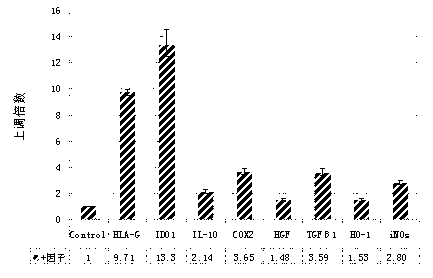Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
288 results about "Proinflammatory cytokine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule (a cytokine) that is excreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Tₕ) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-12, and IL-18, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interferon gamma (IFNγ), and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and play an important role in mediating the innate immune response. Inflammatory cytokines are predominantly produced by and involved in the upregulation of inflammatory reactions.
Nerve stimulation techniques
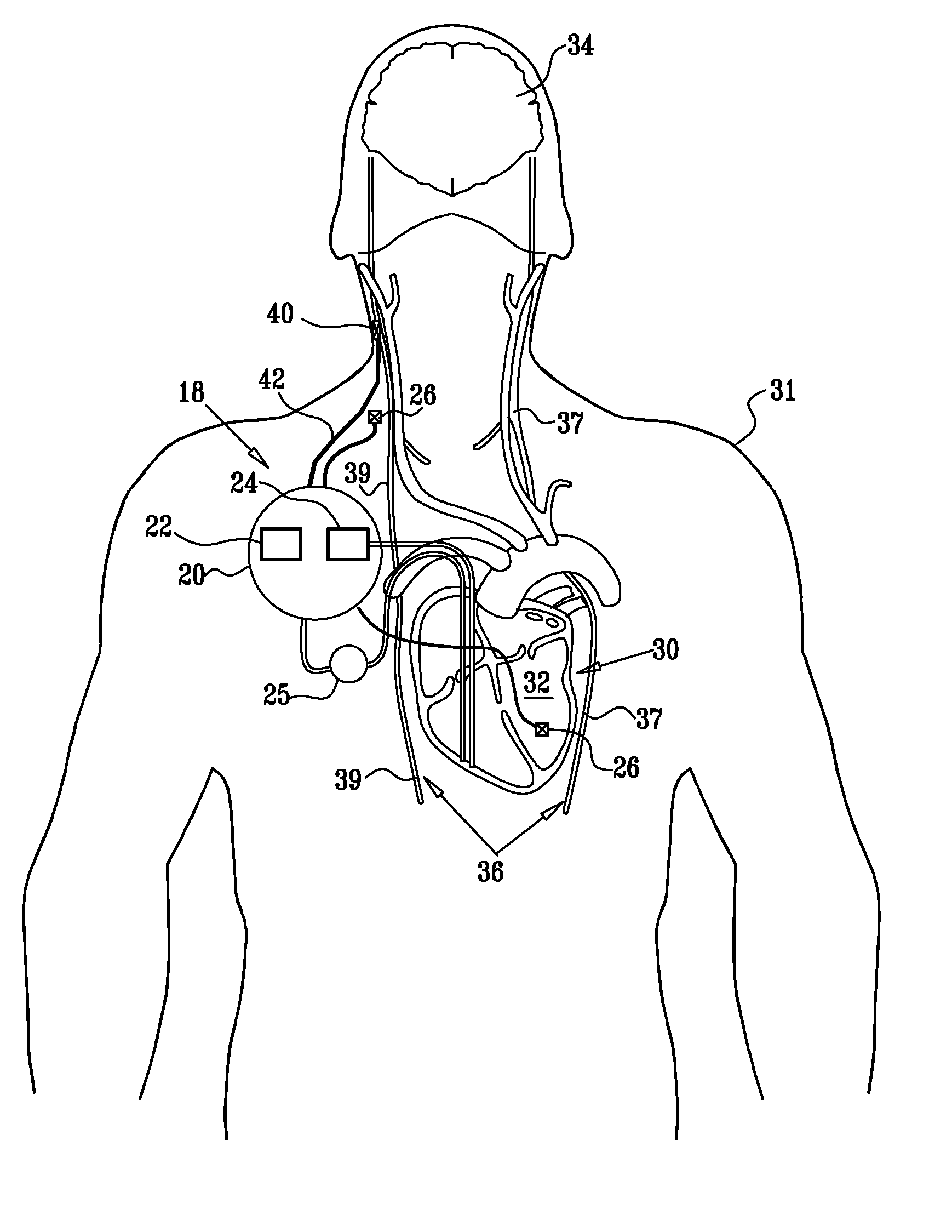
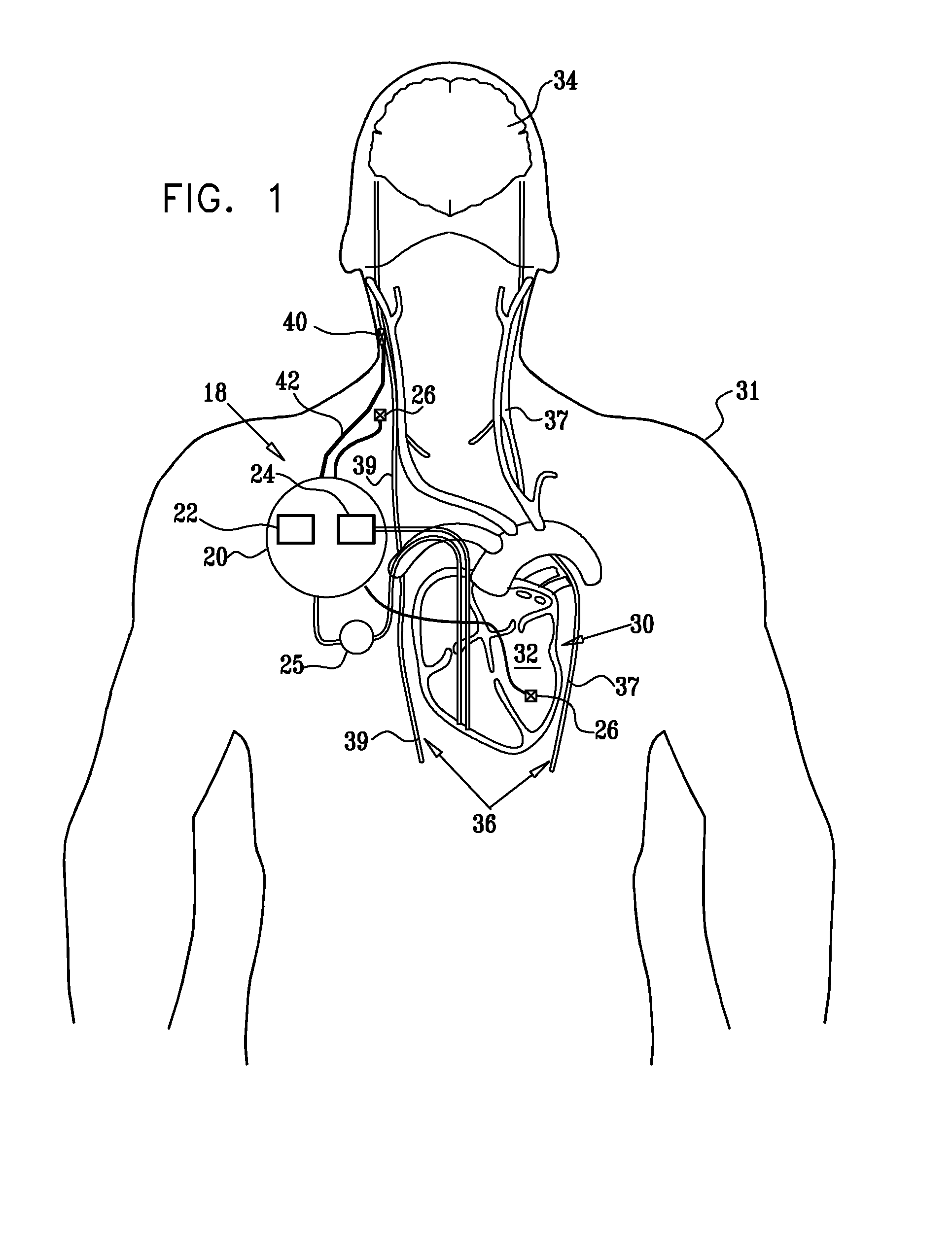
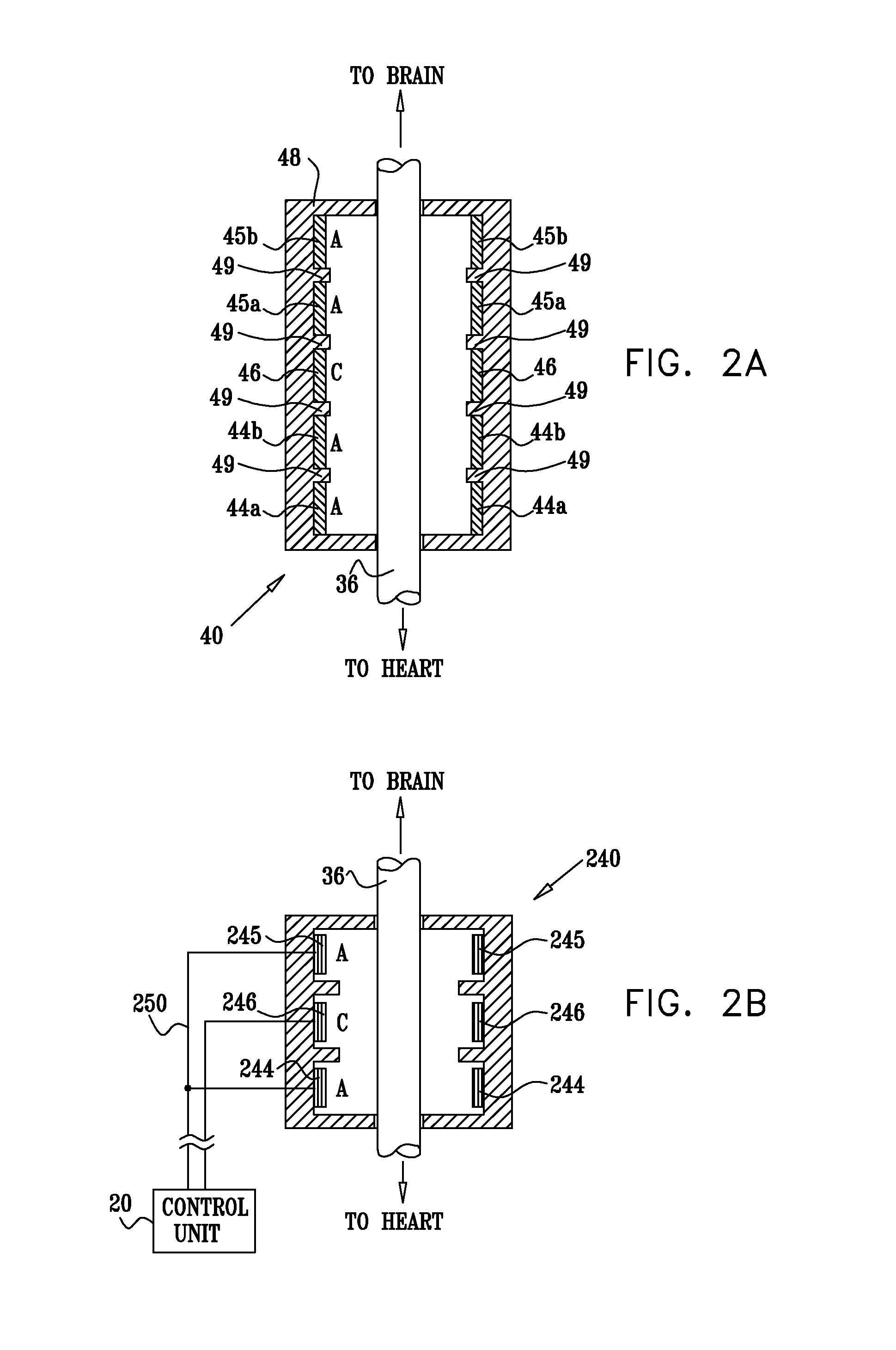
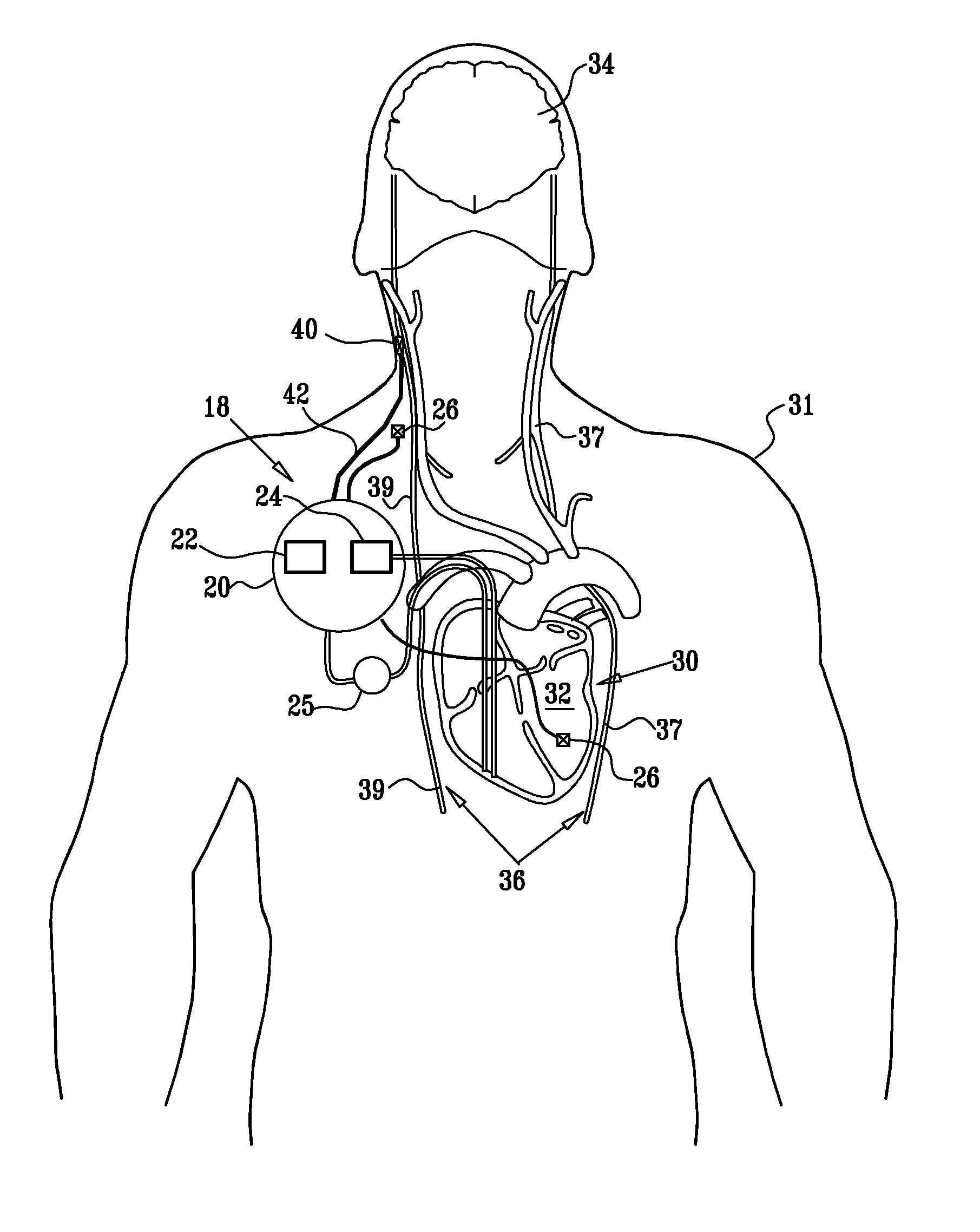
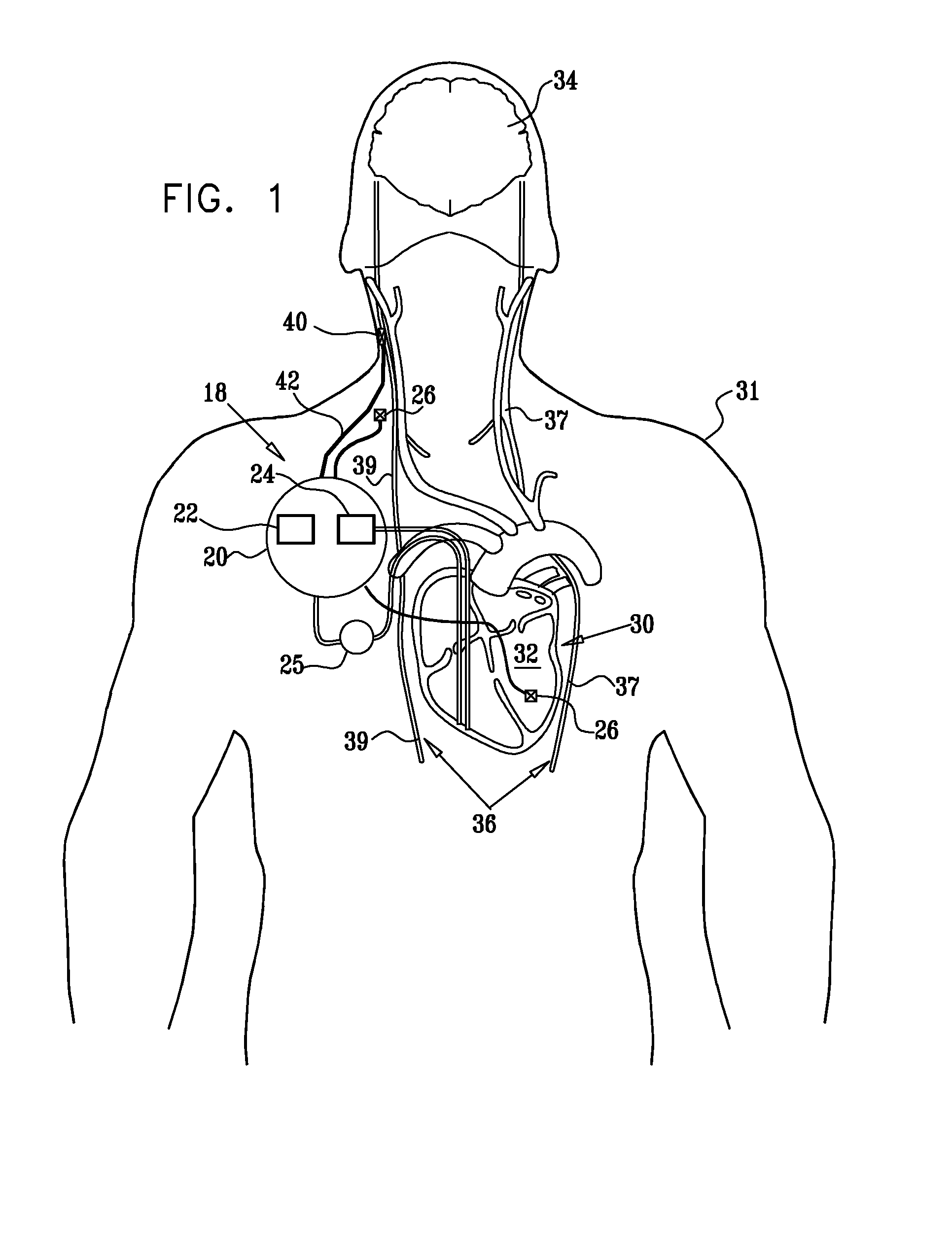
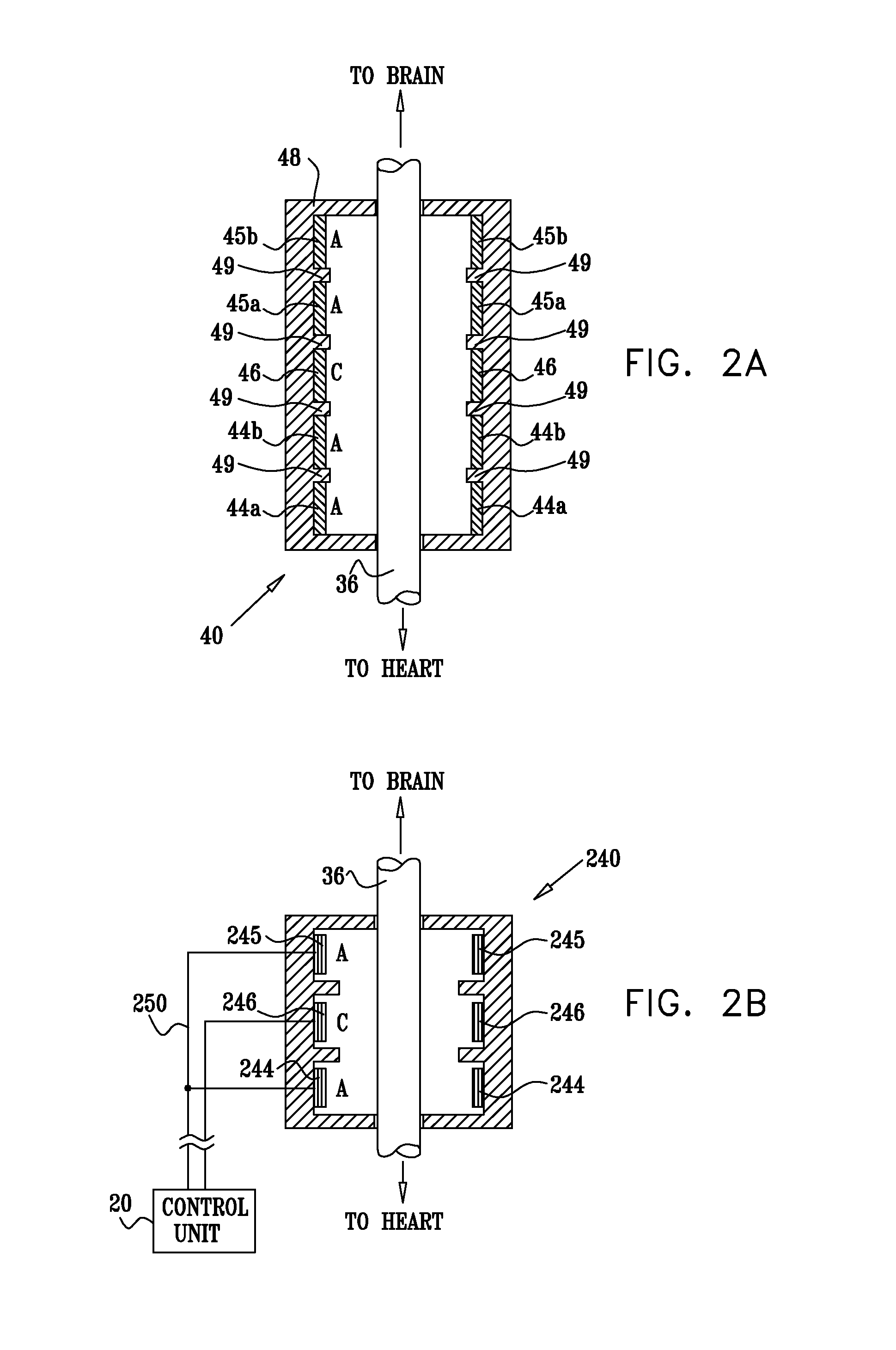
InactiveUS20110224749A1Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialHeart stimulatorsMedicineCytokine
A method is provided for treating heart failure in a subject in need of such treatment, including applying a stimulating current to parasympathetic nervous tissue of the subject, selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve and an epicardial fat pad. The stimulating current is configured to inhibit release of at least one proinflammatory cytokine sufficiently to the treat heart failure of the subject. A level of the at least one proinflammatory cytokine is measured. Optionally, the stimulating current is configured to change a level of Connexin 43 of the subject, and the level of Connexin 43 is also measured. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
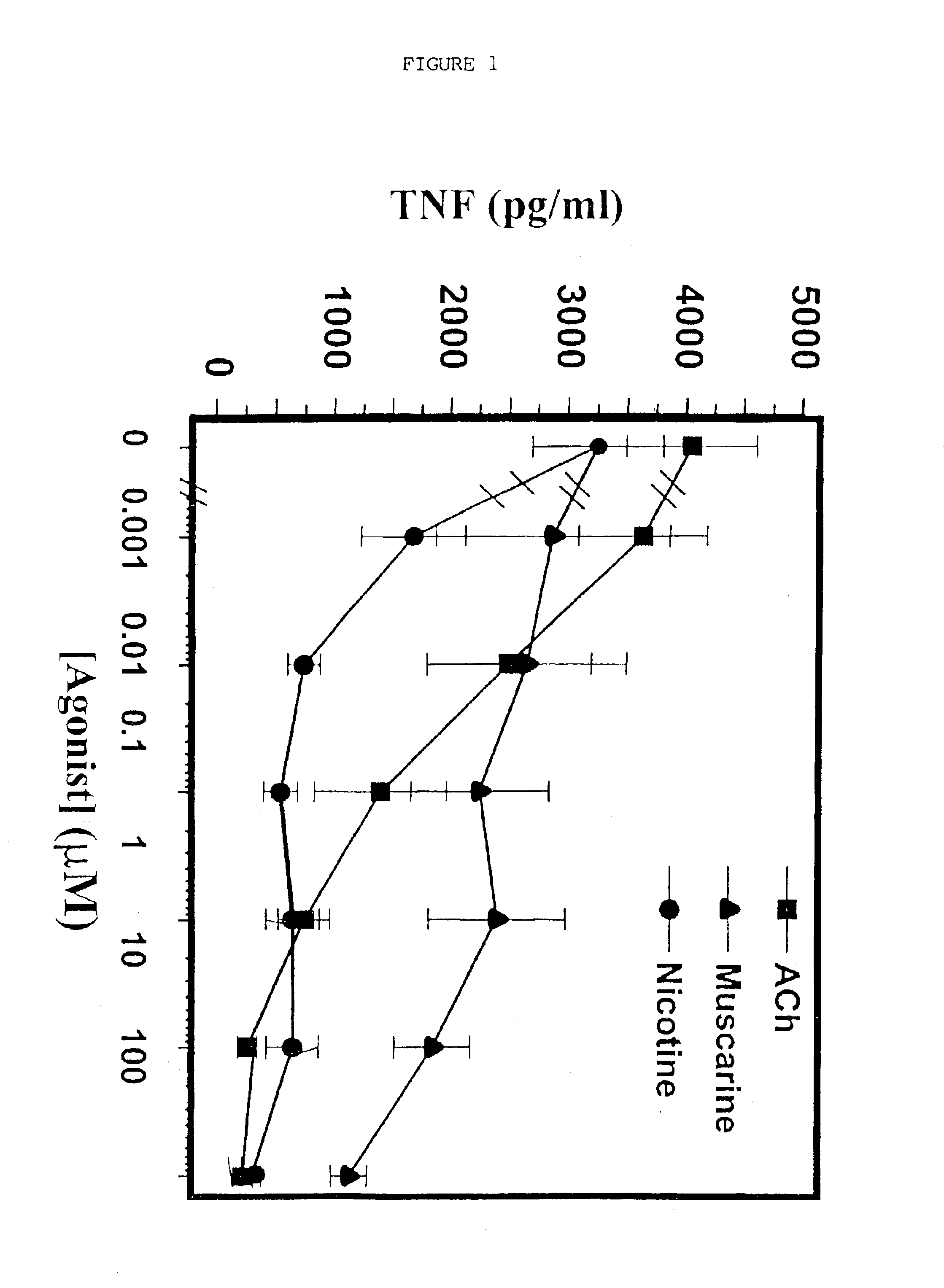
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by cholinergic agonists and vagus nerve stimulation
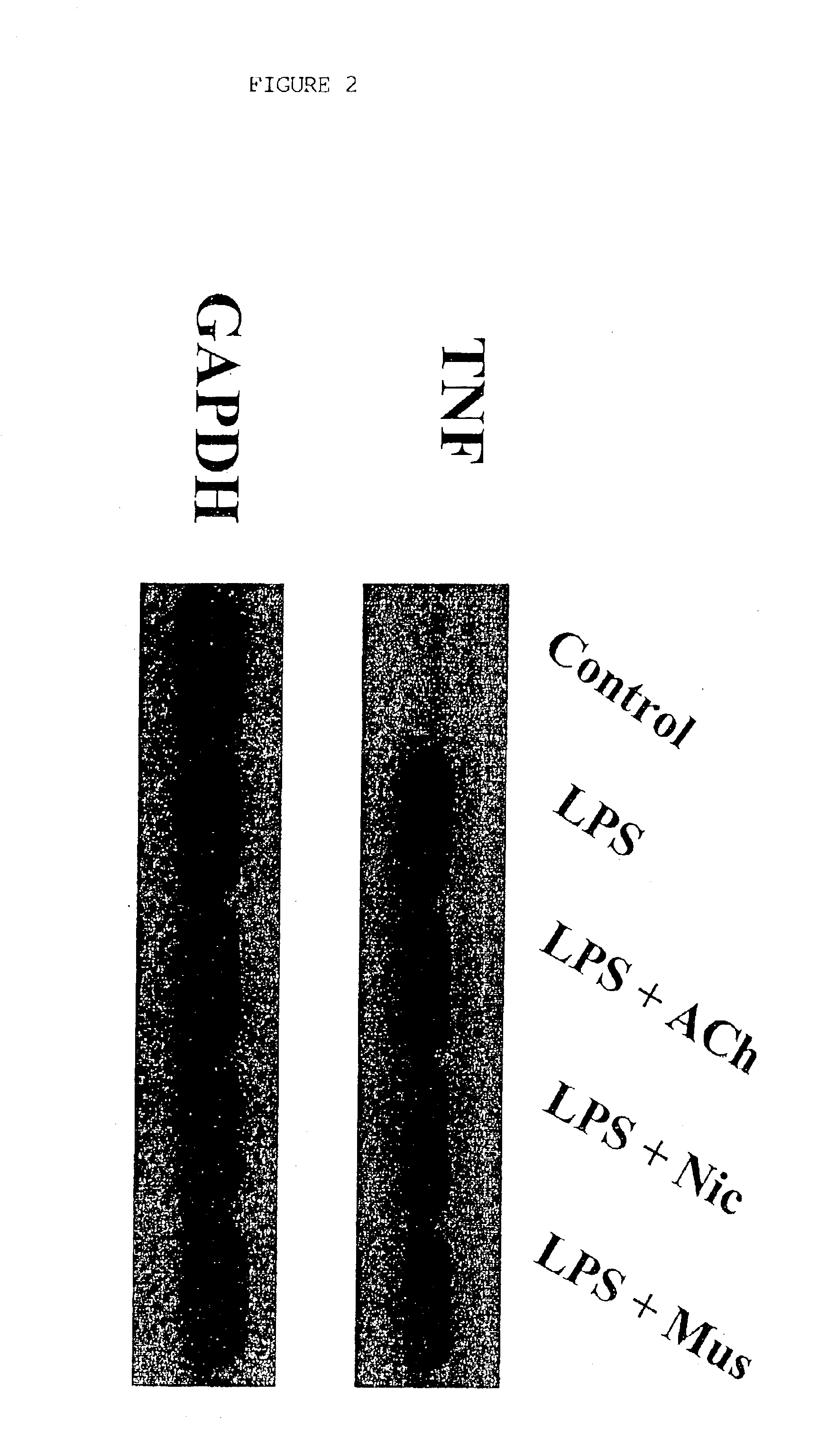
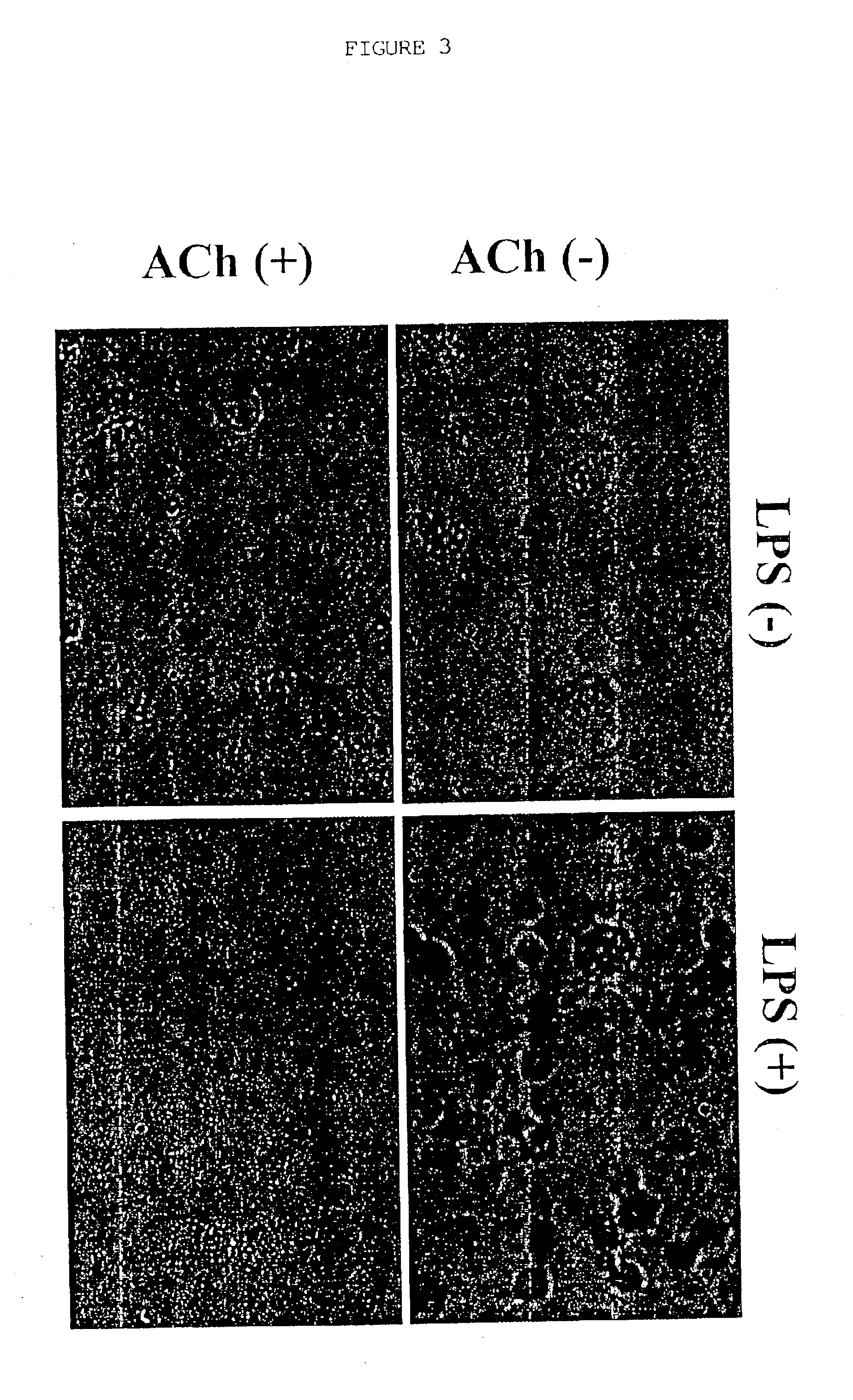
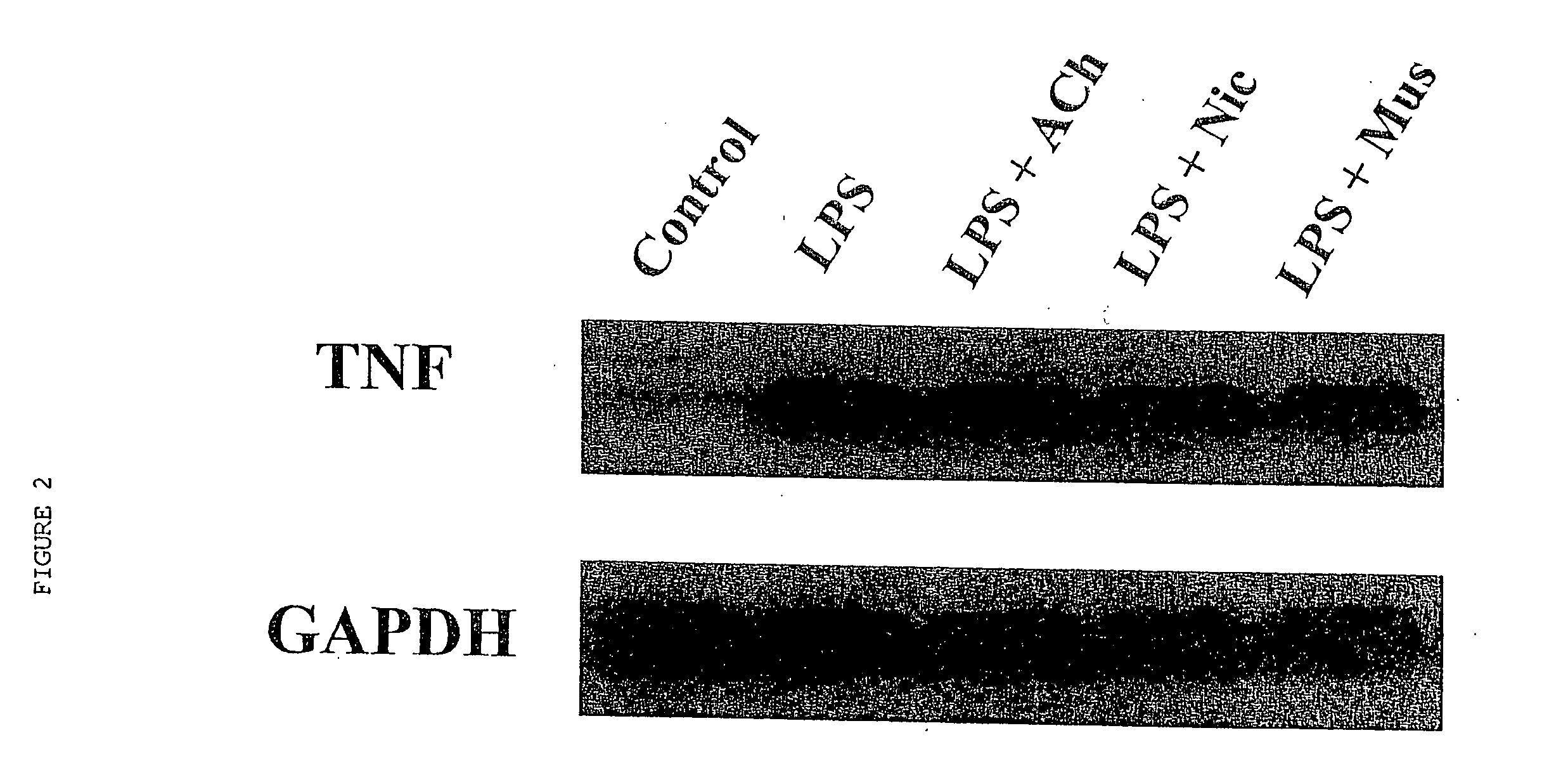
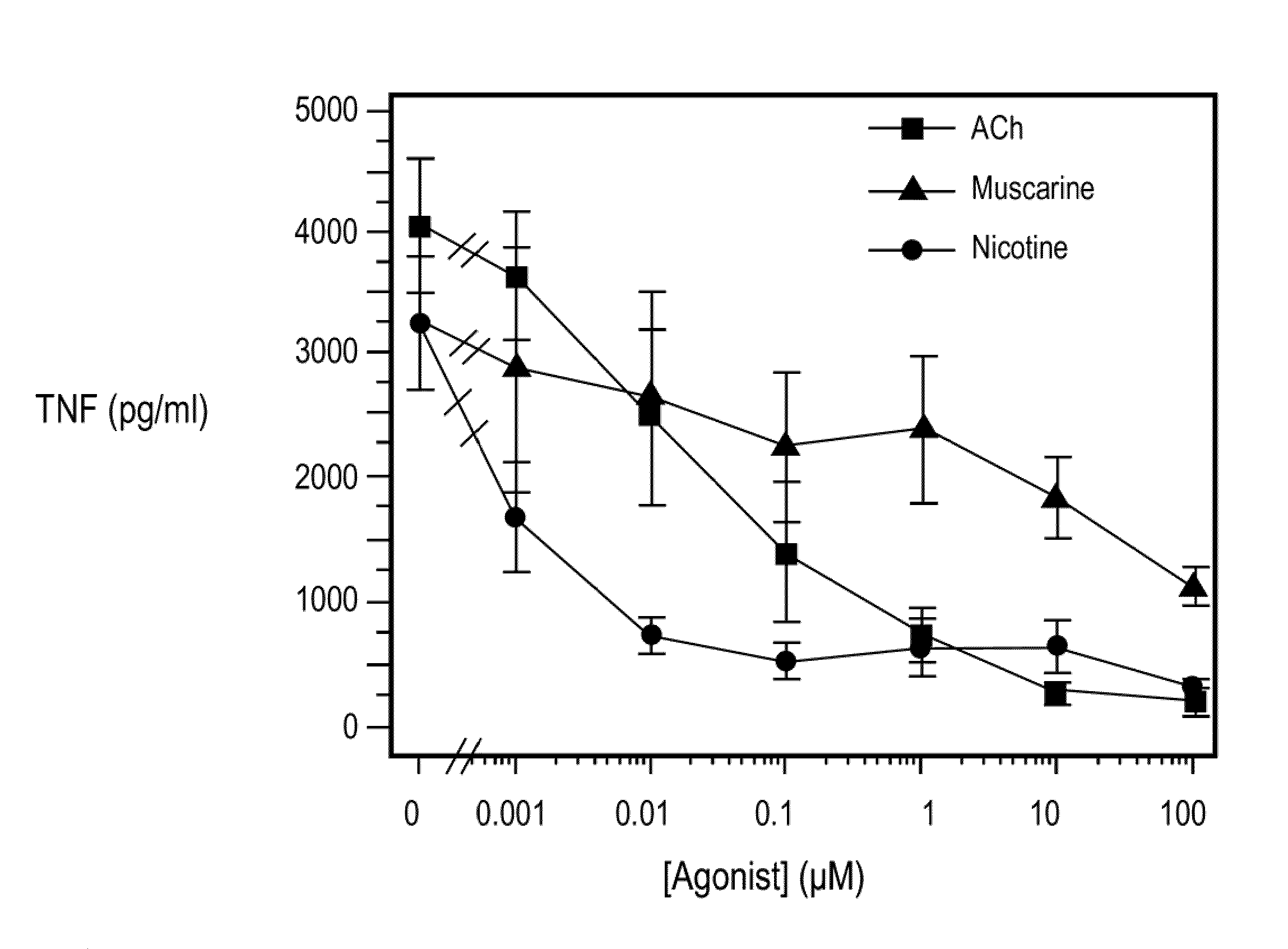
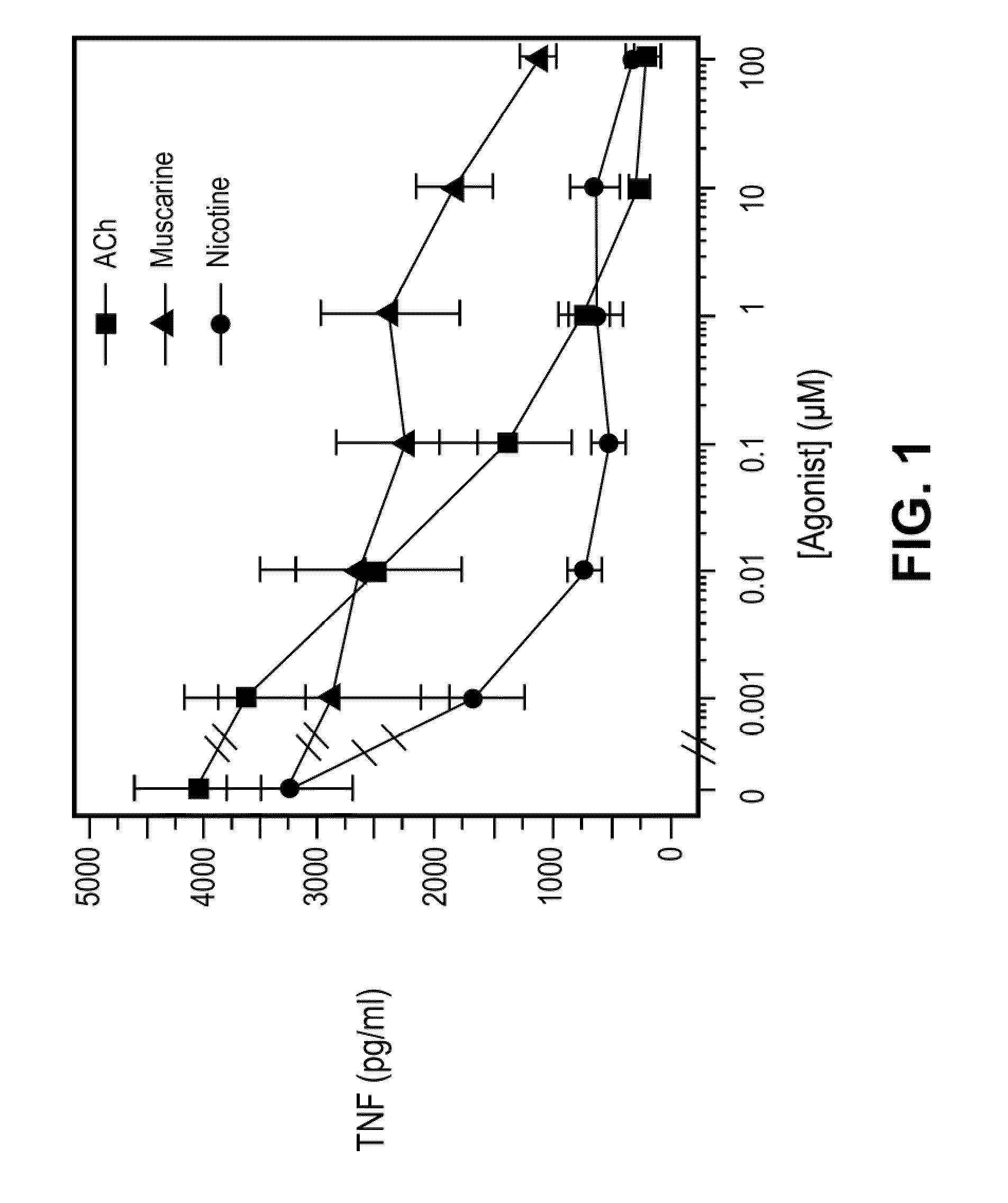
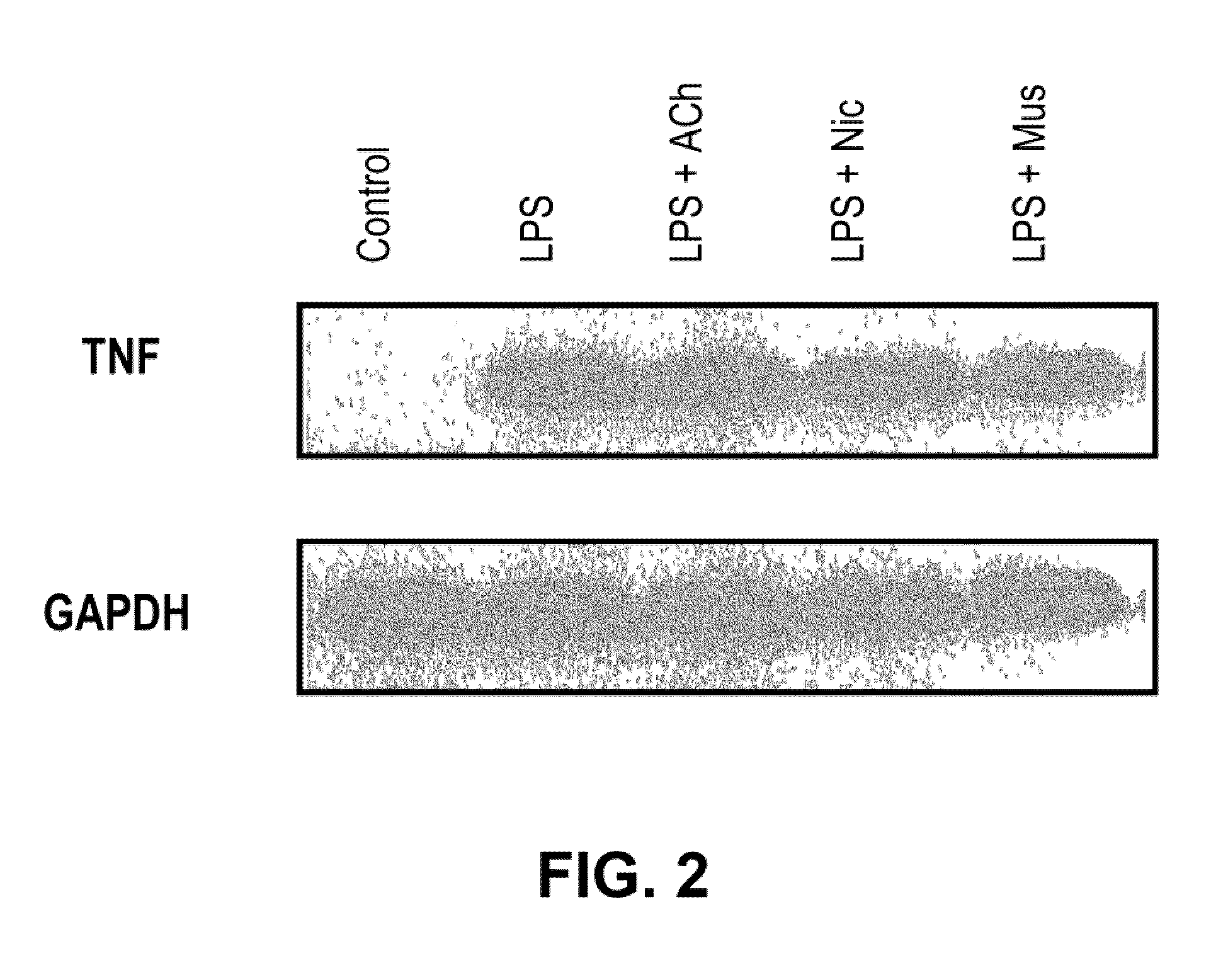
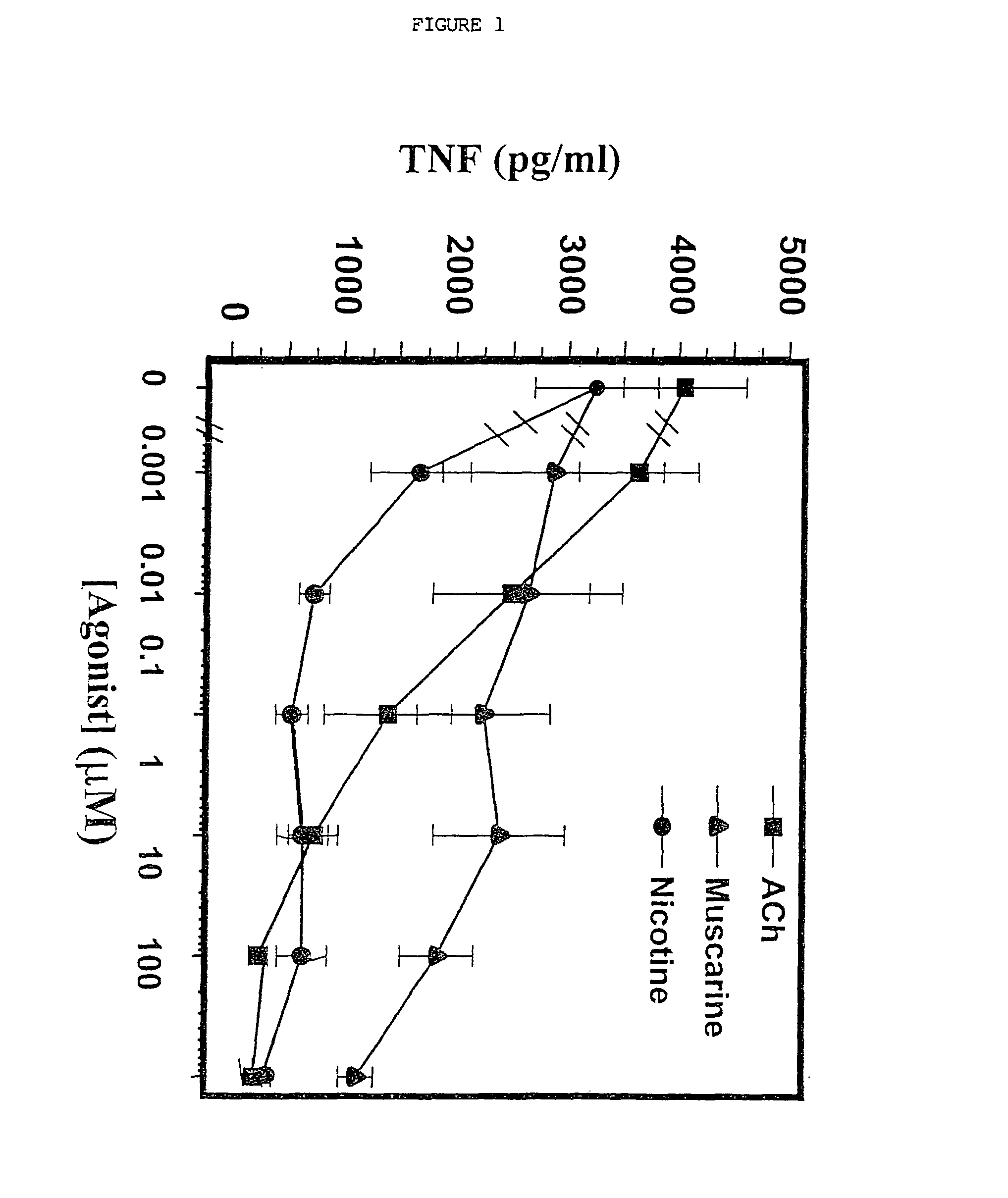
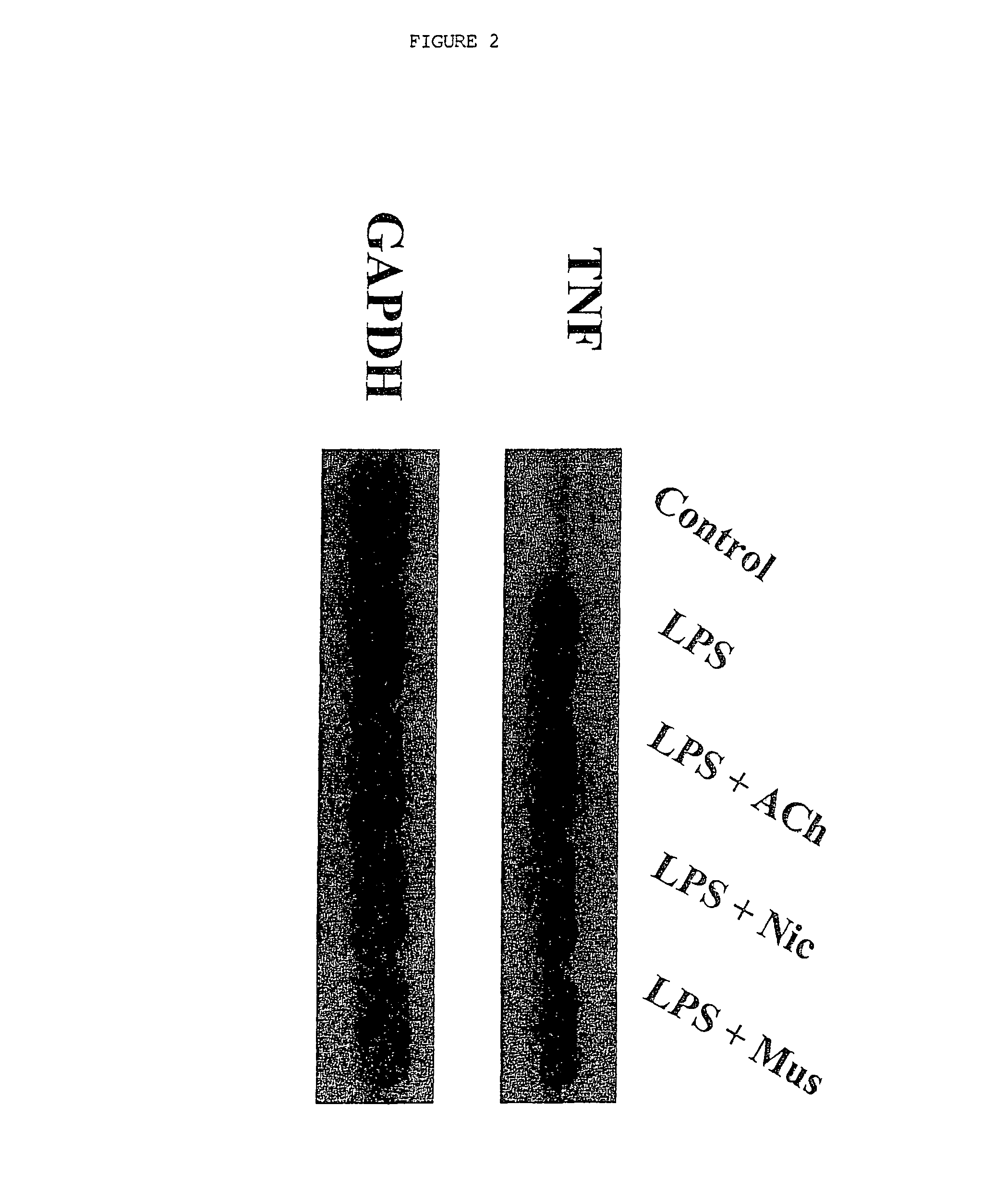
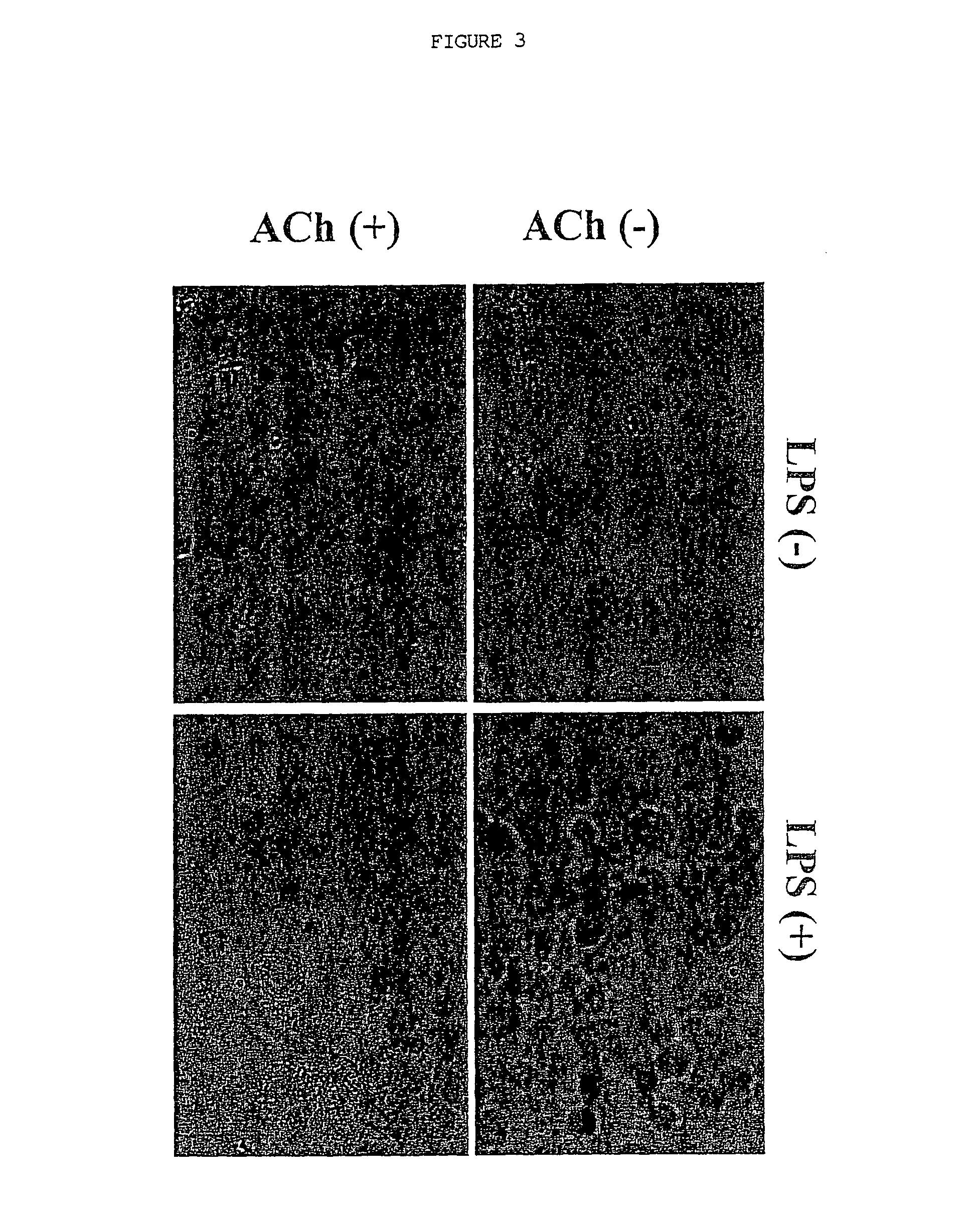
A method of inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine in a cell is disclosed. The method comprises treating the cell with a cholinergic agonist. The method is useful in patients at risk for, or suffering from, a condition mediated by an inflammatory cytokine cascade, for example endotoxic shock. The cholinergic agonist treatment can be effected by stimulation of an efferent vagus nerve fiber, or the entire vagus nerve.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by cholinergic agonists and vagus nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20050125044A1Inhibition releaseImplantable neurostimulatorsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsEfferentEndotoxic shock
A method of inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine in a cell is disclosed. The method comprises treating the cell with a cholinergic agonist. The method is useful in patients at risk for, or suffering from, a condition mediated by an inflammatory cytokine cascade, for example endotoxic shock. The cholinergic agonist treatment can be effected by stimulation of an efferent vagus nerve fiber, or the entire vagus nerve.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Treatment of inflammation by non-invasive stimulation
InactiveUS20080249439A1Reduces proinflammatory cytokineInhibits the inflammatory reflexDevices for pressing relfex pointsChiropractic devicesInflammatory reflexFacial nerve
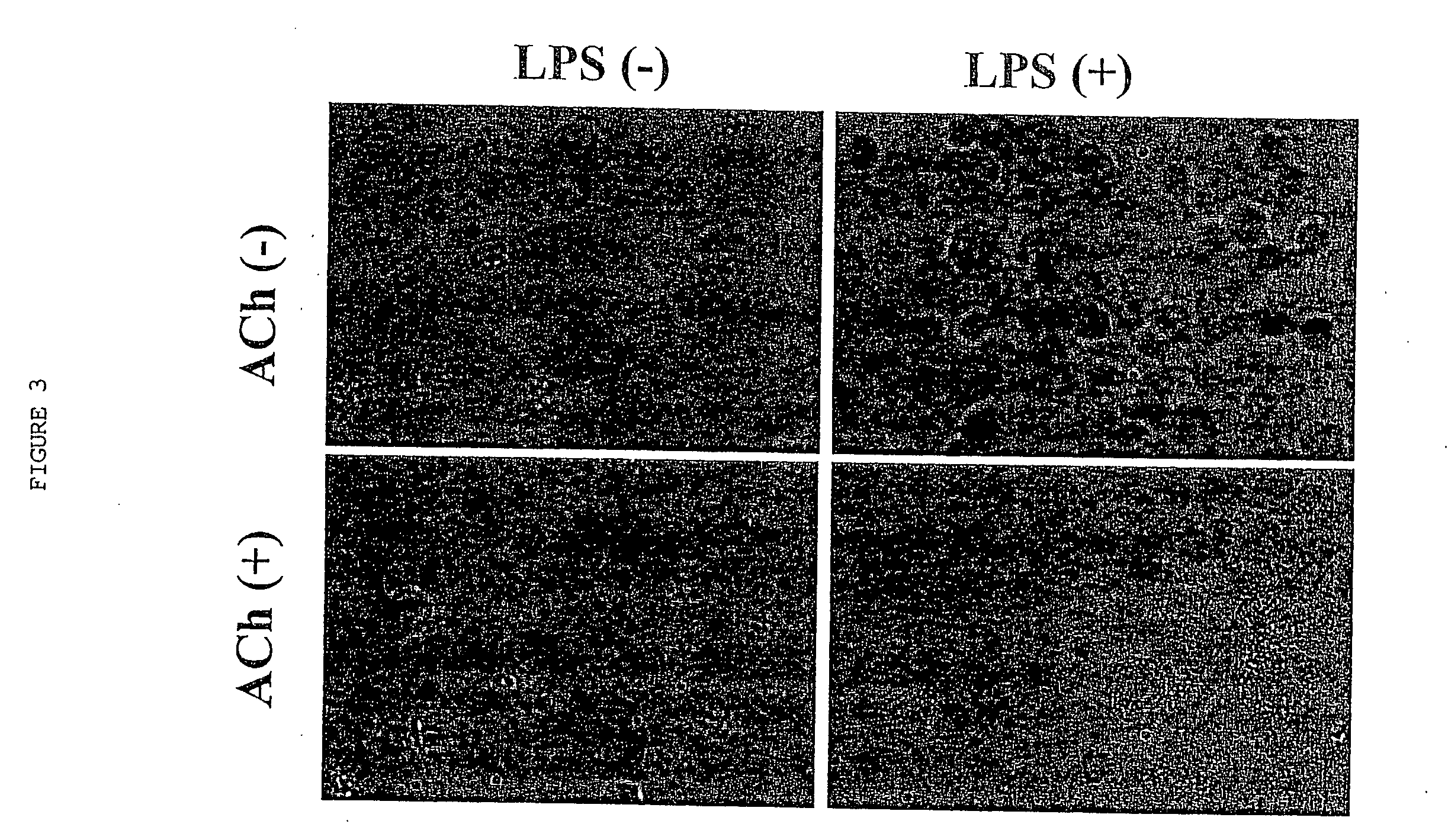
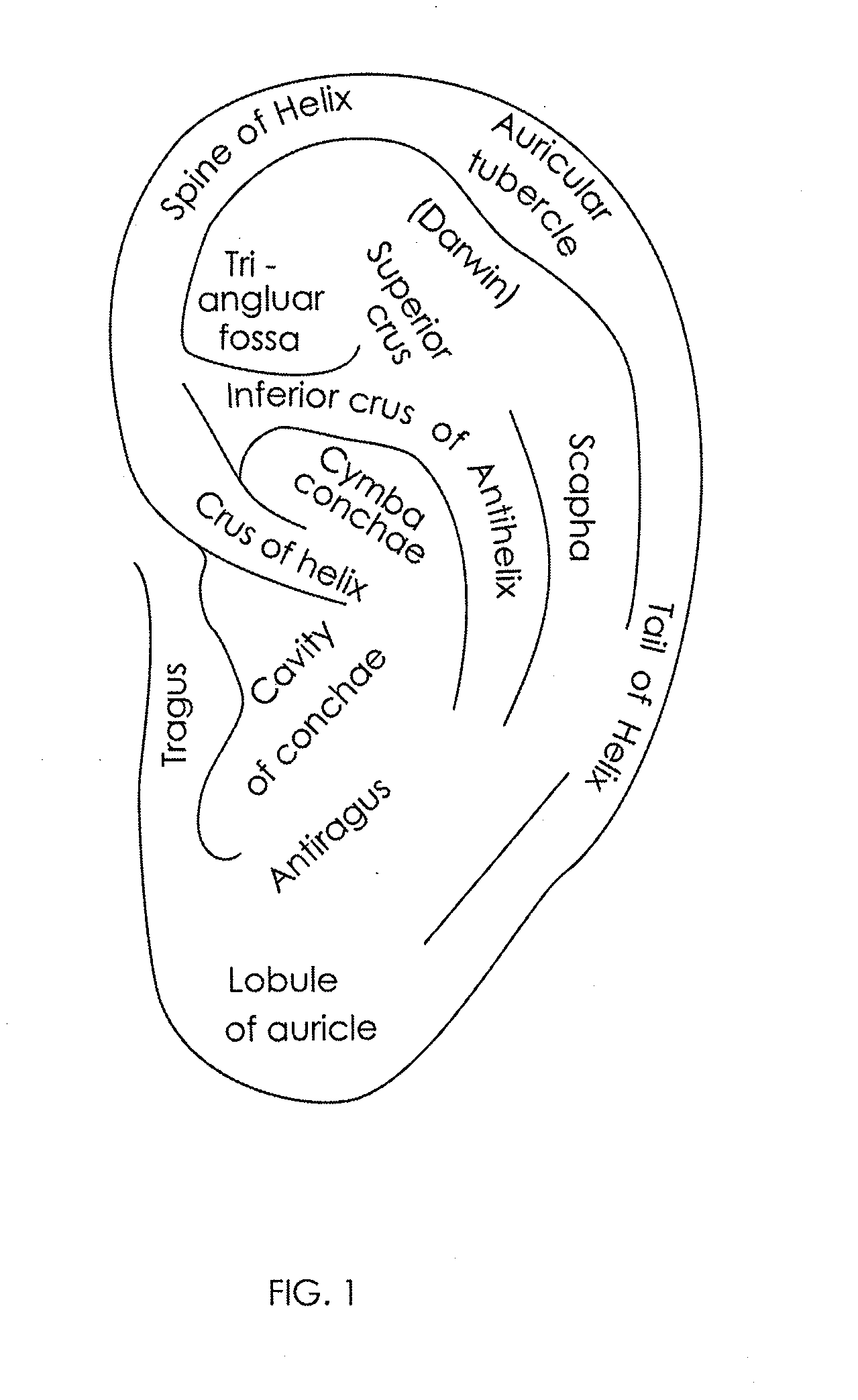
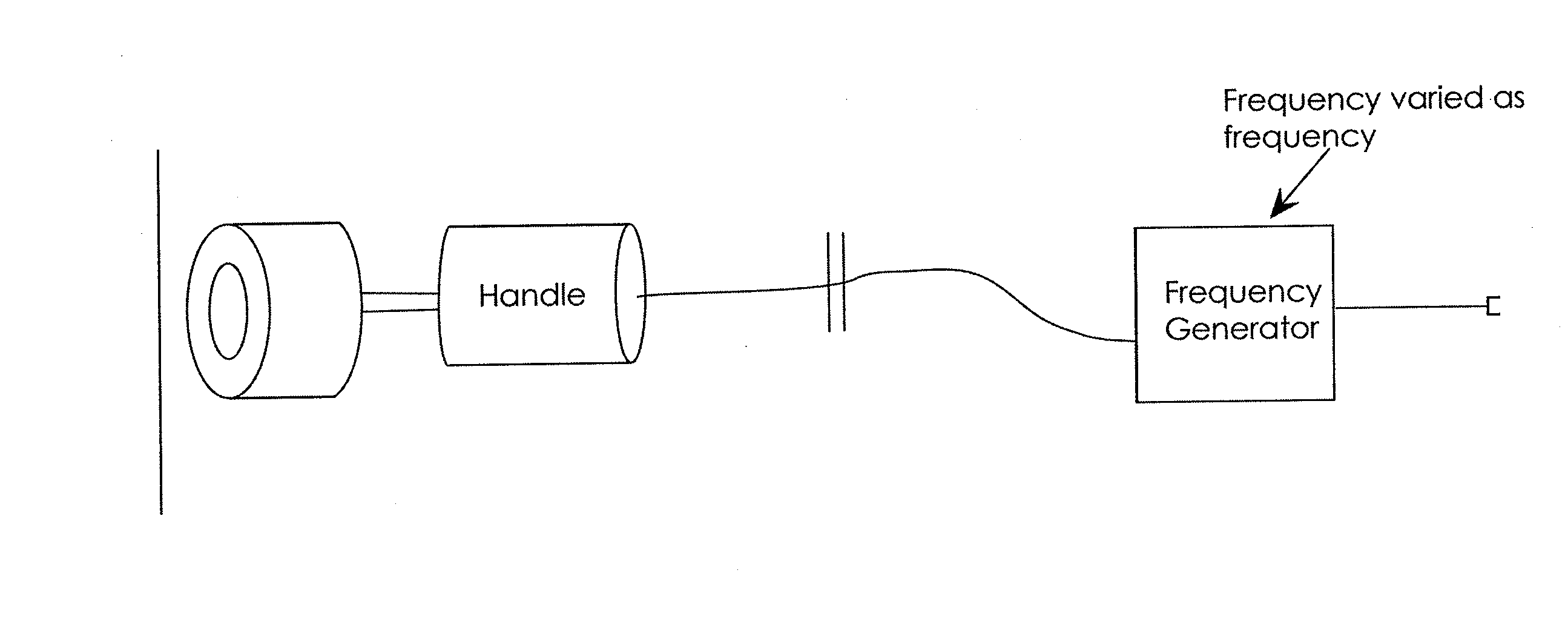
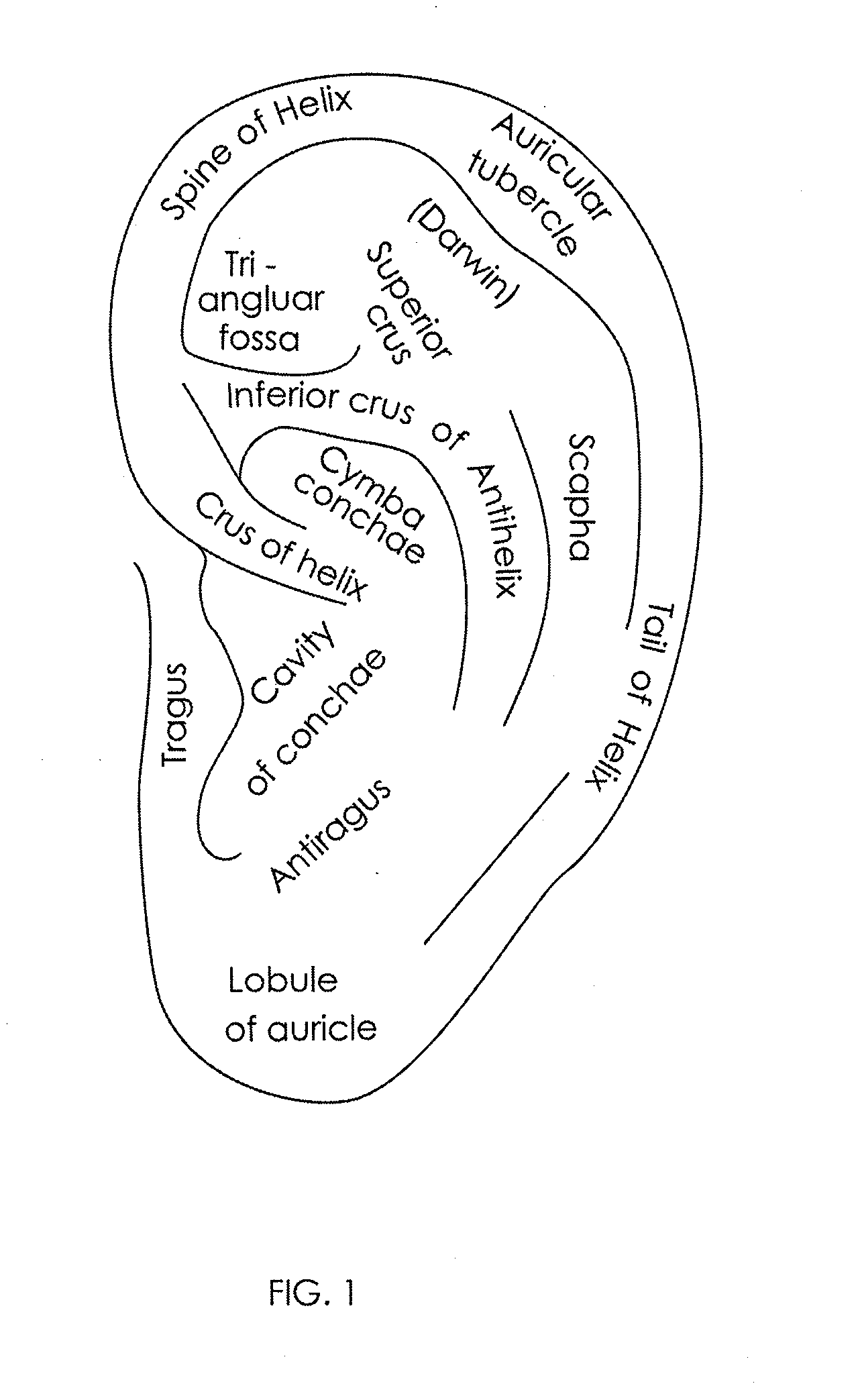
Described herein are devices, systems and method for treating inflammatory disorders by modulating a subject's inflammatory reflex. The method may include the step of non-invasively stimulating the inflammatory reflex (e.g., the vagus nerve, the splenic nerve, the hepatic nerve, the facial nerve, and the trigeminal nerve) of a subject in a manner which significantly reduces proinflammatory cytokines in the subject and / or provides a therapeutically effective treatment for the subject. Devices for non-invasively stimulating the inflammatory reflex may include a movable tip or actuator that is controlled to mechanically stimulate the ear. The devices may be hand-held or wearable, and may stimulate the cymba conchae region of the subject's ear.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by cholinergic agonists and vagus nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20090248097A1Implantable neurostimulatorsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsEfferentEndotoxic shock
A method of inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine in a cell is disclosed. The method comprises treating the cell with a cholinergic agonist. The method is useful in patients at risk for, or suffering from, a condition mediated by an inflammatory cytokine cascade, for example endotoxic shock. The cholinergic agonist treatment can be effected by stimulation of an efferent vagus nerve fiber, or the entire vagus nerve.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
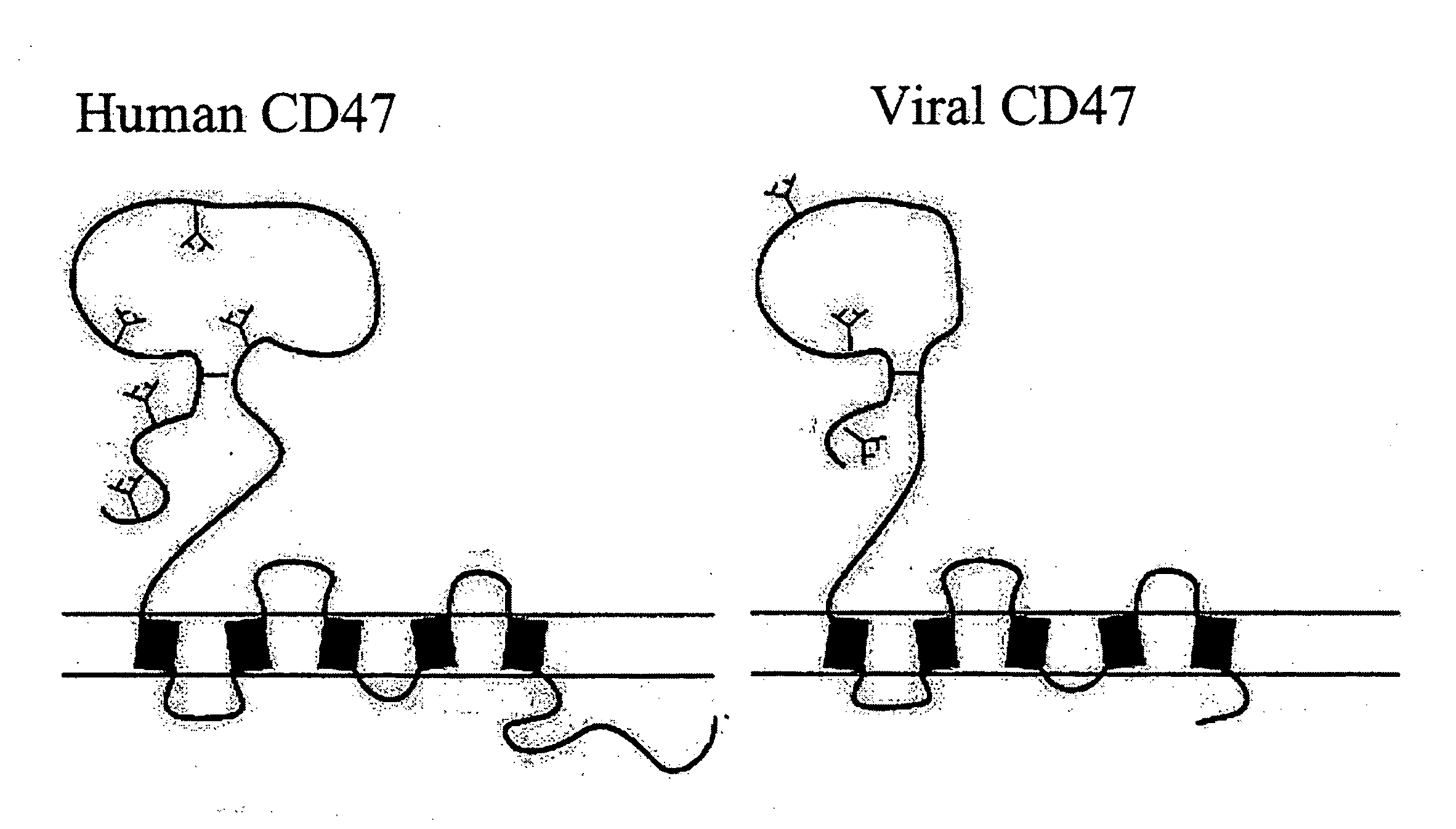
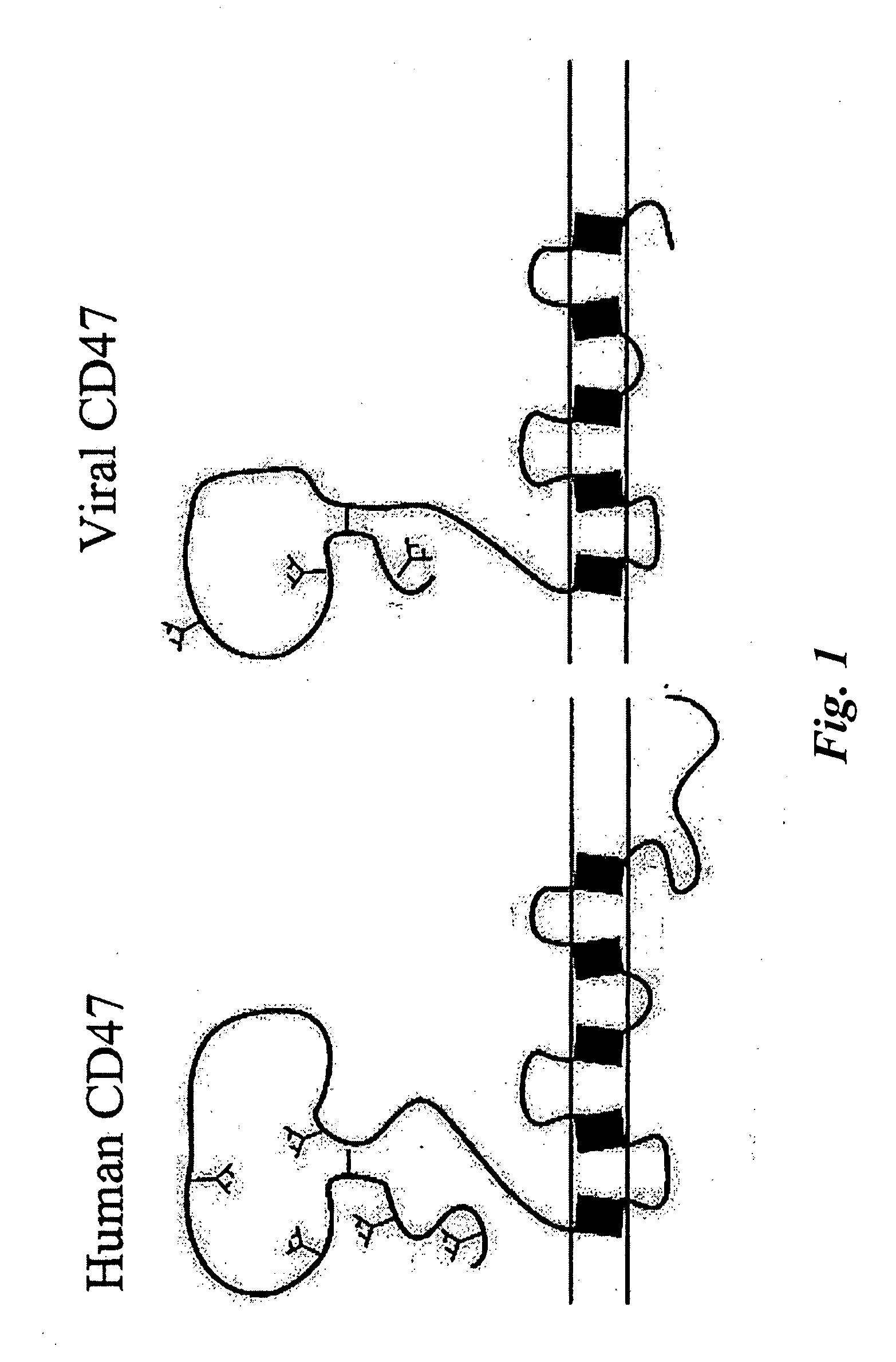
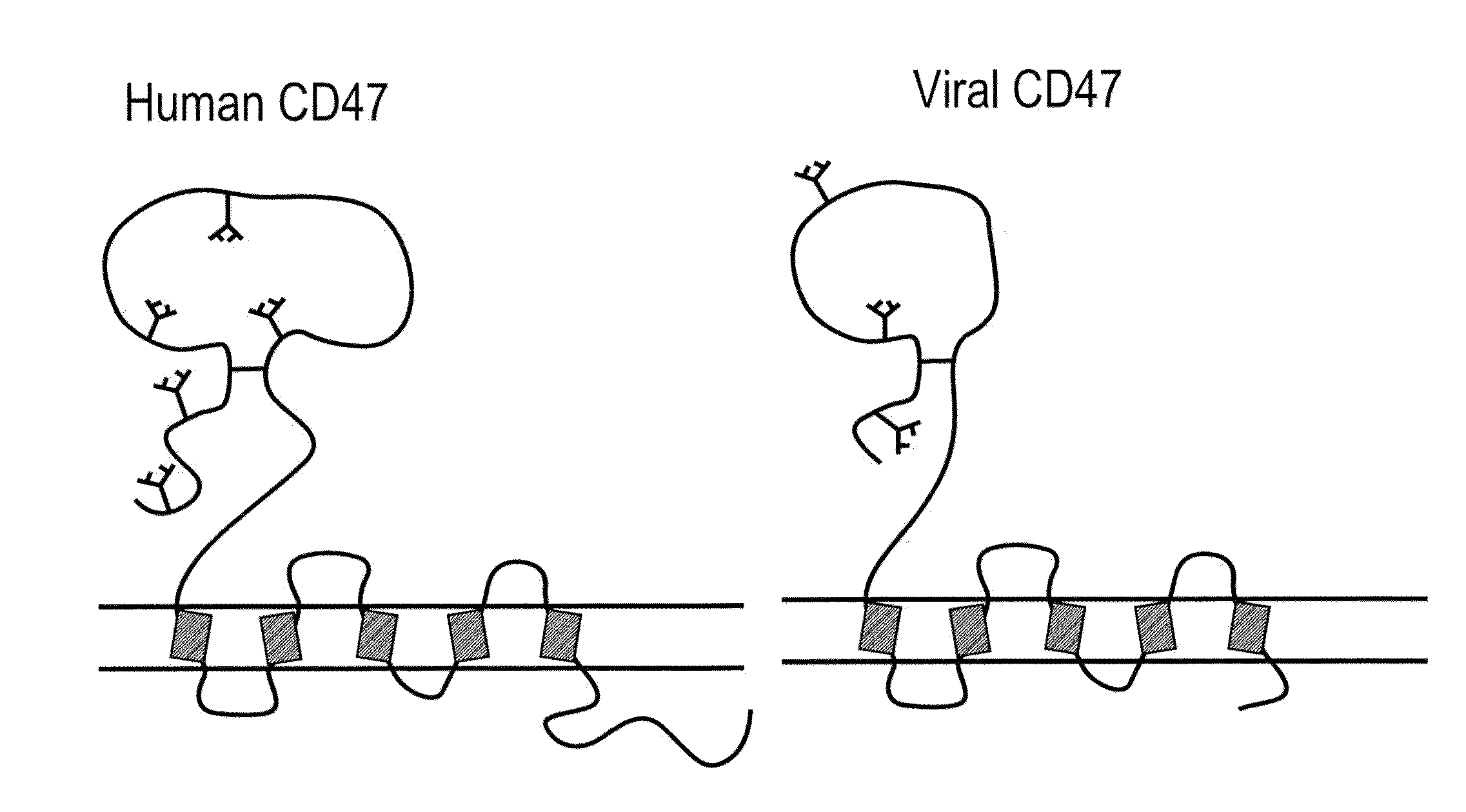
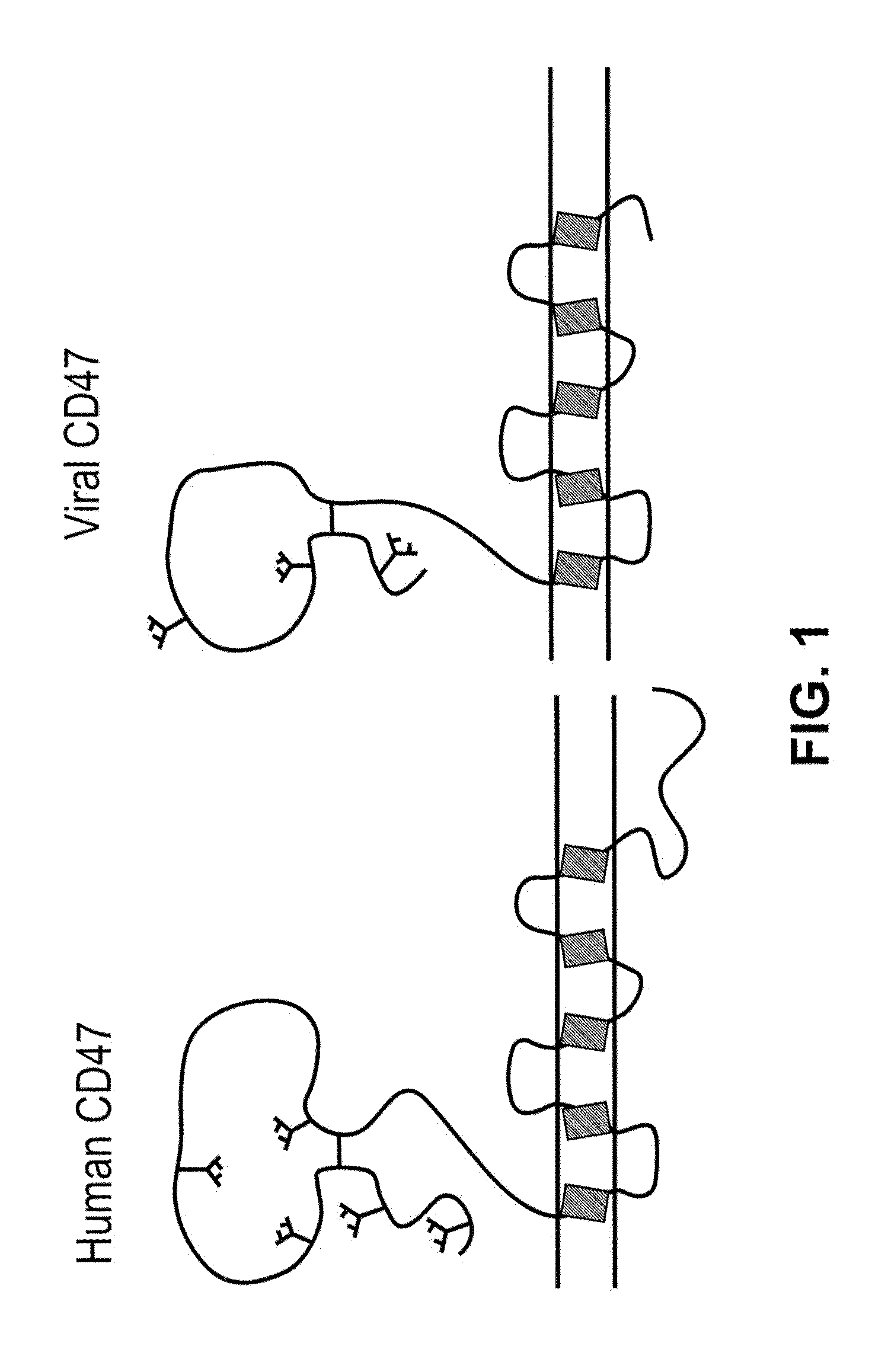
CD47 related compositions and methods for treating immunological diseases and disorders
InactiveUS20080131431A1Lower capability requirementsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderImmune complex depositionImmune complex
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CD47 Related Compositions and Methods for Treating Immunological Diseases and Disorders
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Reagents, methods and systems to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines
ActiveUS20080124370A1Inhibit inflammationInhibit expressionAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsMedicineCytokine
The present invention relates to reagents, methods and systems to treat inflammation and pain in a subject using small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules targeted to either TNFα, IL1, IL6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
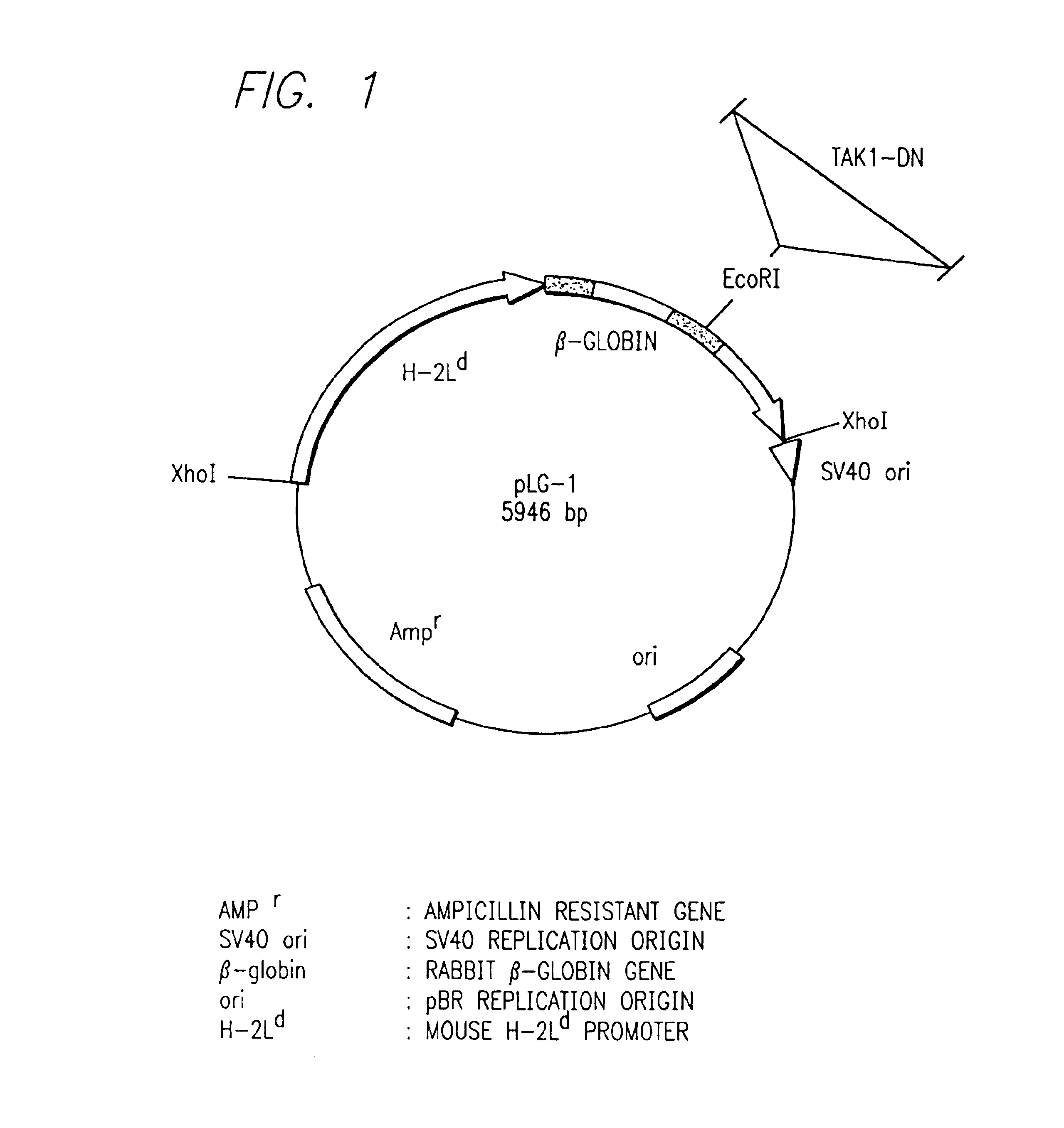
Method for screening compounds inhibiting signal transduction through inflammatory cytokines
InactiveUS6989244B1Avoid low activityHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCytokineProinflammatory cytokine
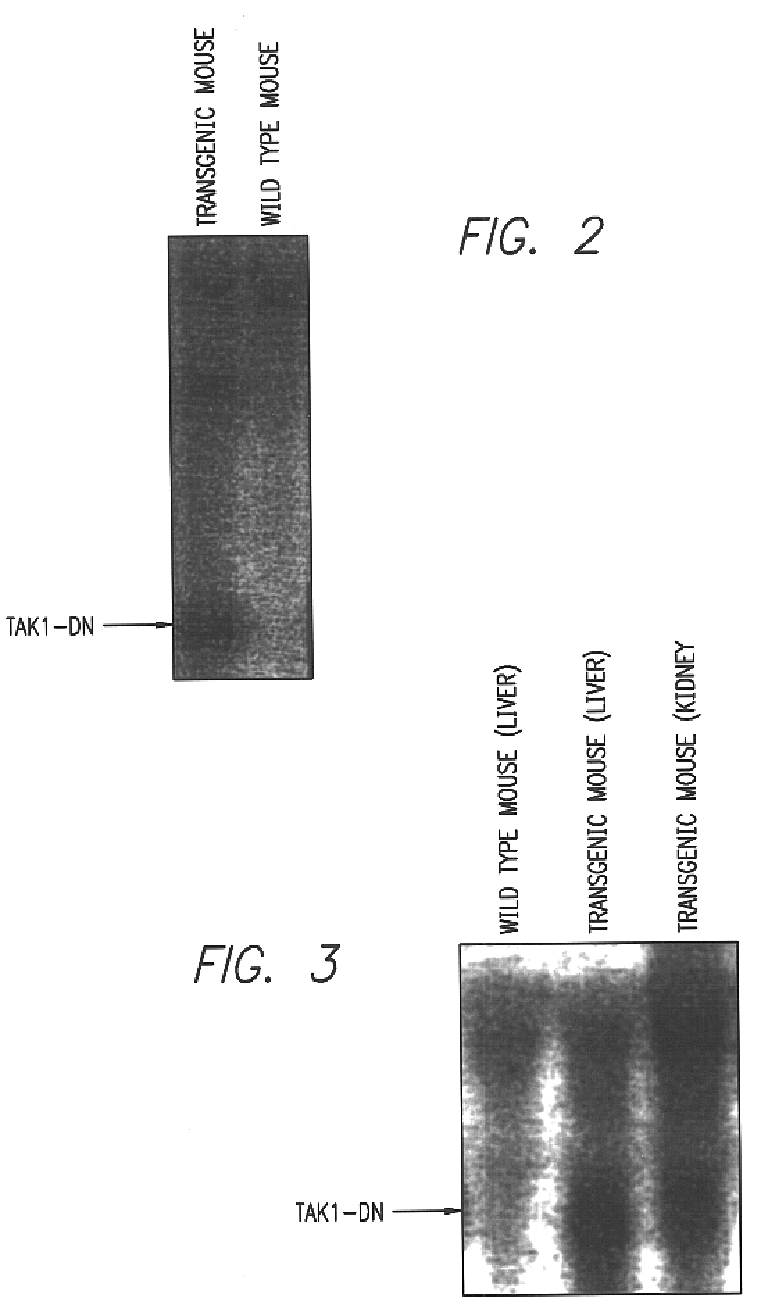
The present invention relates to methods of screening for compounds that inhibit signal transduction by inflammatory cytokines. The methods include providing a sample that contains a TAK1 and a TAB1; contacting the sample with a compound; detecting binding between the TAK1 and the TAB1; and selecting the compound if binding between the TAK1 and TAB1 is inhibited in the sample compared to a control.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
High affinity antibodies against HMGB1 and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060099207A1Reduce bone loss and/or cartilage damageAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReperfusion injuryAllograft rejection
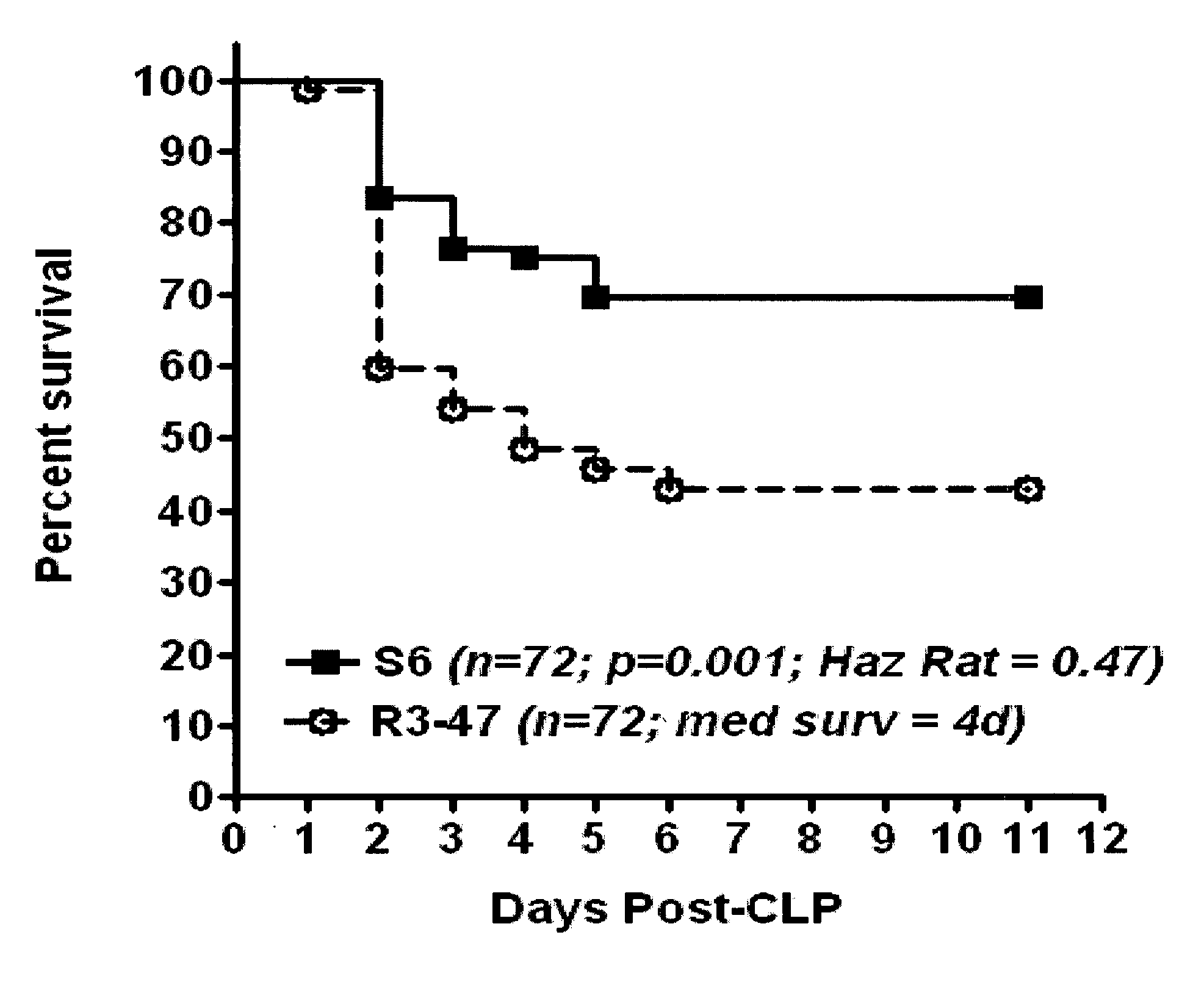
Compositions and methods are disclosed for inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine from a vertebrate cell, and for inhibiting an inflammatory cytokine cascade in a patient. The compositions comprise, for example, high affinity antibodies that specifically bind HMG1 and antigenic fragments thereof. The high affinity antibodies of the present invention and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same are useful for many purposes, for example, as therapeutics against a wide range of inflammatory diseases and disorders such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, peritonitis, Crohn's disease, reperfusion injury, septicemia, endotoxic shock, cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, arthritis, anaphylactic shock, organ ischemia, reperfusion injury, and allograft rejection. In addition, the high affinity antibodies of the present inventions are useful as diagnostic antibodies.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20060140936A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory diseases, using multispecific antagonists that target at least two different markers are disclosed. The different targets include (i) proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system, (ii) coagulation factors, and (iii) targets specifically associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, wherein the targets included in group (iii) are neither a proinflammatory effector of the immune system nor a coagulation factor. When the multispecific antagonist reacts specifically with a target associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, it also binds specifically with at least one proinflammatory effector of the immune system or at least one coagulation factor. Thus, the multispecific antagonist contains at least one binding specificity related to the diseased cell or condition being treated and at least one specificity to a component of the immune system, such as a receptor or antigen of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, and dendritic cells, a modulator of coagulation, or a proinflammatory cytokine. The multispecific antagonists are used in the treatment of various diseases that are generated or exacerbated by, or otherwise involve, proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system or coagulation factors. Such diseases more particularly include acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, giant cell arteritis, septicemia and septic shock, coagulopathies (including diffuse intravascular coagulation), neuropathies, graft versus host disease, infectious diseases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, granulomatous diseases, transplant rejection, asthma, cachexia, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Other diseases also responsive to these therapies include cancers and conditions with pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Nerve stimulation techniques
InactiveUS8571653B2Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialElectrotherapyPower flowMedicine
A method is provided for treating heart failure in a subject in need of such treatment, including applying a stimulating current to parasympathetic nervous tissue of the subject, selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve and an epicardial fat pad. The stimulating current is configured to inhibit release of at least one proinflammatory cytokine sufficiently to the treat heart failure of the subject. A level of the at least one proinflammatory cytokine is measured. Optionally, the stimulating current is configured to change a level of Connexin 43 of the subject, and the level of Connexin 43 is also measured. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
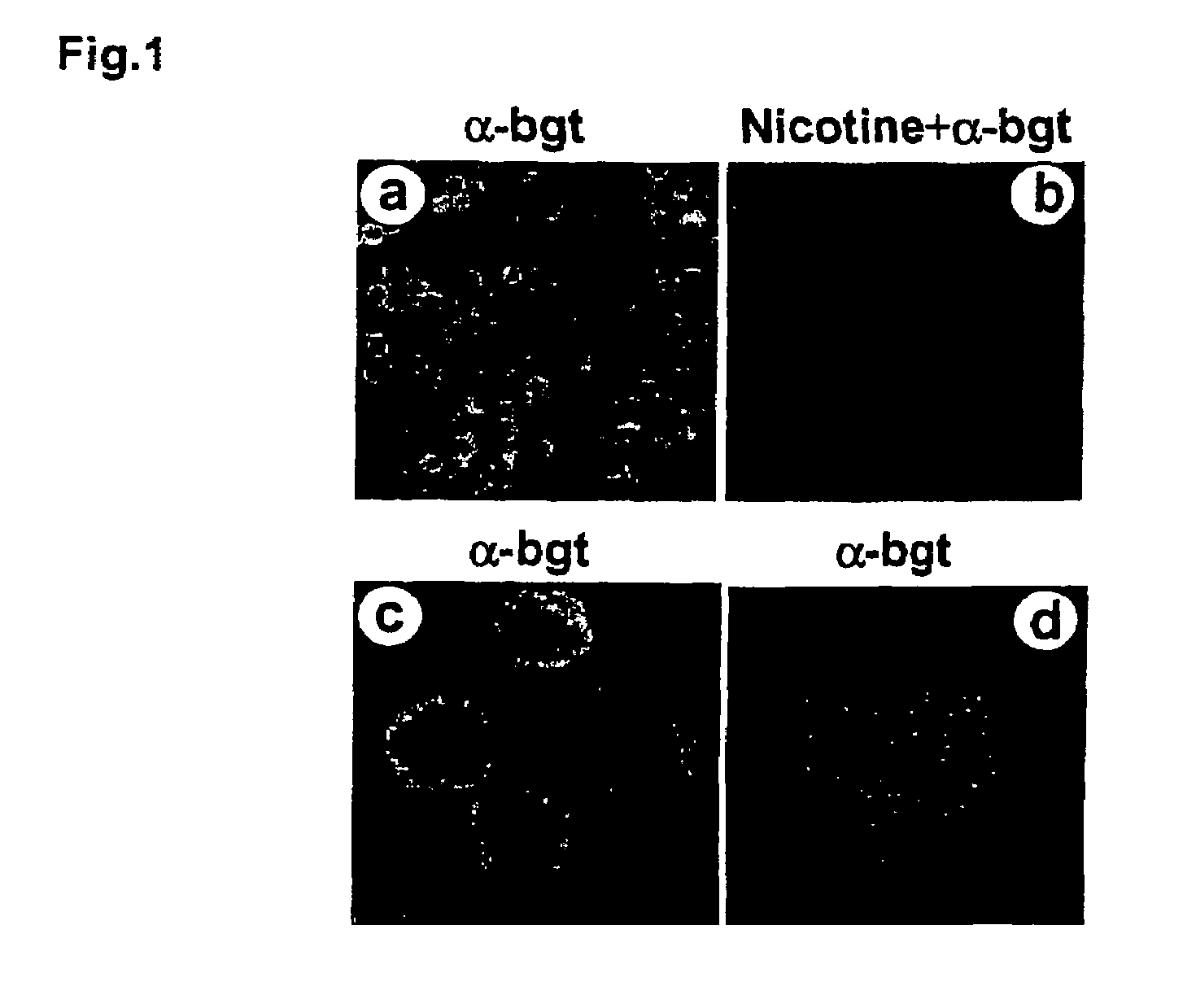
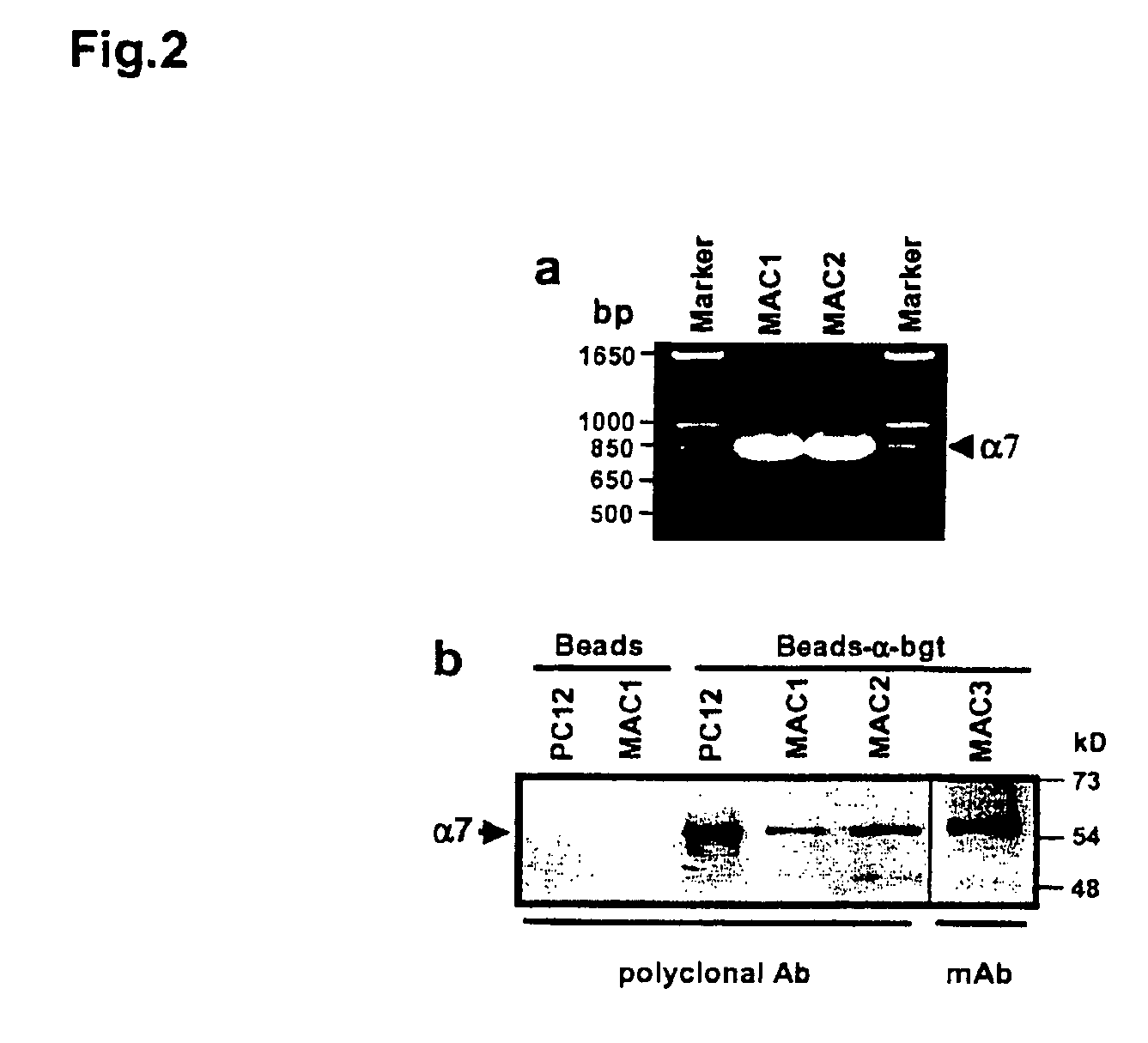
Treatment of pancreatitis using alpha 7 receptor-binding cholinergic agonists
A method of treating a patient suffering from pancreatitis comprising treating said patient with a therapeutically effective amount of a cholinergic agonist selective for an α7 nicotinic receptor in an amount sufficient to decrease the amount of the proinflammatory cytokine that is released from a macrophage wherein said condition is acute pancreatitis. The compounds of the present invention include a quaternary analog of cocaine; (1-aza-bicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)-carbamic acid 1-(2-fluorophenyl)-ethyl ester; a compound of formula (I), a compound of formula (II), a compound of formula (III), a compound of formula (IV), and an oligonucleotide or mimetic capable of attenuating the symptoms of acute pancreatitis wherein the oligonucleotide or mimetic consists essentially of a sequence greater than 5 nucleotides long that is complementary to an mRNA of an α7 cholinergic receptor. The variables of formulae (I), (II), (III) and (IV) are described herein
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Method for increasing therapeutic gain in radiotherapy and chemotherapy
InactiveUS20050272644A1Inhibit tumor growthReduced radiation-induced normal tissue fibrosisBiocideAntipyreticAbnormal tissue growthTumor therapy
The present invention provides compositions and methods for increasing therapeutic gain in radiotherapy and chemotherapy for proliferating malignant or nonmalignant disease to produce high probability of tumor control with low frequency of sequelae of therapy by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a histone deacetylase inhibitor. The compounds are capable of simultaneously stimulating the epithelium regrowth, inhibiting the fibroblast proliferation, decreasing the collagen deposit, suppressing the fibrogenic growth factor, subsiding the proinflammatory cytokine and modulating the expression of cell cycle genes, tumor suppressors and oncogenes, and are useful to increase the therapeutic gain in radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which results in decrease of skin swelling and inflammation, promotion of epithelium healing in mucosa and dermis, decrease of xerostomia, prevention / reduction of severity of plantar-palmar syndrome, prevention of tissue fibrosis, ulceration, necrosis and tumorigenesis, and increase of tumor growth inhibition and tumor therapy effectiveness.
Owner:SUNNY PHARMTECH
Transdiscal administration of specific inhibitors of pro-inflammatory cytokines
ActiveUS7344716B2Prevent degradationFree from painPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesCytokine SuppressionIntervertebral disc
The present invention relates to injecting a high specificity cytokine antagonist into a diseased intervertebral disc.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by cholinergic agonists and vagus nerve stimulation
InactiveUS8914114B2Implantable neurostimulatorsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSacral nerve stimulationEfferent
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
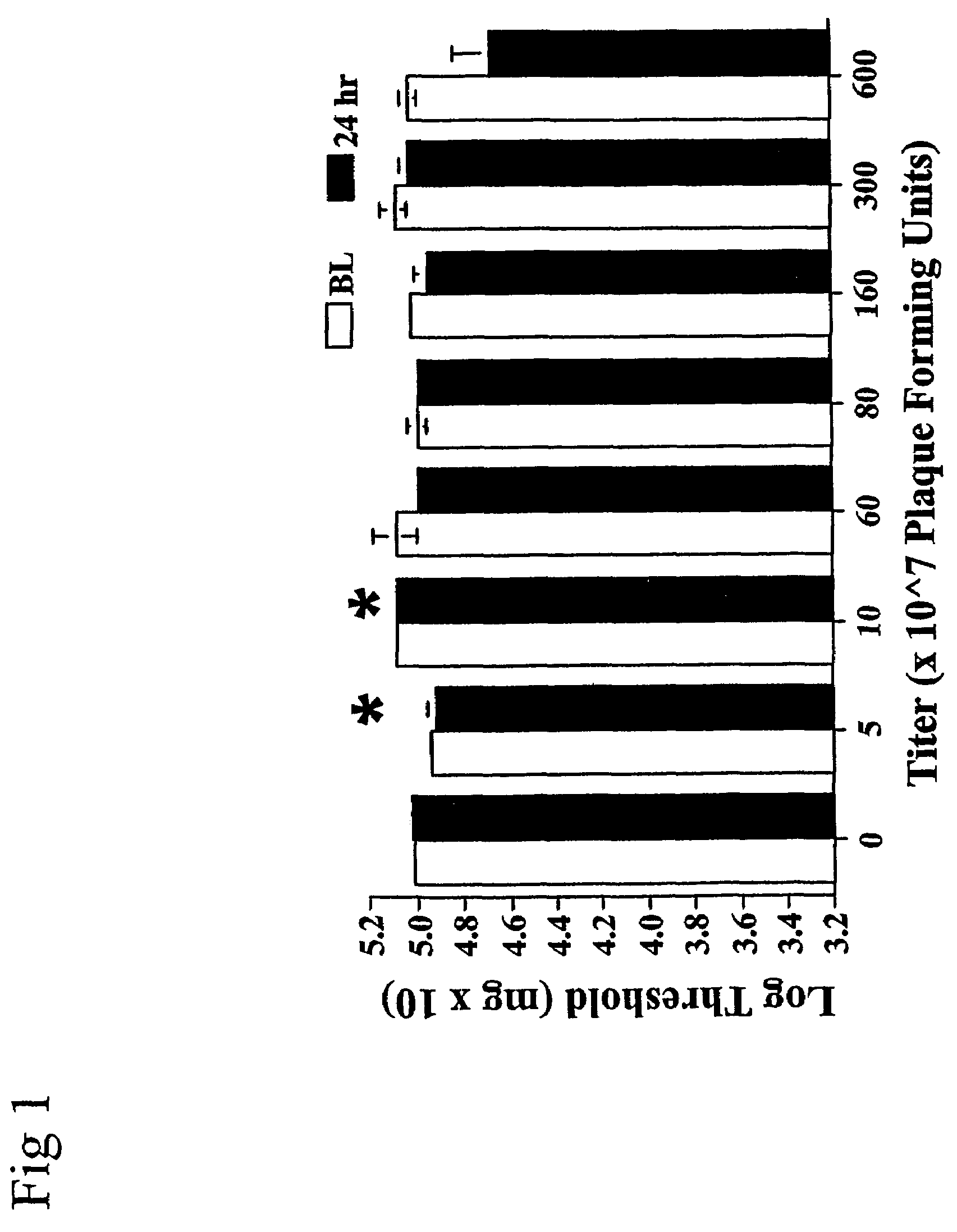
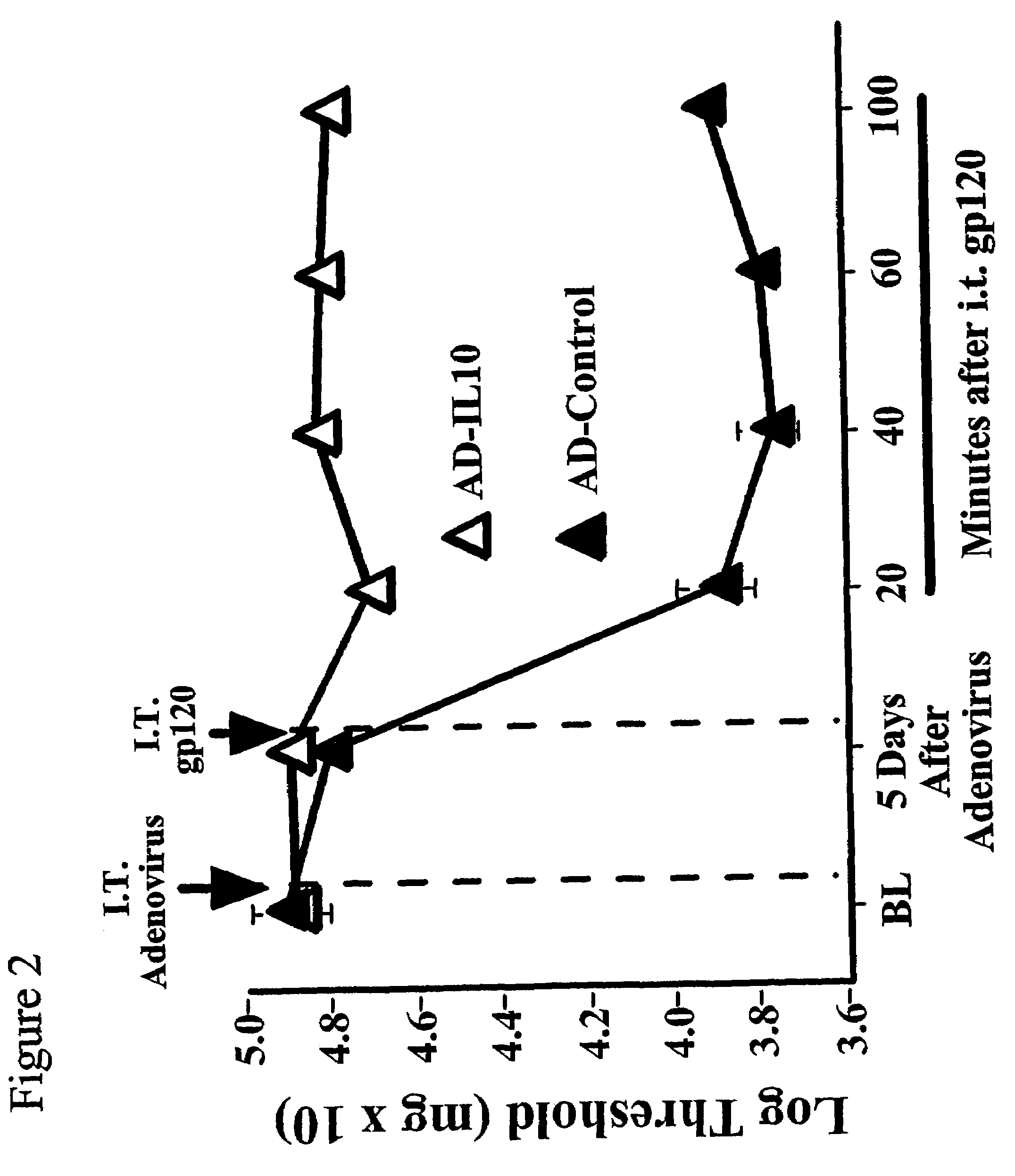
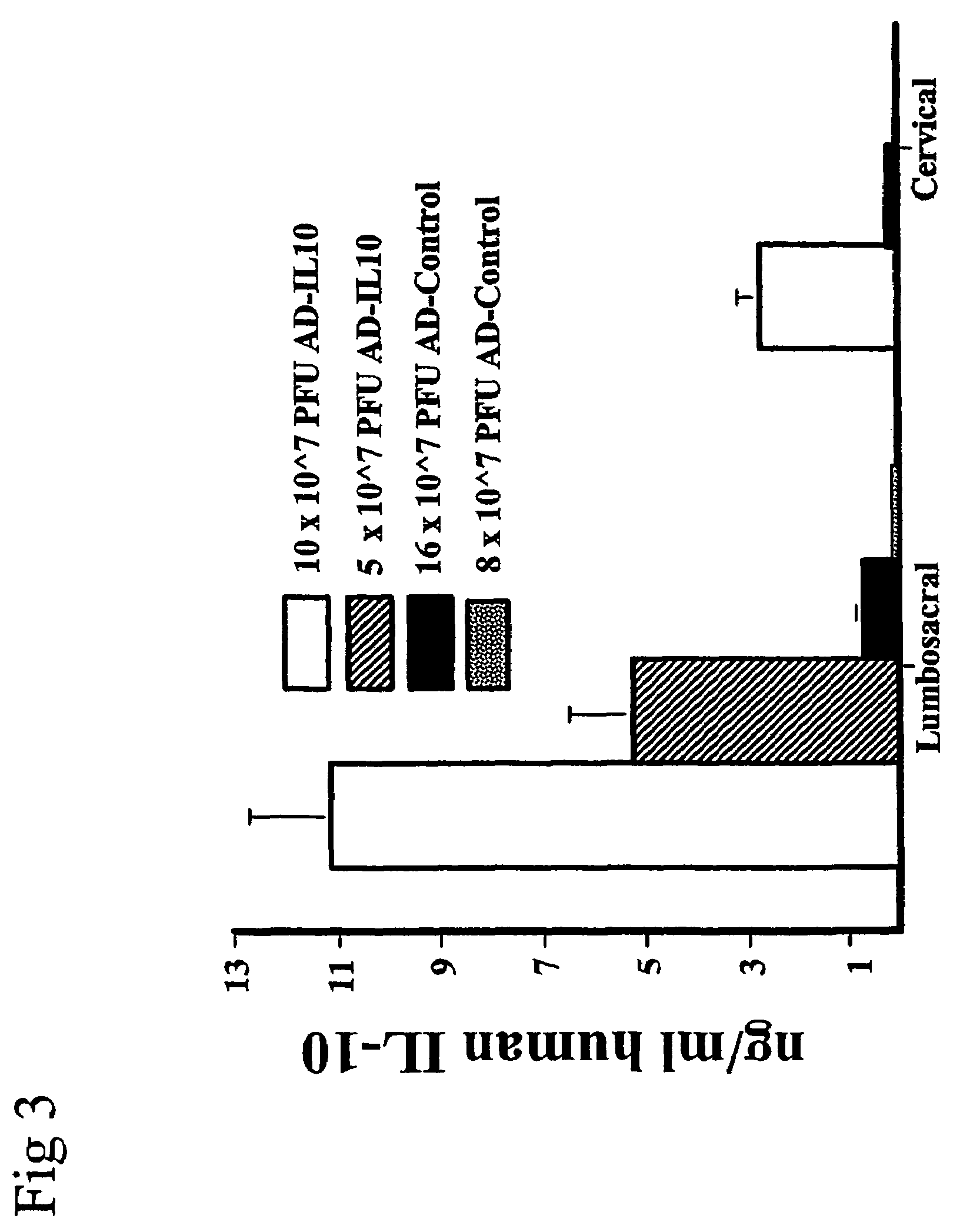
Methods for treating neuropathic pain by administering IL-10 polypeptides
ActiveUS7261882B2Avoid painSuccessful treatmentVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemProtein composition
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method for treating or preventing inflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20050080140A1BiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsProstacyclin synthasePeroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
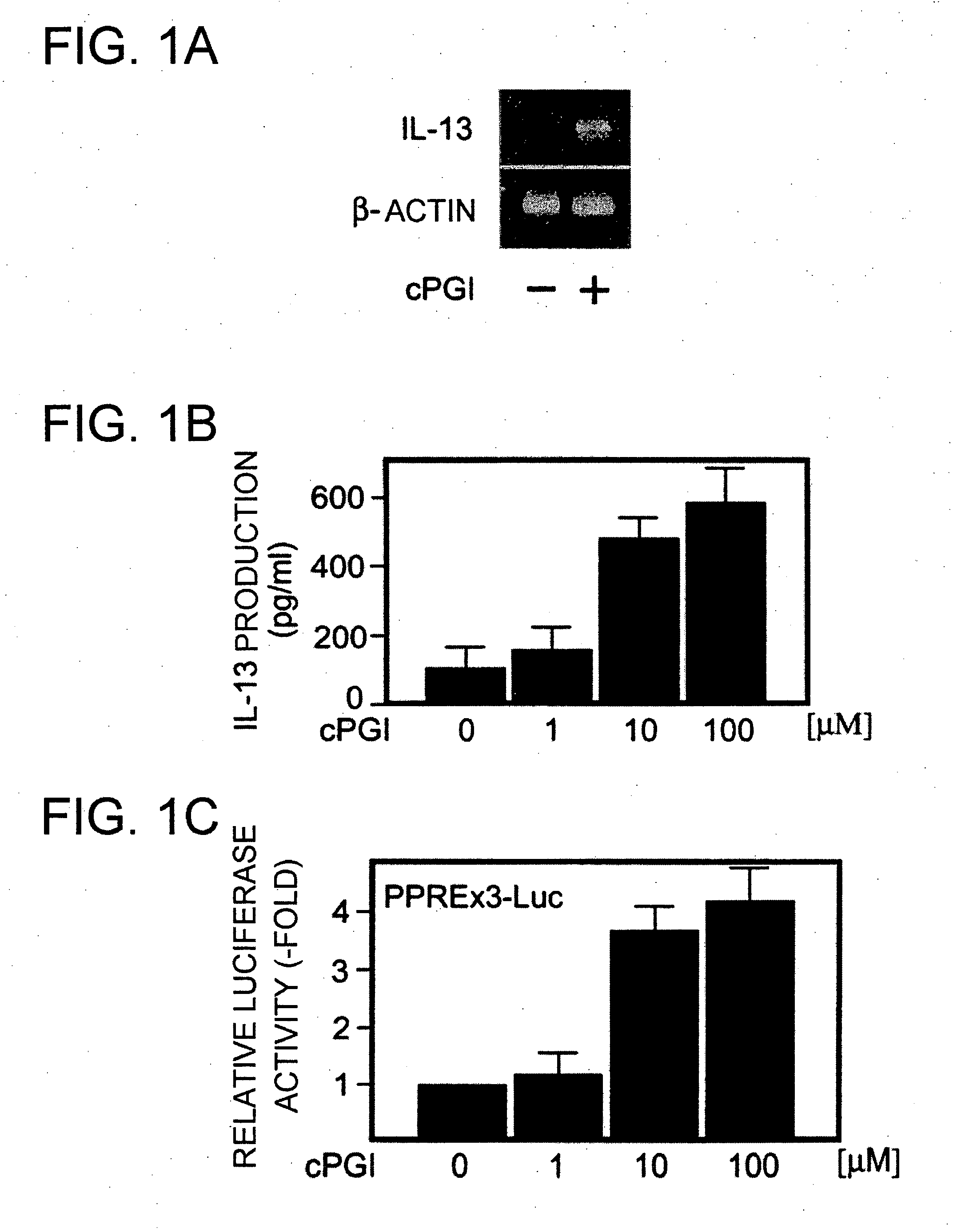
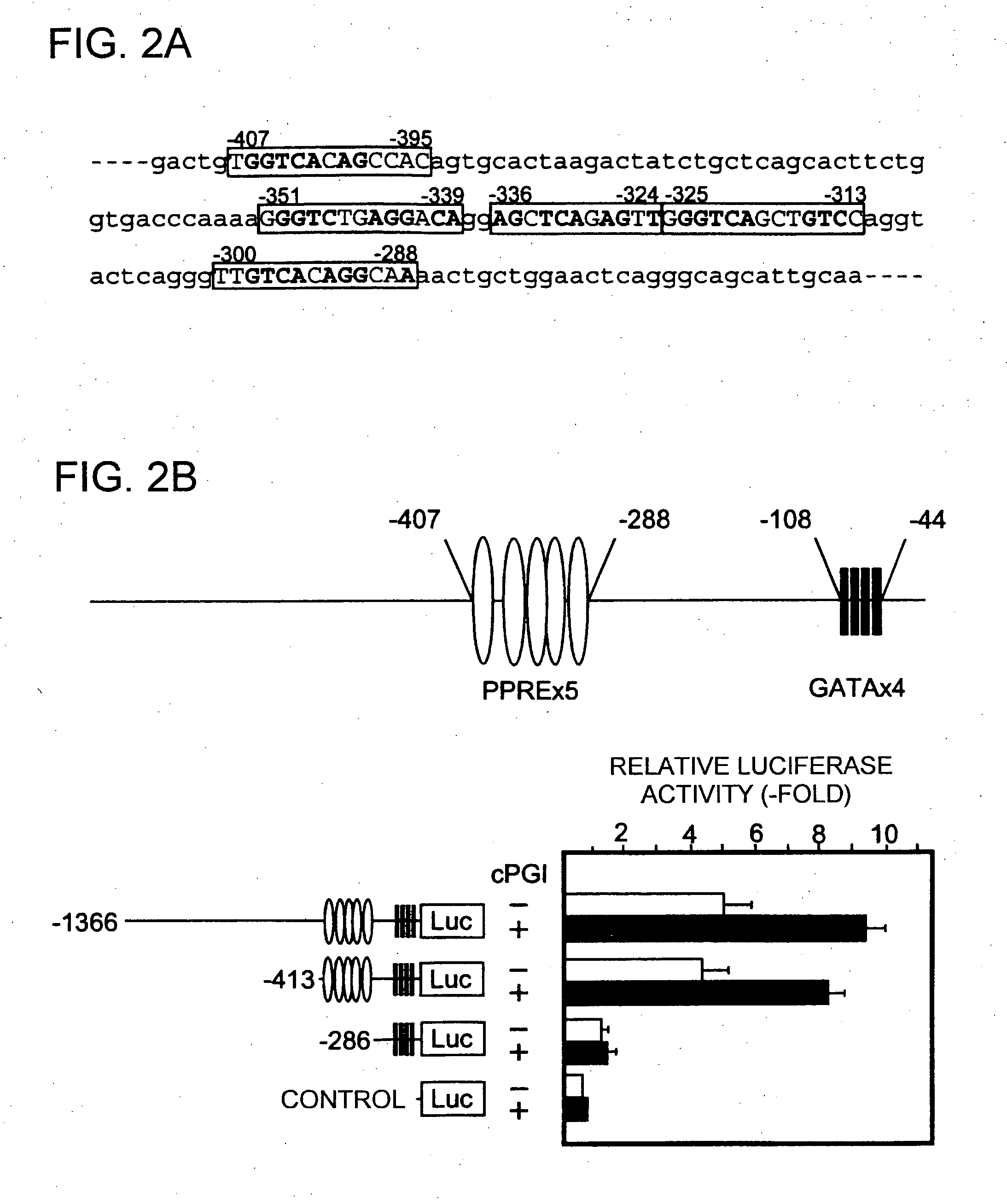
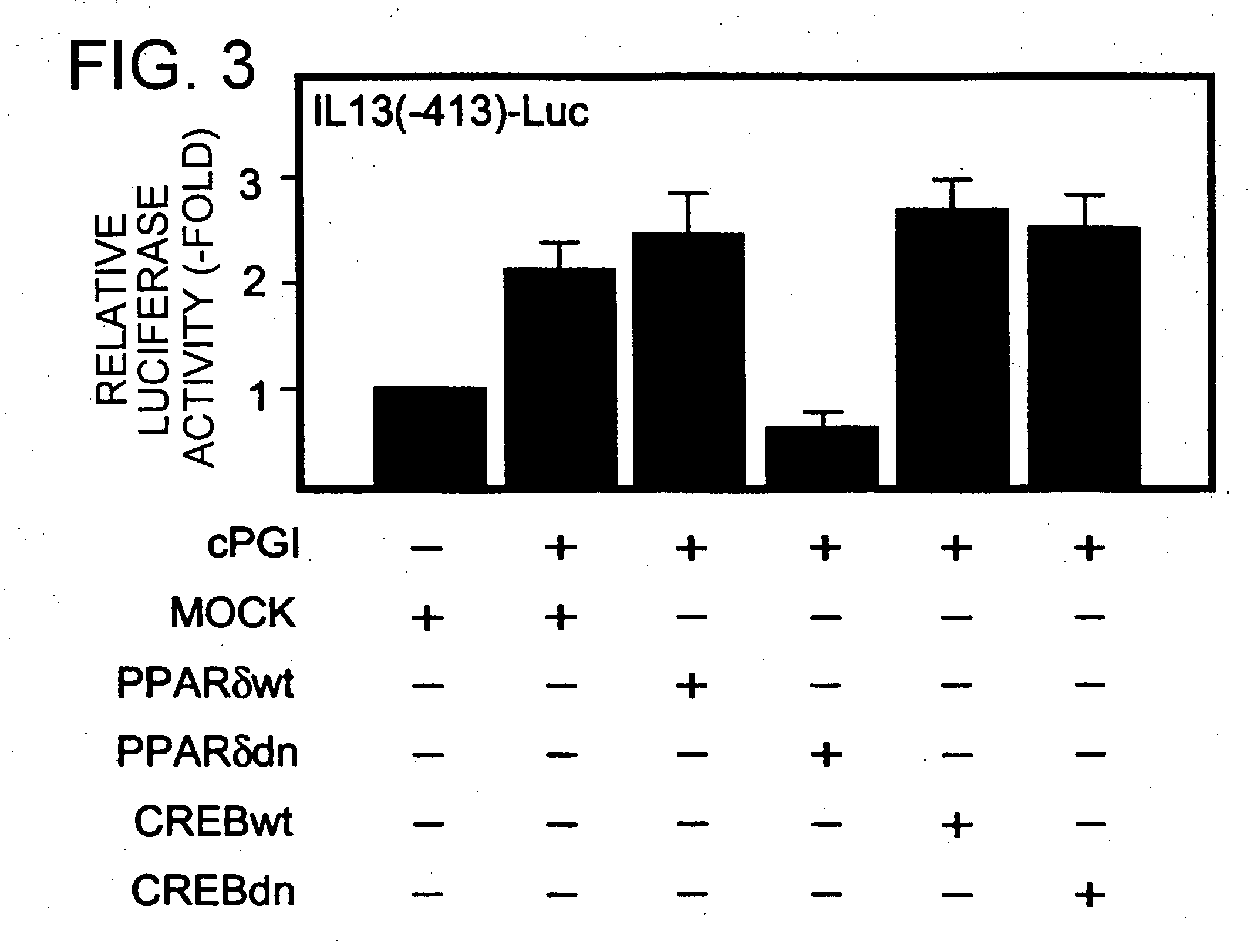
According to the present invention, the gene for IL-13, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, was shown to be a target of prostacyclin (PGI2)-activated Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) δ. Furthermore, the PGI2-PPARδ signaling pathway was revealed to regulate the expression of IL-13 gene in human vascular endothelial cells, and controls inflammatory responses induced by proinflammatory cytokines through the production of IL-13 in an autocrine or paracrine manner. Thus, the present invention provides a method for treating or preventing inflammatory disorders, which comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of PPARδ agonist into a subject. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method for treating or preventing inflammatory disorders, which comprises administering a prostacyclin synthase gene or a protein encoded by the gene into a subject.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
Use of HMGB fragments as anti-inflammatory agents
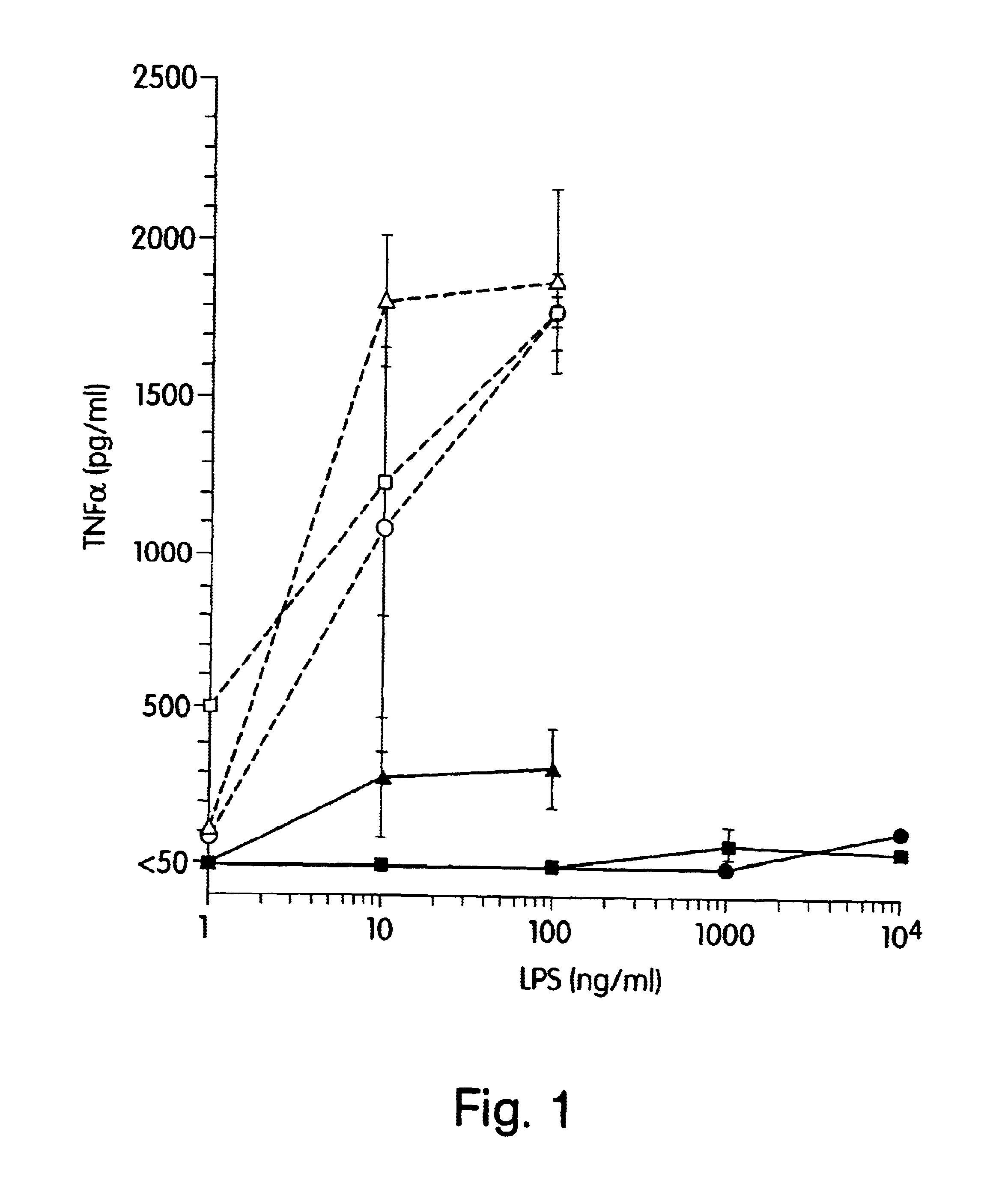
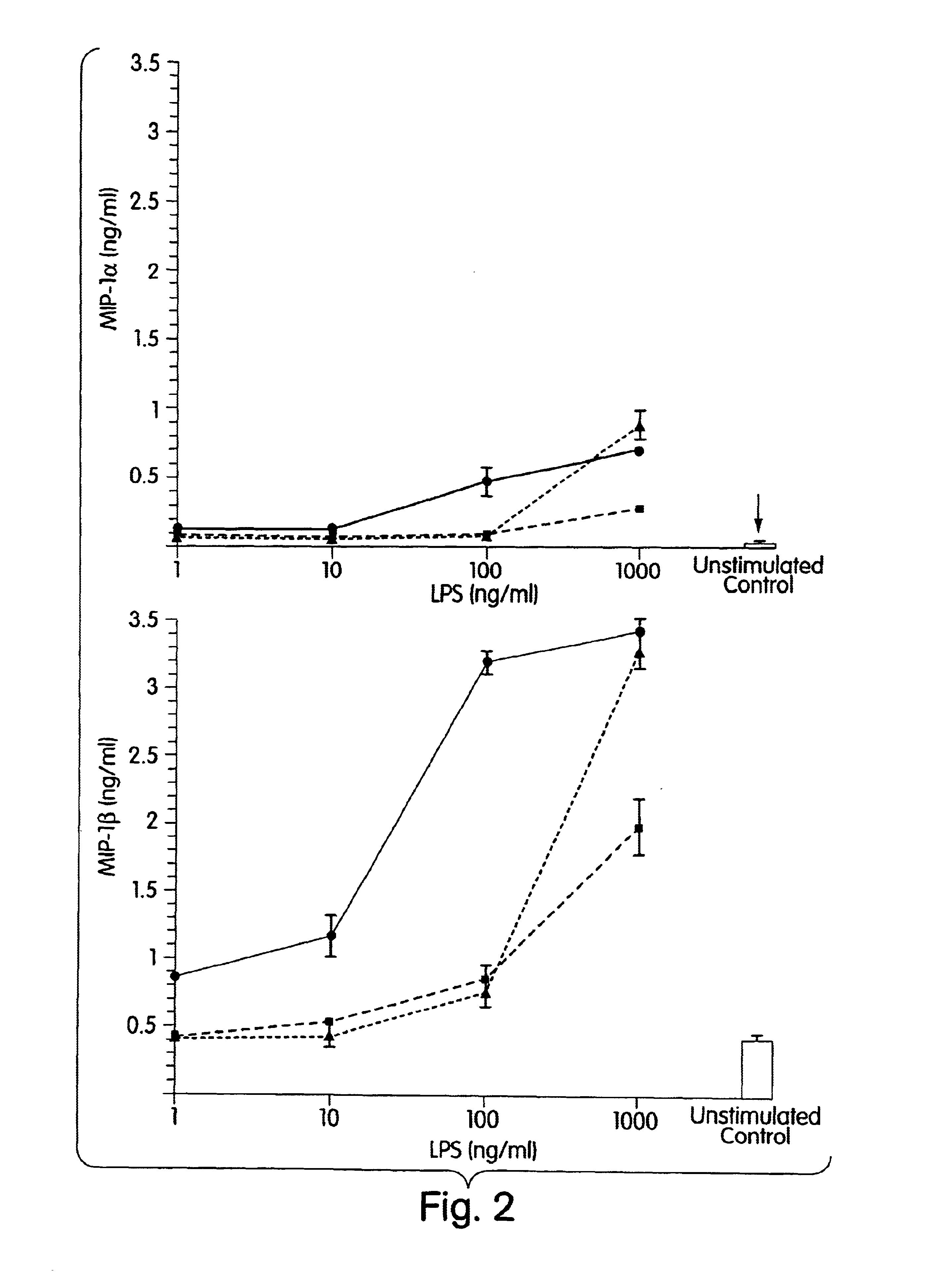
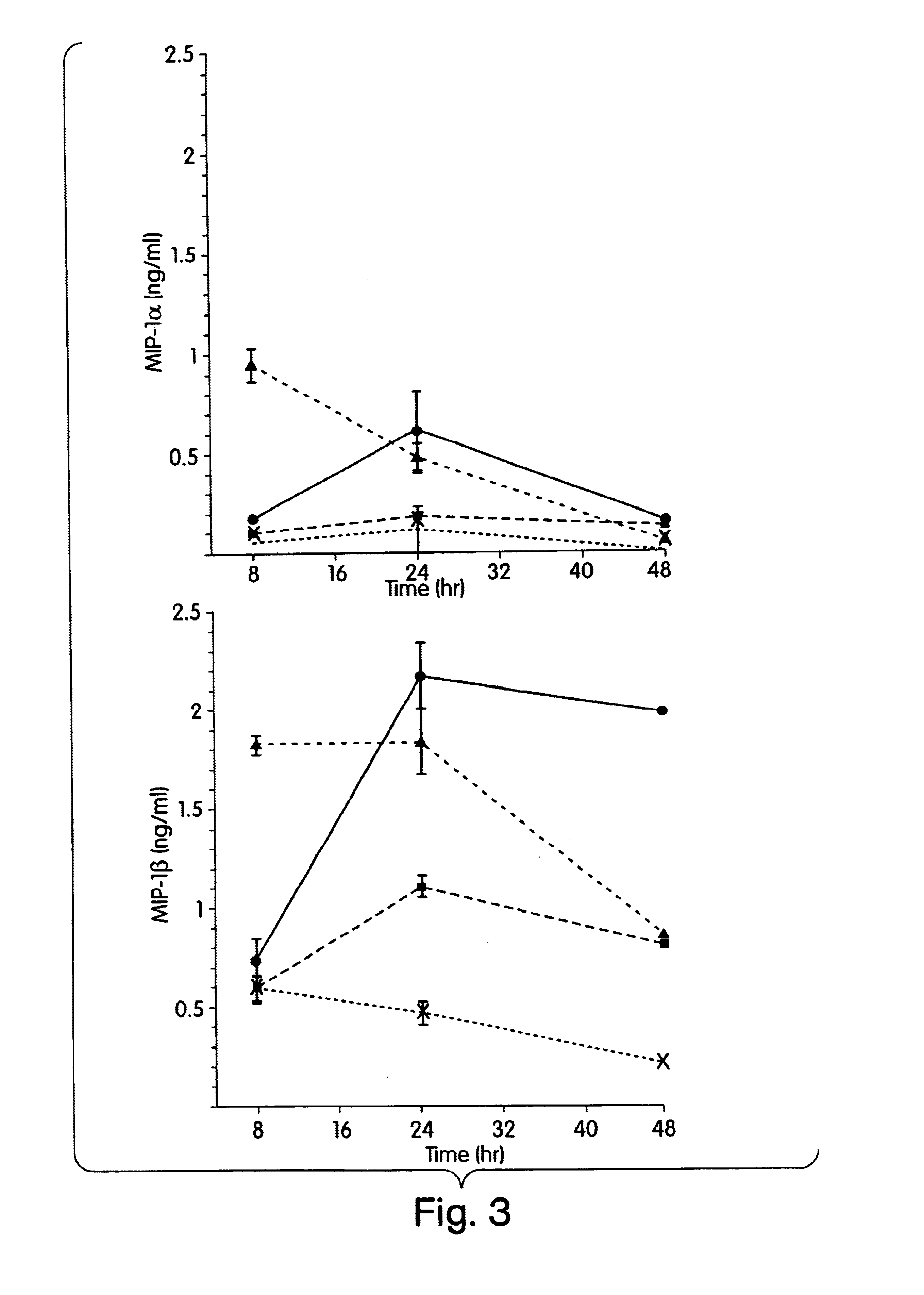
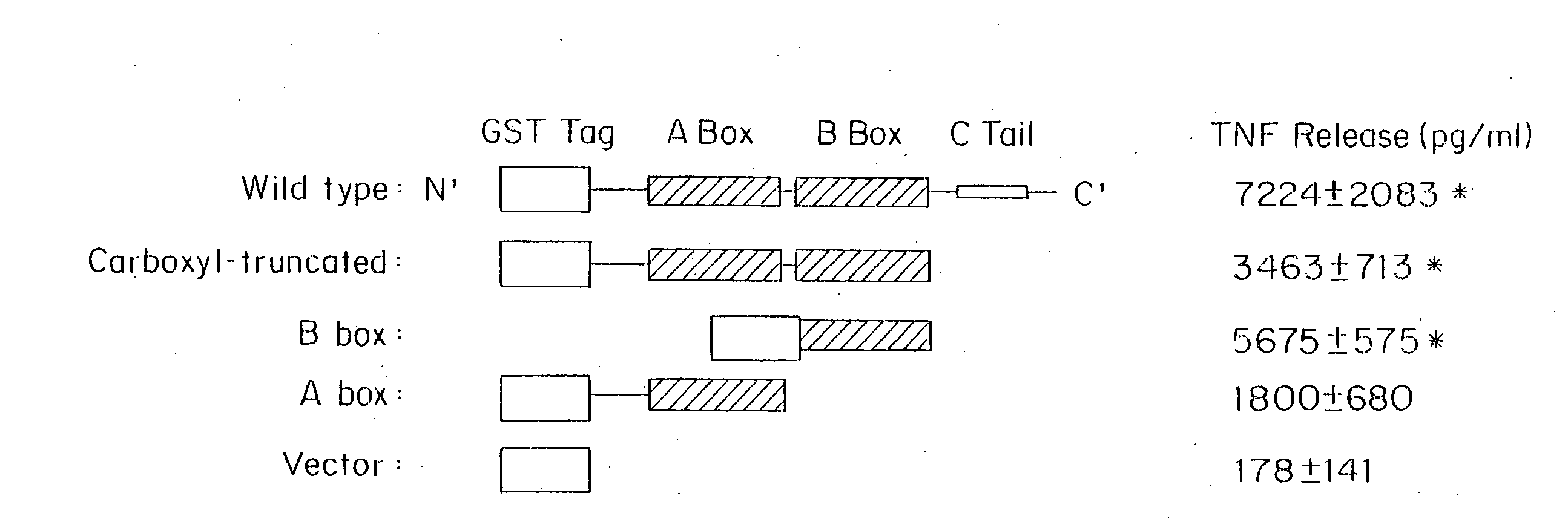
InactiveUS7304034B2Avoid adjustmentInhibition releaseBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCytokineProinflammatory cytokine
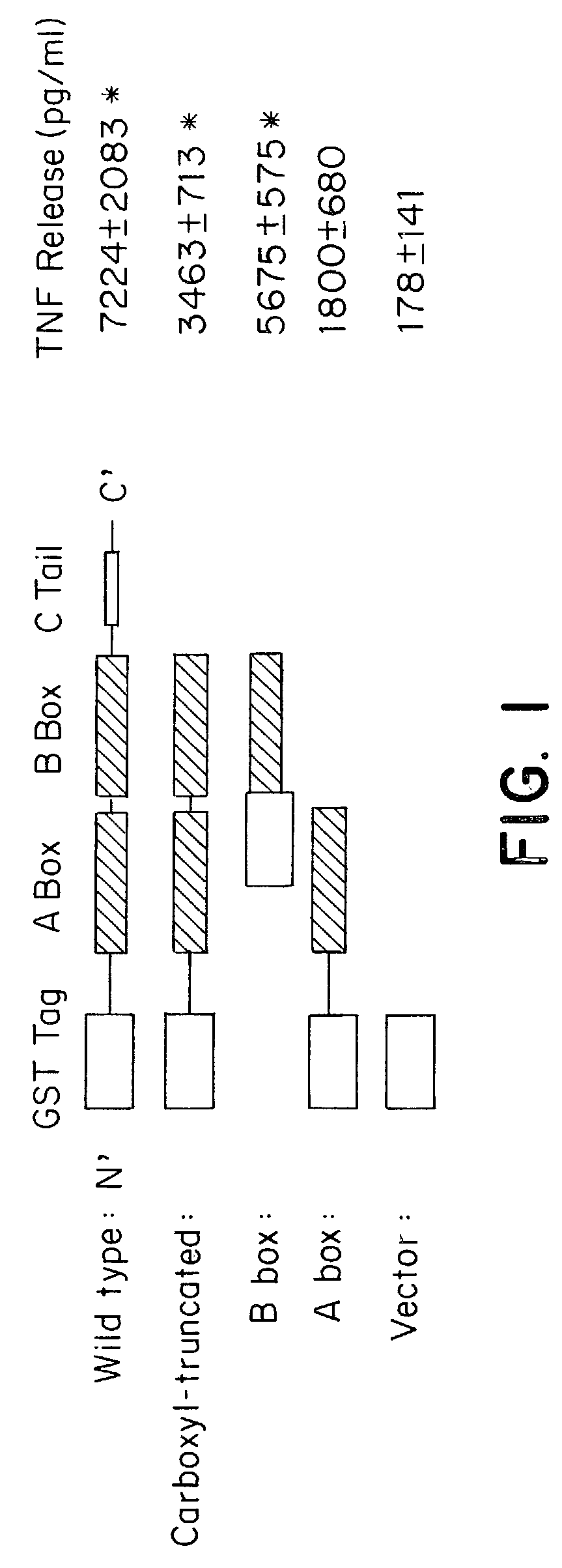
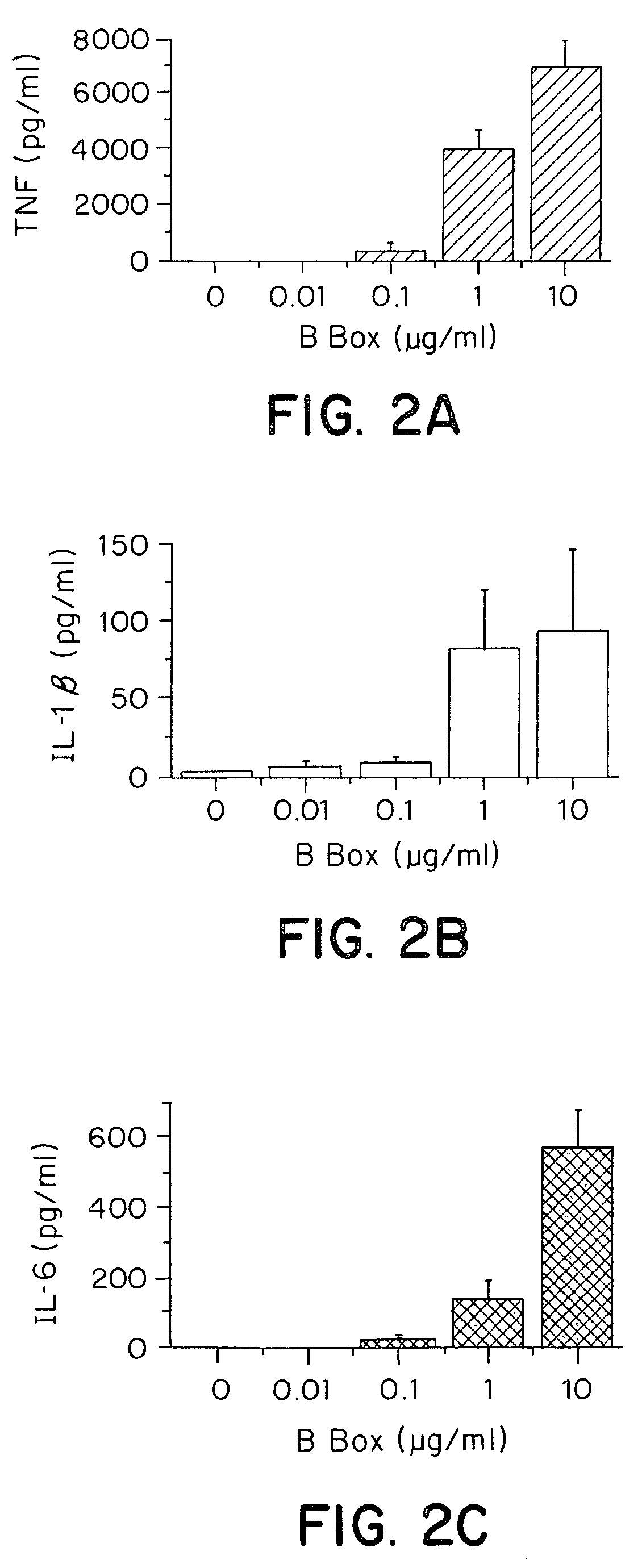
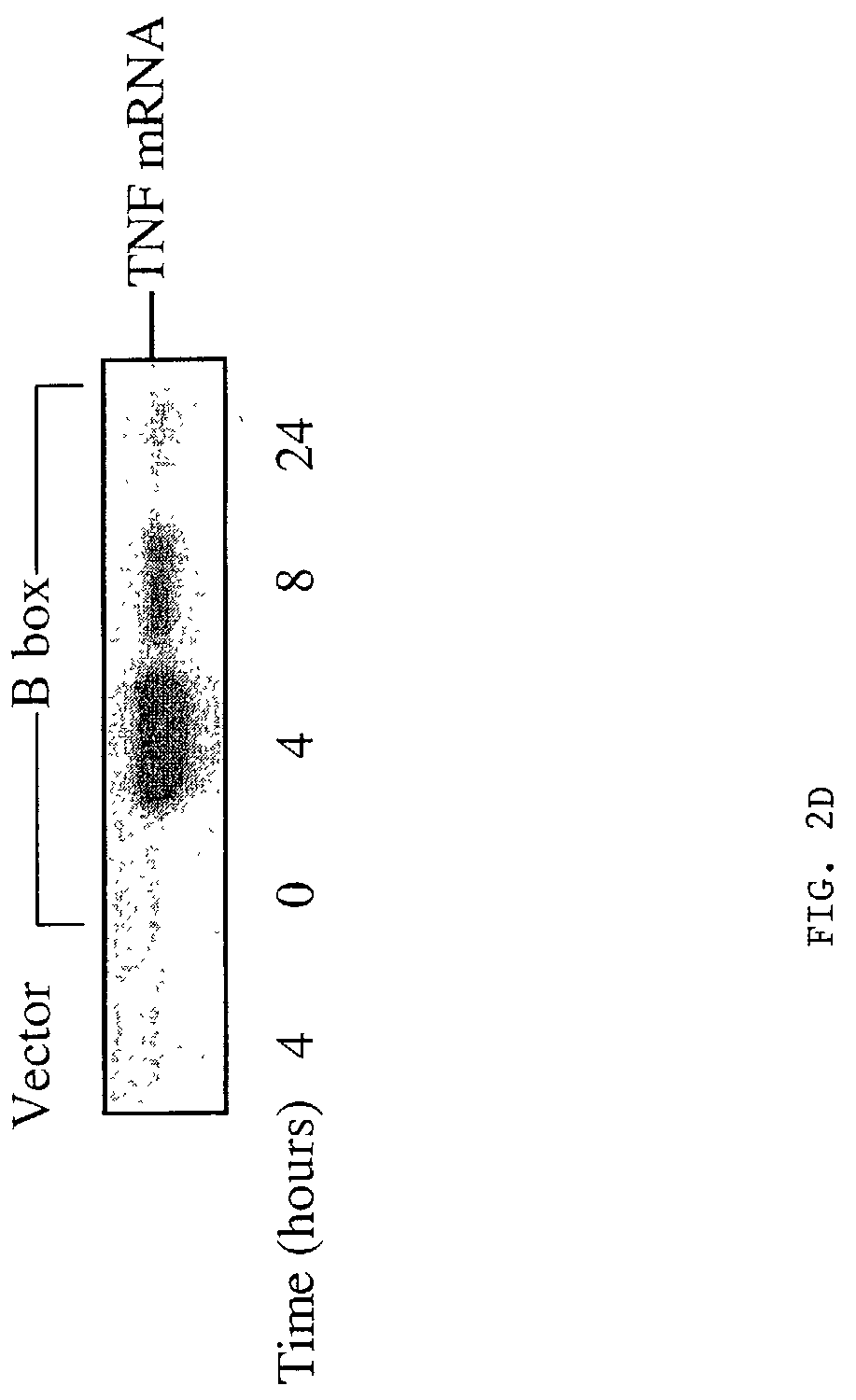
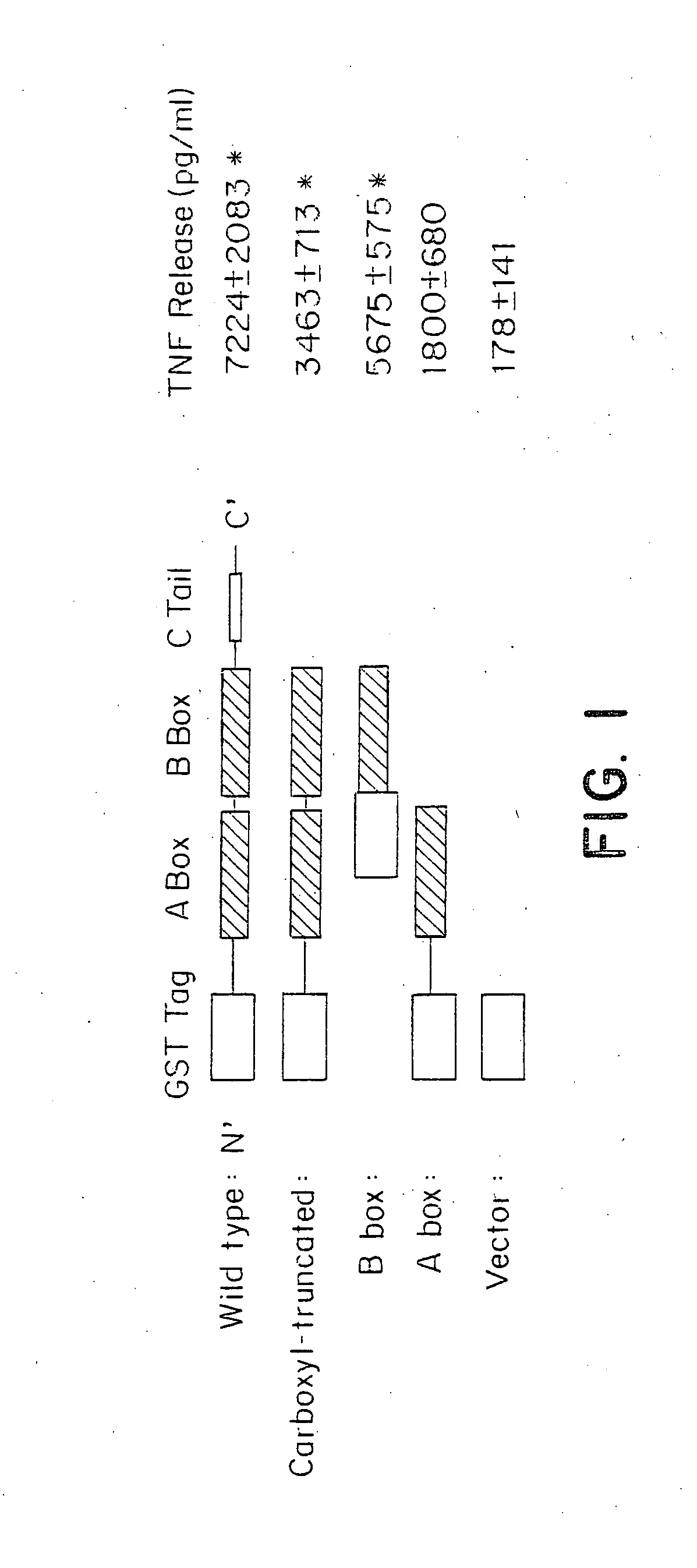
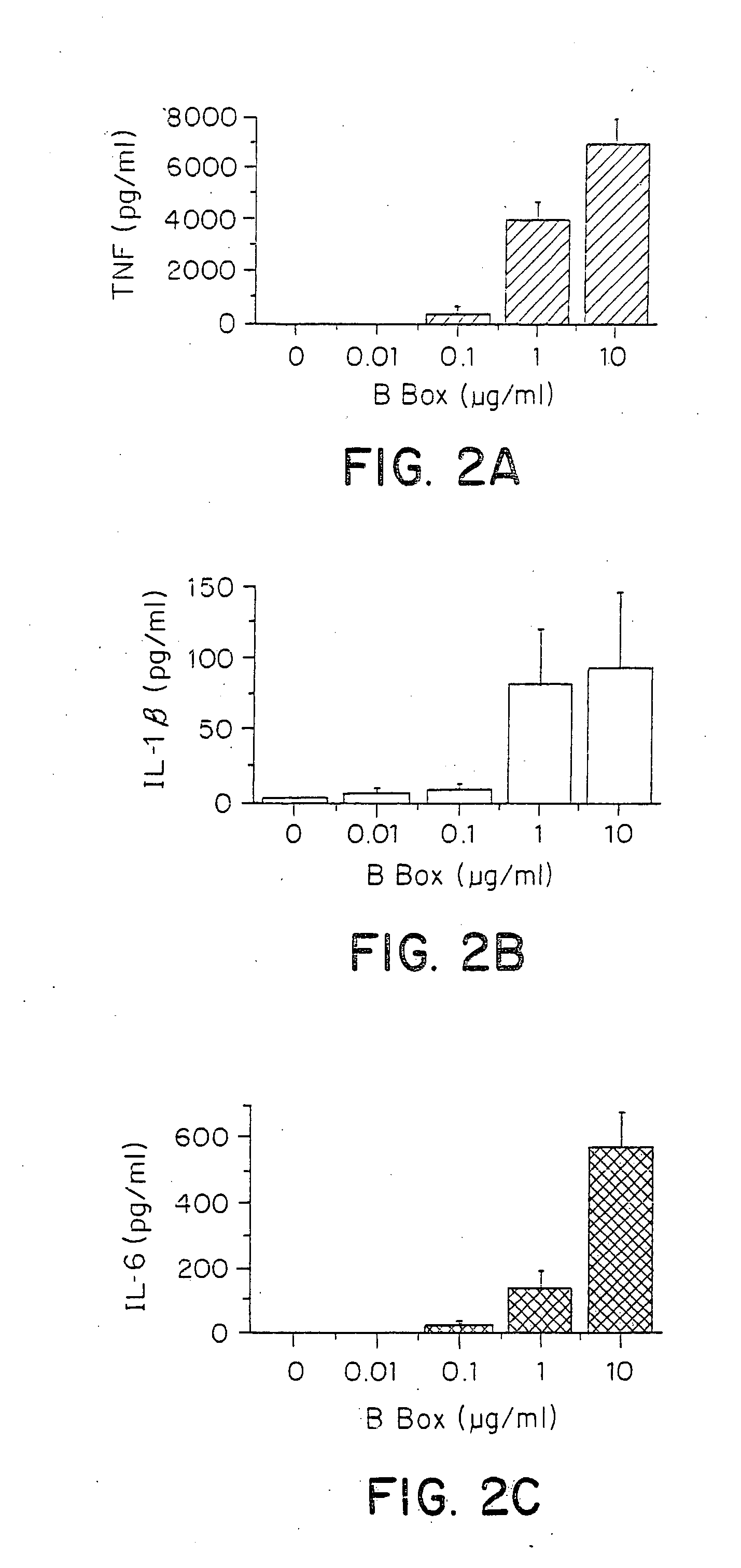
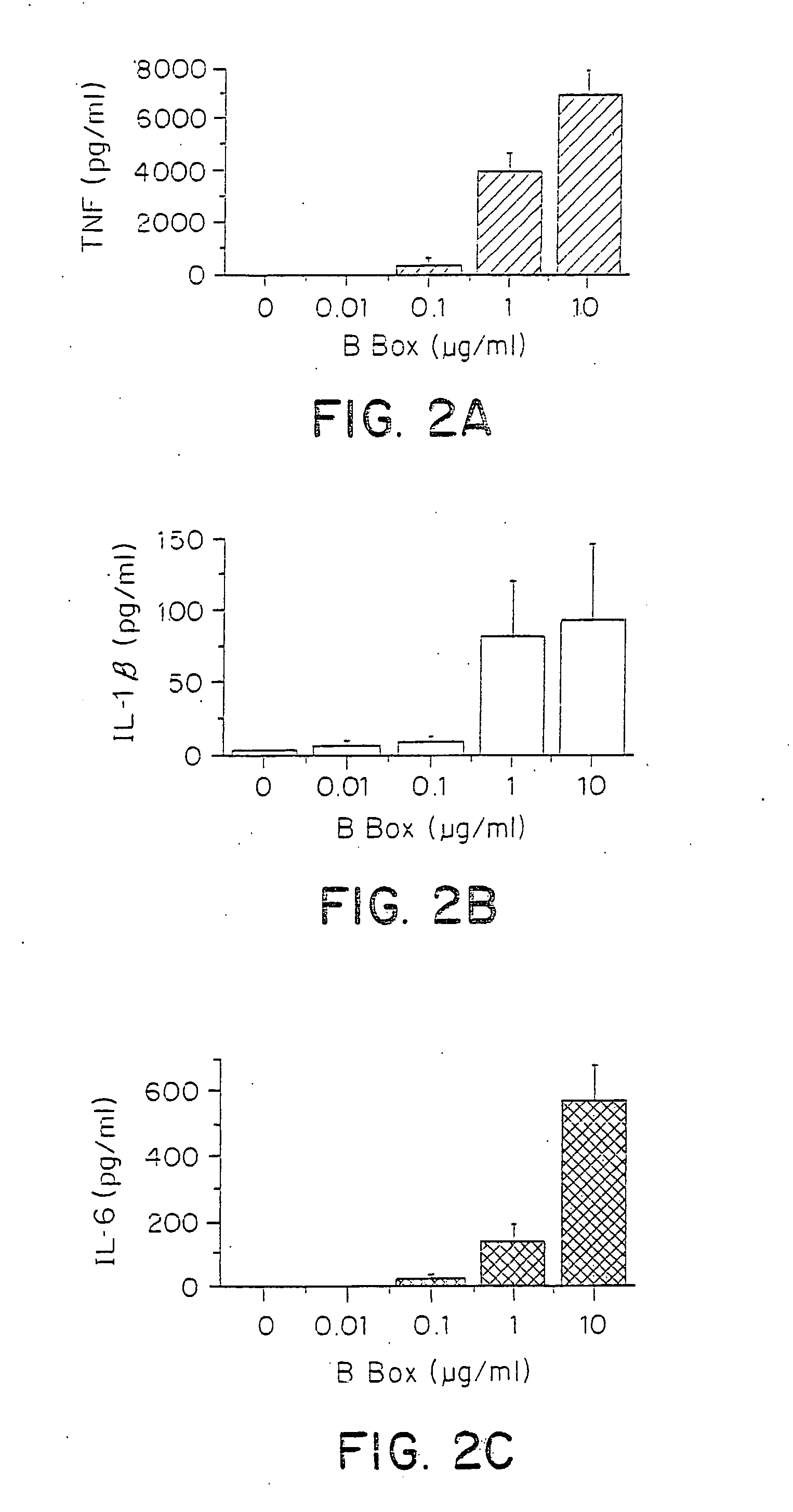
Compositions and methods are disclosed for inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine from a vertebrate cell, and for inhibiting an inflammatory cytokine cascade in a patient. The compositions comprise a vertebrate HMGB A box, and an antibody preparation that specifically binds to a vertebrate HMGB B box. The methods comprise treating a cell or a patient with sufficient amounts of the composition to inhibit the release of the proinflammatory cytokine, or to inhibit the inflammatory cytokine cascade.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +2
Methods and reagents for the treatment of immunoinflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20050271661A1High expressionIncrease and decrease expression levelBiocideAntipyreticNFAT PathwaySignalling pathways
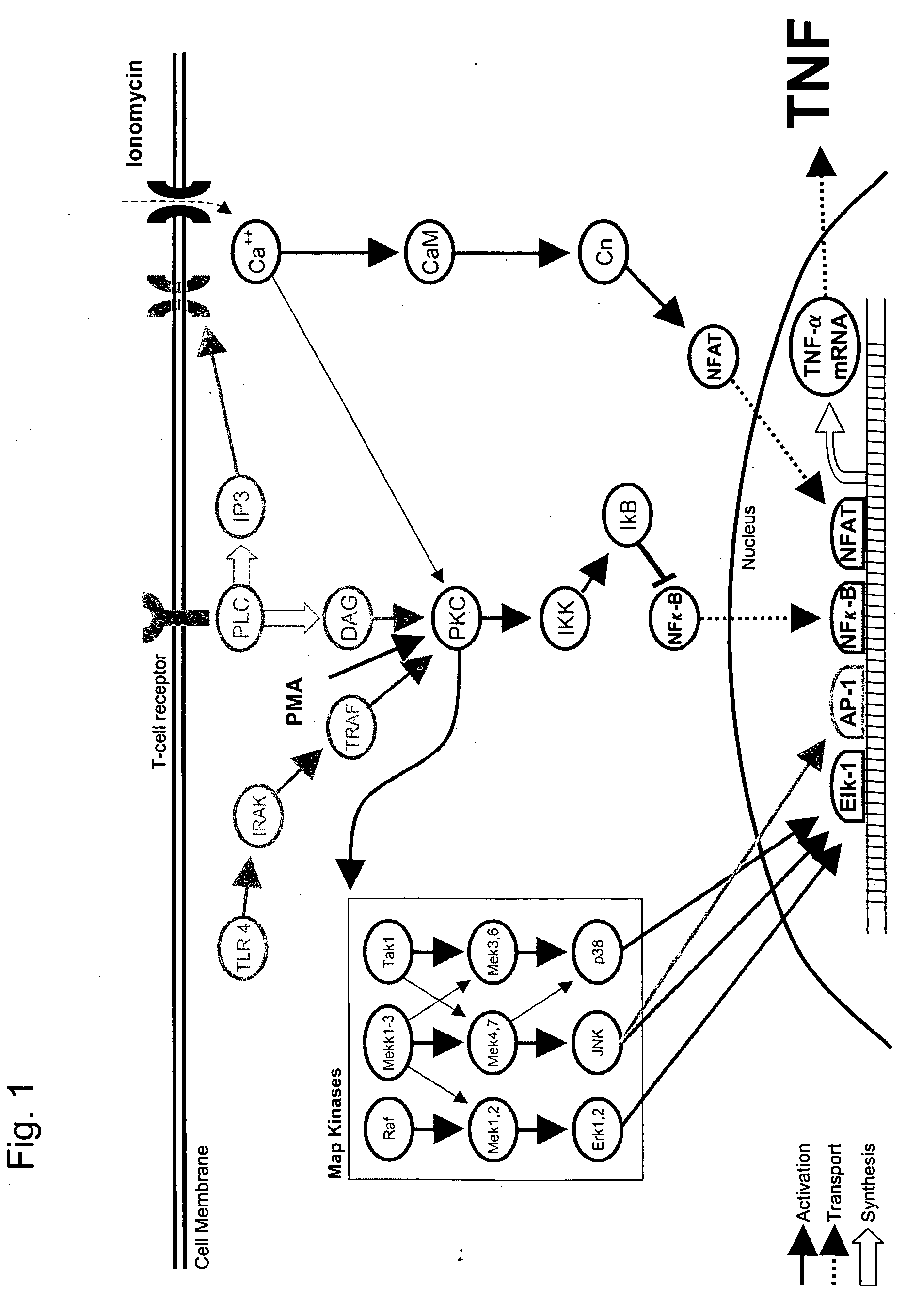
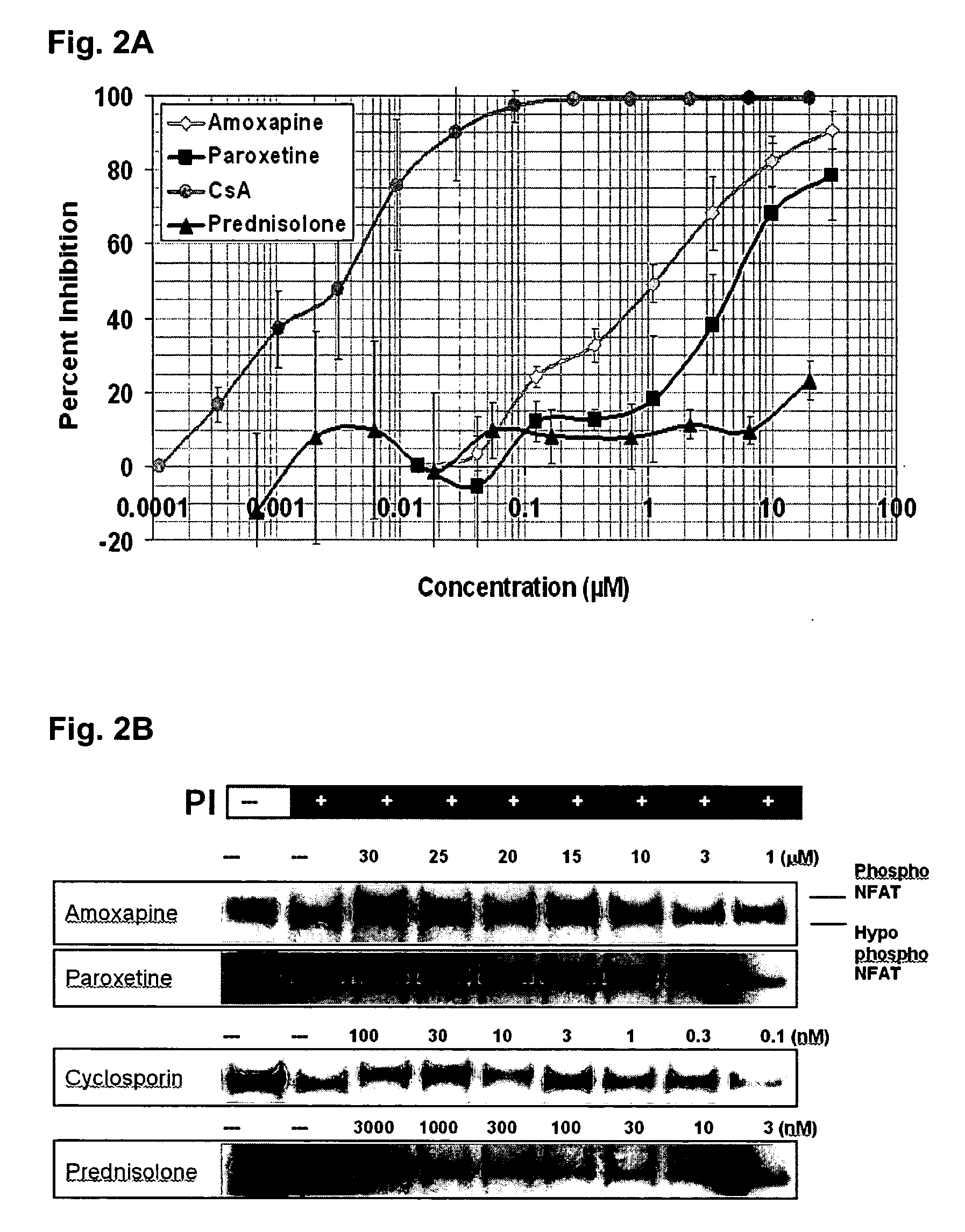
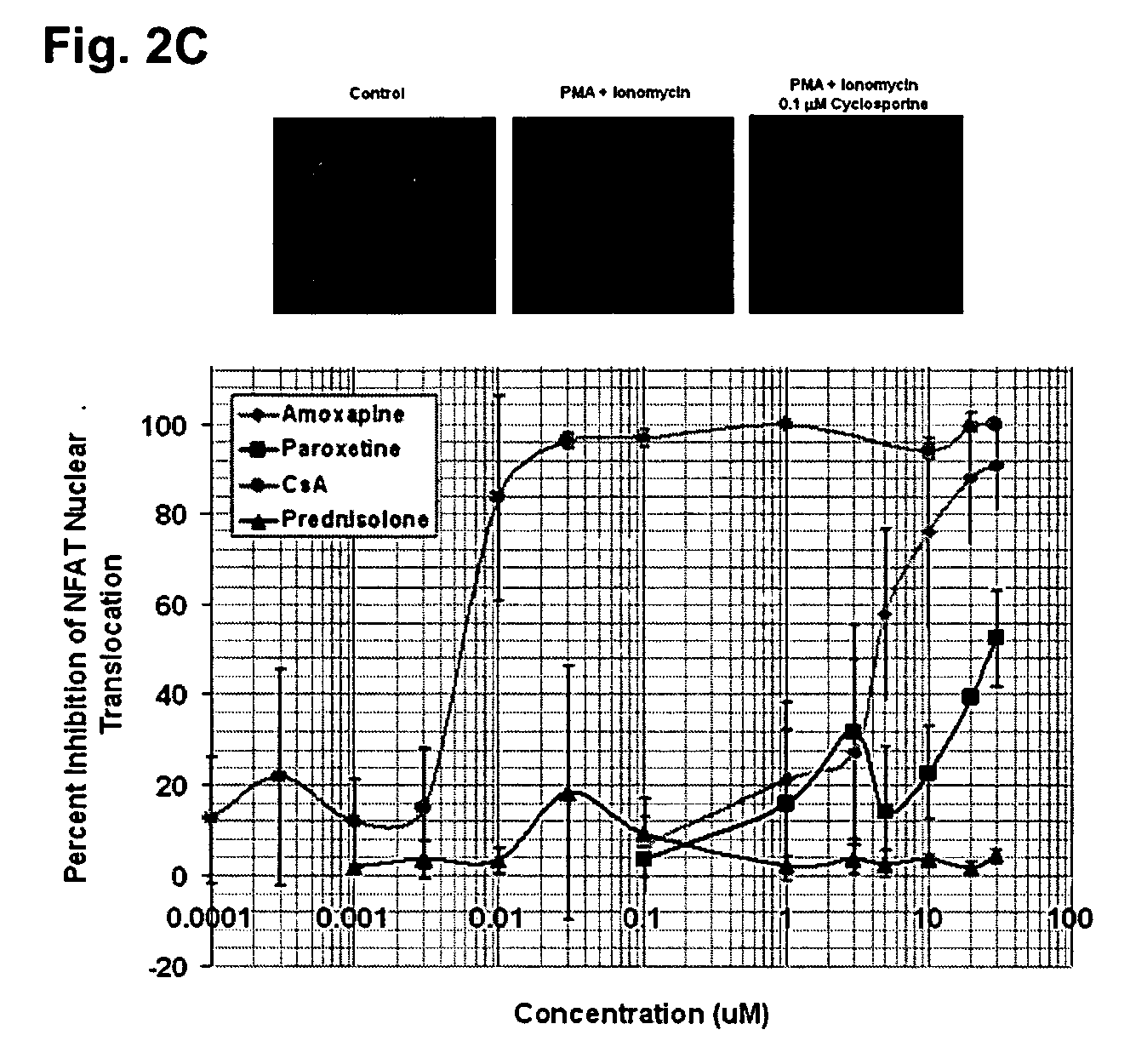
The invention involves the treatment, prevention, and reduction of immunoinflammatory disorders involving the combination of an agent that increases the signal activity of a glucocorticoid receptor (e.g., glucocorticoid receptor agonist) and an agent that modulates the signaling activity of one or more signaling pathways selected from the NF-κB pathway, NFAT pathway, AP-1 pathway, and Elk-1 pathway such that proinflammatory cytokine secretion or production, or any other inflammatory response, is reduced. Further, screening methods are provided for identifying candidate compounds and strategies useful for treating, preventing, or reducing such conditions.
Owner:COMBINATORX
Treatment of inflammation by non-invasive stimulation
InactiveUS20160250097A9Reduces proinflammatory cytokineInhibits the inflammatory reflexDevices for pressing relfex pointsChiropractic devicesInflammatory reflexFacial nerve
Described herein are devices, systems and method for treating inflammatory disorders by modulating a subject's inflammatory reflex. The method may include the step of non-invasively stimulating the inflammatory reflex (e.g., the vagus nerve, the splenic nerve, the hepatic nerve, the facial nerve, and the trigeminal nerve) of a subject in a manner which significantly reduces proinflammatory cytokines in the subject and / or provides a therapeutically effective treatment for the subject. Devices for non-invasively stimulating the inflammatory reflex may include a movable tip or actuator that is controlled to mechanically stimulate the ear. The devices may be hand-held or wearable, and may stimulate the cymba conchae region of the subject's ear.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
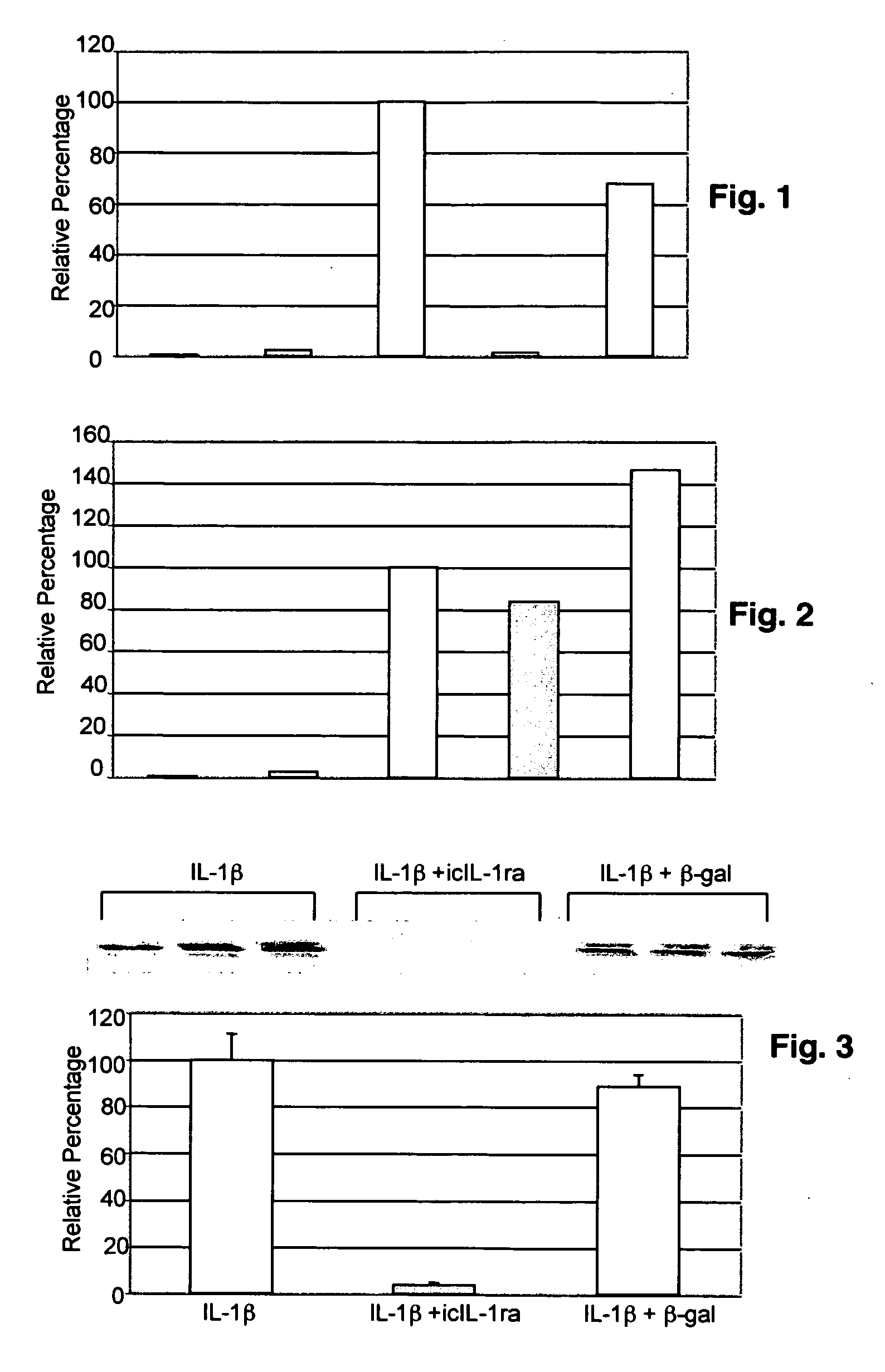
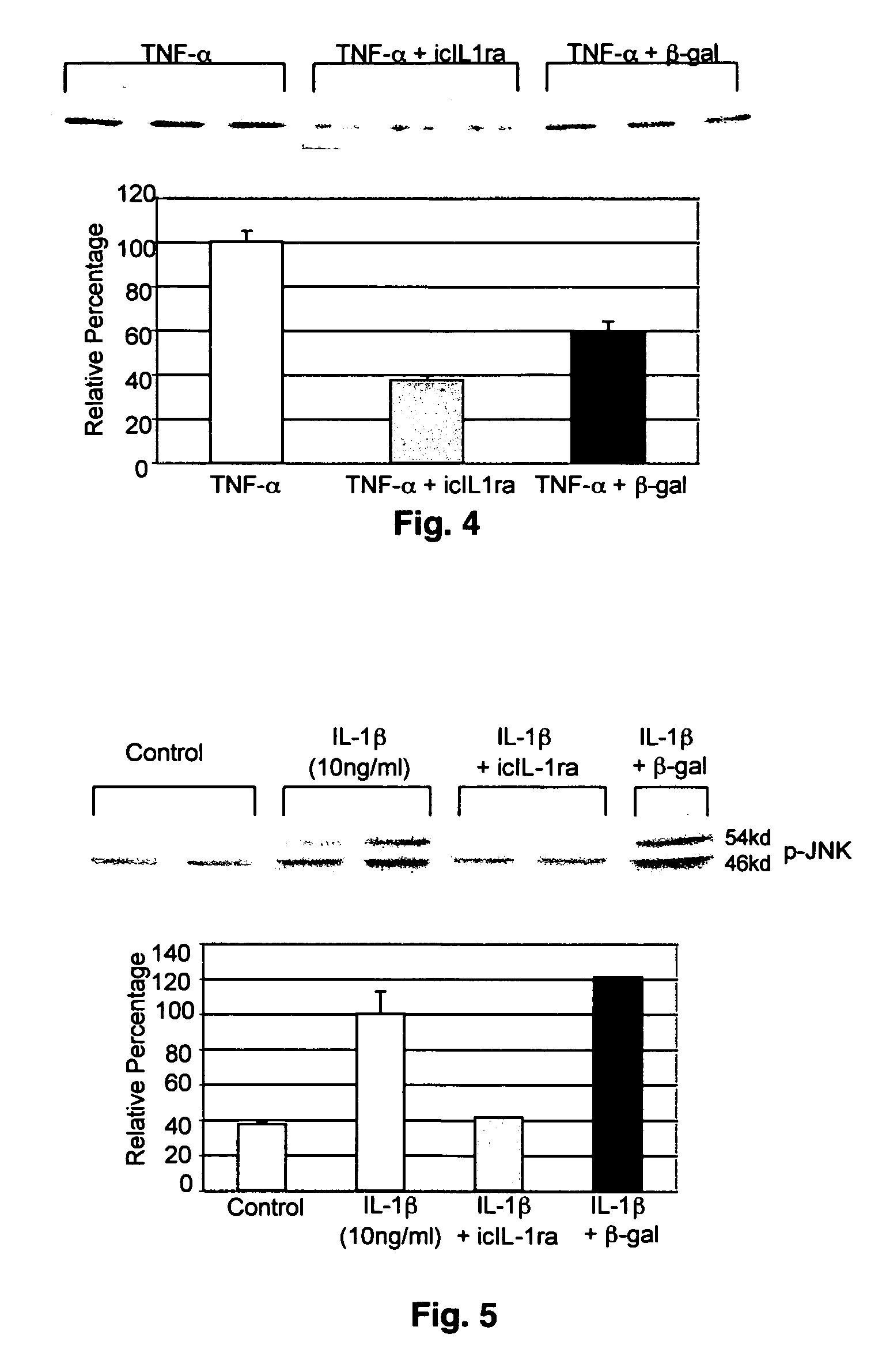
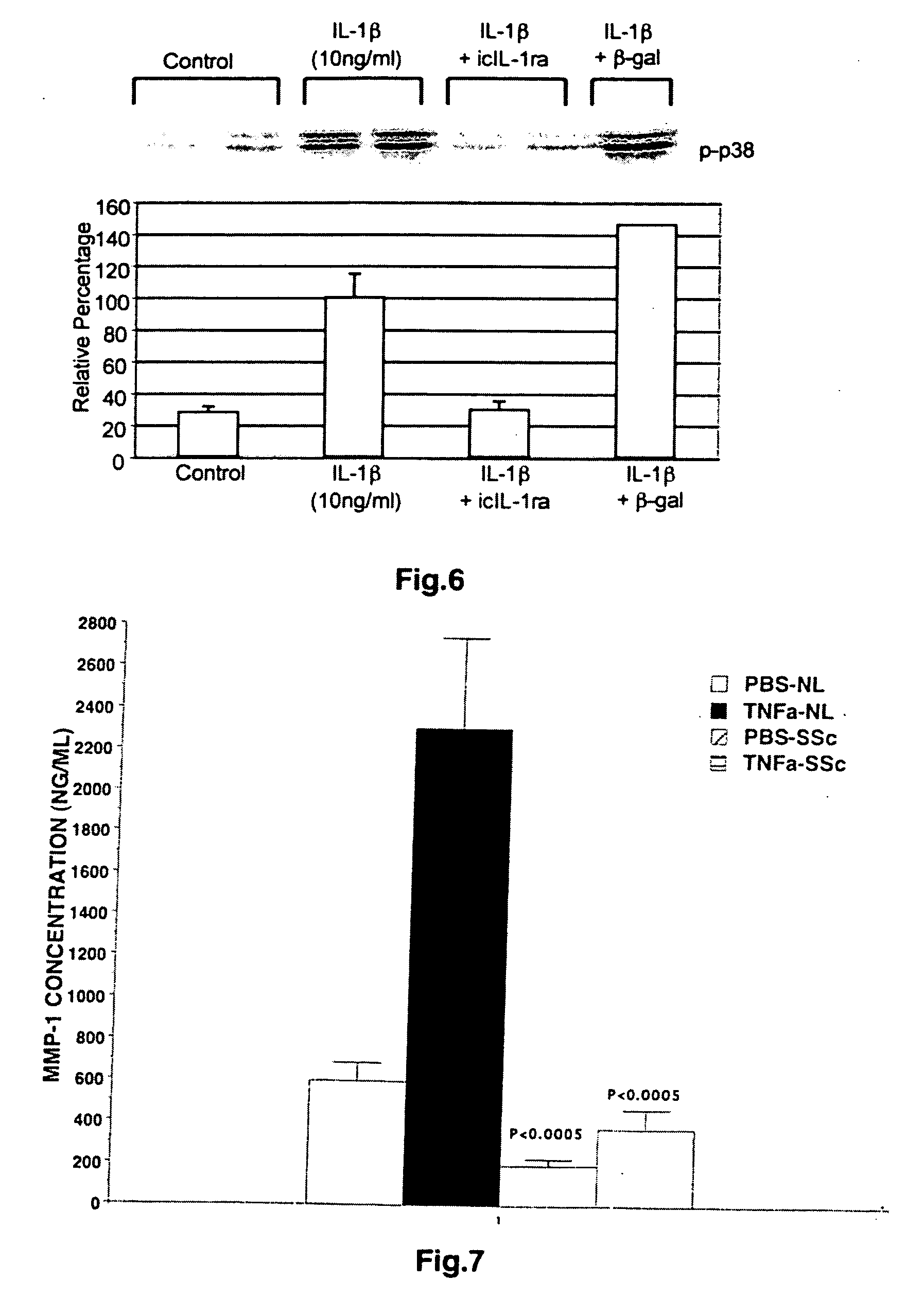
Intracellular interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and uses thereof
Matrix metalloproteinases are major mediators of tissue destruction in various chronic inflammatory disorders. The present invention demonstrates that over- expression of intracellular isoform of IL-1 receptor antagonist confers to recipient cells resistance to signaling pathways of proinflammatory cytokines (such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-1 beta) that induce matrix metalloproteinase and subsequent tissue degradation. Hence, over-expression of intracellular IL-1 receptor antagonist may inhibit tissue destruction in various inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, other arthritides, degenerative intervertebral disc disease and chronic skin ulcers that occurs in diabetes mellitus and bed-ridden patients.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Treatment and prevention of immunodeficiency virus infection by administration of non-pyrogenic derivatives of lipid A
InactiveUS20040120924A1BiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellImmunodeficiency virus
The present inventors have found that certain preparations containing LPS and / or lipid A variants, derivatives, and / or analogs demonstrate non-pyrogenic properties and exhibit anti-viral activities. In particular, non-pyrogenic preparations of LPS, lipid A, LPS antagonists and lipid A antagonists, and derivatives thereof induce beta chemokine secretion, such as MIP-1beta, but not proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNFalpha, IL-1beta and IL-6. Non-pyrogenic preparations of the invention have been demonstrated by the Applicant to suppress HIV replication in human peripheral blood monocytes, as described by way of example herein. The present invention provides preparations of LPS or lipid A variants, analogs and derivatives of decreased or absent pyrogenicity which can be used as therapeutics for the treatment or prevention of immunodeficiency virus infection and its consequences.
Owner:HONE DAVID M +2
Treatment and prevention of immunodeficiency virus infection by administration of non-pyrogenic derivatives of lipid A
The present inventors have found that certain preparations containing LPS and / or lipid A variants, derivatives, and / or analogs demonstrate non-pyrogenic properties and exhibit anti-viral activities. In particular, non-pyrogenic preparations of LPS, lipid A, LPS antagonists and lipid A antagonists, and derivatives thereof induce β chemokine secretion, such as MIP-1β, but not proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6. Non-pyrogenic preparations of the invention have been demonstrated by the Applicant to suppress HIV replication in human peripheral blood monocytes, as described by way of example herein. The present invention provides preparations of LPS or lipid A variants, analogs and derivatives of decreased or absent pyrogenicity which can be used as therapeutics for the treatment or prevention of immunodeficiency virus infection and its consequences.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
Use of HMGB fragments as anti-inflammatory agents
InactiveUS20080214454A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSpinal cordProinflammatory cytokine
Compositions and methods are disclosed for inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine from a vertebrate cell, and for inhibiting an inflammatory cytokine cascade in a patient. The compositions comprise a vertebrate HMGB A box, and an antibody preparation that specifically binds to a vertebrate HMGB B box. The methods comprise treating a cell or a patient with sufficient amounts of the composition to inhibit the release of the proinflammatory cytokine, or to inhibit the inflammatory cytokine cascade.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES +2
Localized Therapy of Lower Airways Inflammatory Disorders with Proinflammatory Cytokine Inhibitors
ActiveUS20100209357A1Reduce expressionReduced activityPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryCytokine SuppressionNebulizer
The present invention is drawn to methods and compositions for treating inflammatory disorders of the lower airways, comprising administering an effective amount of an agent, which modulates the expression and / or activity of a proinflammatory cytokine or fragment thereof, preferably in a human. The proinflammatory cytokine contemplated by the invention includes IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha. The present invention describes a kit comprising a delivery device and a pharmaceutical composition for administration of the agent. The pharmaceutical composition includes at least one proinflammatory cytokine inhibitor, optionally one or more additional active ingredients, and at least one pharmaceutically active carrier. The delivery device further comprises a nebulizer, an inhaler, a powder dispenser, an intrapulmonary aerosolizer and a sub-miniature aerosolizer.
Owner:ONSPIRA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for strengthening immune-suppression function of mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN102936578AEnhanced Contact InhibitionLower immune responseChemical cell growth stimulationLymphocyte proliferationIntracellular
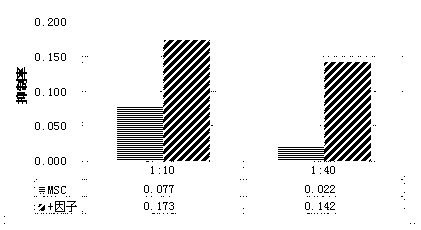
The invention relates to the technical field of mesenchymal stem cells for cell therapy, in particular to a method for strengthening an immune-suppression function of the mesenchymal stem cells. Separated mesenchymal stem cells are sub-cultured and then cultured in a culture medium containing IFN-gamma, IL-1beta and progesterone. After subjected to co-cultivation and activation of the IFN-gamma, theIL-1beta and the progesterone, the suppression ratio of the MSC cells to lymphocyte proliferation is improved by 2-7 times, the expression of immune-suppression protein in the MSC cells is improved by 2-12 times, the capacity of cell secretion anti-inflammatory cytokines is improved by 5-20 times, and the capacity of secretion proinflammatory cytokines is reduced by 10%-30%, and the immune-suppression activity of the MSC cells is increased greatly.
Owner:SHANDONG QILU STEM CELL ENG
CD47 related compositions and methods for treating immunological diseases and disorders
InactiveUS8377448B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmune complex depositionImmune complex
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for the treatment of malignant melanoma, breast, prostate, colon, papillary thyroid and pancreatic cancer
InactiveUS20100004304A1Mitigating and preventing complicationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLymphatic SpreadGrowth cell
It is now recognized that chronic inflammation is an important risk factor for the development of cancer. The proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 is implicated in cancer because it is important for the activation of STAT, a key regulator of cancer growth, survival, metastasis, immune evasion and angiogenesis. Increased IL-6 and Stat-3 exists in vitro in pancreatic cancer, malignant melanoma, papillary thyroid cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, and prostate cancer cells with high basal expression of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and Wnt5a. IL6 / STAT3 activation, mediated by overexpressed TLR3 signaling, appears important in the tumor growth process, it may increase Wnt5a signaling, and be associated with increased cellular growth and migration. Using a novel inhibitor of pathologic TLR3 signaling (5-phenylmethimazole [C10]) we have demonstrated decreases in these markers plus suppression of cell growth and migration in human pancreatic cancer, malignant melanoma, papillary thyroid cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, and prostate cancer cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Use of HMGB fragments as anti-inflammatory agents
Compositions and methods are disclosed for inhibiting the release of a proinflammatory cytokine from a vertebrate cell, and for inhibiting an inflammatory cytokine cascade in a patient. The compositions comprise a vertebrate HMGB A box, and an antibody preparation that specifically binds to a vertebrate HMGB B box. The methods comprise treating a cell or a patient with sufficient amounts of the composition to inhibit the release of the proinflammatory cytokine, or to inhibit the inflammatory cytokine cascade.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com