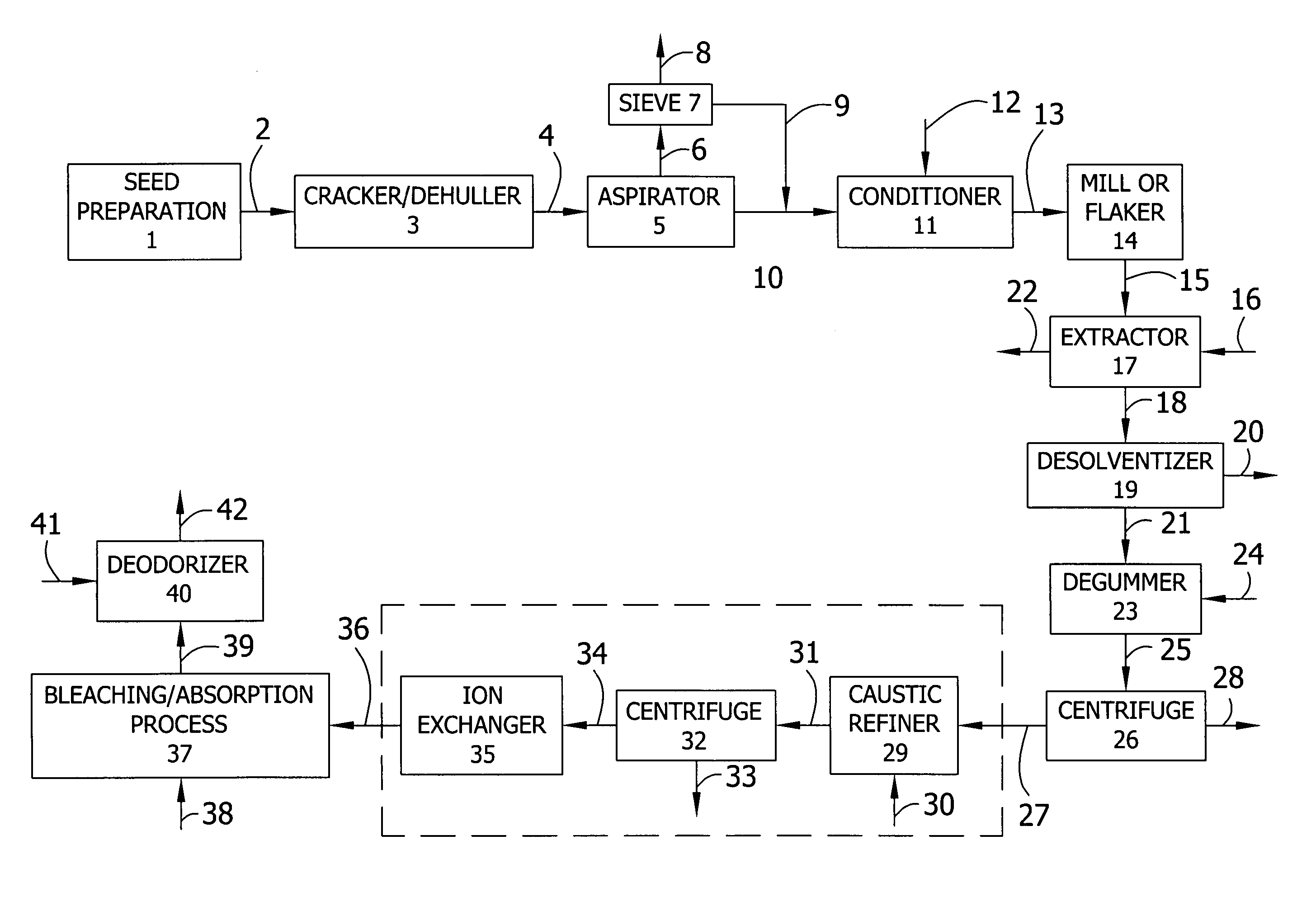
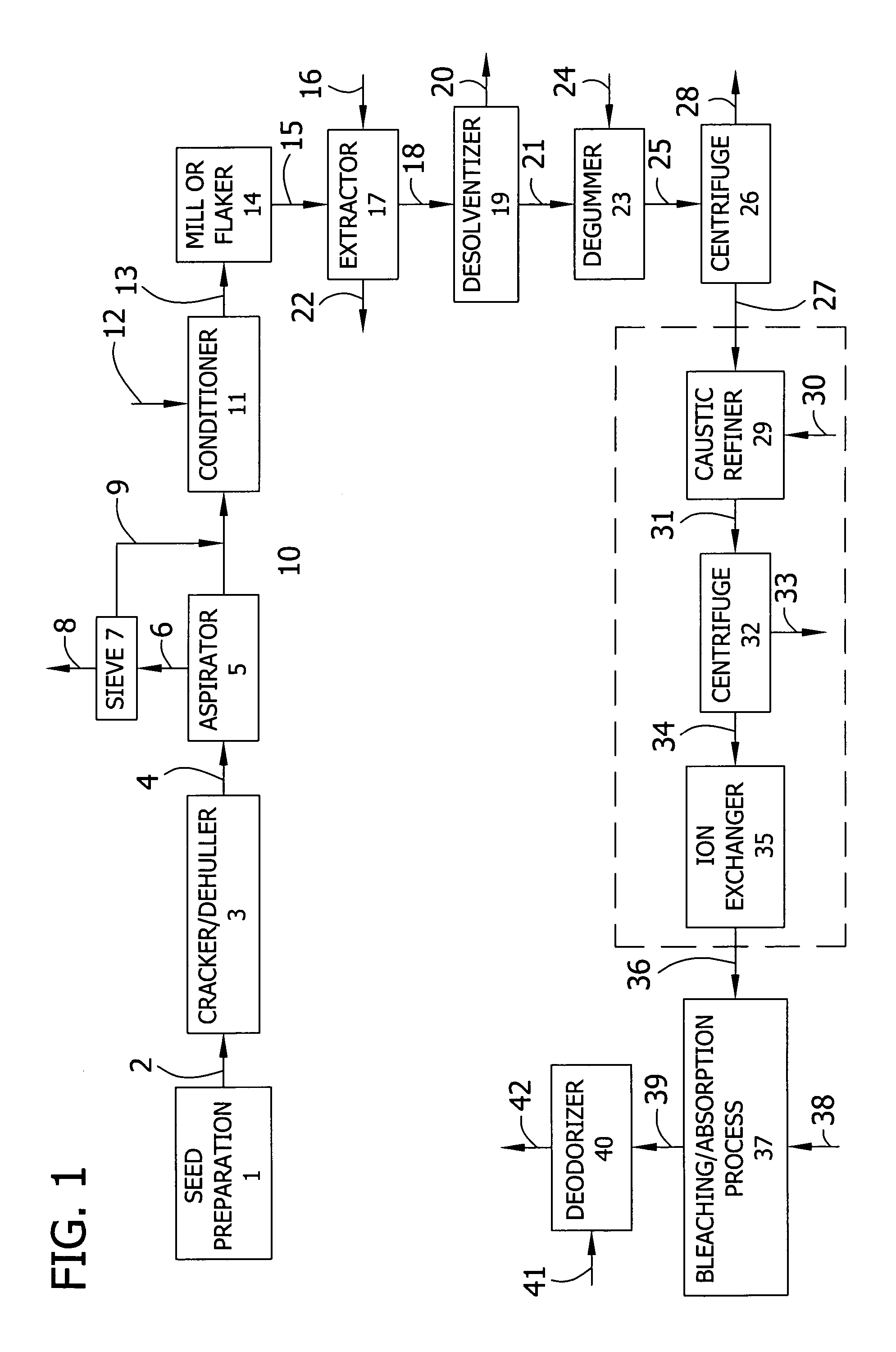
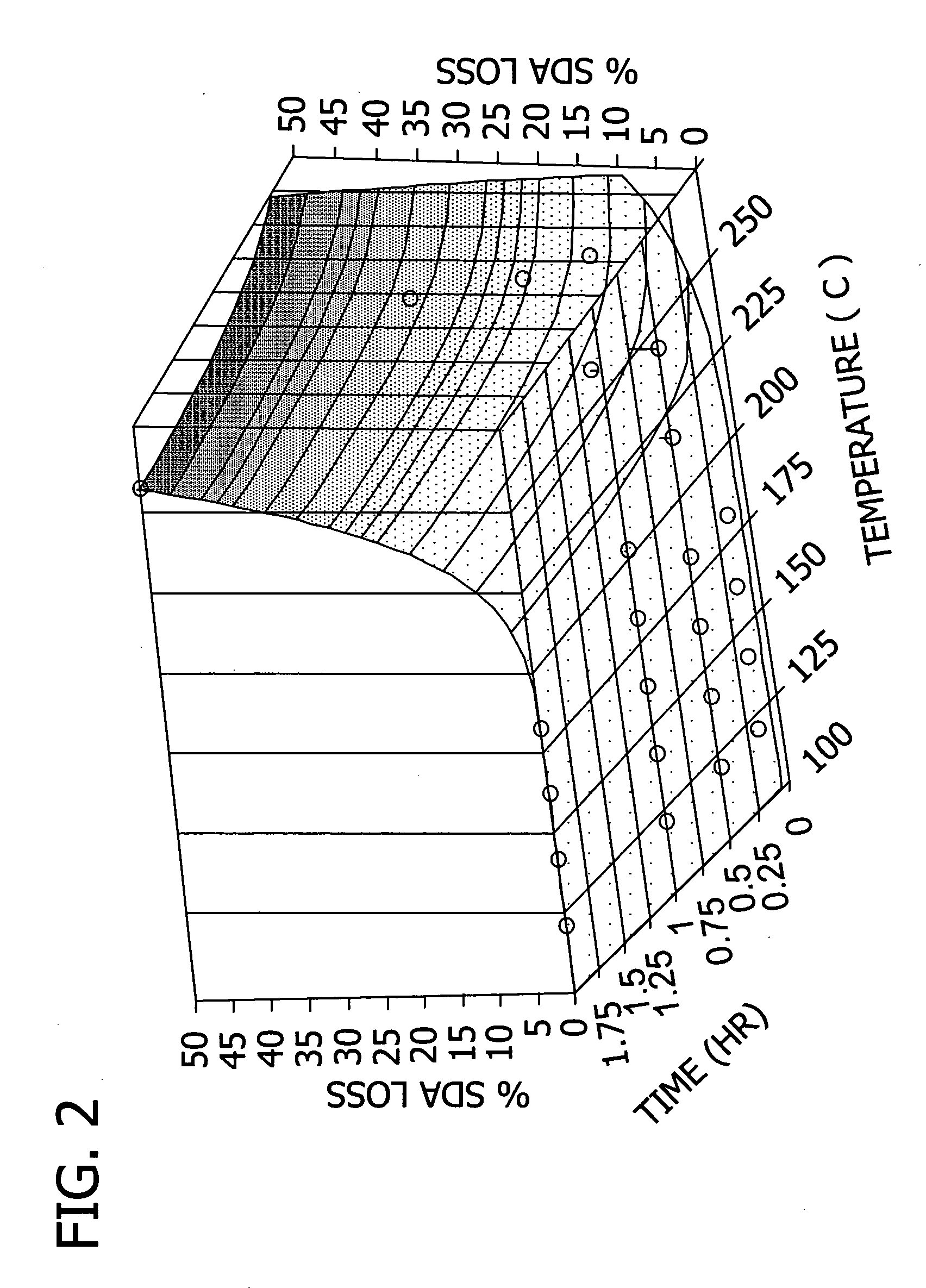
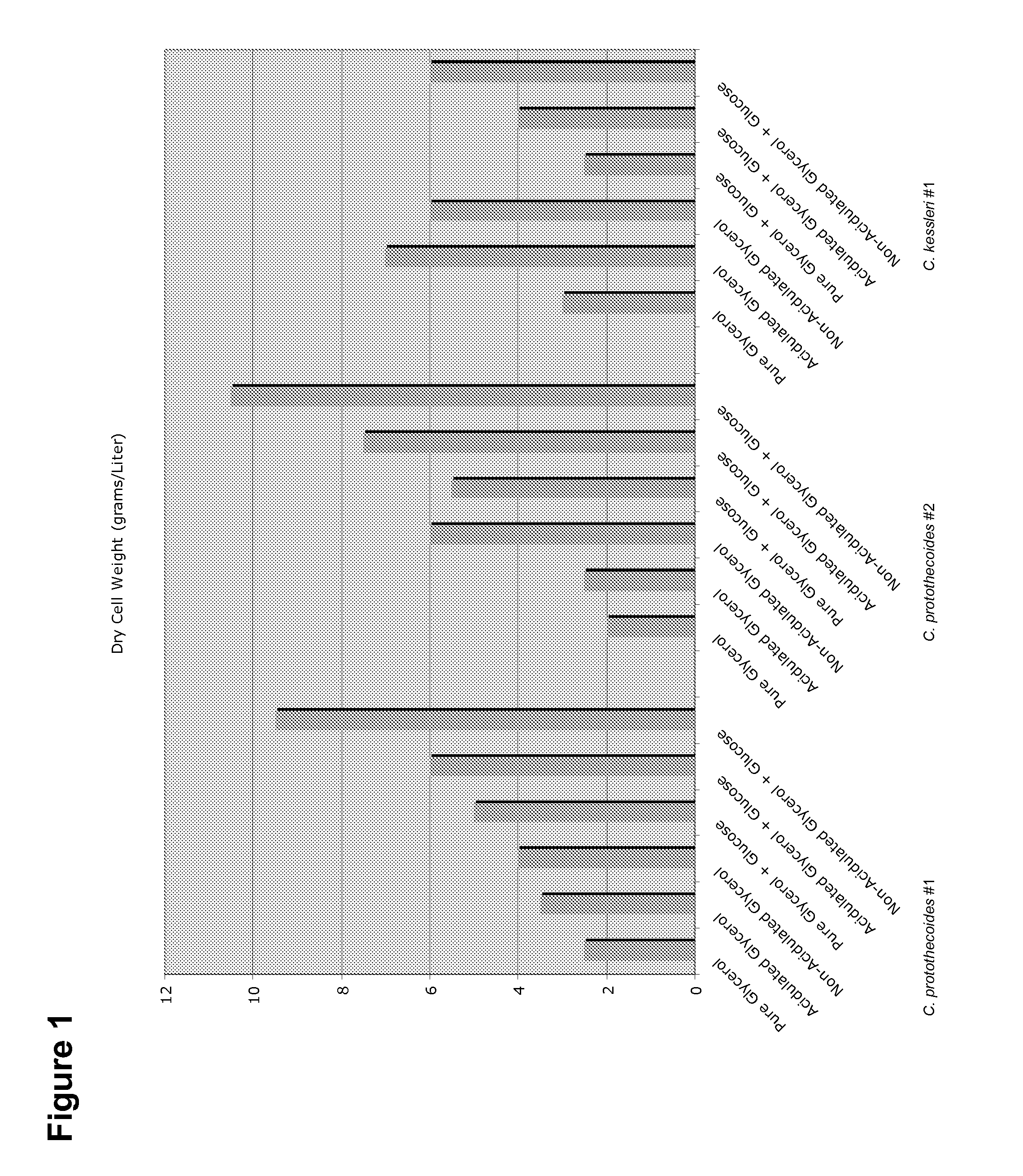
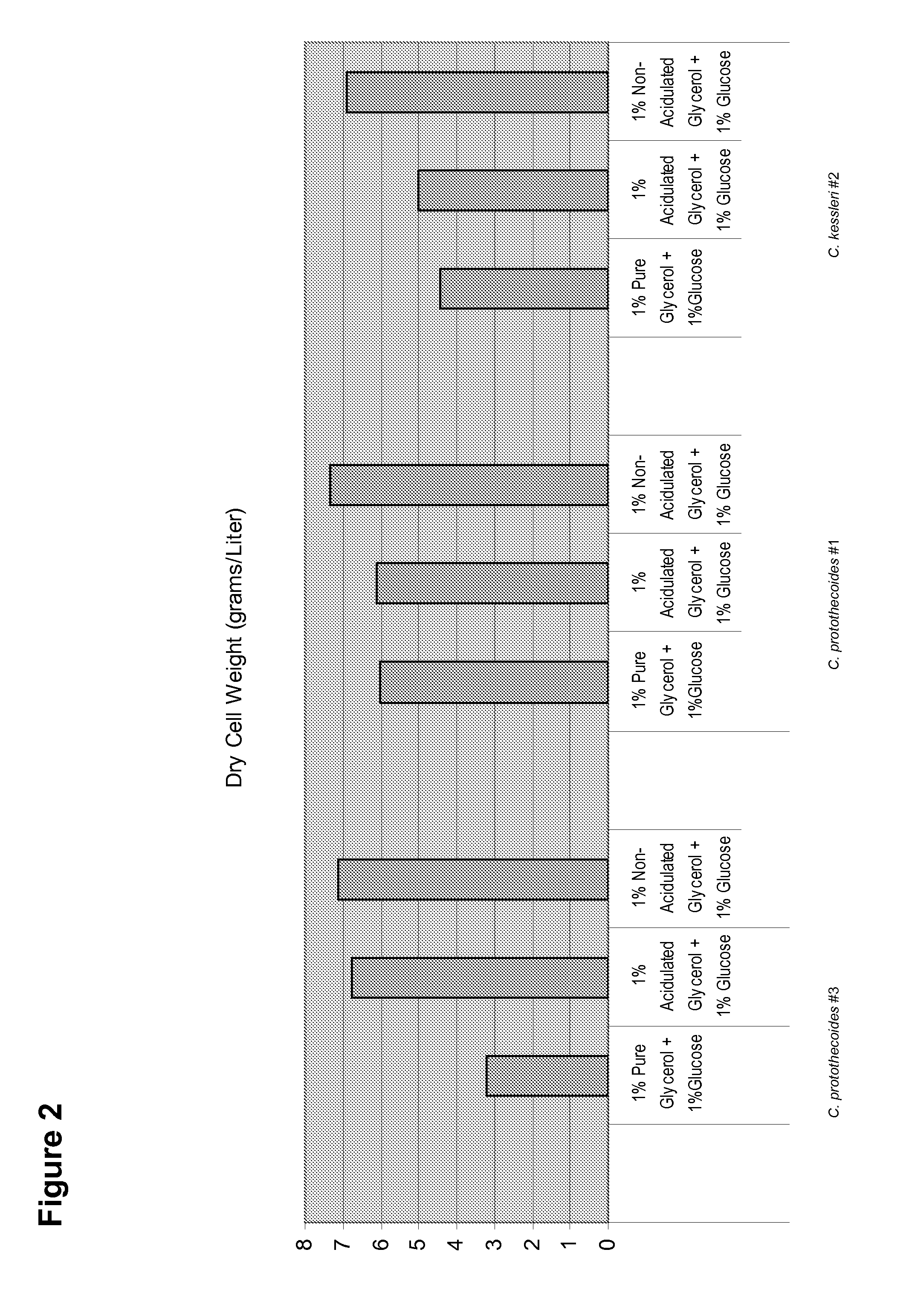
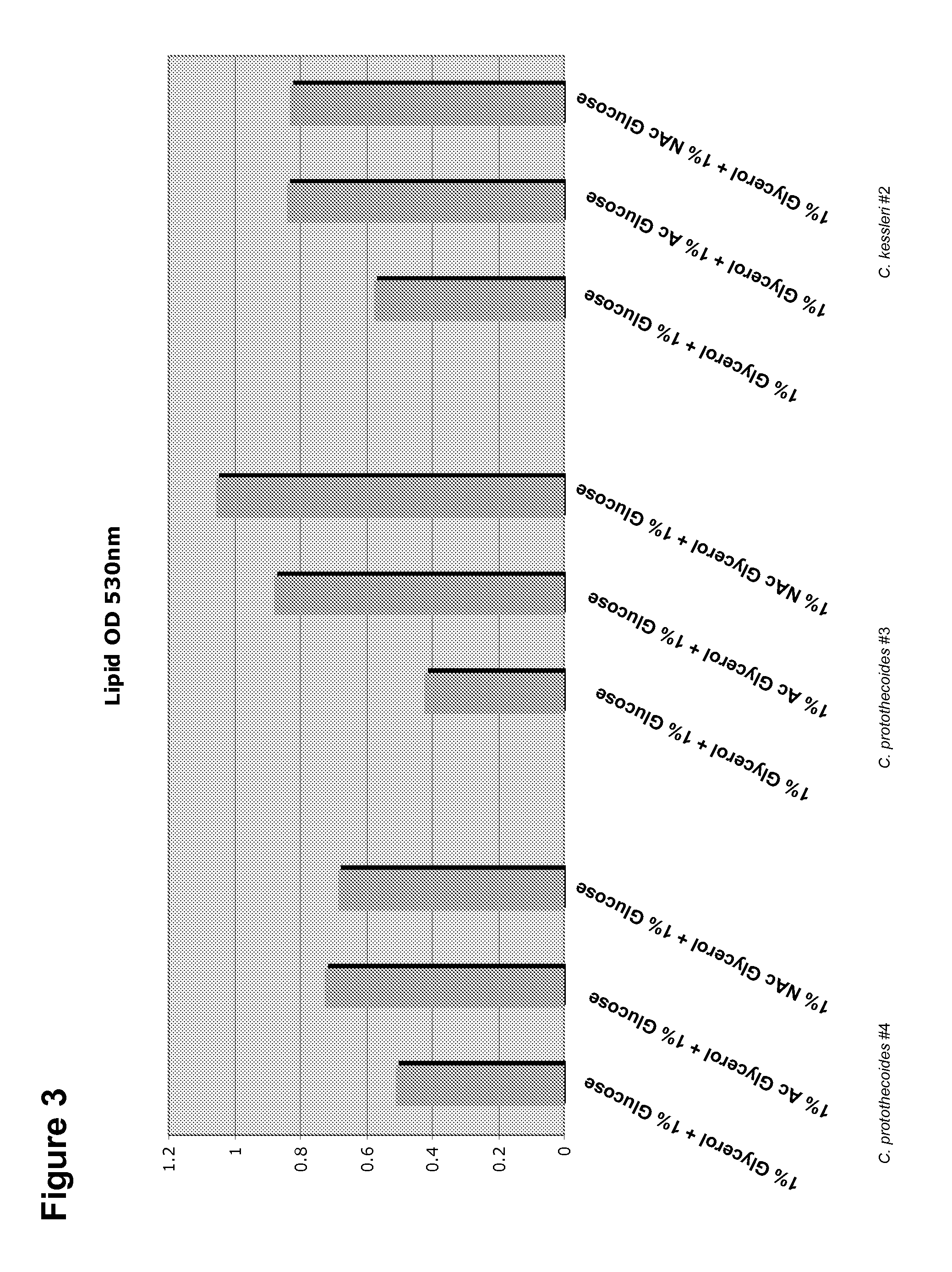
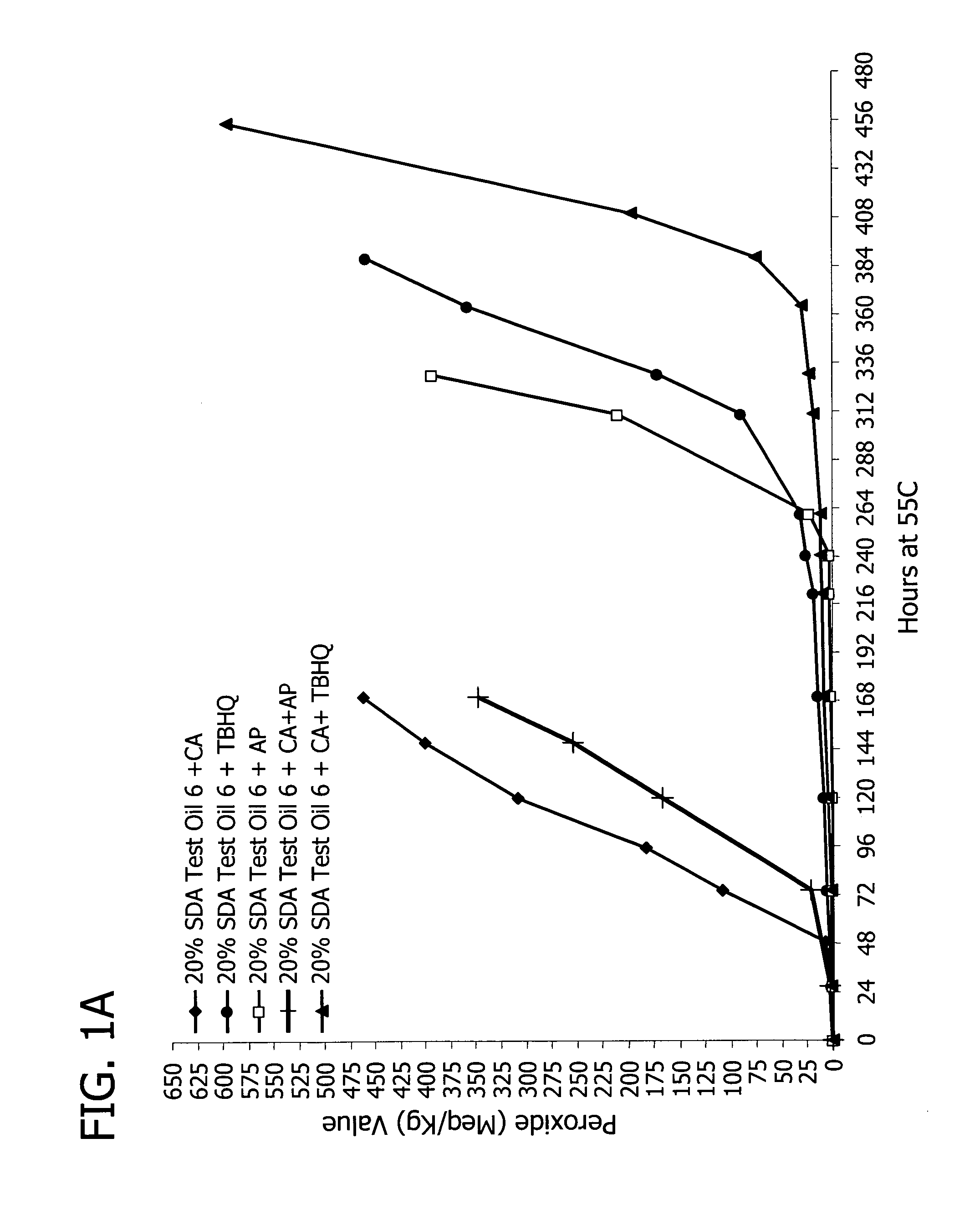
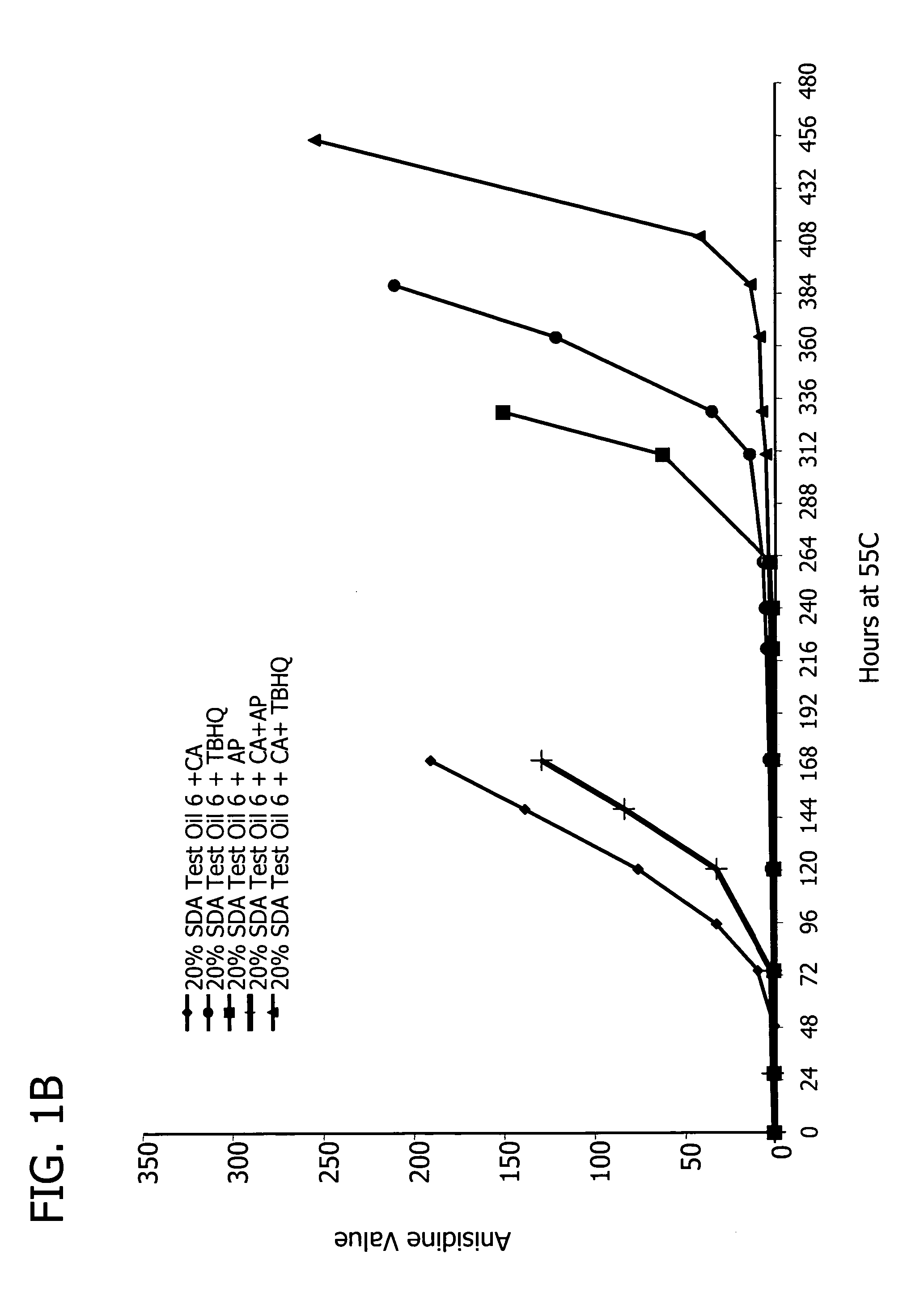
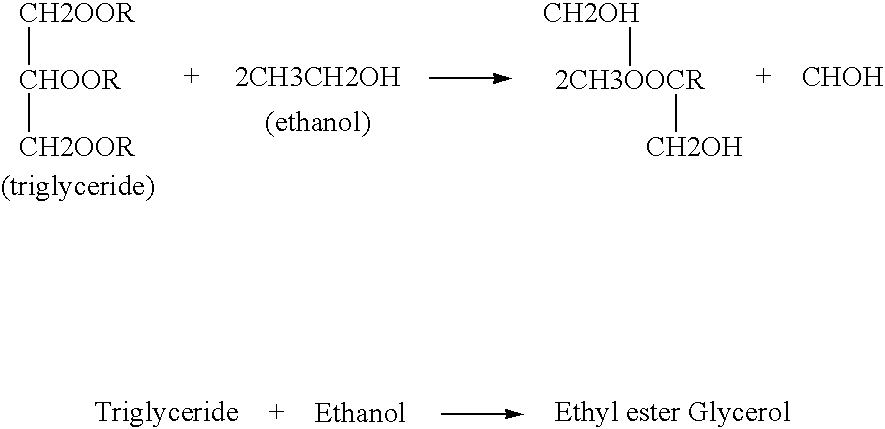
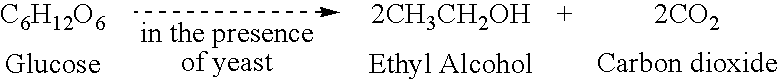Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7599results about "Fatty-oils/fats refining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
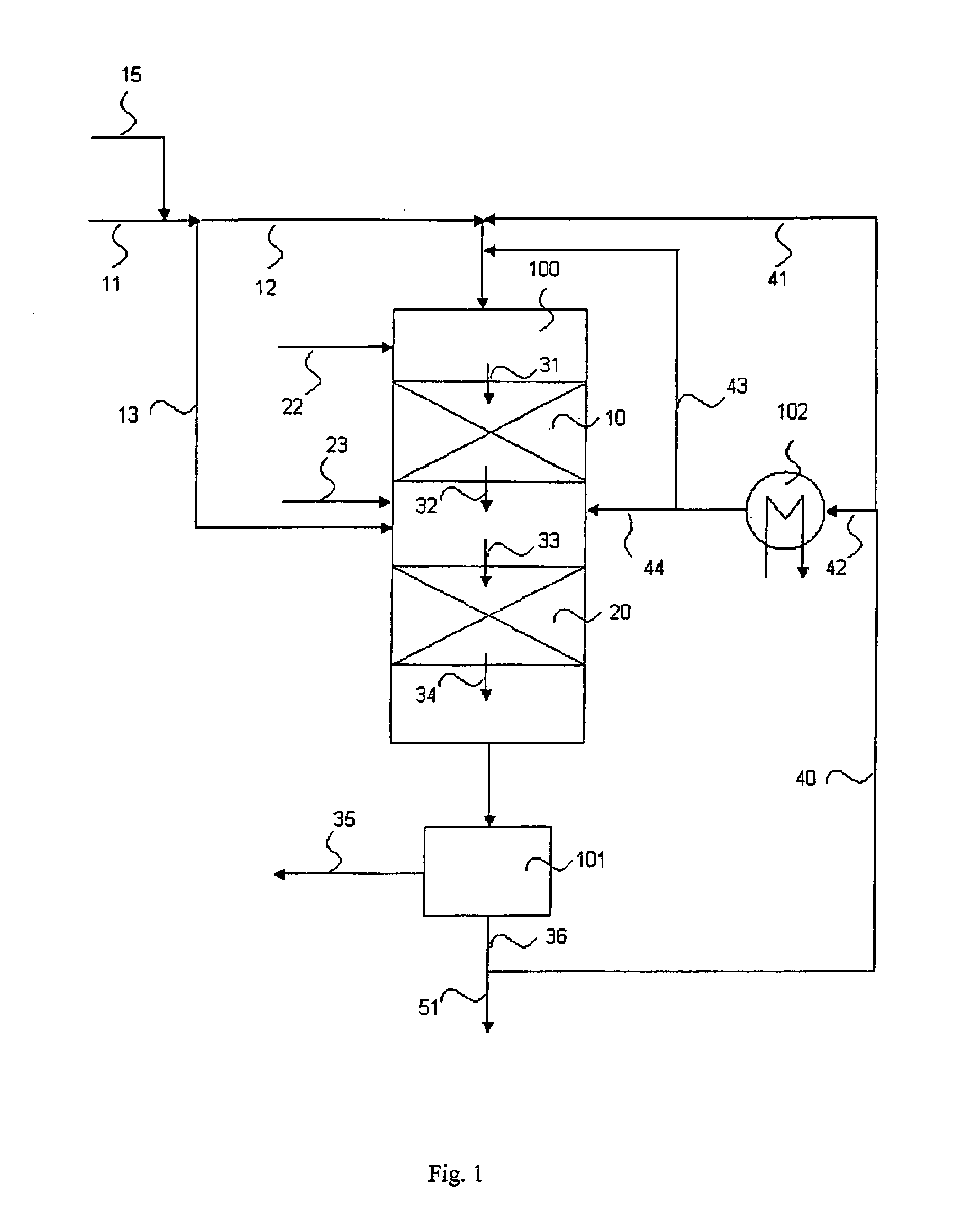
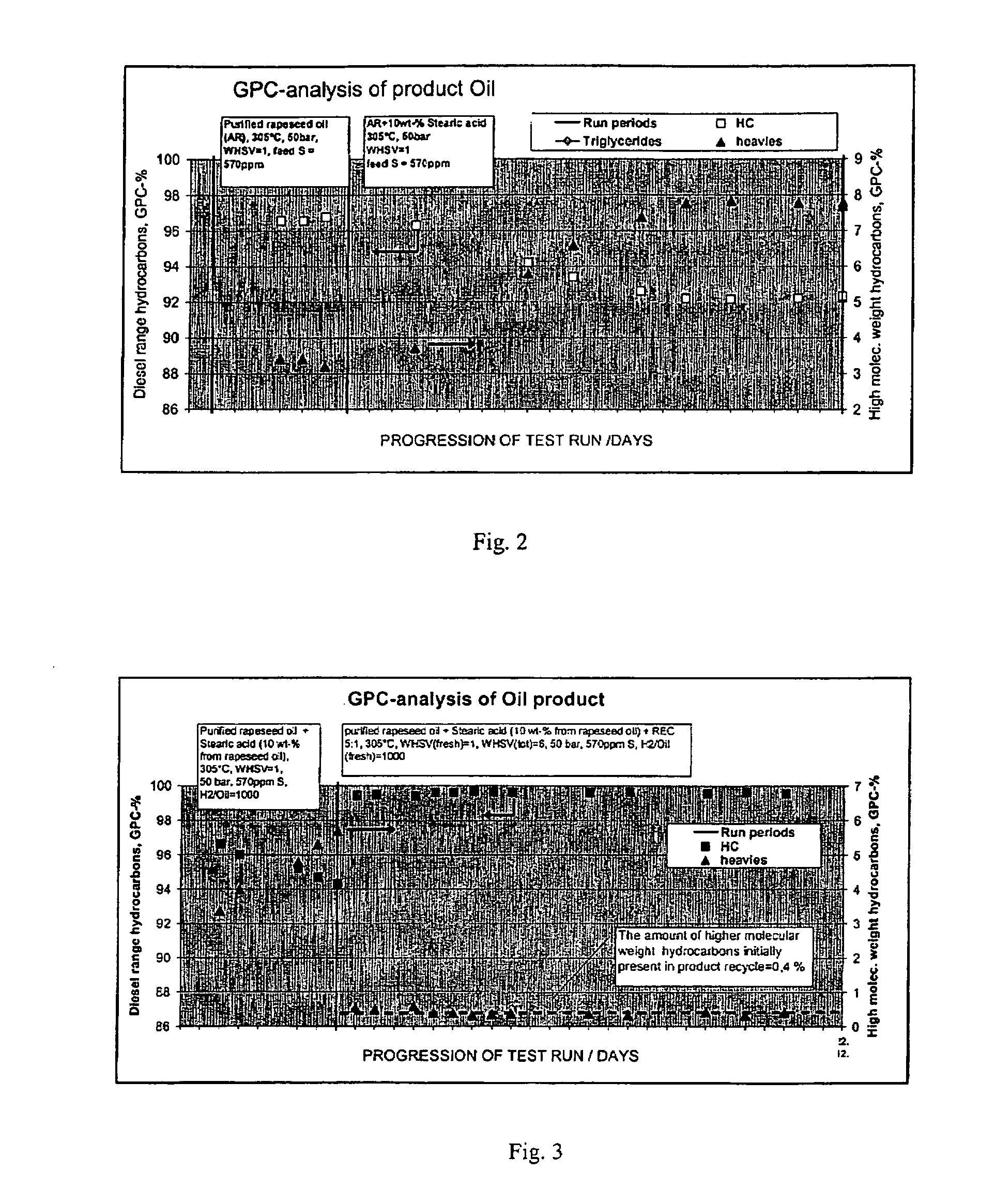
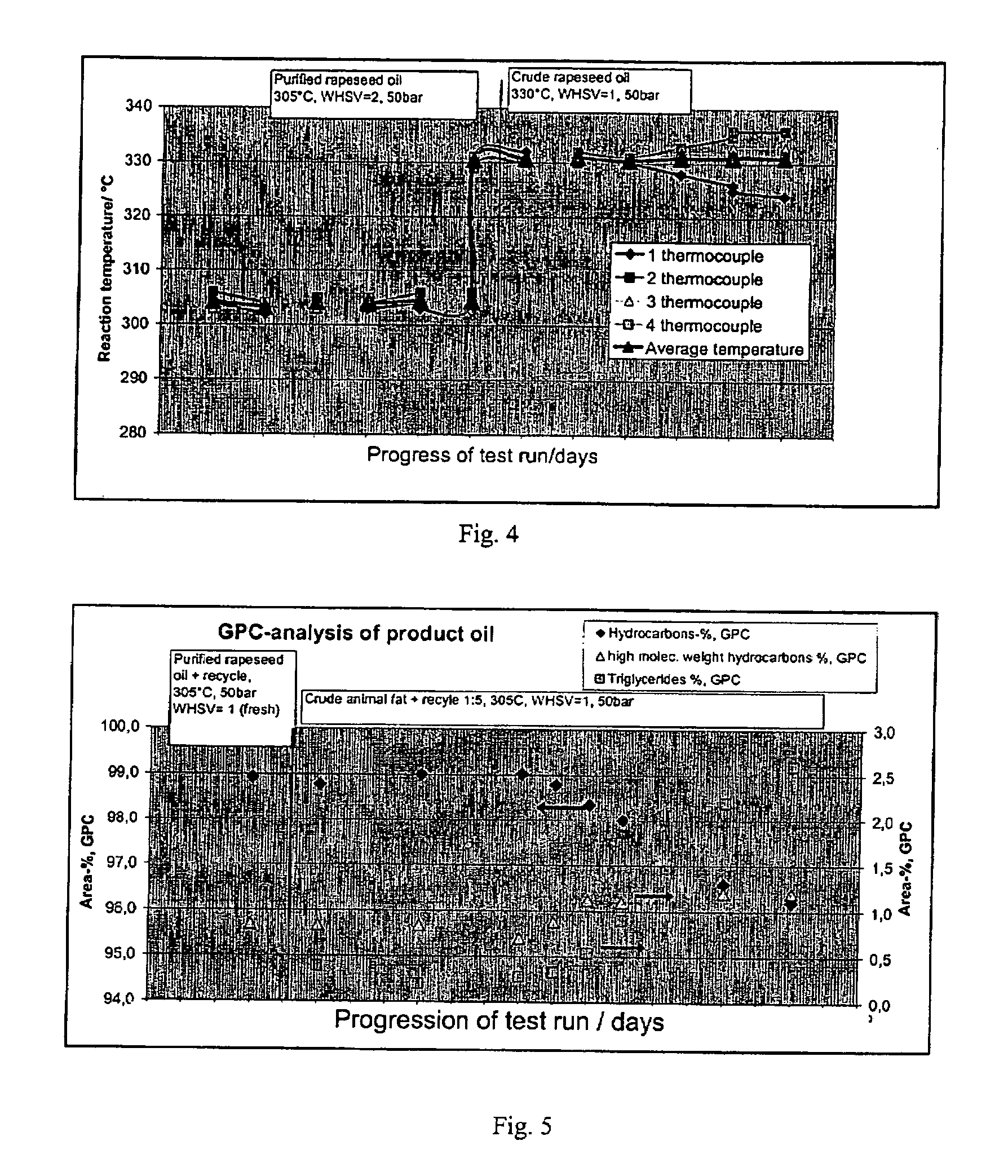
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20070010682A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons wherein a feed is hydrotreated in a hydrotreating step and isomerised in an isomerisation step, and a feed comprising fresh feed containing more than 5 wt % of free fatty acids and at least one diluting agent is hydrotreated at a reaction temperature of 200-400° C., in a hydrotreating reactor in the presence of catalyst, and the ratio of the diluting agent / fresh feed is 5-30:1.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Methods and compositions for extraction and transesterification of biomass components
InactiveUS20090234146A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationBiofuel
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the direct transesterification and extraction of bio-lipids and bio-oils in the production of biofuel, particularly fatty acid methyl ester products.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
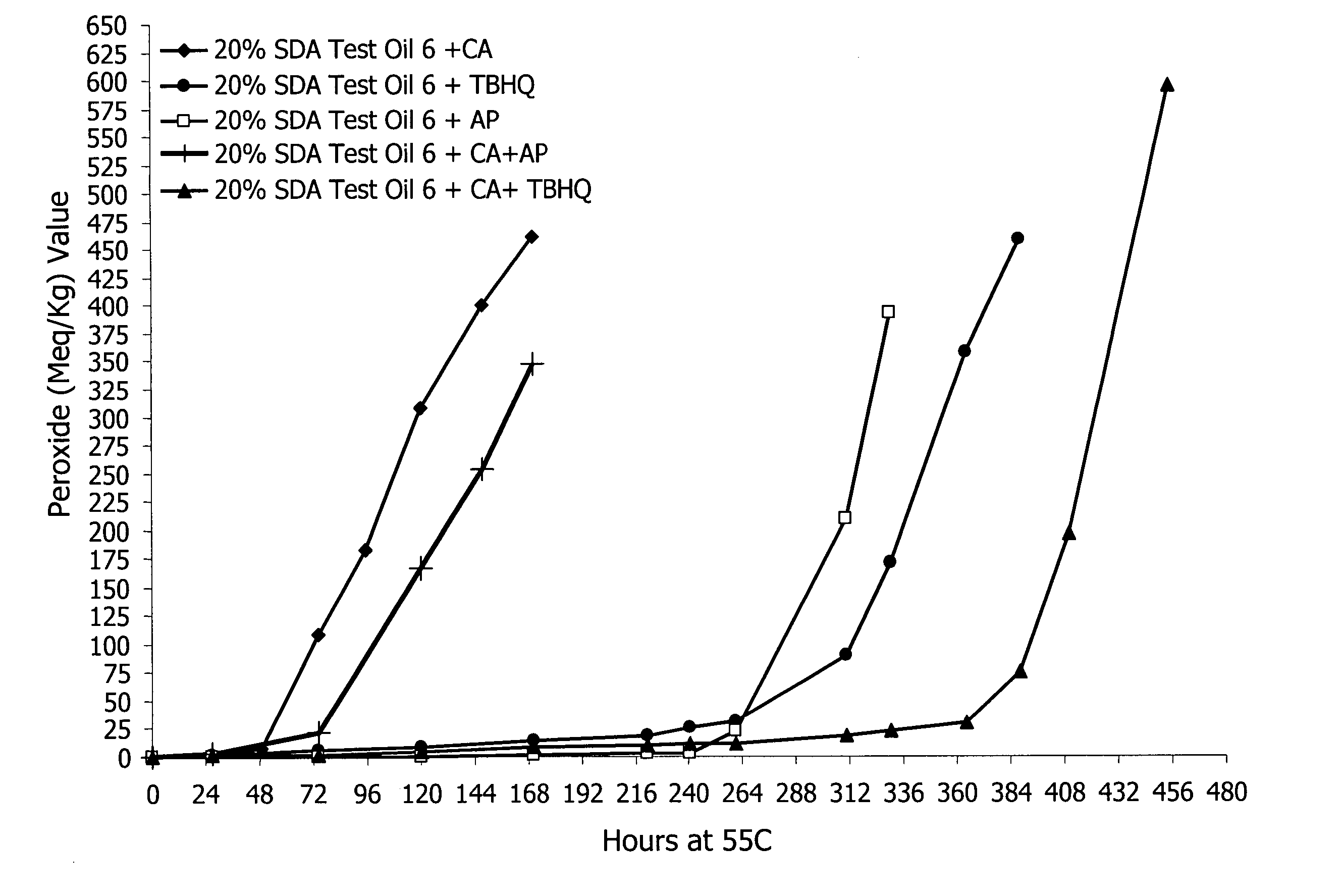
Chemical methods for treating a metathesis feedstock
ActiveUS20110160472A1Reduce starting peroxide valueFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationChemical treatmentNatural oils
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
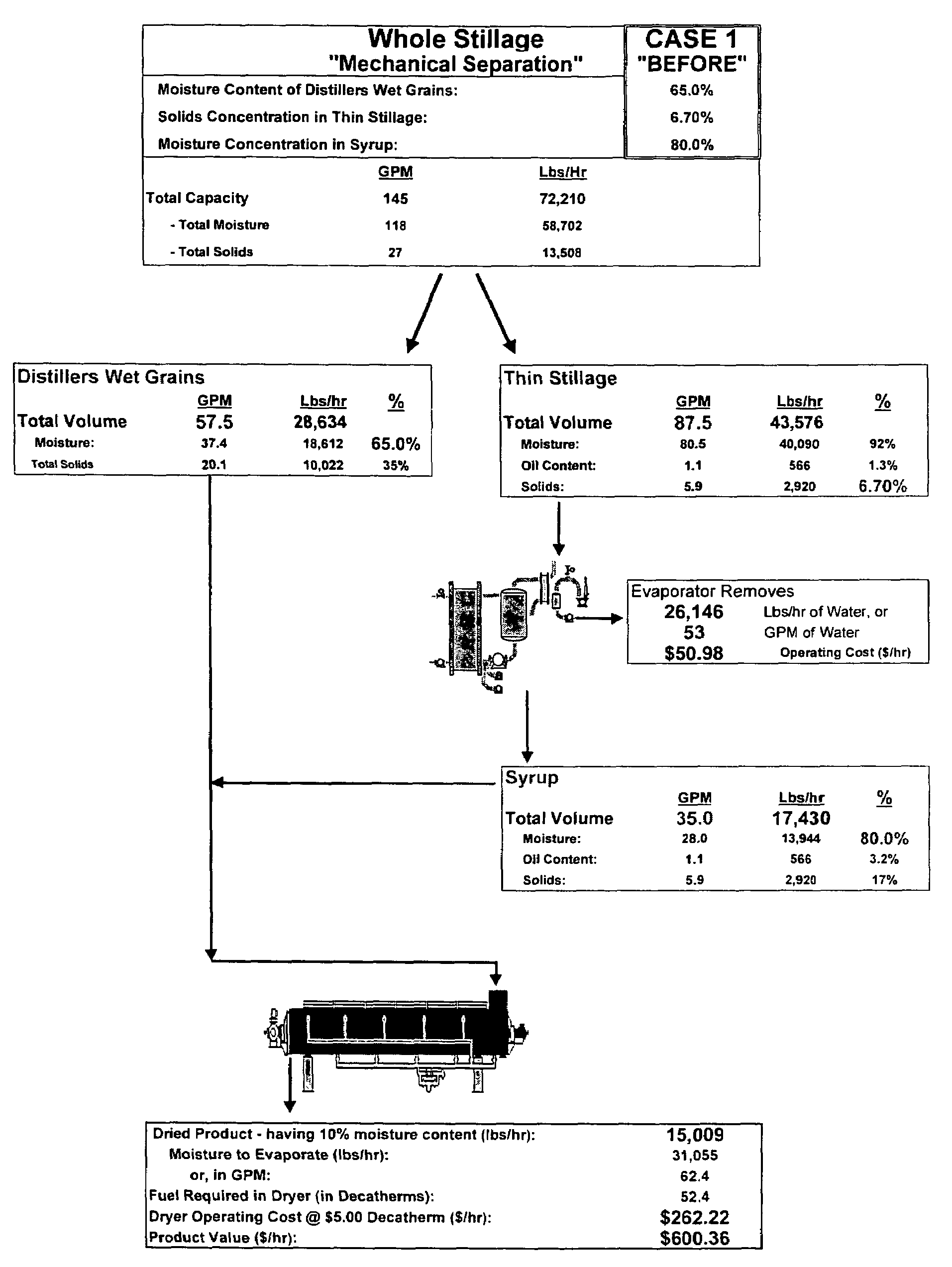
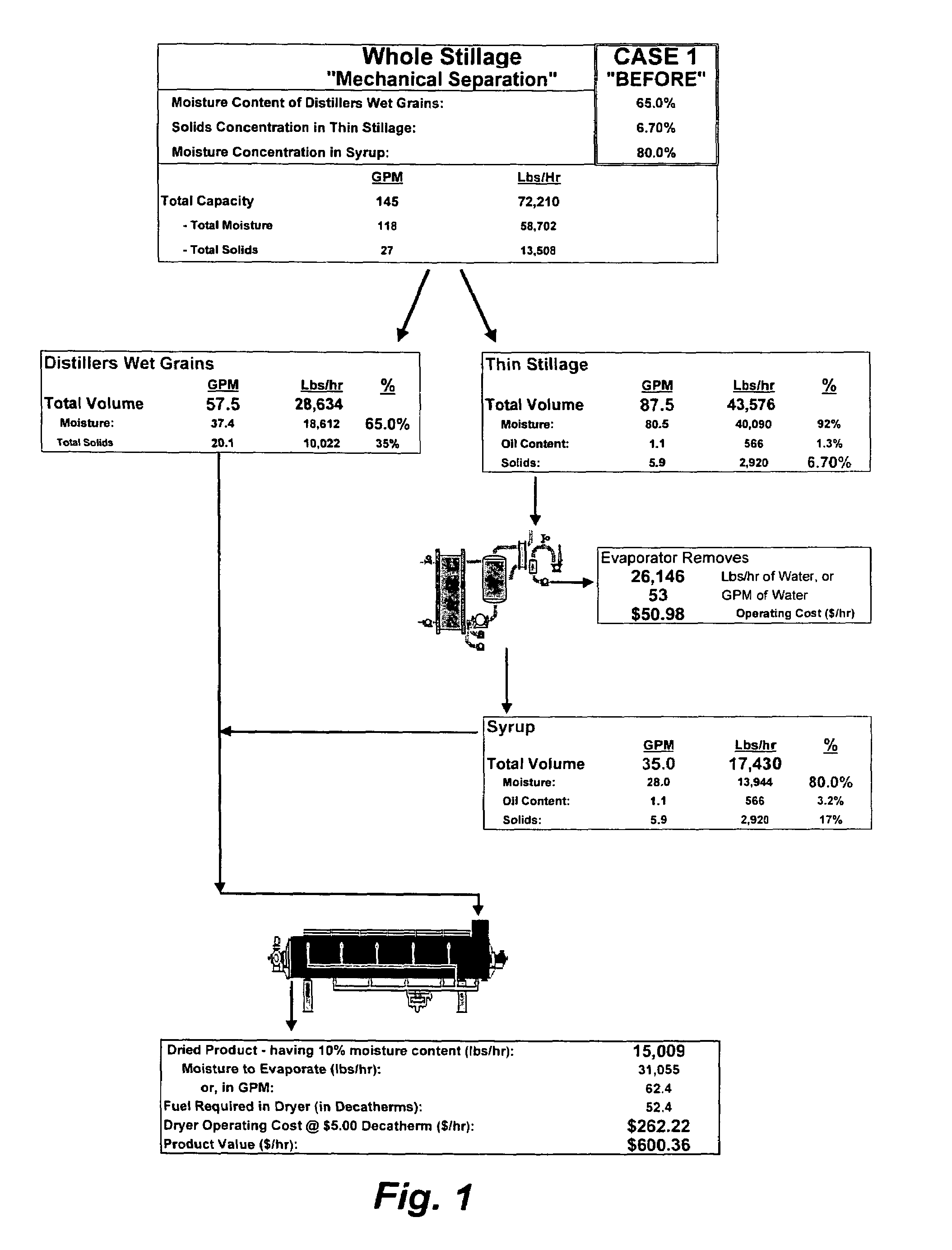
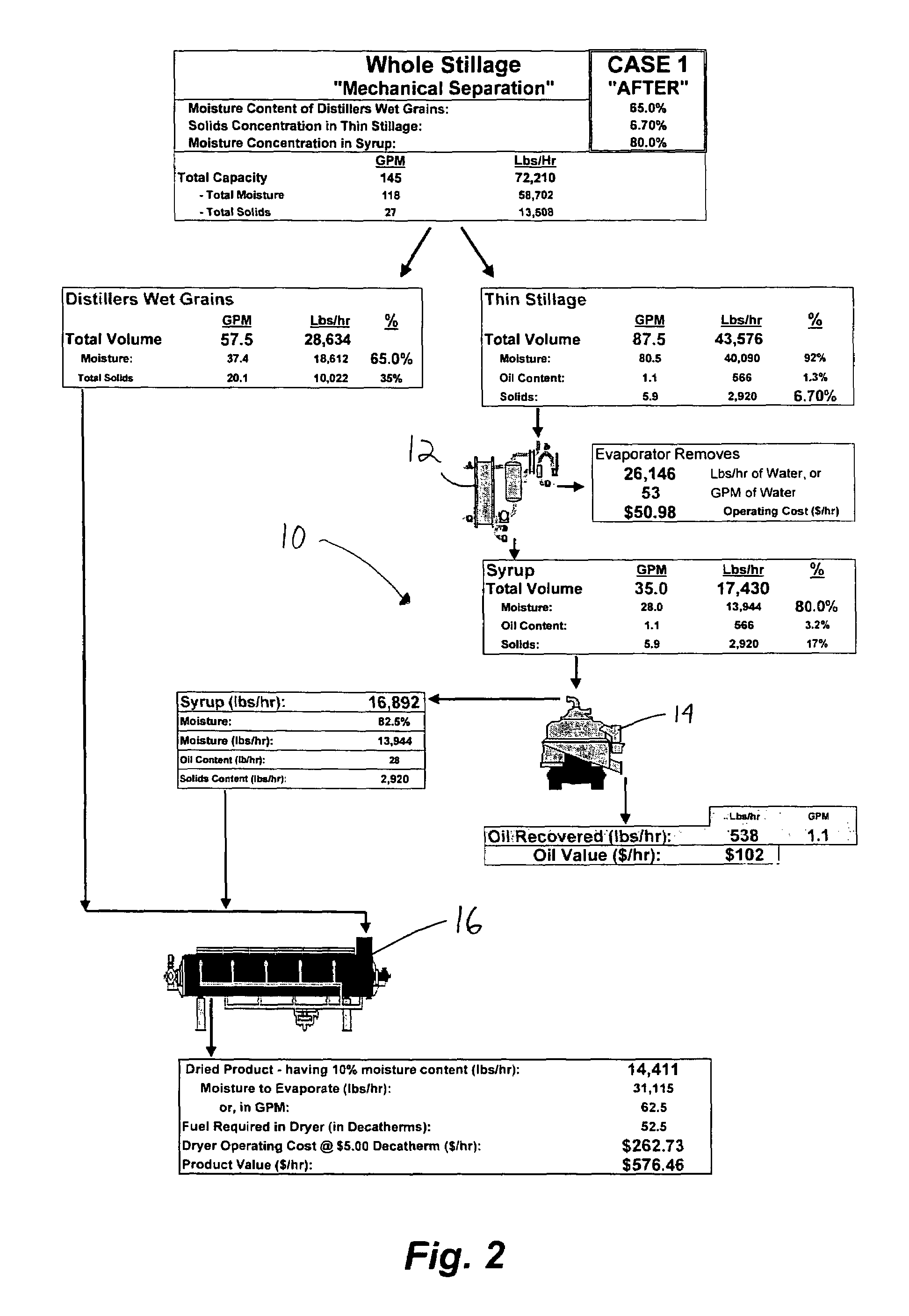
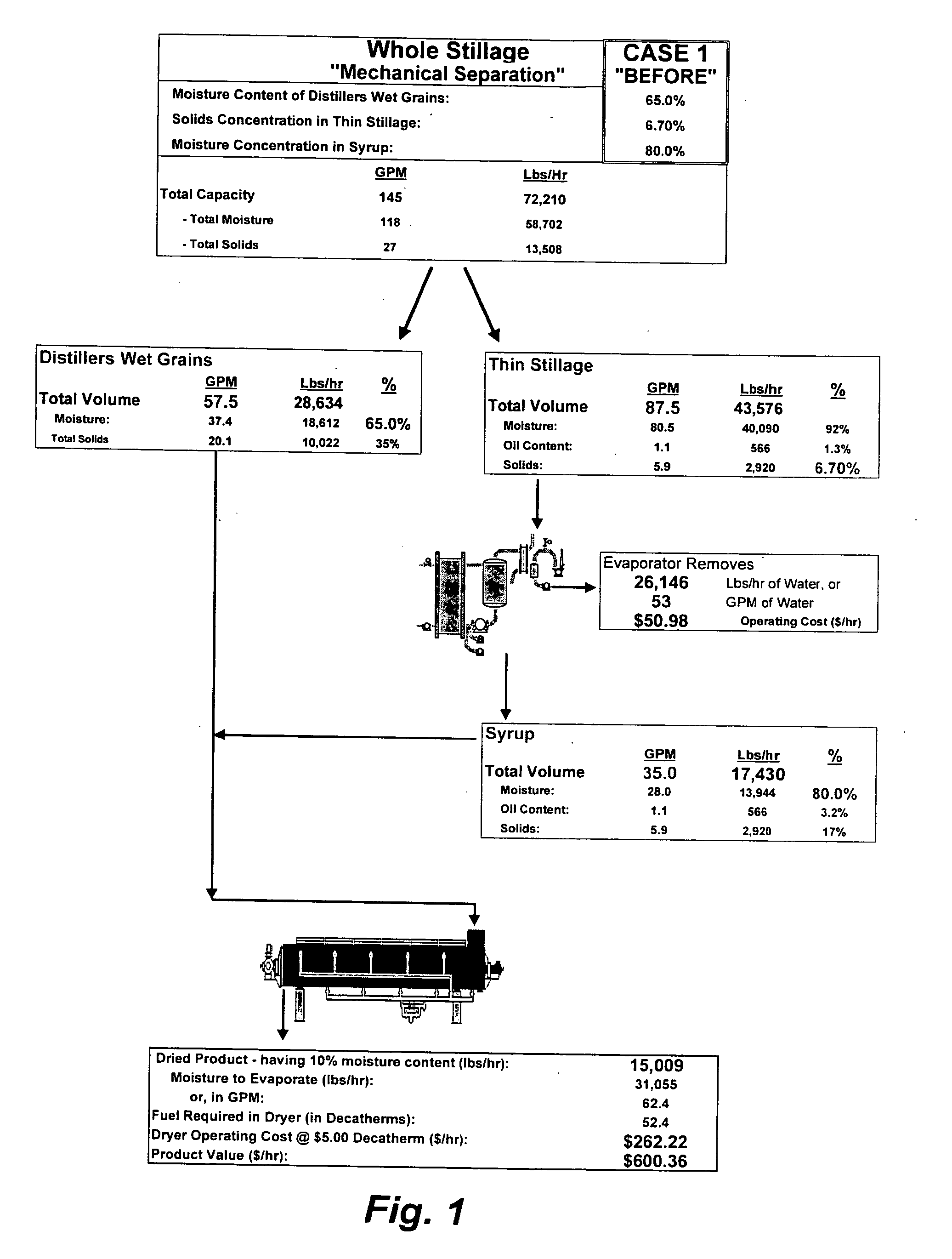
Method of processing ethanol byproducts and related subsystems
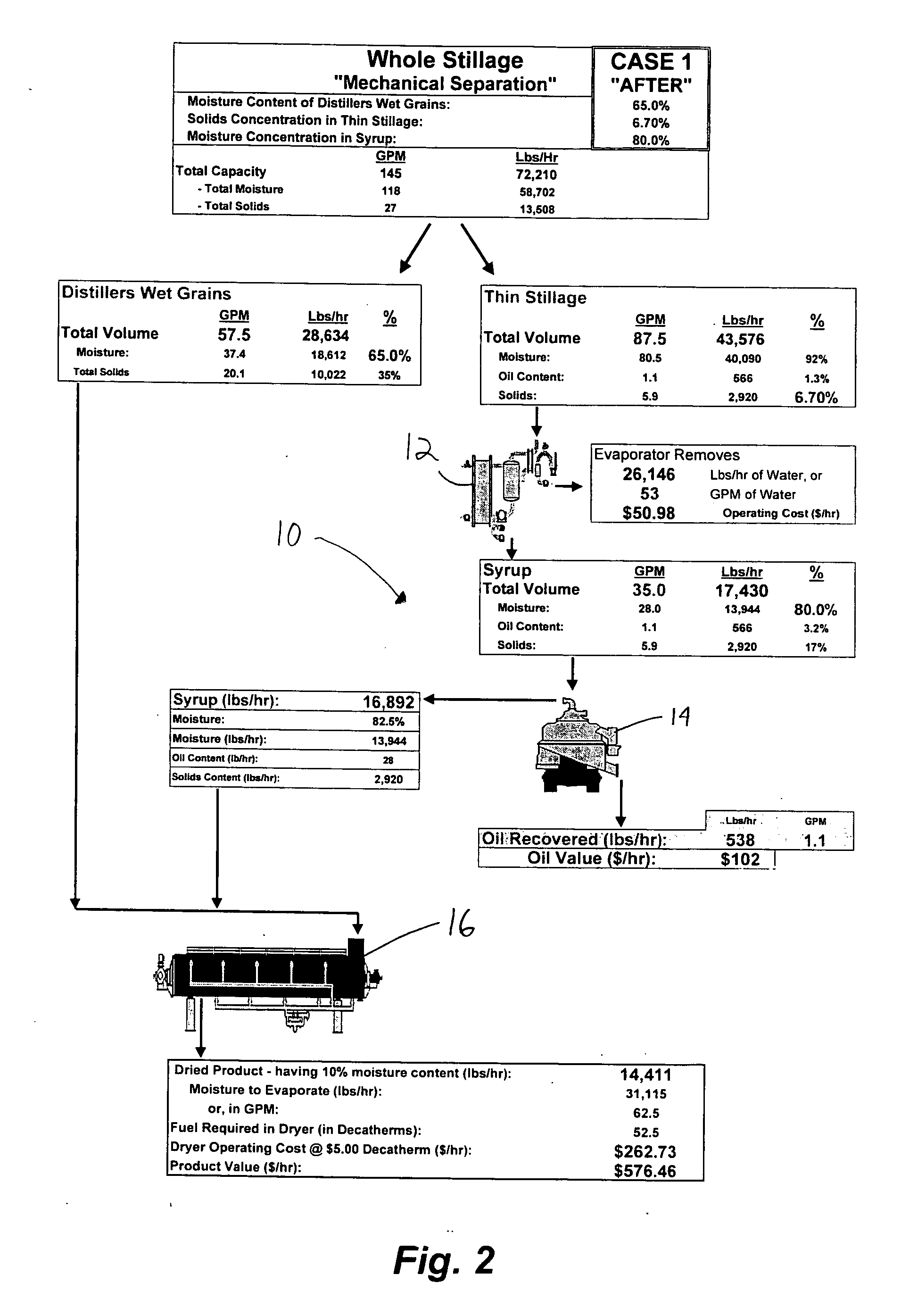
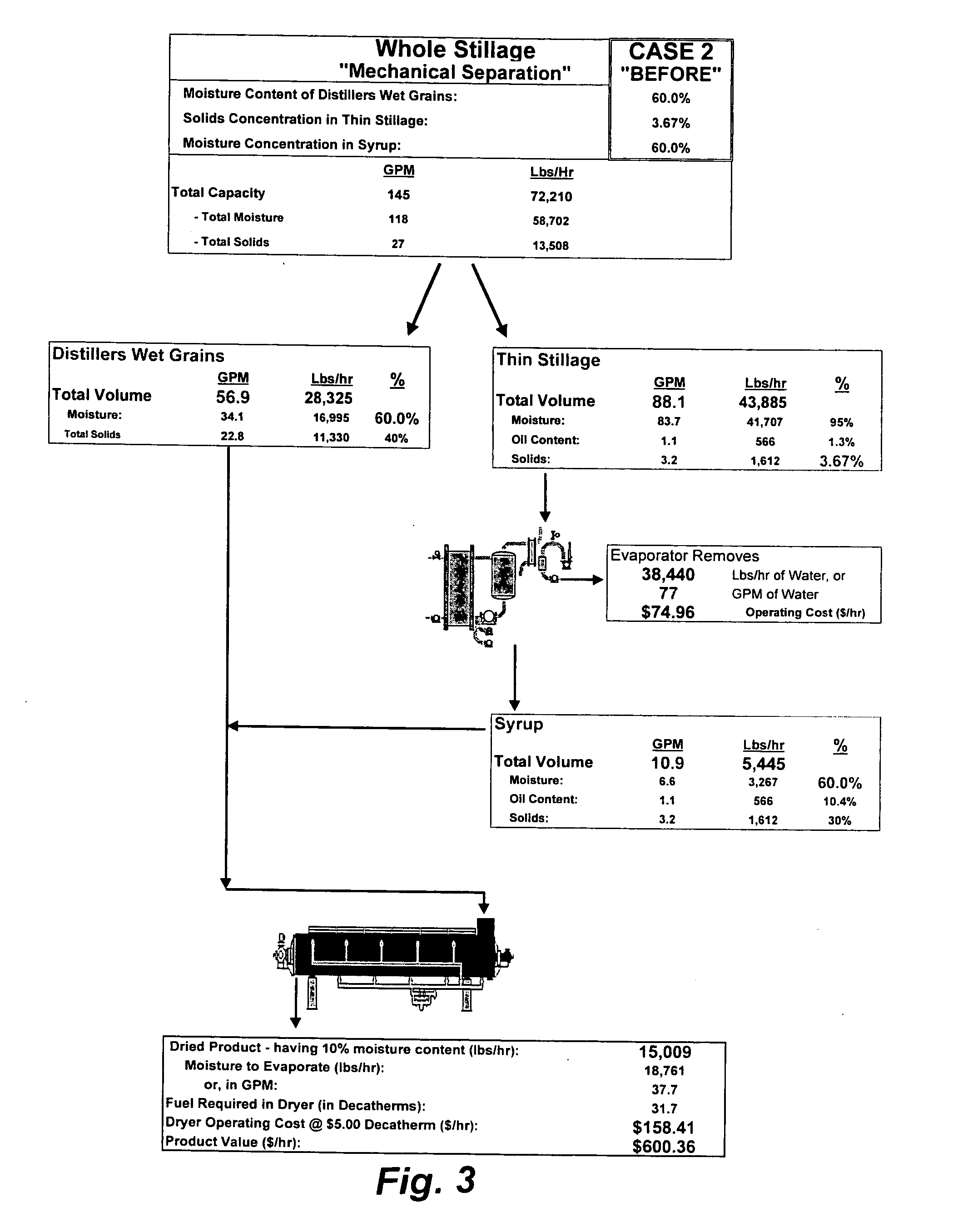
In one aspect of the invention, a method recovers oil from a concentrated byproduct, such as evaporated thin stillage formed during a dry milling process used for producing ethanol. The method includes forming a concentrate from the byproduct and recovering oil from the concentrate. The step of forming the concentrate may comprise evaporating the byproduct. Further, the step of separating the oil from the concentrate may comprise using a centrifuge and, in particular, a disk stack centrifuge. Other aspects of the invention include related methods and subsystems for recovering oil from thin stillage.
Owner:GS CLEANTECH CORP
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
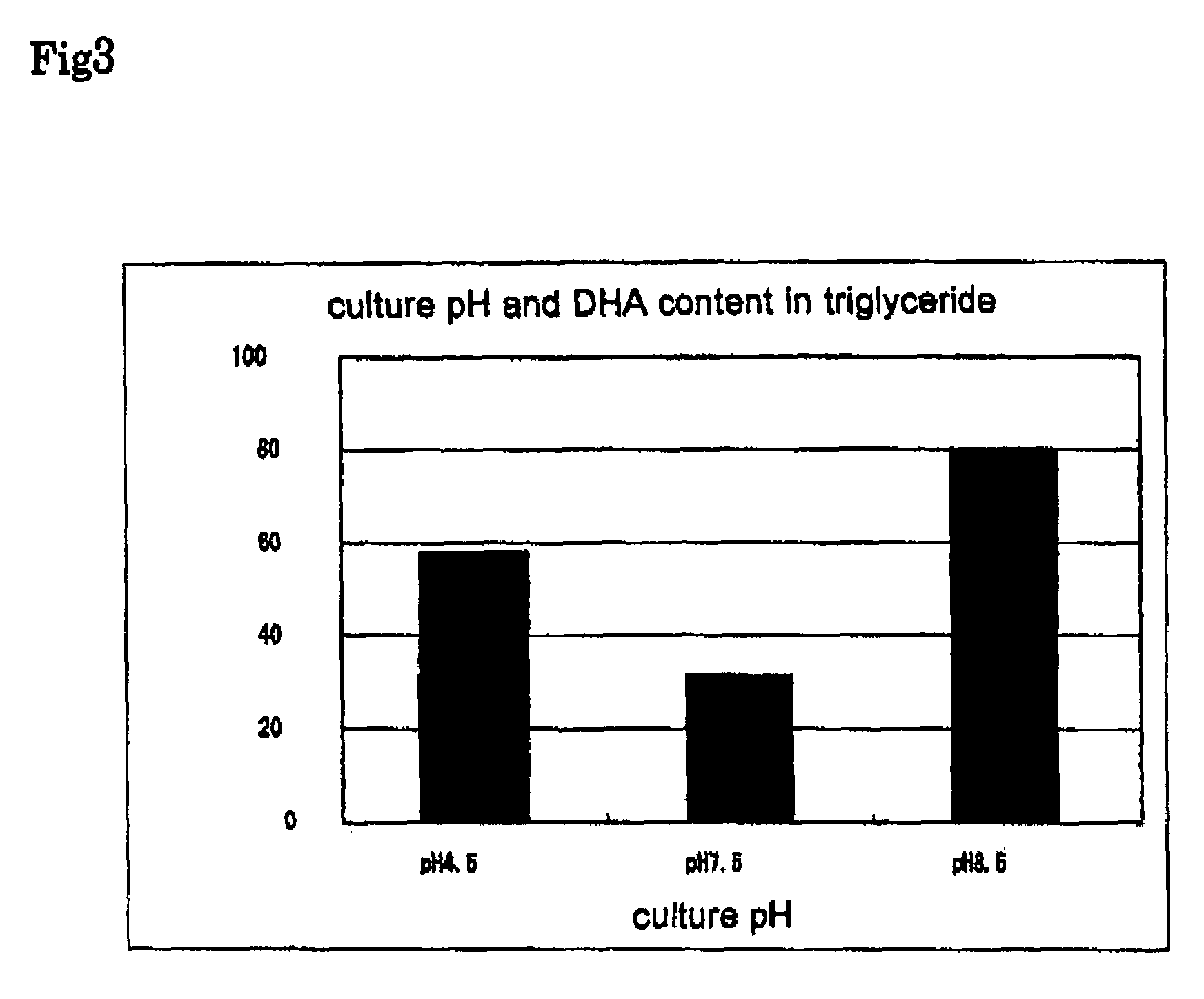
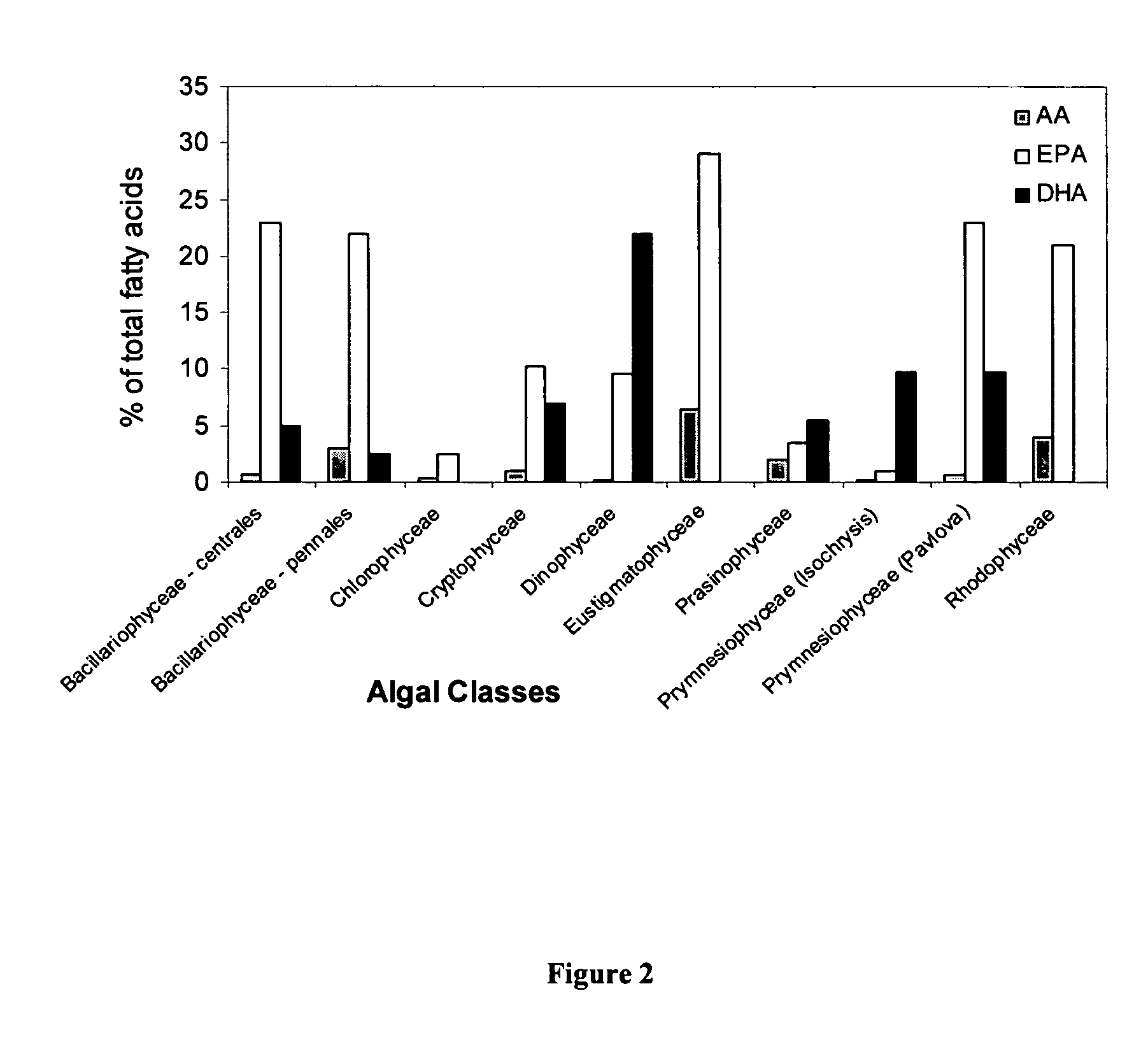
Method for preparing pure EPA and pure DHA
InactiveUS6846942B2Easy to disassembleSimple procedureFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acids production/refiningSolubilitySolvent
Pure DHA and pure EPA can be obtained from a mixture of EPA and DHA in a solution by forming salts of DHA and EPA which have different solubilities in the solvent, cooling the solution until the salt of EPA is formed, filtering the solution to recover the salt of EPA, and acidifying the EPA salt and the DHA salt to obtain pure EPA and pure DHA.
Owner:RUBIN DAVID
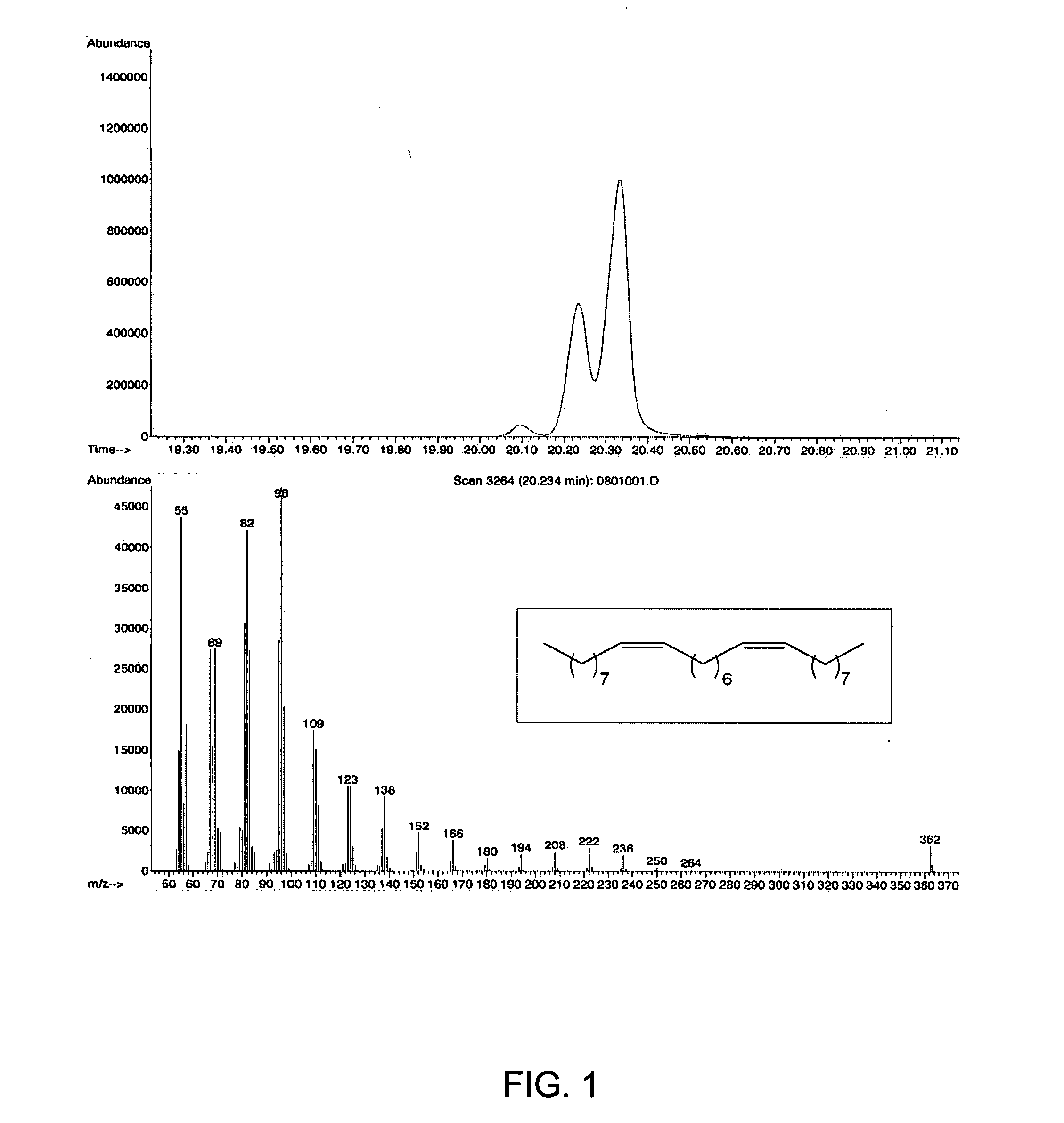
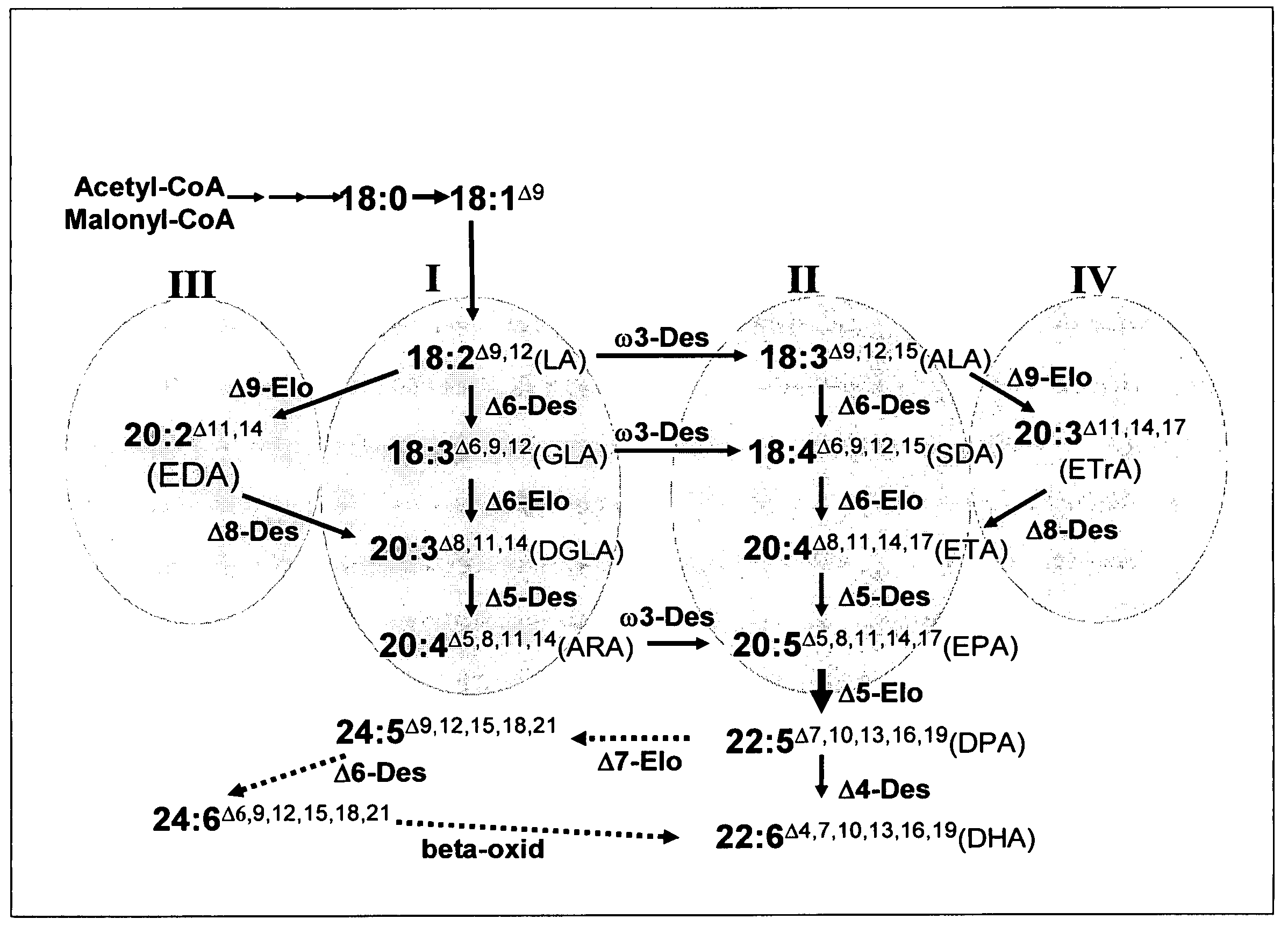
Synthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by recombinant cells
ActiveUS20050273885A1Reduce enzyme activityImprove efficiencyNervous disorderAntipyreticYeastPlant cell
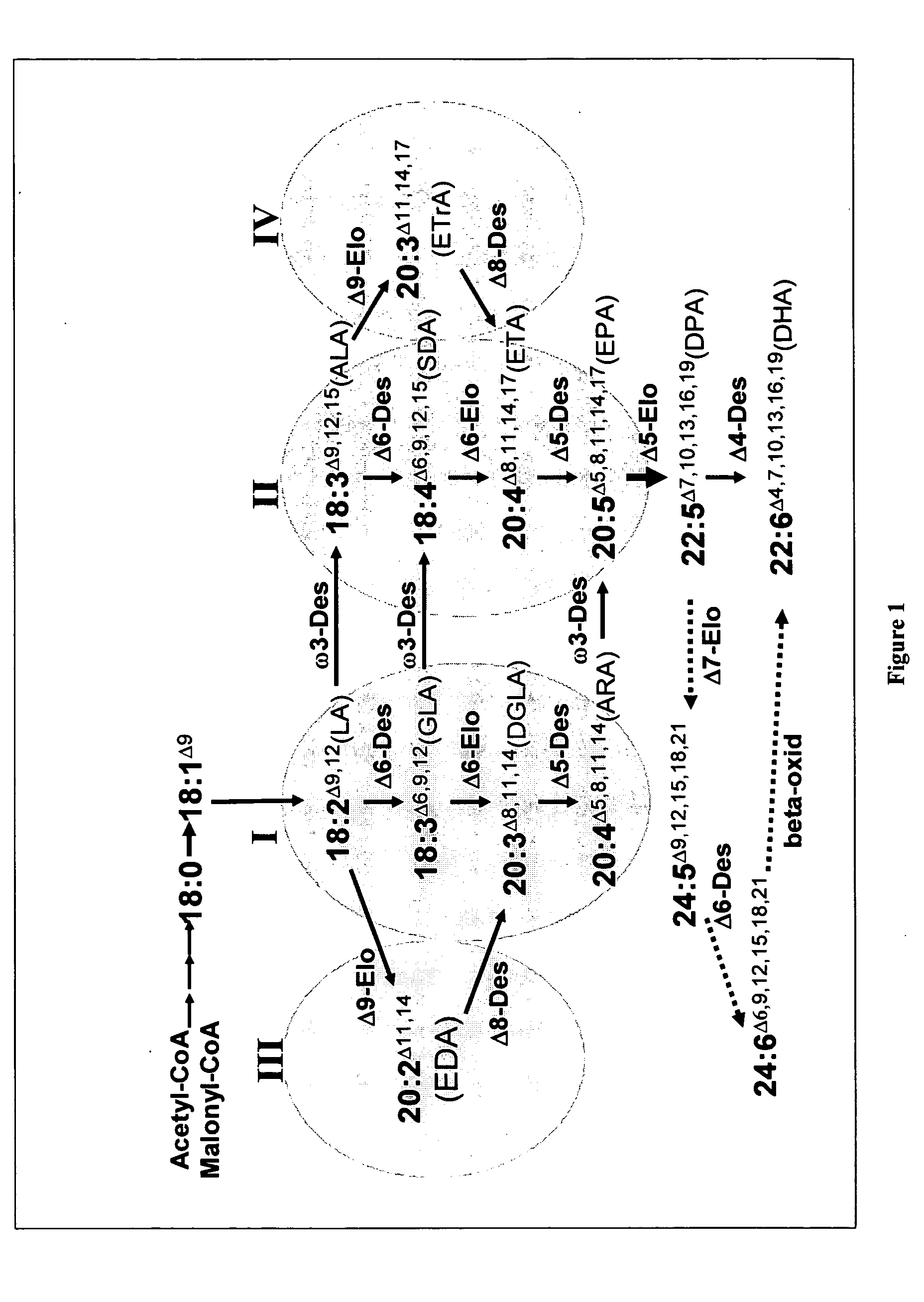
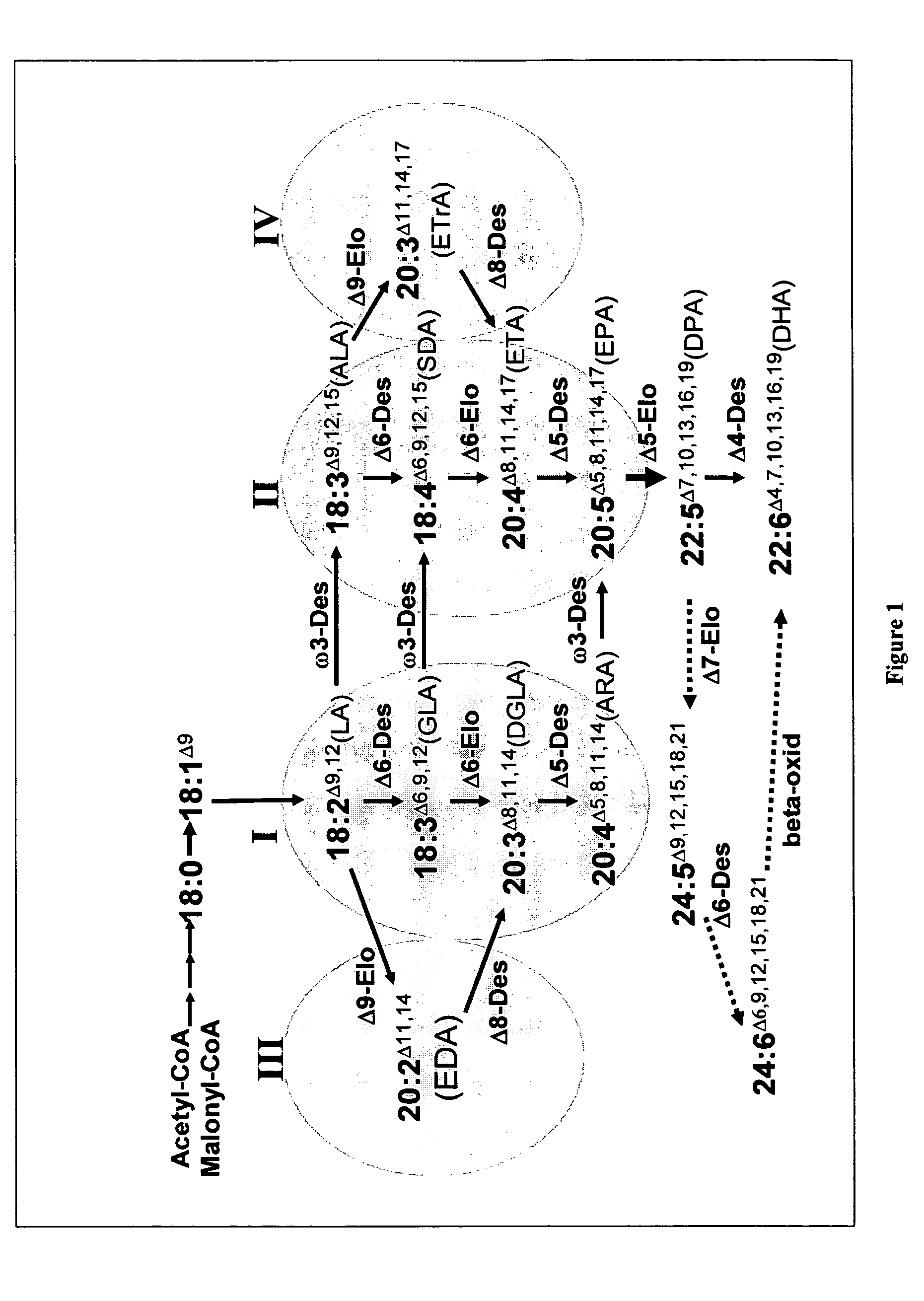
The present invention relates to methods of synthesizing long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, in recombinant cells such as yeast or plant cells. Also provided are recombinant cells or plants which produce long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a group of new enzymes which possess desaturase or elongase activity that can be used in methods of synthesizing long-chain poly unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Preparation and stabilization of food-grade marine oils
InactiveUS20030161918A1Increases rancimat stabilityIncreased rancimat stabilityMilk preparationDough treatmentFood gradeSilicon dioxide
The present invention relates to stabilizing marine oil by treatment with silica in the presence or absence of carbon and vacuum steam deodorization at a temperature between about 140° C. and about 210° C. in the presence of 0.1-0.4% deodorized rosemary or sage extract. If desired 0.01-0.03% ascorbyl palmitate and 0.05-0.2% mixed tocopherol can be added. A method of using such oil in food applications is provided. A method of identifying the sensory quality of unknown marine oils is also provided.
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD
Processes for preparation of oil compositions
ActiveUS20060111578A1Reduce oxidationMinimizes isomerizationFatty substance preservation using additivesEdible seed preservationHigh concentrationΑ-linolenic acid
The present invention is directed to processes for preparing oil compositions having a high concentration of poly-unsaturated fatty acids and oil compositions having a low concentration of α-linolenic acid. In addition, the present invention is directed to processes for preparing oil compositions having advantageous stability characteristics.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
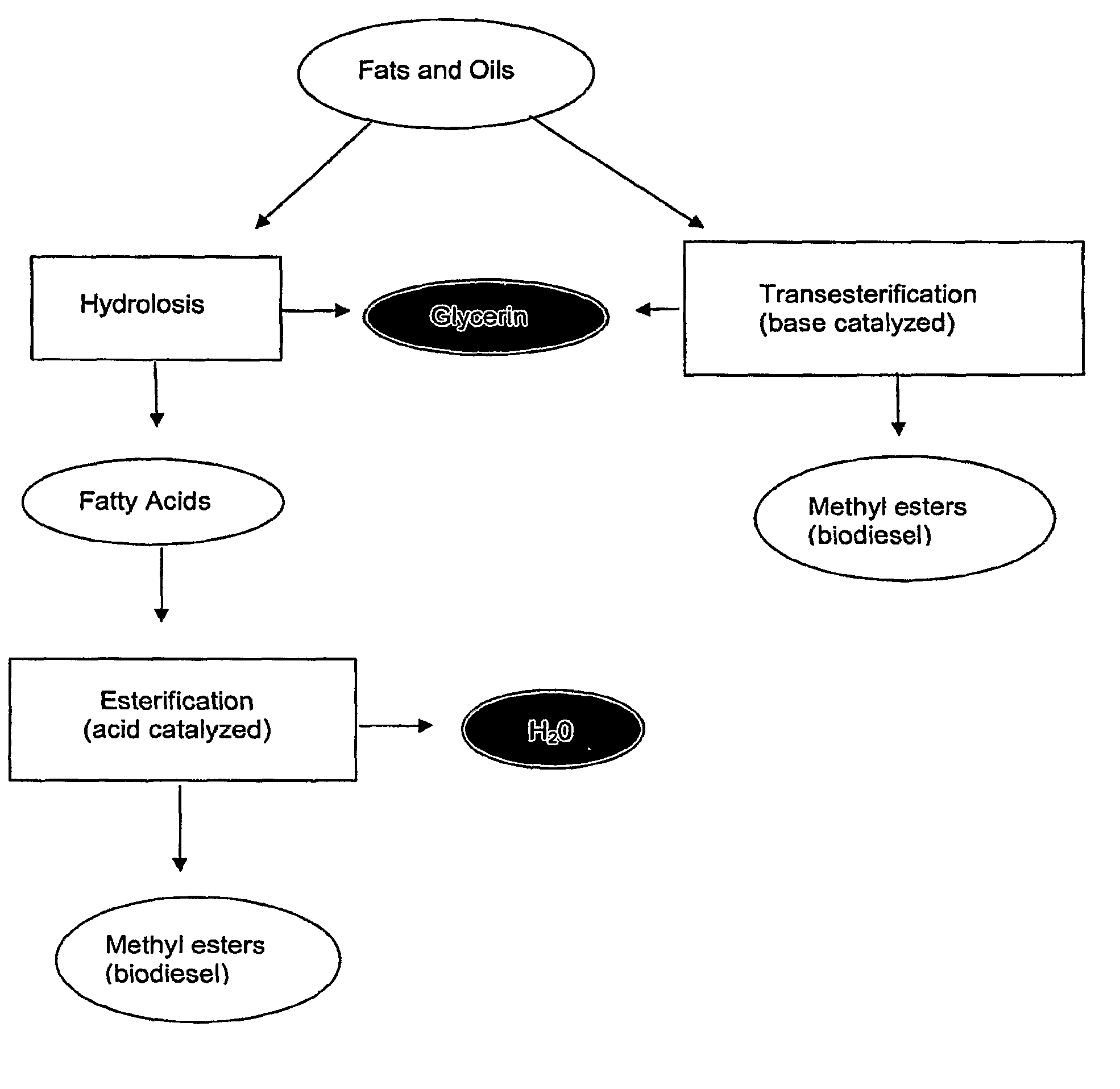
Process for producing biodiesel, lubricants, and fuel and lubricant additives in a critical fluid medium
InactiveUS6887283B1Limited mass transferImprove reaction speedFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselVegetable oil
A process for producing alkyl esters useful in biofuels and lubricants by transesterifying glyceride- or esterifying free fatty acid-containing substances in a single critical phase medium is disclosed. The critical phase medium provides increased reaction rates, decreases the loss of catalyst or catalyst activity and improves the overall yield of desired product. The process involves the steps of dissolving an input glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with an alcohol or water into a critical fluid medium; reacting the glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substance with the alcohol or water input over either a solid or liquid acidic or basic catalyst and sequentially separating the products from each other and from the critical fluid medium, which critical fluid medium can then be recycled back in the process. The process significantly reduces the cost of producing additives or alternatives to automotive fuels and lubricants utilizing inexpensive glyceride- or free fatty acid-containing substances, such as animal fats, vegetable oils, rendered fats, and restaurant grease.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Bioeffective krill oil compositions
InactiveUS20080274203A1Increasing flesh colorationPromote growthBiocideMetabolism disorderInsulin resistanceAnti oxidant
This invention discloses new krill oil compositions characterized by having high amounts of phospholipids, astaxanthin esters and / or omega-3 contents. The krill oils are obtained from krill meal using supercritical fluid extraction in a two stage process. Stage 1 removes the neutral lipid by extracting with neat supercritical CO2 or CO2 plus approximately 5% of a co-solvent. Stage 2 extracts the actual krill oils by using supercritical CO2 in combination with approximately 20% ethanol. The krill oil materials obtained are compared with commercially available krill oil and found to be more bioeffective in a number of areas such as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidant effects, improving insulin resistances and improving blood lipid profile.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Soaps Produced from Oil-Bearing Microbial Biomass and Oils
ActiveUS20090305942A1Improve efficiencyLow costSoap detergents with organic compounding agentsBiofuelsMicroorganismMicrobial oil
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Method of processing ethanol byproducts and related subsystems
In one aspect of the invention, a method recovers oil from a concentrated byproduct, such as evaporated thin stillage formed during a dry milling process used for producing ethanol. The method includes forming a concentrate from the byproduct and recovering oil from the concentrate. The step of forming the concentrate may comprise evaporating the byproduct. Further, the step of separating the oil from the concentrate may comprise using a centrifuge and, in particular, a disk stack centrifuge. Other aspects of the invention include related methods and subsystems for recovering oil from thin stillage.
Owner:GS CLEANTECH CORP
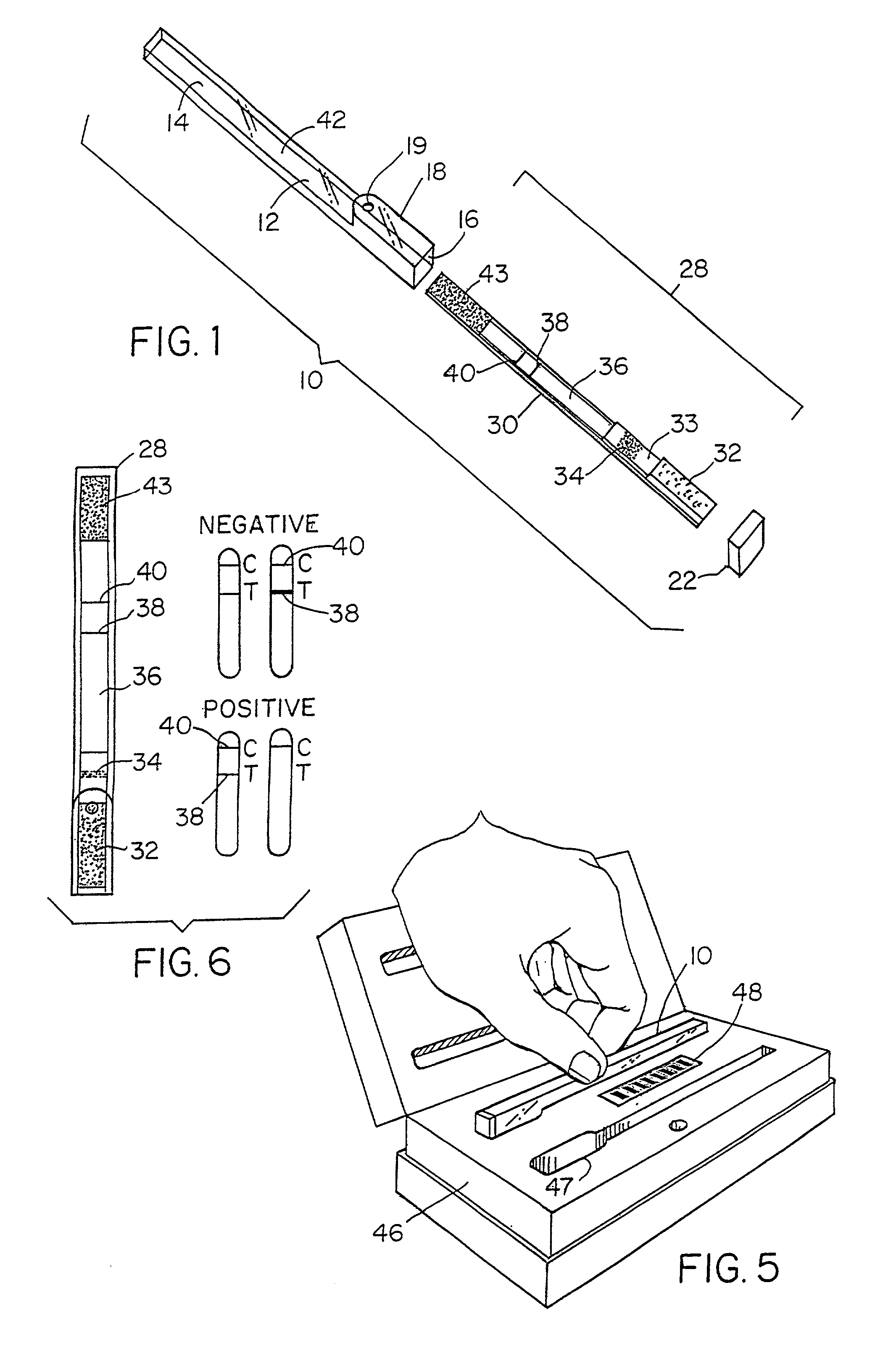
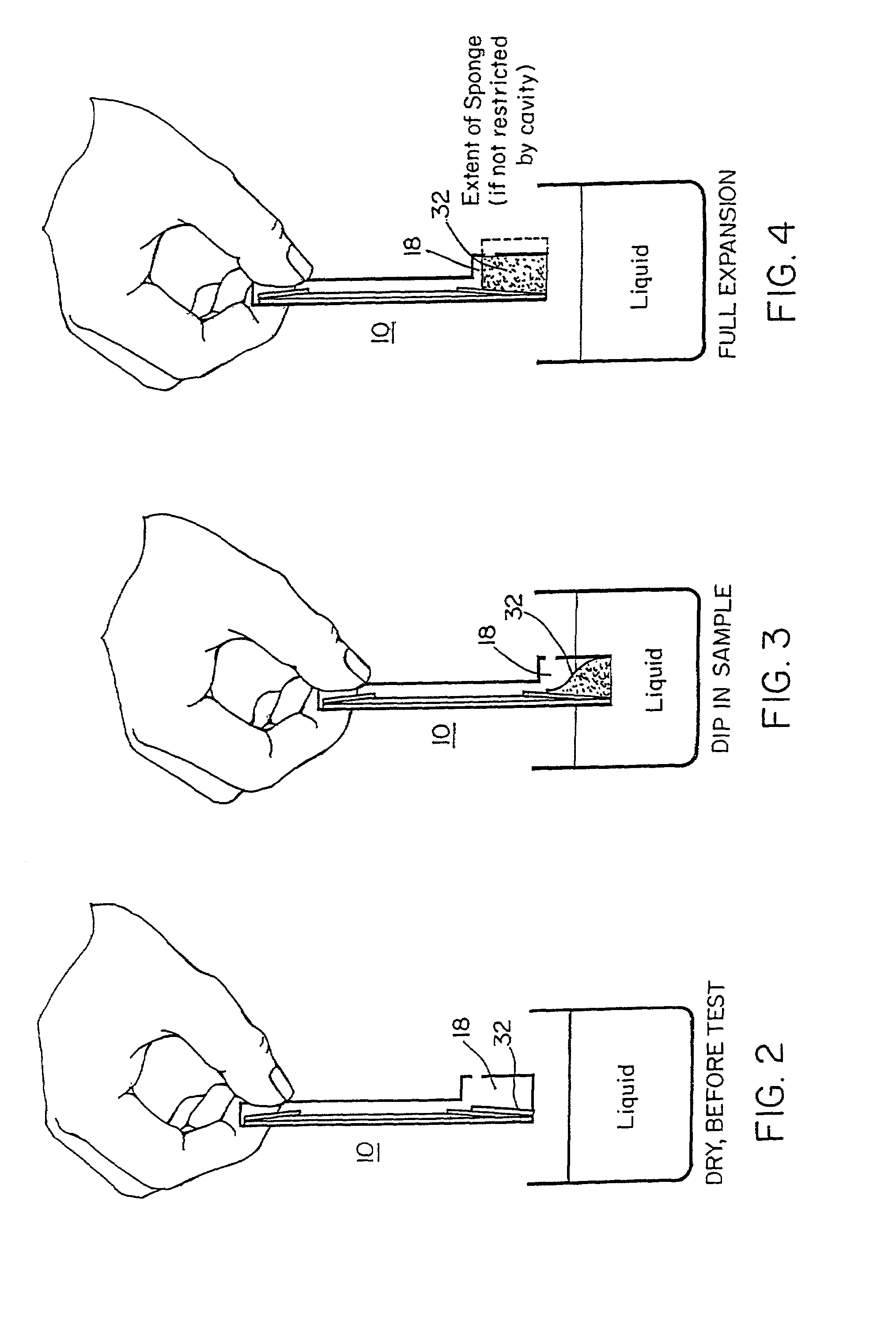
Method for detecting the presence of an analyte in a sample
InactiveUS7097983B2High purityEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid hydrogenationAnalyteBinding site
The invention features a method of determining whether one or more members of an analyte family are present in a sample. The method makes use of a test zone binder, e.g., a receptor that can bind one or a plurality of analytes within an analyte family, the analytes family defined by similar structural binding sites. Members of an analyte family can have different detection level requirements and, therefore, additional analyte binders can be employed to adjust test sensitivity for a subset of the analytes in the analyte family individually, so that each analyte can be detected only if it is present in the sample above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:CHARM SCI
Optimization of biofuel production
InactiveUS20090181438A1Enhance lipid productionEnhance oil extractionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveBiofuel
Embodiments of the present invention includes an apparatuses, compositions, and methods utilizing mechanical and chemical engineering strategies to achieve even greater efficiencies in biofuels production from oleaginous organisms. These increased efficiencies may be achieved through the application of targeted and well-designed chemical and mechanical engineering methods disclosed herein to achieve a non-destructive extraction process (NDEP).
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
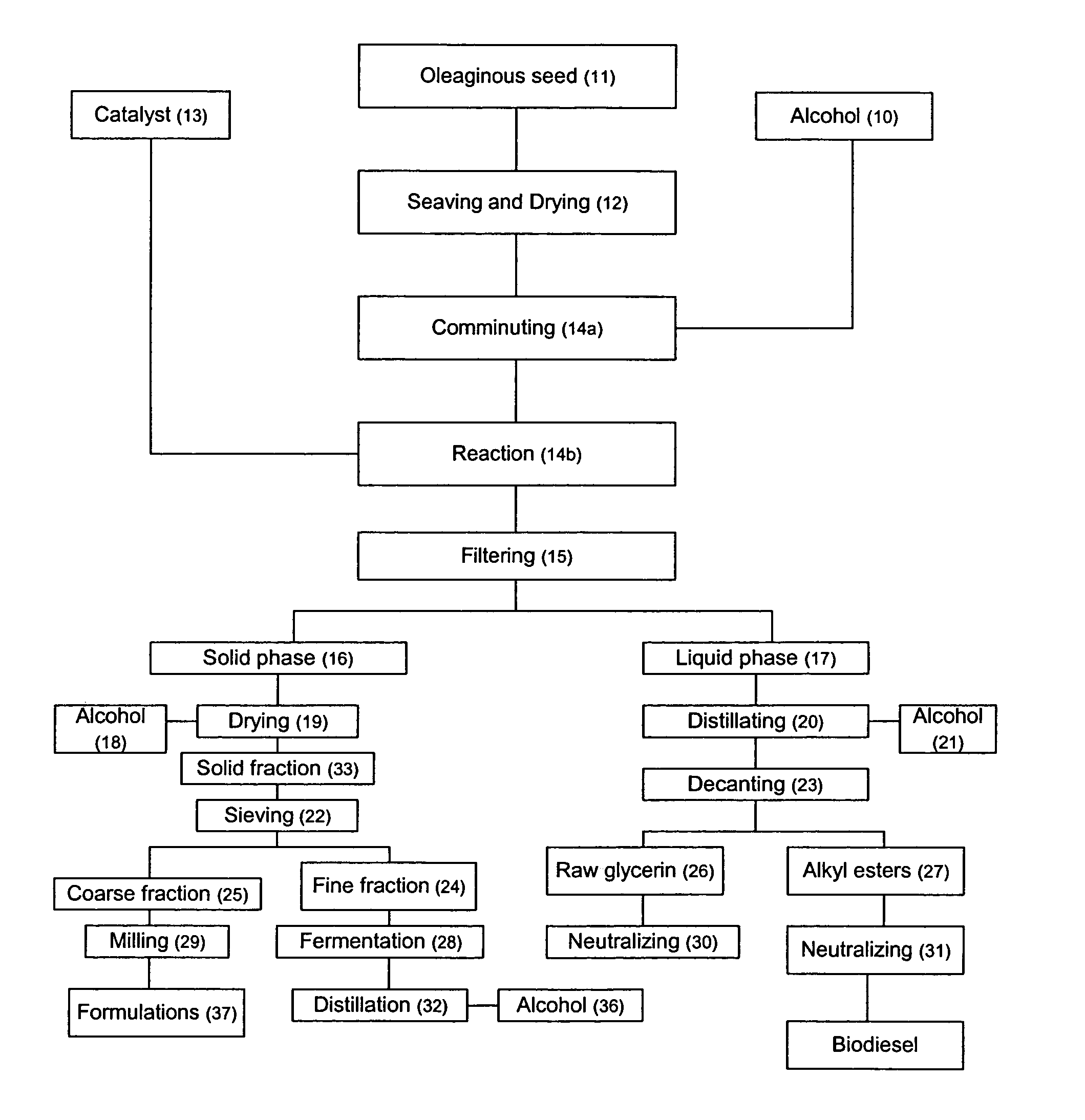
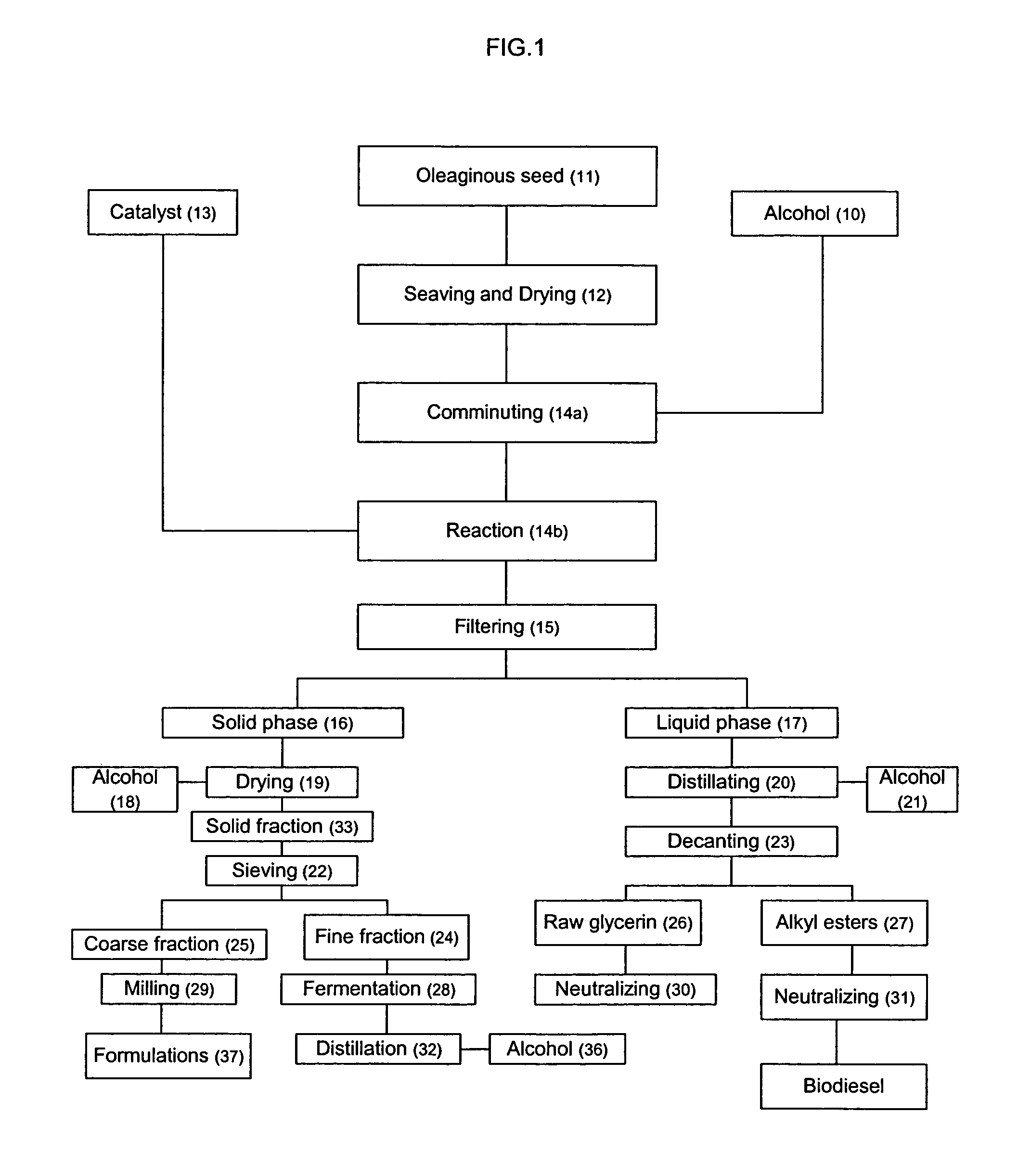
Process for producing biodiesel fuel using triglyceride-rich oleagineous seed directly in a transesterification reaction in the presence of an alkaline alkoxide catalyst
InactiveUS7112229B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationOil and greaseBiodiesel
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds. The inventive process includes a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Thermal methods for treating a metathesis feedstock
ActiveUS20110313180A1Diminish starting peroxide valueOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationOxygenThermal methods
Various methods are provided for metathesizing a feedstock. In one aspect, a method includes providing a feedstock comprising a natural oil, heating the feedstock to a temperature greater than 100° C. in the absence of oxygen, holding the feedstock at the temperature for a time sufficient to diminish catalyst poisons in the feedstock, and, following the heating and holding, combining a metathesis catalyst with the feedstock under conditions sufficient to metathesize the feedstock.
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
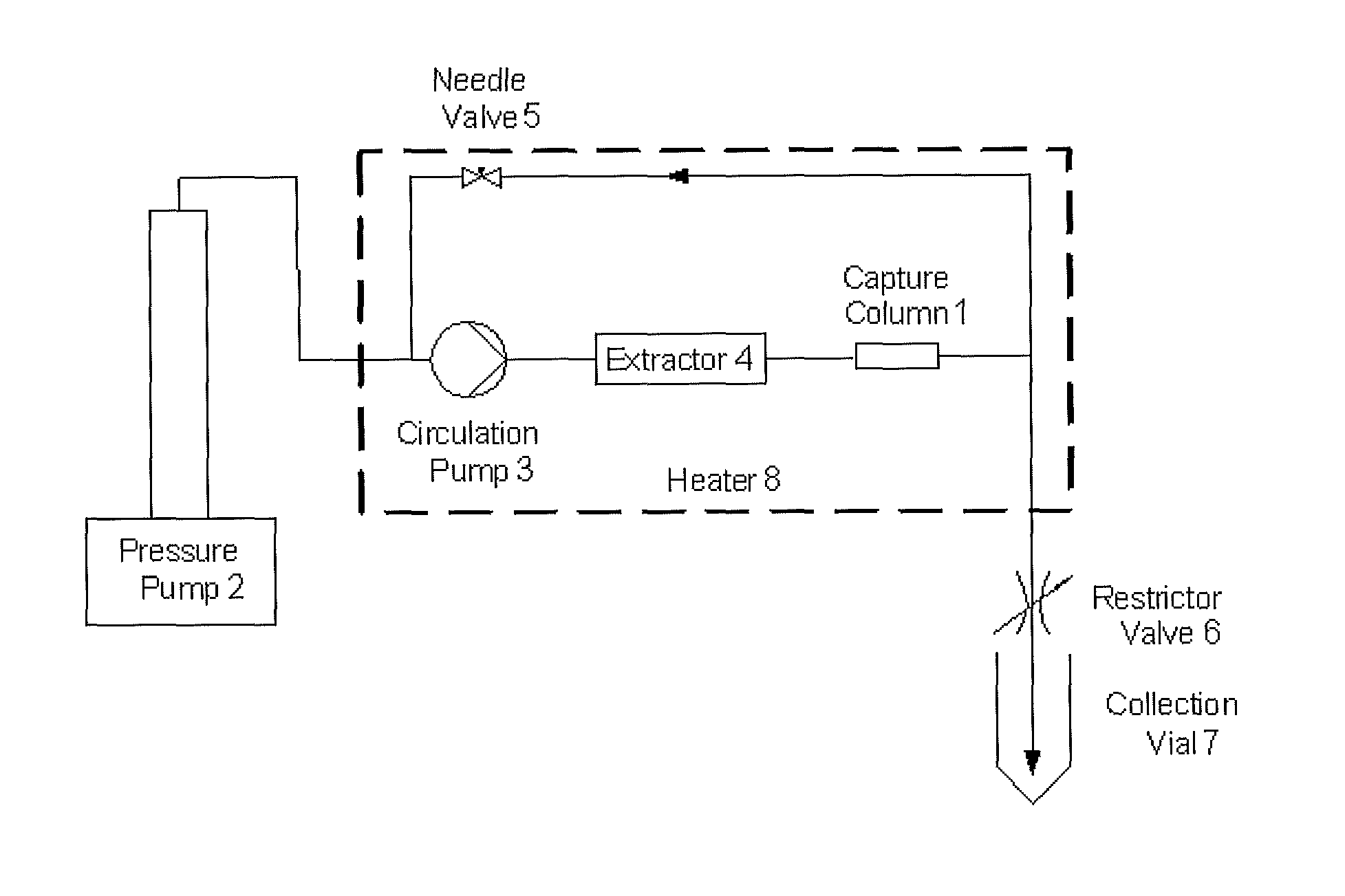
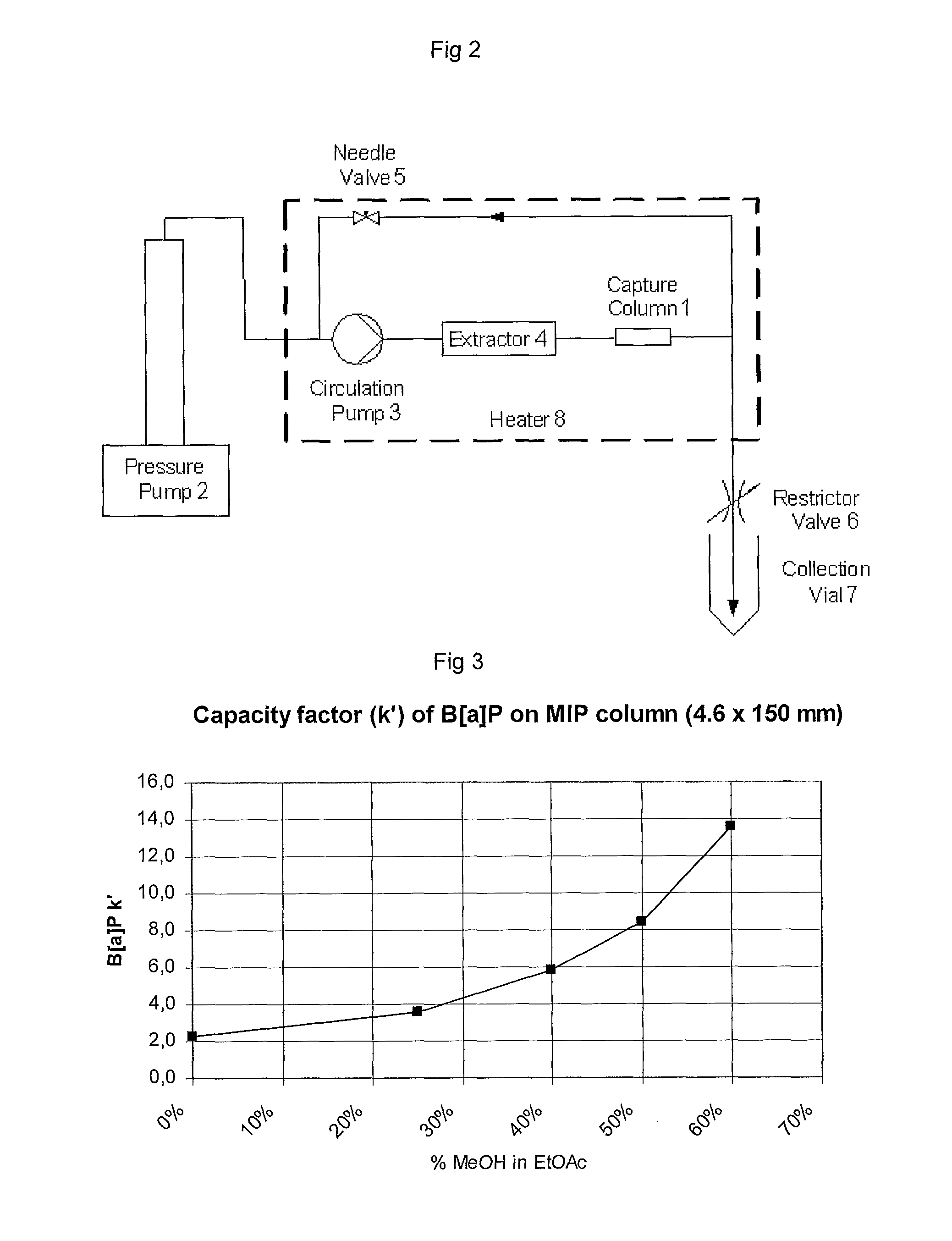
Method for Removing Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20110159160A1Improve performanceReduce in quantityTobacco treatmentSolvent extractionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMolecularly imprinted polymer
A method for extracting a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from a material such as tobacco or tobacco extracts or other materials comprises treating the material with a molecularly imprinted polymer selective for the hydrocarbon in the presence of a low polarity medium.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
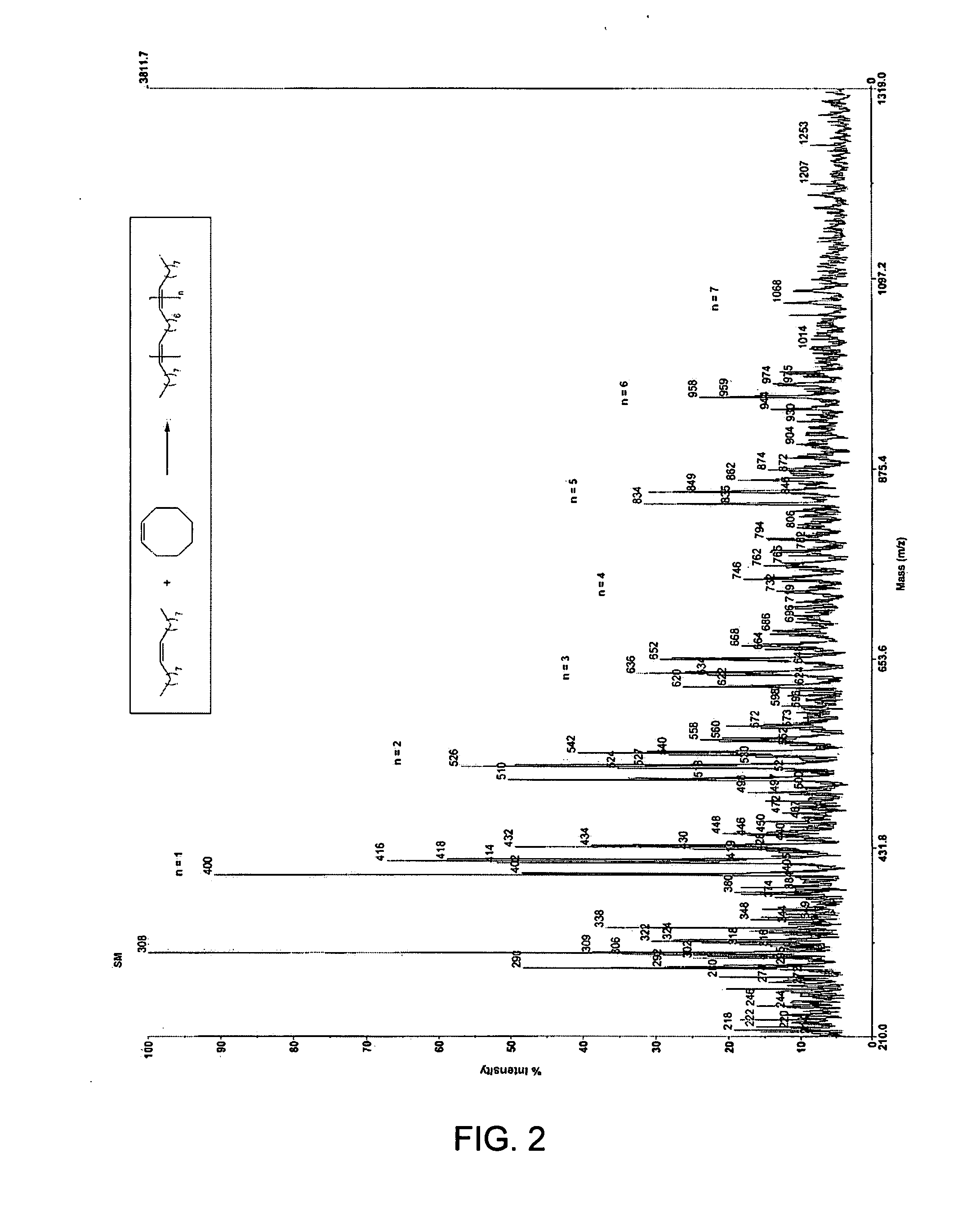
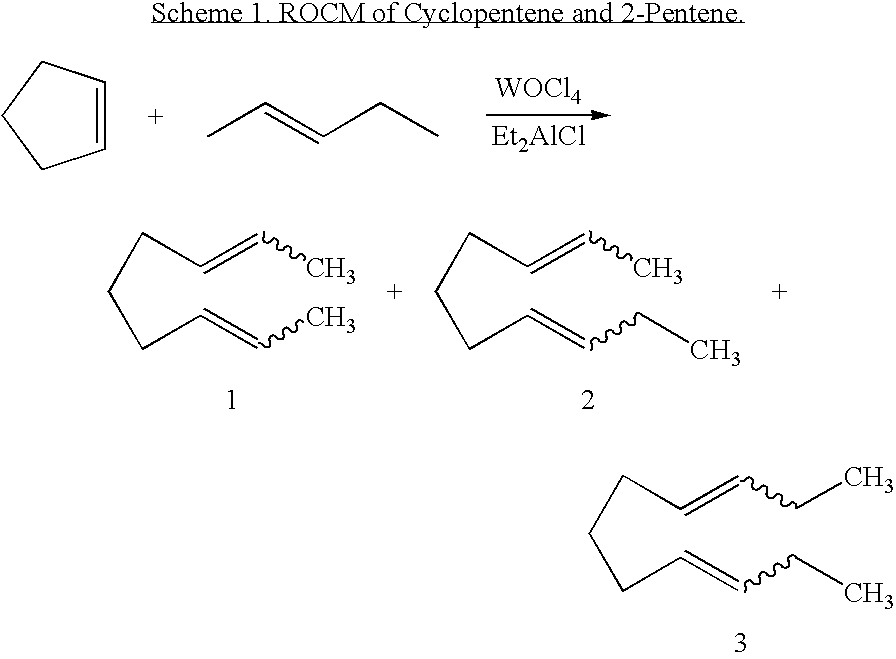
Ring opening cross-metathesis reaction of cyclic olefins with seed oils and the like
ActiveUS20080064891A1Fatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationOrganic synthesisRuthenium
This invention relates generally to olefin metathesis, and more particularly relates to the ring-opening, ring insertion cross-metathesis of cyclic olefins with internal olefins such as seed oils and the like. In one embodiment, a method is provided for carrying out a catalytic ring-opening cross-metathesis reaction, comprising contacting at least one olefinic substrate with at least one cyclic olefin as a cross metathesis partner, in the presence of a ruthenium alkylidene olefin metathesis catalyst under conditions effective to allow ring insertion cross metathesis whereby the cyclic olefin is simultaneously opened and inserted into the olefinic substrate. The invention has utility in the fields of catalysis, organic synthesis, and industrial chemistry.
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
Microorganism having an ability of producing docosahexaenoic acid and use thereof
ActiveUS7259006B2High ability of producing docosahexaenoic acidEfficient productionBiocideFatty acid hydrogenationDocosahexaenoic acidMicroorganism
An object of the present invention is to provide a microorganism which has a high ability of producing docosahexaenoic acid. The present invention provides a Thraustochytrium strain which has an ability of producing docosahexaenoic acid, and use thereof.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Process for producing alkyl esters from a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol
InactiveUS6878837B2High purityImpact on overall process costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationAluminateTransesterification
Alkyl esters of fatty acids, and high purity glycerin, are produced using a process comprising a set of transesterification reactions between a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol employing a heterogeneous catalyst, for example based on zinc aluminate, the water content in the reaction medium being controlled to a value that is below a given limiting value.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Synthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by recombinant cells
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Fatty acid blends and uses therefor
ActiveUS8029579B2Maintain good propertiesEffect cold flow propertyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationPolymer scienceFatty acid methyl ester
Owner:CIBUS
High PUFA oil compositions
ActiveUS20060110521A1Organic chemistryFatty substance preservation using additivesHigh concentrationFatty acids.polyunsaturated
The present invention is directed to oil compositions having a high concentration of poly-unsaturated fatty acids. In addition, the oils of the present invention have advantageous stability characteristics and minimal trans-fatty acids.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Production of biodiesel from combination of corn (maize) and other feed stocks
InactiveUS20070099278A1Increase Biodiesel production outputStable year round productionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationProcess systemsSodium Bentonite
A method and system to produce biodiesel from a combination of corn (maize) and other agro feedstock may be simarouba, mahua, rice, pongamia etc. Germ is separated (either by wet process or dry process) from corn, crude corn oil extracted from germ and corn starch milk / slurry is heated and cooked in jet cooker to about 105 degree Celsius, enzymes added to convert starch into fermentable sugars in liquification and saccharification process and rapidly cooled down to about 30 degree Celsius. Simarouba fruits syrup, mahua syrup is mixed with corn starch milk (after saccharification). When yeast is added the fermentation takes place for about 72 hours. Thereafter the fermented wash is distilled to produce ethanol. Water consumed in dry process is very less compared to traditional wet process system. Corn oil and mixture of other oils is fed into transesterification (reaction) vessels where ethanol with catalyst, usually sodium hydroxide is added and reaction takes place for about a period of 2-8 hours. Crude biodiesel and crude glycerin as by-products is produced. Excess ethanol removed by distillation process. Crude biodiesel washed with warm water to remove residual soaps or unused catalyst, dried and biodiesel stored for commercial use. Oil extracted from spent bleach mud (used sodium bentonite), a waste product of edible oil refineries may also be utilized for economical production of biodiesel in combination of corn oil and ethanol.
Owner:AARE PALANISWAMY RAMASWAMY
Soaps produced from oil-bearing microbial biomass and oils
ActiveUS8119583B2Low costImprove efficiencySoap detergents with organic compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsMicrobial oilGlycerol
Soap and cosmetic products can be made from oil-bearing microbial biomass via the alkaline hydrolysis of glycerolipids and fatty acid esters to fatty acid salts. The saponified microbial oils / lipids can be combined with a variety of additives to produce compositions for use as soaps and other cosmetic products, which may also contain other constituents of the biomass, including unsaponified oils, glycerol and carotenoids, among others.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
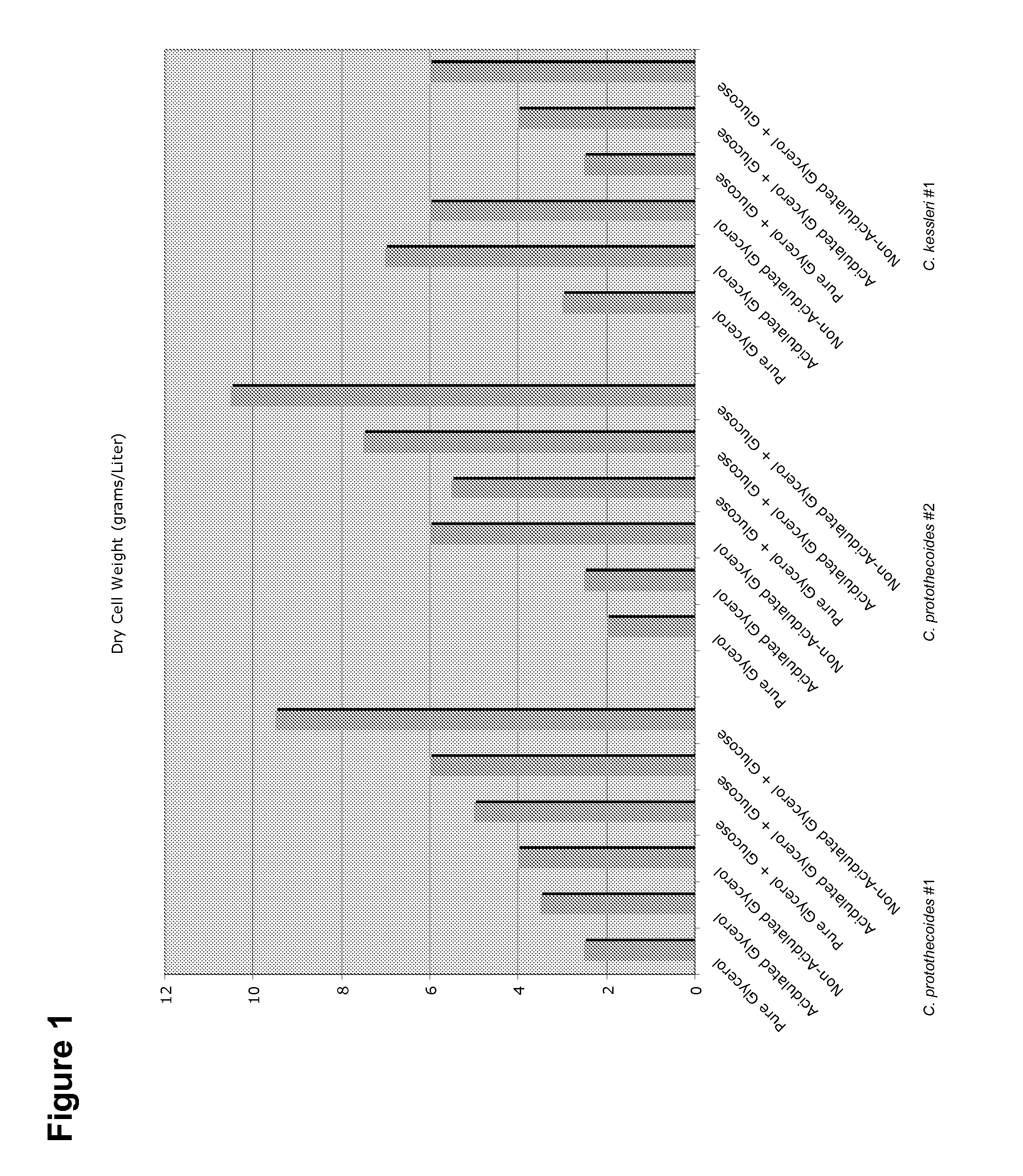
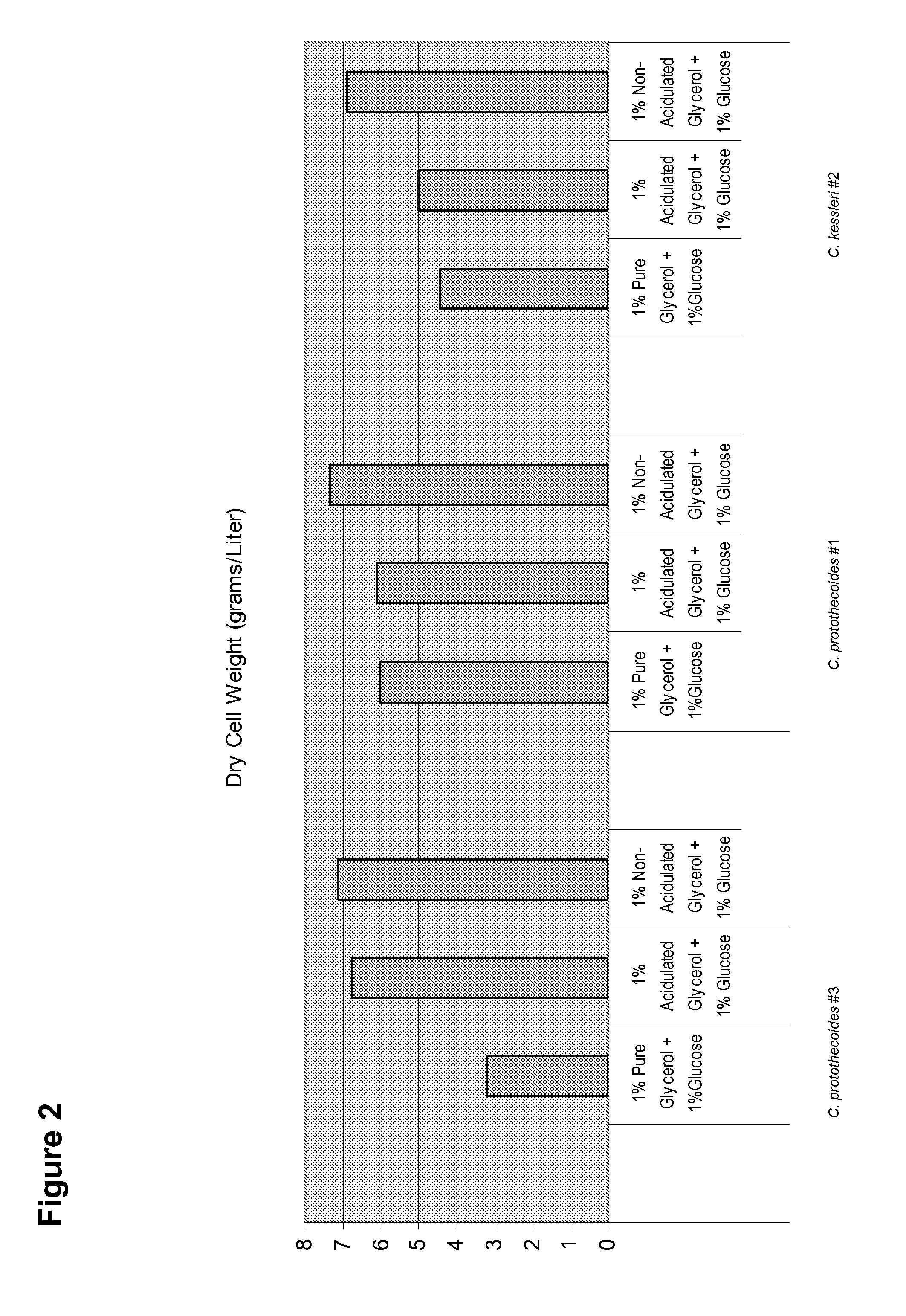
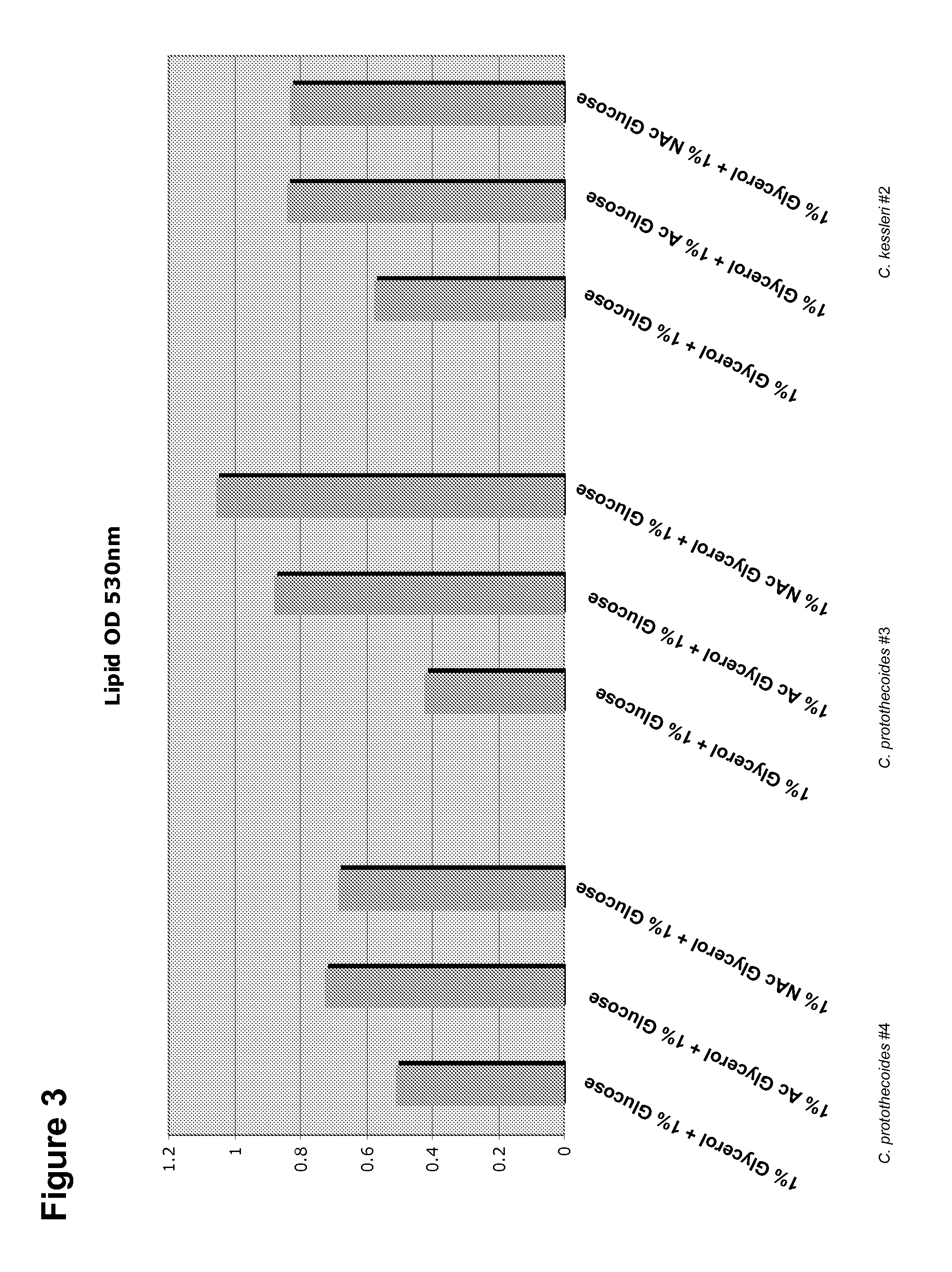
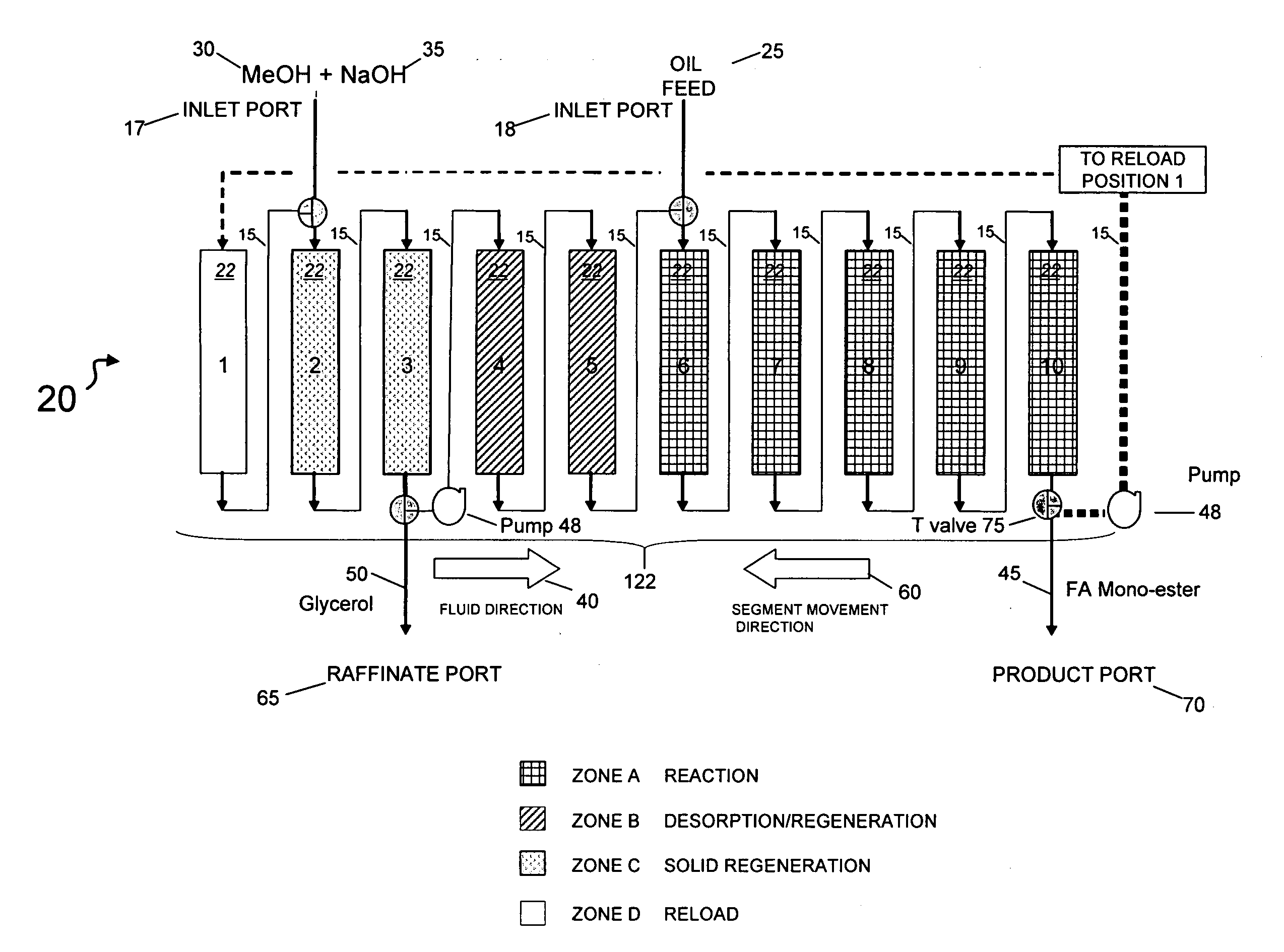
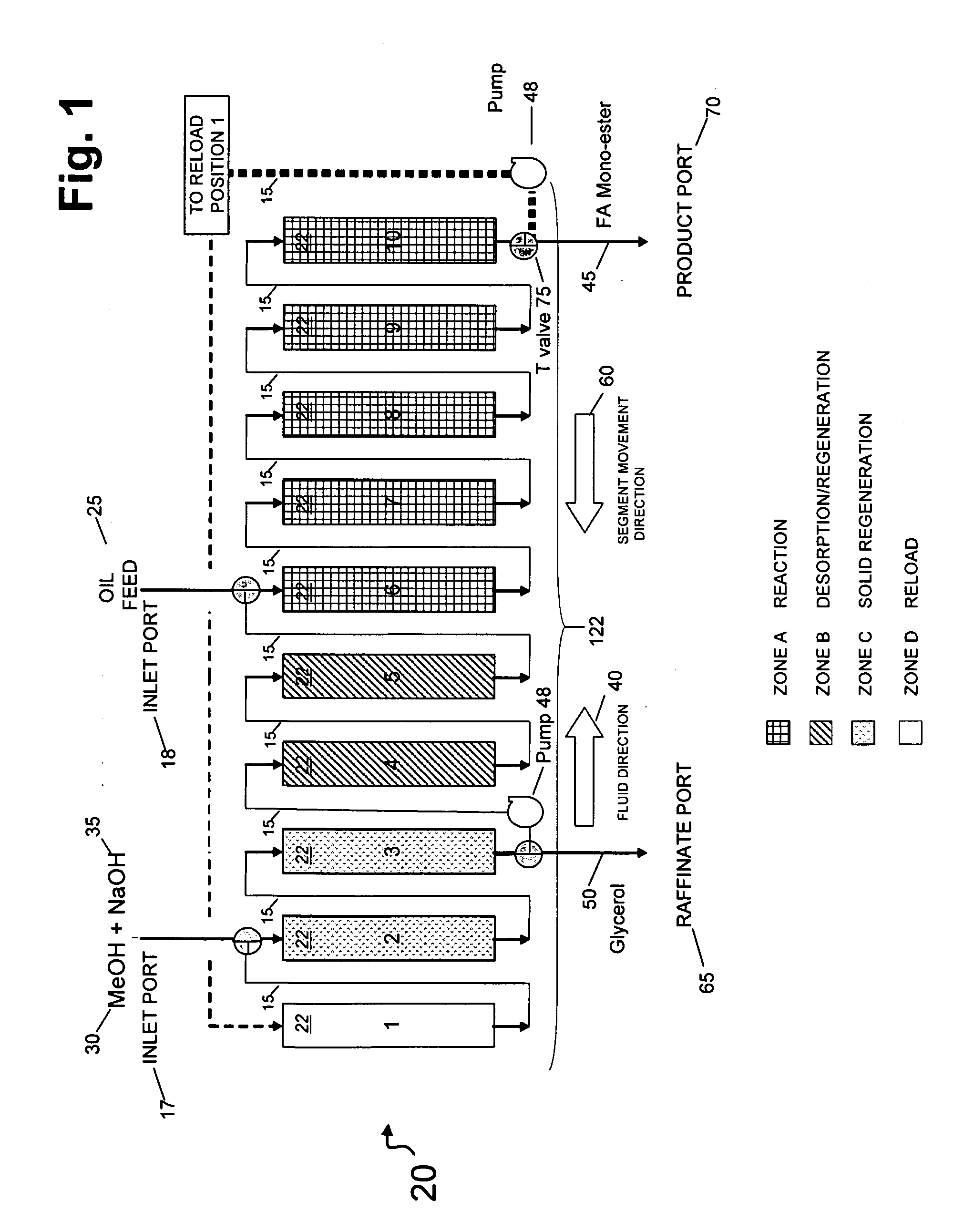
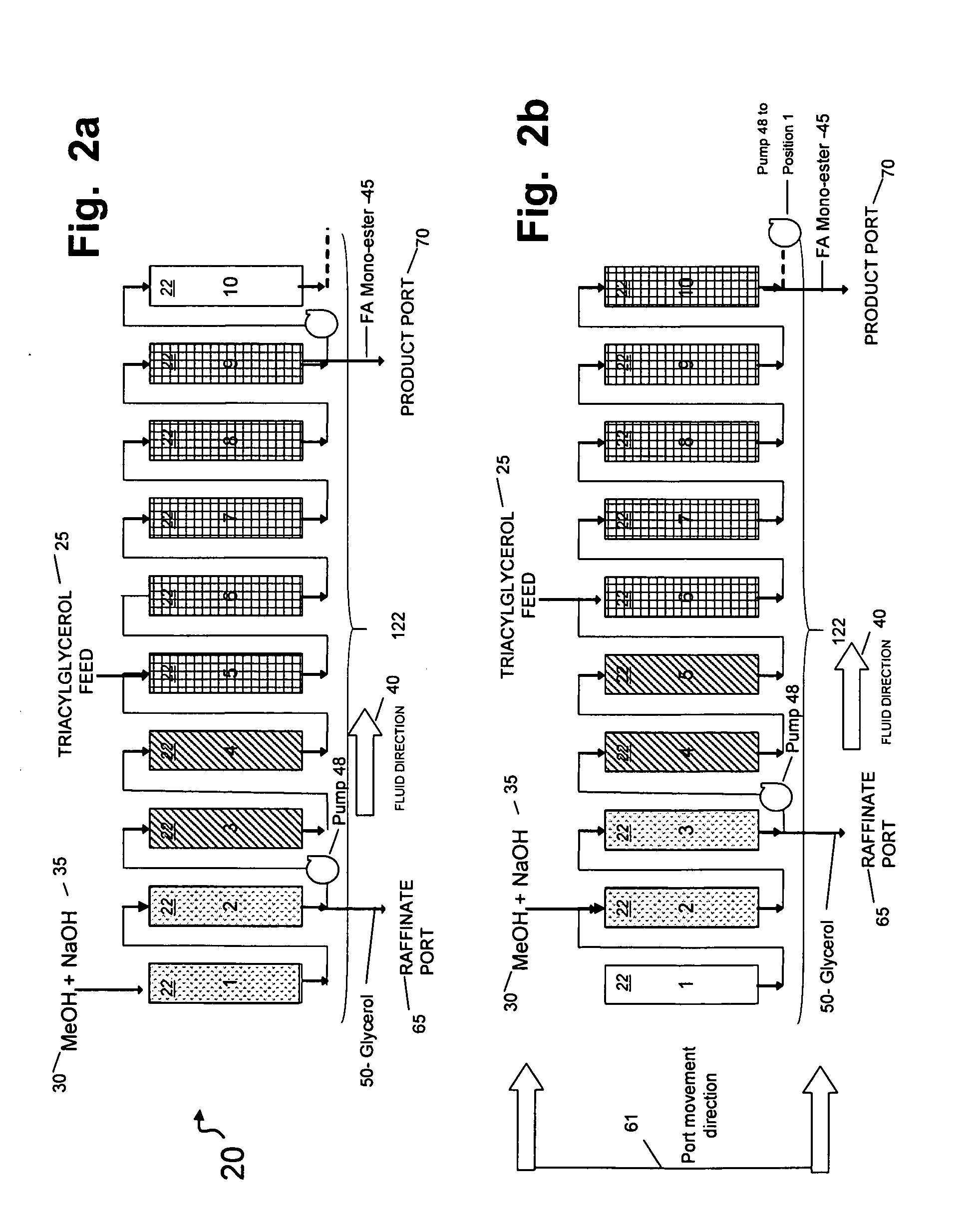
Simultaneous synthesis and purification of a fatty acid monoester biodiesel fuel
ActiveUS20070158270A1Reduce contentLow costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselAlcohol
Simultaneous synthesis and purification of a fatty acid monoester biodiesel fuel from a triacylglycerol feedstock is described. In an exemplary method, the triacylglycerol feedstock is continuously contacted with a catalytic chromatographic bed comprising a first (solid phase) basic catalyst through a first port of a simulated moving bed chromatographic apparatus. A monohydric alcohol and optional second (mobile phase) basic catalyst is continuously contacted with the catalytic chromatographic bed through a second port and pumped in a first direction toward the triacylglycerol feedstock to contact the triacylglycerol in a reaction zone of the catalytic chromatographic bed where the fatty acid monoester and glycerol coproduct are formed. The fatty acid monoester is removed from the reaction zone through a product port of the simulated moving bed apparatus. Segments of the catalytic chromatographic bed are incrementally moved in a second direction, opposite the first direction, and the glycerol is removed from a raffinate port located opposite the product port of the apparatus.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
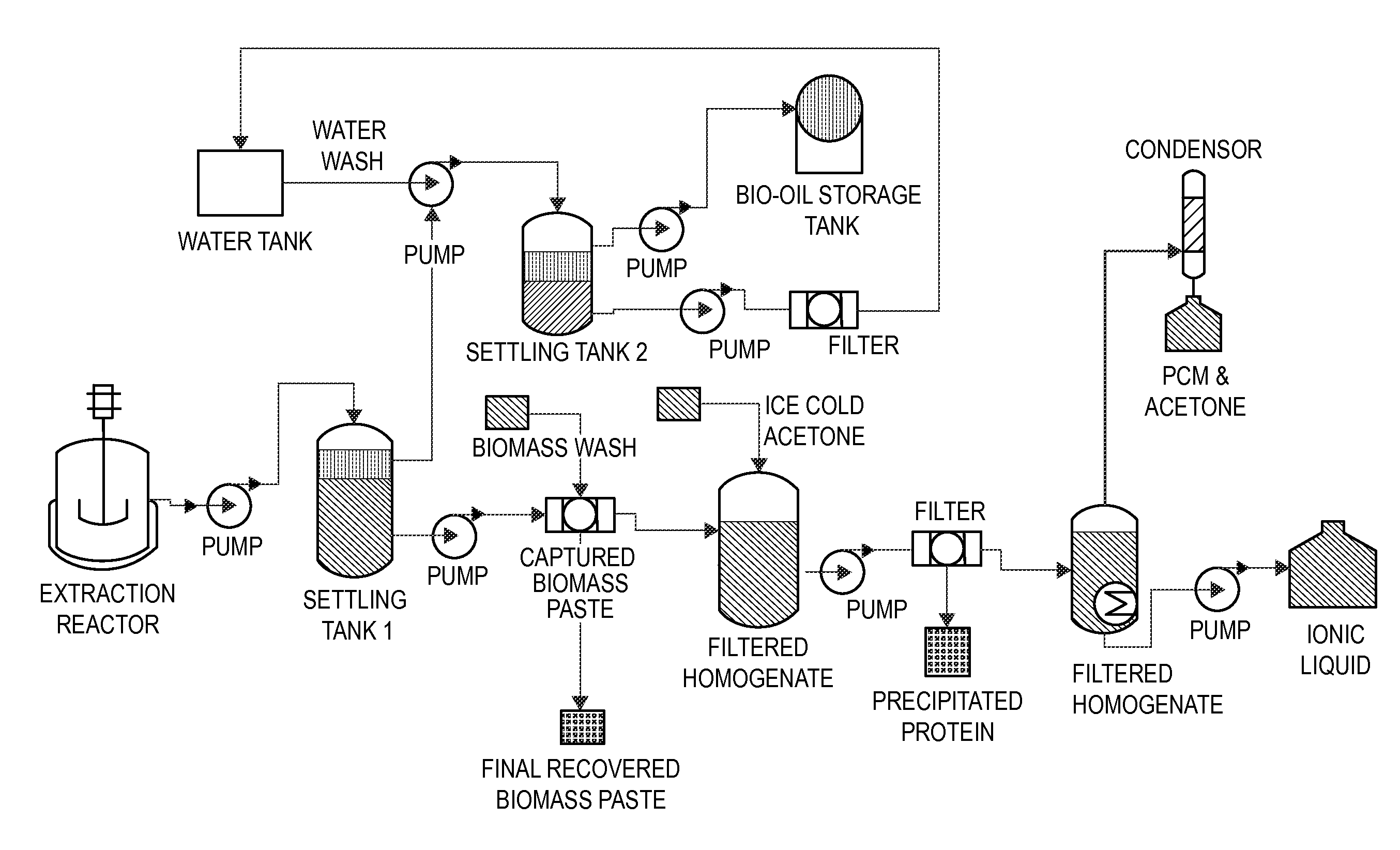
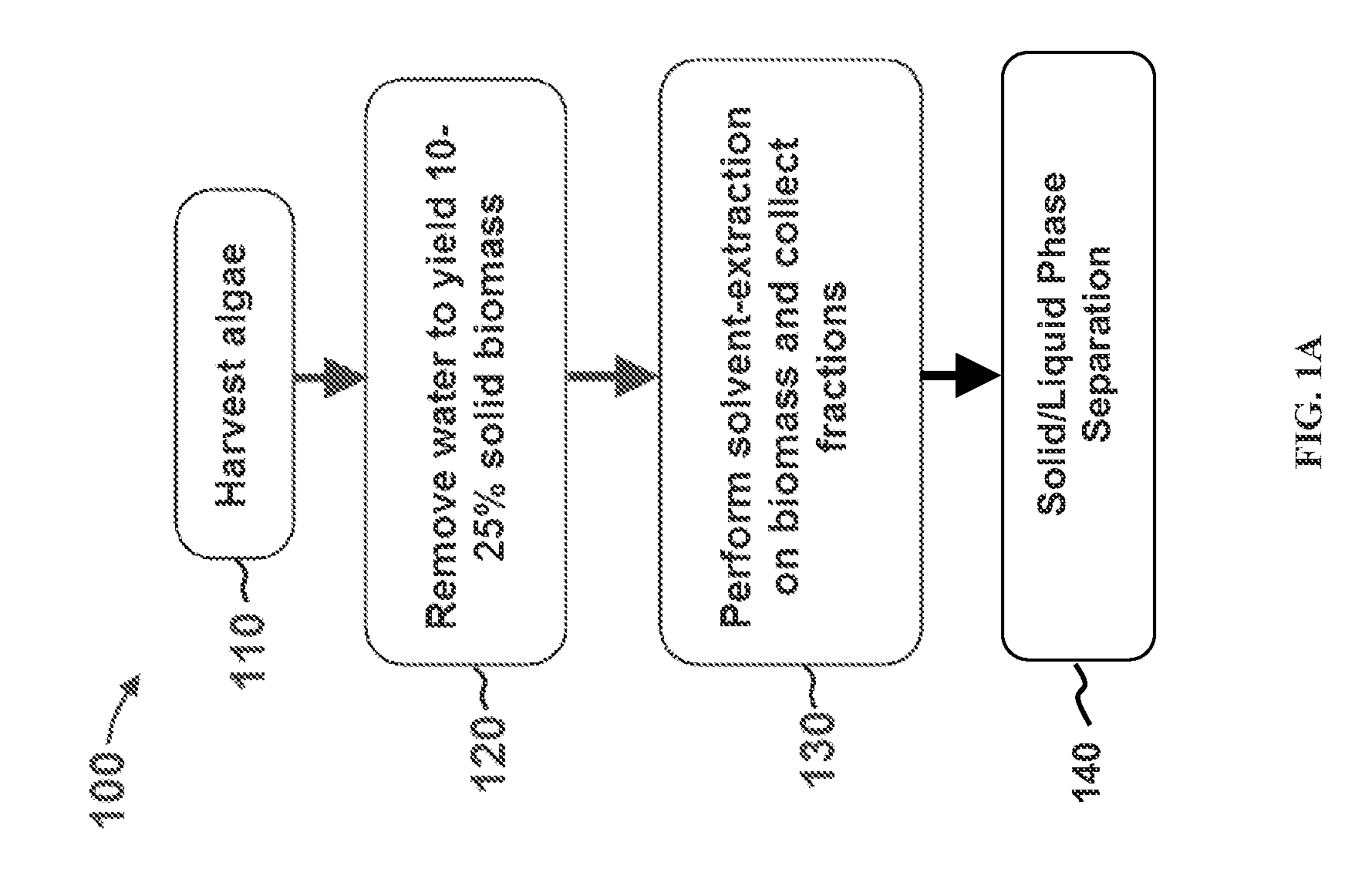
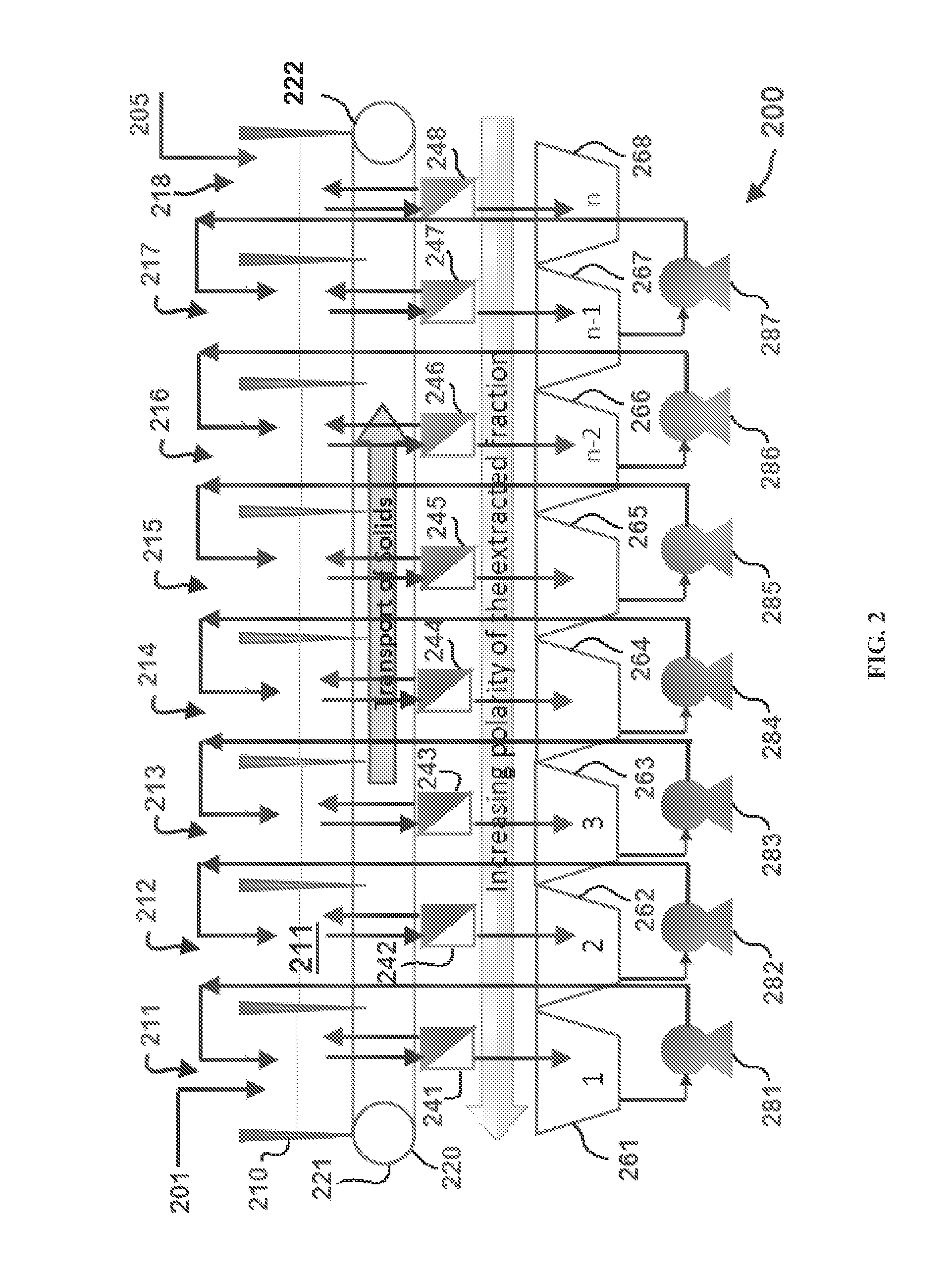
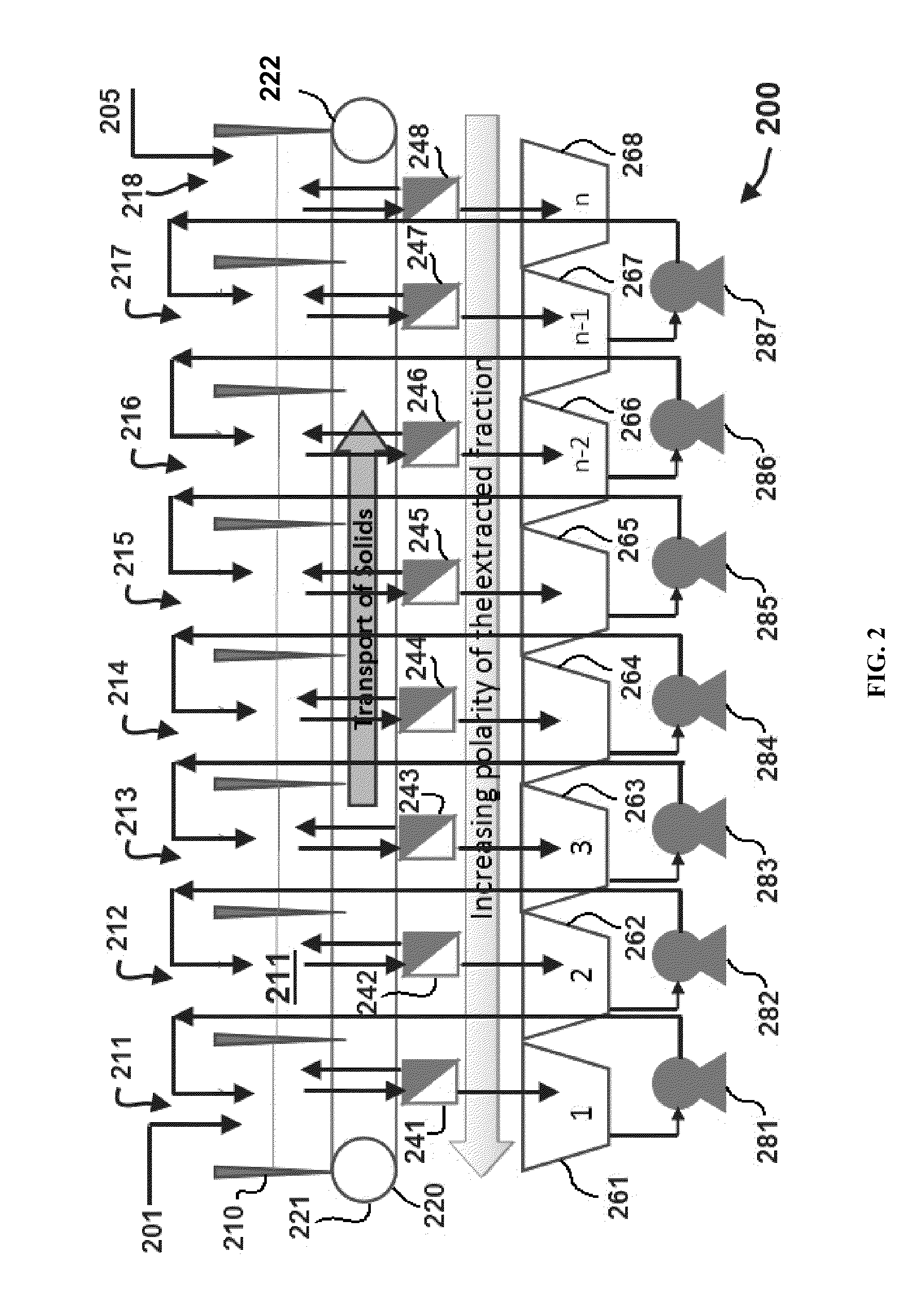
Extraction with fractionation of oil and proteinaceous material from oleaginous material
Methods for selective extraction and fractionation of algal lipids and algal products are disclosed. A method of selective removal of products from an algal biomass provides for single and multistep extraction processes which enable efficient separation of algal components. Among these components are neutral lipids synthesized by algae, which are extracted by the methods disclosed herein for the production of renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Process of converting rendered triglyceride oil from marine sources into bland, stable oil
Triglyceride oil derived from marine sources, mammalian and fish, is treated with a silica at relatively low temperature under vacuum and is then further treated with a bleaching clay under vacuum and at higher temperature. The silica and the bleaching clay are then separated from the oil. The oil treated by this method is essentially free of proteinaceous materials, phosphatides and mucilage, pro-oxidant metals and very low in colored compounds, and is suitable for deodorizing. The deodorized oil is completely bland, unchanged in the concentration of the long-chain highly unsaturated fatty acids (EPA, DPA and DHA), very low in color, peroxides and secondary oxidation products, free of pesticides and has very good flavor stability. The method avoids the use of any chemicals, such as in the acid and base treatments required in conventional degumming and alkali refining of oils of marine origin. This avoids the formation of artifacts in the oil and trace contamination with chemicals. It also reduces the number of process steps required to produce deodorized food oil from marine sources, which is advantageous in respect to oil quality, process losses and processing costs. The method is especially environmentally advantageous, since it avoids the need for soapstock and waste water processing entirely. Refined oil produced by the method is useful as a nutritional supplement and in methods of therapy or medical treatment.
Owner:MAG TED
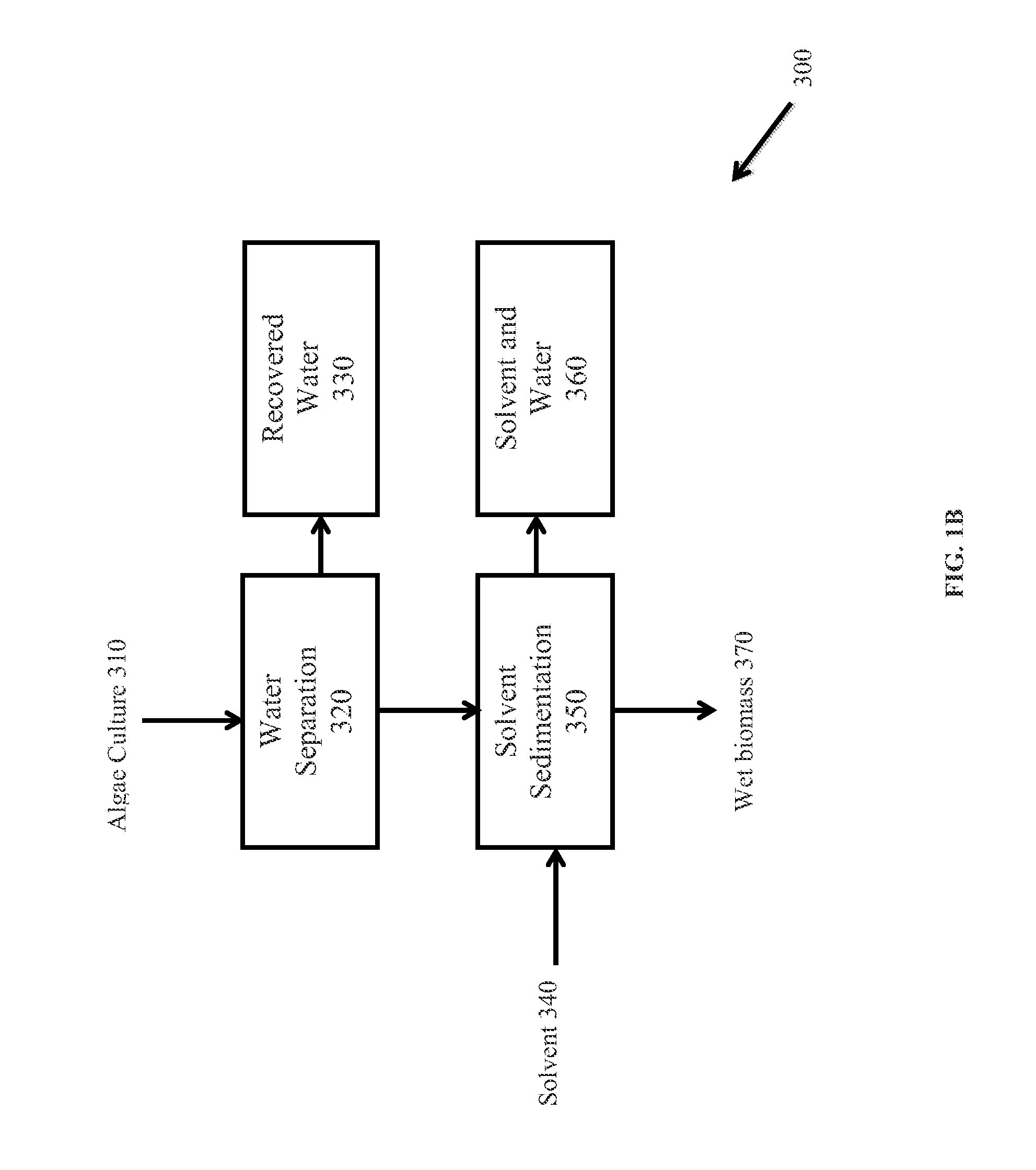
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Popular searches
Refining to change hydrocarbon structural skeleton Hydrocarbon by hydrogenation Fatty-oils/fats refining Fatty-oils/fats separation Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Bio-feedstock Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Refining to eliminate hetero atoms Molecular sieve catalyst
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com