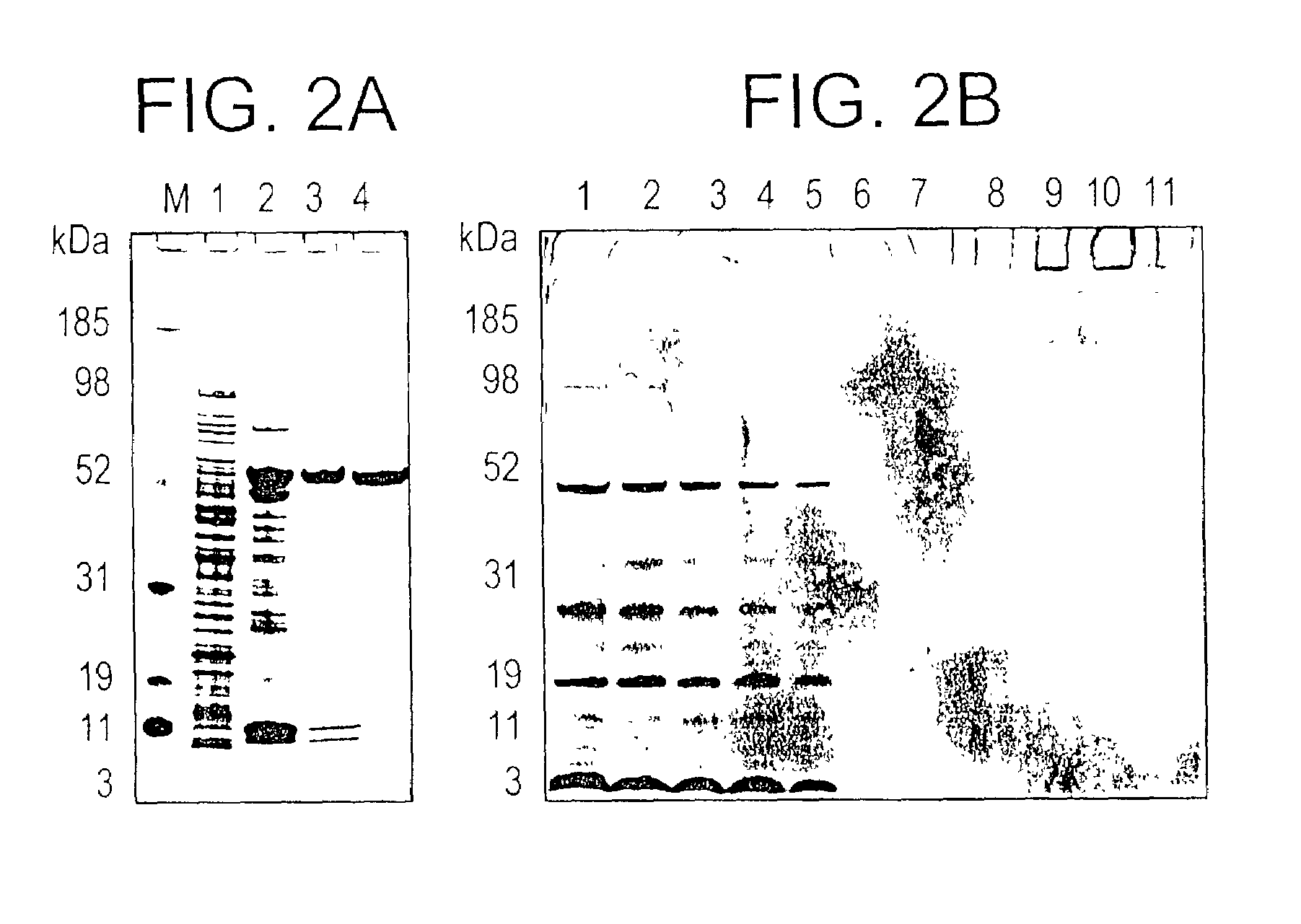
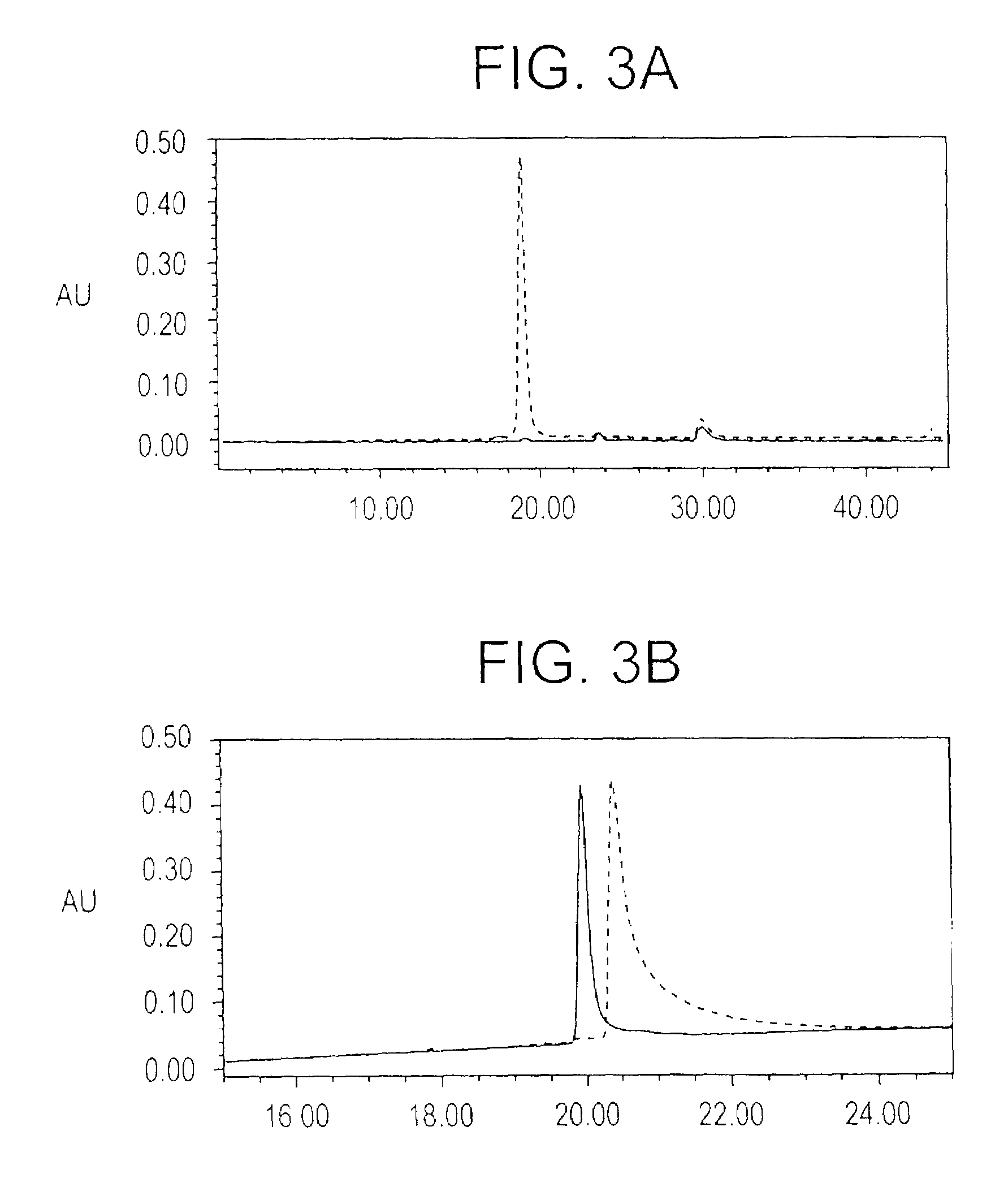
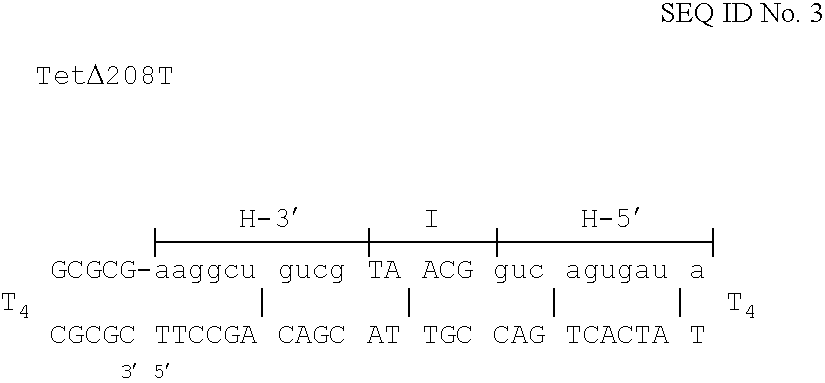Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
581results about "Protozoa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
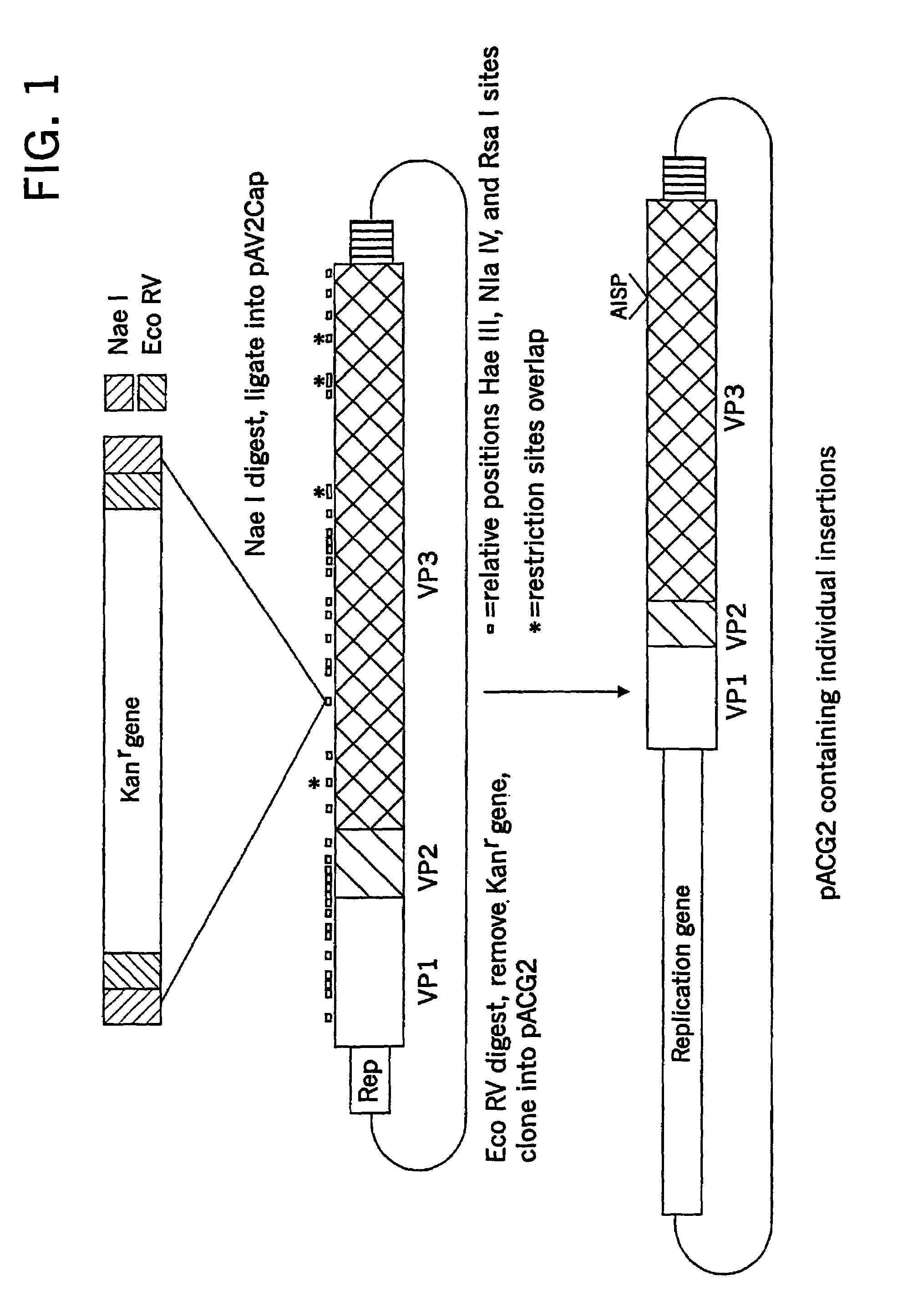
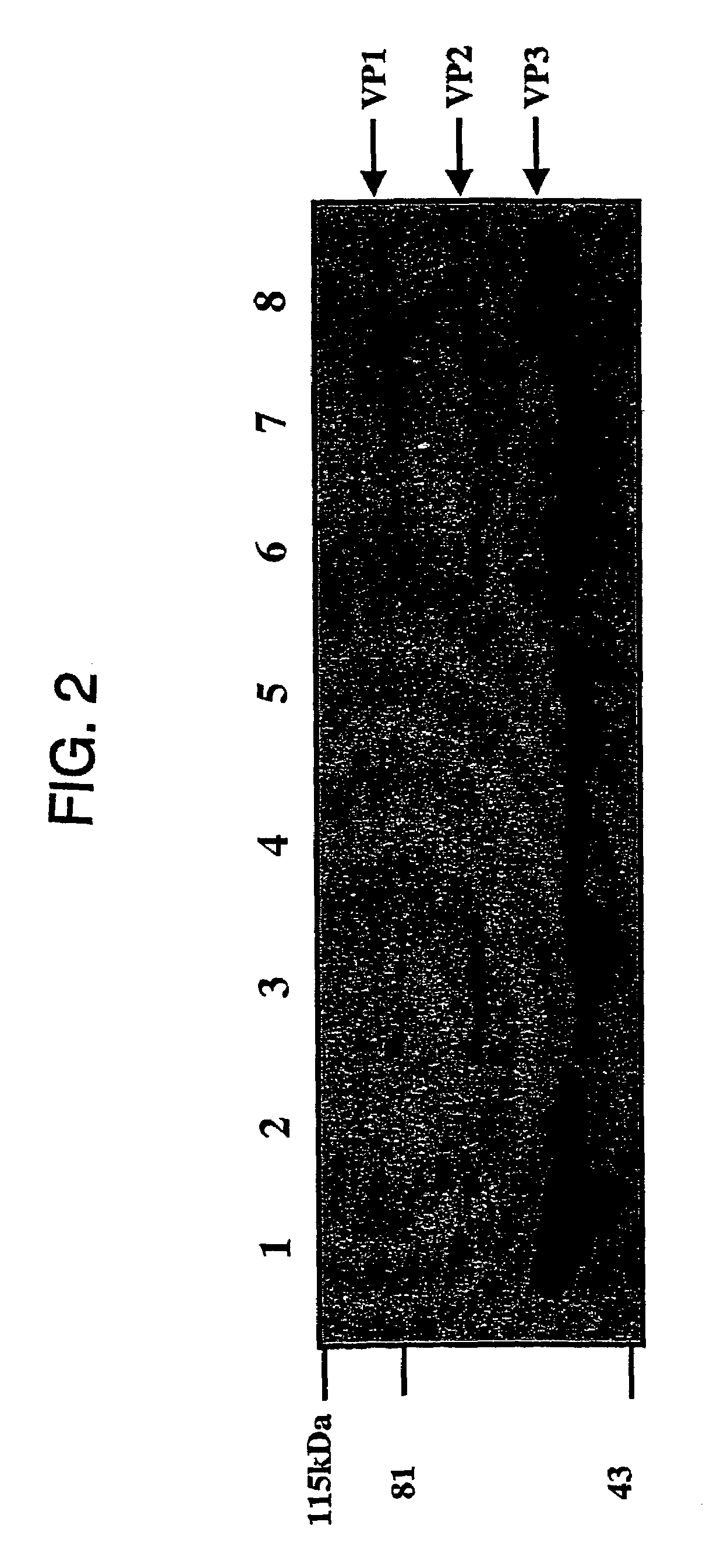
Virus vectors and methods of making and administering the same
The present invention provides genetically-engineered parvovirus capsids and viruses designed to introduce a heterologous gene into a target cell. The parvoviruses of the invention provide a repertoire of vectors with altered antigenic properties, packaging capabilities, and / or cellular tropisms as compared with current AAV vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Herbal and pharmaceutical drugs enhanced with probiotics
The curative action of drugs, including herbal remedies, allopathic remedies, and periodontal remedies, is enhanced and accelerated by administering such drugs in combination or association with probiotics, especially those of genus Lactococcus, Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, Streptococcus, Propionibacterium, Brevibacterium, Penicillium, and Saccharomyces.
Owner:REDDY MALIREDDY S
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
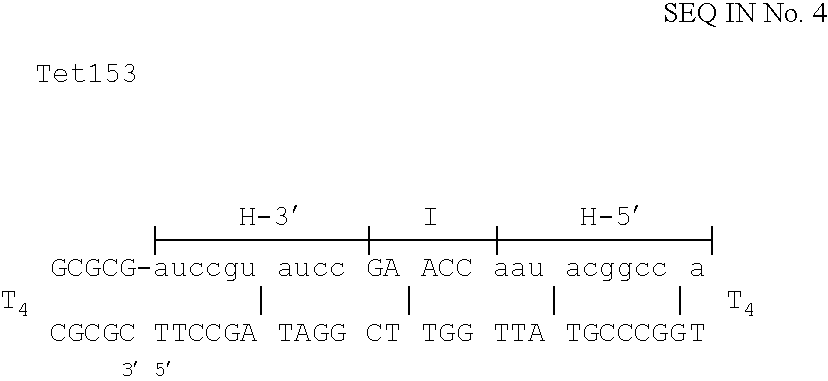
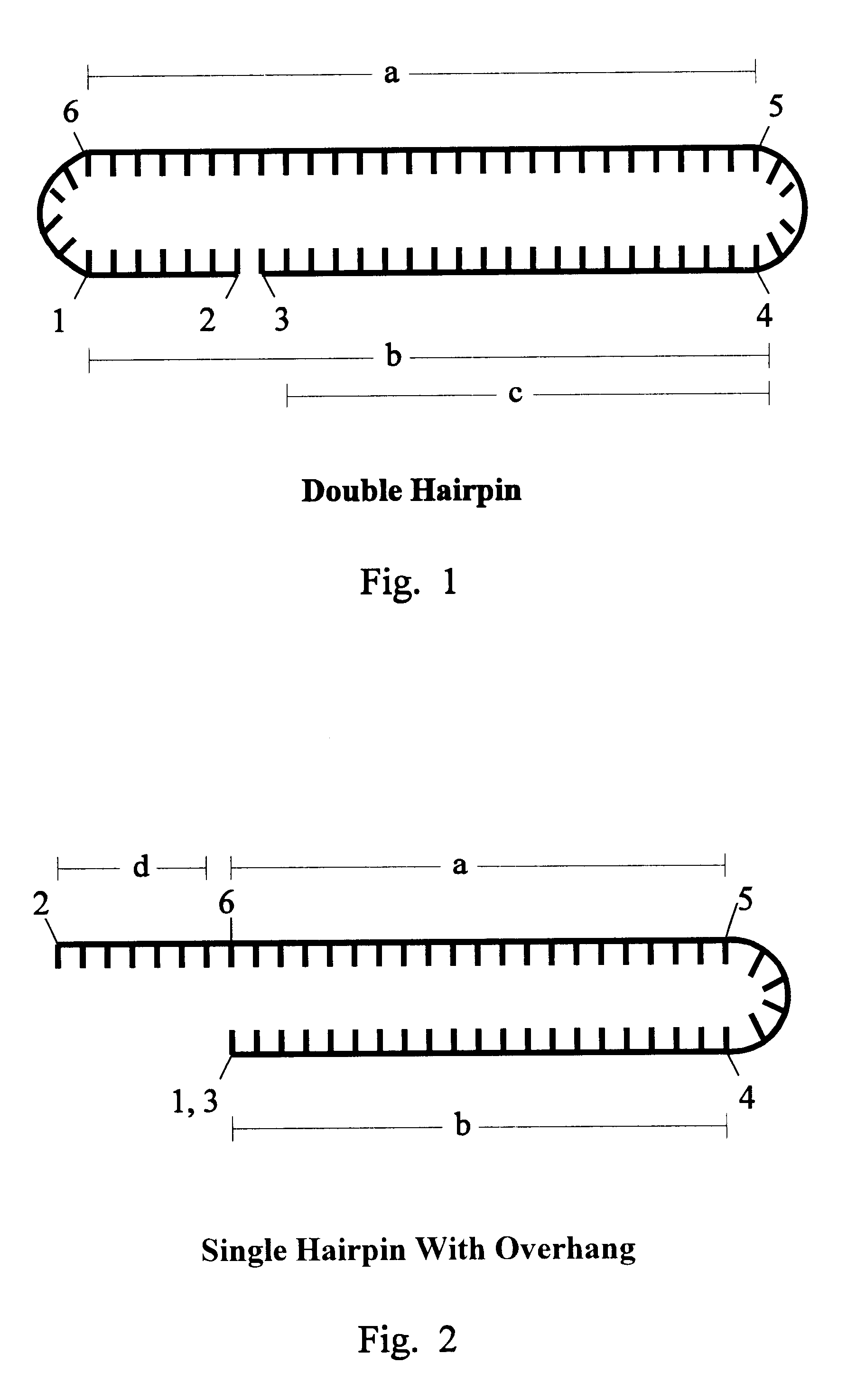
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
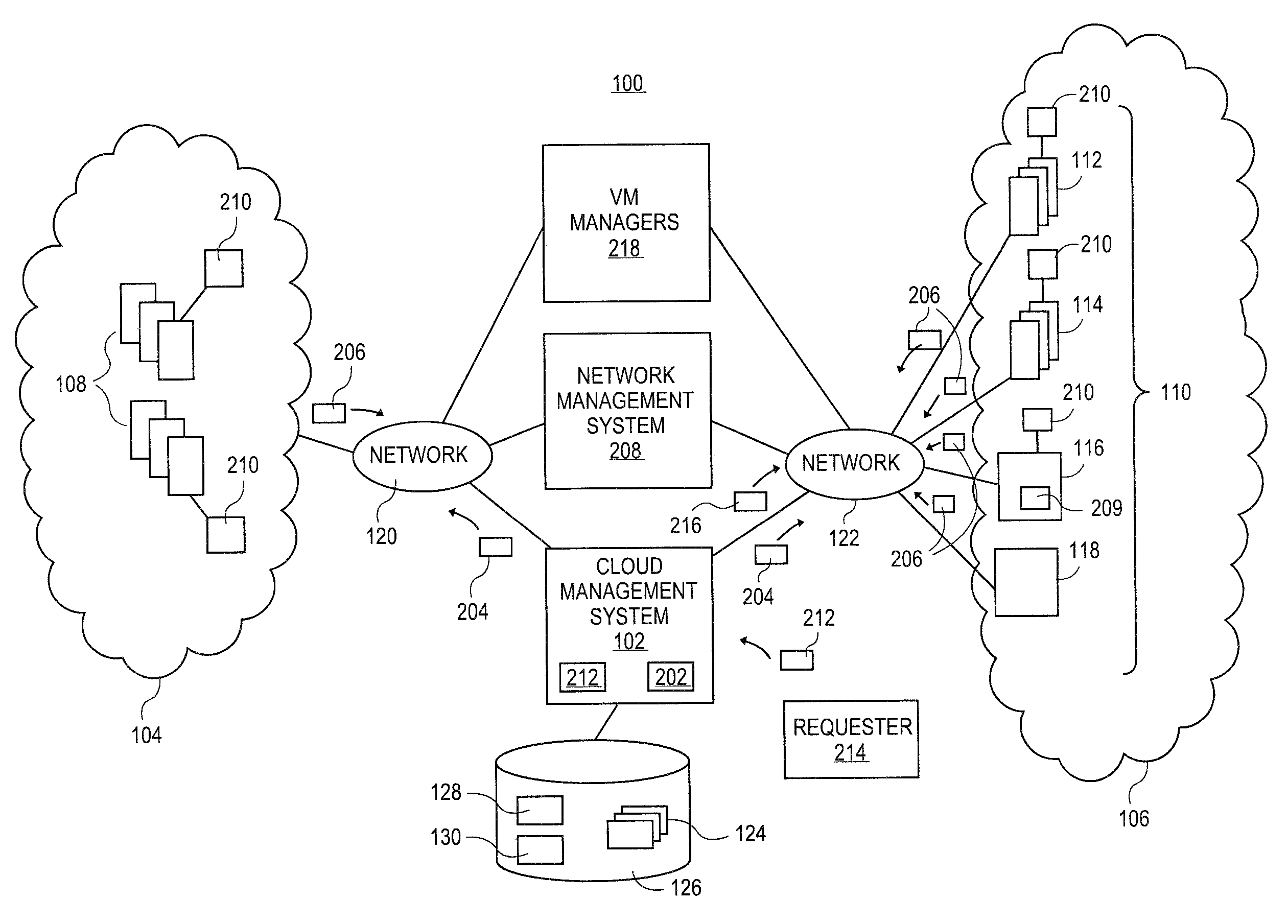
Methods and systems for flexible cloud management with power management support
A cloud management system can determine if the operational state of the virtual machines and / or the computing systems needs to be altered in order to instantiate virtual machines. If the operational state of the computing systems needs to be altered, the cloud management system retrieves an identification of the power management systems supporting the computing systems. The cloud management system can utilize the identification of the power management systems to instruct the power management systems to alter the power state of the computing system in order to instantiate the virtual machines.
Owner:RED HAT
Continuous-Batch Hybrid Process for Production of Oil and Other Useful Products from Photosynthetic Microbes
InactiveUS20080118964A1Lower potentialIncreased complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCarrying capacity
A process for cultivating photosynthetic microbes comprising Closed Systems for continuous cultivation and Open Systems for batch cultivation, in which (a) the Closed System Area occupies no more than 20% of the Total Land Area of the cultivation facility; (b) batch cultures in the Open Systems are initiated with an inoculum from the Closed Systems containing a cell biomass of no less than 5% of the carrying capacity of said Open System; (c) the doubling rate of said photosynthetic microbe is no less than once every 16 hours; and (d) the residence time of the batch culture in said Open System is no more than a period of 5 days.
Owner:CELLANA
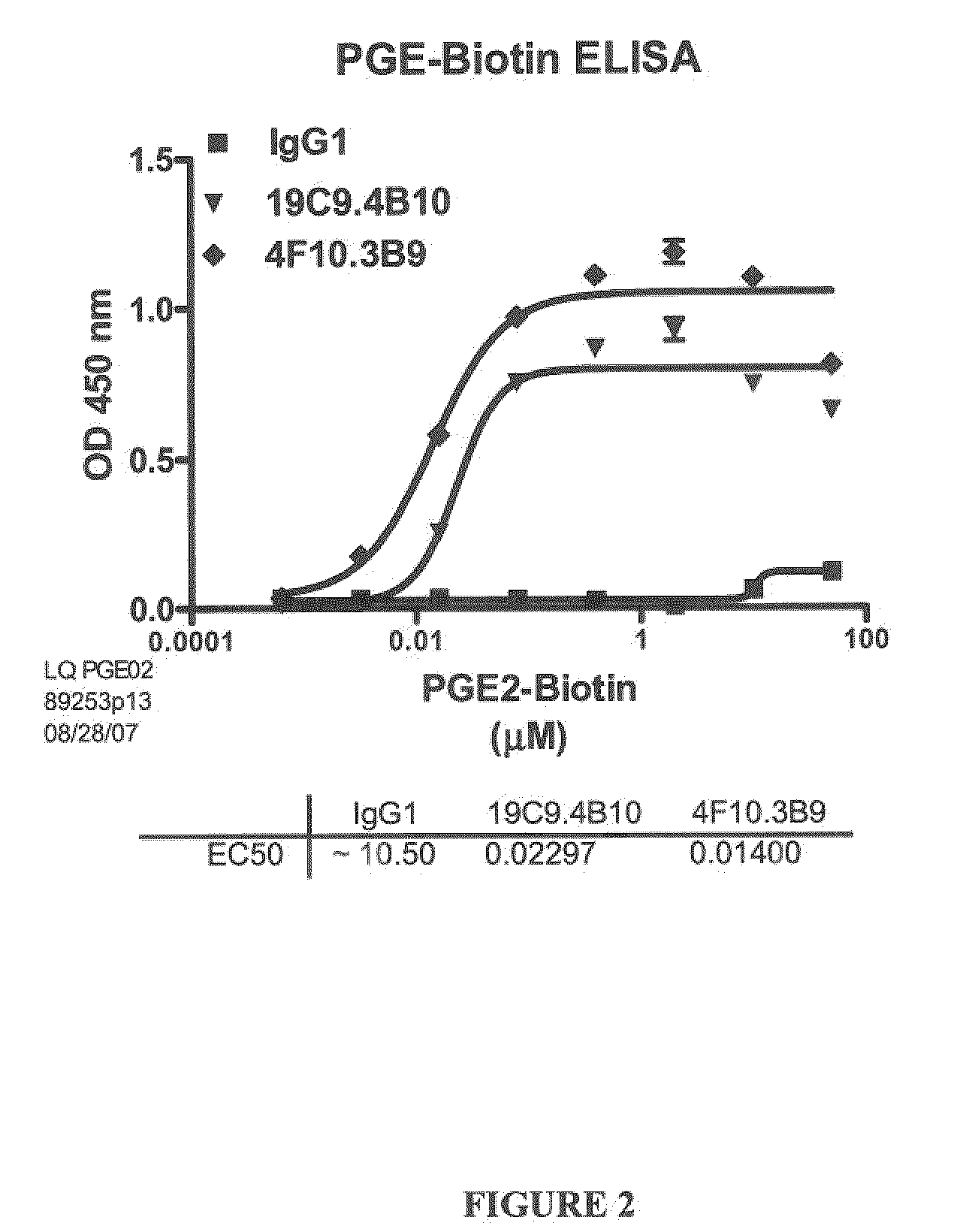
Prostaglandin E2 Binding Proteins and Uses Thereof
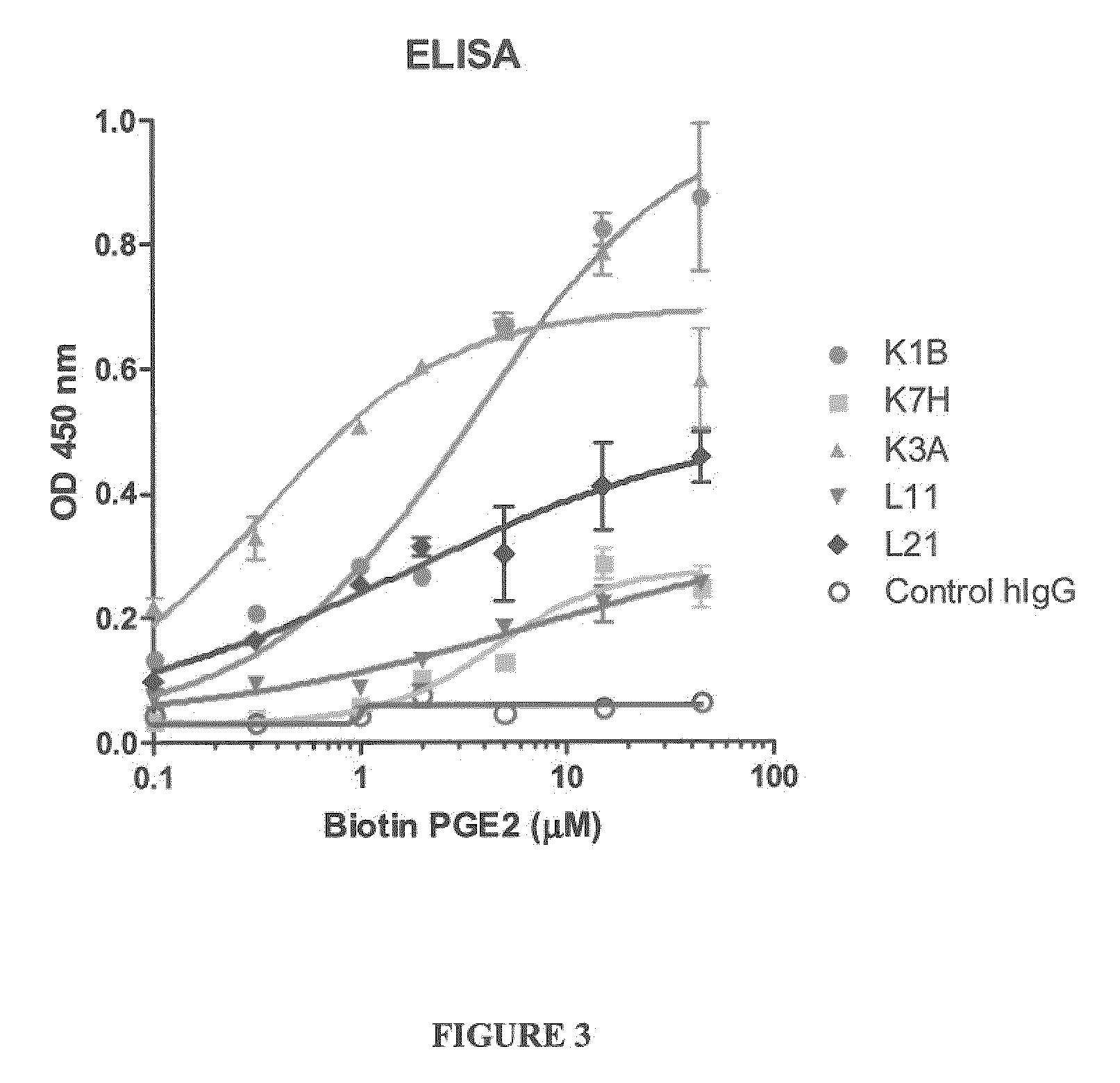
ActiveUS20100040537A1Prevent and more symptomAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsWild typeAntigen binding
The present invention encompasses prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) binding proteins. The invention relates to antibodies that are wild-type, chimeric, CDR grafted and humanized. Preferred antibodies have high affinity for prostaglandin E2 and neutralize prostaglandin E2 activity in vitro and in vivo. An antibody of the invention can be a full-length antibody, or an antigen-binding portion thereof. Methods of making and methods of using the antibodies of the invention are also provided. The antibodies, or antigen-binding portions, of the invention are useful for detecting prostaglandin E2 and for inhibiting prostaglandin E2 activity, e.g., in a human subject suffering from a disorder in which prostaglandin E2 activity is detrimental.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
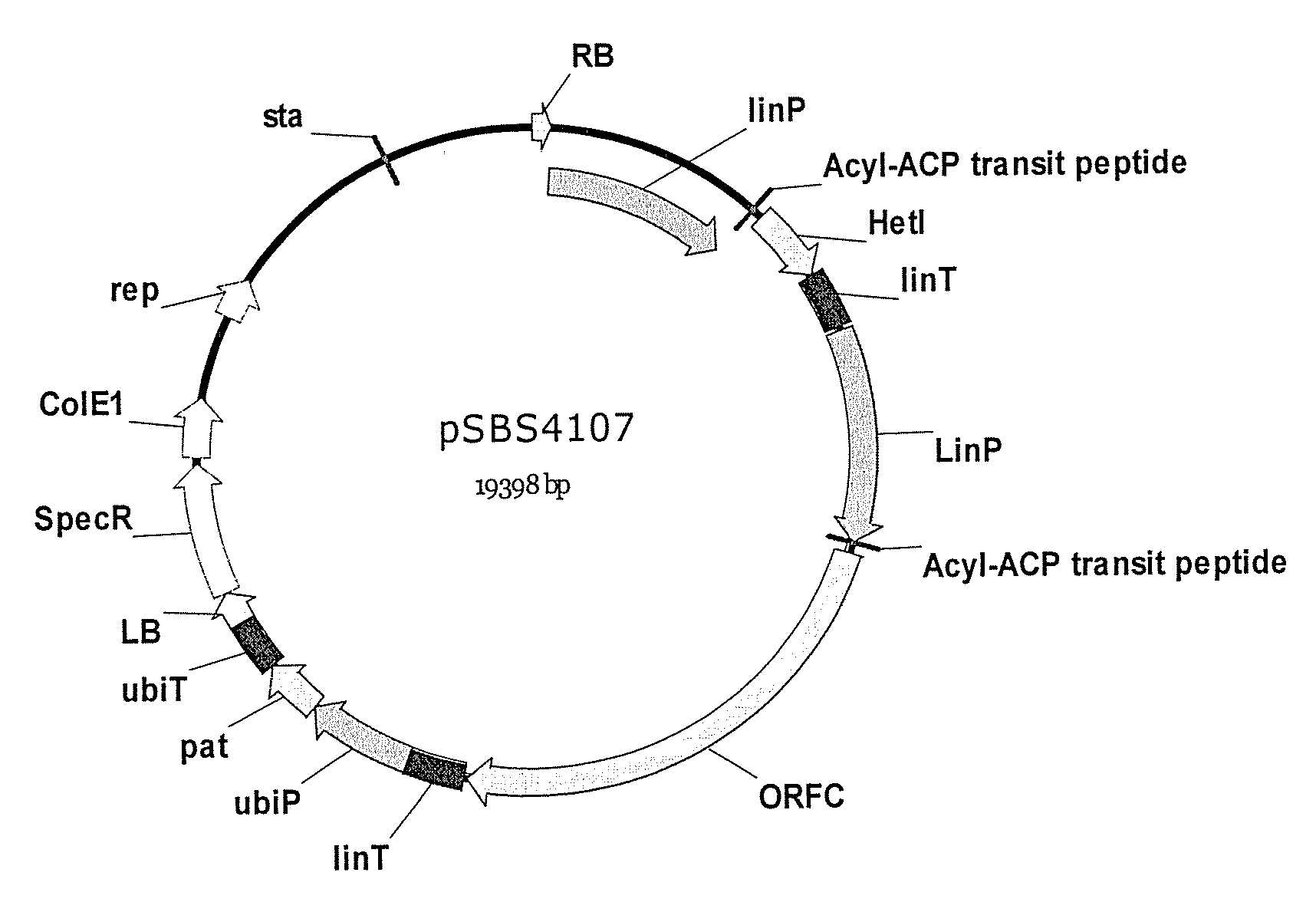
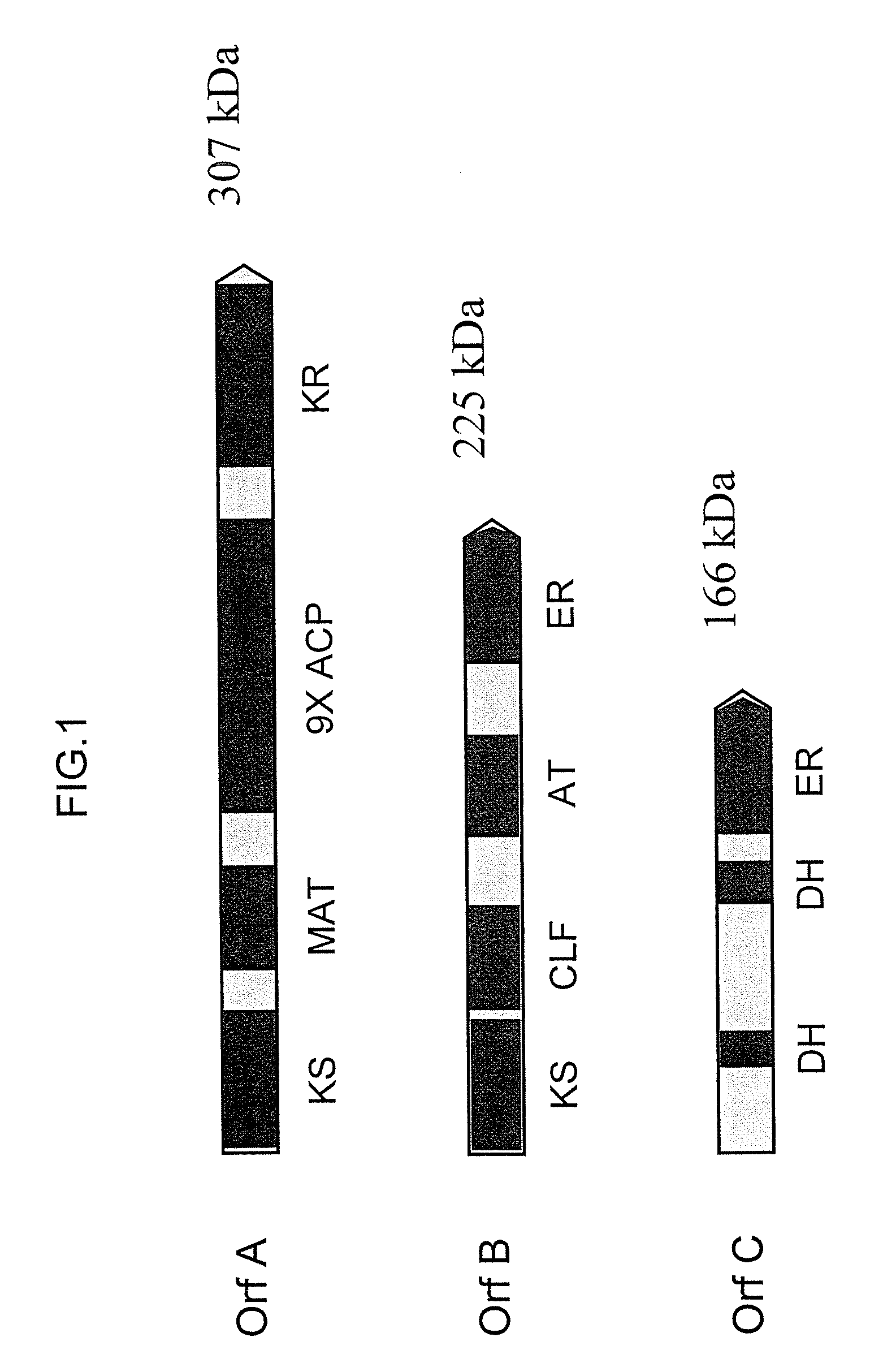
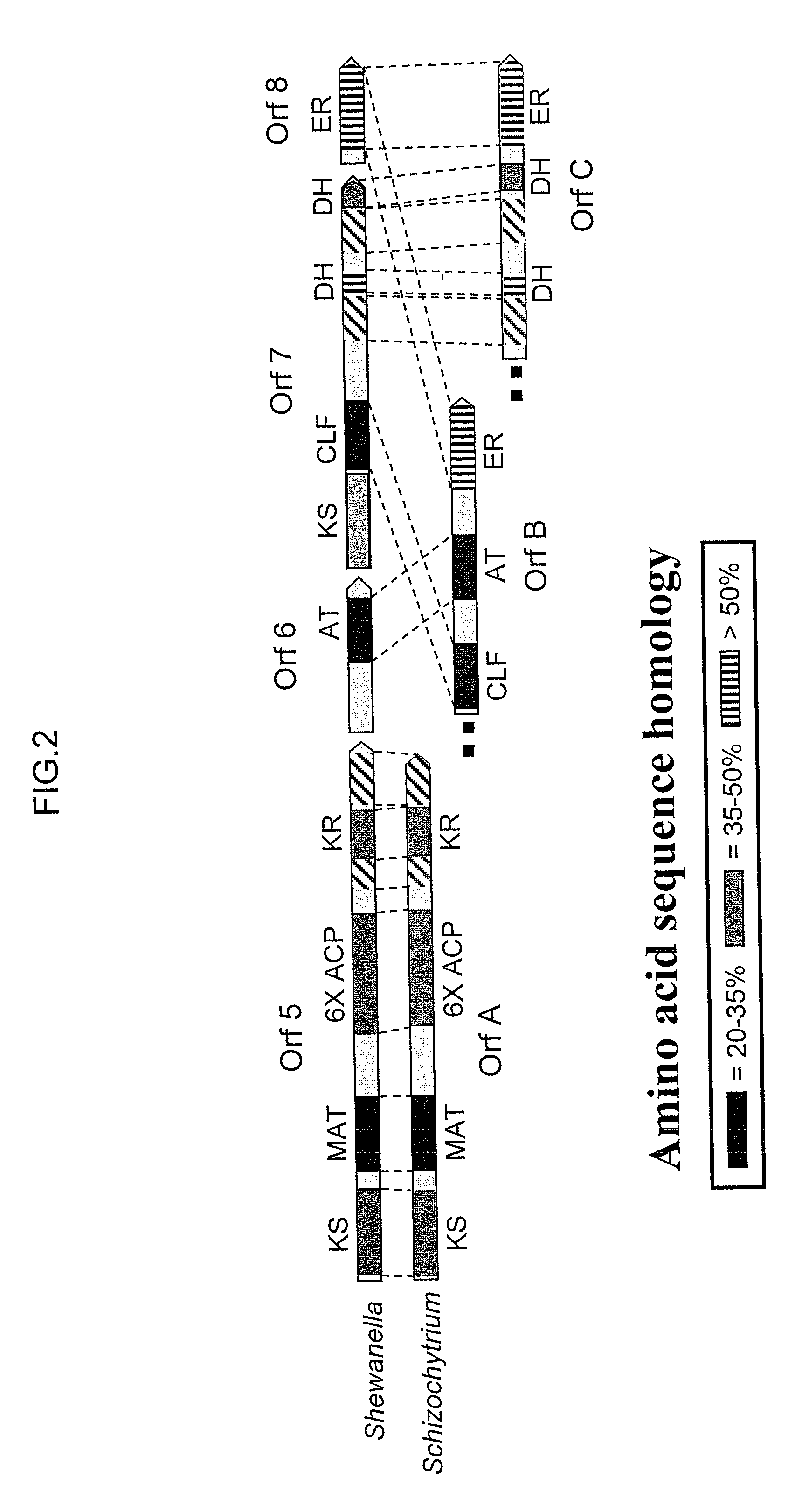
Disclosed are the complete polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems from Schizochytrium, and biologically active fragments and homologues thereof. More particularly, this invention relates to nucleic acids encoding such PUFA PKS systems, to proteins and domains thereof that comprise such PUFA PKS systems, to genetically modified organisms (plants and microorganisms) comprising such PUFA PKS systems, and to methods of making and using the PUFA PKS systems disclosed herein. This invention also relates to genetically modified plants and microorganisms and methods to efficiently produce lipids enriched in various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as well as other bioactive molecules by manipulation of a PUFA polyketide synthase (PKS) system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
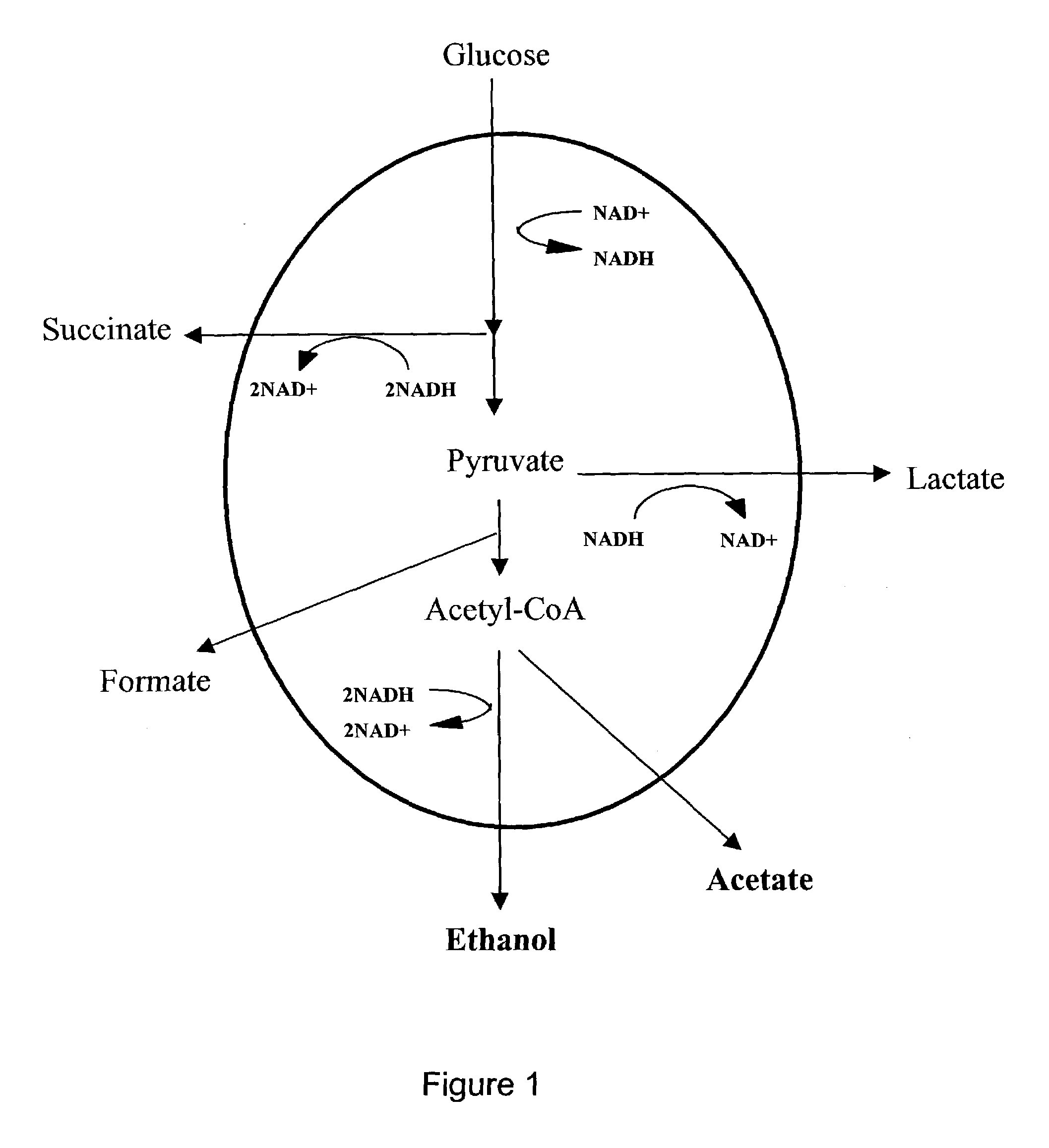
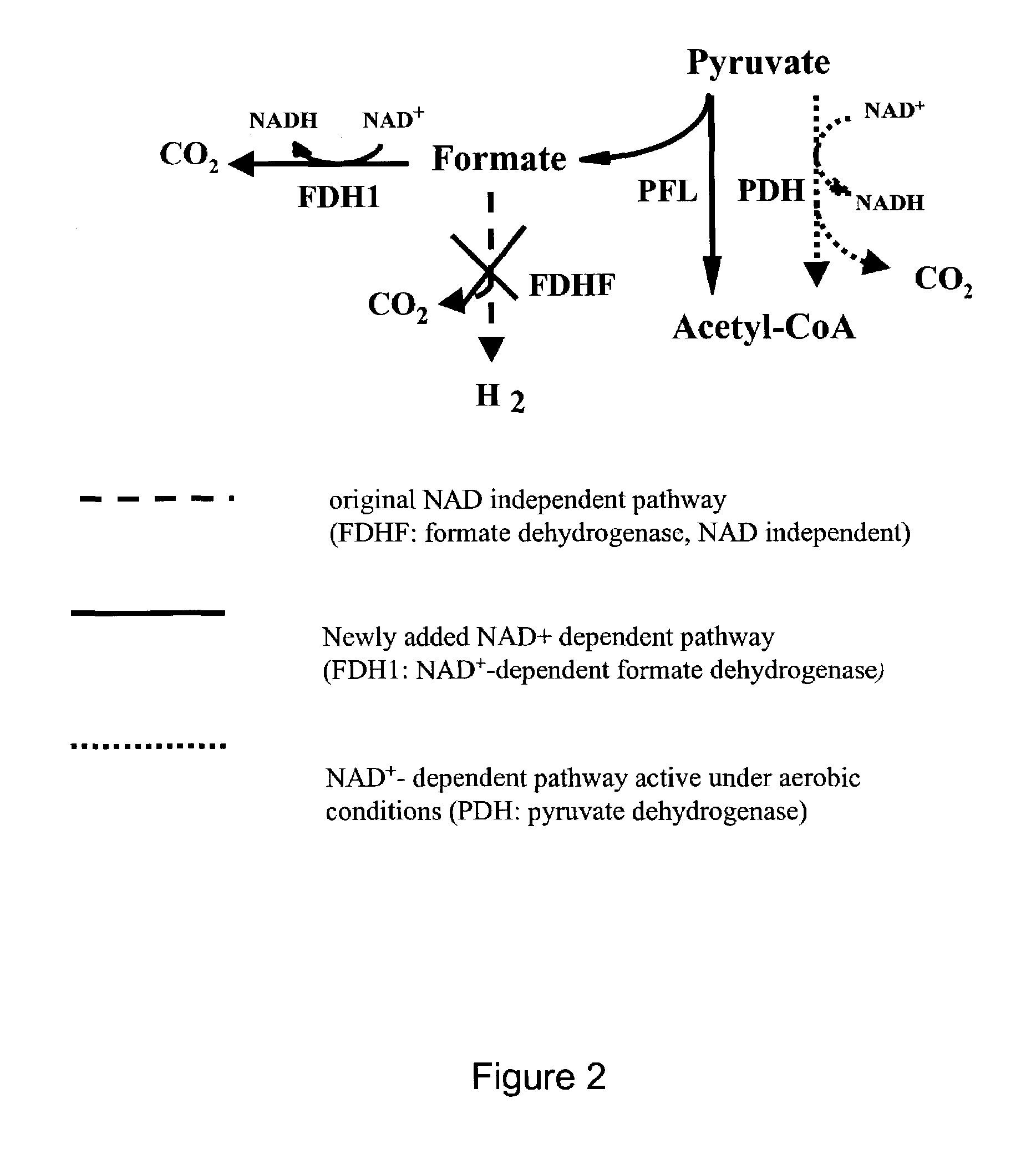
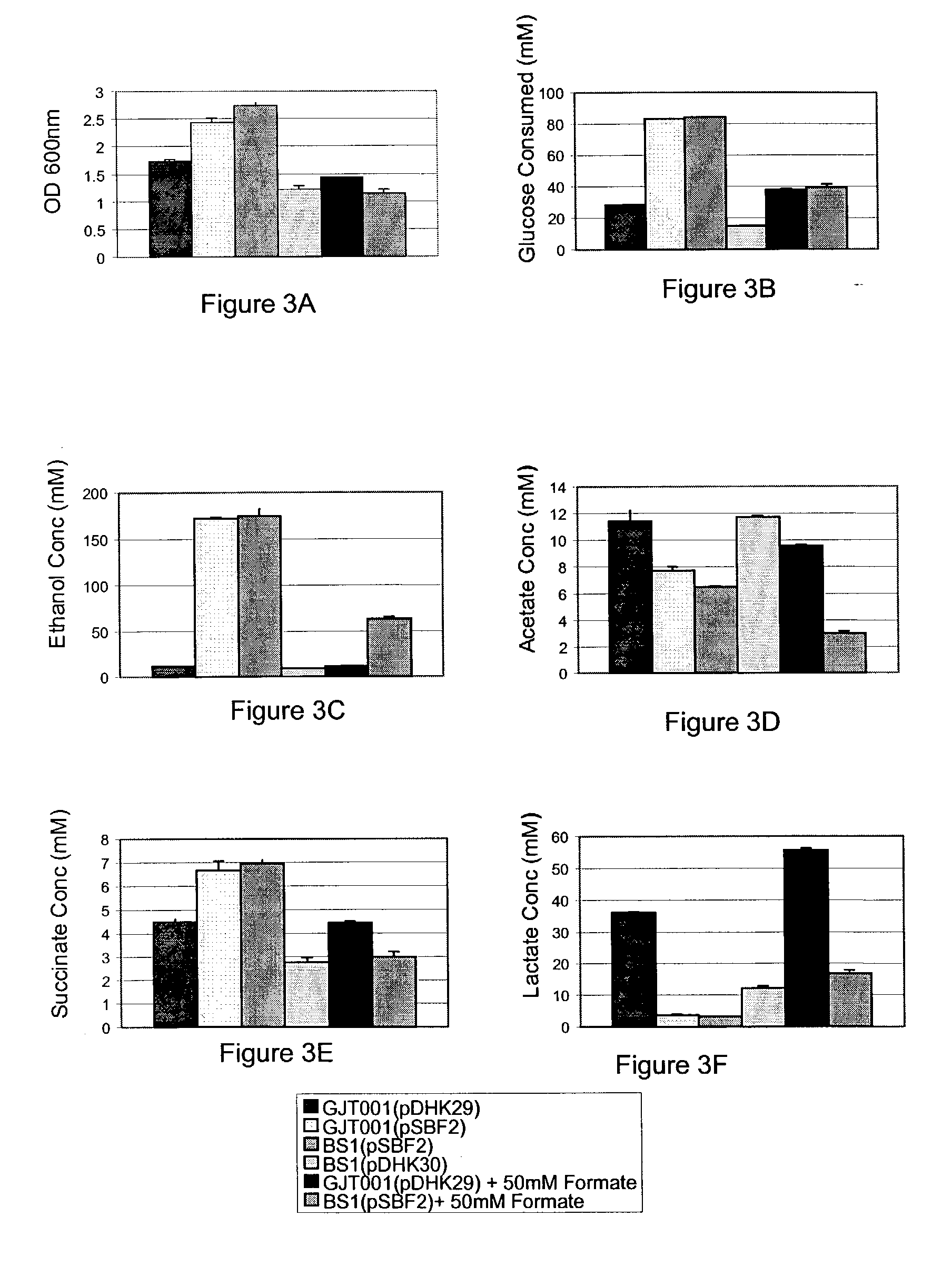
Recycling system for manipulation of intracellular NADH availability
ActiveUS7256016B2Increases intracellular availabilityImprove usabilityBacteriaProtozoaVitaminBiology
The present invention describes a novel recombinant NADH recycling system that is used as a process for producing reduced compounds. In a specific embodiment, the reduced compounds include ethanol, succinate, lactate, a vitamin, a pharmaceutical and a biodegraded organic molecule. The NADH recycling system effects metabolic flux of reductive pathways in aerobic and anaerobic environments.
Owner:RICE UNIV
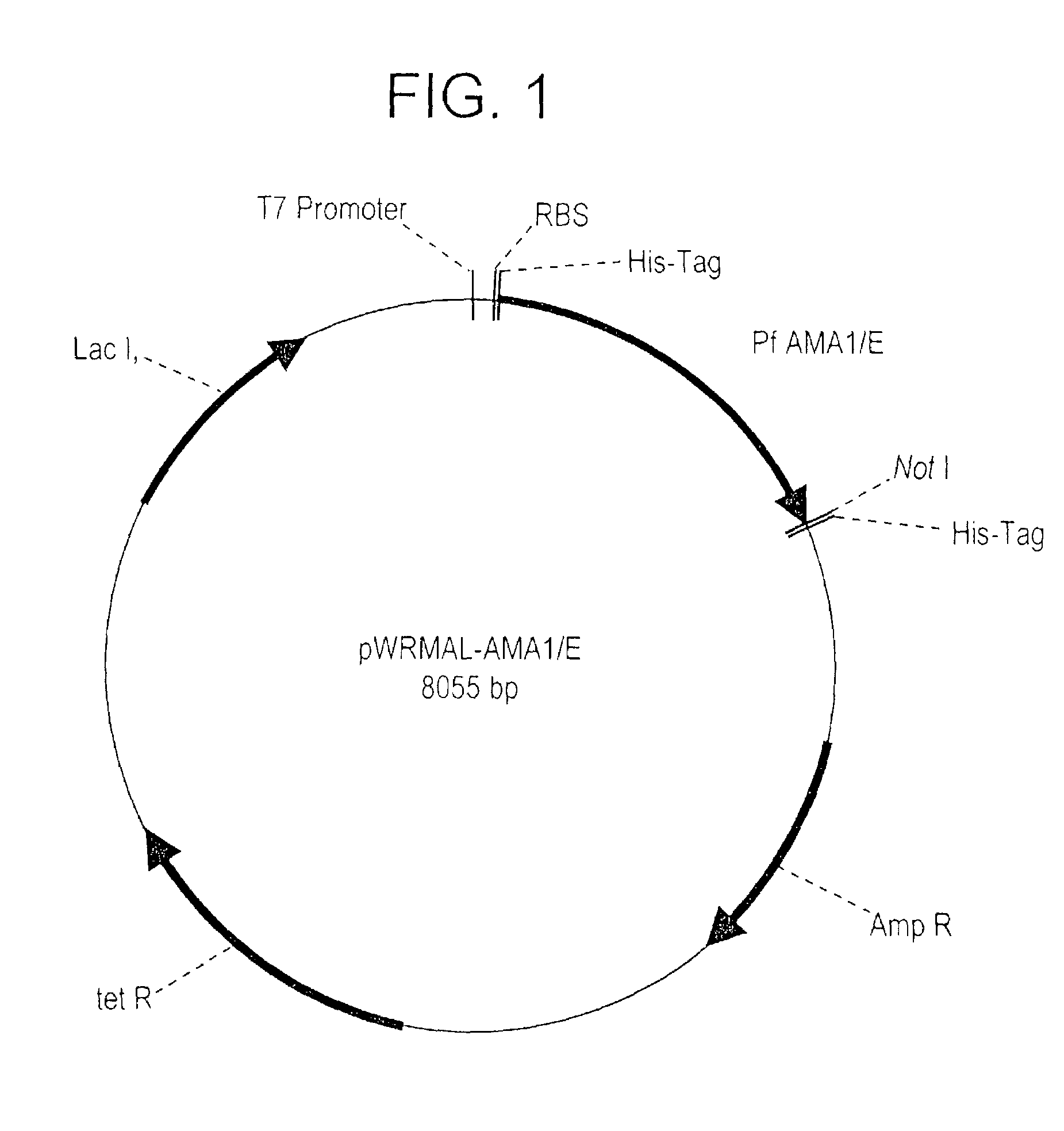
Plasmodium falciparum AMA-1 protein and uses thereof
InactiveUS7029685B2Eliminate the problemImprove responseProtozoaFermentationADAMTS ProteinsMalarial parasites
In this application is described the expression and purification of a recombinant Plasmodium falciparum (3D7) AMA-1 ectodomain. The method of the present invention produces a highly purified protein which retains folding and disulfide bridging of the native molecule. The recombinant AMA-1 is useful as a diagnostic reagent, for use in antibody production, and as a protein for use alone, or as part of, a vaccine to prevent malaria.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Thraustochytrids, Fatty Acid Compositions, and Methods of Making and Uses Thereof
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
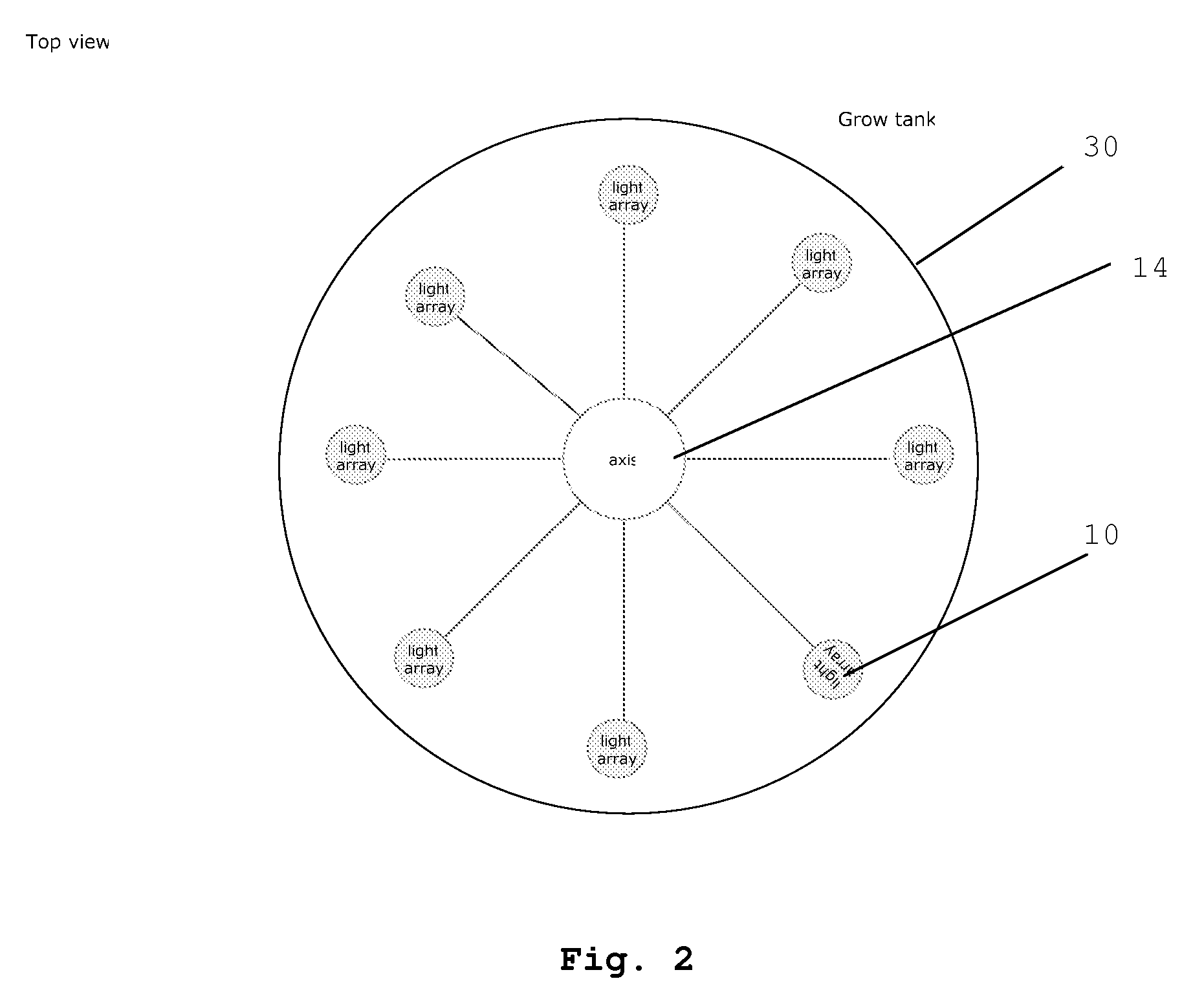
Apparatus and method for optimizing photosynthetic growth in a photo bioreactor
InactiveUS20090291485A1Light utilization efficiencyReduce energy costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess systemsPhotosynthetic growth
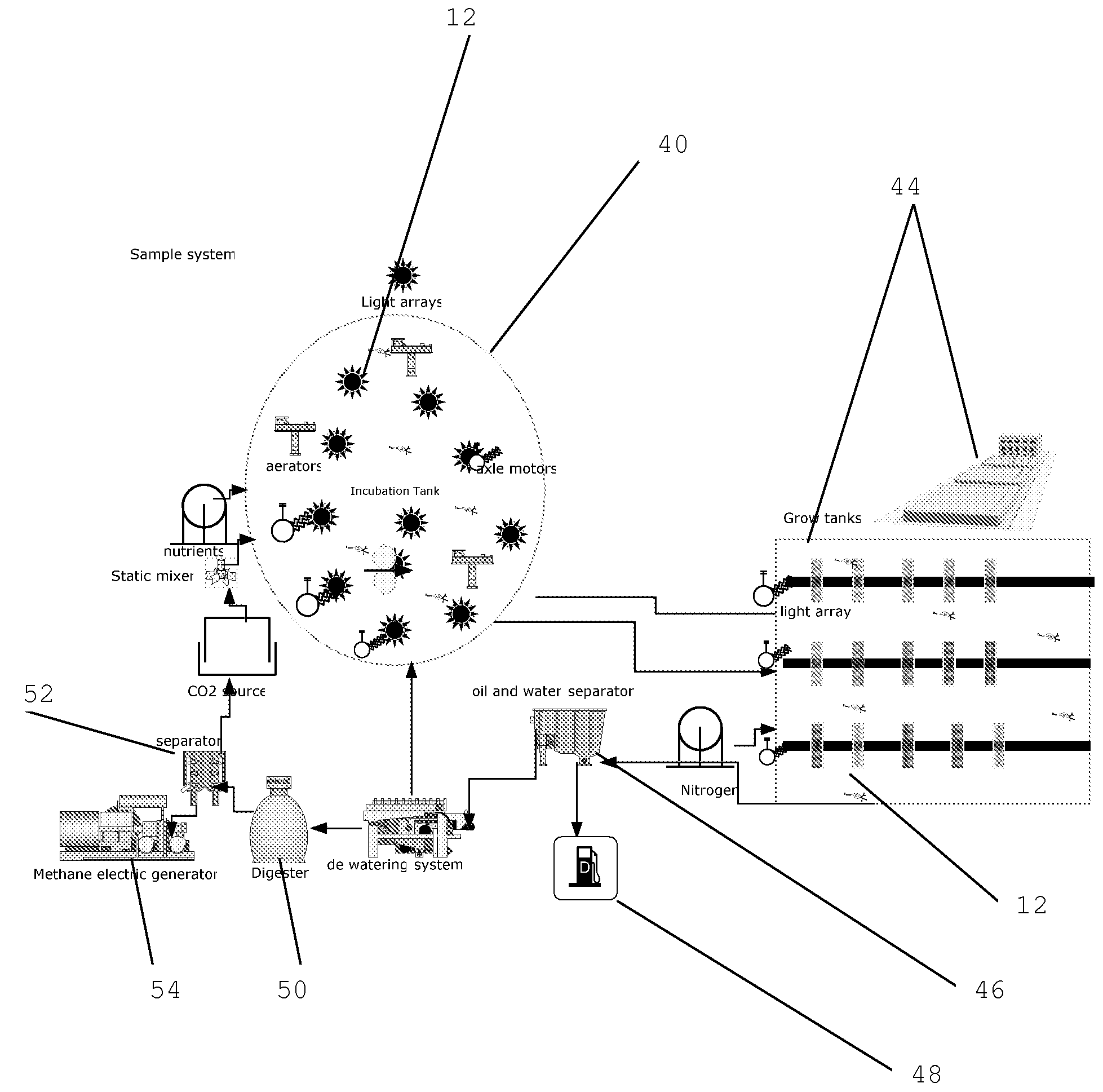
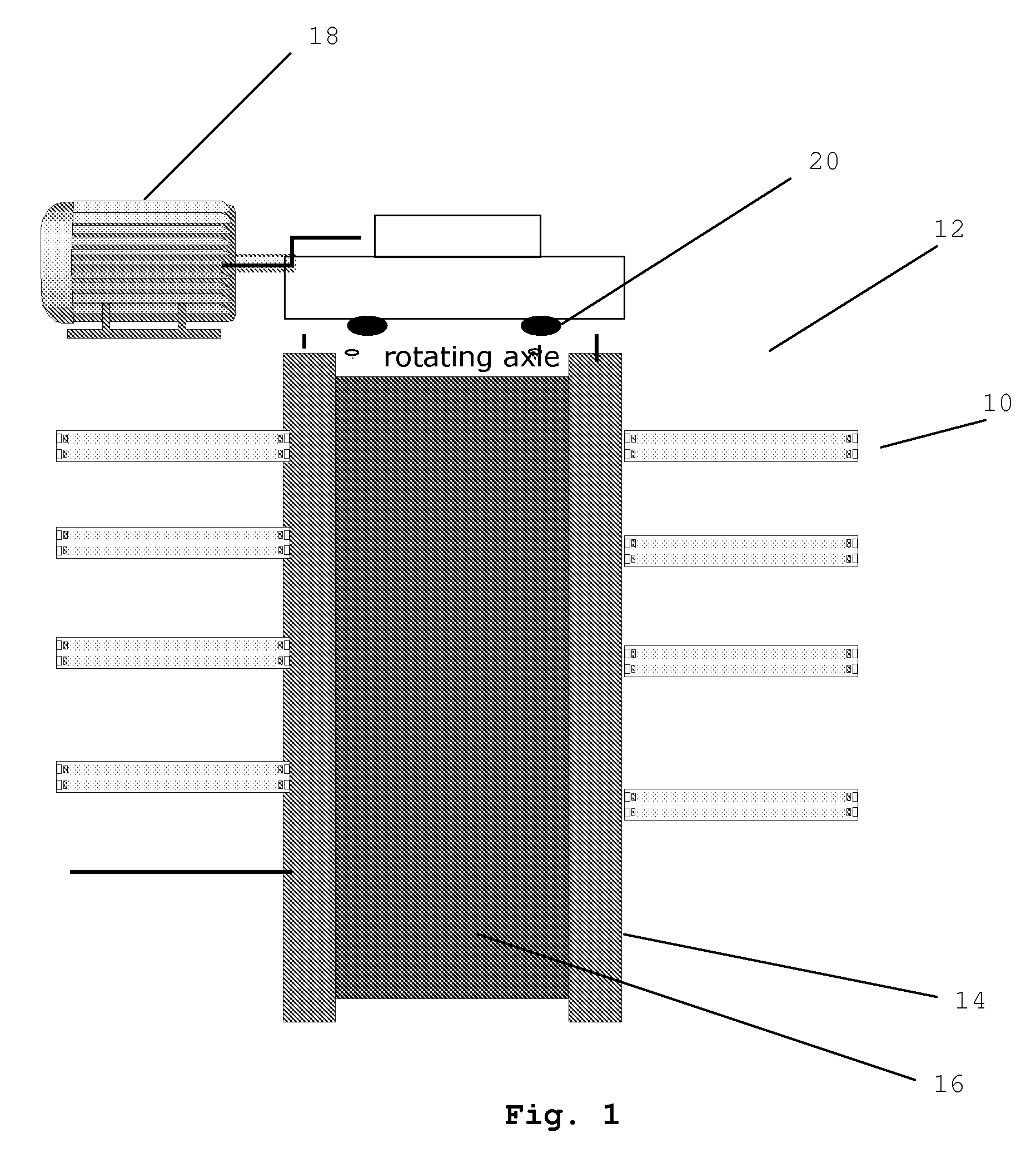
A system and methods for enhancing mass production of algae, diatoms or other photosynthetic organism is described. The system and methods are useful in applications such as energy production, fuels, foods, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and CO2 fixation. The system and methods involve the use of a submersed rotating pole(s) on which lights are branched out at strategic intervals in order to appropriately increase contact between photosynthetic water-based organisms and light. Rotation can timed so as to disperse light and / or nutrients when the organism is in a receiving mode. A process flow system is also described which can be scaled for the mass production of photosynthetic based organism. This process system makes use of centralized automatable controls and linear or parallel growth tanks. The system can be used for continuous or batch methods of production of bio-mass whose values such as lipids or carbohydrate can be extracted for the production of fuels or other byproducts.
Owner:ENNESYS
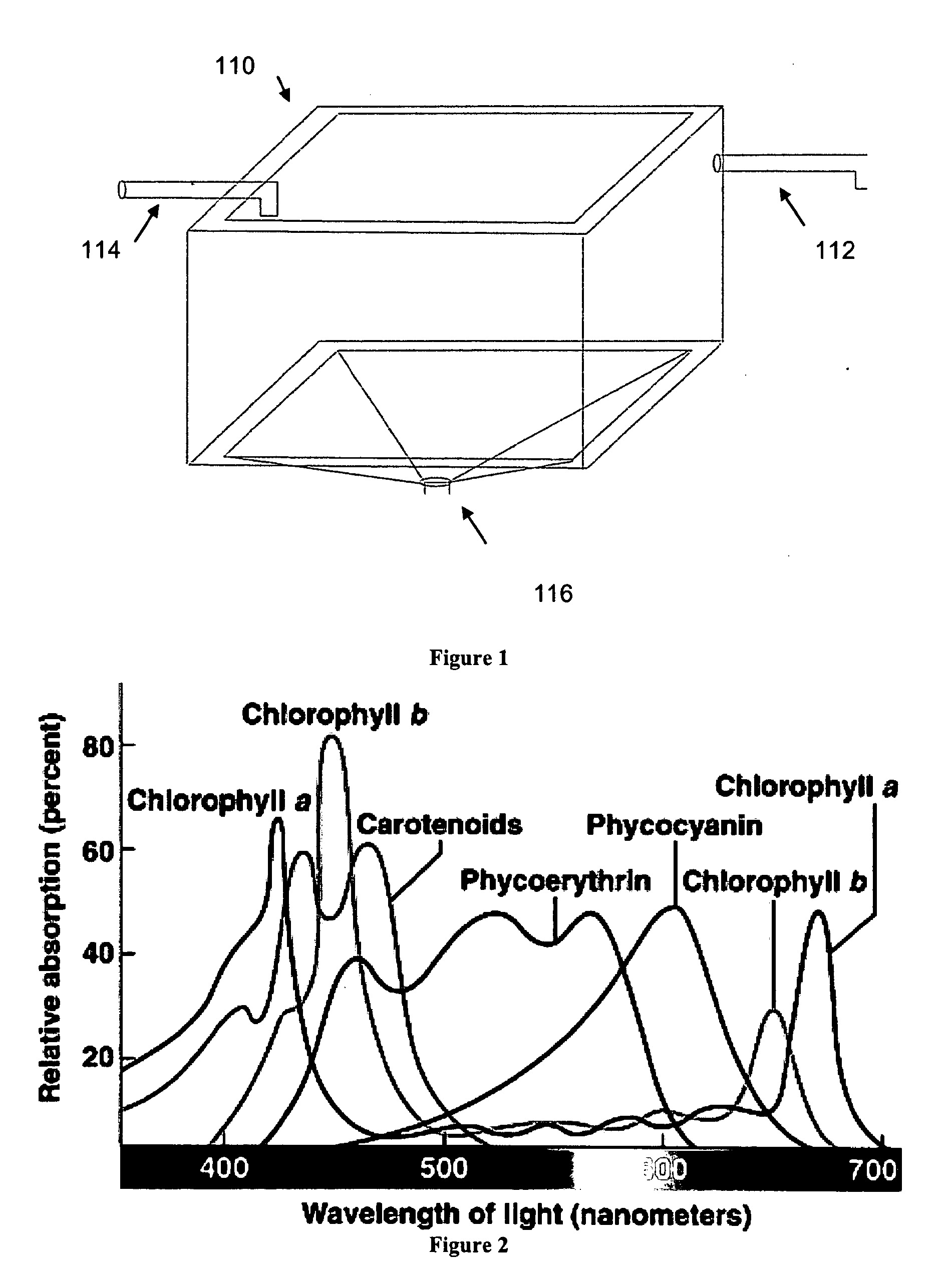
Bioreactor
InactiveUS20100255458A1Maximizing growth rateMaximize growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSolar heating energyOrganismBioreactor
The invention provides devices and methods for the growth of photoautotrophic organisms. The devices and methods address issues related to the design of bioreactors, selection of a photoautotrophic organism, growth of the photoautotrophic organisms, extraction of biomass products, and / or use of the biomass products as a renewable energy source.
Owner:ALGAEDYNE CORPORTION
Marine actinomycete taxon for drug and fermentation product discovery
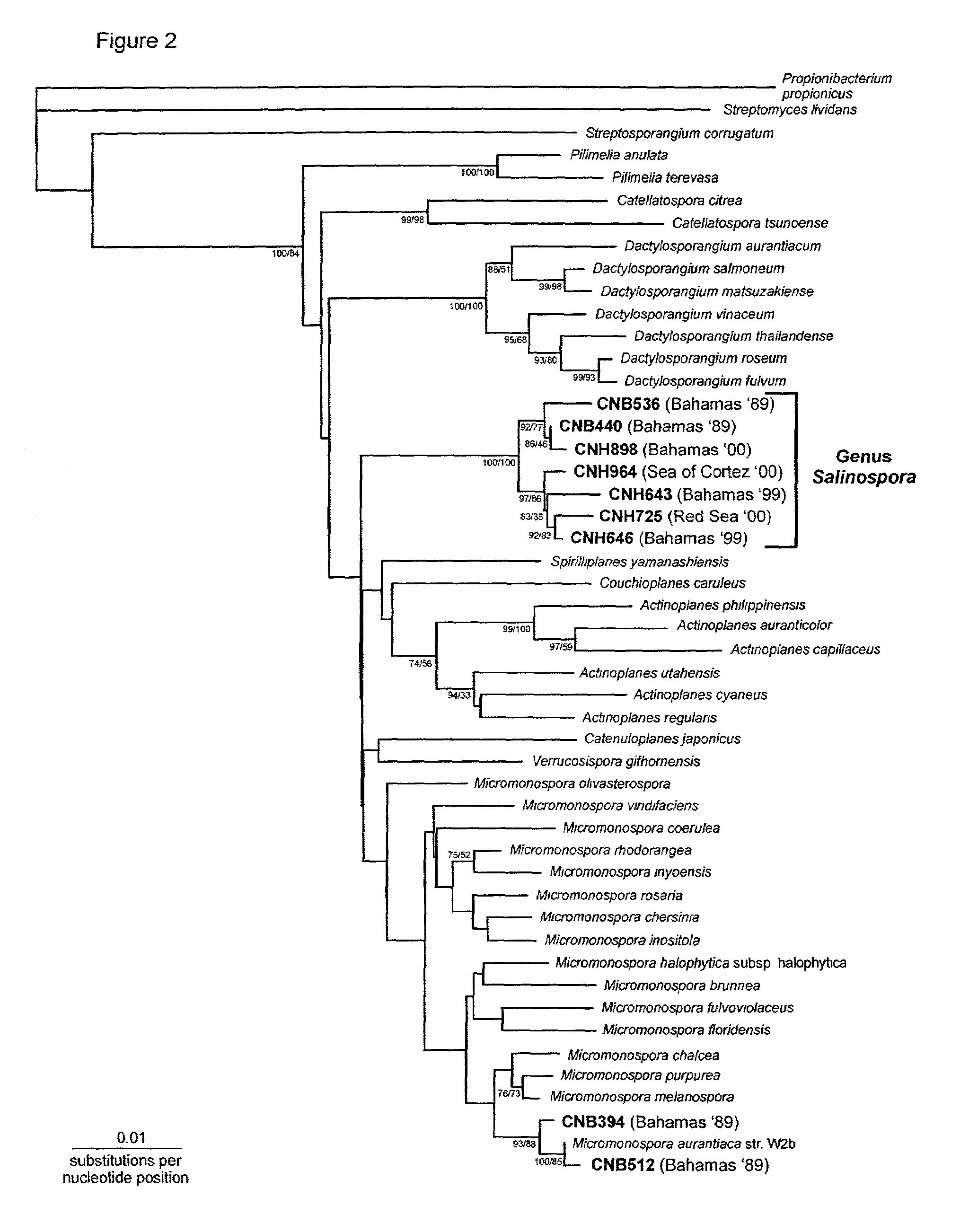
The invention is the discovery of an actinomycete genus, given the name Salinospora gen. nov., that displays an obligate requirement of seawater (Na+) for growth and unique 16S rRNA signature nucleotides. The invention is also the use of the genus for the production and discovery of active biomolecules such as pharmaceutical agents, agrichemicals, immunomodifiers, enzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
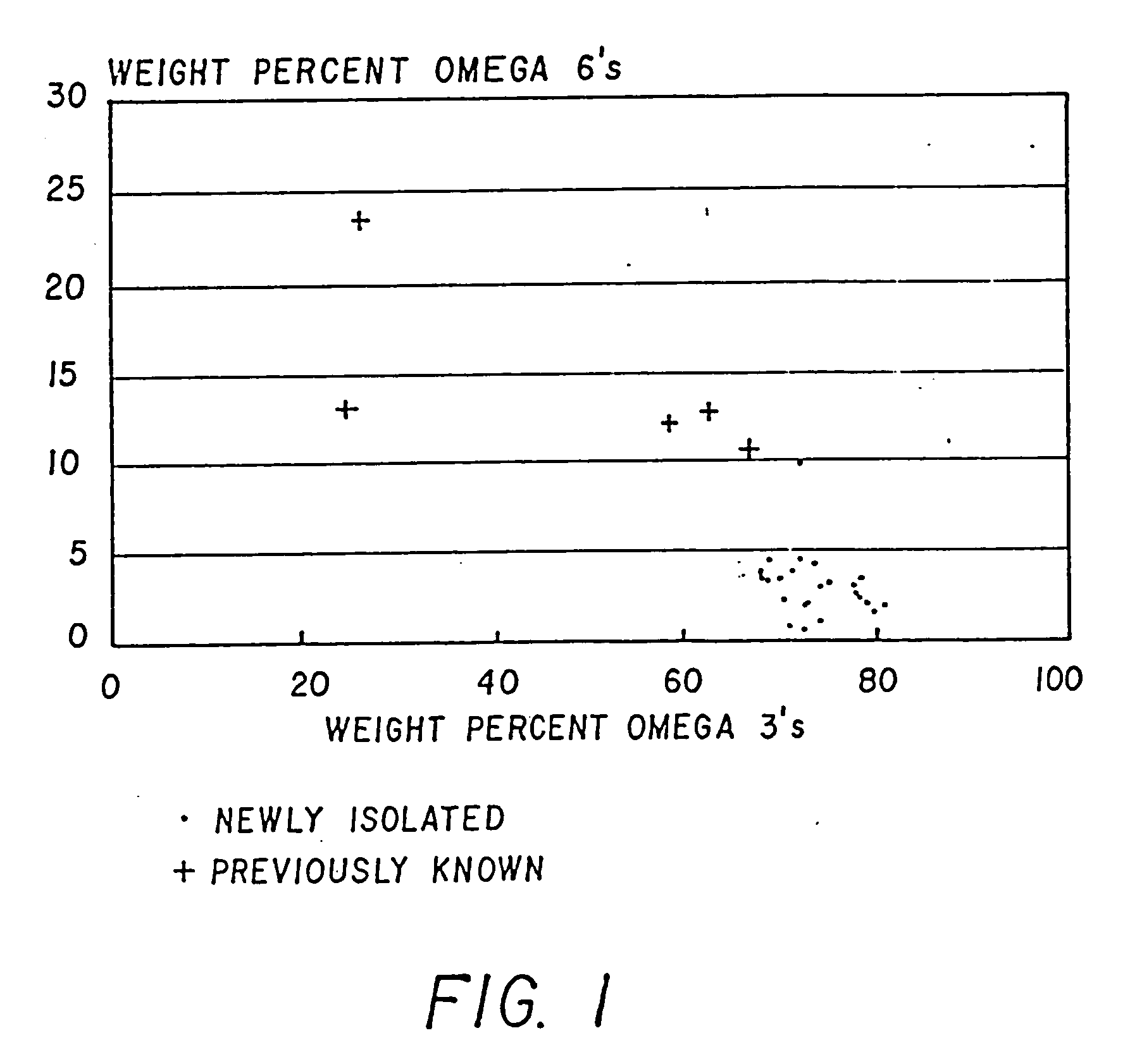
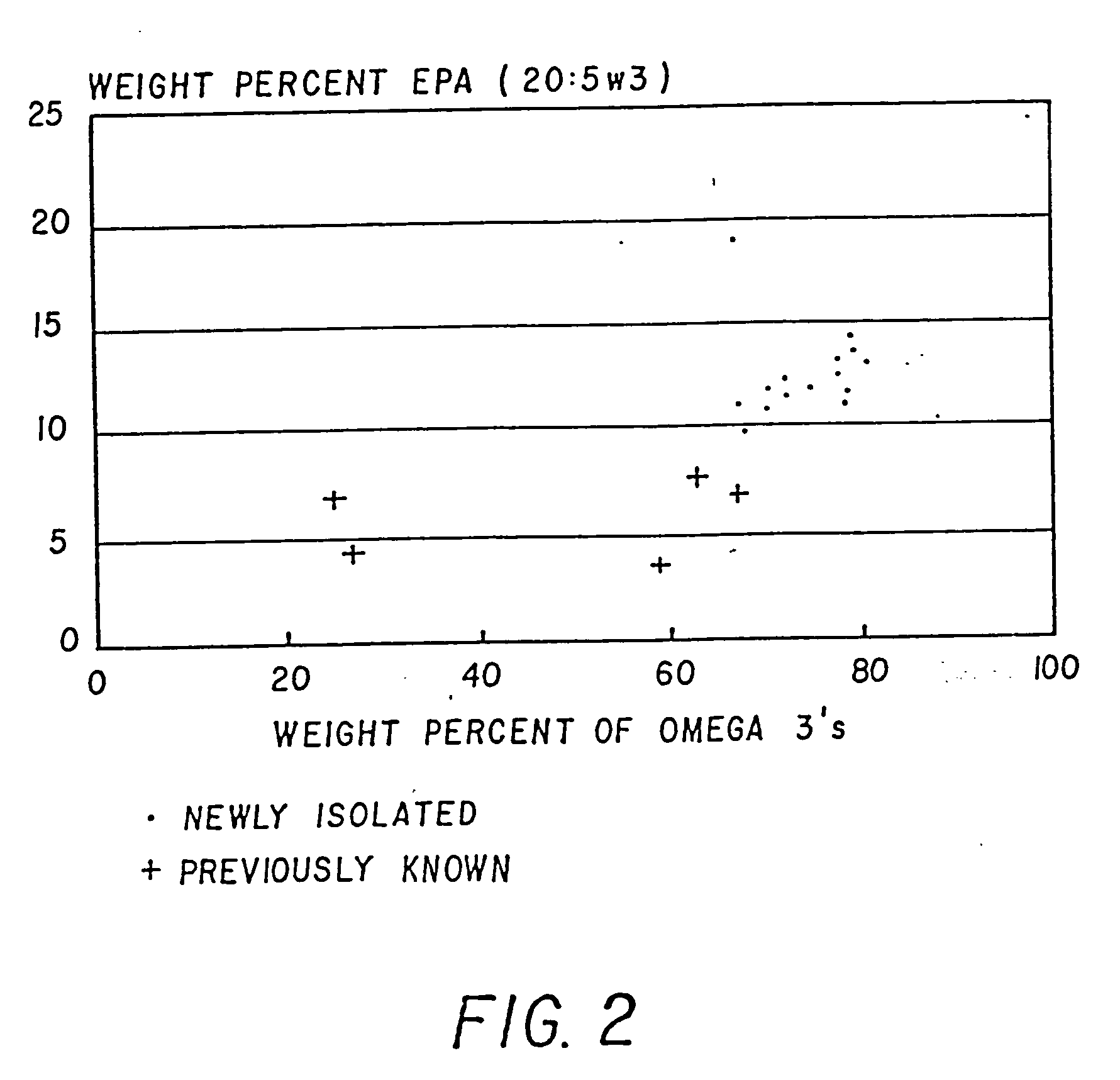
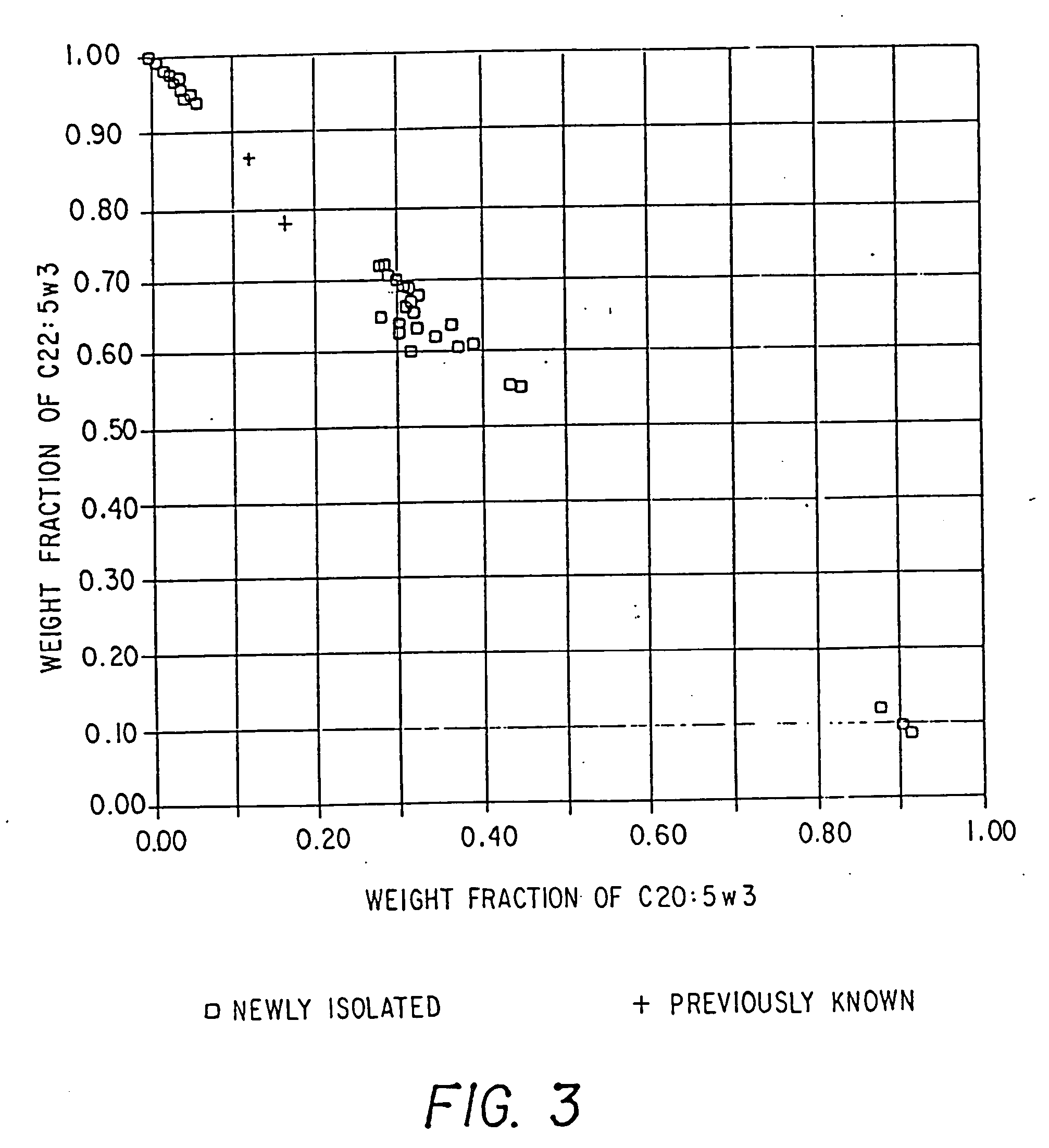
Process for the heterotrophic production of microbial products with high concentrations of omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20060160203A1Improve filtering effectLipid content can be increasedFungiBacteriaHigh concentrationRapeseed
Disclosed is a process for growing the microflora Thraustochytrium, Schizochytrium, and mixtures thereof, which includes the growing of the microflora in fermentation medium containing non-chloride containing sodium salts, in particular sodium sulfate. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the process produces microflora having a cell aggregate size useful for the production of food products for use in aquaculture. Further disclosed is a food product which includes Thraustochytrium, Schizochytrium, and mixtures thereof, and a component selected from flaxseed, rapeseed, soybean and avocado meal. Such a food product includes a balance of long chain and short chain omega-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Eukaryotic use of improved chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of recombinagenic oligonucleotides in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test duplex DNA on a plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria and allows for the rapid and quantitative comparison of recombinagenic oligonucleobases. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Heteroduplex Mutational Vector, was shown to be more active in than the types of mutational vectors heretofore tested. Further improvements in activity were obtained by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the Duplex Mutational Vector and removal of the DNA-containing intervening segment. The claims concern Duplex Mutational Vectors that contain the above improvements. In an alternative embodiment the claims concern a reaction mixture containing a recombinagenic oligonucleobase, a cell-free enzyme mixture and a duplex DNA containing a target sequence. In yet an alternative embodiment, the invention concerns the use of such mixture to test improvements in recombinagenic oligonucleobases, as well as to test the effects of compounds on the activity of the cell-free enzyme mixture and also to make specific changes in the target DNA sequence.
Owner:CIBUS
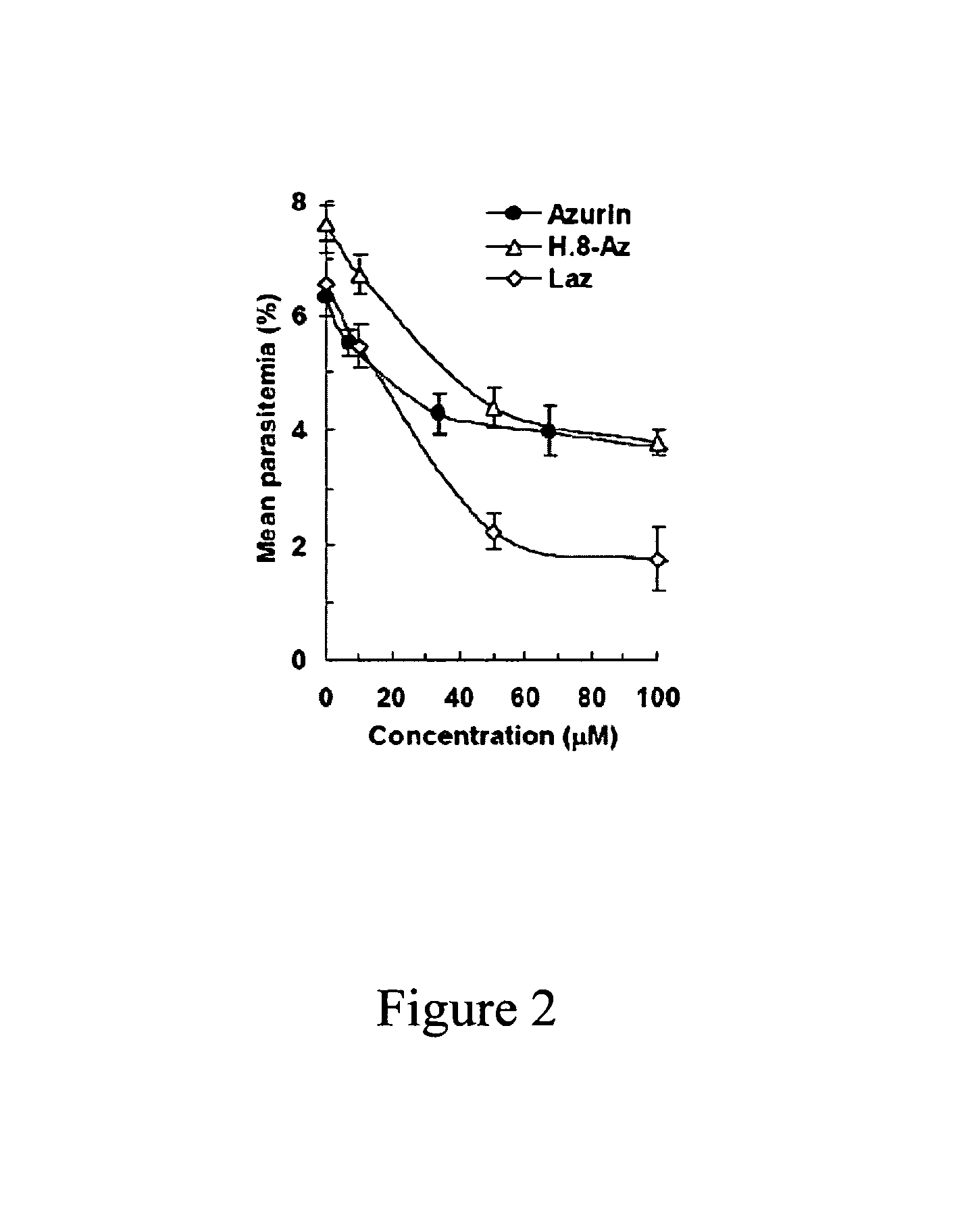
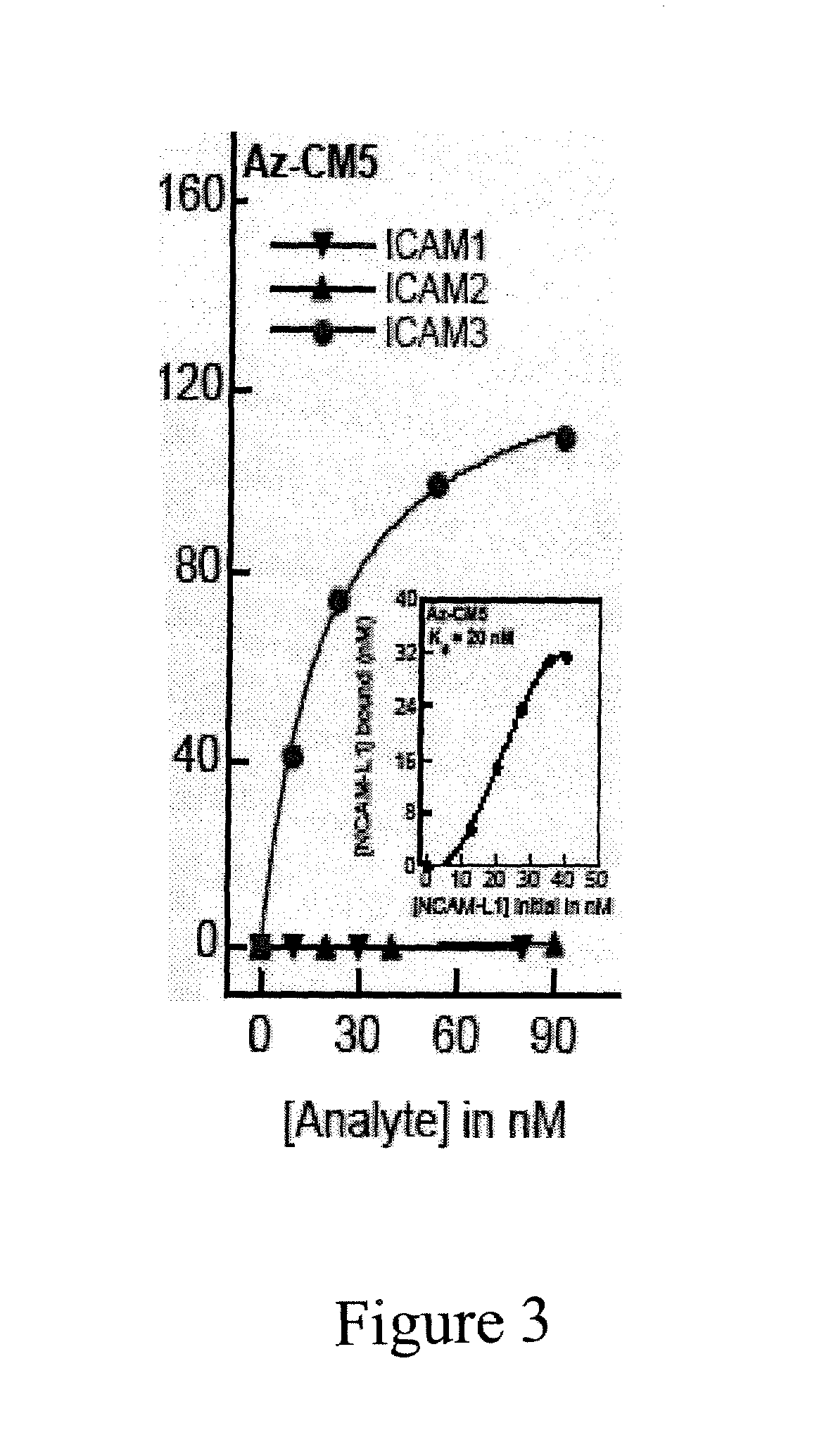
Compositions and methods for treating malaria with cupredoxin and cytochrome
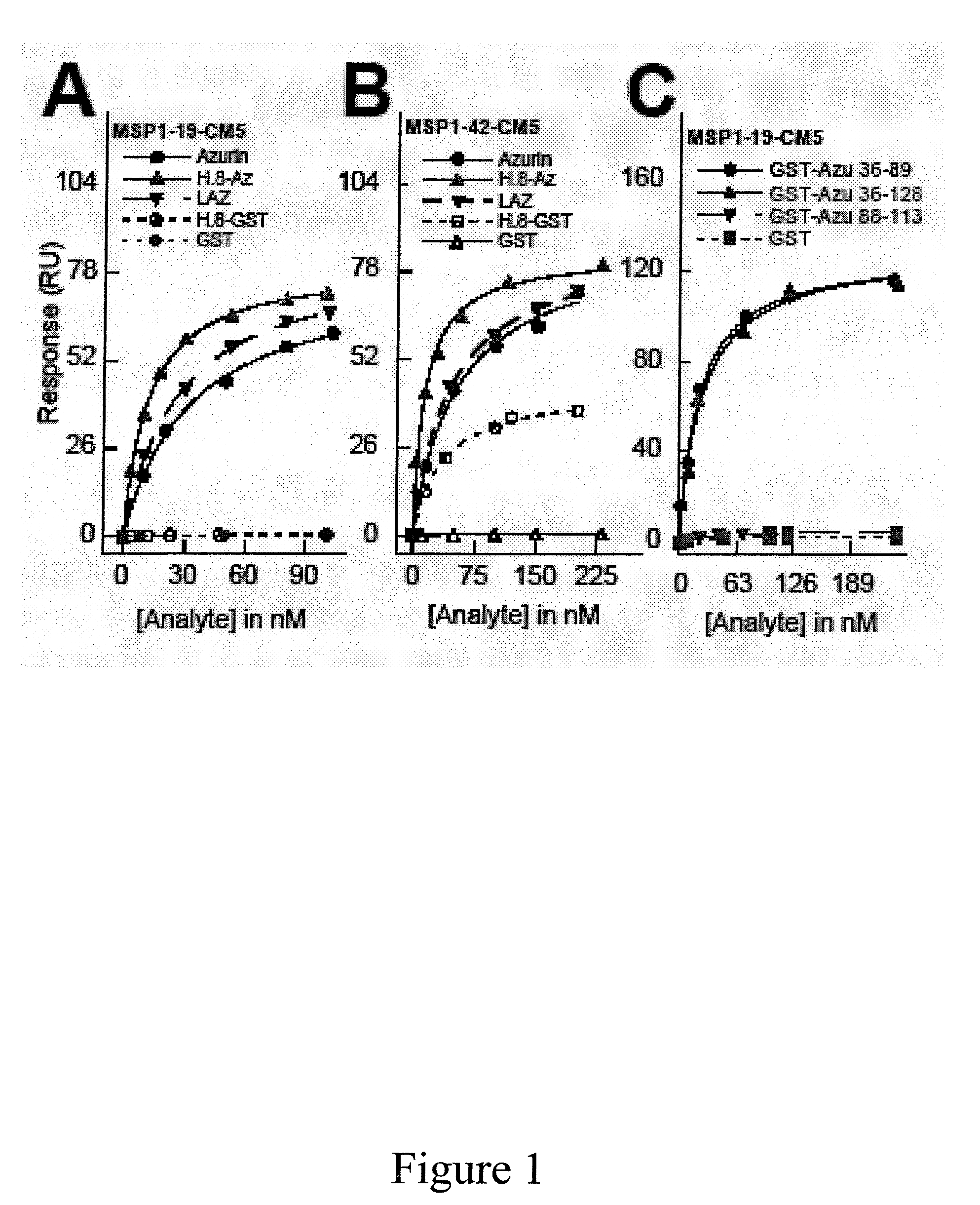
The present invention relates to cupredoxin and cytochrome and their use, separately or together, to inhibit the spread of parasitemia in mammalian red blood cells and other tissues infected by the malaria parasite, and in particular the parasitemia of human red blood cells by P. falciparum. The invention provides isolated peptides that are variants, derivatives or structural equivalents of cupredoxins or cytochrome c, and compositions comprising cupredoxins and / or cytochrome c, or variants, derivatives or structural equivalents thereof, that are useful for treating or preventing malaria infection in mammals. Further, the invention provides methods to treat mammalian patients to prevent or inhibit the growth of malarial infection in mammals. The invention also provides methods to prevent the growth of malaria infection in insect vectors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
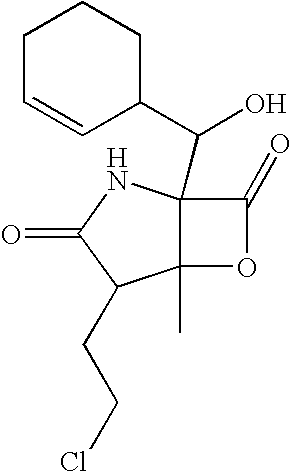
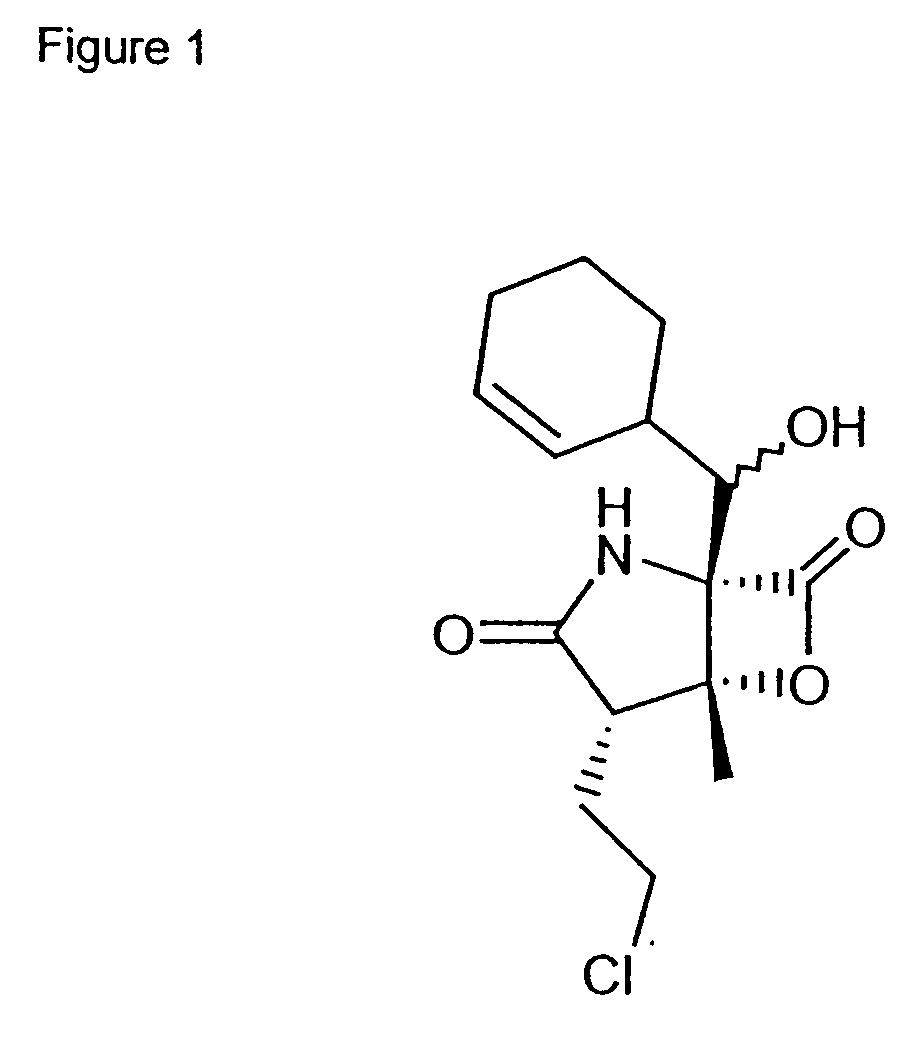
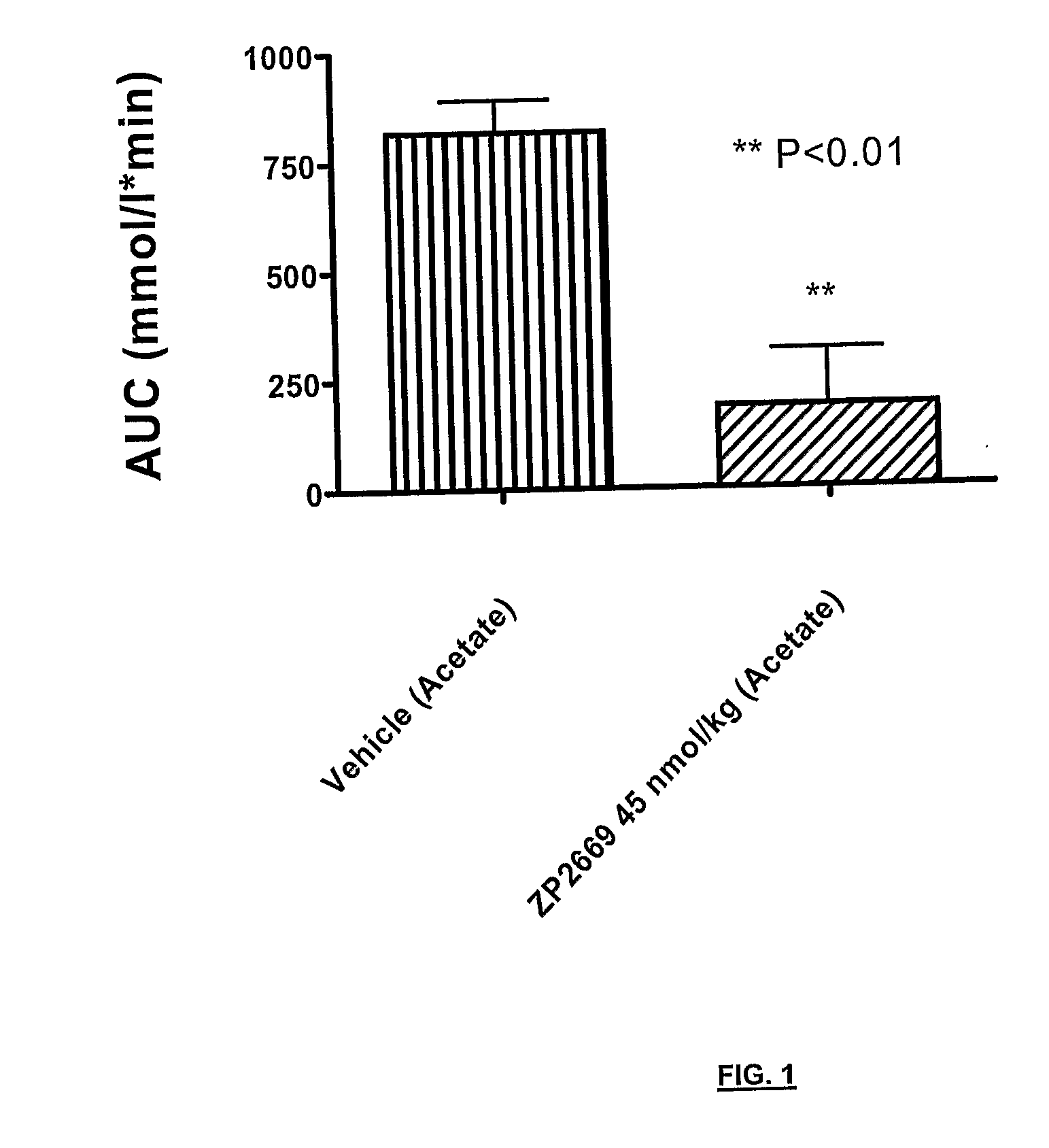
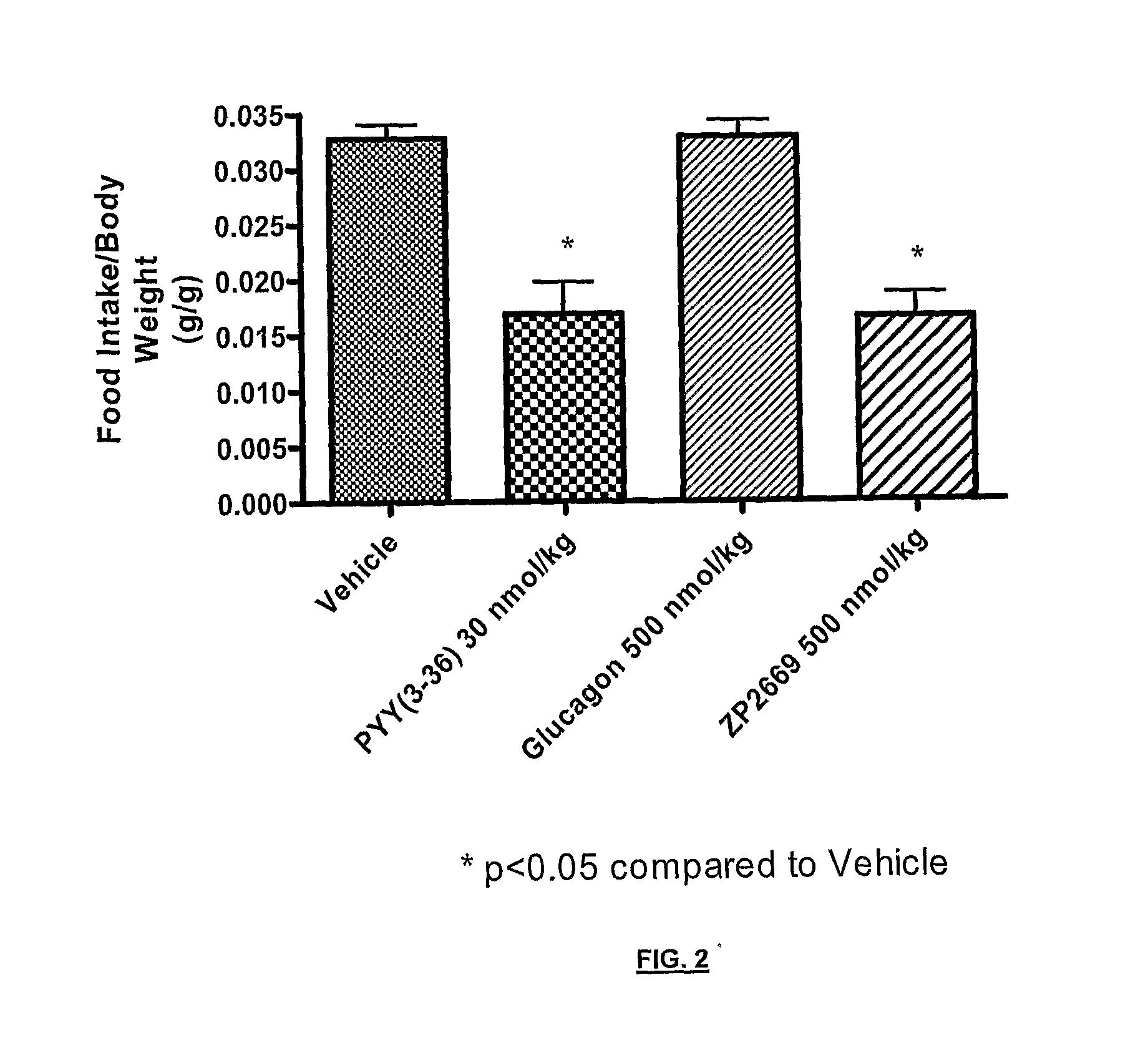
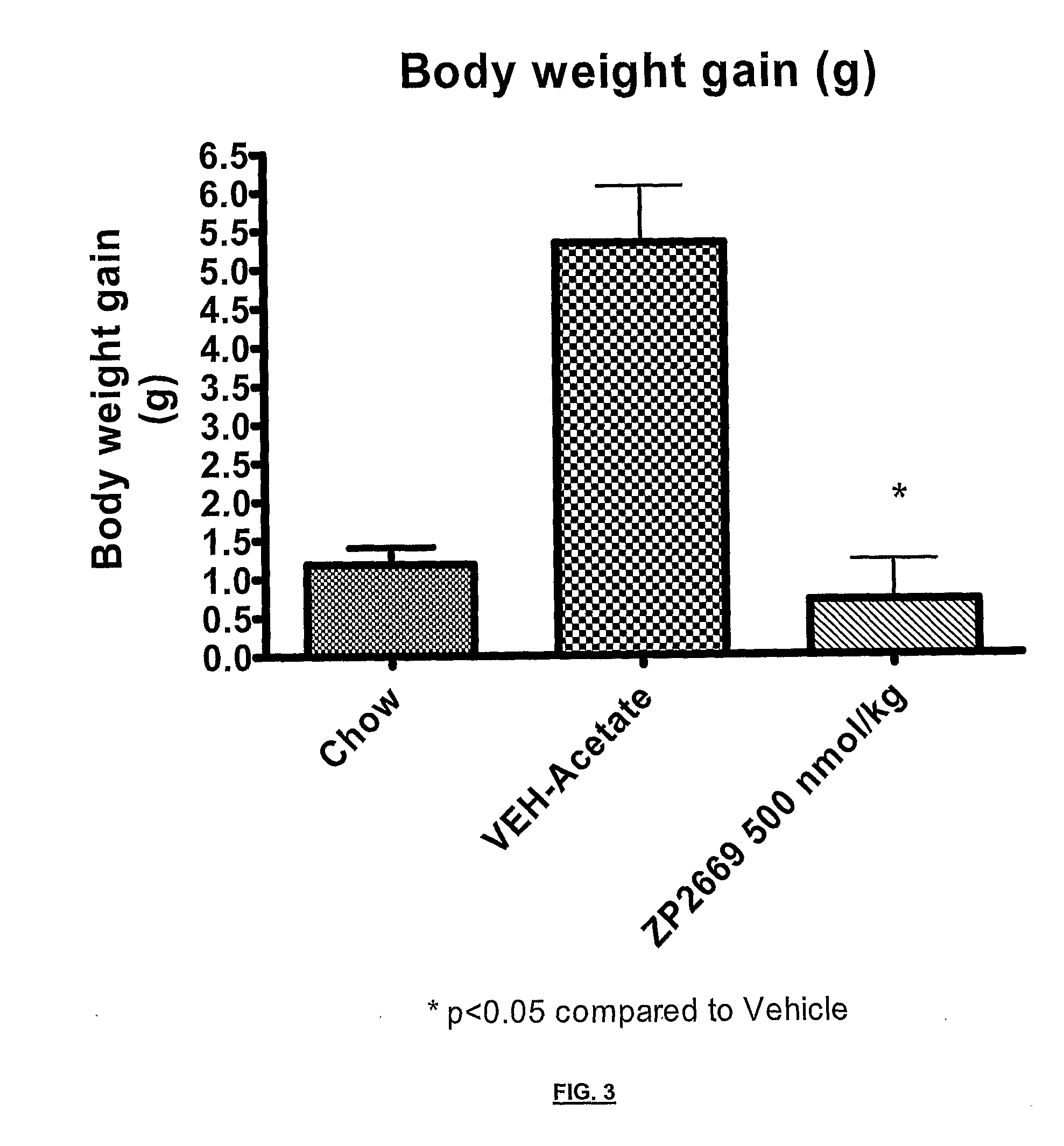
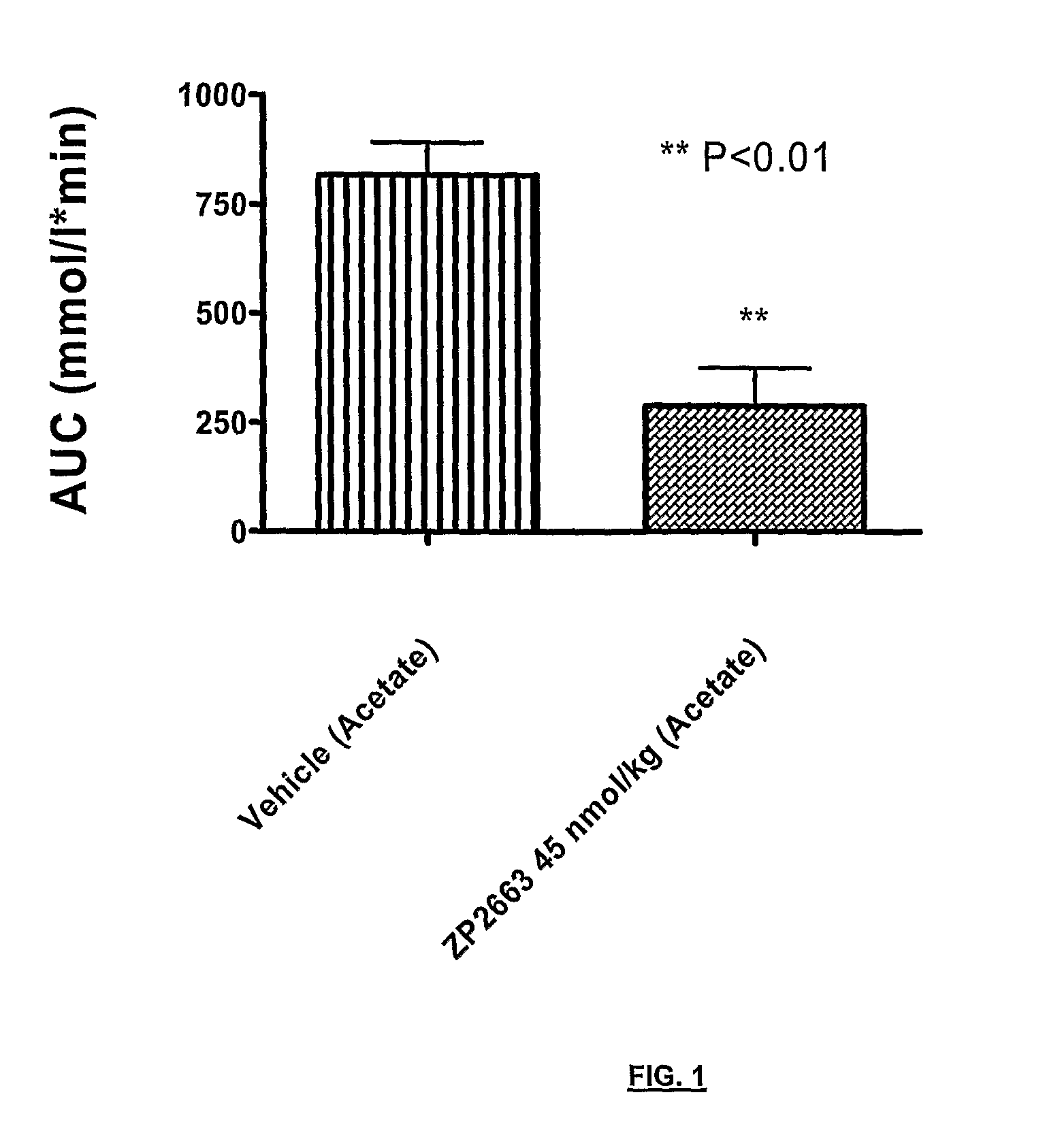
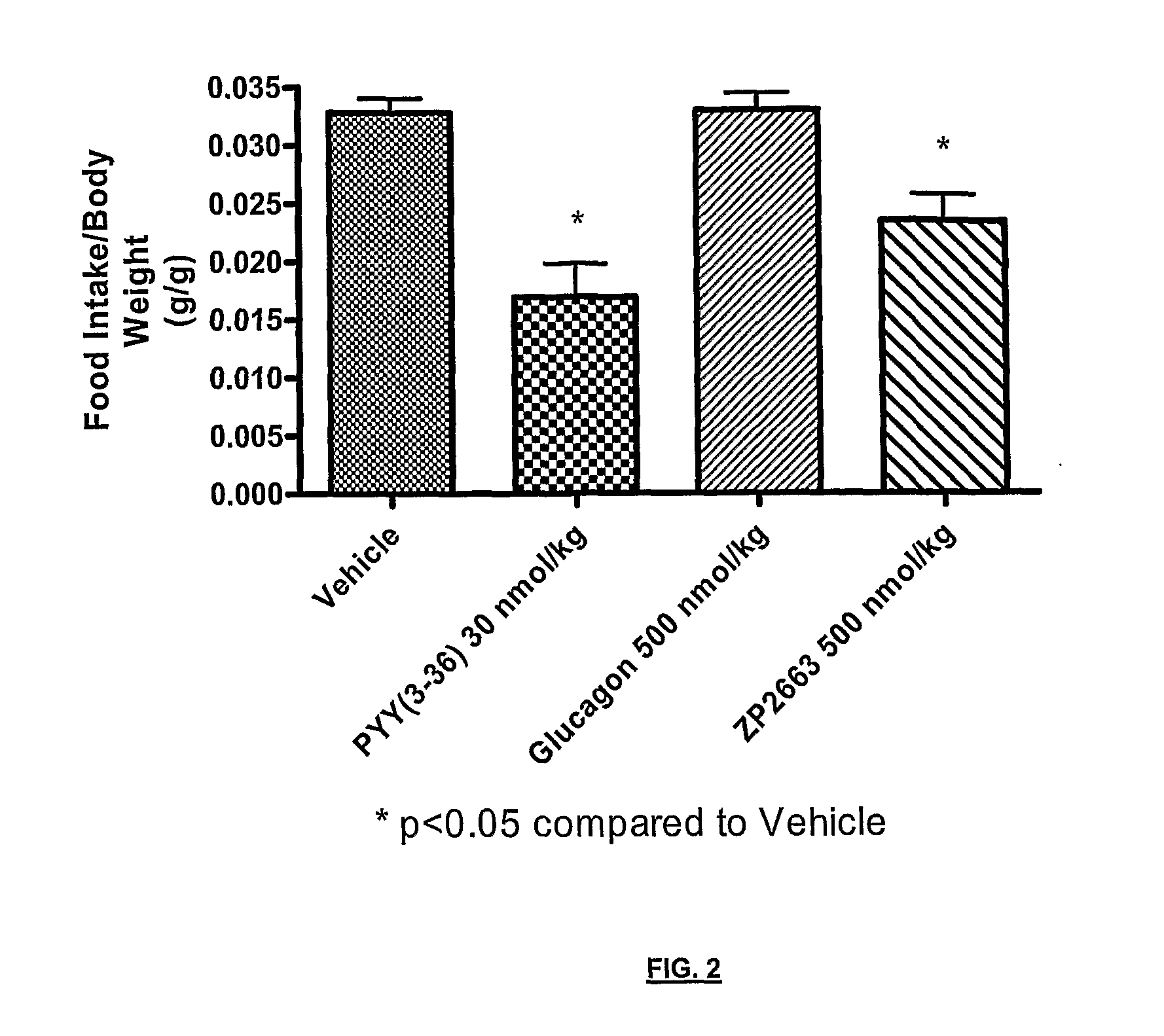
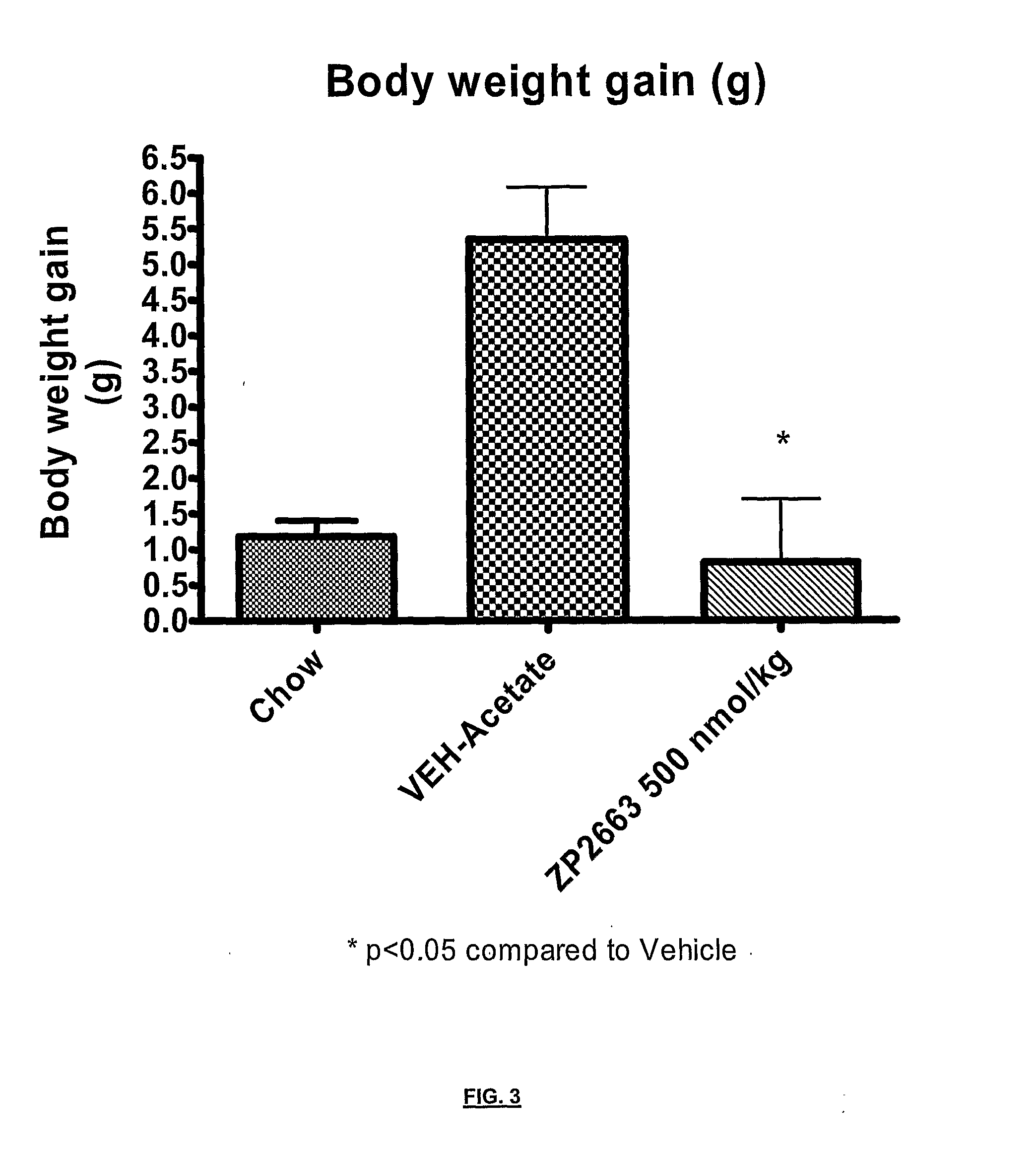
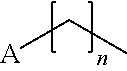
Glucagon analogues
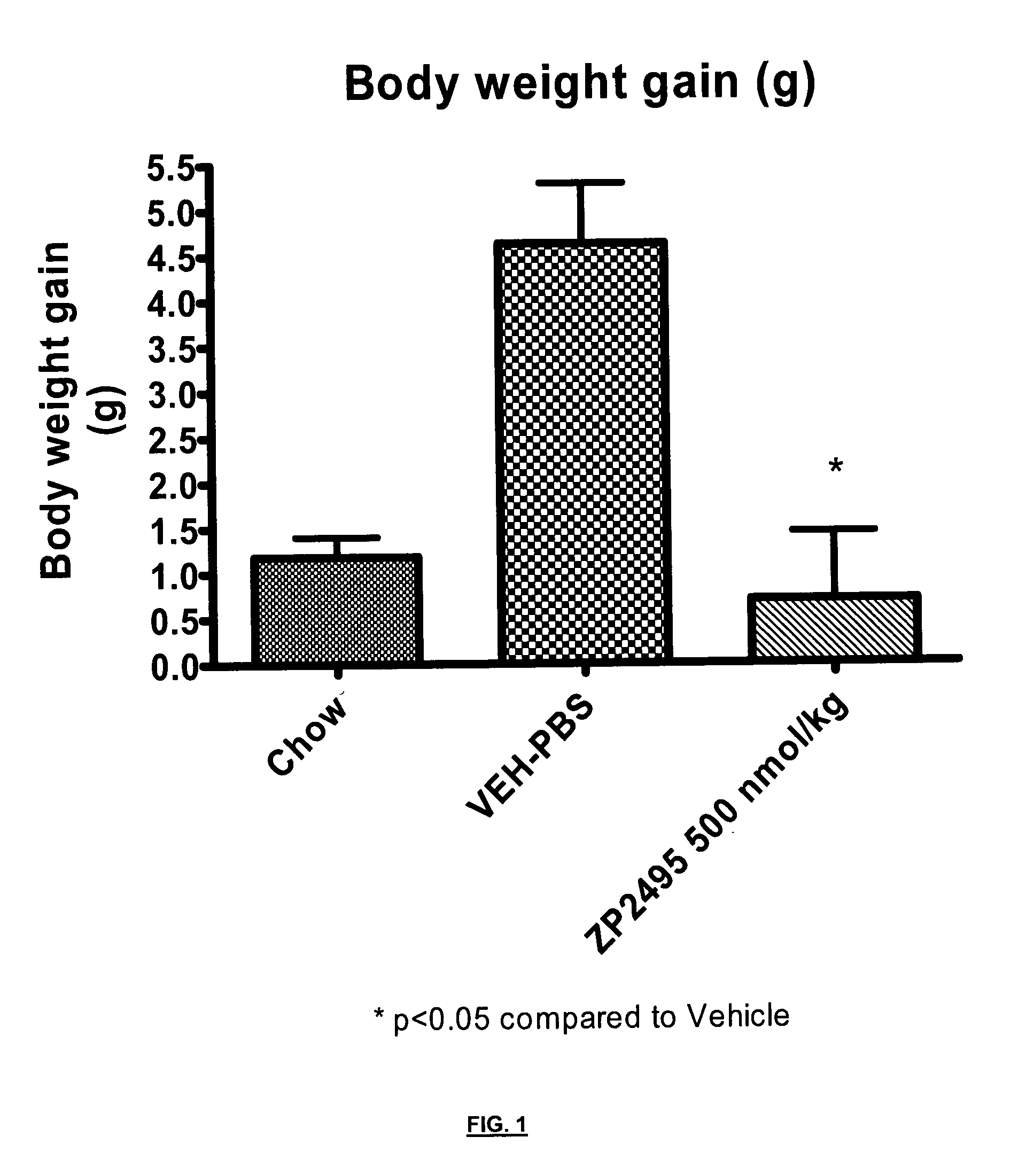
ActiveUS20140080757A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsProviding materialObesity
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Method for generating a parvovirus b19 virus-like particle
InactiveUS20130273109A1Lower Level RequirementsPrevent correction of the anemiaBacteriaProtozoaParvovirusImmunogenicity
The invention provides a process for generating parvovirus VP1 / VP2 virus like particles (VLPs). The invention further provides methods for purification of the parvovirus VLPs and immunogenic compositions that contain the VLPs. The invention also includes recombinant nucleic acid molecules that encode parvovirus VP1 and VP2, and host cells that contain the recombinant nucleic acids.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Marine actinomycete taxon for drug and fermentation product discovery
The invention is the discovery of an actinomycete genus, given the name Salinospora gen. nov., that displays an obligate requirement of seawater (Na+) for growth and unique 16S rRNA signature nucleotides. The invention is also the use of the genus for the production and discovery of active biomolecules such as pharmaceutical agents, agrichemicals, immunomodifiers, enzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Glucagon analogues
InactiveUS20110286982A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossOrganic active ingredientsFungiWeight gain preventionProviding material
The invention provides materials and methods for promoting weight loss or preventing weight gain, and in the treatment of diabetes, metablic syndrome and associated disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Glucagon analogues
InactiveUS20110286981A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossOrganic active ingredientsFungiWeight gain preventionProviding material
The invention provides materials and methods for promoting weight loss or preventing weight gain, and in the treatment of diabetes, metabolic syndrome and associated disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Glucagon analogues
The invention provides materials and methods for promoting weight loss or preventing weight gain, and in the treatment of diabetes, metablic syndrome and associated disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
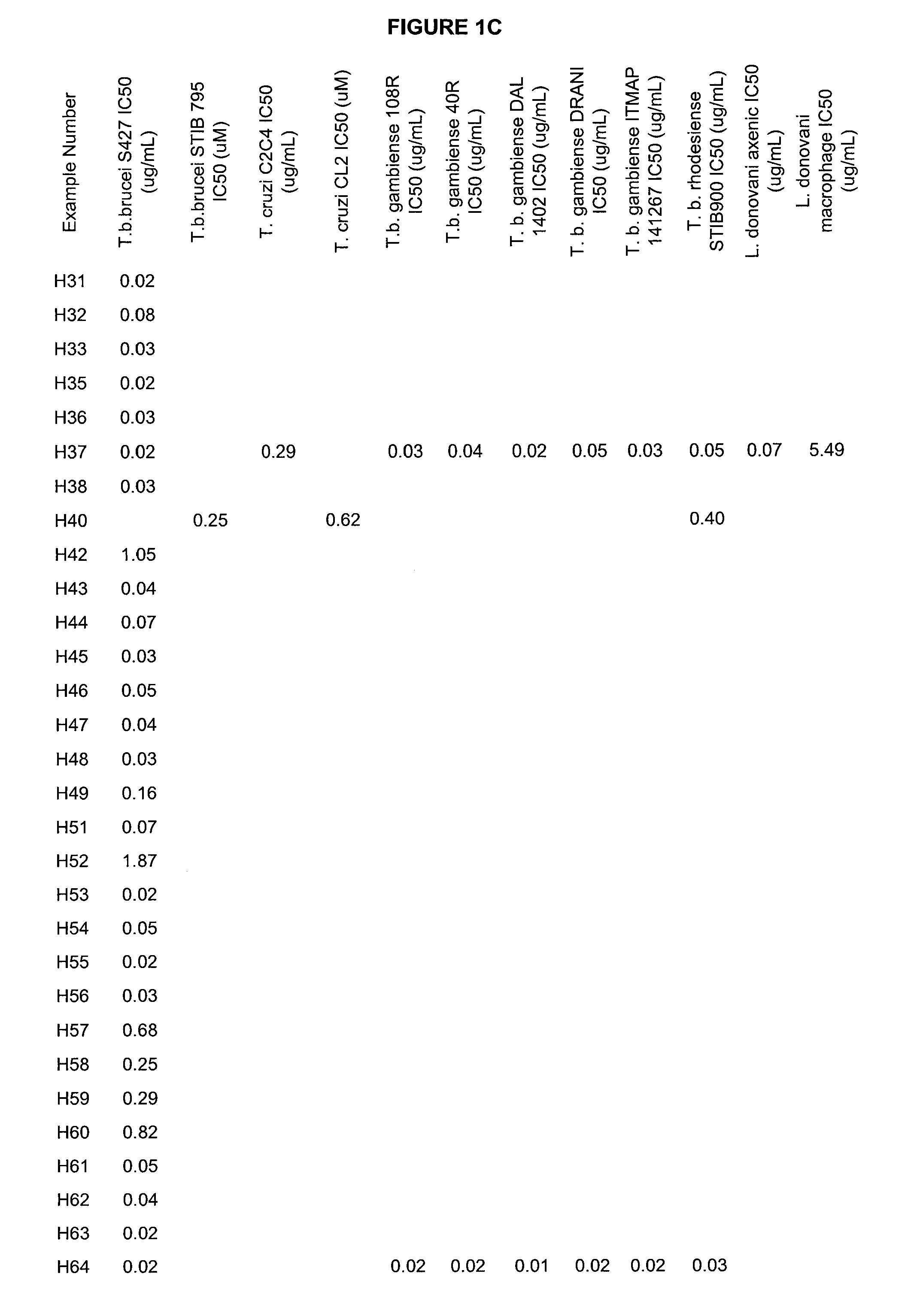
Boron-containing small molecules as Anti-protozoal agents
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA INC
Targeted genomic rearrangements using site-specific nucleases
The present invention relates to a method for genomic DNA rearrangements, and more particularly, to a method for deletion, duplication, inversion, replacement, or rearrangement of genomic DNA using pairs of site-specific nucleases targeting two or more sites in the genome, a cell in which genomic DNA is deleted, duplicated, inverted, replaced, or rearranged by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells. Further, the present invention relates to a method for inserting synthetic DNA molecules into the genome using site-specific nucleases targeting a pre-determined site in the genome, a cell in which DNA insertion occurs by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Continuous-batch hybrid process for production of oil and other useful products from photosynthetic microbes
InactiveUS7770322B2Minimize complexityOperation minimizedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCarrying capacity
Owner:CELLANA
Glucagon analogues
ActiveUS20150111817A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossNervous disorderBacteriaProviding materialObesity
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Method for preparing salt-tolerant microbial agent
InactiveCN103540555ARapid industrialization startSimple stepsFungiBacteriaInorganic saltsMixed culture
The invention discloses a method for preparing a salt-tolerant microbial agent. The method comprises the following steps of in an open culture device, directly carrying out mixed culture on a salt-tolerant microbial flora in a high-salt environment sample under the condition that total salt concentration is 1%-30%; and adding an organic carbon source, nutrient elements and trace elements according to the needs in a culture process, controlling and keeping proper pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen relatively stable. The salt-tolerant microbial agent prepared by adopting the method has good salt tolerance and salinity impact resistance, can degrade organic substances in water without being restrained by high-concentration inorganic salt under the condition that total salt concentration is 1%-30%, and can be directly used for purifying high-salt-content wastewater with salt concentration of 1%-30%. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, short in implementation period and capable of quickly carrying out industrial application.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Methods for control of flux in metabolic pathways through enzyme relocation
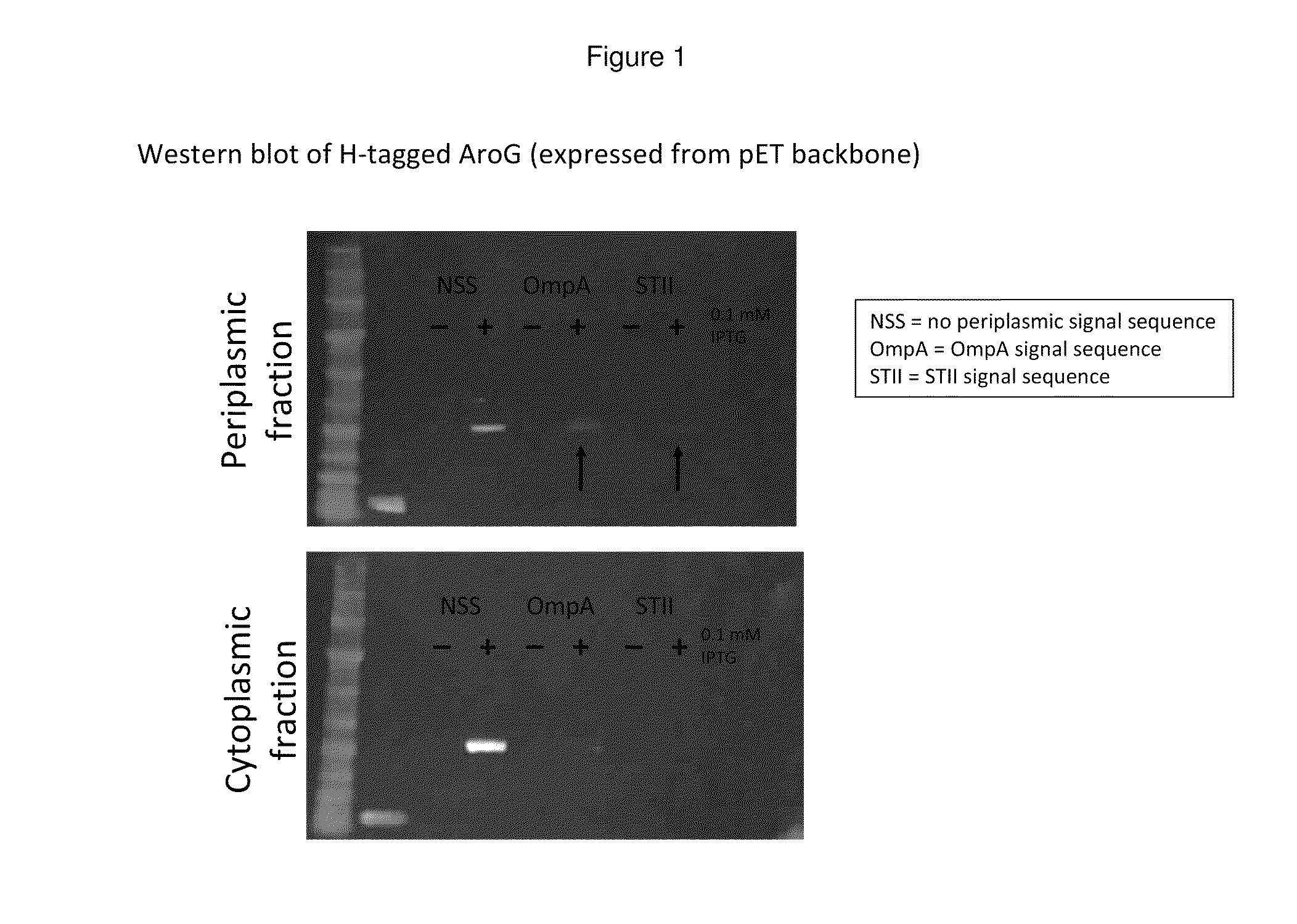
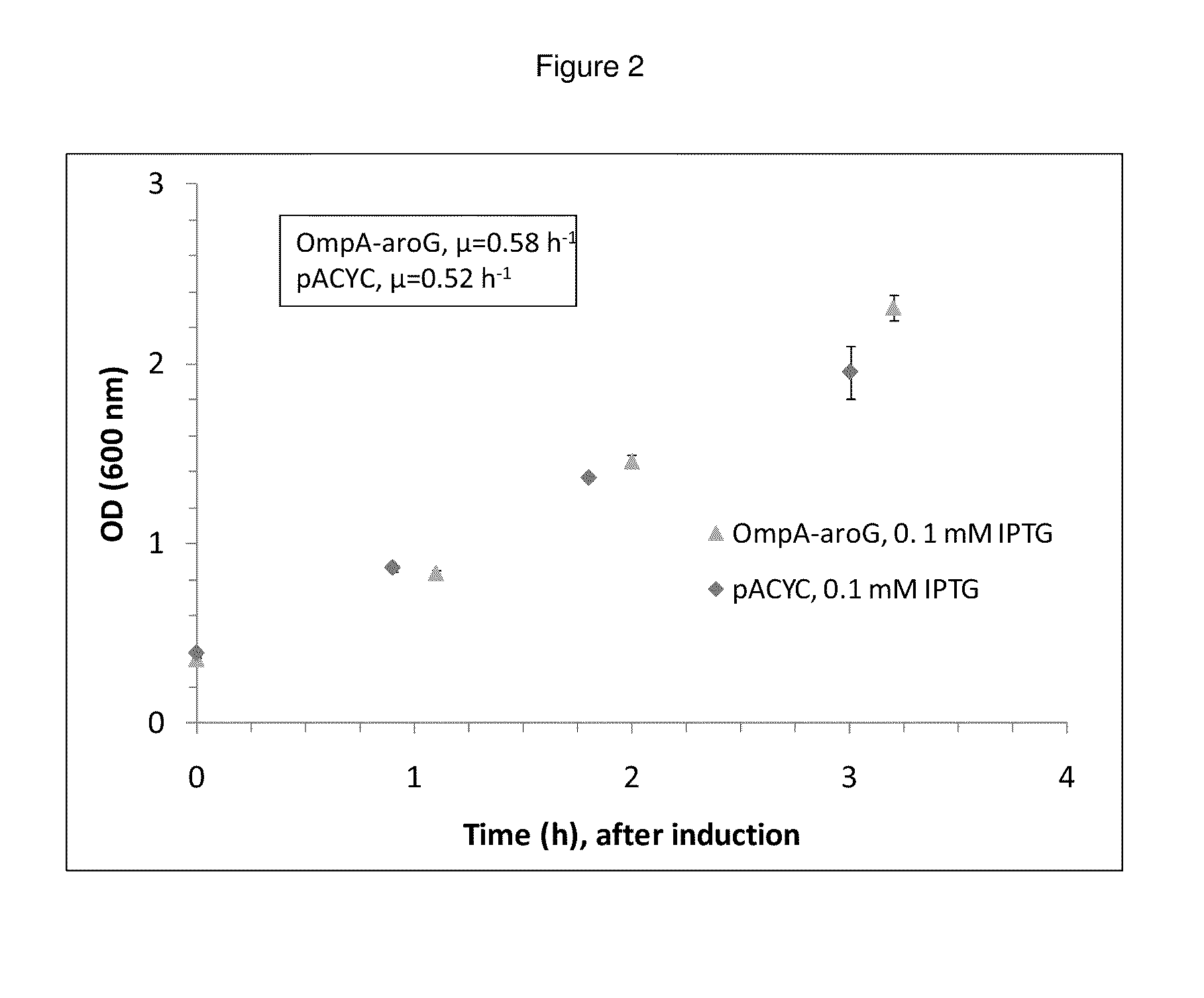
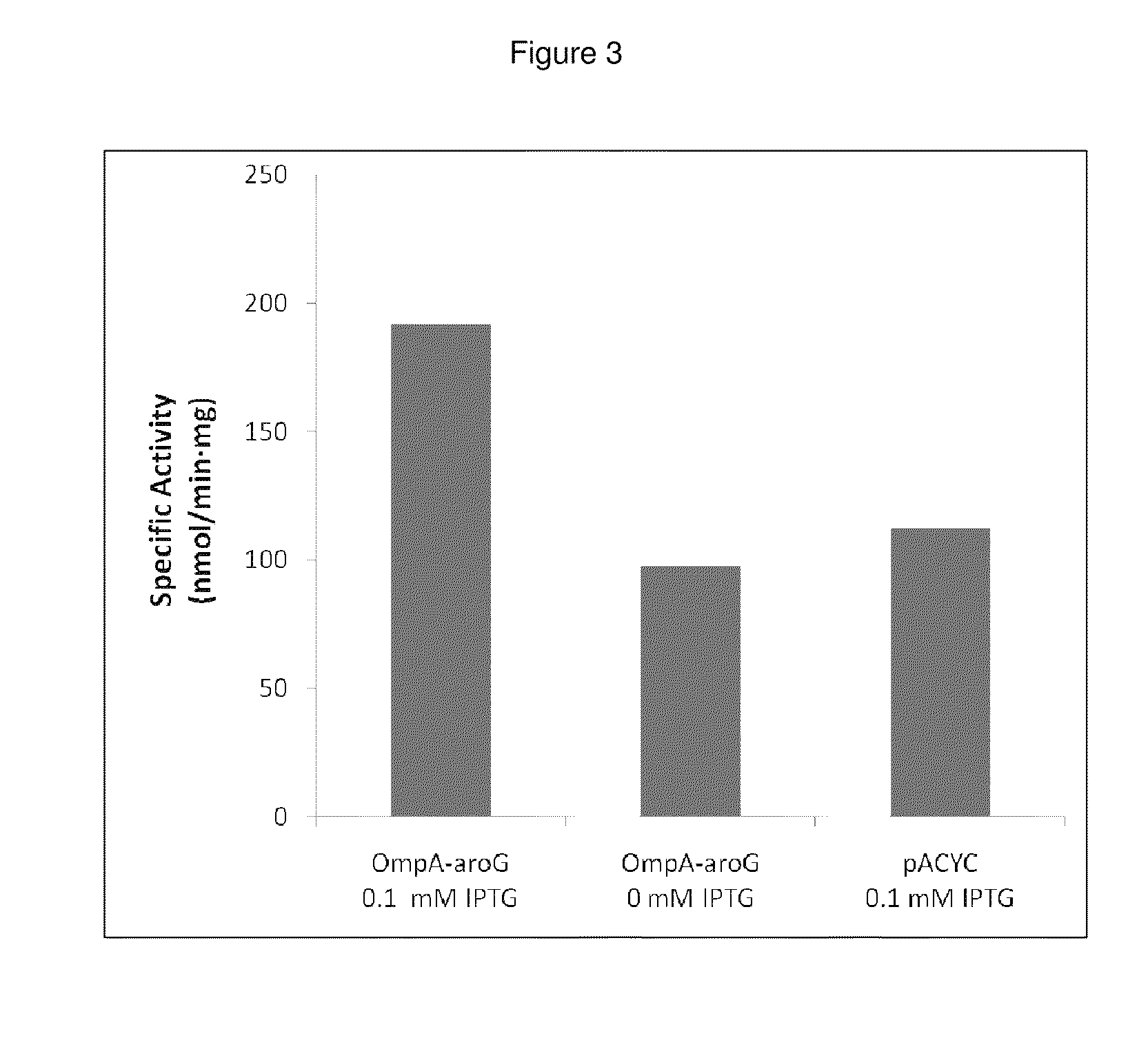
Genetically manipulated cells, lysates of such cells, systems, and methods of use thereof are provided, where one or more enzymes in a pathway of interest are genetically modified to incorporate a peptide sequence that provides for relocation of the protein, e.g., to the periplasm, so as to sequester the enzyme, and where the enzyme controls flux in the pathway of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
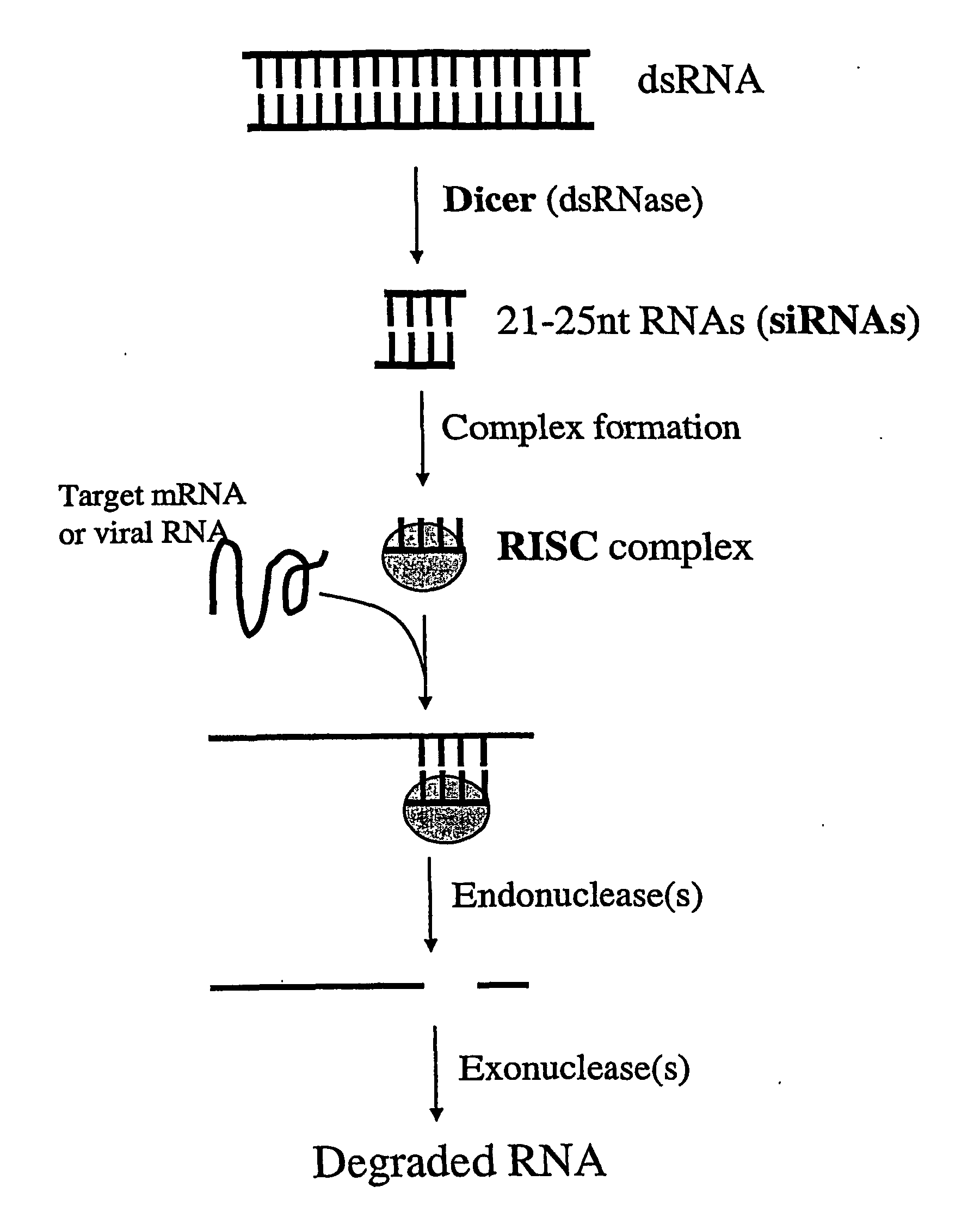
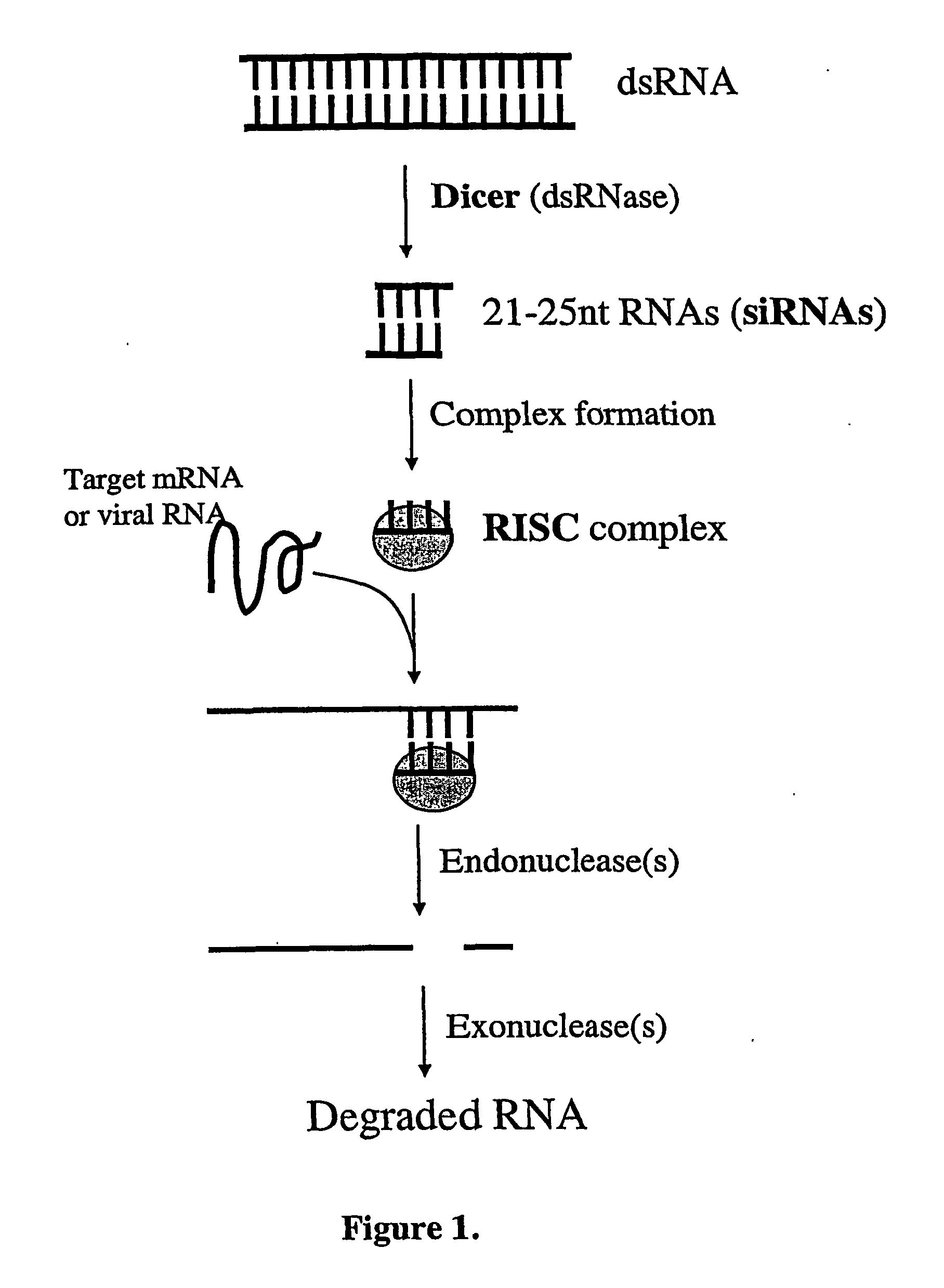
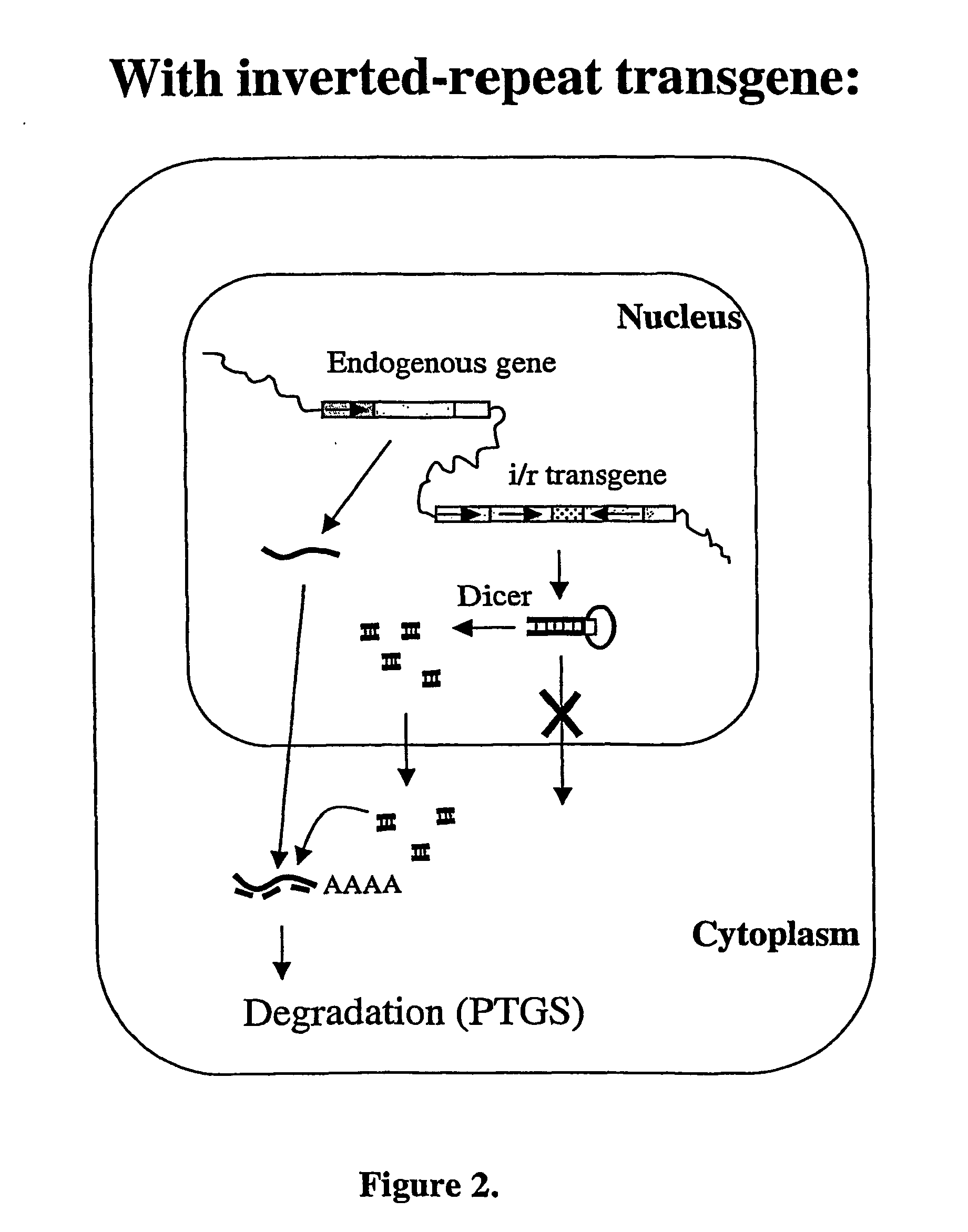
Modified Gene-Silencing Nucleic Acid Molecules and Uses Thereof
Methods and means for efficiently downregulating the expression of a target gene of interest in cell from an organism that is an animal, fungus and protist. The invention provides chimeric nucleic acid molecules for downregulating target genes. The invention also provides modified cells and organisms comprising the chimeric nucleic acid molecules and compositions comprising the chimeric molecules.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com