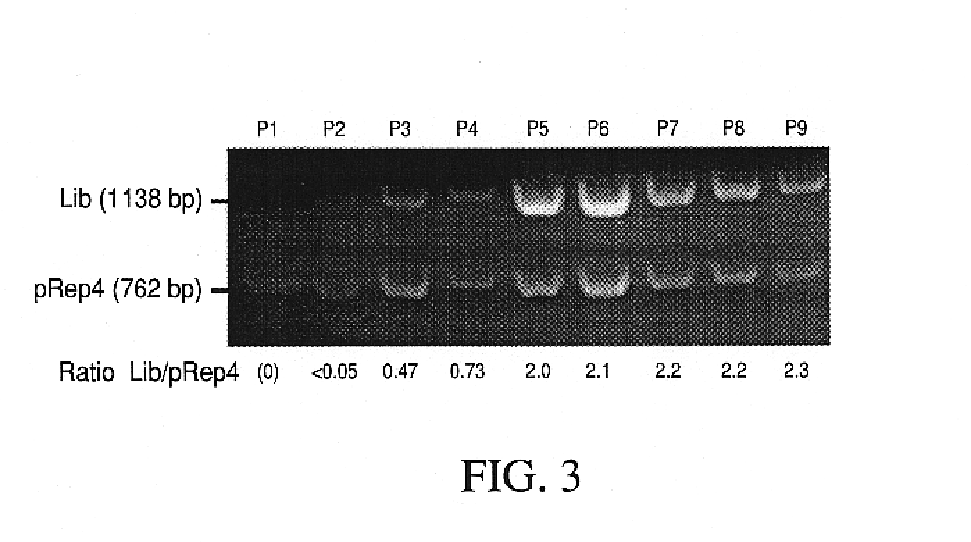
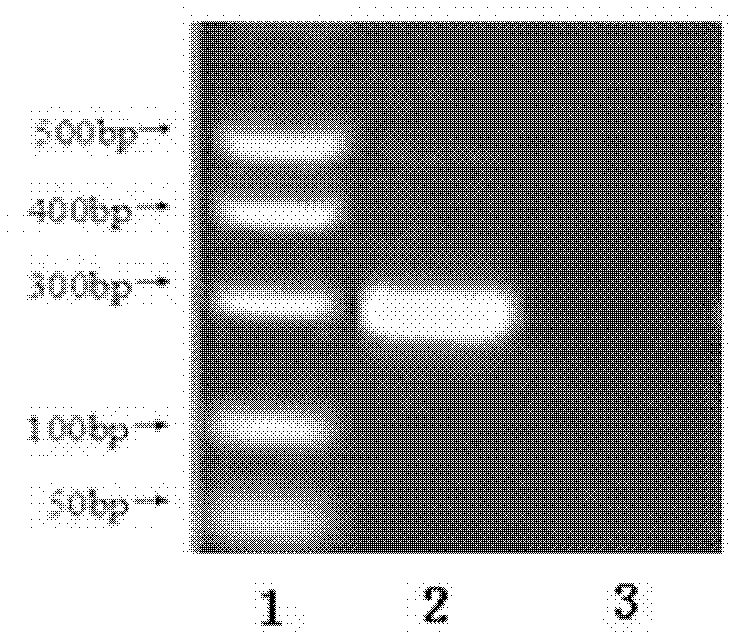
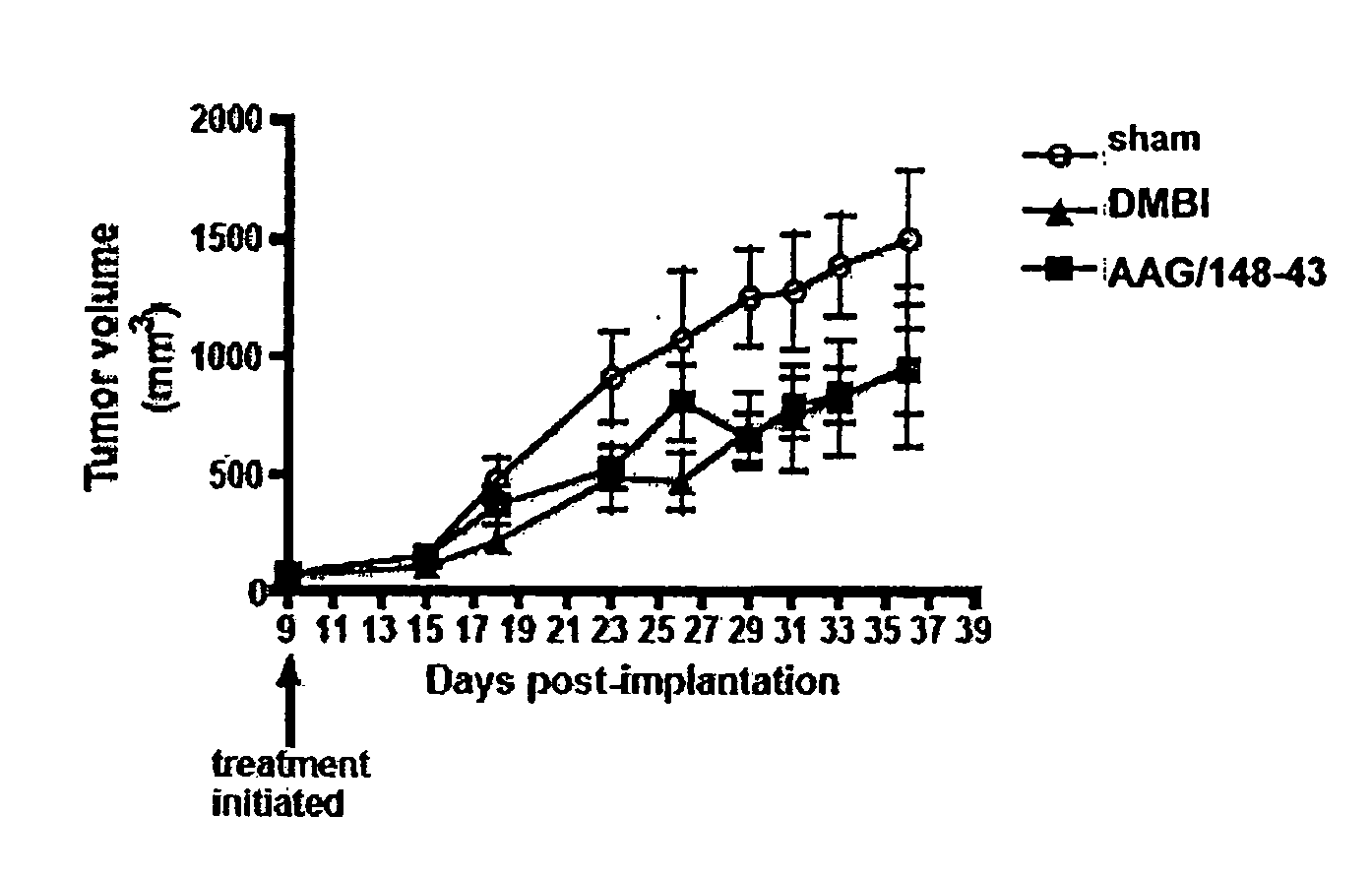
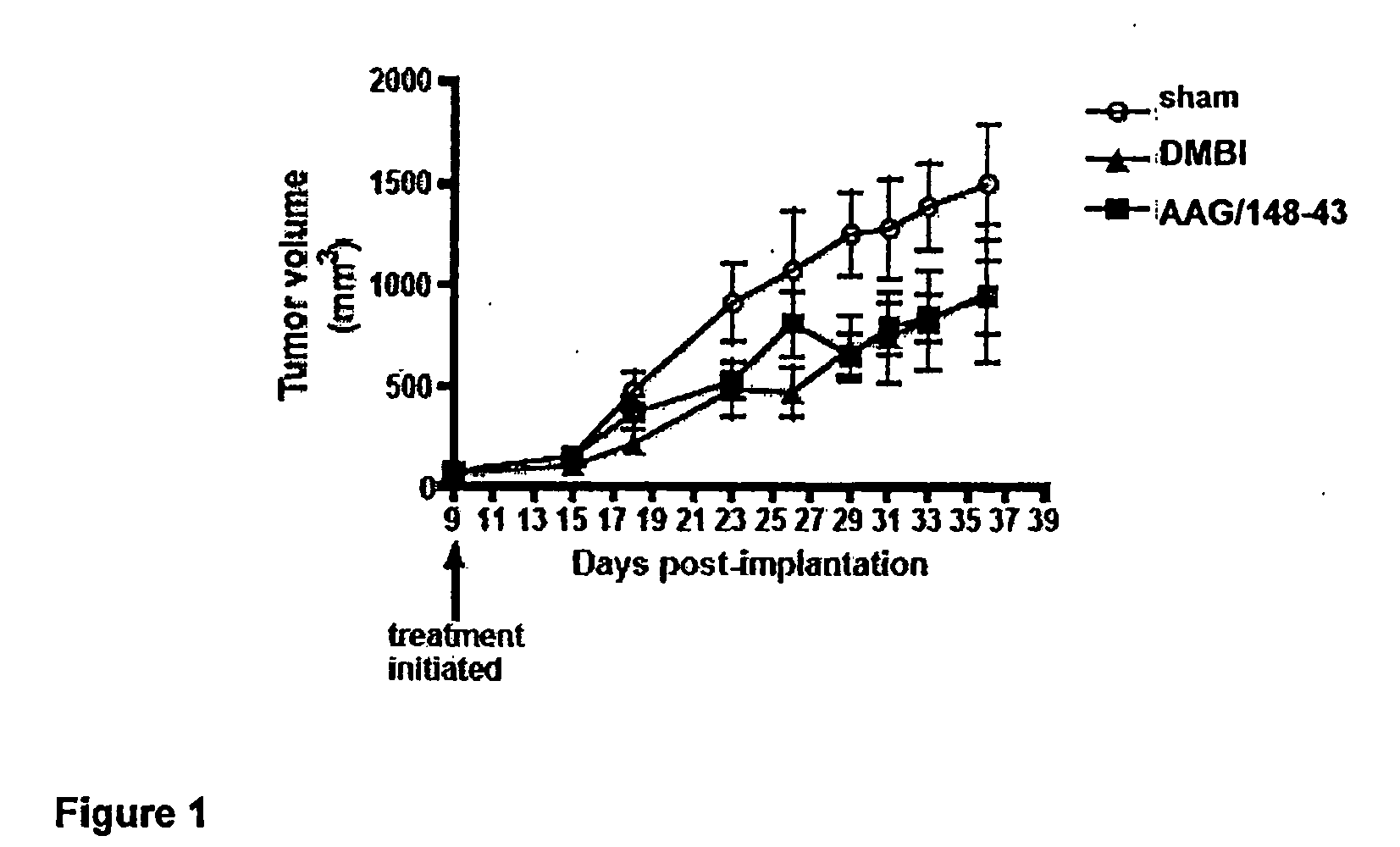
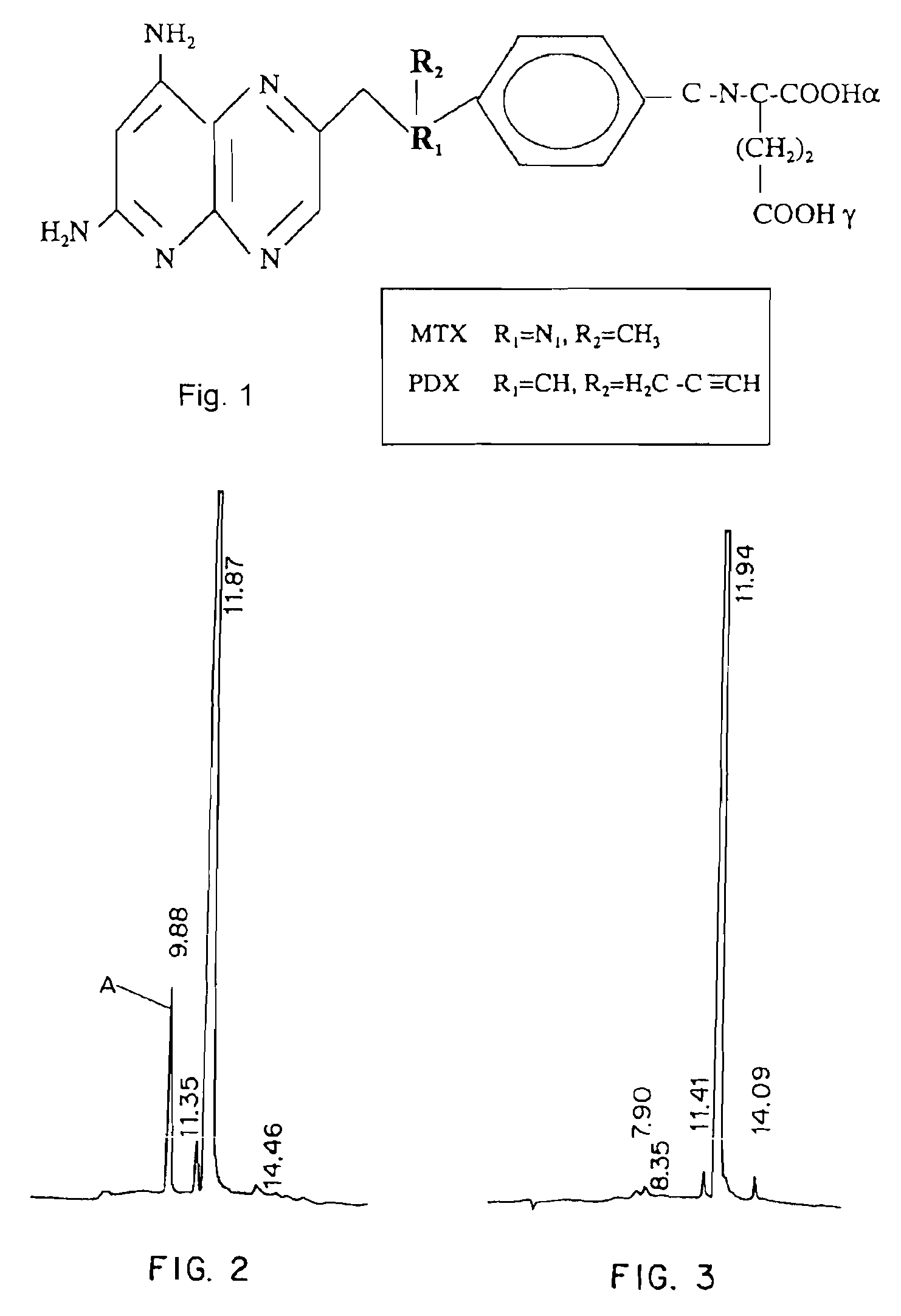
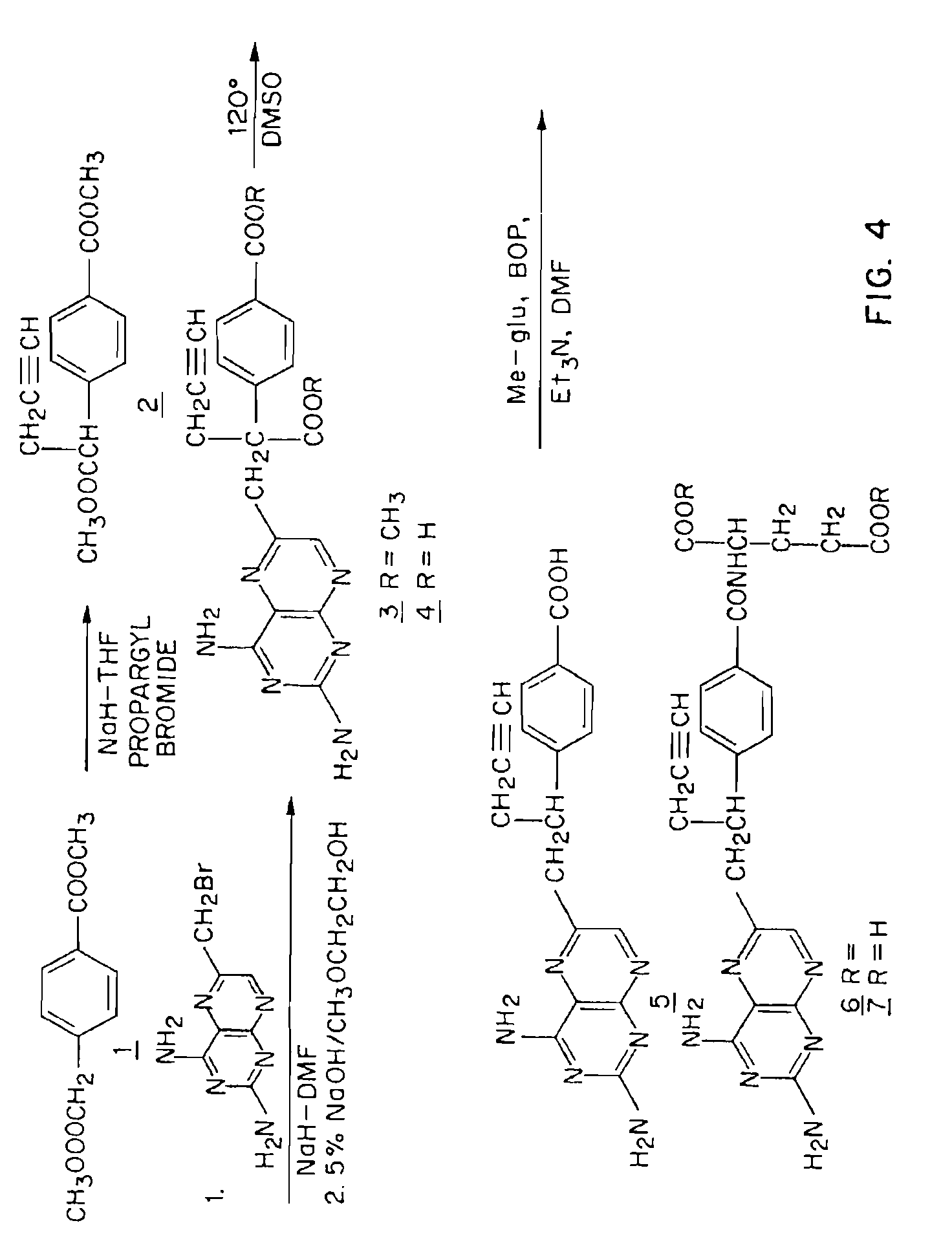
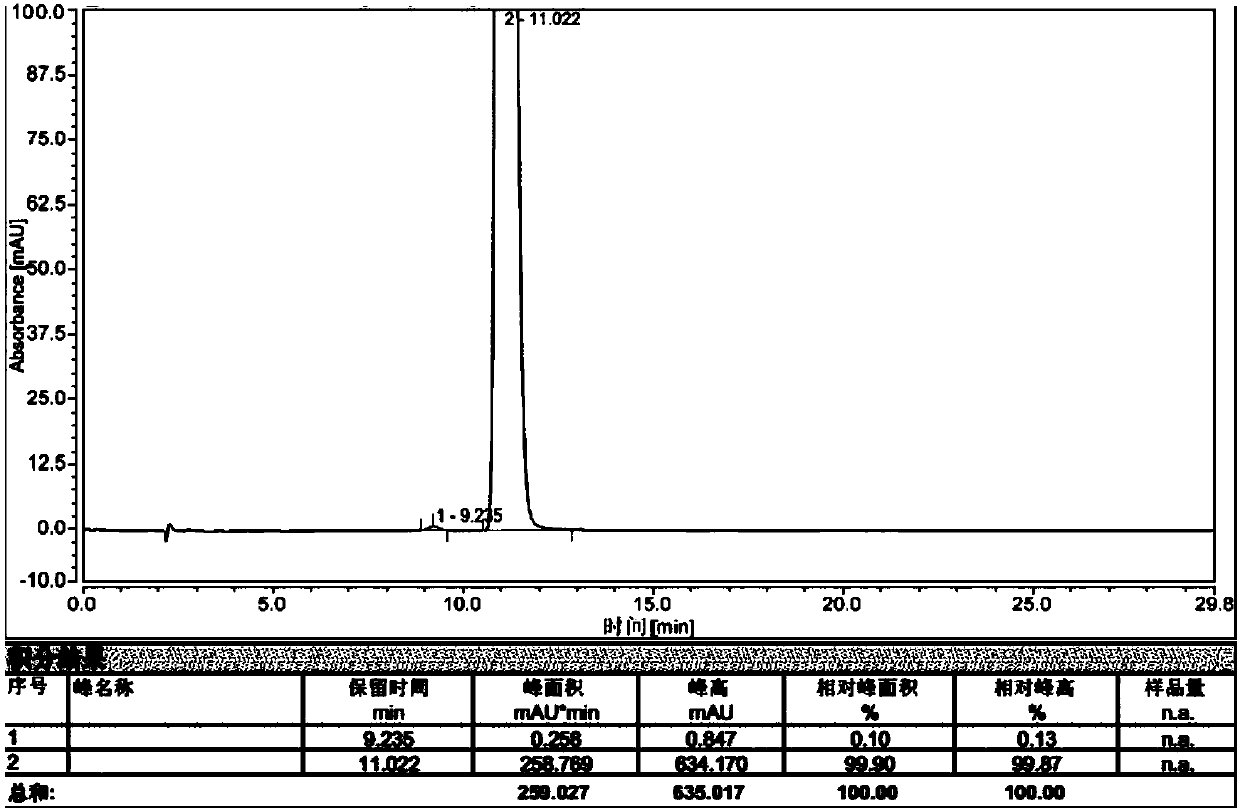
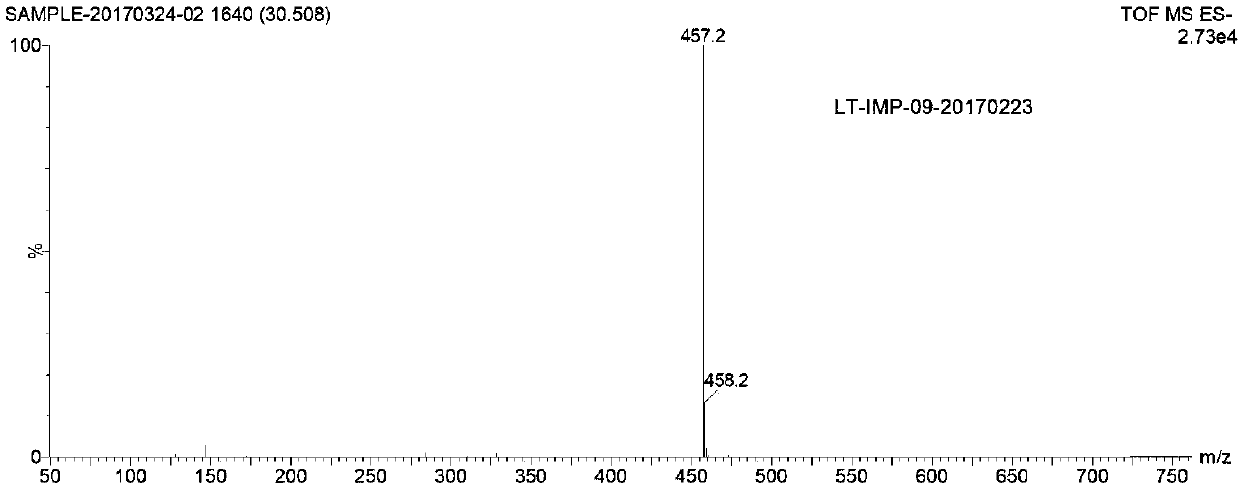
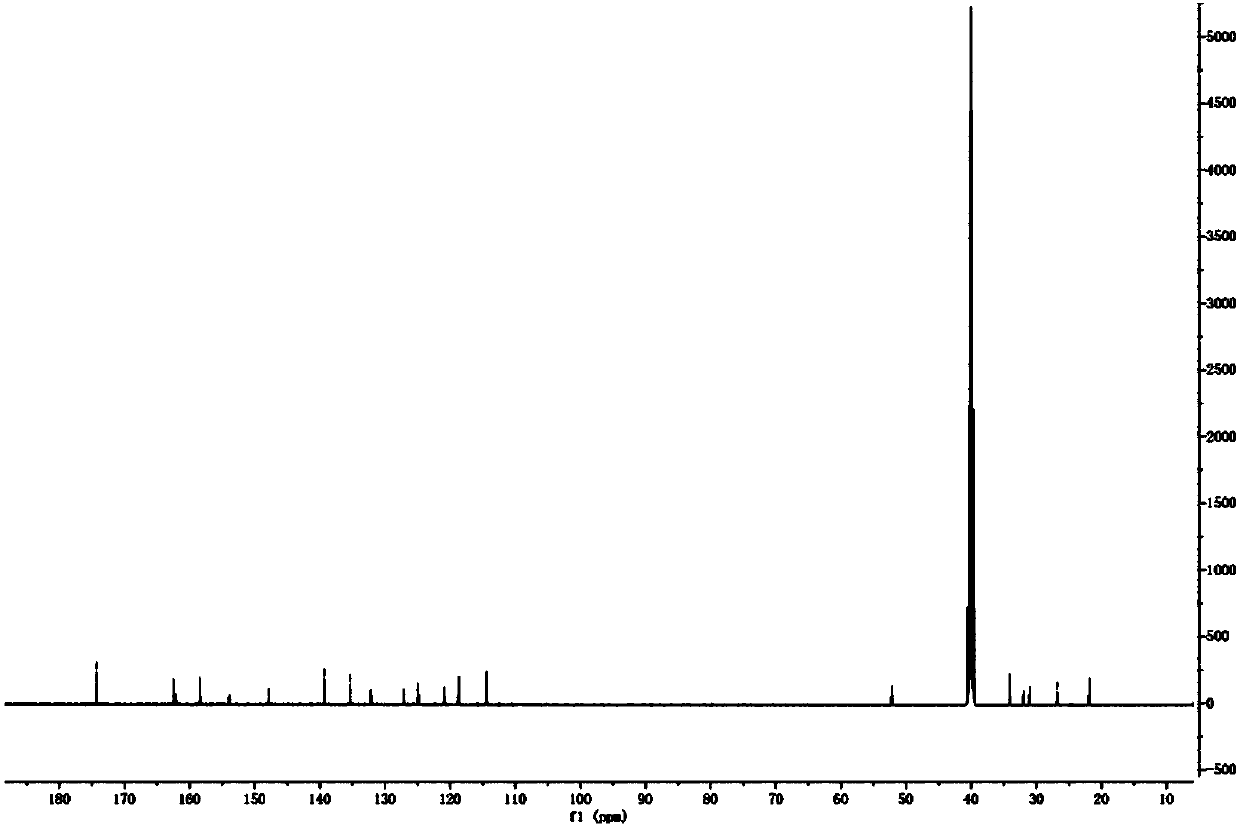
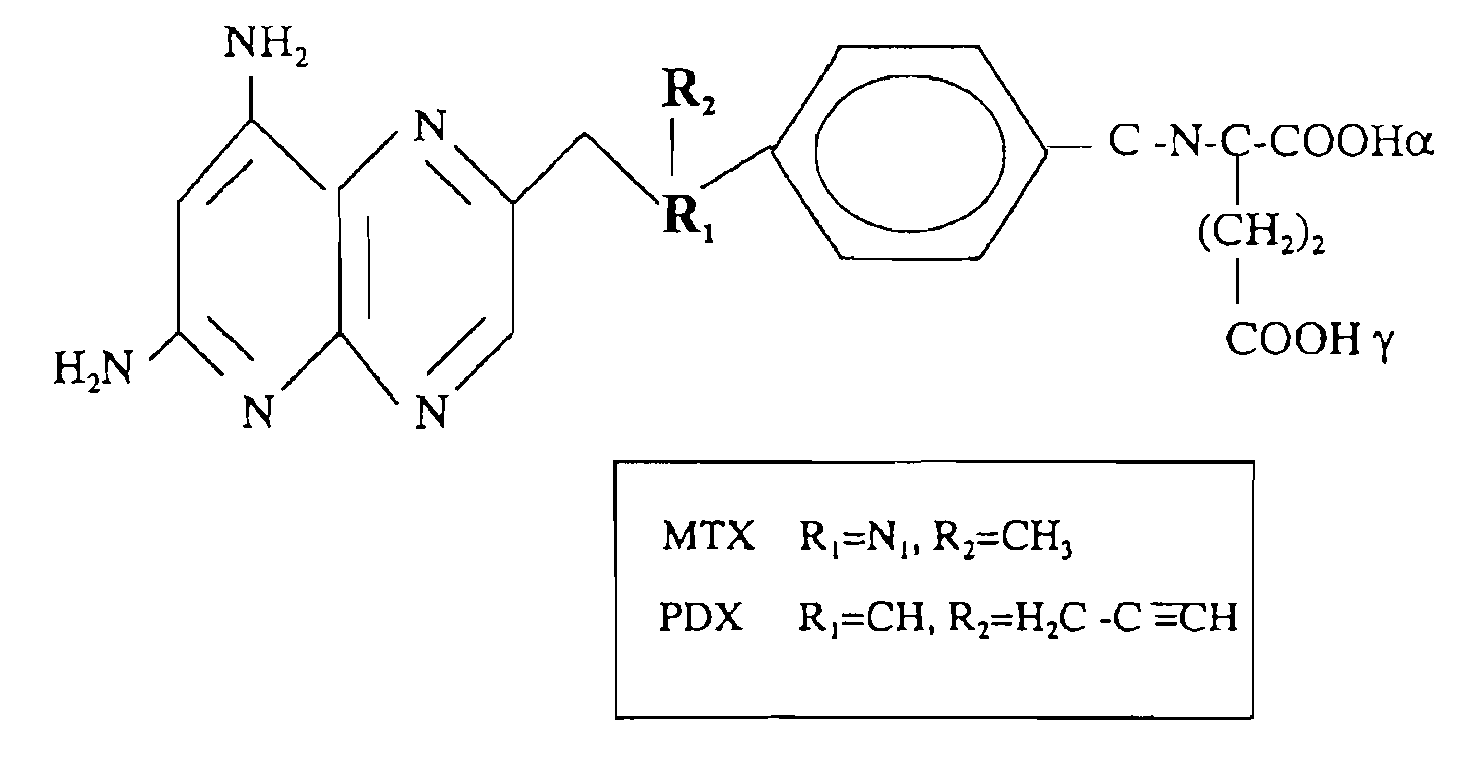Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Dihydrofolate reductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
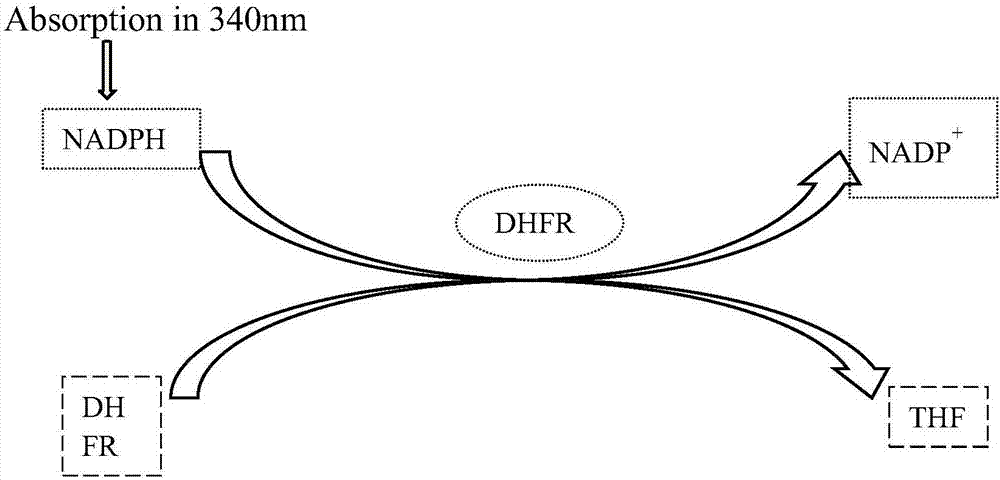
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. In humans, the DHFR enzyme is encoded by the DHFR gene. It is found in the q11→q22 region of chromosome 5. Bacterial species possess distinct DHFR enzymes (based on their pattern of binding diaminoheterocyclic molecules), but mammalian DHFRs are highly similar.
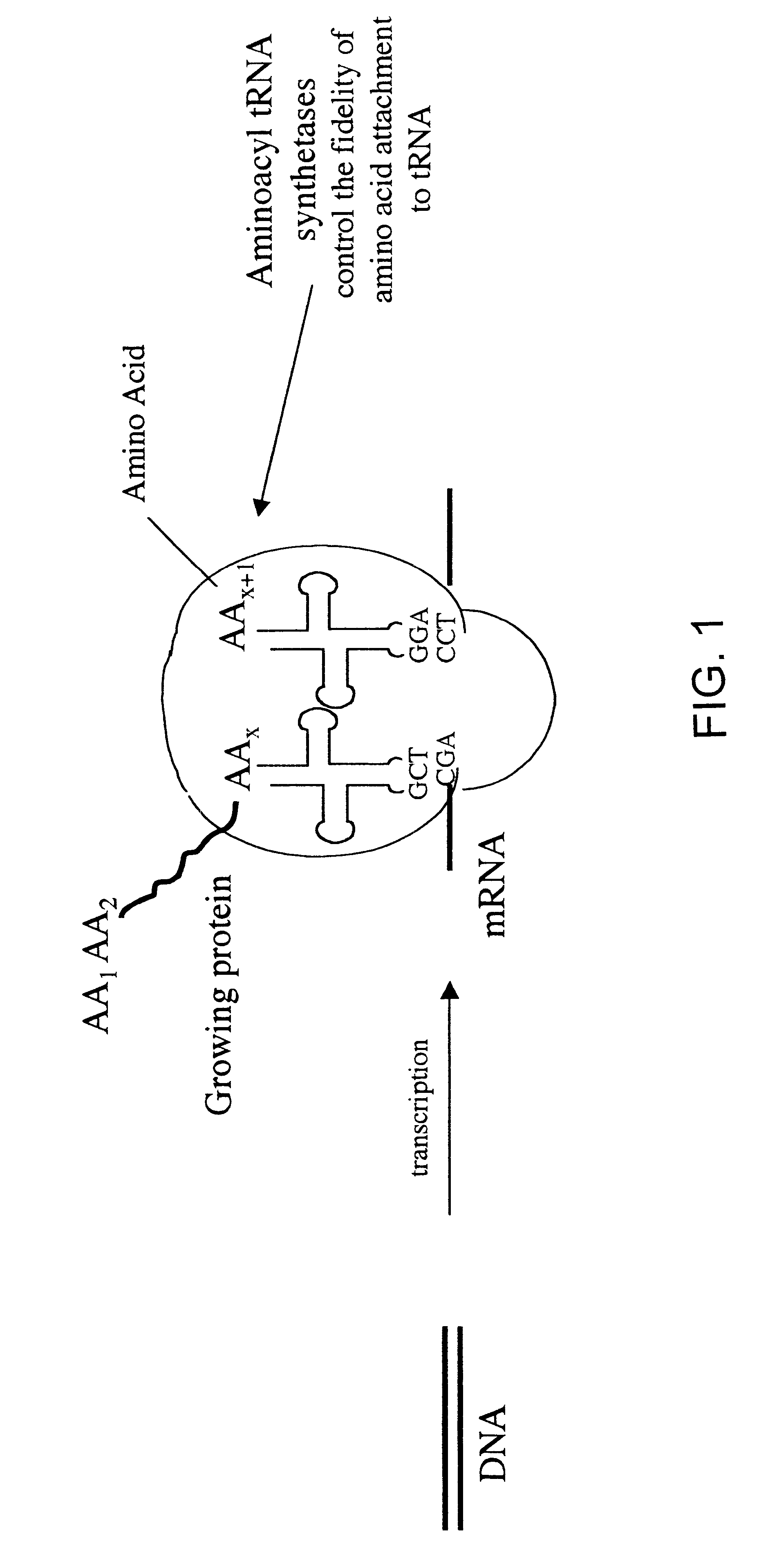
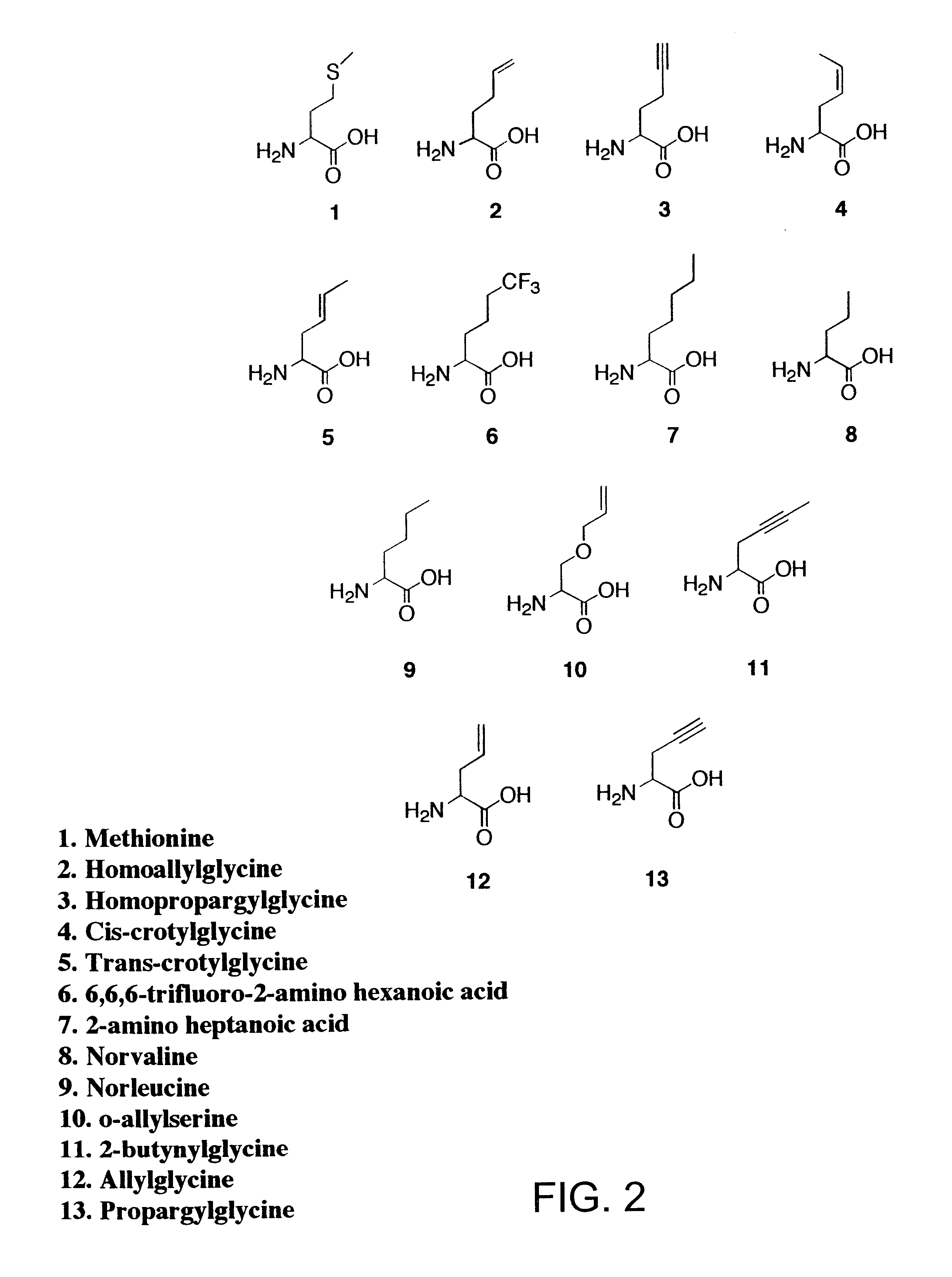
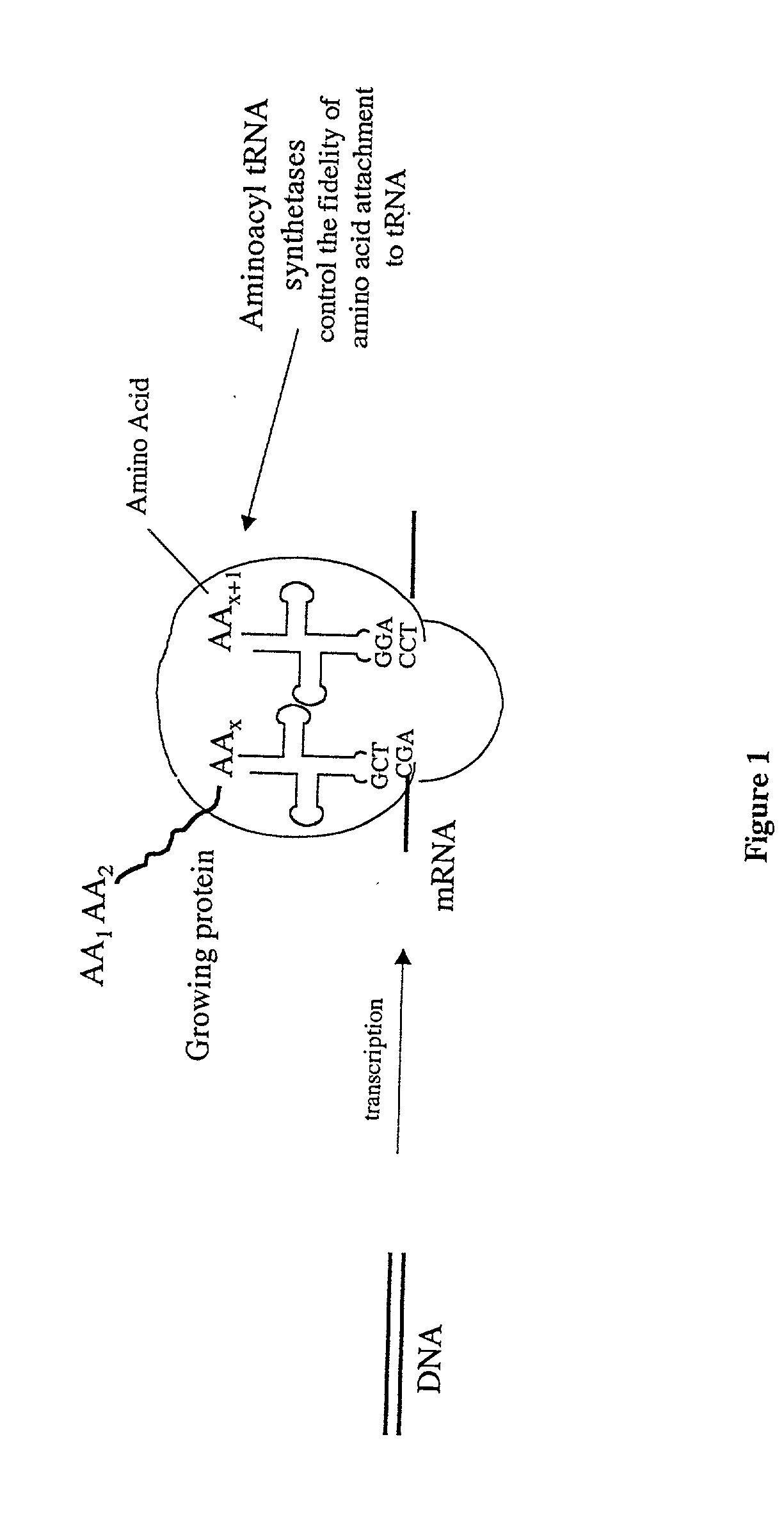
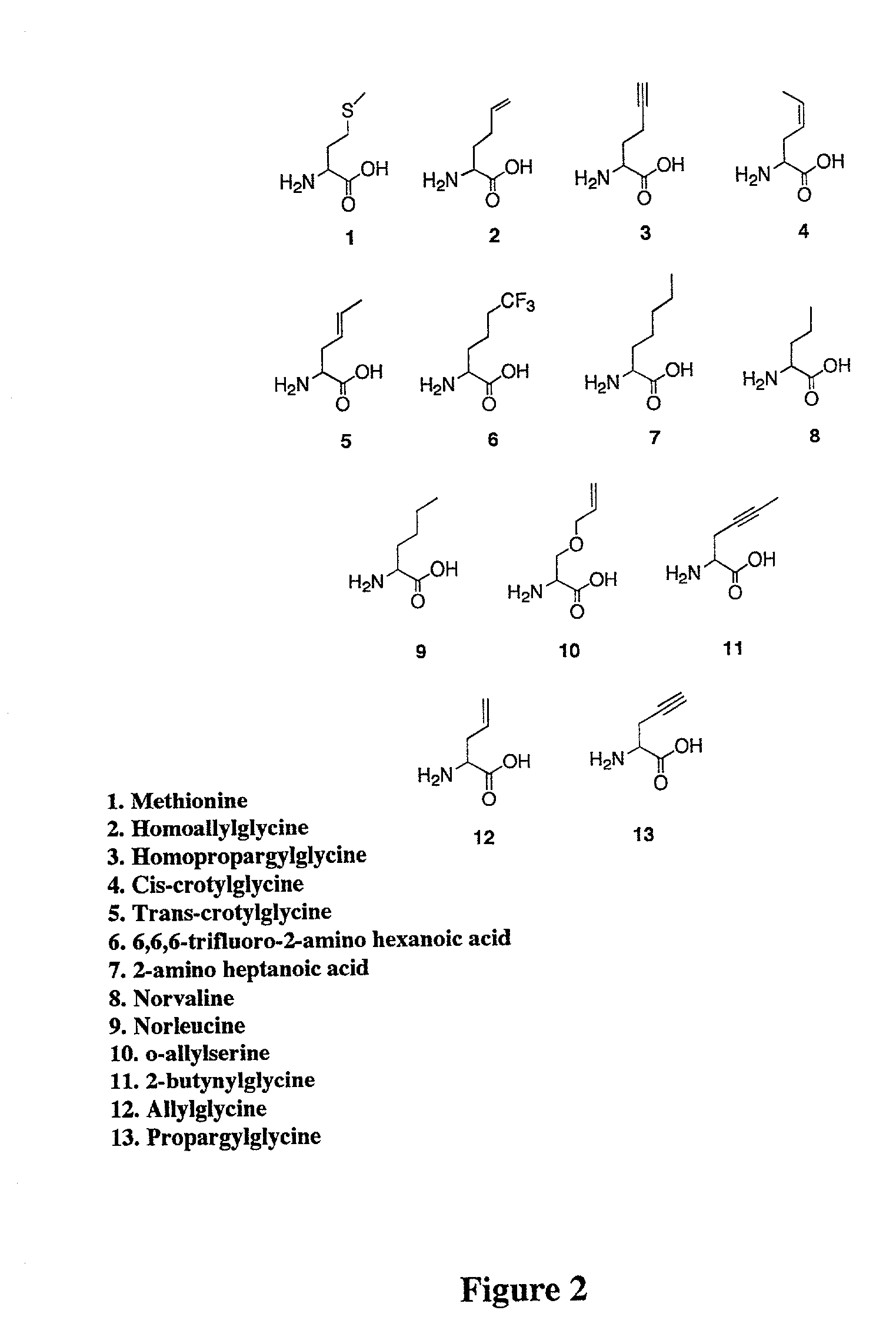
Overexpression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for efficient production of engineered proteins containing amino acid analogues
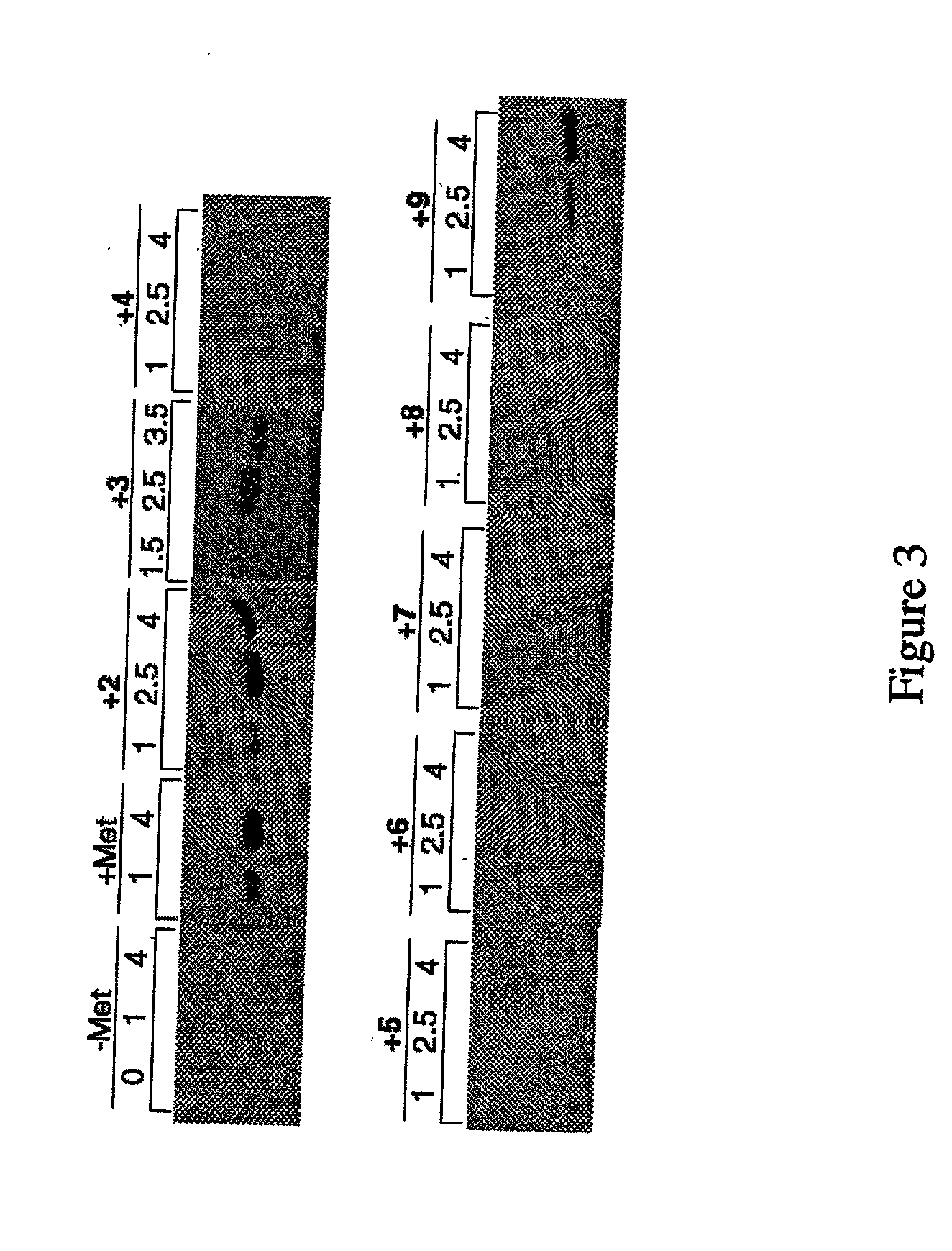
InactiveUS6586207B2High yieldRapid and predictable approachBacteriaOxidoreductasesMethionine biosynthesisDihydrofolate reductase
Methods for producing modified polypeptides containing amino acid analogues are disclosed. The invention further provides purified dihydrofolate reductase polypeptides, produced by the methods of the invention, in which the methionine residues have been replaced with homoallyglycine, homoproparglycine, norvaline, norleucine, cis-crotylglycine, trans-crotylglycine, 2-aminoheptanoic acid, 2-butynylglycine and allylglycine.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Overexpression of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for efficient production of engineered proteins containing amino acid analogues
InactiveUS20020042097A1High yieldRapid and predictable approachFungiBacteriaMethionine biosynthesisDihydrofolate reductase
Methods for producing modified polypeptides containing amino acid analogues are disclosed. The invention further provides purified dihydrofolate reductase polypeptides, produced by the methods of the invention, in which the methionine residues have been replaced with homoallyglycine, homoproparglycine, norvaline, norleucine, cis-crotylglycine, trans-crotylglycine, 2-aminoheptanoic acid, 2-butynylglycine and allylglycine.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Antisense antibacterial cell division composition and method
Antisense oligomers directed to bacterial cell division and cell cycle-encoding nucleic acids are capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and are useful in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. The antisense oligomers are substantially uncharged, and contain from 8 to 40 nucleotide subunits, including a targeting nucleic acid sequence at least 10 nucleotides in length which is effective to hybridize to (i) a bacterial tRNA or (ii) a target sequence, containing a translational start codon, within a bacterial nucleic acid which encodes a protein associated with cell division or the cell cycle. Such proteins include zipA, sulA, secA, dicA, dicB, dicC, dicF, ftsA, ftsI, ftsN, ftsK, ftsL, ftsQ, ftsW, ftsZ, murC, murD, murE, murF, murG, minC, minD, minE, mraY, mraW, mraZ, seqA, ddlB, carbamate kinase, D-ala D-ala ligase, topoisomerase, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, thioredoxin reductase, dihydrofolate reductase, and cell wall enzyme.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
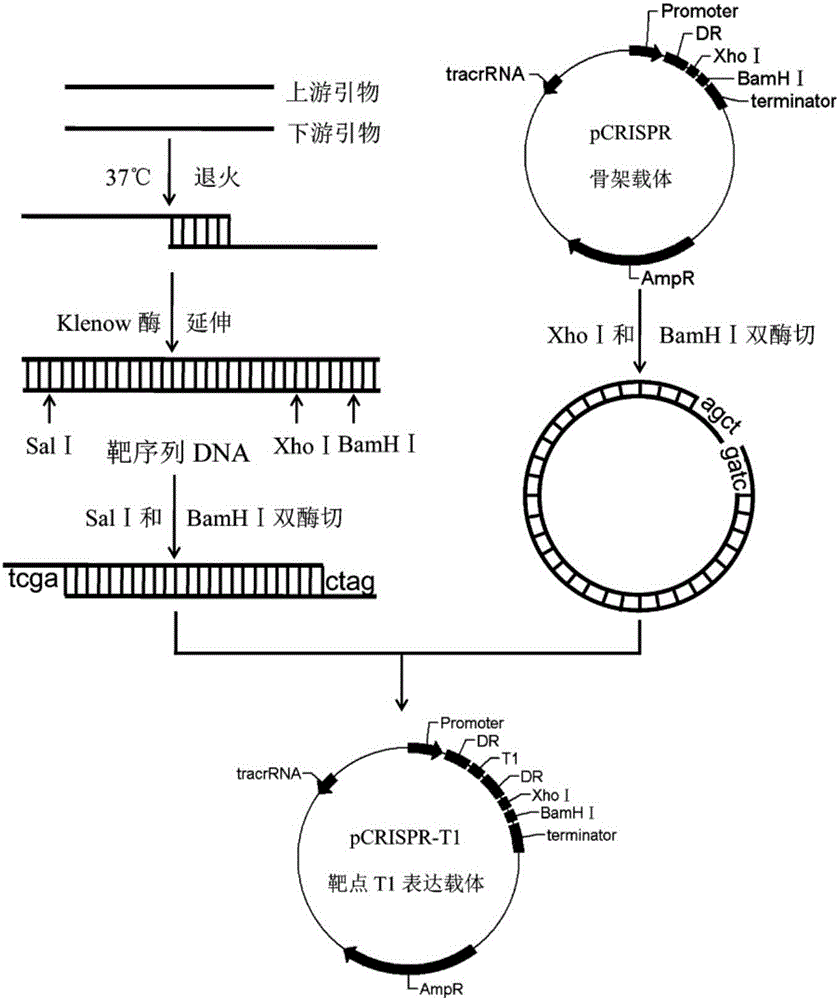
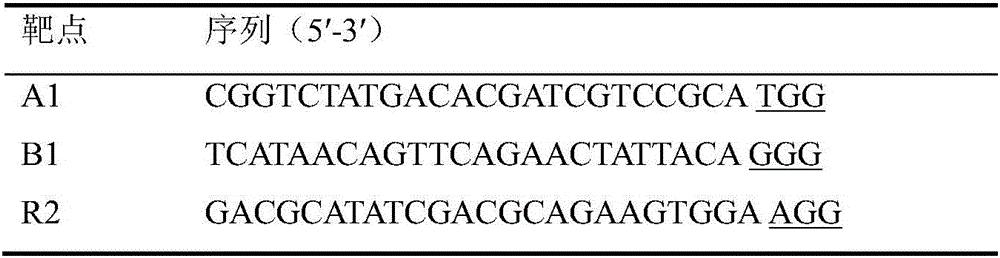
Multi-target-point CRISPR/Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization
InactiveCN106554969ATo achieve the effect of antibacterial and bactericidalVectorsOxidoreductasesA-DNADihydrofolate reductase
The invention discloses a multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization. The gene sequence of the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO1 and the gene sequence of a Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO2. A construction method of the expression vector comprises: using a DNA segment of an oriented RNA specific recognition gene, mediating Cas9 protein to cut a DNA double strand to produce a double strand incision and break a DNA sequence, and therefore breaking the principle of DNA coding of functional protein to construct the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector. Through comparison with a negative contrast, after CRISPR / Cas9 acts on DNA gyrase and dihydrofolate reductase, the survival rate of bacteria is only 10%, and the sterilization effect can reach no less than 90%.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
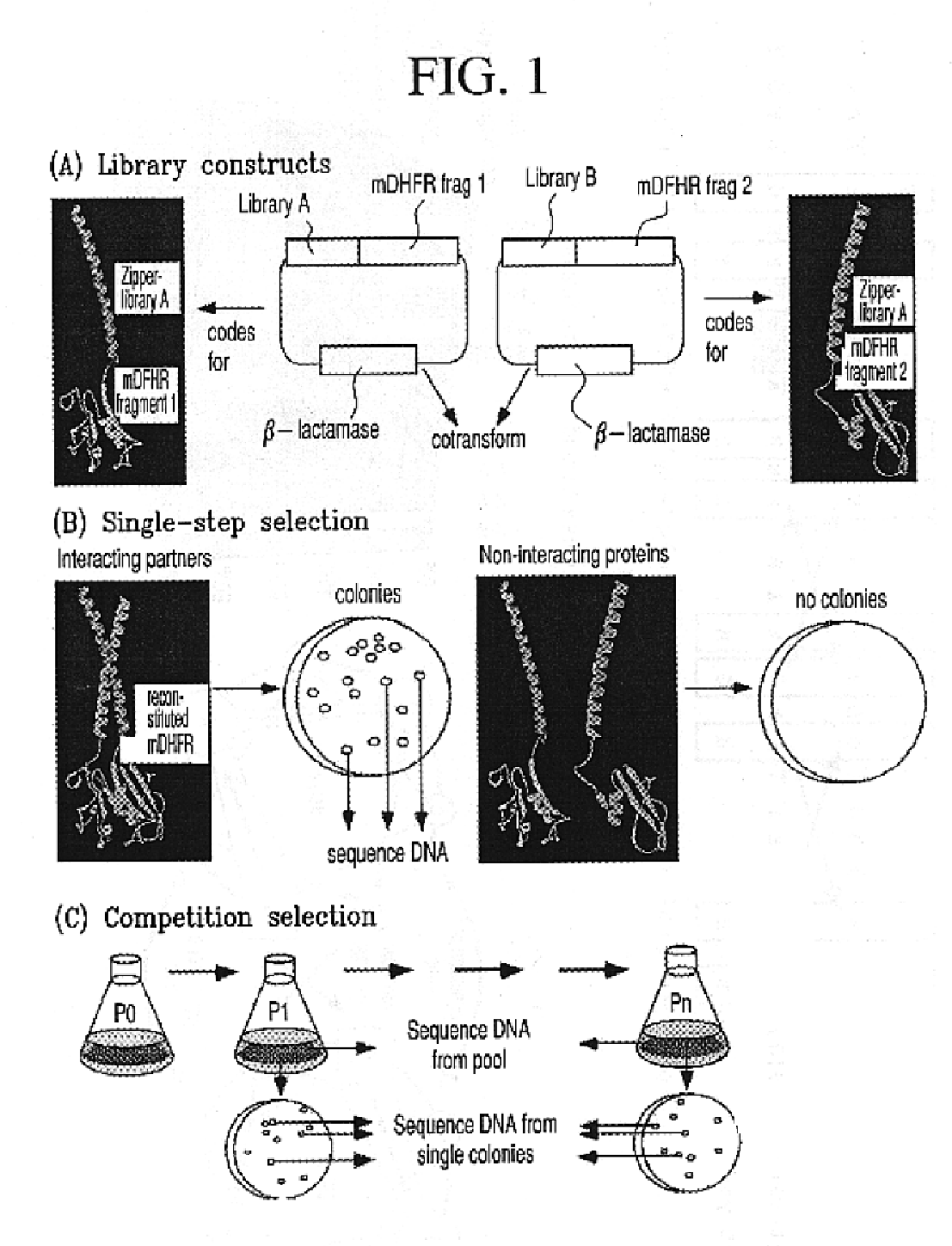
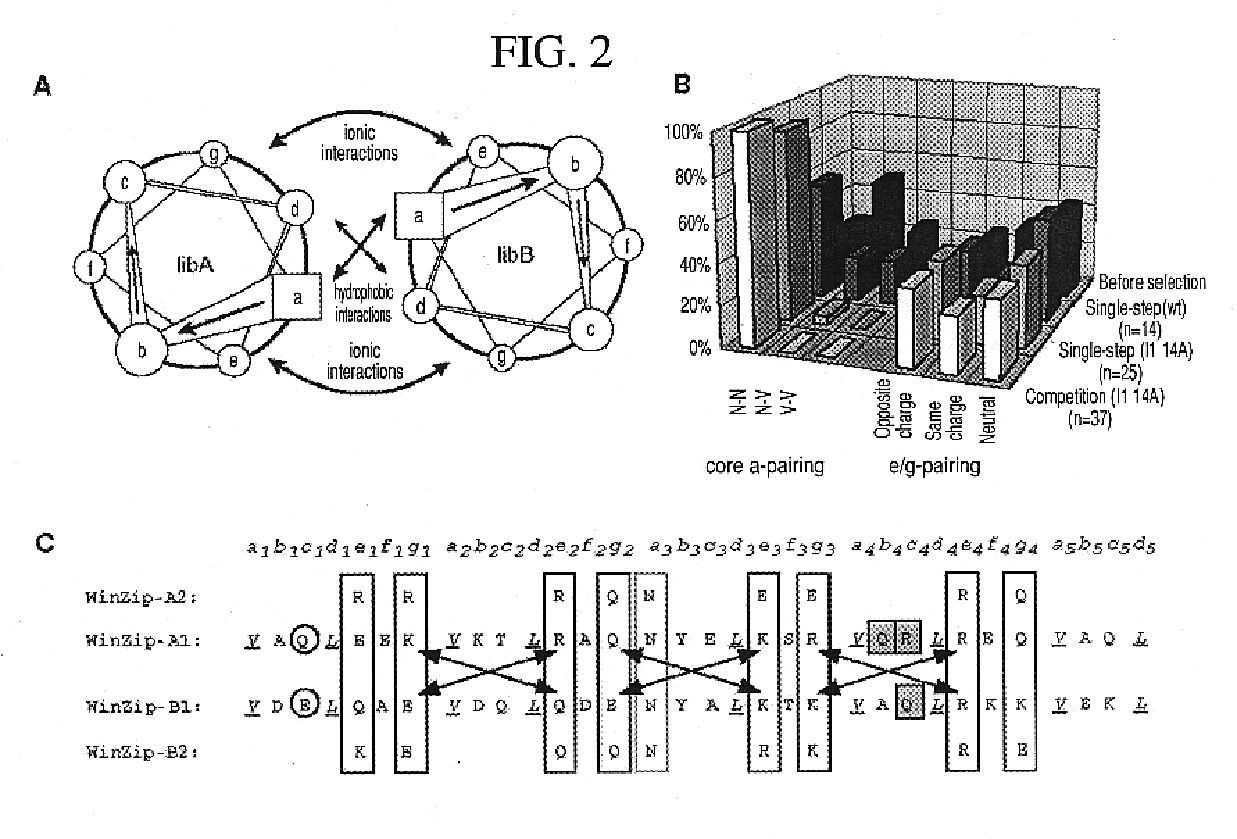
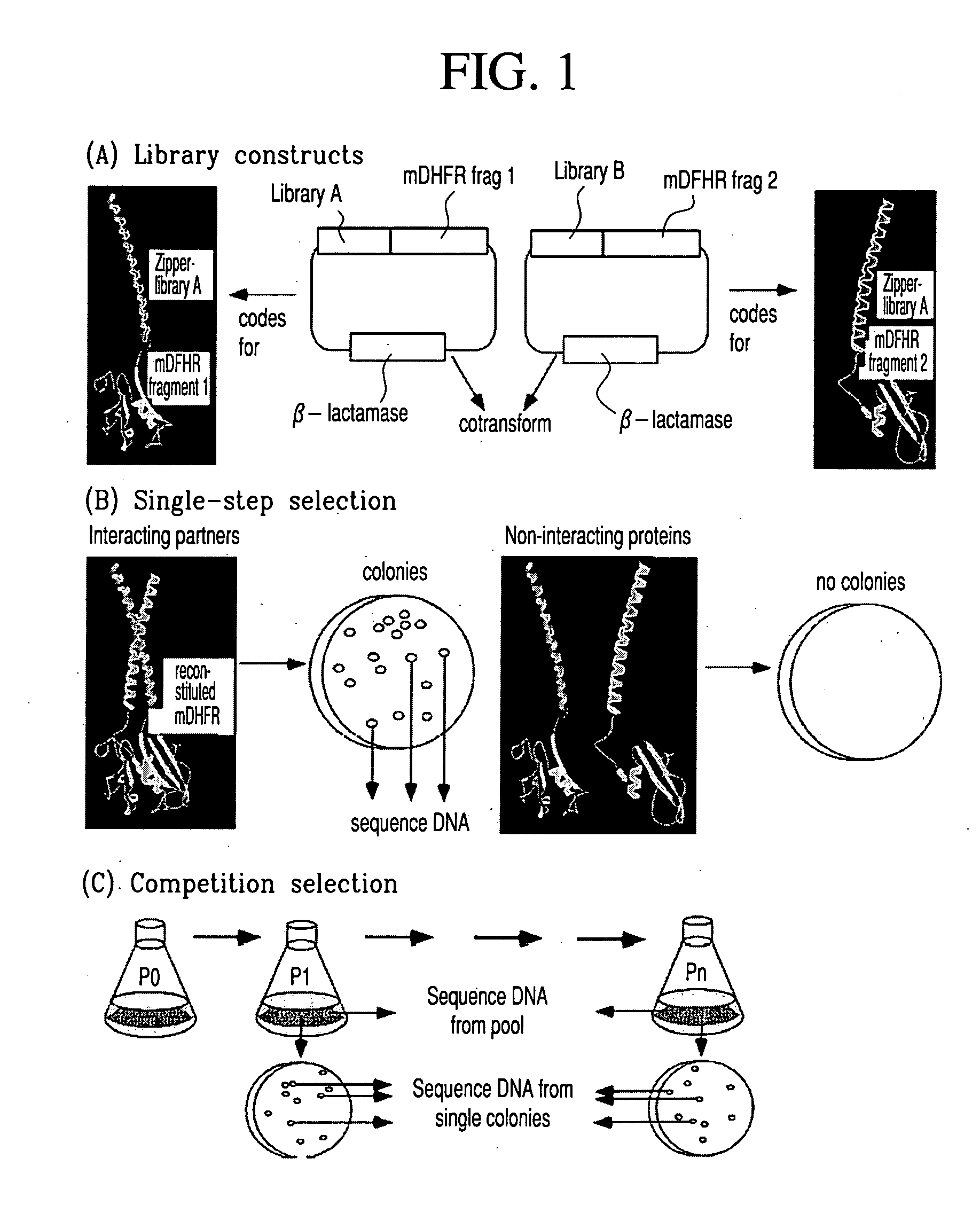
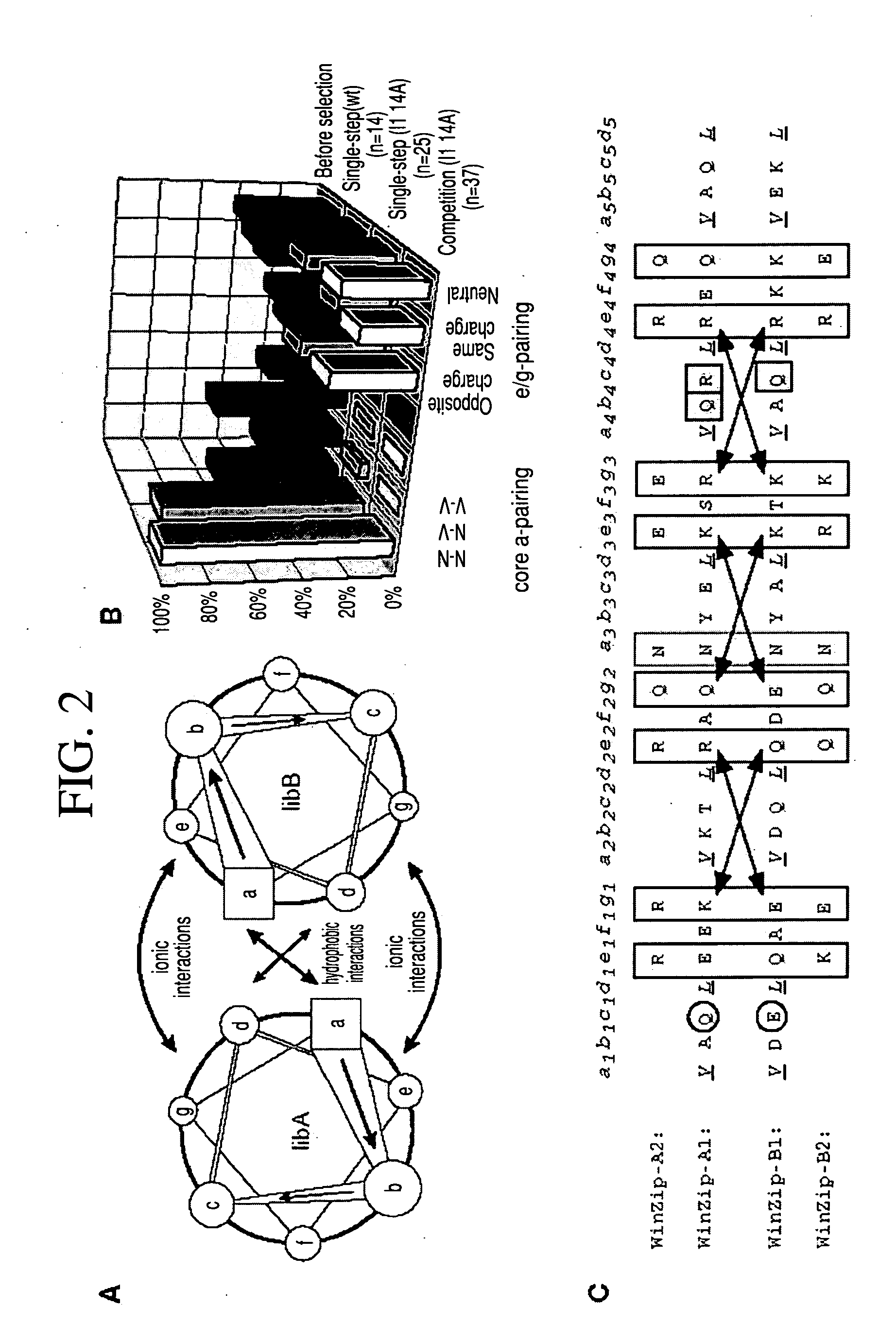
Vivo library-versus-library selection of optimized protein-protein interactions
The present invention describes a rapid and efficient in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy for identifying optimally interacting pairs of heterodimerizing polypeptides. It allows for the screening of a protein library against a second protein library, rather than against a single bait protein, and thus has numerous applications in the study of protein-protein interactions. Additionally, it allows for the application of different selection stringencies. Two leucine zipper libraries, semi-randomized at the positions adjacent to the hydrophobic core, were genetically fused to either one of two designed fragments of the enzyme murine dihydrofolate reductase (mDHFR), and cotransformed into E. coli. Interaction between the library polypeptides was required for reconstitution of the enzymatic activity of mDHFR, allowing bacterial growth. Analysis of the resulting colonies revealed important biases in the zipper sequences relative to the original libraries, which are consistent with selection for stable, heterodimerizing pairs. Using more weakly associating mDHFR fragments, we increased the stringency of selection. We enriched the best performing leucine zipper pairs by multiple passaging of the pooled, selected colonies in liquid culture, as the best pairs allowed for better bacterial propagation. This competitive growth allowed small differences among the pairs to be amplified, and different sequence positions were enriched at different rates. We applied these selection processes to a library-versus-library sample of 2.0×106 combinations, and selected a novel leucine zipper pair which may be appropriate for use in further in vivo heterodimerization strategies.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Chinese hamster ovary genetic engineering cell line for performing high-level secretory expression on AcAPc2
InactiveCN102321588AAdaptableExtended half-lifeVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHigh level expressionHamster
The invention discloses a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) genetic engineering cell line for performing high-level secretory expression on AcAPc2 and relates to a CHO cell line for performing high-level secretory expression on the AcAPc2. The invention aims to solve the problems that the expression level of an exogenous gene product expressed by using CHO is low at present and the industrialized production cannot be realized. The CHO genetic engineering cell line for performing high-level secretory expression on the AcAPc2 is obtained by the following step of: screening dihydrofolate reductase-deficient CHO cells which are taken as host cells, and amplifying to obtain the cell line for performing stable and high-level expression on the AcAPc2. The CHO cell line can perform high-level expression on the AcAPc2; the expression level can be up to 10mg / L.72h; and the CHO cell line can be industrially produced. The cell line is used for resisting blood coagulation and treating tumor, septicaemiaand the like.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and/or cytotoxic activity and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20090062318A1Reduce resistanceOvercome costsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsThymidylate synthaseDihydrofolate reductase
The present invention provides tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and cytotoxic activity in a single molecule having receptor tyrosine kinase(s), dihydrofolate reductase, thymidylate synthase and / or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory activity, which are useful as anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor agents. Also provided are methods of utilizing these inhibitors to treat tumor cells and other proliferative diseases and disorders.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
Mapping molecular interactions in plants with protein fragments complementation assays
InactiveUS6872871B2Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesFluorescenceADAMTS Proteins
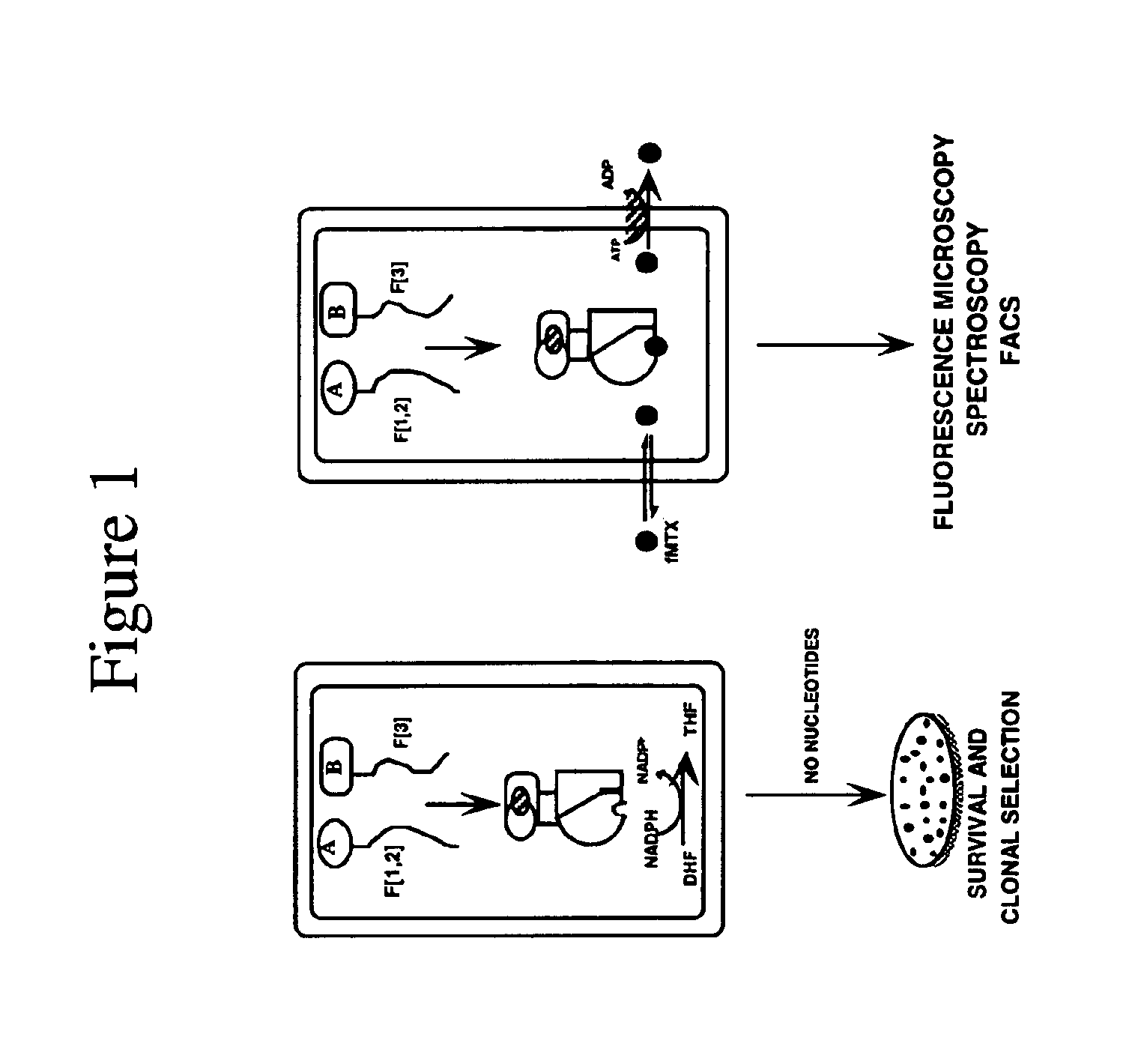
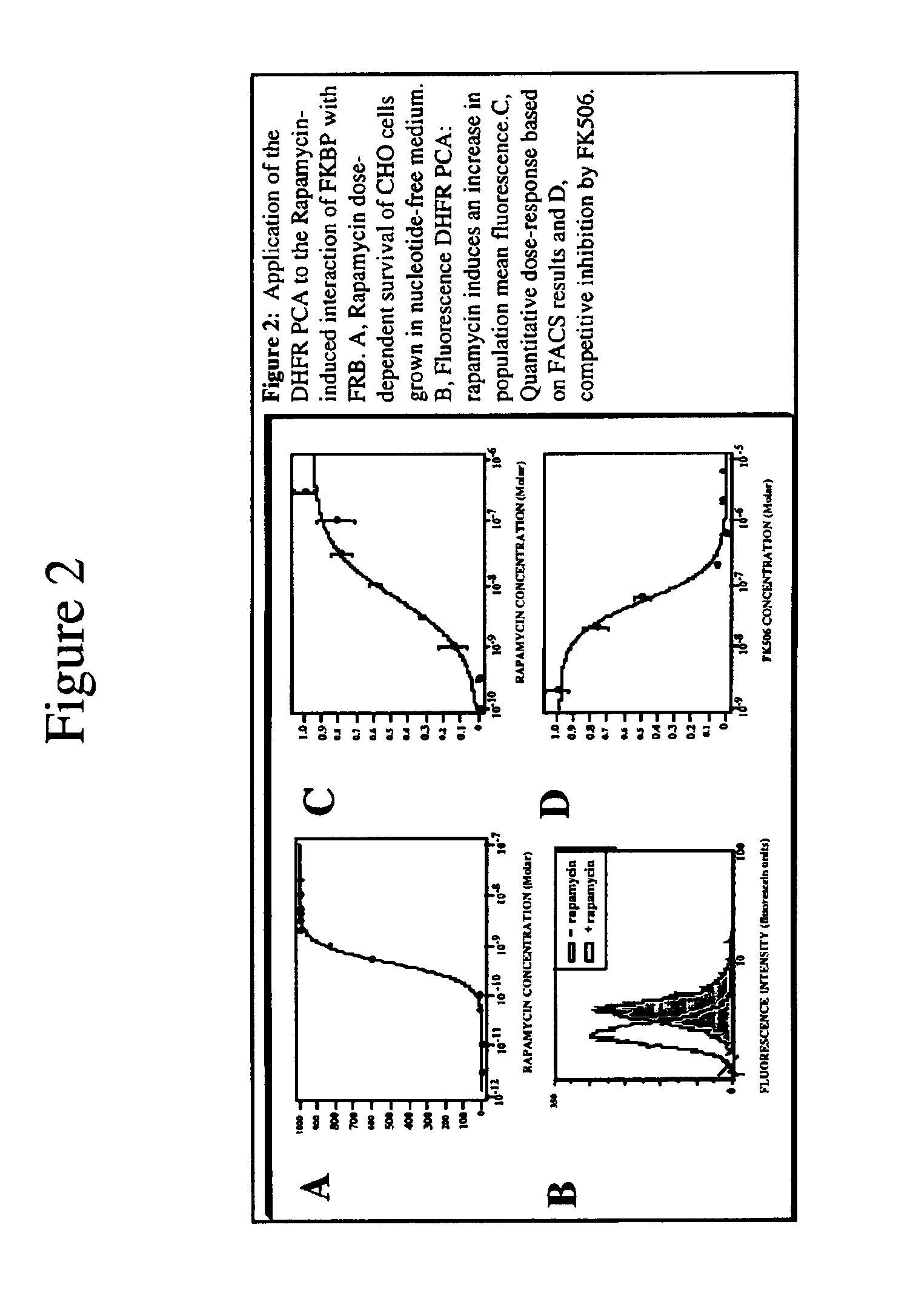
Protein Fragment Complementation Assays (PCA) are done in plant material using enzyme fragment constructs, for example, dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) fragment constructs. Plant material is transformed with at least two different constructs that form different products capable of interacting to reconstitute enzymatic activity in the plant material. Detection of the activity can be done using a substrate for the enzyme in the culture medium which, when reacted with the enzyme, is converted to a detectable product. One embodiment uses a substrate that can be enzymatically converted to a detectable fluorescent product. An inducer such as rapamycin or salicylic acid can be added to the culture medium to increase the level of detectable product.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Application of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)-PKcs in preparation of medicine for changing drug resistance of tumor cells on MTX (Methotrexate)
ActiveCN103301447AReduce the degree of amplificationDouble minute reductionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh concentrationResearch Object
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for assessing cancer for increased sensitivity to 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin
ActiveUS20110111436A1Disease diagnosisGlycinamide Ribonucleotide FormyltransferaseThymidylate synthase
Sensitivity of a patient's cancer to treatment with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin is assessed and patients are selected for treatment of cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin, by determining the amount of a selected polypeptide expressed by the cancer and comparing the amount with the amount of the selected polypeptide expressed by a reference cancer. The polypeptide includes a member of a folate pathway polypeptide within a cell and may include at least one of reduced folate carrier-1 enzyme (RFC-1), dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase (FPGS), thymidylate synthase (TS), γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT).
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and/or cytotoxic activity and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7960400B2Reduce resistanceOvercome costsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDihydrofolate reductaseThymidylate synthase
The present invention provides tricyclic compounds having cytostatic and cytotoxic activity in a single molecule having receptor tyrosine kinase(s), dihydrofolate reductase, thymidylate synthase and / or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitory activity, which are useful as anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor agents. Also provided are methods of utilizing these inhibitors to treat tumor cells and other proliferative diseases and disorders.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
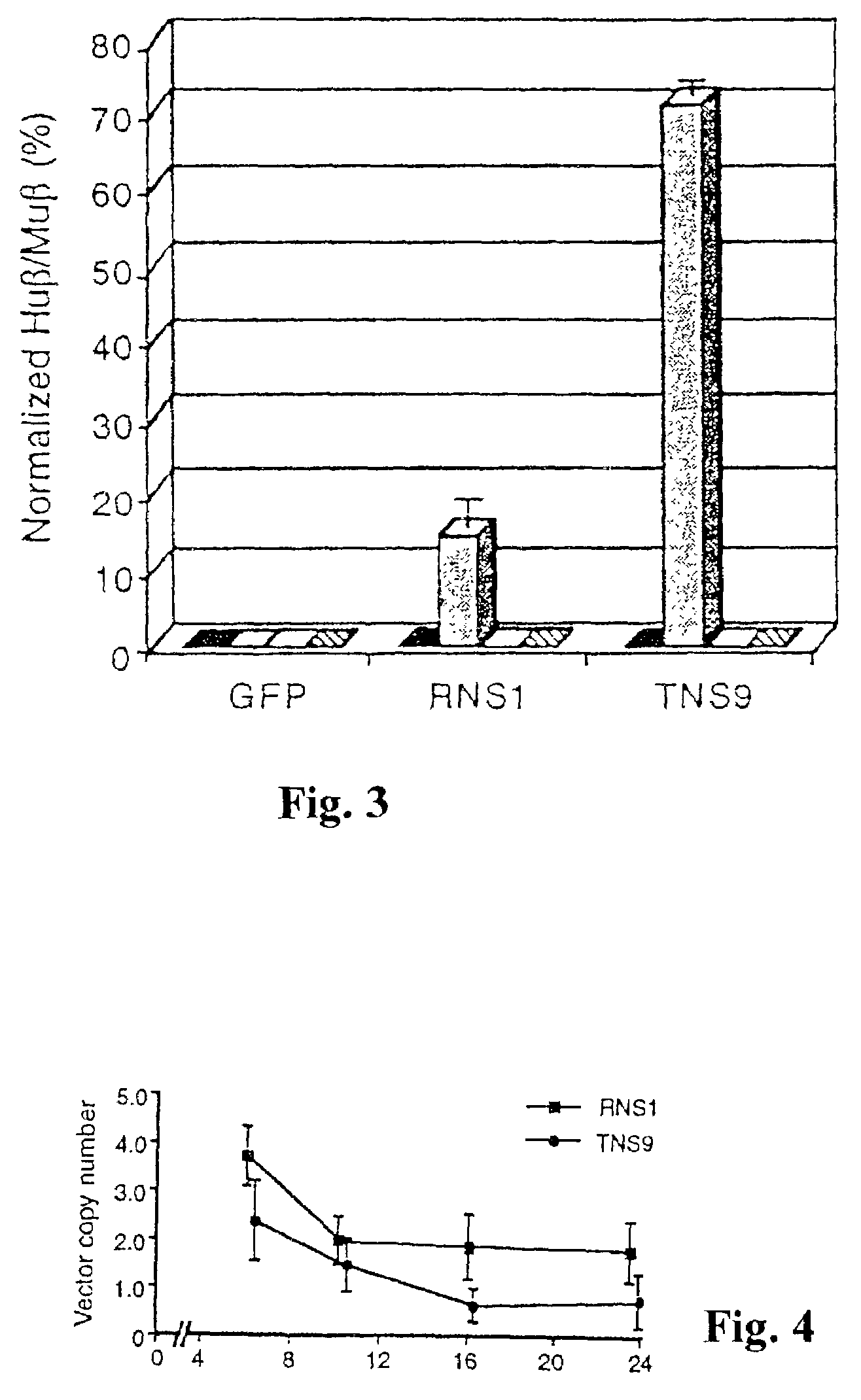
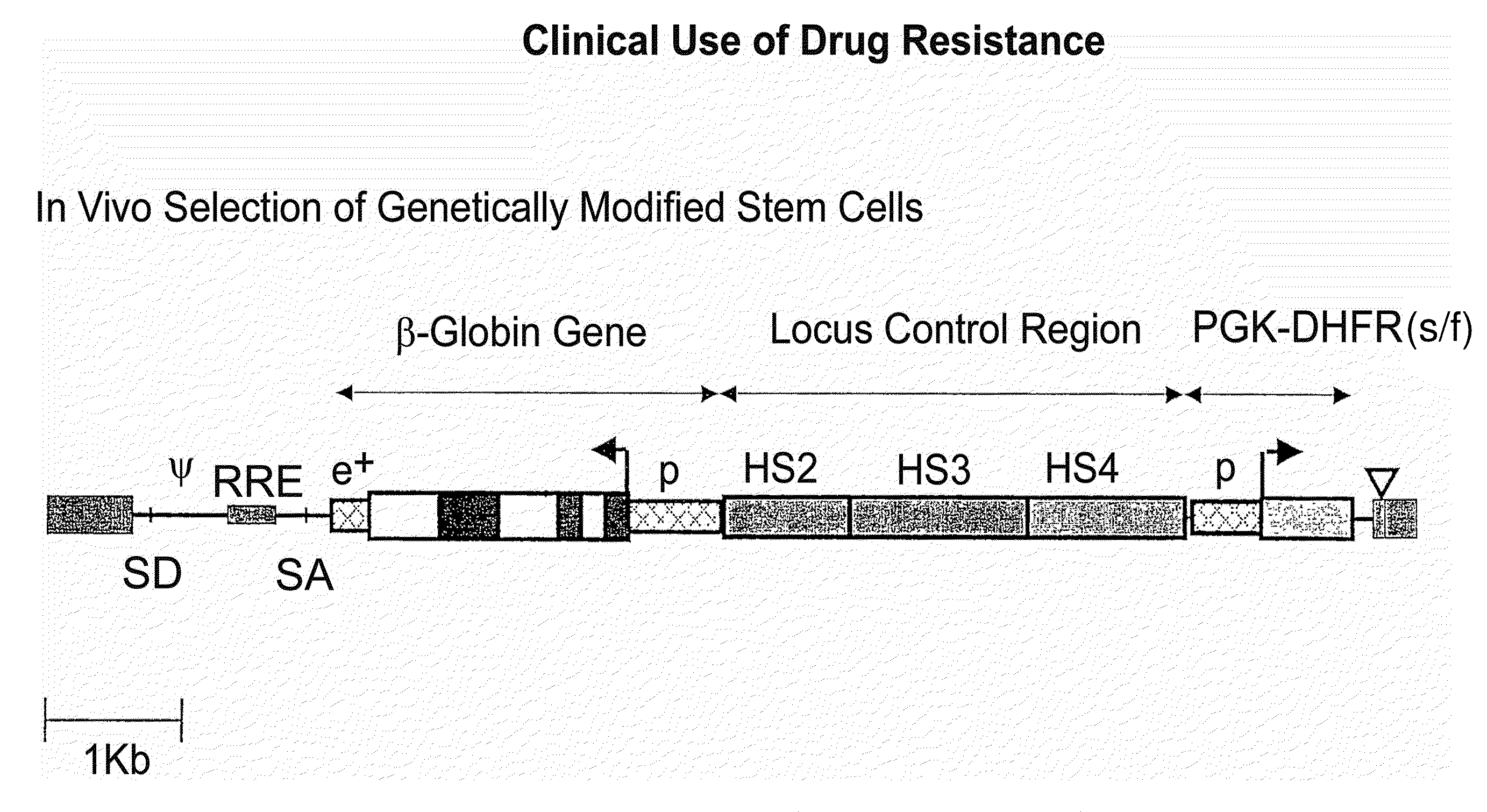
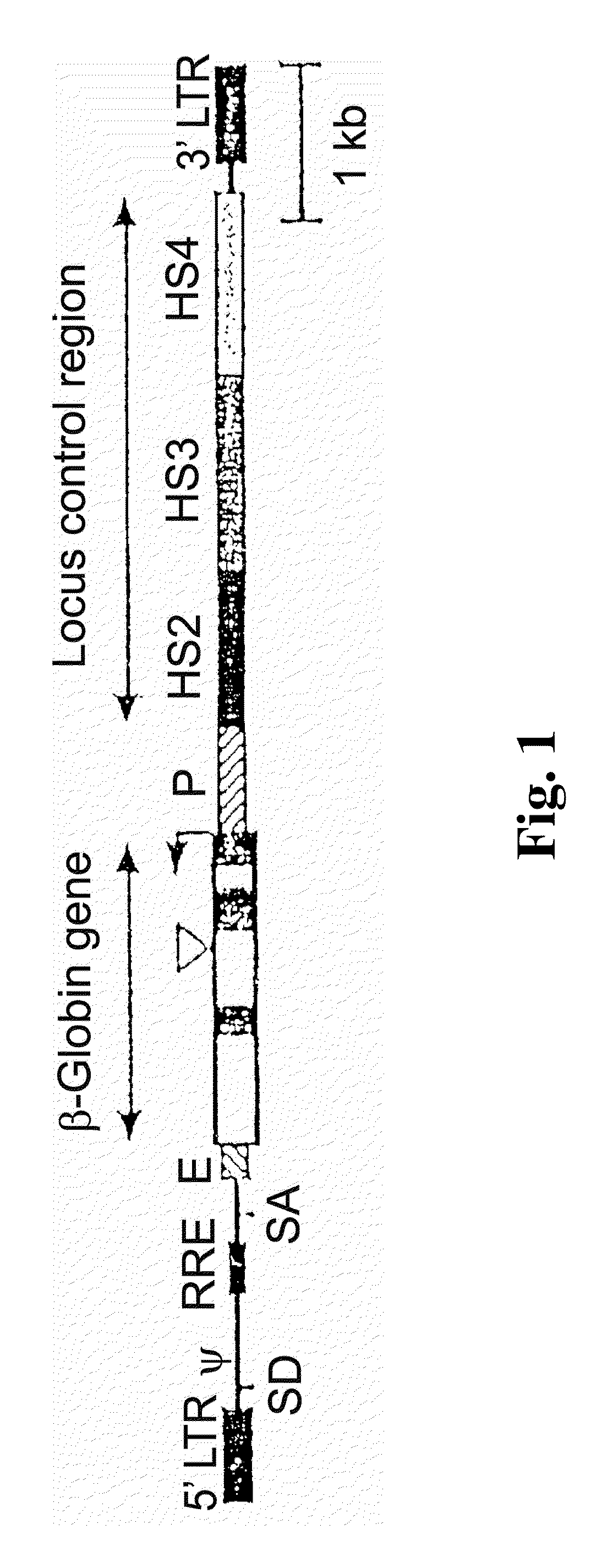
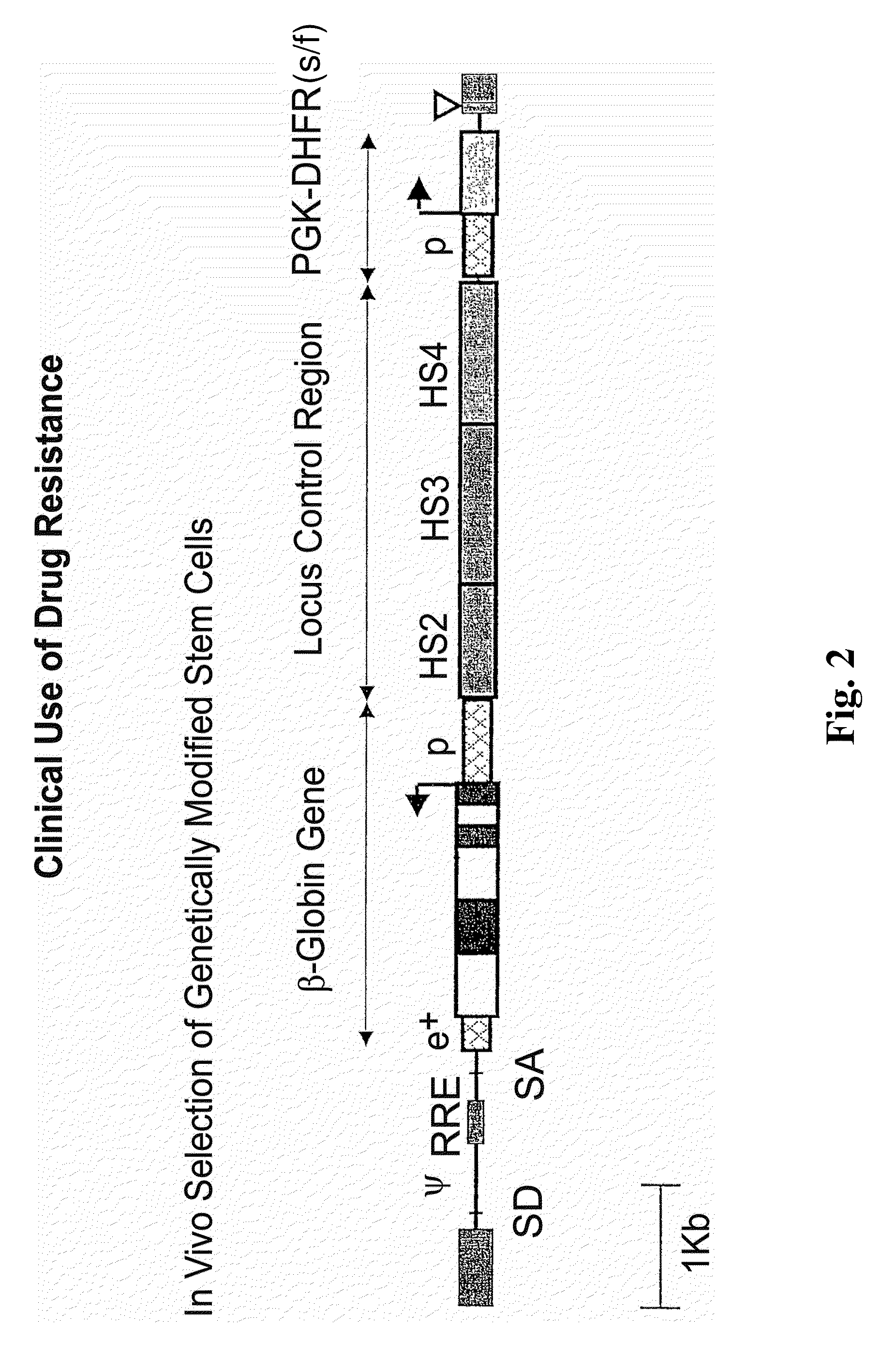
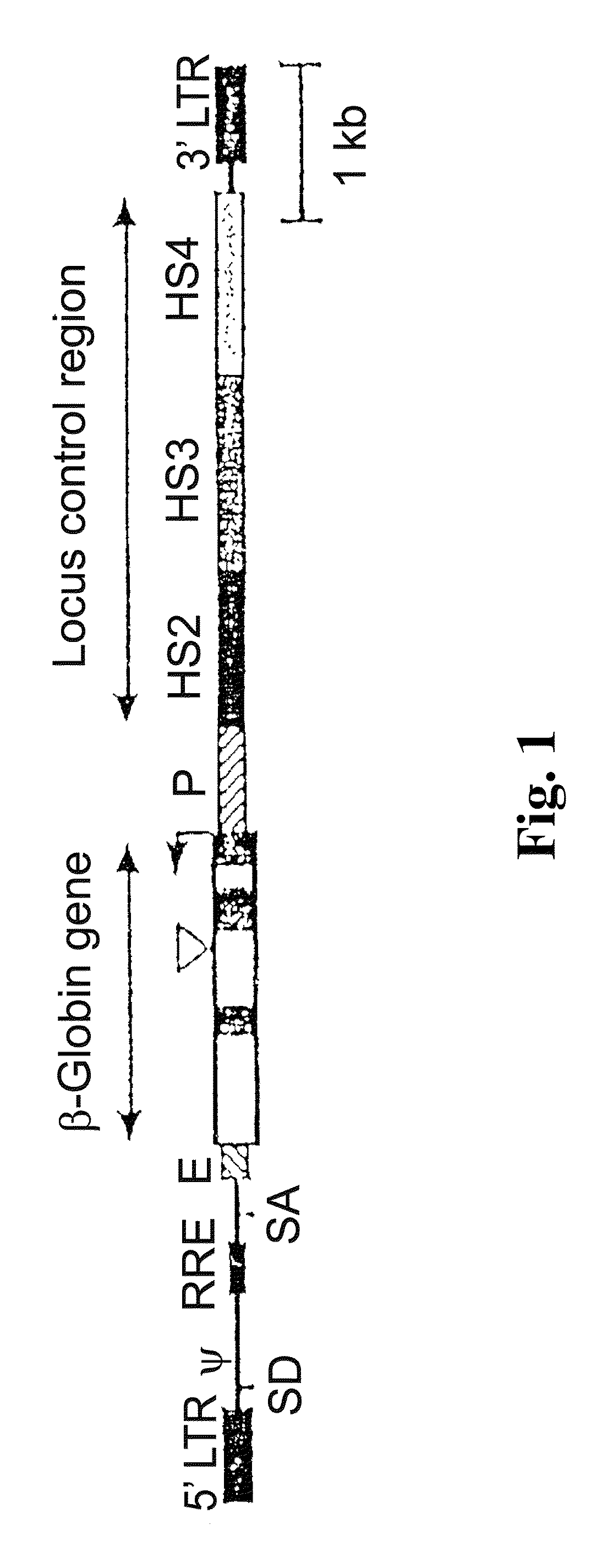
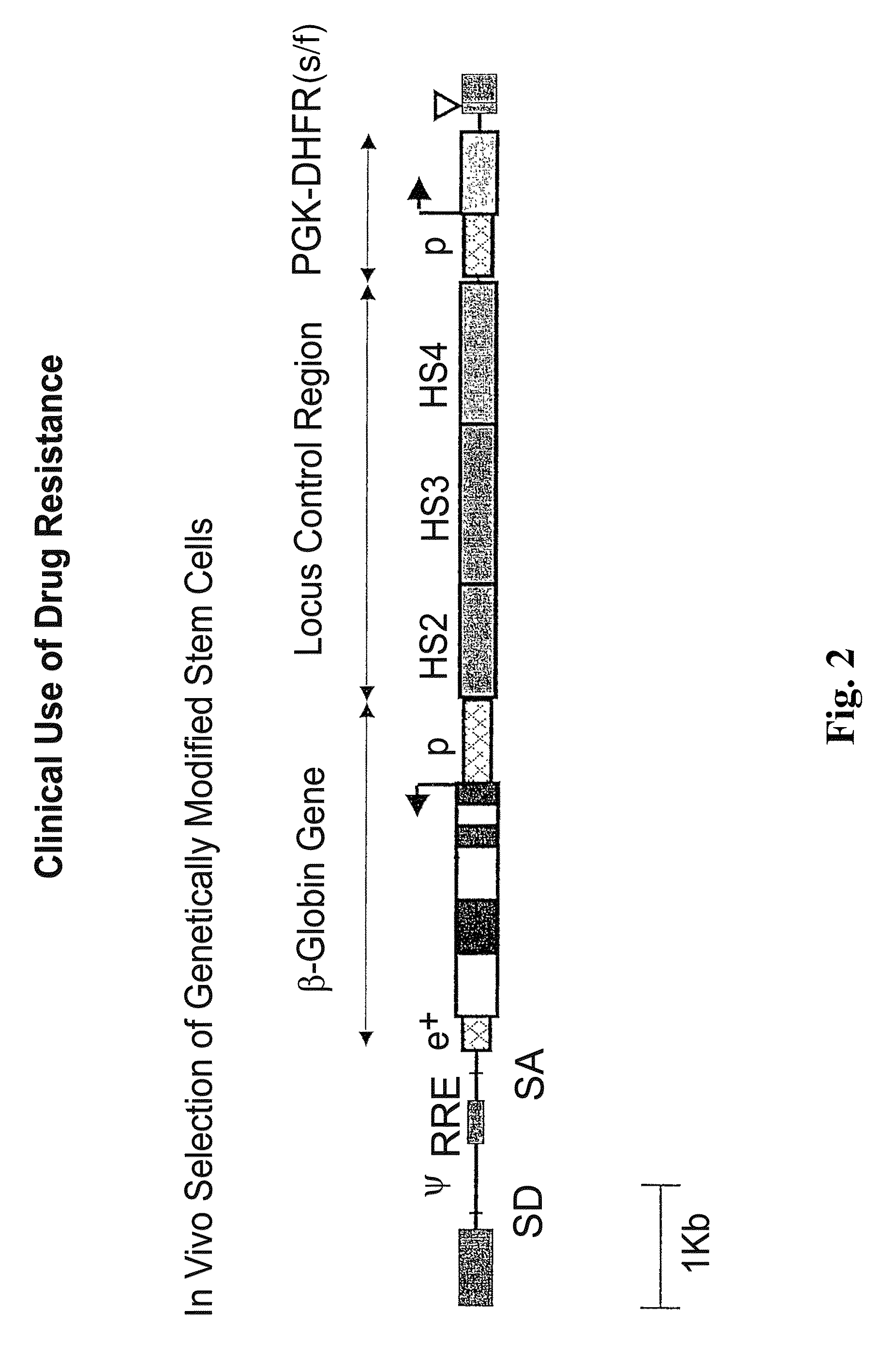
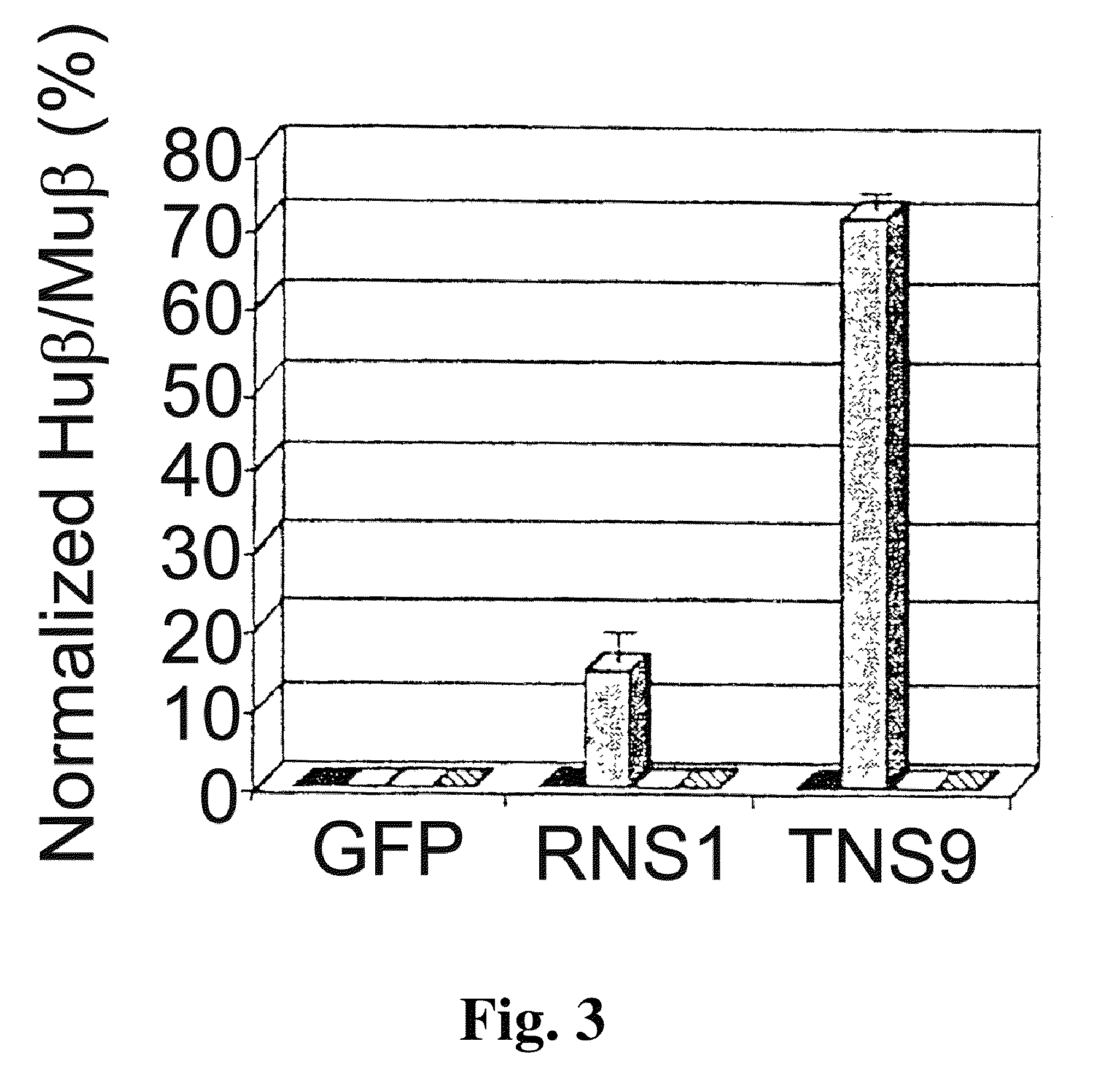
Vector encoding human globin gene and use thereof in treatment of hemoglobinopathies
ActiveUS7541179B2Increase percentageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlobin genesDihydrofolate reductase
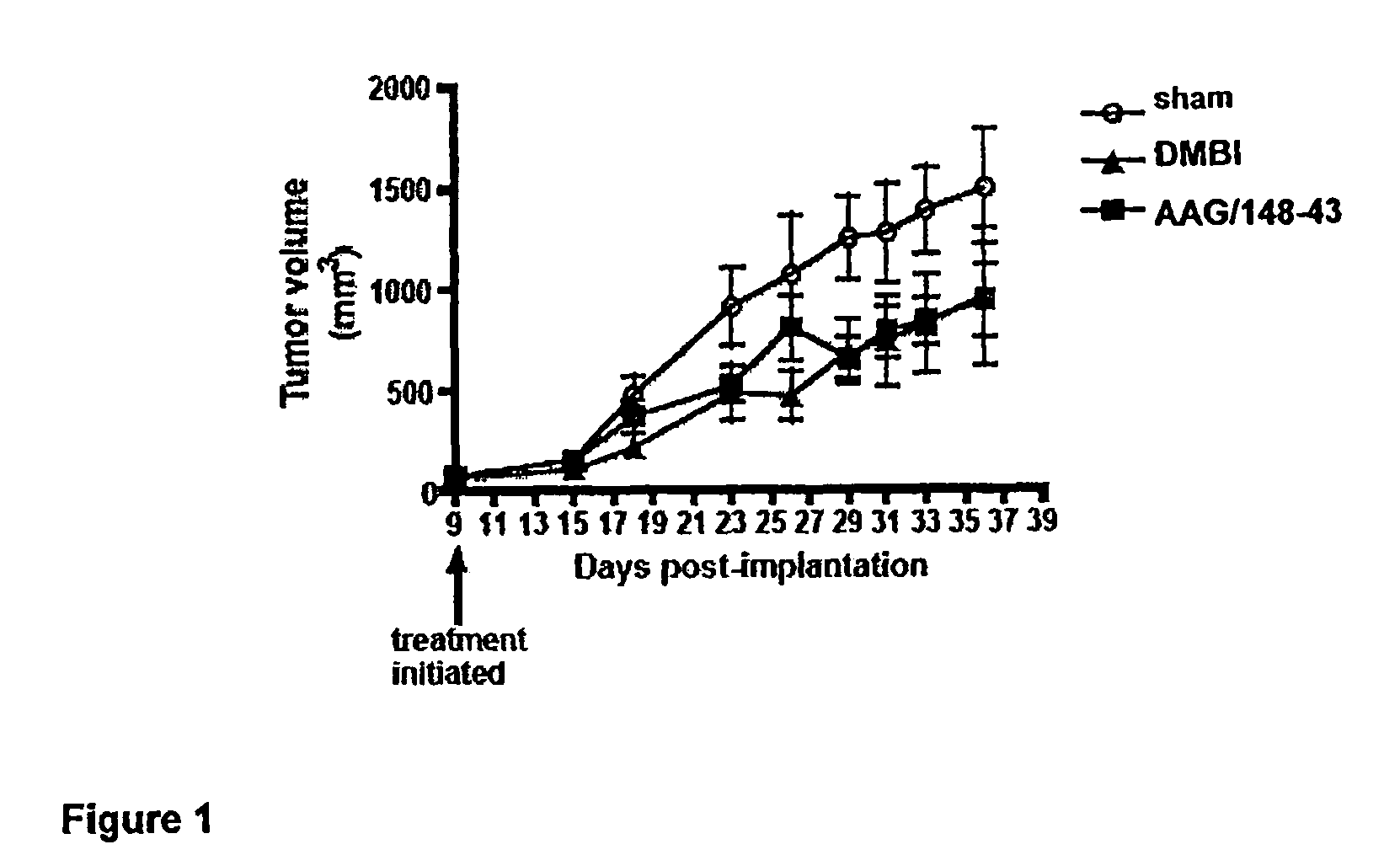
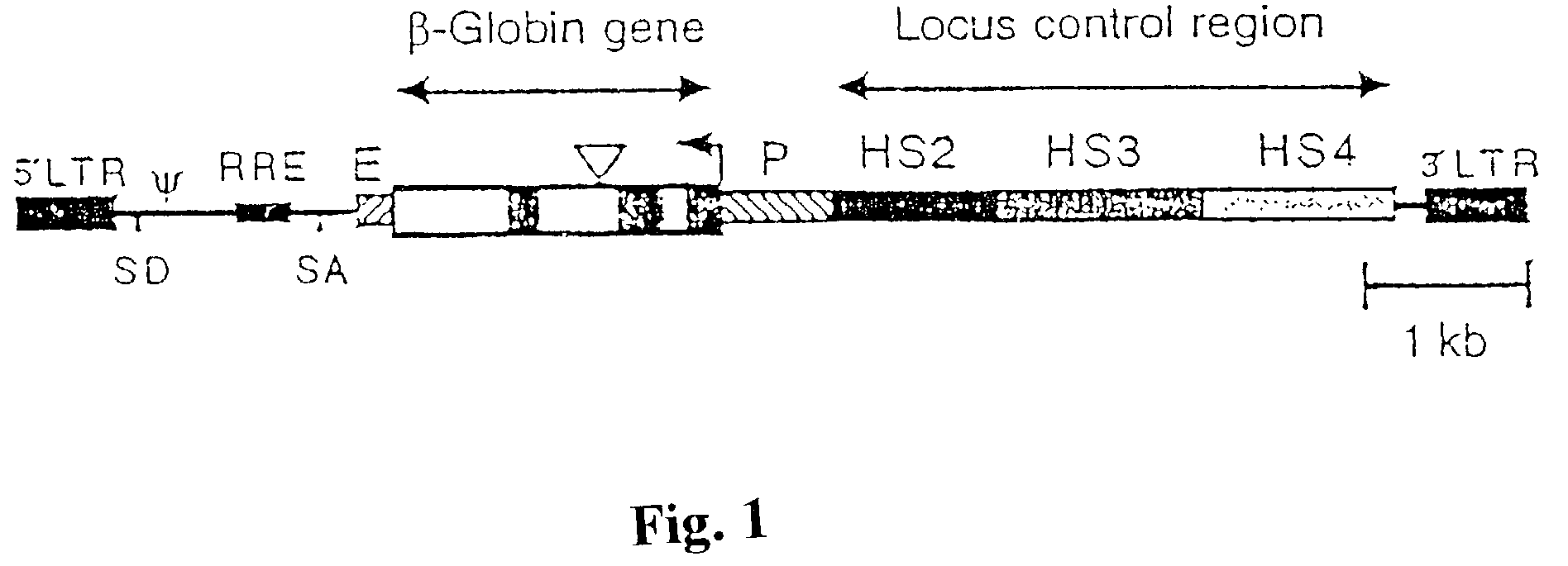
Recombinant lentiviral vectors having a region encoding a functional β-globin gene; and large portions of the β-globin locus control regions which include DNase I hypersensitive sites HS2, HS3 and HS4 provides expression of β-globin when introduced into a mammal, for example a human, in vivo. Optionally, the vector further includes a region encoding a dihydrofolate reductase. The vector may be used in treatment of hemoglobinopathies, including β-thalessemia and sickle-cell disease. For example, hematopoietic progenitor or stem cells may be transformed ex vivo and then restored to the patient. Selection processes may be used to increase the percentage of transformed cells in the returned population. For example, a selection marker which makes transformed cells more drug resistant than un-transformed cells allows selection by treatment of the cells with the corresponding drug.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Gene expression system and regulation thereof
InactiveUS20170114346A1Eliminate fluctuationsPromote resultsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNucleotide
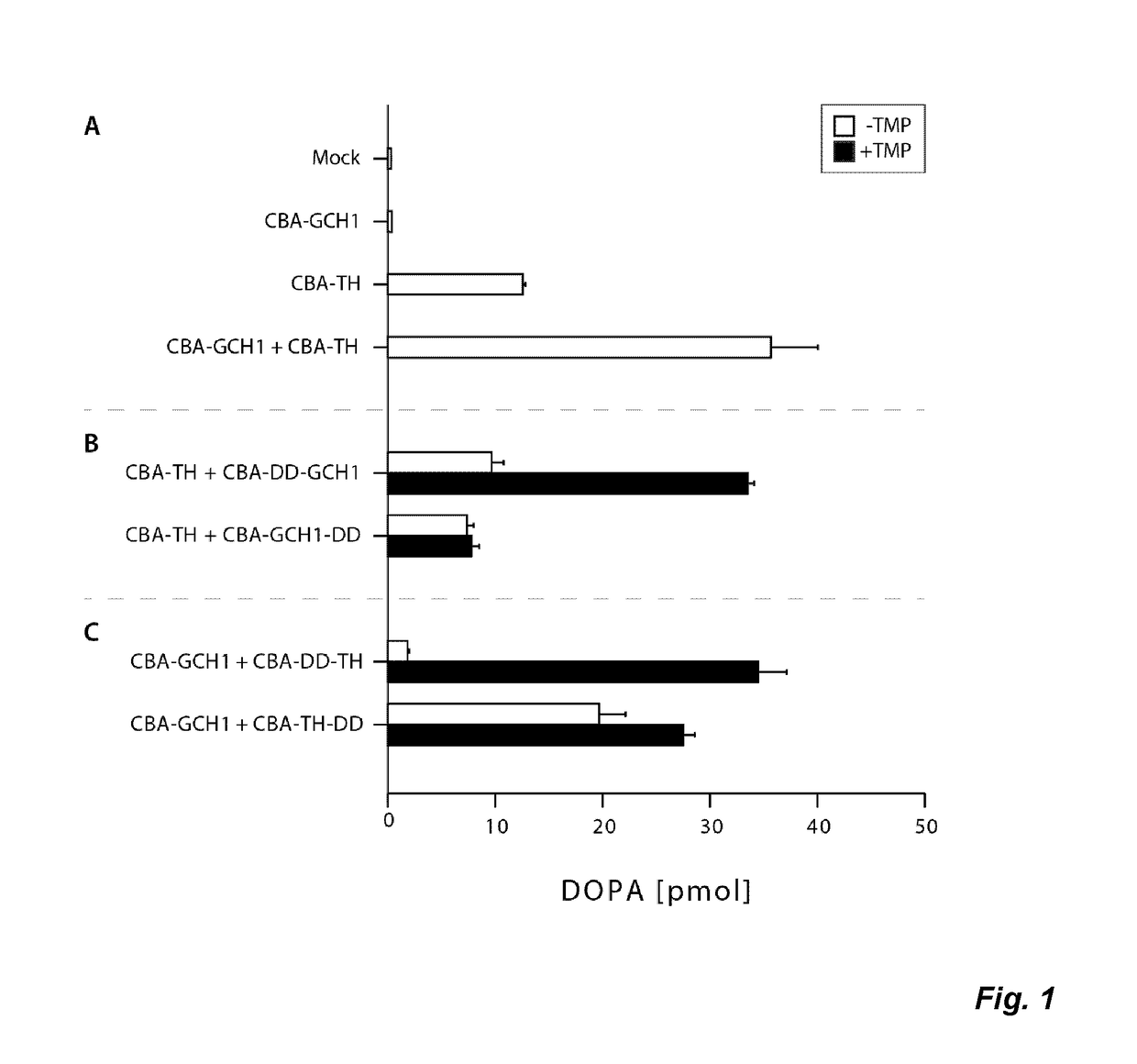
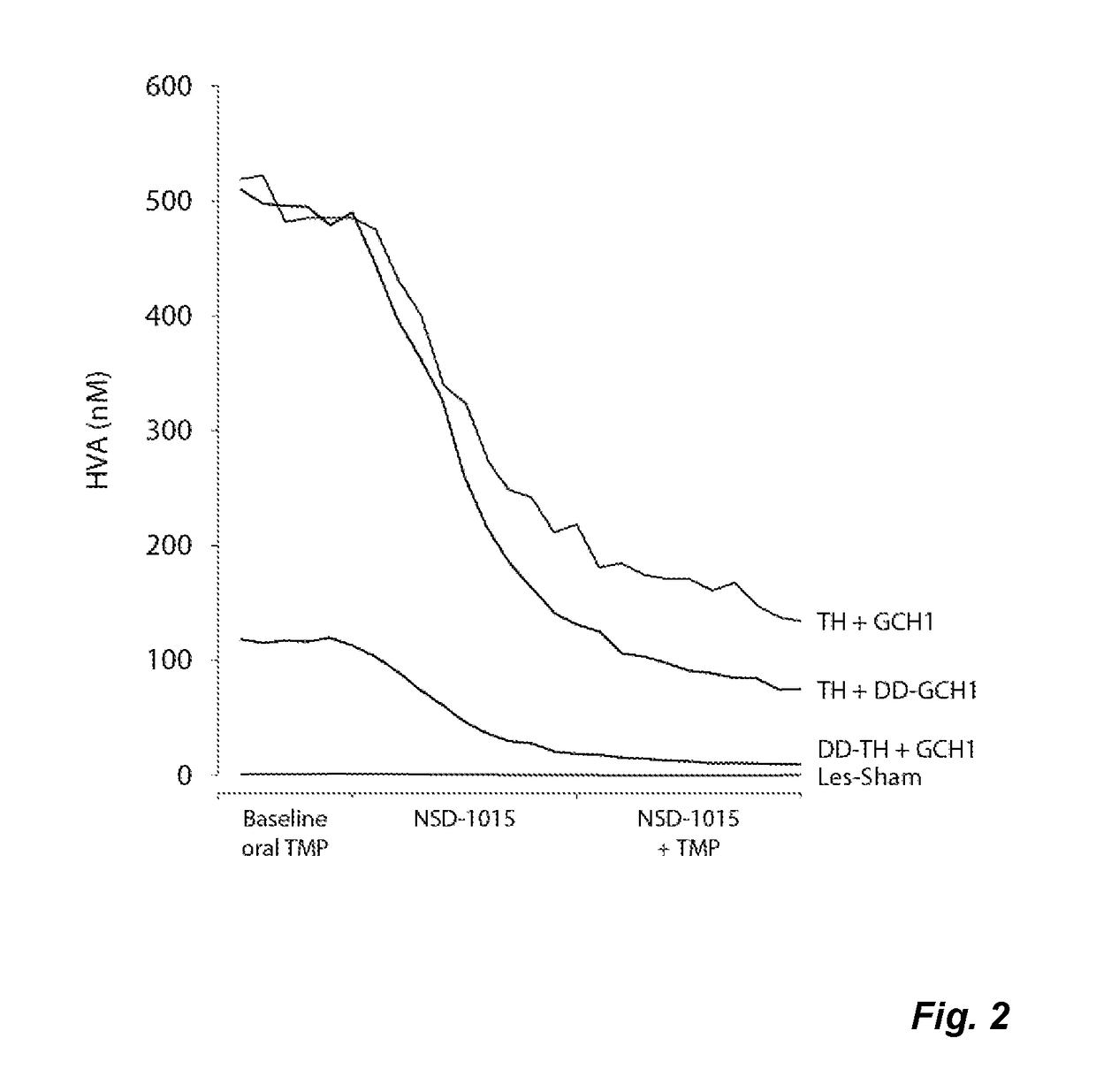
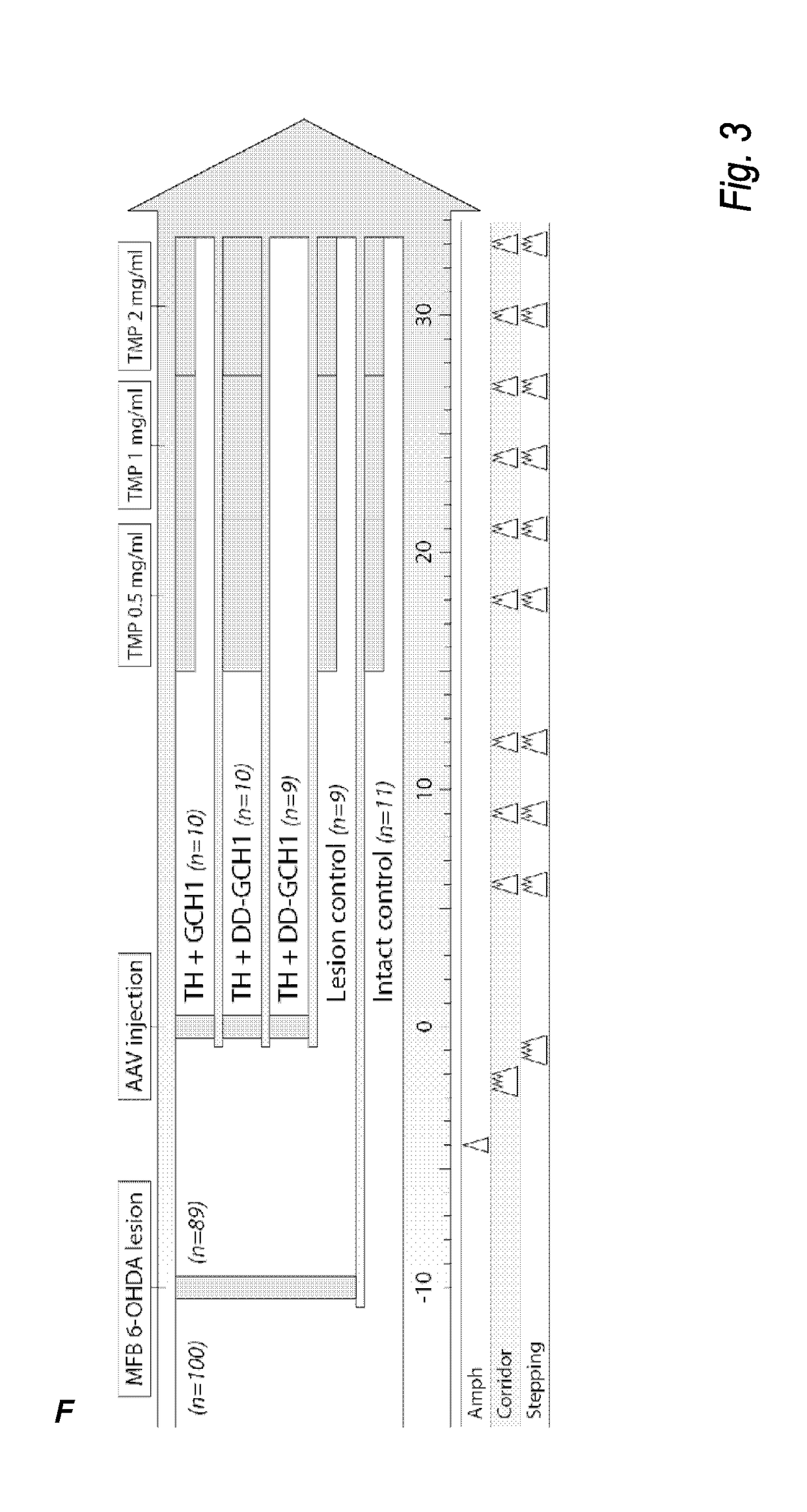
The present invention relates to a novel gene expression system comprising: a) a first nucleotide sequence encoding a fusion polypeptide of: a1) a destabilizing domain (DD) based on DHFR, and a2) a GTPcyclohydrolase 1 (GCH1) polypeptide, or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof; and b) a second nucleotide sequence encoding a tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) polypeptide, or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof. The invention also relates to use of this gene expression system together with a ligand binding to a destabilizing domain (DD) based on dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) for treatment of diseases associated with a reduced dopamine level, such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:BRAINGENE AB
Acetamides compound and application thereof
The invention relates to an acetamides compound and application thereof, and discloses an N-(4-substituted phenyl ethyl) amides compound with a novel structure. An in vitro activity test experiment proves that the compound has the enzyme inhibitory activity on cysteine proteinase (FP-2) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR); a malaria-killing experiment result proves that the compound has an inhibition effect on wild and drug-resistant malaria protozoon.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Antimalarial compounds with flexible side-chains
ActiveUS20090099220A1Low toxicityLittle and no antibacterial activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMalarial parasiteSide chain
The present invention relates to novel compounds that are inhibitors of wild type and mutant dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) of Plasmodium falciparum, which are useful for the treatment of malaria. It also relates to processes of making and using such compounds. The antimalarial compounds of the present invention have low toxicity to a host infected with the malarial parasite, and are potent when administered in pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:NAT SCI & TECH DEV AGENCY
Protein regulation system as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107312797AImprove expression levelHigh expressionGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid vectorProtein targetProtein regulation
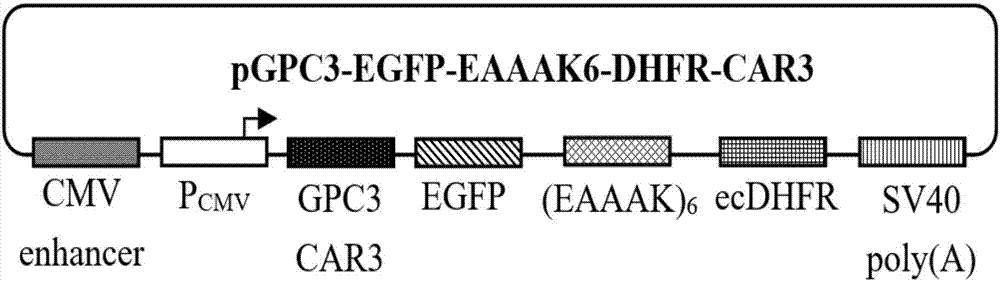
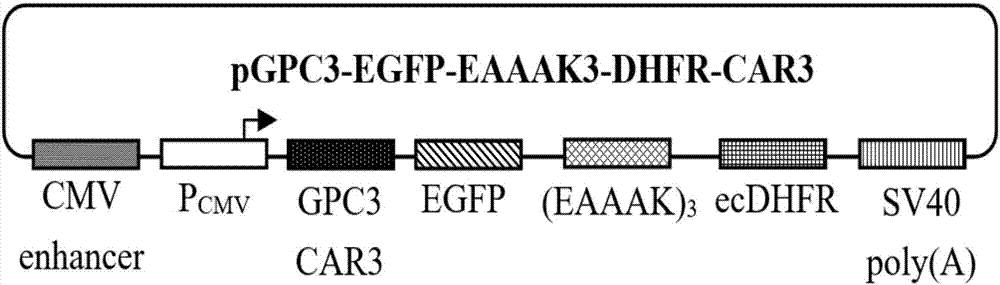
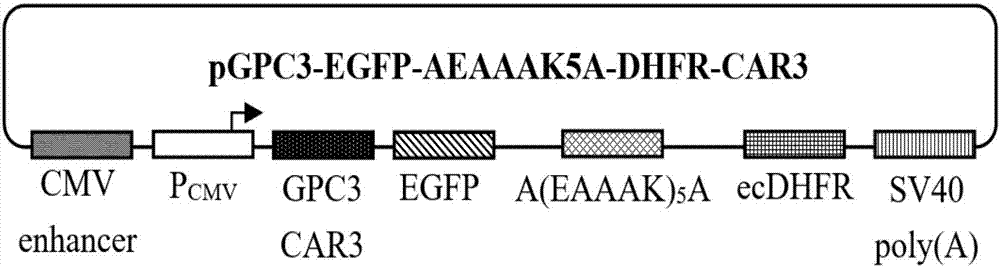
The invention relates to a protein regulation system as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Dihydrofolate reductase in a protein regulation system and to-be-regulated target protein are connected by adopting rigid connecting peptide; the rigid connecting peptide is (EAAAK)n or A(EAAAK)nA, wherein n is an arbitrary integer ranging from 1 to 6, and preferably, n is 6. The protein regulation system disclosed by the invention has higher target protein expression quantity, higher regulation ratio, higher regulation amplitude and very wide application value.
Owner:BLUE ELEGANT BIOTECH CO LTD
Antisense antibacterial cell division composition and method
Antisense oligomers directed to bacterial cell division and cell cycle-encoding nucleic acids are capable of selectively modulating the biological activity thereof, and are useful in treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. The antisense oligomers are substantially uncharged, and contain from 8 to 40 nucleotide subunits, including a targeting nucleic acid sequence at least 10 nucleotides in length which is effective to hybridize to (i) a bacterial tRNA or (ii) a target sequence, containing a translational start codon, within a bacterial nucleic acid which encodes a protein associated with cell division or the cell cycle. Such proteins include zipA, sulA, secA, dicA, dicB, diCc, dicF, ftsA, ftsl,ftsN, ftsK, ftsL, ftsQ, ftsw, ftsZ, murC, murD, murE, murF, murg, minC, minD, minE, mraY, mraW, mraZ, seqA, ddlB, carbamate kinase, D-ala D-ala ligase, topoisomerase, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, thioredoxin reductase, dihydrofolate reductase, and cell wall enzyme.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
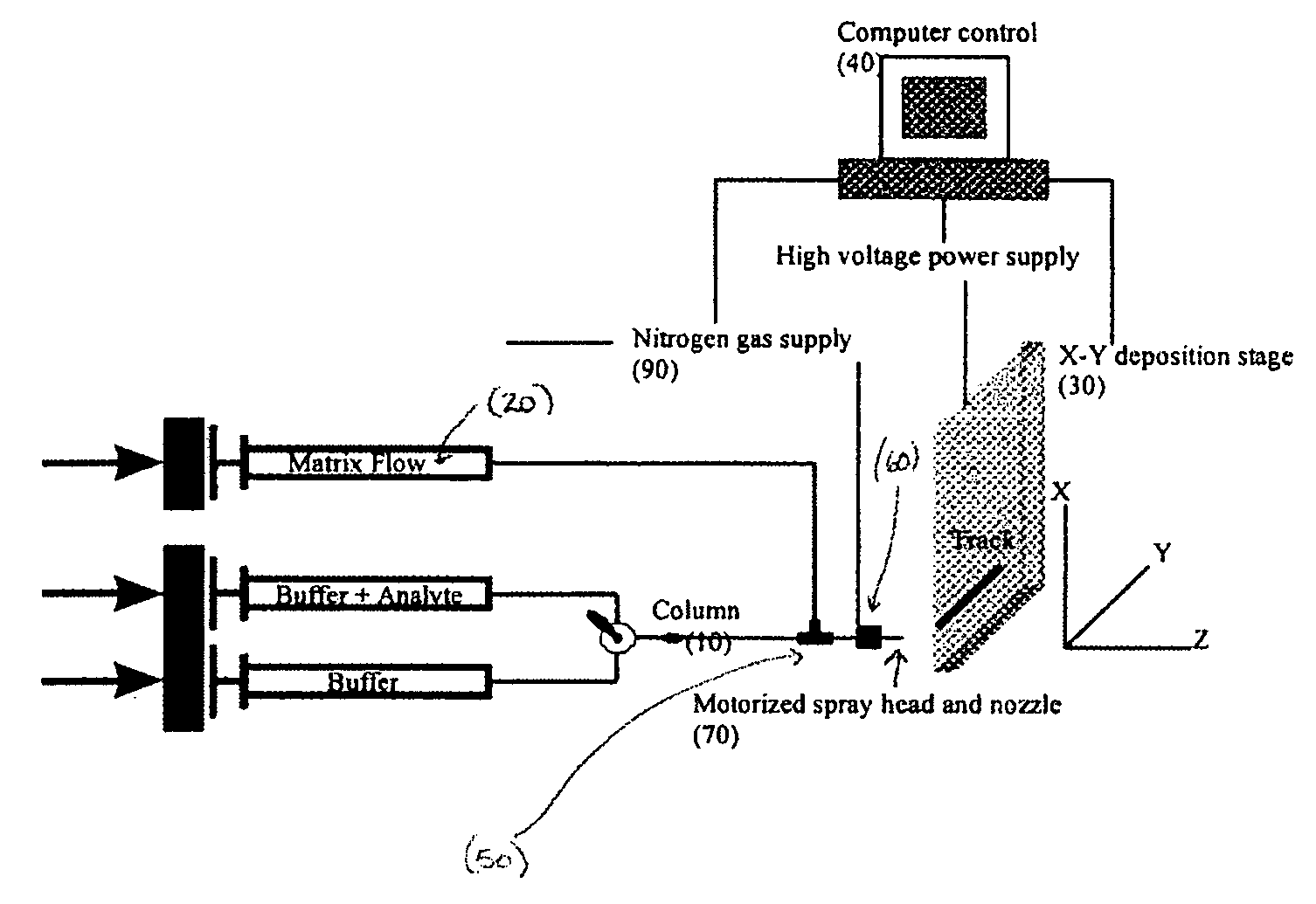
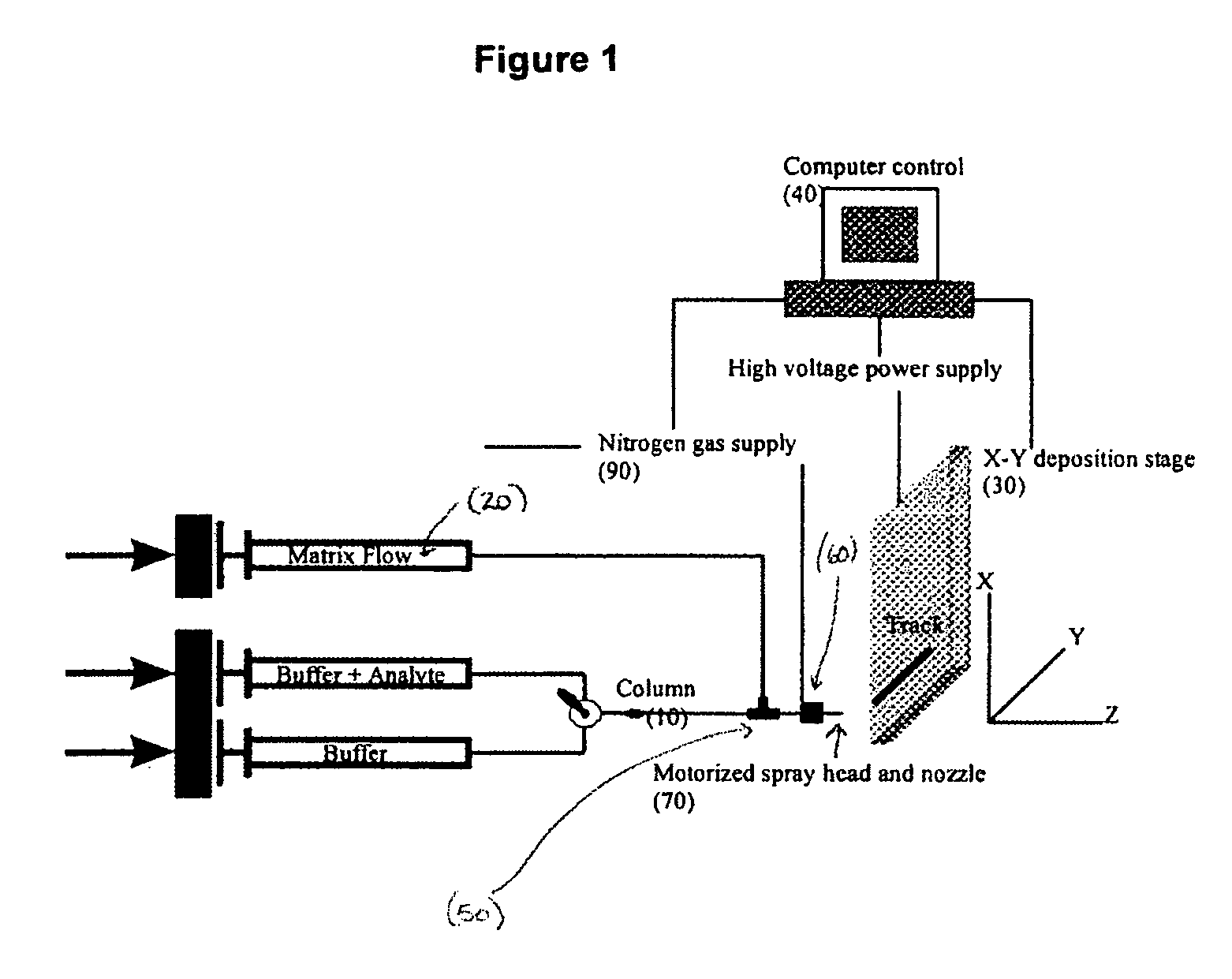
Frontal affinity chromatography/MALDI tandem mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20050269507A1DetectabilityMaximum track homogeneityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationDihydrofolate reductaseMass spectrometry imaging
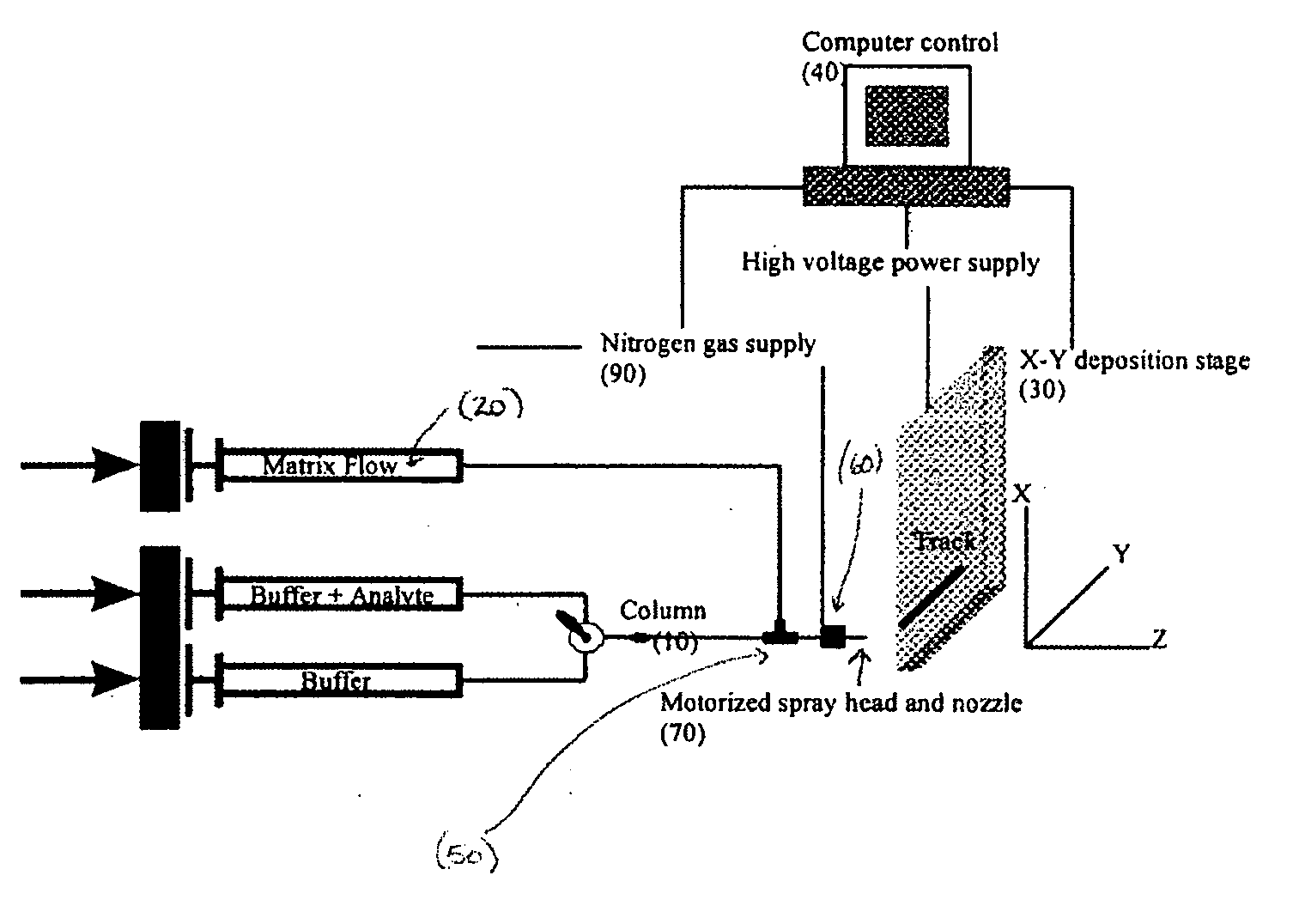
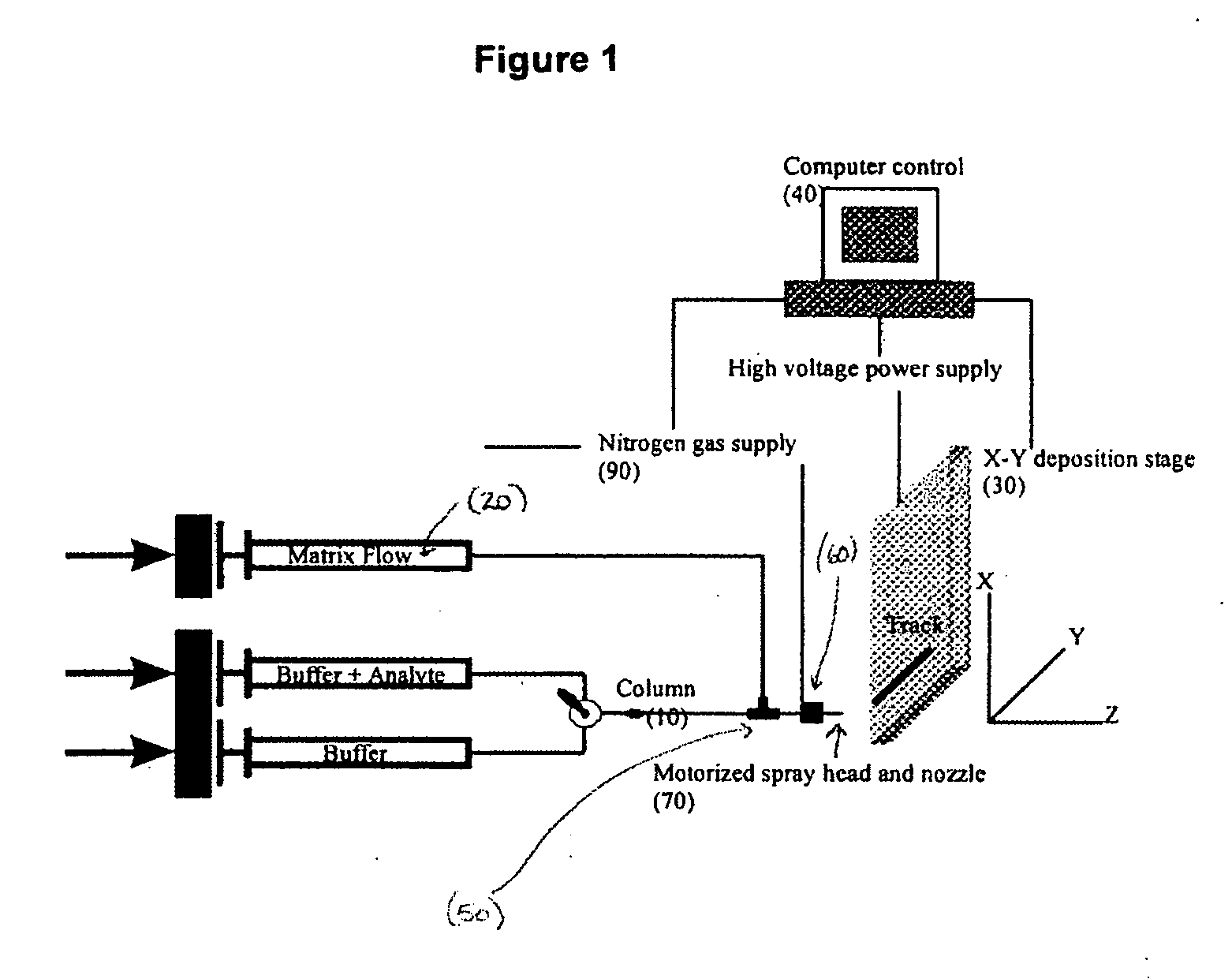
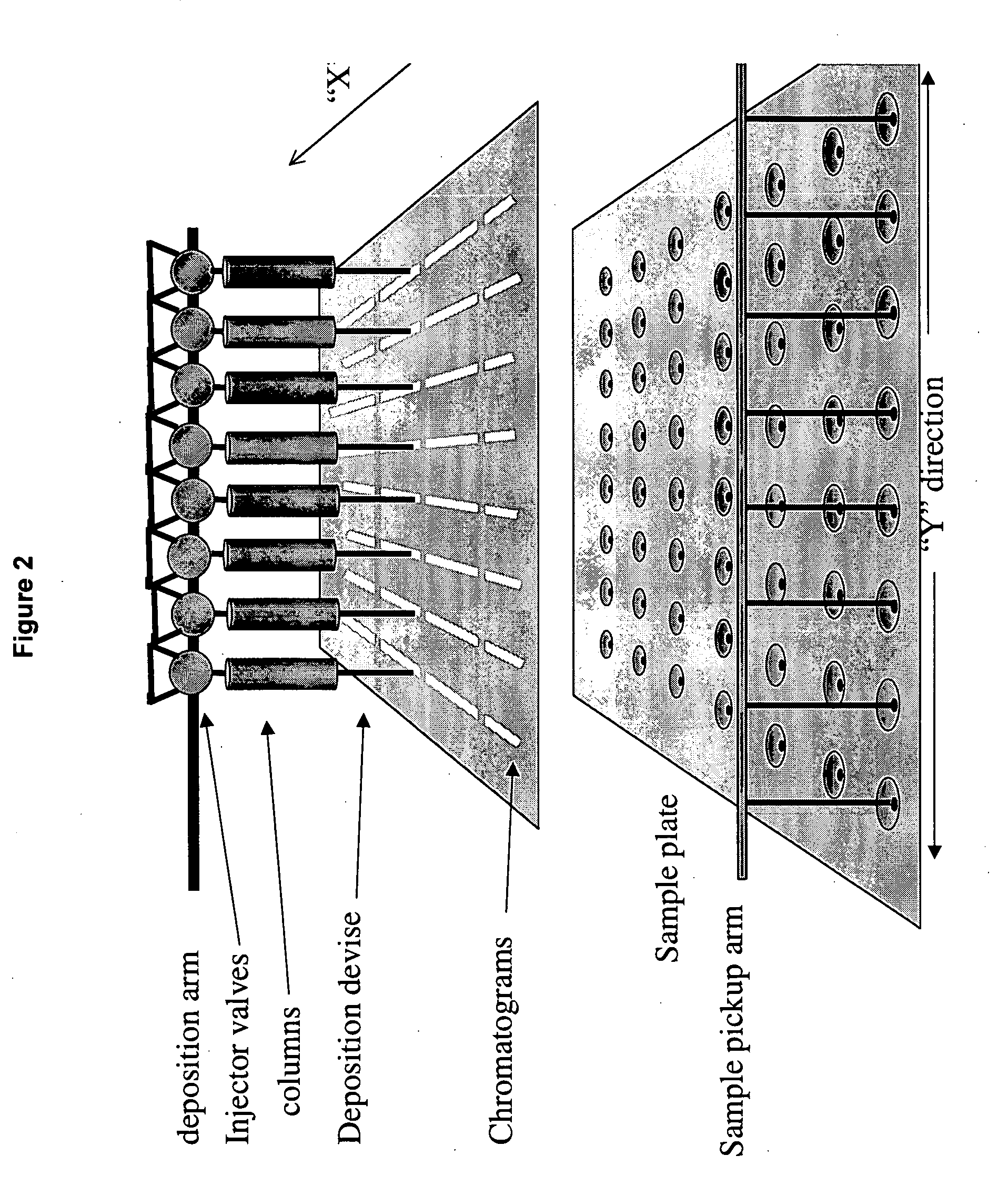
Sol-gel derived monolithic silica columns containing entrapped dihydrofolate reductase were used for frontal affinity chromatography of small molecule mixtures. The output from the column combined with a second stream containing the matrix molecule (HCCA) and was directly deposited onto a conventional MALDI plate that moved relative to the column via a computer controlled x-y stage, creating a semi-permanent record of the FAC run. The use of MALDI MS allowed for a decoupling of the FAC and MS methods allowing significantly higher ionic strength buffers to be used for FAC studies, which allowed for better retention of protein activity over multiple runs.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
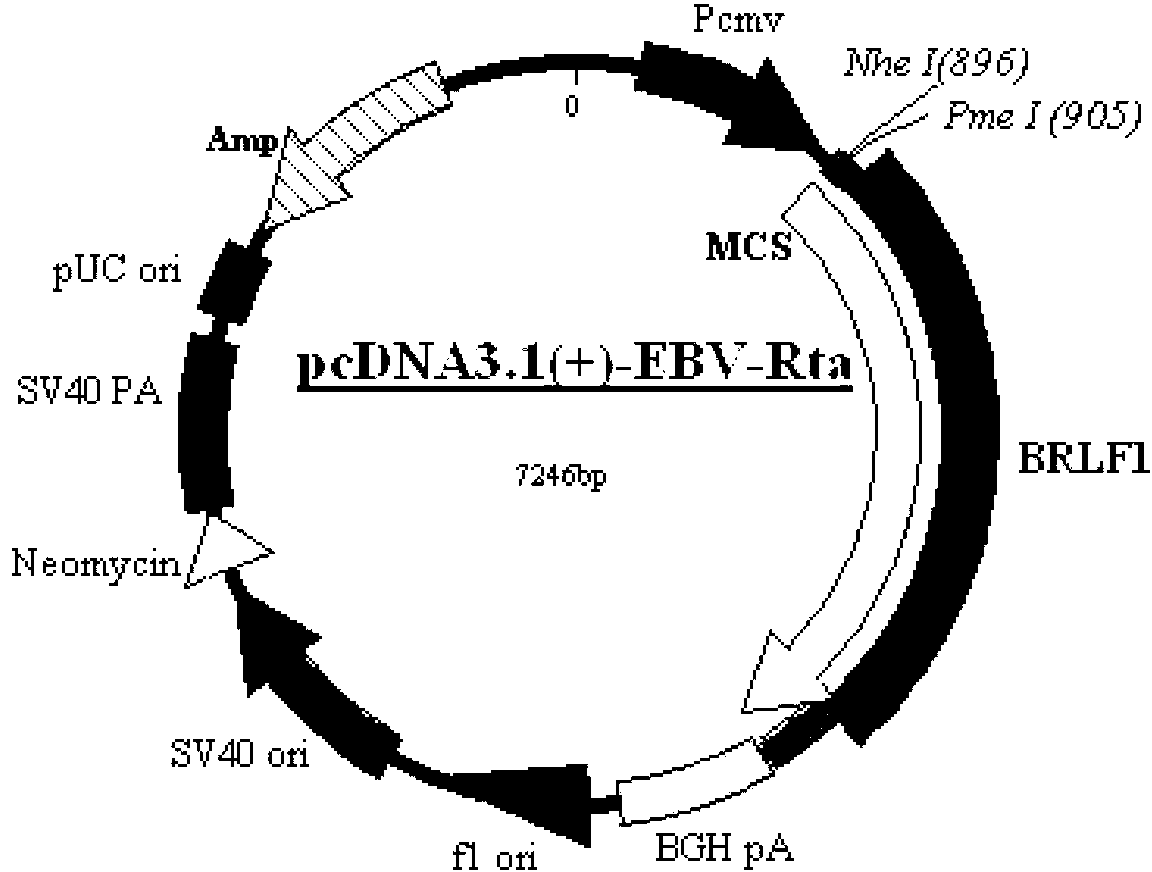
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line capable of expressing Rta albumen of Elzatein-Barn (EB) virus stably and efficiently, creation method and application thereof and cell base built by CHO cell line
ActiveCN103131674AConducive to screeningEasy diagnosisMicroorganism librariesVector-based foreign material introductionDihydrofolate reductaseCell strain
The invention relates to a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line capable of showing Rta albumen of Elzatein-Barn (EB) virus stably and efficiently, a creation method and application thereof and a cell base built by the CHO cell line, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Preservation number of the recombination cell line CHO / RTA is CGMCC6955, the CHO cell base expressing the Rta albumen of the EB virus can be used for practical production and formed by the recombination cell line CHO / RTA. The invention further provides a method for creating the CHO cell line. Dihydrofolate reductase defect type Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO / dhfr-) serve as host cells, and the cell line capable of expressing the Rta albumen of the EB virus stably and efficiently is obtained after screening and amplification of the host cells.
Owner:同昕生物技术(北京)有限公司
Vector encoding human globin gene and use thereof in treatment of hemoglobinopathies
InactiveUS20090274671A1Increase percentageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTransformation cellGlobin genes
Recombinant lentiviral vectors having a region encoding a functional β-globin gene; and large portions of the β-globin locus control regions which include DNase I hypersensitive sites HS2, HS3 and HS4 provides expression of β-globin when introduced into a mammal, for example a human, in vivo. Optionally, the vector further includes a region encoding a dihydrofolate reductase. The vector may be used in treatment of hemoglobinopathies, including β-thalessemia and sickle-cell disease. For example, hematopoietic progenitor or stem cells may be transformed ex vivo and then restored to the patient. Selection processes may be used to increase the percentage of transformed cells in the returned population. For example, a selection marker which makes transformed cells more drug resistant than untransformed cells allows selection by treatment of the cells with the corresponding drug.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
3-methoxy-4-(N-substituted amino sulfonyl)fenalamide compounds and application thereof
InactiveCN102086166AOrganic chemistryAmide active ingredientsReduction ActivityHemoglobin hydrolysis
The invention relates to a preparation method and pharmacological application of novel 3-methoxy-4-(N-substituted amino sulfonyl)fenalamide derivatives. The structural general formula of the derivatives is shown in a formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are defined as the specifications. The compounds can serve as small molecular double inhibitors for Falcipain-2 and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), simultaneously blocks hemoglobin hydrolysis under the action of cysteine protease and inhibits the reduction activity of the DHFR, so as to inhibit multiplication of plasmodium. Therefore, the compounds can be expected to be developed into double-target-based novel antimalarial medicines.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Frontal affinity chromatography/MALDI tandem mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7317187B2Increase ionic strengthDetectabilityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationDihydrofolate reductaseMass spectrometry imaging
Sol-gel derived monolithic silica columns containing entrapped dihydrofolate reductase were used for frontal affinity chromatography of small molecule mixtures. The output from the column combined with a second stream containing the matrix molecule (HCCA) and was directly deposited onto a conventional MALDI plate that moved relative to the column via a computer controlled x-y stage, creating a semi-permanent record of the FAC run. The use of MALDI MS allowed for a decoupling of the FAC and MS methods allowing significantly higher ionic strength buffers to be used for FAC studies, which allowed for better retention of protein activity over multiple runs.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Methods to Treat Cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin and Methods for Assessing Cancer for Increased Sensitivity to 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin
InactiveUS20080188479A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycinamide Ribonucleotide FormyltransferaseThymidylate synthase
The present invention relates to a method for assessing the sensitivity of a patient's cancer to treatment with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin and a method for selecting a patient for treatment of cancer with 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin, by determining the amount of a selected polypeptide expressed by the cancer and comparing the amount with the amount of the selected polypeptide expressed by a reference cancer, wherein the polypeptide includes a member of folate pathways within cells and may include at least one of reduced folate carrier-1 enzyme (RFC-1), dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), folylpoly-gamma-glutamate synthetase (FPGS), thymidylate synthase (TS), γ-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase (GARFT). The present invention also relates to the use of 10-propargyl-10-deazaaminopterin in the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
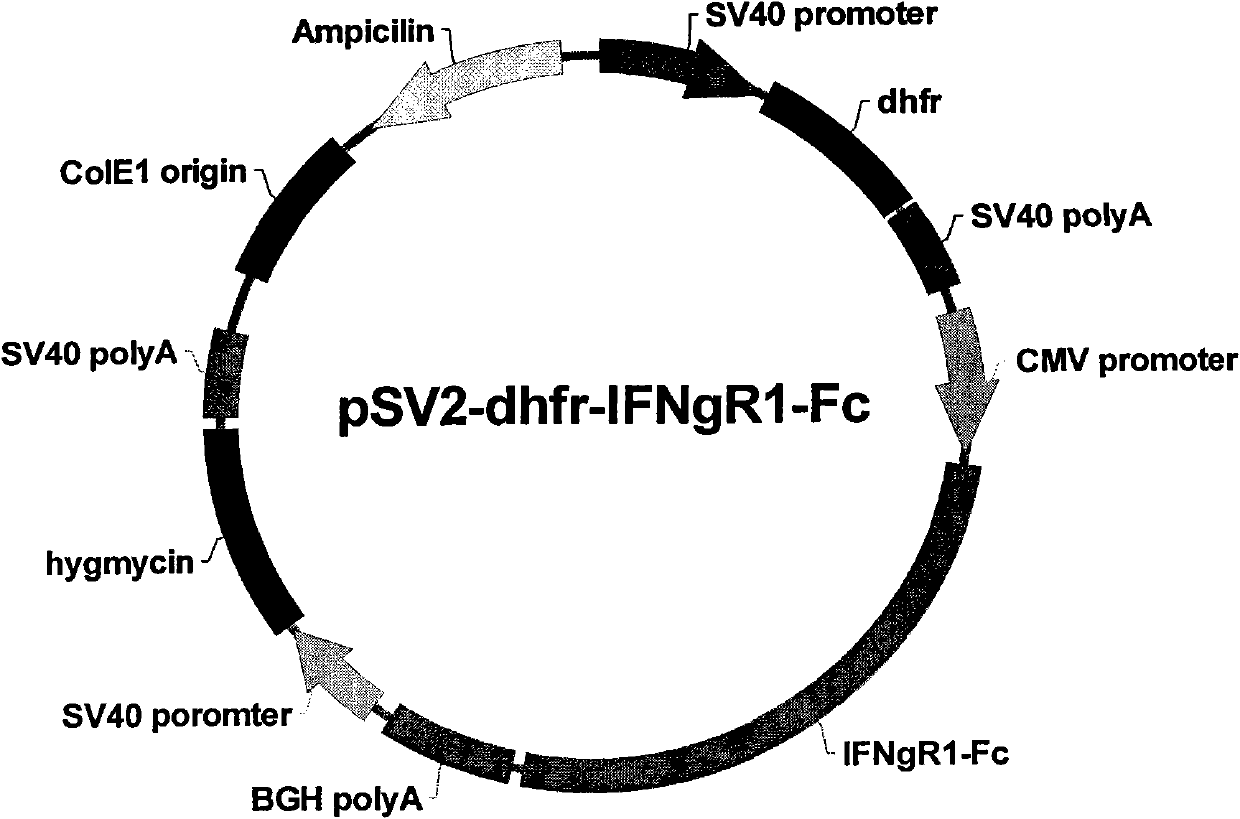
Recombinant Expression Vector for Animal Cell
ActiveUS20110117643A1Advantageous effects on cost reductionReduce concentrationSugar derivativesNucleic acid vectorProtein targetDihydrofolate reductase
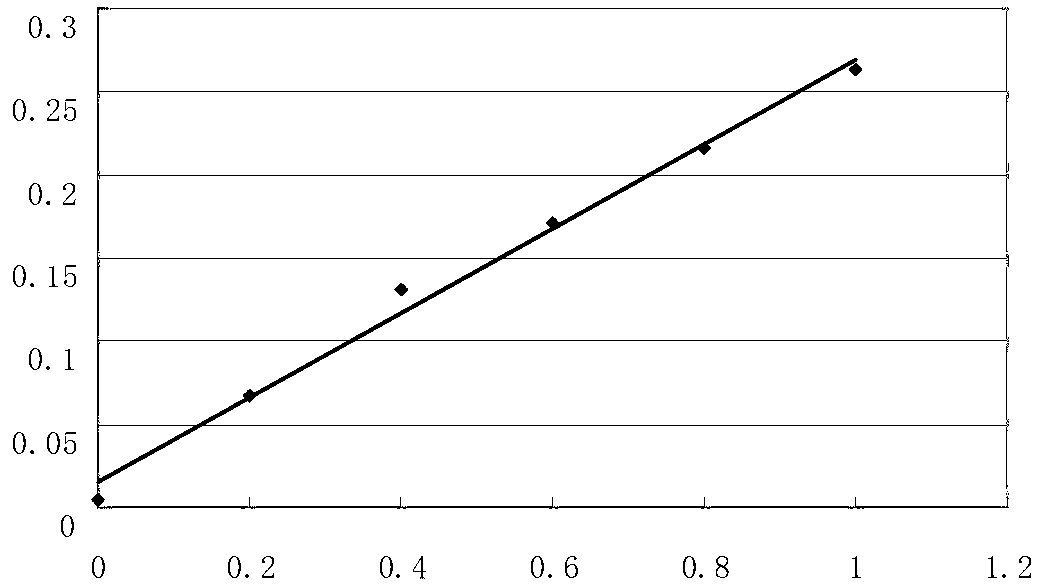
The present invention relates to a recombinant expression vector for an animal cell containing a dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) coding nucleotide sequence operatively linked to a DHFR promoter, to an animal cell line transformed by the vector, and to a method for preparing a target protein using the same. As compared with existing animal cell expression vectors, the vector of the present invention enables an effective screening of a cell line clone in which foreign genes are amplified together with DHFR genes even at a much lower methotrexate concentration. The present invention exhibits excellent effects in cell line preparation as high-productivity cell lines can be ensured in a short time through the use of a lower concentration of methotrexate in the process of protein production cell line establishment.
Owner:APROGEN INC
Raltitrexed related substance C as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN107721995AHas inhibitory activityHigh yieldOrganic chemistryComponent separationDihydrofolate reductaseDihydrofolate reductase deficiency
The invention discloses a raltitrexed related substance C with inhibition activity on dihydrofolate reductase and methionine synthetase, a preparation method and application thereof as an impurity control group.
Owner:NANJING CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA
In vivo library-versus-library selection of optimized protein-protein interactions
The present invention describes a rapid and efficient in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy for identifying optimally interacting pairs of heterodimerizing polypeptides. It allows for the screening of a protein library against a second protein library, rather than against a single bait protein, and thus has numerous applications in the study of protein-protein interactions. Additionally, it allows for the application of different selection stringencies. Two leucine zipper libraries, semi-randomized at the positions adjacent to the hydrophobic core, were genetically fused to either one of two designed fragments of the enzyme murine dihydrofolate reductase (mDHFR), and cotransformed into E. coli. Interaction between the library polypeptides was required for reconstitution of the enzymatic activity of mDHFR, allowing bacterial growth. Analysis of the resulting colonies revealed important biases in the zipper sequences relative to the original libraries, which are consistent with selection for stable, heterodimerizing pairs. Using more weakly associating mDHFR fragments, we increased the stringency of selection. We enriched the best performing leucine zipper pairs by multiple passaging of the pooled, selected colonies in liquid culture, as the best pairs allowed for better bacterial propagation. This competitive growth allowed small differences among the pairs to be amplified, and different sequence positions were enriched at different rates. We applied these selection processes to a library-versus-library sample of 2.0×106 combinations, and selected a novel leucine zipper pair which may be appropriate for use in further in vivo heterodimerization strategies.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
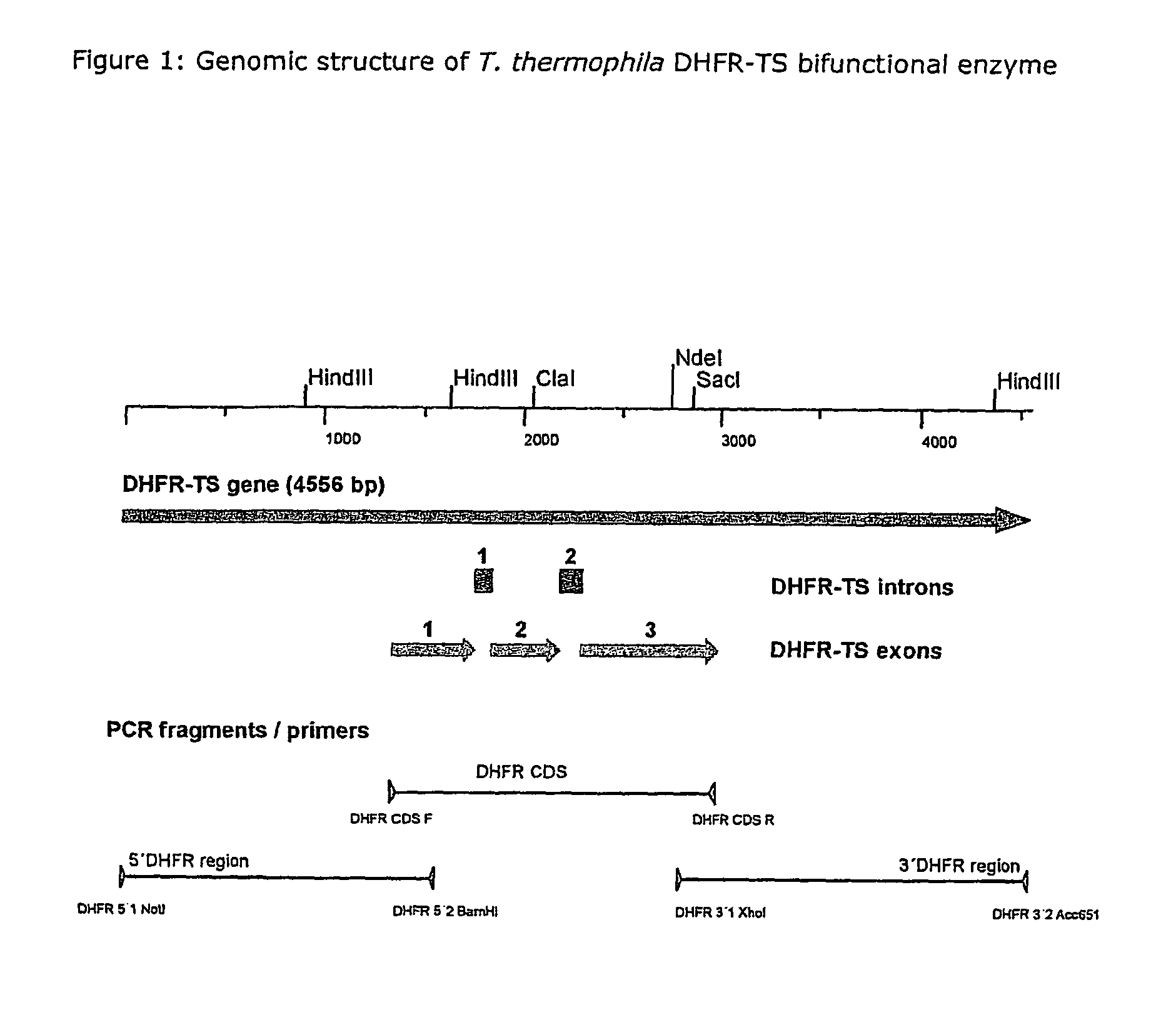
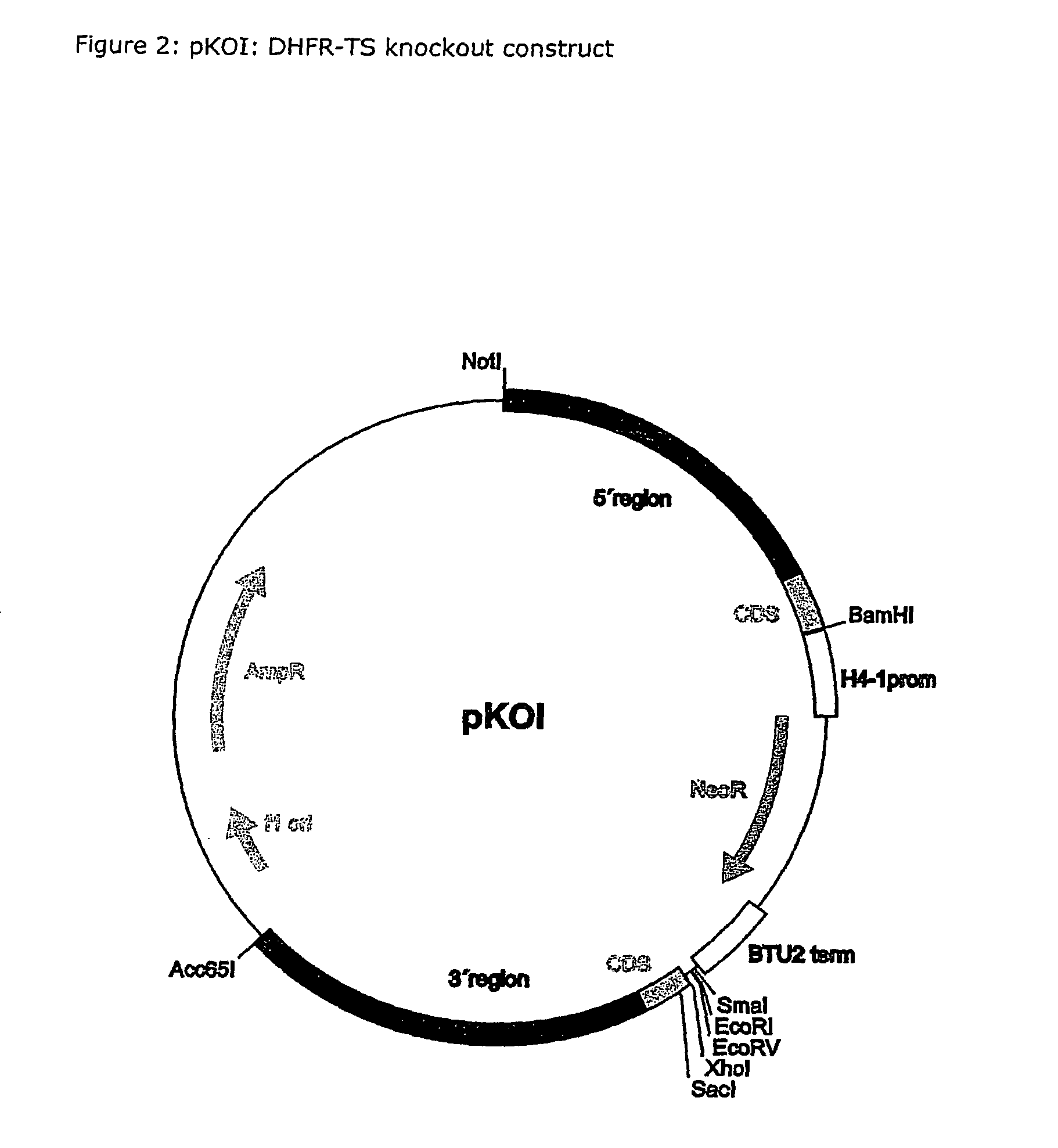
Nucleic acid and its use effecting ciliate tetrahymena bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase deficiency
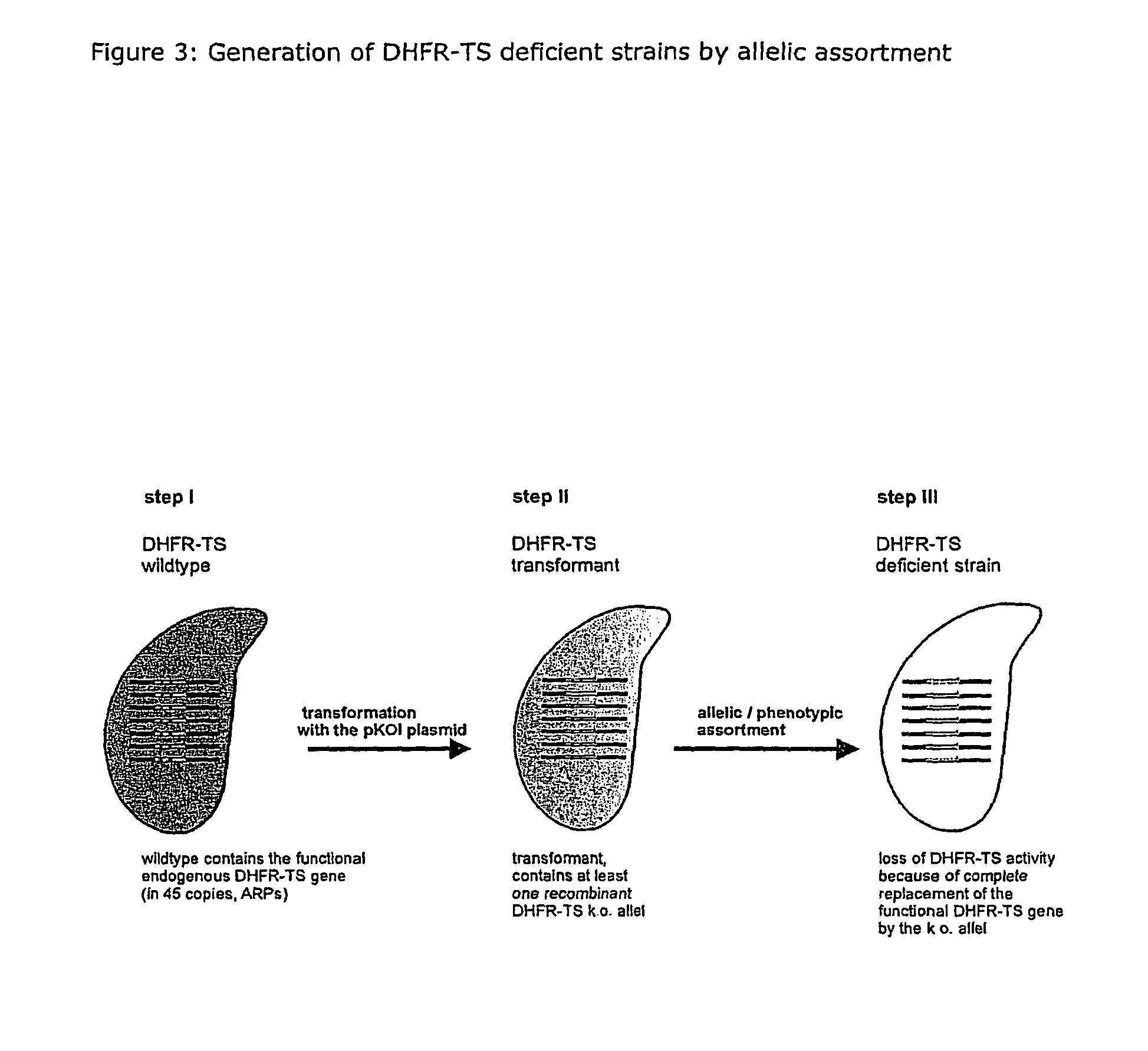
A method for producing a ciliate cell with reduced or essentially no dihydrofolate reductase (DHFS) activity or reduced or essentially no thymidylate synthase (TS) activity or both reduced or essentially no dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase (DHFR-TS) activity is claimed, comprising the steps ofa) transforming ciliate cells by inserting a construct containing an allele altering the gene encoding the endogenous DHFR-TS into at least one of the endogenous DHFR-TS genes of the ciliate macronucleus (MAC),b) inducing an allelic assortment process in the transformed ciliate cells to generate cells having the construct inserted in most or all functional DHFR-TS genes of the MAC, andc) identifying the cells generated in step b) by cultivation with or without thymidine.
Owner:CILIAN
C829T single nucleotide polymorphism assay kit of DHFR
ActiveCN102876779AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayNucleotide
The invention discloses a C829T single nucleotide polymorphism assay kit of DHFR (dihydrofolate reductase). The kit comprises a red blood cell lysate, a DNA extracting solution, a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reagent, a single-chain purification reagent and a sequencing reagent, and is characterized in that the PCR reagent comprises specific augmentation primers SEQNO.1 and SEQNO.2, whose sequences are respectively ACTAAGTGCTTCTCCAAGACC and Biotin-AATGTCAAGGACTGGCAAGAG; and the sequencing reagent comprises a specific sequencing primer SEQNO.3 whose sequence is AGTCCCCAGCACCTG.
Owner:北京艾迪康医学检验实验室有限公司
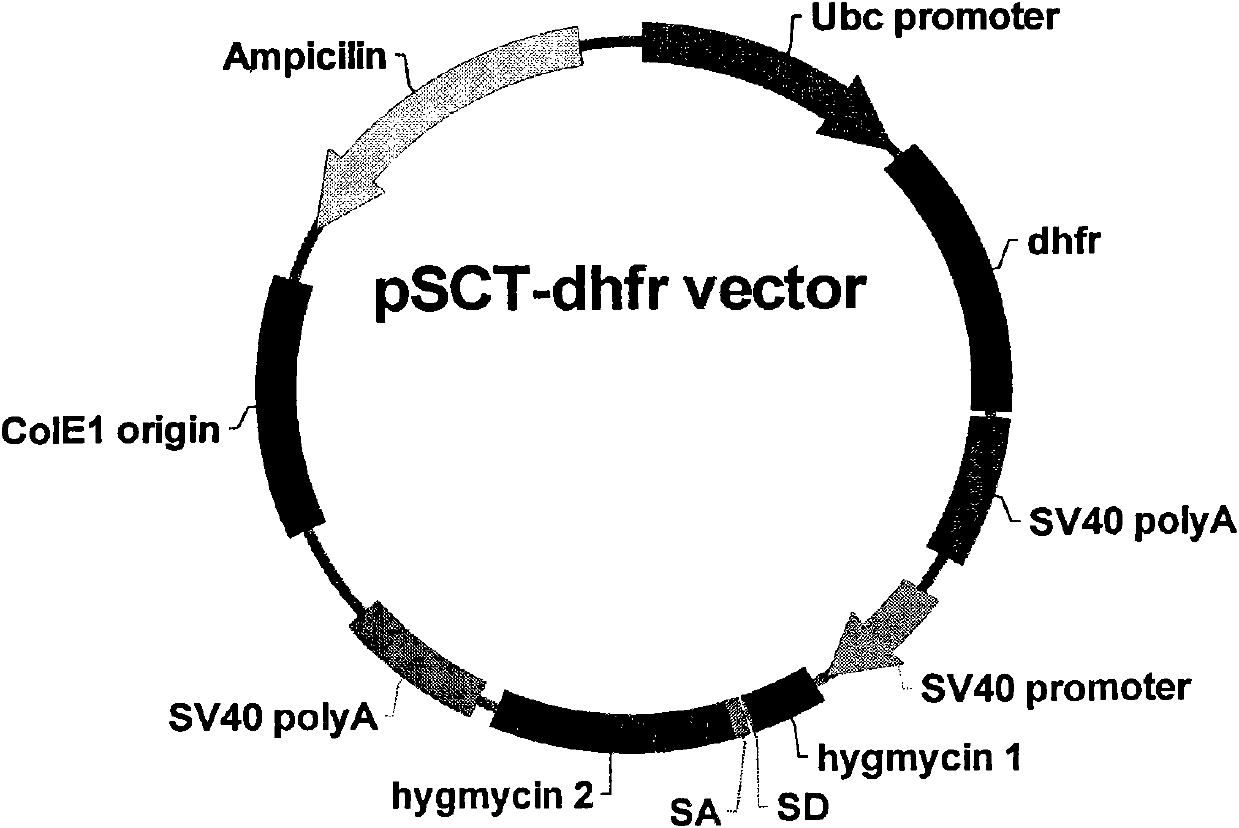
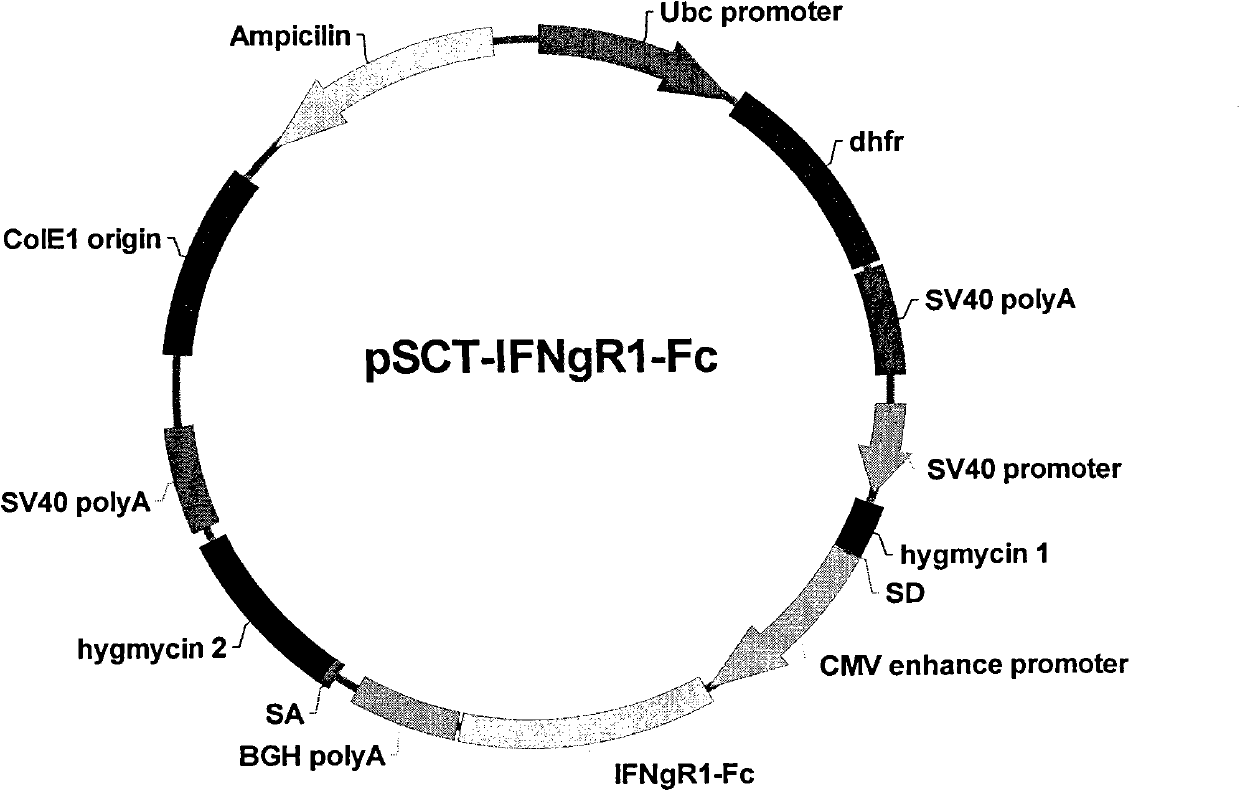
Vector capable of being used for expressing foreign gene and cell line screening method
ActiveCN102559734AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHigh level expressionScreening method
The invention provides a vector capable of being used for expressing a foreign gene. The vector is used for tightly connecting expression of a target gene with expression of hygromycin B phosphotransferase of a screening gene. According to the vector, a technology of avianizing the expression of an amplified gene enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) for increasing the MTX (methotrexate) screening efficiency and reducing the MTX use concentration is adopted. The invention provides a screening method for obtaining high-level expression cloning after a cell is transfected by an expression vector optimized by adopting the technology.
Owner:SINO CELL TECH INC
Vector encoding human globin gene and use thereof in treatment of hemoglobinopathies
InactiveUS8058061B2Increase percentageOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGlobin genesDihydrofolate reductase
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com