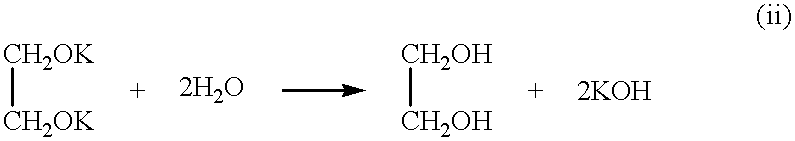
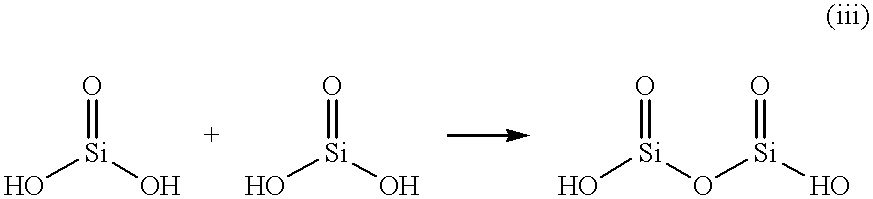
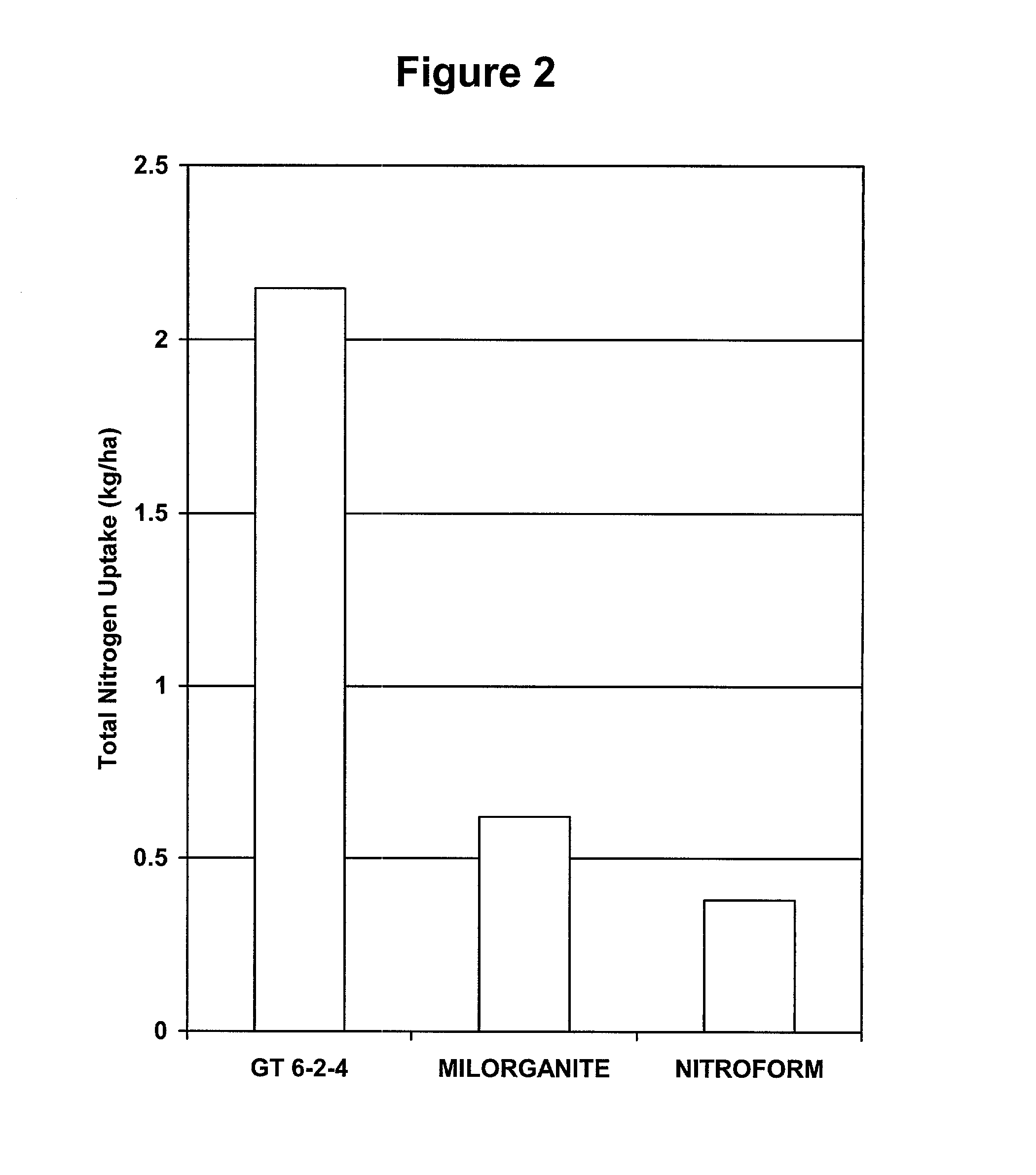
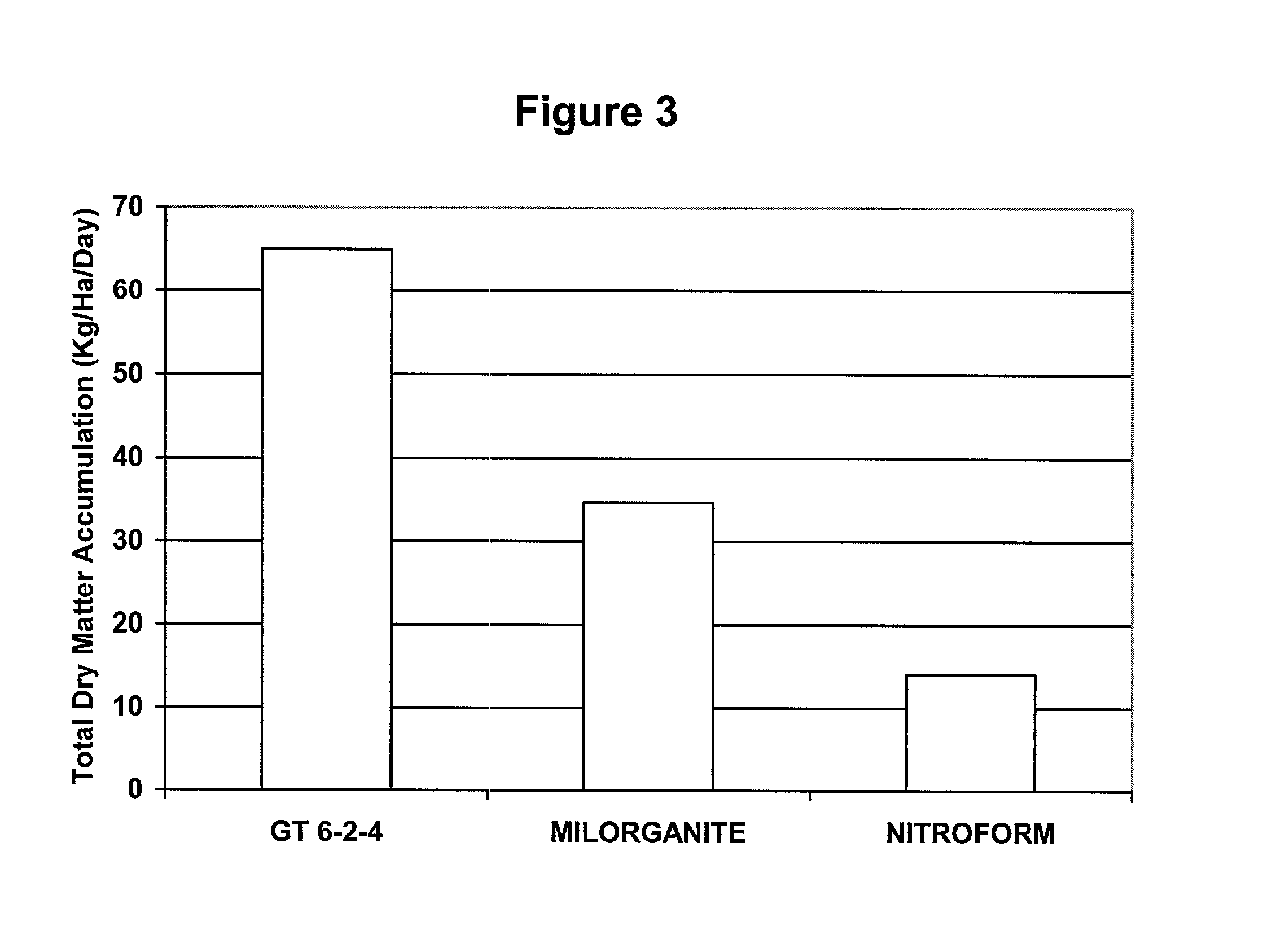
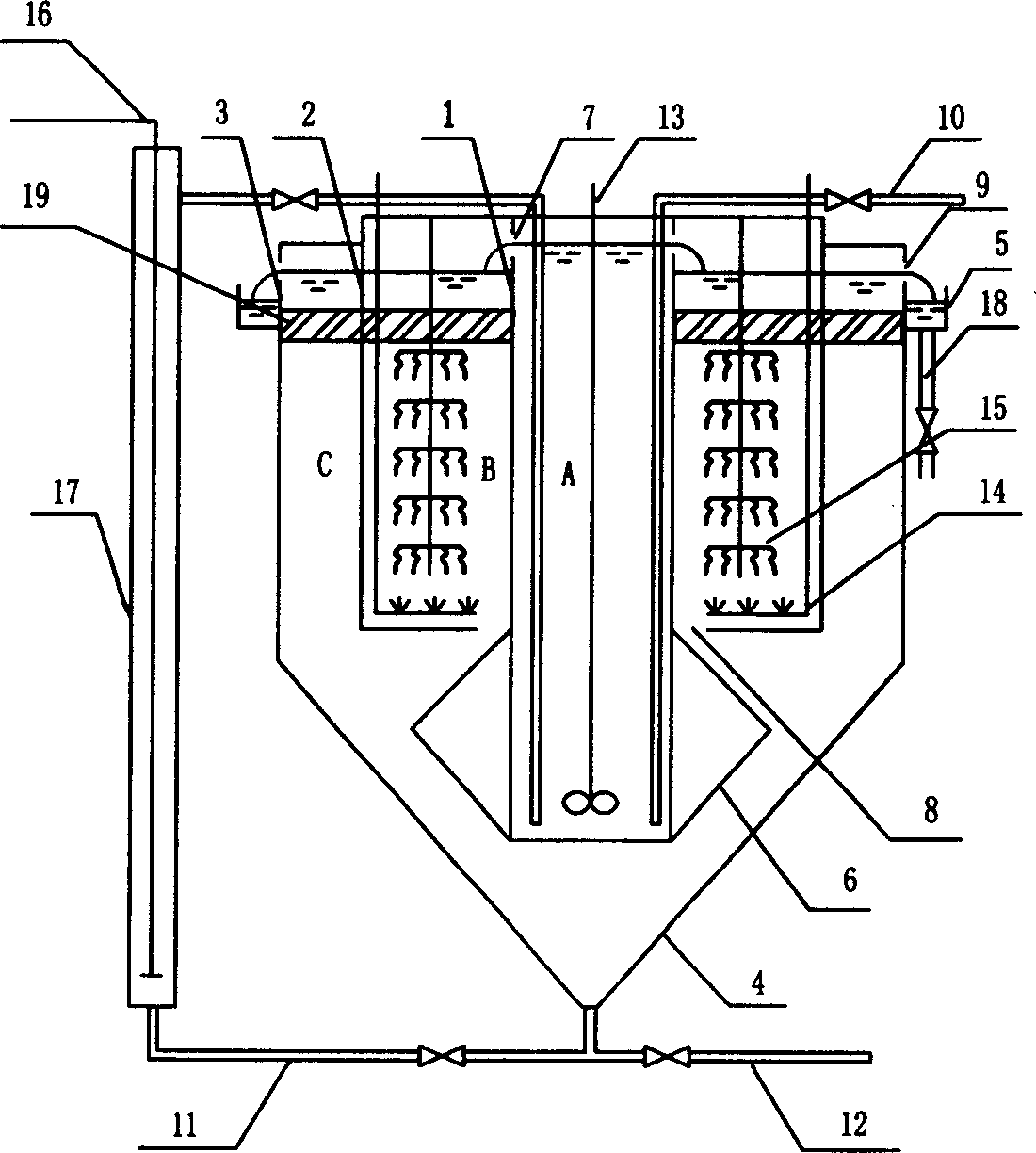
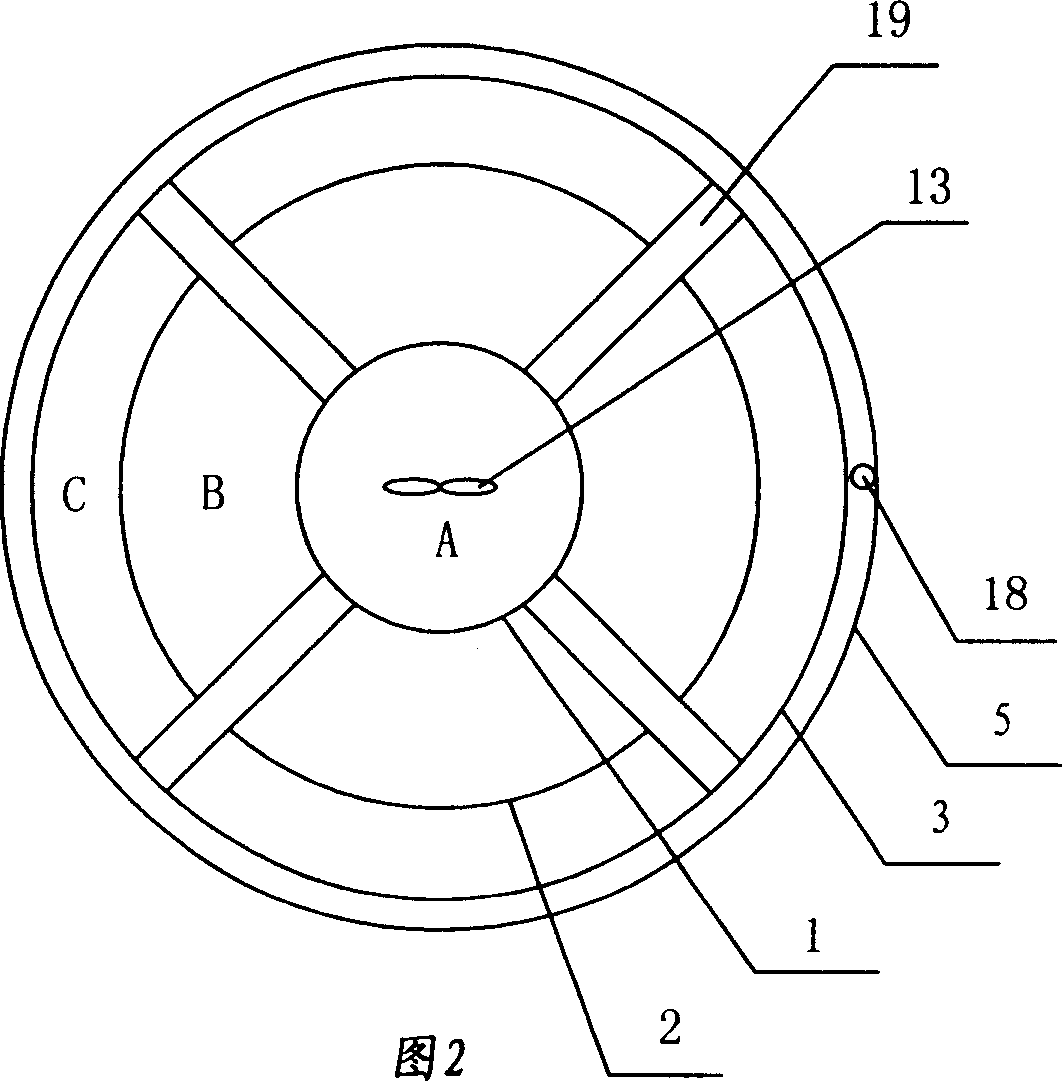
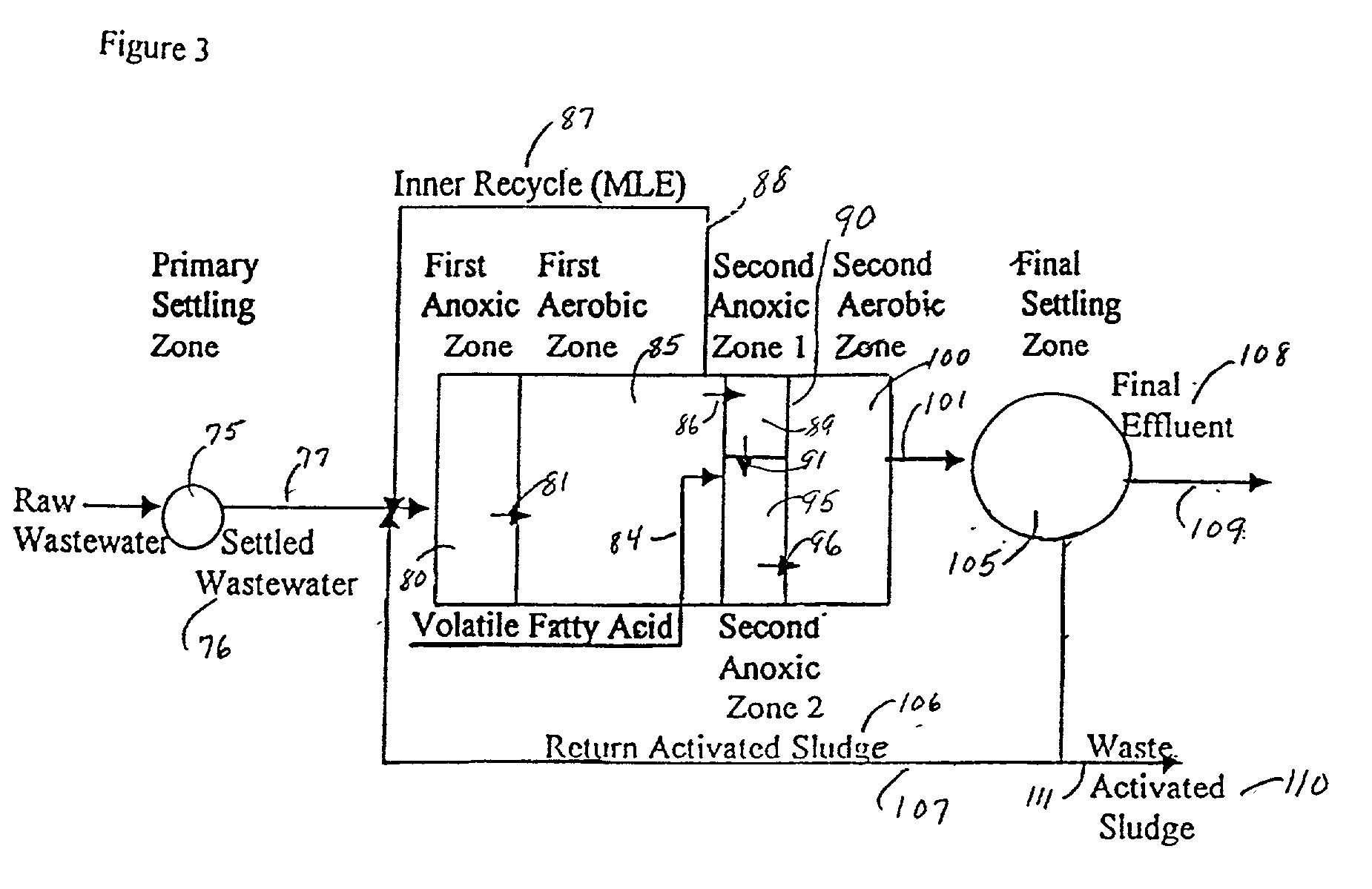
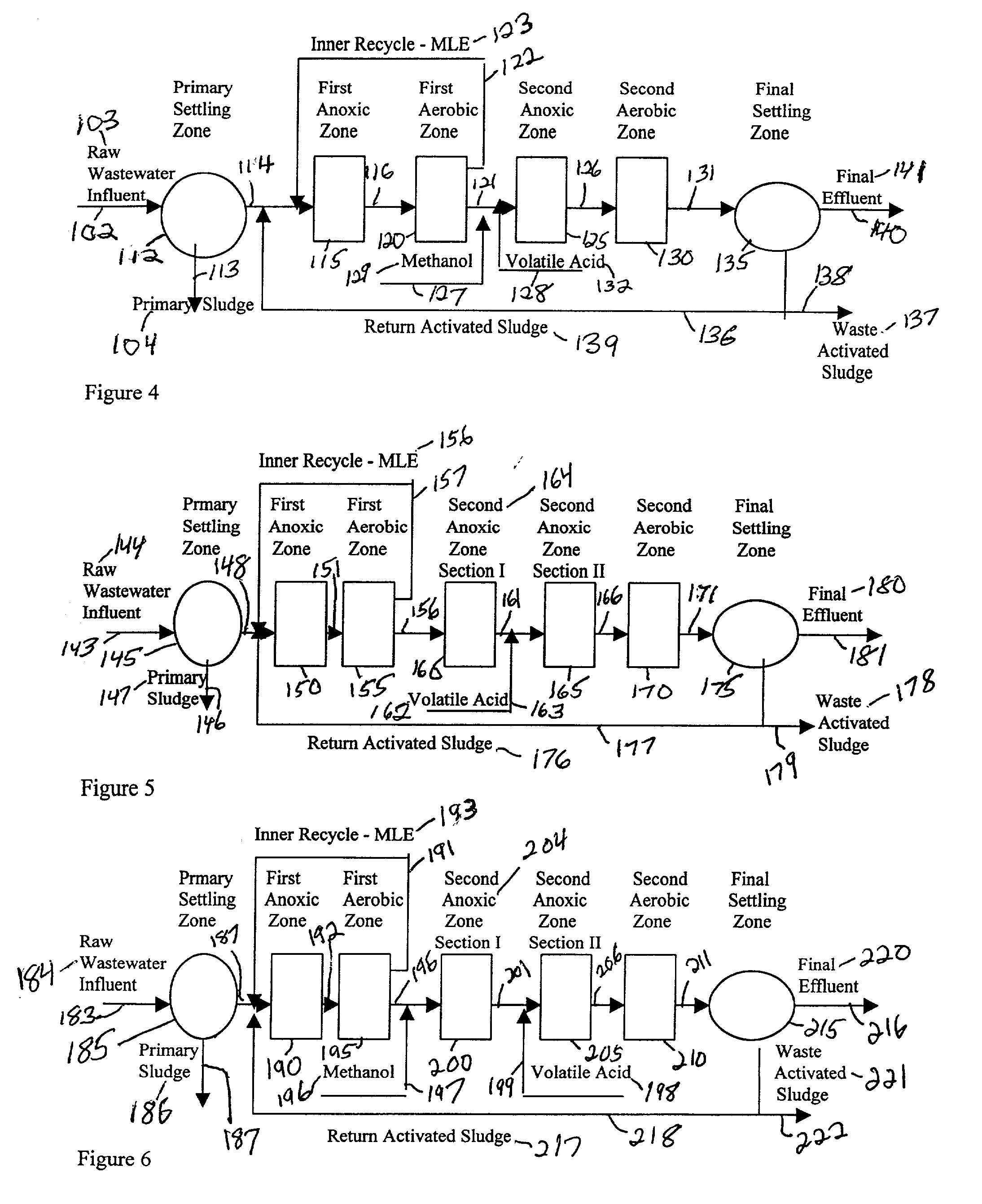
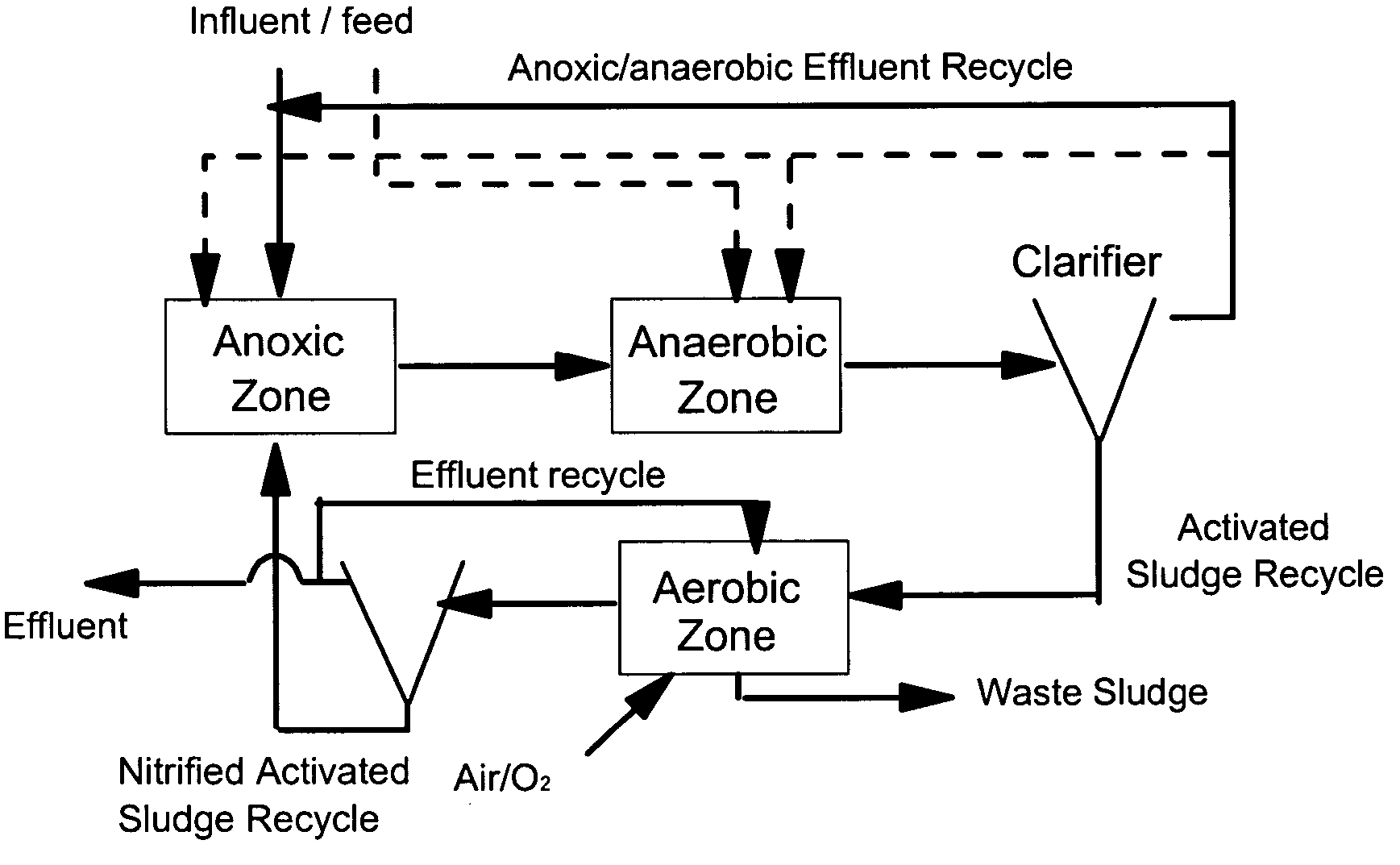
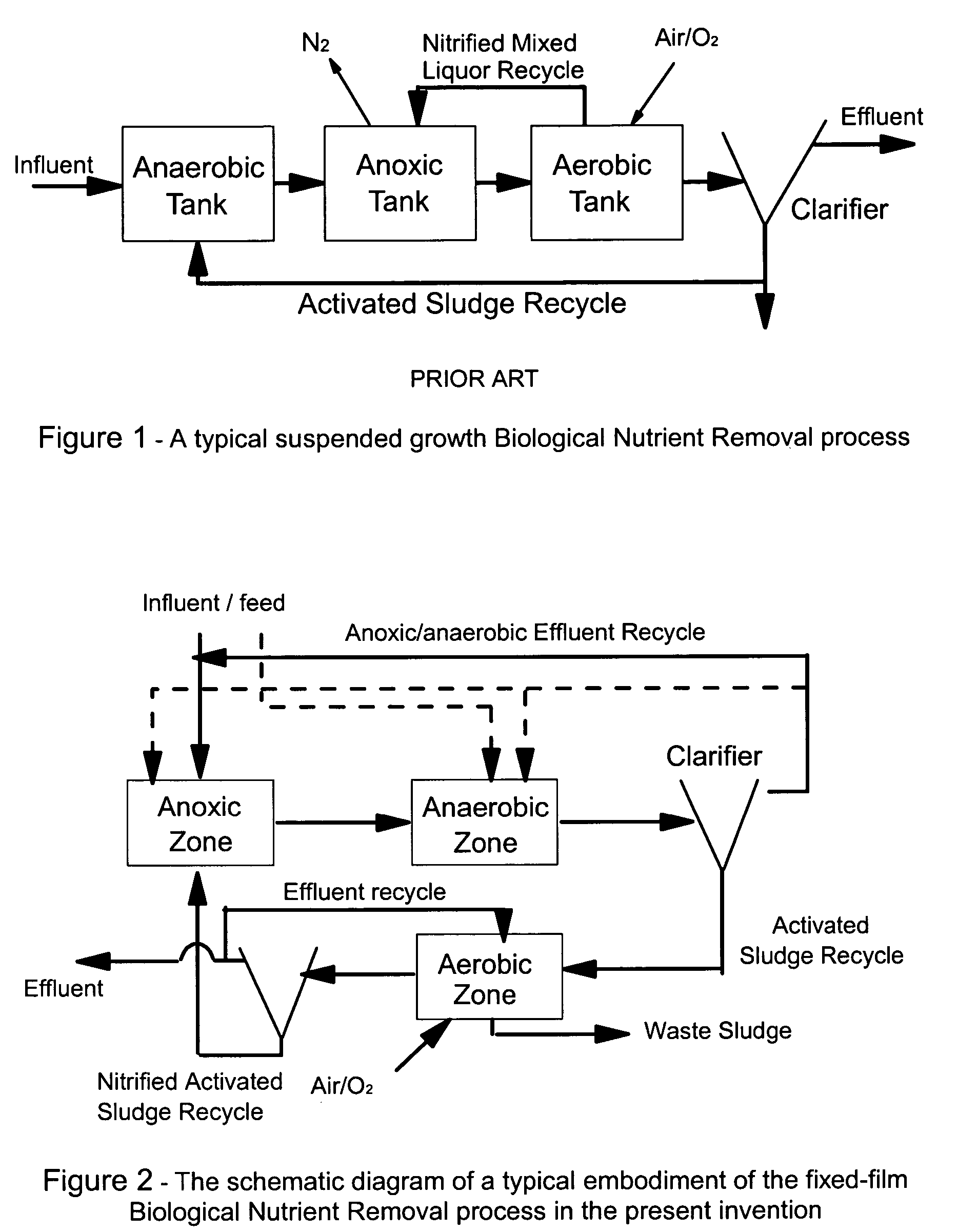
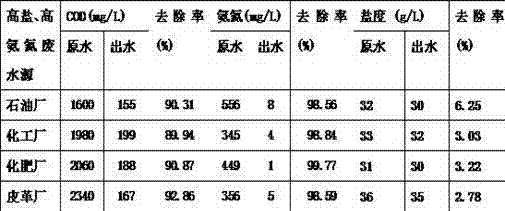
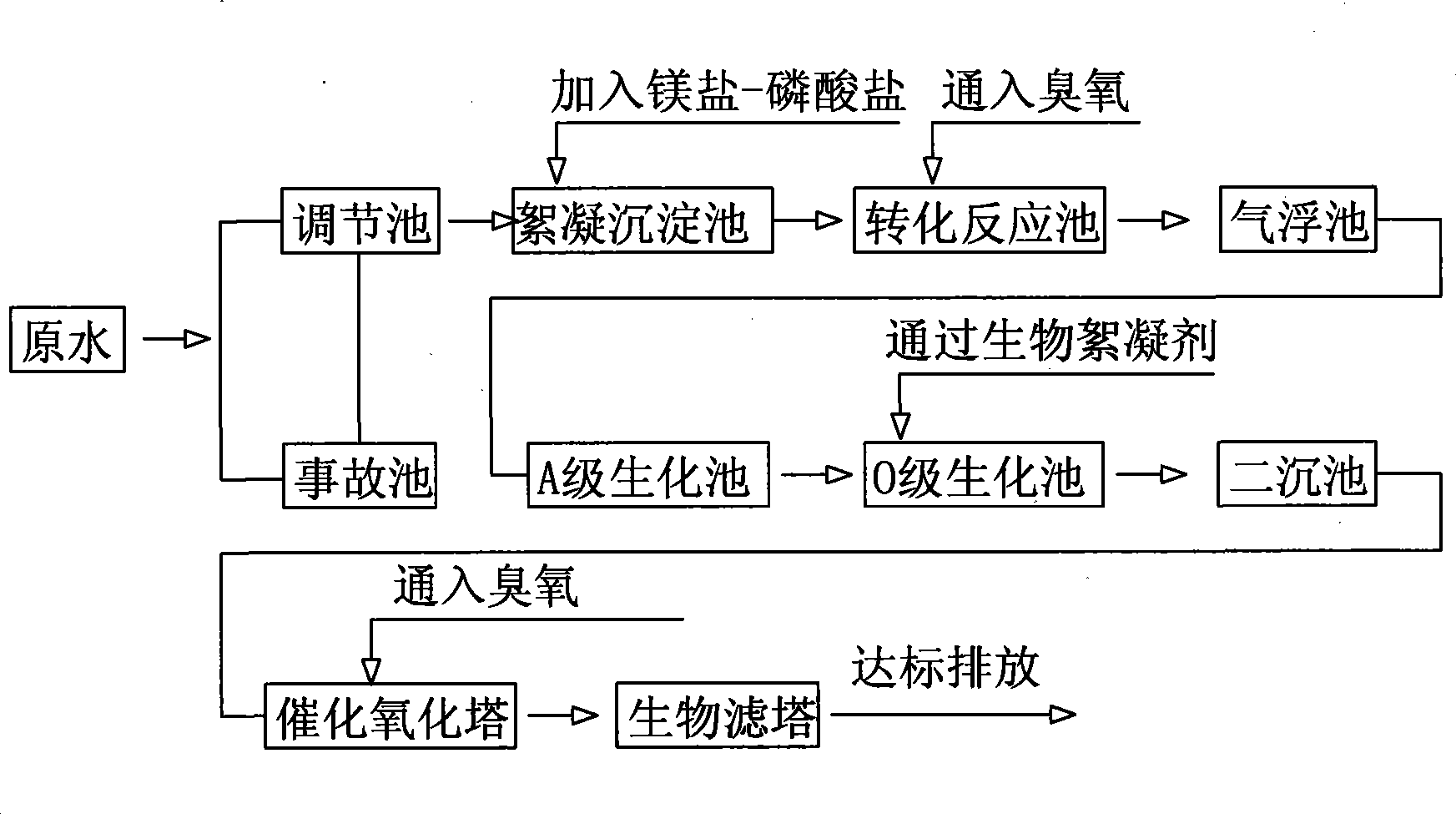
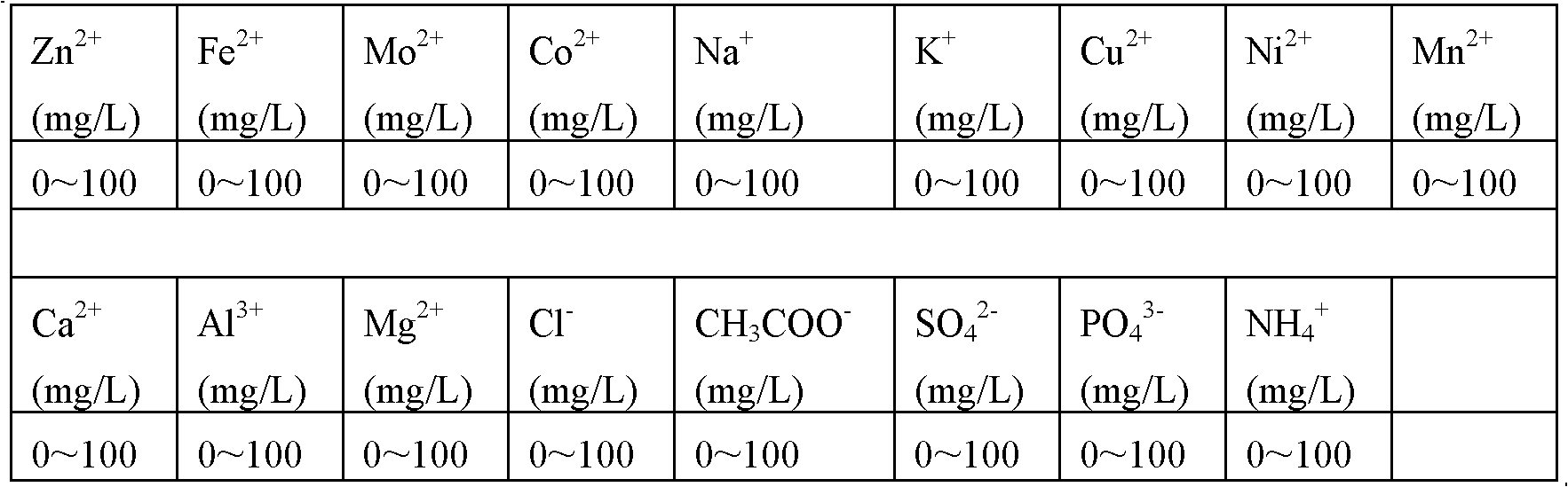Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5010 results about "Activated sludge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
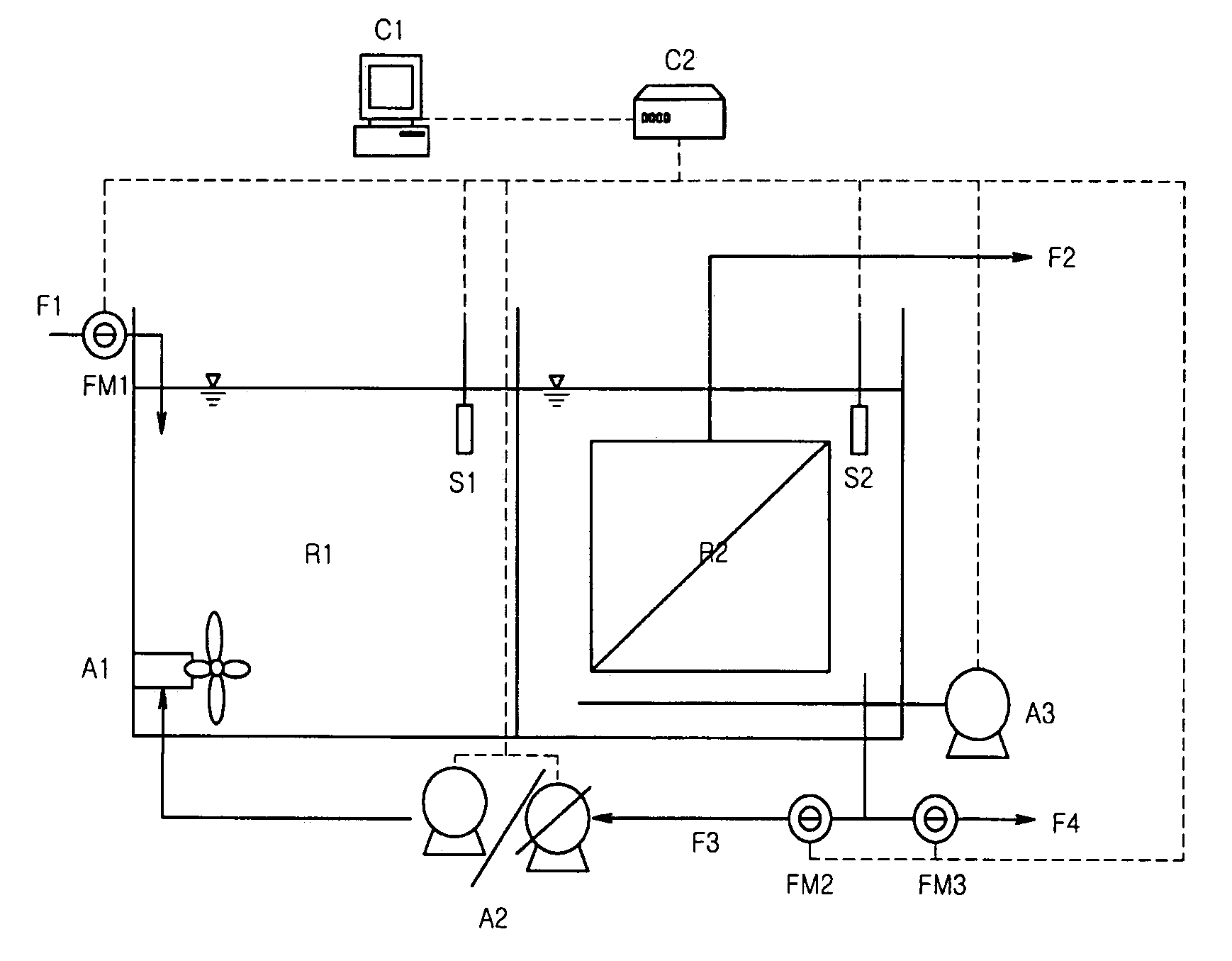
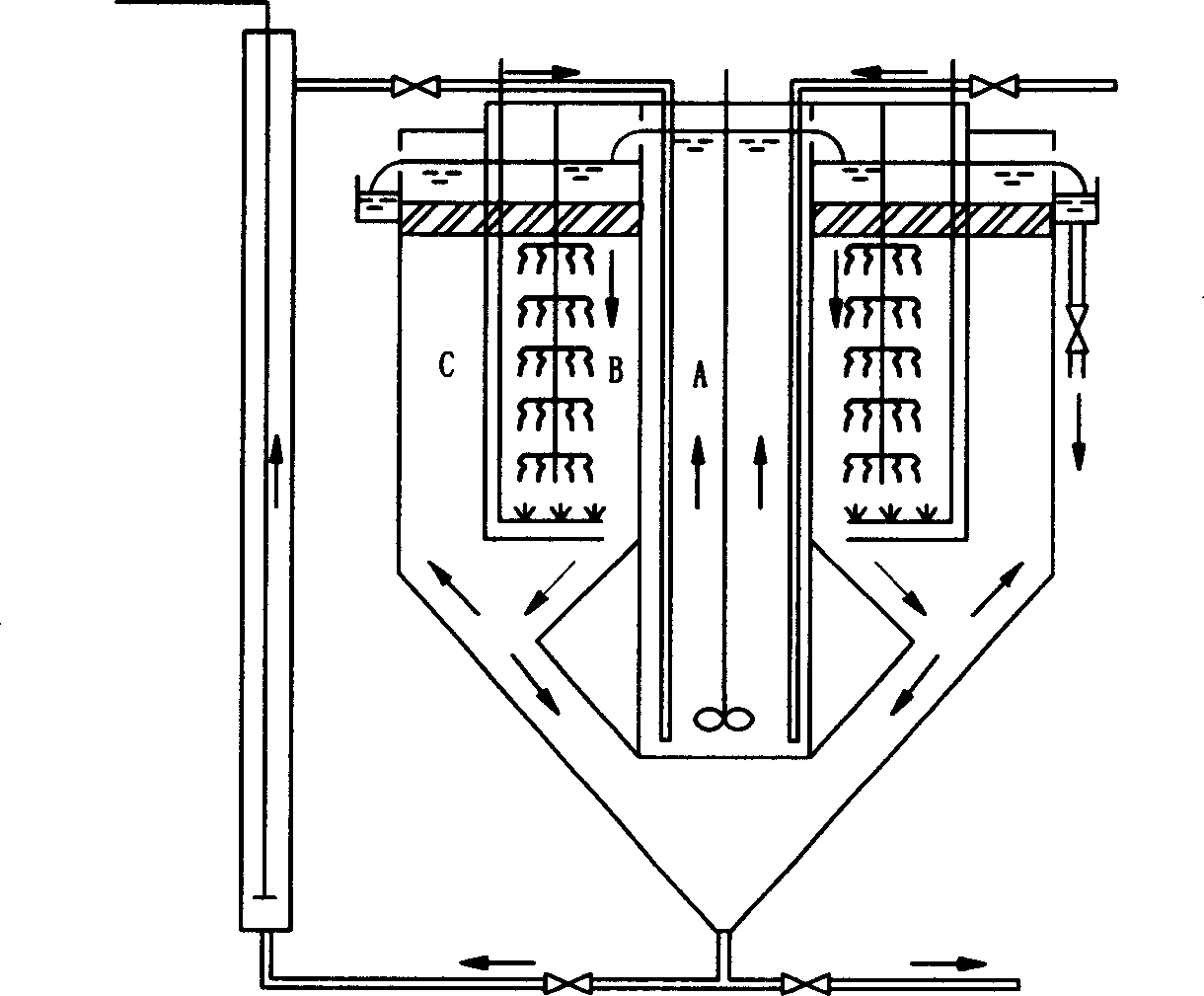
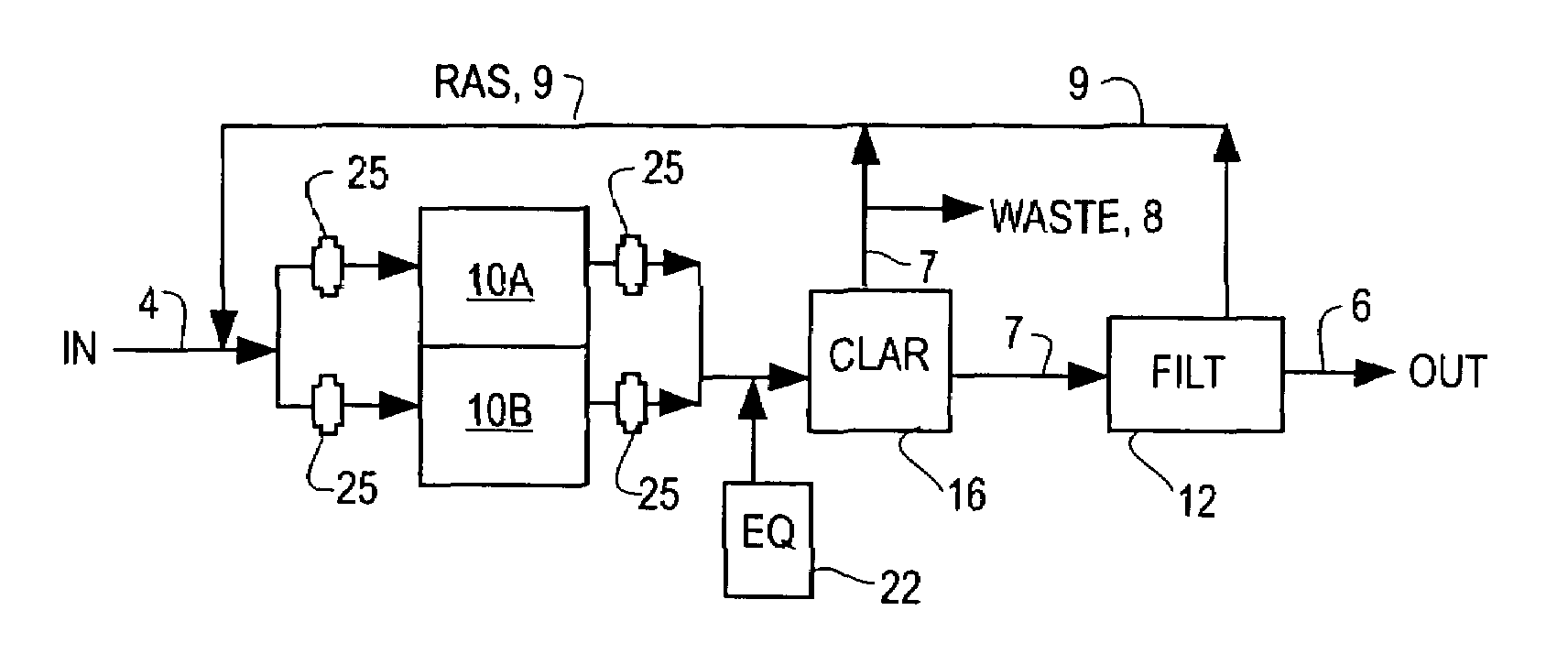
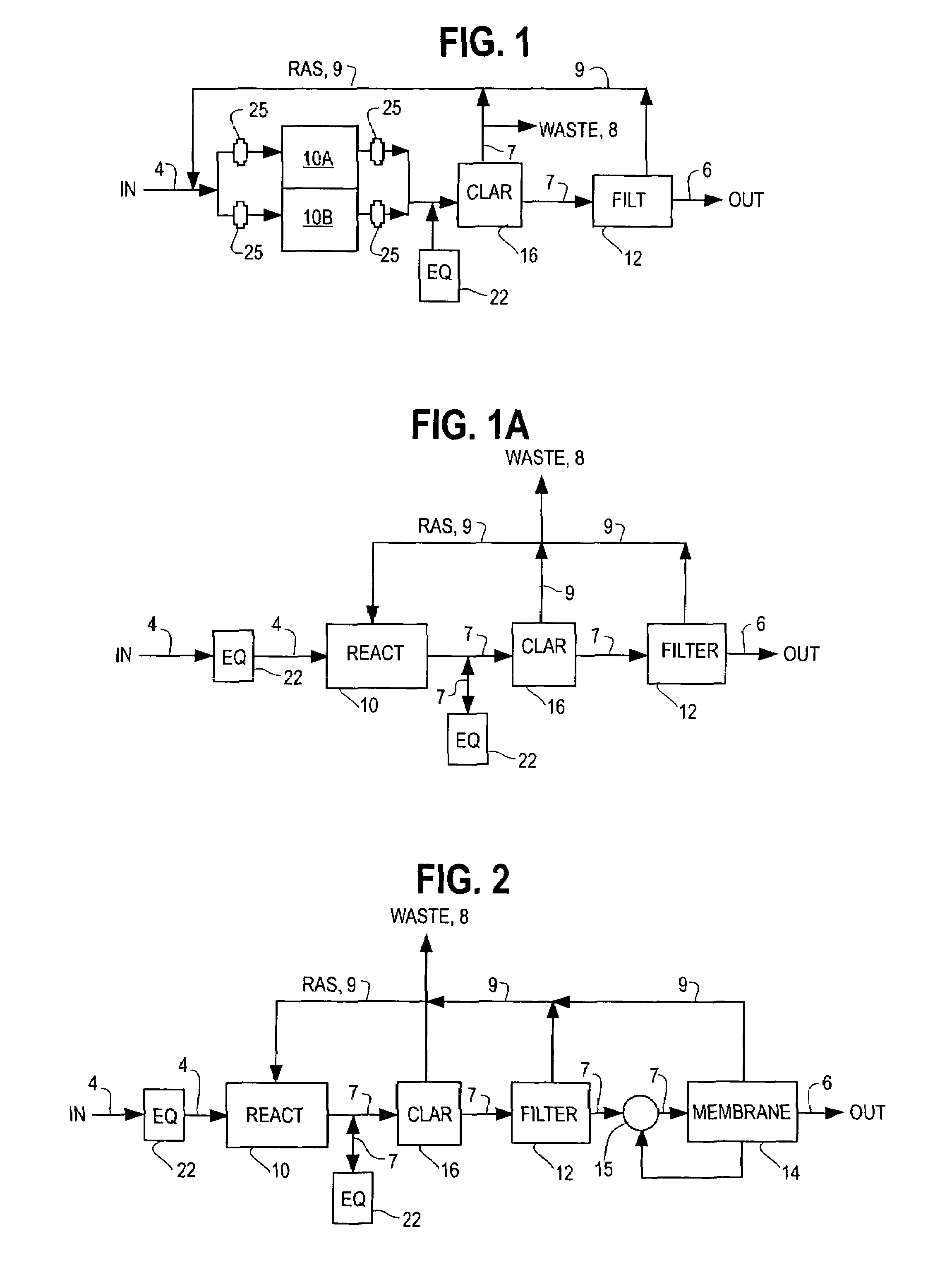
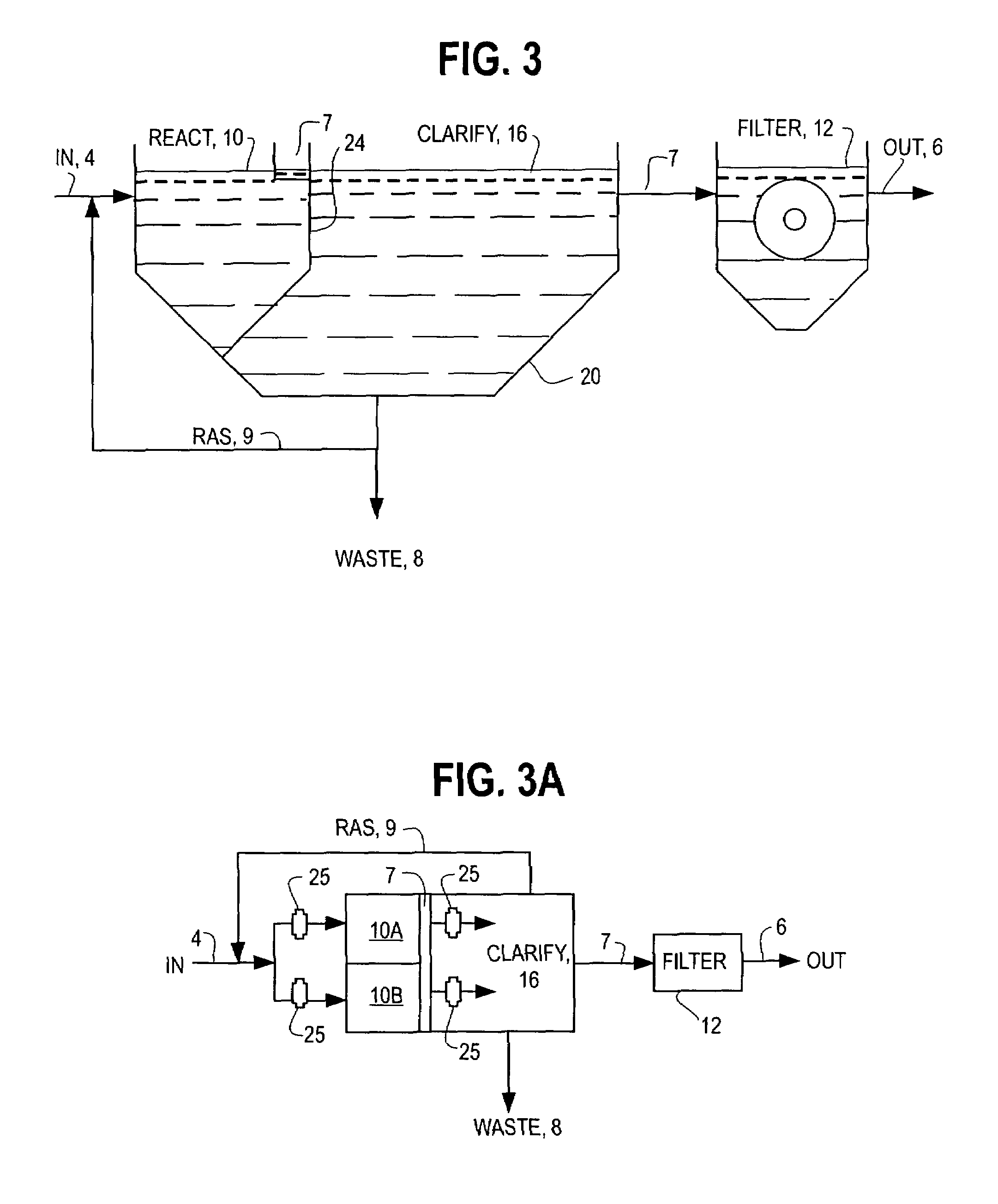
The activated sludge process is a type of wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. The general arrangement of an activated sludge process for removing carbonaceous pollution includes the following items: An aeration tank where air (or oxygen) is injected in the mixed liquor. This is followed by a settling tank (usually referred to as "final clarifier" or "secondary settling tank") to allow the biological flocs (the sludge blanket) to settle, thus separating the biological sludge from the clear treated water.
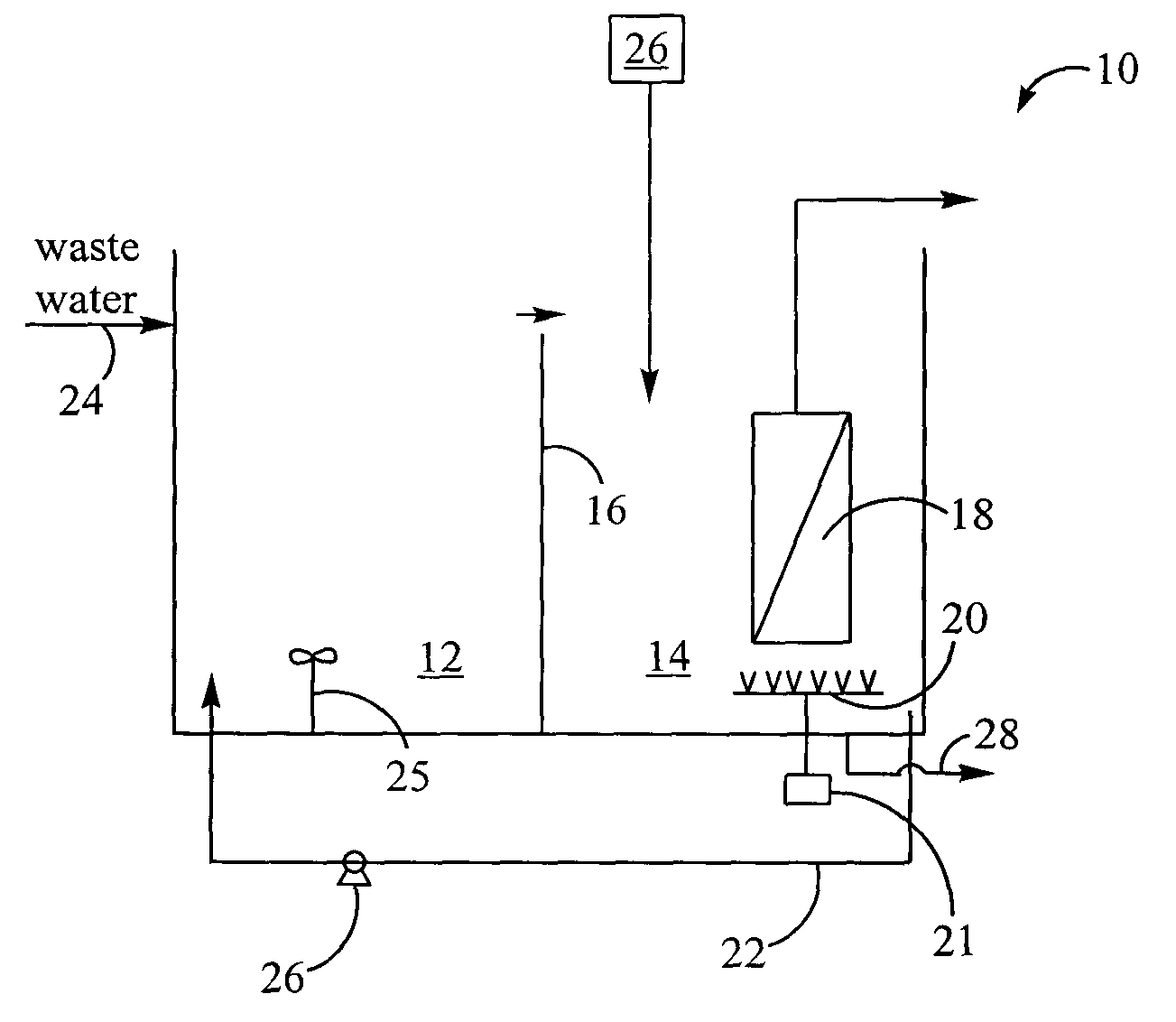
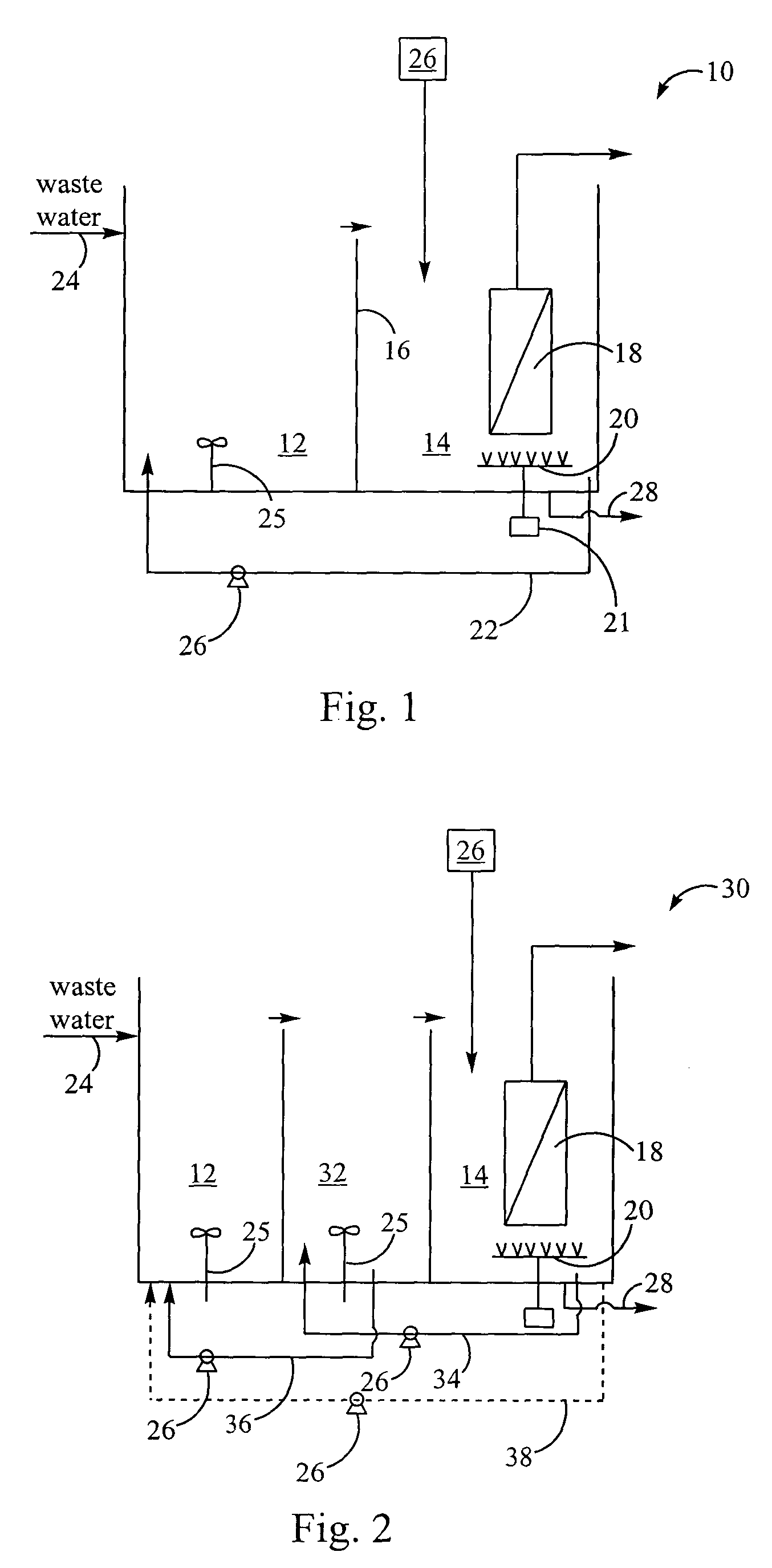
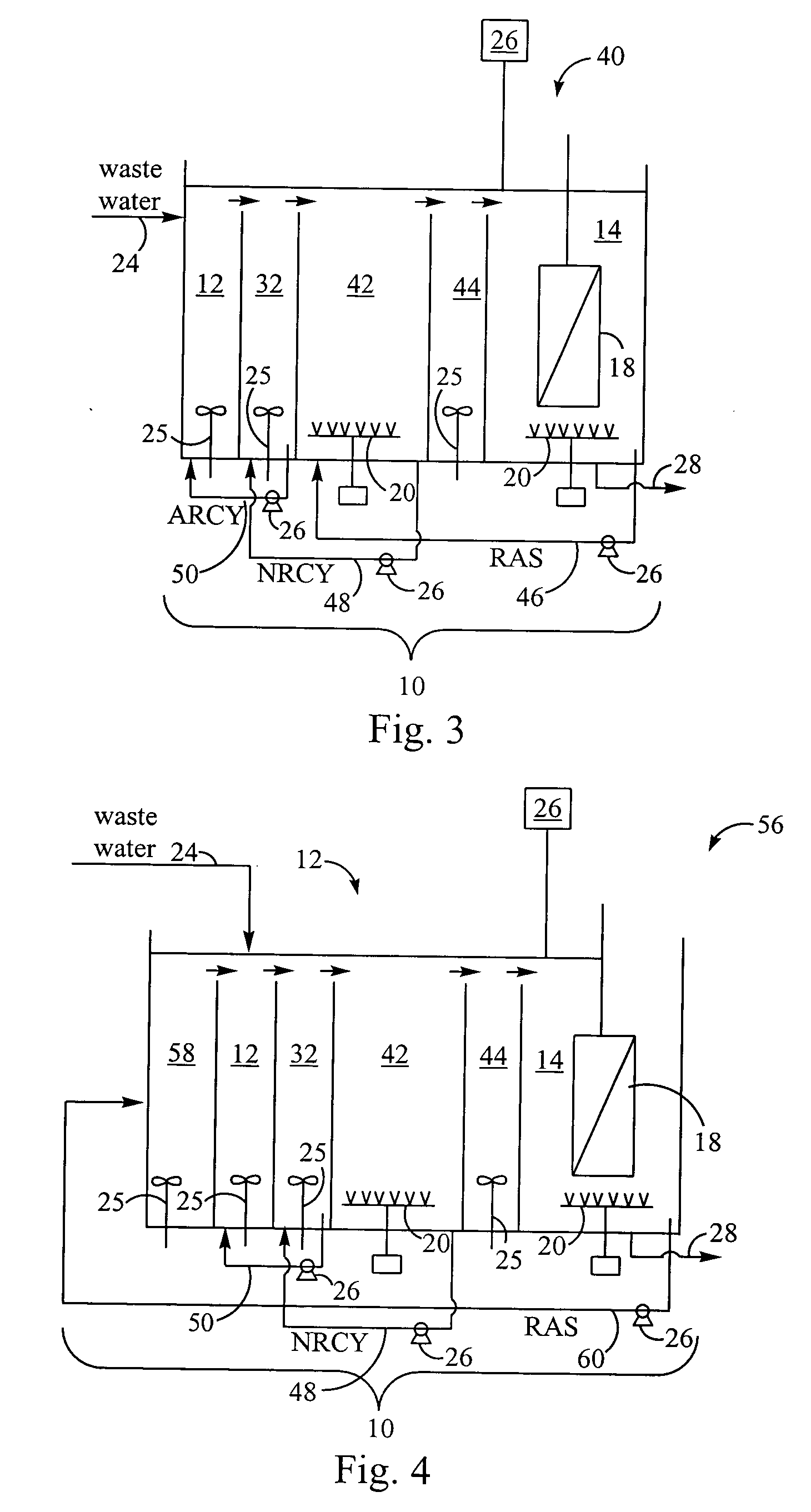
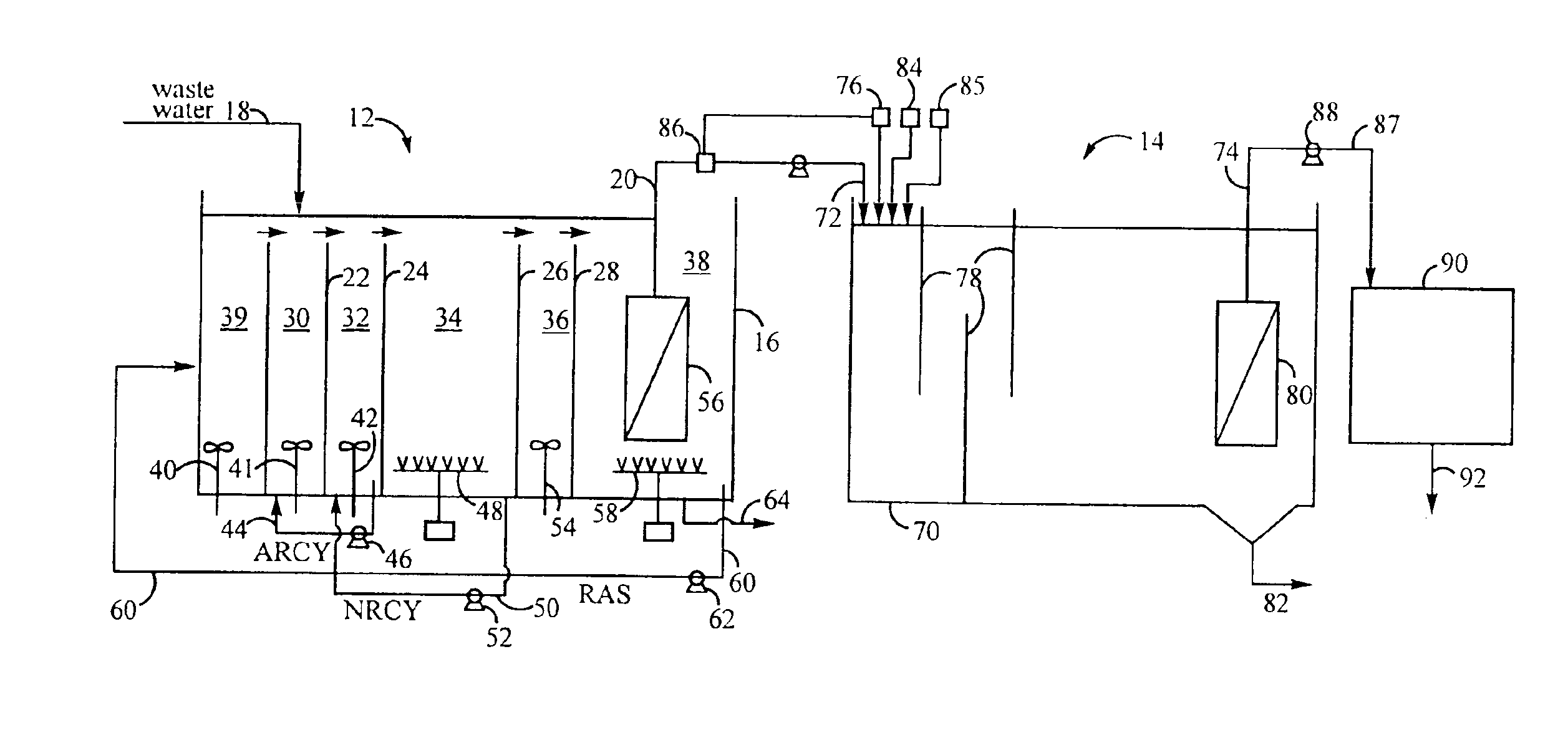
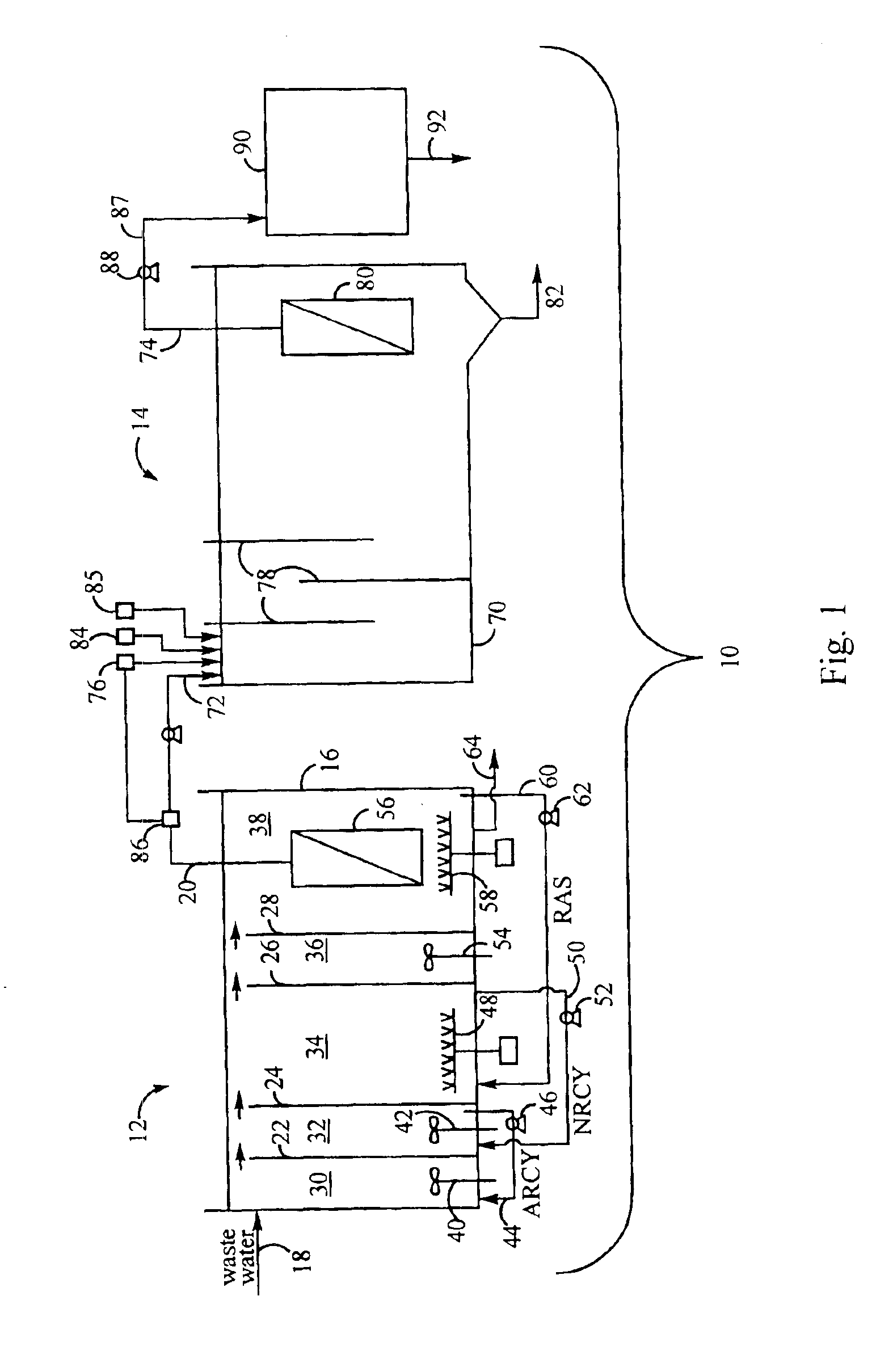
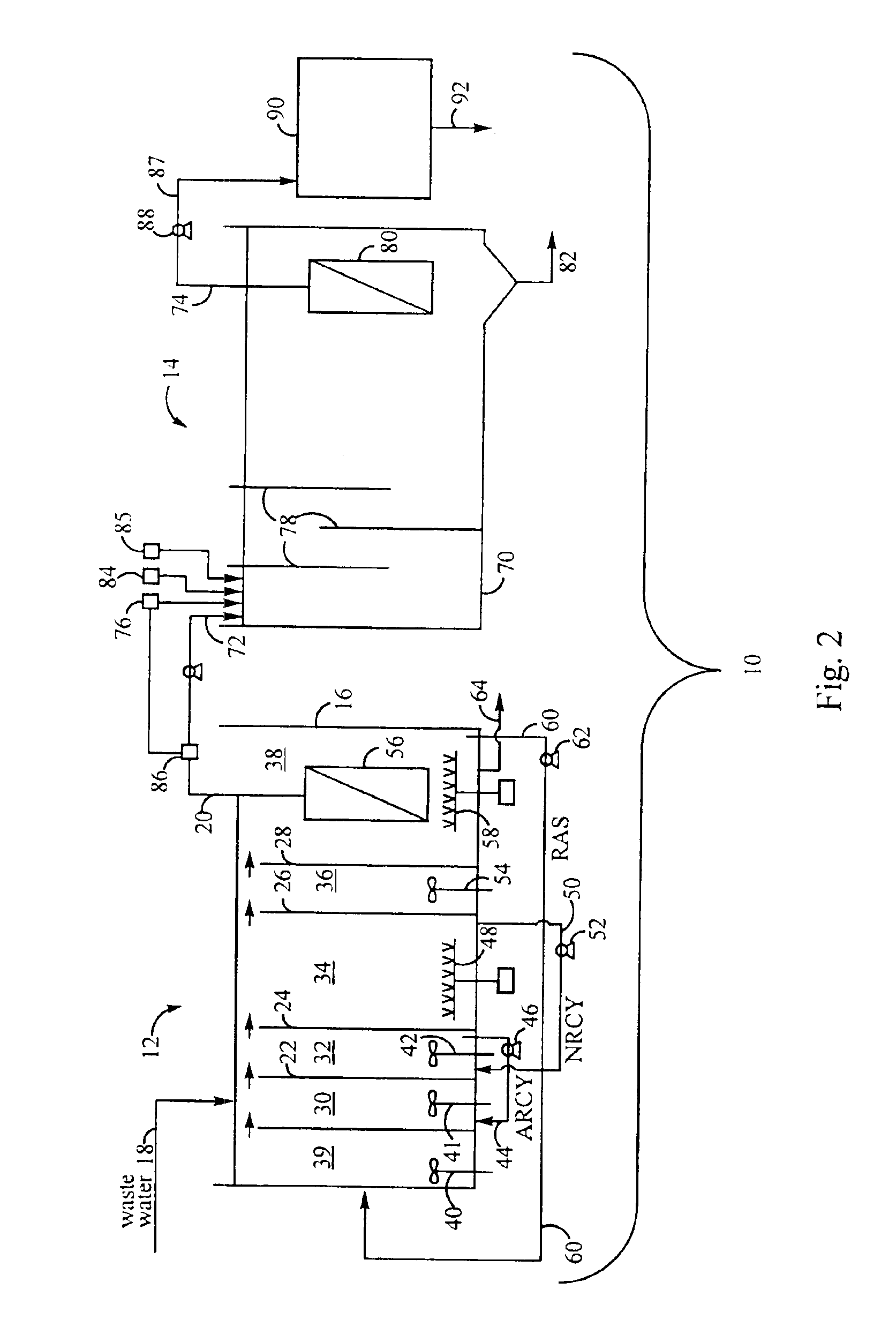
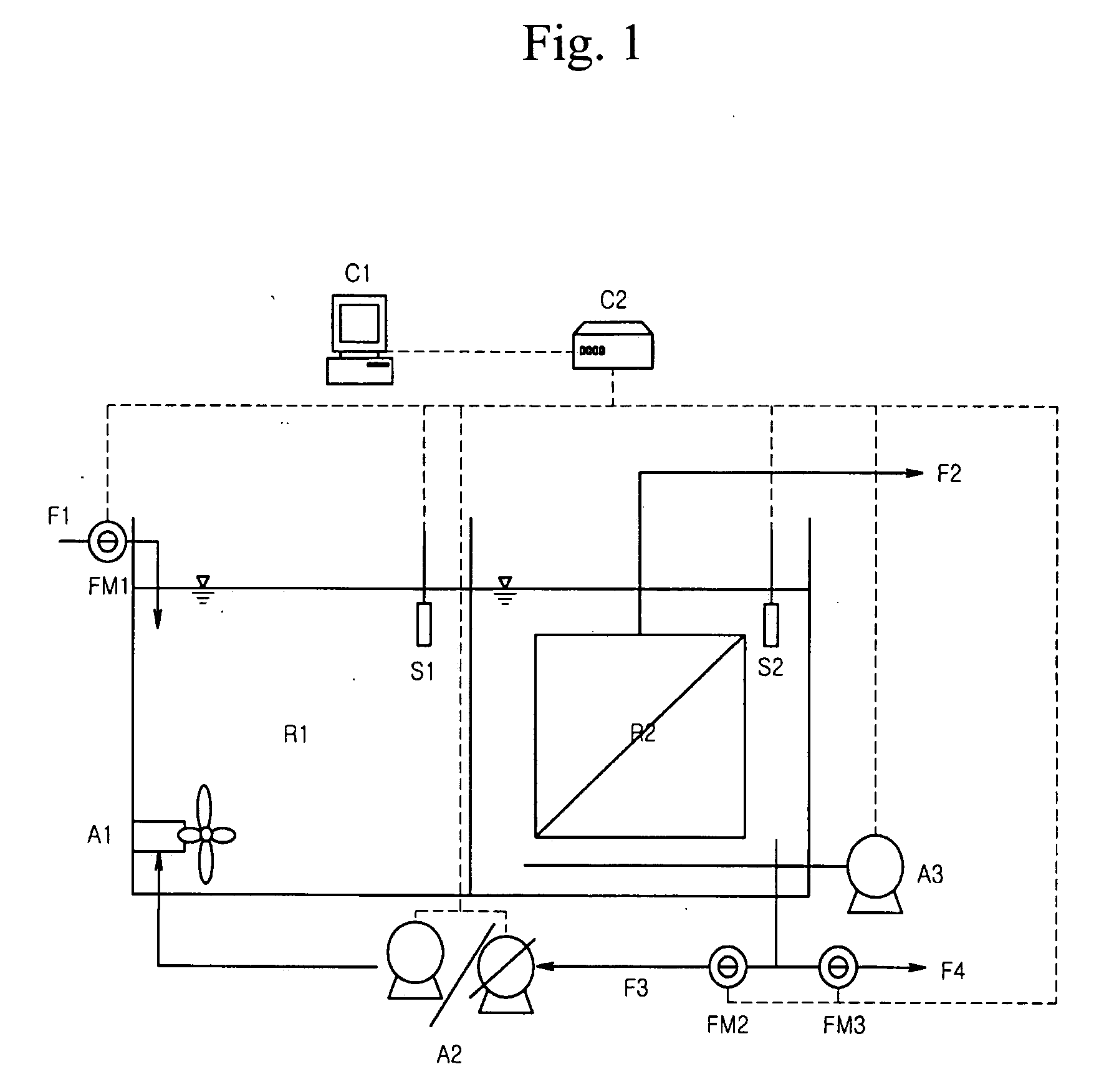
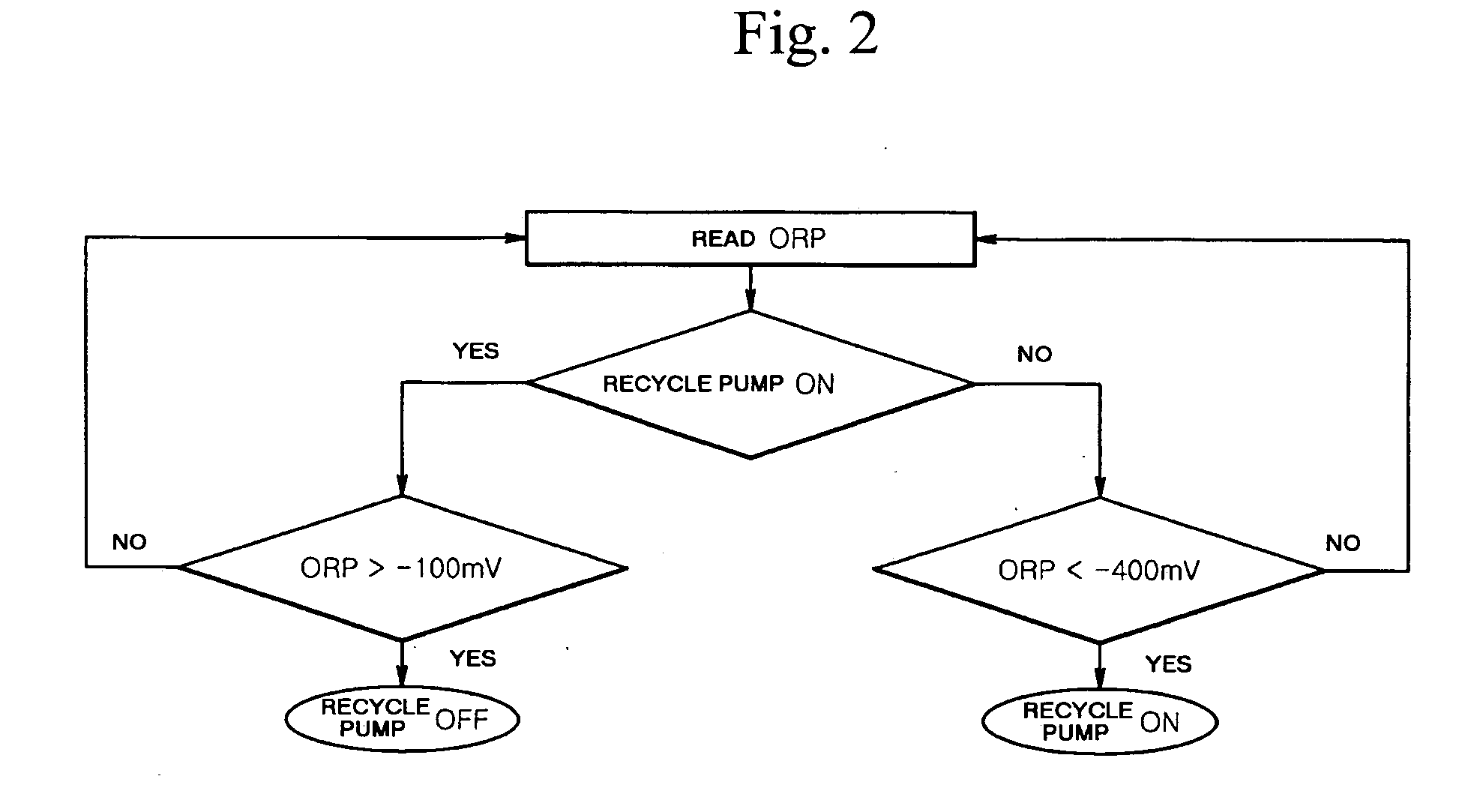
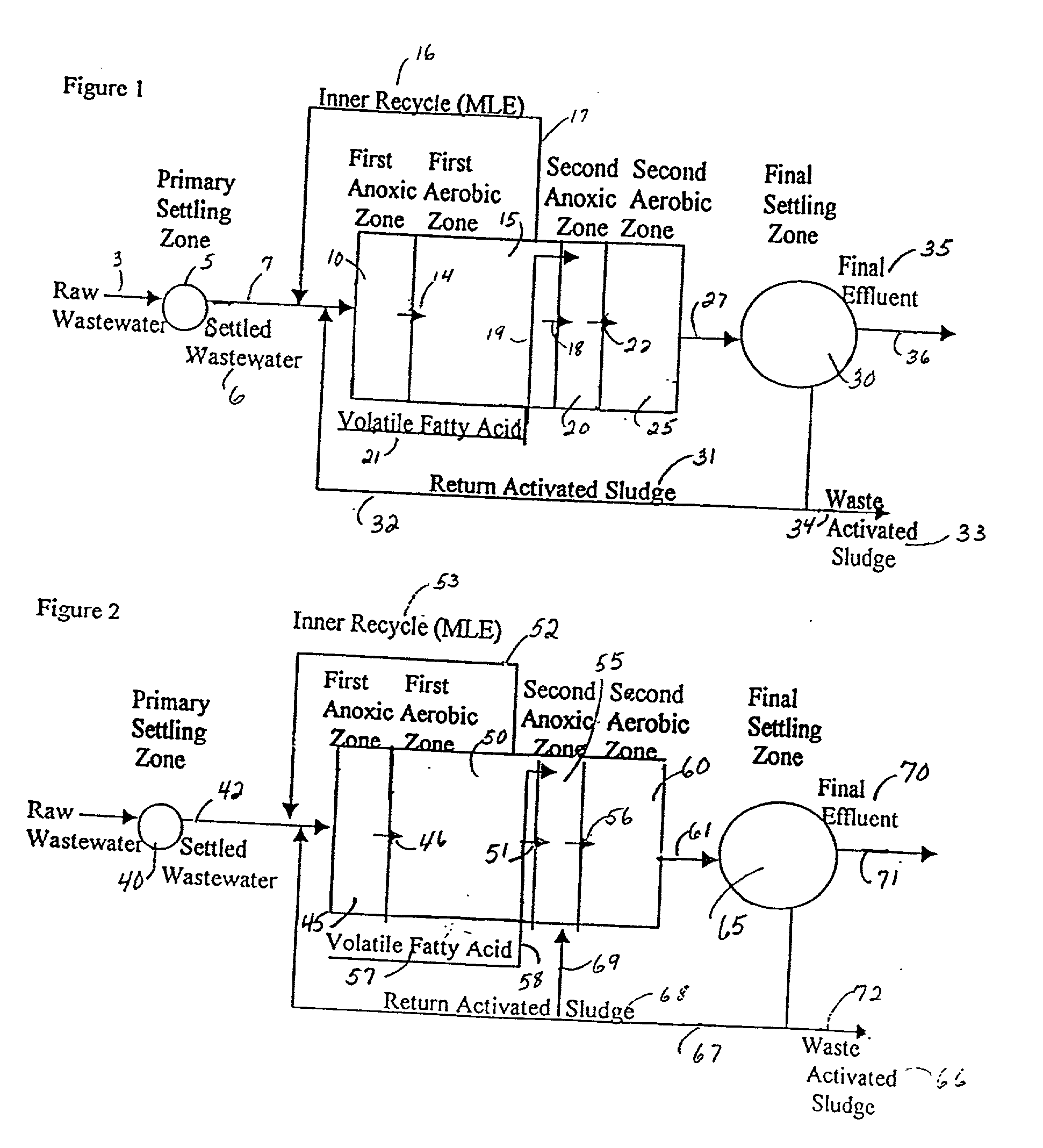
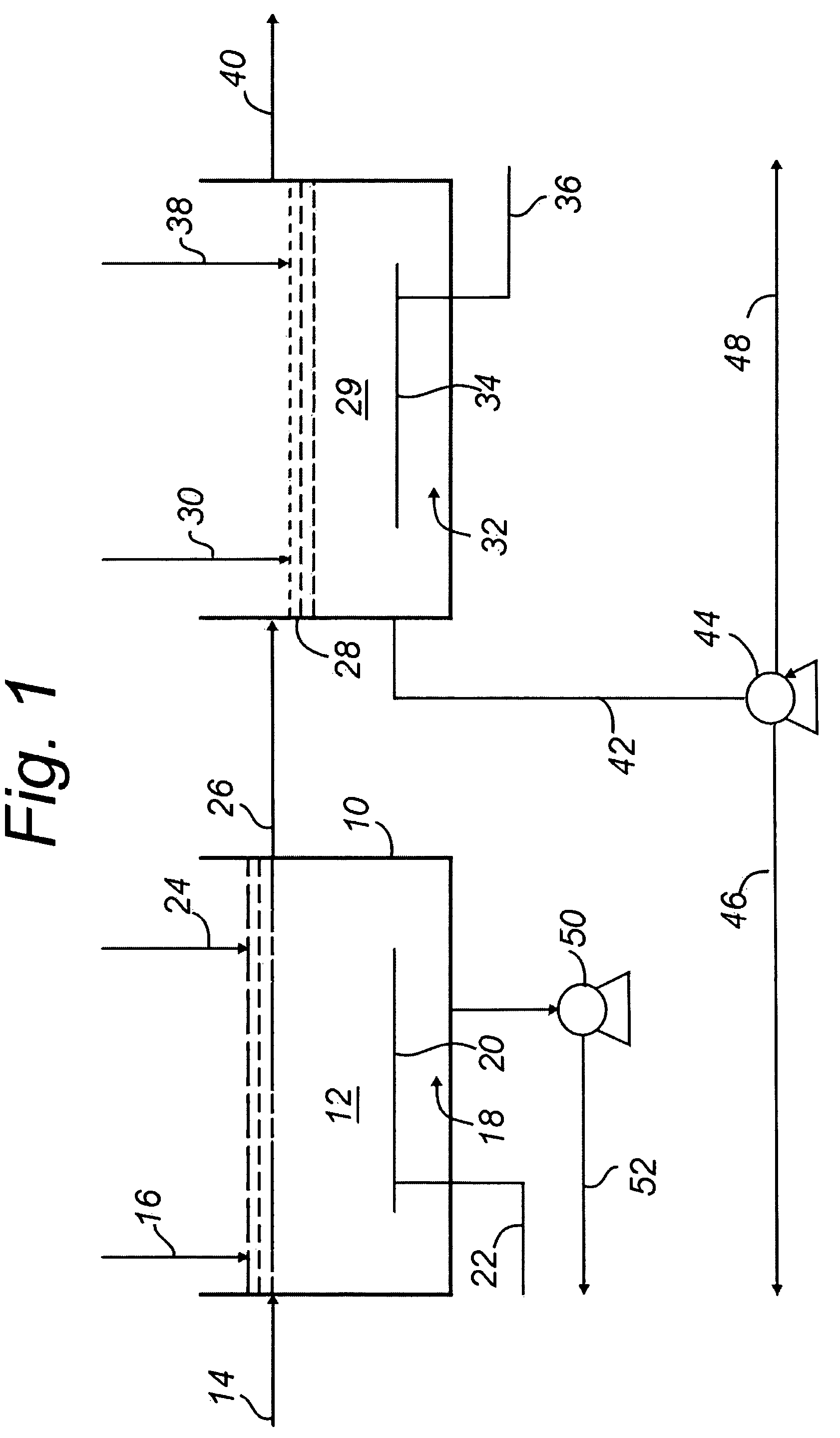
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
ActiveUS20050045557A1Minimizing space requirementMinimizing attendant costTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
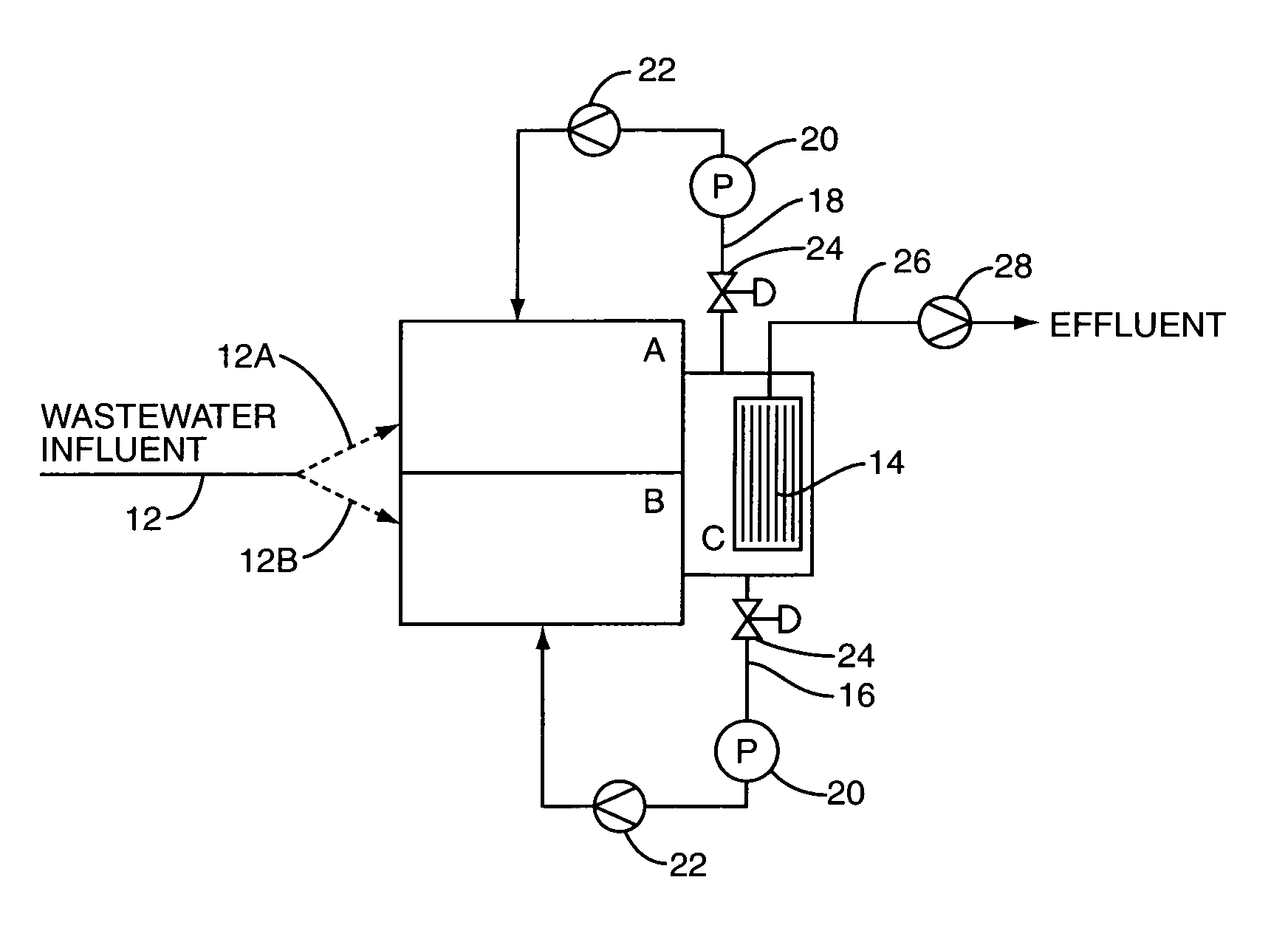
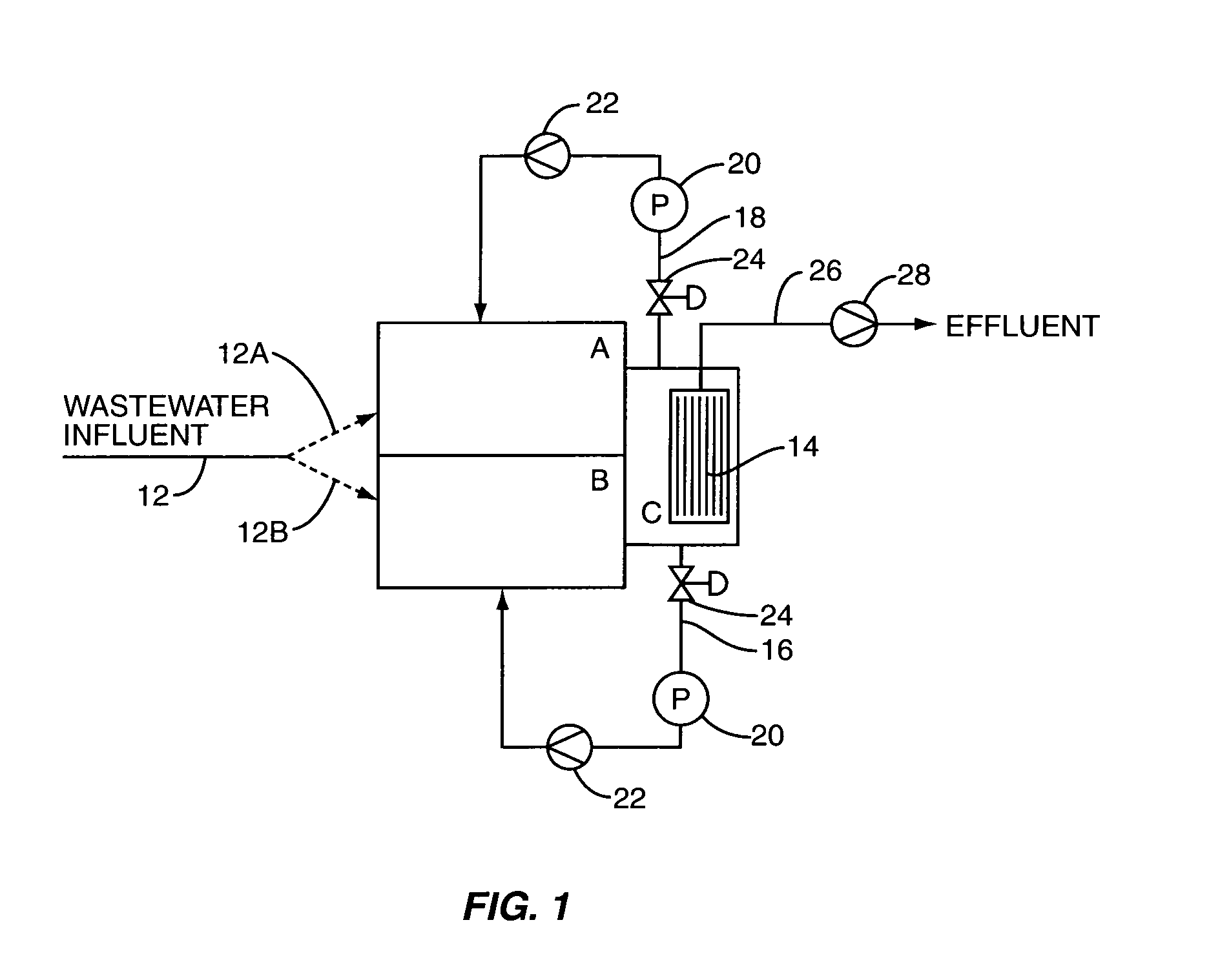
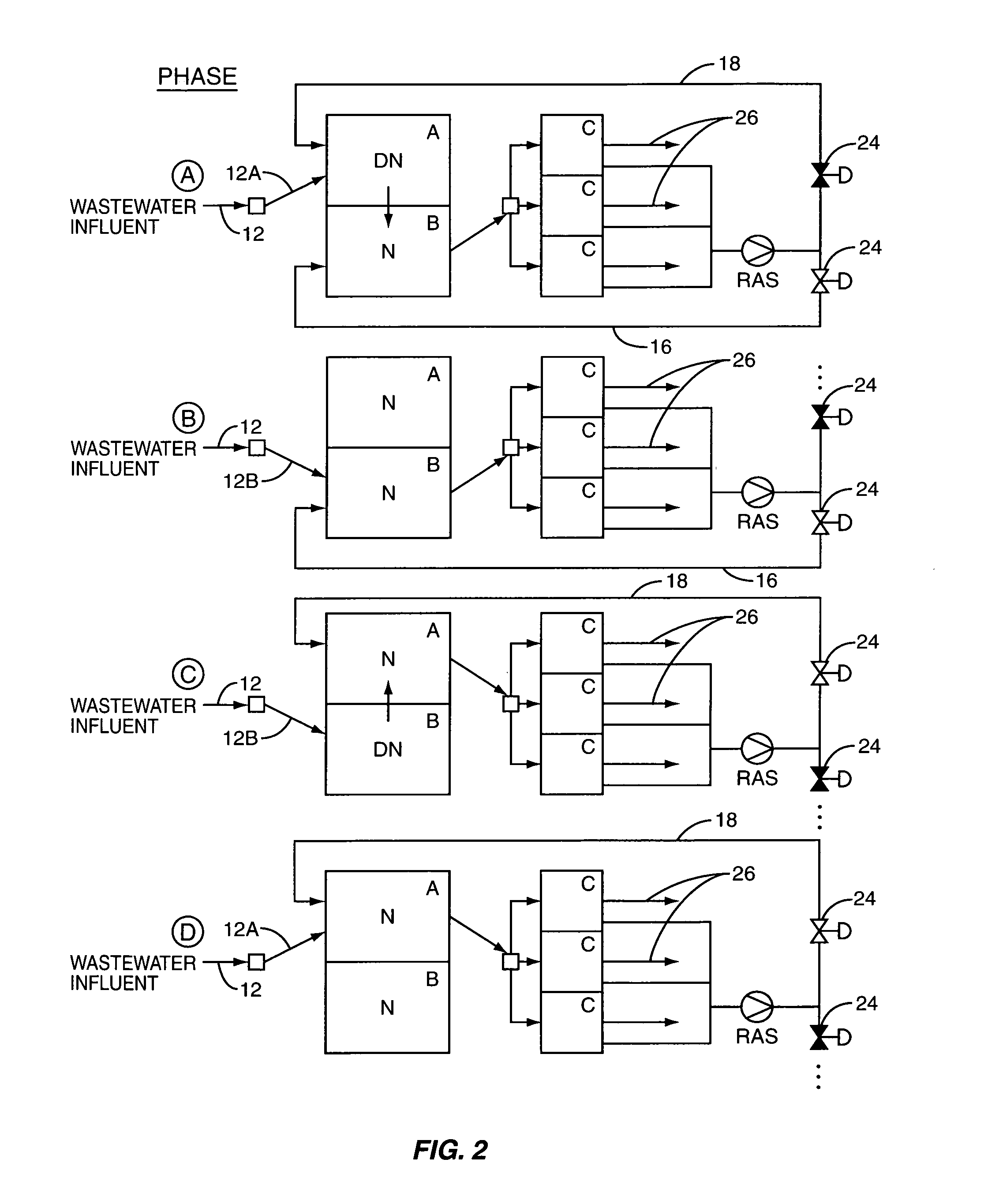
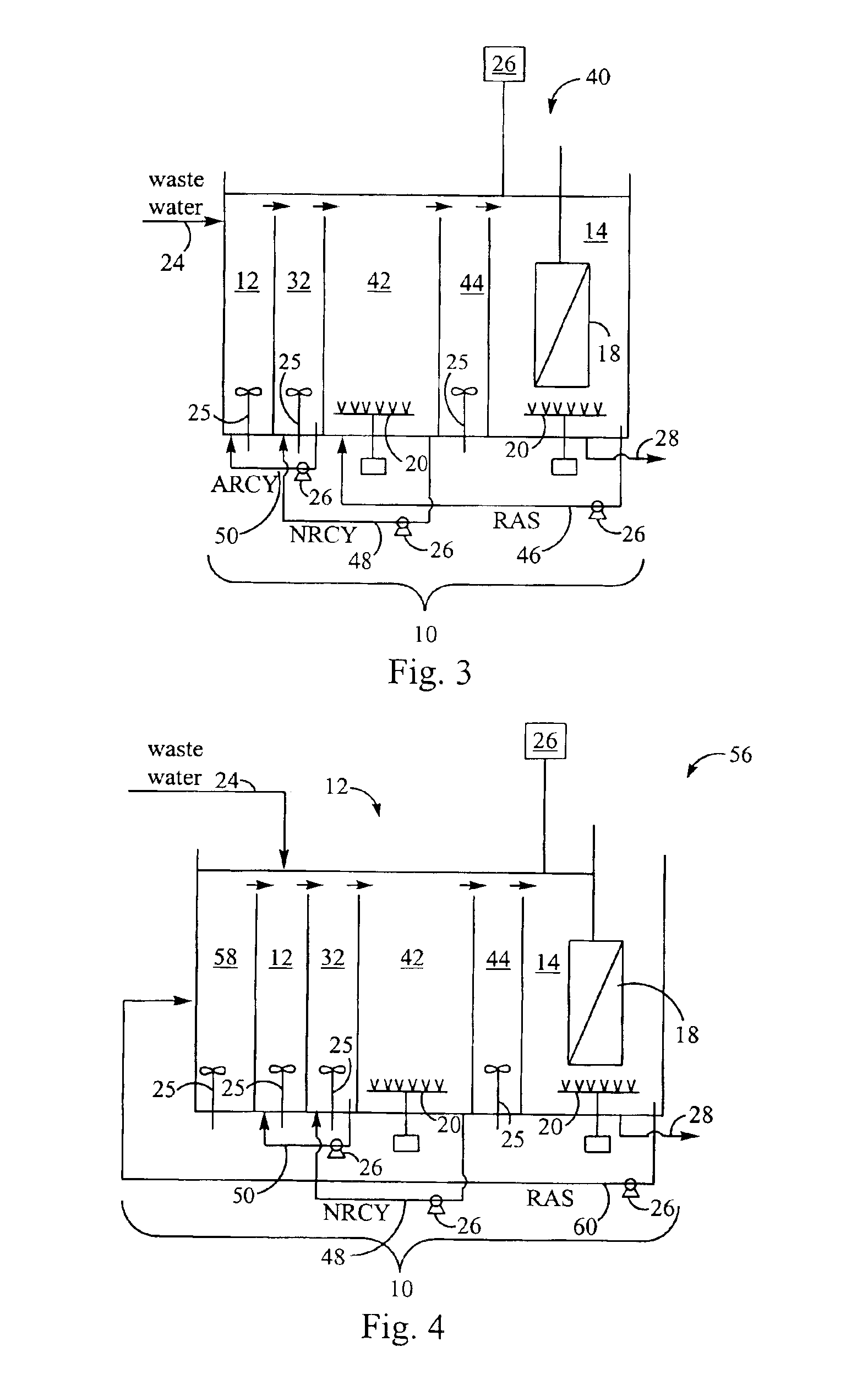
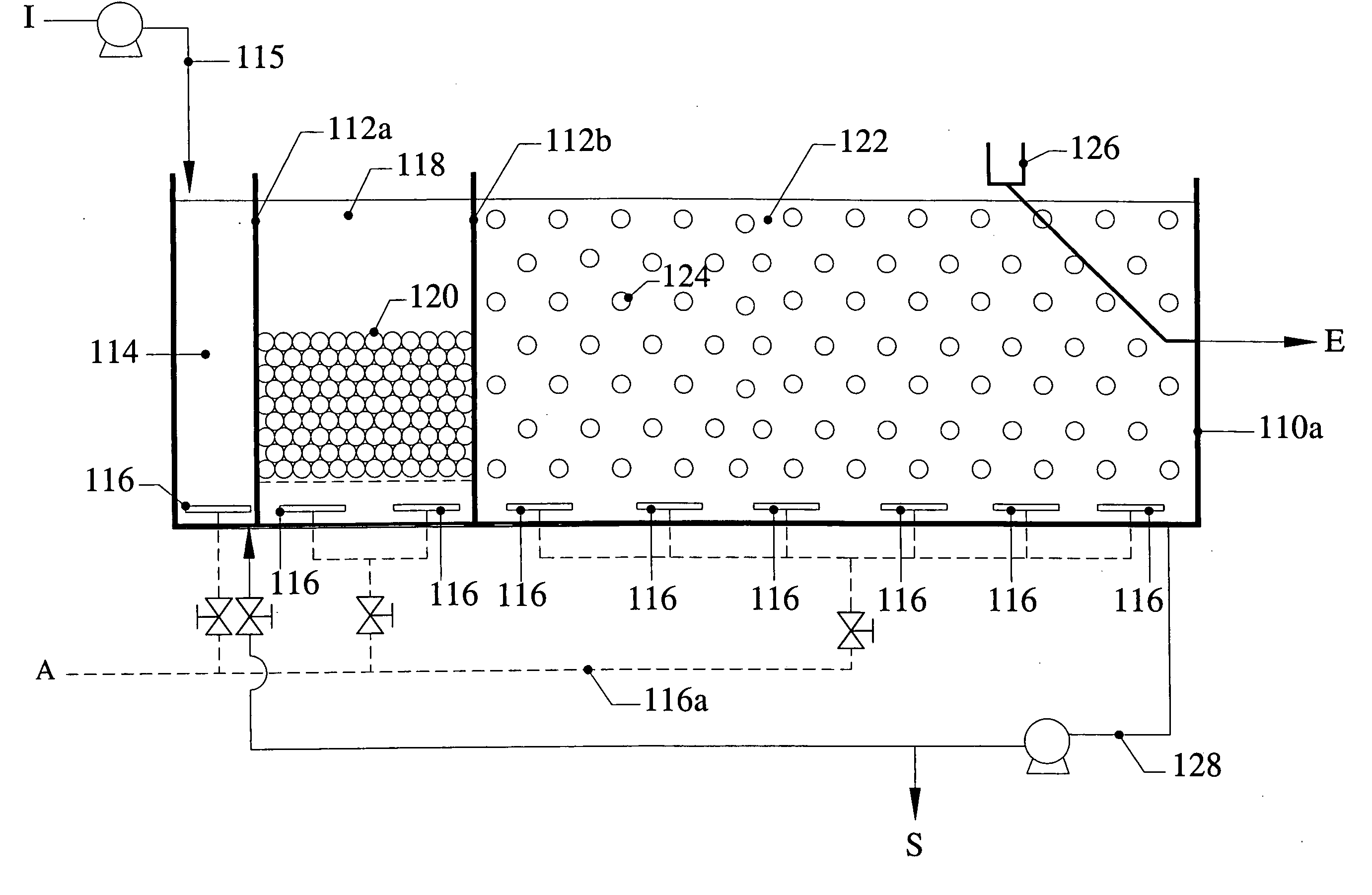
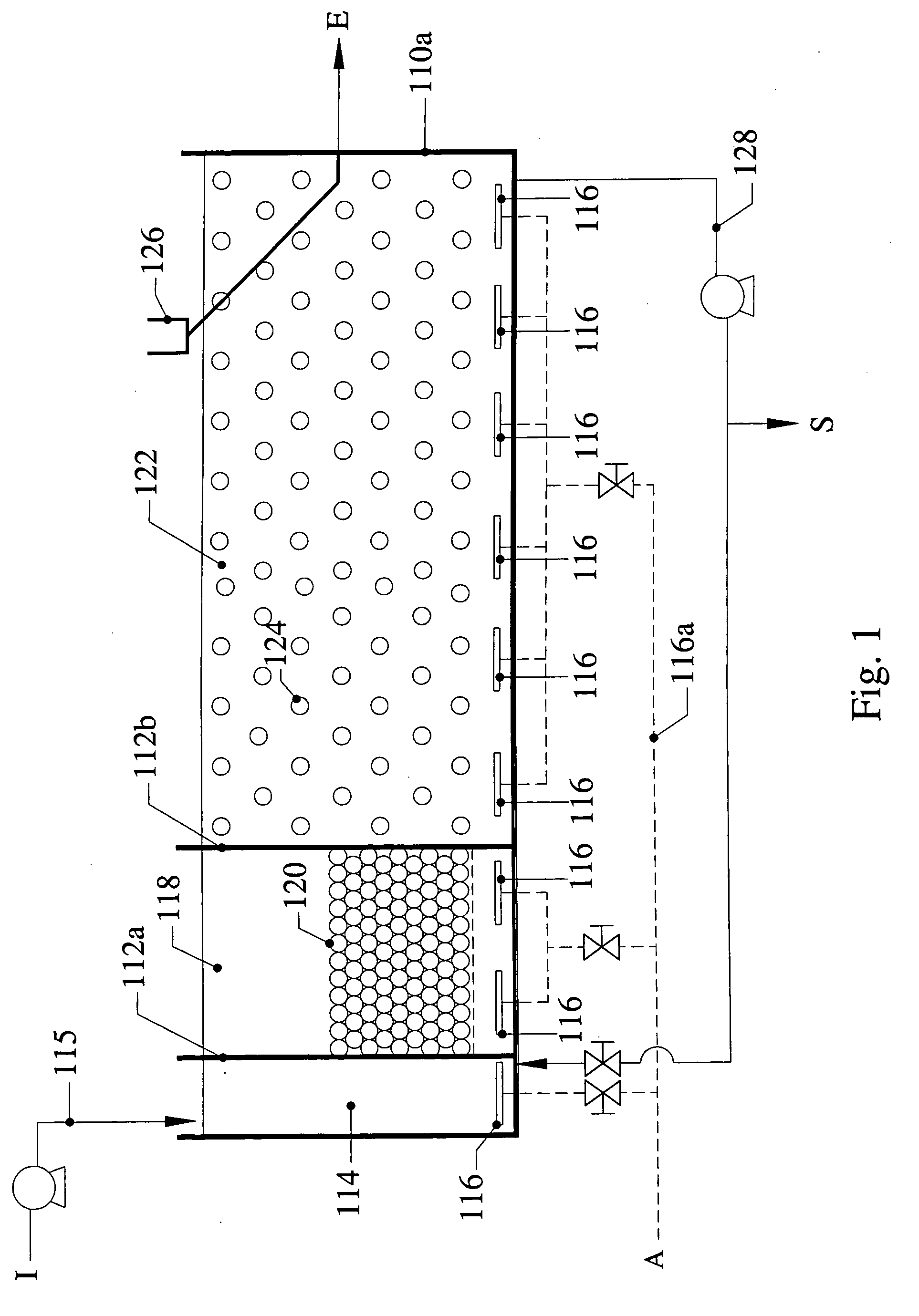
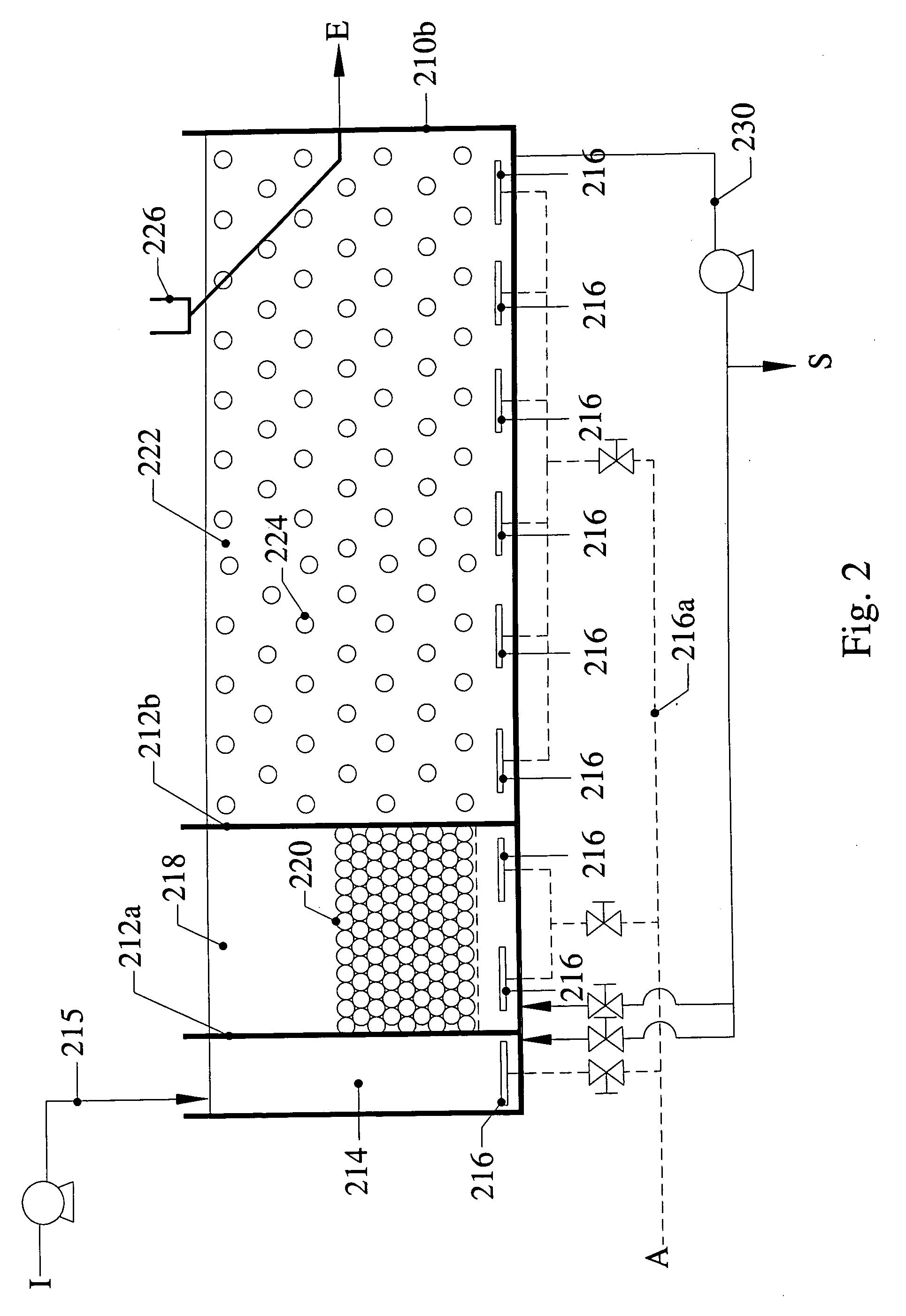
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Aqueous compositions, aqueous cutting fluid using the same, method for preparation thereof, and cutting method using the cutting fluid
InactiveUS6221814B1Promote degradationSimple treatmentOther chemical processesWork treatment devicesActivated sludgeLiquid waste
An aqueous cutting fluid which can reduce the impact on working environment and the global environment, and can achieve both preventing precipitates from becoming a hard cake and keeping high dispersibility for abrasive grains is provided. Such an aqueous cutting fluid is obtained by a method comprising dispersing abrasive grains (G) in an aqueous composition comprising a dispersion medium (M) containing a hydrophilic alcohol compound such as ethylene glycol, a lipophilic alcohol compound such as propylene glycol and water, and silica colloid particles dispersed stably in the medium. The dispersion medium (M) is odorless and not flammable. The abrasive grains (G) may settle out after a time, but they do not closely contact with one another, and therefore the resulting precipitates do not become a hard cake, which allows the re-dispersion and reuse of precipitated grains. The instant aqueous cutting fluid is inherently low viscous, and the reduction of viscosity owing to the contamination of water and the increase of viscosity owing to contamination of shavings are both moderate. As a result, the cutting fluid has a long life. And articles which have been cut using the cutting fluid can be washed with water. Further, as the dispersion medium (M) is a biodegradable low molecular weight organic compound, a waste liquid from a process using the cutting fluid can be disposed with an activated sludge.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD +1
Process to enhance phosphorus removal for activated sludge wastewater treatment systems
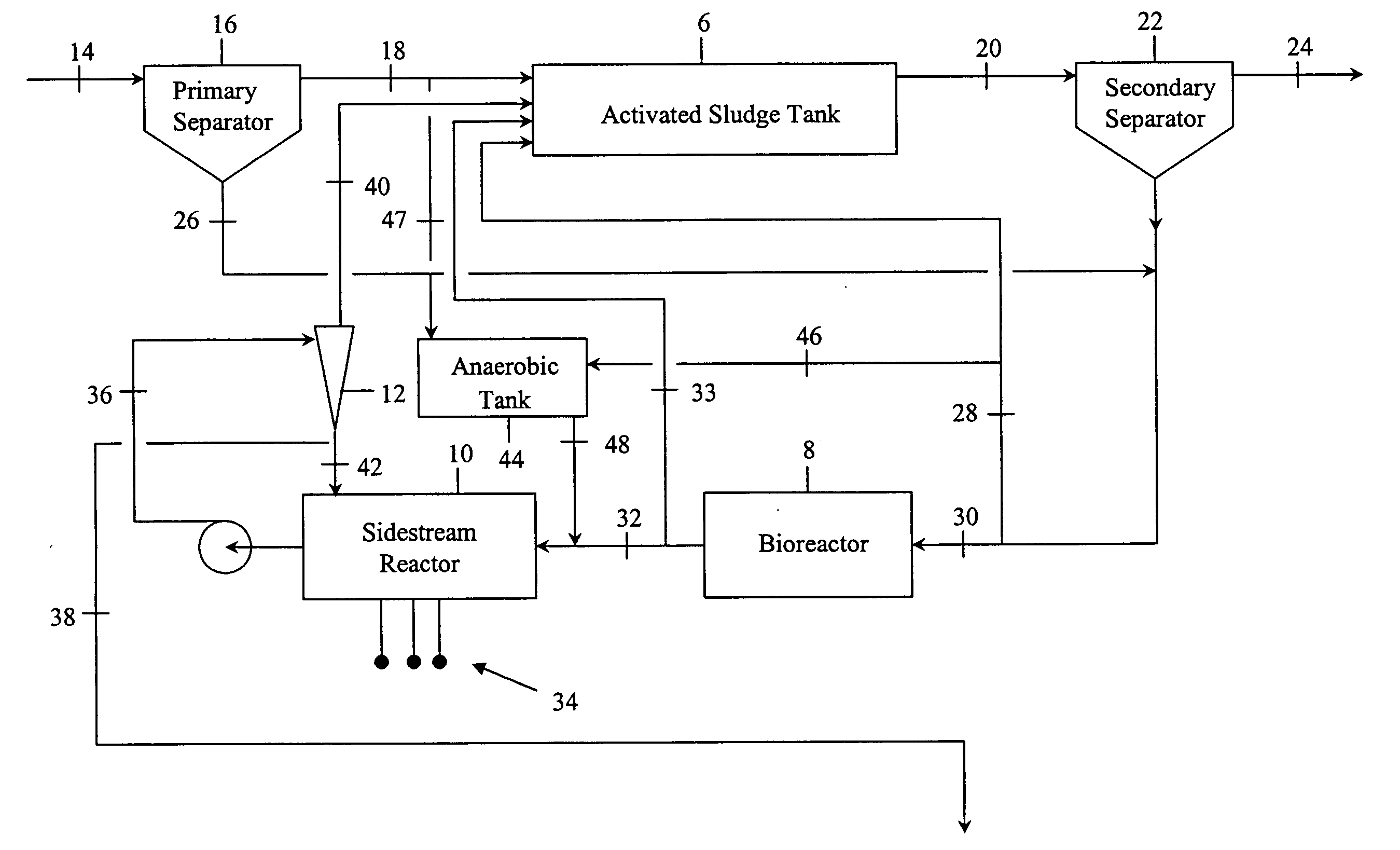
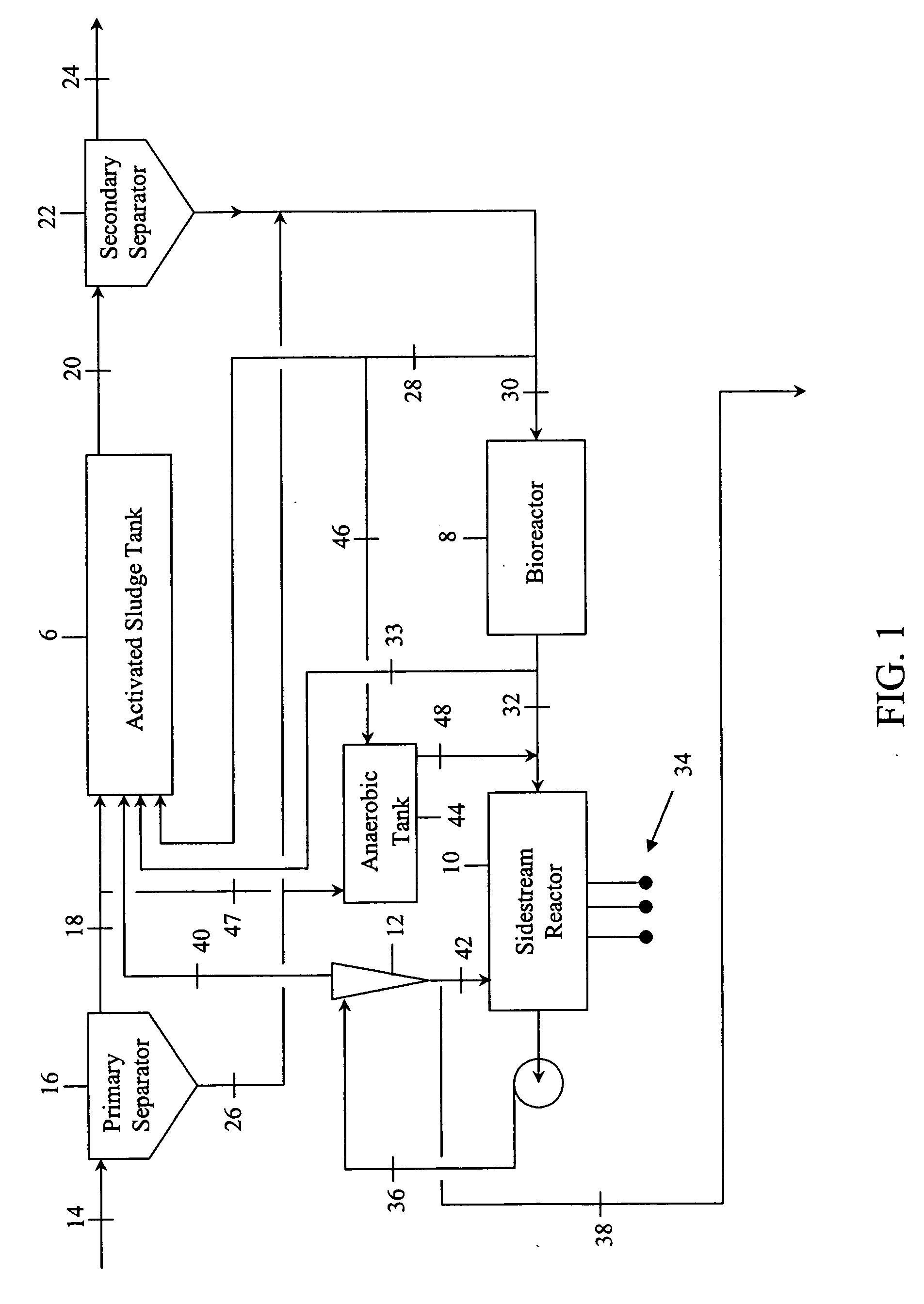
InactiveUS20070000836A1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlActivated sludgePhosphate
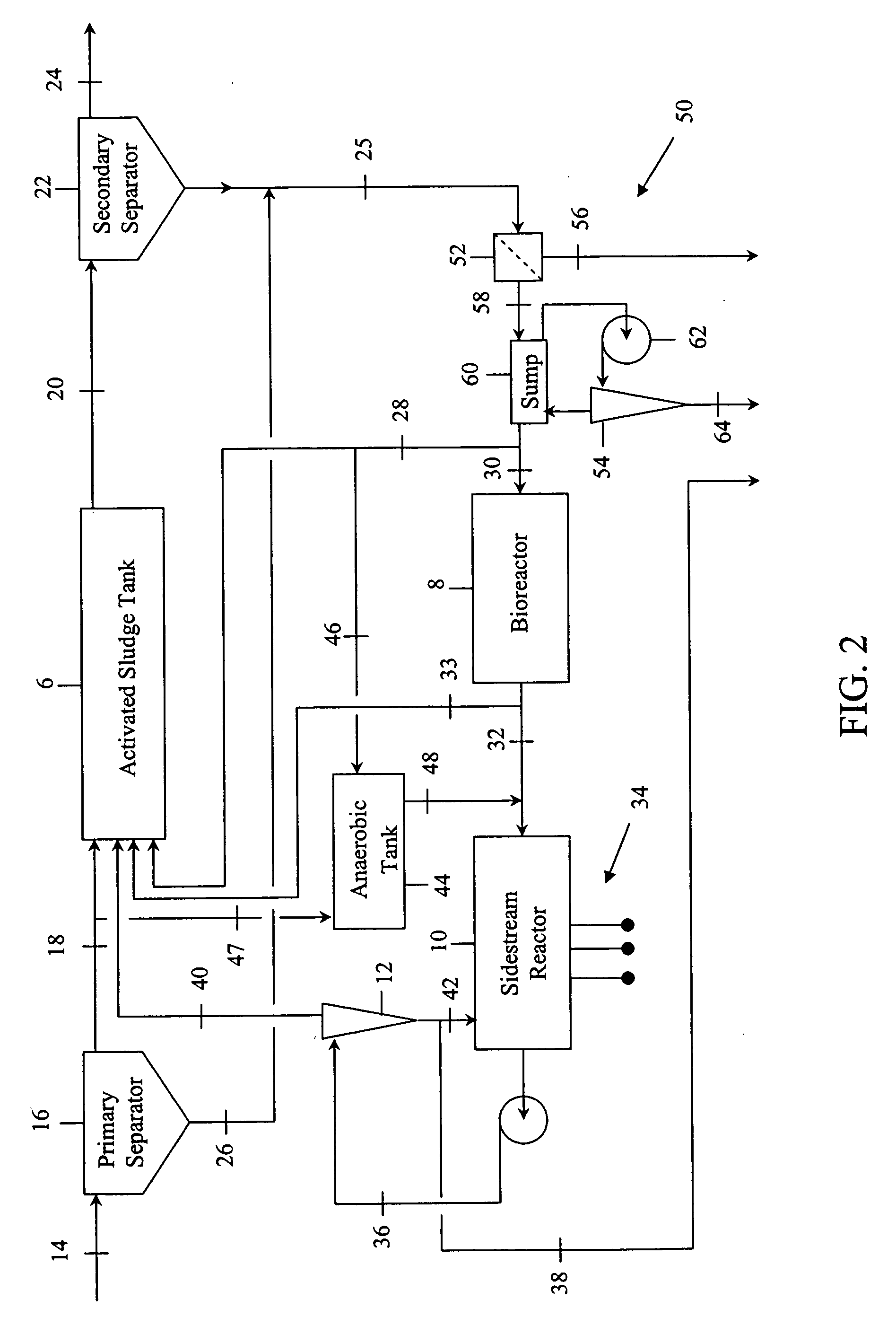
Contaminated wastewaters comprising biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), nitrogen and phosphorus are treated by an activated sludge process. The process utilizes an activated sludge tank, a solid-liquid separator, and a bioreactor to significantly reduce, or eliminate, waste activated sludge (WAS) within a sludge stream. A sidestream reactor is employed downstream from the bioreactor to remove soluble phosphates left in the sludge stream by the low WAS process. Within the sidestream reactor, a source of multivalent metal ions is added to a slightly alkaline sludge stream to precipitate the phosphates. The solid phosphates have a specific gravity higher than that of the organic matter in the sludge stream and may be separated from the sludge stream based upon differential settling velocity.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method and system for nitrifying and denitrifying wastewater
ActiveUS7147778B1Reducing and minimizing dissolved oxygen concentrationReduces and minimizes dissolved oxygen concentrationTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesActivated sludgeOxygen
A wastewater treatment system is provided that includes first and second reactors, each operative to nitrify or denitrify wastewater contained therein. Downstream from the first and second reactors is a membrane reactor that operates under aerobic conditions and includes one or more submersed membranes for separating solids. Extending between the membrane reactor and each of the first and second reactors is a return activated sludge line with appropriate controls for permitting return activated sludge to be directed to one of the reactors at a time. To nitrify and denitrify wastewater, a wastewater influent stream is alternatively directed to the anoxic reactors which are alternatively operated under aerobic and anoxic conditions so as to nitrify or denitrify the wastewater contained therein. To reduce or minimize the dissolved oxygen return from the membrane reactor to the first and second reactors, the flow of return activated sludge is controlled such that generally return activated sludge is returned to the reactor operating under aerobic conditions.
Owner:KRUGER I INC
Method and apparatus for treating wastewater using membrane filters
InactiveUS6863818B2Good removal effectEfficient workTreatment using aerobic processesBiological treatment regulationActivated sludgeBioreactor
An apparatus using activated sludge for the removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater includes a bioreactor for containing a mixture of wastewater under treatment and activated sludge. The bioreactor is divided into a plurality of serially connected treatment zones and includes a wastewater inlet, a downstream aerobic zone and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone. A method for removal of nutrients from a wastewater includes providing a wastewater to an inlet of a serial, multi-zone, activated sludge bioreactor containing an activated sludge. The bioreactor has a downstream aerobic zone from which water is removed and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic/anaerobic process alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosphorous
ActiveUS20070108125A1Quality improvementSimple processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsActivated sludgeNitrogen
Disclosed are a membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic / anaerobic processes alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosporus, wherein nitrogen and phosphorous together with organics in the sewage, wastewater, filthy water etc. can be simultaneously removed with an economic and efficient manner, an operation thereof is easy and efficient, a capacity thereof is high and the method is economic due to the reduced operating costs with performing measurement and control of a recycle rate, a recycle time of alternate operation of the anoxic and anaerobic process, an amount of sludge, an amount of aeration and an operation of a blower for an intermittent membrane cleaning.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
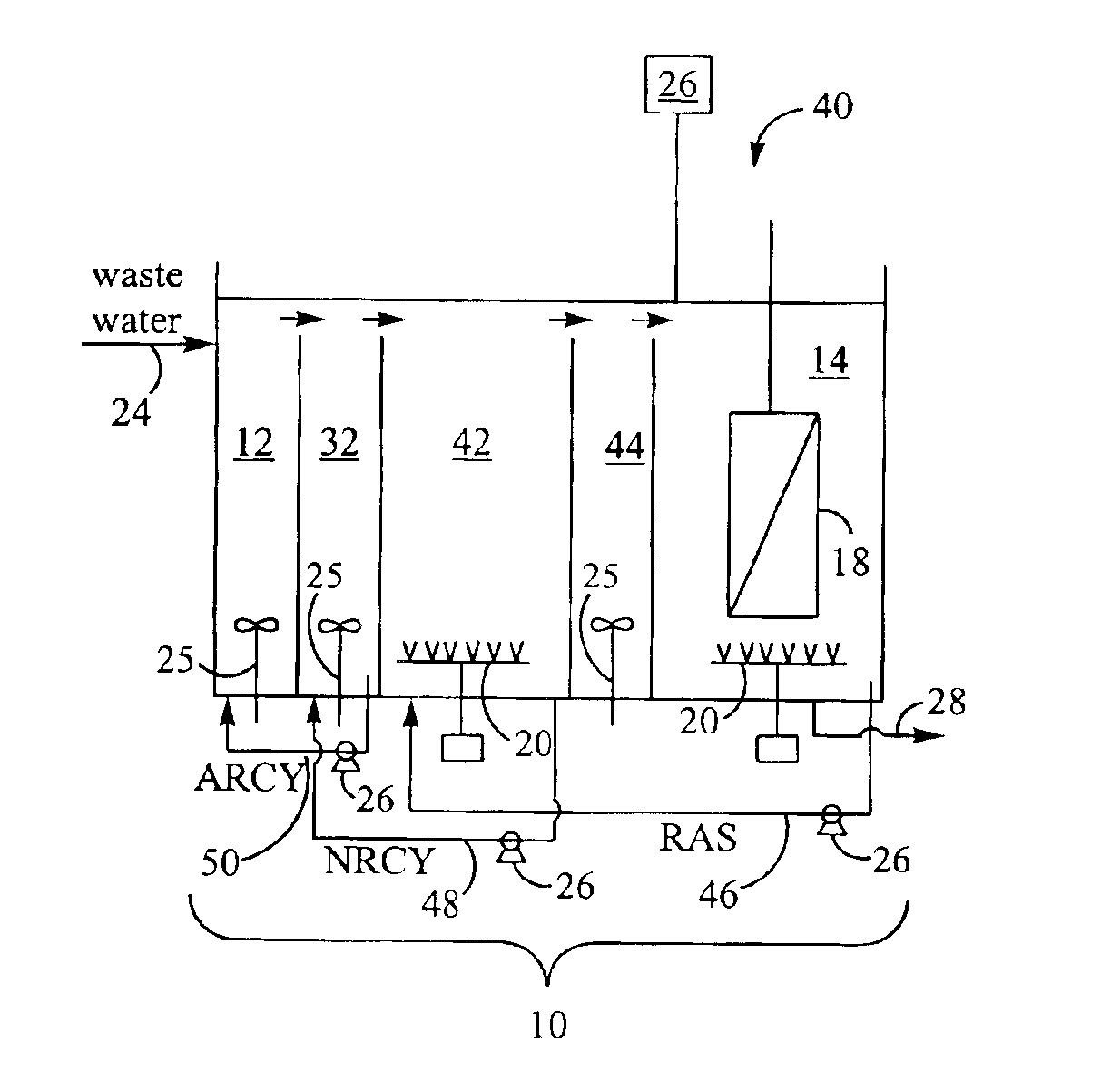
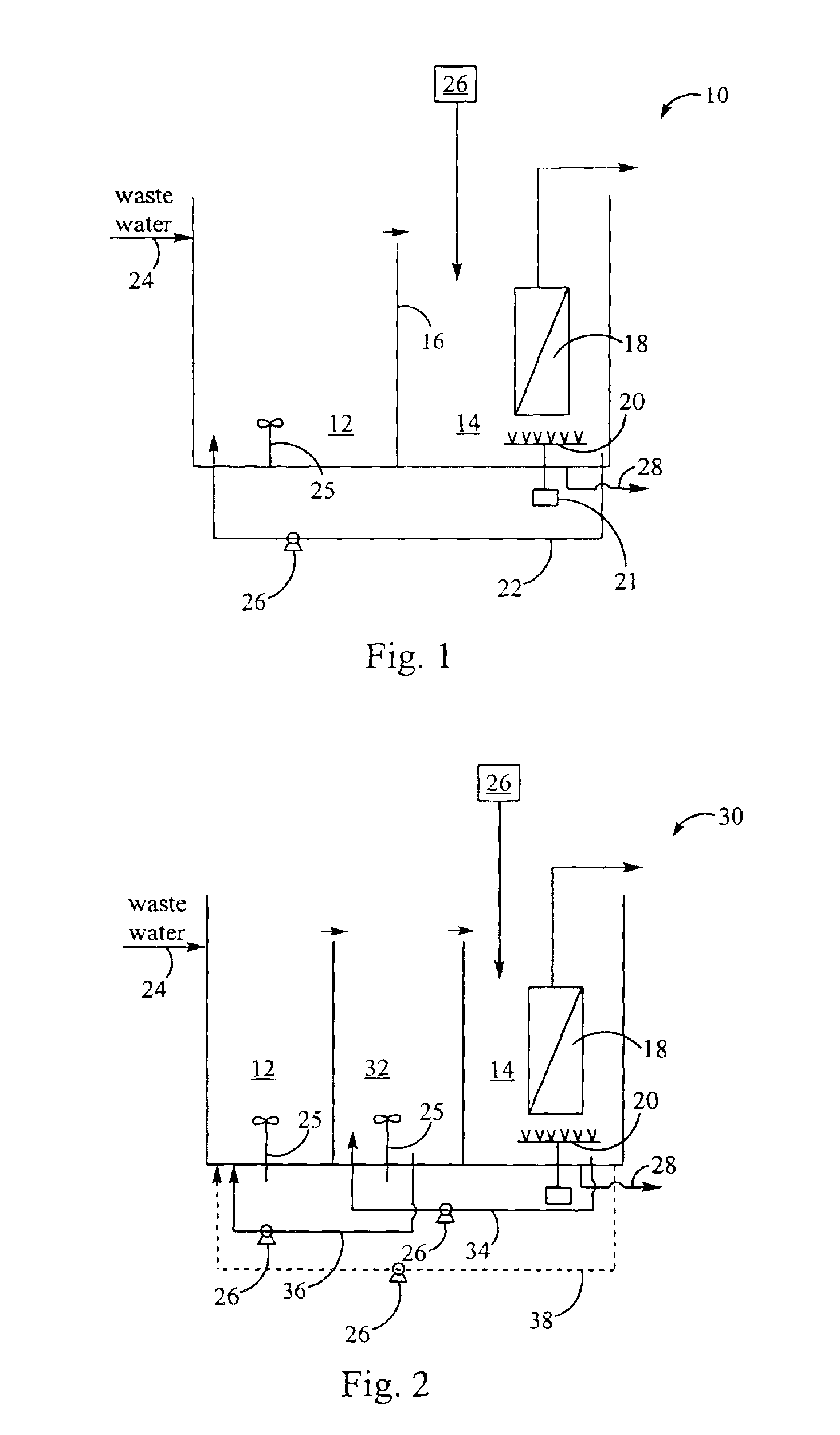
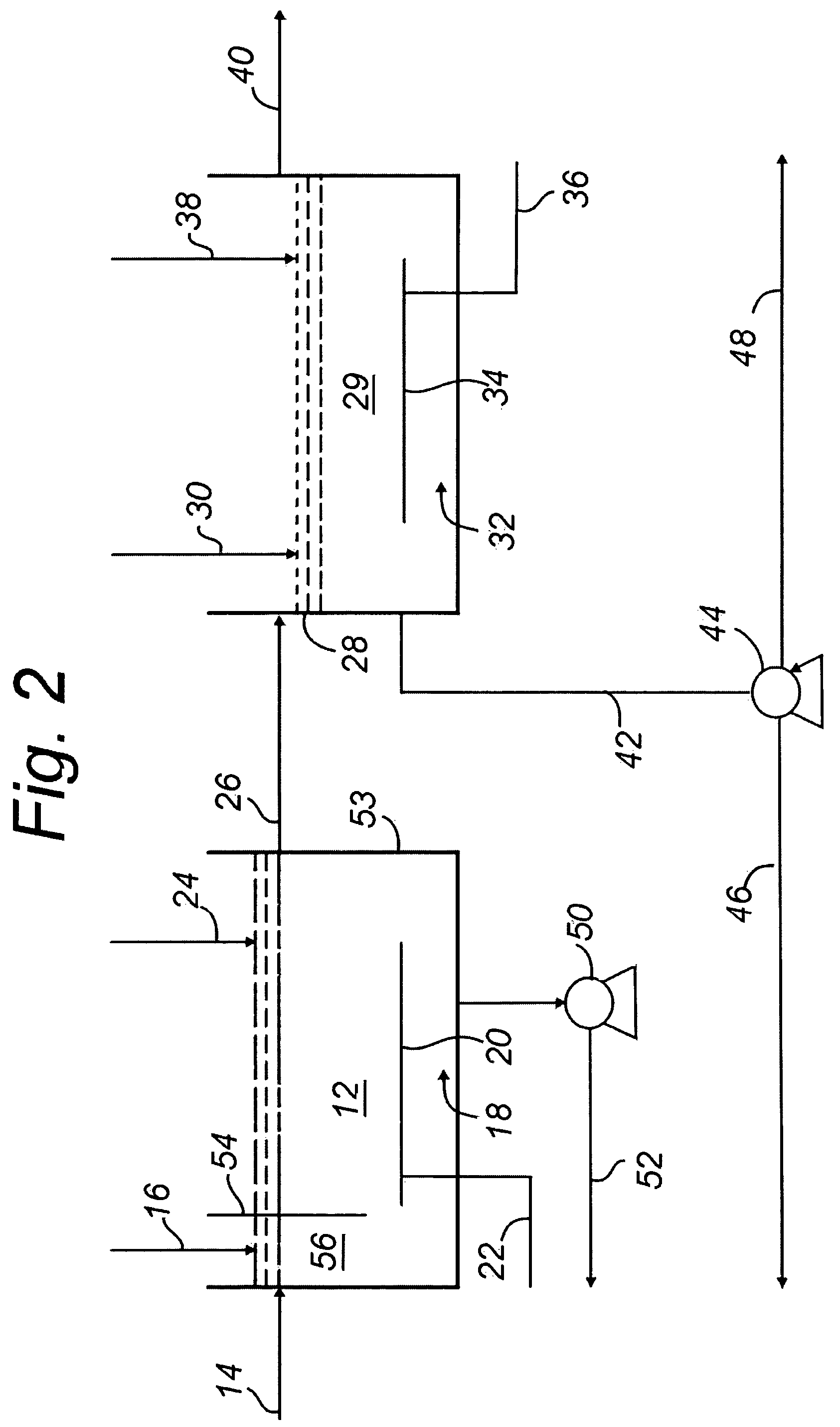
Method for treating wastewater in a membrane bioreactor to produce a low phosphorus effluent
InactiveUS6946073B2Reduce outputPromoting robust nutrient uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesActivated sludgeMembrane bioreactor
Removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater yielding a low phosphorous (e.g., less than 0.25 mg / L) output includes providing a serial multistage bioreactor containing activated sludge having in hydraulic series an anaerobic zone and a downstream aerobic zone, with each zone having an upstream inlet and a downstream outlet. The wastewater is provided to the anaerobic zone inlet. A quantity of chemical sufficient to precipitate soluble and particulate phosphorous is added to the downstream aerobic zone in an amount sufficient to yield a low phosphorous output. Treated water is separated from the activated sludge and precipitated phosphorous and a return activated sludge separated from the treated water is recycled to the anaerobic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
Combined activated sludge-biofilm sequencing batch reactor and process
InactiveUS20040206699A1Similar oxygen transfer efficiencyRemoval can be promoted and increasedTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
A new biofilm-activated sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) treatment process for sewage or wastewater has successfully been developed as the third generation SBR (SBR3). This new SBR3 process utilizes a multi-stage and multi-sludge SBR configuration receiving either continuous or intermittent inflow of wastewater. Each stage has individually controlled continuous or alternating anaerobic / anoxic / aerobic operation, with or without mixing and recycling from the other stage(s). The configuration and operation is dependent upon the treatment objectives and effluent discharge requirements. In the preferred embodiment, carriers are used to facilitate control of operating conditions.
Owner:KINGSFORD ENVIRONMENTAL H K
Membrane coupled activated sludge method and apparatus operating anoxic/anaerobic process alternately for removal of nitrogen and phosphorous
ActiveUS7314563B2Quality improvementSimple processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsActivated sludgeNitrogen
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Organic-based fertilizer
The subject invention provides methods for producing homogenous organic base fertilizer for plant nutrition and soil fertility. Also provided by the subject invention are value added fertilizer products for plant nutrition and soil fertility and concentrated liquid formulations / nutrient supplements that provide the value added nutrients to fertilizer products. Methods according to the invention involve the application of concentrated liquid(s) and / or dry formulation(s) comprising a mixture of one or more plant nutrient(s), one or more additional organic compound(s), one or more penetrate(s), and one or more optional supplement(s) into one or more organic base material(s). These organic base materials include, and are not limited to, biosolids, activated sludge, municipal compost, animal manures (e.g., horse, cow, chicken, pig, and sheep), and composted organic byproducts.
Owner:GREEN TECH LLC
Active sludge-biomembrane compounding integral sewage treating method and apparatus
InactiveCN1887739AIncrease sludge concentrationAvoid churnTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeEngineering
The active sludge-biomembrane compounding integral sewage treating method includes the first leading the sewage to be treated to the anoxic area through stirring for mixing sewage to be treated and active sludge, the subsequent leading the sewage to aerobic area with stuffing for aeration treatment with combined active sludge and biomembrane, and final leading the sewage to the precipitation area for natural deposition to separate sludge and water, leading out purified water, reflowing the mixed sludge liquid to the anoxic area and draining the residual sludge. The present invention also relates to the corresponding sewage treating apparatus. The present invention has the advantages of high treating capacity, resistance to impact load, simple operation, etc. and is especially suitable for use in medium and small towns.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Multiple barrier biological treatment systems
InactiveUS7014763B2Small footprintReduce construction costsTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorSingle vessel
The inventions separate the activated sludge, biochemical reaction stages of the batch treatment process of a sequencing batch reactor from the clarification and sedimentation stages by separating the locations where each process takes place. The separation may be accomplished in a variety of ways including constructing separate basins for each process, installing baffles or other partitions in a single vessel to isolate the areas where each process takes place, or other methods of process separation as are known in the art. In each process, treatment occurs through the performance of a series of operations. The operations are repeated for each batch of wastewater processed by the SBR. In a conventional SBR process, the cycle of operations for clarification and sedimentation are dependent on a preceding biochemical reaction step. However, in the present invention the clarification and sedimentation operations are independent of the biochemical reaction operations. It remains possible to coordinate operations so that the process cycles are coincident, however the benefits of the invention are more readily realized by the practice of independent operation.
Owner:AQUA AEROBIC SYST
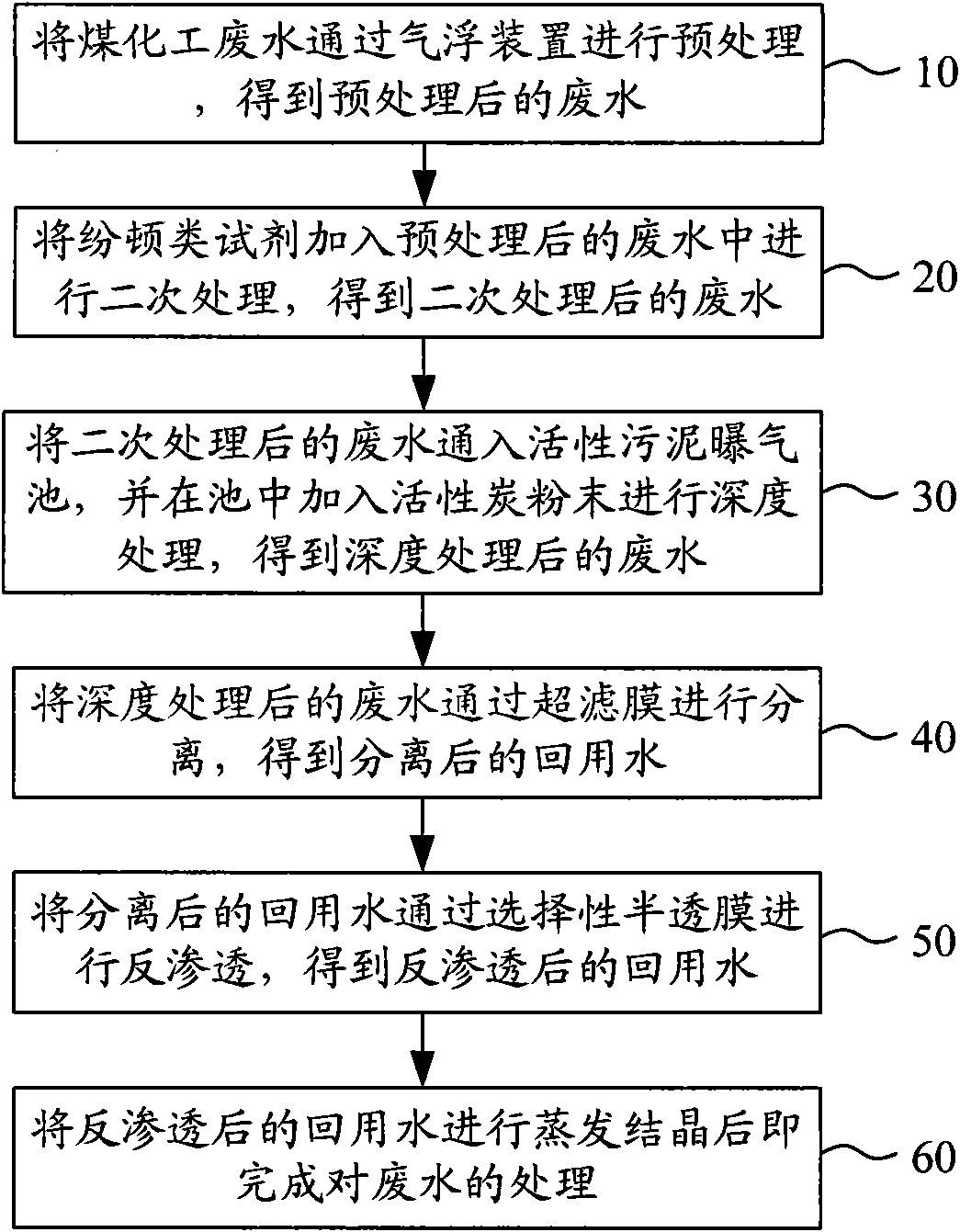
Coal chemical wastewater treating technique
InactiveCN101560045AMeet environmental protection requirementsWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeActivated carbon
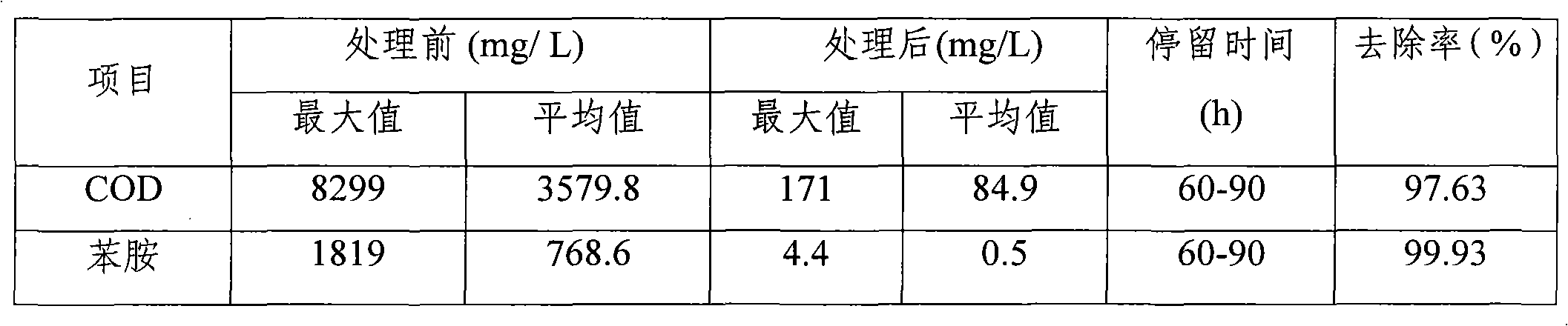
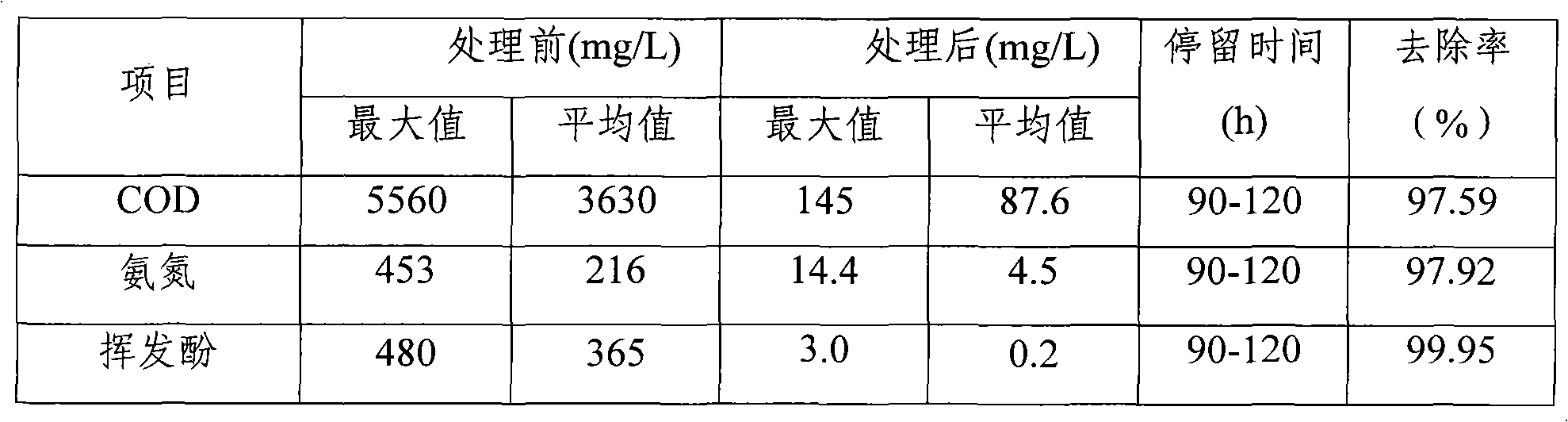
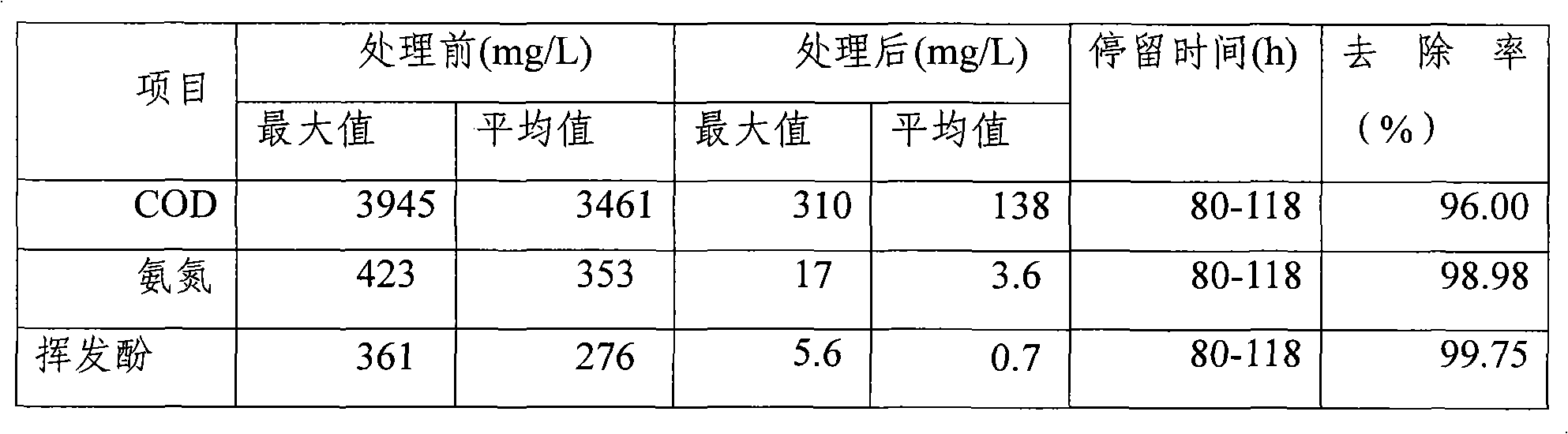
The invention relates to a coal chemical wastewater treating technique, which comprises the following steps of: pretreating the coal chemical wastewater by an air-floatation device and obtaining pretreated wastewater; adding a fenton reagent into the pretreated wastewater to carry out secondarily treatment and obtaining secondarily treated wastewater; putting the secondarily treated wastewater into an activated sludge aeration pool and adding active carbon powder into the pool for deep treatment to obtain deeply treated wastewater; separating the deeply treated wastewater with a hyperfiltration membrane and obtaining separated recycled water; reversely penetrating the separated recycled water with a selective semi-permeable membrane and obtaining reversely penetrated recycled water; evaporating and crystallizing the reversely penetrated recycled water and finishing the wastewater treatment. The wastewater, after treated by the coal chemical wastewater treating technique, can realize the 'zero discharge' standard, meet the national environmental requirements, and obtain good economic and social benefits.
Owner:POTEN ENVIRONMENT GRP
Composite efficient microbial preparation for treating difficultly-degradable waste water and preparation and application
The invention discloses a composite efficient microbial preparation for treating difficultly-degradable waste water. The composite efficient microbial preparation comprises the following active ingredients of: bacillus, pseudomonas, alcaligenes eutrophus, aspergillus and yeast. The composite efficient microbial preparation has a unique treating effect on high-concentration organic sewage and highammonia and nitrogen sewage which are difficult to treat by the conventional activated sludge process and contain macromolecules and difficultly-degradable harmful constituents.
Owner:北京三泰正方生物环境科技发展有限公司
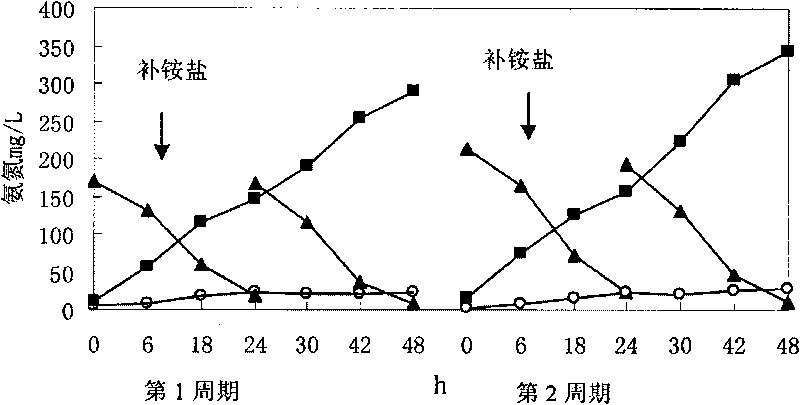
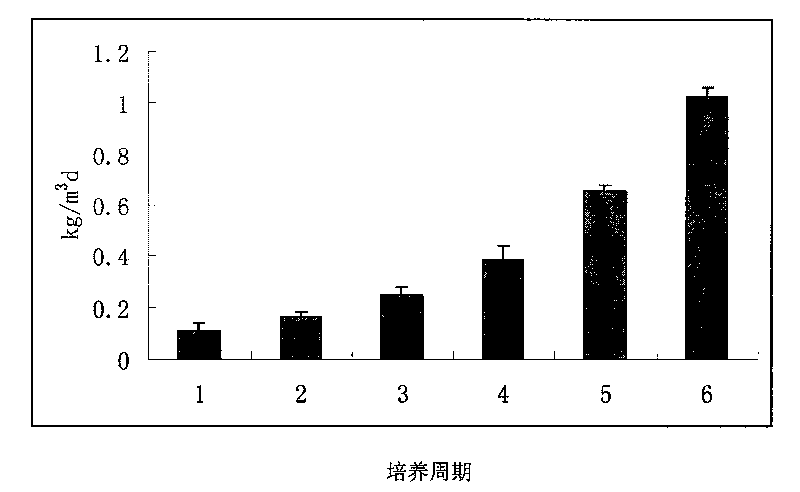
Large-scaled culture method of high-concentration nitrosobacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN101709278AIncrease concentrationHigh activityBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeHigh concentration
The invention discloses a large-scaled culture method of high-concentration nitrosobacteria and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding an enrichment culture solution with initial ammonia nitrogen mass concentration of 30-500mg / L in a reaction device with functions of stirring, heating and aeration; preparing activated sludge of a waste water treatment plant in activated sludge of 0.5-20% for primary inoculation to conduct the enrichment culture of the nitrosobacteria by 2-6d as a culture cycle, wherein extra ammonium salts and a growth promoter are added during the enrichment culture of the nitrosobacteria; (2) ending the culture when the concentration of NO2-N in the solution is accumulated to reach 70-95% of the concentration of total nitrogen; adding a flocculating agent for flocculation and sedimentation; and allowing to stand still to remove supernate, and then adding the enrichment culture solution to start the culture of the second cycle; and (3) continuously conducting 3-8 cycles of the enrichment culture to obtain the high-concentration nitrosobacteria. By adopting the nitrosobacteria to strengthen the bi-nitrification treatment of ammonia nitrogen contained waste water, the method has the advantages of high stress resistance, low cost and high efficiency and is suitable for the complicated treatment of ammonia nitrogen contained industrial waste water.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS20010045390A1Improve efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
Owner:KIM SUNGTAI +2
Method and apparatus for treating oil refining sewerage
ActiveCN101434443AReduce shockFacilitate deep processing and reuseWater/sewage treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationActivated sludge
The invention relates to a treatment method and a device for refinery sewage. The refinery sewage is sent into an electrolytic catalysis oxidation reactor which is provided with an anode, a cathode and solid catalyst particles, wherein, the lower part of the reactor is provided with an oxygenation aeration device, the solid catalyst particles are filled between the anode and the cathode, and the solid catalyst particles adopts particle activated carbon loaded with metals having catalytic and oxidation function. The effluent of the electrolytic catalysis oxidation can be further treated by adopting an activated sludge process. The method is used for treating high-concentration salt-containing mixed wastewater such as the draining water of a refinery electrical desalting unit, the alkali washing waste alkali liquid of oils, liquefied petroleum gas and dry gas, and cutting water in an oils tank farm, and the like, the wastewater after treatment satisfies the requirement of direct discharging, thus alleviating impact on a wastewater treatment plant. The method put forward by the invention has the advantages that high-concentration wastewater can reach disposable treatment standard and does not need any dilution biochemical treatment, treatment effluent is not polluted secondarily by metal ions, and investment and running cost are lower, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
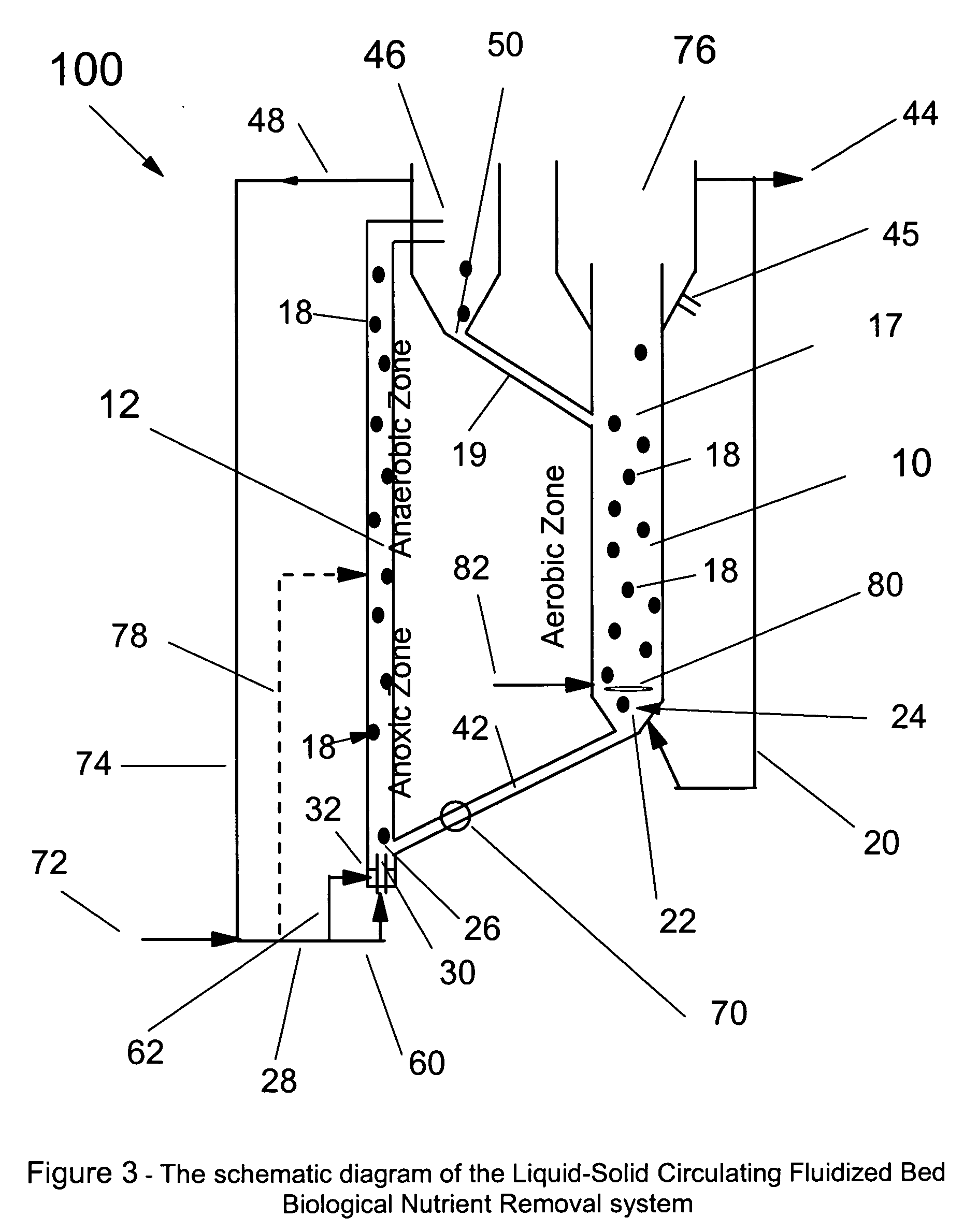
Liquid-solid circulating fluidized bed waste water treatment system for simultaneous carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus removal
InactiveUS20040178132A1Easy to adaptIncrease contactTreatment using aerobic processesIon-exchanger regenerationActivated sludgeOxygen
Biological nutrient removal (BNR) in municipal wastewater treatment to remove carbonaceous substrates, nutrients and phosphorus, has recently become increasingly popular worldwide due to increasingly stringent regulations. Biological fluidized bed (BFB) technology, which could be potentially used for BNR processes, can provide some advantages such as high efficiency and compact structure. This present invention incorporates the fixed-film biological fluidized bed technology with the biological nutrient removal in a liquid-solid circulating fluidized bed, which has achieved the simultaneous elimination of organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, in a very efficient manner and with very compact space requirements. The BNR-LSCFB has two fluidized beds, running as anoxic / anaerobic and aerobic processes to accomplish simultaneous nitrification and denitrification and to remove carbonaceous substrates, nutrients and phosphorus, with continuous liquid and solids recirculation through the anoxic / anaerobic bed and the aerobic bed. The new BNR-LSCFB system is not only an excellent alternative for conventional activated sludge type BNR technologies but is also capable of processing much higher loadings and suitable for industrial applications.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Method for concentrating highly effective nitrobacteria in active sludge
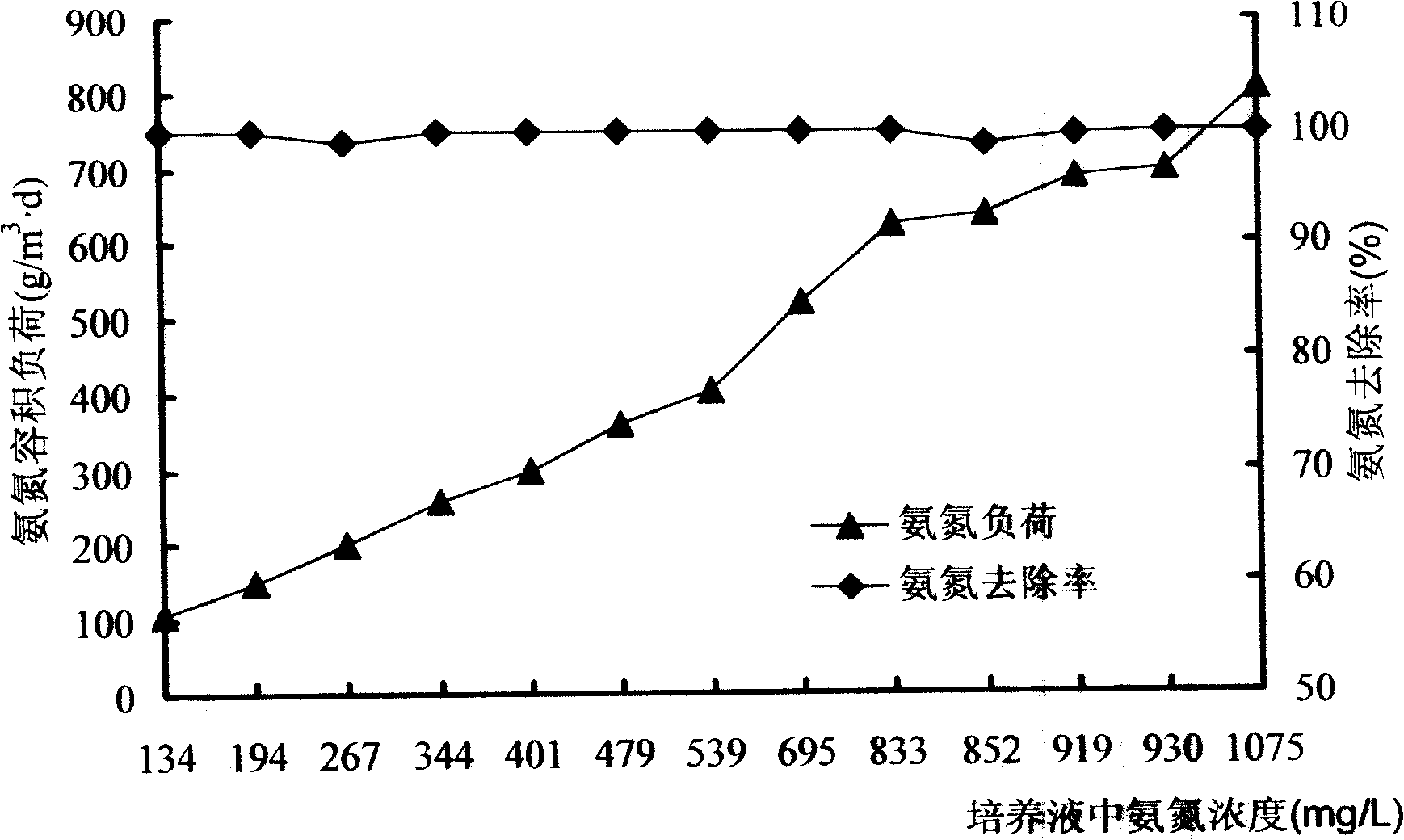
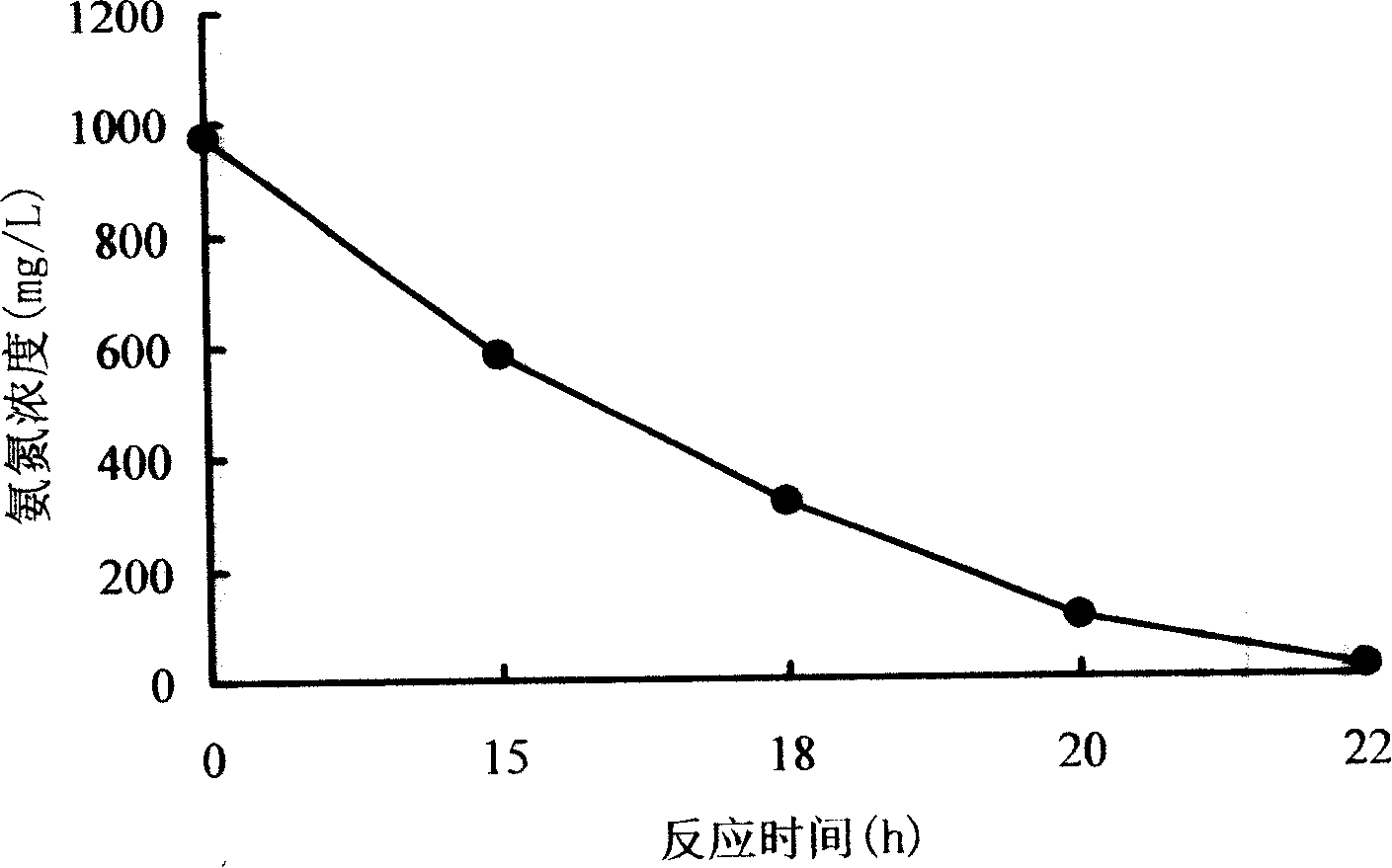
ActiveCN101240253AGrowth inhibitionGood removal effectBacteriaSustainable biological treatmentActivated sludgeHigh concentration
The invention discloses a enrichment method of nitrifying organism. The method adapts discontinuous activated sludge process by gradually improving ammonia nitrogen ph indicator in nutrient fluid to enrich. The main component of the enrichment nutrient fluid is inorganic salt comprising microelement Fe, Mg, Na, K and amortization liquor, in which inceptive concentration of NH(4)(+-N) is 100mg / L to 200mg / L, final concentration is 500mg / L to 1200mg / L and COD is less than or equal to 200mg / L. The method can restrain evidence the growth of sundry bacterium such as carbonizing bacterium, is propitious for nitrifying organism to become ascendency bacterium and resist more and more high ammonia nitrogen concentration, and finally disposing concentration of the ammonia nitrogen wasted water is up to 1200mg / L and high concentration ammonia nitrogen in wasted water can be reduce to less 10mg / L.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
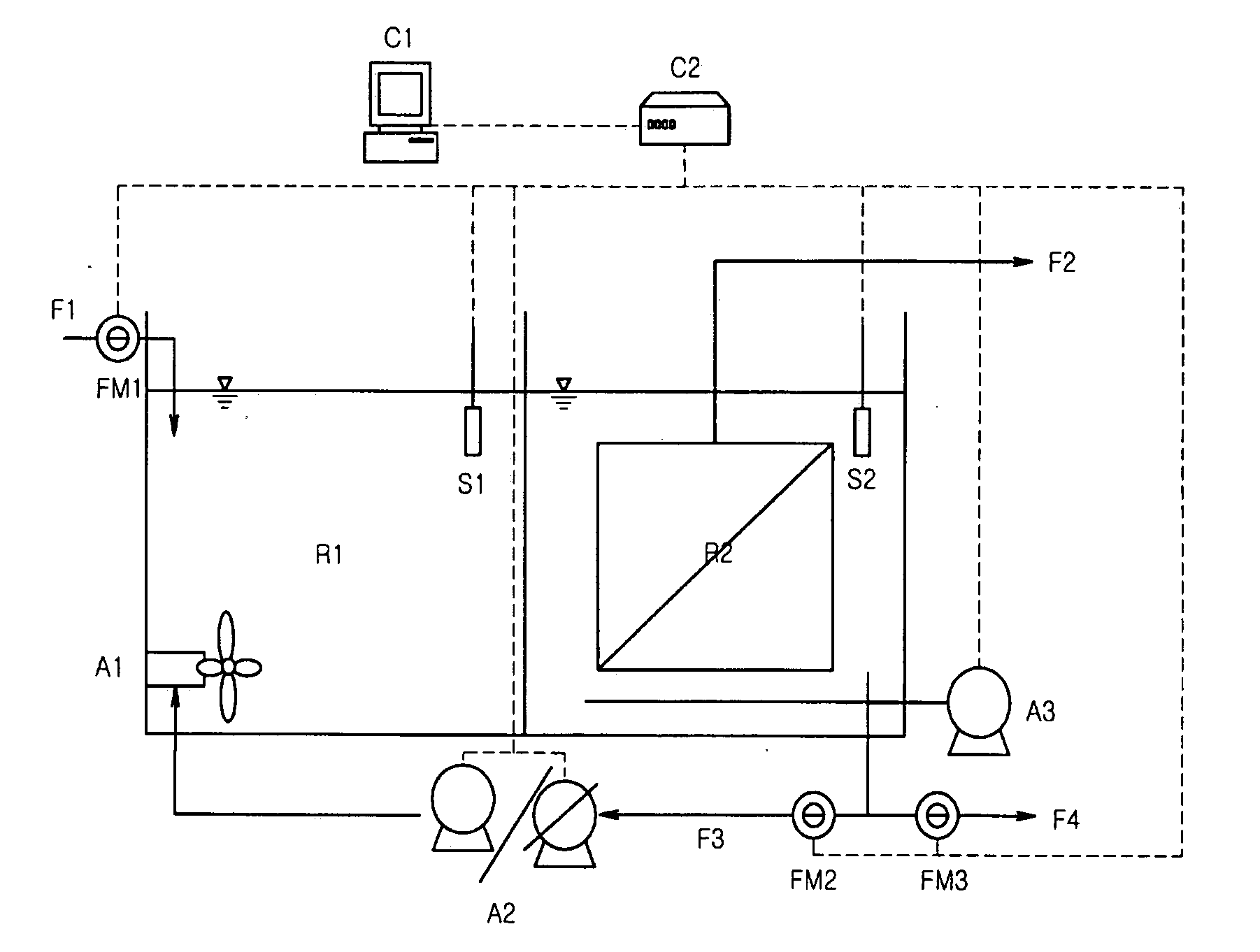
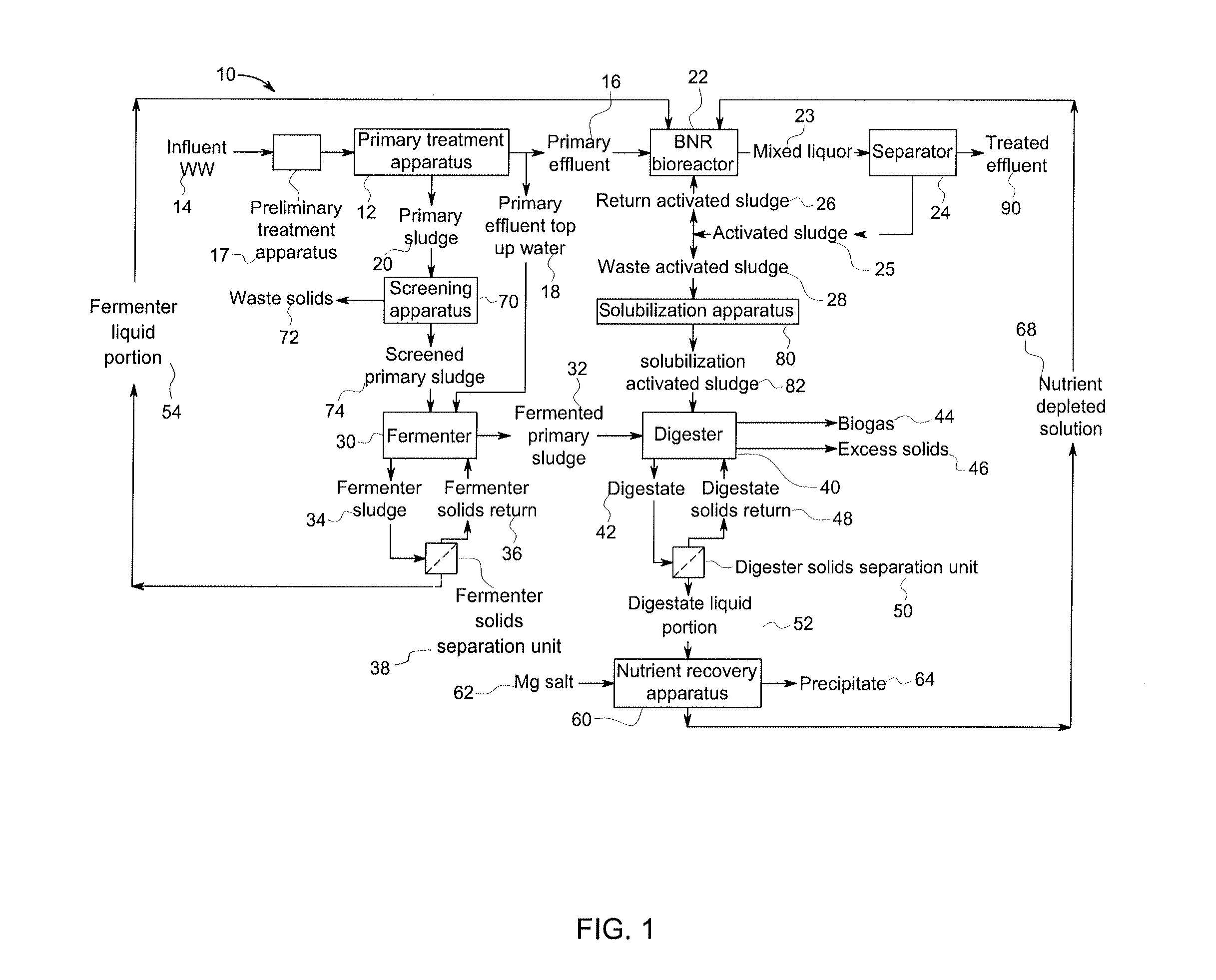
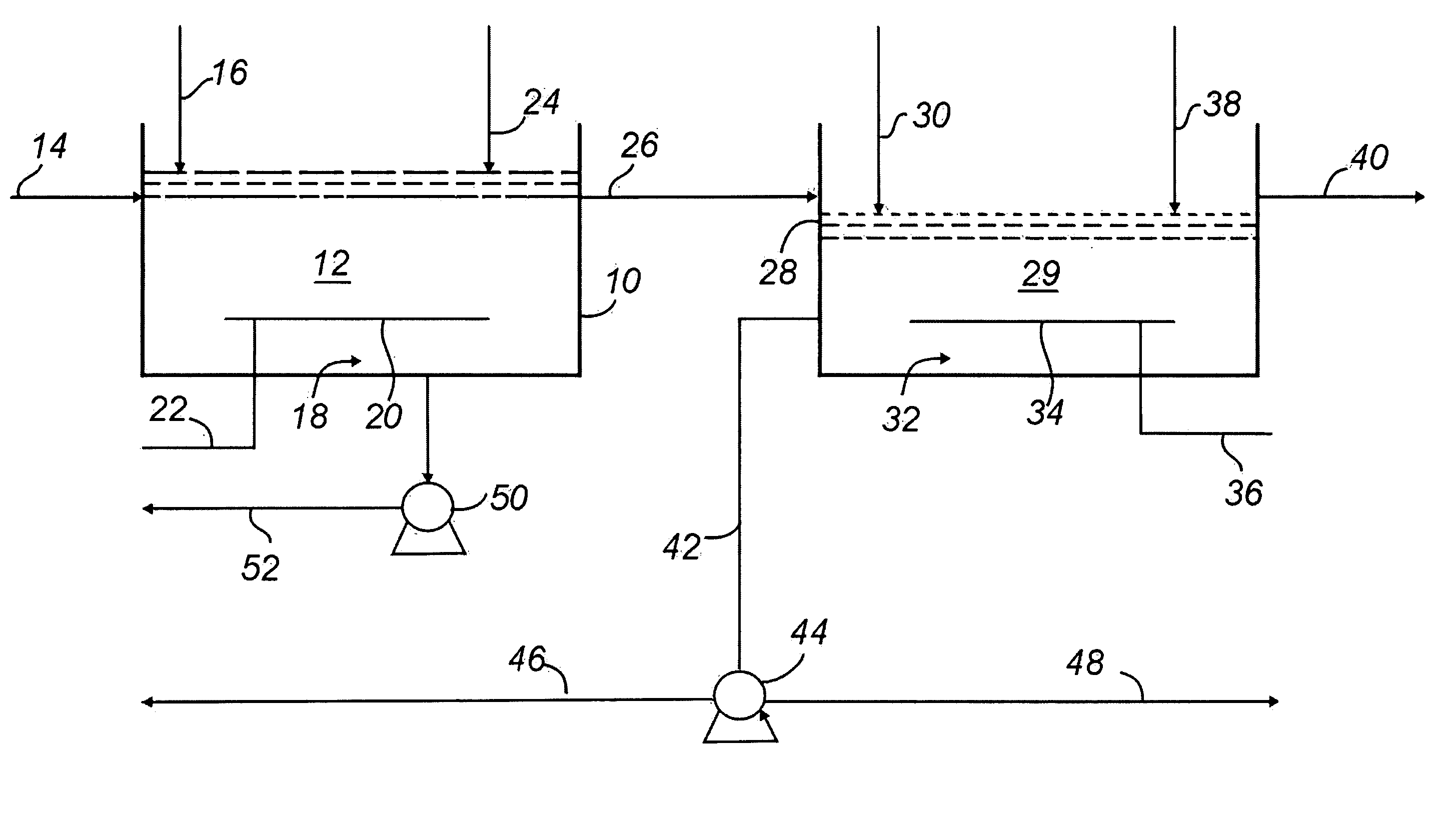
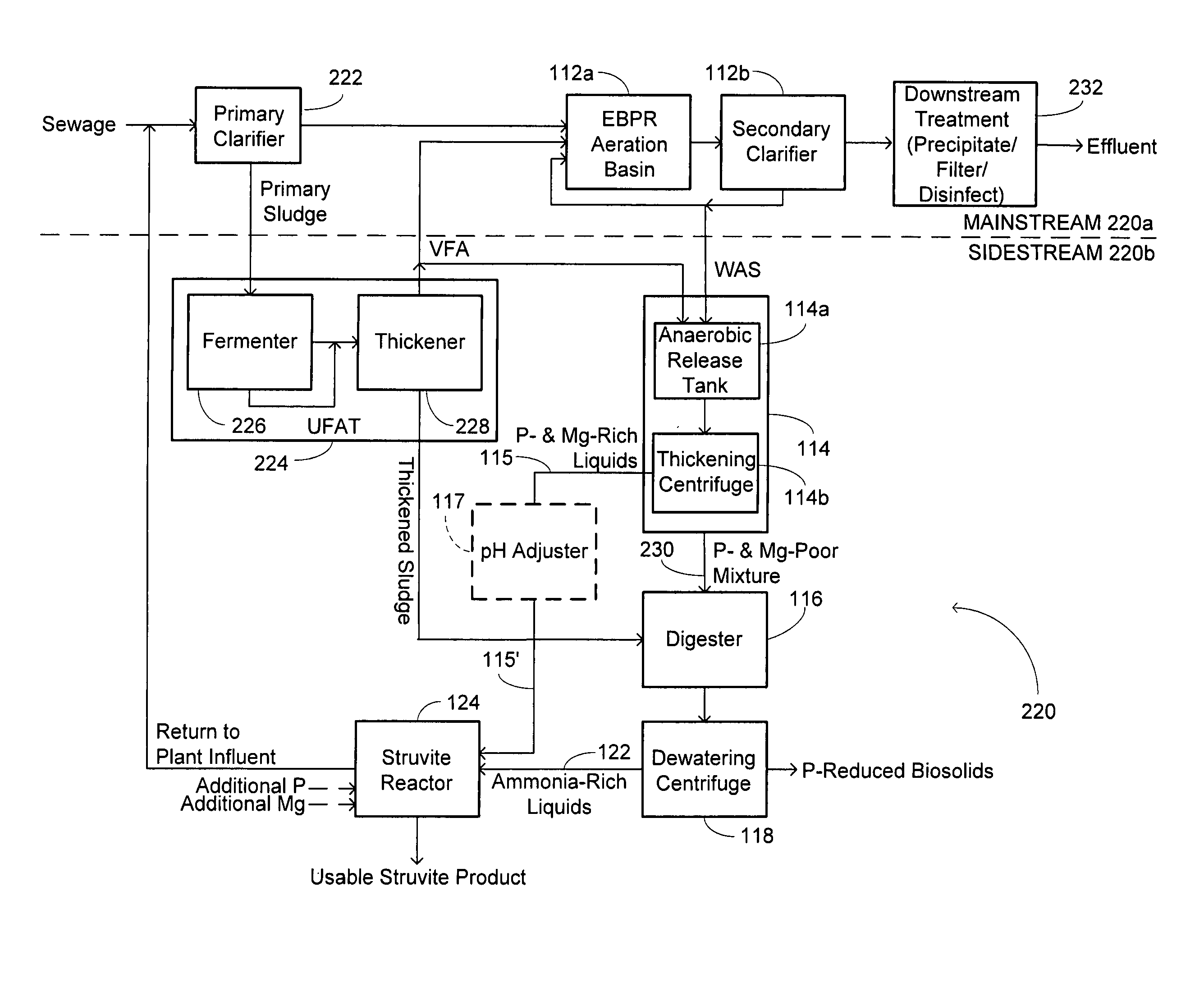
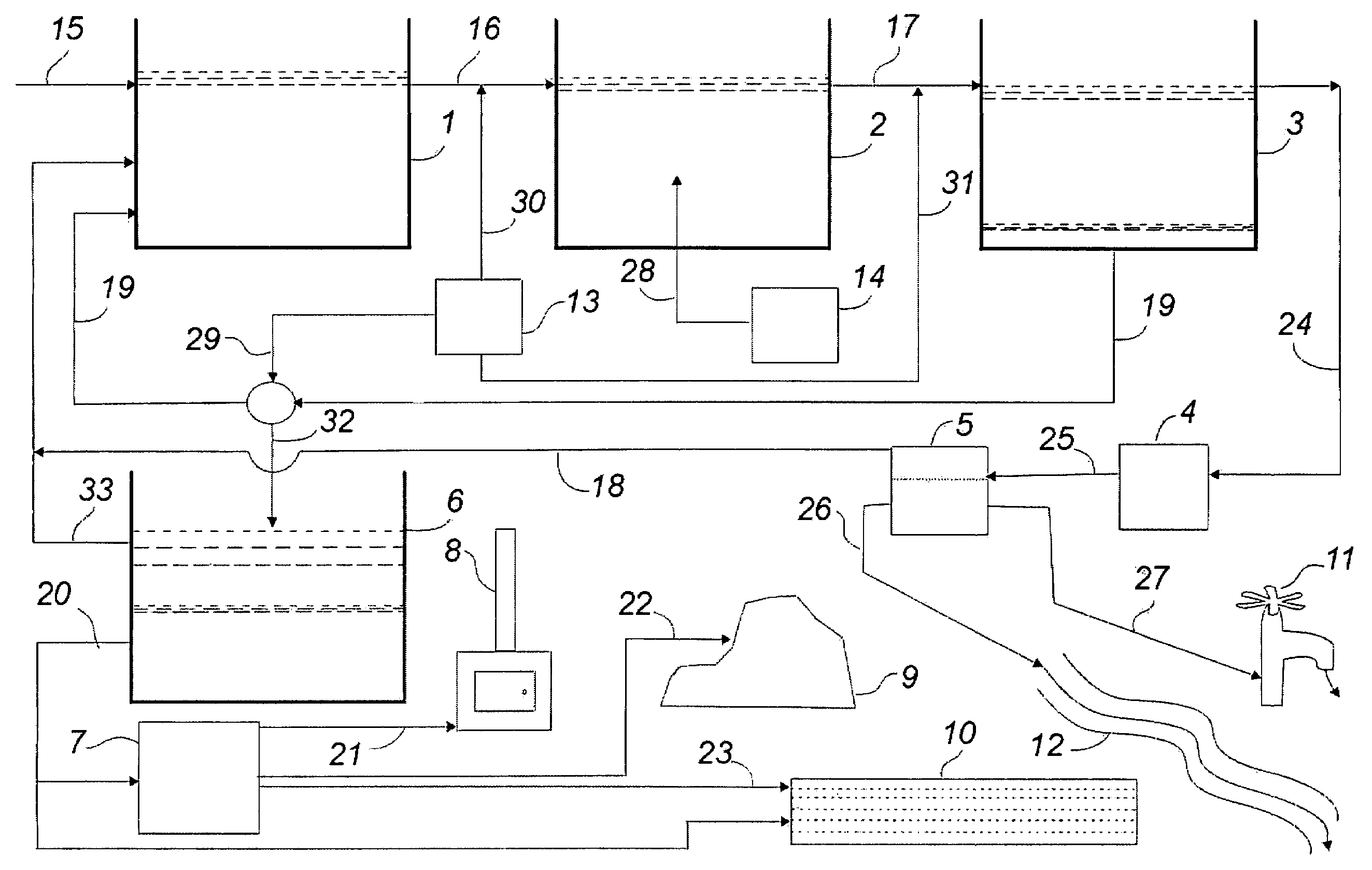
Method and system for treating wastewater
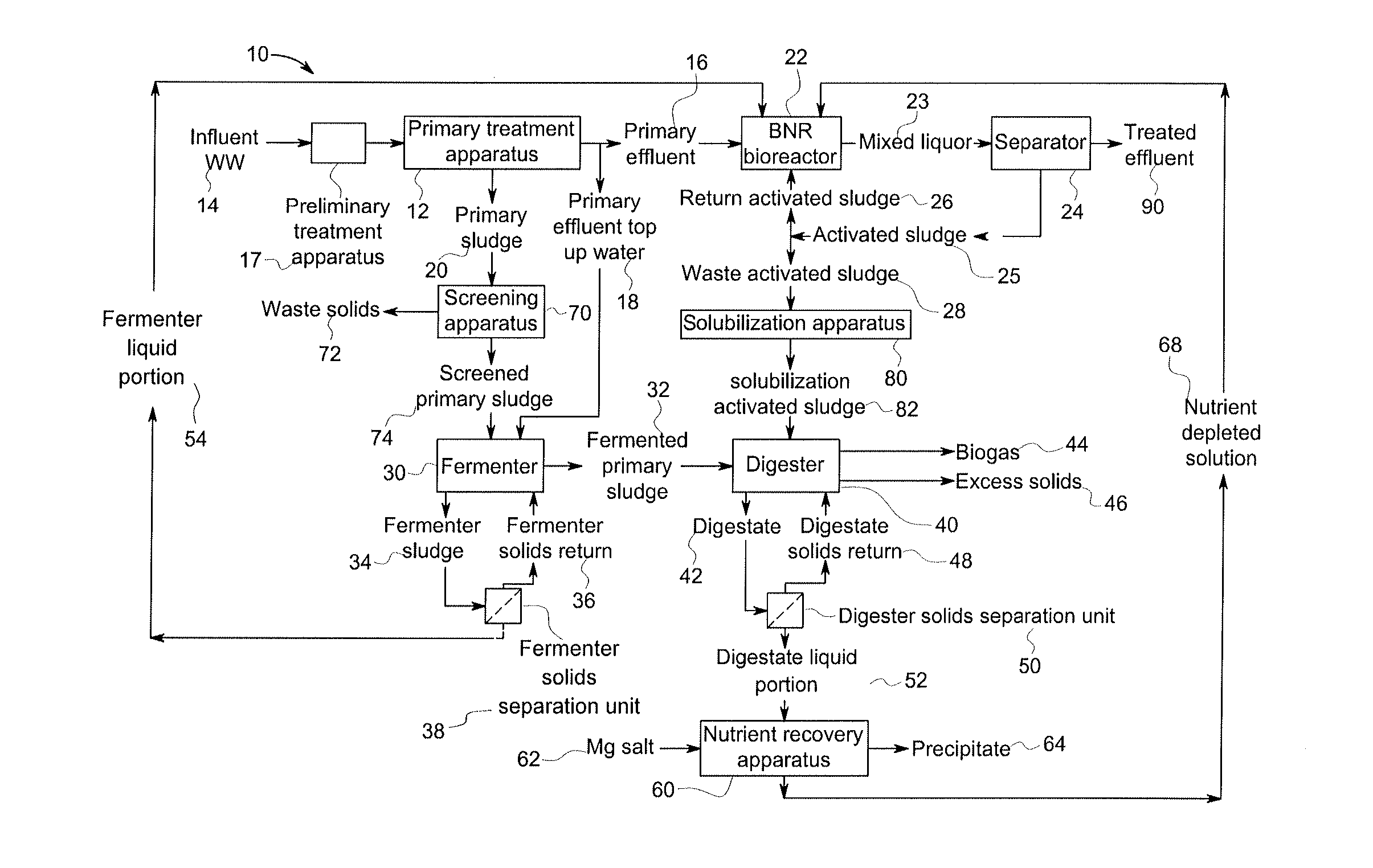
InactiveUS20130134089A1Water treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
A wastewater treatment process uses enhanced primary treatment to remove suspended solids from raw wastewater. Primary sludge is treated in a fermenter. Primary effluent is treated by biological nutrient removal (BNR) to produce a treated effluent and waste activated sludge (WAS). The WAS is treated in an anaerobic digester, which also treats sludge from the fermenter. Anaerobic digestate is separated to provide a liquid effluent. The liquid effluent is stripped of phosphorous and returned to the BNR as a source of readily biodegradable carbon. Liquid in the fermenter may also be separated to provide a liquid rich in volatile fatty acids (VFAs). This liquid is returned to the BNR when additional VFAs are required.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
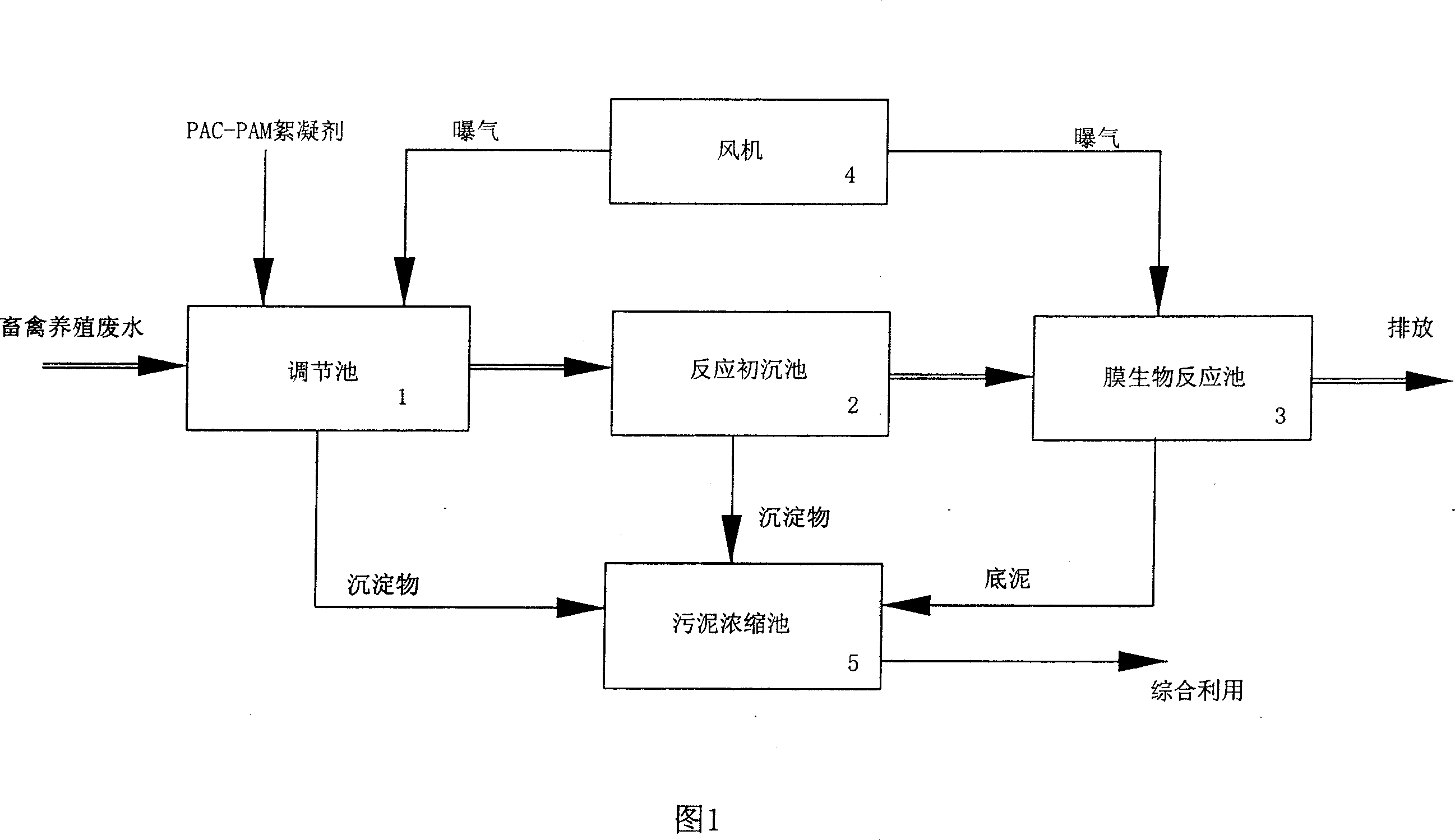
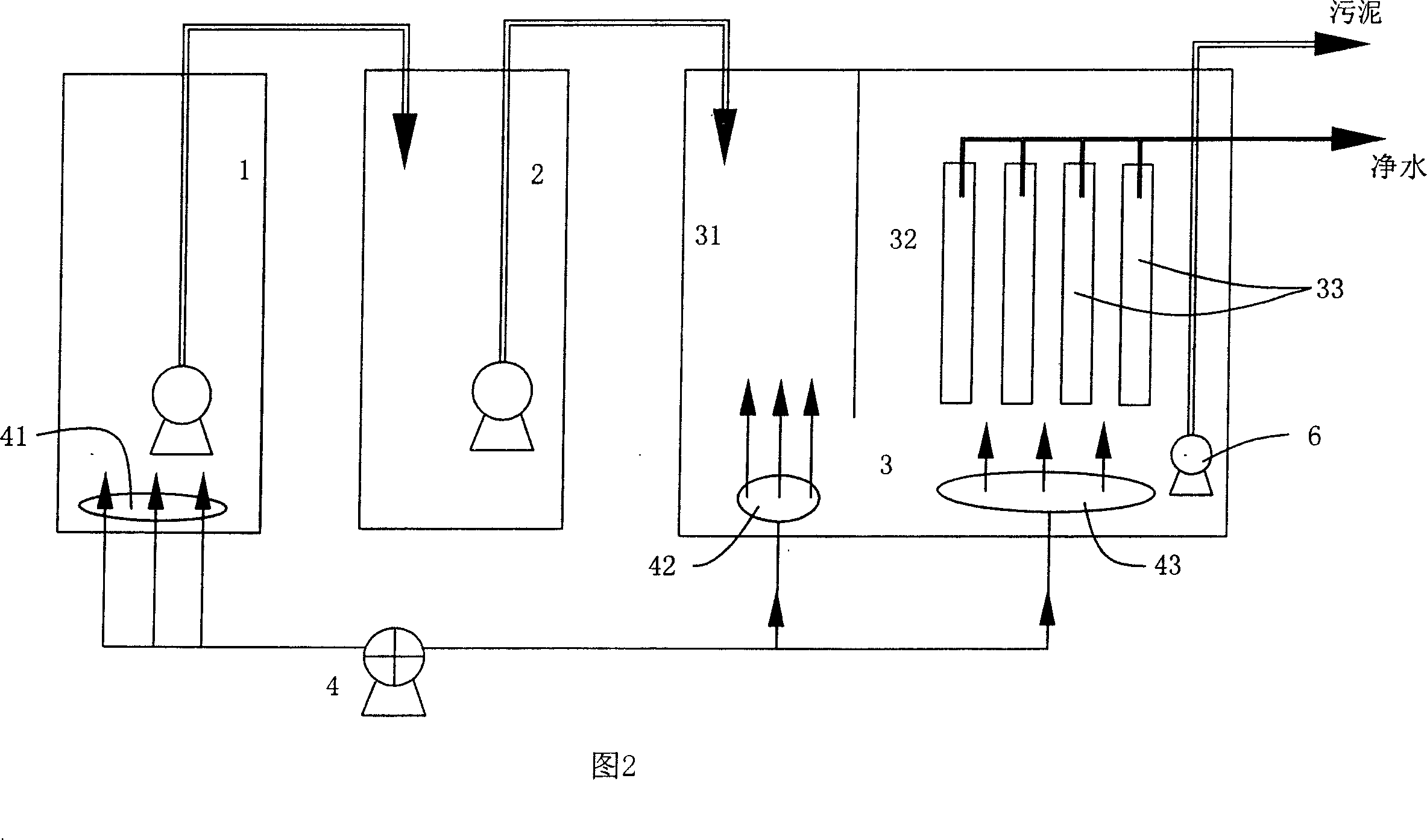
Method for treating waste water of livestock and fowl cultivation
InactiveCN101148302AIncrease concentrationBiochemical improvementTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeFowl
The process of treating animal raising waste water includes the following steps: aerating animal raising waste water through stirring in a regulating pond, flocculating and precipitating in a reacting preliminary sedimentation tank, biodegrading inside a membrane bioreactor with active sludge, filtering through ultrafiltering membrane, and discharging. The present invention combines the active sludge process and the membrane bioreactor process well to degrade animal raising waste water completely, and the treating process is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:SHENZEN JDL ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION LTD +1
Methods for treatment of wastewater with powdered natural lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS20070170115A1Efficiently economically decontaminateProlong total treatment processTreatment using aerobic processesWaste water treatment from animal husbandryActivated sludgeCellulose
A process for treating wastewater through the use of powdered natural ligno-cellulosic materials (PNLM) for (a) physically removing colloidal and suspended volatile solids through adsorption and enhanced floc-formation and settling during pretreatment; (b) adsorbing toxic substances and elements that interfere with biological processes, thus serving to reduce their contact with and exposure to activated sludge organisms effecting wastewater treatment functions; (c) providing fixed surfaces in activated sludge wastewater treatment bioreactors for bacteria and other organisms favoring attached growth in circumstances devoid of such surfaces; (d) reducing production of biological sludge, while also helping to maintain high treatment efficiencies; and (e) following aeration, enhancing the settling characteristics of sludge with respect both to speed of settling and the vertical profile of the settled sludge.
Owner:NUVODA LLC
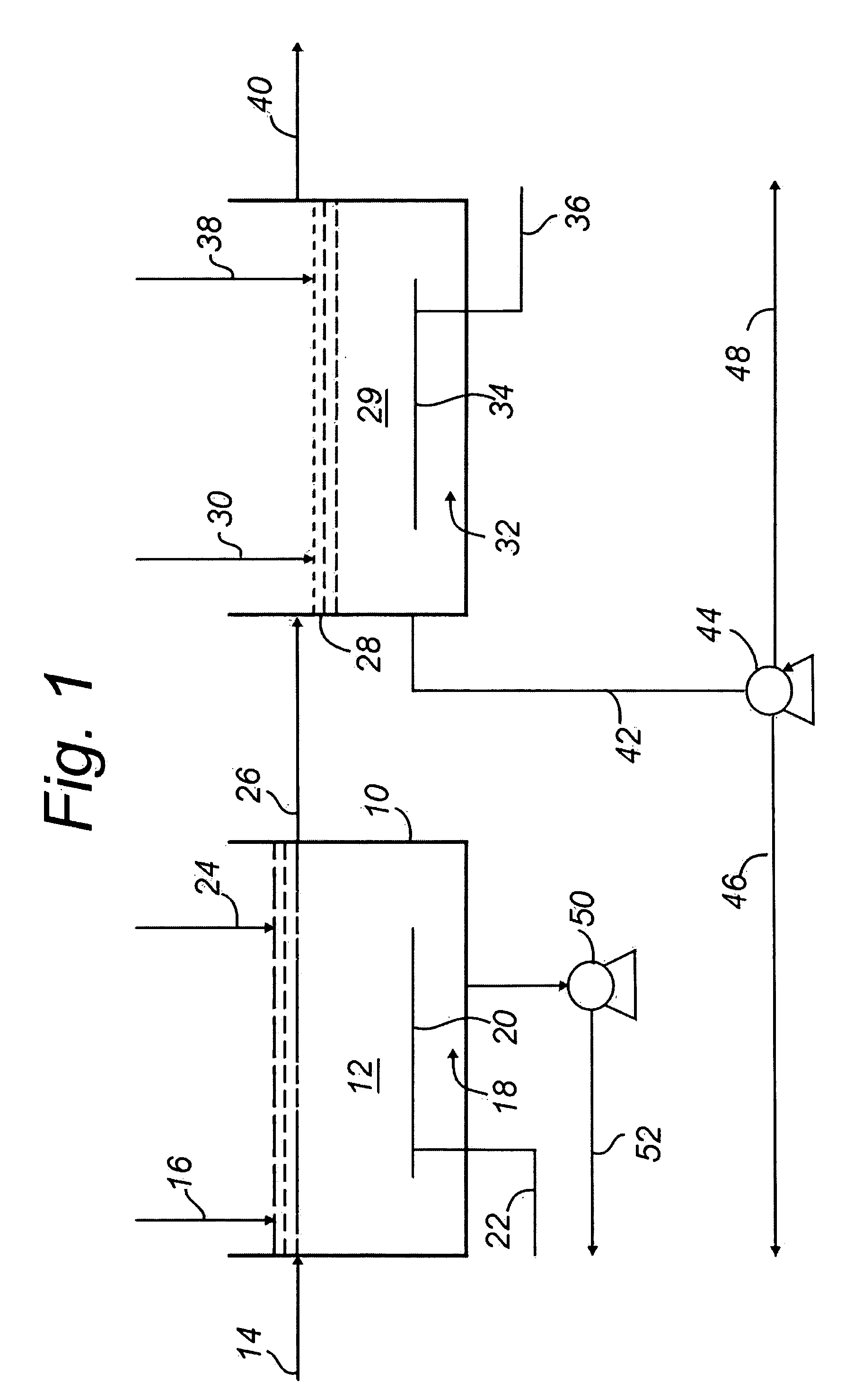
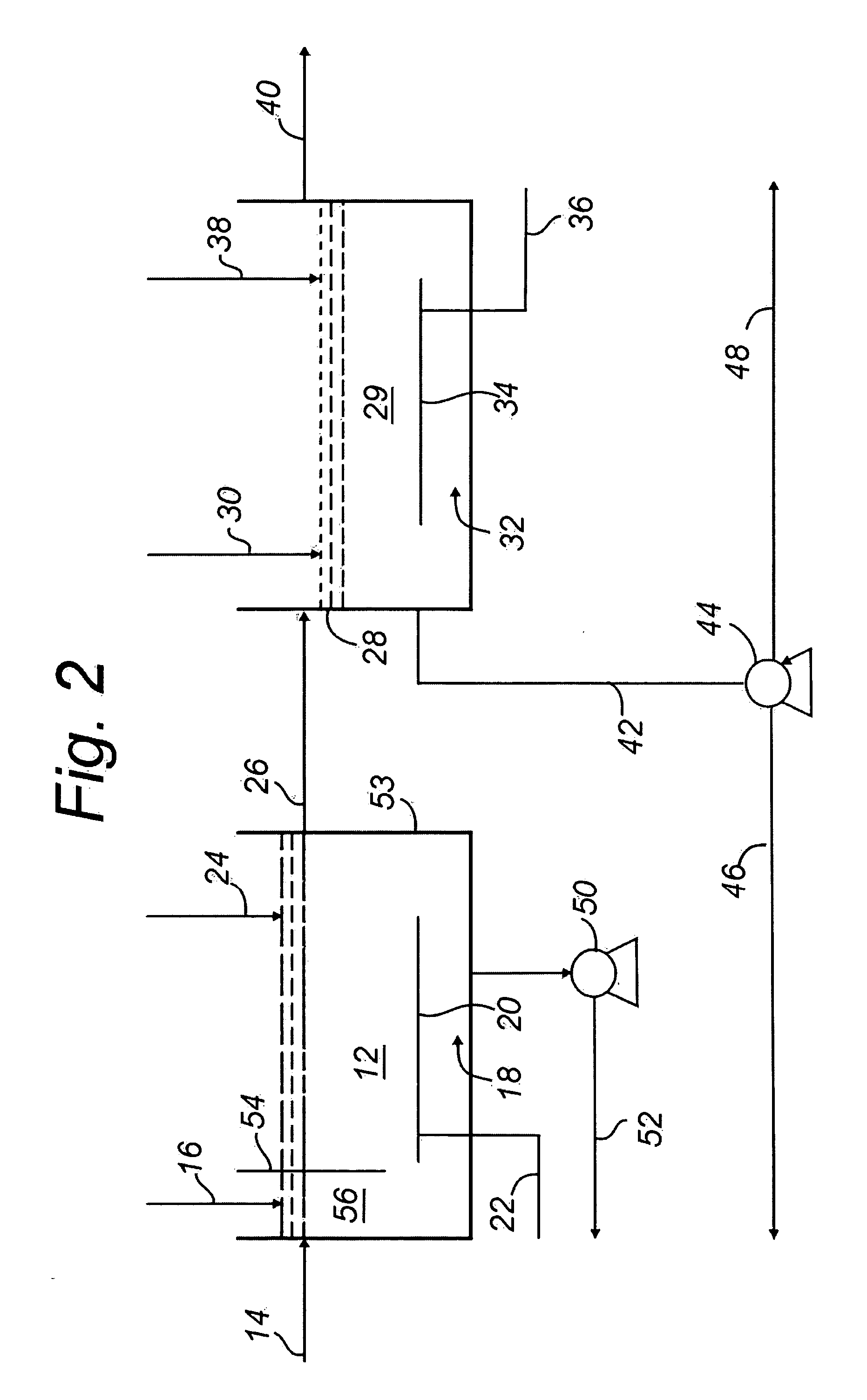
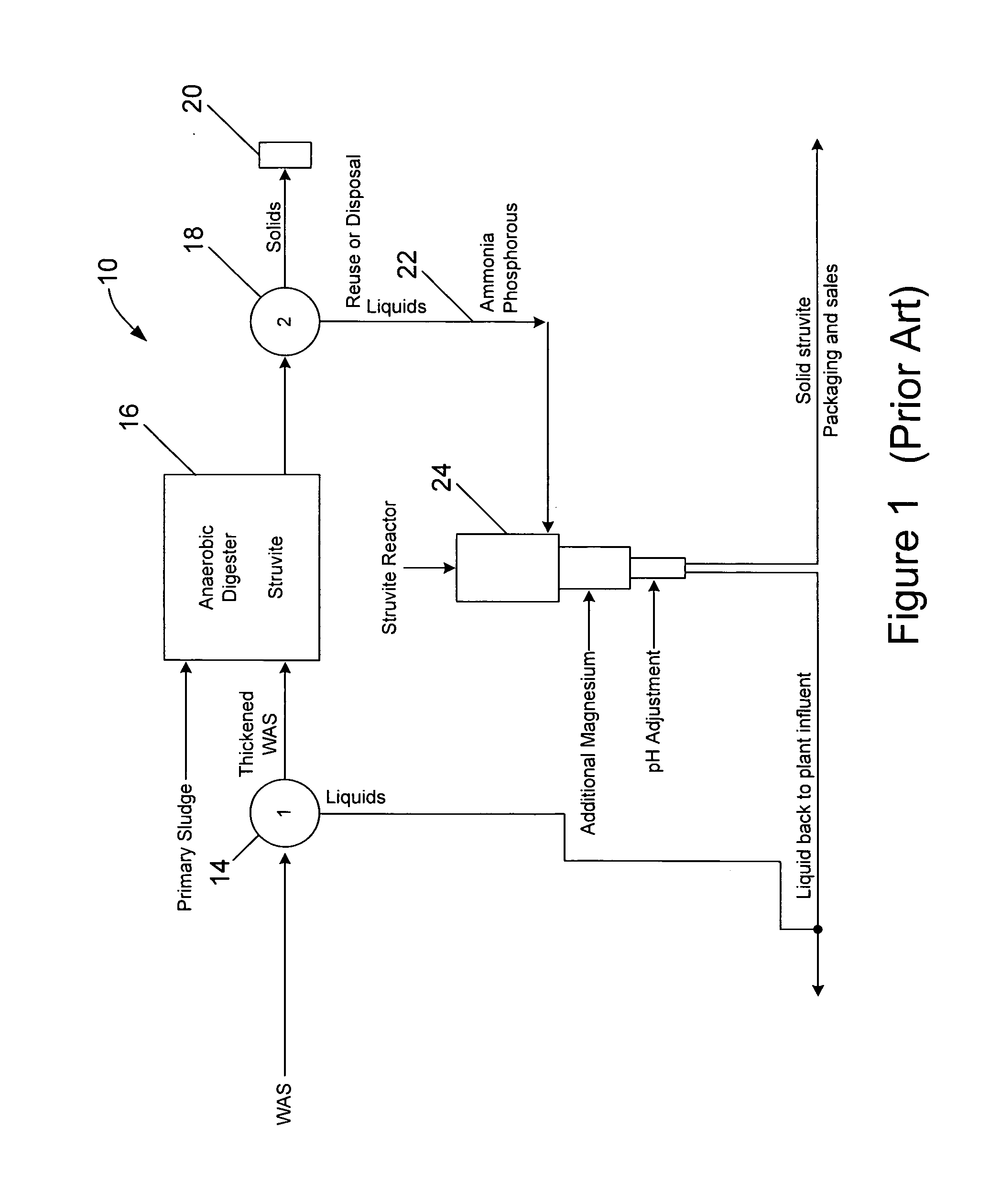
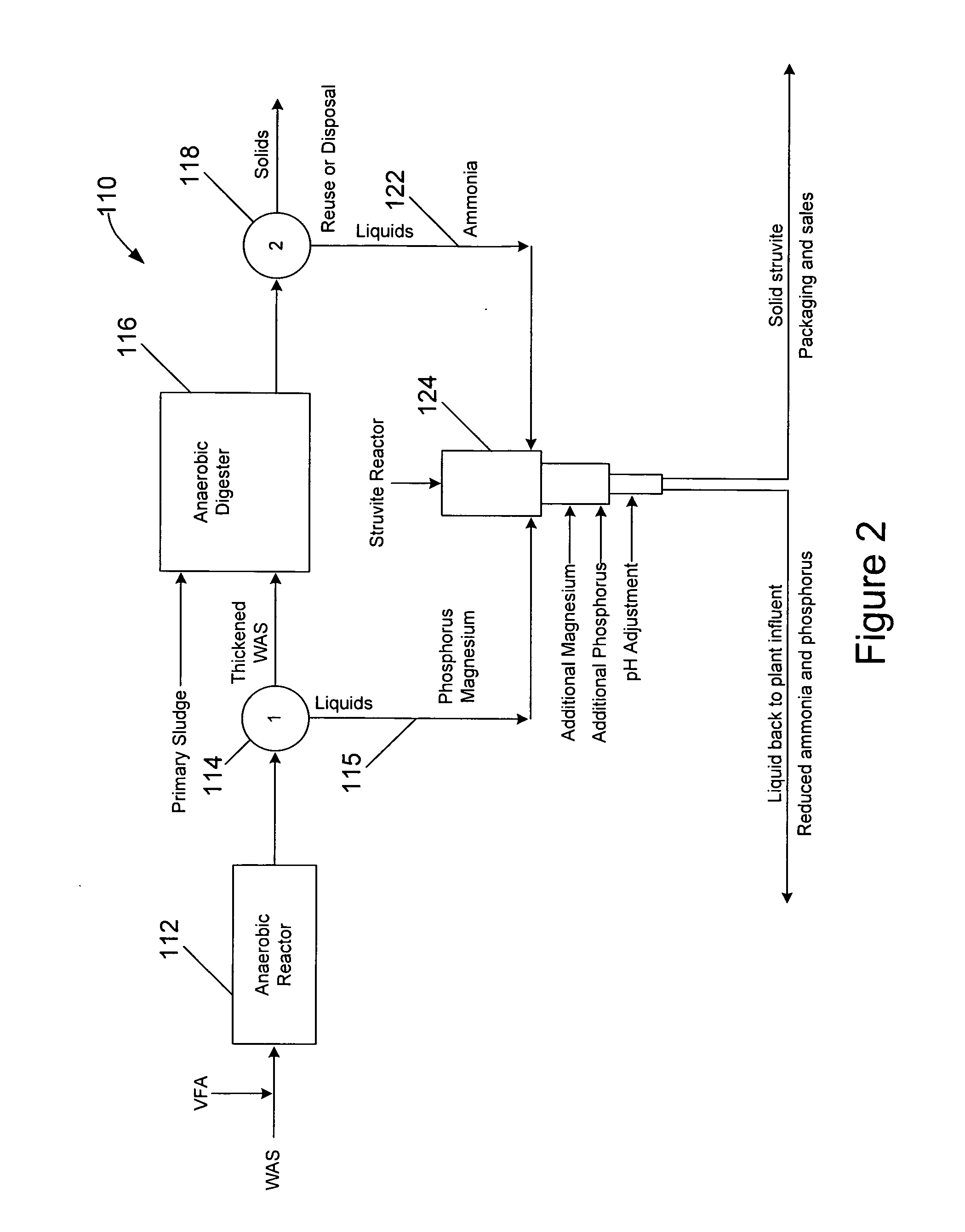
Waste activated sludge phosphorus and magnesium stripping process and struvite production system
ActiveUS20100170845A1Reduce productionBio-organic fraction processingTreatment using aerobic processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
A method of treating a mixture of microorganisms with readily biodegradable carbon compounds (RBCs) in the form of one or more volatile fatty acids (VFAs), by first inducing the mixture microorganisms to release phosphorus and magnesium which is then tapped o as the mixture is thickened, to produce a phosphorus / magnesium-nch liquid and a phosphorus / magnesium-reduced treated mixture This treated mixture is placed in an anaerobic digester where ammonia is formed, but combines very little with phosphorus or magnesium Next the high-ammonia mixture is dewatered to produce an ammonia-rich liquid, which is combined with the phosphorus and magnesium-rich liquid and reacted to form struvite In one preferred embodiment, VFAs are formed in situ via an upstream unified fermentation and thickening (UFAT) process and added to the waste sidestream to strip phosphorus and magnesium found therein In another preferred embodiment a usable struvite product is harvested.
Owner:CLEAN WATER SERVICES
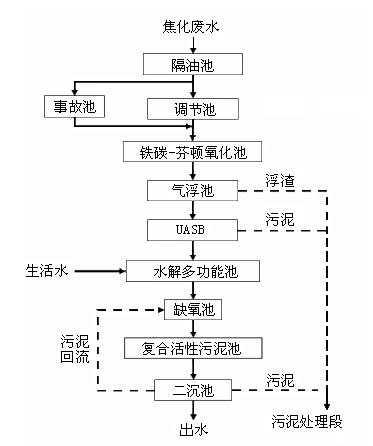
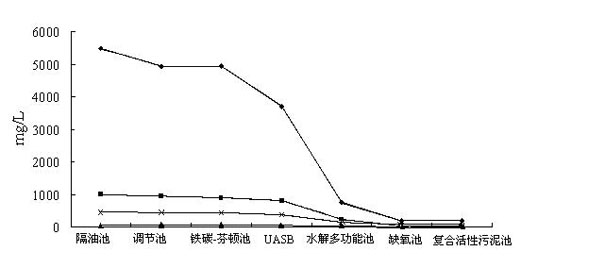
Method for treating coking wastewater
InactiveCN101781067AReduce CODPromotes electrochemical corrosionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeCyanide compound
The invention discloses a method for treating coking wastewater, which relates to the method for treating wastewater and aims to solve the problems that an activated sludge method for treating the coking wastewater has the disadvantage of relatively poorer effect on the removal of organic substances and the treated water is difficult to reach the secondary discharge standard of the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB8978-96). The method comprises that: the coking wastewater is discharged after passing through an oil separation tank, an adjusting tank, an iron carbon-Fenton oxidation pond, an up-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor, a multifunctional hydrolyzing pond, an anaerobic tank, a composite active sludge tank and a secondary sedimentation tank, wherein the coking wastewater can also pass through a floatation tank. The coking wastewater treated by the method of the invention has a pH value of 5 to 8 and the rate of removal of Cu2+ from the coking wastewater of 69 to 85 percent, contains 300 to 450mg / L phenol and less than 15mg / L cyanide and therefore reaches the secondary discharge standard of the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB8978-96).
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Methods for treatment of wastewater with powdered natural lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS7481934B2Efficiently economically decontaminateSpeed up the processTreatment using aerobic processesWaste water treatment from animal husbandryActivated sludgeBiological body
A process for treating wastewater through the use of powdered natural ligno-cellulosic materials (PNLM) for (a) physically removing colloidal and suspended volatile solids through adsorption and enhanced floc-formation and settling during pretreatment; (b) adsorbing toxic substances and elements that interfere with biological processes, thus serving to reduce their contact with and exposure to activated sludge organisms effecting wastewater treatment functions; (c) providing fixed surfaces in activated sludge wastewater treatment bioreactors for bacteria and other organisms favoring attached growth in circumstances devoid of such surfaces; (d) reducing production of biological sludge, while also helping to maintain high treatment efficiencies; and (e) following aeration, enhancing the settling characteristics of sludge with respect both to speed of settling and the vertical profile of the settled sludge.
Owner:NUVODA LLC
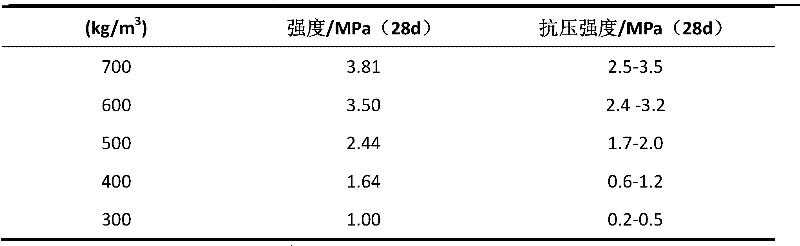
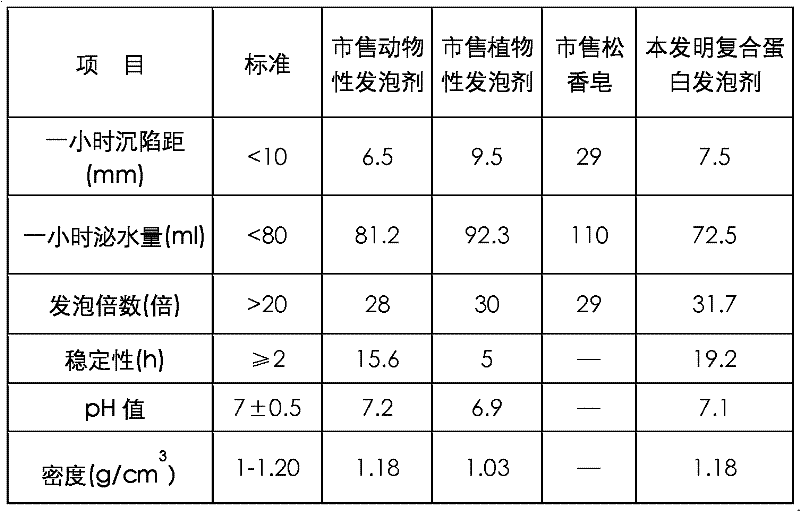
Method for preparing light foam concrete by using compound protein foaming agent
ActiveCN102515827AImprove foam stabilityNo autoclaving requiredCeramicwareFoam concreteActivated sludge
The invention relates to a method for preparing light foam concrete by using a compound protein foaming agent. The light foam concrete comprises 1-10 weight parts of foaming agent, 20-50 weight parts of concrete, 25-60 weight parts of fly ash, 1-10 weight parts of lime, 1-5 weight parts of gypsum, 0.5-2 weight parts of additive, and 27-40 weight parts of water, wherein the foaming agent comprises2.5-25 weight parts of activated sludge protein with a mass concentration 15-25 %, 0.1-1 weight parts of vegetable protein with a mass concentration of 20-40 %, 0.1-0.5 weight parts of stabilizing agent, and 73.5-97.3 weight parts of water. According to the invention, the compound protein foaming agent uses activated sludge protein and vegetable protein as the main components, and the stabilizingagent is used for modification, thus the foam stability of the protein foaming agent is raised. The preparation method has no need of steam pressure curing.
Owner:天津市裕川环境科技有限公司
Flower nutrient soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103553767AImprove the cultivation effectRich in nutrientsFertilizer mixturesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil, and specifically relates to flower nutrient soil and a preparation method thereof. The flower nutrient soil comprises the following components in parts by mass: 30-35 parts of leaf mold, 25-30 parts of garden soil, 25-30 parts of river sand, 10-15 parts of activated sludge, 5-10 parts of bone meal, 10-15 parts of decayed farmyard manure, 10-15 parts of sawdust and 2-5 parts of active microorganisms. By using the technical scheme, the flower nutrient soil disclosed by the invention is rich in nutrient substances and short in fermentation time; leaf mold, garden soil, river sand and activated sludge are mixed, so that the flower nutrient soil is good in water retention and nutrient preserving capability, good in soil permeability, and low in cost; and by using the flower nutrient soil, flowers are robust and good cultivation effect is achieved.
Owner:DANYANG RUIQING GARDEN ENG
Method for treating high-salinity high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater
InactiveCN102849857AOvercoming processingOvercome the shortcomings of wastewater resistant to high ammonia nitrogenBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationActivated sludge
The invention discloses a method for treating high-salinity high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, characterized by: adopting sequencing batch reactor, accumulating nitrification sludge by alternately increasing the concentration of a nutrient solution or ammonia-nitrogen concentration, and domesticating to obtain high salinity-resisting high ammonia nitrogen-resisting nitrobacteria. According to the invention, the nitrobacteria can treat high-salinity wastewater having ammonia-nitrogen concentration of 500mg / L and having the salt content of no larger than 35g / L to make the effluent have the ammonia-nitrogen concentration of no larger than 10mg / L, thus the effluent achieve national level of discharging standard; the method has good effect on treating high-salinity high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater in chemical plant, leather factory, oil refinery and the like, can overcome the shortage that the nitrobacteria cannot simultaneously treat high-salinity and high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater existing in the prior art, and has important economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Immobilized-cultivation method for aerobic granular sludge
ActiveCN102583722AAccelerated settlementSmall footprintSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeSewage
The invention relates to a rapid cultivation method for aerobic granular sludge in waste water with higher organic load fluctuation. In the method, through a special cultivation technology that at first, the immobilized-cultivation is conducted on multiple microbes in activated sludge so as to obtain early-stage seed grains of sludge, and then the grains are promoted to further grow rapidly with the addition of an agglomerator and / or a dominant consortium, the aerobic granular sludge with high activity and strong load fluctuation tolerance is obtained successfully in objective waste water. The aerobic granular sludge is suitable for various kinds of organic sewage with higher organic load fluctuation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Novel process for treating coking waste water by charging activated sludge process
InactiveCN101417850AQuality improvementBulk volumeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeNitration
The utility model discloses a technology for treating coking wastewater by using a novel feeding activated sludge method, which comprises the following steps: biochemical treatment process is carried out on the pretreated wastewater, the coking wastewater first enters an A-grade biochemical pond to provide carbon sources for denitrification, and then the coking wastewater enters a 0-grade biochemical pond for carrying out oxidation and nitration under aerobic environment, the effluent water of the 0-grade biochemical pond enters a secondary sedimentation tank; the supernatant from the secondary sedimentation tank enters a subsequent-stage treatment system and one part of settling sludge refluxes and enters the A-grade biochemical pond and 0-grade biochemical pond; the other part of the settling sludge enters a sludge thickener. As flocculants are added into the biochemical pond, the ability of tolerating loads is greatly improved, and shock resistance is also greatly enhanced; the area of the biochemical reaction pond is reduced to 70 percent of the area of the reaction pond of traditional feeding activated sludge method, so investment costs are saved and operation costs are decreased; while the decolorizing ratio of the technology to coking wastewater, black liquor and chloromycetin wastewater can reach to more than 80 percent.
Owner:江苏百纳环境工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com