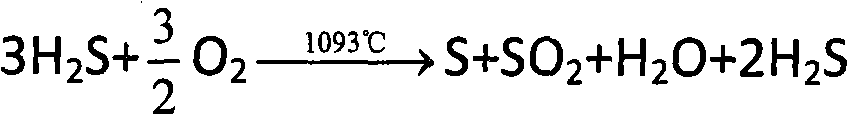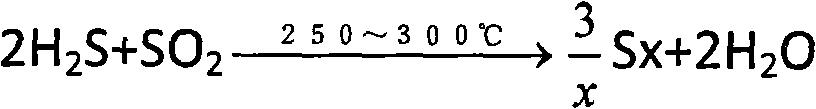Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
603 results about "Selective reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Selective reduction is the practice of reducing the number of fetuses in a multiple pregnancy, say quadruplets, to a twin or singleton pregnancy. The procedure is also called multifetal pregnancy reduction. The procedure is most commonly done to reduce the number of fetuses in a multiple pregnancy to a safe number, when the multiple pregnancy is the result of use of assisted reproductive technology; outcomes for both the mother and the babies are generally worse, the higher the number of fetuses. The procedure is also used in multiple pregnancies when one of the fetuses has a serious and incurable disease, or in the case where one of the fetuses is outside the uterus, in which case it is called selective termination.
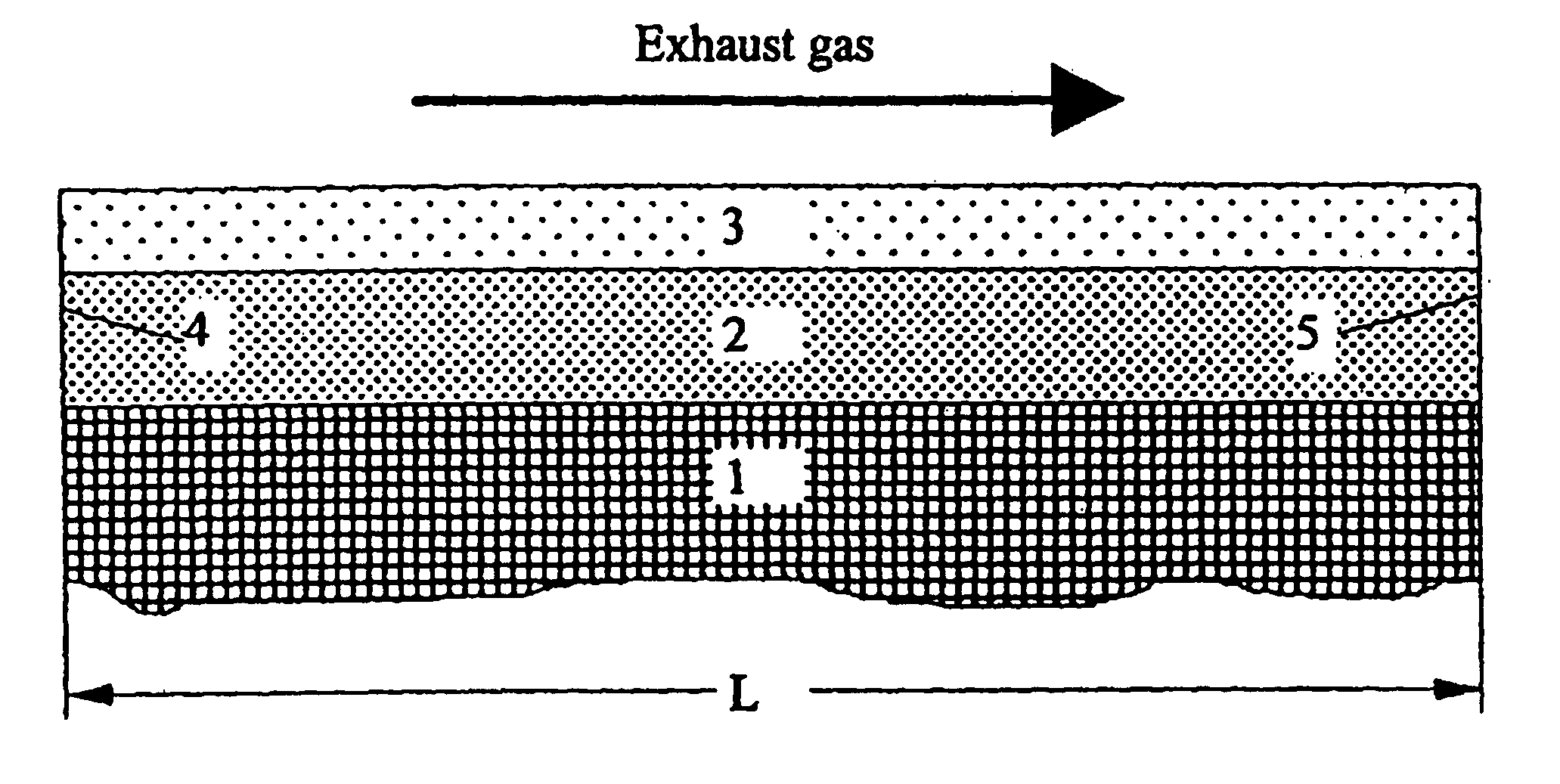
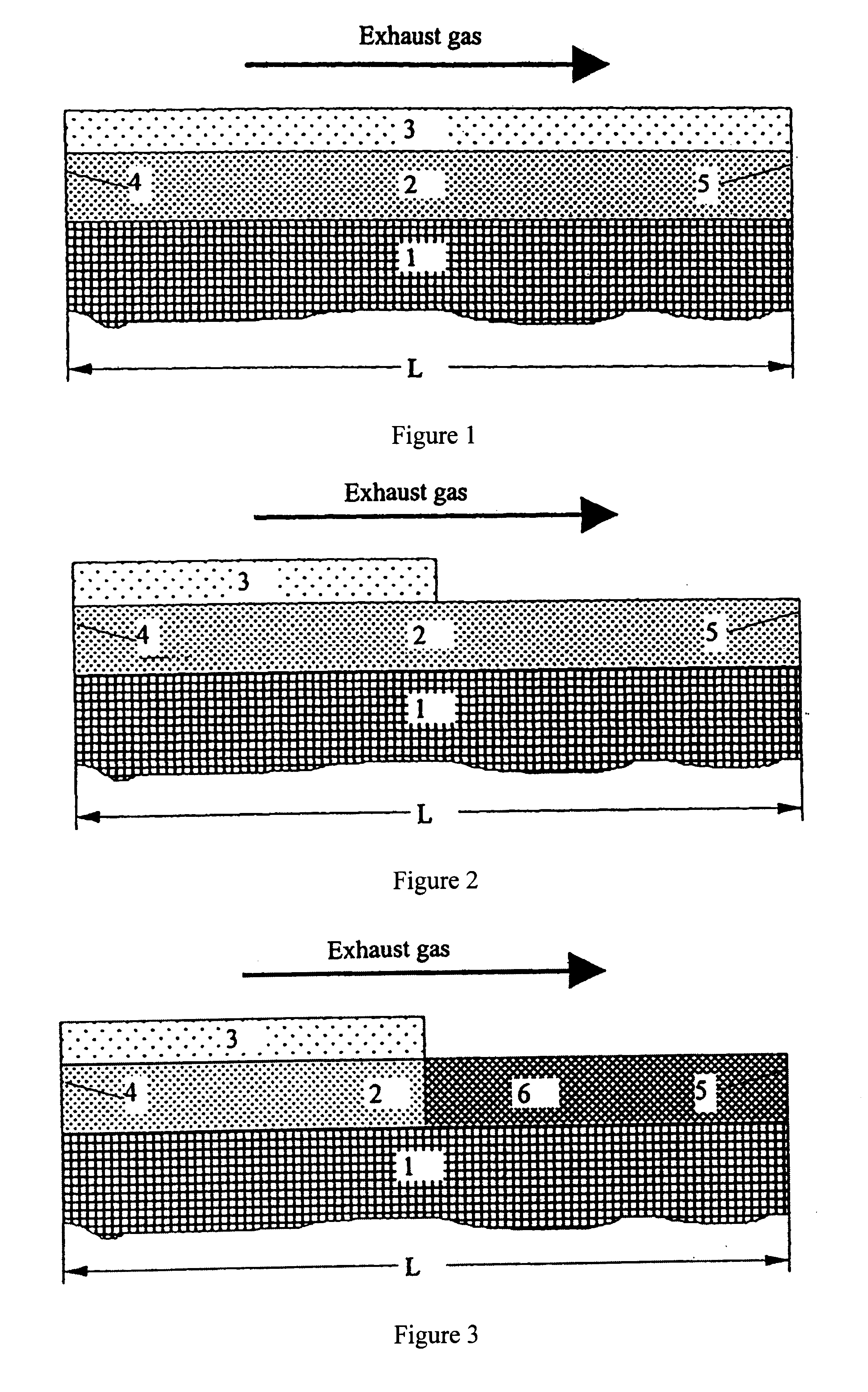
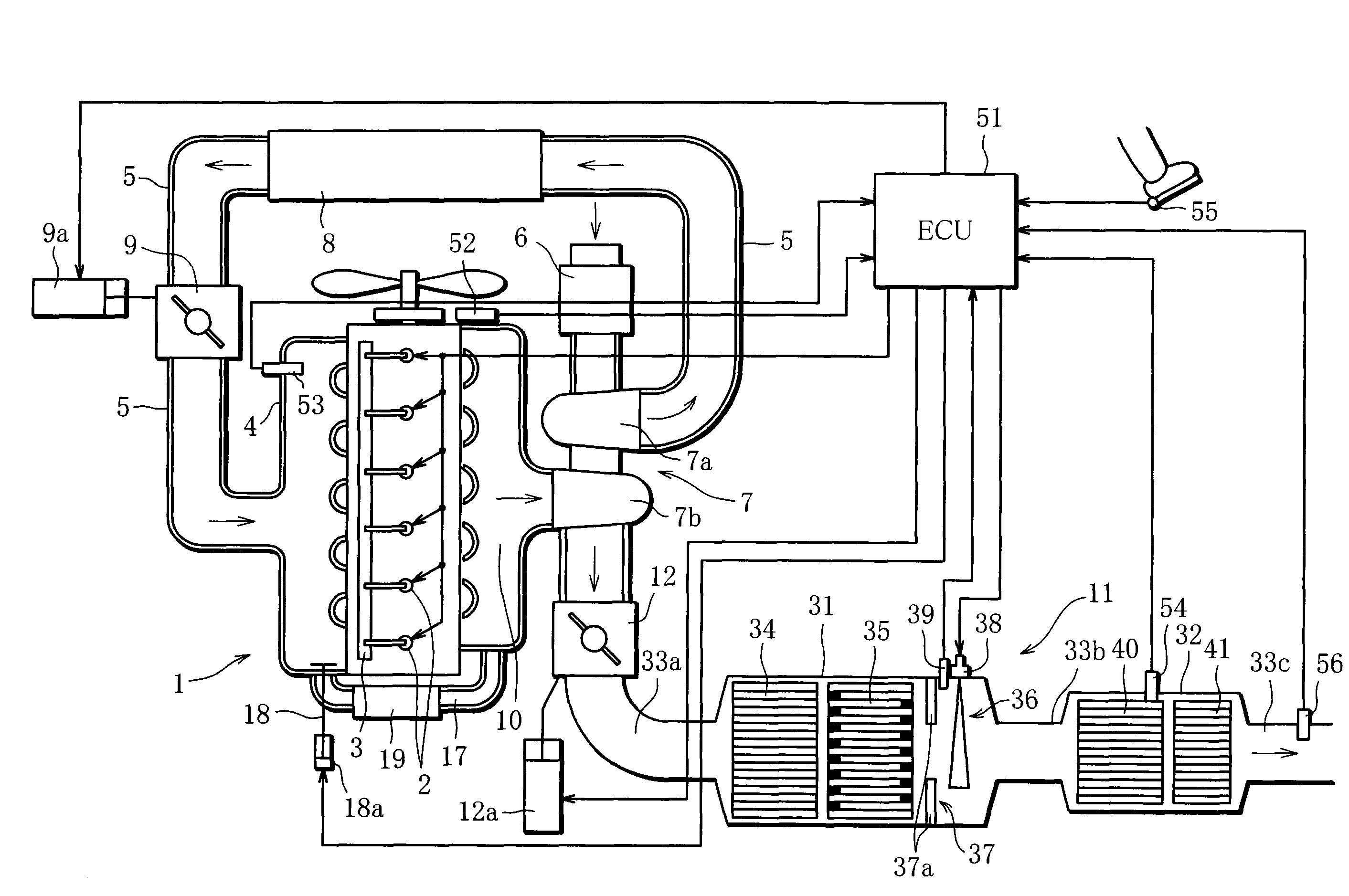
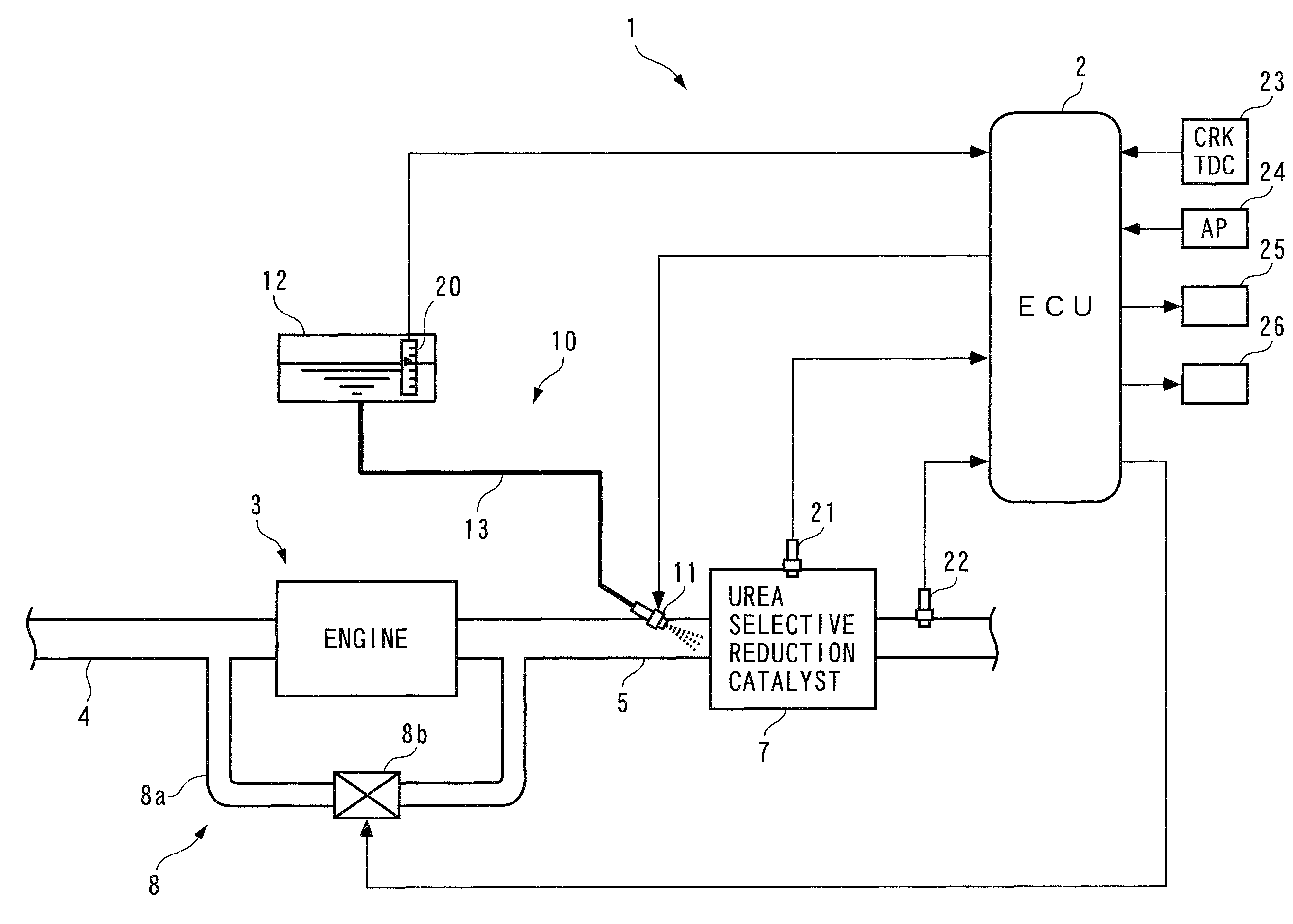
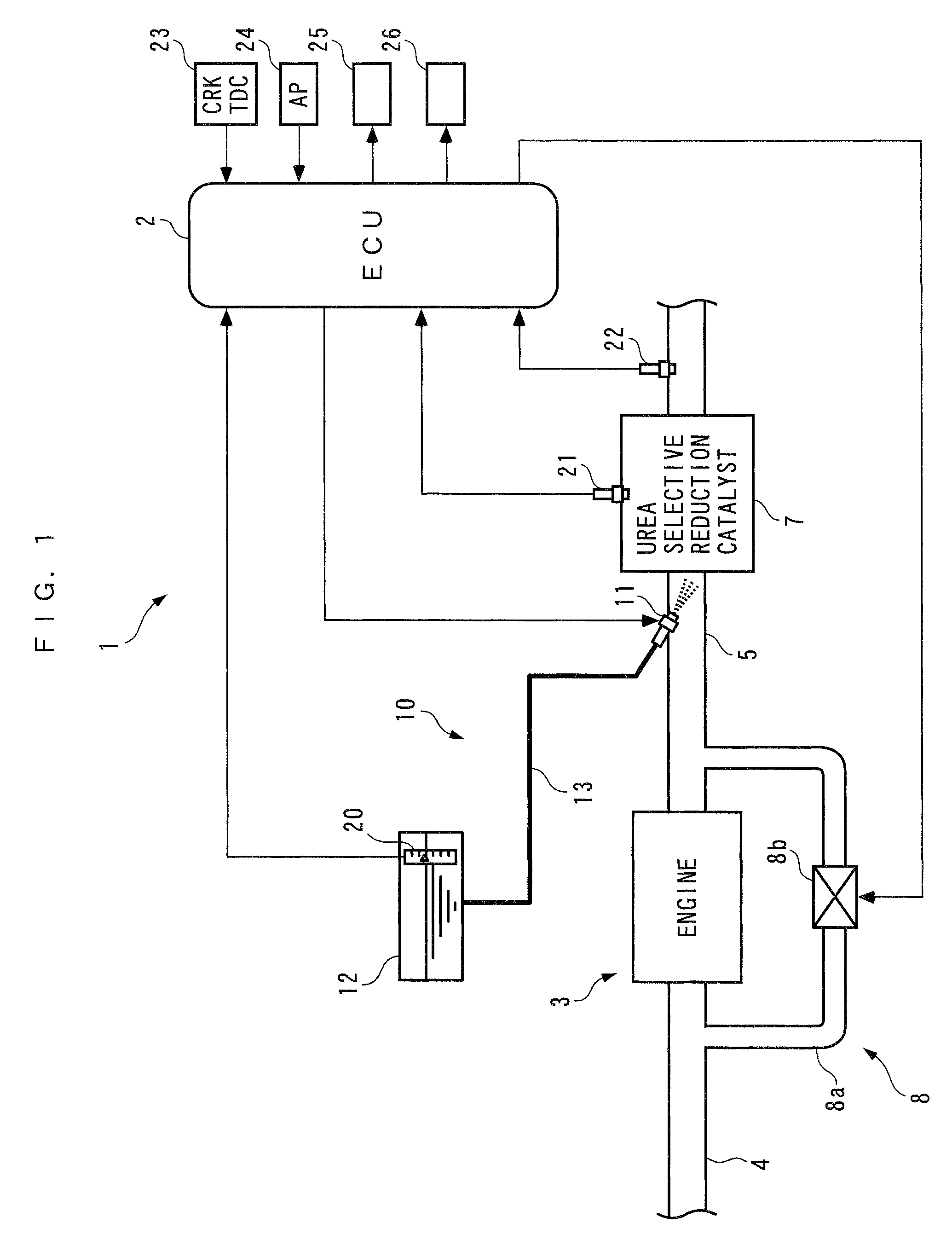
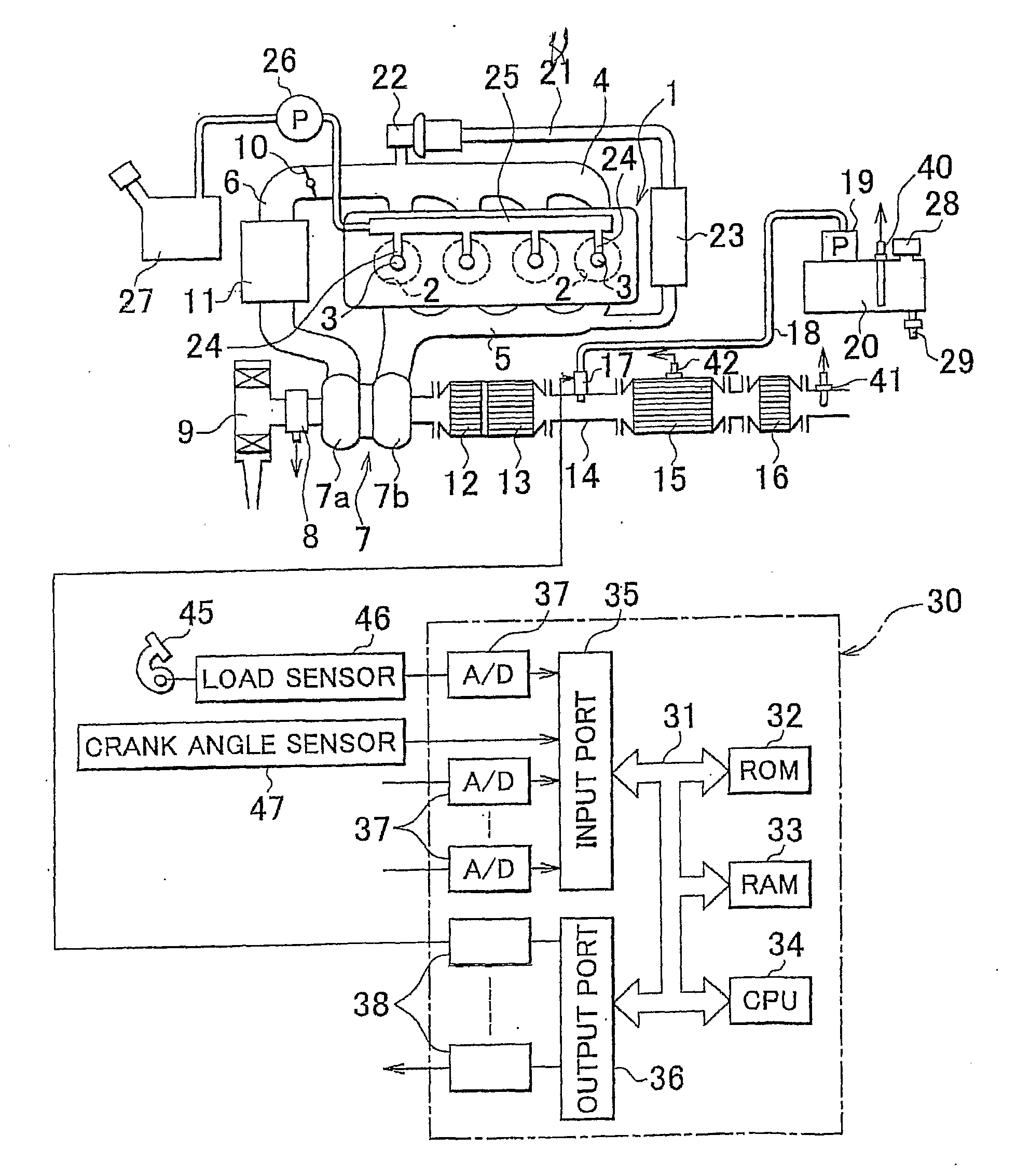
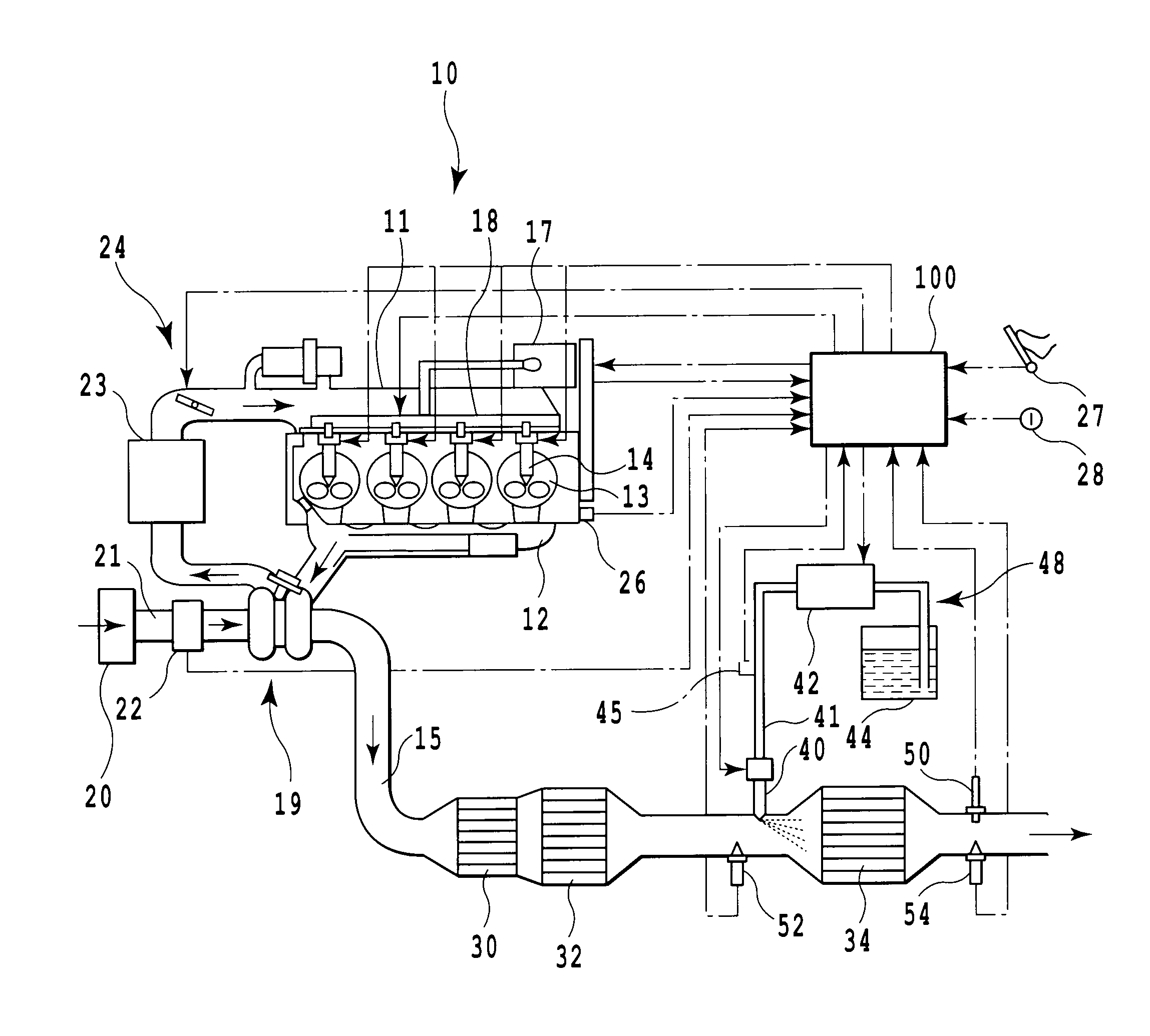
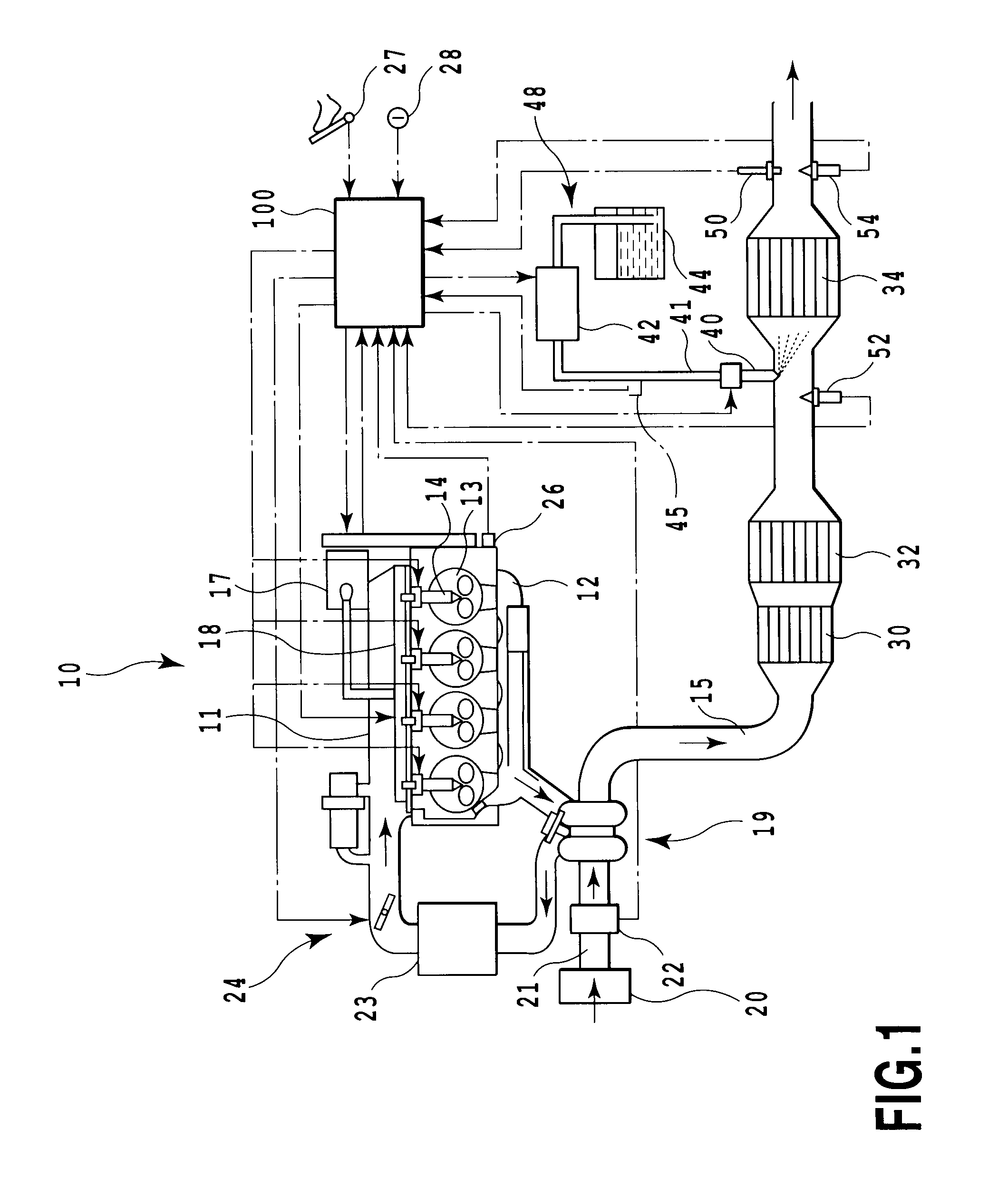
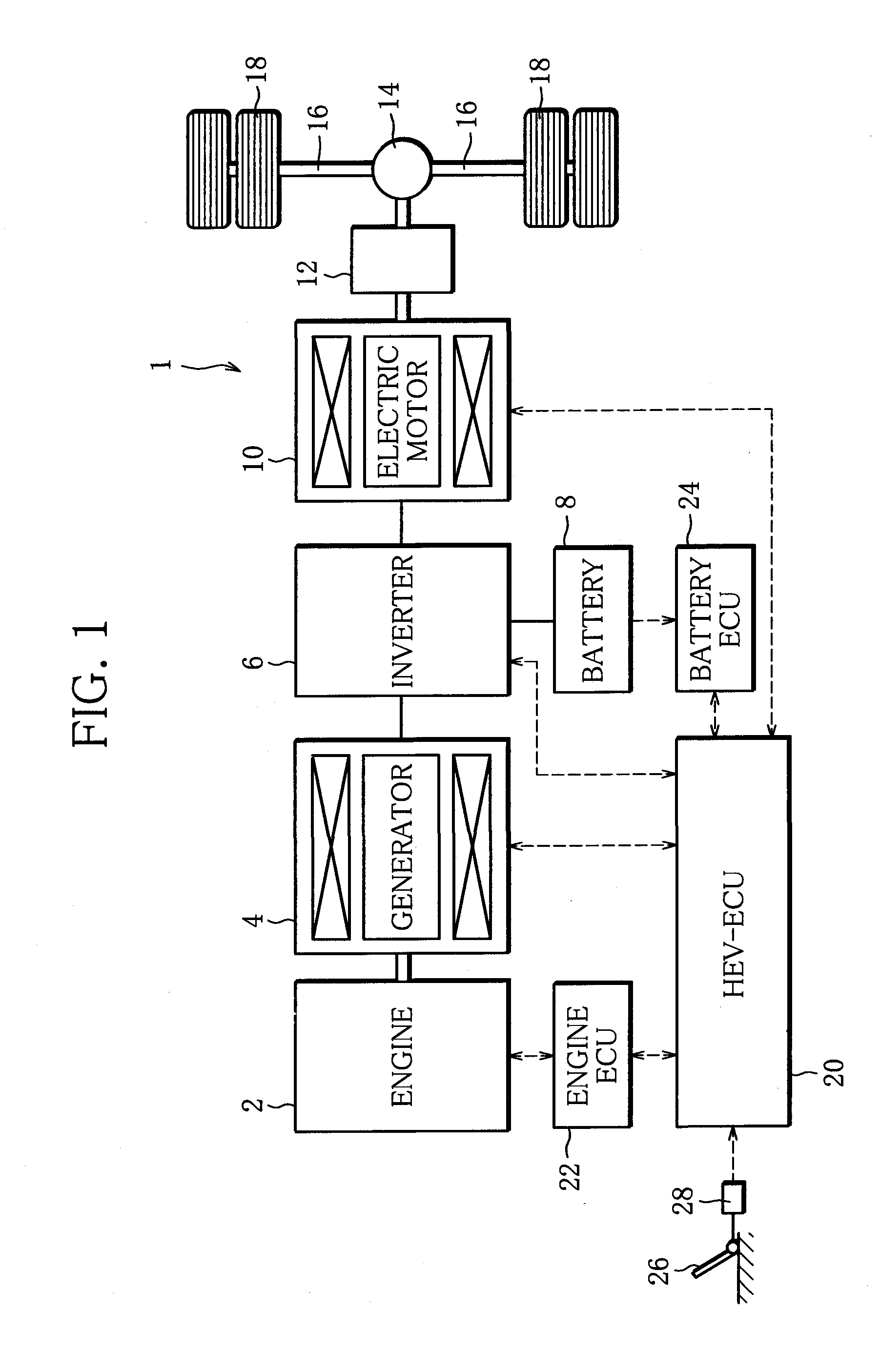
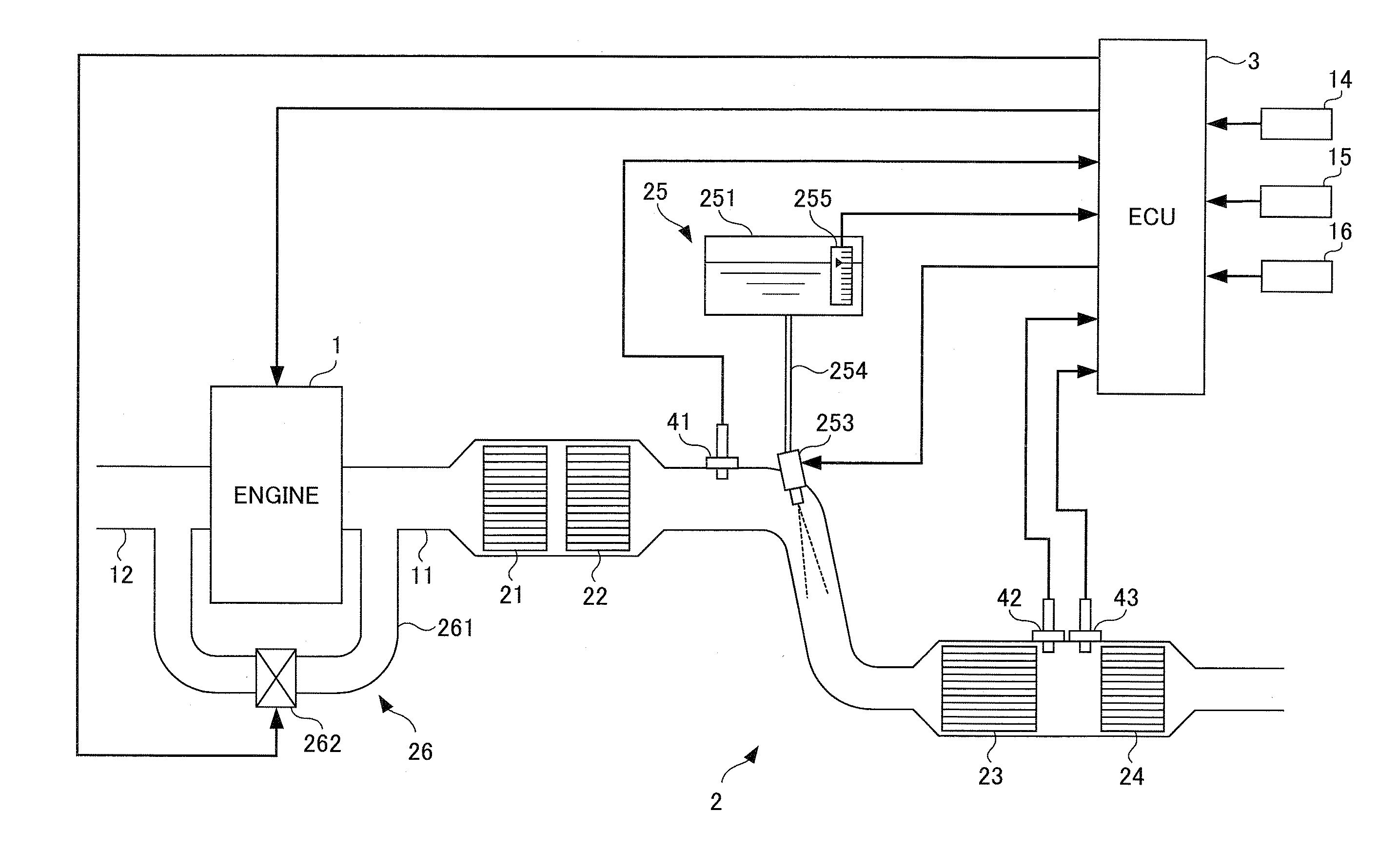
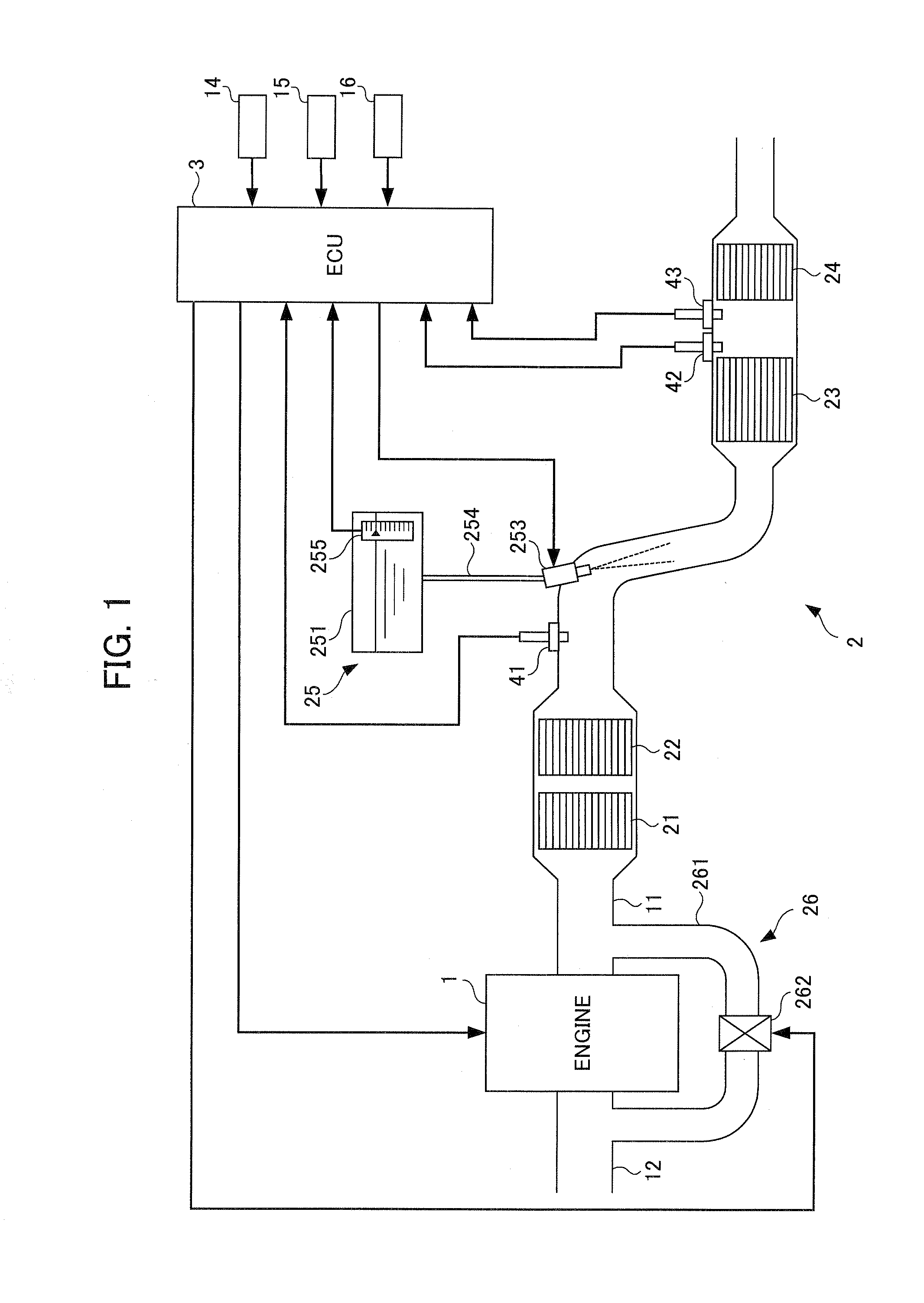
Exhaust emission control device
ActiveUS20090313979A1Well mixedIncrease flow rateGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesEnvironmental engineering
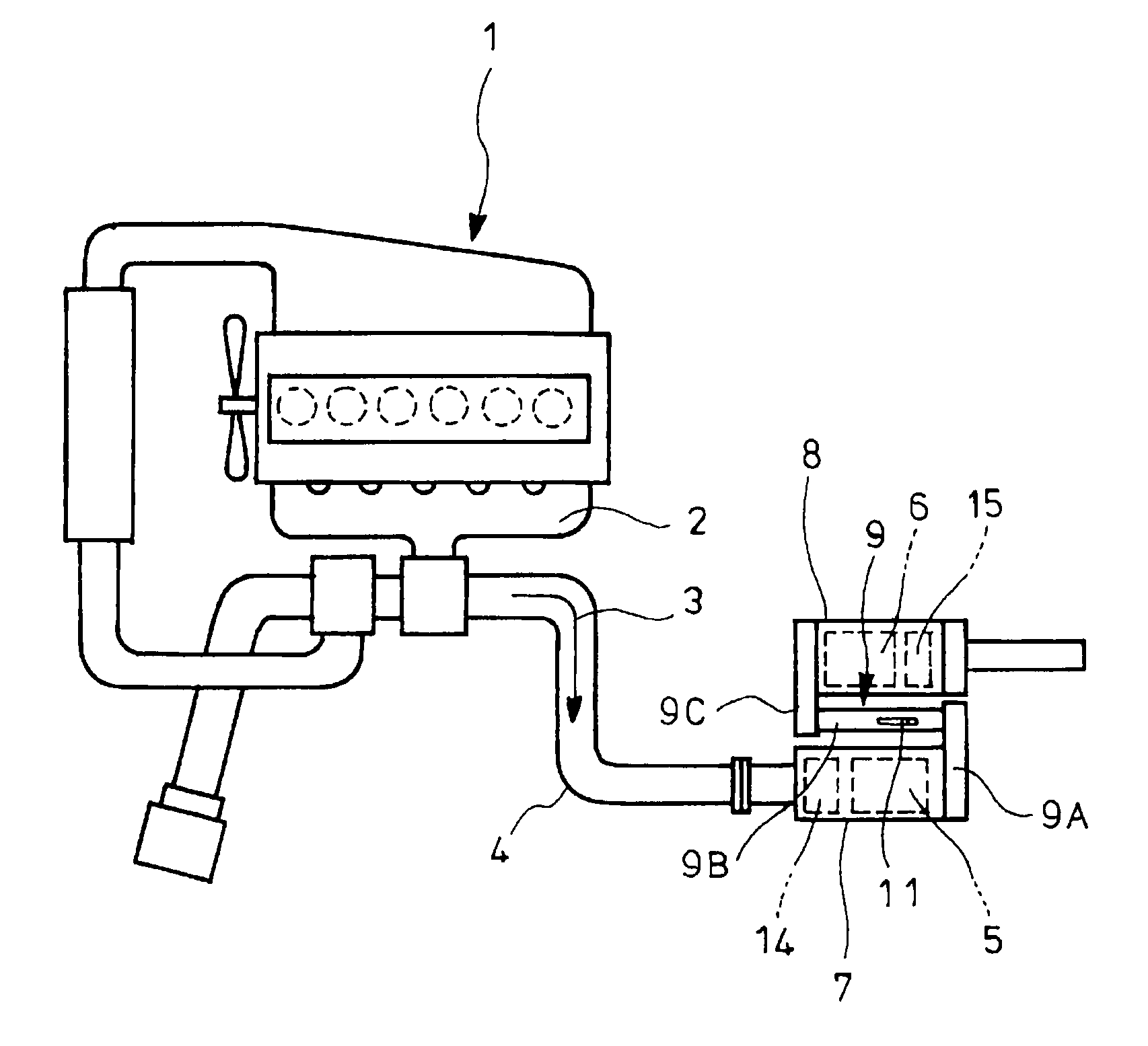
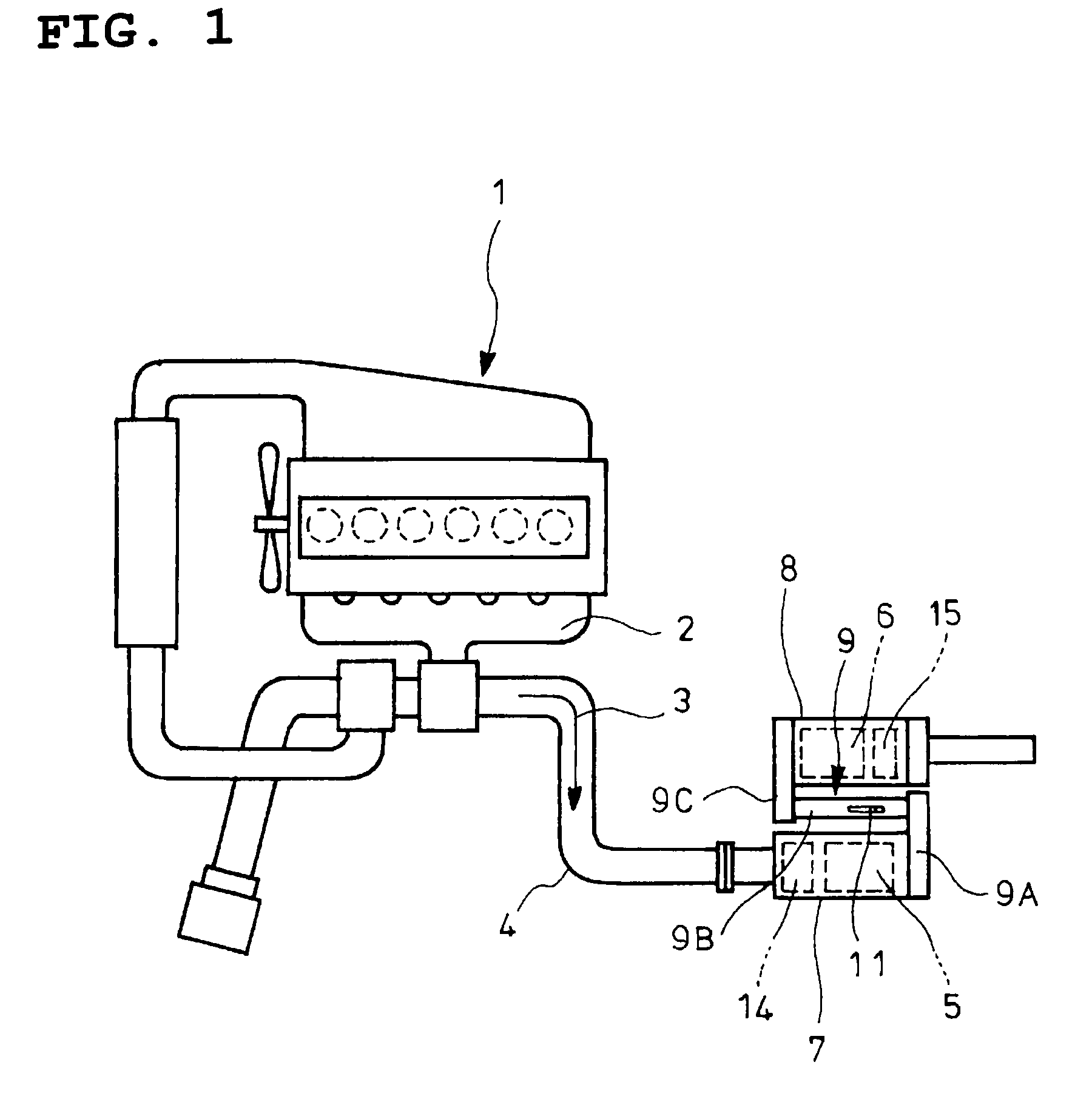
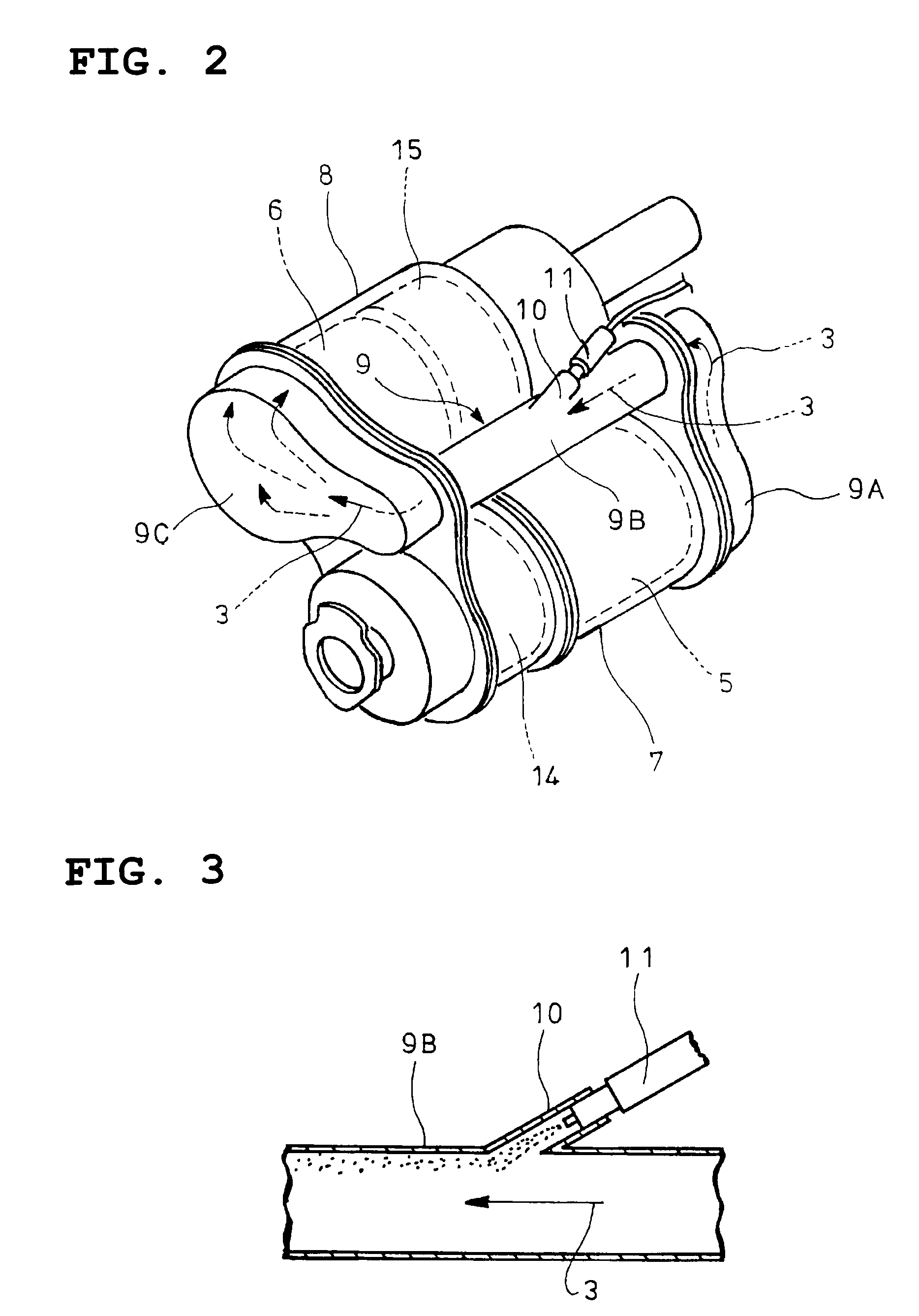
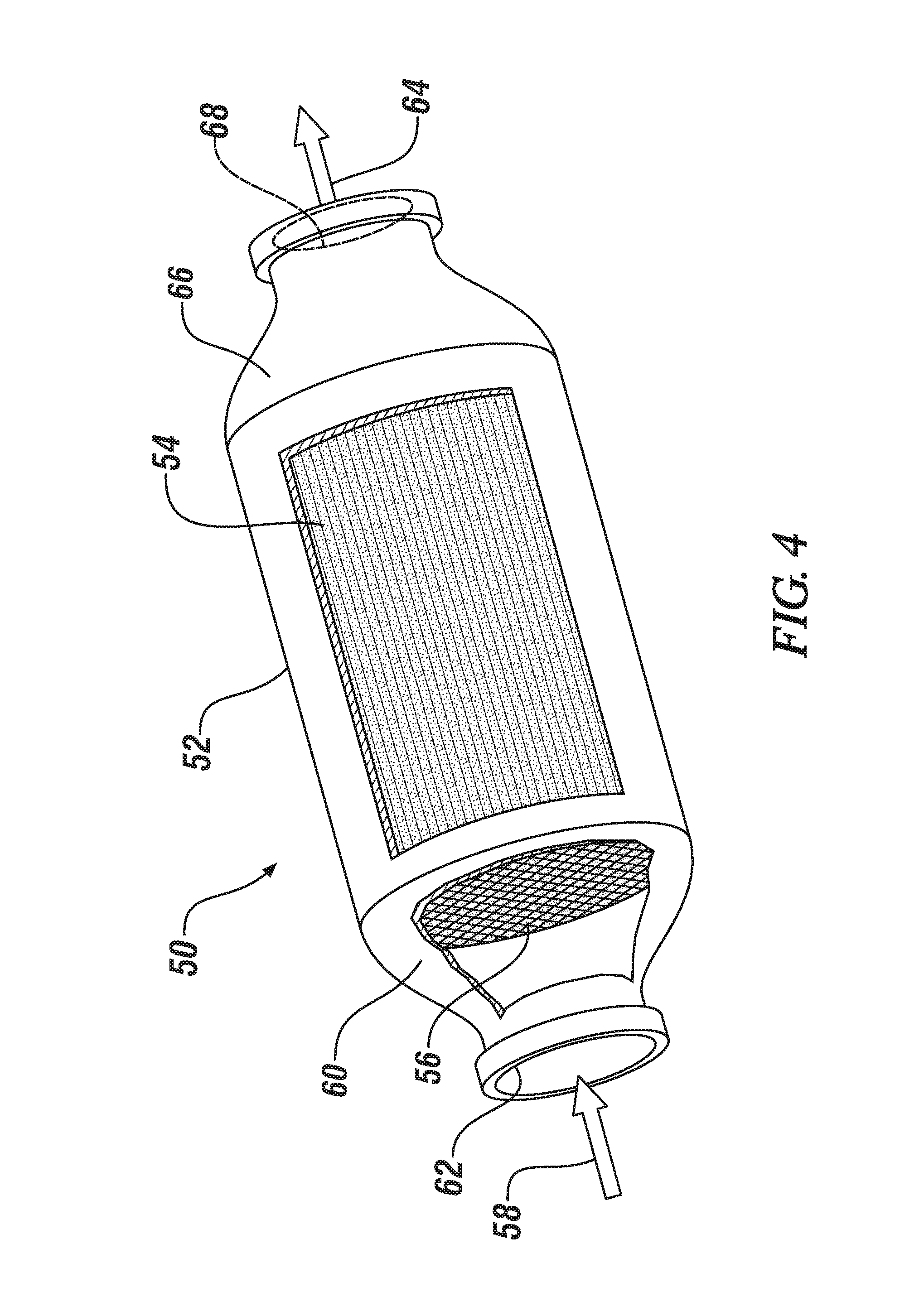
An exhaust emission control device has a particulate filter 5 and a selective reduction catalyst 6 arranged side by side. An S-shaped communication passage 9 is arranged for introduction of exhaust gas 3 from a rear end of the filter 5 to a front end of the adjacent catalyst 6 in a forward fold-back manner and with a urea water addition injector 11 arranged midway of the passage 9. In order to satisfactorily disperse the urea water with enhanced mixing with the exhaust gas 3 even if the flow rate is increased, slits 12 are formed in circumferentially spaced positions on a rear end of a mixing pipe 9B constituting an upstream portion of the communication passage 9 so as to introduce the exhaust gas 3. A downstream end 9a of a gas gathering chamber 9A is connected to the rear end of the mixing pipe 9B such that the slits 12 are encased and the rear end of the mixing pipe 9B is closed.
Owner:HINO MOTORS LTD
Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation method and apparatus with improved dosing
InactiveUS6955642B1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMagnetic field amplitudeTreatment duration
A noninvasive method and apparatus for treating living tissue with pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) having selectively reduced high-frequency signal components, with improved bioresponse provided by magnetic field amplitudes less than approximately 40 μT, and most preferably in the range of 4–10 μT. Such amplitude levels for the disclosed PEMF signal are particularly effective with a treatment duration in the range of 0.25–2 hours / day.
Owner:EUROPEAN BIOINFORMATICS INSTITUTE
Advanced catalysts for fine chemical and pharmaceutical applications
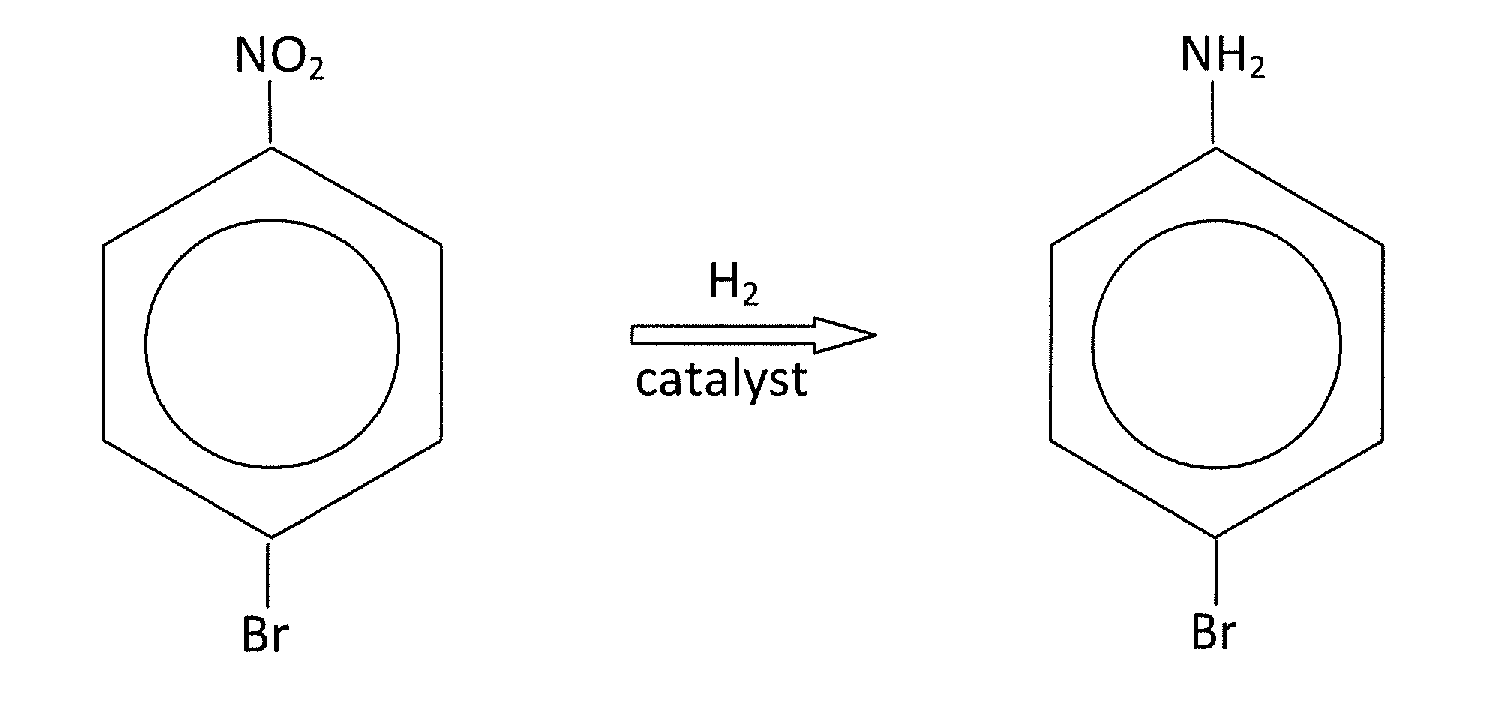
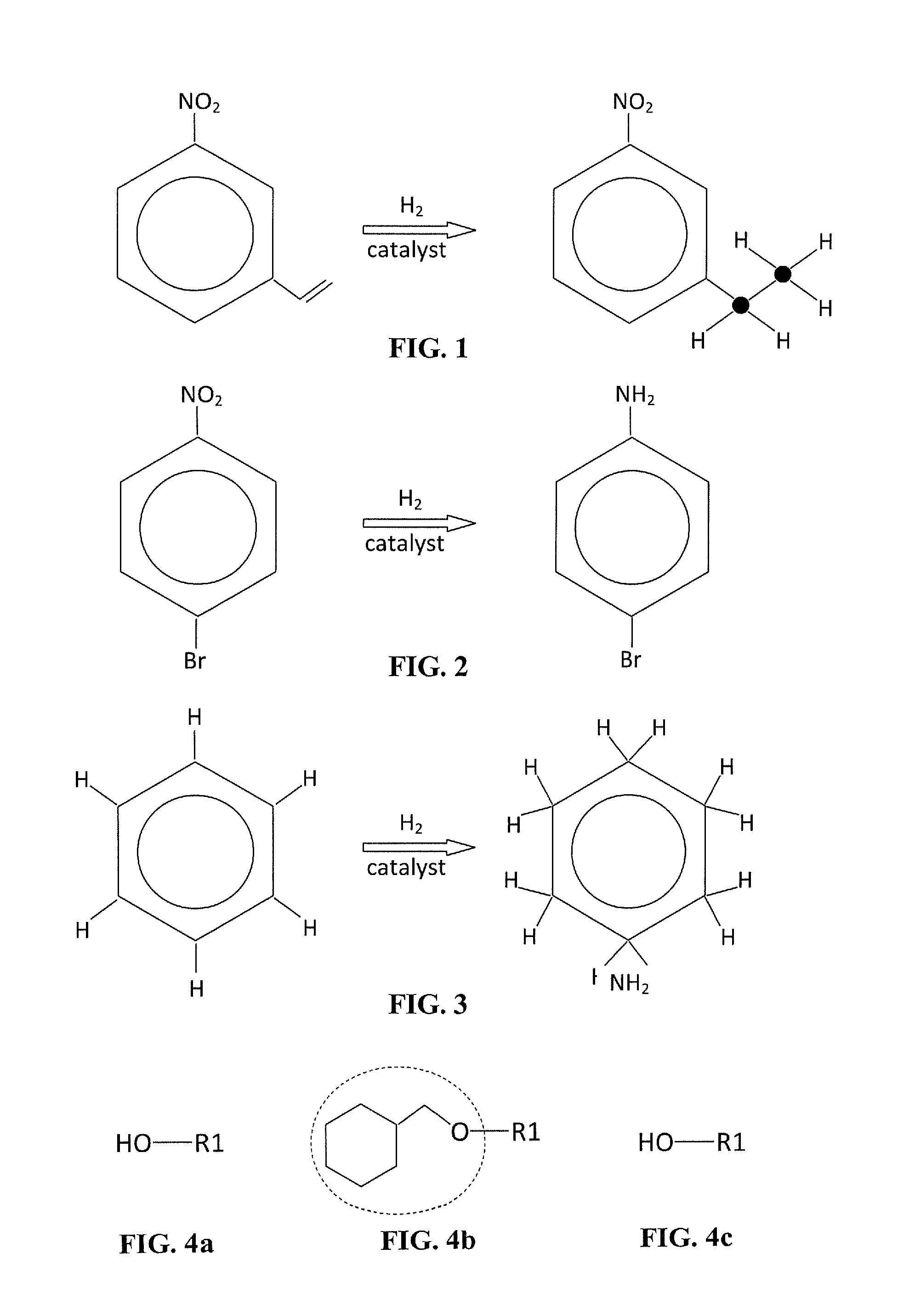
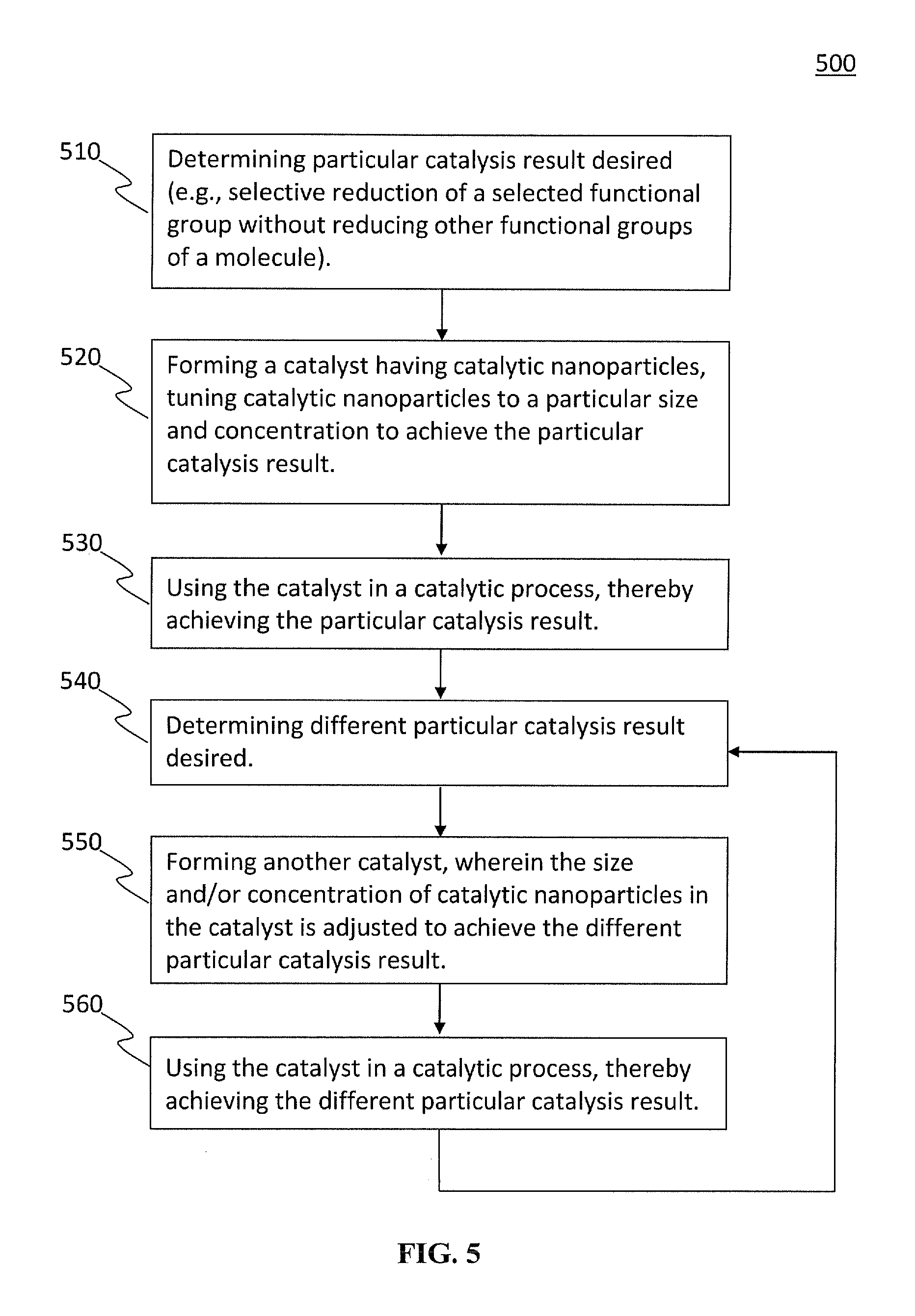
A catalyst comprising a plurality of support nanoparticles and a plurality of catalytic nanoparticles. At least one catalytic nanoparticle is bonded to each support nanoparticle. The catalytic particles have a size and a concentration, wherein a first configuration of the size and the concentration of the catalytic nanoparticles enables a first catalysis result and a second configuration of the size and the concentration of the catalytic nanoparticles enables a second catalysis result, with the first and second configurations having a different size or concentration, and the first and second catalysis results being different. In some embodiments, the first catalysis result is a selective reduction of a first selected functional group without reducing one or more other functional groups, and the second catalysis result is a selective reduction of a second selected functional group without reducing one or more other functional groups.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS
Structured catalysts for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides by ammonia using a compound that can be hydrolyzed to ammonia
InactiveUS20020025905A1Shorten the lengthImprove catalytic performanceCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsCatalytic functionNitrogen oxide
A structured catalyst for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia using an ammonia-supplying compound. The catalyst is preferably used for exhaust gas treatment of diesel vehicles powered by diesel motors. The catalyst is characterized by the fact that it contains a reduction catalyst for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia and a hydrolysis catalyst for the hydrolysis of urea, where the hydrolysis catalyst is applied in the form of a coating onto the reduction catalyst. By this arrangement of the two catalytic functions in one catalyst the exhaust gas system can be made very compactly and space saving. Moreover, advantageous synergistic effects result from the direct contact of the hydrolysis catalyst and the reduction catalyst.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
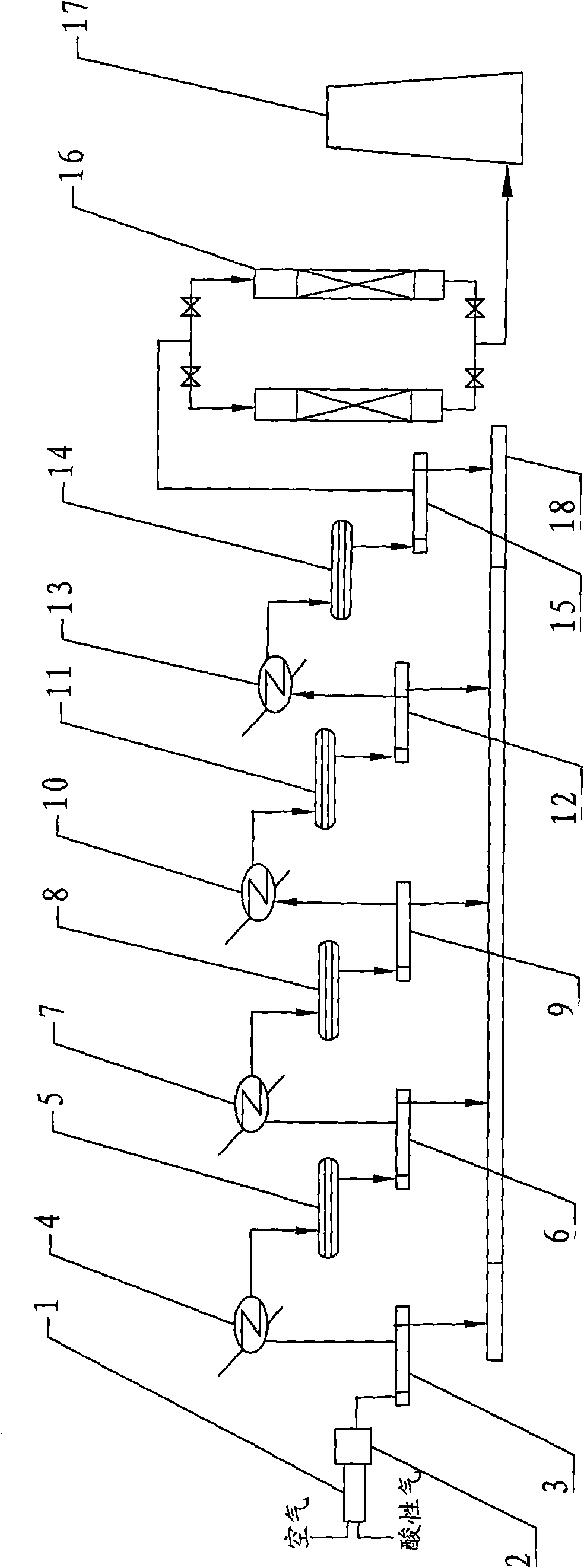
Catalyst combination process of sulfur recovering device
ActiveCN101659400AMeet the requirements of total sulfur recoveryAchieve complete hydrolysisPhysical/chemical process catalystsSulfur preparation/purificationCombustionSulfur
The invention relates to a catalyst combination process of a sulfur recovering device, belonging to the technical field of sulfur recovery, and comprising a combustion furnace, a primary clotz reactorand a secondary clotz reactor connected in series with each other. The catalyst combination process is characterized in that: behind the secondary clotz reactor, a selective hydrogenation reduction reactor, a selective oxidation reactor and two absorption desulfurizing towers connected in parallel are connected in series; a deoxygenation protection-type sulfur recovery catalyst is filled in the upper part of the primary clotz reactor, and a TiO2 sulfur recovery catalyst is filled in the lower part; an auxiliary agent type sulfur recovery catalyst is filled in the secondary clotz reactor; a SO2 selective reduction catalyst is filled in the selective hydrogenation reduction reactor and selectively reduces the SO2 into elemental sulfur; H2S selective oxidation catalyst is filled in the selective oxidation reactor and selectively oxidizes the H2S into elemental sulfur. In the invention, the recovery rate of sulfur is high, and the tail gas after desulfuration can completely reach the national discharge requirement of GB16297-1996.
Owner:山东迅达化工集团有限公司
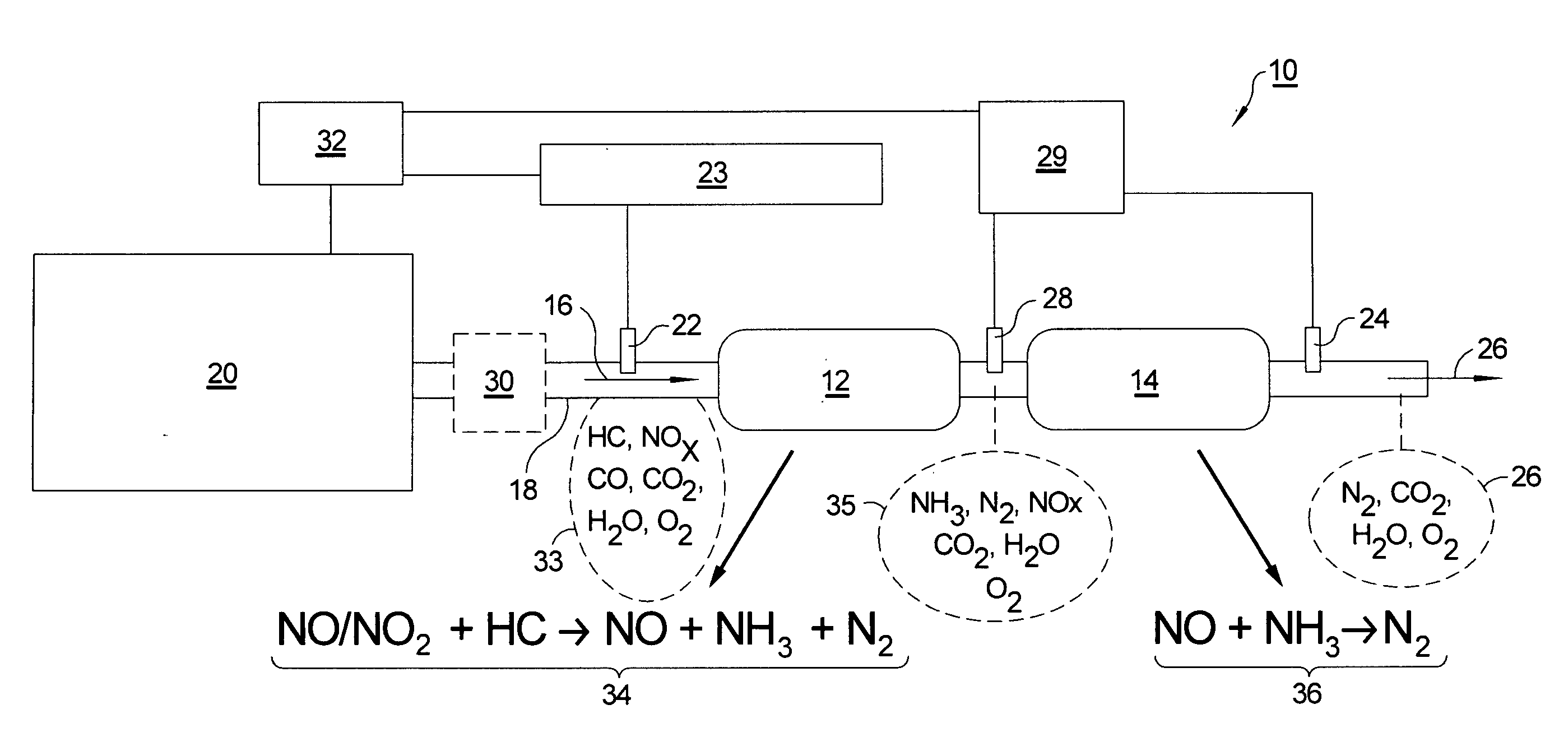
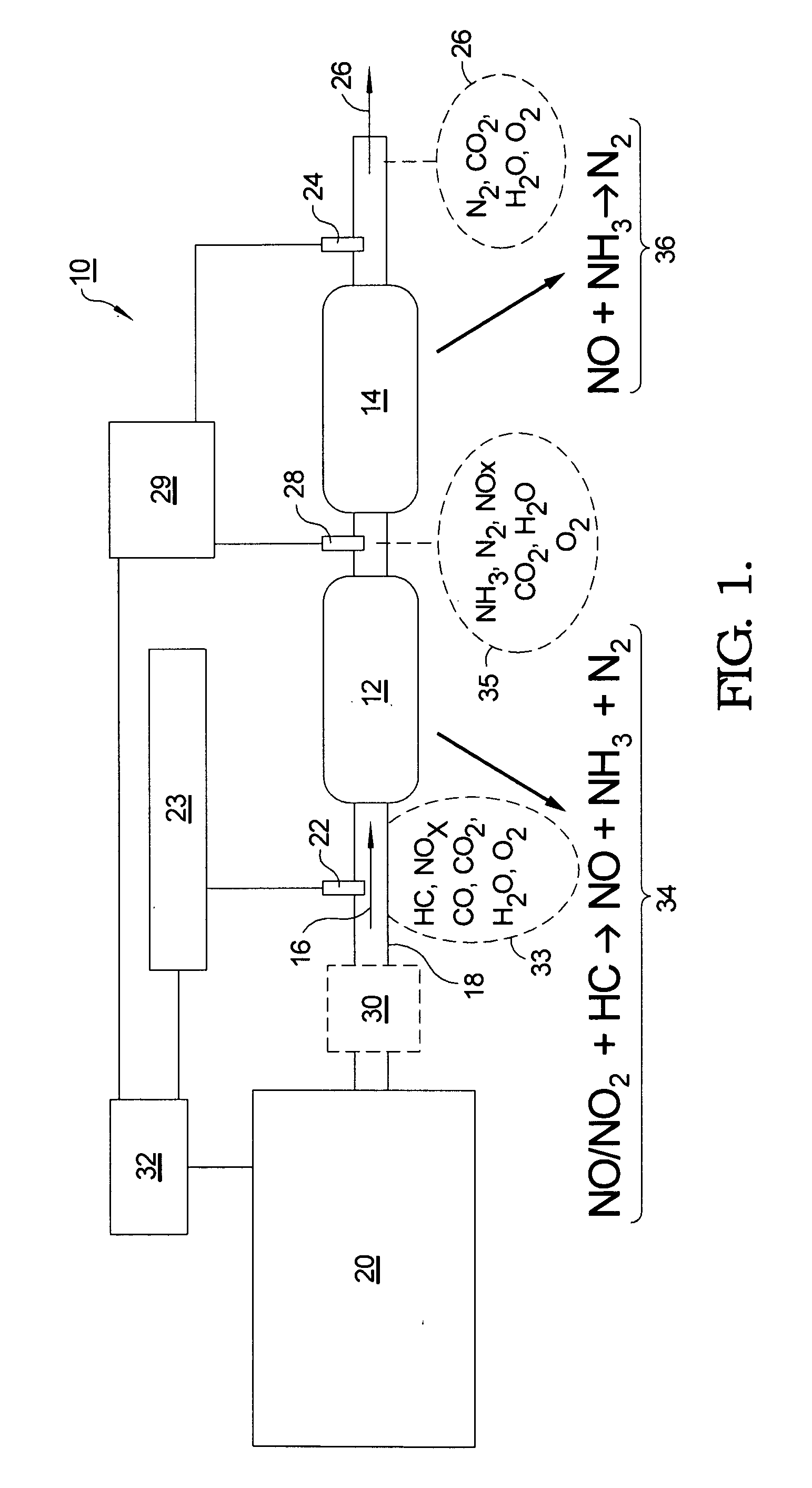
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for internal combustion engine, and engine control unit
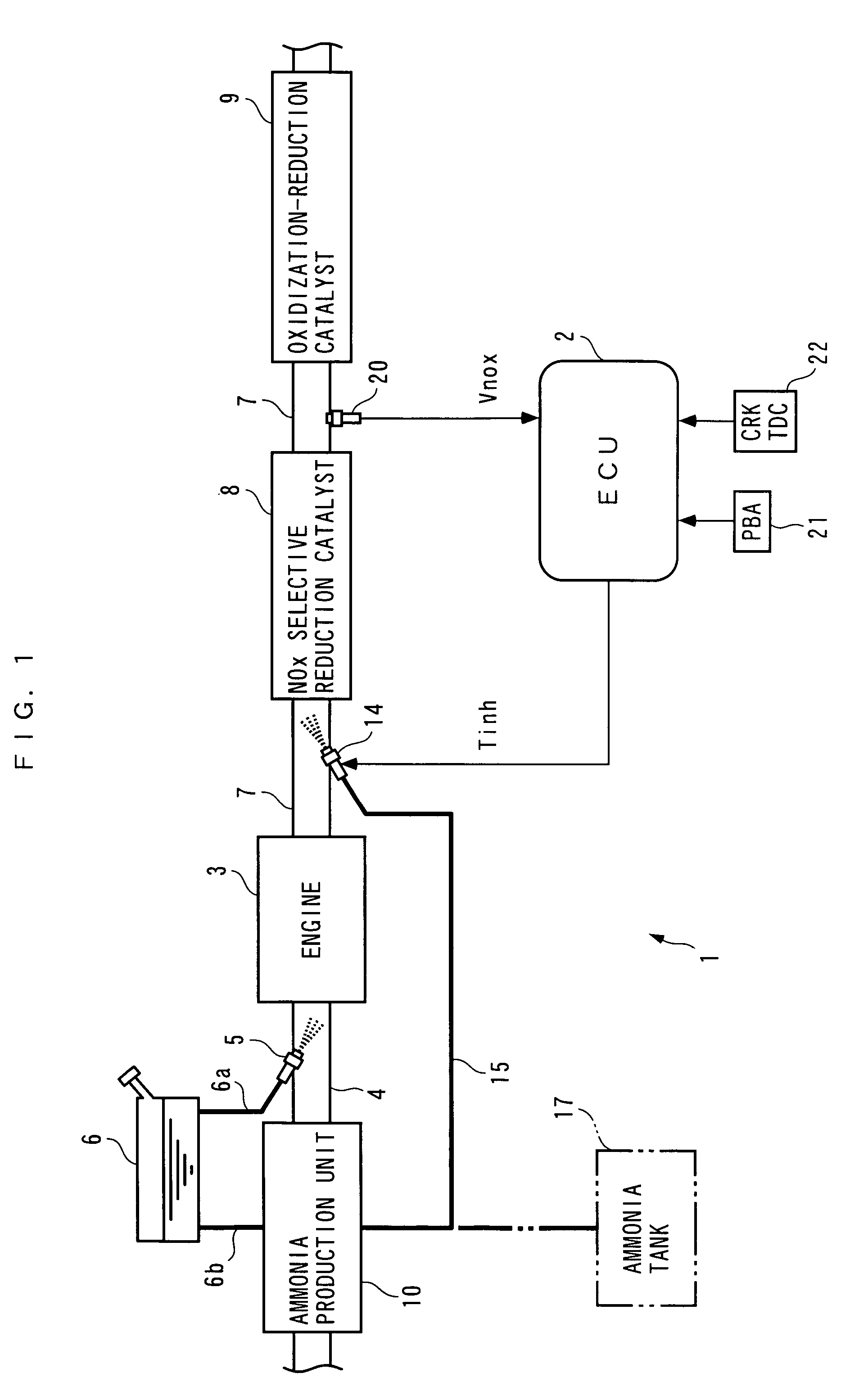
InactiveUS7204081B2Accurate detectionReduce supplyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia productionExhaust fumes
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
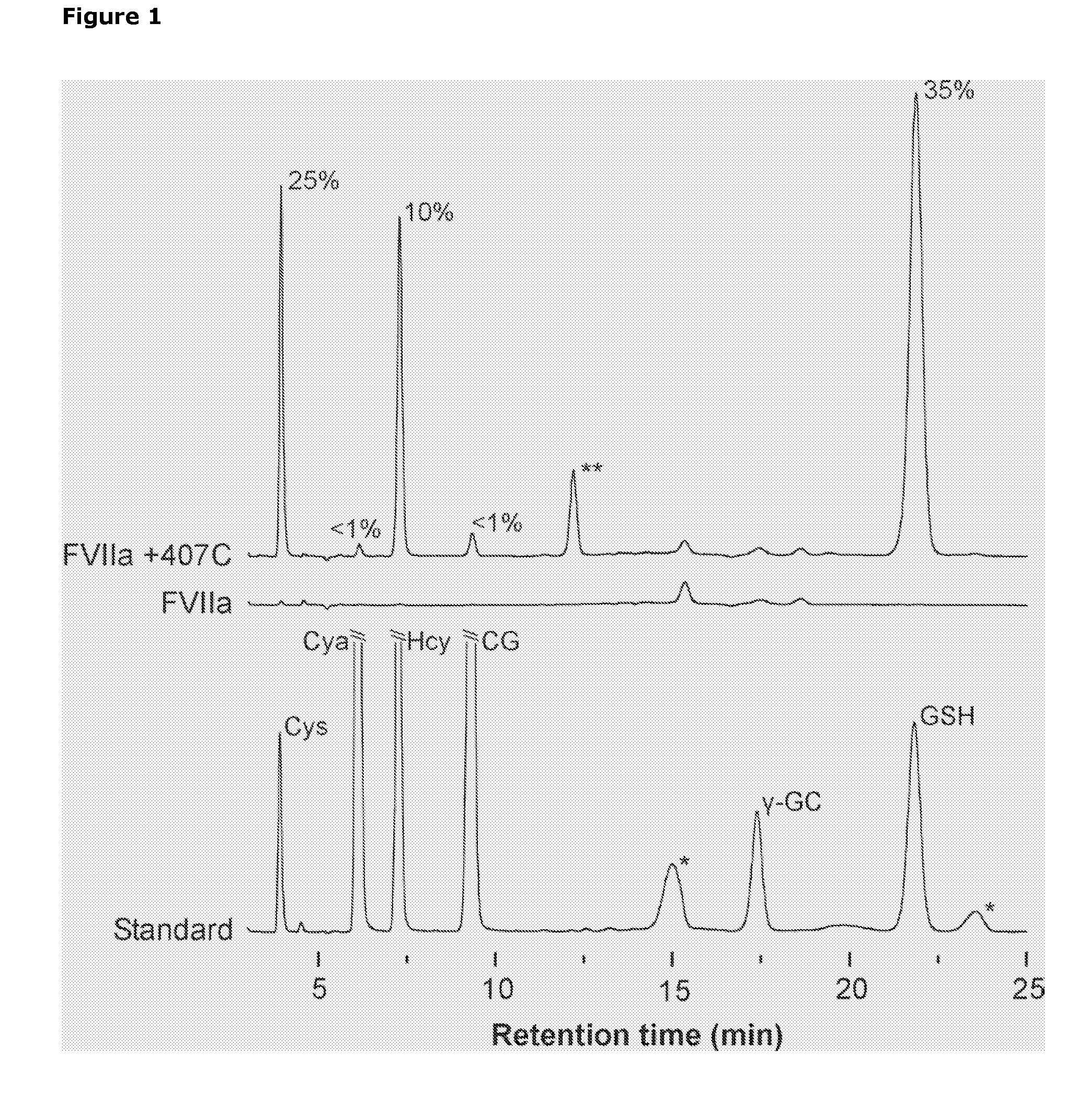
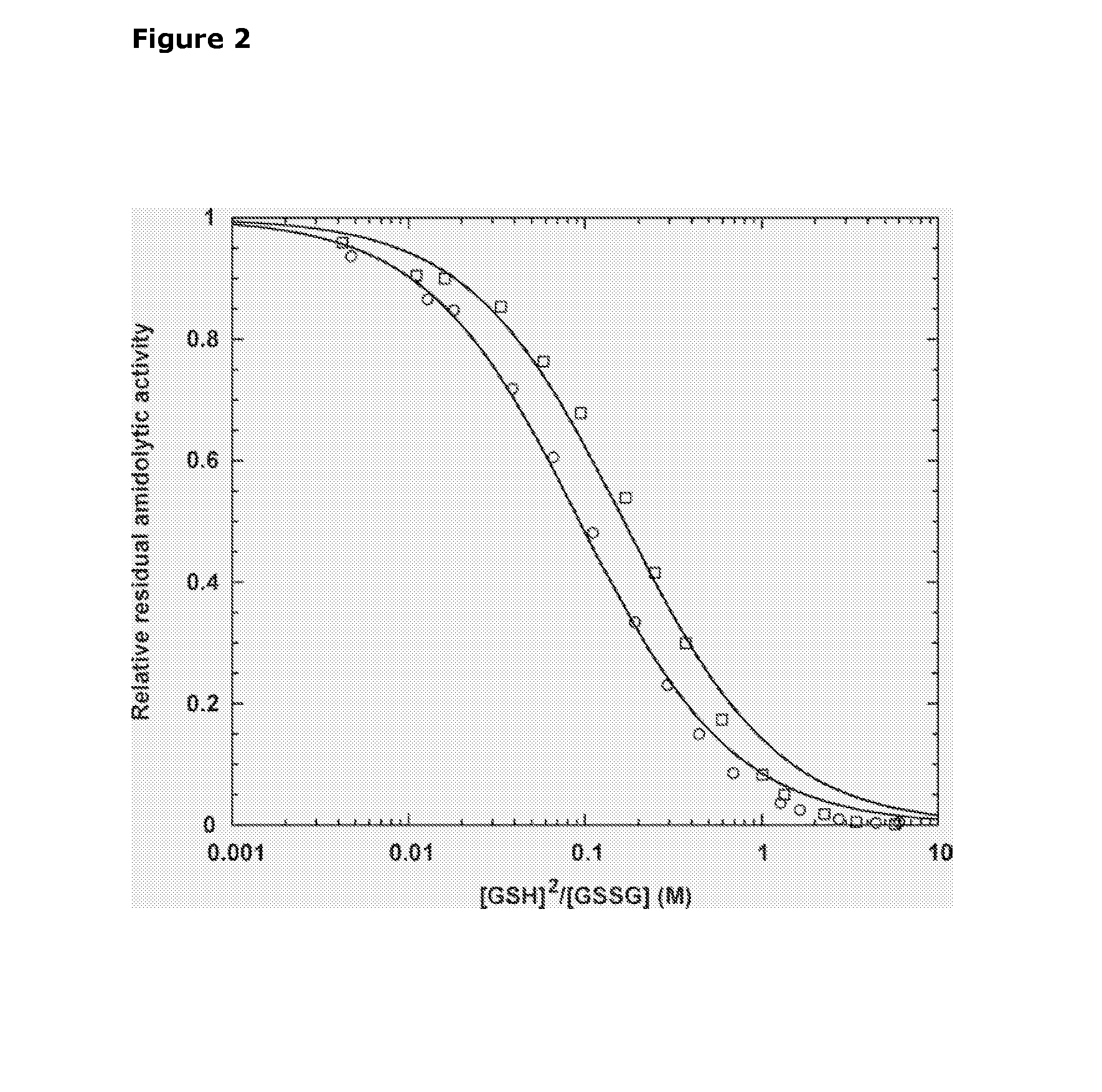
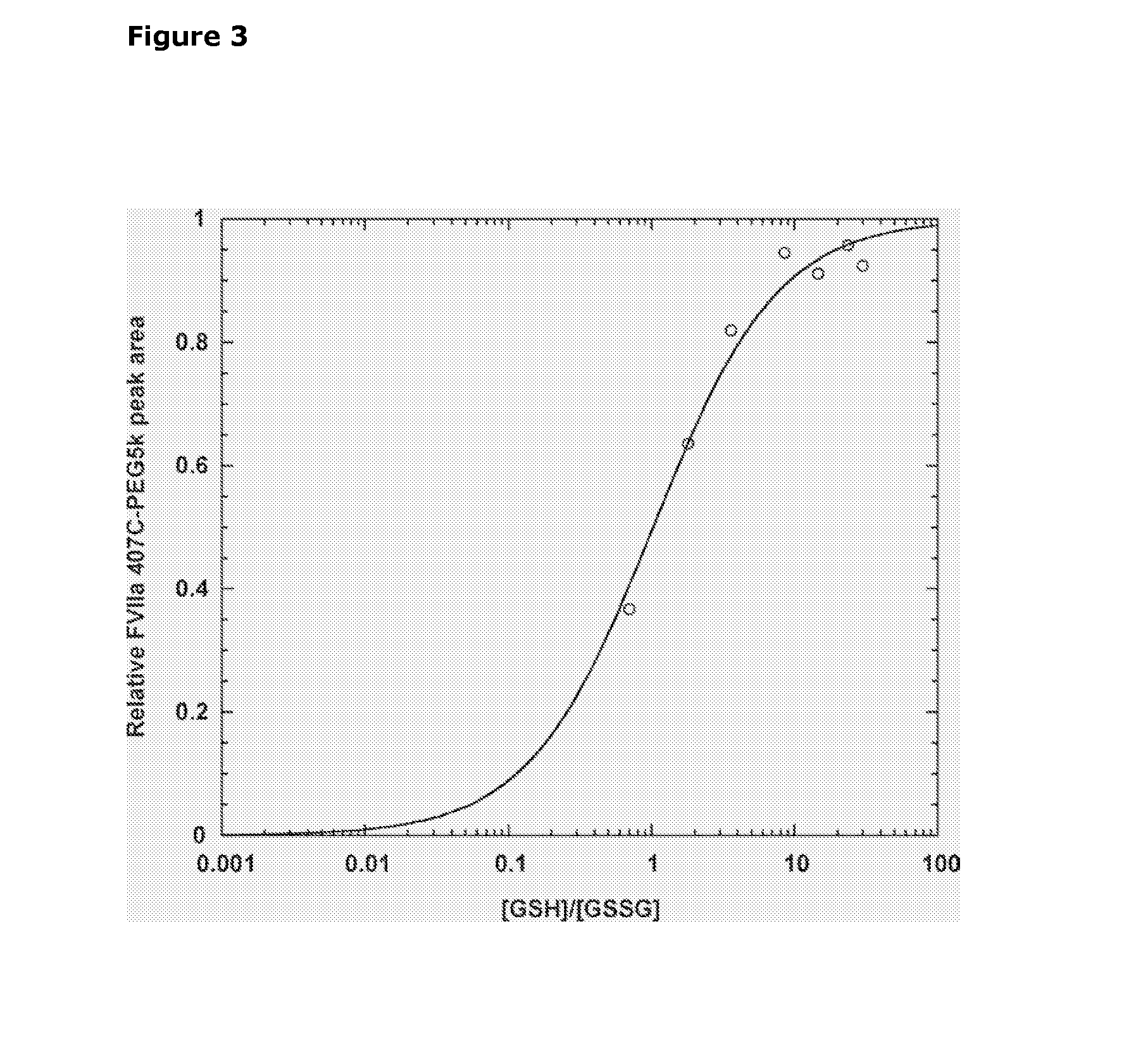
Selective Reduction and Derivatization of Engineered Proteins Comprising at Least One Non-Native Cysteine
InactiveUS20080200651A1Reduce decreasePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsRedoxDerivatization
The present invention relates to method for selective reduction and derivatization of recombinantly prepared engineered proteins comprising at least one non-native cysteine, wherein the reduction reaction is conducted in the presence of a redox buffer or in the presence of a triarylphosphine reducing agent.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
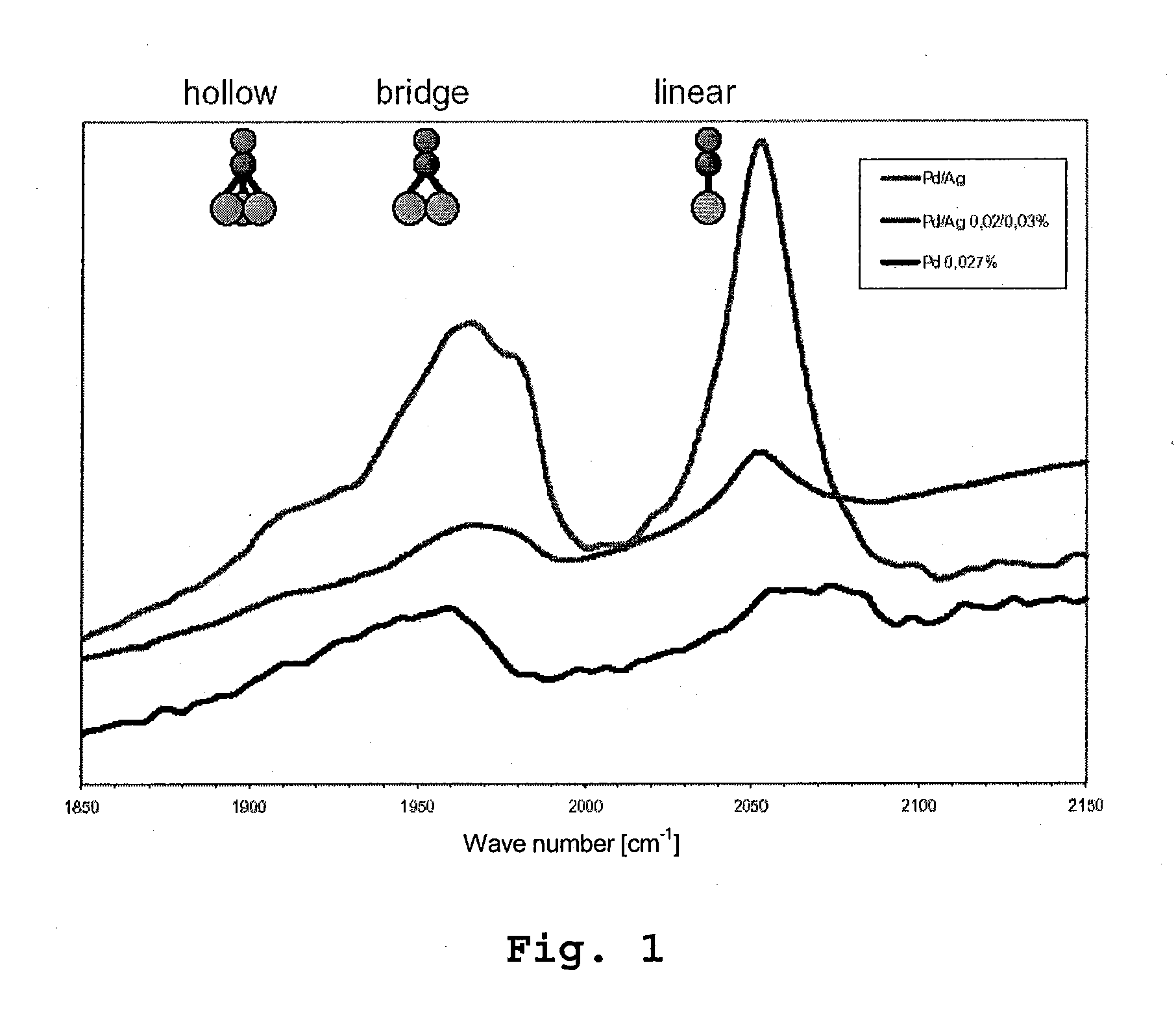
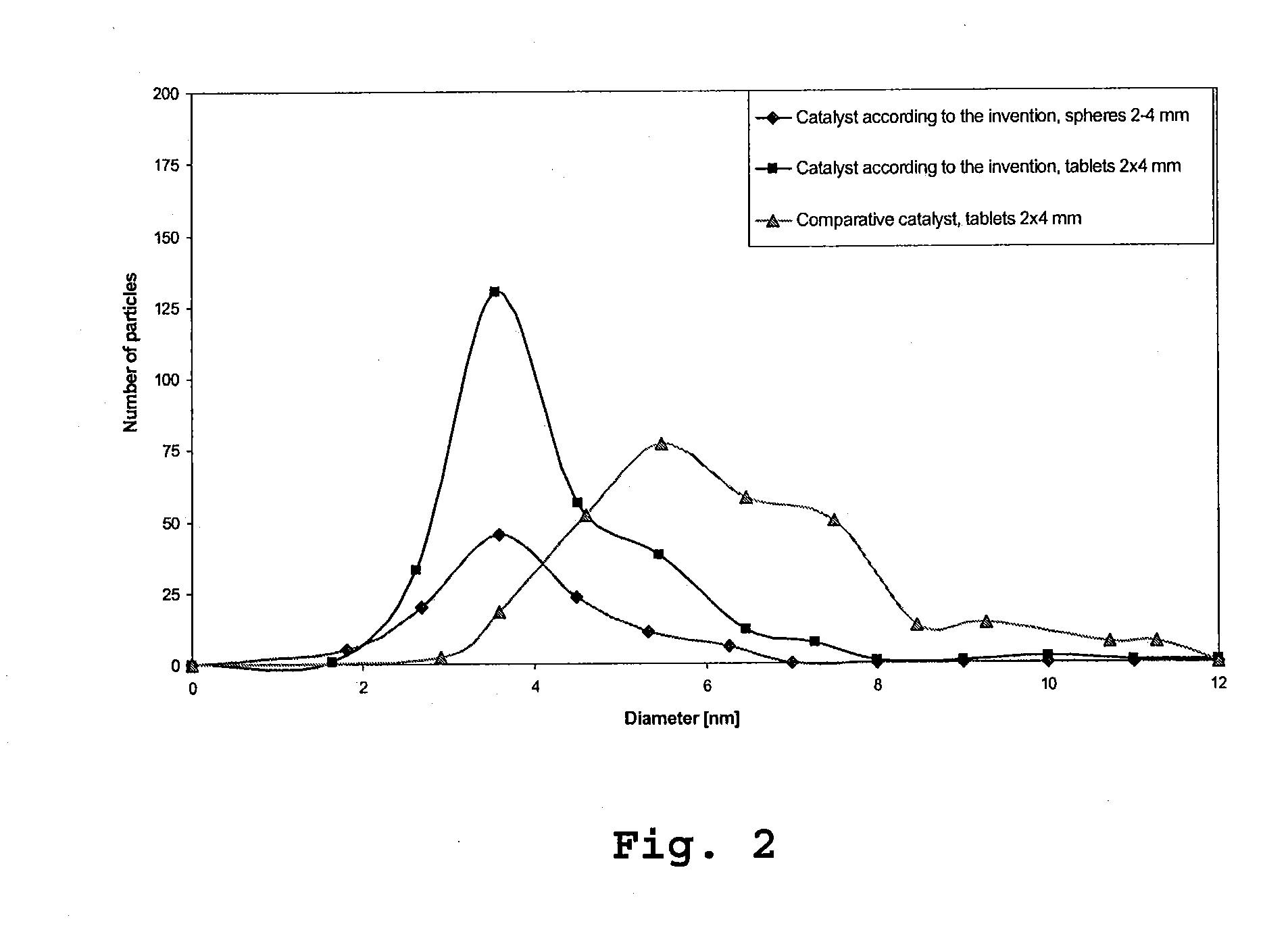
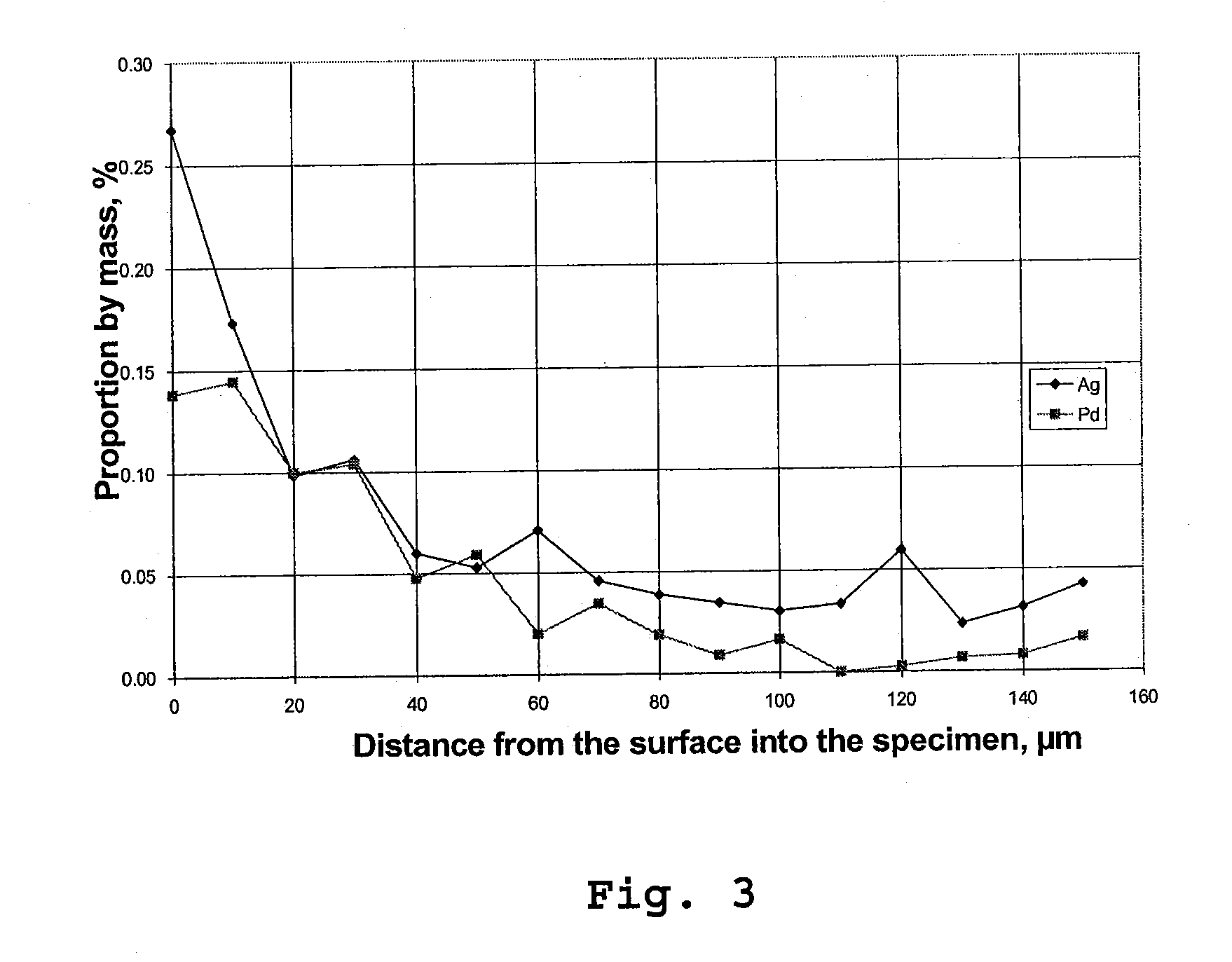
Catalyst For The Selective Hydrogenation Of Acetylenic Hydrocarbons And Method For Producing Said Catalyst
InactiveUS20100217052A1Narrow particle size distributionReduced tendency to form by-productOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationOrganic solventAcetylenic Compounds
A method for producing a catalyst, in particular for the selective reduction of acetylenic compounds in hydrocarbon streams. An impregnation solution is provided, which contains a mixture of water and at least one water-miscible organic solvent as solvent in which at least one active metal compound and also preferably at least one promoter metal compound is dissolved. A support is provided, the support is impregnated with the impregnation solution, and the impregnated support is calcined. Palladium is preferably used as active metal and silver is preferably used as promoter metal. Also, a catalyst as is obtained by the method and also its preferred use for the selective hydrogenation of acetylenic compounds.
Owner:SUED CHEM IP GMBH & CO KG
Structured catalysts for selective reduction of nitrogen oxides by ammonia using a compound that can be hydrolyzed to ammonia
InactiveUS6713031B2Shorten the lengthImprove catalytic performanceCyanogen compoundsNitrogen compoundsCatalytic functionNitrogen oxide
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Dual catalyst NOx reduction system for exhaust from lean burn internal combustion engines
ActiveUS20100000202A1Remove loadGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesMolecular nitrogenInternal combustion engine
A method and apparatus for reducing the percentage of nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen monoxide in an exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine, comprising the steps of injecting a hydrocarbon compound and optionally hydrogen into the exhaust gas stream; passing the exhaust gas through a first catalyst for selective reduction of a portion of the nitrogen oxides to nitrogen, ammonia, and N-containing species; passing the exhaust gas through a second catalyst for selective reduction of a portion of the nitrogen oxides with ammonia to molecular nitrogen; sensing ammonia concentration in the exhaust gas stream after passage through either or both of the first and second catalysts; and controlling by a controller in a feedback loop the injecting to an amount of hydrocarbon that will produce a predetermined concentration of ammonia and nitrogen oxides at the sensor that will lead to high NOx conversion.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
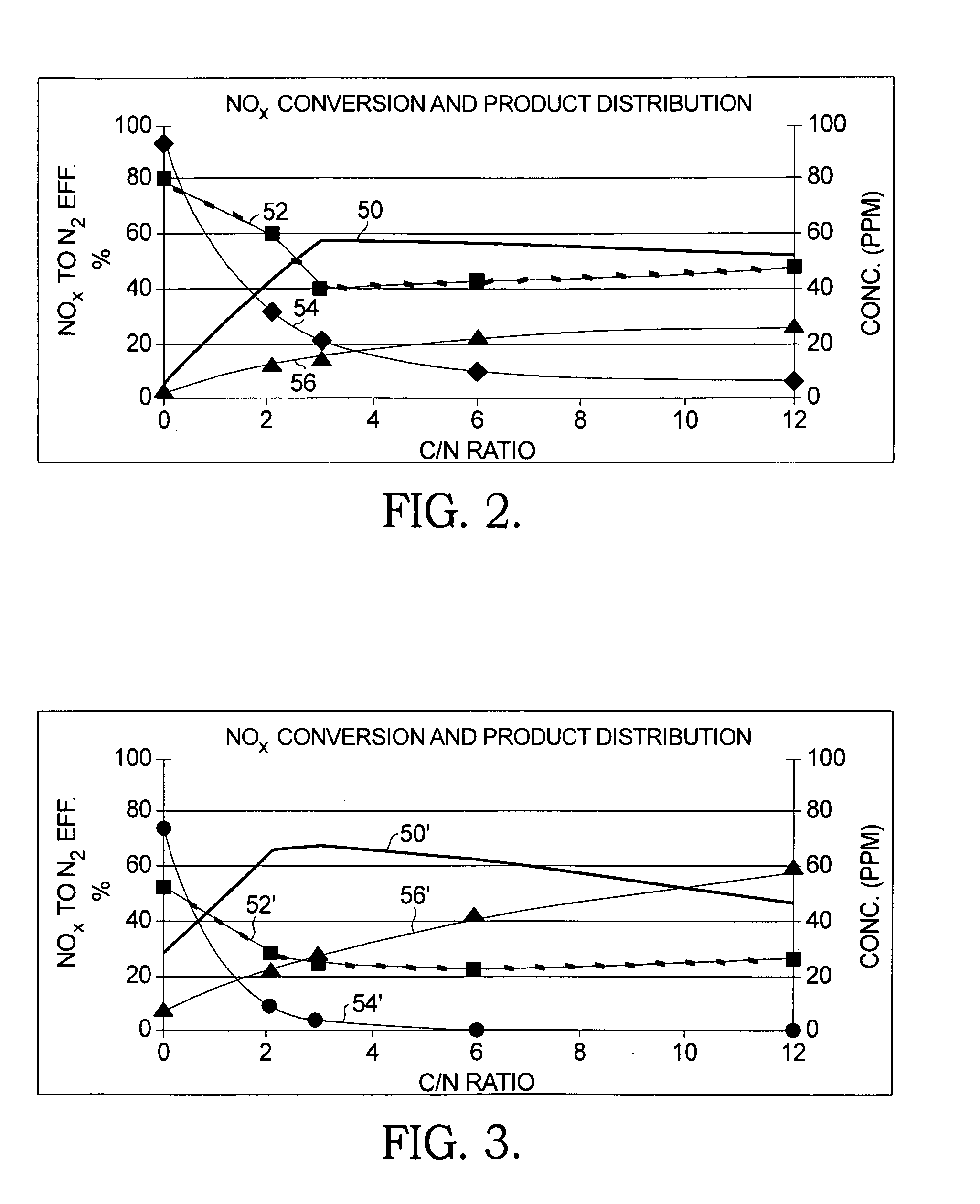
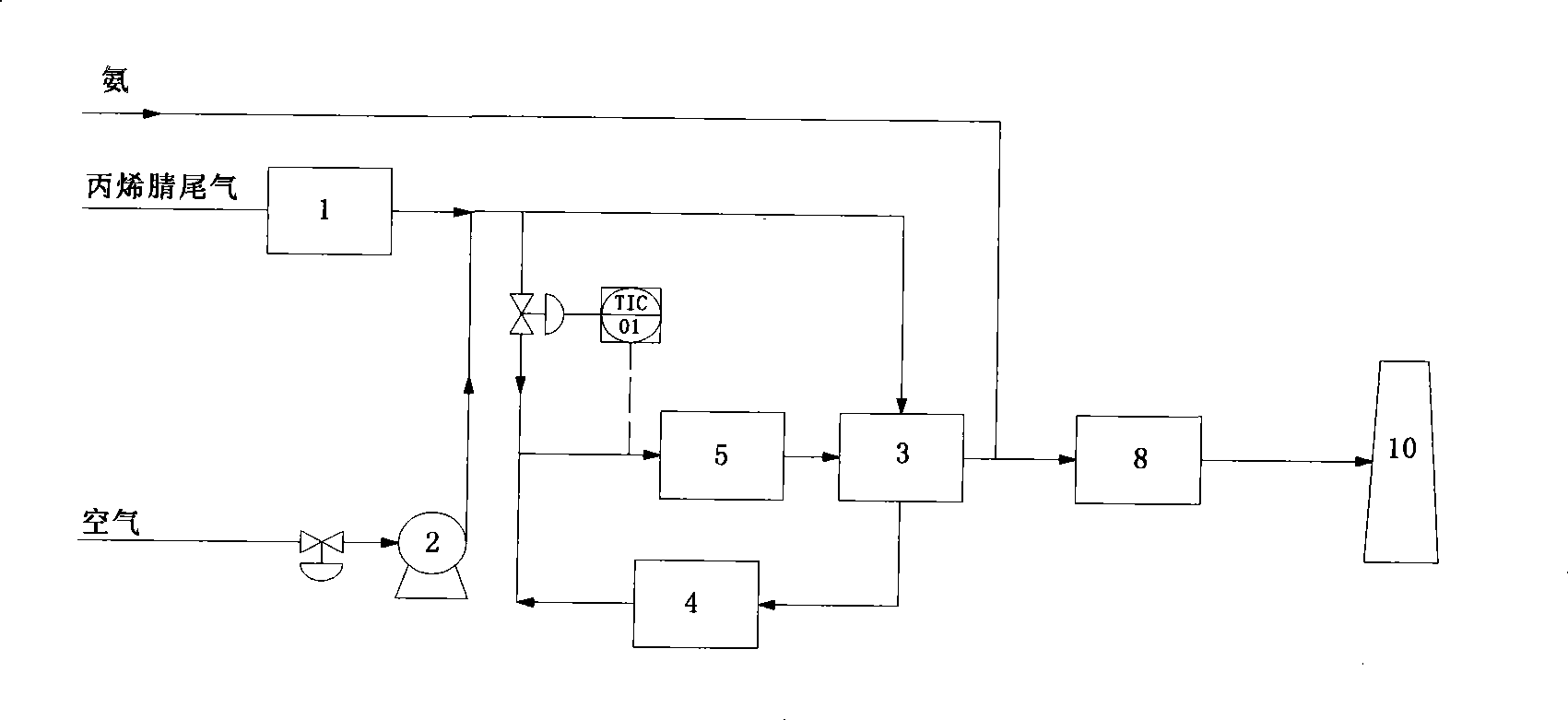
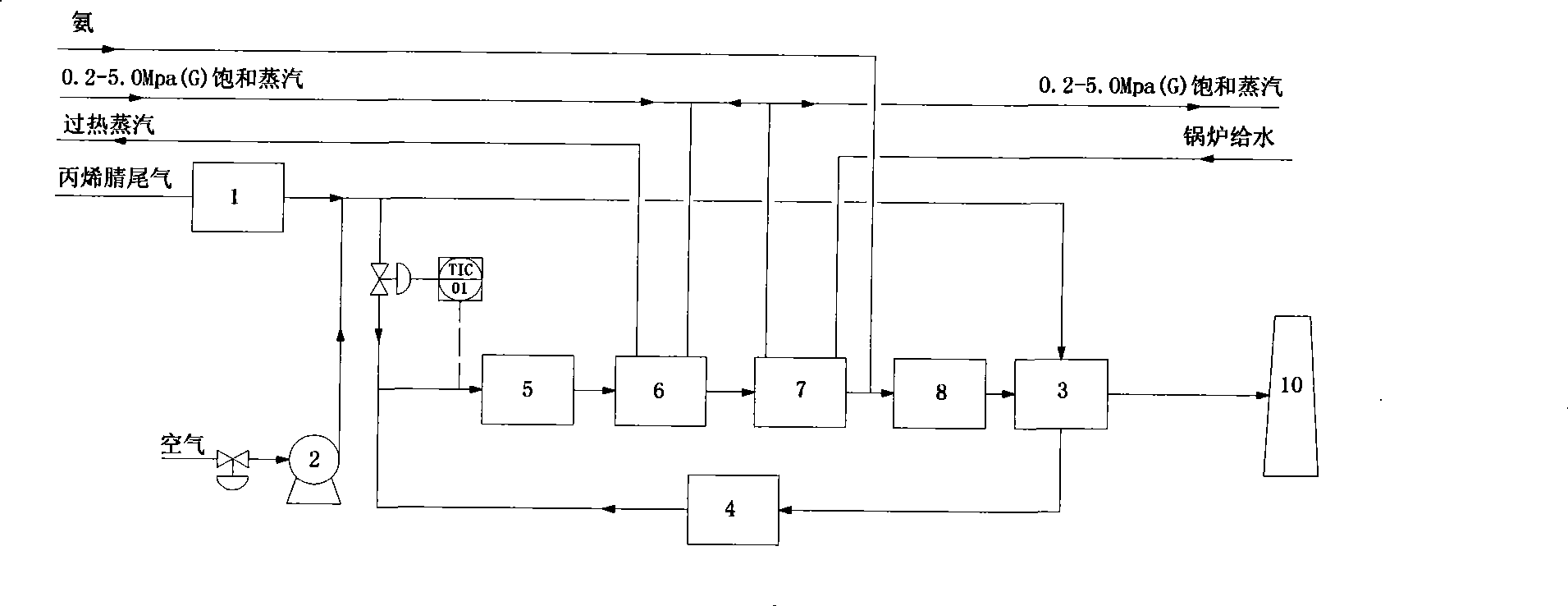
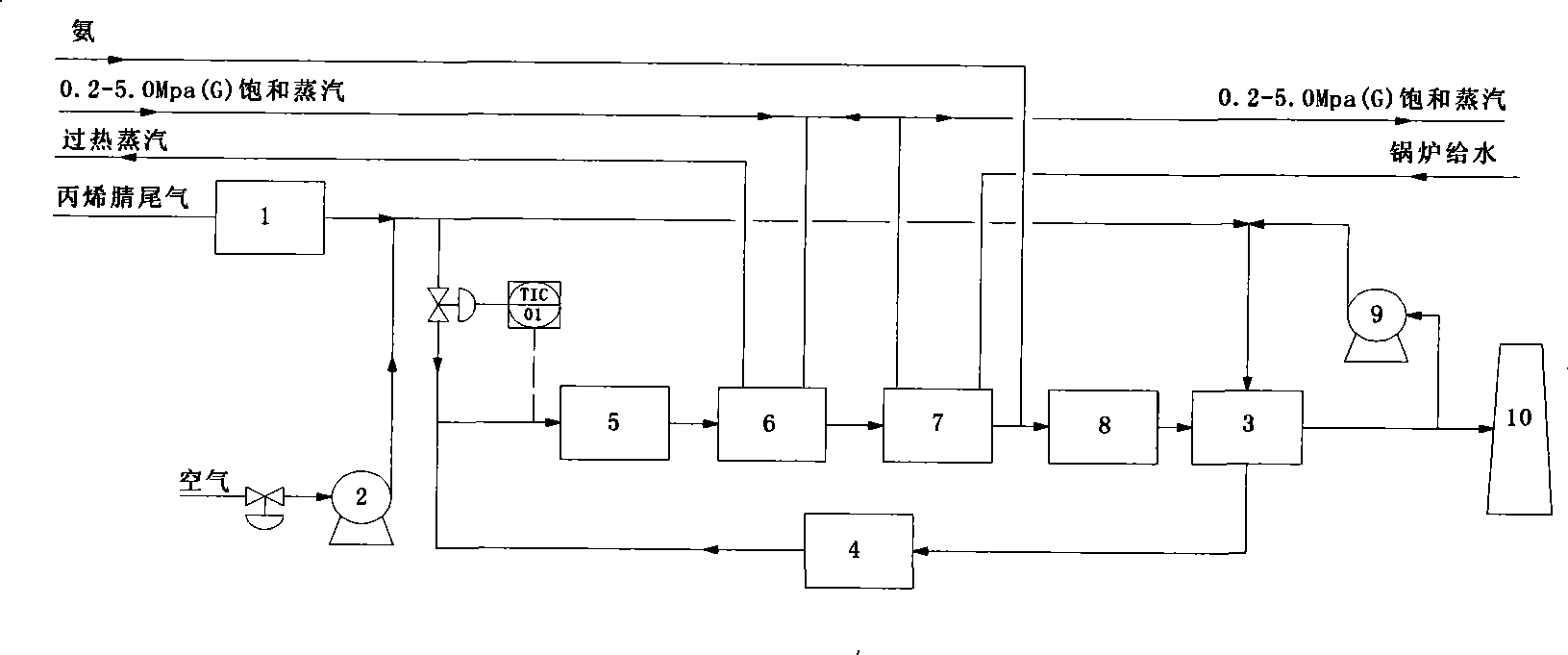
Acrylonitrile device tail-gas treatment technique
InactiveCN101362051AHigh mechanical strengthExtended service lifeChemical industryDispersed particle separationAcrylonitrileCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a technique for treating the tail gas of an acrylonitrile device, which is suitable for treating acrylonitrile tail gas discharged by the acrylonitrile device. The technique is characterized in that: after free water is separated out by a gas-liquid separator, the acrylonitrile tail gas is mixed with air, a noble metal monolithic catalyst is taken as a catalyst and catalytic oxidation reaction is carried out to turn harmful volatile organic compounds into carbon dioxide and water; then a selective reduction monolithic catalyst is taken as a catalyst and selective catalytic reduction reaction with added ammonia is carried out to reduce nitrogen oxide in the tail gas into nitrogen and water. The technique has the advantages of simple technique, turning the harmful volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxide in the tail gas into carbon dioxide, nitrogen and water, without secondary pollution, the test results totally meeting the environmental protection control requirements of the State Standard of China, adopting a tail gas heat exchanger to recycle reaction heat to heat input tail gas, needing no additional fuel during the normal operation process, small system resistance and low operation cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG
Ammonia SCR catalyst and method of using the catalyst
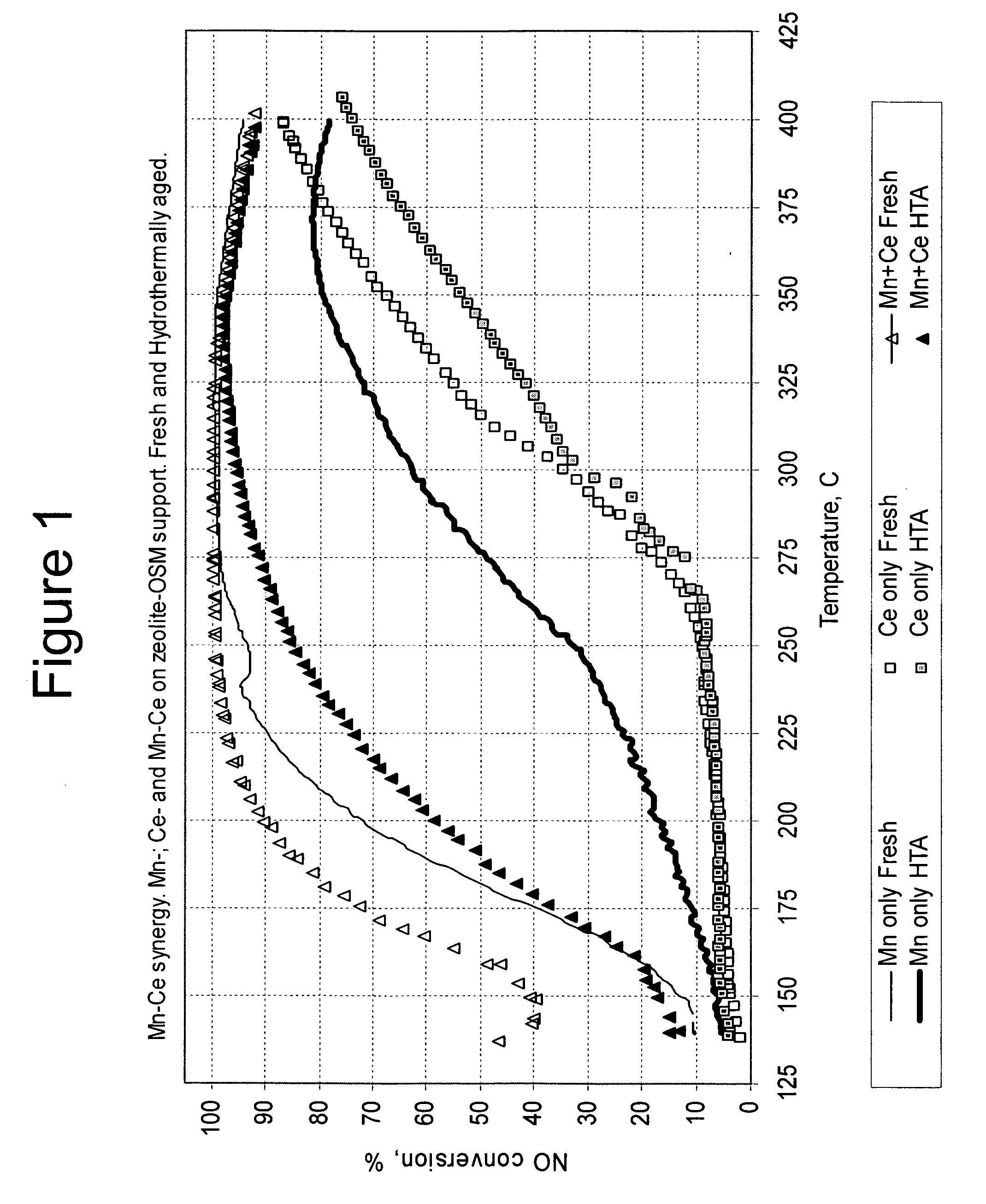
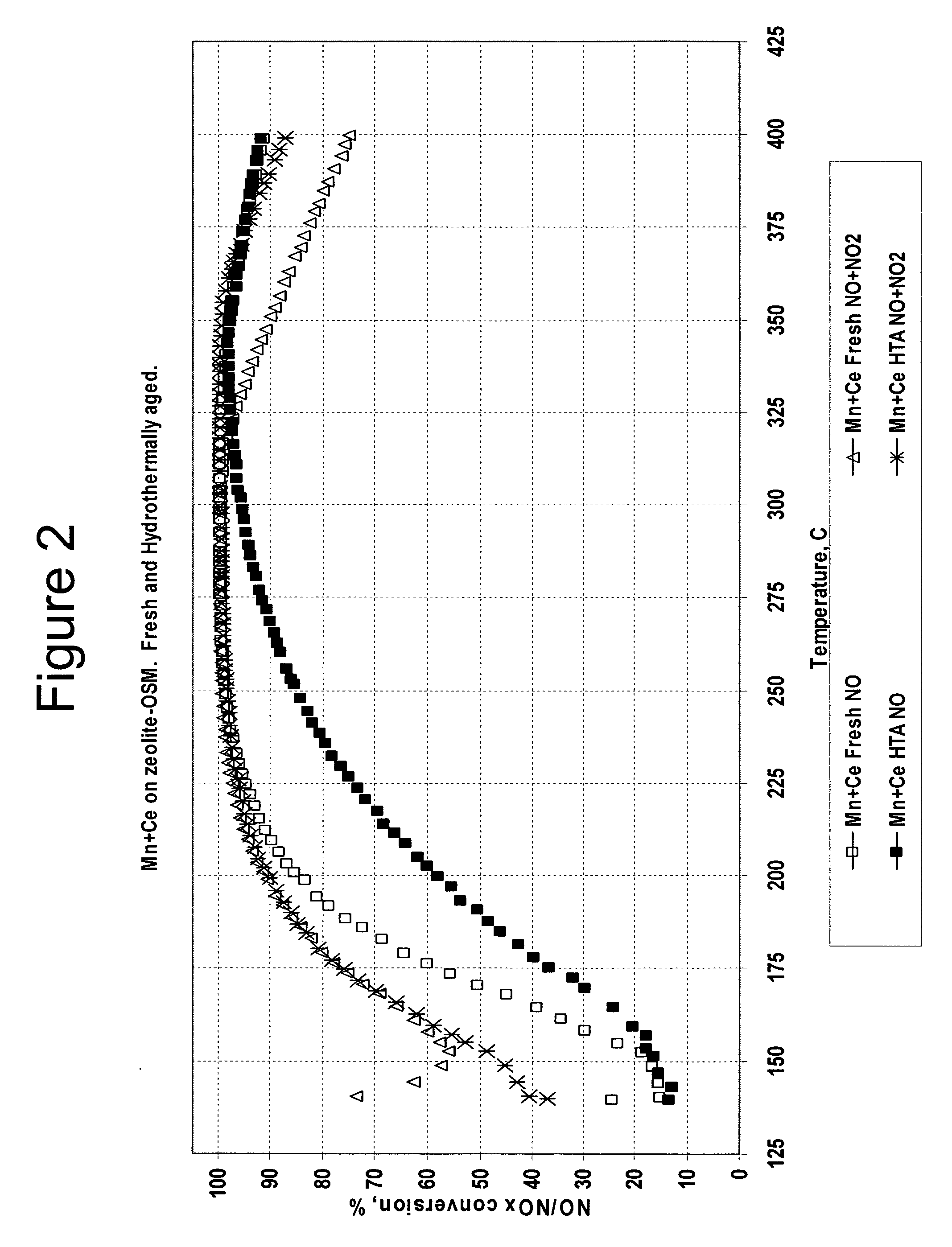
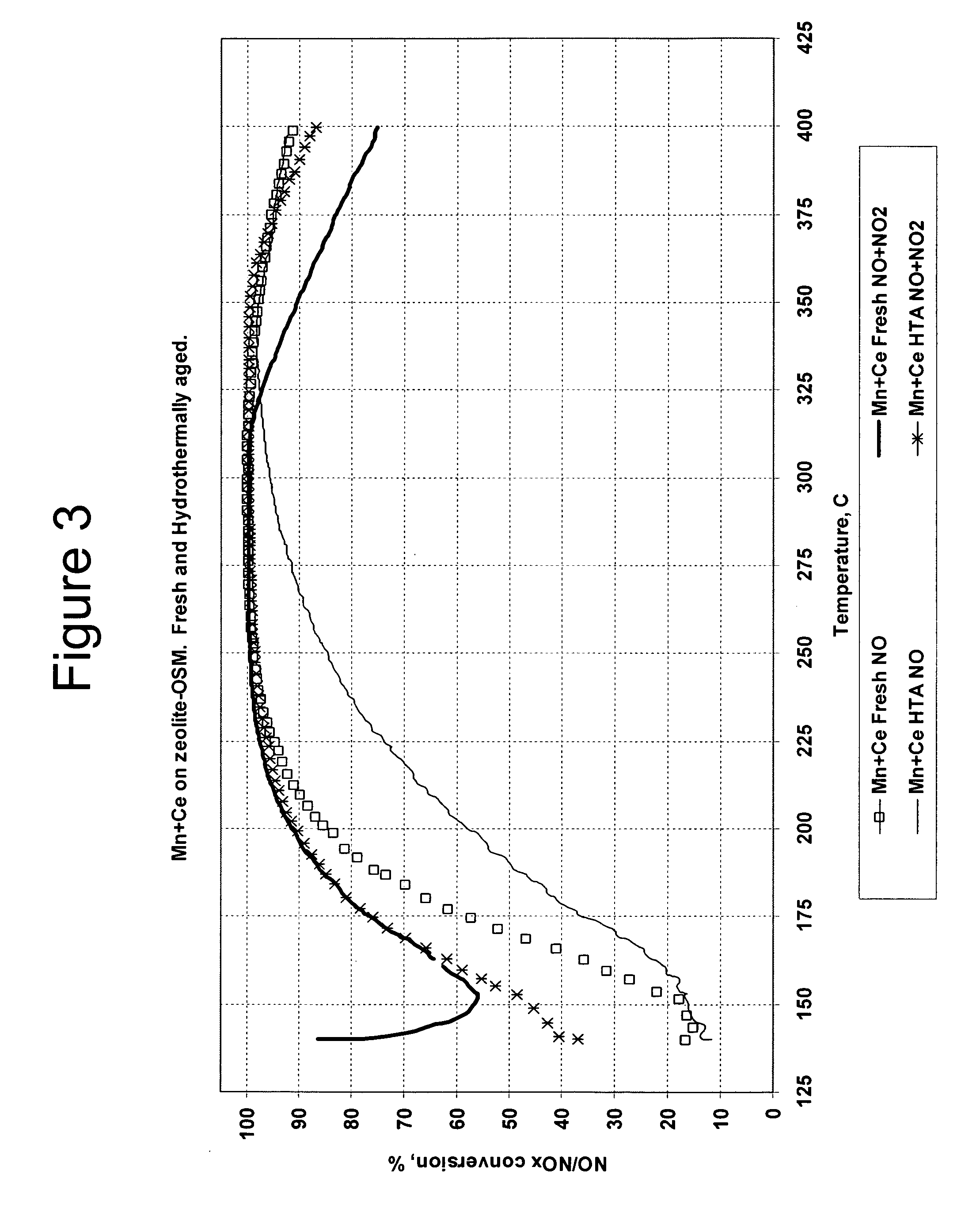
A catalyst and a method for selectively reducing nitrogen oxides with ammonia are provided. The catalyst includes a first component of copper, chromium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, iron, niobium, or mixtures thereof, a second component of cerium, a lanthanide, a mixture of lanthanides, or mixtures thereof, and a zeolite. The catalyst may also include strontium as an additional second component. The catalyst selectively reduces nitrogen oxides to nitrogen with ammonia at low temperatures. The catalyst has high hydrothermal stability. The catalyst has high activity for conversion of nitrogen oxides in exhaust streams, and are not significantly influenced by the NO / NO2 ratio. The catalyst and the method may have special application to selective reduction of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas from diesel vehicles, although the catalyst and the method have broad application to a wide range of gas streams that contain nitrogen oxides. The temperature of exhaust gas from diesel vehicles is low, and the exhaust gas generally has a high NO / NO2 ratio. Both the low temperature and the high NO / NO2 ratio are challenging for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Exhaust purification apparatus for engine
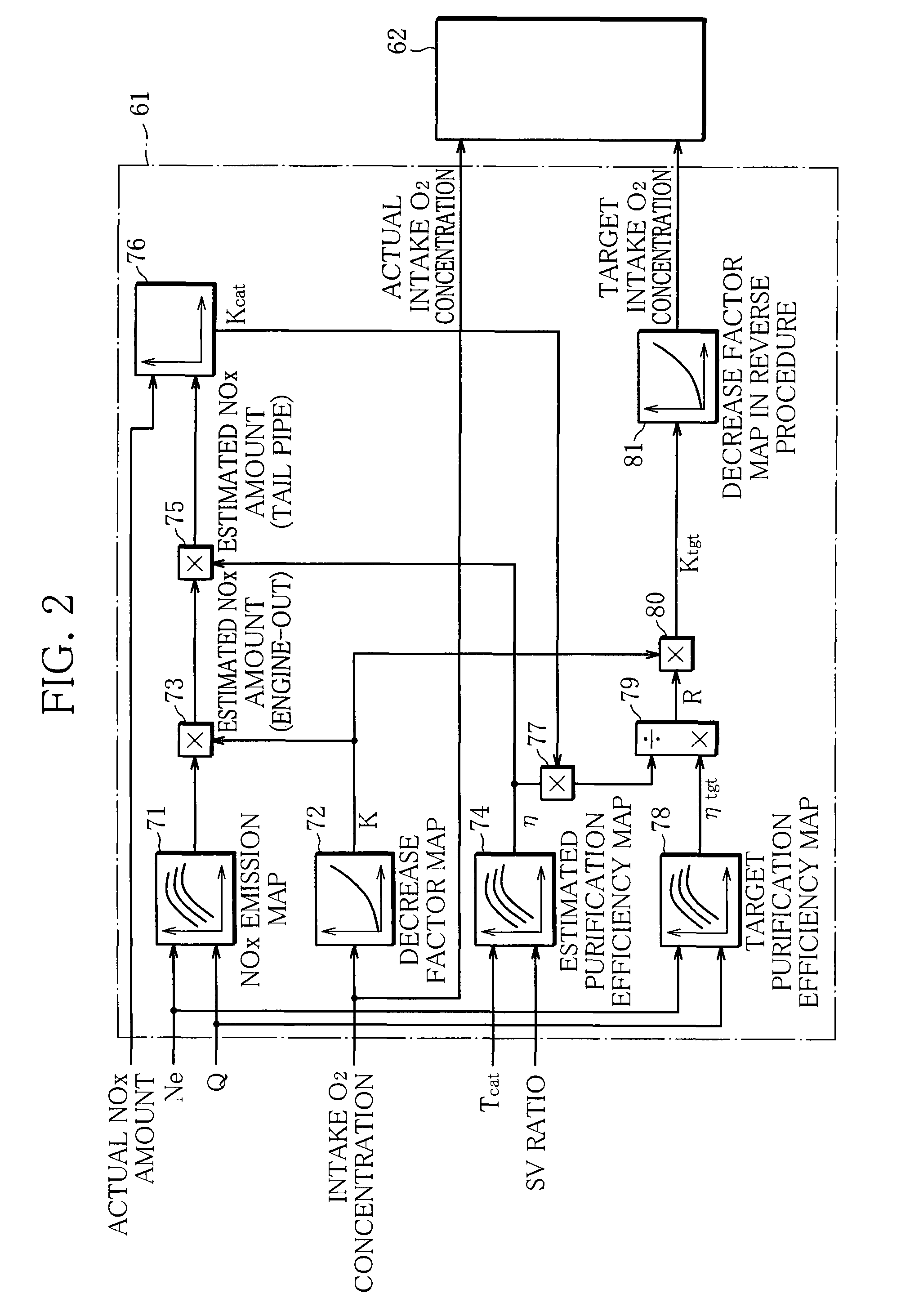
InactiveUS20090158710A1Reduces NOx containedElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gas recirculationSelective reduction
An exhaust purification apparatus for an engine comprises a selective reduction-type NOx catalyst that is interposed in an exhaust passage of the engine and selectively reduces NOx contained in exhaust gas of the engine, an EGR device that recirculates exhaust gas of the engine to an intake side of the engine, an exhaust-purification-efficiency estimation unit that estimates exhaust purification efficiency of the NOx catalyst with respect to NOx, a target-exhaust-purification-efficiency calculation unit that calculates target exhaust purification efficiency with respect to NOx on the basis of an operational state of the engine, and a control unit that controls the EGR device to compensate a decrease amount of the estimated exhaust purification efficiency to the target exhaust purification efficiency.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
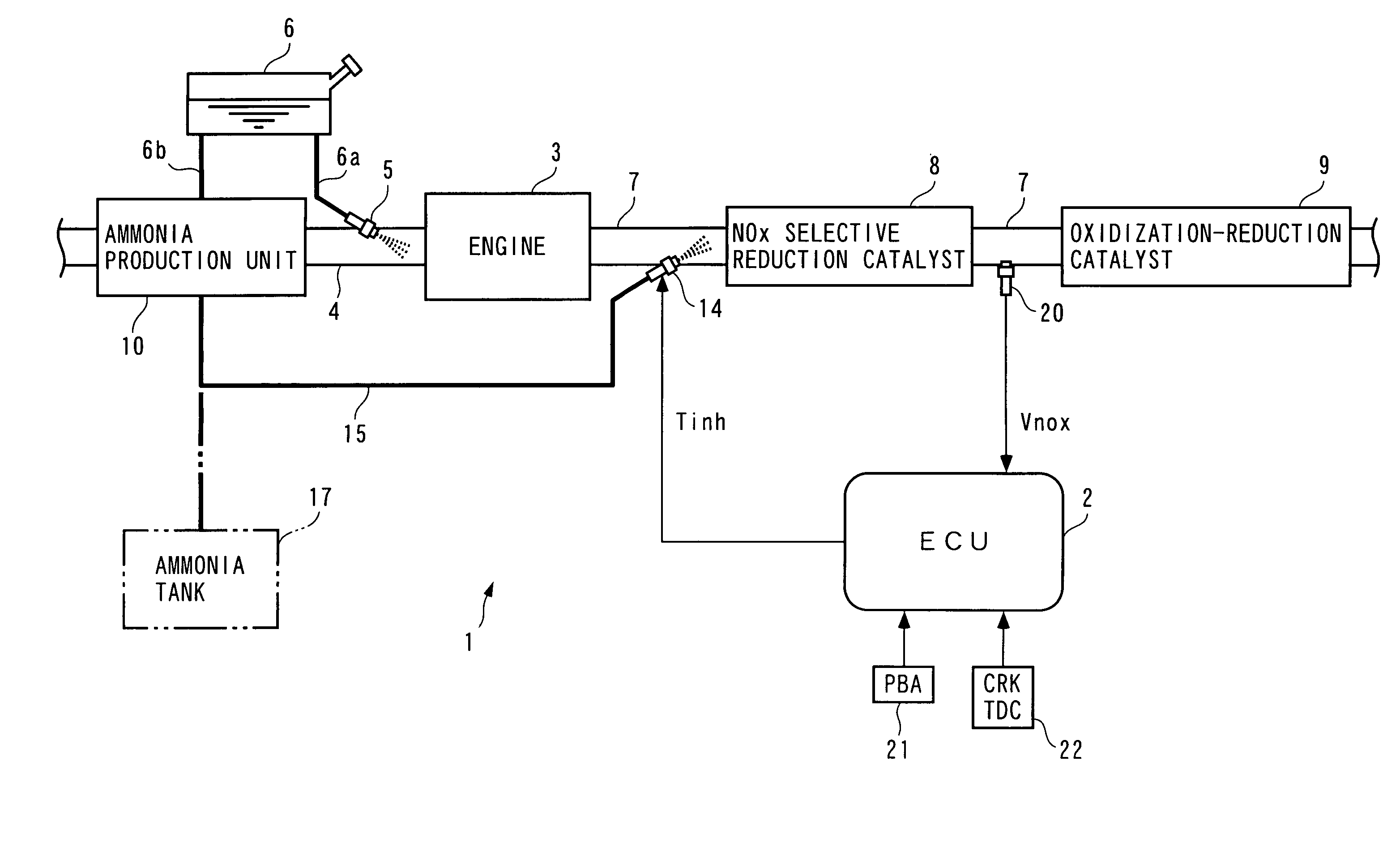
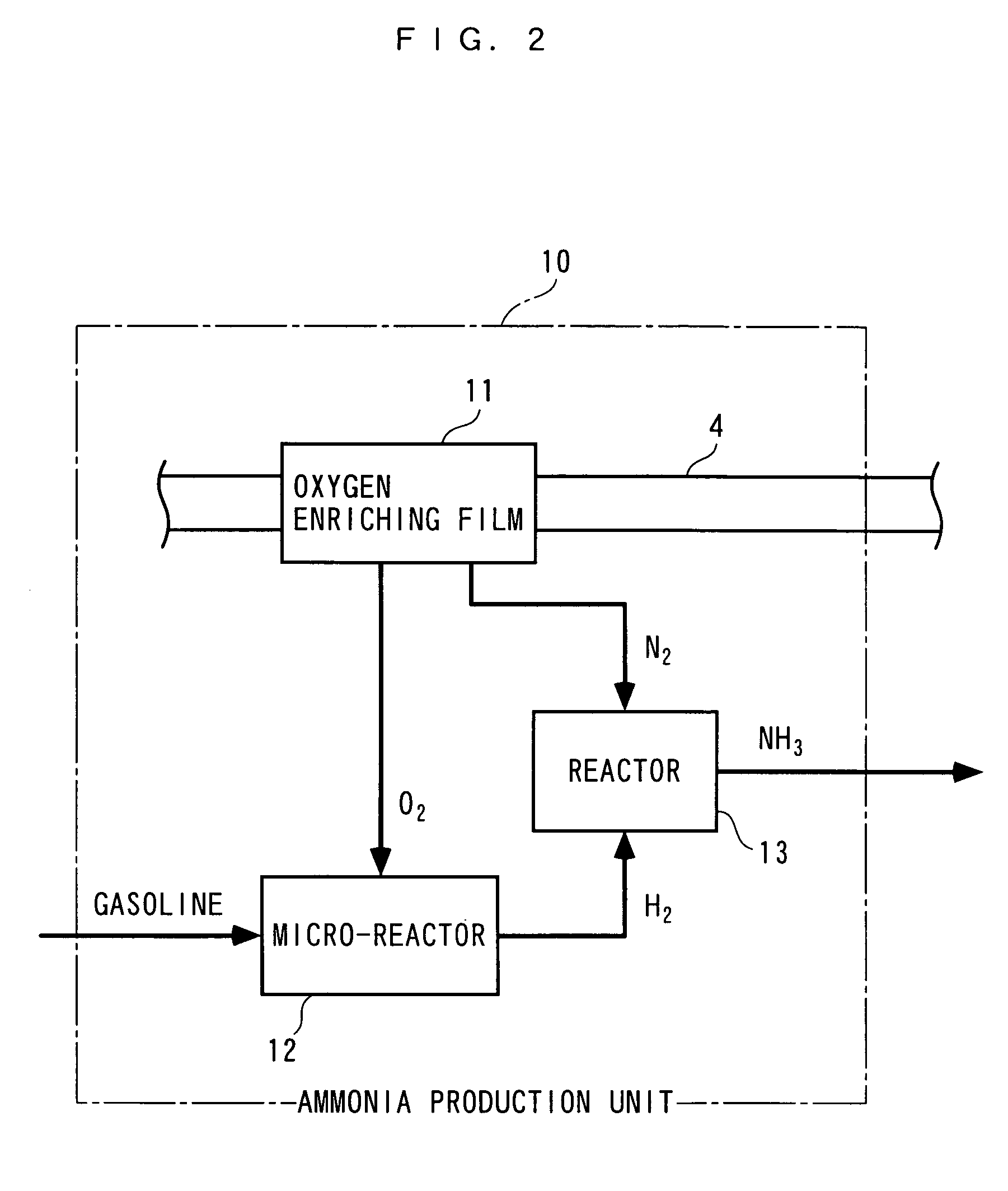
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for internal combustion engine, and engine control unit
InactiveUS20040159096A1Improve performanceImprove featuresInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia productionExhaust fumes
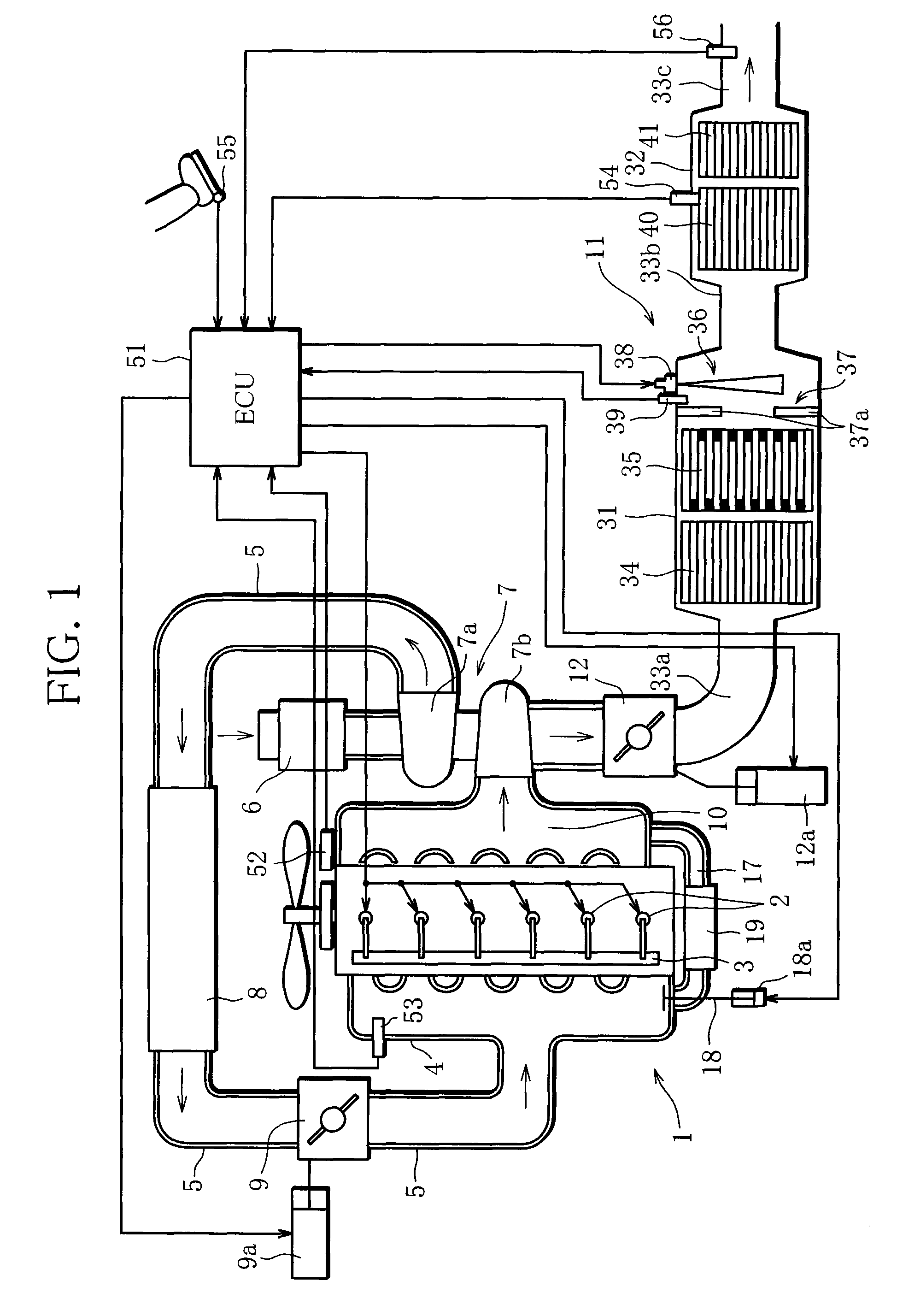
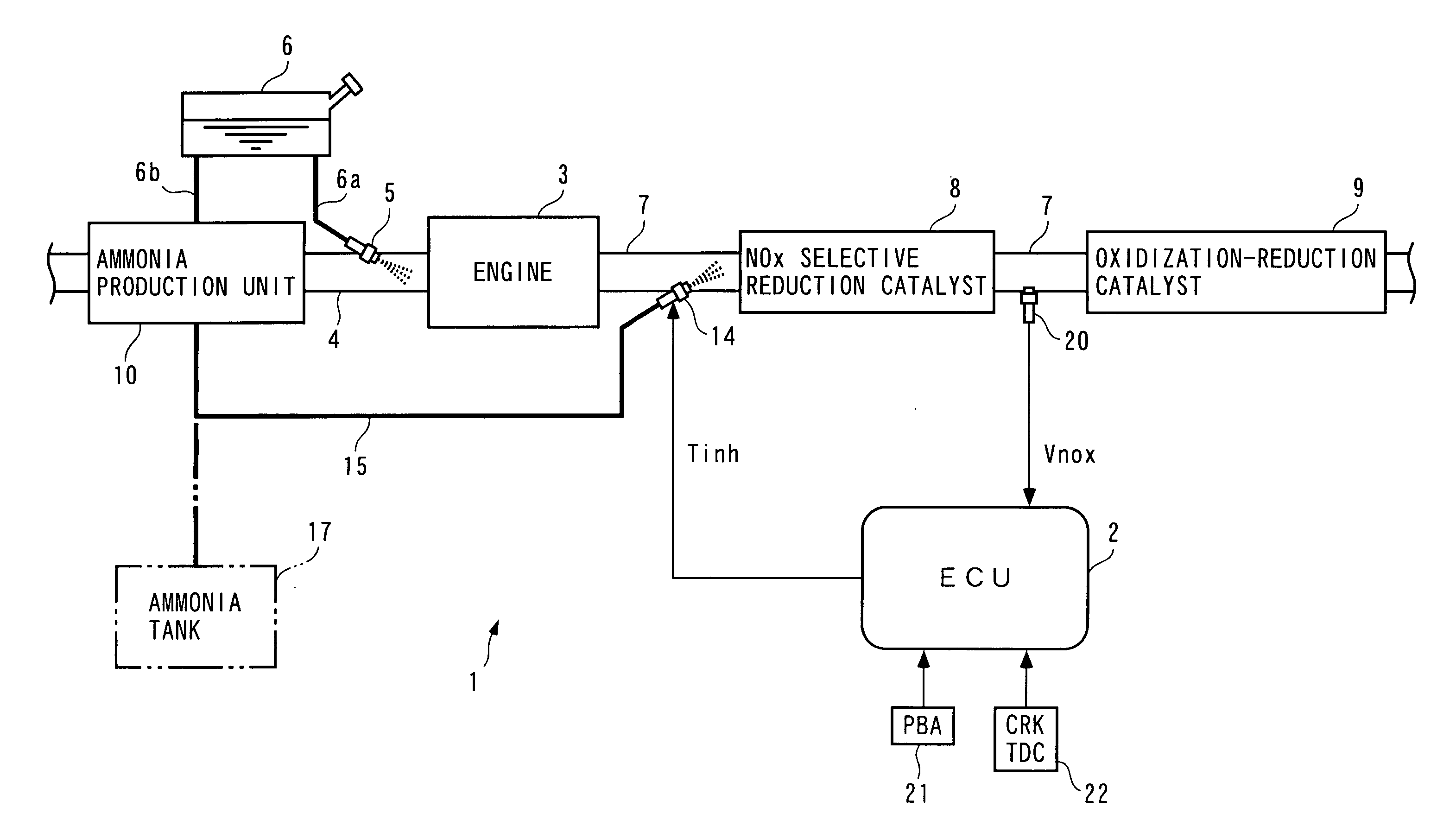
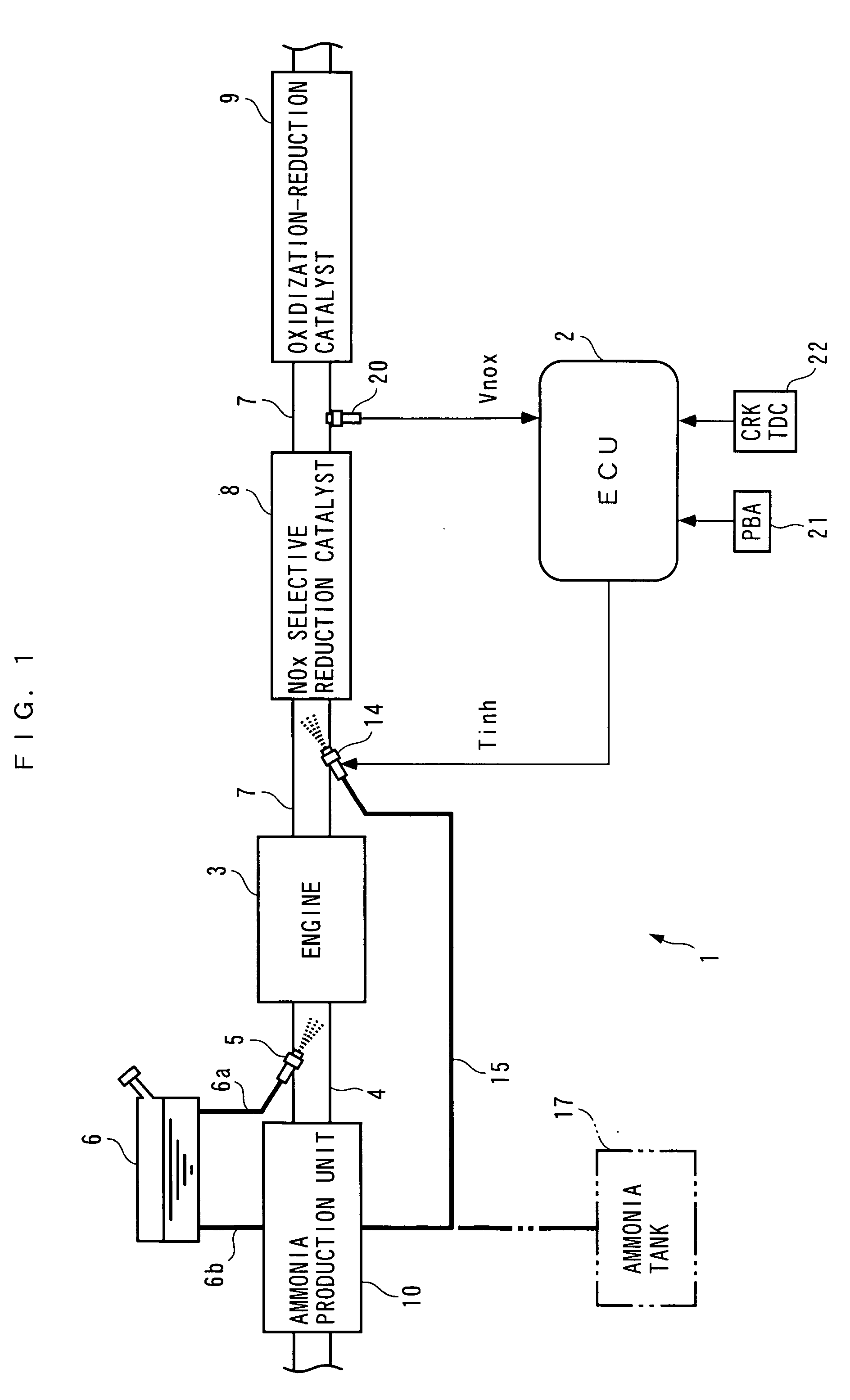
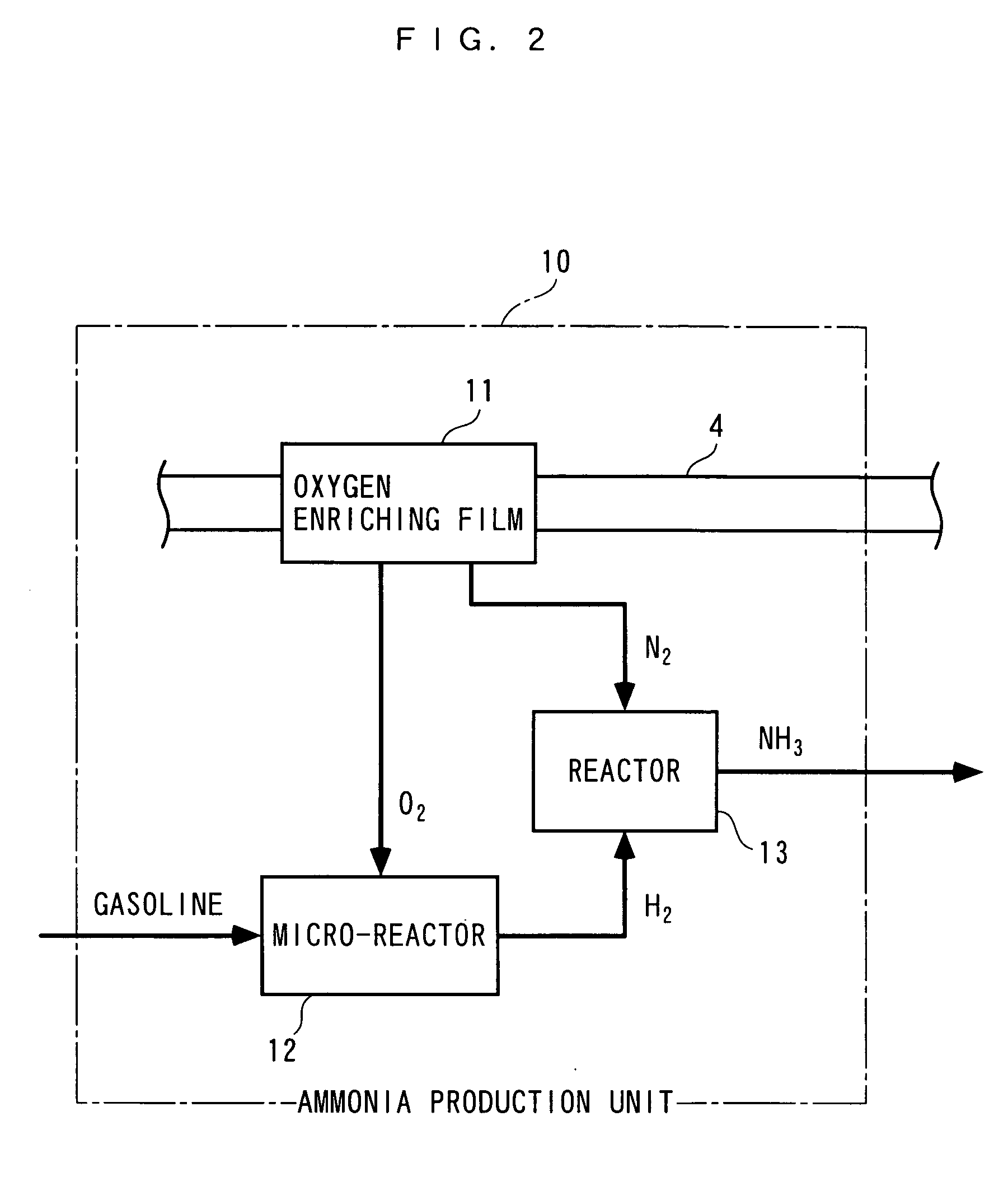
An exhaust gas purifying apparatus and method for an internal combustion engine, and an engine control unit are provided for appropriately determining the amount of reducing agent supplied to a NOx selective reduction catalyst to ensure good exhaust gas characteristics. The exhaust gas purifying apparatus comprises an ECU; a NOx selective reduction catalyst for purifying NOx in exhaust gases in an exhaust pipe; a NOx sensor disposed in the exhaust pipe at a location downstream of the NOx selective reduction catalyst for detecting a NOx concentration in exhaust gases; and an injector for supplying the NOx selective reduction catalyst with ammonia produced in an ammonia production unit. The ECU determines the amount of ammonia injected to the NOx selective reduction catalyst by the injector such that an estimate of the NOx concentration detected by the NOx sensor reaches a minimum value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Selective catalytic reduction catalyst system with expanded temperature window
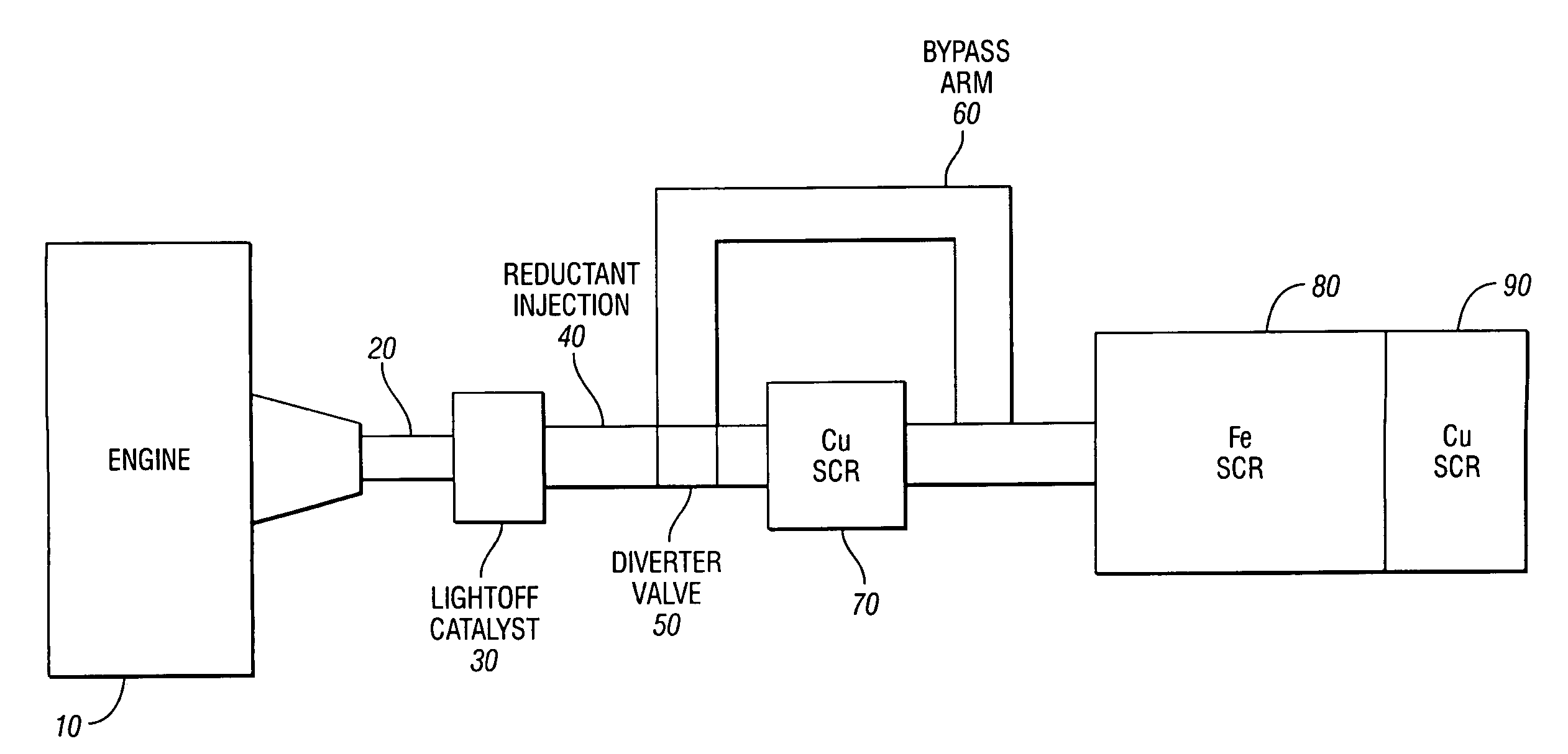
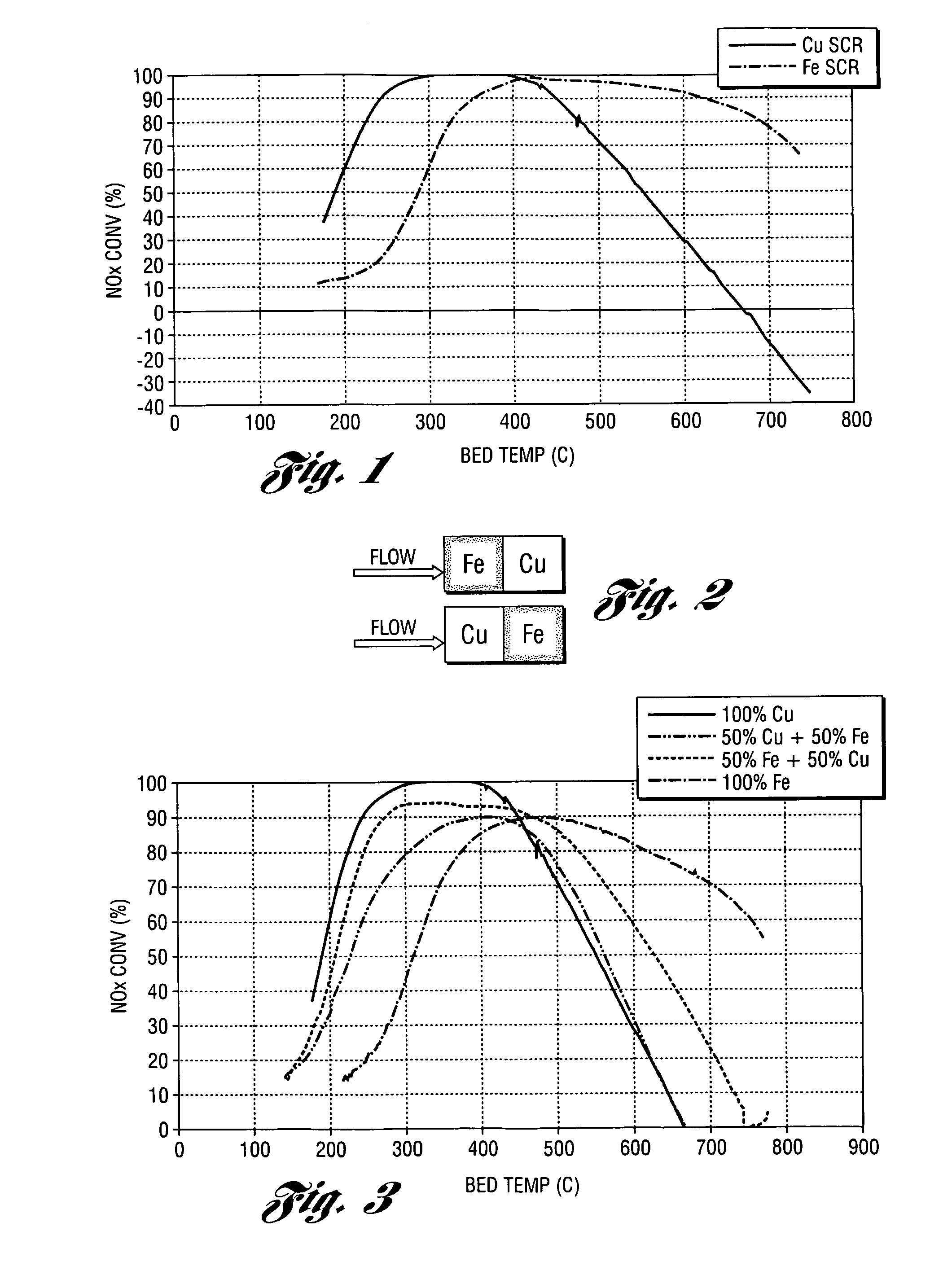
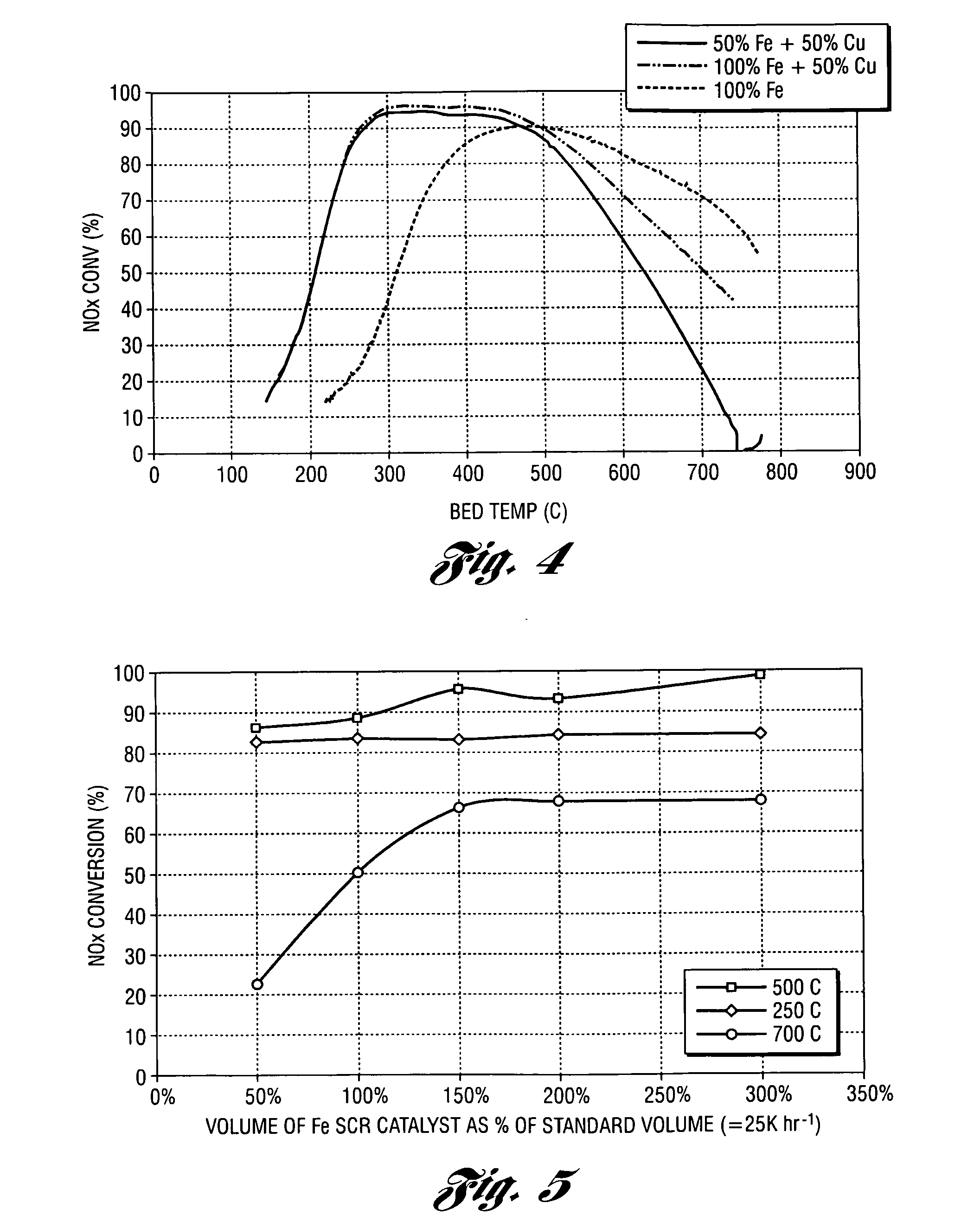
According to one embodiment of the present invention a selective reduction catalyst system with a broad temperature window for lean-burn gasoline and diesel engines is disclosed. The system includes a first and second zone, wherein the first zone is composed of an iron SCR catalyst and a second zone is composed of a copper SCR catalyst, and wherein the second zone is positioned downstream of the first zone. In another embodiment, a small copper SCR catalyst is placed in front of a second zone composed of an iron SCR catalyst and a third zone composed of a copper SCR catalyst, wherein the volume of the first copper SCR catalyst is a fraction of the volume of the second copper SCR catalyst. In yet another embodiment, a diverter valve would be included in the system to eliminate any NOx penalty produced by the front Cu SCR catalyst.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
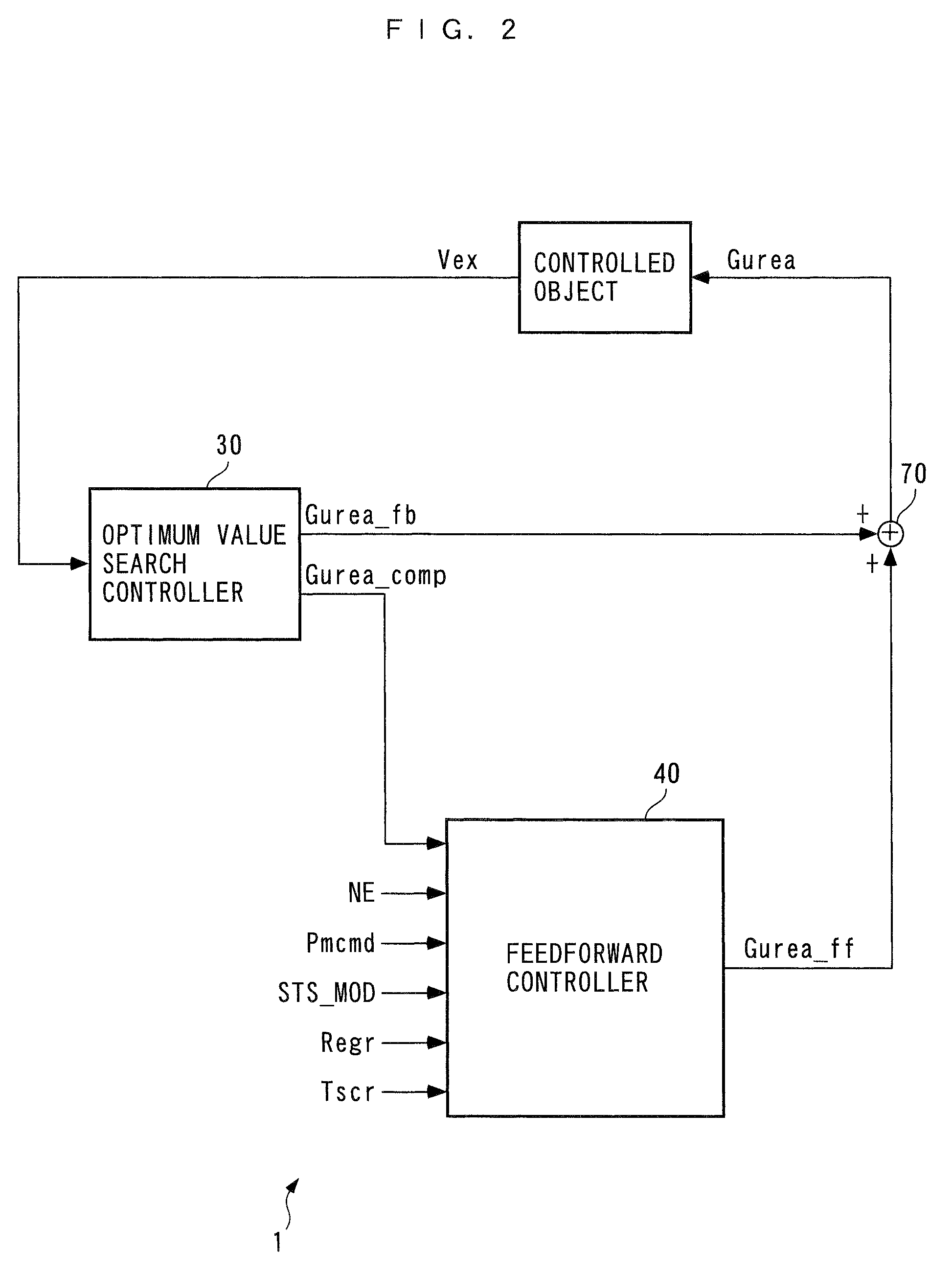
Exhaust emission control device for internal combustion engine
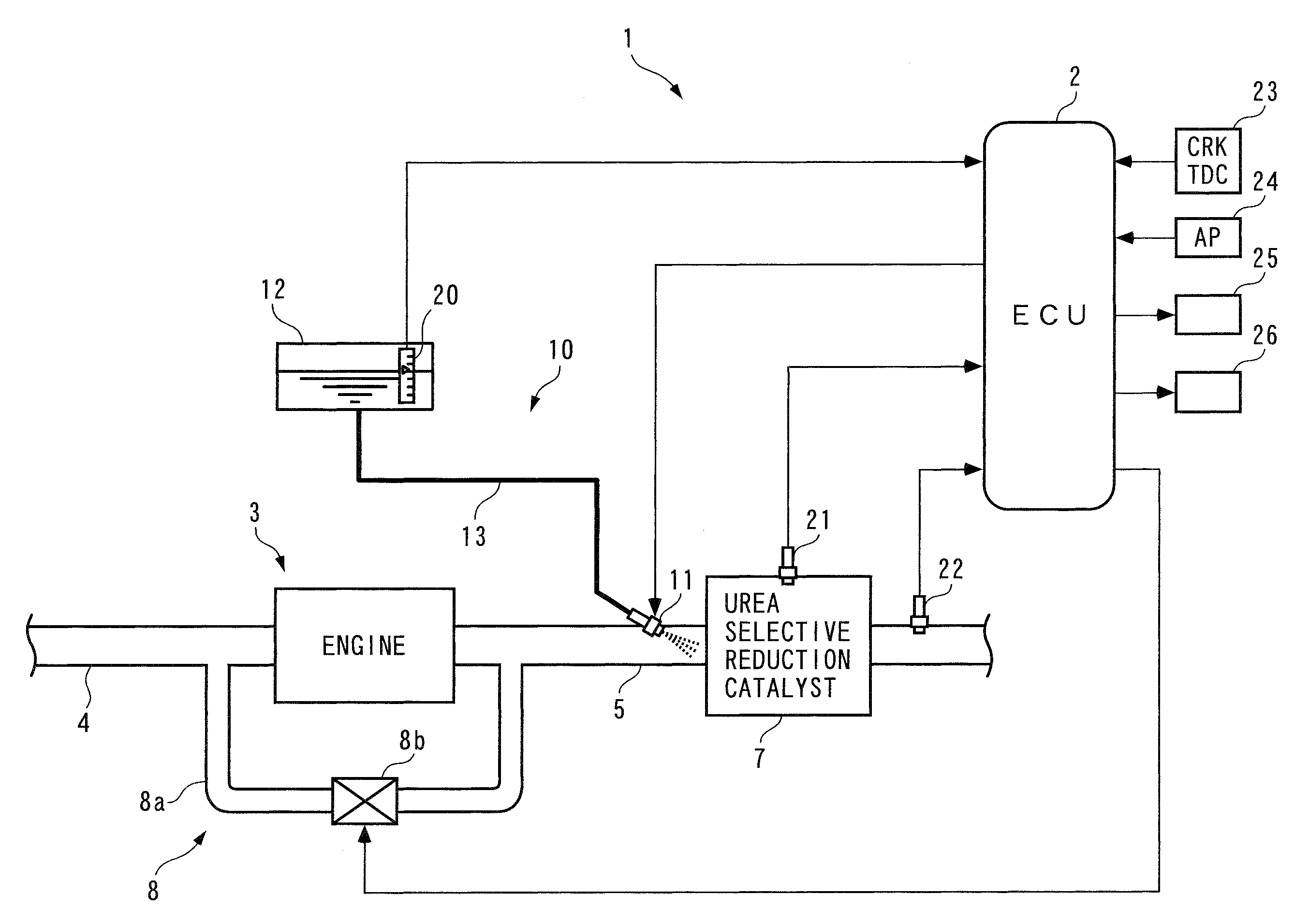
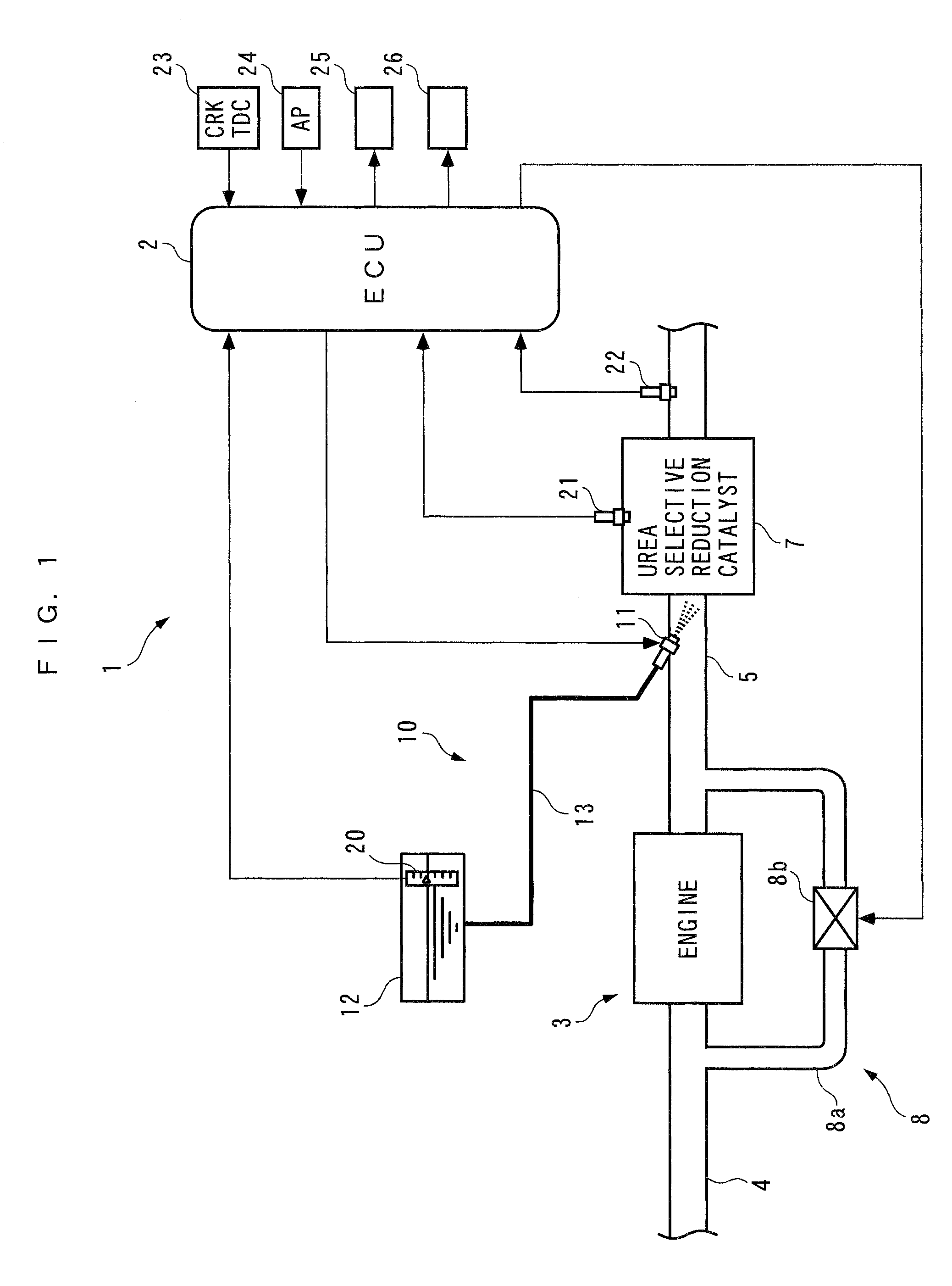
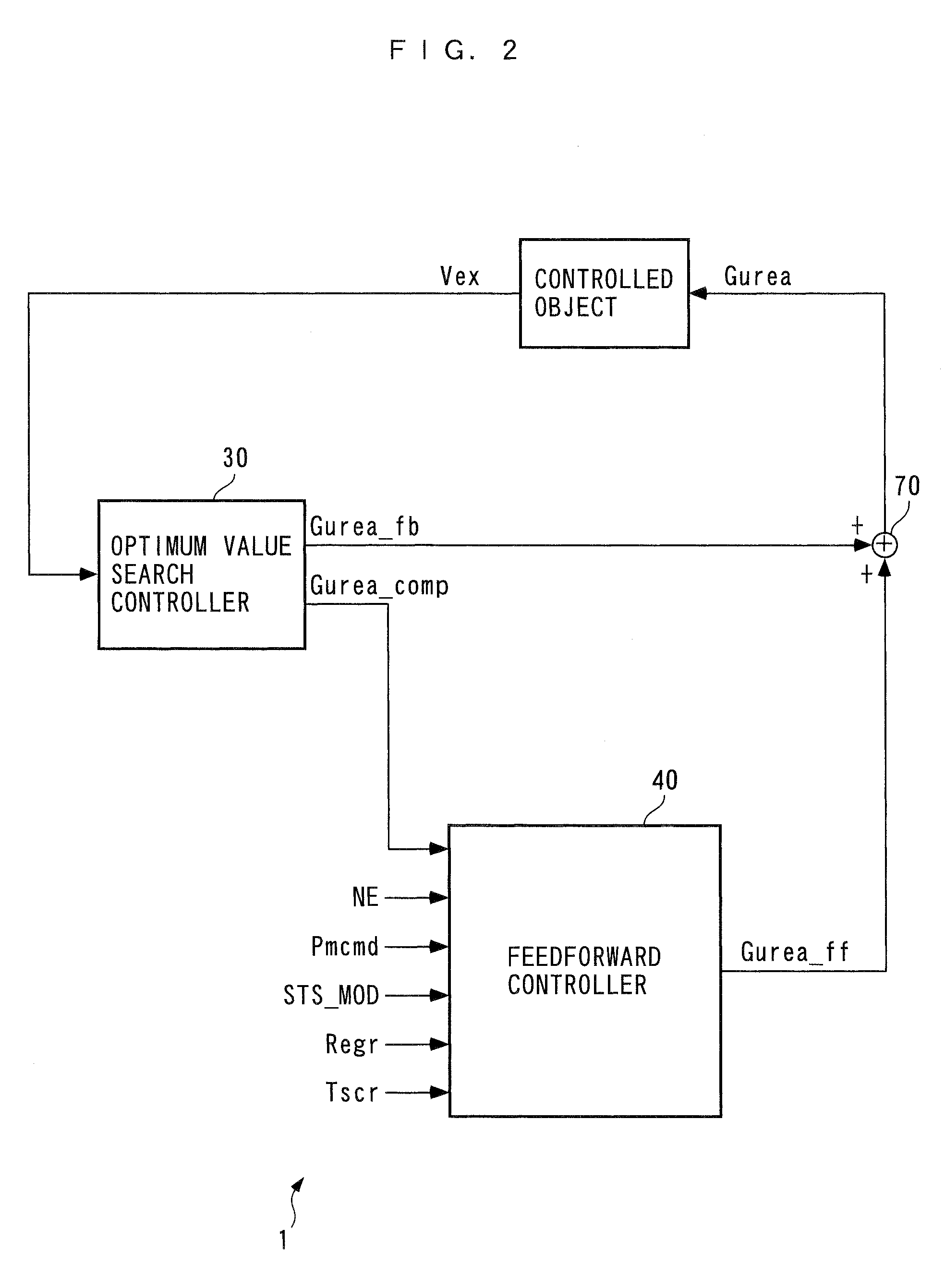
InactiveUS7997070B2Reduce the valueImprove concentrationAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesMoving averageExhaust fumes
An exhaust emission control device for an internal combustion engine, capable of supplying a just enough amount of reducing agent to a selective reduction catalyst even when a NOx purification ratio of the catalyst is changed by various causes, thereby enabling a high NOx purification ratio and very low exhaust emissions to be maintained. An ECU calculates a filtered value based on a signal from an exhaust gas concentration sensor, calculates a moving average value of a product of the filtered value and a reference input, calculates a control input such that the moving average value becomes equal to 0, and adds a reference input to the control input to calculate an FB injection amount. The ECU calculates an FF injection amount with a predetermined feedforward control algorithm, and adds the FF injection amount to the FB injection amount, to thereby calculate a urea injection amount.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
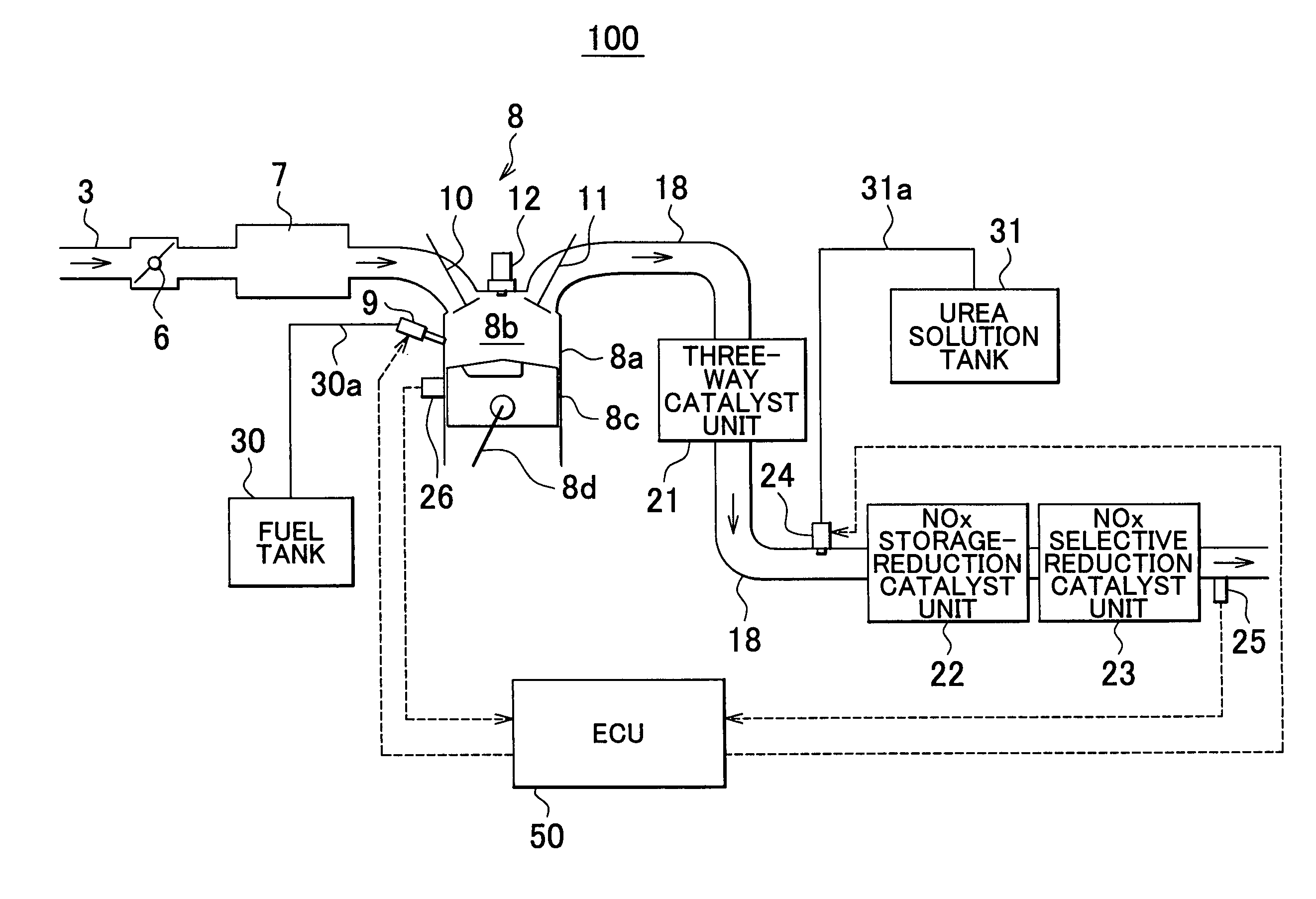
Internal combustion engine exhaust gas purification apparatus and method for controlling same
InactiveUS7892508B2Lightweight productionContainment leakNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineSelective reduction
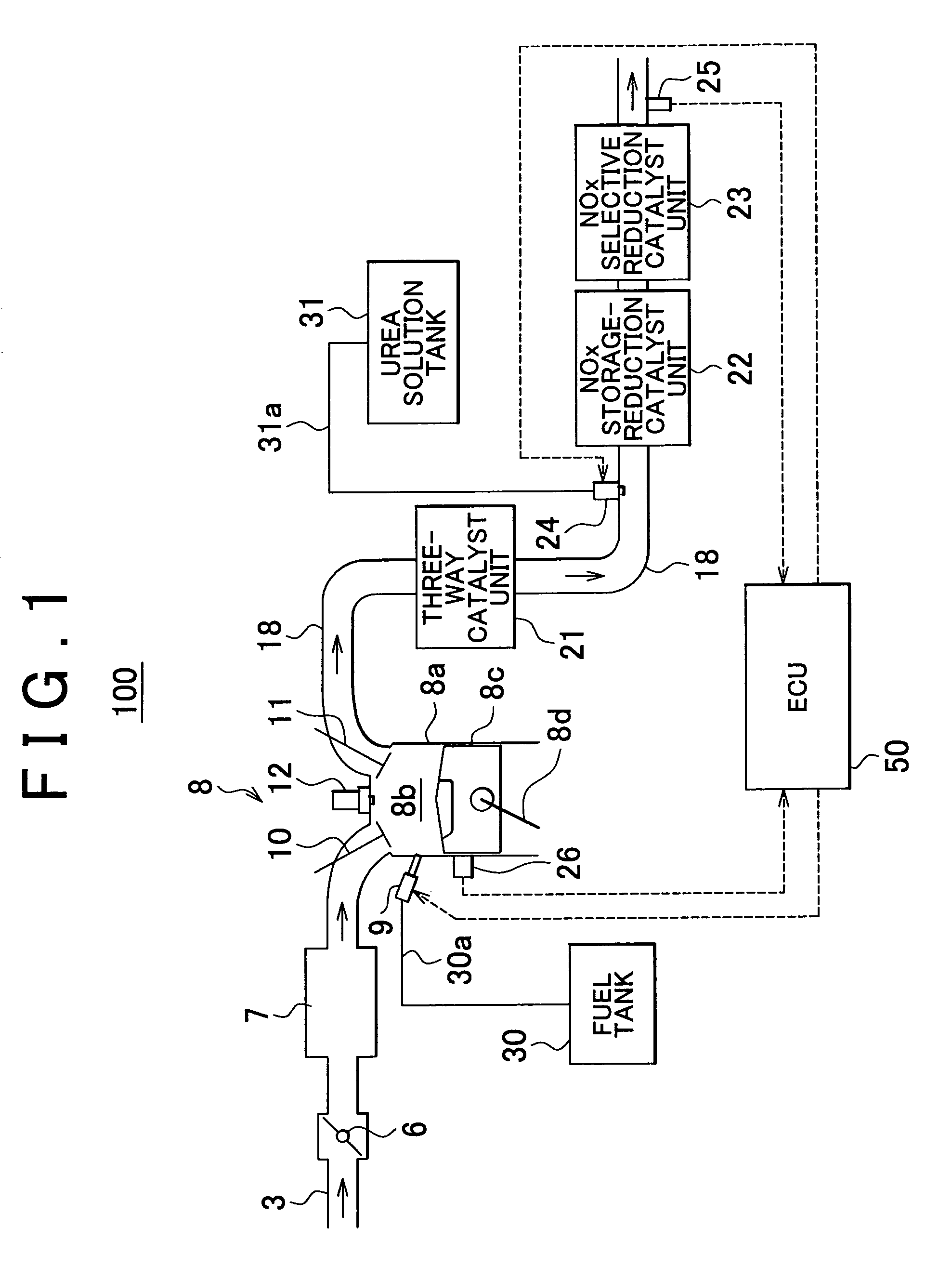
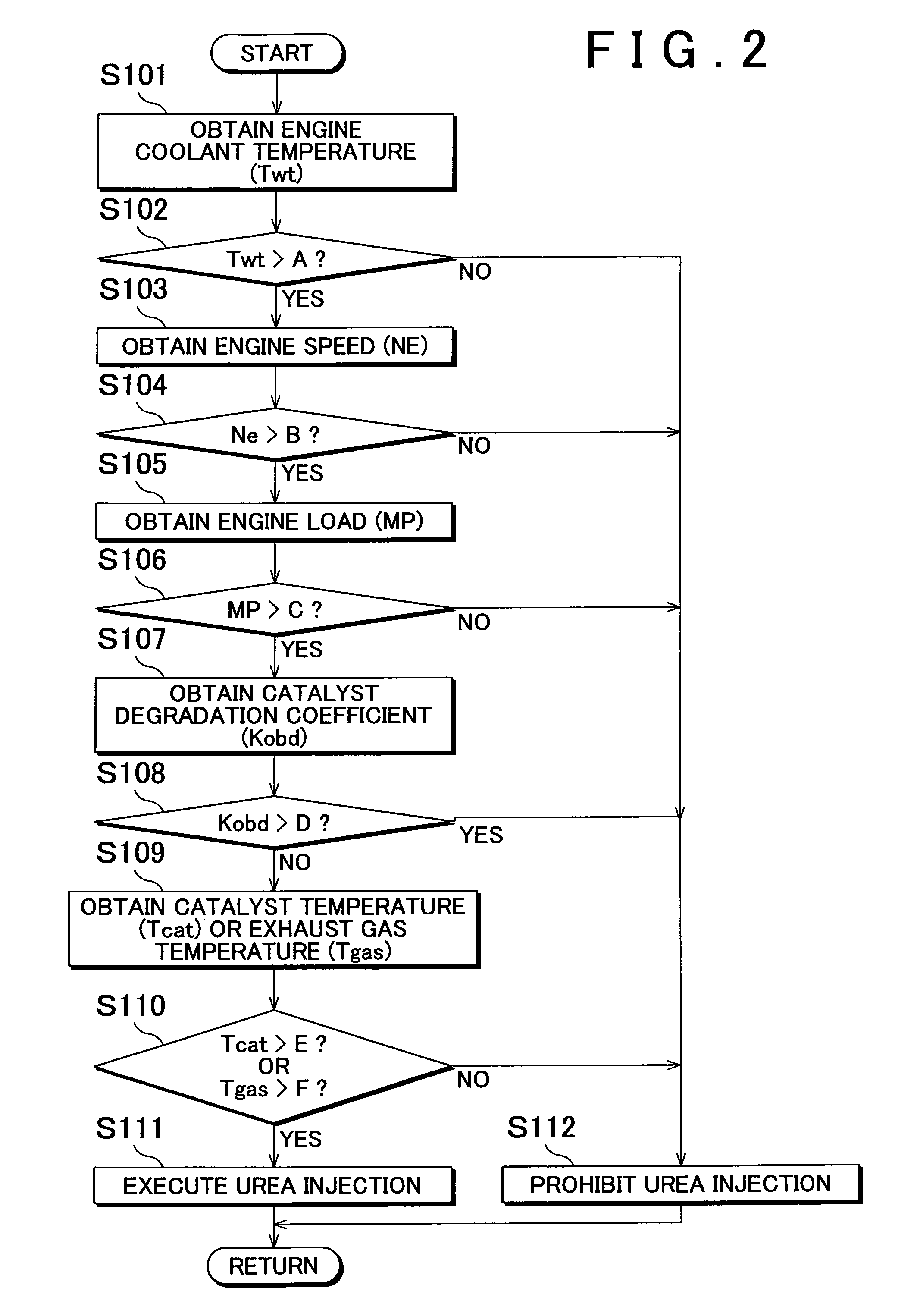
An internal combustion engine exhaust gas purification apparatus purifies exhaust gas using a NOx storage-reduction catalyst unit and a NOx selective reduction catalyst unit. The NOx selective reduction catalyst unit is provided downstream of the NOx storage-reduction catalyst unit in an exhaust gas passage. An urea injecting mechanism, for example an injection valve, injects urea into the exhaust gas passage. An urea injection controller prohibits urea injection from the urea injecting mechanism if at least one of the temperatures of the NOx storage-reduction catalyst unit and the NOx selective reduction catalyst unit is equal to or lower than a reference temperature. As such, production of cyanic acid is minimized, and therefore leaks of cyanic acid from the NOx storage-reduction catalyst unit and / or the NOx selective reduction catalyst unit can be suppressed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Nitric oxide oxidation over silver-based catalysts
InactiveUS20130294989A1Reduce tailpipe emission of NOxEfficient oxidationCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsHydrogenNitrogen
Ag / Al2O3 materials may be packaged in a suitable flow-through reactor, close coupled to the exhaust manifold of a diesel engine, and upstream of other exhaust gas treatment devices, such as a diesel oxidation catalyst and a selective reduction catalyst for NOx. The silver / alumina catalyst material uses hydrogen in a cold-start engine exhaust and serves to oxidize NO to NO2 in the relatively low temperature, hydrocarbon-containing, exhaust during a short period following the engine cold start, and to temporarily store NOx during the start-up period. After the exhaust has heated downstream catalytic devices, the silver yields its nitrogen oxides for conversion to nitrogen by the then-operating devices before NOx is discharged to the atmosphere.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
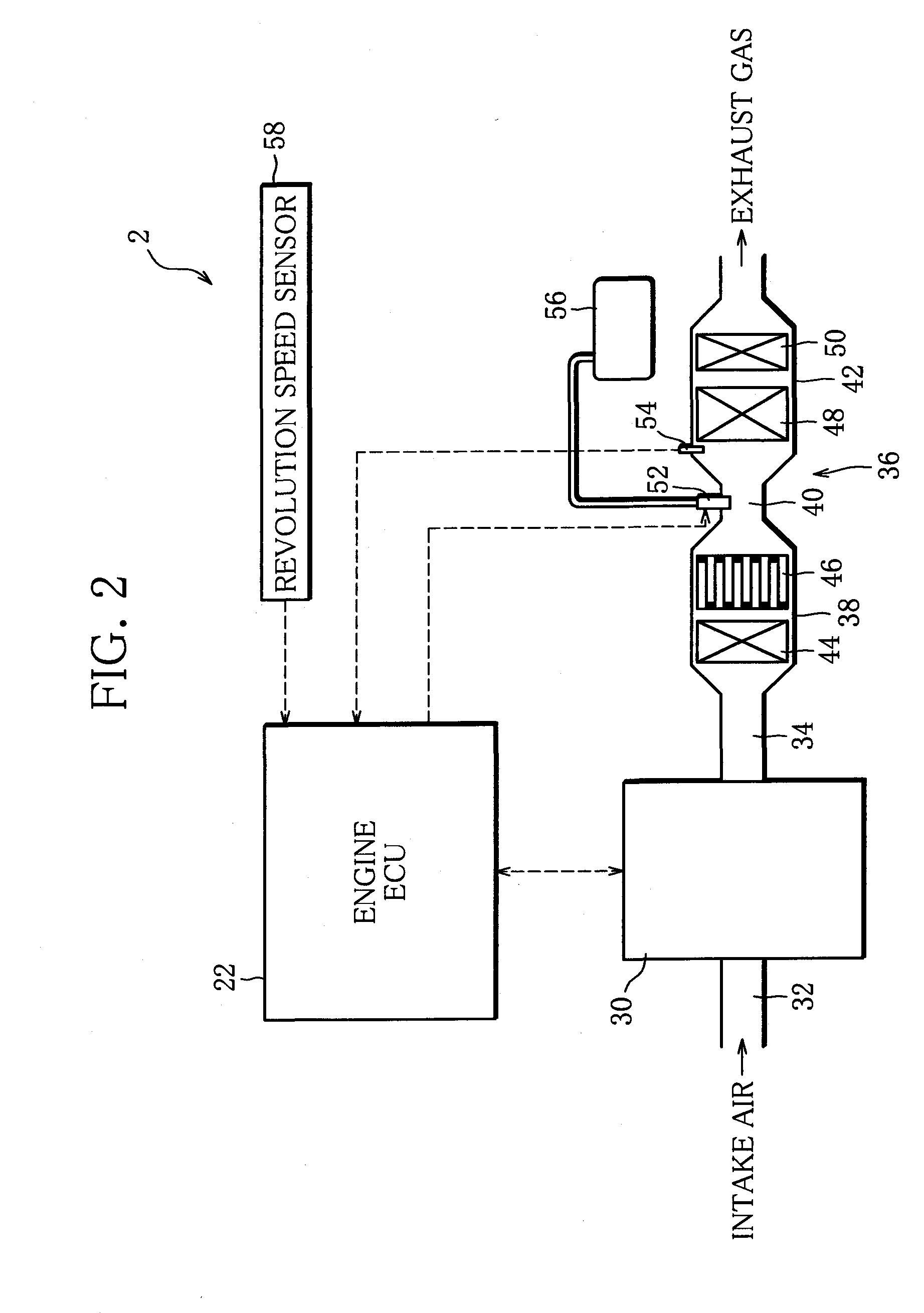
Exhaust emission control device
ActiveUS20100000203A1Sufficient reaction timeClosely arrangedGas treatmentElectrical controlParticulatesOxygen
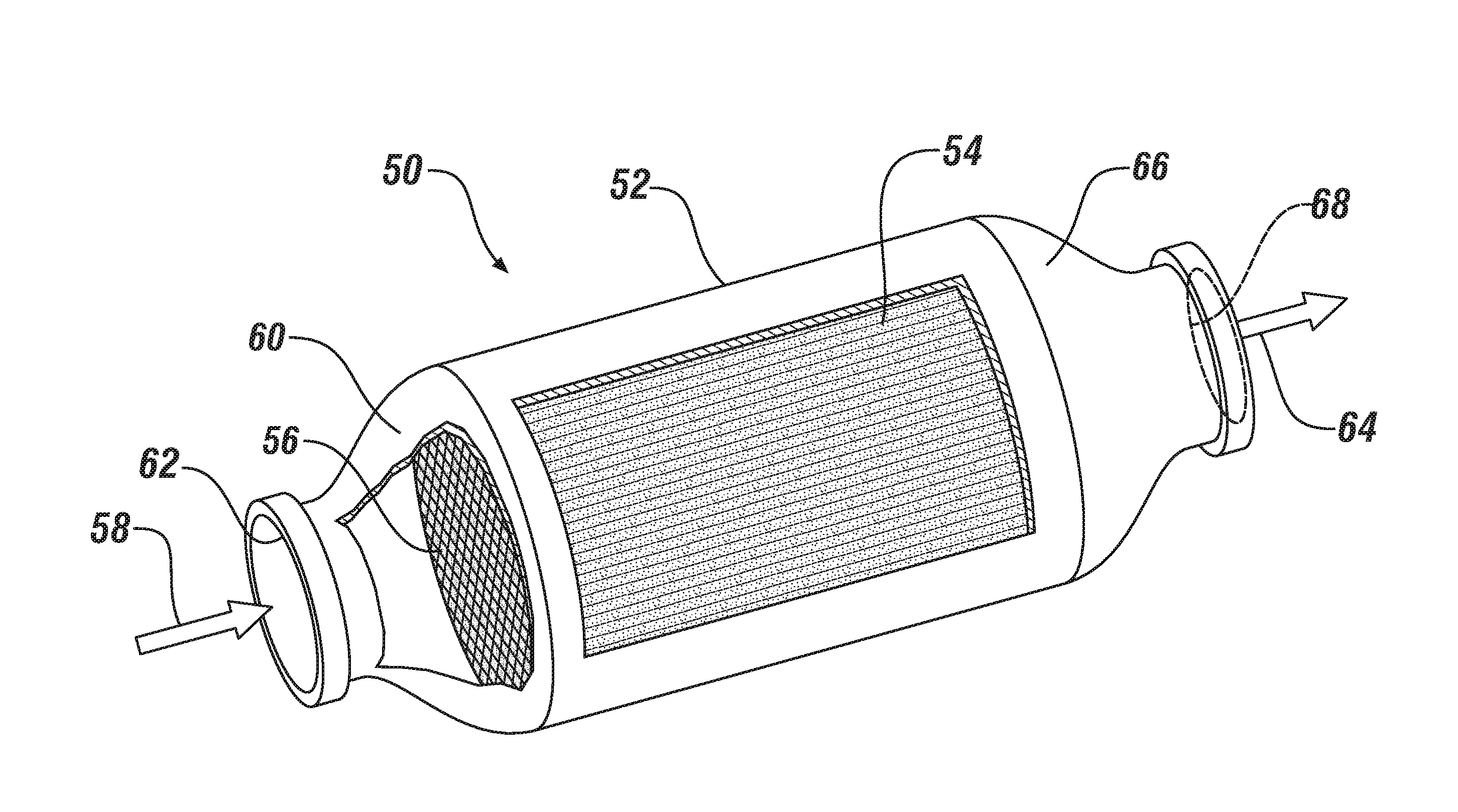
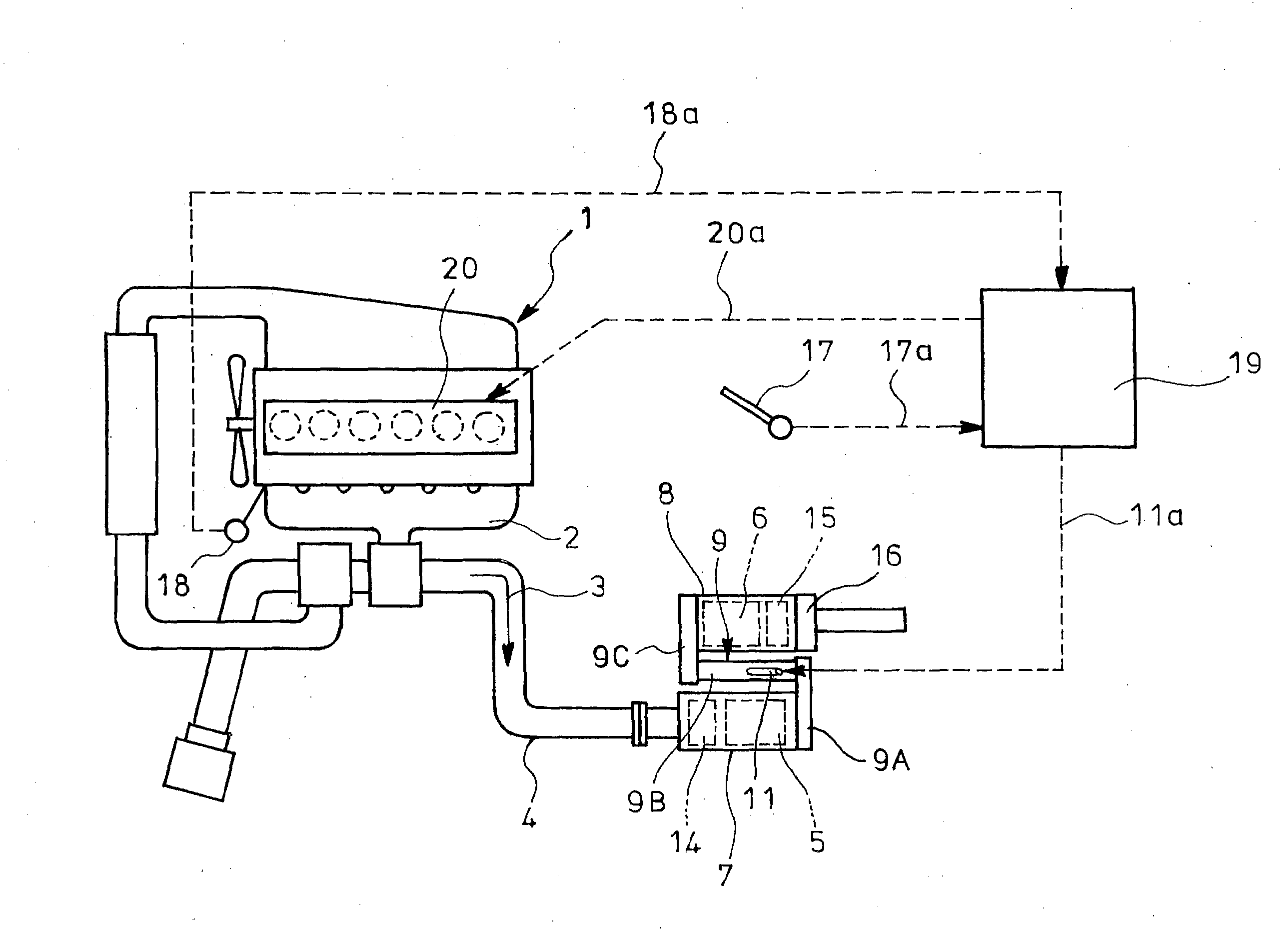
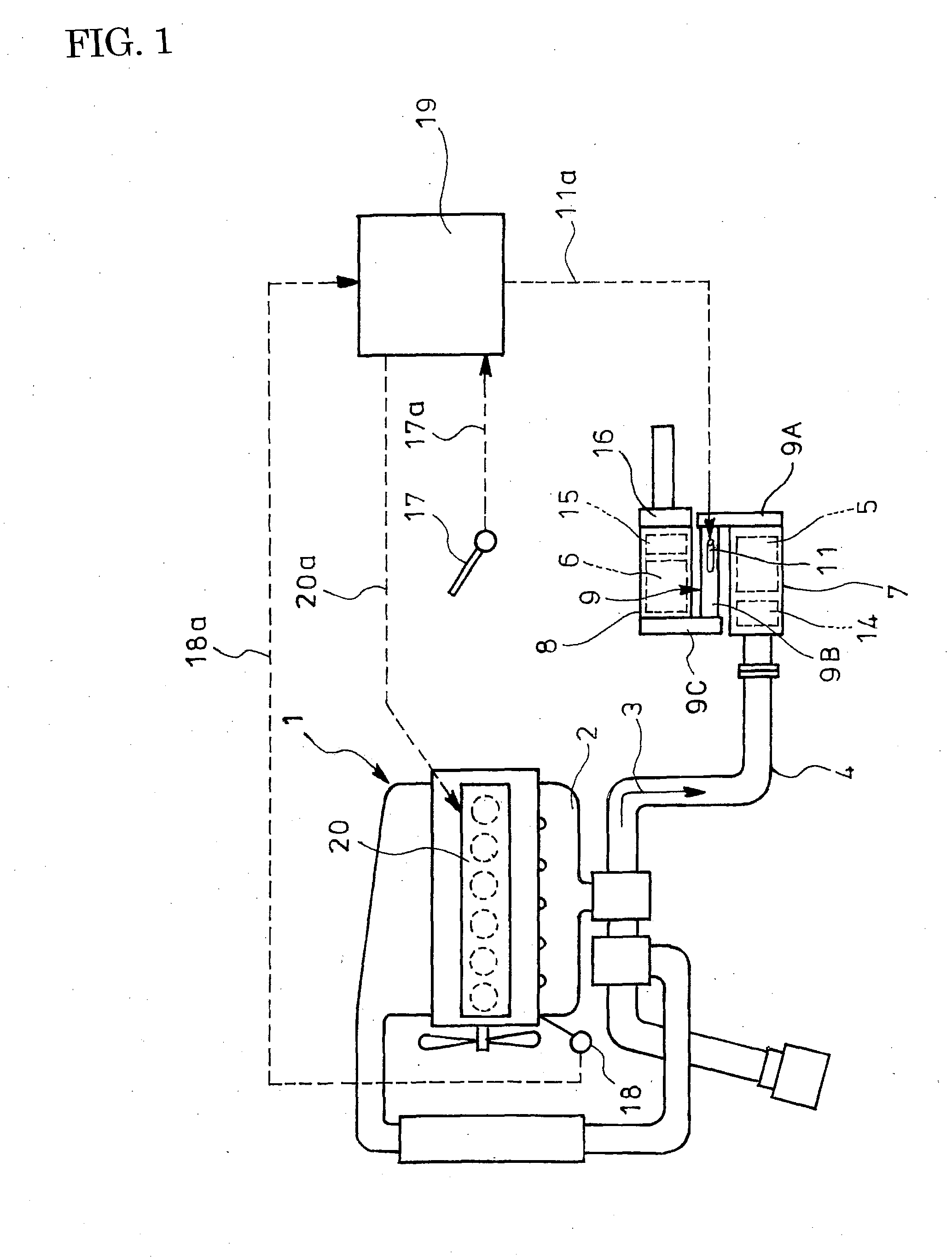
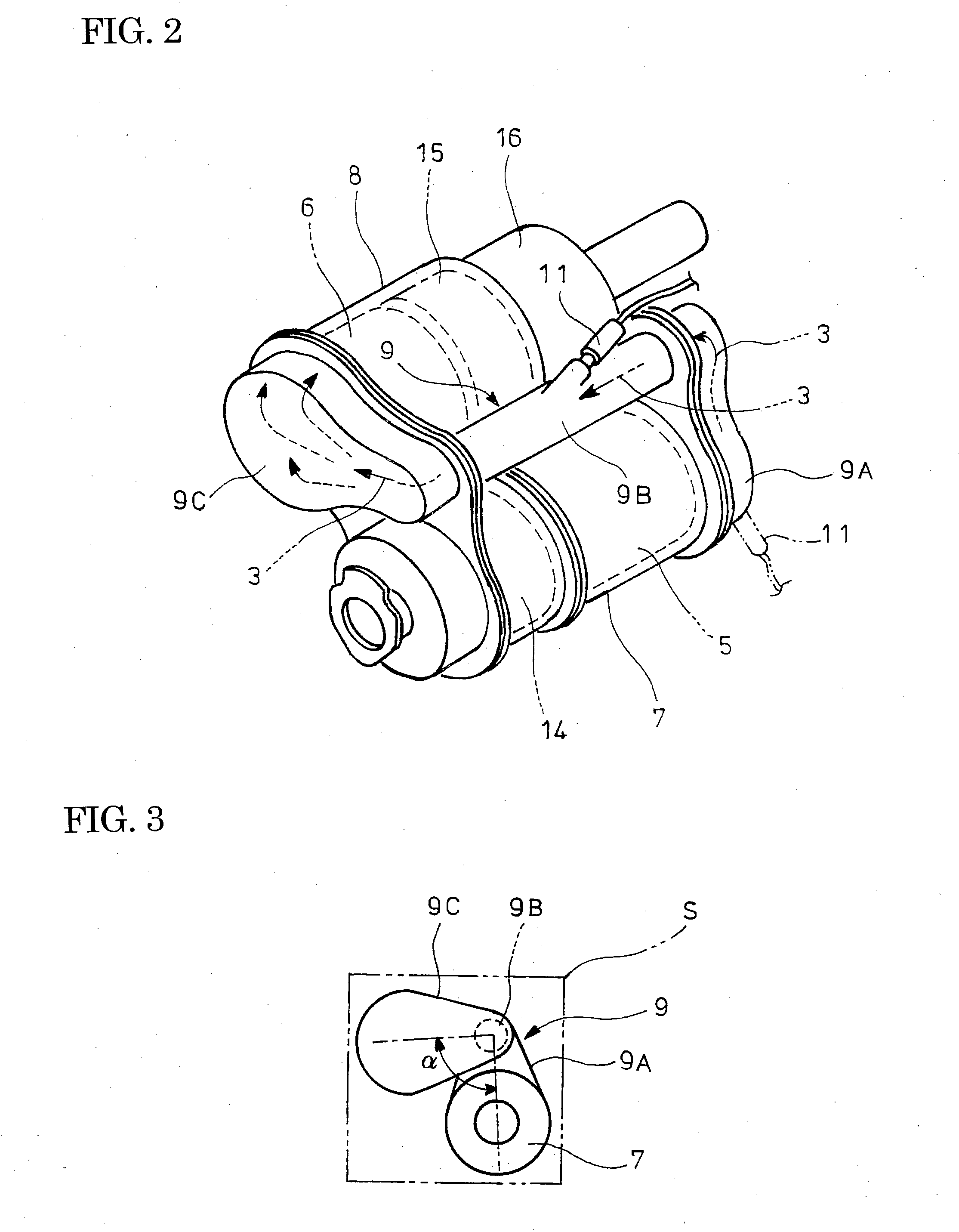
The object of the invention is to improve mountability on a vehicle by realizing a compact arrangement of a particulate filter 5 and selective reduction catalyst 6 while ensuring satisfactory reaction time for generation of ammonia from urea water. In an exhaust emission control device having particulate filter 5 incorporated in an exhaust pipe 4, selective reduction catalyst 6 capable of selectively reacting NOx with ammonia under the presence of oxygen being arranged downstream of the particulate filter, urea water as reducing agent being adapted to be added between the selective reduction catalyst 6 and the particulate filter 5, the particulate filter 5 is arranged in parallel with the selective reduction catalyst 6. An S-shaped communication passage 9 is arranged for introduction of the exhaust gas 3 from a rear end of the particulate filter 5 to a front end of the adjacent selective reduction catalyst 6 in a forward folded manner. A urea water addition injector 11 is arranged midway of the communication passage 9.
Owner:HINO MOTORS LTD
Exhaust emission control system of internal combustion engine and exhaust emission control method
InactiveUS20100205940A1Low costReduce conversionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemExhaust fumes
In an exhaust emission control system of an internal combustion engine, a NOx selective reduction catalyst is disposed in an engine exhaust passage, and an aqueous solution of urea stored in an aqueous-urea tank is supplied to the NOx selective reduction catalyst so as to selectively reduce NOx. A NOx sensor is provided in the engine exhaust passage downstream of the NOx selective reduction catalyst for detecting the NOx conversion efficiency of the NOx selective reduction catalyst, and the concentration of aqueous urea in the aqueous-urea tank is estimated from the detected NOx conversion efficiency. The exhaust emission control system and method make it possible to detect the concentration of aqueous urea at reduced cost.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
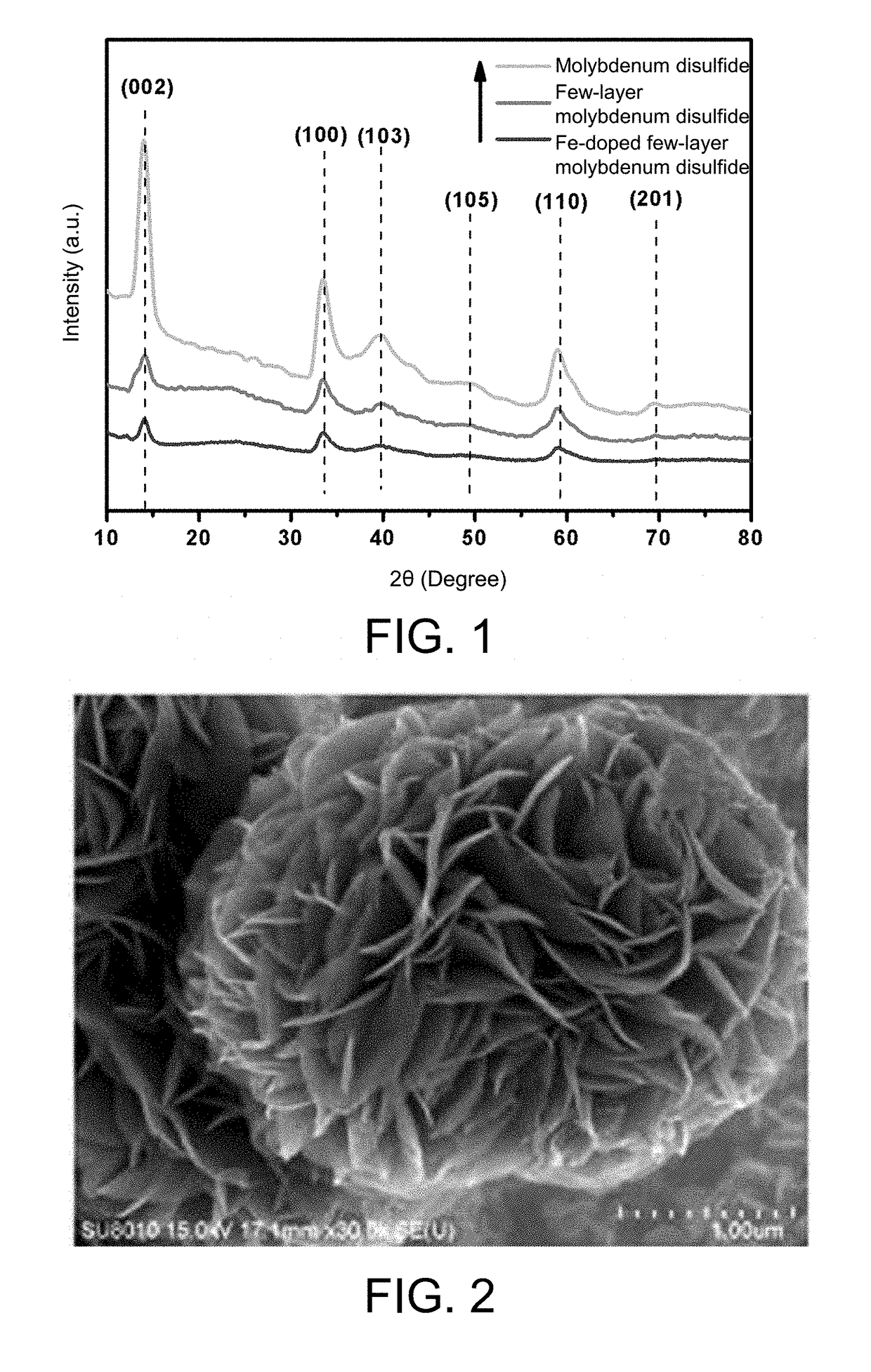
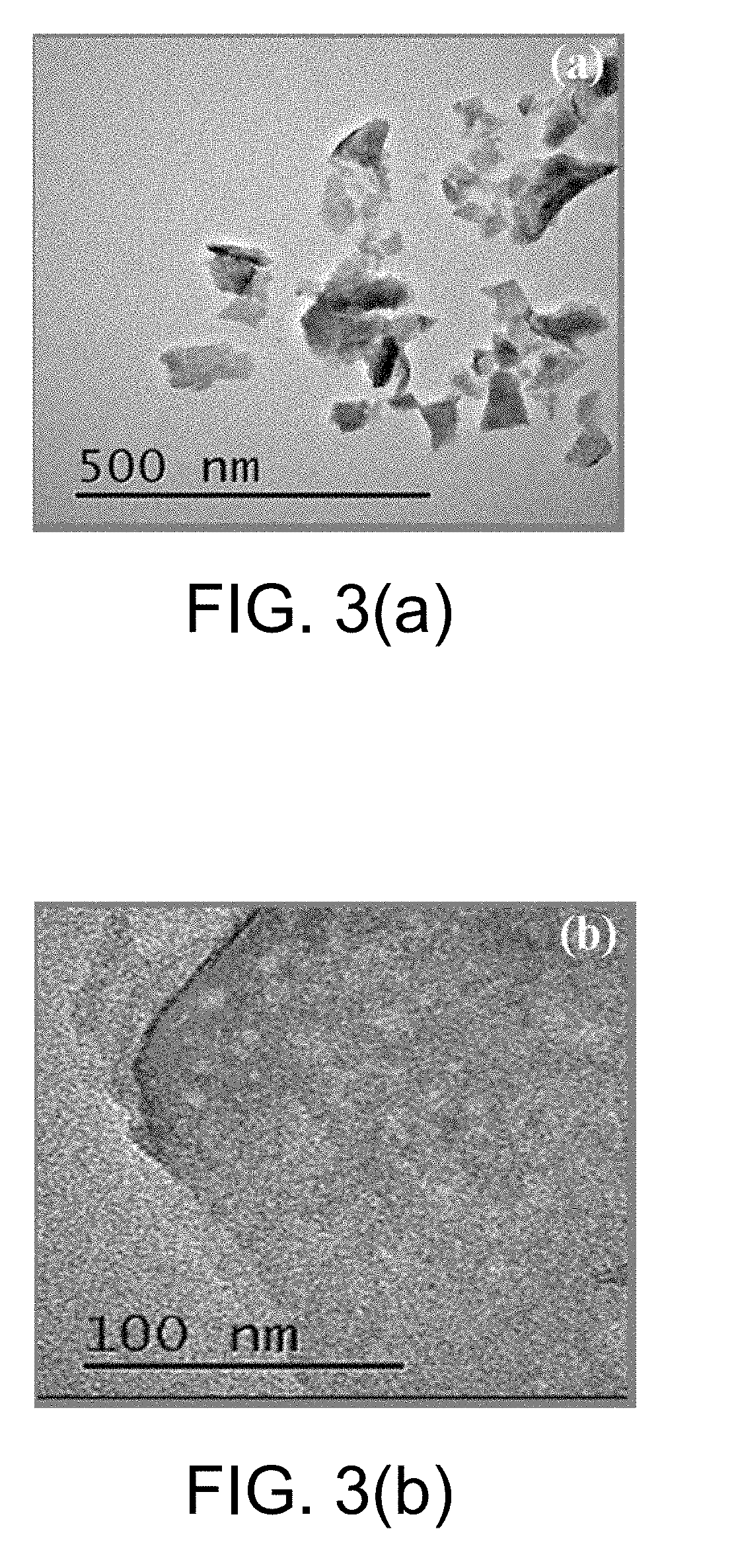
Monatomic metal-doped few-layer molybdenum disulfide electrocatalytic material, preparing method thereof, and method for electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation
ActiveUS20190030516A1Readily availableLow costHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationFaraday efficiencySelective reduction
The present invention provides a monatomic metal-doped few-layer molybdenum disulfide electrocatalytic material, a preparing method thereof, and a method for electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation. The material has a few-layer ultra-thin and irregular flake-like microstructure with a length and a width of nanometer scale. A doping metal in the monatomic metal-doped few-layer molybdenum disulfide electrocatalytic material is dispersed in a form of single atoms. When the catalyst is used in electrochemical reduction of N2, a Faradic efficiency in selective reduction of N2 into NH4+ is 18% or above, and stability of the catalyst is better.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
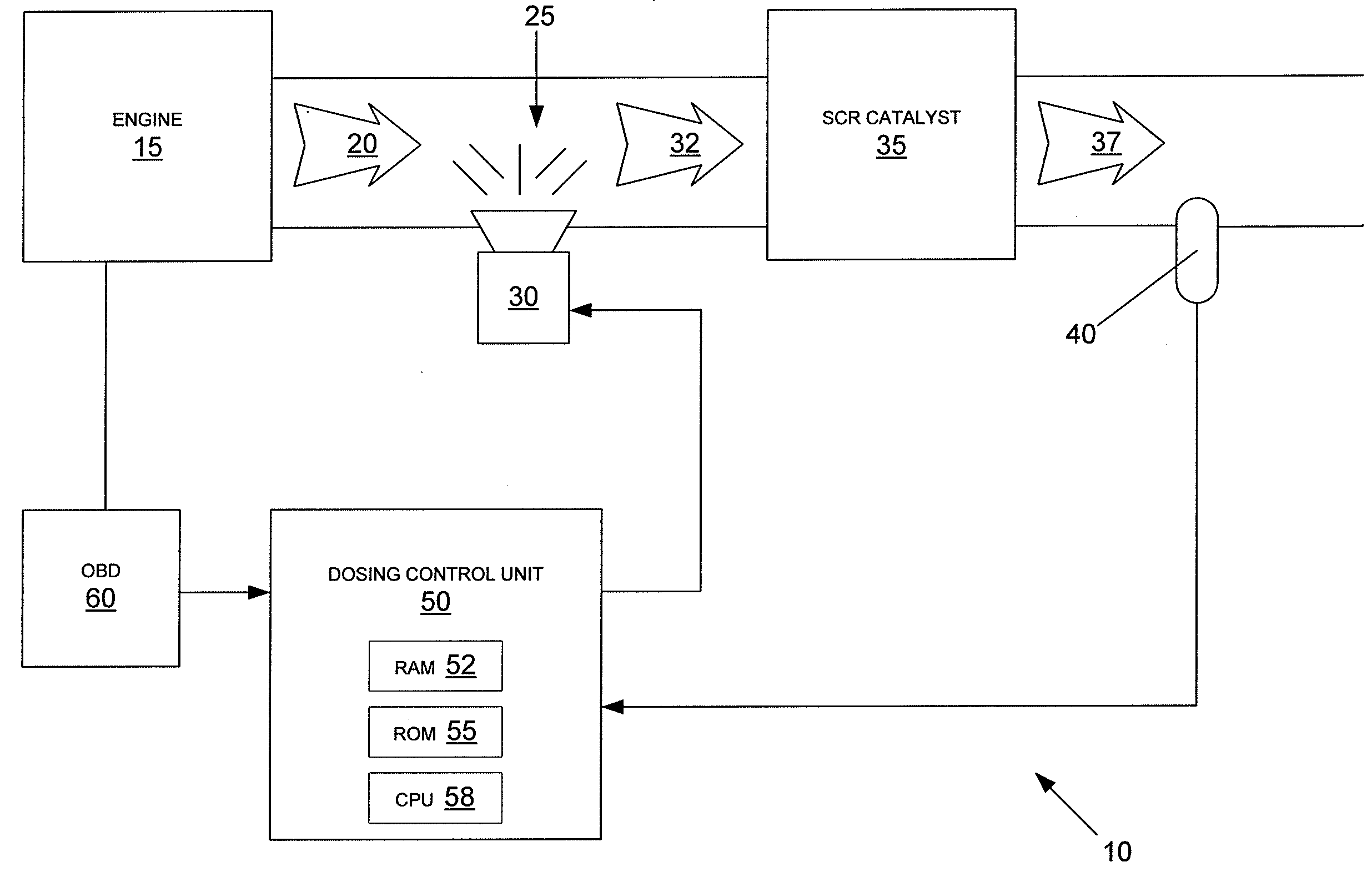
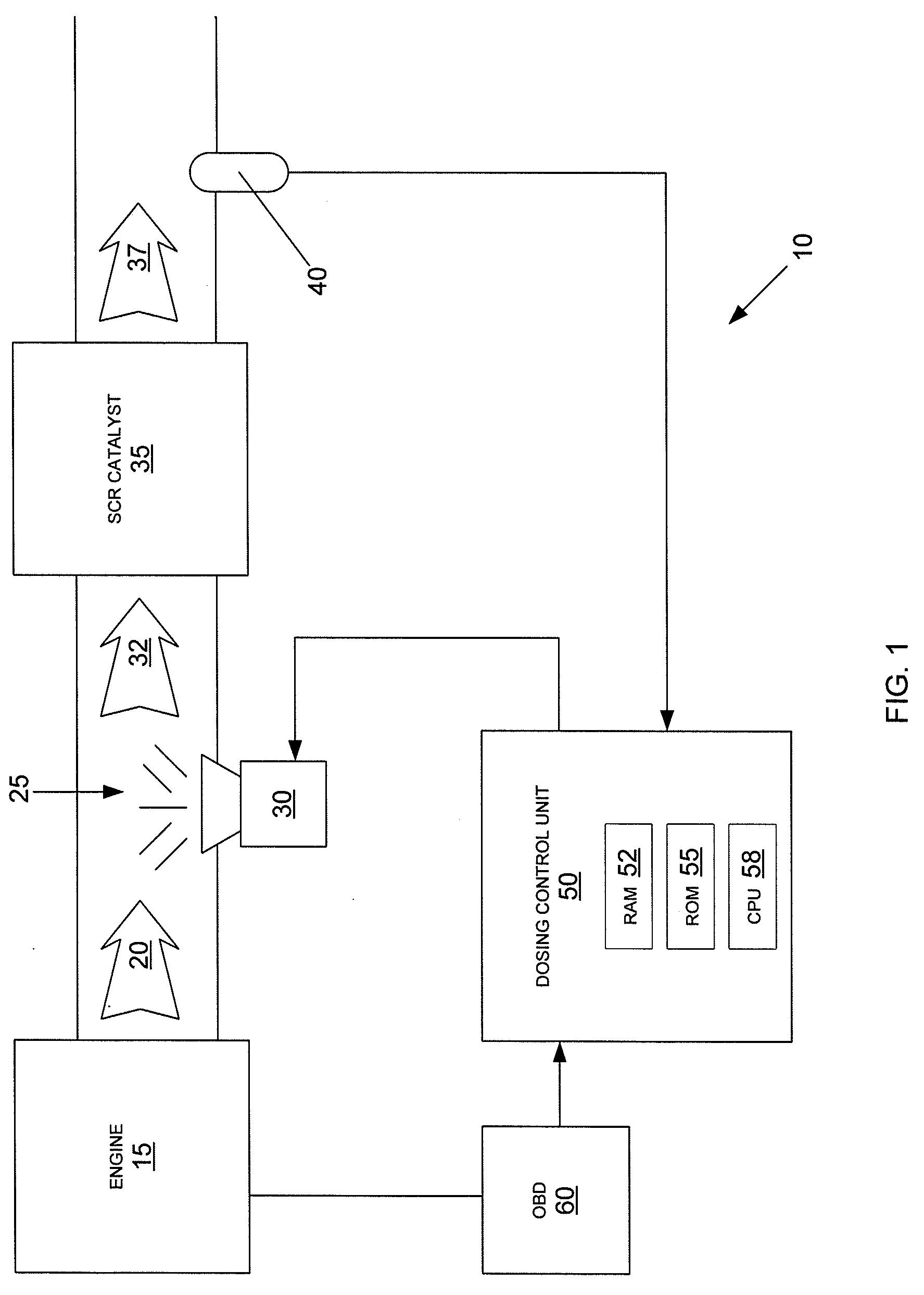
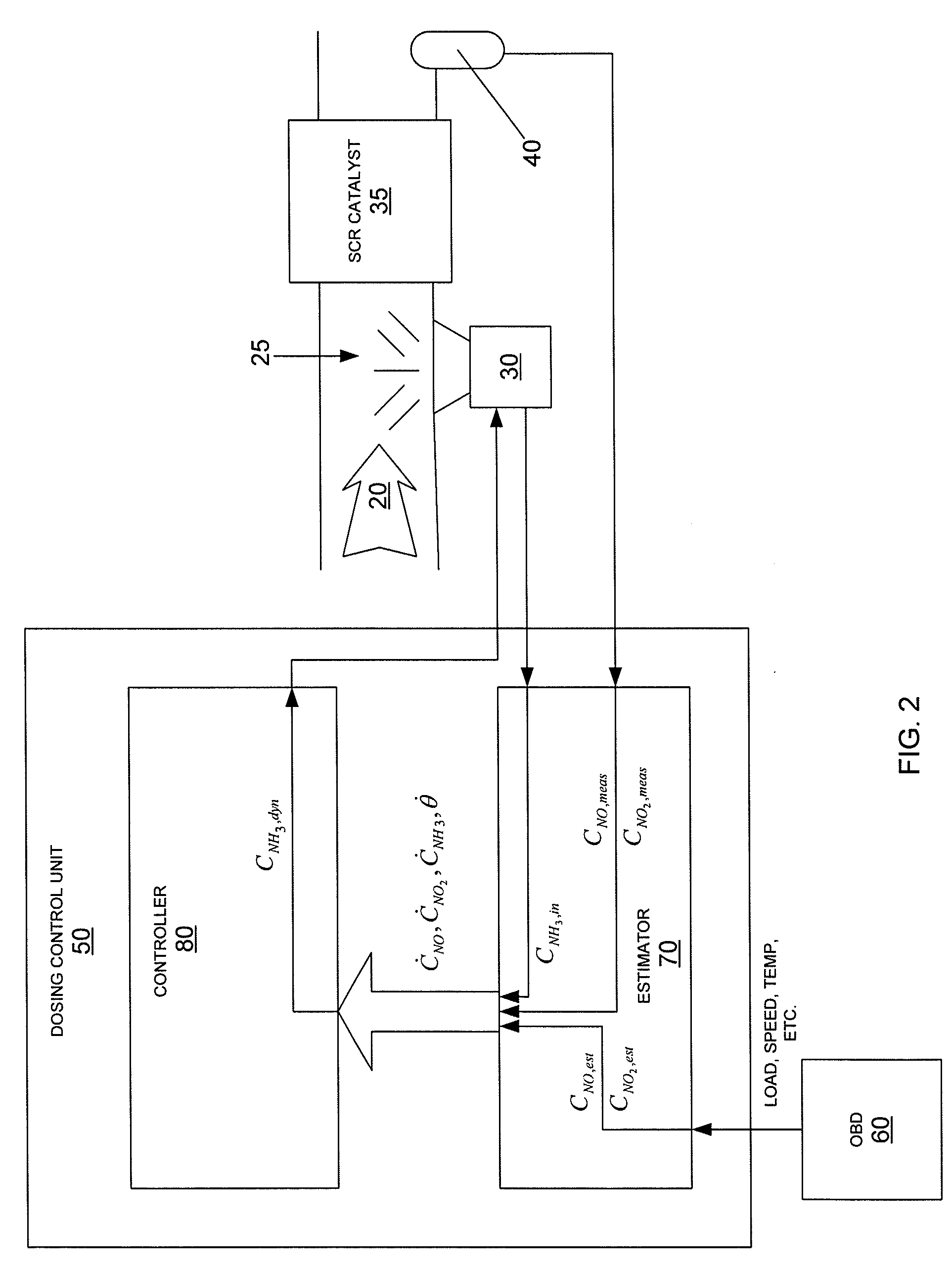
NOx CONTROL SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR CONTROLLING NOx EMISSIONS
InactiveUS20090133384A1Minimize NOx emissionInternal combustion piston enginesLighting and heating apparatusControl systemEnvironmental engineering
An exhaust aftertreatment system comprising a selective reduction catalyst, a NOx sensor or an NH3 sensor, a urea injector, and a dosing control unit, wherein the dosing control unit calculates the rate of urea injection by estimating the concentrations of NO and NO2 in the exhaust downstream of the SCR catalyst.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
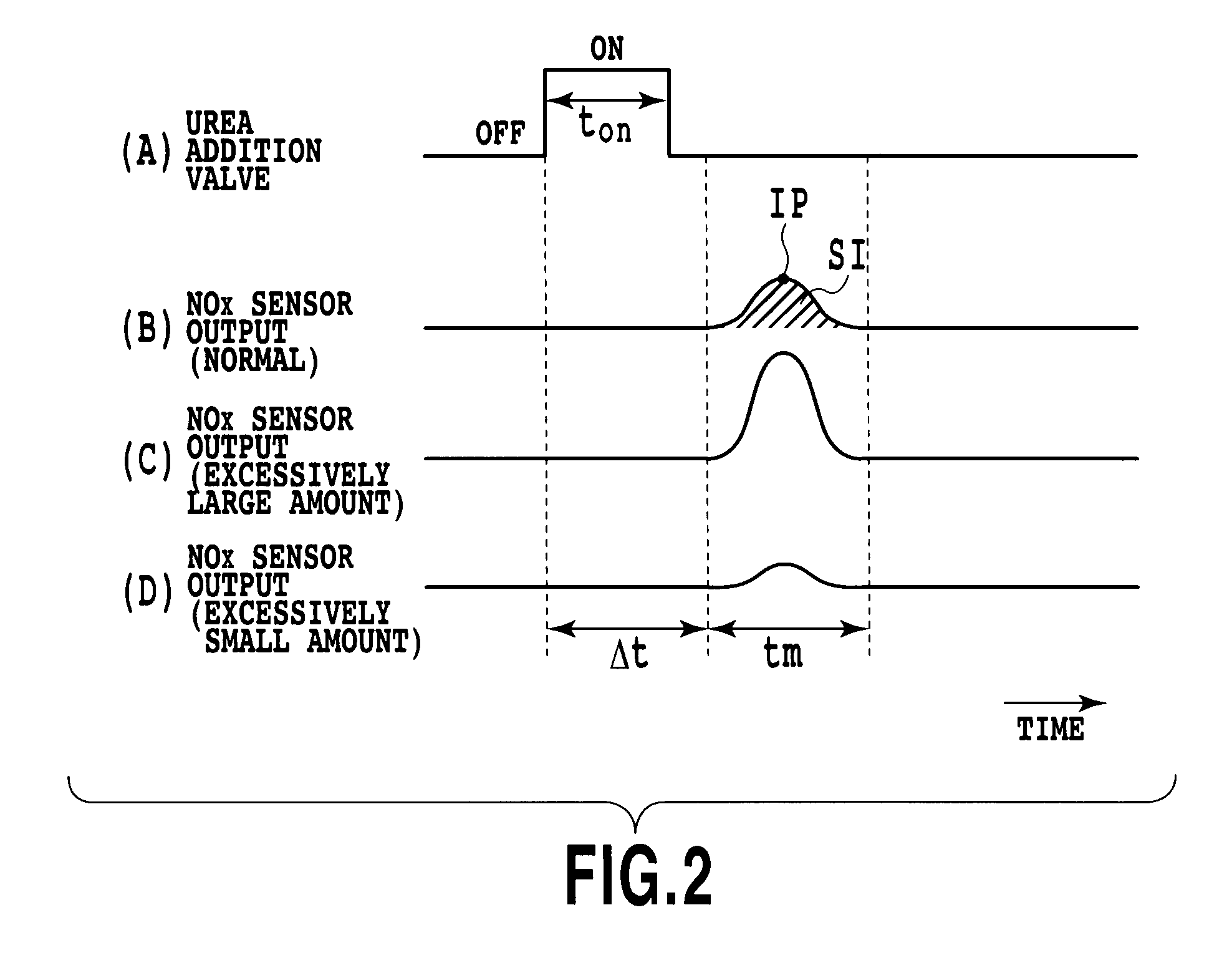
Abnormality diagnosis apparatus for exhaust purification system
ActiveUS20100115918A1Easy to detectAvoid spendingInternal-combustion engine testingInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineAqueous solution
In an exhaust purification system having a urea addition device adding a urea aqueous solution to an NOx catalyst of selective reduction type provided in an exhaust passage in an internal combustion engine, a sensor detecting an ammonia concentration is provided at the downstream side of the NOx catalyst. During fuel cut, a predetermined amount of urea aqueous solution is added. Then, based on a sensor output obtained at this time, an abnormality in at least one of the urea addition device and the urea aqueous solution is detected. The addition of the urea aqueous solution during the fuel cut prevents reactive consumption between urea and NOx. The sensor output corresponding to the amount of the urea aqueous solution is obtained. This output condition is compared with a normal one to allow determination of whether or not an appropriate amount of urea aqueous solution of appropriate quality has been added.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Exhaust gas purification method using selective reduction catalyst
InactiveUS20090269265A1Efficient purificationImprove efficiencyNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentPurification methodsEngineering
An exhaust gas purification method which is capable of purifying nitrogen oxide to be included in exhaust gas from a lean burn engine such as a boiler, a gas turbine or a lean-burn-type gasoline engine, a diesel engine, effectively, in particular, even at low temperature, with spray-supplying an aqueous solution of urea as the reducing component to the selective reduction catalyst.The exhaust gas purification method for reducing selectively NOx in exhaust gas, which is exhausted from a lean burn engine, with a selective reduction catalyst and ammonia, characterized in thatan aqueous solution of urea is spray-supplied to the selective reduction catalyst, comprising at least the following zeolite (A) and the hydrolysis promotion component of urea (B), and it is contacted at 150 to 600° C., and ammonia is generated in a ratio of [NH3 / NOx=0.5 to 1.5] to NOx in exhaust gas, as converted to ammonia, and a nitrogen oxide is decomposed into nitrogen and water.zeolite (A): zeolite comprising an iron elementhydrolysis promotion component (B): a complex oxide comprising at least one kind selected from titania or titanium, zirconium, tungsten, silicon or alumina
Owner:BASF AG +1
Ferrotitanium composite oxides catalyst for ammonia selective reduction nitric oxides
ActiveCN101380578ALow priceSimple preparation processDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitric oxideHigh activity
The invention relates to a catalyst of selective reduction of nitrogen oxide by ammonia, which mainly solves the existing problems that the commonly used NH3-SCR catalyst system is toxic to environment and human body, the anti-SO2 poisoning ability of the catalyst system is poor in the reference and the catalyst system can not adapt to the conditions of high space velocity. The invention adopts cheap and non-toxic raw materials to prepare a Fe-Ti oxide catalyst with high activity, selectivity, stability and anti-S2 poisoning ability by the simple and practicable co-precipitation method, which can better solve the existing technical problems. If the catalyst is loaded on honeycomb ceramics after being made into pulp, the catalyst is hopeful to be put into practical application of flue gas denitrification of coal-fired power plants.
Owner:江西中科鸿虔新材料有限公司
Exhaust emission control device for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20080306673A1Reduce the valueImprove concentrationAnalogue computers for vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesMoving averageExternal combustion engine
An exhaust emission control device for an internal combustion engine, capable of supplying a just enough amount of reducing agent to a selective reduction catalyst even when a NOx purification ratio of the catalyst is changed by various causes, thereby enabling a high NOx purification ratio and very low exhaust emissions to be maintained. An ECU calculates a filtered value based on a signal from an exhaust gas concentration sensor, calculates a moving average value of a product of the filtered value and a reference input, calculates a control input such that the moving average value becomes equal to 0, and adds a reference input to the control input to calculate an FB injection amount. The ECU calculates an FF injection amount with a predetermined feedforward control algorithm, and adds the FF injection amount to the FB injection amount, to thereby calculate a urea injection amount.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Exhaust purification device for hybrid electric vehicle
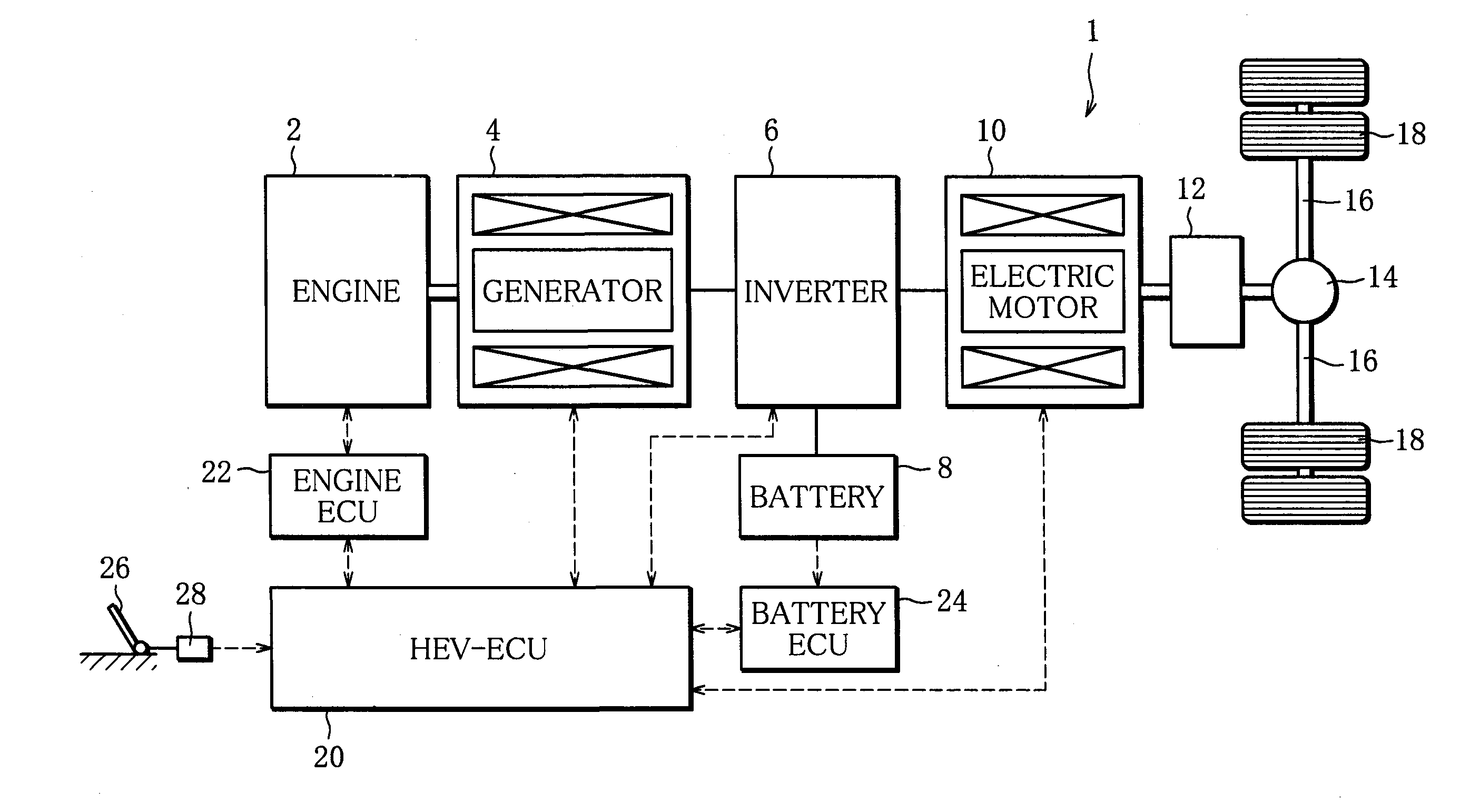
InactiveUS20100268438A1Reliably prevent occurrenceIncrease exhaust temperatureAuxillary drivesInternal combustion piston enginesHybrid electrical vehicleAmmonia
An ammonia selective reduction-type NOx catalyst (48) is interposed in an exhaust passage of an engine (2) provided in a series-type hybrid electric vehicle (1), and a urea water injector (52) is disposed in the exhaust passage to supply a urea water into exhaust gas existing upstream of the ammonia selective reduction-type NOx catalyst (48). The engine (2) is started and stopped in accordance with the storage state of a battery (8), and the urea water injector (52) is controlled in accordance with the operating state of the engine (2). When the engine (2) is to be stopped, an adsorption increasing operation for increasing the amount of ammonia adsorbed by the ammonia selective reduction-type NOx catalyst (48) is executed over a predetermined period before the engine (2) is stopped.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
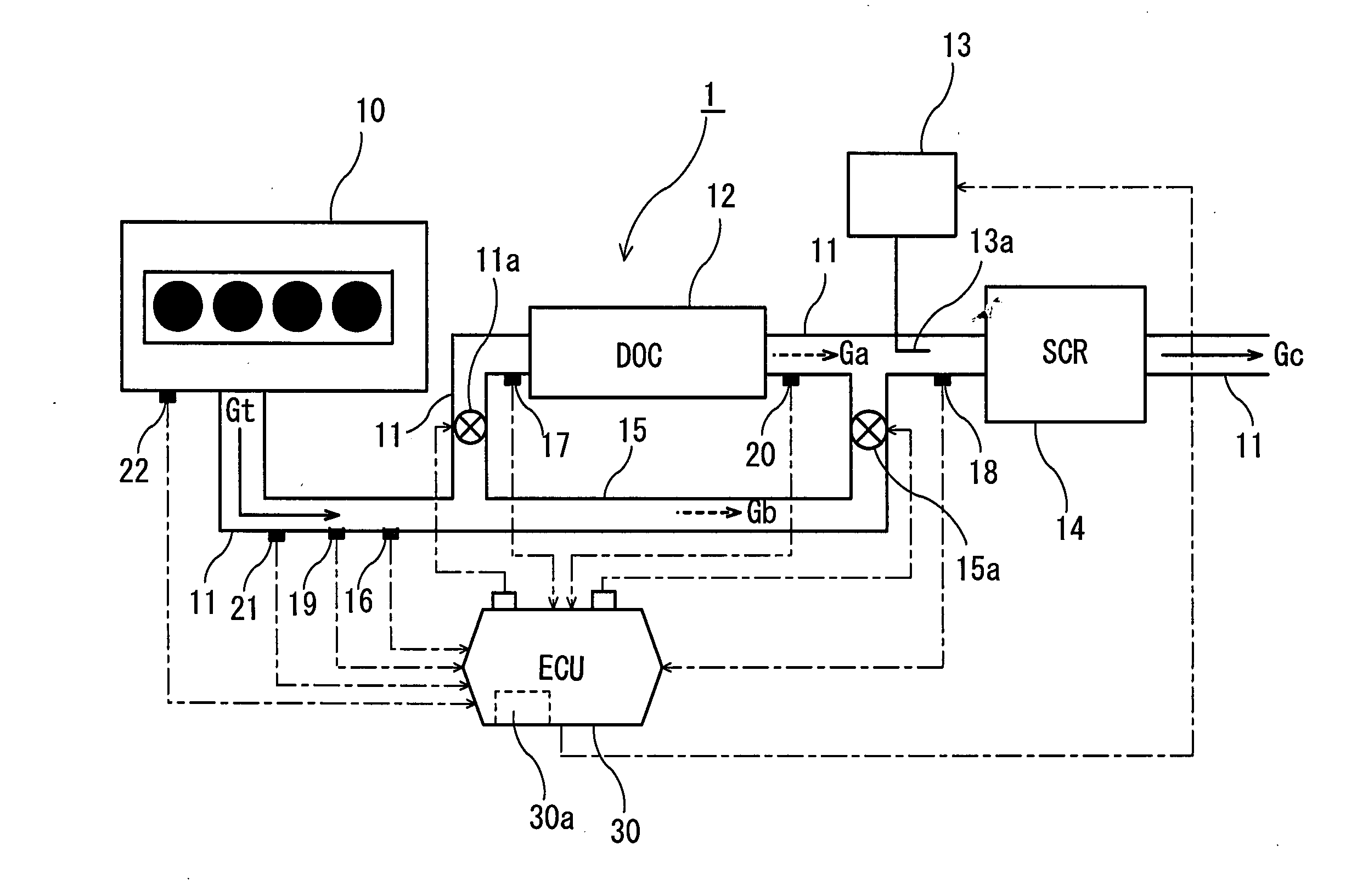
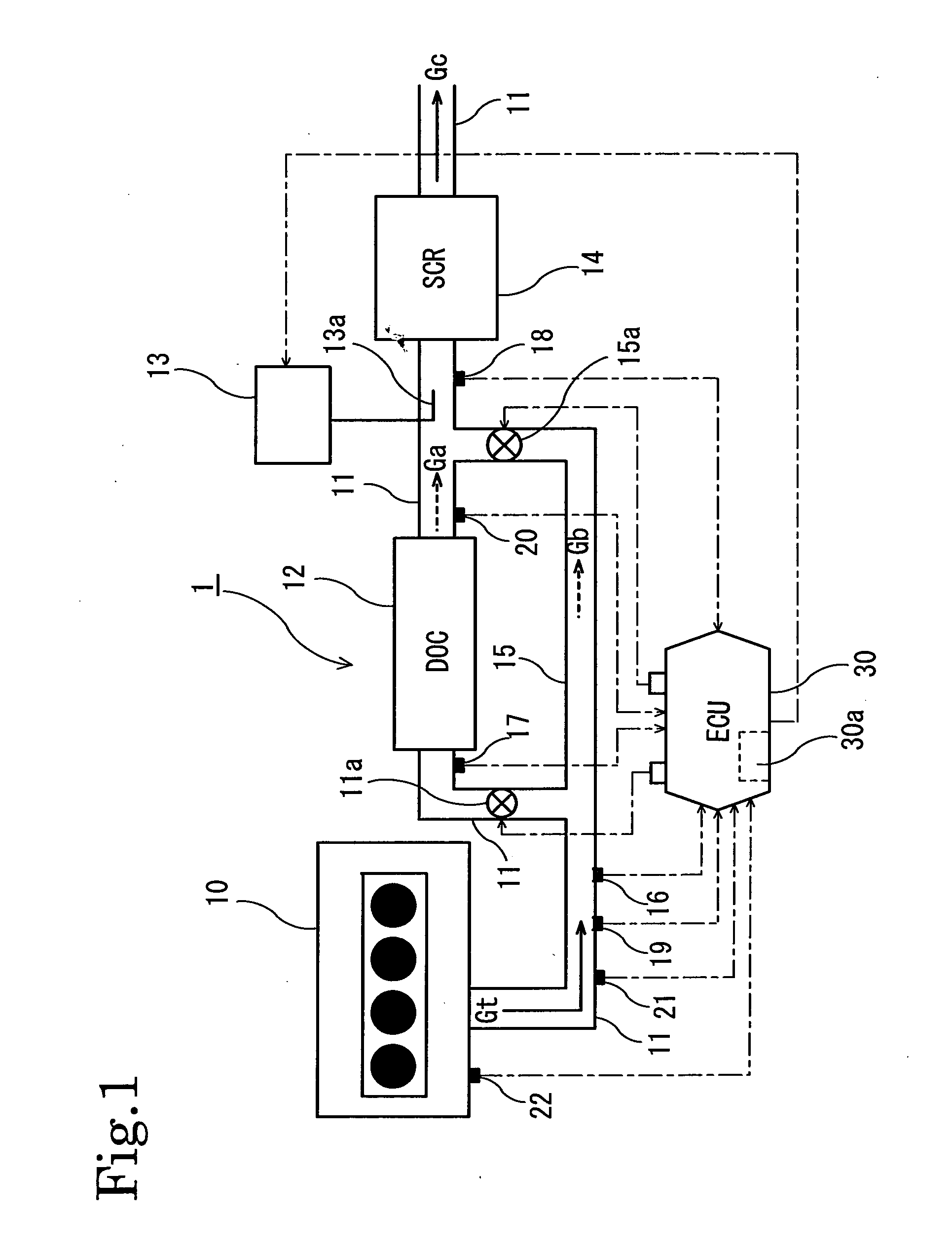
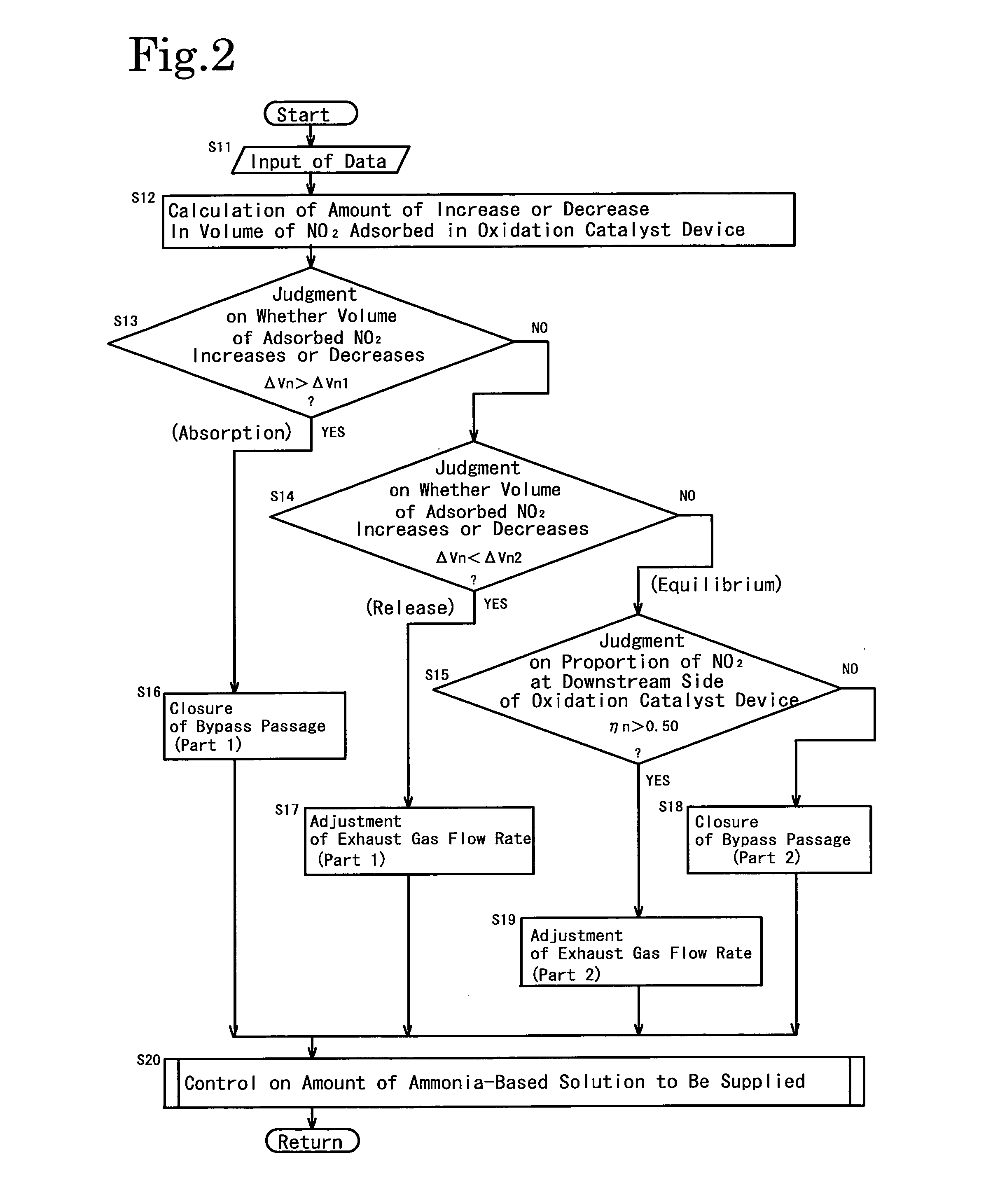
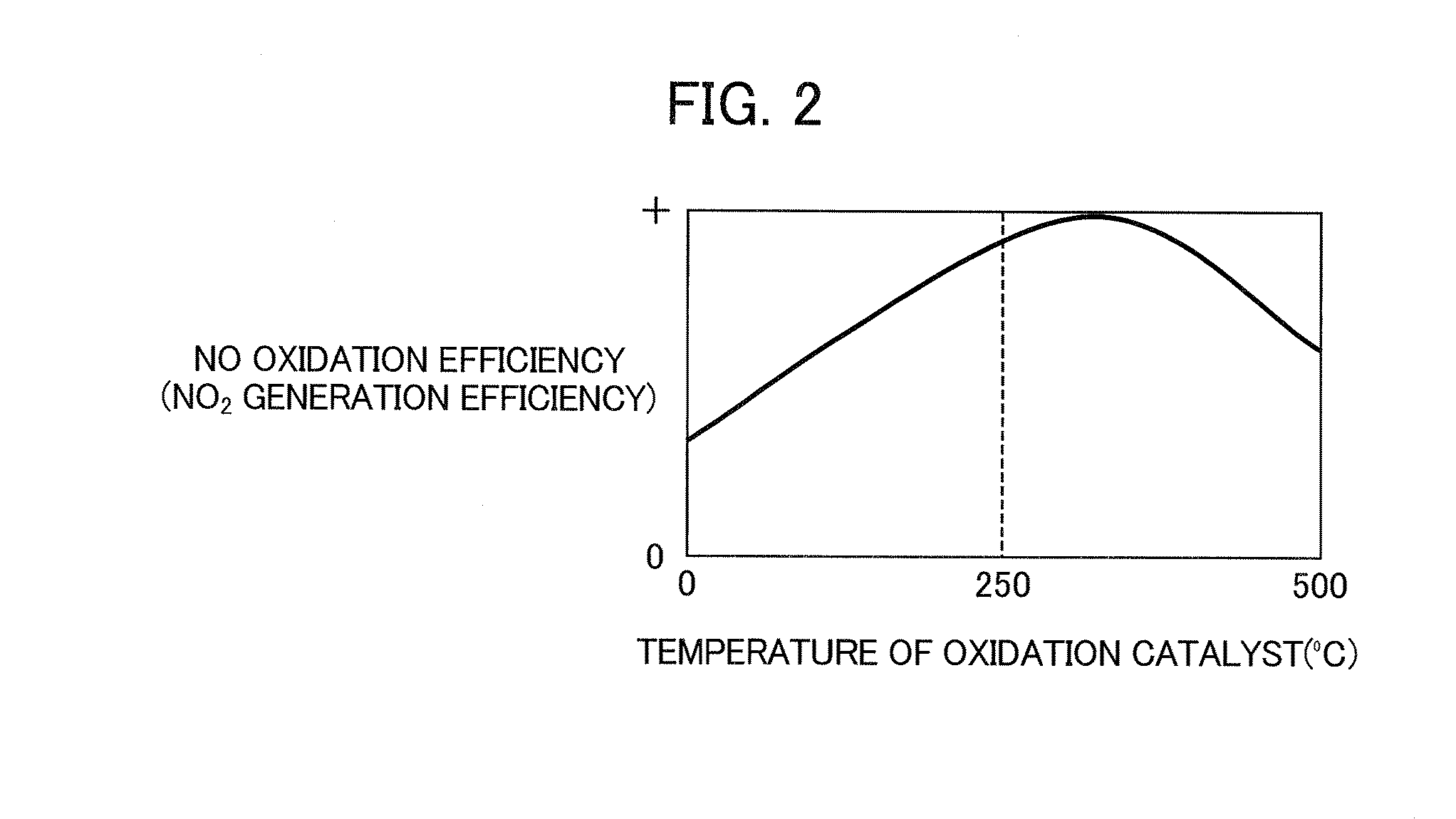
Method of controlling nox purification system, and nox purification system
ActiveUS20110041481A1Improve abilitiesLower the volumeGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesAmmoniaSelective reduction
Provided is a method of controlling a NOx purification system configured to reduce NOx contained in an exhaust gas by including an oxidation catalyst device (12) and a selective reduction type NOx catalyst device (14), which are arranged in this order from the upstream side, as well as the NOx purification system (1). The method and the system estimates whether a volume (Vn) of NO2 adsorbed in the oxidation catalyst device (12) increases or decreases, and controls a flow rate (Vgb) of exhaust gas which bypasses the oxidation catalyst device (12) on the basis of the increase or decrease in the estimated volume (Vn) of adsorbed NO2. Thereby, the method and the system avoid problems which occur due to shortage and excessive supply of ammonia by: estimating how much of NO2 is adsorbed in the oxidation catalyst device; thus making the ratio of NO to NO2 in NOx, which flows into the selective reduction type NOx catalyst device, closer to 1:1 as much as possible; and adding a necessary amount of ammonia-based solution.
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
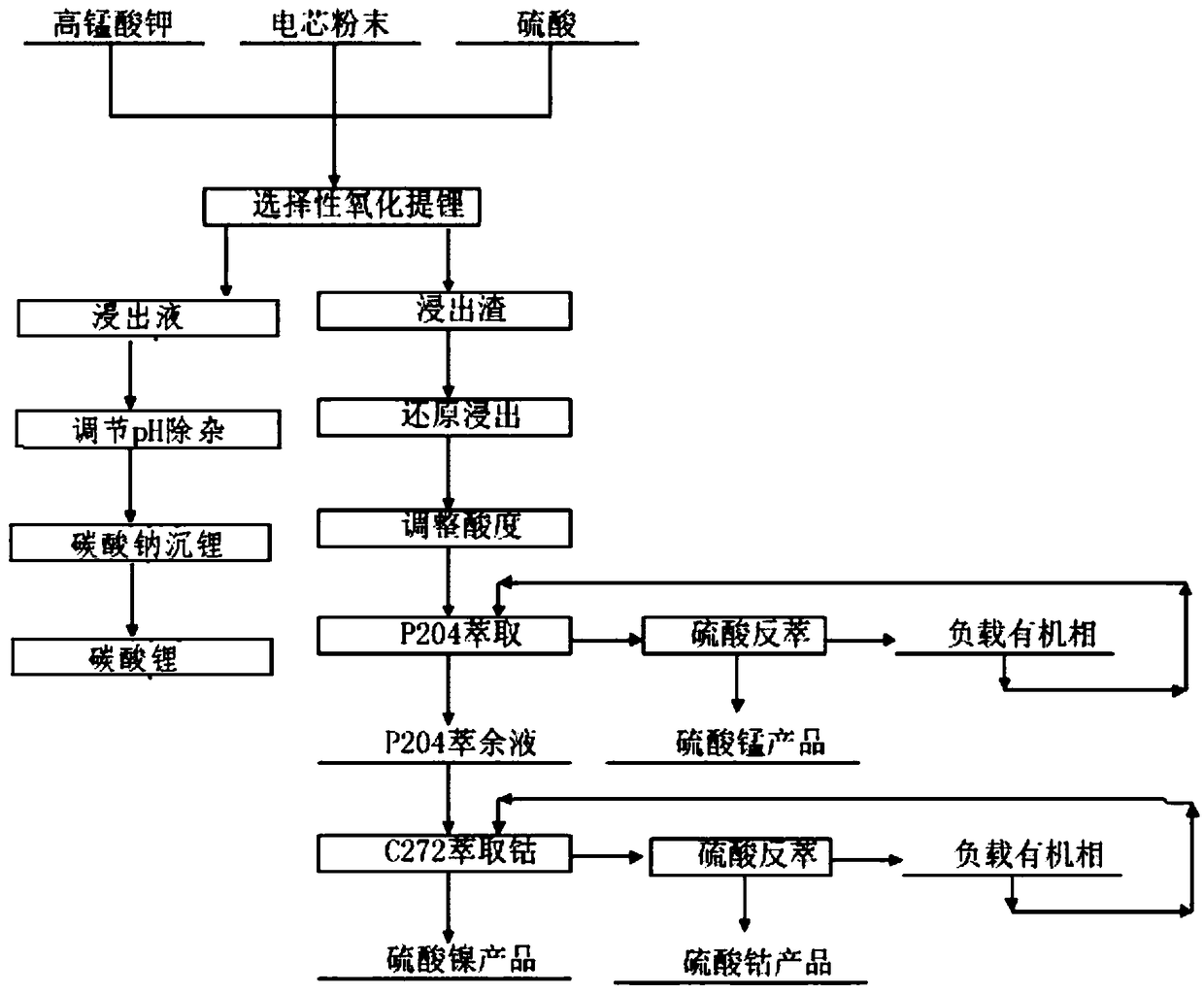
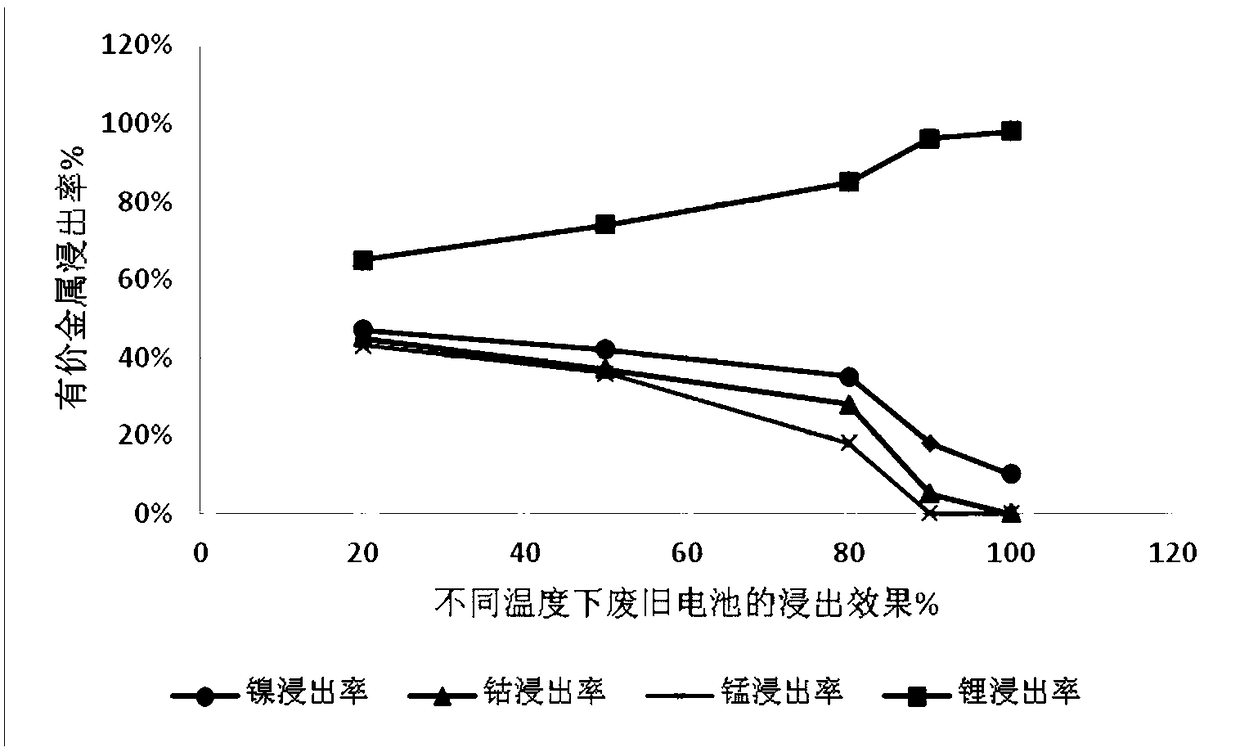
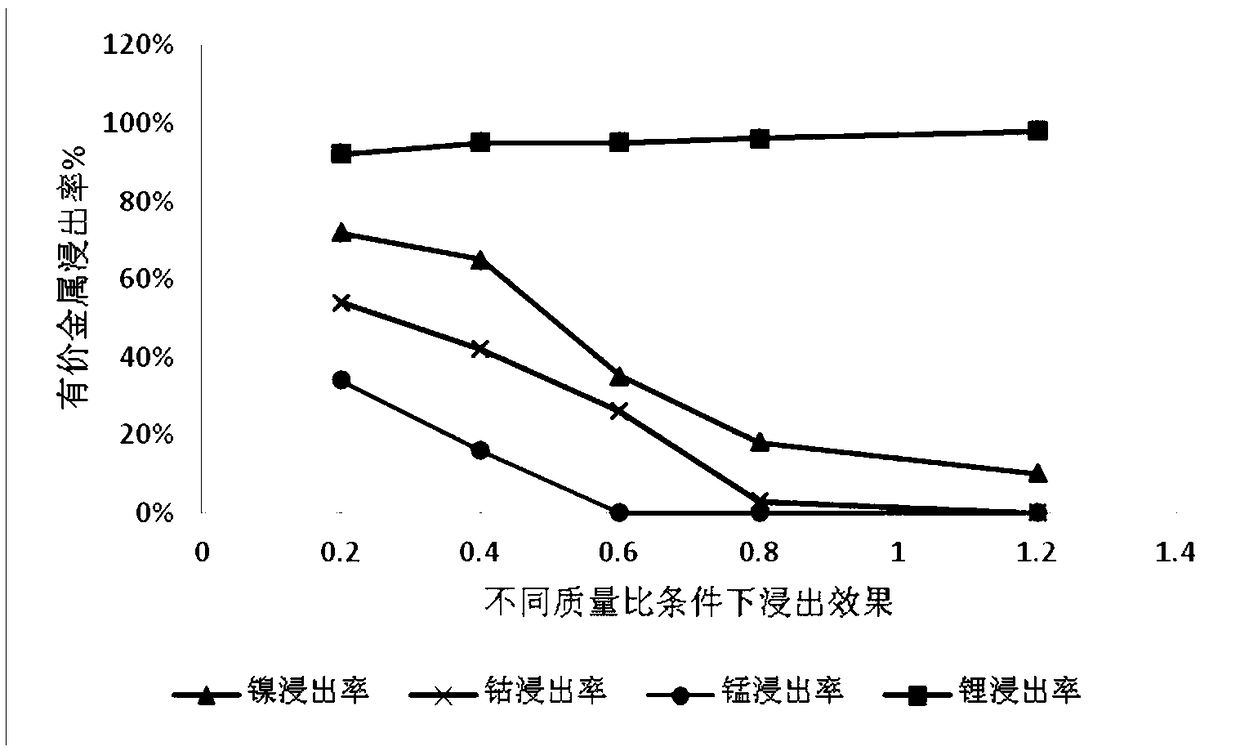
Comprehensive recovery method for waste lithium ion battery
ActiveCN109449523ASolve the problem of high concentration enrichment recoveryRealize harmless disposalWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodLithium-ion battery
The invention provides a comprehensive recovery method for a waste lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: three-element waste lithium battery cell powder is leached by sulfuricacid and potassium permanganate for the first time so as to obtain a first leaching solution and a first leaching residue; sodium carbonate is used for carrying out lithium precipitation on the firstleaching solution to obtain lithium carbonate; selective reduction leaching is carried out on the first leaching residue by using hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid so as to obtain a second leachingsolution and a second leaching residue; the pH value of the second leaching solution is adjusted to be 4.2-4.5, and P204 is used for extracting the second leaching solution so as to obtain a P204 raffinate and a P204 loaded organic phase; reverse extraction is carried out on the P204 loaded organic phase by using sulfuric acid, and evaporating and crystallizing are carried out to prepare manganese sulfate; the pH value of the P204 raffinate is adjusted to be 4.5-5, and the P204 raffinate is extracted by using C272 so as to obtain a C272 extracting solution and a C272 loaded organic phase; reverse extraction is carried out on a C727 loaded organic phase by sulfuric acid to obtain a cobalt sulfate solution, and evaporating and crystallizing are carried out to prepare battery-grade cobalt sulfate; and the pH value of a C272 raffinate is adjusted to be 5-5.5, the C272 extracting solution is extracted by using P507 to obtain a P507 loaded organic phase, sulfuric acid back-extraction is carried out on the P507 loaded organic phase to obtain a nickel sulfate solution, and evaporating and crystallizing are carried out to obtain nickel sulfate.
Owner:天齐锂业资源循环技术研发(江苏)有限公司
Exhaust purification system for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20120255286A1Function increaseHigh NOx purification rateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
An exhaust purification system for an internal combustion engine is provided that can steadily maintain a NOx purification rate of a selective reduction catalyst to be high without allowing the fuel economy or marketability to deteriorate. The exhaust purification system includes a NO2—NOx ratio adjustment mechanism that causes a NO2—NOx ratio to change; and a NO2—NOx ratio perturbation controller that executes NO2—NOx ratio perturbation control so that a NO2 balance of the selective reduction catalyst in a predetermined time period, with NO2 adsorption being positive and NO2 release being negative, is 0. Herein, NO2—NOx ratio perturbation control is defined as control that alternately executes NO2 increase control to cause the NO2—NOx ratio to be greater than a reference value near 0.5, and NO2 decrease control to cause the NO2—NOx ratio to be less than the reference value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com