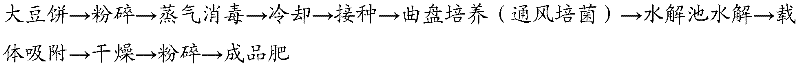Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Molecular nitrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular nitrogen makes up 78% of the gases in the atmosphere. Let's look at this molecule more closely. Molecular nitrogen is made up of 2 nitrogen atoms.
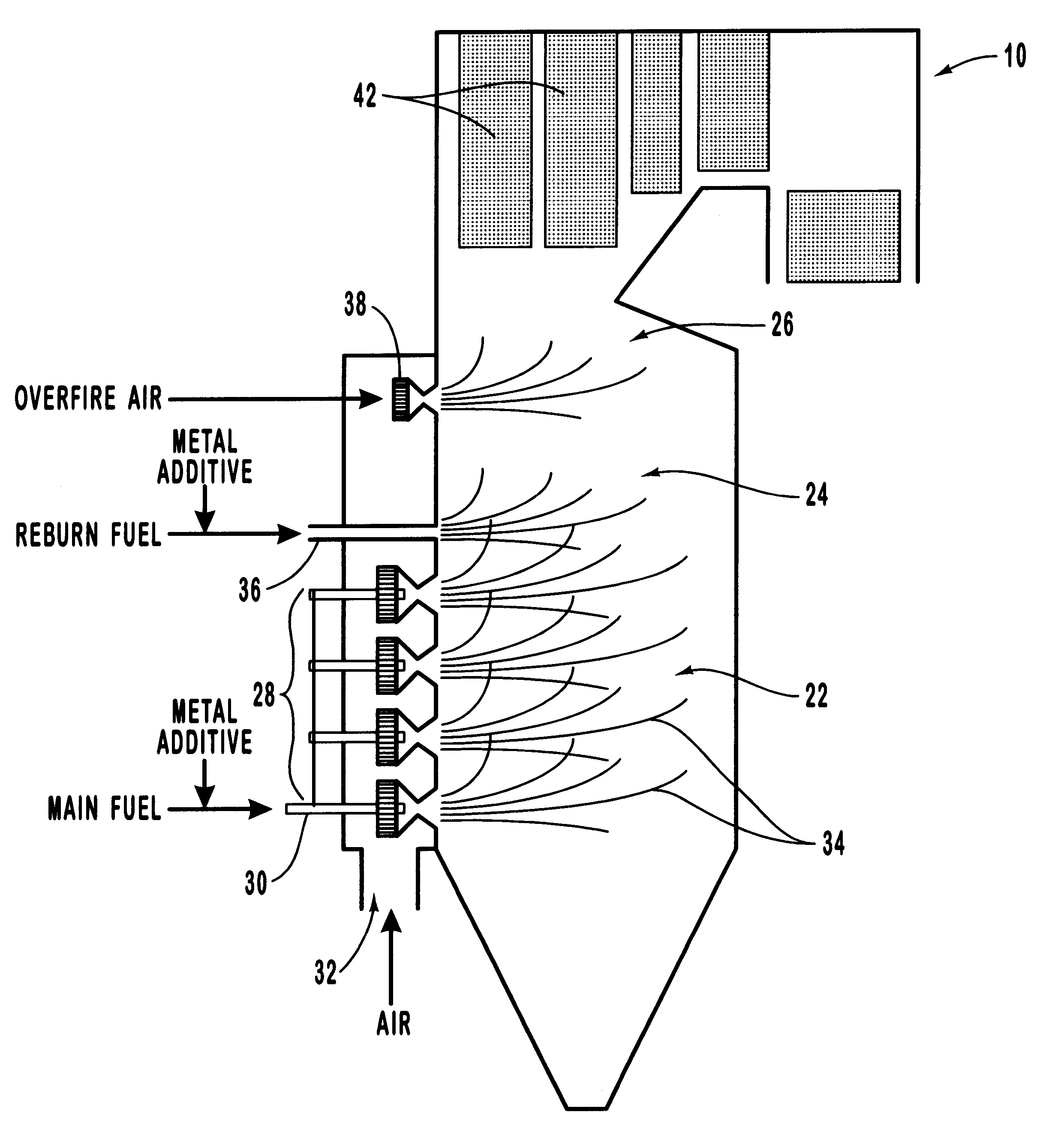
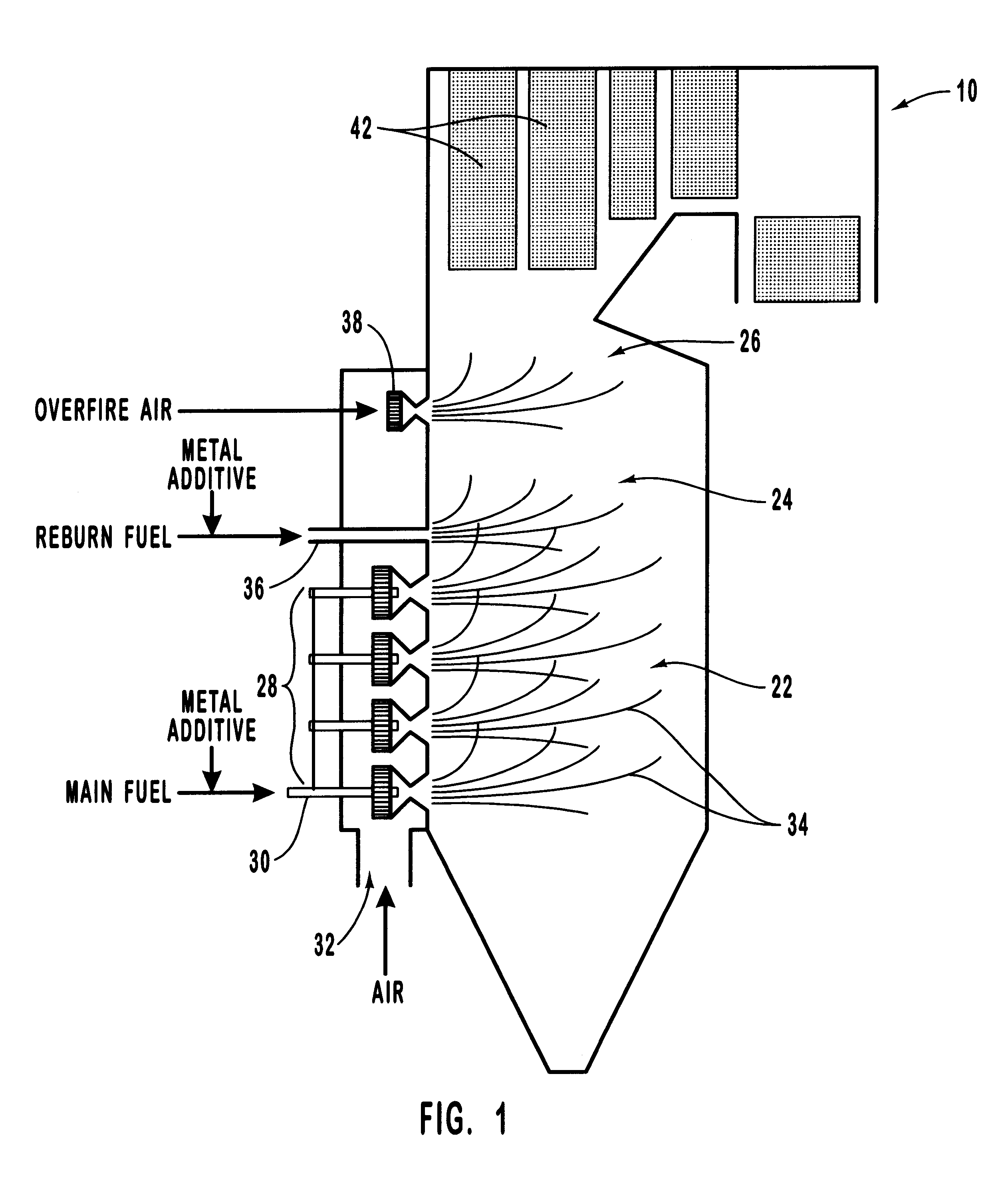
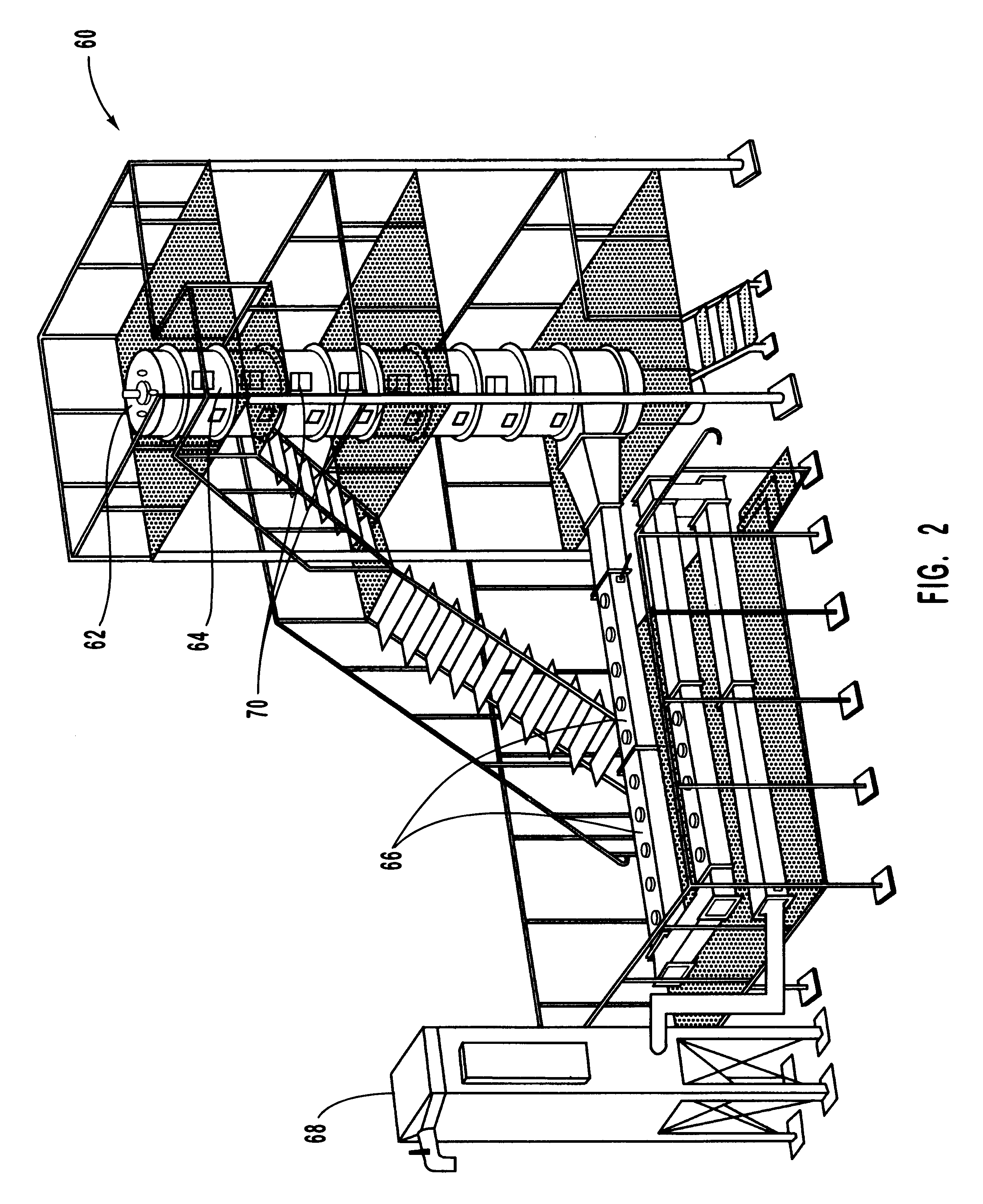
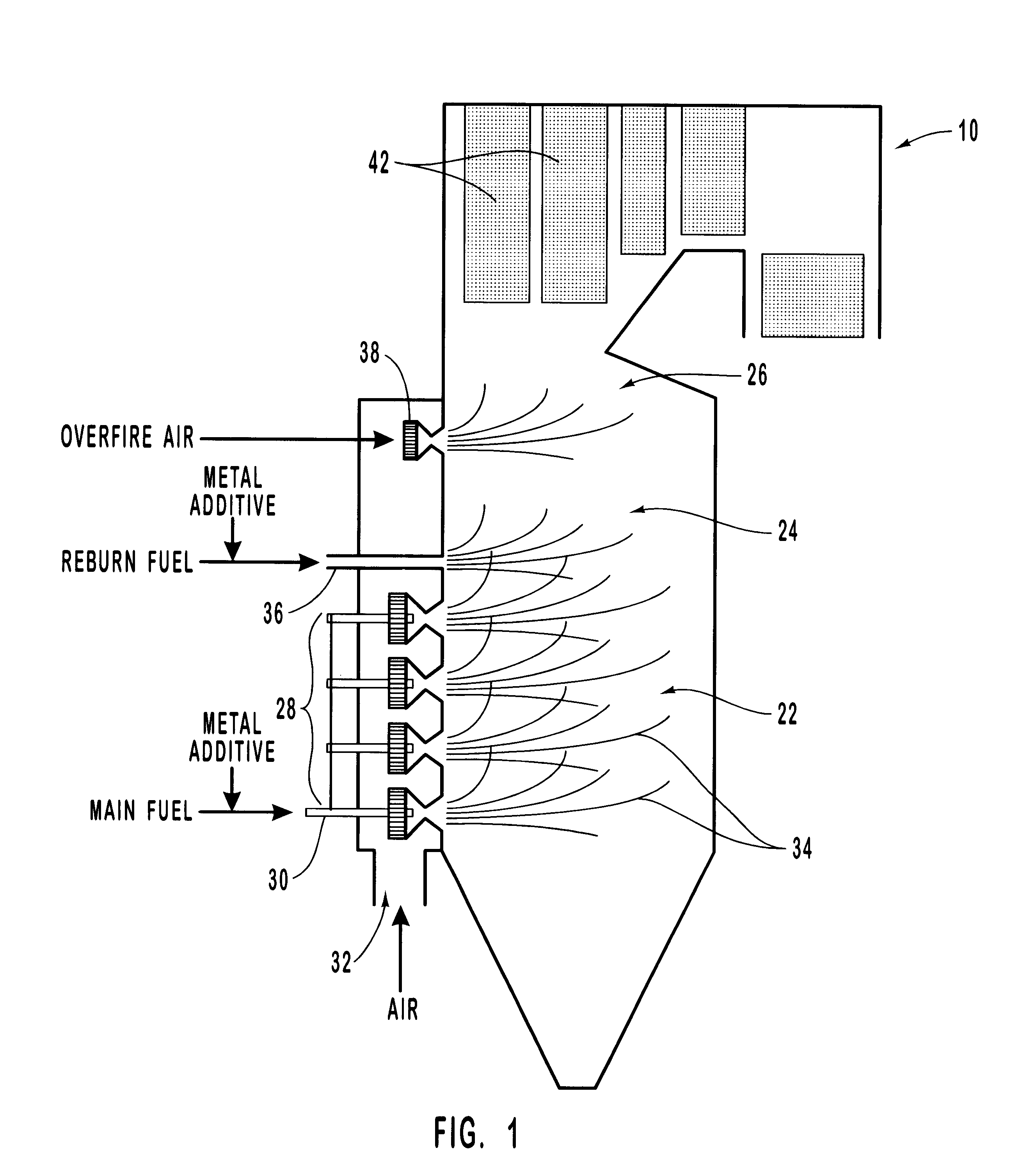
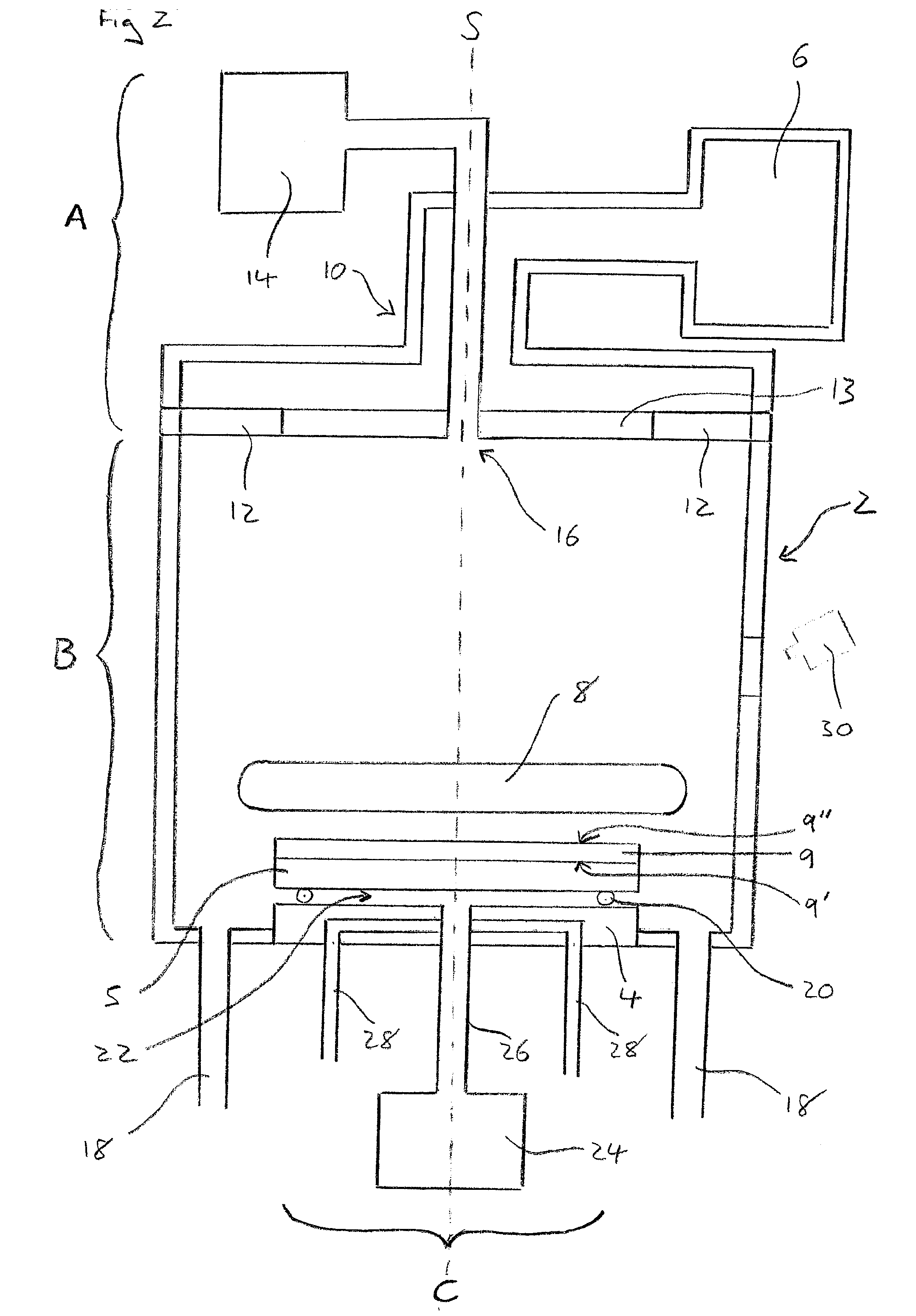
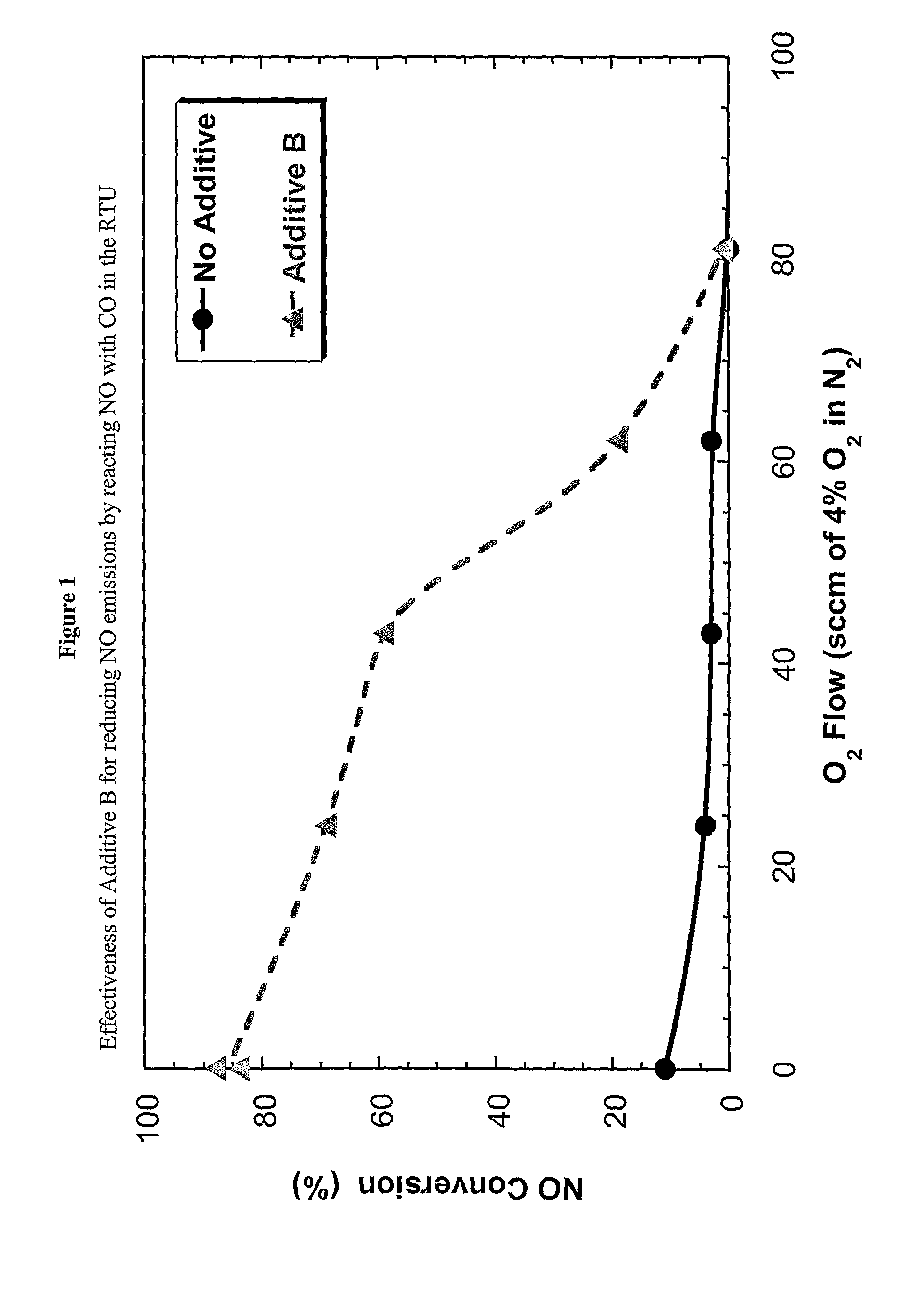
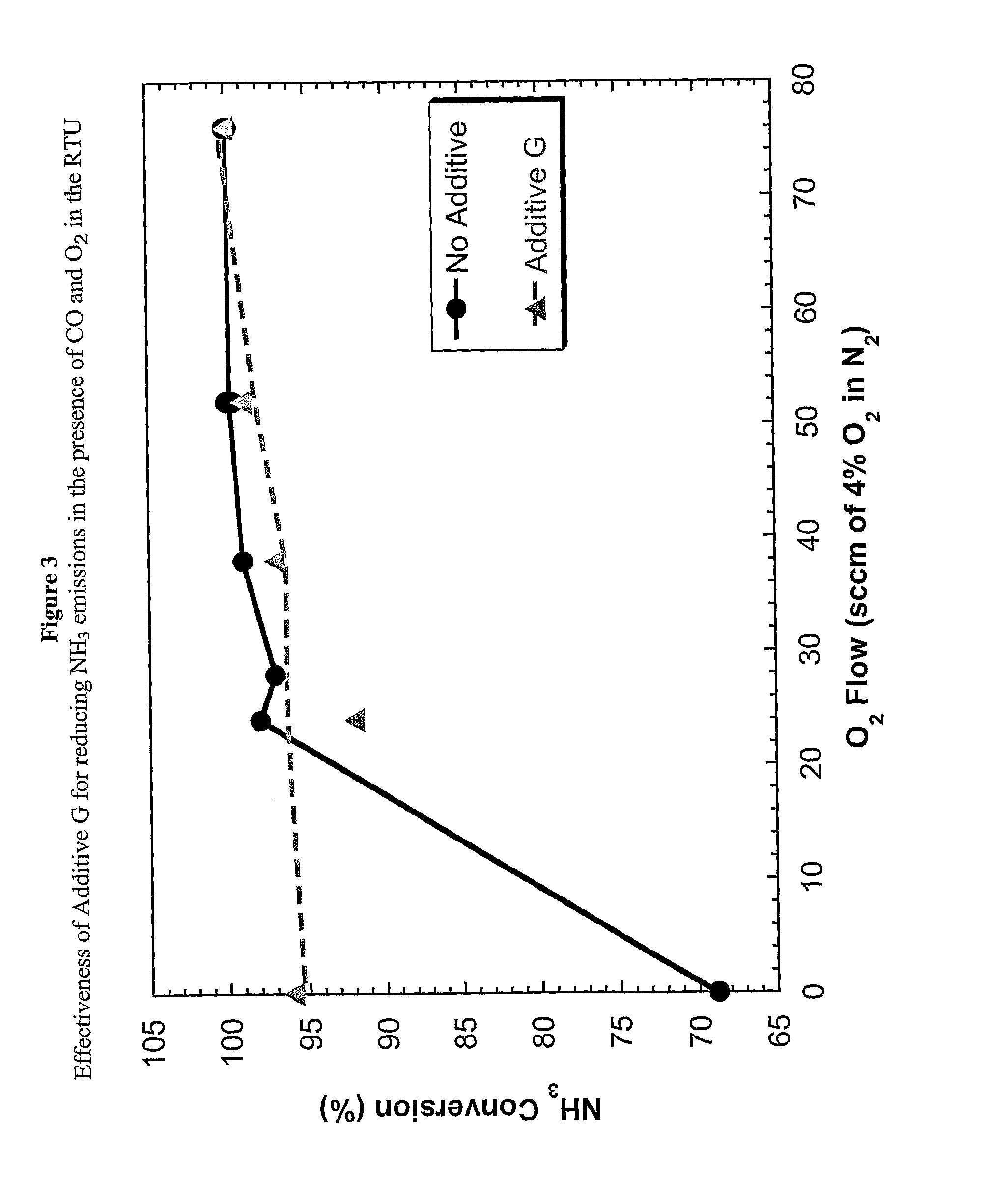
Method for reducing NOX in combustion flue gas using metal-containing additives
InactiveUS6206685B1Improved control deviceSure easyDispersed particle separationSolid fuel combustionAtmospheric airNitric oxide
Various methods for decreasing the amount of nitrogen oxides released to the atmosphere as a component of combustion gas mixtures are provided. The methods specifically provide for the removal of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) from gas mixtures emitted from stationary combustion systems. In particular, methods for improving efficiency of nitrogen oxide reduction from combustion systems include injecting metal-containing compounds into the main combustion zone and / or the reburning zone of a combustion system. The metal containing compounds react with active combustion species, and these reactions change radical concentrations and significantly improve NOx conversion to molecular nitrogen. The metal-containing additives can be injected with the main fuel, in the main combustion zone, with secondary or reburning fuel addition, or at several locations in the main combustion zone and reburning zone. Optionally, nitrogenous reducing agents and / or overfire air can be injected downstream to further increase NOx reduction.
Owner:GE ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES
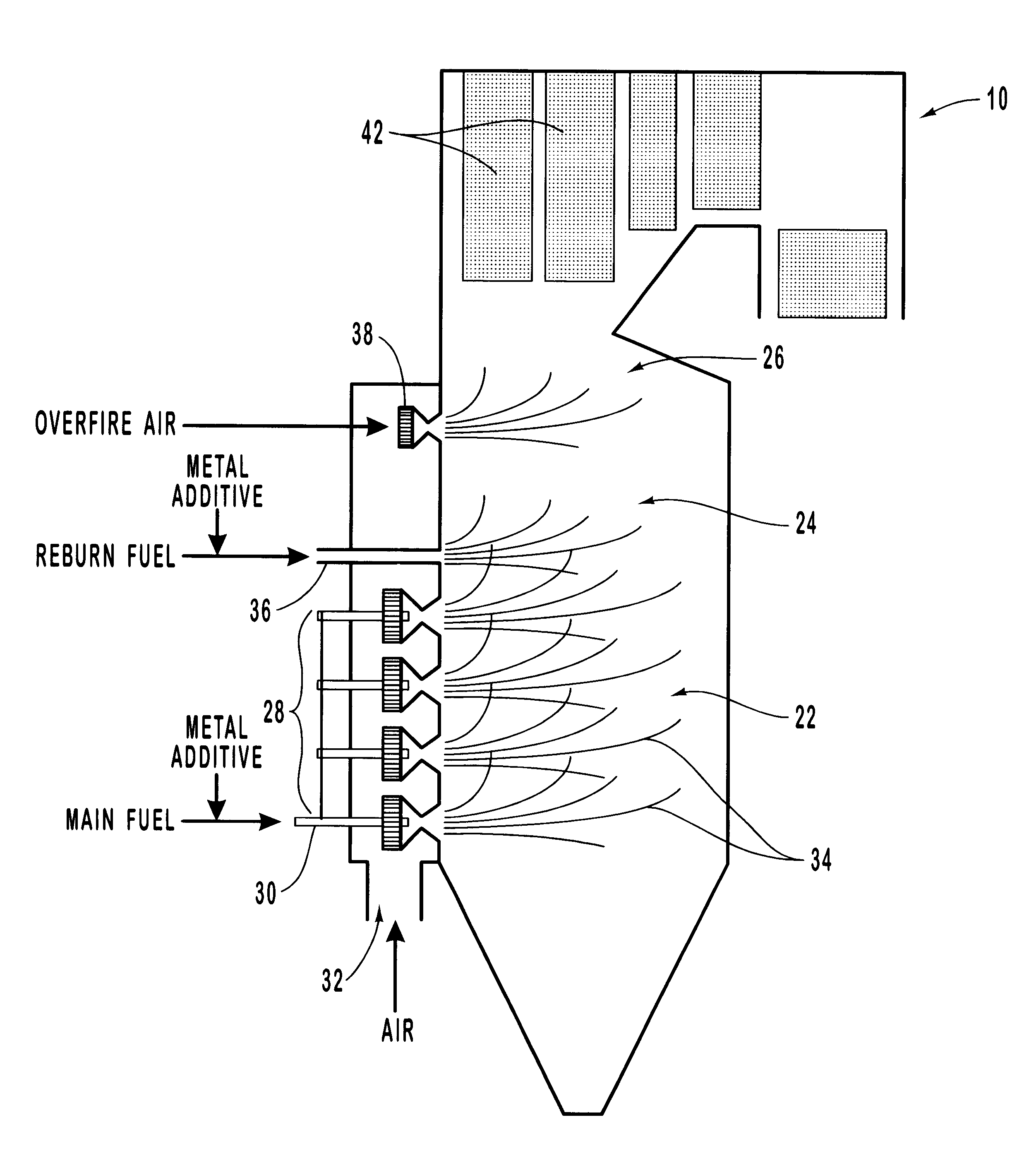
Methods for reducing NOx in combustion flue gas using metal-containing additives
InactiveUS6471506B1Simple and inexpensive methodReduce penetrationDispersed particle separationIncinerator apparatusAtmospheric airMolecular nitrogen
Various methods for decreasing the amount of nitrogen oxides released to the atmosphere as a component of combustion gas mixtures are provided. The methods specifically provide for the removal of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) from gas mixtures emitted from stationary combustion systems. In particular, methods for improving efficiency of nitrogen oxide reduction from combustion systems include injecting metal-containing compounds into the main combustion zone and / or the reburning zone of a combustion system. The metal containing compounds react with active combustion species, and these reactions change radical concentrations and significantly improve NOx conversion to molecular nitrogen. The metal-containing additives can be injected with the main fuel, in the main combustion zone, with secondary or reburning fuel addition, or at several locations in the main combustion zone and reburning zone. Optionally, nitrogenous reducing agents and / or overfire air can be injected downstream to further increase NOx reduction.
Owner:GE ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES
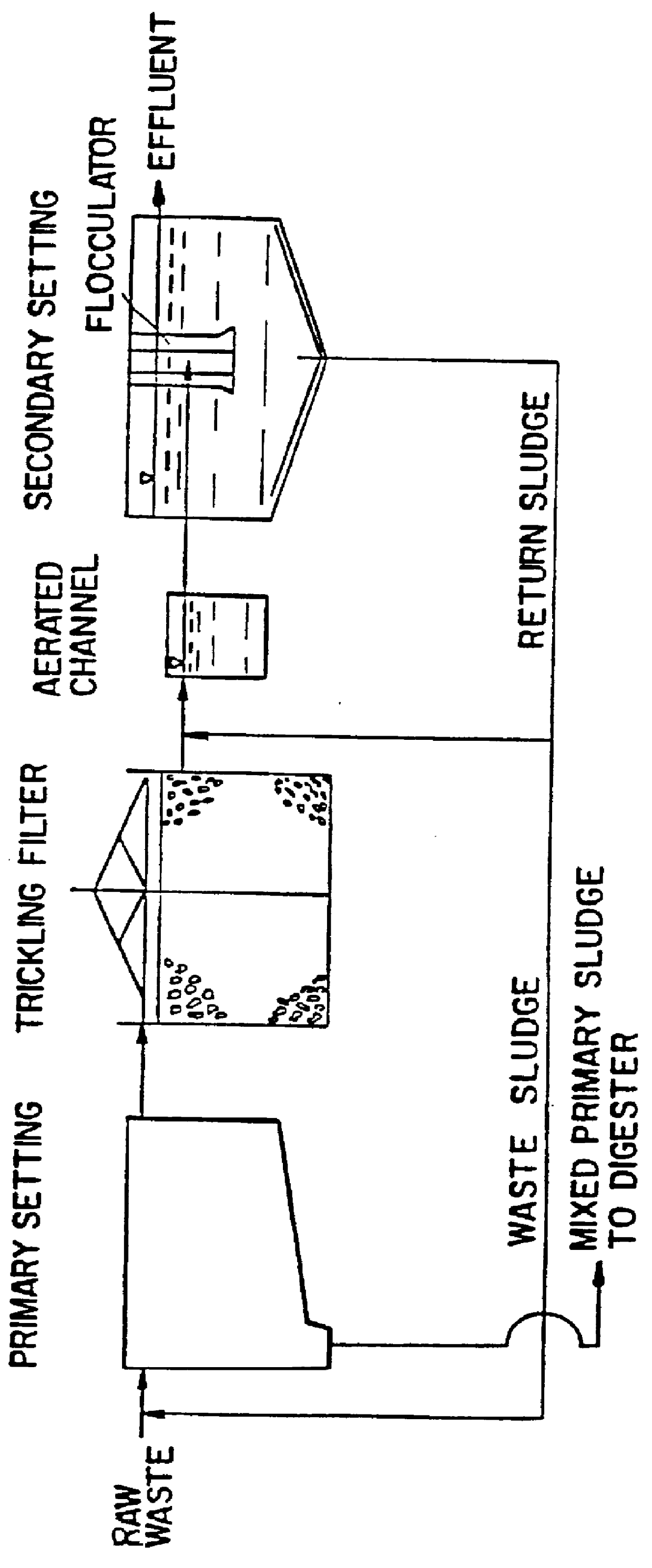
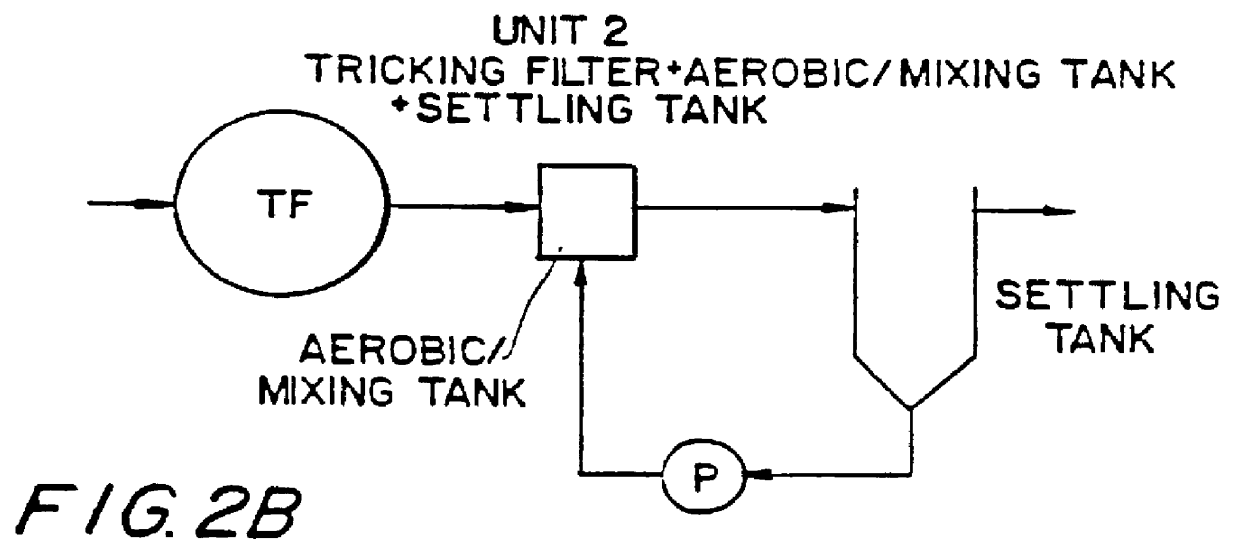
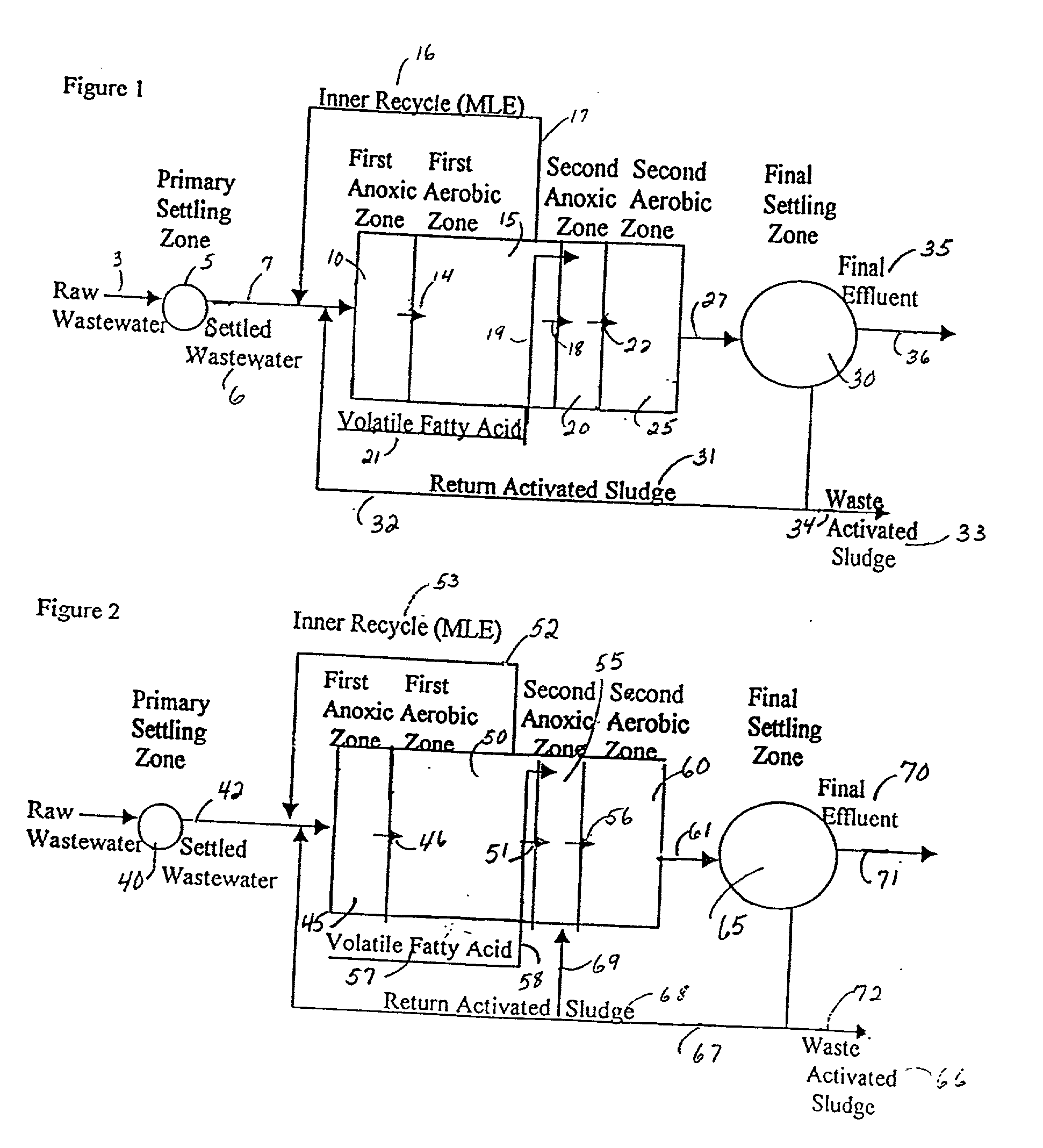
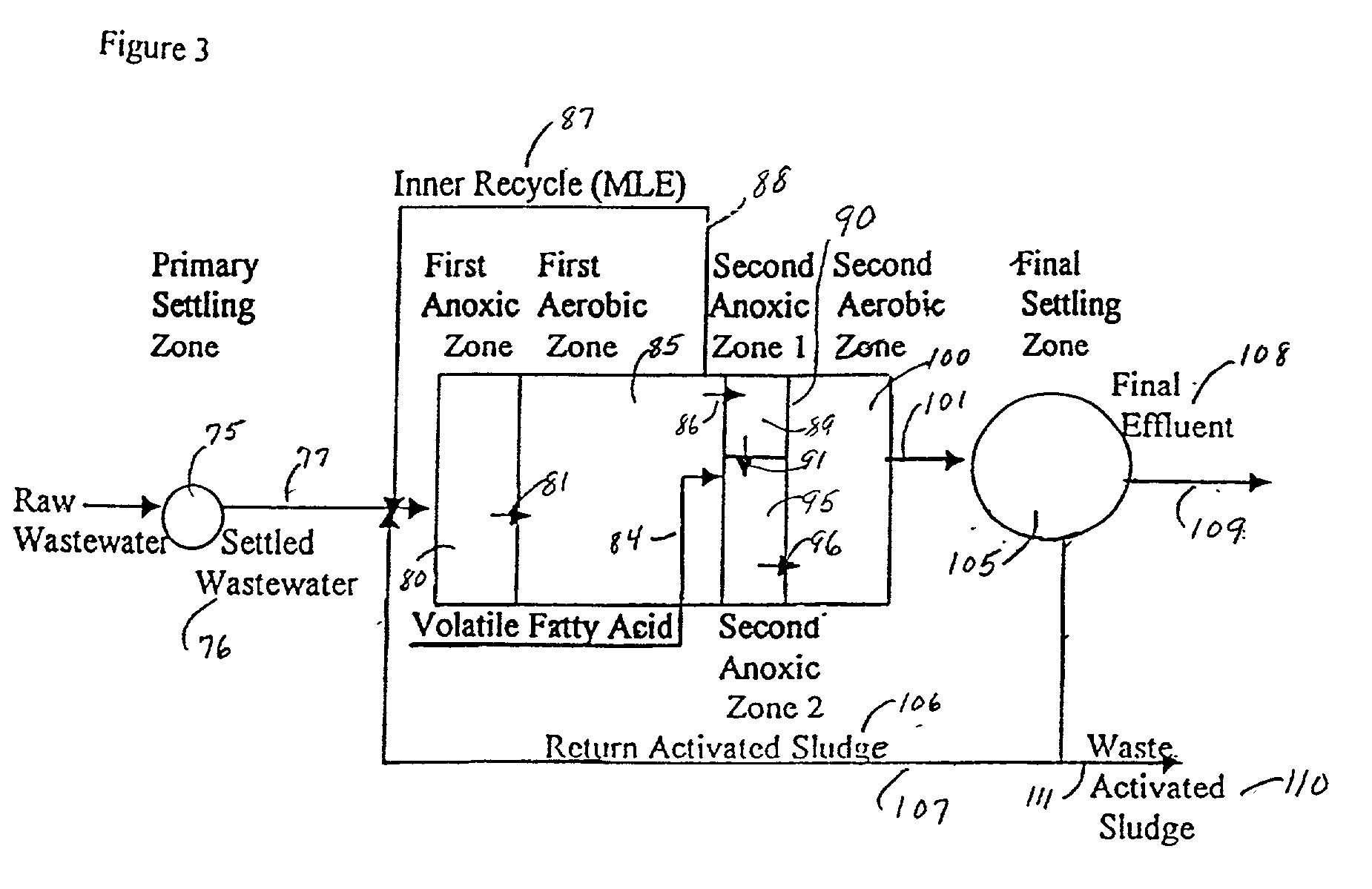
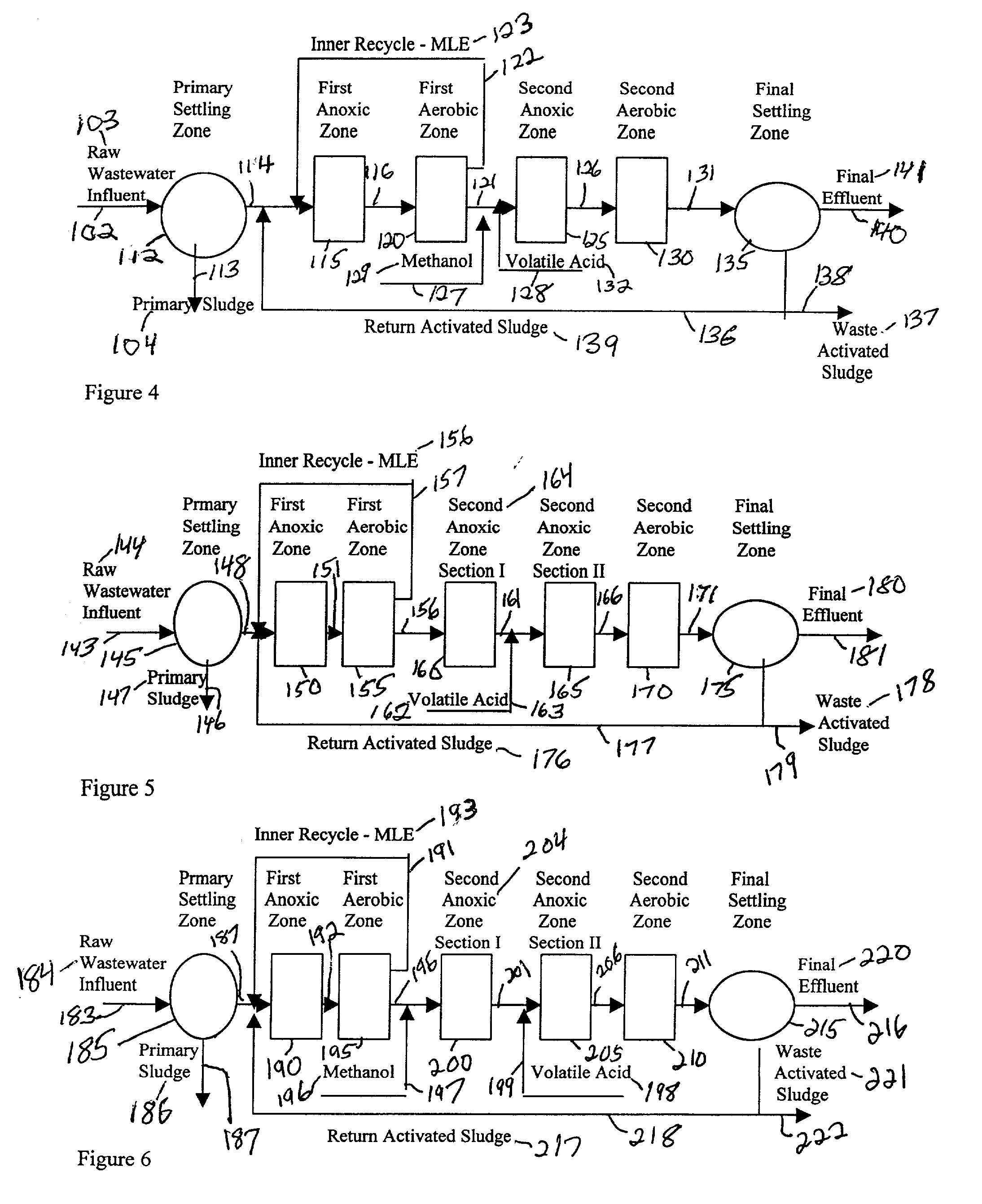
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS6113788AImprove efficiencyFacilitated releaseTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSludgePhosphate
A wastewater treatment process having improved solids separation characteristics and reduced biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in the purified wastewater comprising the steps of: passing wastewater through a main aerobic biological oxidation zone and therein oxidizing a portion of the BOD a portion of the ammonia nitrogen content (NH3-N); passing the effluent from said aerobic biological oxidation zone to an aerobic / mixing zone and therein mixing said effluent with effluent from the anoxic / anaerobic zone; passing the effluent from said aerobic / mixing zone to a settling zone and therein separating purified wastewater having reduced BOD and suspended solids, and sludge containing suspended solids; passing a portion of the sludge formed in the settling zone and volatile acids to an anoxic / anaerobic zone and therein increasing the extracellular polymer content of said sludge, the release of phosphorus into solution and the reduction of nitrate nitrogen to molecular nitrogen gas; and recycling an effective amount of the effluent from said anoxic / anaerobic zone to said aerobic / mixing zone. In an alternative embodiment, a volatile acid is added to a zone to which no additional oxygen has been added that is in the flow path from the main aerobic biological oxidation zone or, alternatively, it may be added to the anoxic / anaerobic zone and the thus-treated effluent is passed to the aerobic / mixing zone wherein phosphate is removed from the effluent.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
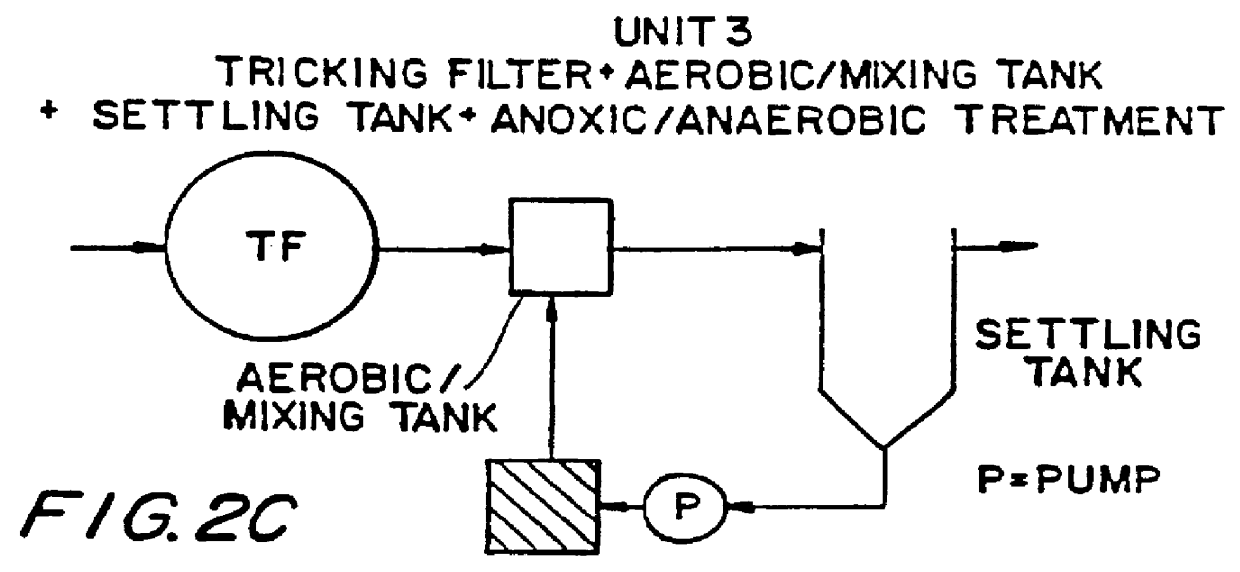
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS20010045390A1Improve efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
Owner:KIM SUNGTAI +2
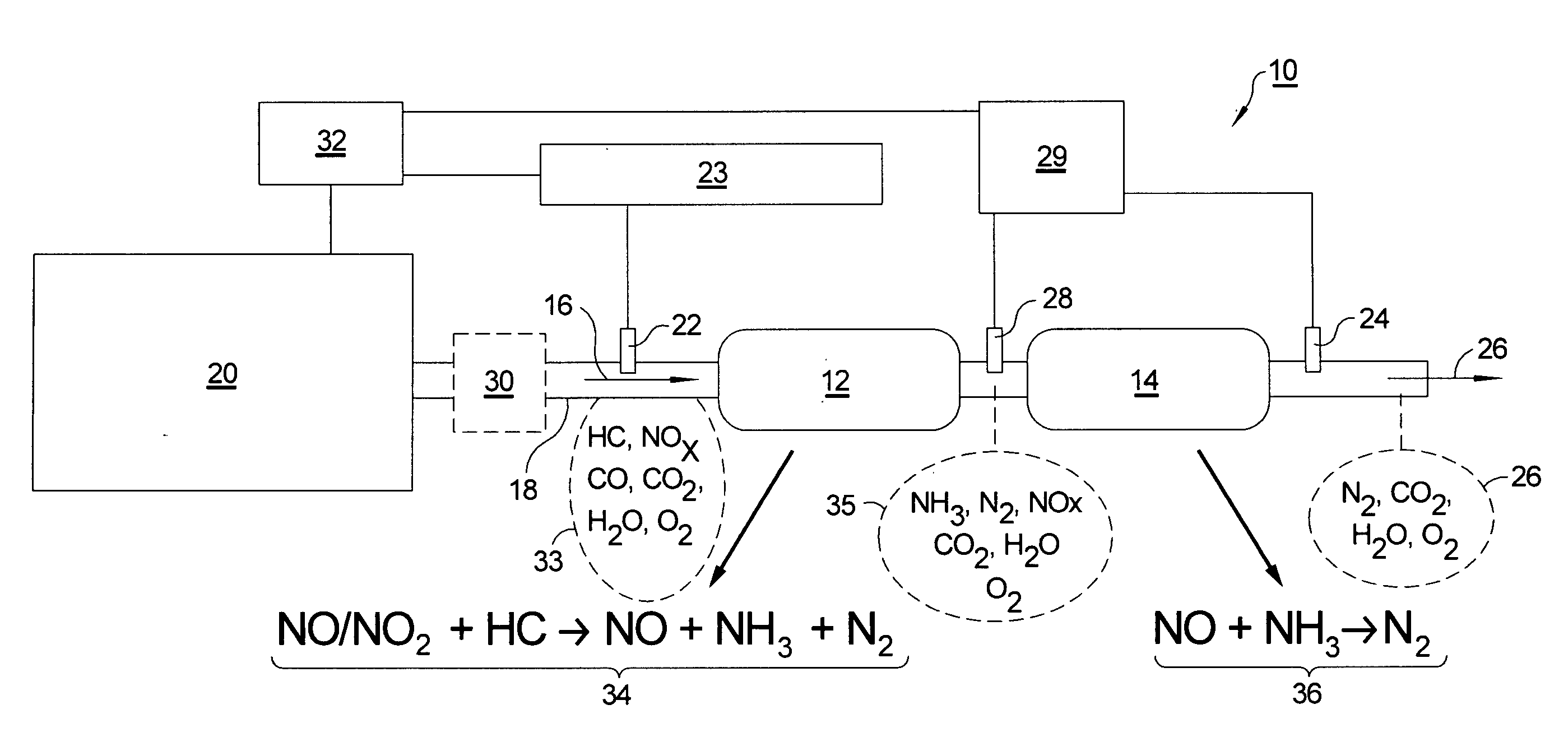
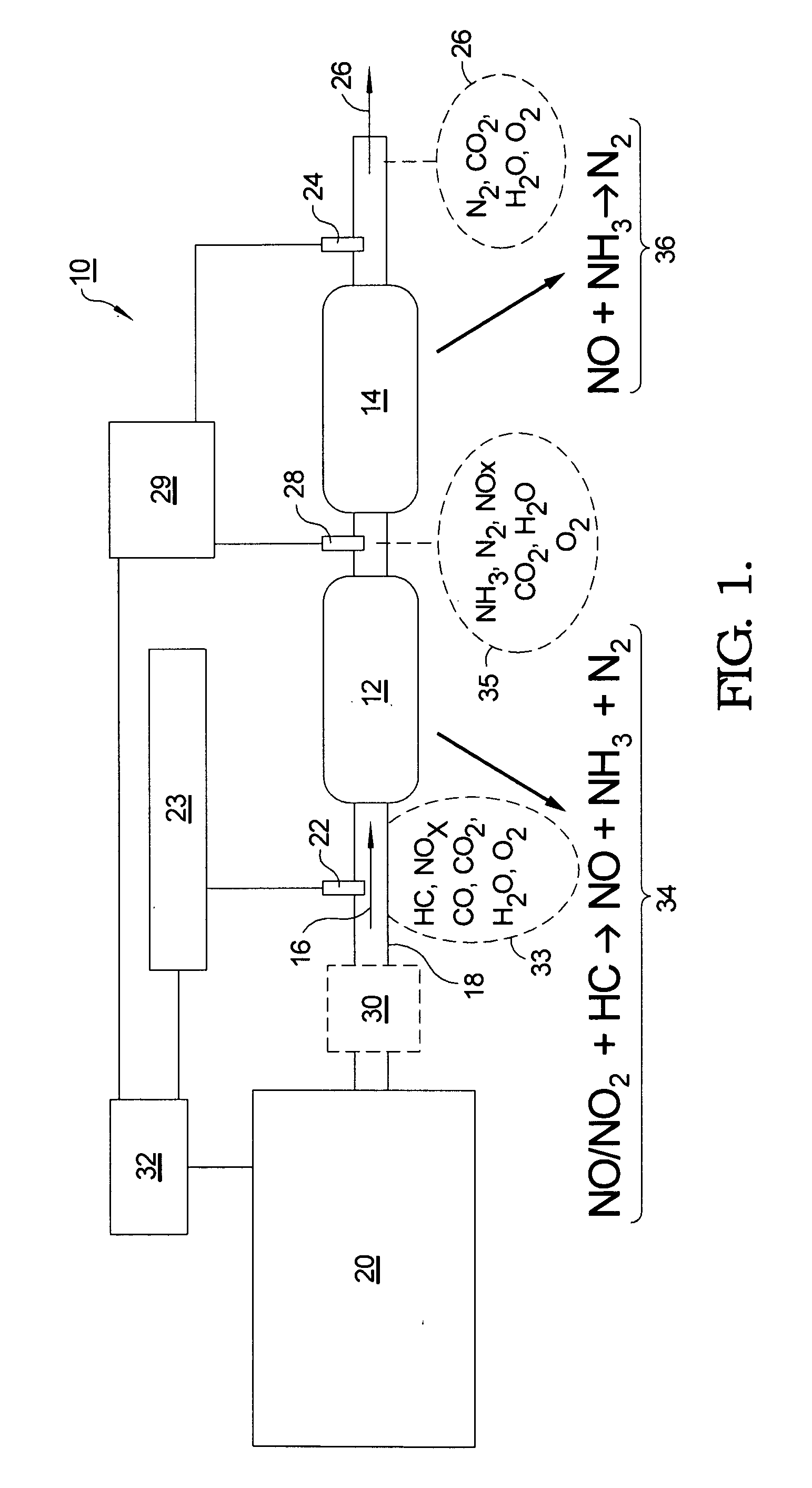
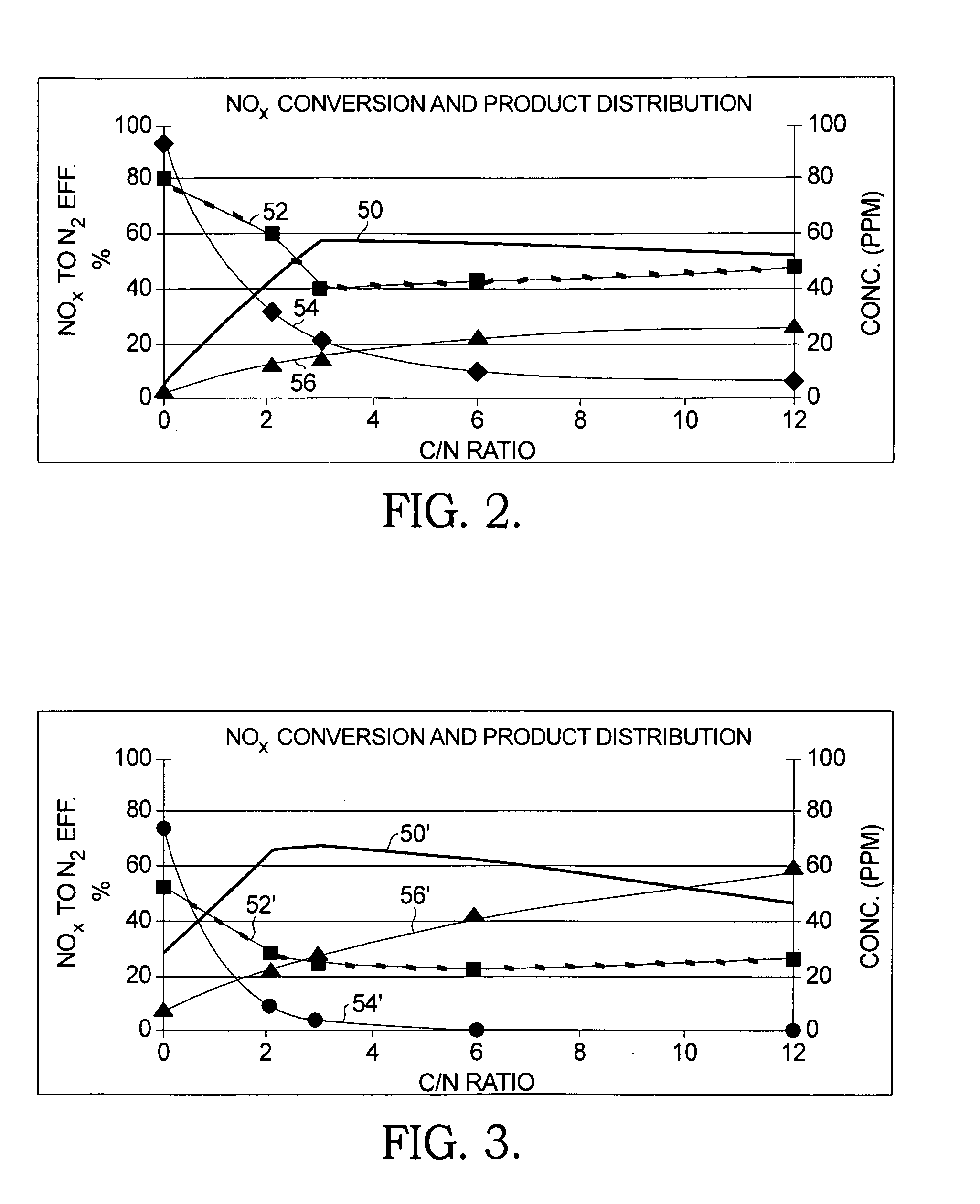
Dual catalyst NOx reduction system for exhaust from lean burn internal combustion engines
ActiveUS20100000202A1Remove loadGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesMolecular nitrogenInternal combustion engine
A method and apparatus for reducing the percentage of nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen monoxide in an exhaust gas stream of an internal combustion engine, comprising the steps of injecting a hydrocarbon compound and optionally hydrogen into the exhaust gas stream; passing the exhaust gas through a first catalyst for selective reduction of a portion of the nitrogen oxides to nitrogen, ammonia, and N-containing species; passing the exhaust gas through a second catalyst for selective reduction of a portion of the nitrogen oxides with ammonia to molecular nitrogen; sensing ammonia concentration in the exhaust gas stream after passage through either or both of the first and second catalysts; and controlling by a controller in a feedback loop the injecting to an amount of hydrocarbon that will produce a predetermined concentration of ammonia and nitrogen oxides at the sensor that will lead to high NOx conversion.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
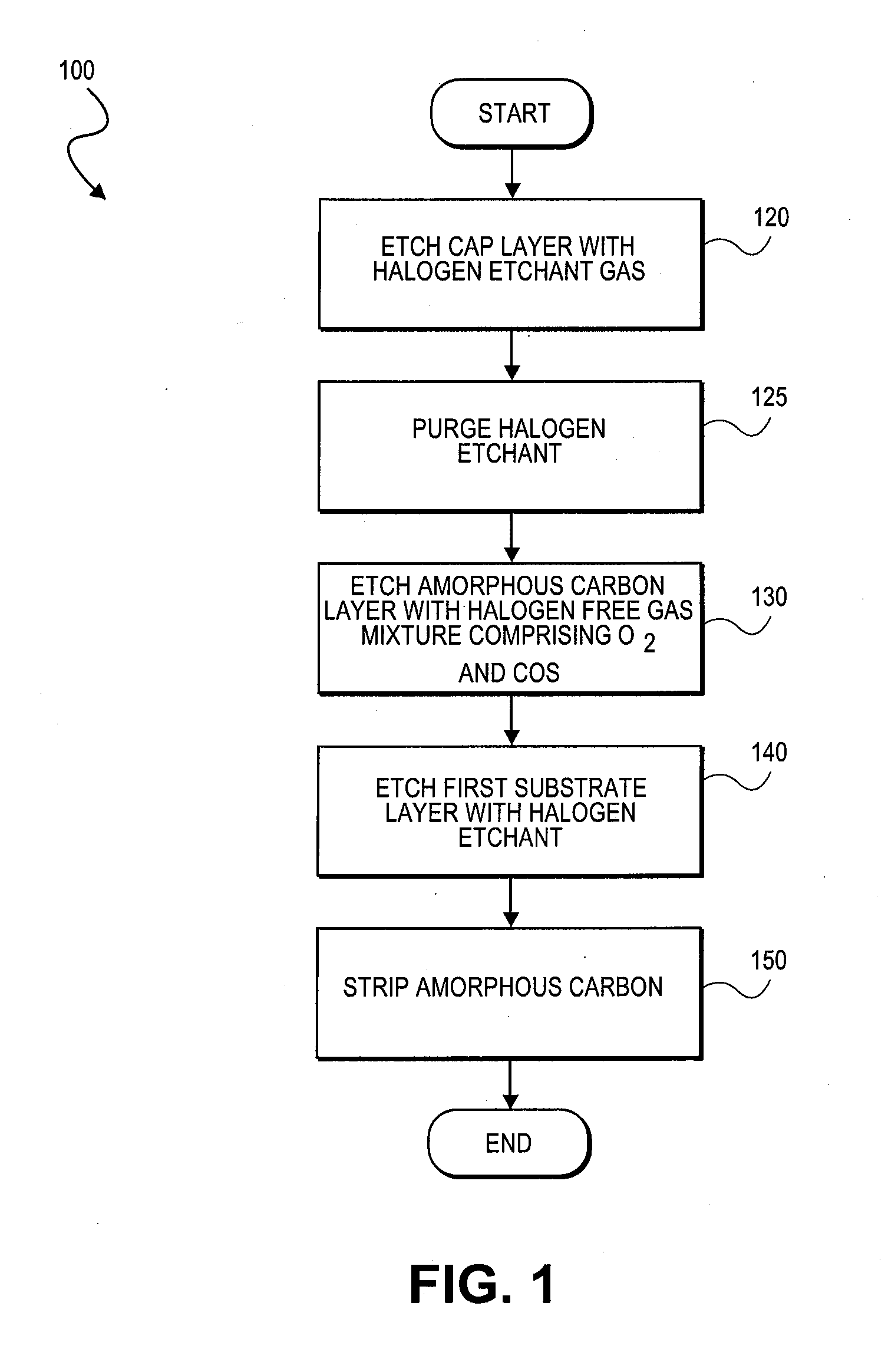
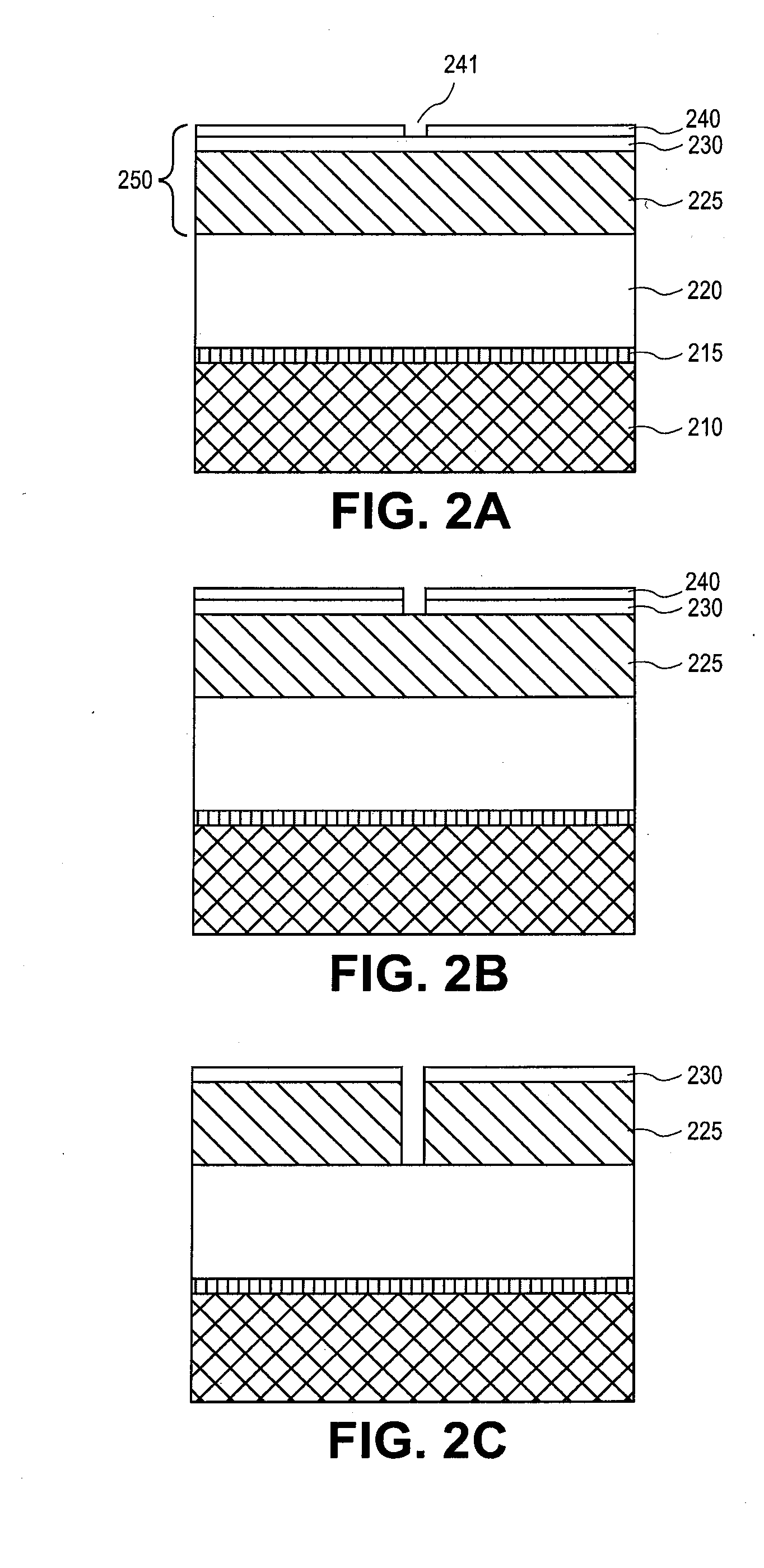
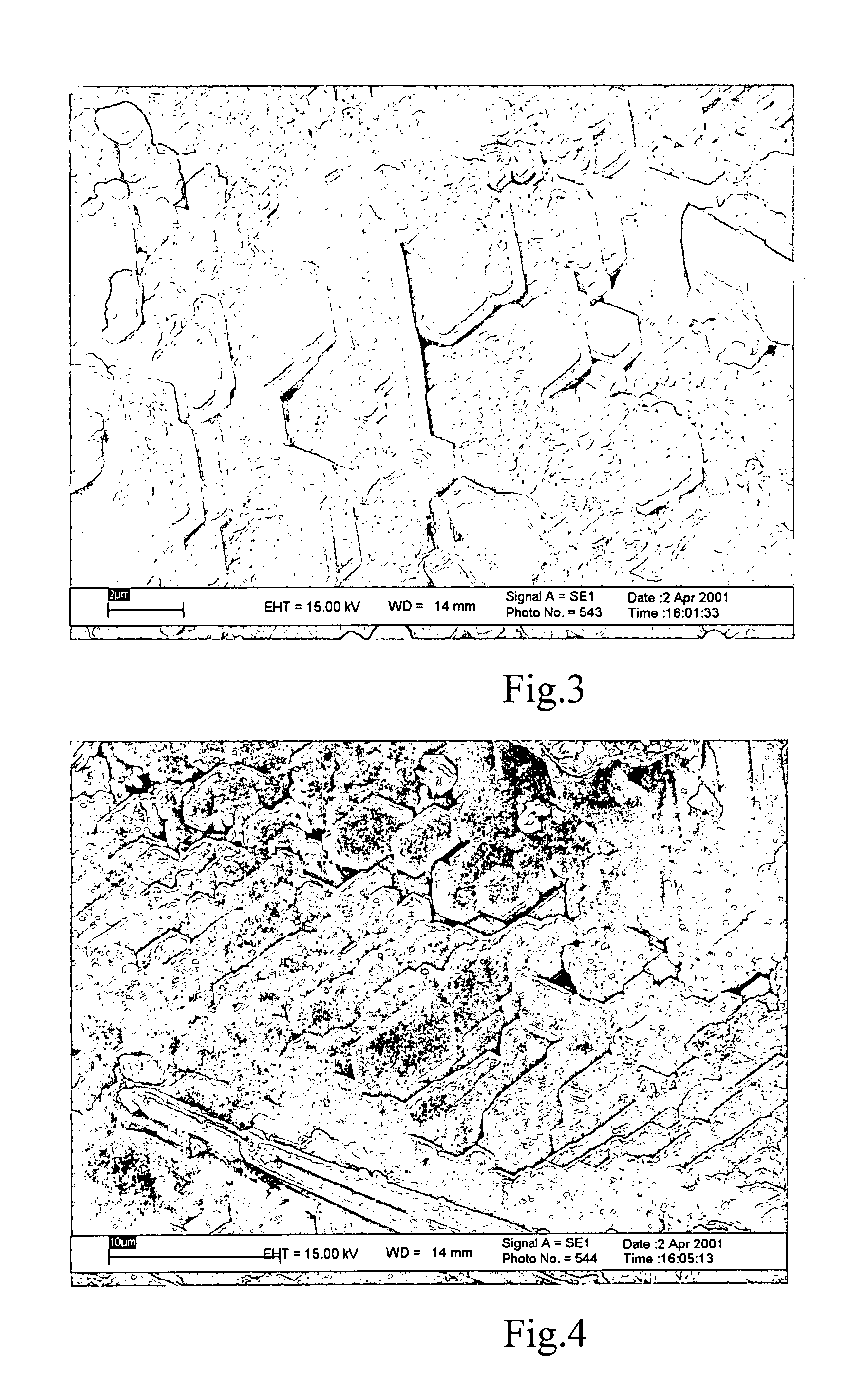
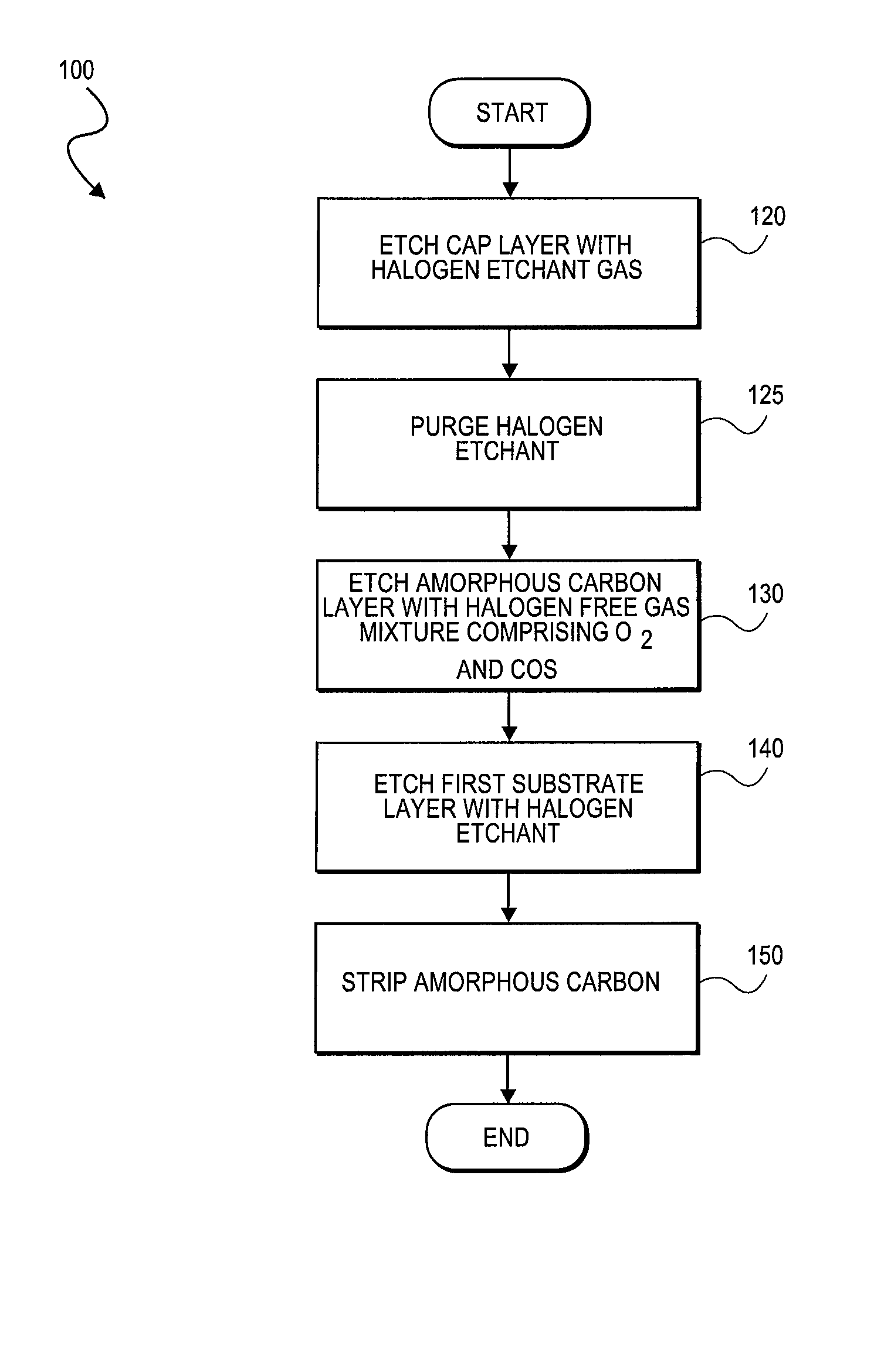
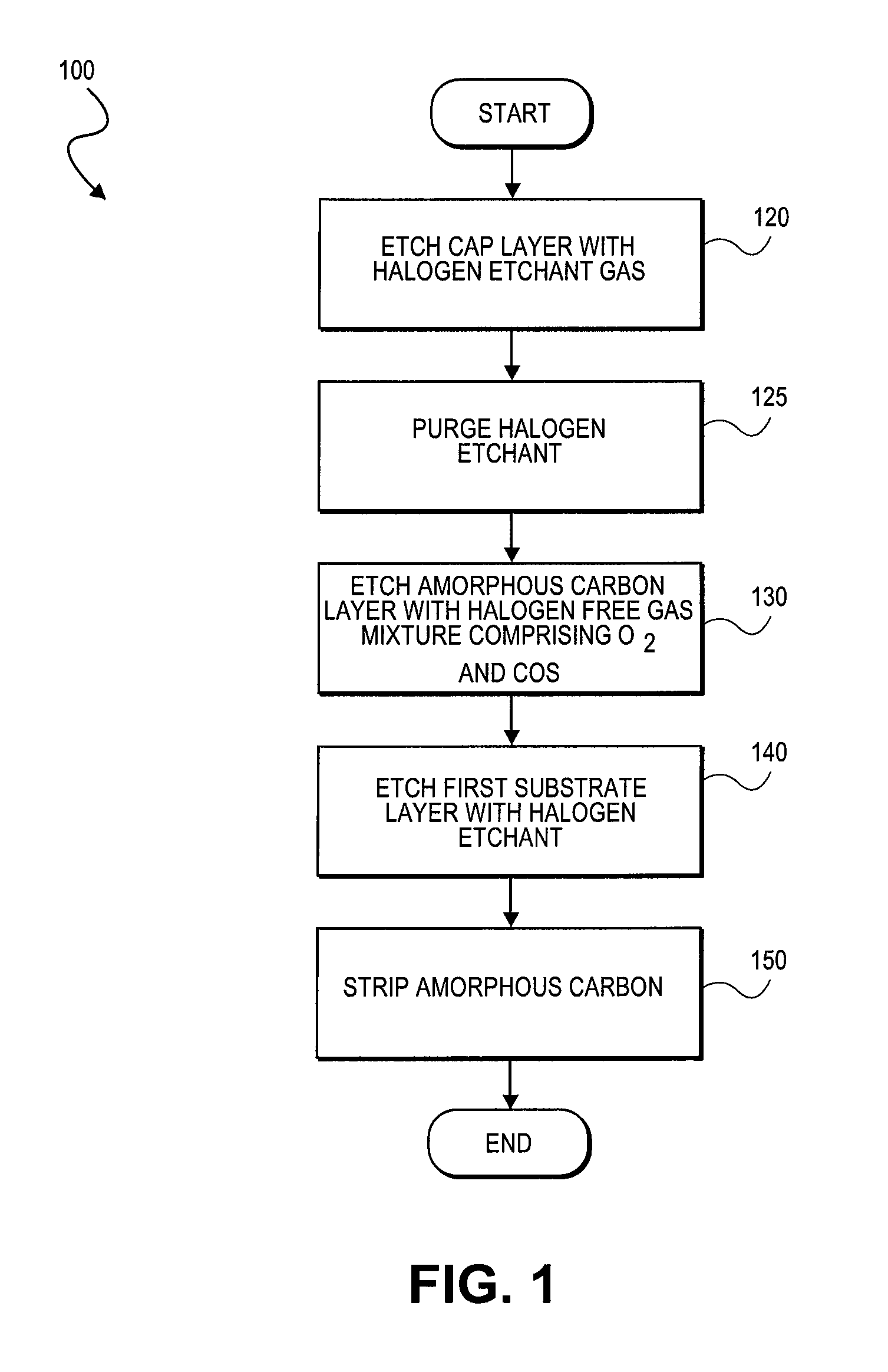
Plasma etching carbonaceous layers with sulfur-based etchants
InactiveUS20090212010A1Improve uniformityMinimal bowingDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfurMolecular nitrogen
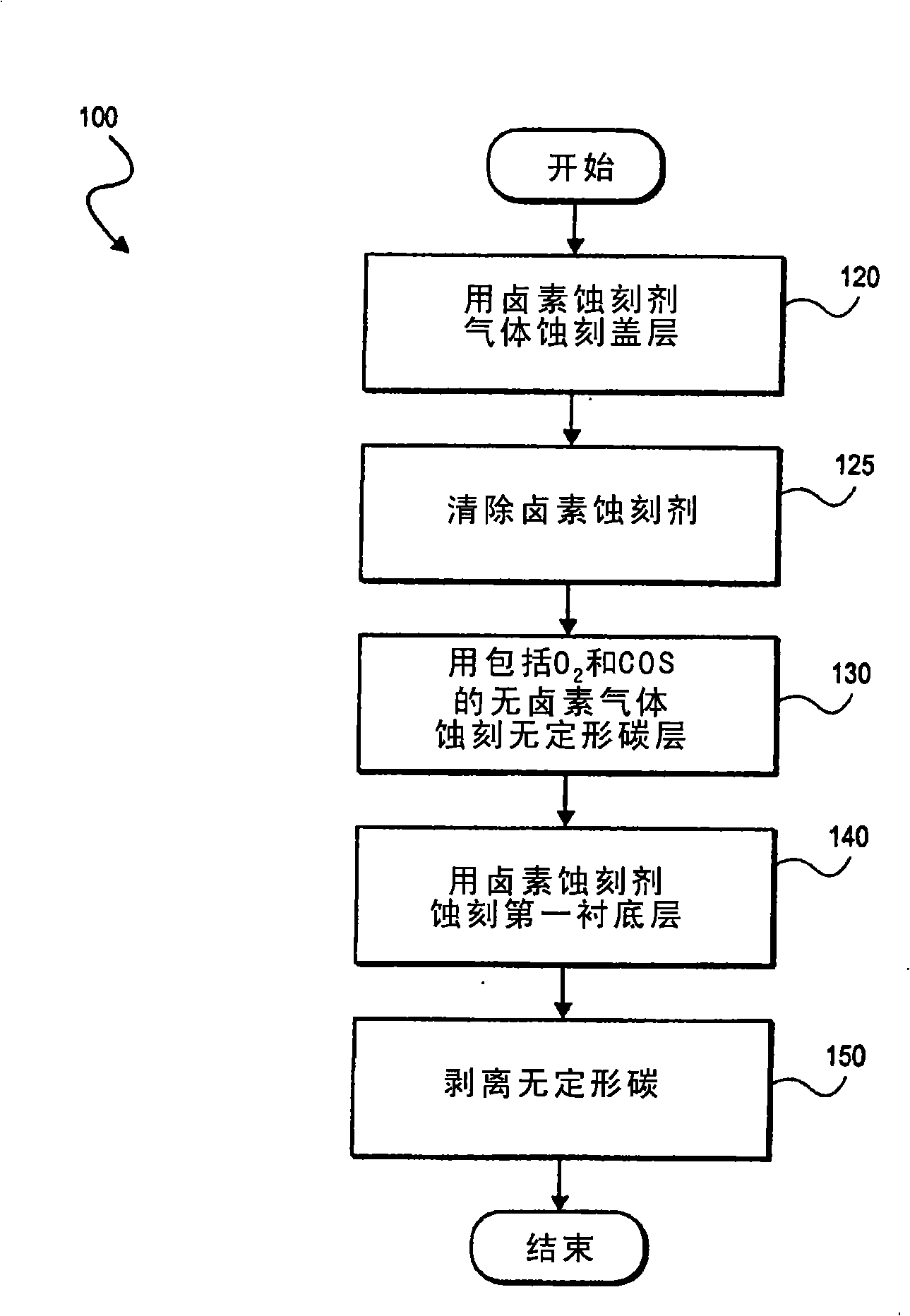
Etching of carbonaceous layers with an etchant gas mixture including molecular oxygen (O2) and a gas including a carbon sulfur terminal ligand. A high RF frequency source is employed in certain embodiments to achieve a high etch rate with high selectivity to inorganic dielectric layers. In certain embodiments, the etchant gas mixture includes only the two components, COS and O2, but in other embodiments additional gases, such as at least one of molecular nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide (CO2) may be further employed to etch to carbonaceous layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Thick polycrystalline synthetic diamond wafers for heat spreading applications and microwave plasma chemical vapour depositon synthesis techniques
ActiveUS20150222087A1Low costNegating economic benefitPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsMolecular nitrogenGas concentration
A method of fabricating a polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material having an average thermal conductivity at room temperature through a thickness of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material of at least 2000 Wm−1K−1, the method comprising: loading a refractory metal substrate into a CVD reactor; locating a refractory metal guard ring around a peripheral region of the refractory metal substrate, the refractory metal guard ring defining a gap between an edge of the refractory metal substrate and the refractory metal guard ring having a width 1.5 mm to 5.0 mm; introducing microwaves into the CVD reactor at a power such that the power density in terms of power per unit area of the refractory metal substrate is in a range 2.5 to 4.5 W mm−2; introducing process gas into the CVD reactor wherein the process gas within the CVD reactor comprises a nitrogen concentration in a range 600 ppb to 1500 ppb calculated as molecular nitrogen N2, a carbon containing gas concentration in a range 0.5% to 3.0% by volume, and a hydrogen concentration in a range 92% to 98.5% by volume; controlling an average temperature of the refractory metal substrate to lie in a range 750° C. to 950° C. and to maintain a temperature difference between an edge and a centre point on the refractory metal substrate of no more than 80° C. growing polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material to a thickness of at least 1.3 mm on the refractory metal substrate; and cooling the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material to yield a polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material having a thickness of at least 1.3 mm, an average thermal conductivity at room temperature through the thickness of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material of at least 2000 Wm−1K−1 over at least a central area of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material, wherein the central area is at least 70% of a total area of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material, a single substitutional nitrogen concentration no more than 0.80 ppm over at least the central area of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material, and wherein the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material is substantially crack free over at least the central area thereof such that the central area has no cracks which intersect both external major faces of the polycrystalline CVD synthetic diamond material and extend greater than 2 mm in length.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
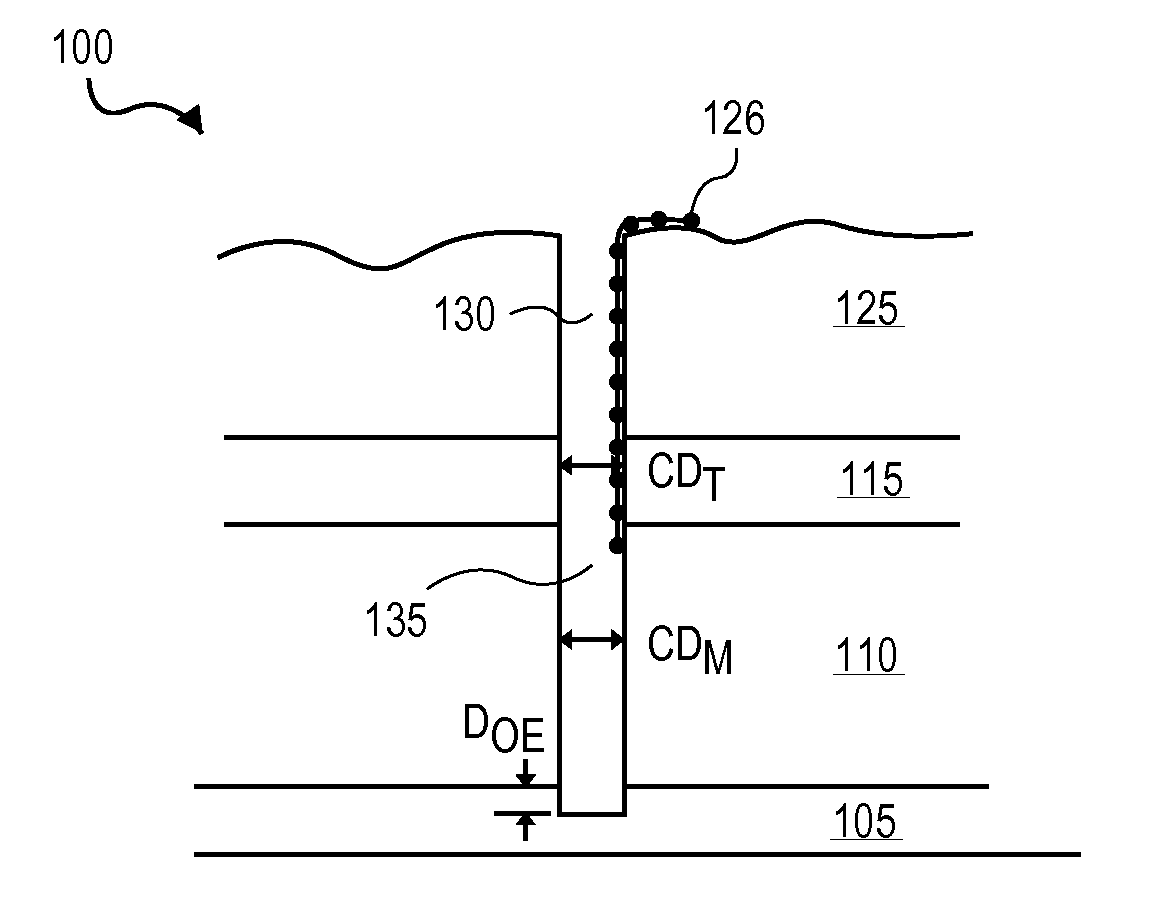
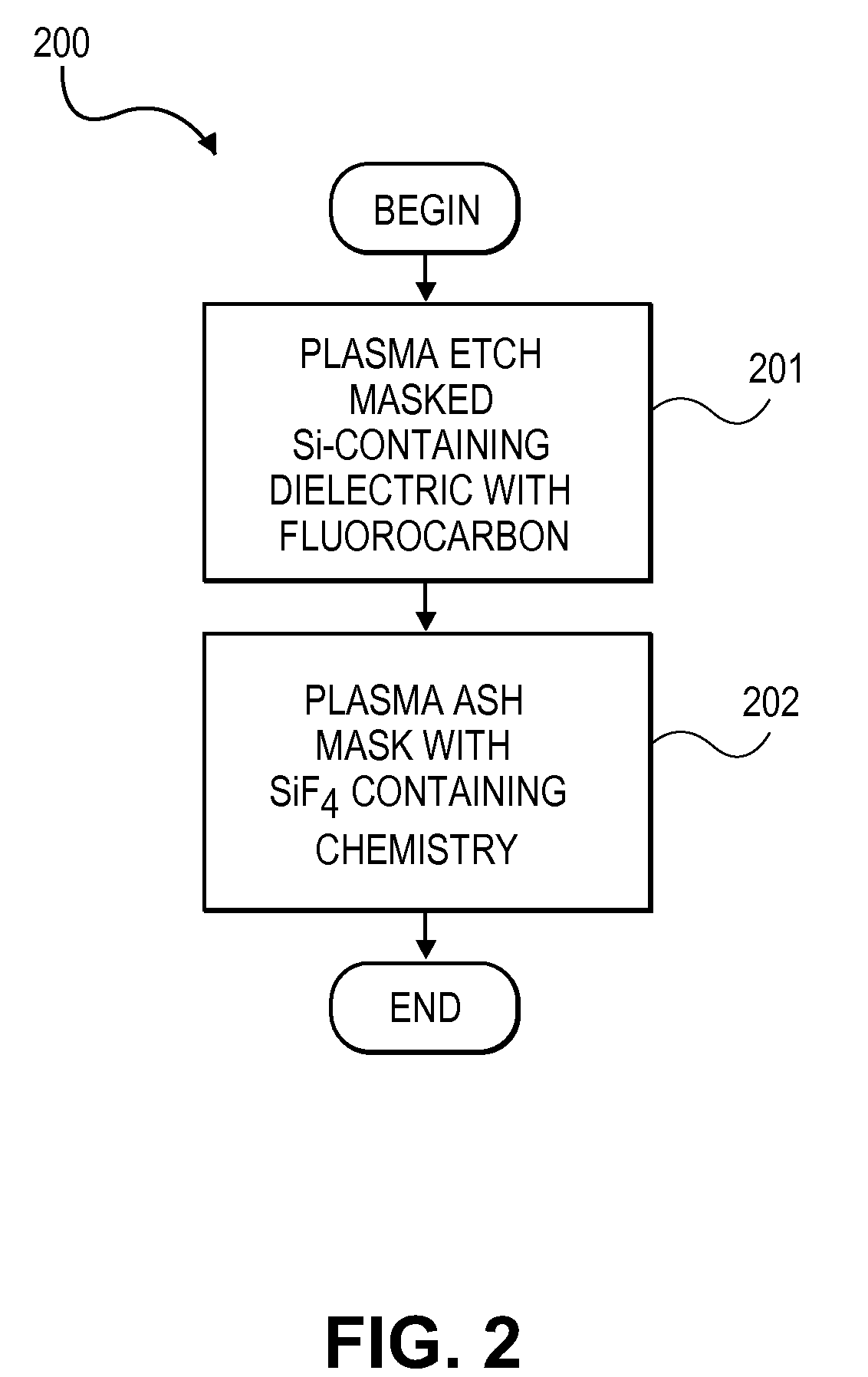
Plasma-based organic mask removal with silicon fluoride
InactiveUS20110079918A1Reduce lateral etchReduce harmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhysical chemistryMolecular nitrogen
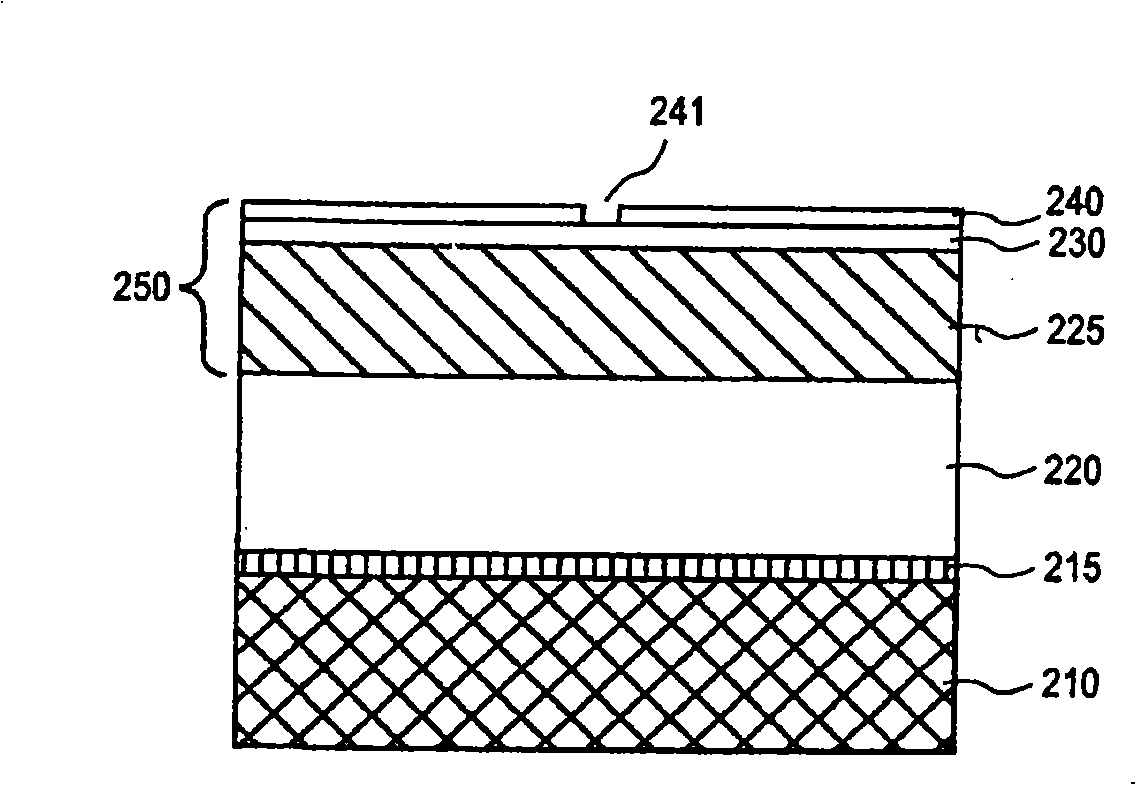
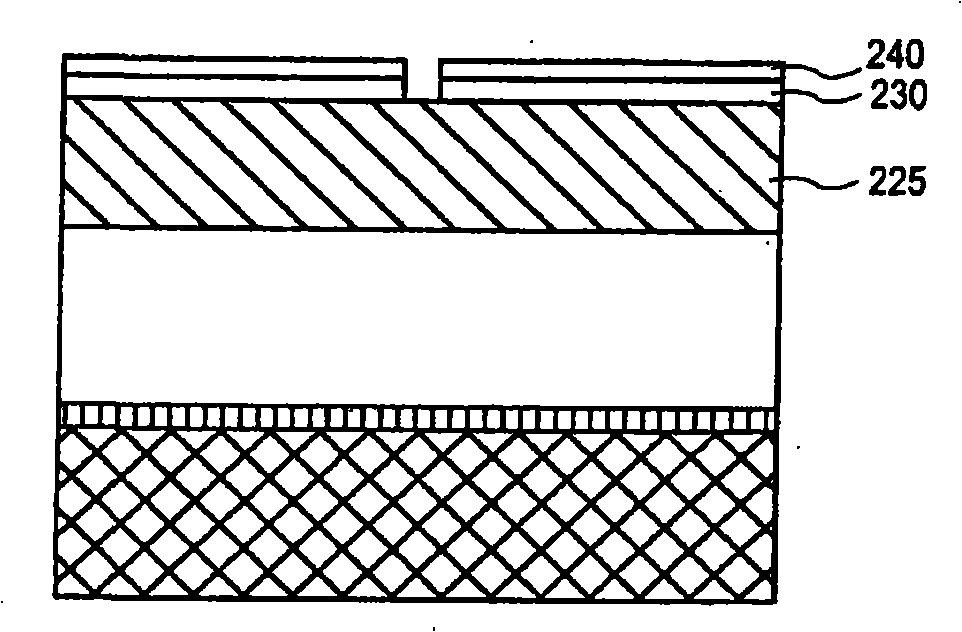
Removal of organic mask material from an etched dielectric film with an etchant gas mixture including silicon fluoride (SiF4). In certain embodiments, SiF4 is combined in an etchant gas mixture of molecular nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2) to in-situ strip an organic mask material from a porous low-k dielectric film that has been etched to form a damascene interconnect structure with reduced etch profile bowing and reduced ashing damage to the low-k dielectric film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
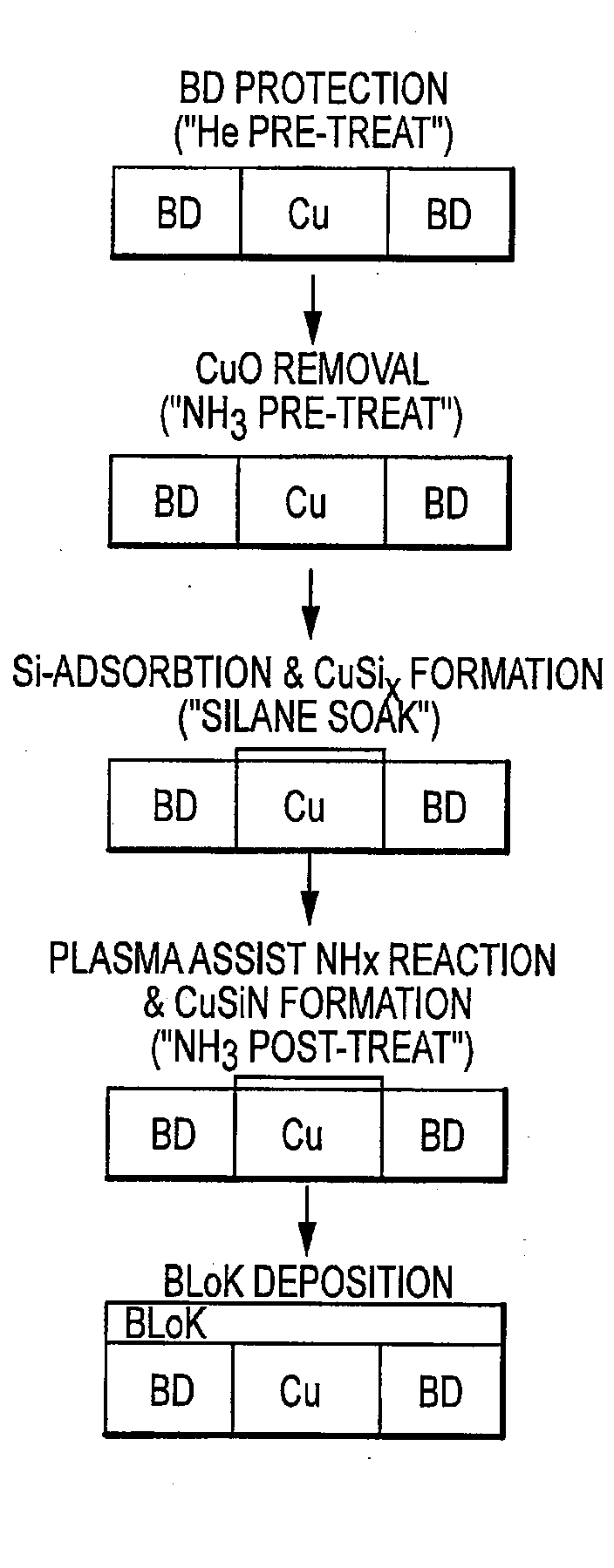
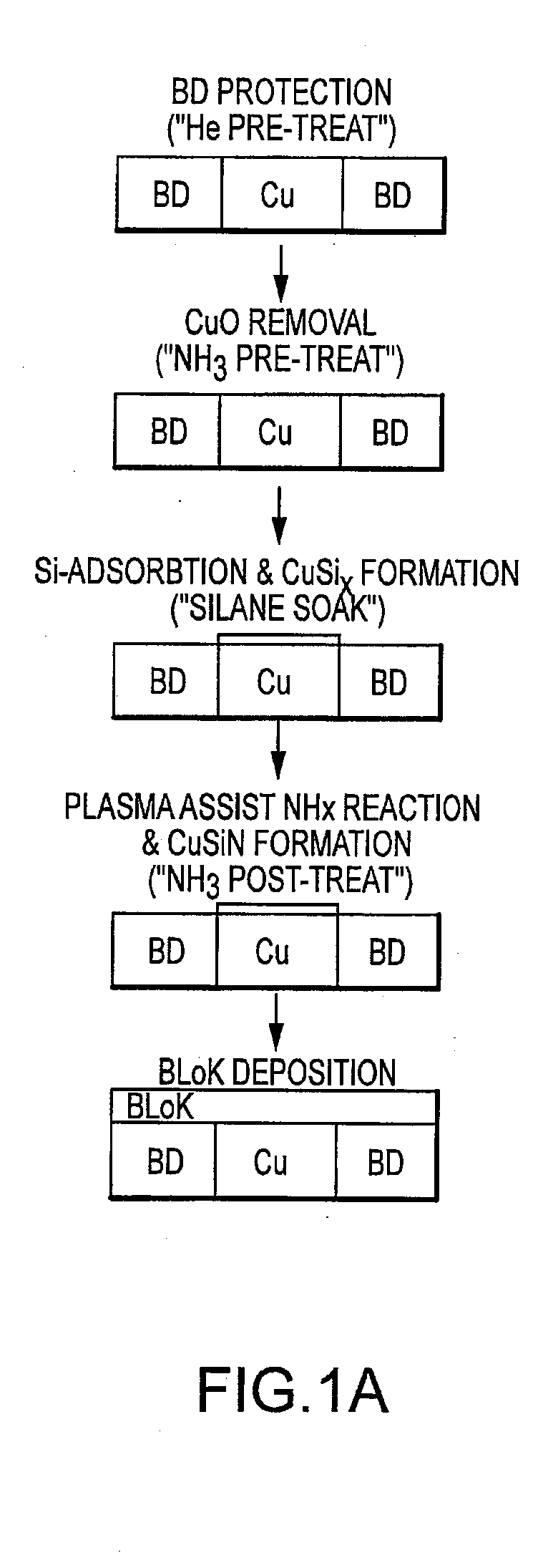
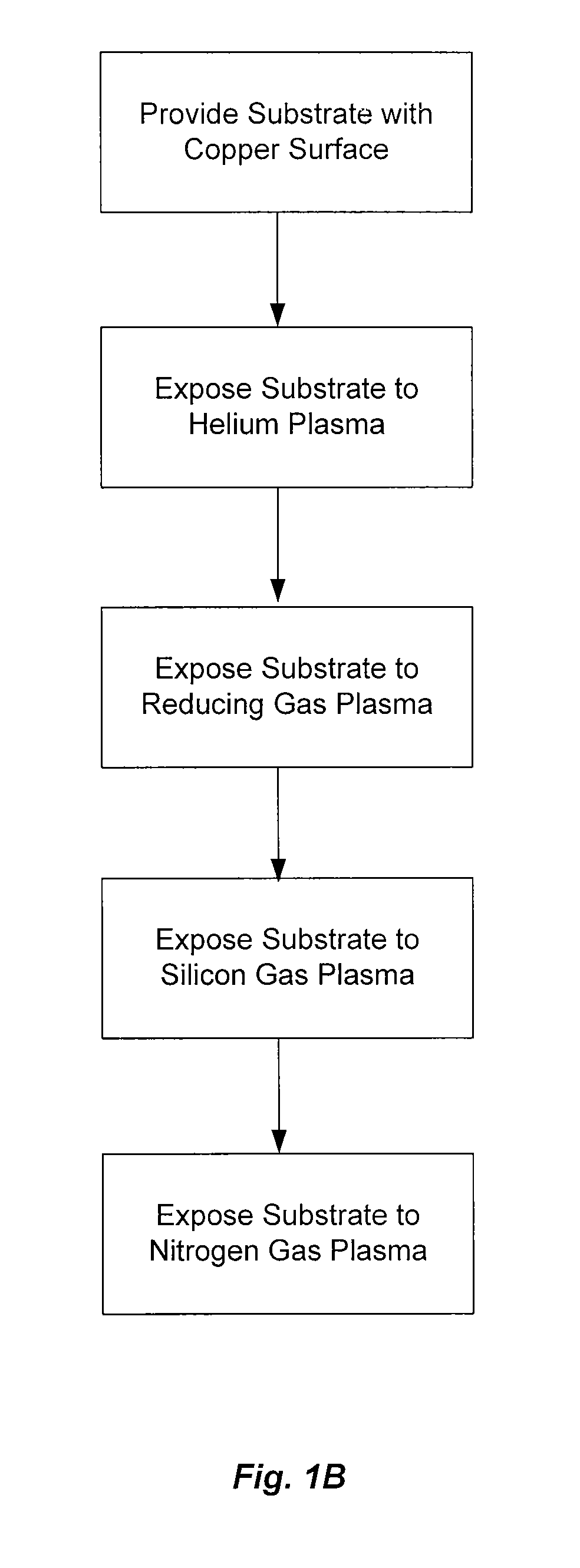
Selective copper-silicon-nitride layer formation for an improved dielectric film/copper line interface
InactiveUS20080213997A1Improve adhesionLow dielectric constantPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesCopper oxide
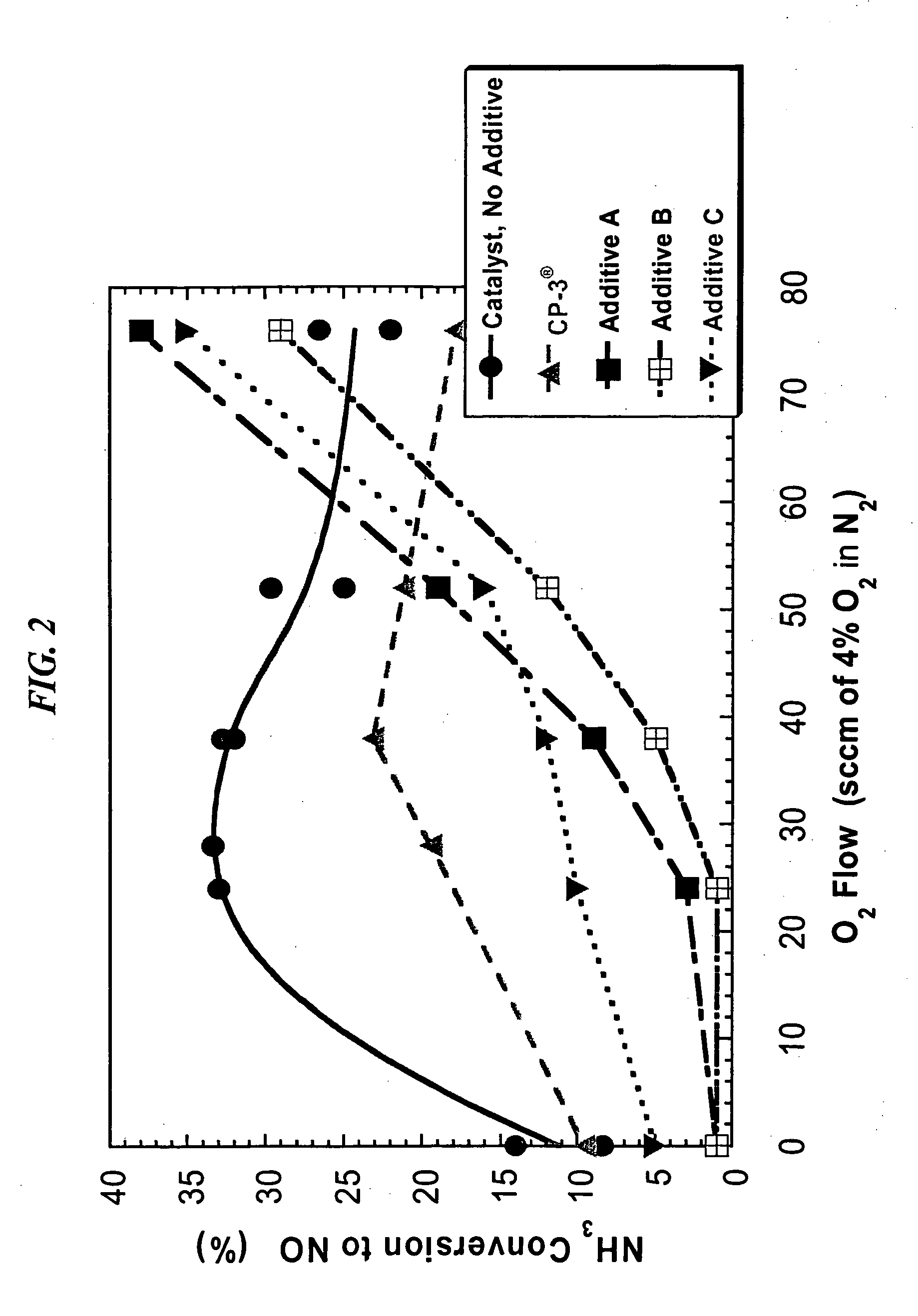
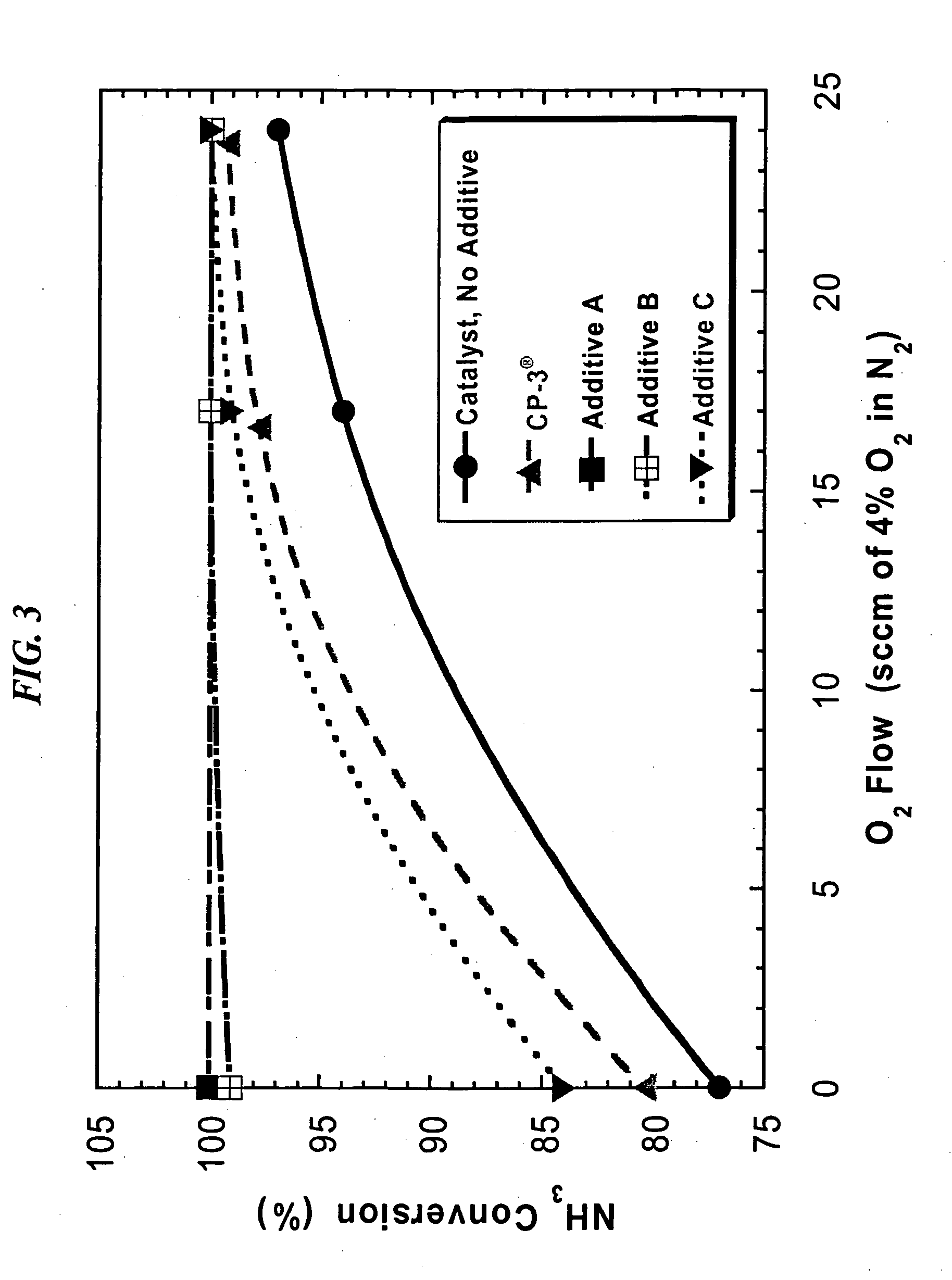
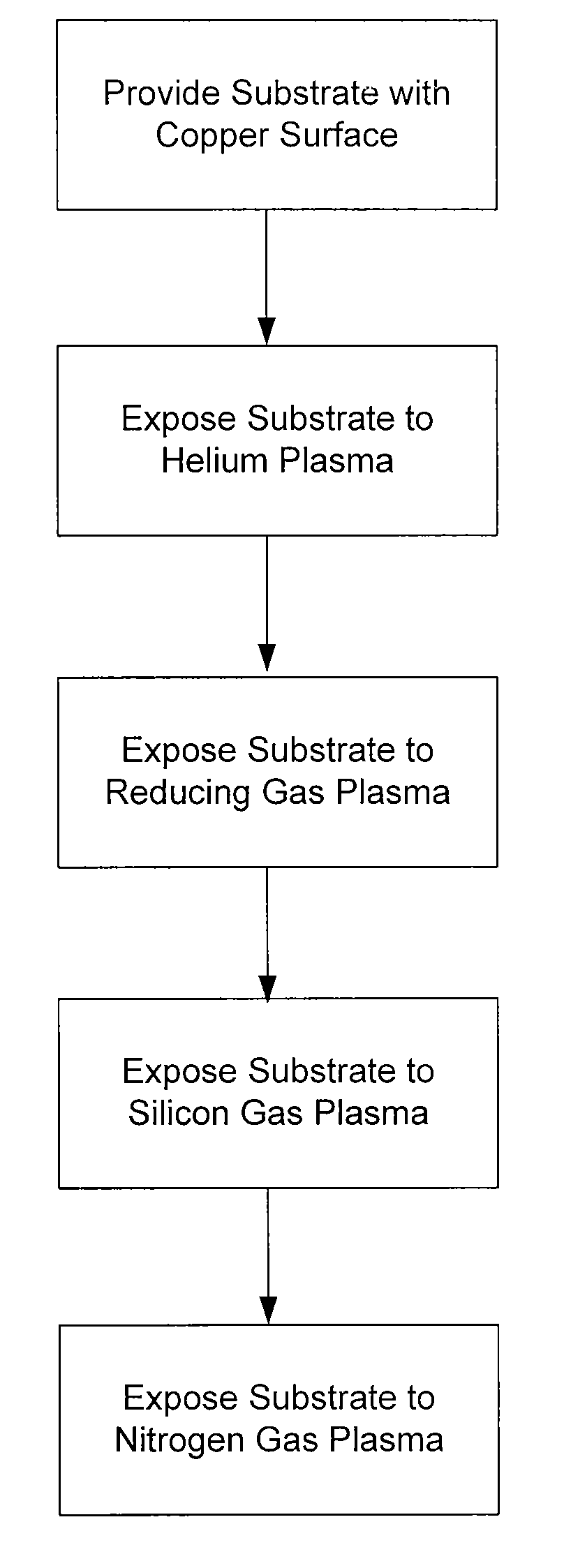
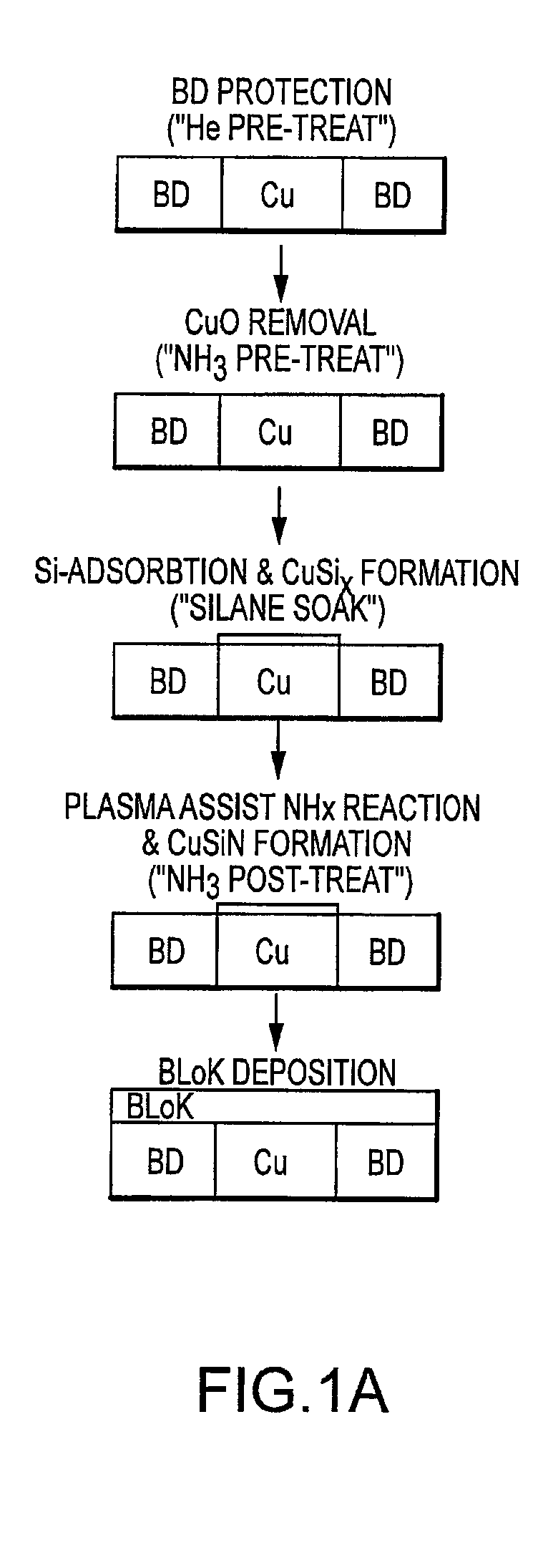
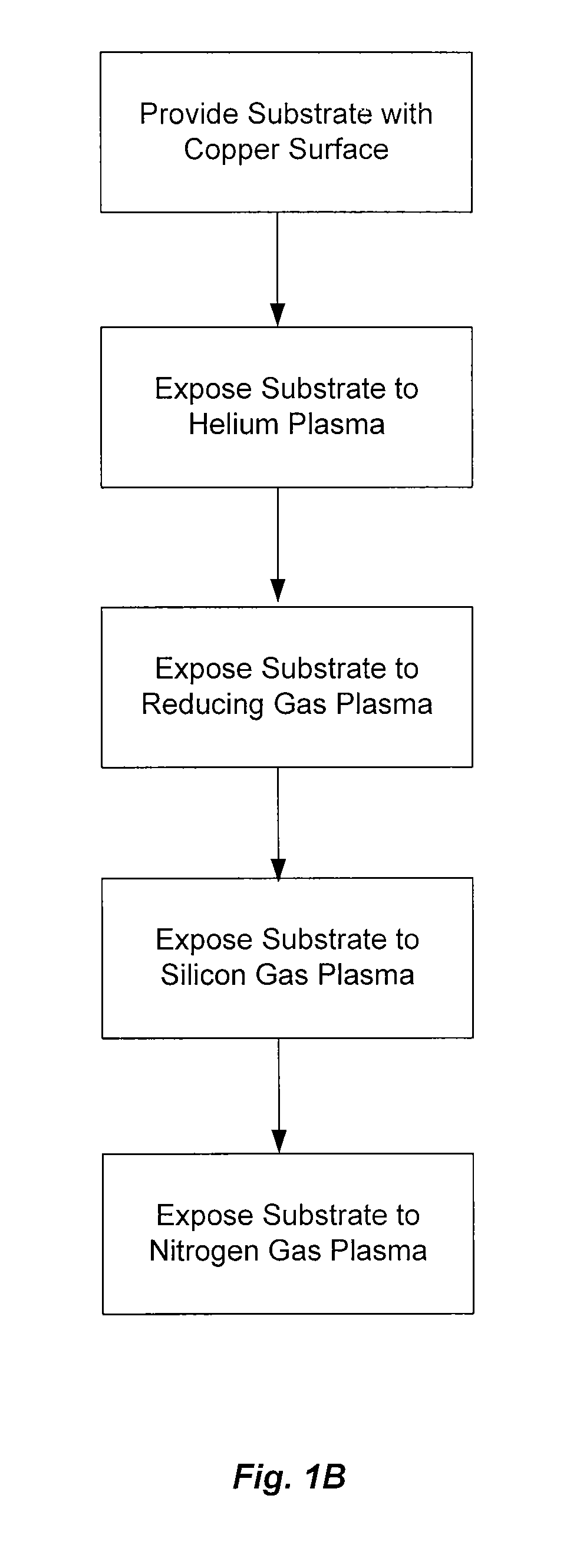
A process to form a copper-silicon-nitride layer on a copper surface on a semiconductor wafer is described. The process may include the step of exposing the wafer to a first plasma made from helium. The process may also include exposing the wafer to a second plasma made from a reducing gas, where the second plasma removes copper oxide from the copper surface, and exposing the wafer to silane, where the silane reacts with the copper surface to selectively form copper silicide. The process may further include exposing the wafer to a third plasma made from ammonia and molecular nitrogen to form the copper silicon nitride layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Bamboo forest biological fertilizer
InactiveCN1443729AIncrease nitrogen fixation intensityIncrease productionBacteriaHorticulture methodsBacillus licheniformisK pneumoniae
The bamboo forest biolgoical fertilizer capable of meeting the requirements for biological organic fertilizer in production of nuisance-free green bamboo shoots and organic bamboo shoots for reducingor substituting chemical fertilizer is formed from matrix and bamboo plant rhizospheric combined nitrogen-fixing bacteria which are separated from bamboo plant rhizosphere, can be used for fixing molecular nitrogen in atmosphere and are any one strain or combination of any two kinds of strains or more than two kinds of (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-1 strain, (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-2 strain, (Bacillus licheniformis Chester) WG-3 strain and (Klebsiella pneumoniae (Schroeter) Trevisan) WG-4 strain. Said fertilizer can be used for cultivating bamboo forest.
Owner:吴晓丽 +1
Growth of textured gallium nitride thin films and nanowires on polycrystalline substrates
InactiveUS20080194085A1Polycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthNanowireMolecular nitrogen
A synthesis route to grow textured thin film of gallium nitride on amorphous quartz substrates and on single crystalline substrates such as c-sapphire and polycrystalline substrates such as pyrolytic boron nitride (PBN), alumina and quartz using the dissolution of atomic nitrogen rather than molecular nitrogen to allow for growth at subatmospheric pressure.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
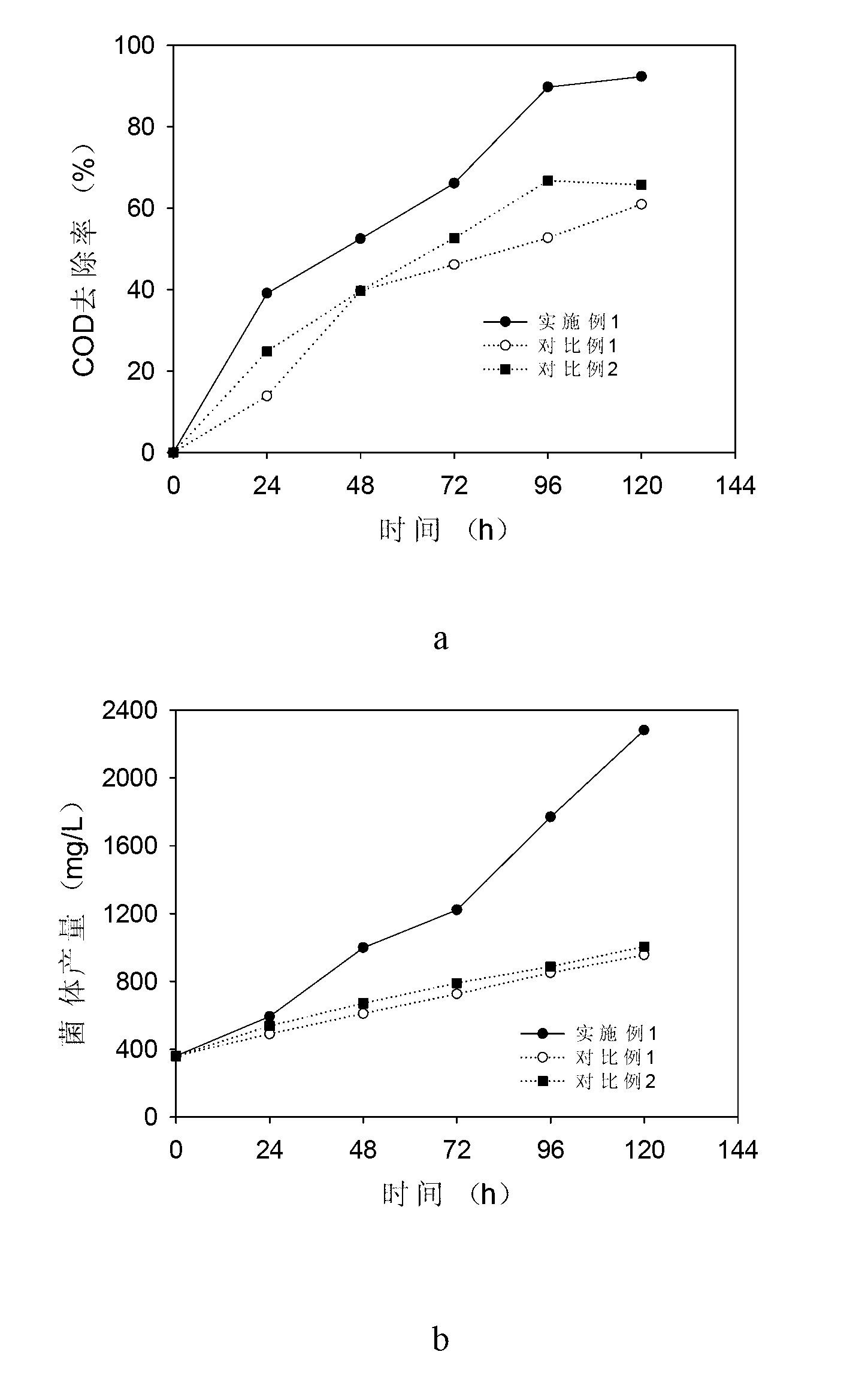
Method of treating and recycling food processing waste water by using photosynthetic bacterium
InactiveCN103058387AImprove processing efficiencyHigh degree of processingBiological water/sewage treatmentMolecular nitrogenOxygen
The invention discloses a method of treating and recycling food processing waste water by using a photosynthetic bacterium, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps: adding a micro-molecular carbon source substance into food processing waste water until a final concentration of the micro-molecular carbon source substance is 160 to 2000 mg / L and adding a micro-molecular nitrogen source substance into the food processing waste water until a final concentration of the micro-molecular nitrogen source substance is 55 to 1000 mg / L; adjusting the pH value of the waste water to be 7.0 to 9.0; then adding Rhodopseudomonas palustris in a logarithmic phase into the waste water until a final concentration of Rhodopseudomonas palustris is 240 to 2000 mg / L; carrying out treatment at a temperature of 25 to 30 DEG C for 96 to 120 h; and controlling externally applied illumination intensity to be 500 to 1500 lux by using an electric incandescent lamp and controlling the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the waste water to be 0.5 to 1.0 mg / L. The method provided by the invention is simple and easily practicable, enables process flow to be simplified and a recycling degree of sewage to be improved, the problem of secondary pollution in traditional sewage treatment processes is avoided, and energy consumption is lowered down.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plasma etching carbonaceous layers with sulfur-based etchants
InactiveUS8133819B2Minimal bowingImprove uniformityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfurMolecular nitrogen
Etching of carbonaceous layers with an etchant gas mixture including molecular oxygen (O2) and a gas including a carbon sulfur terminal ligand. A high RF frequency source is employed in certain embodiments to achieve a high etch rate with high selectivity to inorganic dielectric layers. In certain embodiments, the etchant gas mixture includes only the two components, COS and O2, but in other embodiments additional gases, such as at least one of molecular nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide (CO2) may be further employed to etch to carbonaceous layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
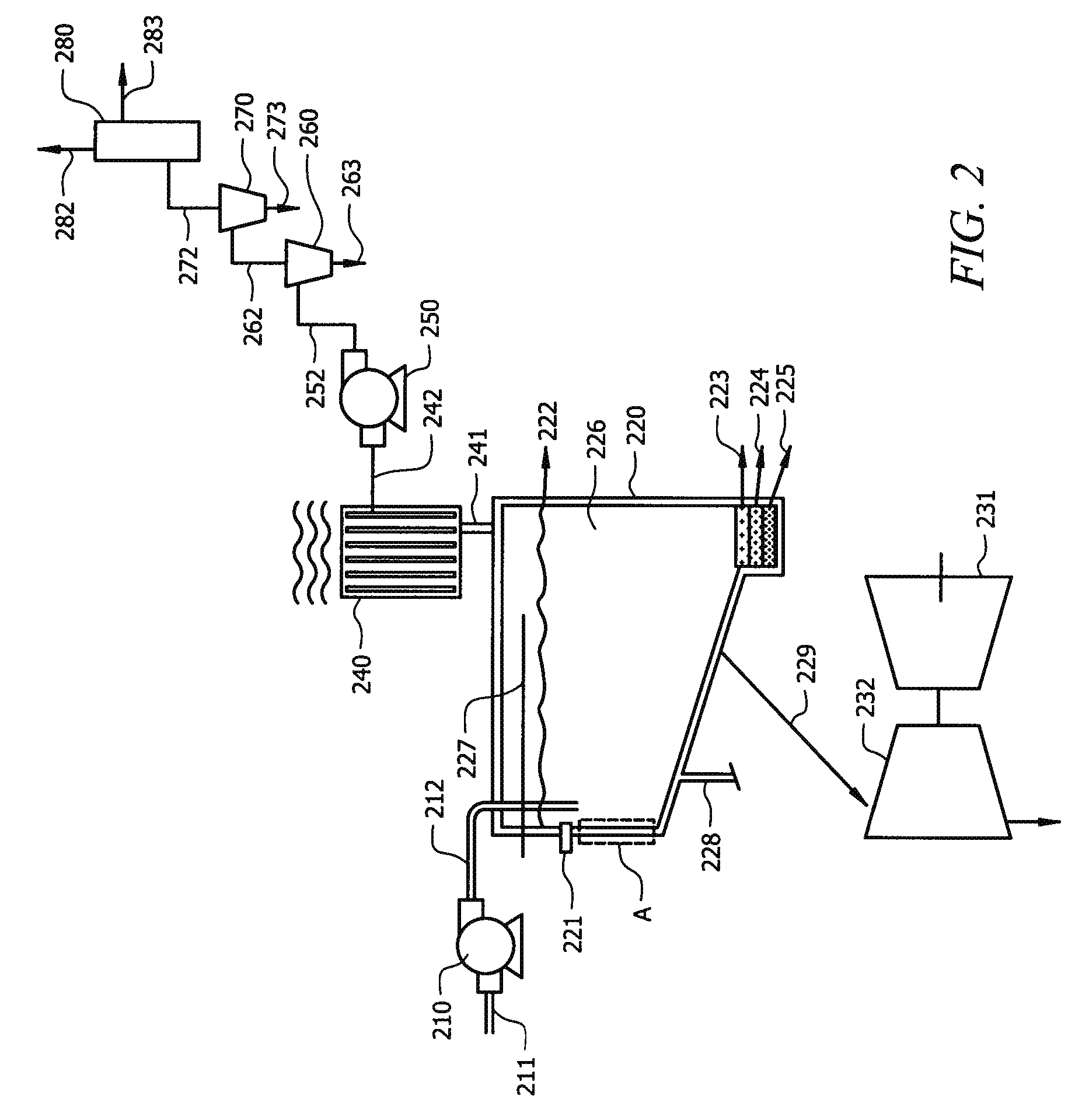
Method for Controlling Nox Emissions in the Fccu
InactiveUS20080213150A1Increase productionEfficiently oxidizedThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingMolecular nitrogenHeterogeneous Combustion
Processes for the reduction of NOx emissions from a regeneration zone during a fluid catalytic cracking of a hydrocarbon feedstock into lower molecular weight components are disclosed. The processes comprise contacting during a fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process where NOx emissions are released from a regeneration zone of a fluid catalytic cracking unit (FCCU) operating in a heterogeneous combustion mode under FCC conditions, a hydrocarbon feedstock with a circulating inventory of a FCC cracking catalyst and a NOx reduction composition. The NOx reduction composition comprises: (1) at least one reduced nitrogen species component having the ability to reduce the content of reduced nitrogen species to molecular nitrogen under reducing or partial burn FCC conditions and (2) at least one NOx reduction component having the ability to convert NOx to molecular nitrogen under oxidizing or full burn FCC conditions. The reduced nitrogen species and the NOx reduction components do not significantly increase the content of reduced nitrogen species or NOx under any mode of combustion during a FCC process.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
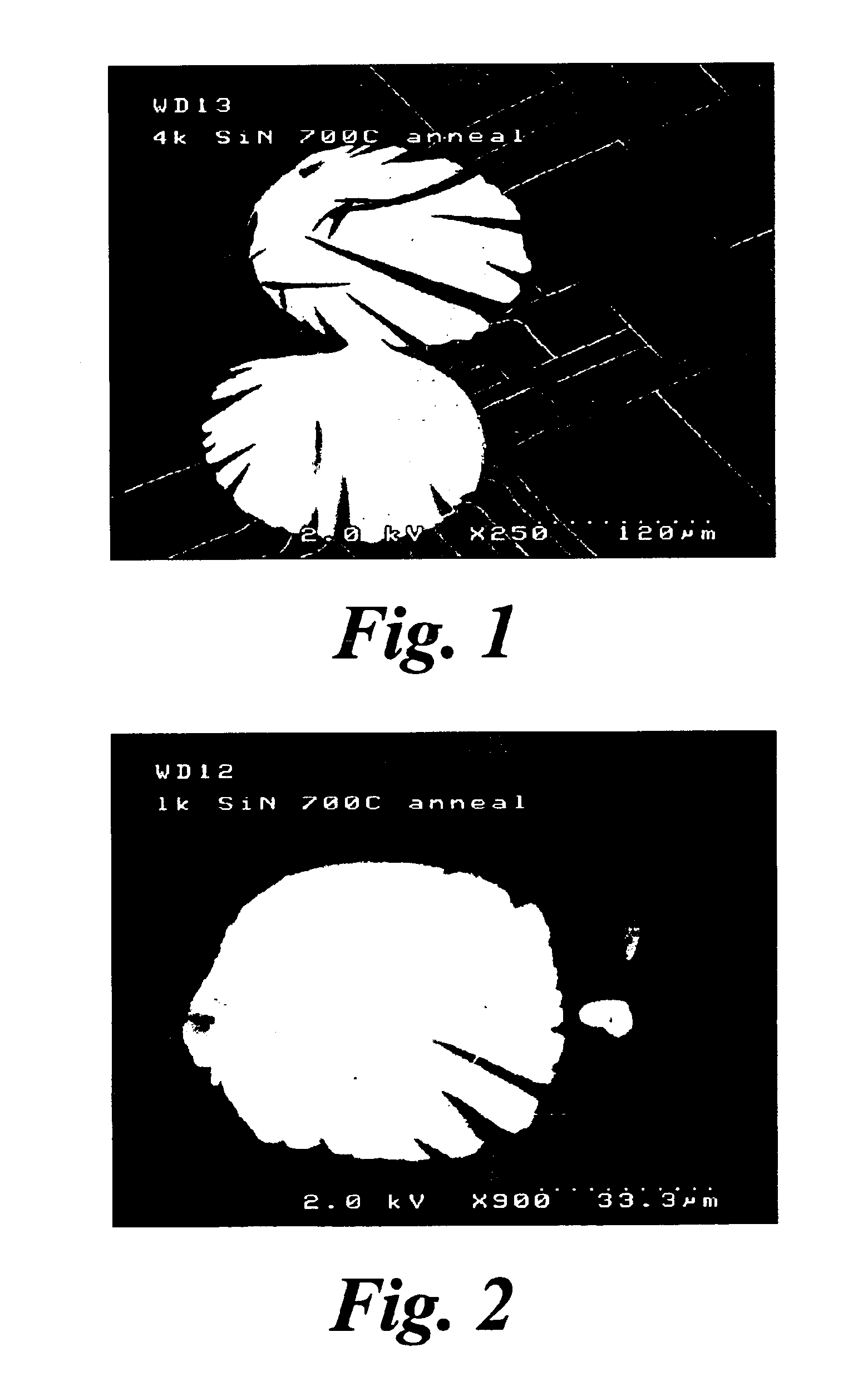
Methods of forming nitride films
InactiveUS6929831B2Change surface structureRemove blisteringVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesSilicon nitrideMolecular nitrogen
A silicon nitride film, for example, is deposited by introducing into a plasma region of a chamber a silicon containing gas, molecular nitrogen and sufficient hydrogen to dissociate the nitrogen to allow the silicon and nitrogen to react to form a silicon nitride film on a surface adjacent the plasma region. The thus deposited film may then be subjected to an activation anneal.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
Reduction of gas phase reduced nitrogen species in partial burn FCC processes
InactiveUS20060021910A1Speed up the processCatalytic crackingOther chemical processesCombustionGas phase
Reduced emissions of gas phase reduced nitrogen species in the off gas of an FCC regenerator operated in a partial or incomplete mode of combustion is achieved by contacting the off gas with an oxidative catalyst / additive composition having the ability to reduce gas phase nitrogen species to molecular nitrogen and to oxidize CO under catalytic cracking conditions. The oxidative catalyst / additive composition is used in an amount less than the amount necessary to prevent afterburn. Fluidizable particles of the oxidative catalyst / additives are circulated throughout the partial or incomplete burn FCC unit along with the FCC catalyst inventory. The flue gas having a reduced content of gas phase reduced nitrogen species and NOx is passed to a downstream CO boiler, preferably a low NOx CO boiler. In the CO boiler, as CO is oxidized to CO2, a reduced amount of gas phase reduced nitrogen species is oxidized to NOx, thereby providing an increase in the overall reduction of NOx emitted into the environment.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO
Selective copper-silicon-nitride layer formation for an improved dielectric film/copper line interface
InactiveUS7718548B2Improve adhesionLow dielectric constantPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesCopper oxide
A process to form a copper-silicon-nitride layer on a copper surface on a semiconductor wafer is described. The process may include the step of exposing the wafer to a first plasma made from helium. The process may also include exposing the wafer to a second plasma made from a reducing gas, where the second plasma removes copper oxide from the copper surface, and exposing the wafer to silane, where the silane reacts with the copper surface to selectively form copper silicide. The process may further include exposing the wafer to a third plasma made from ammonia and molecular nitrogen to form the copper silicon nitride layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
System and process for generation of electrical power
A system and process for generation of electrical power is provided. Electrical power is generated by a system including two integrated power cycles, a first power cycle utilizing water / steam as a working fluid and the second power cycle utilizing a fluid selected from the group consisting of molecular nitrogen, argon, a chemical compound having a boiling point of at most 65° C. at 0.101 MPa and a latent heat of vaporization of at least 350 kJ / kg, and a chemical compound having a boiling point of at most 65° C. at 0.101 MPa and a specific heat capacity as a liquid of at least 1.9 kJ / kg-° K as a working fluid. The working fluid of the second power cycle is expanded through a two-phase expander to produce power in the second power cycle, where the expanded working fluid of the second cycle has a temperature of at most 10° C.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
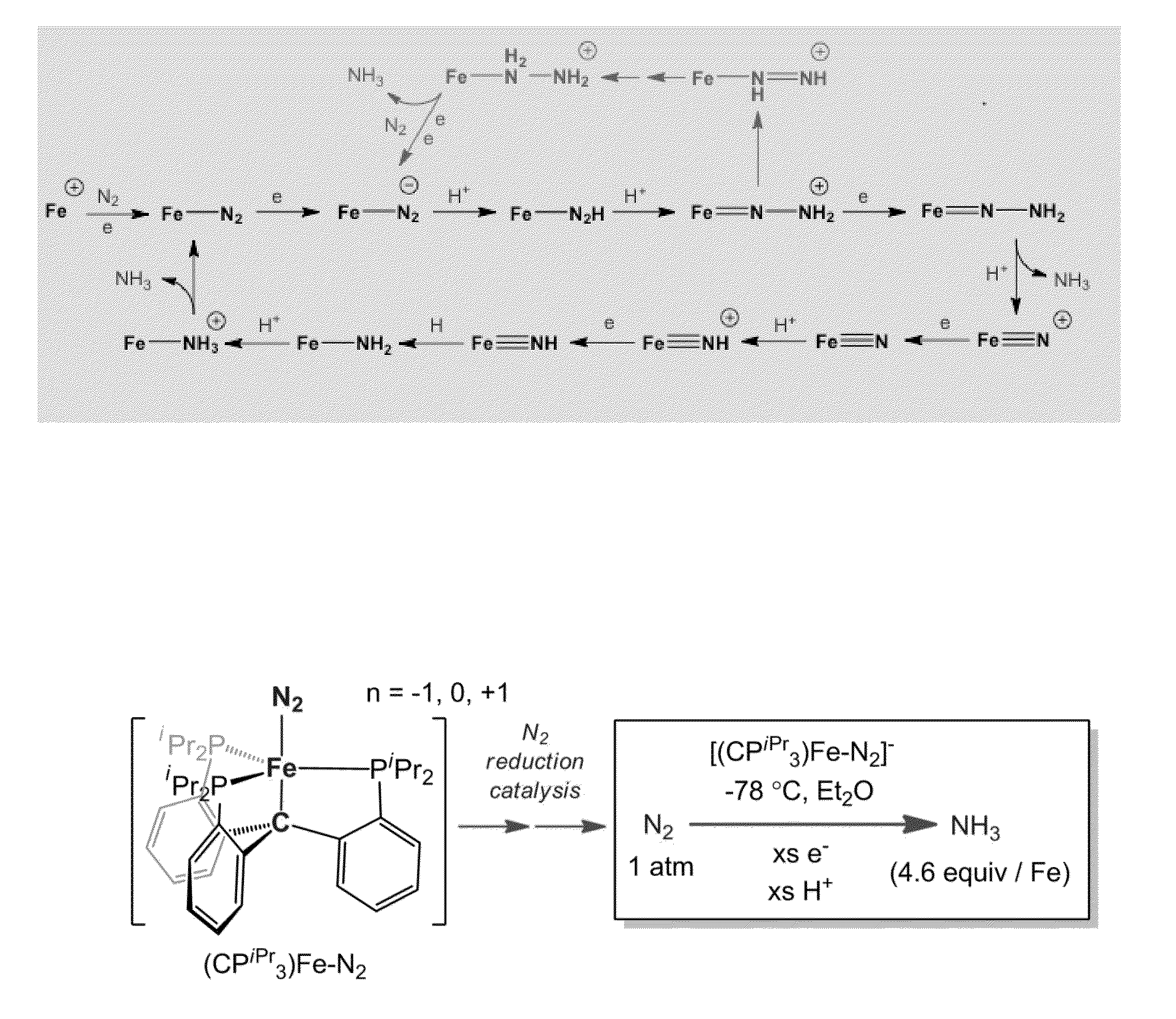
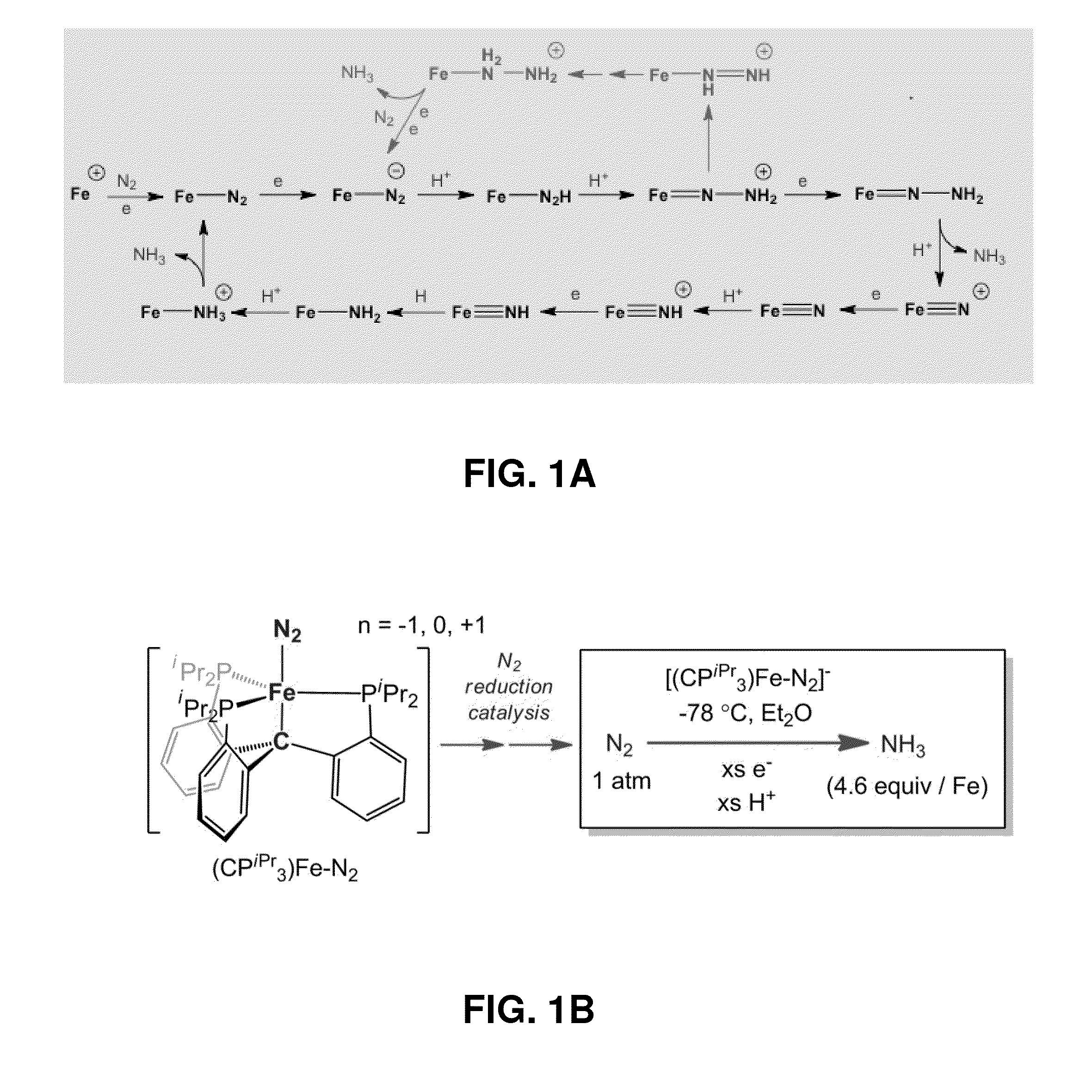
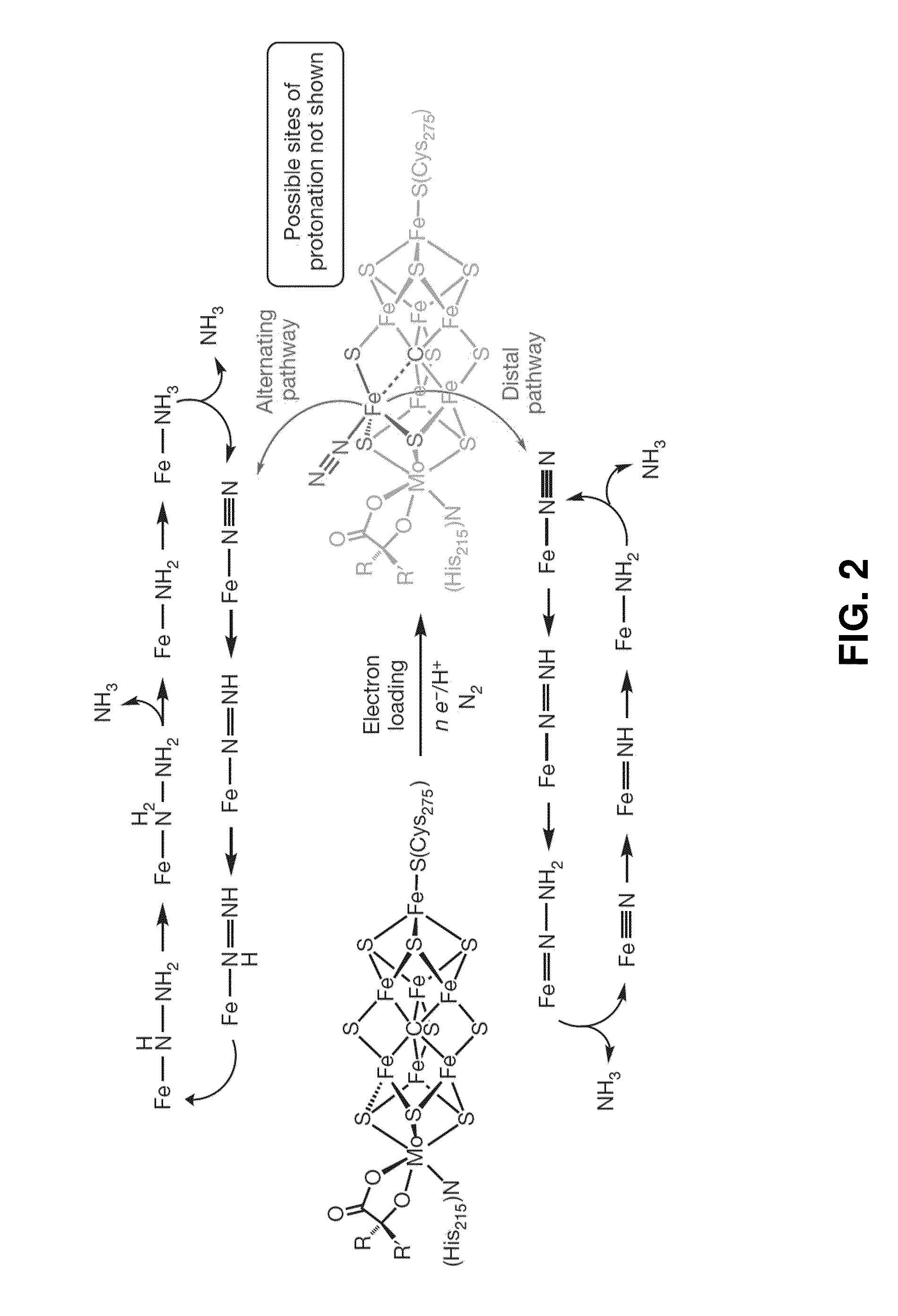
Catalytic ammonia synthesis by transition metal molecular complexes
ActiveUS20150104371A1Useful catalytic efficiencyGood turnover ratioSilicon organic compoundsOther chemical processesChemical reactionCatalytic method
This invention relates to molecular catalysts and chemical reactions utilizing the same, and particularly to catalysts and catalytic methods for reduction of molecular nitrogen. The molecular catalytic platform provided herein is capable of the facile reduction of molecular nitrogen under useful conditions such as room temperature or less and atmospheric pressure or less.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Highly dispersible inorganic compound nanoparticles and method of production thereof
Highly dispersible inorganic compound nanoparticles include a high molecular nitrogen compound having at least two amino groups selected from primary amino groups, secondary amino groups and tertiary amino groups; and inorganic compound nanoparticles bonded to at least one amino group of the at least two amino groups. The inorganic compound nanoparticles are covered with the high molecular nitrogen compound.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
System and method for converting system management data to be viewed and updated before or during runtime of an operating system
InactiveUS7241431B2Reduce the temperatureBroken down more effectivelyNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesOperational systemSystems management
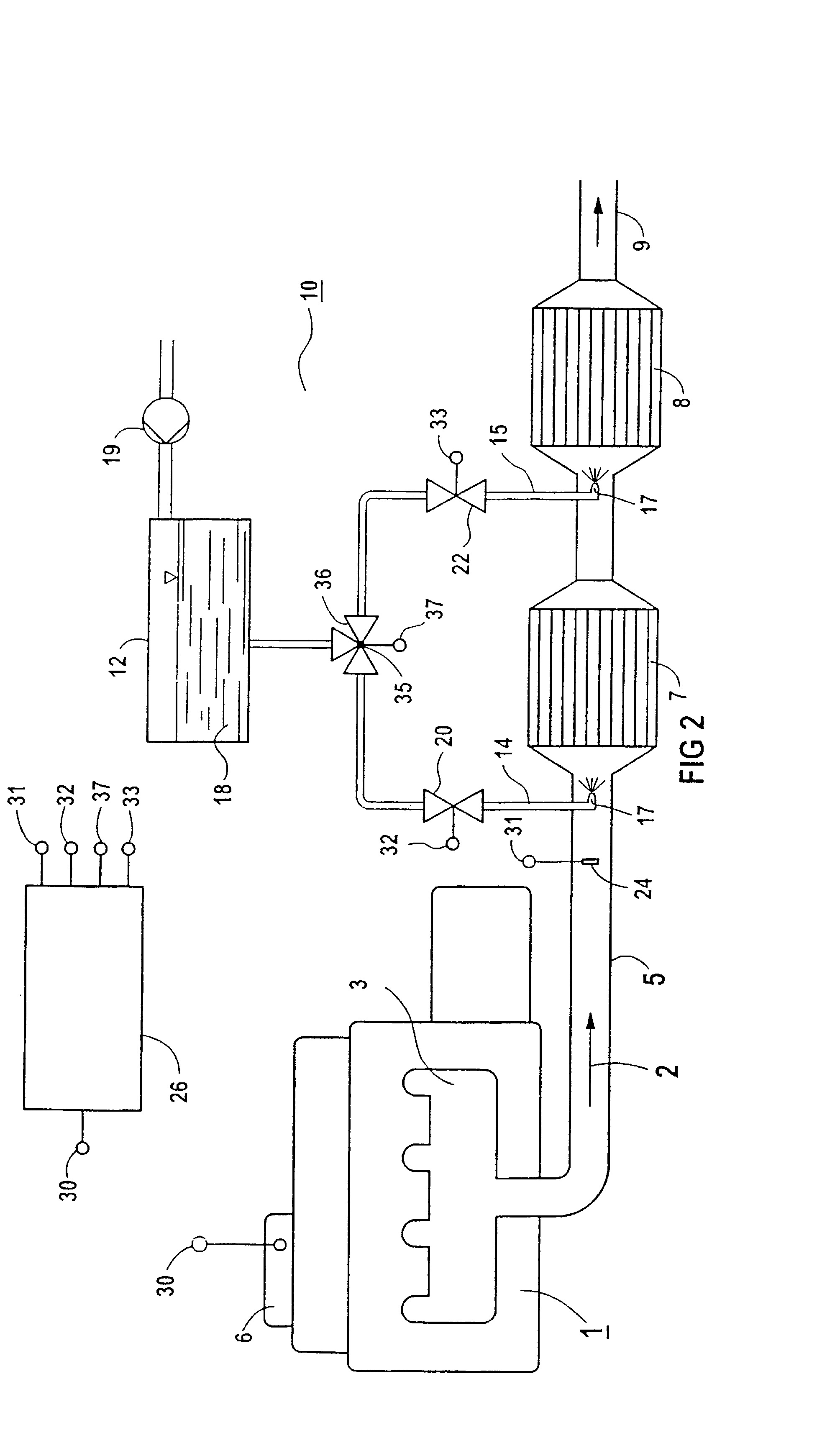
A method and an emission control system are for catalytically reducing nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas of a combustion system, especially a diesel motor. An oxidation catalyst is arranged upstream in relation to the reduction catalyst and in the exhaust gas channel. A reaction agent for decomposing nitrogen oxides according to the method of the selective catalytic reduction is added according to the temperature and upstream or downstream in relation to the oxidation catalyst and upstream in relation to the reduction catalyst. The selectivity of the oxidation catalyst is used for decomposing nitrogen oxides to form molecular nitrogen.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Plasma etching carbonaceous layers with sulfur-based etchants
Etching of carbonaceous layers with an etchant gas mixture including molecular oxygen (O2) and a gas including a carbon sulfur terminal ligand. A high RF frequency source is employed in certain embodiments to achieve a high etch rate with high selectivity to inorganic dielectric layers. In certain embodiments, the etchant gas mixture includes only the two components, COS and O2, but in other embodiments additional gases, such as at least one of molecular nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide (CO2) may be further employed to etch to carbonaceous layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Adsorbent for purifying coal ethylene glycol and preparation method of adsorbent for purifying coal ethylene glycol
InactiveCN104275157AImprove qualityMeet the quality requirementsOther chemical processesHydroxy compound separation/purificationPolyesterSorbent
The invention relates to an adsorbent for purifying coal ethylene glycol and a preparation method of the adsorbent for purifying the coal ethylene glycol. The adsorbent is used for removing trace impurities including aldehydes, esters, acids, micro-molecular nitrogen oxides or organic amine compounds and the like in a coal ethylene glycol product. The invention relates to modified active carbon which is used as the adsorbent; the ethylene glycol passes through a bed layer filled with the adsorbent at a room temperature and the trace impurities which can influence the light transmittance can be electively remained in the bed layer so that the content of the impurities of the product is reduced; and the ultraviolet light transmittance and the acidity of the coal ethylene glycol are improved and the chromaticity of an ethylene glycol distilled residual solution is reduced. The refining temperature is 20-50 DEG C and the liquid-phase air speed is 1.5hr<-1>. After the treatment of the method, the purity of the ethylene glycol is improved by 0.5% and the ultraviolet light transmittance (UV) reach 88% at 220nm, reach 96% at 275nm and reach 99.5% at 350nm; the acidity can reach 1ppm-8ppm; and the chromaticity of the distilled residual solution reaches the level equal to that of petroleum ethylene glycol and the standards of polyester-grade products are reached.
Owner:JIANGSU JINJU ALLOY MATERIAL
Preparation of acrolein or acrylic acid or a mixture thereof by heterogeneously catalyzed partial gas phase oxidation of propylene
InactiveUS7592483B2Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidationGas phaseAcrolein
A process for preparing acrolein or acrylic acid or a mixture thereof by heterogeneously catalyzed partial gas oxidation of propylene, in which the starting reaction gas mixture has the following contents:from 6 to 9% by volume of propylene,from 8 to 18% by volume of molecular oxygen,from 6 to 30% by volume of propane andfrom 32 to 72% by volume of molecular nitrogen.
Owner:BASF AG
Hexagonal flaky cobalt hydroxide synthesis method
InactiveCN106186085AEasy alignmentEasy to separateMaterial nanotechnologyCobalt oxides/hydroxidesHigh concentrationSynthesis methods
The present invention relates to a hexagonal flaky cobalt hydroxide synthesis method, which comprises: dissolving a cobalt salt in deionized water to obtain a cobalt salt solution; dissolving caustic alkali and one or a plurality of small molecular nitrogen-containing ligands in deionized water so as to be adopted as a precipitant solution; and adding the precipitant solution into the cobalt salt solution to react with the cobalt ions so as to generate the cobalt hydroxide. According to the present invention, during the reaction precipitation process of the hydroxide ions and the cobalt ions, a certain amount of the one or the plurality of the small molecular nitrogen-containing ligands are added, and the nitrogen-containing ligands are strongly matched with the cobalt ions to make the cobalt hydroxide grow according to a certain direction, such that finally the hexagonal flaky structure having the edge length of 100-400 nm is formed; and the flaky structure can be obtained at the room temperature under the high concentration, the reaction time is short, and the mass production can be achieved.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Growth of textured gallium nitride thin films on polycrystalline substrates
InactiveUS7238232B1Polycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthMolecular nitrogenDissolution
A synthesis route to grow textured thin film of gallium nitride on amorphous quartz substrates and on single crystalline substrates such as c-sapphire and polycrystalline substrates such as pyrolytic boron nitride (PBN), alumina and quartz using the dissolution of atomic nitrogen rather than molecular nitrogen to allow for growth at subatmospheric pressure.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Micro-molecular biological controlled-release composite fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a micro-molecular biological controlled-release composite fertilizer which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 10-20% of urea, 15-30% of monoammonium phosphate, 10-25% of potassium sulfate and / or potassium chloride, 5-10% of micro molecular nitrogen powder, 15-20% of medium trace element powder, 15-20% of a slow-release organic matter mixed material and 0.2-0.6 per mill of a composite bacterium, wherein the content of nitrogen of micro molecular nitrogen powder is 30-40%; the medium trace elements comprise raw material powder of potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, zinc, iron, boron, manganese and ore; the slow-release organic matter mixing material comprises byproducts of stevia rebaudiana powder, humic acid and soyabean protein; the effective bacterium content of the composite bacterium is 30-40 billion / gram. The invention further provides a preparation method of the micro-molecular biological controlled-release composite fertilizer. Therefore, the micro-molecular biological controlled-release composite fertilizer is not only relatively high in fertilizer efficiency, but also capable of ensuring that plants relatively well absorb metal elements.
Owner:SHANDONG CREATE YIFENG FERTILIZER GRP CO LTD
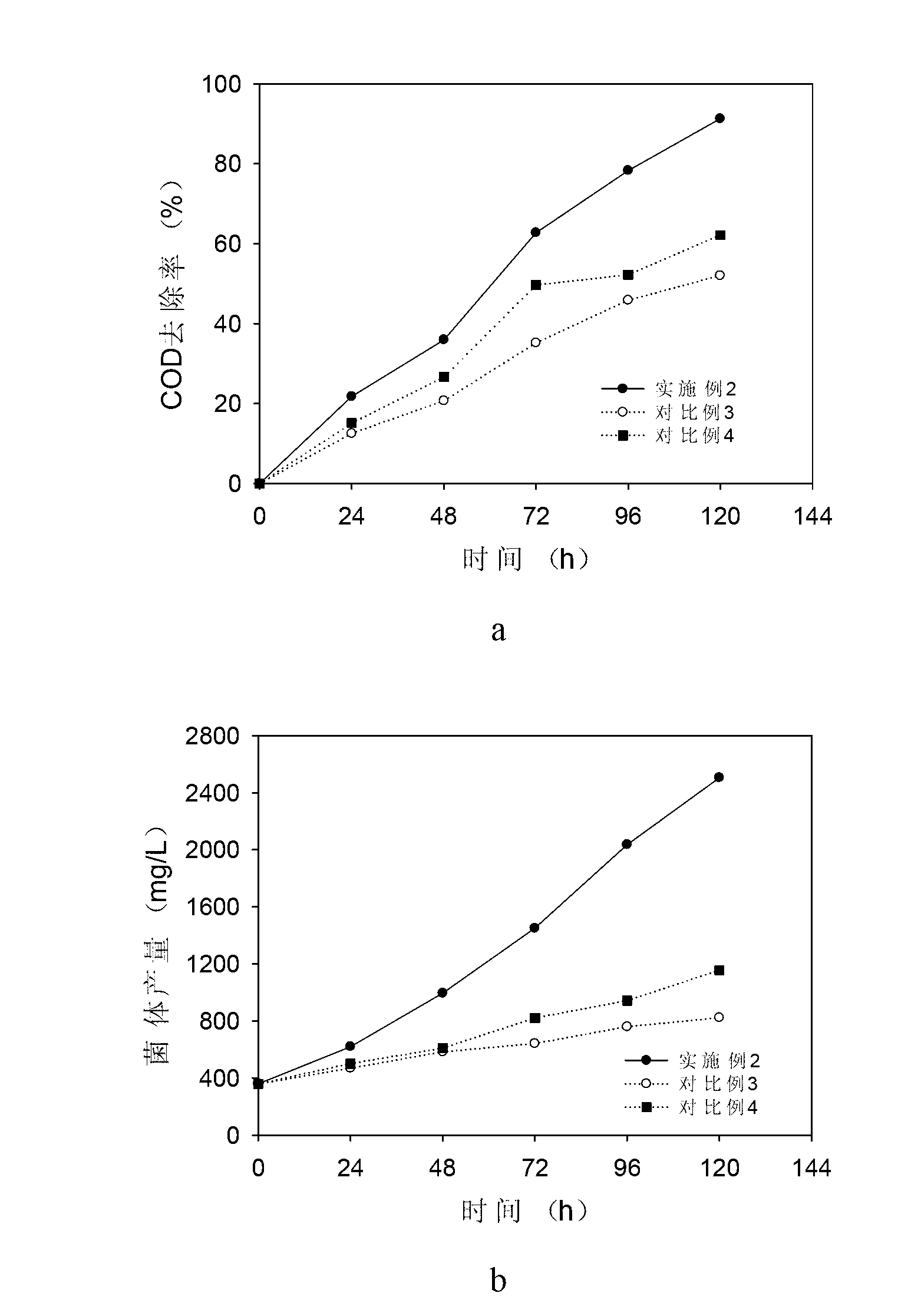
Method for treating soybean processing wastewater by utilizing photosynthetic bacteria and recycling wastewater
InactiveCN103043804ARealize resourcesImprove processing efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentRhodobacterMolecular nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for treating soybean processing wastewater by utilizing photosynthetic bacteria and recycling the wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises the steps as follows: adding small molecular carbon source substances with the final concentration of 400-1200 mg / L and small molecular nitrogen source substances with the final concentration of 200-2000 mg / L into the soybean processing wastewater at first; adjusting the pH value of the wastewater to be 7.0-9.0; adding rhodobacter sphaeroides with the final concentration of 400-1500 mg / L during logarithmic growth phase into the wastewater; treating for 96-120 h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C; and micro-aerating in the wastewater and controlling the dissolved oxygen concentration in the soybean processing wastewater to be 0.5-1.0 mg / L during the treatment process. According to the method, the energy consumption is reduced, the process of treating sewage with the photosynthetic bacteria is simplified, a large amount of bacterial resources capable of being directly and comprehensively utilized are produced, and the problem of secondary pollution is avoided, so that the sewage recycling rate is increased.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Off gas treatment using a metal reactant alloy composition
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for treating a flue gas stream containing oxygen containing greenhouse gases. In particular, the method comprises reacting a flue gas steam with a molten aluminum or aluminum alloy bath, creating alumina and elemental carbon, elemental sulfur, and molecular nitrogen. The apparatus includes a reaction vessel for carrying out the reaction, as well as other equipment necessary for capturing and removing the reaction products. Further, the process can be used to cogenerate electricity using the excess heat generated by the process.
Owner:ELEMENTAL RECYCLING INC
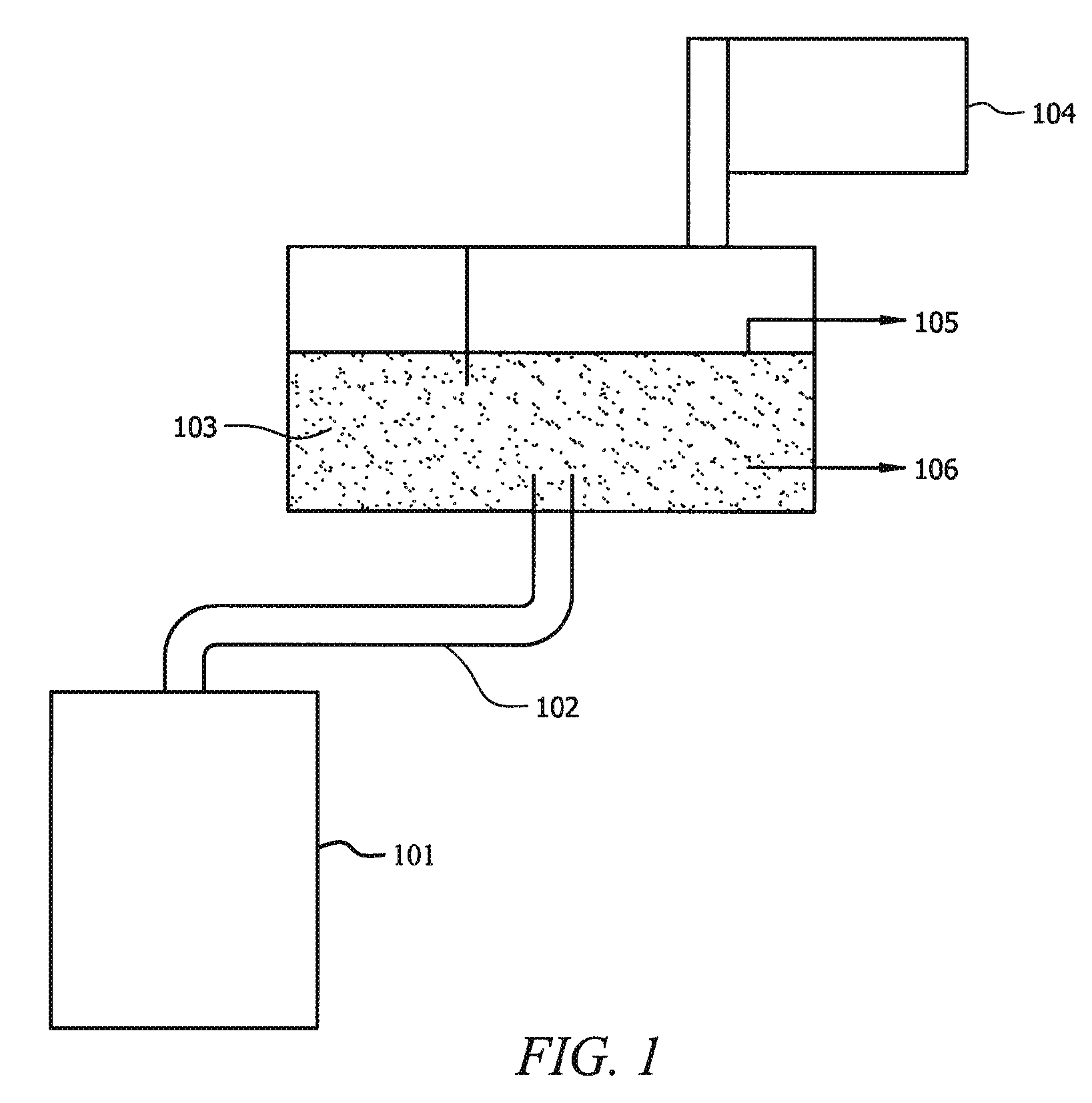
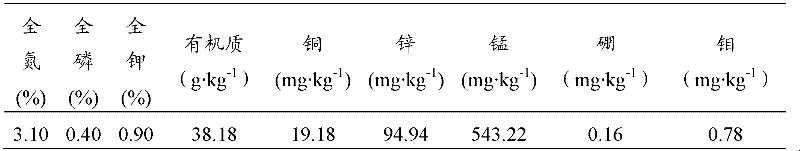
Fermented cake fertilizer, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102515896ASolve nitrogenSolving the Contradictions of Flue-cured Tobacco Needing NitrogenMolecular nitrogenFermentation
The invention discloses a fermented cake fertilizer, its preparation method and application. The invention overcomes the defects of the prior art and provides a fermented cake fertilizer which is suitable for tobacco growth. The fermented cake fertilizer is characterized in that a bean cake is subject to microbial strain fermentation, then macro-molecular compounds in the cake fertilizer are converted into micro-molecular compounds, nitrogen in protein is converted into amino acid to release nitrogen in the cake fertilizer in advance, thus the releasing rule of nitrogen is consistent with the nitrogen absorption rule of tobacco; and microbes generate protease in the process of growth, fermented materials are put in water, protease converts protein in the bean cake into amino acid or micro-molecular nitrogen containing compounds, plants can directly adsorb amino acid, or the micro-molecular nitrogen containing compounds are easy to be converted into absorbable nitrogen of plants in soil. According to the invention, the purpose of improving the tobacco quality can be achieved, and simultaneously the effects of increasing soil biological activity, improving soil structure, and raising soil fertility are achieved.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com