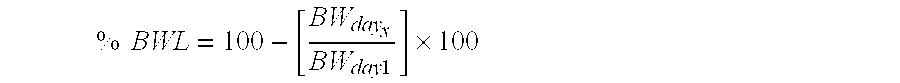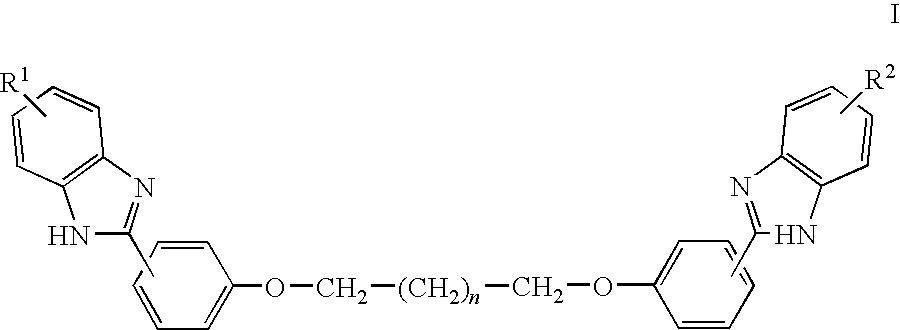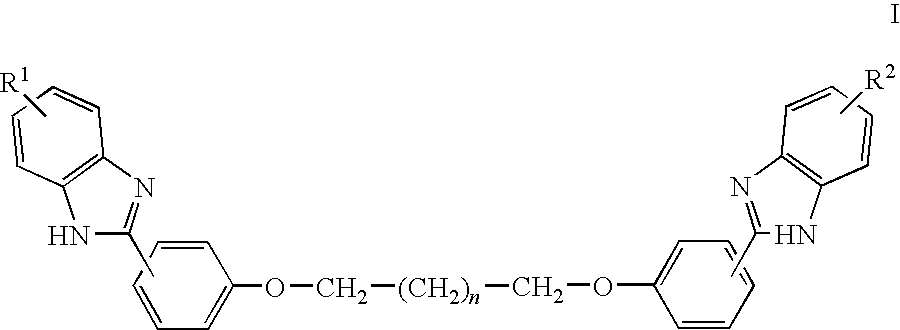Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Antimalarial Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
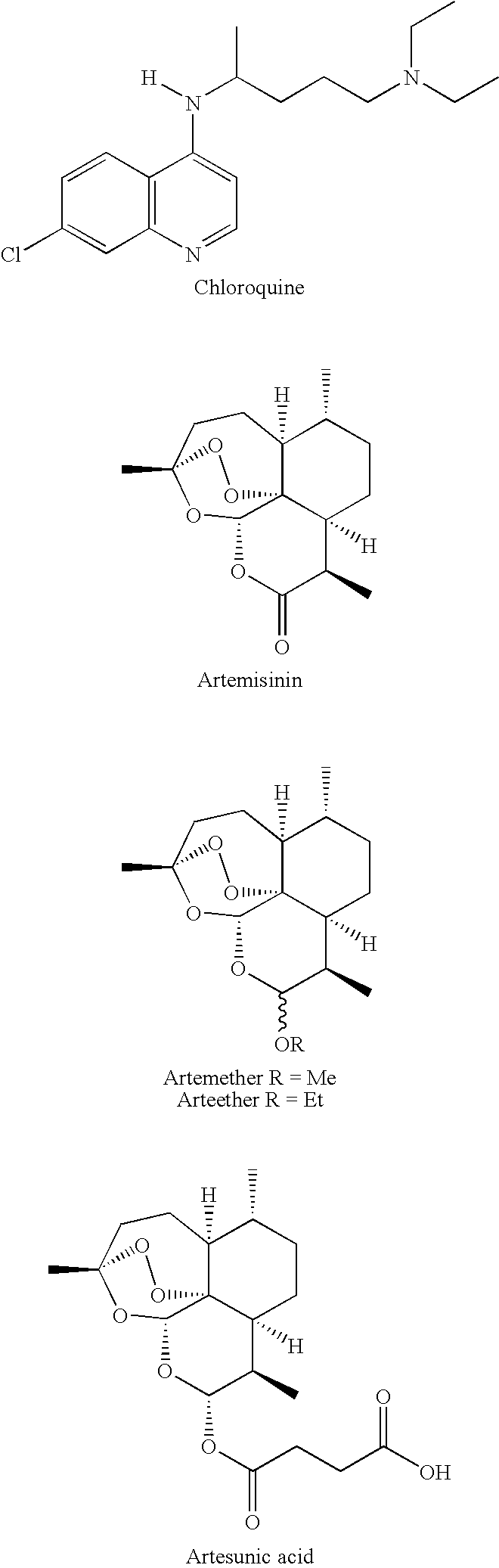
A pharmaceutical agent that cures or prevents malaria. Certain anti-malarials, specifically chloroquine derivatives, have been used in the treatment of autoimmune disease.
Substituted 1,2,4-trioxanes useful as antimalarial agents and a process for the preparation thereof
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
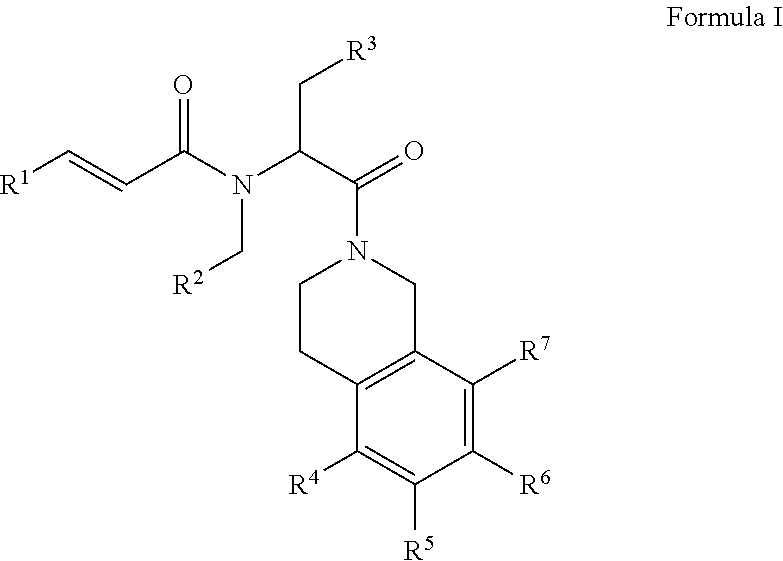
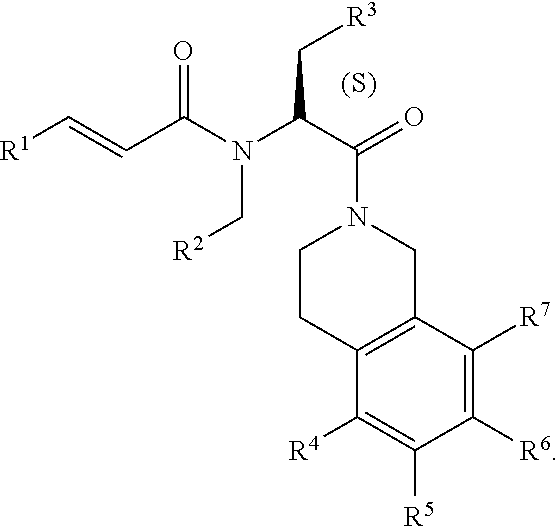
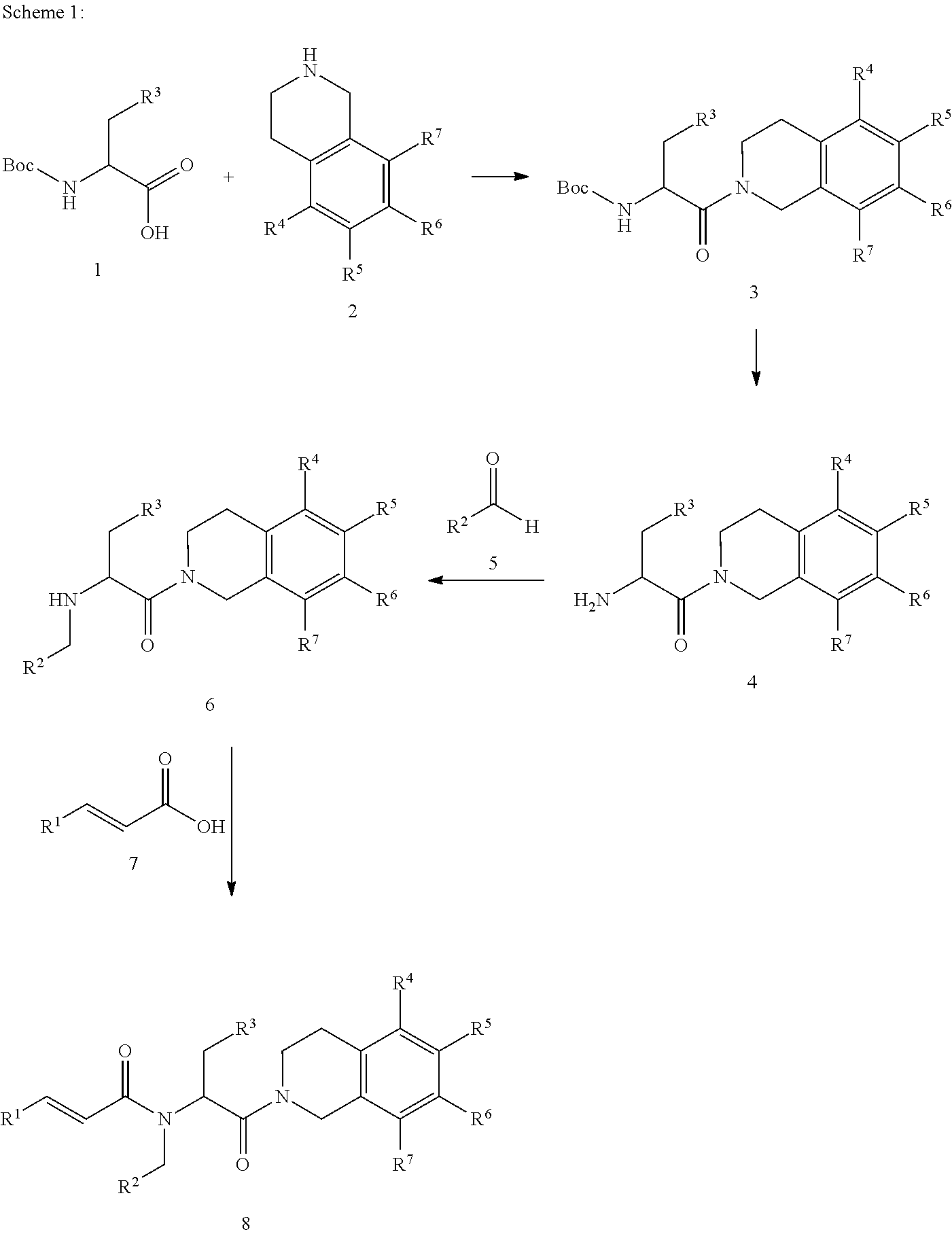
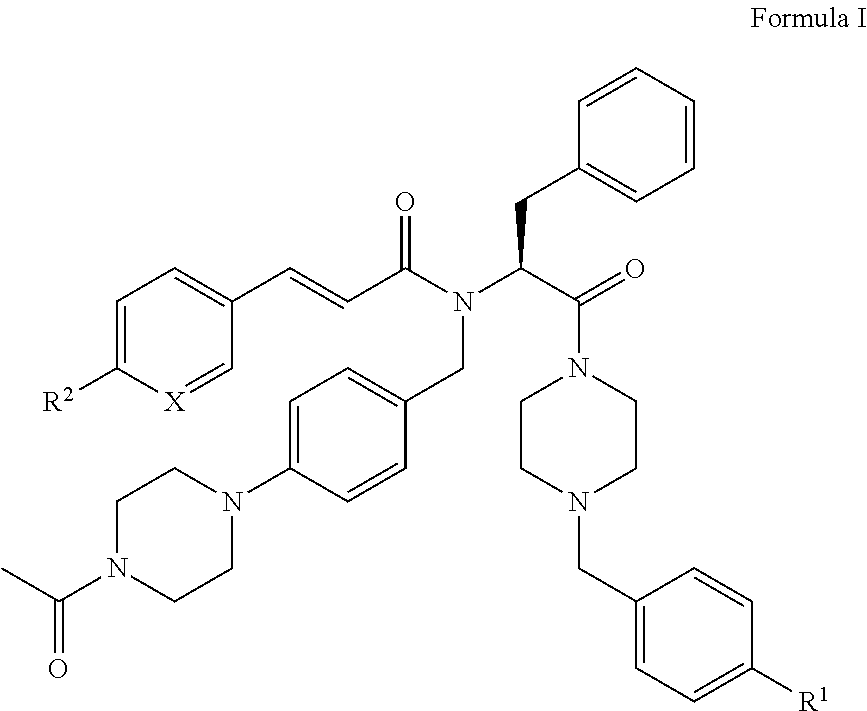
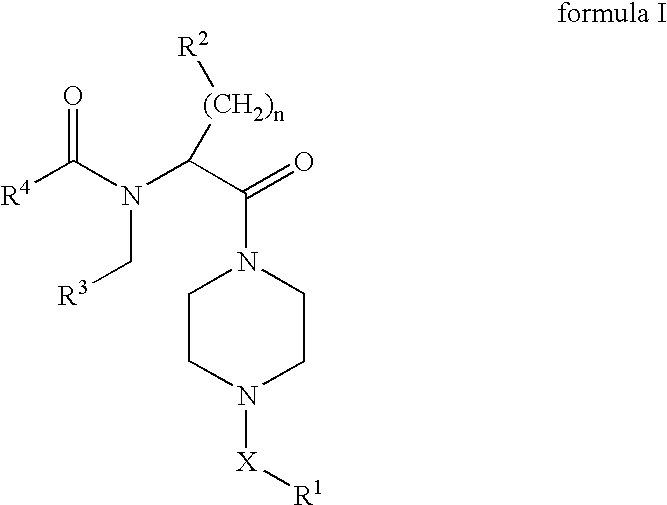
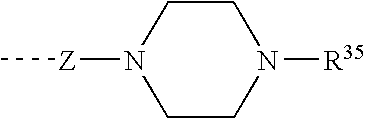
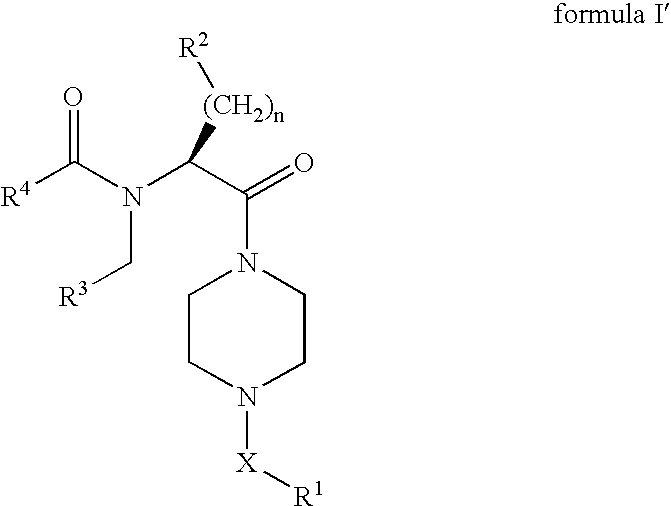
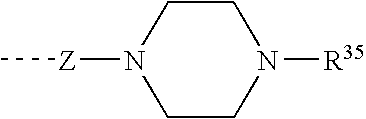
Piperazines as antimalarial agents
Owner:IDORSIA PHARM LTD
Novel Piperazines as Antimalarial Agents
The invention relates to novel piperazine derivatives and their use as active ingredients in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also concerns related aspects including pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more of those compounds and their use as medicaments for the treatment or prevention of protozoal infections, especially malaria.
Owner:IDORSIA PHARM LTD
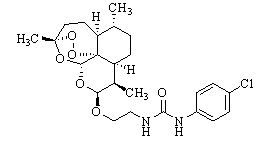
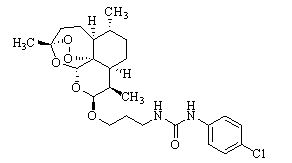
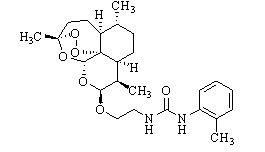
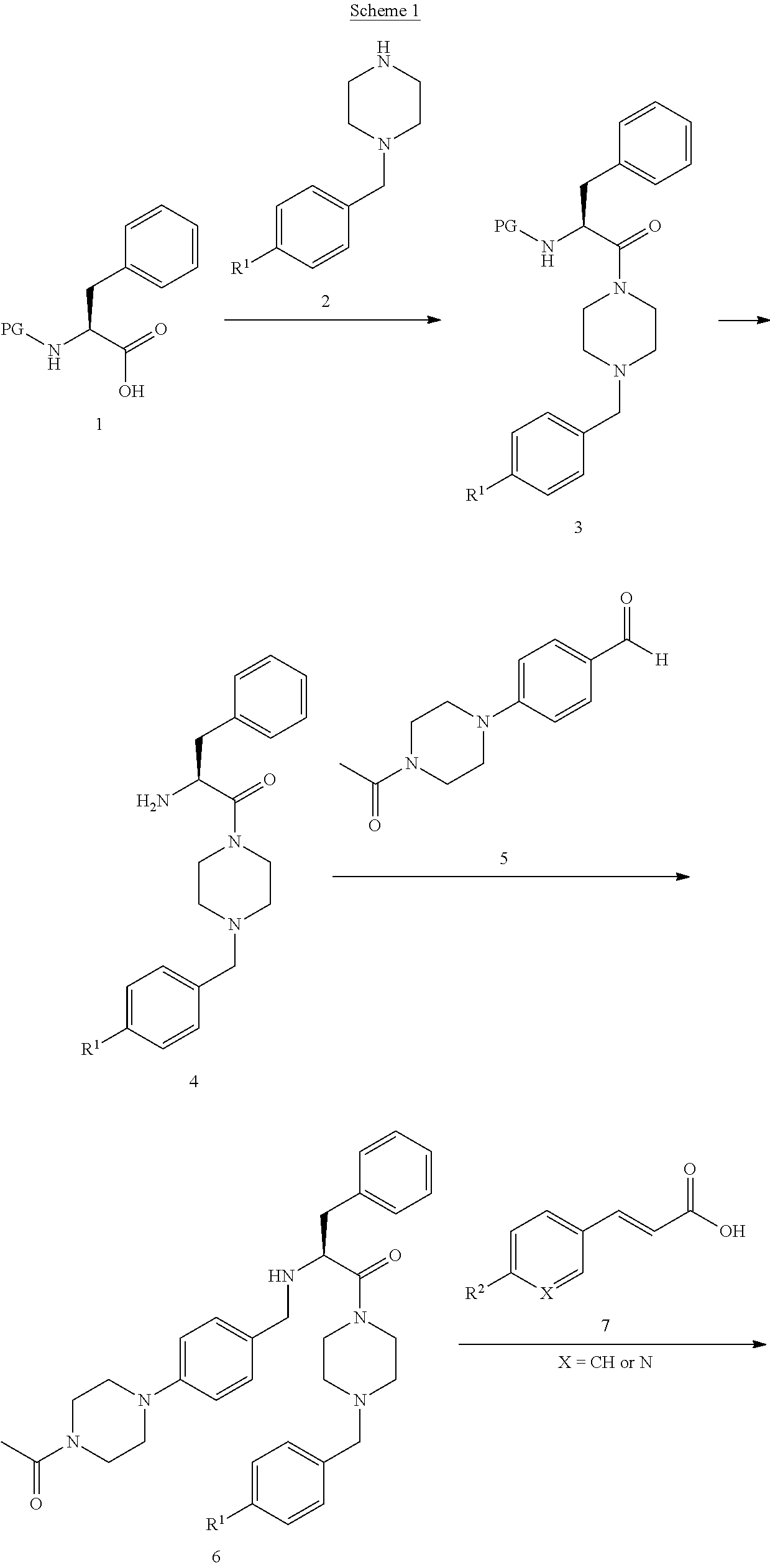
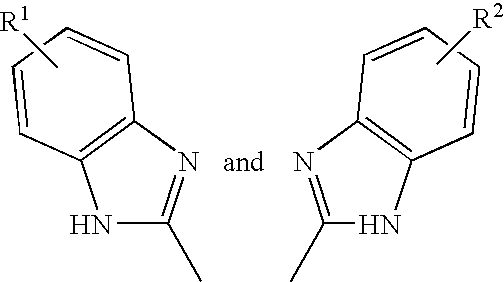
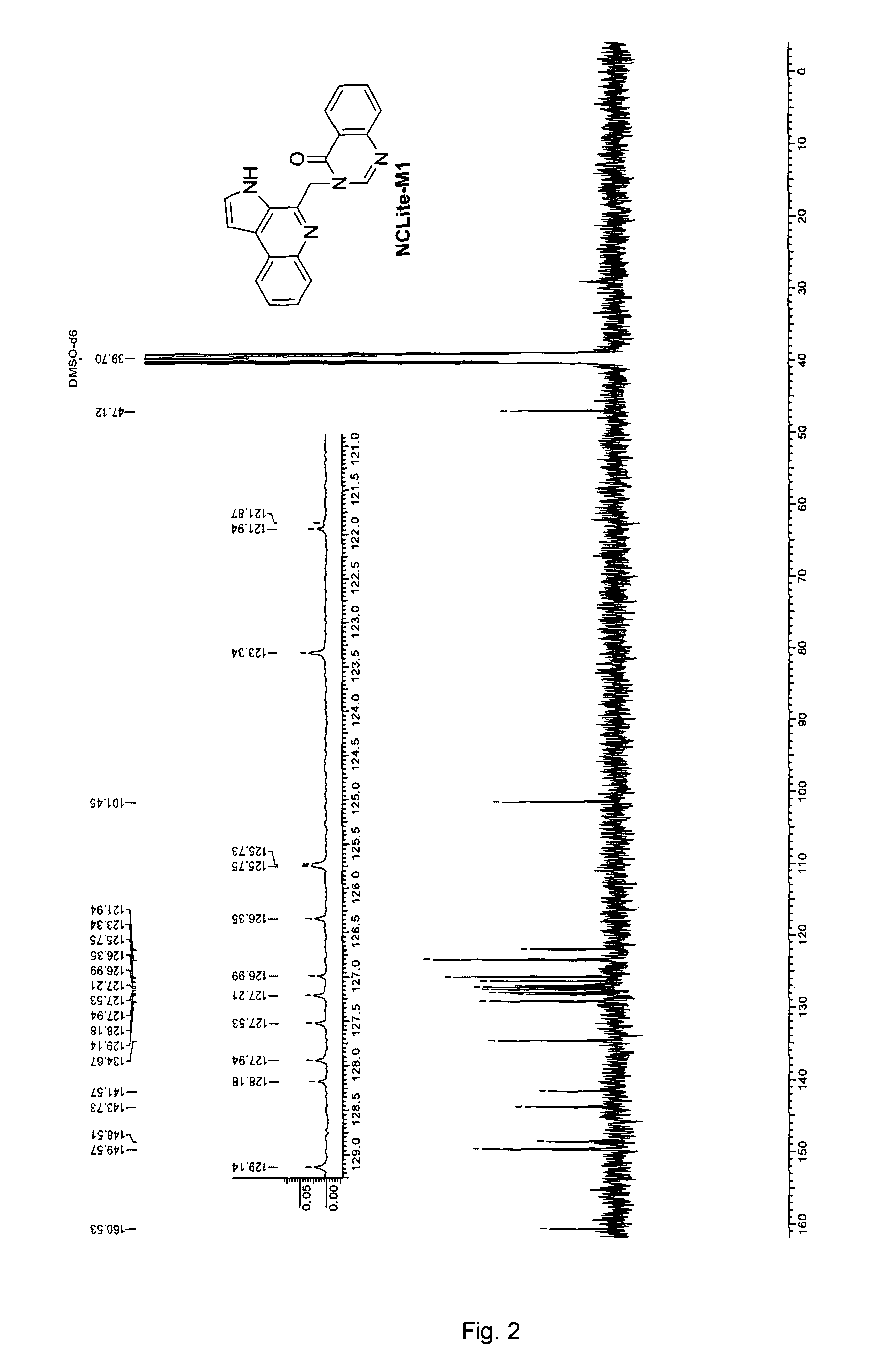
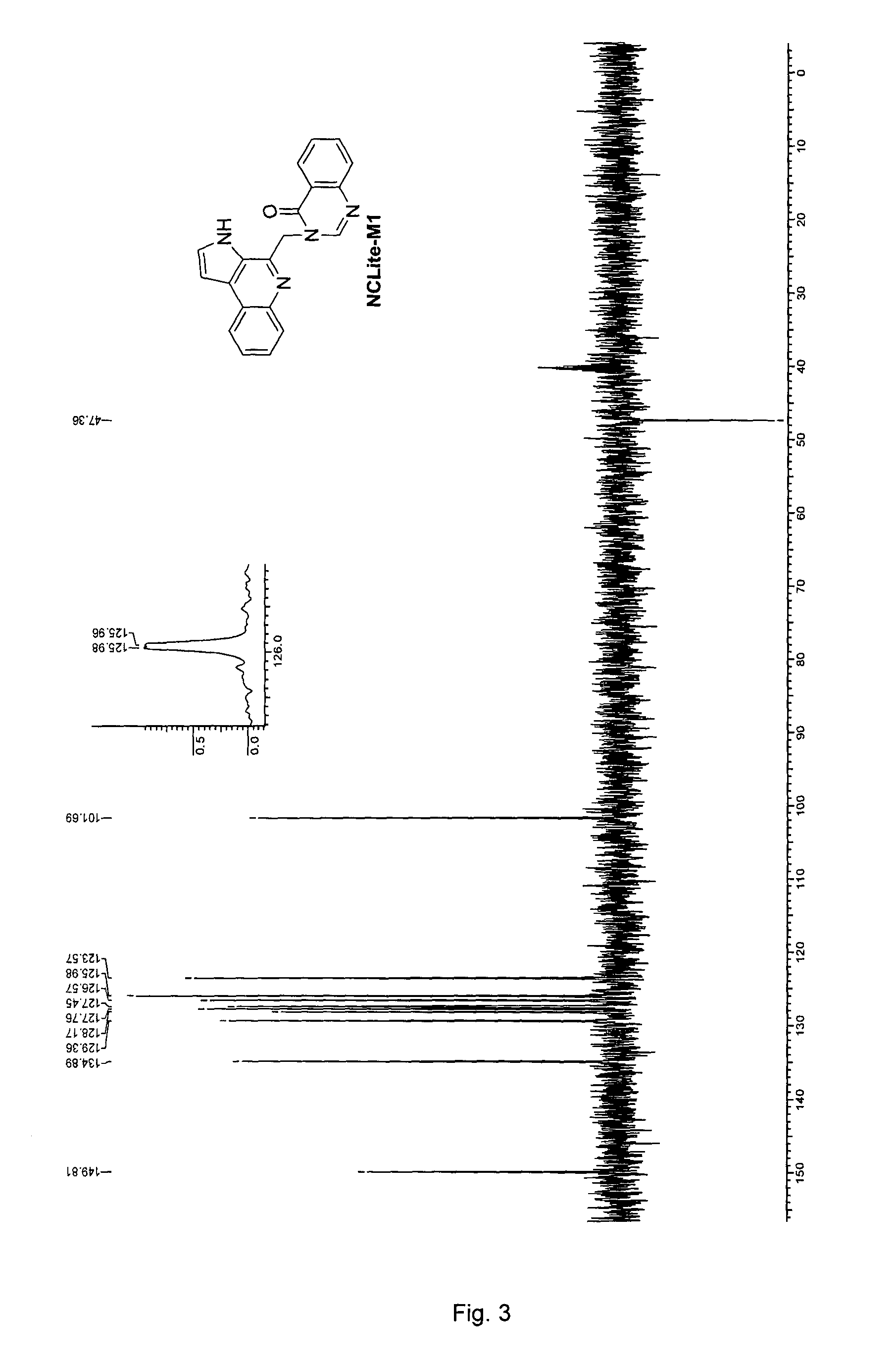
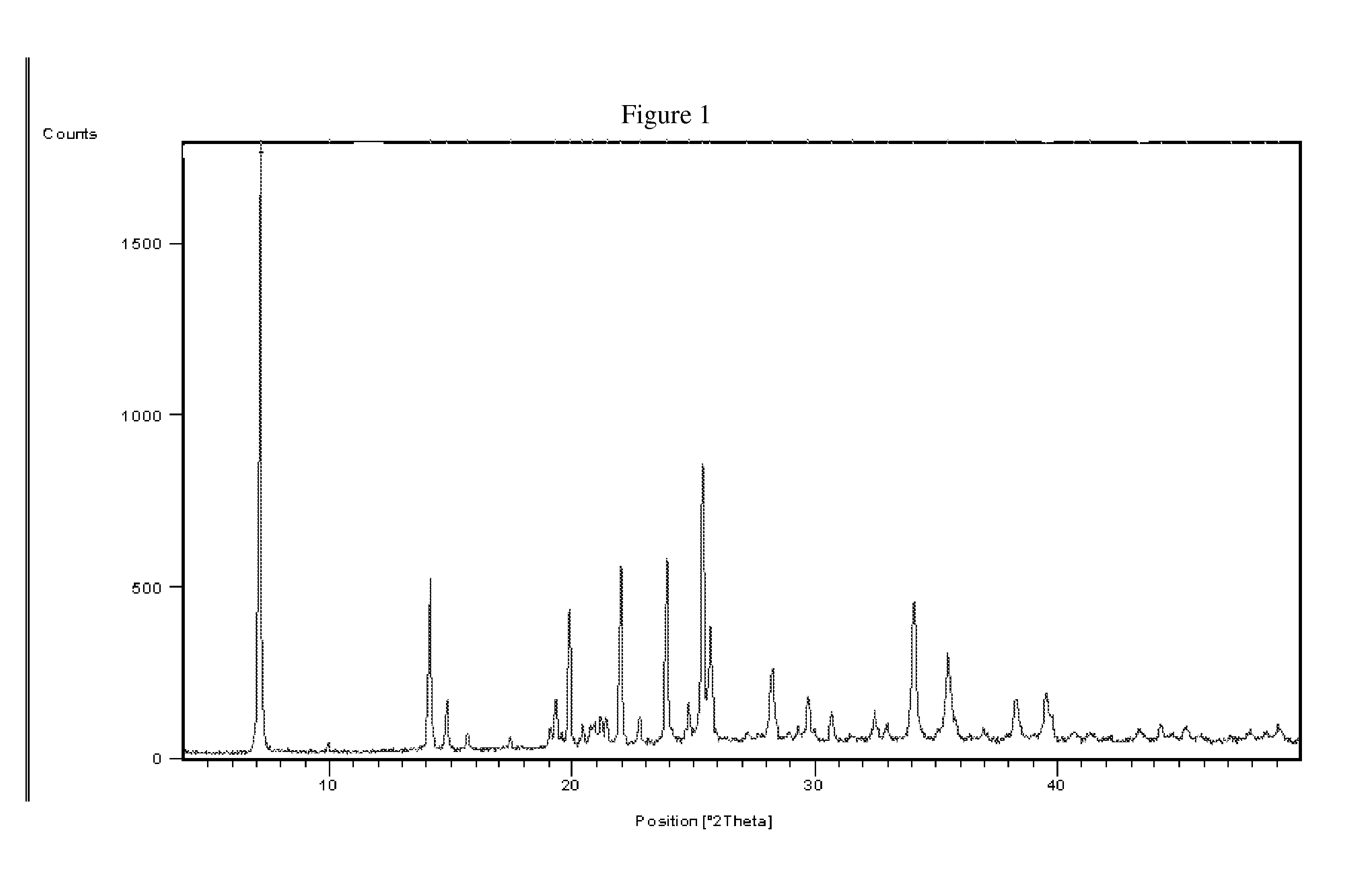
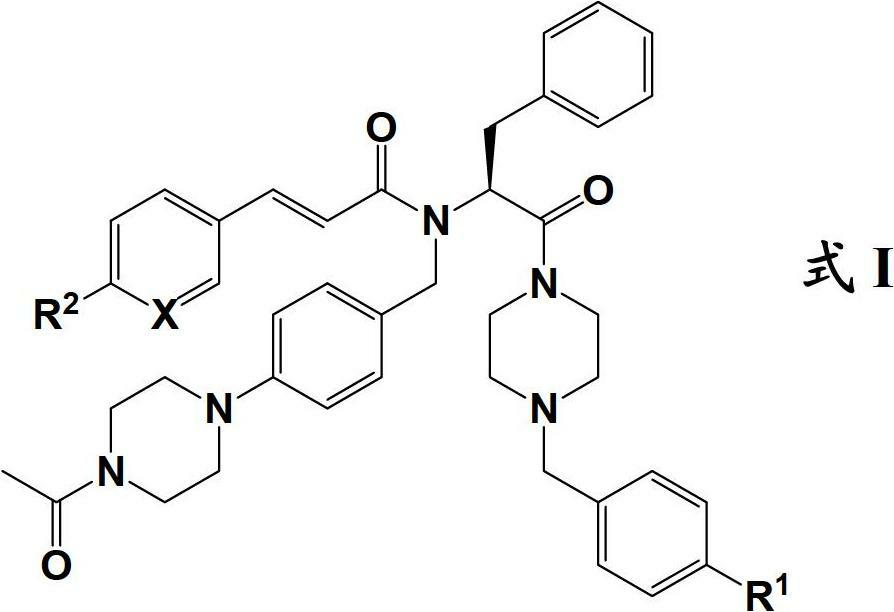
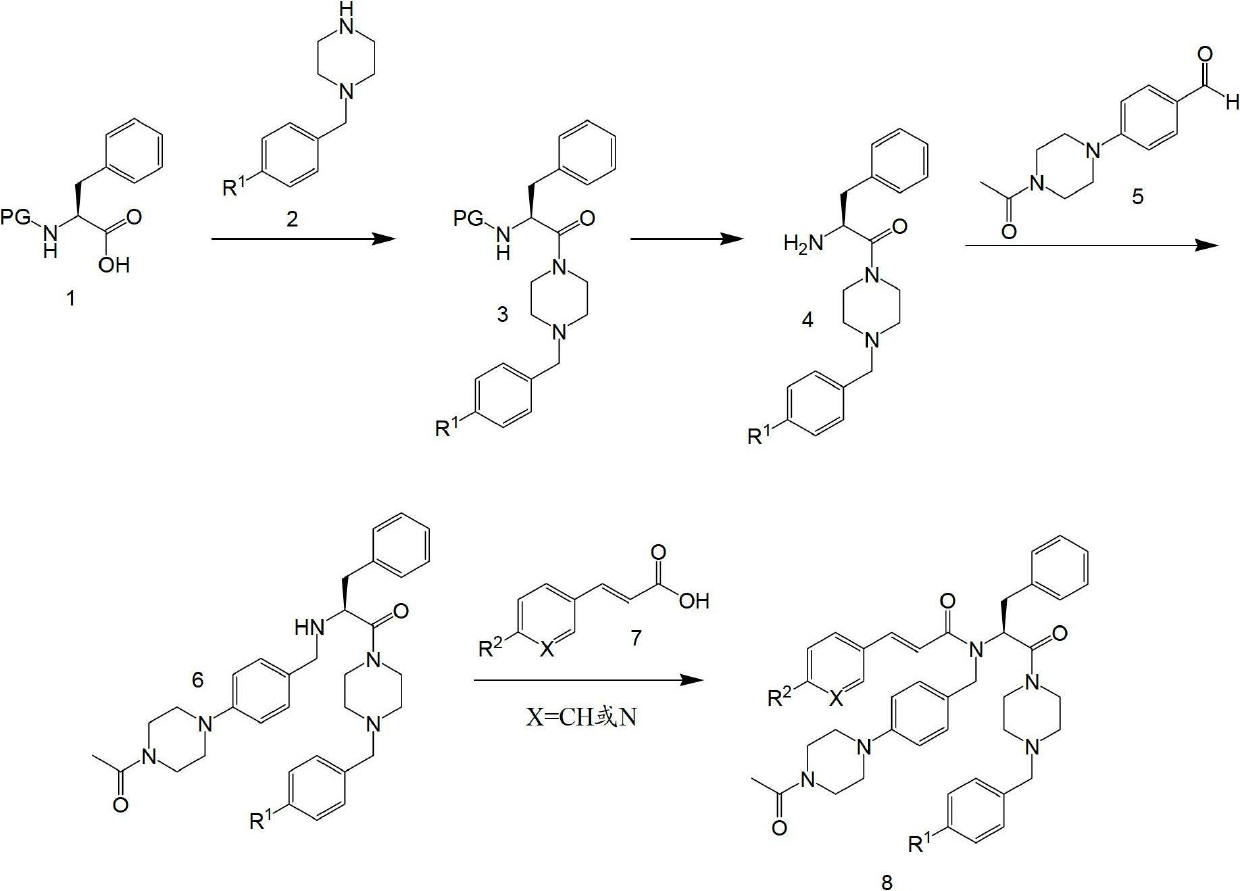
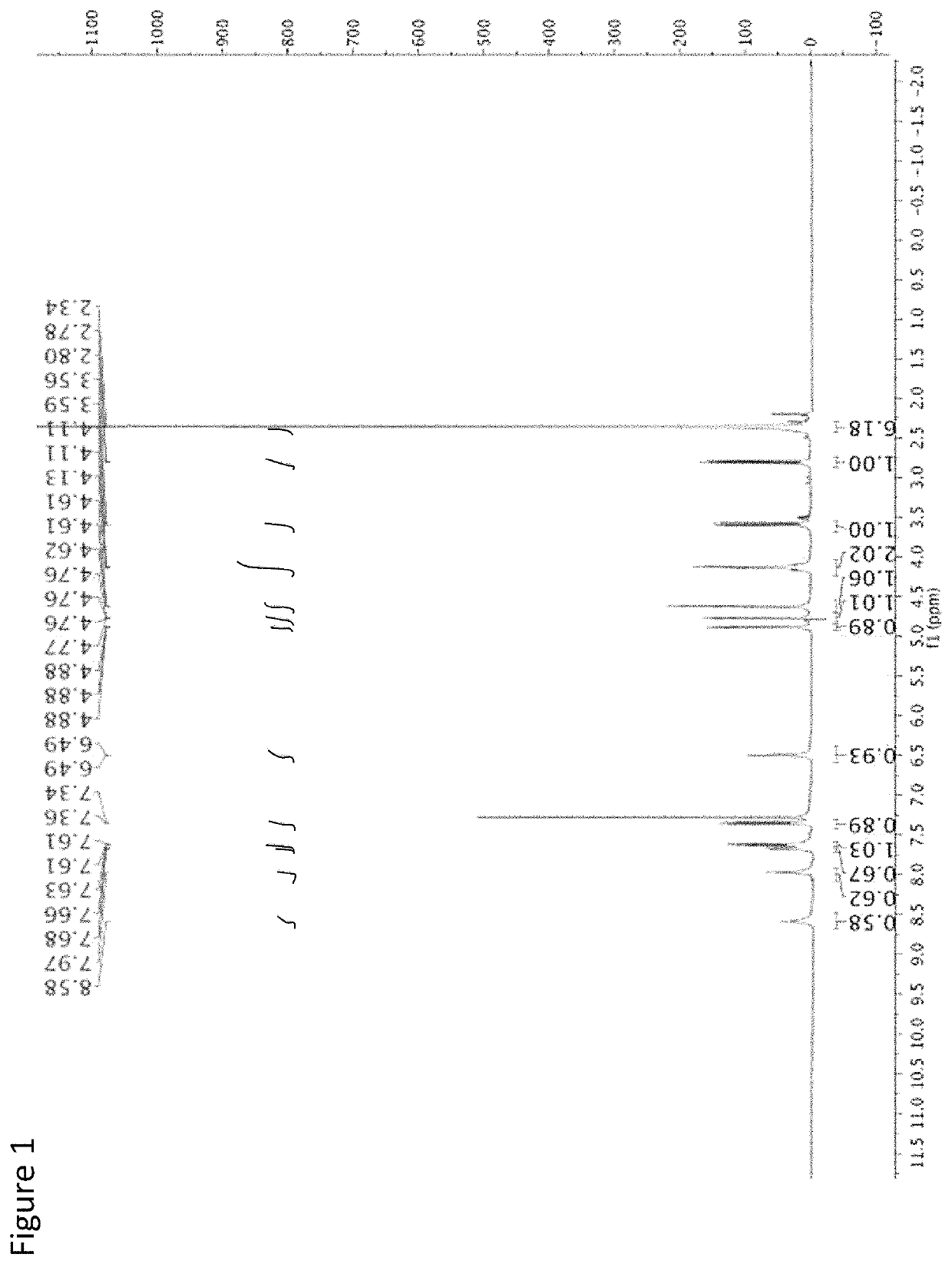
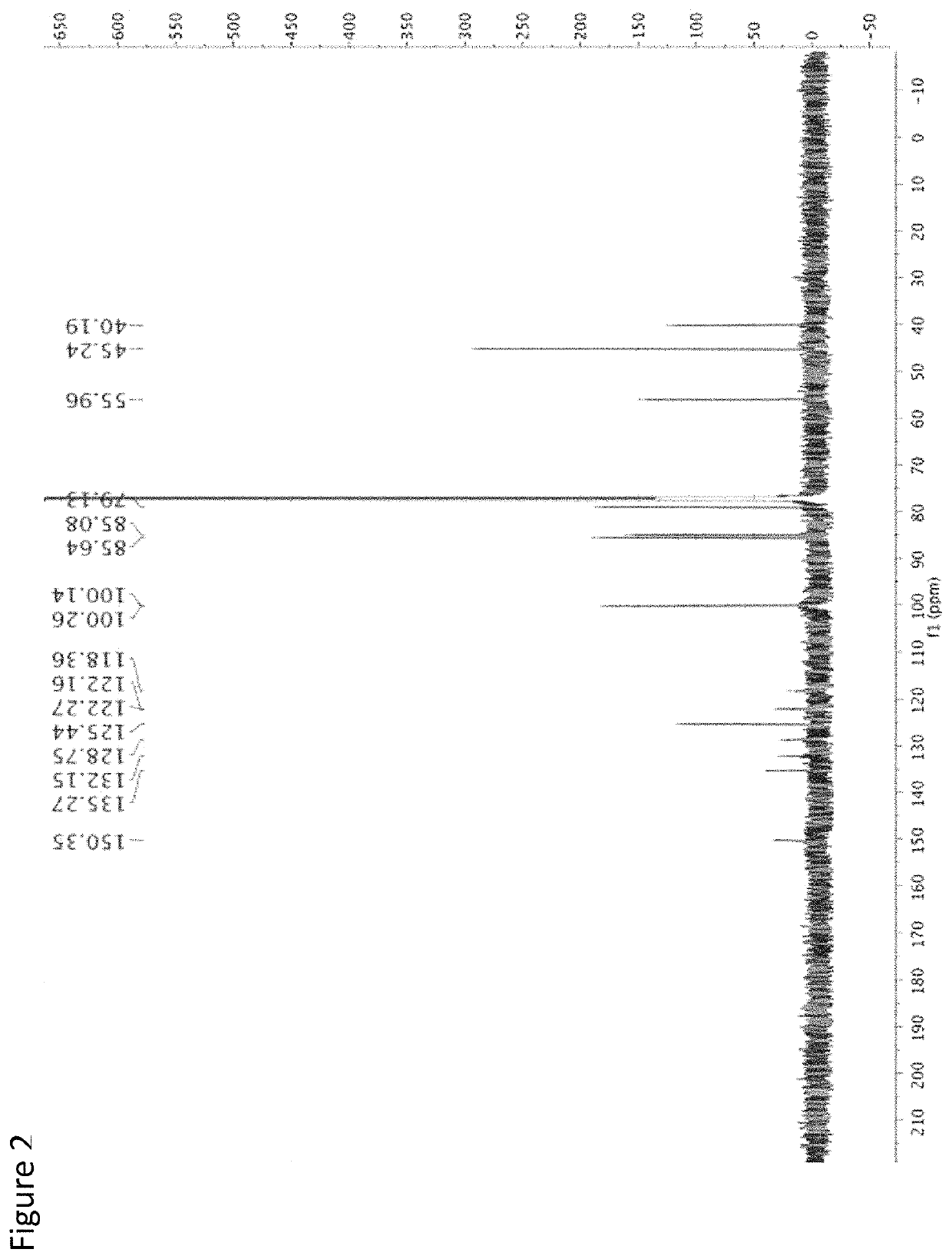
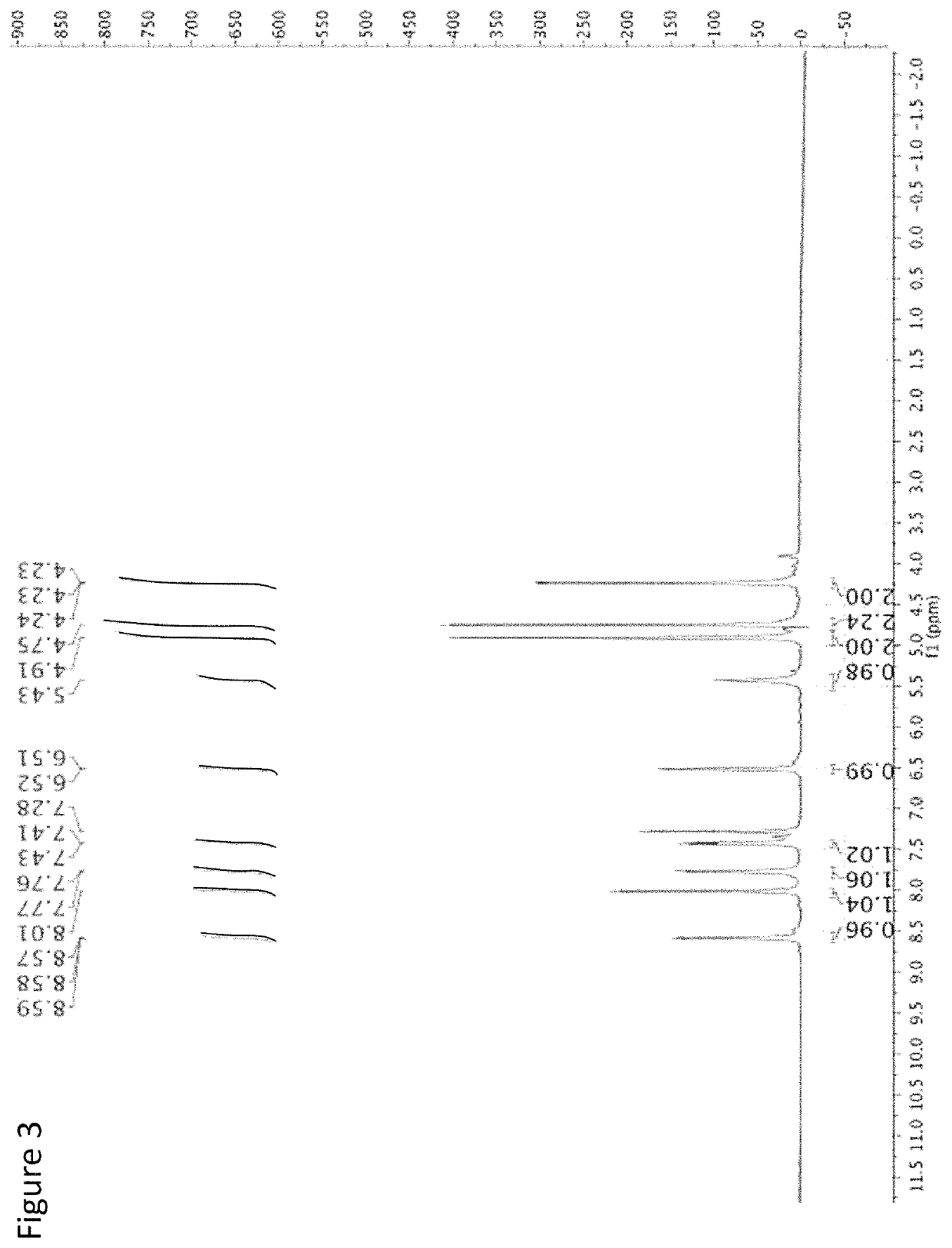
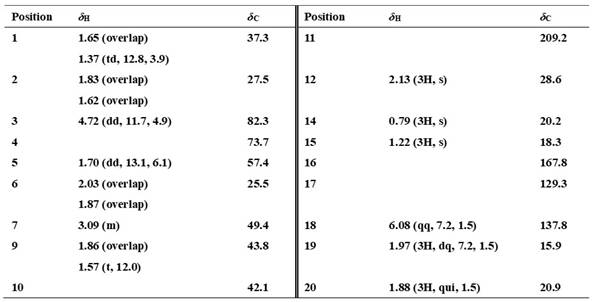
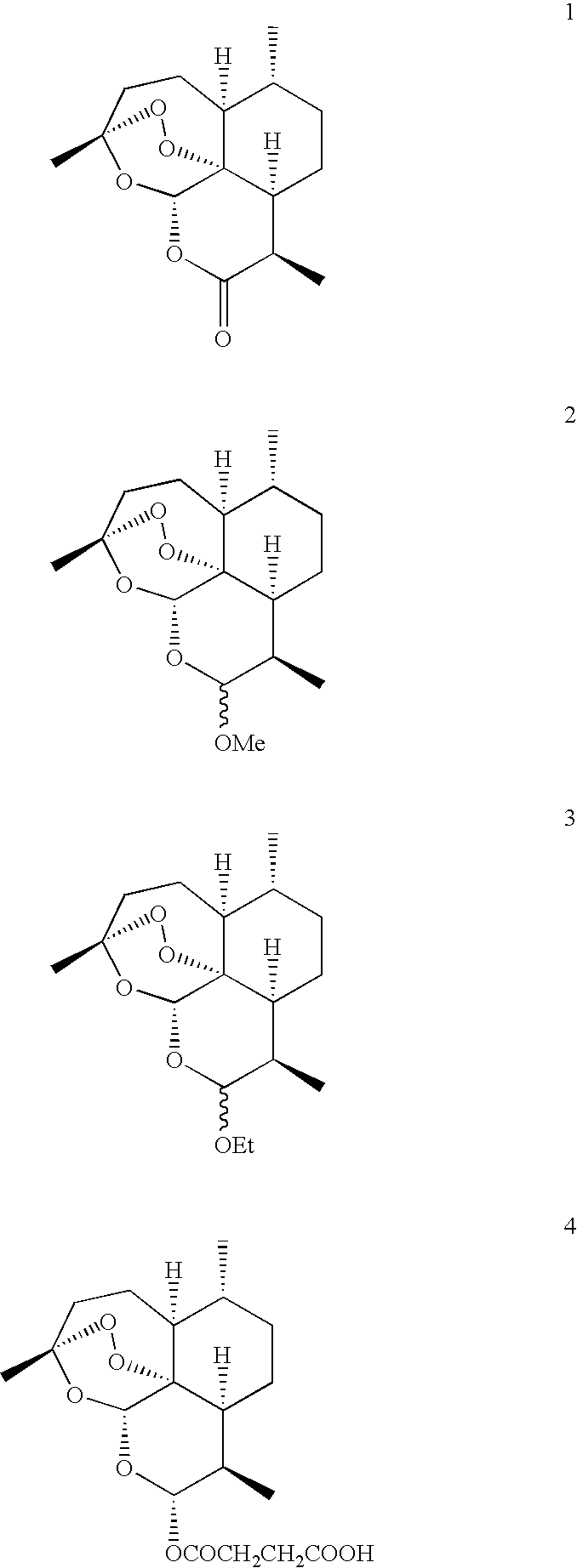
[(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof
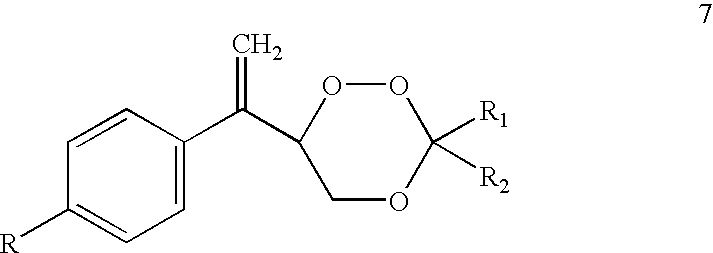
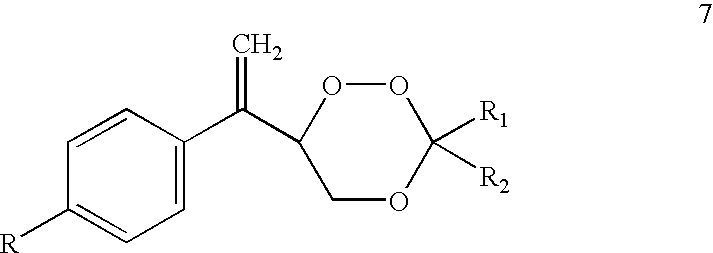
The invention relates to [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances and provides a structure, a preparation method and application of a novel artemisinine 10-locus derivative. The structural formula of the [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substance is shown in a formula I. The invention also relates to pharmaceutically-acceptable slats, a solvate, an optical isomer or a polymorphic substance of the [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances and a medicinal composition by taking the compounds as active components. As novel antimalarial agents, anti-tumor agents and antifungal agents, the compounds can be used for treating or preventing malaria, mycotic infection, malignant tumor and the like. The compounds can be prepared by reacting dihydroartemisinine as an initial raw material with trifluoroacetic anhydride / triethylamine to obtain 10(R)-trifluoro-acetoxyl-9,10-dihydroartemisinine, directly reacting the 10(R)-trifluoro-acetoxyl-9,10-dihydroartemisinine with hydroxy benzaldehyde without separation to obtain (10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde, and reacting the (10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde with the substituted amino (sulfur) urea compounds in acid catalysts and alcohol solvents to obtain target compounds.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Water-soluble trioxanes as potent and safe antimalarial agents
InactiveUS6136847AGood water solubilityImprove efficacyBiocideOrganic chemistryArylAntiparasite agent
Biologically-active, water soluble, 3-substituted trioxanes of the formula wherein R represents a COOH- substituted aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group or an alkyl group, and C12-(p-carboxy)benzyloxy trioxanes of formula wherein R represents a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, alkenyl, aryl or heteroaryl group and methods for their use as antiparasitic agents, particularly for the treatment of malaria.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Process for isolating artemisinin from Artemisia annua
InactiveUS6685972B2Simple and rapid and cost-effective and practicalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideArtemisia annuaBiology
The present invention relates to a process for the isolation of artemisinin, an antimalarial agent from the herb of the Artemisia annua plant, comprising of extracting the herb with ethanol, partitioning of the extract between water and hexane, followed by evaporative crystallization of artemisinin from hexane phase to produce substantially pure artemisinin.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
C-10 site carbamido substituted artemisinin derivative, preparation method and application
The invention relates to a C-10 site carbamido substituted artemisinin derivative (I), and relates to a structure, a preparation method and an application of the novel artemisinin 10 site derivative. The structural formula is shown as a formula I, and relates to its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a solvate, an optical isomer or a polymorphic substance and a pharmaceutical composition which takes the compound as an active component. Being as a new antimalarial agent, an antitumor agent and an antifungal agent, the compound can be used for treating or preventing malaria, fungal infection, malignant tumor and the like. The compound takes substituted carbamide as an initial raw material, and is obtained by reacting with dihydroartemisinin under catalysis of Et2O.BF3.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
Anticancer combination of artemisinin-based drugs and other chemotherapeutic agents
InactiveUS9023861B2Heavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAlkylating antineoplastic agentChemotherapeutic drugs
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Carbohydrate-metallocene-antimalarial conjugates
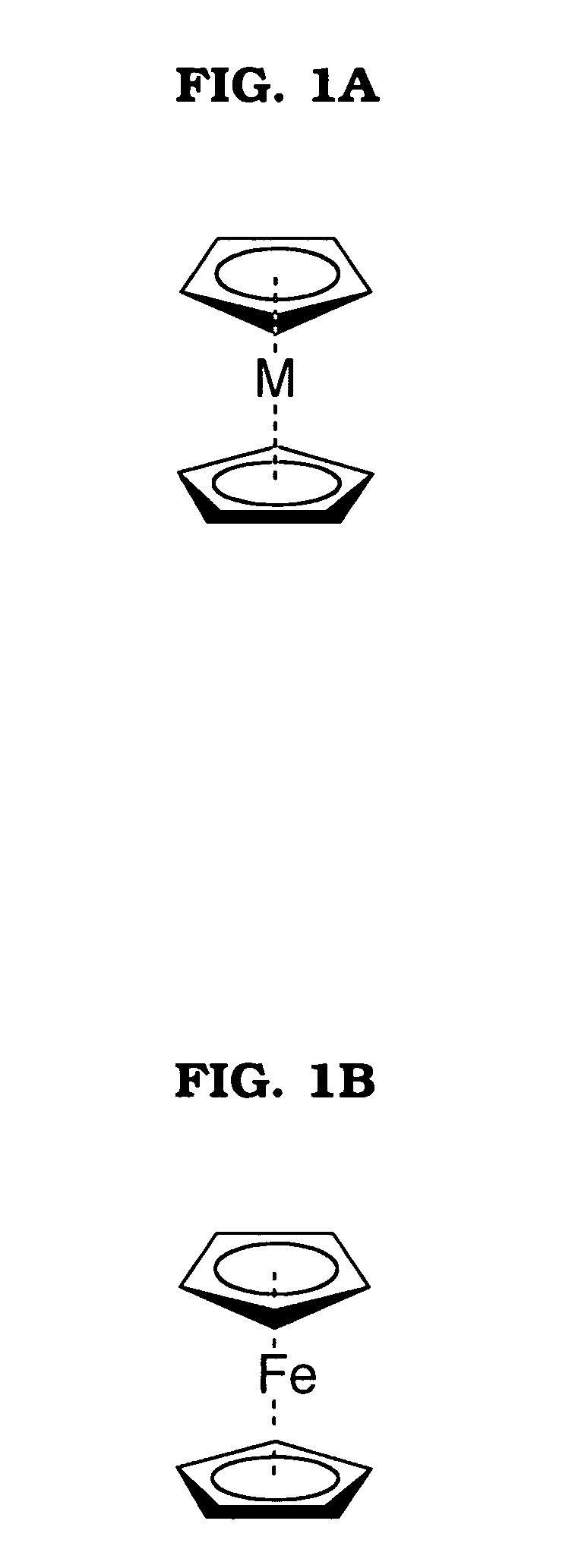
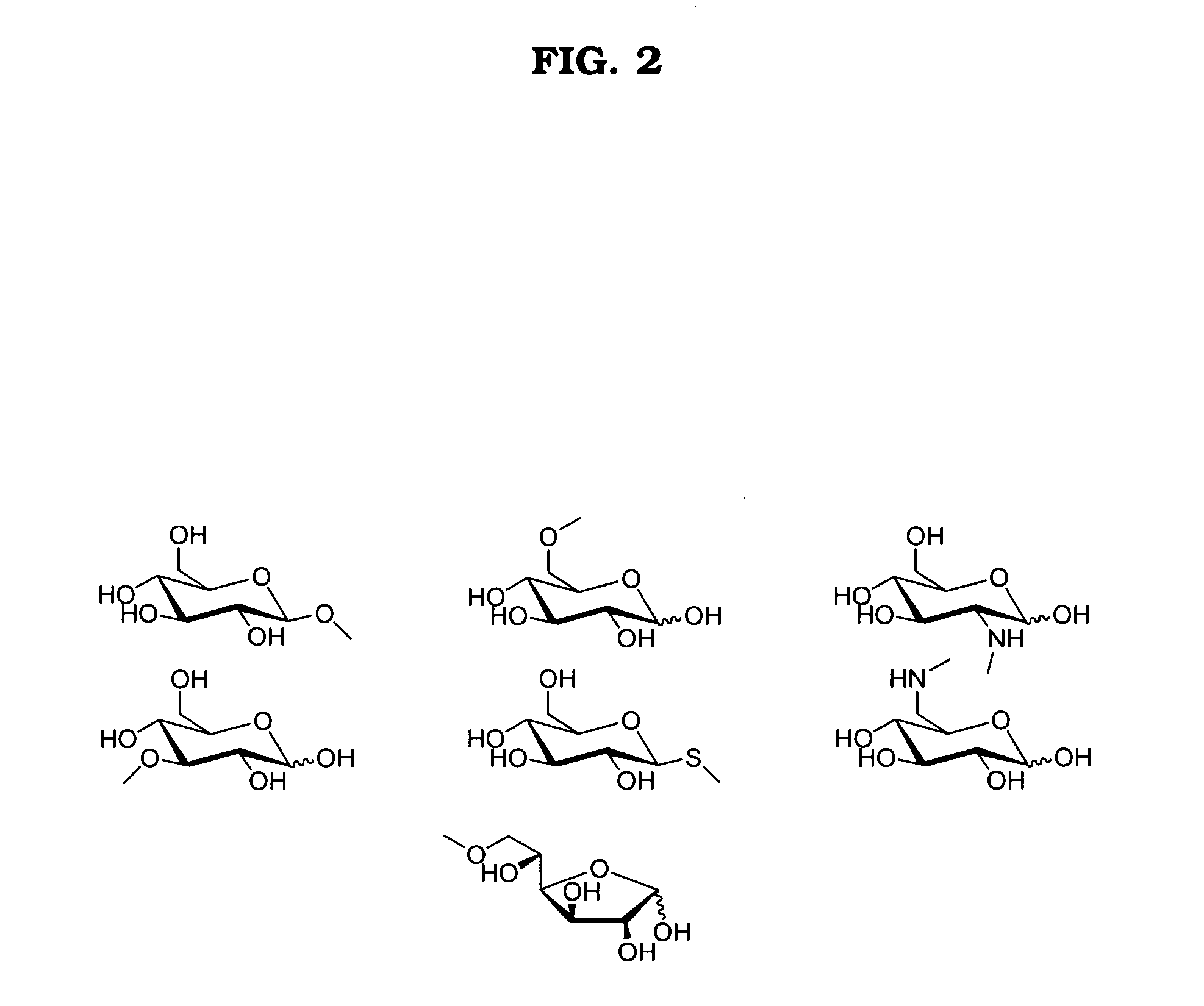
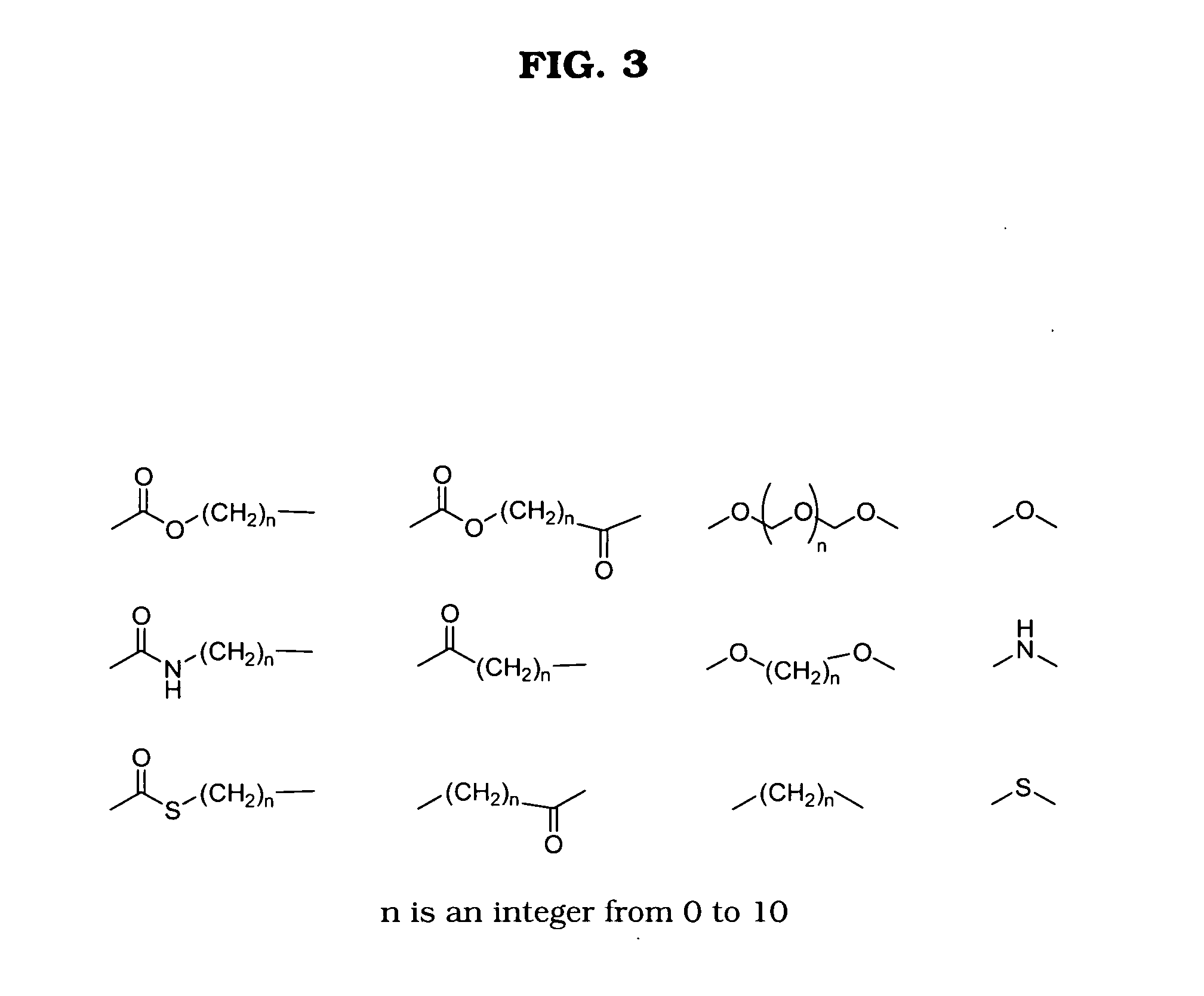
An antimalarial conjugate according to a non-limiting embodiment of the present invention may include a metallocene, a carbohydrate, and an antimalarial agent. The metallocene may include two cyclopentadienyl rings bound to a central metal atom. The carbohydrate and the antimalarial agent may be appended to at least one of the cyclopentadienyl rings of the metallocene, wherein the antimalarial agent has therapeutic properties directed to treating and / or preventing malaria. The metallocene may be ferrocene, the carbohydrate may be glucose, and the antimalarial agent may be chloroquine.
Owner:ADVANCED APPLIED PHYSICS SOLUTIONS
Combination kit used in the treatment of malaria
A combination kit for the treatment of malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax (P. vivax) having individual doses of an anti-malarial agent, 3-[1-[[4-[(6-methoxy-8-quinolinyl)amino]pentyl]amino]ethylidene]-dihydro-2(3H)-furanone (I) in the form of capsules; individual doses of the anti-malarial agent, chloroquine in the form of tablets; and instruction material for the administration of the two anti-malarial drugs. The combination kit is particularly suited for a 6 days treatment regimen where the treatment is rendered by five tablets containing 500 mg of chloroquine phosphate (equivalent to 300 mg base), three to be taken on day one and one each on days two and three; and five capsules containing 25 mg of 3-[1-[[4-[(6-methoxy-8-quinolinyl)amino]pentyl]amino]ethylidene]-dihydro-2(3H)-furanone (I), one each to be taken on days two to six.
Owner:NICHOLAS PIRAMAL INDIA LTD +1
Novel medicine for treating malaria controlling malaria spreading
InactiveCN1616101AStop transmissionRapid spread controlOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismRegimenHalf-life
The medicine for treating malaria and controlling malaria spreading consists of artemisinin or its derivative, or the mixture of artemisinin or its derivative and antimalarial agent with long or medium half life, or separated packed artemisinin or its derivative and antimalarial agent with long or medium half life, in 1-500 weight portions; and lower dosage of primaqine or its salt in 0.1-1 weight portions. Clinical experiment shows that the medicine has the features of high and fast curative effect, low toxicity, short treating period, convenient taking and fast killing gametophyte to block the spreading of malaria.
Owner:广州青蒿医药科技有限公司
Novel compounds and antimalarials
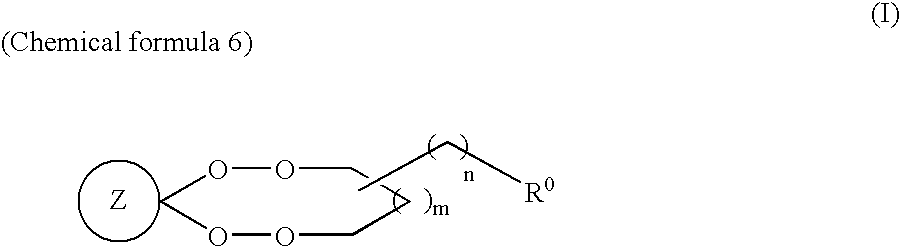
The present invention is to provide an antimalarial agent having excellent antimalarial activity with little side effects, in particular, having remarkable antimalarial activity against drug-resistant malaria parasites, and being capable of increasing solubility not only to organic solvent including olive oil, but also to water, and therefore, being usable not only as oral drugs but also as injectable solutions. The antimalarial agent of the present invention contains a compound represented by the following general formula (I) [wherein Z represents an unsubstituted or optionally substituted alicyclic hydrocarbon group, R0 represents a water-soluble functional group, m represents anyone of integers of from 0 to 6, n represents any one of integers of from 0 to 10.].
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
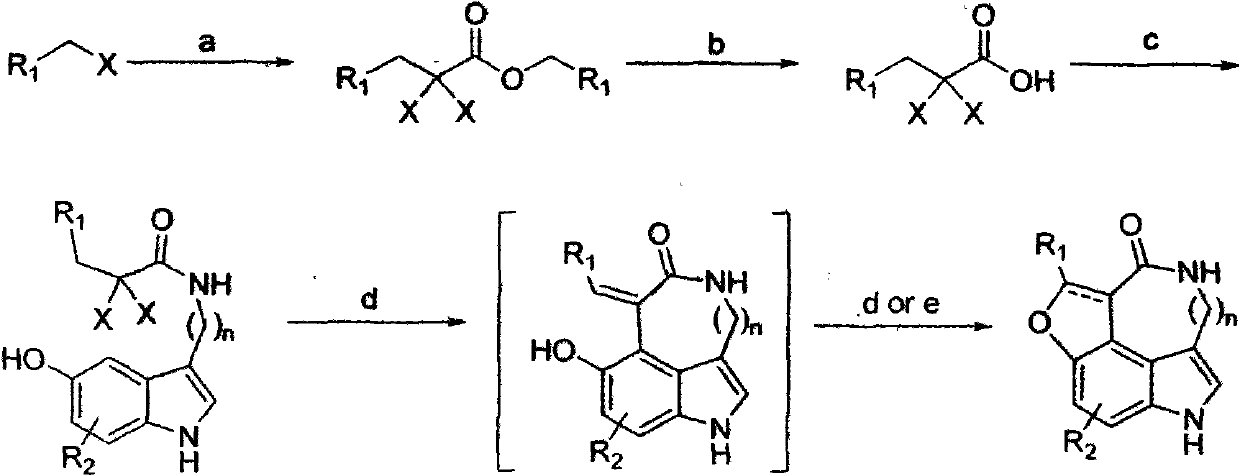
Preparation of substituted indole lactam derivative and application of substituted indole lactam derivative as antimalarial agent
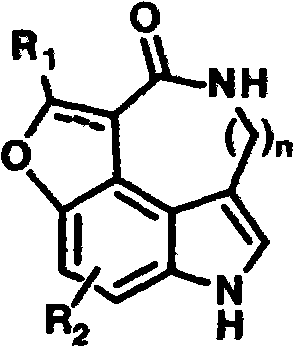
The invention designs an efficient synthesis method for preparing a compound shown as a general formula (I) and an application of a derivative of the compound to the research and development of an antimalarial active medicament. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a reactant into an appropriate solvent; and reacting under the irradiation condition of a high-voltage mercury lamp (ultraviolet lamp). In the method disclosed by the invention, a series of poly-substituted indole lactam compounds taking 3,4,5-trisubstituted indole as a basic framework are efficiently synthesized with a one-pot method under an illumination condition, so that the defects of complex steps, difficulty in operating and low total yield existing in synthesis of the type of compounds under the condition of the prior art are overcome. Derivatives containing different substituted functional groups are obtained only through a four-step reaction, and the type of compounds has potential antimalarial activity, so that necessary material bases are provided for the researches of active screening, acting mechanisms and structure-activity relationships of a large quantity of analogues, and the type of compound can possibly become a new type of antimalarial candidate medicament. The general formula (I) is shown in the specifications.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Process for isolating srtemisinin from artemisia annua
InactiveCN1627942ALight in massProgressiveOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMalariaArtemisia annua
The present invention relates to a process for the isolation of artemisinin, an antimalarial agent from the herb of the Artemisia annuaplant, comprising of extracting the herb with ethanol, partitioning of thextract between water and hexane, followed by evaporative crystallization of artemisinin from hexane phase to produce substantially pure artemisinin.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
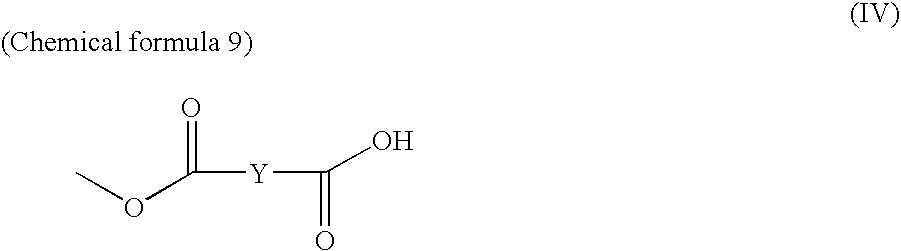
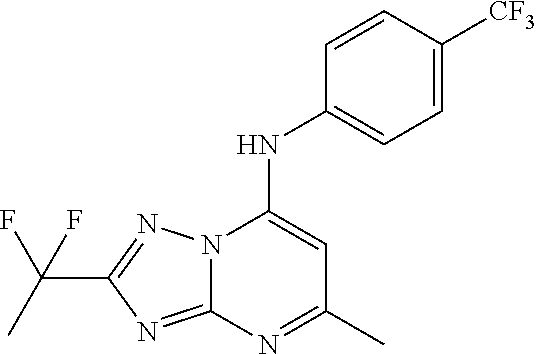
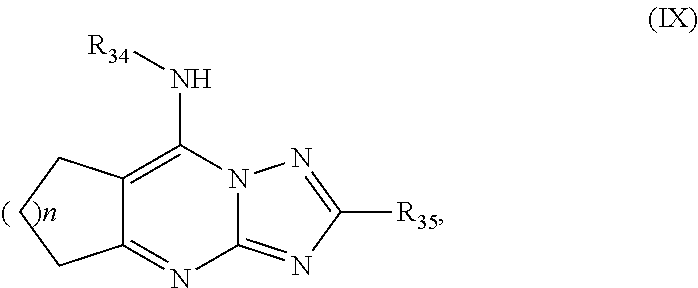
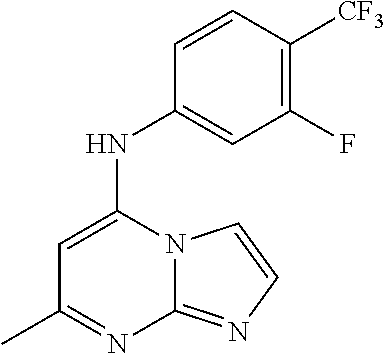
Antimalarial agents that are inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
Inhibitors of parasitic dihydroorotate dehydrogenase enzyme (DHOD) are candidate therapeutics for treating malaria. Illustrative of such therapeutic agents include the compound:and a triazolopyrimidine class of compounds that conform to Formula IX:and their solvates, stereoisomers, tautomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:MMV MEDICINES FOR MALARIA VENTURE +2
Process for isolating artemisinin from artemisia annua
InactiveUS20030185914A1Simple and rapid and cost-effective and practicalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideArtemisia annuaBiology
The present invention relates to a process for the isolation of artemisinin, an antimalarial agent from the herb of the Artemisia annua plant, comprising of extracting the herb with ethanol, partitioning of the extract between water and hexane, followed by evaporative crystallization of artemisinin from hexane phase to produce substantially pure artemisinin.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Tetrahydroisoquinolines as antimalarial agents
The invention relates to novel tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives and their use as active ingredients in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also concerns related aspects including pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more of those compounds and their use as medicaments for the treatment or prevention of protozoal infections, such as especially malaria.
Owner:AISSAOUI HAMED +3
Piperazines as antimalarial agents
The invention relates to novel piperazine derivatives and their use as active ingredients in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also concerns related aspects including pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more of those compounds and their use as medicaments for the treatment or prevention of protozoal infections, such as especially malaria.
Owner:IDORSIA PHARM LTD
Bisbenzimidazoles as antimalarial agents
InactiveUS20100160402A1Overcomes drawbackReduce usageOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHalogenMalaria
Owner:XAVIER UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA
Process for preparation of ring-substituted 8-aminoquinoline analogs as antimalarial agents
ActiveUS6979740B2Low toxicityReduced methemoglobin toxic side effectBiocideOrganic chemistryResistant strainMalaria
The present invention is concerned with the development of novel 8-aminoquinoline analogs in the treatment and prevention of malaria and the said compound has broad spectrum of activity against the blood as well as tissue stages of the human malaria parasites makes these compounds very attractive in the cure and prevention of malaria caused by drug-sensitive and multidrug resistant strains and also it is expected that development of these compounds as ideal antimalarial agents may lead to suppression as well as radical cure of the malaria infection with single drug therapy.
Owner:NAT INST OF PHARMA EDUCATION & RES DEPT OF PHARMA TECH
Pyrroloquinoline alkaloids as antimalarial agents and process for the preparation thereof
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
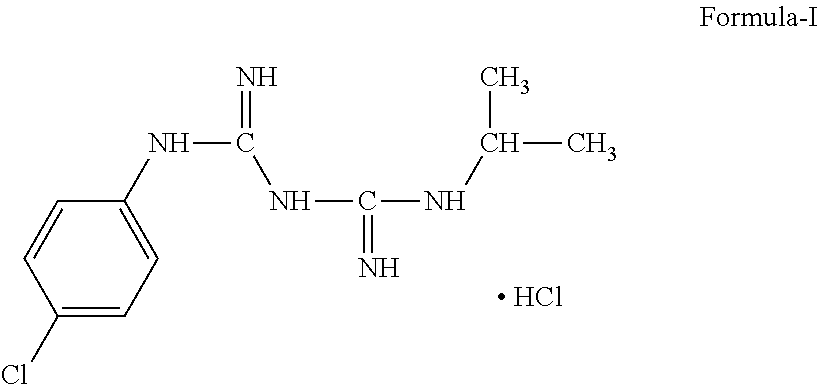
Process of Preparation of Proguanil
InactiveUS20110263901A1High purityHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationProguanil HydrochlorideHydrochloride
Disclosed herein is the process for the preparation of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-biguanide hydrochloride (Proguanil hydrochloride), Formula-I, an antimalarial agent.
Owner:USV LTD
Piperazines as antimalarial agents
The invention relates to piperazine derivatives of Formula I and their use as active ingredients in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also concerns related aspects including pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more of those compounds and their use as medicaments for the treatment or prevention of protozoal infections, such as especially malaria.
Owner:IDORSIA PHARM LTD
Use of cymanquine compounds as antimalarial agents
ActiveUS10512652B2Improve permeabilitySmall structureOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsRheniumManganese
Owner:DREXEL UNIV +1
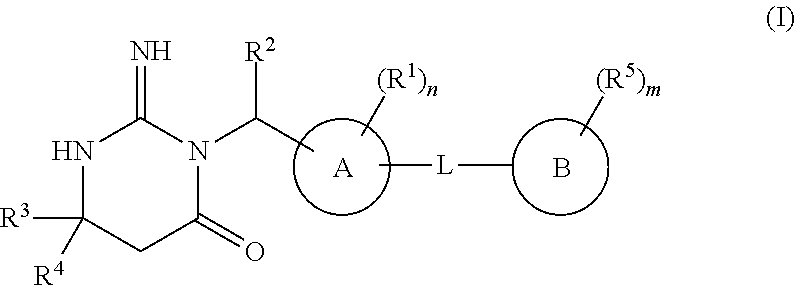
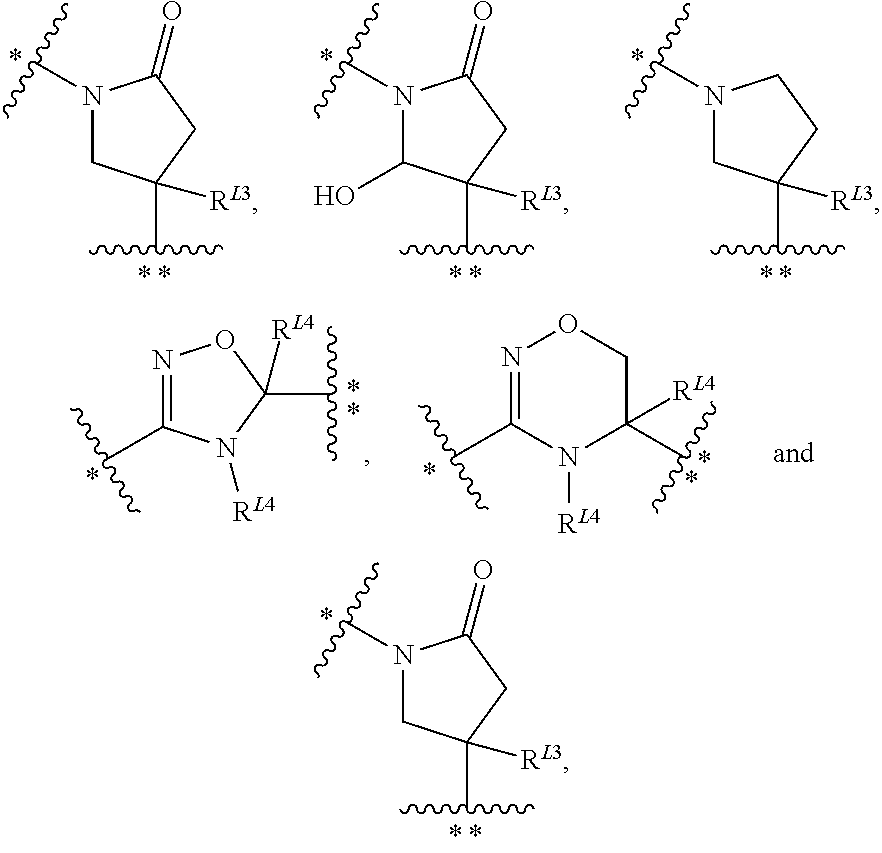
N3-substituted iminopyrimidinones as antimalarial agents
ActiveUS20200230140A1Impair proteolytic functionUseful in treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMalarial parasitePharmaceutical medicine
The present invention provides methods of treating malaria comprising administration of an N3-substituted iminopyrimidinone of Formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, to a subject in need thereof, wherein the variables R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, A, B, L, m, and n are as defined herein. The invention also provides uses of the compounds of Formula (I), as defined herein, for inhibiting plasmepsin V activity, for treating a Plasmodium infection, and for treating malaria. Also provided are methods of treatment further comprising administration of one or more additional anti-malarial compounds.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
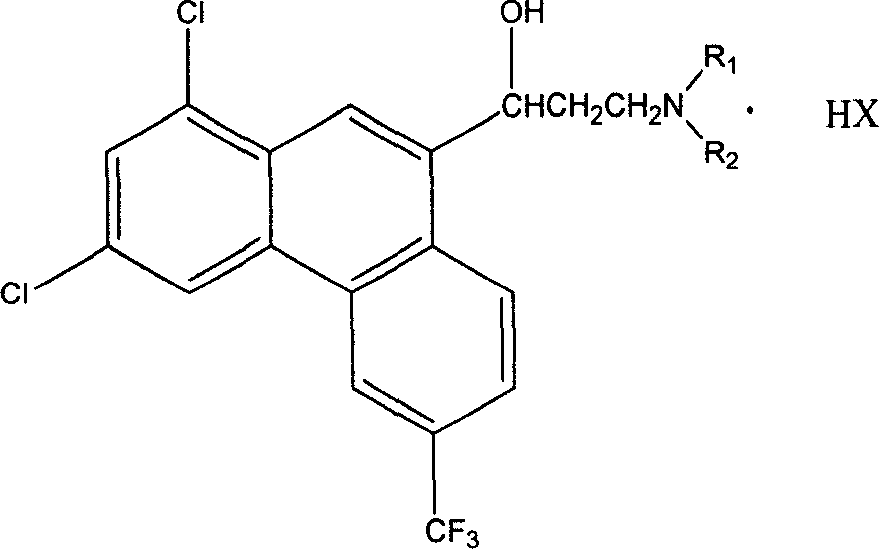
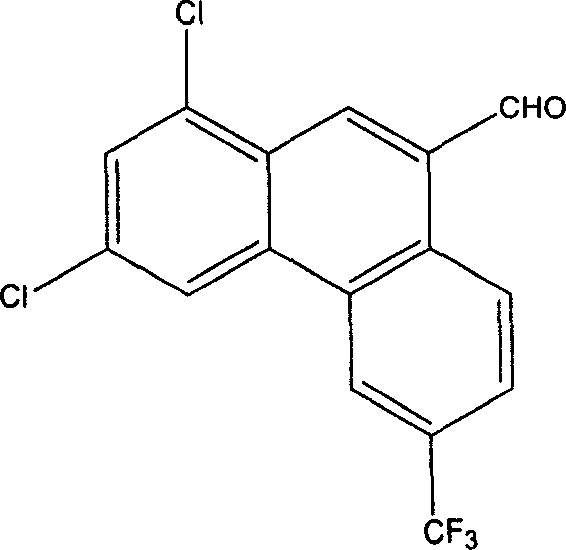
1,3-dichlor-6-trifluomethyl-9-phenanthrene formaldehyde preparation method
InactiveCN1765866ANo pollution in the processMild reaction conditionsCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationOrganic solventMethanol
The invention discloses a preparation method for 1, 3-dichloro- 6- trifluoromethyl ¿C 9 - phenanthryl formaldehyde as intermediate of antimalarial agent by 1, 3-dichloro- 6- trifluoromethyl ¿C 9 ¿C phenanthryl carbinol with active manganese bioxide. This method is simple with mild reaction condition, and has high purity and yield.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD
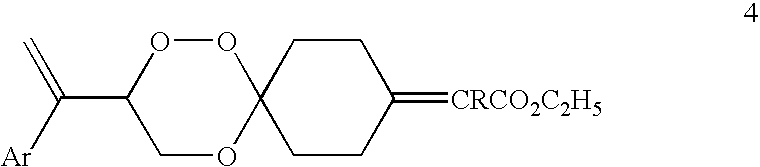
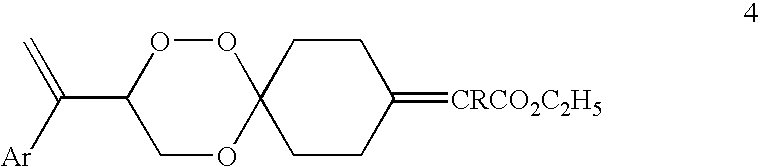
Spiro-1,2,4-trioxanes
The present invention relates to spiro 1,2,4-trioxanes of general formula 4. This invention more particularly relates to a process for the preparation of a series of spiro 1,2,4-trioxanes.Wherein, Ar represents aryl groups such as phenyl, 4-biphenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-methylphenyl, 4-cyclohexylphenyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl and the like and R represents hydrogen or the alkyl group such as methyl, ethyl and the like. Several of these compounds show high order of antimalarial activity against multidrug-resistant malaria in mice and thus hold promise as antimalarial agents against multidrug-resistant malaria.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Norcenane sesquiterpenes, pharmaceutical composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110305017BOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationEthyl acetateBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a class of norcine sesquiterpenes and a pharmaceutical composition thereof, belonging to the field of natural medicine chemistry. Formula (I) noreucalyptane sesquiterpenoids, a pharmaceutical composition with such compounds as active ingredients, and its preparation method is to take the root or rhizome or the whole plant of the Anacardiaceae genus genus, and use the organic solvent petroleum ether Or chloroform or ethyl acetate or acetone or methanol or ethanol or water direct cold immersion or heat reflux or ultrasonic or microwave auxiliary extraction, or use the above-mentioned organic solvent or water cold immersion or reflux or ultrasonic or microwave auxiliary extraction and then use acetic acid The total extract was obtained by extraction with ethyl ester, and the compound of the present invention was obtained from the total extract through repeated chromatography. An antimalarial drug compound with the compound of the present invention as an active ingredient. Use of the compound of the present invention in the preparation of antimalarial agents.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Combination therapies for malaria
InactiveUS9918989B2Reduce developmentEfficient reductionCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningRegimenPTK Inhibitors
The present disclosure provides methods for treating or preventing malaria by administration of a protein kinase inhibitor and optionally one or both of a further protein kinase inhibitor and an antimalarial drug to a mammalian subject infected with or at risk of exposure to Plasmodium sp. In some aspects, the therapeutic and prophylactic regimens of the present disclosure are effective in reducing parasite development in mosquitoes feeding on recipients of the regimens. Additionally, the present disclosure provides methods for screening candidate antimalarial agents.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
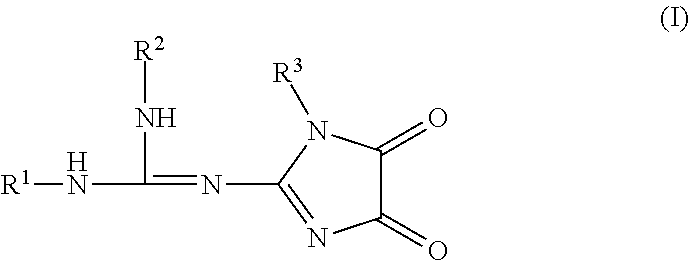
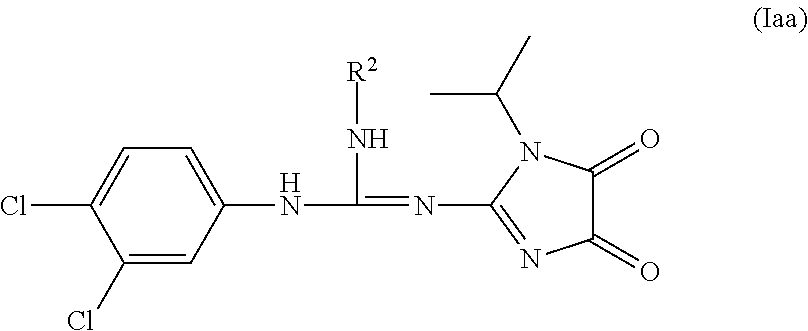
Imidazolidinedione derivatives as antimalarial agents, preparation thereof, and methods of use
Embodiments disclosed herein relate to new imidazolidinedione derivatives, methods of making these compounds, and methods of using the same to prevent, treat, or inhibit malaria in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![[(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/eb64c4a8-e8b1-40f0-8f34-a589ab94d906/DSA00000298513800011.png)
![[(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/eb64c4a8-e8b1-40f0-8f34-a589ab94d906/FSA00000298513900011.png)
![[(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof [(10S)-9,10-dihydroartemisinine-10-oxyl]benzaldehyde semicarbazones (sulfur) series substances as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/eb64c4a8-e8b1-40f0-8f34-a589ab94d906/BSA00000298514000011.png)