Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
627results about "Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeleton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Premium synthetic lubricant base stock having at least 95% non-cyclic isoparaffins
InactiveUS6080301ARefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationParaffin waxAlkane
A premium synthetic lubricating oil base stock having a high VI and low pour point is made by hydroisomerizing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesized waxy, paraffinic feed wax and then dewaxing the hydroisomerate to form a 650-750 DEG F.+ dewaxate. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750 DEG F., from which it continuously boils up to at least 1050 DEG F. and has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350 DEG F. The feed is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The 650-750 DEG F.+ dewaxate is fractionated into two or more base stocks of different viscosity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Production of synthetic lubricant and lubricant base stock without dewaxing
InactiveUS6103099AThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAutomatic transmissionBoiling point
A lubricating base stock useful for forming lubricants such as a multigrade automotive oils, automatic transmission oils, greases and the like is prepared by hydroisomerizing a waxy hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the 650-750 DEG F. range and an end point of at least 1050 DEG F., synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch hydrocarbon synthesis process. The hydroisomerization forms a hydroisomerate containing the desired base stock which is recovered, without dewaxing the hydroisomerate. The hydroisomerization is conducted at conditions effective to convert at least 67 wt. % of the 650-750 DEG F.+ waxy feed hydrocarbons to lower boiling hydrocarbons. When combined with a standard lubricant additive package, these base stocks have been formed into multigrade automotive crankcase oils, transmission oils and hydraulic oils meeting the specifications for these oils.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Catalytic dewaxing with trivalent rare earth metal ion exchanged ferrierite
InactiveUS6013171AMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCation-exchange capacityIon exchange
A process for dewaxing waxy hydrocarbonaceous materials, such as hydrocarbon fuel and lubricating oil fractions to reduce their cloud and pour points comprises reacting the material with hydrogen in the presence of a dewaxing catalyst comprising at least one metal catalytic component and ferrierite in which at least a portion of its cation exchange positions are occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations. The rare earth ion exchanged ferrierite catalyst has good selectivity for lubricating oil production, particularly when dewaxing a Fischer-Tropsch wax hydroisomerate. Preferably at least 10% and more preferably at least 15% of the ferreirite cation exchange capacity is occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons
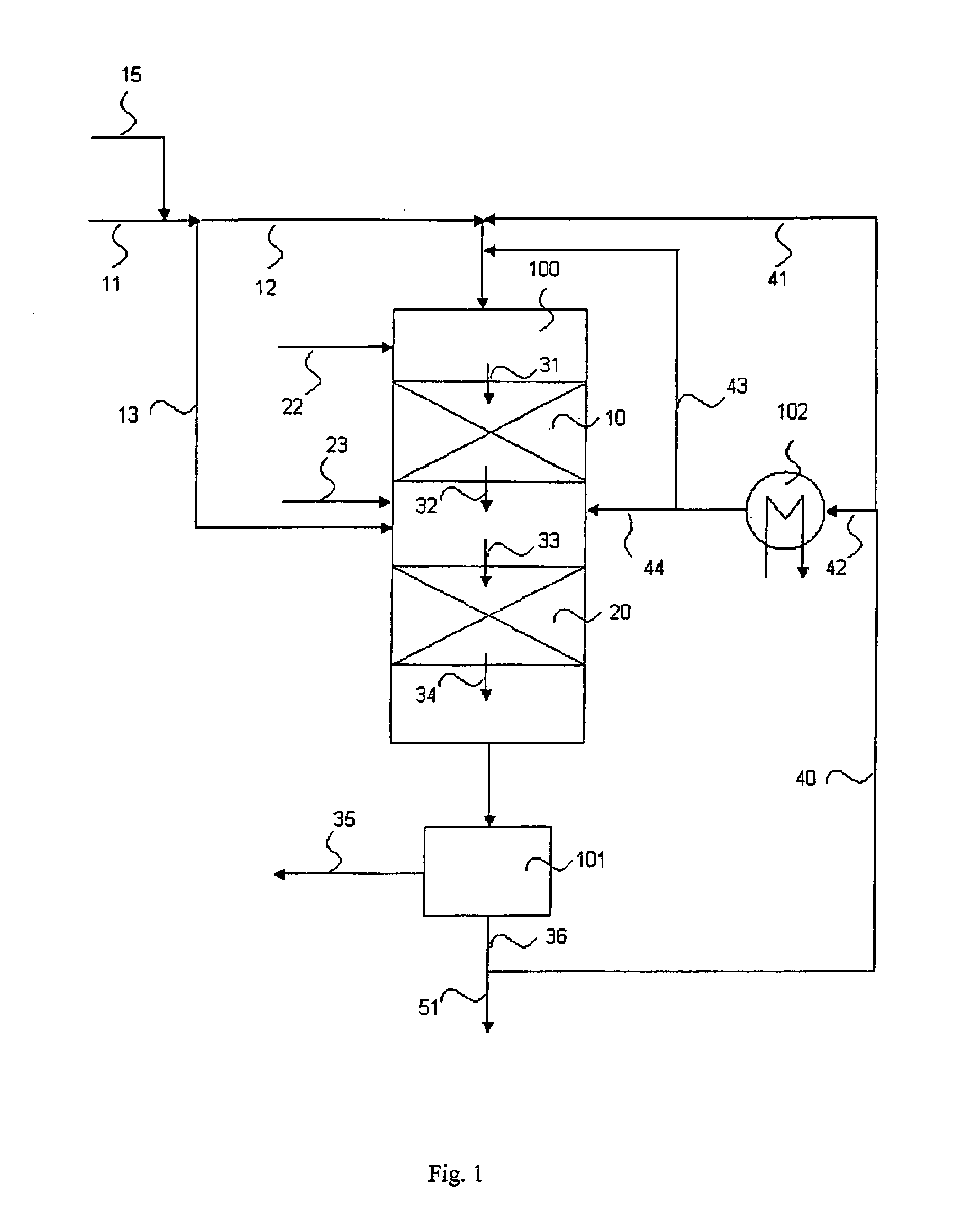
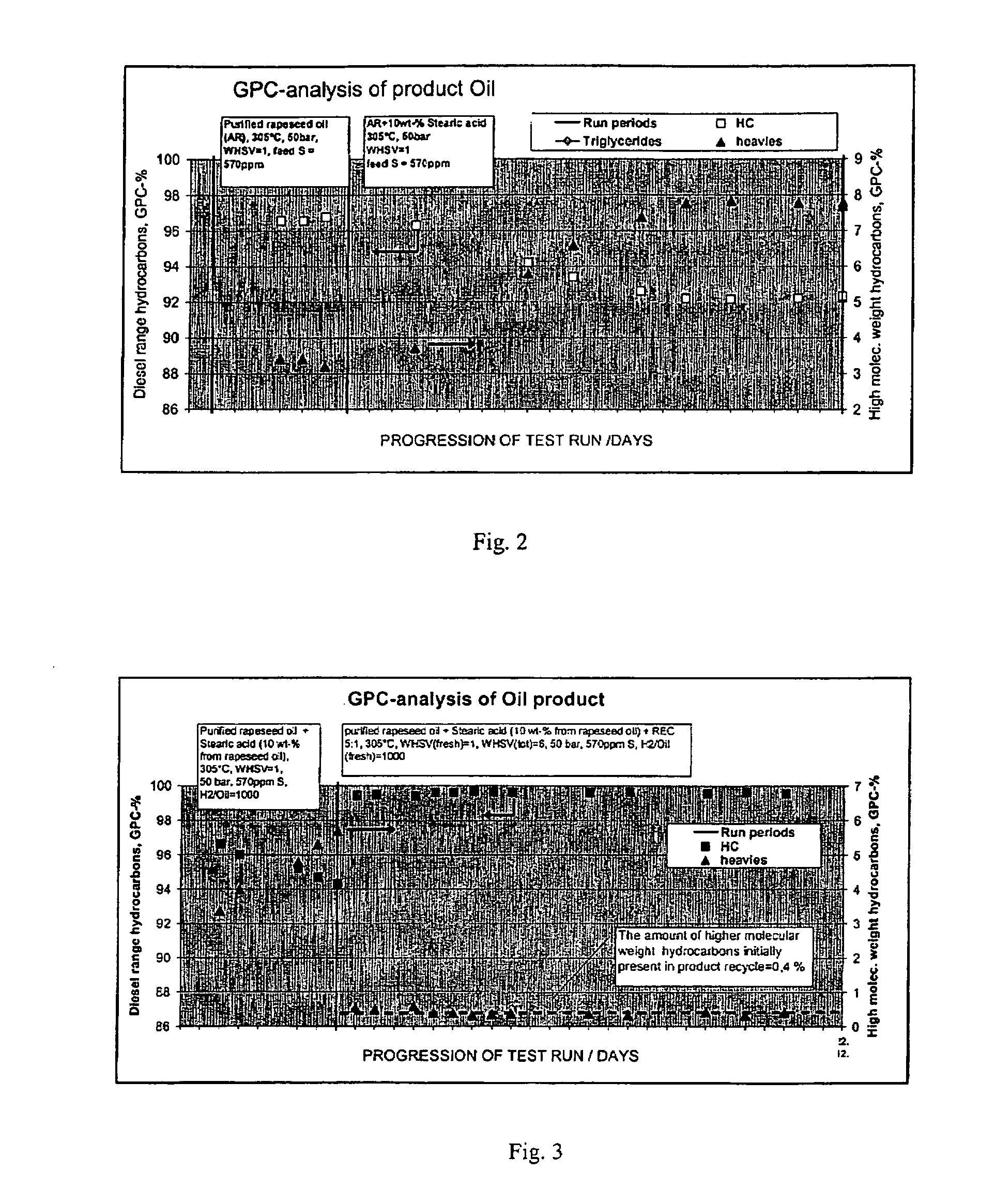
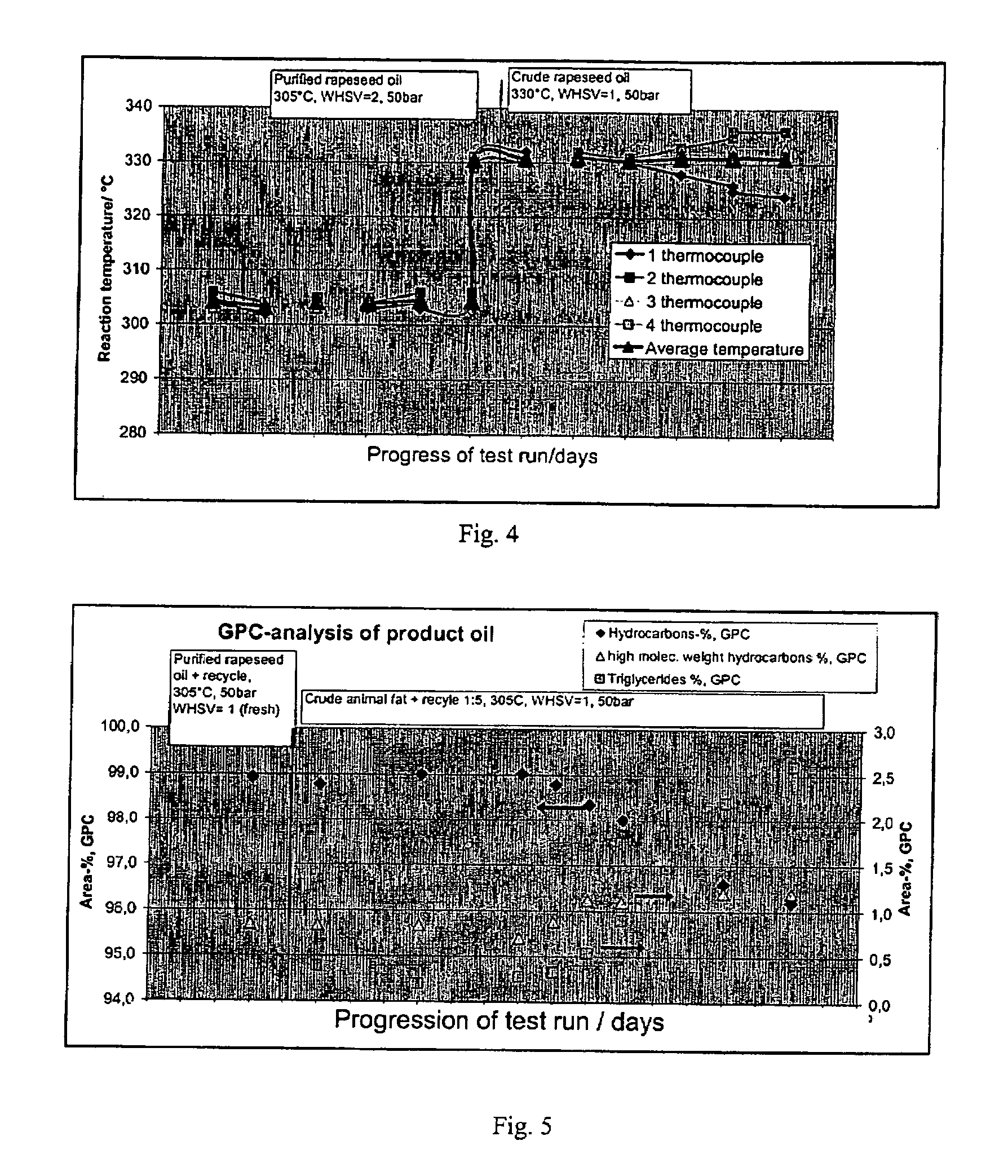
ActiveUS20070010682A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons wherein a feed is hydrotreated in a hydrotreating step and isomerised in an isomerisation step, and a feed comprising fresh feed containing more than 5 wt % of free fatty acids and at least one diluting agent is hydrotreated at a reaction temperature of 200-400° C., in a hydrotreating reactor in the presence of catalyst, and the ratio of the diluting agent / fresh feed is 5-30:1.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Finished lubricating comprising lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
ActiveUS20050133407A1Improve Oxidation StabilityReduce wearRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMolecular sieveWax
A process for manufacturing a finished lubricant by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an isomerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil, whereby a lubricating base oil is produced having specific desired properties; and e) blending the lubricating base oil with at least one lubricant additive.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for reducing haze point in bright stock
InactiveUS6051129ASuperior lube oil yieldHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenHaze
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS7816570B2Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Premium synthetic lubricants
InactiveUS6475960B1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationAntioxidantBoiling point
Premium synthetic lubricants comprise a synthetic isoparaffinic hydrocarbon base stock and an effective amount of at least one, and typically a plurality of lubricant additives such as a detergent, dispersant, antioxidant, antiwear additive, pout point depresant, VI improver and the like. The base stock is derived from a waxy, paraffinic, Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon feed fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F. and continuously boiling up to at least 1050° F., by a process which comprises hydroisomerizing the feed and dewaxing the isomerate. The waxy feed has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. and is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The lubricant may also contain hydrocarbonaceous and synthetic base stock material. Lubricants, such as fully formulated multigrade automotive crankcase and transmission oils formed by adding a suitable additive package to the isoparaffinic base stock have exhibited performance superior to similar fully formulated oils based on both PAO and conventional, petroleum derived base stocks.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Production of Aviation Fuel from Biorenewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090158637A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationAlkaneVegetable oil
A process has been developed for producing aviation fuel from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils and animal fats and oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating to provide n-paraffins having from about 8 to about 24 carbon atoms. At least some of the n-paraffins are isomerized to improve cold flow properties. At least a portion of the paraffins are selectively cracked to provide paraffins meeting specifications for different aviation fuels such as JP-8.
Owner:UOP LLC
Production of Blended Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090301930A1Minimize the numberReduce the amount requiredRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonBiofuelsParaffin waxEngineering
A process for producing a blended fuel from a paraffin rich component and a cyclic rich component, where each of the components are generated from a renewable feedstock, is presented. The paraffin rich component is generated from glycerides and free fatty acids in feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The cyclic rich component is generated from biomass derived pyrolysis oil. The source of the animal or plant oil and the biomass may be the same renewable source.
Owner:UOP LLC
Production of high viscosity lubricating oil stock with improved ZSM-5 catalyst
InactiveUS6294077B1Low pour pointHigh viscosity indexMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenParaffin oils
The present invention is a process for producing a high viscosity index and low pour point lubricating oil base stock which comprises catalytically converting a hydrotreated hydrocarbon lube oil feedstock containing waxy paraffins in the presence of hydrogen and in the presence of a low acidity ZSM-5 catalyst having a highly dispersed noble metal component. The ZSM-5 catalyst is subjected to controlled acidity reduction to an alpha value below 15 prior to incorporation of the noble metal component.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Method for the manufacture of hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20060161032A1Reduce hydrogen consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenDistillation
Feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to hydrocarbons in diesel fuel distillation range by contacting with a supported catalyst comprising VIII group metal / metals, whereby the consumption of hydrogen is decreased.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Process for conversion of biomass to fuel
ActiveUS20090069610A1Meet growth needsEasy to processFatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneChain length
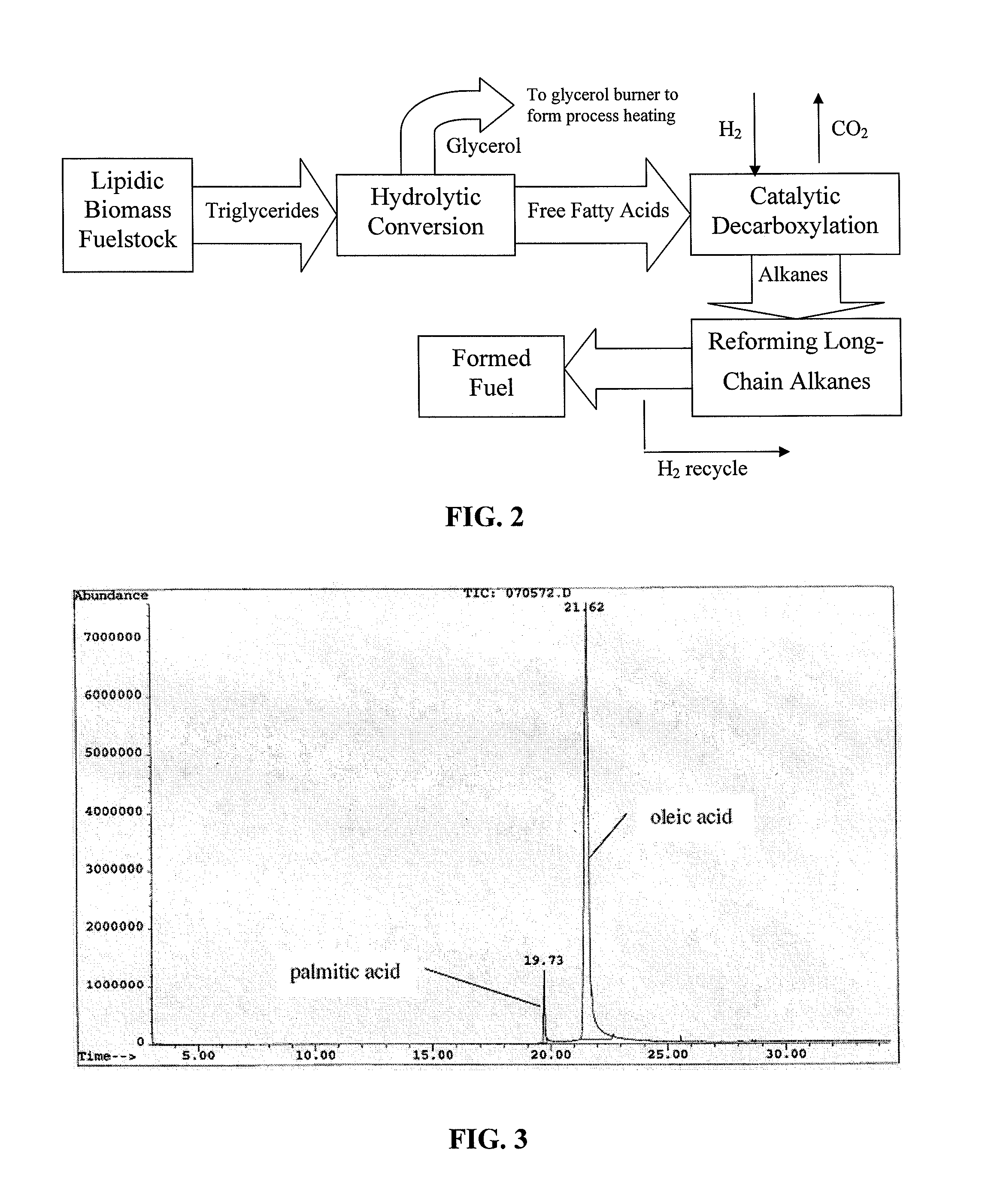
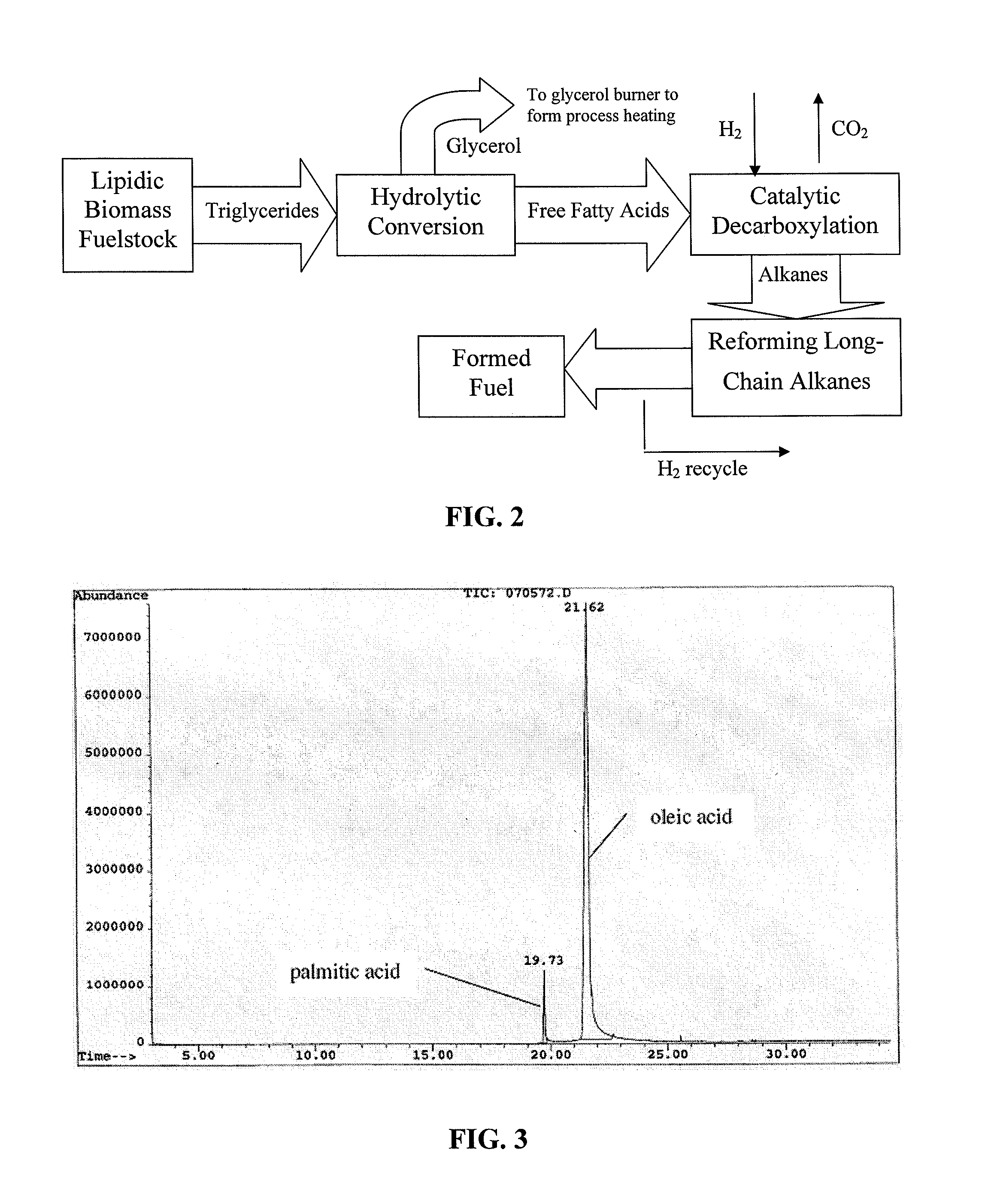
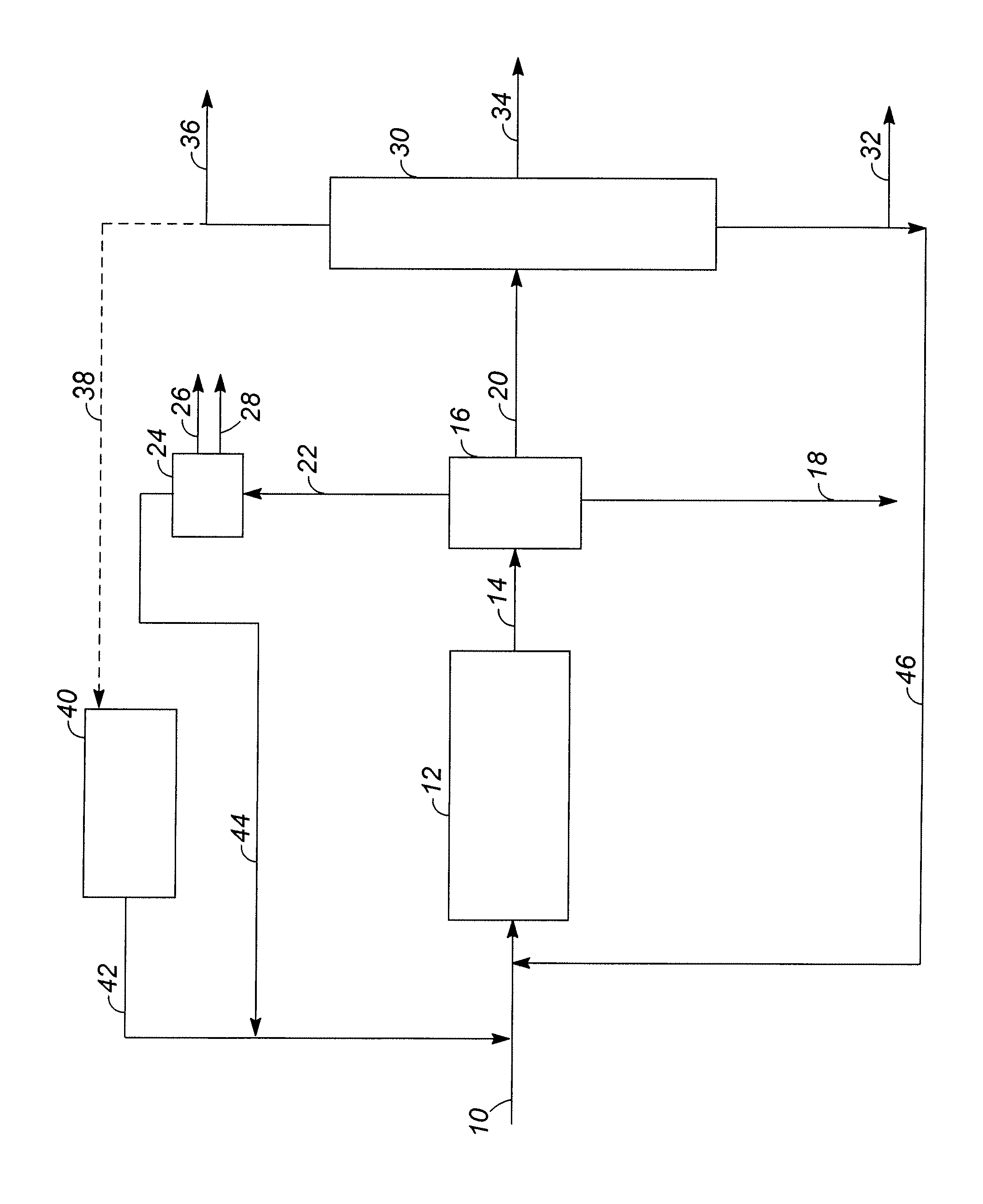
The present invention is directed to processes for the direct conversion of lipidic biomass fuelstock to combustible fuels. In particular, the invention provides a process for the direct conversion of animal fats to transportations fuels suitable as replacement for petroleum-derived transportation fuels. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of hydrolyzing a lipidic biomass to form free fatty acids, catalytically deoxygenating the free fatty acids to form n-alkanes, and reforming at least a portion of the n-alkanes into a mixture of compounds in the correct chain length, conformations, and ratio to be useful transportation fuels. Particularly, the product prepared according to the invention comprises mixtures of hydrocarbon compounds selected from the group consisting of n-alkanes, isoalkanes, aromatics, cycloalkanes, and combinations thereof.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Production of Aviation Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090283442A1Improve solubilityMinimize severityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonIsomerizationBoiling point
A hydrocarbon product stream having hydrocarbons with boiling points in the aviation fuel range is produced from renewable feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating, deoxygenating, isomerization, and selectively hydrocracking the feedstock to produce paraffinic hydrocarbons having from about 9 to about 16 carbon atoms and a high iso / normal ratio in a single reaction zone containing a multifunctional catalyst, or set of catalysts, having hydrogenation, deoxygenation, isomerization and selective hydrocracking functions.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for the manufacture of hydrocarbons
ActiveUS7491858B2Reduce hydrogen consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenDistillation
Feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to hydrocarbons in diesel fuel distillation range by contacting with a supported catalyst comprising VIII group metal / metals, whereby the consumption of hydrogen is decreased.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Composition of lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
ActiveUS7083713B2Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationCycloparaffinsBase oil
A composition of lubricating base oil having a weight percent of all molecules with at least one aromatic function less than 0.30, a weight percent of all molecules with at least one cycloparaffin function greater than 10, and a ratio of weight percent of molecules with monocycloparaffins to weight percent of molecules with multicycloparaffins greater than 15.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Premium synthetic lubricant base stock (Law734) having at least 95% noncyclic isoparaffins
A premium synthetic lubricating oil base stock having a high VI and low pour point is made by hydroisomerizing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesized waxy, paraffinic feed wax and then dewaxing the hydroisomerate to form a 650-750° F.+ dewaxate. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F., from which it continuously boils up to at least 1050° F. and has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. The feed is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The 650-750° F.+ dewaxate is fractionated into two or more base stocks of different viscosity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Production of Diesel Fuel from Biorenewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090077866A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon by hydrogenationSolubilityHydrogen
A process has been developed for producing diesel boiling range fuel from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils and animal oils, fats, and greases. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating i.e. decarboxylating, decarbonylating, and / or hydrodeoxygenating to provide a hydrocarbon fraction useful as a diesel boiling range fuel or diesel boiling range fuel blending component. If desired, the hydrocarbon fraction can be isomerized to improve cold flow properties. A portion of the hydrogenated and deoxygenated feedstock is selectively separated and then recycled to the treatment zone to increase the hydrogen solubility of the reaction mixture.
Owner:UOP LLC
Lithium aluminate layered catalyst and a selective oxidation process using the catalyst
InactiveUS6858769B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrogenDehydrogenation
A catalyst for the selective oxidation of hydrogen has been developed. It comprises an inert core such as cordierite and an outer layer comprising a lithium aluminate support. The support has dispersed thereon a platinum group metal and a promoter metal, e.g. platinum and tin respectively. This catalyst is particularly effective in the selective oxidation of hydrogen in a dehydrogenation process.
Owner:UOP LLC
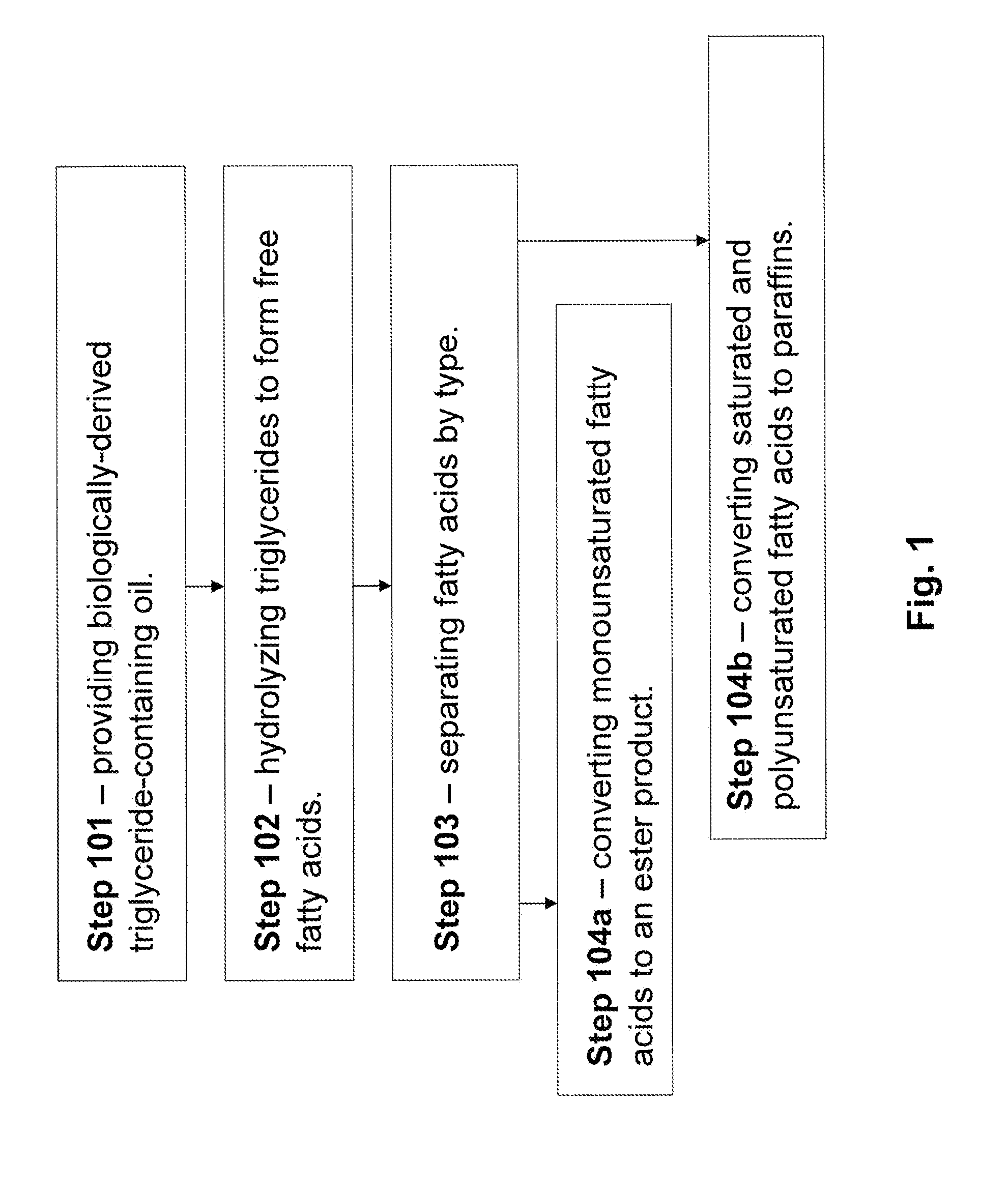
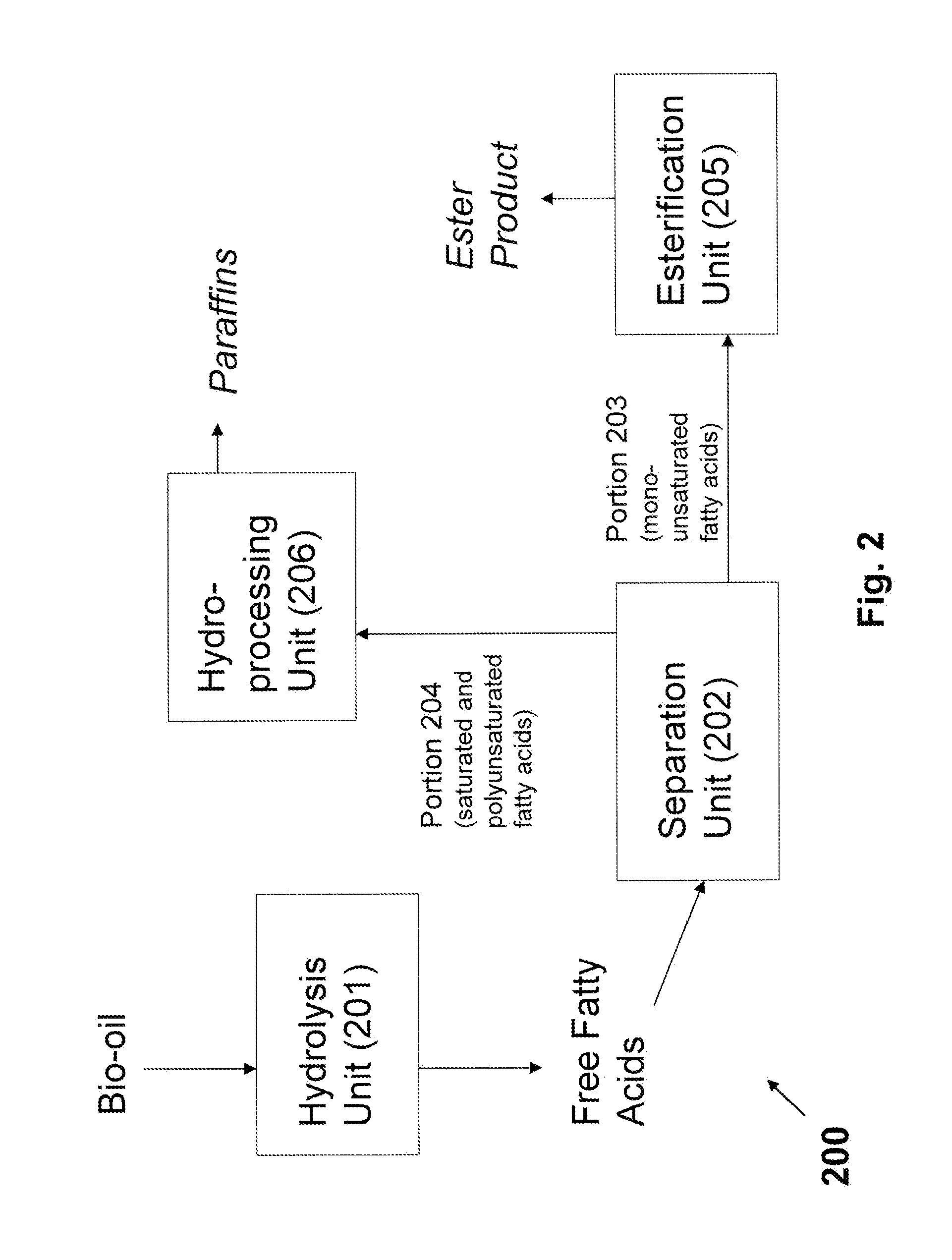
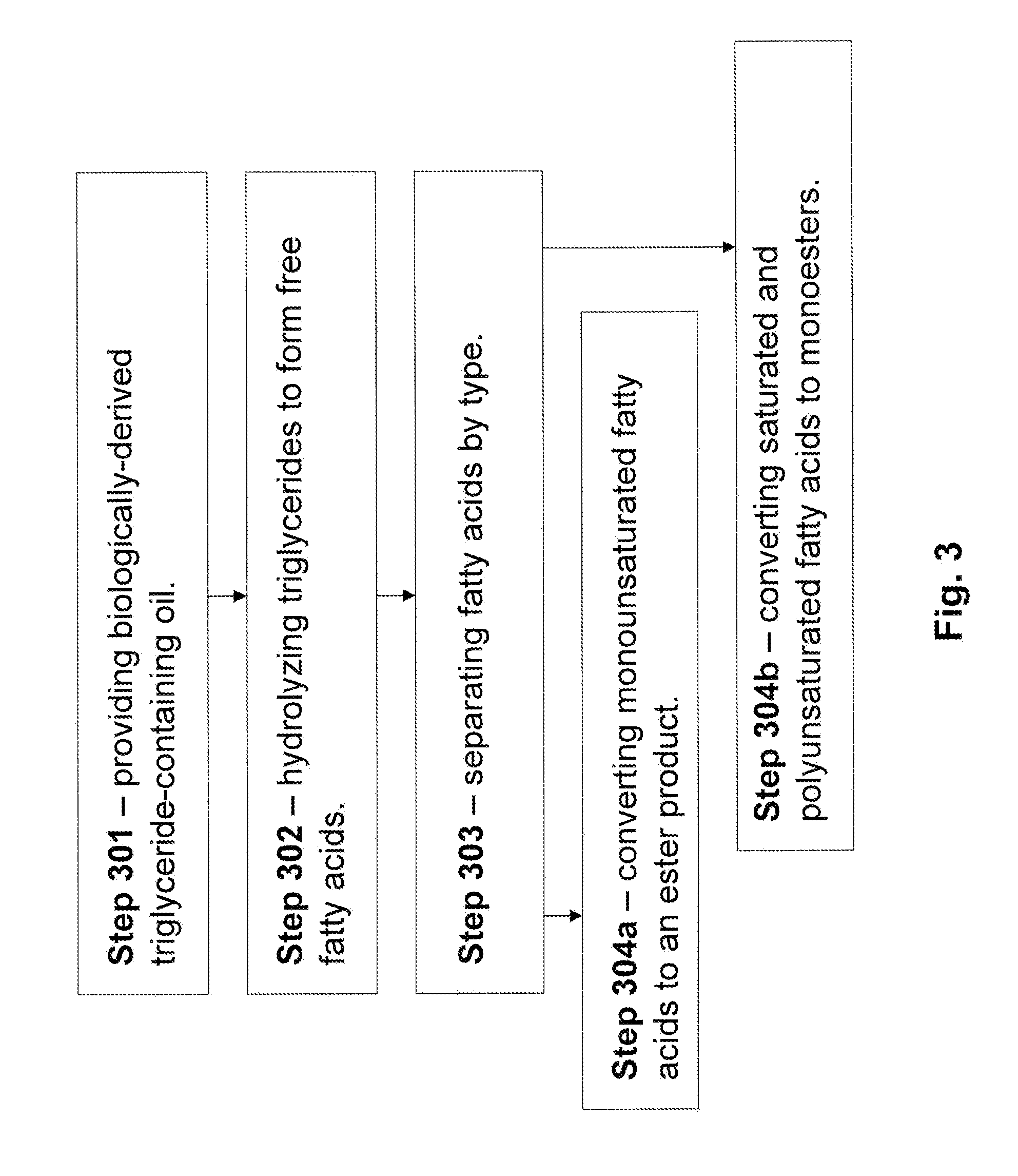
Production of Biofuels and Biolubricants From a Common Feedstock
InactiveUS20090084026A1Fatty acid esterificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonChemistryCommon source
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for processing triglyceride-containing, biologically-derived oils, wherein such processing comprises conversion of triglycerides to free fatty acids and the separation of these fatty acids by saturation type. Such separation by type enables the efficient preparation of both lubricants and transportation fuels from a common source using a single integrated method and / or system.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
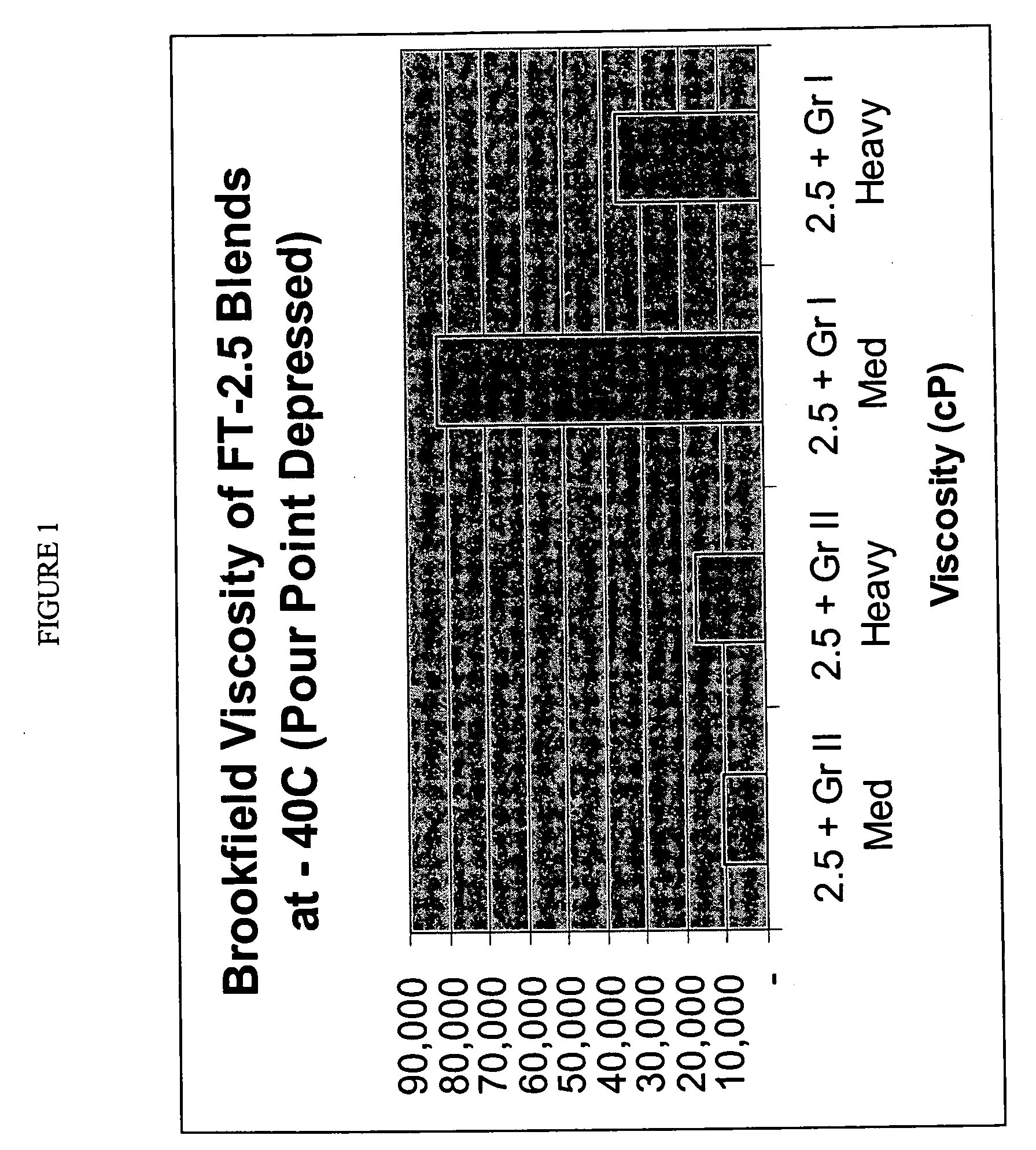
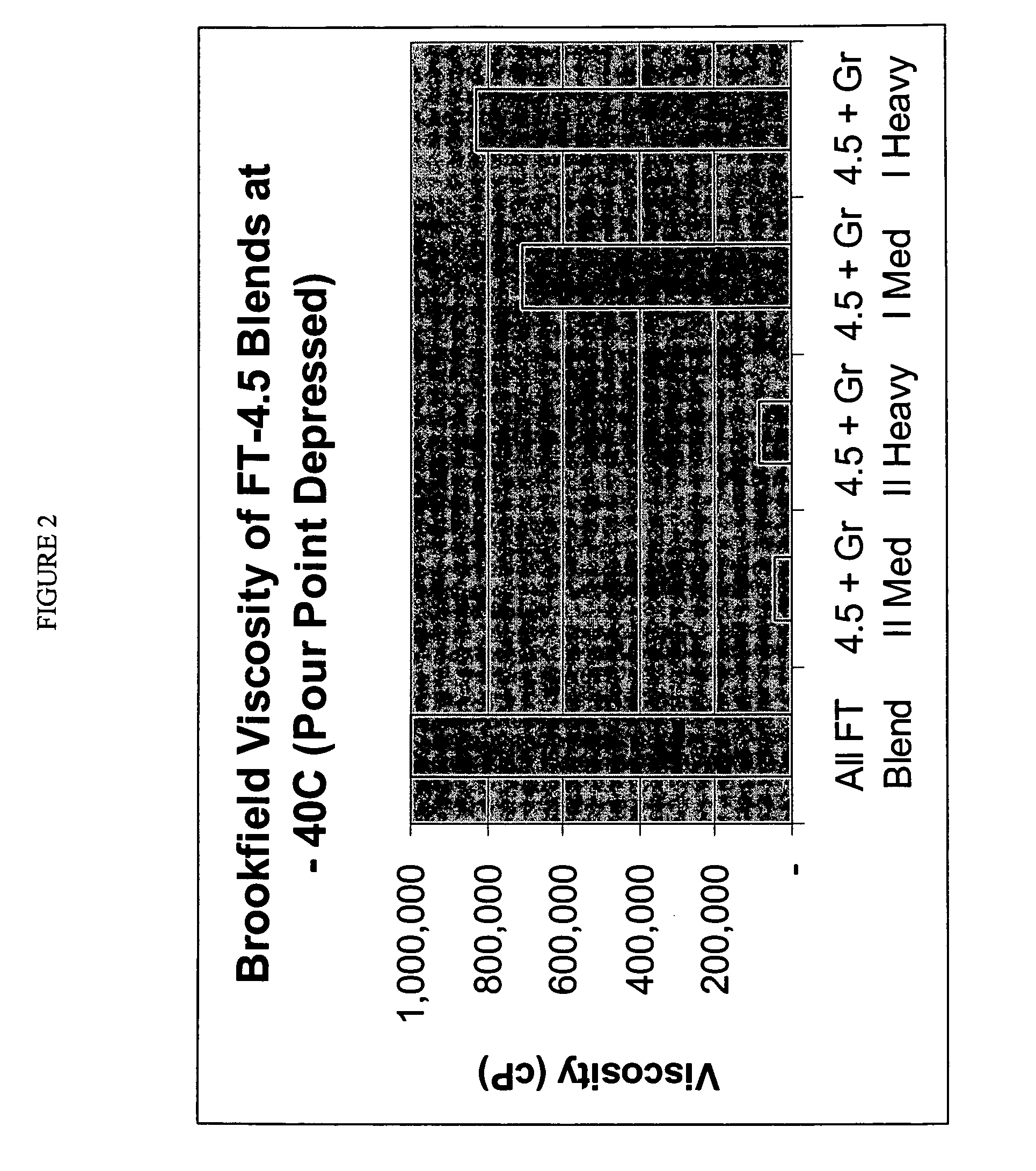
Processes for making lubricant blends with low brookfield viscosities
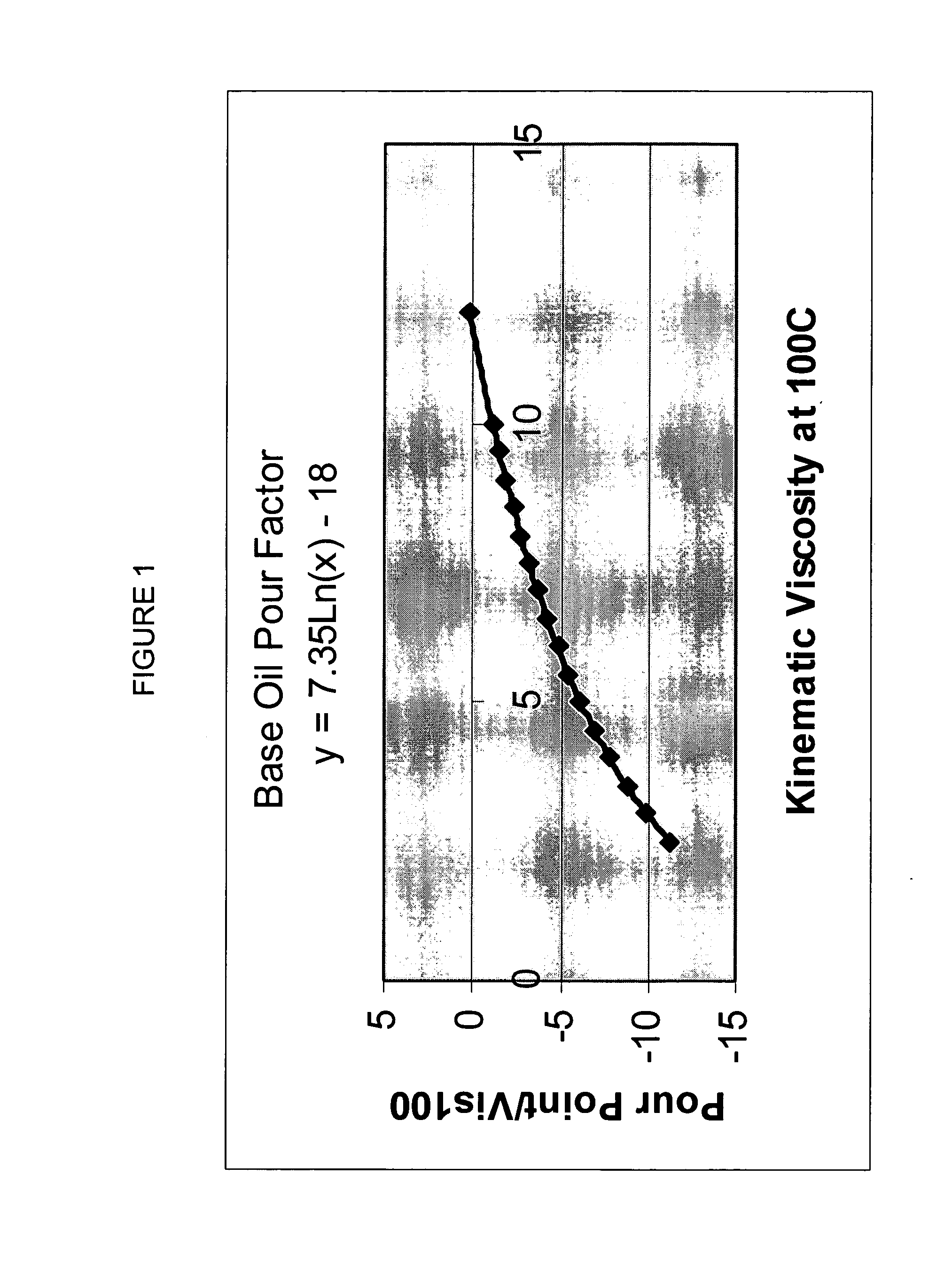
InactiveUS20050261146A1Improve low temperature performanceLow viscosityRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationParaffin waxSulfur
Lubricant blends and finished gear oils comprising a lubricant base oil fraction derived from highly paraffinic wax, a petroleum derived base oil, and a pour point depressant are provided. The lubricant base oil fraction derived from highly paraffinic wax comprises less than 0.30 weight percent aromatics, greater than 5 weight percent molecules with cycloparaffinic functionality, and a ratio of weight percent of molecules with monocycloparaffinic functionality to weight percent of molecules with multicycloparaffinic functionality greater than 15. The petroleum derived base oils comprises greater than 90 weight percent saturates and less than 300 ppm sulfur and is preferably selected from the group consisting of a Group II base oil, a Group III base oil, and mixtures thereof. These lubricant blends have surprising low Brookfield viscosities at −40° C.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
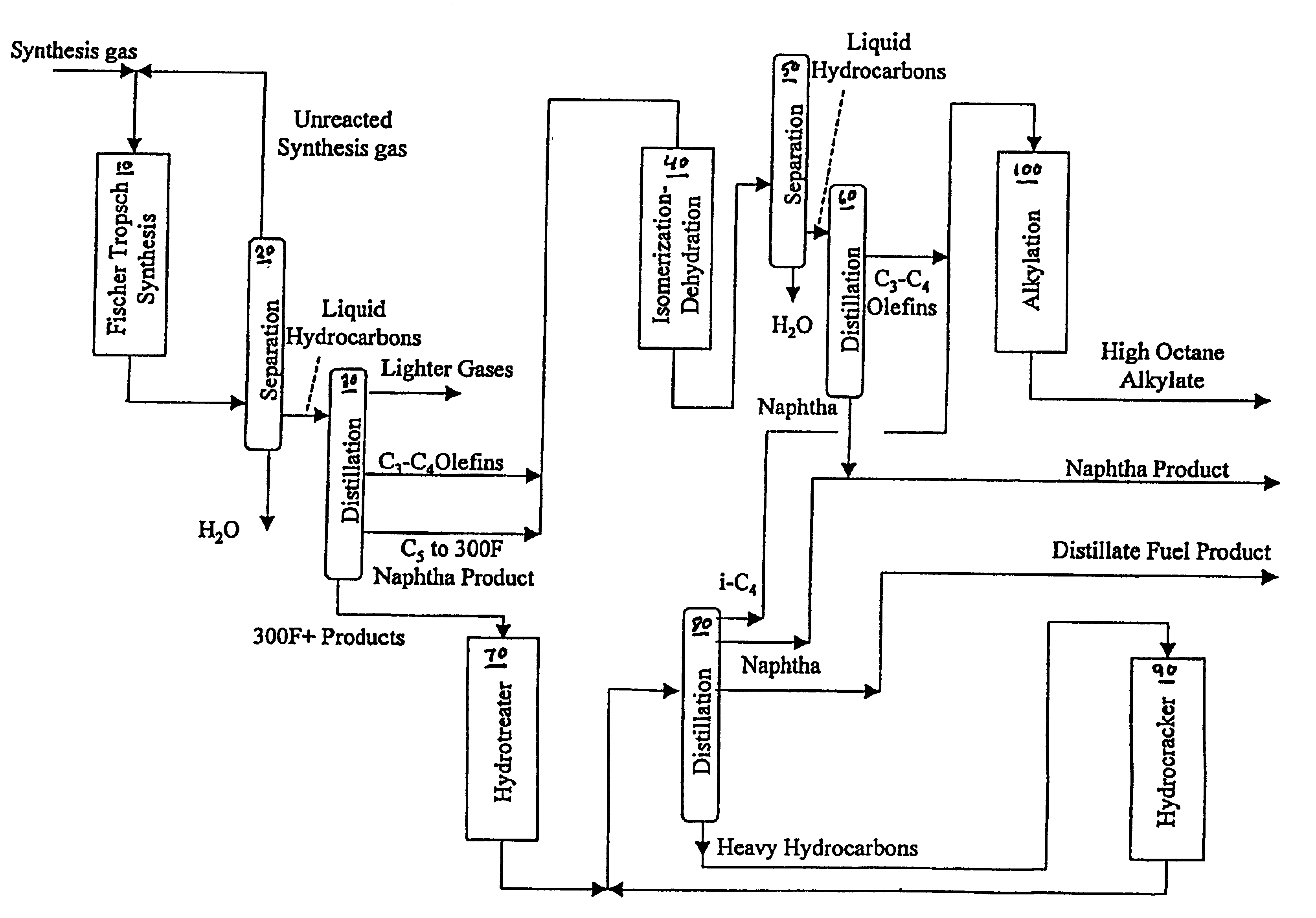
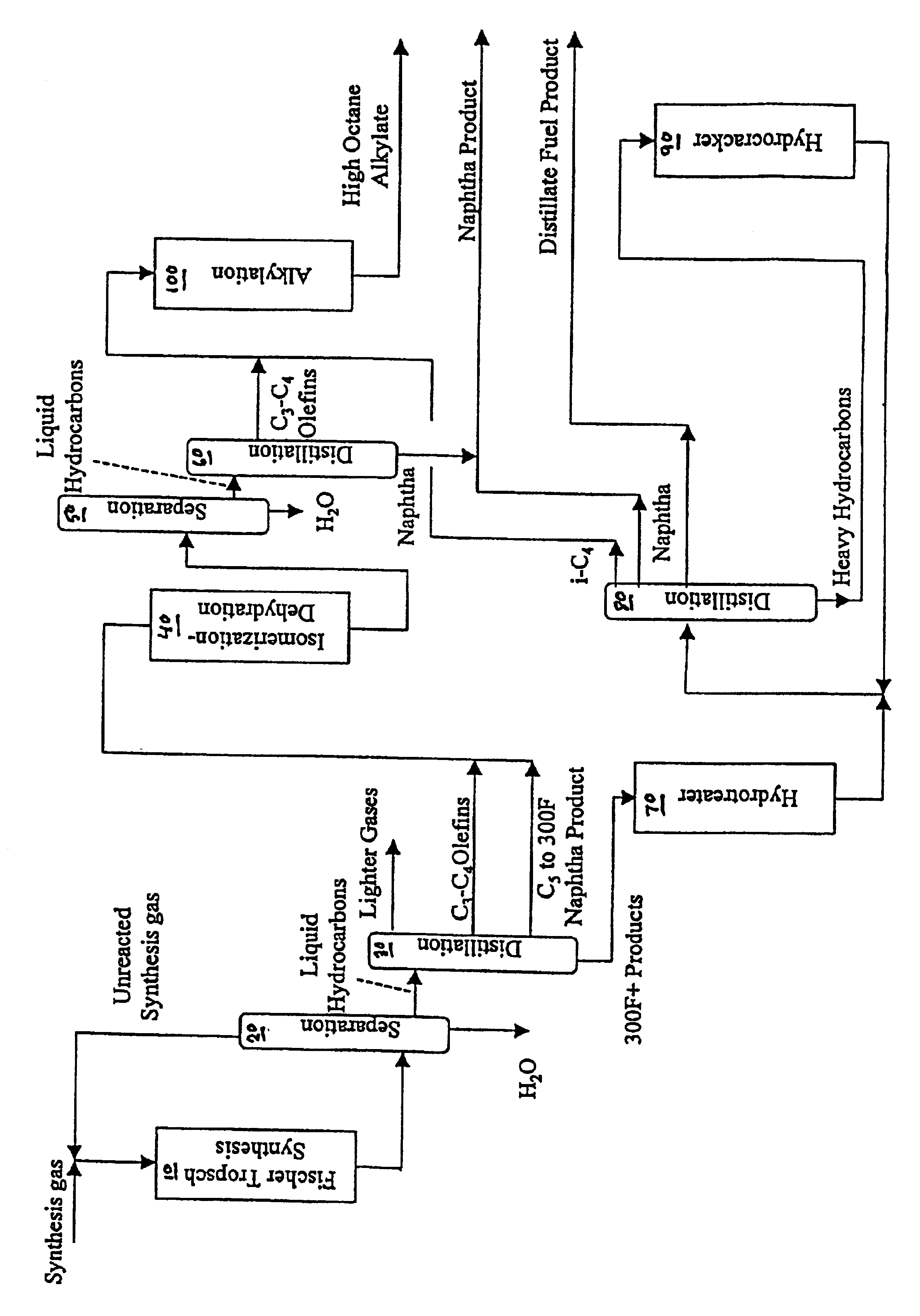
Manufacture of high octane alkylate
InactiveUS6768035B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlcoholGasoline
A Fischer-Tropsch C3-C4 olefin stream is simultaneously dehydrated and isomerized to convert alcohols to olefins and 1-butenes to 2-butenes and thereby lower the oxygenate content. Another Fischer-Tropsch fraction is hydrotreated and hydrocracked to provide an isobutane stream. The treated C3-C4 olefin stream having an oxygenate content less than 4000 ppm, is reacted with the isobutane stream to provide a highly branched, high octane isoparaffinic alkylate. The alkylate is useful as a blending component in motor gasoline.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
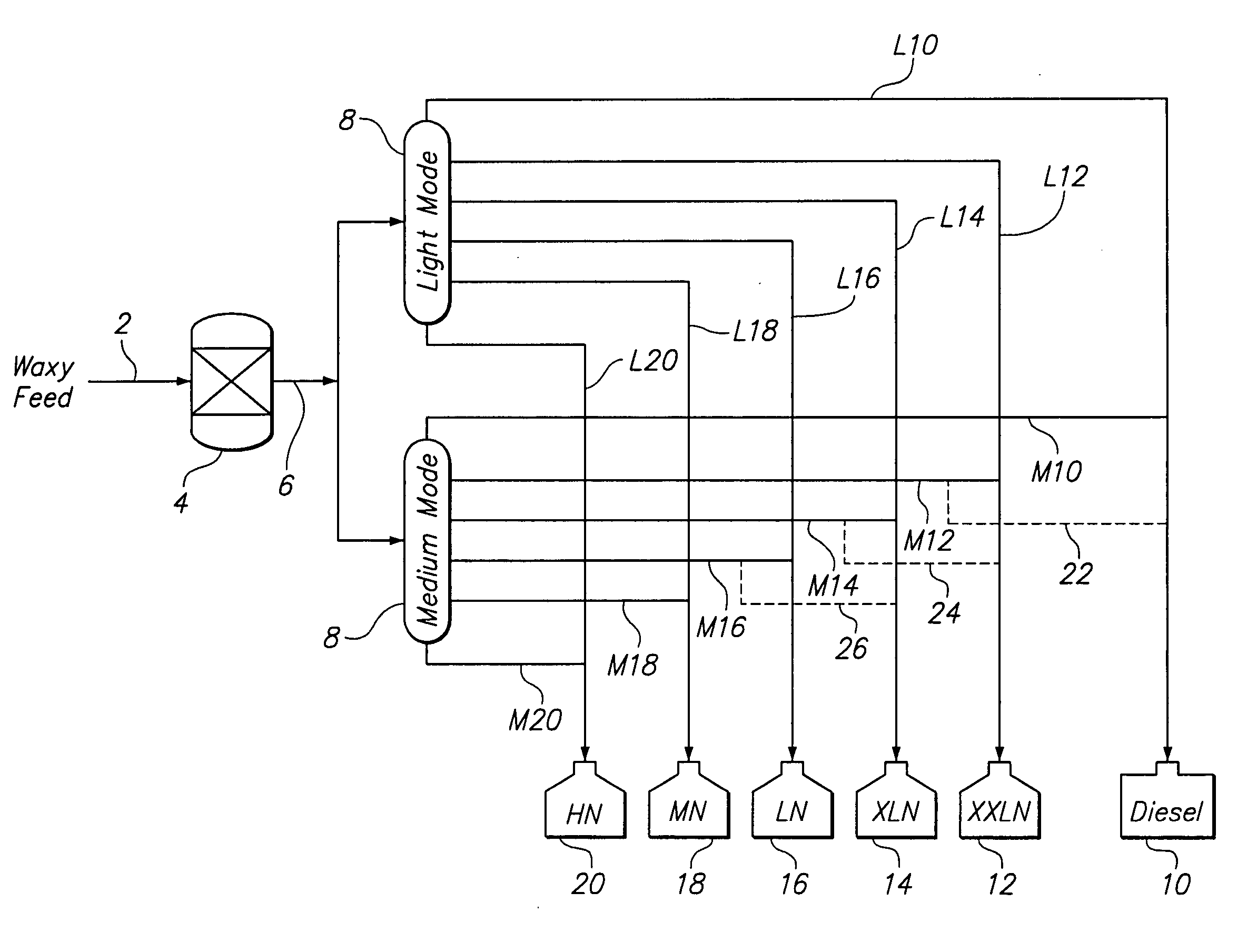
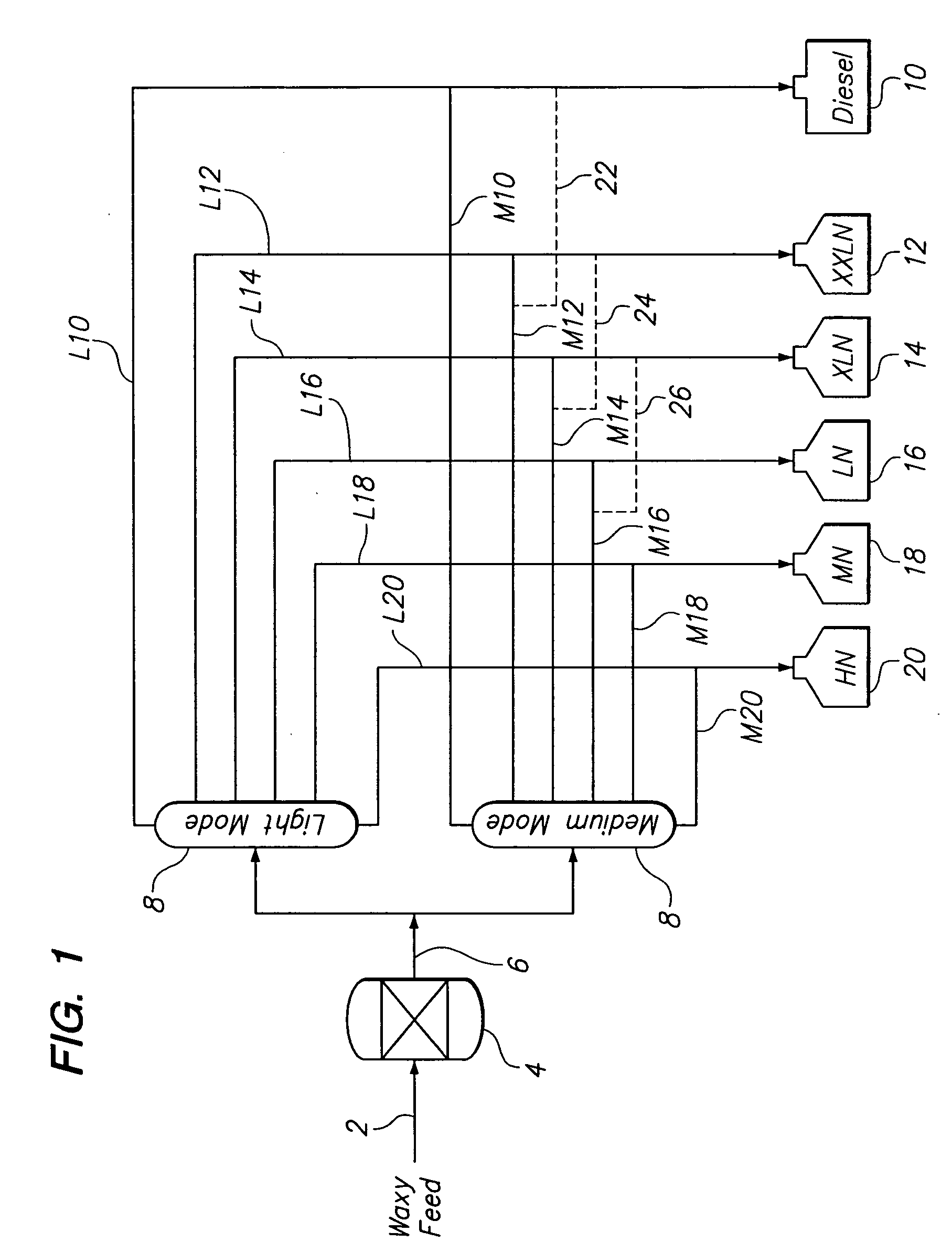
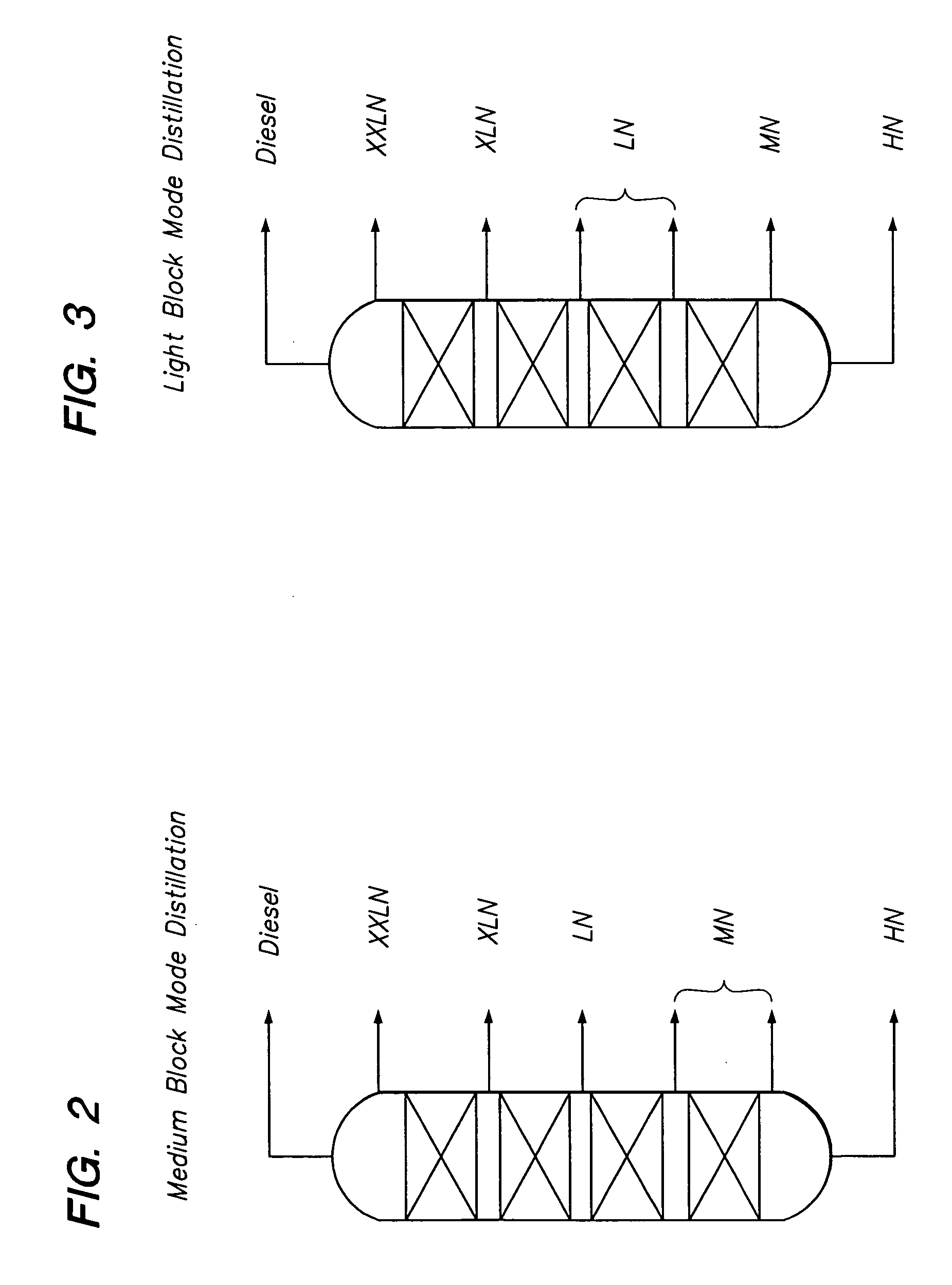
Multiple side draws during distillation in the production of base oil blends from waxy feeds
InactiveUS20060201851A1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonPetroleum wax refiningIsomerizationDistillation
A process for producing a product slate, which includes at least three base oil grades having kinematic viscosities at 100° C. within the range between about 1.8 cSt and 30 cSt, from a waxy feed having an initial boiling point of about 340° C. or less and a final boiling point of about 560° C. or higher, said process comprising (a) isomerizing at least a portion of the waxy feed, whereby the amount of isoparaffins present are increased; (b) distilling a first portion of the isomerized waxy feed in light block mode operation into at least three base oil fractions having different boiling ranges; (c) distilling a second portion of the isomerized waxy feed in medium block mode operation into at least three base oil fractions having different boiling ranges; and (d) blending at least one base oil fraction produced from light block mode with at least one base oil fraction produced from medium block mode to produce a lubricating base oil blend meeting a target value for at least one pre-selected property.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Paraffinic Biologically-Derived Distillate Fuels With Bio-Oxygenates For Improved Lubricity And Methods Of Making Same
ActiveUS20090031617A1Improve the lubrication effectImprove efficiencyFatty acid chemical modificationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonParaffin waxIsomerization
The present invention is generally directed to methods for making fuels from biomass comprising triglyceride species, whereby the biomass is subjected to partial hydrodeoxygenation and (optionally) catalytic isomerization. The partial-hydrodeoxygenation of the triglyceride species produces a fuel that retains some oxygenates for enhanced lubricity.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Biodegradable high performance hydrocarbon base oils
InactiveUS6506297B1Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionAlkaneWax
Discloses novel biodegradable high performance hydrocarbon base oils useful as lubricants in engine oil and industrial compositions, and process for their manufacture. A waxy, or paraffinic feed, particularly a Fischer-Tropsch wax, is reacted over a dual function catalyst to produce hydroisomerization and hydrocracking reactions, at 700° F.+ conversion levels ranging from about 20 to 50 wt. %, preferably about 25-40 wt. %, sufficient to produce a crude fraction, e.g., a C5-1050° F.+ crude fraction, containing 700° F.+ isoparaffins having from about 6.0 to about 7.5 methyl branches per 100 carbon atoms in the molecule. The methyl paraffins containing crude fraction is topped via atmospheric distillation to produce a bottoms fraction having an initial boiling point between about 650° F. and 750° F. which is then solvent dewaxed, and the dewaxed oil is then fractionated under high vacuum to produce biodegradable high performance hydrocarbon base oils.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Production of diesel fuel from biorenewable feedstocks
ActiveUS7999142B2Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon by hydrogenationSolubilityHydrogen
A process has been developed for producing diesel boiling range fuel from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils and animal oils, fats, and greases. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating i.e. decarboxylating, decarbonylating, and / or hydrodeoxygenating to provide a hydrocarbon fraction useful as a diesel boiling range fuel or diesel boiling range fuel blending component. If desired, the hydrocarbon fraction can be isomerized to improve cold flow properties. A portion of the hydrogenated and deoxygenated feedstock is selectively separated and then recycled to the treatment zone to increase the hydrogen solubility of the reaction mixture.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for improving the lubricating properties of base oils using a Fischer-Tropsch derived bottoms
InactiveUS20050098476A1High viscosityReduce pointsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon purification/separationProcess engineeringBase oil
A method for improving the lubricating properties of a distillate base oil characterized by a pour point of 0 degrees C. or less and a boiling range having the 10 percent point falling between about 625 degrees F. and about 790 degrees F. and the 90 percent point falling between about 725 degrees F. and about 950 degrees F., the method comprises blending with said distillate base oil a sufficient amount of a pour point depressing base oil blending component to reduce the pour point of the resulting base oil blend at least 3 degrees C. below the pour point of the distillate base oil, wherein the pour point depressing base oil blending component is an isomerized Fischer-Tropsch derived bottoms product having a pour point that is at least 3 degrees C. higher than the pour point of the distillate base oil.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Synthetic isoparaffinic premium heavy lubricant base stock
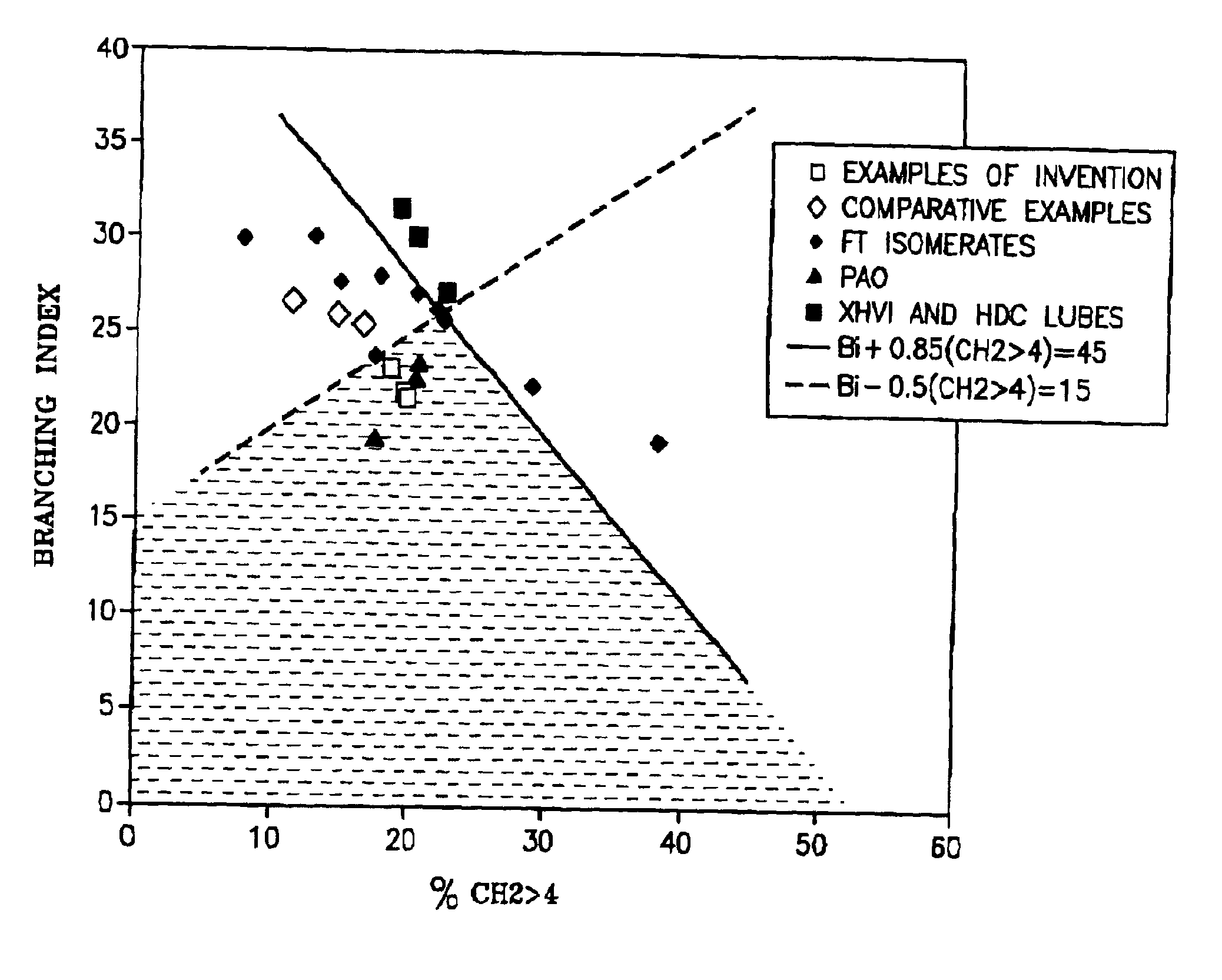
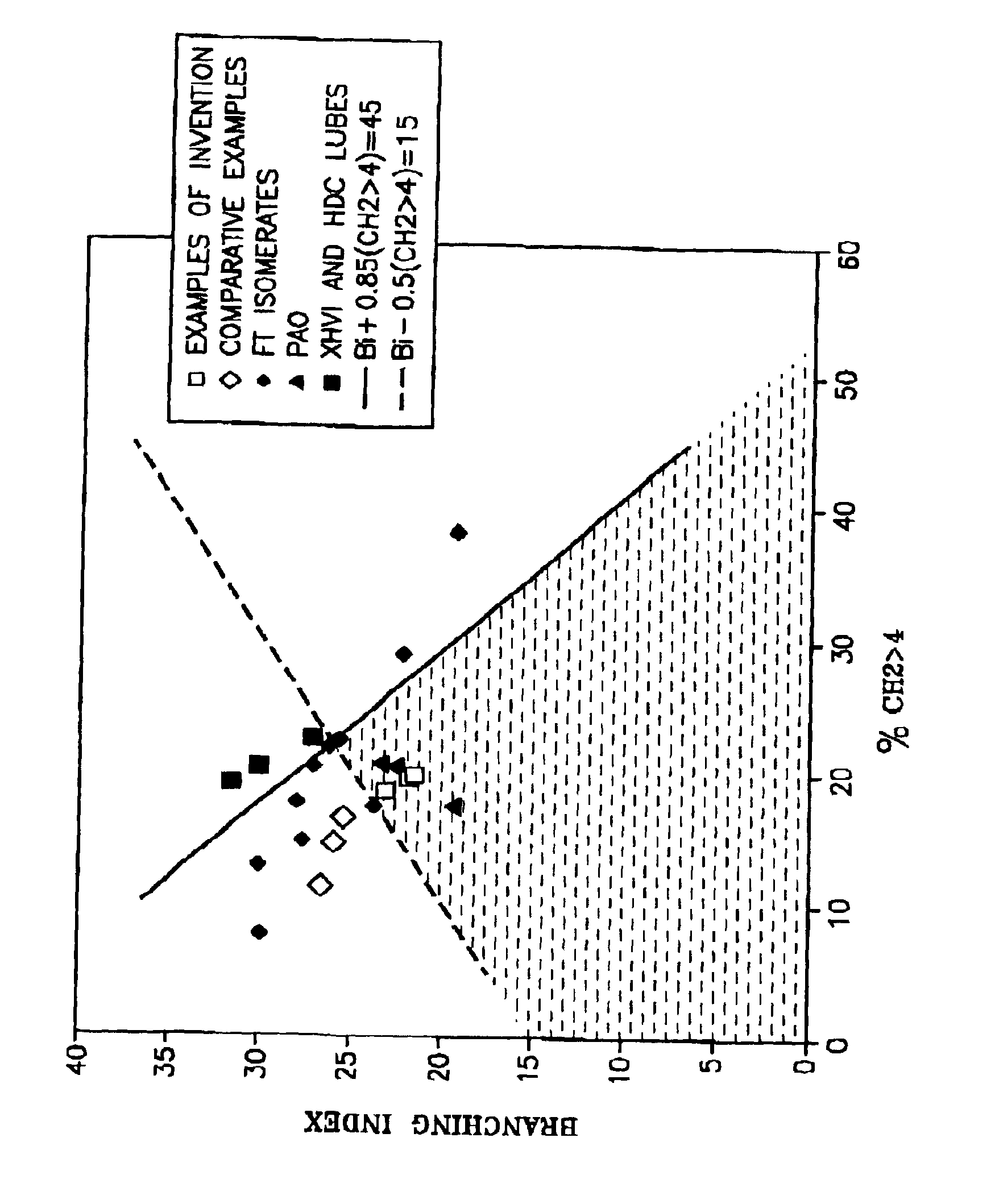
A synthetic, isoparaffinic heavy hydrocarbon composition useful as a heavy lubricant base stock contains hydrocarbon molecules having consecutive numbers of carbon atoms, is a liquid at 100° C., at which temperature its kinematic viscosity is above 8 cSt and has respective initial and end boiling points of at least 850 and 1000° F. (454 and 538° C.). The branching index BI and the branching proximity CH2>4 of the isoparaffinic hydrocarbon molecules, are such that:BI−0.5(CH2>4)<15; and (a)BI+0.85(CH2>4)<45; (b)as measured over the hydrocarbon composition as a whole.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Extremely low acidity USY and homogeneous, amorphous silica-alumina hydrocracking catalyst and process
InactiveUS6902664B2High catalytic activityLow pollution rateMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonSingle stageAmorphous silica-alumina
A catalyst composition comprising a minor amount of a low acidity, highly dealuminated ultra stable Y zeolite having an Alpha value of less than about 5, preferable less than about 3 and Broensted acidity measured by FT-IR from about 1 to about 20, preferably from about 1-10, micro mole / g of, a homogeneous, amorphous silica-alumina cracking component having an SB ratio of from about 0.7 to about 1.3, wherein a crystalline alumina phase is present in an amount of no greater than about 10%, preferably no greater than 5% and a catalytic amount of hydrogenation component selected from the group consisting of a Group VI metal, a Group VIII metal, and mixtures thereof is disclosed. The present invention provides for a process for converting hydrocarbonaceous oils comprising contacting the hydrocarbonaceous oils with the catalyst under suitable hydrocarbon conversion conditions. Such processes in include, but are not limited to, single stage hydrocracking, two-stage hydrocracking, series-flow hydrocracking, mild hydrocracking, lube hydrocracking, hydrotreating, lube hydrofinishing, hydrodesulphurization, hydrodenitrification, catalytic dewaxing and catalytic cracking.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for the conversion of ethane to aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20090209794A1Limit initial cracking activitySacrificing activityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystBenzenePlatinum
A process for producing aromatic hydrocarbons which comprises (a) contacting ethane with a dehyroaromatization aromatic catalyst which is comprised of about 0.005 to about 0.1 wt % platinum, an amount of gallium which is equal to or greater than the amount of the platinum, from about 10 to about 99.9 wt % of an aluminosilicate, and a binder, and (b) separating methane, hydrogen, and C2-5 hydrocarbons from the reaction products of step (a) to produce aromatic reaction products including benzene.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com