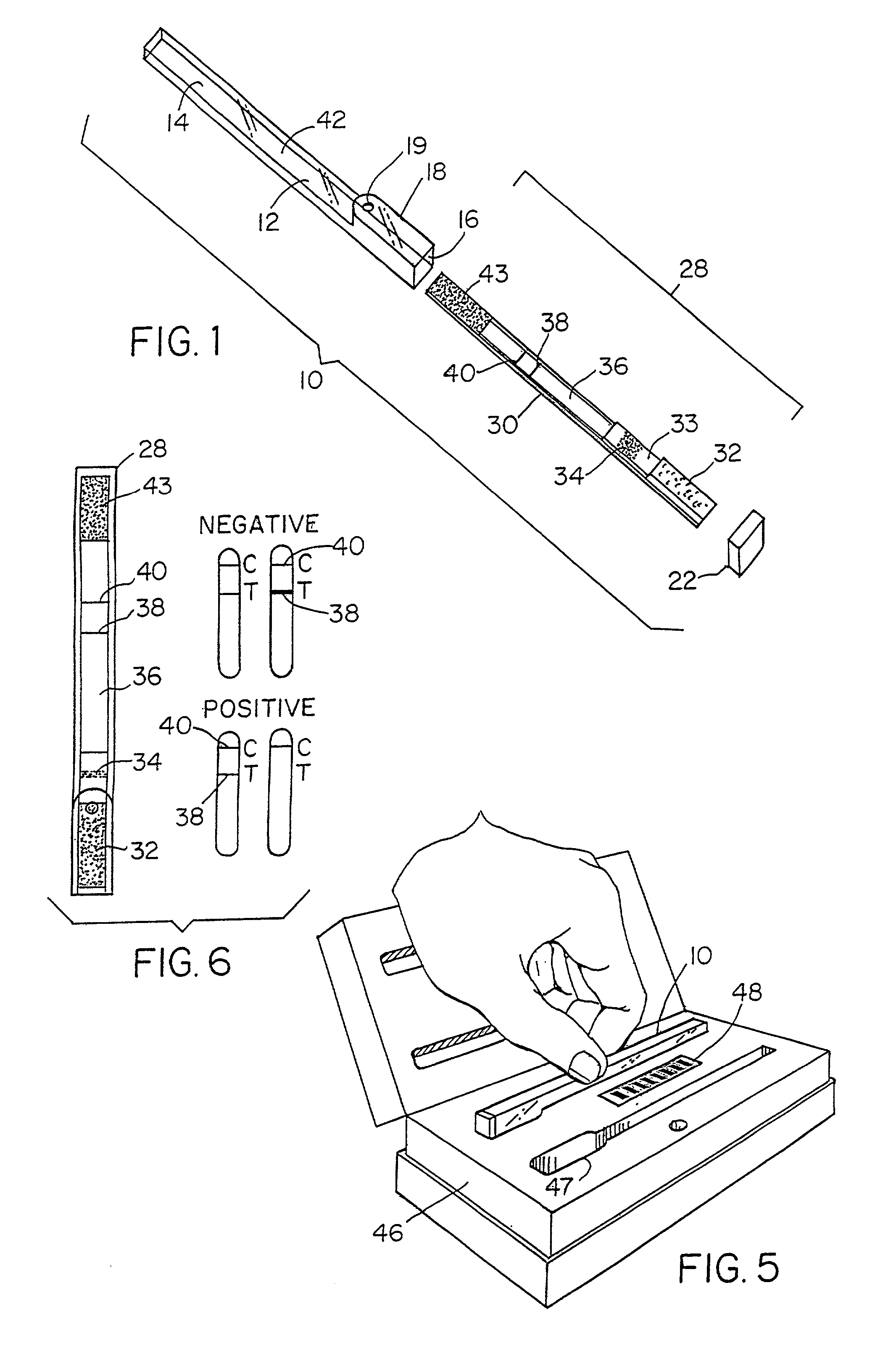
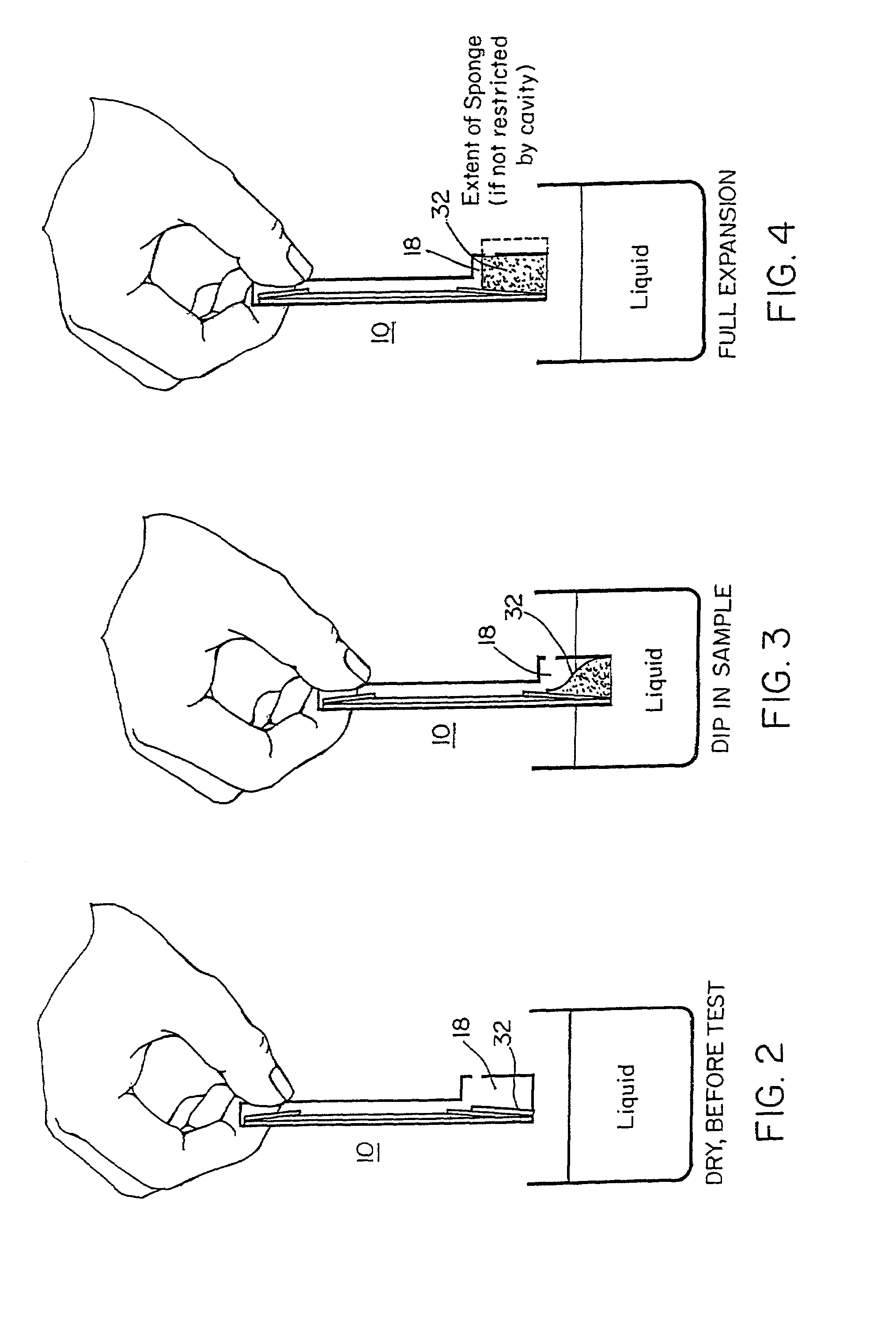
Method for detecting the presence of an analyte in a sample
InactiveUS7097983B2High purityEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid hydrogenationAnalyteBinding site
The invention features a method of determining whether one or more members of an analyte family are present in a sample. The method makes use of a test zone binder, e.g., a receptor that can bind one or a plurality of analytes within an analyte family, the analytes family defined by similar structural binding sites. Members of an analyte family can have different detection level requirements and, therefore, additional analyte binders can be employed to adjust test sensitivity for a subset of the analytes in the analyte family individually, so that each analyte can be detected only if it is present in the sample above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:CHARM SCI
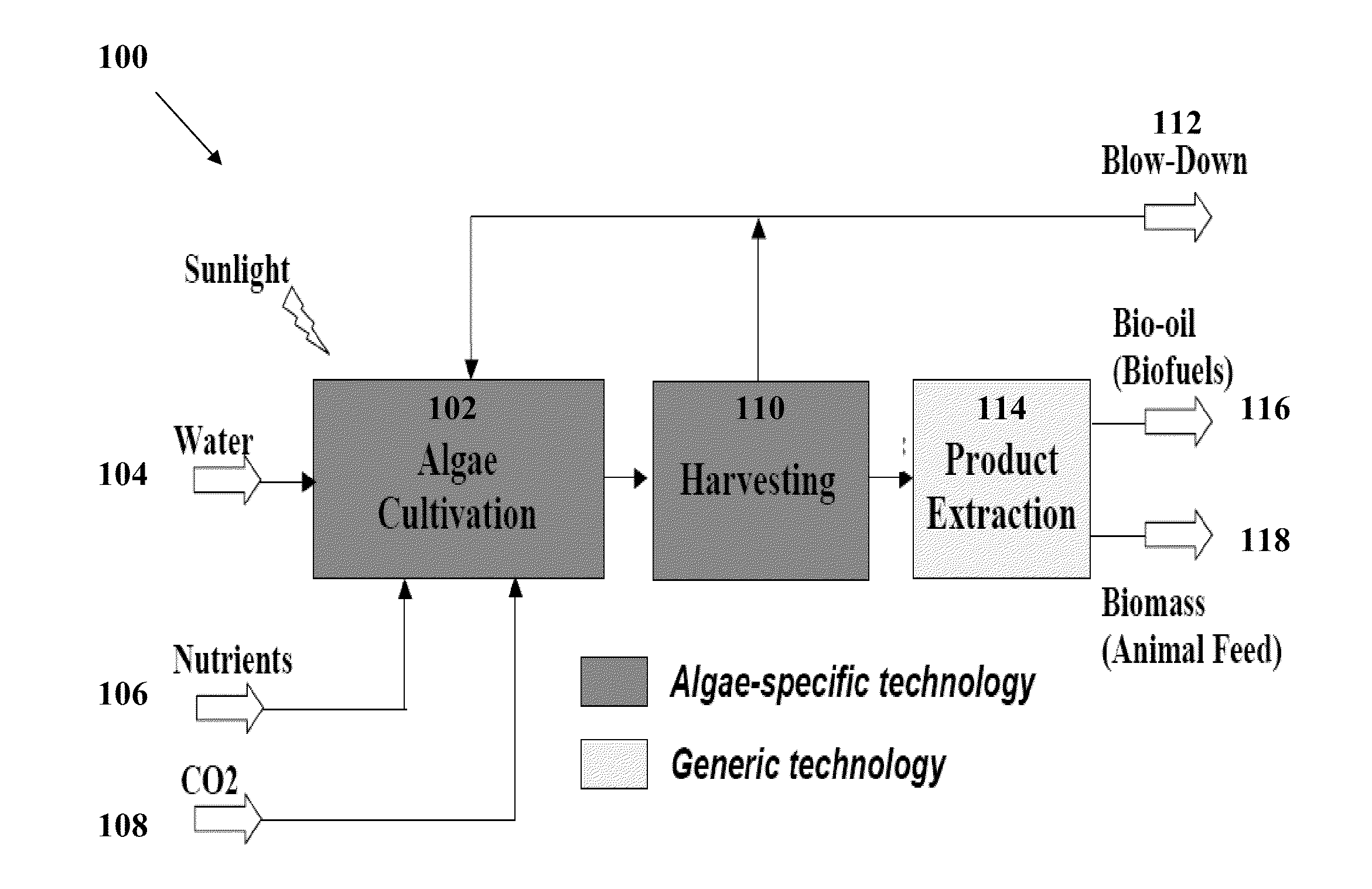
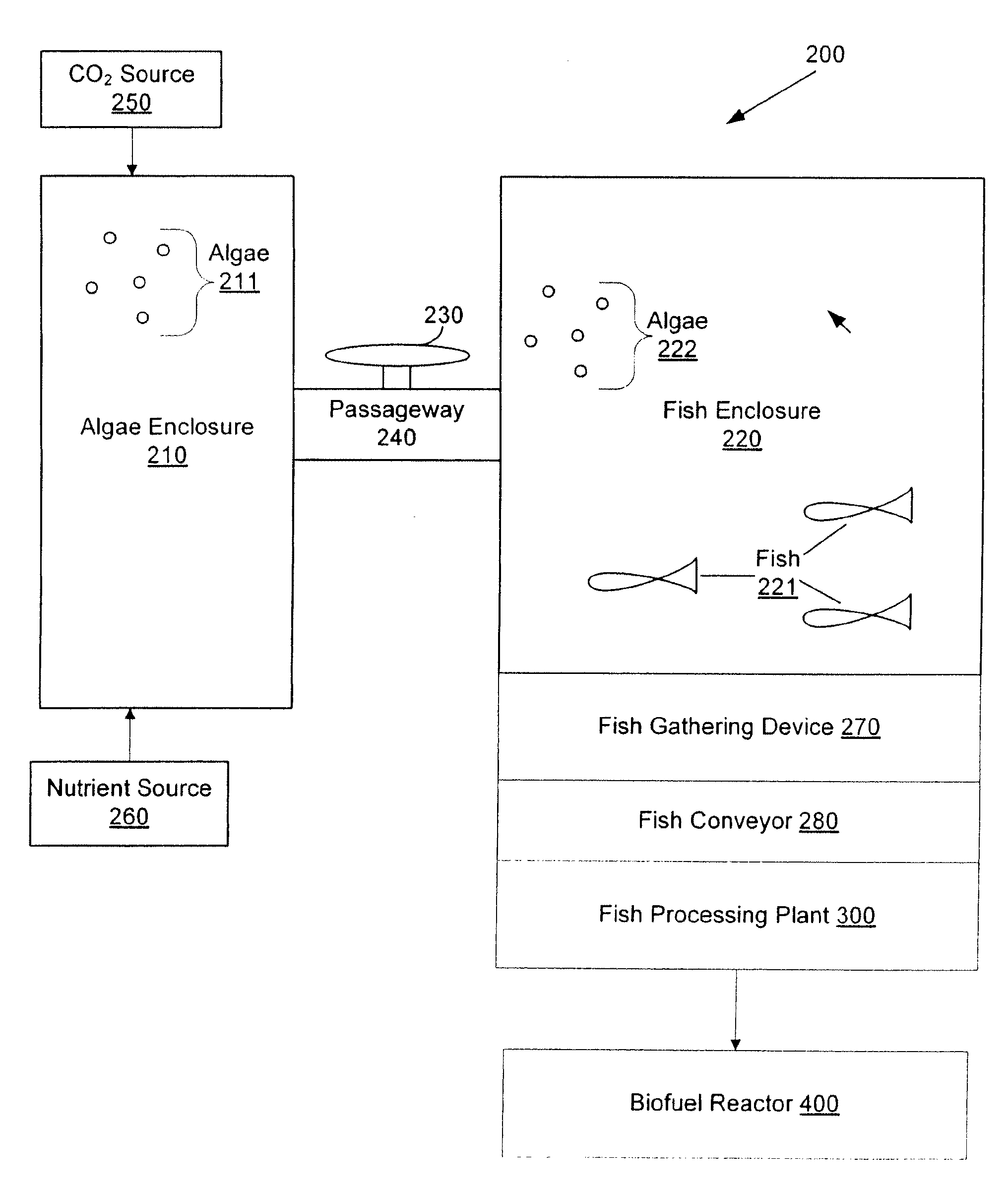
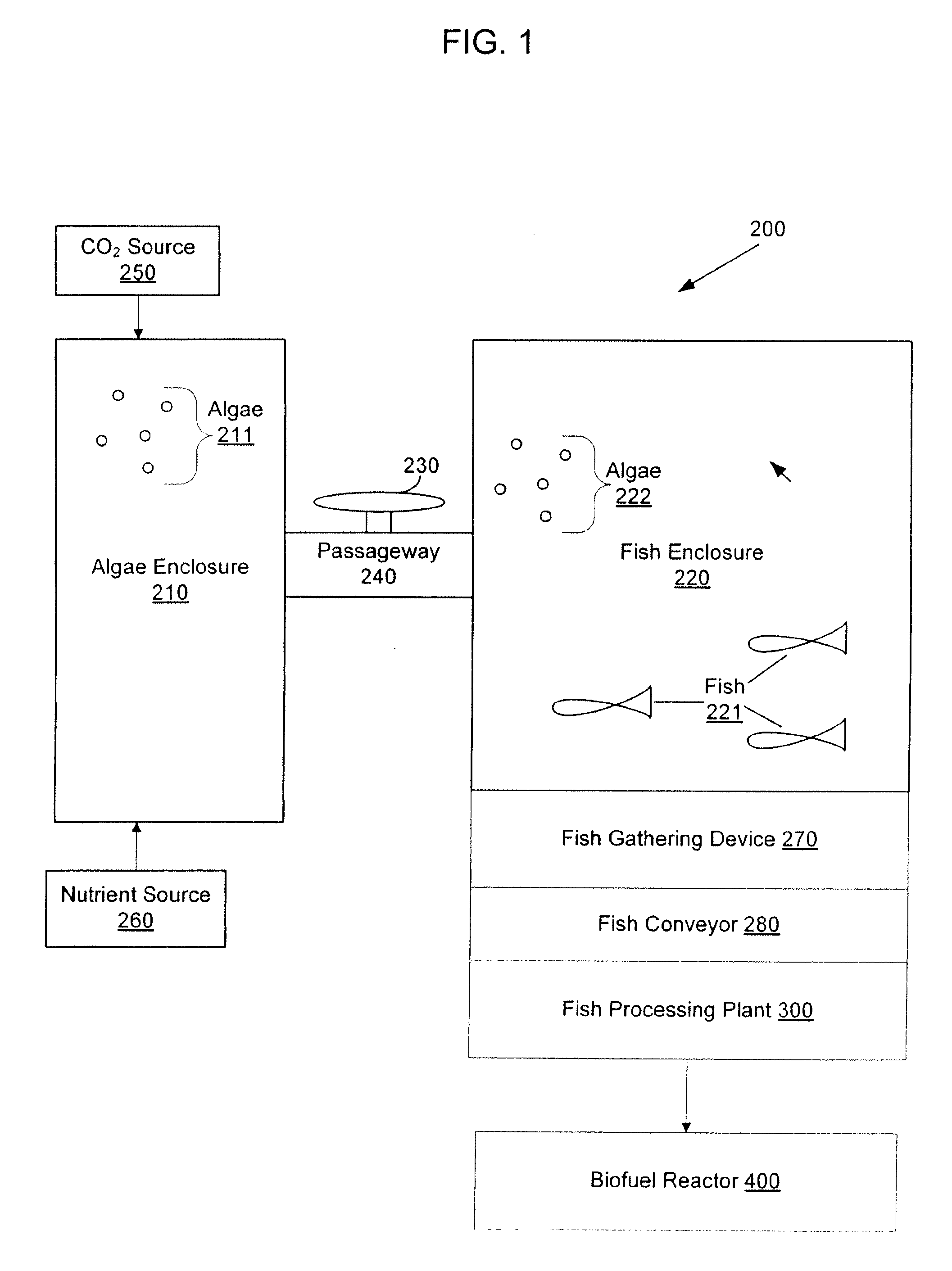
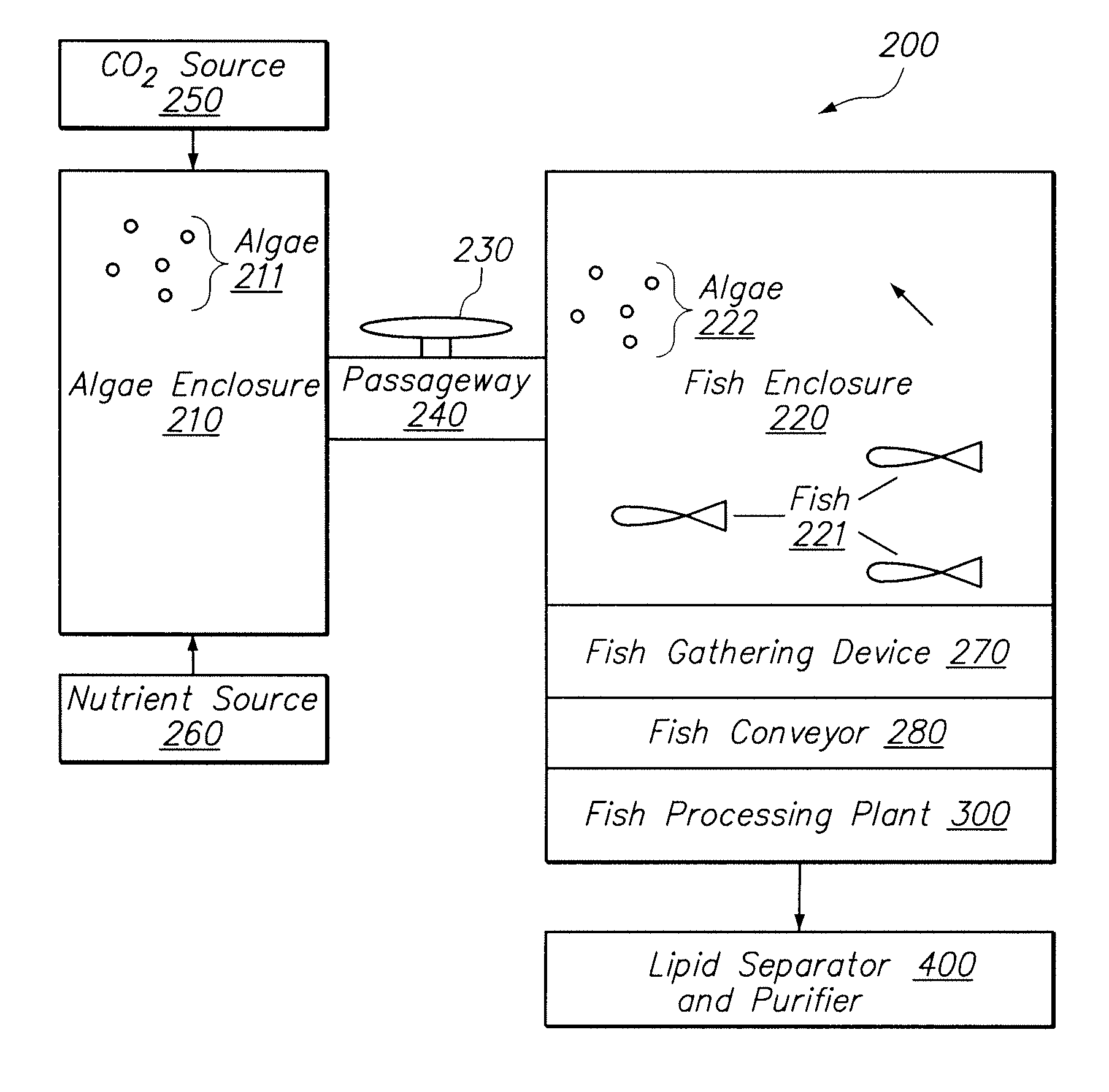
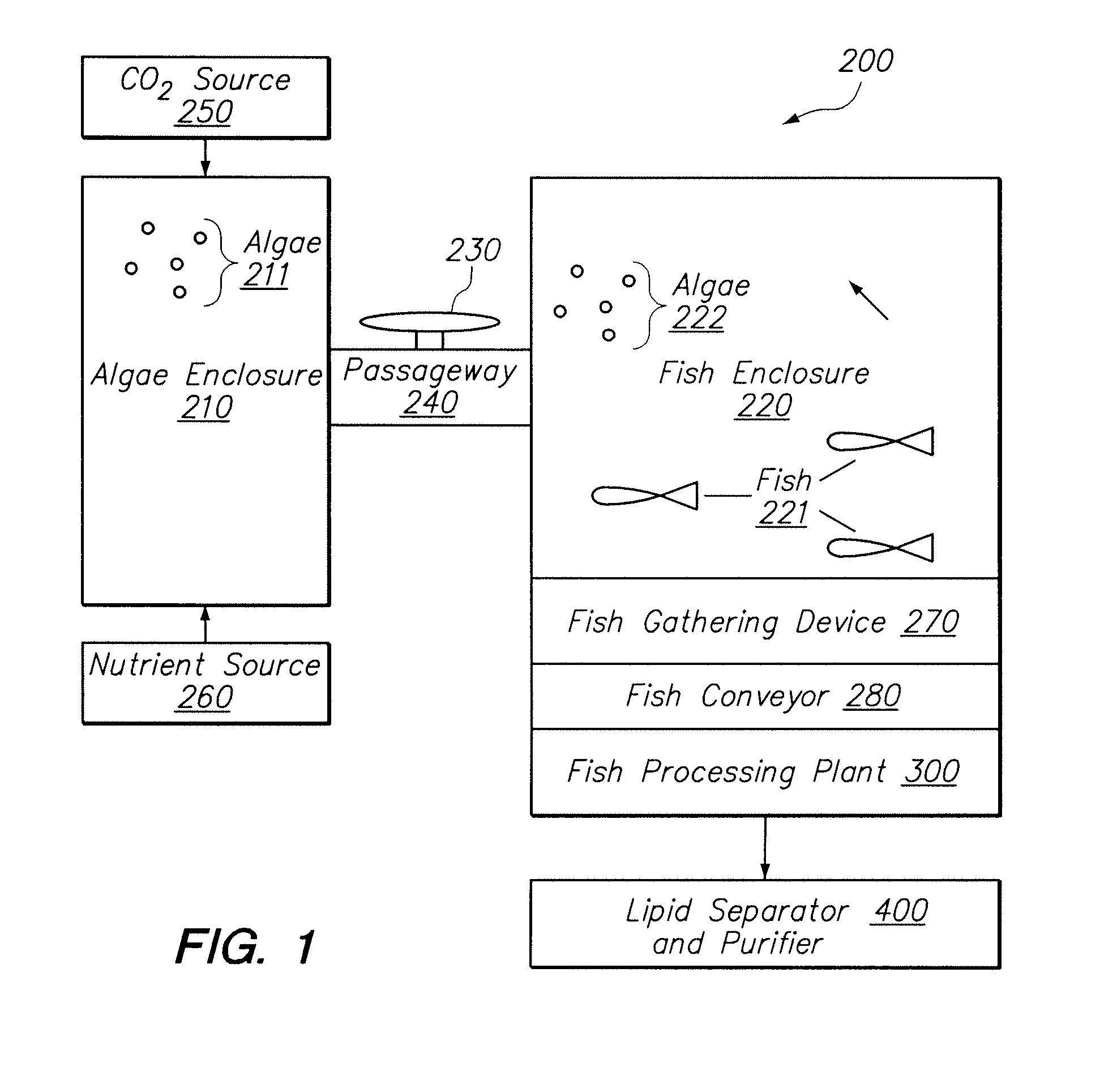
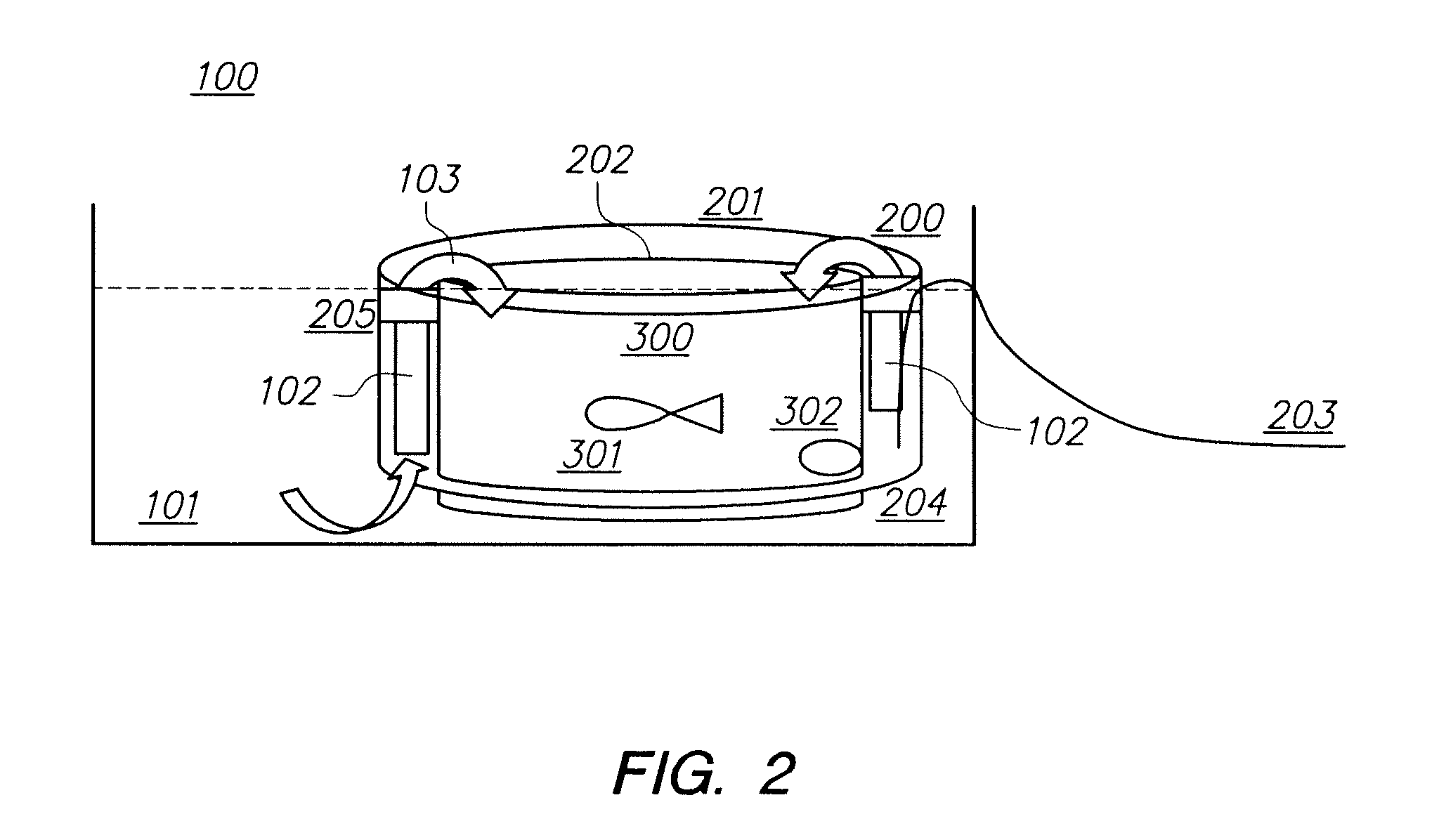
Systems and methods for producing biofuels from algae
The invention provides systems and methods for producing biofuel from algae that use cultured fish to harvest algae from an algal culture. The methods further comprise gathering the fish, extracting lipids from the fish, and processing the lipids to form biofuel. The multi-trophic systems of the invention comprises at least one enclosure that contains the algae and the fishes, and means for controllably feeding the algae to the fishes. The lipid compositions extracted from the fishes are also encompassed.
Owner:LIVEFUELS
Fatty acid blends and uses therefor
ActiveUS20100058651A1Maintain good propertiesEffect cold flow propertyFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningFatty acid methyl esterMedium chain fatty acid
Provided herein are blends oils or fatty acids comprising more than 50% medium chain fatty acids, or the fatty acid alkyl esters thereof, and having low melting points. Such blends are useful as a fuel or as a starting material for the production of, for example, a biodiesel. Also provided genetically altered or modified plants, modified such that the amount of medium chain fatty acids generated by the plant are increased. Further provided is a method of predicting the melting point of a blend of fatty acid methyl esters and the use of such a method for identifying blends suitable for use as, for example, a biodiesel.
Owner:CIBUS
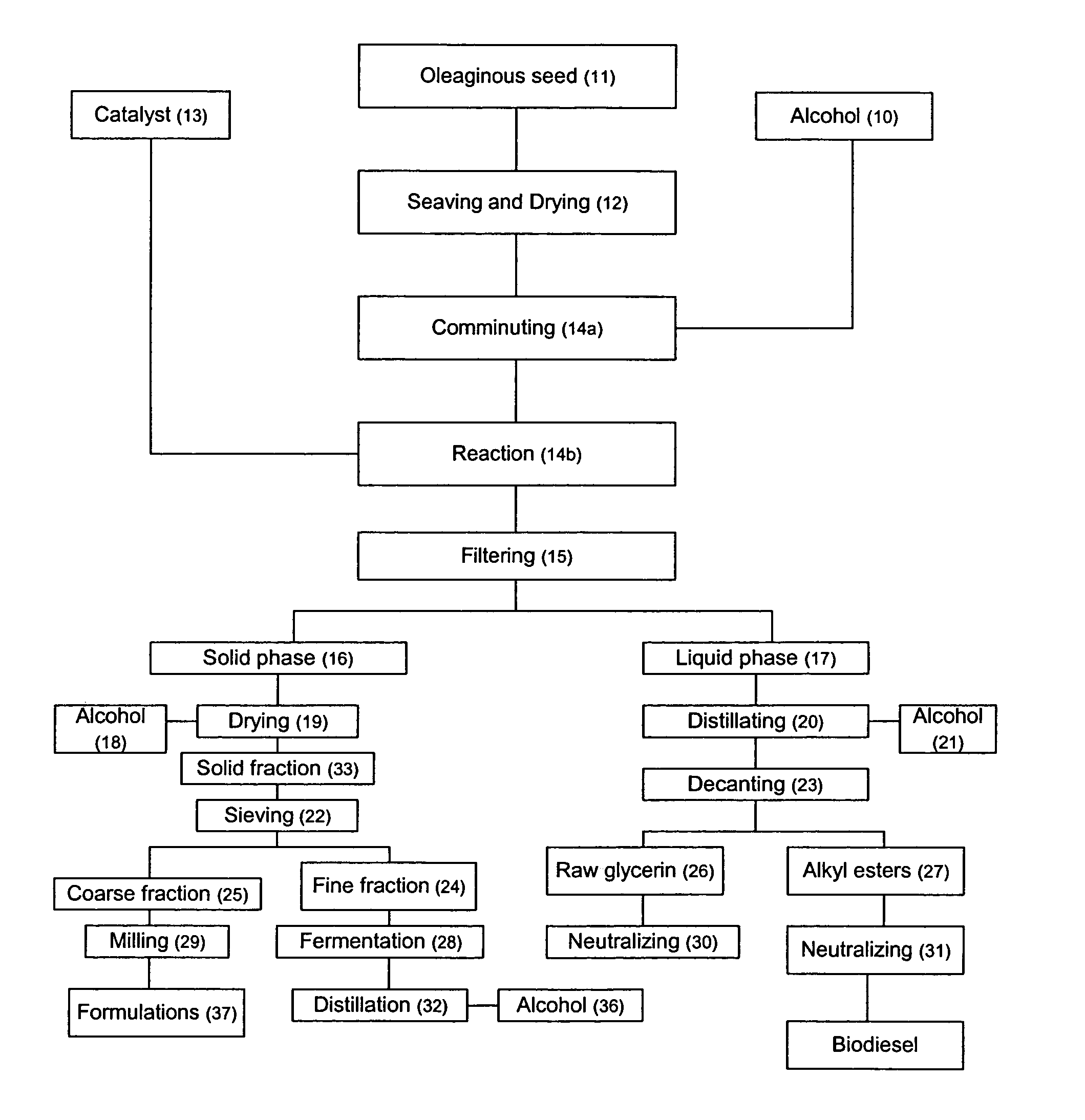
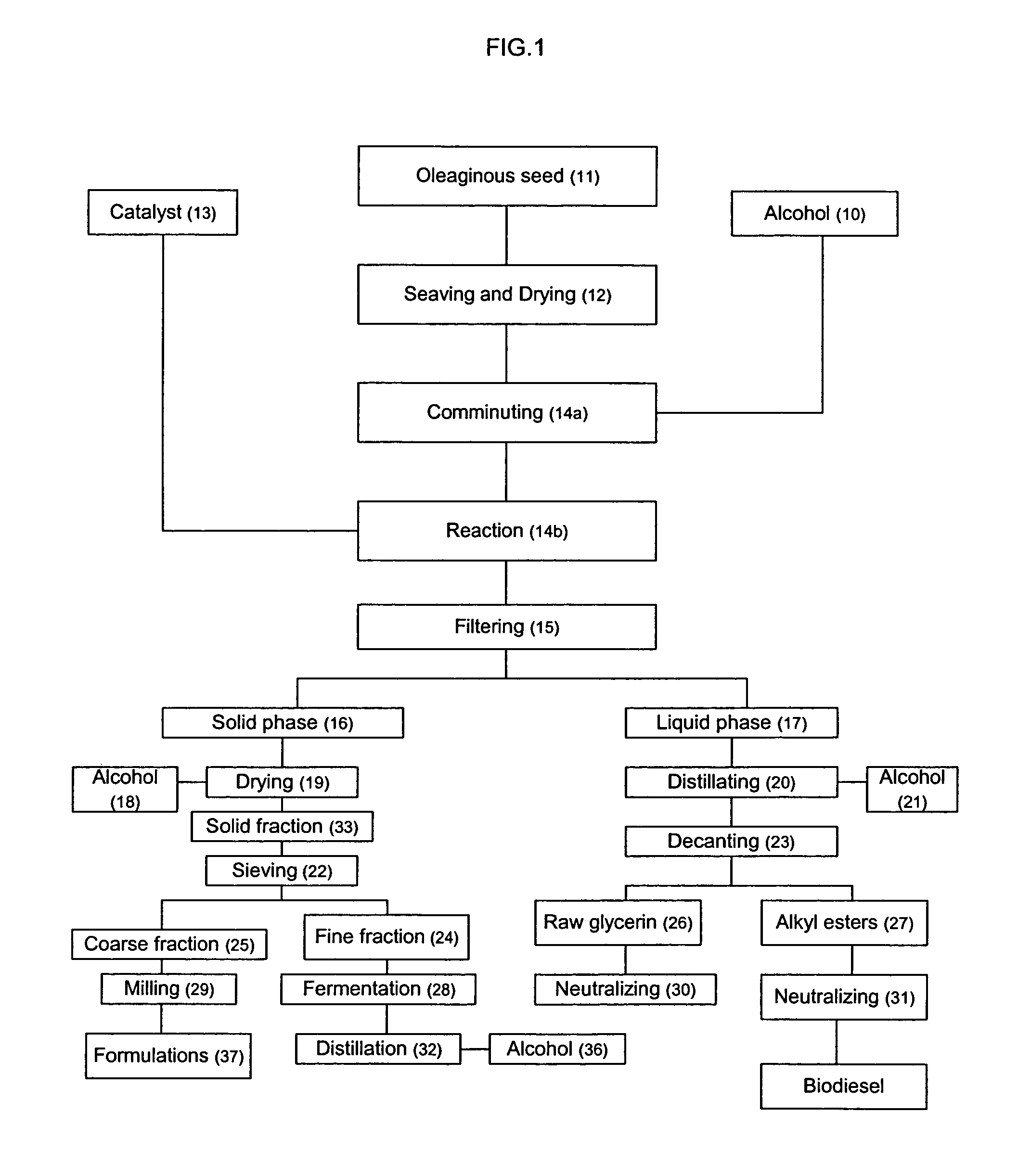
Process for producing biodiesel fuel using triglyceride-rich oleagineous seed directly in a transesterification reaction in the presence of an alkaline alkoxide catalyst
InactiveUS7112229B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationOil and greaseBiodiesel
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds. The inventive process includes a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
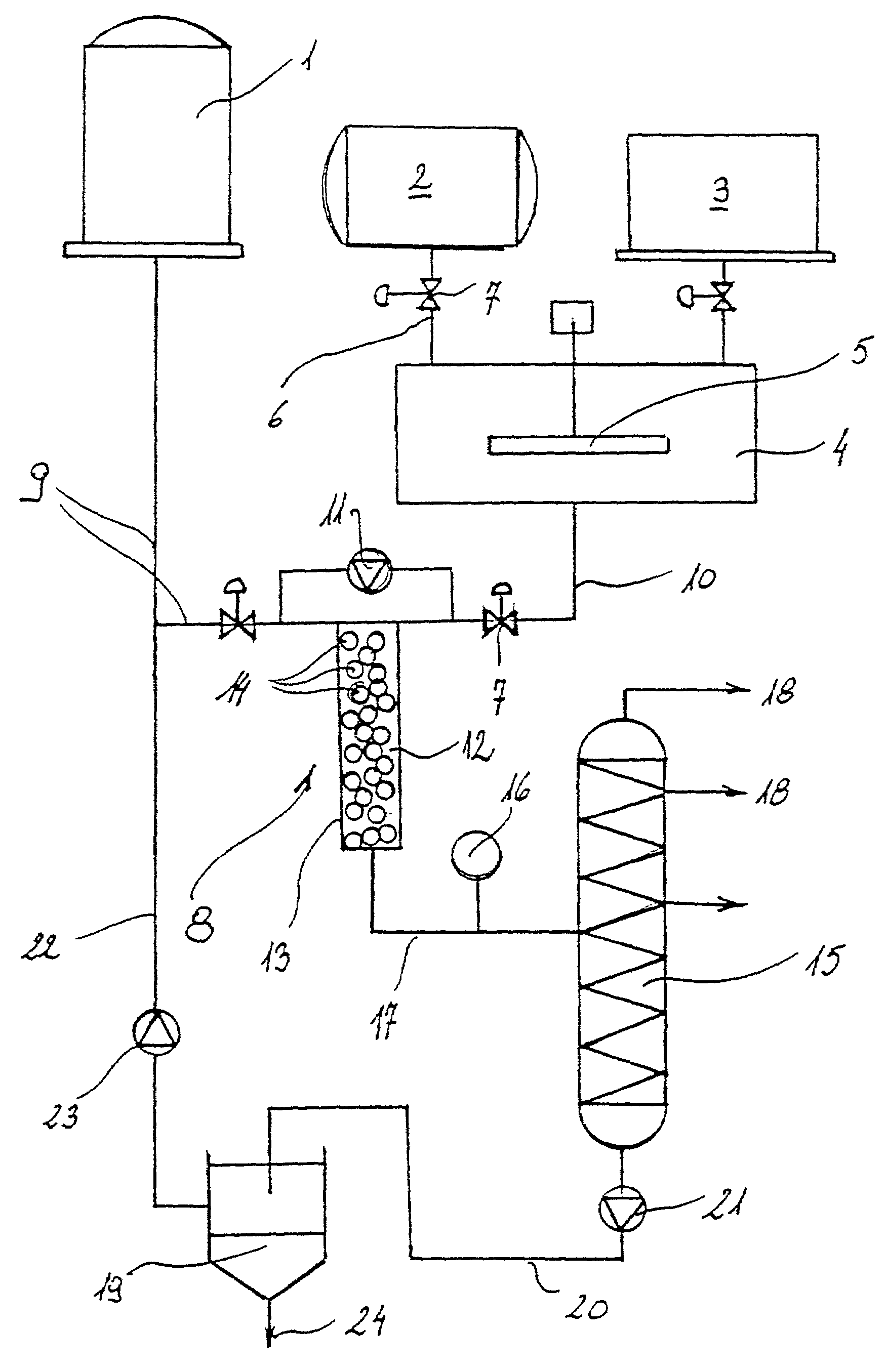
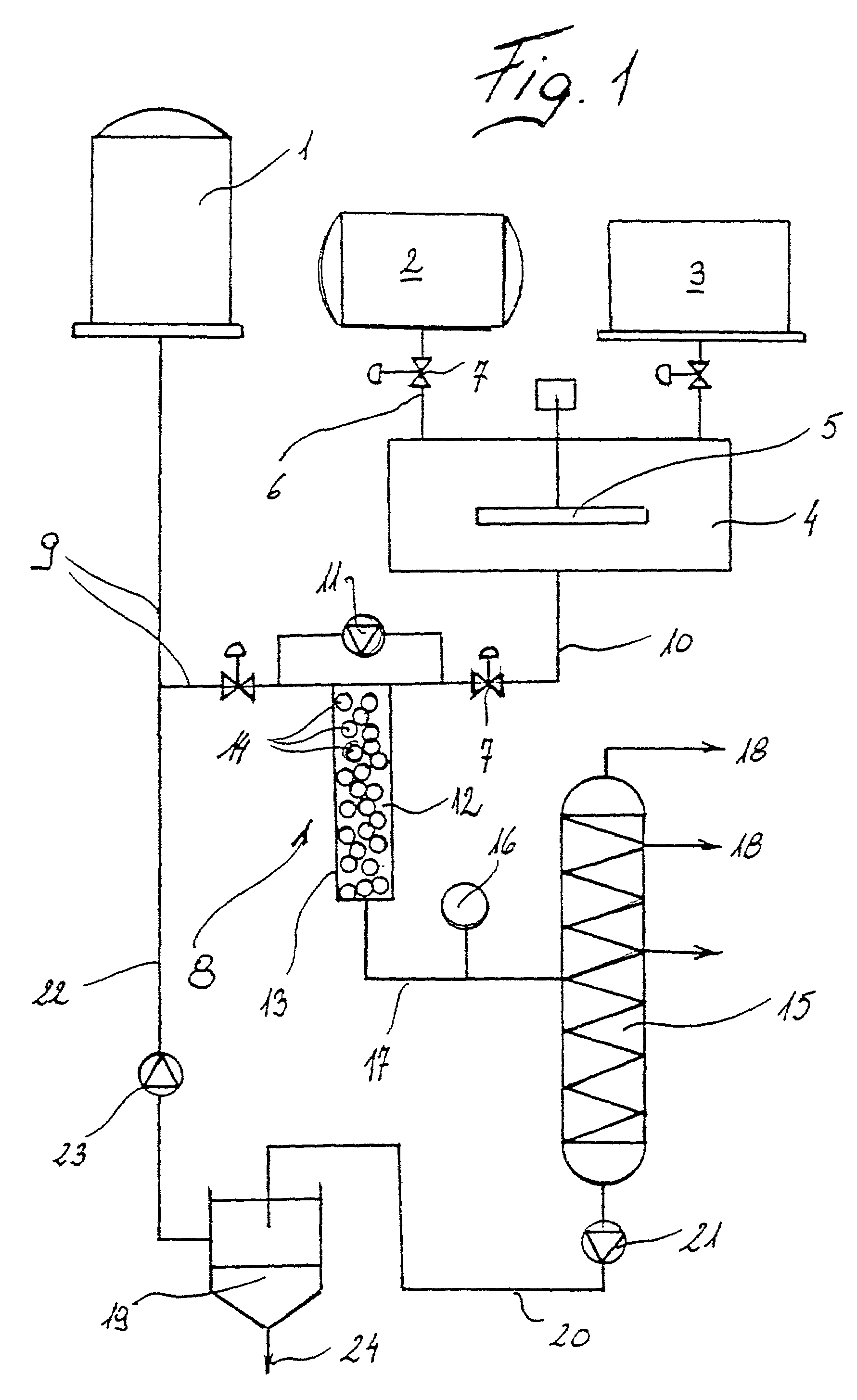
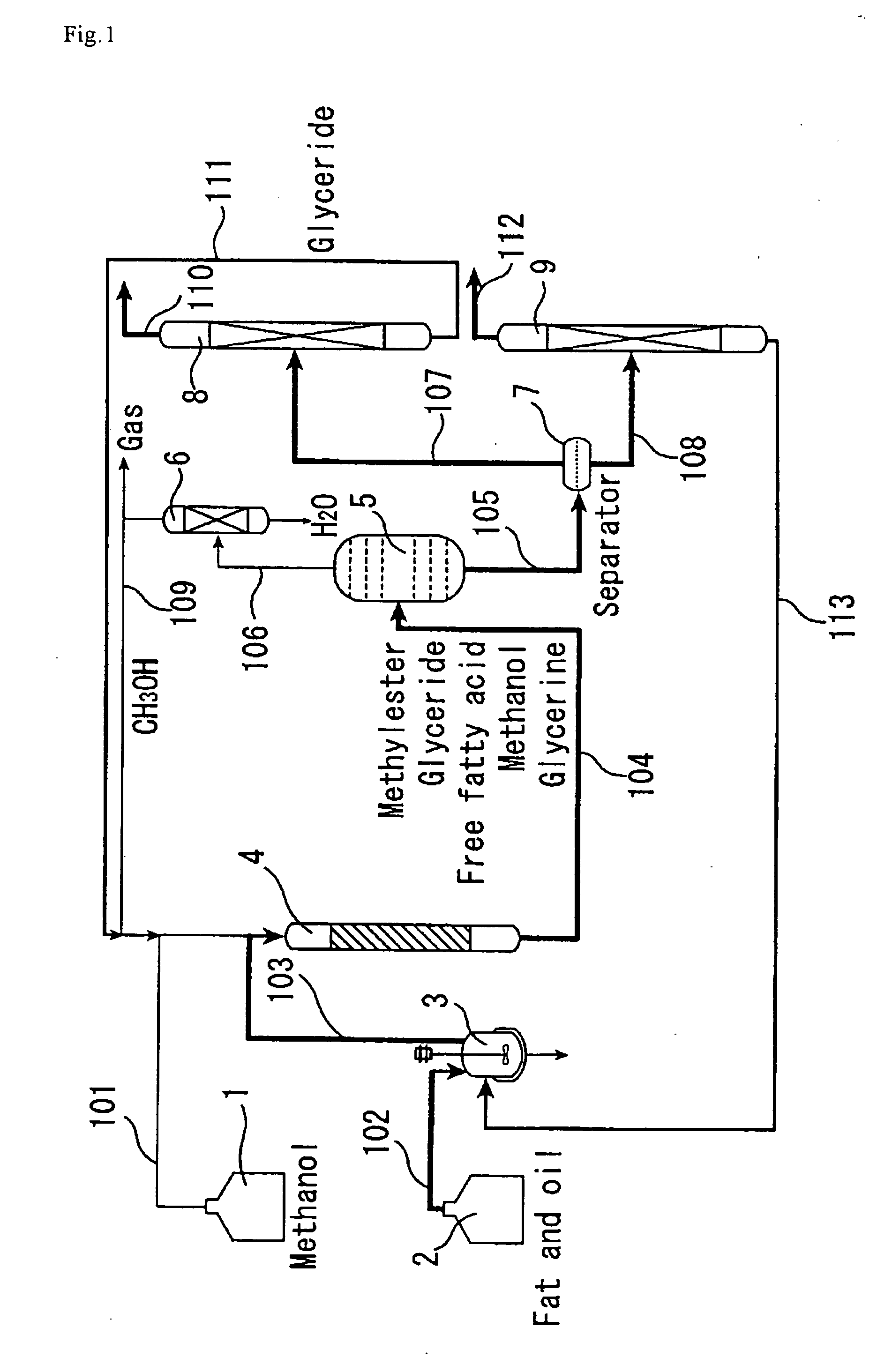
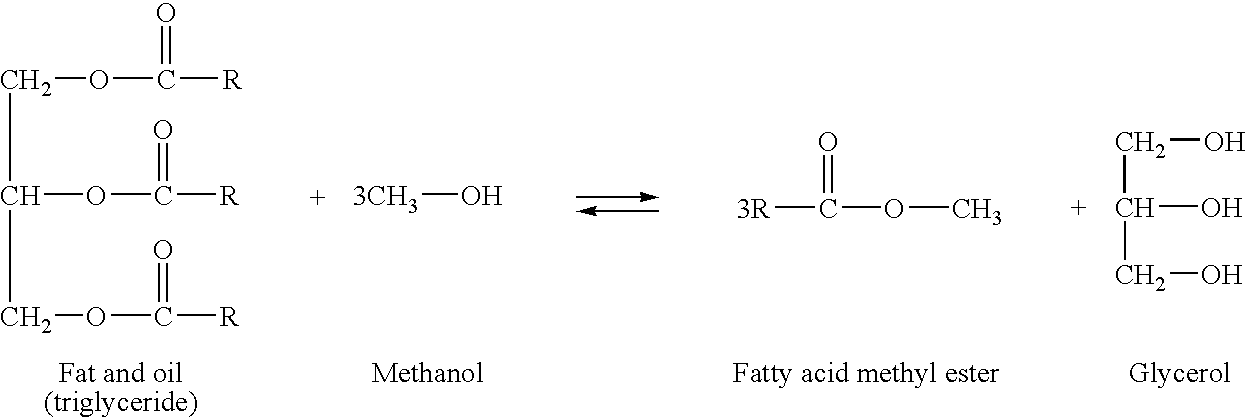
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester and equipment for realizing the same
InactiveUS7045100B2Avoid disadvantagesRational productionPressurized chemical processFatty acid esterificationAlcoholTransesterification
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester, including compounding saturated and unsaturated higher fatty substances from at least one of vegetable and animal with an alkaline solution dissolved in alcohol to form a mixture. The method also includes emulsifying the mixture to reach a chemical balance state in a reaction section, wherein fats are transesterified into fatty acid methyl ester, wherein border surfaces of the mixture are enlarged by dynamic turbulence in the reaction section and the transesterification is performed under pressure, and wherein the pressure is reduced during transesterification. The method further includes after reaching a chemical balance state, separating residues from the fatty acid methyl ester in a phase separation section. Apparatus for producing fatty acid methyl ester.
Owner:AMERICAN RENEWABLE FUELS
Method for producing biodiesel using high-cell-density cultivation of microalga Chlorella protothecoides in bioreactor
InactiveUS20090211150A1Reduce acidityAdjust pHFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeHigh cellHigh density
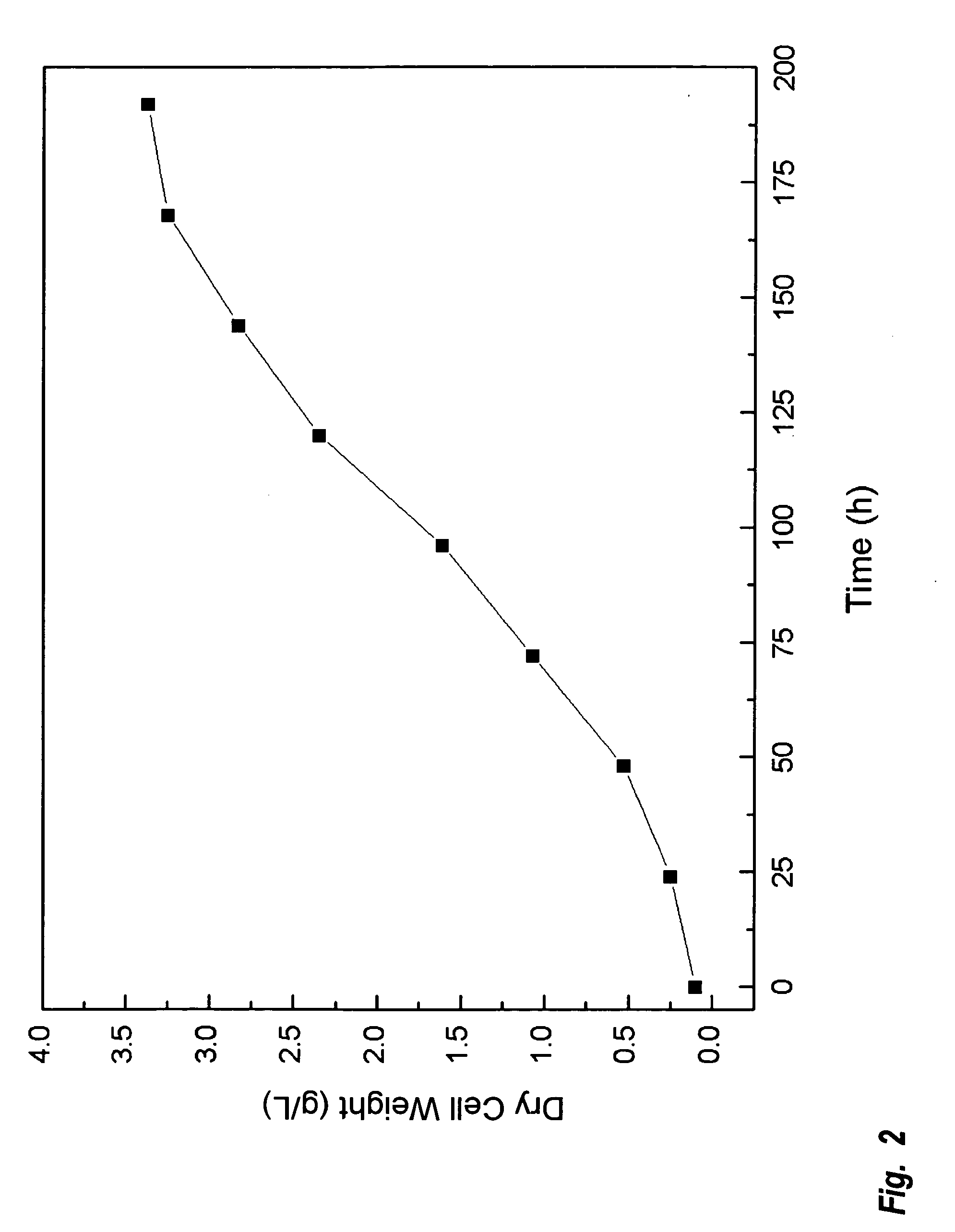
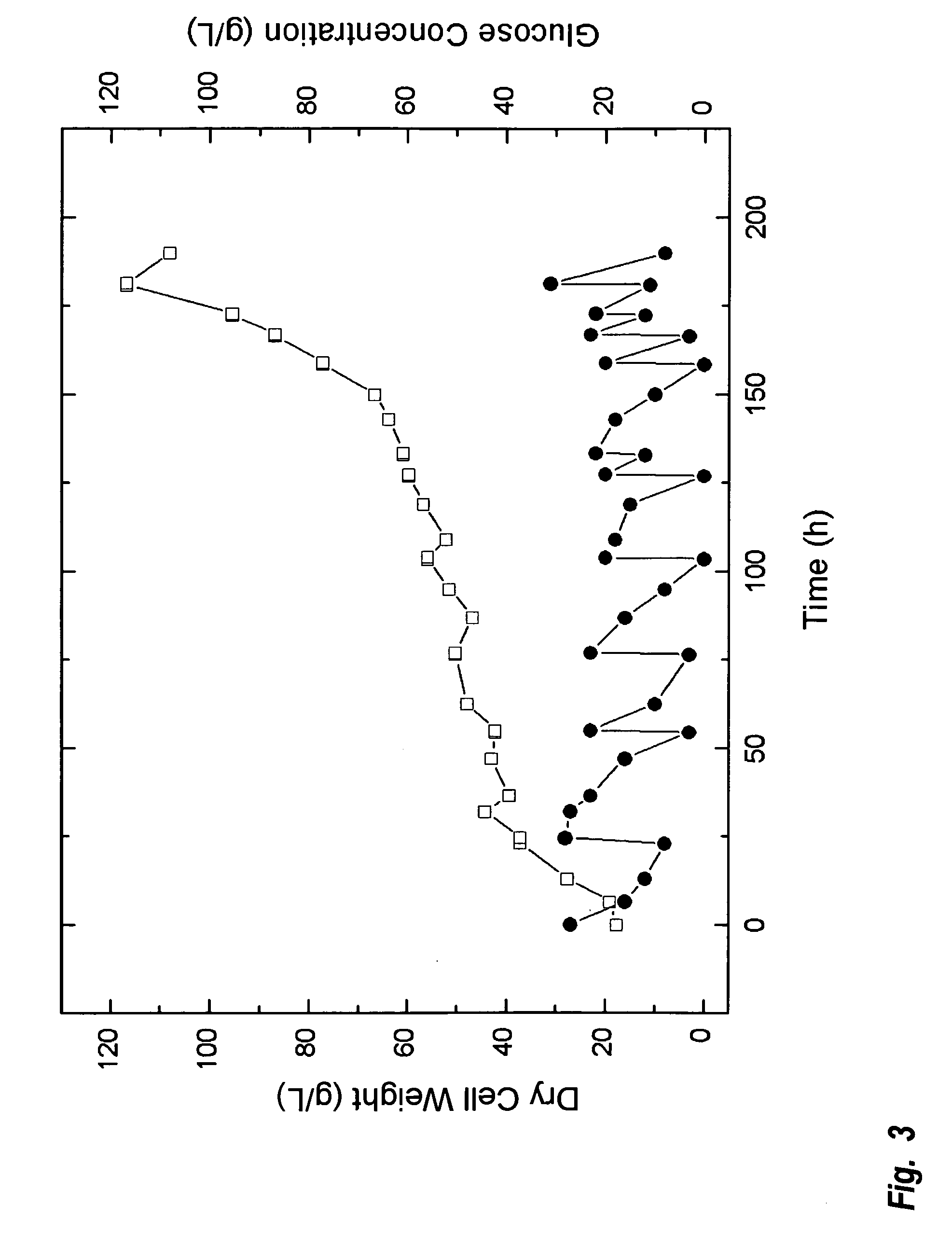
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a strain of microalga chlorella protothecoids, by screening a specific strain with characteristics of high yield of biomass and high oil content, cultivating the screened strain for high-cell-density growth for up to 108 grams of dry cell weight per liter of the suspension in a bioreactor using solutions containing carbohydrates as feed, harvesting and drying the high density cultivated algal cells to extract oil from the dried algal cells, and producing the biodiesel by reaction of catalyzed transesterification using the extracted oil as feedstock.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
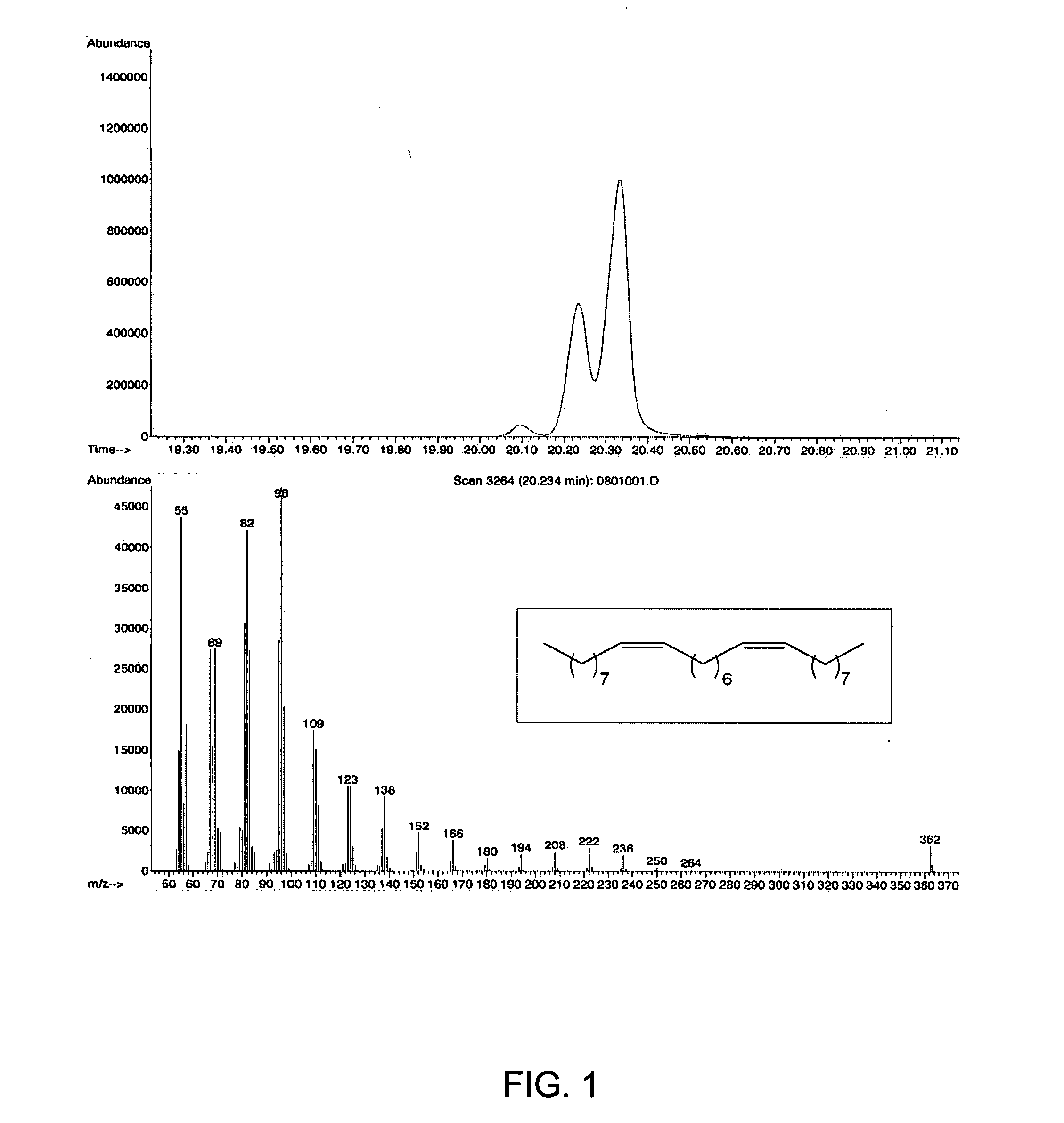
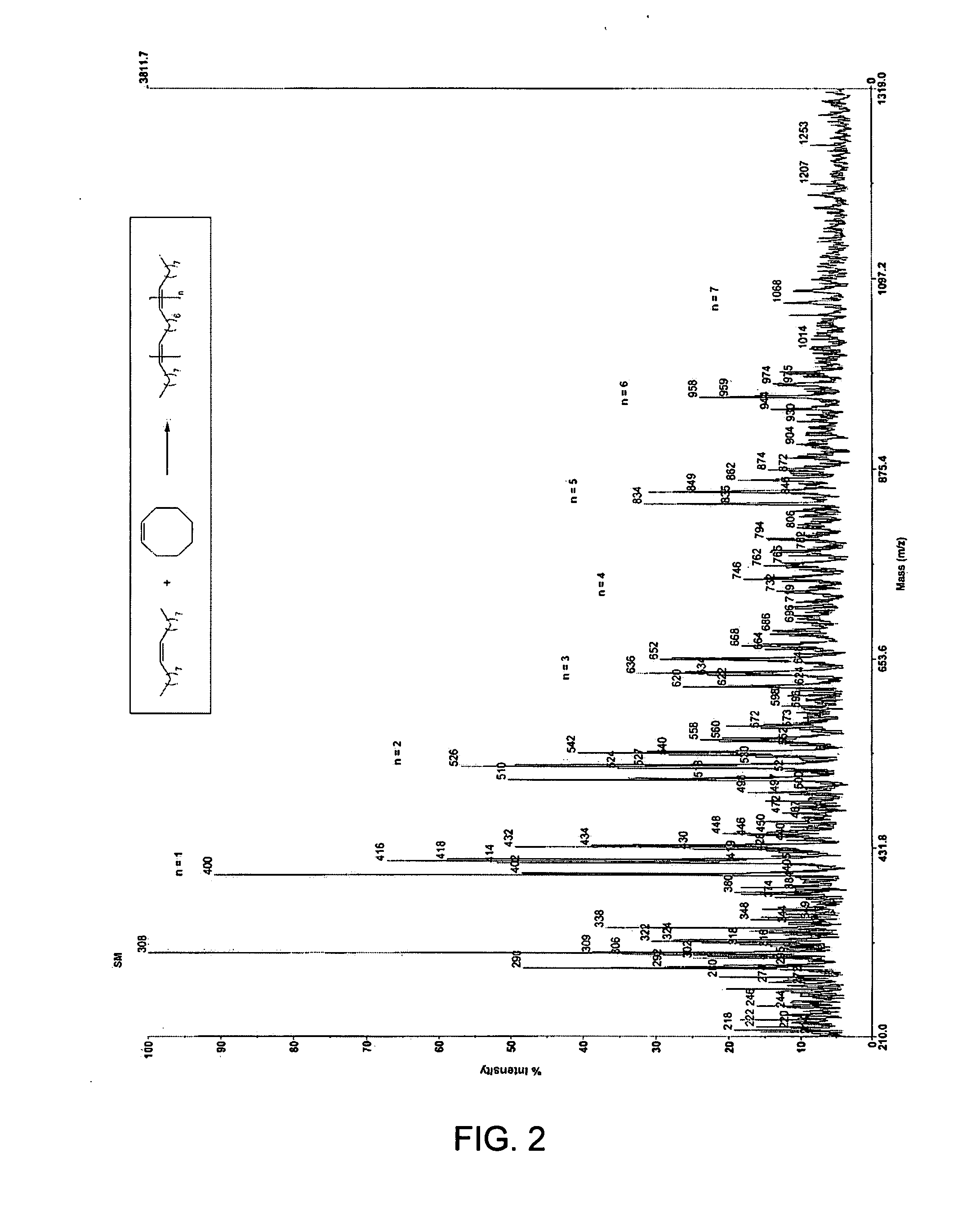
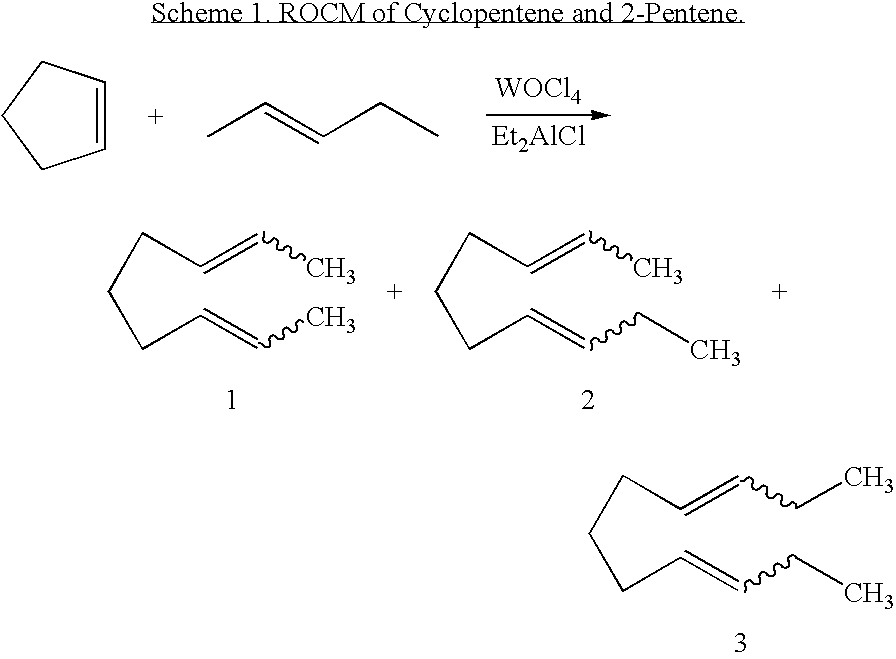
Ring opening cross-metathesis reaction of cyclic olefins with seed oils and the like
ActiveUS20080064891A1Fatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationOrganic synthesisRuthenium
This invention relates generally to olefin metathesis, and more particularly relates to the ring-opening, ring insertion cross-metathesis of cyclic olefins with internal olefins such as seed oils and the like. In one embodiment, a method is provided for carrying out a catalytic ring-opening cross-metathesis reaction, comprising contacting at least one olefinic substrate with at least one cyclic olefin as a cross metathesis partner, in the presence of a ruthenium alkylidene olefin metathesis catalyst under conditions effective to allow ring insertion cross metathesis whereby the cyclic olefin is simultaneously opened and inserted into the olefinic substrate. The invention has utility in the fields of catalysis, organic synthesis, and industrial chemistry.
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
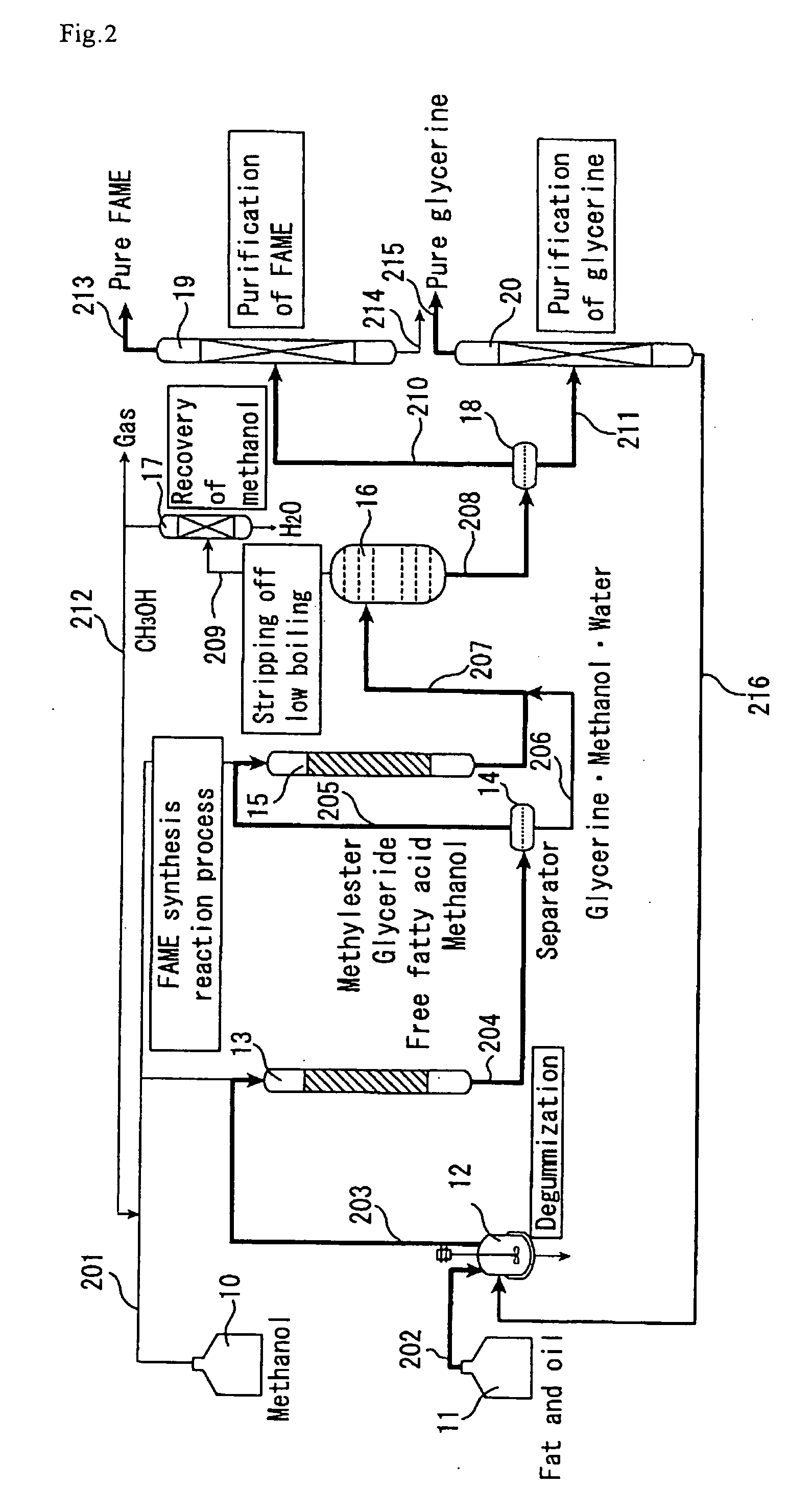
Method of production of fatty acid alkyl esters and/or glycerine and fatty acid alkyl ester-containing composition
InactiveUS20070167642A1Reduce energy consumptionIncrease contentFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBoiling pointGlycerol
The method of producing fatty acid alkyl esters and / or glycerine of the present invention is a method of producing high-purity fatty acid alkyl esters and / or glycerine advantageously from the energy viewpoint while reducing the energy consumption of the production, and the products can be used in various fields of application, for example in biodiesel fuels, foods, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. The above-mentioned method of producing fatty acid alkyl esters and / or glycerine by reacting a fat or oil with an alcohol using an insoluble solid catalyst in a reaction apparatus comprising at least one reactor, comprises (a) a step of obtaining low-boiling components removed liquid by removing low-boiling components or fraction from an effluent liquid of a reactor and (b) a step of separating the fatty acid alkyl esters and glycerine from the low-boiling components removed liquid, wherein an eluted active metal component of the insoluble solid catalyst in the effluent liquid of a reactor amounts to a level not higher than 1,000 ppm.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Lipid composition for infant formula and method of preparation
InactiveUS6034130AImprove stabilityBiocideFatty acid esterificationDocosahexaenoic acidLipid composition
Synthetic lipid composition in which the content and the distribution of the fatty acids are similar to those of human milk fat, containing less than 2% by weight of free fatty acids, in which palmitic acid is predominantly at the 2-position of the triacylglycerols and the arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids are distributed between the 1-, 2- and 3-positions and in particular predominantly at the 2-position of the triacylglycerols.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Process for producing alkyl esters from a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol
InactiveUS6878837B2High purityImpact on overall process costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationAluminateTransesterification
Alkyl esters of fatty acids, and high purity glycerin, are produced using a process comprising a set of transesterification reactions between a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol employing a heterogeneous catalyst, for example based on zinc aluminate, the water content in the reaction medium being controlled to a value that is below a given limiting value.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
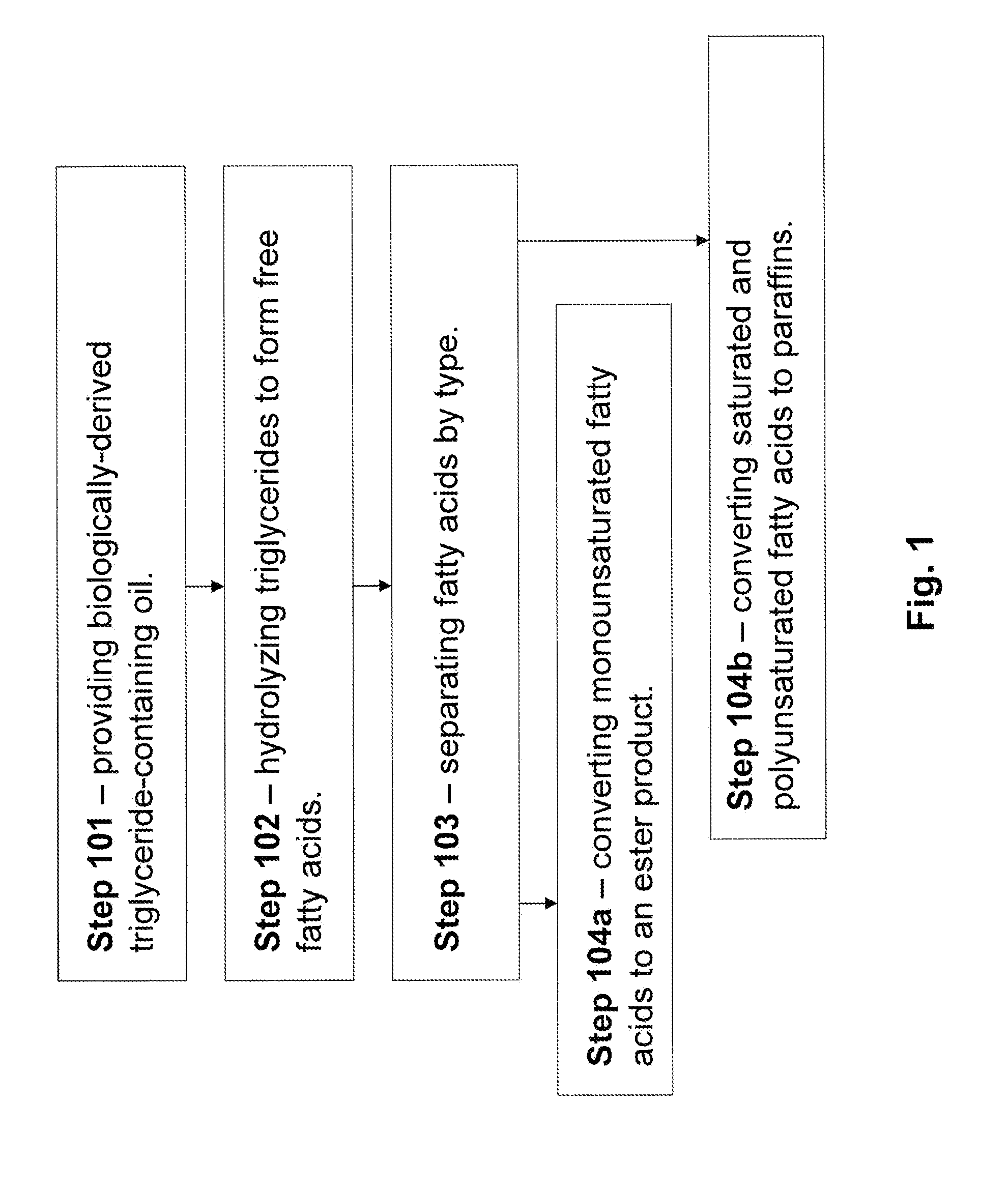
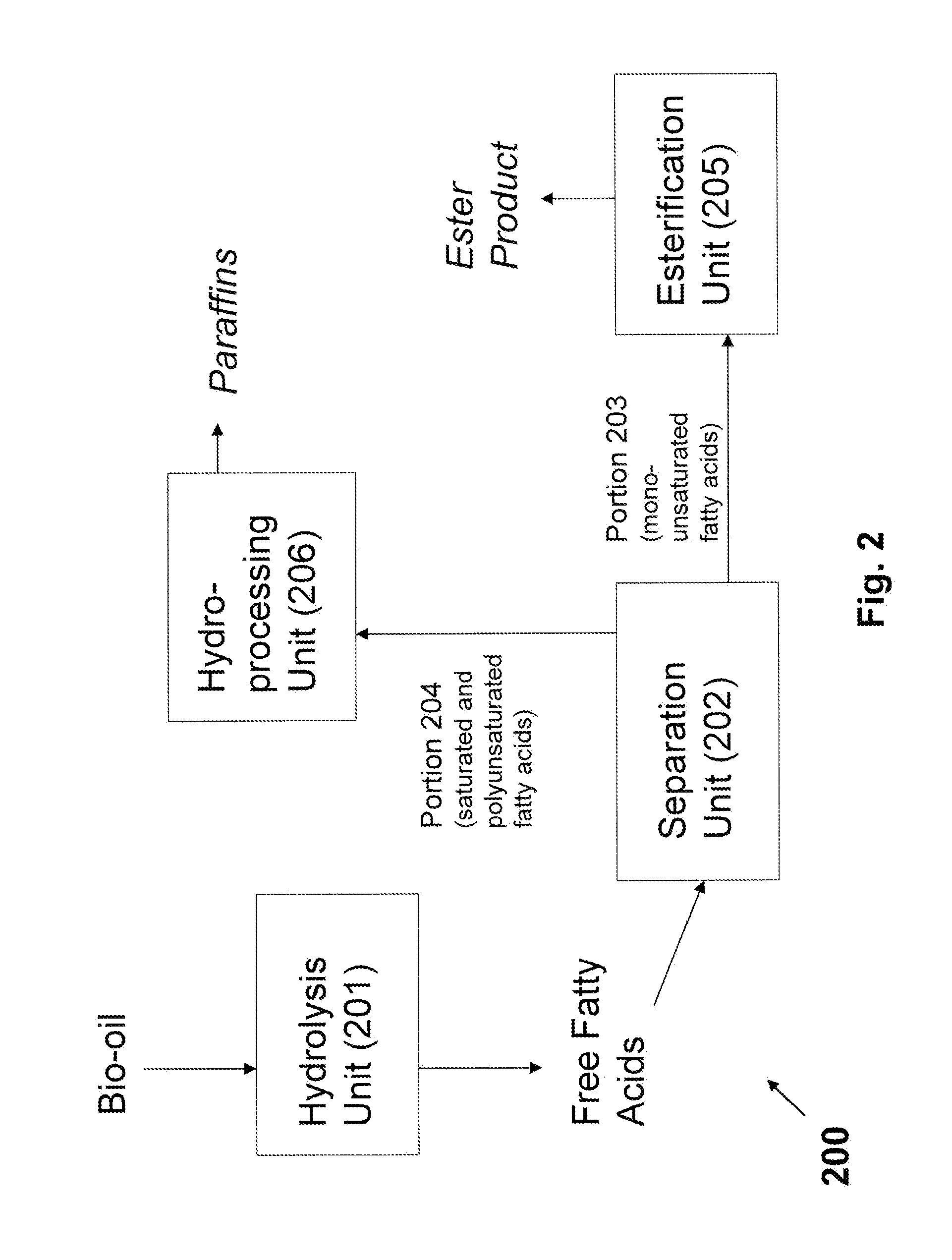
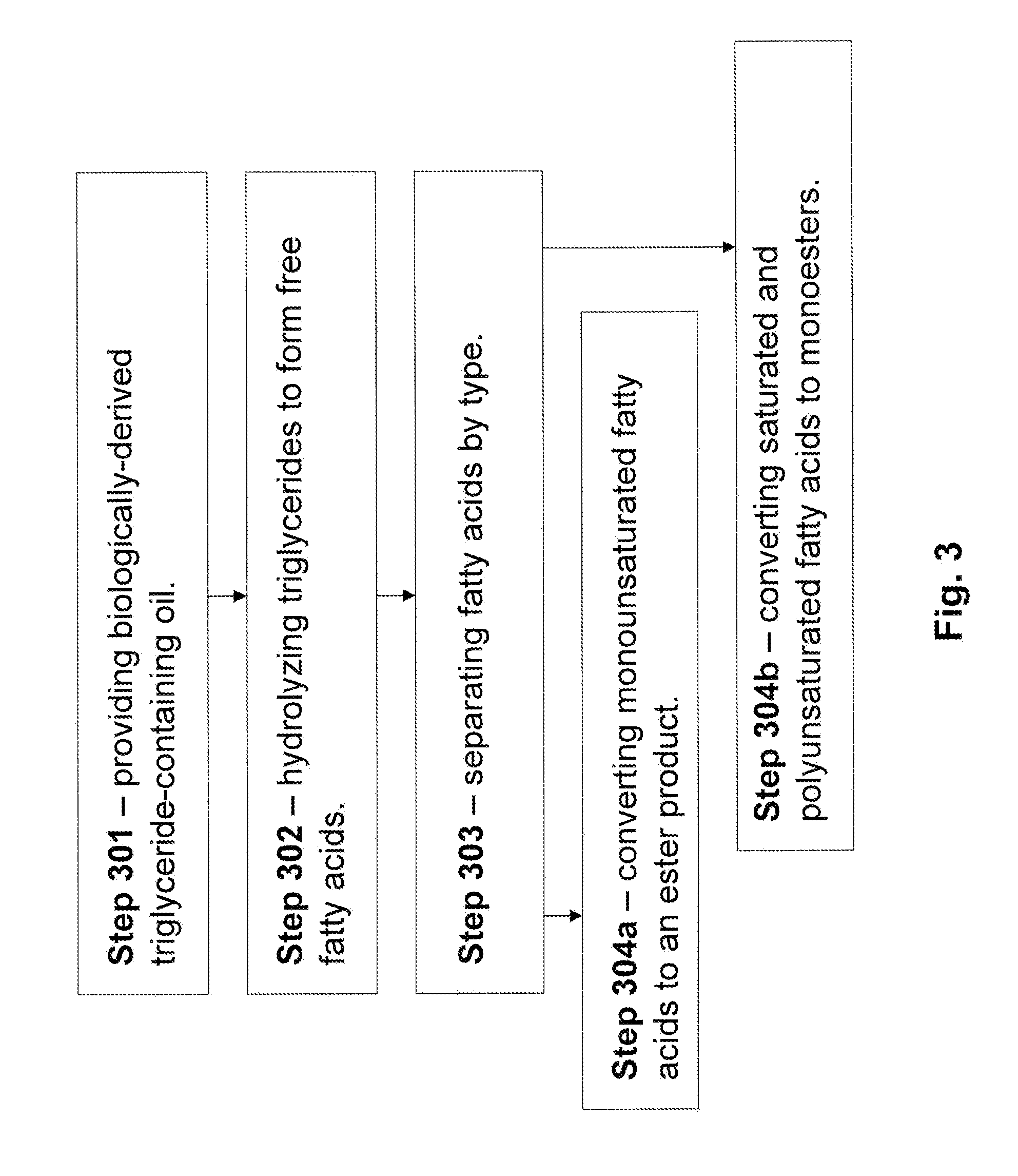
Production of Biofuels and Biolubricants From a Common Feedstock
InactiveUS20090084026A1Fatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonChemistryCommon source
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for processing triglyceride-containing, biologically-derived oils, wherein such processing comprises conversion of triglycerides to free fatty acids and the separation of these fatty acids by saturation type. Such separation by type enables the efficient preparation of both lubricants and transportation fuels from a common source using a single integrated method and / or system.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Fatty acid blends and uses therefor
ActiveUS8029579B2Maintain good propertiesEffect cold flow propertyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationPolymer scienceFatty acid methyl ester
Owner:CIBUS
Production and Purification of Esters of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
The present invention includes methods for producing and purifying esters of polyunsaturated fatty acids that include reacting a composition having triglycerides with polyunsaturated fatty acid residues in the presence of an alcohol and a base to produce an ester of a polyunsaturated fatty acid from the triglycerides. The composition can be a polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing composition that has not been conventionally processed. The reacted composition can be further processed by distillation.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Systems and methods for producing eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from algae
InactiveUS20100236137A1Inexpensive and energy-efficient methodOrganic chemistryFatty acid esterificationDocosahexaenoic acidEicosapentaenoic acid
Provided herein are systems and methods for producing eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and / or derivatives and / or mixtures thereof by growing algae that produce the oils containing EPA and / or DHA and / or derivatives and / or mixtures thereof, harvesting the algae with fish in one or more enclosed systems, and then processing fish to separate and purify the EPA and / or DHA. The multi-trophic systems provided herein comprise at least one enclosure that contains the algae and the fishes, and means for controllably feeding the algae to the fishes. Also provided herein are the lipid compositions extracted from the fishes.
Owner:LIVEFUELS
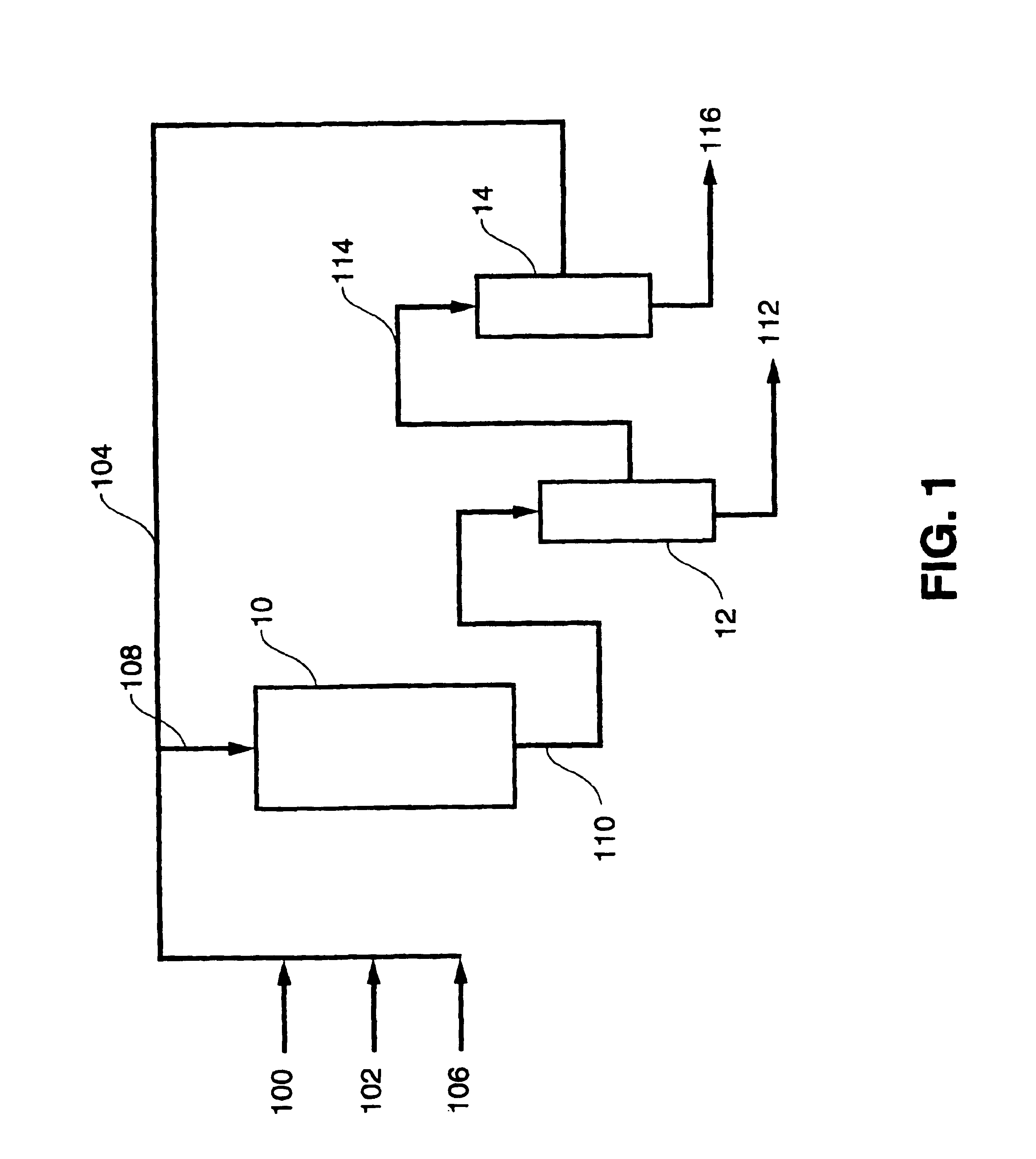
Continuous algal biodiesel production facility
Embodiments of the present invention concern methods, compositions, and apparatus for the continuous conversion of algal lipids into biodiesel. In some embodiments, the biodiesel is formed in a multi-step sequence, the first steps occurring in the presence of water and a strong acid wherein the lipids are released from the algae by means of mechanical and chemical action and are then hydrolyzed to free fatty acids. In a subsequent step, this free fatty acid mixture is reacted with methanol to generate fatty acid methyl esters (also known as biodiesel). Such methods produce biodiesel from algal lipids without the requirement for separate algal cell lysis or lipid extraction or purification prior to the acid catalysis sequence. In other embodiments, the multi-step acid catalysis sequence occurs at 100° C. at two atmospheres of pressure.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Glyceride compositions and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20040209953A1Fast absorptionImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMonoglycerideDiglyceride
Disclosed are glyceride compositions, methods of making the glyceride compositions, and nutritional formulations containing the glyceride compositions. The glyceride compositions contain predominantly monoglycerides and diglycerides carrying one or more long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Also disclosed are methods of using the glyceride compositions and nutritional formulations.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Simultaneous synthesis and purification of a fatty acid monoester biodiesel fuel
ActiveUS20070158270A1Reduce contentLow costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselAlcohol
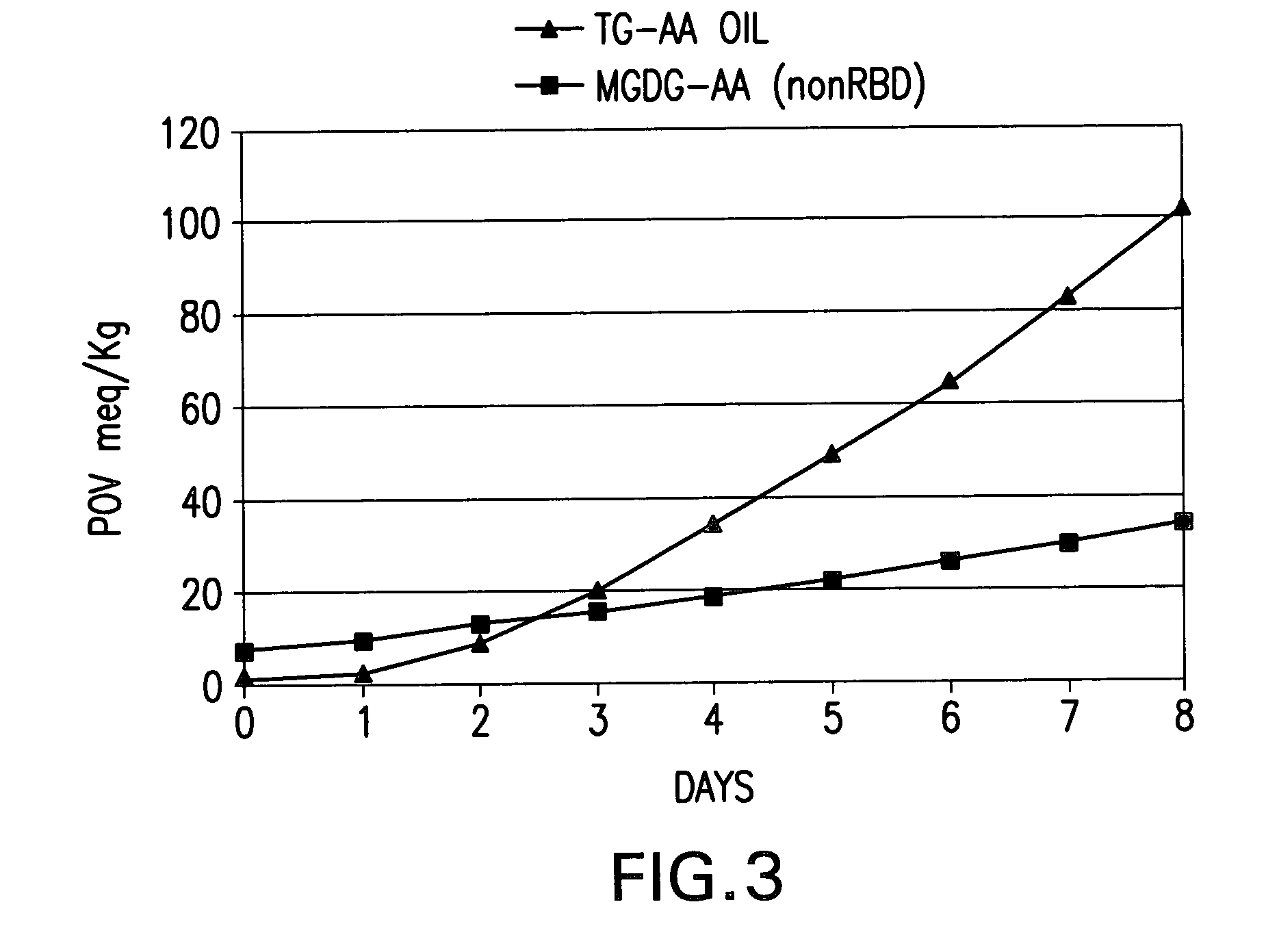
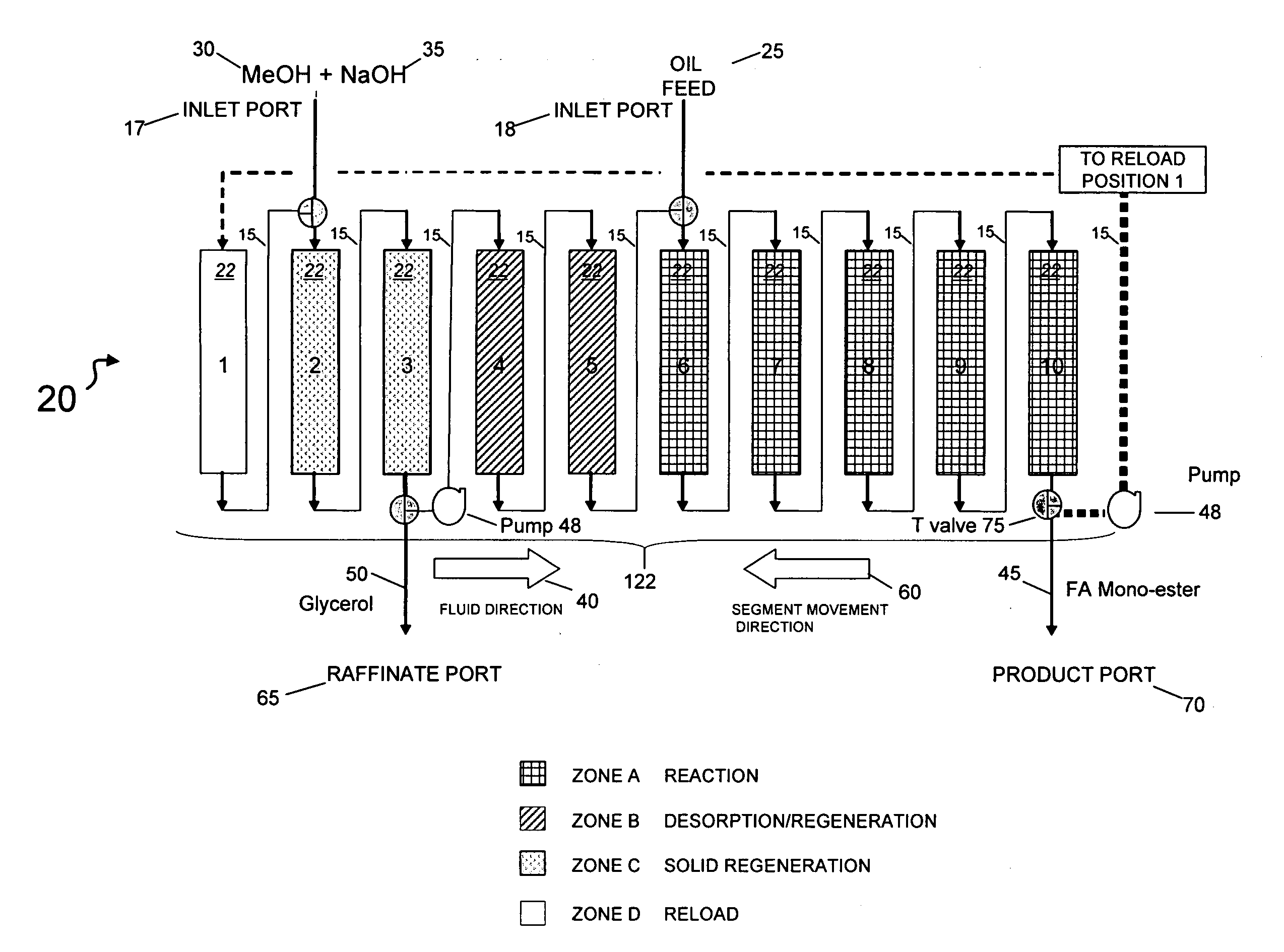
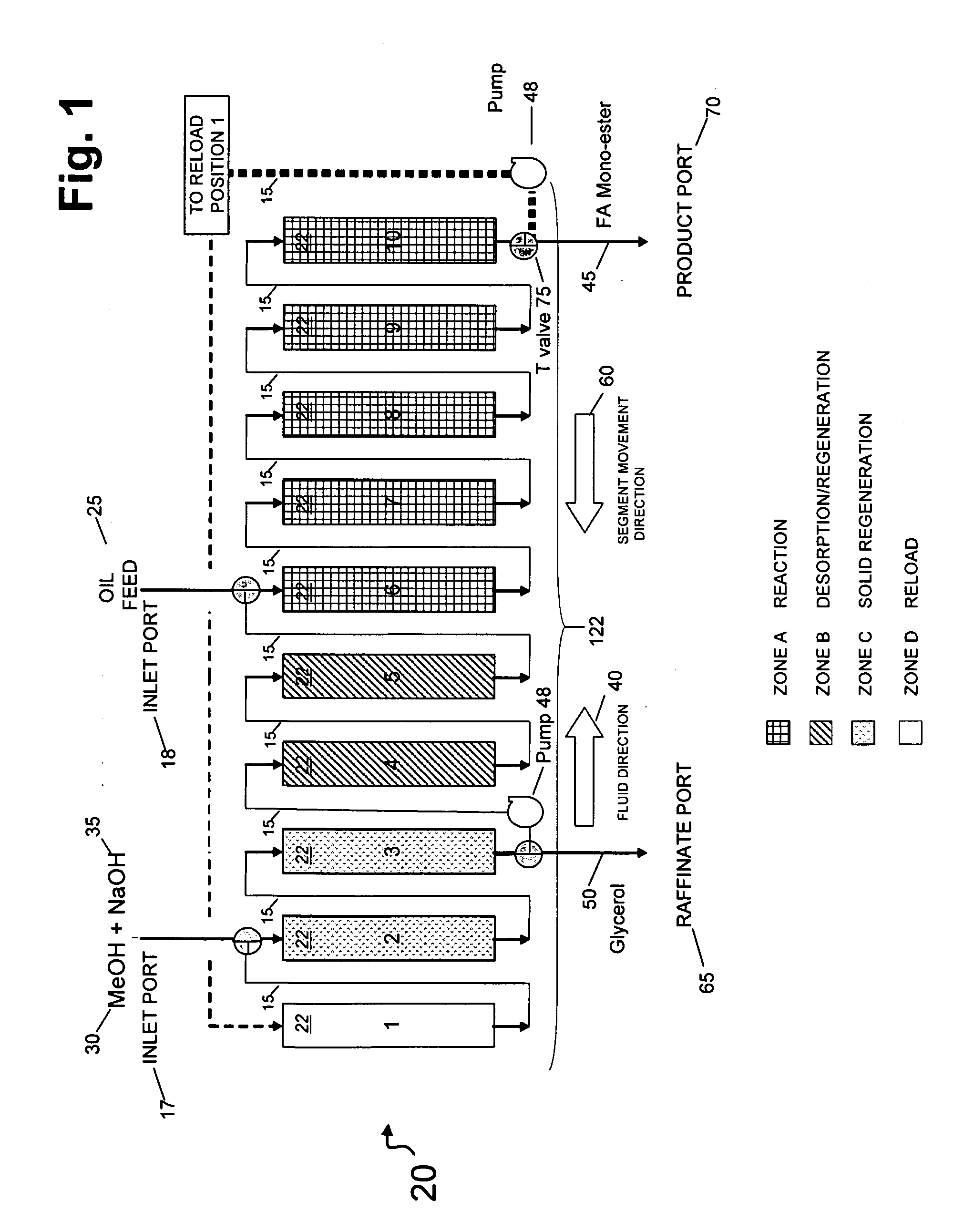
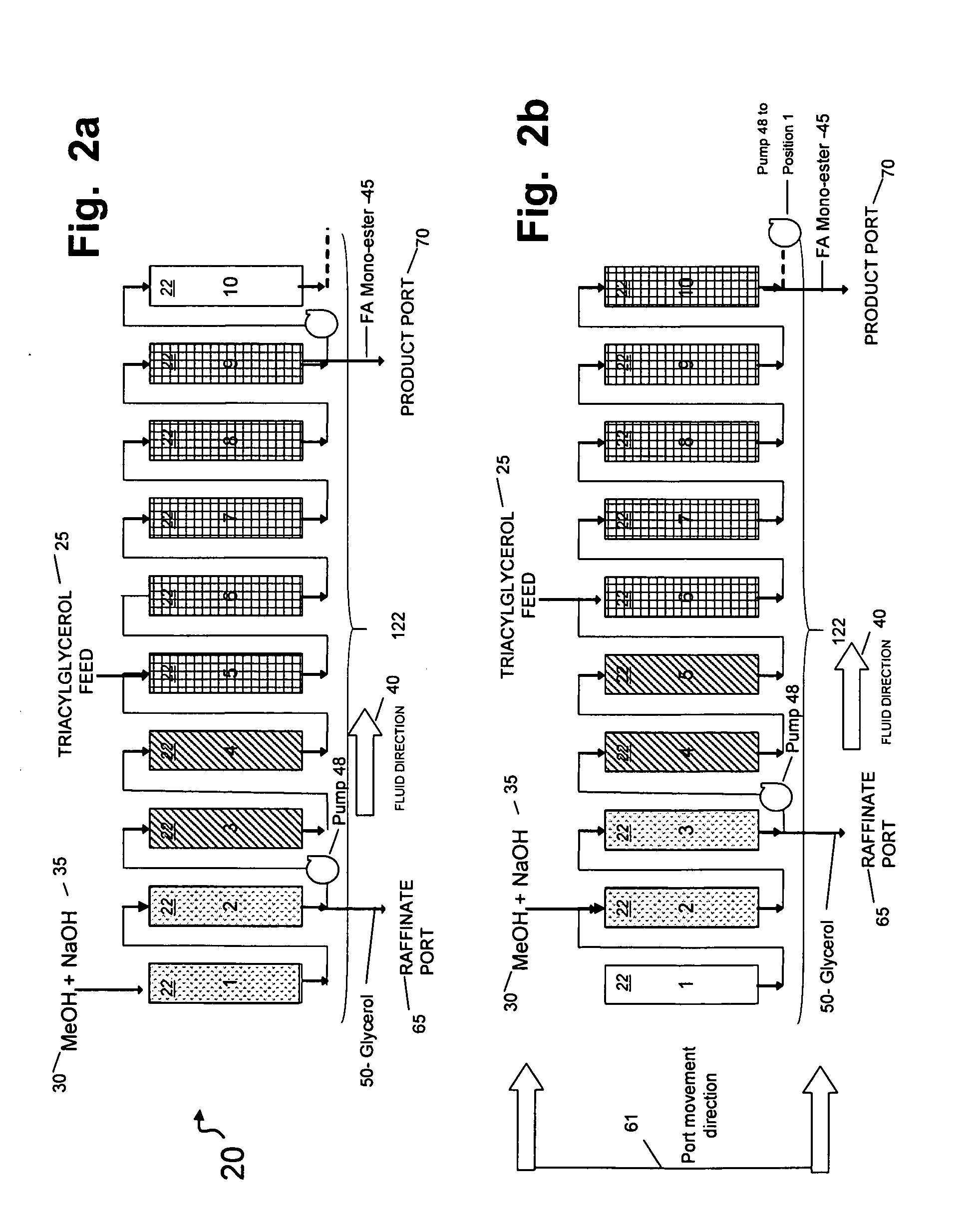
Simultaneous synthesis and purification of a fatty acid monoester biodiesel fuel from a triacylglycerol feedstock is described. In an exemplary method, the triacylglycerol feedstock is continuously contacted with a catalytic chromatographic bed comprising a first (solid phase) basic catalyst through a first port of a simulated moving bed chromatographic apparatus. A monohydric alcohol and optional second (mobile phase) basic catalyst is continuously contacted with the catalytic chromatographic bed through a second port and pumped in a first direction toward the triacylglycerol feedstock to contact the triacylglycerol in a reaction zone of the catalytic chromatographic bed where the fatty acid monoester and glycerol coproduct are formed. The fatty acid monoester is removed from the reaction zone through a product port of the simulated moving bed apparatus. Segments of the catalytic chromatographic bed are incrementally moved in a second direction, opposite the first direction, and the glycerol is removed from a raffinate port located opposite the product port of the apparatus.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com