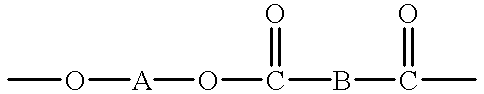
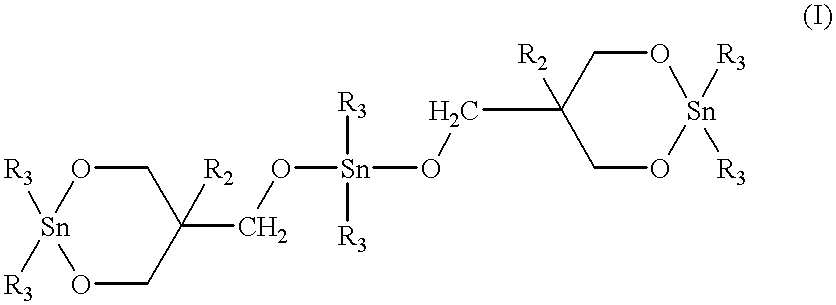
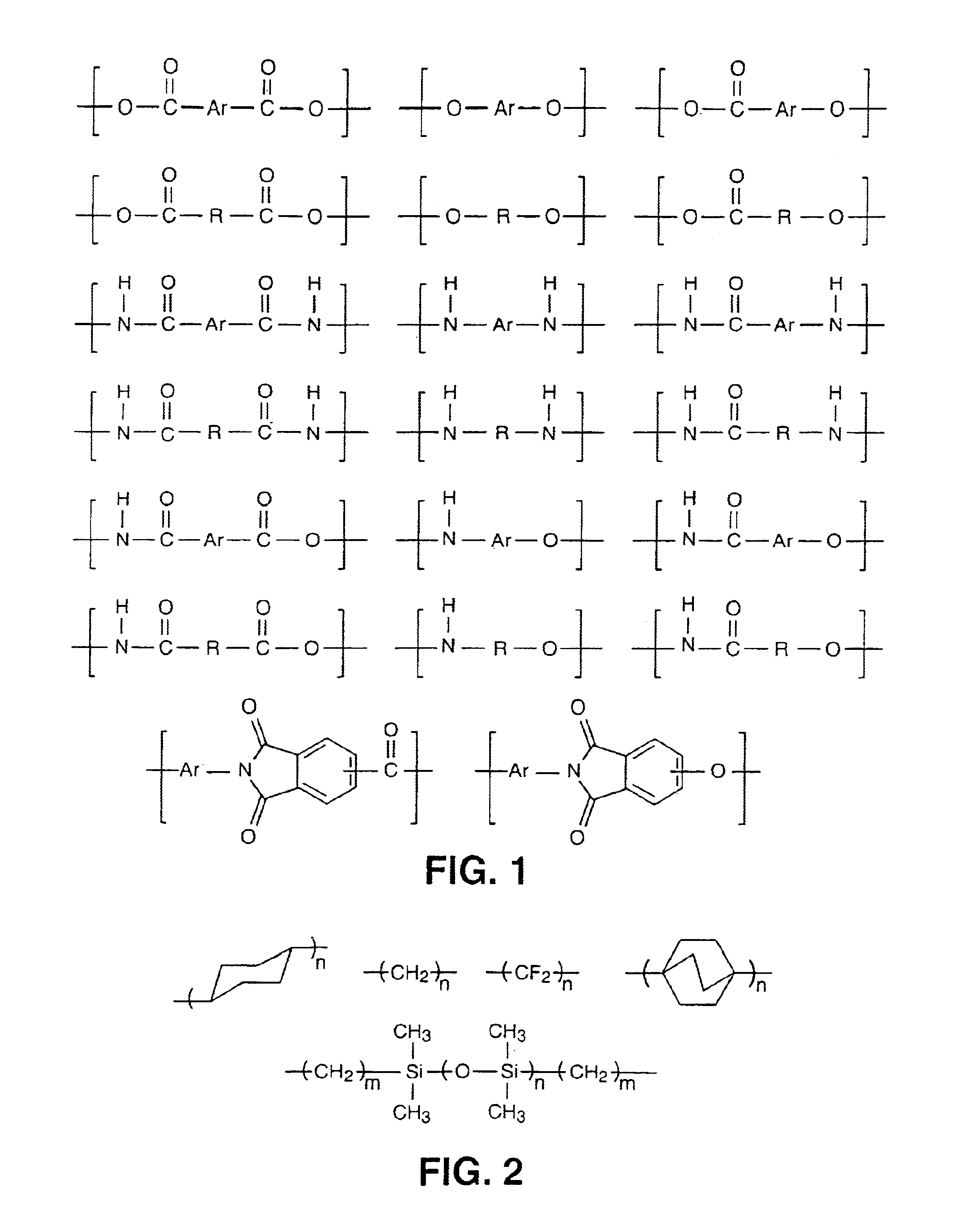
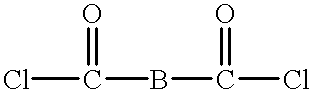Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
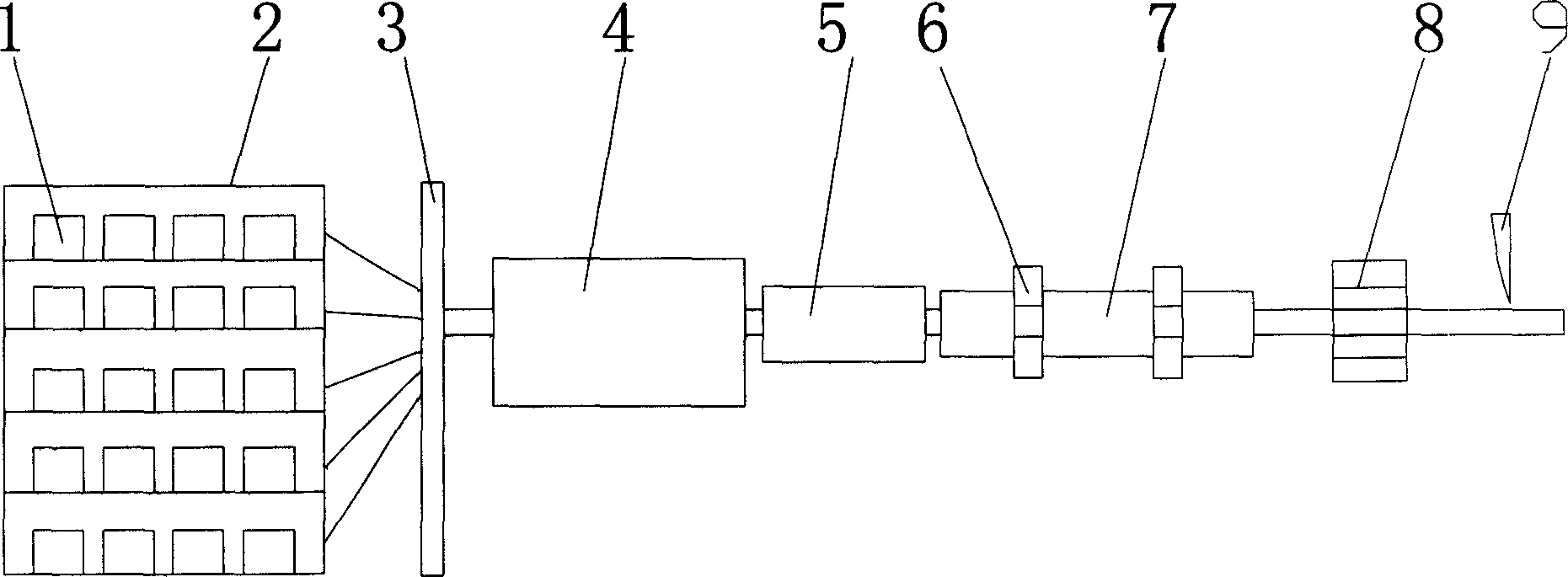
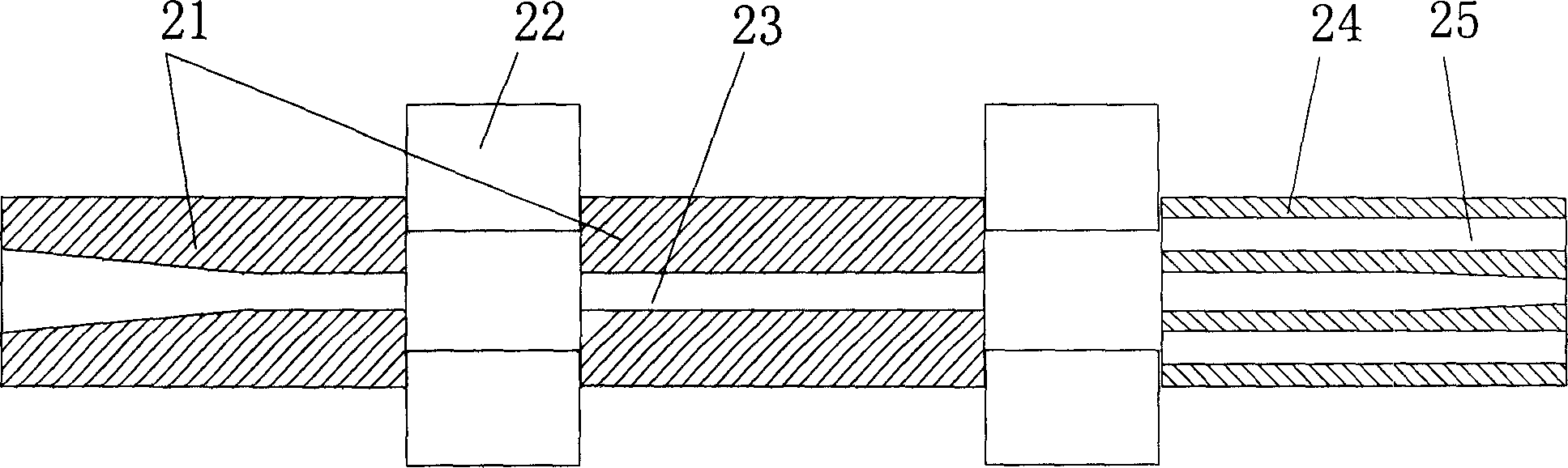
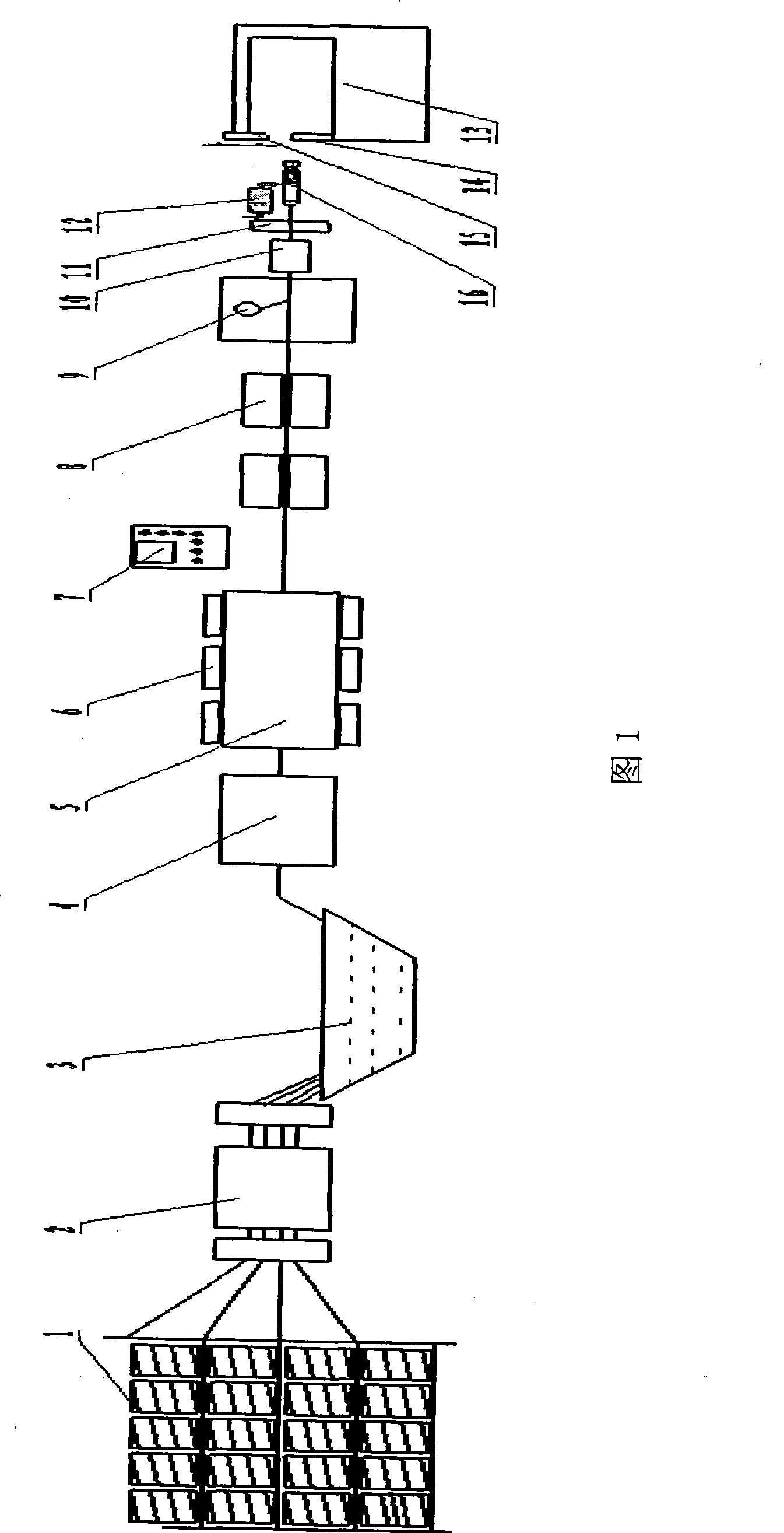
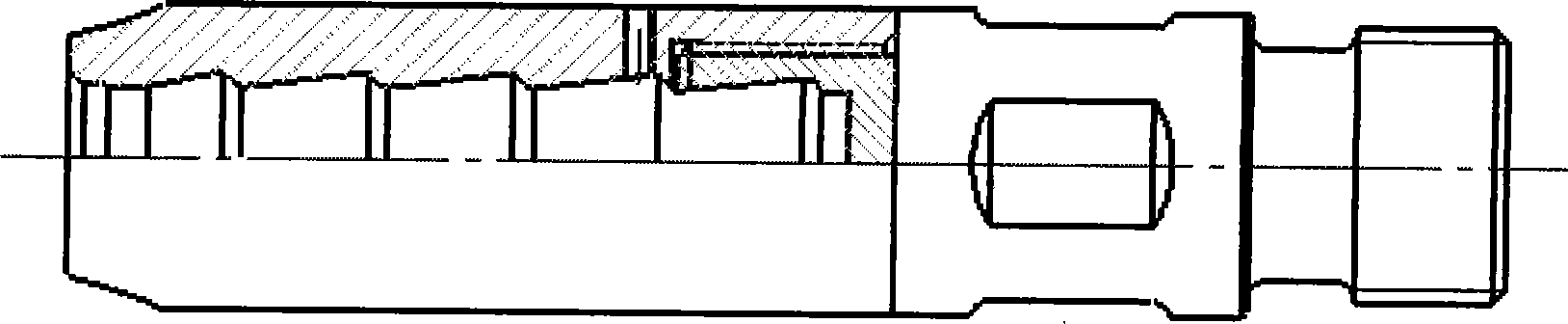
1506 results about "Pultrusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
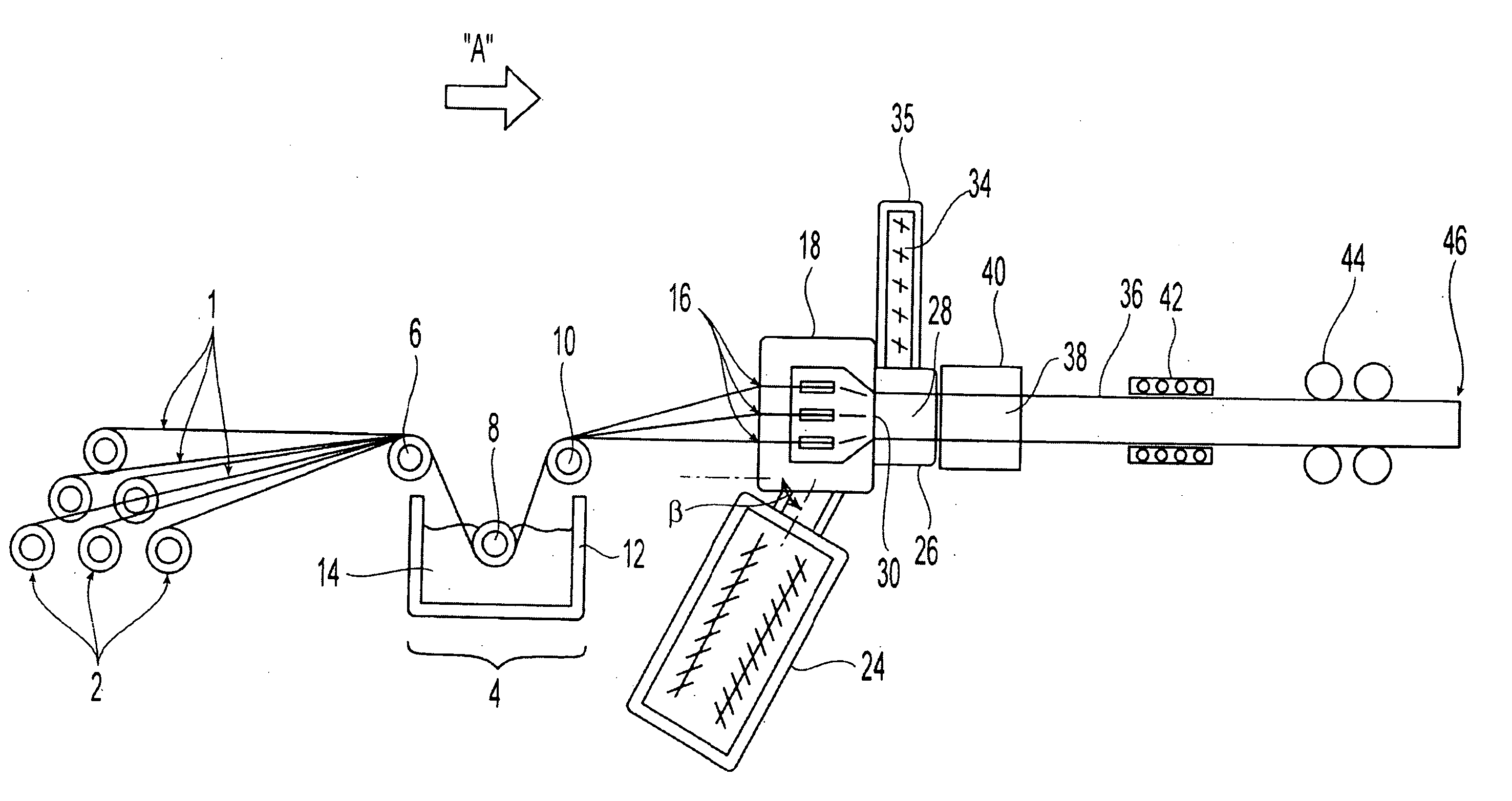
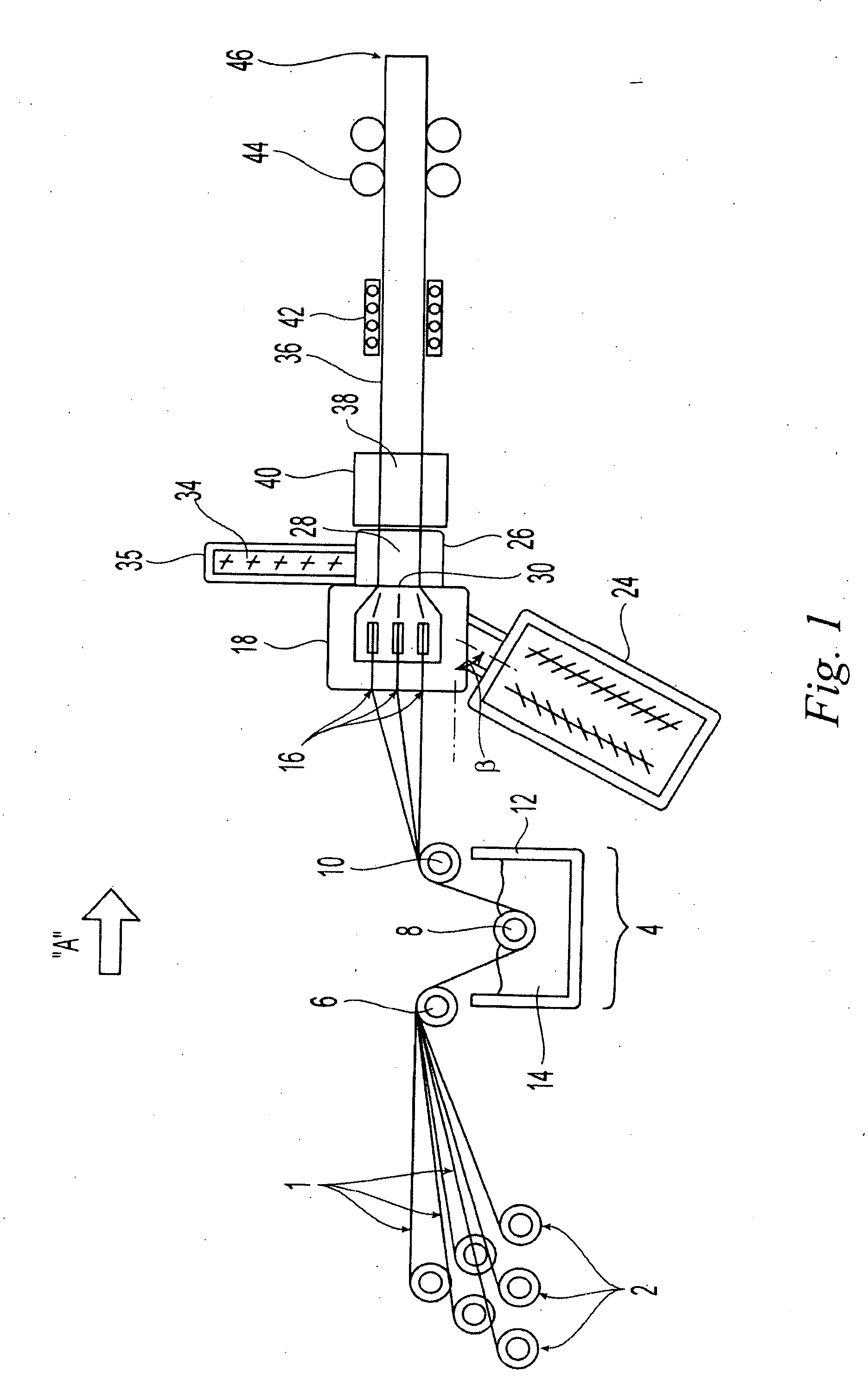
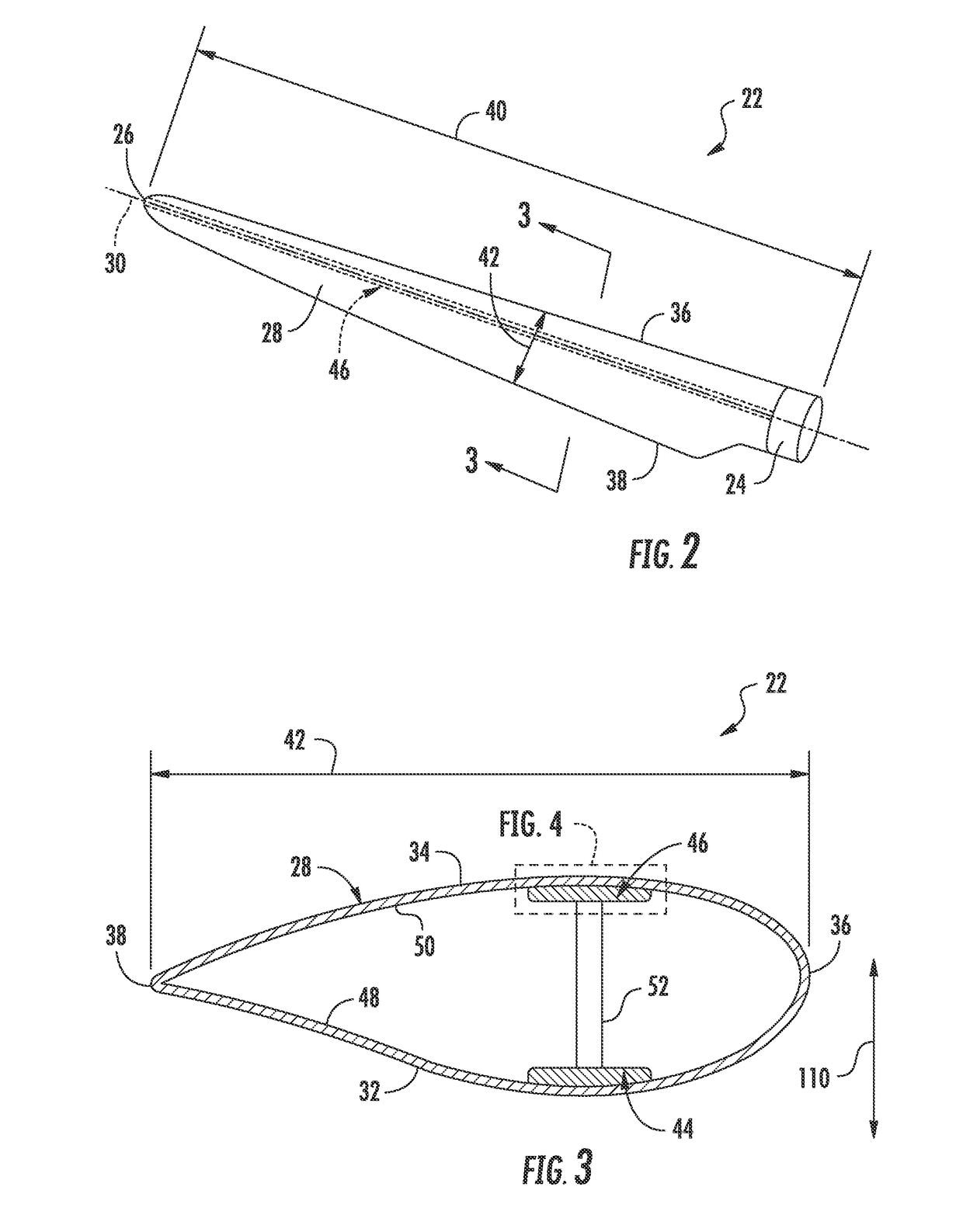
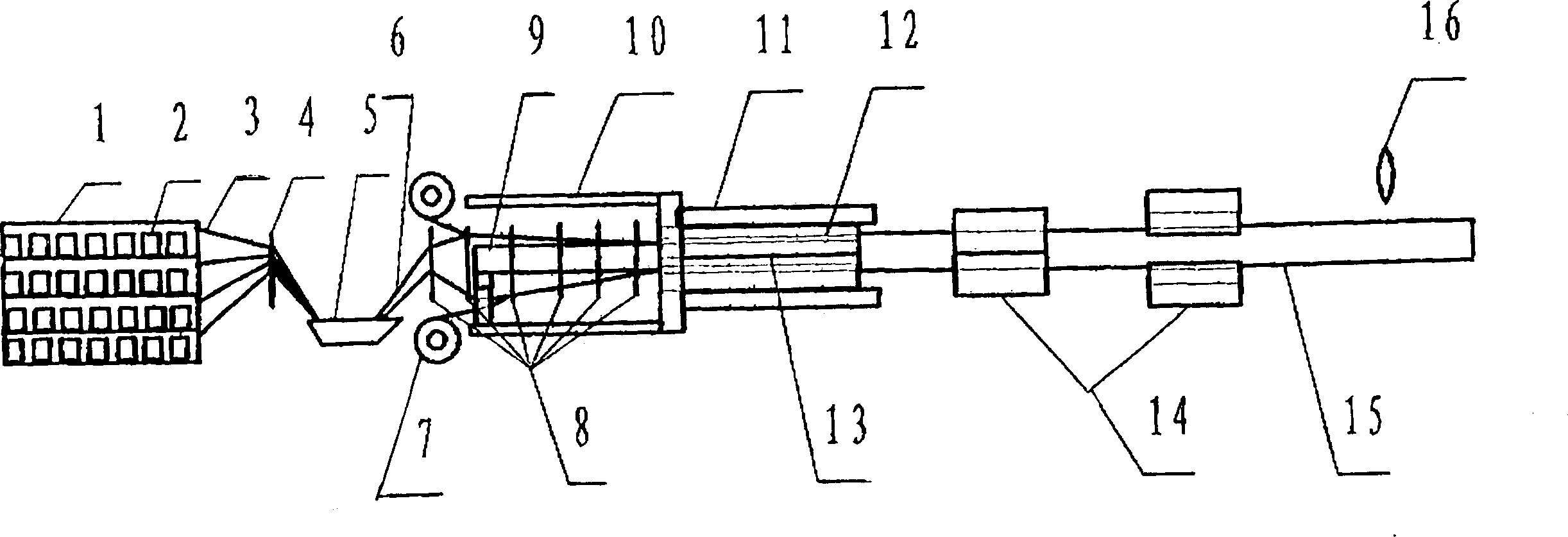
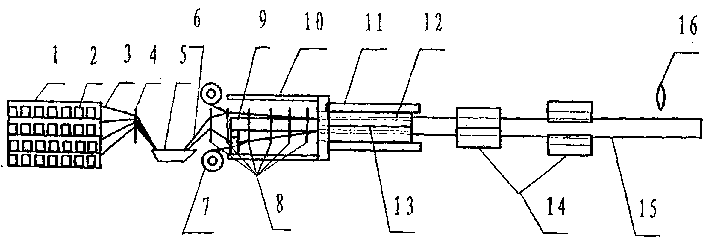
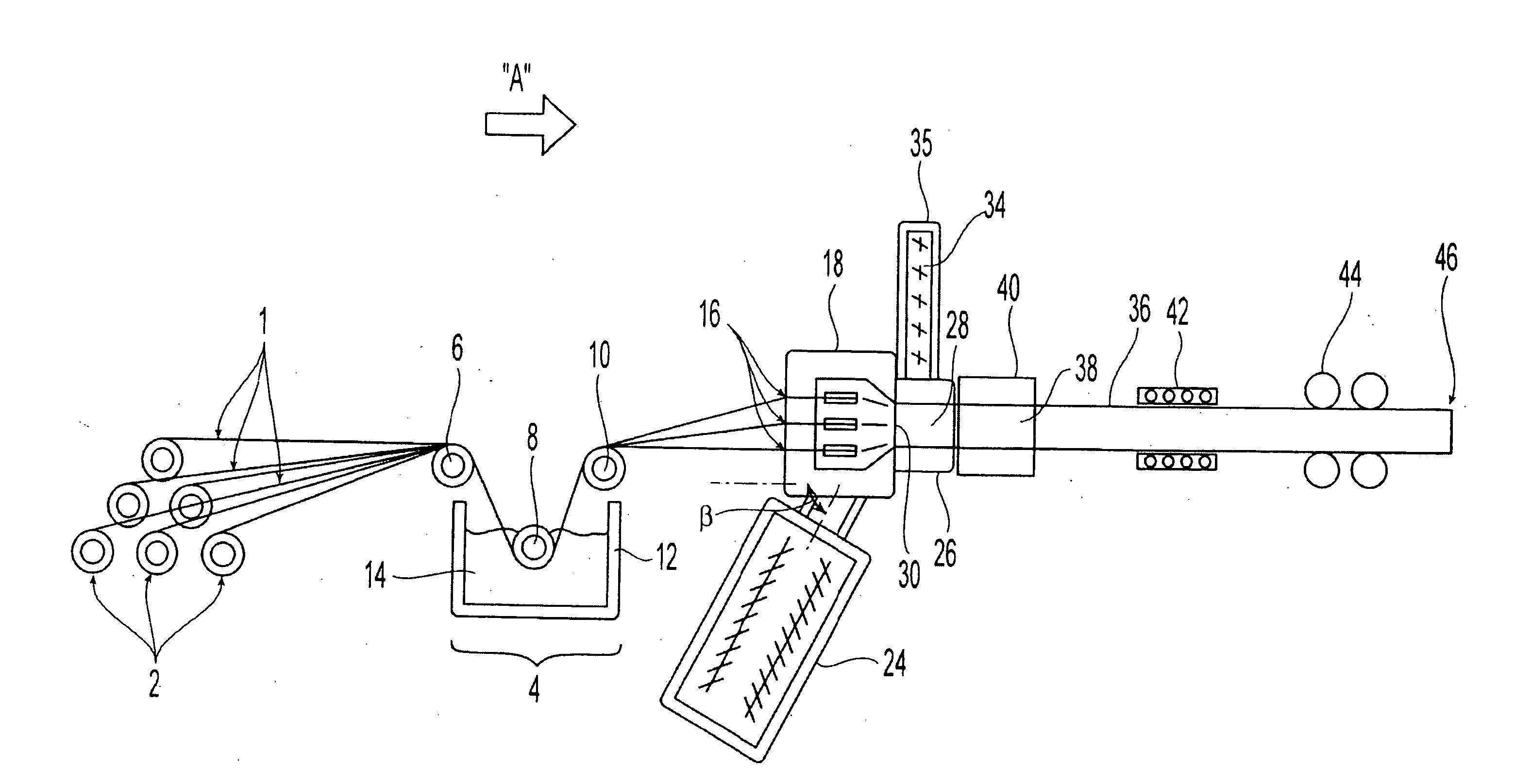
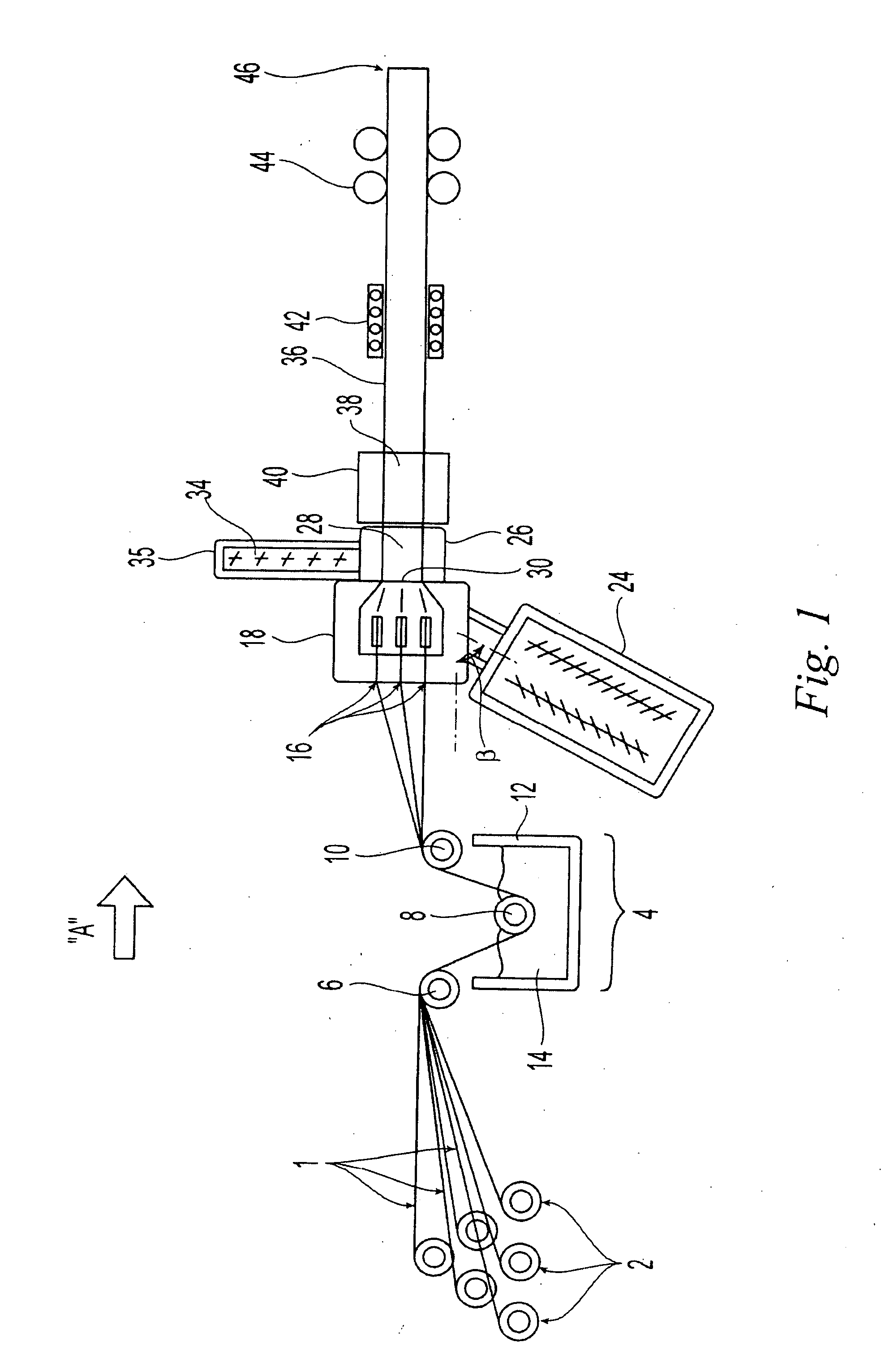
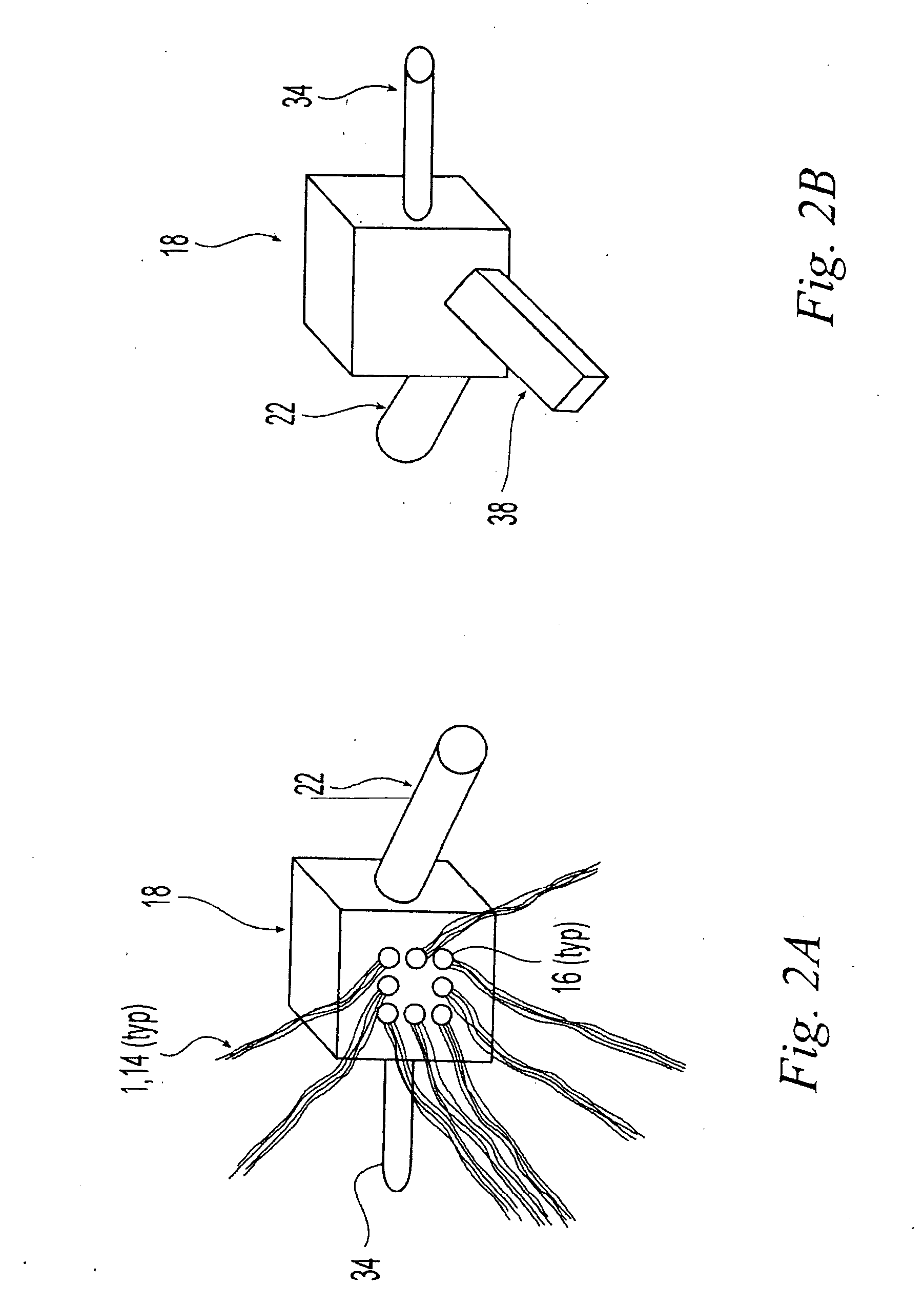
Pultrusion is a continuous process for manufacture of spendere materials with constant cross-section. The term is a portmanteau word, combining "pull" and "extrusion". As opposed to extrusion, which pushes the material, pultrusion pulls the material.
Blend material including macrocyclic polyester oligomers and processes for polymerizing the same
A blend of a macrocyclic polyester oligomer and a polymerization catalyst as a one component ready-to-use material with a long shelf life enables production of parts from macrocyclic polyester oligomers without the modification of existing equipment, thereby reducing time and cost of manufacture while expanding the application of macrocyclic polyester oligomers. In this blend material, the macrocyclic polyester oligomer remains intact in solid state at ambient conditions. Upon melting, the blend material initially forms low viscosity fluid, and then rapidly polymerizes to form high molecular weight polyesters which subsequently solidify to form crystalline polymers. In the case of certain macrocyclic polyester oligomers, for example, poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate), demolding can take place at the polymerization temperature, e.g., at about 180° C. to 200° C., because the resulting polyester polymer solidifies fairly rapidly at that temperature without cooling. In one aspect, the invention generally features a blend material that includes a macrocyclic polyester oligomer, a polymerization catalyst, and optionally, a filler. In another aspect, the invention generally features a process for preparing a blend material. In yet another aspect, the invention features processes such as rotational molding, resin film infusion, pultrusion, resin transfer molding, filament winding, making and using powder-coated or hot melt prepreg, compression molding, and roll wrapping, which use the blend material.
Owner:CYCLICS CORP
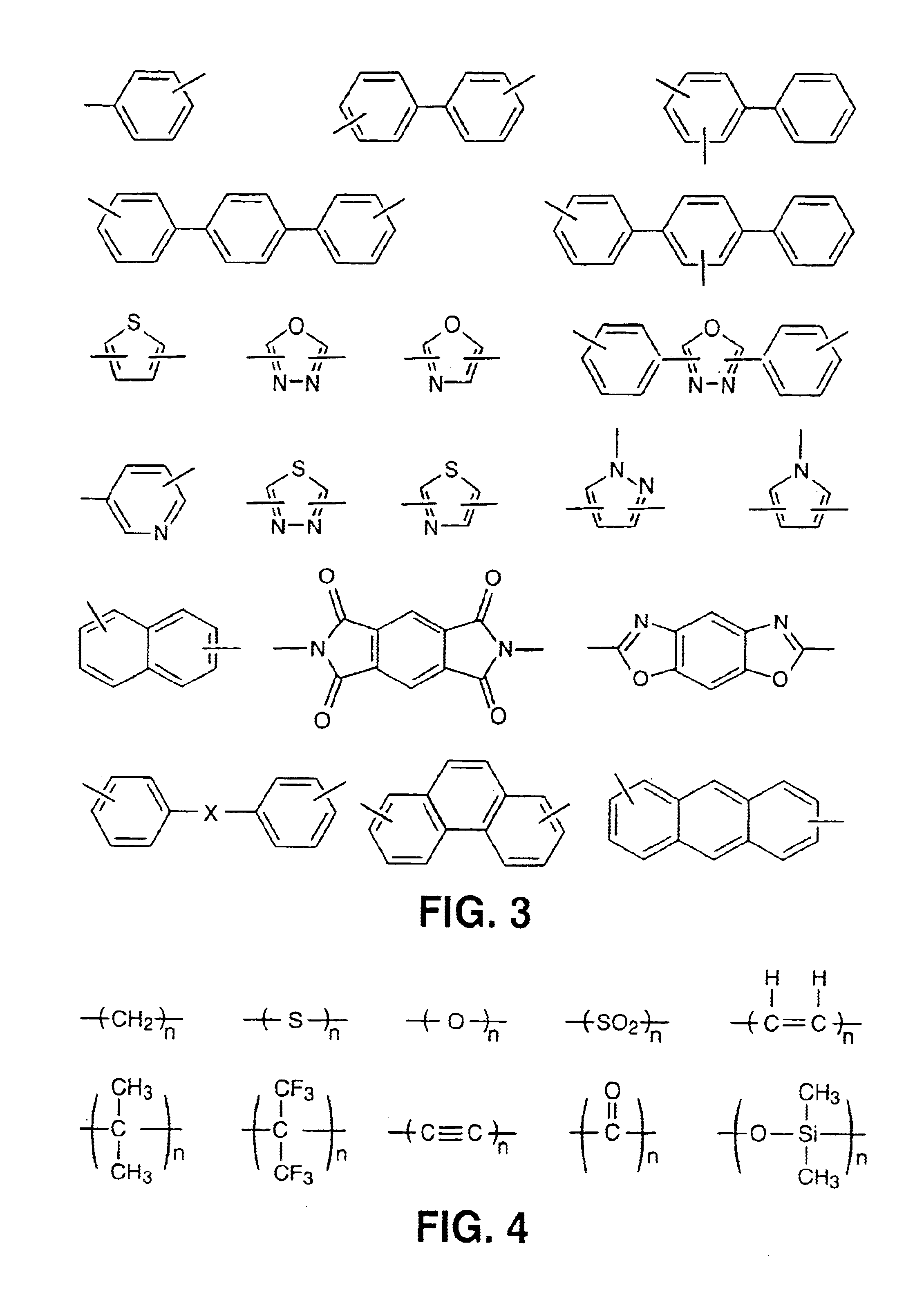
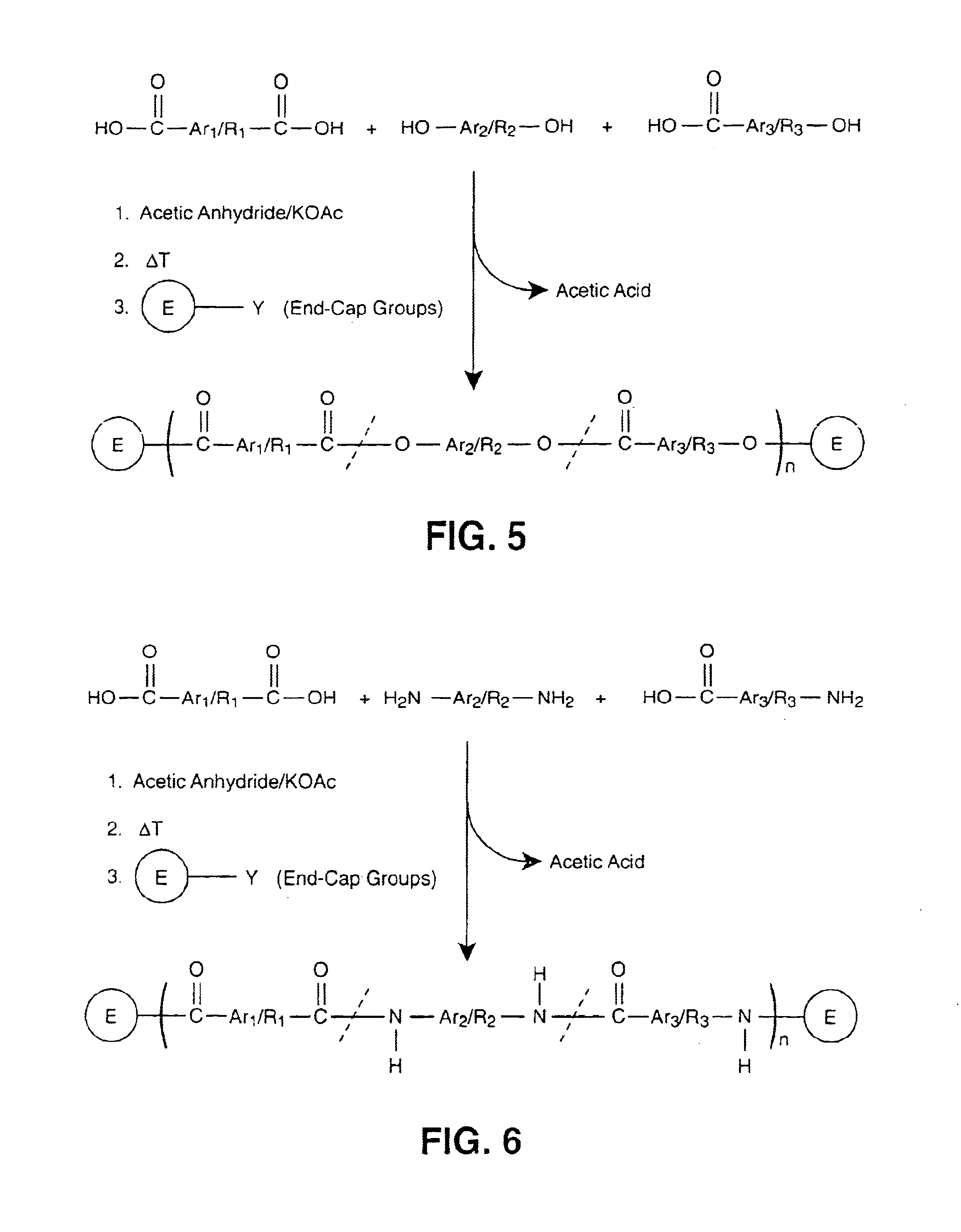
Liquid crystalline thermosets from ester, ester-imide, and ester-amide oligomers
InactiveUS6939940B2Low viscosityLow dielectric constantLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineEnd-group
Main chain thermotropic liquid crystal esters, ester-imides, and ester-amides were prepared from AA, BB, and AB type monomeric materials and were end-capped with phenylacetylene, phenylmaleimide, or nadimide reactive end-groups. The resulting reactive end-capped liquid crystal oligomers exhibit a variety of improved and preferred physical properties. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are thermotropic and have, preferably, molecular weights in the range of approximately 1000-15,000 grams per mole. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers have broad liquid crystalline melting ranges and exhibit high melt stability and very low melt viscosities at accessible temperatures. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are stable for up to an hour in the melt phase. These properties make the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers highly processable by a variety of melt process shape forming and blending techniques including film extrusion, fiber spinning, reactive injection molding (RIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), resin film injection (RFI), powder molding, pultrusion, injection molding, blow molding, plasma spraying and thermo-forming. Once processed and shaped, the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers were heated to further polymerize and form liquid crystalline thermosets (LCT). The fully cured products are rubbers above their glass transition temperatures. The resulting thermosets display many properties that are superior to their non-end-capped high molecular weight analogs.
Owner:NASA
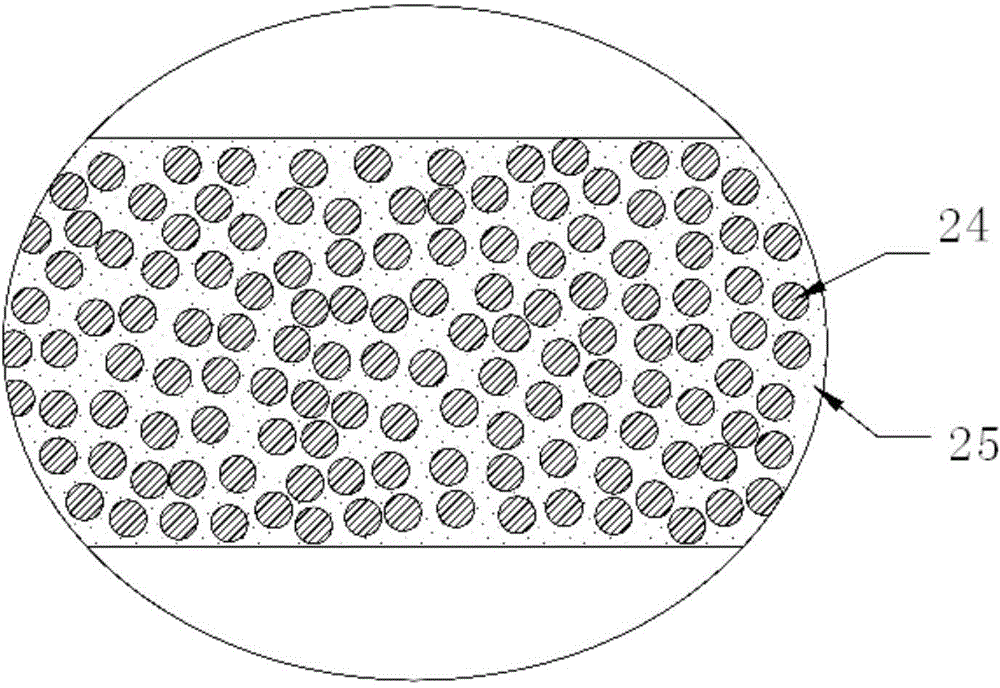
Fiber thermoset reinforced thermoplastic structural member
InactiveUS6106944AHigh strengthImprove mechanical propertiesLayered productsSpecial ornamental structuresYoung's modulusEngineering
In the manufacture of a structural member comprising a thermoplastic composite core with an exterior reinforcing layer, the core member is initially extruded in the shape of a profile. The profile is then contacted with reinforcing fiber and resin to form the exterior reinforcing layer. The exterior thermosetting layer is cured to form a reinforcing layer. The structural member is preferably manufactured using a pultrusion method in which a tractor device is used to provide linear movement of the profile from the extrusion head to the exterior coating operation. The fiber-reinforced thermoset is coated on the entirety of the exterior of the profile or is applied only on a portion of the profile requiring reinforcement in a defined load-bearing direction. A preferred thermoplastic core comprises a polymer-fiber composite material. A structural member of the invention has significantly improved Young's modulus providing strength for applications such as telephone poles, electric poles, electric lighting poles, boat mast or keel applications, lumber replacements, structural members used in window and door manufacture, etc.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
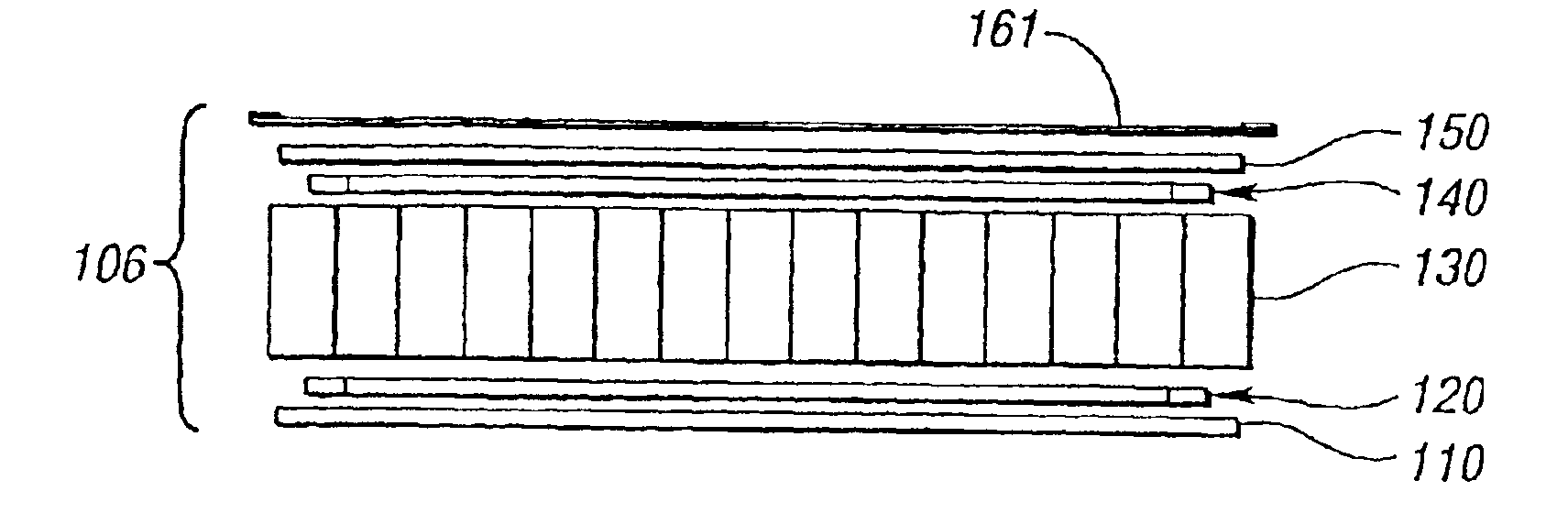
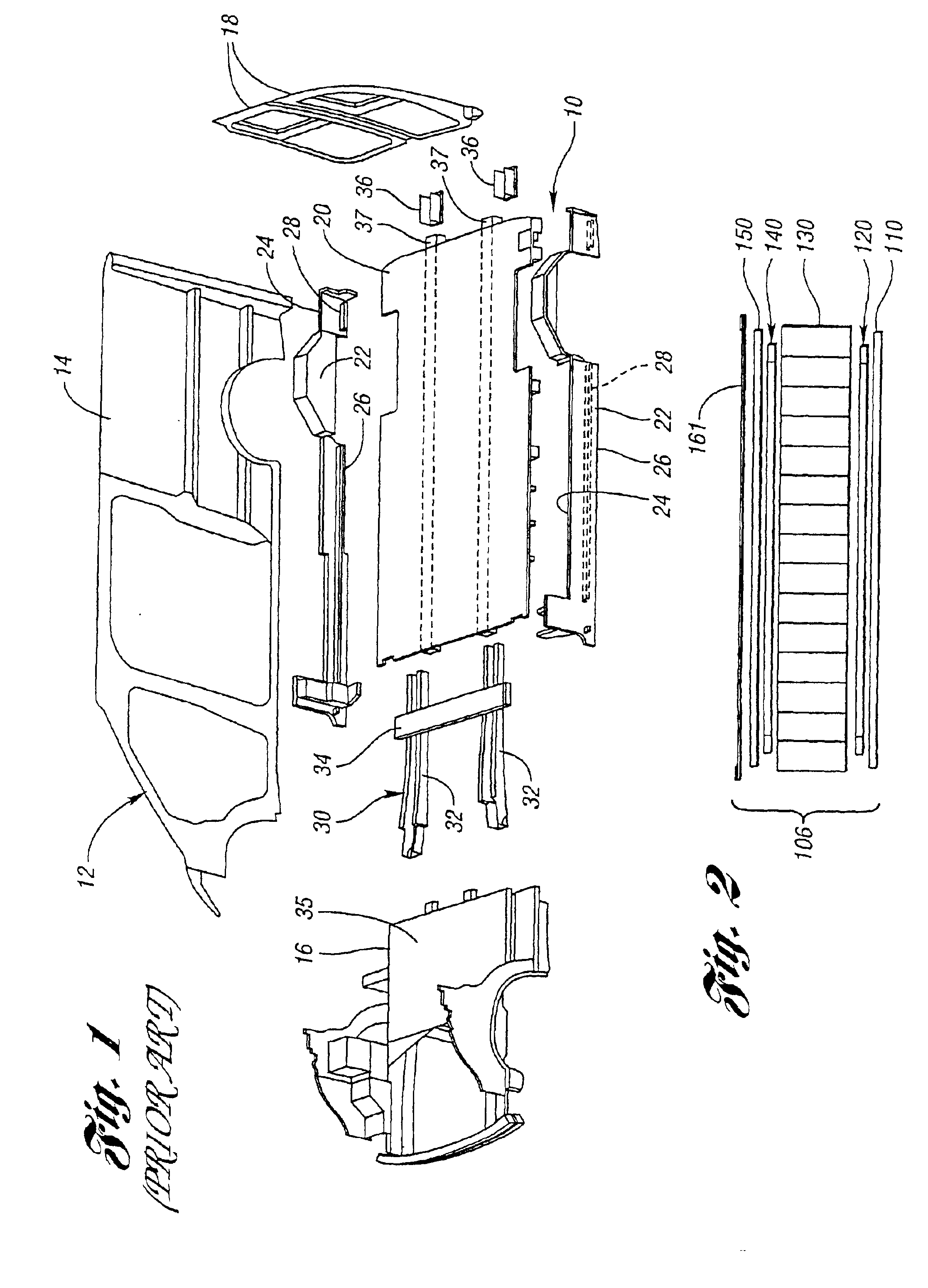
Reinforced composite vehicle load floor of the cellular core sandwich-type
The invention relates to reinforced composite vehicle load floors of the sandwich-type having a cellular core. In a method for making a load floor of the invention, a stack is formed that is made up of: a load-bearing upper skin made of a reinforced thermoplastics material; an upper skeletal frame structure of reinforcing slats each of which is made of a reinforced thermoplastic composite or pultrusion; a cellular core made of a thermoplastic material; a lower skeletal frame structure of reinforcing slats each of which is also made of a reinforced thermoplastic composite or pultrusion; and a bottom skin made of a reinforced thermoplastic material. Each of the frame structures of reinforcing slats has a surface area that is smaller than the surface area of each of the skins. The frame structures of reinforcing slats are positioned symmetrically about a plane formed by the cellular core against the skins.
Owner:GLOBAL IP HLDG
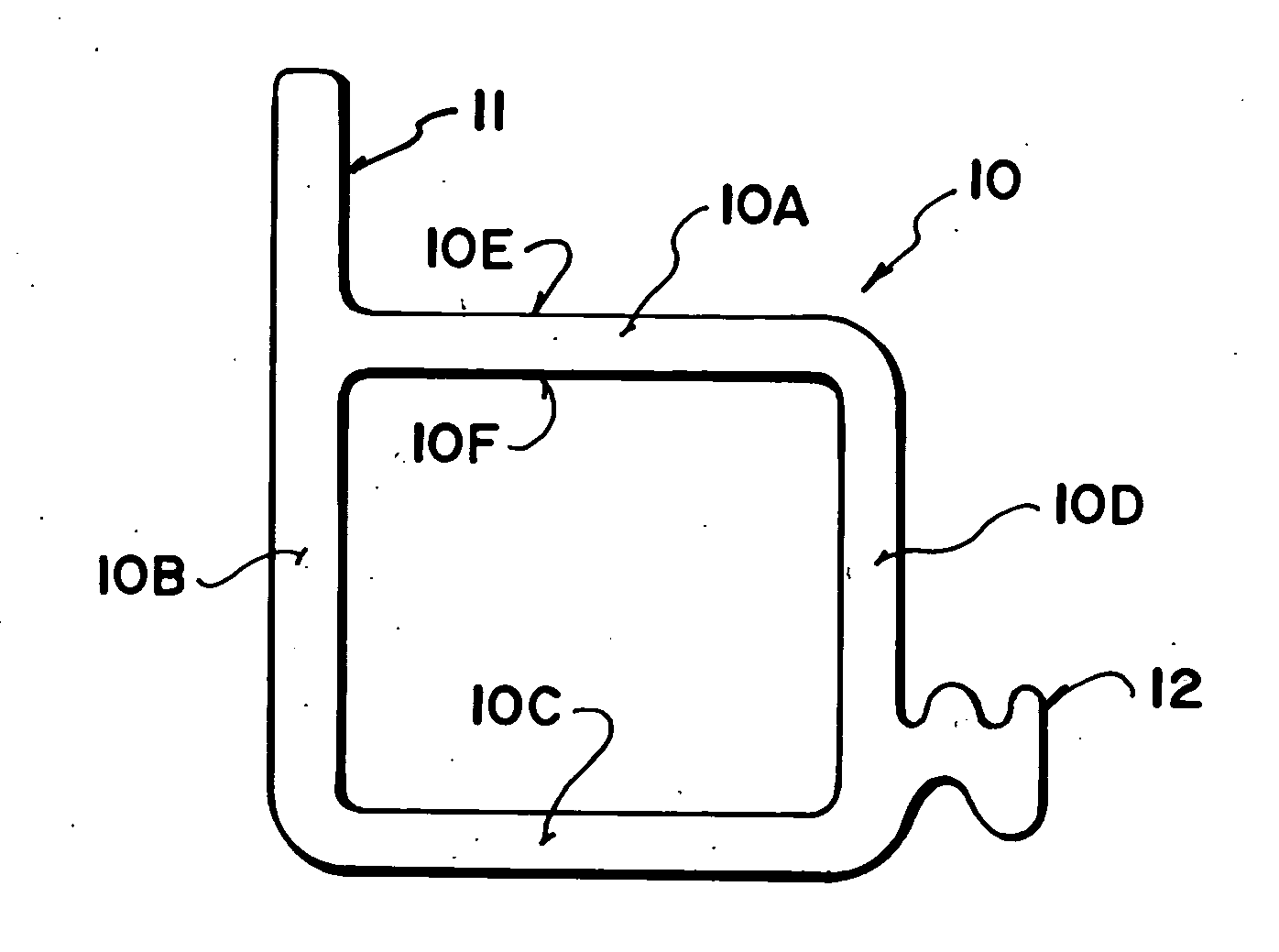
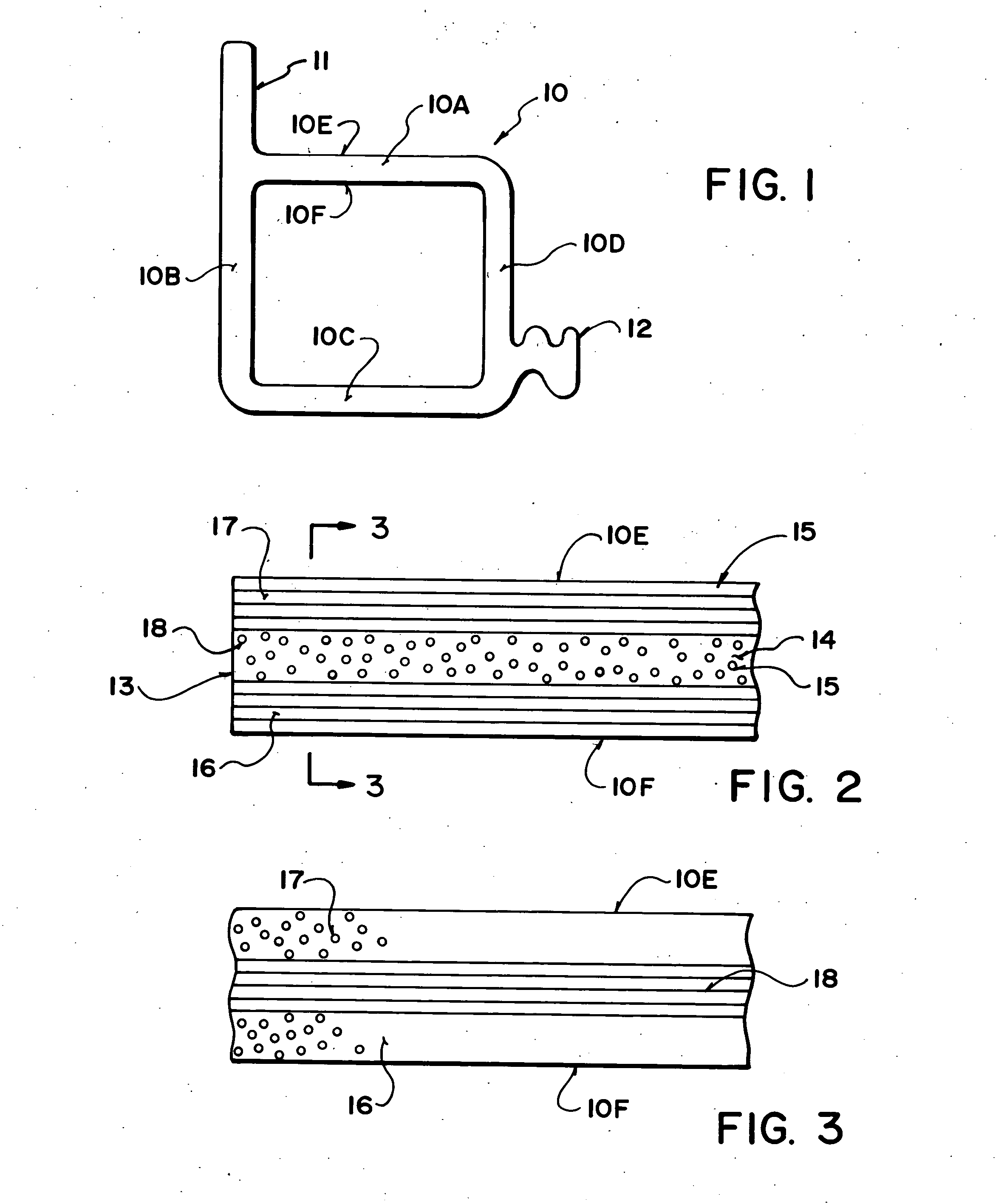
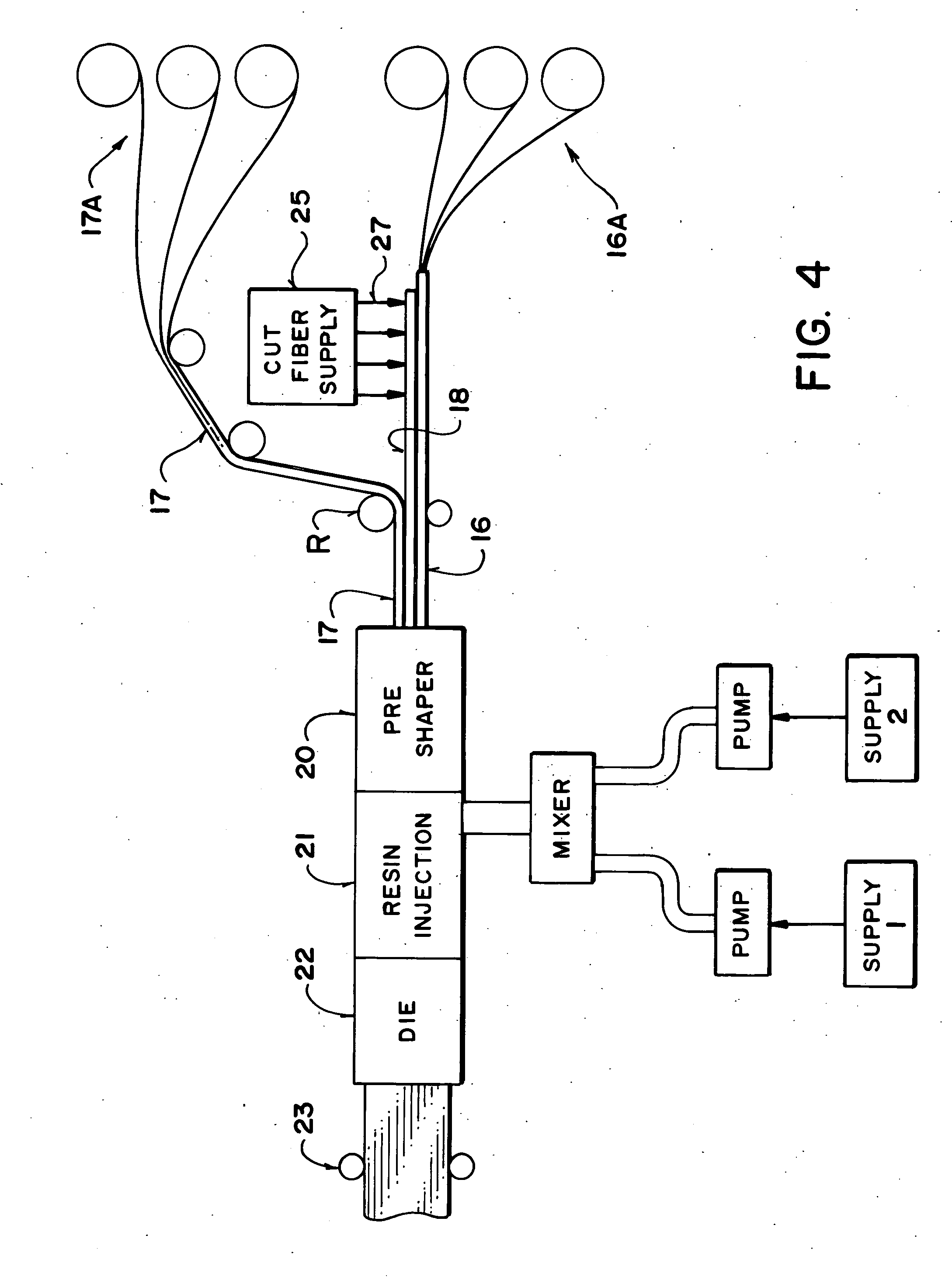
Aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable and method of manufacture
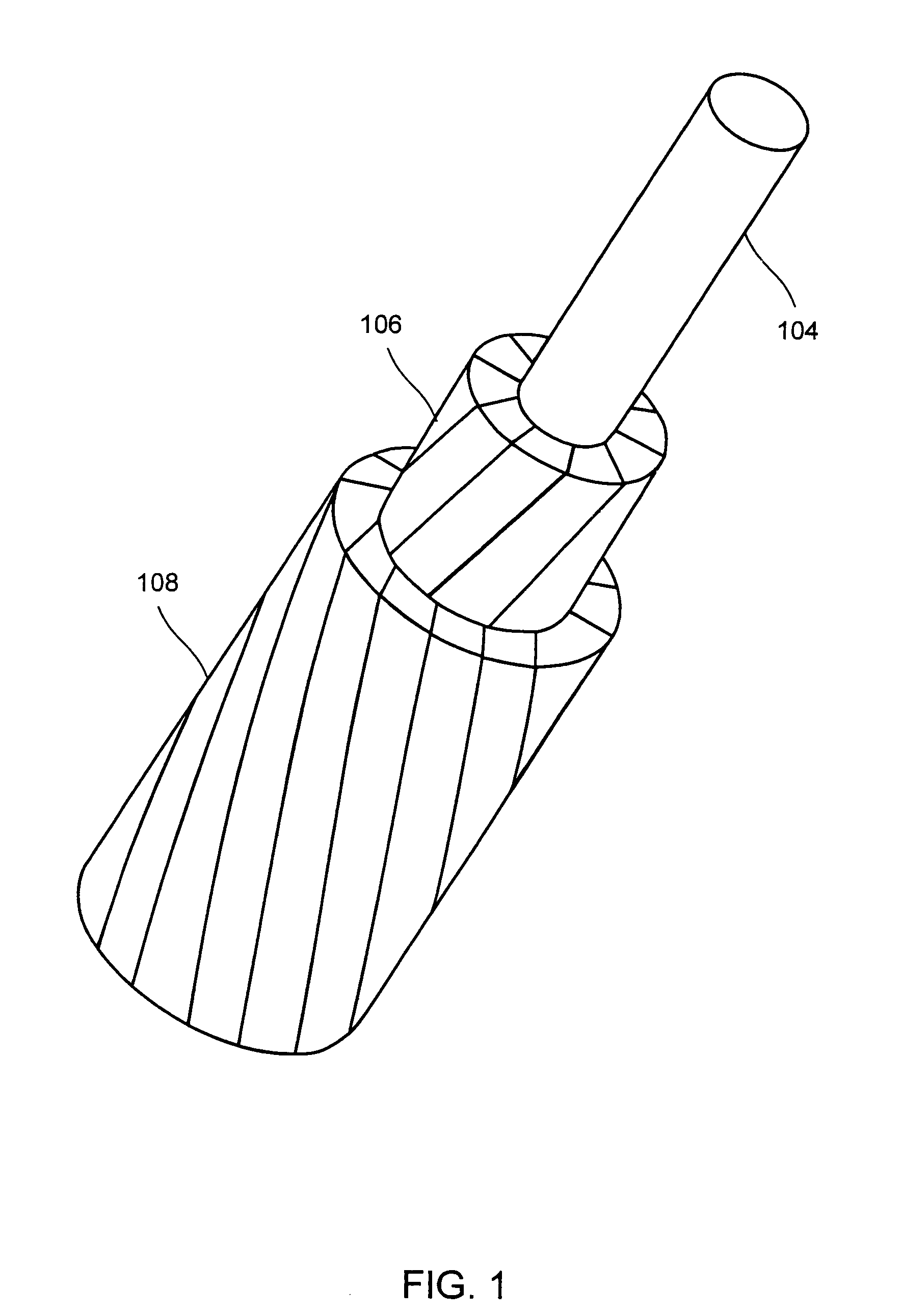
This invention relates to an aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable and method of manufacture. The composite core comprises a plurality of longitudinally extending fibers embedded in a resin matrix. The composite core comprises the following characteristics: tensile strength ranging from about 250 to about 350 Ksi; a tensile modulus of elasticity ranging from about 12 to about 16 Msi; and a coefficient of thermal expansion less than or equal to about 6×10−6 cm / cm·° C. The composite core is further manufactured according to a two die pultrusion system, the system comprising tooling designed in accordance with the processing speed, selection of composite core fibers and resin and desired physical characteristics of the end composite core.
Owner:CTC GLOBAL CORP
Plastic rail system and other building products reinforced with polymer matrix composites
InactiveUS20040009338A1Reduce air pressureBalustersSynthetic resin layered productsBuilding productUltimate tensile strength
Polymeric building materials are provided which include a composite reinforcement comprising continuous filaments of fibers substantially oriented in at least a first direction within a polymeric matrix. The composite reinforcement includes a higher tensile strength and a lower rigidity than aluminum. The building material further includes a capstock polymeric material disposed substantially over the composite reinforcement. The building material is resistant to heat deformation and corrosion. This invention also includes methods for constructing such polymeric composite building materials, including in the preferred embodiments, pultrusion and extrusion steps.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7438971B2Non-insulated conductorsSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical conductorResin matrix
This invention relates to an aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable and method of manufacture. The composite core comprises a plurality of longitudinally extending fibers embedded in a resin matrix. The composite core comprises the following characteristics: tensile strength ranging from about 250 to about 350 Ksi; a tensile modulus of elasticity ranging from about 12 to about 16 Msi; and a coefficient of thermal expansion less than or equal to about 6×10−6 cm / cm·° C. The composite core is further manufactured according to a one or more die pultrusion system, the system comprising tooling designed in accordance with the processing speed, selection of composite core fibers and resin and desired physical characteristics of the end composite core.
Owner:CTC GLOBAL CORP
Thermoplastic pultrusion die system and method
ActiveUS8747098B1High compression forceFacilitated releaseAdhesive processesConfectioneryNumerical controlEngineering
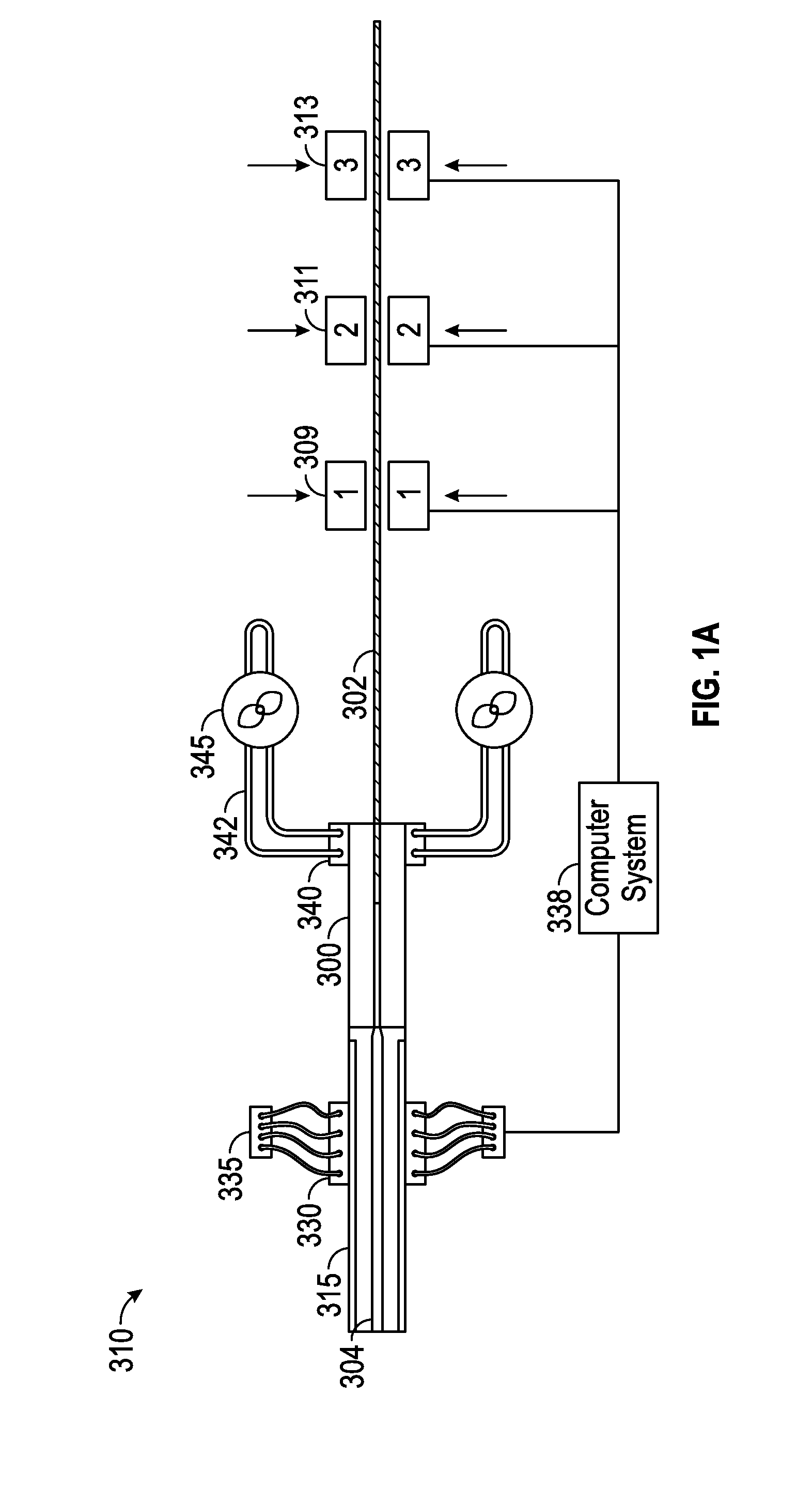
A thermoplastic pultrusion die system for pultruding a thermoplastic composite includes a first pultrusion die member with a curved, concave top surface; a second pultrusion die member with a curved, convex bottom surface; a curved die cavity gap formed between the a curved, concave top surface of the first pultrusion die member and the curved, convex bottom surface of the second pultrusion die member; a die cavity gap adjustment mechanism that imparts movement to at least one of the first pultrusion die member and the second pultrusion die member to vary the die cavity gap from closed to a specified location to open at a specified location; a pultrusion gripper mechanism having one or more grippers in series, and a computer numerical control (CNC) computer system controlling the die cavity gap adjustment mechanism.
Owner:EBERT COMPOSITES
Aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20040131834A1High strengthIncrease ampacityNon-insulated conductorsApparatus for heat treatmentElectrical conductorThermal expansion
This invention relates to an aluminum conductor composite core reinforced cable (ACCC) and method of manufacture. An ACCC cable has a composite core surrounded by at least one layer of aluminum conductor. The composite core comprises a plurality of fibers from at least one fiber type in one or more matrix materials. The composite core can have a maximum operating temperature capability above 100° C. or within the range of about -45° C. to about 230° C., at least 50% fiber to resin volume fraction, a tensile strength in the range of about 160 Ksi to about 370 Ksi, a modulus of elasticity in the range of about 7 Msi to about 37 Msi and a coefficient of thermal expansion in the range of about -0.7x10<-6 >m / m / ° C. to about 6x10<-6 >m / m° C. According to the invention, a B-stage forming process may be used to form the composite core at improved speeds over pultrusion processes wherein the speeds ranges from about 9 ft / min to about 60 ft / min.
Owner:CTC GLOBAL CORP
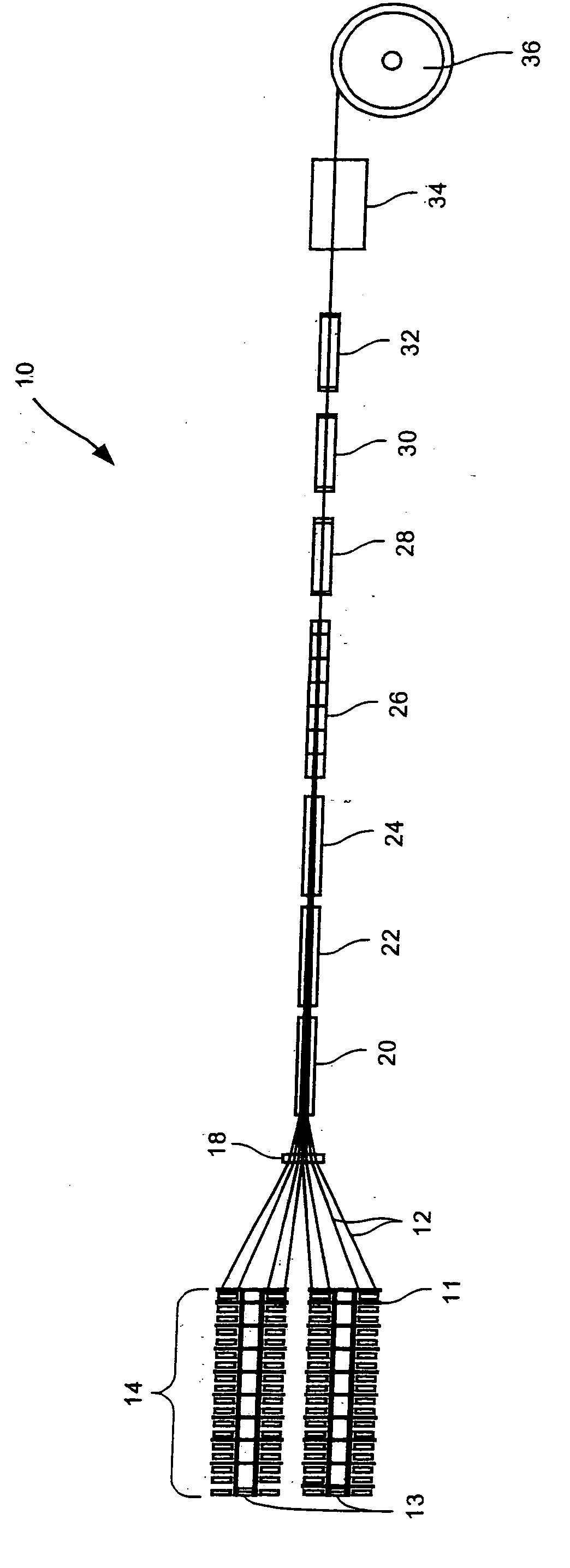
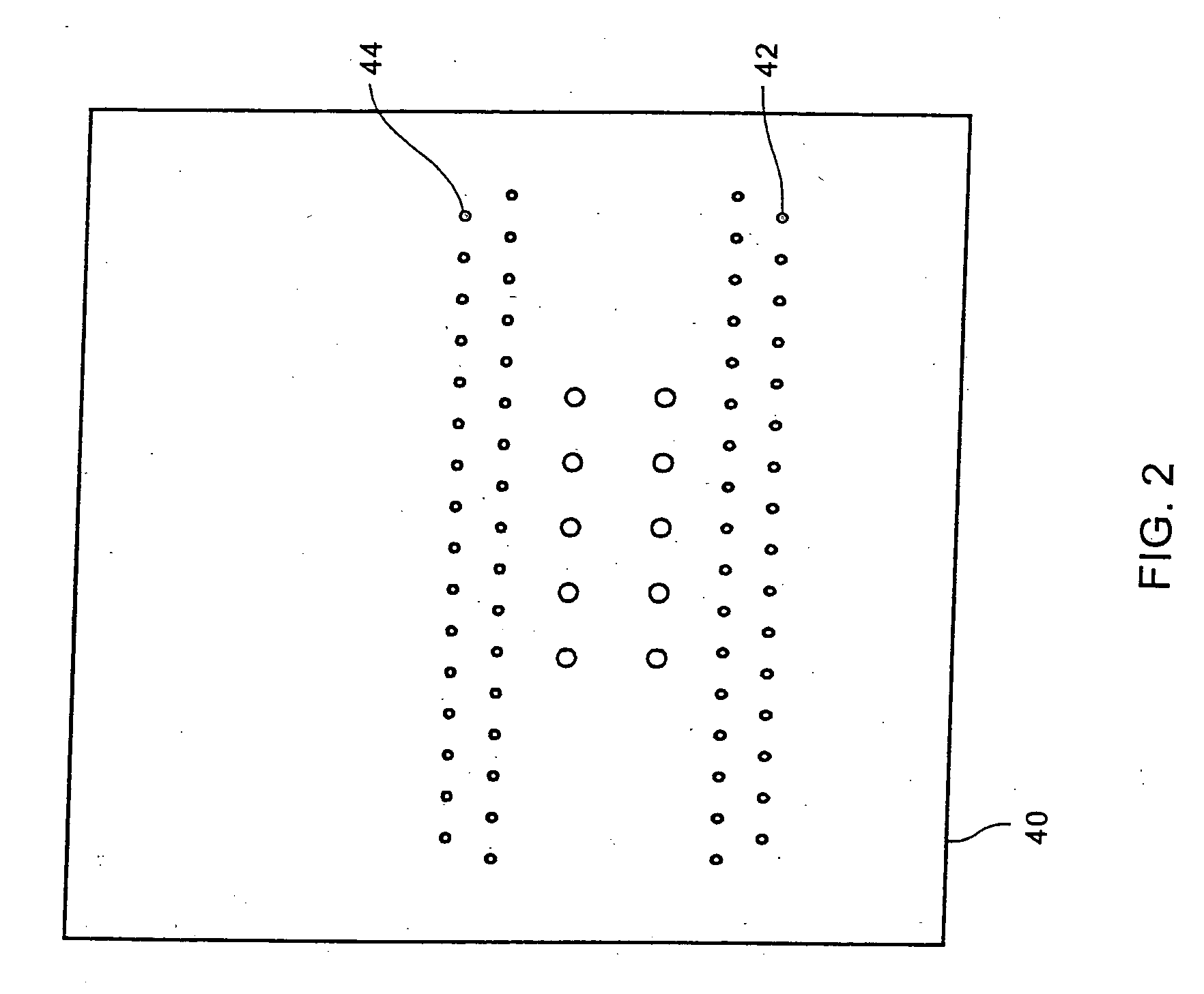
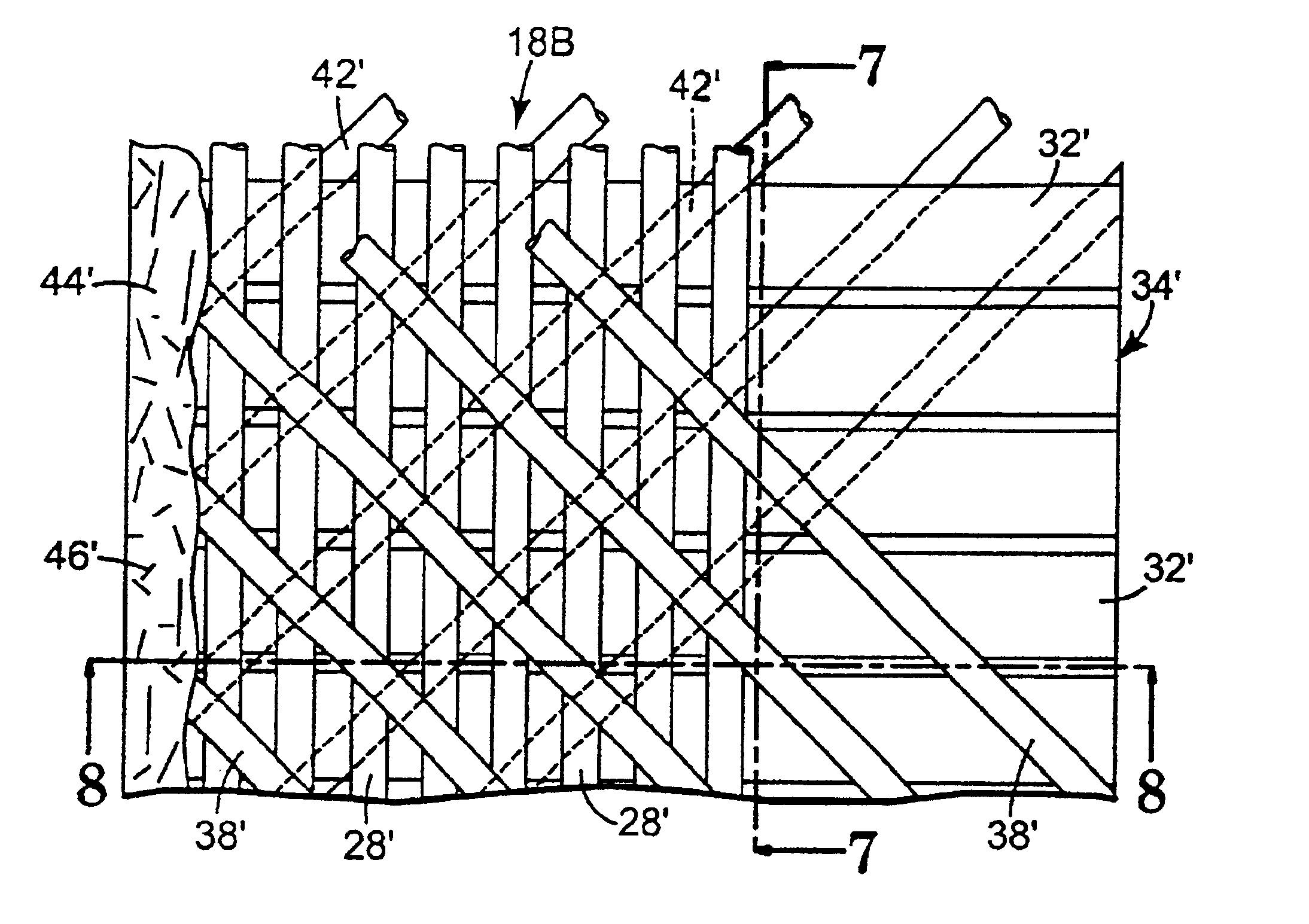
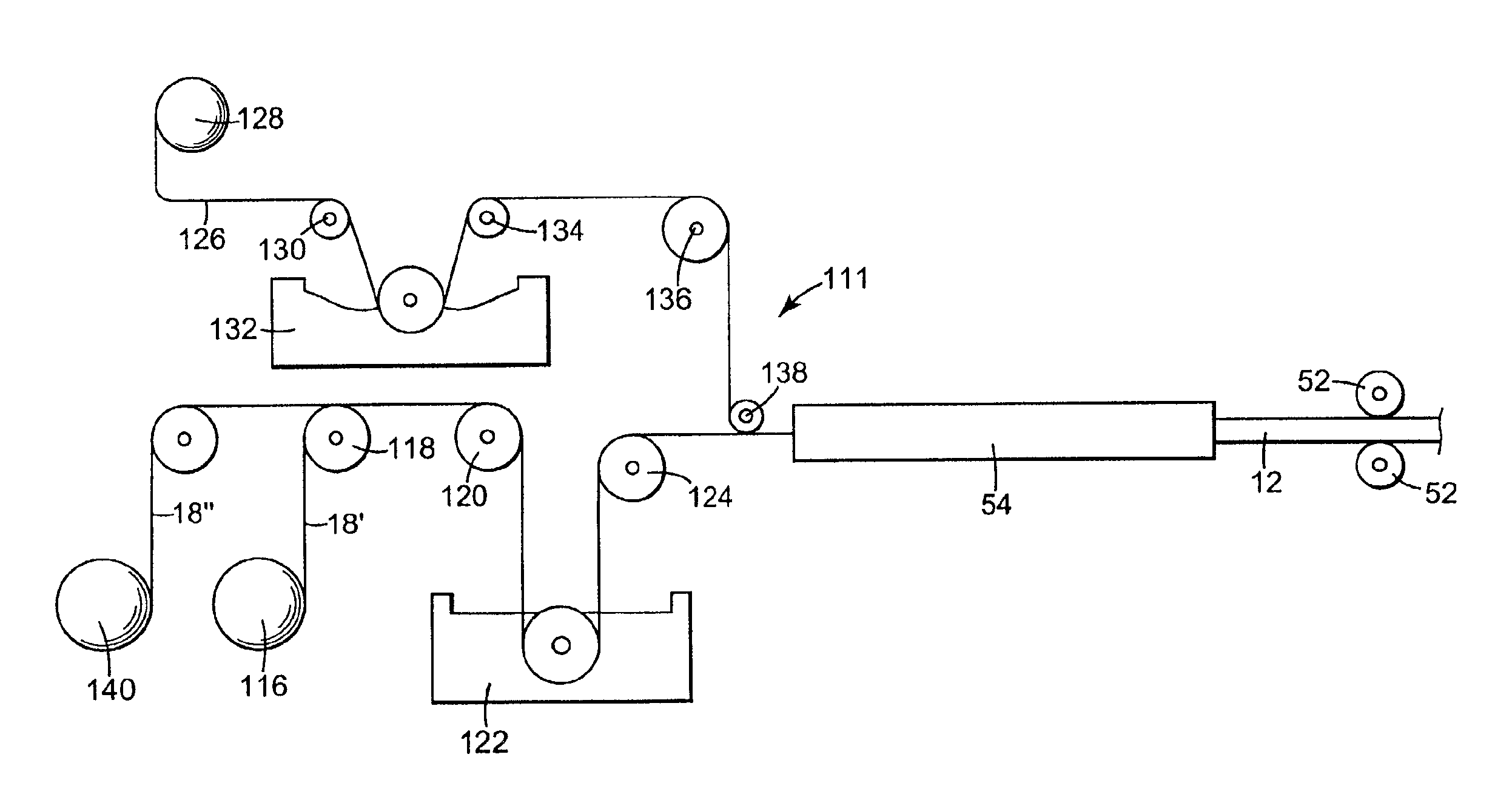
Method of making a reinforcing mat for a pultruded part
A method of preparing a reinforcing structure for use in manufacture a pultruded part where the reinforcing structure is pulled through a pultrusion die in a continuous longitudinal pull direction. The method includes arranging a plurality of first reinforcing fibers in a transverse direction and attaching a permeable transport web of staple fibers to the first reinforcing fibers such that the portion of the first reinforcing fibers oriented in the direction transverse comprises at least 40% of a volume of materials comprising the reinforcing structure.
Owner:PELLA
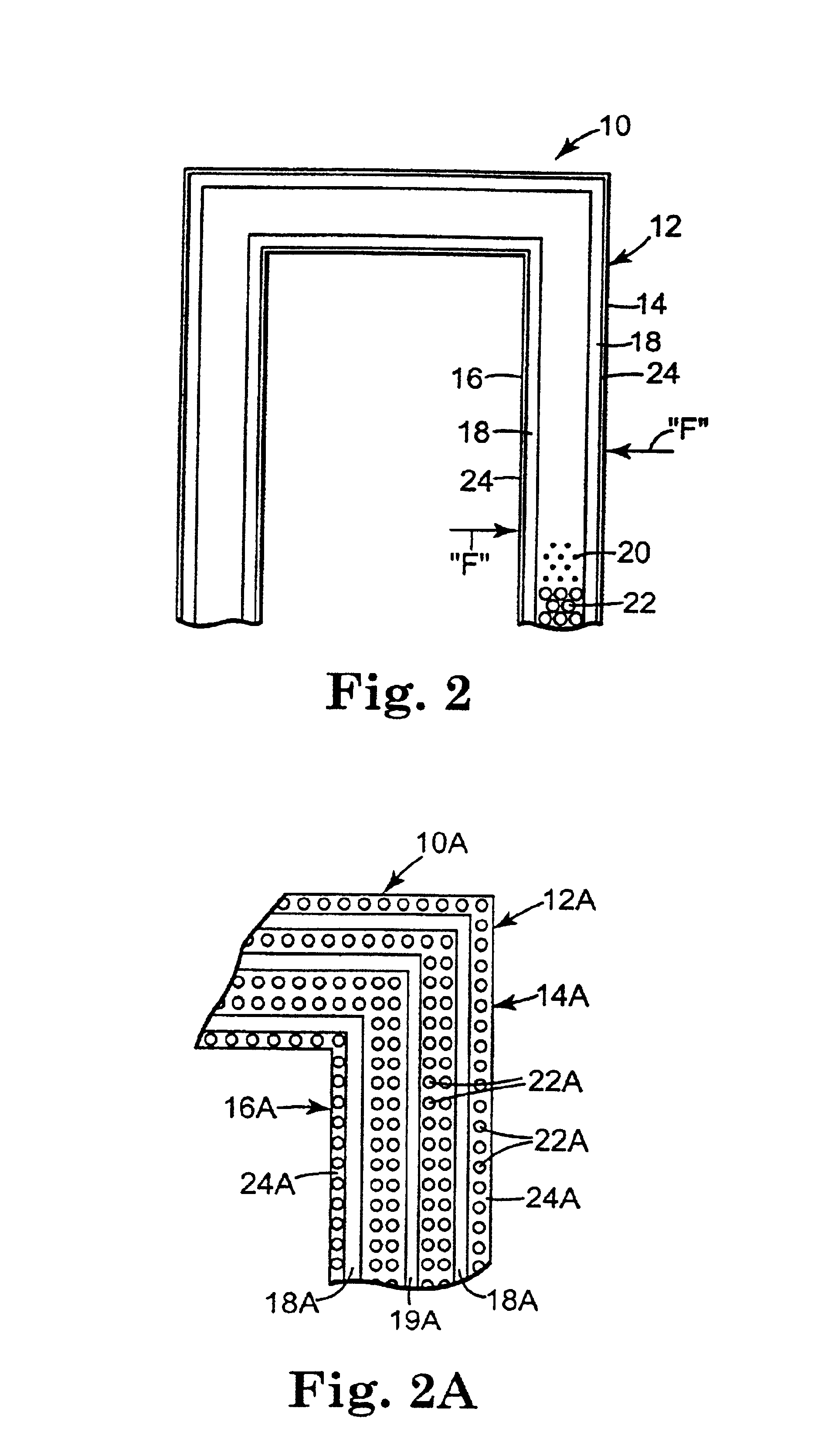
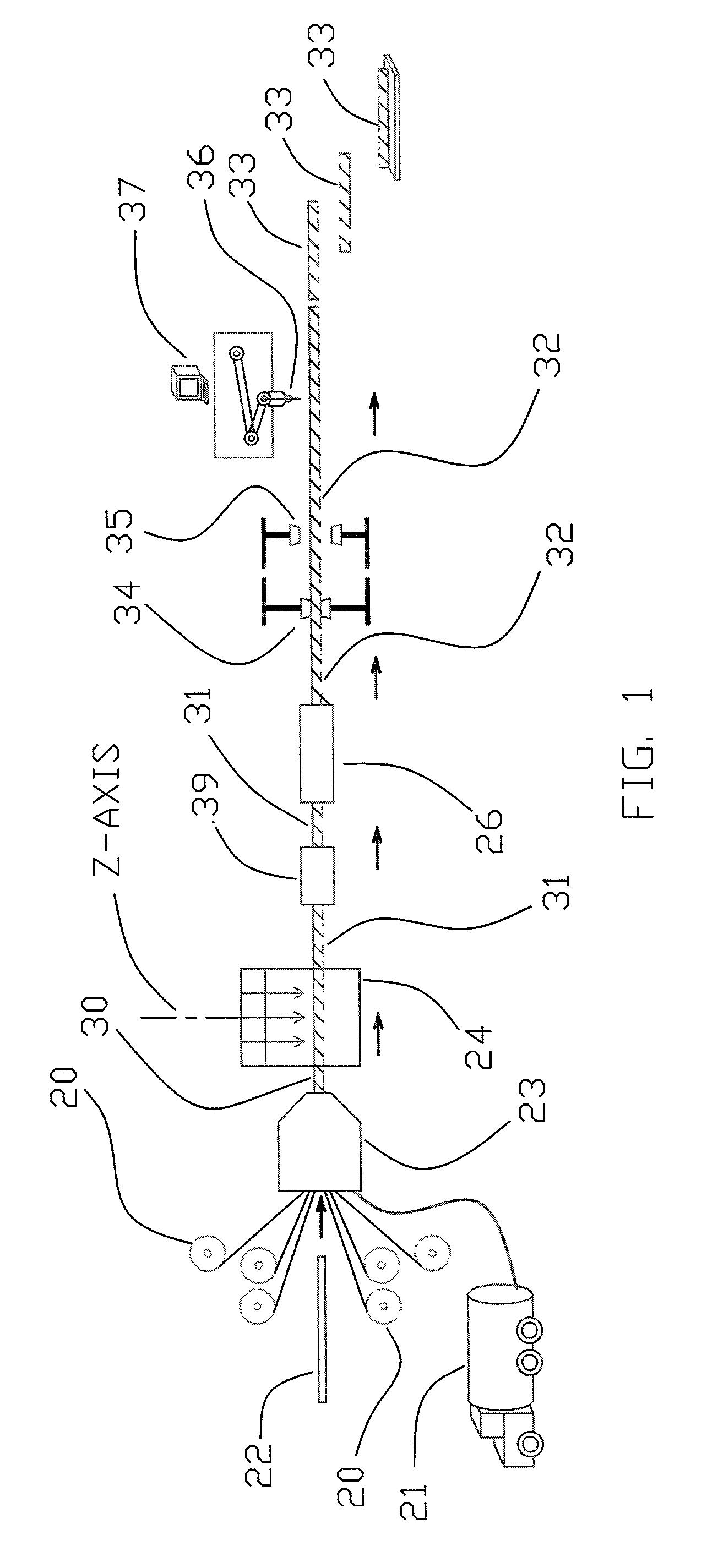
Method of clinching the top and bottom ends of Z-axis fibers into the respective top and bottom surfaces of a composite laminate
InactiveUS20020144767A1Improve the immunityEasy to assembleLayered productsTemporary pavingsComposite laminatesFiber-reinforced composite
A method and apparatus for forming an improved pultruded and clinched Z-axis fiber reinforced composite laminate structure. The upper and lower skins and the core are pulled automatically through tooling where the skin material is wetted-out with resin and the entire composite laminate is preformed in nearly its final thickness. The preformed composite laminate continues to be pulled into an automatic 3-dimensional Z-axis fiber deposition machine that deposits "groupings of fiber filaments" at multiple locations normal to the plane of the composite laminate structure and cuts each individual grouping such that a extension of each "grouping of fiber filaments" remains above the upper skin and below the lower skin. The preformed composite laminate then continues to be pulled into a secondary wet-out station. Next the preformed composite laminate travels into a pultrusion die where the extended "groupings of fiber filaments" are all bent over above the top skin and below the bottom skin producing a superior clinched Z-axis fiber reinforcement as the composite laminate continues to be pulled, catalyzed, and cured at the back section of the pultrusion die. The composite laminate continues to be pulled by grippers that then feed it into a gantry CNC machine that is synchronous with the pull speed of the grippers and where computerized machining, drilling, and cutting operations take place. This entire method is accomplished automatically without the need for human operators.
Owner:EBERT COMPOSITES
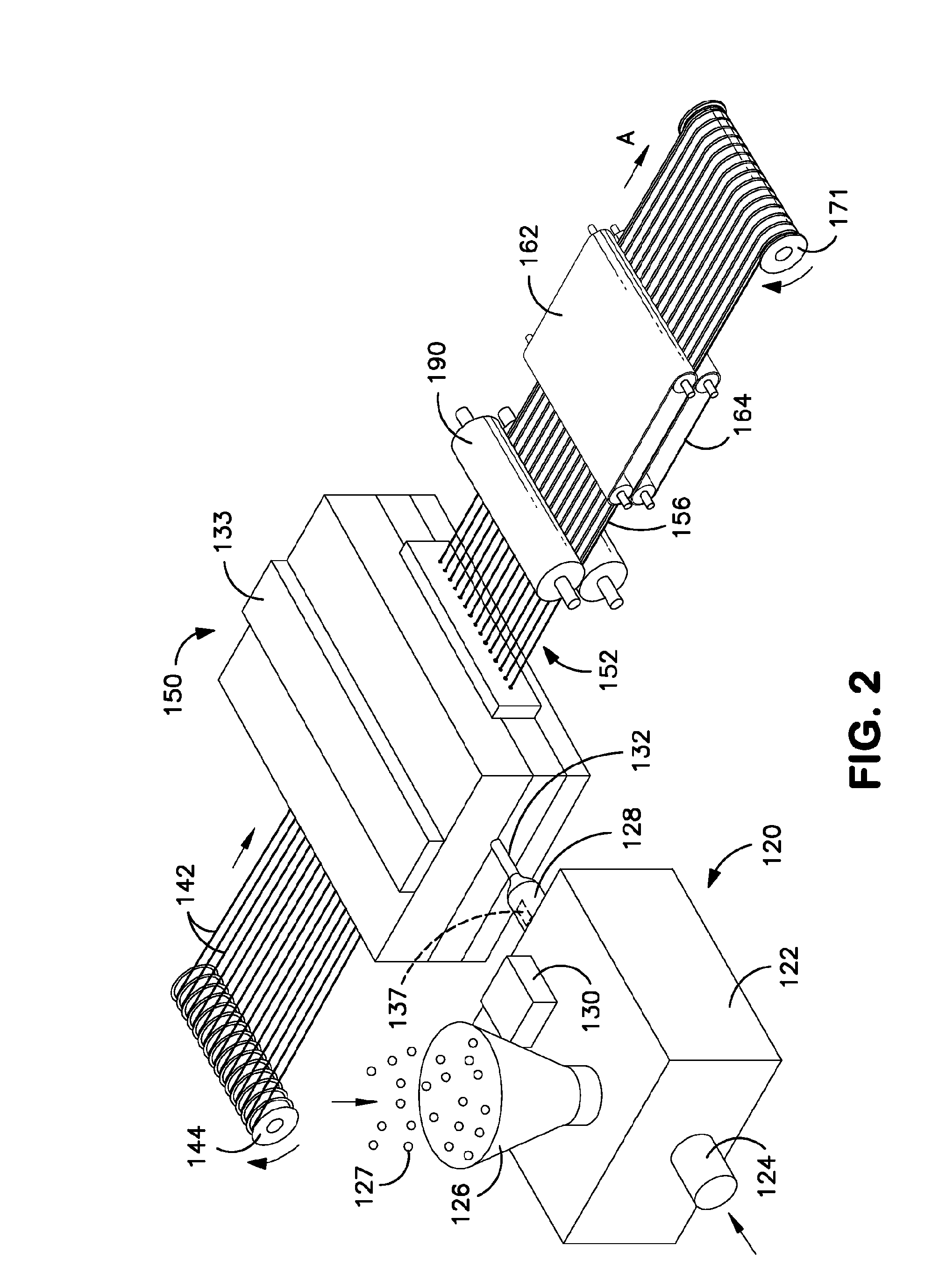
Method of making continuous filament reinforced structural plastic profiles using pultrusion/coextrusion
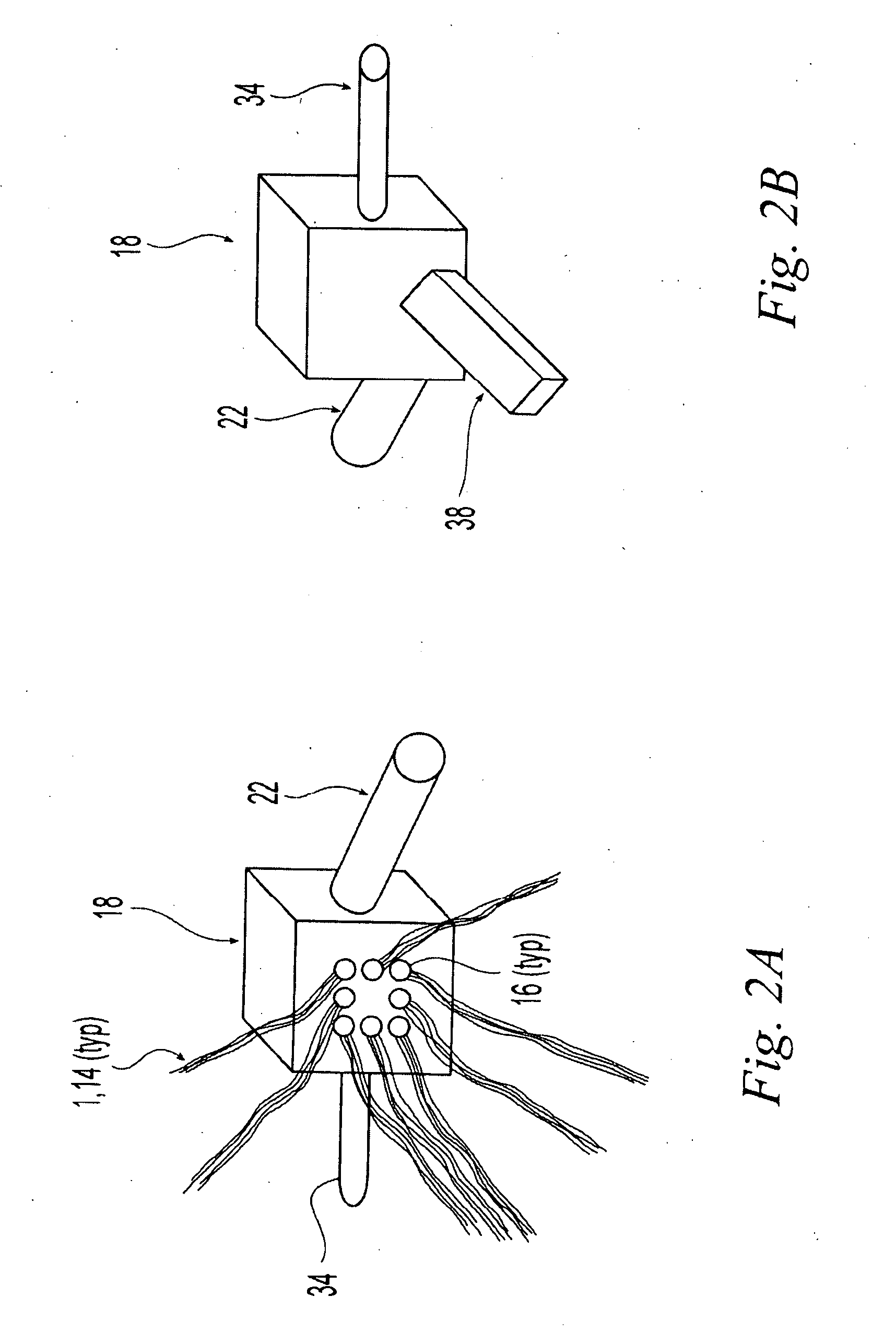
A system and method are disclosed for producing a continuous filament reinforced thermoplastic profile having consistent cross section. A continuous reinforcing filament is pre-wetted with a first thermoplastic resin and introduced into a die, where it is contacted with a second thermoplastic resin extruded from an extruder at melt state. The temperature of the die is carefully controlled so that the pre-wetted filament and first resin do not cure or solidify until after they have contacted and mixed with the second thermoplastic resin. The mixture temperature is then controlled to make a substantially solidified profile pre-shape. A capping layer comprising a third thermoplastic resin is then co-extruded onto the outer surface of the pre-shape. A multistage die for bringing together the filament and thermoplastic resins and for maintaining appropriate temperatures at each stage of the profile-forming process is also disclosed.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CORP
High-transverse-strength pultrusion structural sheet material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103589127AImprove longitudinal strengthReduce weightForming/stuttering elementsYarnGlass fiber
The invention relates to a high-transverse-strength pultrusion structural sheet material and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises that: alkali-free glass fiber roving, knitting felt and composite felt are drawn out from a creel and a felt shaft, and successively pass a yarn-guiding rack, a gum dipping tank, a pre-forming die apparatus; and glass fiber yarn and glass fiber felt subjected to infiltration and pre-forming enter a structural sheet material pultrusion die heated to a preset temperature, and sheet materials subjected to solidification forming are subjected to traction by a traction mechanism, fixed-length cutting and the like for being processed into a structural sheet material product with relatively large size and with a same shape as the die shape. The product is relatively high in transverse strength, light and high in strength, and can be subjected to secondary processing such as cutting, boring and the like. Additionally, concave-convex bayonets are arranged at the two sides of the sheet material, and the sheet material is widely applicable to buildings such as large-area building templates, wall plates, roof boards, furniture plates, decorative plates and the like, and also is applicable to other industries such as energy field and transportation field.
Owner:上海事升新材料有限公司
Reinforced composites and system and method for making same
InactiveUS20050048273A1Easy to smoothFacilitates rapidTailstocks/centresConfectioneryMechanical engineeringPressure sensitive
A detailed embodiment of the invention described herein includes a method and apparatus for pultrusion of a plastic member having a non-wood (e.g., bamboo) reinforced core. The apparatus includes an input and series of die assemblies for taking bamboo tape and embedding it in an appropriately shaped composite member. The die assembly may include a finger die, an encapsulation die, a forming die, and a chilling die. A pultrusion unit maintains production at an efficient and desired rate by use of pressure sensitive clamps to pull the product forward through the prior die units. A colorizer unit and embossing unit allow particular appearances to be produced in the end product. Alternative embodiments are also shown including the processing of bamboo into tape and ribbon forms usable by a pultrusion machine.
Owner:CORLYTE PRODS
Fibre enhancement modifying method for polyurethane foam plastic
The invention relates to a fiber reinforced and modified method of a polyurethane foam plastic. The formula of raw materials added into raw materials of the polyurethane foam plastic is: 80-90 portions of polyether polyol 1; 10-20 portions of polyether polyol 2; 0.01-0.03 portions of catalyst; 0.5-2 portions of hard foam silicon oil; 0.2-0.5 portions of foaming agent; 5-20 portions of flame retardant; 0.1-0.2 portions of antioxidant; 115-150 portions of isocyanate; 230-300 portions of reinforcing materials. compression molding forming is that: each component in the formula after mixed evenly is fast sprayed on the surface of reinforcing fiber, which is dipped uniformly and then put into the die for curing molding under room temperature; pulling and extruding molding is carried out through a pulling and extruding device; each component in the formula after mixed evenly is fast sprayed on the surface of the reinforcing fiber running with certain speed, which is dipped uniformly and then put into a die cavity for foaming, curing and molding.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Method for Forming Reinfoced Pultruded Profiles
A method and apparatus for forming a profile that contains at least one layer of continuous fibers and at least one layer of discontinuous fibers. Said method allowing the selective control of features to achieve a profile that has increased transverse strength and flexural modulus. The layer of continuous fibers may be formed from one or more continuous fiber reinforced ribbons (“CFRT”) (12) that contain fibers embedded within a thermoplastic polymer matrix, whereby a void fraction and in turn is minimized and flexural modulus is optimized Further, the ribbon (s) are consolidated so that the continuous fibers remain fixed in alignment in a substantially longitudinal direction (e.g., the direction of pultrusion). In addition to enhancing the tensile properties of the profile, the use of such ribbons also allows an improved handability when placing them into the desired position within the pultrusion die. The discontinuous fibers are also embedded within a thermoplastic matrix, in such a way as to assist in bonding of the layers to achieve the desired strength. At least a portion of the fibers are oriented in the transverse direction to provide increased transverse strength.
Owner:TICONA LLC
Method of making a pultruded part with a reinforcing mat
A method of making a pultruded part having a uniform cross-section using a novel reinforcing mat. The method comprises orienting a plurality of longitudinal rovings along a longitudinal axis of a pultrusion die; providing a reinforcing structure comprising a permeable transport web of staple fibers attached to a plurality of first reinforcing fibers oriented so that the portion of the first reinforcing fibers oriented in a direction transverse to the longitudinal axis comprises at least 40% of a volume of materials comprising the reinforcing structure; shaping the reinforcing structure to generally conform with a profile of the pultrusion die; combining a resin matrix with the longitudinal rovings and the reinforcing structure in the pultrusion die so that the longitudinal rovings and the reinforcing structure are substantially surrounded by the resin matrix; at least partially curing the resin matrix in the pultrusion die; and pulling the pultruded part from the pultrusion die.
Owner:PELLA
Process for in-line forming of pultruded composites
InactiveUS6872343B2Increase the number ofSimple formatLaminationLamination apparatusPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
Pultruded composites of longitudinally oriented reinforcing fibers in a matrix of a thermoplastic resin are shaped in-line during the pultrusion process to provide a variety of non-linear or variable cross-section articles.
Owner:FULCRUM COMPOSITES
Pultrusion method for thermoplastic composite material and forming die thereof
InactiveCN1730270AImprove impregnation effectImprove mechanical propertiesPolymer scienceFiber bundle
The invention relates to a pultrusion method for thermoplastic composite, which takes fortifying fiber and matrix fiber as raw material, including the following steps: a. placing matrix fiber and fortifying fiber on the creel in the weight ratio of 95-20:5-80; b. loading the fortifying fiber and matrix fiber to demand scale into the preheat chamber by the thread wire and board and preheating them; c. loading the preheated mixed fiber tuft into the preforming die, so the tuft near to the entrance shape of the forming die; d. loading the preformed mixed fiber into the forming die. Certainly the performing die and forming die can be diad, with performing segment and forming segment in one die; e. after loading out from the forming die the section bar cooling and shaping to get products. The invention overcomes the socking problem of high molecular polymer, improving the socking effects of thermoplastic composites, and the mechanical property enhances dramatically.
Owner:SINOMA SCI & TECH
Preparation method and device of eccentric wear prevention pumping rod
InactiveCN101396874AExcellent performance of anti-eccentric wearPrevent slippageDrilling rodsDomestic articlesPre stressResin matrix
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite material sucker rod which can prevent camber wear and a device thereof. Combining pultrusion and winding, fibre is immersed by resin matrix, and the composite material sucker rod is prepared by pultrusion, curing and shaping; the surface of the rod body is continuously wound with wearing fibre immersed by resin matrix glue after shaping; the rod body of the sucker rod, the surface of which is provided with a camber wear preventing layer of a spiral bar shape is obtained by curing; the rod body of the sucker rod is cut to be in fixed length, is connected with a metal joint by glue, and is treated in a joint curing furnace; the whole sucker rod is stretched by inherent stress. The surface of the rod body of the sucker rod is provided with the camber wear preventing layer of a spiral bar shape, thus having excellent camber wear preventing performance while ensuring a high intensity of the sucker body; the inverse cone structure of the metal joint and the pressure injection glue connection process ensure the joint part has the properties of high intensity and fatigue proof, the service life of which is consistent with the composite material rod body, and the reliability of the products is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A kind of high temperature resistant epoxy resin composition for rapid pultrusion
InactiveCN102286138AHigh strength, high toughness and impact resistanceImprove high temperature resistanceEpoxyEther
The invention relates to a high temperature resistant epoxy resin composition for rapid pultrusion and a preparation method thereof. The epoxy resin composition consists of 100 parts by mass of epoxy resin, 30-50 parts by mass of amine curing agent, 0.5-5.0 parts by mass of latent curing agent, 0.5-5.0 parts by mass of small epoxy group It is composed of molecular compound and 0.5-5.0 parts by mass of inorganic filler. The mixed epoxy resin of glycidyl ether epoxy resin and glycidyl amine resin or glycidyl ester epoxy resin is used as the resin matrix of the pultruded product, so that the pultruded product has high strength and high toughness impact resistance, and has Excellent high temperature resistance. Using a latent curing agent together with a mixed amine curing agent can make the pultruded product have a lower curing temperature and be cured quickly within a certain period of time, shortening the curing time, thereby improving the pultrusion speed and production efficiency.
Owner:BLUESTAR BEIJING CHEM MACHINERY
Fibers treated with polymerization compounds and fiber reinforced composites made therefrom
InactiveUS20110045275A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsFiber-reinforced compositePolymer chemistry
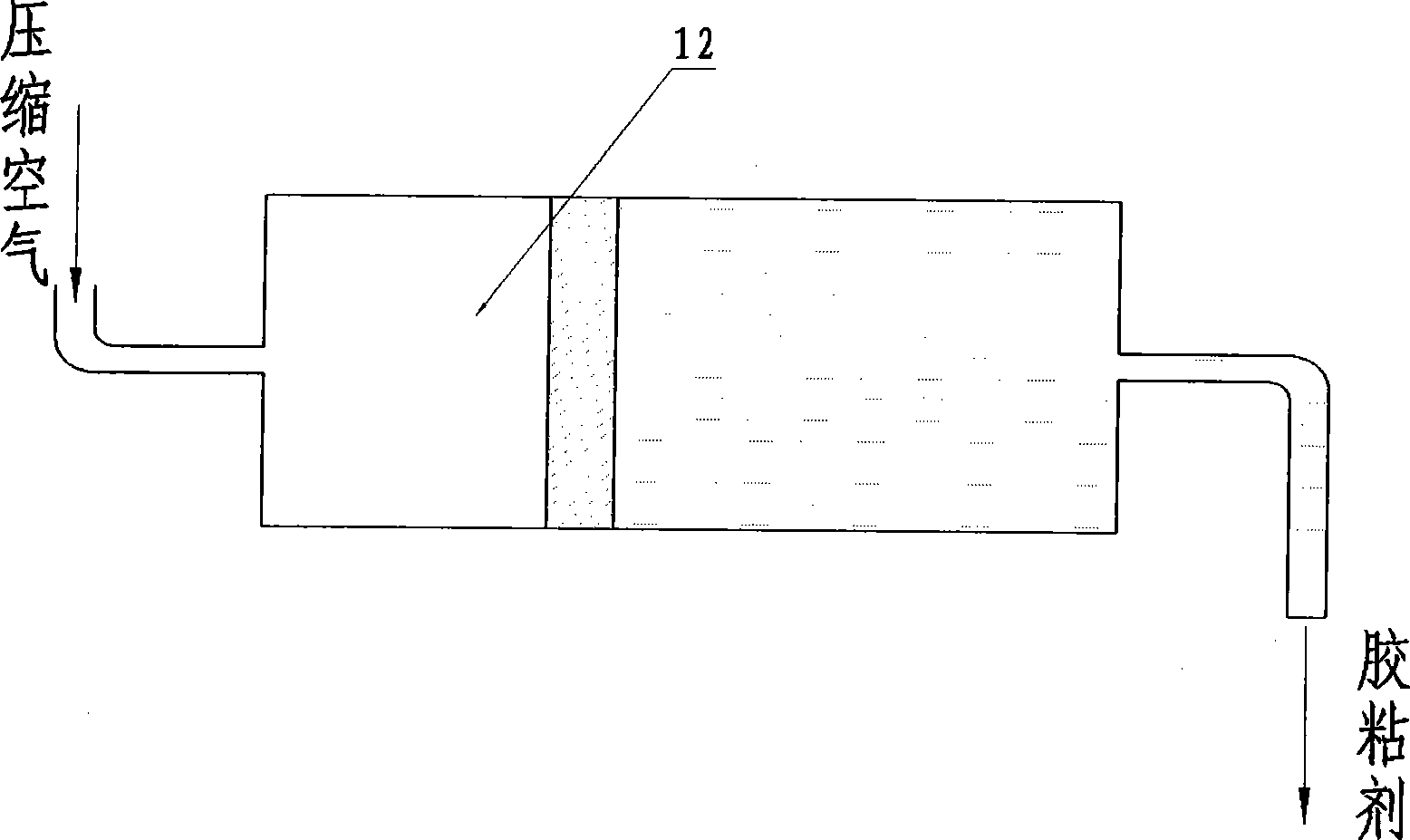
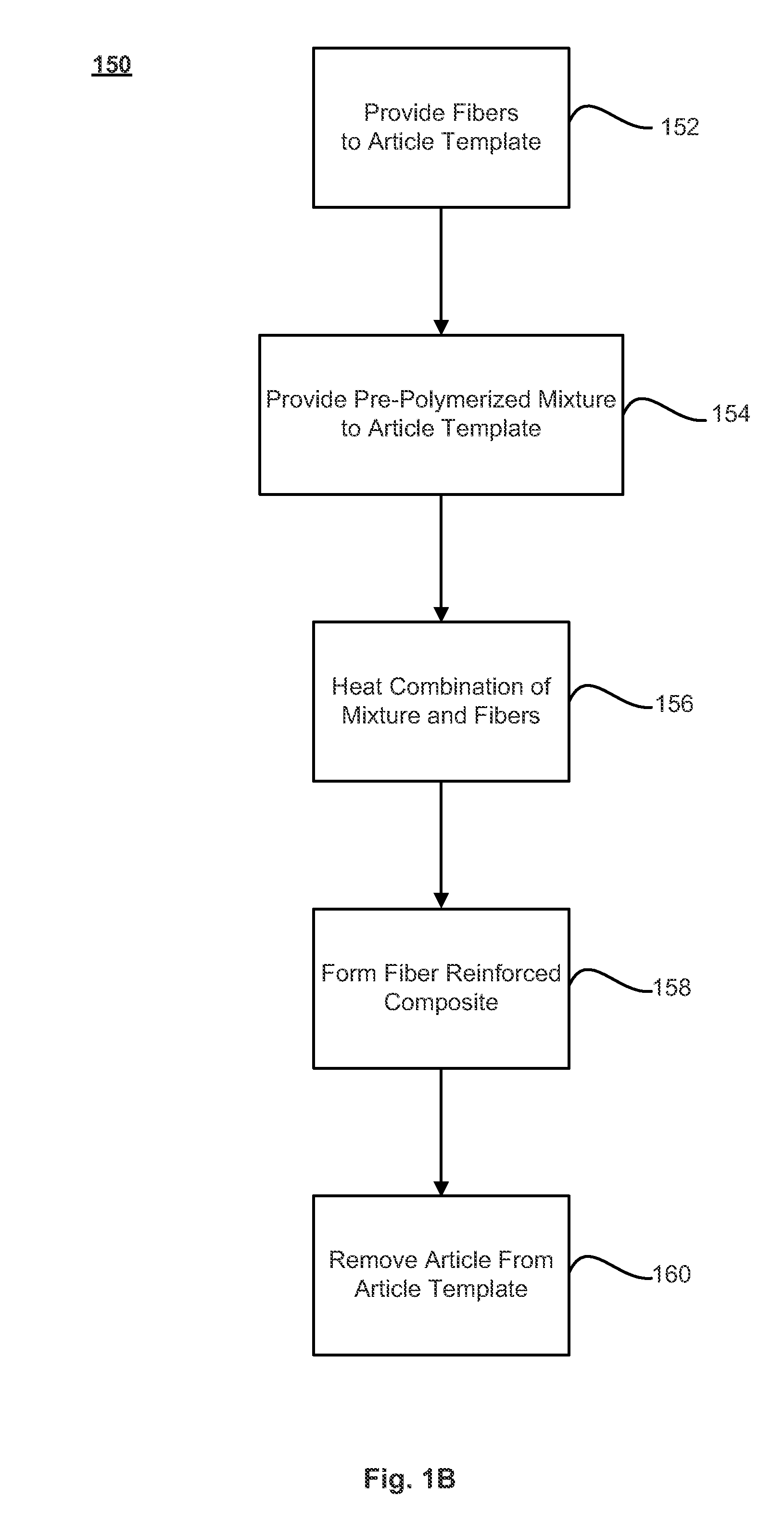
Methods of making fiber reinforced composite articles are described. The methods may include treating fibers with a sizing composition that includes a polymerization compound, and introducing the treated fibers to a pre-polymerized composition. The combination of the treated fibers and pre-polymerized composition may then undergo a temperature adjustment to a polymerization temperature at which the pre-polymerized composition polymerizes into a plastic around the fibers to form the fiber-reinforced composite article. Techniques for introducing the treated fibers to the pre-polymerized composition may include pultrusion, filament winding, reactive injection molding (RIM), structural reactive injection molding (SRIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM), long fiber injection (LFI), sheet molding compound (SMC) molding, bulk molding compound (BMC) molding, a spray-up application, and / or a hand lay-up application, among other techniques.
Owner:TADEPALLI RAJAPPA +3
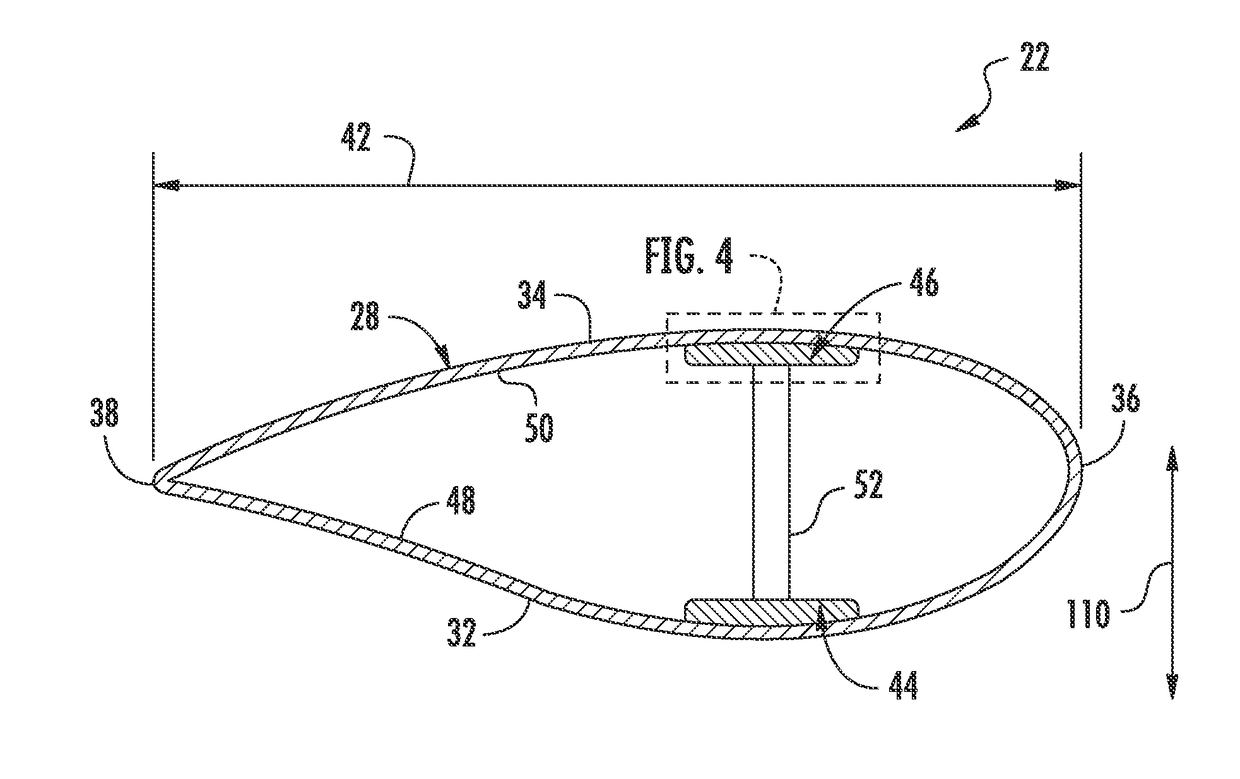
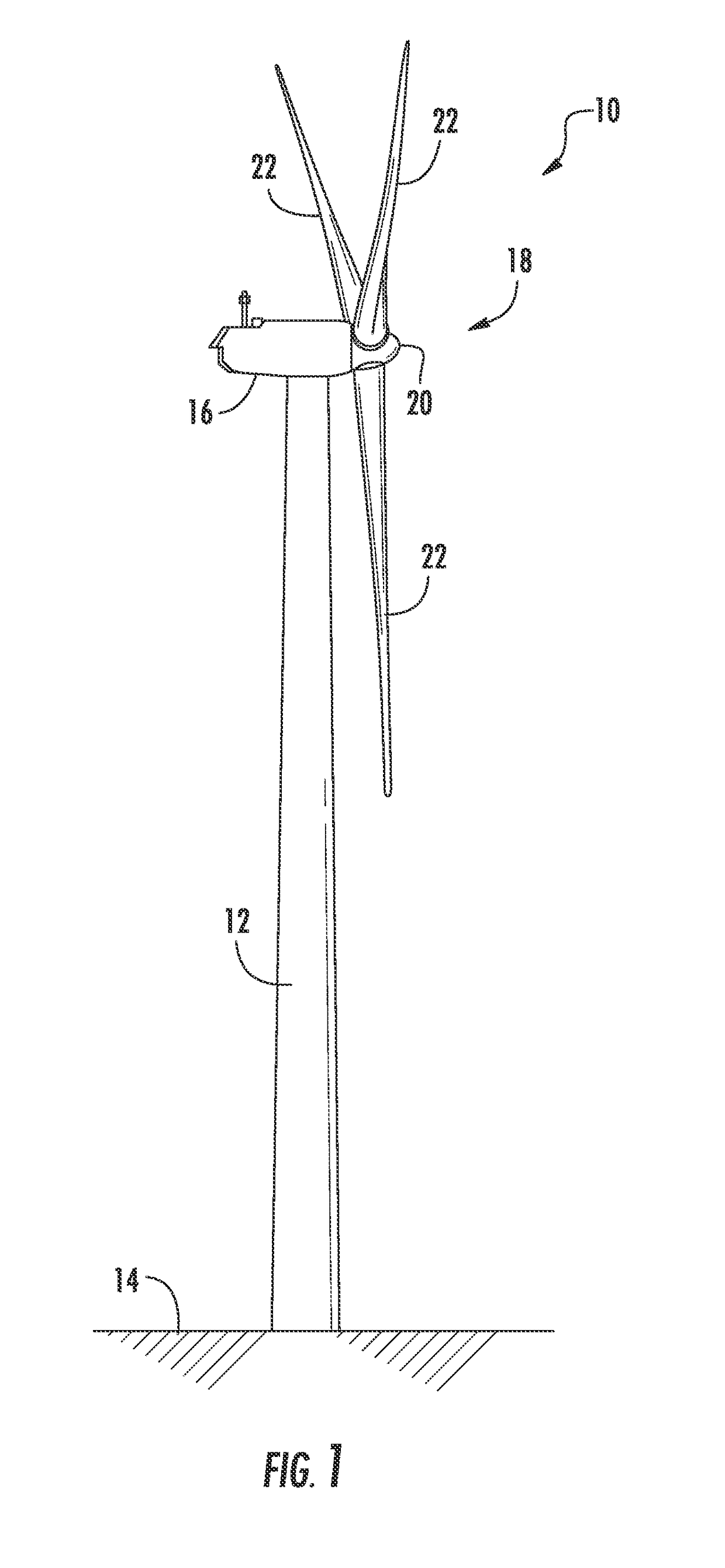
Wind turbine rotor blade components formed from pultruded hybrid-resin fiber-reinforced composites
ActiveUS20170082089A1Final product manufactureWind motor assemblyEngineeringFiber-reinforced composite
A rotor blade component for a wind turbine rotor blade may generally include an assembly of pre-formed pultruded products. Each pultruded product may include an interior pultruded portion formed from a first fiber-reinforced composite including a first plurality of fibers surrounded by a thermoset resin material and an exterior pultruded portion encapsulating the interior pultruded portion. The exterior pultruded portion may be formed from a second fiber-reinforced composite including a second plurality of fibers surrounded by a thermoplastic resin material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
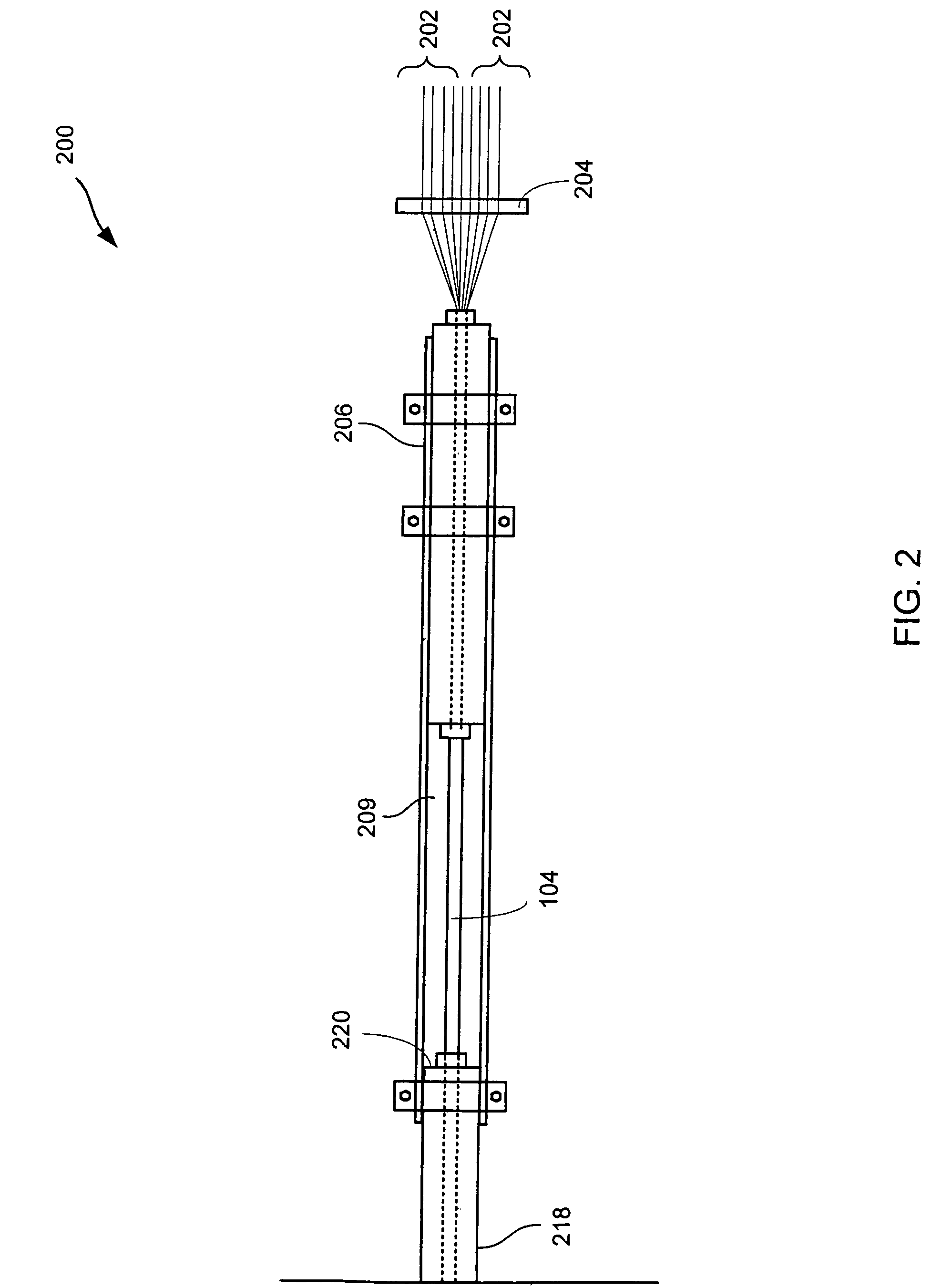
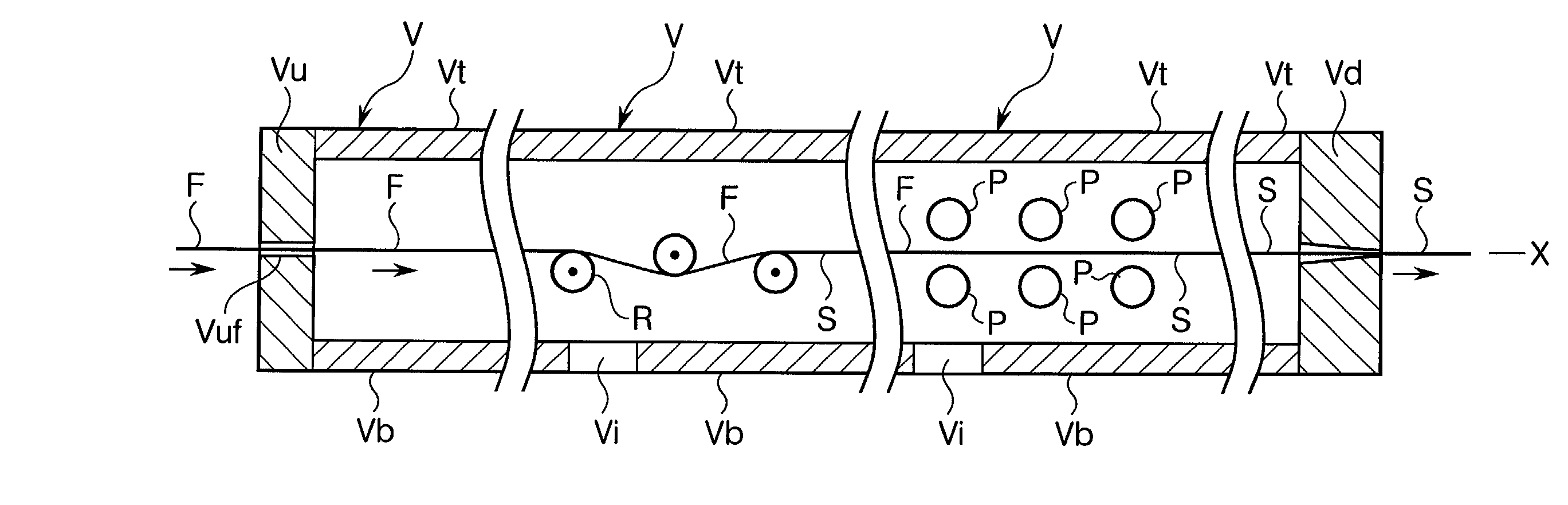
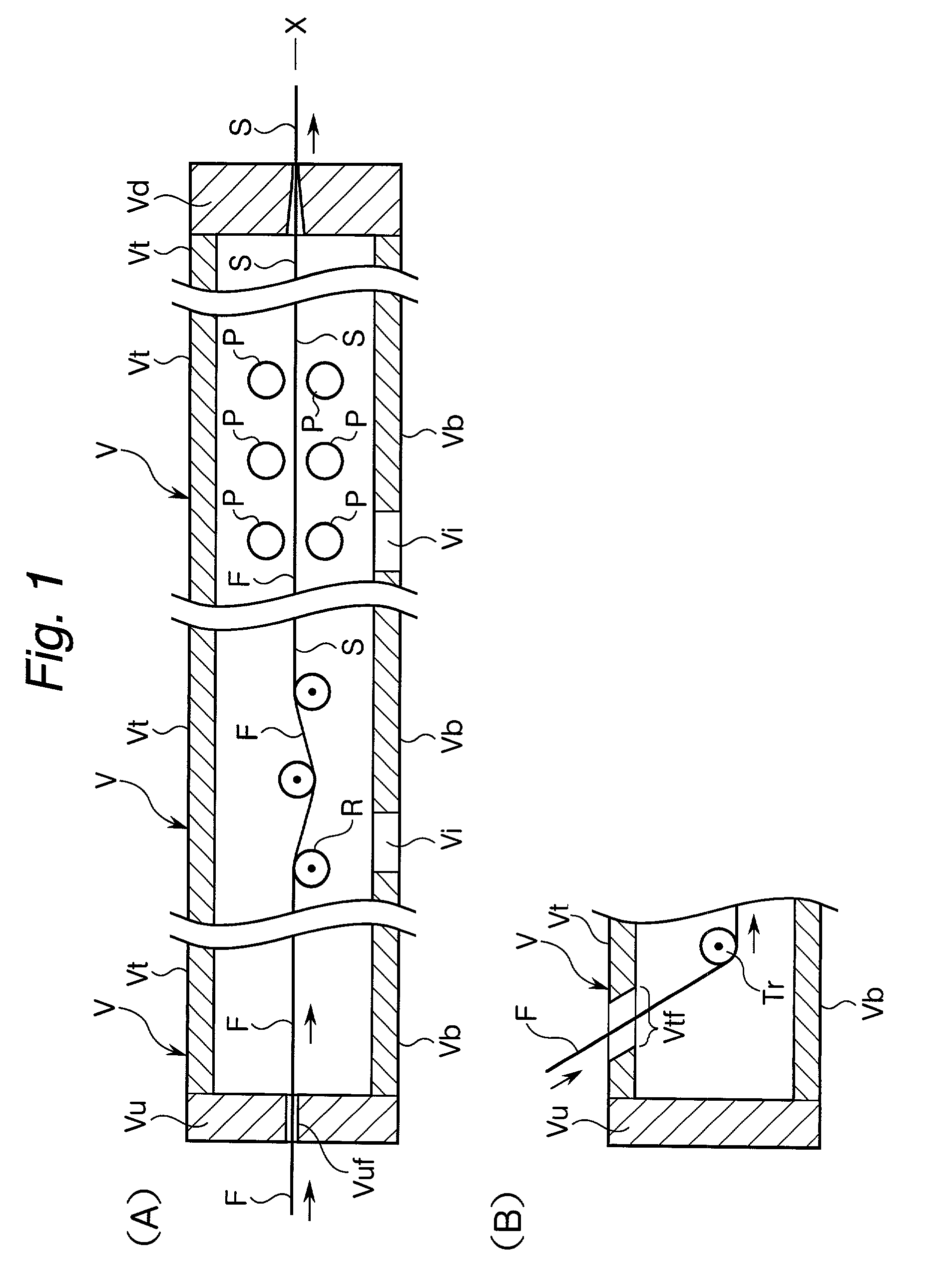
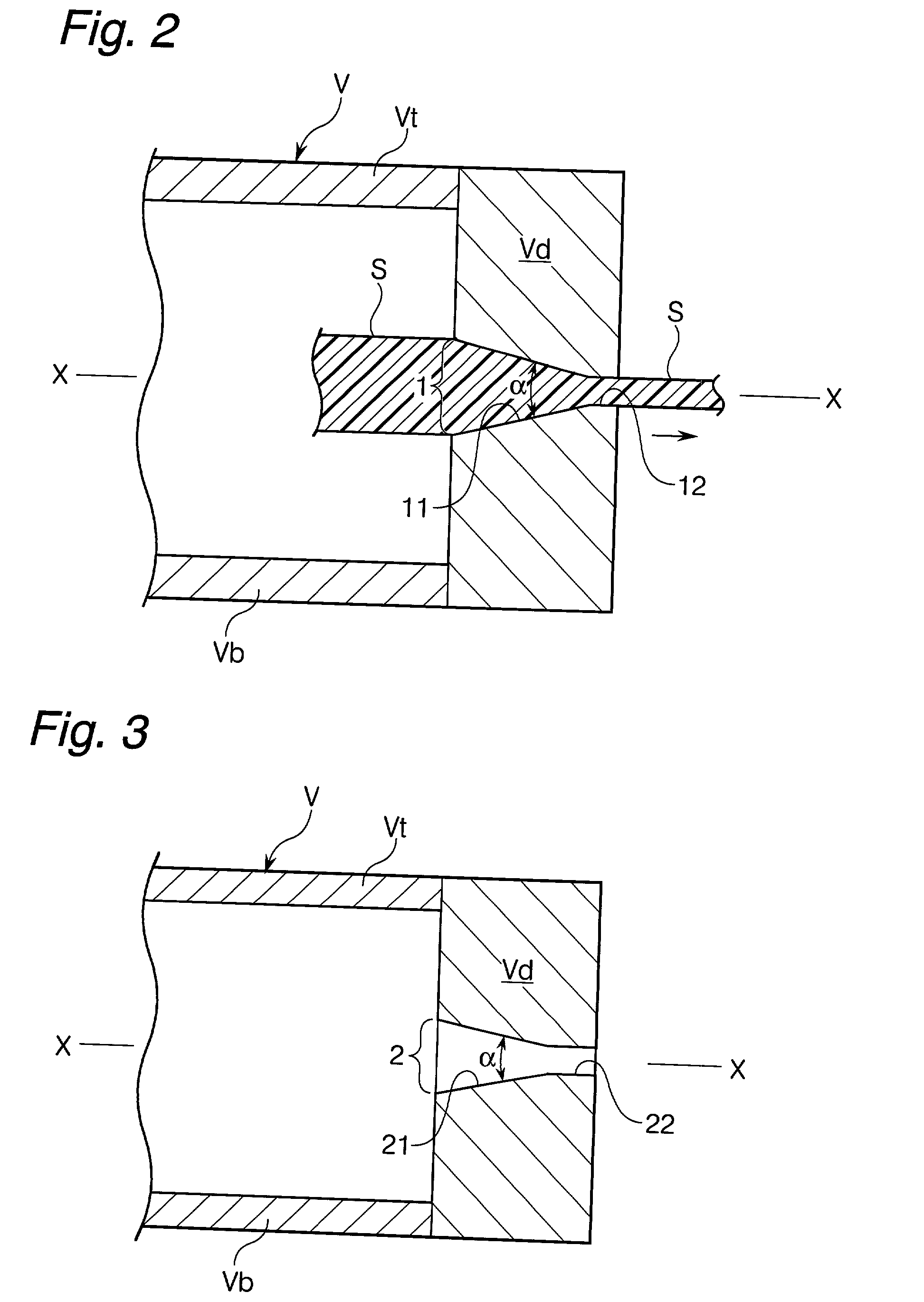
Device for producing thermoplastic resin continuous length sections reinforced with long fibers
In a pultrusion device for producing continuous length sections prepared from thermoplastic resins reinforced with long fibers, the vertical angle (.alpha.) of an upstream conical surface of a conical portion, which constitutes a shaping nozzle perforated through the downstream end wall of the device ranges from 15 to 35 degrees and the shaping nozzle has a land portion having a length of 1 to 5 mm in the downstream area subsequent to the upstream conical surface. According to this pultrusion device for producing continuous length sections prepared from thermoplastic resins reinforced with long fibers, the long fibers never undergo any breakage nor fluffing during the opening treatment and this accordingly leads to the substantial reduction of pill-formation. As a result, the opening-impregnation device of the present invention provided at least with the downstream end wall carrying the shaping nozzle (including the land portion) can stably and continuously be operated over a long period of time, without any trouble such as those encountered in the conventional devices.
Owner:JNC CORP
Water-clear aliphatic polyurethane pultrusion formulations and processes
InactiveUS20140265000A1Excellent weathering property propertyGood physical propertiesPolyolFiber-reinforced composite
Clear polyurethane fiber reinforced composites are produced by a pultrusion process with a polyurethane-forming system that includes: (a) a clear, aliphatic polyisocyanate having a viscosity at 25° C. of no more than 1000 centipoise, (b) a colorless polyol component comprising an amine-initiated polyol having a molecular weight of from about 150 to about 400 and an OH functionality greater than or equal to 3, and (c) a catalyst. These fiber-reinforced composites are characterized by both excellent weathering characteristics and excellent physical properties.
Owner:COVESTRO LLC
Sleeper synthesized by enhanced fiber
InactiveCN101457504AAvoid defectsIncrease elasticityBallastwayUltimate tensile strengthMaterials science
The invention relates to a reinforced fiber composite sleeper for supporting railway tracks. The reinforced fiber composite sleeper is one made from reinforced fiber materials, fiber felts or weaving cloth through resin impregnation, formed by the pultrusion of a forming die for designing the shape of the section and solidified in the forming die. The invention overcomes the defects of the known techniques, has ideal strength and elasticity and good insulating property compared with the common concrete sleeper and the anticorrosive wooden sleeper, and ensures the safe running of the trains. In addition, with the good elasticity, the reinforced fiber composite sleeper greatly enhances the whole elasticity of the track structure and reduces the influence on roadbeds from the vibration of the trains and the environmental pollution from the noise of the trains during running; with the good insulating property, the reinforced fiber composite sleeper has no influence on the track circuits so as to ensure the safe running of the trains. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacturing, easy forming and short production period, and is capable of realizing the mechanical and continuous production. Besides, the length of the reinforced fiber composite sleeper can be cut and processed according to the determined length requirements, and the waste sleepers can be treated and recycled easily.
Owner:RAILWAY ENG RES INST CHINA ACADEMY OF RAILWAY SCI +1
Preparation method and preparation system for ultralight composite traction belt
ActiveCN104552988AReduce internal defectsImprove tensile propertiesRope making machinesBeltsYarnAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method and a preparation system for an ultralight composite traction belt, and provides a preparation method and a preparation system for the ultralight composite traction belt with uniform bearing and long service life. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a twist-free continuous monofilament is led out of a fiber yarn group, unfolded uniformly, and introduced into an impregnation tank for impregnation, wherein the impregnation tank is added with a glue solution, then arrangement is performed, and composite enhanced pieces are obtained after pultrusion and curing; the composite enhanced pieces are led out respectively, preheated and introduced into a head die of an extruder, an extruding die core corresponding to the section of the traction belt is arranged in the head die, the composite enhanced pieces are uniformly coated with molten thermoplastic resin in the head die and led out of the head die of the extruder, preliminary forming is realized, and the traction belt is obtained after cooling setting and cooling. The prepared traction belt is light in weight, high in strength, easy to bend, anti-fatigue, long in service life, low in maintenance cost and more applicable to a long-distance elevator.
Owner:TIANJIN GOLDSUN WIRE ROPE
Pultruded part reinforced by longitudinal and transverse fibers and a method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20050008804A1Excessive degradationSuitablePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkEngineering
A method for forming a pultruded part includes collating reinforcing fibers by providing a first layer of reinforcing rovings extending in the longitudinal pultrusion direction, applying onto the first layer an intermediate layer of reinforcing fibers at least some of which include at least portions thereof which extend in the transverse direction and covering the intermediate layer with a second layer of rovings extending in the longitudinal direction. Alternatively the transverse fiber layer is formed on the inside surface of a hollow part. To the collated fibers is applied a urethane resin so as to permeate through the layers and the materials are passed through a die to form a thermo-set cross-linked poly-urethane. The transverse layer or layers are relatively thin having a weight less than or equal to 0.5 ounces per square foot and more preferably as low as 0.25 ounces or 0.1 ounces.
Owner:OMNIGLASS
Technological method for pultrusion of glass fibre reinforced plastics pipe and die thereof
The present invention relates to a pultrusion process for making glass fibre reinforced plastics tube and its special-purpose die equipment. Said process includes the steps of soaking yarn, felt-yarncombination, preforming, solidfying and forming and tube-discharging and coaling. Its special-purpose die equipment includes a die cavity whose internal diameter is equal to the external diameter of formed glass fibre reinforced plastic tube, the periphery of said die cavity is equipped with heating device, a die core whose external diameter is equal to the internal diameter of formed glass fibrereinforced plastic tube is cover-mounted in the interior of die cavity, the centre of said die core is hoelow, and its interior is equipped with heating device. Said invention adopts common heating method in exterior and interior of said die cavity, so that the interior and exterior of glass fibre reinforced plastic tube are solidified well, and its surface is smooth.
Owner:柳惠平
System and die for forming a continuous filament reinforced structural plastic profile by pultrusion/coextrusion
InactiveUS20070125301A1Reinforced thermoplasticAvoid reverse motionLiquid surface applicatorsConfectioneryThermoplasticPolymer science
A system and method are disclosed for producing a continuous filament reinforced thermoplastic profile having consistent cross section. A continuous reinforcing filament is pre-wetted with a first thermoplastic resin and introduced into a die, where it is contacted with a second thermoplastic resin extruded from an extruder at melt state. The temperature of the die is carefully controlled so that the pre-wetted filament and first resin do not cure or solidify until after they have contacted and mixed with the second thermoplastic resin. The mixture temperature is then controlled to make a substantially solidified profile pre-shape. A capping layer comprising a third thermoplastic resin is then coextruded onto the outer surface of the pre-shape. A multistage die for bringing together the filament and thermoplastic resins and for maintaining appropriate temperatures at each stage of the profile-forming process is also disclosed.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com