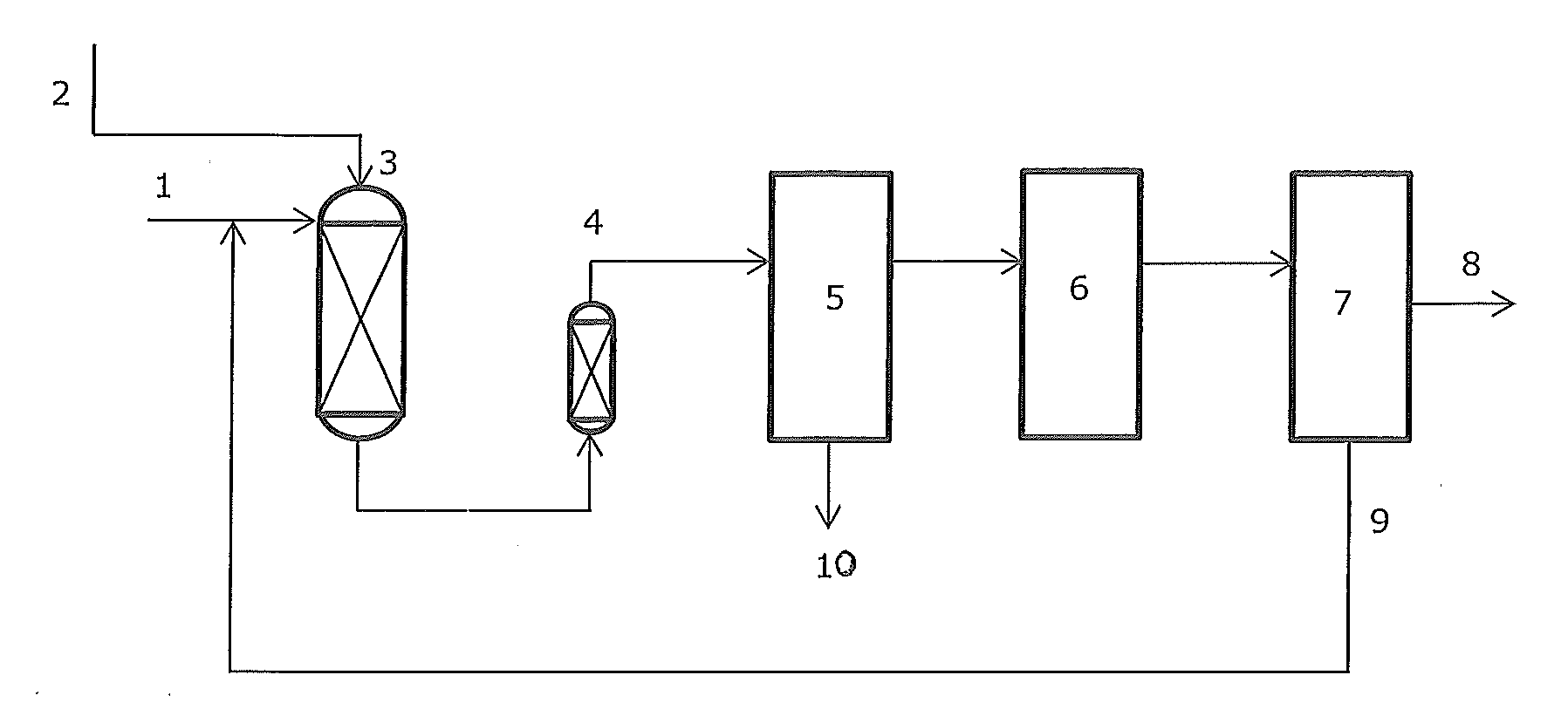
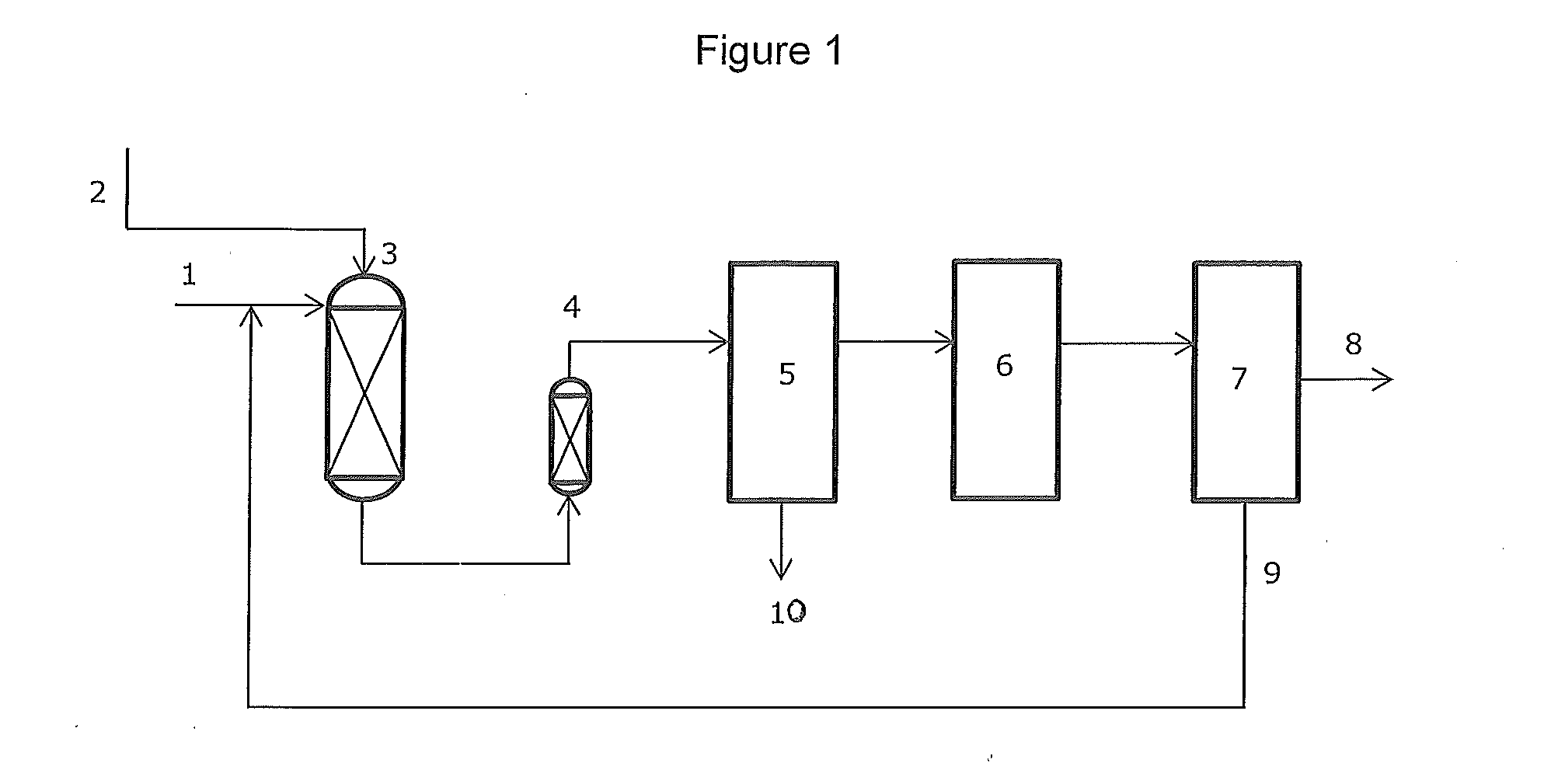
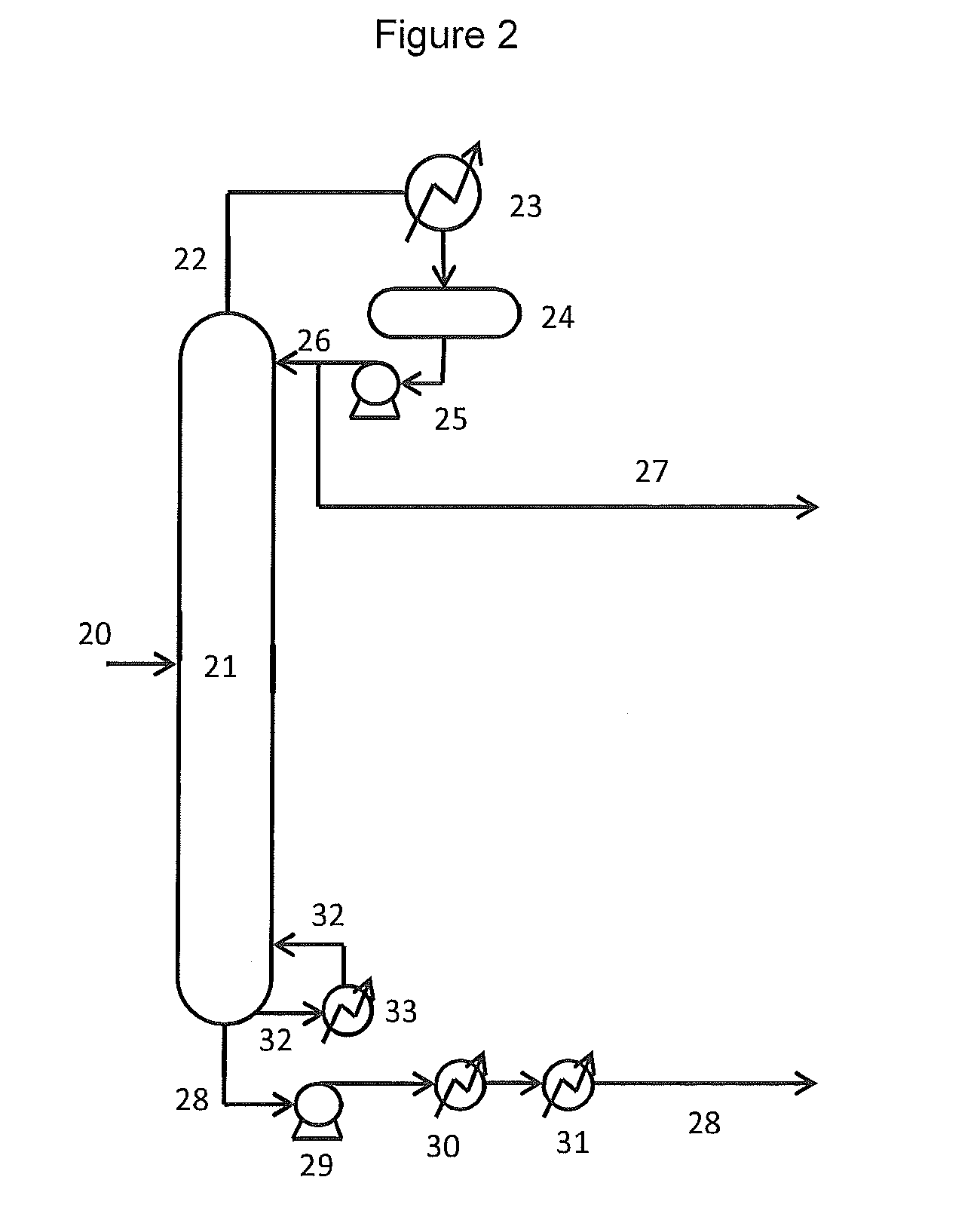
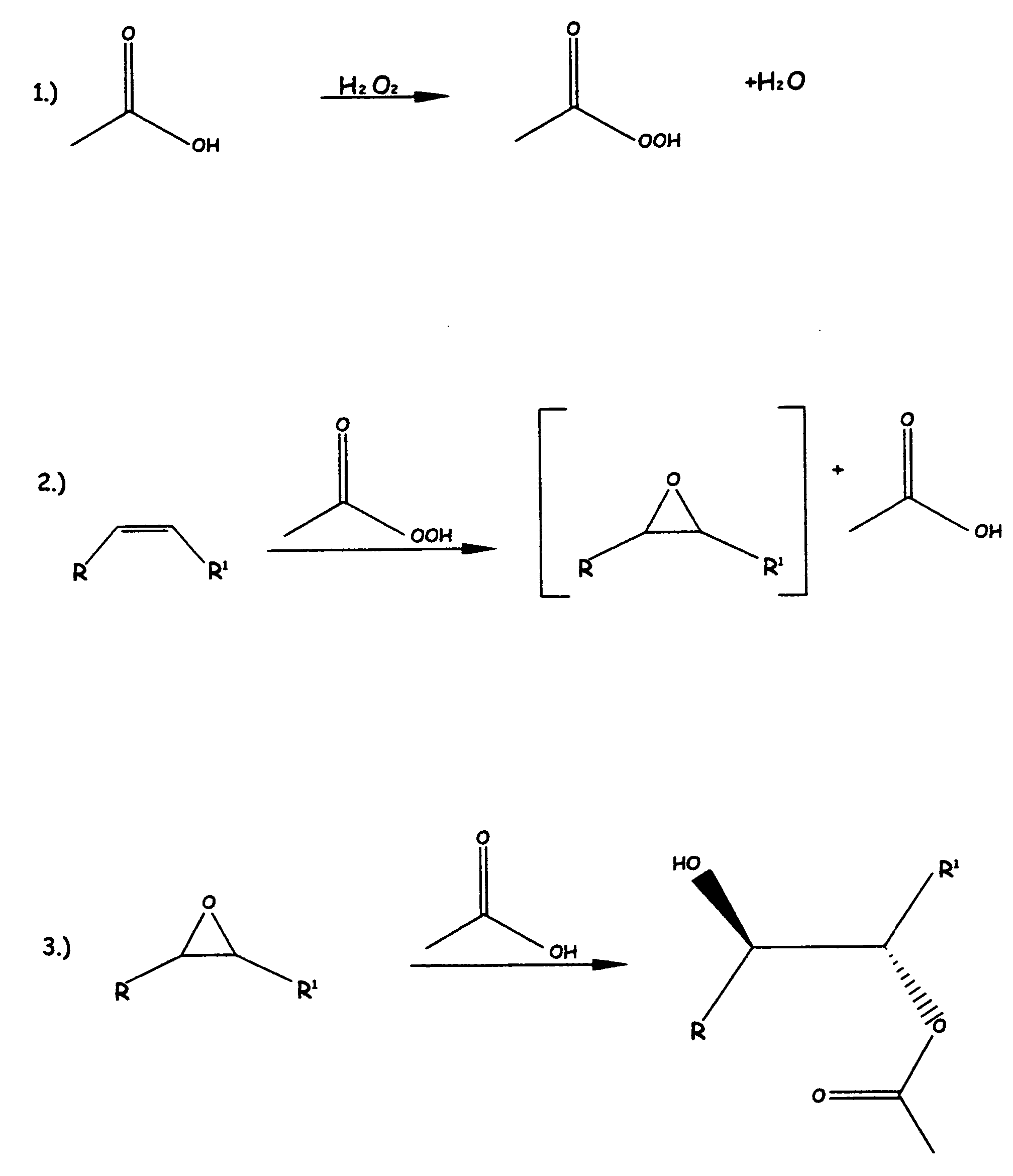
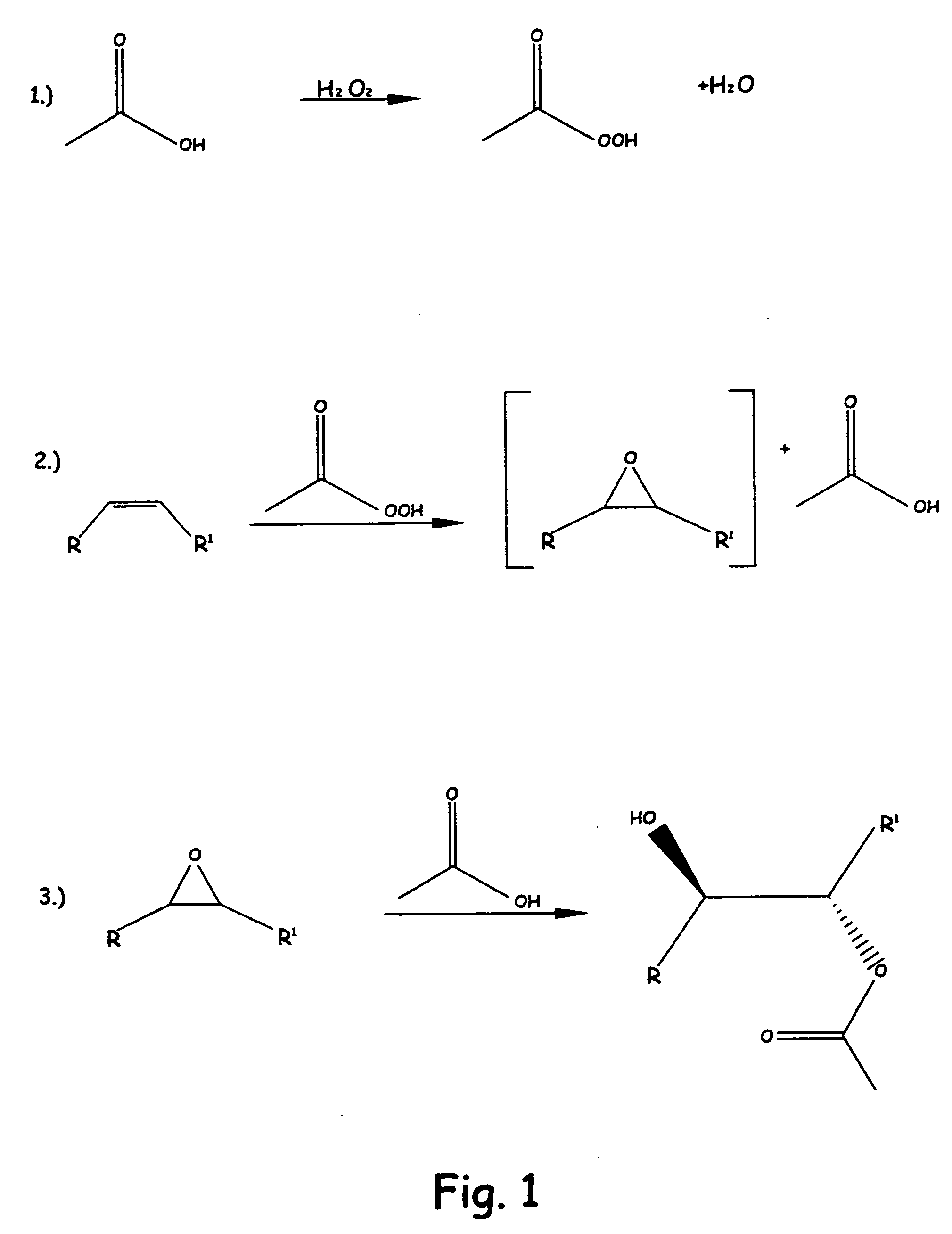
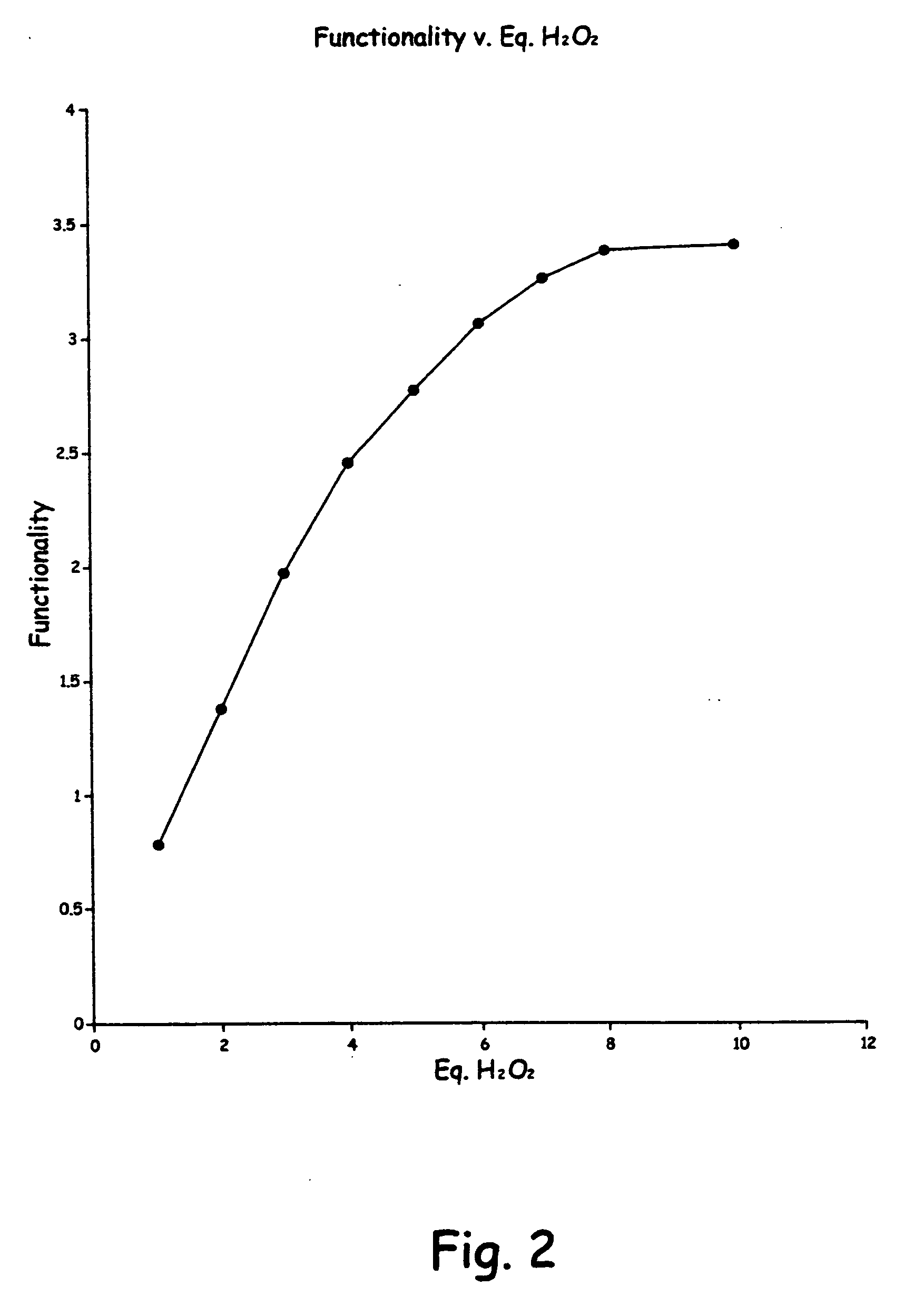
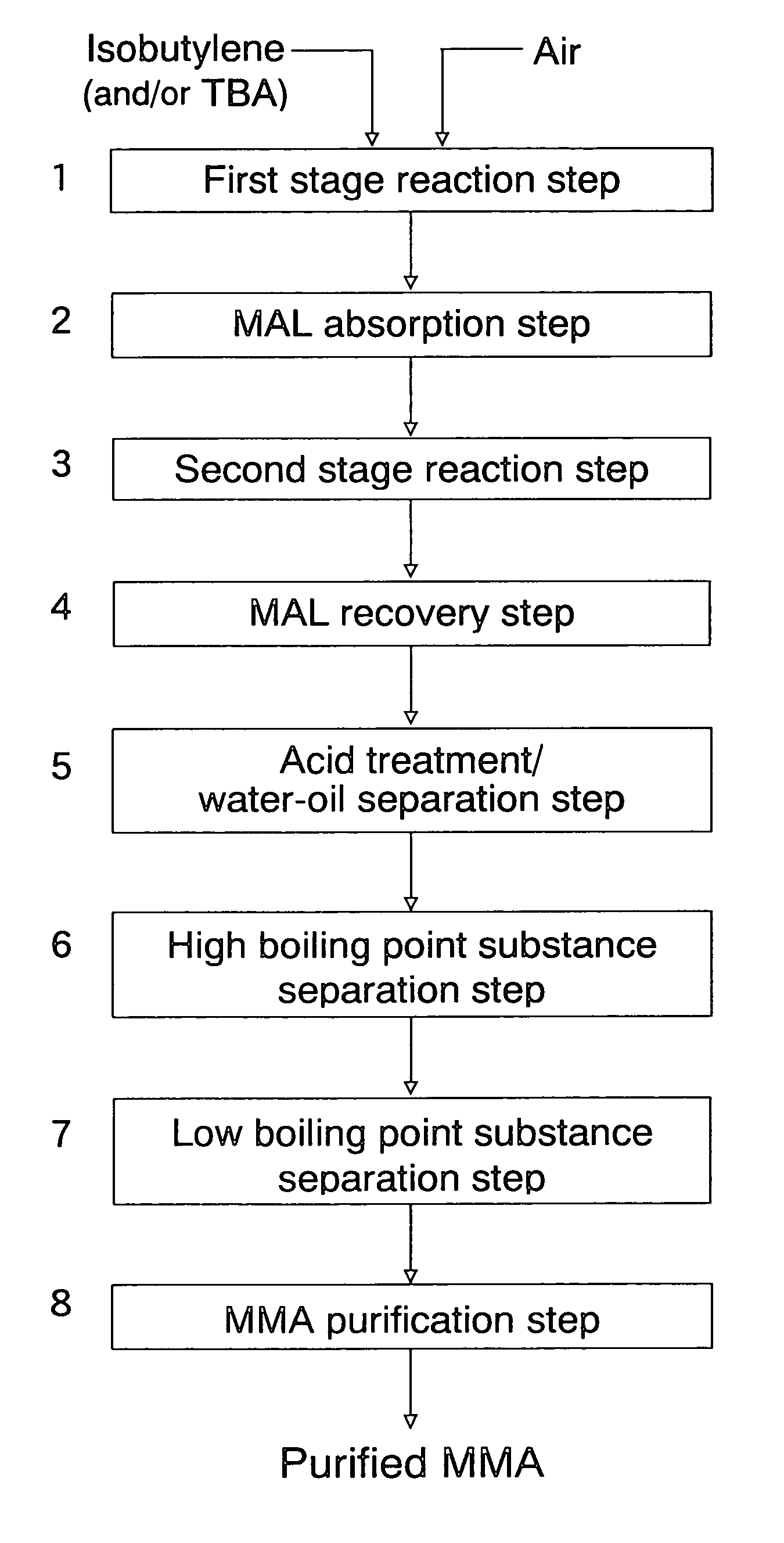
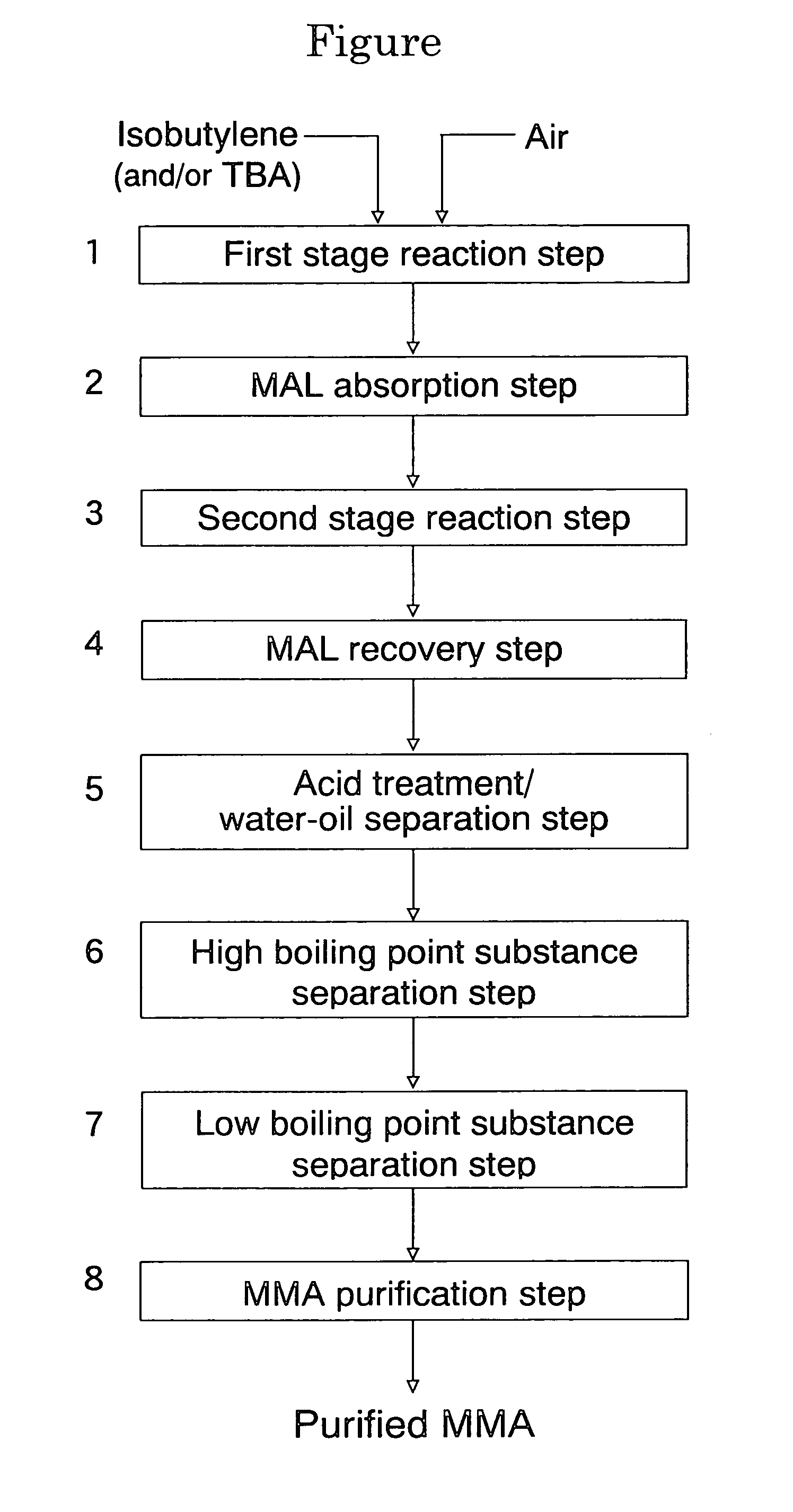
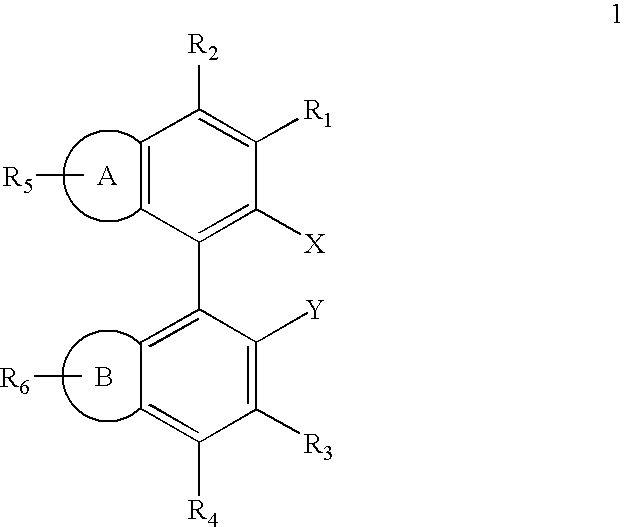
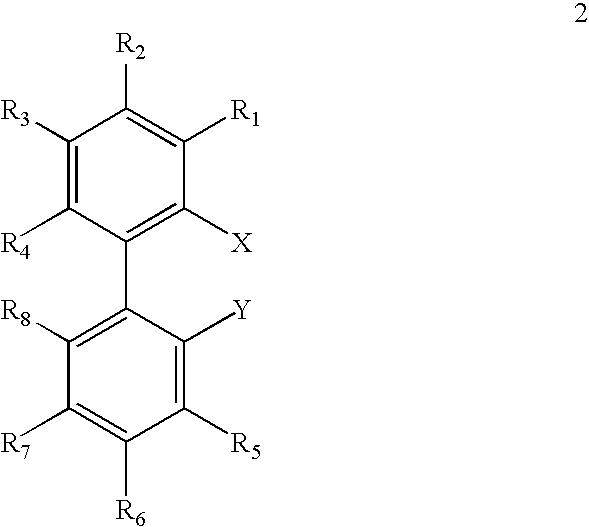
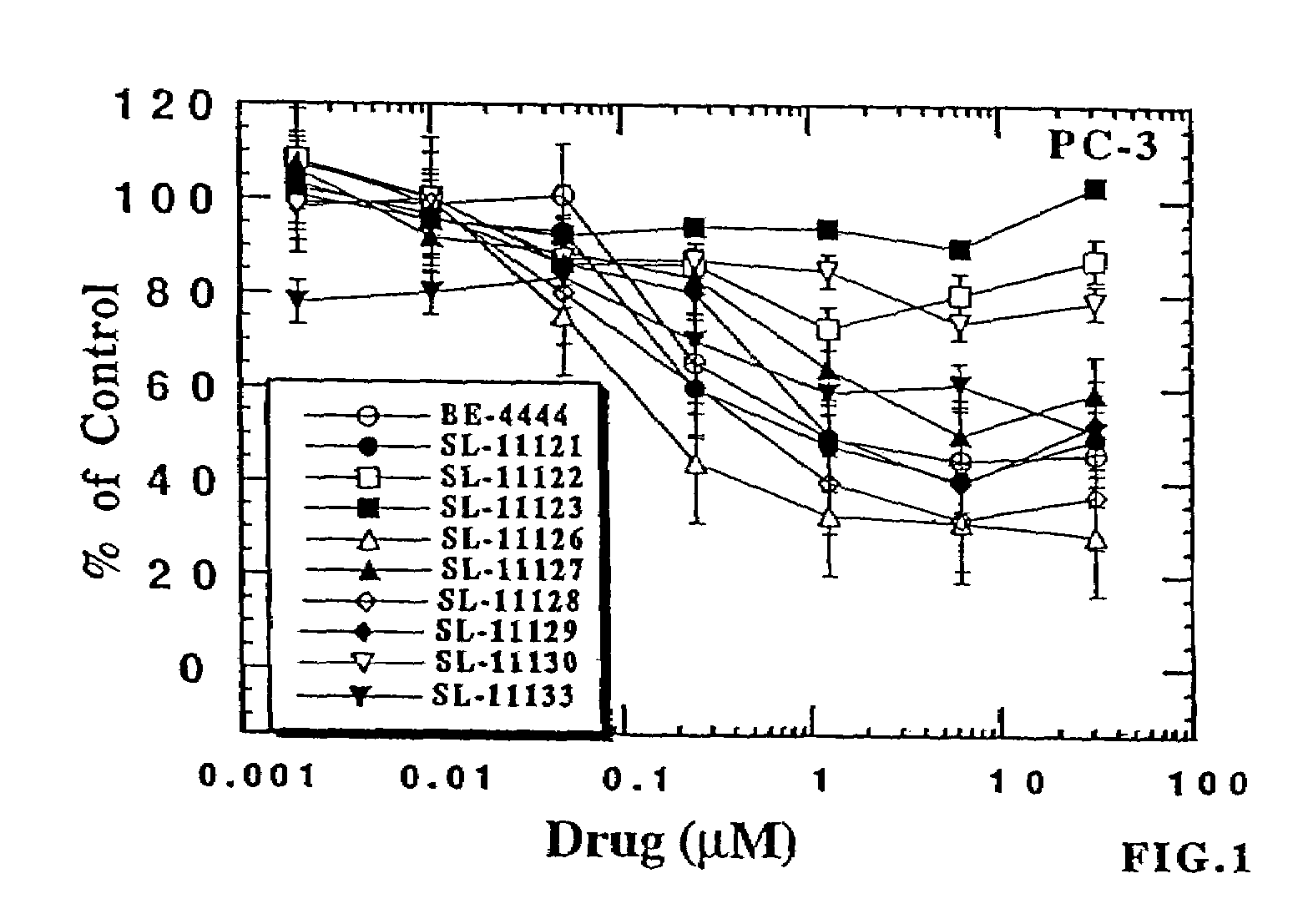
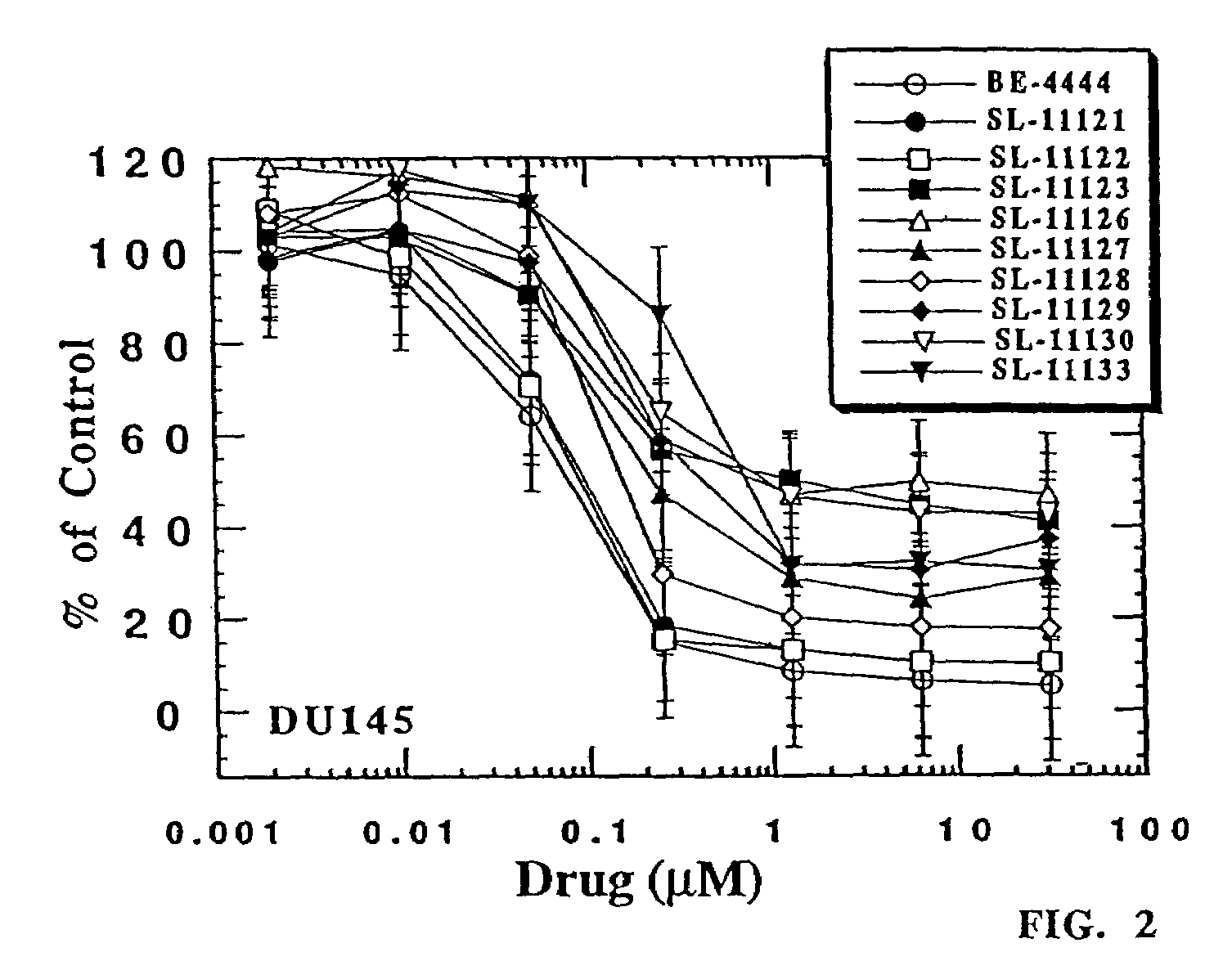
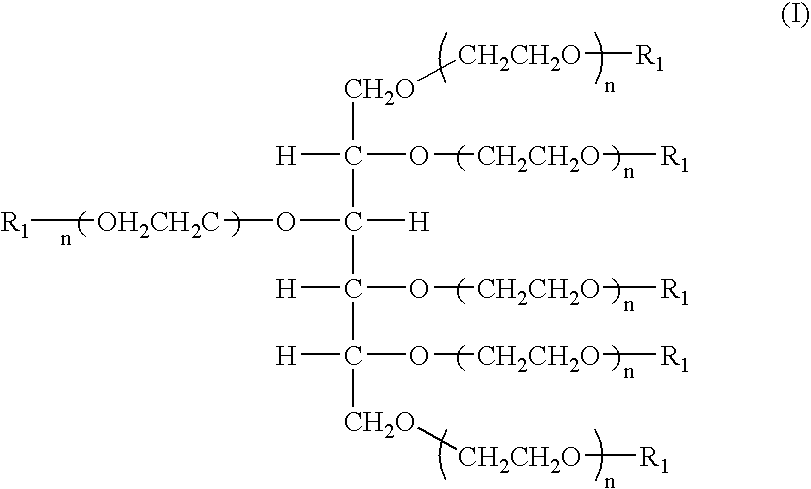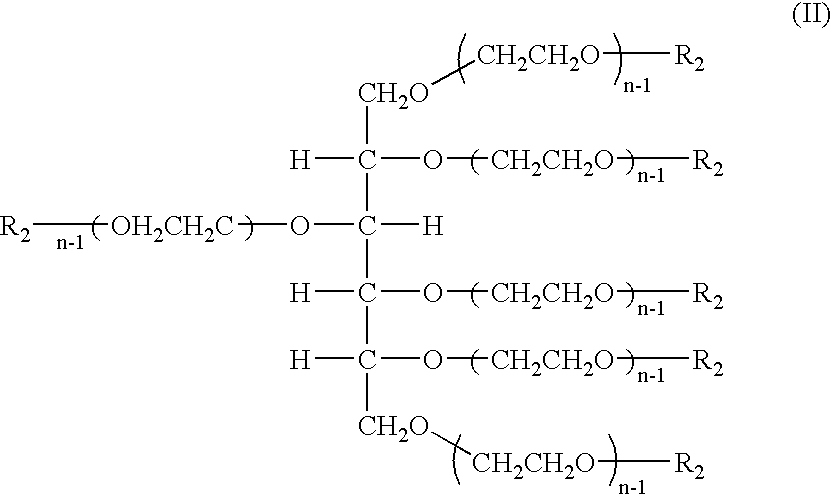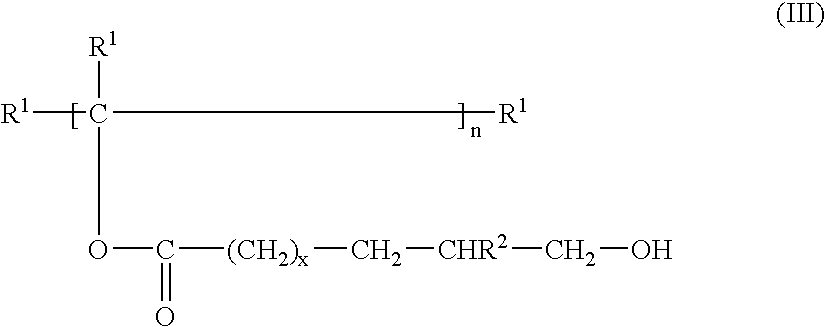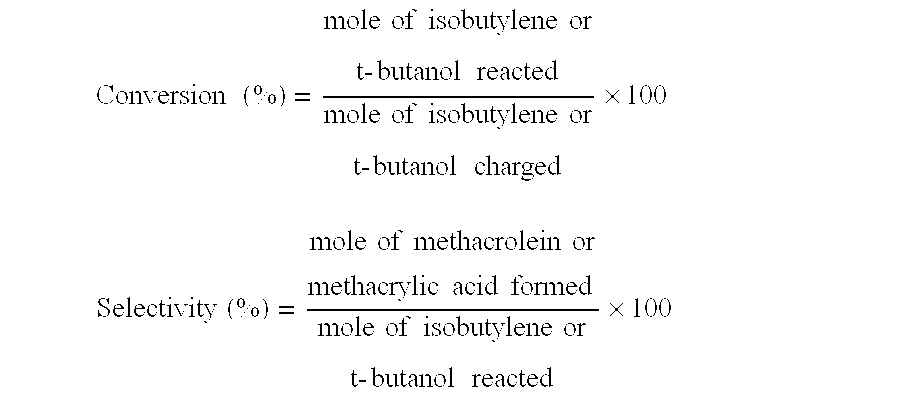Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
16413results about "Carboxylic acid esters preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
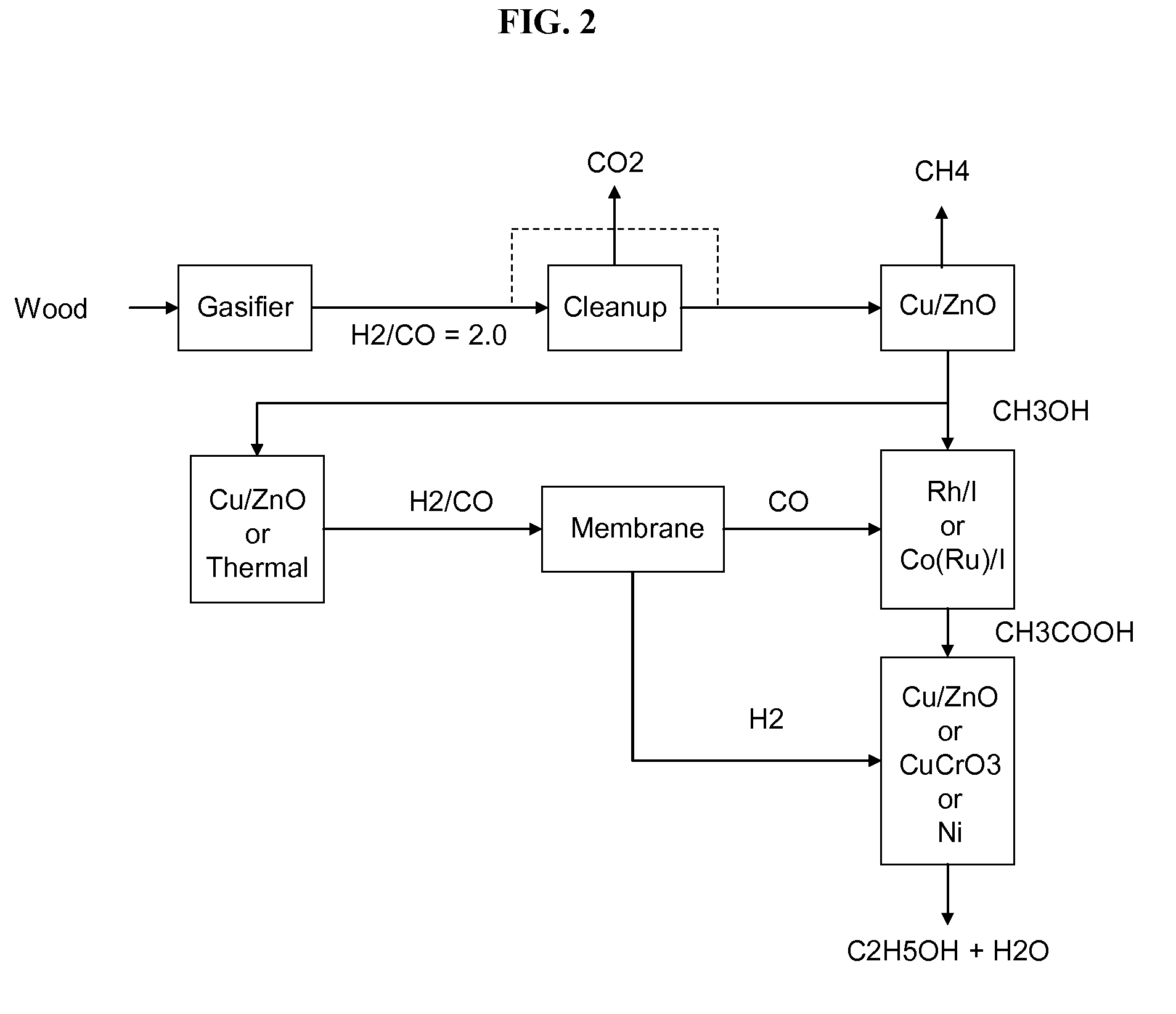
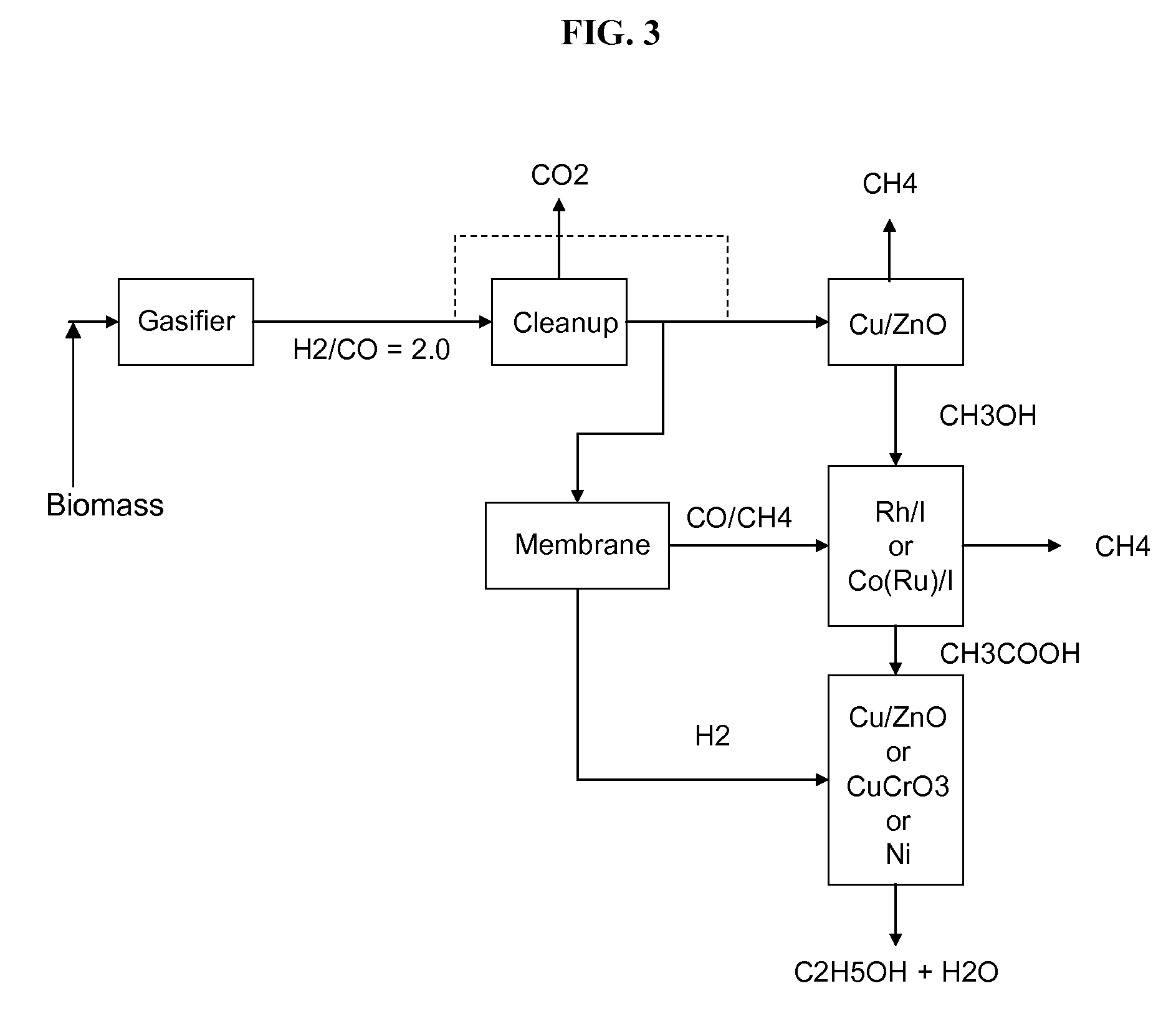
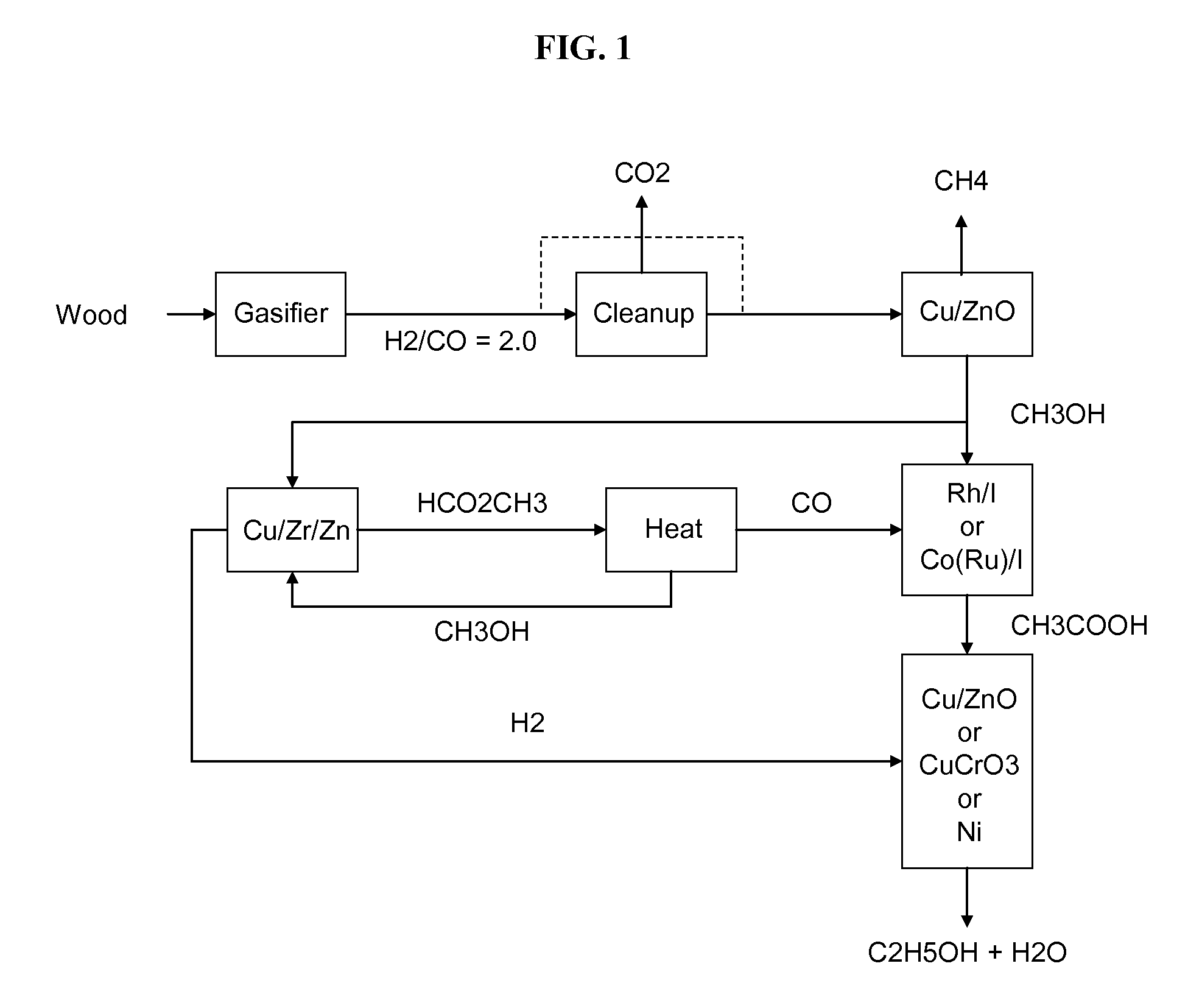
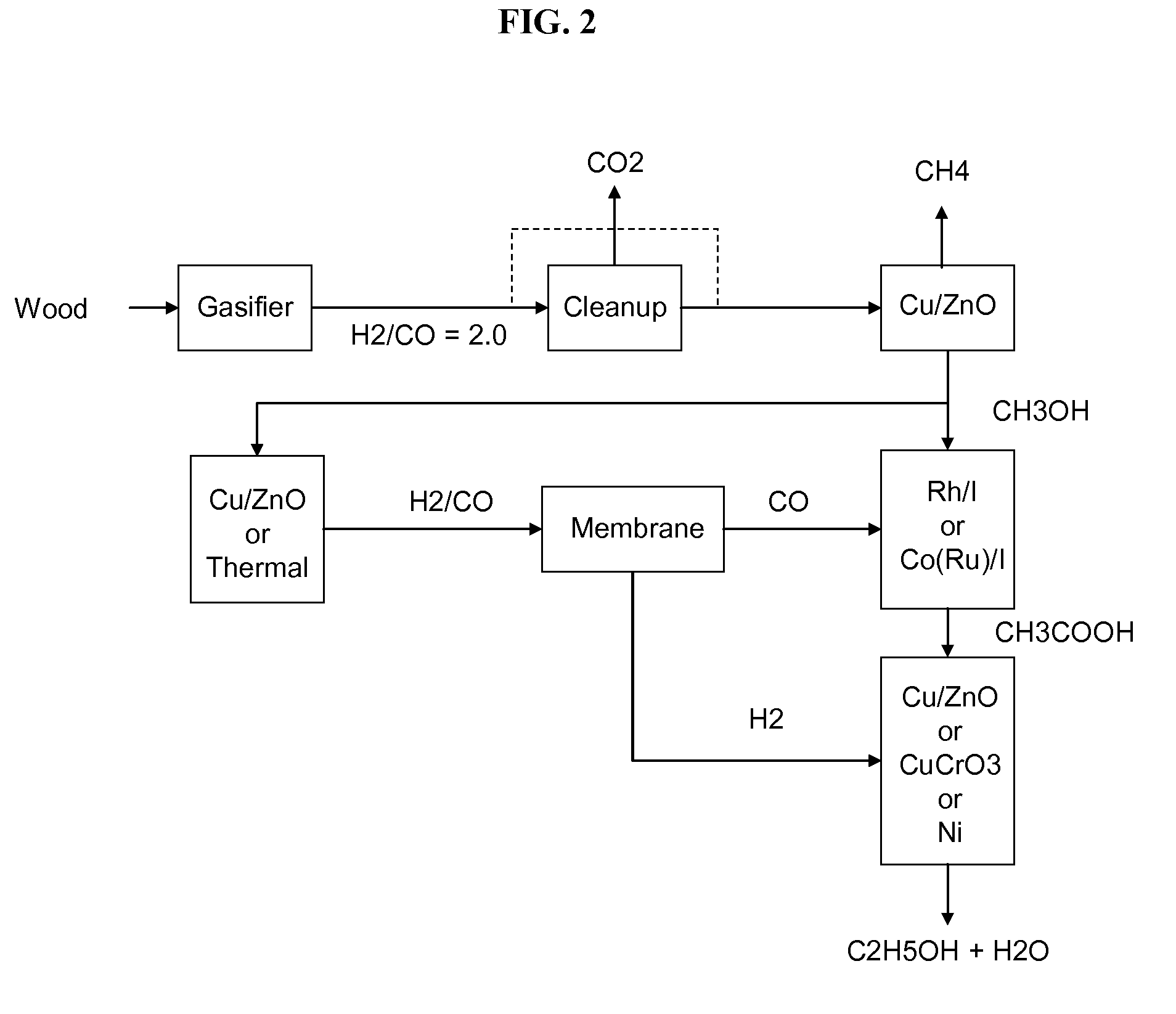
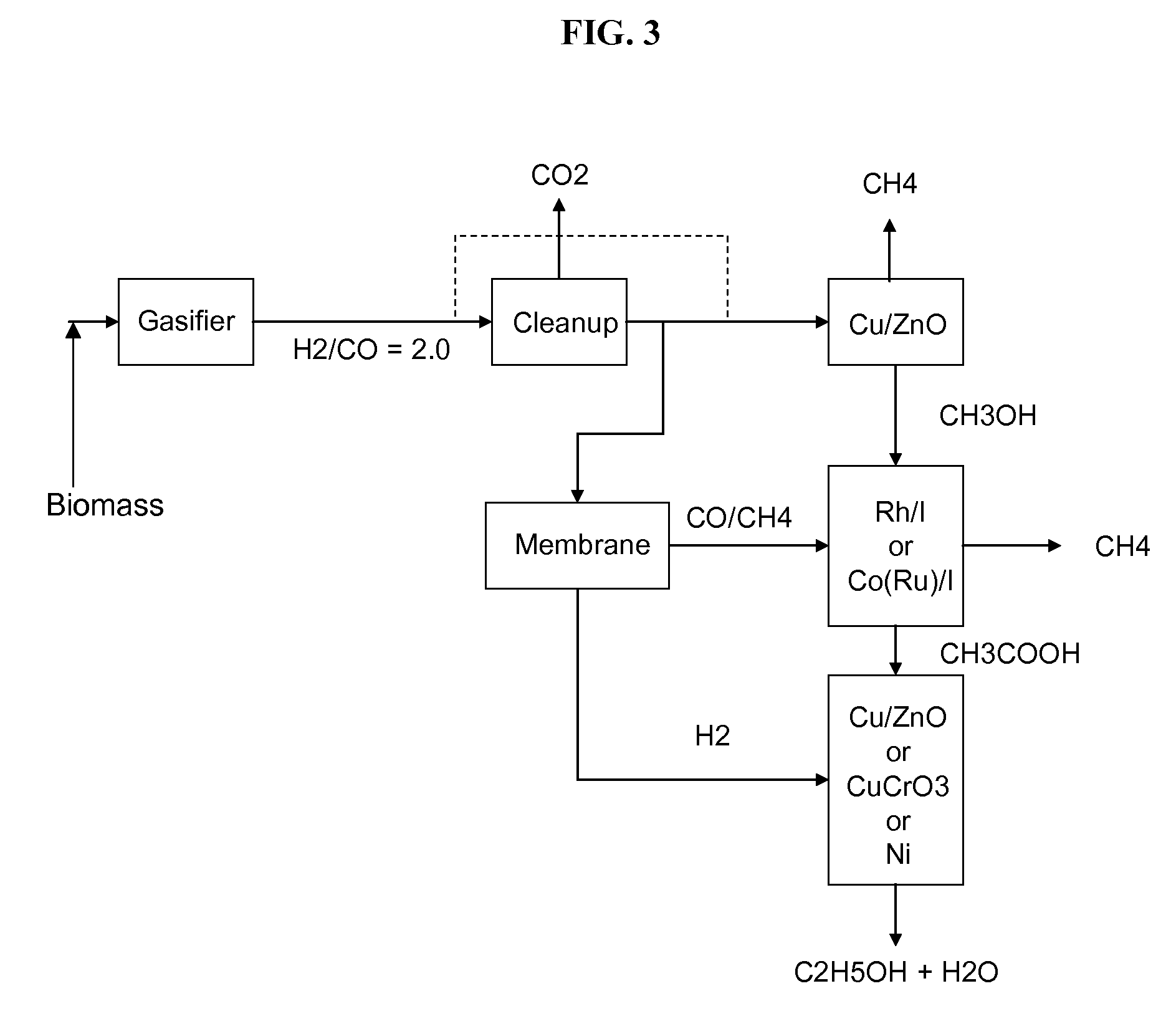
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS6927048B2High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
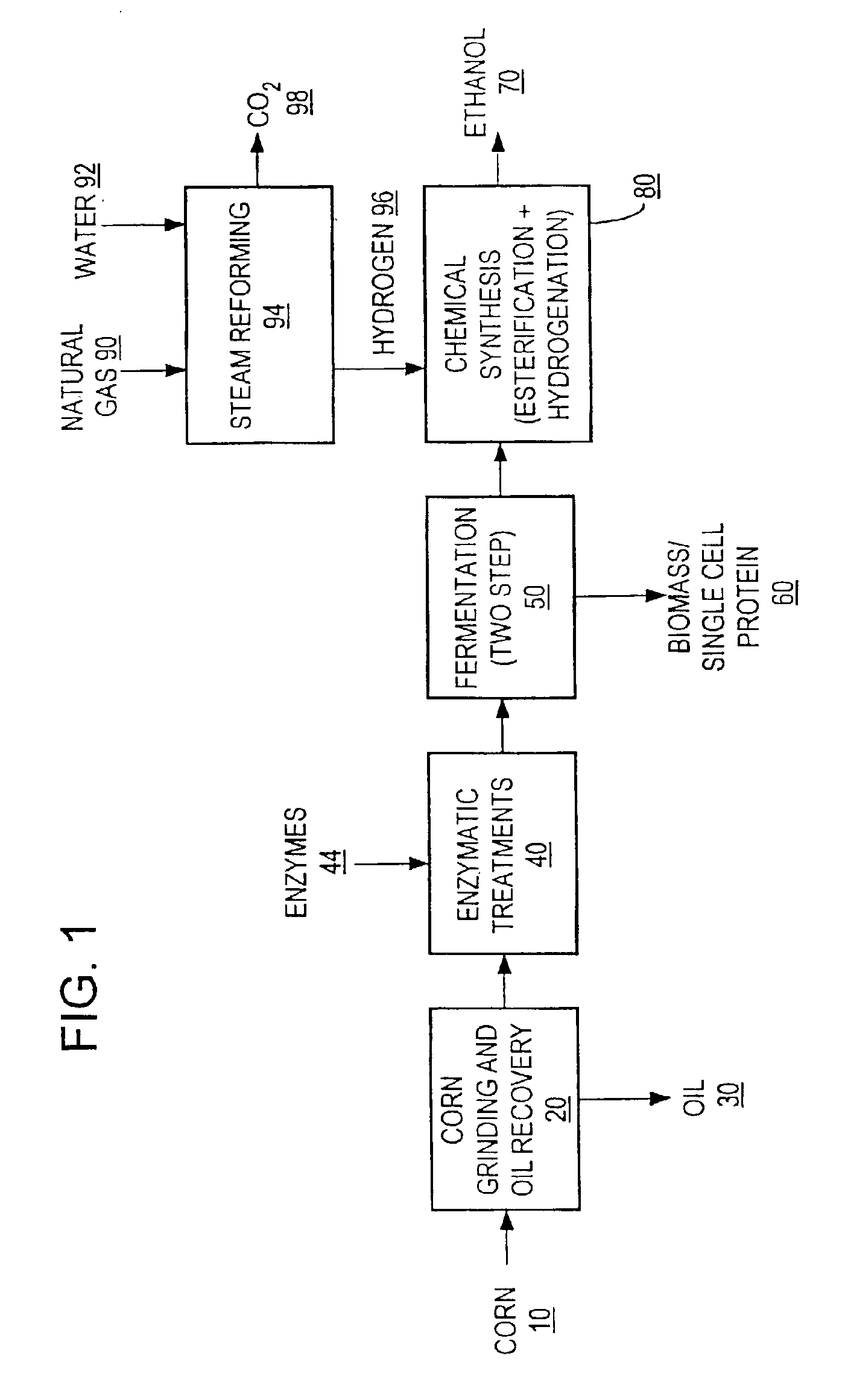
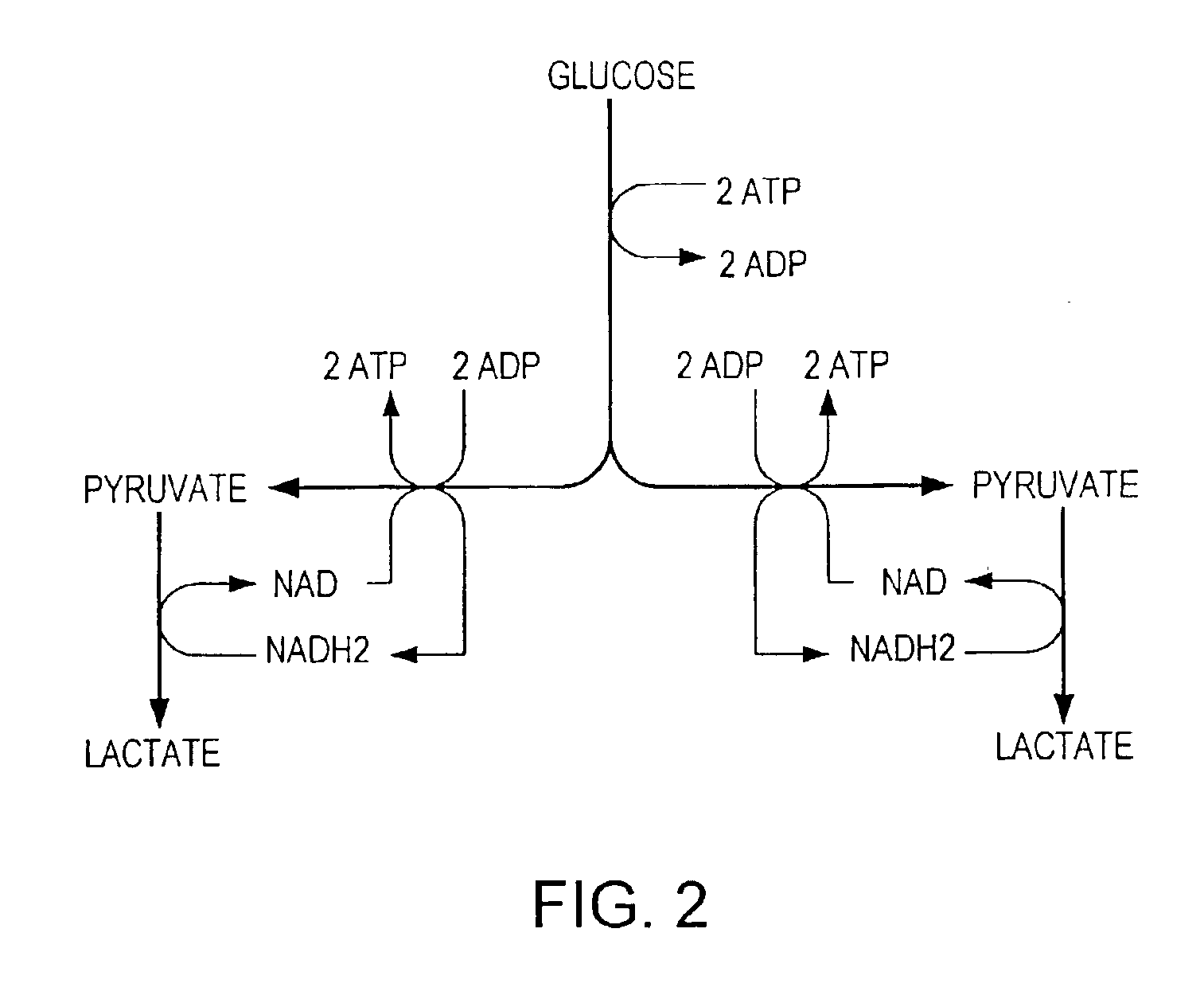
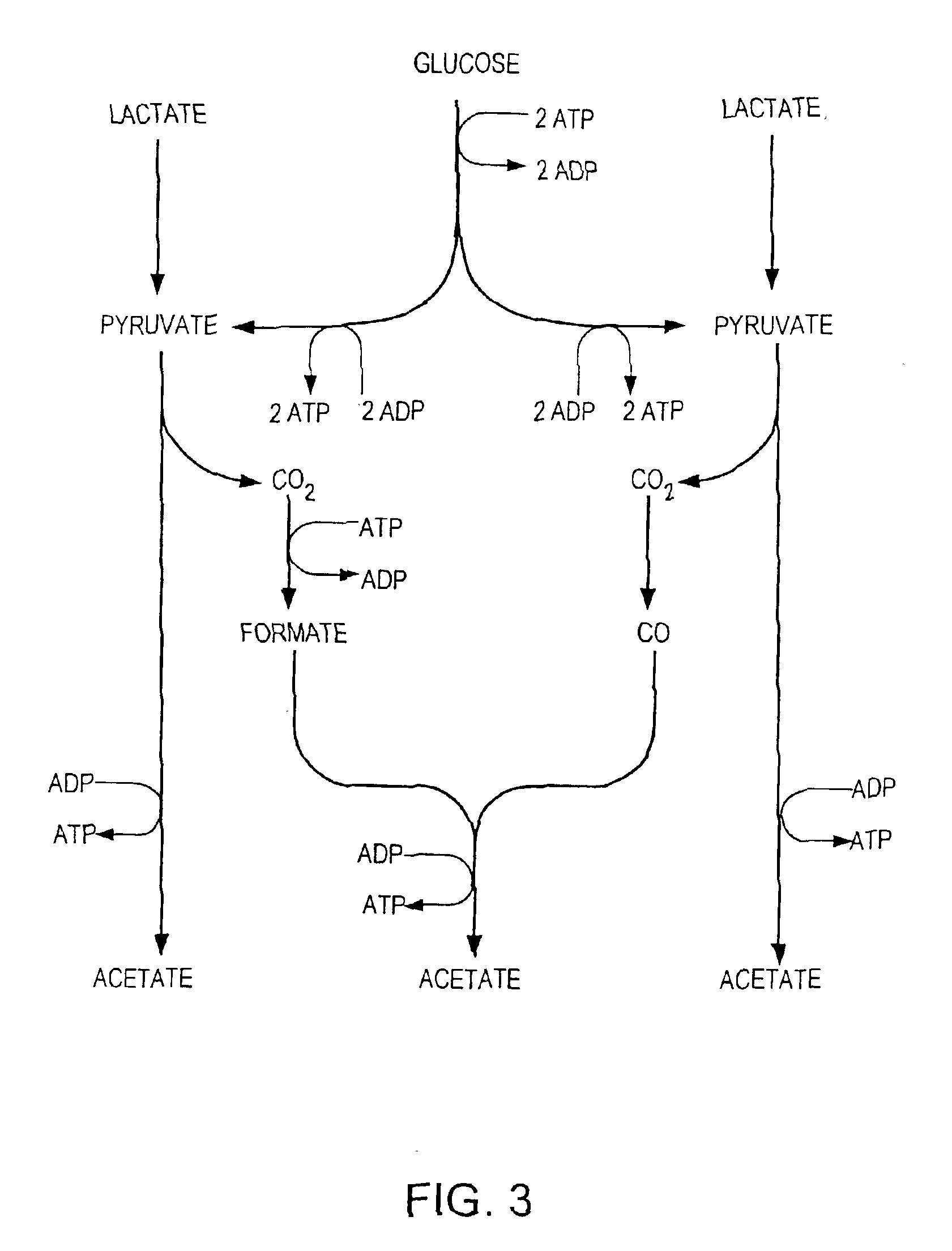
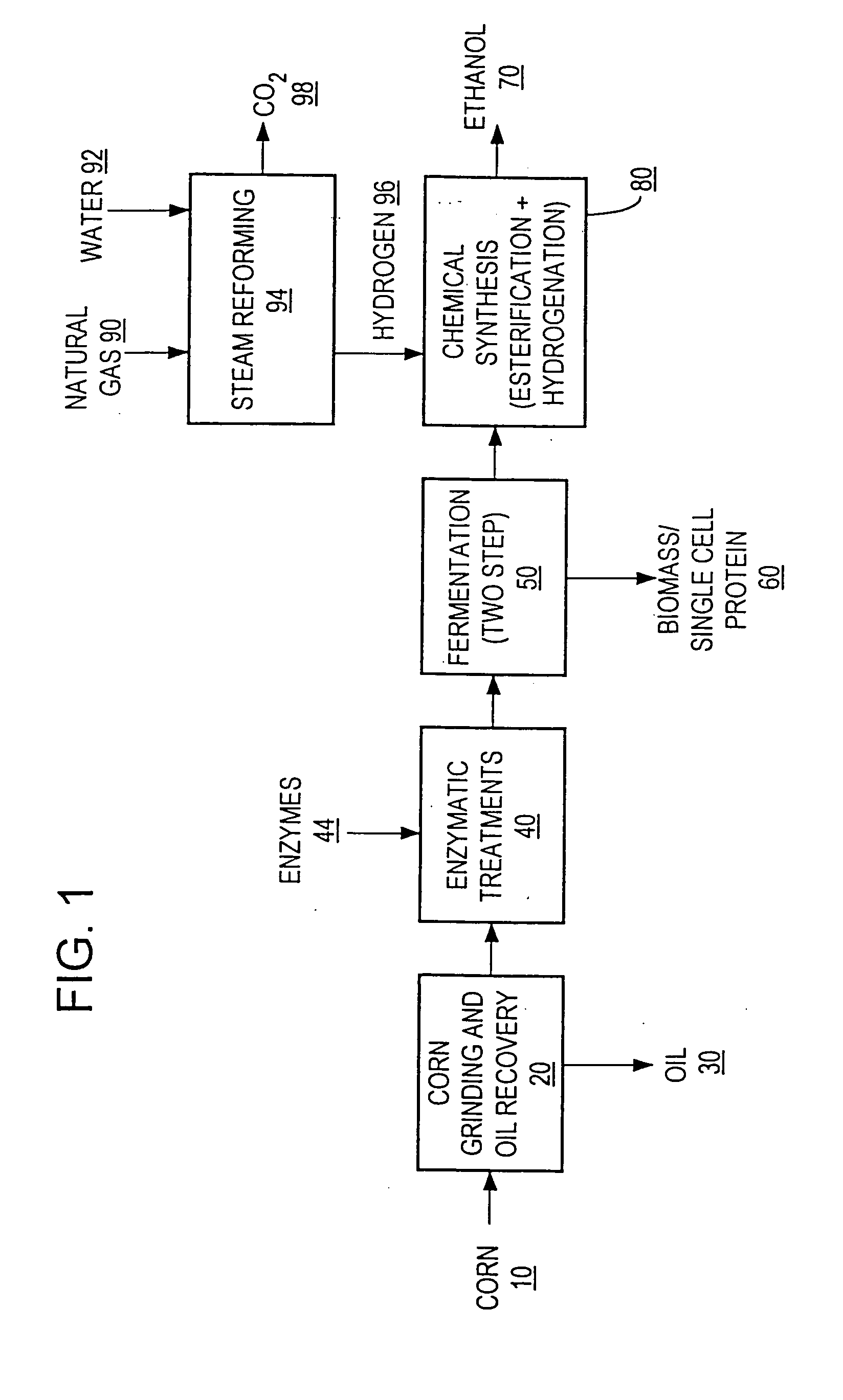
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
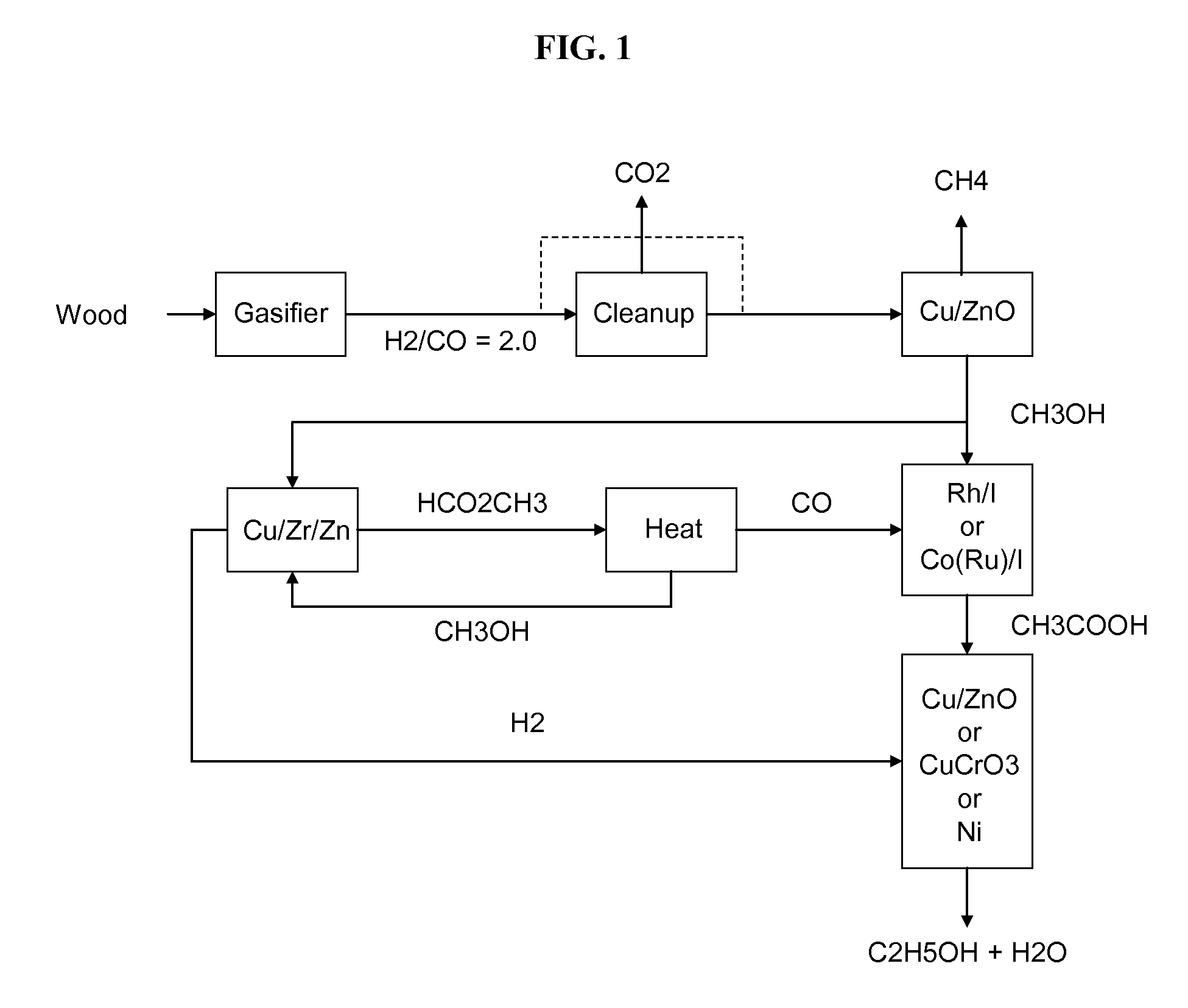
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for Making Ethanol From Acetic Acid Using Acidic Catalysts
InactiveUS20110082322A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidMetal
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid by hydrogenating acetic acid in the presence of a catalyst comprises a first metal on an acidic support. The acidic support may comprise an acidic support material or may comprise an support having an acidic support modifier. The catalyst may be used alone to produced ethanol via hydrogenation or in combination with another catalyst. In addition, the crude ethanol product is separated to obtain ethanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
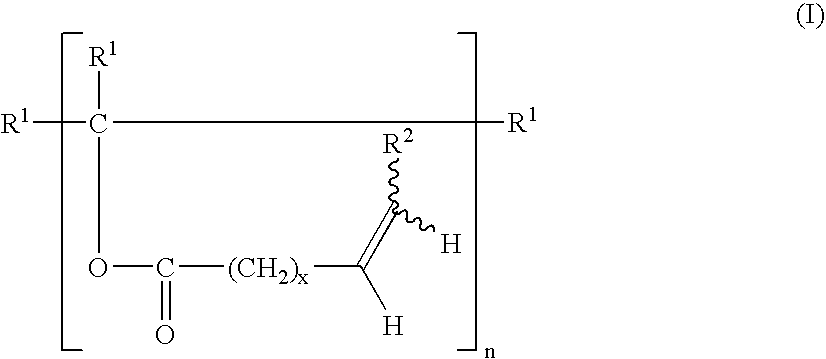
Novel Polymers
ActiveUS20080015315A1Sufficient amountReduce the amount requiredOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention relates to novel crosslinkable copolymers which are obtainable by (a) copolymerizing at least two different hydrophilic monomers selected from the group consisting of N,N-dimethyl acrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP), acrylic acid (AA) and a C1-C4-alkoxy polyethylene glycol (meth)acrylate having a weight average molecular weight of from 200 to 1500, and at least one crosslinker comprising two or more ethylenically unsaturated double bonds in the presence of a chain transfer agent having a functional group; and (b) reacting one or more functional groups of the resulting copolymer with an organic compound having an ethylenically unsaturated group.
Owner:ALCON INC
Chemical methods for treating a metathesis feedstock
ActiveUS20110160472A1Reduce starting peroxide valueFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationChemical treatmentNatural oils
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS20060019360A1High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationChemical industryAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
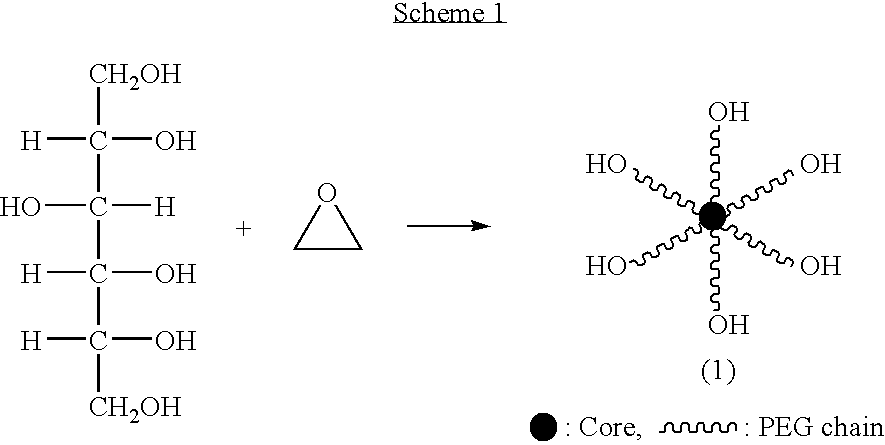
Hexa-arm polyethylene glycol and its derivatives and the methods of preparation thereof
The present invention relates to novel hexa-arm polyethylene glycol (6-arm PEG) and its derivatives. The core of 6-arm PEG derivatives is sorbitol and the end groups can be derivatized into many different reactive functionalities that are useful in conjugating with many different targets. The present invention also provides a biodegradable polymeric hydrogel-forming composition comprising the 6-arm PEG and its derivatives, and methods of using such 6-arm PEG derivatives as surgical or biological implants or sealants.
Owner:SUN BIO INC
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
InactiveUS20090318573A1Increased ethanol yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSyngasChemistry
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
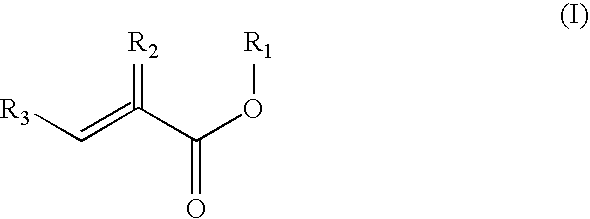
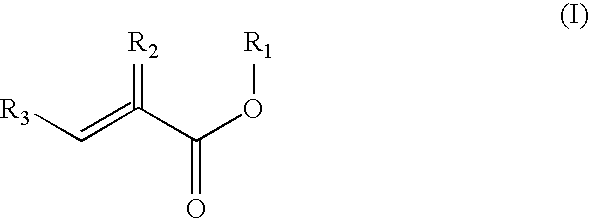
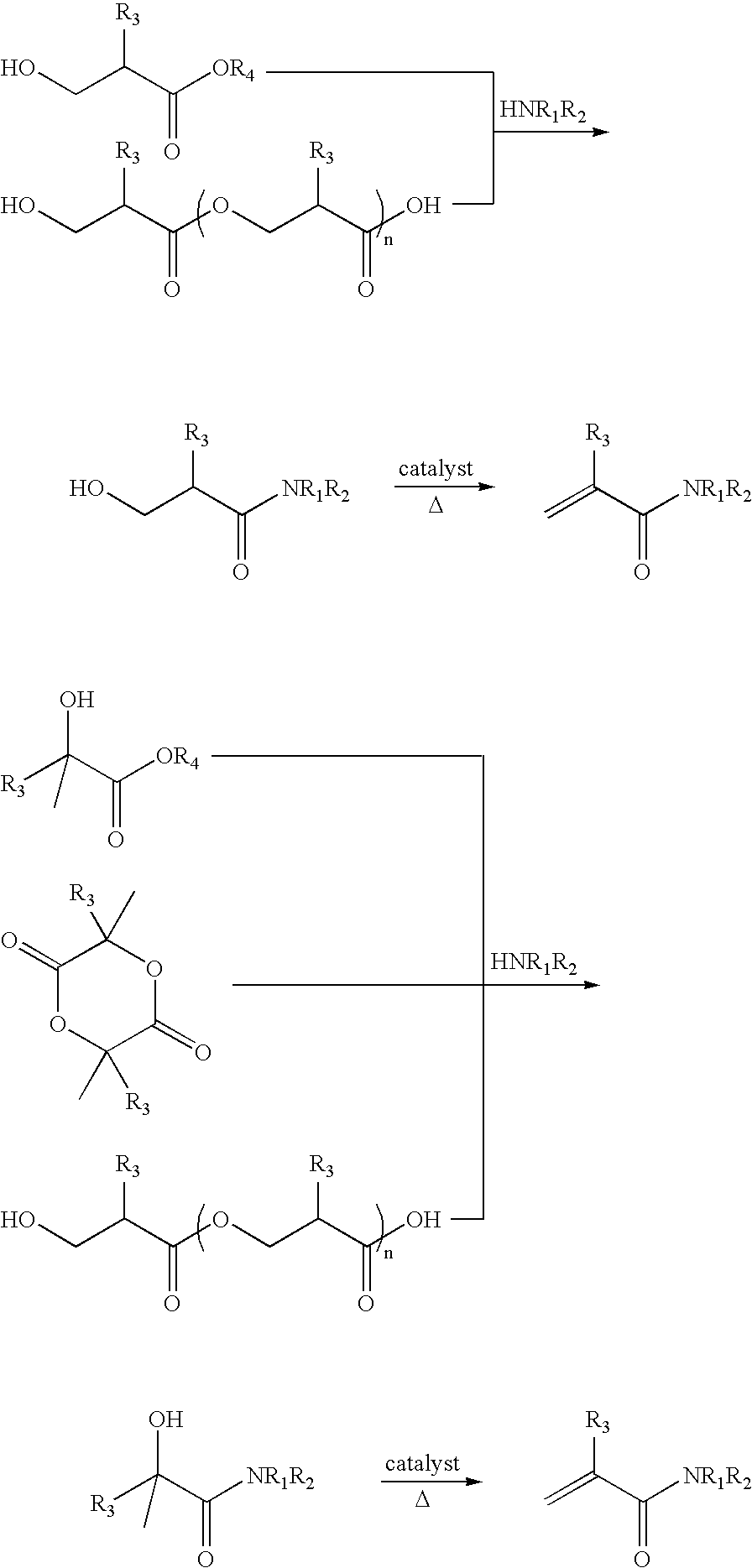
Preparation of acrylic acid derivatives from alpha-or beta-hydroxy carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20050222458A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCarboxylic acidMedicinal chemistry
The invention is directed to a process for the preparation of α,β-unsaturated acids, esters and amides from α- or β-hydroxycarboxylic acids or esters or precursors in high yields and high selectivity. The α,β-unsaturated acids or esters are optionally prepared in the presence of specific dehydration and / or esterification catalysts. The α,β-unsaturated amides or substituted amides are prepared optionally in the presence of a dehydration and / or amidation catalyst. The source of α- or β-hydroxycarboxylic acids or precusor is preferably from a renewable resource. The precursor is defined herein.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM WATER TRATMENTS
Supported palladium-gold catalysts and preparation of vinyl acetate therewith
InactiveUS20100121100A1High activity selectivityImproves oxygen selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTungsten trioxidePalladium
Disclosed is a catalyst. The catalyst comprises palladium, gold, and a support comprising titanium dioxide and tungsten trioxide. The support preferably comprises from 75 wt % to 99 wt % of titanium dioxide and from 1 wt % to 25 wt % of tungsten trioxide. A method for preparing the catalyst is also disclosed. The method comprises impregnating the support with a palladium compound and a gold compound, calcining the impregnated support, and then reducing the calcined support. Further disclosed is a method for preparing vinyl acetate with the catalyst. The catalyst exhibits improved catalytic activity and selectivity.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ACETYLS
Complex comprising oxidative dehydrogenation unit
ActiveUS20140249339A1Consumes lotThermal non-catalytic crackingSequential/parallel process reactionsAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins provides a lower energy route to produce olefins. Oxidative dehydrogenation processes may be integrated with a number of processes in a chemical plant such as polymerization processes, manufacture of glycols, and carboxylic acids and esters. Additionally, oxidative dehydrogenation processes can be integrated with the back end separation process of a conventional steam cracker to increase capacity at reduced cost.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Catalyst used for synthesis of vinyl acetate and its prepn. method
ActiveCN1903435AHigh activityReduce consumptionOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAcetic acidActivated carbon
A catalyst for synthesizing vinyl acetate from acetylene and acetic acid is prepared from activated carbon, zinc acetate and alkaline bismuth carbonate in mass ratio of 100: (27-40): 0.026 by excessive solution dipping method.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +2
Methods of preparing hydroxy functional vegetable oils
Simple, economical preparative processes for the provision of pure hydroxyl functional materials that are derived by converting the alkene groups of the unsaturated molecules found in vegetable oils, into hydroxyl groups.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Oxide catalyst composition
InactiveUS7012039B2High selectivityLow selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationLanthanideMethacrolein
An oxide catalyst composition for use in producing methacrolein or a mixture of methacrolein and methacrylic acid, wherein the oxide catalyst composition is represented by the formula (Mo+W)l2BiaAbBcFedXeSbfOg, wherein: A is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Y and the elements of the lanthanoid series exclusive of Pm; B is at least one member selected from the group consisting of K, Rb and Cs; X is Co solely, or a mixture of Co and at least one member selected from the group consisting of Mg and Ni; and a, b, c, d, e, f and g are, respectively, the atomic ratios of Bi, A, B, Fe, X, Sb and O, relative to twelve atoms of the total of Mo and W, wherein the atomic ratios (a to f) of the elements and the relationship between the amounts of the elements are chosen so as to satisfy specific requirements.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
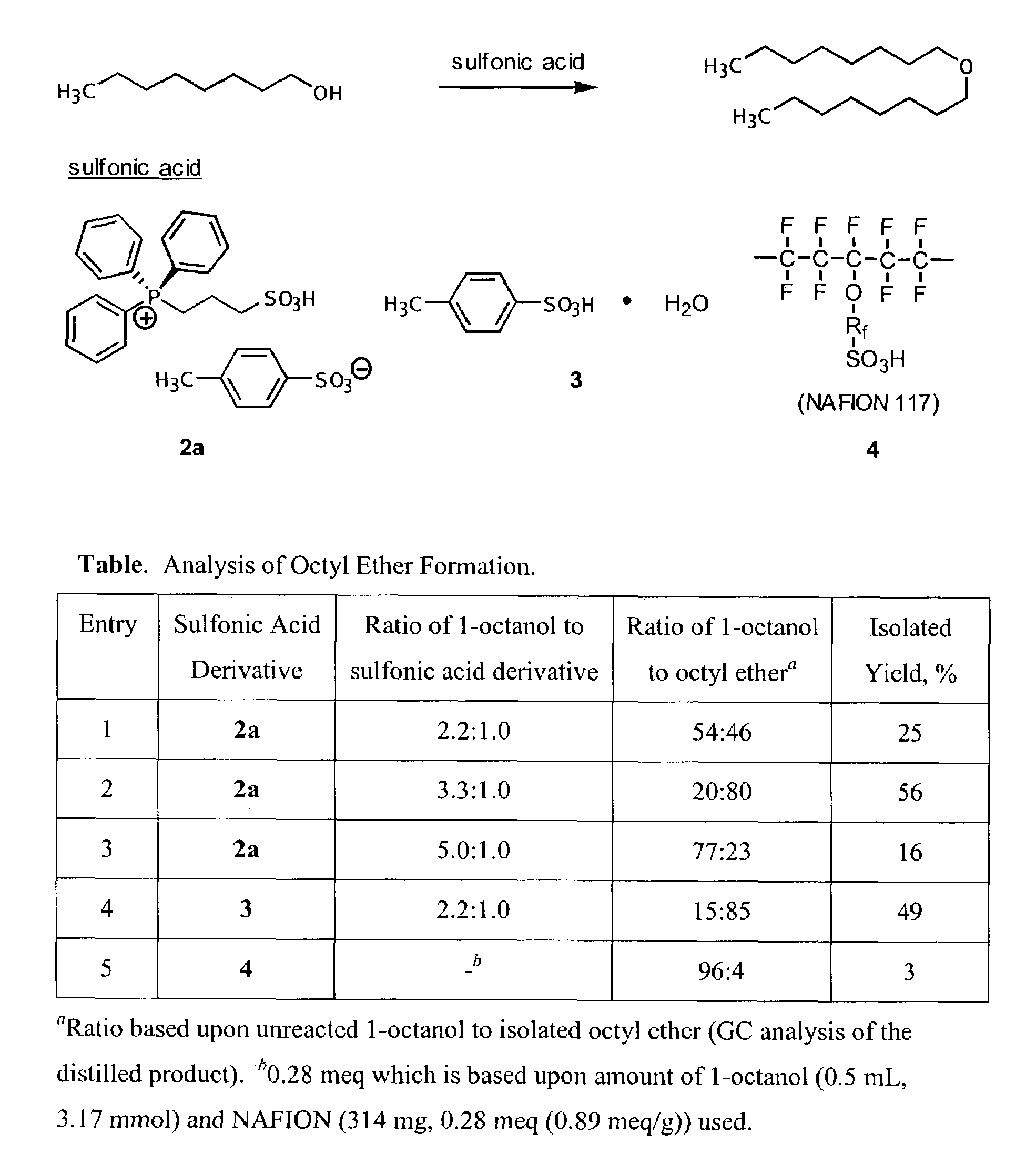
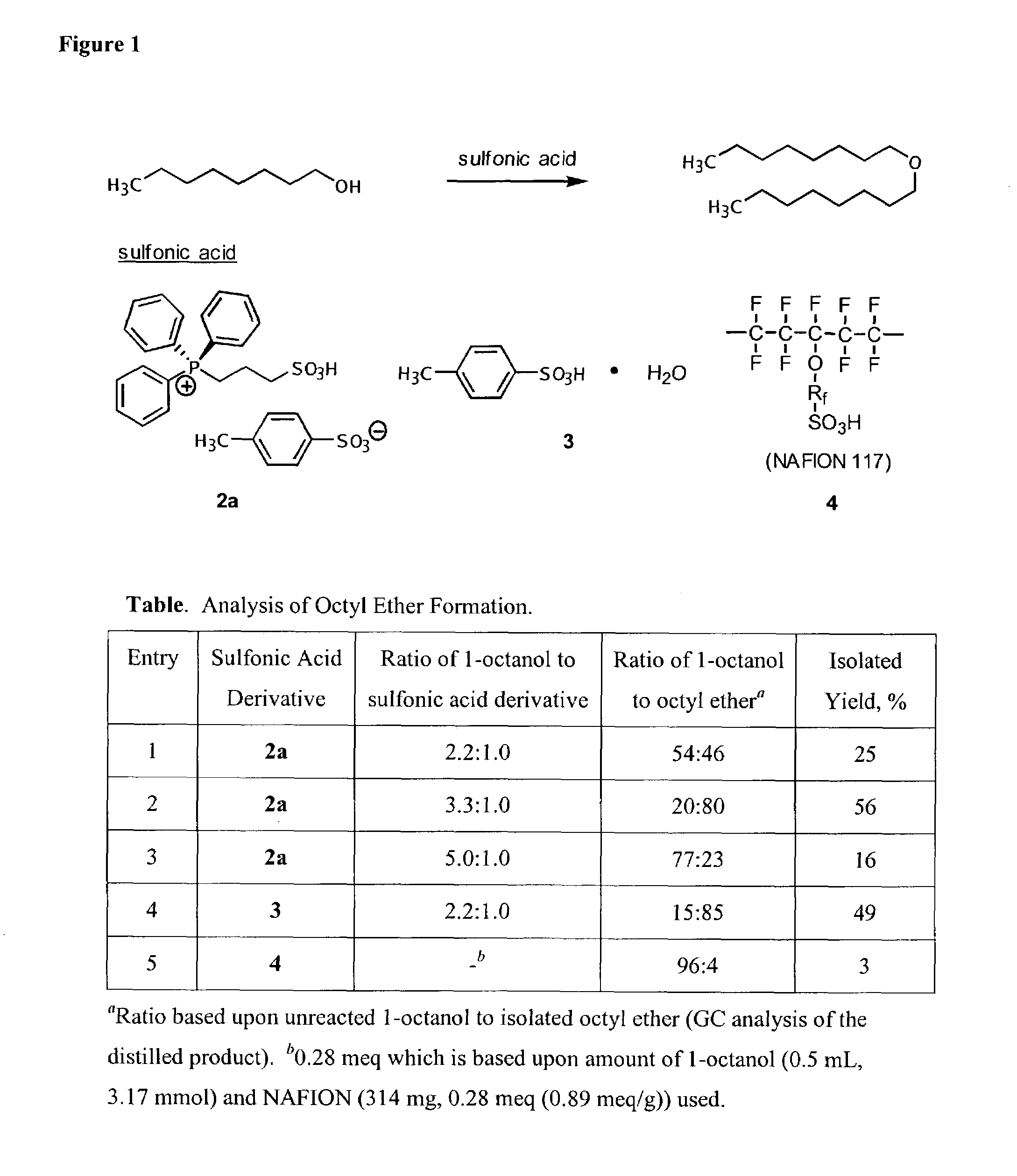
Functionalized ionic liquids, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to ionic liquids comprising a pendant Bronsted-acidic group, e.g., a sulfonic acid group. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant Bronsted-acidic group to catalyze a Bronsted-acid-catalyzed chemical reaction. A third aspect of the present invention relates to ionic liquids comprising a pendant nucleophilic group, e.g., an amine. Still another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant nucleophilic group to catalyze a nucleophile-assisted chemical reaction. A fifth aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant nucleophilic group to remove a gaseous impurity, e.g., carbon dioxide, from a gas, e.g., sour natural gas.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH ALABAMA
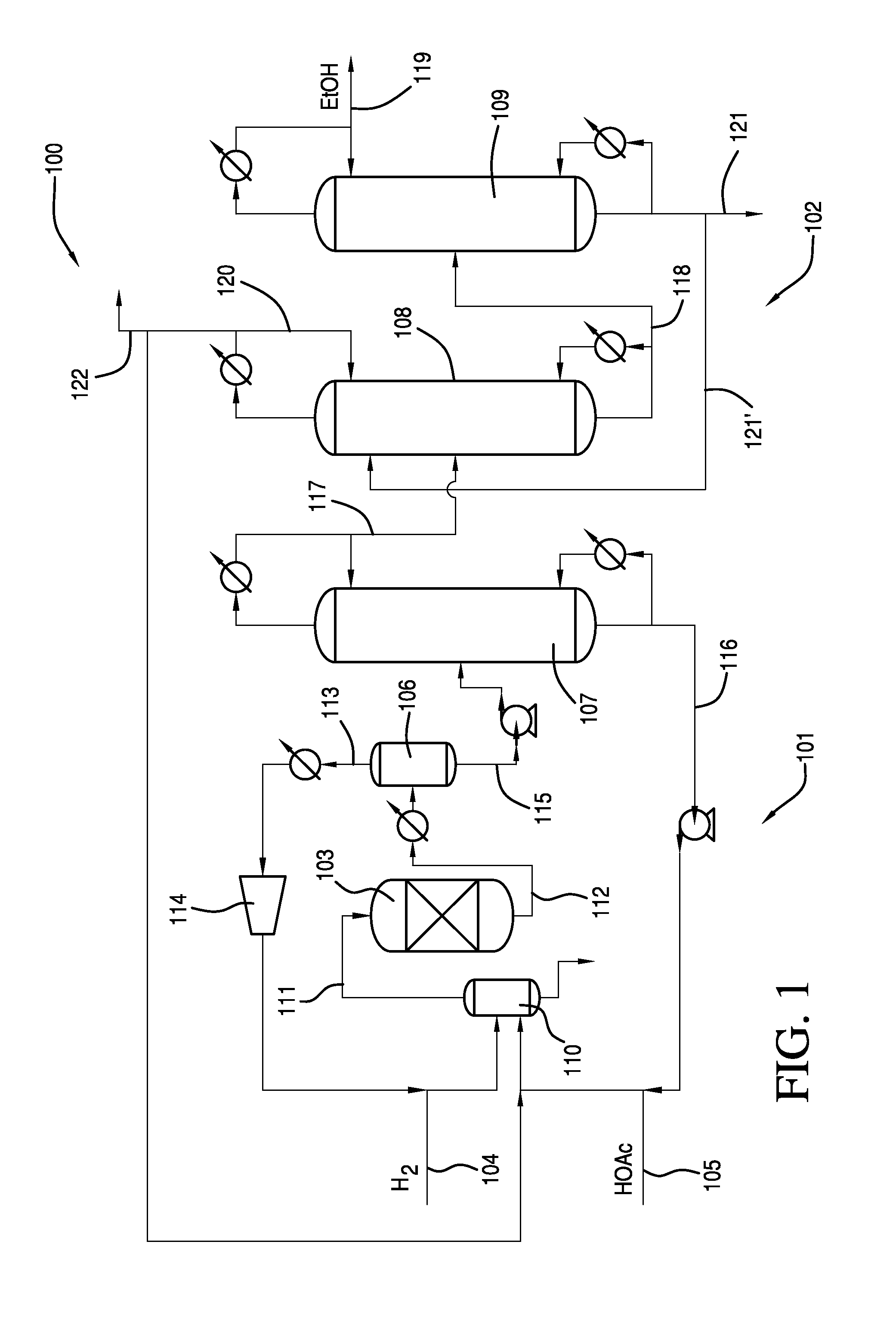
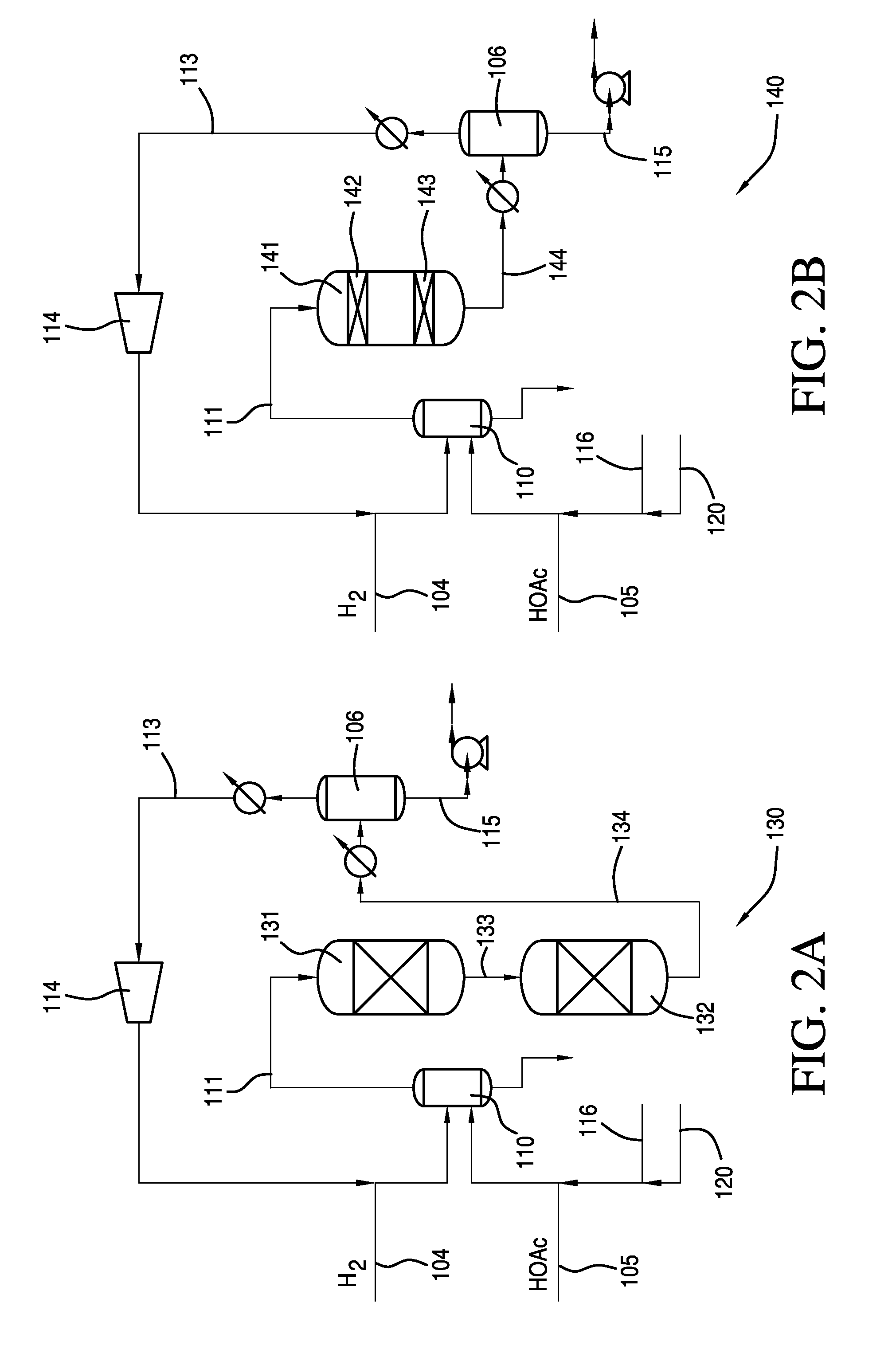
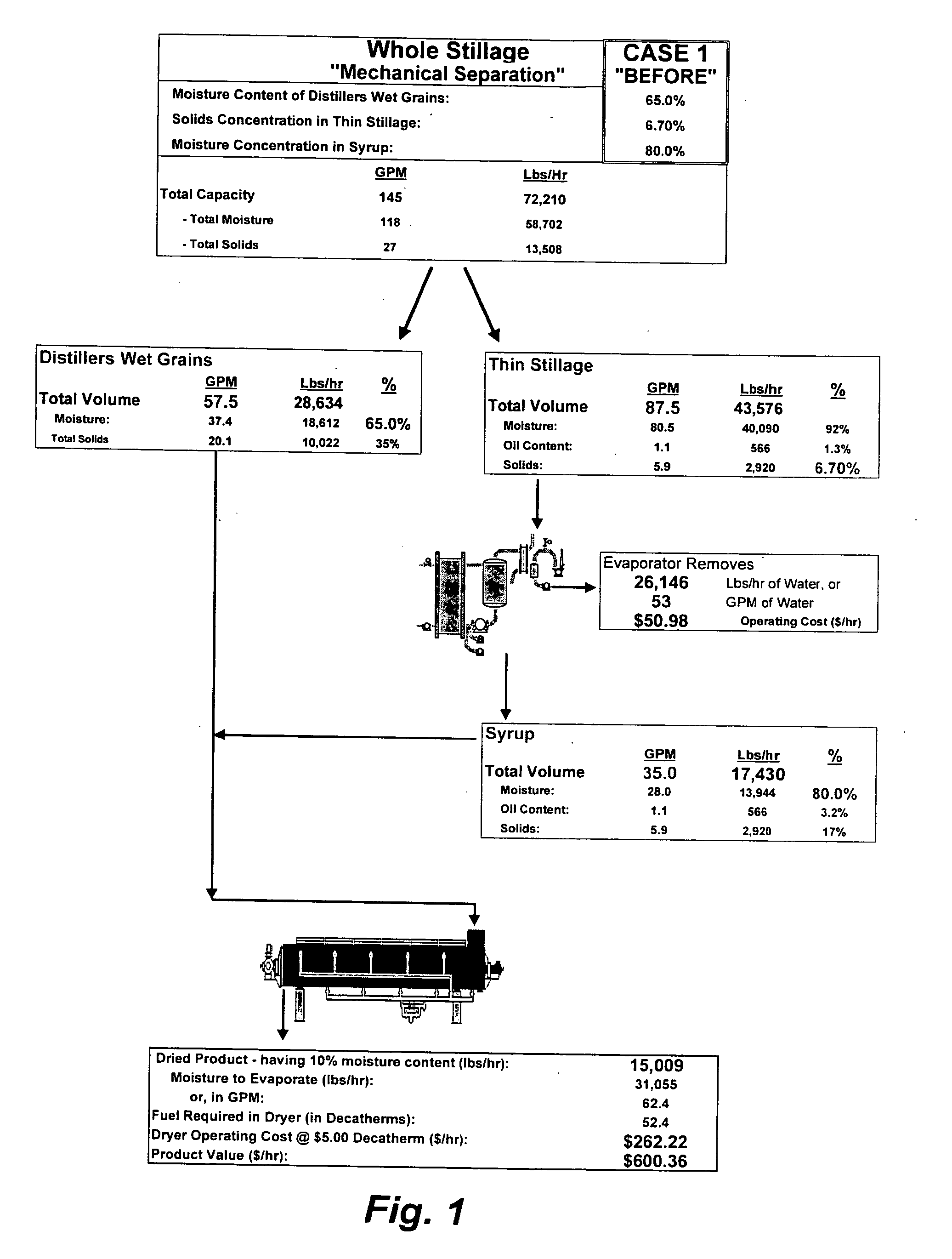
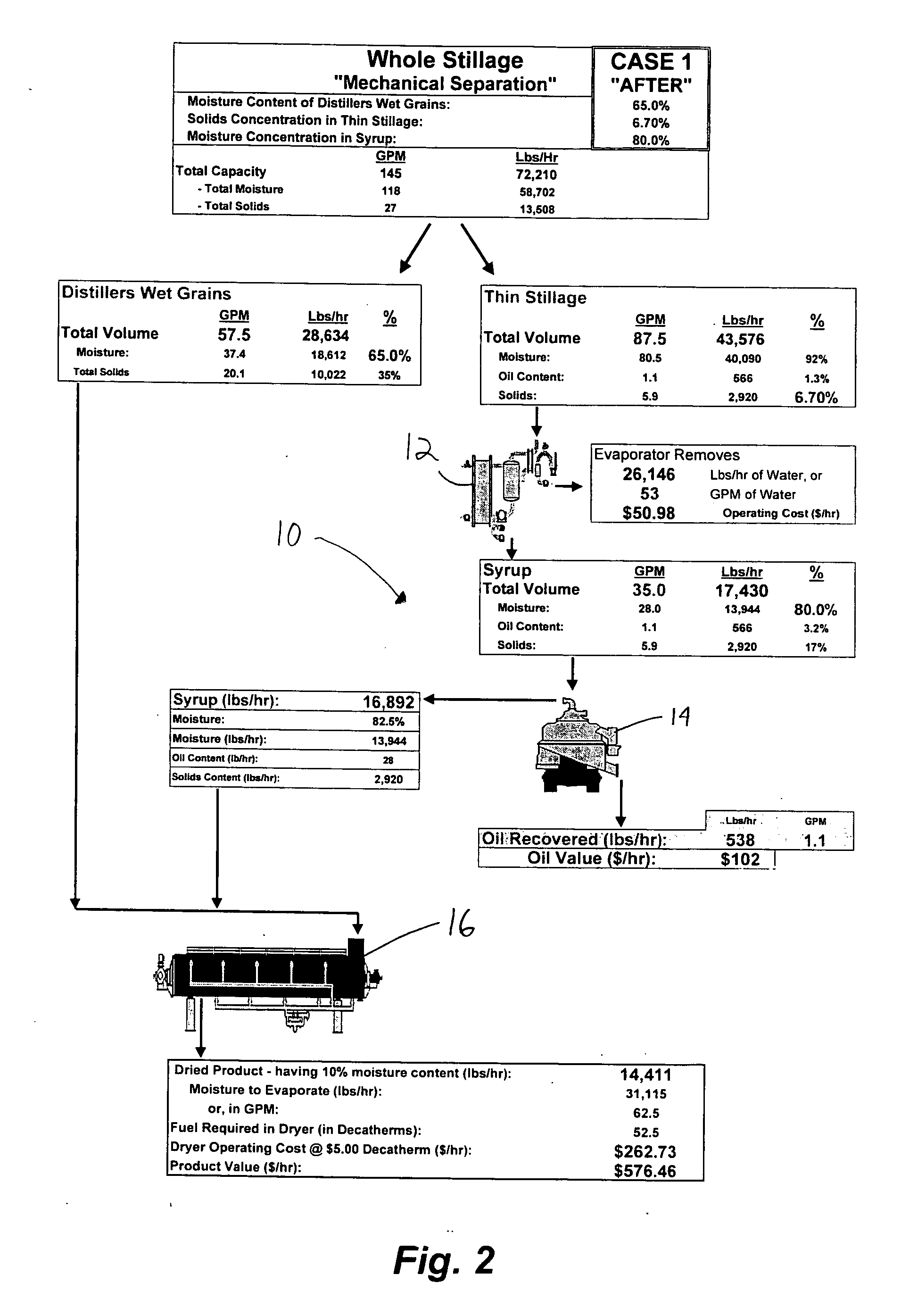
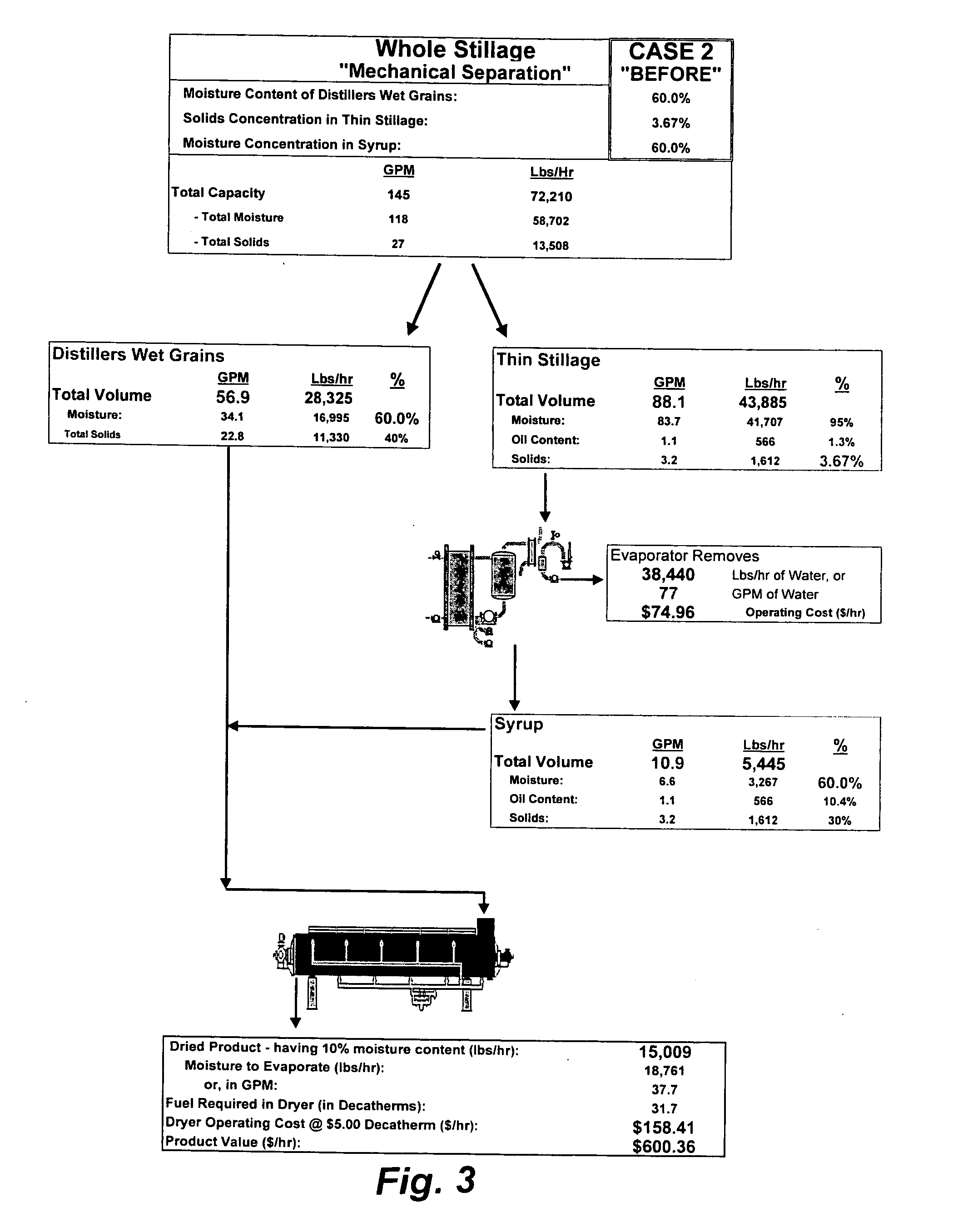
Method of processing ethanol byproducts and related subsystems
In one aspect of the invention, a method recovers oil from a concentrated byproduct, such as evaporated thin stillage formed during a dry milling process used for producing ethanol. The method includes forming a concentrate from the byproduct and recovering oil from the concentrate. The step of forming the concentrate may comprise evaporating the byproduct. Further, the step of separating the oil from the concentrate may comprise using a centrifuge and, in particular, a disk stack centrifuge. Other aspects of the invention include related methods and subsystems for recovering oil from thin stillage.
Owner:GS CLEANTECH CORP
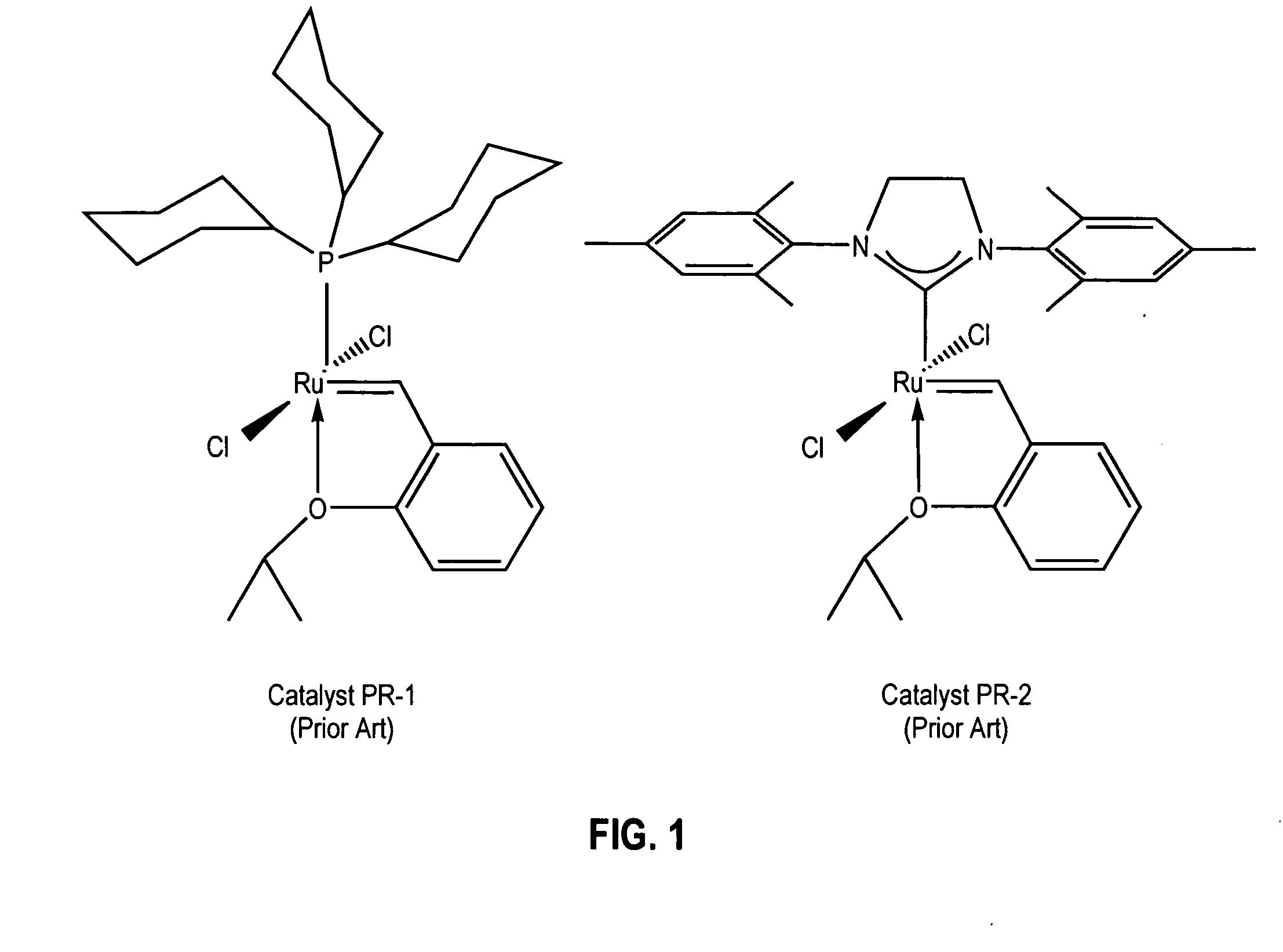
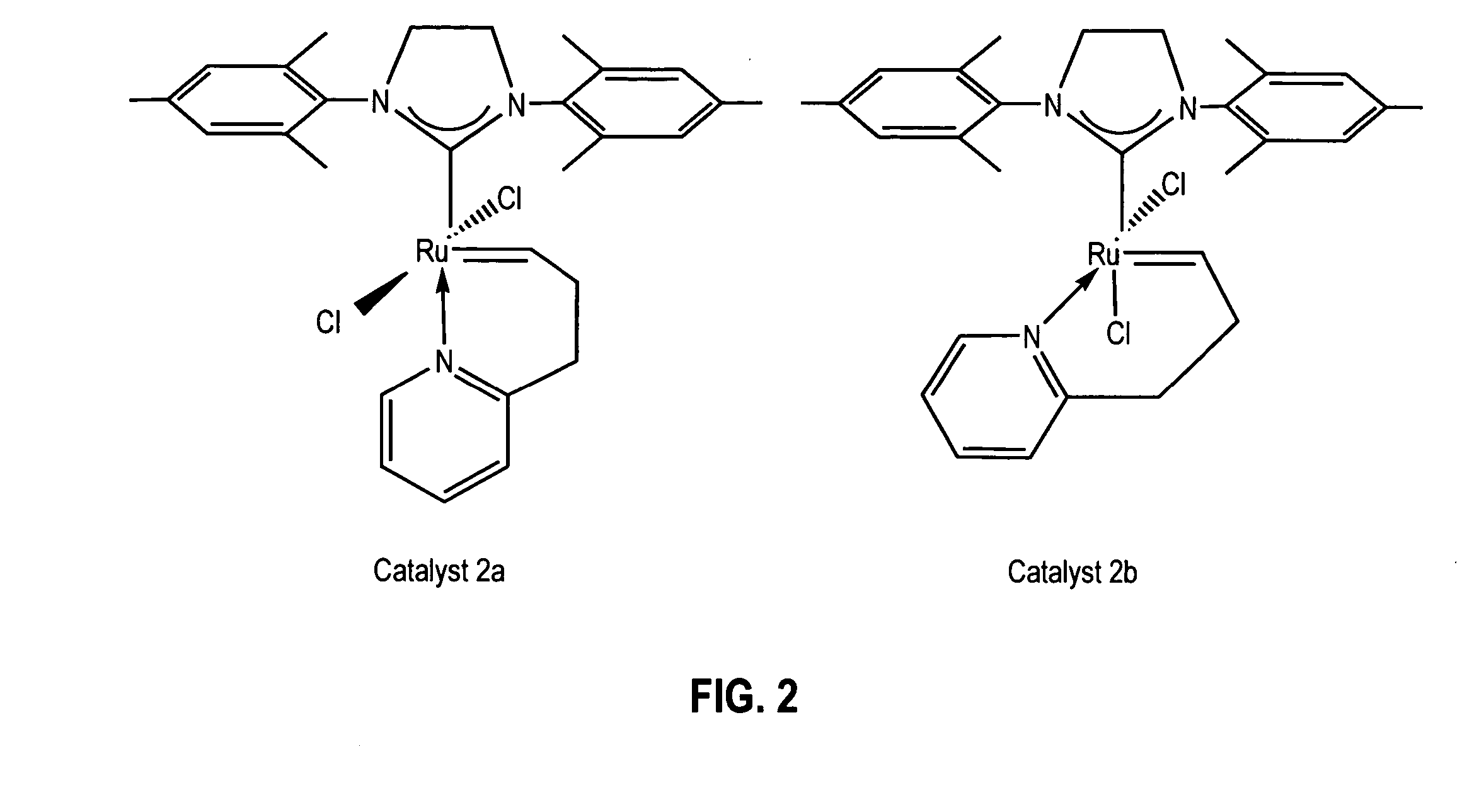
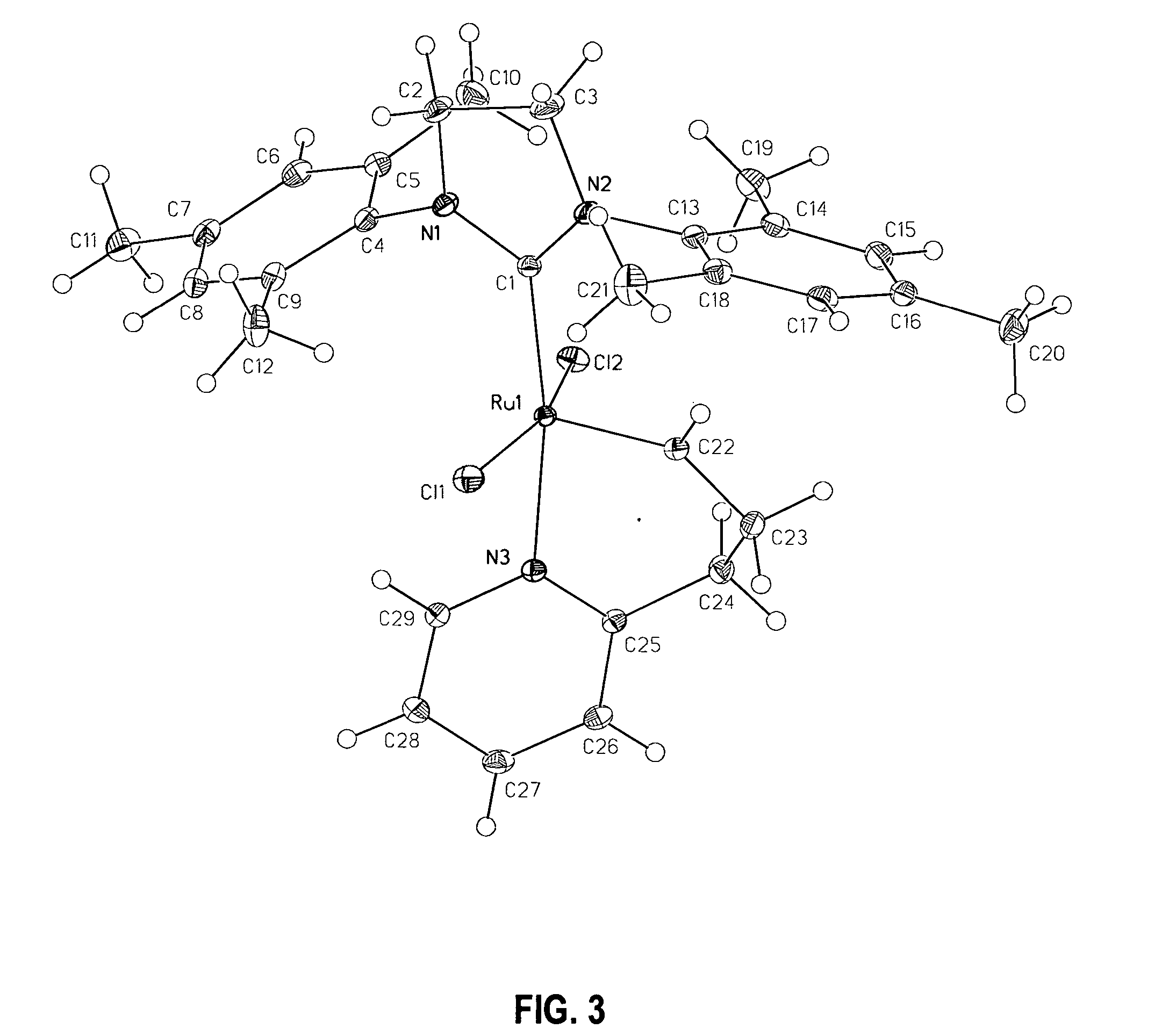
Latent, high-activity olefin metathesis catalysts containing an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand
InactiveUS20050261451A1Ruthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationRing-closing metathesisAlkene
The invention provides novel organometallic complexes useful as olefin metathesis catalysts. The complexes have an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand and a chelating carbene ligand associated with a Group 8 transition metal center. The molecular structure of the complexes can be altered so as to provide a substantial latency period. The complexes are particularly useful in catalyzing ring closing metathesis of acyclic olefins and ring opening metathesis polymerization of cyclic olefins.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Tricyclic compounds and their use in medicine process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them
Novel beta -aryl- alpha -oxysubstituted alkylcarboxylic acids of the formula (I) and compositions containing them. The compounds have hypolipidemic, antihyperglycemic uses.
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB LTD
Thermal methods for treating a metathesis feedstock
ActiveUS20110313180A1Diminish starting peroxide valueOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationOxygenThermal methods
Various methods are provided for metathesizing a feedstock. In one aspect, a method includes providing a feedstock comprising a natural oil, heating the feedstock to a temperature greater than 100° C. in the absence of oxygen, holding the feedstock at the temperature for a time sufficient to diminish catalyst poisons in the feedstock, and, following the heating and holding, combining a metathesis catalyst with the feedstock under conditions sufficient to metathesize the feedstock.
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
Method for preparing salvianolic acid A by catalytically converting salvianolic acid B
InactiveCN102212004AShorten the timeHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSalvianolic acid KSalvianolic acid B
The invention discloses a method for preparing salvianolic acid A by catalytically converting salvianolic acid B. The method is characterized in that the converted raw material is a salvia miltiorrhiza aqueous extract (salvianolic acid B=>50%) primarily purified through combined chromatography; the concentration of the raw material salvianolic acid B is 0.5-2%; urea is taken as the catalyst; the mole ratio of urea to the salvianolic acid B is 0.3-0.7; the conversion reaction temperature is 100-125 DEG C; and the reaction time is 3-6 hours. The method has the following beneficial effects: urea is taken as the catalyst, thus greatly shortening the time for which the salvianolic acid B is in easily destroyed state and remarkably increasing the yield of the salvianolic acid A; the primarily purified salvia miltiorrhiza extract is taken as the converted raw material, thus not only removing the metal ions which are not beneficial to conversion but also removing most colloid-like impurities and frontal impurities which are not beneficial to following separation of the salvianolic acid; and the directional conversion rate of the salvianolic acid B to the salvianolic acid A prepared by the method is not less than 10% and even reaches 60%.
Owner:SUZHOU LEINA PHARMA RES DEV +1
Ring opening cross-metathesis reaction of cyclic olefins with seed oils and the like
ActiveUS20080064891A1Fatty acid esterificationOrganic compound preparationOrganic synthesisRuthenium
This invention relates generally to olefin metathesis, and more particularly relates to the ring-opening, ring insertion cross-metathesis of cyclic olefins with internal olefins such as seed oils and the like. In one embodiment, a method is provided for carrying out a catalytic ring-opening cross-metathesis reaction, comprising contacting at least one olefinic substrate with at least one cyclic olefin as a cross metathesis partner, in the presence of a ruthenium alkylidene olefin metathesis catalyst under conditions effective to allow ring insertion cross metathesis whereby the cyclic olefin is simultaneously opened and inserted into the olefinic substrate. The invention has utility in the fields of catalysis, organic synthesis, and industrial chemistry.
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
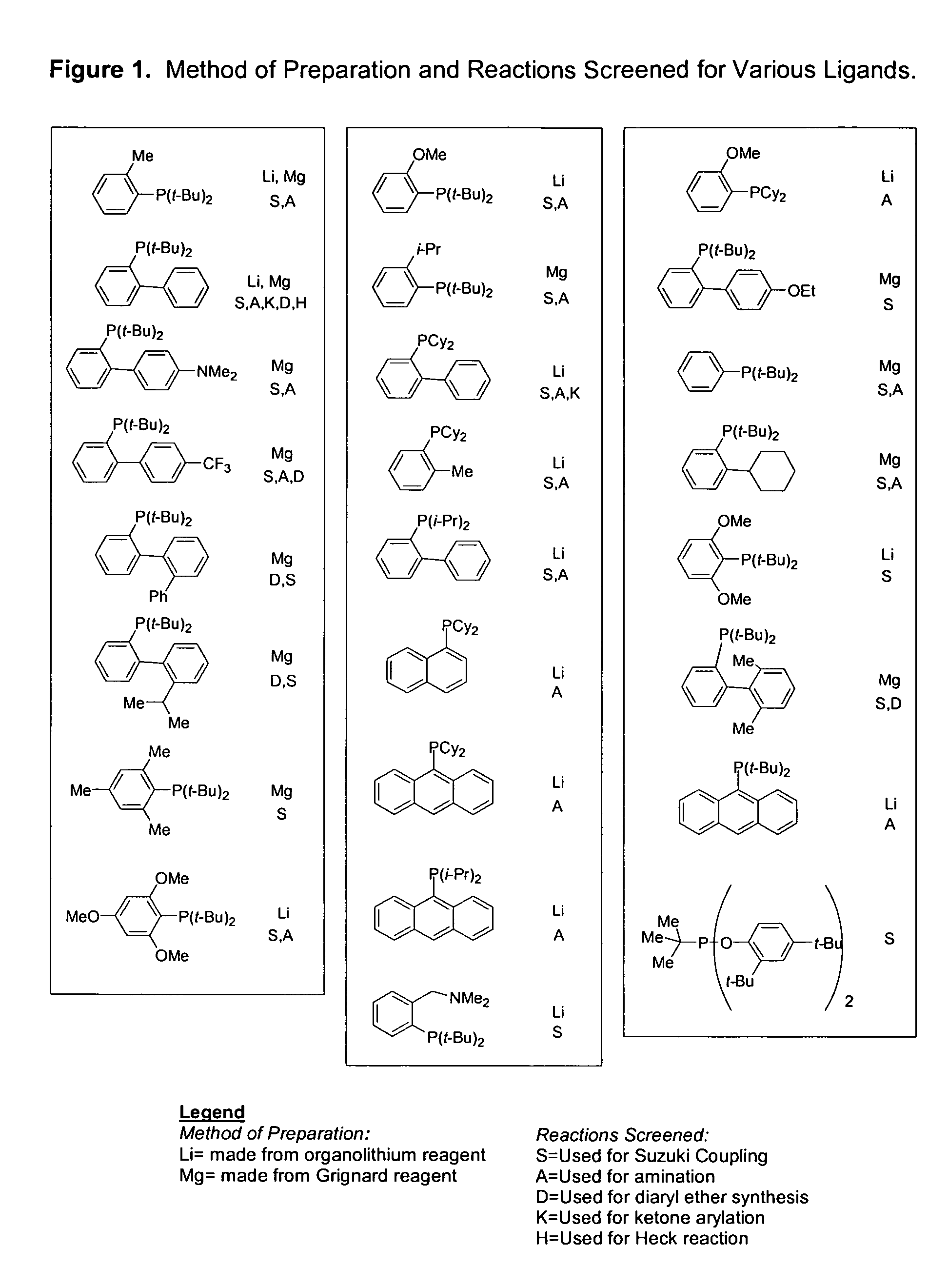
Ligands for metals and improved metal-catalyzed processes based thereon
InactiveUS7223879B2More featureEasy to useCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarbon–carbon bondHeteroatom
One aspect of the present invention relates to ligands for transition metals. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of catalysts comprising these ligands in transition metal-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The subject methods provide improvements in many features of the transition metal-catalyzed reactions, including the range of suitable substrates, reaction conditions, and efficiency.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
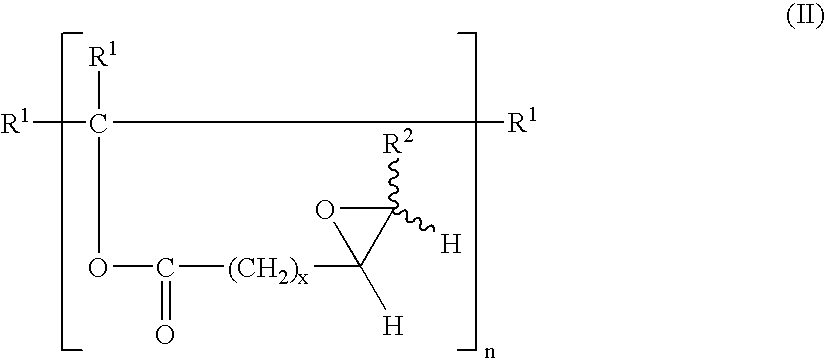
Synthesis of terminal alkenes from internal alkenes and ethylene via olefin metathesis
This invention relates generally to olefin metathesis, and more particularly relates to the synthesis of terminal alkenes from internal alkenes using a cross-metathesis reaction catalyzed by a selected olefin metathesis catalyst. In one embodiment of the invention, for example, a method is provided for synthesizing a terminal olefin, the method comprising contacting an olefinic substrate comprised of at least one internal olefin with ethylene, in the presence of a metathesis catalyst, wherein the catalyst is present in an amount that is less than about 1000 ppm relative to the olefinic substrate, and wherein the metathesis catalyst has the structure of formula (II) wherein the various substituents are as defined herein. The invention has utility, for example, in the fields of catalysis, organic synthesis, and industrial chemistry.
Owner:MATERIA
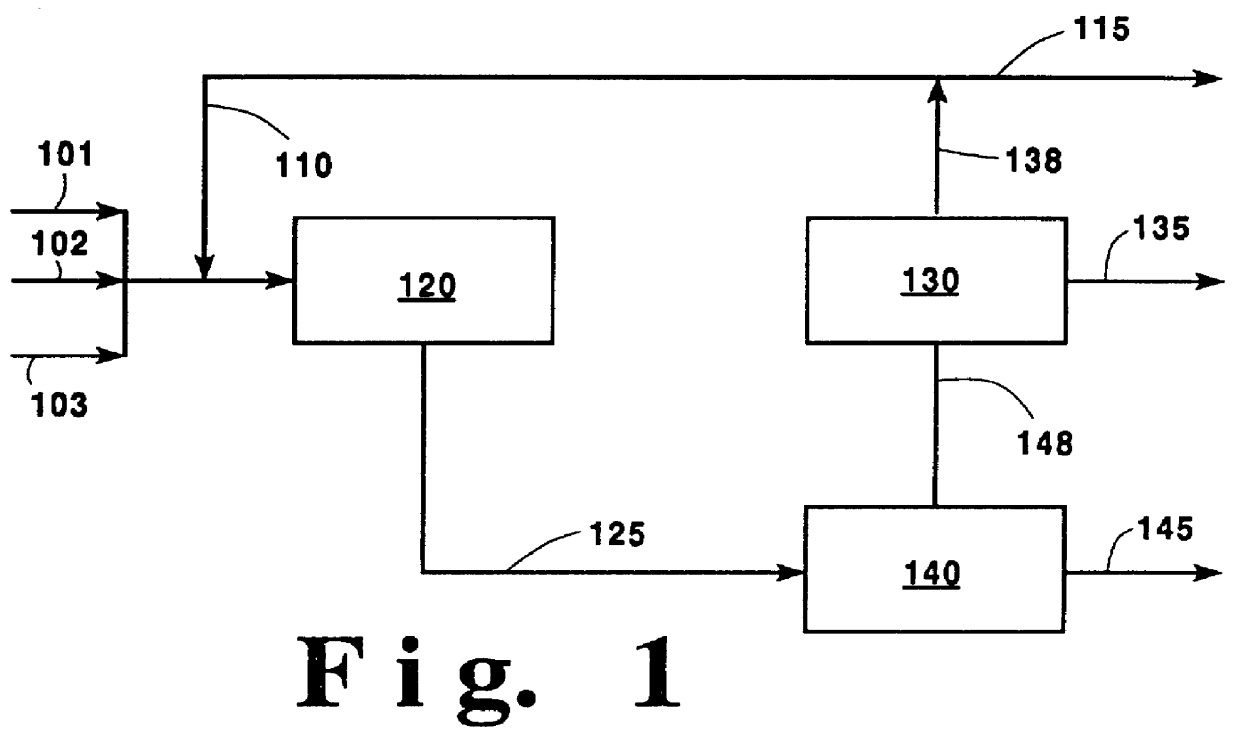
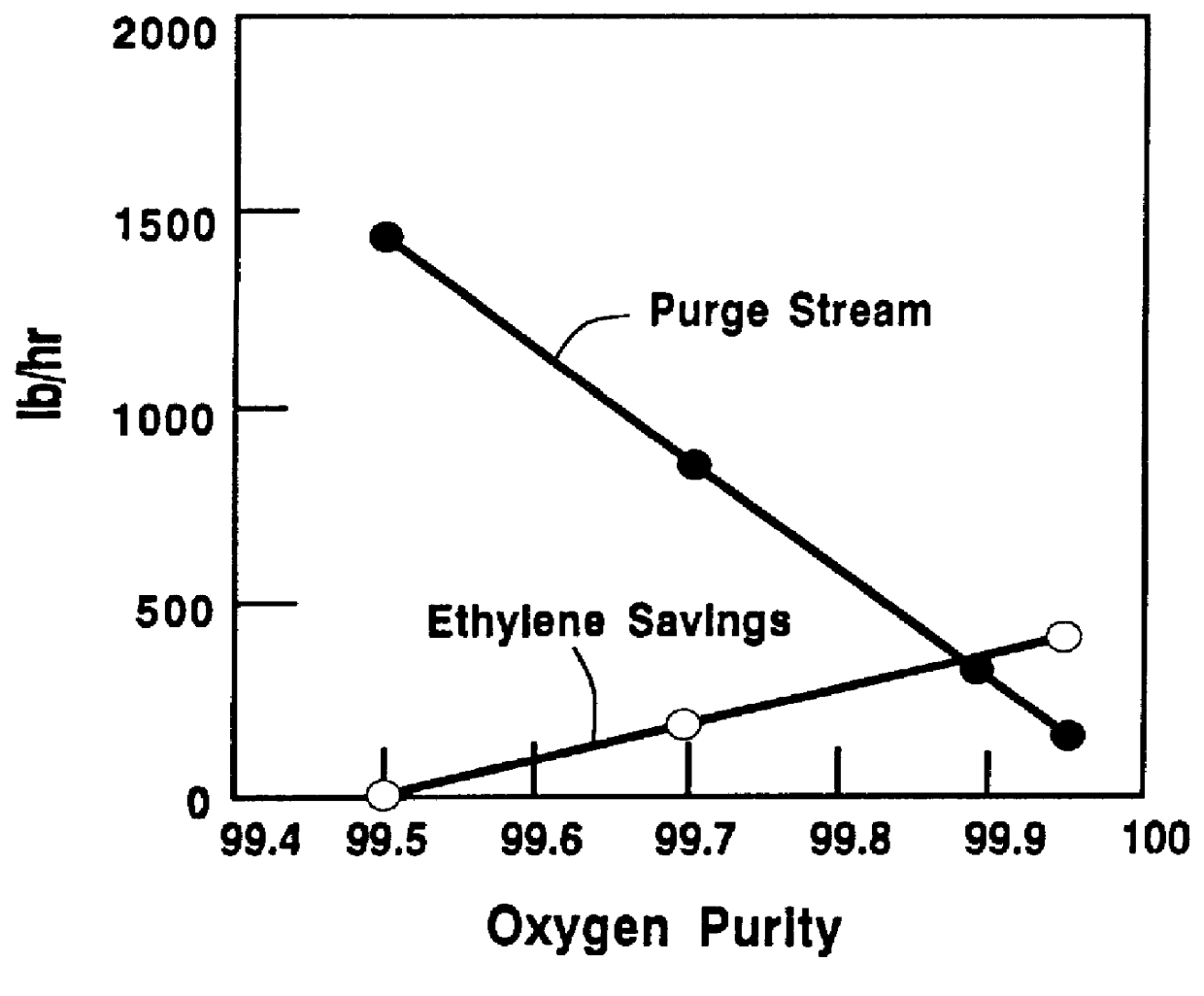
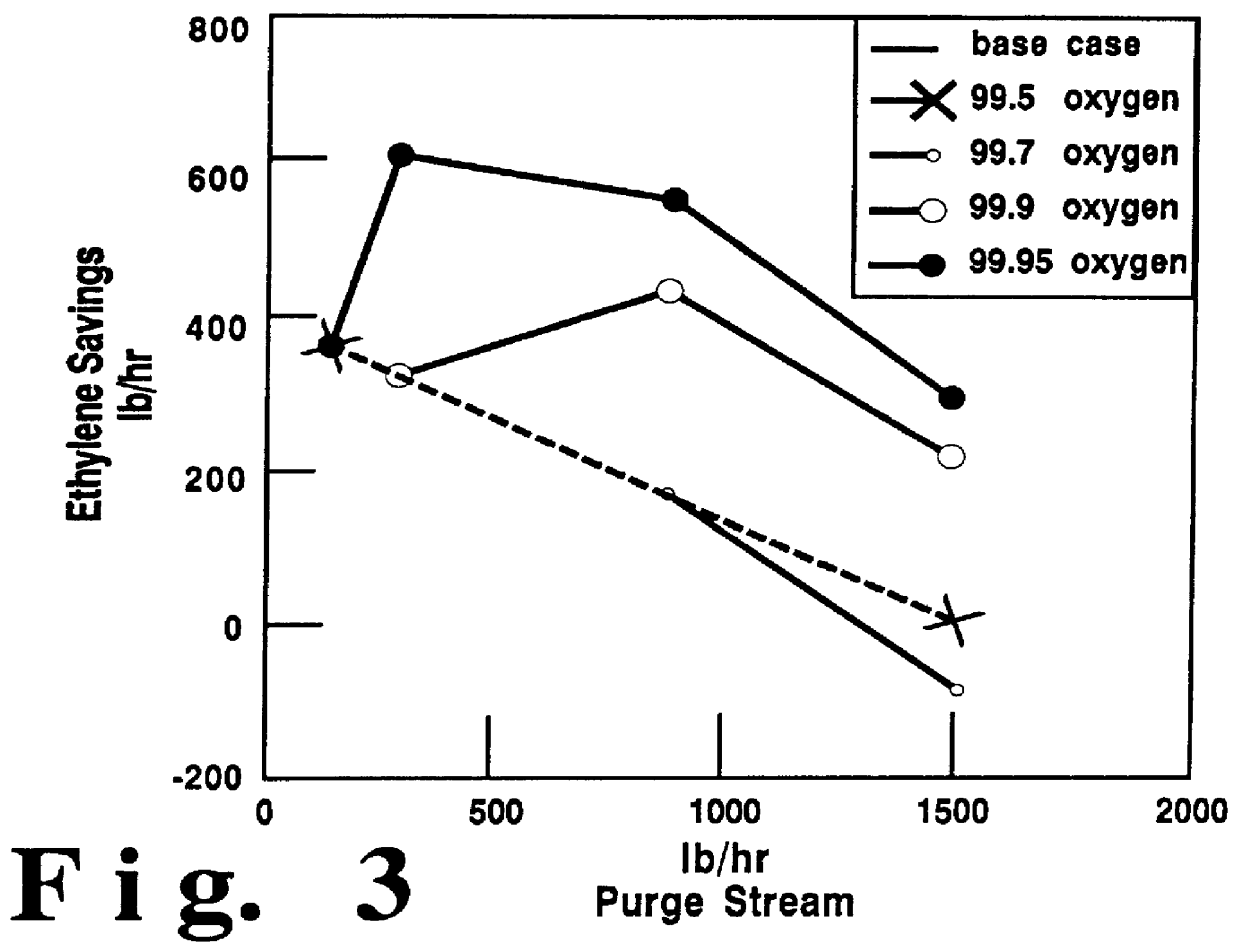
High purity oxygen for ethylene oxide production
InactiveUS6040467AIncrease productionReduces required capital investmentOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationEthylene oxideProduct gas
This invention is directed to a method for producing ethylene oxide comprising feeding ethylene, high purity oxygen and a ballast gas with a recycle gas in a catalyst filled reactor to form a gaseous mixture; passing the gaseous mixture from the reactor to a recovery unit to selectively separate ethylene oxide and carbon dioxide containing gas; passing at least a portion of the carbon dioxide containing gas to a stripping unit to selectively separate carbon dioxide and a waste gas; passing at least a portion of the waste gas to purge and another portion for recycling as the recycle gas; and recovering ethylene oxide from the recovery unit.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Ligands for metals and improved metal-catalyzed processes based thereon
InactiveUS6946560B2More featureEasy to useCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCarbon–carbon bondHeteroatom
One aspect of the present invention relates to novel ligands for transition metals. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of catalysts comprising these ligands in transition metal-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. The subject methods provide improvements in many features of the transition metal-catalyzed reactions, including the range of suitable substrates, reaction conditions, and efficiency.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Polyamine analog conjugates and quinone conjugates as therapies for cancers and prostate diseases
Peptide conjugates in which cytocidal and cytostatic agents, such as polyamine analogs or naphthoquinones, are conjugated to a polypeptide recognized and cleaved by enzymes such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and cathepsin B are provided, as well as compositions comprising these conjugates. Methods of using these conjugates in the treatment of prostate diseases are also provided.
Owner:CELLGATE
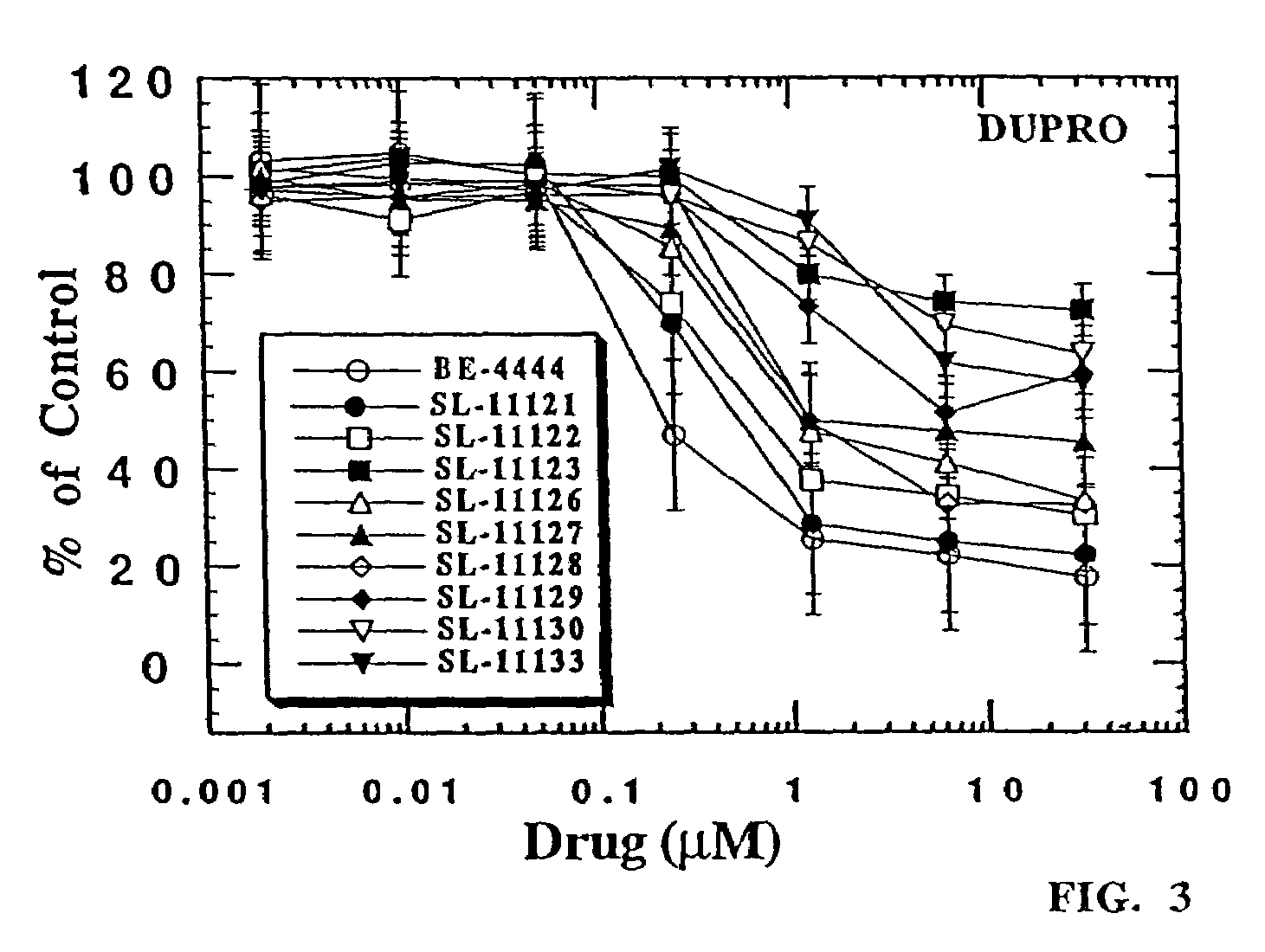
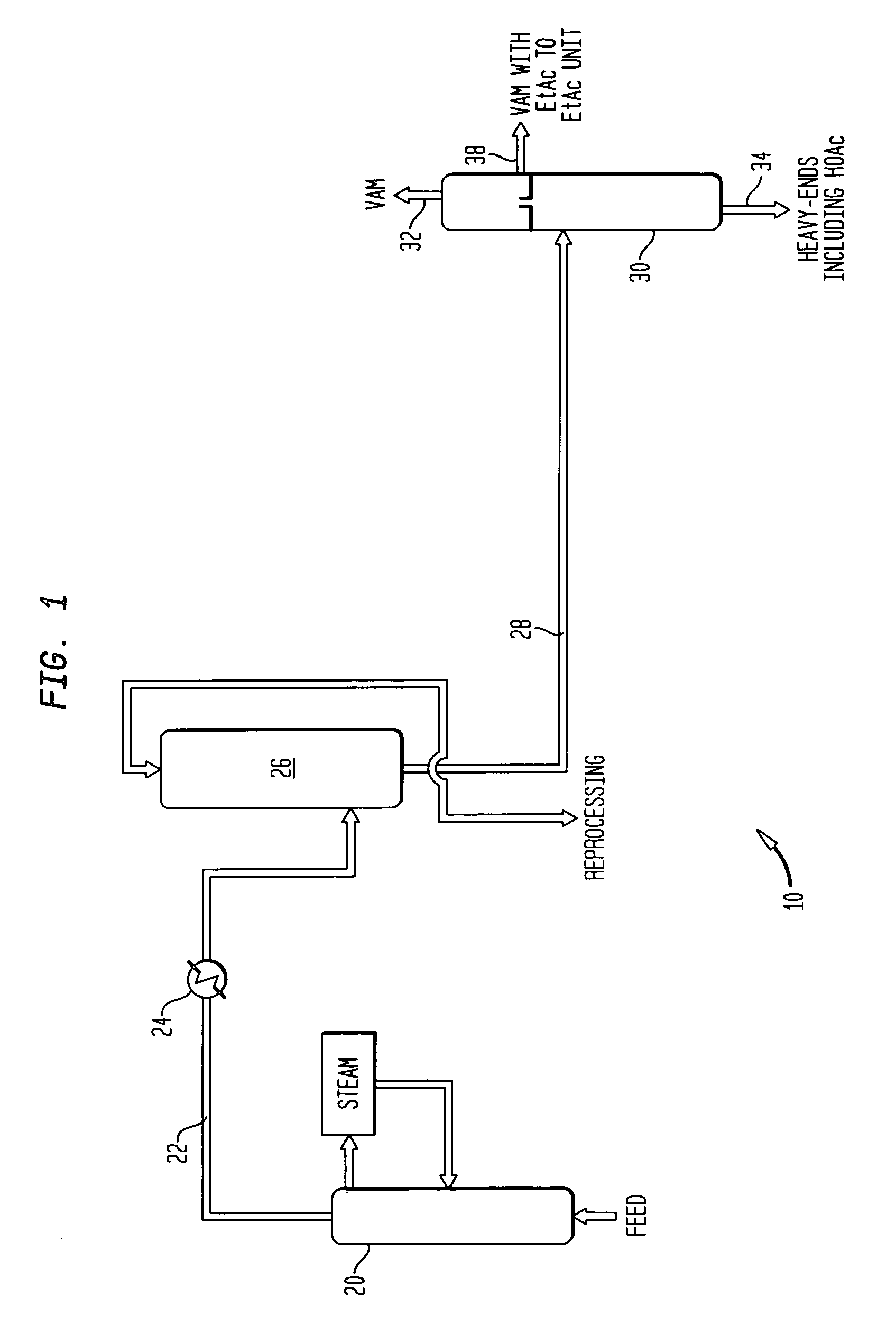
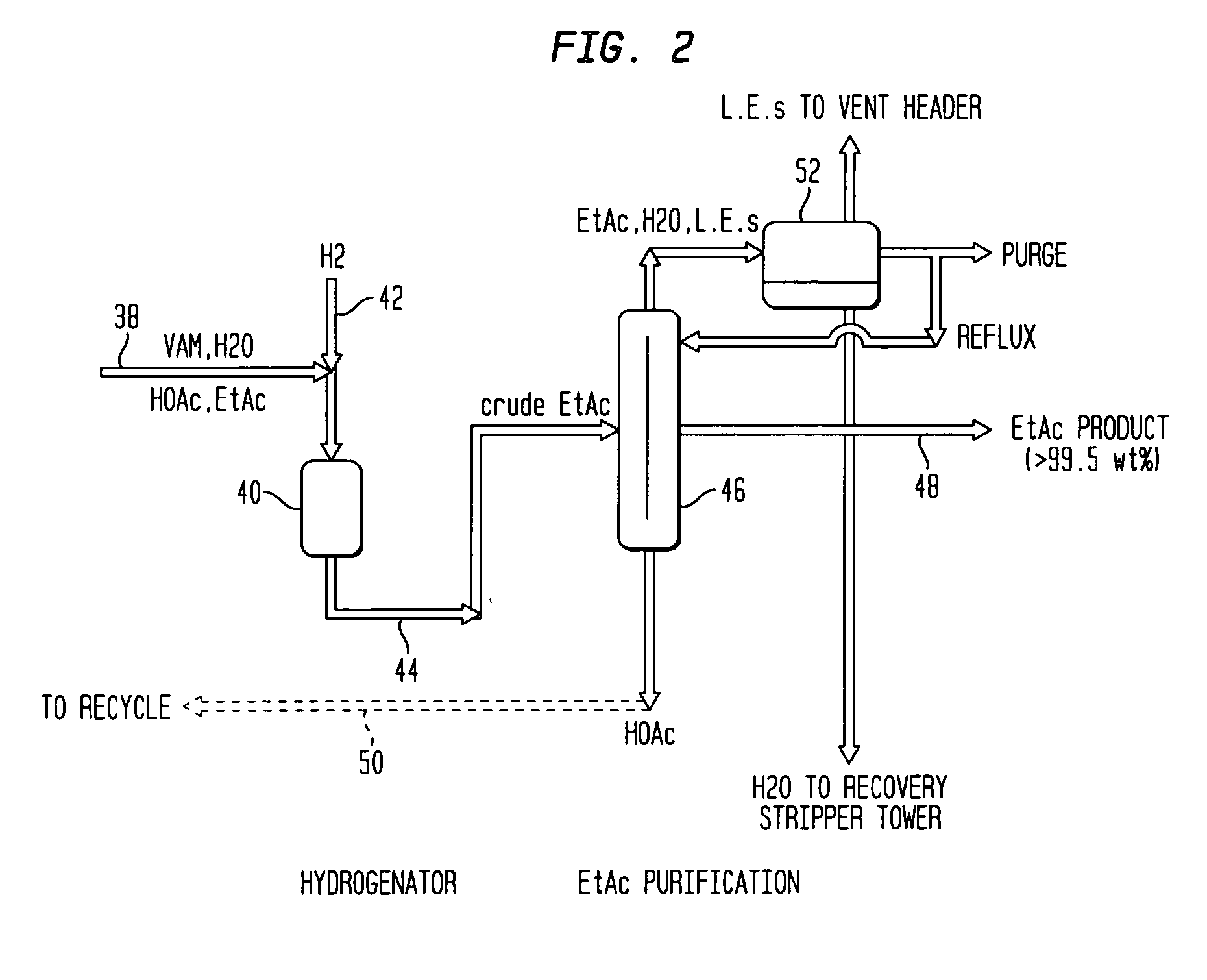
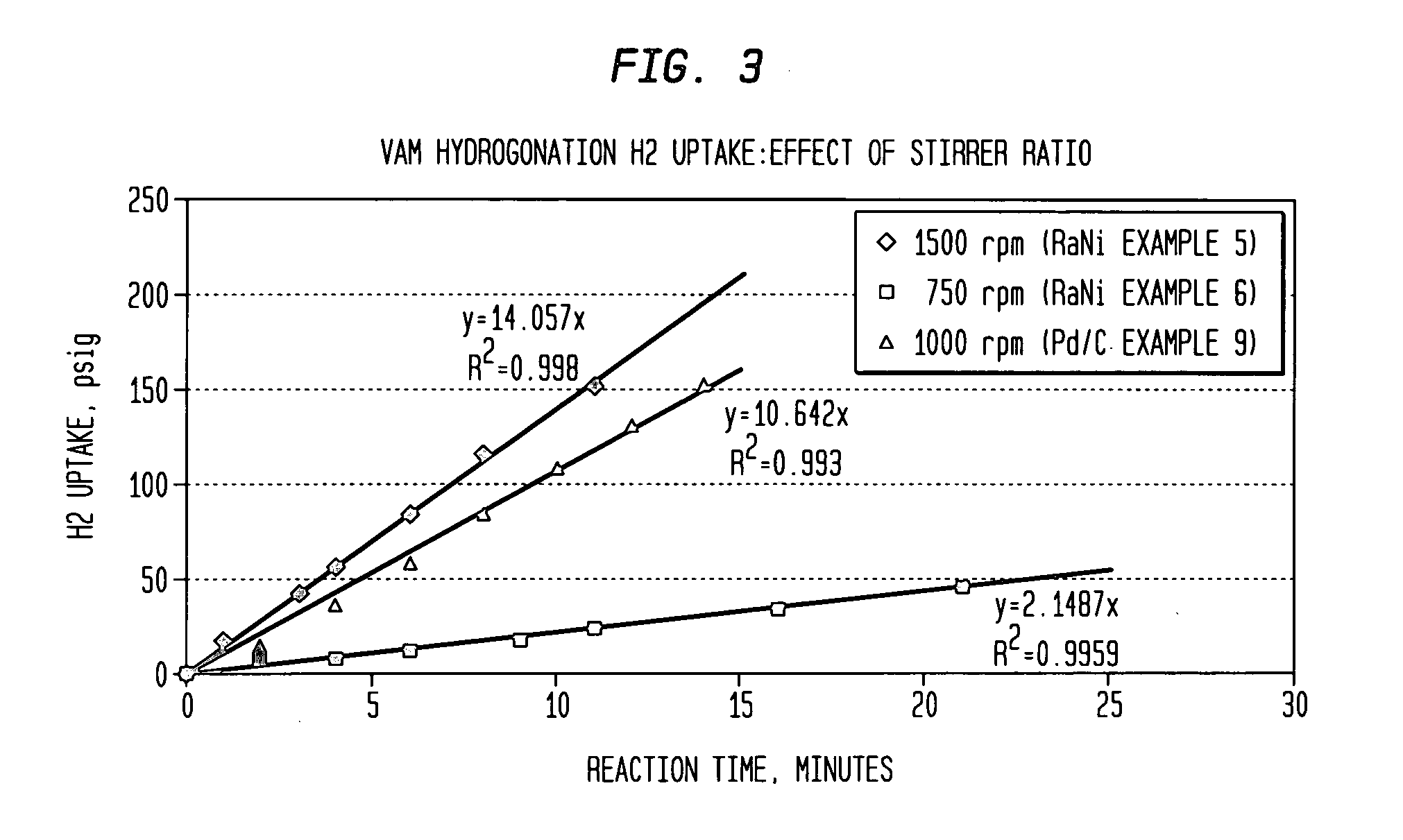
Co-production of vinyl acetate and ethyl acetate
InactiveUS20060106246A1Improve throughputReduce purification costsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidDistillation
A method of co-producing vinyl acetate and ethyl acetate includes: (a) reacting ethylene, acetic acid and oxygen to form vinyl acetate and at least a minor amount of ethyl acetate; (b) providing a crude product stream containing the vinyl acetate and ethyl acetate of step (a) and acetic acid to a distillation tower; (c) separating the crude product stream into: (i) a vinyl acetate product stream enriched in vinyl acetate with respect to the crude product stream; (ii) an acid recycle stream enriched in acetic acid with respect to the crude product stream; (iii) a mixed sidestream containing vinyl acetate and ethyl acetate, the mixed sidestream being enriched in ethyl acetate with respect to the vinyl acetate product stream; and (d) hydrogenating vinyl acetate in the mixed sidestream to provide an ethyl acetate product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Advanced catalysts for fine chemical and pharmaceutical applications
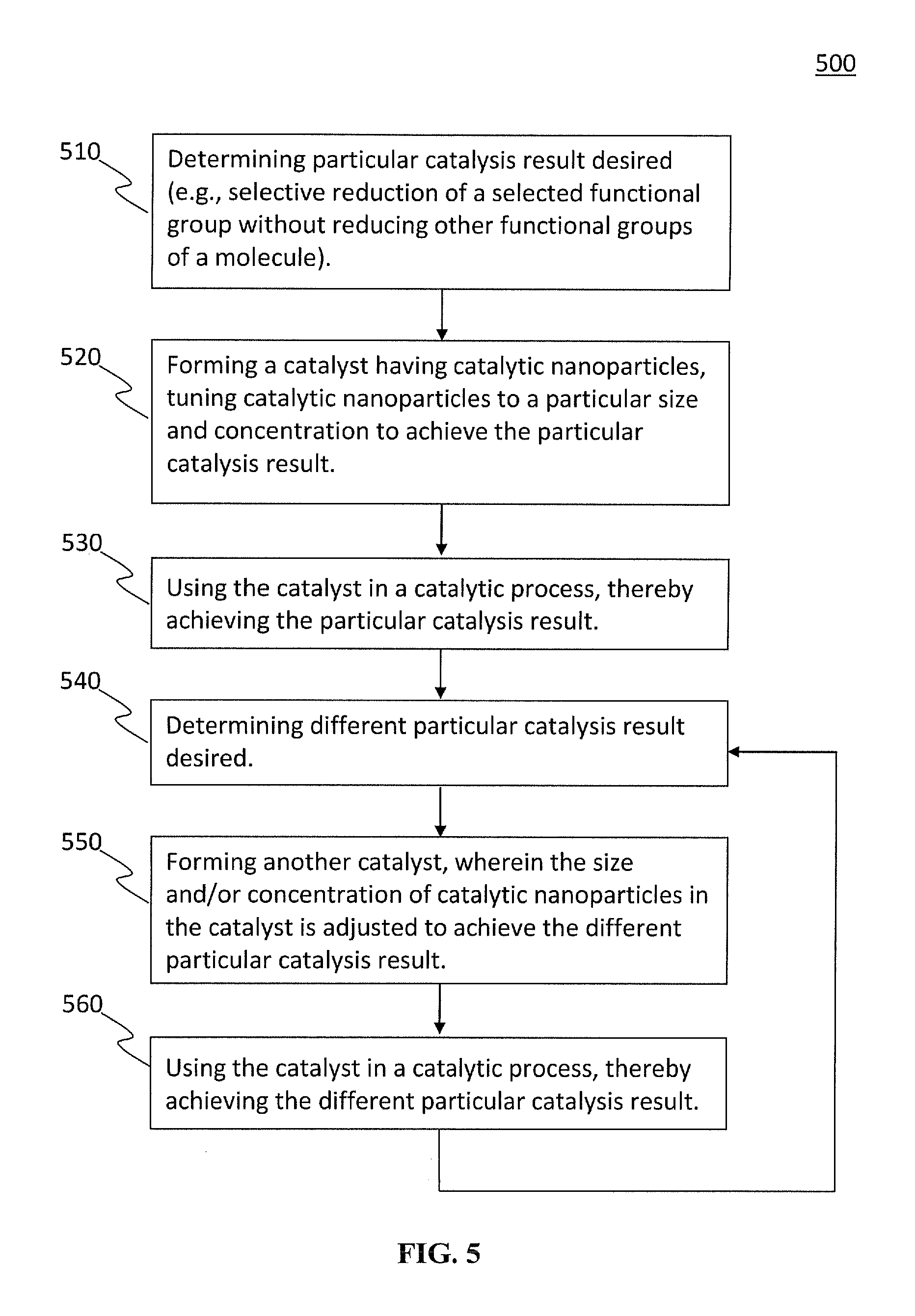
A catalyst comprising a plurality of support nanoparticles and a plurality of catalytic nanoparticles. At least one catalytic nanoparticle is bonded to each support nanoparticle. The catalytic particles have a size and a concentration, wherein a first configuration of the size and the concentration of the catalytic nanoparticles enables a first catalysis result and a second configuration of the size and the concentration of the catalytic nanoparticles enables a second catalysis result, with the first and second configurations having a different size or concentration, and the first and second catalysis results being different. In some embodiments, the first catalysis result is a selective reduction of a first selected functional group without reducing one or more other functional groups, and the second catalysis result is a selective reduction of a second selected functional group without reducing one or more other functional groups.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS
Process for the manufacture of base oil
ActiveUS20070299291A1Decreased global warming impactEmission reductionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDistillationHydrocarbon
A feedstock originating from renewable sources is converted to branched and saturated hydrocarbons without heteroatoms in the base oils distillation range by converting the fatty acids to olefins, which are subsequently oligomerised.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Popular searches
Biofuels Hydroxy compound preparation Fermentation Oxygen compounds preparation by reduction Waste based fuel Preparation by hydrogenolysis Carboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reaction Preparation by oxygen reduction Oxygen compounds purification/separation Hydroxy compound separation/purification
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com