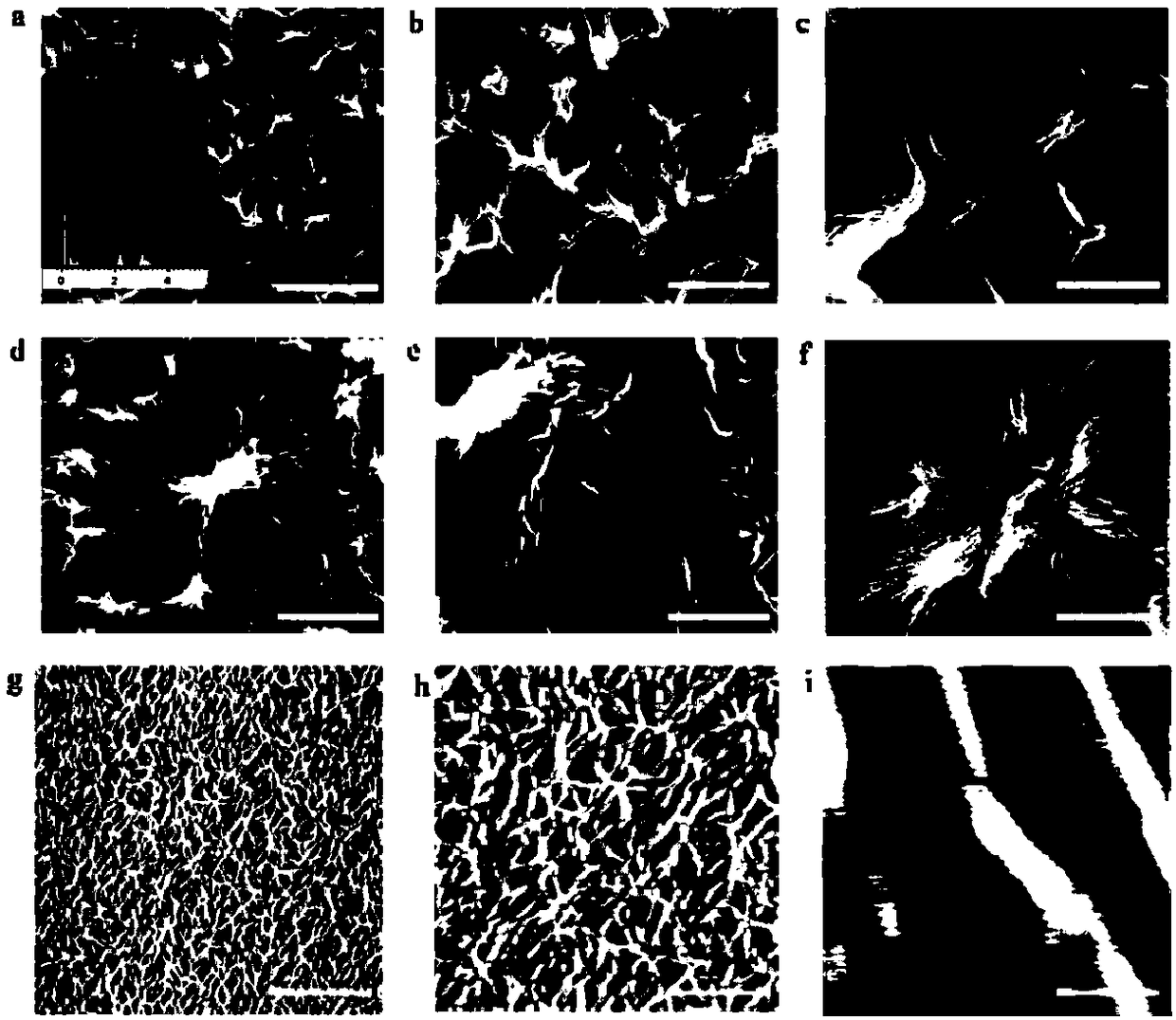
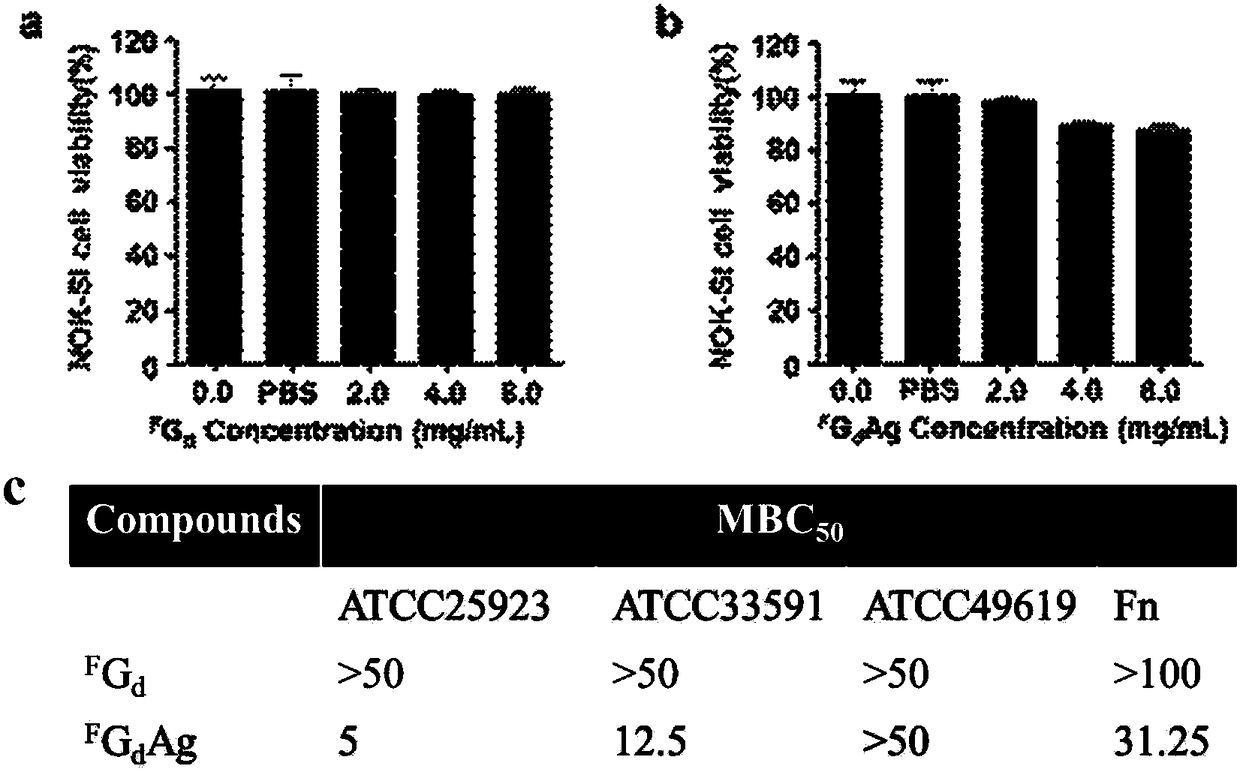
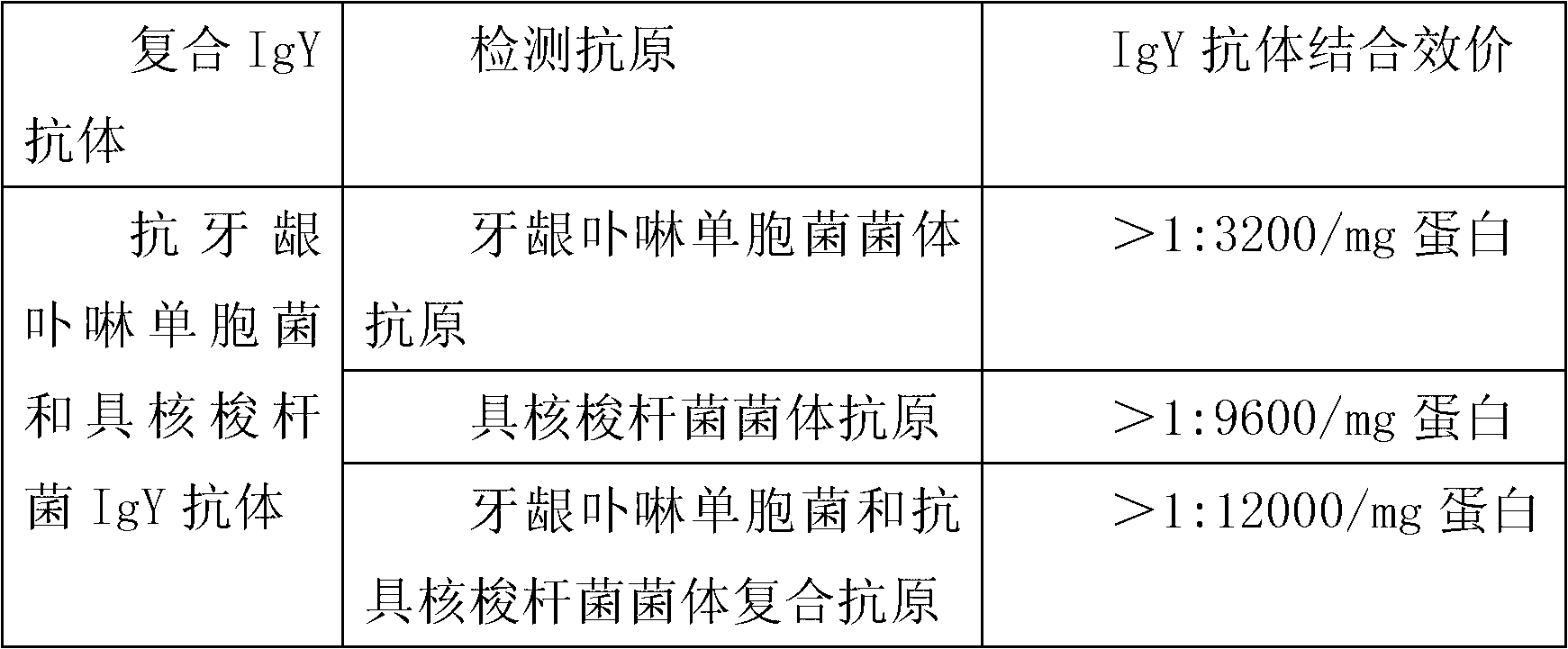
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
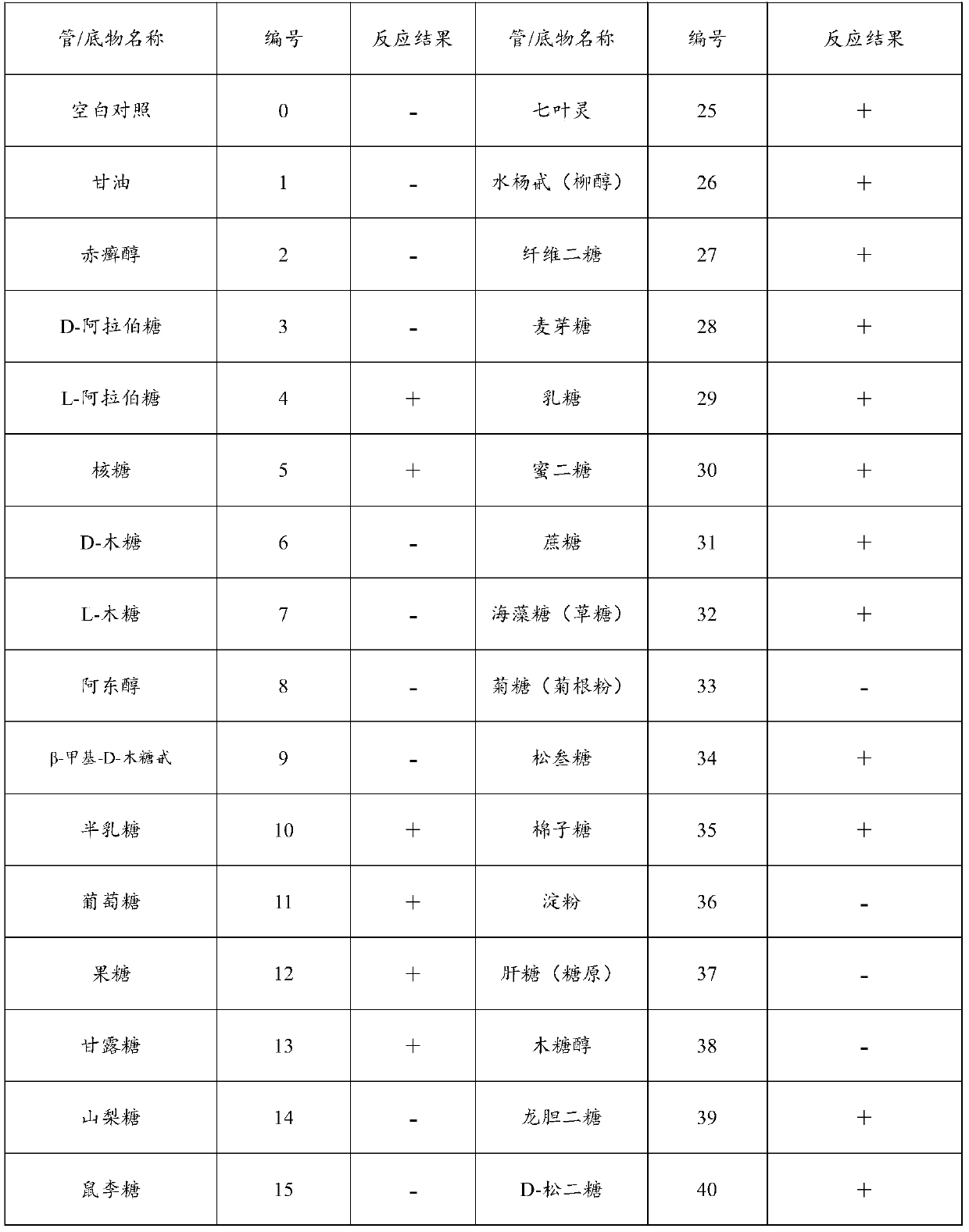
129 results about "Fusobacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
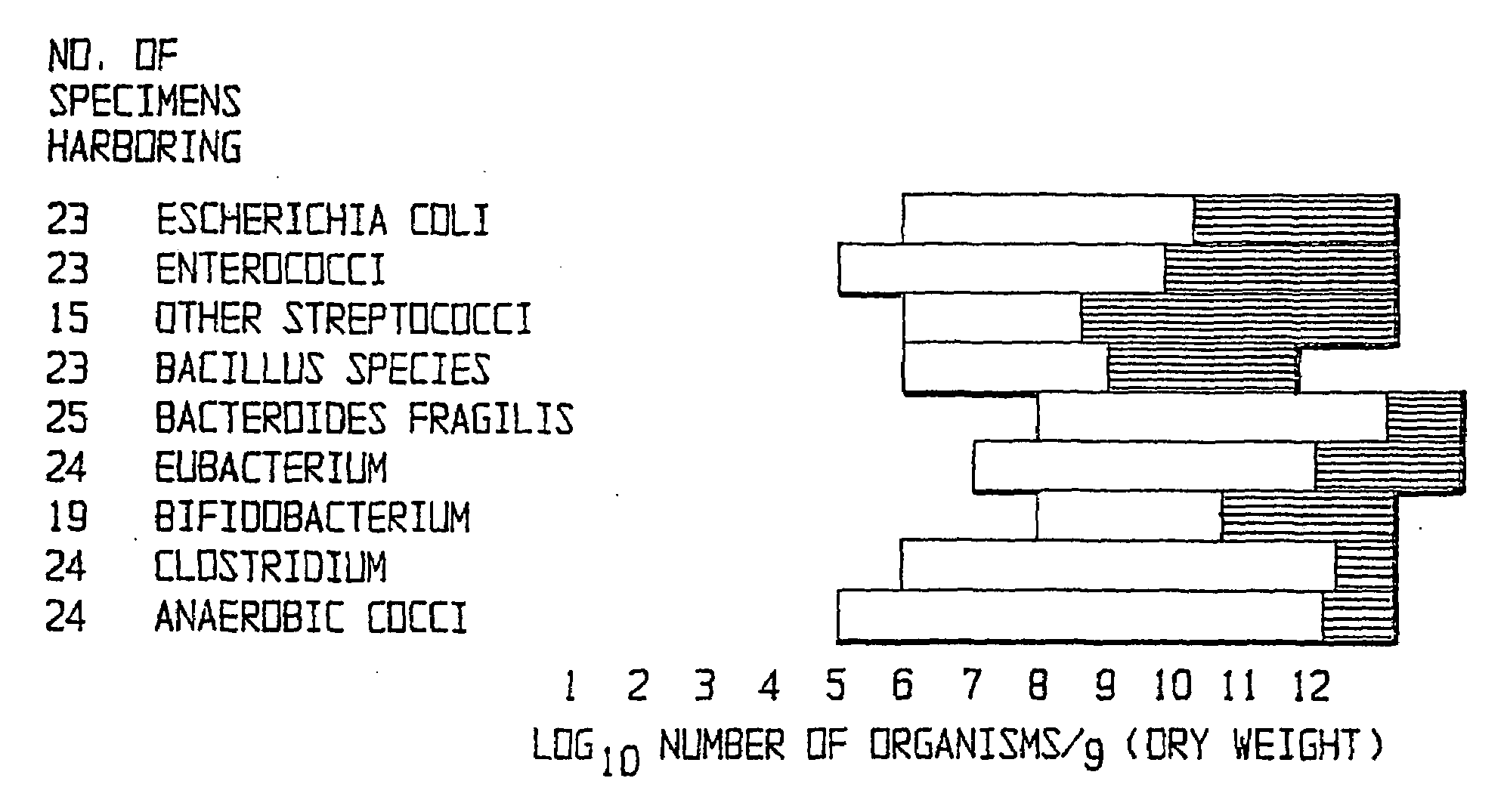
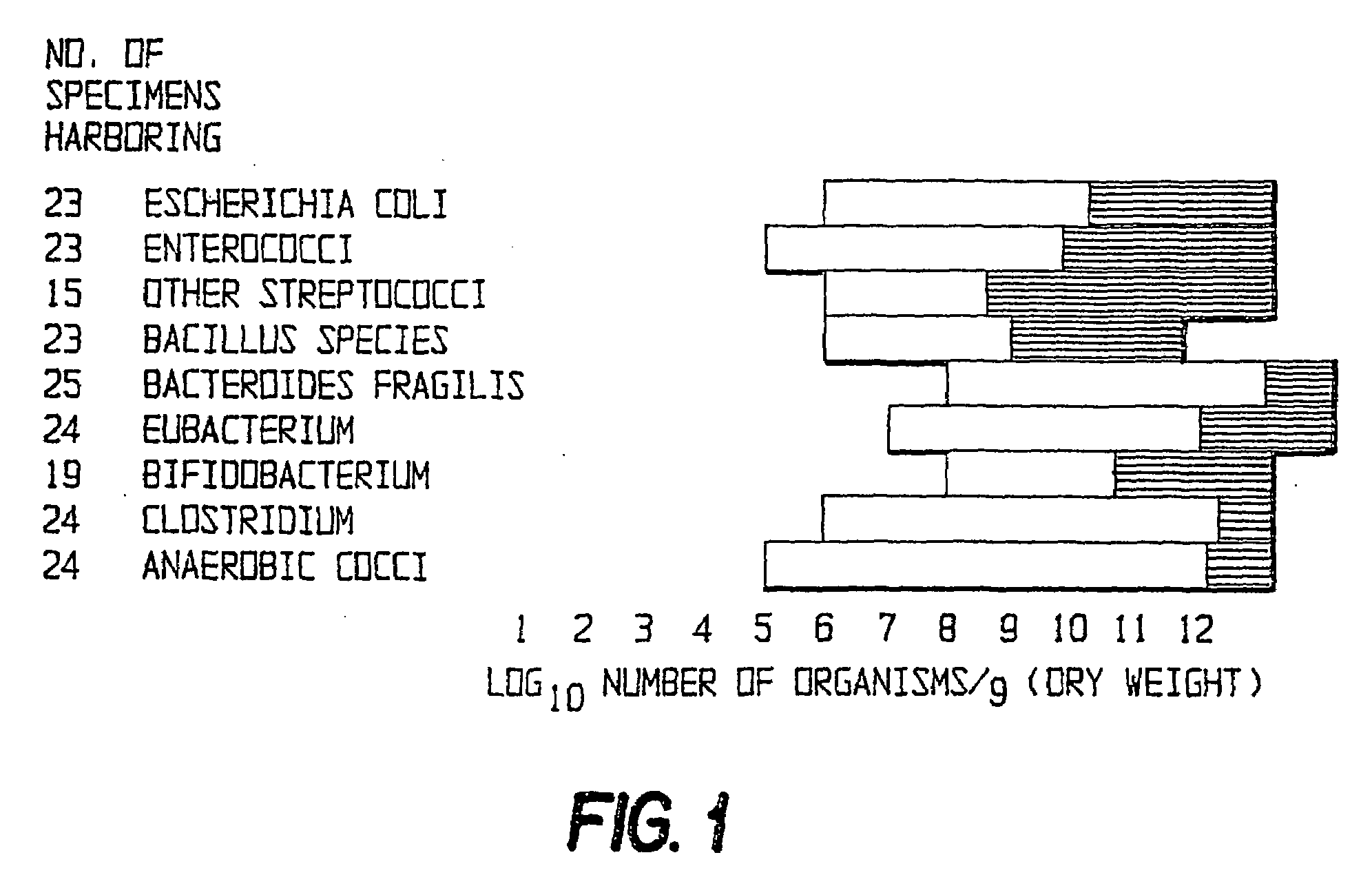
Fusobacteria are obligately anaerobic non-sporeforming Gram-negative bacilli. Since the first reports in the late nineteenth century, various names have been applied to these organisms, sometimes with the same name being applied to different species. More recently, not only have there been changes to the nomenclature, but also attempts to differentiate between species which are believed to be either pathogenic or commensal or both. Because of their asaccharolytic nature, and a general paucity of positive results in routine biochemical tests, laboratory identification of the fusobacteria has been difficult. However, the application of novel molecular biological techniques to taxonomy has established a number of new species, together with the subspeciation of Fusobacterium necrophorum and F. nucleatum, and provided new methods for identification. The involvement of fusobacteria in a wide spectrum of human infections causing tissue necrosis and septicaemia has long been recognised, and, more recently, their importance in intra-amniotic infections, premature labour and tropical ulcers has been reported.
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus clostridium
The invention includes a method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus Clostridium such as clostridium deficit in human patients with gastrointestinal disorders having an etiological component such as a microbial agent producing a toxin where treated with an antimicrobial composition an amount effective to inhibit or eliminate the microbial agent. The antimicrobial composition in a form of probiotic mixture can be administrated alone or in combination with an antimicrobial agent, such as a bacteriophage which is specific for a bacterium producing toxin or antibiotics which are then used to eliminate or inhibit the clostridial species overgrown in a patient's gastrointestinal tract. Disorders that can be treated by the method of the invention include diarrhea or inflammatory bowel diseases such as colitis or Crohn's disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E. Coli, Gemmiger, Desulfamonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Antibacterial composition and method of production
An electrolysis method is described for generating an aqueous solution of copper citrate that has bacteriocidal activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. Gram positive bacteria are known to be relatively more sensitive to the bacteriocidal activities of copper ions than are Gram negative bacteria. Situations exist in which a disinfectant that is relatively more toxic for Gram positive bacteria will be advantageous over a more broadly active disinfectant, such as that provided by most other disinfectants. In particular, a disinfectant that is relatively selective for Gram positive bacteria could help preserve various non-pathogenic Gram negative microbial populations. The residual Gram negative bacteria can potentially compete with, and thereby lessen the chances of the reintroduction of pathogenic Gram positive bacteria, such as MRSA, Streptococcus, Clostridium difficile and Listeria monocytogenes.
Owner:MI HOPE
Method for evaluating stable state of flora in excrement sample and application of method in colorectal cancer screening
PendingCN108690864ALow costGood Gut Health ScreeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium leptumFeces
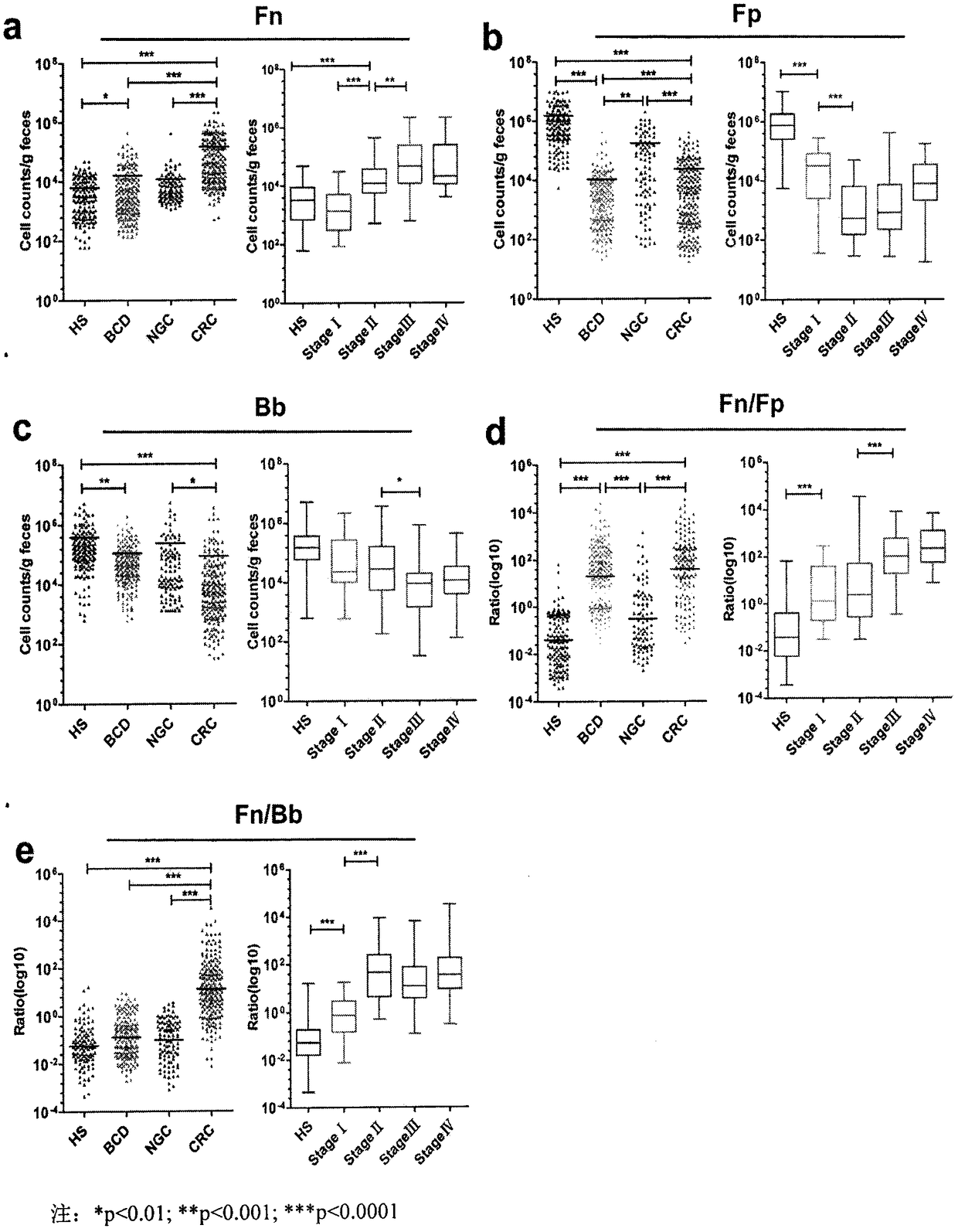
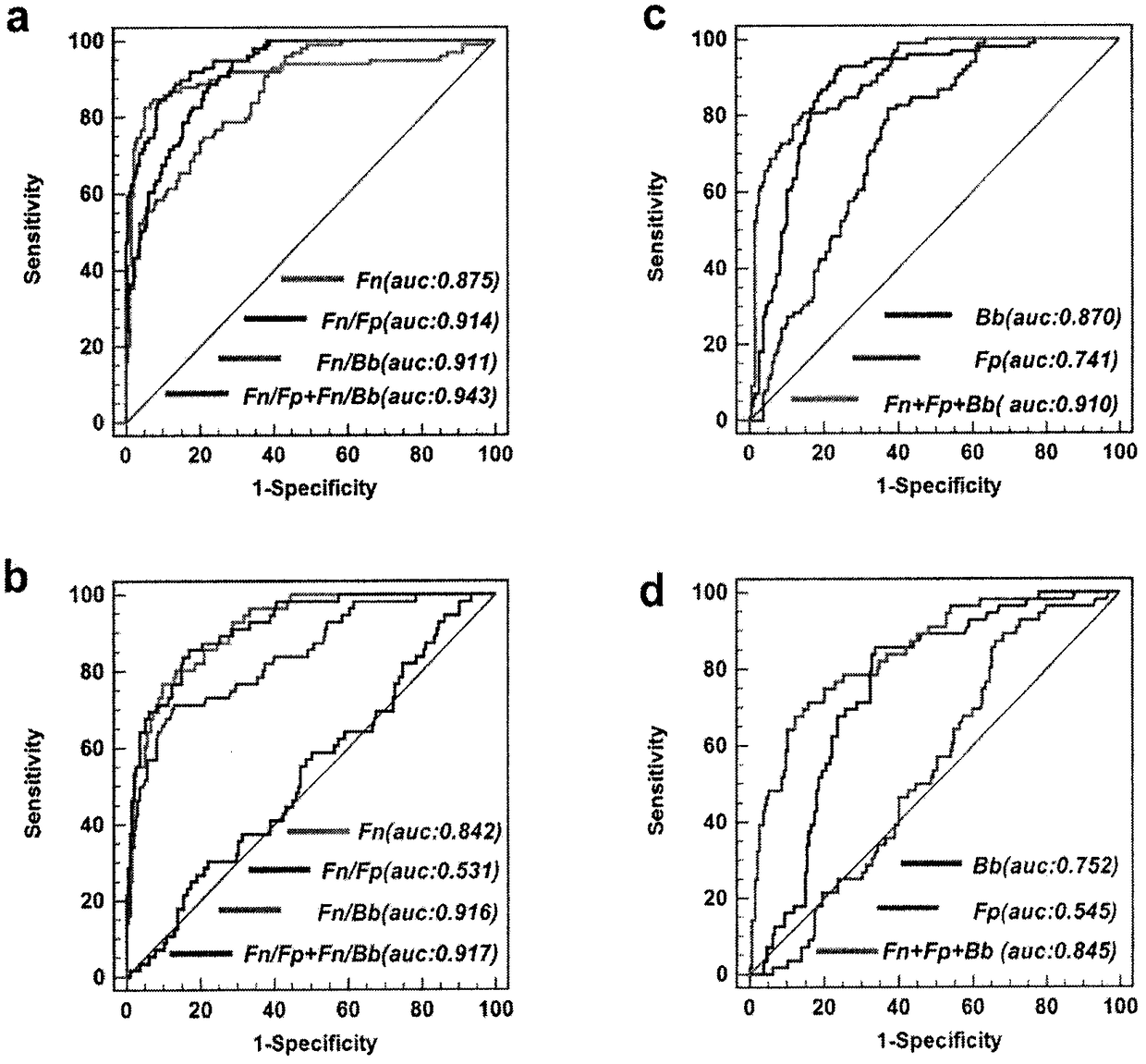
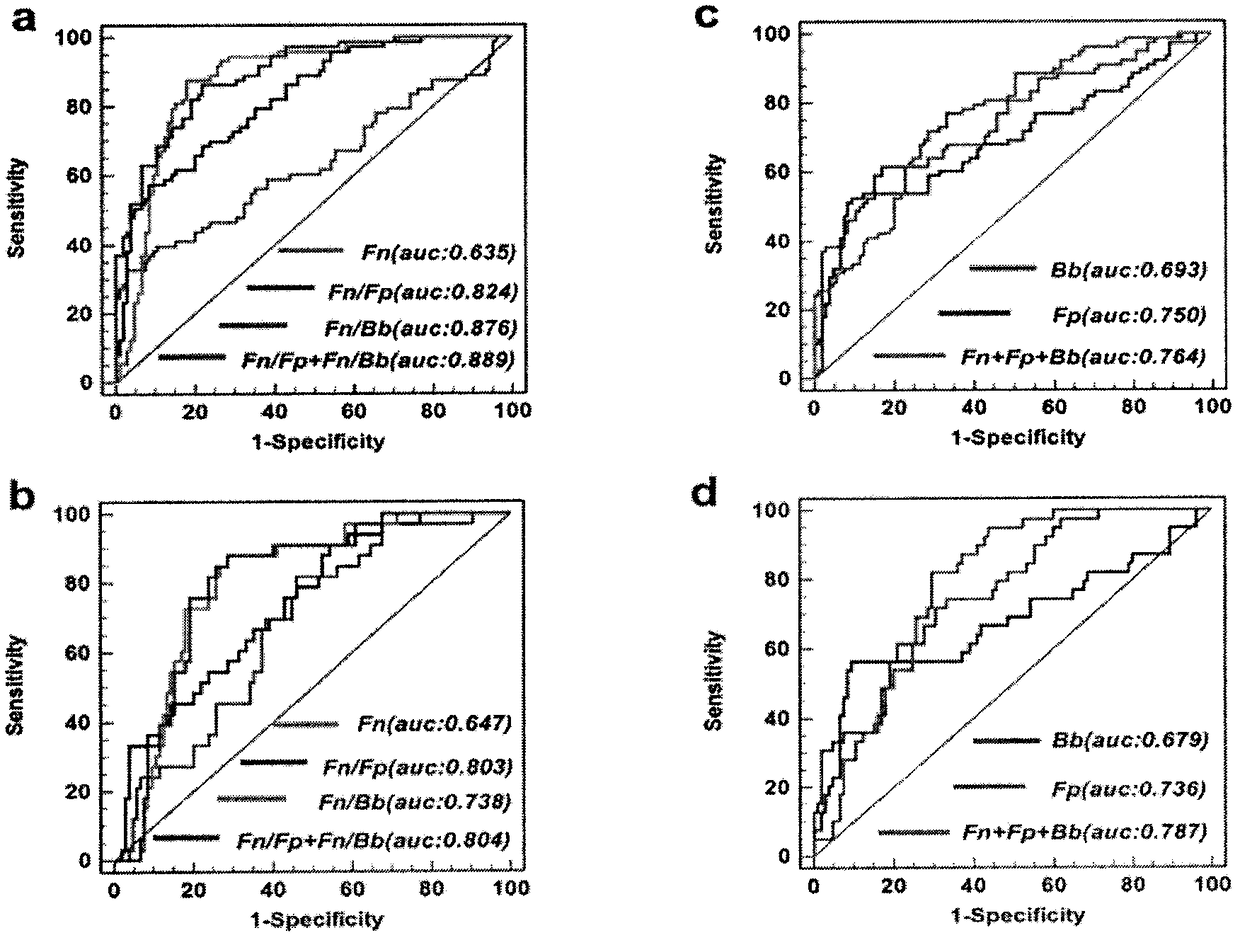
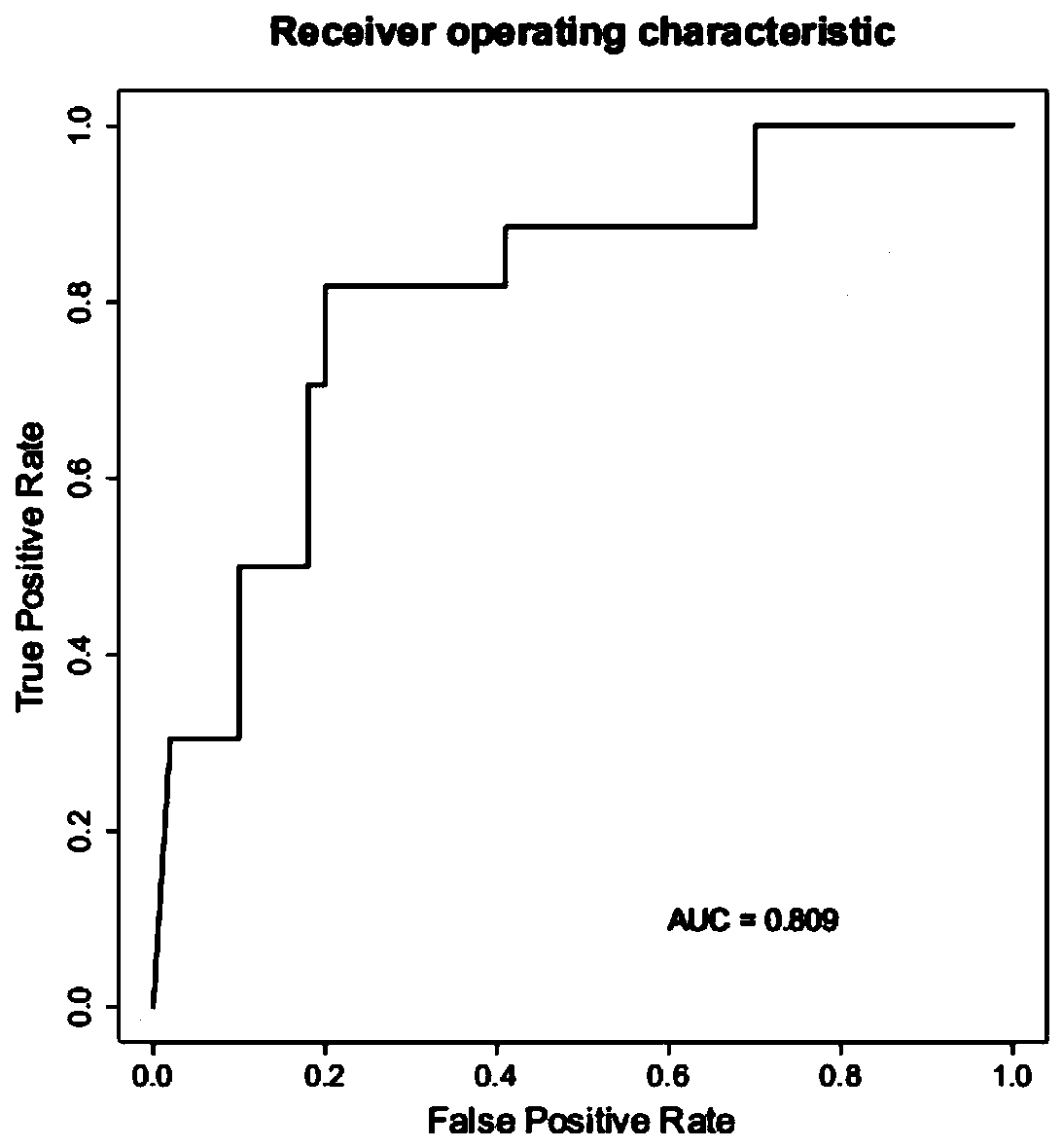
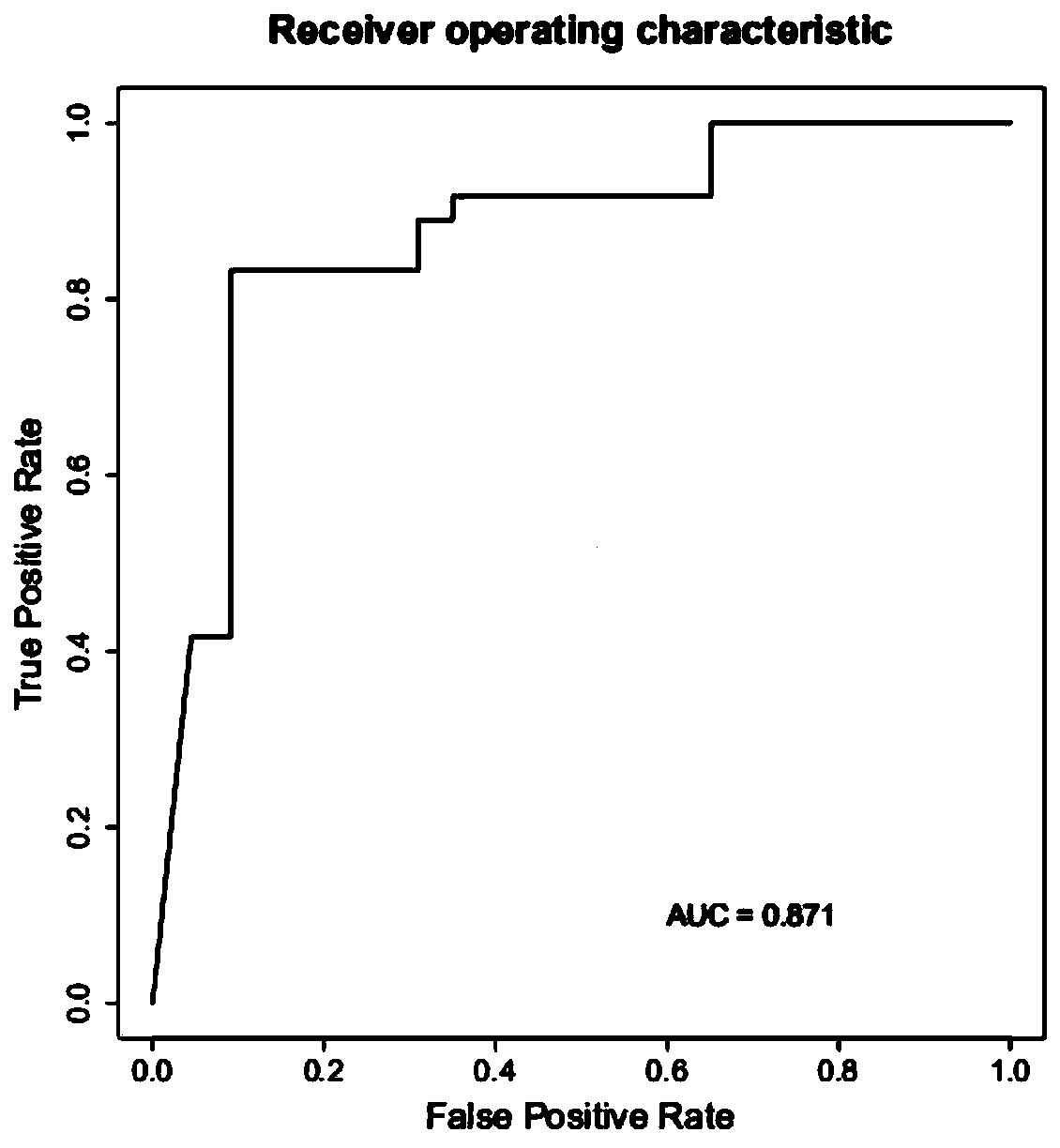
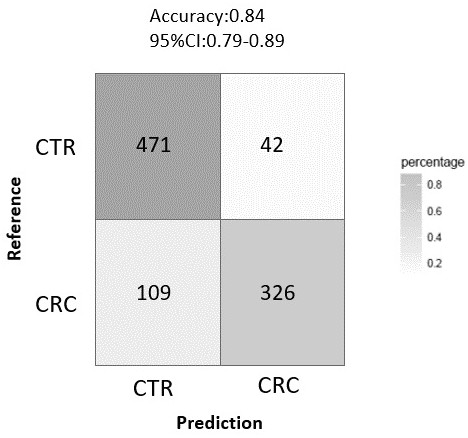
The invention relates to a method for calculating a flora balanced relation index in an individual excrement sample, and an application of the method in screening, diagnosis or auxiliary diagnosis incolorectal cancer (CRC). By extracting bacteria in excrement during DNA sequencing, the types and quantity characteristics of the bacteria can be obtained, and a CRC diagnosis by taking quantity ratiocharacteristic of a plurality of bacteria as a base is carried out. Compared with the methods used in clinical diagnosis or noninvasive screening of CRC with an applied patent, the method is completely noninvasive, and can realize accurate diagnosis of CRC. The analysis result displays that a ratio of fusobacterium nucleatum Fn to bifidobacteria Bb quantity (Fn / Bb) has high susceptibility and specificity on CRC screening, which can respectively reach 84.6% and 92.3% (AUC=0.911). the ratio of fusobacterium nucleatum Fn to clostridium leptum Fp (Fn / Fp) quantity is combined to increase the diagnosis value on CRC, and the Area Under Curve (AUC) of a subject work characteristic curve can reach 0.943. In addition, combination of Fn / Bb and Fn / Fp quantity ratio for screening I-stage CRC has 60% of specificity and 90% of sensitivity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Chenopodium quinoa saponin with enhanced antibacterial effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106176847AImprove antibacterial effectEfficient preparationAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemChemistryPathogen
The invention discloses Chenopodium quinoa saponin with enhanced antibacterial effect and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of subjecting Chenopodium quinoa bran to 70% ethanol extraction, filtration and concentration for acquiring extract, cleaning with ethyl acetate and normal butanol, modification with alkaline solution, desalting, and purification with macroporous resin, and is finally lyophilized to obtain the Chenopodium quinoa saponin. It is possible to quickly and efficiently prepare the Chenopodium quinoa saponin with enhanced antibacterial effect. Bacterial culture experiments prove that the Chenopodium quinoa saponin treated with alkali is higher in antibacterial effect than the saponin not treated with alkali; particularly, in-vitro culture experiments via three oral pathogens (Porphyromonas gingivalis, Clostridium perfringens and Fusobacterium nucleatum) prove that the Chenopodium quinoa saponin treated with alkali is higher in antibacterial effect than the Chenopodium quinoa saponin not treated with alkali.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of prevention and treatment of clostridium difficile infection
InactiveUS20140112985A1Improve developmentGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsSurgical needlesClostridial infectionMicroorganism
This invention relates to prophylactic and / or therapeutic application of microorganism species that are, for example, administered orally as delayed release formulation designed to release its microbial content to the distal small intestine and / or colon in high quantities and density, which is a “normalized” approach to repopulate the colonic flora as a method of prevention and / or treatment of, for example, Clostridium difficile colitis.
Owner:POLONEZ THERAPEUTICS
Strain marker for assisting COVID-19 diagnosis and application thereof
ActiveCN111378788AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesMake up for the defect of false negative testMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPrevotella nigrescensAggregatibacter
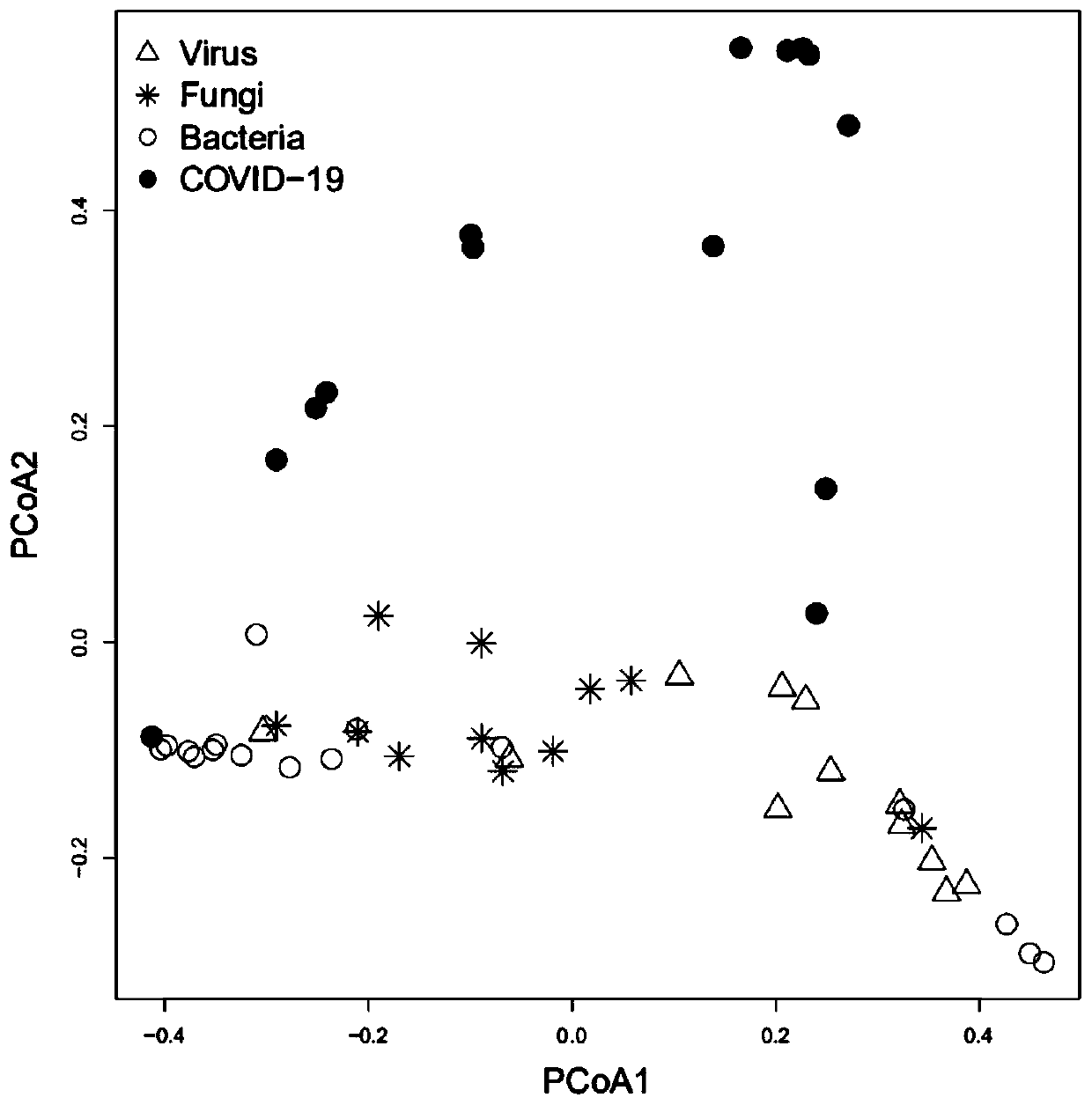
The invention relates to a strain marker for assisting COVID-19 diagnosis and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of pathogenic microorganism infection detection. The strain markercomprises at least one of haemophilus parainfluenzae, propionibacterium, veillonella atypica, aggregatibacter segnis, alloprevotellatannerae, campylobacter showae, fusobacteria, fusobacterium nucleatum, fusobacterium periodonticum, gemella sanguinis, haemophilus parahaemolyticus, haemophilus sputorum, porphyromonas gingivalis, prevotella intermedia, prevotella multifurmis, prevotella nanceiensis,prevotella nigrescens and prevotella timonensis. A prediction model ROC obtained by the strain marker has an AUC value being 0.910, and the strain marker can be used for assisting diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, so that the diagnosing performance on COVID-19 pneumonia can be improved, and the defect that viral nucleic acid detection is false negative can be overcome to a certain extent.
Owner:广州微远医疗器械有限公司 +4
Silver-ion supramolecular antibacterial hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108498543AEasy to makeLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses supramolecular hydrogel and also discloses a preparation method and application of the supramolecular hydrogel. The supramolecular hydrogel disclosed by the invention is prepared from a 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-guanosine analogue and silver ions. The silver-ion supramolecular antibacterial hydrogel provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in preparation, low toxicity, good biocompatibility, excellent stable performance and the like; the silver ions can be effectively alleviated and the antibacterial activity is good; especially, the silver-ion supramolecular antibacterial hydrogel has relatively high antibacterial activity on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 and ATCC33591, and fusobacterium nucleatum; the silver-ion supramolecular antibacterial hydrogel is prepared into an antibacterial material and has a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Anti-porphyromonas gingivalis and fusobacterium nucleatum compound specific IgY antibody, preparation method and toothpaste thereof
The invention discloses an anti-porphyromonas gingivalis and fusobacterium nucleatum compound specific IgY preparation. According to the preparation, 10-70 parts by weight of porphyromonas gingivalis thalli and thalli fragments, and 30-90 parts by weight of fusobacterium nucleatum thalli and thalli fragments are compounded into an antigen to immune an egg laying hen. The invention also discloses the specific preparation method of the anti-porphyromonas gingivalis and fusobacterium nucleatum compound specific IgY preparation, and toothpaste containing the anti-porphyromonas gingivalis and fusobacterium nucleatum compound specific IgY preparation. By the IgY toothpaste which is used for treating and preventing gingivitis and ozostomia has obvious effects in preventing and treating the gingivitis and the ozostomia.
Owner:上海美加净日化有限公司
Lactobacillus plantarum SD26 as well as product and application thereof
ActiveCN112175884AEnhanced inhibitory effectGreat application potentialAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBiotechnologyFusobacteria
The invention provides lactobacillus plantarum SD26 as well as a product and application thereof, and relates to the field of microorganisms. The lactobacillus plantarum SD26 provided by the inventionhas a preservation number of CGMCC No.19328, is derived from pickled vegetables, has an obvious inhibiting effect on oral pathogenic bacteria including streptococcus mutans, candida albicans, fusobacterium nucleatum and porphyromonas gingivalis and food-borne pathogenic bacteria including salmonella typhimurium, escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and listeria monocytogenes, and has good application potential in the aspects of prevention and treatment of the oral pathogenic bacteria and the food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:BEIJING BEINONG HONGZE BIOTECH CO LTD
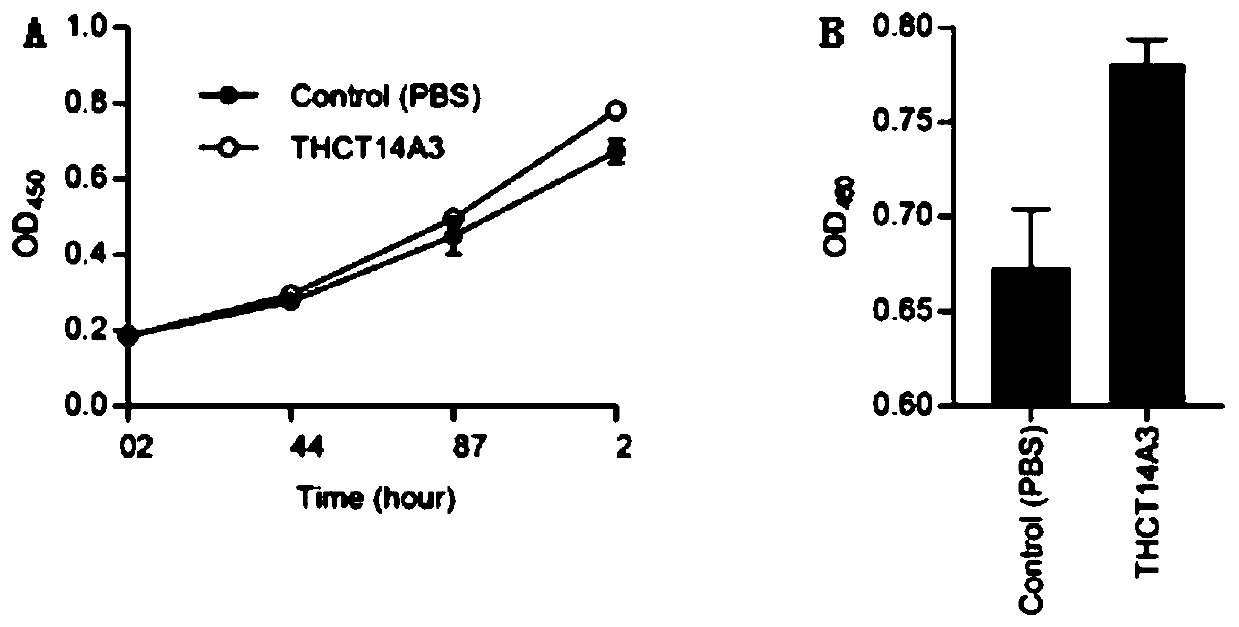
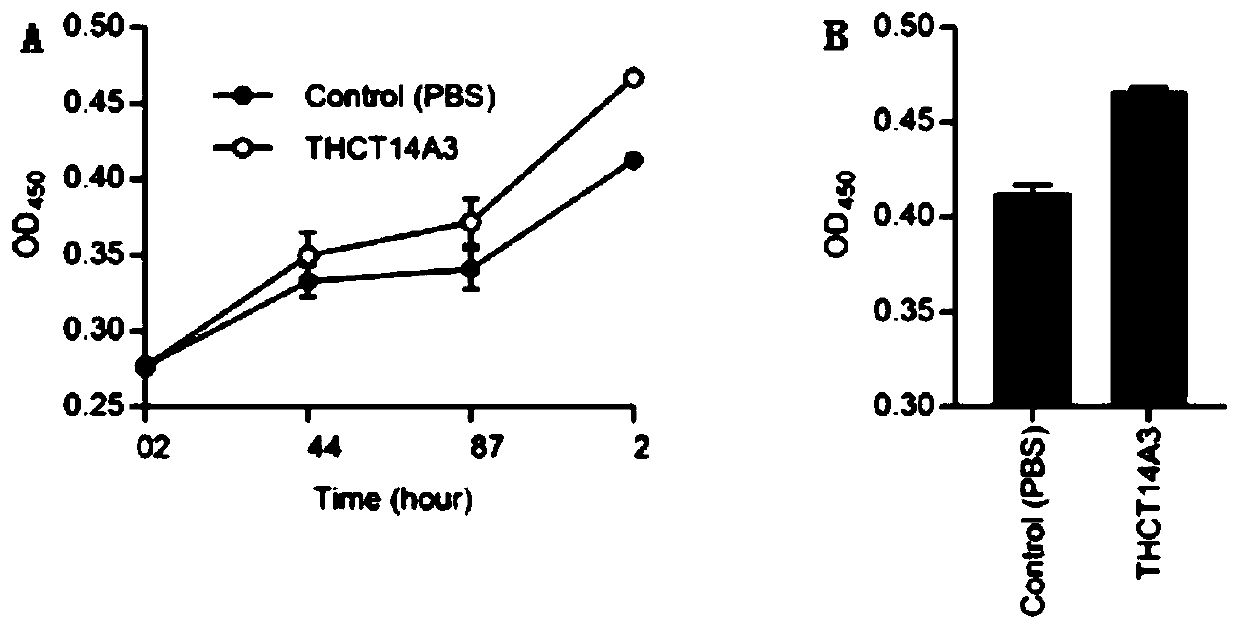
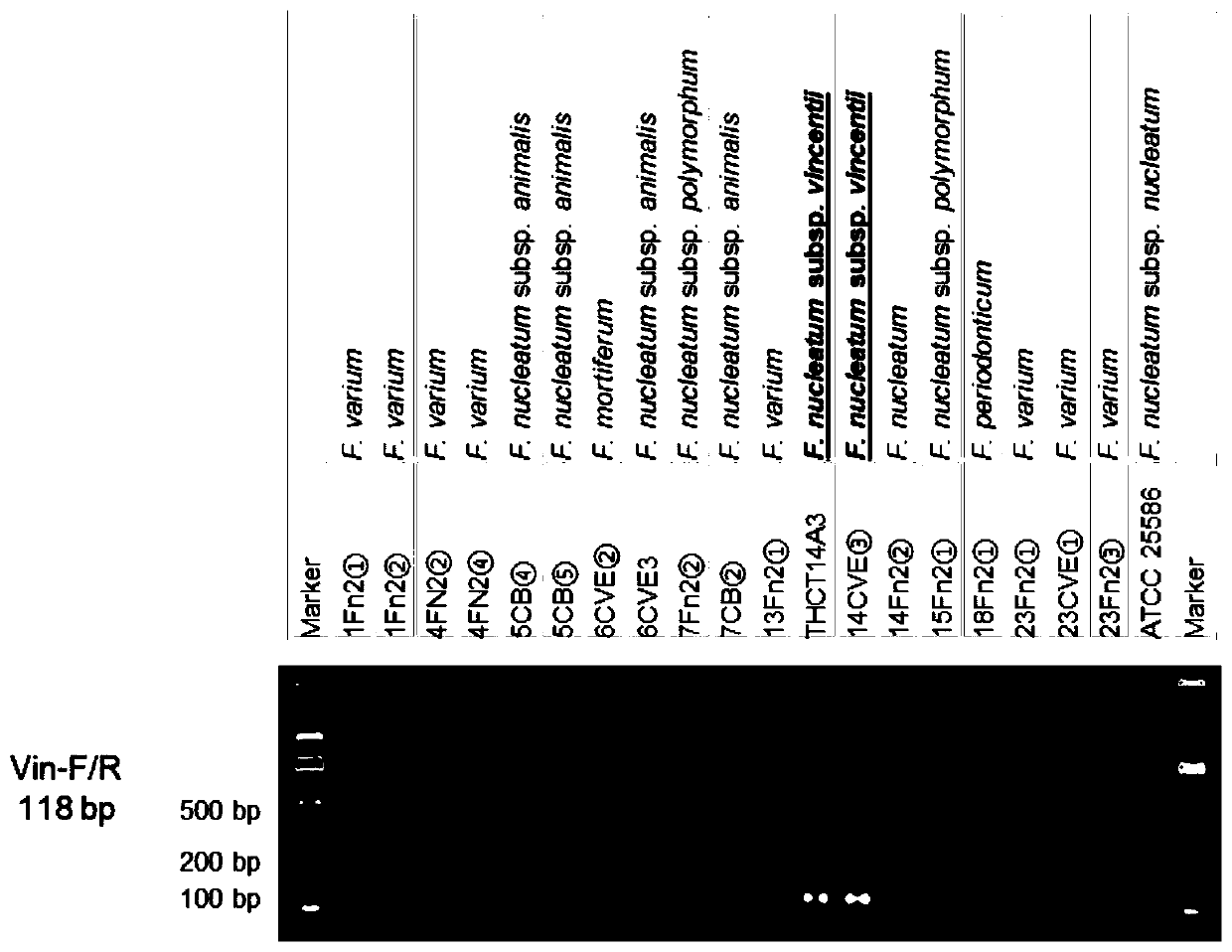
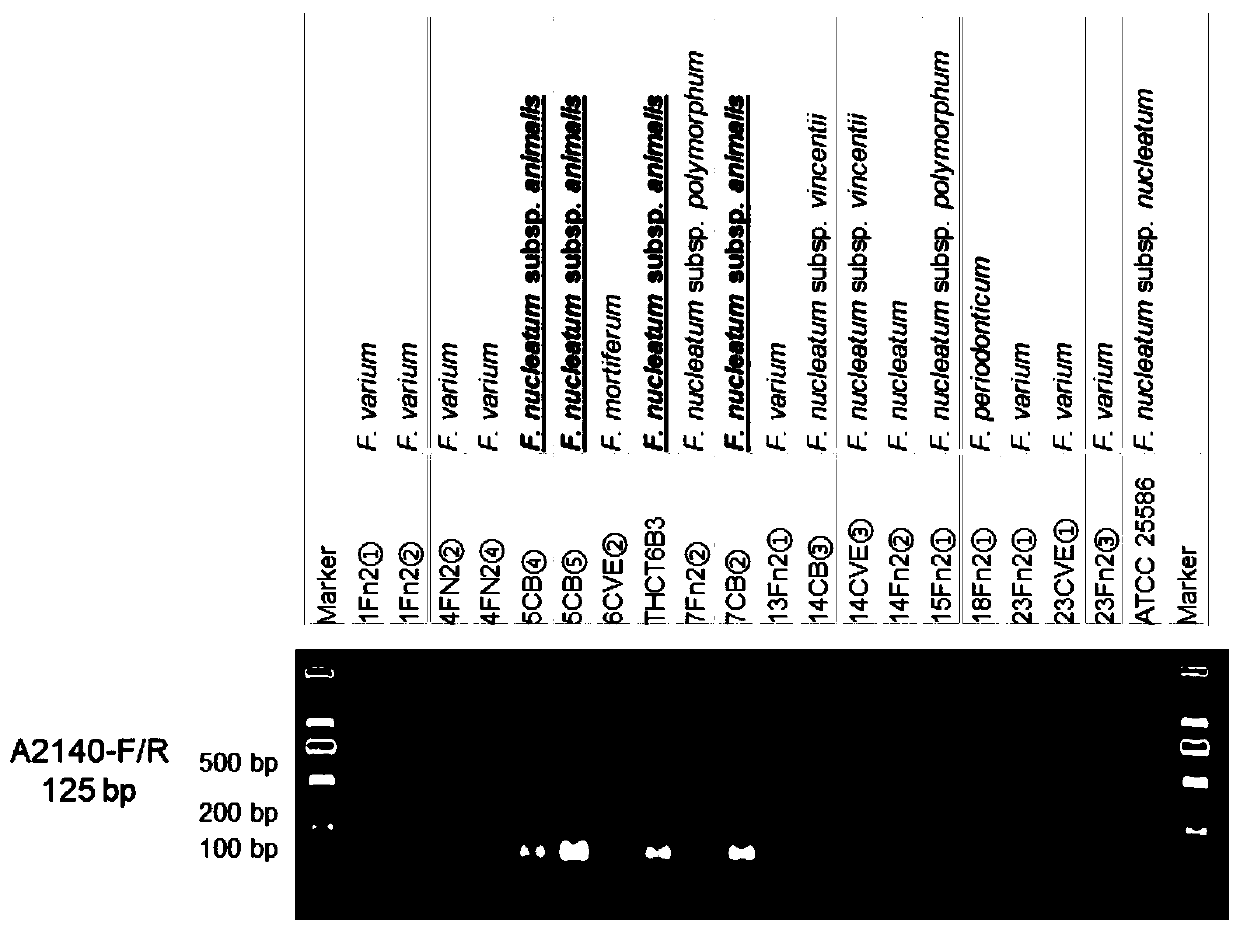
Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii strain for intestinal tract separation and application of fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii strain for intestinal tract separation
The invention provides a fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii strain THCT14A3 for intestinal tract separation. The classification designation is Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019363, the preservation date is May 17th, 2019, and the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection. The 16SrRNA gene sequence of the strain is as shownin SEQID NO:1. The invention further provides a specific DNA sequence for identifying the fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii and a primer sequence corresponding to the specific DNA sequences. Thecolorectal cancer cell line and THCT14A3 co-culture result show that the THCT14A3 can significantly promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Therefore, the THCT14A3 provided by the invention canfacilitate micro-ecology research of intestinal tracts suffering from colorectal cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
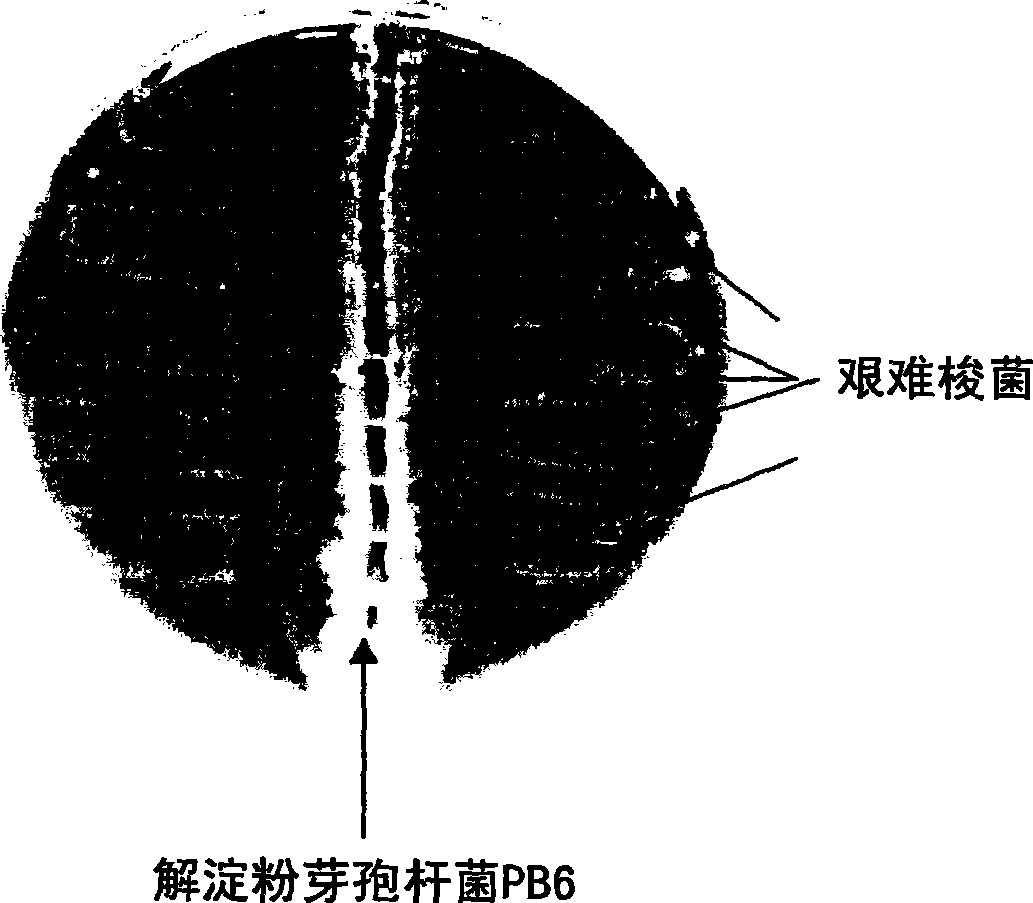
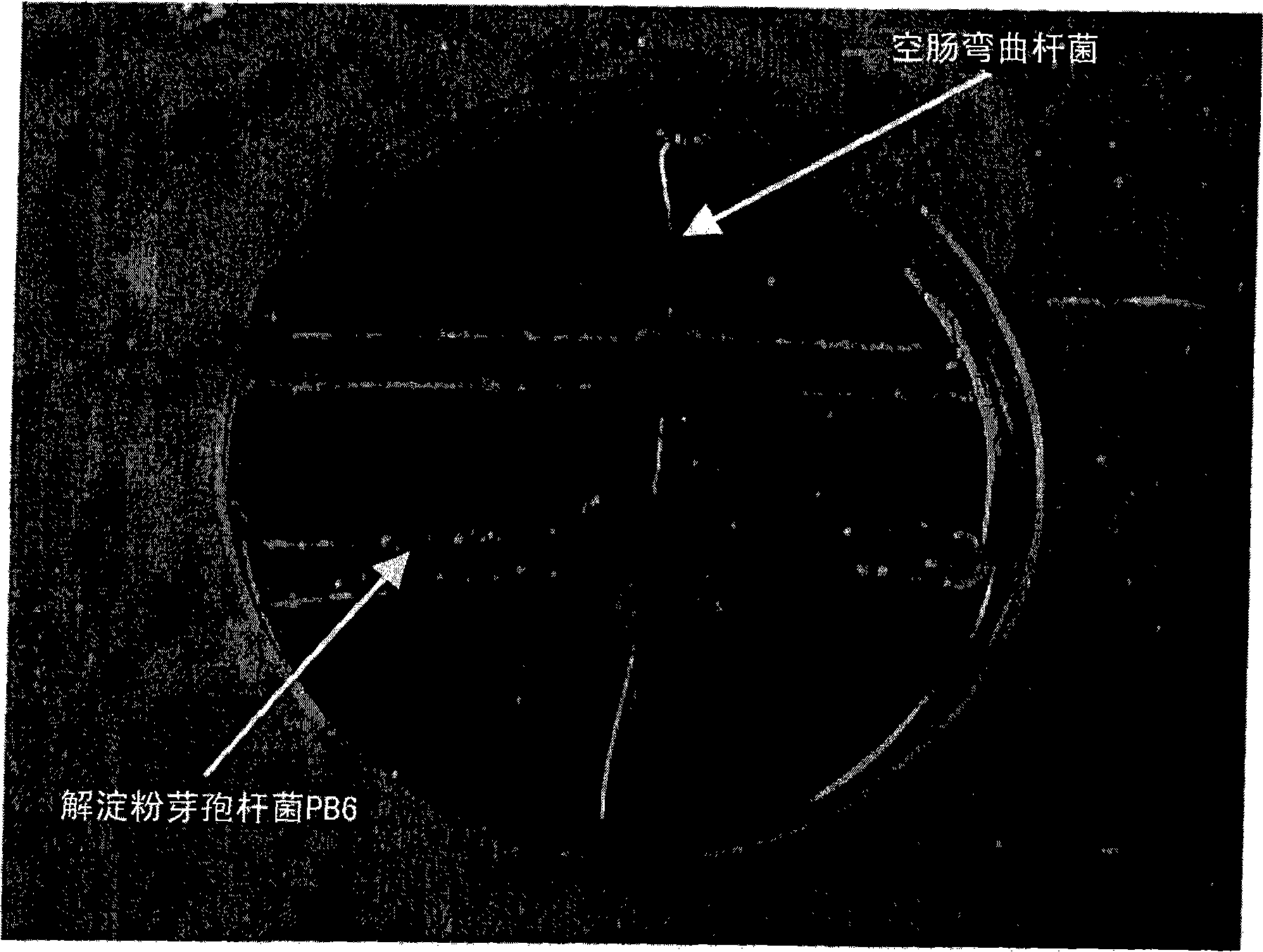
The use of bacillus PB6 for the prophylaxis or treatment of gastrointestinal and immuno-related diseases
Bacteria of the sp. Bacillus that produce a lipopeptide are found to be effective in the treatment and prophylaxis of gastro-intestinal disease when administered as a probiotic. In particular, a strain of Bacillus bacteria identified as PB6 is useful for the treatment of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea (AAD) or the more serious condition Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) when administered as a probiotic. Additionally, these bacteria have been found efficient for the treatment of immunorelated diseases such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Butyrogenic bacteria as probiotics to treat clostridium difficile
The subject invention pertains to the use of certain bacterial strains, particularly butyrogenic bacteria, for preparing a composition to treat and / or prevent Clostridium difficile infection. In particular, the invention relates to the use of butyrate-producing anaerobic fermenters of gut commensals in pharmaceutical or food compositions.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis strain separated from human intestines and application of F. nucleatum subsp. animalis strain
ActiveCN110903999AHelps analyze molecular epidemiological featuresBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationHuman intestine
The invention provides a Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis strain THCT6b3 separated from human intestines. A 16SrRNA gene sequence of the strain is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The classification nameof the strain is Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis and collected on May 17, 2019 with the collection number of CCTCC NO:M 2019363 in the China Center for Type Culture Collection. The invention further provides application of the strain in detection of Fusobacterium nucleatum. A PCR-based molecular identification method for Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis is established for the firsttime. The strain can promote disclosing of composition and sources of the Fusobacterium nucleatum in intestines of colorectal cancer patients, and contributes to analysis of molecular epidemiologic characteristics of the Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Egg yolk antibody mouth wash capable of preventing and treating ozostomia and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106214510AInhibit the growth of bacteriaAvoid breedingAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsNormal floraBooster immunizations
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and discloses an egg yolk antibody mouth wash capable of preventing and treating ozostomia and a preparation method of the egg yolk antibody mouth wash. The mouth wash comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-10 parts of specific complex egg yok antibody preparation, 1-10 parts of a Chinese herb extract, and 100 parts of sterile water. The specific complex egg yolk antibody preparation is a complex antigen prepared from porphyromonas gingivalis, fusobacterium nucleatum and a bacterium internationally named Solobacterium moorei, a laying hen is primarily immunized and then immunized in a booster manner for five times all together, an egg is collected from the first booster immunization, an egg yolk liquid is obtained, separated and purified to obtain a specific complex egg yolk antibody. The egg yolk antibody mouth wash contains both the specific complex egg yolk antibody and an important extract, the breeding of microorganisms in an oral cavity is effectively inhibited, the ozostomia is prevented and treated, the normal flora of the oral cavity is not affected, and the mouth wash is safe and harmless.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Primer group and method for rapidly detecting fusobacterium nucleatum of excrement and application of primer group and method
InactiveCN109680083AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseFeces
The invention discloses primer group information of fusobacterium nucleatum, a quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method and application of primer group and method. According to a16S rRNA (ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid) nucleotide sequence and a BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) function of bacteria in an NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information) database, a fusobacterium nucleatum related primer and V3 to V4 primers are designed according to primer design software Primer Primer 5, and the primers are identified. Genome information of total bacteria is extracted from an excrement sample; the qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) is carried out through utilizing the primers and the relative content of the fusobacterium nucleatum is calculated andobtained. The detection method is used as a principle and an intestinal micro-ecological detection kit is prepared by utilizing the fusobacterium nucleatum primer. A kit is used for carrying out actual detection and a result shows that the content of the fusobacterium nucleatum in the excrement samples of an intestinal micro-ecological patient and a patient with intestinal cancer is remarkably different from that of normal people. A specific primer of the fusobacterium nucleatum, a rapid and accurate detection method and research and development of an intestinal micro-ecological kit provide methods for knowing the distribution of an intestinal micro-ecology and predicating and primarily screening diseases.
Owner:JIANGXI PRECISION GENE CO LTD
Colorectal cancer auxiliary diagnosis kit for fecal nucleic acid detection and use method thereof
ActiveCN110904228AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFusobacteriaLogistische regression
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer auxiliary diagnosis kit for fecal nucleic acid detection and a use method of the colorectal cancer auxiliary diagnosis kit. The kit comprises a KRAS gene mutation detection reagent, a fusobacterium nucleatum detection reagent, a DNA sulfite conversion reagent and a Septin9, SDC2, HOXA11 and NDRG4 gene methylation detection reagent. The use method comprises the following steps: collecting an excrement sample, and then completing DNA purification, KRAS gene mutation detection, fusobacterium nucleatum abundance detection and Septin9, SDC2, HOXA11 and NDRG4 gene methylation detection of the sample by using reagents in the kit; and calculating the obtained data through a logistic regression model, and performing result evaluation and analysis. The colorectal cancer detection sensitivity reaches 89% or above, the specificity reaches 94% or so, high-sensitivity and high-specificity colorectal cancer detection can be achieved, and doctors can be helped to guide follow-up treatment medication of patients.
Owner:GENETALKS BIO TECH CHANGSHA CO LTD
Lactobacillus plantarum for preventing and/or treating periodontitis as well as culture, preparation and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN113005055AReduce the content of inflammatory factorsHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyOral disease
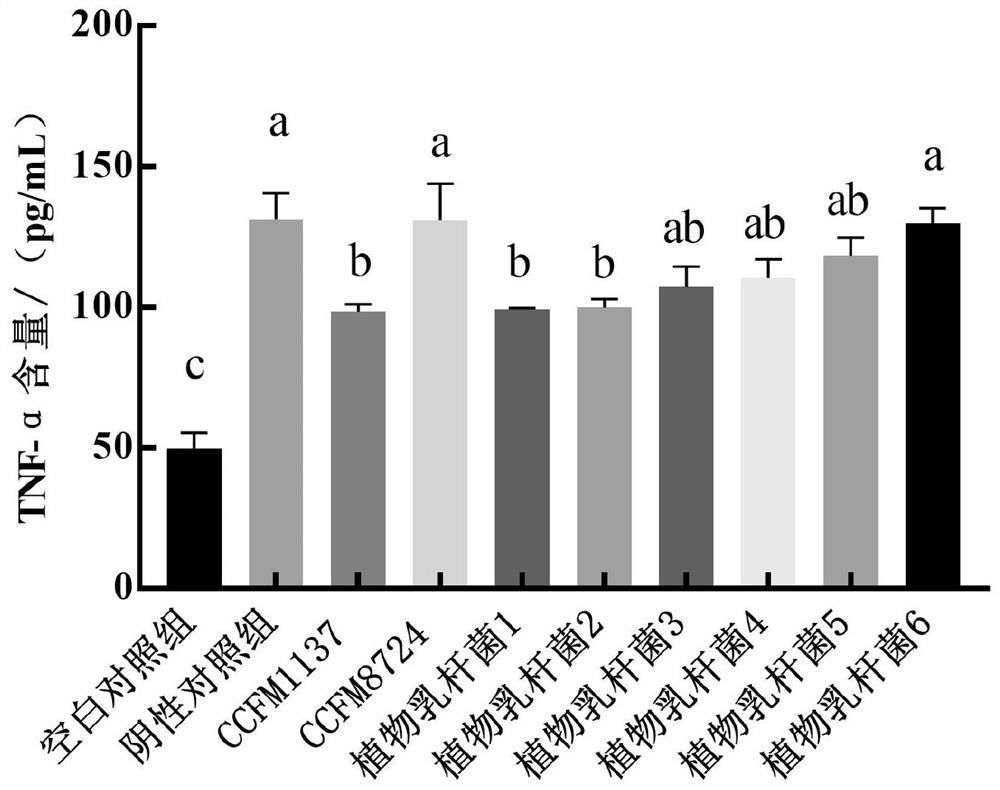
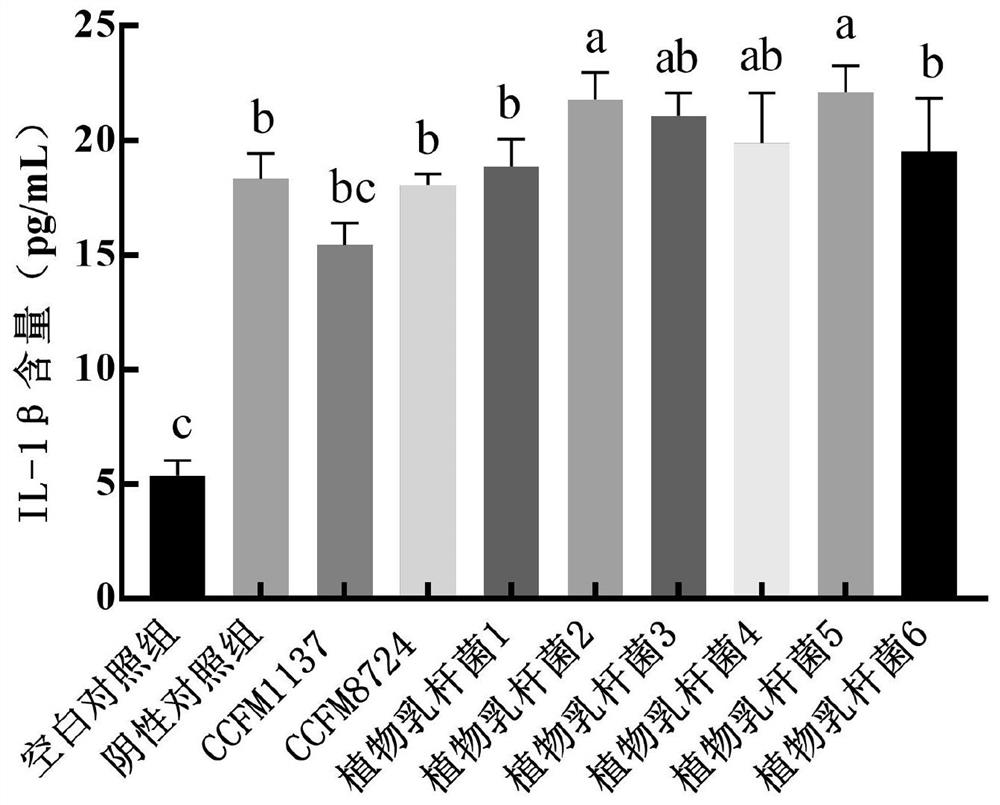
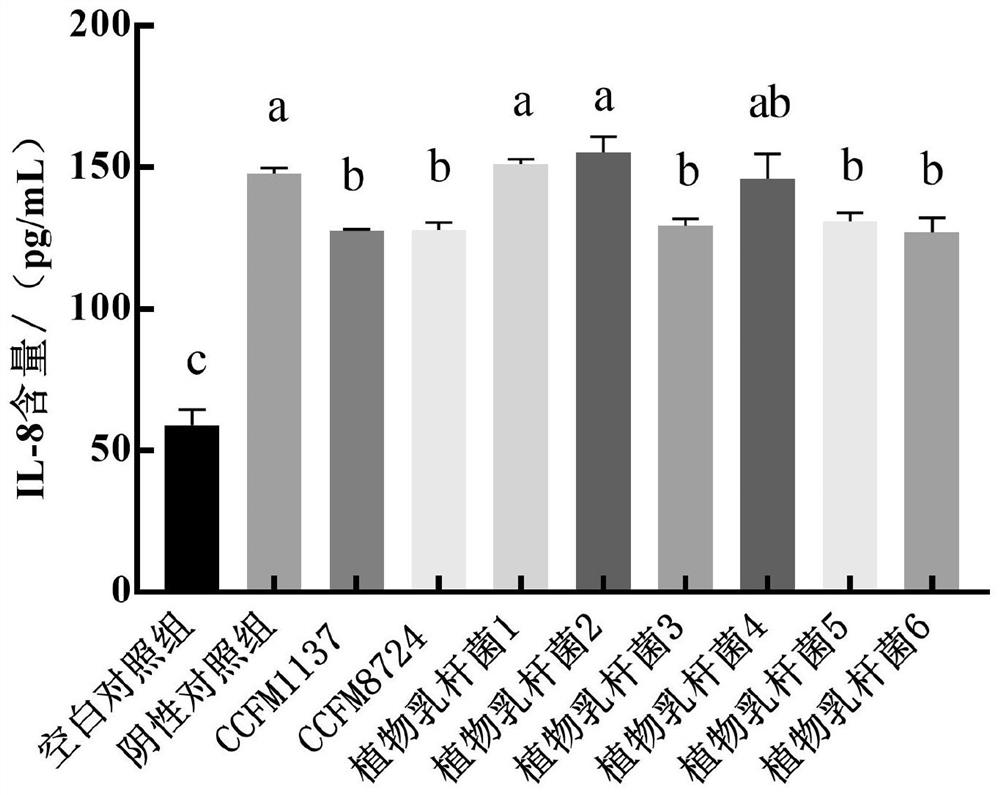
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and discloses lactobacillus plantarum for preventing and / or treating periodontitis as well as a culture, preparation and application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The name of the lactobacillus plantarum is Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM1137, the lactobacillus plantarum is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on the 5th floor of the Building 59, No. 100 Courtyard, Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou on August 1, 2020, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61114. The lactobacillus plantarum can be used for inhibiting the formation of a mixed bacterium biological membrane of porphyromonas gingivalis, prevotella intermedia and fusobacterium nucleatum; the content of inflammatory factors in a periodontitis cell model can be reduced; the expression quantity of transmembrane transport protein in a periodontitis cell model can be increased; and the lactobacillus plantarumcan be used for preventing and / or treating oral diseases and inhibiting prevotella intermedia, porphyromonas gingivalis and / or fusobacterium nucleatum.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis strain and application thereof
ActiveCN111205994APromote proliferationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseColorectal cancer cell line
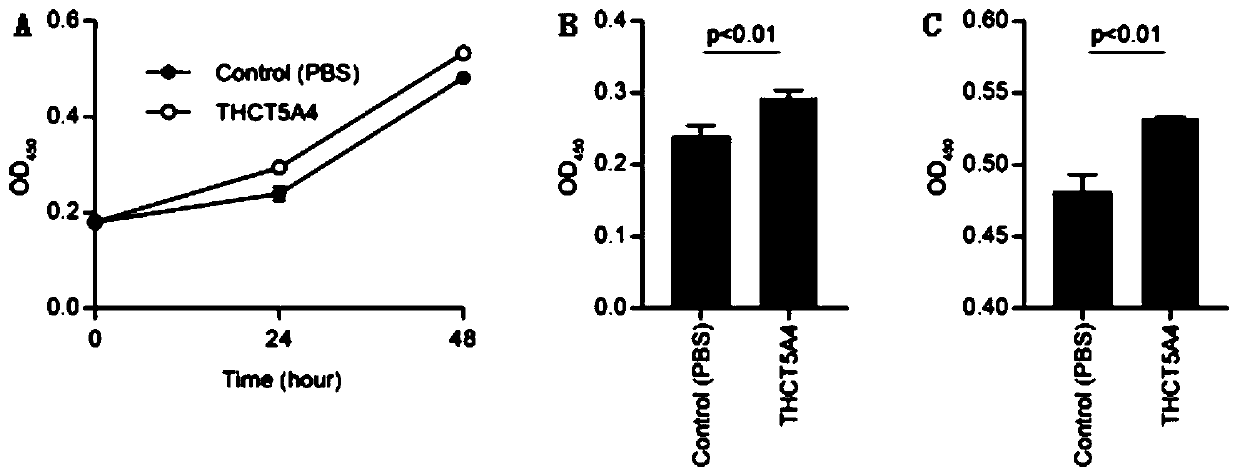
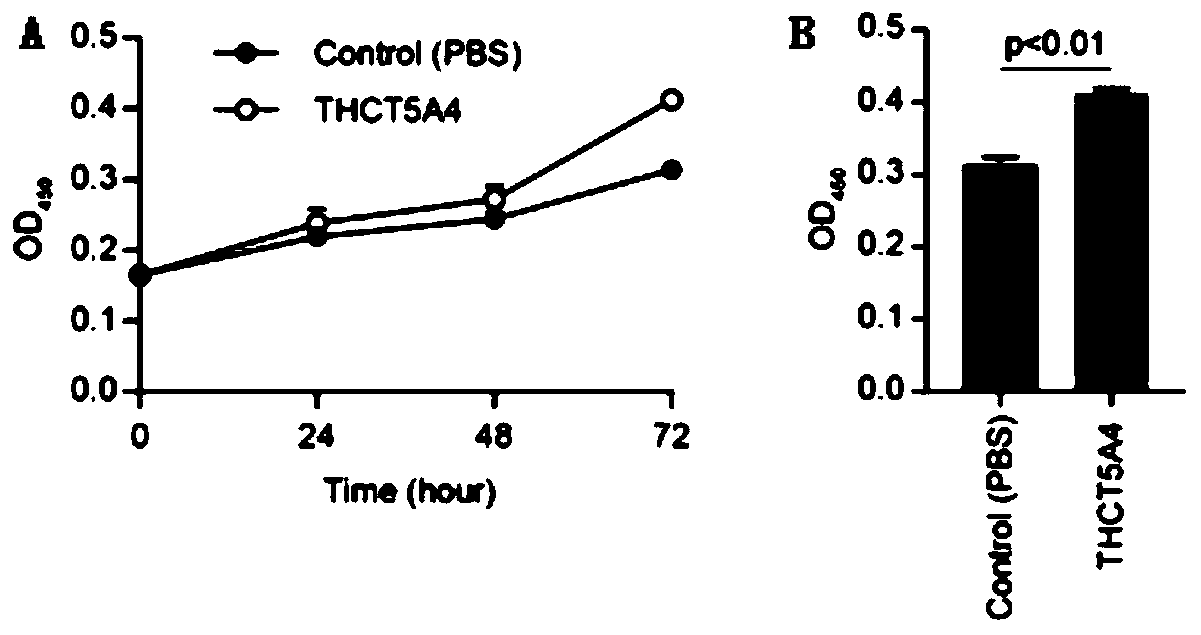
The invention provides a fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis strain THCT5A4 separated from human rectal cancer tumor tissue. A classification name is Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis THCT5A4,a preservation number of the fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis strain THCT5A4 separated from the human rectal cancer tumor tissue is CCTCC NO: M 2019366, the preservation date is May 17th, 2019,the preservation organization is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and a 16SrRNA gene sequence of the fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis strain THCT5A4 separated from the human rectal cancer tumor tissue is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 as shown in the description. A separation method of the fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.animalis strain is provided. A result of co-culture of a colorectal cancer cell line and the THCT5A4 shows that the THCT5A4 can significantly promote proliferation of colorectal cancer cells, therefore, the THCT5A4 can provide diverse in-vitro or in-vivo experimental conditions for simulating an intestinal environment for studies of colorectal cancer, and a colorectal cancer disease model can be built for screening medicines for treating colorectal cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Fusobacterium nucleatum polymorphic subspecies isolate and application thereof
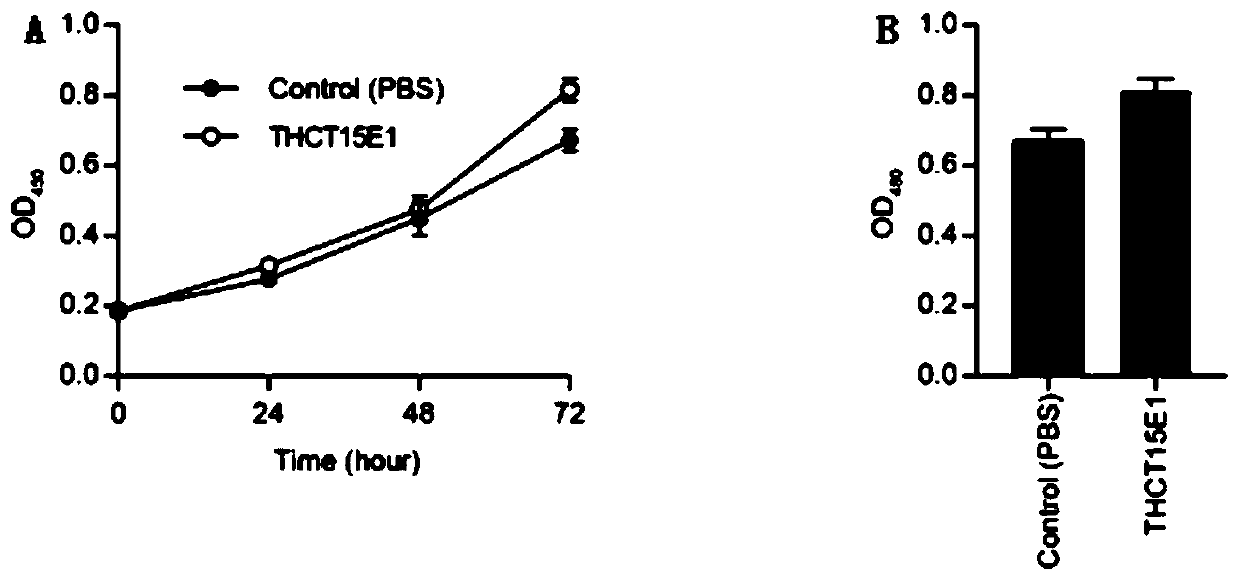
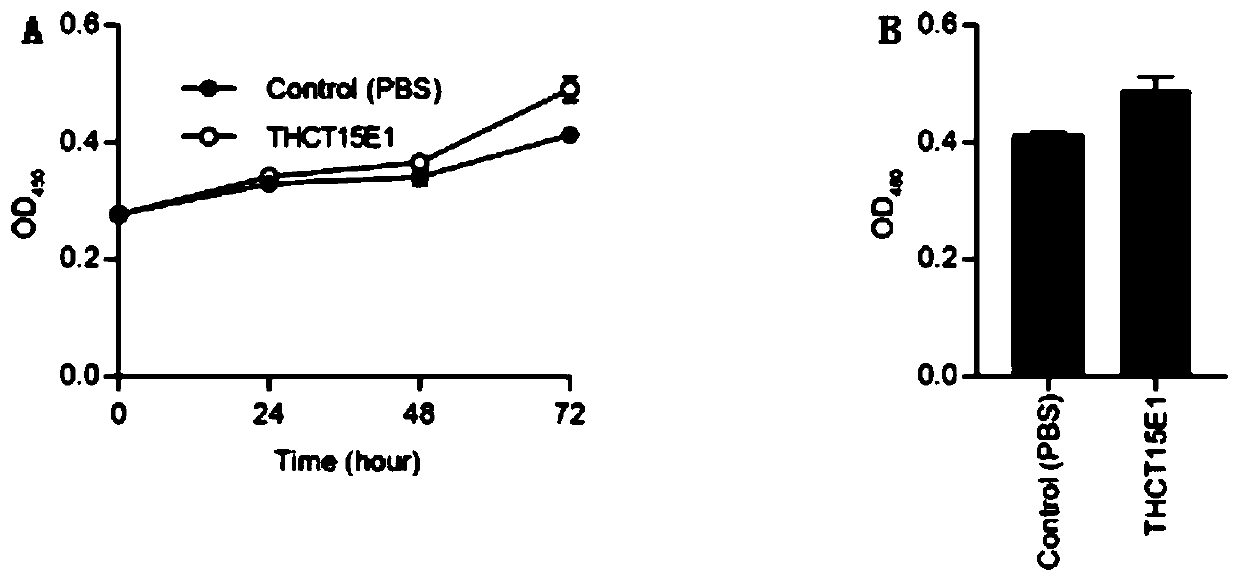
ActiveCN111004738APromote proliferationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a fusobacterium nucleatum polymorphic subspecies isolate THCT15E1, a classification name is Fusobacterium nuucleates subsp.nucleatum THCT15E1, a preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M 2019362, a preservation date is May 17, 2019, a preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the 16SrRNA gene sequence of the strain is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The result of co-culture of the colorectal cancer cell line and THCT15E1 shows that THCT15E1 can significantly promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation; therefore, the THCT15E1 can provide diversified experimental conditions for in-vitro or in-vivo intestinal environment simulation for colorectal cancer research, and can also construct a colorectal cancer disease model to screen drugs for treating colorectal cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
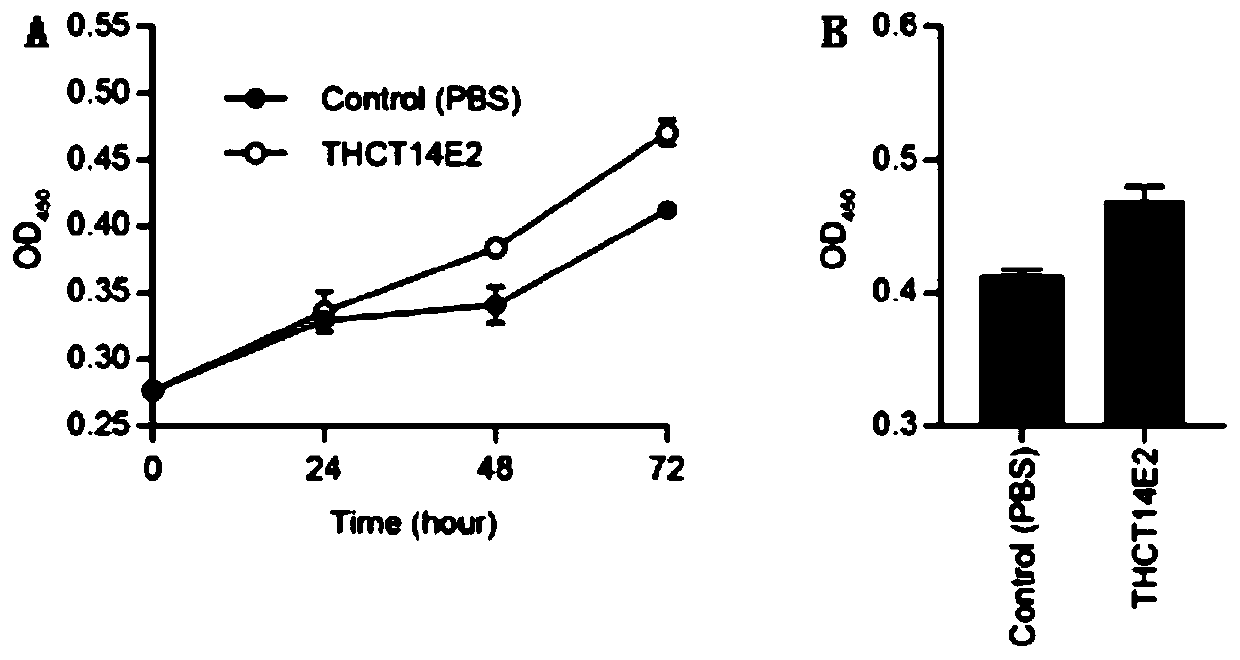
Fusobacterium nucleatum obtained from large intestine cancer tumor tissue and application of fusobacterium nucleatum obtained from large intestine cancer tumor tissue
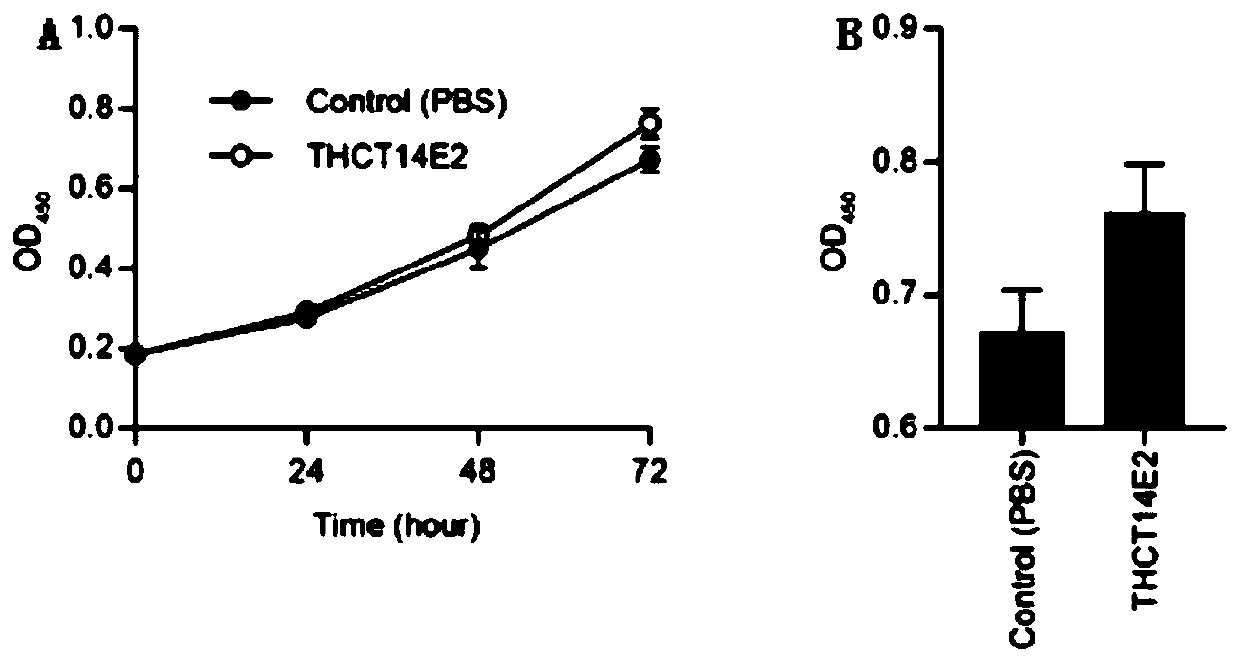
ActiveCN110903997AAids in functional studiesPromote proliferationBacteriaCulture processLarge Intestine CancerColorectal cancer cell line
The invention provides fusobacterium nucleatum THCT14E2 which is obtained from large intestine cancer tumor tissue and does not belong to known fusobacterium nucleatum subsp.vincentii. The 16SrRNA gene sequence of the strain is as shown in SEQID NO:1. The classification designation of the THCT14E2 is Fusobacterium nucleatum, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019361, the preservation date is May 17th, 2019, and the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection. The colorectal cancer cell line and THCT14E2 co-culture result shows that the THCT14E2 can significantly promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Therefore, the THCT14E2 can promote understanding of micro-ecology diversity of rectum cancer, and facilitate function research of the fusobacterium nucleatum fromthe colorectal cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Transcription factor decoys for the treatment and prevention of infections caused by bacteria including clostridium difficile
Decoy nucleic acid sequences comprising a binding site for a target transcription factor, wherein the binding site is not operably linked to a gene, and wherein the transcription factor comprises a regulator of expression of a gene or genes in Clostridium difficile encoding one or more of: (i) a cellular growth factor; (ii) a cellular toxin; (iii) a cellular sporulation factor; (iv) a cellular stress response; and / or (v) a cellular essential gene are described. Uses of the decoys in antibacterial complexes for the treatment of bacterial infections are also described.
Owner:PROCARTA BIOSYST
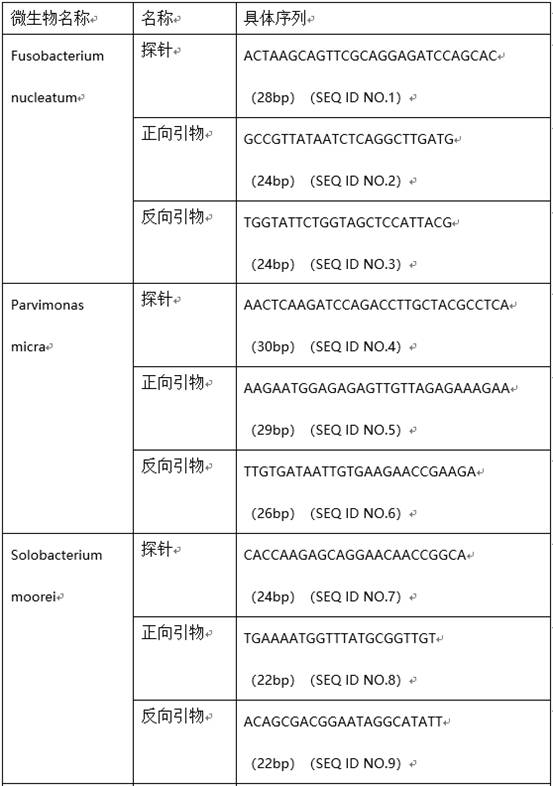
Microbial markers for predicting risk of colorectal cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN112609015AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismAIDS diagnosis
The invention provides microbial markers for predicting the risk of colorectal cancer and application of the microbial marker. The microbial markers comprise the following three types: fusobacterium nucleatum, parvimonas micra and solobacter moorei. The abundance of the above three bacteria in a colorectal cancer patient is remarkably increased; corresponding microbial marker expression abundance values are obtained through an experimental method and input into a machine learning model established by the invention; and a risk value is given after the model conducts comprehensive calculation, so colorectal cancer is diagnosed in an assisted manner. The microbial markers provided by the invention are high in sensitivity and good in specificity, have the potential of serving as colorectal cancer markers, and provide a means for non-invasive auxiliary diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Owner:天津奇云诺德生物医学有限公司
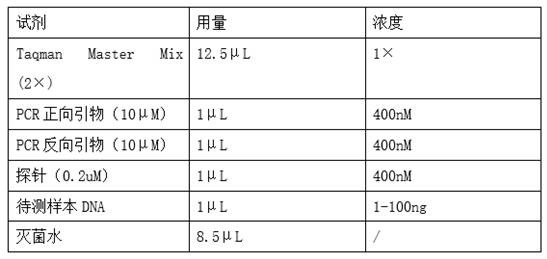
Establishment of methodology for carrying out joint detection on bacterial genus genes and toxin genes of clostridium difficile by using TaqMan-MGB probe real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology
InactiveCN103215362AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFecesClostridium difficile toxin B
A TaqMan / MGB probe PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology can carry out bacterial genus identification on clostridium difficile in fecal genomes, simultaneously detect the carrying situation of toxin genes, and can judge whether a toxin A has deletion. A fecal specimen is not required to be purely cultured, and the strain identification and the toxin detection are completed in a reaction system. The method has the characteristics of simple operation, good repeatability, high flux detection specimens, short report time, and the like, and is applicable to the screening of pathogenesis of patients with diarrhea caused by clinically unexplained causes. The invention solves the technical problems that fecal specimens can be subjected to strain identification and strain toxin carrying situation screening simultaneously without being purely cultured, and a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) detection method for fecal genomes, which is high in sensibility, is provided. Because traditional anaerobic culture is uneasy to perform, and an enzyme immunoassay has methodology defects, according to the invention, the diagnosis rate of clostridium difficile associated diarrhea is significantly increased. Meanwhile, the invention also can be applied to the monitoring of drug used in the process of treating the diseases.
Owner:AEROSPACE CENT HOSPITAL
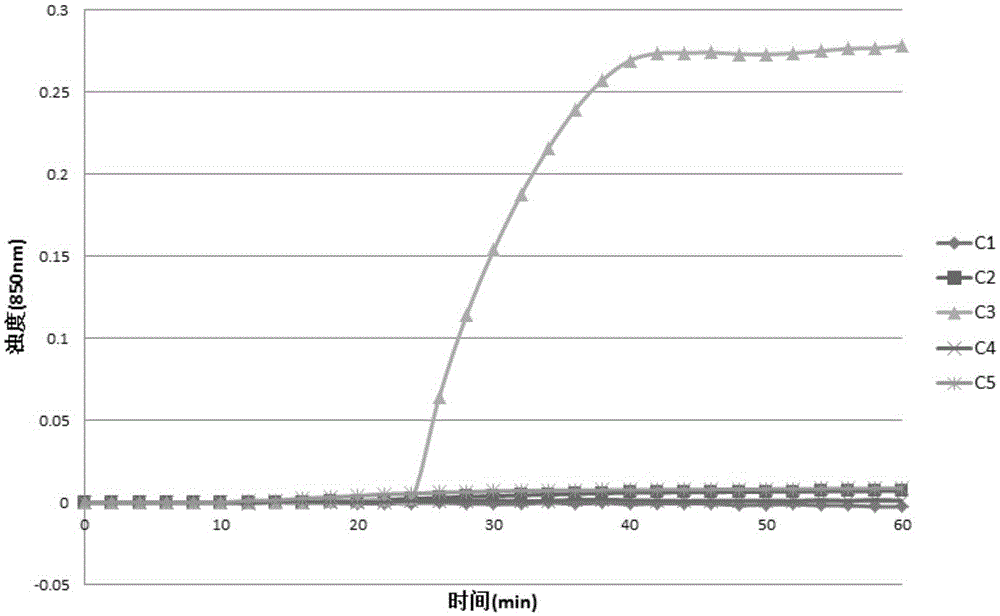
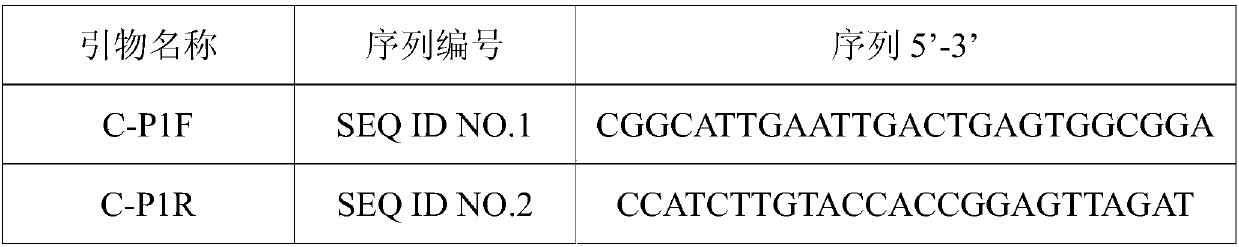
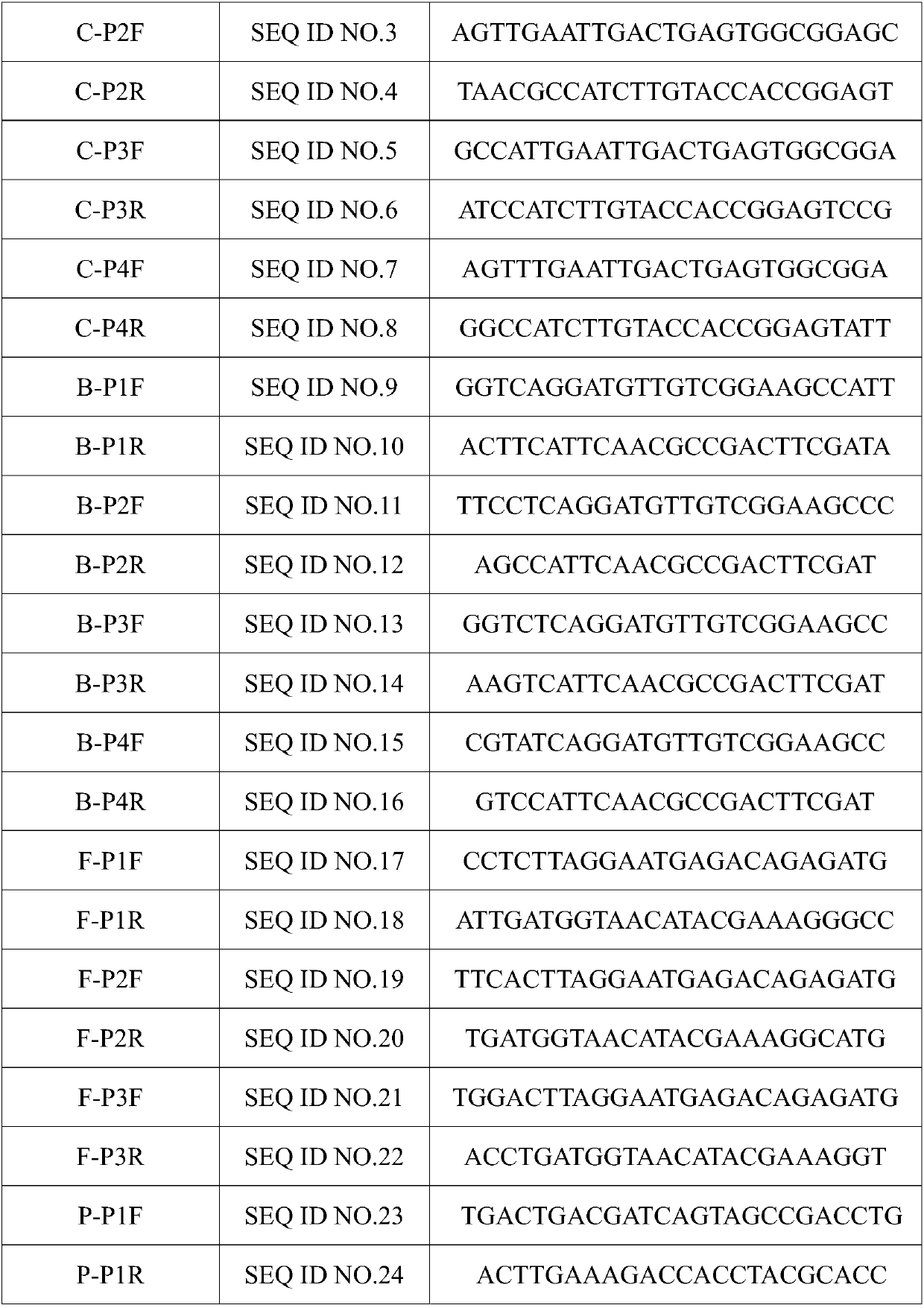
Constant-temperature detecting method for fusobacterium nucleatum, as well as special primer and kit thereof
InactiveCN105256046AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSocial benefitsDisease
The invention discloses a constant-temperature detecting method for fusobacterium nucleatum, as well as a special primer and a kit thereof. The invention provides a circular mediate constant-temperature amplification primer for detecting the fusobacterium nucleatum, which is composed of a primer 1, a primer 2, a primer 3, a primer 4 and a primer 5, wherein the sequence 2, sequence 3, sequence 4, sequence 5 and sequence 6 in a sequence table are respectively taken as the nucleotide sequences of the primer 1, the primer 2, the primer 3, the primer 4 and the primer 5. According to the constant-temperature detecting method provided by the invention, the fusobacterium nucleatum can be quickly, conveniently, efficiently, high-peculiarly and high-sensitively detected under a constant temperature condition; no complex instrument is required; a new technical platform is supplied for detecting the fusobacterium nucleatum; the constant-temperature detecting method can be used for screening and detecting the fusobacterium nucleatum for the basic medical treatment enterprises and various disease control and prevention centers; the constant-temperature detecting method has wide market prospect, has higher economic and social benefits and is suitable for wide-scope popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
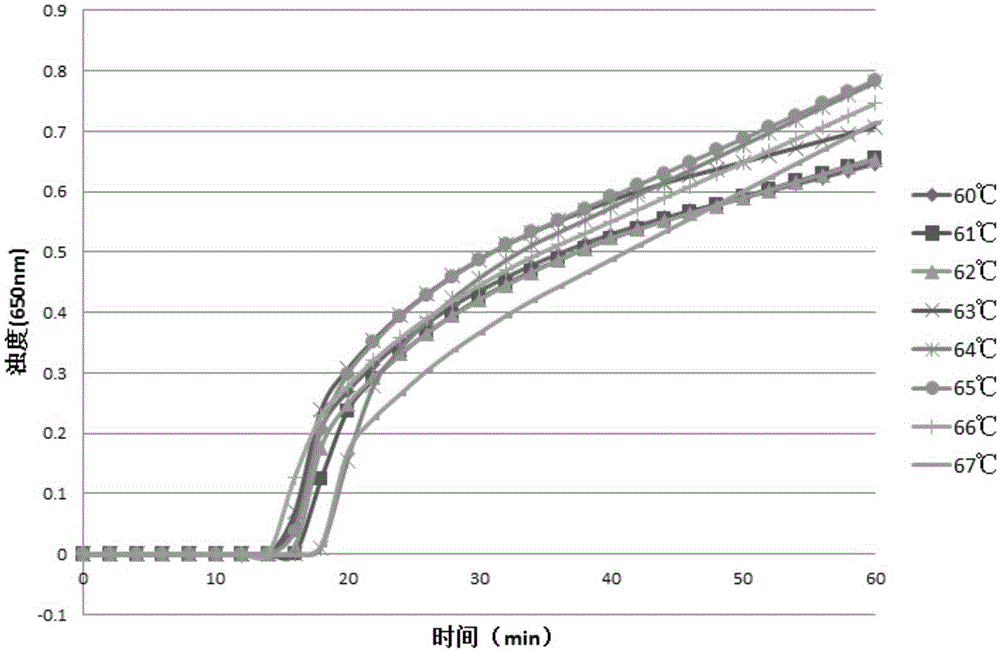
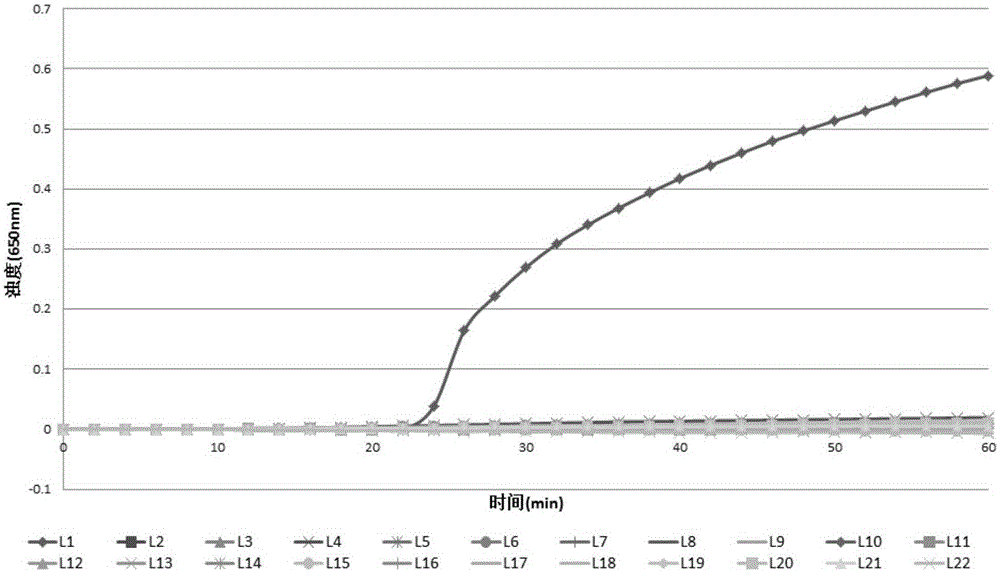
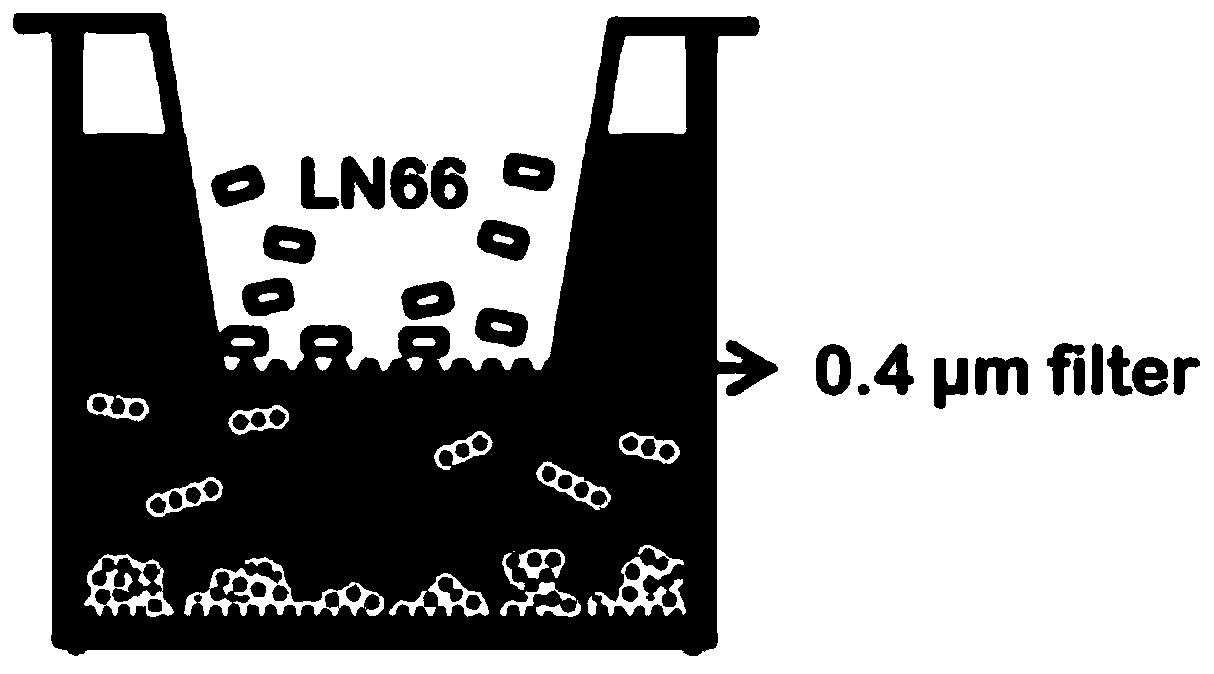
Lactobacillus plantarum LN66 and application thereof to product reducing halitosis risk
The invention provides a lactobacillus plantarum LN66 and an application thereof to a product reducing a halitosis risk and relates to the technical field of halitosis prevention and treatment. An LN66 strain is preserved with the number of CGMCC No. 17369. The LN66 strain is directly separated from a healthy human body, is a Gram staining positive bacillus, is incapable of generating spores and is capable of growing in both aerobiotic and anaerobic environments. The LN66 strain has good tolerance to lysozyme and adapts to the oral environment, not aims at killing fusobacterium nucleatum, butaims at reducing the occurrence and development risks of halitosis by reducing the expression level of genes relevant to the formation of a biological film in the fusobacterium nucleatum, reducing thesecretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) of the fusobacterium nucleatum and specifically inhibiting or reducing the formation of fusobacterium nucleatum biological films.
Owner:JIAXING INNOCUL PROBIOTICS CO LTD
Primer compound for identifying intestinal microecological state and application thereof
ActiveCN109576386AEfficient and convenient identificationHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesClostridium symbiosum
The invention provides a primer compound for identifying intestinal microecological state and an application thereof. The primer compound is a specific primer designed for intestinal bacterium 16S rRNA; the specific primer includes random basic groups; the quantity of random basic groups is 3-5; the intestinal bacterium includes any one of or combination of at least two of symbiotic clostridia, bifidobacterium adolescentis, fusobacterium nucleatum, peptostreptococcus anaerobius or klebsiella. A kit researched and developed on the basis of the primer compound provided by the invention has a specificity for detecting intestinal microecological imbalance reaching up to 92.5% and a sensitivity reaching up to 80.43%.
Owner:SUZHOU PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
Clostridium perfringen alpha toxin genetic engineering vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN103861094AImprove immunityTargeted optimizationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseAlpha-toxin
The invention relates to a clostridium perfringen alpha toxin genetic engineering vaccine and application thereof. The clostridium perfringen alpha toxin genetic engineering vaccine is prepared by designing a specific primer, implementing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on A-type clostridium perfringen DNA to obtain an alpha toxin gene segment, cloning the gene segment onto a pMD18-T Vector, selecting a positive recon and linking the positive recon onto a PET-28 alpha (+) plasmid; introducing the recombinant plasmid to a receptor strain to successfully construct a recombinant strain BL21 (DE3)-alpha; emulsifying the prepared alpha toxin protein and an aluminum hydroxide adjuvant at a volume ratio of 9:1, and adding 0.01% thiomersal to obtain the clostridium perfringen alpha toxin genetic engineering vaccine. The clostridium perfringen alpha toxin genetic engineering vaccine is easy for realization of industrial production, simple to operate and good in safety, and is capable of effectively preventing such diseases as animal necrotic enteritis, enterotoxemia, and human and animal traumatic gas gangrene caused by the A-type clostridium perfringens.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com