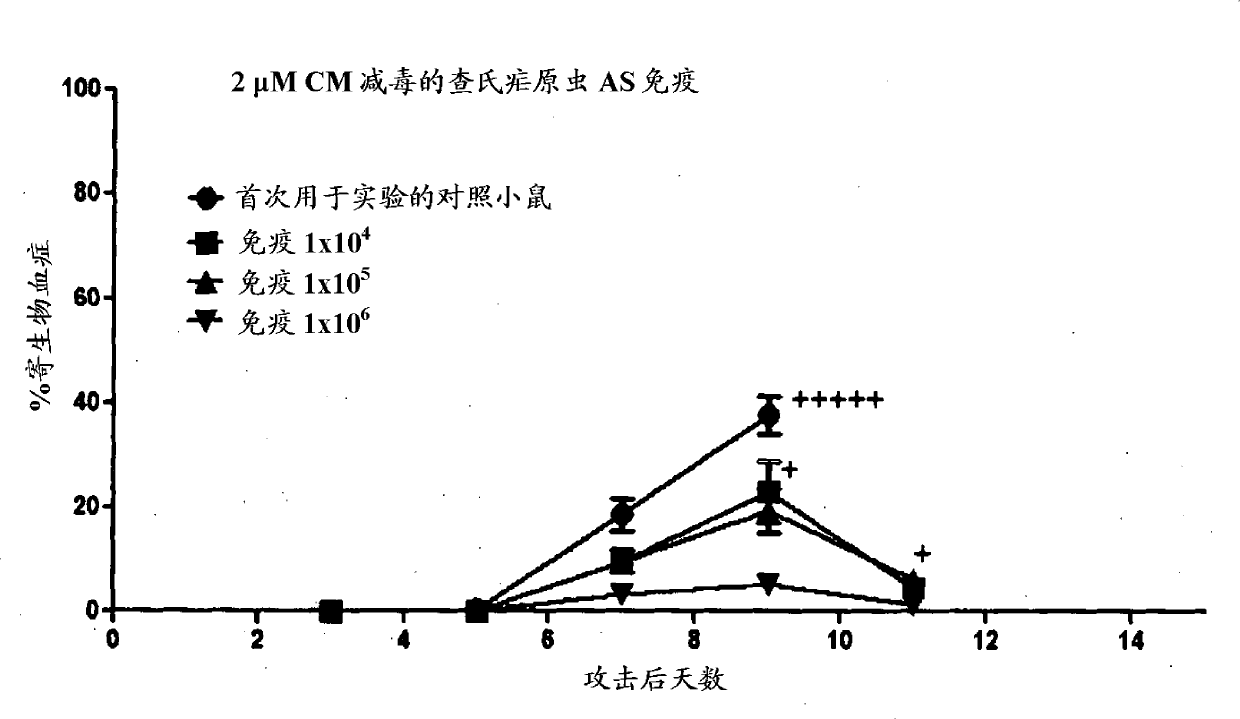
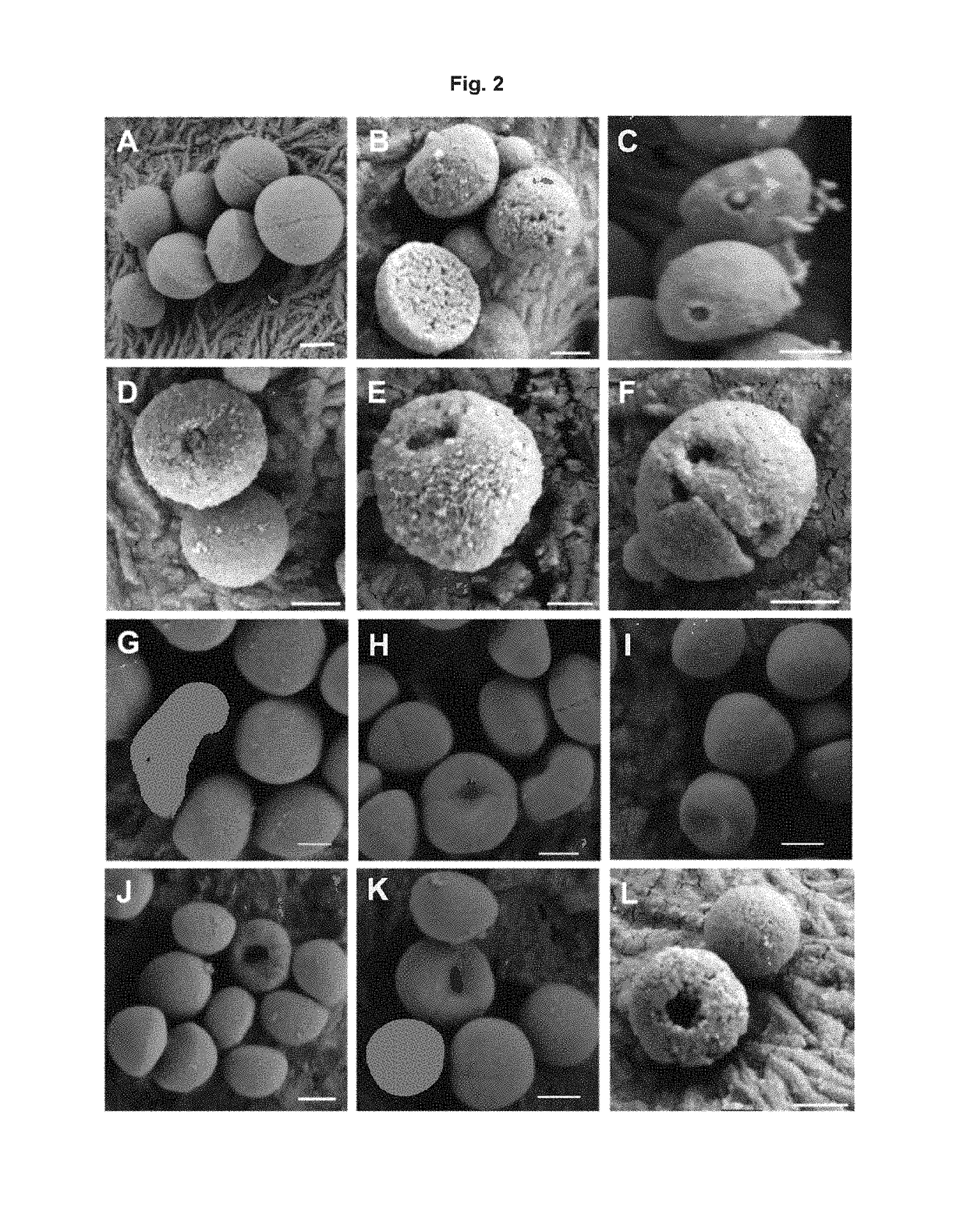
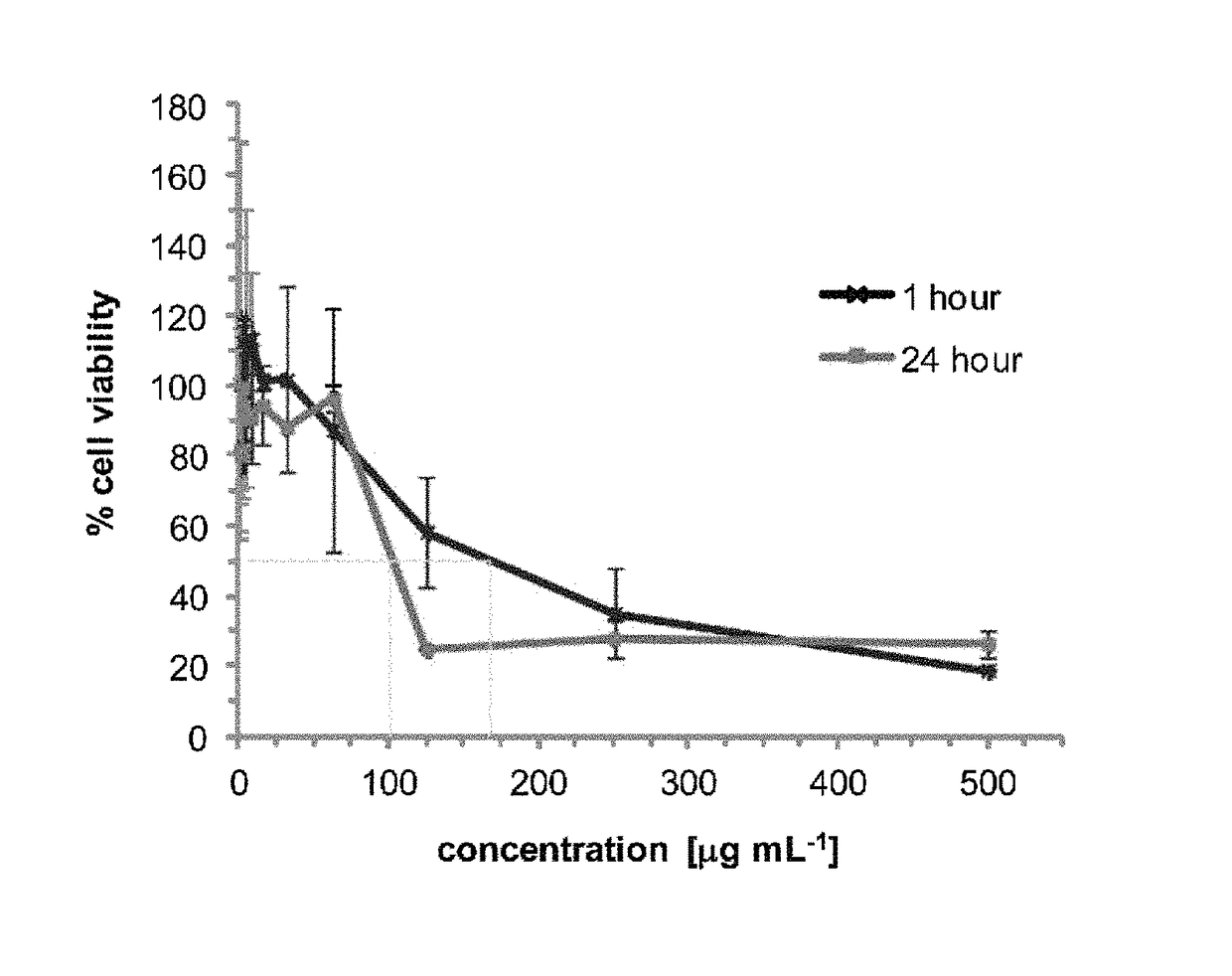
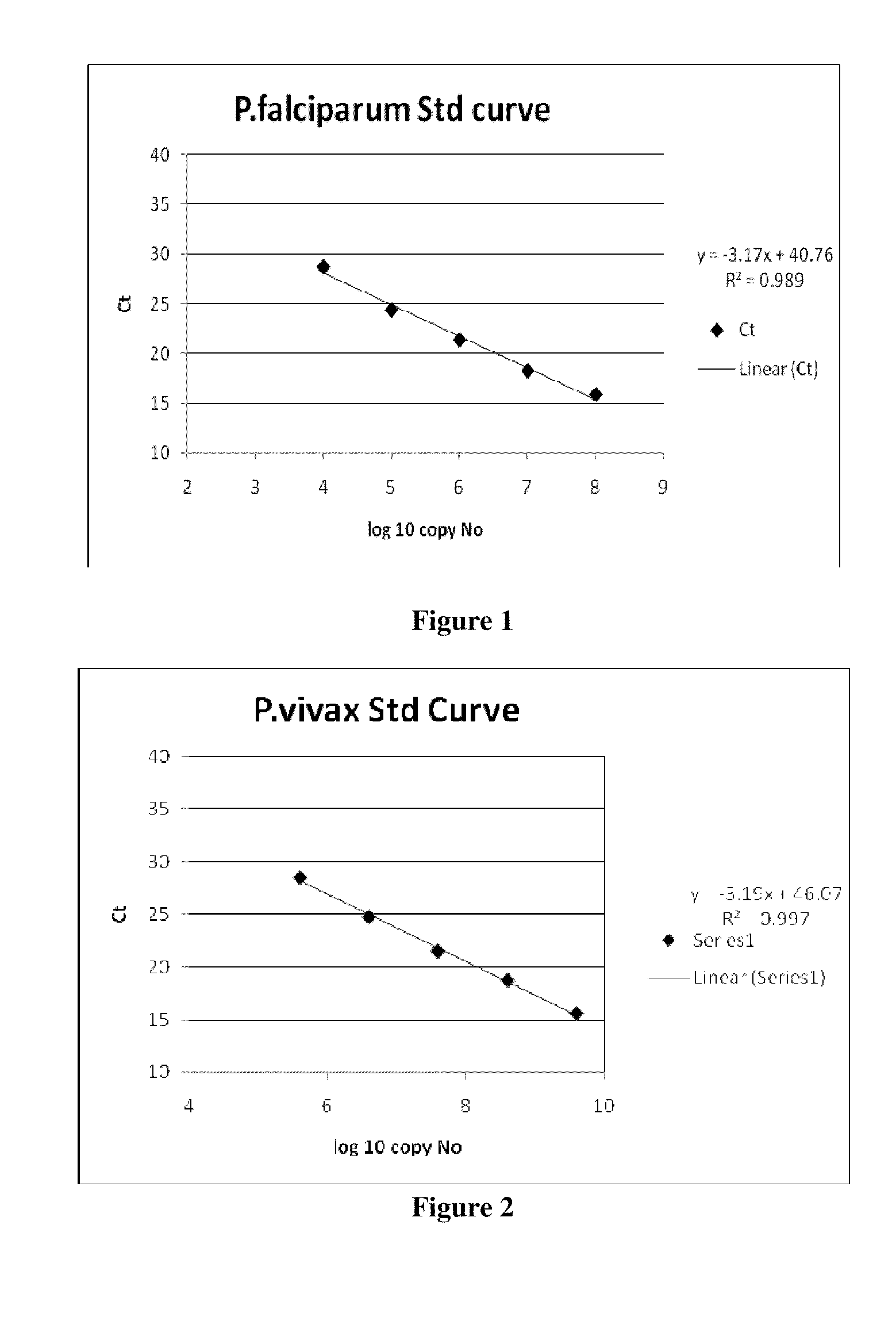
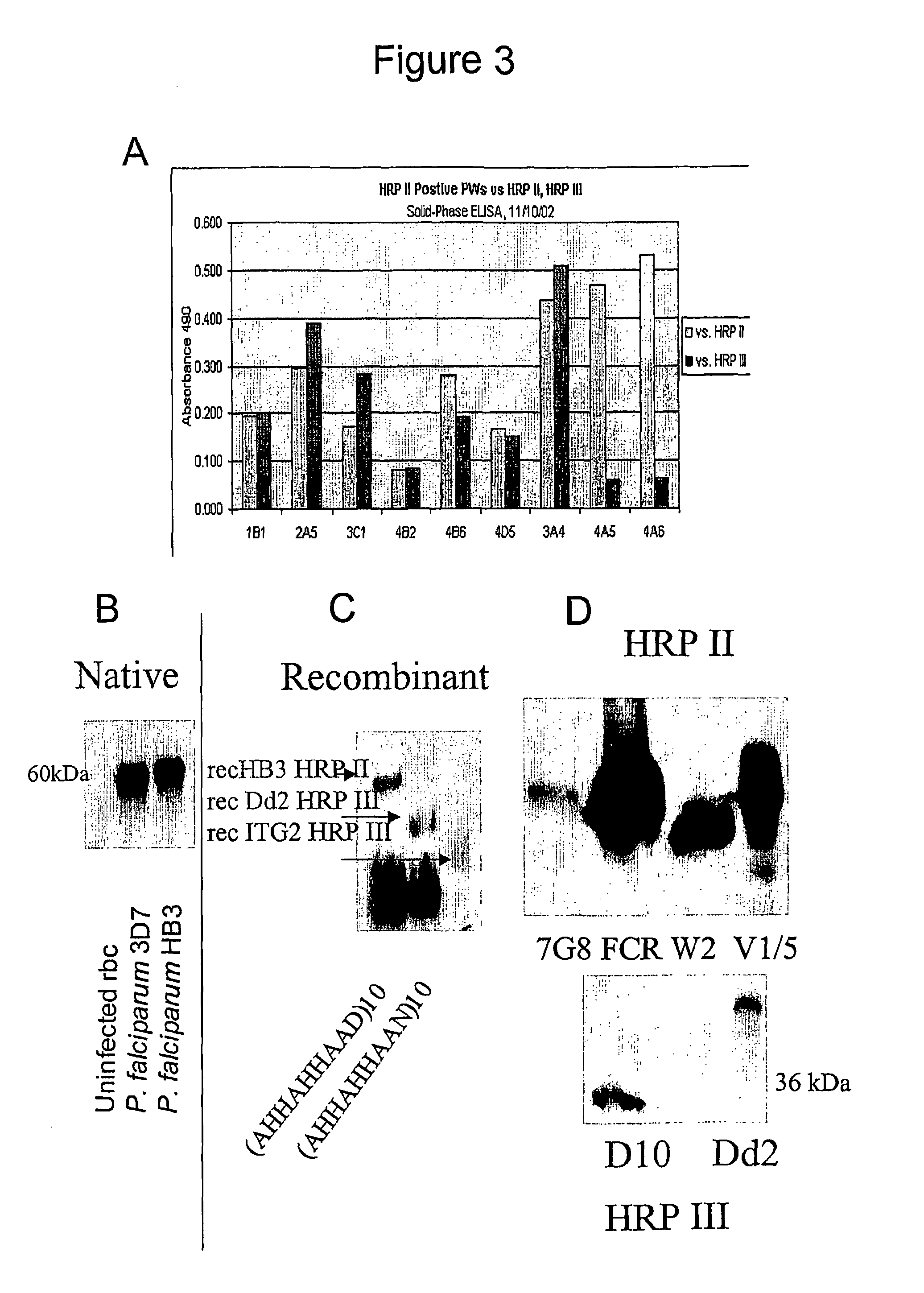
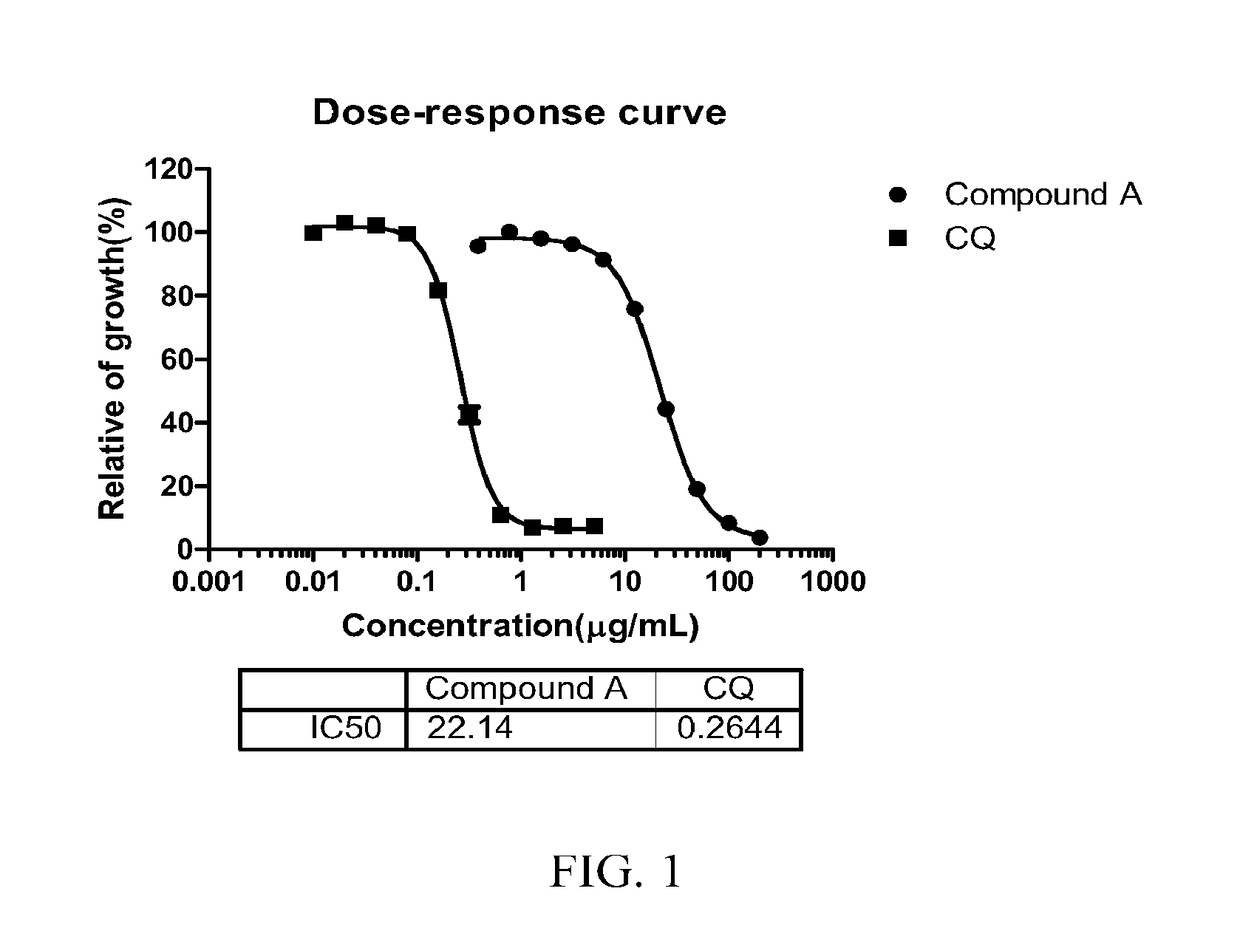
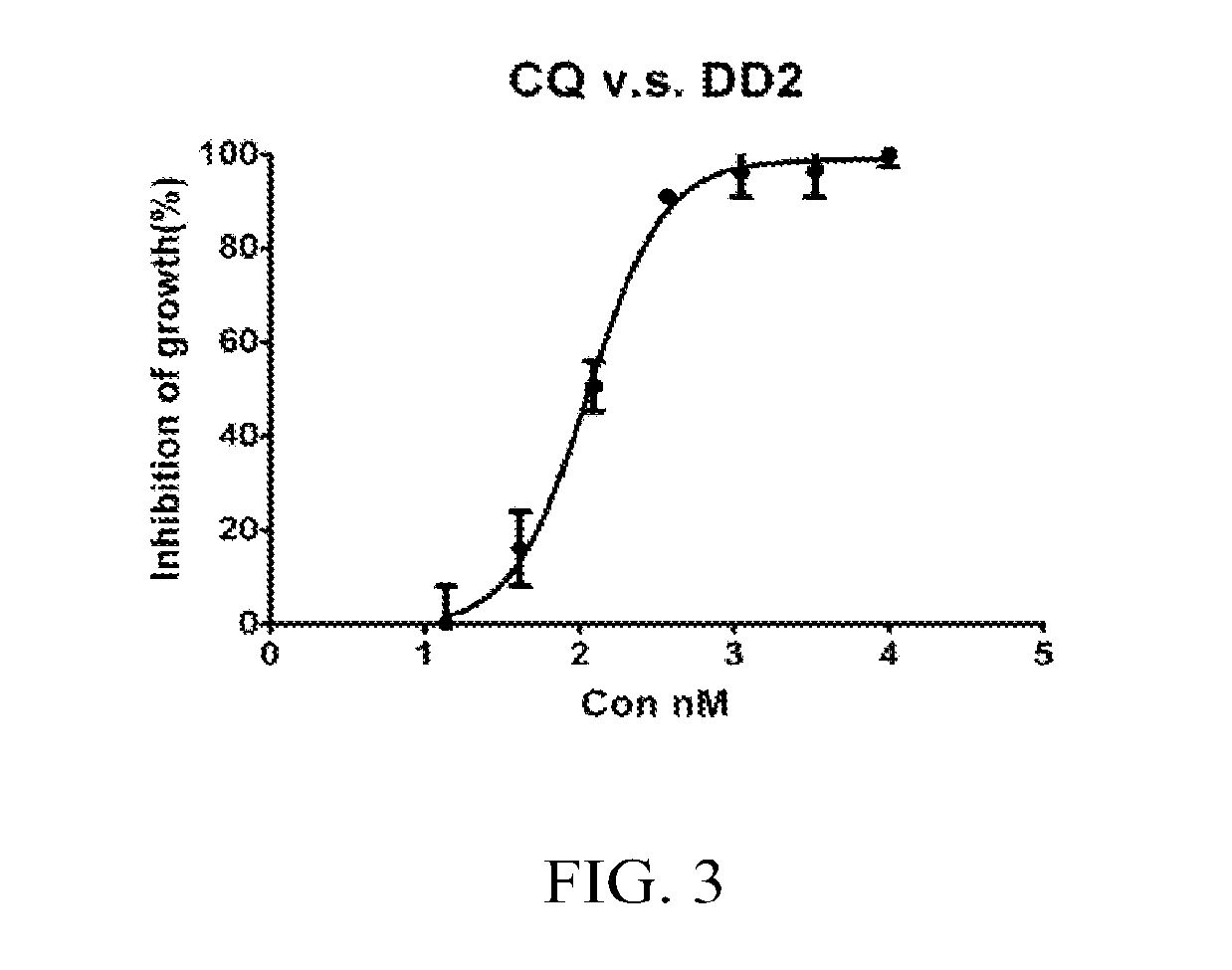
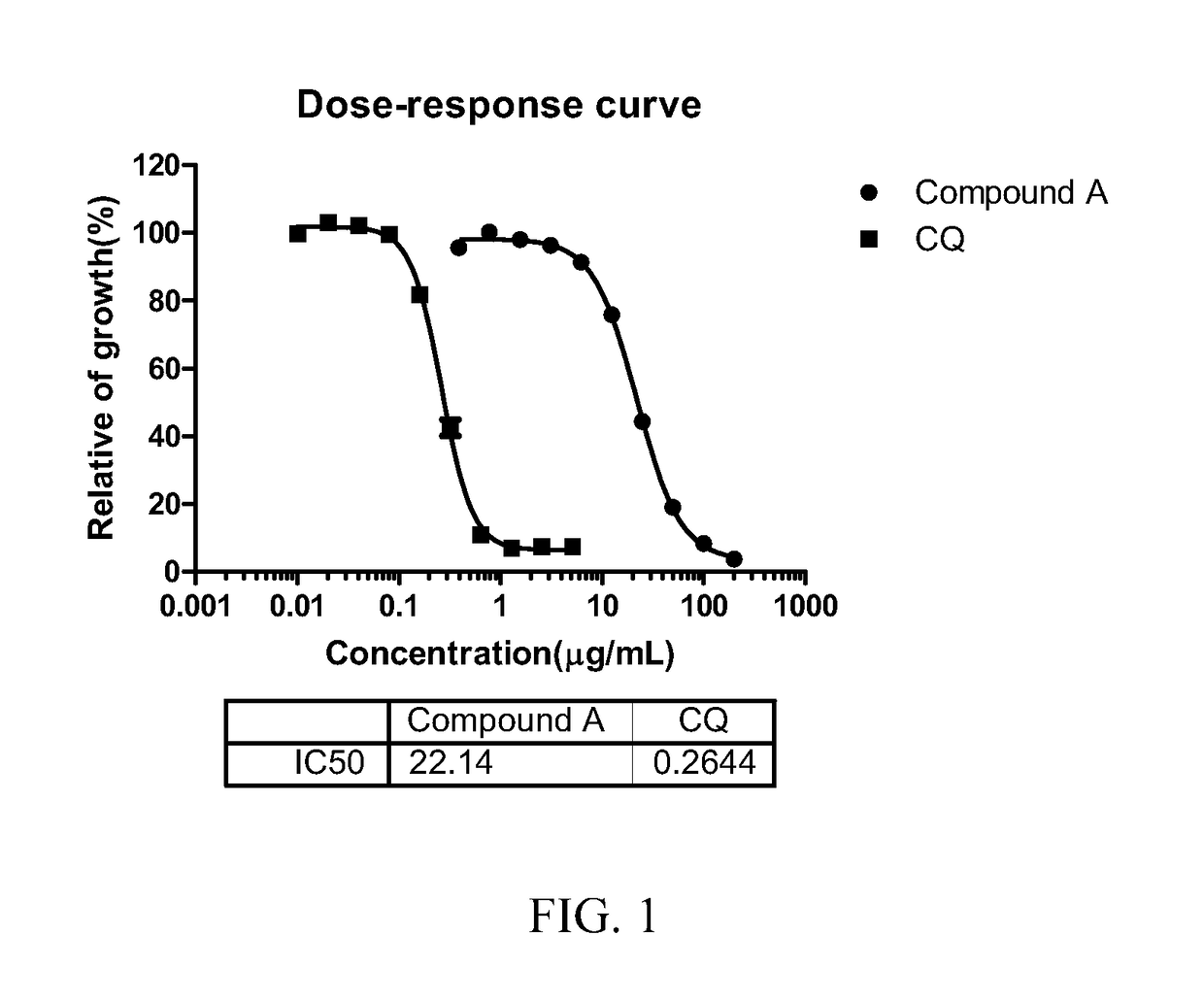
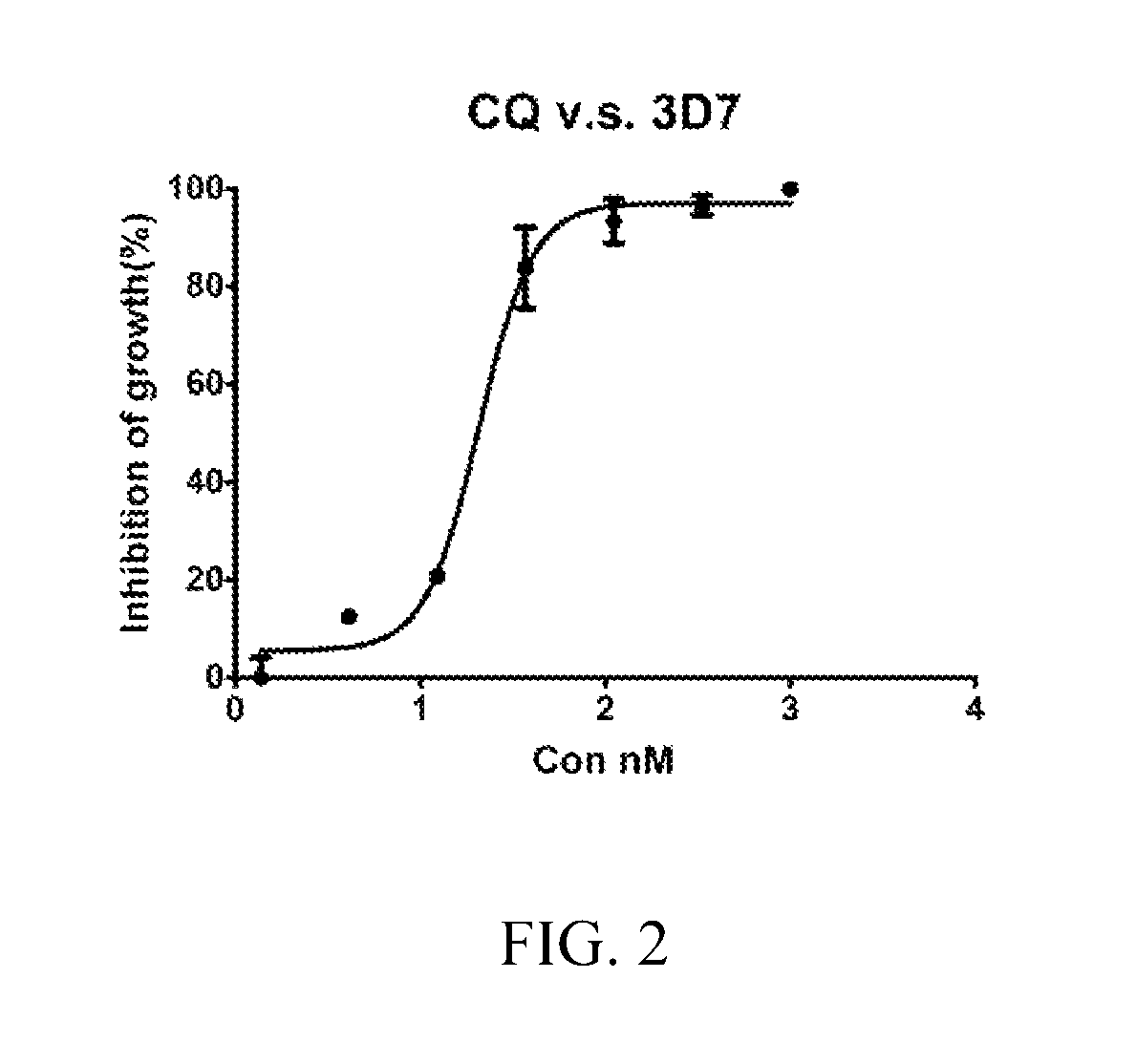
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Malarial infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Malaria is an infection caused by single-celled parasites that enter the blood through the bite of an Anopheles mosquito. These parasites, called plasmodia, belong to at least five species. Most human infections are caused by either Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax.
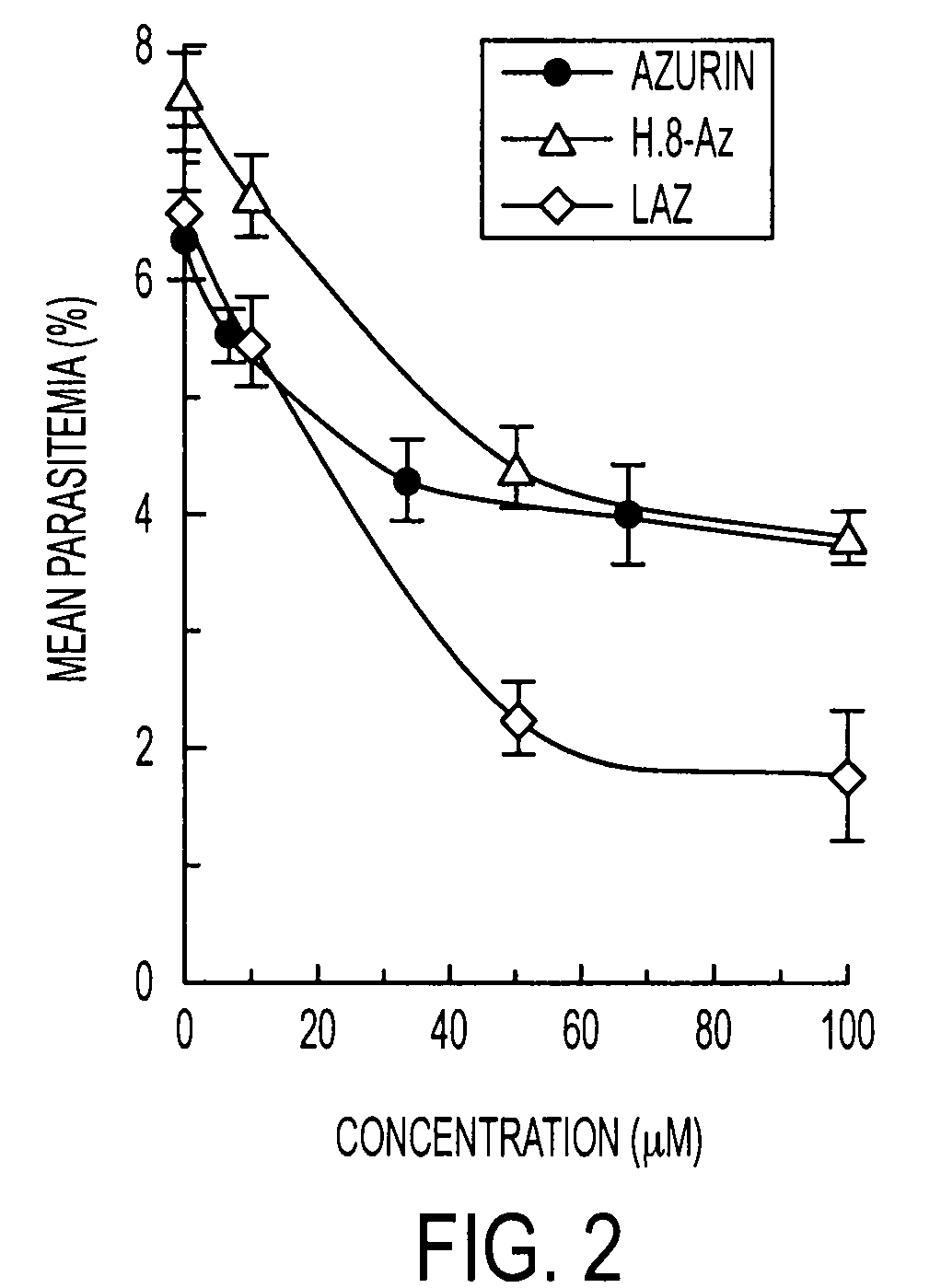
Compositions and methods for treating malaria with cupredoxin and cytochrome
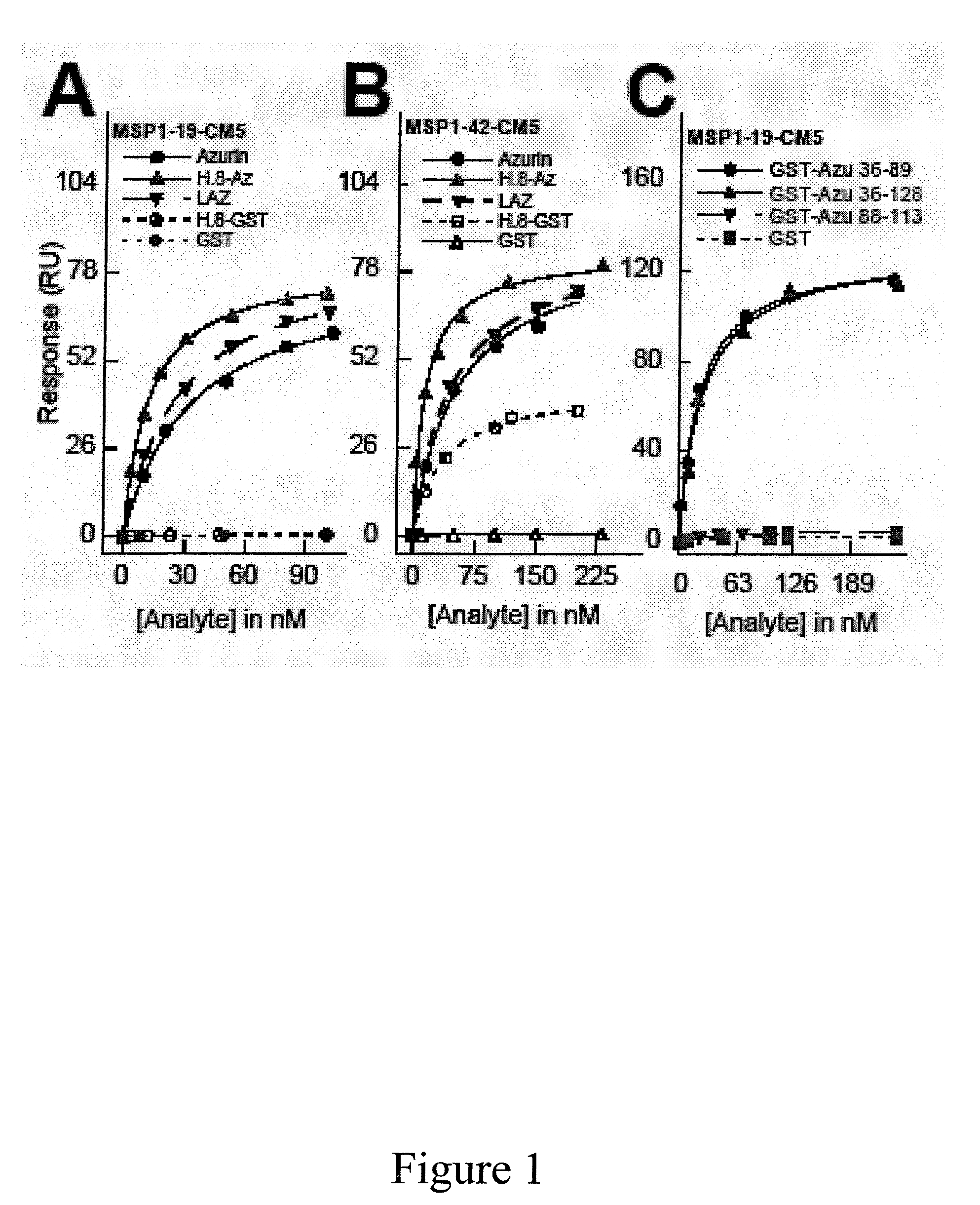
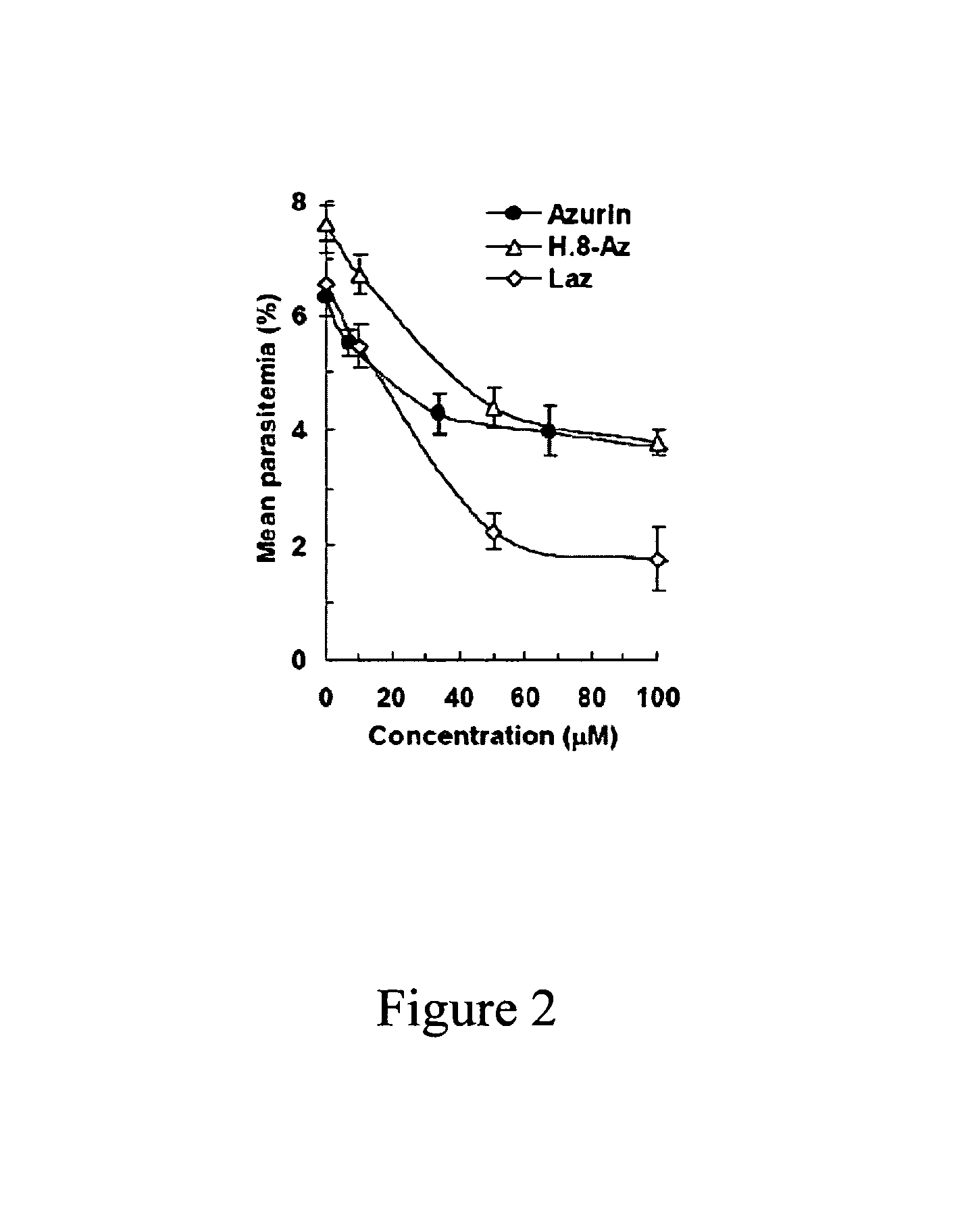
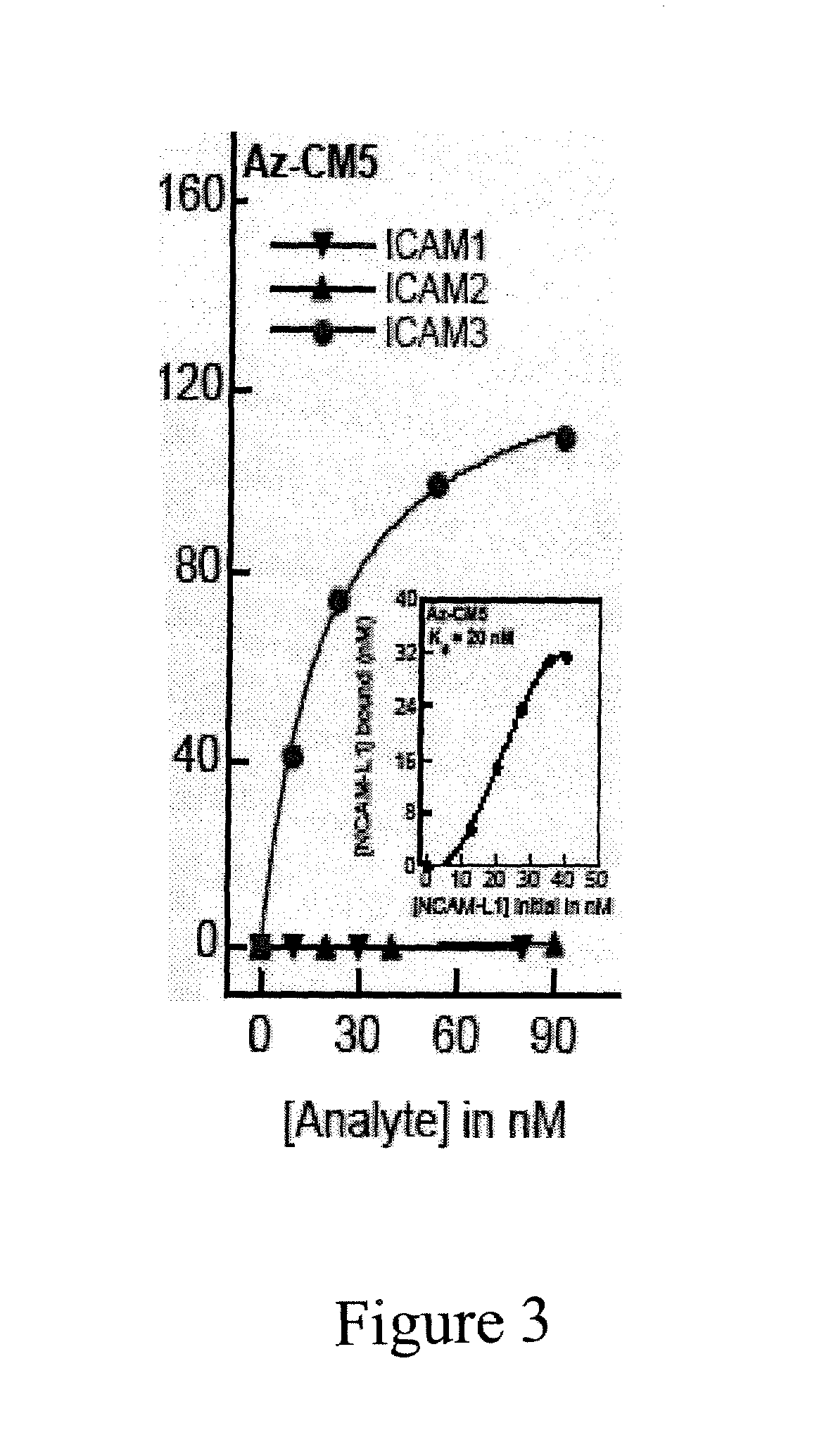
The present invention relates to cupredoxin and cytochrome and their use, separately or together, to inhibit the spread of parasitemia in mammalian red blood cells and other tissues infected by the malaria parasite, and in particular the parasitemia of human red blood cells by P. falciparum. The invention provides isolated peptides that are variants, derivatives or structural equivalents of cupredoxins or cytochrome c, and compositions comprising cupredoxins and / or cytochrome c, or variants, derivatives or structural equivalents thereof, that are useful for treating or preventing malaria infection in mammals. Further, the invention provides methods to treat mammalian patients to prevent or inhibit the growth of malarial infection in mammals. The invention also provides methods to prevent the growth of malaria infection in insect vectors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
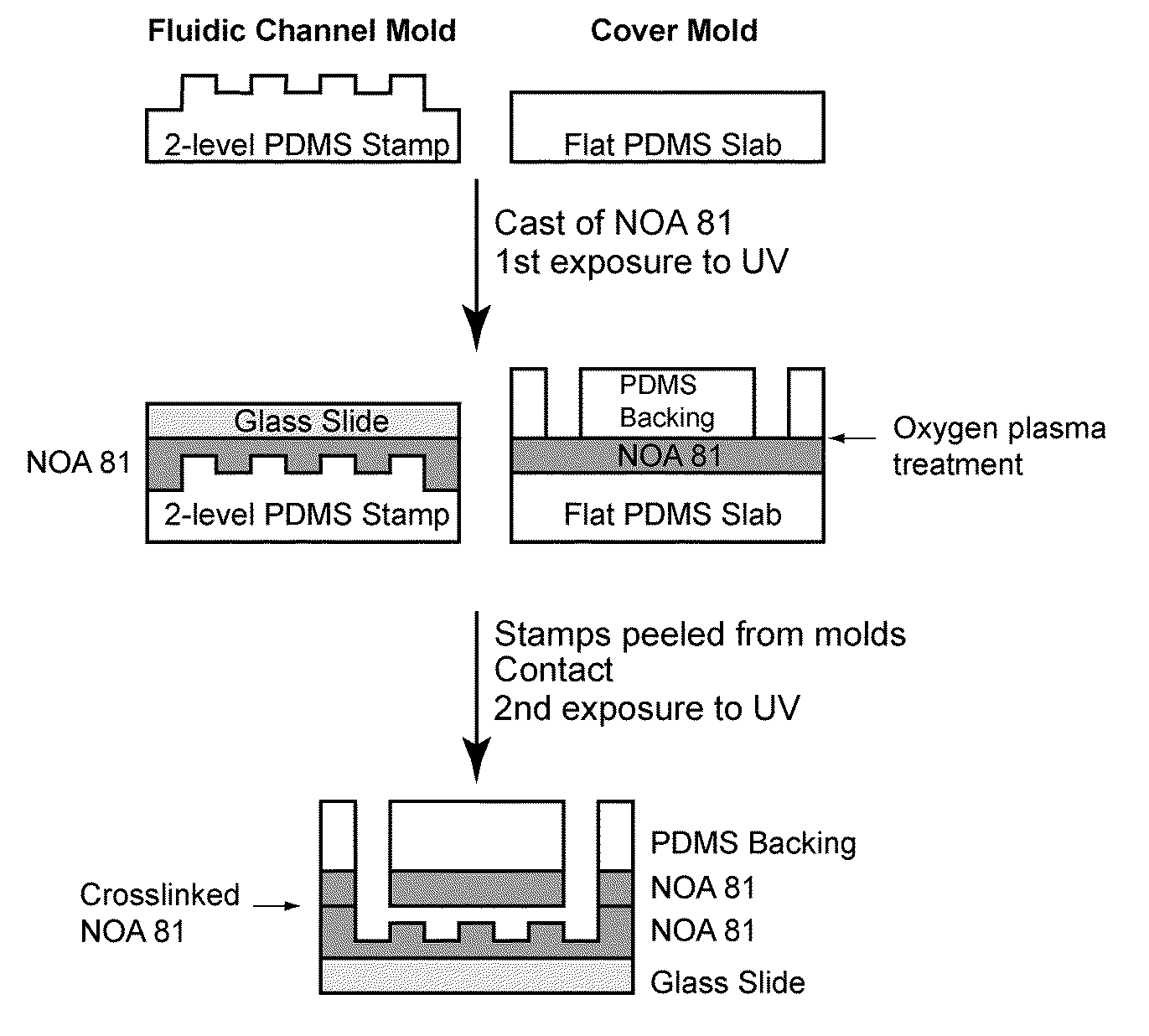
Continuous-flow deformability-based cell separation
InactiveUS20110081674A1Reduces and eliminates cloggingMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsContinuous flowCell separation
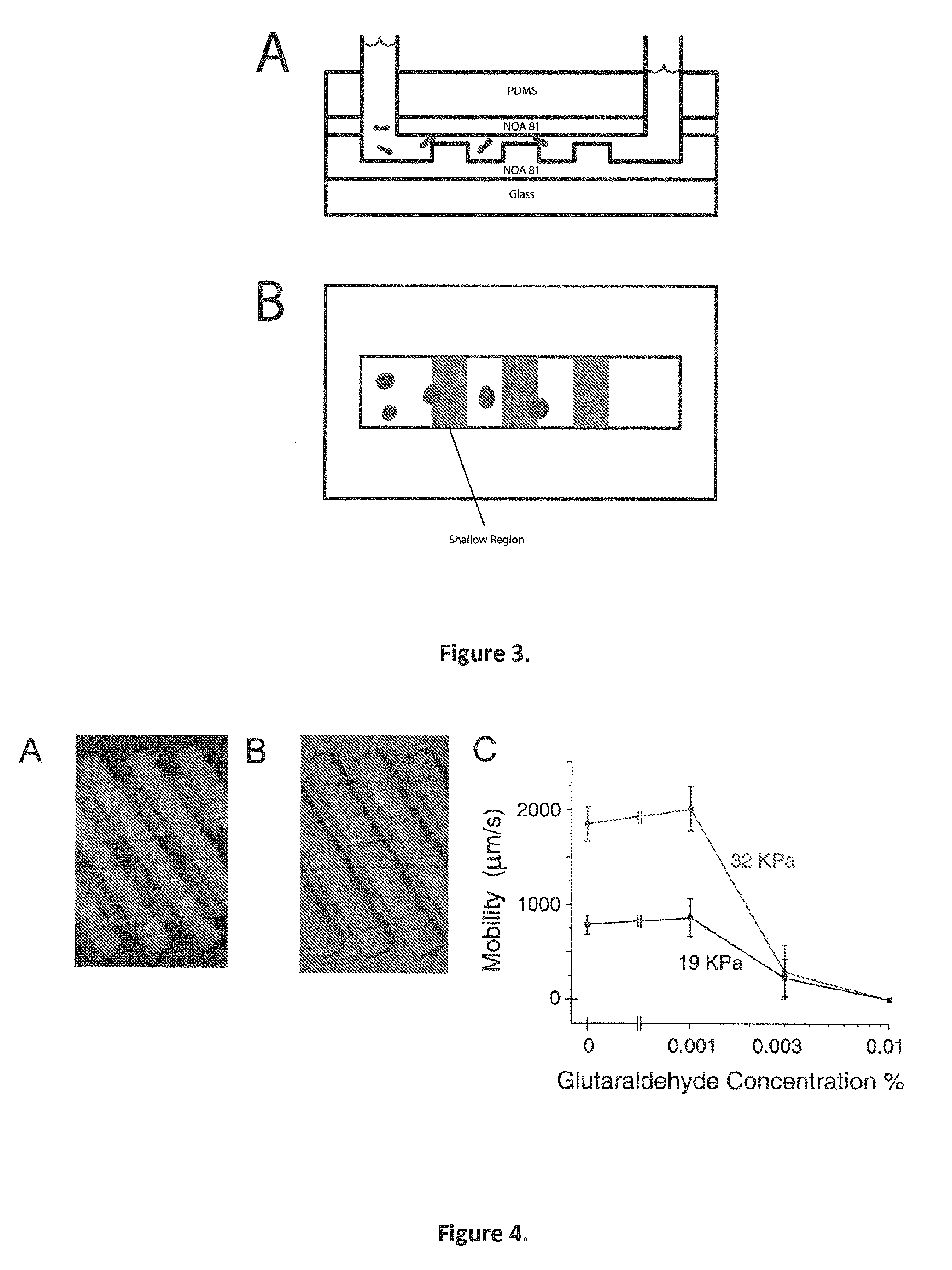
This invention provides methods utilizing a microfluidic device that can quickly and accurately discern differences in deformability between individual cells and sets of cells and continuously fractionate populations of cells based on their deformability. This information may be important in disease diagnosis and treatment efficacy monitoring. For example such a device may be able to determine the stage of malarial infection by using red blood cell deformability. Additionally, methods of the invention may be used as a tool to screen drugs that can make cells more flexible in diseases such as sickle cell anemia that causes sickle cell crises. The relatively low manufacturing and operation costs of methods of the invention enable this device to be used in resource-limited settings to diagnose and monitor disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods for vaccinating against malaria
ActiveUS20060188527A1Reduce chanceReduce severityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsVaccinationA-DNA
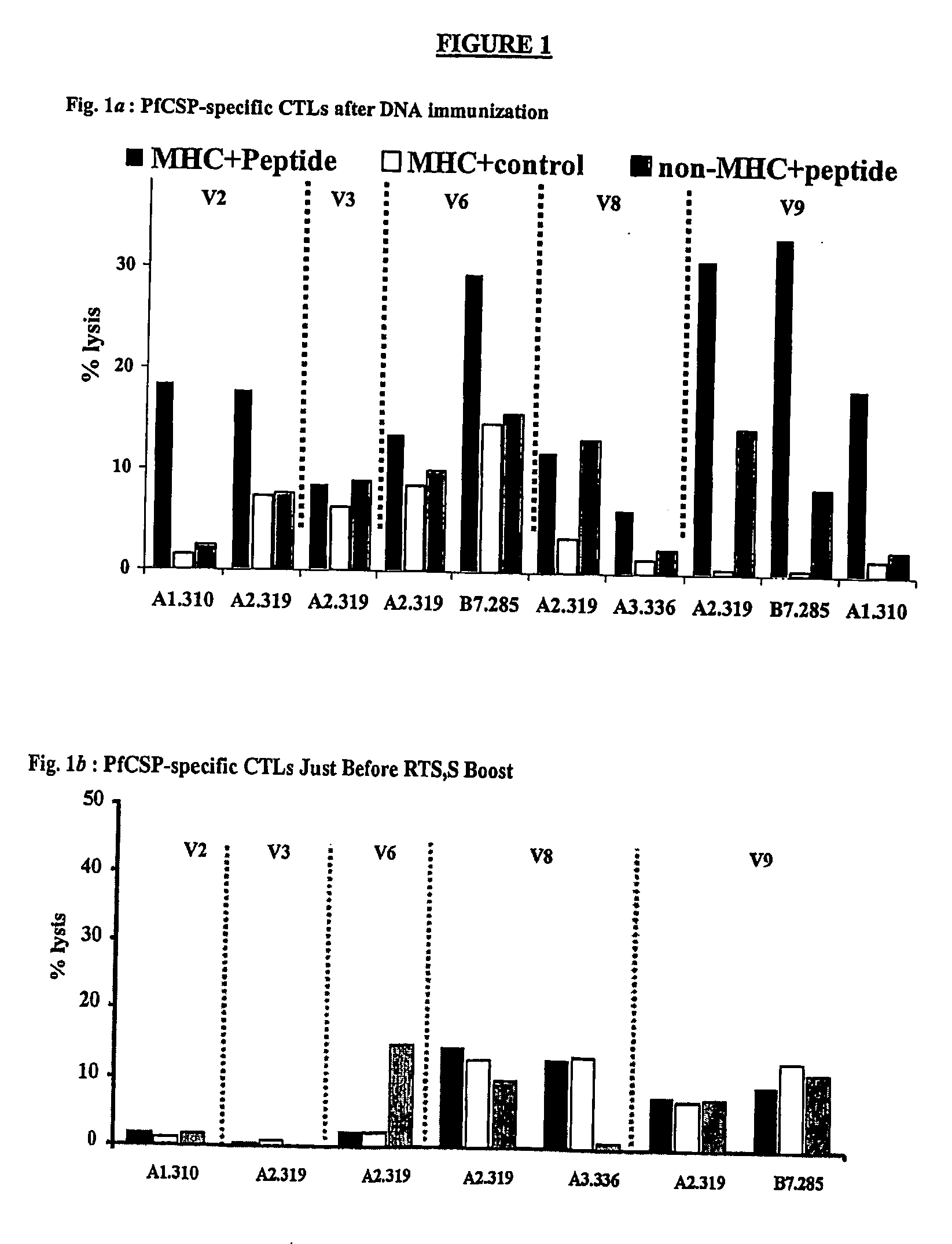
The invention pertains to methods for protecting against malaria infection by vaccination. The method of the invention involves priming an anti-malaria immune response with a DNA-based vaccine and boosting that response with a protein-based a vaccine. The method of the invention also relates to broadening the resulting immune response by boosting with a protein-based vaccine.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA +1
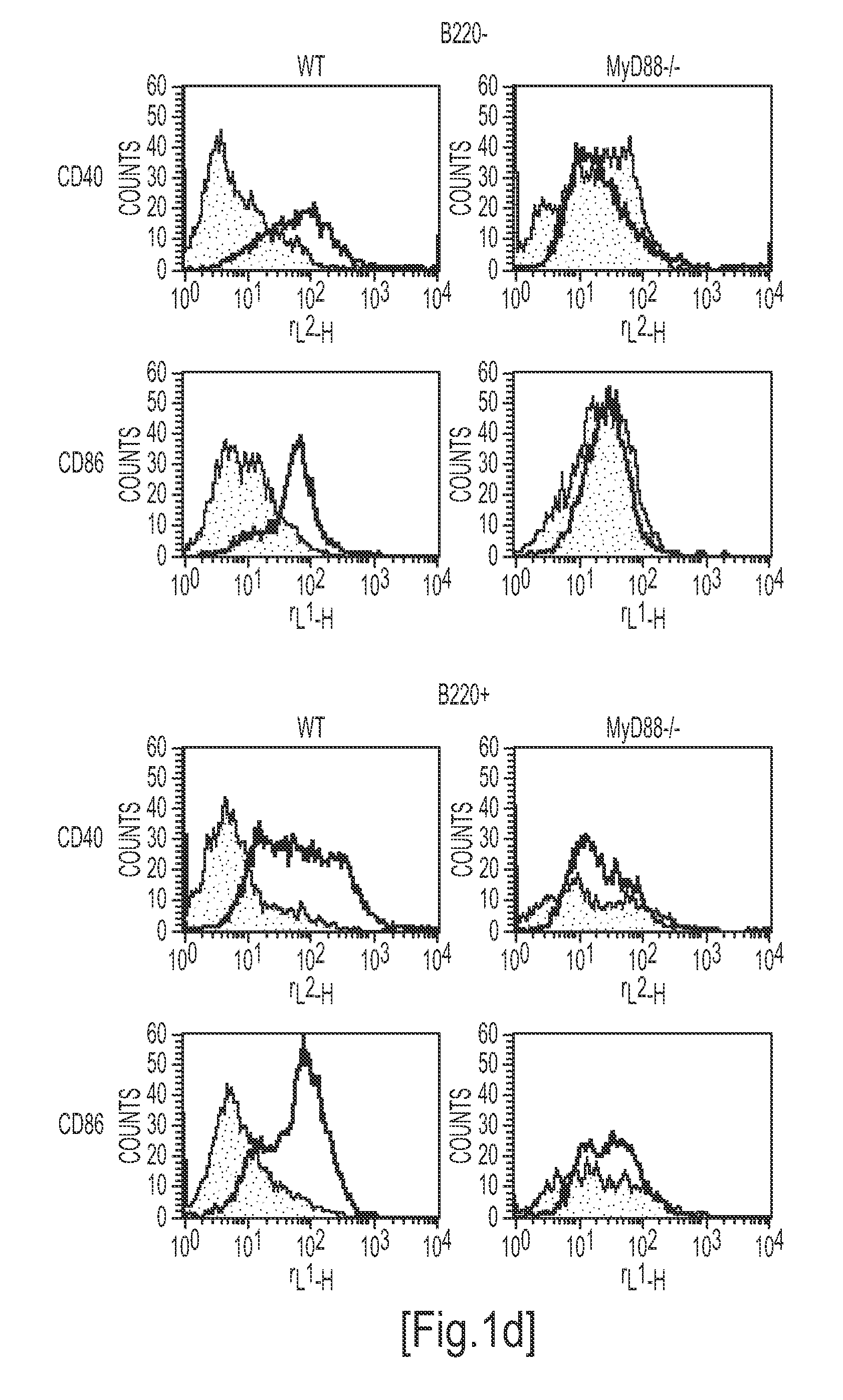
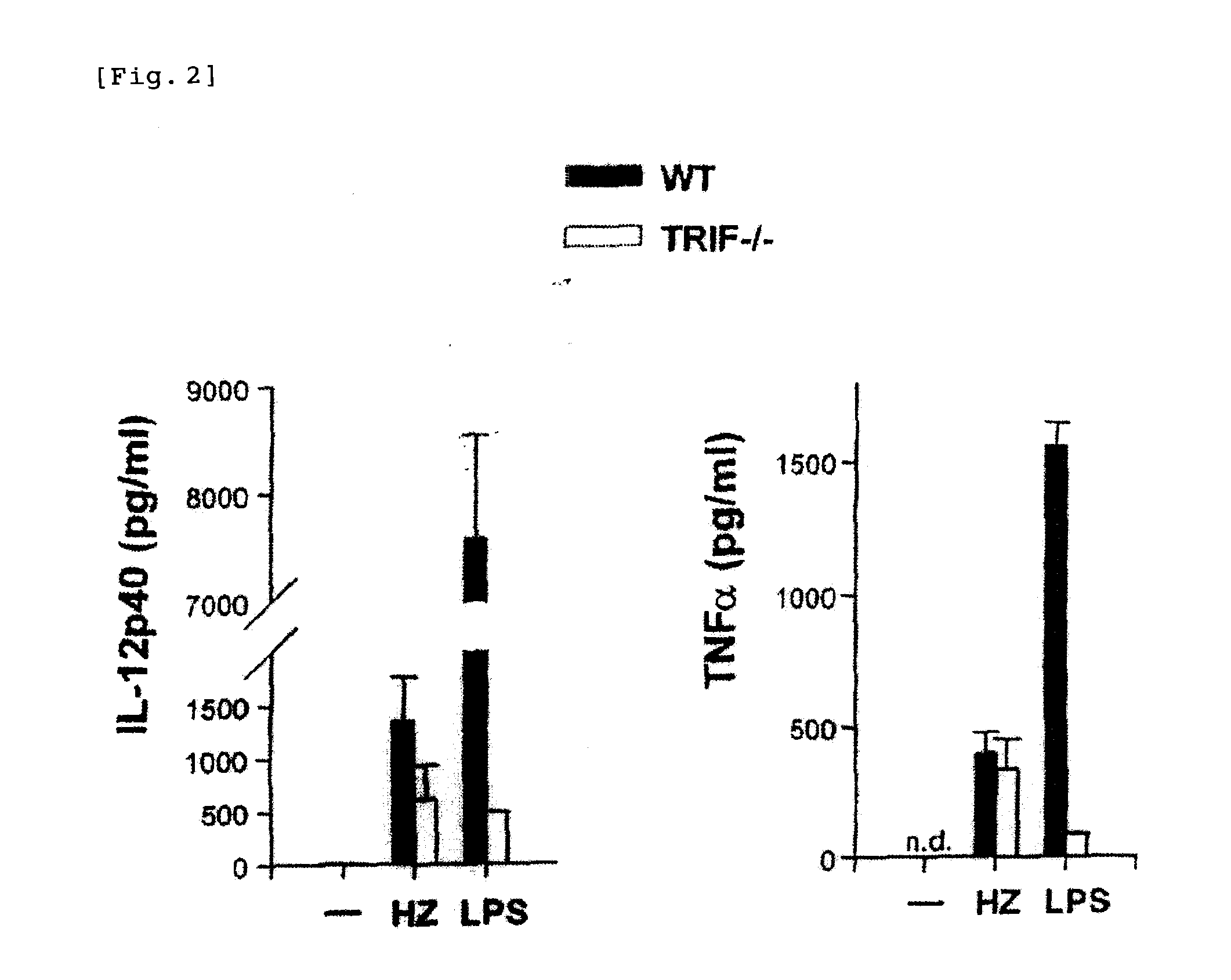
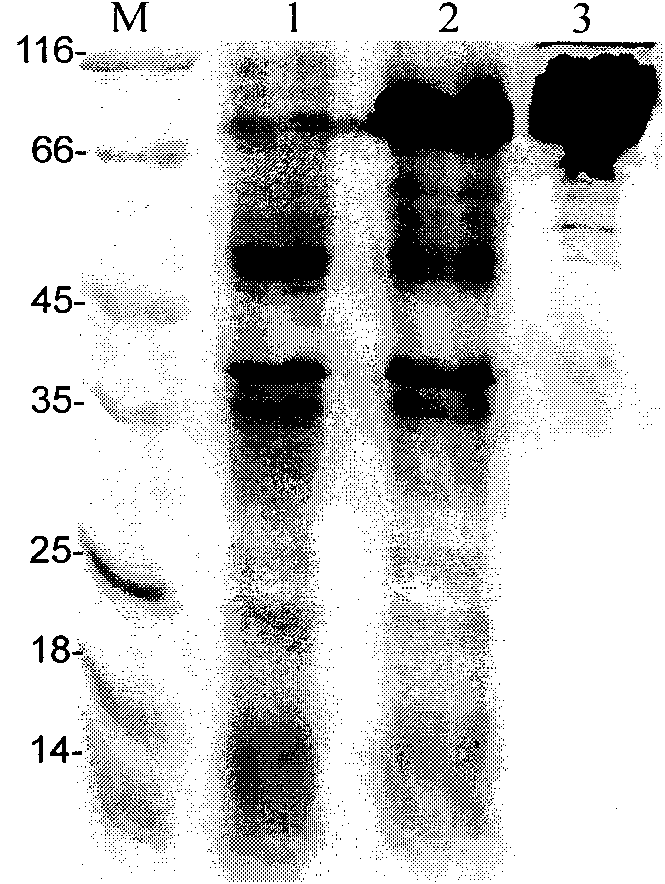
Detection/Measurement Of Malaria Infection Disease Utilizing Natural Immunity By Hemozoin Induction, Screening Of Preventative Or Therapeutic Medicine For Malaria Infection Disease, And Regulation Of Natural Immunity Induction
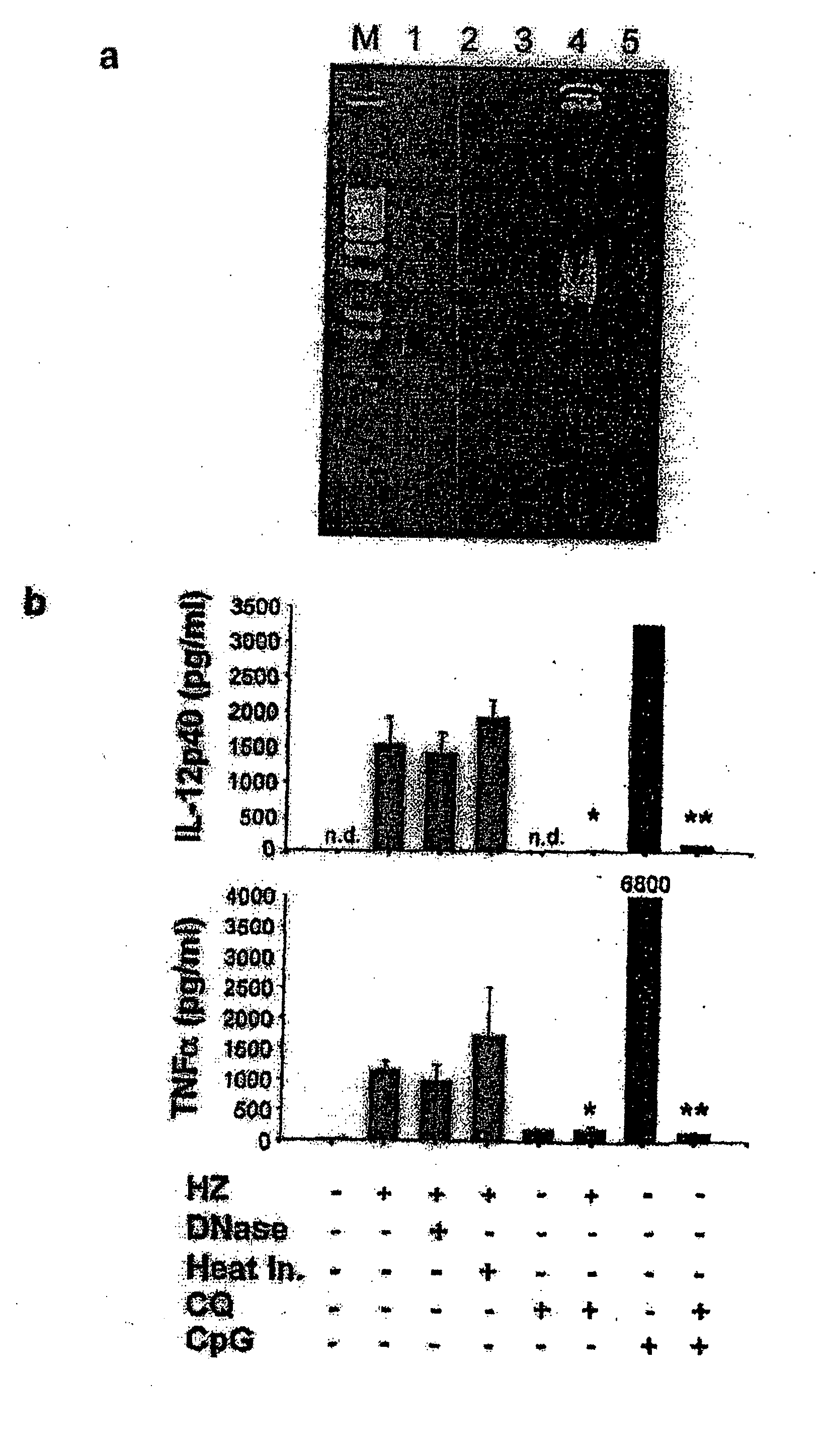
The instant invention is to provide a method for detecting and measuring malaria infection utilizing the induction by hemozoin (HZ); a method for screening a vaccine for malaria infection and a preventative or therapeutic agent for malaria infection using the method for detecting and measuring; and a means for regulating the induction of innate immunity using the HZ, synthetic HZ, or derivatives thereof as an adjuvant or immunostimulant. Malaria infection is detected and measured of by detecting and measuring HZ-induced, TLR9-mediated, and MyD88-dependent innate immune activity. The detection and measurement of malaria infection can be used to diagnose malaria infection. The method for detecting and measuring is also used for screening a vaccine for malaria infection and a preventative or therapeutic agent for malaria infection. Further, HZ, synthetic HZ, or derivatives thereof are used as an adjuvant or immunostimulant to regulate HZ-induced innate immune induction.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating malaria with cupredoxin and cytochrome
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Methods and compositions for malaria prophylaxis
InactiveUS20060122266A1Malaria prophylaxisPreventing cell invasionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCell invasionProteinase activity
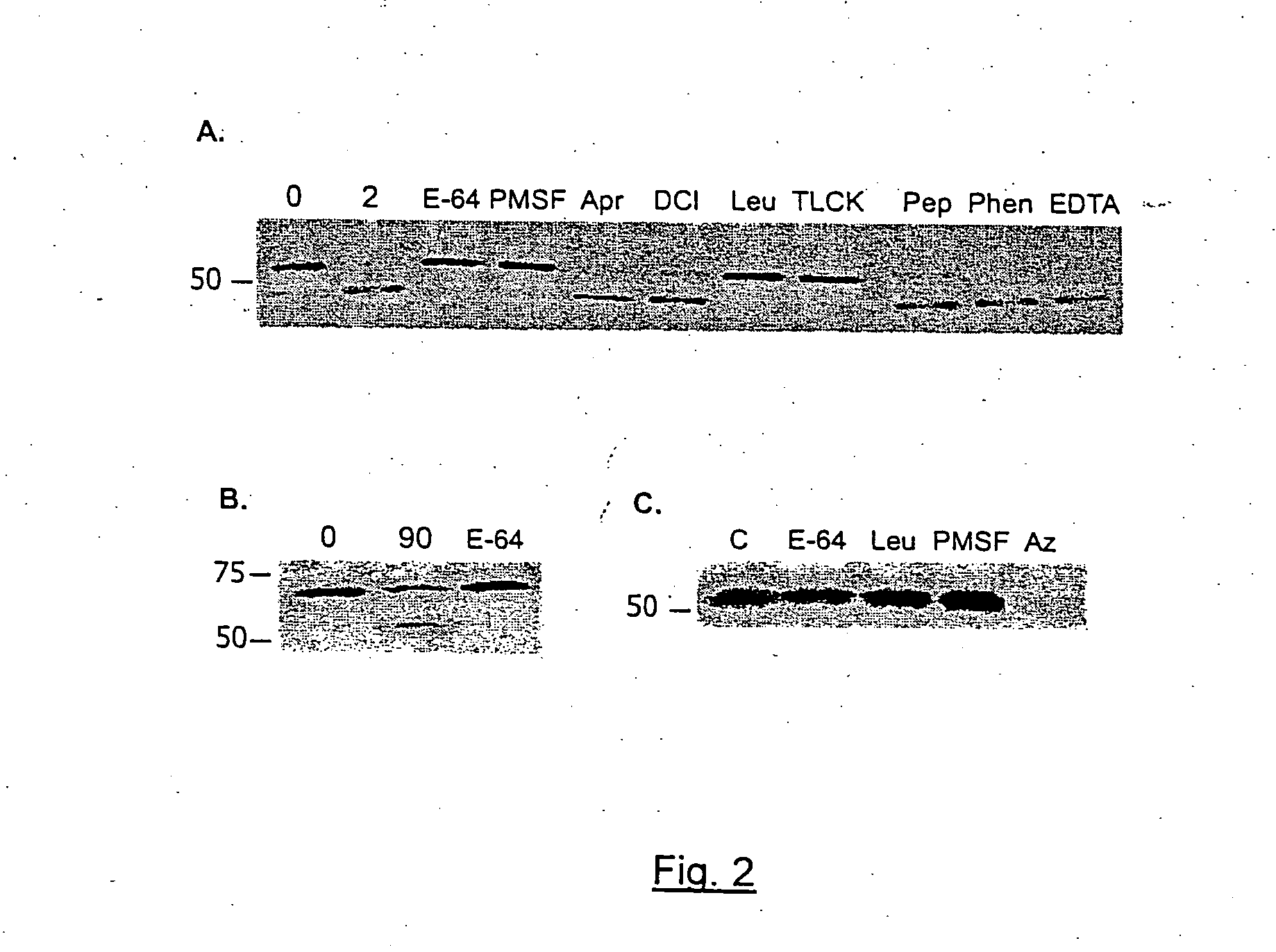
A composition for preventing malaria infection including a protease inhibitor. A pharmaceutical composition for preventing malaria infection including a protease inhibitor and a pharmaceutical carrier. A method of malaria infection prophylaxis including the step of administering an effective amount of the composition of the present invention. A method of malaria prophylaxis by inhibiting circumsporozoite protein processing or by inhibiting a protease of a sporozoite. Methods of preventing sporozoite cell invasion or preventing circumsporozoite processing.
Owner:SINNIS PHOTINI +1
Formulation of dihydroartemisinin for the control of wide spectrum of malaria
The present invention relates to a synergistic formulation useful for the control of wide spectrum of malarial infections, which comprises a pharmaceutically effective amount of dihydroartemisinin and a vegetable oil.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Devices and methods for detecting β-haematin and haemozoin
ActiveUS8214006B2Effects depolarisation occurring within the patient's tissue can be counteredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOptical radiationWhole blood units
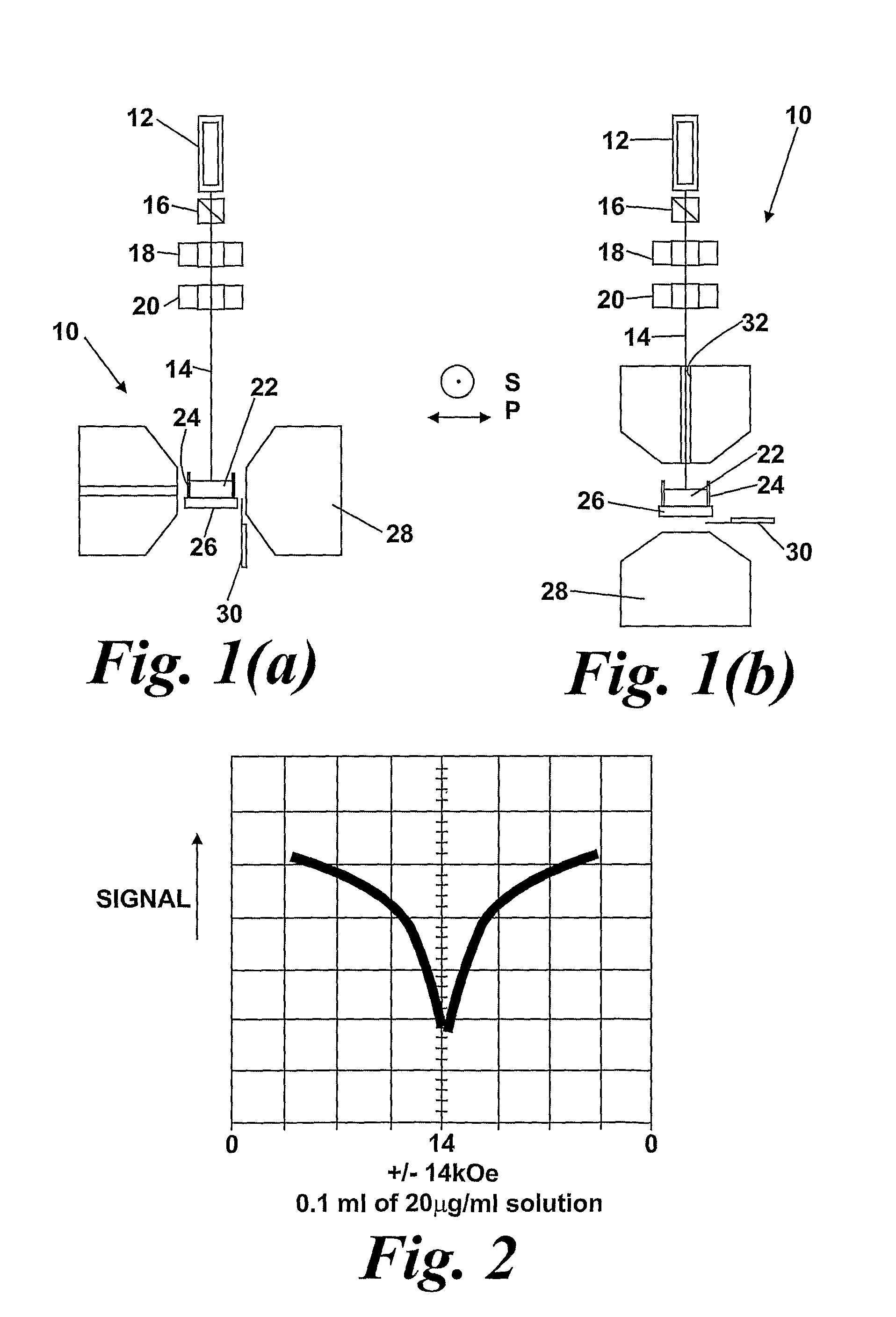
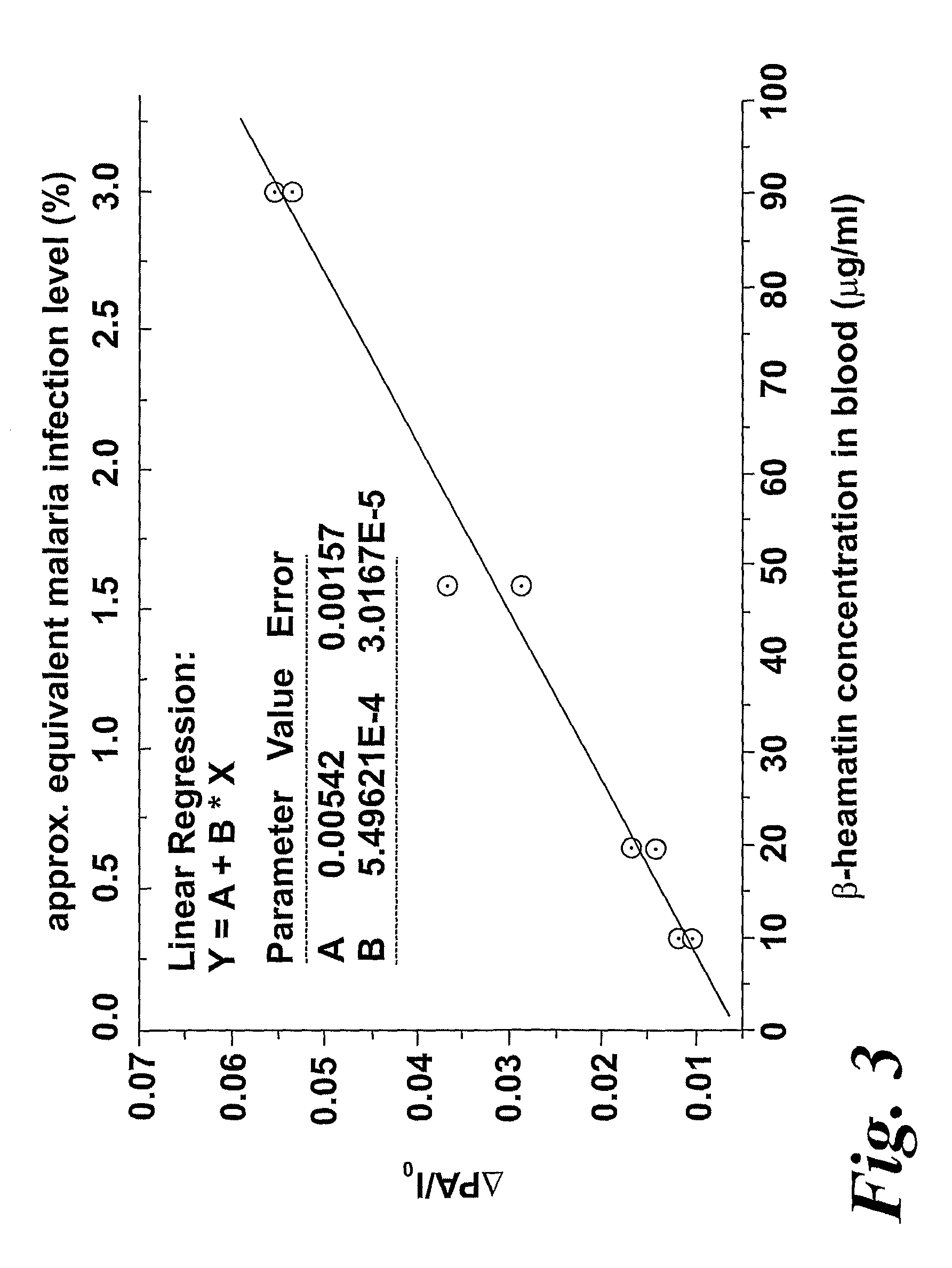
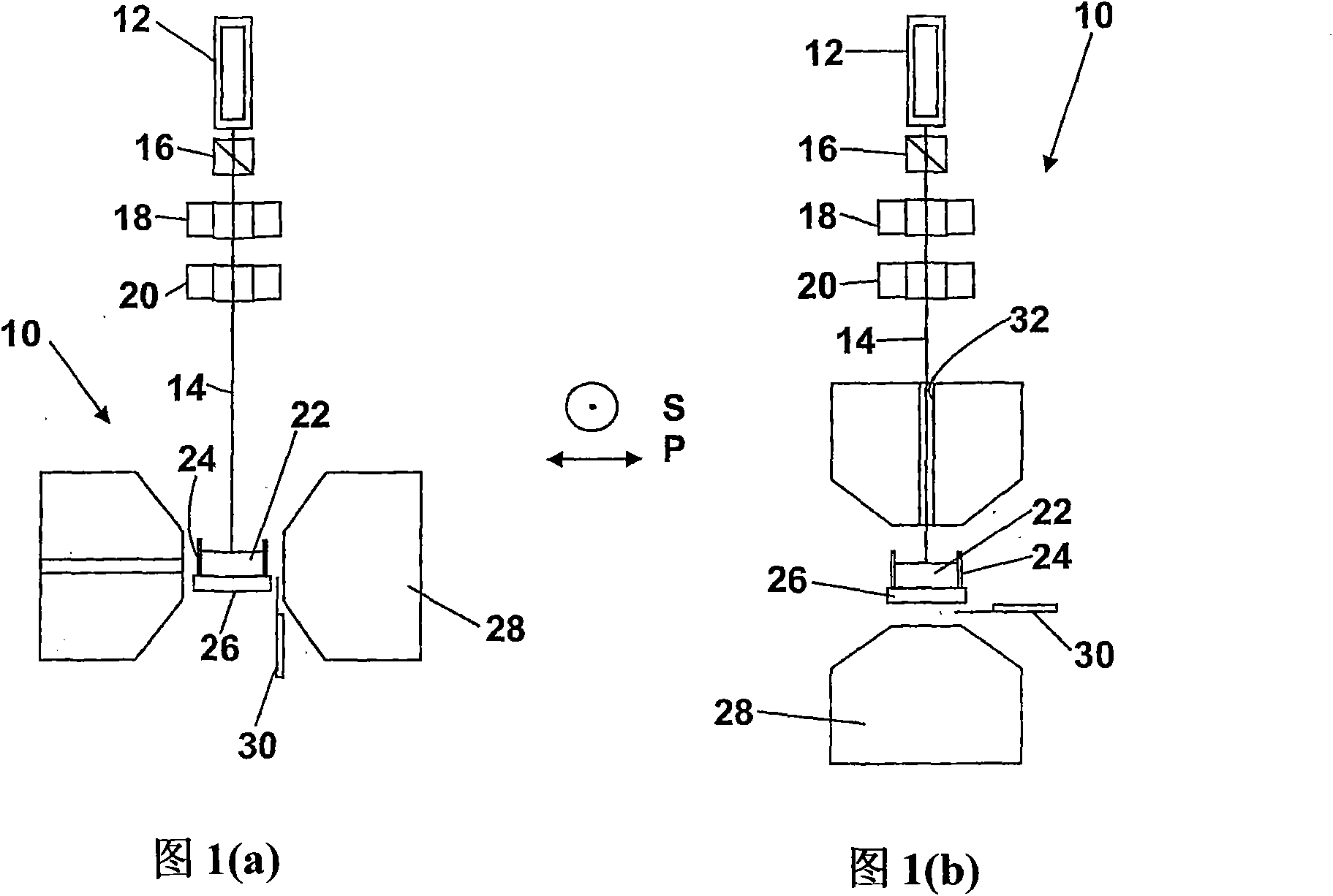
In the application, the change in the magnetic state of the haemoglobin caused by the malarial infection is exploited by detecting suitable properties of haemozoin which are dependent on the application of a magnetic field. FIG. 1 shows apparatus, shown generally at (10), for performing magneto-optical detection using photo-acoustic techniques. The apparatus (10) comprises a light source (12), producing a beam of optical radiation (14) which passes through a polarizer (16), a variable LC retarder (0 or 180° retardance) (18), and a (chopper 20), before impinging on a sample (22) held in a sample holder (24). The sample is in direct contact with an acoustic detector (26). The apparatus (10) further comprises an electromagnet (28), and a Gauss meter (30) can be utilized to measure the applied magnetic field strength. Advantages associated with this approach are the—possibility of making in vivo measurements, and the avoidance of problems of optical scattering associated with conventional optical measurements on turbid liquids such as whole blood.
Owner:COTTON MOUTON DIAGNOSTICS LTD +1
Multi-epitope artificial antigen of plasmodium falciparum and application thereof
ActiveCN102108355AImproving immunogenicityHigh suppression efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaImmunogenicityIn vitro growth
The invention relates to a multi-epitope artificial antigen of plasmodium falciparum and an application thereof. The invention designs a polynucleotide with a sequence as shown in SEQ ID No:1 and a polypeptide with a sequence as shown in SEQ ID No:2, wherein the polynucleotide and the polypeptide are used as artificial antigens to prepare vaccines, and antibodies can be obtained from the antigens and are used to prepare immune preparations against plasmodium falciparum infections and kits for detecting malaria infections. Compared with anti plasmodium falciparum vaccines in the prior art, the multi-epitope artificial antigen of the invention has high immunogenicity and antigen recognition diversity, and the antibody of the invention has high inhibition efficiency on the in vitro growth of plasmodium falciparum.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Devices and methods for detecting ss-haematin and haemozoin
ActiveCN101600962ADiagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptical radiationOptical measurements
In the application, the change in the magnetic state of the haemoglobin caused by the malarial infection is exploited by detecting suitable properties of haemozoin which are dependent on the application of a magnetic field. FIG. 1 shows apparatus, shown generally at (10), for performing magneto-optical detection using photo-acoustic techniques. The apparatus (10) comprises a light source (12), producing a beam of optical radiation (14) which passes through a polariser (16), a variable LC retarder (0 or 180 DEG retardance) (18), and a (chopper 20), before impinging on a sample (22) held in a sample holder (24). The sample is in direct contact with an acoustic detector (26). The apparatus (10) further comprises an electromagnet (28), and a Gauss meter (30) can be utilised to measure the applied magnetic field strength. Advantages associated with this approach are the-possibility of making in vivo measurements, and the avoidance of problems of optical scattering associated with conventional optical measurements on turbid liquids such as whole blood.
Owner:COTTON MOUTON DIAGNOSTICS LTD
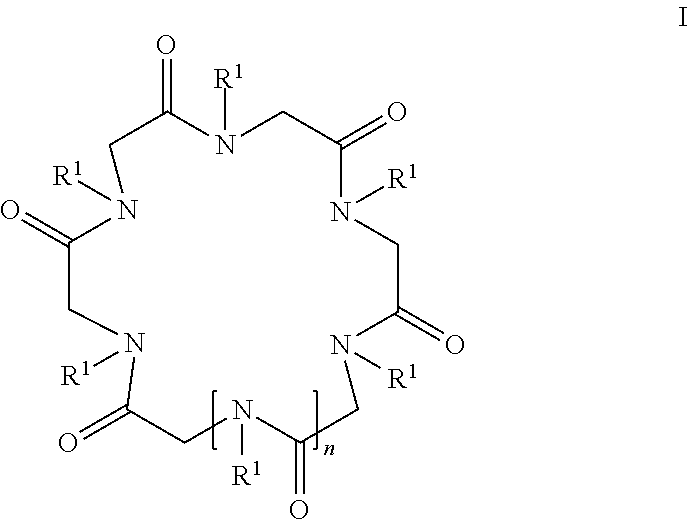
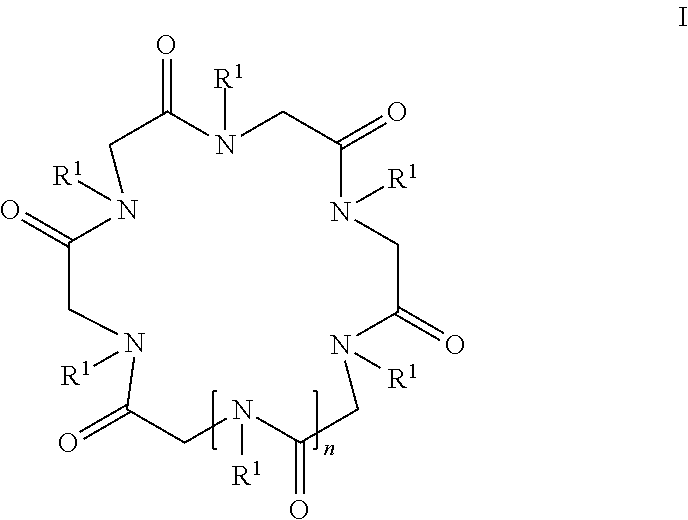
Cyclic peptoid oligomers, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20140274916A1Enhanced anti-microbial activityPotent and selective antimicrobialAntibacterial agentsAntiviralsMicroorganismOligomer
Novel peptoid oligomers are disclosed that have a formula represented by the following formula I:wherein R1 and n are as described herein. The peptoids demonstrate antimicrobial and antimalarial activity and may be prepared as pharmaceutical compositions and used for the prevention or treatment of a variety of conditions in mammals including humans where microbial or malarial infection is involved. The present cyclic peptoids are particularly valuable as their effect is rapid, broad in spectrum and mostly indifferent to resistance provoked by standard antibiotics.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Blood stage malaria vaccine
An immunogenic composition for use as a blood-stage malaria vaccine, a method of producing the immunogenic composition and a method of treatment of malaria are provided. The immunogenic composition includes isolated or purified merozoites, or red blood cells infected with merozoites, treated with centanamycin or tafuramycin A. The immunogenic composition does not include an adjuvant. A single dose of the immunogenic composition is sufficient to protect an animal against subsequent malaria infection by the same isolate, strain or species of Plasmodium used in the immunogenic composition, or by one or more heterologous isolates, strains or species of Plasmodium.
Owner:GRIFFITH UNIVERSITY +2
Cyclic peptoid oligomers, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using the same
ActiveUS9938321B2High activityPotent and selective antimicrobialAntibacterial agentsAntiviralsMicroorganismOligomer
Novel peptoid oligomers are disclosed that have a formula represented by the following formula I:wherein R1 and n are as described herein. The peptoids demonstrate antimicrobial and antimalarial activity and may be prepared as pharmaceutical compositions and used for the prevention or treatment of a variety of conditions in mammals including humans where microbial or malarial infection is involved. The present cyclic peptoids are particularly valuable as their effect is rapid, broad in spectrum and mostly indifferent to resistance provoked by standard antibiotics.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Probes and Primers for Detection of Malaria
InactiveUS20110306046A1Fluorescent signal enhancementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyMalarial infection
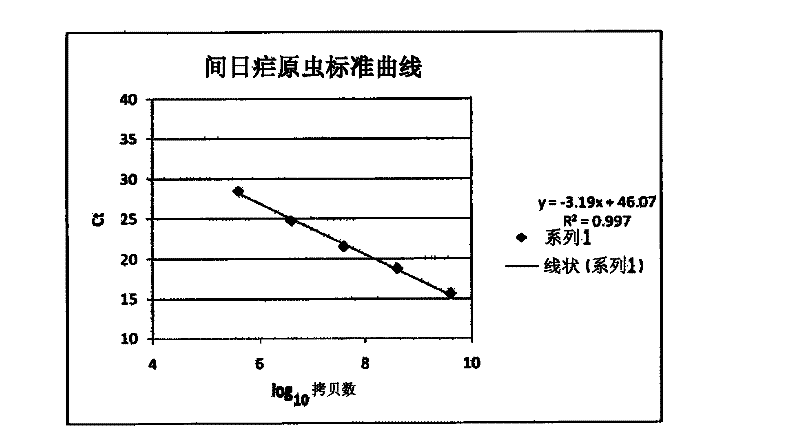
The present disclosure gives description of a method used for the detection and quantification of malarial infection caused either by Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax using nucleic acids isolated from blood samples by employing Oligonucleotide probes. The method employed here for detection is by Real time PCR.
Owner:BIGTEC PTE LTD
Probes and primers for detection of malaria
The present disclosure gives description of a method used for the detection and quantification of malarial infection caused either by Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax using nucleic acids isolated from blood samples by employing oligonucleotide probes. The method employed here for detection is by real time PCR.
Owner:BIGTEC PTE LTD
Continuous-flow deformability-based cell separation
InactiveUS8771933B2Reduces and eliminates cloggingMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationPharmaceutical drugCell based
This invention provides methods utilizing a microfluidic device that can quickly and accurately discern differences in deformability between individual cells and sets of cells and continuously fractionate populations of cells based on their deformability. This information may be important in disease diagnosis and treatment efficacy monitoring. For example such a device may be able to determine the stage of malarial infection by using red blood cell deformability. Additionally, methods of the invention may be used as a tool to screen drugs that can make cells more flexible in diseases such as sickle cell anemia that causes sickle cell crises. The relatively low manufacturing and operation costs of methods of the invention enable this device to be used in resource-limited settings to diagnose and monitor disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
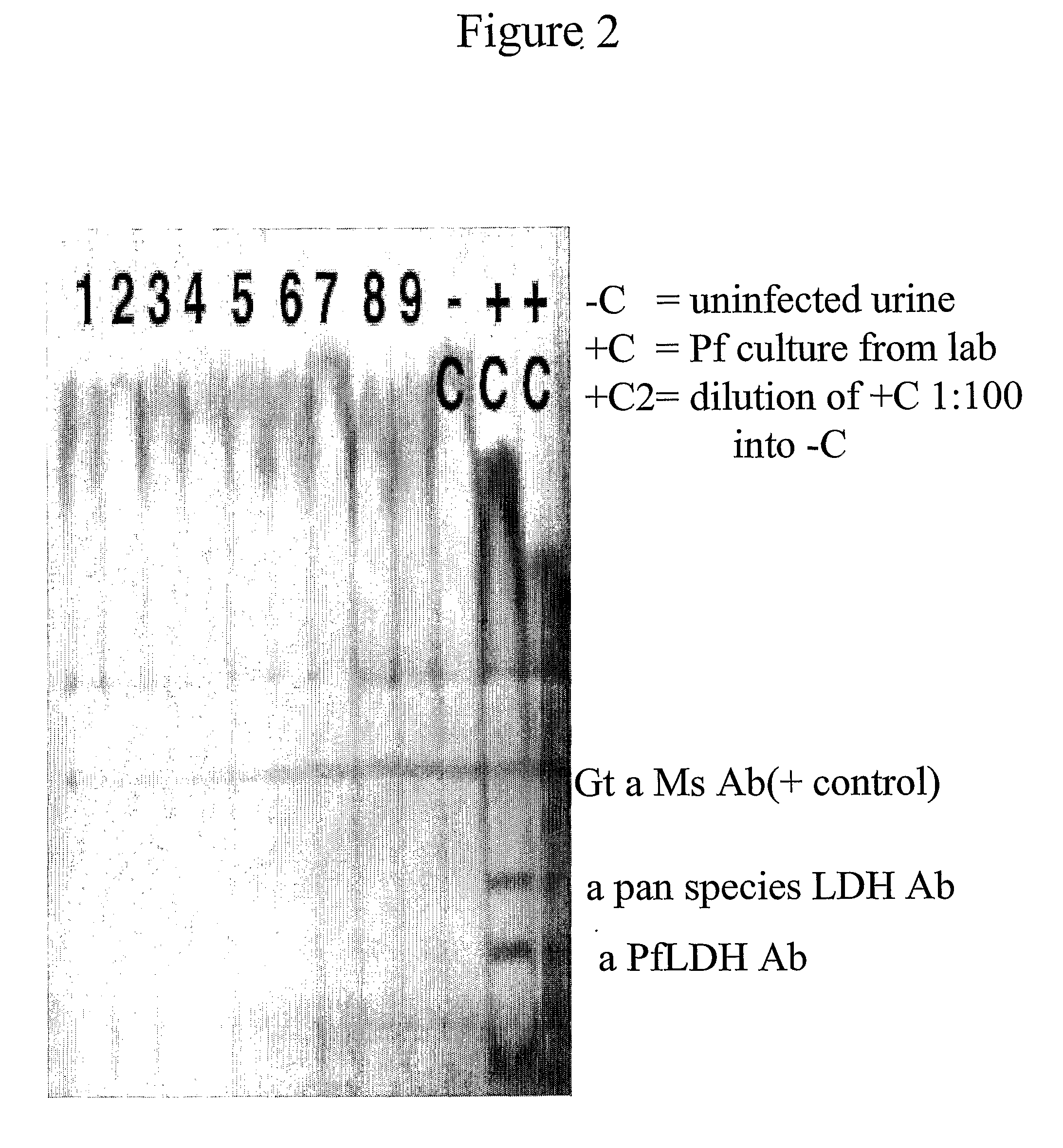
Plasmodium Diagnostic Assay Device
ActiveUS20090117602A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBody fluid
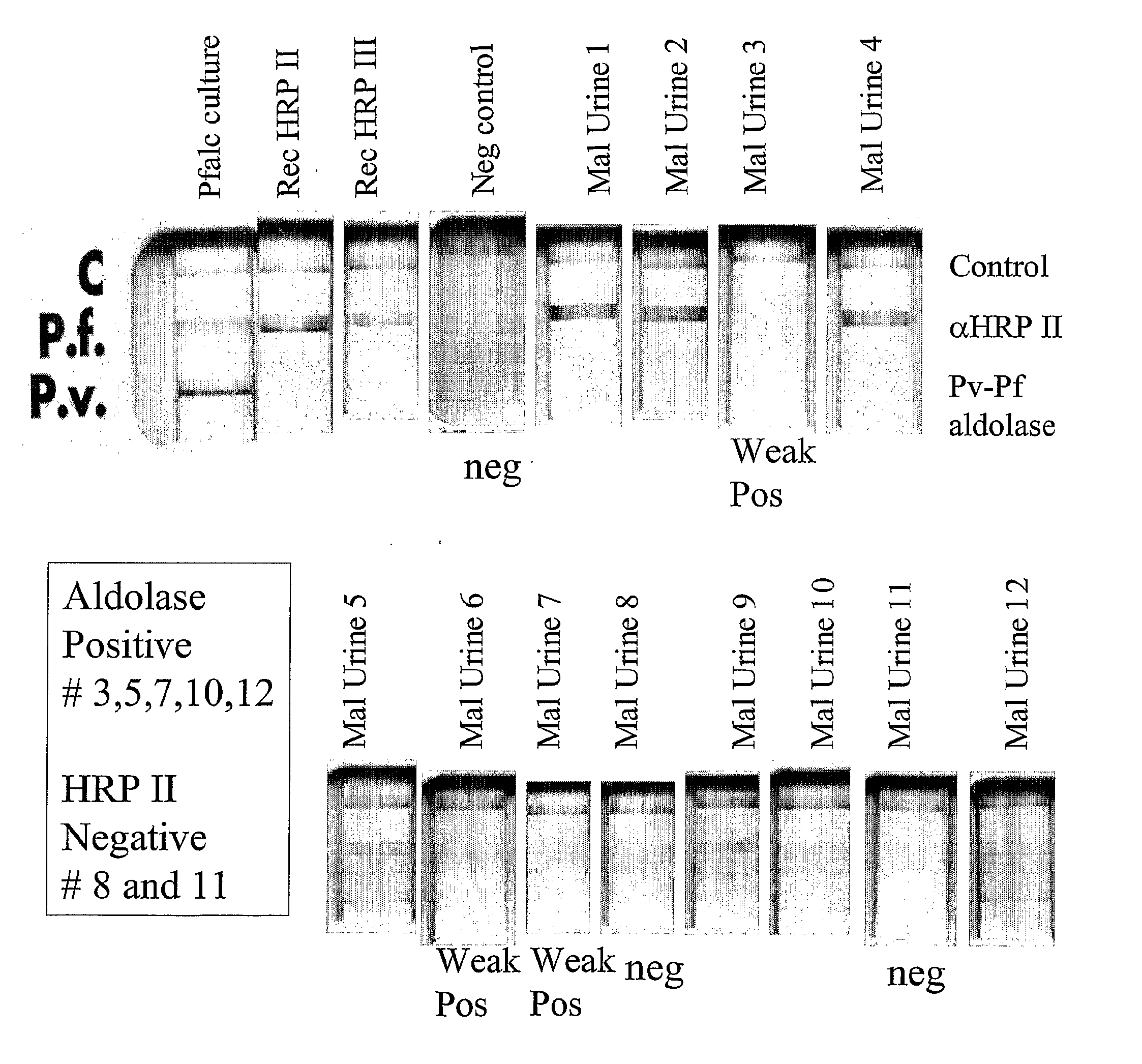
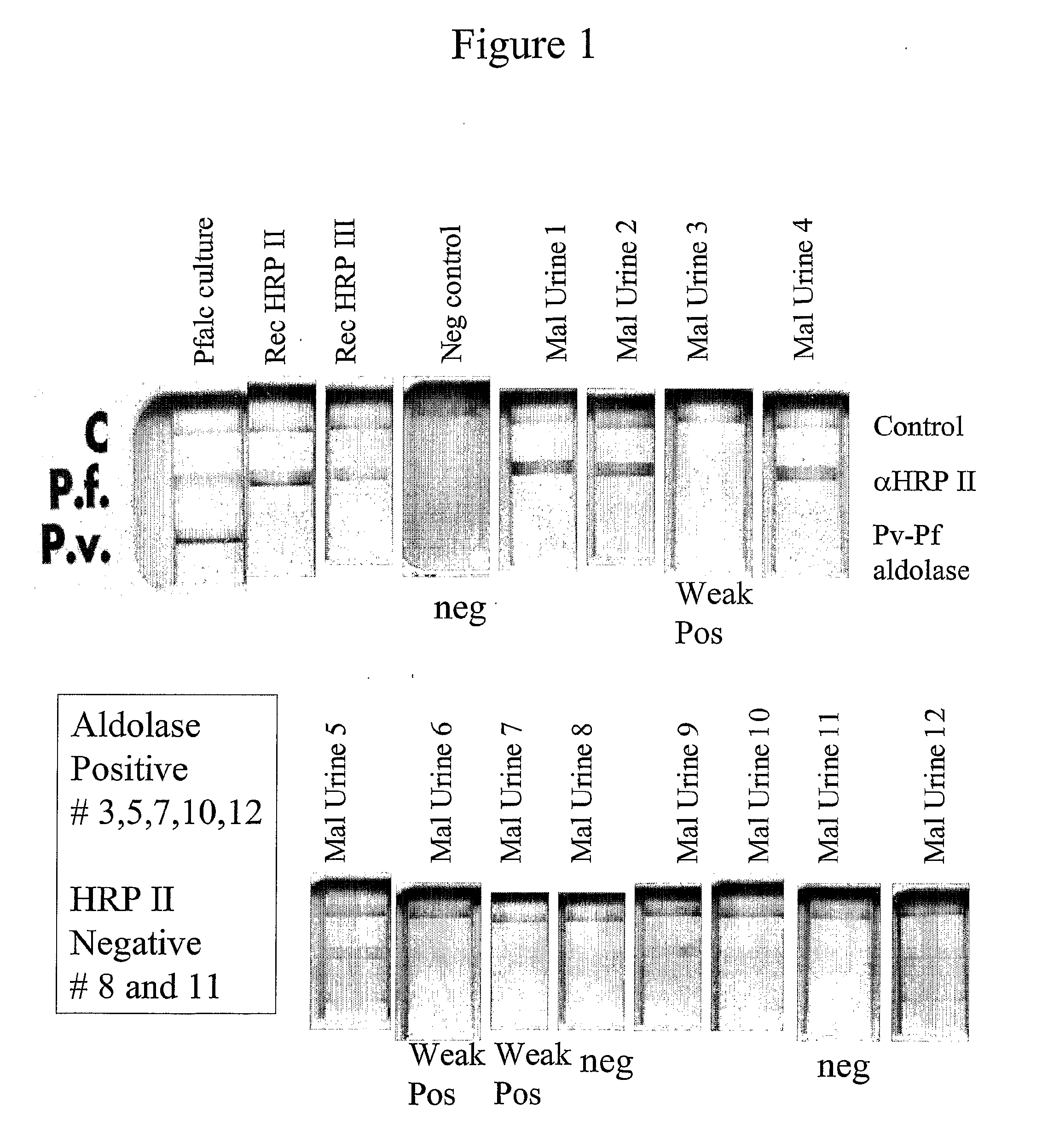
This invention relates to assays for a Plasmodium analyte in a liquid sample such as a body fluid. More particularly, the invention relates to a method and apparatus for the detection of a ligand in a body fluid such as urine or blood, which can diagnose malarial infection.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Detection/measurement of malaria infection disease utilizing natural immunity by hemozoin induction, screening of preventative or therapeutic medicine for malaria infection disease, and regulation of natural immunity induction
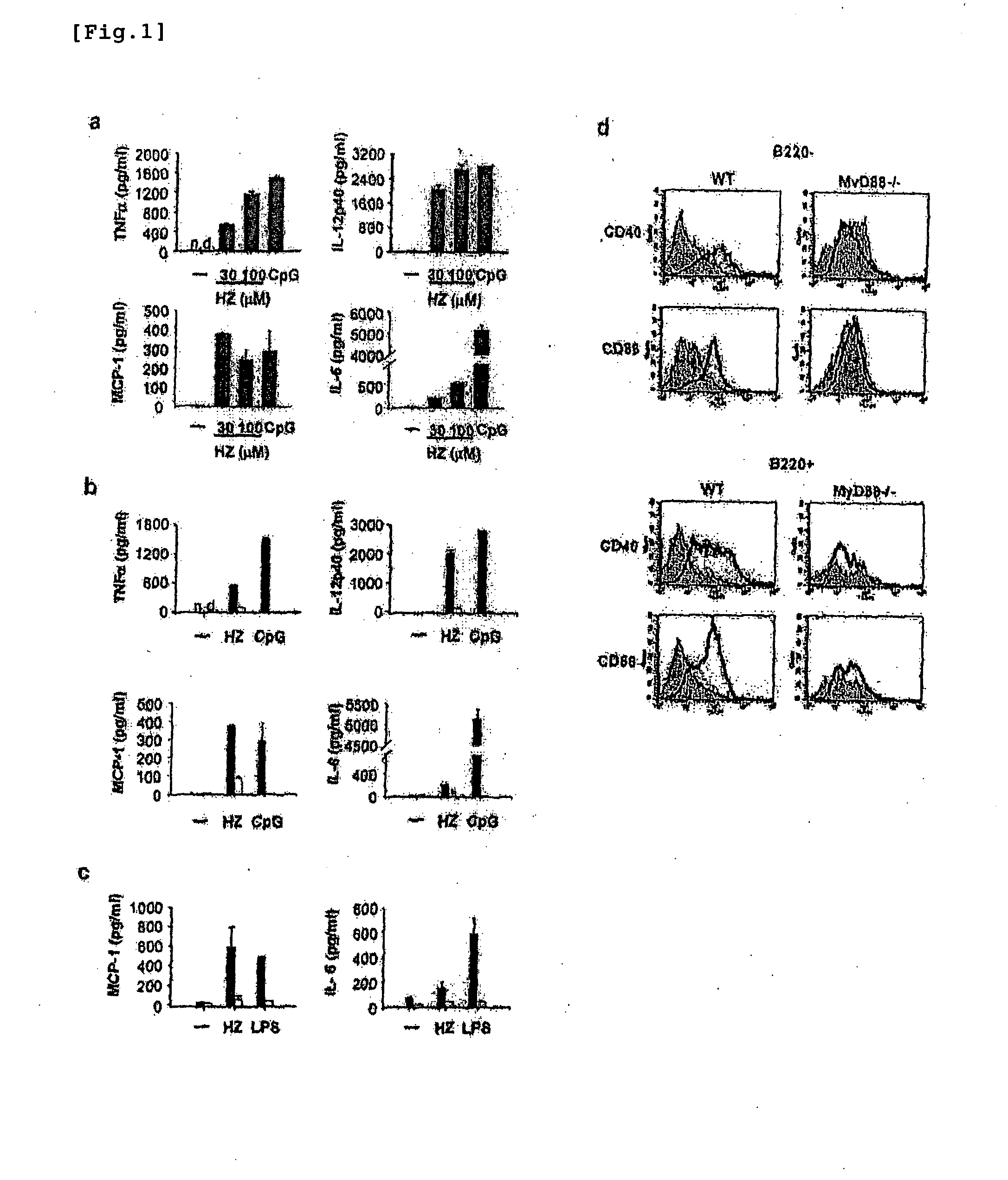
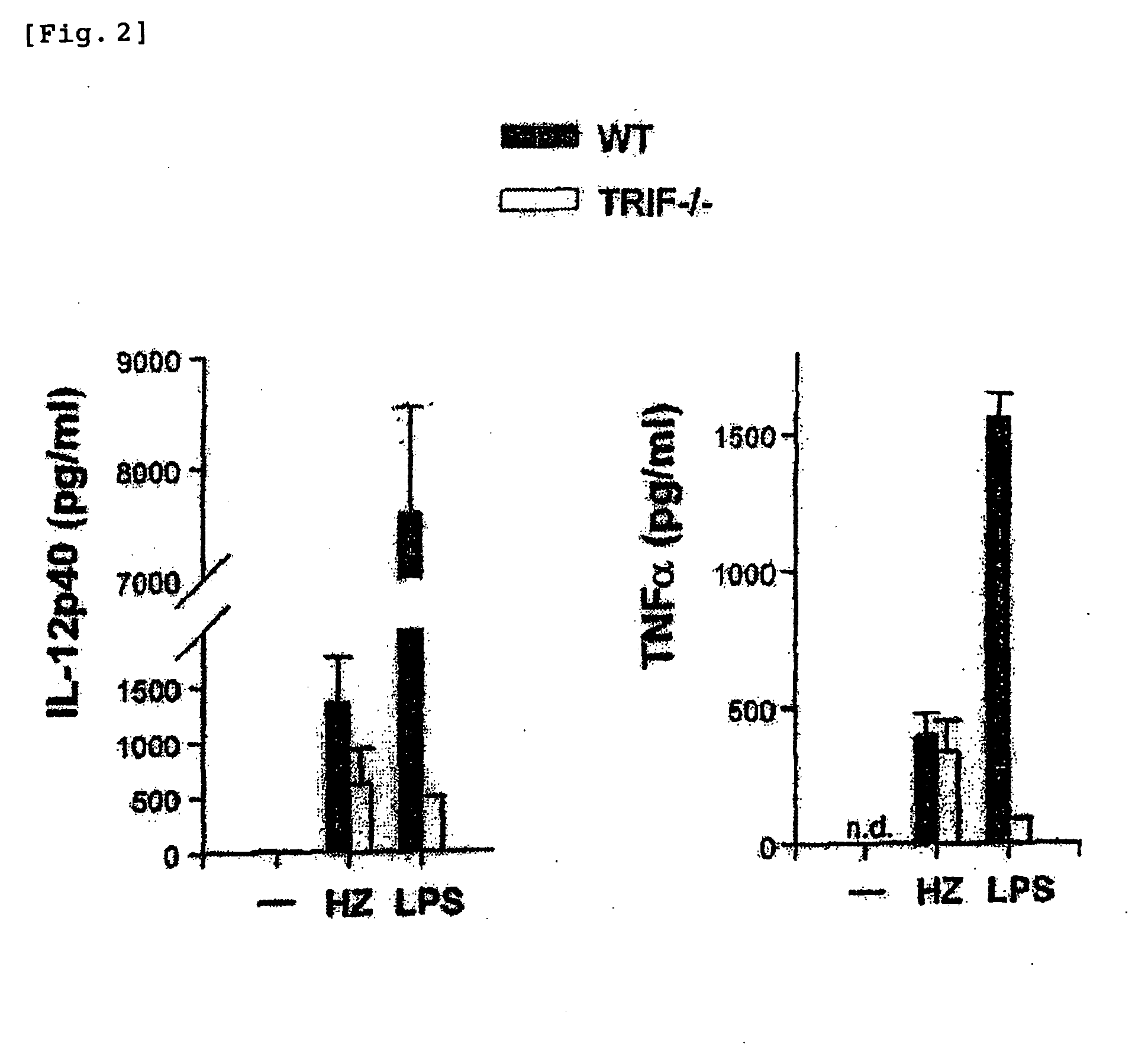
The instant invention is to provide a method for detecting and measuring malaria infection utilizing the induction by hemozoin (HZ); a method for screening a vaccine for malaria infection and a preventative or therapeutic agent for malaria infection using the method for detecting and measuring; and a means for regulating the induction of innate immunity using the HZ, synthetic HZ, or derivatives thereof as an adjuvant or immunostimulant. Malaria infection is detected and measured of by detecting and measuring HZ-induced, TLR9-mediated, and MyD88-dependent innate immune activity. The detection and measurement of malaria infection can be used to diagnose malaria infection. The method for detecting and measuring is also used for screening a vaccine for malaria infection and a preventative or therapeutic agent for malaria infection. Further, HZ, synthetic HZ, or derivatives thereof are used as an adjuvant or immunostimulant to regulate HZ-induced innate immune induction.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Vaccines for malaria
InactiveUS9364525B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiinfectivesPolyclonal antibodiesLipoprotein particle
The present invention relates to a novel lipoprotein particle, methods for preparing and purifying the same, its use in medicine, particularly in the prevention of malarial infections, compositions / vaccines containing the particle or antibodies against the protein particle such as monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies and use of the same, particularly in therapy. In particular it relates to an immunogenic protein particle comprising the following monomers:a. a fusion protein comprising sequences derived from a CS protein of P. vivax and the S antigen of Hepatitis B (CSV-S), andb. a fusion protein comprising sequences derived from CS protein of P. falciparum and S antigen of Hepatitis B (RTS), andc. optionally the S antigen derived from Hepatitis B.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA +1
Malaria recombinant antigen, IgY immune body and malaria detection kit
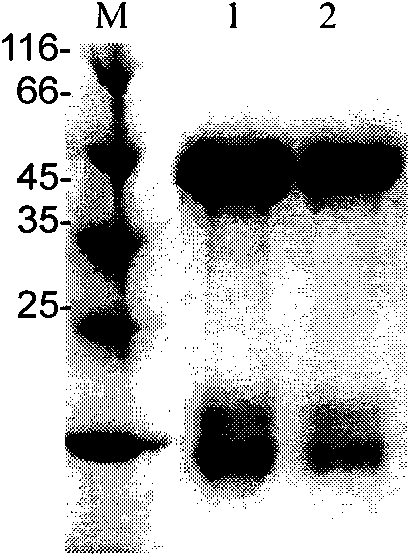
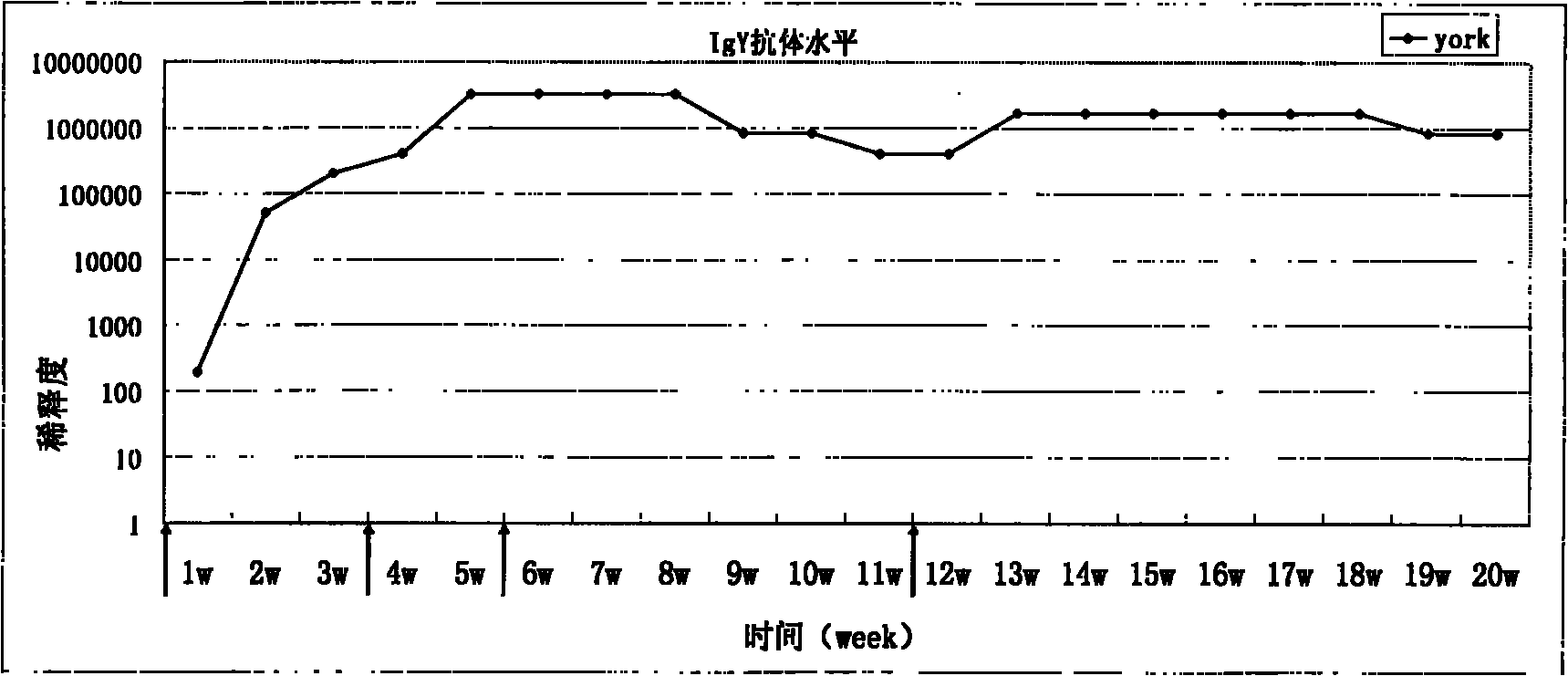
InactiveCN101838322AStrong specificityUniform natureEgg immunoglobulinsMicroorganism based processesAntigenMalaria
The invention relates to a malaria recombinant antigen, an IgY immune body and a malaria detection kit. In the invention, the malaria antigen with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 11 is designed; the IgY immune body is obtained from an antigen-immunized chicken; and a malaria infection detection kit containing the IgY immune body is prepared. The sensitivity of the detection kit of the invention is 1000 times higher than that of the similar rapid detection card in the prior art.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Specific malaria detection with digital holographic microscopy
ActiveUS20200264557A1Individual particle analysisBiological testingDigital holographic microscopyMalarial infection
The present invention relates to a method of detecting a possible infection of malaria in a patient using a digital optical microscope
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Application of circumsporozoite protein polypeptide CSP I-plus of plasmodium in preparing anti-malarial medicine
InactiveCN103611151AReduced number of infecting parasitesPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMalarial parasiteCell invasion
The invention discloses novel application of the peptide fragment CSP I-plus of circumsporozoite protein CSP I-plus of plasmodium in treating plasmodium infection. Researches discover that the circumsporozoite protein CSP plays an important role in adhesion and hepatic cell invasion of plasmodium sporozoite, and the key point of malaria infection is that sporozoite of plasmodium invades liver cells, so that malaria infection can be prevented by stopping invasion of sporozoite. CSP I-plus is an important functional domain of CSP, can be specifically combined with a liver cell surface molecule, namely heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG), and can stop combination of CSP and the liver cells. Therefore, the CSP I-plus is expected to be developed into a novel micro-molecule polypeptide medicine for treating plasmodium falciparum infection by stopping adhesion and liver cell invasion of CSP mediated plasmodium sporozoite, and the recombinant expression plasmid containing CSP I-plus coding genes is expected to be further developed into a novel anti-malarial genetic medicine, so that the circumsporozoite protein polypeptide CSP I-plus has an excellent clinical application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
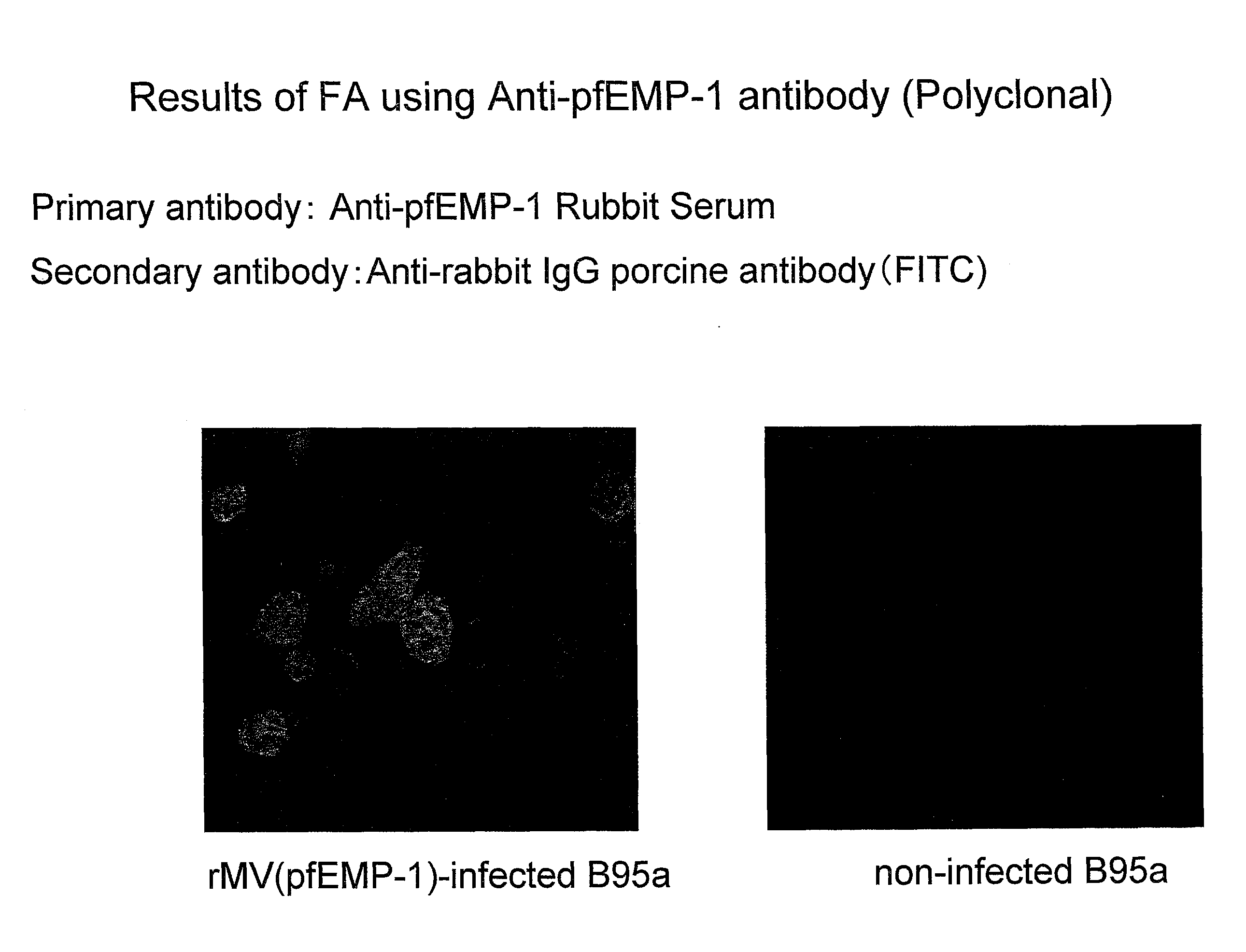
Recombinant Measles Virus Useful as a Bivalent Vaccine Against Measles and Malarial Infections
Provided herein is a vaccine which is safe and effective against malarial infection and a vector which is used in the manufacture of this vaccine and to provide a bivalent vaccine which exhibits an excellent preventive effect against measles virus and malarial infection and which eliminates complexity at the time of inoculation. Also provided is a recombinant measles virus in which is inserted a gene which encodes a protein involved in preventing malarial infection in the measles virus genome. The present invention also provides a bivalent vaccine against measles and malarial infection which contains the recombinant measles virus. It also provides a method of manufacturing a vaccine against malarial infection which is characterized by using a measles virus as a vaccine vector in the manufacture of a vaccine against malarial infection
Owner:ARIGEN PHARMA INC
Plasmodium diagnostic assay device
ActiveUS9568471B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBody fluid
This invention relates to assays for a Plasmodium analyte in a liquid sample such as a body fluid. More particularly, the invention relates to a method and apparatus for the detection of a ligand in a body fluid such as urine or blood, which can diagnose malarial infection.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
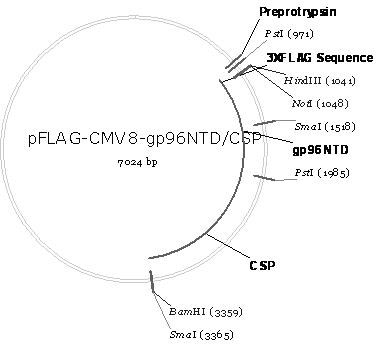
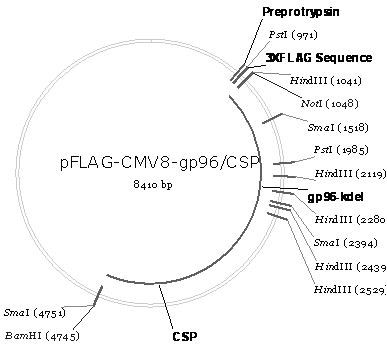
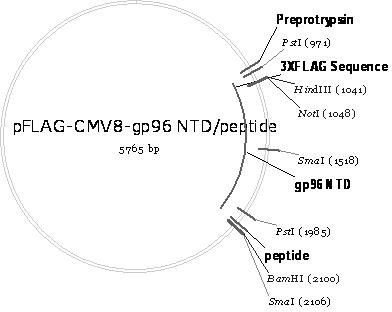
Malaria infrared stage DNA vaccine and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN102166349ASpecific complete protective immunityAvoid infectionAntibody medical ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionCD8T cell
The invention belongs to the biomedicine field, relating to a malaria infrared stage DNA vaccine and a preparing method thereof. The vaccine is obtained by connecting the coding gene of N end segment (amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1) of heat shock protein (gp96) with the coding gene of the circumsporozoite protein (amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 3) in series and inserting into eukaryotic expression plasmid. The preparing method of the invention comprises three steps: the construction of recombinant plasmid pMD19 simple T / CSP, the construction of recombinant plasmid pFLAG-CMV8-gp96NTD, and the construction of recombinant plasmid pFLAG-CMV8-gp96NTD / CSP. The vaccine is able to simultaneously induce anti-CSP antibody generation and CD8+T cell reaction, thereby obtaining the plasmodium-specified complete protective immunization, and has great application prospect in preventing malaria inflection.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Treating Multi-Drug Resistant Malaria
InactiveUS20180207216A1Organic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsMalarial parasitesMulti drug resistant
A method is provided for treating an individual for a malarial infection, in particular drug-resistant species of Plasmodium, including administering to the individual in need of such treatment a composition comprising an extract containing an effective amount of one or more anti-malarial di- or tri-terpene compounds. Potent and effective extracts containing the anti-malarial compounds can be derived from Luo Han fruit and Stevia leaves, including combinations of the same, for treating and preventing malaria in an inexpensive manner from readily available commodities. The composition may be administered orally in a solid or liquid ingestible form.
Owner:FEBRIS BIO TECH
Compositions and methods for treating multi-drug resistant malaria
A method is provided for treating an individual for a malarial infection, in particular drug-resistant species of Plasmodium, including administering to the individual in need of such treatment a composition comprising an extract containing an effective amount of one or more anti-malarial di- or tri-terpene compounds. Potent and effective extracts containing the anti-malarial compounds can be derived from Luo Han fruit and Stevia leaves, including combinations of the same, for the purpose of treating and preventing malaria in an inexpensive manner from readily available commodities. In one embodiment, the composition is administered orally in a solid or liquid ingestible form.
Owner:FEBRIS BIO TECH
Antimalarial heterocyclic compounds and a process for the preparation thereof
The present invention relates to an antimalarial heterocyclic compound of formula I, dimers thereof and process for the preparation thereof. Further, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition of heterocyclic compound of formula I, dimers thereof for treating malarial infection.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Intramuscular depot of decoquinate compositions and method of prophylaxis and treatment thereof
ActiveUS20210059946A1No adverse effectsAdequate levelPill deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseMonoglyceride
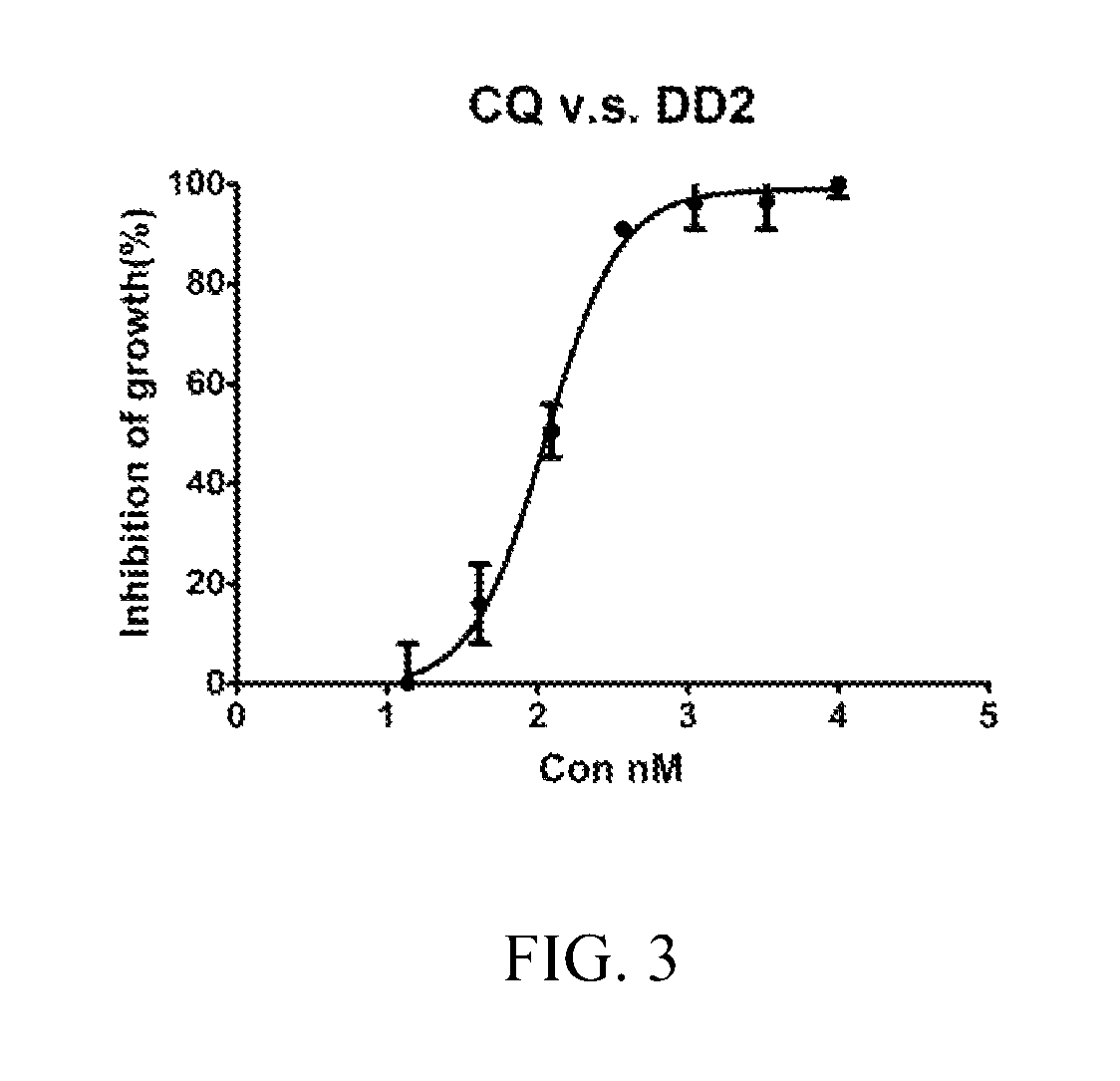
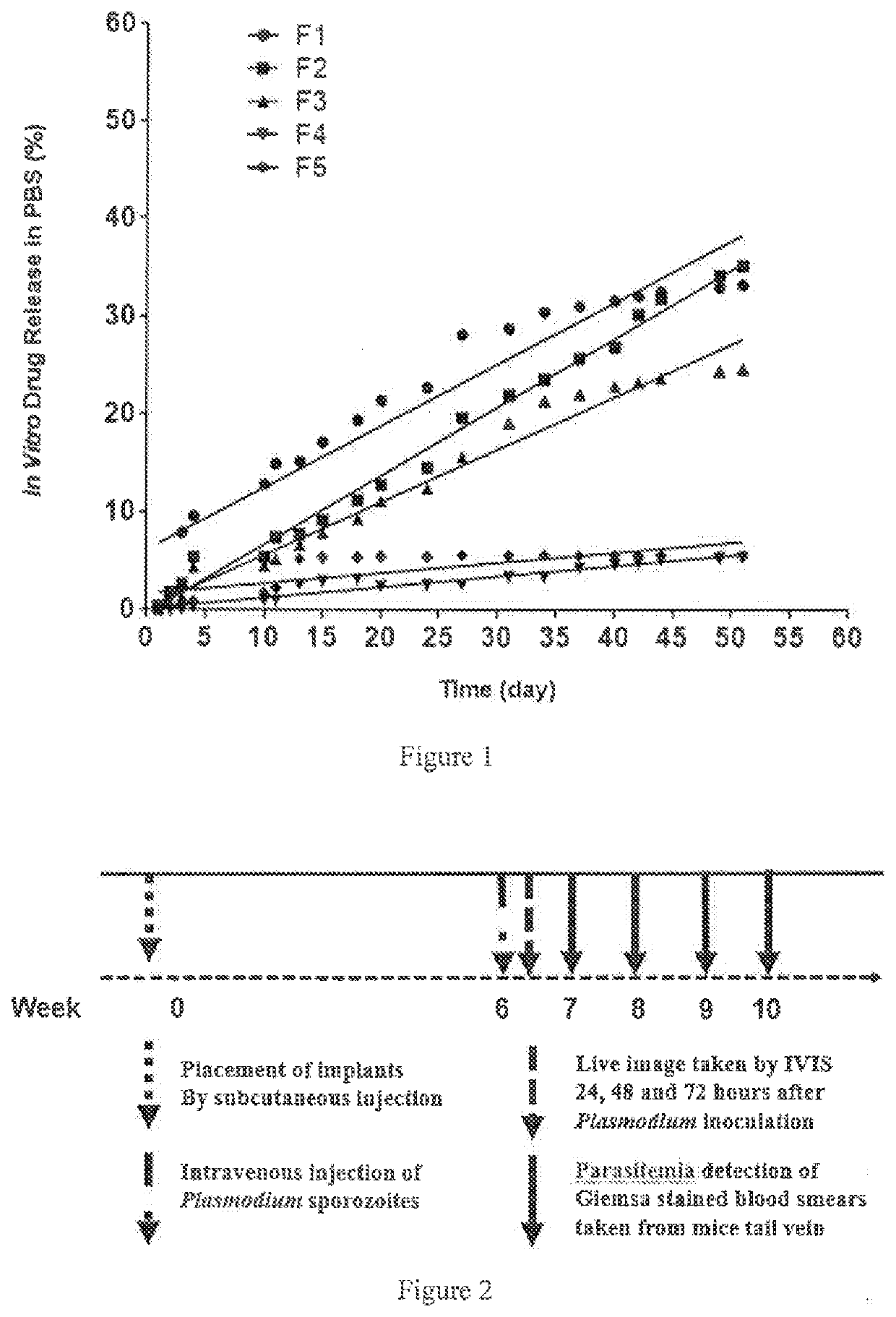
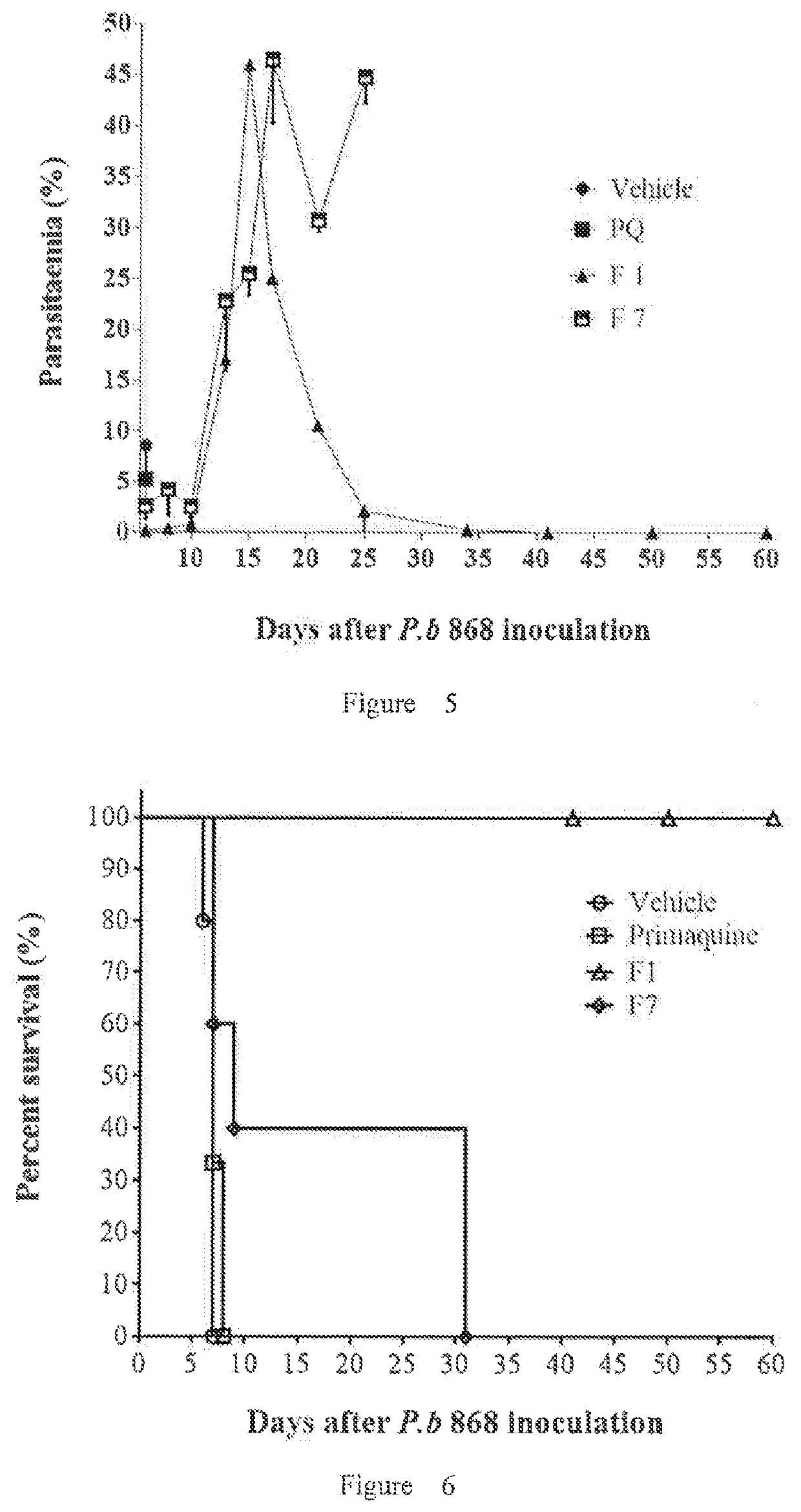
Implants comprising an antimalarial agent such as decoquinate or another therapeutic drug are disclosed. The implants can be in the form of a complex comprising a drug, a lipid or lipids and optionally a polymer carrier. The present invention provides methods for preparing implants wherein the implants comprise decoquinate or another therapeutic drug, and a lipid or lipids such as cholesterol, monoglycerides, or diglycerides, and optionally a small percentage of a biocompatible polymer based on the total implant weight. The implants are useful for releasing a therapeutic drug at a constant level and maintaining a prophylactic or therapeutic level of the drug in a subject, for preventing a malarial infection or treating other diseases or disorders.
Owner:CAS LAMVAC (GUANGZHOU) BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for treating malaria with cupredoxin and cytochrome
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com