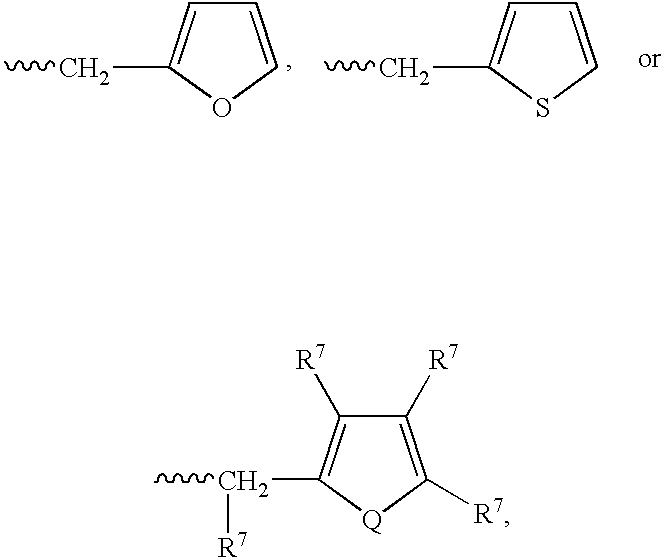
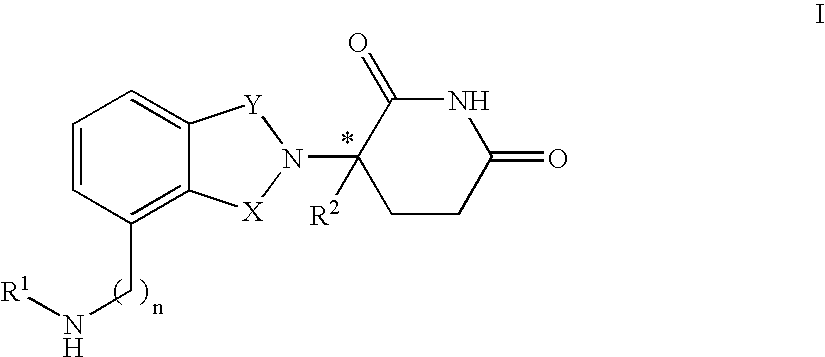
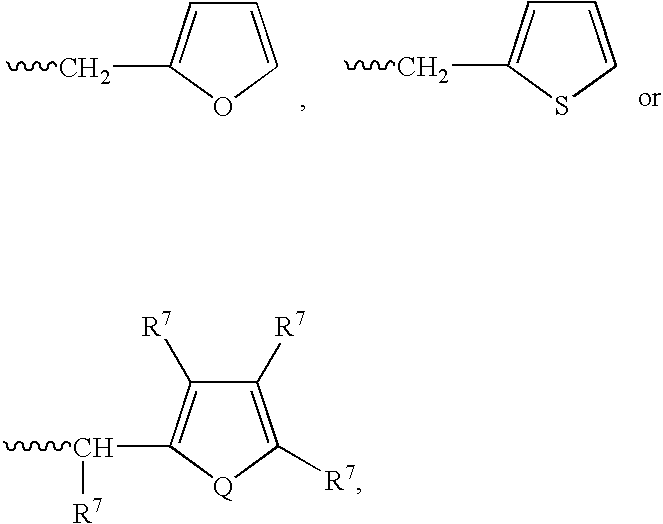
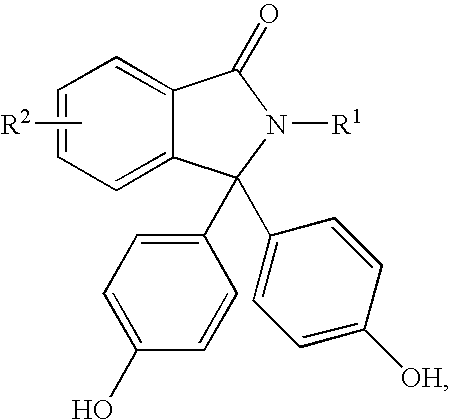
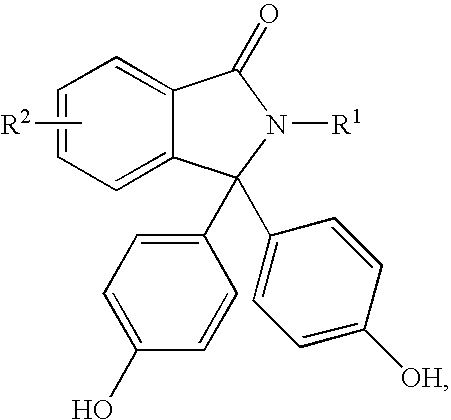
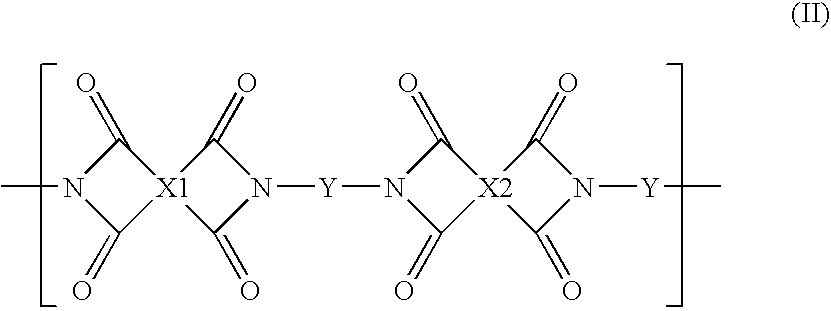
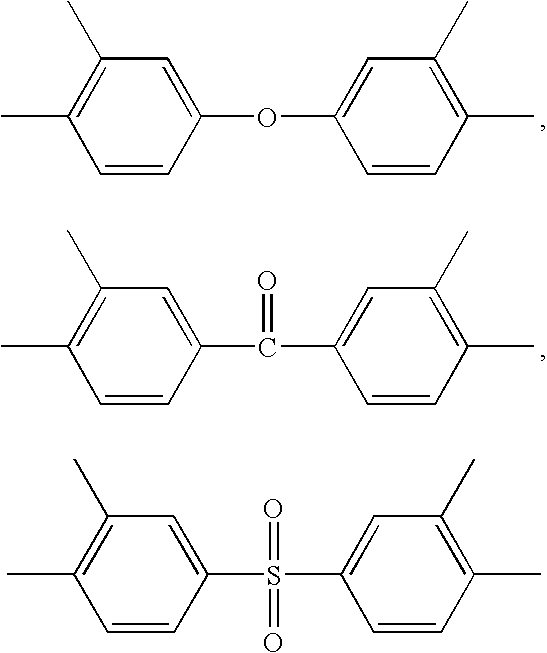
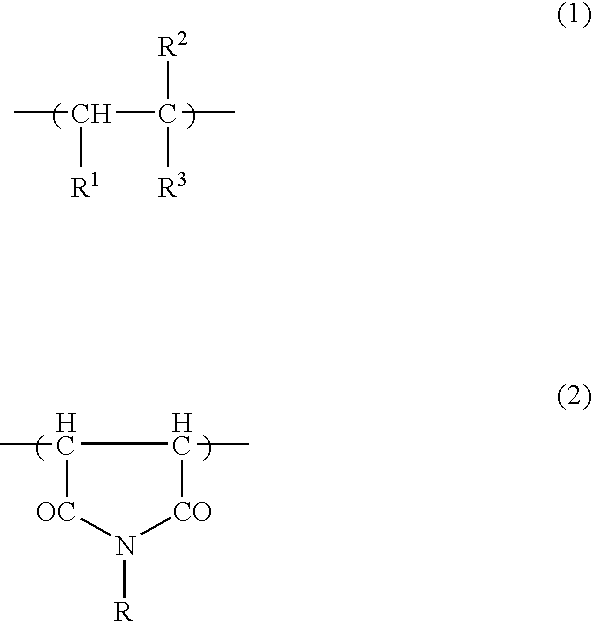
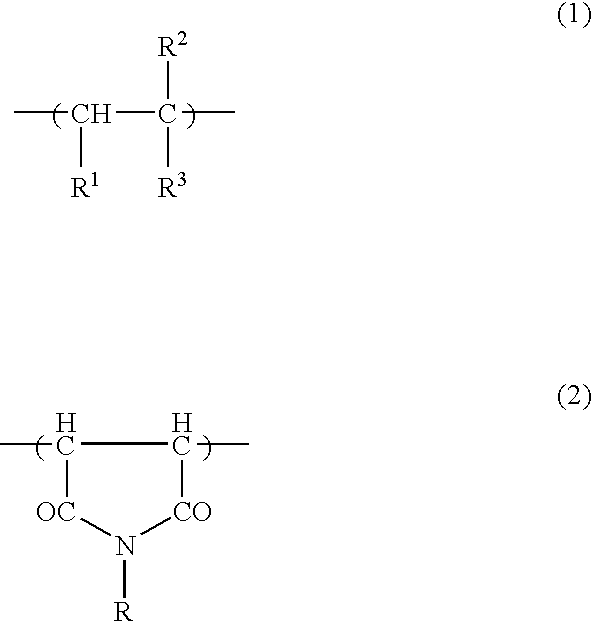
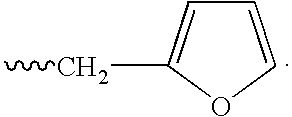Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12291 results about "Imide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
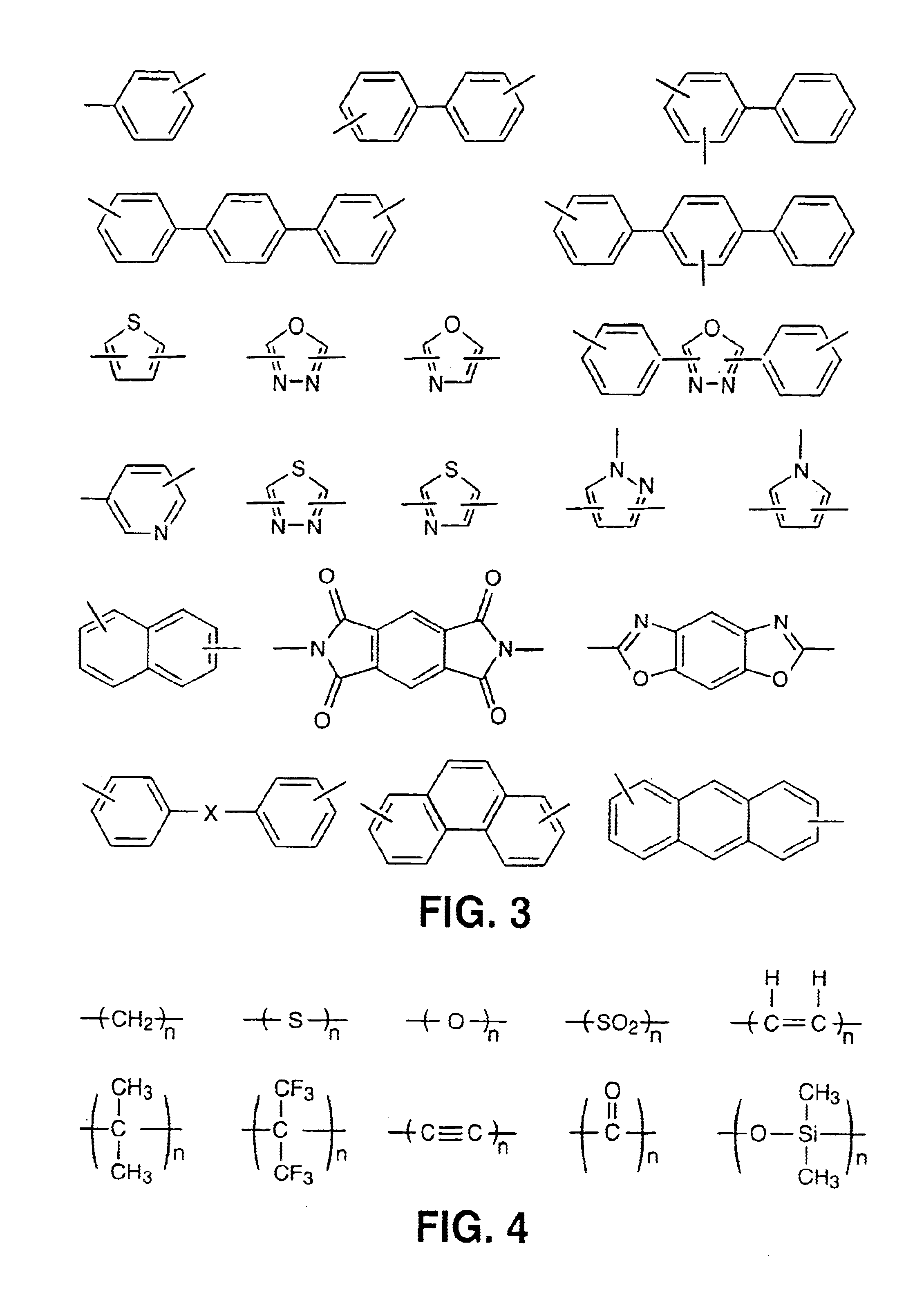
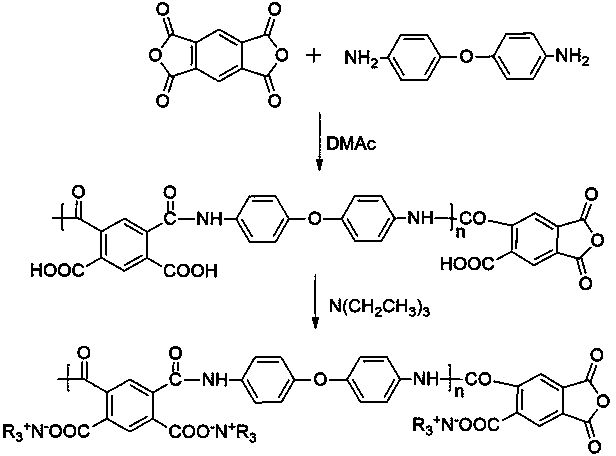
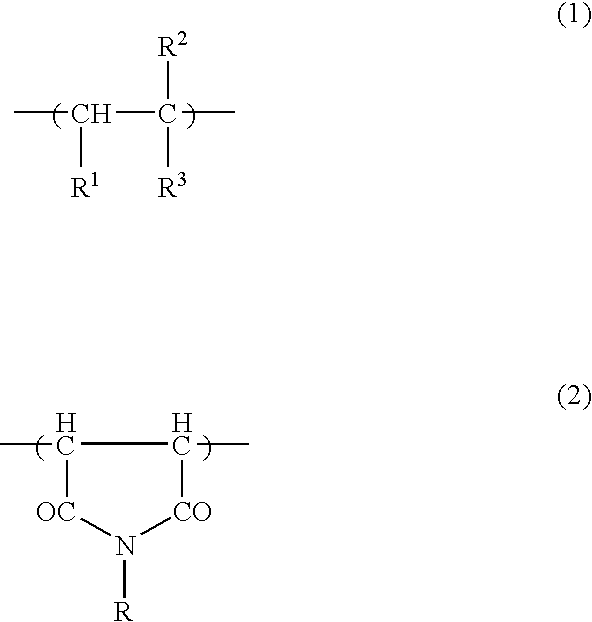
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant toward hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called polyimides.
Aerogel metallic compositions
InactiveUS7071287B2Reduce nitrogen contentSuperior physical and electrical propertyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesImidePolymer science
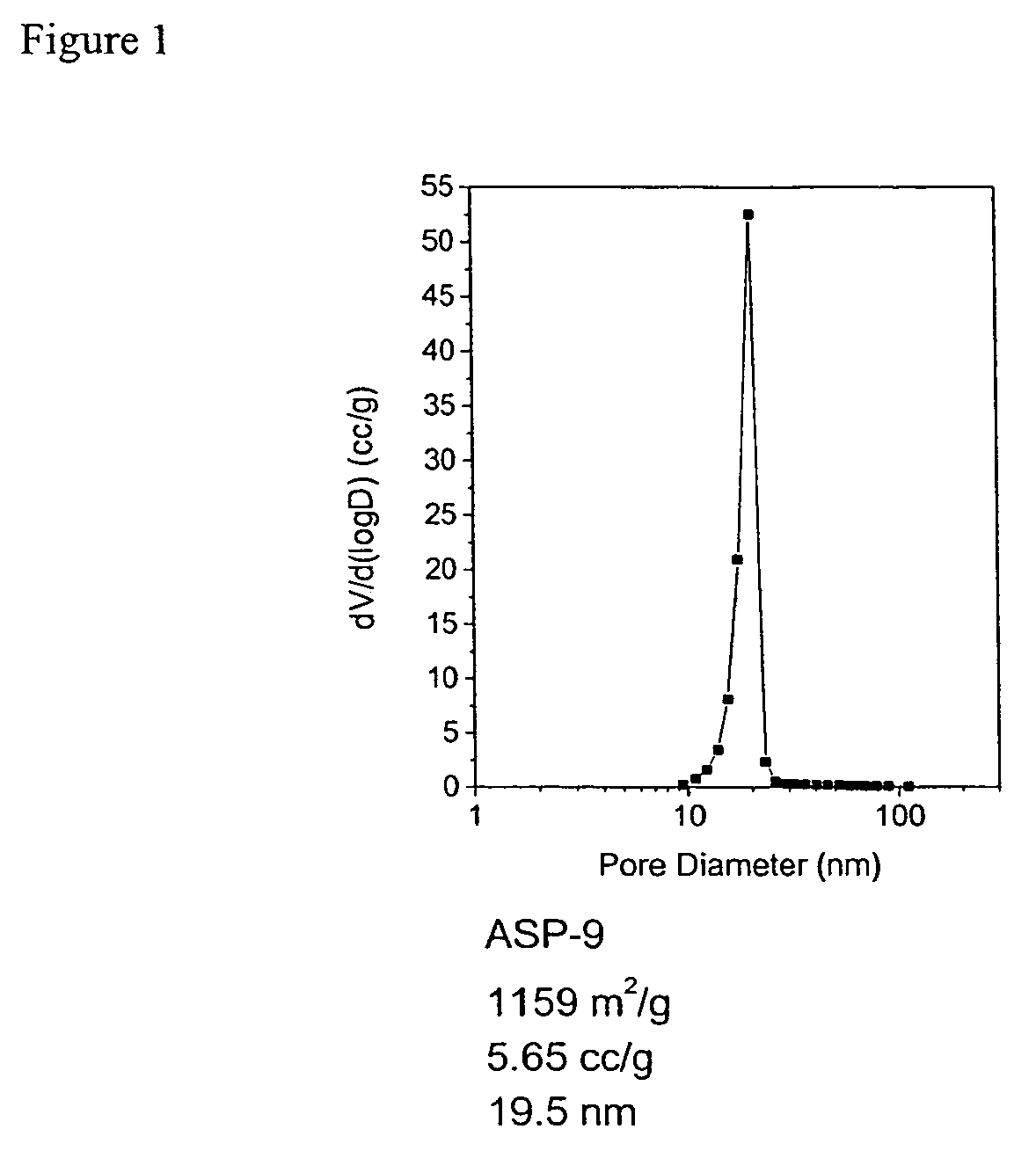
A preparation process of polyimide aerogels that composed of aromatic dianhydrides and aromatic diamines or a combined aromatic and aliphatic diamines is described. Also descried is a process to produce carbon aerogels derived from polyimide aerogel composed of a rigid aromatic diamine and an aromatic dianhydride. Finally, the processes to produce carbon aerogels or xerogel-aerogel hybrid, both of which impregnated with highly dispersed transition metal clusters, and metal carbide aerogels, deriving from the polyimide aerogels composed of a rigid aromatic diamine and an aromatic dianhydride, are described. The polyimide aerogels and the polyimide aerogel derivatives consist of interconnecting mesopores with average pore size at 10 to 30 nm and a mono-dispersed pore size distribution. The gel density could be as low as 0.008 g / cc and accessible surface area as high as 1300 m2 / g.
Owner:ASPEN AEROGELS INC
Isoindole-imide compounds, compositions, and uses thereof
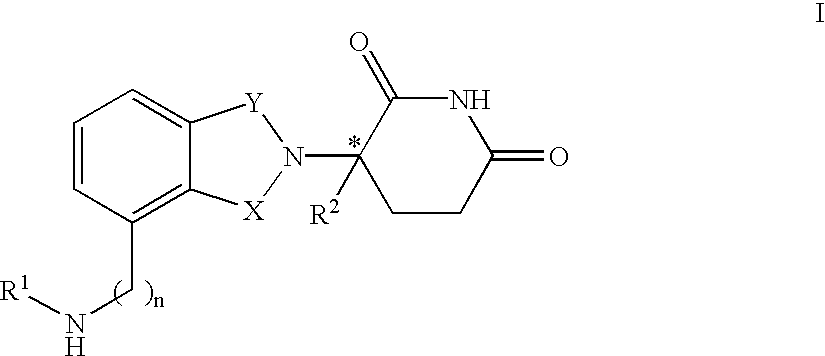
The invention relates to isoindole-imide compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, clathrates, enantiomers, diastereomers, racemates, or mixtures of stereoisomers thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these isoindole-imide compounds, and methods for reducing the level of cytokines and their precursors in mammals. In particular, the invention pertains to isoindole-imide compounds that are potent inhibitors of the production of TNF-alpha in mammals. The isoindole-imides described herein are useful for treating or preventing diseases or disorders in mammals, for example, cancers, such as solid tumors and blood-born tumors; heart disease, such as congestive heart failure; osteoporosis; and genetic, inflammatory; allergic; and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Isoindole-imide compounds, compositions, and uses thereof
The invention relates to isoindole-imide compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, clathrates, enantiomers, diastereomers, racemates, or mixtures of stereoisomers thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these isoindole-imide compounds, and methods for reducing the level of cytokines and their precursors in mammals. In particular, the invention pertains to isoindole-imide compounds that are potent inhibitors of the production of TNF-alpha in mammals. The isoindole-imides described herein are useful for treating or preventing diseases or disorders in mammals, for example, cancers, such as solid tumors and blood-born tumors; heart disease, such as congestive heart failure; osteoporosis; and genetic, inflammatory; allergic; and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Isoindole-imide compounds, compositions, and uses thereof
The invention relates to isoindole-imide compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, clathrates, enantiomers, diastereomers, racemates, or mixtures of stereoisomers thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these isoindole-imide compounds, and methods for reducing the level of cytokines and their precursors in mammals. In particular, the invention pertains to isoindole-imide compounds that are potent inhibitors of the production of TNF-α in mammals. The isoindole-imides described herein are useful for treating or preventing diseases or disorders in mammals, for example, cancers, such as solid tumors and blood-born tumors; heart disease, such as congestive heart failure; osteoporosis; and genetic, inflammatory; allergic; and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
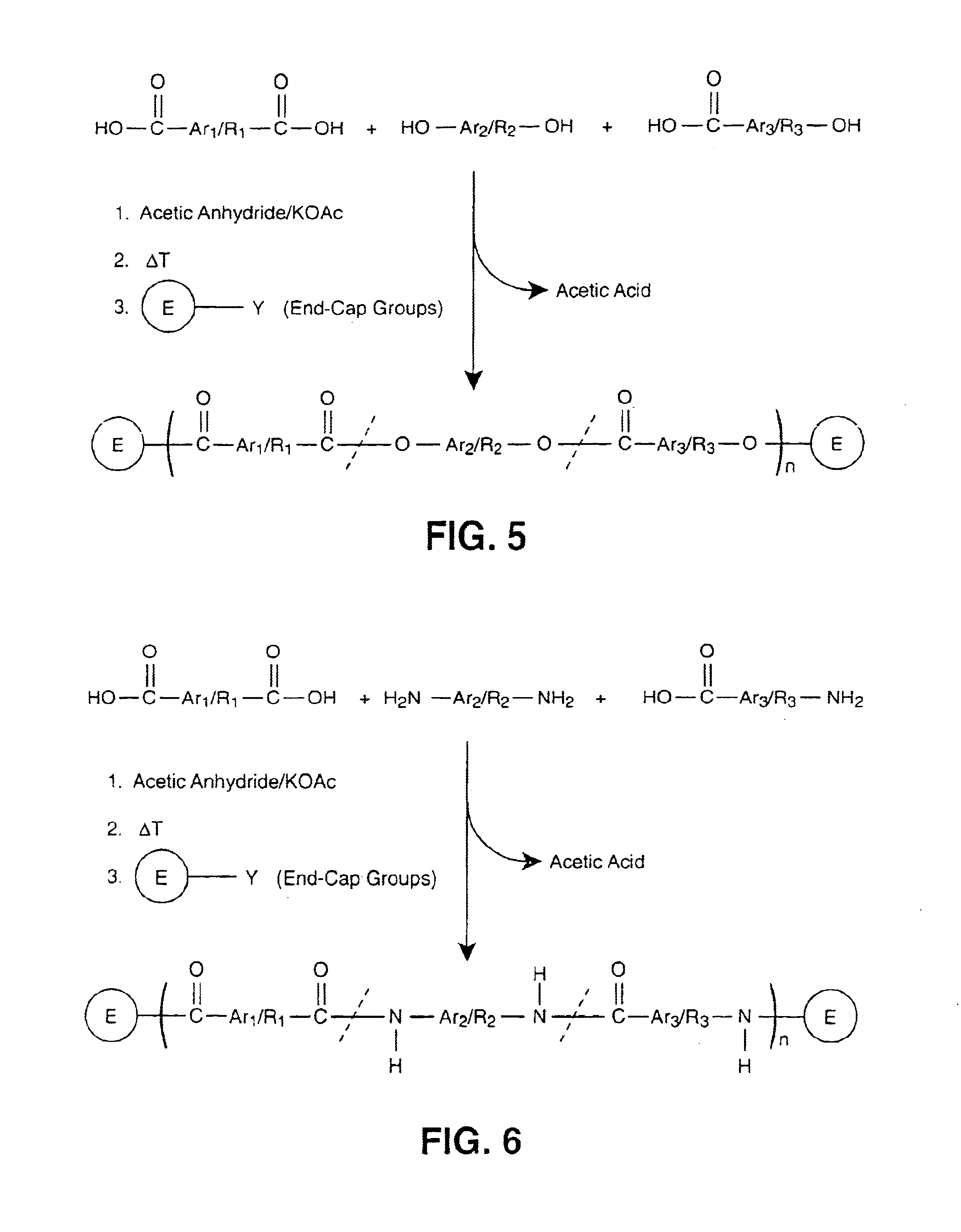
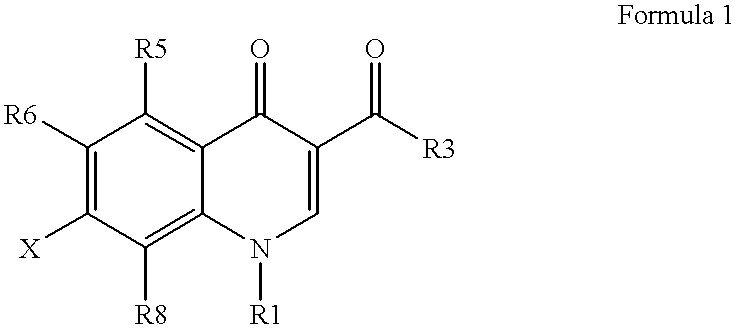
Liquid crystalline thermosets from ester, ester-imide, and ester-amide oligomers
InactiveUS6939940B2Low viscosityLow dielectric constantLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineEnd-group
Main chain thermotropic liquid crystal esters, ester-imides, and ester-amides were prepared from AA, BB, and AB type monomeric materials and were end-capped with phenylacetylene, phenylmaleimide, or nadimide reactive end-groups. The resulting reactive end-capped liquid crystal oligomers exhibit a variety of improved and preferred physical properties. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are thermotropic and have, preferably, molecular weights in the range of approximately 1000-15,000 grams per mole. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers have broad liquid crystalline melting ranges and exhibit high melt stability and very low melt viscosities at accessible temperatures. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are stable for up to an hour in the melt phase. These properties make the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers highly processable by a variety of melt process shape forming and blending techniques including film extrusion, fiber spinning, reactive injection molding (RIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), resin film injection (RFI), powder molding, pultrusion, injection molding, blow molding, plasma spraying and thermo-forming. Once processed and shaped, the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers were heated to further polymerize and form liquid crystalline thermosets (LCT). The fully cured products are rubbers above their glass transition temperatures. The resulting thermosets display many properties that are superior to their non-end-capped high molecular weight analogs.
Owner:NASA
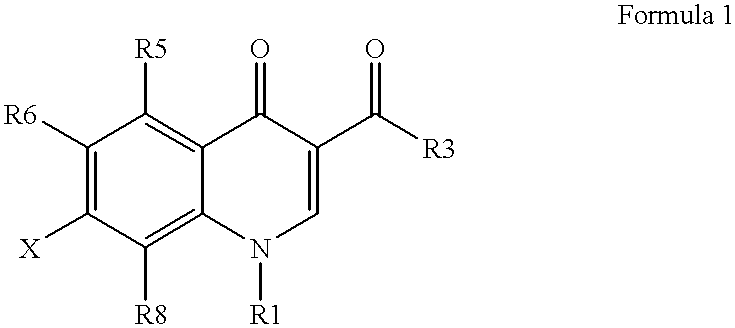
Antimicrobial quinolones, their compositions and uses
InactiveUS6329391B1Low susceptibility to microbial resistanceLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideImideQuinolone
This invention relates to novel antimicrobial compounds of formula;wherein X, R1, R3, R5, R6, and R8 are defined in the claims, and to their optical isomers, diastereomers or enantiomers, as well as pharmaceutically-acceptable salts, hydrates, and biohydrolyzable esters, amides and imides thereof, and to compositions and uses of such compounds. The invention also relates to compounds derived from these compounds having antimicrobial uses.
Owner:TAIGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Composite materials comprising polar polymers and single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6936653B2Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationPolyesterPolymer science
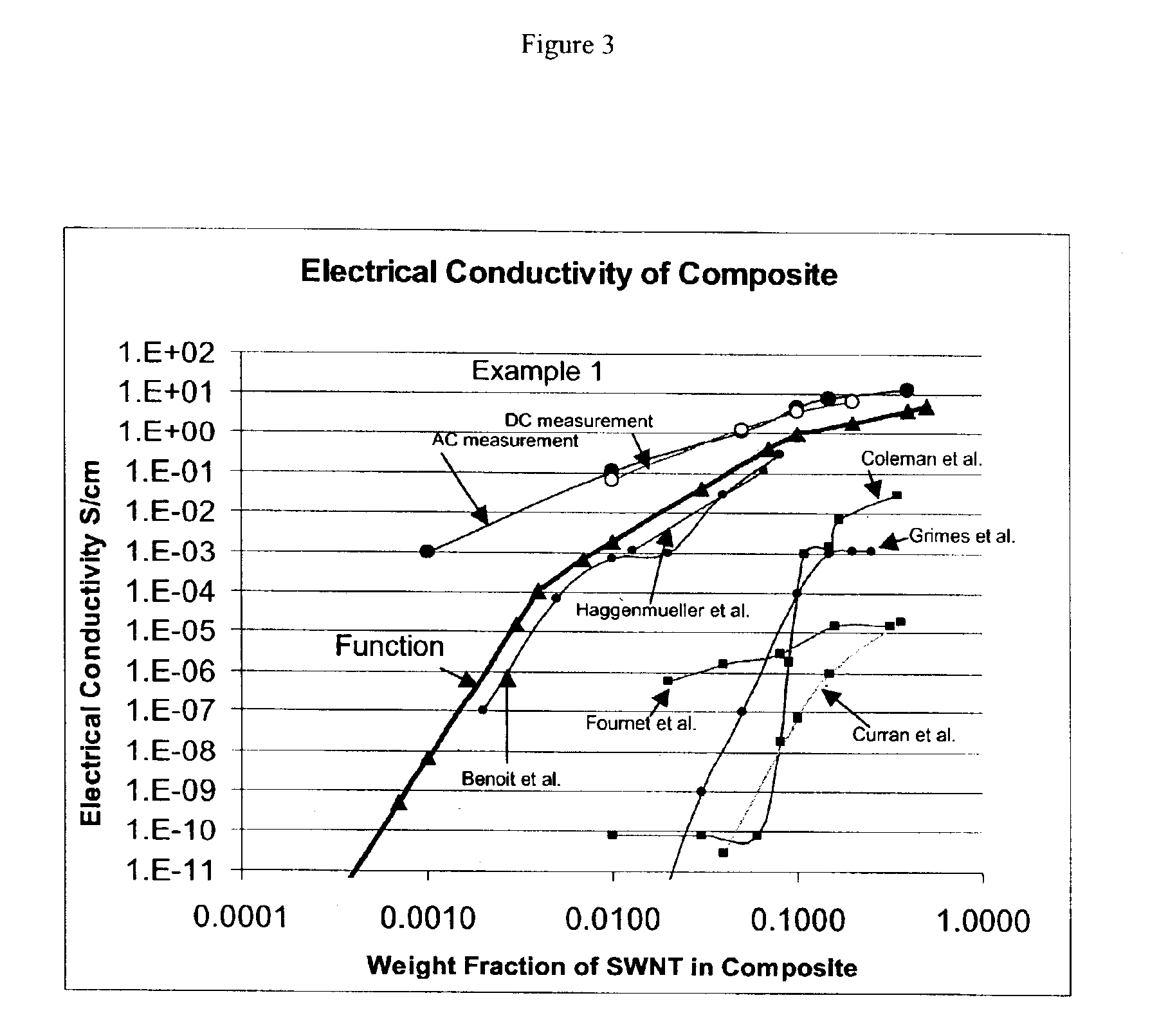
The invention relates to a composite comprising a weight fraction of single-wall carbon nanotubes and at least one polar polymer wherein the composite has an electrical and / or thermal conductivity enhanced over that of the polymer alone. The invention also comprises a method for making this polymer composition. The present application provides composite compositions that, over a wide range of single-wall carbon nanotube loading, have electrical conductivities exceeding those known in the art by more than one order of magnitude. The electrical conductivity enhancement depends on the weight fraction (F) of the single-wall carbon nanotubes in the composite. The electrical conductivity of the composite of this invention is at least 5 Siemens per centimeter (S / cm) at (F) of 0.5 (i.e. where single-wall carbon nanotube loading weight represents half of the total composite weight), at least 1 S / cm at a F of 0.1, at least 1×10−4 S / cm at (F) of 0.004, at least 6×10−9 S / cm at (F) of 0.001 and at least 3×10−16 S / cm (F) plus the intrinsic conductivity of the polymer matrix material at of 0.0001. The thermal conductivity enhancement is in excess of 1 Watt / m-° K. The polar polymer can be polycarbonate, poly(acrylic acid), poly(acrylic acid), poly(methacrylic acid), polyoxide, polysulfide, polysulfone, polyamides, polyester, polyurethane, polyimide, poly(vinyl acetate), poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(vinyl chloride), poly(vinyl pyridine), poly(vinyl pyrrolidone), copolymers thereof and combinations thereof. The composite can further comprise a nonpolar polymer, such as, a polyolefin polymer, polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutene, polyisobutene, polyisoprene, polystyrene, copolymers thereof and combinations thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Crosslinked compositions comprising collagen and demineralized bone matrix, methods of making and methods of use
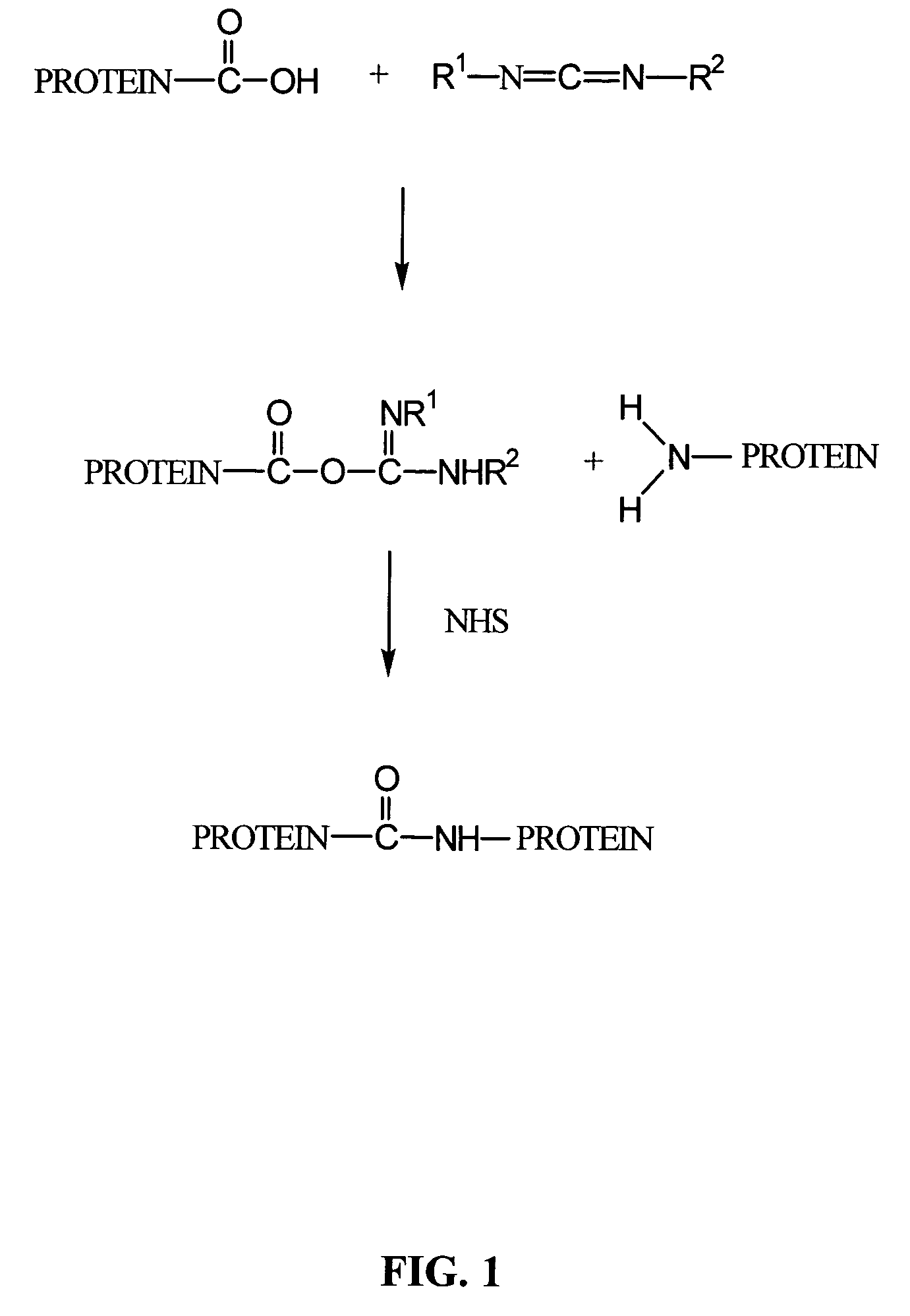
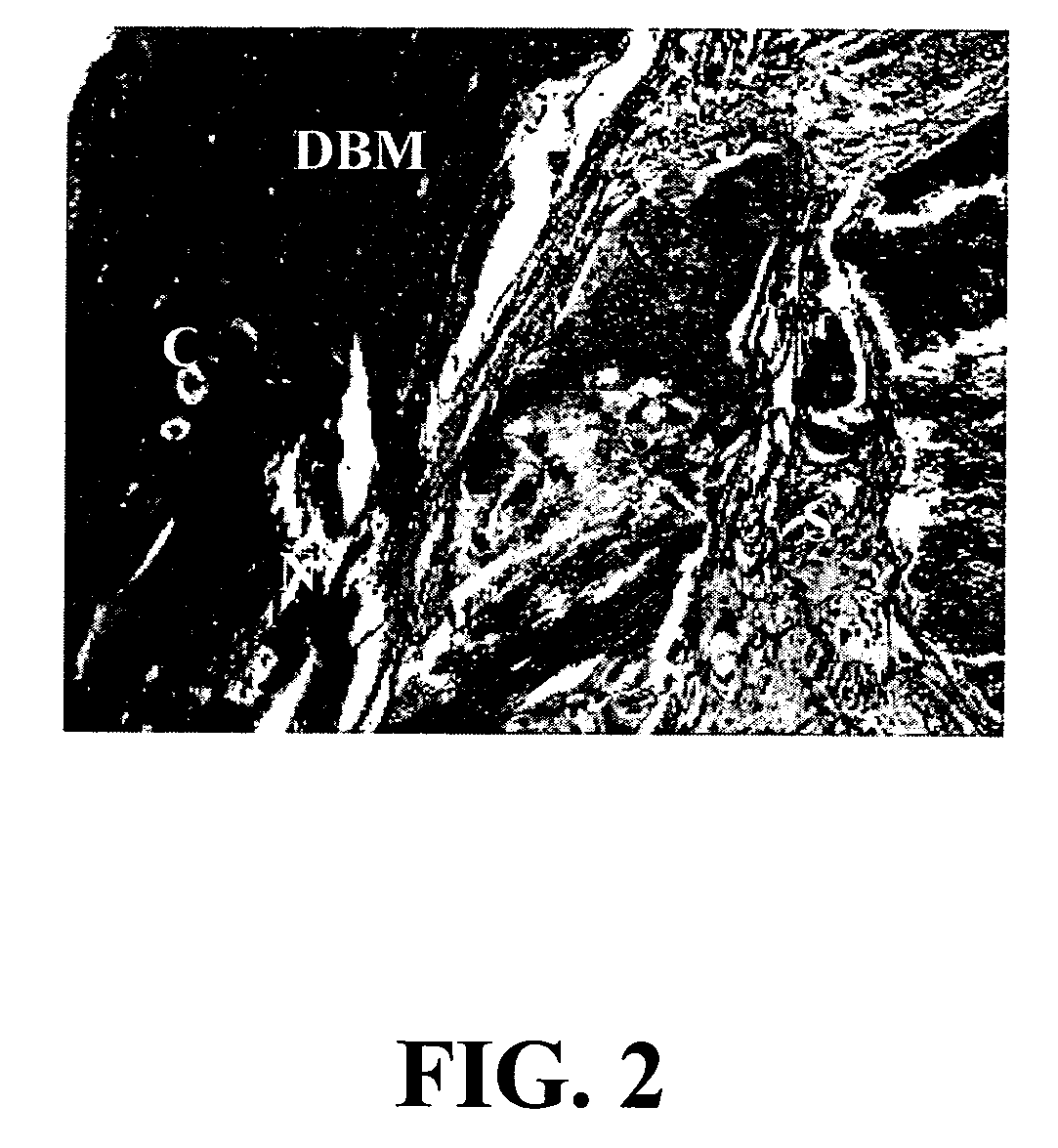
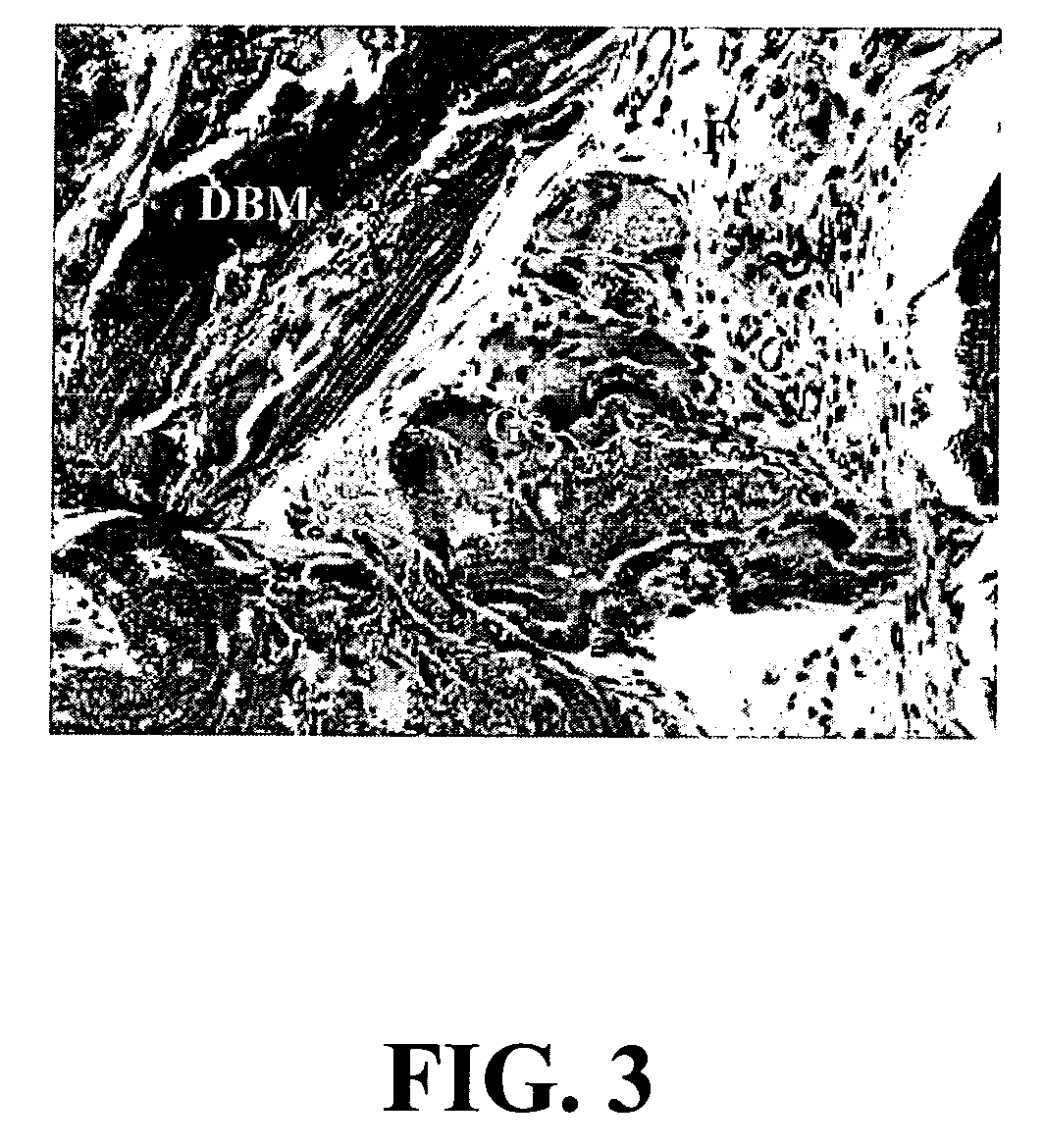
A composition comprising a collagen protein and demineralized bone matrix is described wherein the composition is chemically cross-linked with a carbodiimide such as N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC). The crosslinking reaction can be conducted in the presence of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). The collagen can be in a porous matrix or scaffolding. The DBM can be in the form of particles dispersed in the collagen. A method of making the composition is also described wherein a collagen slurry is cast into the desired shape, freeze dried to form a porous scaffolding and infitrated with a solution comprising the cross-linking agent. The composition can be used as an implant for tissue (e.g., soft tissue or bone) engineering.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
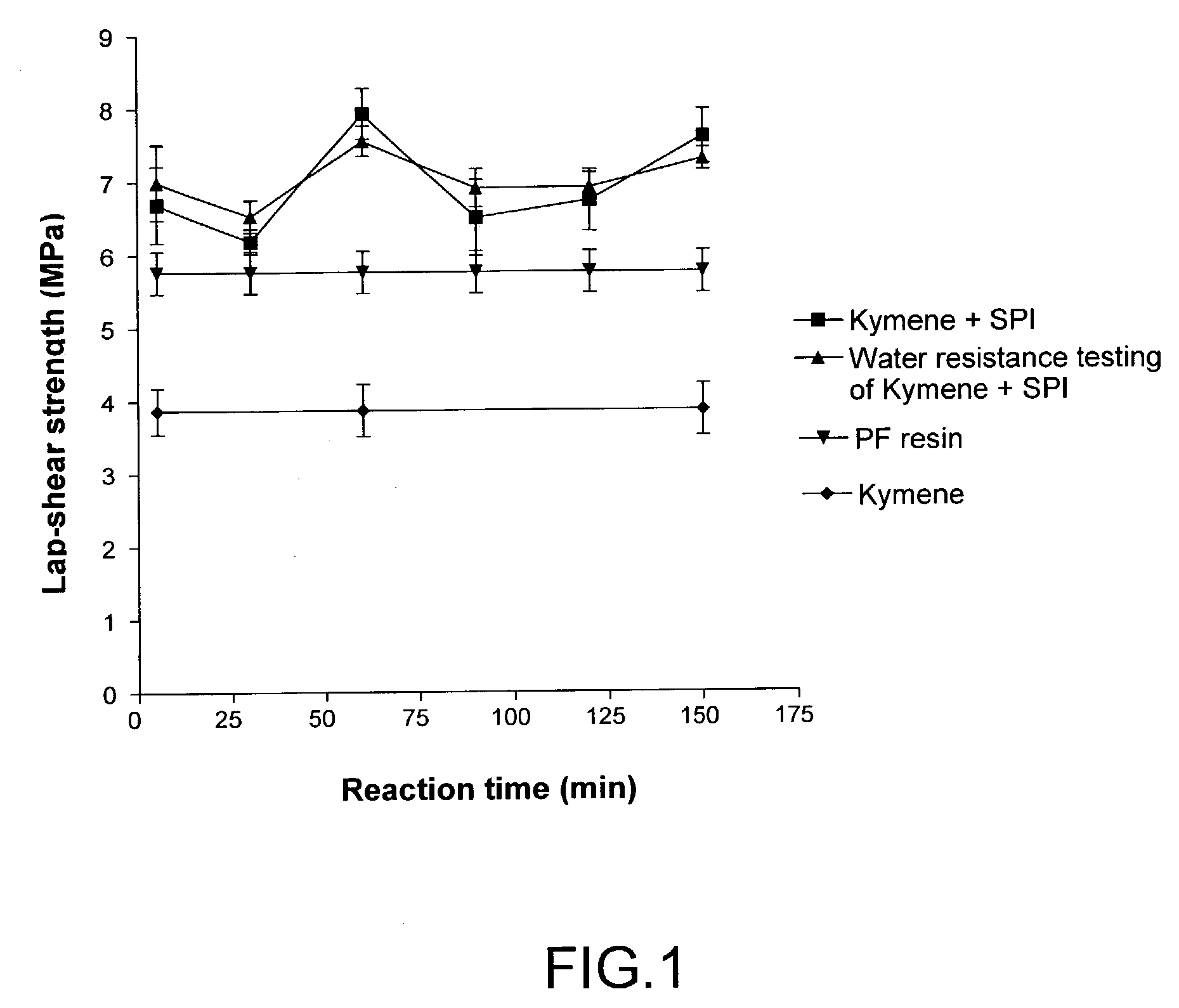
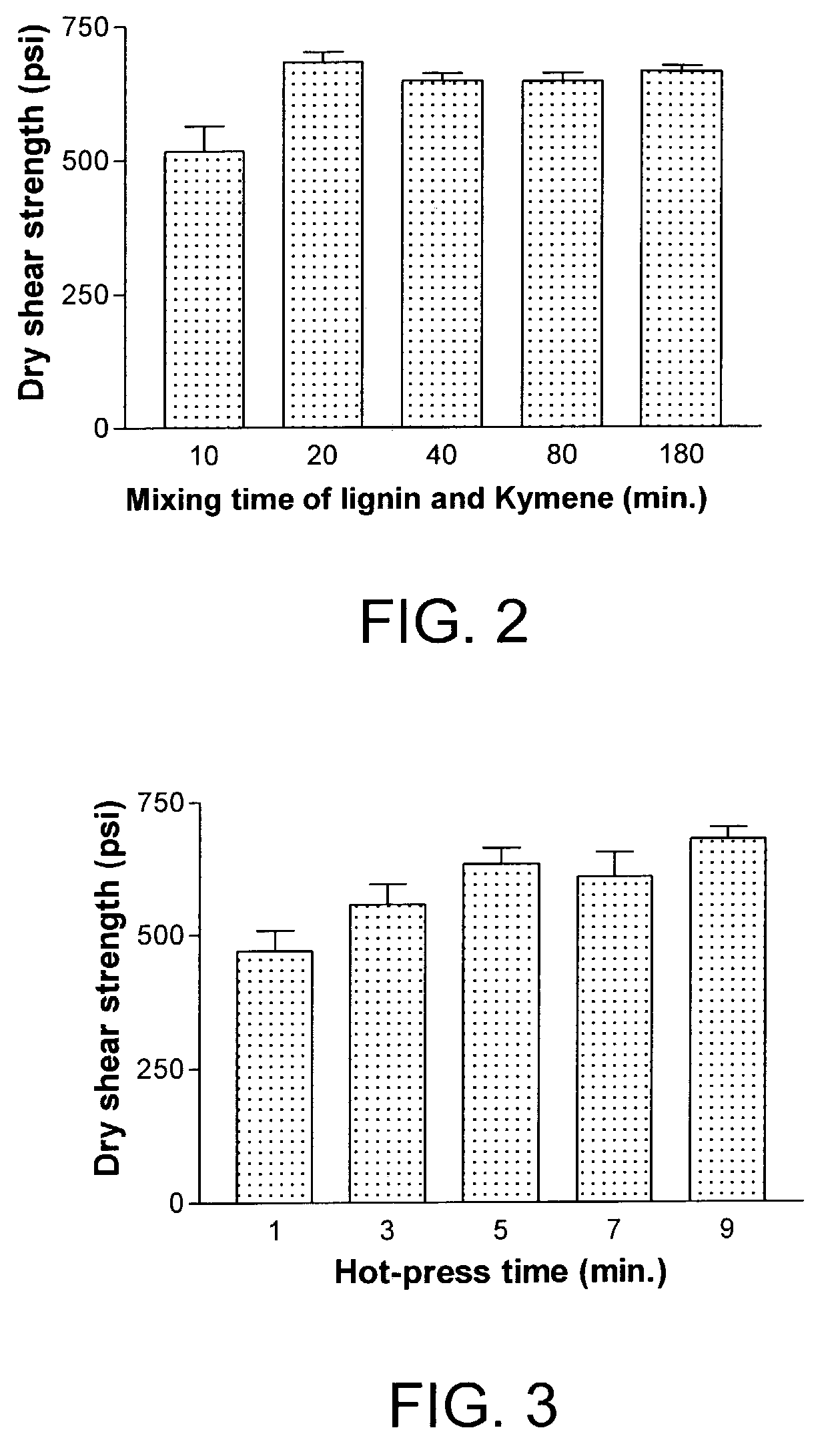
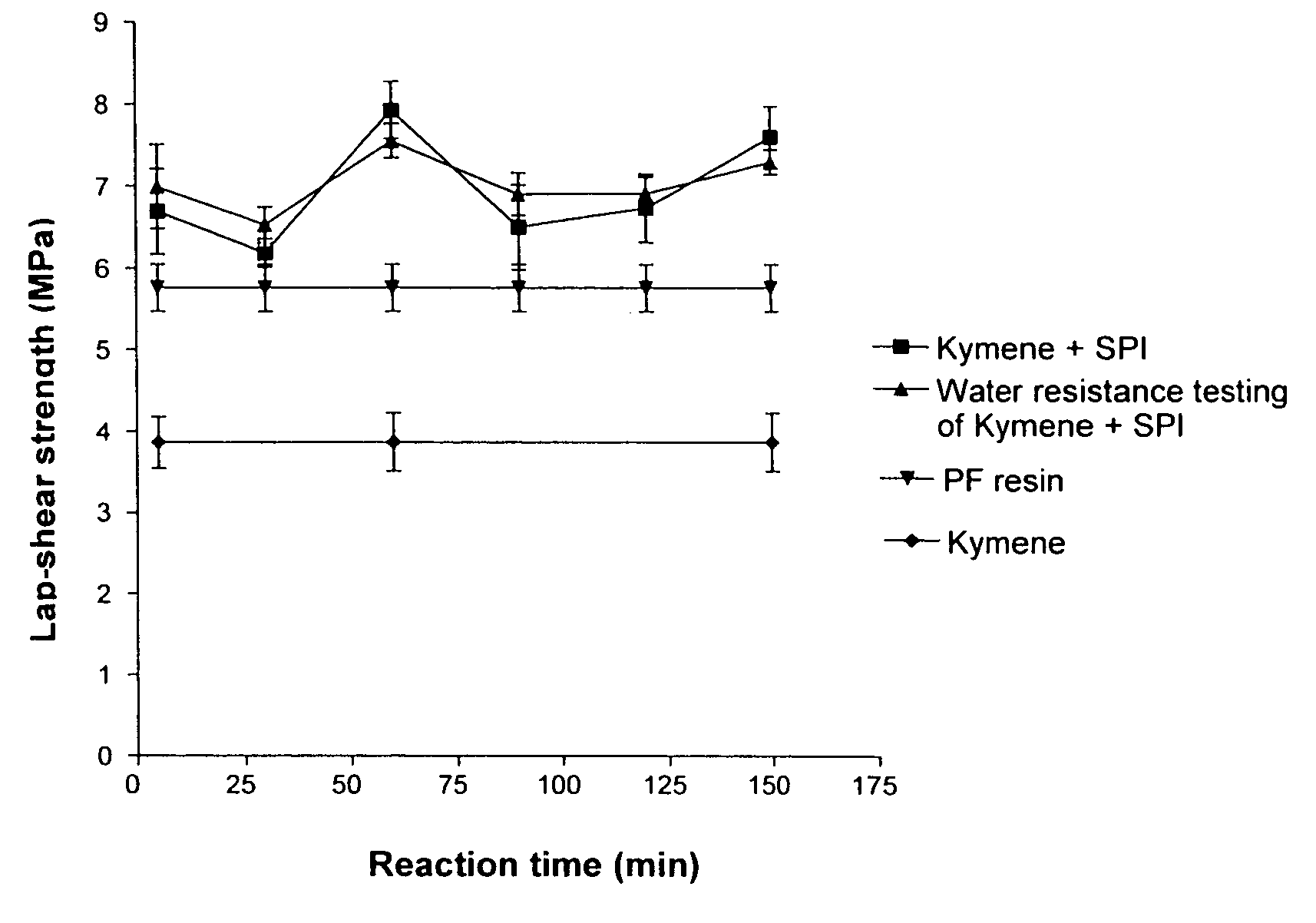
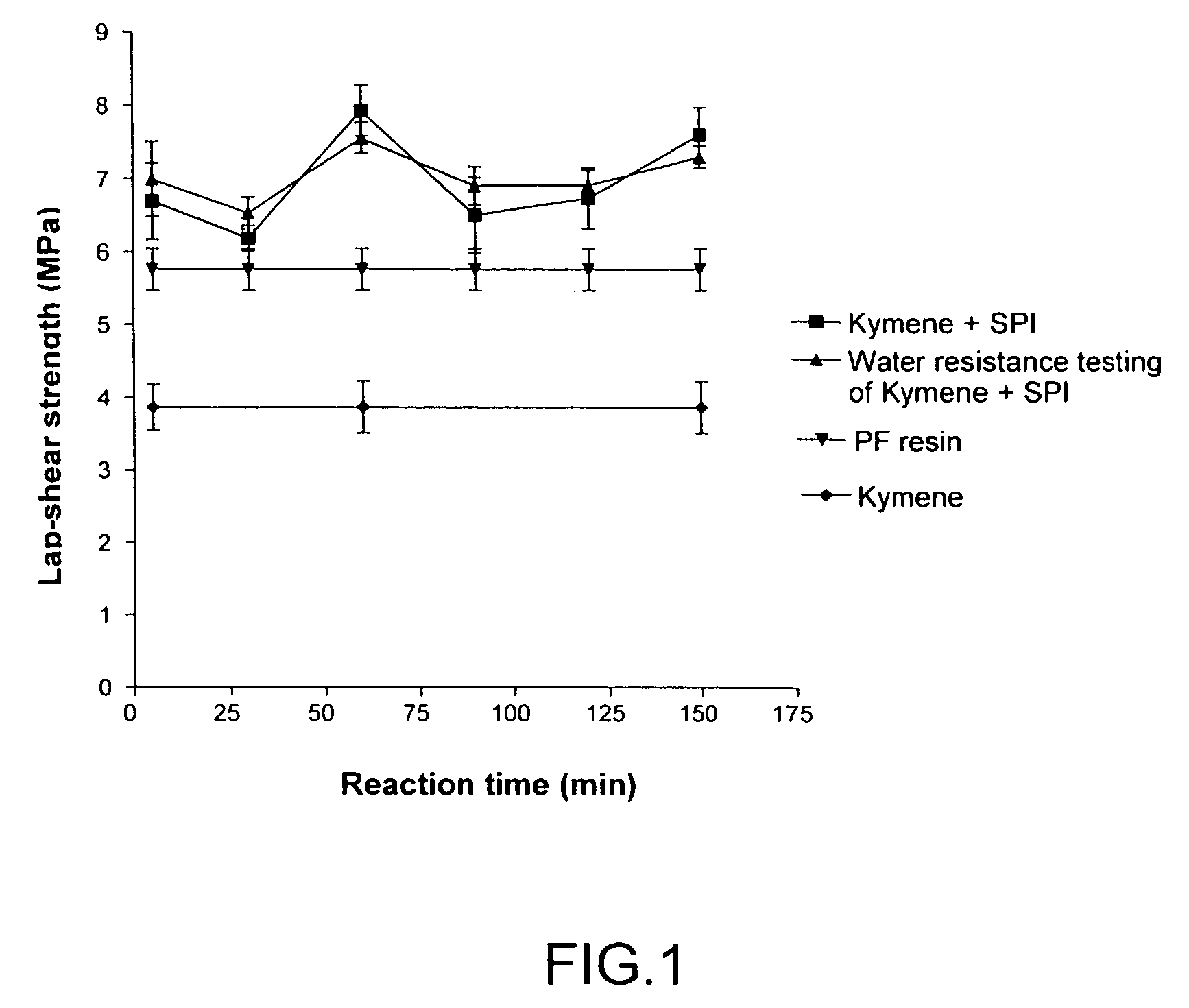
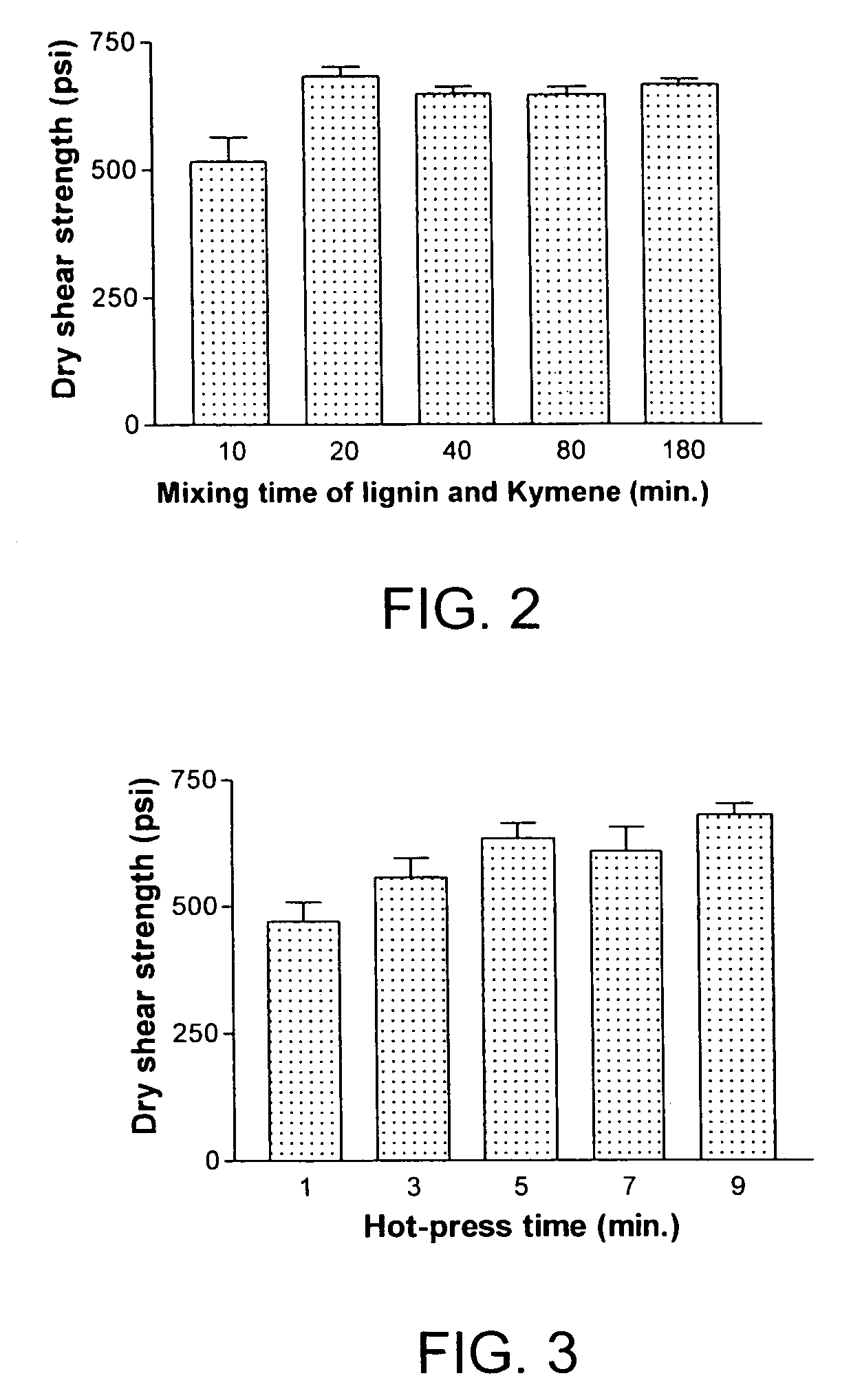
Formaldehyde-free lignocellulosic adhesives and composites made from the adhesives
Method for making lignocellulosic composites by adhering lignocellulosic substrates together. A first variant of the method involves using an adhesive composition that comprises a reaction product of (i) first ingredient selected from a soy protein or lignin and (ii) at least one substantially formaldehyde-free curing agent that includes at least one amine, amide, imine, imide, or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic functional group that can react with at least one functional group of the soy protein. A second variant of the method involves using an adhesive composition that comprises a reaction product of (i) a protein or lignin, (ii) a first compound that includes at least one amine, amide, imine, imide or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic functional group that can react with at least one functional group of the protein and (iii) a curing agent.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
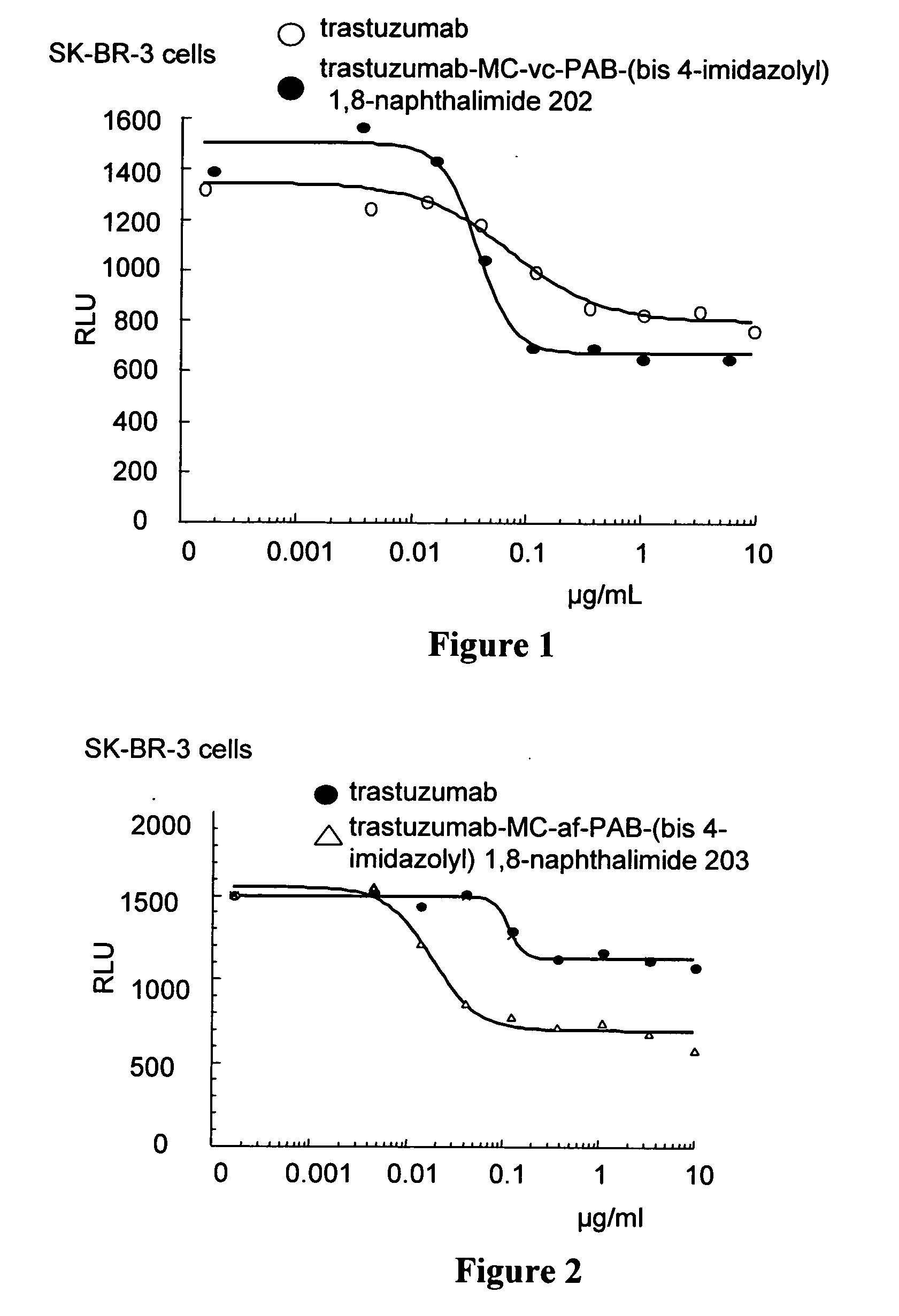
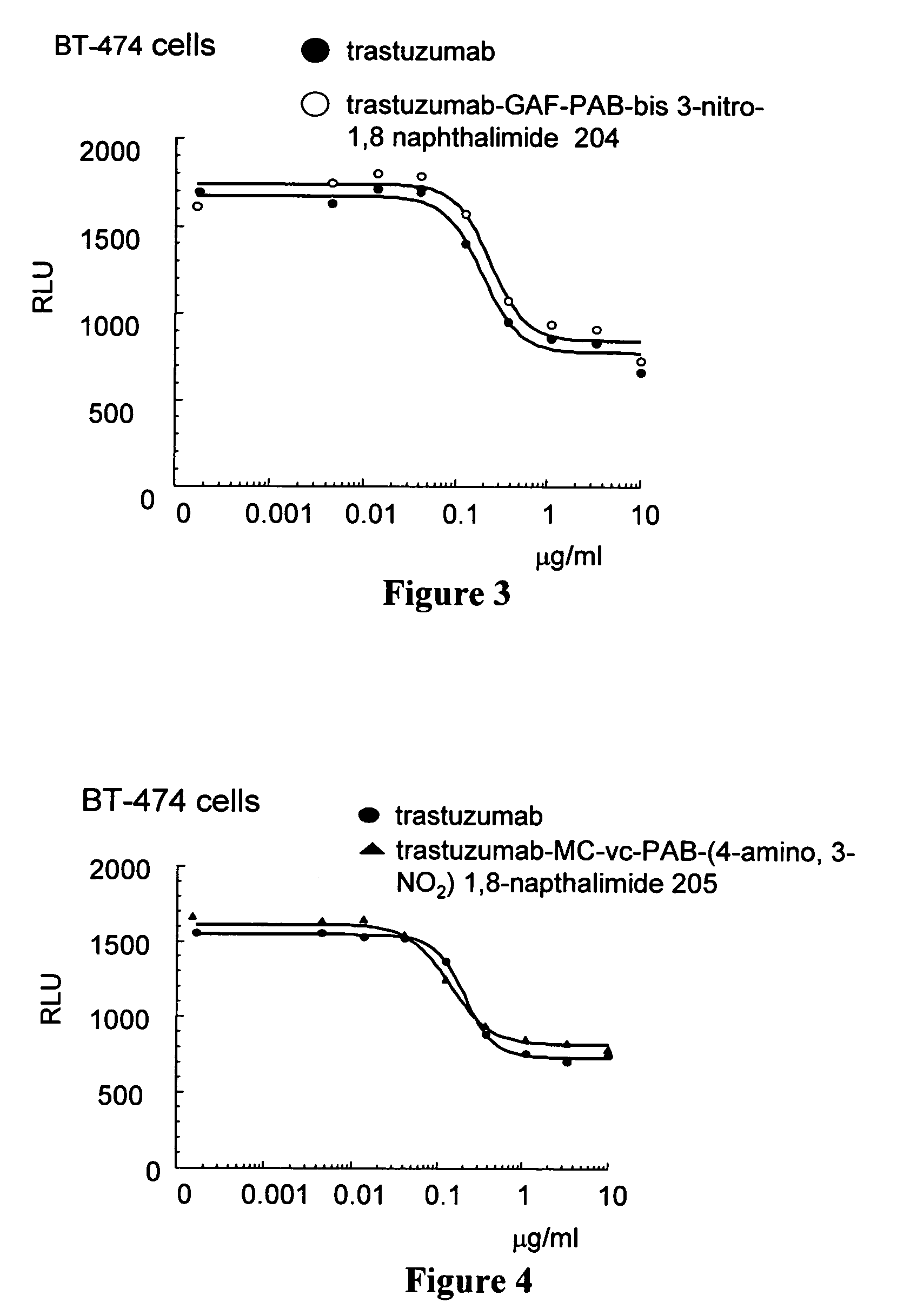
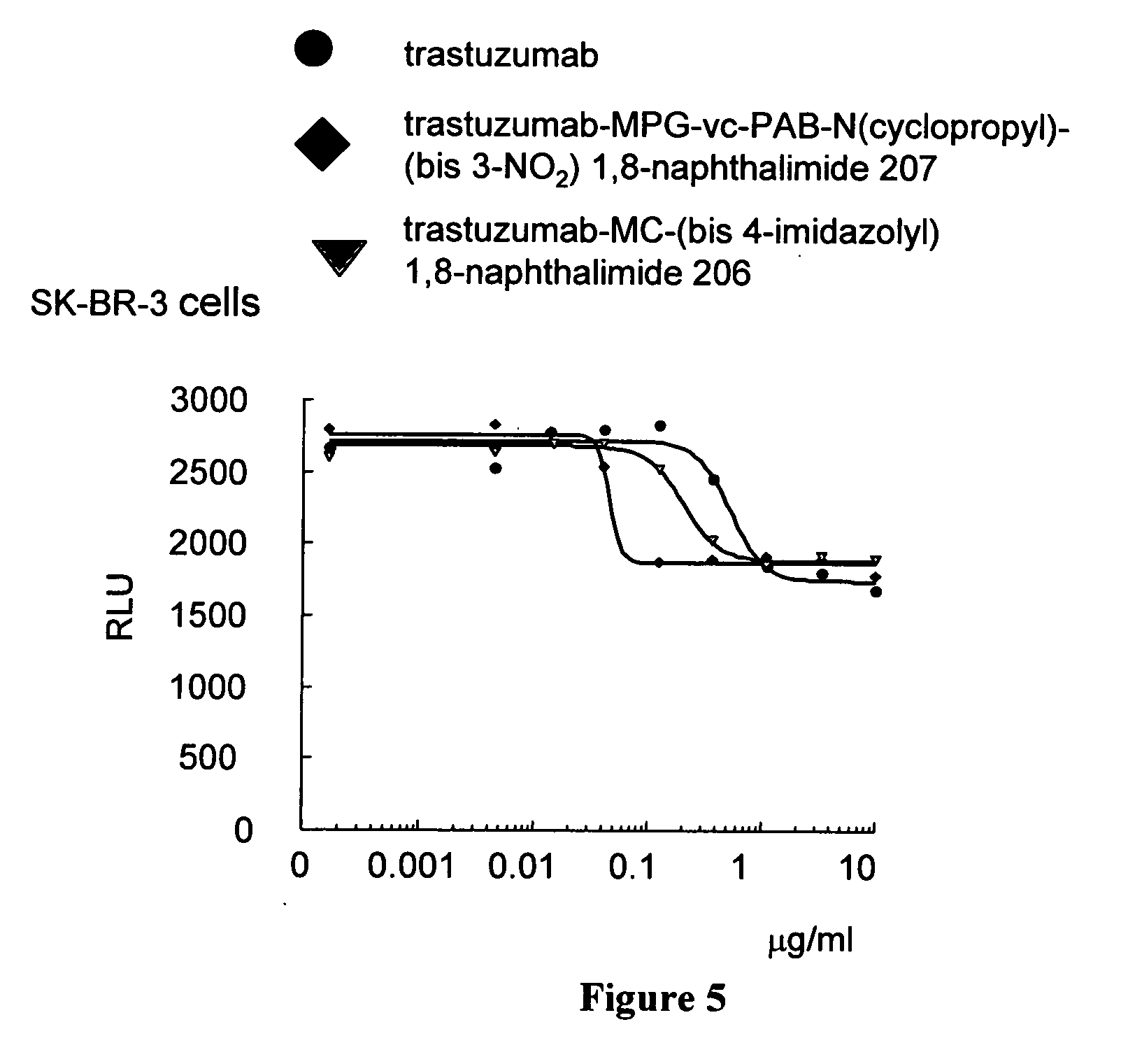
Heterocyclic-substituted bis-1,8 naphthalimide compounds, antibody drug conjugates, and methods of use
InactiveUS20060182751A1Prevent proliferationKill or inhibit the proliferation of the tumor cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseImide
The invention relates to bis 1,8 naphthalimide compounds including antibody drug conjugate (ADC) compounds represented by Formula I: Ab-(L-D)p I where one or more 1,8 bis-naphthalimide drug moieties (D) having Formulas IIa and IIb are covalently linked, through the wavy line, by a linker (L) to an antibody (Ab). The invention also relates to heterocyclic-substituted 1,8 bis-naphthalimide compounds having Formula XV The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of a Formula I ADC or Formula XV heterocyclic-substituted 1,8 bis-naphthalimide compound for treatment of hyperproliferative disorders and other disorders. The invention also relates to methods for killing or inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells or cancer cells including administering to a patient an effective amount of a Formula I ADC or Formula XV compound.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
High carbon content filamentary membrane and method of making the same
A high carbon content membrane and method for making the same are disclosed. The carbon membrane includes an asymmetric hollow filamentary carbon membrane, including a partial carbonization product of an asymmetric hollow filament including an aromatic imide polymer material. The carbon membrane is at least 95 weight percent carbon, and has a dense layer located in the outside surface portion of the hollow filamentary membrane and a porous base layer continued from the dense layer and located in the inside portion of the hollow filamentary membrane. A process for separating CO2 from natural gas is described including: contacting a mixture of CO2 and natural gas with a first side of a carbon membrane in a manner to cause a portion of the mixture to pass through the carbon membrane to a permeate side. The resulting mixture on the permeate side becomes enriched in CO2 over that of the mixture on the first side. The contacting step occurs at a pressure of at least about 200 psia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for preparing bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine alkali metal salt
ActiveCN101747242AAvoid product agglomerationSimple and efficient operationSulfonic acid amide preparationSolventDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine alkali metal salt. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting sulfamide and thionyl chloride and chlorosulfonic acid to prepare bi-(sulfonyl chlorine) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl chlorine sulfonyl) imine, reacting with antimony trifluoride and potassium carbonate (rubidium or caesium) to obtain corresponding high-purity bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt or (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt, performing double decomposition exchange reaction using the potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt with the lithium perchlorate (or sodium) or lithium tetrafluoroborate (or sodium) in the aprotic polar solvent to obtain corresponding lithium (or sodium) salt with high purity. The method in the invention has the characteristics of simple operating steps, easy separation and extraction of output, high purity and yield, no environmental pollution, and the like, and is suitable for mass industrial production.
Owner:武汉市瑞华新能源科技有限公司
Soft compounds derived from polypropylene grafted disubstituted ethylene- maleimide copolymers
The instant invention teaches a method for enabling the formation of a high damping, soft polymer gel. The method includes: reacting a poly(disubstituted ethylene-co-maleimide) polymer with a maleated polyalkylene and an alkyl diamine under substantially dry conditions sufficient to form a polyalkylene grafted poly(disubstituted ethylene-co-maleimide) polymer product; and, dispersing the polyalkylene grafted poly(disubstituted ethylene-co-maleimide) polymer product with an extender oil sufficient to form the gel. The instant invention also contemplates a polymer gel composition, a polymer composition and an article manufactured from the polymer gel composition.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Olefin block copolymers, processes for producing the same and uses thereof
Olefin block copolymers (A-1) are disclosed represented by the formula (I) PO1-g1-B1 . . . (I) wherein PO1 is a segment comprised of repeating units derived from an olefin having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, g1 is an ester, ether, amide, imide, urethane, urea, silylether or carbonyl linkage, and B1 is a segment containing an unsaturated hydrocarbon or a hetero atom. The olefin block copolymers are suitable for uses in adhesives, various molded articles such as construction and civil engineering materials, automobile interior and exterior materials, gasoline tanks, electric and electronic parts, medical care and sanitation materials, materials of miscellaneous goods, resin materials having environmental degradation properties, films and sheets, modifiers and dispersions.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Formaldehyde-free lignocellulosic adhesives and composites made from the adhesives
Method for making lignocellulosic composites by adhering lignocellulosic substrates together. A first variant of the method involves using an adhesive composition that comprises a reaction product of (i) first ingredient selected from a soy protein or lignin and (ii) at least one substantially formaldehyde-free curing agent that includes at least one amine, amide, imine, imide, or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic functional group that can react with at least one functional group of the soy protein. A second variant of the method involves using an adhesive composition that comprises a reaction product of (i) a protein or lignin, (ii) a first compound that includes at least one amine, amide, imine, imide or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic functional group that can react with at least one functional group of the protein and (iii) a curing agent.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
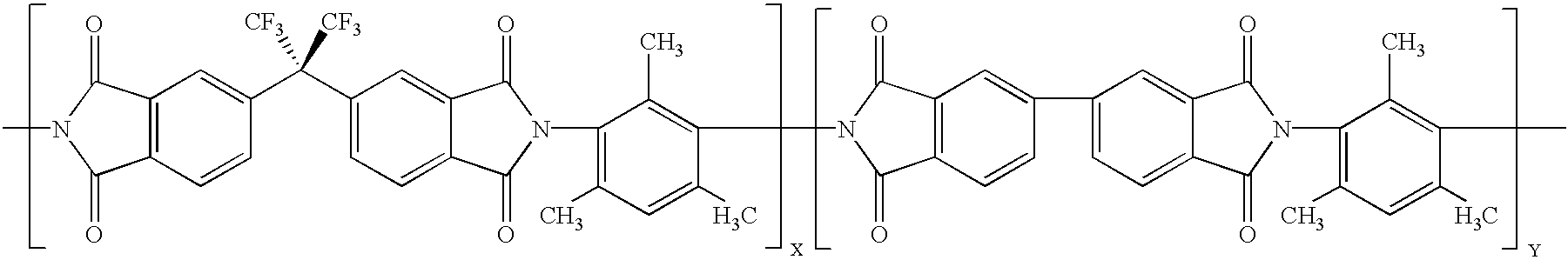
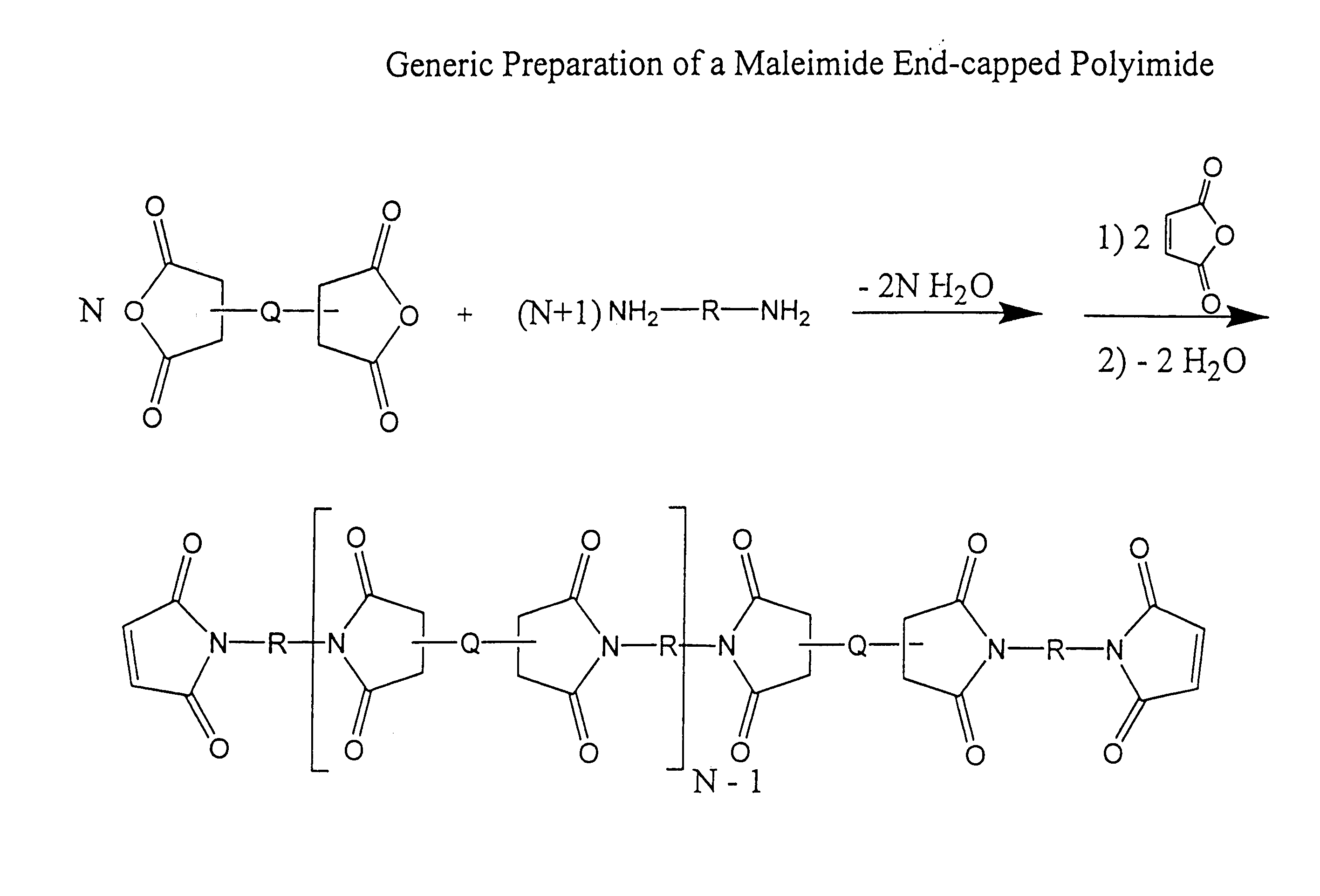
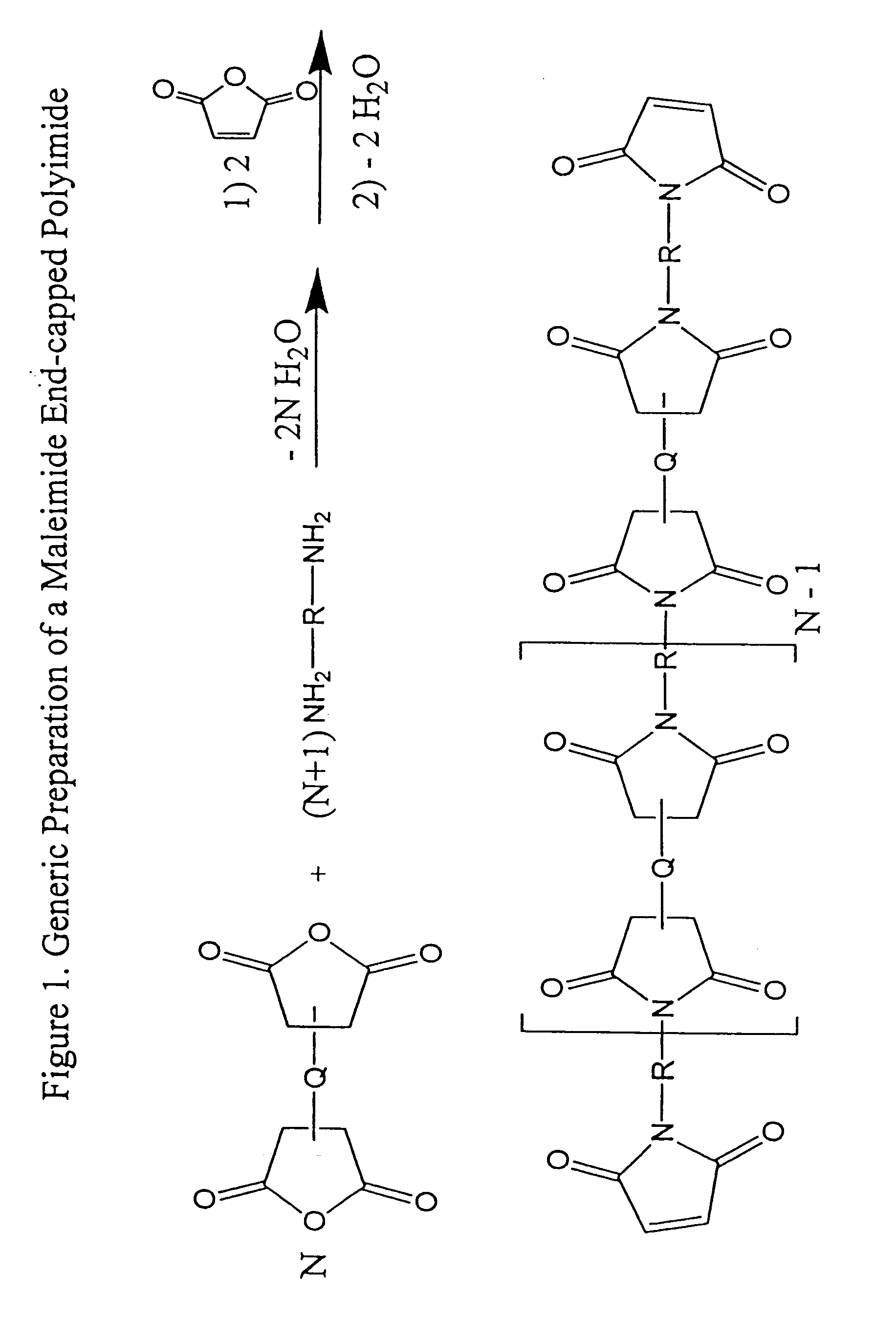
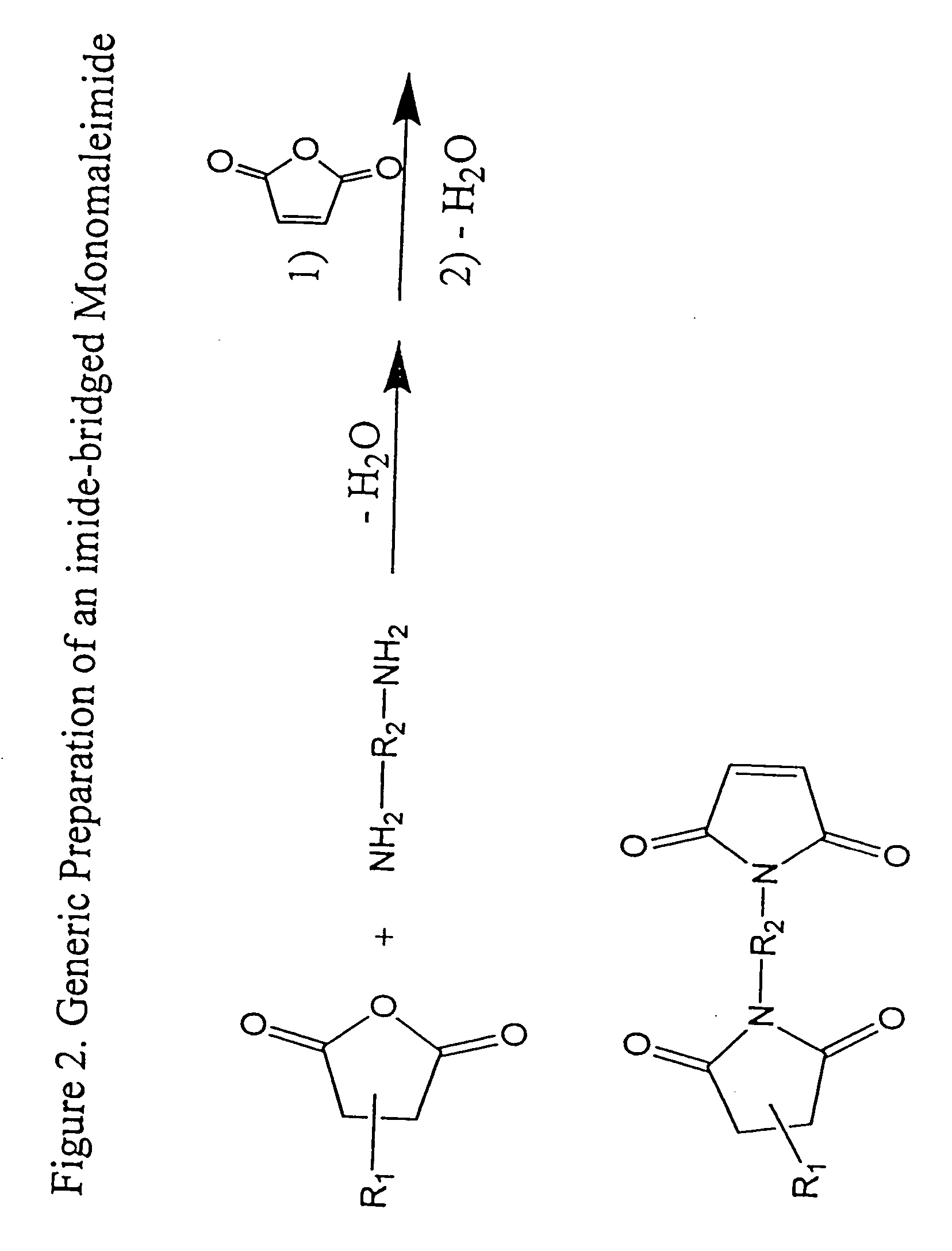
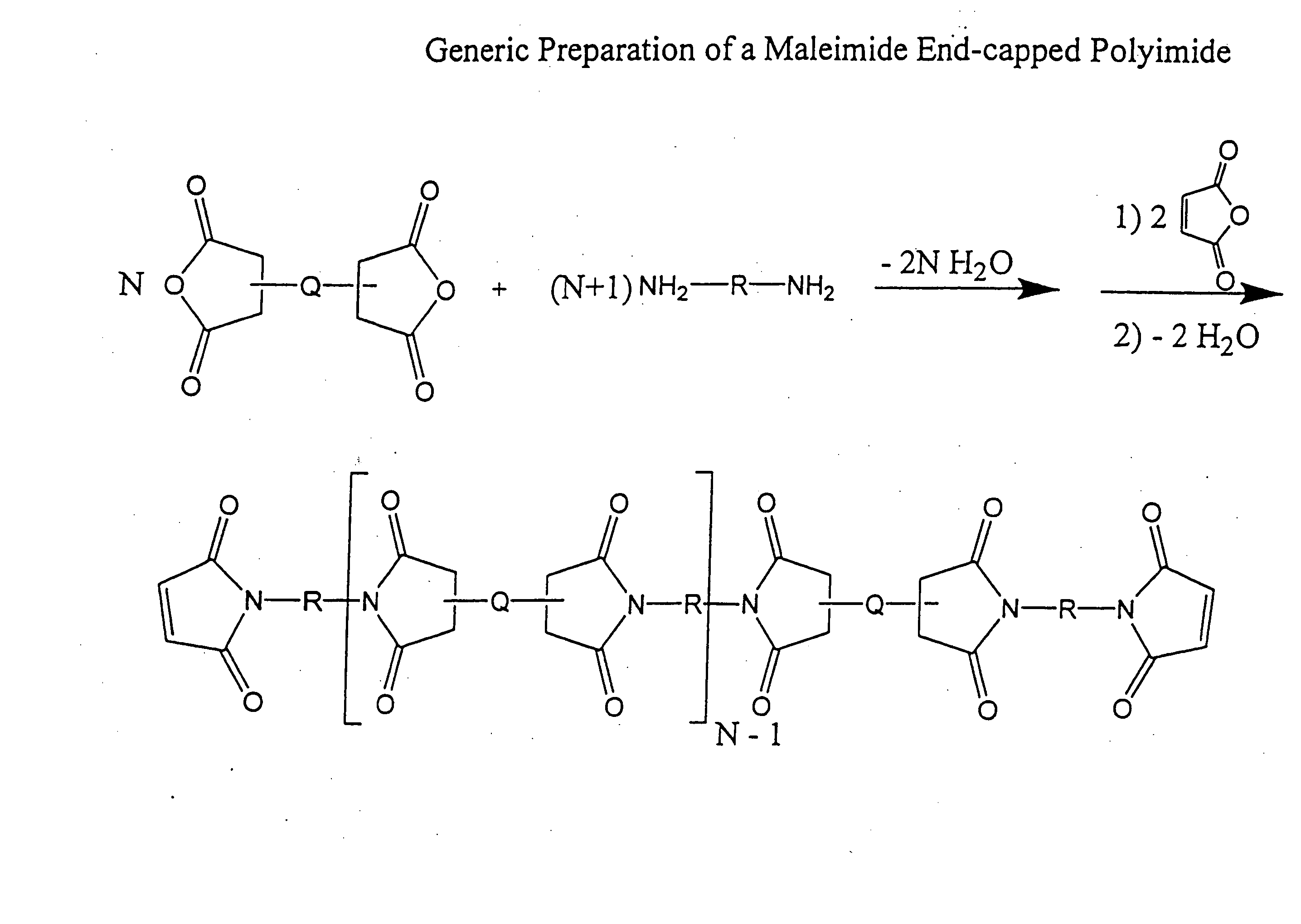
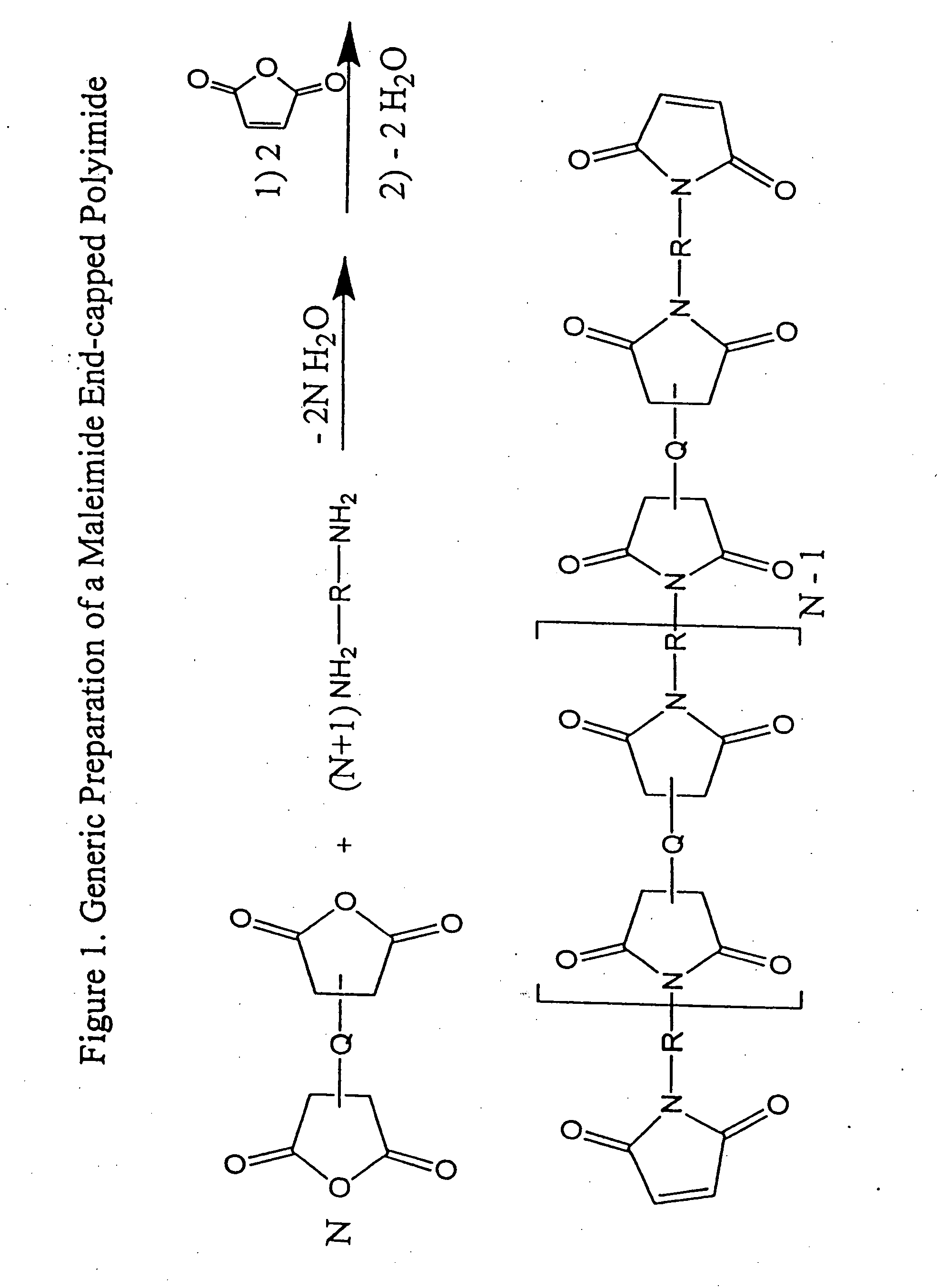
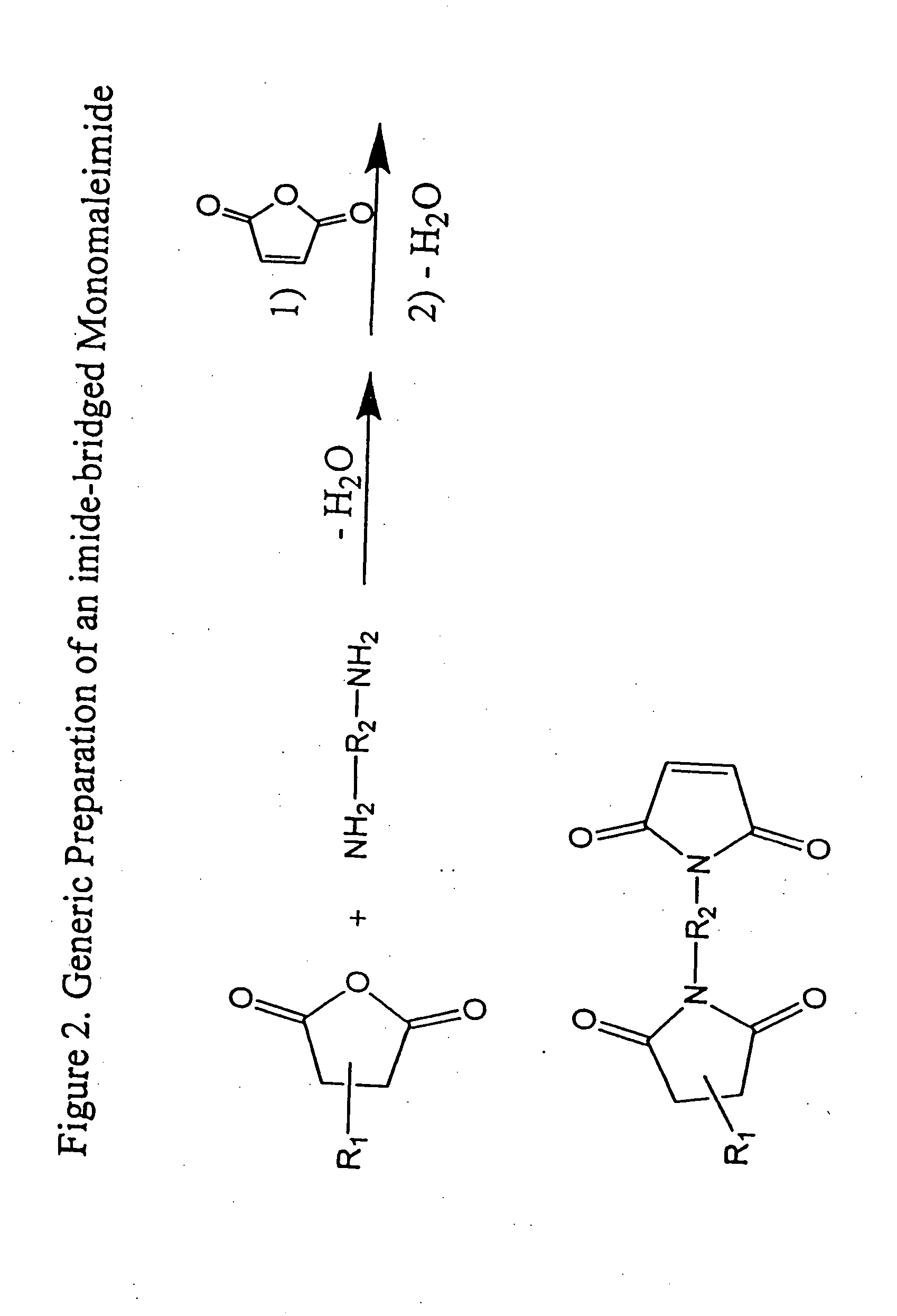
Imide-linked maleimide and polymaleimide compounds
ActiveUS7208566B2Improve toughnessNot sacrificing thermal stabilityOrganic chemistryAdhesivesPolyamine CompoundImide
The invention is based on the discovery that a remarkable improvement in the performance of maleimide thermosets can be achieved through the incorporation of imide-extended mono-, bis-, or polymaleimide compounds. These imide-extended maleimide compounds are readily prepared by the condensation of appropriate anhydrides with appropriate diamines to give amine terminated compounds. These compounds are then condensed with excess maleic anhydride to yield imide-extended maleimide compounds.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
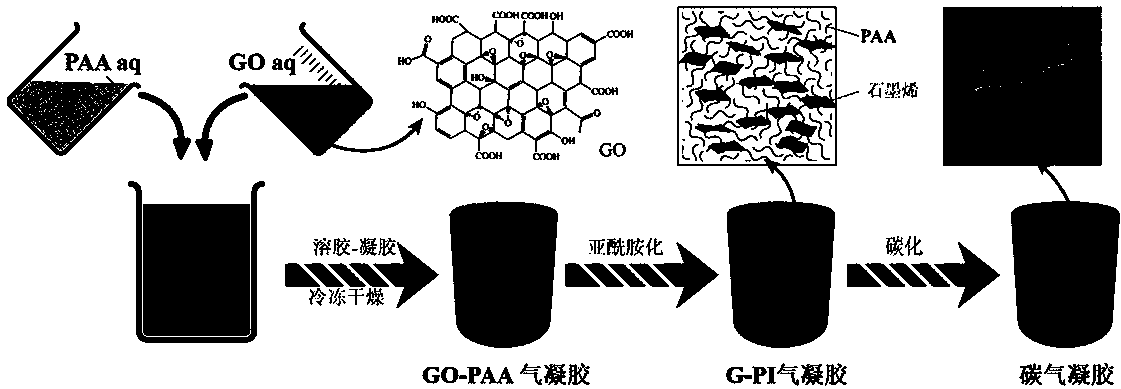
Preparation method of graphene/polyimide-based carbon aerogel
InactiveCN104355302AEasy to makeThe preparation process is environmentally friendlyFreeze-dryingNew energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanoporous material, namely carbon aerogel, and particularly relates to graphene oxide-crosslinked polyimide-based carbon aerogel and a preparation method thereof. The invention carbon aerogel is prepared by crosslinking polyamide acid aerogel by graphene oxide, and comprises the components of graphene oxide and one or more water-soluble polyimide precursor-polyamide acids. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing an aqueous graphene oxide solution with the water-soluble polyimide precursor-polyamide acid, and preparing graphene oxide / polyamide acid aerogel through sol-gel and freeze-drying processes; preparing the graphene / polyimide-based carbon aerogel through thermal imidization and high temperature carbonization. According to the preparation method, a toxic reagent formaldehyde is not used; the prepared carbon aerogel has a mesoporous, microporous and macroporous three-level three-dimensional network porous structure, high specific surface area, high conductivity and stable physical and chemical properties, and is an ideal electrode material for preparing a supercapacitor and other new energy devices and a high-performance adsorbent material.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Automotive-wire insulation
InactiveUS6359230B1Excellent physical toughnessResistant to oxidationPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyesterInter layer
The invention pertains to multi-layer polymeric formulations for protecting or insulating metallic objects, and, more particularly, to an integrated, tri-layer, thin-wall insulation composite, for use in a high temperature, automotive-wire article. The tri-layer design comprises an inner layer of a fluoropolymer, polyether sulfone, polyether-ketone, polyetherimide, or thermoplastic polyester; a middle layer comprising a polyolefin; and an outer layer comprising a fluoropolymer. The inner and outer layers serve to protect the middle polyolefinic layer from degradation.
Owner:CHAMPLAIN CABLE CORP
Electrolytes for electrooptic devices comprising ionic liquids
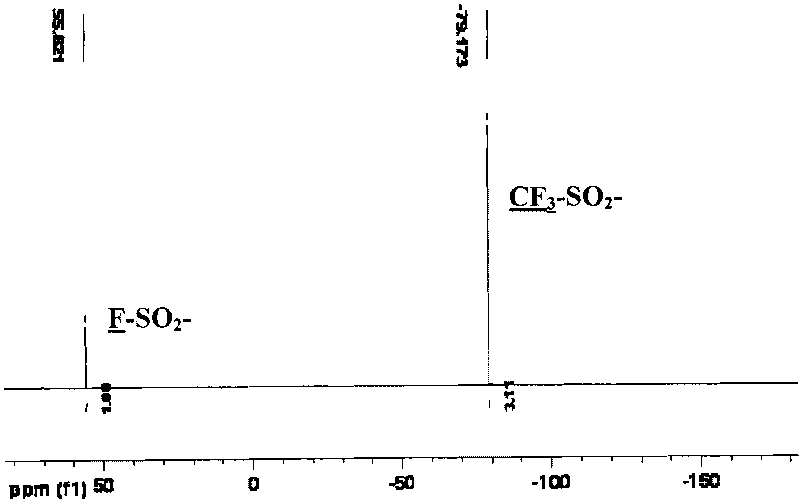
Electrolyte solutions of soluble bifunctional redox dyes in molten salt solvent may be used to prepare electrooptic devices with enhanced stability toward ultraviolet radiation. The solvents include lithium or quaternary ammonium cations, and perfluorinated sulfonylimide anions selected from trifluoromethylsulfonate (CF3SO3−), bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ((CF3SO2)2N−), bis(perfluoroethylsulfonyl)imide ((CF3CF2SO2)2N−) and tris(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)methide ((CF3SO2)3C−).
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Methods for producing and purifying 2-hydrocarbyl-3,3-bis(4-hydroxyaryl)phthalimidine monomers and polycarbonates derived therefrom
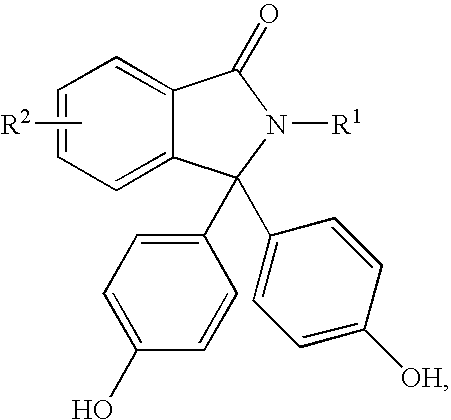
Disclosed herein is a method for producing a 2-hydrocarbyl-3,3-bis(4-hydroxyaryl)phthalimidine. The method comprises forming a reaction mixture comprising at least one substituted or unsubstituted phenolphthalein, at least one substituted or unsubstituted primary hydrocarbyl amine, and an acid catalyst; and heating the reaction mixture to a temperature of less than 180° C. to remove a distillate comprising water and form a crude 2-hydrocarbyl-3,3-bis(4-hydroxyaryl)phthalimidine product; where the 2-hydrocarbyl-3,3-bis(4-hydroxyaryl)phthalimidine has a formula: where R1 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen and a hydrocarbyl group, and R2 is selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen, a hydrocarbyl group, and a halogen.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
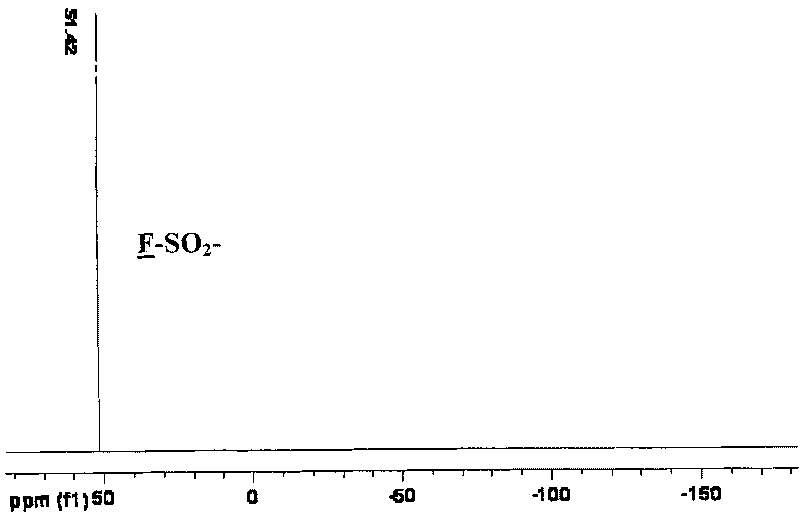
Synthesis of bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide
The present invention provides methods for producing bis(fluorosulfonyl) compounds of the formula:F—S(O)2—Z—S(O)2—F Iby contacting a nonfluorohalide compound of the formula:X—S(O)2—Z—S(O)2—Xwith bismuth trifluoride under conditions sufficient to produce the bis(fluorosulfonyl) compound of Formula I, where Z and X are those defined herein.
Owner:SES HLDG PTE LTD
High performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes
In the present invention high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes and methods for making and using these membranes have been developed. The cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes are prepared by: 1) first synthesizing polyimide polymers comprising pendent functional groups (e.g., —OH or —SH) ortho to the heterocyclic imide nitrogen and cross-linkable functional groups in the polymer backbone; 2) fabricating polyimide membranes from these polymers; 3) converting the polyimide membranes to polybenzoxazole or polybenzothiazole membranes by heating under inert atmosphere such as nitrogen or vacuum; and 4) finally converting the membranes to high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole or polybenzothiazole membranes by a crosslinking treatment, preferably UV radiation. The membranes can be fabricated into any convenient geometry. The high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes of the present invention are suitable for a variety of liquid, gas, and vapor separations.
Owner:UOP LLC
Copolymerized polyimide nanofiber nonwoven and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101974828AHigh mechanical strengthElectrospun copolyimide nanofiber nonwovens with this property are tear-resistantMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentCell component detailsPorosityTear resistance
The invention relates to a copolymerized polyimide nanofiber nonwoven and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: reacting a tetracid dianhydride monomer with a diamine monomer by taking a high-polar solvent as a reaction medium; performing condensation polymerization through mechanical agitation in a reaction kettle to form copolymerized polyimide acid solution; performing electrostatic spinning on the copolymerized polyimide acid solution in a high-voltage electric field so as to obtain the copolymerized polyimide nanofiber nonwoven; performing imidization on the nonwoven at a high temperature to prepare the copolymerized polyimide nanofiber nonwoven which has the characteristics of high tear resistance, high porosity, high temperature and low temperature resistance and high mechanical properties. The copolymerized polyimide nanofiber nonwoven is mainly used for battery diaphragms and capacitor diaphragms.
Owner:JIANGXI XIAN CAI NANOFIBERS TECH
High performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes
InactiveUS8127936B2High selectivityImprove stabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesImidePolymer science
In the present invention high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes and methods for making and using these membranes have been developed. The cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes are prepared by: 1) first synthesizing polyimide polymers comprising pendent functional groups (e.g., —OH or —SH) ortho to the heterocyclic imide nitrogen and cross-linkable functional groups in the polymer backbone; 2) fabricating polyimide membranes from these polymers; 3) converting the polyimide membranes to polybenzoxazole or polybenzothiazole membranes by heating under inert atmosphere such as nitrogen or vacuum; and 4) finally converting the membranes to high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole or polybenzothiazole membranes by a crosslinking treatment, preferably UV radiation. The membranes can be fabricated into any convenient geometry. The high performance cross-linked polybenzoxazole and polybenzothiazole polymer membranes of the present invention are suitable for a variety of liquid, gas, and vapor separations.
Owner:UOP LLC
Transparent film
InactiveUS20050096431A1Small retardationMeasurement wavelength dependence can be easily controlledSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsImideSide chain
A film is provided which comprises a thermoplastic resin A having a substituted or non-substituted imide group at a side chain of the resin A, and a thermoplastic resin B having a substituted or non-substituted phenyl group and a nitrile group at a side chain of the resin B. The film has a retardation value of 0 to 1000 nm, a light transmission of 85% or more, and a haze of 2% or less.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Adhesive polyethylene compositions and multi-layer laminated films using the same
InactiveUS6210765B1Improve adhesion strengthHigh heat sealing strength heatWrappers shrinkageShrinkage connectionsElastomerPolyamide
Disclosed is a specific adhesive polyethylene composition comprising [1] a modified ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer resin or elastomer obtained by modifying a specific ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer resin or elastomer, each of which comprises ethylene and an alpha-olefin of 3 to 20 carbon atoms, with an unsaturated carboxylic acid or anhydride, ester, amide, imide or metallic salt derivative of a unsaturated carboxylic acid thereof, [2] an unmodified ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer resin and / or an unmodified ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer elastomer and [3] a tackifier. Also disclosed is a multi-layer laminated film of 3 or more layers in which a layer of the above composition is interposed between an ethylene polymer layer and either a polyamide resin layer, an ethylene / vinyl alcohol copolymer layer or a layer of a mixture of polyamide resin and ethylene / vinyl alcohol copolymer. The adhesive polyethylene composition shows excellent adhesion strength to ethylene polymers, polyamide resins and ethylene / vinyl alcohol copolymers, high heat-sealing strength and heat resistance. The multi-layer laminated film shows excellent strength, heat resistance and gas barrier properties, and besides this film has heat shrinkability, so that the film is suitably used as a shrink film.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Halogen-free resin composition and copper clad laminate and printed circuit board using same
ActiveUS20130075138A1Low dissipation factorHigh heat resistancePrinted circuit aspectsSynthetic resin layered productsLow dissipationStyrene maleic anhydride
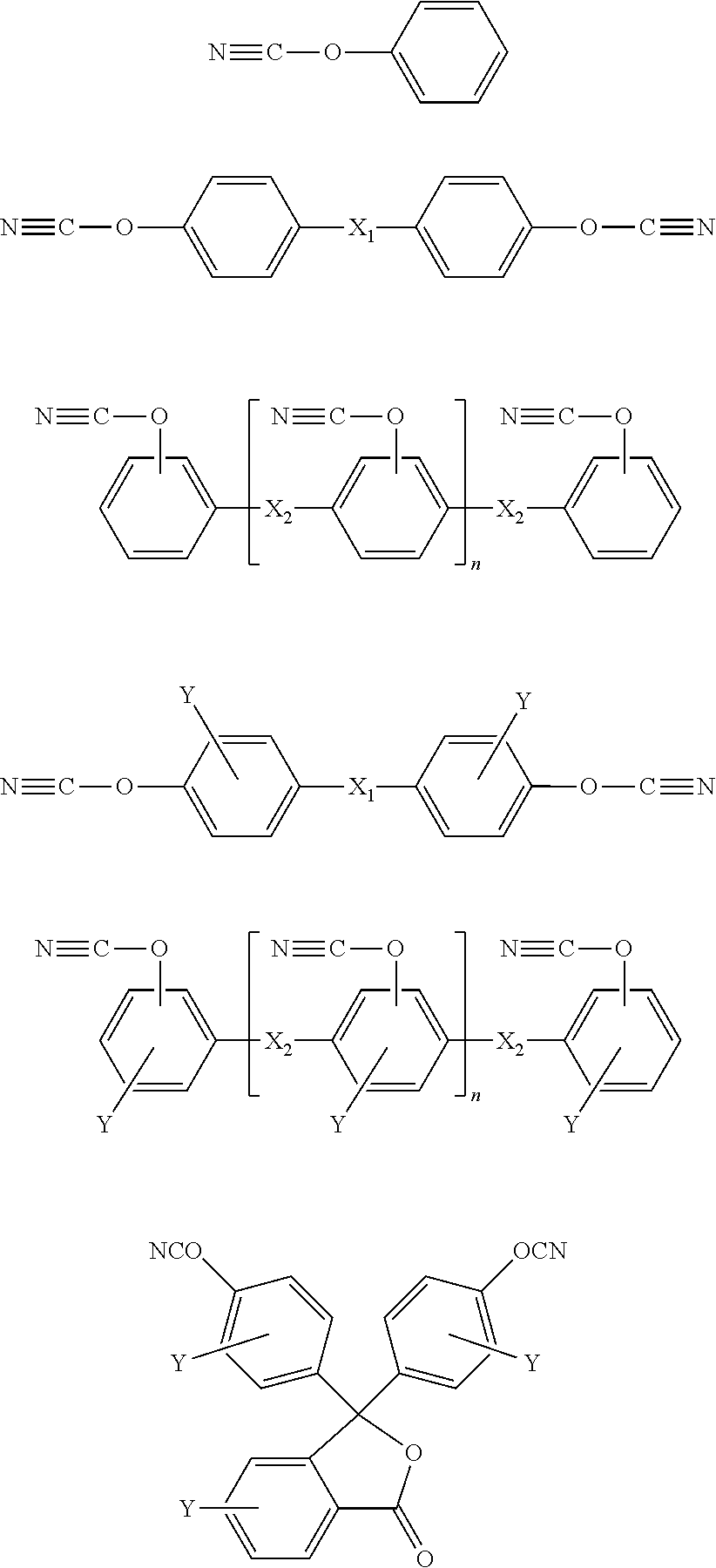
The halogen-free resin composition comprises (A)100 parts by weight of cyanate ester resin; (B) 5 to 50 parts by weight of styrene-maleic anhydride; (C) 5 to 100 parts by weight of polyphenylene oxide resin; (D) 5 to 100 parts by weight of maleimide; (E) 10 to 150 parts by weight of phosphazene; and (F) 10 to 1000 parts by weight of inorganic filler. By using specific components at specific proportions, the halogen-free resin composition of the invention offers the features of low dielectric constant, low dissipation factor, high heat resistance and high flame retardancy, and can be made into prepreg or resin film, and thereby used in copper clad laminate or printed circuit board.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
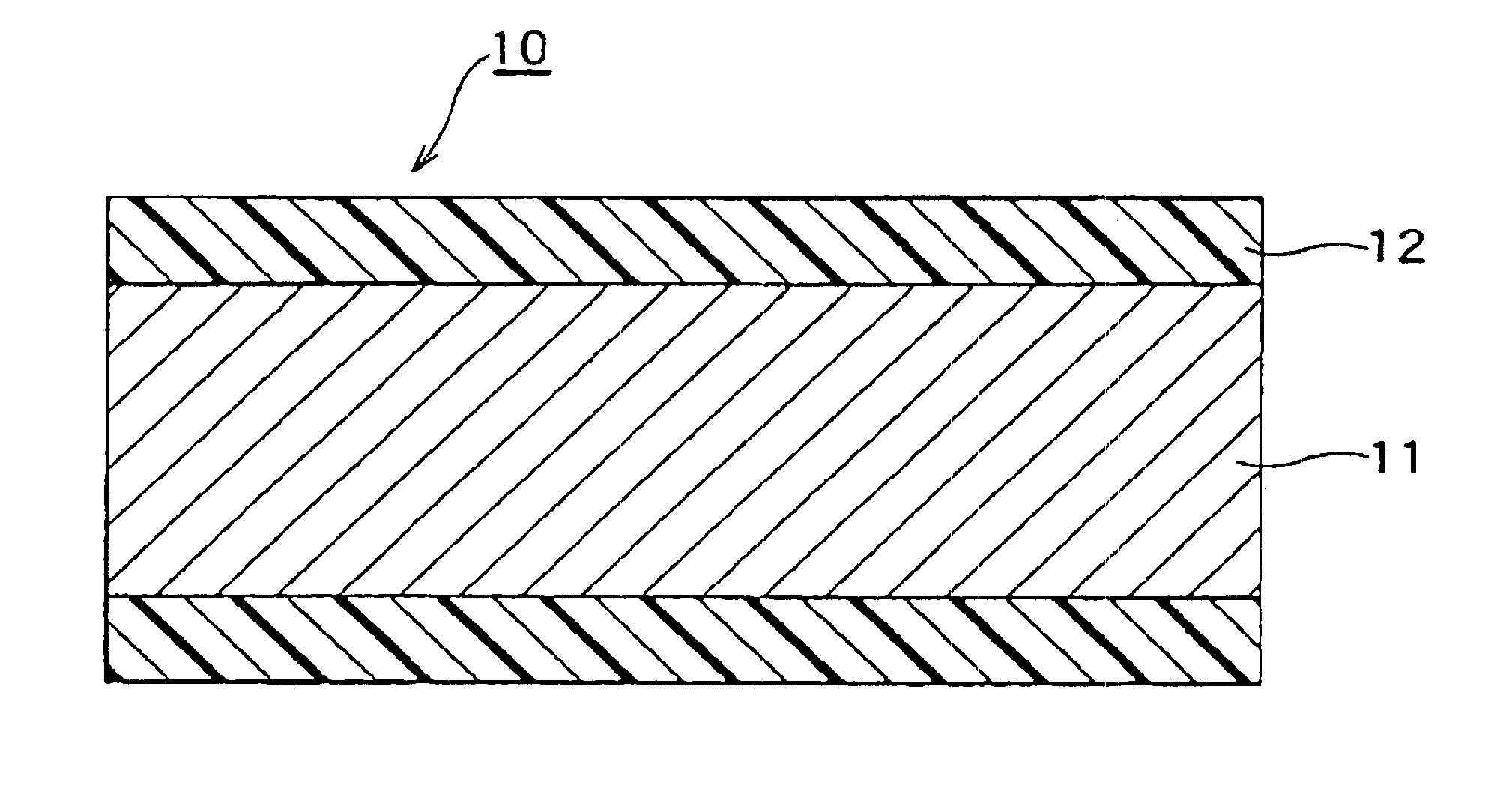
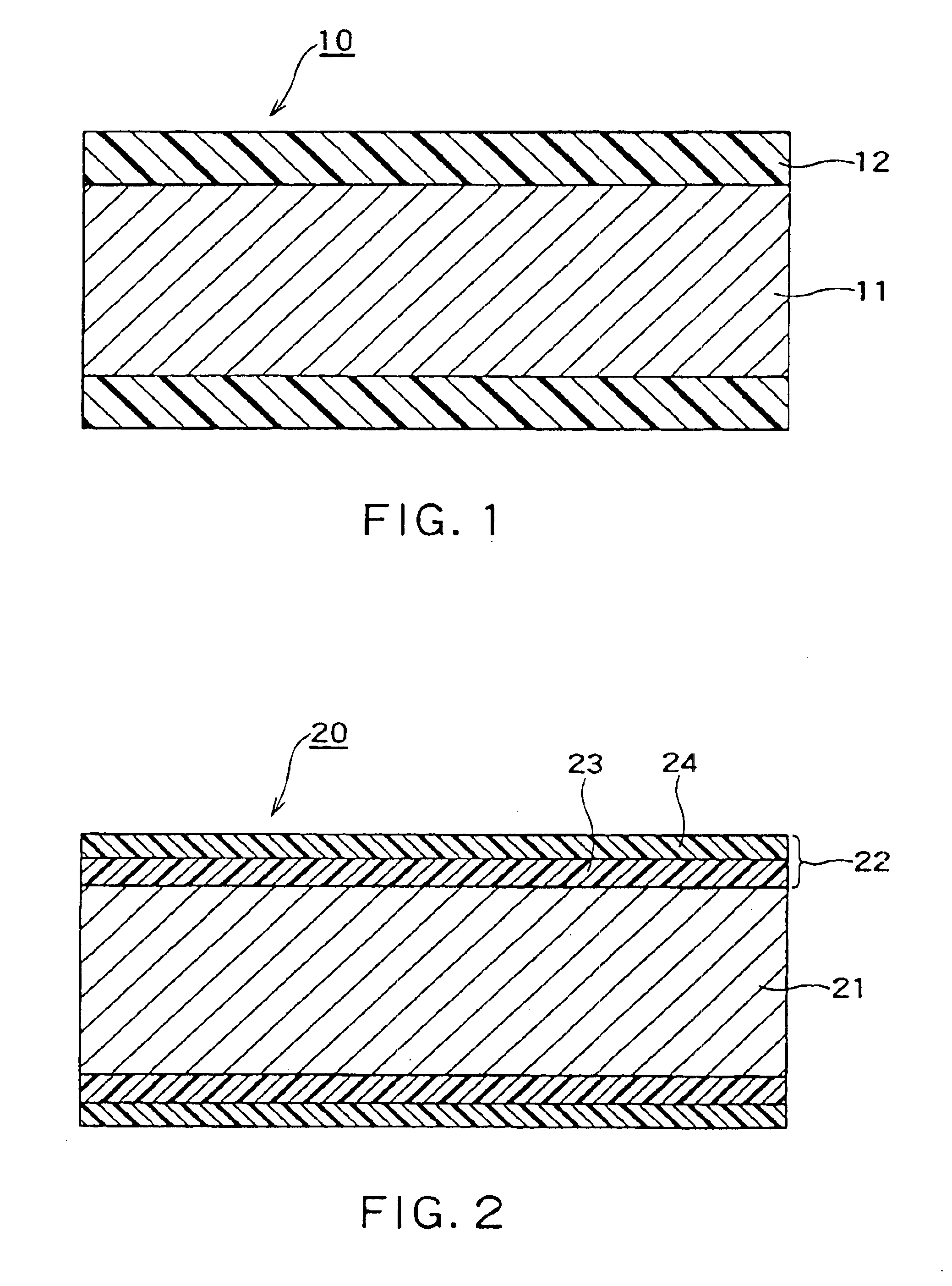
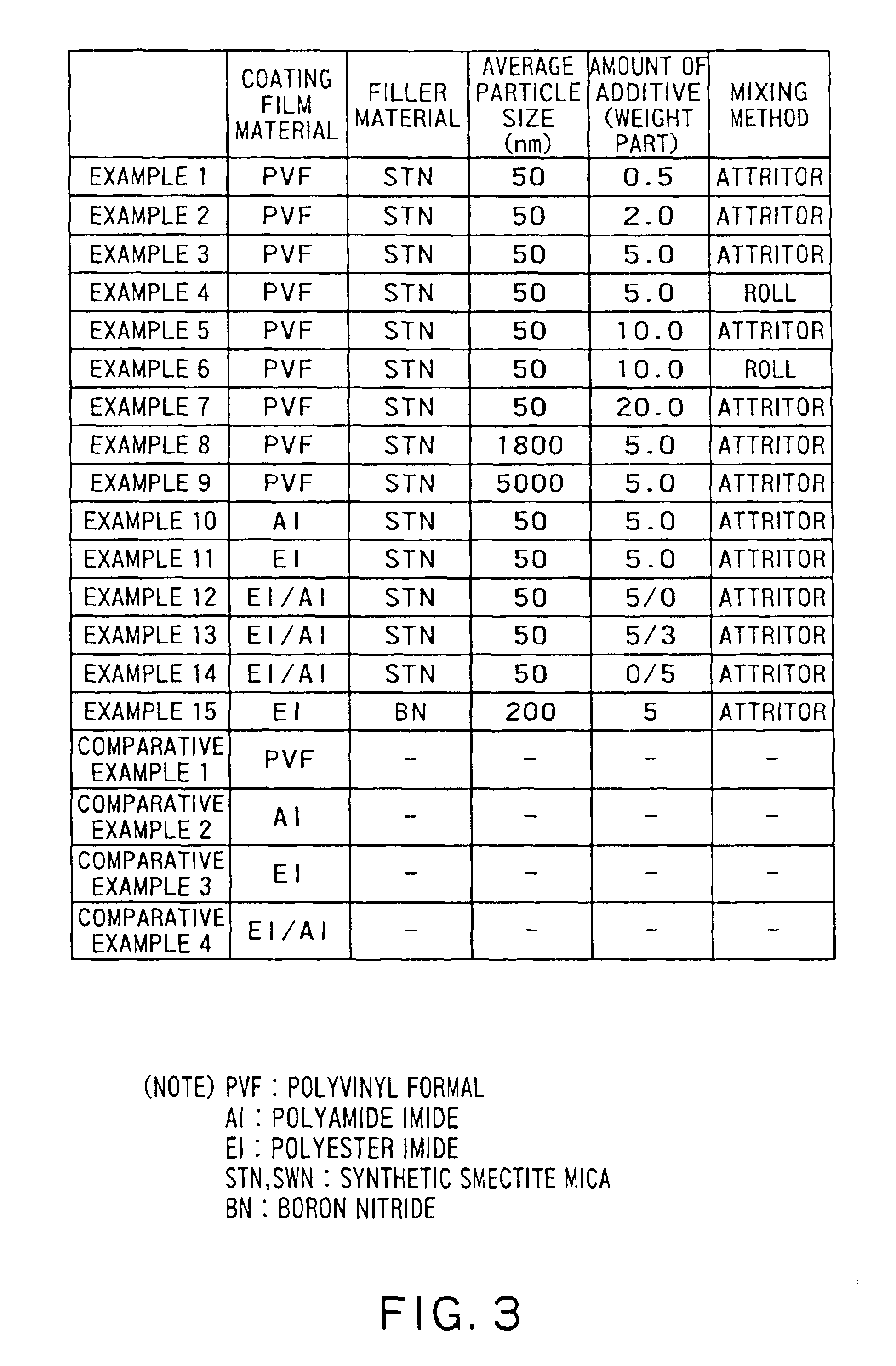
Enameled wire
InactiveUS6906258B2Improve withstand lifetimeLimited amountPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyesterImide
An enameled wire capable of improving withstand lifetime with respect to the application of surge voltage of an inverter and thermal degradation thereof while restricting an amount of an inorganic filler material is provided. The enameled wire includes an electrically conductive wire (11) and a coating (12) formed of a high molecular compound uniformly mixed with an inorganic filler material in the form of fine flat particles provided around the electrically conductive wire (11). The enameled wire may include an electrically conductive wire (21), a coating (23) formed of a polyester imide resin solution mixed with an inorganic filler material in the form of fine flat particles and provided on the conductive wire and a coating (24) formed of polyamide imide and provided on the coating (23).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Imide-linked maleimide and polymaleimide compounds
ActiveUS20080075961A1Reduce brittlenessImprove toughnessOrganic chemistrySynthetic resin layered productsImideDiamine
The invention is based on the discovery that a remarkable improvement in the performance of maleimide thermosets can be achieved through the incorporation of imide-extended mono-, bis-, or polymaleimide compounds. These imide-extended maleimide compounds are readily prepared by the condensation of appropriate anhydrides with appropriate diamines to give amine terminated compounds. These compounds are then condensed with excess maleic anhydride to yield imide-extended maleimide compounds.
Owner:DESIGNER MOLECULES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com