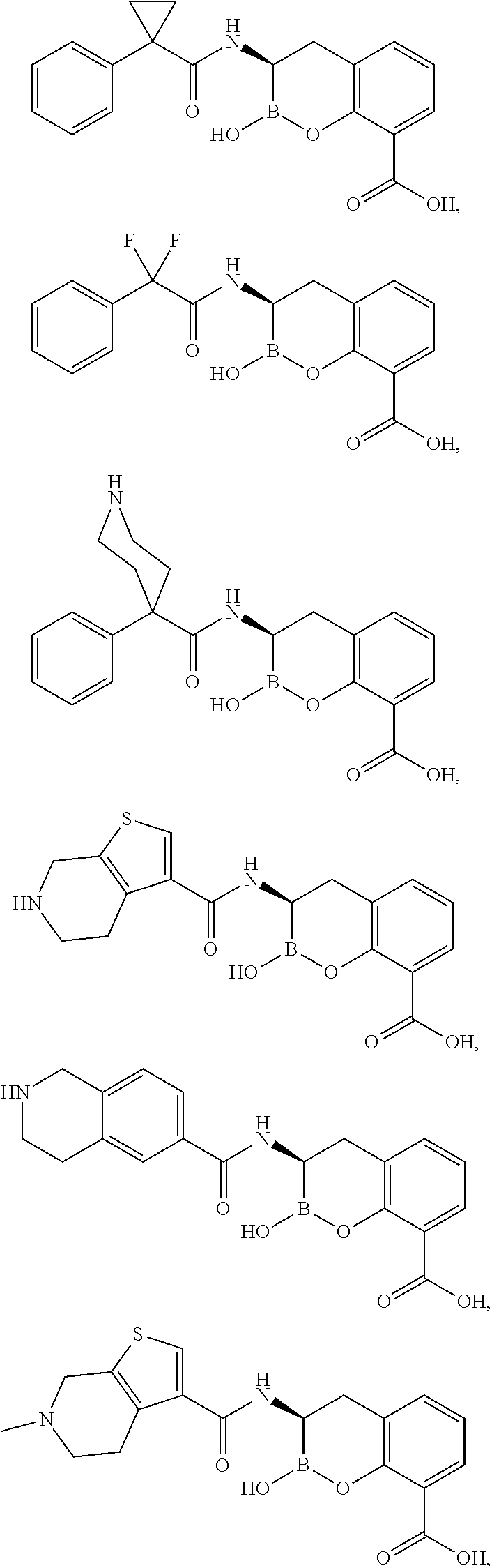
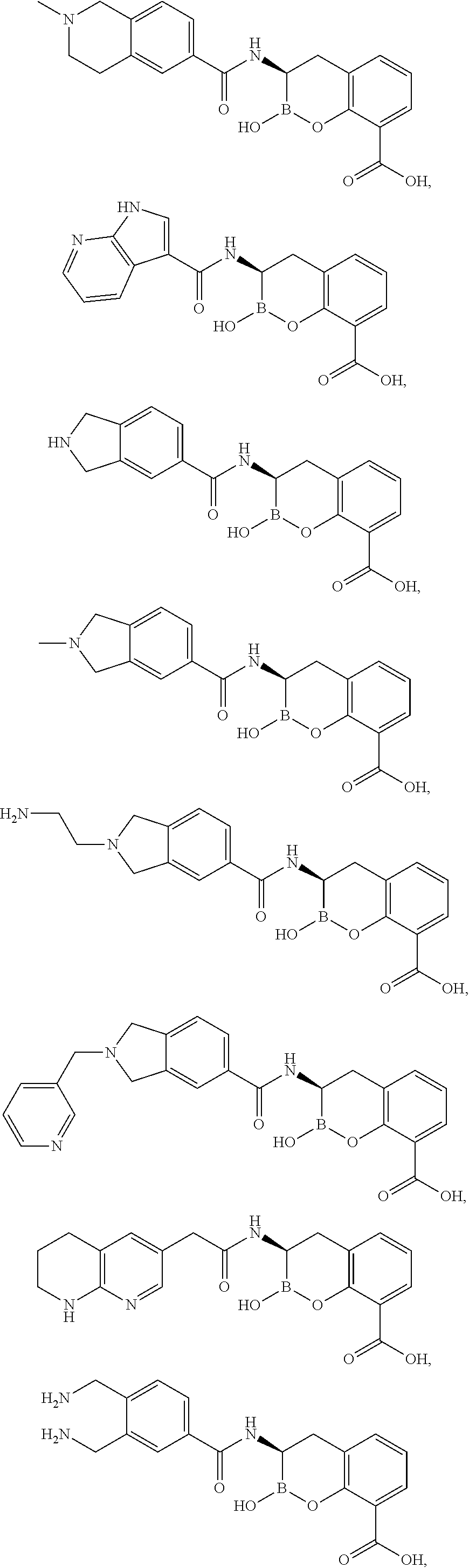
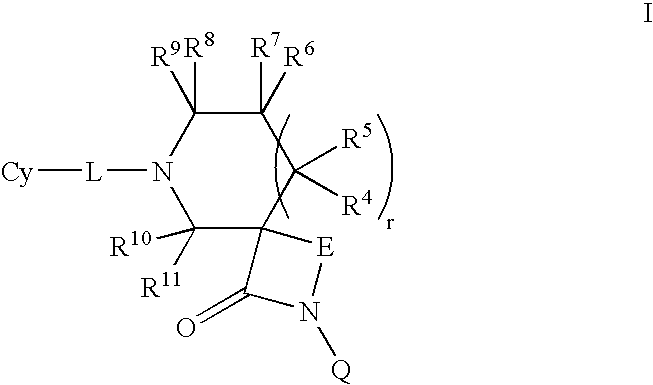
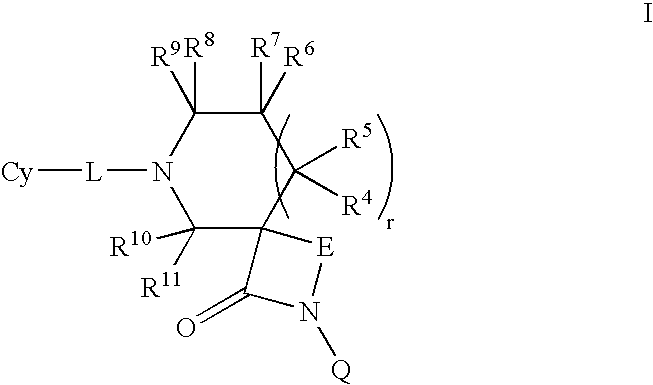
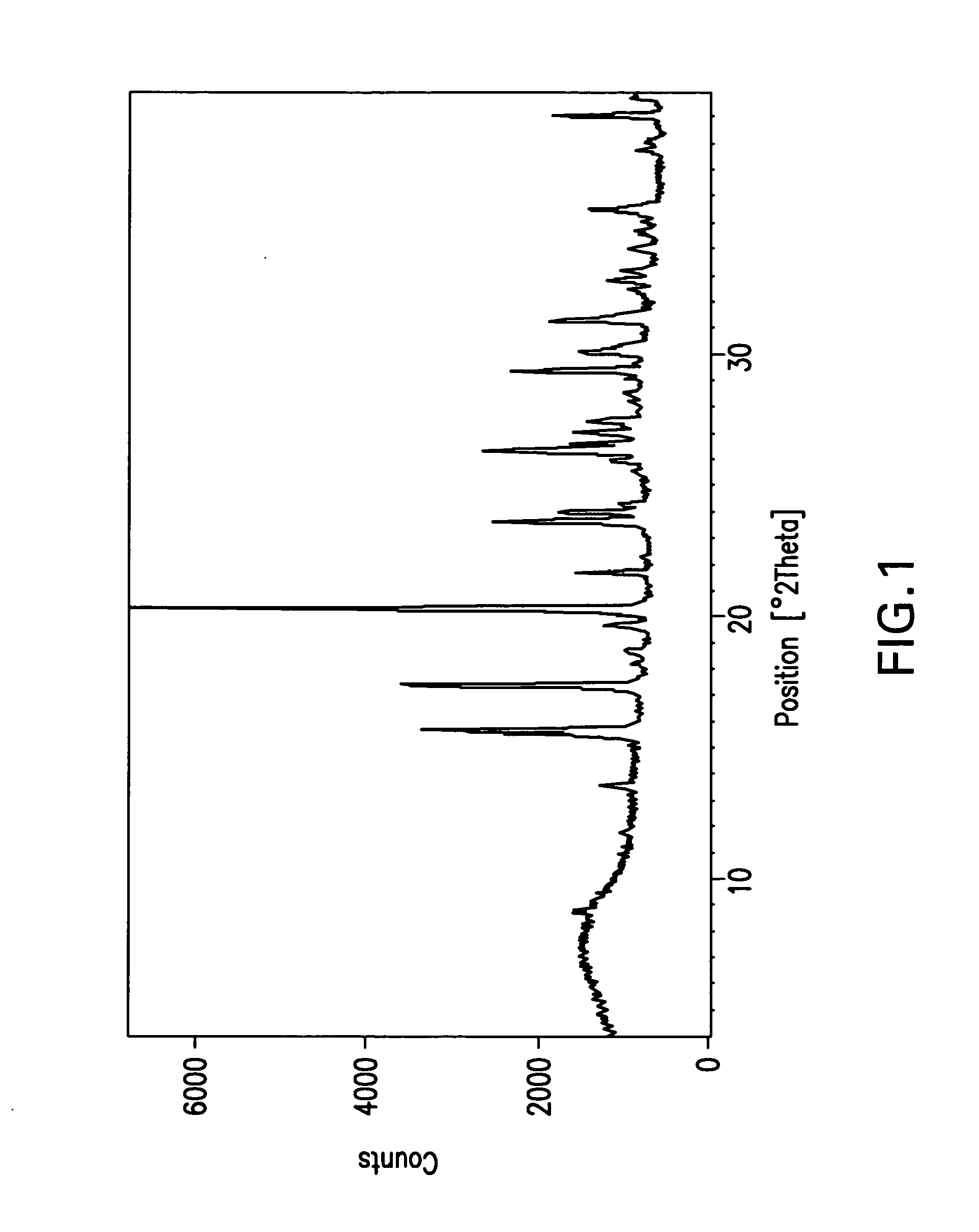
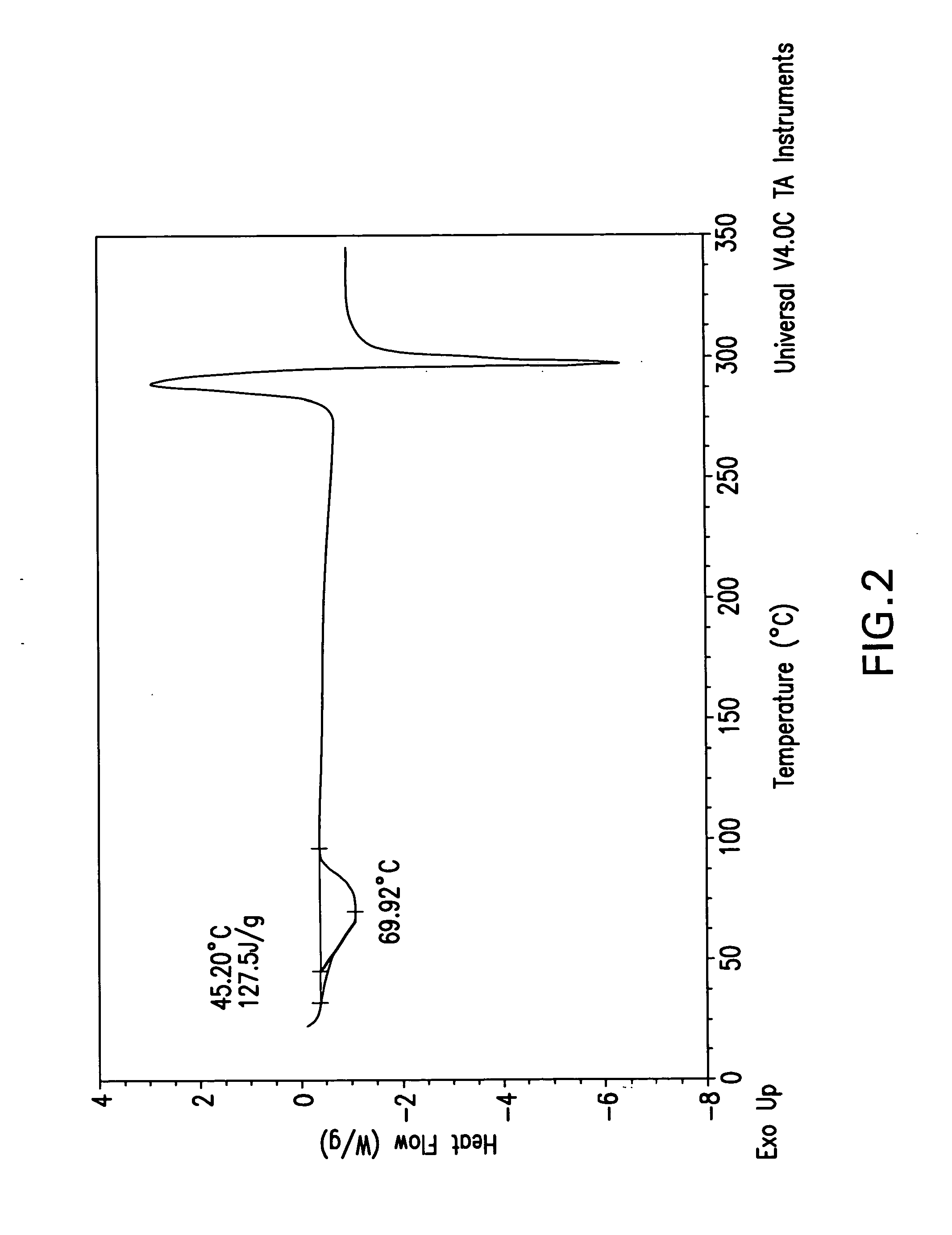
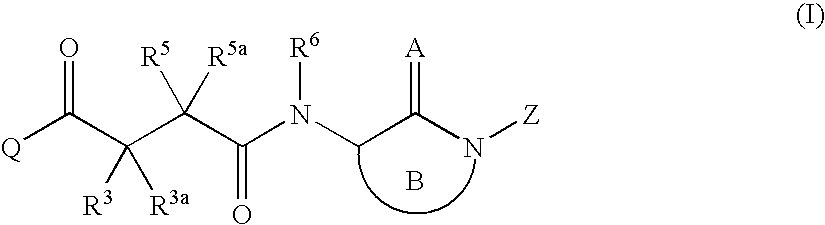
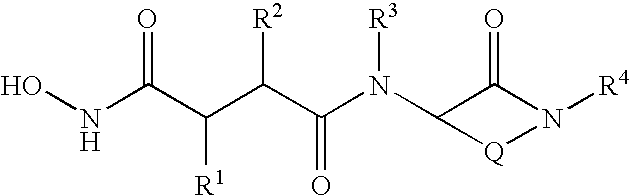
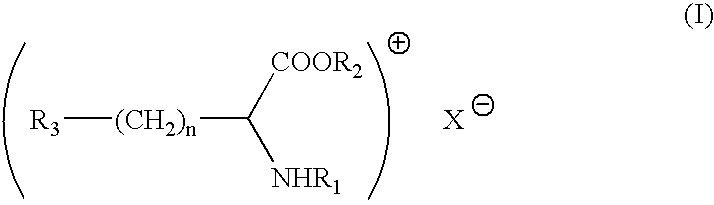Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2492 results about "Lactam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
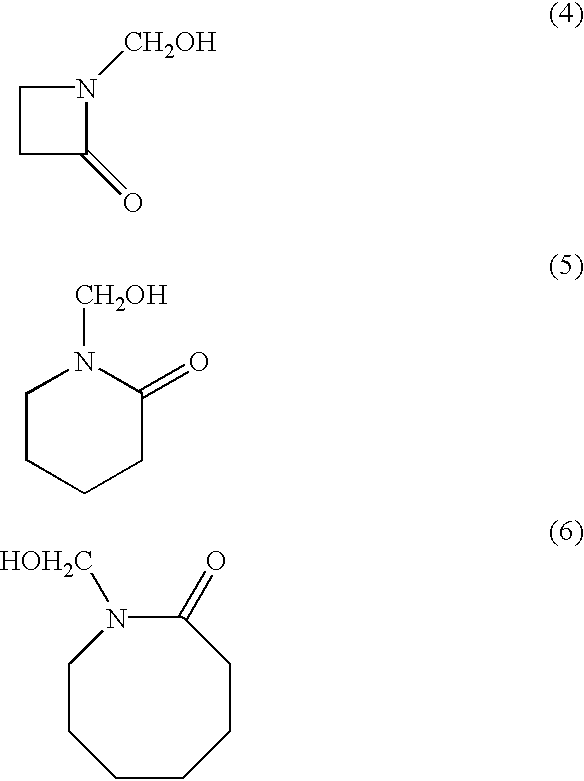
A lactam is a cyclic amide. The term is a portmanteau of the words lactone + amide.
Glucagon/glp-1 receptor co-agonists
InactiveUS20100190701A1High activityEnhanced biophysical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCarboxylic acid
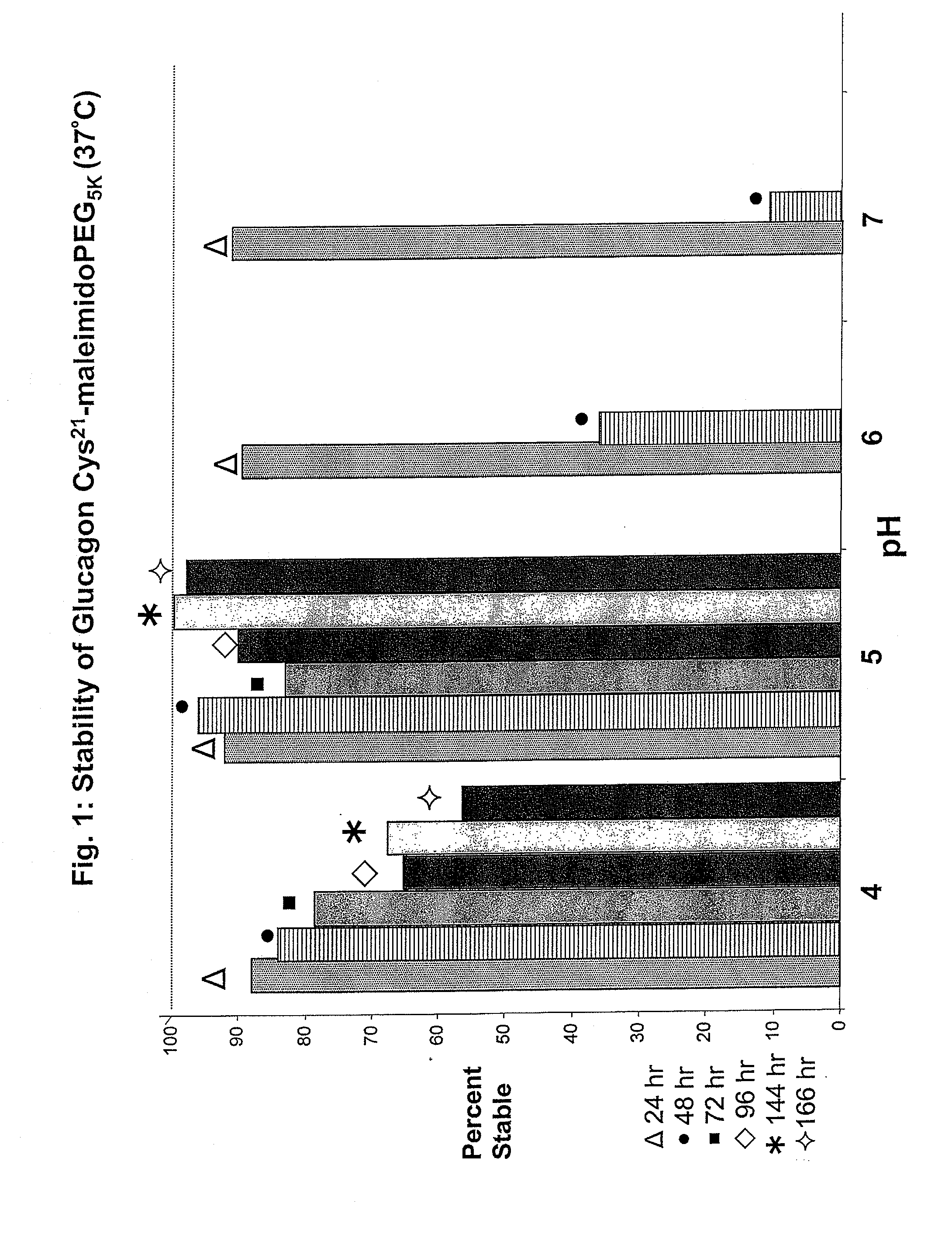
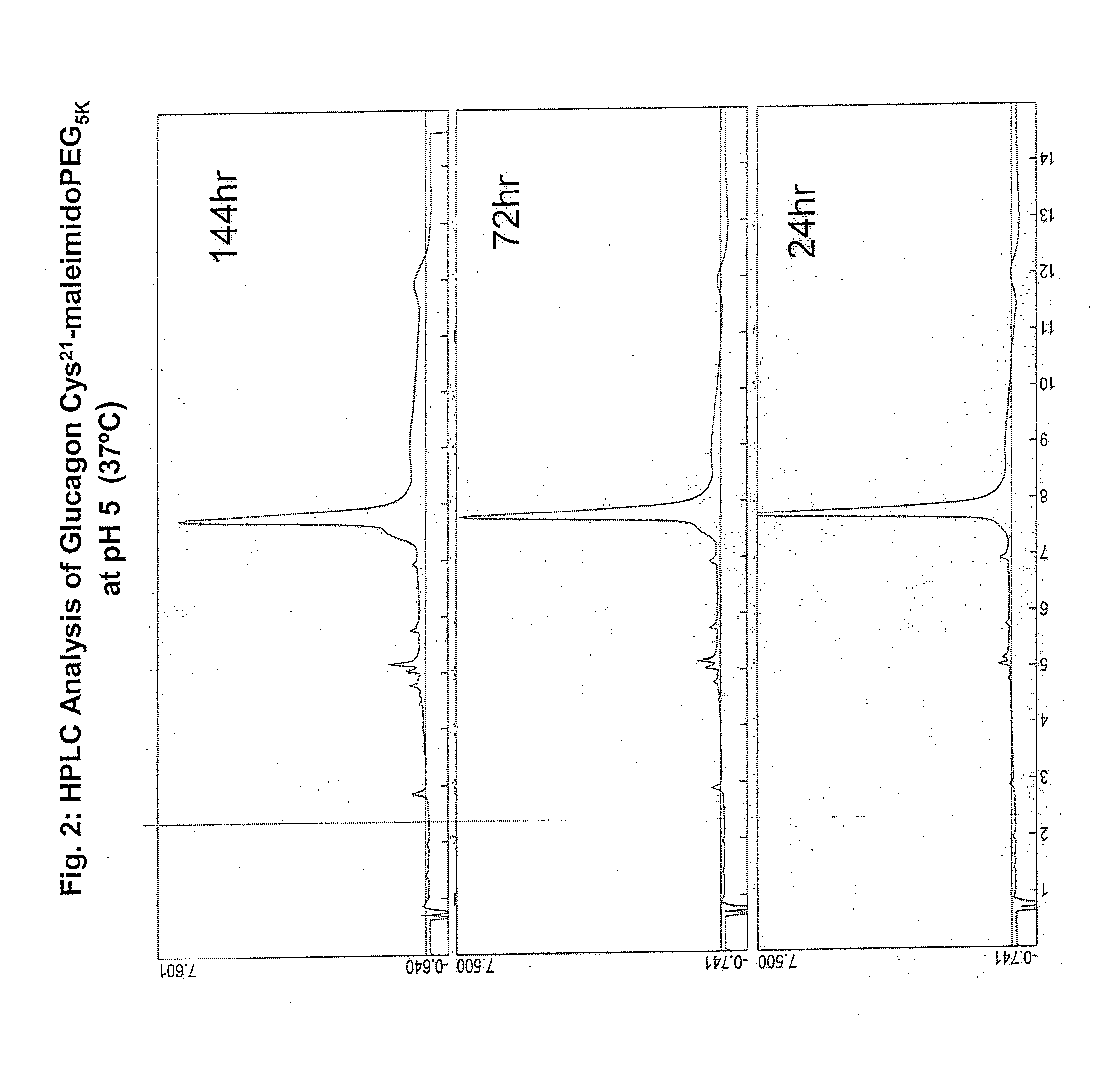
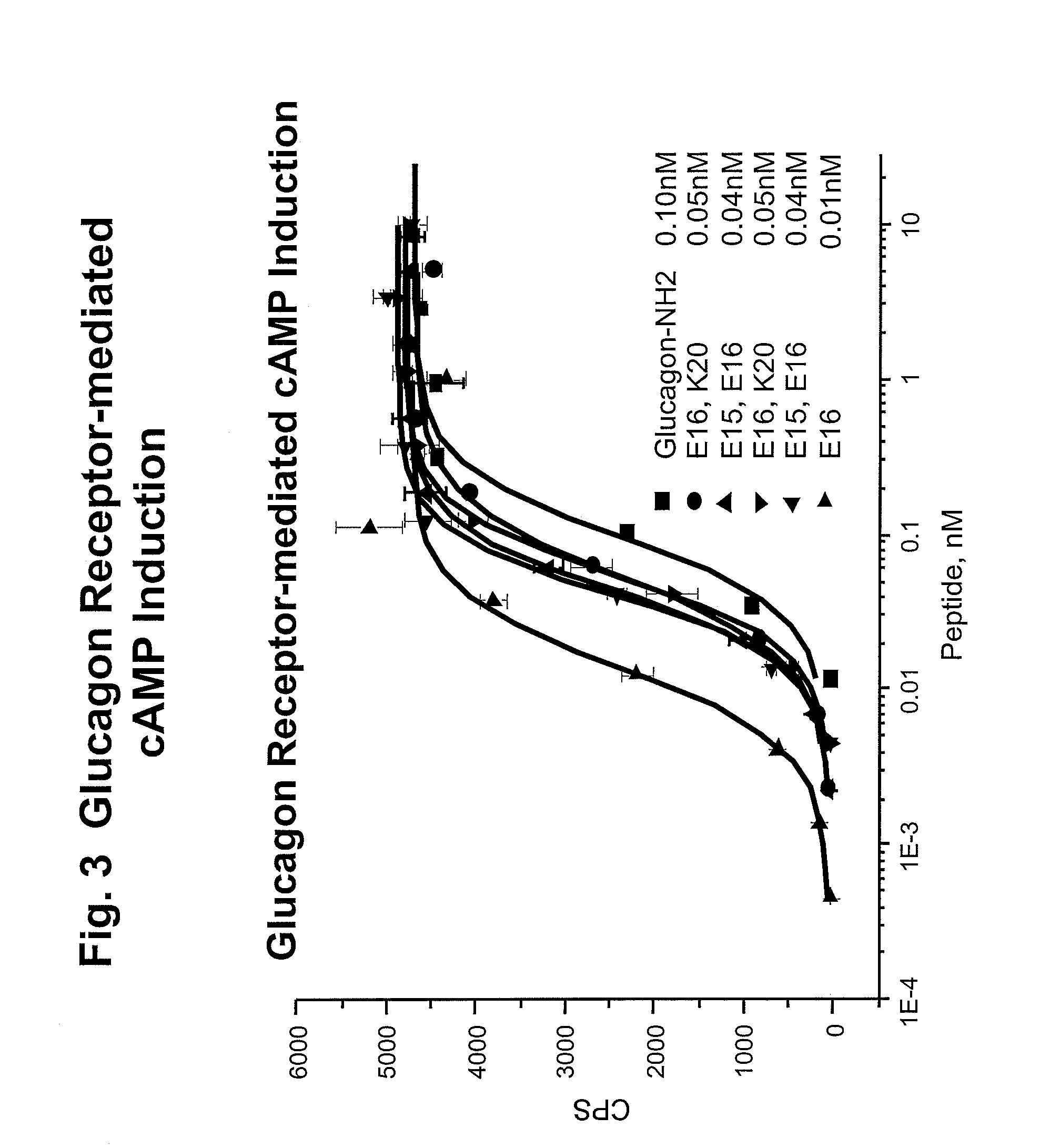
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having enhanced potency at the glucagon receptor relative to native glucagon. Further modification of the glucagon peptides by forming lactam bridges or the substitution of the terminal carboxylic acid with an amide group produces peptides exhibiting glucagon / GLP-1 receptor co-agonist activity. The solubility and stability of these high potency glucagon analogs can be further improved by modification of the polypeptides by pegylation, substitution of carboxy terminal amino acids, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 26 (GPSSGAPPPS), SEQ ID NO: 27 (K-RNRNNIA) and SEQ ID NO: 28 (KRNR).
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Semiaromatic polyamide molding compositions and their use
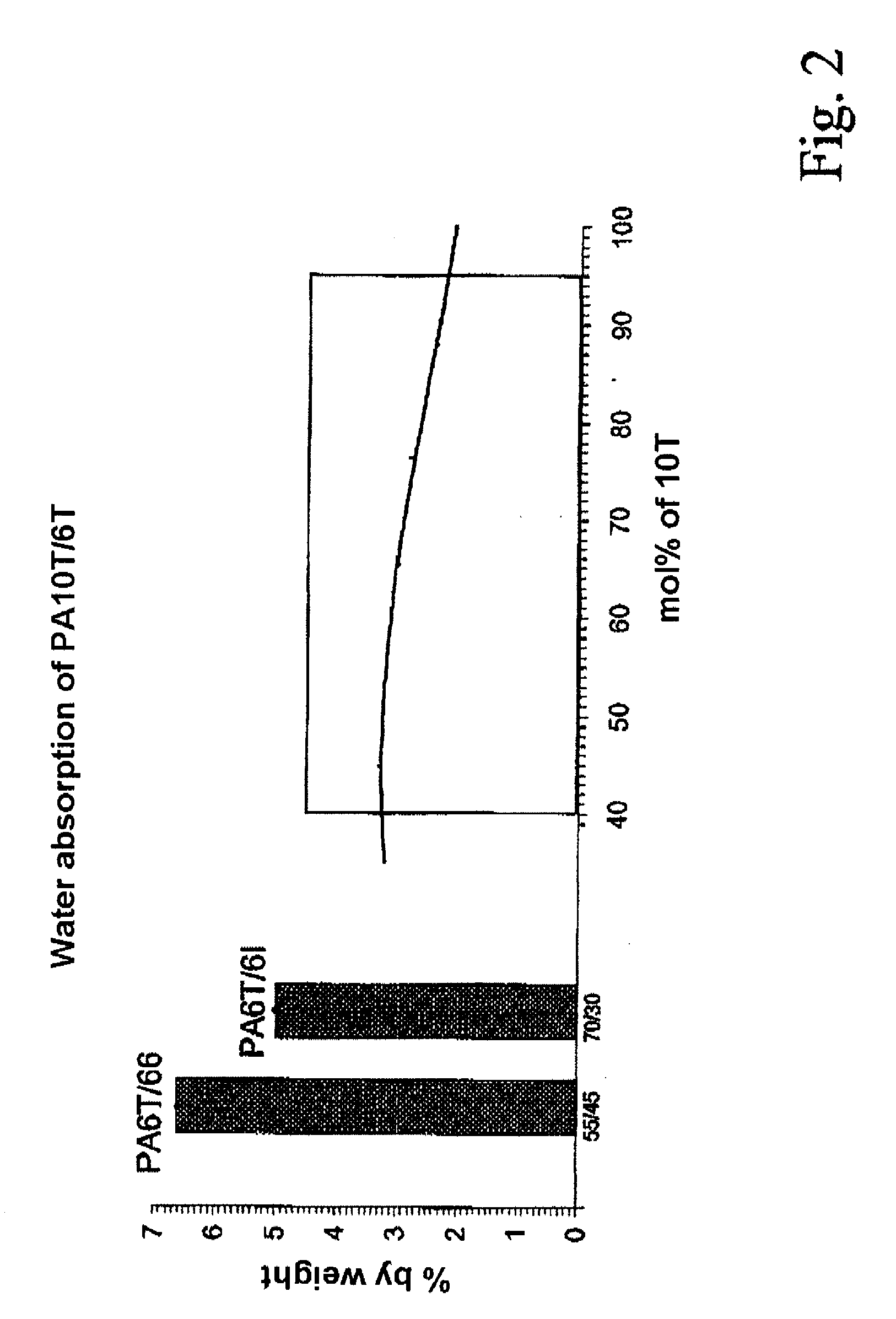
ActiveUS20080274355A1High strengthLow water absorptionPigmenting treatmentNon-fibrous pulp additionHexamethylenediamineAramides
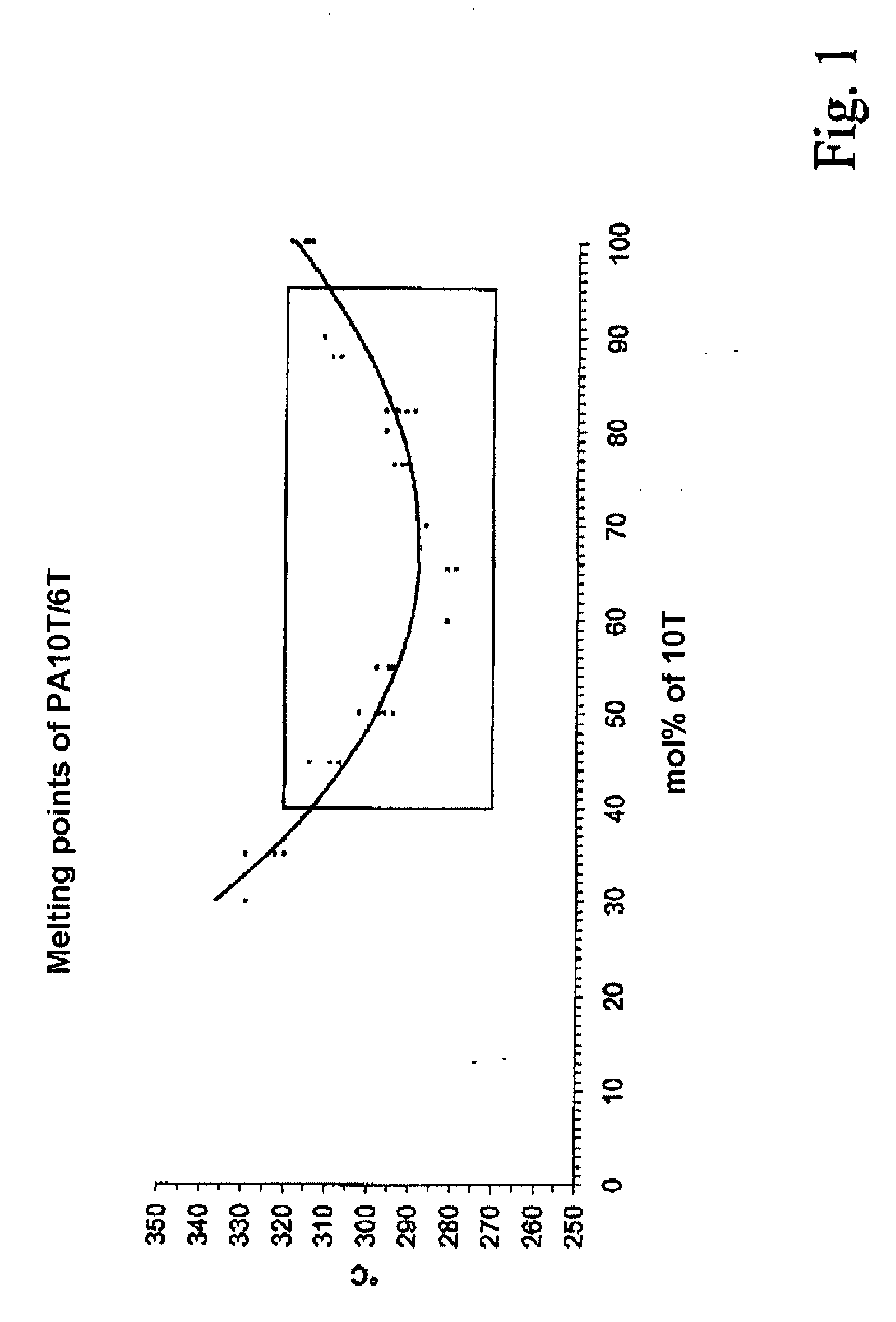
A polyamide molding composition with the following constitution is described:(A) from 30 to 100% by weight of at least one 10T / 6T copolyamide, where this is composed of(A1) from 40 to 95 mol % of 10T units, formed from the monomers 1,10-decanediamine and terephthalic acid(A2) from 5 to 60 mol % of 6T units, formed from the monomers 1,6-hexanediamine and terephthalic acid(B) from 0 to 70% by weight of reinforcing materials and / or fillers(C) from 0 to 50% by weight of additives and / or further polymerswhere the entirety of components A to C is 100%, with the proviso that in component (A) up to 30 mol %, based on the entirety of the dicarboxylic acids, of the terephthalic acid can have been replaced by other aromatic, aliphatic, or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids, and with the proviso that in component (A) up to 30 mol % of 1,10-decanediamine and respectively 1,6-hexanediamine, based on the entirety of the diamines, can have been replaced by other diamines, and with the proviso that not more than 30 mol % in component (A), based on the entirety of the monomers, can have been formed via lactams or amino acids. Uses of this polyamide molding composition are moreover described, as also are processes for the preparation of these polyamide molding compositions.
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
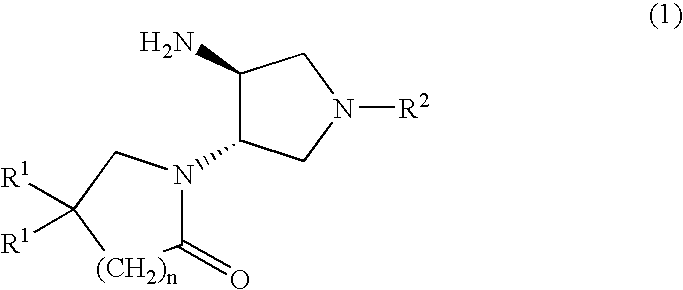
Substituted 3-Amino-Pyrrolidino-4-Lactams
InactiveUS20070299076A1Prevention and mitigation of disease progressionBiocideOrganic chemistryPyrrolidineLactam
Owner:PFIZER INC
New bicyclic compounds and their use as antibacterial agents and beta-lactamase inhibitors
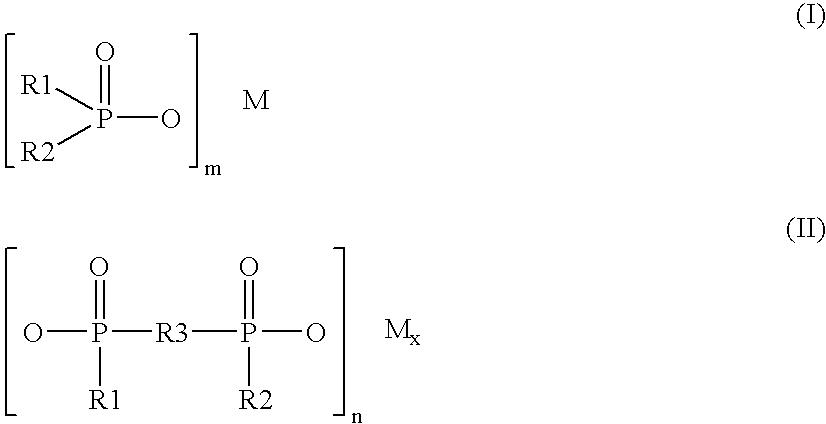
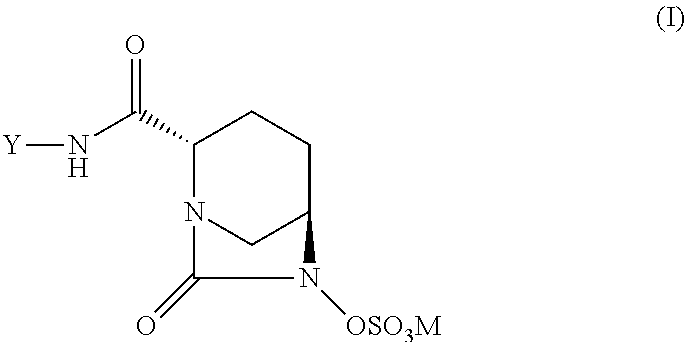
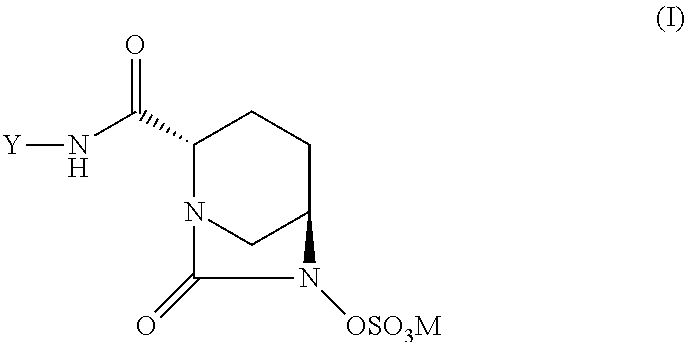
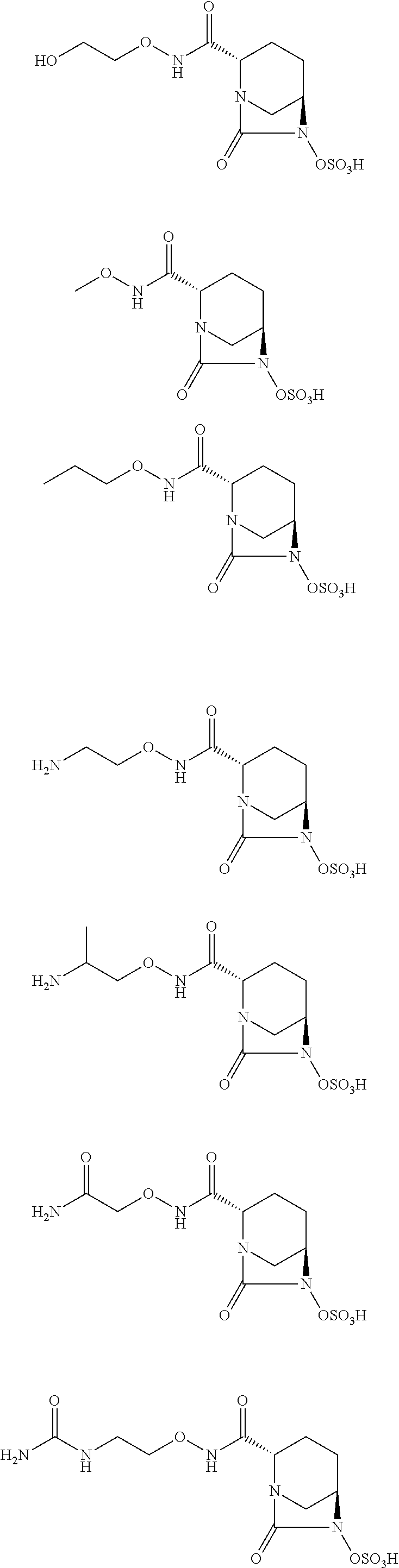
A compound of formula (I):wherein:M is hydrogen or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt-forming cation;Y is OR1 or NR2R3,and R1, R2, R3 and M are as defined herein. Also, methods of treating bacterial infection, pharmaceutical compositions, molecular complexes and processes for preparing compounds.
Owner:FEDORA PHARMA
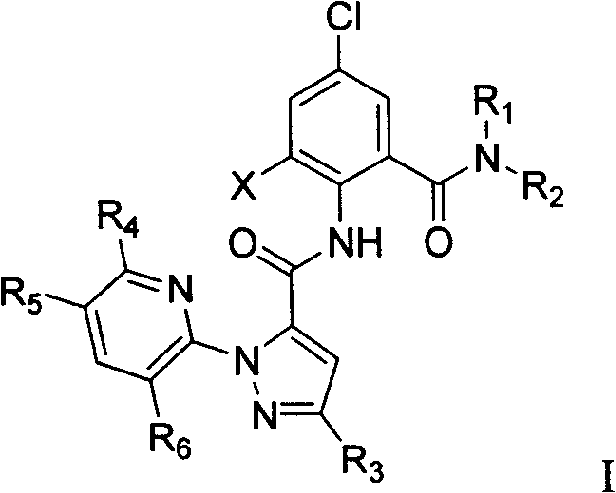
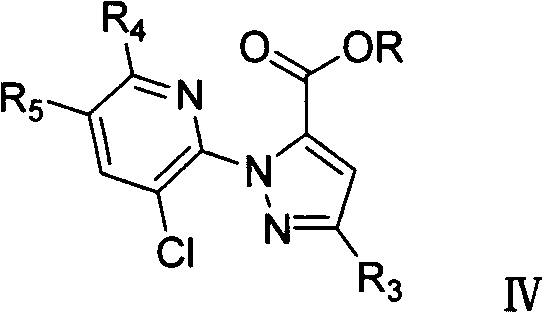
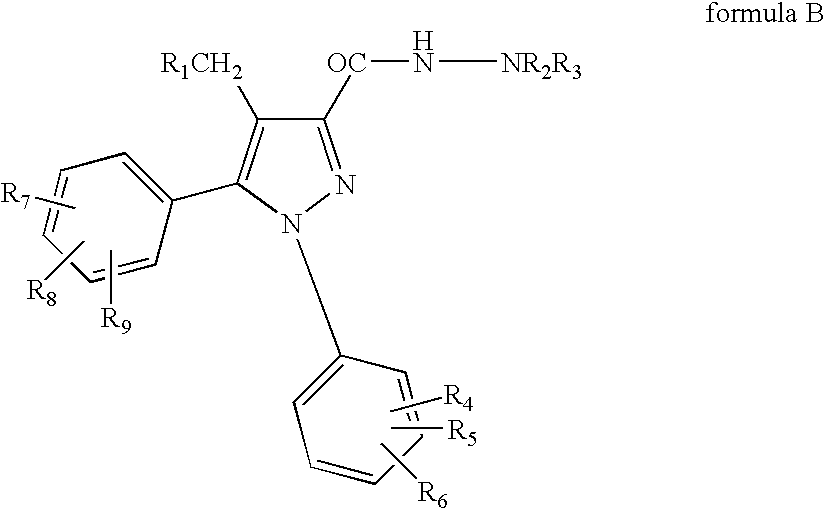
1-substituted pyridyl-pyrazol acid amide compounds and use thereof
The invention discloses a novel-structured 1-substituent pyridyl-lactam pyrazole compound, with the structure shown in the general formula I; the definitions of each substituent group are stated in the instruction book. The compound in the general formula I is provided with excellent insecticidal and sterilizing activity and can be used to control pests and diseases. The technical proposal of the invention also comprises an intermediate for preparing the compound in the general formula I; the structure of the intermediate is shown in the general formula IV, and the definitions of each substituent group in the formula IV are stated in the instruction book.
Owner:SHENYANG SINOCHEM AGROCHEMICALS R&D CO LTD
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
InactiveUS20140194386A1Modulate activityUseful in treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideOrganic chemistryBeta-Lactamase Inhibitors
Described herein are compounds and compositions that modulate the activity of beta-lactamases. In some embodiments, the compounds described herein inhibit beta-lactamase. In certain embodiments, the compounds described herein are useful in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Owner:VENATORX PHARMA INC
Anti-infectious hydrogel compositions
InactiveUS20050191270A1Optical visibilityReduce riskAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyOrganism
The present invention provides a hydrogel composition capable of preventing the intrusion of micro-organisms into body cavities or body openings of mammals comprising of a poly(N-vinyl lactam), a polysaccharide and water.
Owner:HYDROMER INC
Lactam compounds and their use as pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS20060116382A1Avoid conversionInhibit productionBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseMineralocorticoid receptor
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1, antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and / or diseases associated with aldosterone excess.
Owner:INCYTE
Lactam compounds and methods of using the same
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1.
Owner:INCYTE
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
InactiveUS20100292185A1Reduce bacterial resistanceAntibacterial agentsSilicon organic compoundsStereochemistryBeta-Lactamase Inhibitors
Disclosed herein are α-aminoboronic acids and their derivatives which act as inhibitors of beta-lactamases. Also disclosed herein are pharmaceutical compositions comprising α-aminoboronic acids and methods of use thereof.
Owner:NOVARTIS INT PHARM LTD
Resorcinolic derivatives and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6605670B1Reduce molecular weightReduce contentOrganic chemistryFibre treatmentPhenolMedicinal chemistry
Methods of making low molecular weight methylene acceptors are provided. The methylene acceptors are prepared by reacting a polyhydric phenol with an aromatic olefinic compound in the presence of an acid catalyst, and then further reacting the products of the first reaction with an N-methylol lactam derivative. Derivatives made by the above method, as well as rubber compositions using these derivatives are also provided.
Owner:INDSPEC CHEM CORP
Poly-beta-peptides from functionalized beta-lactam monomers and antibacterial compositions containing same
InactiveUS20070087404A1Control over polymerization conditionLarge molecular weightAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMonomerTetrahydrofuran
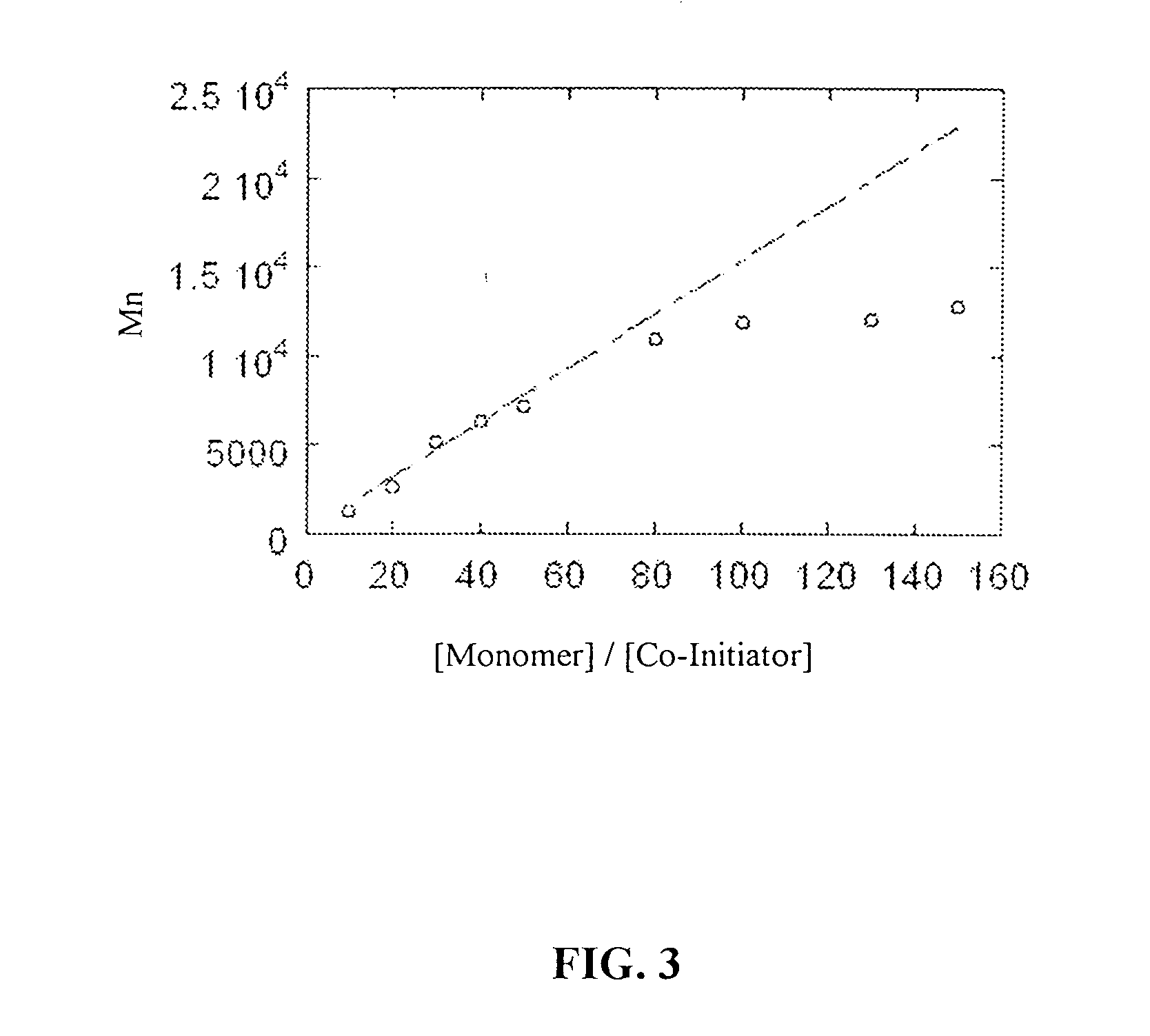
Disclosed is a method of making β-polypeptides. The method includes polymerizing β-lactam-containing monomers in the presence of a base initiator and a co-initiator which is not a metal-containing molecule to yield the product β-polypeptides. Specifically disclosed are methods wherein the base initiator is potassium t-butoxide, lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (LiN(TMS)2), potassium bis(trimethyl-silyl)amide, and sodium ethoxide, and the reaction is carried out in a solvent such as chloroform, dichloromethane, dimethylsulfoxide, or tetrahydrofuran.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
Substituted bicyclic beta-lactams of Formula I: (I), are β-lactamase inhibitors, wherein a, X, R1 and R2 are defined herein. The compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are useful in the treatment of bacterial infections in combination with β-lactam antibiotics. In particular, the compounds can be employed with a β-lactam antibiotics (e.g., imipenem, piperacillin, or ceftazidime) against microorganisms resistant to β-lactam antibiotics due to the presence of the β-lactamases.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Transparent molding composition
ActiveUS20060281873A1Sufficient crystallinityAdequate stress crackingEnvelopes/bags making machineryClosuresPolyamideCarboxylic acid
A polyamide molding composition which can be used for production of a printable or printed item contains a) at most 90 parts by weight of a polyamide obtained from a lactam or from an amino carboxylic acid having at least 10 carbon atoms; and b) from 10 to 100 parts by weight of PA1010, wherein a total of components a) and b) is 100 parts by weight.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Skin adherent hydrogels
There is disclosed hydrogel compositions comprising a combination of at least two of three components selected from non-acidic poly (N-vinyl lactam), chitosan derivatives and water-soluble multifunctional amine-containing polymers in various ratios. The hydrogels are useful as cavity-filling wound dressings, burn dressings, drug delivery systems, cosmetic masks, conductive electrodes, prostheses and wraps.
Owner:HYDROMER INC
Succinoylamino benzodiazepines as inhibitors of Aβ protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Copolyamide powder and its preparation, use of copolyamide powder in a shaping process and mouldings produced from this copolyamide powder
ActiveUS20090236775A1Low viscosityHigh dimensional accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingLaurolactamPolyamide
A task often encountered in very recent times is the rapid provision of prototypes. Particularly suitable processes are those based on pulverulent materials and in which the desired structures are produced layer-by-layer through selective melting and solidification. The invention provides the constitution, production and use of a copolyamide powder which was produced using the following monomer units: a) laurolactam or ω-aminoundecanoic acid, and also b) dodecanedioic acid, and either c) decanediamine or dodecanediamine, in shaping processes, and also to mouldings produced through a layer-by-layer process which selectively melts regions of a powder layer, using this specific powder. Once the regions previously melted layer-by-layer have been cooled and solidified, the moulding can be removed from the powder bed. The mouldless layer-by-layer processes for the production of components using the copolyamide powder result in simplified and more reliable conduct of the process and better recyclability.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
1,2,4-oxadiazole and 1,2,4-thiadiazole beta-lactamase inhibitors
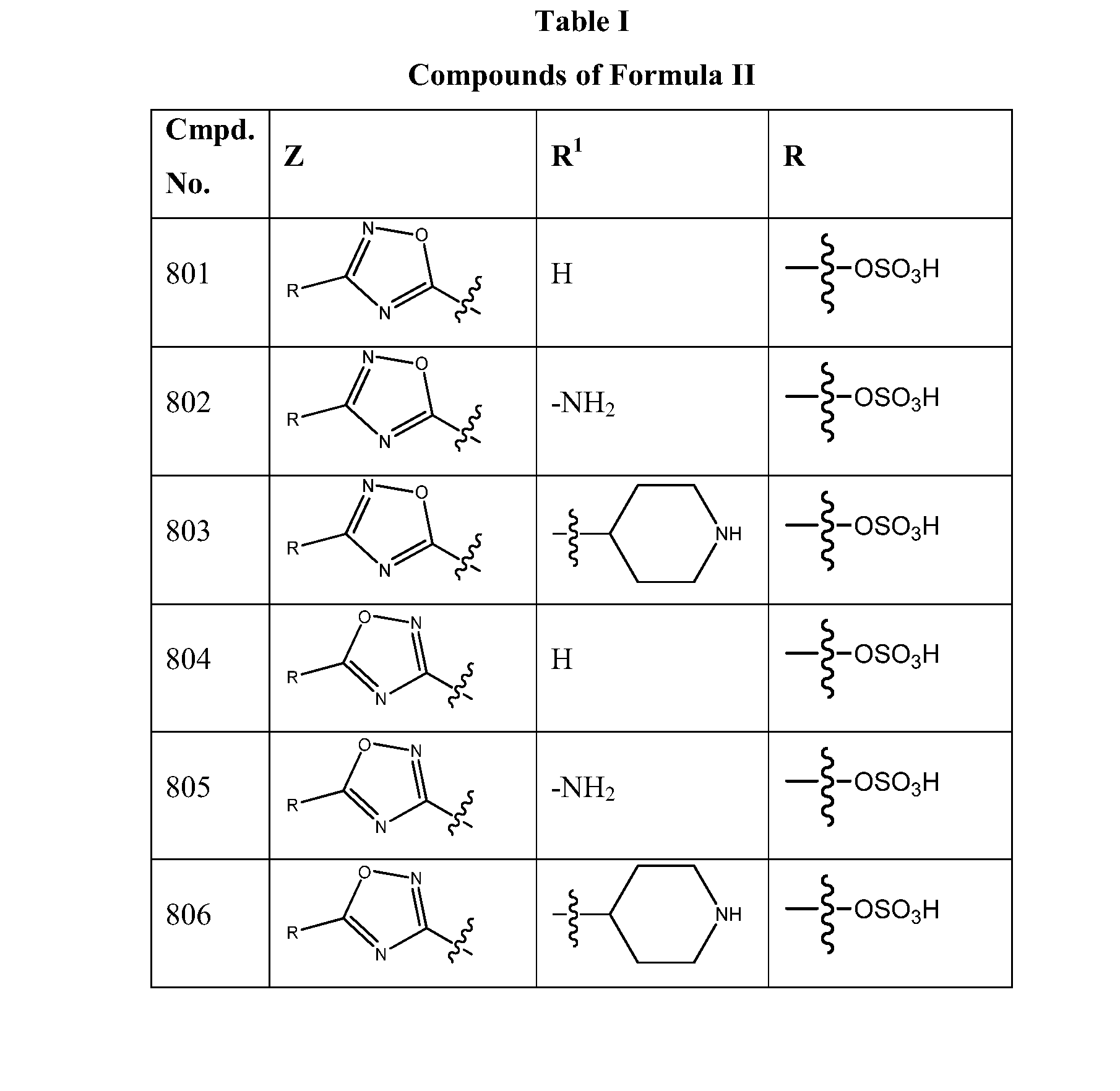
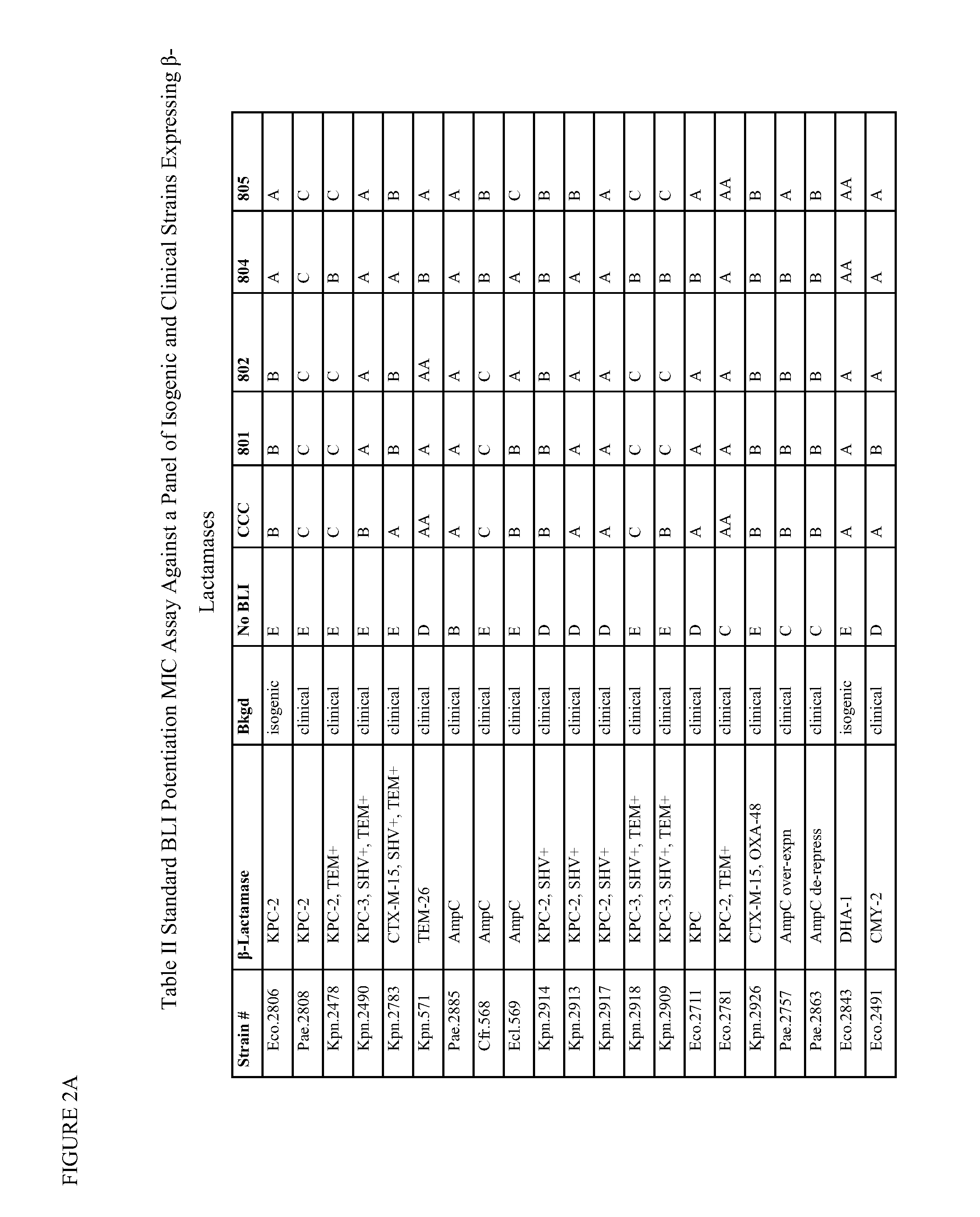
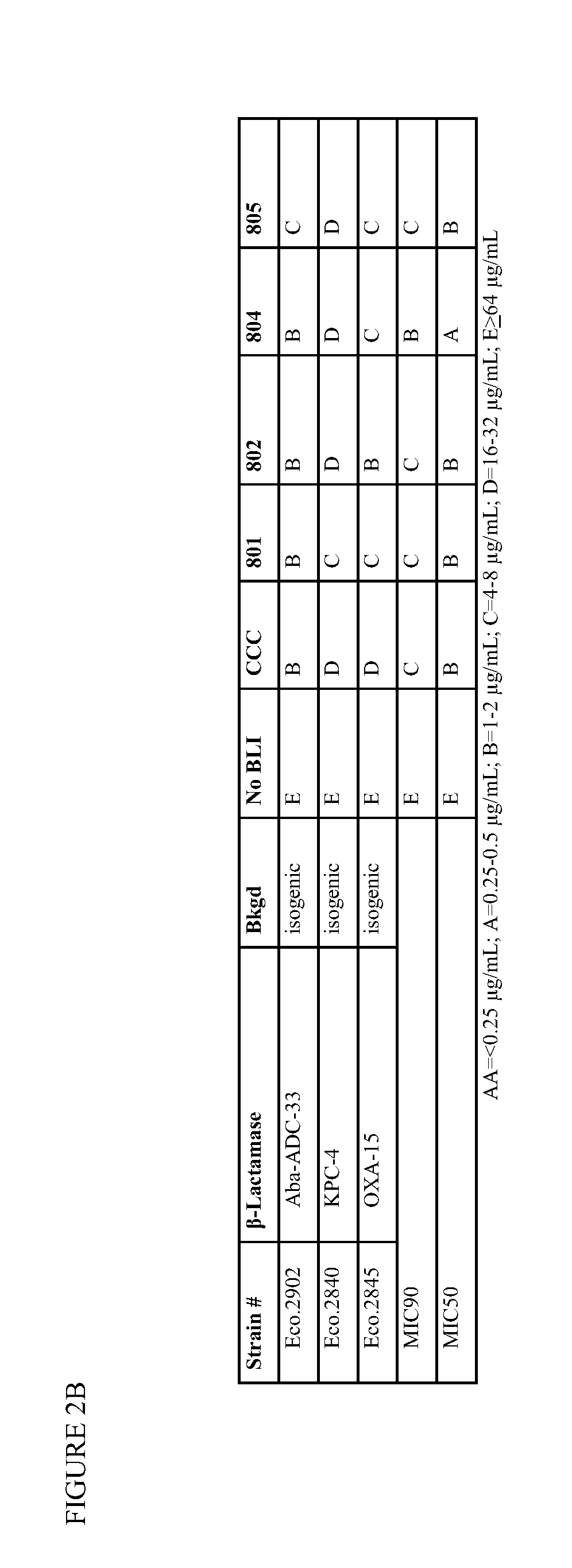
β-Lactamase inhibitor compounds (BLIs) are disclosed, including compounds that have activity against class A, class C or class D β-lactamases. Methods of manufacturing the BLIs, and uses of the compounds in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions and antibacterial applications are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Antimicrobial composition
An antimicrobial composition comprising (a) a cationic surfactant derived from the condensation of fatty acids and esterified dibasic amino acids, such as lauric arginate and (b) an antibiotic, such as of β-lactam antibiotics, polypeptides, quinolones. The composition may be used as a stand alone antimicrobial formulation, or in combination with medical articles or medical devices.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Combinations of substituted azetidinones and CB1 antagonists
The present invention provides compositions, therapeutic combinations and methods including: (a) at least one selective CB1 antagonist; and (b) at least one substituted azetidinone or substituted β-lactam sterol absorption inhibitor which can be useful for treating vascular conditions, diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome and lowering plasma levels of sterols or 5α-stanols.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Prodrugs of nh-acidic compounds: ester, carbonate, carbamate and phosphonate derivatives
ActiveUS20110319422A1Long duration of actionReduce polarityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderImideCarbamate
The invention provides a method of sustained delivery of a lactam, imide, amide, sulfonamide, carbamate or urea containing parent drug by administering to a patient an effective amount of a prodrug compound of the invention wherein upon administration to the patient, release of the parent drug from the prodrug is sustained release. Prodrug compounds suitable for use in the methods of the invention are labile conjugates of parent drugs that are derivatized through carbonyl linked prodrug moieties. The prodrug compounds of the invention can be used to treat any condition for which the lactam, imide, amide, sulfonamide, carbamate or urea containing parent drug is useful as a treatment.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Transparent polyamide molding materials having improved transparency, resistance to chemicals and high permanent fatigue strength
ActiveUS6943231B2High transparencyHigh permanent fatigue strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionFramesPolyamideCarboxylic acid
Transparent polyamide molding materials are provided which are characterized in that they have a melting enthalpy between 0 and 12 J / g and the polyamides are constituted of100 mole-% of a diamine mixture having 10-70 mole-% of PACM [bis-(4-amino-cyclohexyl)-methane] with less than 50 wt.-% of trans,trans-isomer and 90-30 mole-% of MACM [bis-(4-amino-3-methyl-cyclohexyl)-methane], wherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aliphatic diamines having 6 to 12 C atoms, cycloaliphatic, alkyl-substituted cycloaliphatic, branched aliphatic diamines or multiamines having 3 to 12 amino groups or mixtures thereof, and100 mole-% of long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 14 C atoms or mixtures of these dicarboxylic acids, wherein 0-10 mole-% can be replaced by other aromatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids having 8 to 16 C atoms, which are especially selected from the group consisting of isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, naphthalenedicarboxylic acid, cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid or mixtures thereof, andwherein, optionally, 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic diamines and 0-10 mole-% of the other long-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acids can be added as 0-20 mole-% of ω-aminocarboxylic acids having 6 to 12 C atoms or lactams having 6 to 12 C atoms.Further, methods for producing the polyamide moulding materials and methods for producing and further treating moulded articles from the polyamide moulding materials are provided. Especially, the present invention relates to glasses and lenses which are obtainable from the polyamide moulding materials.
Owner:EMS CHEM AG
Beta-lactam antibiotic-containing tablet and production thereof
InactiveUS6423341B1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLow-substituted hydroxypropylcelluloseEngineering
This invention provides beta-lactam antibiotic-containing tablets capable of being orally taken either as such owing to their being small-sized, hence still easily swallowable, or, in the case of administration to the aged encountering some difficulty in swallowing, in the form of dispersions resulting from easy self-disintegration upon being dropped into water in a glass as well as a method of producing the same. The tablets of this invention comprise, on the per-tablet basis, 60-85% by weight of a beta-lactam antibiotic, 1-10% by weight of low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose and / or crosslinked polyvinylpyrrolidone as a disintegrator, and 0.5-2% by weight of a binder. Granules to be compressed for tableting are prepared using water or an aqueous solution of ethanol or the like.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
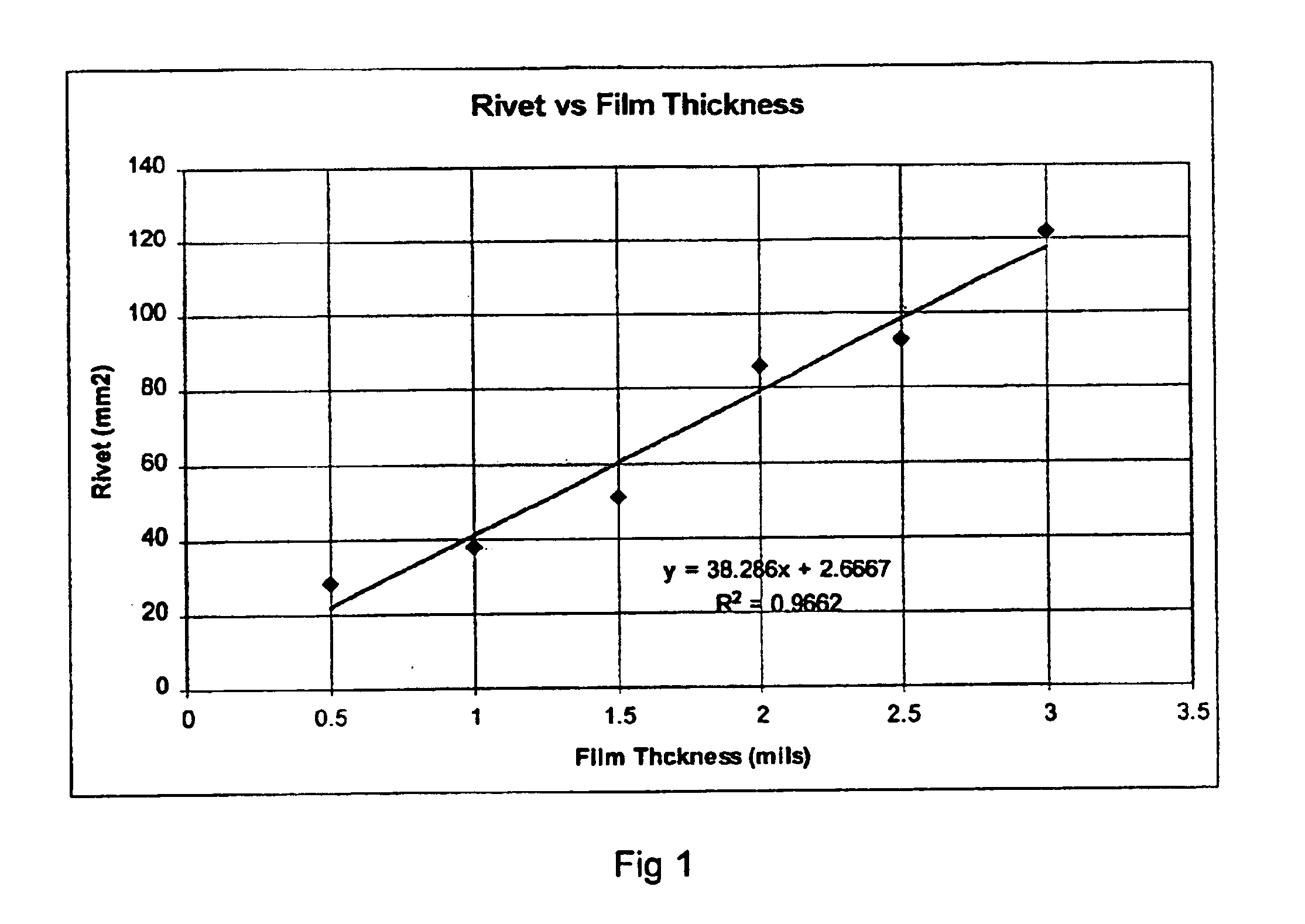
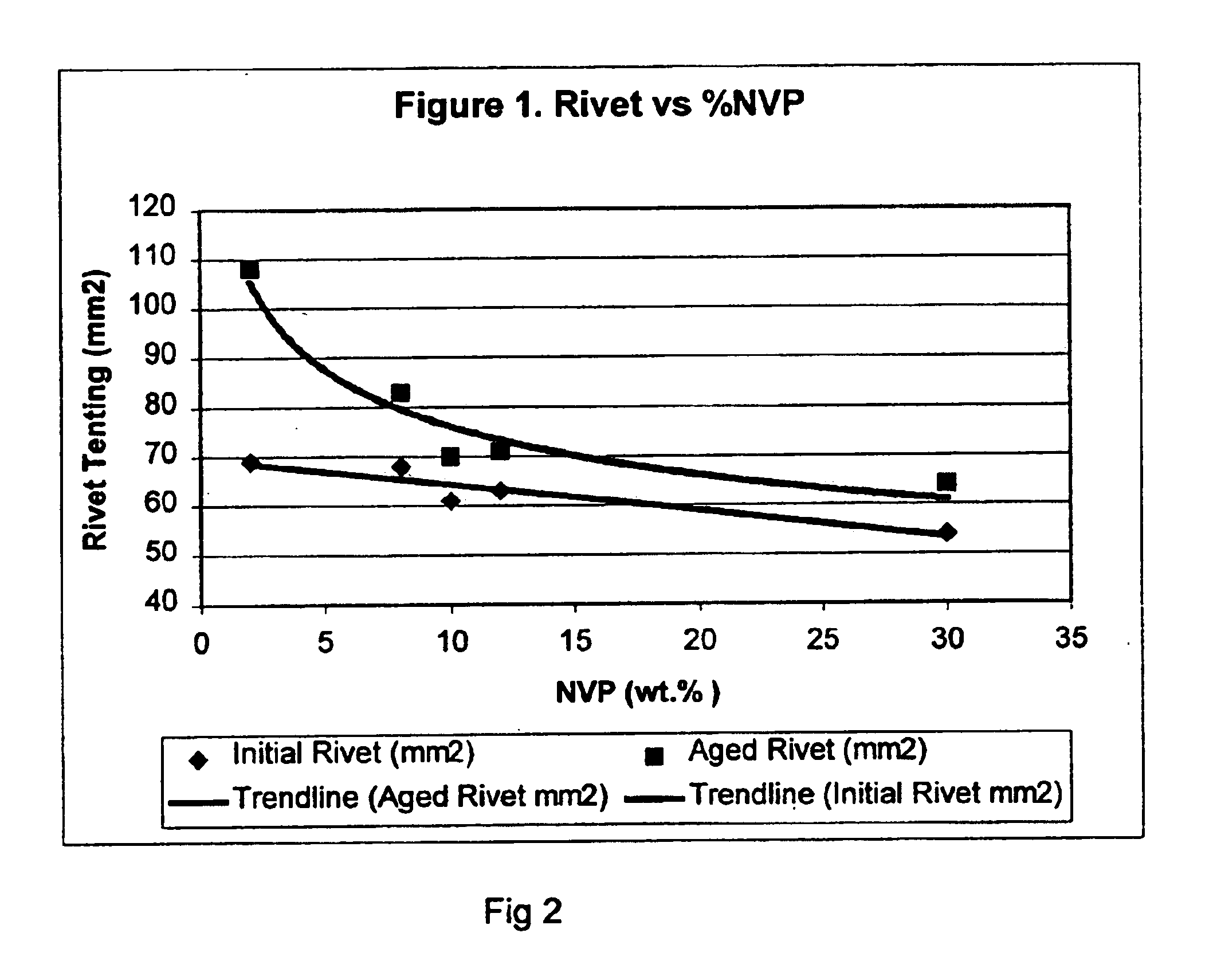
Adhesives with improved rivet properties and laminates using the same
InactiveUS6844391B1Improve performanceOutstanding removal characteristicLiquid surface applicatorsChemical liquid solidificationMethacrylateCohesive strength
Acrylate copolymer pressure-sensitive adhesive constructions are described which provide excellent retention of rivet properties. Tenting around rivets is minimized even after undergoing thermal aging while in contact with additive rich films like PVC. This is achieved by the inclusion of a synergistic amount of an N-vinyl lactam monomer and acid monomer with the bulk of the monomers being an alkyl acrylate save and / or methacrylate esters. A concomitant increase in cohesive strength is also achieved which affords good removal characteristics. The use of appropriate adhesive blends is further disclosed which allows retention of these features while also improving cold temperature properties.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
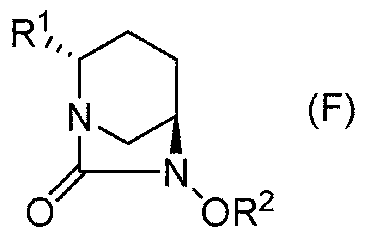
Optically-active diazabicyclooctane derivative and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN103328476APromote crystallizationImprove effectivenessAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHydrogen atomBenzyl group
Provided are an optically-active diazabicyclooctane derivative represented by a formula (F) that is useful as a medicinal intermediate of a ss-lactamase inhibitor, and a method for manufacturing the same. In the formula (F), R1 represents CO2R, CO2M, or CONH2; R represents a methyl group, a tert-butyl group, an allyl group, a benzyl group, or a 2,5-dioxopyrrolidine-1-yl group; M represents a hydrogen atom, an inorganic cation, or an organic cation; and R2 represents a benzyl group or an allyl group.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modifi-cation of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and inser-tion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA pro-duction system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also de-scribed. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intes-tine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
Process for synthesizing oxidized lactam compounds
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
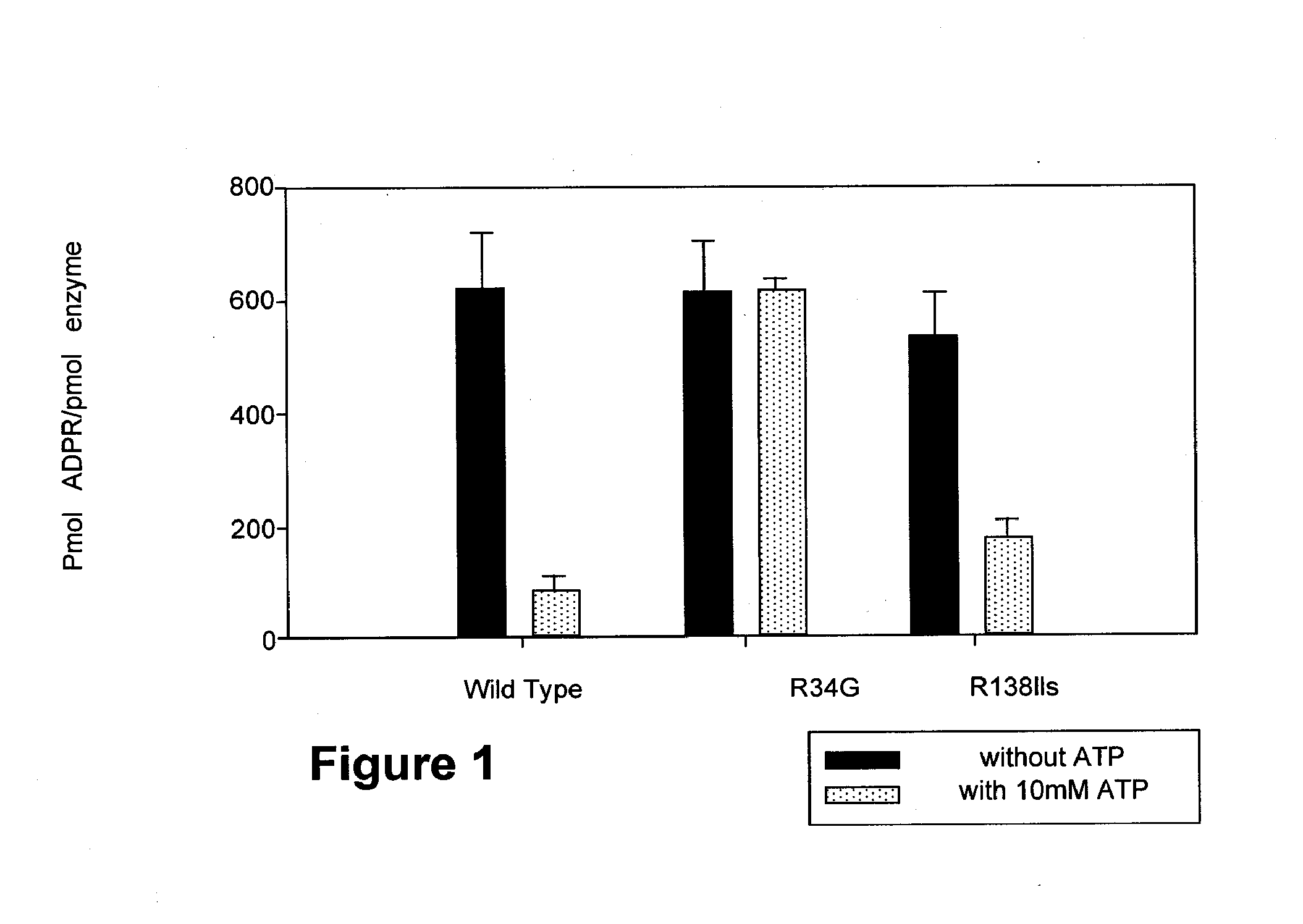
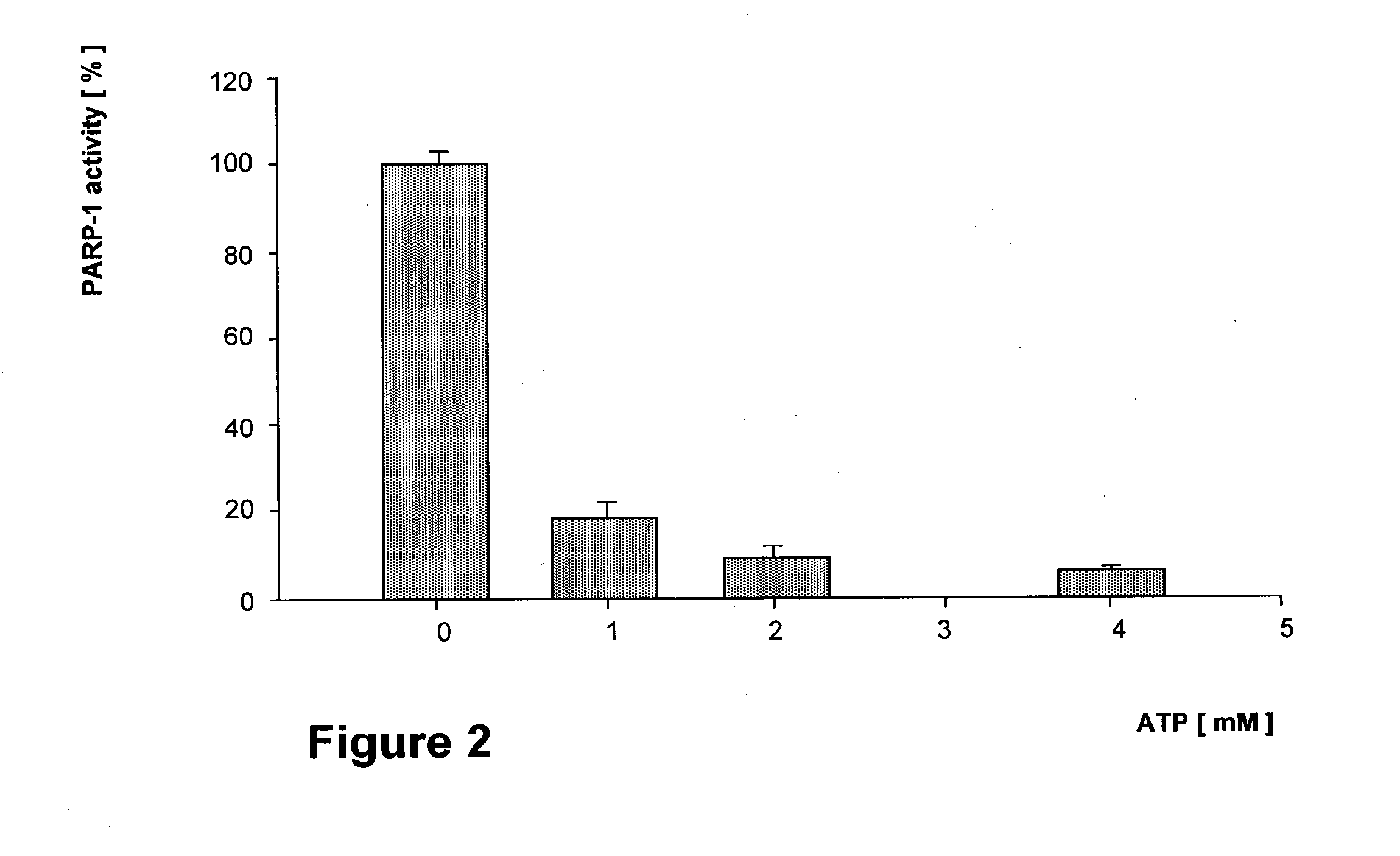
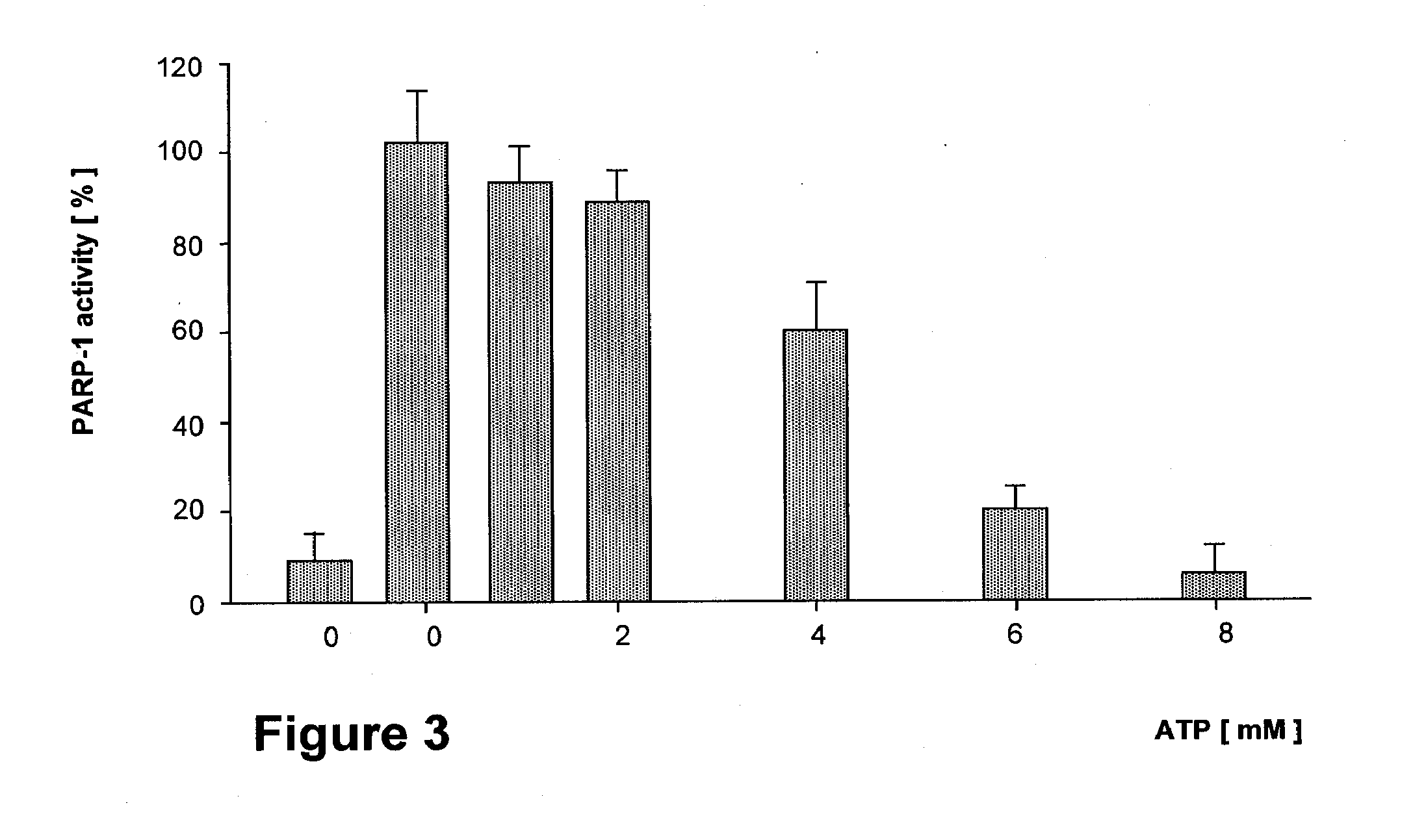
Parp Modulators and Treatment of Cancer
The invention relates to a method of modulating poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activity in a mammal comprising administering to a mammal an effective amount of an organic aromatic compound having from 4 to about 35 carbon atoms, wherein said organic aromatic compound is capable of binding the arginine-34 moiety located in Zinc finger-1 of the PARP-1 enzyme and wherein said organic aromatic compound has electron donating capabilities such that it's π-electron system will interact with the positively charged (cationic) guanidinium moiety of the specific arginine-34 residue of the Zinc-1 finger of PARP-1 and does not contain benzamide or lactam substituents. In particular, substituted benzopyrones and substituted indoles and their pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds that modulate the activity of PARP-1, are described. The invention is also directed to the composition of matter, kits and methods for their therapeutic and / or prophylactic use in treating diseases and disorders described herein, by administering effective amounts of such compounds. Preferably, the compositions and methods provided herein inhibit PARP activity.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
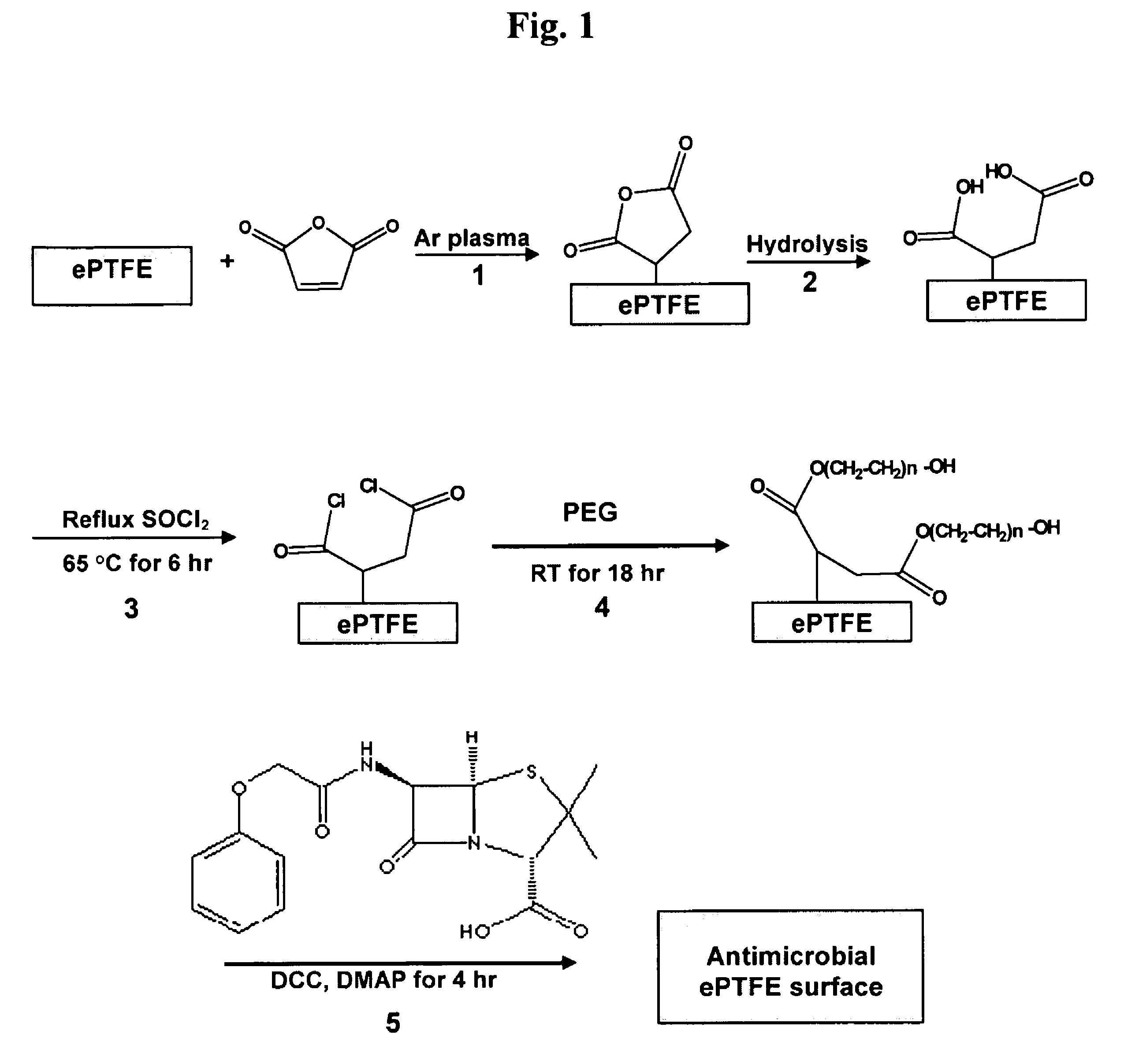
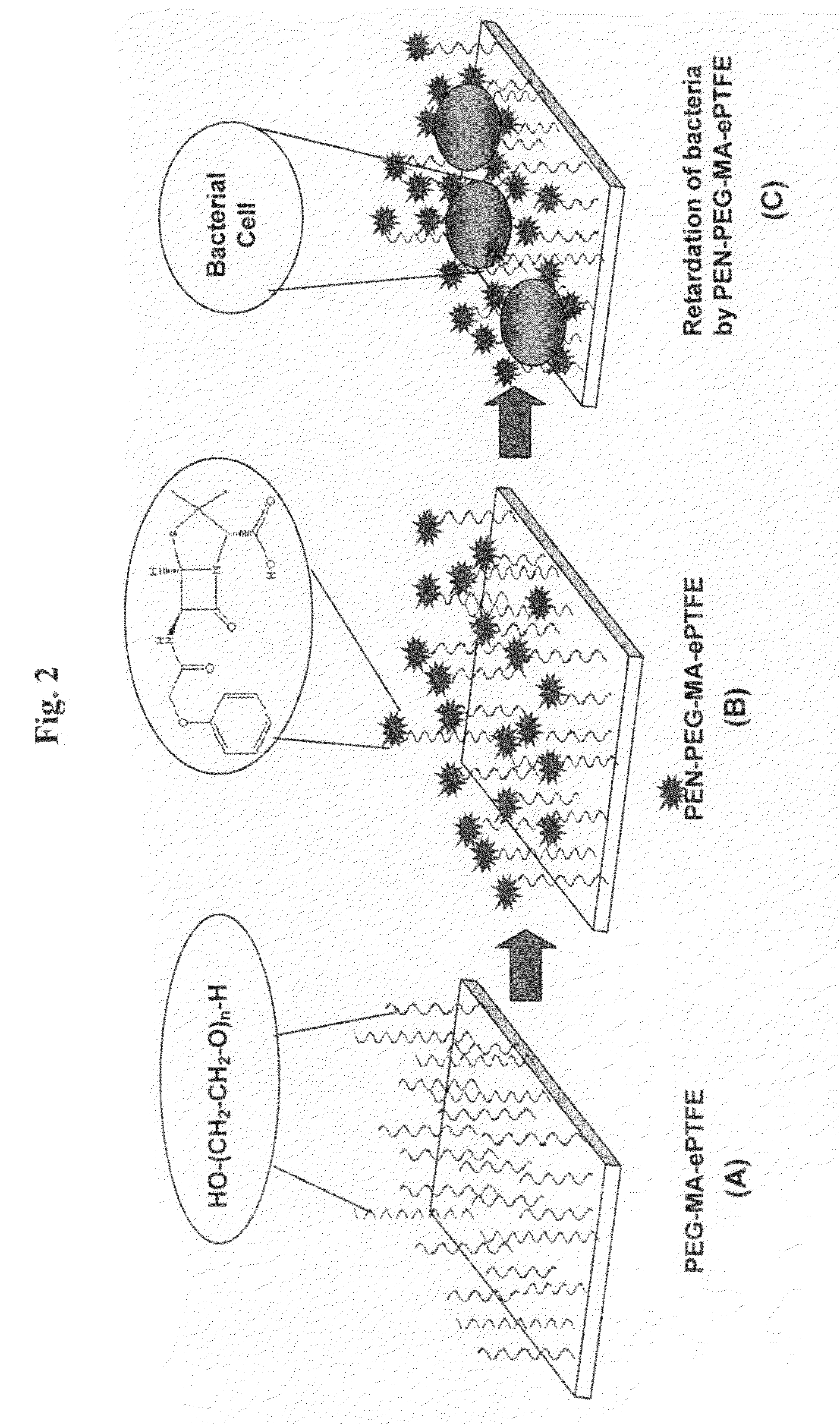
Method of attaching drug compounds to non-reactive polymer surfaces
Polymers are disclosed that are chemically modified to retard bacterial growth. Such modified polymers (e.g. ePTFE and polypropylene) are produced by first creating acid groups on the polymer surface through reactions with an anhydride. The acid groups are then linked to polyethylene glycol (PEG) through esterification or other reactions such as amidation. Preferably, at least two different molecular weight PEG species are employed. The antimicrobial surface is completed by linking antibiotics (e.g. β-lactam antibiotics) to the PEG extensions. One preferred embodiment of such a modified polymer is produced using ePTFE, maleic anhydride (MA), and penicillin (PEN) to yield PEN-PEG-MA-ePTFE, which inhibits gram-positive bacteria. The PEG spacer is critical for PEN function in this context, since PEN-ePTFE is ineffective against bacterial growth. Another preferred embodiment incorporates ampicillin (AMP) and a heterobifunctional PEG, HOOC—(CH2—CH2—O)n—NH2, to yield AMP-PEG-MA-ePTFE. This latter example inhibits both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHERN MISSISSIPPI THE UNIV OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com