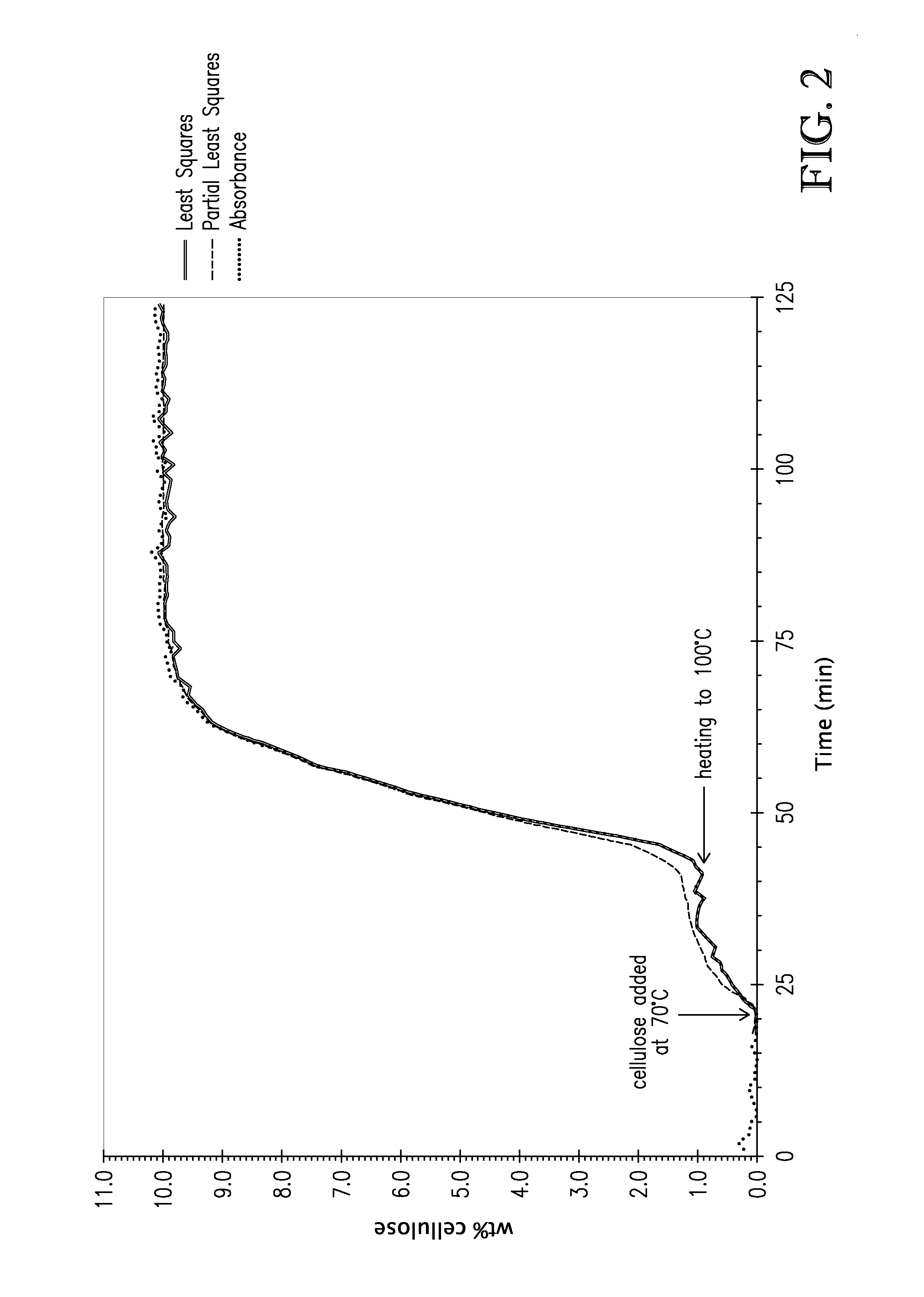
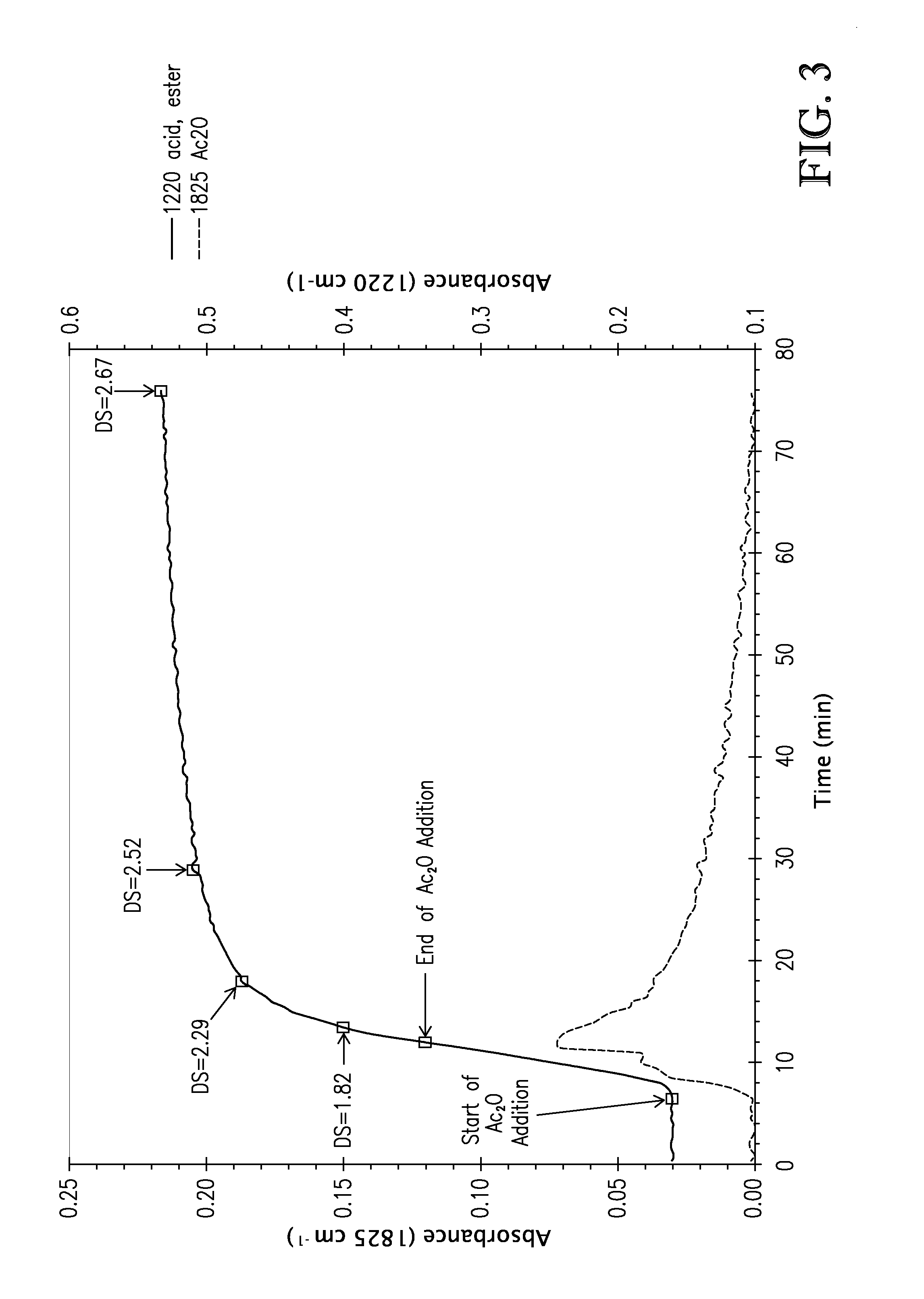
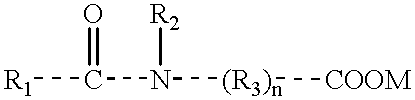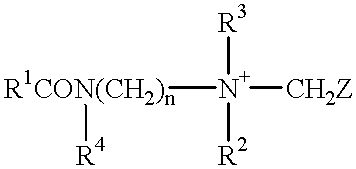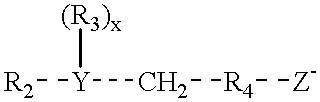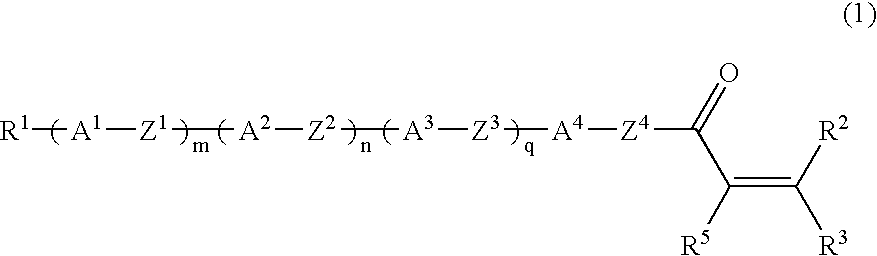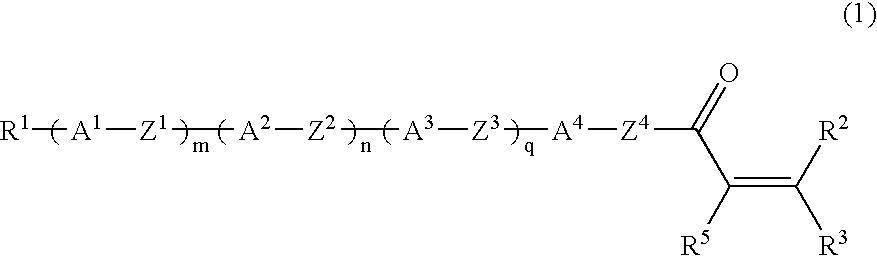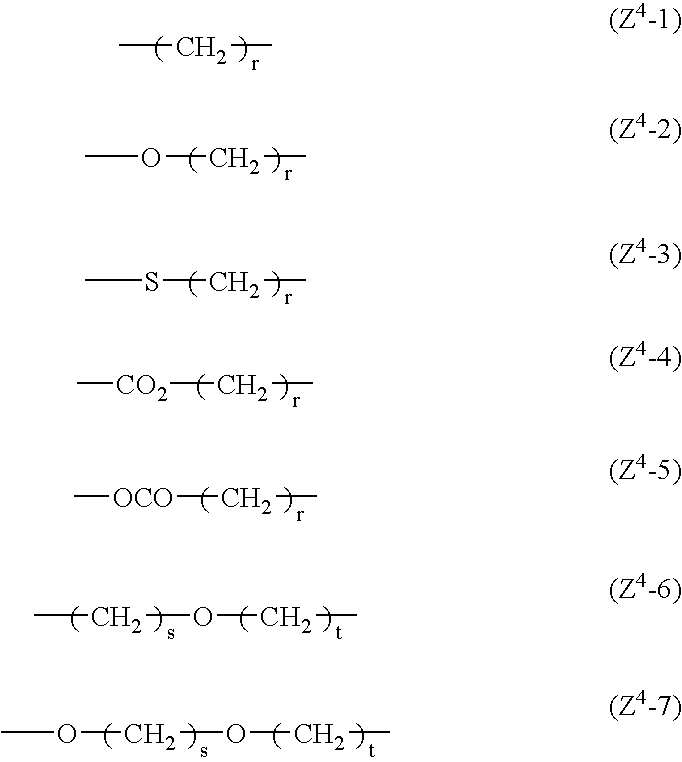Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2258 results about "Liquid crystalline" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
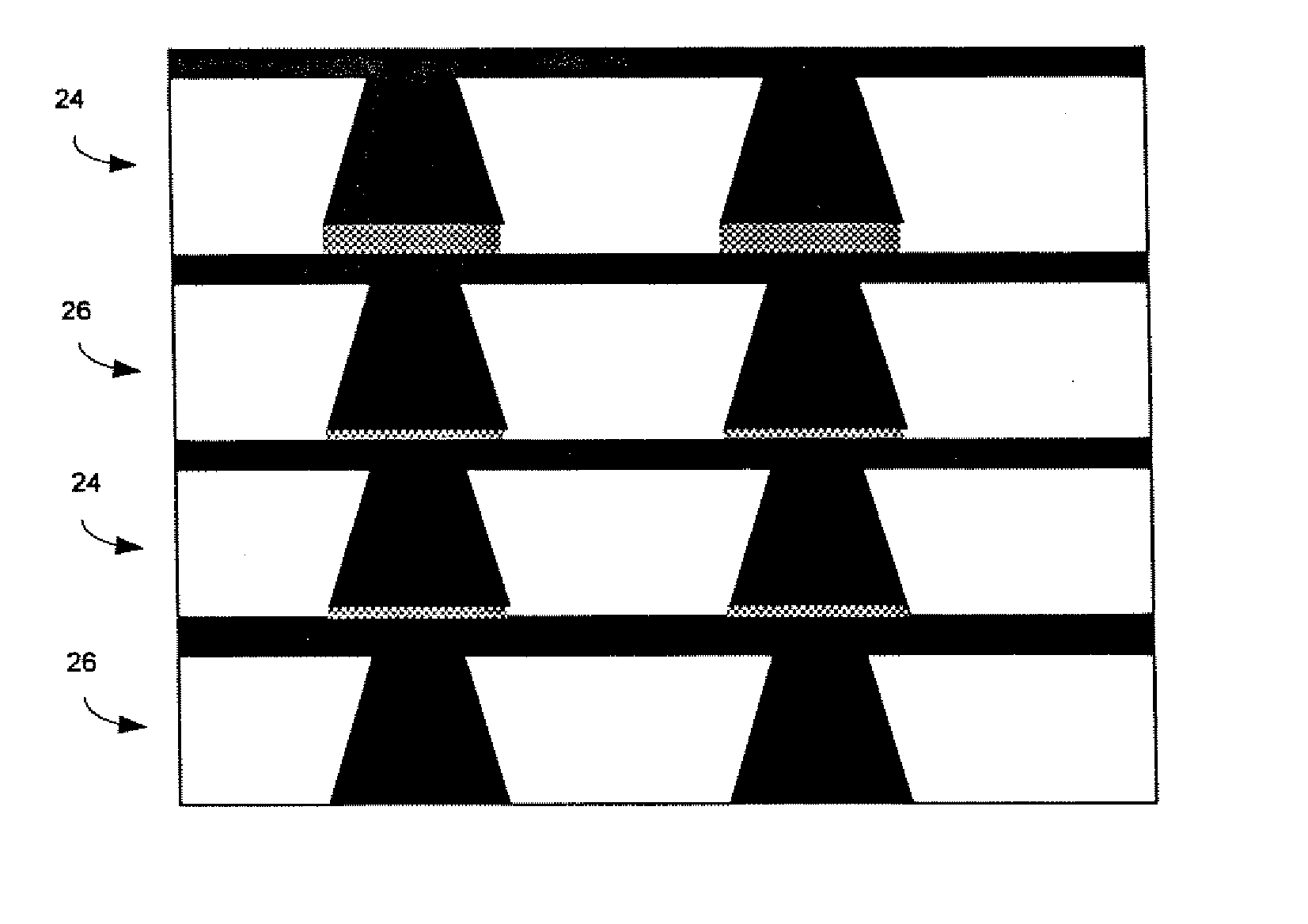
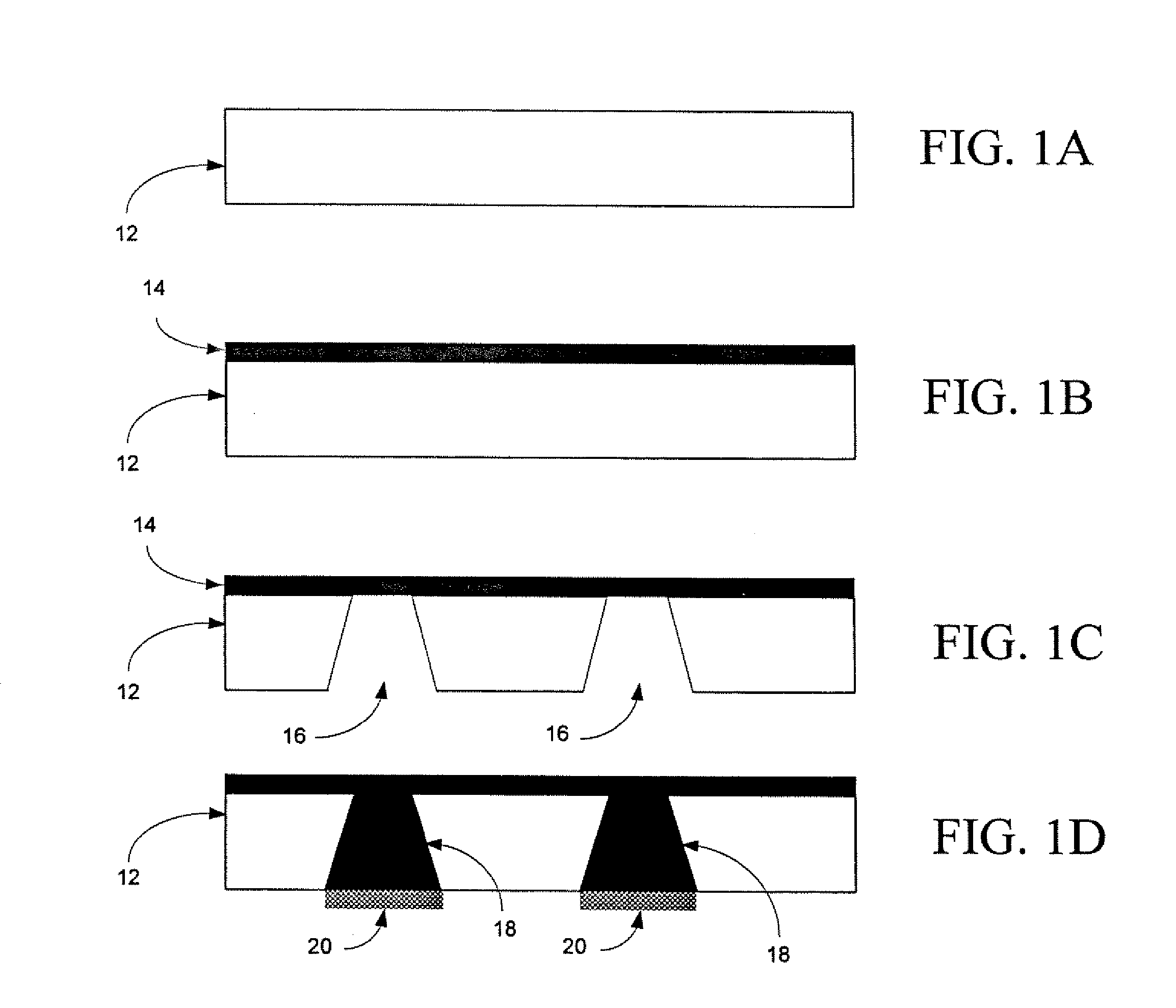
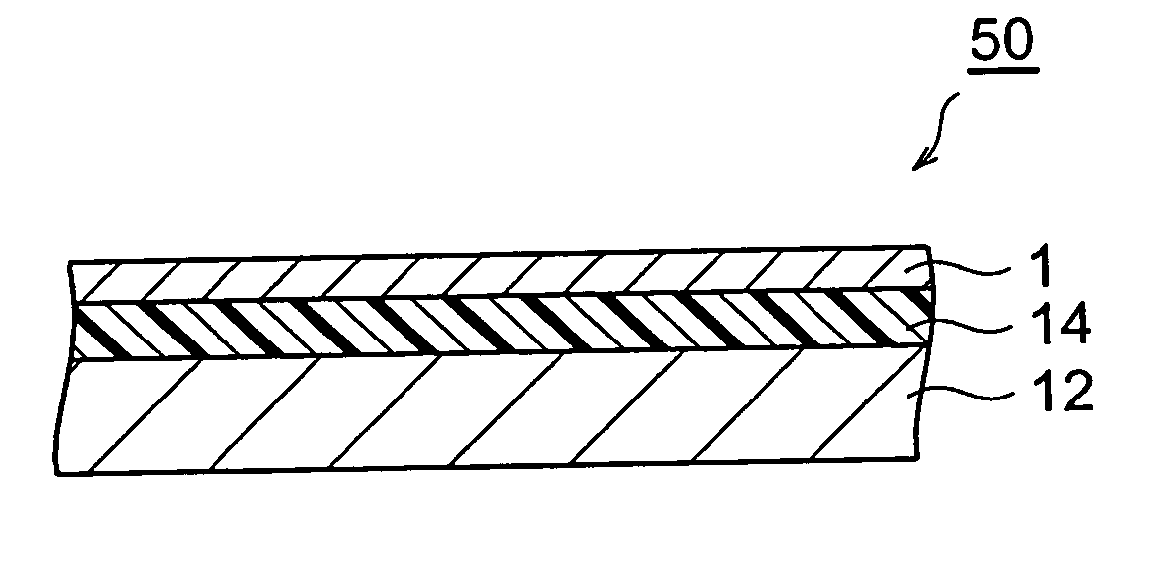
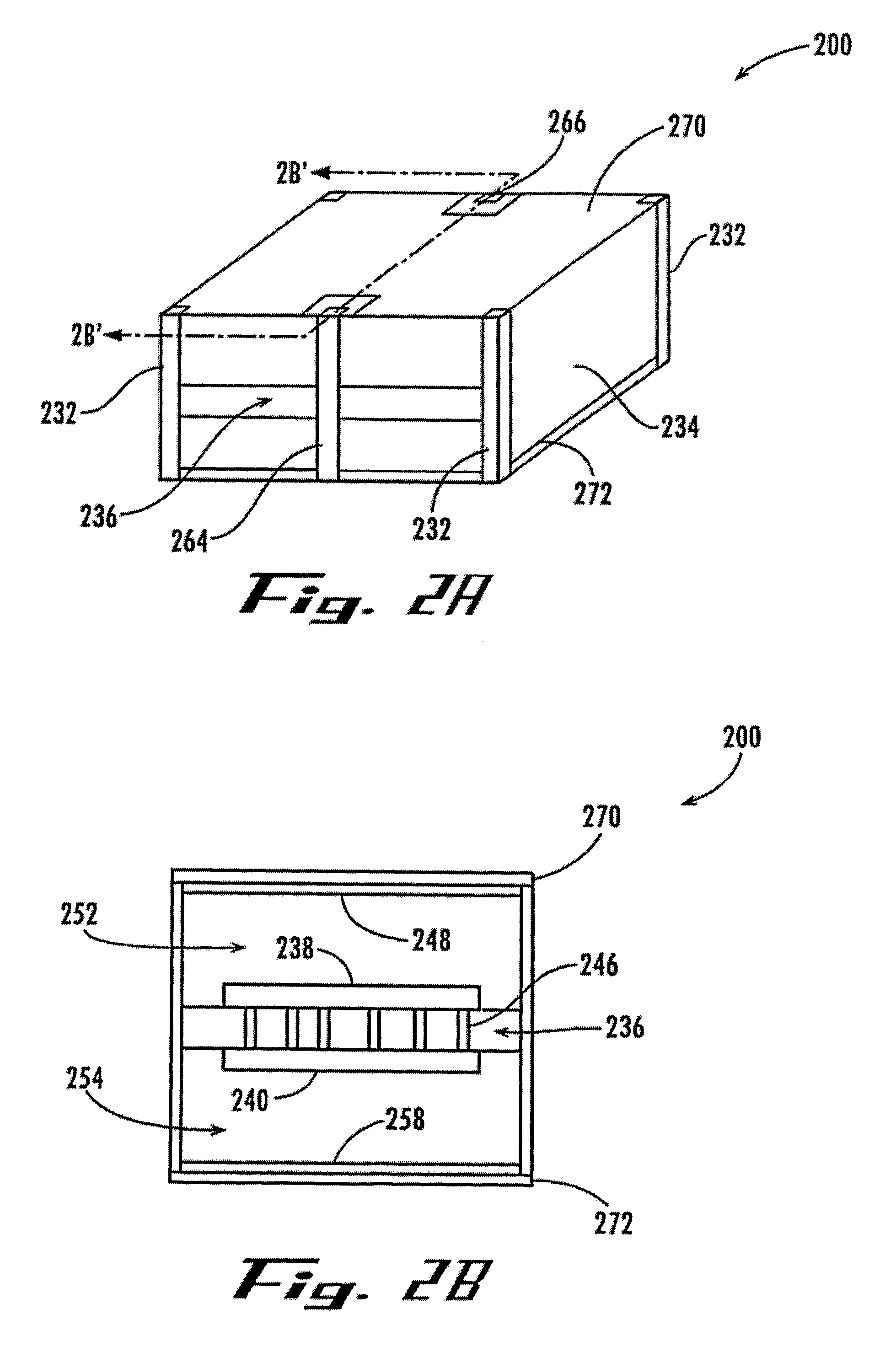
Phase difference film and production method therefor
InactiveUS20060192913A1Low costElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLiquid crystallinePhase difference
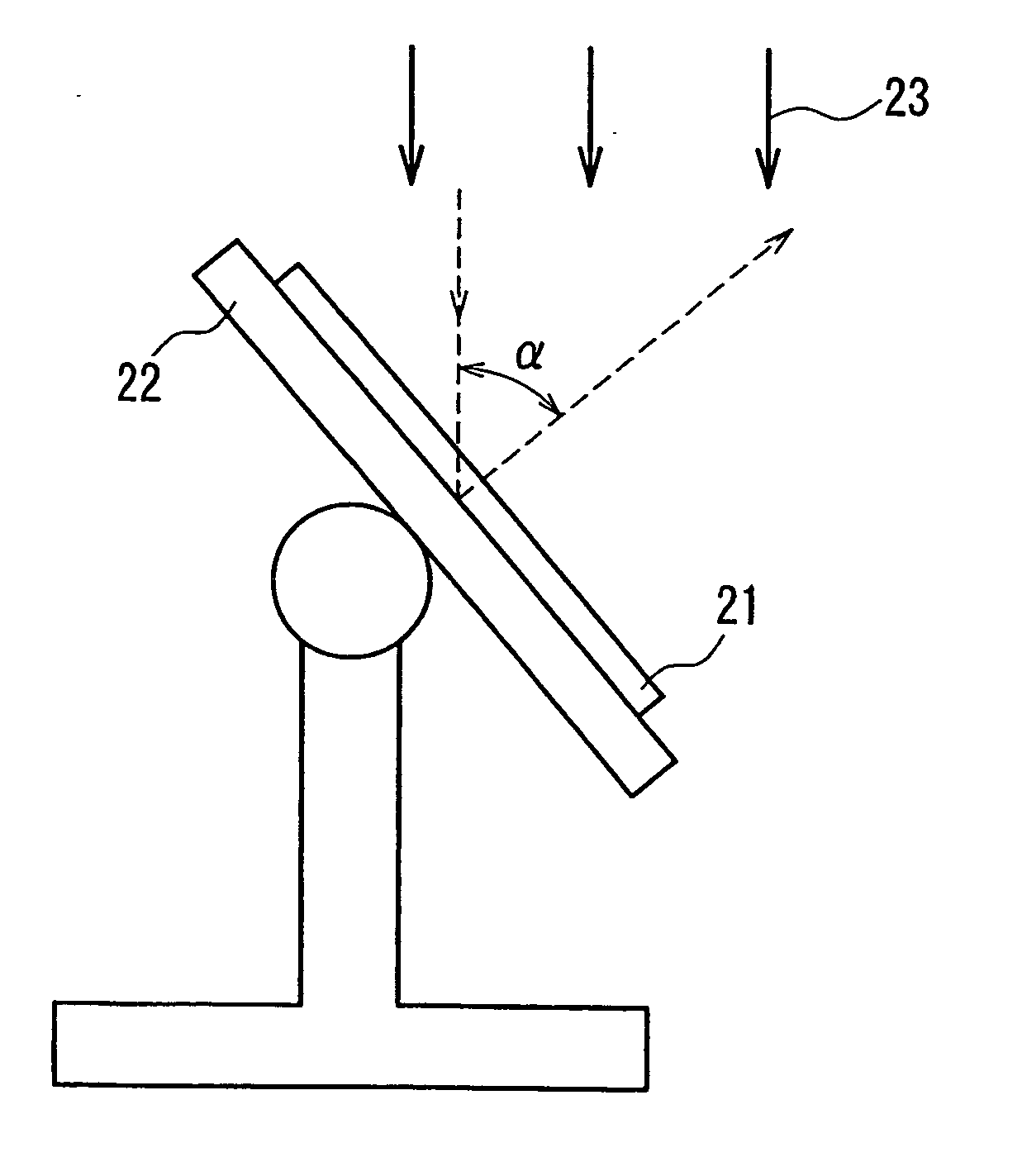
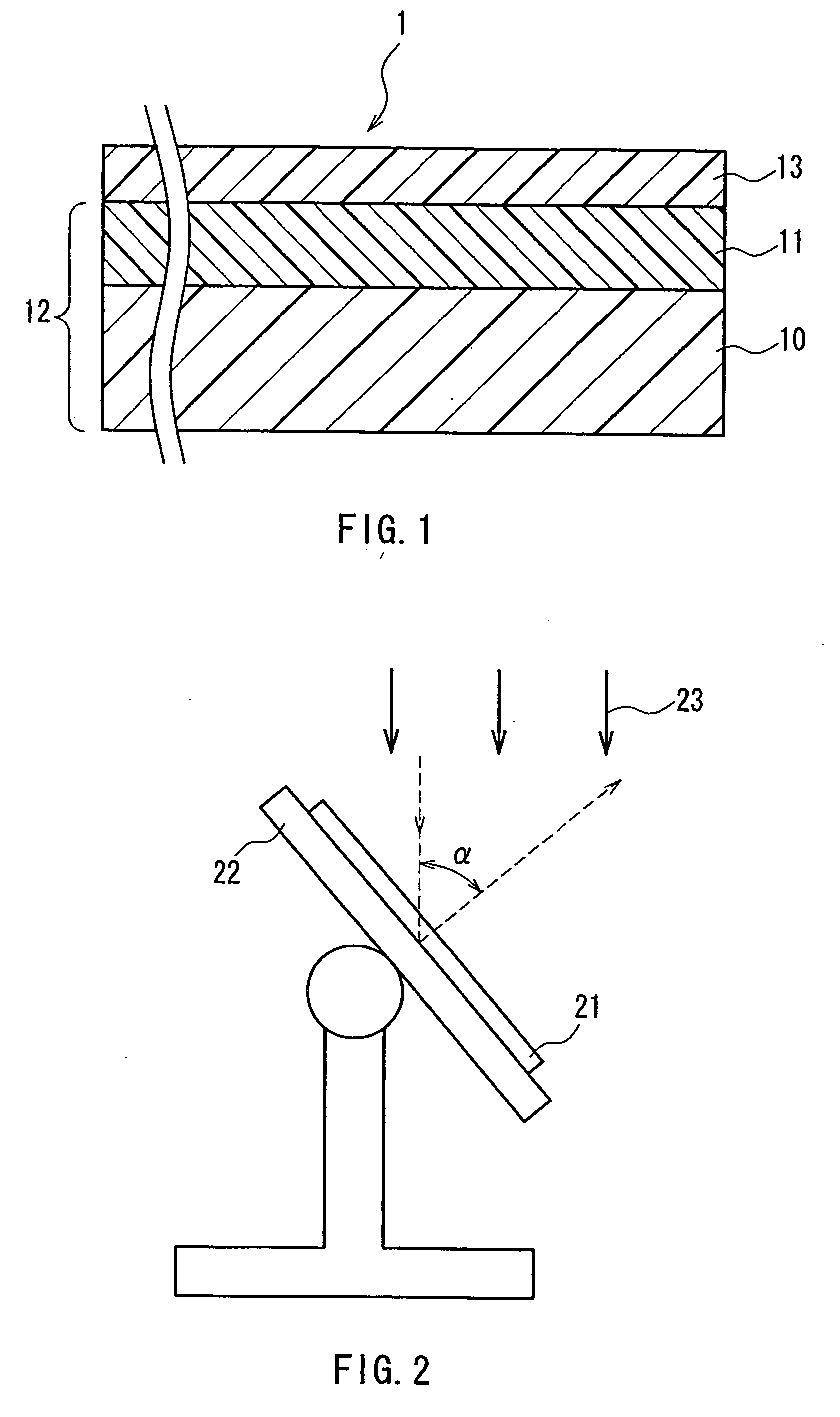
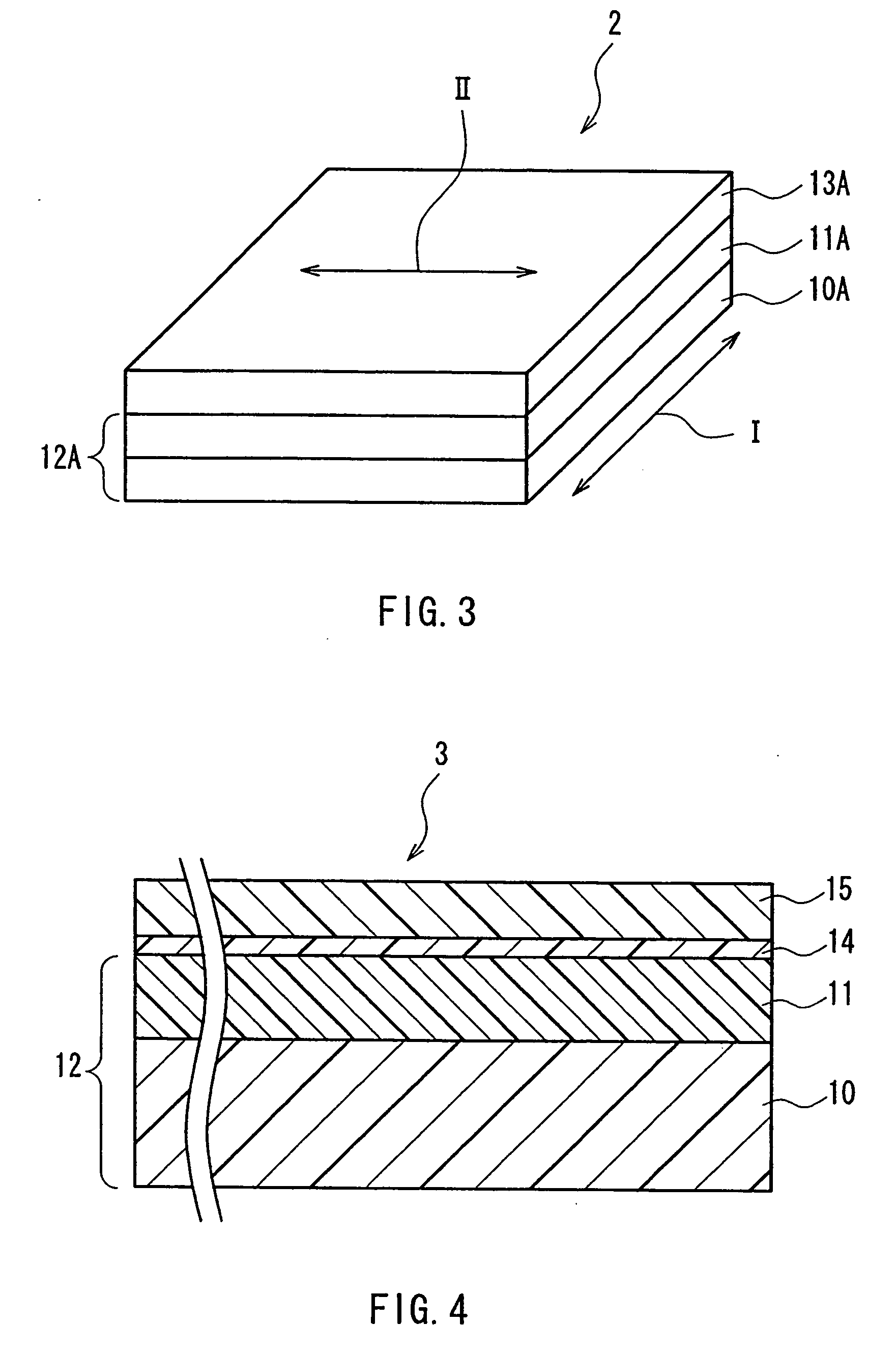
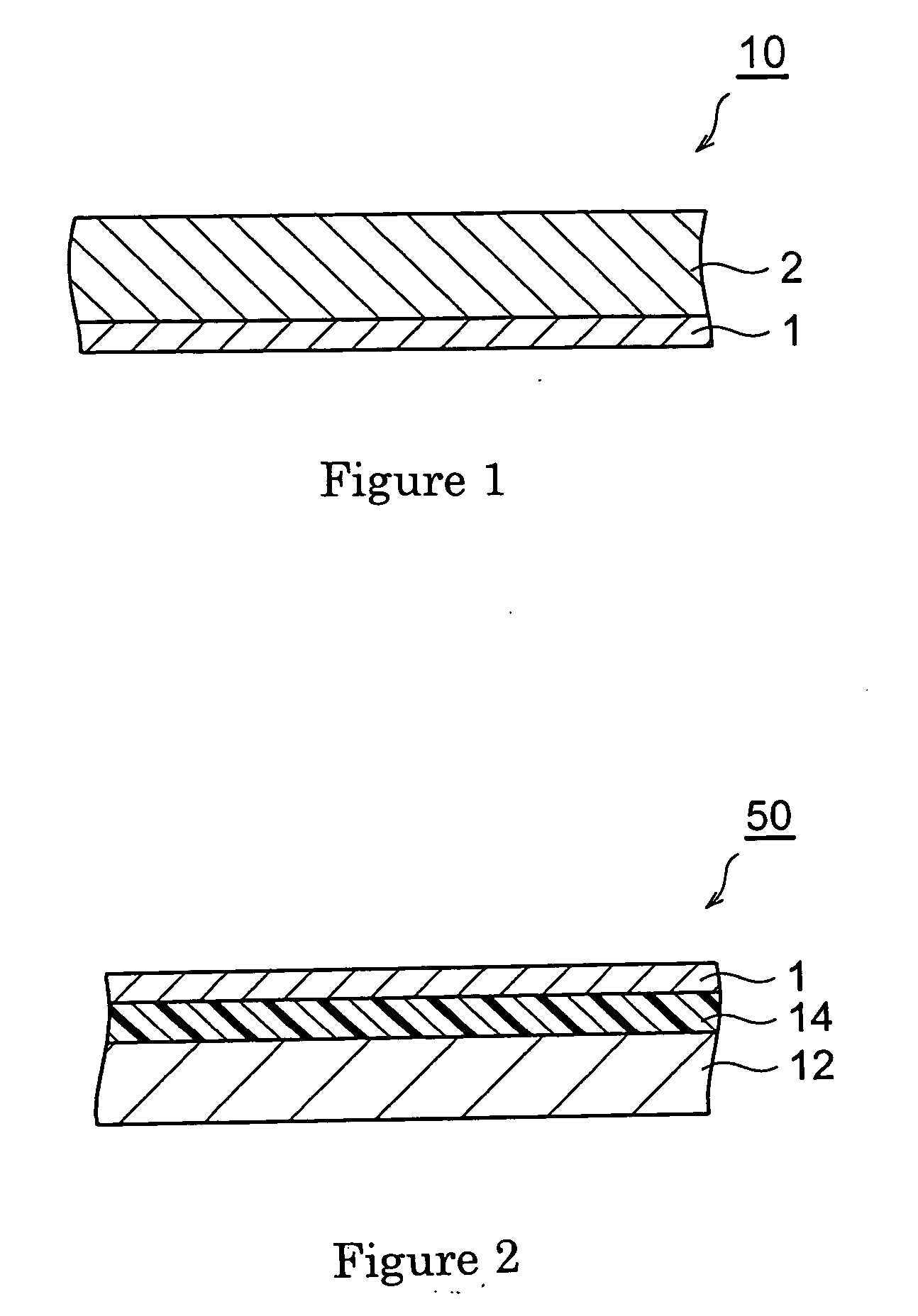
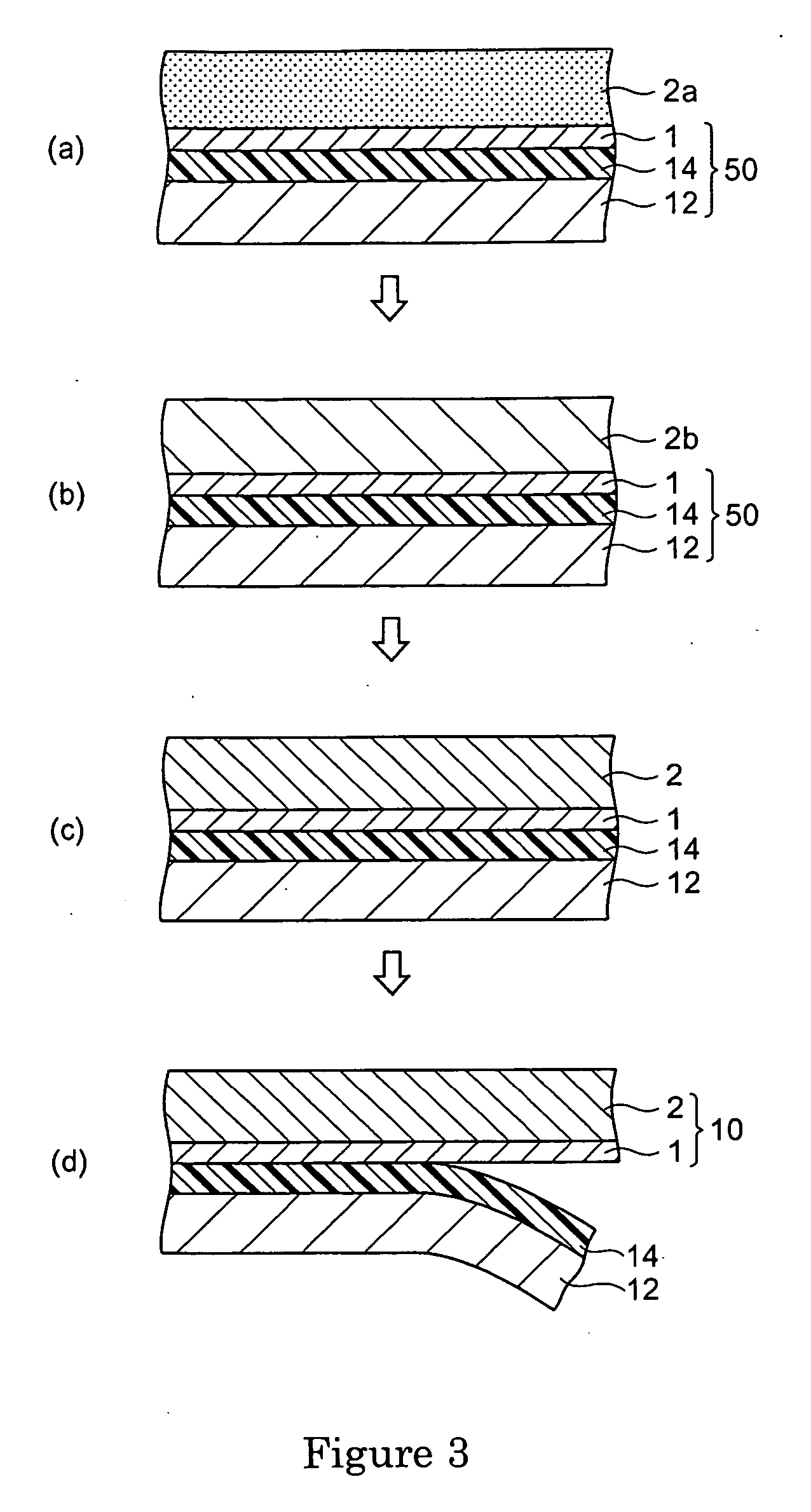
A retardation film that has an optical retardation layer whose alignment direction is controlled precisely and that is produced at a low cost, and also a method for producing the same, are provided. The explanation below relates to FIG. 1. First, a base-attached anisotropic layer 12 is prepared by laminating an optically anisotropic layer 11 on a transparent base 10. Next, on the optically anisotropic layer 11, a solution containing a polymer reacting with polarized ultraviolet light and a liquid crystalline compound is coated and dried. Then, it is irradiated with polarized ultraviolet light so as to align the liquid crystalline compound, and irradiated further with unpolarized ultraviolet light as required to crosslink the liquid crystalline compound, thereby forming a retardation film 1 having an optical retardation layer 13 that is directly formed on the optically anisotropic layer 11.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Thermally conductive polymer based printed circuit board
InactiveUS20100012354A1Prevent unwanted solderingImprove mechanical propertiesPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufactureLiquid crystallineConductive polymer
A printed circuit board has a liquid crystalline polymer layer that is bonded to an electrically conductive layer that includes traces that electrically connect components mounted on the printed circuit board. The liquid crystalline polymer material is thermally conductive and dielectric. When the components produce heat, the liquid crystalline polymer layer absorbs and dissipates the heat produced by the electrical components mounted on the printed circuit board. The thermal equilibrium of the printed circuit board is lower than the maximum operating temperature of the components.
Owner:HEDIN LOGAN BROOK +1
Liquid crystalline peroxide compositions and methods for coloring and/or bleaching hair
InactiveUS6238653B1Shorten the timeCosmetic preparationsHair removalLiquid crystallineAdditive ingredient
An aqueous peroxide composition for coloring or lightening hair comprising (a) 1-99% of an aqueous phase containing (ii) 1-55% by weight of the total composition of water, (ii) 1-45% hydrogen peroxide, and (iii) a water soluble cosolvent; and (b) 0.1-60% of an oil phase; and (c) 1-65% of an organic, amphiphilic, surface active ingredient capable of interacting with the water phase and the oil phase to form lyotropic liquid crystals containing said water phase ingredients; a method for coloring or lightening hair using the peroxide composition, and a method for reducing the amount of time necessary to permanently color hair using the peroxide composition.
Owner:REVLON CONSUMER PROD CORP
Liquid crystalline thermosets from ester, ester-imide, and ester-amide oligomers
InactiveUS6939940B2Low viscosityLow dielectric constantLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineEnd-group
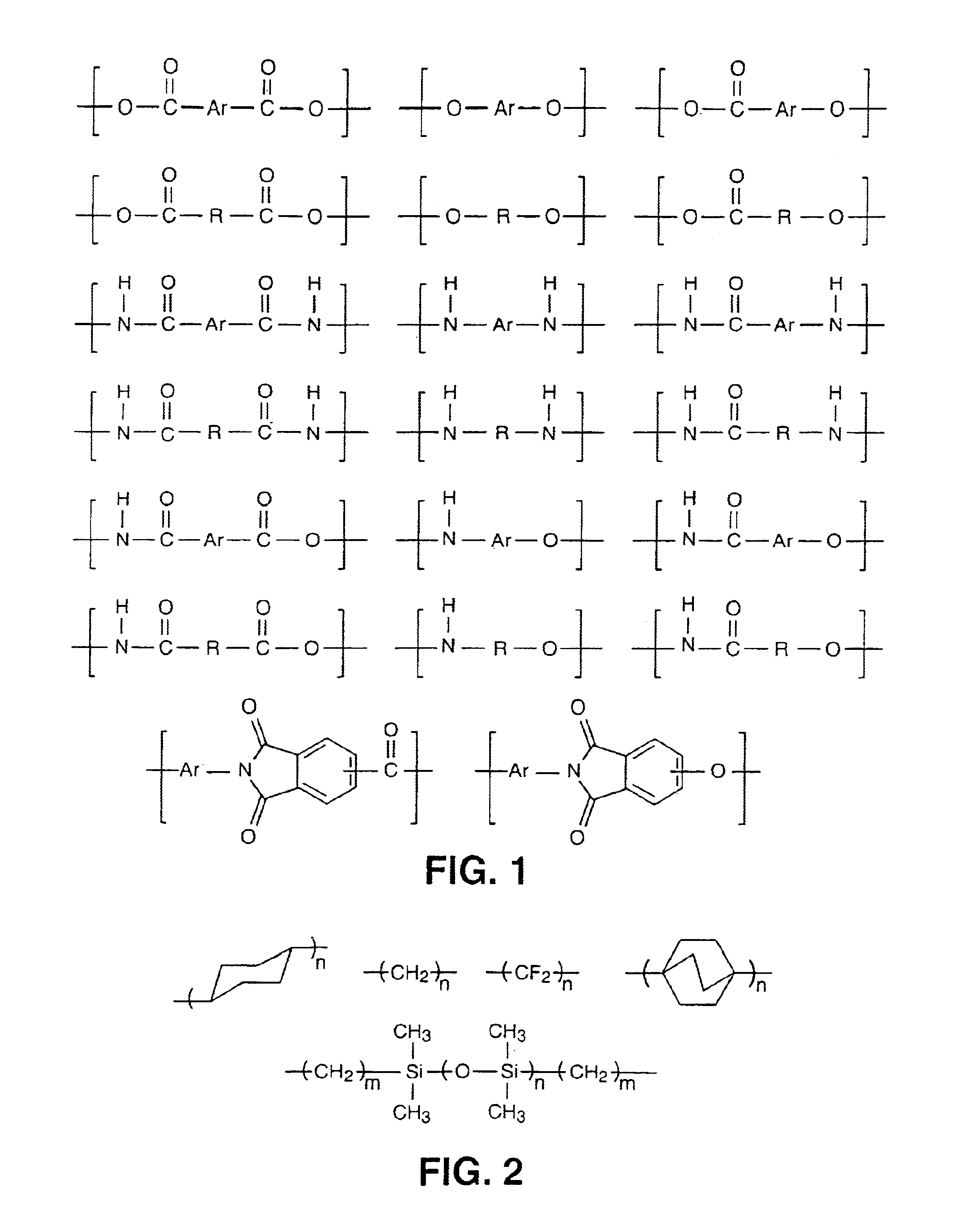
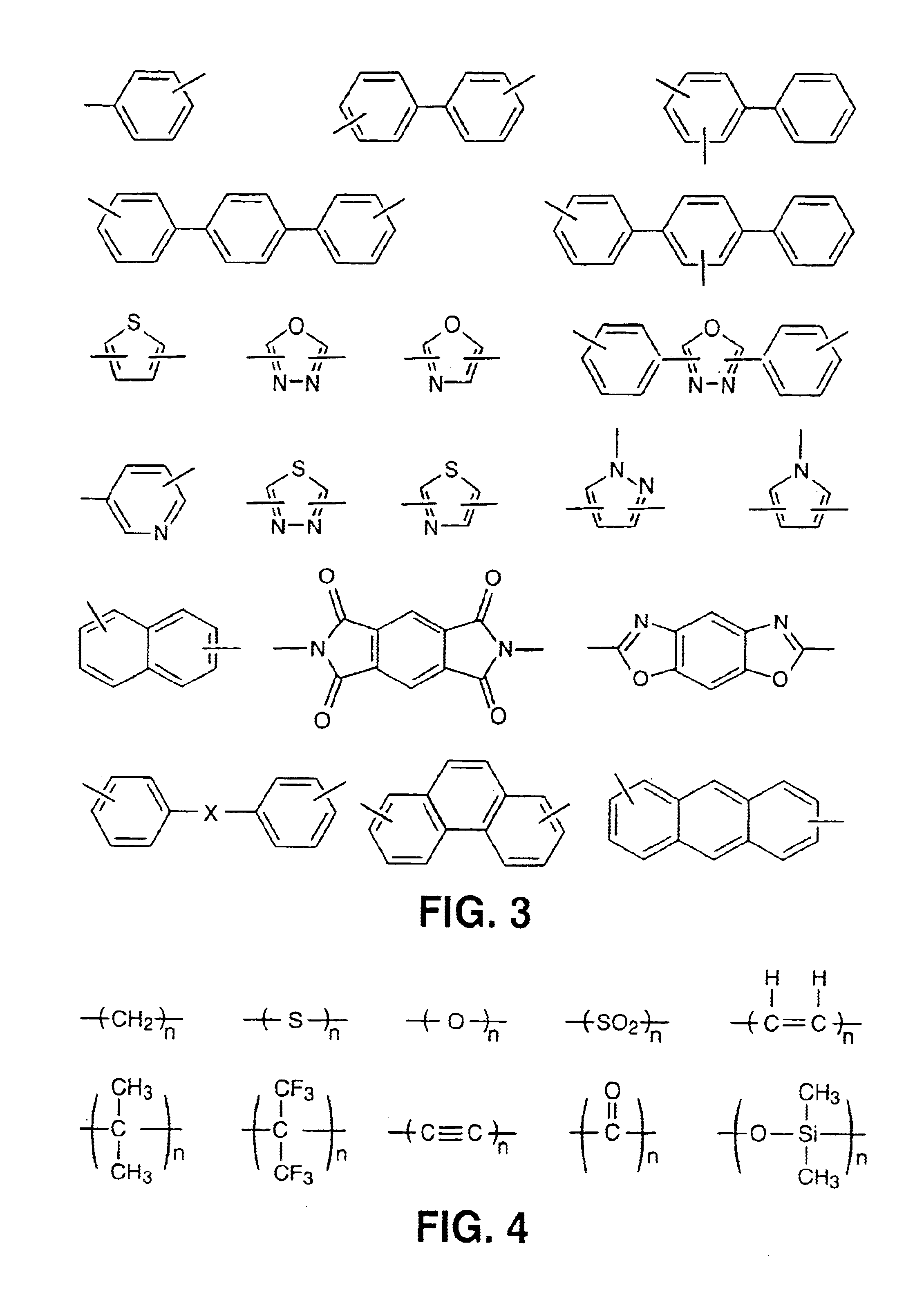
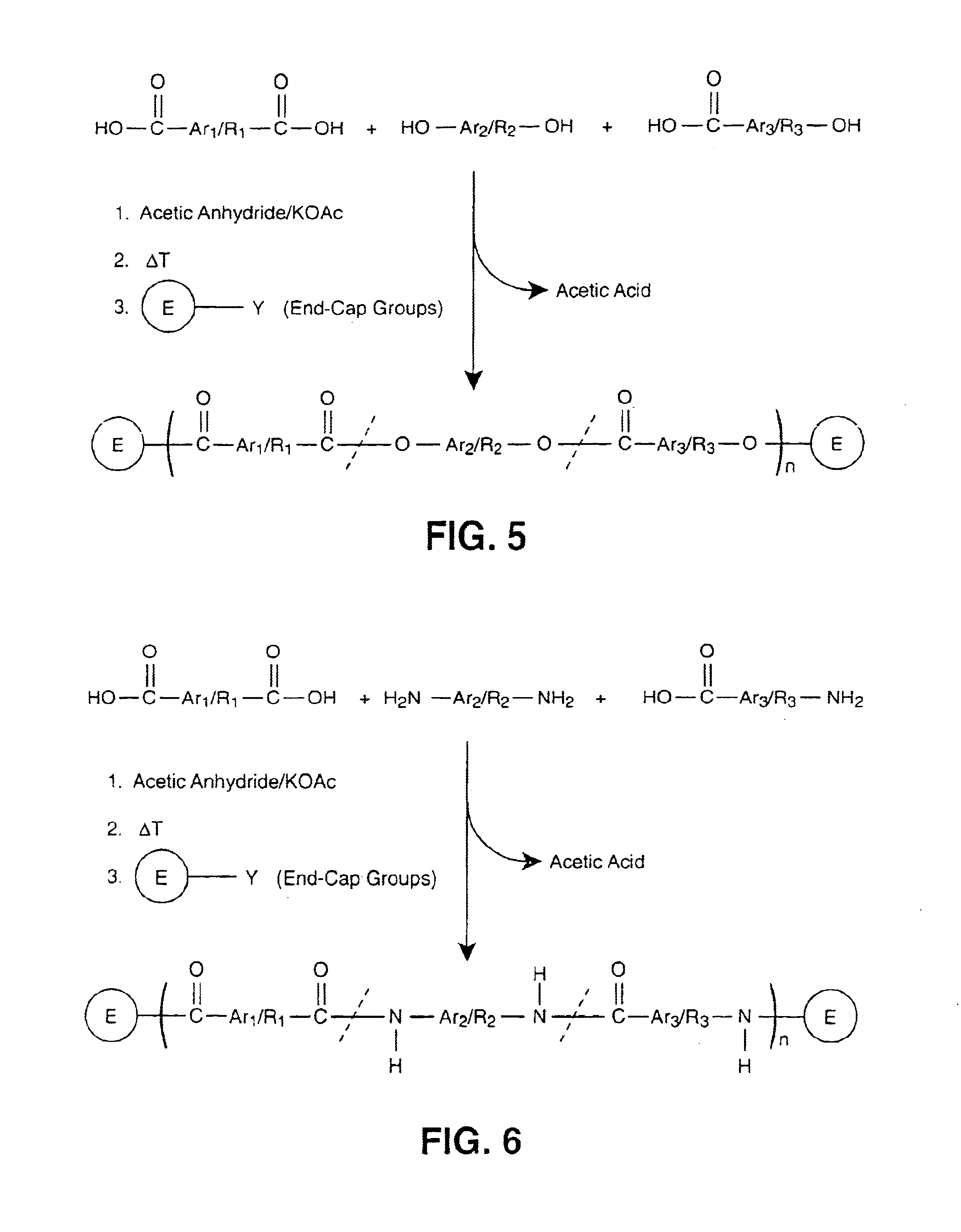
Main chain thermotropic liquid crystal esters, ester-imides, and ester-amides were prepared from AA, BB, and AB type monomeric materials and were end-capped with phenylacetylene, phenylmaleimide, or nadimide reactive end-groups. The resulting reactive end-capped liquid crystal oligomers exhibit a variety of improved and preferred physical properties. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are thermotropic and have, preferably, molecular weights in the range of approximately 1000-15,000 grams per mole. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers have broad liquid crystalline melting ranges and exhibit high melt stability and very low melt viscosities at accessible temperatures. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are stable for up to an hour in the melt phase. These properties make the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers highly processable by a variety of melt process shape forming and blending techniques including film extrusion, fiber spinning, reactive injection molding (RIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), resin film injection (RFI), powder molding, pultrusion, injection molding, blow molding, plasma spraying and thermo-forming. Once processed and shaped, the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers were heated to further polymerize and form liquid crystalline thermosets (LCT). The fully cured products are rubbers above their glass transition temperatures. The resulting thermosets display many properties that are superior to their non-end-capped high molecular weight analogs.
Owner:NASA
Thermostable pigments, films and effect coatings, and mixtures for their production
InactiveUS6423246B1Reduce interactionDegrade solventLiquid crystal compositionsBoltsLiquid crystallineColor shift
A mixture of crosslinkable liquid-crystalline substances having a chiral phase (LC mixture), containing polymerizable groups, where at least 90% of the polymerizable groups are part of molecules containing at least two polymerizable groups (crosslinker molecules), wherein from 3.2 to 15 mmol of polymerizable groups are present per g of LC mixture. The crosslinked pigments show little color shift in the presence of solvents or upon application to substrate different temperatures.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Thermally conductive thermoplastic resin compositions
InactiveUS20050176835A1Plastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid crystallinePolymer chemistry
Thermally conductive thermoplastic polymer resin compositions comprising thermoplastic polymer, calcium fluoride, and, optionally, one or more of fibrous filler, liquid crystalline polymer, and polymeric toughening agent. The compositions are particularly useful for molded or extruded parts.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
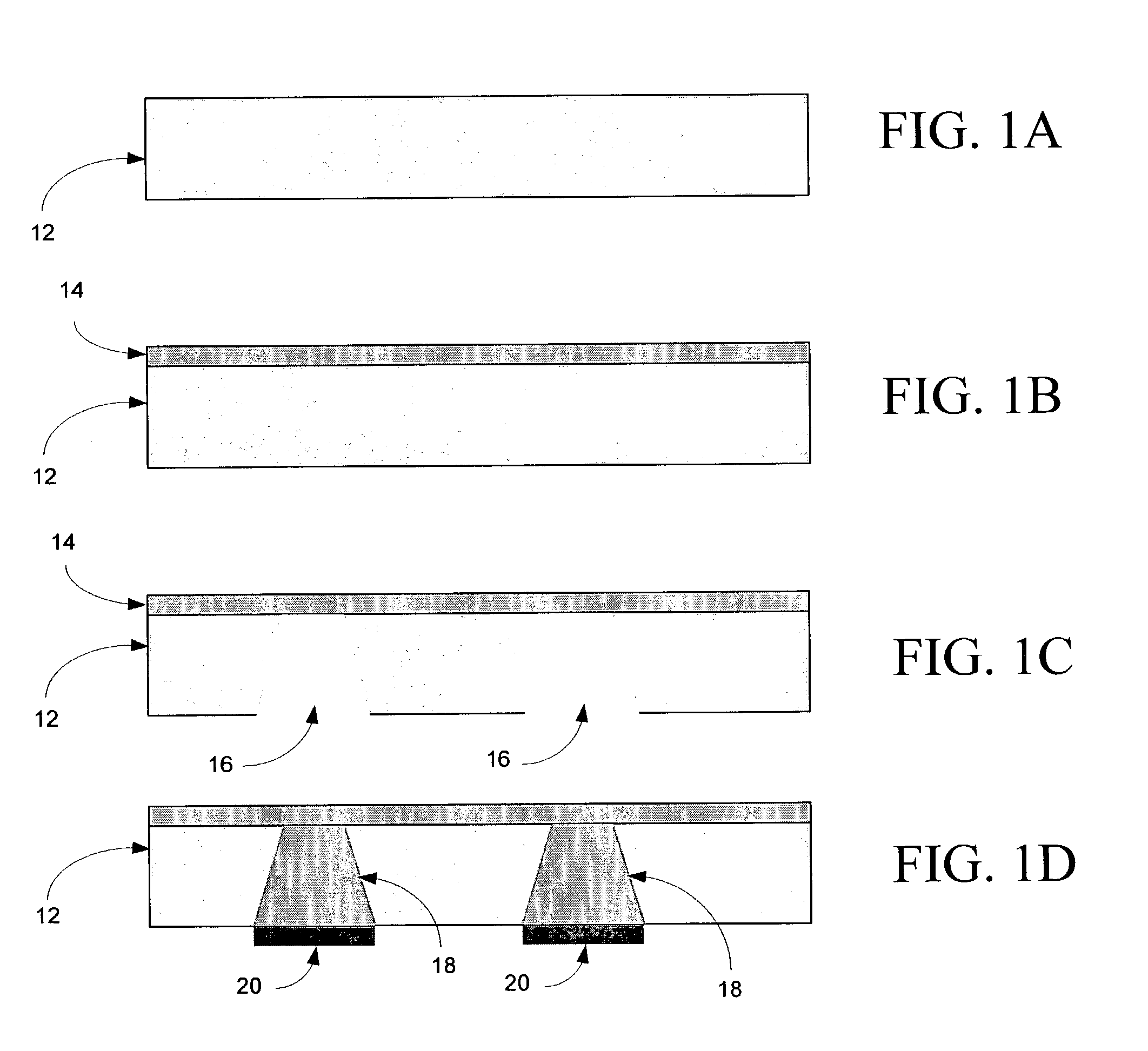
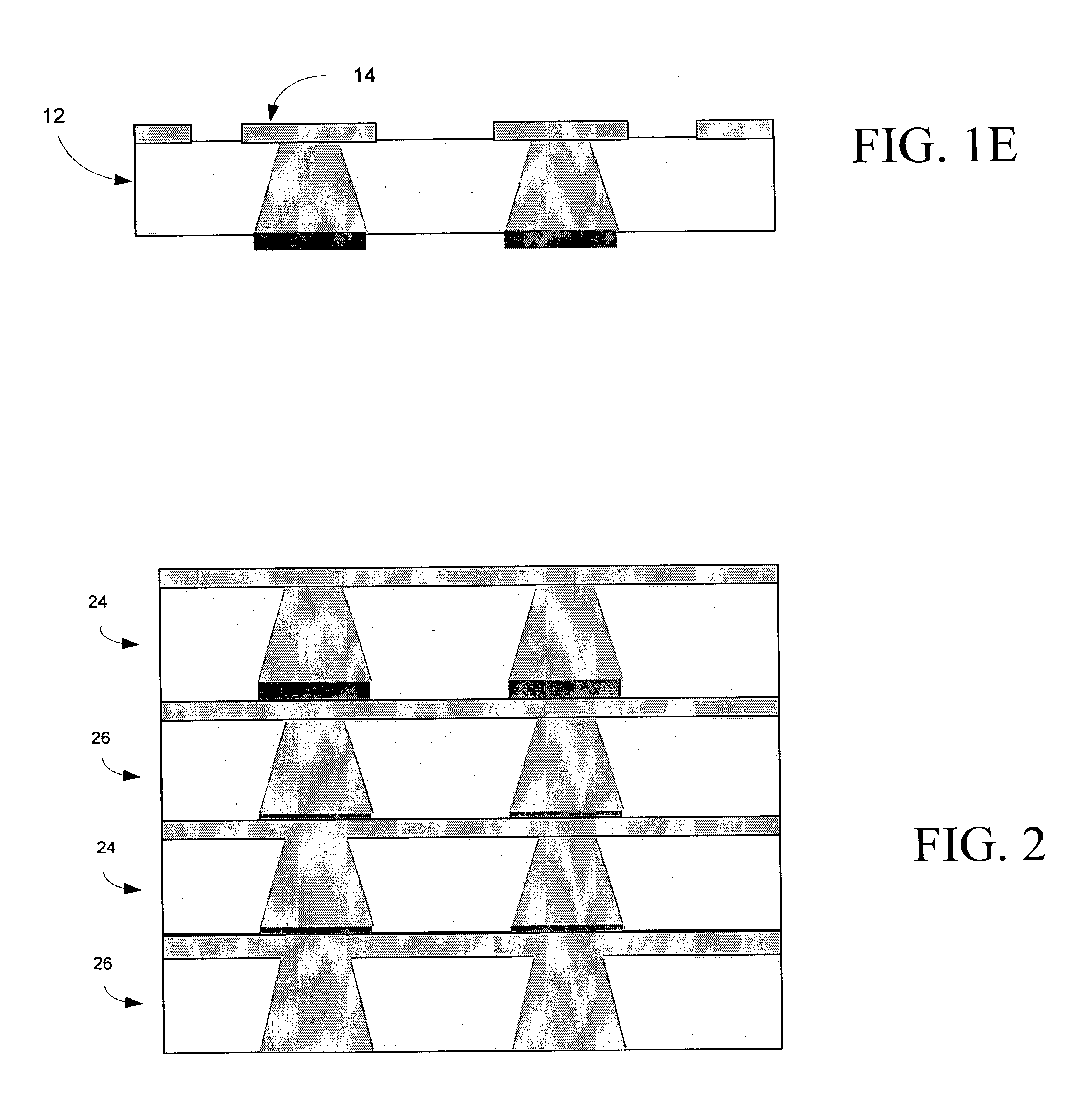
Methods for Fabricating Three-Dimensional All Organic Interconnect Structures
InactiveUS20070267138A1High frequency and high bandwidth applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLiquid crystallineMaterials science
The present invention includes methods for making liquid crystalline polymer (LCP) interconnect structures using a high temperature and low temperature single sided LCP, where both the high and low temperature LCP are provided with a z-axis connection. The single sided conductive layer is a bus layer to form z-axis conductive stud within the high and low temperature LCP. High and low temperature LCP layers are etched or built up to form circuit patterns and subsequently bonded together to form final multilayer circuit pattern where the low temperature LCP melts to form both dielectric to dielectric bond to high temperature LCP circuit layer, and dielectric to conductive bond.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
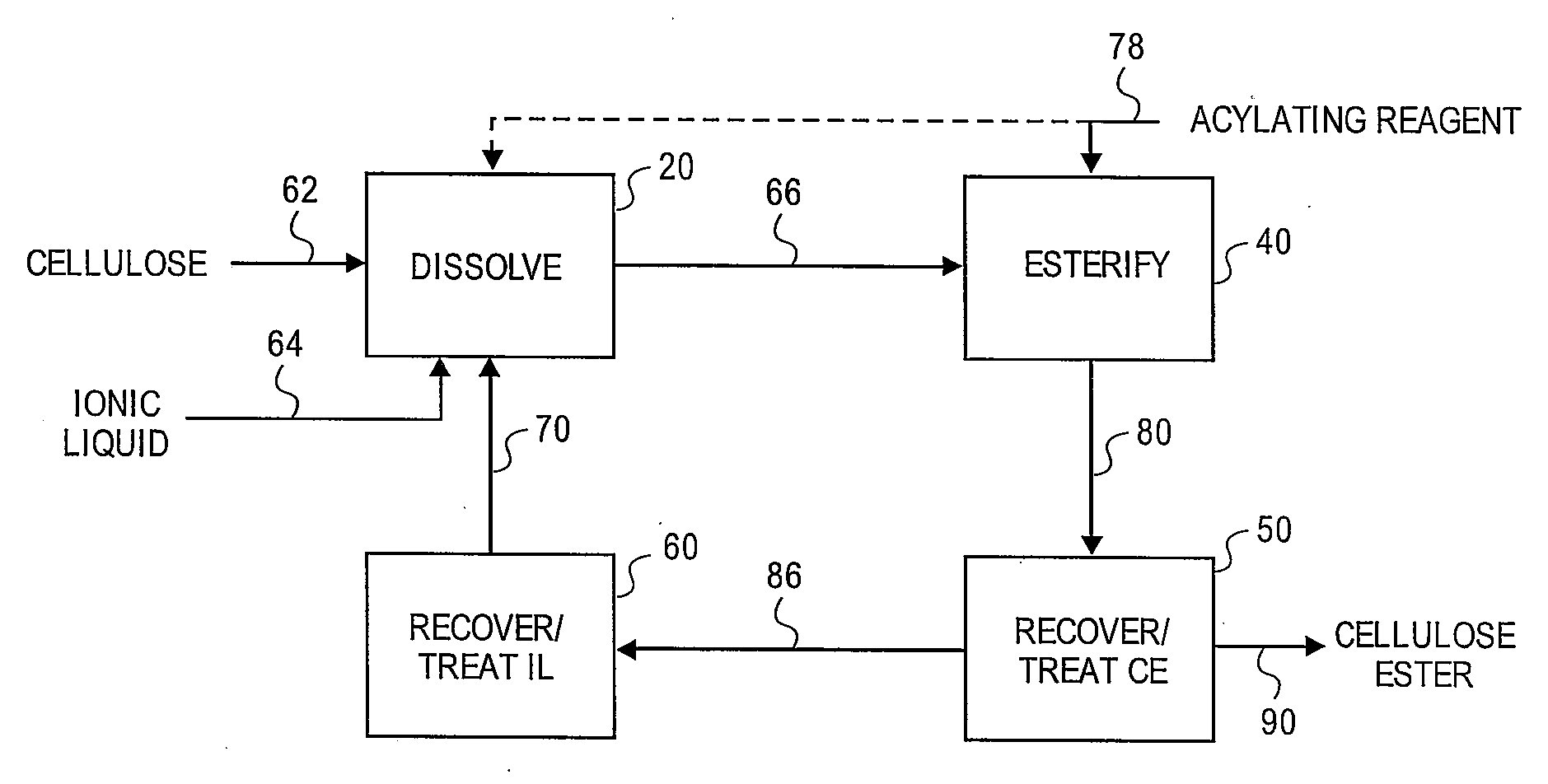
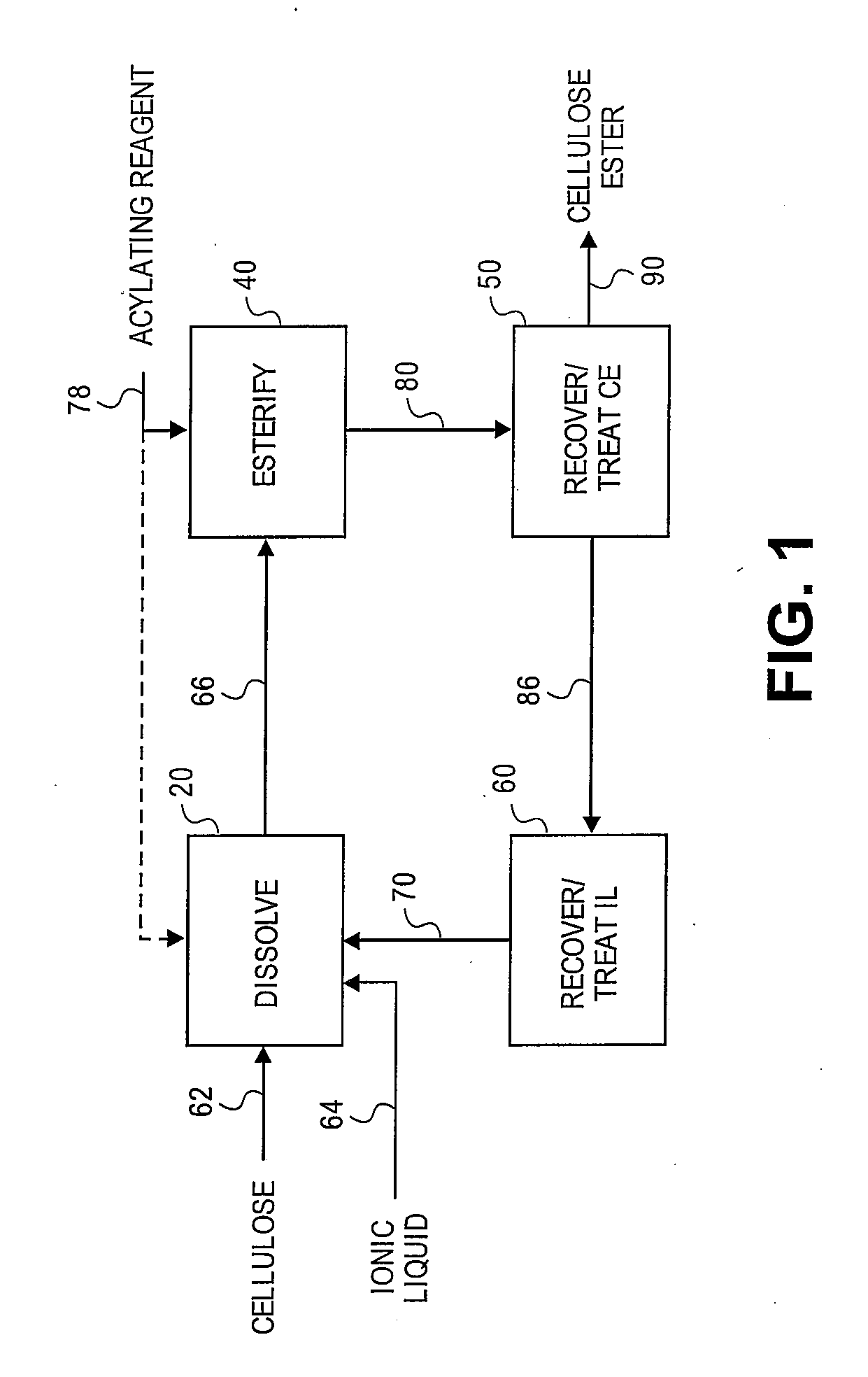
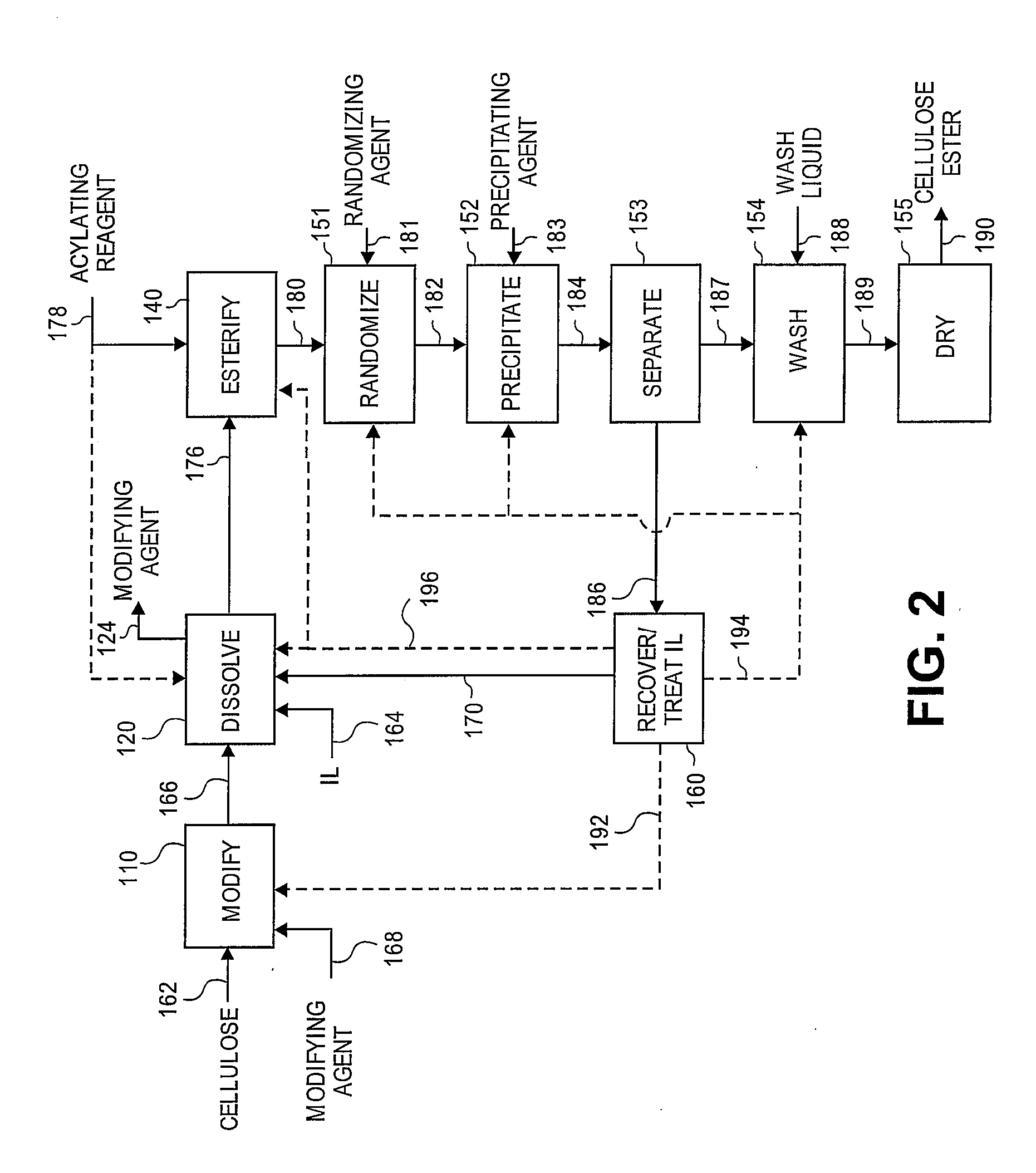
Regioselectively substituted cellulose esters produced in a carboxylated ionic liquid process and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS20100029927A1Increase ratingsPrevent gelOrganic chemistryOptical elementsCelluloseLiquid crystalline
This invention relates to novel compositions comprising regioselectively substituted cellulose esters. One aspect of the invention relates to processes for preparing regioselectively substituted cellulose esters from cellulose dissolved in ionic liquids. Another aspect of the invention relates to the utility of regioselectively substituted cellulose esters in applications such as protective and compensation films for liquid crystalline displays.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
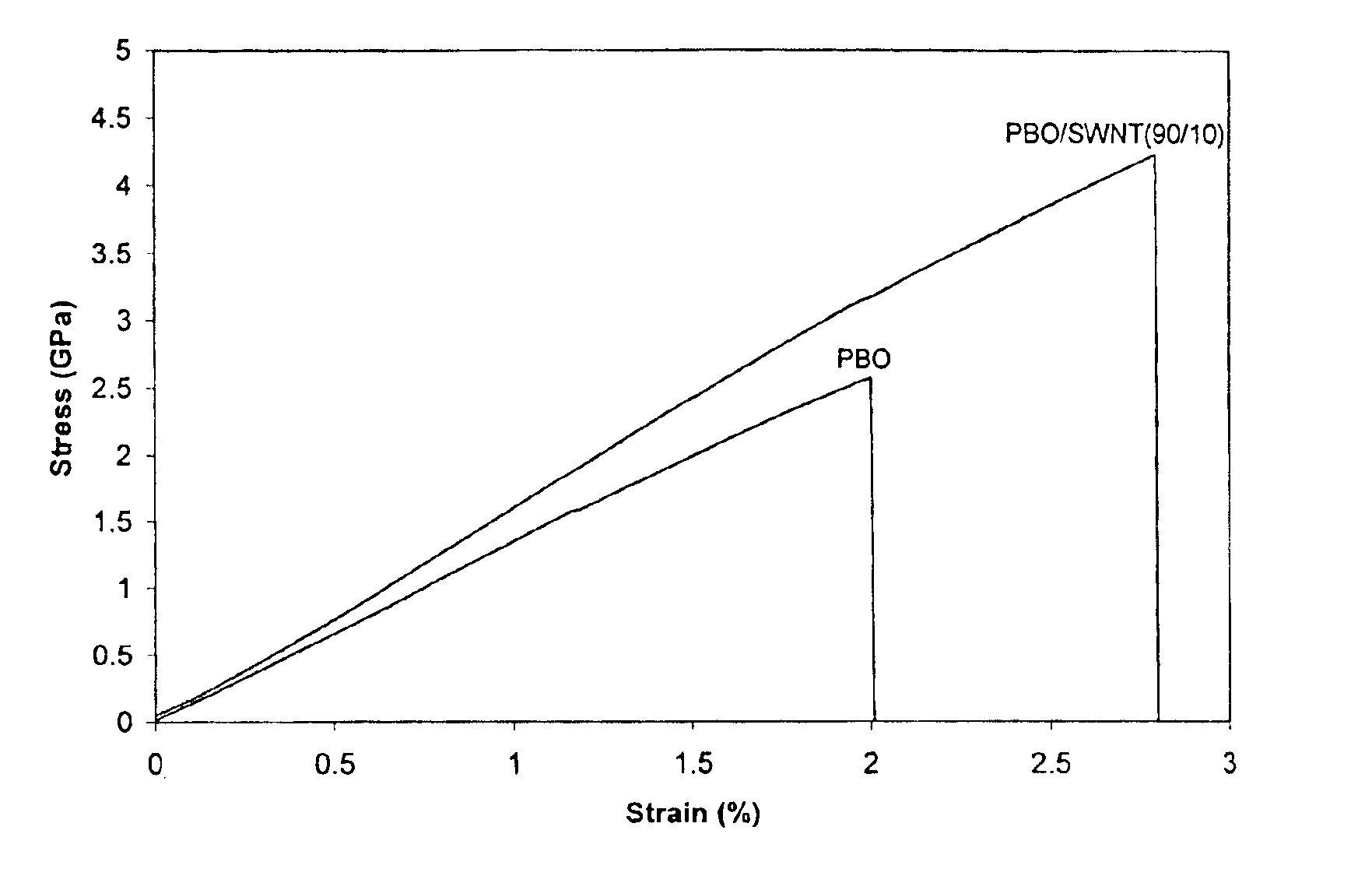
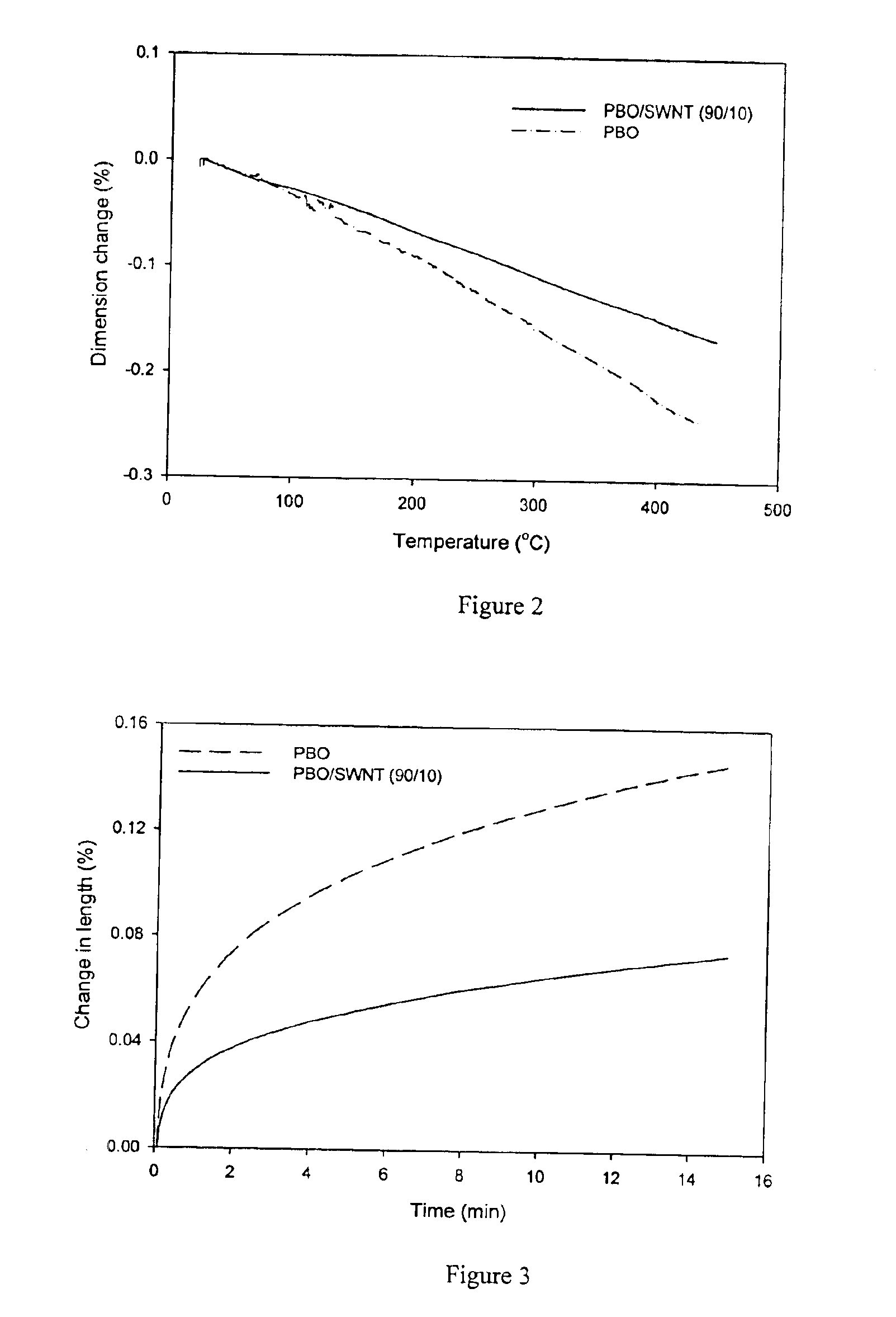
Compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes and process for making the same
InactiveUS6900264B2High modulusHigh stiffnessMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresFiberLiquid crystalline
The present invention relates to compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes. The compositions comprise dispersed carbon nanotubes aligned with rigid-rod polymers. The alignment of the nanotubes and polymers can be liquid crystalline. The rigid-rod polymers of this invention include, but are not limited to, polymers and copolymers comprising benzobisazole, pyridobisimidazole and benzamidazobenzo-phenanthroline repeat units. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes is achieved by in-situ polymerization in the presence of the carbon nanotubes, which may be either single-wall or multi-wall or a combination of both. The polymer compositions comprising carbon nanotubes may be spun into fibers or formed into films. The strength of the resulting fibers of the present invention is significantly greater than that of fibers without carbon nanotubes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
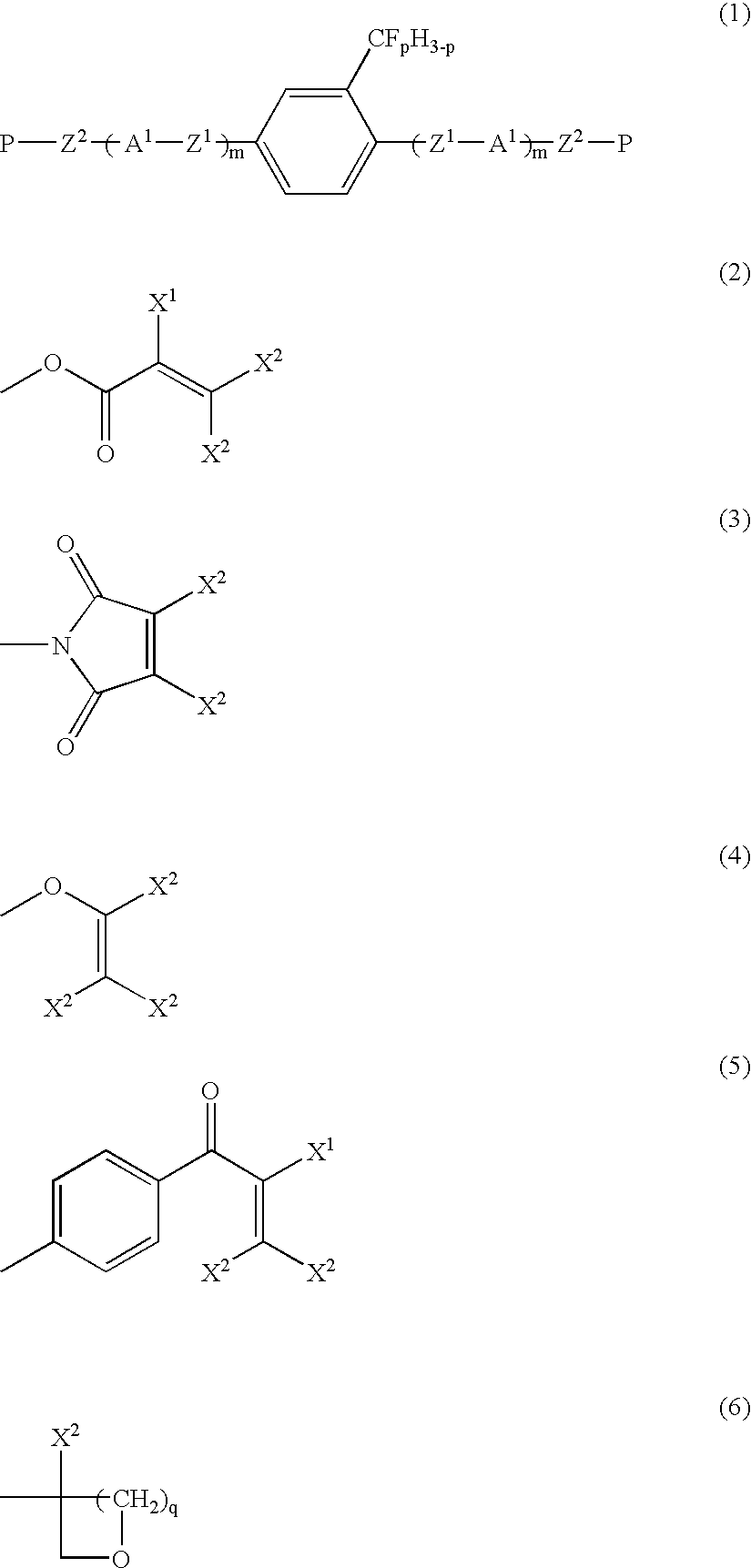
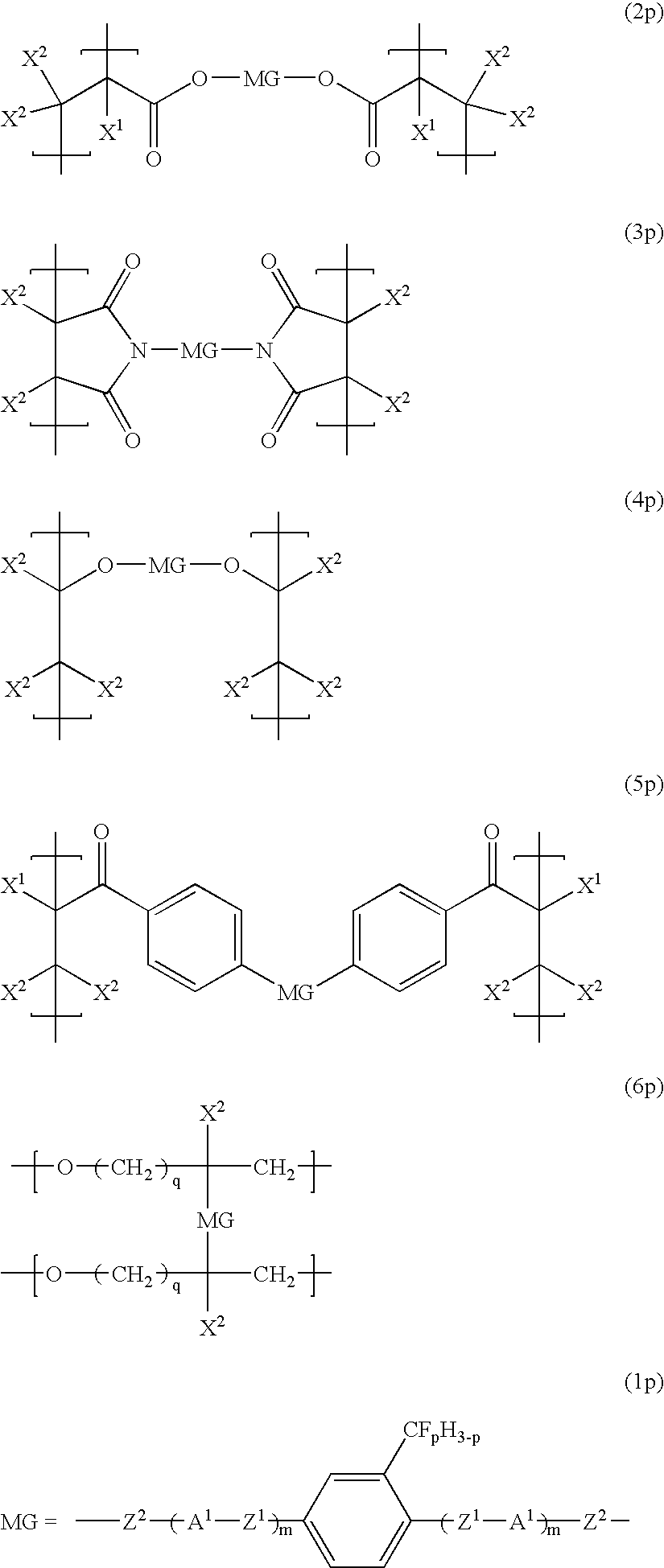
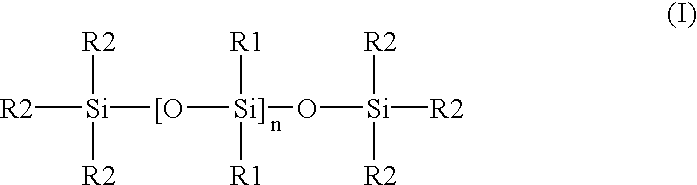
Liquid crystalline compound, liquid crystal composition and their polymers
The present invention provides a compound represented by formula (1) defined in the specification and a liquid crystal composition comprising the compound. The invention further provides a polymer obtained by polymerization of compound or composition above, and further the present invention provides a film, an optical anisotropic material, A ¼ or ½ wavelength functional plate, an optical compensation element, an optical element and a liquid crystal display element employing the polymer.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM CORP +1
Coated particles, methods of making and using
InactiveUS6989195B2Simple processOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryLiquid crystallineActive agent
A particle coated with a nonlamellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material includes an internal matrix core having at least one a nanostructured liquid phase, or at least on nanostructured liquid crystalline phase or a combination of the two is used for the delivery of active agents such as pharmaceuticals, nutrients, pesticides, etc. The coated particle can be fabricated by a variety of different techniques where the exterior coating is a nonlamellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Composition in the form of an oil-in water emulsion containing a silicone copolymer and showing a liquid crystalline phase and uses thereof
InactiveUS7087650B2Good cosmetic effectGood flexibilityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsLiquid crystallineSURFACTANT BLEND
A composition in the form of an oil-in-water emulsion containing, in a physiologically acceptable medium, an oily phase dispersed in an aqueous phase, the aqueous phase containing particles of a noncrosslinked silicone copolymer and at least one amphiphilic surfactant capable of forming liquid crystals.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Methods for fabricating three-dimensional all organic interconnect structures
InactiveUS20040000425A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLiquid crystallineAdhesive
The present invention comprises methods for making three-dimensional (3-D) liquid crystalline polymer (LCP) interconnect structures using a high temperature singe sided liquid crystalline polymer, and low temperature single sided liquid crystalline polymer, whereas both the high temperature LCP and the low temperature LCP are drilled using a laser or mechanical drill or mechanically punch to form a z-axis connection. The single sided Conductive layer is used as a bus layer to form z axis conductive stud conductive stud within the high temperature and low temperature LCP, followed by deposition of a metallic capping layer of the stud that serves as the bonding metal between the conductive interconnects to form the z-axis electrical connection. High temperature and low temperature LCP circuit layers are etched or built up to form circuit patterns and subsequently bonded together to form final 3-D multilayer circuit pattern whereas the low temperature LCP melts to form both dielectric to dielectric bond to high temperature LCP circuit layer, and dielectric to conductive bond, whereas, metal to metal bonding occurs with high temperature metal capping layer bonding to conductive metal layer. The resultant structure is then packaged using two metallized organic cores that are laminated onto either side of the device using a low temperature adhesive with similar electrical properties and subsequently metallized to form the input output terminals and EM shielding.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Regioselectively substituted cellulose esters produced in a tetraalkylammonium alkylphosphate ionic liquid process and products produced therefrom
InactiveUS20100267942A1Sugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLiquid crystallineLiquid-crystal display
This invention relates a cellulose solution comprising cellulose and at least one tetraalkylammonium alkylphosphate and processes to produce the cellulose solution. Another aspect of this invention relates to shaped articles prepared from a cellulose solution comprising cellulose and at least one tetraalkylammonium alkylphosphate. Another embodiment of this invention relates to compositions comprising derivatives of cellulose prepared from a cellulose solution comprising at least one tetraalkylammonium alkylphosphate. Another embodiment of this invention relates to compositions comprising regioselectively substituted cellulose esters prepared from a cellulose solution comprising cellulose and at least one tetraalkylammonium alkylphosphate. In another embodiment of the invention, the cellulose esters of the present invention are used as protective and compensation films for liquid crystalline displays.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Light scattering sheet, light scattering composite sheet, and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6723392B1Improve clarityQuality improvementLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsSolid componentElectricity
A light-scattering sheet having a phase separation structure comprised of a plurality of solid components varying in refractive index is used to construct a liquid crystal display device. In a first embodiment, the light-scattering sheet is disposed in a defined position within a reflecting LCD device. Thus, in a reflecting LCD device comprising a liquid crystal cell constituted of a transparent front electrode plate having a substrate carrying a transparent conductive layer, a back electrode plate having a substrate carrying a conductive layer and a liquid crystal and, as disposed forwardly of the liquid crystal cell, a polarizer, the light-scattering sheet is interposed (i) between the polarizer and the front electrode plate or (ii) between the back electrode plate and a reflector disposed behind the back electrode plate. Alternatively, (iii) the substrate sheet may be constituted of the light-scattering sheet. In a second embodiment, a light-scattering sheet having an isotropic bicontinuous phase structure comprised of a plurality of polymers varying in refractive index is used.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Display device having optical waveguides and light-emitting units
InactiveUS7592988B2Improve viewing angle characteristic and brightness characteristicStatic indicating devicesCoupling light guidesLiquid crystallineDisplay device
A display device is provided that includes a display panel having a light-emitting unit for emitting light according to predetermined display data, an elongated optical waveguide unit which guides the light incident from the light-emitting unit and has a core layer and an addressing unit for selecting the light from the light waveguide unit according to the predetermined display data. The core layer is composed of light scattering liquid crystal, and the addressing unit allows the light to be emitted from a predetermined part of the optical waveguide unit by using the light scattering operation of the light scattering liquid crystal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Reversed liquid crystalline phases with non-paraffin hydrophobes
Compounds which are otherwise difficult to solubilize, such as, for example, pharmaceutical actives difficult for the body to absorb, are solubilized into a composition using a solvent system that is a structured fluid. The structured fluid is a reversed cubic phase or reversed hexagonal phase material, or a combination thereof, which includes a polar solvent, a surfactant and a non-paraffinic liquid with a high octanol-water partition coefficient which does not qualify as a surfactant. The compositions thus formed are able to enhance absorption of drugs by the induction of local, transient nanopores in biomembrane absorption barriers and particularly those in which efflux mechanisms, such as those associated with P-glycoprotein and / or cytochrome 3A4, are active. The compositions and methods that are used for solubilizing pharmaceutical actives in structured fluids can simultaneously accomplish solubilization of difficultly soluble drugs and enhancement of absorption.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
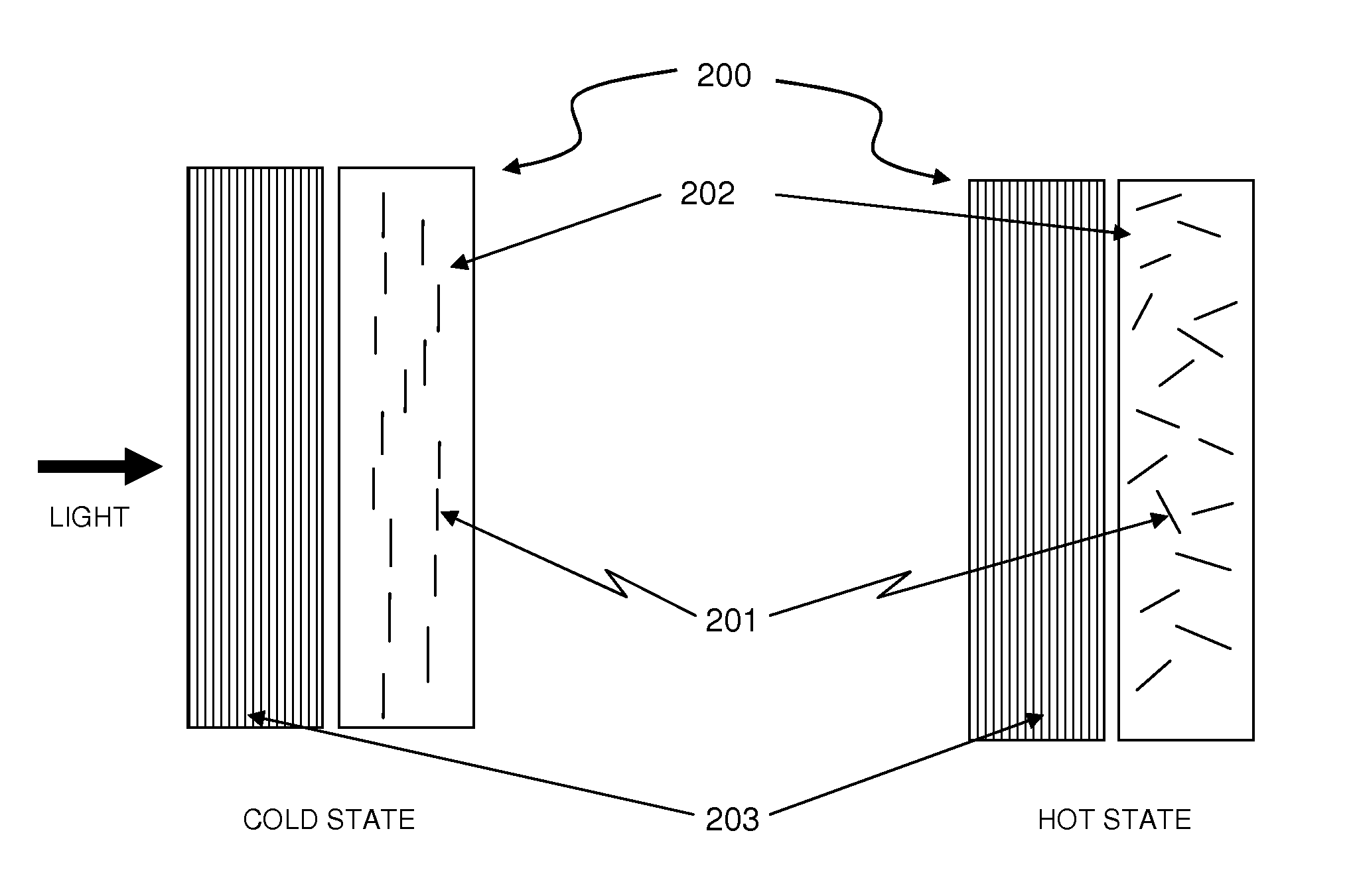
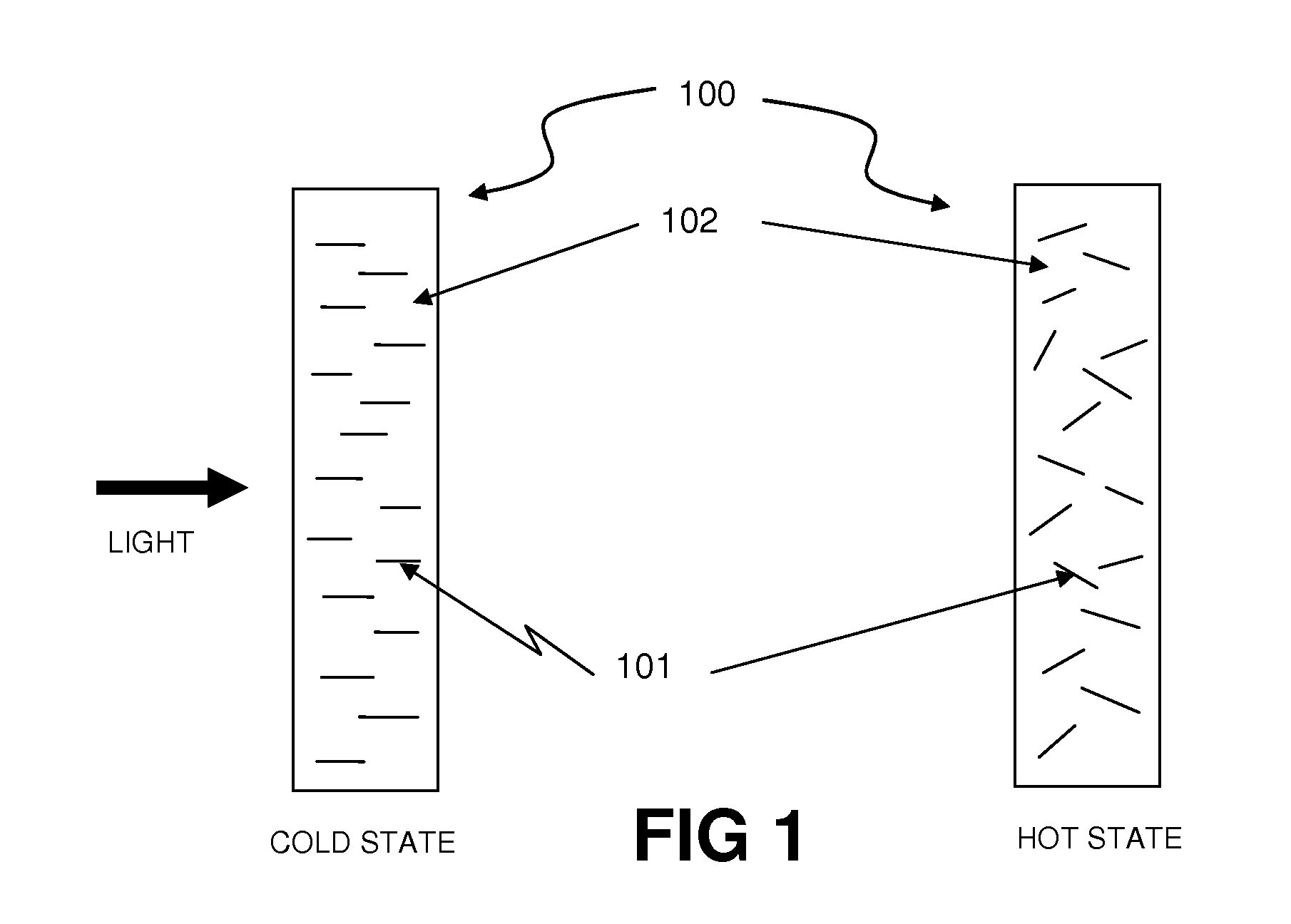
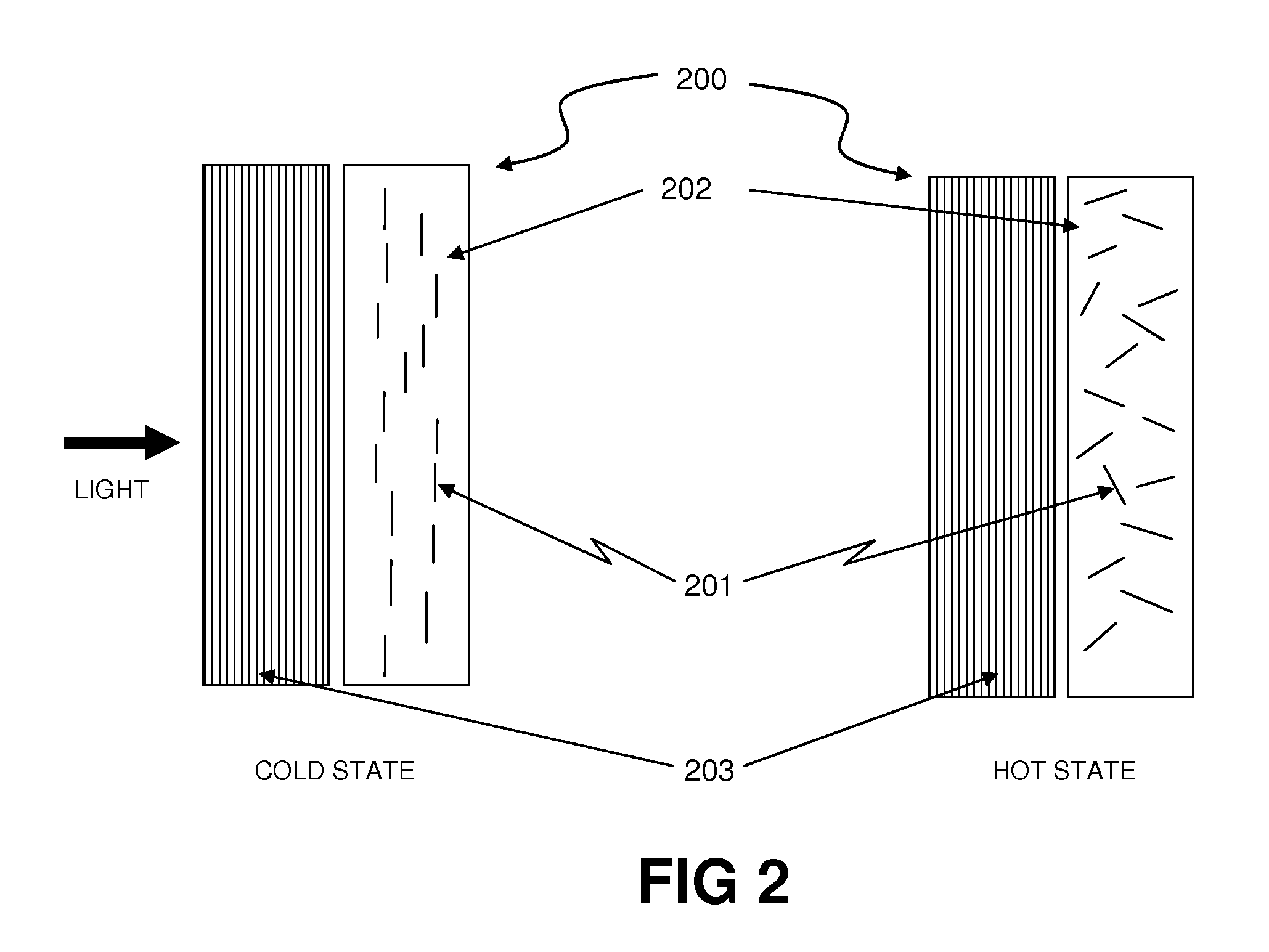
Thermally Switched Optical Filter Incorporating a Guest-Host Architecture
InactiveUS20100259698A1Avoid concentrationLess transmissiveLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid crystallineSelective reflection
Thermochromic filters are constructed using absorptive, reflective, or fluorescent dyes, molecules, polymers, particles, rods, or other orientation-dependent colorants that have their orientation, order, or director influenced by carrier materials, which are themselves influenced by temperature. These order-influencing carrier materials include thermotropic liquid crystals, which provide orientation to dyes and polymers in a Guest-Host system in the liquid-crystalline state at lower temperatures, but do not provide such order in the isotropic state at higher temperatures. The varying degree to which the absorptive, reflective, or fluorescent particles interact with light in the two states can be exploited to make many varieties of thermochromic filters. Thermochromic filters can control the flow of light and radiant heat through selective reflection, transmission, absorption, and / or re-emission. The filters have particular application in passive or active light-regulating and temperature-regulating films, materials, and devices, and particularly as construction materials and building and vehicle surfaces.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
Substrate for flexible wiring and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070077416A1Low water absorptionLayer be enoughPretreated surfacesGlass/slag layered productsPolyesterLiquid crystalline
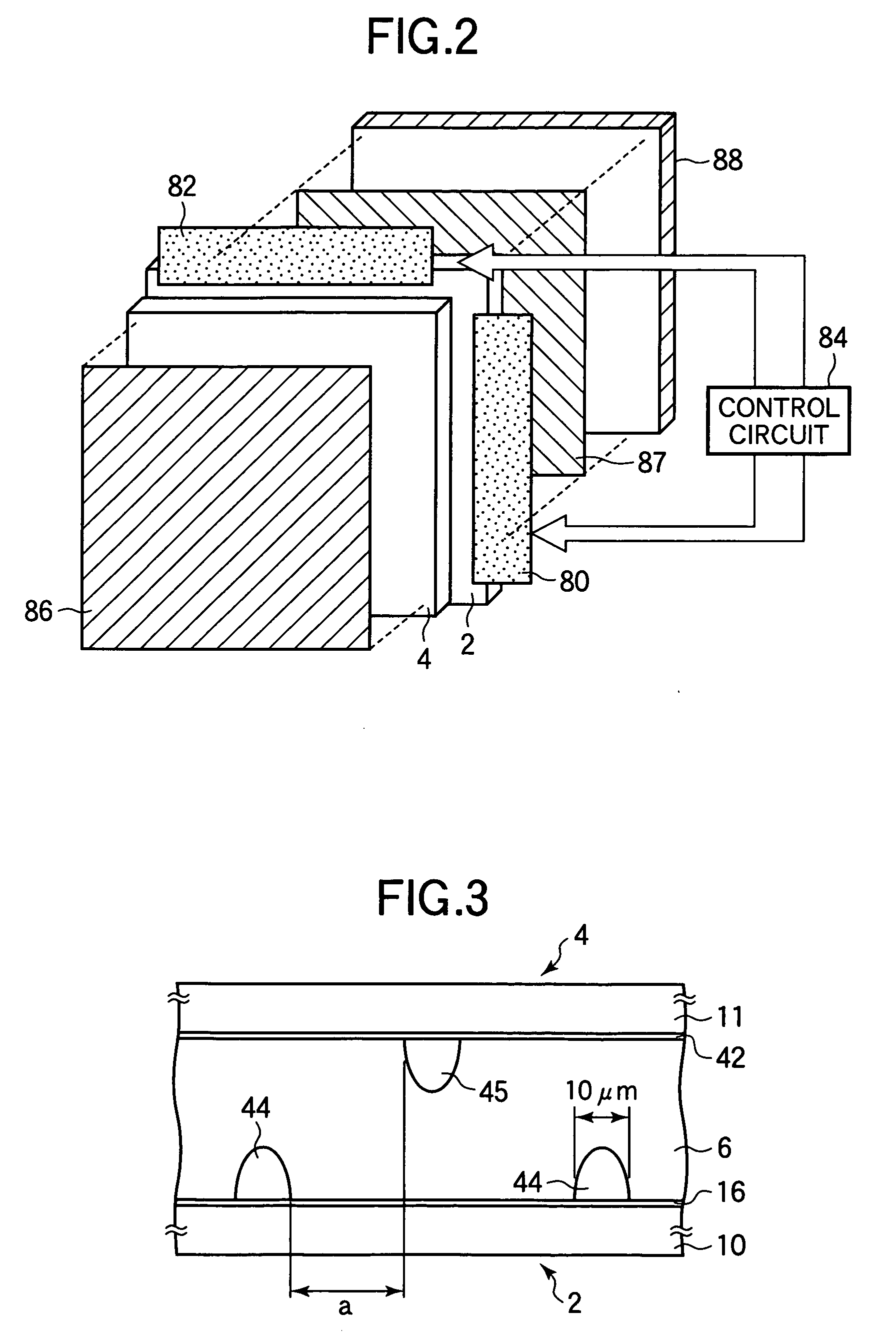
The present invention provides a substrate for flexible wiring comprises a liquid crystalline polyester layer and a copper foil with a thickness of 5 μm or less. The substrate has a large adhesion between the resin layer and the copper foil, and is sufficient in water absorbing property and electrical properties.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Color filter comprising retardation control layer, method for manufacturing the same, and display
ActiveUS20050142464A1Change thicknessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLiquid crystallineVisibility
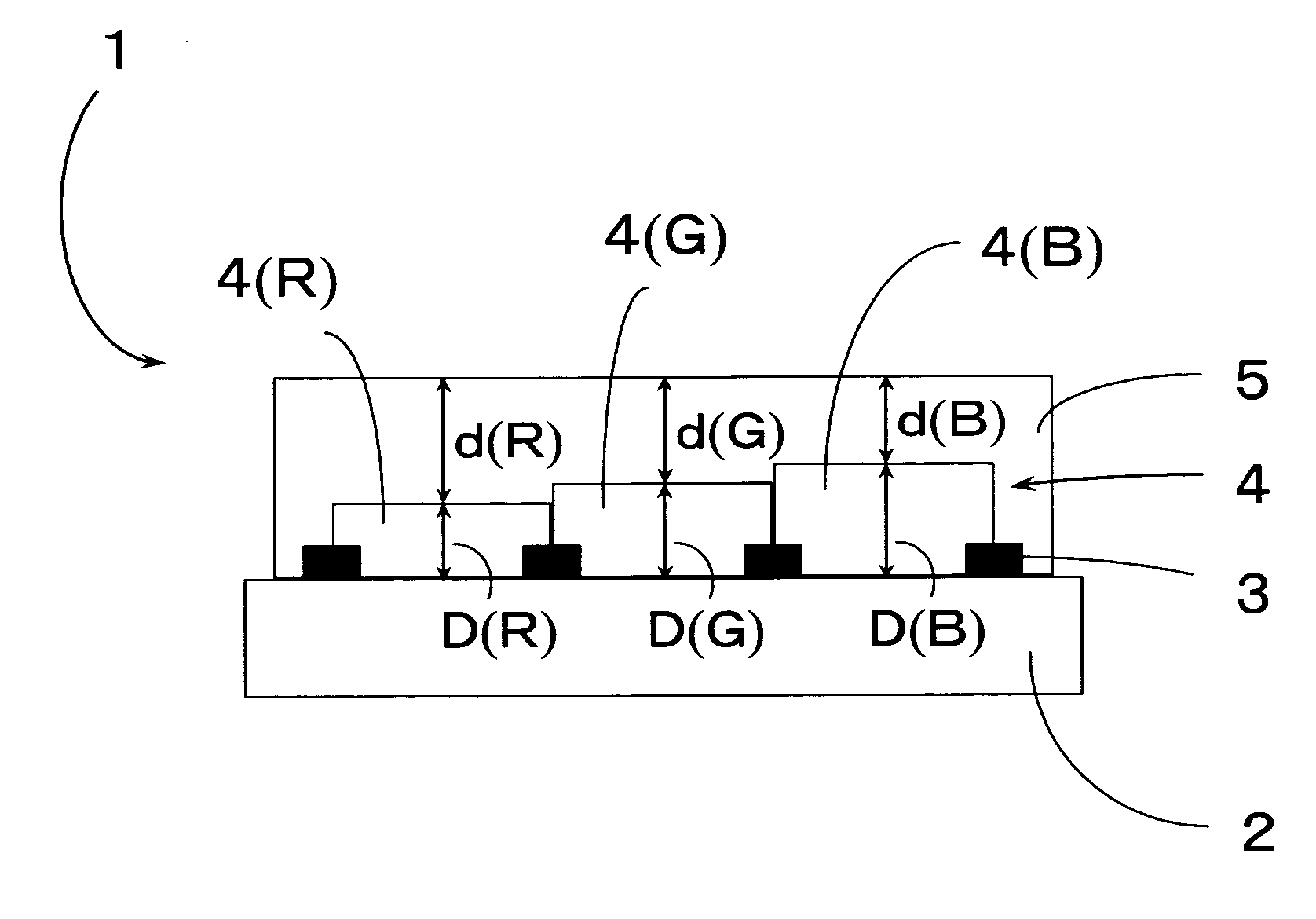
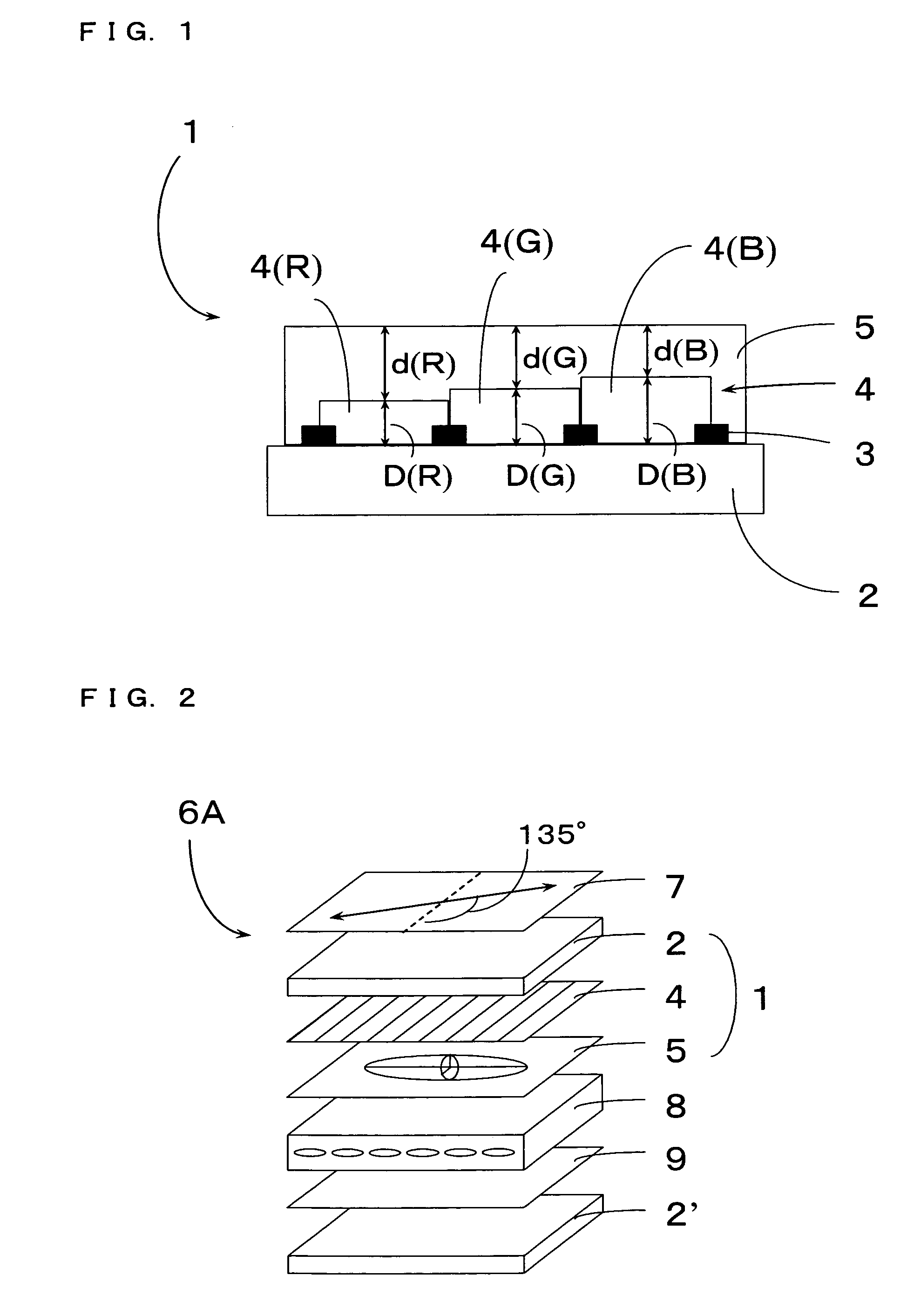
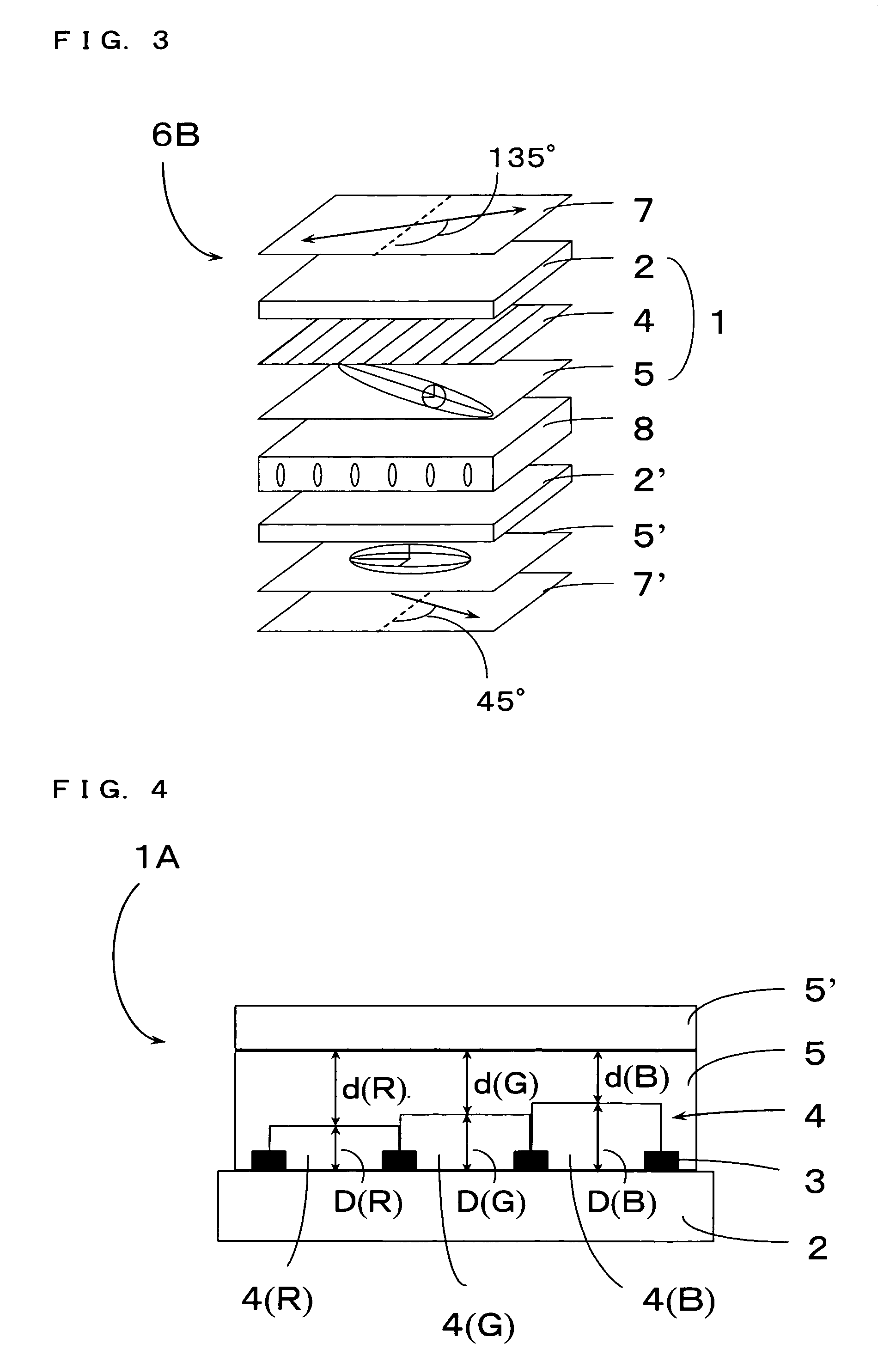
The thickness of a retardation layer made of a liquid crystalline polymer used in improving visibility in a liquid crystalline display or the like is changed every color pattern of a color filter layer laminated with the retardation layer without adding a special process therefor to realize retardation suitable for each color pattern as the problem of the invention. This problem is solved in the invention by making the total thickness of the layers 4 and 5 constant in a structure having black matrix 3, color filter layer 4 and retardation control layer 5 laminated on substrate 2, and changing the thickness of the color filter layer 4 depending on each pattern, such that each region of the retardation control layer 5 has predetermined thickness.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Composition and method employing membrane structured solid nanoparticles for enhanced delivery of oral care actives
An oral care composition containing membrane-structured solid nanoparticles formed from a lyotropic liquid-crystalline mixed phase having an average particle diameter in the range of 10 to 1,000 nm. The nanoparticles are generally solid at 25° C. and are a combination of agent-carrier particles and emulsifiers. The membranes penetrate the nanoparticles so that the emulsifiers are present in the interior and on the surface of the nanoparticles.
Owner:RECKITT BENCKISER (UK) LTD
Liquid crystalline media with homeotropic alignment
ActiveCN105001879ASimple manufacturing methodShort response timeLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic compound preparationDielectric anisotropyLiquid crystalline
The present invention relates to liquid-crystalline media (LC media) having negative or positive dielectric anisotropy, comprising a low-molecular-weight component and a polymerizable component. The polymerizable component comprises self-aligning, polymerizable mesogens (polymerizable self-alignment additives) which effect homeotropic (vertical) alignment of the LC media at a surface or the cell walls of a liquid-crystal display (LC display). The invention therefore also encompasses LC displays having homeotropic alignment of the LC medium without alignment layers. The invention discloses novel structures for self-alignment additives which have a certain position of the functional groups.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
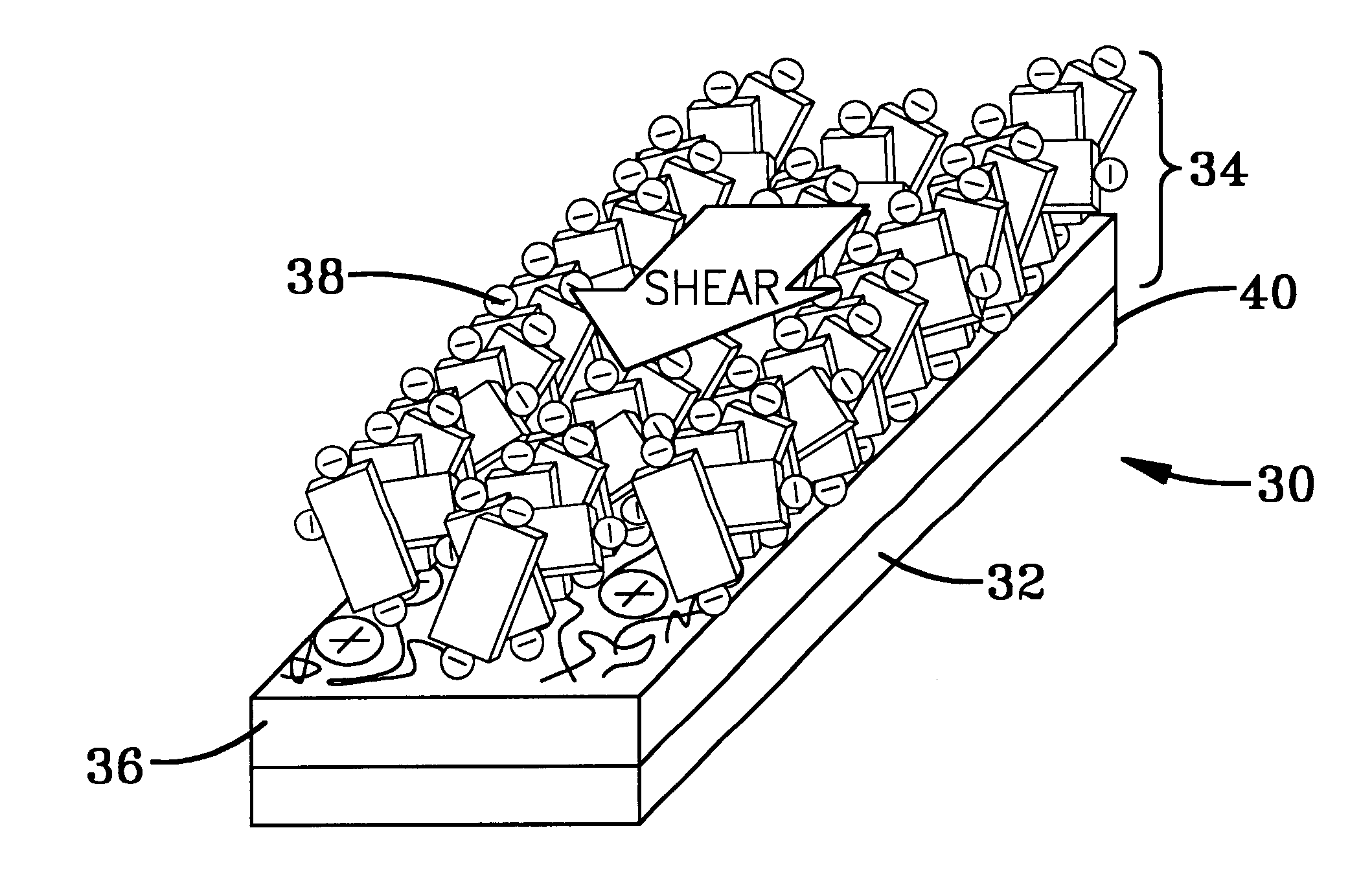
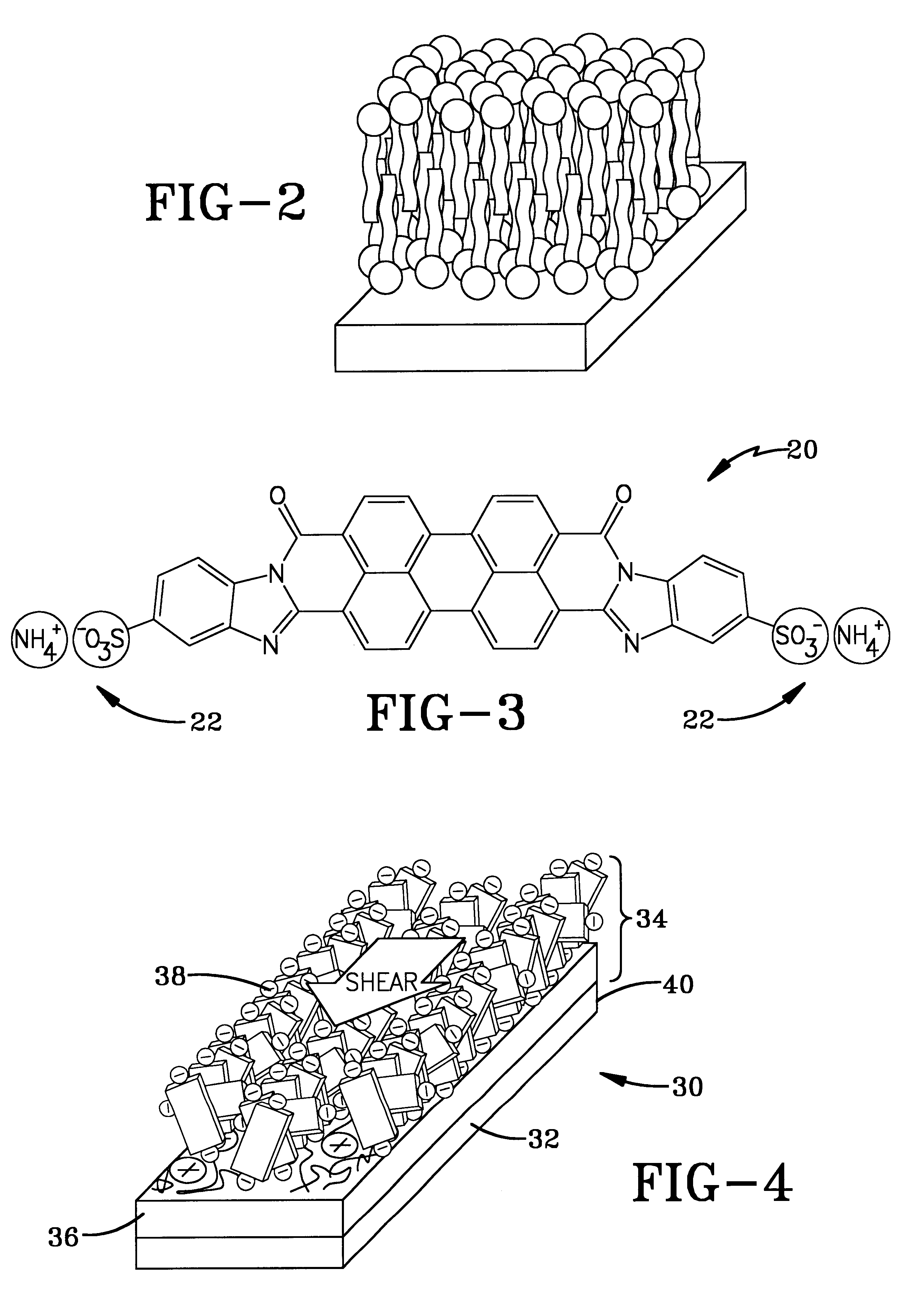
Alignment of lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals at surfaces as monolayers and multilayered stacks
InactiveUS6673398B2Eliminate needEasy to controlLiquid crystal compositionsMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid crystallineChemical physics
A broad class of lyotropic liquid crystals of a non-surfactant nature, the so-called lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals (LCLCs), are alignable with the techniques, in particular, LCLCs can be aligned at a surface as one monomolecular layer as a stack of monomolecular layers. The method for monolayer alignment is based on alternate layer-by-layer adsorption of polyions and dyes from aqueous solutions that have liquid crystalline structure. Using this method, one is able to stack alternate monolayers of dye and polyion while controlling the long-range in-plane orientation of the dye molecules within the plane of each layer. The feature of controlling the alignment of LCLCs enables one to create practical devices from them. For example, alignment of multilayered stacks allows one to use the resulting dried LCLC films in optical devices, for example, as internal polarizers, color filters, optical compensators, band-gap filters, and the like.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
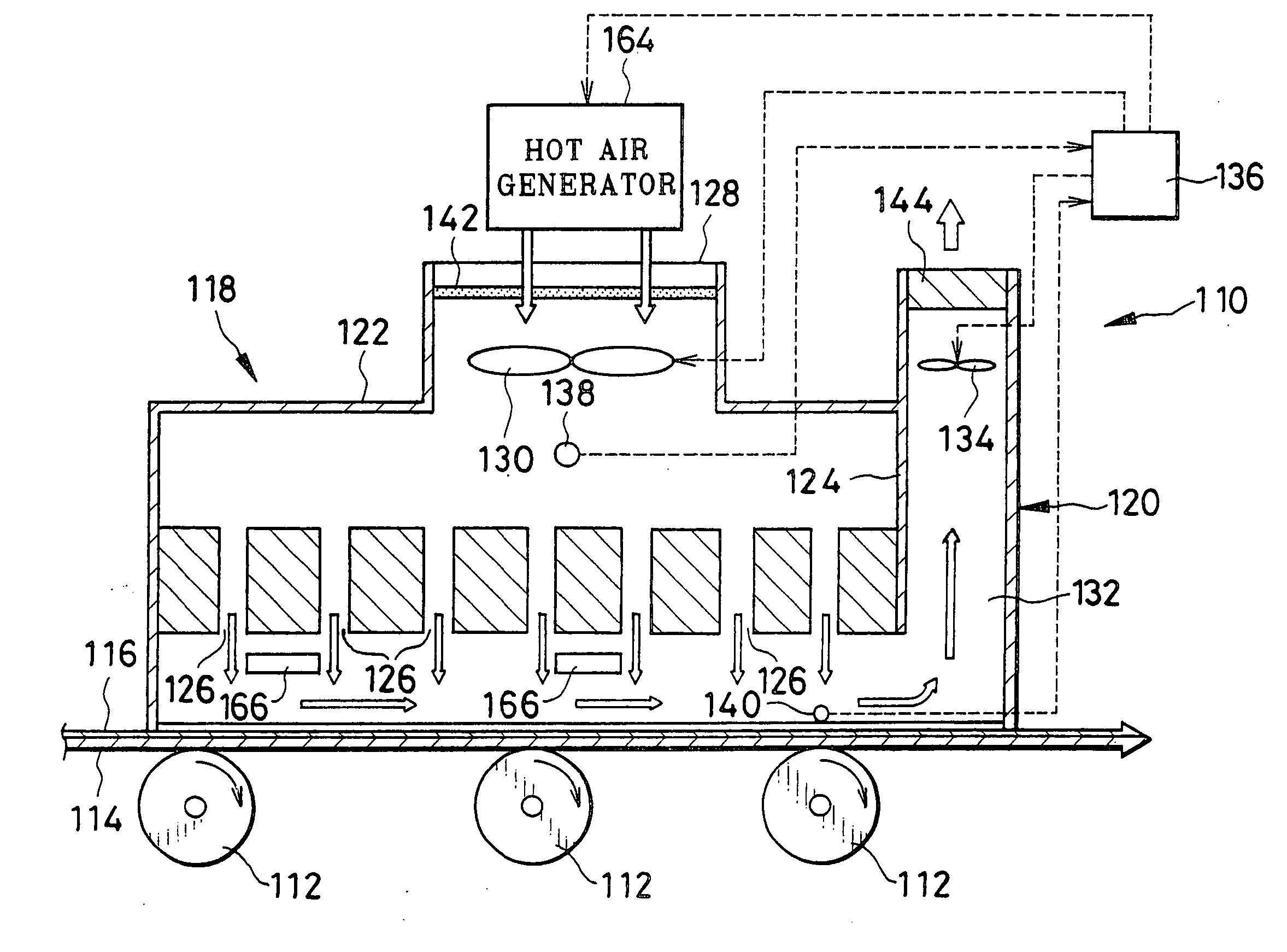
Optical compensatory sheet producing method and apparatus, thermal treating method and apparatus, and dust removing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060177587A1Increase contrastGood colorLighting and heating apparatusPretreated surfacesLiquid crystallineEngineering
An optical compensatory sheet producing apparatus produces an optical compensatory sheet having a liquid crystal layer. In the apparatus, a rubbing unit is supplied with resin film having a first layer including resin, and subjects the first layer to a rubbing process, so as to form an orientation layer. A dust remover removes dust from the orientation layer by use of liquid such as perfluorocarbon, to which the orientation layer is insoluble. A liquid crystal layer coater is disposed downstream from the dust remover, for coating the orientation layer with coating liquid including liquid crystalline compound, so that the liquid crystal layer is formed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid crystal display and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050030458A1Improve viewing angle characteristicsWiden perspectiveDoor/window protective devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid crystallineCrystallography
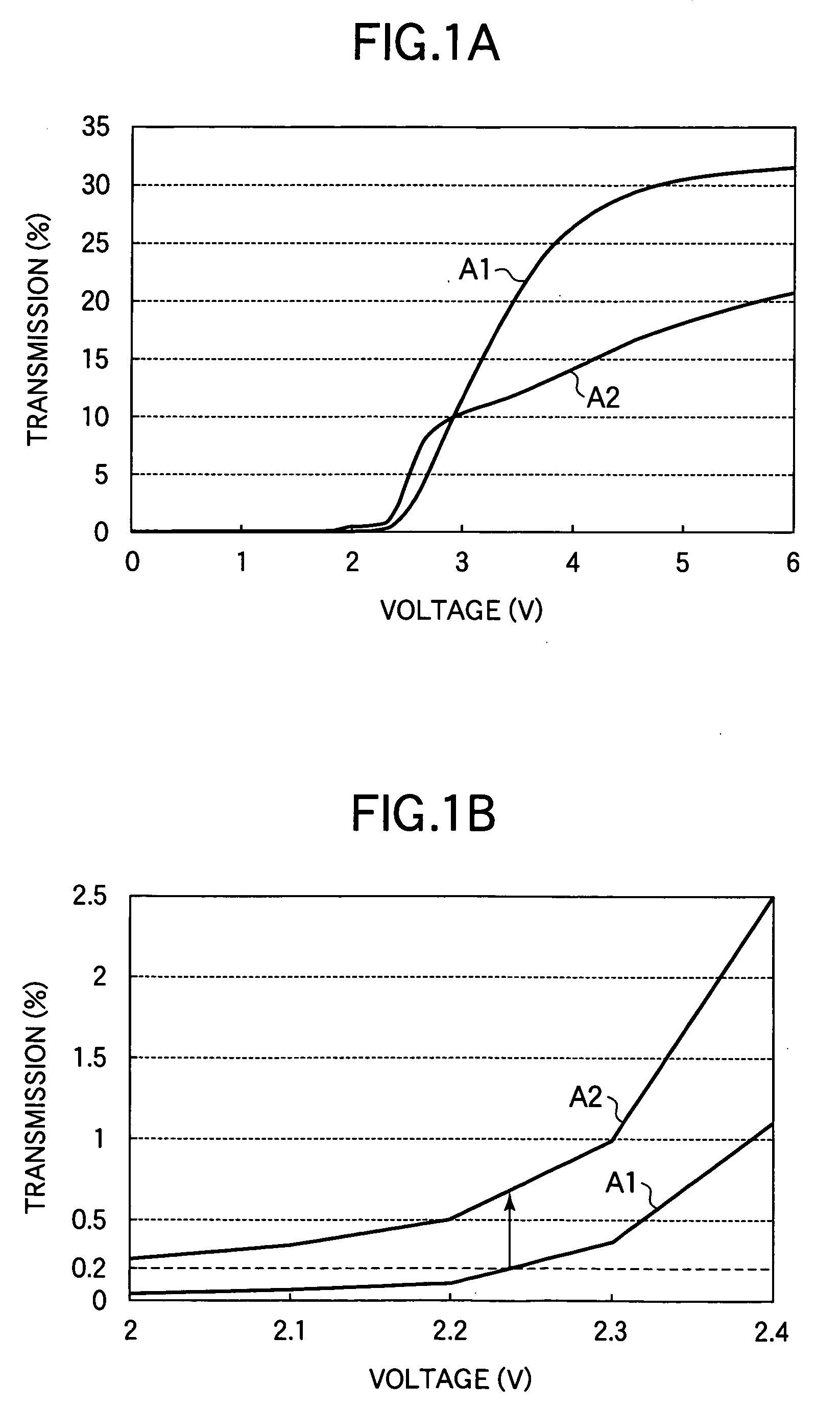
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display used as a display section of an electronic apparatus and a method of manufacturing the same, and it is aimed at providing a liquid crystal display which can achieve high viewing angle characteristics and a method of manufacturing the same. A configuration is employed which includes a pair of substrates provided opposite to each other, a liquid crystal sealed between the pair of substrates, protrusions formed on at least one of the pair of substrates for regulating the alignment of the liquid crystal, and a plurality of pixel regions having both of a first area in which the protrusions are disposed at first intervals a2 and which has a first threshold voltage for driving of the liquid crystal and a second area in which the protrusions are disposed at second intervals a2 smaller than the first intervals and which has a second threshold voltage lower than the first threshold voltage.
Owner:SHARP KK
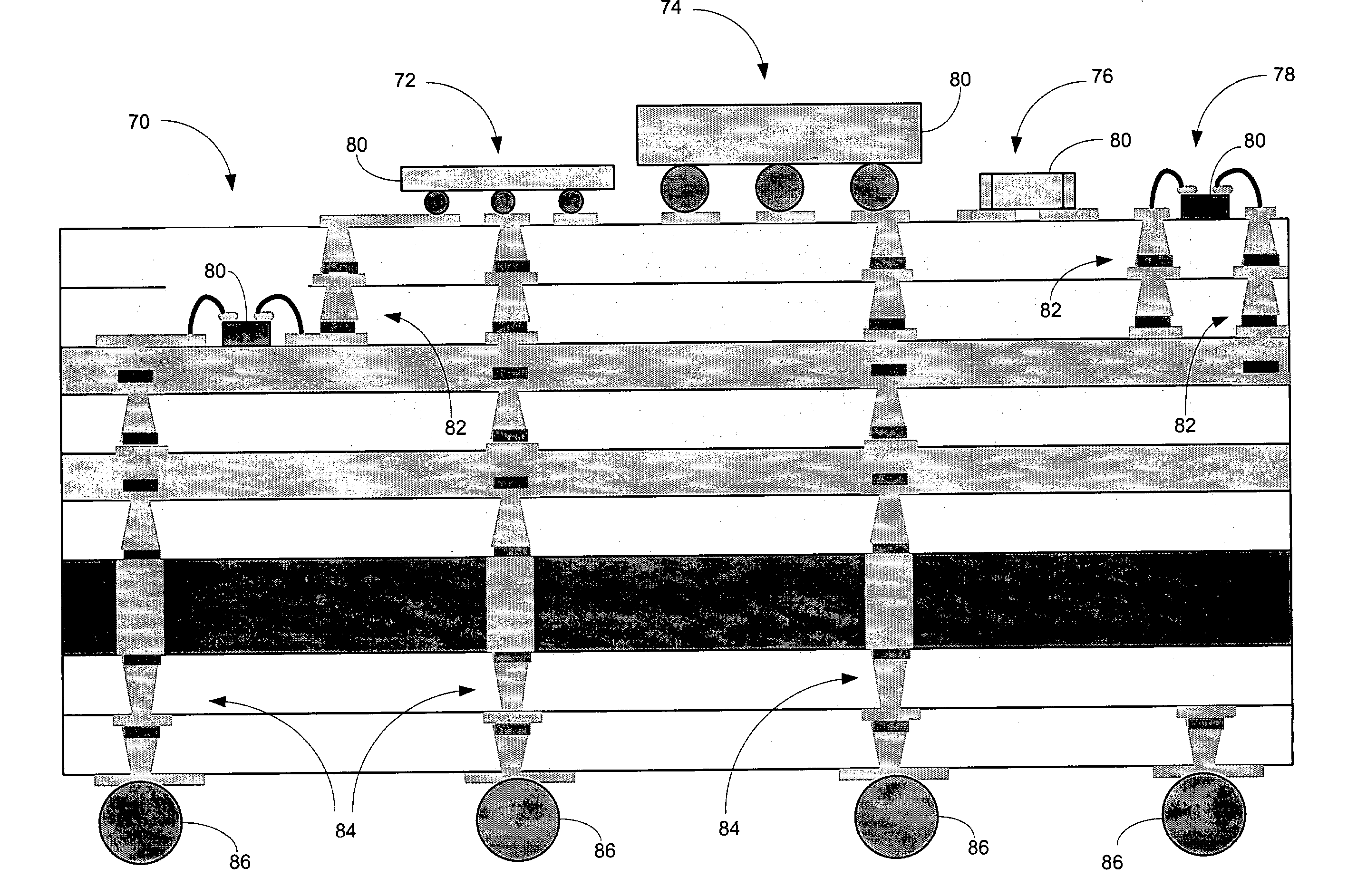
Liquid crystalline polymer and multilayer polymer-based passive signal processing components for RF/wireless multi-band applications
ActiveUS7795995B2Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMulti bandBandpass filtering
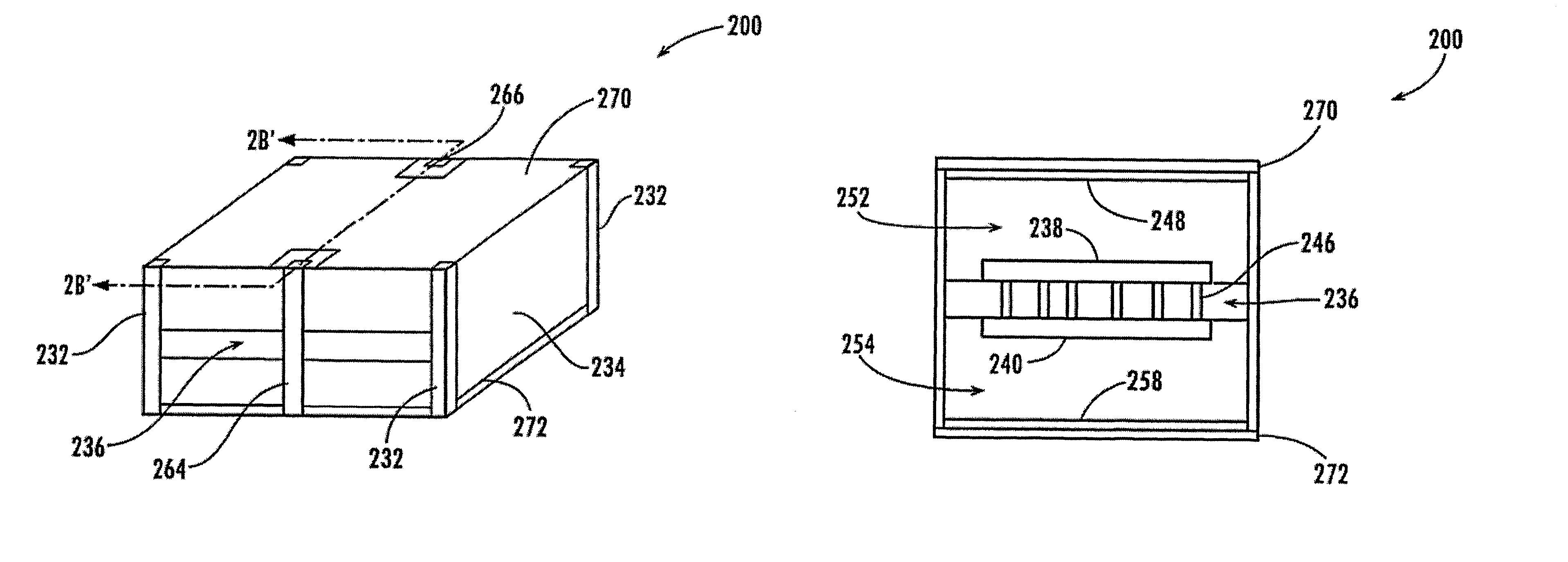
The present invention provides all organic fully-packaged miniature bandpass filters, baluns, diplexers, multiplexers, couplers and a combination of the above manufactured using liquid crystalline polymer (LCP) and other multilayer polymer based substrates. These devices are manufactured using one or more LCP layers having integrated passive components formed thereon to provide the density and performance necessary for multi-band wireless devices. In the designs involving multiple LCP layers, the LCP layers are separated by prepeg layers. In accordance with an aspect of the present invention, coplanar waveguide, hybrid stripline / coplanar waveguide and / or microstrip topologies are utilized to form the integrated passive components, and the devices can be mass produced on large area panels at least 18 inches by 12 inches with line widths smaller than 10 um.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
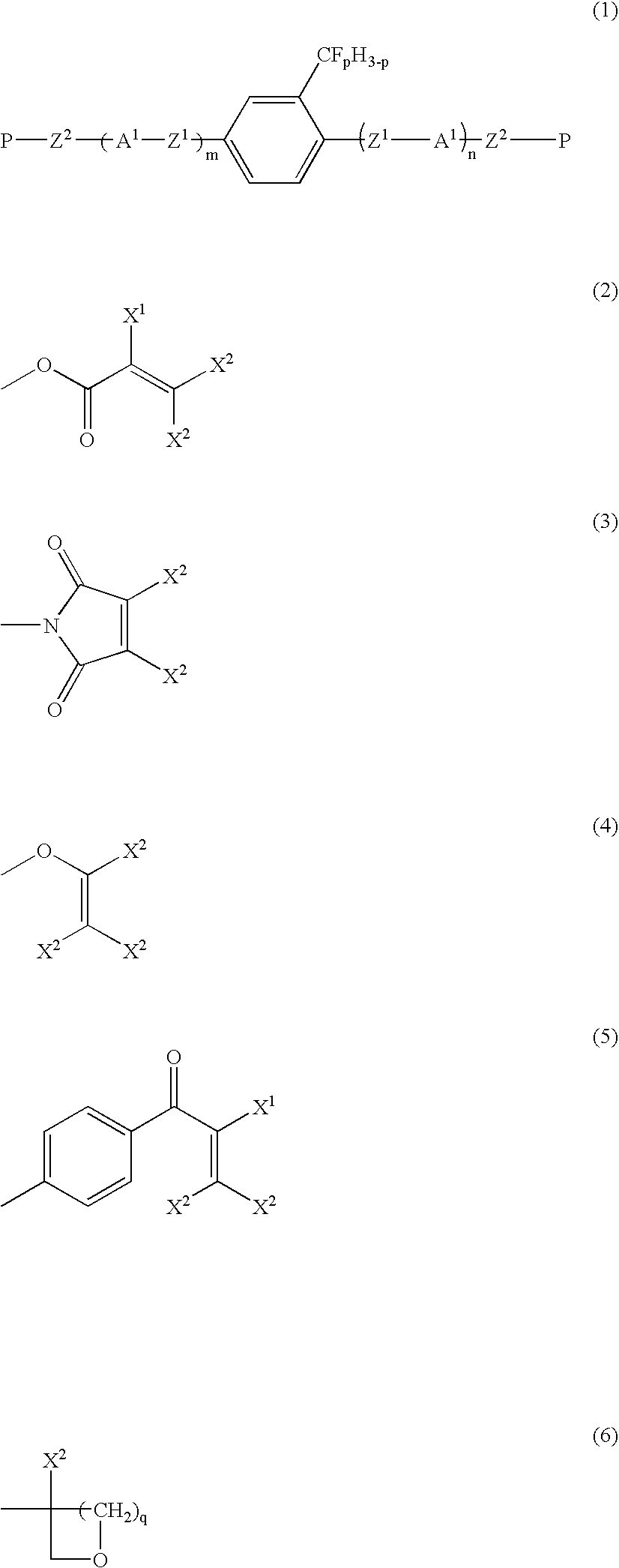
Liquid-crystalline vinyl ketone derivatives and their polymers
ActiveUS20050012070A1Improve compatibilityExcellent characteristicsLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistrySolubilityLiquid crystalline
Provided is a liquid-crystalline, polymerizable vinyl ketone compound of formula (1): Preferably, R1 is hydrogen, halogen, —CN, —CF3, —CF2H, —CFH2, —OCF3, —OCF2H, or alkyl, alkoxy, alkoxyalkyl or alkenyl having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms; R2, R3 and R5 are hydrogen; A1 to A4 are independently 1,4-cyclohexylene, 1,4-cyclohexenylene or 1,4-phenylene where any hydrogen may be substituted with halogen; Z1 to Z3 are independently a single bond, —(CH2)2—, —CH═CH—, —CF═CF—, —OCF2— or —CF2O—; Z4 is a single bond, —(CH2)3— or —(CH2)4—; m, n and q are independently 0, 1 or 2. The uppermost temperature of the liquid crystalline phase of the compound is high, and the compound has good compatibility with other compounds and has the necessary characteristics such as optical anisotropy. Also provided are a polymer having many good characteristics of transparency, mechanical strength, coatability, solubility, crystallinity, shrinkage, water permeability, water absorption, melting point, glass transition point, clearing point and chemical resistance; an optically-anisotropic material of the polymer; a liquid-crystal display device that comprises the polymer; and a method for producing the liquid-crystalline compound.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
Coated particles, methods of making and using
InactiveUS20060073333A1Simple processOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryLiquid crystallineActive agent
A particle coated with a nonlamellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material includes an internal matrix core having at least one a nanostructured liquid phase, or at least on nanostructured liquid crystalline phase or a combination of the two is used for the delivery of active agents such as pharmaceuticals, nutrients, pesticides, etc. The coated particle can be fabricated by a variety of different techniques where the exterior coating is a nonlaliellar material such as a nonlamellar crystalline material, a nonlamellar amorphous material, or a nonlamellar semi-crystalline material
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Thermally conductive liquid crystalline polymer compositions and articles formed therefrom
InactiveUS20060014876A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove conductivityLiquid crystal compositionsCooking-vessel materialsLiquid crystallinePolymer science
This invention relates to thermally conductive liquid crystalline polymer compositions. The composition is comprised of a liquid crystalline polymer and metal particles. At least about 90% by weight of the metal particles have an average particle size larger than 200 μm. In other embodiments of the invention, the average particle size of the metal particles is larger than 420 μm. Aluminum flakes are exemplary metal particles for use in this invention. The thermally conductive liquid crystalline polymer composition is useful for the manufacture of cookware and has sufficient thermal conductivity to provide browning during cooking. The composition is useful for the manufacture of oven cookware such as cooking pans, sheets, trays, dishes, casseroles, and the like.
Owner:SOLVAY ADVANCED POLYMERS LLC
Alignment of lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals at surfaces as monolayers and multilayered stacks
InactiveUS20020168511A1Easy fashionLiquid crystal compositionsMaterial nanotechnologyIn planeLiquid crystalline
A broad class of lyotropic liquid crystals of a non-surfactant nature, the so-called lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals (LCLCs), are alignable with the techniques, in particular, LCLCs can be aligned at a surface as one monomolecular layer as a stack of monomolecular layers. The method for monolayer alignment is based on alternate layer-by-layer adsorption of polyions and dyes from aqueous solutions that have liquid crystalline structure. Using this method, one is able to stack alternate monolayers of dye and polyion while controlling the long-range in-plane orientation of the dye molecules within the plane of each layer. The feature of controlling the alignment of LCLCs enables one to create practical devices from them. For example, alignment of multilayered stacks allows one to use the resulting dried LCLC films in optical devices, for example, as internal polarizers, color filters, optical compensators, band-gap filters, and the like.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com