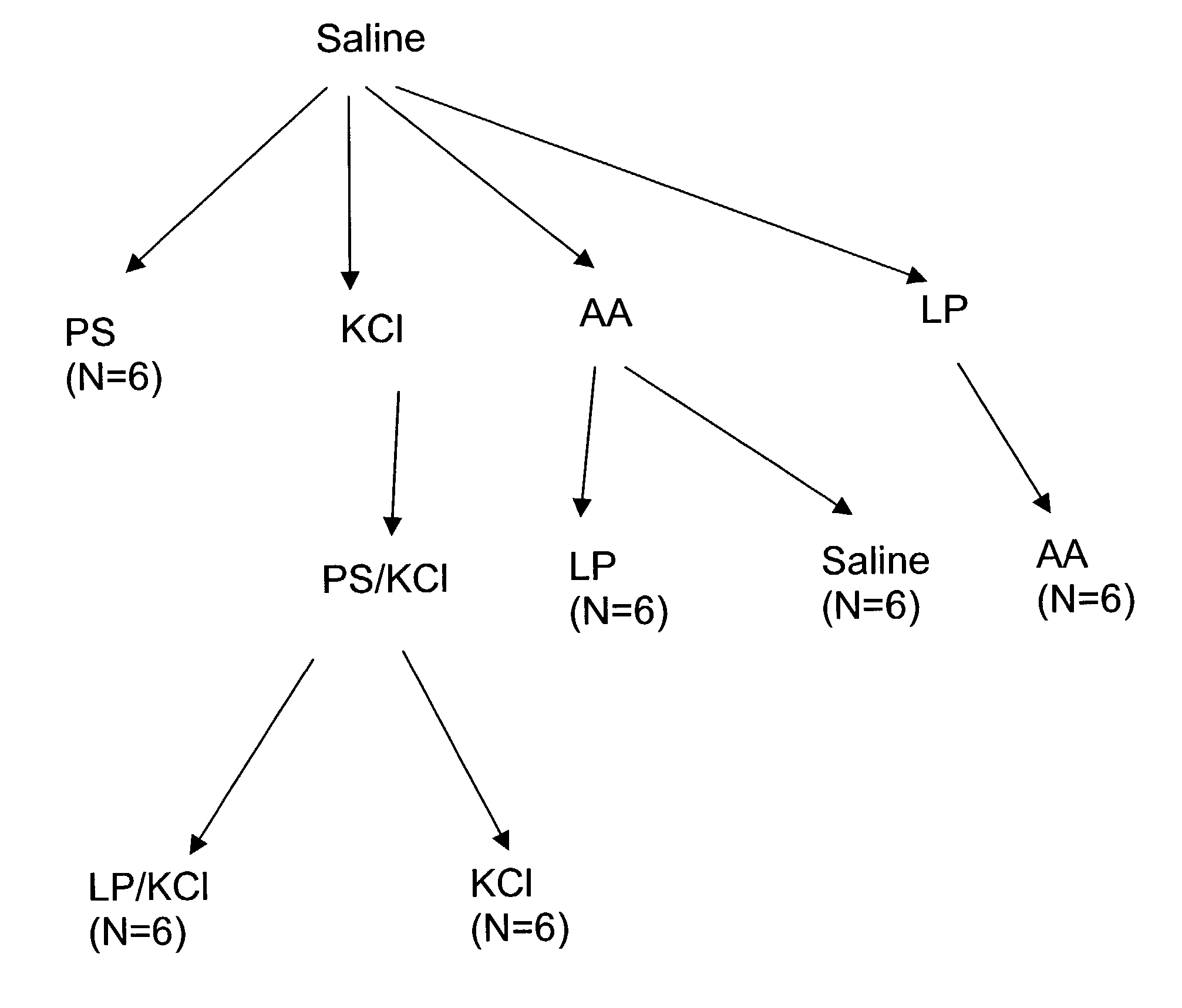
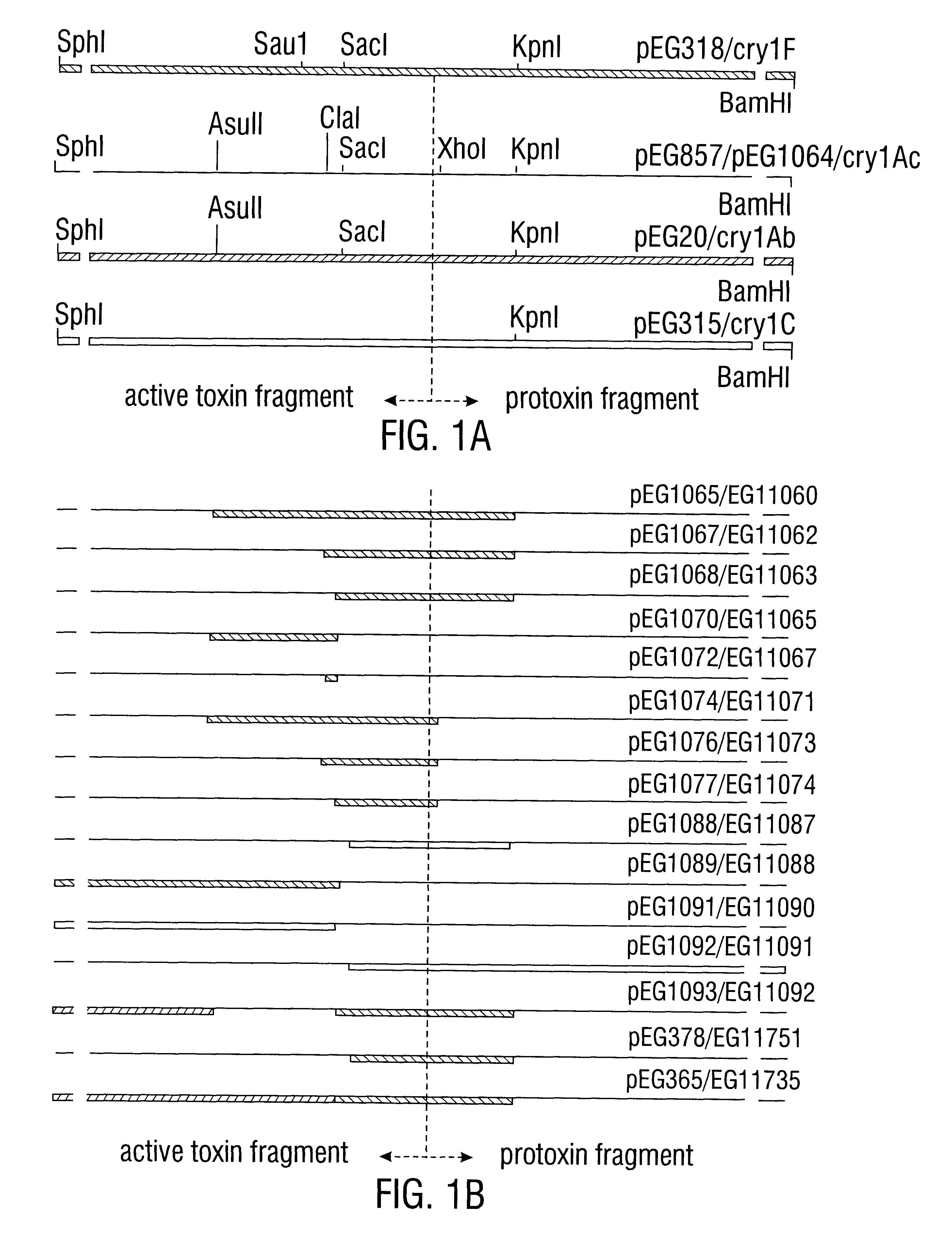
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13562 results about "Toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; synthetic toxicants created by artificial processes are thus excluded. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from the word toxic.
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
Disulfide prodrugs and linkers and stabilizers useful therefor
The present invention provides analogues of duocarmycins that are potent cytotoxins. Also provided are peptidyl and disulfide linkers that are cleaved in vivo. The linkers are of use in forming prodrugs and conjugates of the cytotoxins of the invention as well as other diagnostic and therapeutic moieties. The invention provides prodrugs and conjugates of the duocarmycin analogues with the linker arms of the invention.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Methods and materials for the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells in feeder-free culture
Methods and materials for culturing primate-derived primordial stem cells are described. In one embodiment, a cell culture medium for growing primate-derived primordial stem cells in a substantially undifferentiated state is provided which includes a low osmotic pressure, low endotoxin basic medium that is effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells. The basic medium is combined with a nutrient serum effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells and a substrate selected from the group consisting of feeder cells and an extracellular matrix component derived from feeder cells. The medium further includes non-essential amino acids, an anti-oxidant, and a first growth factor selected from the group consisting of nucleosides and a pyruvate salt.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functions or binding specificities
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Broad-spectrum delta-endotoxins
InactiveUS6713063B1Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityImproving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity and broader insect host range against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Insect-resistant transgenic plants
The invention provides transgenic plants and transformed host cells which express modified cry 3B genes with enhanced toxicity to Coleopteran insects. Also disclosed are methods of making and using these transgenic plants, methods of making recombinant host cells expressing these delta -endotoxins, and methods of killing insects such as Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi Barber) and western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Application of lipid vehicles and use for drug delivery
InactiveUS7063860B2Reduce and prevent antibody-mediated resistanceIncrease stimulationBiocideAntipyreticAnticarcinogenCapsaicin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the administration of lipid-based vehicles to treat various disorders, including bladder inflammation, infection, dysfunction, and cancer. In various aspects, the compositions and methods of the invention are useful for prolonged delivery of drugs, e.g., antibiotics, pain treatments, and anticancer agents, to the bladder, genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal system, pulmonary system, and other organs or body systems. In particular, the present invention relates to liposome-based delivery of vanilloid compounds, such as resiniferatoxin, capsaicin, or tinyatoxin, and toxins, such as botulinum toxin, for the treatment of bladder conditions, including pain, inflammation, incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. Further related are methods of using these vehicles alone or in conjunction with antibodies, e.g., uroplakin antibodies, to improve duration of liposome attachment, and provide a long-term intravesical drug delivery platform. The present invention specifically relates to antibody-coated liposomes that are useful for targeting specific receptors for drug, peptide, polypeptide, or nucleic acid delivery. In one particular aspect, the present invention relates to liposomes coated with antibodies against nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor and containing NGF antisense nucleic acids, which are used as a treatment for neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET33 and CryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode respectively the coleopteran-toxic proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and CryET34 (14-kDa) crystal protein. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plants and methods of their production using modified Bacillus thuringiensis Cry3Bb nucleic acids
Disclosed are nucleic acid segments comprising synthetically-modified genes encoding modified Coleopteran-toxic B. thuringiensis Cry 3Bb* delta-endotoxins. Also disclosed are methods of using these genes for preparing a Coleopteran-resistant transgenic plant and reducing insect in restations, and plants thereby produced.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis cryET33 and cryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode the colepteran-toxic crystal proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and the cryET34 gene encodes the 14-kDa CryET34 crystal protein. The CryET33 and CryET34 crystal proteins are toxic to red flour beetle larvae and Japanese beetle larvae. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
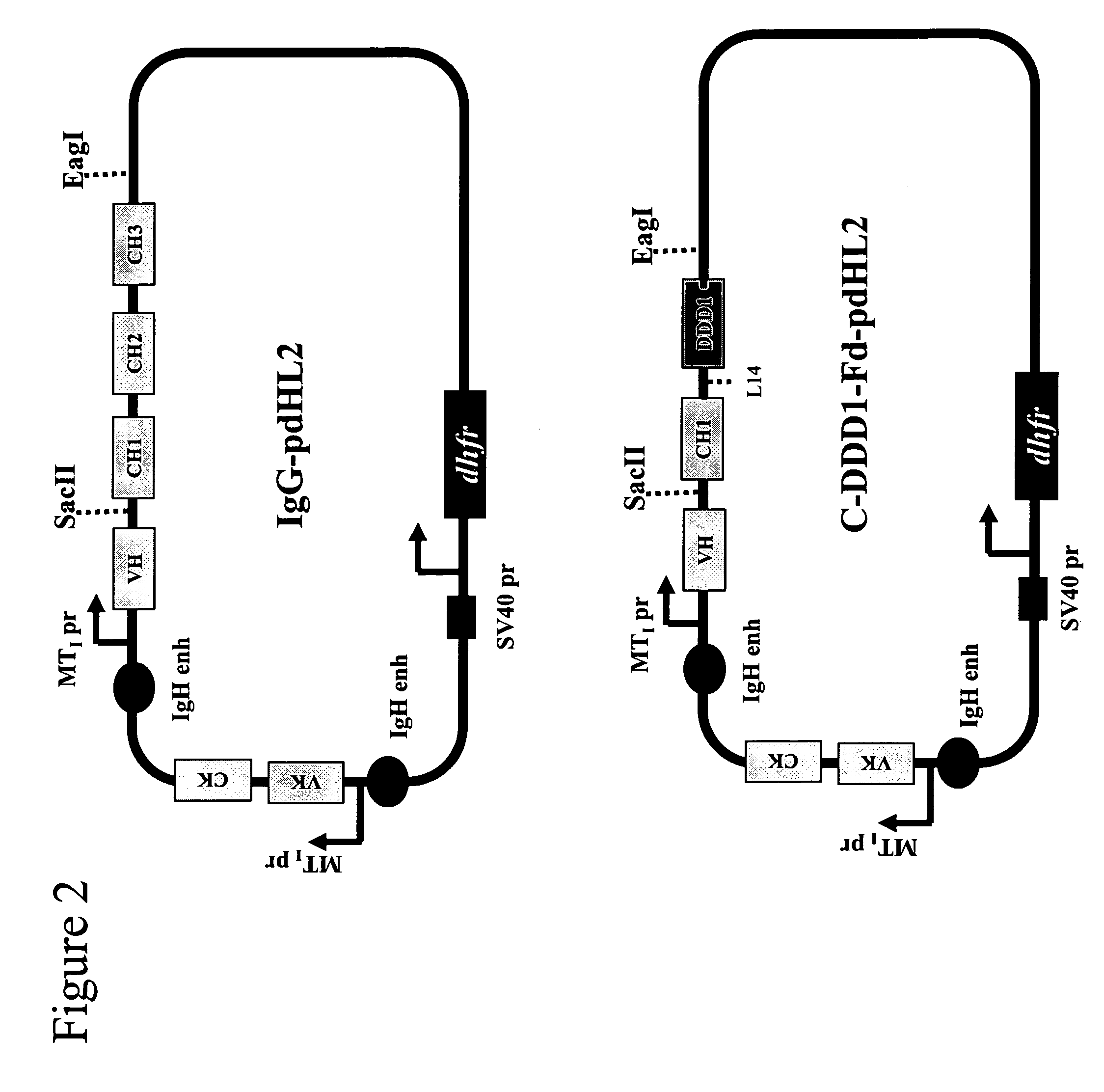
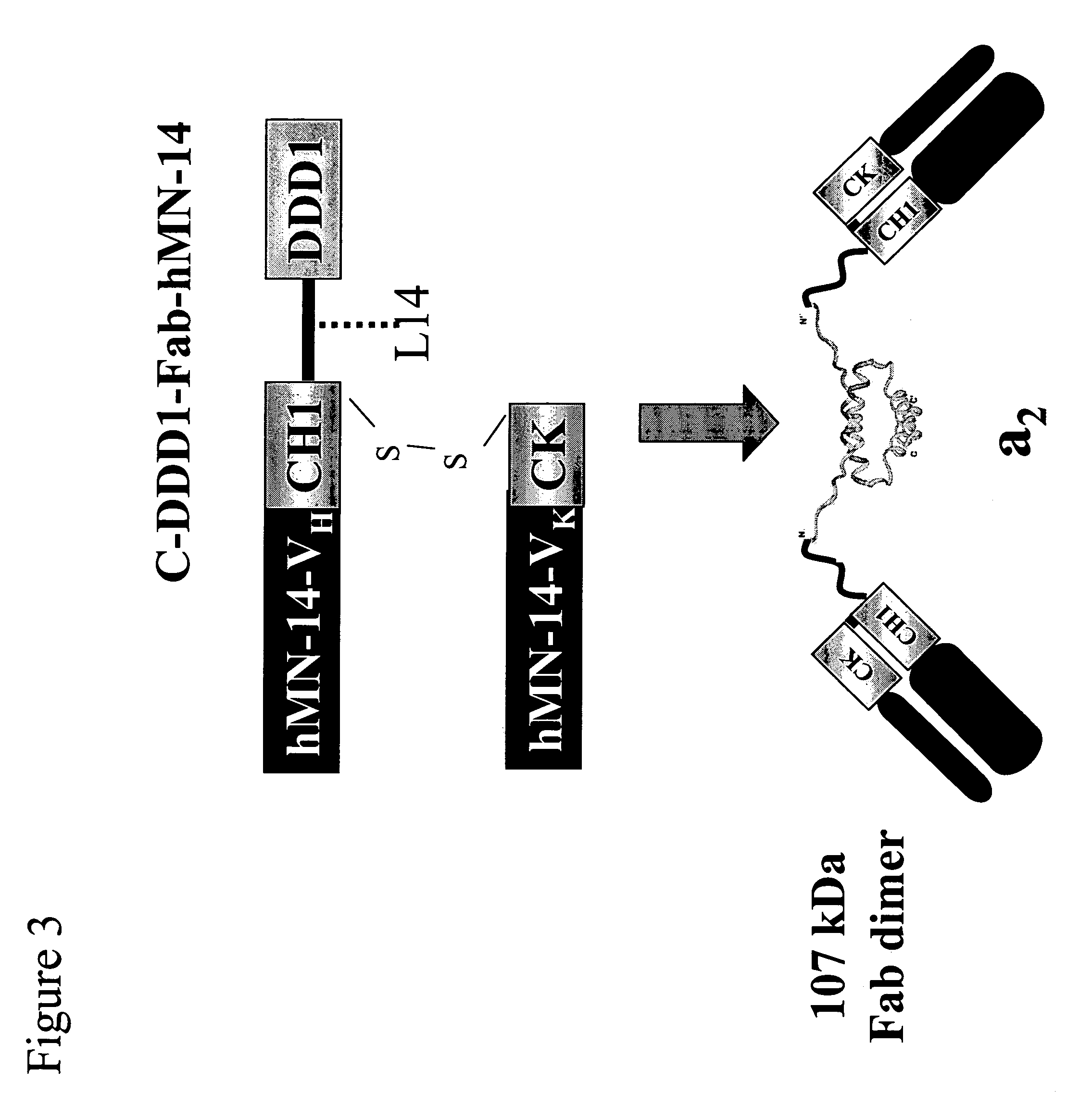
Multipurpose antibody derivatives
InactiveUS6809185B1Efficient preparationEfficient productionHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsSignalling moleculesHormones regulation
The present invention relates to a class of molecules specified as novel multipurpose antibody derivatives. This class of molecules is created by heterodimerization of two constituting components. Heterodimerization is obtained by the specific heterotypic interaction of a chosen VH-CH1 combination of immunoglobulin domains, with a chosen VL-CL combination of immunoglobulin domains. The appropriate VH and VL domains in the VHCH1 and VLCL context, a binding specificity can be constitituted by the heterodimerization scaffold itself. One or both of the comprising VHCH1 and VLCL chains can thus be extended at either the N- or the C-terminus or both with other molecules, such as a toxin polypeptide, an enzyme, a hormone, a cytokine, a signaling molecule, or a single chain linked Fv fragment with the same or a different specificity.
Owner:BIOTECNOL LTD +1
Methods for generating stably linked complexes composed of homodimers, homotetramers or dimers of dimers and uses
ActiveUS7550143B2Improve functionalityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHomotetramerAptamer
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions, which may have multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Particular embodiments concern homodimers comprising monomers that contain a dimerization and docking domain attached to a precursor. The precursors may be virtually any molecule or structure, such as antibodies, antibody fragments, antibody analogs or mimetics, aptamers, binding peptides, fragments of binding proteins, known ligands for proteins or other molecules, enzymes, detectable labels or tags, therapeutic agents, toxins, pharmaceuticals, cytokines, interleukins, interferons, radioisotopes, proteins, peptides, peptide mimetics, polynucleotides, RNAi, oligosaccharides, natural or synthetic polymeric substances, nanoparticles, quantum dots, organic or inorganic compounds, etc. Other embodiments concern tetramers comprising a first and second homodimer, which may be identical or different. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a facile and general way to obtain homodimers, homotetramers and heterotetramers of virtually any functionality and / or binding specificity.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Polynucleotide compositions encoding broad spectrum delta-endotoxins
InactiveUS7070982B2Improved insecticidal activity and broader host-range activityHigh insecticidal activitySugar derivativesBacteriaNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
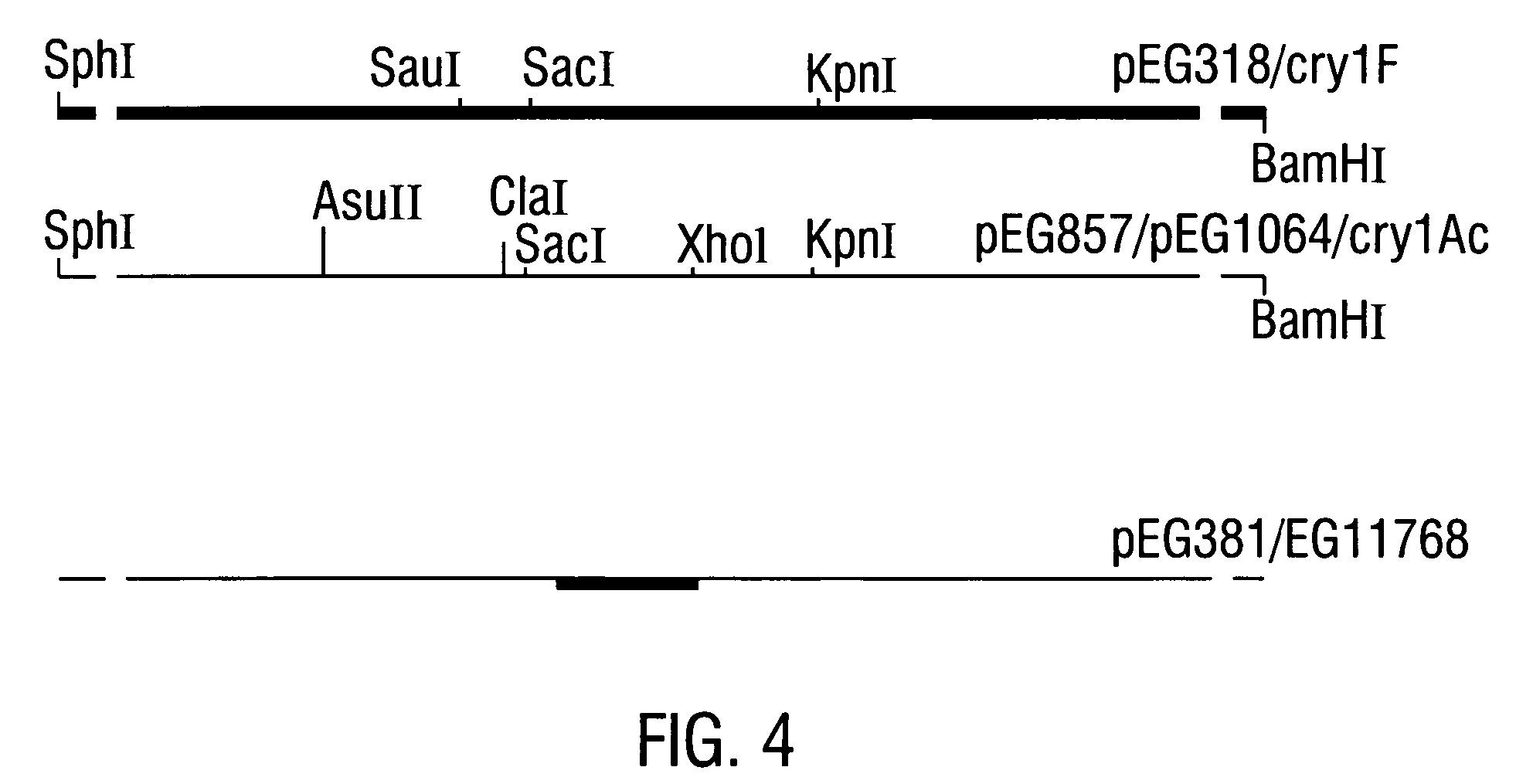
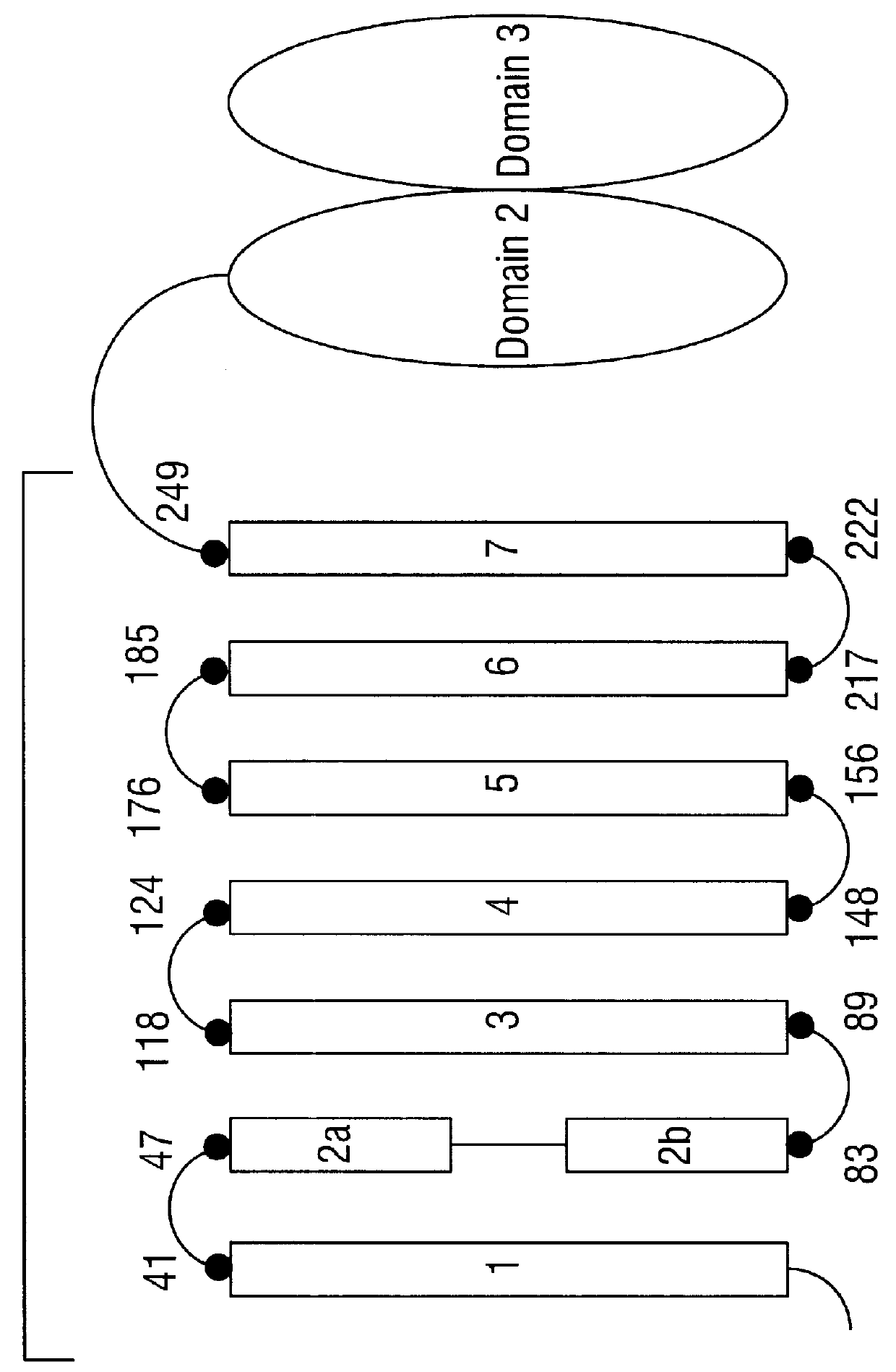
CRY1C polypeptides having improved toxicity to lepidopteran insects
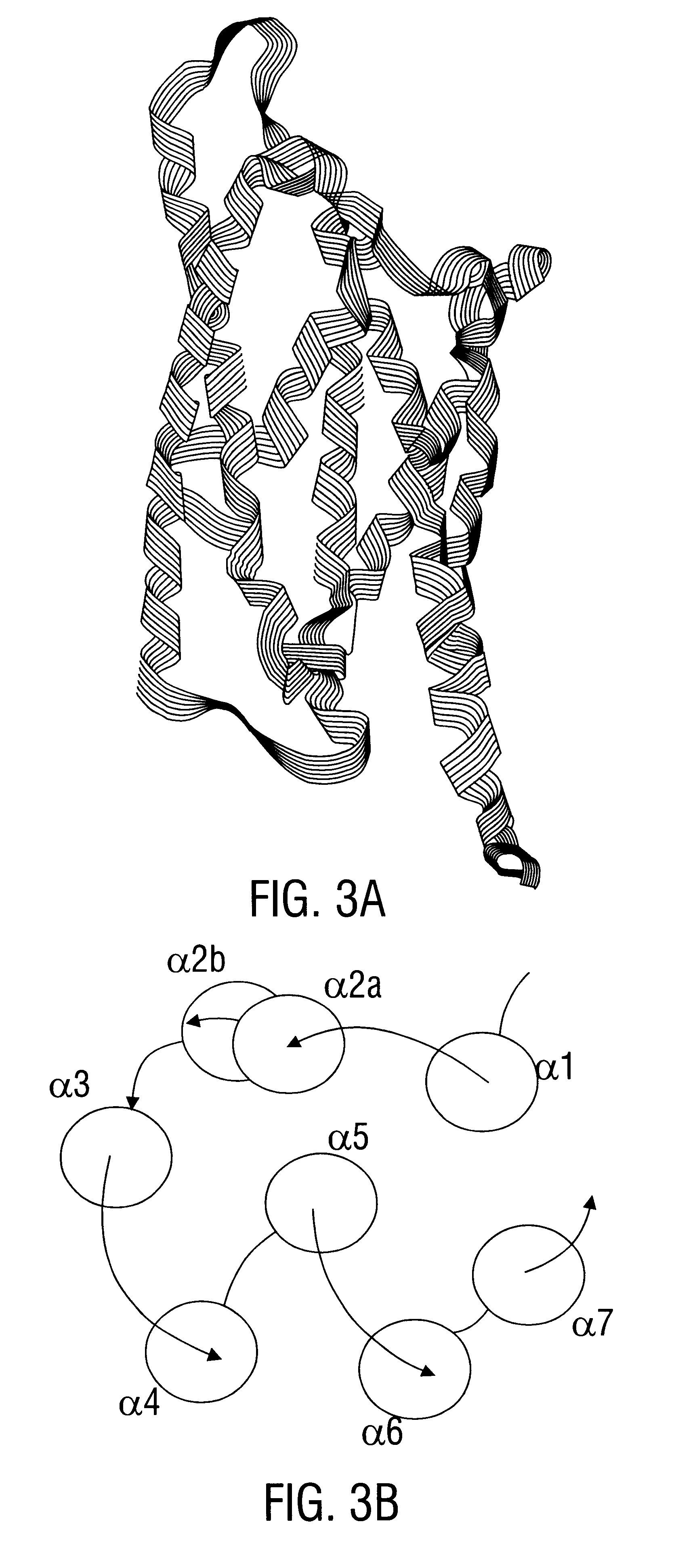
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis nucleic acid segments encoding delta -endotoxins having insecticidal activity against lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are synthetic crystal proteins encoded by these novel nucleic acid sequences. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention. Also disclosed are methods for modifying, altering, and mutagenizing specific loop regions between the alpha helices in domain 1 of these crystal proteins, including Cry1C, to produce genetically-engineered recombinant cry* genes, and the proteins they encode which have improved insecticidal activity. In preferred embodiments, novel Cry1C* amino acid segments and the modified cry1C* nucleic acid sequences which encode them are disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Broad-spectrum insect resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6281016B1Improve insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityBiocideNanotechAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and tansgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
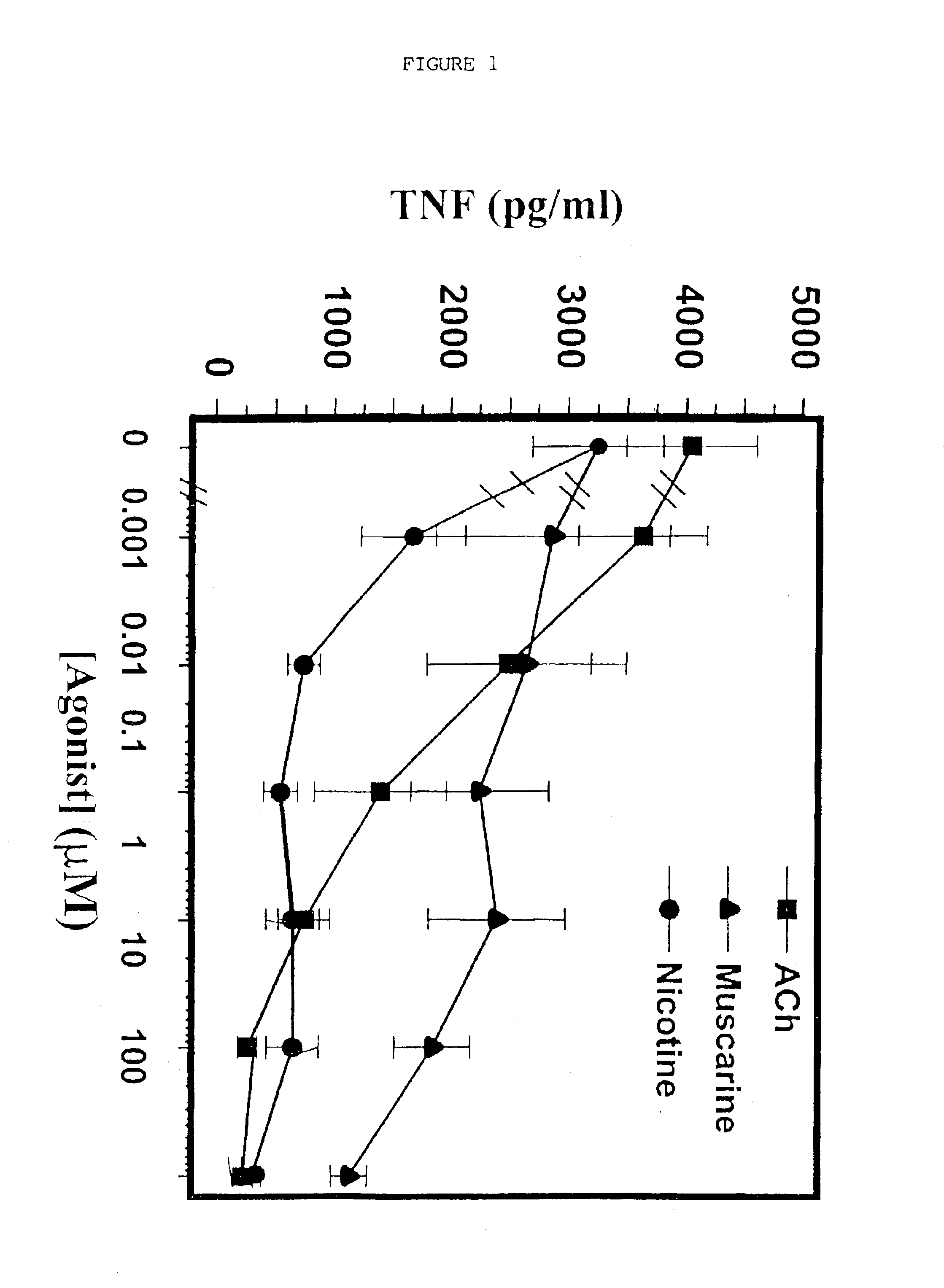
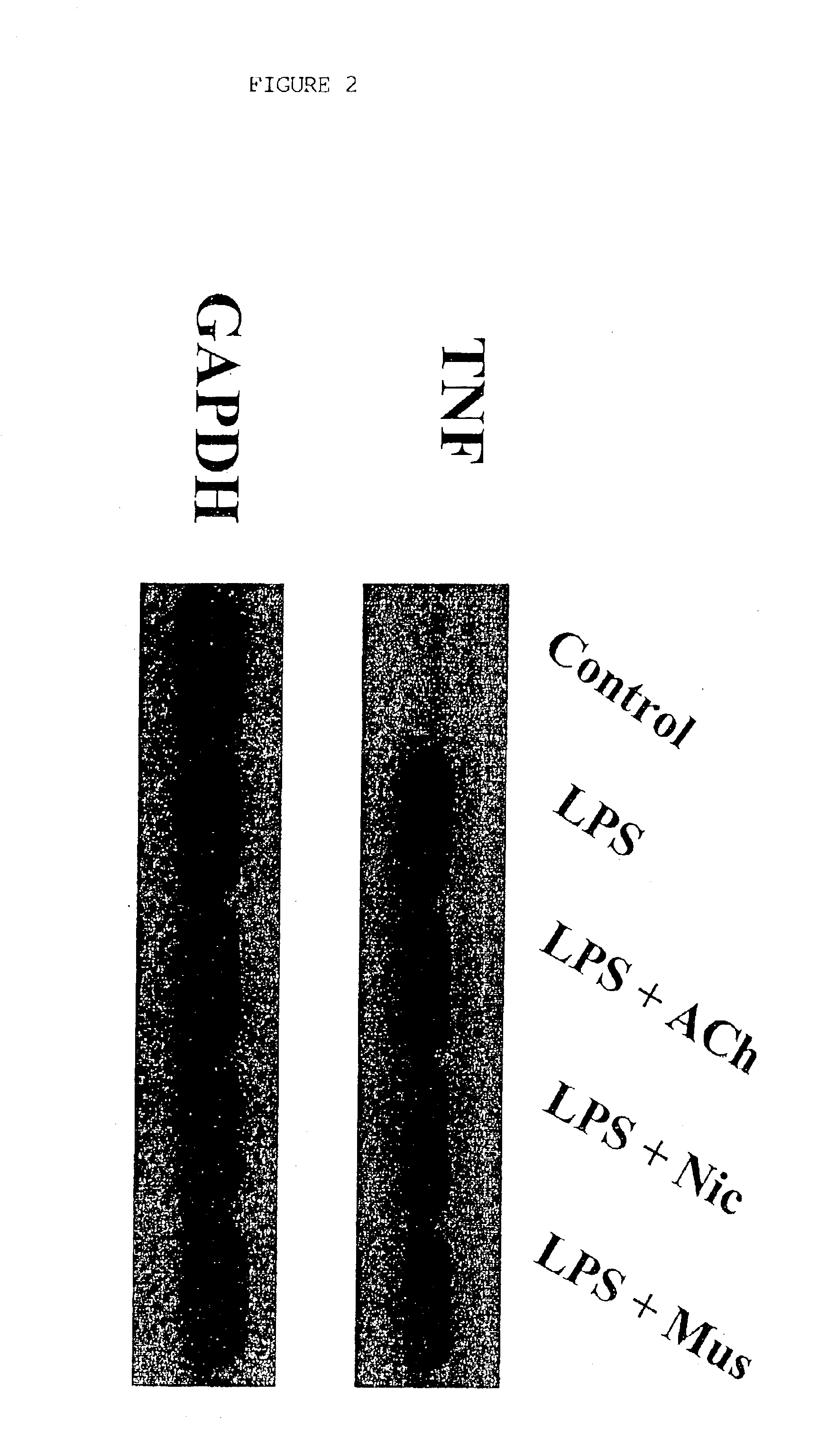
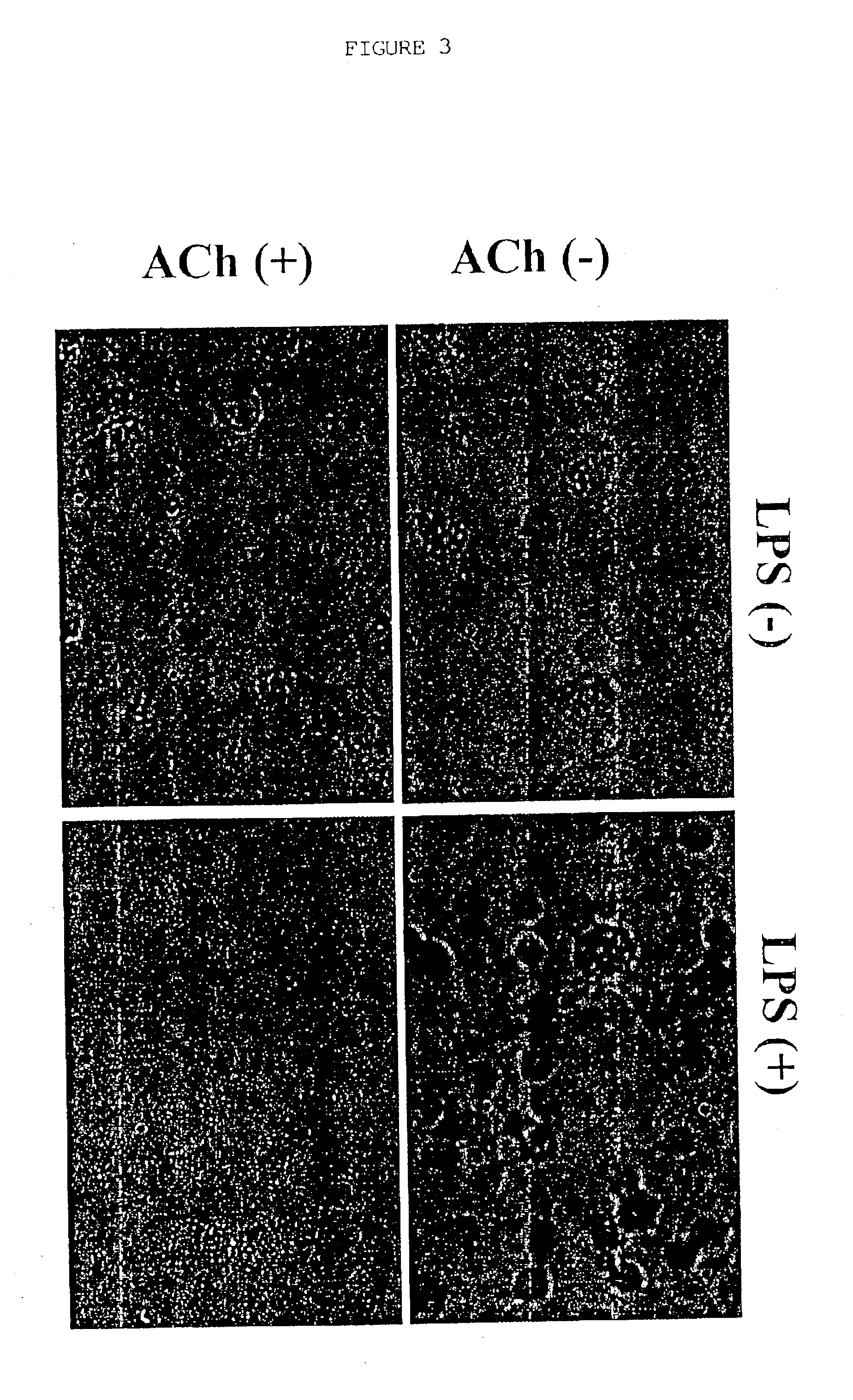
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by cholinergic agonists and vagus nerve stimulation
A method of inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine in a cell is disclosed. The method comprises treating the cell with a cholinergic agonist. The method is useful in patients at risk for, or suffering from, a condition mediated by an inflammatory cytokine cascade, for example endotoxic shock. The cholinergic agonist treatment can be effected by stimulation of an efferent vagus nerve fiber, or the entire vagus nerve.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Broad-spectrum delta -endotoxins
InactiveUS6110464AImprove insecticidal effectBroad-range specificityNanotechBacteriaAureobasidium sp.Toxin
Disclosed are novel synthetically-modified B. thuringiensis chimeric crystal proteins having improved insecticidal activity against coleopteran, dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Also disclosed are the nucleic acid segments encoding these novel peptides. Methods of making and using these genes and proteins are disclosed as well as methods for the recombinant expression, and transformation of suitable host cells. Transformed host cells and transgenic plants expressing the modified endotoxin are also aspects of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods and compositions for the treatment and management of hemoglobinopathy and anemia
InactiveUS20050143420A1Good effectRelieve symptomsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRed blood cellThalassemia
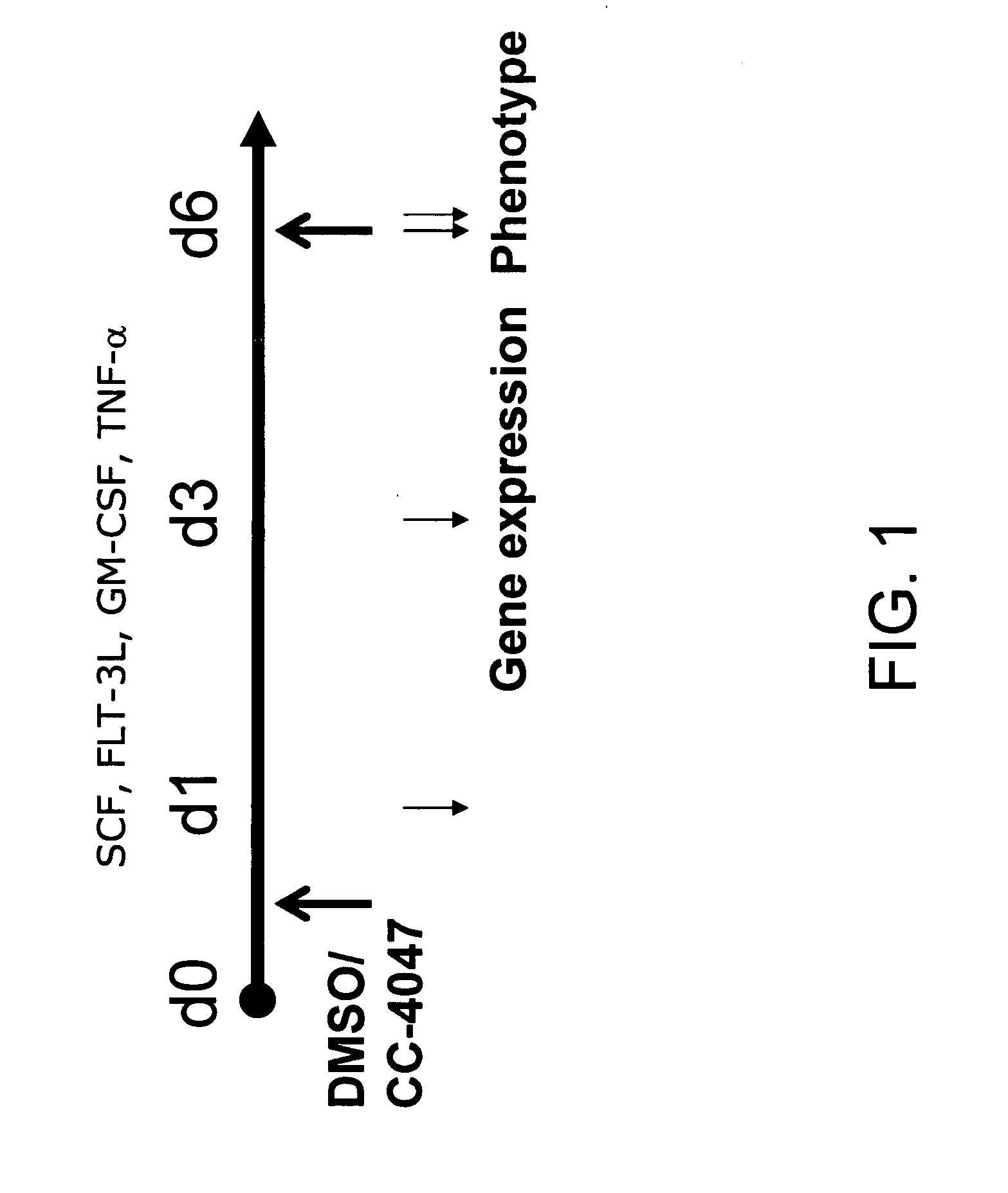
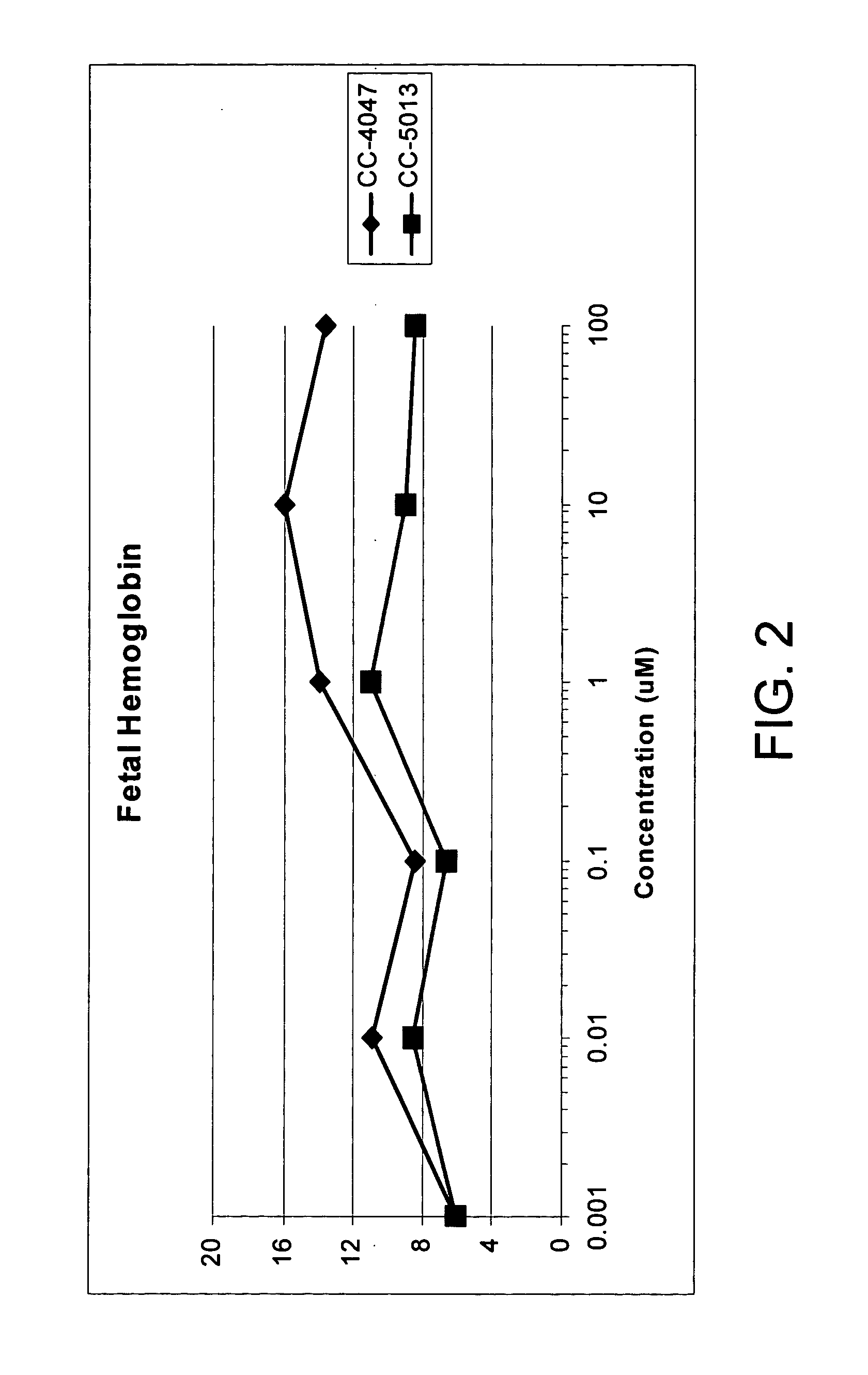
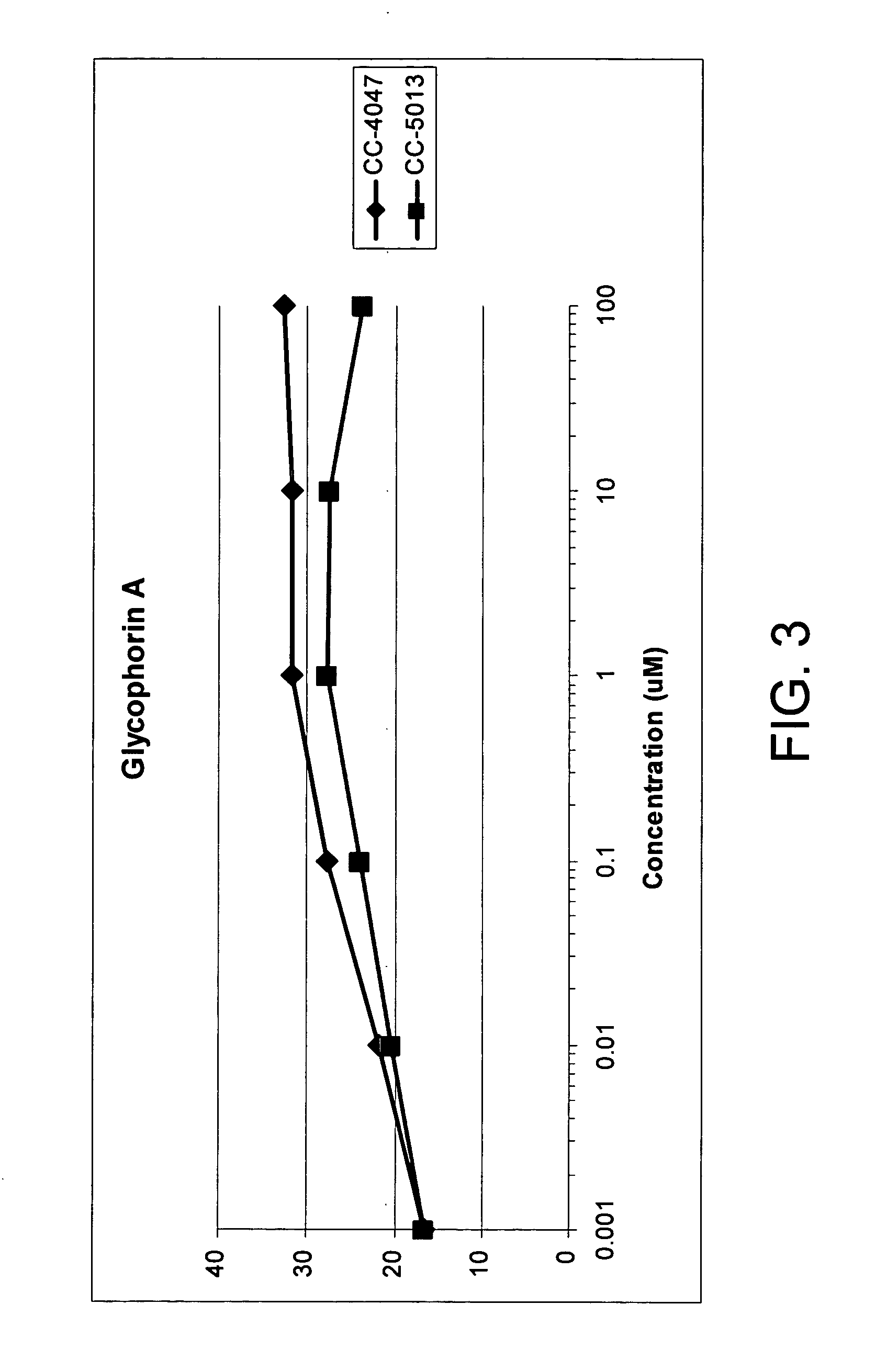
The present invention is directed to the use of immunomodulatory compounds, particularly members of the class of compounds known as IMiDs™, and more specifically the compounds 4-(Amino)-2-(2,6-dioxo(3-piperidyl))-isoindoline-1,3-dione and 3-(4-amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydroisoindol-2-yl)-piperidine-2,6-dione, to induce the expression of fetal hemoglobin genes, genes essential for erythropoiesis, and genes encoding alpha hemoglobin stabilizing protein, within a population of CD34+ cells. These compounds are used to treat hemoglobinopathies such as sickle cell anemia or β-thalassemia, or anemias caused by disease, surgery, accident, or the introduction or ingestion of toxins, poisons or drugs.
Owner:SIGNAL PHARMA LLC
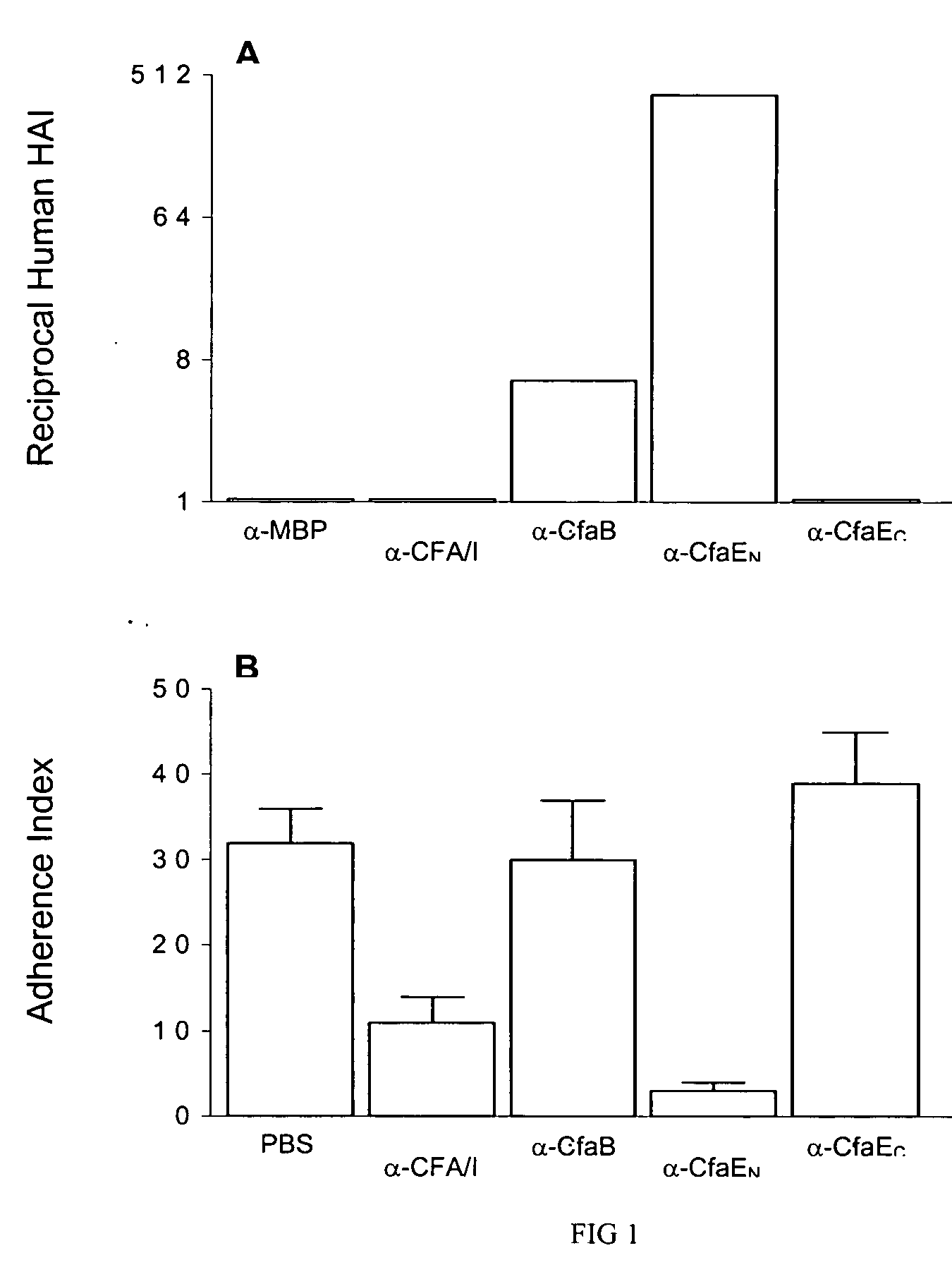
Adhesin as immunogen against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
ActiveUS20060153878A1Inhibition of colonizationAvoid stickingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliDiarrhea
The inventive subject matter relates to the methods for the induction of immunity and prevention of diarrhea resulting from Escherichia coli. The inventive subject matter also relates to the use Escherichia coli adhesins as immunogens and to the construction of conformationally stability and protease resistant Escherichia coli adhesin constructs useful for inducing immunity to Escherichia coli pathogenic bacteria. The methods provide for the induction of B-cell mediated immunity and for the induction of antibody capable of inhibiting the adherence and colonization of Escherichia coli including enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, to human cells.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Olefin metathesis reaction catalyst and preparation method therefor
ActiveUS20190217277A1Separated/recovered readilyEasy to useMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRheniumUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The present invention relates to an olefin metathesis reaction catalyst where rhenium (Re) oxide or molybdenum (Mo) oxide is supported, as a catalyst main component, on a surface-modified mesoporous silica or mesoporous alumina support, and a preparation method therefor. The olefin metathesis reaction catalyst of the present invention allows highly efficient metathesis of long-chain unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least eight carbons at a low temperature of 150° C. or lower. The catalyst can be separated readily from reaction solution, regenerated at a low temperature of 400° C. or lower by removing toxins accumulated on it during the metathesis reaction, and used repeatedly in metathesis reaction many times, thereby being made good use in commercial olefin metathesis processes.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Compositions and methods for topical application and transdermal delivery of botulinum toxins
ActiveUS20050196414A1Reduce hypersecretionReduce sweatingCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderEpitheliumMedicine
A composition for topical application of a botulinum toxin (including botulinum toxin derivatives) comprises a botulinum toxin and a carrier comprising a polymeric backbone comprising a long-chain polypeptide or nonpeptidyl polymer having attached positively charged branching or “efficiency” groups. The invention also relates to methods for reducing muscle paralysis and other conditions that may be treated with a botulinum toxin, particularly paralysis of subcutaneous, and most particularly, facial, muscles, by topically applying an effective amount of the botulinum toxin and carrier, in conjunction, to the subject's skin or epithelium. Kits for administration are also described.
Owner:REVANCE THERAPEUTICS INC
DIG-3 insecticidal Cry toxins
DIG-3 Cry toxins, polynucleotides encoding such toxins, and transgenic plants that produce such toxins are useful to control insect pests.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
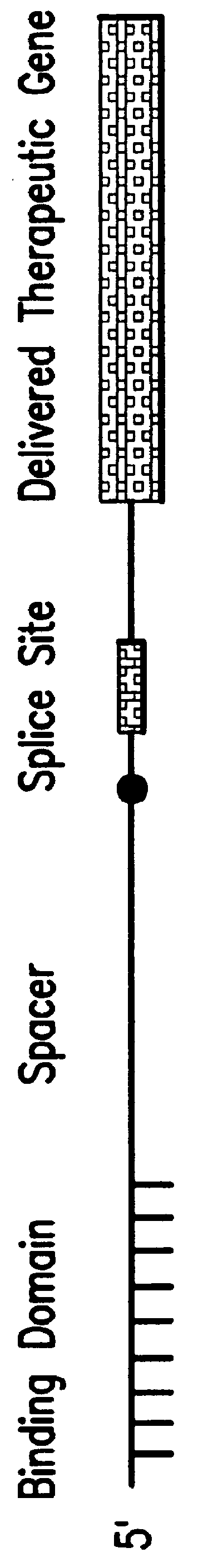
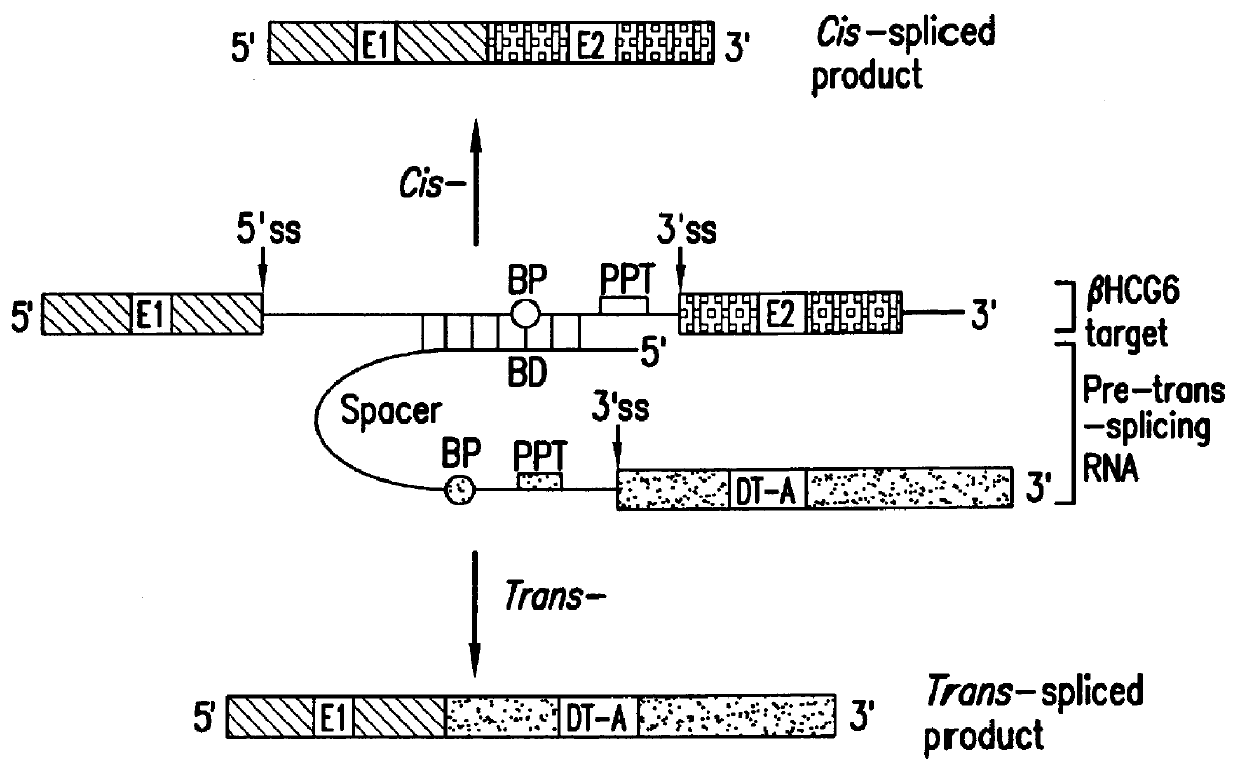
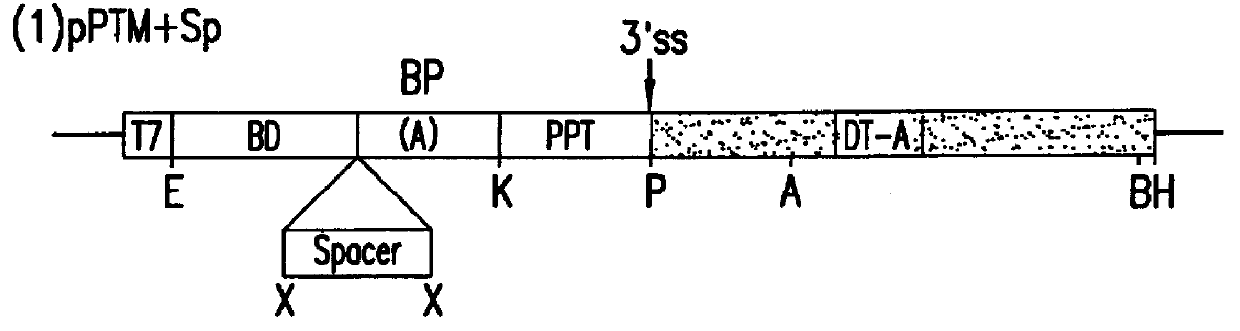
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
Stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functions or binding specificities
ActiveUS20060228300A1Reduce exposureReduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntibody fragmentsBinding peptide
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Particular embodiments concern stably tethered structures comprising a homodimer of a first monomer, comprising a dimerization and docking domain attached to a first precursor, and a second monomer comprising an anchoring domain attached to a second precursor. The first and second precursors may be virtually any molecule or structure, such as antibodies, antibody fragments, antibody analogs or mimetics, aptamers, binding peptides, fragments of binding proteins, known ligands for proteins or other molecules, enzymes, detectable labels or tags, therapeutic agents, toxins, pharmaceuticals, cytokines, interleukins, interferons, radioisotopes, proteins, peptides, peptide mimetics, polynucleotides, RNAi, oligosaccharides, natural or synthetic polymeric substances, nanoparticles, quantum dots, organic or inorganic compounds, etc. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a simple, easy to purify way to obtain any binary compound attached to any monomeric compound, or any trinary compound.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Activatable recombinant neurotoxins
InactiveUS7132259B1Minimize security riskEnhanced efficiency and rateSenses disorderNervous disorderToxinNeurotoxin
The invention provides, in part, compositions comprising activatable recombinant neurotoxins and polypeptides derived therefrom. The invention also provides, in part, nucleic acid molecules encoding such polypeptides, and methods of making such polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
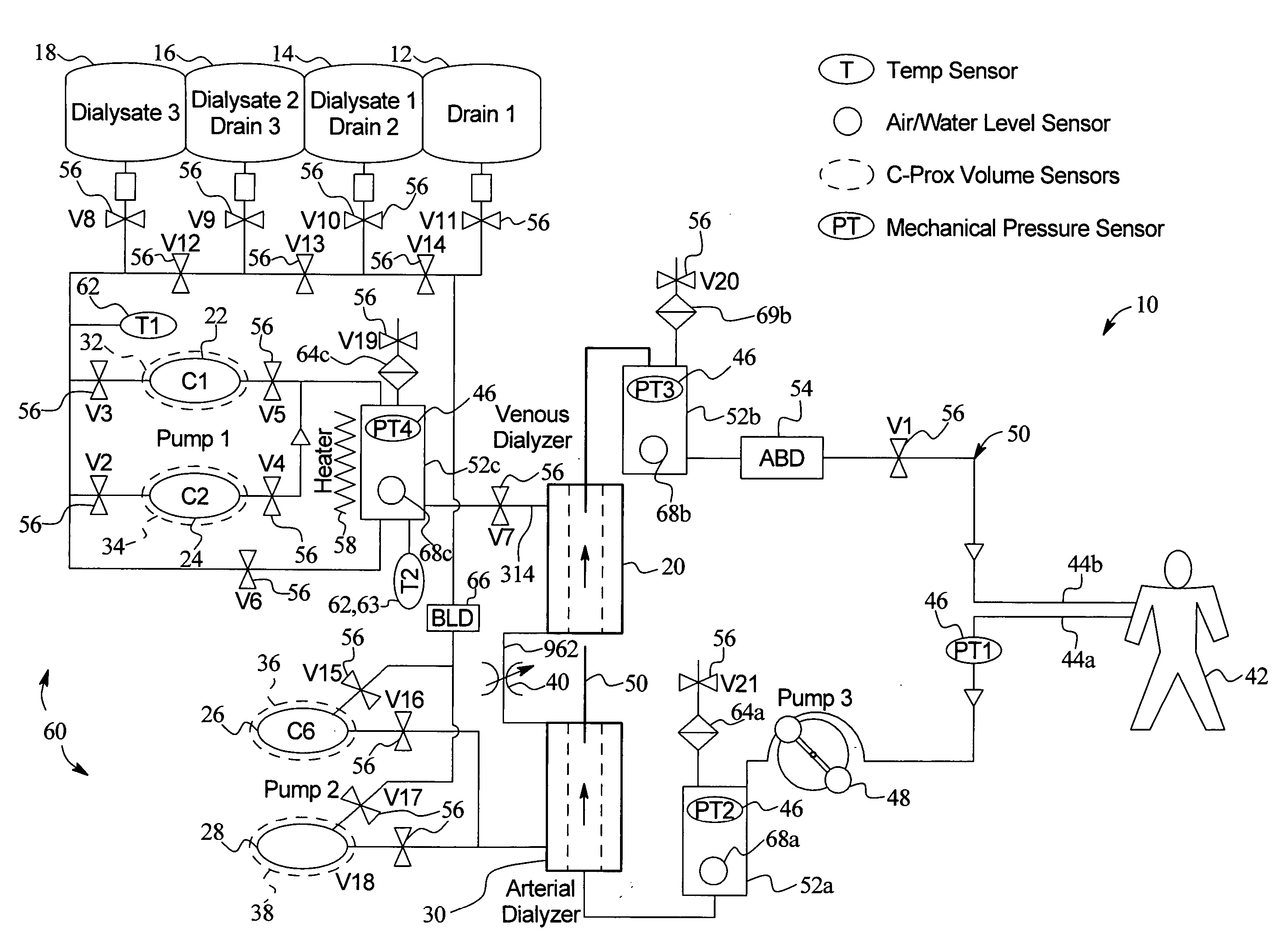
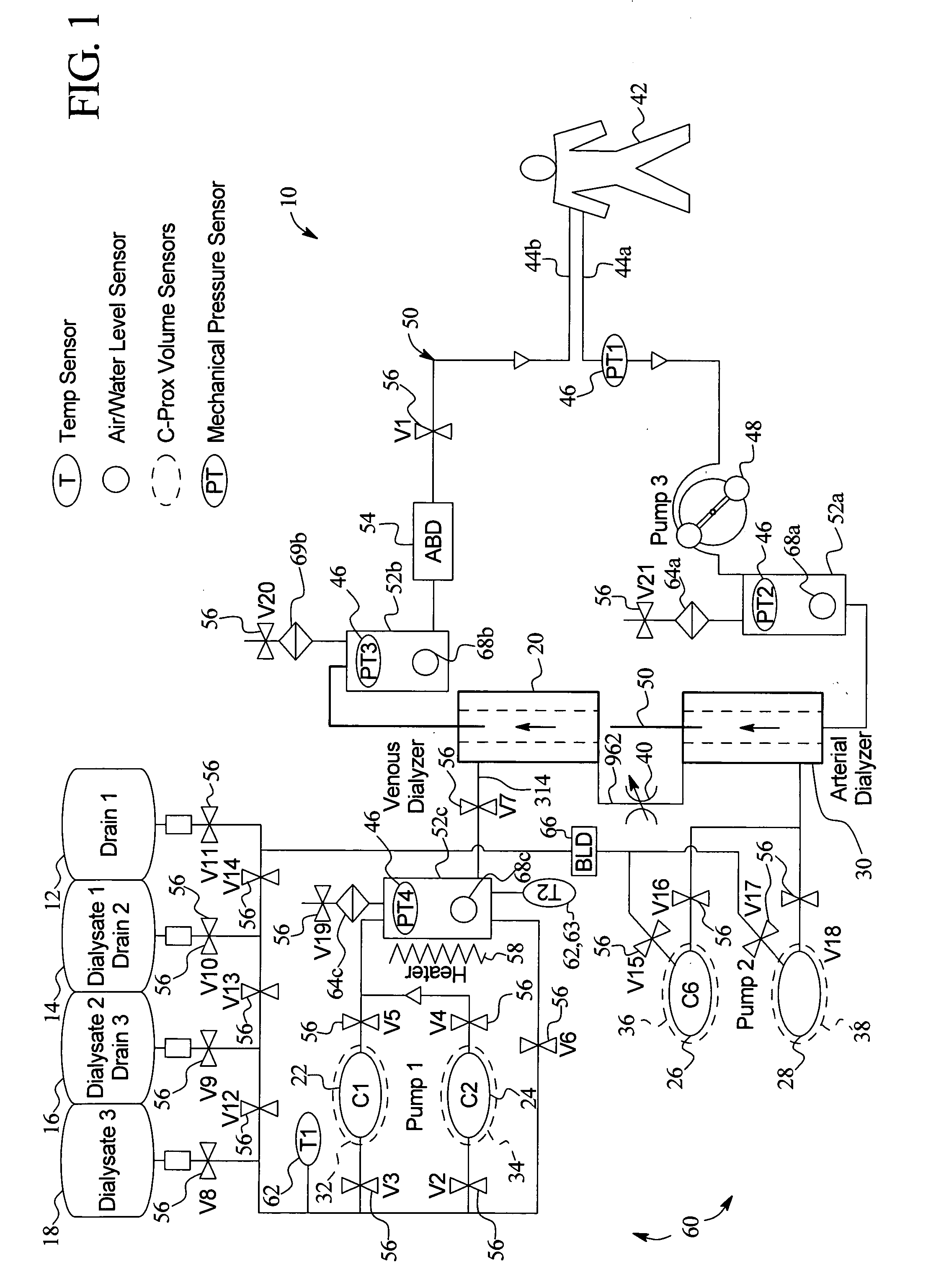
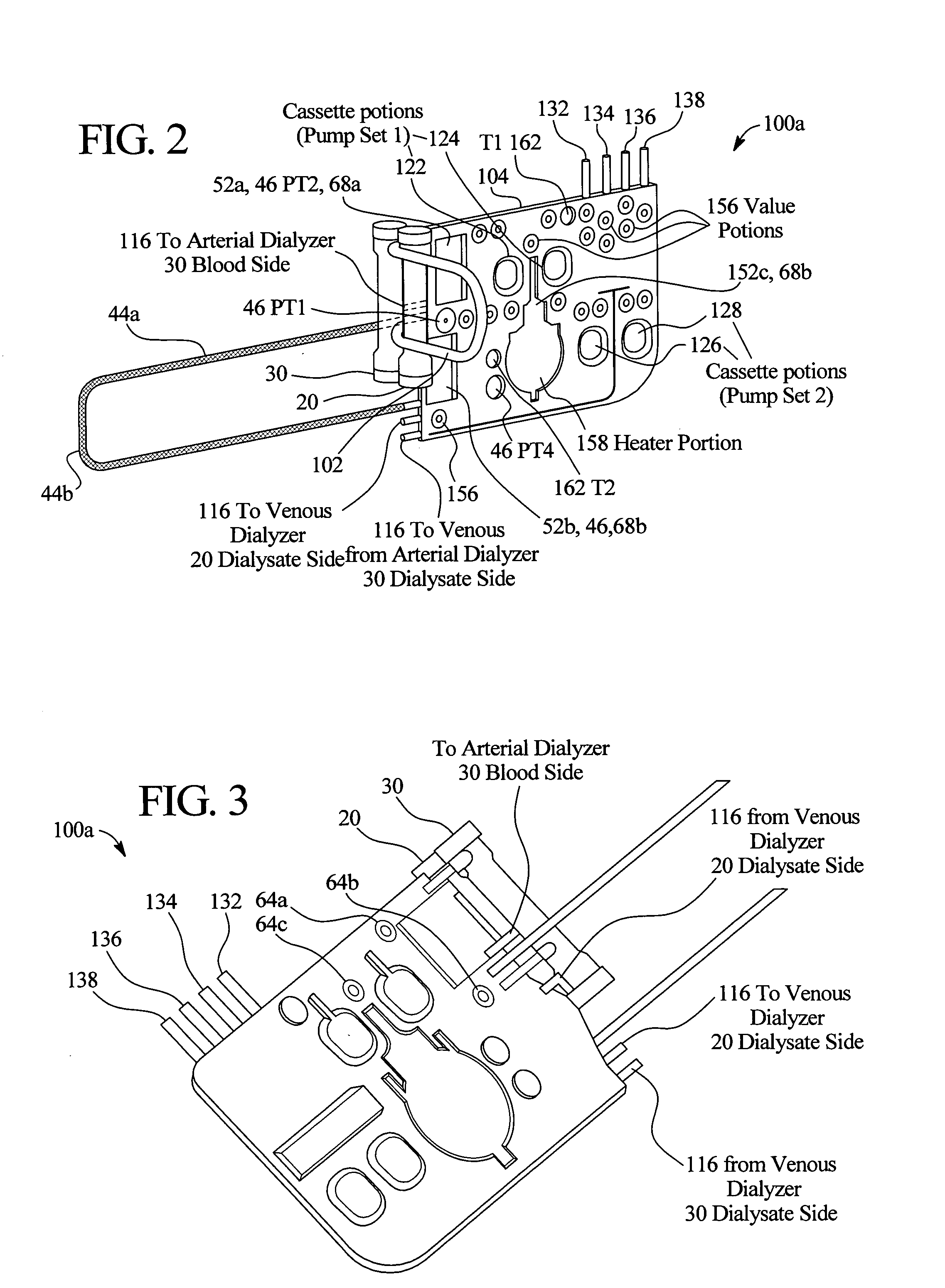
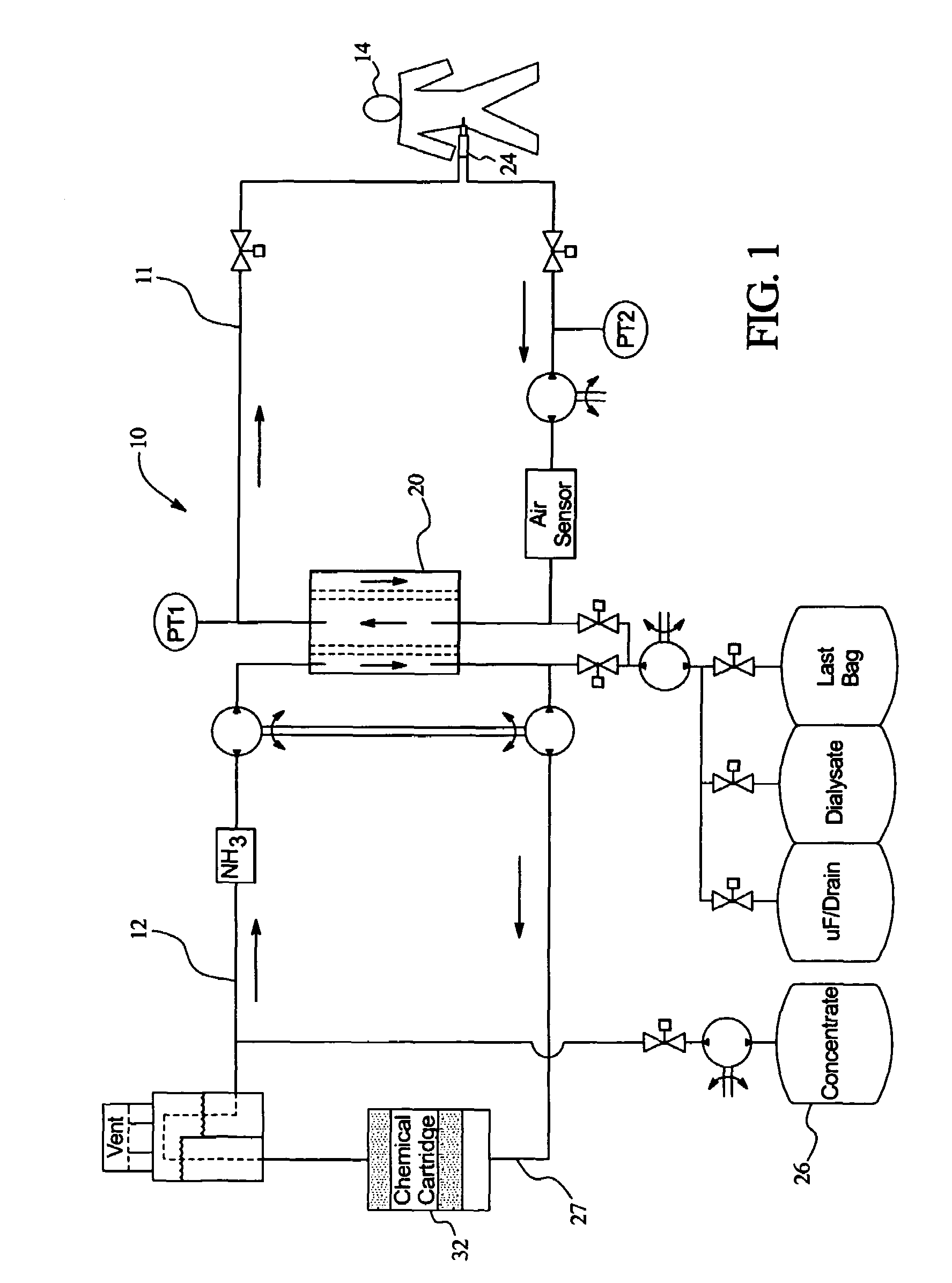
Method and composition for removing uremic toxins in dialysis processes
ActiveUS7241272B2Improved dialysis procedureReduce impurityOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesToxinUrease
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com