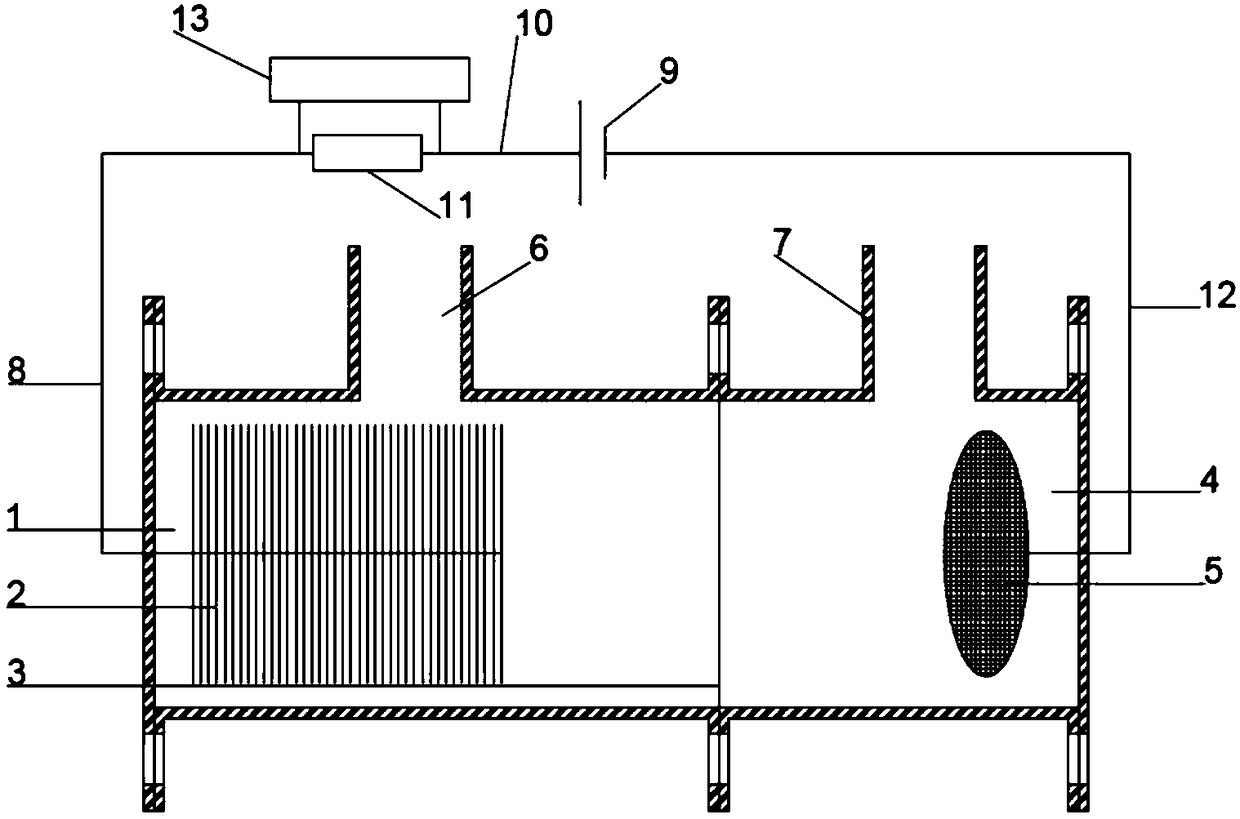
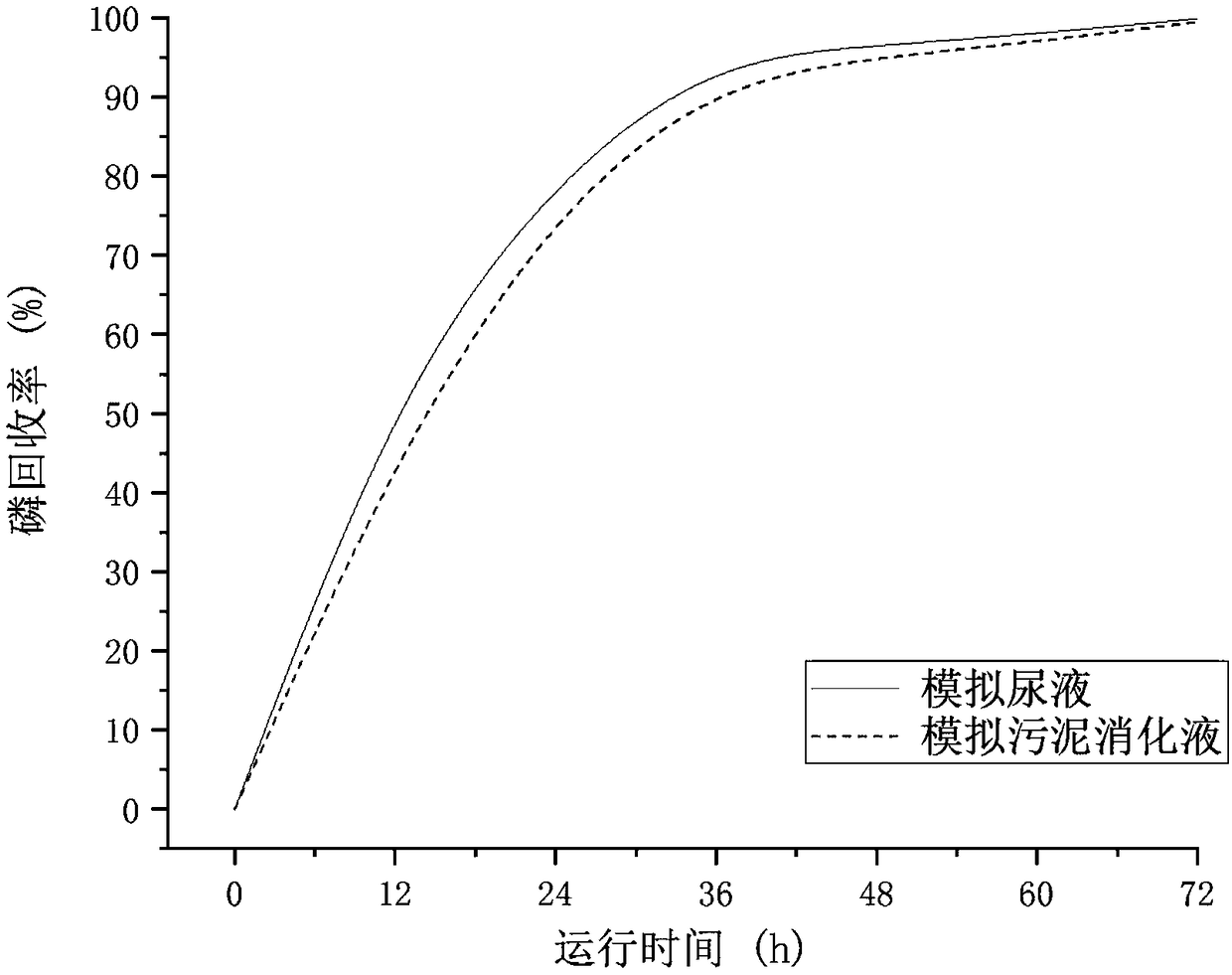
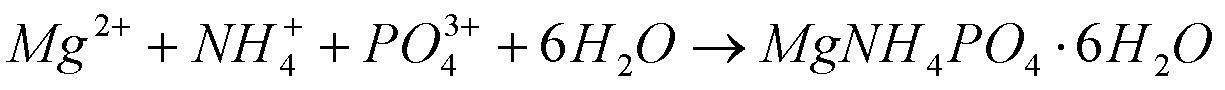Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
314 results about "Struvite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) is a phosphate mineral with formula: NH₄MgPO₄·6H₂O. Struvite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as white to yellowish or brownish-white pyramidal crystals or in platey mica-like forms. It is a soft mineral with Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2 and has a low specific gravity of 1.7. It is sparingly soluble in neutral and alkaline conditions, but readily soluble in acid.
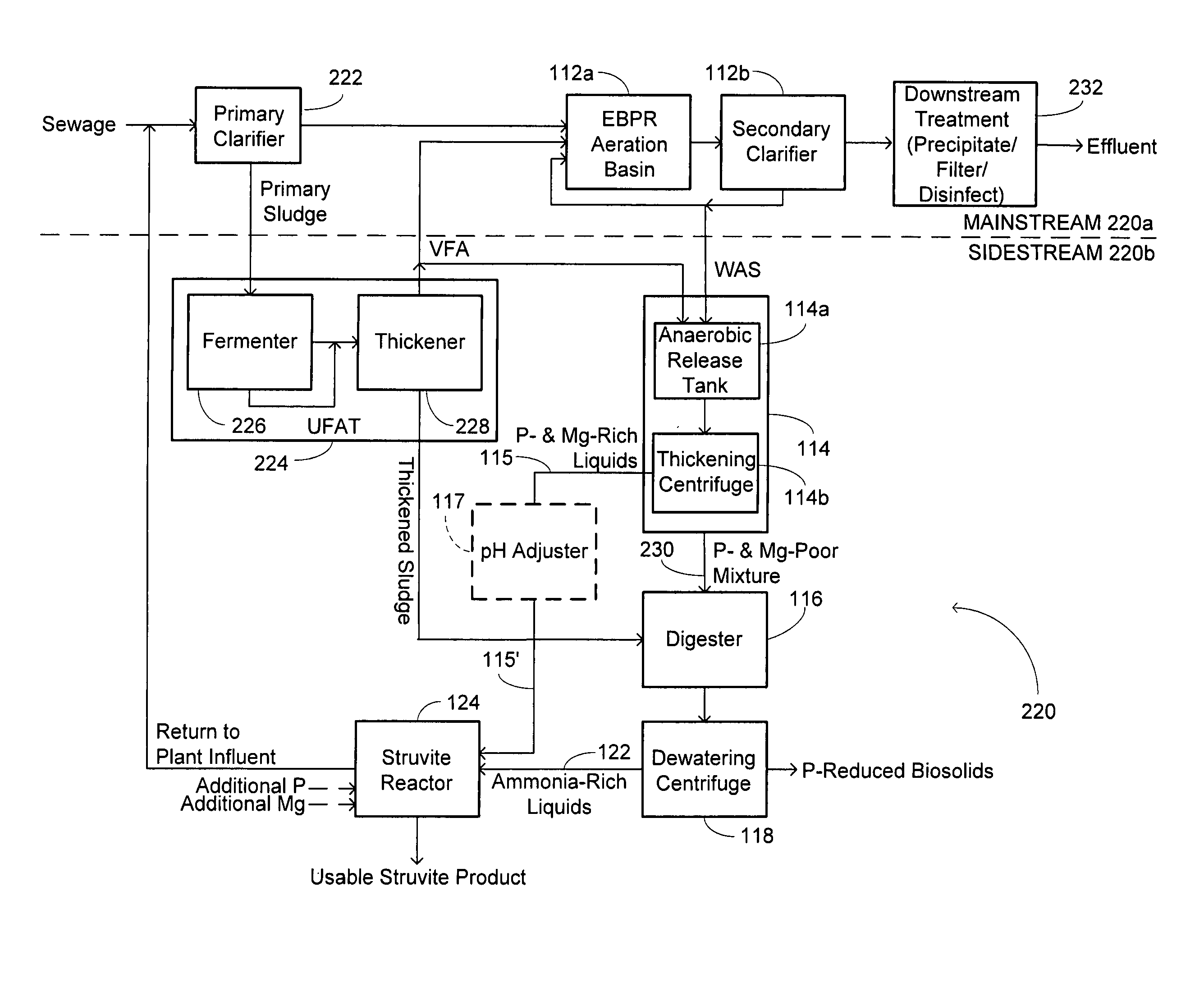
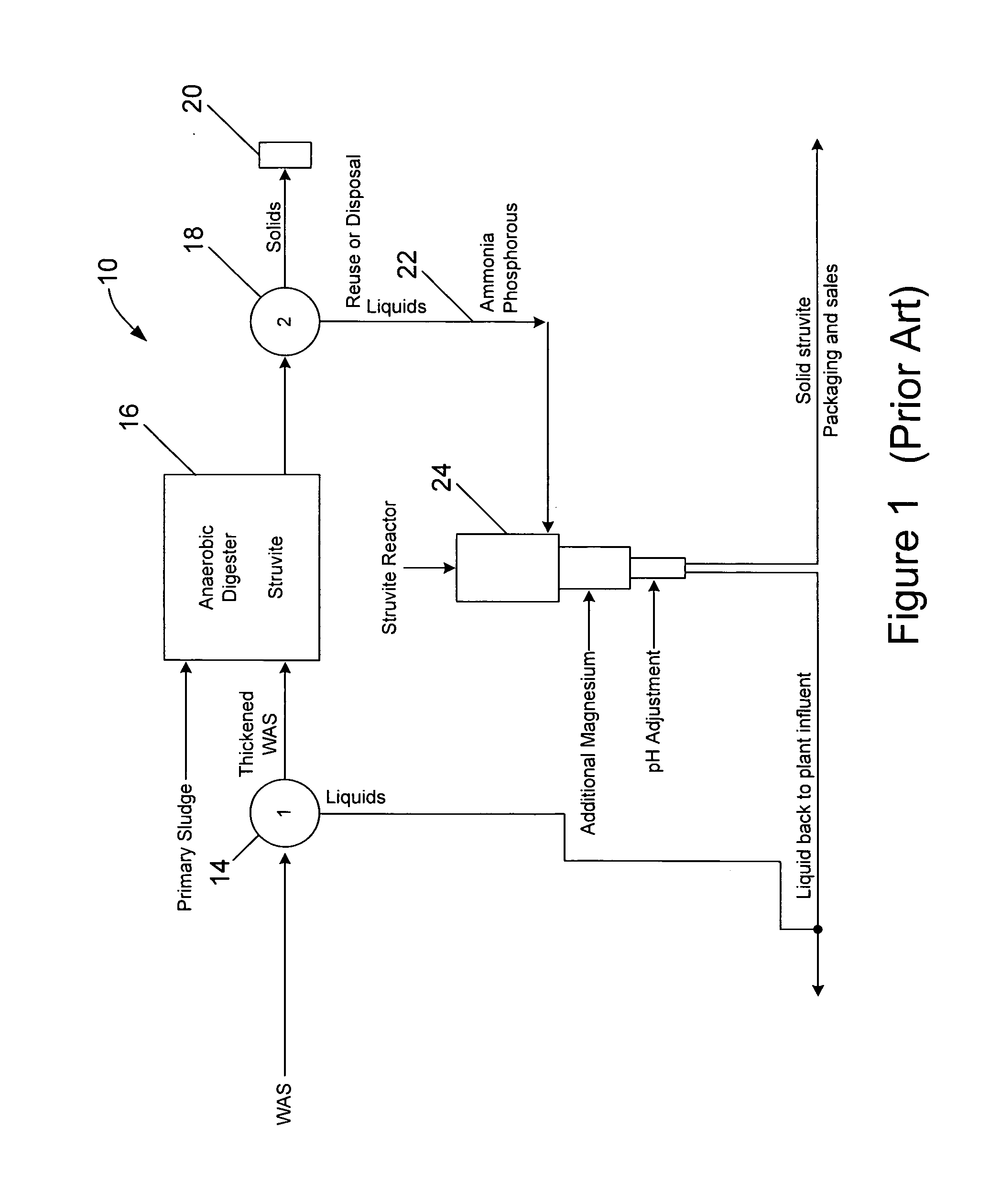
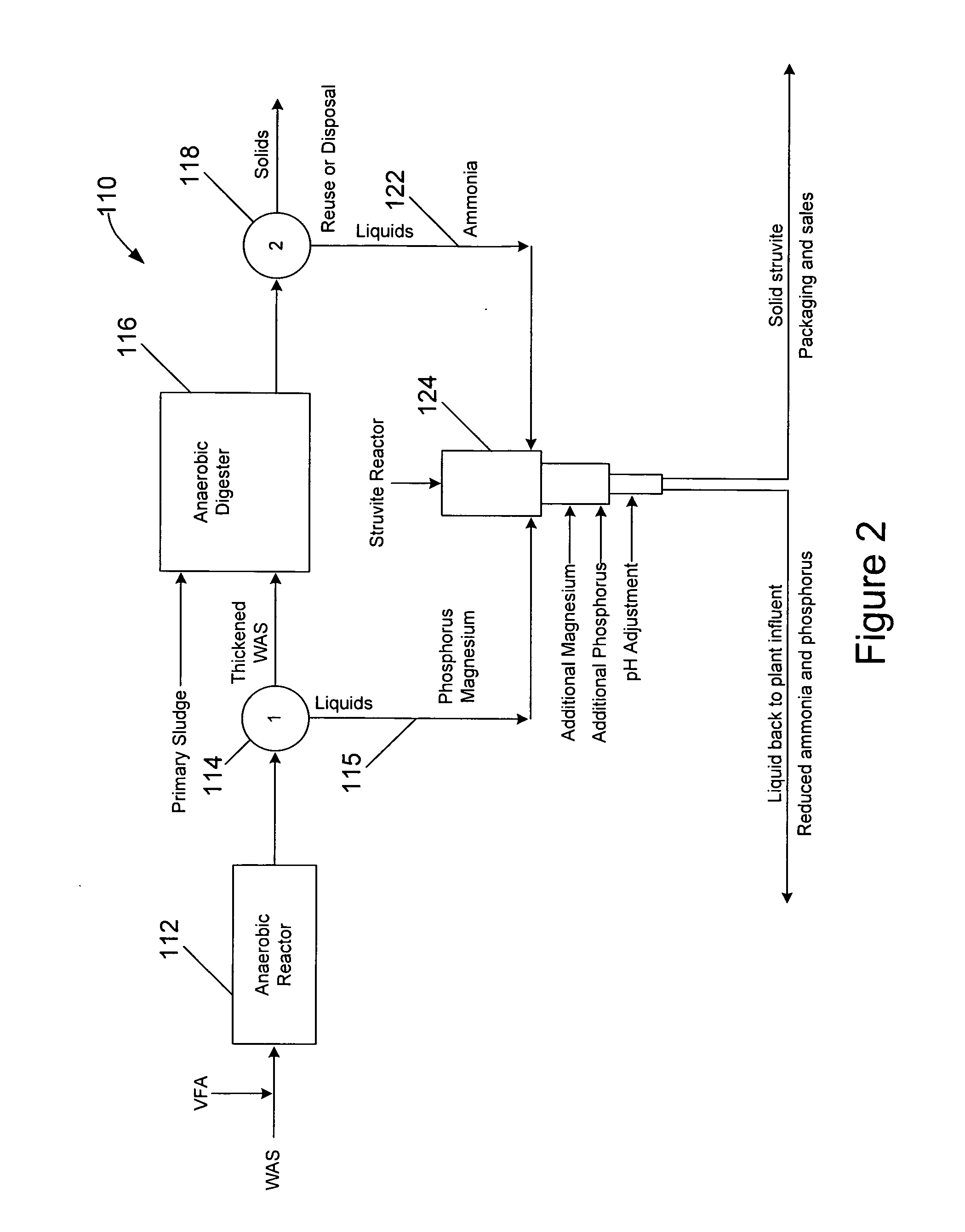
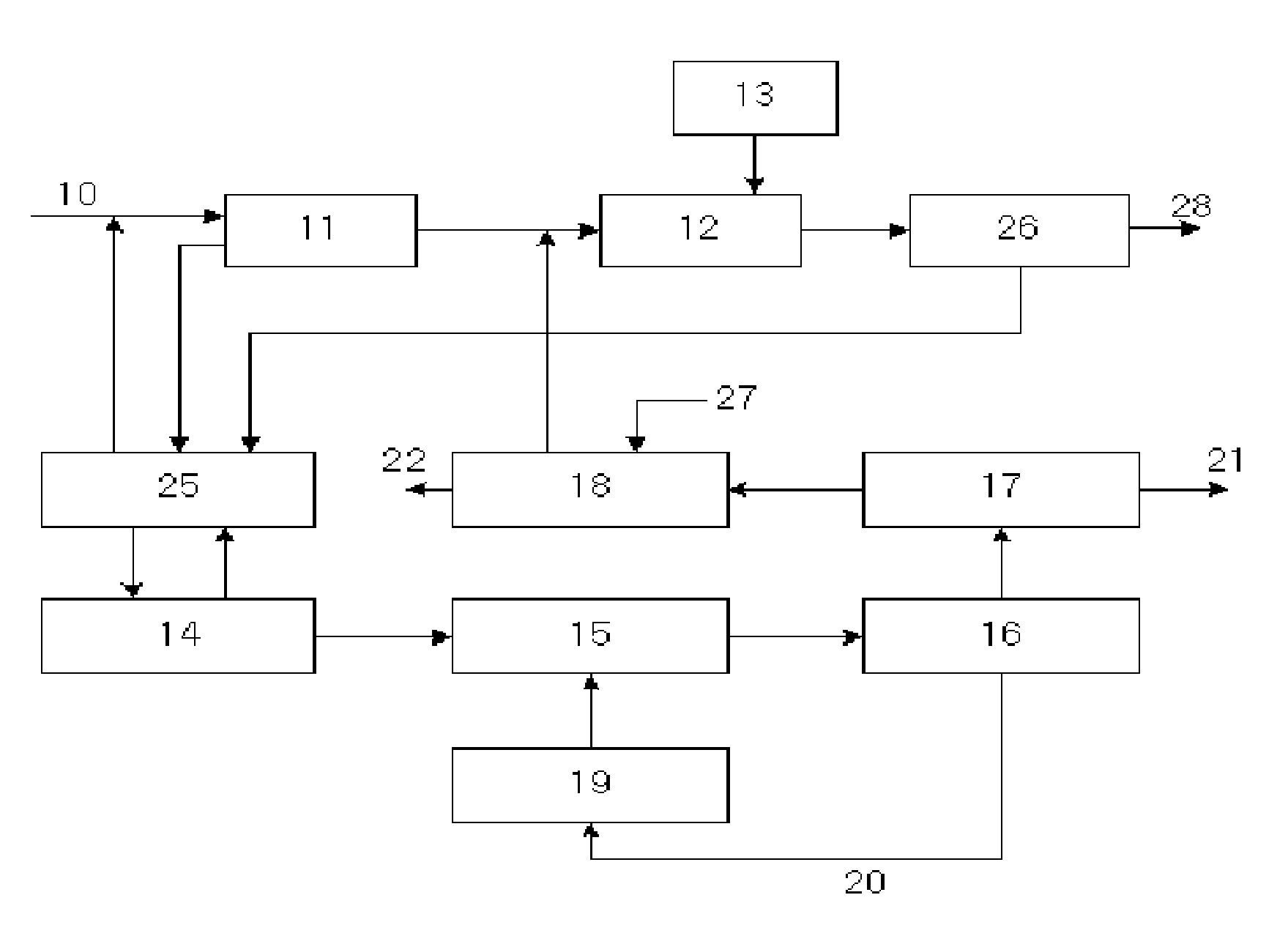
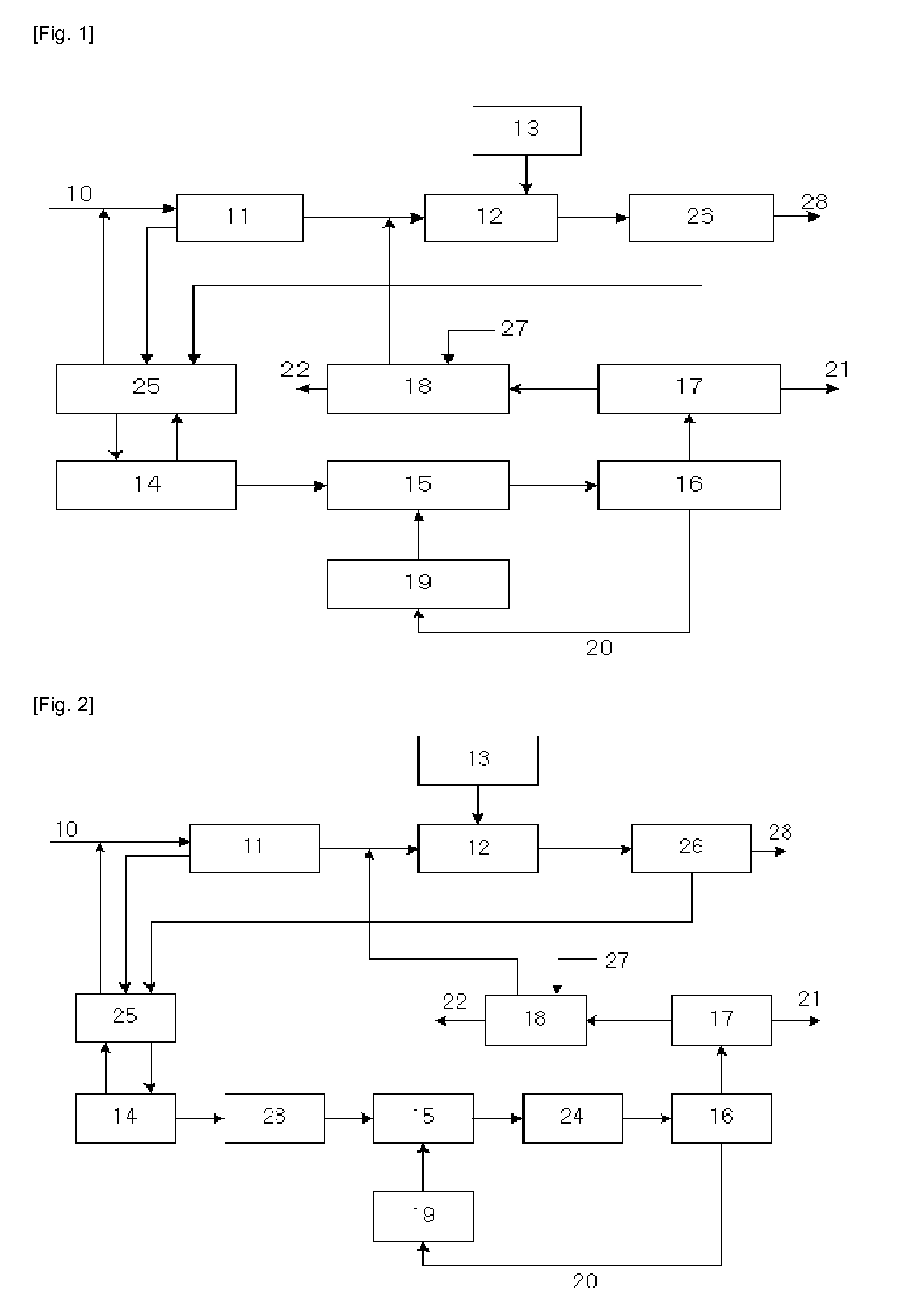
Waste activated sludge phosphorus and magnesium stripping process and struvite production system
ActiveUS20100170845A1Reduce productionBio-organic fraction processingTreatment using aerobic processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
A method of treating a mixture of microorganisms with readily biodegradable carbon compounds (RBCs) in the form of one or more volatile fatty acids (VFAs), by first inducing the mixture microorganisms to release phosphorus and magnesium which is then tapped o as the mixture is thickened, to produce a phosphorus / magnesium-nch liquid and a phosphorus / magnesium-reduced treated mixture This treated mixture is placed in an anaerobic digester where ammonia is formed, but combines very little with phosphorus or magnesium Next the high-ammonia mixture is dewatered to produce an ammonia-rich liquid, which is combined with the phosphorus and magnesium-rich liquid and reacted to form struvite In one preferred embodiment, VFAs are formed in situ via an upstream unified fermentation and thickening (UFAT) process and added to the waste sidestream to strip phosphorus and magnesium found therein In another preferred embodiment a usable struvite product is harvested.
Owner:CLEAN WATER SERVICES
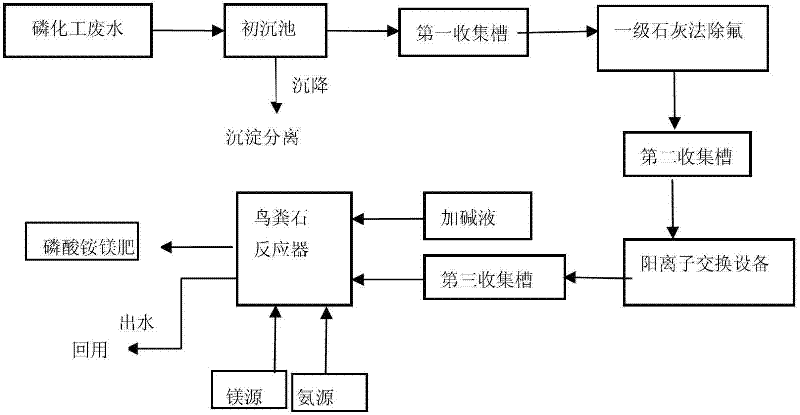
Method for recovering phosphorus in phosphorus chemical wastewater by using struvite production technology
InactiveCN102690000ALess sludgeReduce distractionsMultistage water/sewage treatmentIon exchangeMagnesium ammonium phosphate
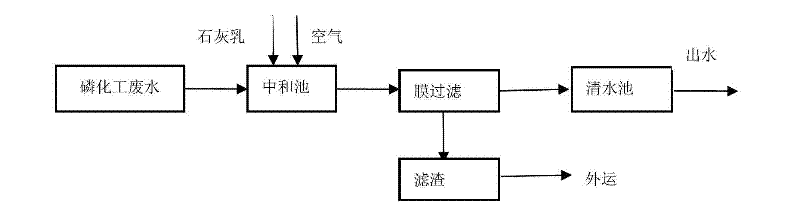
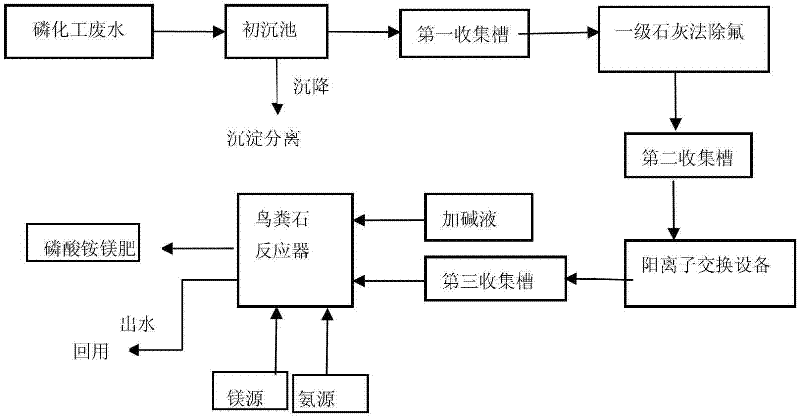
The invention relates to a method for recovering phosphorus in phosphorus chemical wastewater by using a struvite production technology. The method is carried out according to the following steps of: firstly carrying out preliminary sedimentation on the phosphorus chemical wastewater, removing impurity precipitation in the wastewater, and collecting the processed wastewater in a first collecting tank; removing inorganic fluoride ion in wastewater in the first collecting tank by adopting a first-level quick lime method, and collecting the processed wastewater into a second collecting tank; removing inorganic cations in the wastewater in the second collecting tank via a cation exchange device, and collecting the processed ion exchange wastewater into a third collecting tank; finally adjusting pH value of the ion exchange wastewater to 7-9 in a struvite reactor by alkali liquor and adding magnesium source and nitrogen source, wherein the molar ratio of magnesium / phosphorus is 1.0-1.5; and the molar ratio of nitrogen / phosphorus is 1.0-1.5; and generating a magnesium ammonium phosphate granulated fertilizer in a crystalline state in the reactor. The water from the struvite reactor achieves the secondary standard of the national wastewater discharge standard and can be directly reused in a phosphorus chemical production system or discharged up to the standard.
Owner:HUBEI FORBON TECH
Method for biologically purifying municipal sewage and recovering resources
ActiveCN101891343AAchieve disposalWaste based fuelMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeMagnesium salt
The invention discloses a method for biologically purifying municipal sewage and recovering useful resources. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) discharging excess sludge into a sludge activation tank to perform aerobic aeration; 2) discharging the activated sludge and the raw sewage into a sludge adsorption tank to perform aerobic aeration; 3) precipitating sludge-water mixed solution in a precipitation tank, putting supernatant into a sewage treatment system, purifying the supernatant, then discharging the sewage, and purifying the excess sludge circularly; 4) mixing the sludge at the bottom of the precipitation tank with the sludge in an anaerobic digestion tank to perform anaerobic fermentation; 5) converting an organic substance after the anaerobic fermentation into methane gas and recovering the methane gas; 6) discharging the supernatant into a crystallizing pond, adding a magnesium salt into the crystallizing pond, adjusting the pH value to ensure that the mixture is turned into guanite deposit, and recovering the guanite deposit; 7) putting the supernatant in the crystallizing pond into the sewage treatment system; and 8) discharging the excess sludge after the anaerobic fermentation. By using the excess sludge to treat the municipal sewage, the method not only solves the problems in sewage purification, makes use of pollutants in the sewage, but also realizes sludge disposal and extracts effective resources in the sewage.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for whole-process recycling of multiple biogas slurry components
InactiveCN102795725ASolving Biotoxicity IssuesIncrease nitrogen and phosphorus contentUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationUltrafiltrationSlurry
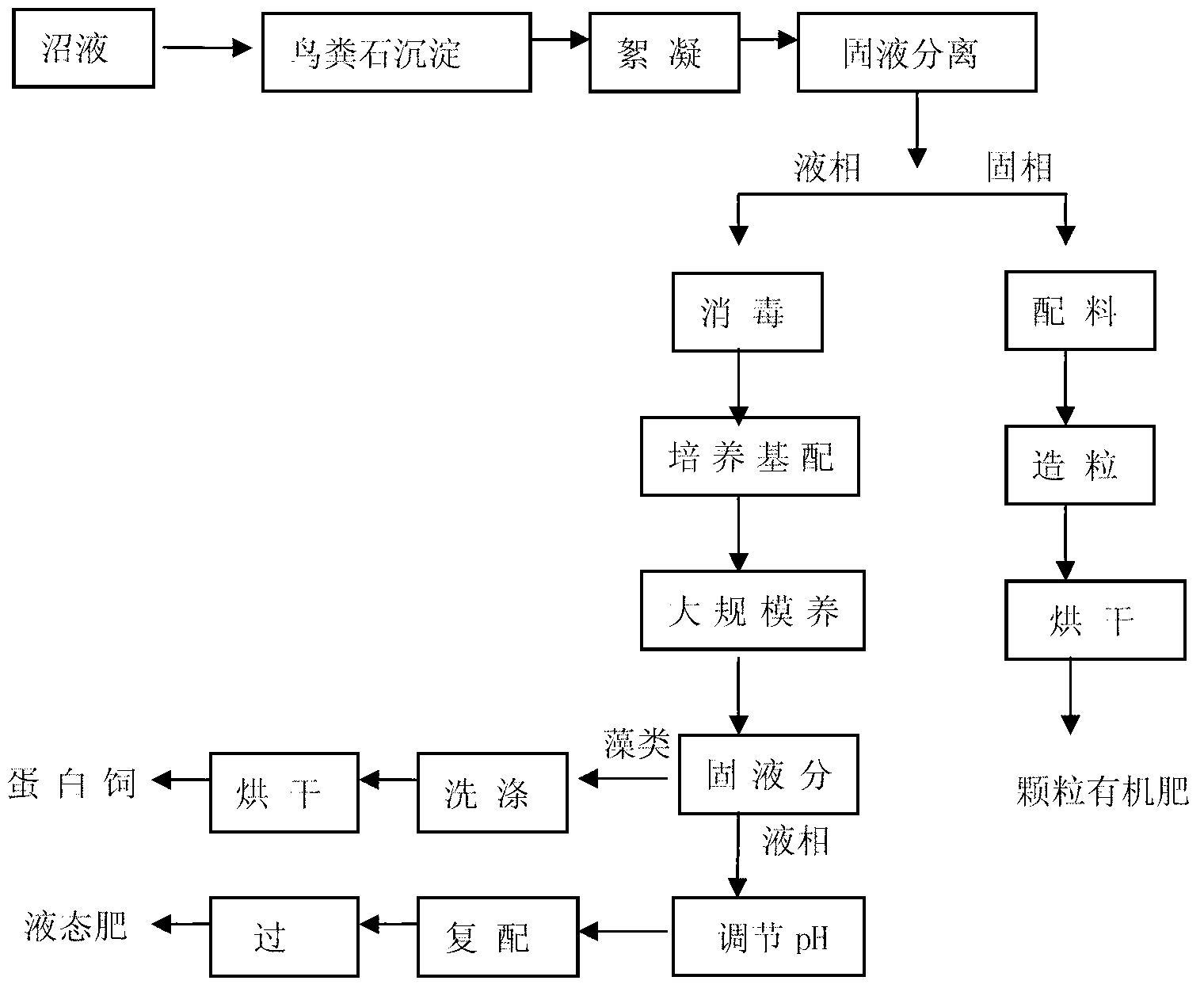
The invention discloses a method for whole-process recycling of multiple biogas slurry components and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. The method comprises the following steps of pre-treating biogas slurry by struvite precipitation and flocculation, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain biogas residues, carrying out blending, granulation and drying of the biogas residues to obtain organic fertilizer particles satisfying the NY525-2012 ''organic fertilizer'' standard, disinfecting a clear liquid obtained by solid-liquid separation, adding nutrients into the disinfected clear liquid to obtain an alga medium, separating out cultured algae, carrying out washing, drying and crushing of the cultured algae to obtain protein feed satisfying a feed hygiene standard, adding nutrients into the remaining liquid as a liquid fertilizer production mother liquor obtained by alga separation, adjusting a pH value of the mixed liquid, and carrying out ultrafiltration to obtain a liquid fertilizer product satisfying the GB / T17419-1998 ''foliar microelement fertilizer'' standard. The method provided by the invention realizes comprehensive, efficient and integrated utilization of biogas slurry components. Through marketing or utilization, organic fertilizer particles, foliar fertilizer and protein feed prepared by the method further improve the income and a return rate of biogas engineering.
Owner:中国科学院生态环境研究中心鄂尔多斯固体废弃物资源化工程技术研究所
Struvite circulating crystallization method for treating synthetic ammonia wastewater
InactiveCN102336504AReduce processing costsGuaranteed removal rateBio-organic fraction processingMultistage water/sewage treatmentMagnesium saltRaw material
The invention relates to a struvite circulating crystallization method for treating synthetic ammonia wastewater. The method comprises the following steps of: A, adding soluble phosphate and magnesium salt into the synthetic ammonia wastewater at the ammonium nitrogen concentration of 1,000-2,065mg / L; B, adding alkali into the acquired struvite solid, and performing pyrolysis at the temperature of between 80 and 100DEG C for 1 to 3 hours; C, treating the synthetic ammonia wastewater by using a pyrolysis solid product, and adding a small amount of magnesium salt, wherein ammonia generated in the pyrolysis process is absorbed by a dilute acid solution, and the obtained ammonium salt is used as a raw material for producing a fertilizer; and D, using struvite which cannot be recycled as a sustained-release fertilizer. For the synthetic ammonia wastewater at the ammonium nitrogen concentration of 1,000-2,065mg / L, the struvite can be recycled for 3 to 6 times, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate is higher than 87 percent, the ammonium nitrogen concentration of effluent is lower than 200mg / L, agents are saved through recycle, and nitrogen resources are recycled. The pretreated wastewater meets the requirement of an A / O biochemical treatment process on nitrogen and phosphorus, and can be subjected to biochemical treatment further.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Struvite crystallization
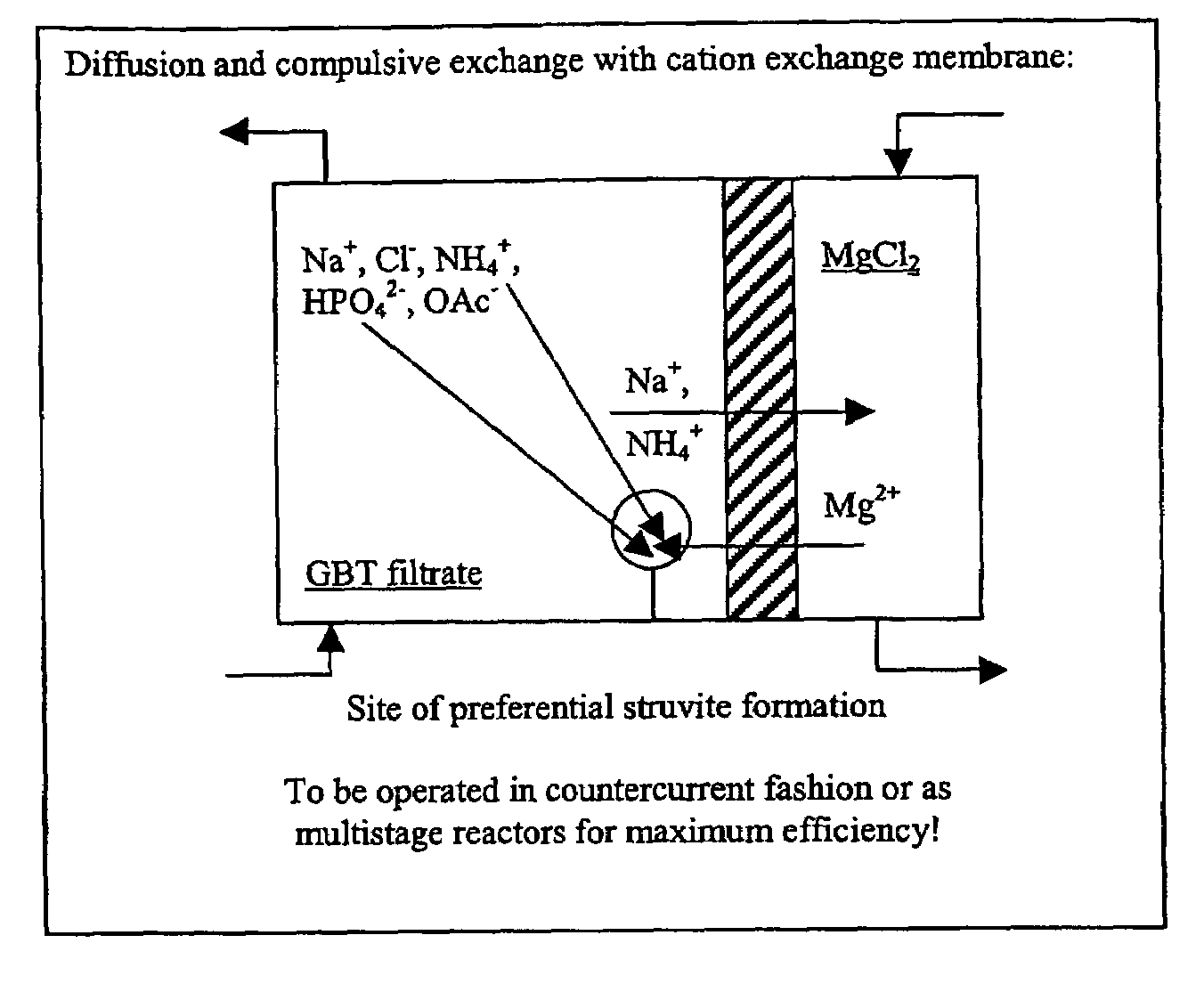
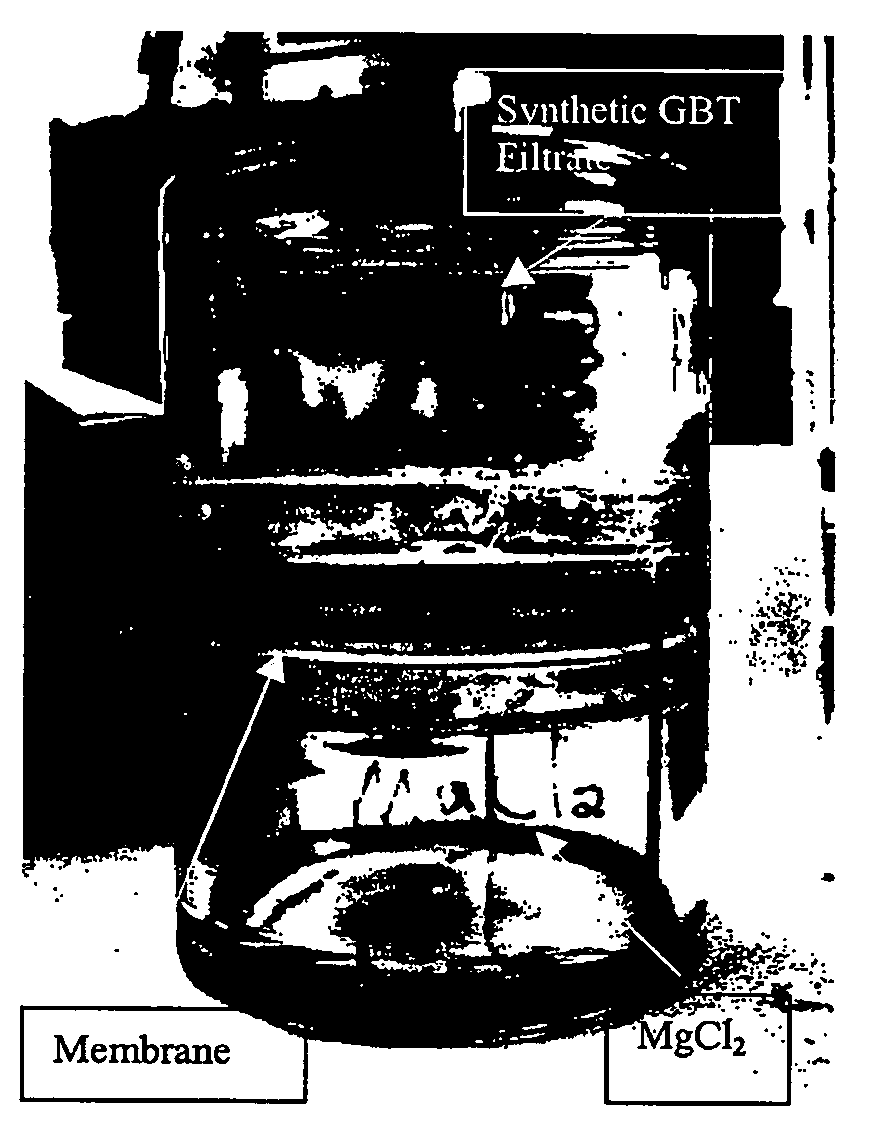
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for removing phosphorus from phosphorus containing waste. In one embodiment, the method is preferably carried out by contacting the phosphorus containing waste with a non-cellular membrane and precipitating phosphorus from the waste as struvite. Another aspect of the invention includes a method of removing phosphorus from phosphorus containing sewage comprising filtrates and biosolids. The removal of phosphorus as struvite occurs in two stages as primary and secondary removal. In the primary removal process, the sewage from a dewatering unit is contacted with a first polymeric membrane reactor and the phosphorus is removed as primary struvite. Subsequently Mg is added so as promote struvite formation and the secondary removal process of struvite. In the secondary removal process, the sewage from GBT Filtrate well or Centrifuge Liquor well is contacted with a second monomolecular membrane and the phosphorus is removed as secondary struvite.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for reclaiming nitrogen and phosphorus in nitrogen and phosphorus-containing wastewater by using bittern as magnesium source
InactiveCN102092871AHigh recovery purityMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationResource recoveryNitrogen
The invention discloses a method for reclaiming nitrogen and phosphorus in nitrogen and phosphorus-containing wastewater by using bittern as a magnesium source, and belongs to the technical field of environmental engineering water treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: regulating the initial pH value of the nitrogen and phosphorus-containing wastewater, fully stirring the wastewater, adding a certain amount of bittern, controlling the reaction time and the reaction pH value, then standing, performing solid-liquid separation, and reclaiming struvite sediment. Compared with the prior art, the waste can be treated by using the other waste, the wastewater treatment cost is saved, the struvite serving as a reaction product can be used as a fertilizer, and the method lays a foundation for practical application and can fulfill the purpose of recycling the resources.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispersible struvite particles
A water-dispersible particle is provided that includes struvite in an amount ranging from 5% to 99.9% by weight of the total dry weight of the particle. A binder component is present in an amount from 1% to 95% by weight. The struvite and the binder component on that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. A process for making a water-dispersible particle includes mechanical aggregation of a struvite into a pellet. A binder component is present in the particle in an amount ranging from 1% to 95% by weight. The struvite and the binder component are present in a form such that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. The particle is then dried and ready to be applied.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Struvite crystallization
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for removing phosphorus from phosphorus containing waste. In one embodiment, the method is preferably carried out by contacting the phosphorus containing waste with a non-cellular membrane and precipitating phosphorus from the waste as struvite. Another aspect of the invention includes a method of removing phosphorus from phosphorus containing sewage comprising filtrates and biosolids. The removal of phosphorus as struvite occurs in two stages as primary and secondary removal. In the primary removal process, the sewage from a dewatering unit is contacted with a first polymeric membrane reactor and the phosphorus is removed as primary struvite. Subsequently Mg is added so as promote struvite formation and the secondary removal process of struvite. In the secondary removal process, the sewage from GBT Filtrate well or Centrifuge Liquor well is contacted with a second monomolecular membrane and the phosphorus is removed as secondary struvite.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for reclaiming phosphorous compound
ActiveCN101927992AHigh agricultural use valueSludge treatmentPhosphorus compoundsLivestock manureMunicipal sewage
The invention discloses a method for reclaiming a phosphorous compound, which comprises the following steps of: analyzing a phosphorous-containing sample, adding a magnesium source and a nitrogen source into the phosphorous-rich extraction solution, and meanwhile controlling the pH value of the solution so that the phosphorous compound in the extraction solution is reclaimed for utilization in a form of struvite precipitation. The method for reclaiming the phosphorous compound has the advantages of simple, convenient and quick operation, reliable experiment result and the like; the reclaimed phosphorous product has extremely high agricultural utilization value; and the method can be used for extracting and reclaiming phosphorous in sludge ash of a municipal sewage plant, phosphorous-rich sewage and livestock manure, and has strong universality.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Process for recovery of nutrients from wastewater
InactiveUS7135116B2Less producedNew technologyExcrement fertilisersSedimentation separationGaseous ammoniaNutrient
The present invention relates to a process for treating a wastewater comprising an ammonium ion species and a phosphorus ion species. The process comprises the steps of: (i) treating the effluent in a first stage of the process to convert the phosphorus to a phosphorus-containing salt; (ii) treating the wastewater in a second stage of the process to convert the ammonium ion species to gaseous ammonia; (iii) removing the struvite and / or other phosphorous containing salts from the effluent; and (iv) removing the gaseous ammonia from the wastewater.
Owner:HAGGERTY KENNETH
Industrial high-concentration phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment method
InactiveCN104086019ASimple processGood effectWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationMagnesium phosphate
The invention discloses an industrial high-concentration phosphorus-containing wastewater treatment method. The method comprises the following steps: adding a fluorine removal agent to high-concentration acidic phosphorus-containing wastewater with the P by P2O5 content of 0.15-2.2%, the F content of 0.01-0.35% and the Ca content of 0.1-0.45% to adjust the pH value of the wastewater to 4.5-6.5, allowing obtained wastewater to stand, and discharging formed fluorine-containing sludge; continuously adding a precipitating agent to the obtained upper layer clear liquid to adjust the pH value of the wastewater to 8.0-9.0, converting P to a magnesium phosphate precipitate, flocculating the obtained clear liquid to realize standard reaching emission or factory reuse; and dissolving the magnesium phosphate precipitate in fertilizer-grade phosphoric acid to obtain a P and Mg-containing mixed liquid, and carrying out metric N source addition to make struvite. The fluorine removal agent is magnesium oxide, magnesium carbonate, magnesian marble or dolomite; and the precipitating agent is magnesium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide. The wastewater treatment method has the advantages of simple process flow, good fluorine and calcium effects, and maximal recovery of the P resource on the premise that standard reaching of emitted water is guaranteed.
Owner:HUBEI FORBON TECH
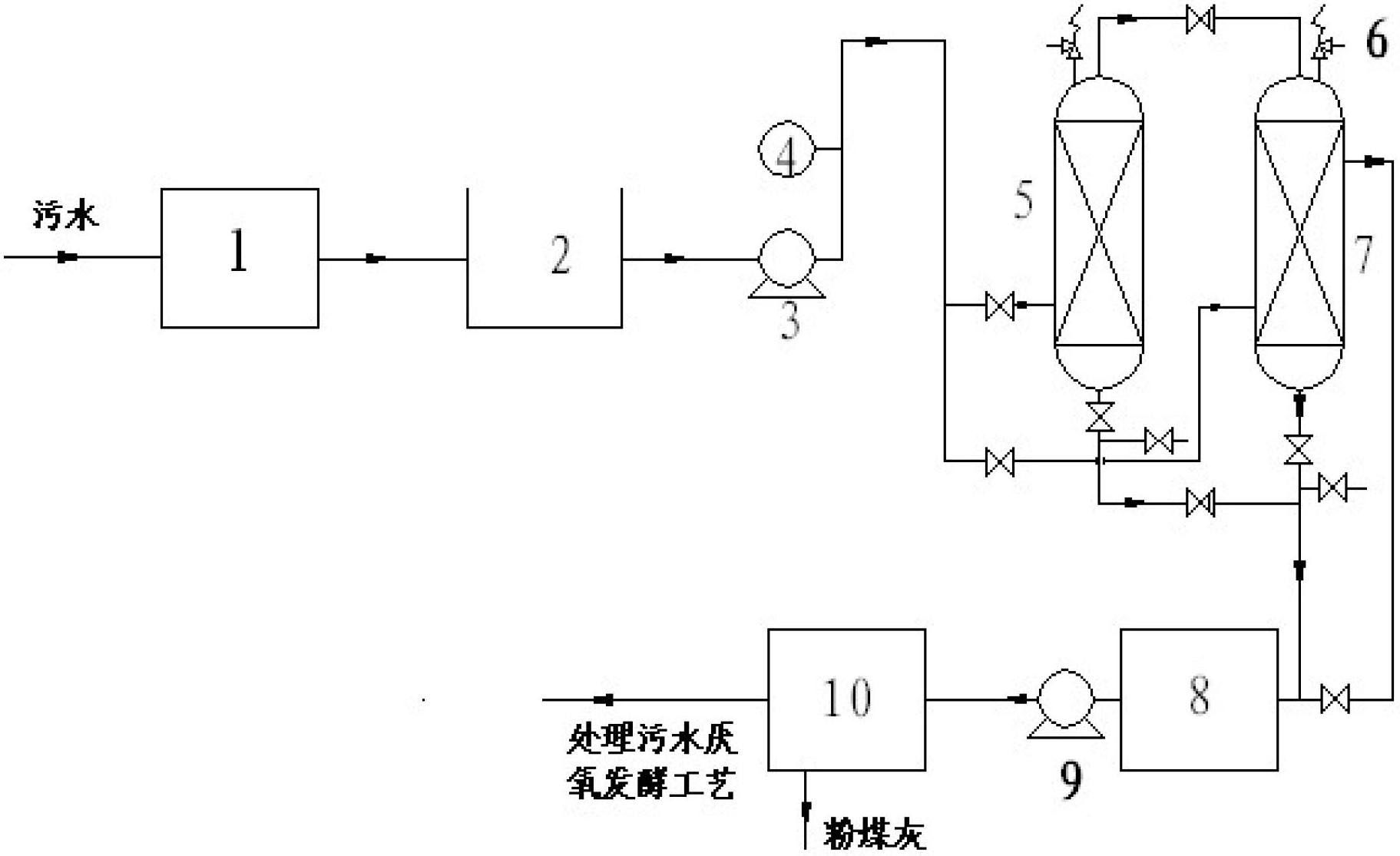
Sludge resource recovery method based on hydrothermal treatment of digested sludge
InactiveCN106746467AEfficient recyclingHigh yieldSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by pyrolysisRecovery methodFiltration
The invention discloses a sludge resource recovery method based on hydrothermal treatment of digested sludge. The method comprises the following steps: performing dehydration treatment on sludge so as to obtain dehydrated sludge with the solid content of 15-20%; mixing the dehydrated sludge and a press filtrate in which nitrogen and phosphorus are removed in a slurrying and tempering reactor, preheating, slurrying and tempering; pumping the sludge subjected to slurrying and tempering into an anaerobic digestion system so as to produce biogas; introducing the sludge subjected to anaerobic digestion into a pyrohydrolysis reactor for performing hydrothermal treatment, relieving pressure and cooling after pyrohydrolysis so as to obtain a mixed solution, and performing plate-frame pressure filtration dehydration so as to form high-dryness biogas residues; regulating the pH value of the press filtrate to 9-11, adding a magnesium salt to produce struvite so as to realize phosphorus recovery; regulating the pH value to 11-13, and performing ammonia stripping, thereby realizing nitrogen recovery; and refluxing the press filtrate in which nitrogen and phosphorus are removed back to the slurrying and tempering reactor, mixing with the dehydrated sludge, and performing cycle treatment. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the sludge degradation rate and methane yield are effectively improved, and nitrogen and phosphorus resources are recovered.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Process for the simultaneous removal of BOD and phosphate from waste water
InactiveUS7722768B2Reduce usageTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsChemical measurementNuclear chemistry
The invention is directed to a process for the simultaneous removal of BOD and phosphate from a liquid containing ammonium, BOD, phosphate and magnesium, the method comprising: feeding the liquid to a reactor containing BOD-oxidising biomass; ensuring that the liquid in the reactor contains an excess to stoichiometry of ammonium and magnesium relative to phosphate, wherein the stoichiometry is related to the stoichiometry of struvite; oxidising at least part of the BOD; adjusting the pH of the liquid in the reactor at a desired value; forming solid material in the reactor, the solid material comprising struvite; separating at least part of the solid material from the reactor effluent; returning a part of the solid material to the reactor. The invention is also directed to a reactor for this process. The advantage of the process and the apparatus is that in one reactor both BOD and phosphate are removed from the liquid.
Owner:PAQUES I P
Method for recycling surplus sludge hydrothermal carbonization solution
InactiveCN108558162AOvercoming the technical bottle diameter of low biological nitrogen removal efficiencyOvercoming the technical bottle diameter with low nitrogen removal efficiencyWater treatment compoundsSludge treatment by pyrolysisHigh concentrationChar
The invention provides a method for recycling a surplus sludge hydrothermal carbonization solution, which belongs to the technical field of environment engineering sludge treatment. The hydrothermal carbonization solution is appropriately circularly utilized in the hydrothermal carbonization process of the surplus sludge, so that while the yield of hydrothermal carbon is increased, the high-concentration hydrothermal carbonization solution which is easy to recycle is generated, nitrogen and phosphorus in the high-concentration hydrothermal carbonization solution are recycled through a struvitemethod, and a liquid phase part is used as a denitrification supplementary carbon source in the sewage biological denitrification. The method has the beneficial effects that the zero emission of thesurplus sludge in the sewage treatment can be realized, the technical bottleneck that the low-carbon-nitrogen-ratio waste water biological denitrification efficiency is low can be effectively overcome; and moreover, the hydrothermal carbon can be used as fuel for heating a hydrothermal carbonization reactor, so that the energy self-supply can be realized, and the application prospect in the aspectof recycling the surplus sludge in an urban sewage treatment factory is wide.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Technique for processing ammonia-nitrogen wastewater employing struvite formation
InactiveCN103848540ARealize resource reuseEasy to handleMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationHigh concentrationSodium hydroxide
The invention relates to a technique for processing an ammonia-nitrogen wastewater employing struvite formation. The technique comprises the following steps: adding certain magnesium source and phosphorus source to the wastewater, controlling a certain pH value; participating the sediments at the bottom of a reactor after reaction; separating out struvite by solid-liquid separation; entering the wastewater to an anaerobic tank to further process, and marketing the discharged struvite as a controlled release fertilizer, wherein the magnesium source and the phosphorus source respectively are magnesium chloride and sodium hydrogen phosphate; the optimal molar ratio of Mg to N to P is 1.2:1:0.8; the initial ammonia-nitrogen concentration is 210-1260mg / L; the pH of the wastewater is controlled to be 8-9; the solution for adjusting the pH to 2-6mol / L is a sodium hydroxide solution. The technical scheme provided by the invention cannot be limited by the temperature and toxin in water, the design and operation are simple, high-concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater can be effectively processed, and the generated struvite sediment is a good controlled release fertilizer. Thus, resource recycling of ammonia-nitrogen is achieved.
Owner:洛阳智方环保技术有限公司
MAP (guano) crystal precipitating stuffing and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101376531AHigh porosityRaw materials are cheap and easy to getWater/sewage treatmentSustainable biological treatmentGuanoPorous particle
The invention relates to a pre-filming MAP filler which can improve the crystallization sedimentation performance of MAP (struvite) and a preparation method. The pre-filming MAP filler and the preparation method are characterized in that porous particles such as waste zeolite, waste active carbon, coke, fly ashes, etc. are used as carriers, magnesium, phosphate and ammonia-nitrogen are used as raw materials, the mol ratio among N, P and Mg is 1:1:1.0 to 2.0, and an MAP film is formed on the surface of the carriers through fluidized reaction. The filler is put in ammonia-containing phosphorus wastewater, so the crystallization sedimentation performance of the MAP (struvite) on the surface of the pre-filming filler can be enhanced obviously; the test shows that the crystal nucleus growth velocity is increased about 20 percent compared with a common amorphous filler carriers. In addition, the carriers are pre-filmed, thereby being beneficial for the MAP film-forming and increasing the firmness of the film. The pre-filming MAP filler and the preparation method adopt external circulation fluidized reaction to prepare the pre-film, and the friction between the carriers is reduced, thereby being also beneficial for the film-forming on the carriers. Air is added before reaction for pressurizing, thereby being beneficial for the formation of the porous pre-filmed MAP carriers and increasing the porosity of the pre-filmed carriers obviously.
Owner:江苏金环科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for treatmet of sludge
InactiveUS20100255562A1Rapidly and efficientlyImprove efficiencyBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersEutrophicationCell membrane
Disclosed are an enhanced apparatus and a method for treating organic sludge, which is constructed so that concentrated sludge is first dewatered with a dewatering device in order to to lower percentage of moisture content of the sludge, which is included in foul water or wastewater sludge such as sewage, food waste, and livestock excretion, etc. thereby causing eutrophication; dewatered sludge is passed through a thermal hydrolysis reactor to decompose a polymer formed spontaneously in the dewatered sludge and cell membrane of an organism; since microorganisms discharge absorbed phosphorus, at least one selected from magnesium, potassium, zinc, calcium carbonate, phosphoric acid and calcium is poured in order to remove phosphorus, nitrogen and various material contained in a solution generated during dewatering by crystallization into struvite, and is passed through a crystallization reactor to crystallize into struvite and then remove it; a is remaining solution after crystallization is fed back to a step prior to the biological reactor or the digester.
Owner:KANG SEOK WOONG
Recycling technique of lithium iron phosphate production wastewater
ActiveCN104628206AAchieve recyclingZero emissionWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention relates to a recycling technique of lithium iron phosphate production wastewater, belonging to the field of advanced wastewater treatment. The technique comprises the following steps: regulating the pH value of wastewater to neutrality by using cheap magnesite, adding a magnesium hydroxide emulsion to regulate the pH value to 8-9 to obtain guano recycled ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus, and completely precipitating phosphoric acid; adding sodium alkali into the residual high-concentration ammonia nitrogen, evaporating ammonia to recycle ammonia water, removing magnesium from the residual high-concentration sodium sulfate, and crystallizing by evaporation to obtain the sodium sulfate product, thereby implementing zero discharge of wastewater. The magnesite is utilized to treat the high-concentration phosphorus salt and ammonium salt to recycle the guano, and the ammonia evaporation and evaporative crystallization are combined to recycle the components in the wastewater, thereby implementing zero discharge of wastewater. Compared with the existing method, the technique is lower in cost and can implement all-component recycling.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Method for recycling high concentration ammonia nitrogen and making ammonia nitrogen into large granule high purity struvite
ActiveCN103935974AAvoid lostAvoid breakingWater/sewage treatmentPhosphorus compoundsHigh concentrationChemistry
The invention relates to a method for recycling high concentration ammonia nitrogen and making ammonia nitrogen into large granule high purity struvite. At first, a granulating main body is changed to a three-section tapered fluidized bed reactor. The reactor is composed of a feeding tube, a granulating tube, and a sediment tube; the connection part between the sediment tube and the granulating tube is in a truncated cone shape, the inclined angel theta of the generatrix of the connection part is 25 degree to 45 degree; the ratio of the external diameter of the big end of the granulating tube to the external diameter of the small end of the granulating tube is equal to 3:1; the ratio of the length of the granulating tube to the external diameter of the small end of the granulating tube is equal to 50:1; a pH probe is arranged in the granulating tube, the bottom of the granulating tube and the top of the feeding tube are both provided with a granulating tube valve; the bottom of the feeding pipe which is provided with five material inlets is provided with a discharging valve; and the length ratio of the sediment tube to the granulating tube to the feeding tube is equal to 2:5:1. High concentration nitrogen-phosphor wastewater with a NH4<+>-N concentration of 1000 to 1600 mg / L and a magnesium chloride solution are simultaneously pumped into the granulating main body, at the same time the mole ratio of NH4<+>-N: PO4<3>-P:Mg<2+> is controlled at 1.5:1:1.1-1.5:1:1.3, the pH value is controlled at 6 to 7, the reflux ratio is controlled at 12 to 30, the diameter of the formed struvite particle is in a range of 3 to 8 mm, the purity of the struvite particle can reach 97.5% or more, and the hardness of the struvite particle is (20.3 + / - 1) kg / mm2. The method can used to prepare struvite from high concentration ammonia nitrogen industrial and poultry culture wastewater, garbage leachate, or sludge fermentation broth.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Treatment of phosphate-containing wastewater with fluorosilicate and phosphate recovery
ActiveCN103813987ARaise the pHWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisPhosphateWastewater
A method for treating phosphate-containing wastewater, such as phosphogypsum pond water. The method includes the steps of: (a) adding a first cation to the wastewater to precipitate fluorosilicate from the wastewater; (b) adding a second cation to the wastewater to precipitate fluoride from the wastewater; (c) raising the pH of the wastewater to precipitate the second cation from the wastewater; (d) removing residual silica from the wastewater; and (e) precipitating phosphate from the wastewater. The precipitated fluorosilicate may be sodium fluorosilicate. The precipitated phosphate may be struvite.
Owner:OSTARA NUTRIENT RECOVERY TECH INC
Struvite-K and Syngenite Composition for Use in Building Materials
A composition and process for the manufacture thereof for use in a hybrid building material comprising at least in part Syngenite (K2Ca(SO4)2.H2O) and Struvite-K (KMgPO4.6H2O). Specified constituents, including magnesium oxide (MgO), monopotassium phosphate (MKP) and stucco (calcium sulfate hemihydrate) are mixed in predetermined ratios and the reaction proceeds through multiple phases reactions which at times are proceeding simultaneously and in parallel and reaction may even compete with each other for reagents if the Struvite-K reaction is not buffered to slow down the reaction rate). A number of variable factors, such as water temperature, pH mixing times and rates, have been found to affect resultant reaction products. Preferred ratios of chemical constituents and manufacturing parameters, including predetermined and specified ratios of Struvite-K and Syngenite may be provided for specified purposes, optimized in respect of stoichiometry to reduce the combined heat of formation to non-destructive levels.
Owner:CERTAINTEED GYPSUM INC
Method for treating sewage with high ammonia, nitrogen and phosphorus contents in livestock and poultry farms by chemical precipitation
ActiveCN102690001AHigh removal rateWide variety of sourcesWaste water treatment from animal husbandryMultistage water/sewage treatmentFixed bedSettling basin
The invention discloses a method for treating sewage with high ammonia, nitrogen and phosphorus contents in livestock and poultry farms by chemical precipitation. The method comprises the following steps of: performing solid-liquid separation on the sewage by using a solid-liquid separator, wherein liquid is discharged into a sedimentation tank for further separation; pumping the sewage which is obtained after separation and deposition into a fixed bed reaction tower in which calcium, magnesium and phosphate fertilizers serve as main reactants, wherein substances which contain the ammonia, the nitrogen or the phosphorus are removed from the sewage in the reaction tower simultaneously; importing sediment and the sewage into a crystallizing pond, and crystallizing to generate struvite; separating the struvite by using the solid-liquid separator; and performing a sewage anaerobic fermentation process on the liquid for further treatment. According to the method, the removal rate of the phosphorous can reach 80 to 90 percent, the removal rate of the ammonia and the nitrogen can reach 70 to 80 percent, and the discharged water can meet the requirement of anaerobic fermentation. The method is high in reaction speed, not influenced by temperatures and low in cost, raw materials are readily available, and the generated sediment, namely the struvite is an efficient sustained-release fertilizer.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for recovering nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage by electrochemical struvite crystallization
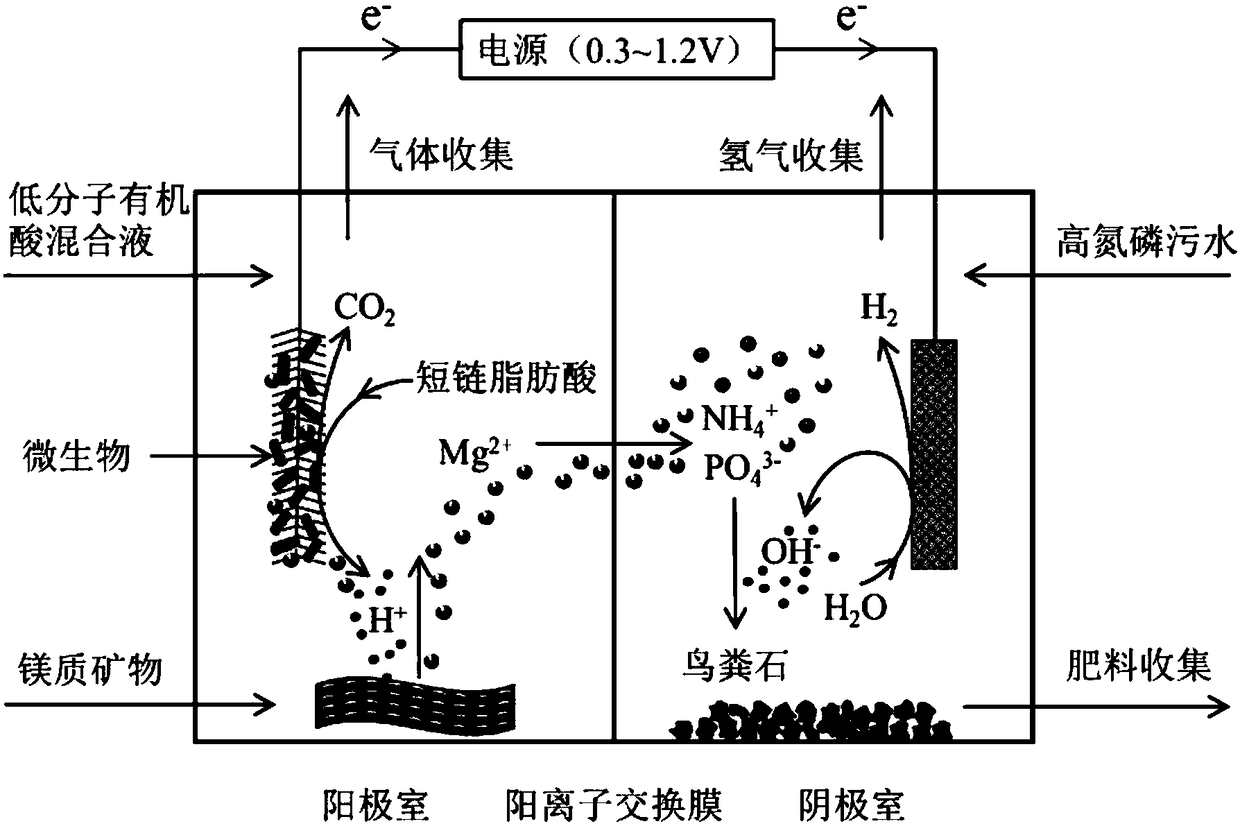
ActiveCN108675403APH dropUniform and rapid precipitation recoveryWater contaminantsWaste based fuelOverpotentialMagnesium ion
The invention discloses a method for recovering nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage by electrochemical struvite crystallization. The method is used for solving the problems of large overpotential and high magnesium source cost of existing electrochemical struvite crystallization recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage, and acidolysis of cheap magnesium mineral in an anolyte is used to significantly reduce the overpotential and reduce the cost of the magnesium source. The method is based on the conditions of acidification of the anolyte and alkalization of a catholyte, formed by electrode reactions in a dual-chamber electrolytic tank, and the magnesium mineral is added into an anode chamber to prevent preventing acidification of the anolyte and stabilize the pH value of the anolyte; andmagnesium ions released by the acidolysis of the magnesium mineral go through a cation exchange membrane and migrate to a cathode under the driving of electric field force, the migrated magnesium ions and ammonium ions and phosphate radicals in sewage in a cathode chamber undergo a crystallization reaction under alkaline conditions to form a struvite precipitate and stabilize the pH value of thecatholyte, so the purpose of simultaneously removing and recovering nitrogen and phosphorus in the sewage is achieved. The method makes the electrochemical struvite crystallization recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sewage have great application and promotion values.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for improving efficiency of struvite precipitation method for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater
InactiveCN107601716AIncrease the size of the pelletGood removal effectWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeCoprecipitation
The invention discloses a method for improving the efficiency of a struvite precipitation method for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adding a proper amount of phosphorus sources, controlling the ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus, dropwise adding a small amount of magnesium sources at a relatively high pH value to generate partial precipitates,and dropwise adding the magnesium source at a relatively low pH value until the reaction is complete; and then adding a proper amount of flocculating agents, so as to promote the generation of precipitates and accelerate the sedimentation of precipitates. By utilizing a coprecipitation method, ammonia and nitrogen in the wastewater react to generate the precipitates, the settling of the precipitates is accelerated under the synergistic effect of the flocculating agent, and then the solid-liquid separation purpose is achieved. The process method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the cost is low, the sludge value is high, the waste can be turned into wealth, the settling velocity of struvite can be accelerated, small struvite particles which are difficult to be settled and are suspended in the solution are effectively removed, and the deep denitrification of the wastewater is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
System and Process for Removal of Phosphorous and Ammonia from Aqueous Streams
InactiveUS20080308505A1Degree of reductionReduce solubilityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsWater flowAmmonia
We disclose a process for the removal of phosphorous and ammonia from an aqueous stream by contacting the aqueous stream with magnesium and base in a first zone having a first pH, to form an (n−1)th mixed stream and a first portion of struvite; separating the (n−1)th mixed stream from the first portion of struvite; removing at least some struvite from the first portion of struvite; contacting the (n−1)th mixed stream with base in an nth zone, wherein n is an integer incrementing from 2 to nmax, wherein nmax is an integer from 2 to about 5, and wherein the nth zone has an nth pH higher than the (n−1)th pH, to form an nth mixed stream and an nth portion of struvite, except no base is added and the nth pH need not be higher than the (n−1)th pH when n=nmax; separating the nth mixed stream from the nth portion of struvite; returning the nth portion of struvite to the (n−1)th zone; and, if n<nmax, incrementing n and repeating the second contacting, second separating, and returning steps, or, if n=nmax, releasing the nth mixed stream to a treated water tank. We also disclose a system which can be used for performing the method.
Owner:JANSEN ROBERT +7
Targeted stabilizer for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103710029AReduced activityLow biological toxicityOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsSodium BentoniteStabilizing Agents
The invention discloses a targeted stabilizer for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of governing and repairing of heavy metal contaminated soil. The stabilizer is prepared from bentonite and struvite as main materials assisted by heavy metal chelate, and an organic binder as a skeleton. The targeted stabilizer comprises the following dry substances by weight percent: 20-40% of bentonite, 30-50% of struvite, 5-20% of heavy metal chelate and 5-10% of binder. The preparation technology of the targeted stabilizer comprises the steps of mixing, reacting, baking, crushing and calcining. By adopting the targeted stabilizer and the preparation method thereof, the pollution problem of the heavy metal contaminated soil can be effectively solved, the targeted stabilizer has the characteristics of being wide in material source, low in price, low in cost, high in remediation efficiency, free of secondary pollution, simple in operation method and the like.
Owner:CECEP L&T ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Method for preparing and purifying struvite from residual sludge
The invention relates to a method for preparing and purifying struvite from residual sludge in an urban sewage treatment factory and is characterized in that the method contains the following steps of: controlling pH within the range of 3-5 for releasing nitrogen and phosphor from the residual sludge; modifying a sodium storng-acid cation exchange resin by using an MgCl2 solution; carrying out ion exchange on a supernatant of the sludge containing rich nitrogen and phosphor by using the modified resin so as to reduce the impact of calcium ion on the formation of the struvite substance; controlling pH within the range of 8.5-9.5, stirring a solution obtained after ion exchange until a lot of off-white precipitates, standing for settling, and recovering the off-white precipitates. By adoption of the acid-base adjustment and ion exchange methods for the preparation and purification of the struvite substance from the residual sludge, the high-purity struvite substance can be obtained, and the impact load of supernatant reflux generated during the sludge treatment process on nitrogen and phosphor during the sewage treatment flow can be mitigated, so as to improve operation of the sewage treatment factory.
Owner:TIANJIN URBAN CONSTR COLLEGE
Method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization
ActiveCN108660475APromote acidolysisCrystallize fastCellsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesOverpotentialMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization. The method aims to solve the problems that in existing recycling of phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization, an anode liquid is acidized, the overpotential is large, the magnesium source cost is high, and the like. Cheap magnesium ores are subjected to acidolysis in the anode liquid, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the overpotential is remarkably reduced, and the magnesium source cost is lowered. According to the method, based on a bichamber microbial electrolysis pool, under an extremely low externally applied voltage (0.3-1.2 V), an electrode reaction is performed to form conditions for acidification of the anode liquid and acidification of a cathode liquid; the crushed magnesium ores are added to an anode chamber, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the pH of the anode liquid is stabilized, and microorganisms are promoted to continuously degrade organic matter to generate power; and magnesium ions released through acidolysis of the magnesian cores move to an cathode through a cation exchange membrane under the drive of the electric filed force and has a crystallization reaction with ammonium radials and phosphate radicals under an alkaline condition, struvite deposits are formed, the pH of the cathode liquid is stabilized, and the purposes of removing and recycling the phosphorus from sewage are realized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Struvite Precipitation Using Magnesium Sacrificial Anode
InactiveUS20140076804A1Increases magnitudeWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsActivated sludgeOxygen
A method precipitating struvite in wastewater uses a magnesium sacrificial anode as the only source of magnesium. A high-purity magnesium alloy cast anode was found to be very effective in recovery of high-quality struvite from water solutions and from supernatant of fermented waste activated sludge (WAS) from a high-purity oxygen wastewater treatment plant. Struvite purity was strongly dependent on the pH and the electric current density. Optimum pH of the solution was in the broad range between 7.5 and 9.3, with struvite purities exceeding 90%. The precipitated struvite accumulated in bulk liquid with significant portions attached to the anode surface from which regular detachment occurred.
Owner:KRUK DAMIAN J +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com