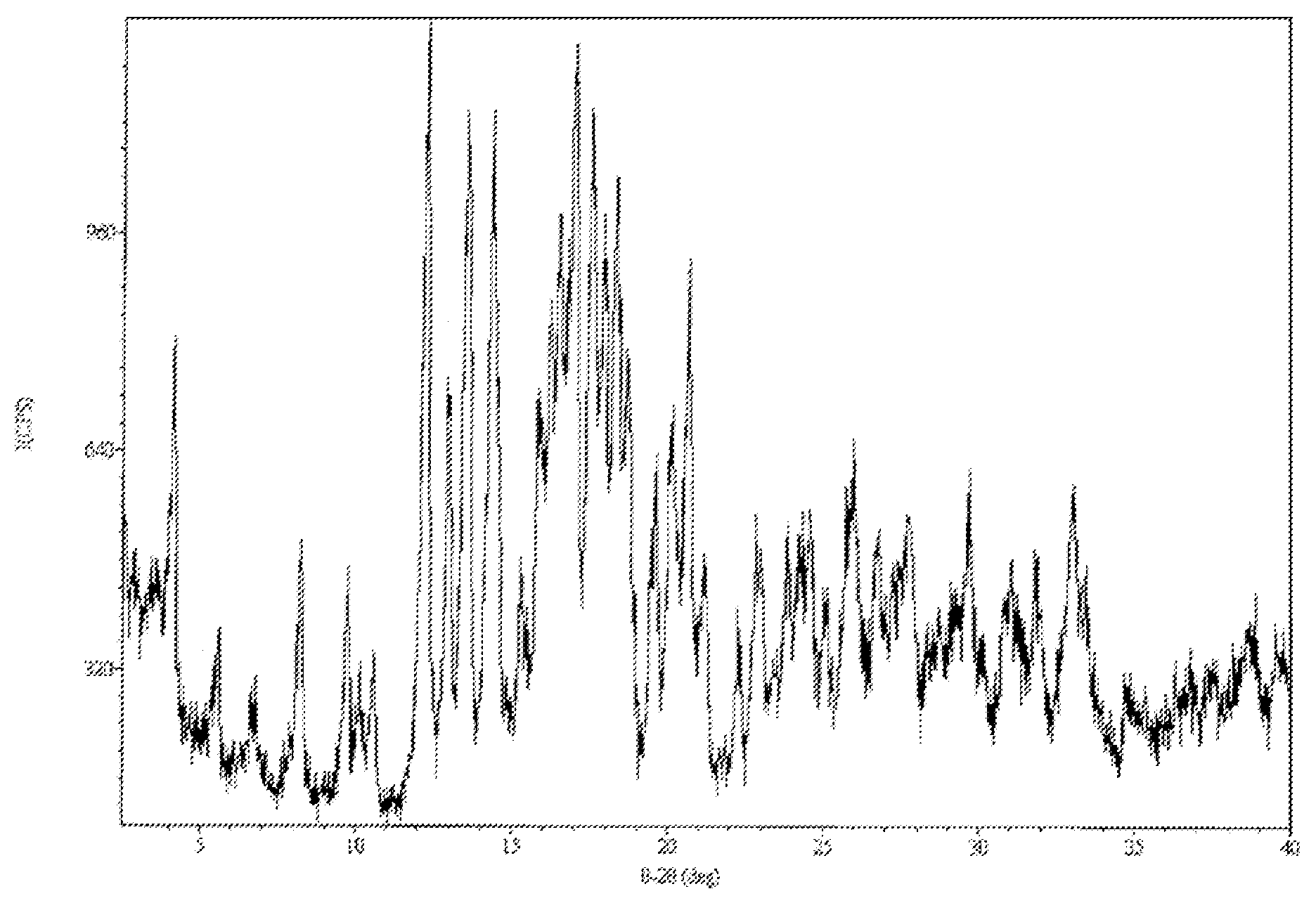
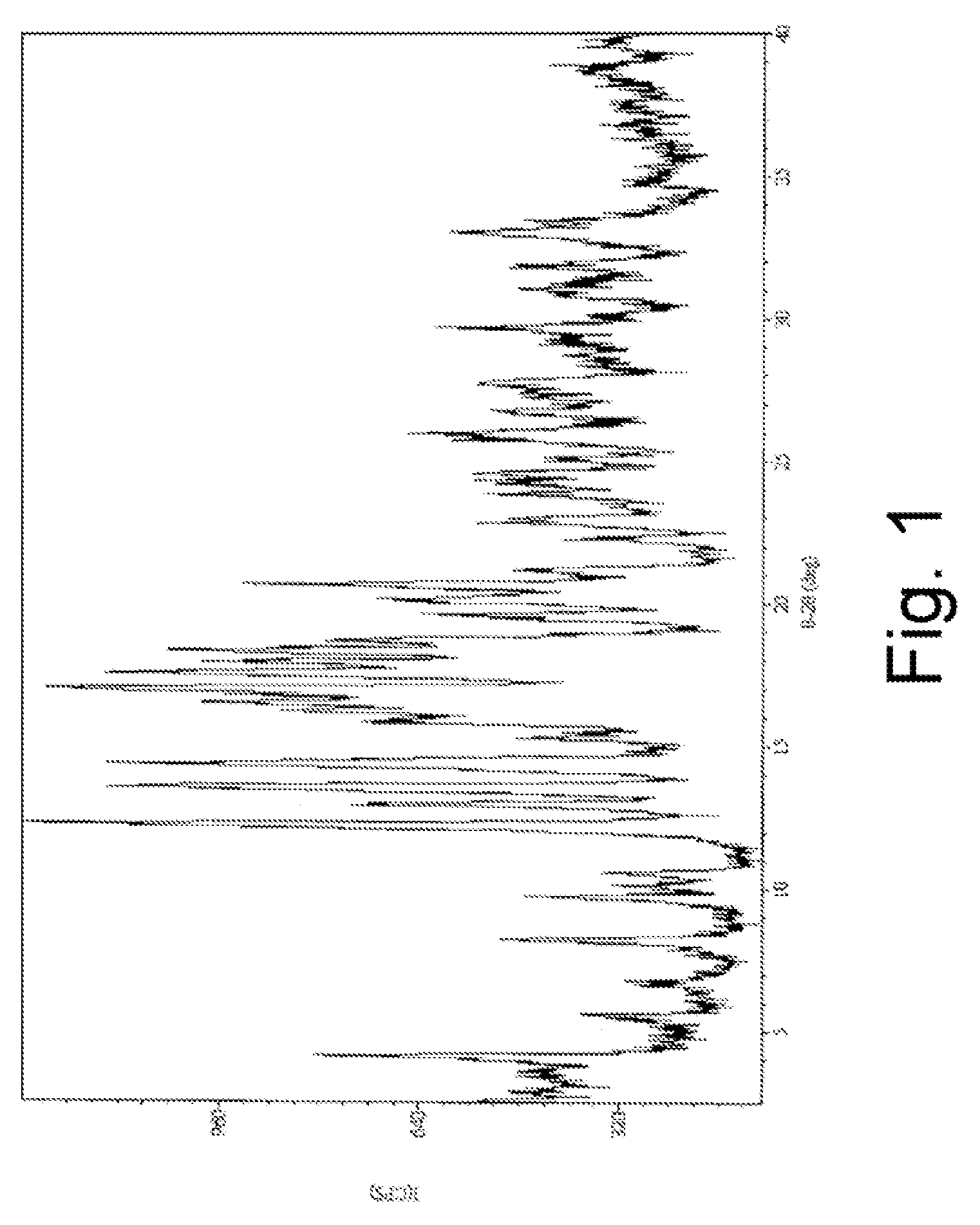
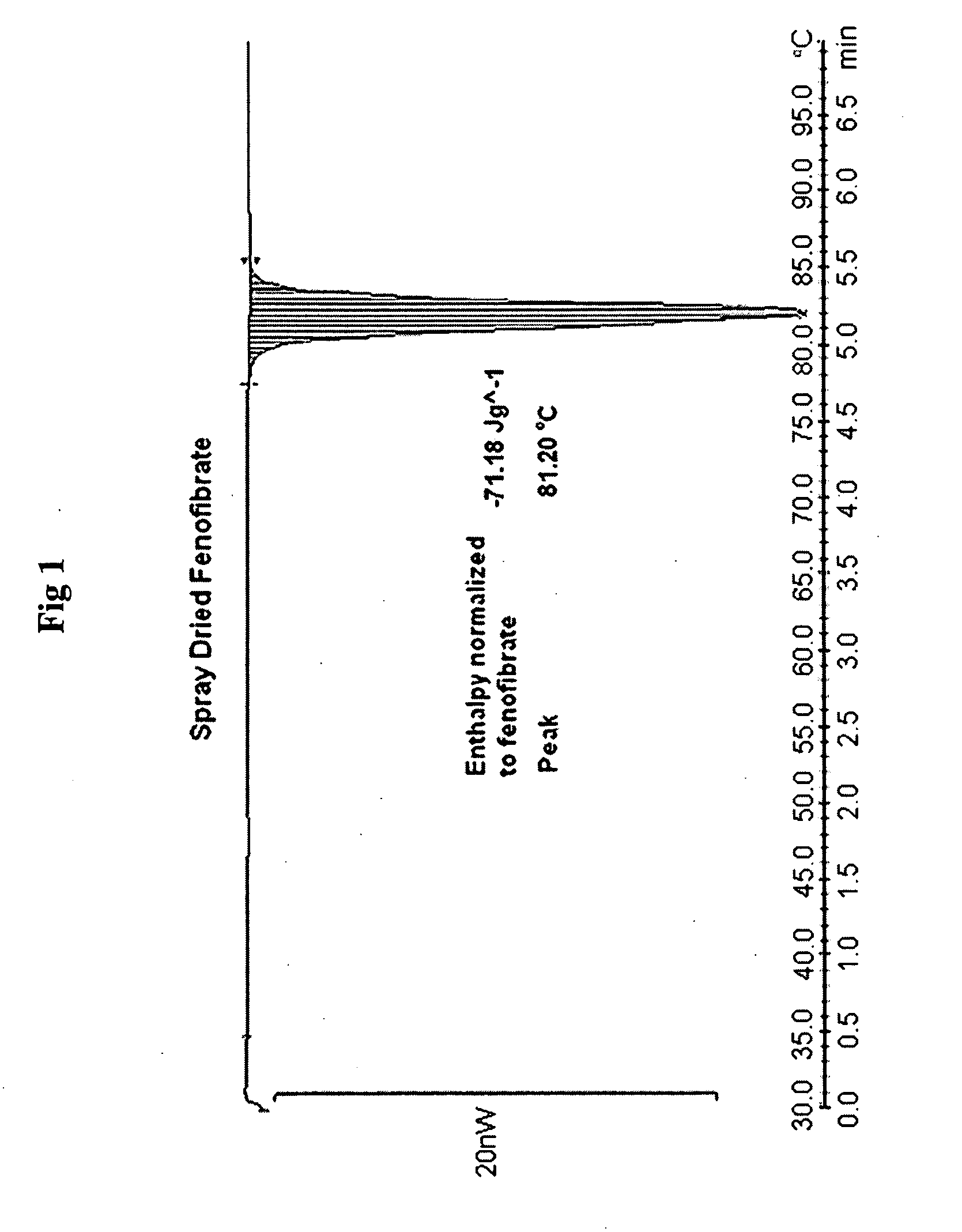
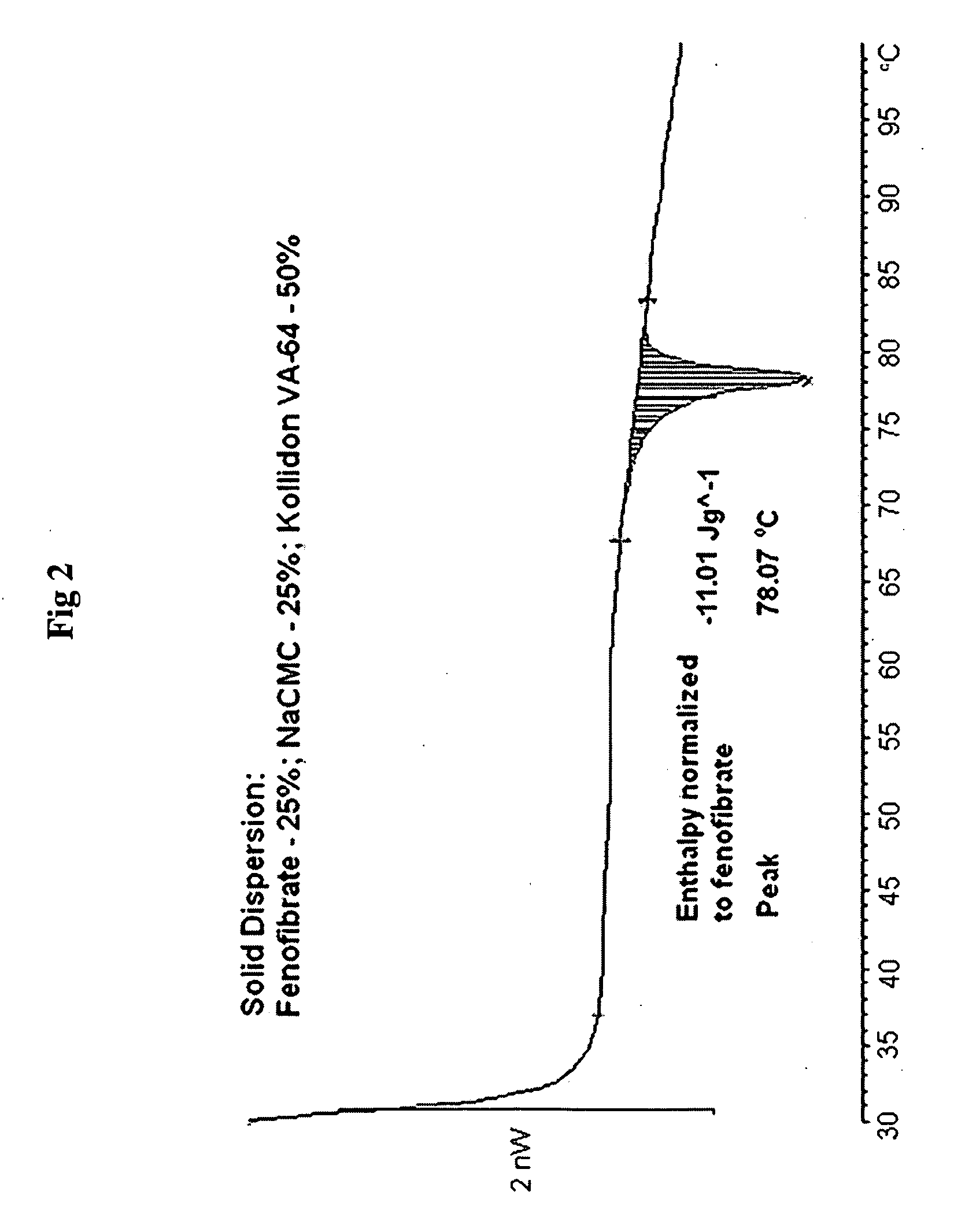
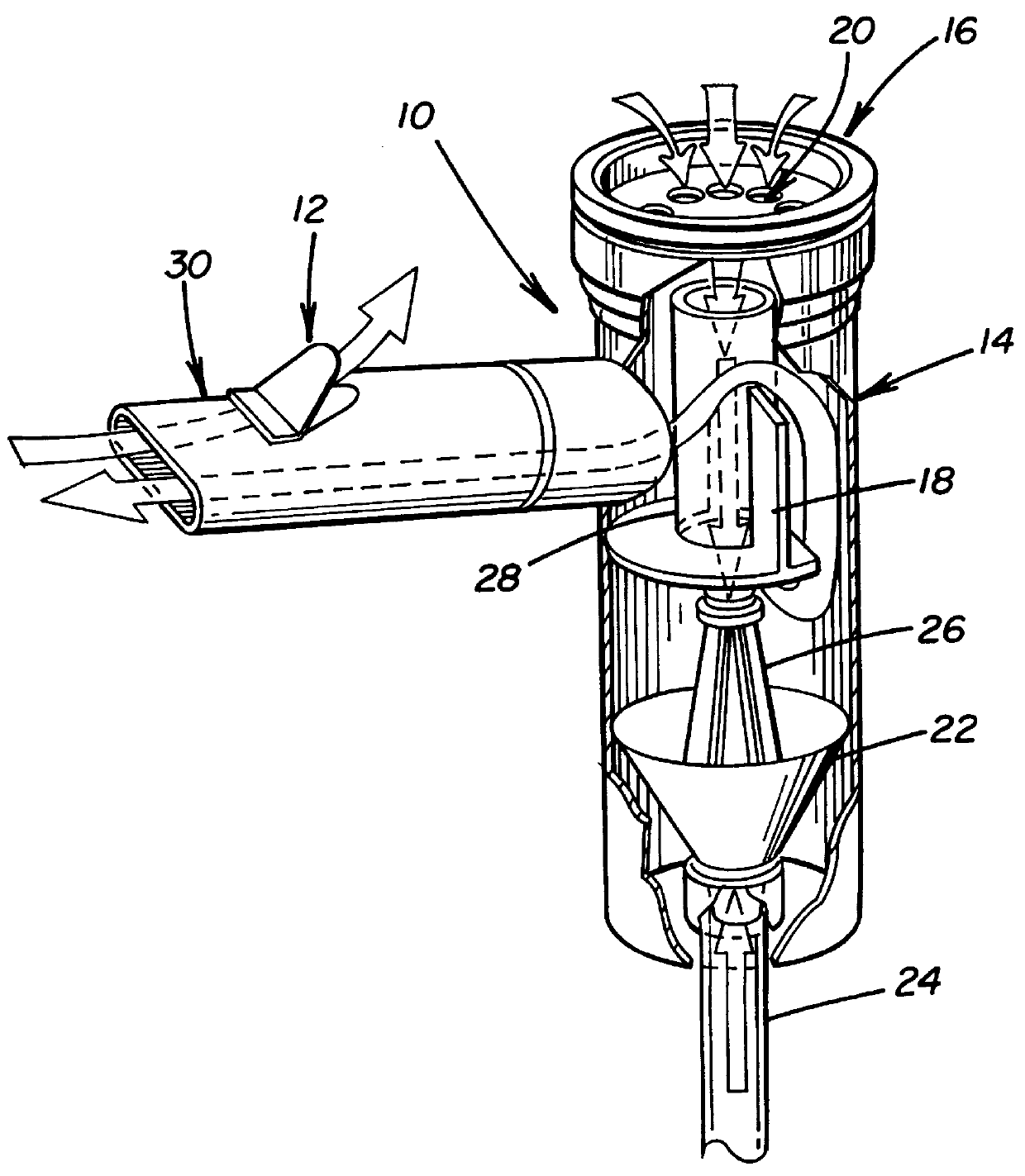
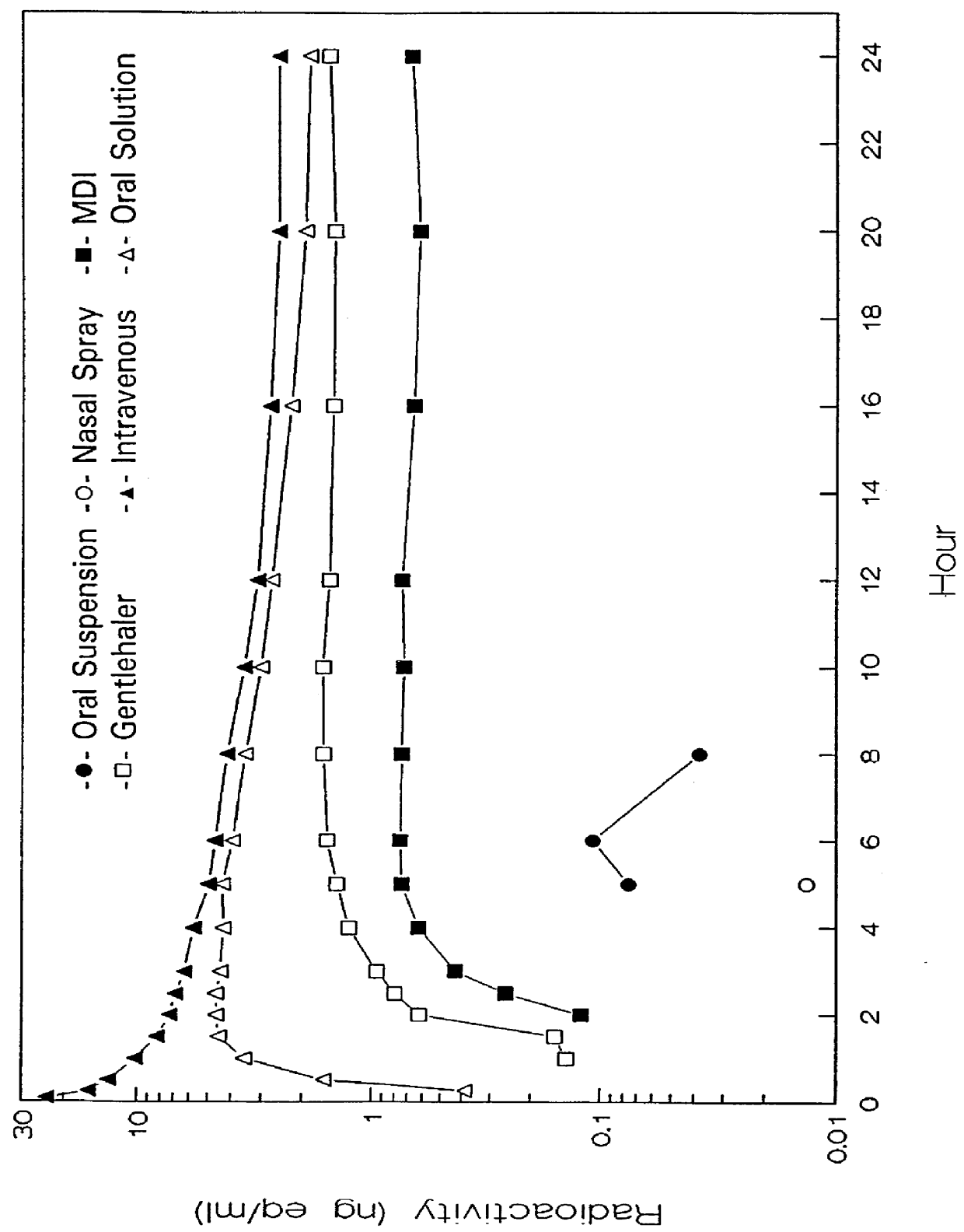
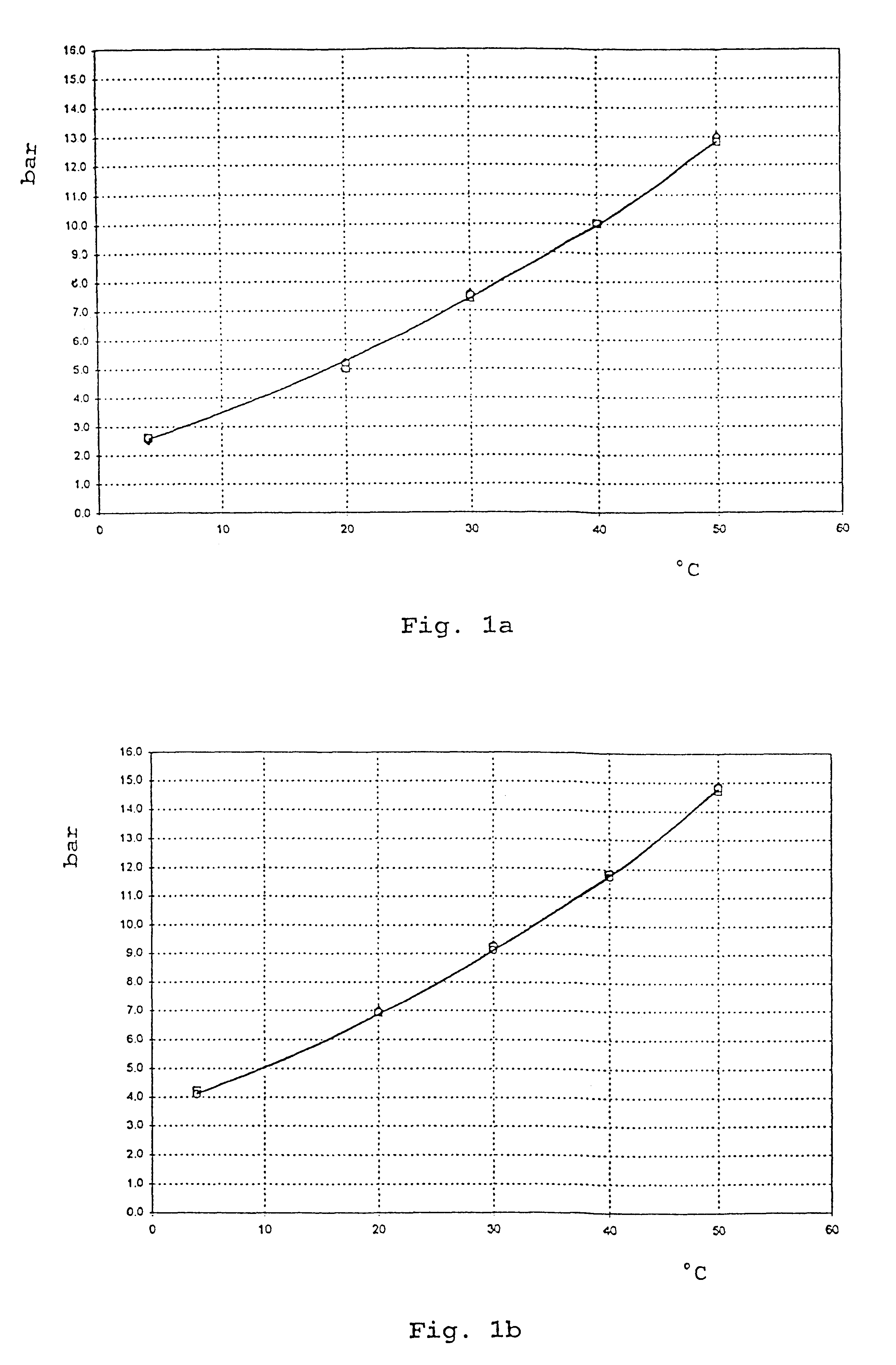
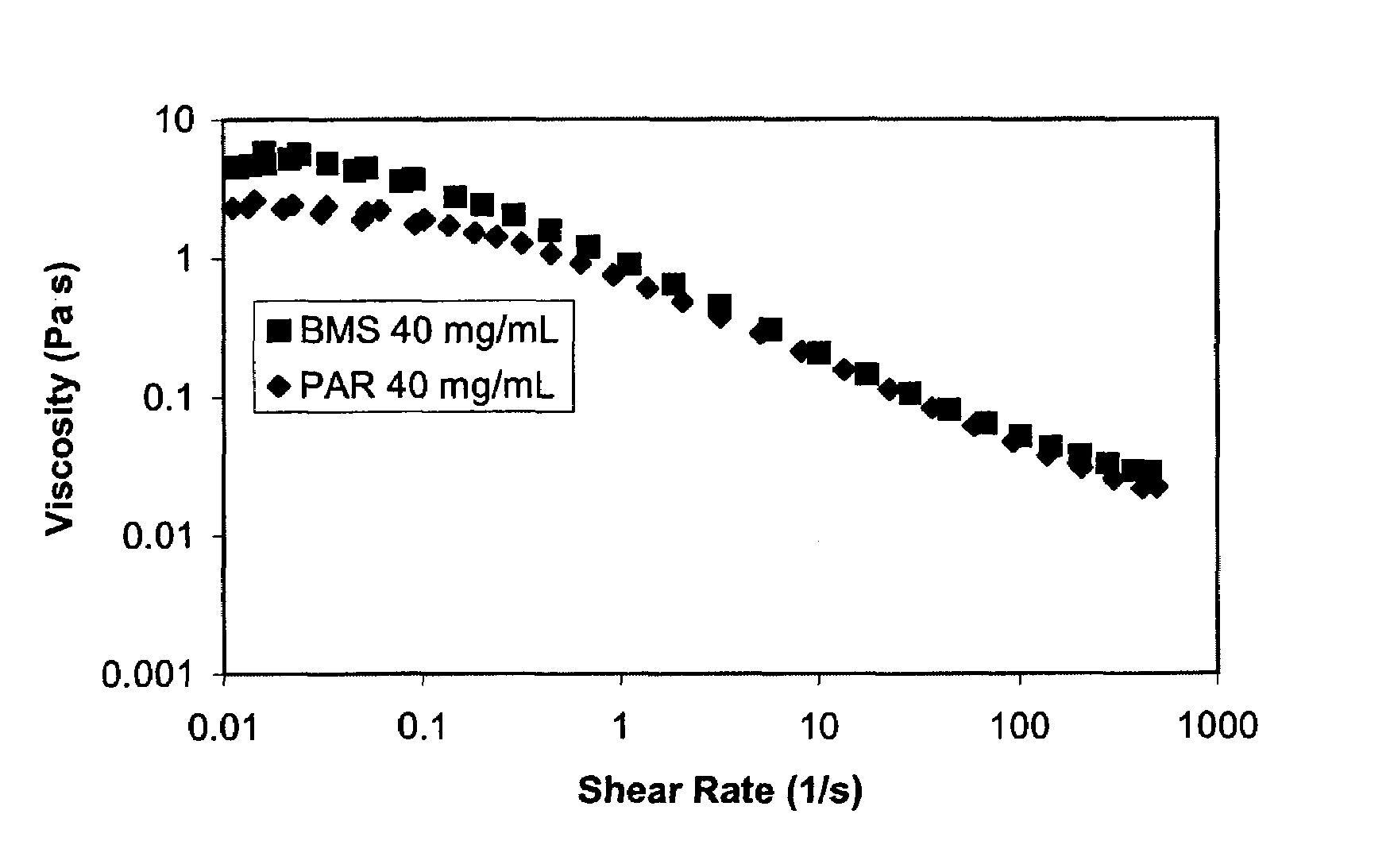
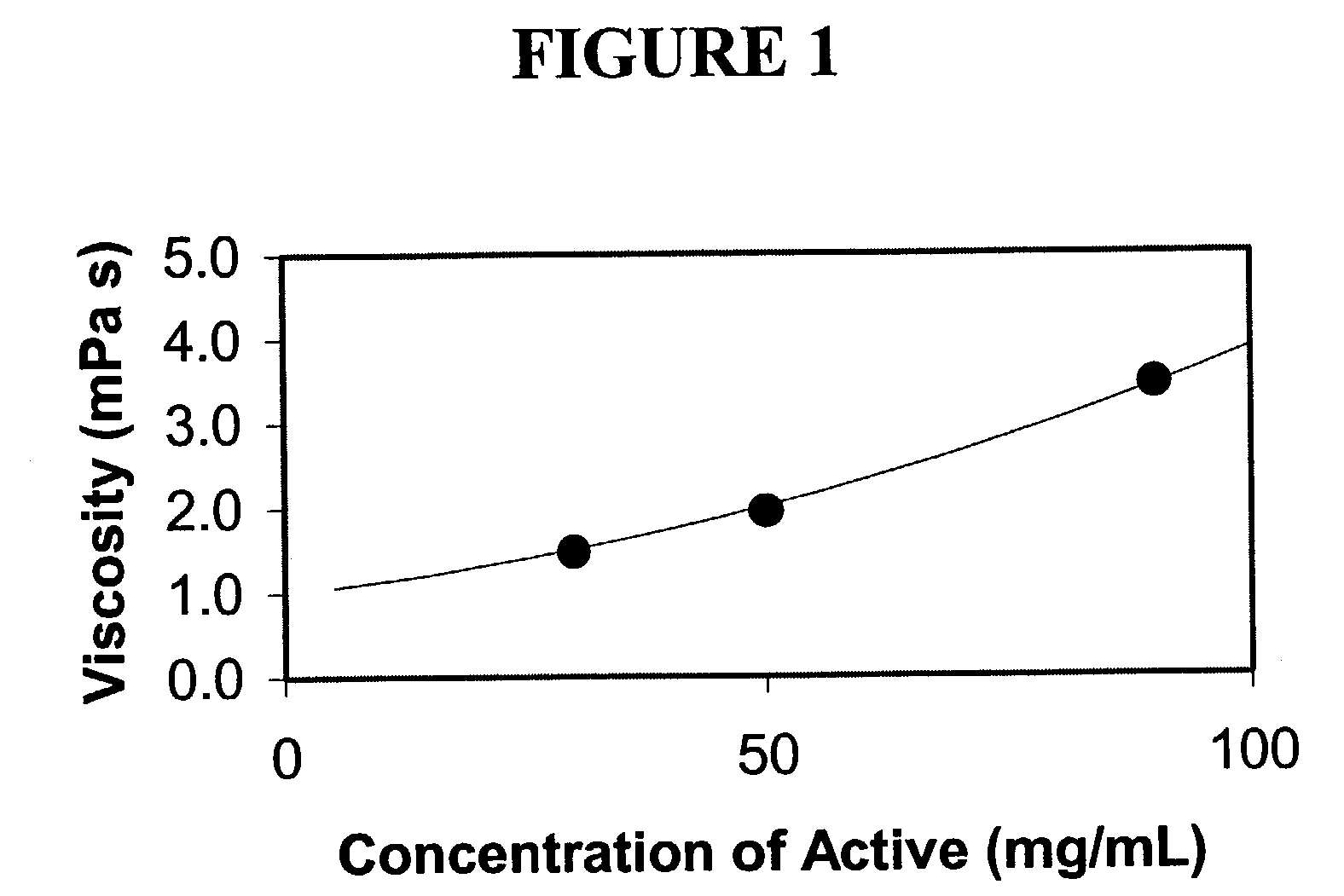
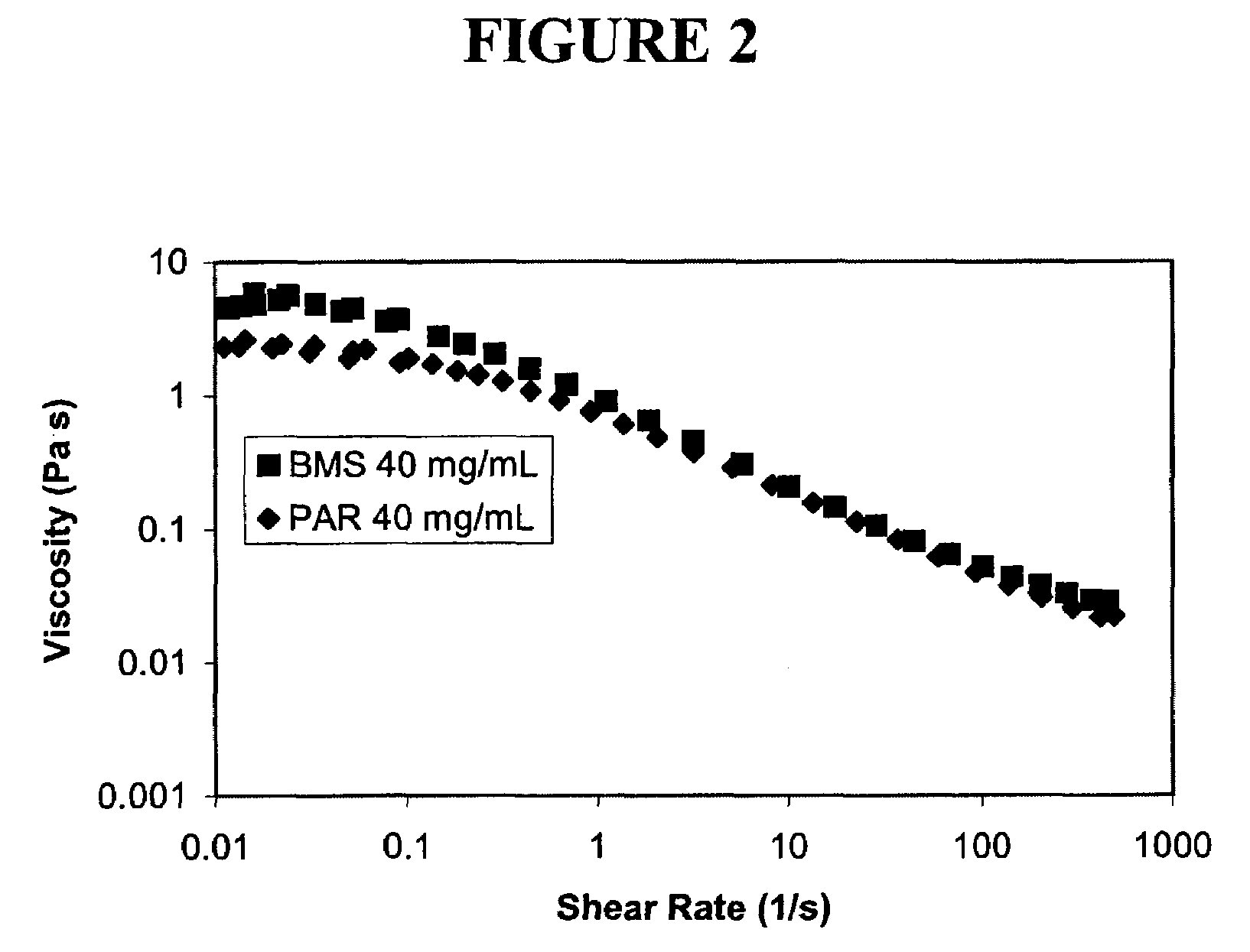
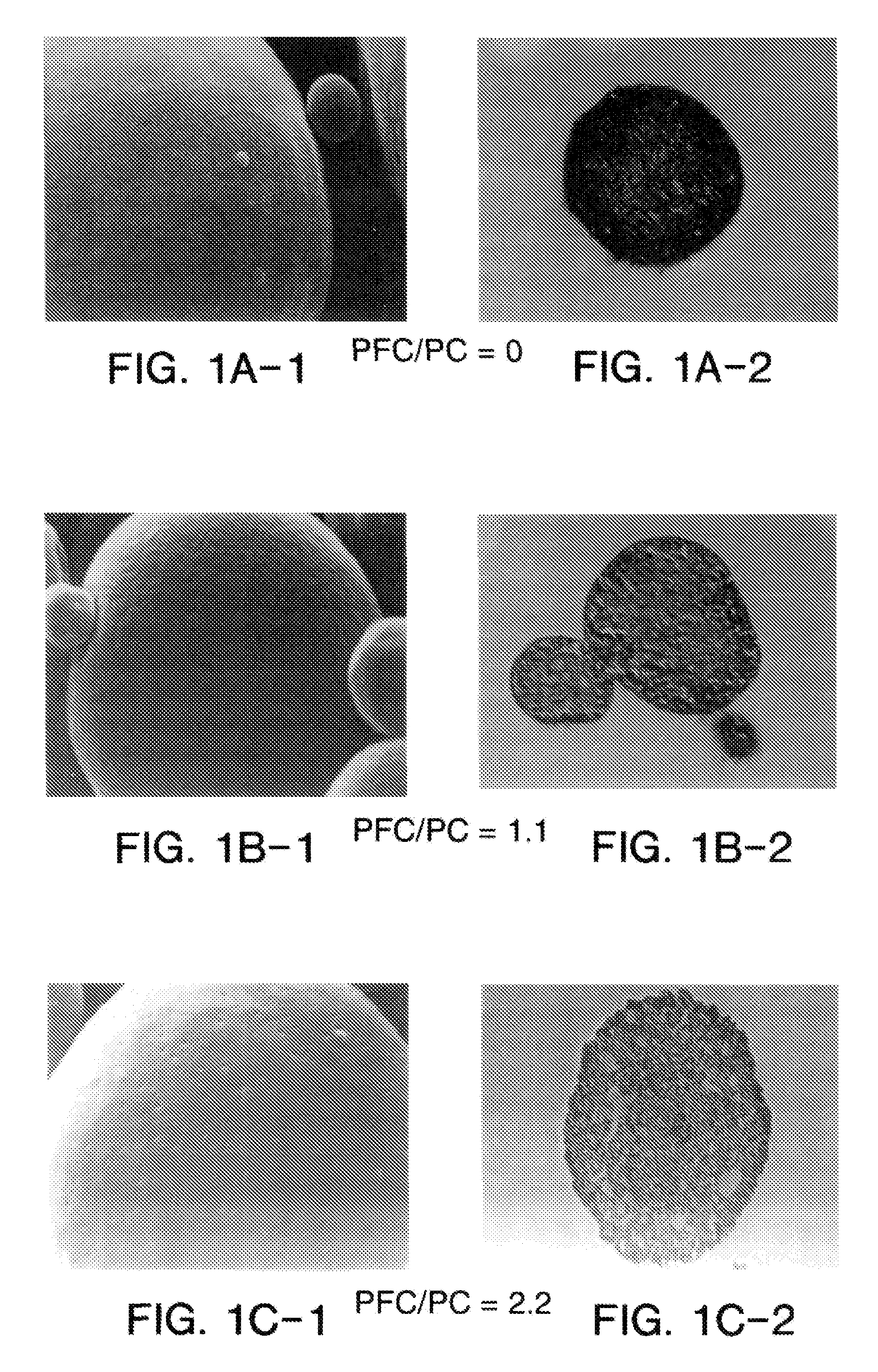
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15898results about "Dispersion delivery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lyophilization process and products obtained thereby
ActiveUS20070116729A1Dissolve fastSuitable for useBiocidePowder deliveryHigh concentrationFreeze-drying
A lyophilization process which comprises dissolving a material in one or more solvents for said material to form a solution; forcing said material at least partially out of solution by combining the solution and a non-solvent for the material, which non-solvent is miscible with the solvent or solvents used and wherein said non-solvent is volatilizable under freeze-drying conditions. In addition, for hydrophobic and / or lipophilic materials, the anti-solvent can be omitted, and the solution of the material in the solvent can be subjected directly to freeze drying. The lyophilizates can then be reconstituted with typical aqueous diluent in the case of hydrophilic materials. Hydrophobic and or lipophilic materials can be initially reconstituted with propylene glycol and / or polyethyleneglycol to form a high concentration solution therein and this is further diluted for use with a diluent of Intralipid, plasma, serum, or even whole blood.
Owner:SCIDOSE PHARMA +1
Compositions and methods of delivery of pharmacological agents
InactiveUS20050004002A1Reducing one or more side effectsInhibiting oxidation in the pharmaceutical compositionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutical agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, which carrier comprises a protein, for example, human serum albumin and / or deferoxamine. The human serum albumin is present in an amount effective to reduce one or more side effects associated with administration of the pharmaceutical composition. The invention also provides methods for reducing one or more side effects of administration of the pharmaceutical composition, methods for inhibiting microbial growth and oxidation in the pharmaceutical composition, and methods for enhancing transport and binding of a pharmaceutical agent to a cell.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
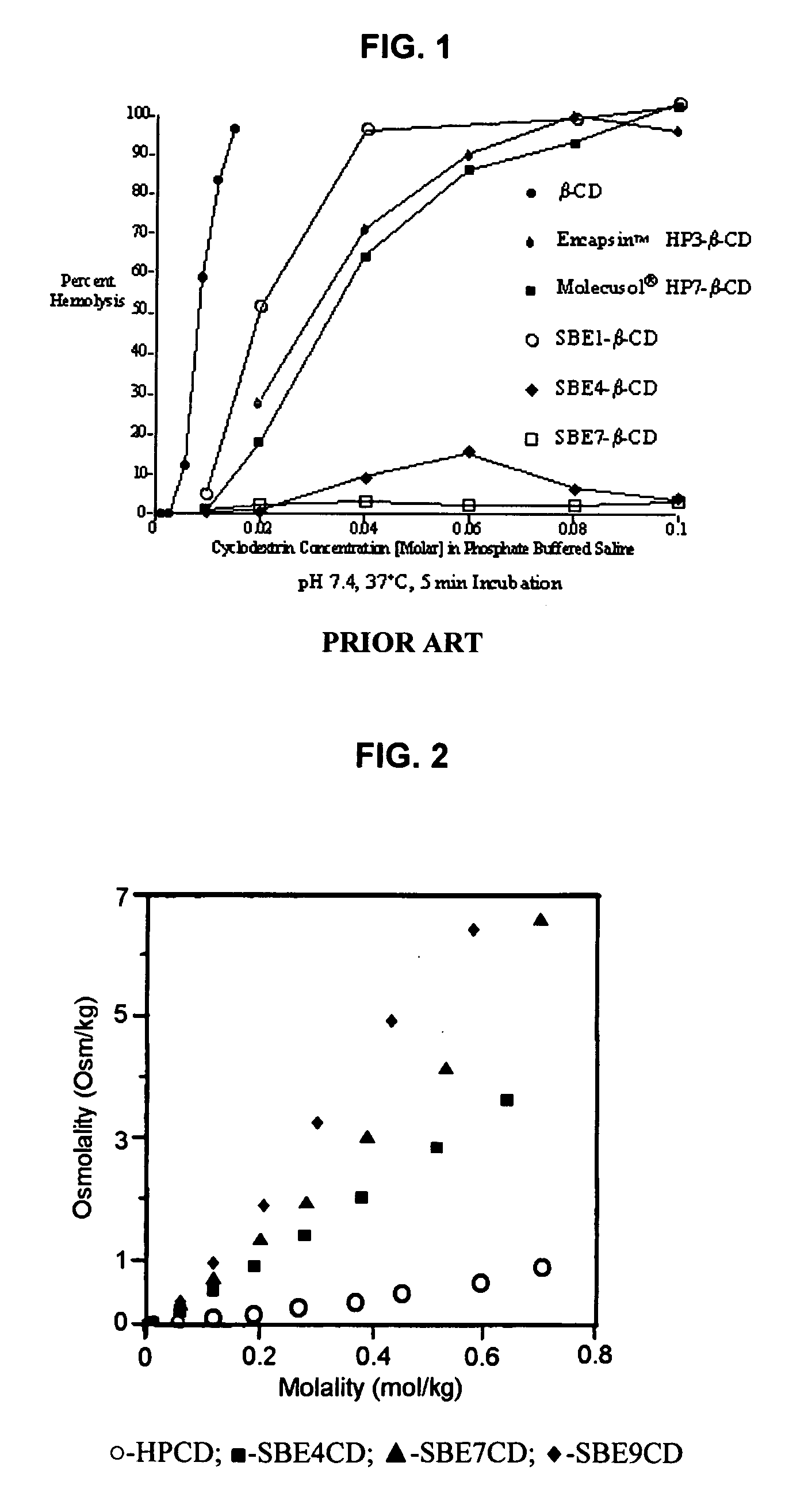
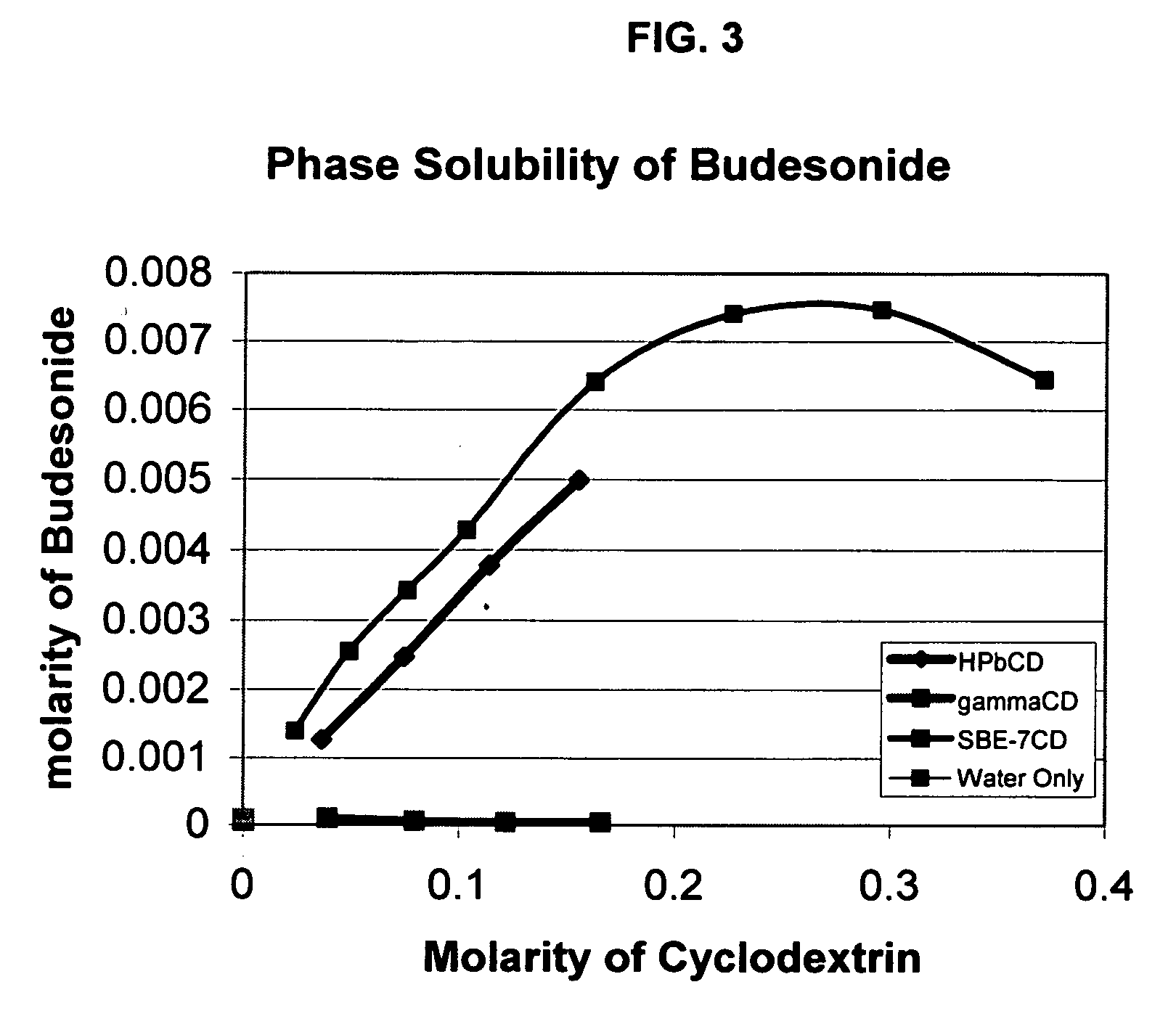
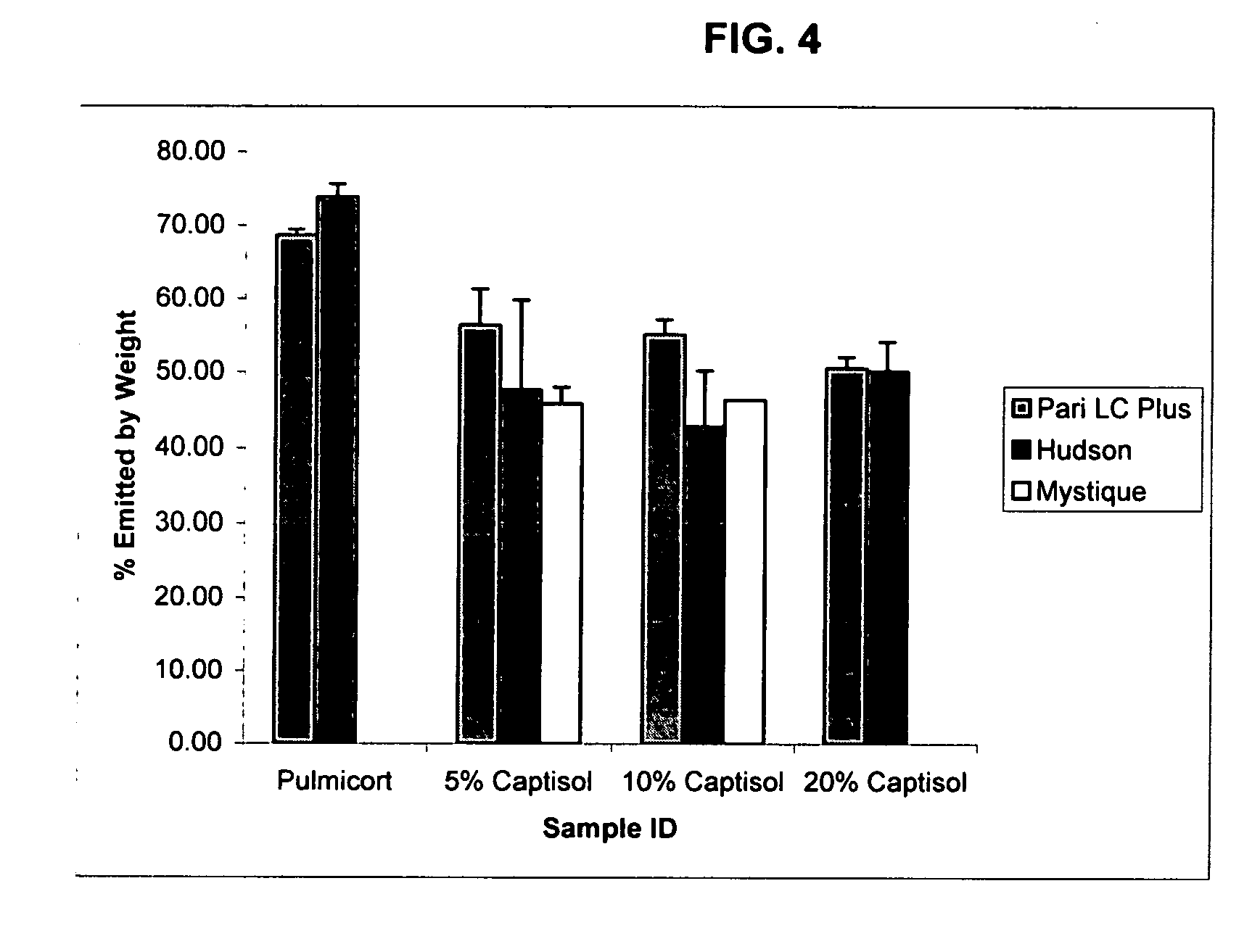
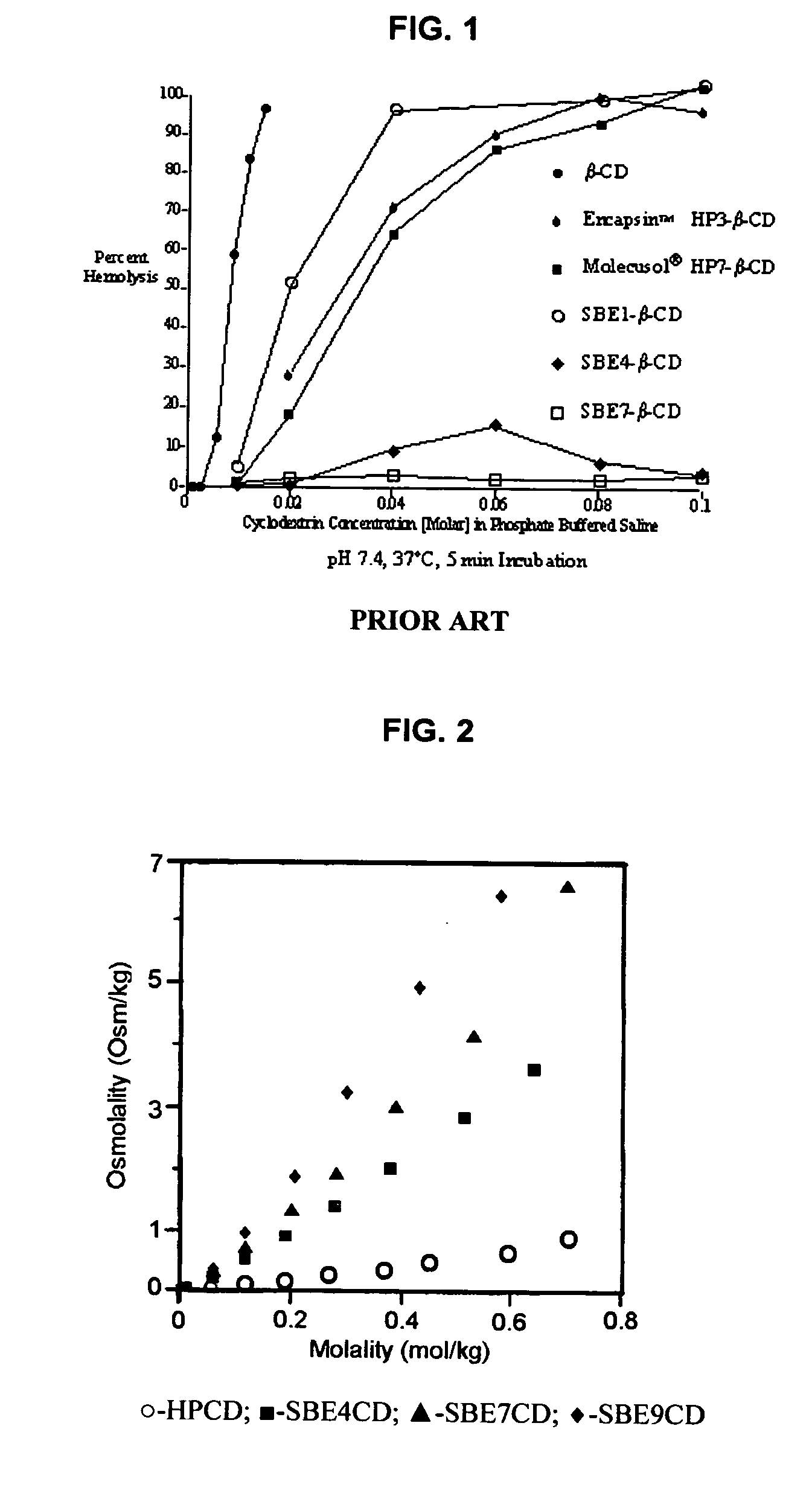
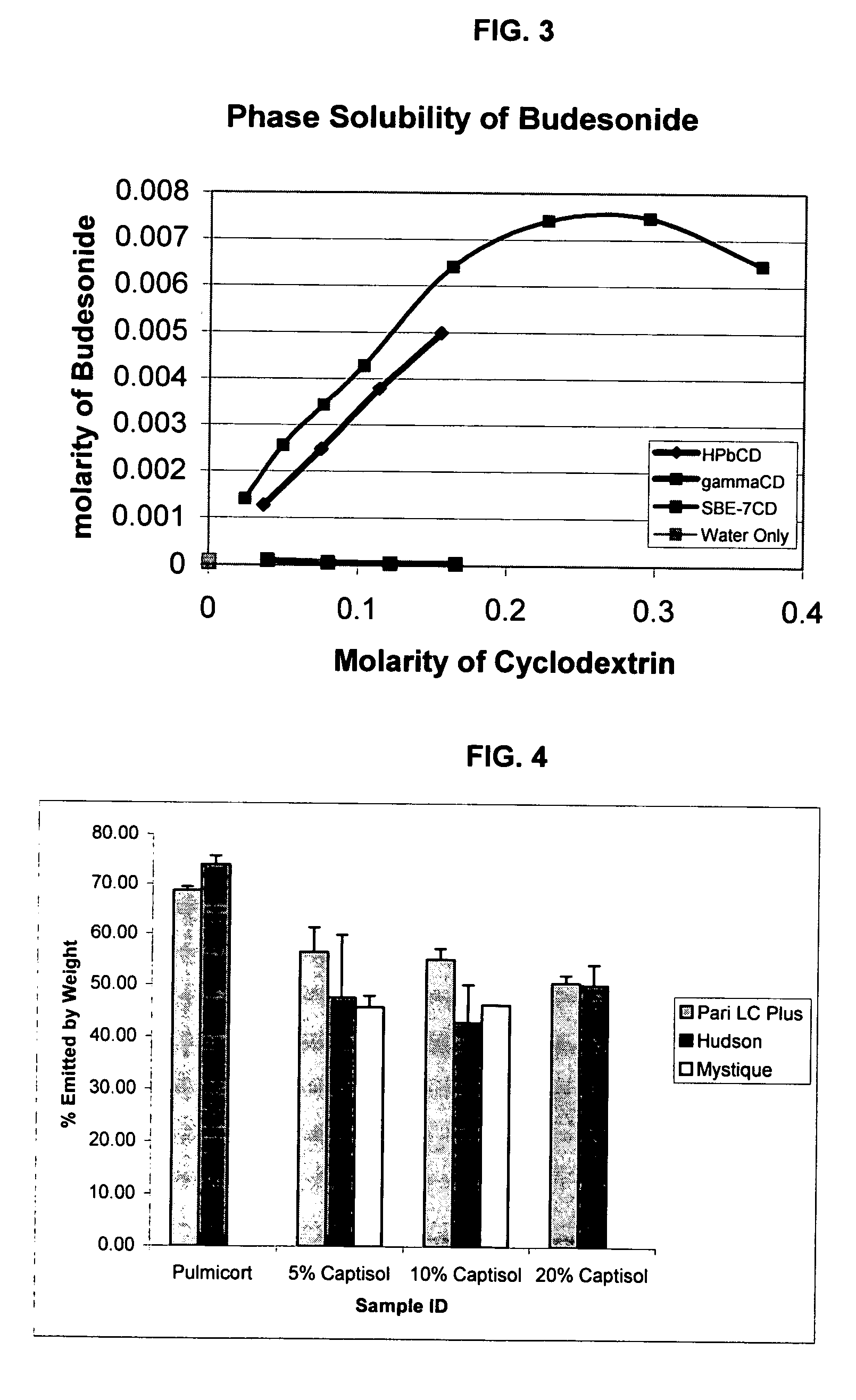
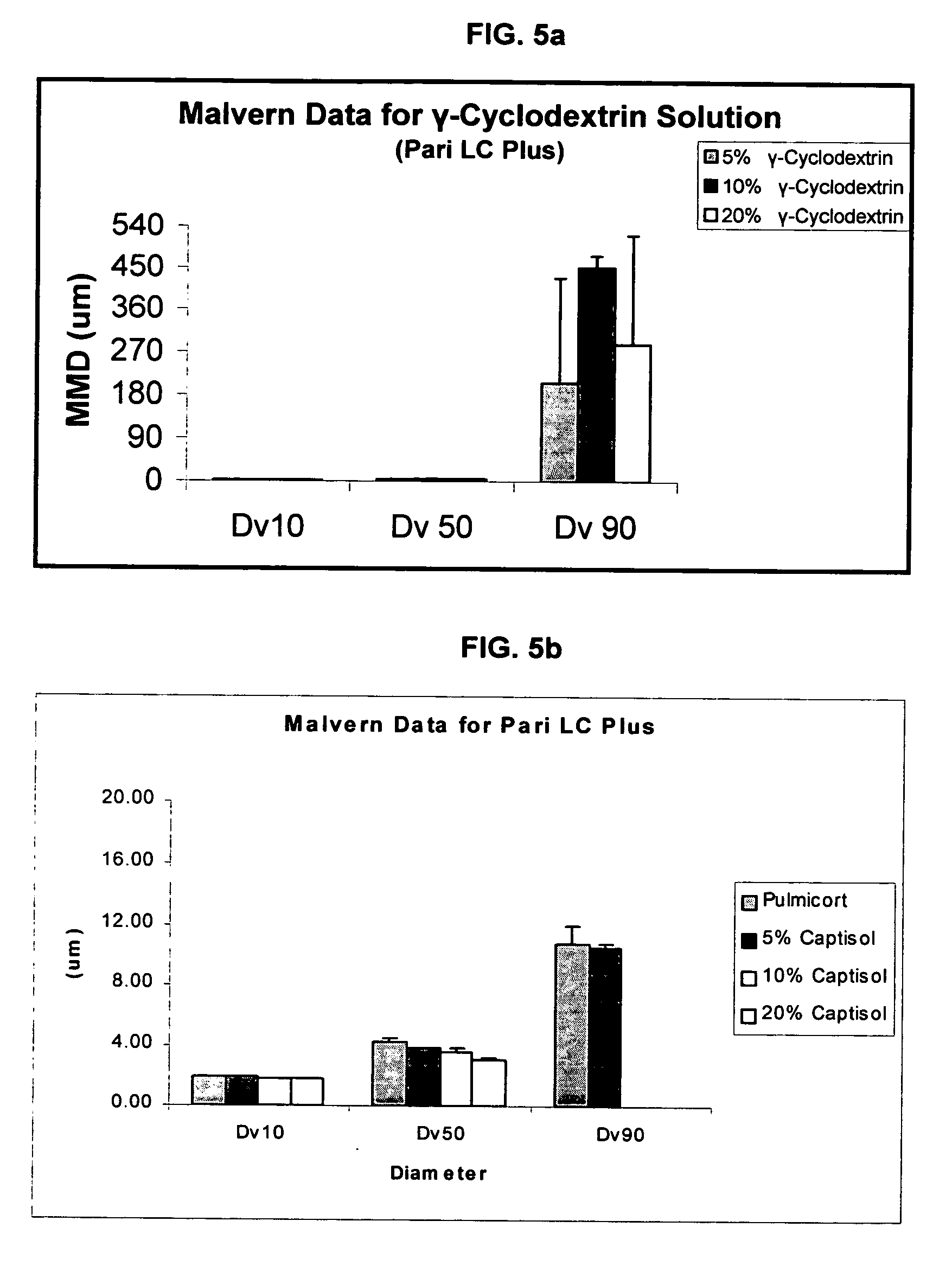
Inhalant formulation containing sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and corticosteroid prepared from a unit dose suspension
InactiveUS20070020196A1Reduce the degradation rateIncrease productivityBiocideDispersion deliveryNebulizerCyclodextrin
An inhalable unit dose liquid formulation containing SAE-CD and corticosteroid is provided. The formulation is adapted for administration to a subject by nebulization with any known nebulizer. The formulation can be included in a kit. The formulation is administered as an aqueous solution or concentrated composition. The formulation is employed in an improved nebulization system for administering corticosteroid by inhalation. SAE-CD present in the formulation significantly enhances the chemical stability of corticosteroid, such as budesonide. A method of administering the formulation by inhalation is provided. The formulation can also be administered by conventional nasal delivery apparatus. The formulation is prepared by mixing SAE-CD, in solid or liquid (dissolved) form, with an inhalable suspension-based unit dose formulation.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Therapeutic delivery systems
InactiveUS6443898B1Low costSuitable for useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryMicrosphereLiposome
Therapeutic delivery systems comprising gaseous precursor-filled microspheres comprising a therapeutic are described. Methods for employing such microspheres in therapeutic delivery applications are also provided. Therapeutic delivery systems comprising gaseous precursor-filled liposomes having encapsulated therein a contrast agent or drug are preferred. Methods of and apparatus for preparing such liposomes and methods for employing such liposomes in therapeutic delivery applications are also disclosed.
Owner:CEREVAST MEDICAL
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Pharmaceutical compositions for buccal and pulmonary application
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a macromolecular pharmaceutical agent in mixed micellar form are disclosed. The mixed micelles are formed from an alkali metal alkyl sulfate, and at least three different micelle-forming compounds as described in the specification. Micelle size ranges between about 1 and 10 nanometers. Methods for making and using the compositions are also disclosed. A preferred method for administering the present composition is through the buccal region of the mouth.
Owner:GENEREX PHARMA INC +1
Sterilized nanoparticulate glucocorticosteroid formulations
InactiveUS20070178051A1Readily heat sterilizedImprove the heating effectOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPediatric patientMicroparticle
The invention is directed sterile to compositions of glucocorticosteroids useful in the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma and other allergic and inflammatory conditions in adults and pediatric patients.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
Spontaneous emulsions containing cyclosporine
A pharmaceutical composition contains cyclosporine as the active ingredient. More specifically, the composition is an orally administered pharmaceutical formulation in the form of a spontaneous emulsion comprising cyclosporine, ethanol ethyl oleate and polyoxyethylene glycerol trioleate. A method for preparing an orally administered pharmaceutical composition involves first dissolving cyclosporine in ethanol. Polyoxyethylene glycerol trioleate and an oil component are then added, mixed and diluted in an aqueous media to form a spontaneous emulsion.
Owner:WOCKHARDT EU OPERATIONS SWISS
Pharmaceutical aerosol composition
Sterile compositions for administration as aerosols are described. They contain an active agent which is poorly water-soluble, a non-ionic surfactant acomponent and a phospholipid component. The compositions are suitable for oral or nasal inhalation, but also for topical or oromucosal administration. They are particulary useful for the efficient pulmonary administration of poorly soluble corticosteroids and can be aerosolized with common nebulizers.
Owner:PARI PHARMA GMBH
Methods and systems for operating an aerosol generator
InactiveUS20050217666A1Improve security levelImprove delivery efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAmikacin
A method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes delivering a dose of aerosolized medicament intermittently to a ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of the patient. Also, a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes taking the patient off a ventilator, and administering to the patient, a nebulized aerosol comprising from about 100 μg to about 500 mg of a medicament. Additionally, an aerosolized medicament for the treatment of a pulmonary disease, where the medicament includes amikacin mixed with an aqueous solution having an adjusted pH from about 5.5 to about 6.3. The pH is adjusted by adding hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to the aqueous solution.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Phenolic antiseptic compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20060052452A1Reduce eliminateReduce and eliminate clinical signAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiphenyl etherSURFACTANT BLEND
Antimicrobial compositions, especially those useful when applied topically, particularly to mucosal tissues (i.e., mucous membranes), including an antiseptic selected from the group consisting of halogenated phenols, bisphenols, diphenyl ethers, anilides and derivatives thereof, and combinations thereof. The compositions can also include an enhancer component, a surfactant, a hydrophobic component, and / or a hydrophilic component. Such compositions provide effective topical antimicrobial activity and are accordingly useful in the treatment and / or prevention of conditions that are caused, or aggravated by, microorganisms (including viruses).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High-Potency Sweetener Composition With Antioxidant and Compositions Sweetened Therewith
ActiveUS20070116838A1Improve flavor profileImproving temporal profile profileCosmetic preparationsDispersion deliveryAdditive ingredientAntioxidant
The present invention relates generally to functional sweetener compositions comprising non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic, high-potency sweeteners and methods for making and using them. In particular, the present invention relates to different functional sweetener compositions comprising at least one non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic, high-potency sweetener, at least one sweet taste improving composition, and at least one functional ingredient, such as antioxidants. The present invention also relates to functional sweetener compositions and methods that can improve the tastes of non-caloric or low-caloric high-potency sweeteners by imparting a more sugar-like taste or characteristic. In particular, the functional sweetener compositions and methods provide a more sugar-like temporal profile, including sweetness onset and sweetness linger, and / or a more sugar-like flavor profile.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Compositions comprising lipophilic active compounds and method for their preparation
ActiveUS20090098200A1Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryBiocideHydrophilic polymersCompound (substance)
Compositions are provided comprising a lipophilic active compound, e.g., a human or veterinary drug or a nutraceutical, interwoven with a polymeric matrix formed by two or more polymers, wherein one of the polymers is an amphiphilic polymer and the other polymer is either an amphiphilic polymer with a different hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance or a hydrophilic polymer, and the active lipophilic compound has modified physicochemical properties. The composition forms colloidal nanodispersion upon contact with aqueous media.
Owner:SOLUBEST
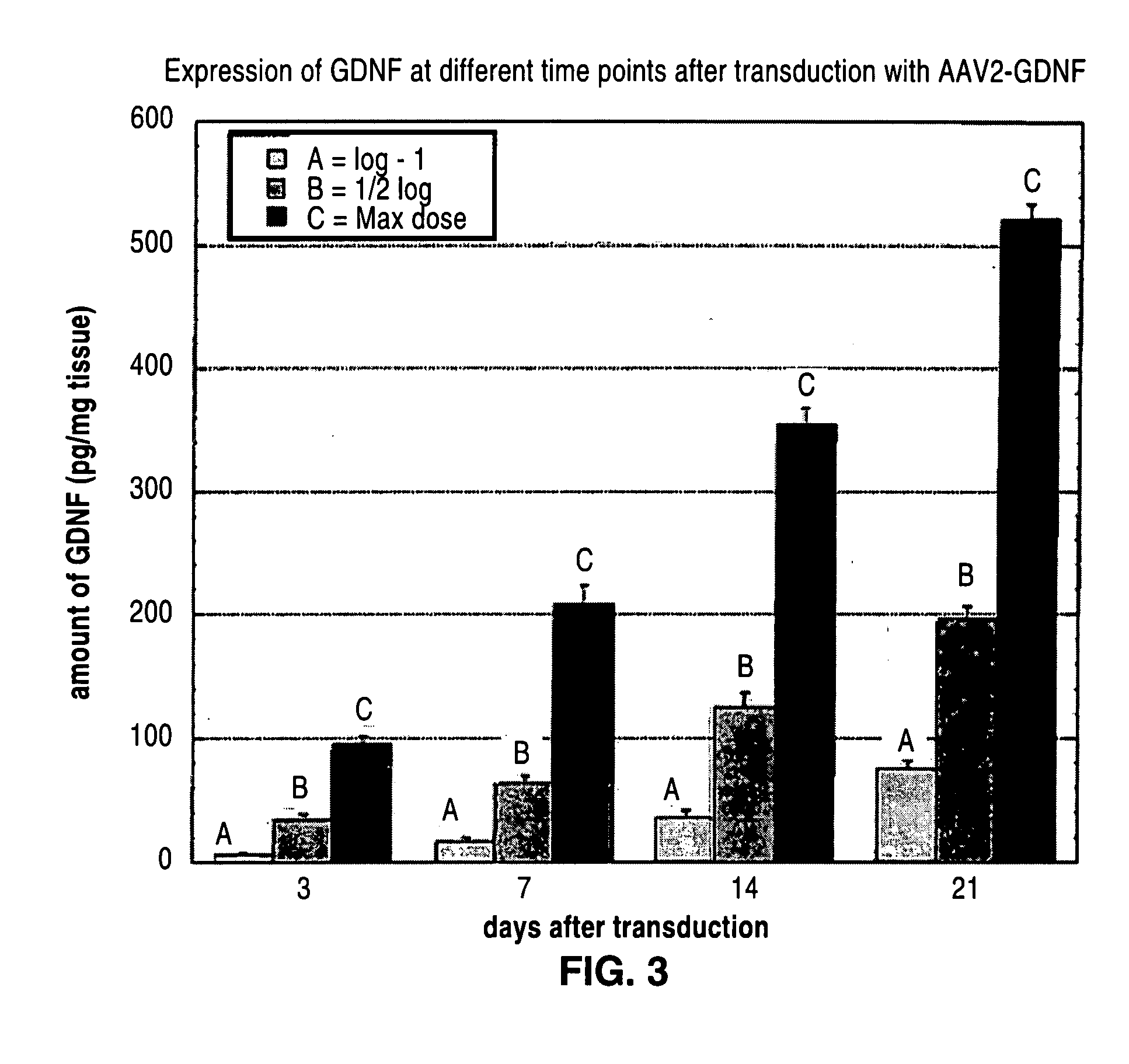
Administration of growth factors for the treatment of CNS disorders
ActiveUS20070254842A1Prevents and delay onsetReduce severityHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseNervous system
A method and system that is directed to the local delivery of growth factors to the mammalian CNS to treat CNS disorders associated with neuronal death and / or dysfunction is described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions containing fluorine substituted olefins
The use to e of tetrafluoropropenes, particularly (HFO-1234) in a variety of applications, including refrigeration equipment, is disclosed. These materials are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and a tobramycin aerosol formulation for treatment prevention and containment of tuberculosis
A method for treatment, prevention and containment of acute and chronic tuberculosis using a preservative-free concentrated tobramycin aerosol formulation delivering tobramycin to the lung endobronchial space including alveoli in an aerosol having mass medium average diameter predominantly between 1 to 5 mu . The method comprises administration of tobramycin in concentration one to ten thousand times higher than the minimal inhibitory concentration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A method for containment of and decreasing infectivity periods of tuberculosis patients to shorter periods of time.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Combination of proton pump inhibitor, buffering agent, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
InactiveUS20050249806A1Preventing gastric acid related disorderReduce riskBiocideSenses disorderNonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs/NSAIDsBuffering agent
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a proton pump inhibitor, one or more buffering agent and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug are described. Methods are described for treating gastric acid related disorders and treating inflammatory disorders, using pharmaceutical compositions comprising a proton pump inhibitor, a buffering agent, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Owner:SANTARUS
Use of mometasone furoate for treating airway passage and lung diseases
InactiveUS6057307AMaximize treating said rhinitisMinimize absorptionPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseAerosolize
The administration of aerosolize particles of mometasone furoate in the form of dry powders, solutions, or aqueous suspension for treating corticosteroid-responsive diseases of the surfaces of upper and / or lower airway passages and / or lungs, e.g., allergic rhinitis and asthma is disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Medical aerosol formulations
InactiveUS6461591B1Improve dosage accuracyIncrease doseBiocideDispersion deliveryAlkaneAerosol spray
A pressure-liquefied propellant mixture for aerosols, comprising a fluorinated alkane, in particular 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane and / or 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane, and carbon dioxide, makes possible an improvement of the wetting properties of pharmaceutically active compounds, with which the formulation problems existing with hydrofluoroalkanes in relation to suspension as well as solution aerosols can be overcome and thus improved medicinal aerosol formulations can be obtained. With the aid of carbon dioxide, it is also possible to specifically influence the pressure and thus the particle size distribution and also by displacement of oxygen from the hydrofluoroalkanes to improve the storage stability of oxidation-sensitive active compounds.
Owner:JAGOTEC AG
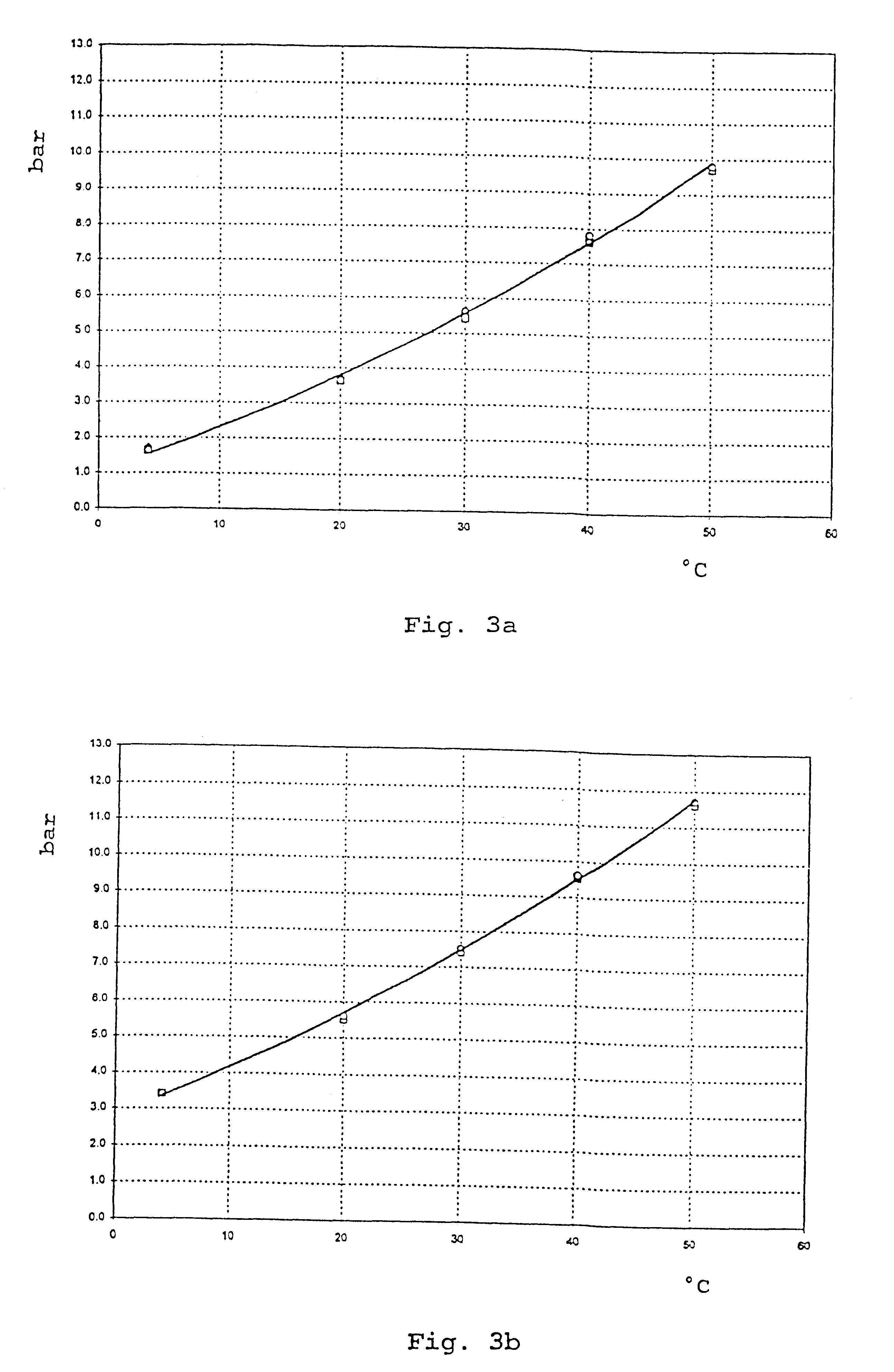
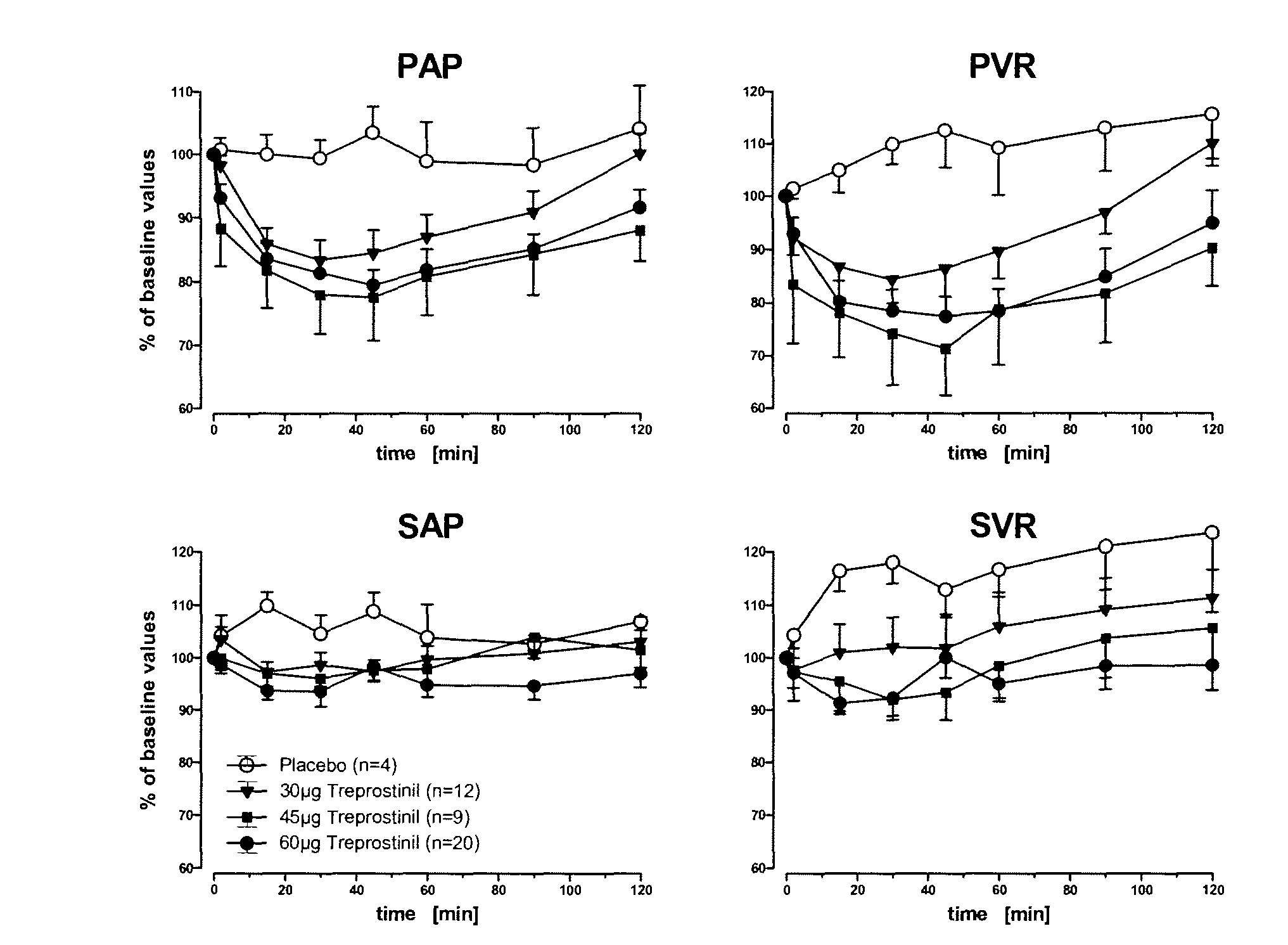
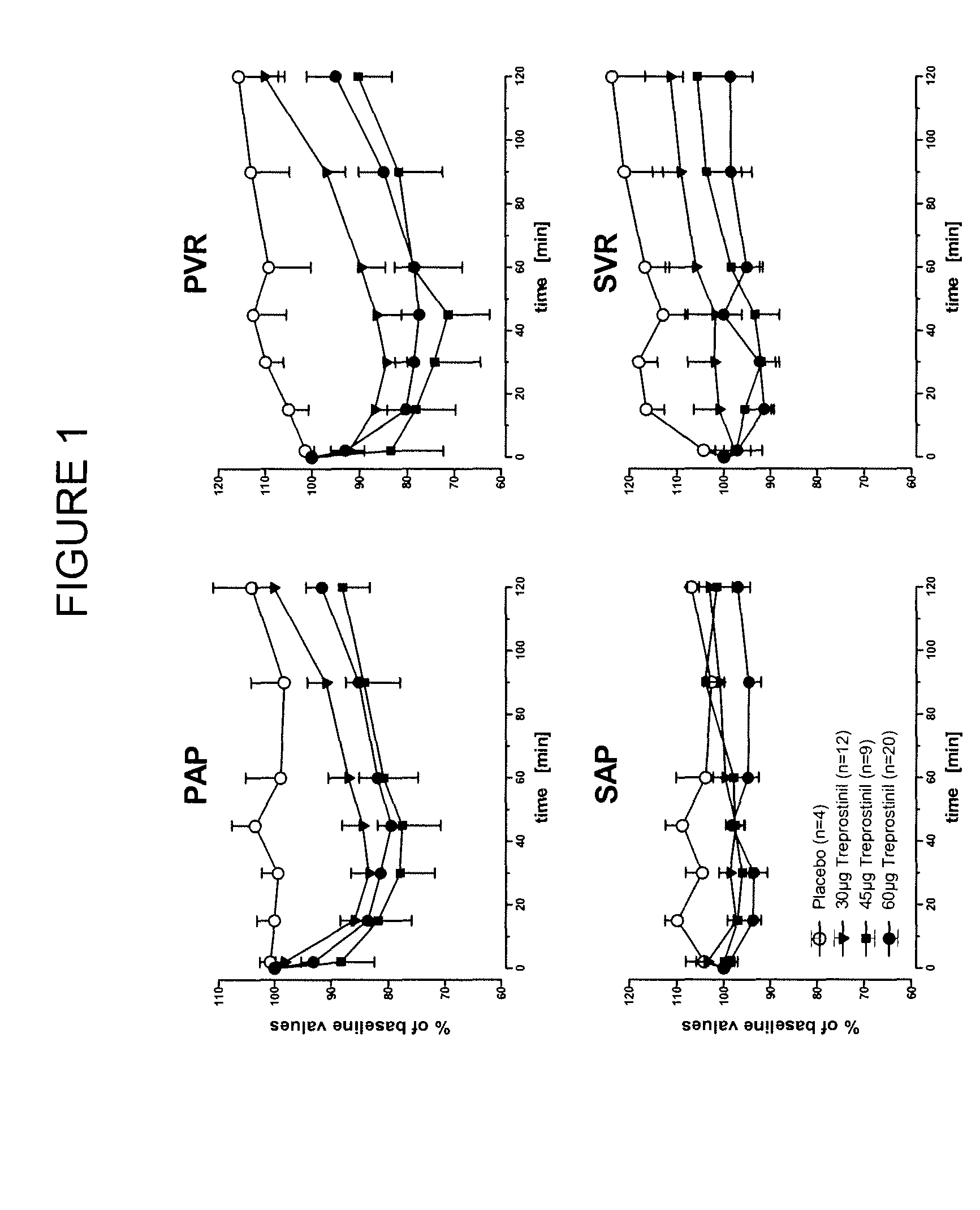
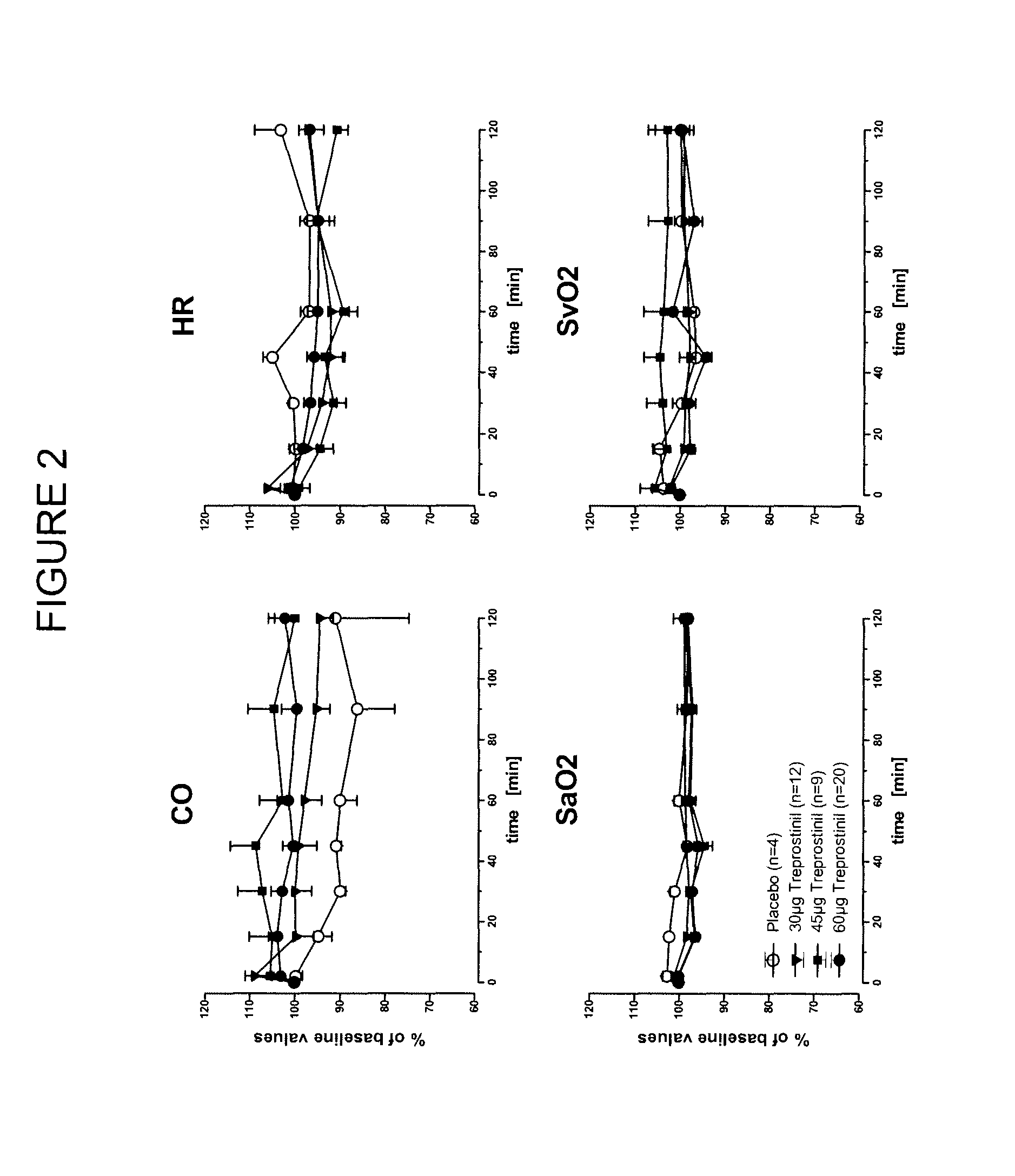
Treprostinil administration using a metered dose inhaler
Treprostinil can be administered using a metered dose inhaler. Such administration provides a greater degree of autonomy to patients. Also disclosed are kits that include a metered dose inhaler containing a pharmaceutical formulation containing treprostinil.
Owner:UNITED THERAPEUTICS CORP
Nanoparticulate megestrol formulations
ActiveUS7101576B2Improved pharmacokinetic profileLess variabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleMegestrol
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Aripiprazole oral solution
The present invention provides for a pharmaceutical solution suitable for oral administration comprising aripiprazole, a pharmaceutically suitable solvent system, one or more taste-enhancing / masking agents and one or more agents selected from the group consisting of lactic acid, acetic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid, wherein said solution has a pH from 2.5 to 4.5.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Engineered particles and methods of use
InactiveUS7306787B2Reduce deliveryLess attractivePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNebulizerActive agent
Engineered particles are provided may be used for the delivery of a bioactive agent to the respiratory tract of a patient. The particles may be used in the form of dry powders or in the form of stabilized dispersions comprising a nonaqueous continuous phase. In particularly preferred embodiments the particles may be used in conjunction with an inhalation device such as a dry powder inhaler, metered dose inhaler or a nebulizer.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Antimicrobial mesoporous silica nanoparticles
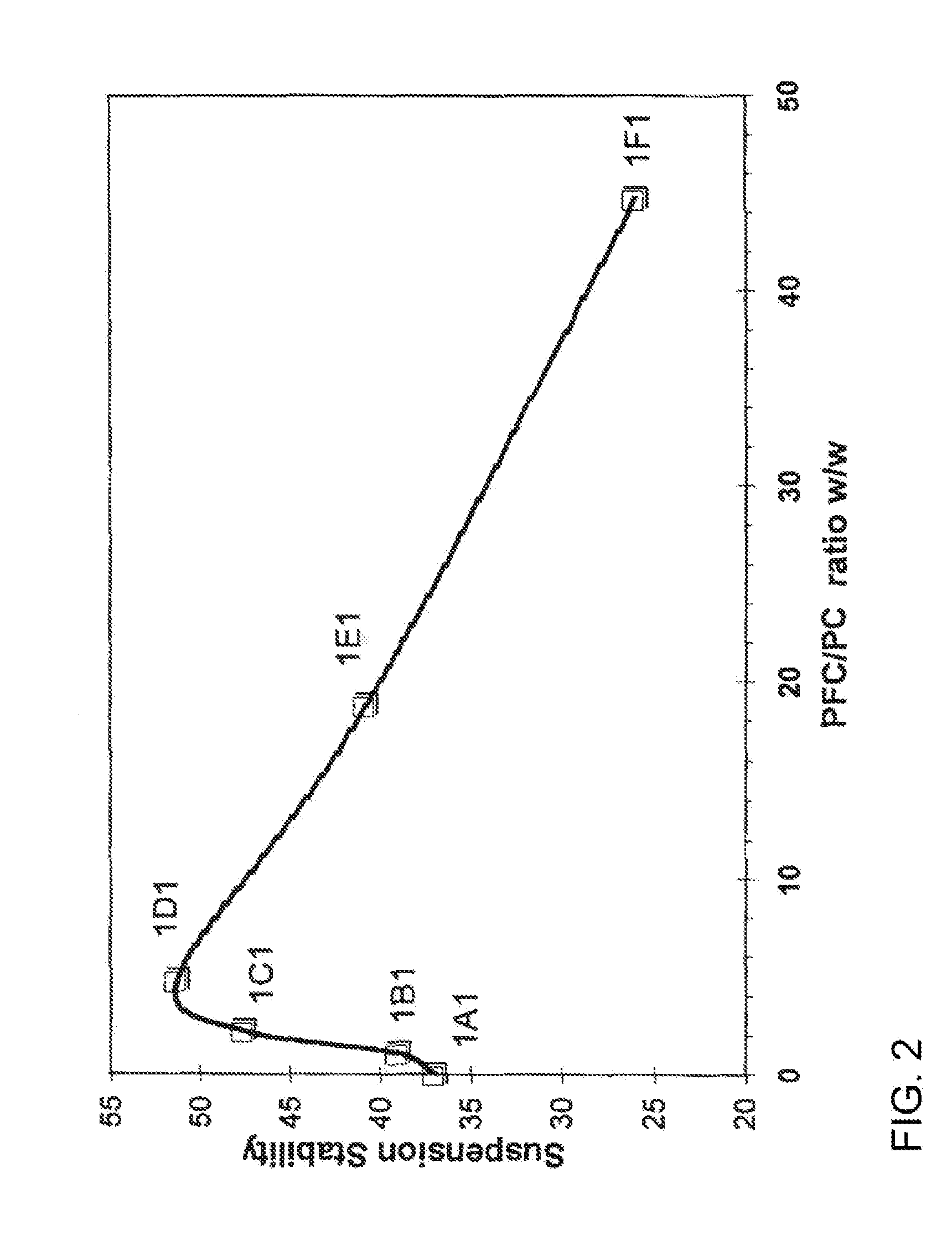
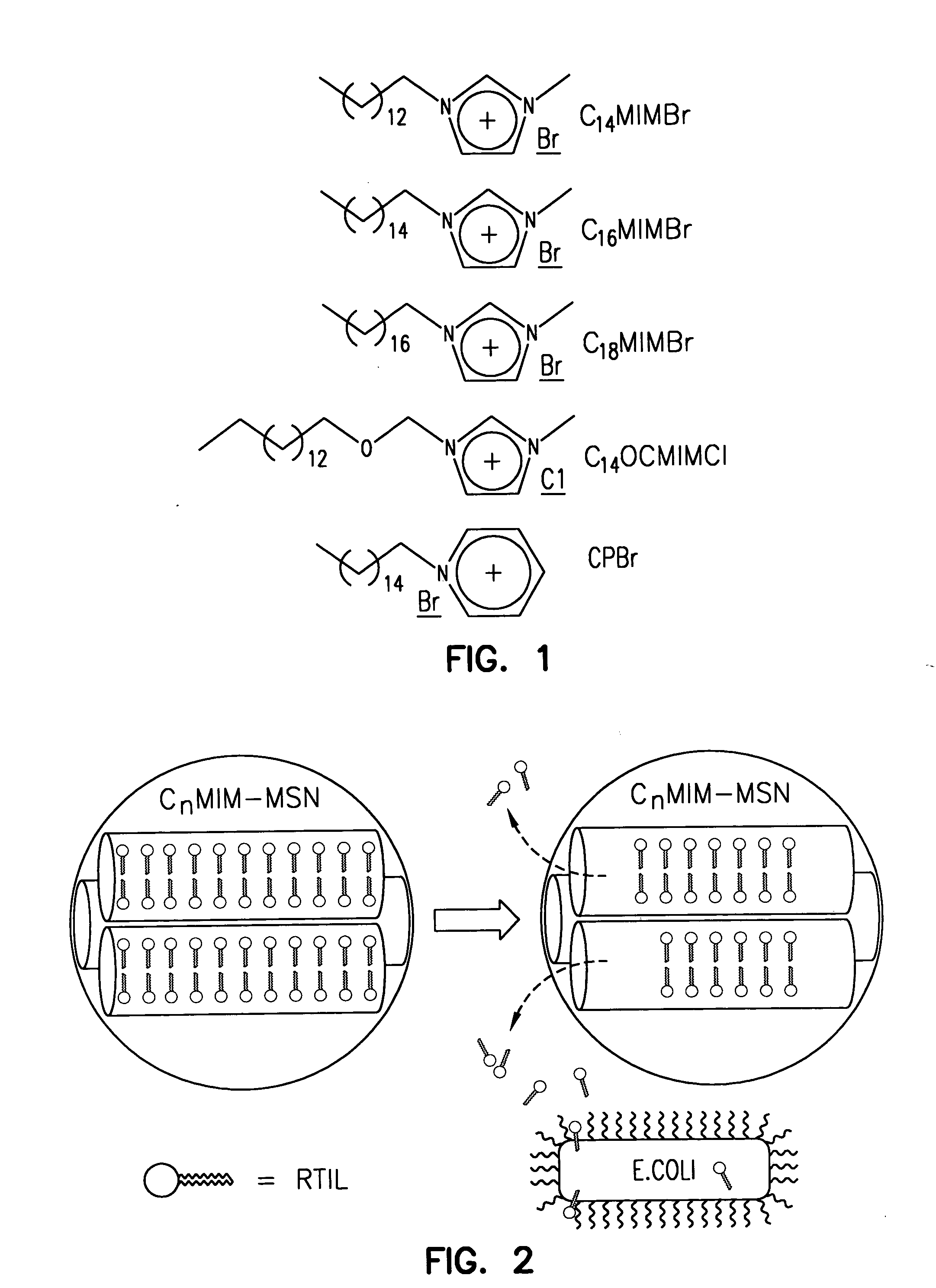
InactiveUS20060018966A1Reduce productionSlow diffusion ratePowder deliveryBiocideMesoporous silicaSilicon dioxide
Methods for preparing a series of mesoporous silicates, such as room-temperature ionic liquid (RTIL)-templated mesoporous silicate particles, with various particle morphologies are provided. Methods for preparing silicate particles with antimicrobial agents within the MSN pores is also provided. The particles can be used as controlled-release nanodevices to deliver antimicrobial agents.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
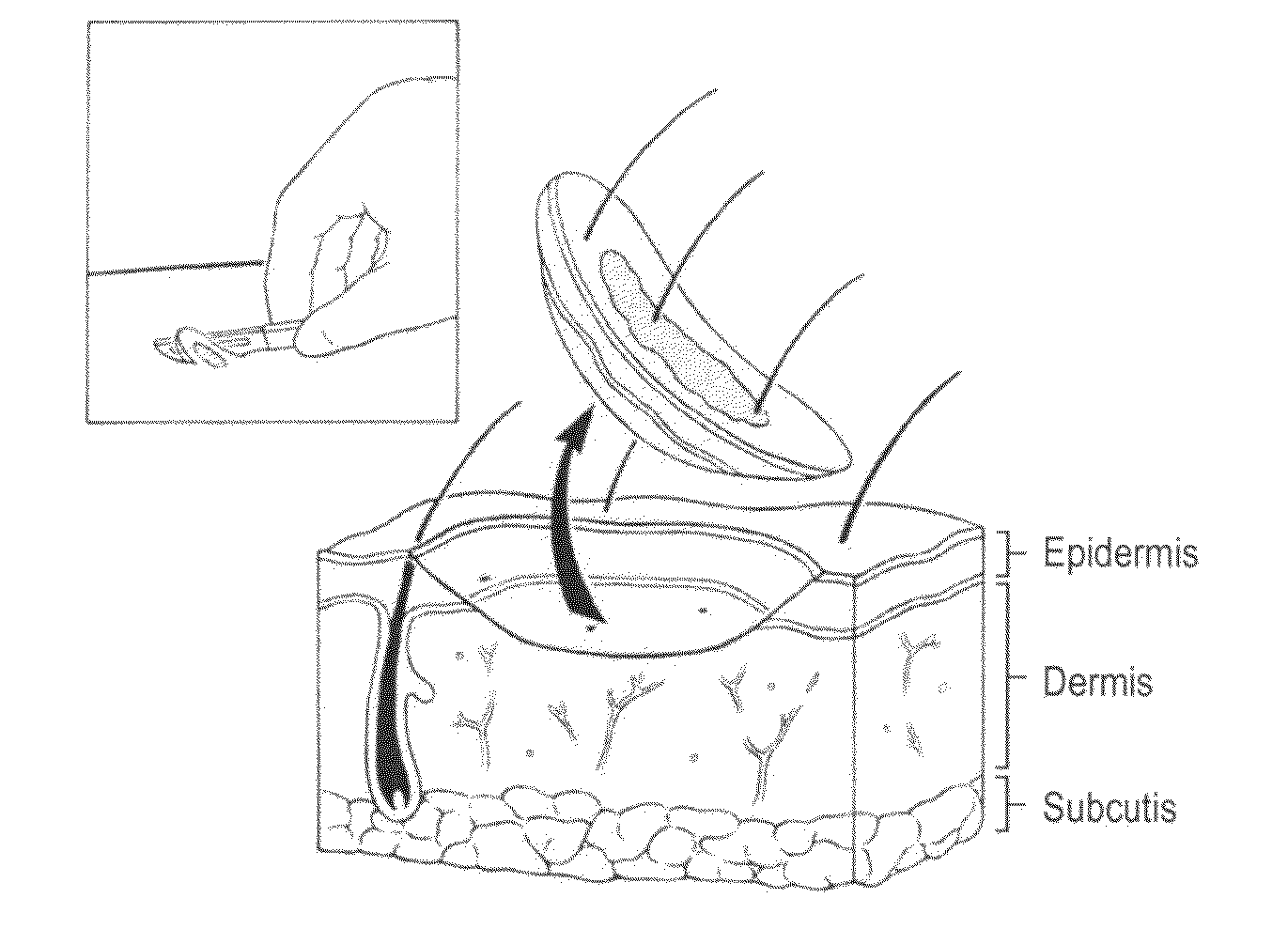
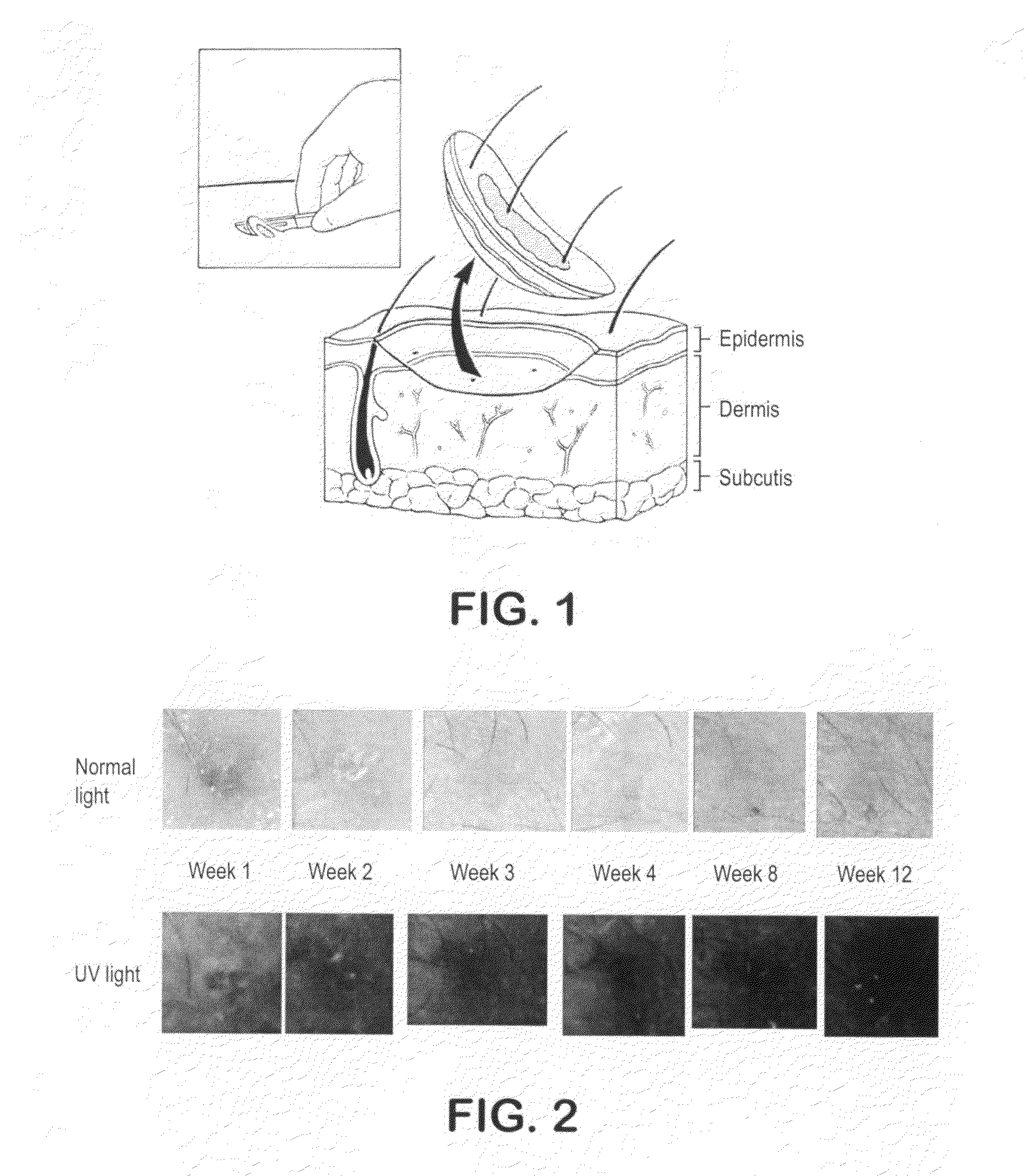
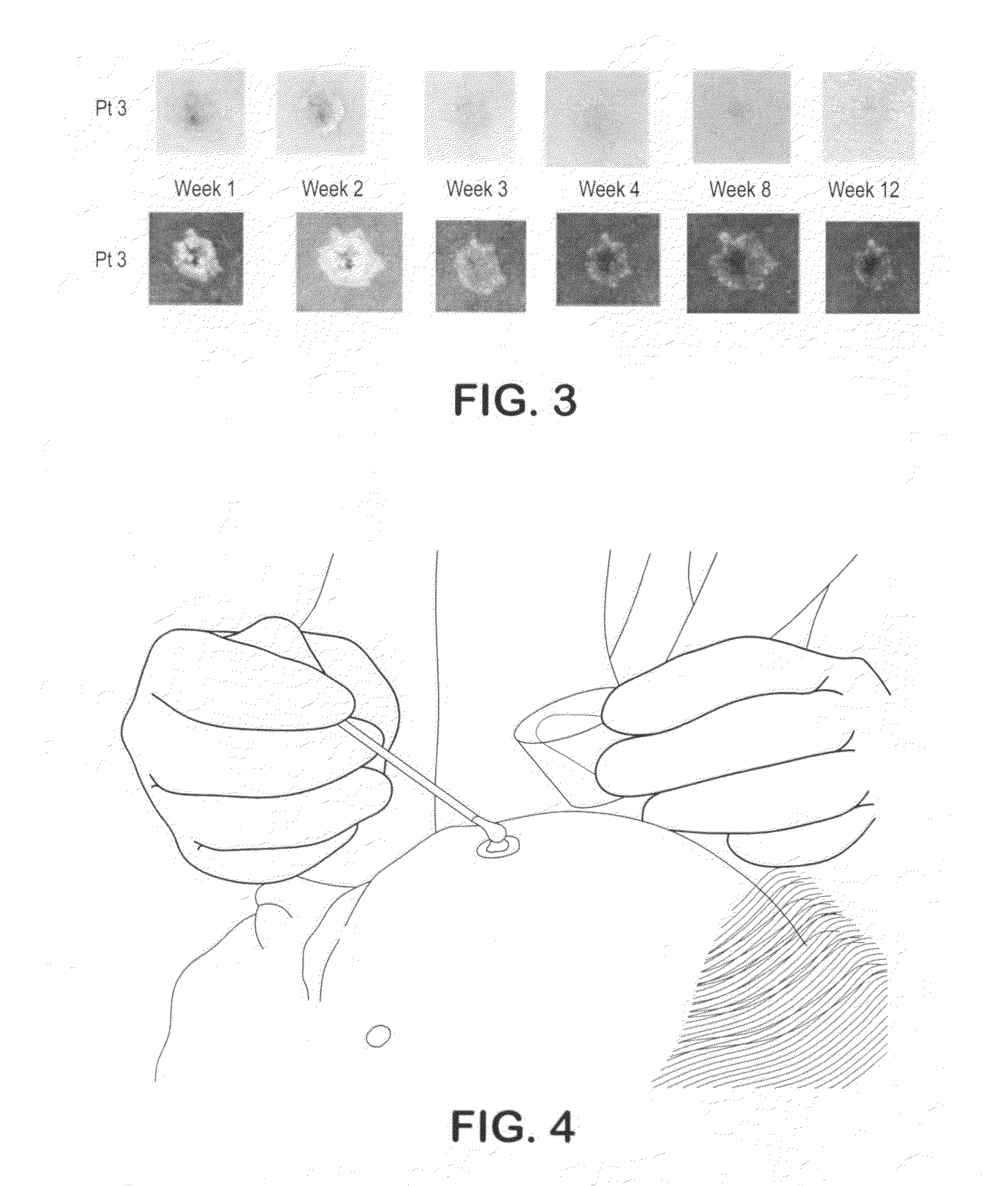
Biopsy marker composition and method of use
InactiveUS20110077512A1Improve efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDispersion deliveryFluorescenceMedicine
An aqueous suspension of titanium dioxide, polymethylmethacrylate and Vitamin E oil is used to mark a location wherein a skin biopsy has been taken to enable subsequent identification of the biopsy location under ultraviolet light. The location is advantageously treated with Vitamin E oil on a daily basis subsequently extend the fluorescing life of the applied titanium dioxide.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
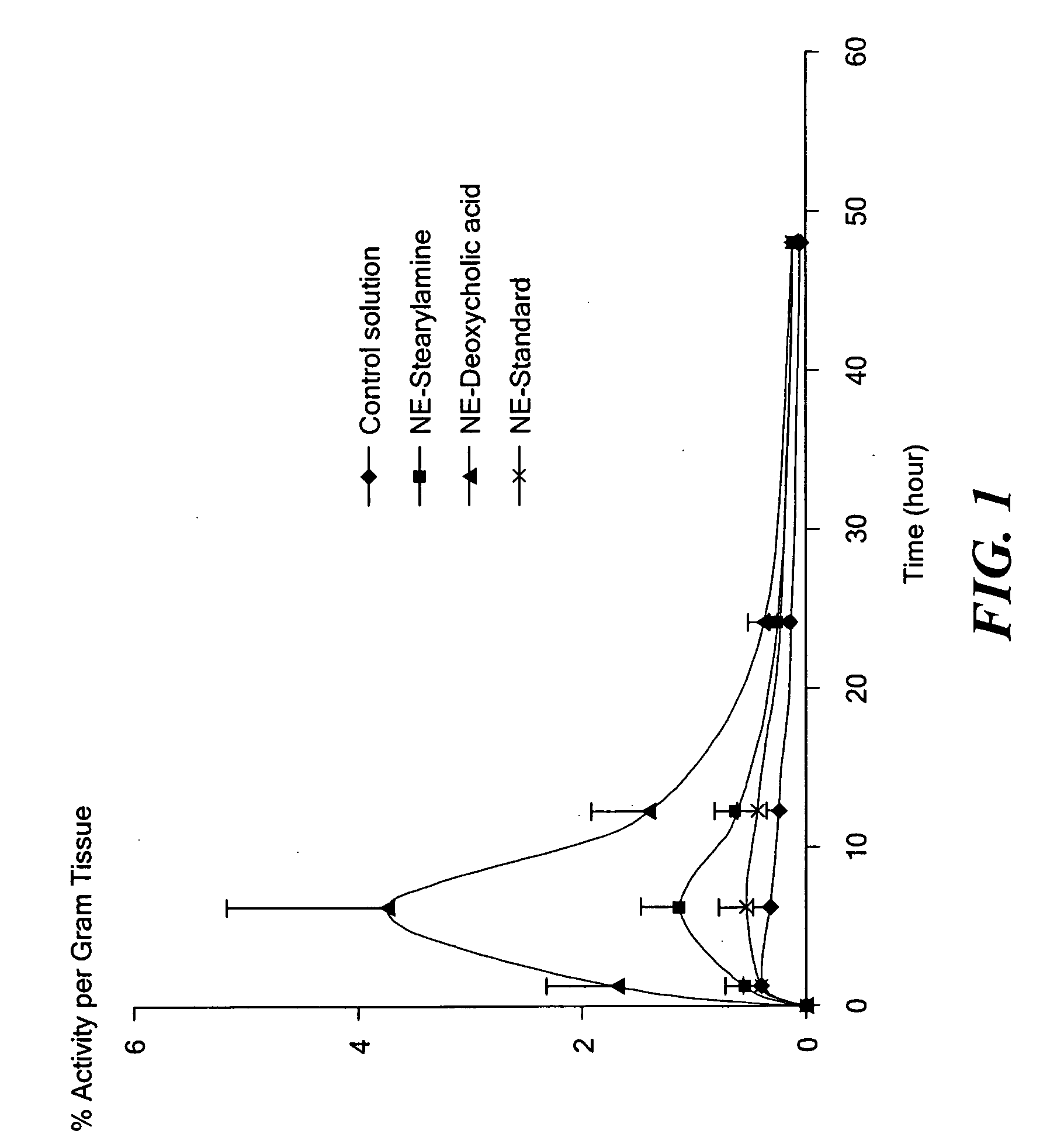
Novel nanoemulsion formulations
InactiveUS20070148194A1Reducing surfactant side-effectsImprove oral bioavailabilityDispersion deliveryEmulsion deliveryBuffering agentAntioxidant
An oil-in-water nanoemulsion delivery system that includes at least one oil having a concentration of greater than or equal to 2% (w / w) of at least one polyunsaturated fatty acid, preferably of the omega-3 or omega-6 family, is disclosed. The delivery system further includes at least one emulsifier and also an aqueous phase. Preferably, one or more hydrophobic therapeutic, monitoring and / or diagnostic agents are dispersed in the oil phase. The nanoemulsions may optionally contain other conventional pharmaceutical aids such as stabilizers, preservatives, buffering agents, antioxidants, polymers, proteins and charge inducing agents. The invention also relates to a process for preparing the nanoemulsions and to their use in the oral, parenteral, opthalmic, nasal, rectal or topical delivery of hydrophobic therapeutic, monitoring or diagnostic agents.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising substituted benzimidazoles and methods of using same
InactiveUS20050054682A1Improve stabilityDecreased time to therapeutic effectBiocideDispersion deliveryBuffering agentPharmacology
The present invention is directed to, inter alia, pharmaceutical compositions comprising at least one proton pump inhibitor and at least one buffering agent. Compositions of the invention are useful in treating, inter alia, gastric acid related disorders.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Phytochemicals for promoting weight loss
New dietary supplement compositions are disclosed that comprise the phytochemical Diindolylmethane (DIM), as well as its precursor, Indole-3-carbinol (I3C), and cogener, 2-(Indol-3-ylmethyl)-3,3' diindolylmethane (LTR-1), dietary supplement acceptable carriers and / or excipients. The use of these dietary supplement compositions facilitate weight loss as part of a nutritional system targeting release and metabolism of stored fat.
Owner:BIORESPONSE
Inhalant formulation containing sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin and corticosteroid
InactiveUS20070020299A1Reduce the degradation rateIncrease productivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNasal cavityNebulizer
An inhalable formulation containing SAE-CD and corticosteroid is provided. The formulation is adapted for administration to a subject by nebulization with any known nebulizer. The formulation can be included in a kit. The formulation is administered as an aqueous solution, however, it can be stored as a dry powder, ready-to-use solution, or concentrated composition. The formulation is employed in an improved nebulization system for administering corticosteroid by inhalation. SAE-CD present in the formulation significantly enhances the chemical stability of budesonide. A method of administering the formulation by inhalation is provided. The formulation can also be administered by conventional nasal delivery apparatus.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com