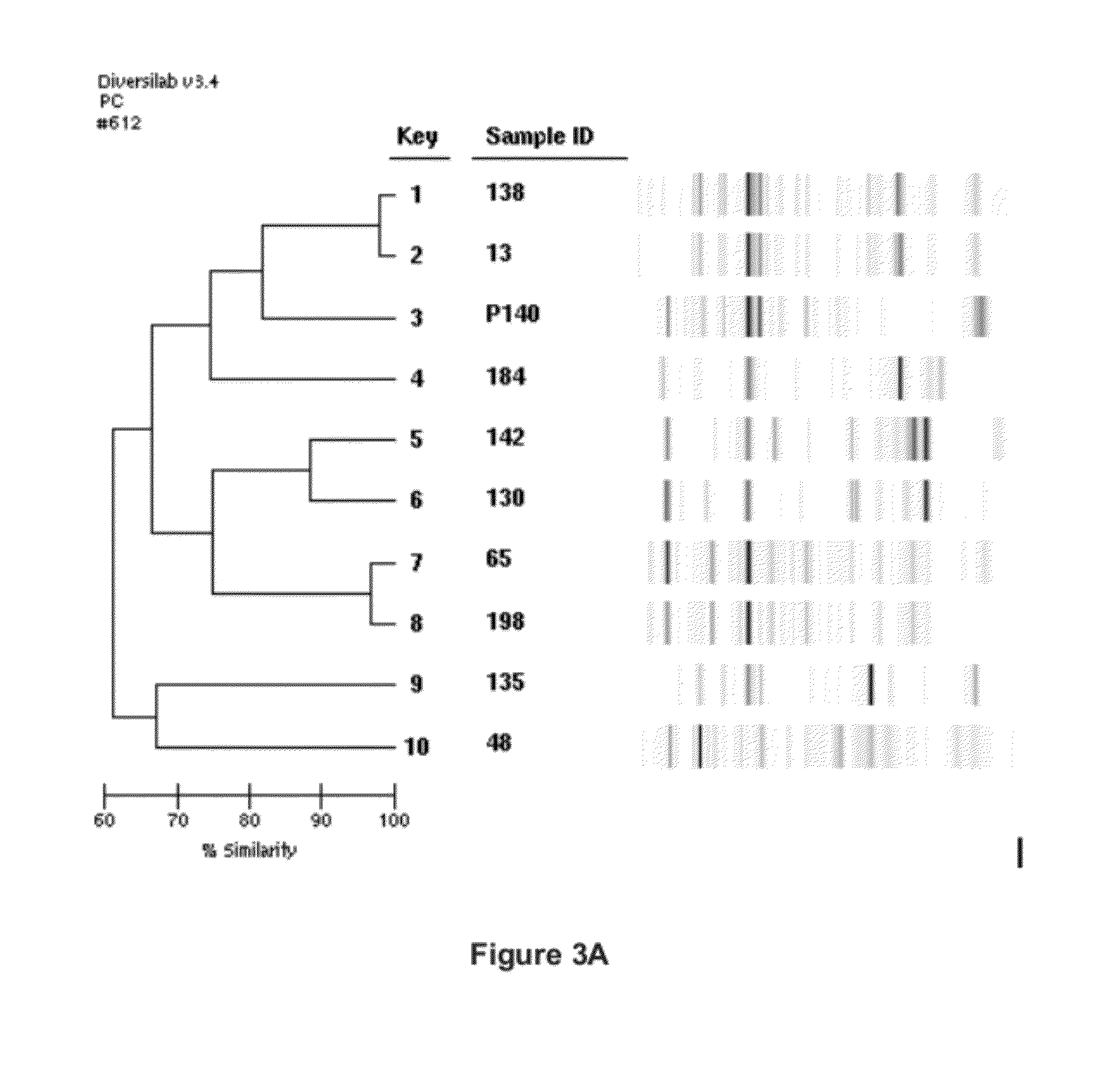
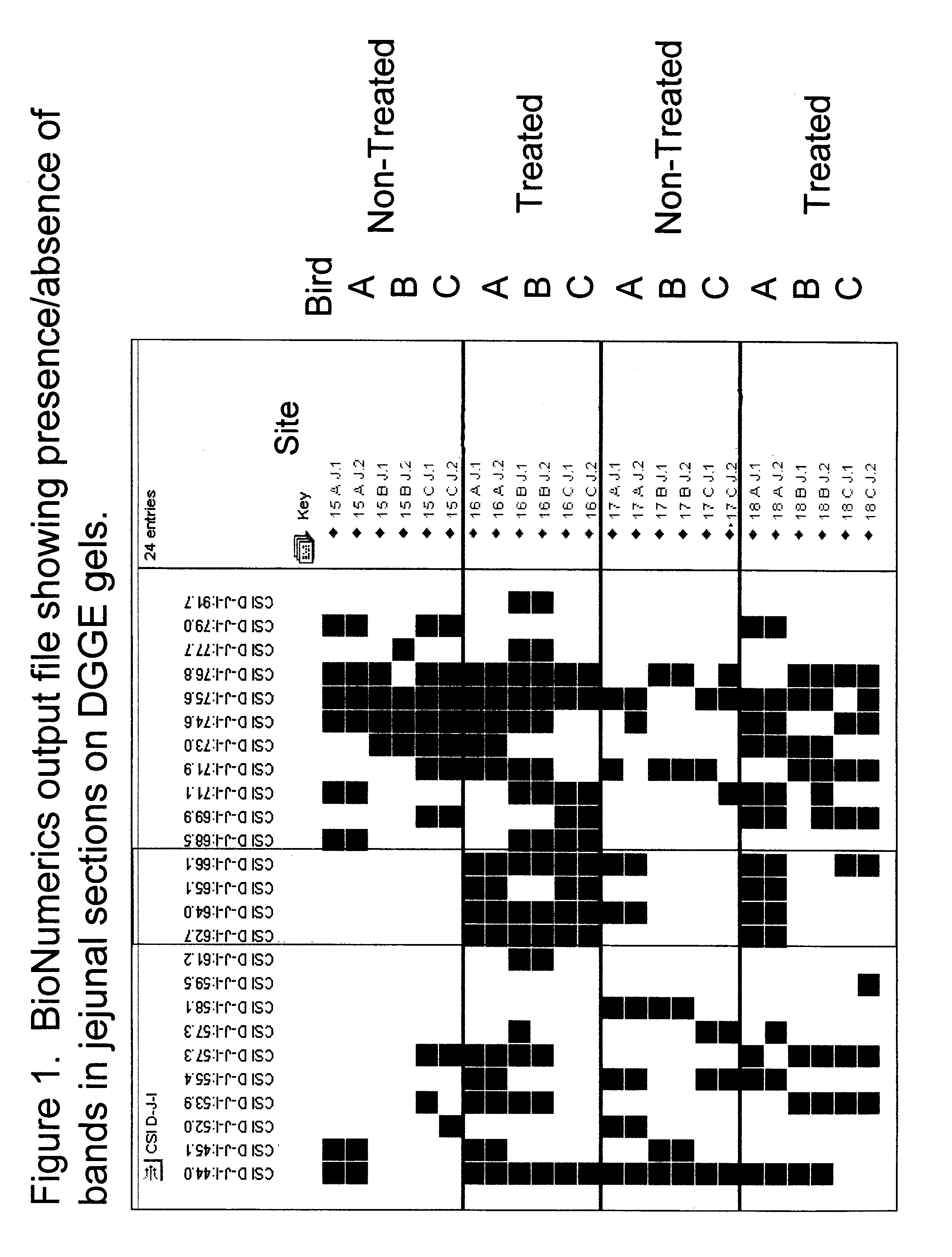
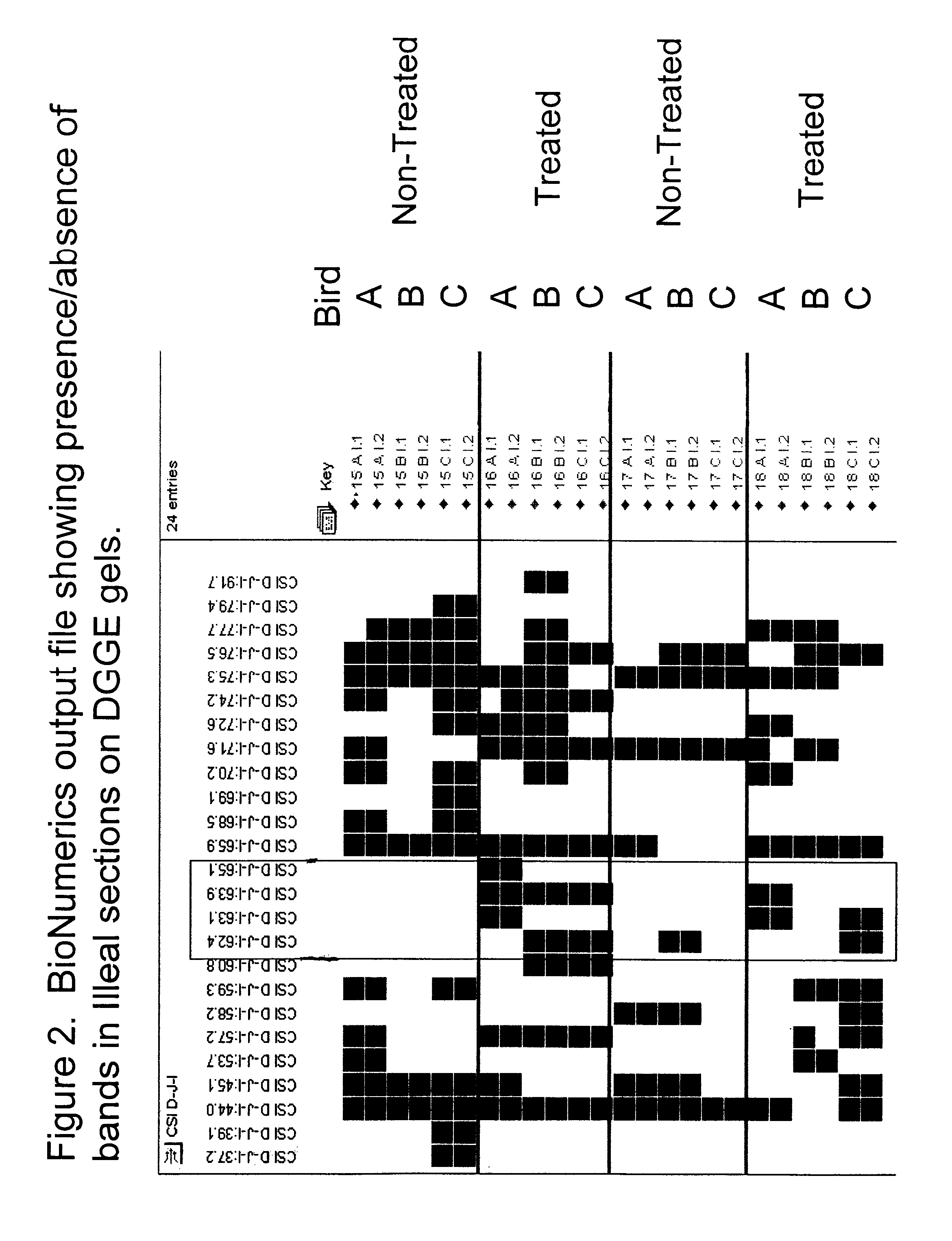
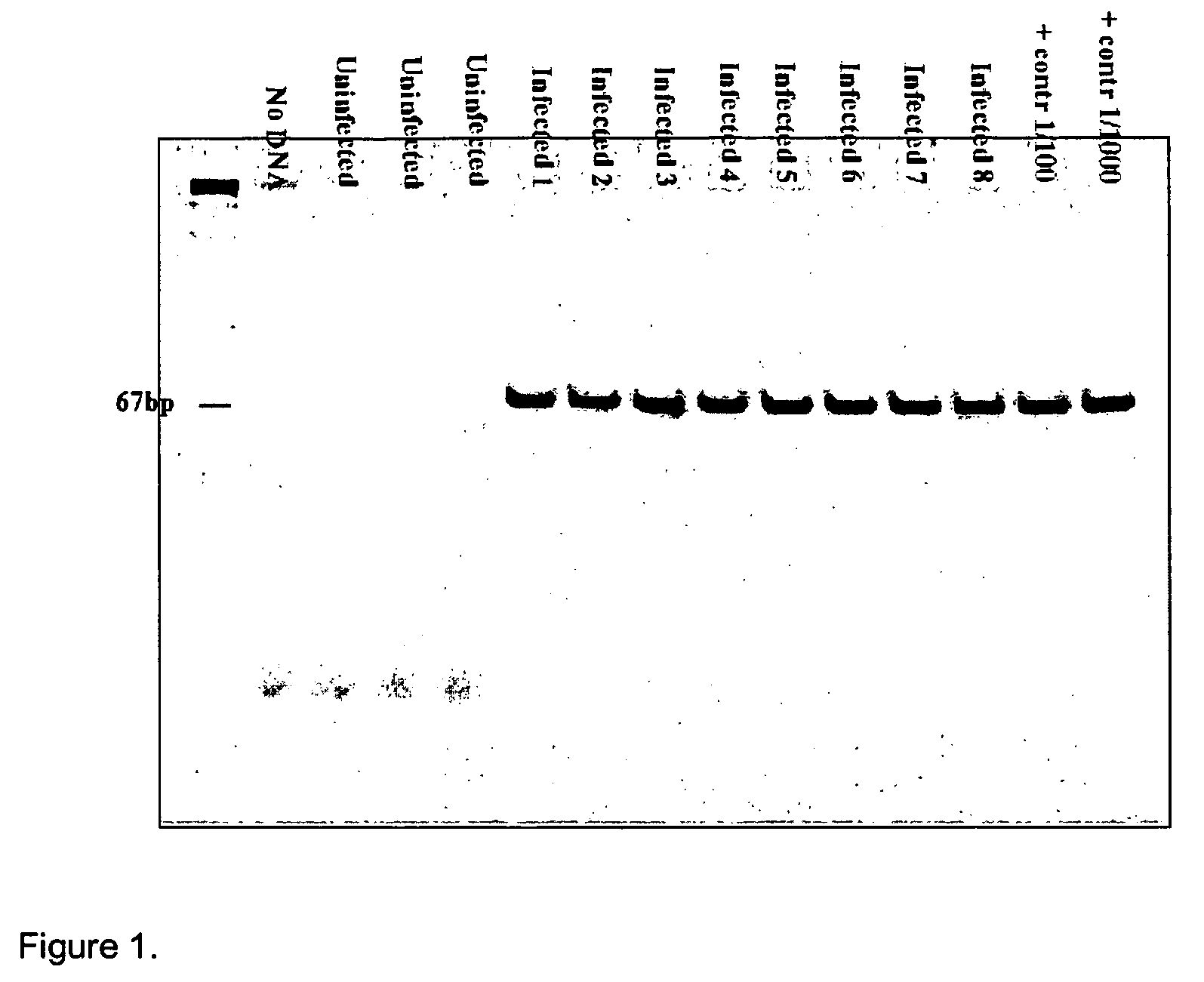
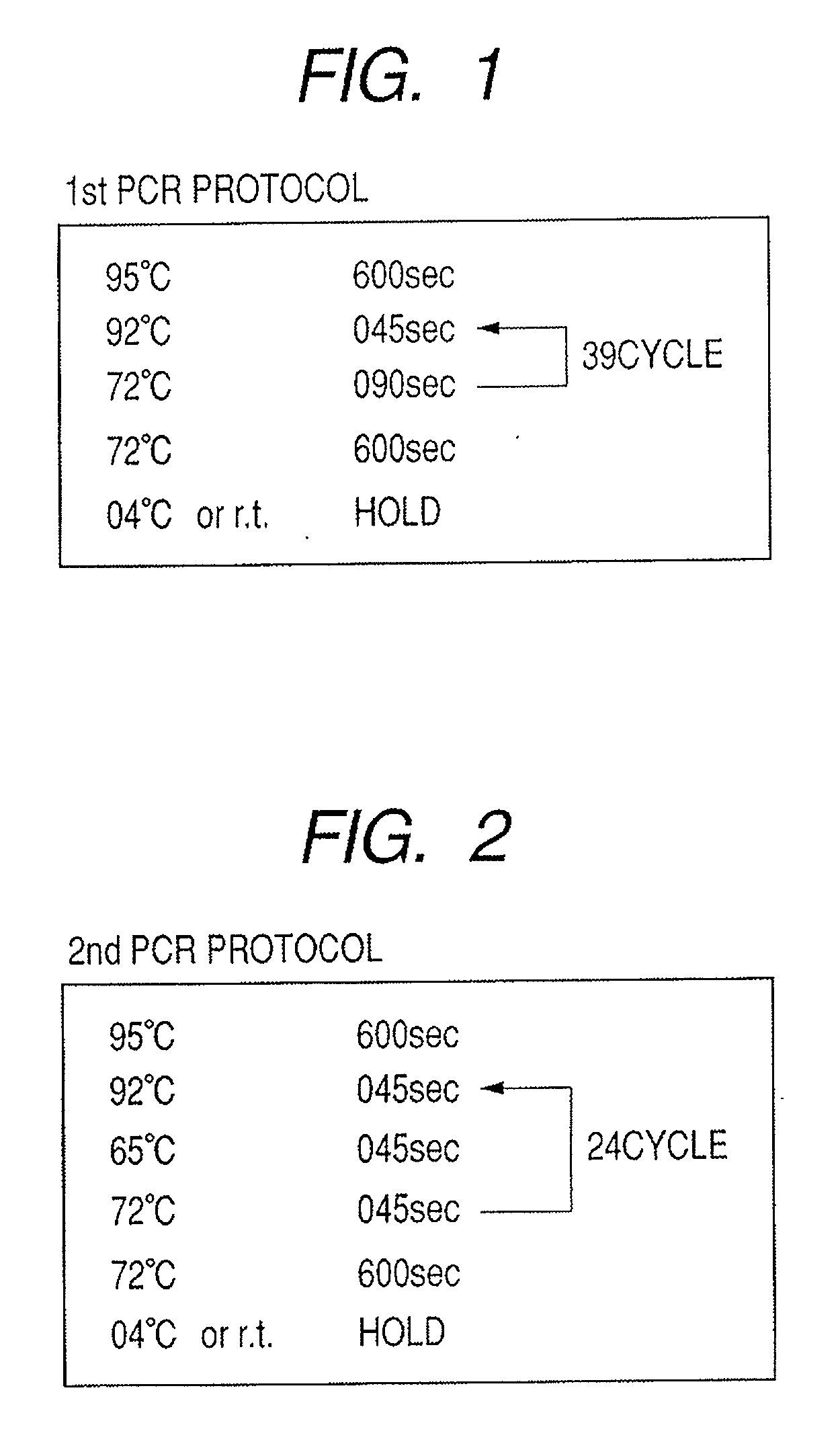
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3525 results about "Photobacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photobacterium is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Vibrionaceae. Members of the genus are bioluminescent, that is they have the ability to emit light. Many species, including Photobacterium leiognathi and Photobacterium phosphoreum, live in symbiosis with marine organisms.
Axmi-028 and axmi-029, a family of novel delta-endotoxin genes and methods for their use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a delta-endotoxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated delta-endotoxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, 15, 17, or 19, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 14, 16, or 18, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
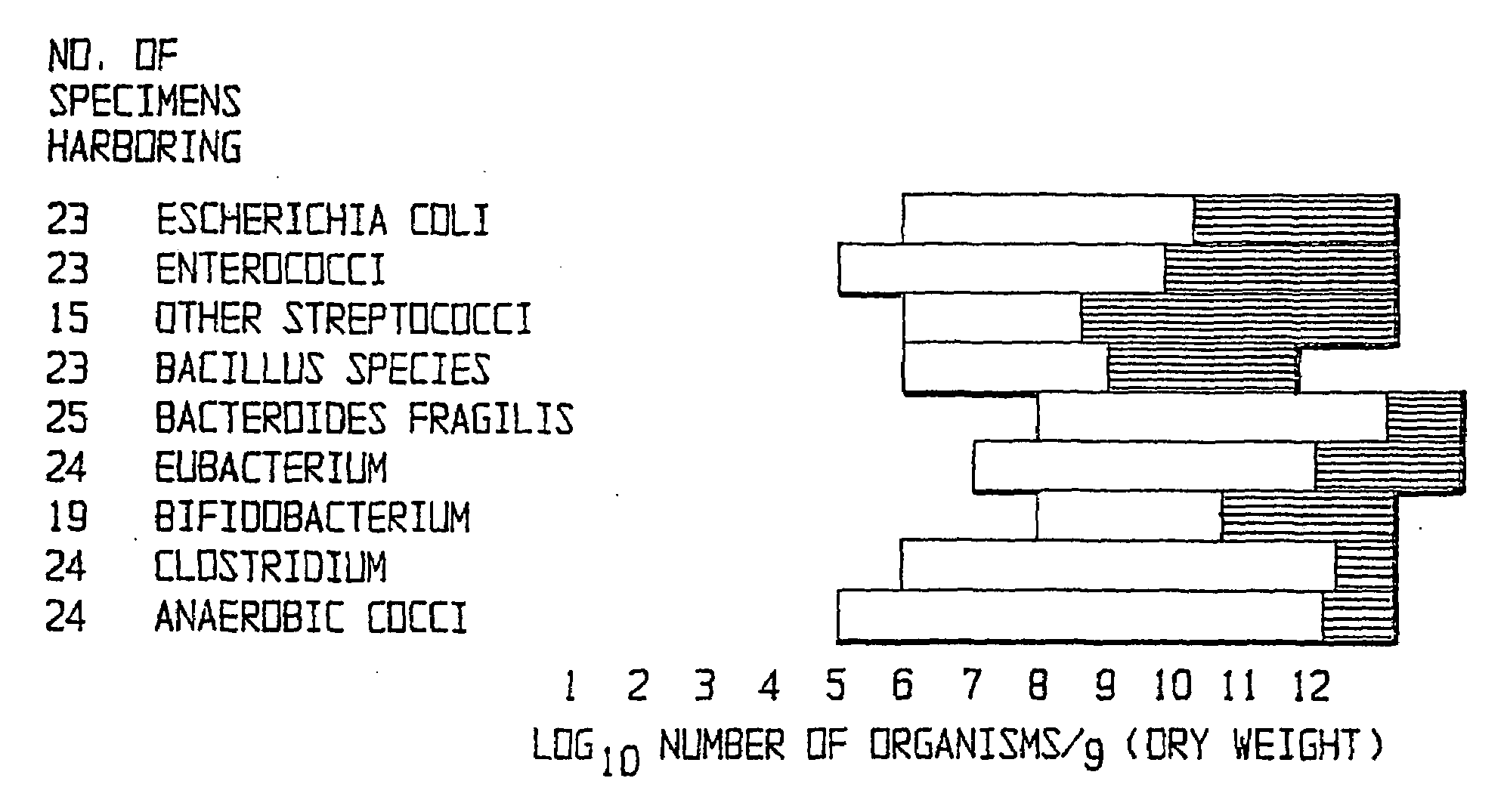
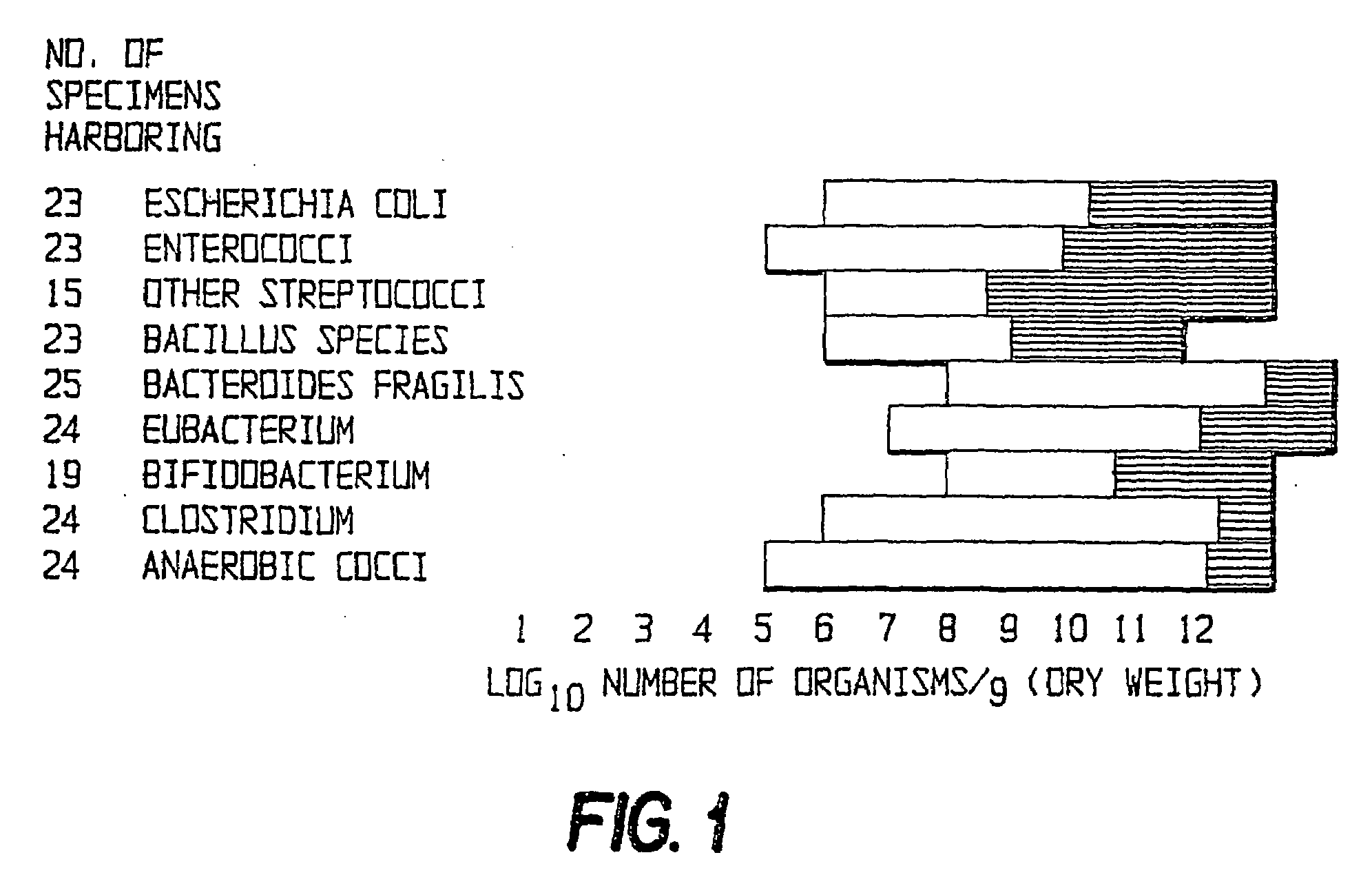
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
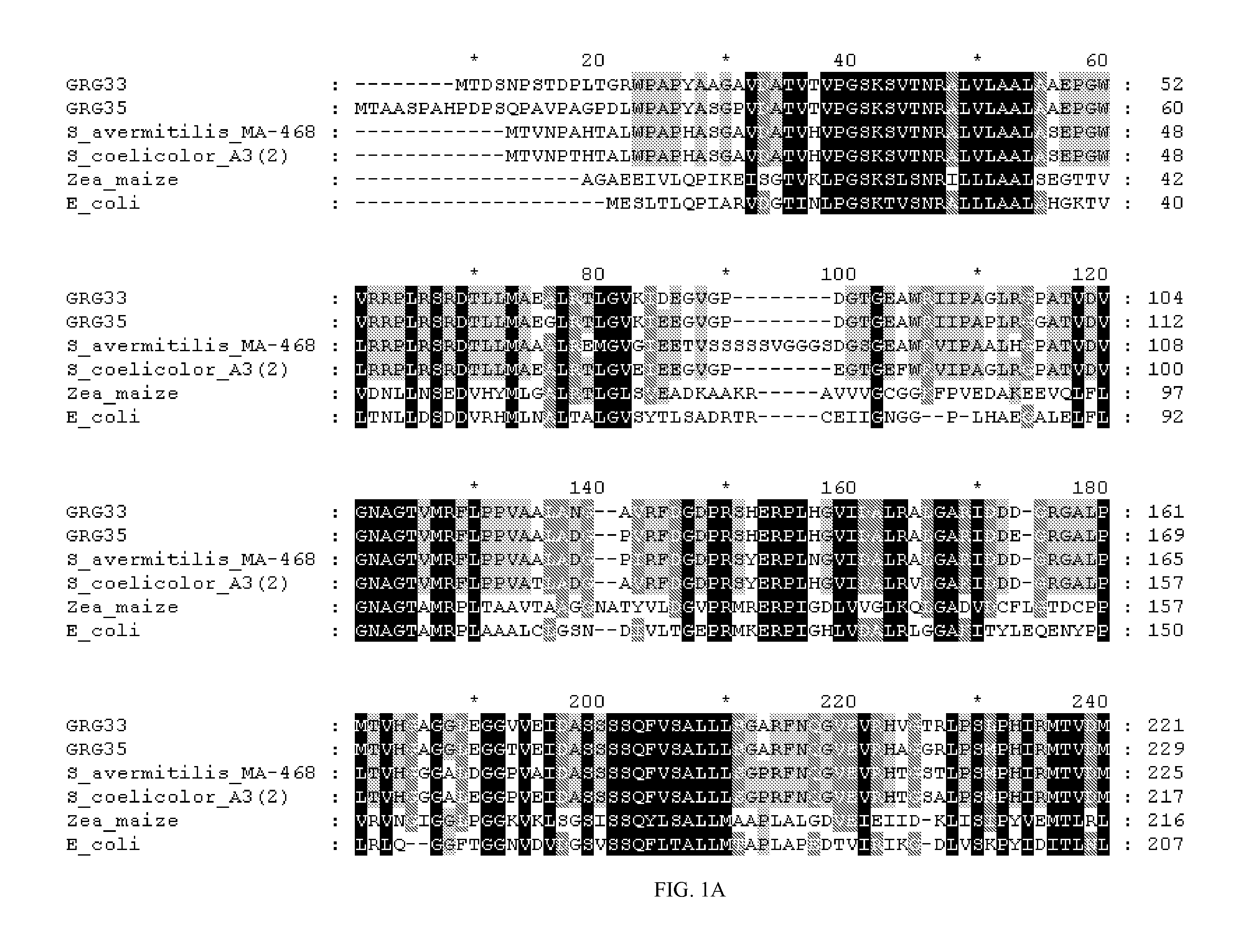
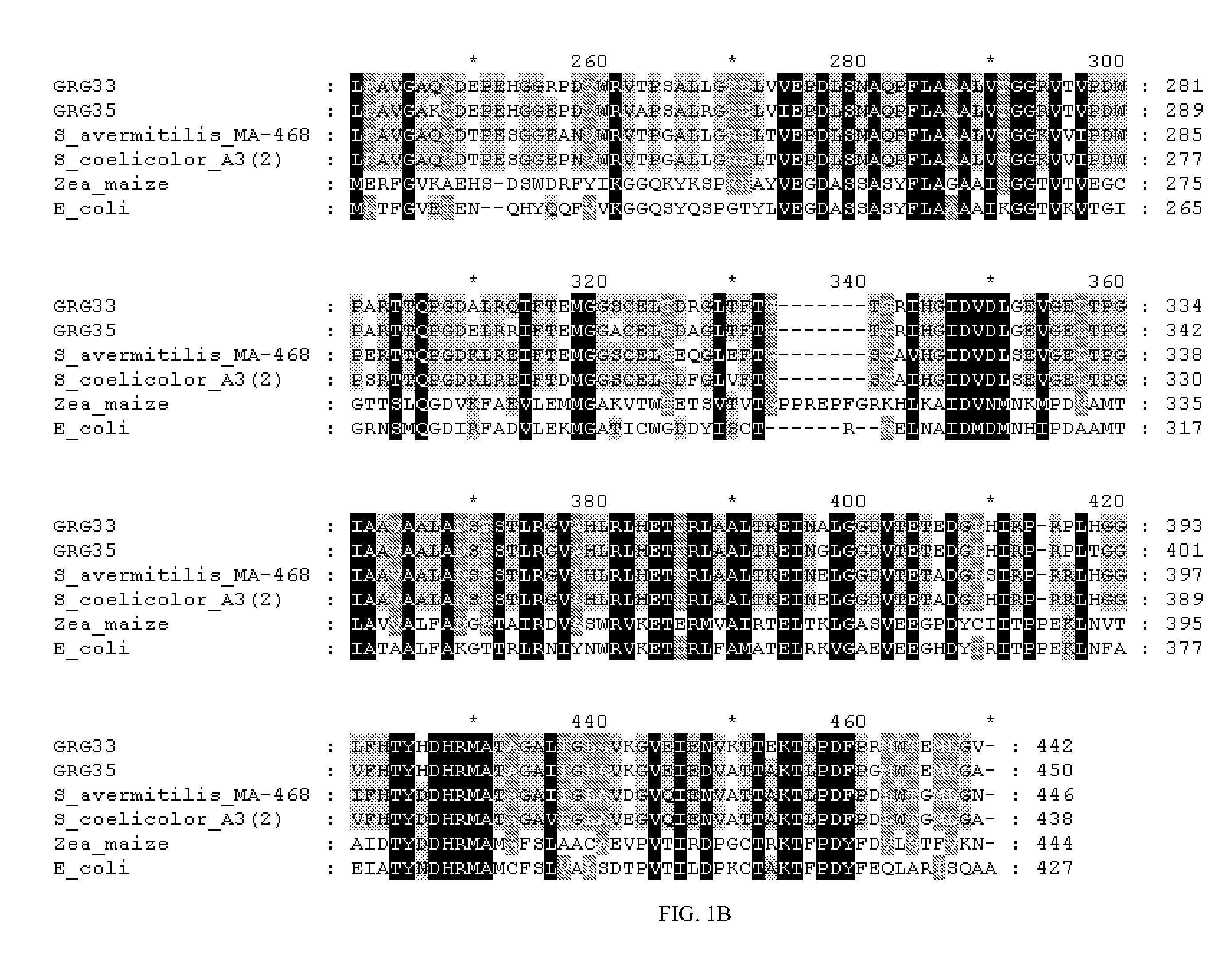
Grg33, grg35, grg36, grg37, grg38, grg39 and grg50: novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Methods of making amino acids using E. coli transformed with csc genes
An amino acid such as threonine, homoserine, isoleucine, lysine, valine and tryptophan is produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has been constructed from sucorse non-assimilative strain belonging to the genus Escherichia and which harbors sucrose non-PTS (phosphoenol pyruvate-dependent sucrose-6-phosphotransferase system) genes and has an ability to produce the amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
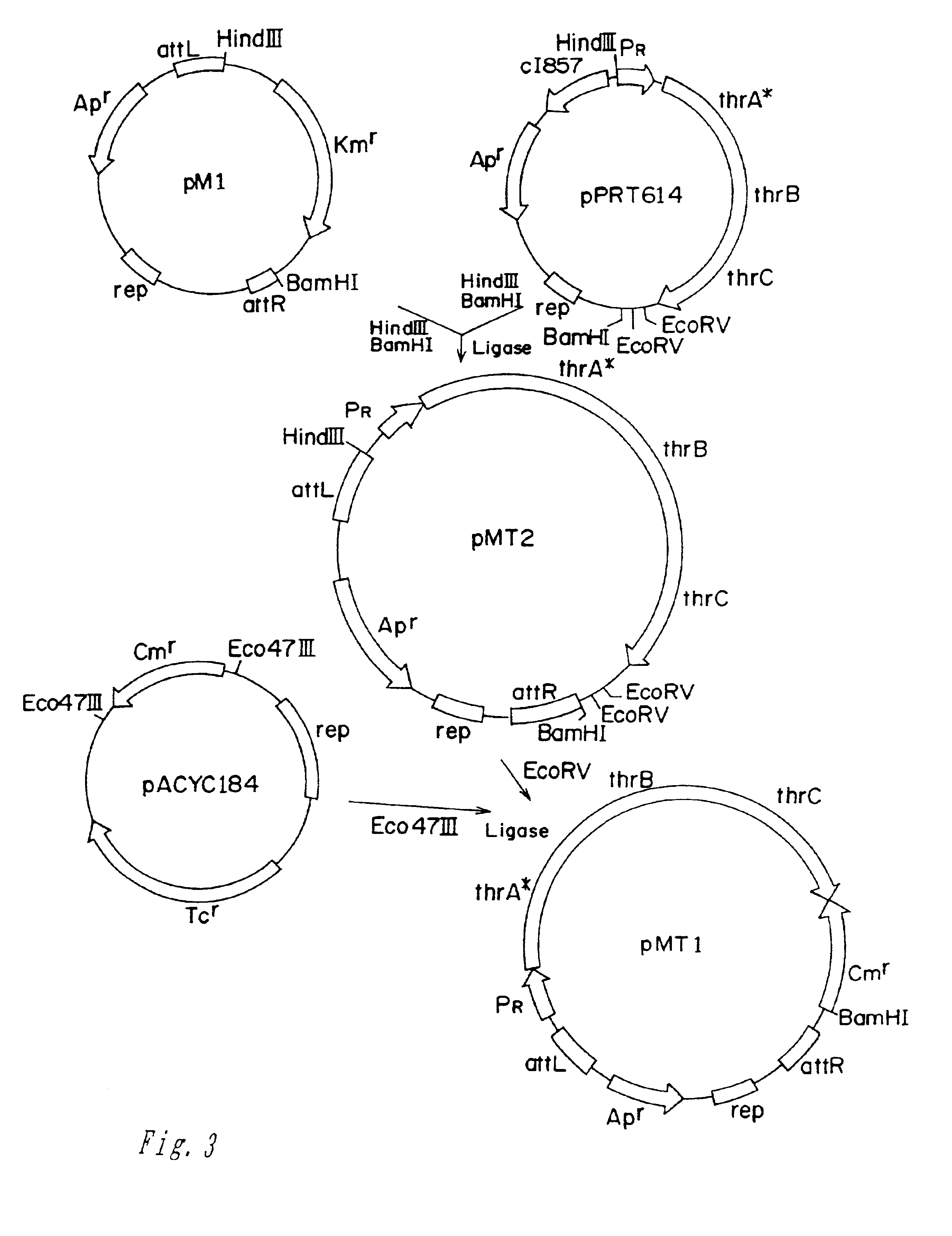
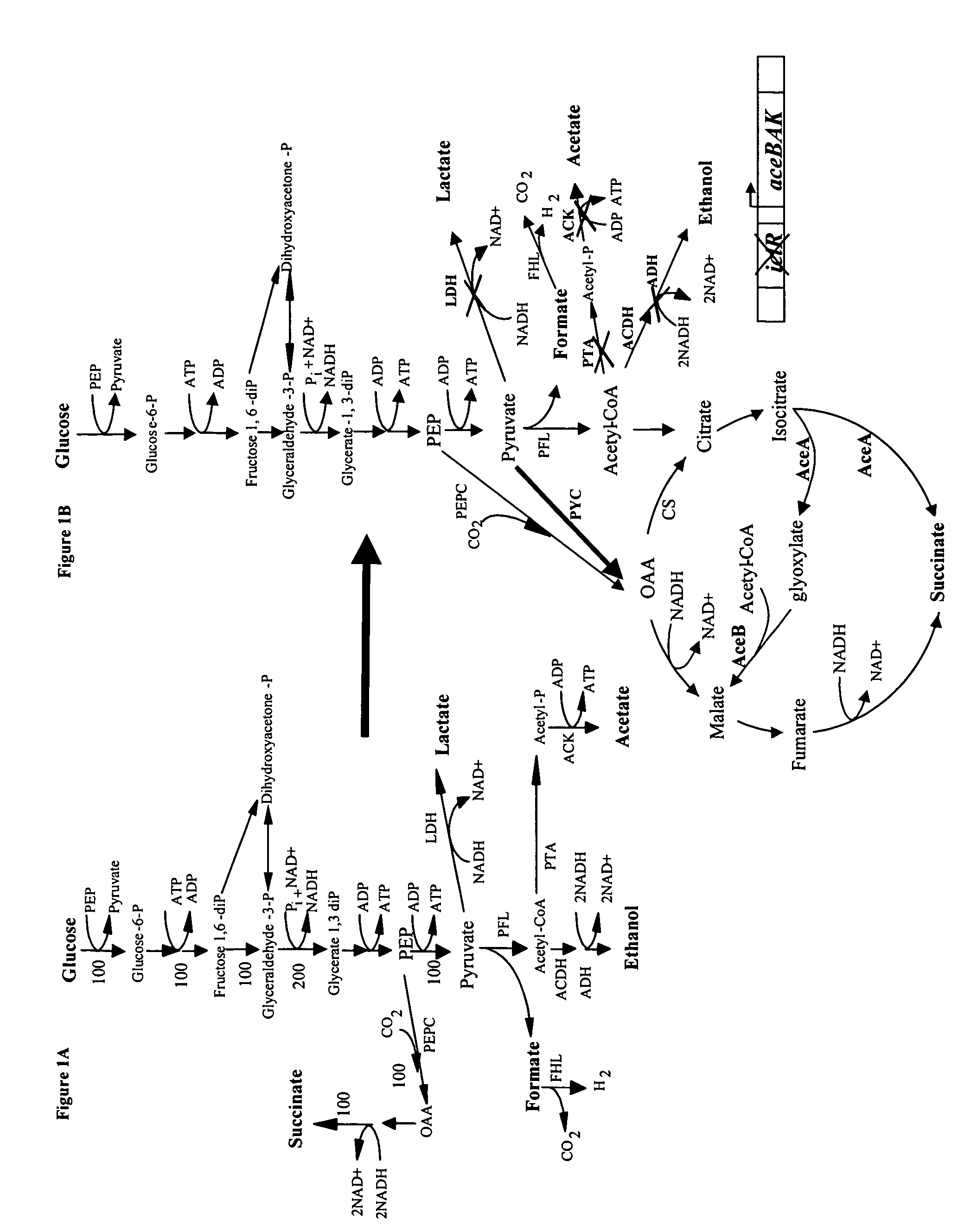
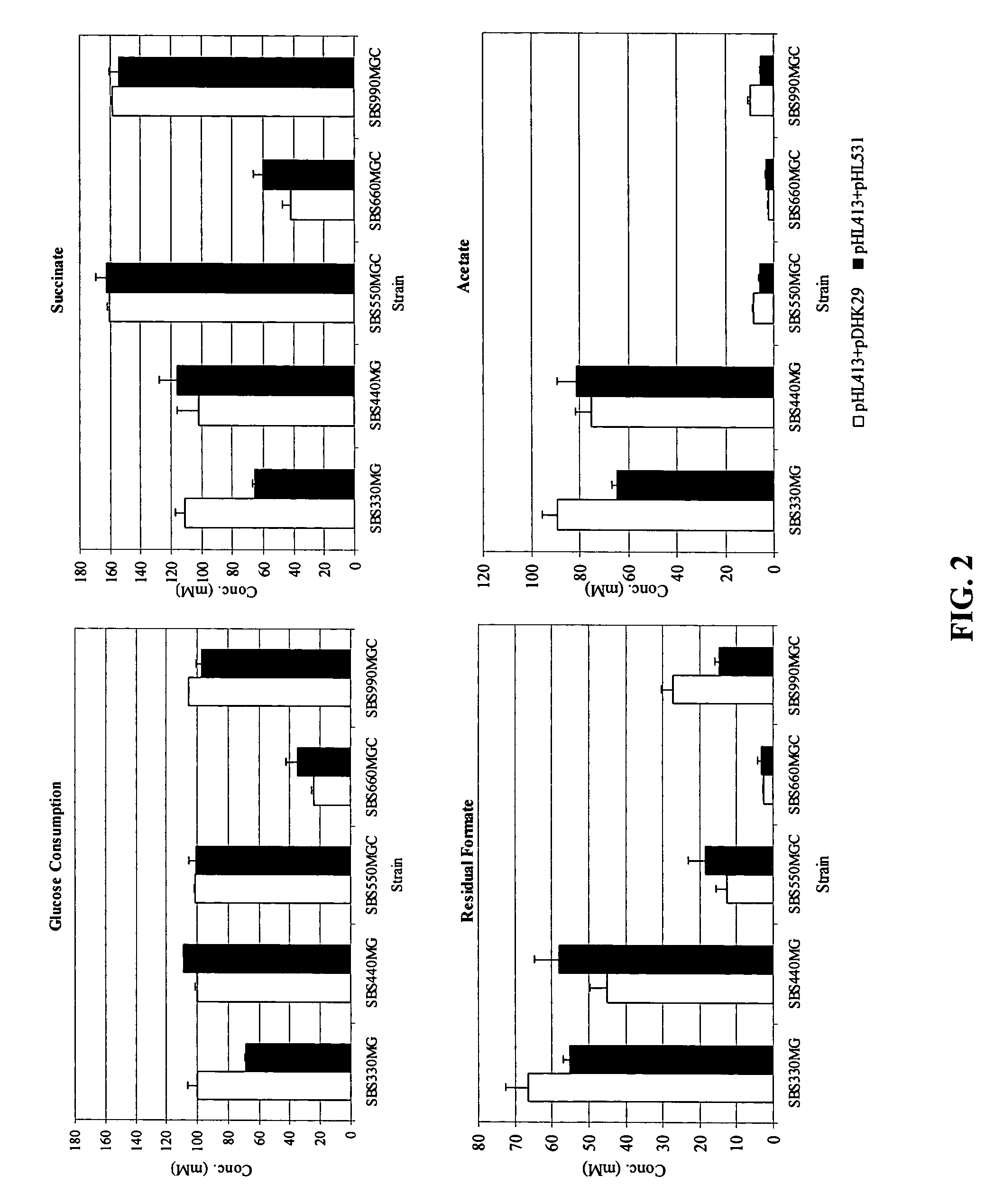
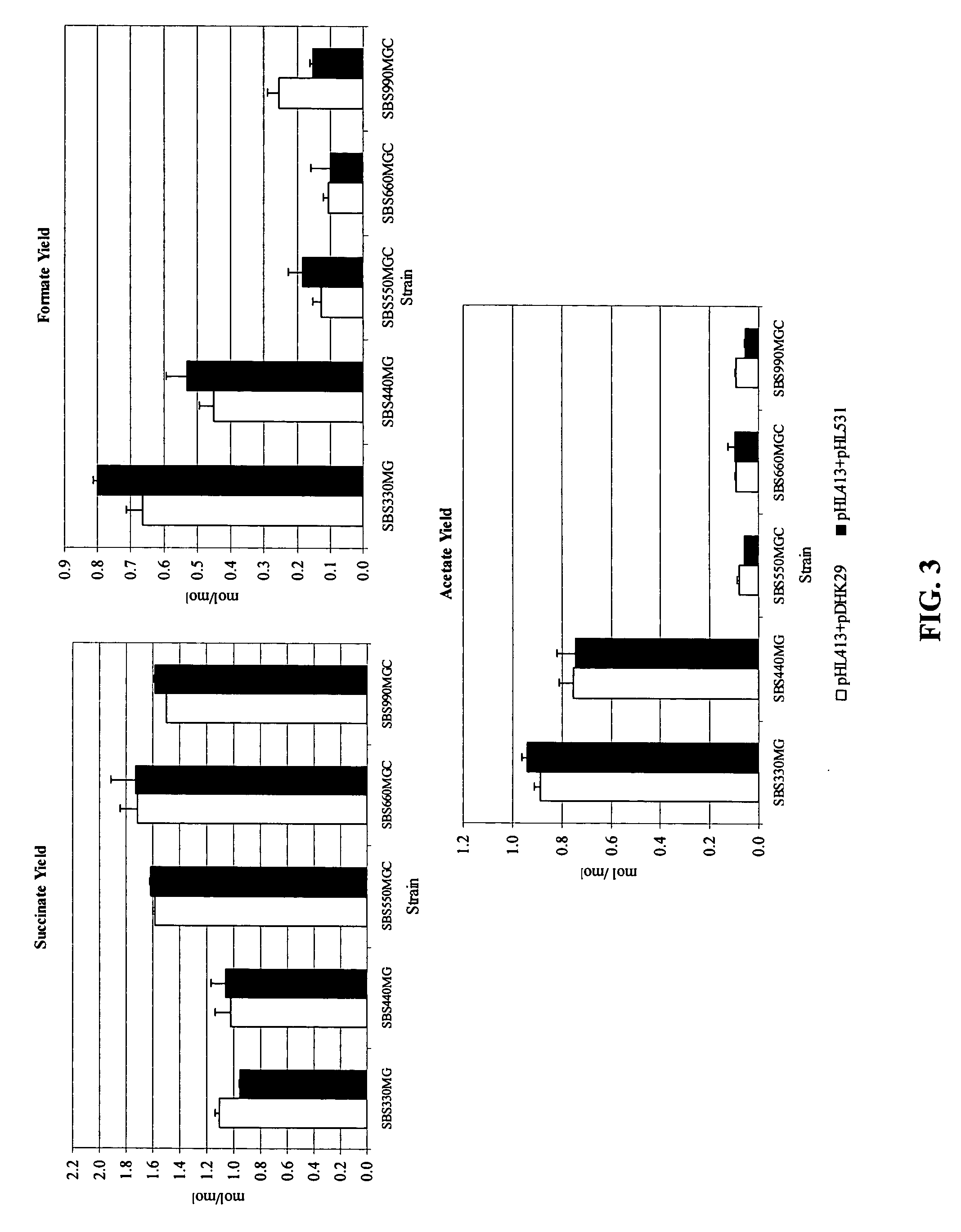
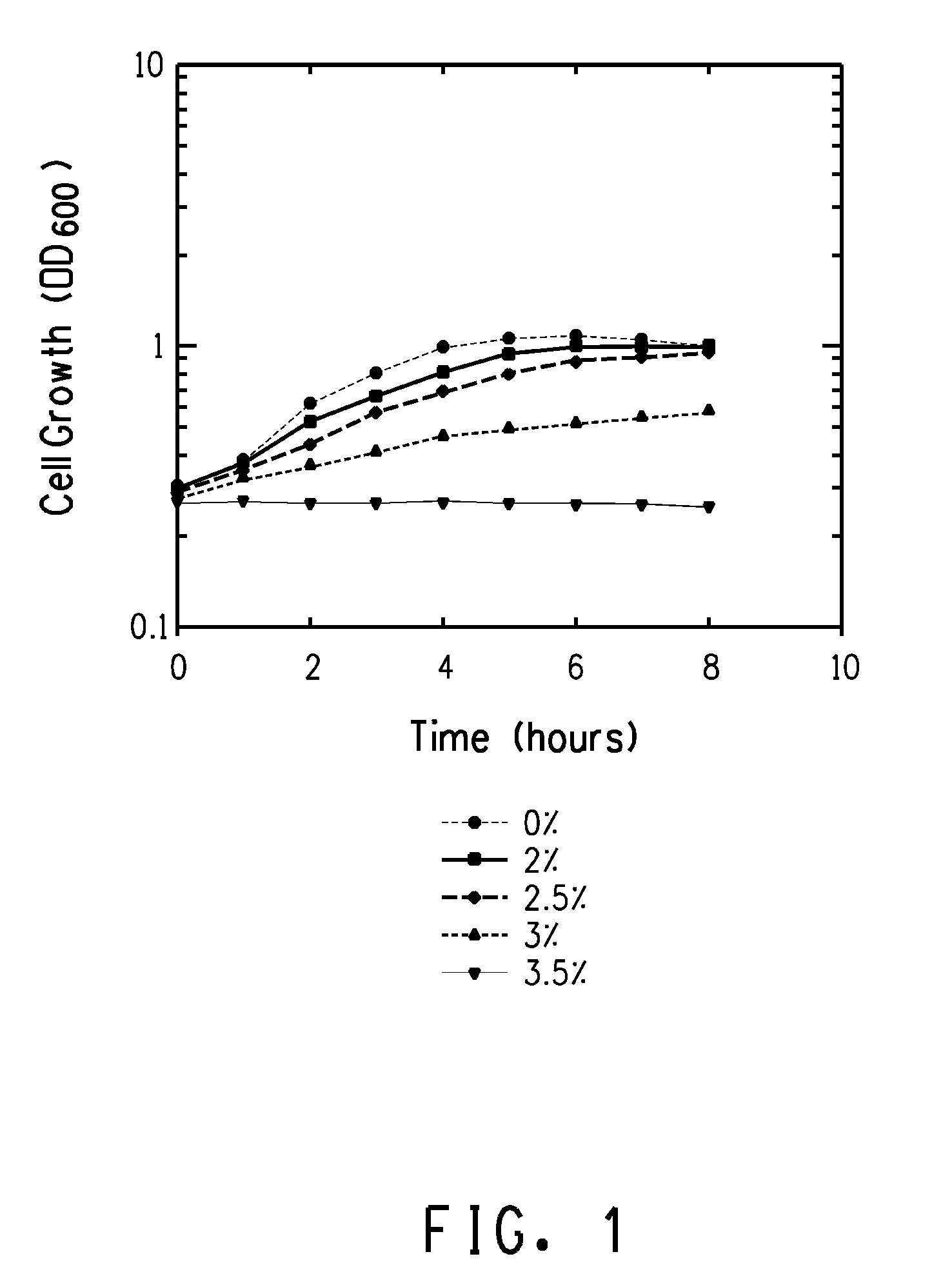
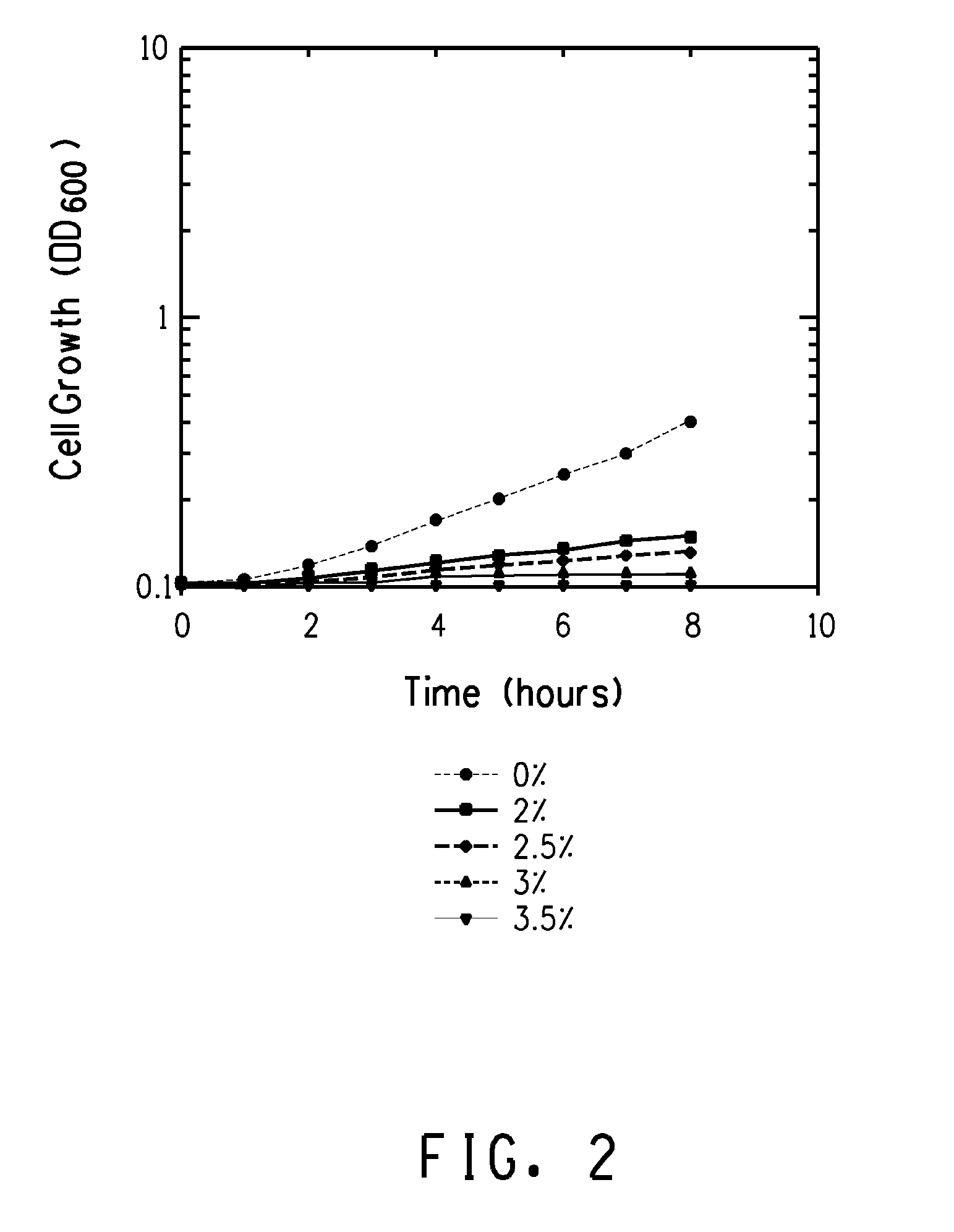
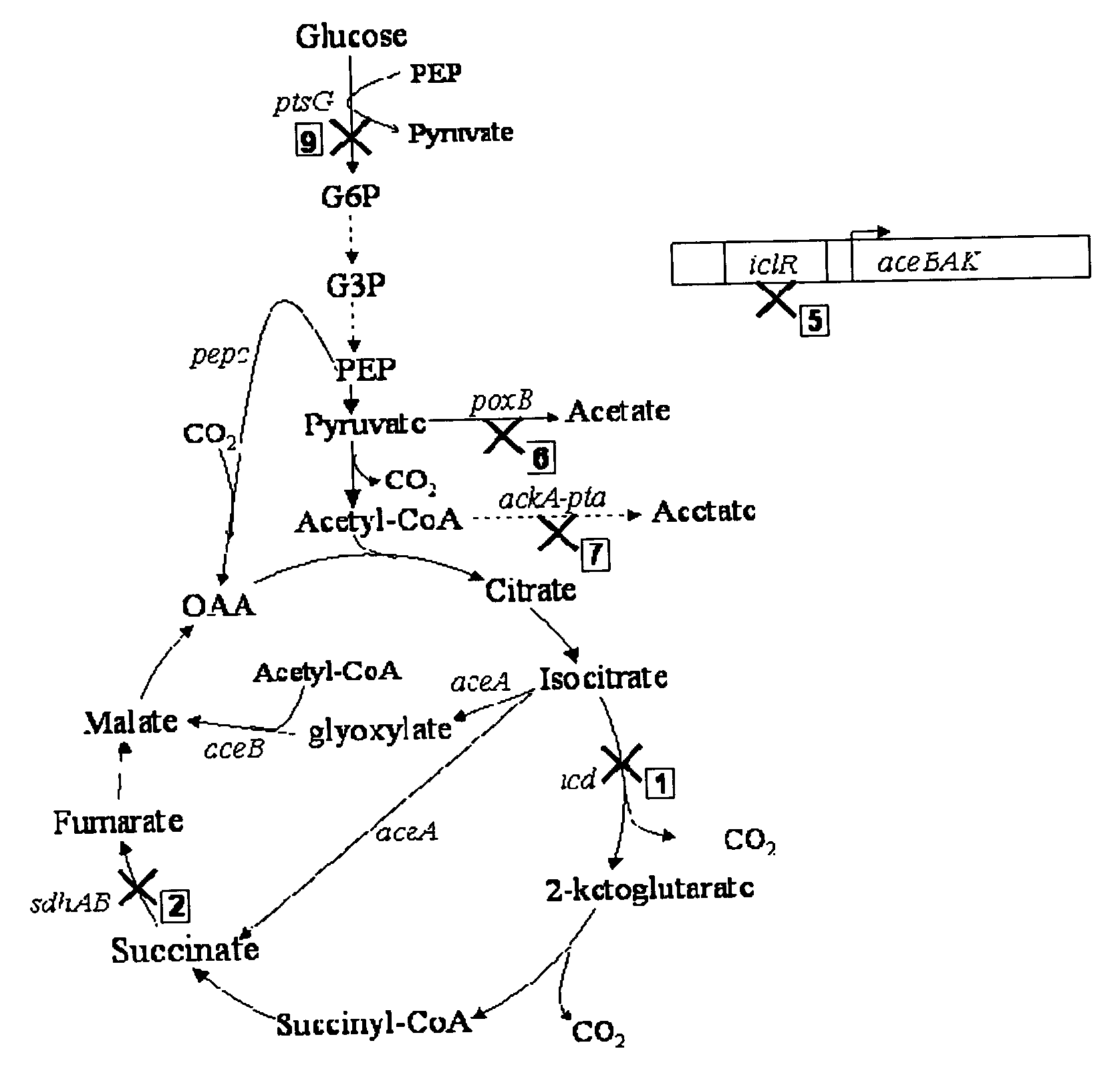
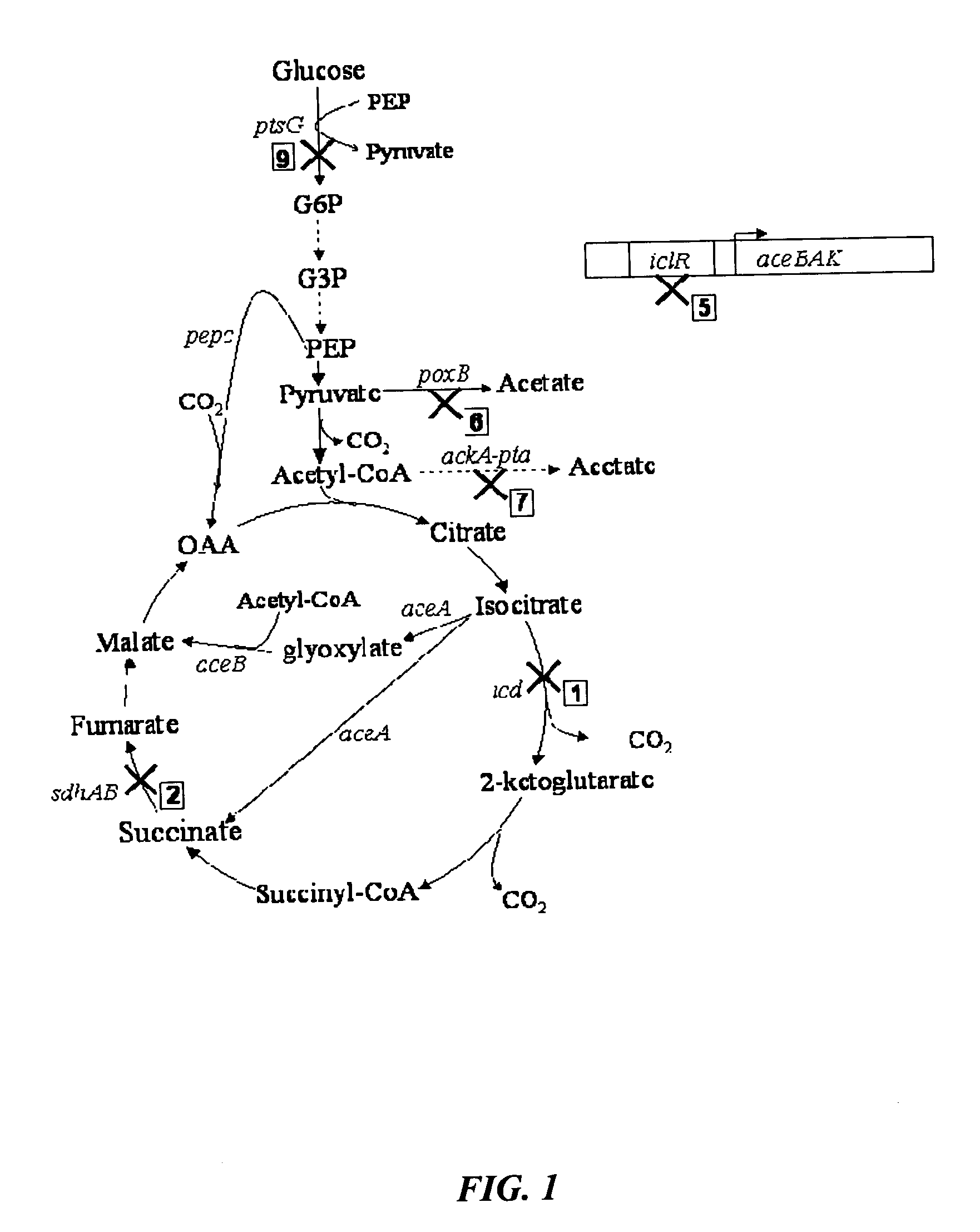
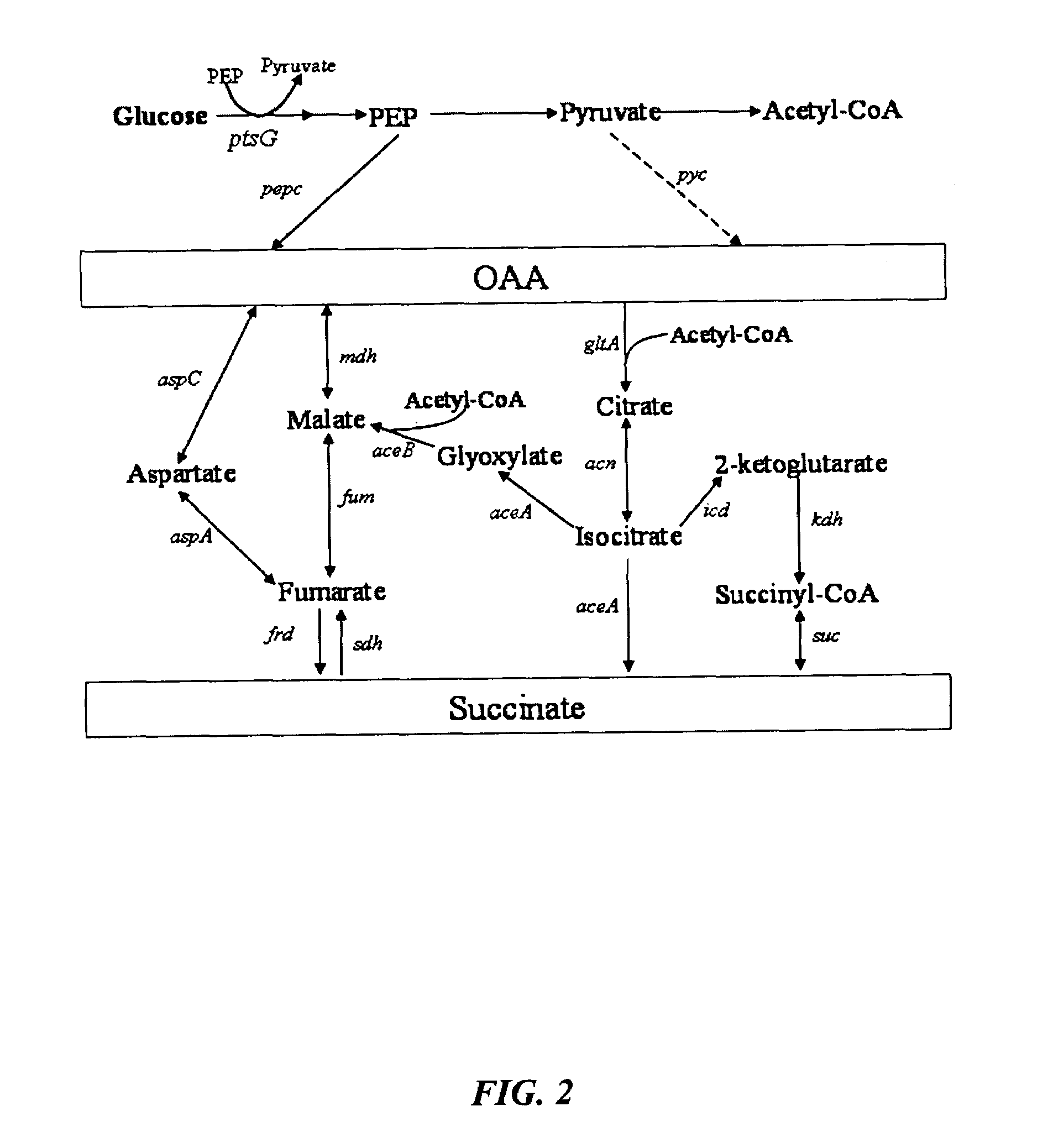
Mutant E. coli strain with increased succinic acid production
The invention relates to a mutant strain of bacteria, which either lacks or contains mutant genes for several key metabolic enzymes, and which produces high amounts of succinic acid under anaerobic conditions.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Microbial pesticidal composition
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
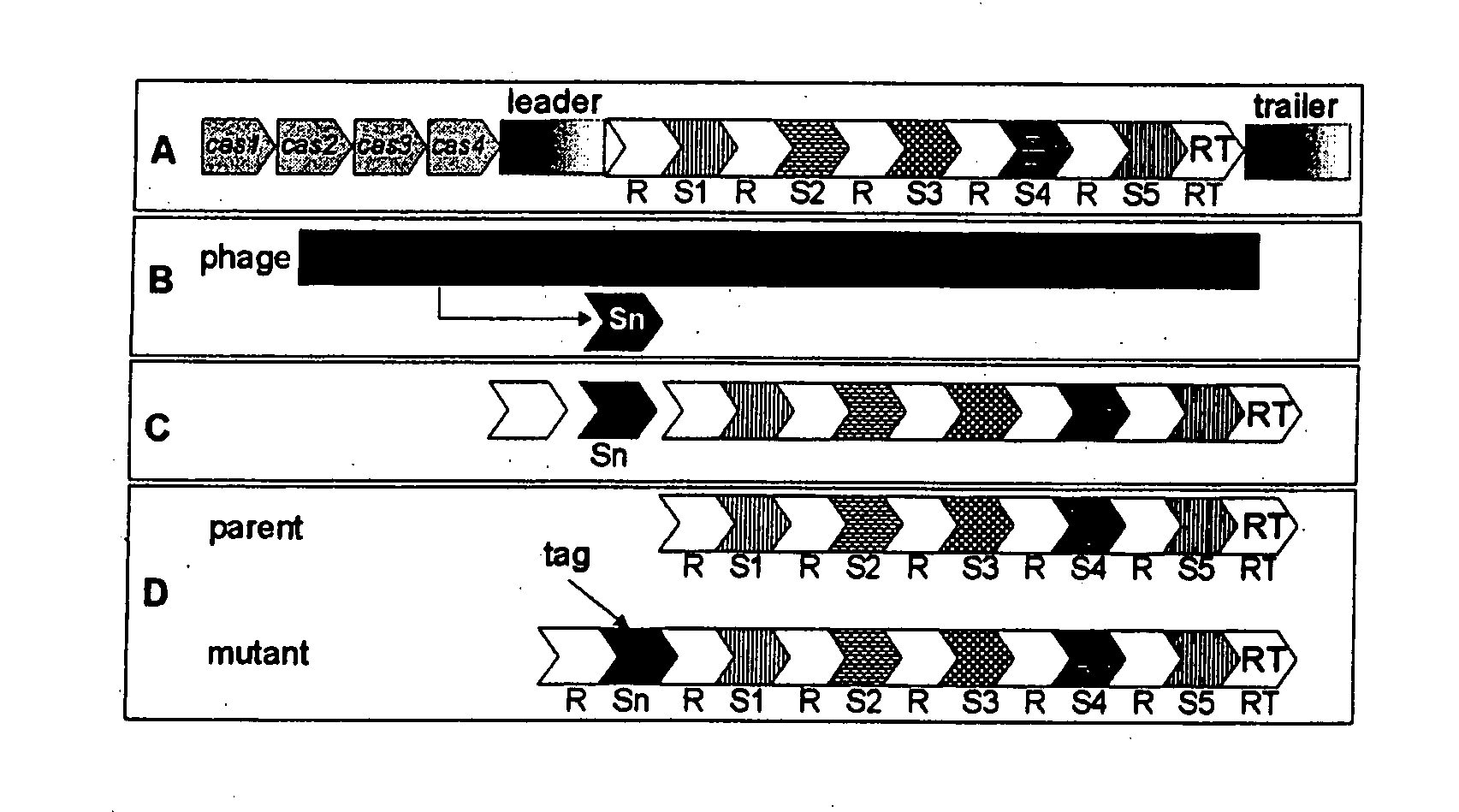
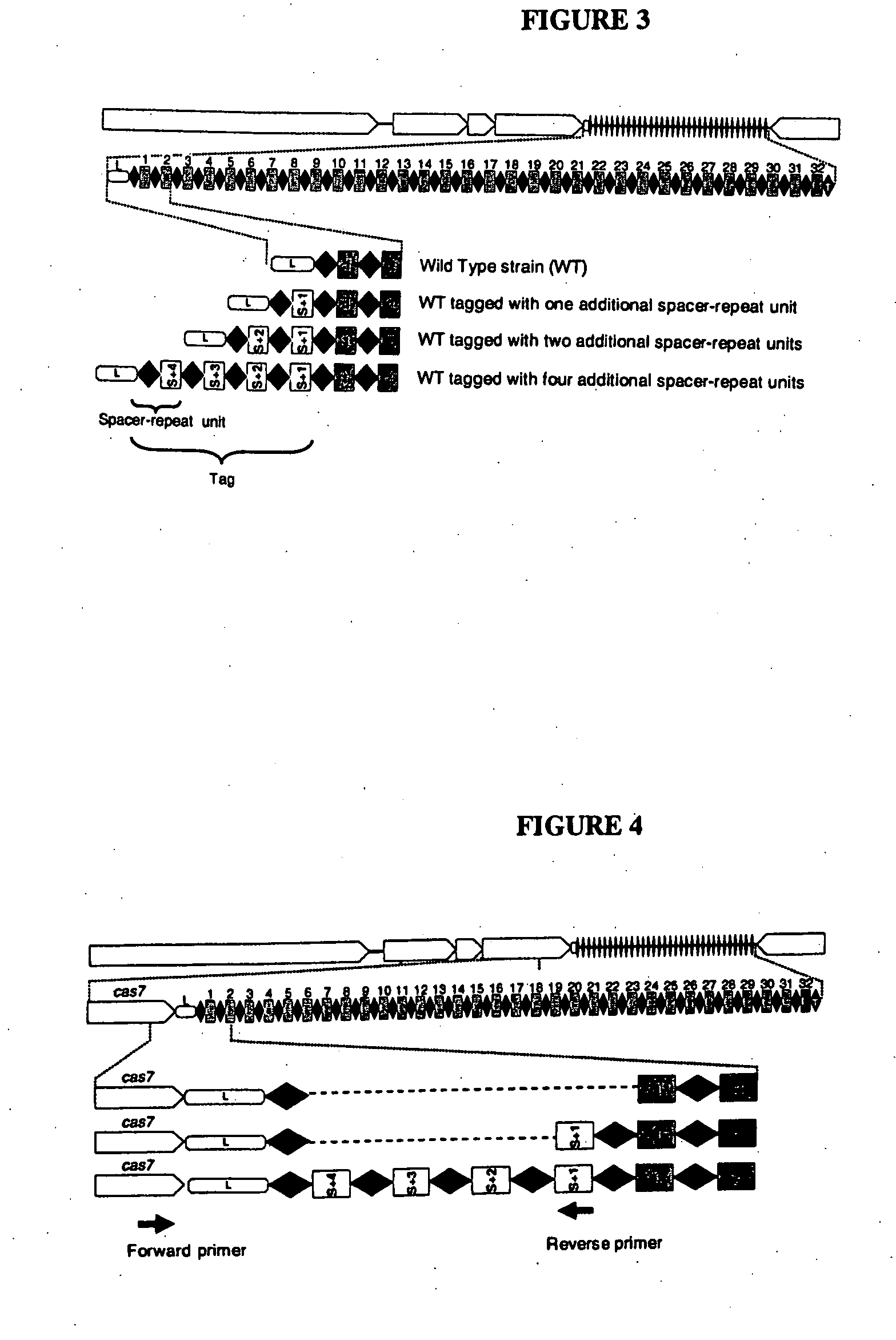
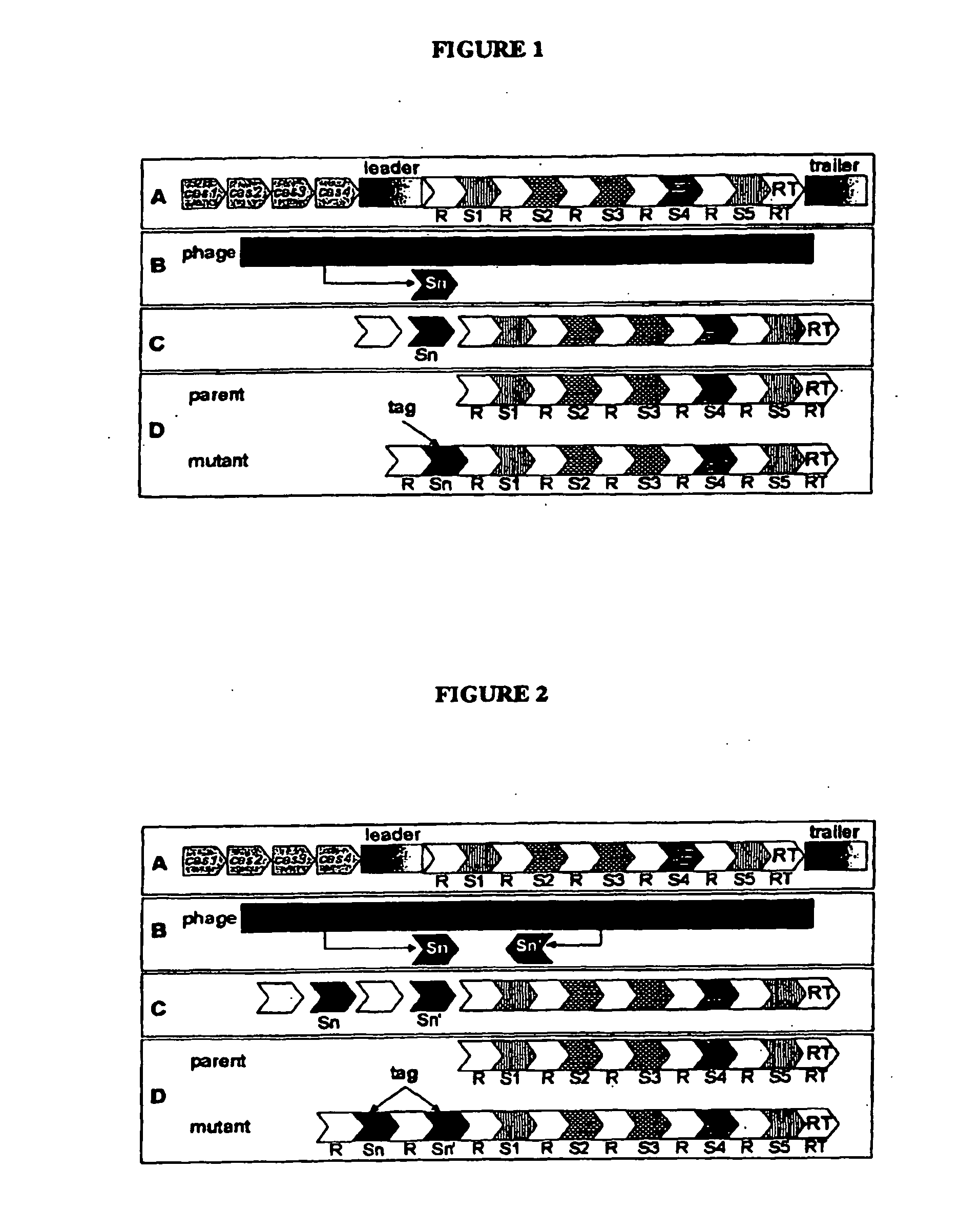
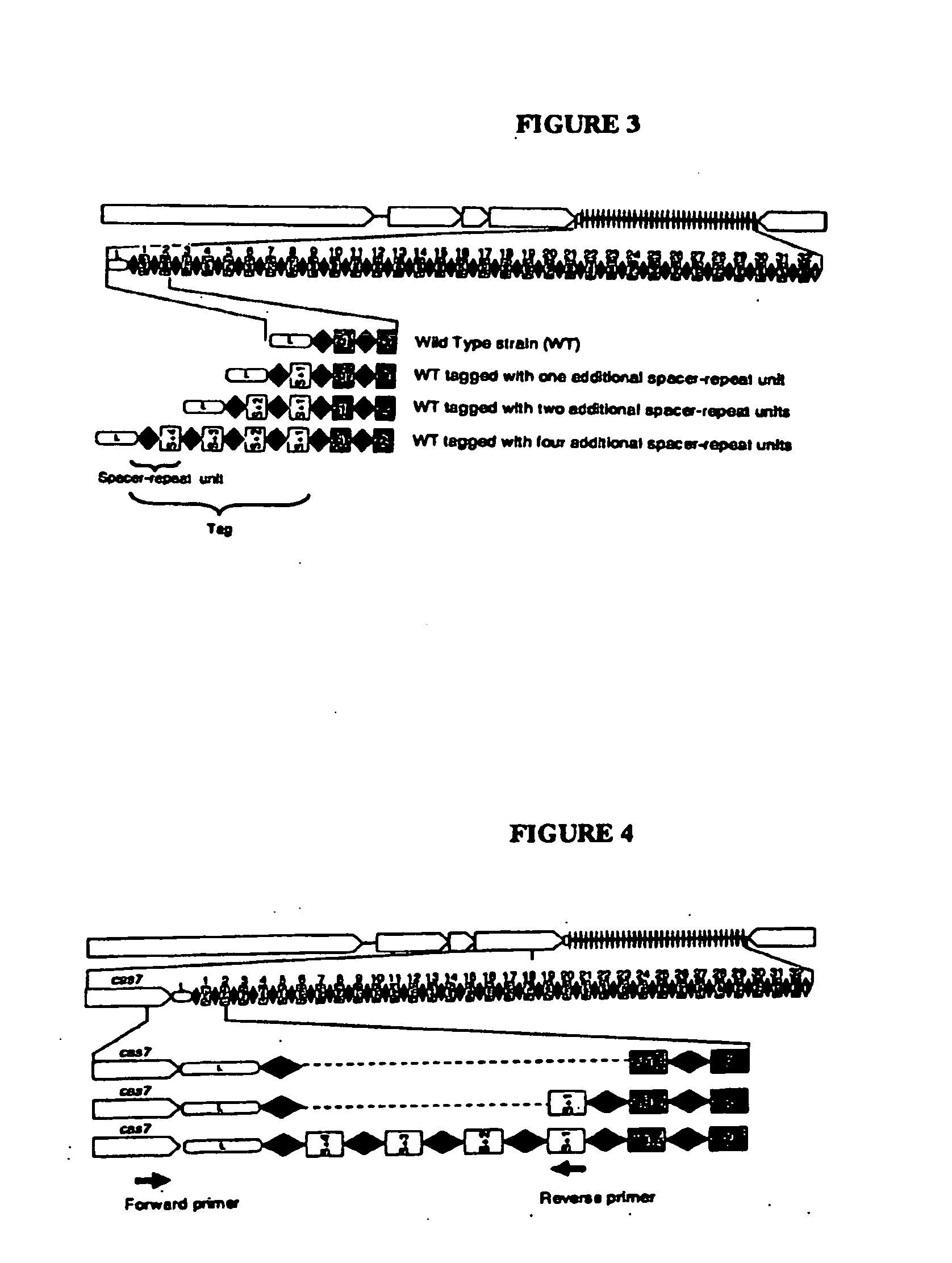
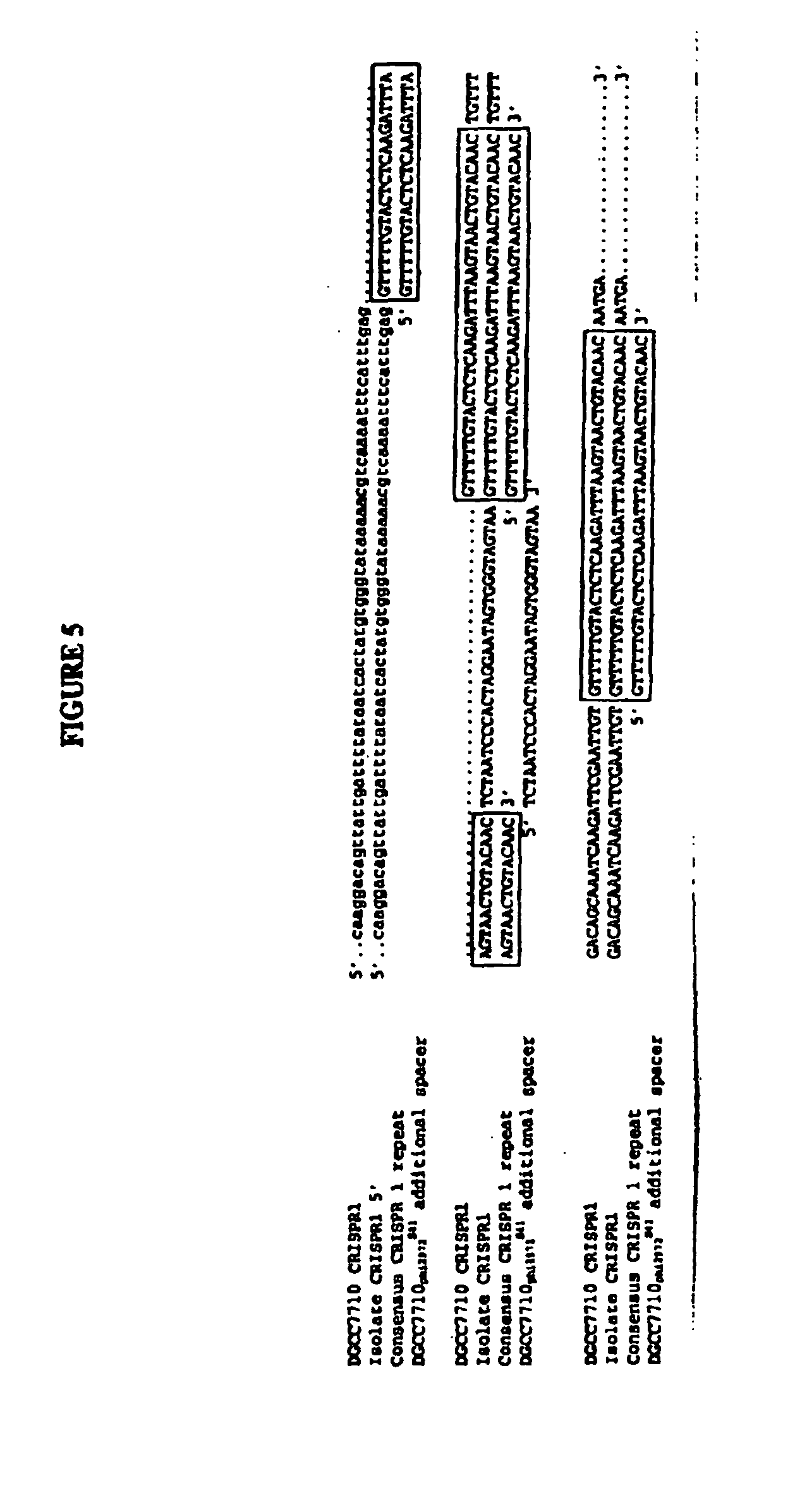
Tagged microorganisms and methods of tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus clostridium
The invention includes a method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus Clostridium such as clostridium deficit in human patients with gastrointestinal disorders having an etiological component such as a microbial agent producing a toxin where treated with an antimicrobial composition an amount effective to inhibit or eliminate the microbial agent. The antimicrobial composition in a form of probiotic mixture can be administrated alone or in combination with an antimicrobial agent, such as a bacteriophage which is specific for a bacterium producing toxin or antibiotics which are then used to eliminate or inhibit the clostridial species overgrown in a patient's gastrointestinal tract. Disorders that can be treated by the method of the invention include diarrhea or inflammatory bowel diseases such as colitis or Crohn's disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Bacillus sp. D747 strain, plant disease controlling agents and insect pest controlling agents using the same and control method using the agents
The present invention relates to a novel strain of Bacillus sp. D747 (deposited as FERM BP-8234) and methods for controlling plant diseases and insect pests, comprising administering cultures of Bacillus sp. D747 (including the viable bacteria) or viable bacteria isolated by culturing, on the plant parts such as roots, stems, leaves, seeds, and the like, or in the culture soil.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Methods and compositions for production of lipo-chito oligosaccharides by rhizobacteria
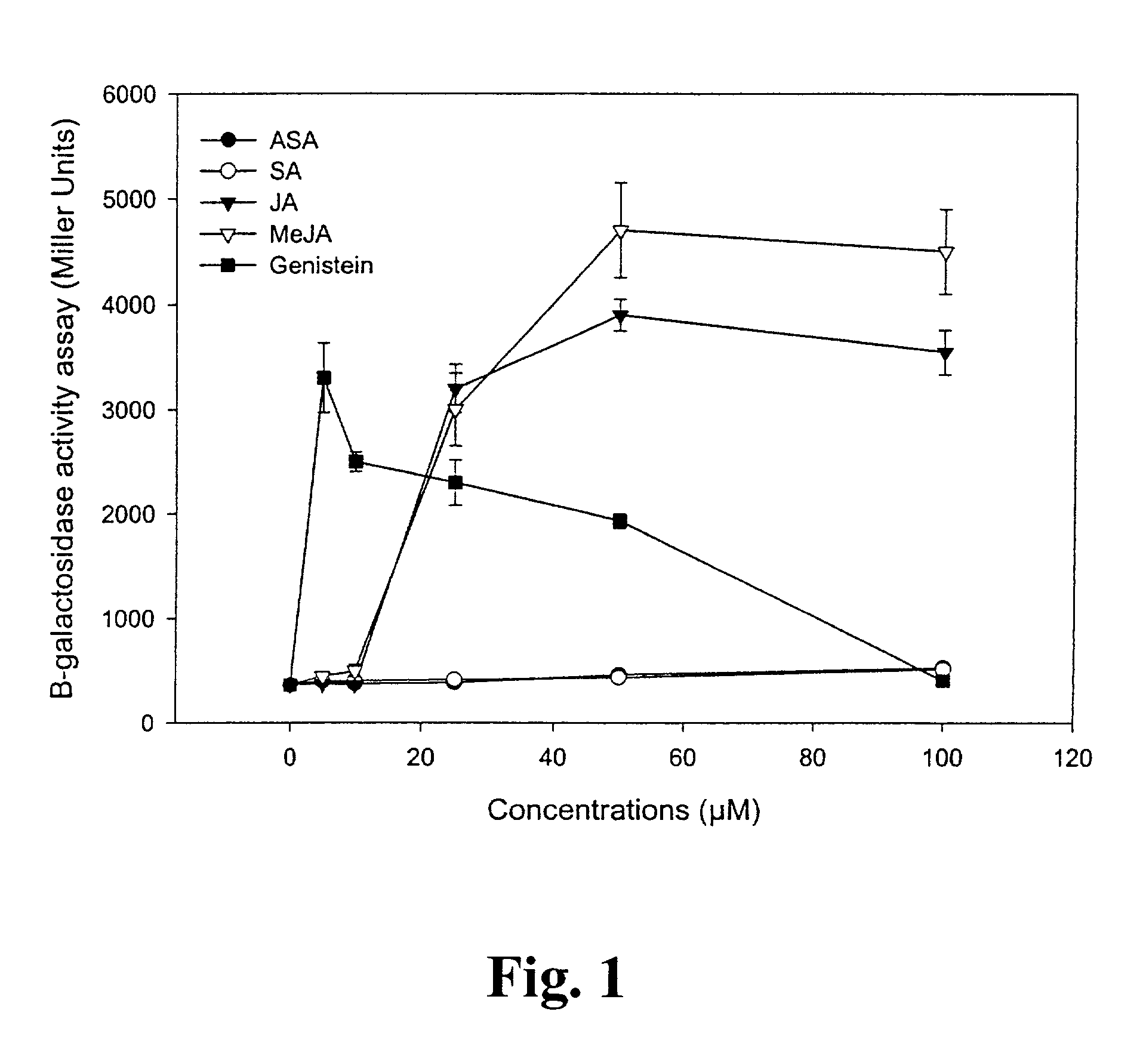
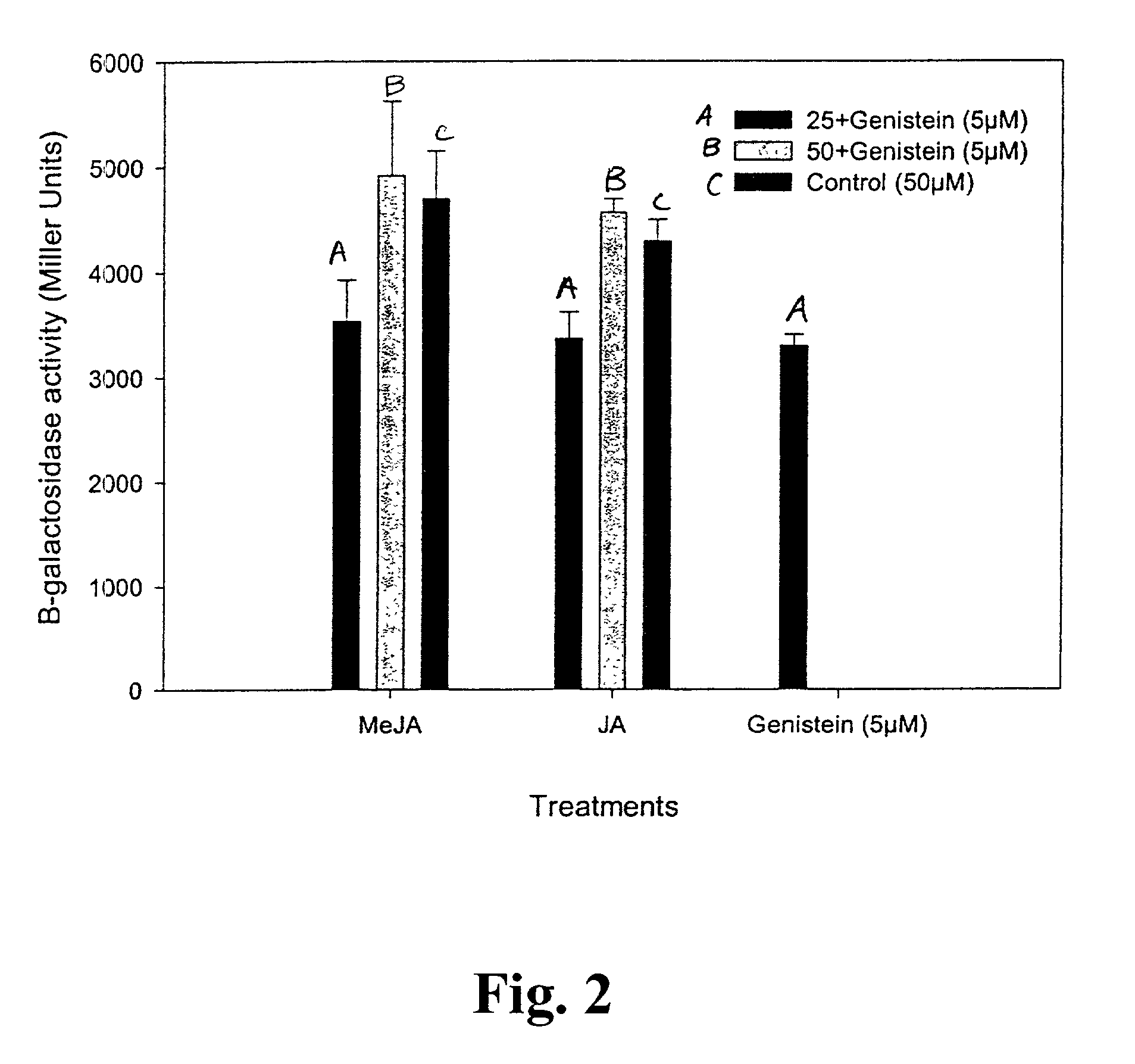
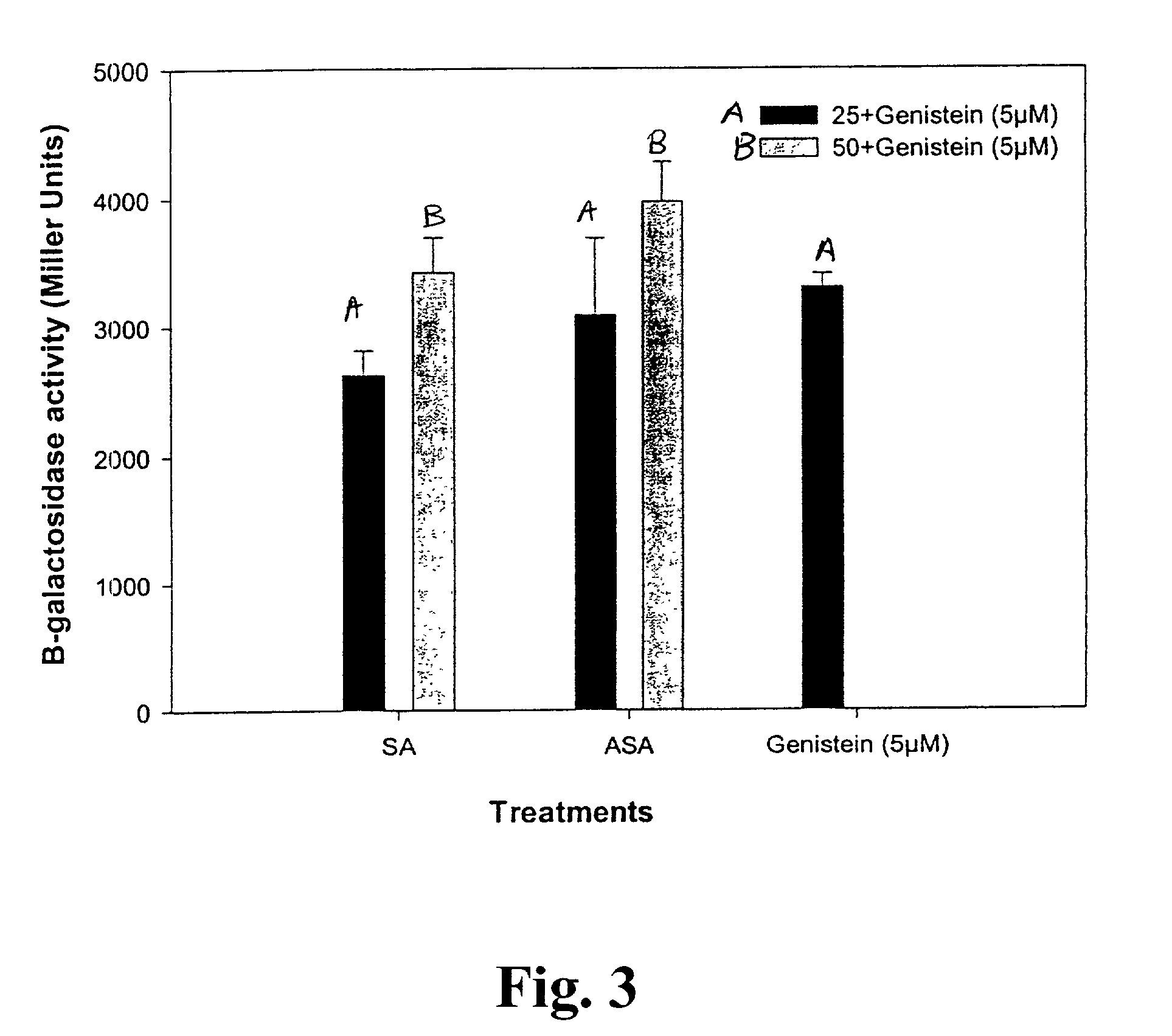
Lipo-chito oligosaccharides (LCOs) are produced by culturing rhizobacteria cells in or on a culture medium comprising at least one of: jasmonic acid or a derivative thereof; linoleic acid or a derivative thereof; or linolenic acid or a derivative thereof. Preferably, the rhizobacteria cells are Bradyrhizobium japonicum cells having the identifying characteristics of B. japonicum strain USDA 3. Preferably, the derivative of jasmonic acid is an ester thereof, preferably methyl jasmonate. Also provided are methods for improving LCO production at low temperatures, particularly temperatures below 25° C.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
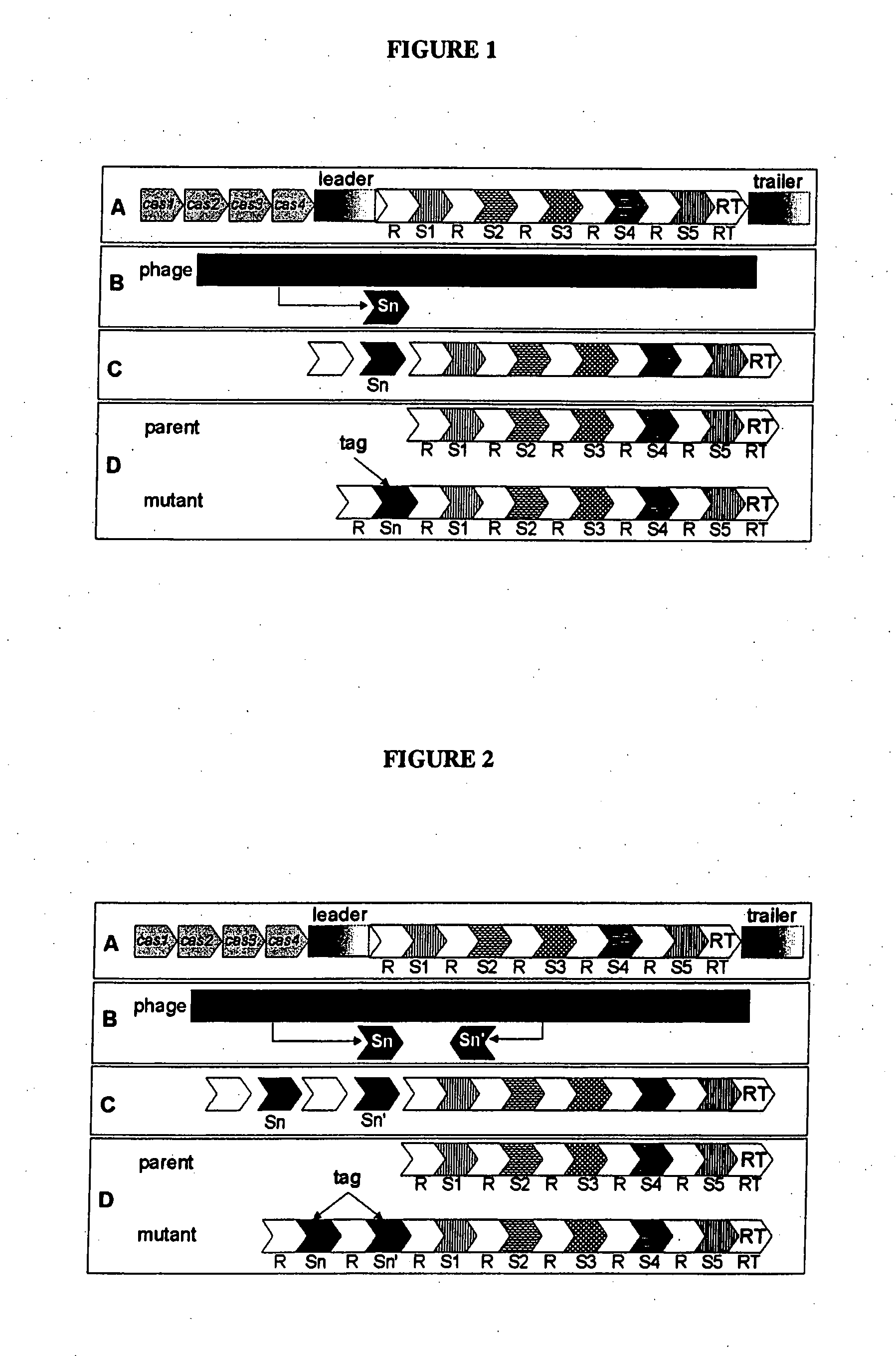
Tagged Microorganisms and Methods of Tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
AXMI-150 delta-endotoxin gene and methods for its use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions including a coding sequence for pesticidal polypeptides are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules having nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
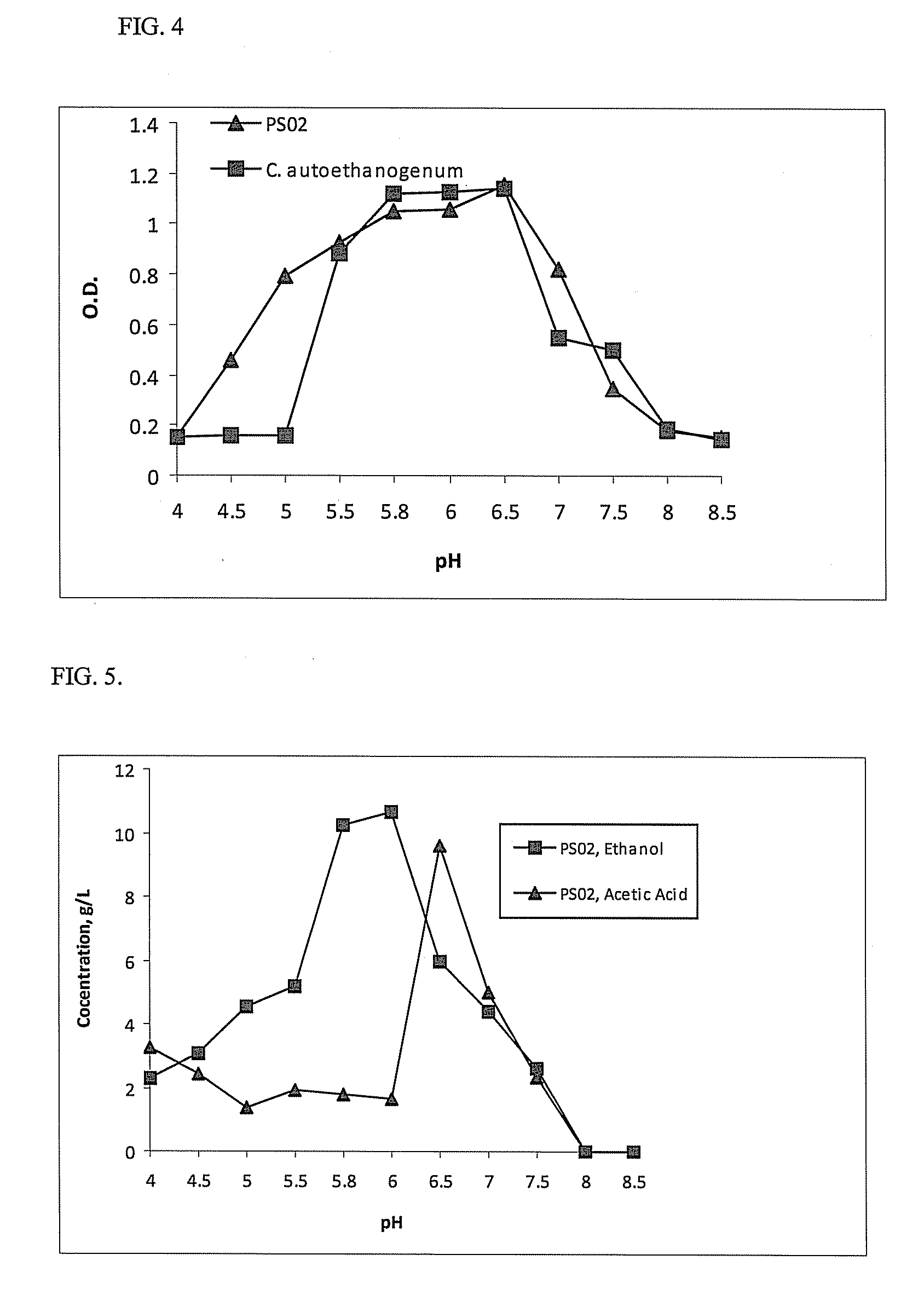
Novel Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium coskatii ATCC No. PTA-10522, “PS02”) is provided. Under anaerobic conditions C. coskatii can convert CO and / or H2 and / or CO2 to ethanol or acetate. Thus, this novel bacterium is capable of transforming waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Bacterium
InactiveUS20100034924A1Resistant to stirringReduce riskBacteriaFrozen sweetsBacteroidesLactobacillus
The present invention relates in one aspect to a fast acidifying lactic acid bacterium that generates a viscosity in fermented milk greater than about 62 Pa·s after 14 days of storage at 6° C.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Glyphosate-tolerant 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthases
InactiveUSRE39247E1Reduce amount of overproductionGlyphosate toleranceSugar derivativesTransferasesPhosphateGenetically modified crops
Genes encoding Class II EPSPS enzymes are disclosed. The genes are useful in producing transformed bacteria and plants which are tolerant to glyphosate herbicide. Class II EPSPS genes share little homology with known, Class I EPSPS genes, and do not hybridize to probes from Class I EPSPS's. The Class II EPSPS enzymes are characterized by being more kinetically efficient than Class I EPSPS's in the presence of glyphosate. Plants transformed with Class II EPSPS genes are also disclosed as well as a method for selectively controlling weeds in a planted transgenic crop field.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Antisense antibacterial cell division composition and method
Antisense oligomers directed to bacterial cell division and cell cycle-encoding nucleic acids are capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and are useful in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. The antisense oligomers are substantially uncharged, and contain from 8 to 40 nucleotide subunits, including a targeting nucleic acid sequence at least 10 nucleotides in length which is effective to hybridize to (i) a bacterial tRNA or (ii) a target sequence, containing a translational start codon, within a bacterial nucleic acid which encodes a protein associated with cell division or the cell cycle. Such proteins include zipA, sulA, secA, dicA, dicB, dicC, dicF, ftsA, ftsI, ftsN, ftsK, ftsL, ftsQ, ftsW, ftsZ, murC, murD, murE, murF, murG, minC, minD, minE, mraY, mraW, mraZ, seqA, ddlB, carbamate kinase, D-ala D-ala ligase, topoisomerase, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, thioredoxin reductase, dihydrofolate reductase, and cell wall enzyme.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Solvent tolerant microorganisms
Pediococcus bacteria having enhanced tolerance to butanols have been isolated. The bacteria are useful for the fermentative production of butanol.
Owner:GEVO INC
Aerobic succinate production in bacteria
Methods of increasing yields of succinate using aerobic culture methods and a multi-mutant E. coli strain are provided. Also provided is a mutant strain of E. coli that produces high amounts of succinic acid.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Competitive and Effective Bacterial Strains
ActiveUS20120252672A1Improve availabilityImprove plant health of plantBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacteroidesGrowth plant
According to the present invention new isolates of bacterial strains have been shown to possess unique properties. These bacterial strains are plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR), posses an enhanced competitive advantage at colonizing leguminous plants, and enhance the overall performance of leguminous plant growth. Further still, the present invention discloses a novel method for screening and selecting bacterial strains having the aforementioned beneficial characteristics.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOLOGICALS
Microorganisms and methods for treating poultry
ActiveUS7754469B2Improve feed conversionIncreasing low G+CBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliBacteroides
An isolated Bacillus strain LSSAO1 is provided. When fed to a bird, this and other Bacillus strains described herein provide benefits to the birds. For example, administration of the one or more Bacillus strain can increase low G+C, gram positive bacteria in the gastrointestinal flora of the bird. These type of bacteria are increased by antibiotics and include beneficial Clostridium. Administration of the one or more Bacillus strain can also inhibit pathogen in the bird, such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium. These benefits can enhance feed conversion in poultry. Useful combinations of Bacillus strains and methods of using one or more Bacillus strain are also provided.
Owner:AGTECH PRODS
Rice containing endophytic bacteria and method of producing it
InactiveUS7084331B2Improve the level ofIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeRice plantsBacteroides
The present invention provides a rice plant that shows enhanced growth and increased seed production, which also enables reduction of the use of chemical fertilizers.In the present invention, a nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacterium is isolated from bacteria symbiotically inhabiting natural plants, the isolated endophytic bacterium is artificially proliferated and then artificially inoculated into rice plants, and thus, the nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacteria are allowed to infect to rice plants.
Owner:SOC FOR TECHNO INNOVATION OF AGRI FORESTRY & FISHERIES +1
Kits for diagnosis and monitoring of pathogenic infection by analysis of cell-free pathogenic nucleic acids in urine
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing and / or monitoring a bacterial or parasitic infection by detection and quantification of the transrenal nucleic acids, derived from bacterial pathogenic agents or from parasites, in urine. The detection method optionally includes the isolation and the purification of the nucleic acids from urine by methods known in the art including pairing with molecular probes that are specific for the pathogenic agents, PCR hybridization, PCR, nested PCR, SSCP, LCR, and SDA. Diagnostic kits based on these detection methods are also claimed.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Detection and typing of bacterial strains
Methods for the detection and typing of bacterial strains from food products and dietary supplements, environmental samples, in vivo / in vitro samples, and for studying the natural diversity of the species are disclosed. Potential applications also include product development and / or detection and differentiation of new bacterial strains.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080161192A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 87 to 89 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
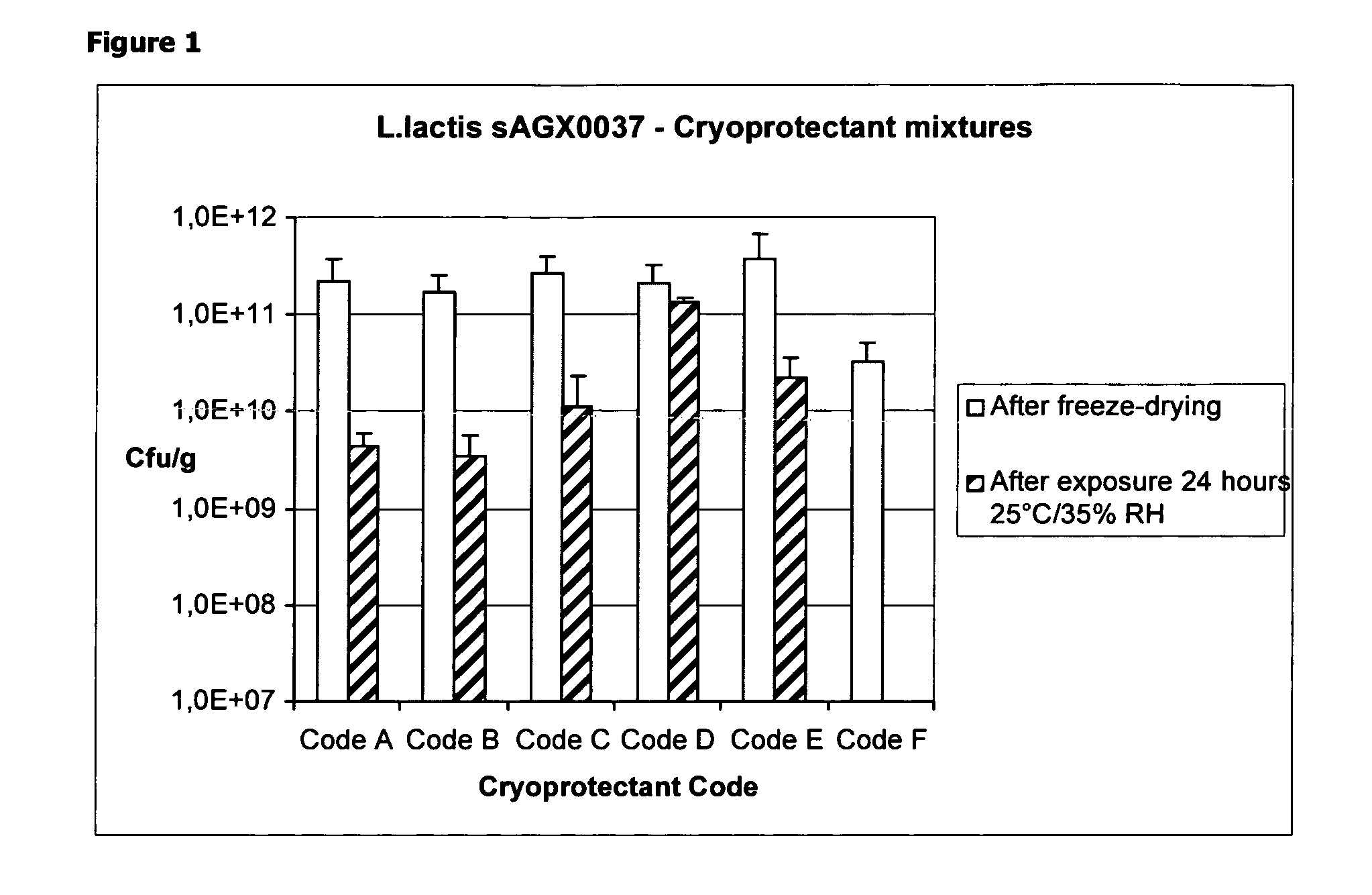
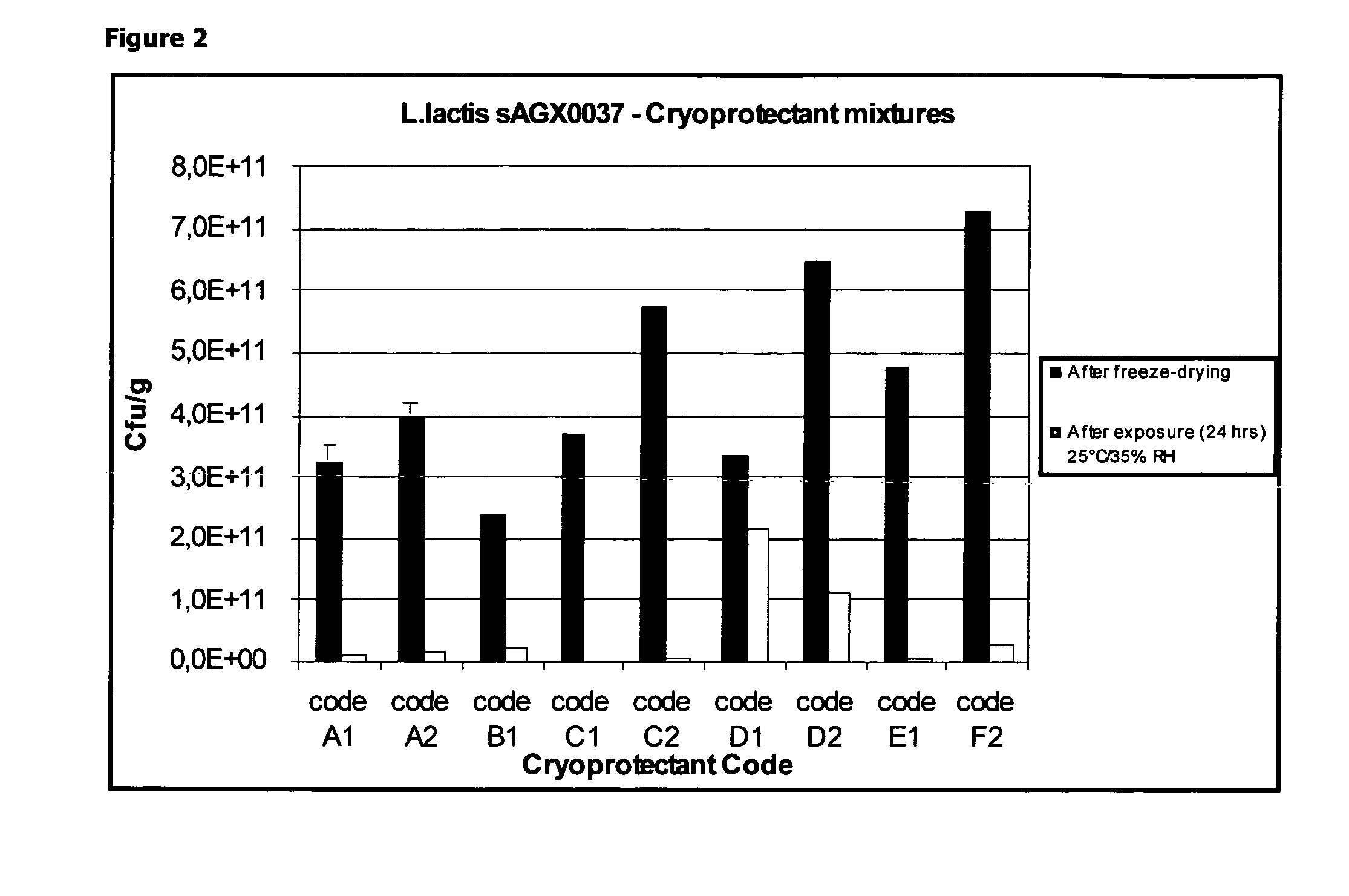
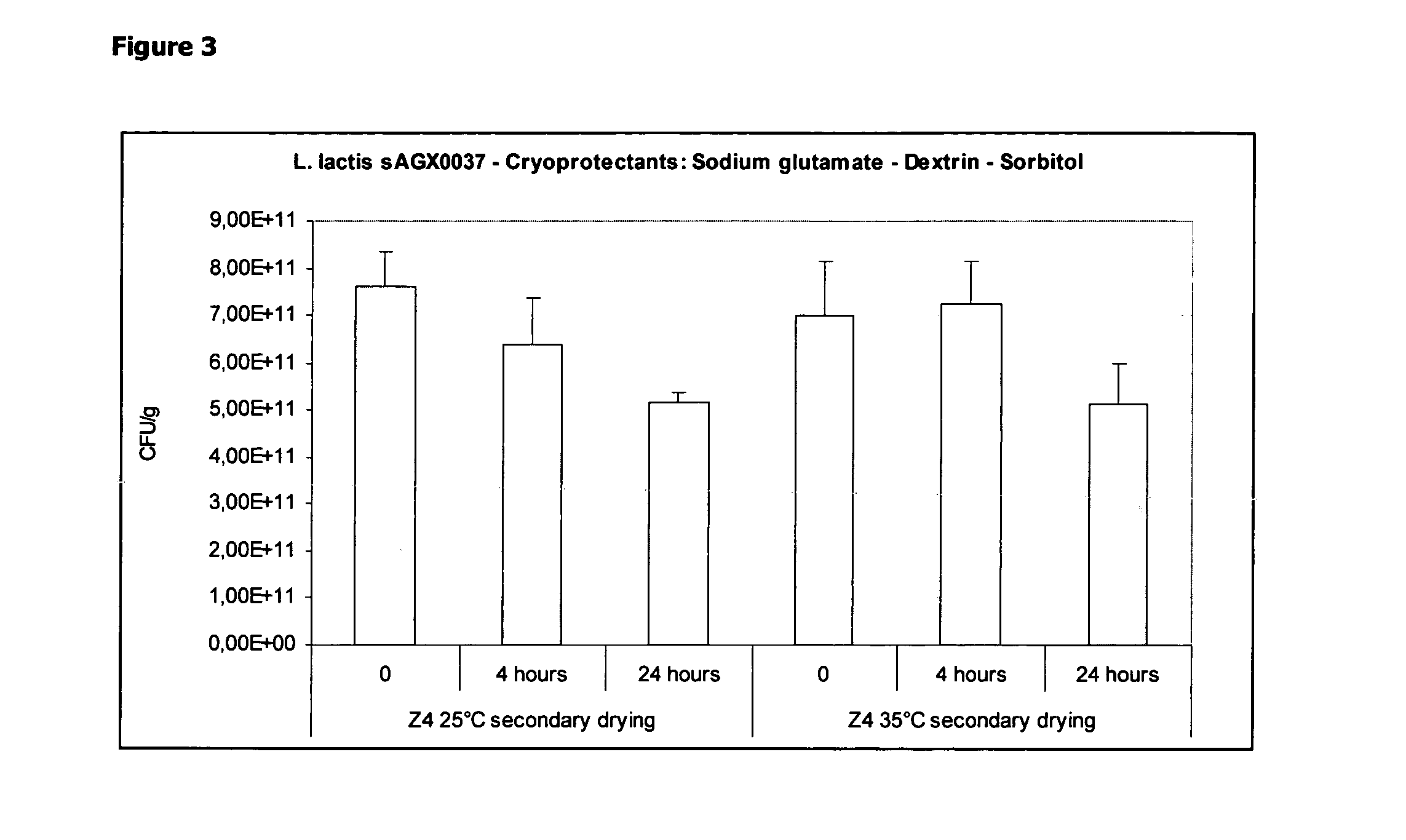
Cryoprotectants for freeze drying of lactic acid bacteria
ActiveUS20120039853A1Improve survivabilityImprove textureBiocideMilk preparationBacteroidesVaccination
The present invention comprises the discovery and development of an effective cryoprotectant composition, without containing skim milk or any other animal-derived compounds, to achieve long-term stability of freeze-dried lactic acid bacteria (LAB), at different temperatures, whereby the retention of viability of the freeze-dried LAB after 6 months of storage, preferably after 9 months of storage, more preferably after 12 months of storage is more than 50%. The invention is in the field of producing freeze dried bacteria, in particular Lactic acid bacteria. More in particular, the invention relates to the use of a novel combination of cryoprotectants for increasing the viability of bacteria after freeze drying, improving the texture of the lyofilized cake for easy grinding and improving the long term stability of the freeze dried bacteria at different temperature conditions. The invention further relates to such freeze dried bacteria for use in food industry or in human or animal health applications. More in particular, the invention relates to the increased viability and long-term storage of recombinant bacteria capable of expressing heterologous proteins or peptides and administered to humans or animals for therapeutic or vaccination purposes.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com