Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
330 results about "Homeotropic alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
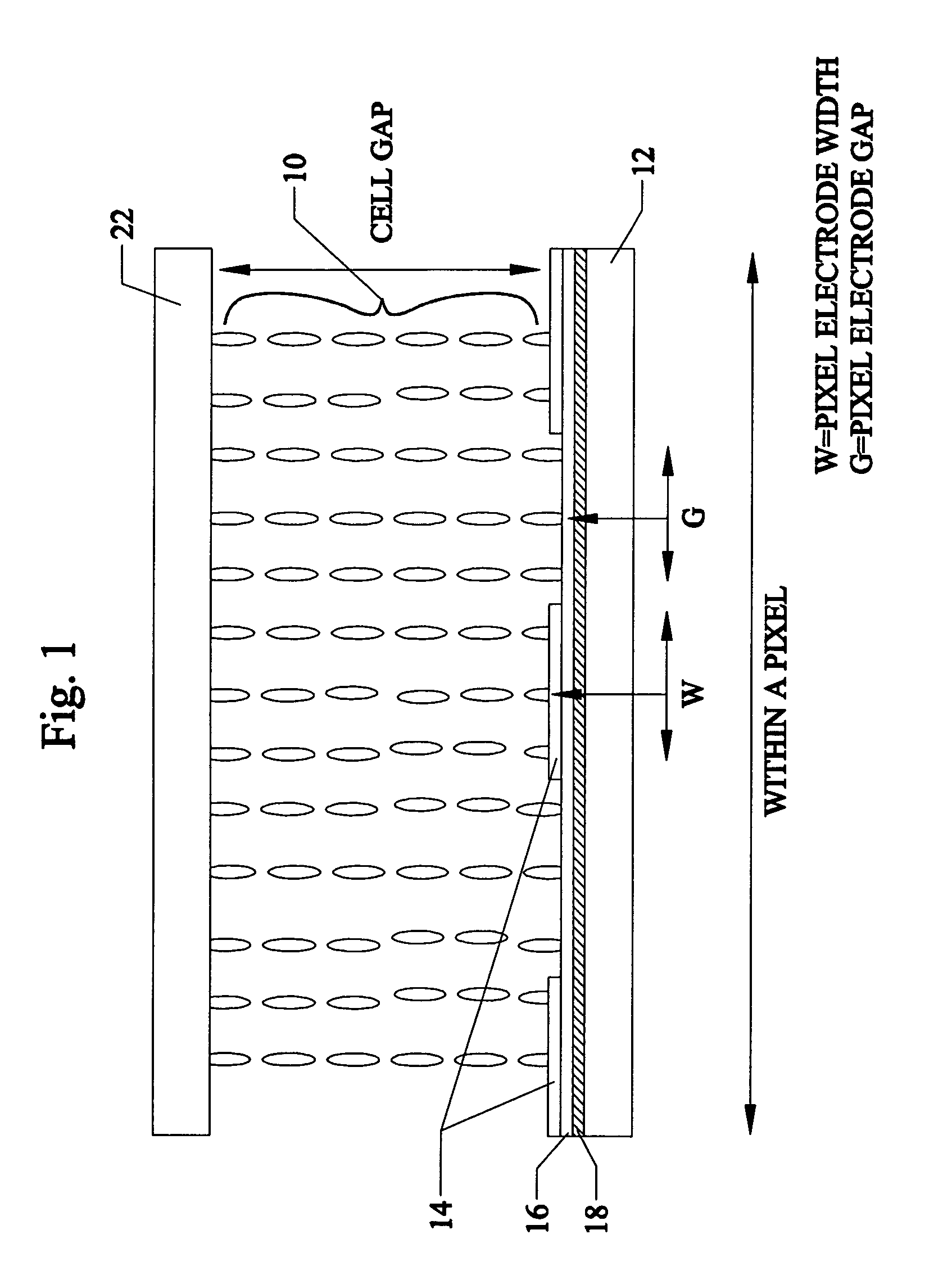
In liquid crystals, homeotropic alignment is one of the ways of alignment of liquid crystalline molecules. Homeotropic alignment is the state in which a rod-like liquid crystalline molecule aligns perpendicularly to the substrate. In the polydomain state, the parts also are called homeotropic domains. In contrast, the state in which the molecule aligns to a substance in parallel is called homogeneous alignment.
Liquid crystal display device with improved viewing angle characteristics
ActiveUS20050253797A1Broad viewing angle characteristicImprove viewing angle characteristicsCathode-ray tube indicatorsCounting objects with random distributionEngineeringImage signal
A liquid crystal display device, in which the liquid crystal molecules are aligned vertically when no voltage is applied, includes pixels each having plural sub-pixel electrodes, a data bus drive circuit for applying drive signals to the sub-pixel electrodes via a data bus line and a switching element, and alignment regulation structure for regulating the direction of alignment of liquid crystal molecules. The first and second sub-pixel electrodes have different areas. The data bus drive circuit applies a first drive signal, which causes luminance to change from minimum to maximum for an increase of input grayscale of image signal, to the first sub-pixel electrode, and a second drive signal, which causes the luminance to be lower than the first drive signal, to the second sub-pixel electrode.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090002588A1Widen perspectiveImprove display characteristicsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceHomeotropic alignment
A display device includes: a first panel having a pixel region including a pixel electrode therein; a second panel having a common electrode facing the first panel; a liquid crystal layer having vertically aligned liquid crystal molecules interposed between the first and second panels; a first alignment layer disposed on the pixel electrode; and a second alignment layer disposed on the common electrode. At least one of the pixel electrode and the common electrode has a micro slit pattern. At least one of the first and second alignment layers divides the pixel region into domains, is formed to have pretilt directions corresponding to a given domain, and pretilts the vertically aligned liquid crystal molecules in the given domain. A direction of summed horizontal components of a fringe field at an edge of the pixel region is substantially equal to a direction of summed horizontal components of a pretilt direction of the at least one of the first and second alignment layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display (LCD) and a liquid crystal panel thereof are provided. The LCD includes a backlight module and the liquid crystal panel disposed thereon. The liquid crystal panel has a first substrate, a second substrate, and a positive liquid crystal layer. The first substrate has a plurality of pixel electrodes, and each pixel electrode has a plurality of first strip-shape portions. The second substrate has a common electrode, and the common electrode has a plurality of second strip-shape portions. The positive liquid crystal layer is interposed between the pixel electrodes of the first substrate and the common electrode of the second substrate and is vertically aligned. The corresponding areas of the first and the second strip-shape portions are staggered.
Owner:WINTEK CORP
Bistable nematic liquid crystal device
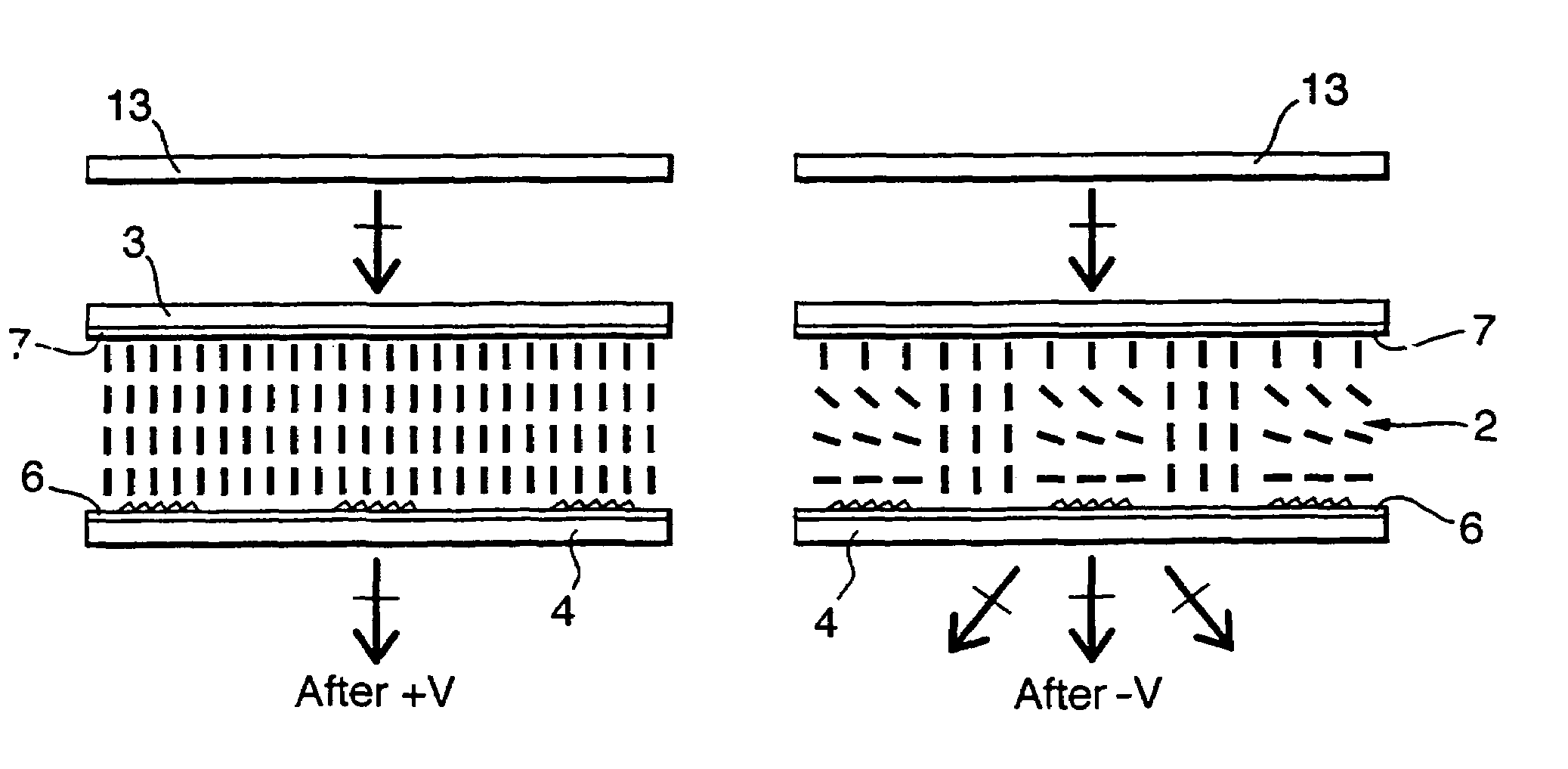
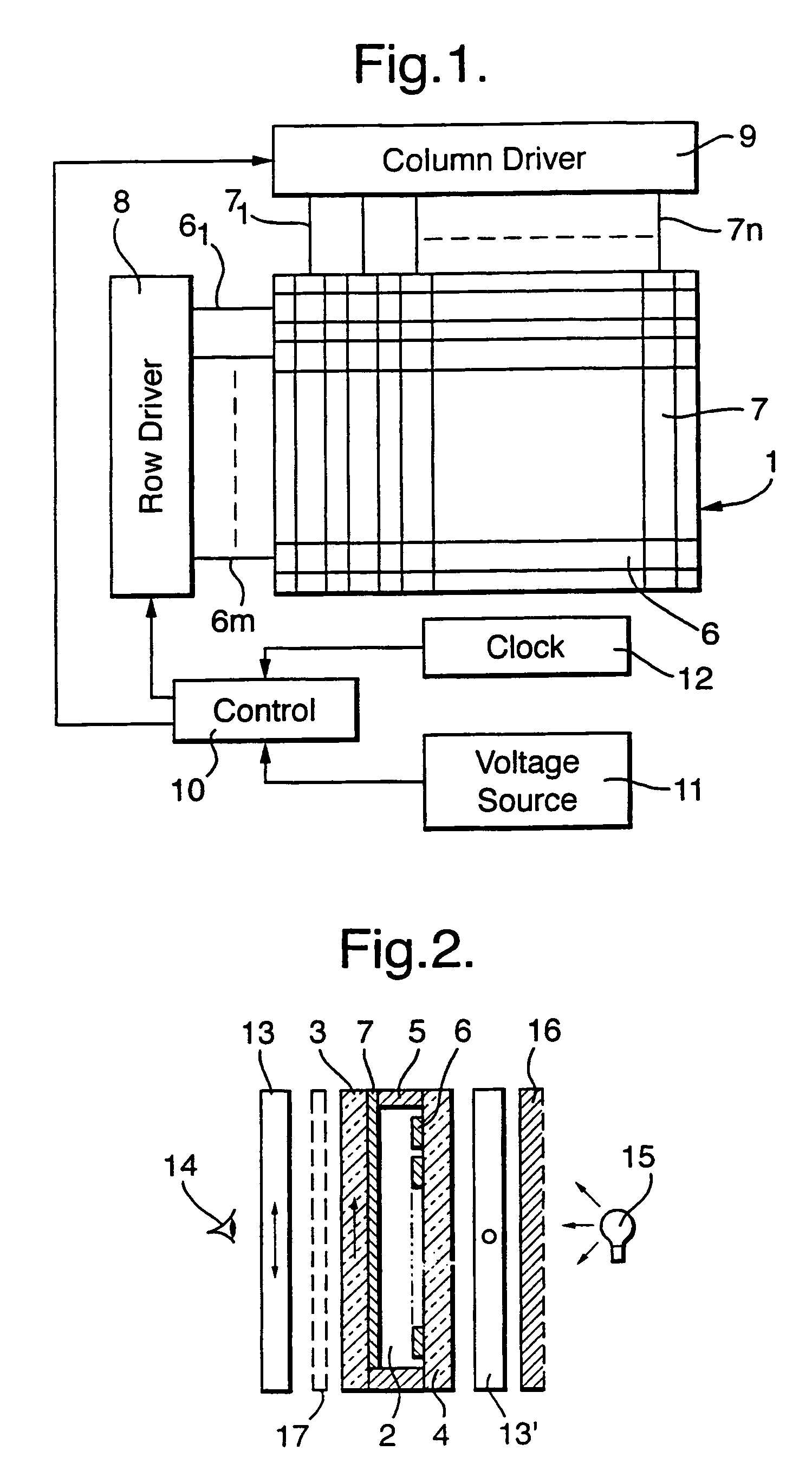
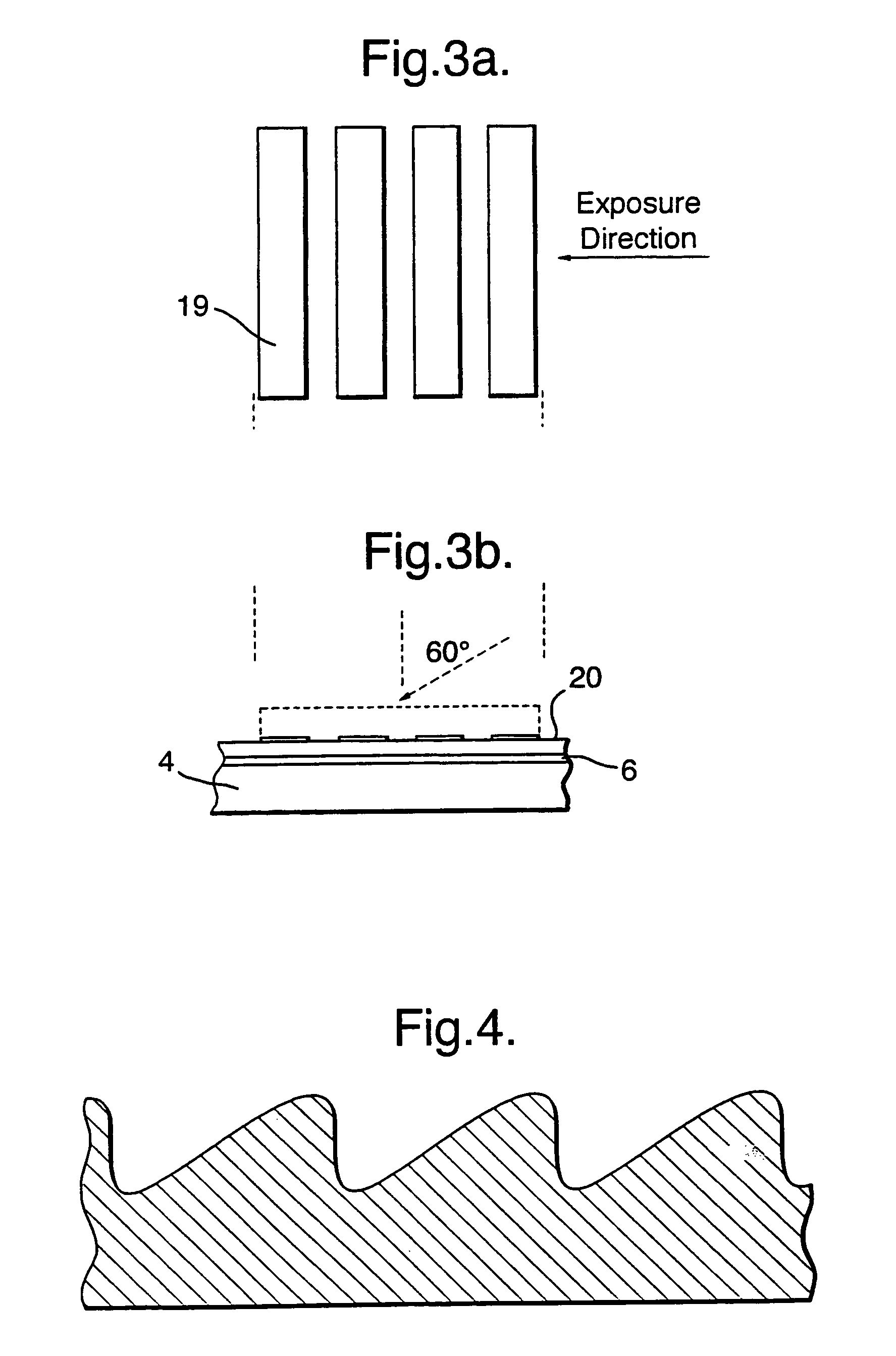
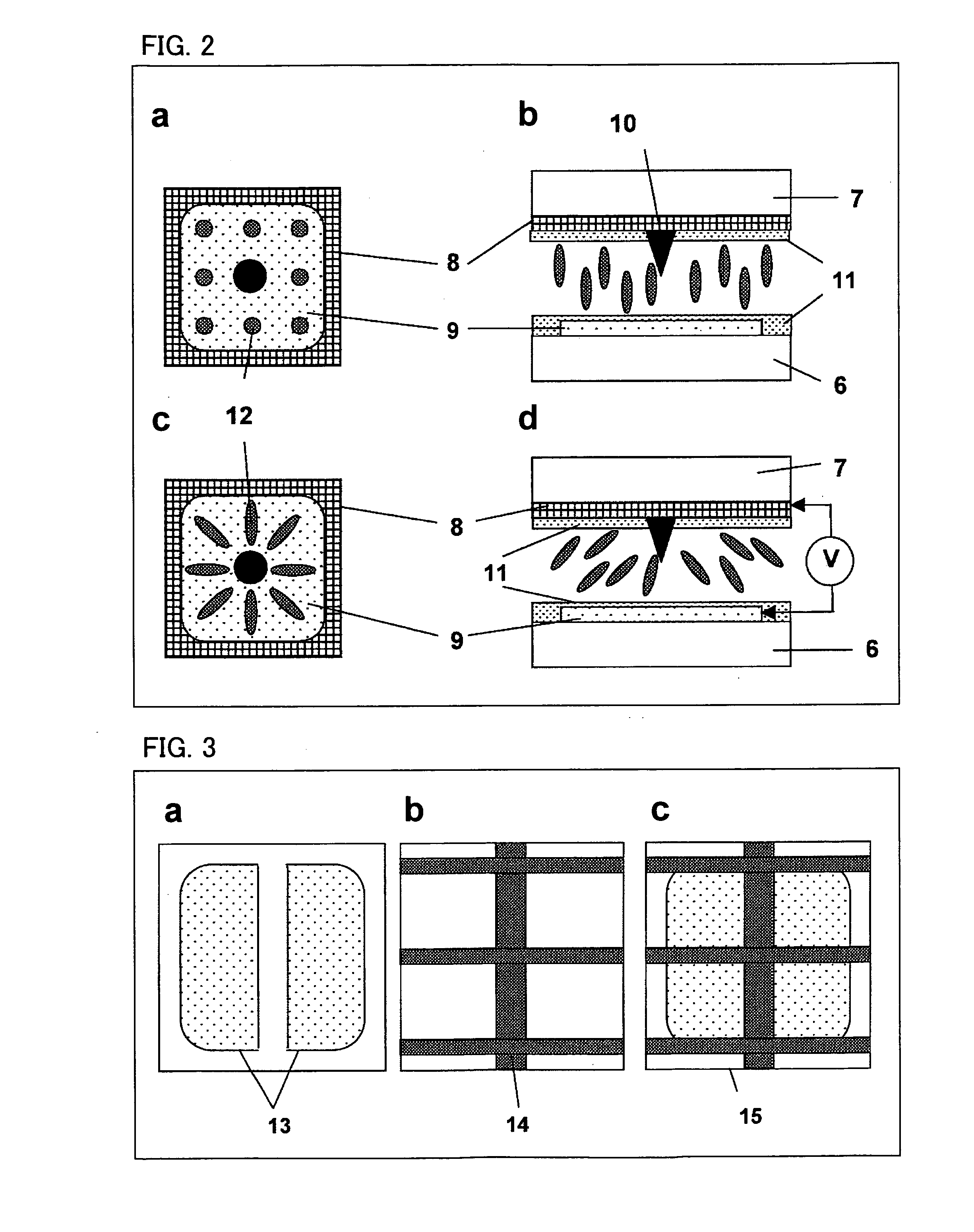
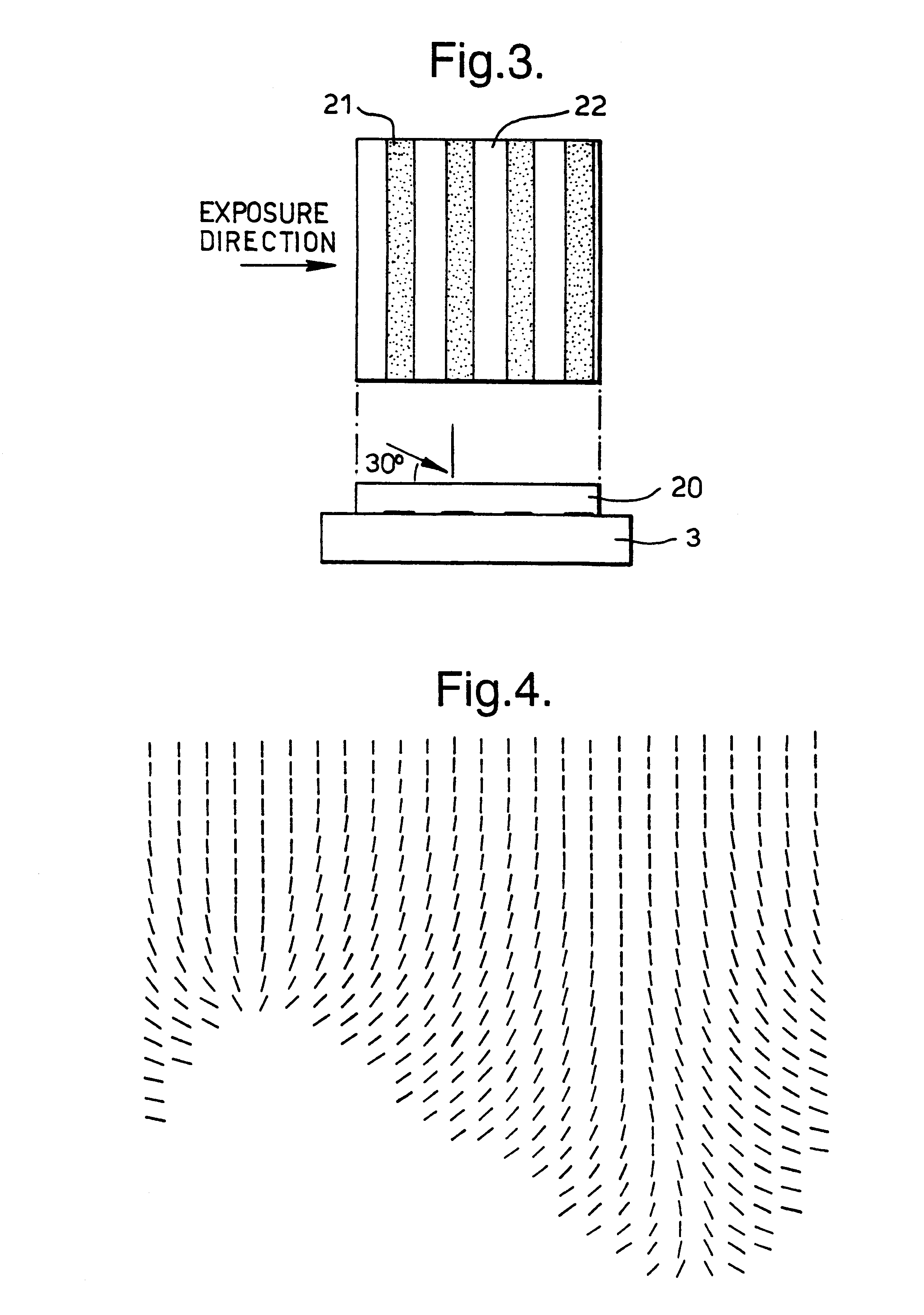
A bistable nematic liquid crystal device cell (1) is provided with a surface alignment grating on at least one cell wall (3) and a surface treatment on the other wall (4). Such treatment may be a homeotropic alignment or a planar alignment with or without an alignment direction, and zero or a non zero pretilt. The surface profile on the monograting is asymmetric with its grove height to width selected to give approximately equal energy within nematic material (2) in its two allowed alignment arrangements. The monograting may be formed by a photolithographic process or by embossing of a plastics material. The cell (1) is switched by dc pulses coupling to a flexoelectric coefficient in the material (2), or by use of a two frequency addressing scheme and a suitable two frequency material. Polarizers (13,13') either side of the cell (1) distinguish between the two switched states. The cell walls (3,4) may be rigid or flexible, and are coated with electrode structures (6,7), e.g. in row and column format giving an x,y matrix of addressable pixels on the cell (1).
Owner:ZBD DISPLAY LTD
Control of liquid crystal alignment in an optical device
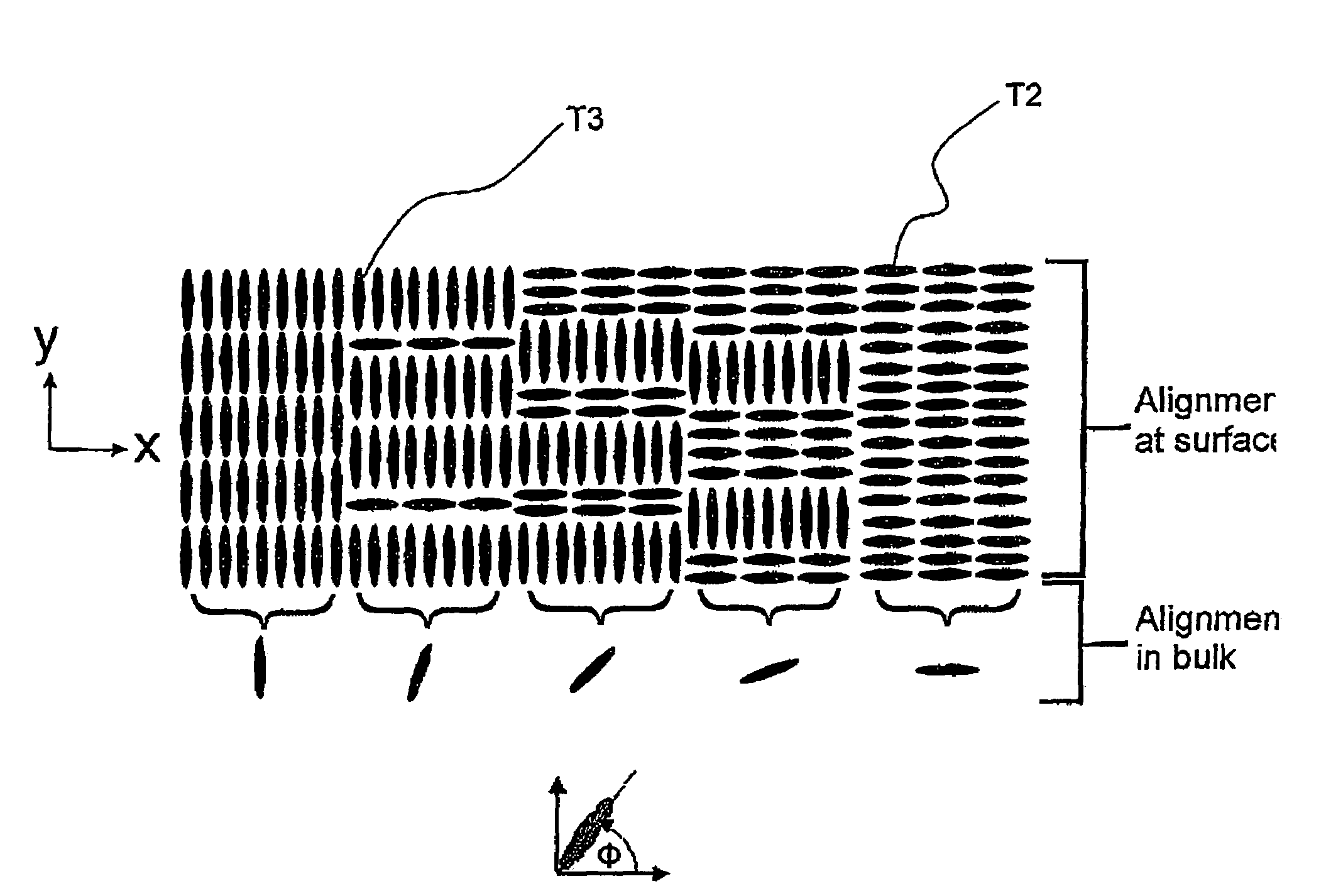
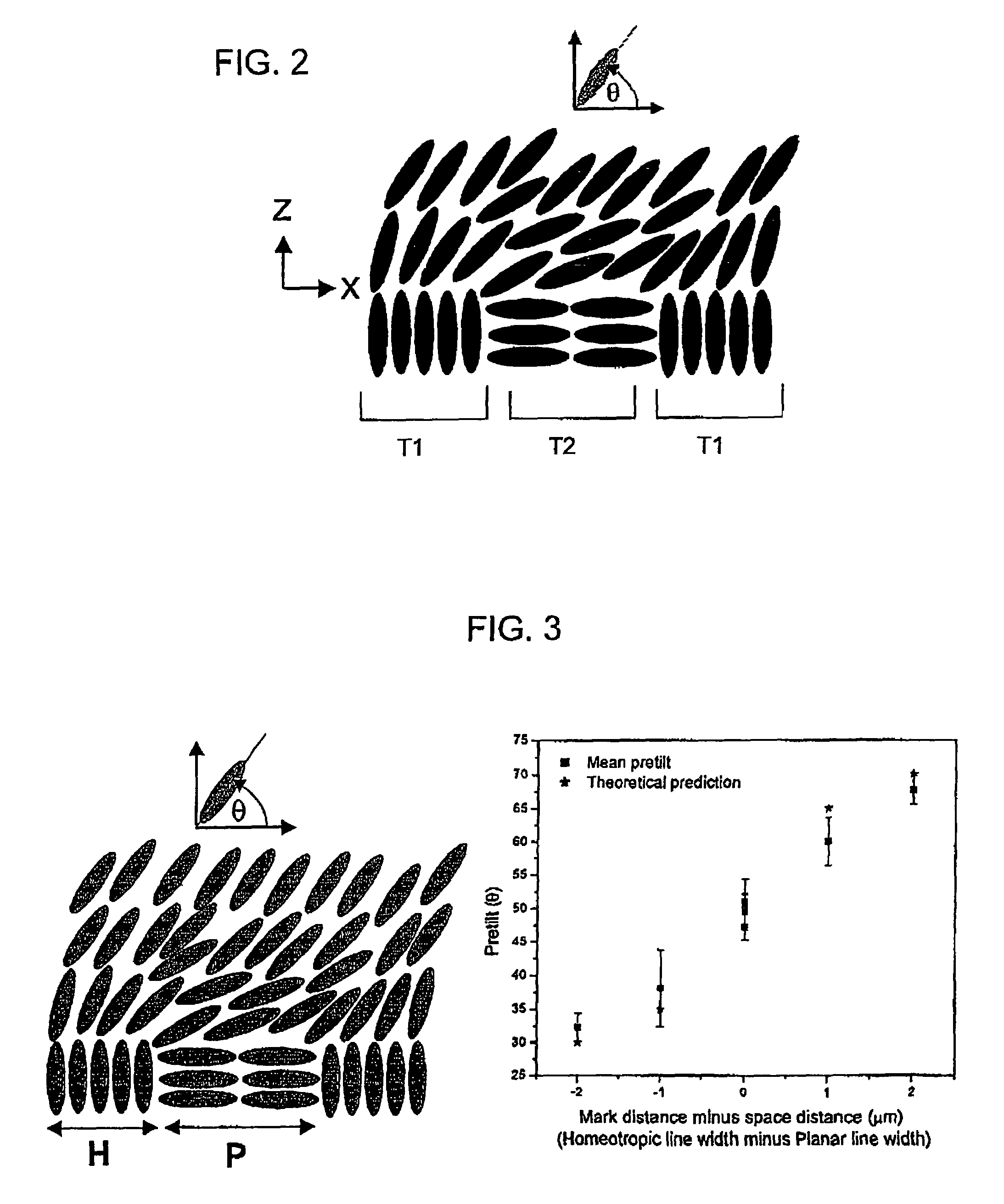
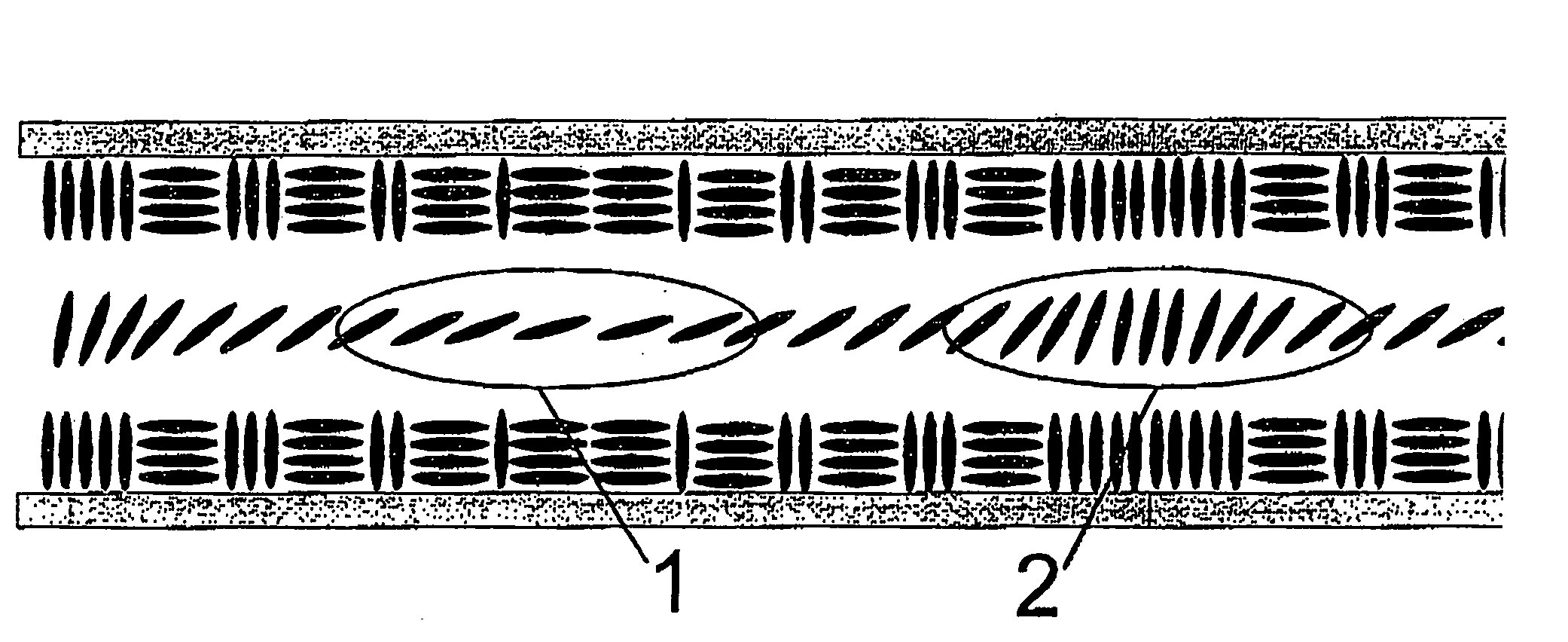
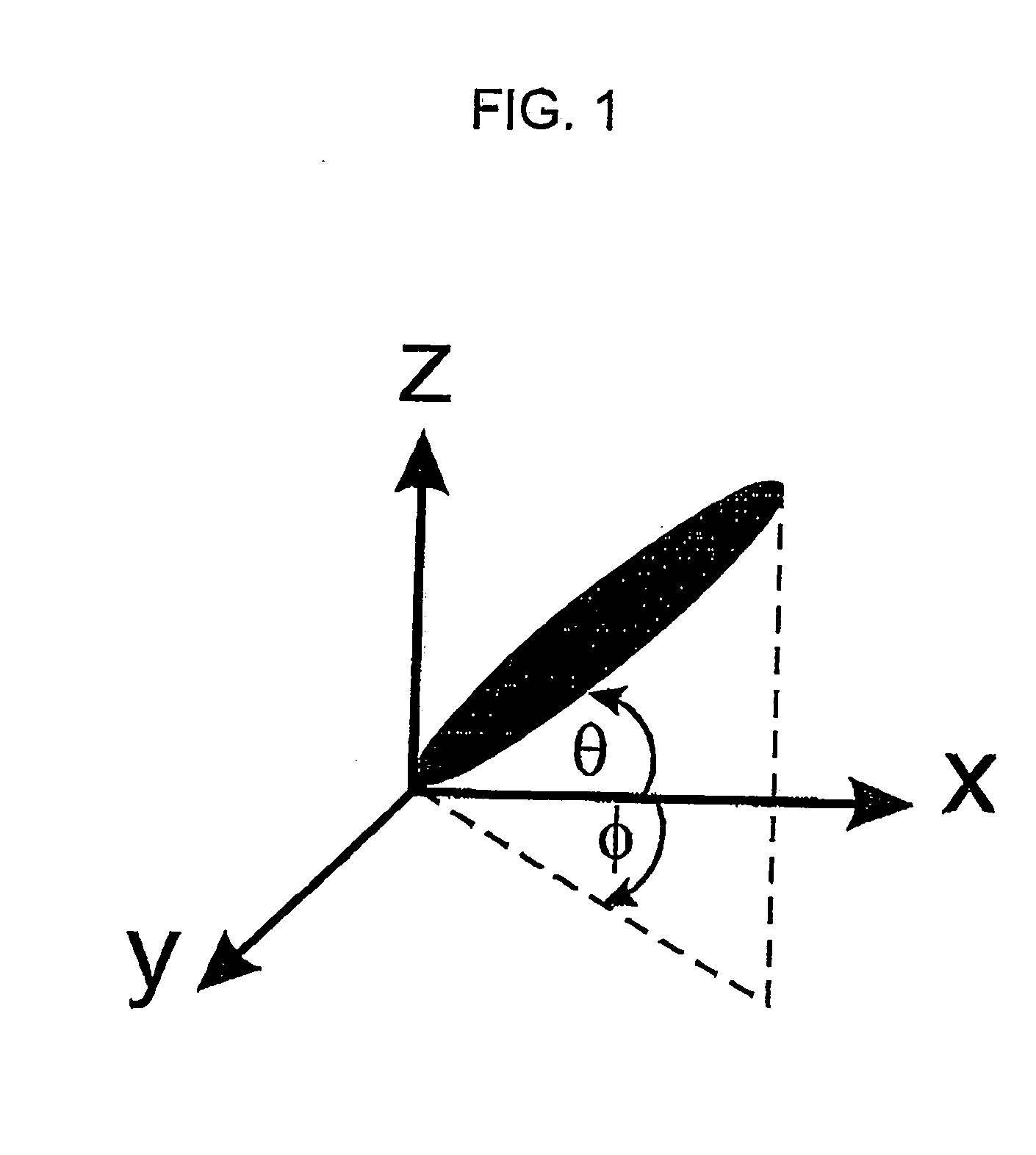
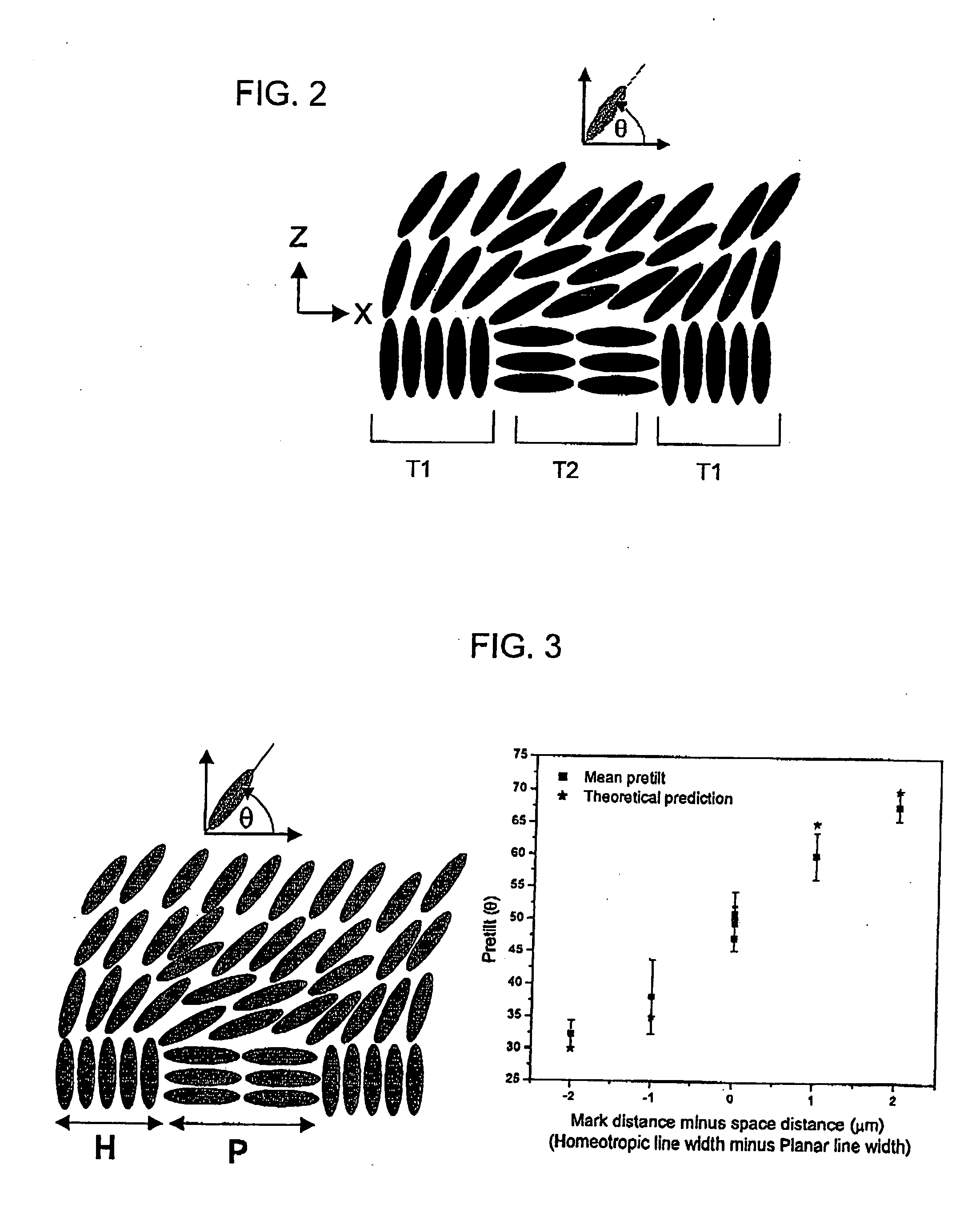
A method is provided that allows simultaneous control of macroscopic azimuthal and zenithal liquid crystal alignment (φ, θ) across a liquid crystal layer by controlling the area ratios between first, second and third different types of alignment region (T1, T2, T3) in a patterned alignment layer, the three different types of alignment region (T1, T2, T3) tending to induce liquid crystal alignment in the liquid crystal layer in three different respective, non-coplanar, principal orientations (z, x, y). In the illustrated example, the first type of alignment region (T1) tends to induce substantially homeotropic alignment (in the z direction) and the second and third types of alignment region (T2, T3) tend to induce substantially planar alignment in different, orthogonal, principal orientations (in the x and y directions). Control of macroscopic zenithal liquid crystal alignment (θ) is achieved by controlling the area ratios between the homeotropic (T1) and planar region types (T2, T3), and control of macroscopic azimuthal liquid crystal alignment (φ) is achieved by controlling the area ratio between the two planar region types (T2, T3).
Owner:SHARP KK
Control of liquid crystal alignment in an optical device
A method is provided that allows simultaneous control of macroscopic azimuthal and zenithal liquid crystal alignment (φ, θ) across a liquid crystal layer by controlling the area ratios between first, second and third different types of alignment region (T1, T2, T3) in a patterned alignment layer, the three different types of alignment region (T1, T2, T3) tending to induce liquid crystal alignment in the liquid crystal layer in three different respective, non-coplanar, principal orientations (z, x, y). In the illustrated example, the first type of alignment region (T1) tends to induce substantially homeotropic alignment (in the z direction) and the second and third types of alignment region (T2, T3) tend to induce substantially planar alignment in different, orthogonal, principal orientations (in the x and y directions). Control of macroscopic zenithal liquid crystal alignment (θ) is achieved by controlling the area ratios between the homeotropic (T1) and planar region types (T2, T3), and control of macroscopic azimuthal liquid crystal alignment (φ) is achieved by controlling the area ratio between the two planar region types (T2, T3).
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical compensator element and liquid crystal display using the same
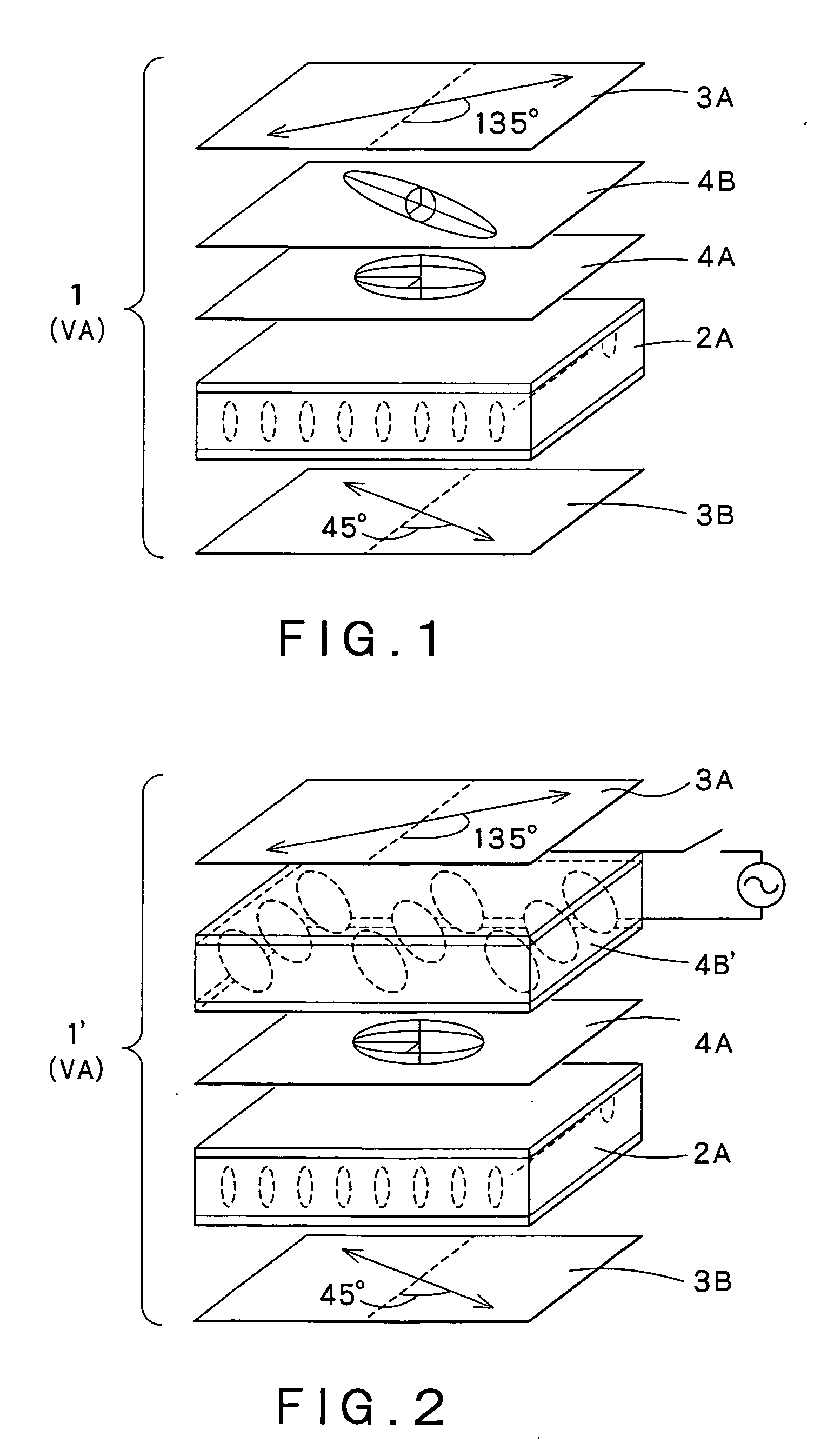
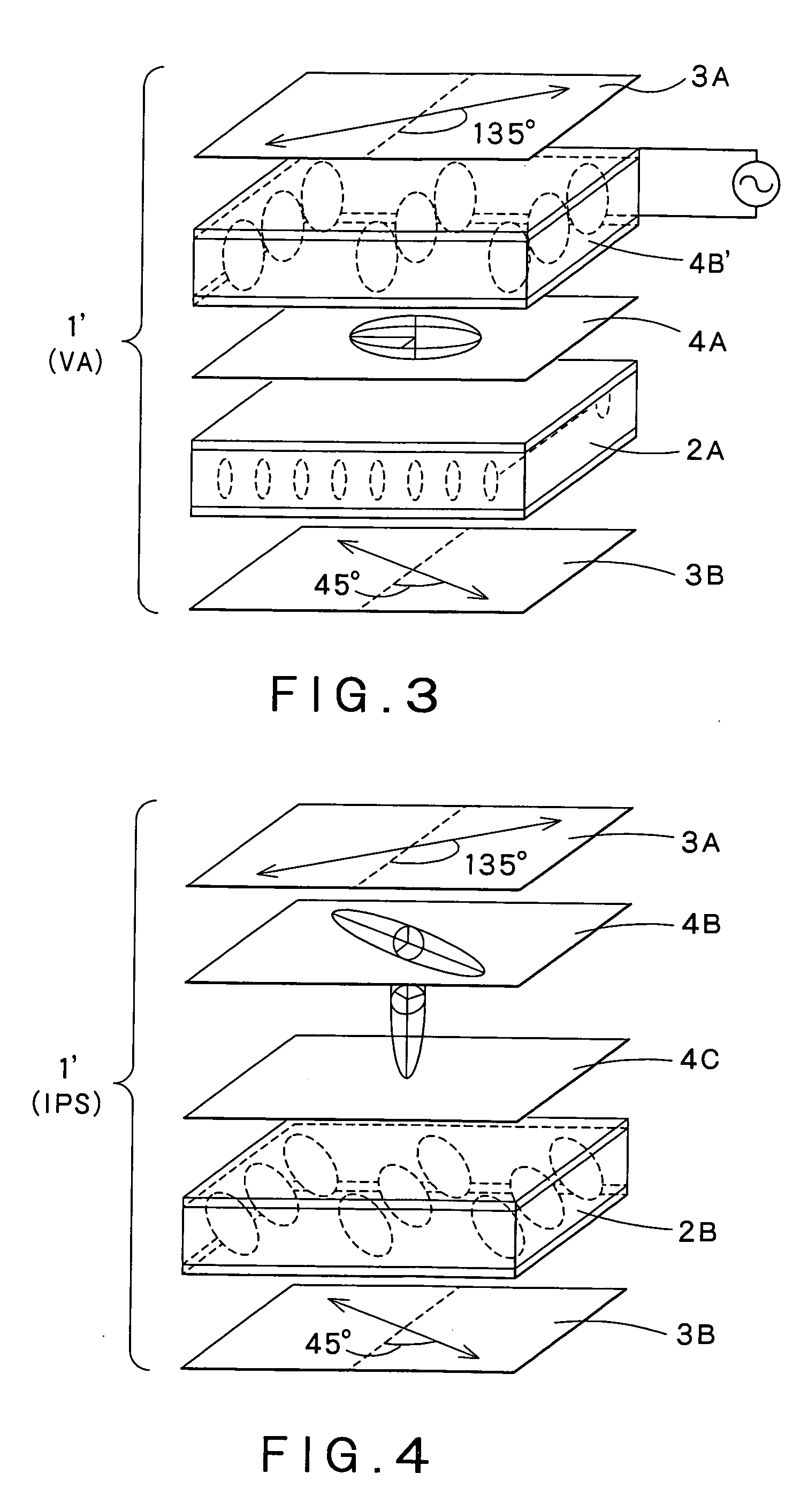
InactiveUS20060066785A1Easy to operateRealize switchingStatic indicating devicesPolarising elementsVisibilityElectricity
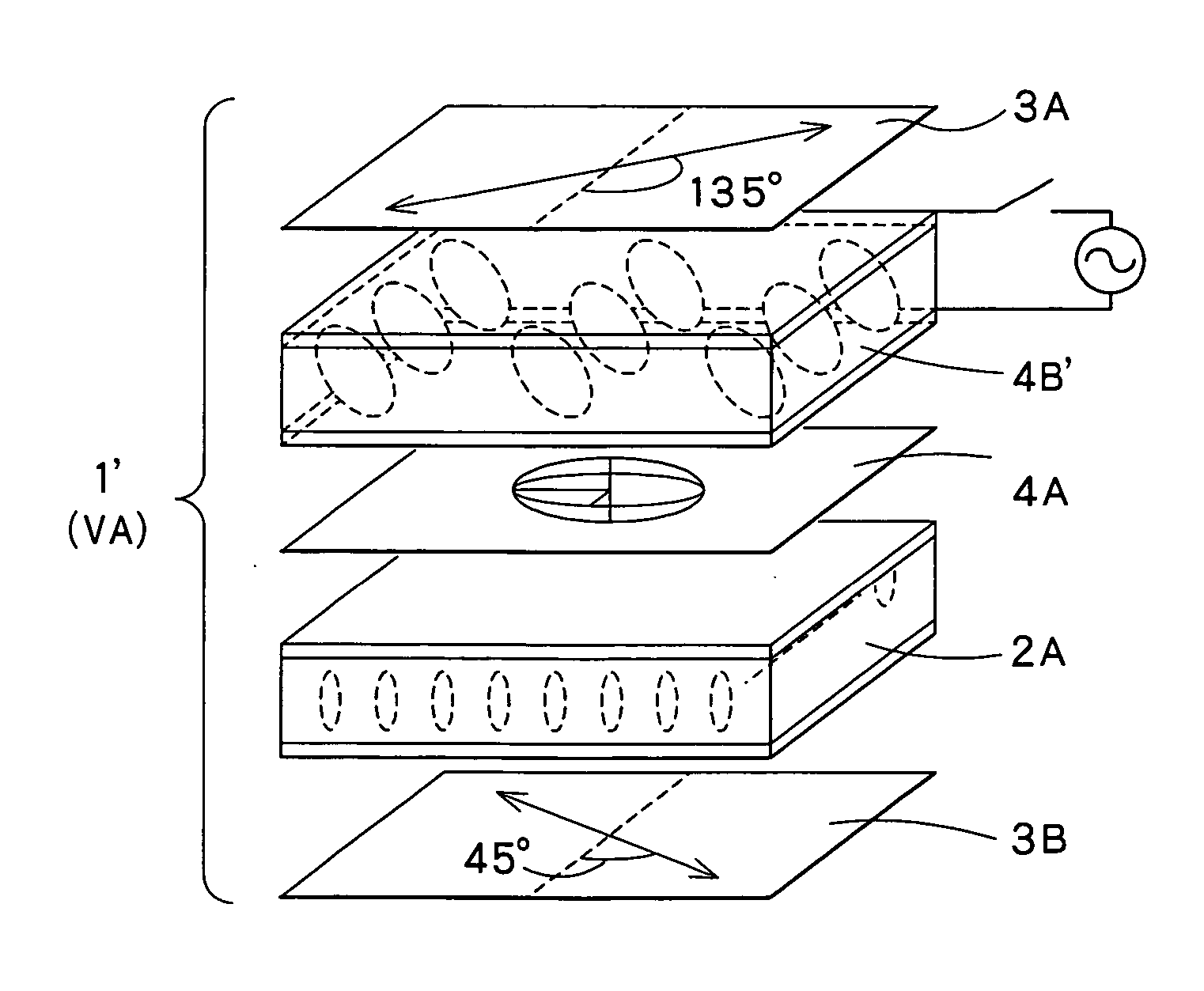
Disclosed are an optical compensator element, which can realize switching between a wide angle of visibility and a narrow angle of visibility through a simple operation, and a liquid crystal display using the same. An optical compensation layer 4B′ comprising, for example, a liquid crystal material having positive dielectric anisotropy sealed between two substrates comprising a transparent electrode and an aligning film stacked on top of each other is provided. An optical compensation layer 4A as a negative C plate and the optical compensation layer 4B′ are stacked in that order on a homeotropically aligned liquid crystal cell 2A to constitute a liquid crystal display 1. Upon the application of voltage to the optical compensation layer 4B′, a narrow angle of visibility is provided, while, when no voltage is applied, a wide angle of visibility is provided.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Vertically aligned liquid crystal display using polynorbornene based polymer film
ActiveUS20050190326A1Improve viewing angle characteristicsEnhanced Contrast FeaturesNon-linear opticsTectorial membranePolynorbornen
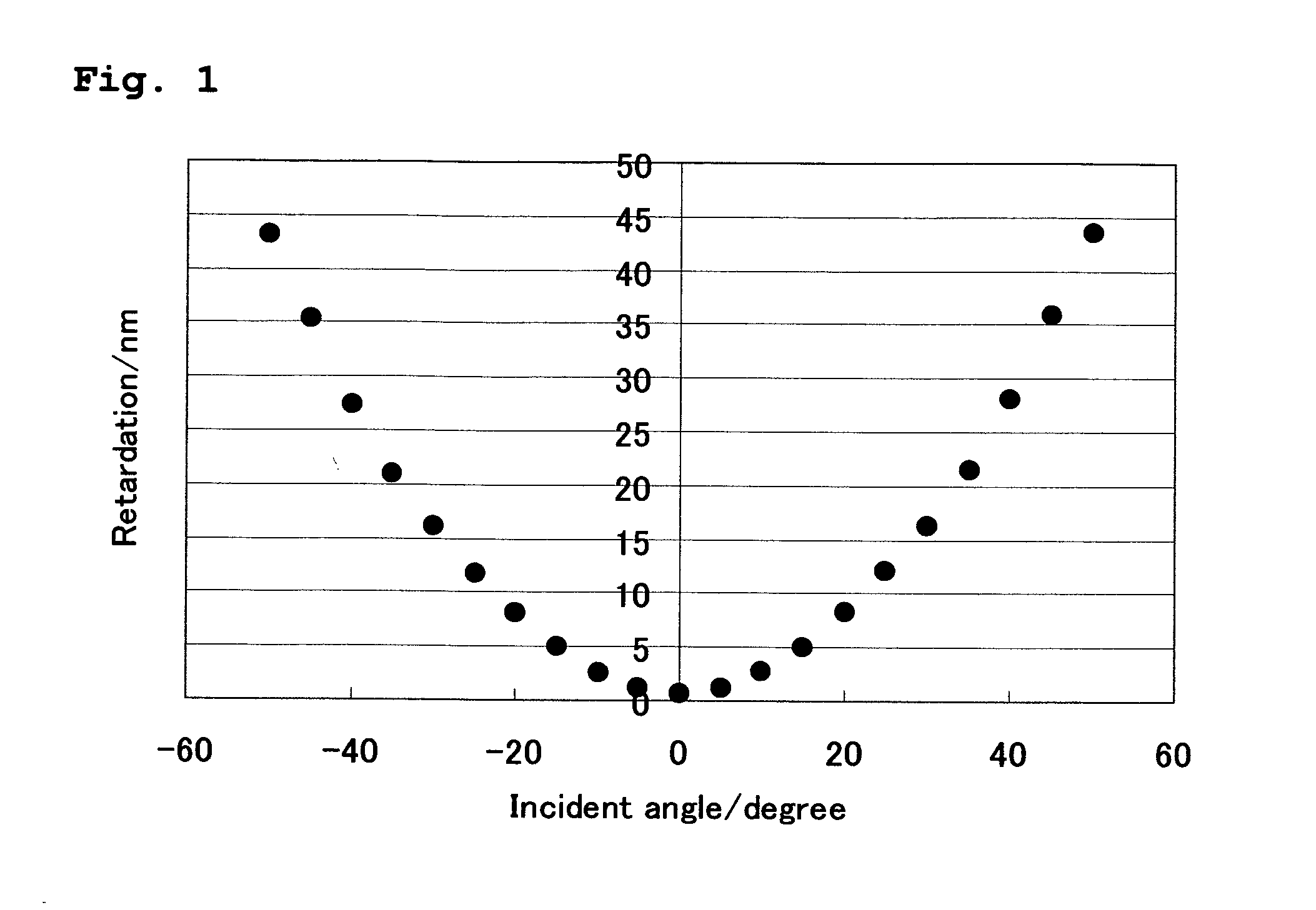
Provided are a vertically aligned liquid crystal display (VA-LCD) with good viewing angle characteristics, which has liquid crystals with negative dielectric anisotropy (Δε<0). In the VA-LCD, a polynorbornene based polymer film is used as a protection film and / or as a negative C-plate retardation film for an upper polarization plate and / or a lower polarization plate. Therefore, high contrast characteristics for a front view and an oblique angle view are realized and color change for an oblique angle view can be minimized.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
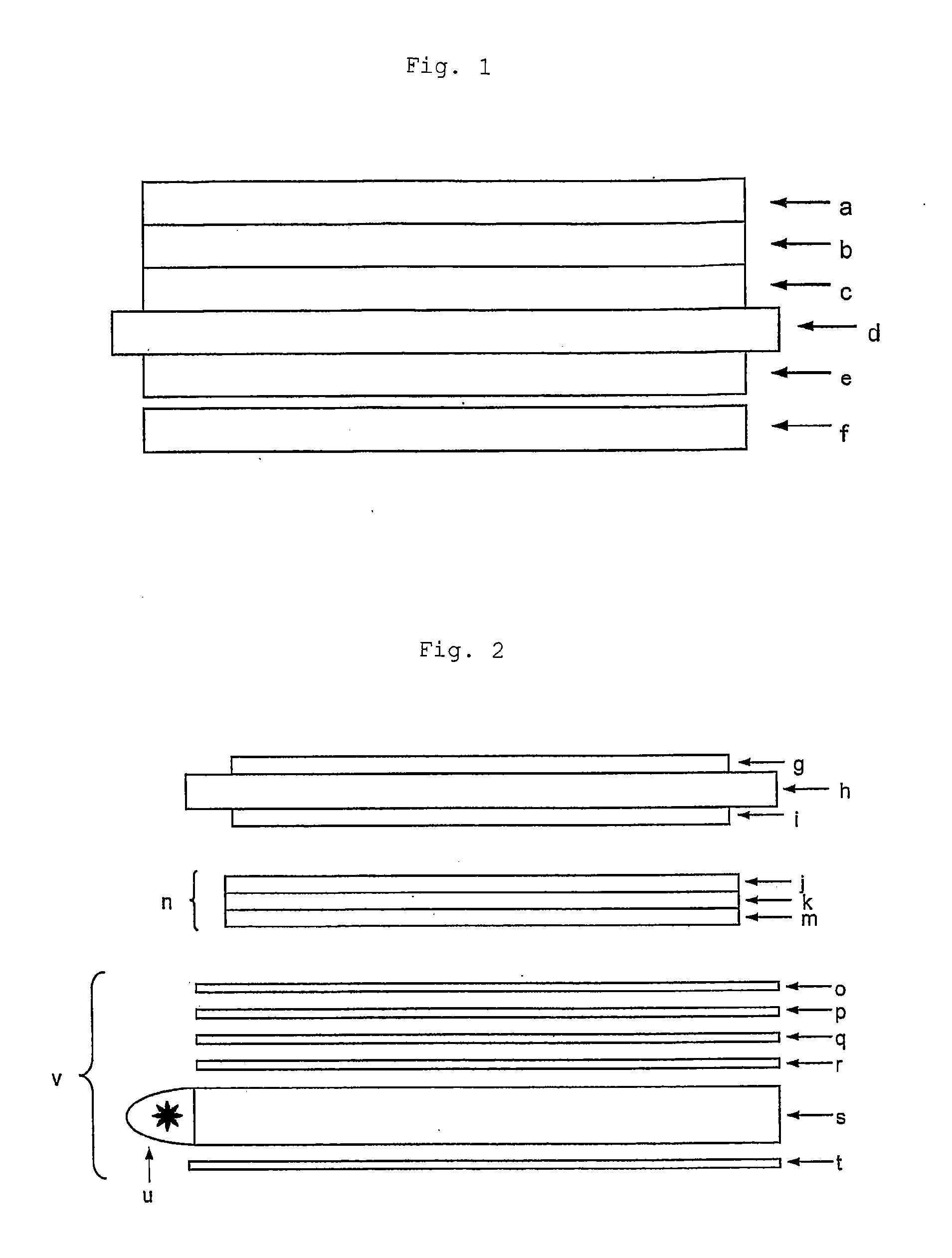
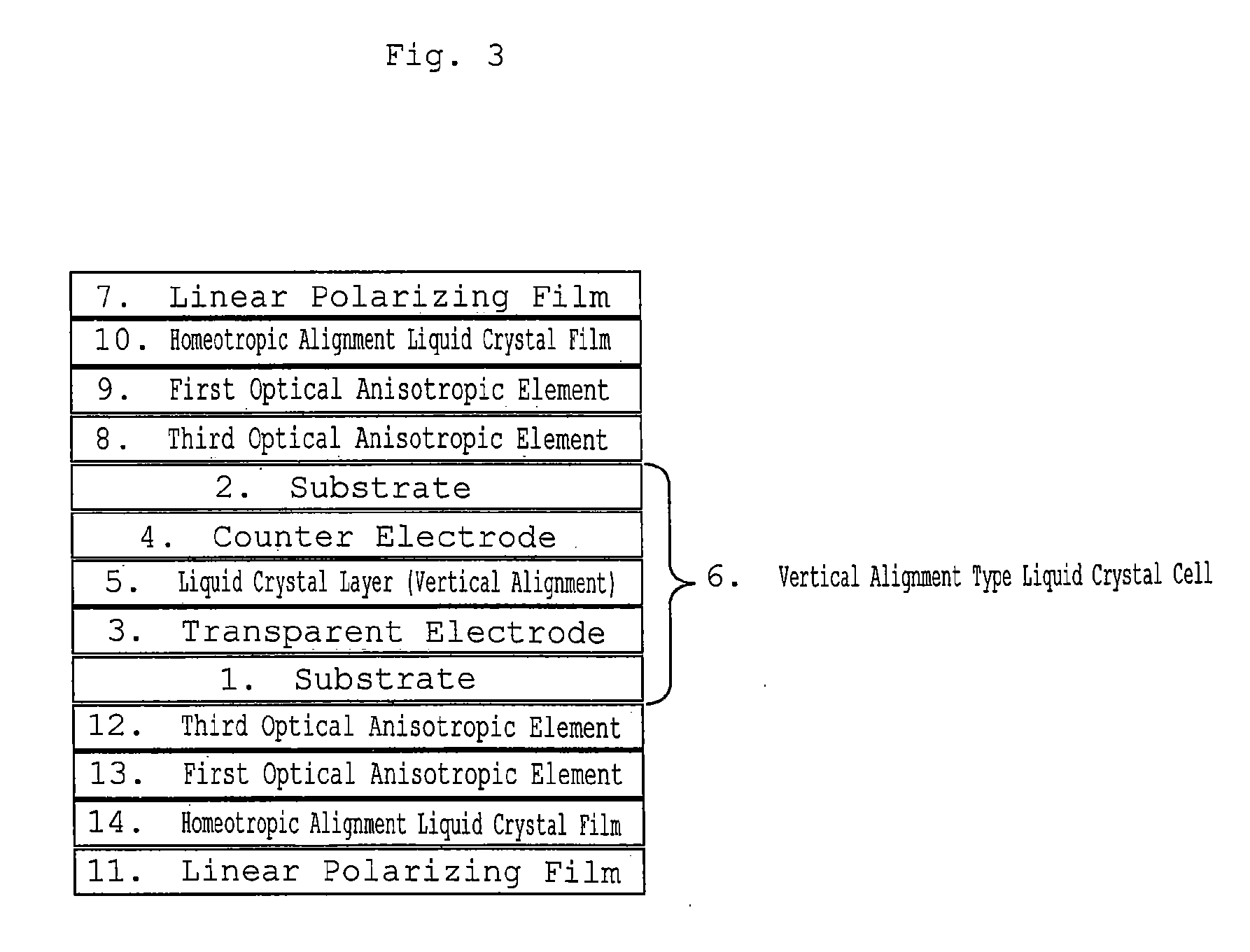
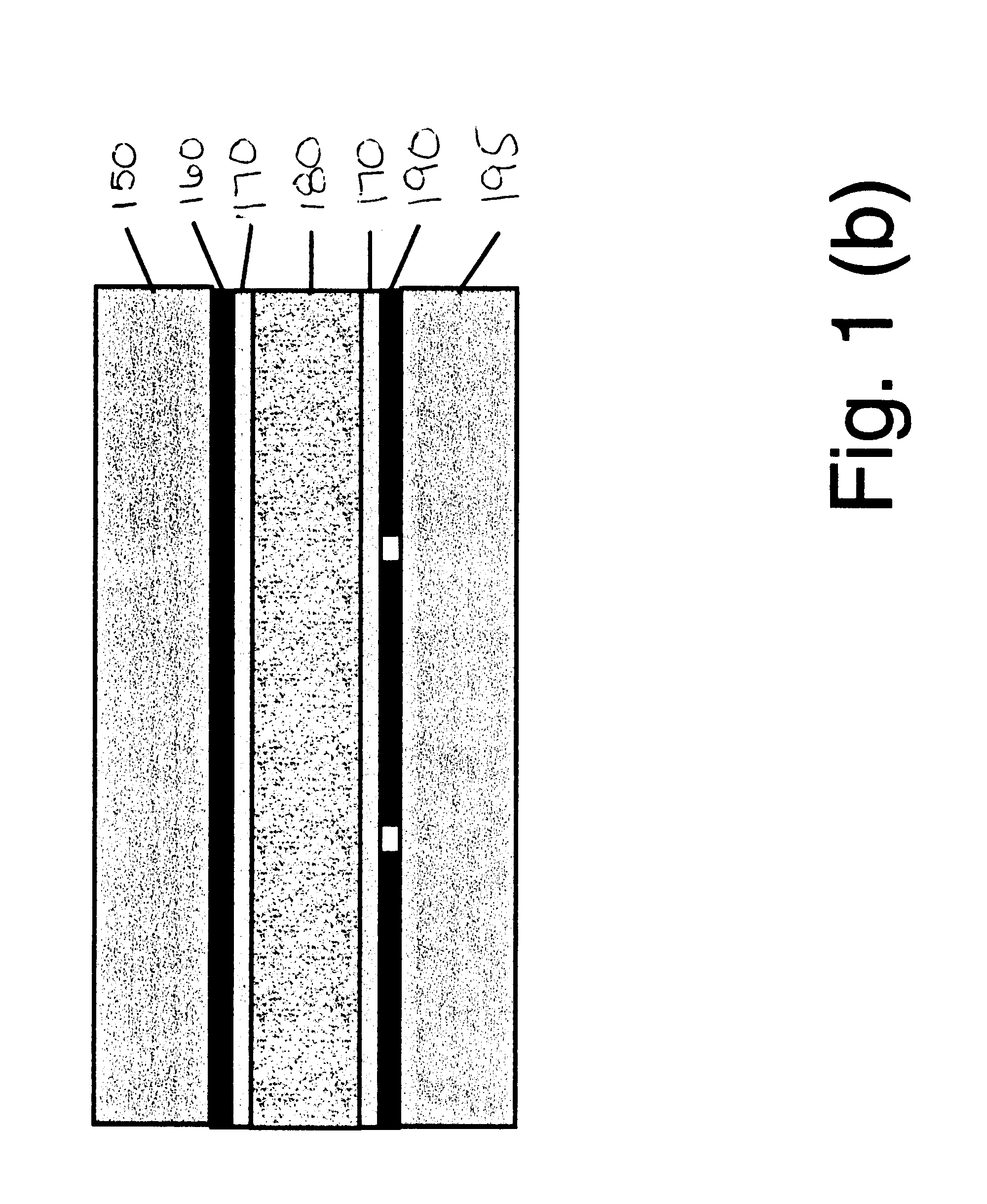
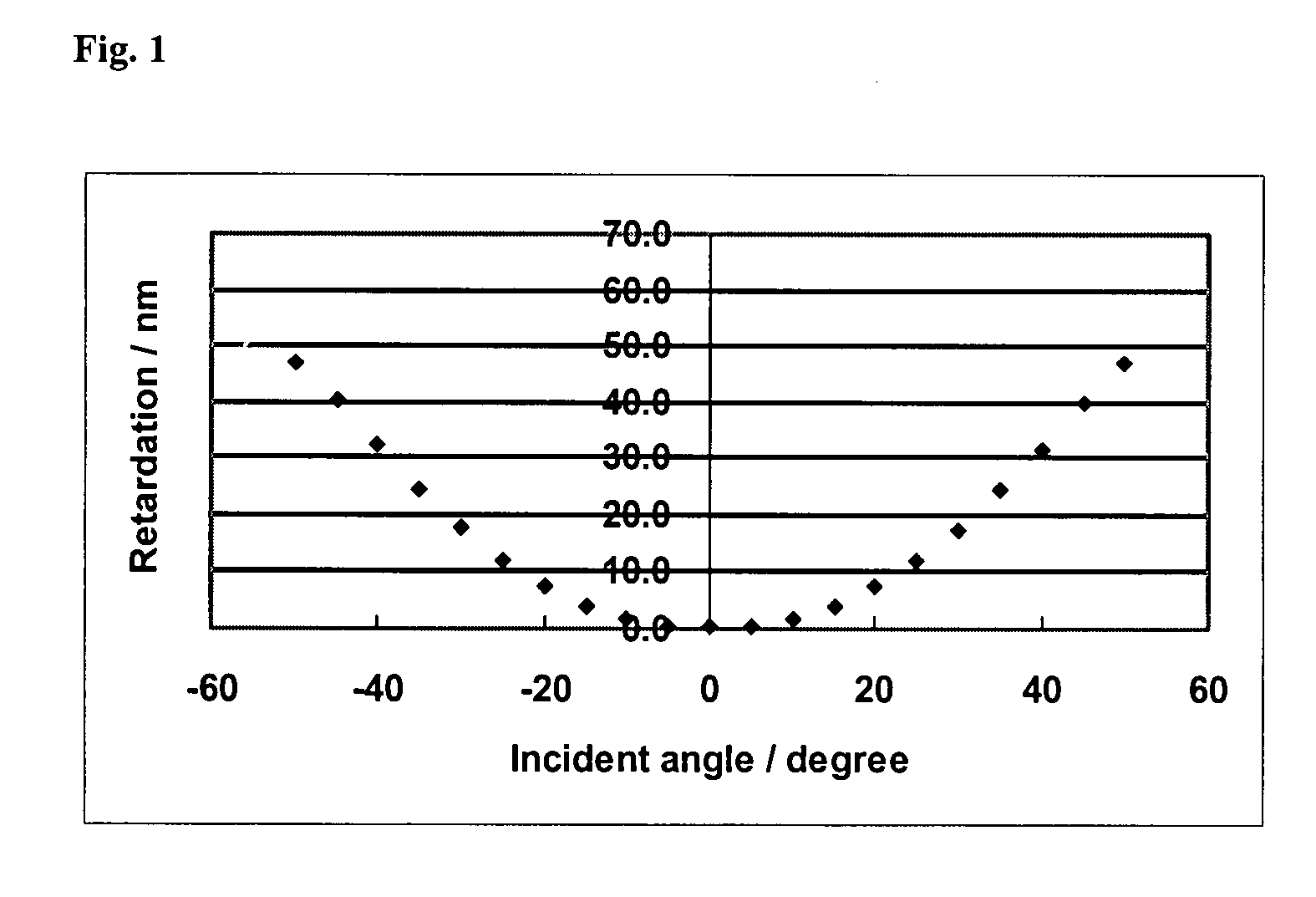
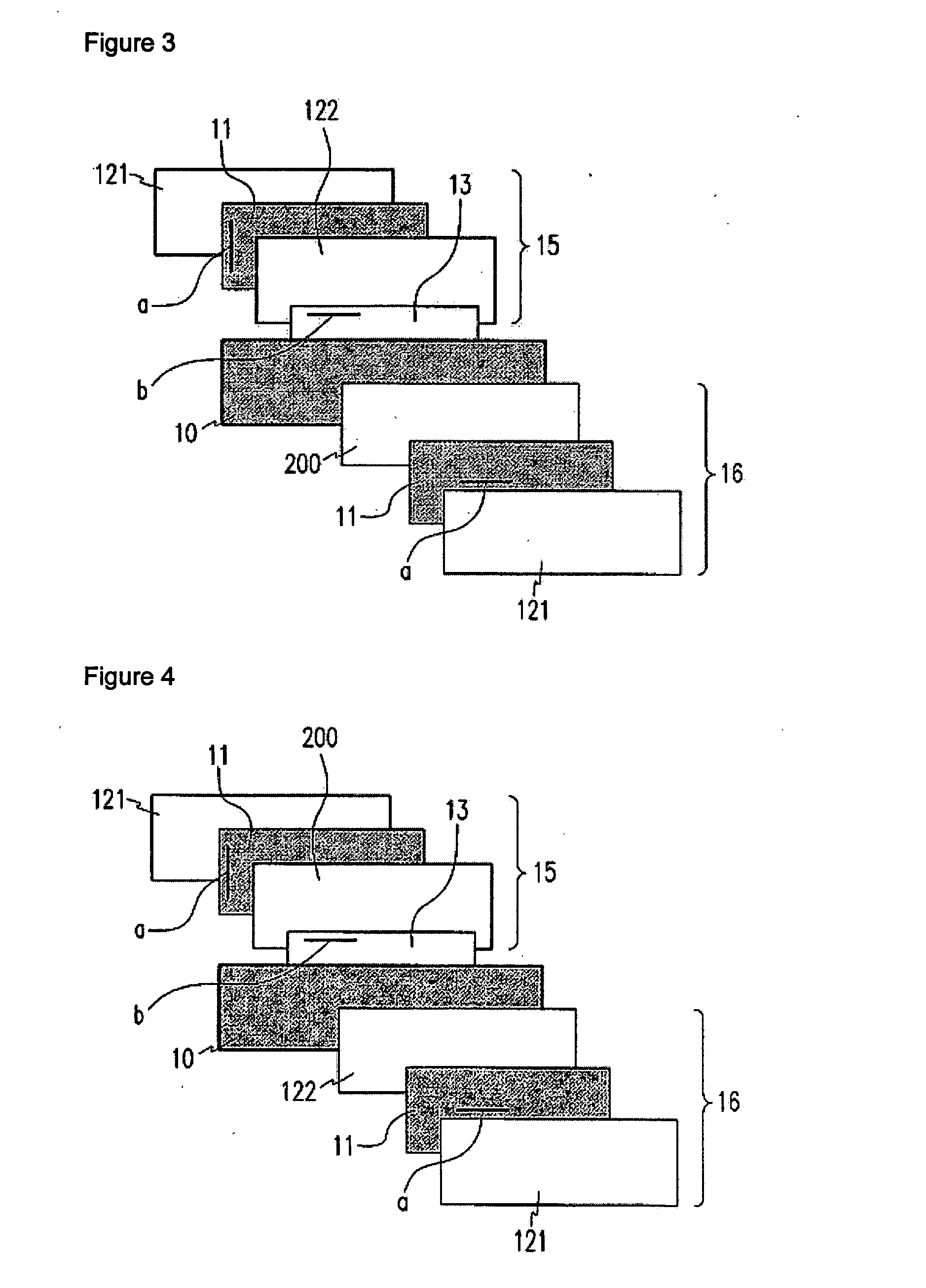
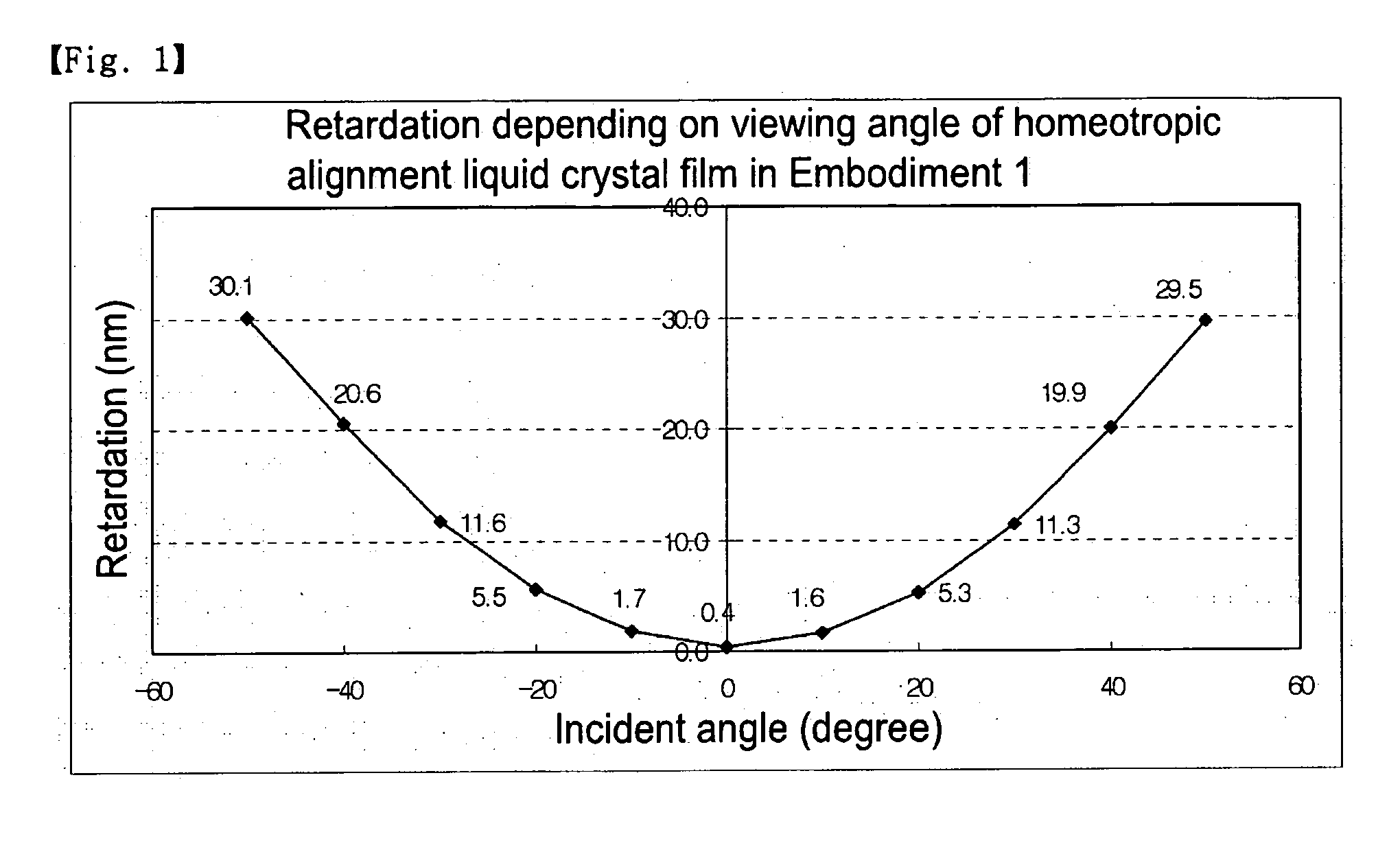
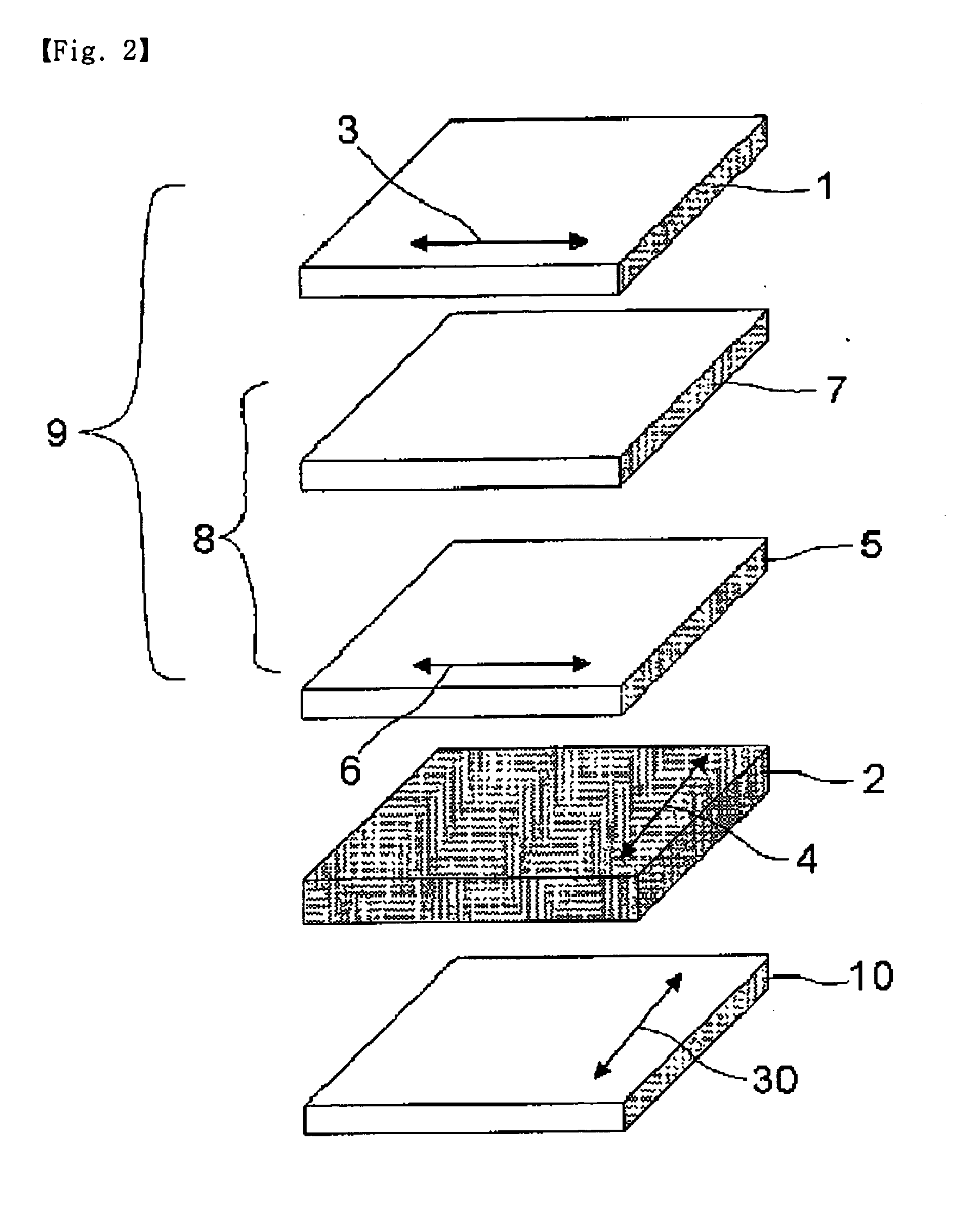
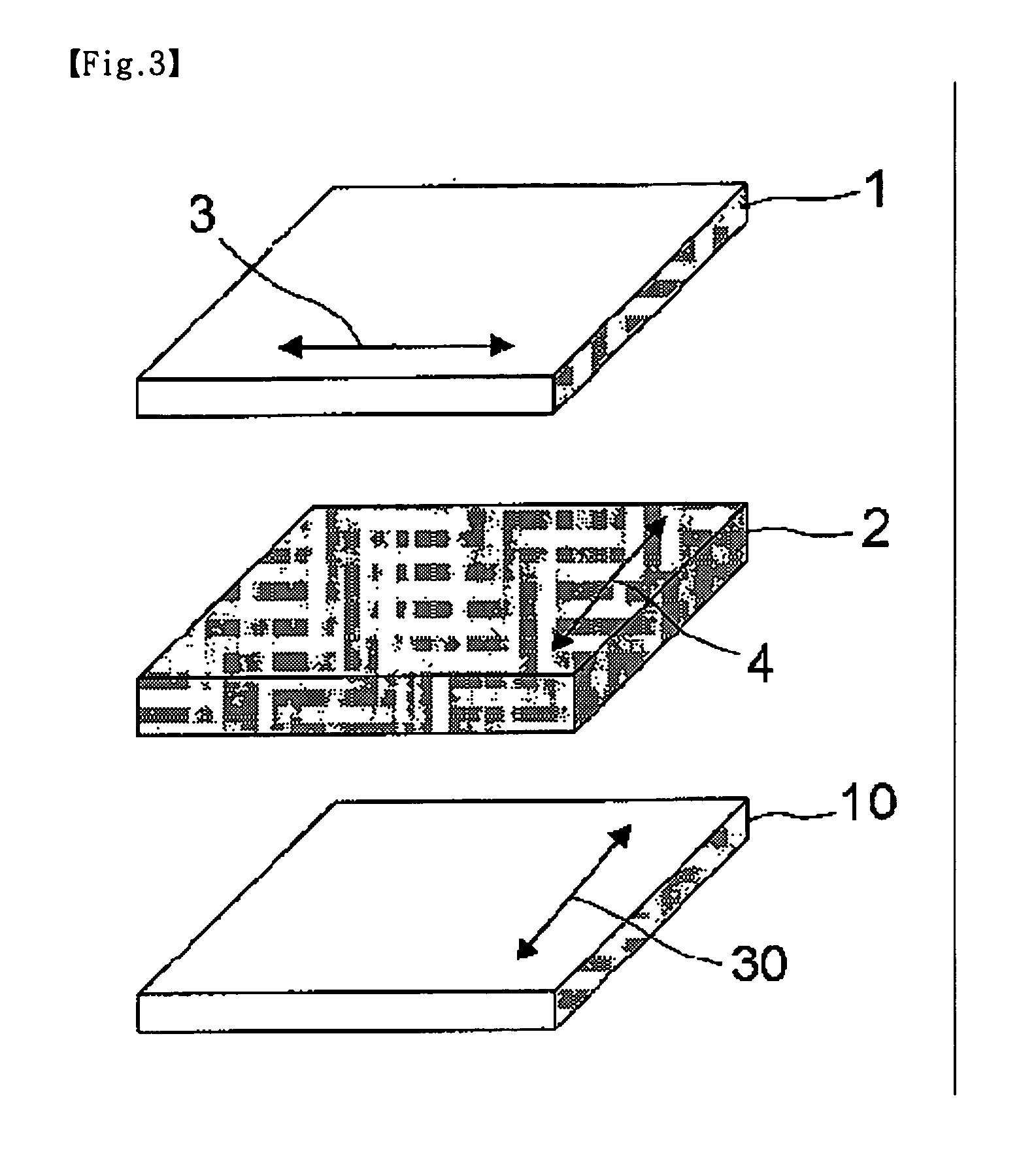
Retardation film having a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film and method for preparing the same
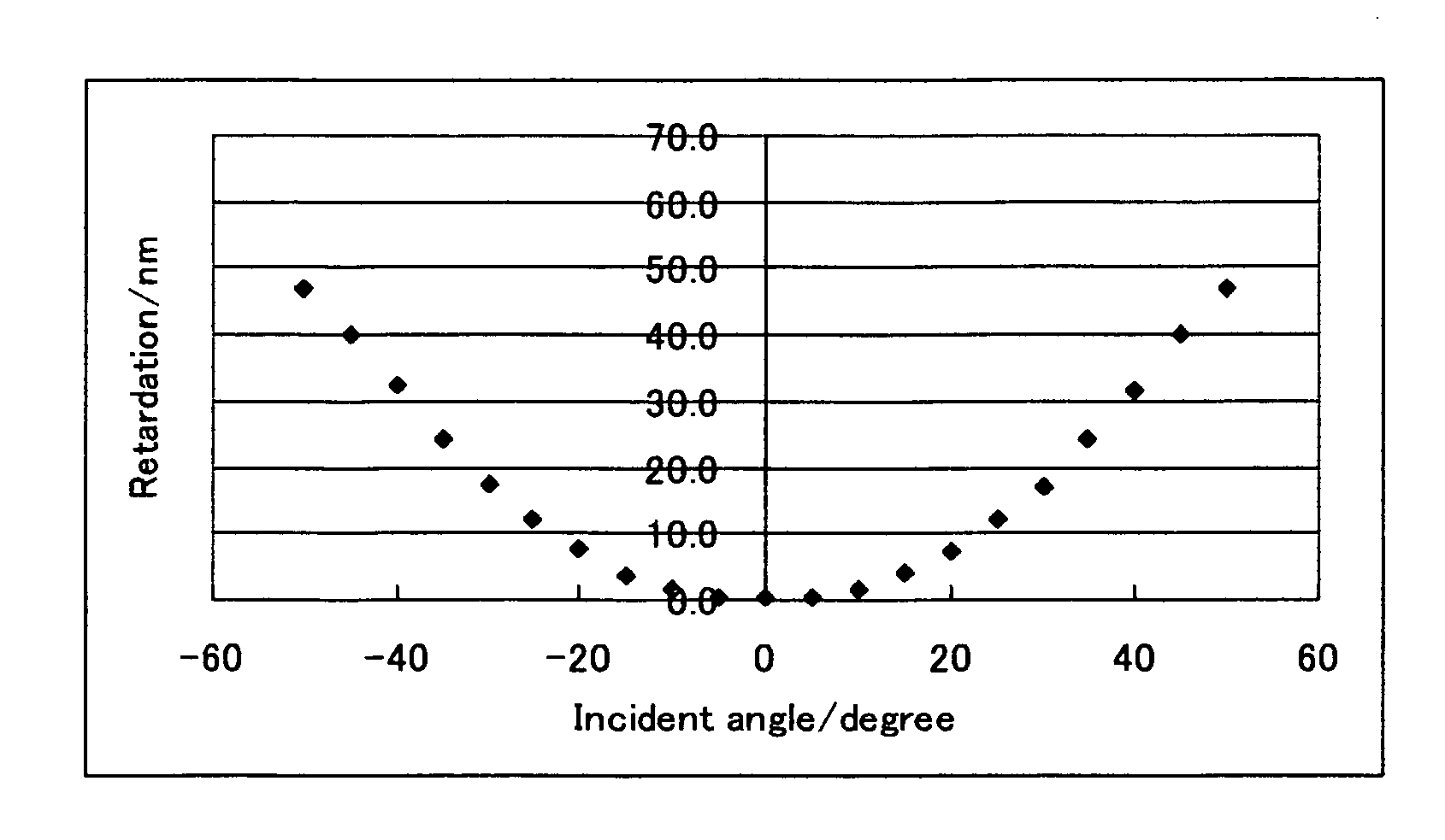
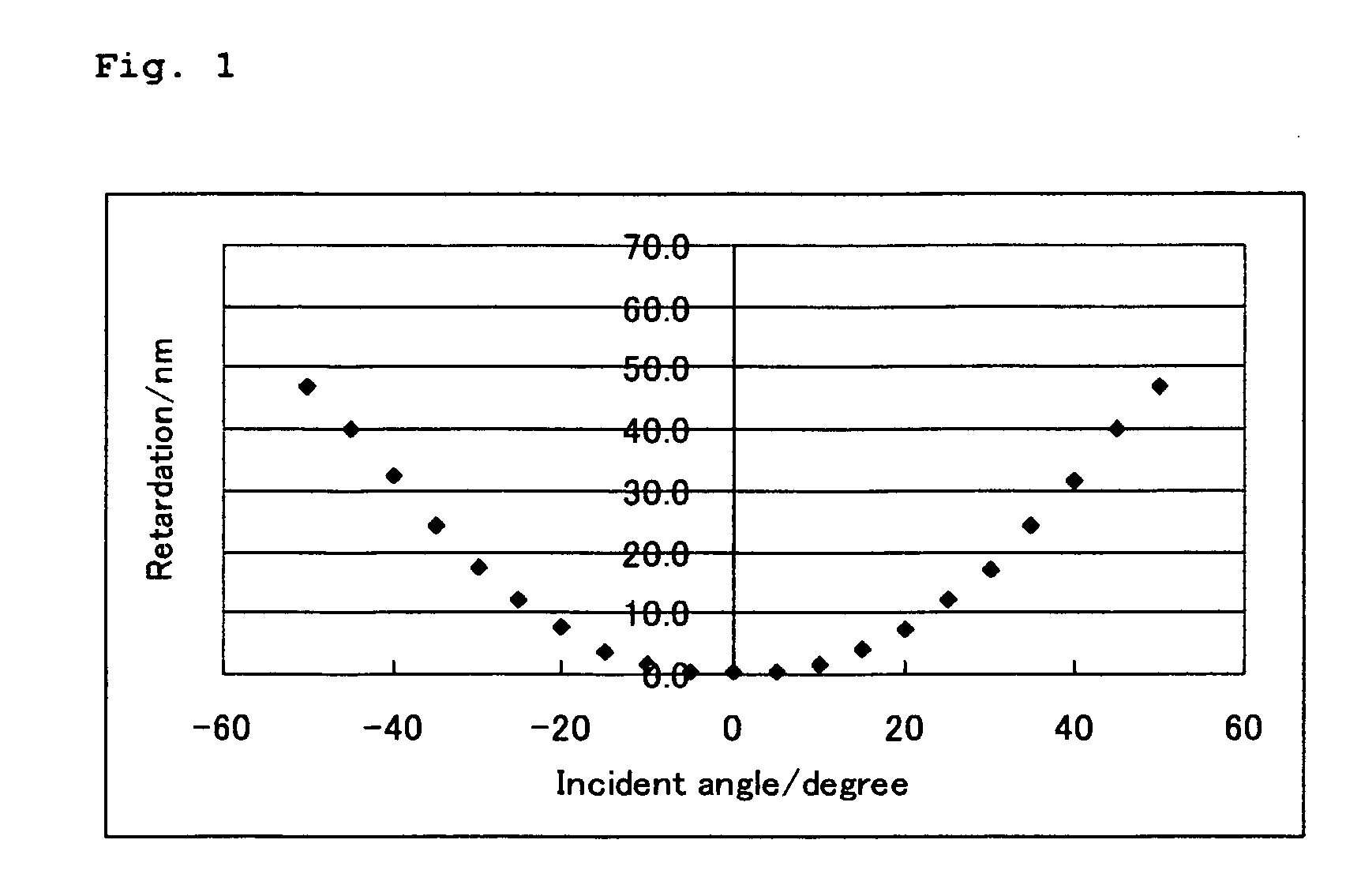
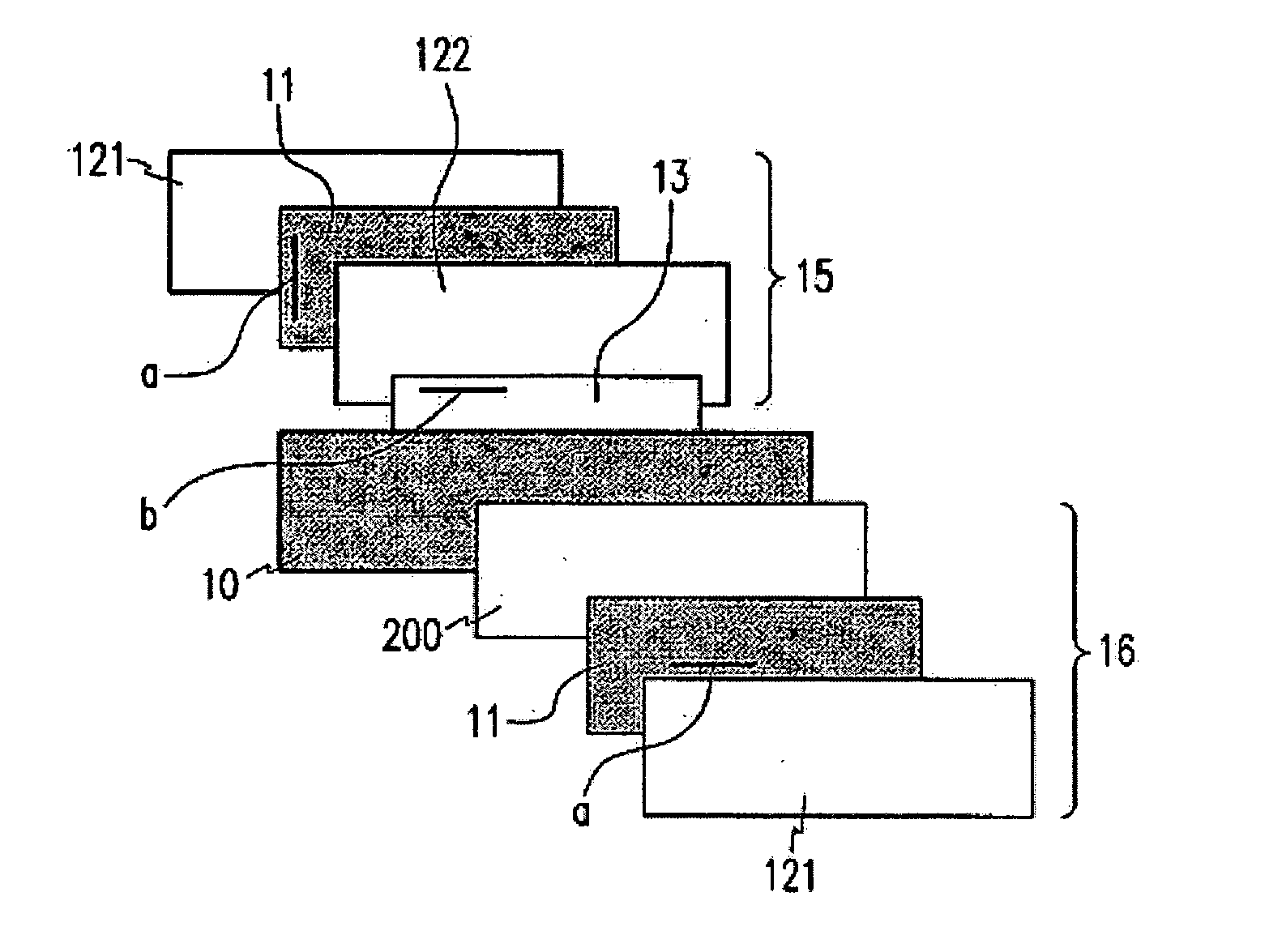
ActiveUS20060182900A1Reduce colorControl thicknessLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingChemistryHomeotropic alignment
The present invention relates to a retardation film having a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film, a polarizing film, an IPS (In-Plane Switching) mode liquid crystal display and a method for preparing the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film prepared from a liquid crystal mixed solution containing a polymerizable reactive liquid crystal monomer so as to improve a viewing angle characteristic of an ISP mode liquid crystal display and reduce a color shift; a retardation film prepared by integrating an oriented retardation film and a method for preparing the same; a polarizing film having the retardation film located between a polarizing element or plate and a liquid crystal cell and a method for preparing the same; and an IPS mode liquid crystal display having the polarizing film. There is an advantage in that since a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film with a retardation of a thickness direction is prepared using a liquid crystal mixed solution containing a reactive liquid crystal monomer, a retardation film according to the present invention is not required for high-temperature heat treatment and cooling processes so that it can be applied to a high-speed continuous process. Further, there is an advantage in that a retardation film having an oriented retardation film integrated with the homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film is arranged between a polarizing element or polarizing plate of an IPS mod liquid crystal display and a liquid crystal cell so that a contrast ratio can be increased up to about 1520%, and a color shift characteristic can be also improved.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
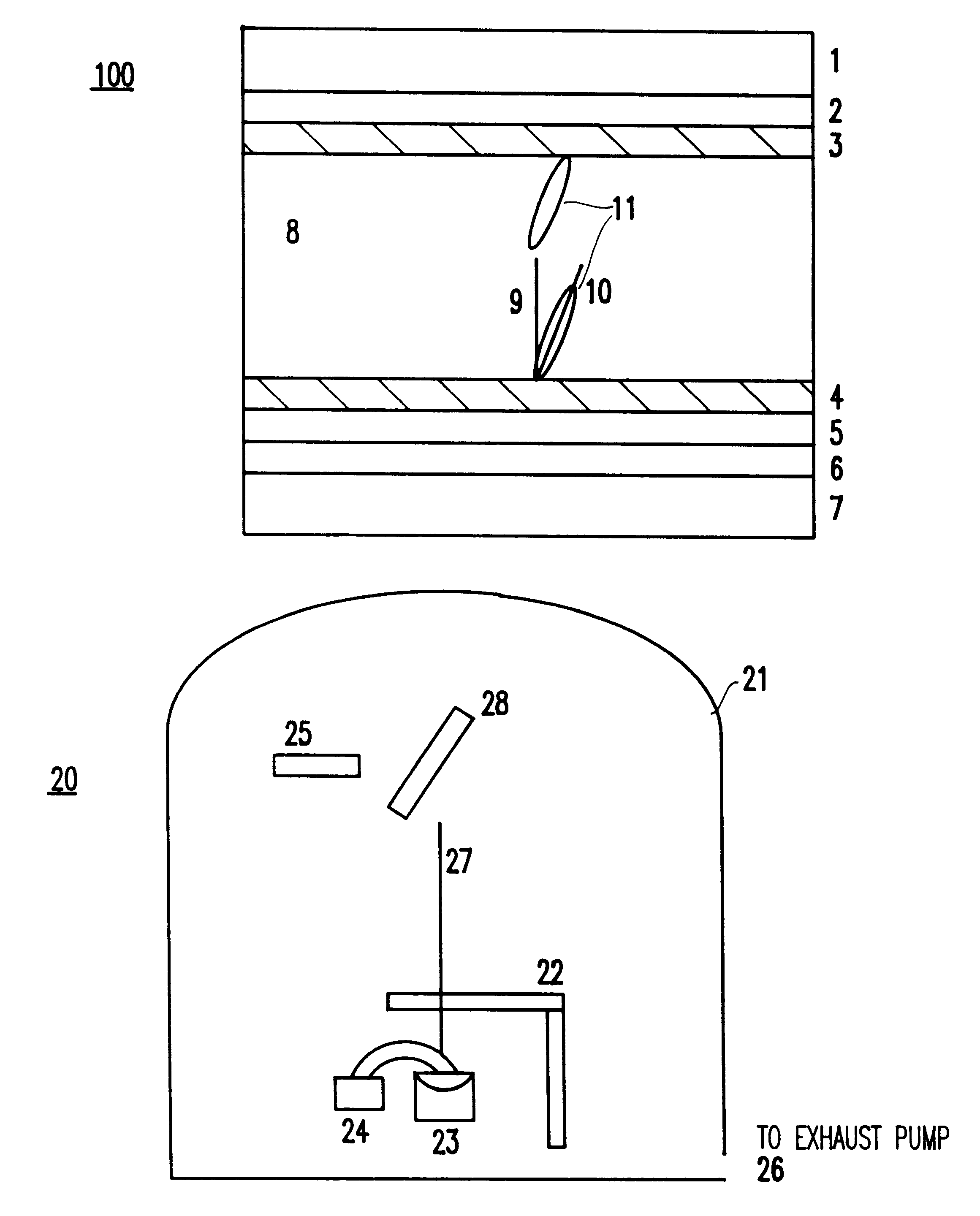
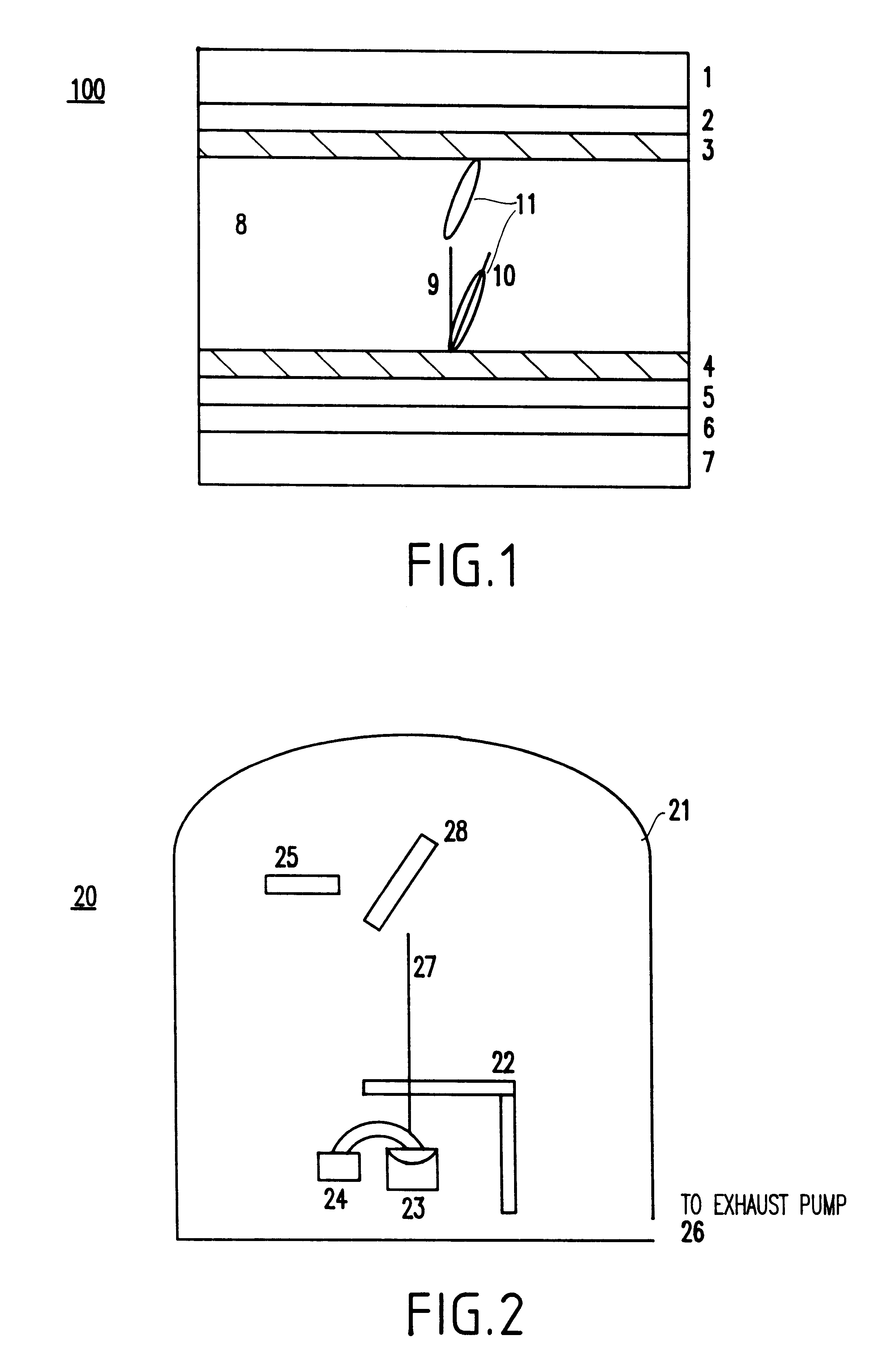
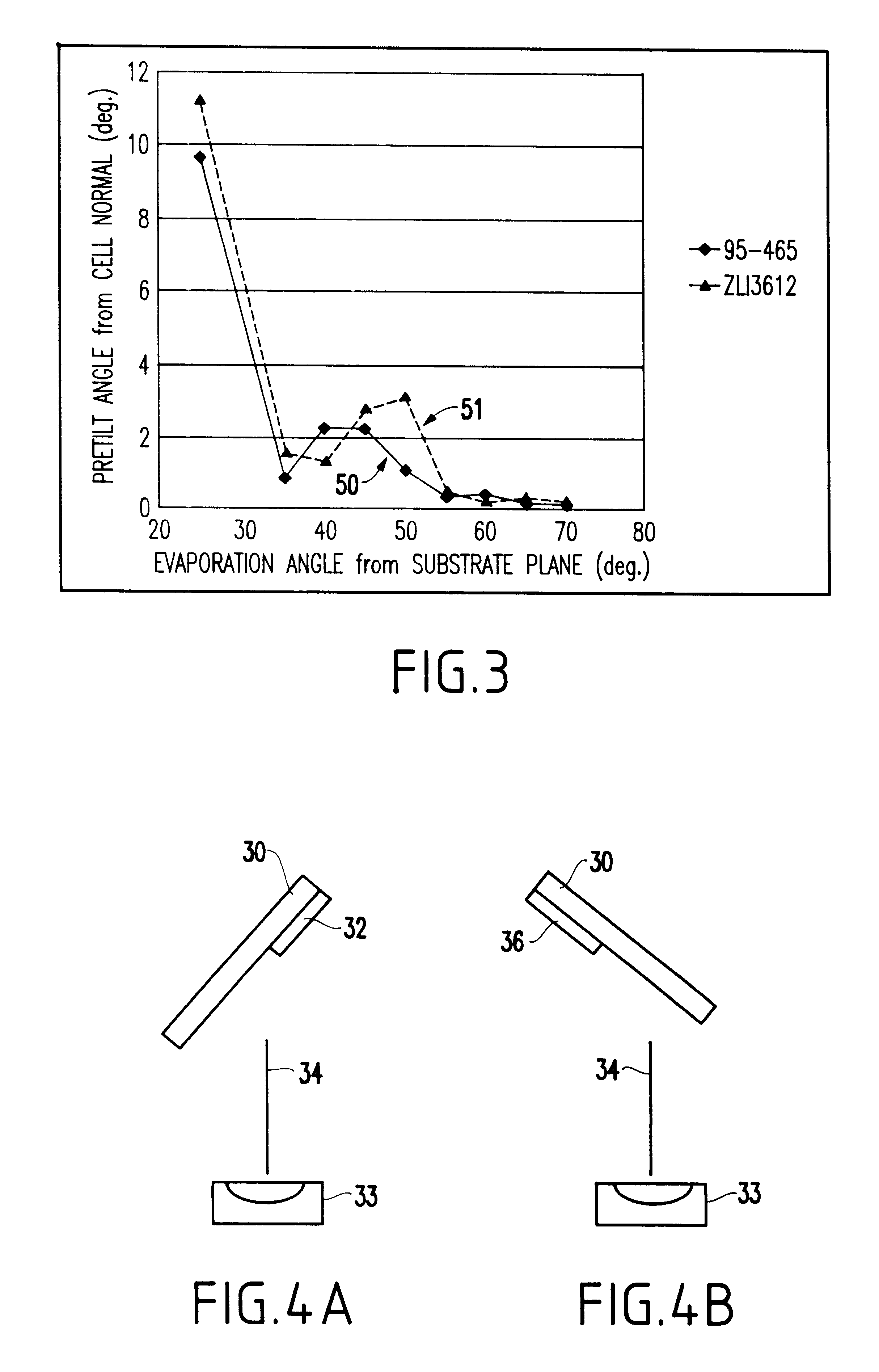
Method of homeotropic alignment or tilted homeotropic alignment of liquid crystals by single oblique evaporation of oxides and liquid crystal display device formed thereby
InactiveUS6426786B1Simple and inexpensiveEasy to useStatic indicating devicesVacuum evaporation coatingLiquid-crystal displayDevice form
A single-domain, two-domain or four-domain homeotropic- or tilted homeotropic-alignment liquid crystal display device of either the transmissive-type or reflective-type having a high contrast ratio, a good display quality, and a high photo-stability (and a method of producing the same), includes a homeotropic- or tilted homeotropic-alignment layer which includes an oxide layer prepared by a single oblique evaporation of an activated oxide source. The angle between the evaporation direction and the substrate plane forms an angle from about ±20° to about ±90°, and the thickness of the oxide layer is from about 10 nm to about 200 nm. A method of homeotropic-alignment or tilted homeotropic-alignment of liquid crystals by a single oblique evaporation process is also provided.
Owner:VIDEOCON GLOBAL
Liquid crystal display having predetermined steepness of light transmittance within a predetermined range on light transmittance gradient for improved visibility
A liquid crystal display is provided, which includes: a first panel including a first signal line, a second signal line intersecting the first signal line, a thin film transistor connected to the first and the second signal lines, and a pixel electrode connected to the thin film transistor and including a first subpixel electrode having a first voltage and a second subpixel electrode capacitively coupled to the first subpixel electrode and having a second voltage; a second panel including a common electrode facing the pixel electrode and supplied with a common voltage; and a vertically aligned liquid crystal layer that is interposed between the pixel electrode and the common electrode, wherein a steepness of light transmittance as function of a voltage applied the first subpixel electrode with respect to the common voltage is lower than about 20.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
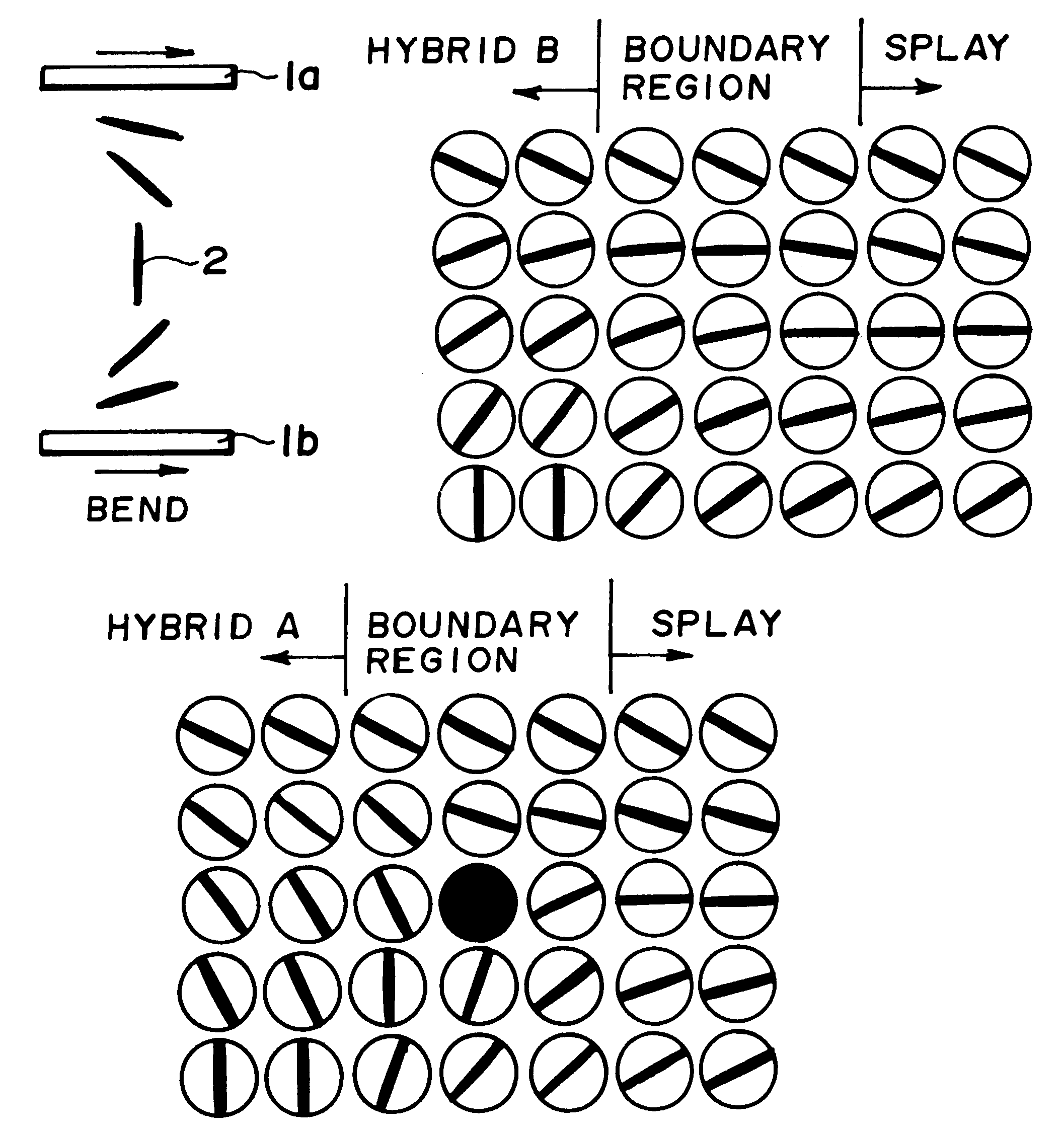
Liquid crystal device and driving method therefor
At least one of a pair of substrates constituting a liquid crystal device is provided with a composite alignment film including a homeotropic alignment film region and a homogeneous alignment film region, whereby the liquid crystal in contact with the homogeneous alignment film region is surrounded by the region of liquid crystal in a hybrid or homeotropic alignment state and is stably held in a twit alignment state under no electric field which can be continuously transformed into a bend alignment state. As a result, it is possible to provide a liquid crystal device capable of display by utilizing bend alignment with reduced bending voltage and voltage for holding the bend alignment.
Owner:CANON KK
Homeotropic alignment type semi-transmissive reflective liquid crystal display device
A liquid crystal display device has a pair of substrates disposed at an observer side and at the opposite side to the observer side, a plurality of pixel electrodes and an opposing electrode which are formed on the internal surfaces of the pair of substrates, a reflective layer, and liquid crystal sealed between these substrates. Each pixel electrode has a reflective display region corresponding to the reflective layer for reflecting light that enters from the observer side to the observer side, and a transmissive display region for allowing light that enters from the opposite side to pass therethrough to the observer side. A liquid crystal layer thickness adjusting layer is formed on the internal surface of the substrate at the observer side, for setting the liquid crystal layer thickness in the reflective display region to be smaller than the liquid crystal layer thickness in the transmissive display region.
Owner:ORTUS TECH
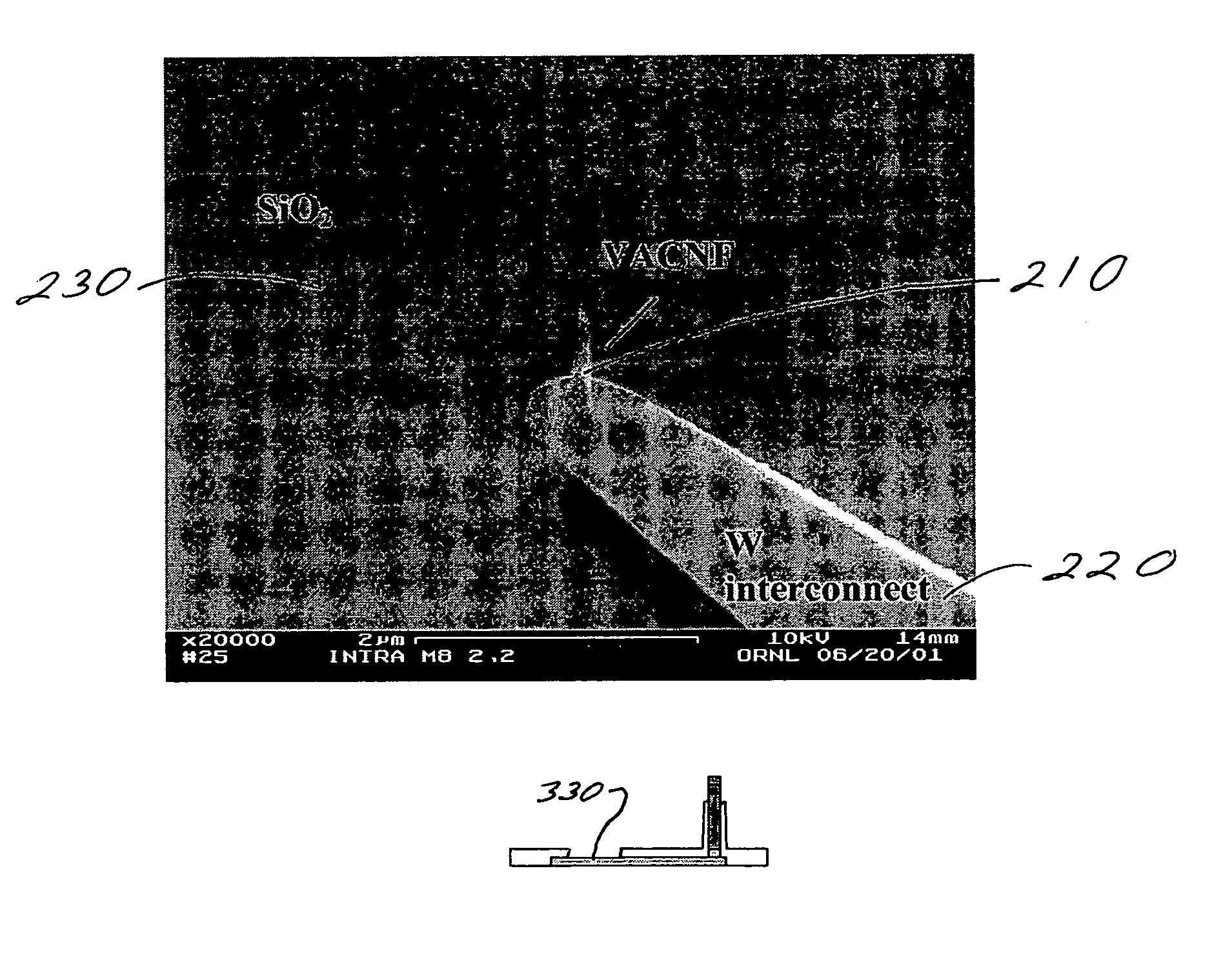
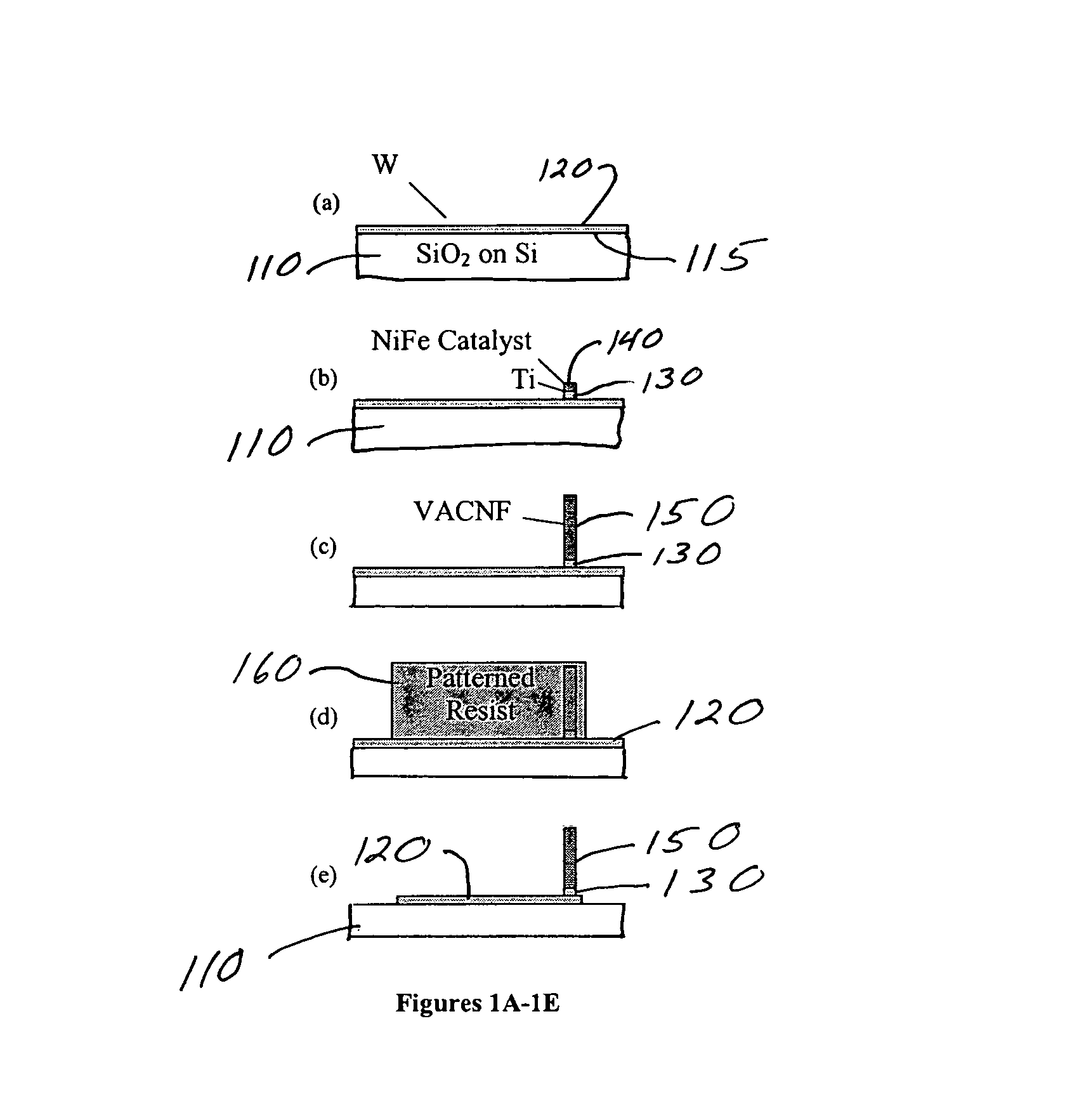
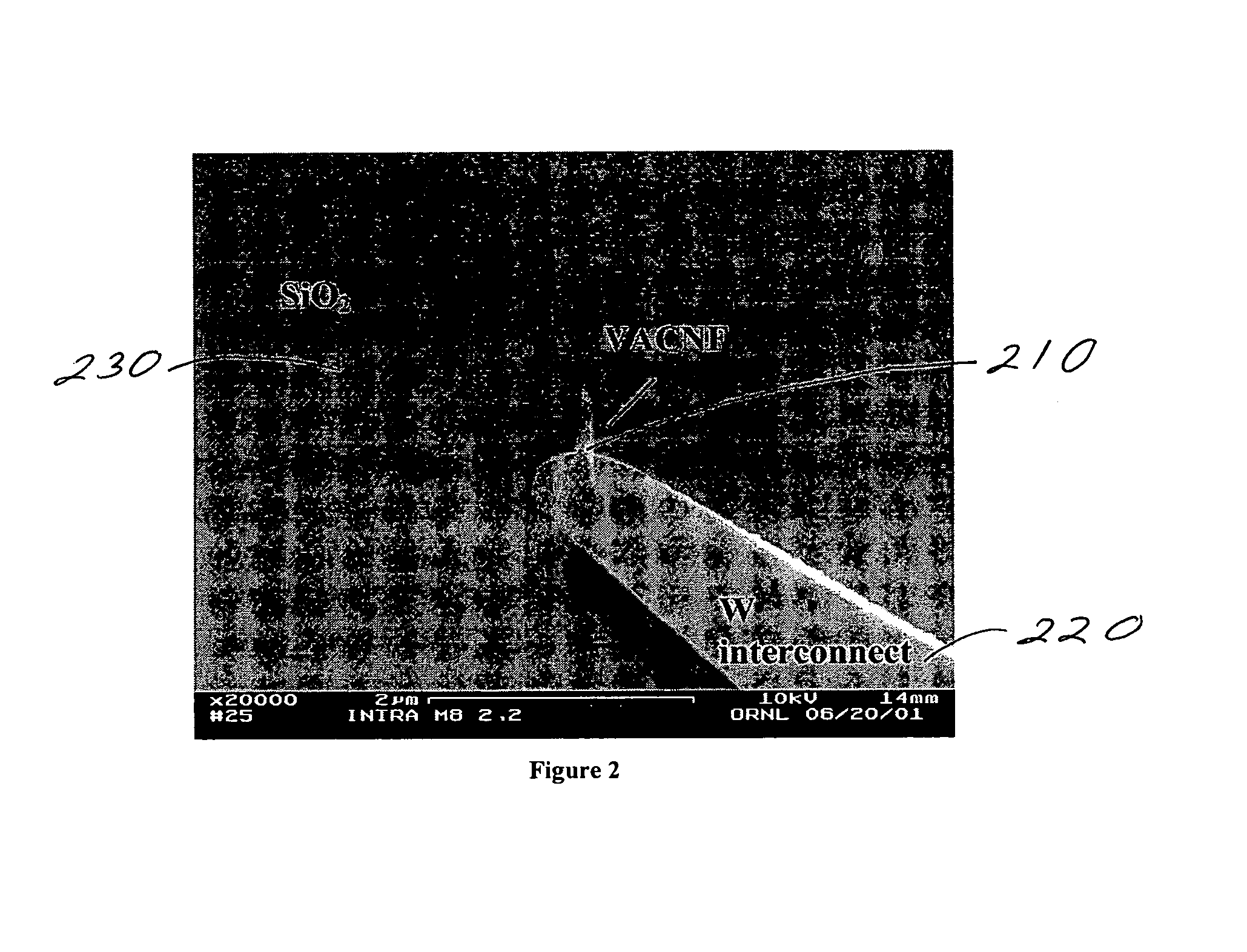
Individually electrically addressable vertically aligned carbon nanofibers on insulating substrates
Systems and methods are described for individually electrically addressable carbon nanofibers on insulating substrates. An apparatus includes an electrically conductive interconnect formed on at least a part of an insulating surface on a substrate; and at least one vertically aligned carbon nanofiber coupled to the electrically conductive interconnect. A kit includes a substrate having an insulating surface; an electrically conductive interconnect formed on at least a part of the insulating surface; and at least one vertically aligned carbon nanofiber coupled to the electrically conductive interconnect.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
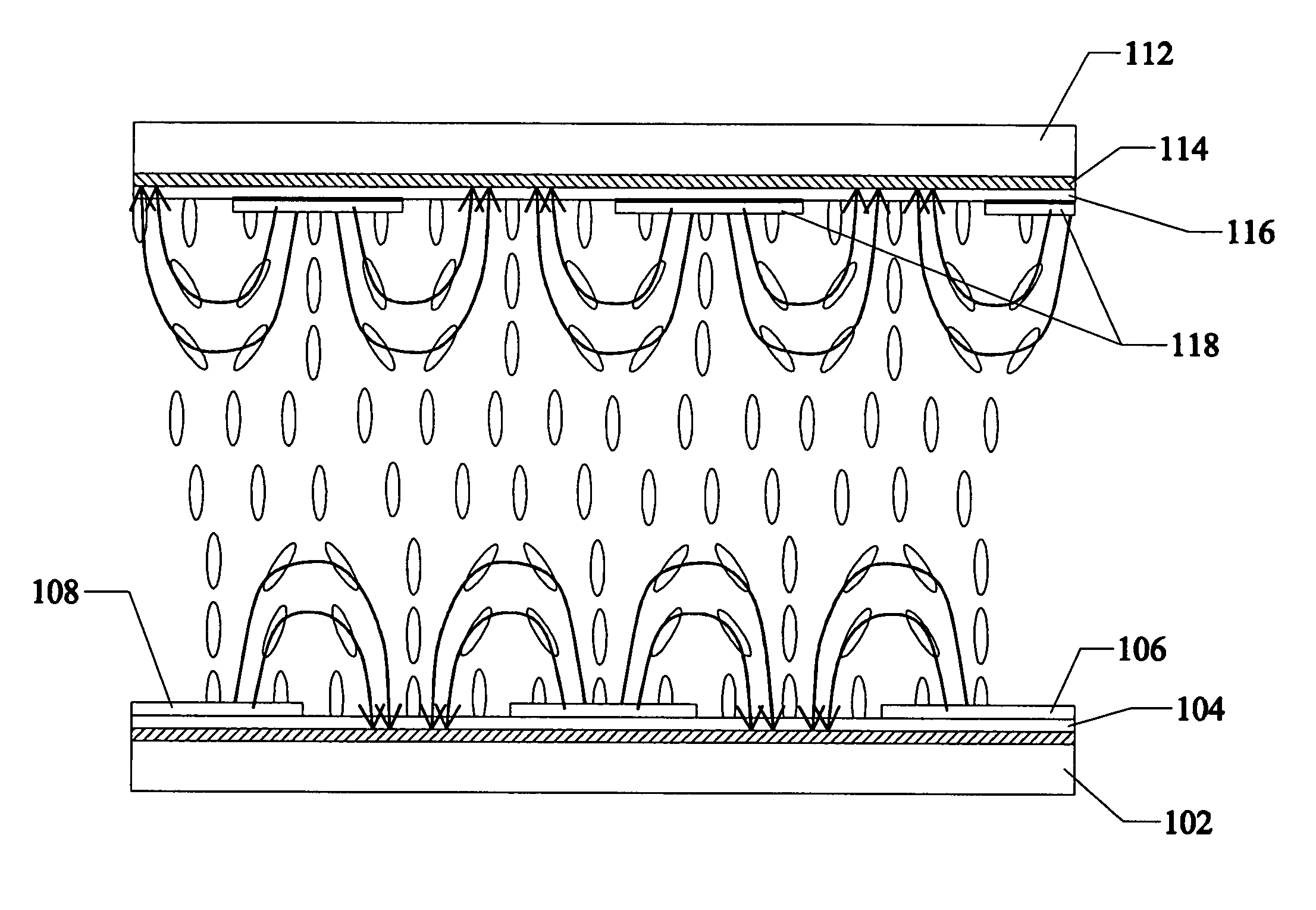
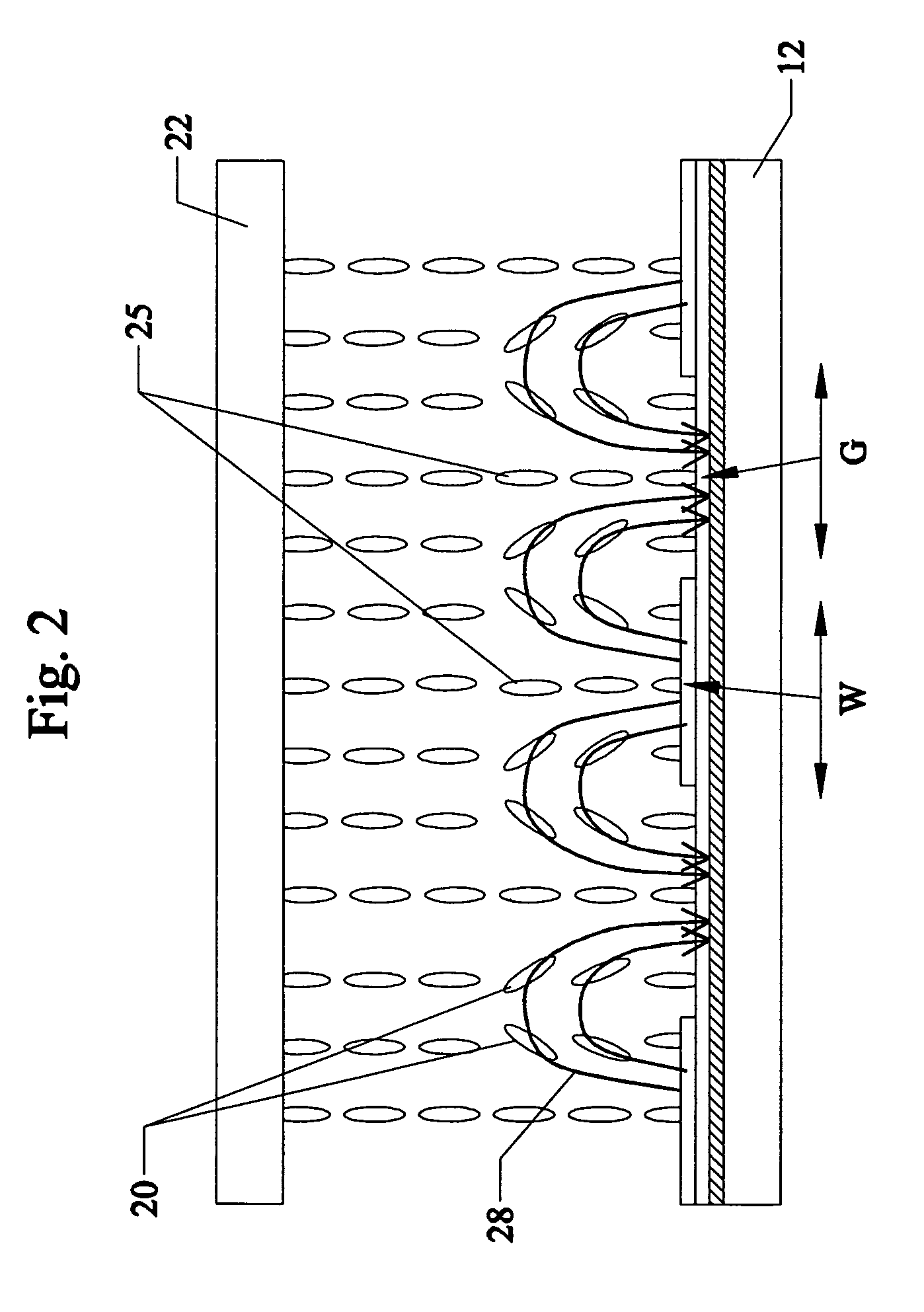
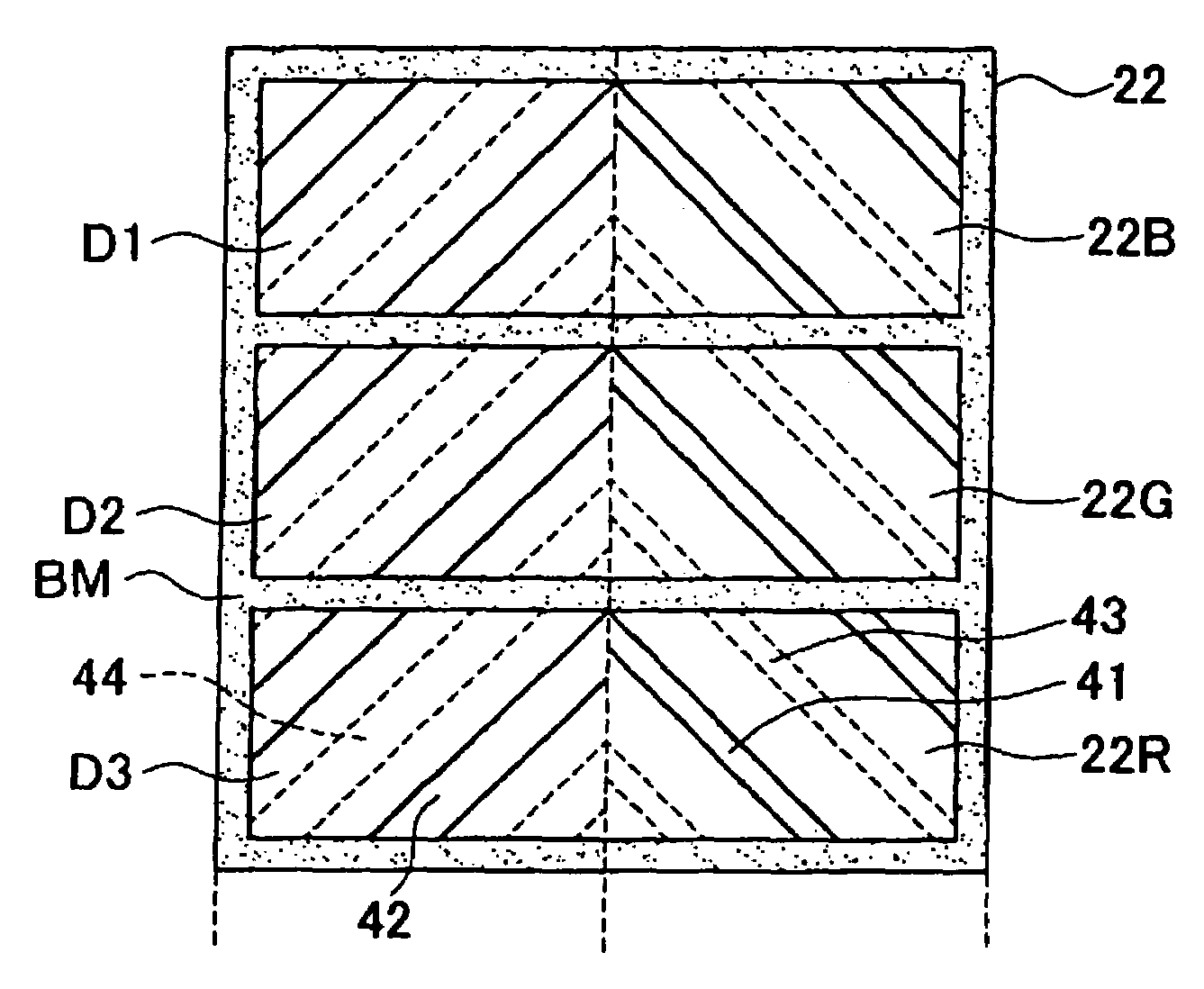
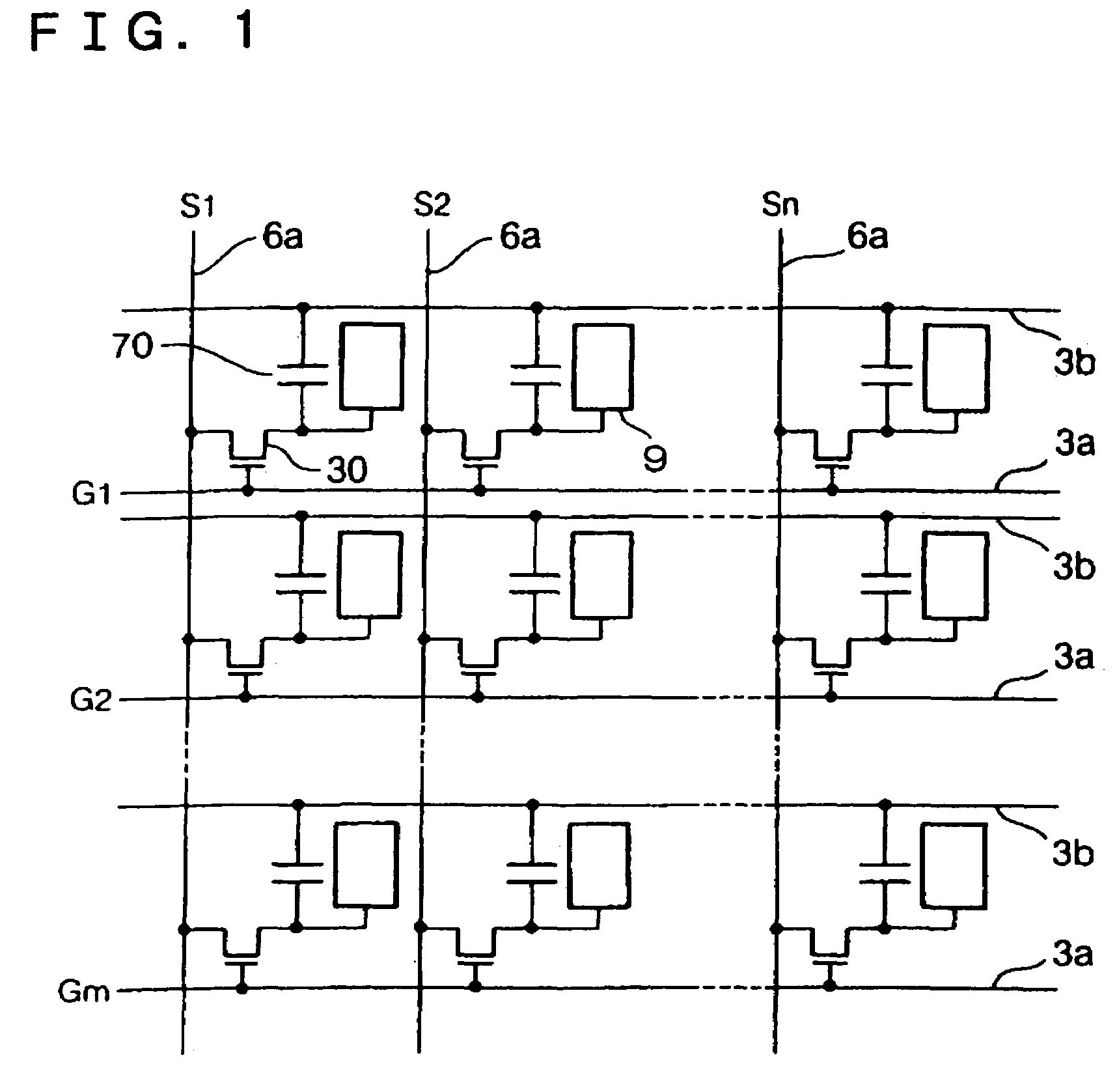
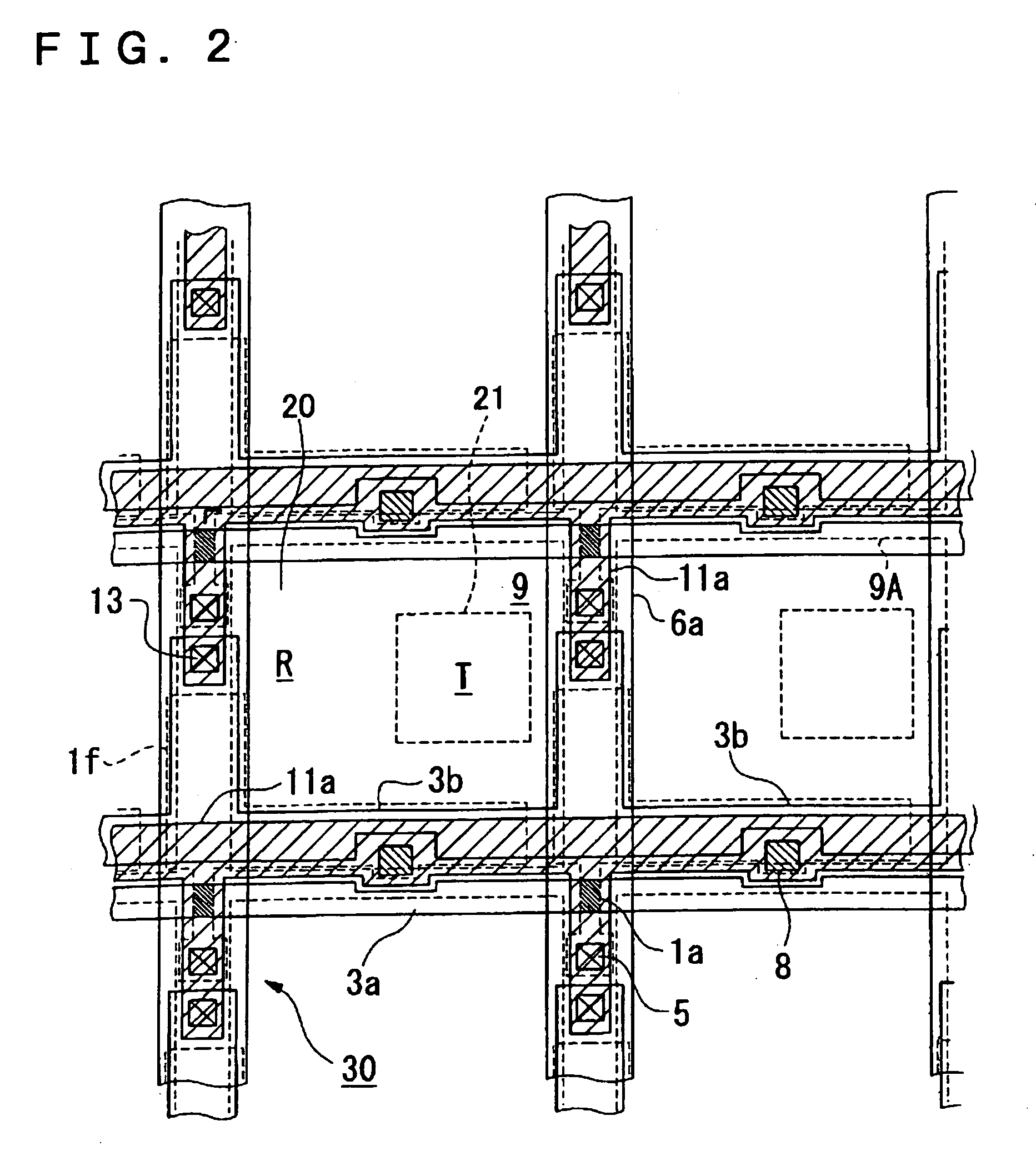
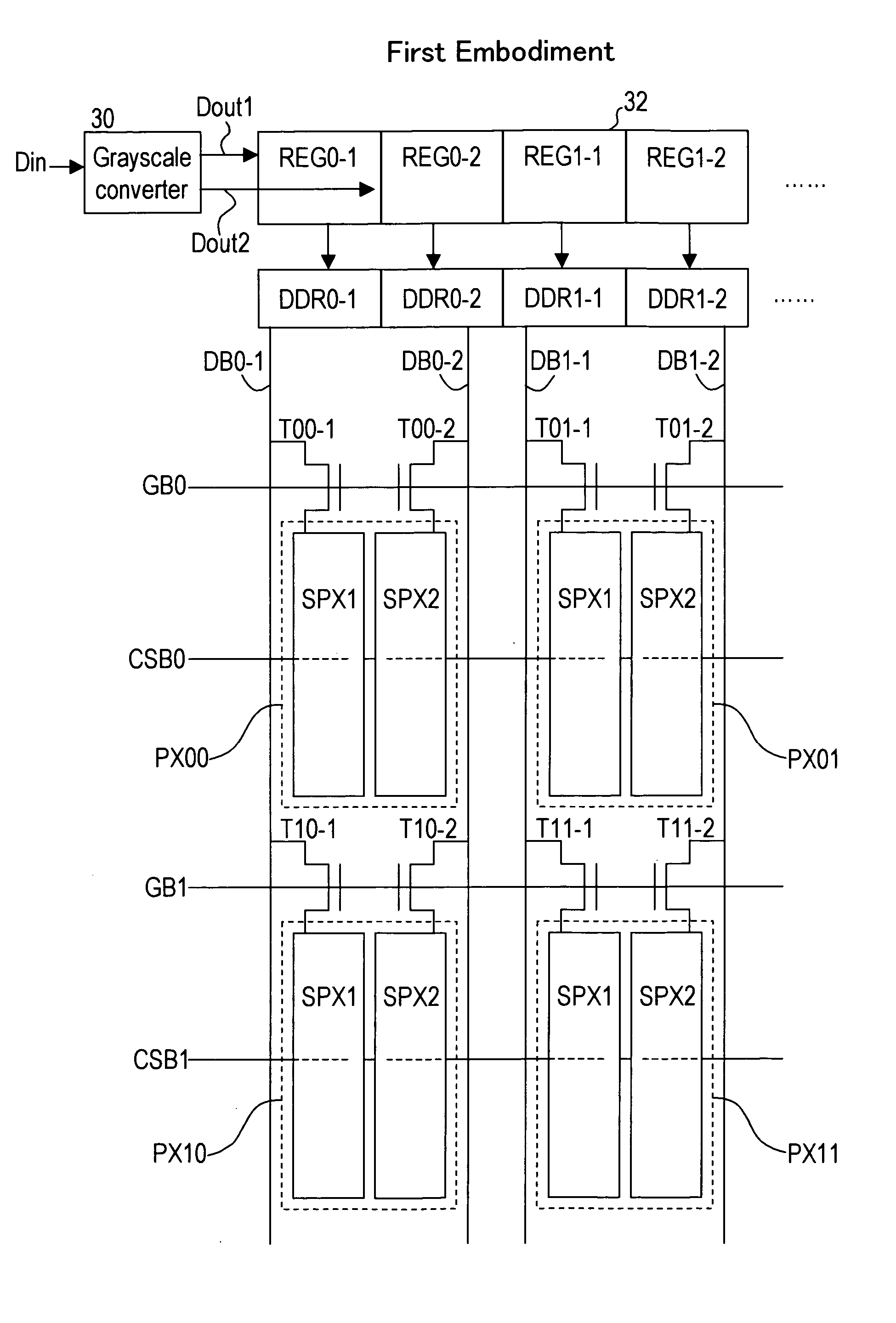
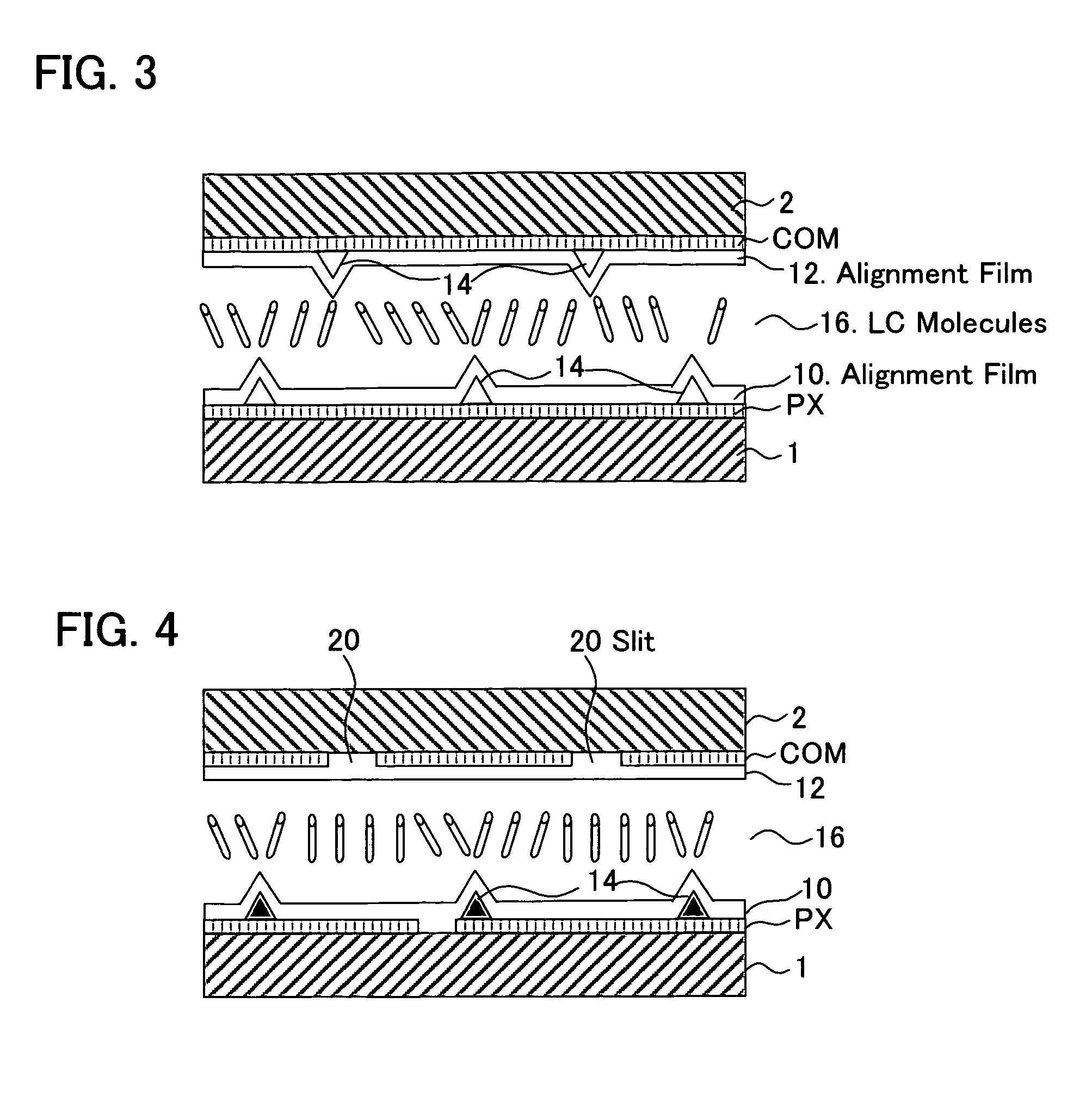
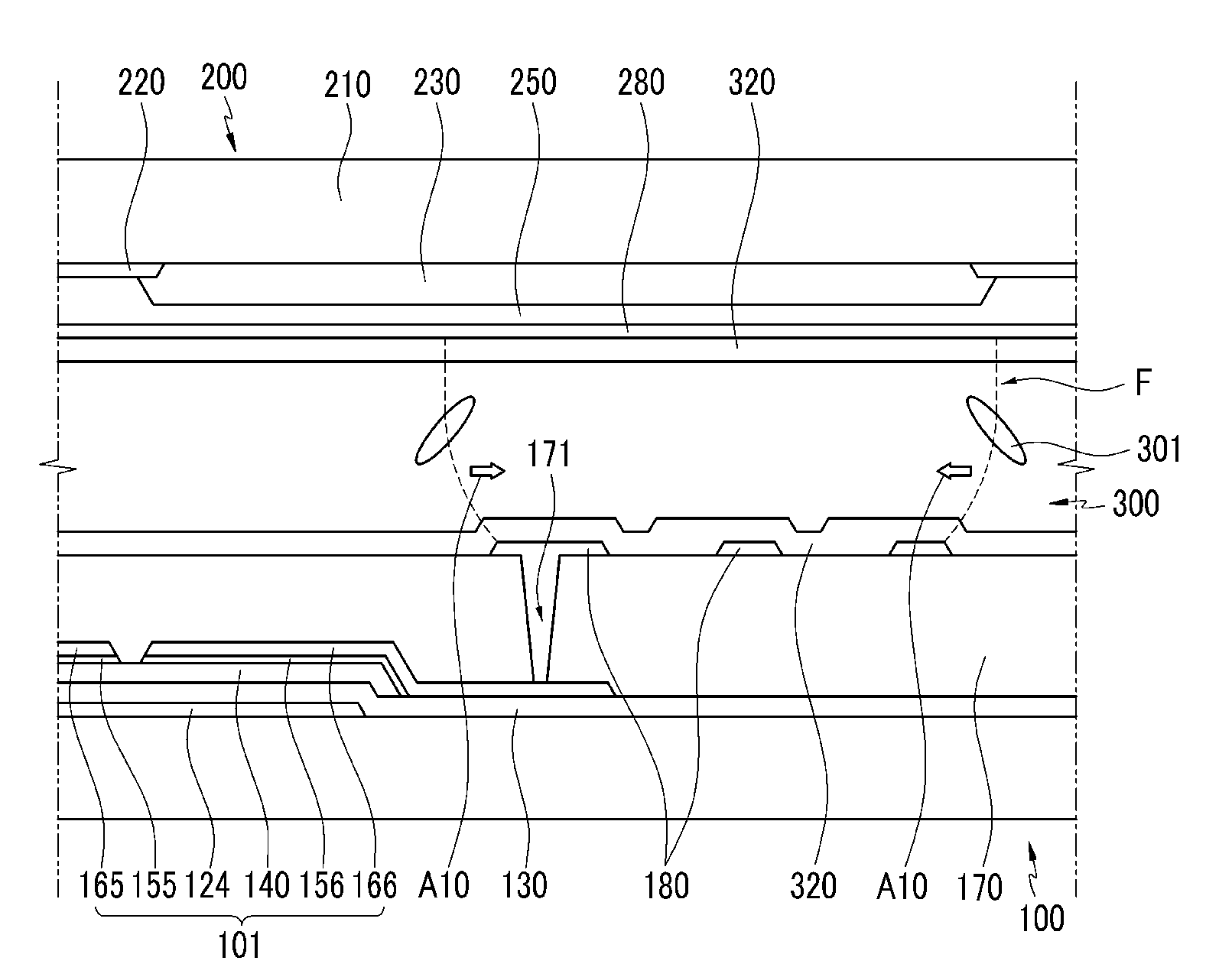
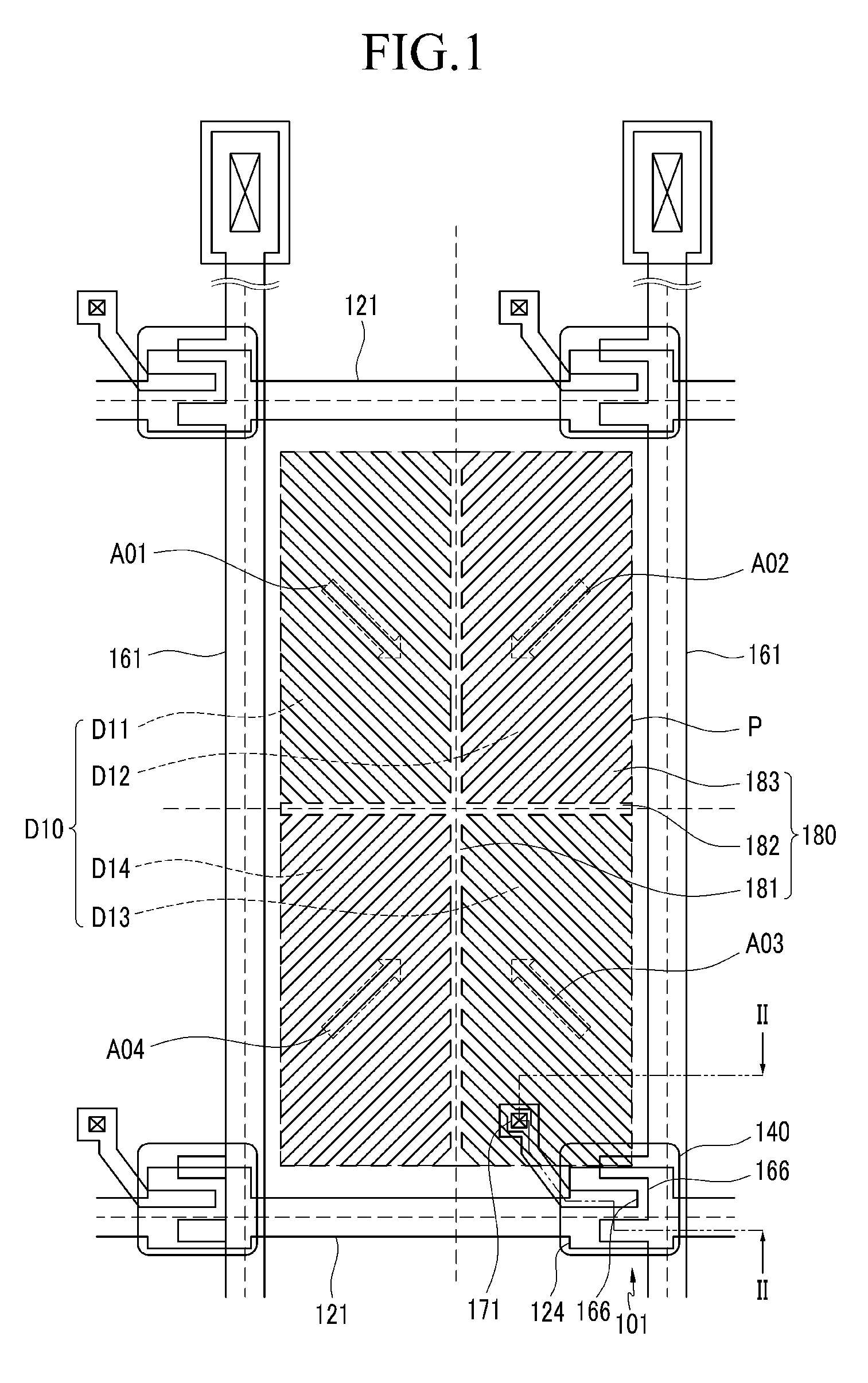
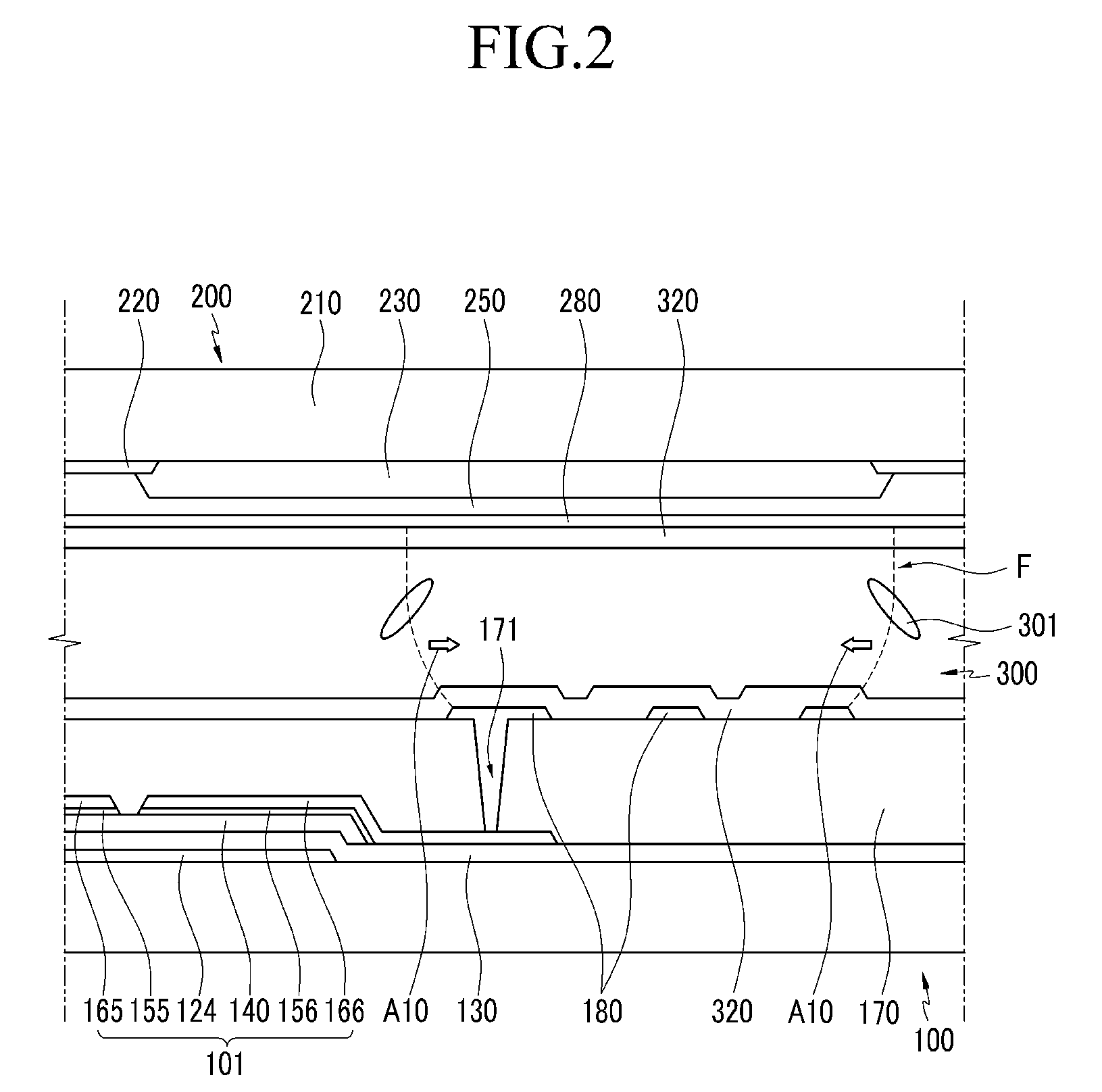
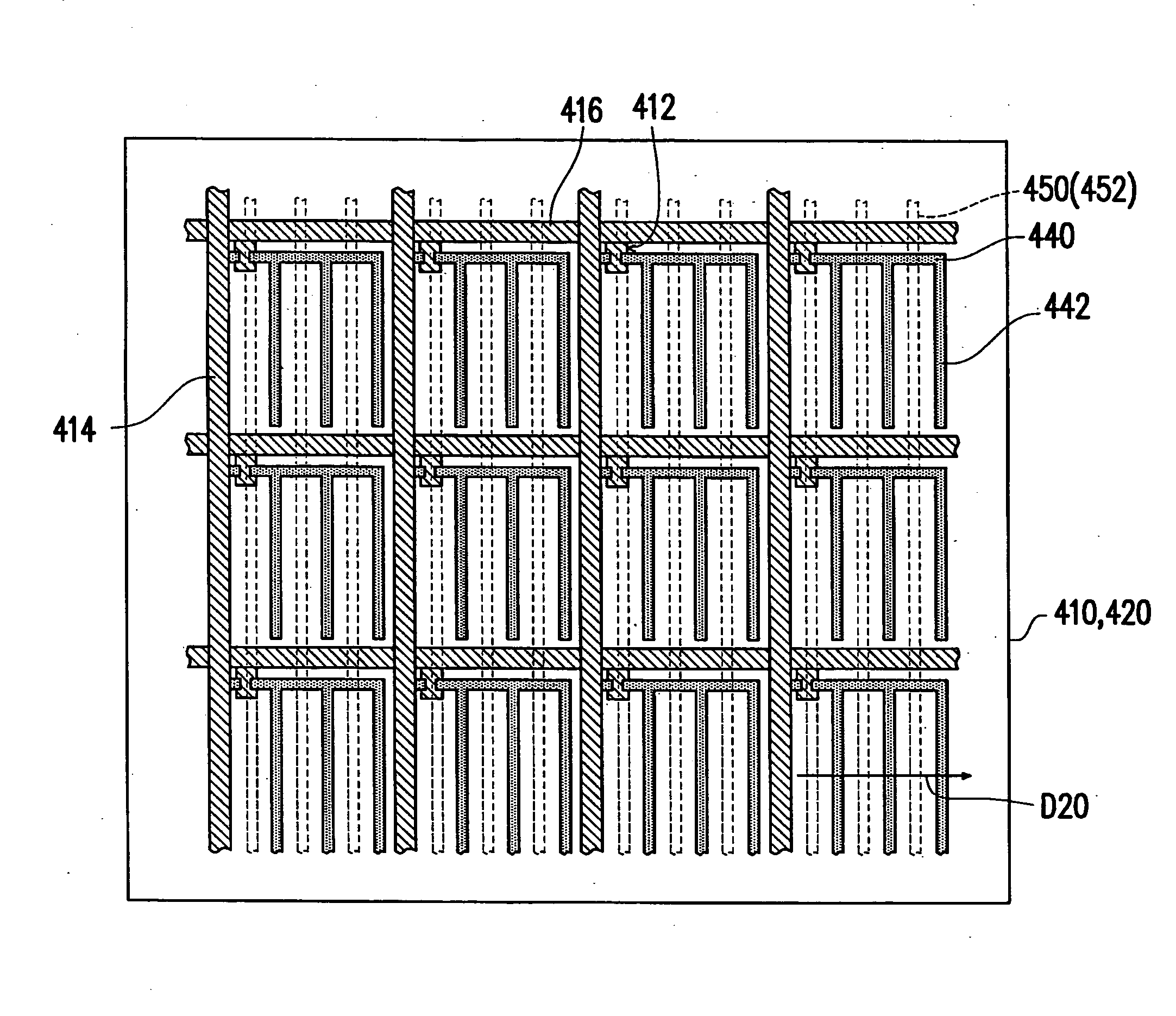
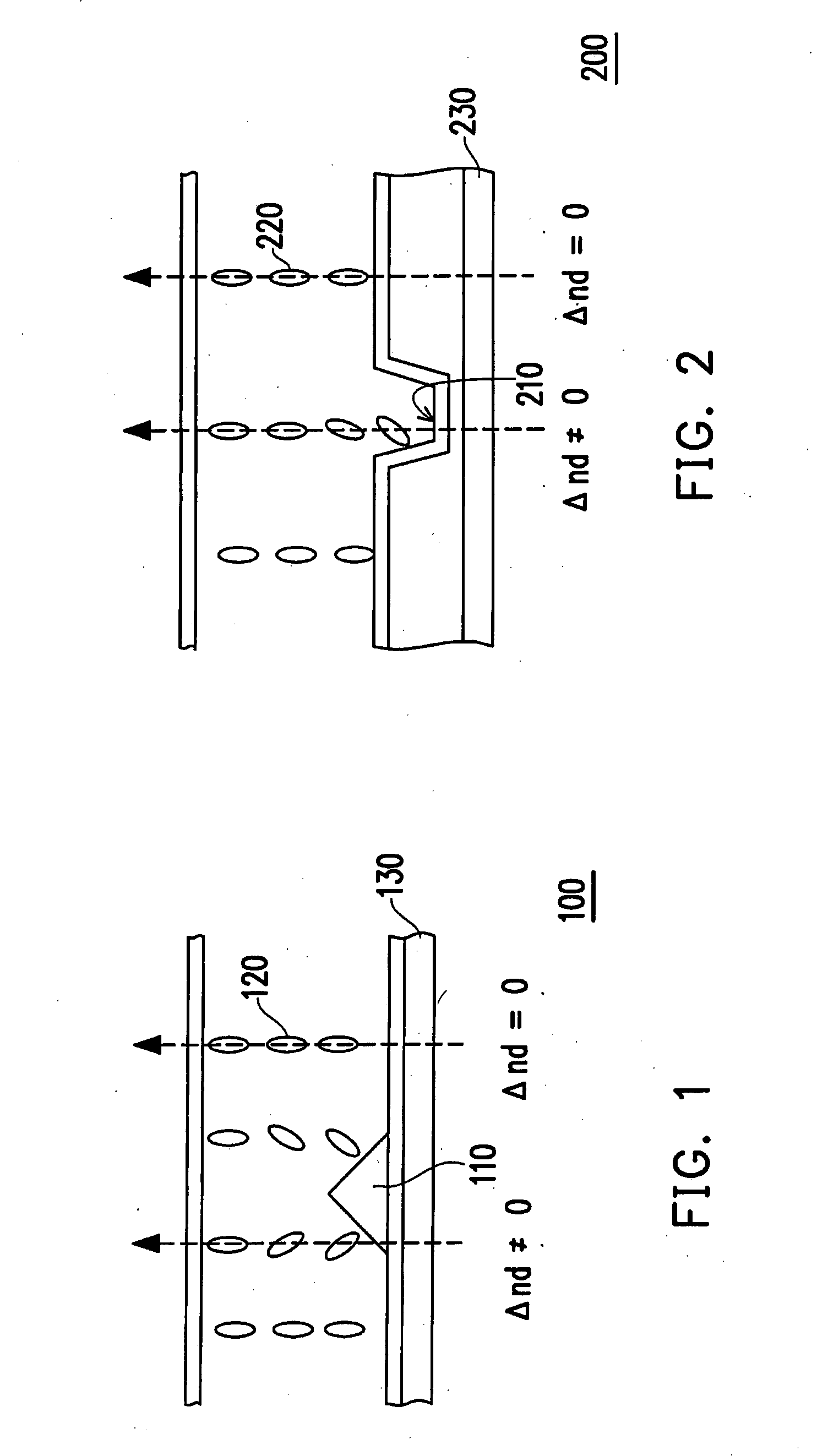
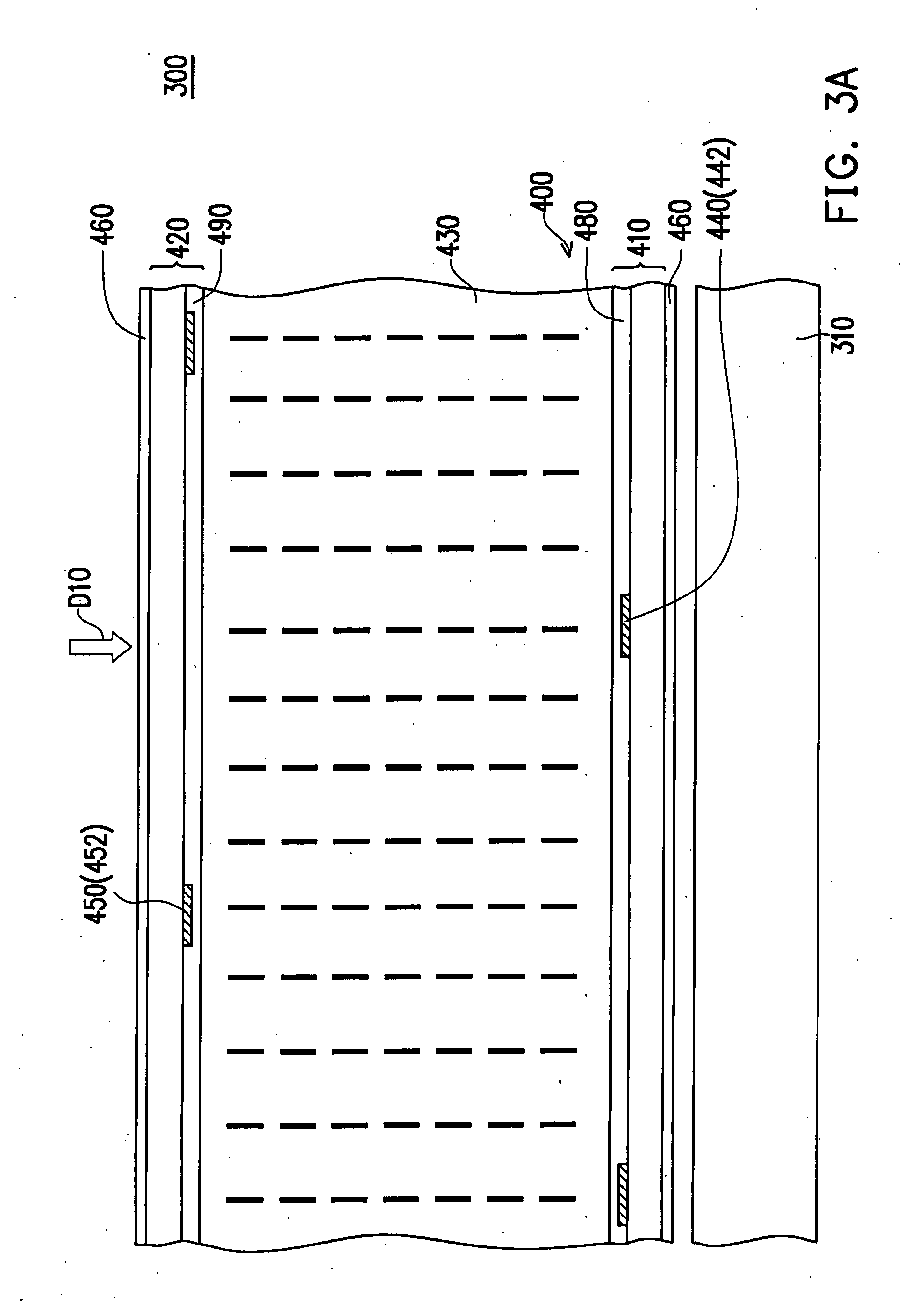
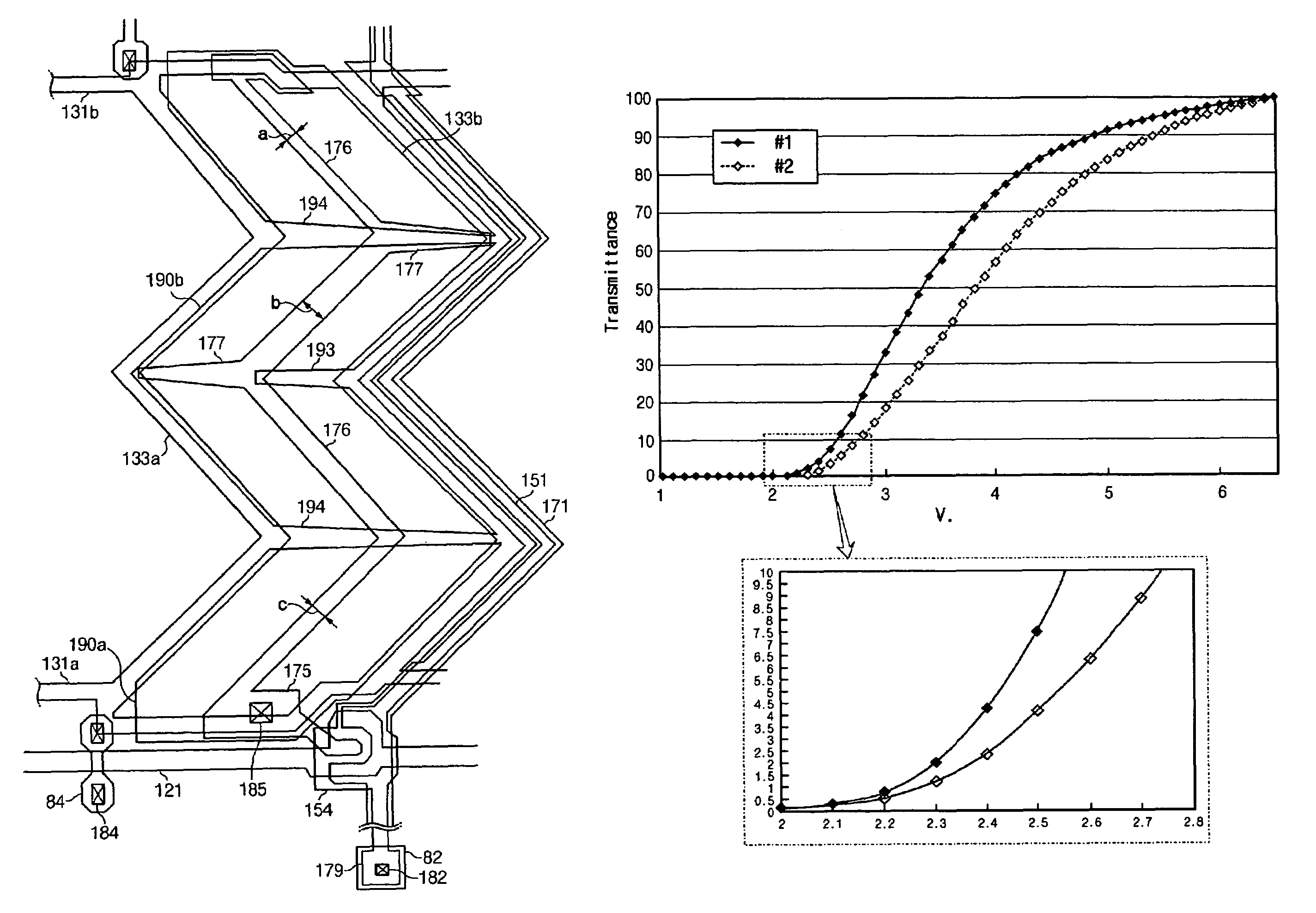
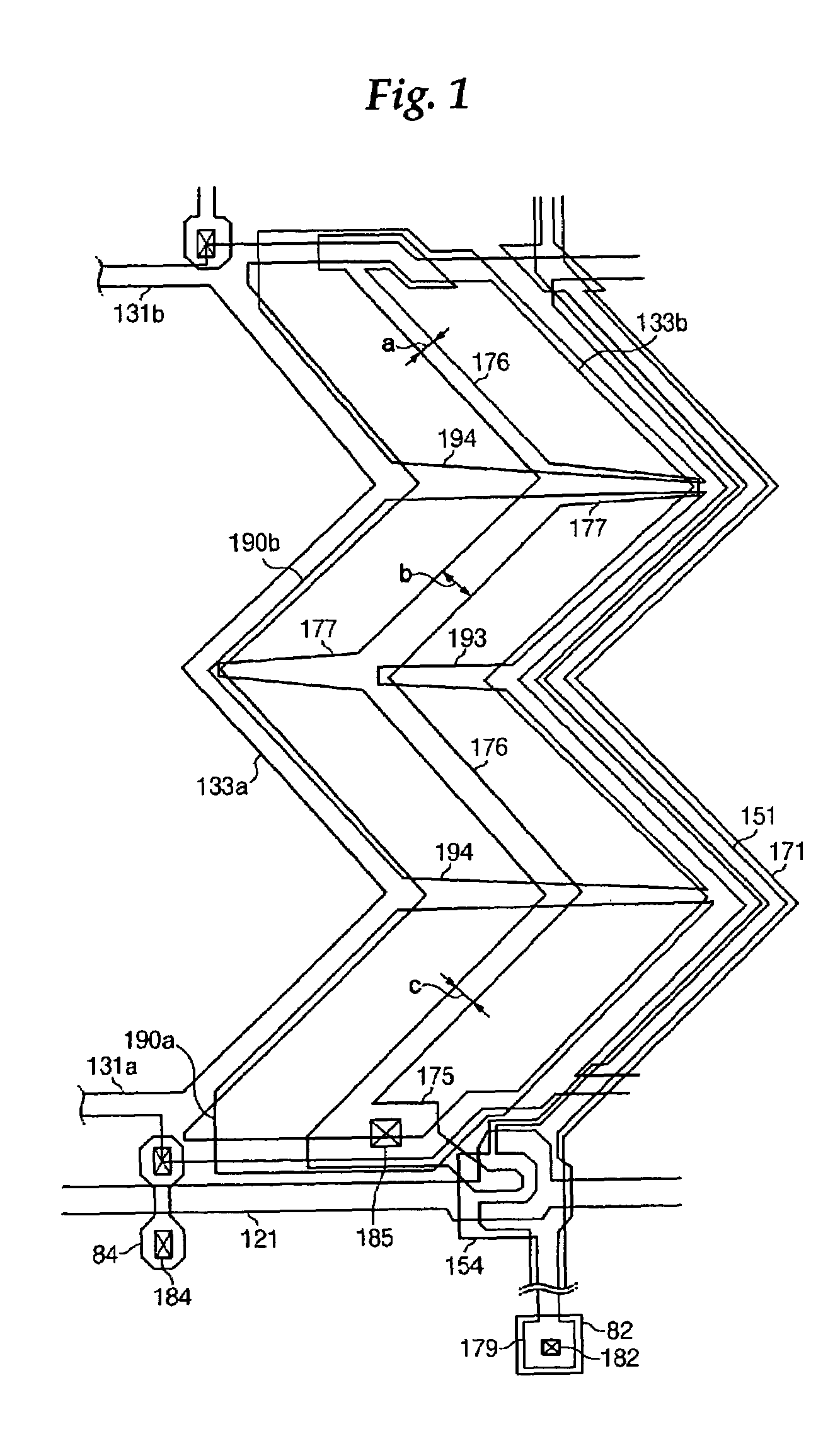
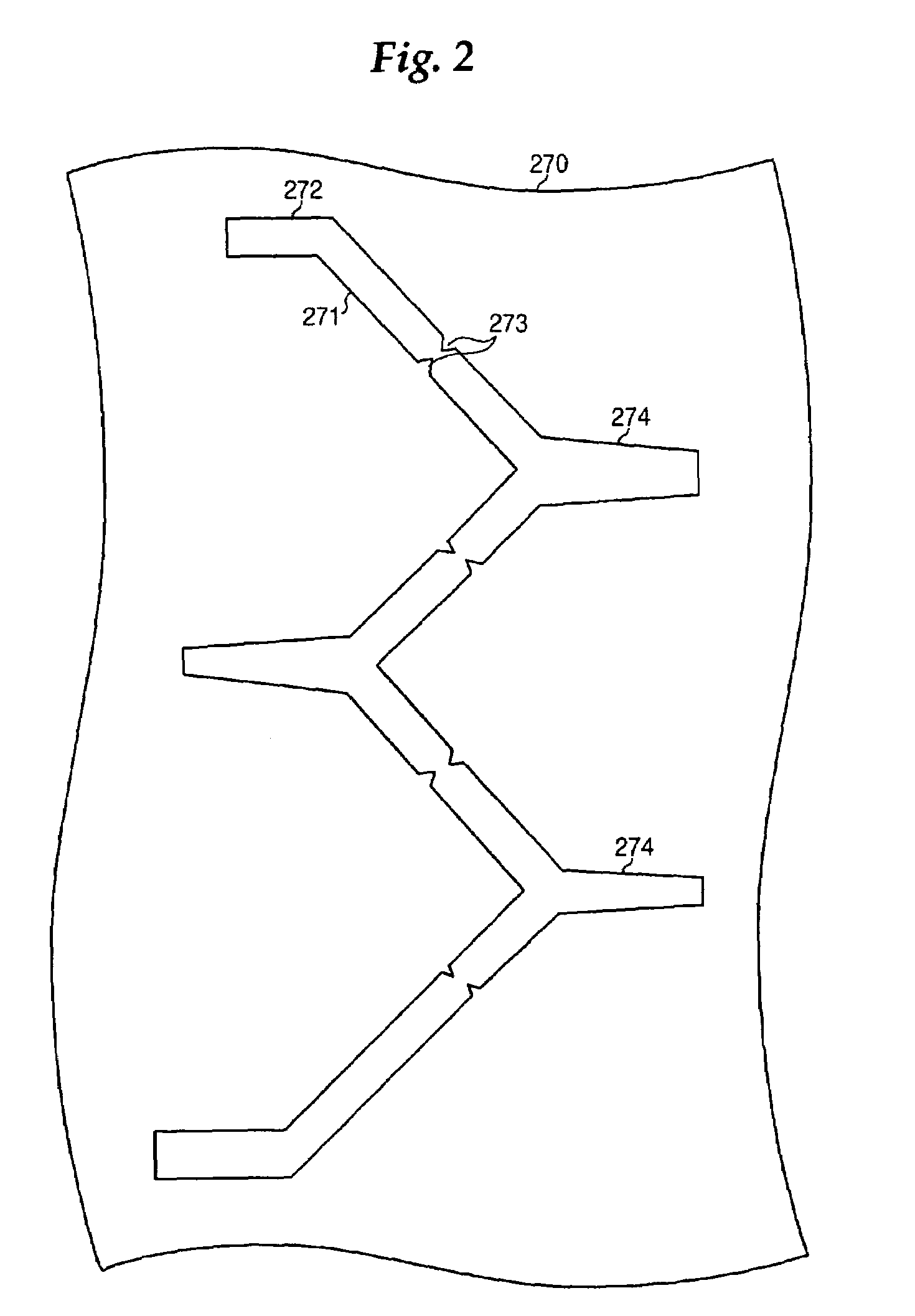
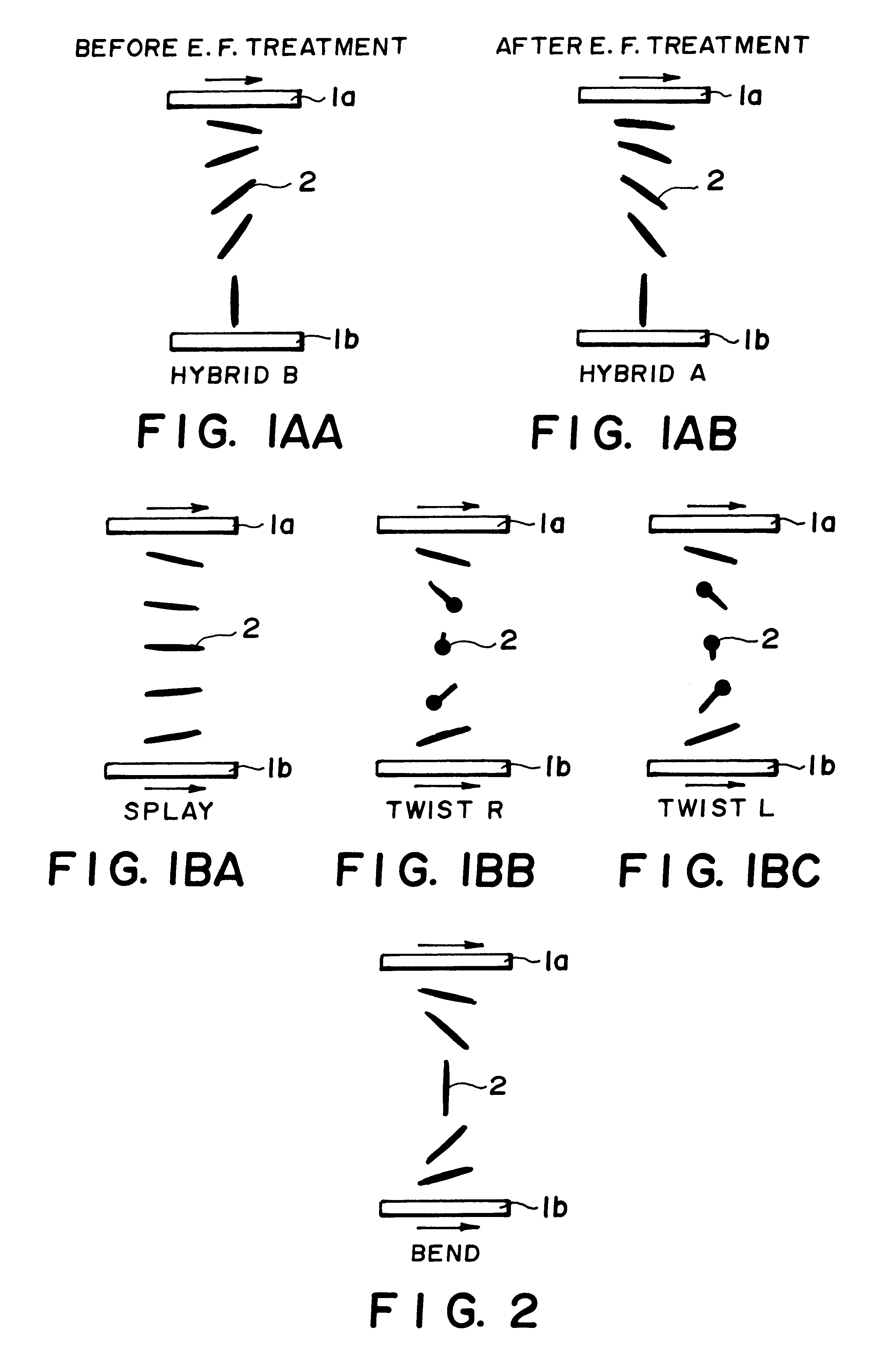
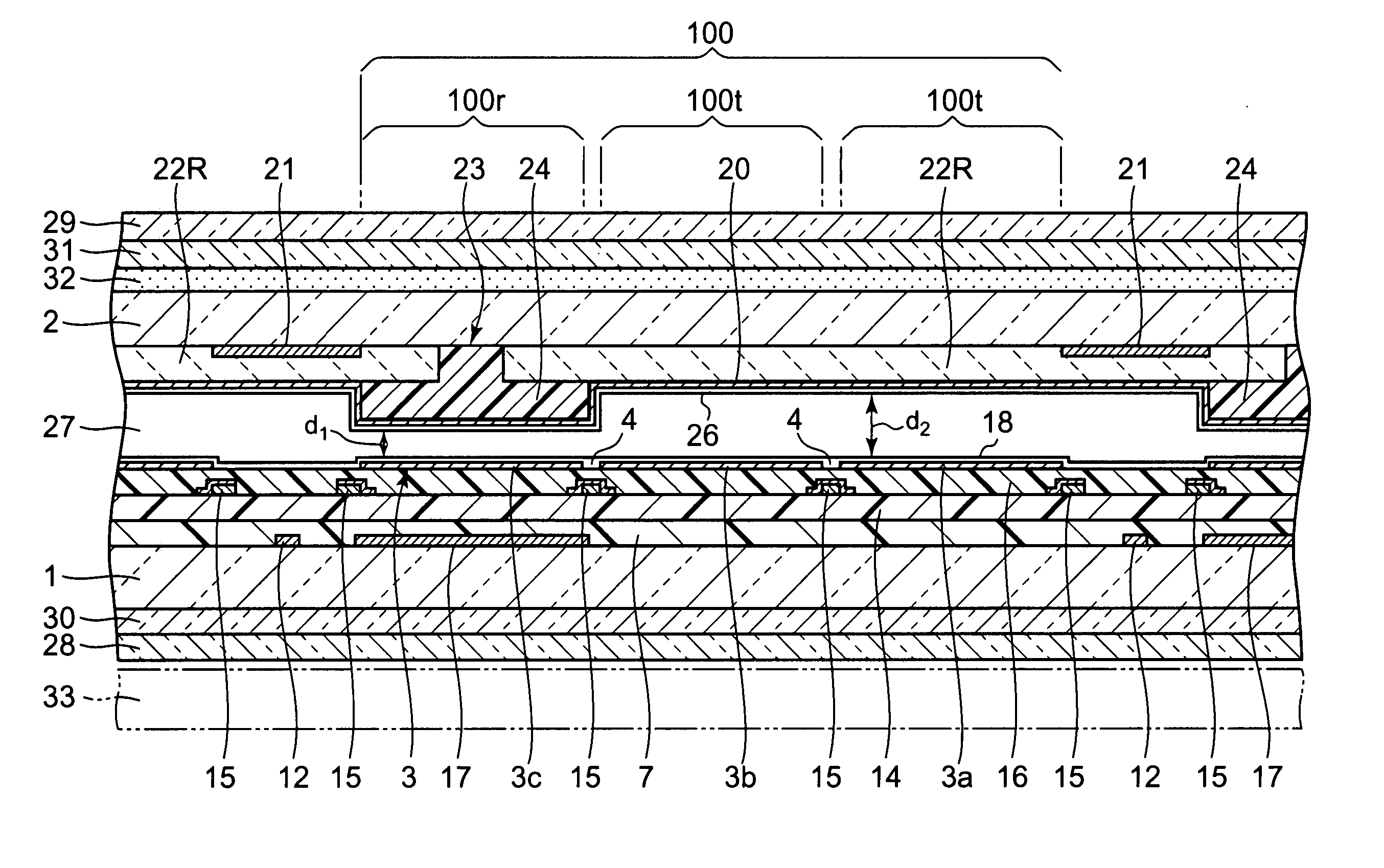
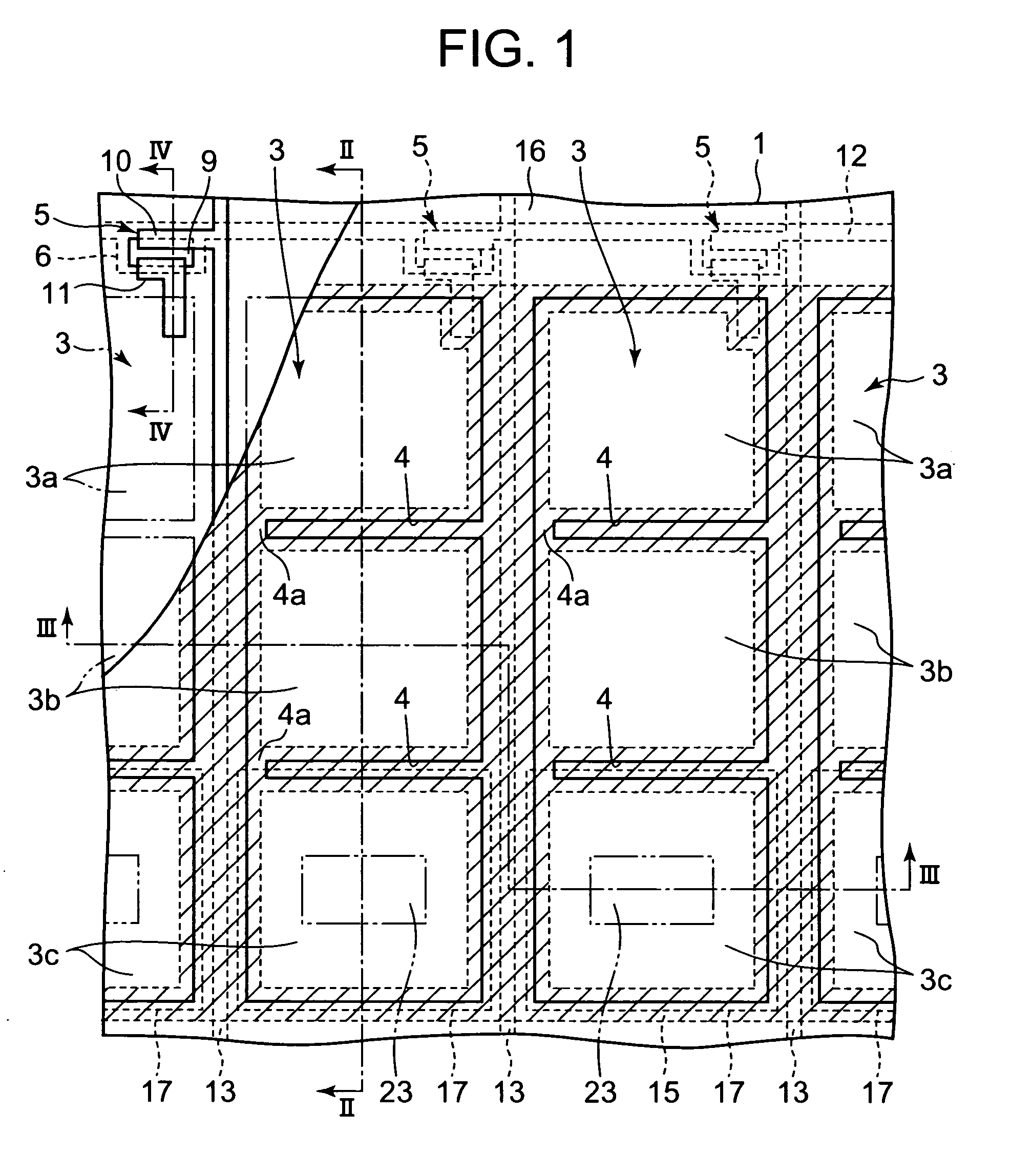
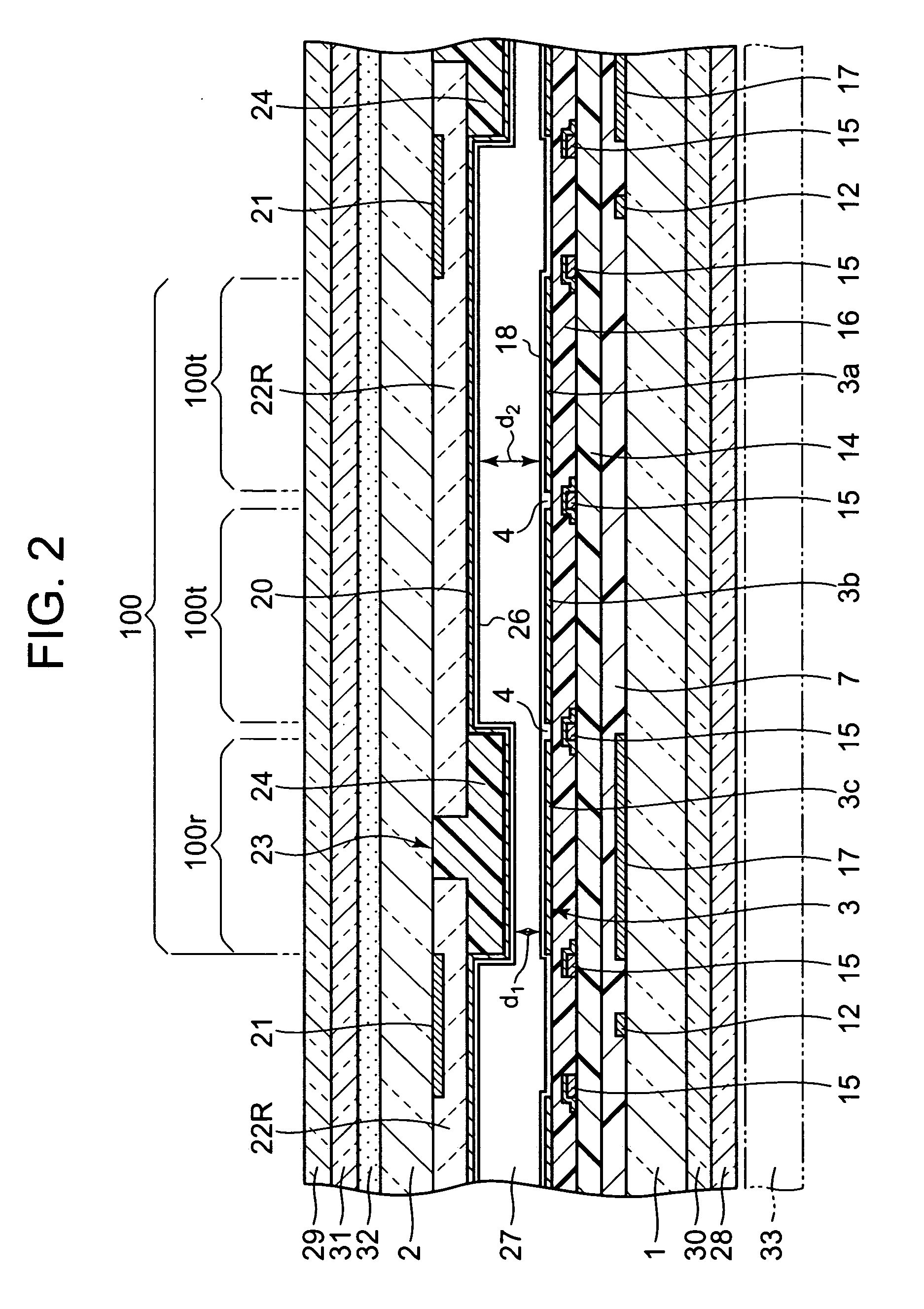
[liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof]
InactiveUS20050088386A1Short response timeStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsVertical alignmentEngineering
A liquid crystal display (LCD) panel and driving circuit having a high response speed is provided. The LC panel at least includes a first group of gate lines, a second group of gate lines, and a first group of source lines, in which gate pulse signals can be fed to the LCD panel through the two groups of gate lines. Preferably, the LC panel further includes a second group of source lines, in which one of the two groups of source lines can be fed with the image data, and the other one is fed with a black image data. Accordingly, the LCD panel can only use the twisted nematic LC or the vertical alignment LC (VA-LC), without need of optically compensated birefringent LC (OCB-LC). Thus, the problems of a fast response speed LC panel using an OCB-LC can be avoided.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
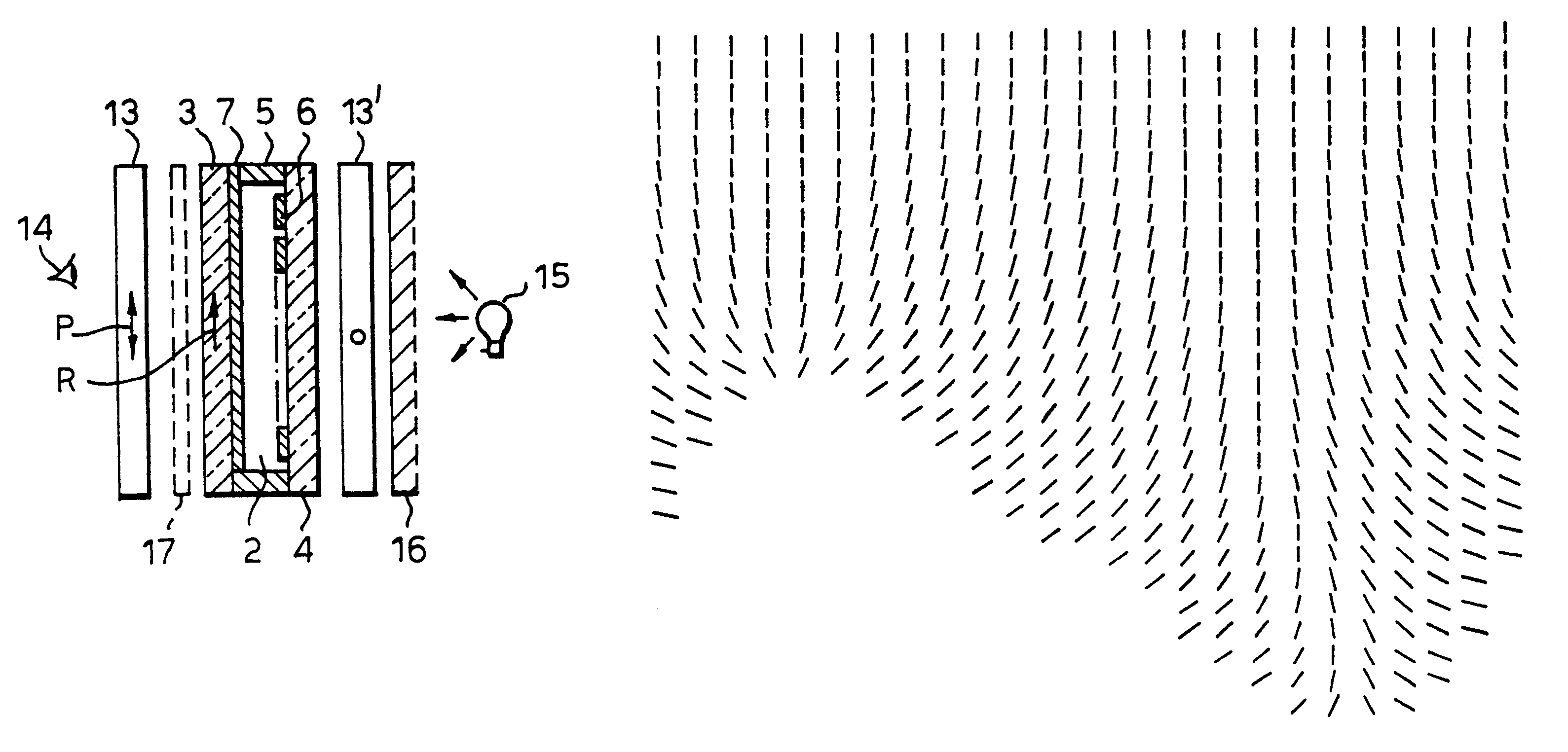
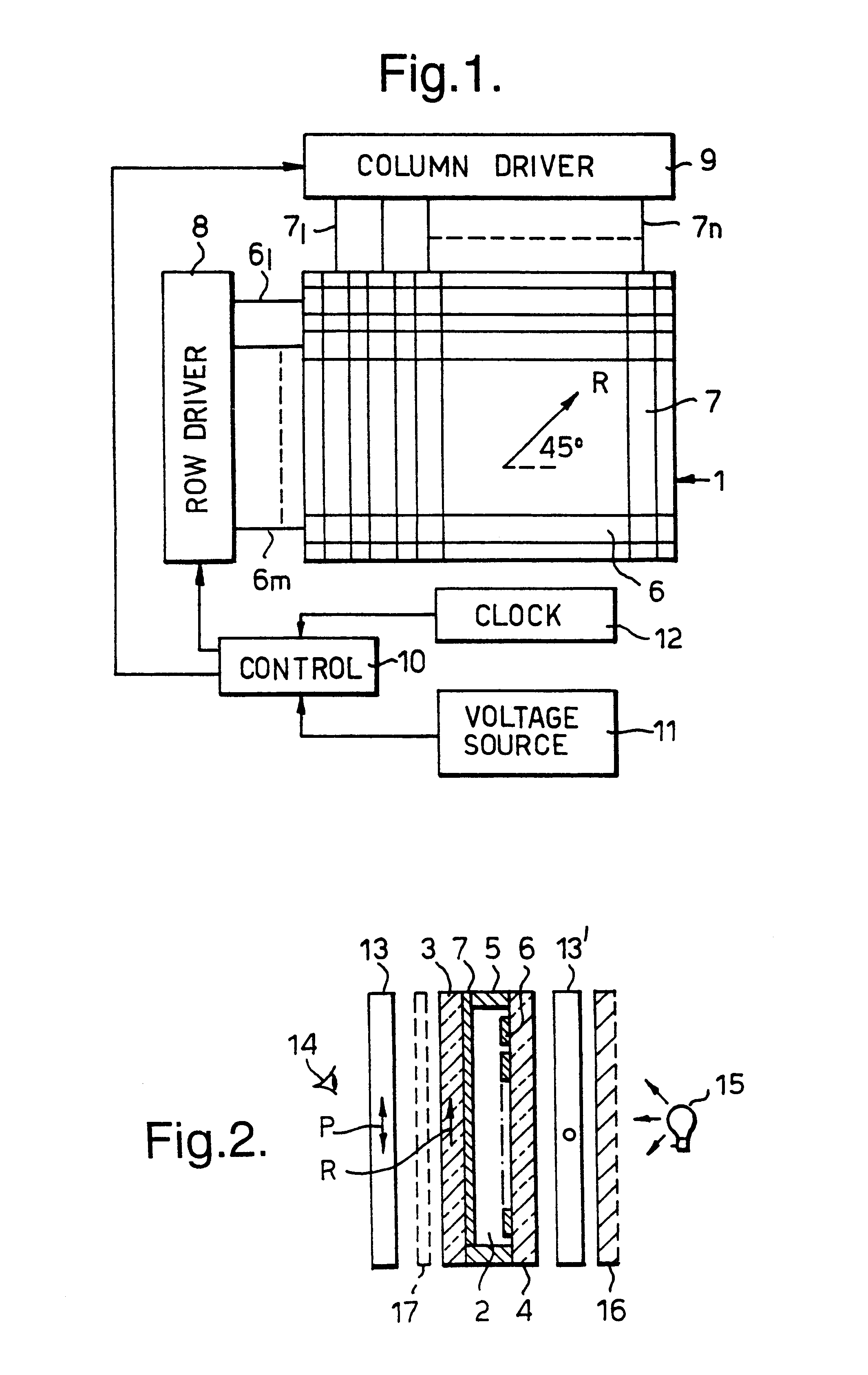
Bistable nematic liquid crystal device
A liquid crystal device comprises a layer (2) of a nematic liquid crystal material contained between two cell walls (3, 4) each carrying electrode structures (6, 7) and an alignment surface (20, 21). The alignment layer (20, 21) on one or both cell wall (4), is formed of a plurality of small (<15 μm) surface features each separably capable of providing a bistable pretilts and an alignment direction and collectively causing larger variations of molecular orientation across the layer (2). The device may be switched between a light transmissive state and a light non-transmissive state. The small surface features may be areas of grating (21), protrusions (25), or blind holes (26), separated by mono stable flat surfaces (Fm) coated with a homeotropic alignment layer. Preferably, the grating etc provides bistable switching operation between a low surface tilt and high surface tilt, and the low tilt alignment direction varies between adjacent grating areas.
Owner:ZBD DISPLAY LTD +1
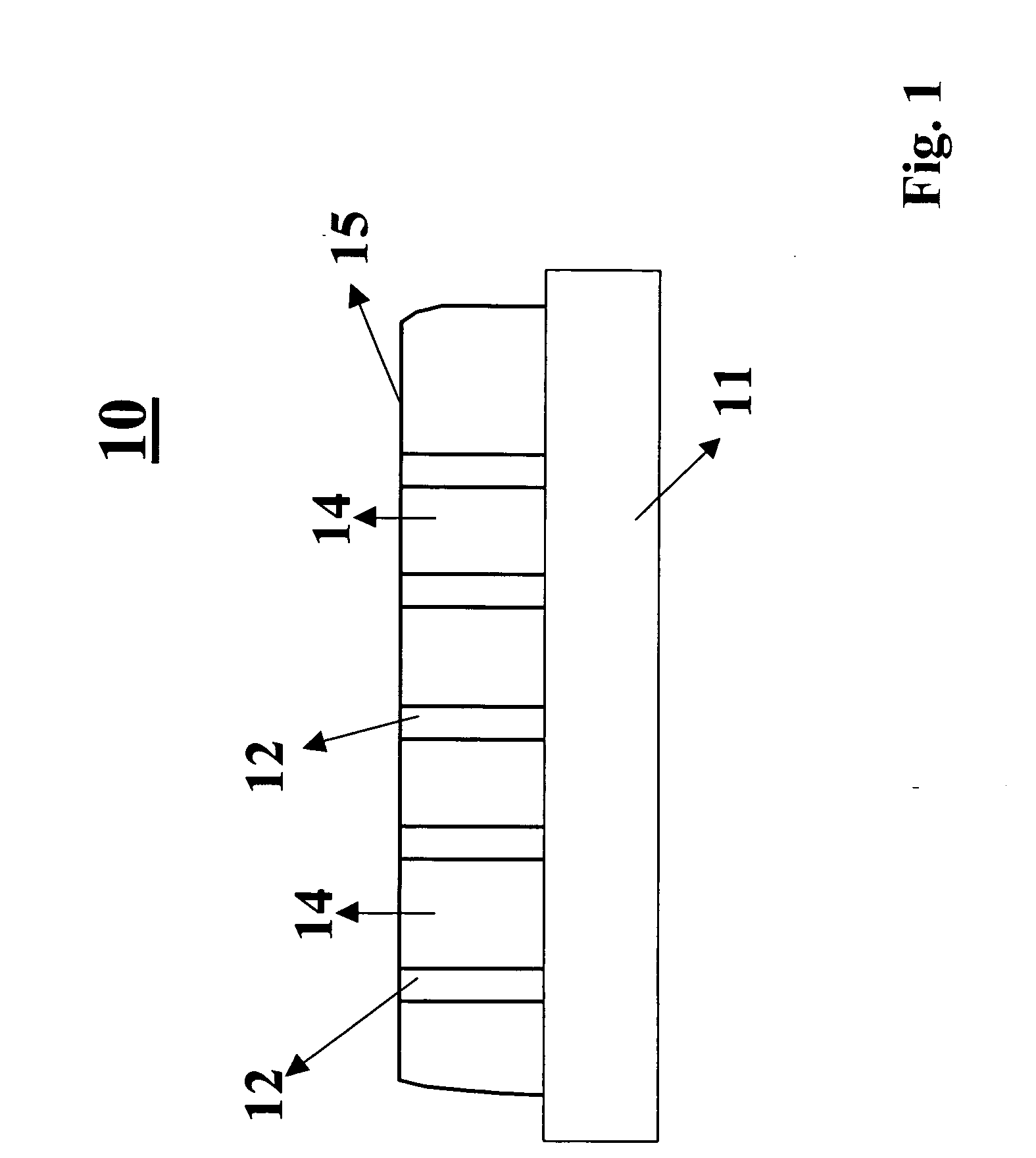
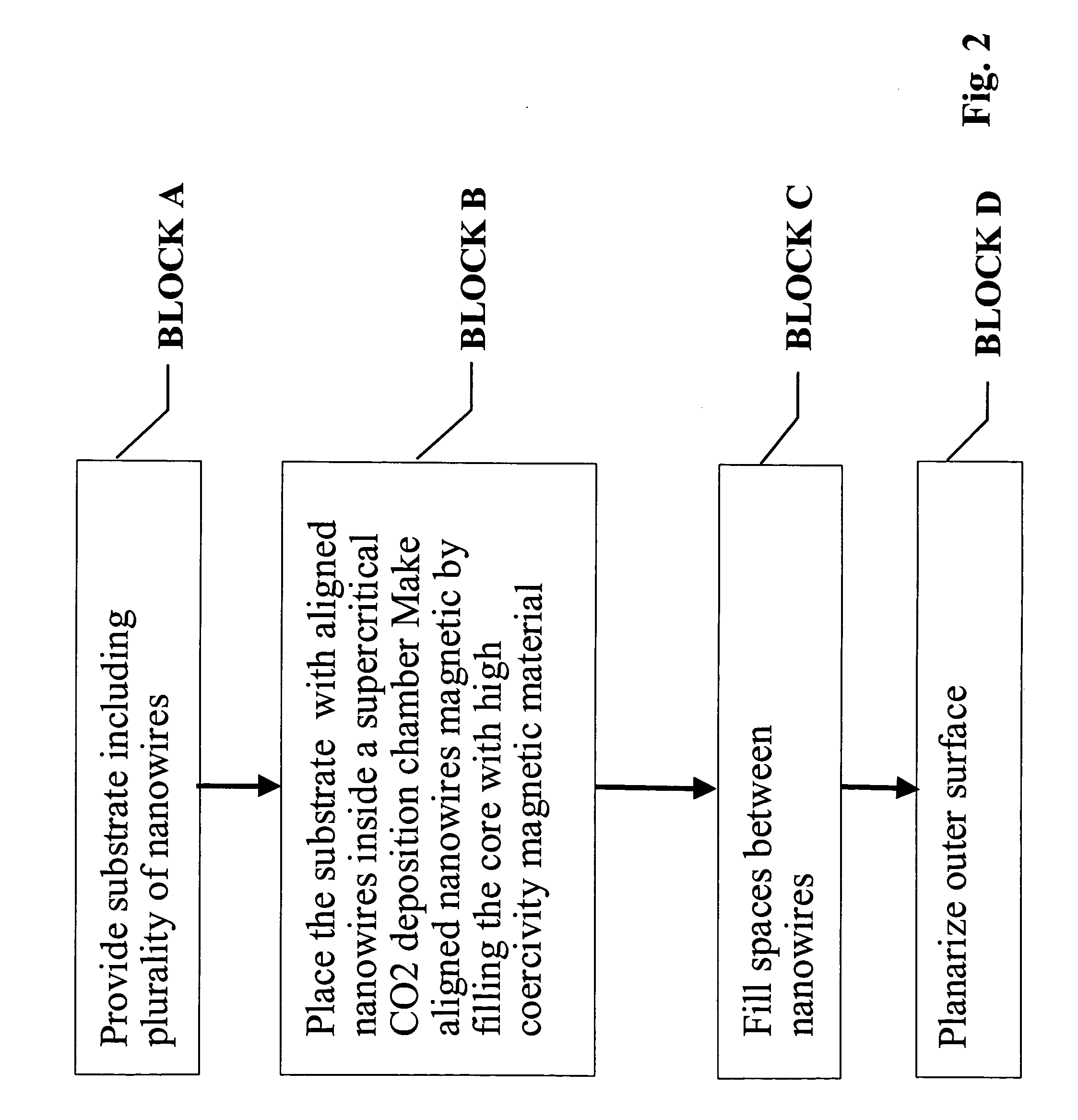
Ultra-high-density magnetic recording media and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20050079282A1High density recordingImprove coercive forceNanoinformaticsRecord information storageNanowireHigh density
In accordance with the invention, a high density recording medium is fabricated by novel methods. The medium comprises an array of nanomagnets disposed within a matrix or on the surface of substrate material. The nanomagnets are advantageously substantially perpendicular to a planar surface. The nanomagnets are preferably nanowires of high coercivity magnetic material inside a porous matrix or an array of vertically aligned nanotubes, or on the surface of flat substrate. Such media can provide ultra-high density recording with bit size less than 50 nm and even less than 20 nm. A variety of techniques are described for making such media.
Owner:JIN SUNGHO
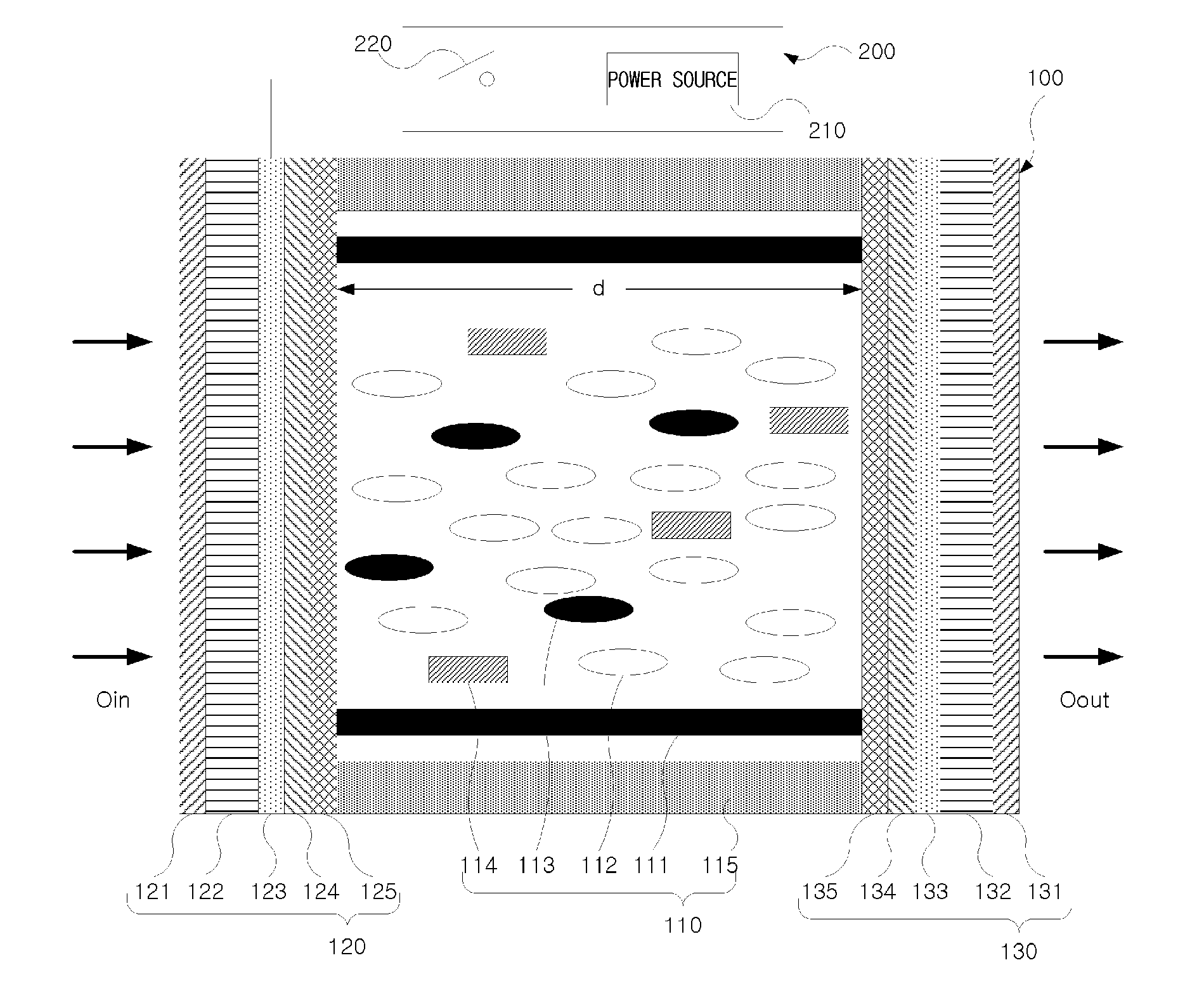
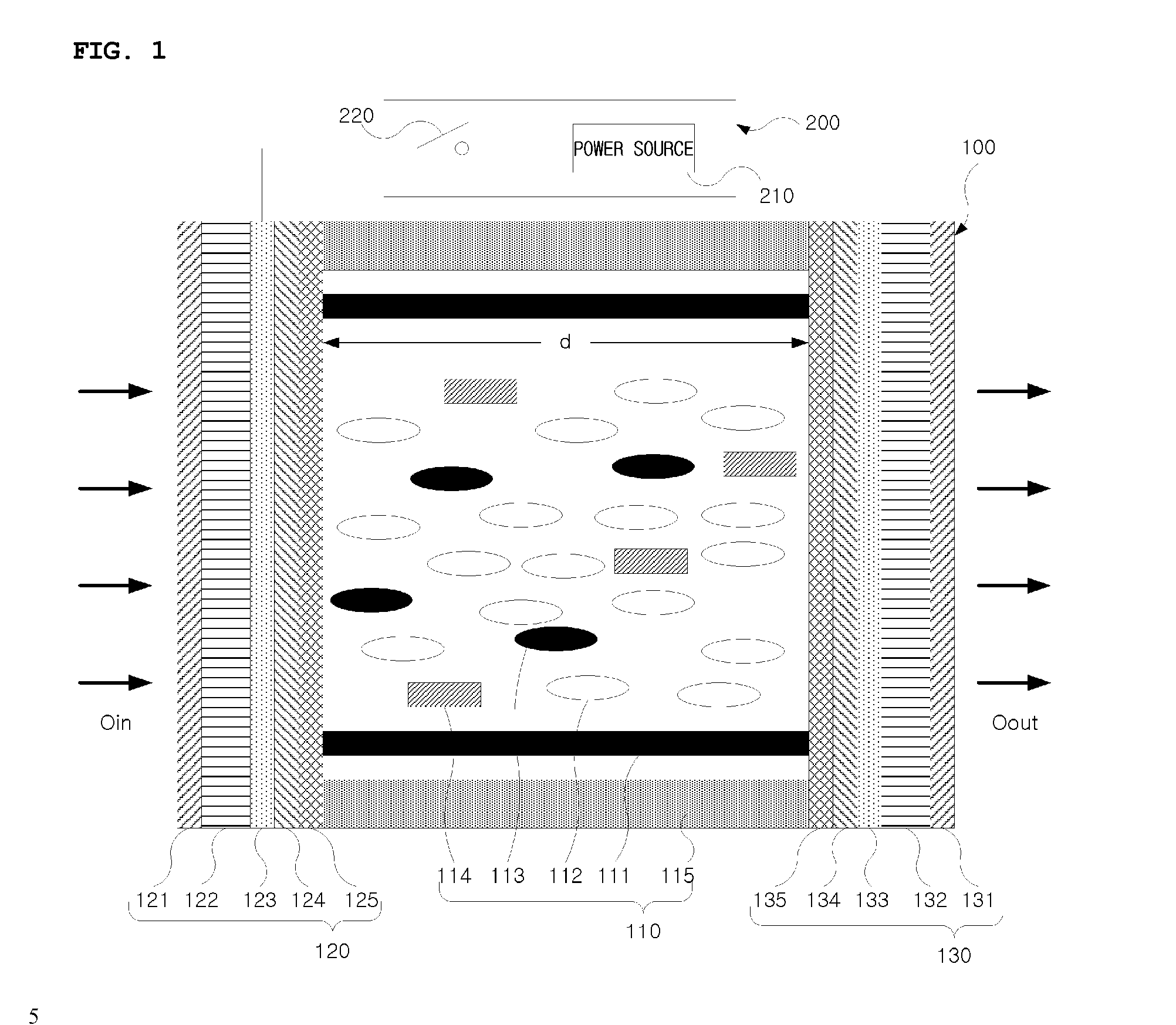
LCD light-reducing apparatus, and vehicle smart mirror using the same
InactiveUS20120257123A1Reduce power consumptionNon-linear opticsOptical viewingDielectric anisotropyEngineering
The present invention relates to an LCD light-reducing apparatus, and to a vehicle smart mirror using the same, which are to be applied to the interior rear-view mirror or exterior side-view mirrors of a vehicle to protect the vision of the driver of the vehicle from bright lights or glares coming from behind him during nighttime drive. The LCD light-reducing apparatus according to the present invention comprises an LCD panel including at least one liquid crystal cell, and a power supply device for supplying a sufficient electric field to the LCD panel. The LCD cell includes a liquid crystal layer; and two substrate layers opposite one another with the liquid crystal layer at center thereof. The liquid crystal layer is filled with a compound including negative dielectric anisotropic nematic liquid crystals, a chiral material for inducing a cholesteric phase of the nematic liquid crystals to have a pitch of 1 to 4 times the cell gap of the liquid crystal layer, and dichromic dyes for being rearranged parallel to the nematic liquid crystals to transmit or absorb light in accordance with whether the electric field is applied or not. The substrate layer includes a tilted homeotropic alignment layer for arranging the respective nematic liquid crystals and dichromatic dyes in a first arrangement that is vertically aligned to the surface of the substrate layer, and an electrode for generating a sufficient electric field that passes through the liquid crystal layer to rearrange the nematic liquid crystals and dichromatic dyes in a second arrangement that is different from the first arrangement.
Owner:SODY
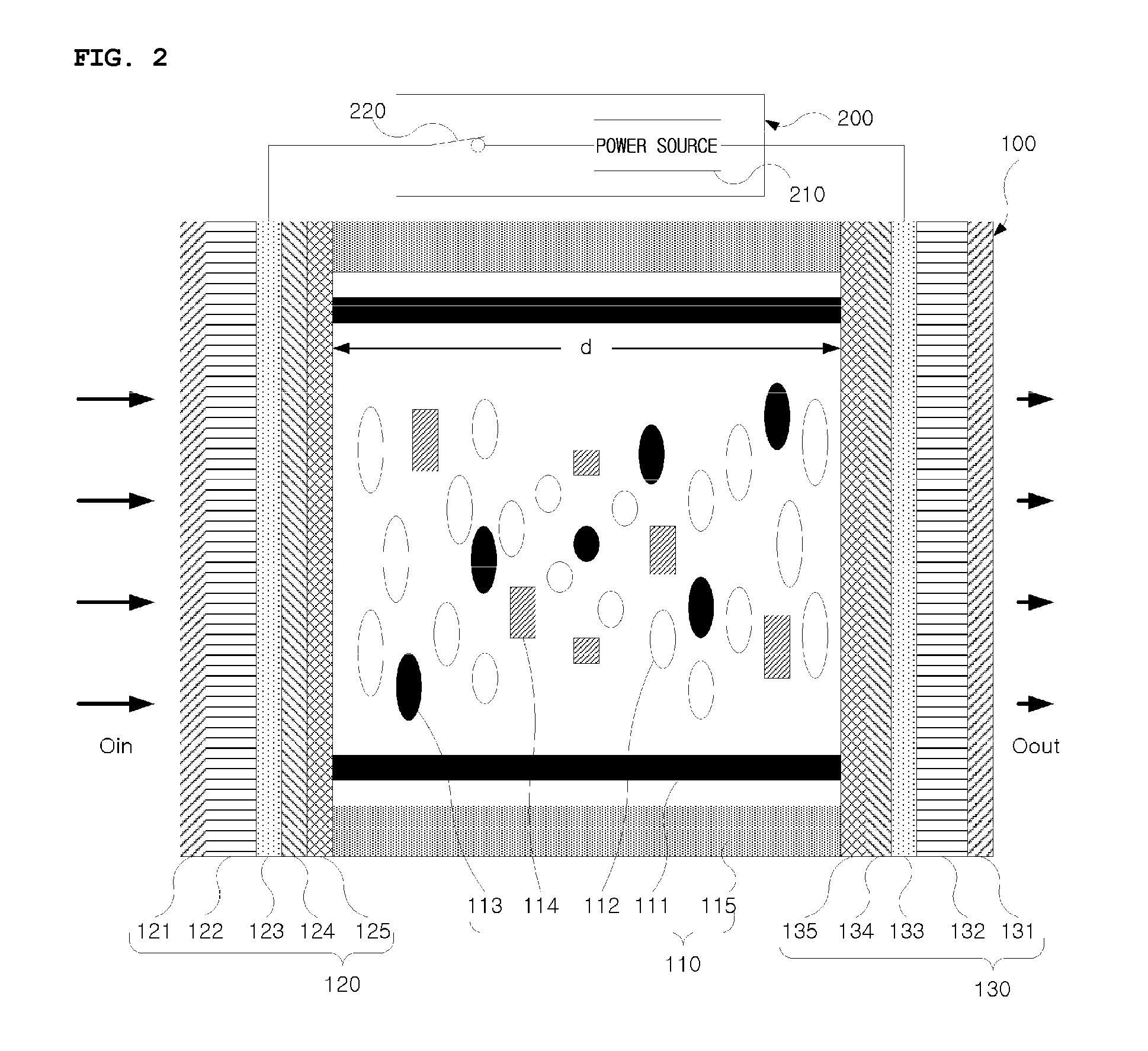
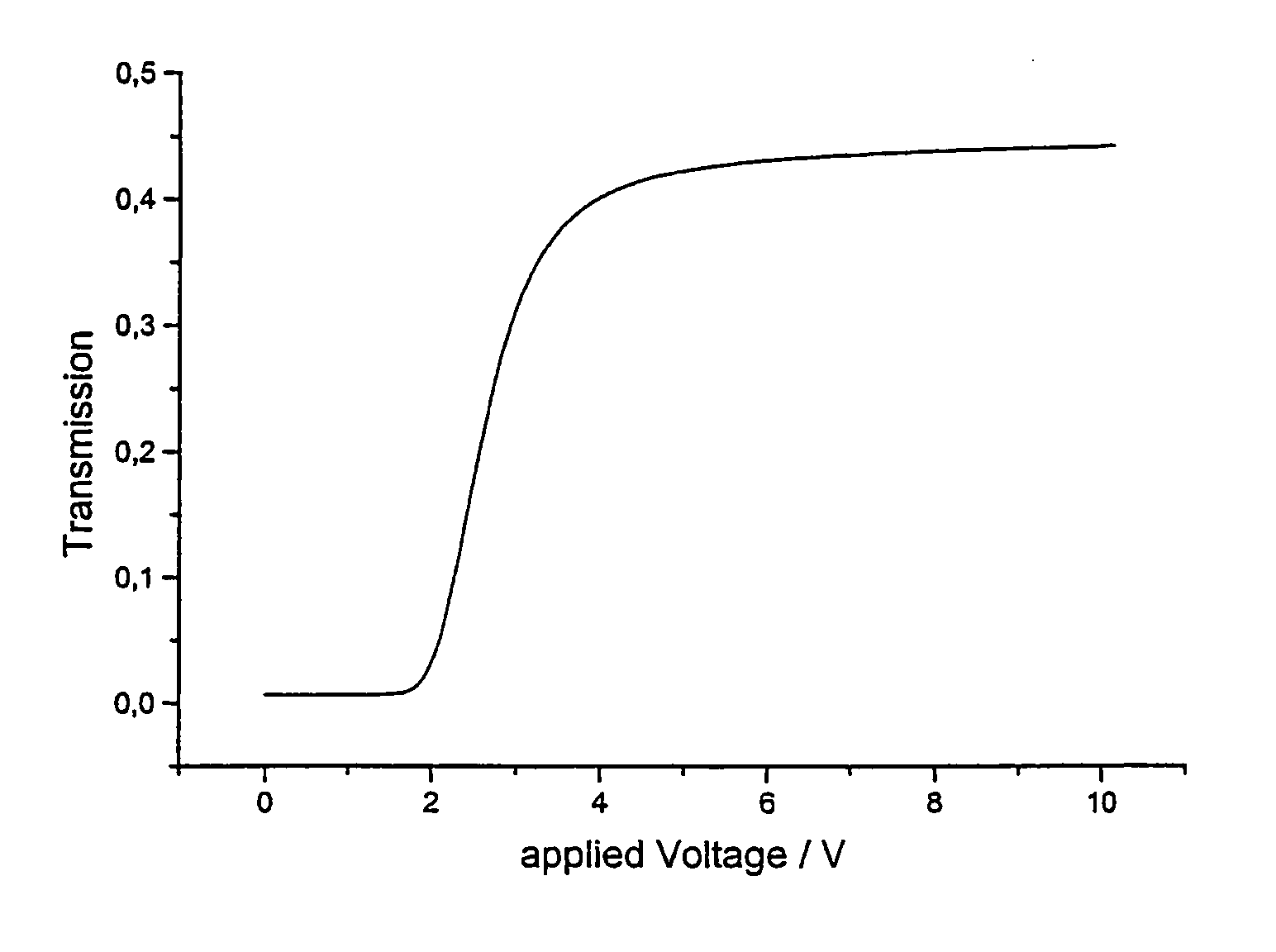
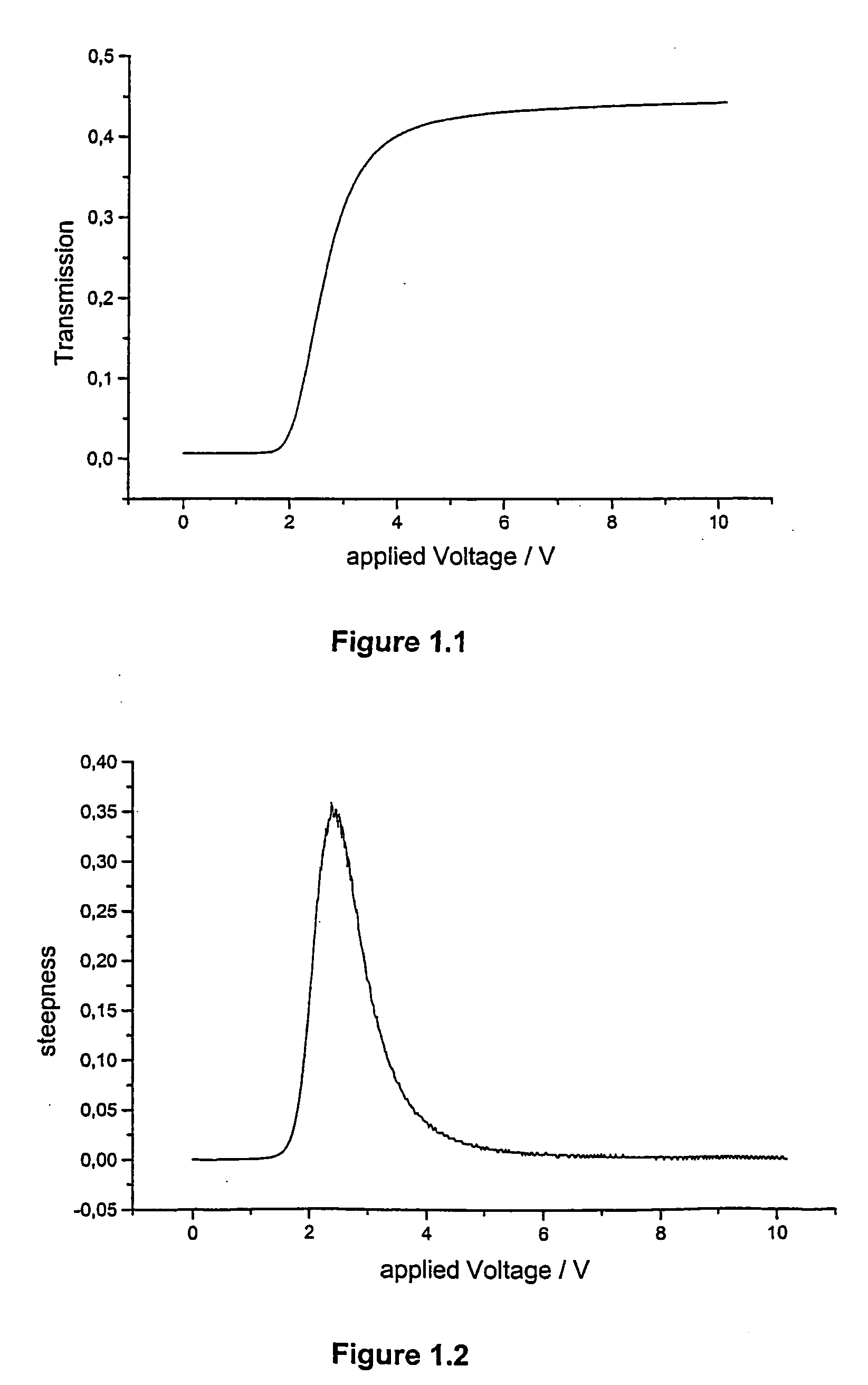
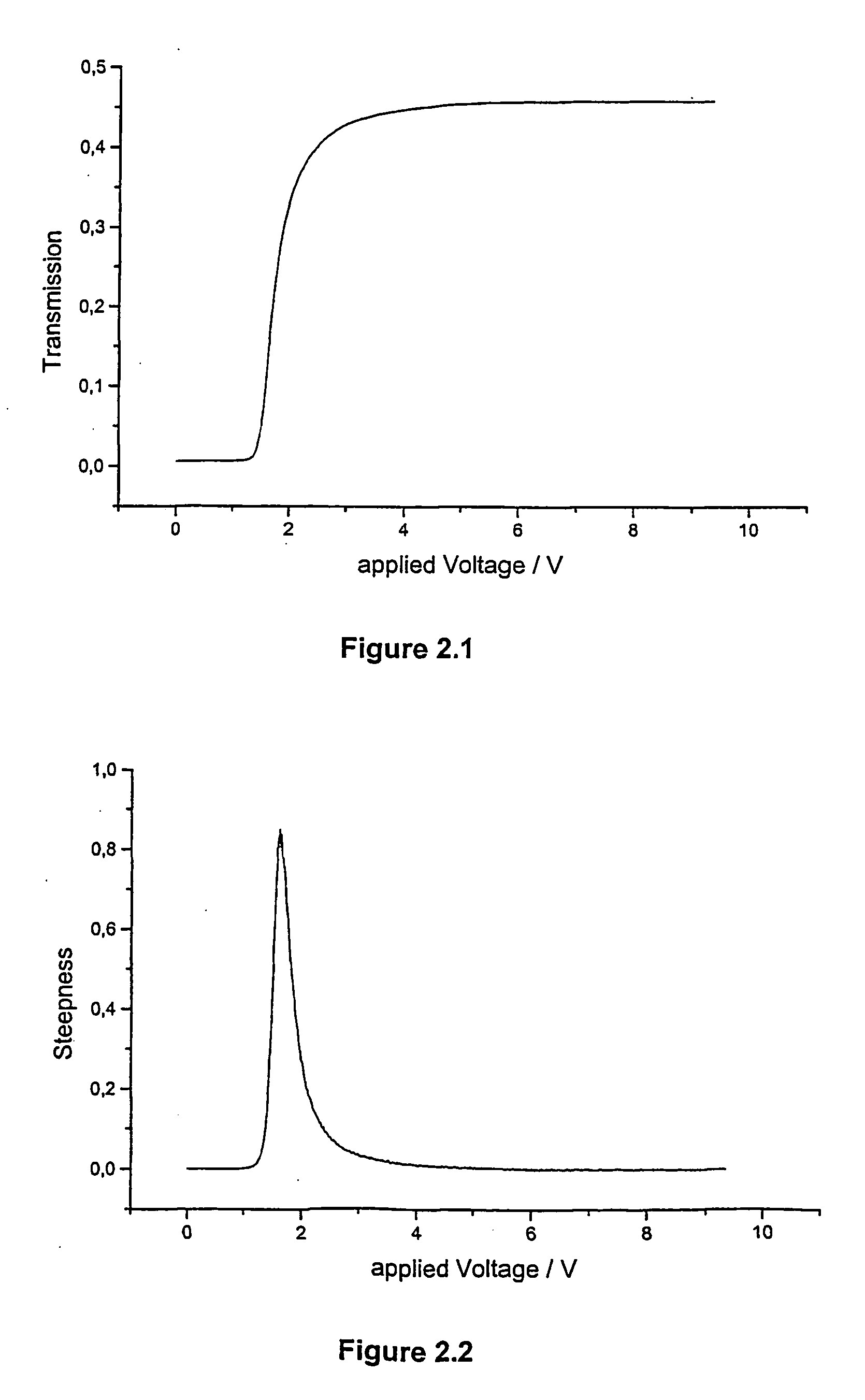
Homeotropic alignment layer
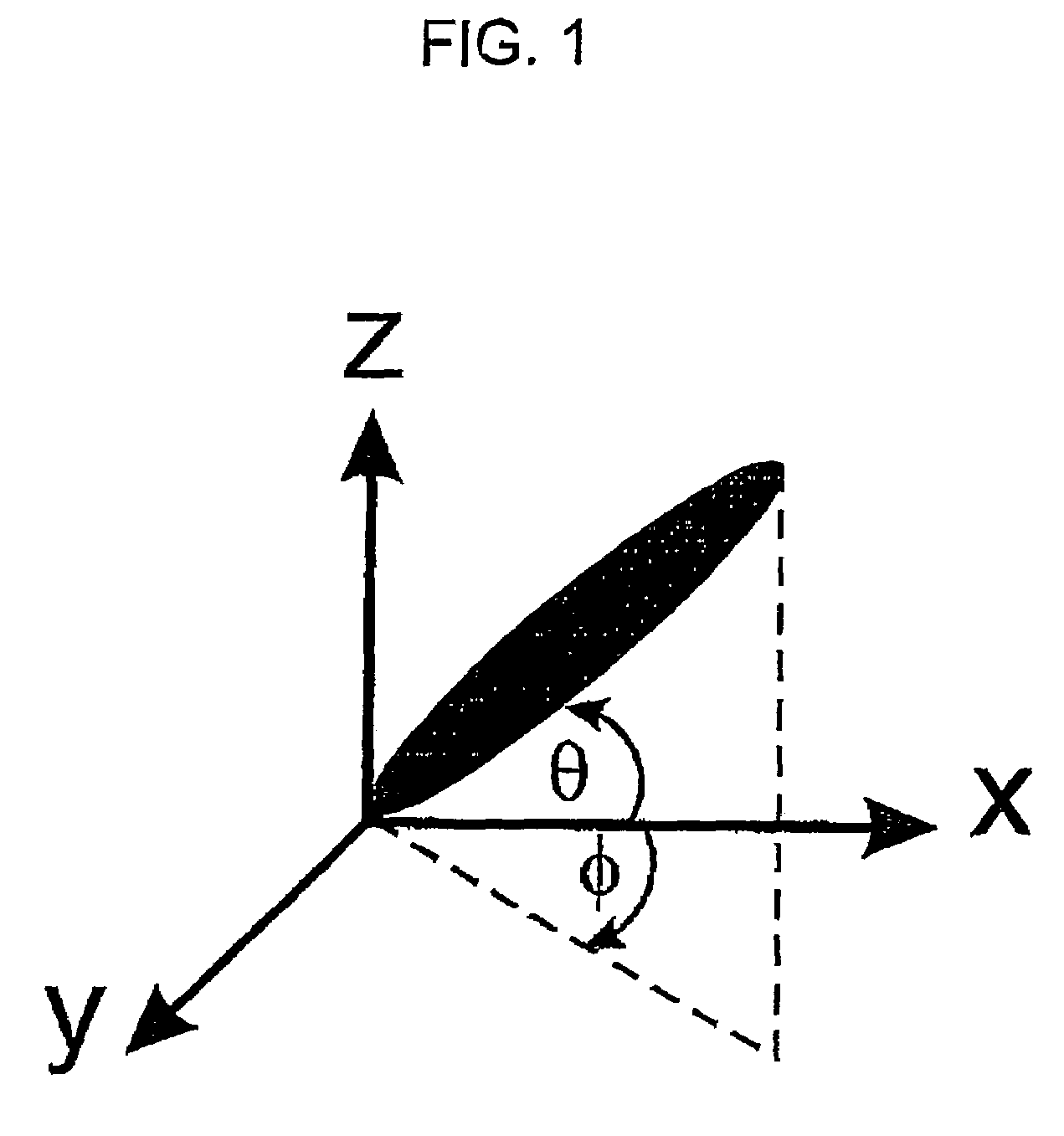
The invention relates to an alignment layer comprising a polymerized liquid crystal material with homeotrophic orientation, to methods of its preparation, to polymerizable liquid crystal compositions and liquid crystal polymers used for the preparation of the alignment layer, to liquid crystal devices comprising the alignment layer, and to a method of controlling the electrooptical steepness of a liquid crystal display comprising at least one alignment layer by varying the surface anchoring energy of the alignment layer.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Three-dimensional coherent plasmonic nanowire arrays for enhancement of optical processes
InactiveUS20120273662A1Avoid large gapsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsNanowireNanopillar
A plasmonic grating sensor having periodic arrays of vertically aligned plasmonic nanopillars, nanowires, or both with an interparticle pitch ranging from λ / 8−2λ, where λ is the incident wavelength of light divided by the effective index of refraction of the sample; a coupled-plasmonic array sensor having vertically aligned periodic arrays of plasmonically coupled nanopillars, nanowires, or both with interparticle gaps sufficient to induce overlap between the plasmonic evanescent fields from neighboring nanoparticles, typically requiring edge-to-edge separations of less than 20 nm; and a plasmo-photonic array sensor having a double-resonant, periodic array of vertically aligned subarrays of 1 to 25 plasmonically coupled nanopillars, nanowires, or both where the subarrays are periodically spaced at a pitch on the order of a wavelength of light.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Homeotropic Alignment Liquid Crystal Film, Optical Film Comprising the Same, and Image Display Device
InactiveUS20070263152A1Improve viewing angleStable productionLiquid crystal compositionsAdhesivesLiquid crystallineLight irradiation
A homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film is provided with a liquid crystalline substance containing a side chain liquid crystalline compound having an oxetanyl group, as a constituent, aligned homeotropically on an alignment substrate while being in a liquid crystal state and fixed in the homeotropic alignment by allowing the oxetanyl group to react. Thus, the homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film can be stably produced without necessitating a complicated step such as light irradiation under an inert gas atmosphere and is excellent in alignment retainability after being fixed in the homeotropic alignment and in mechanical strength.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
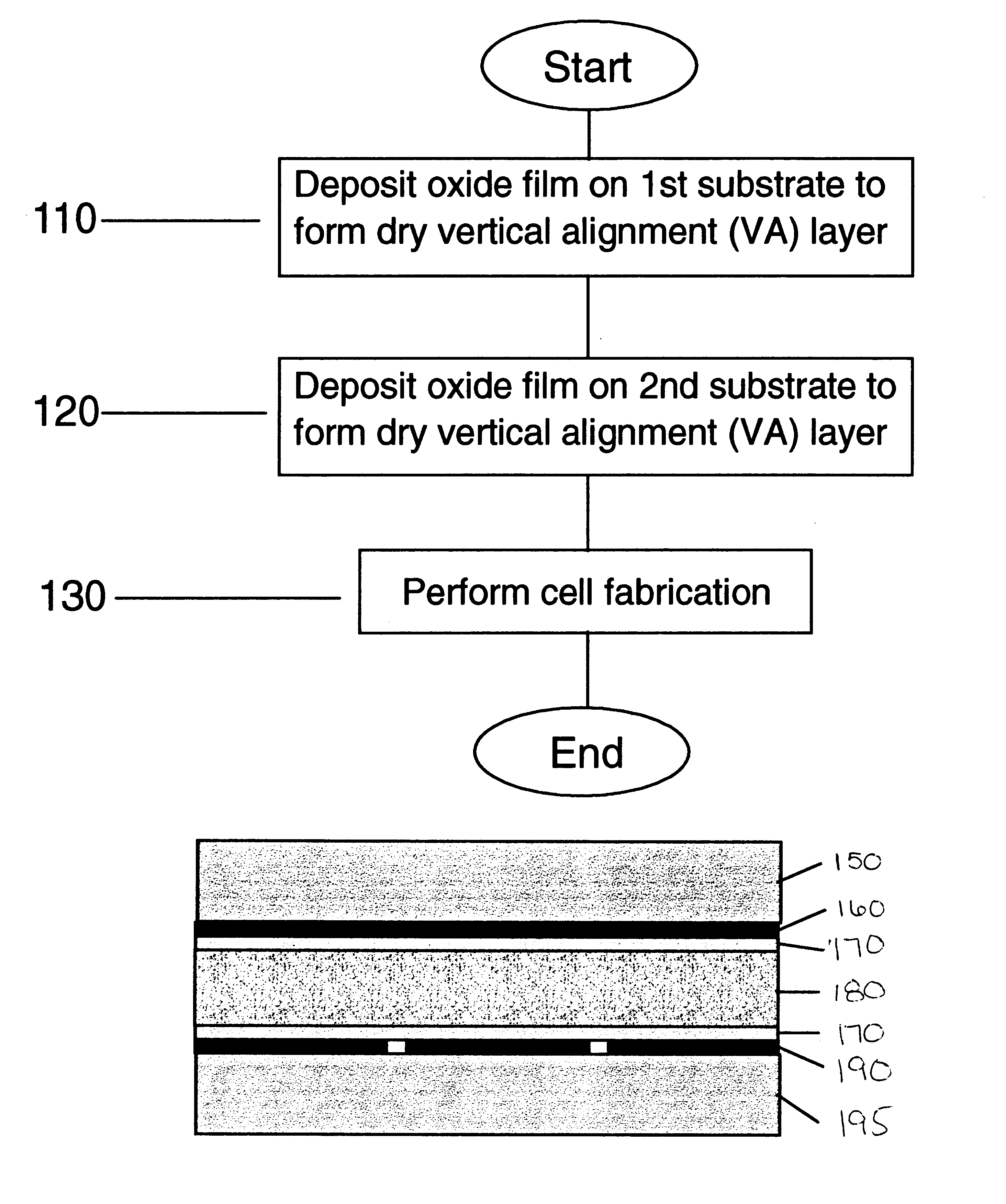
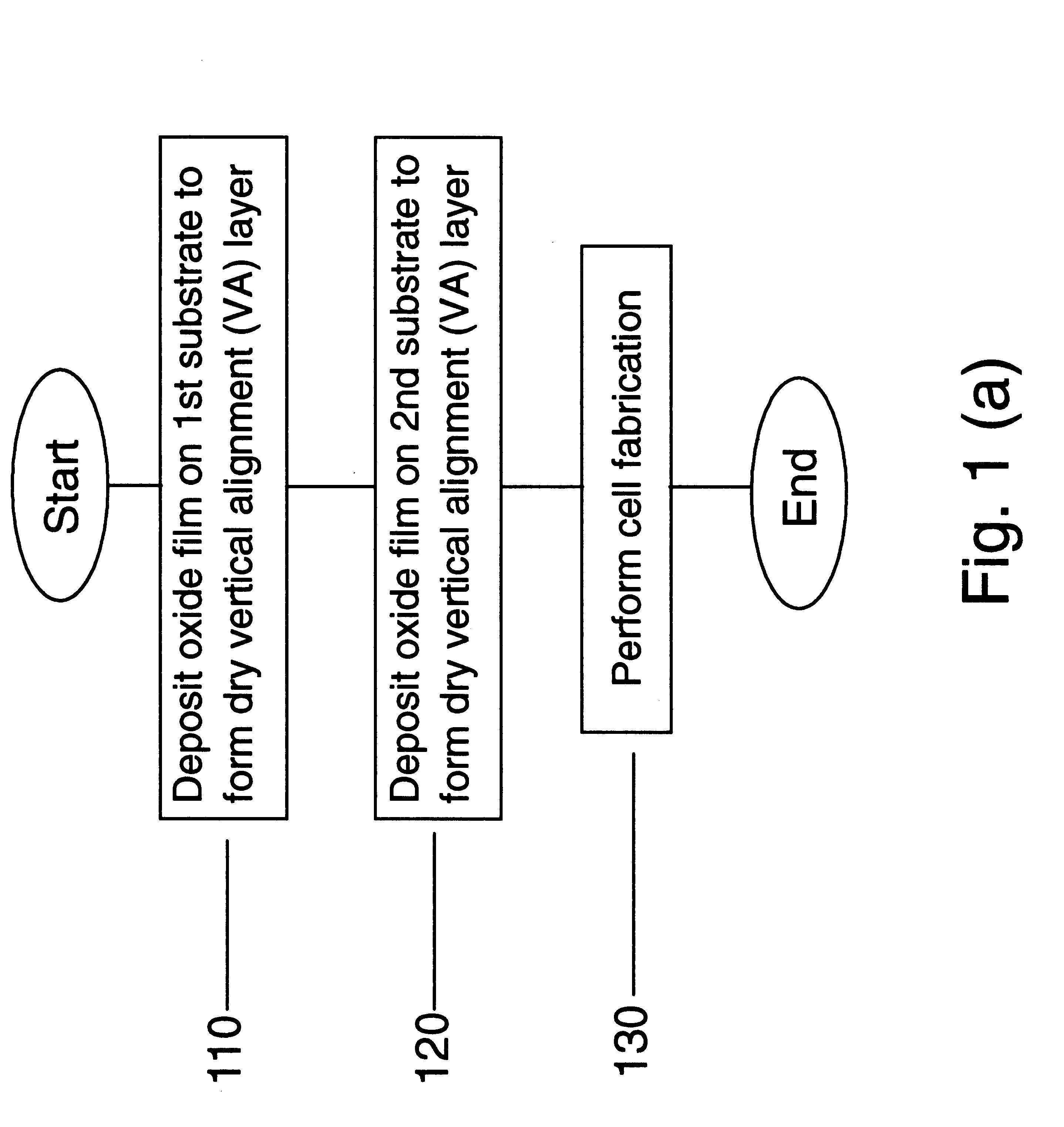
Vertical aligned liquid crystal display and method using dry deposited alignment layer films
InactiveUS6724449B1Reliable alignmentImprove charge retentionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
A liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate, a dry alignment film deposited over the substrate, a second substrate coupled to the first substrate with the dry alignment film deposited over the second substrate therebetween and forming a cell gap, and a liquid crystal material formed in the cell gap. The dry alignment film allows for a truly vertical alignment of molecules of the liquid crystal material such that the molecules form an angle of substantially 90° relative to the substrate. The dry alignment film can be an oxide layer, a nitride layer, an oxynitride layer or a silicon layer. This dry alignment layer can be treated to form a tilted homeotropic alignment, such that the liquid crystal molecules have a pretilt angle of 0.5 to 10 degrees from a substrate normal direction. The truly vertical alignment process can be incorporated with a ridge and fringe field process method to form a multidomain Vertical Alignment (VA) Liquid Crystal Display's (LCDs) which have wide viewing angles.
Owner:INFOVISION OPTOELECTRONICS HLDG LTD +1
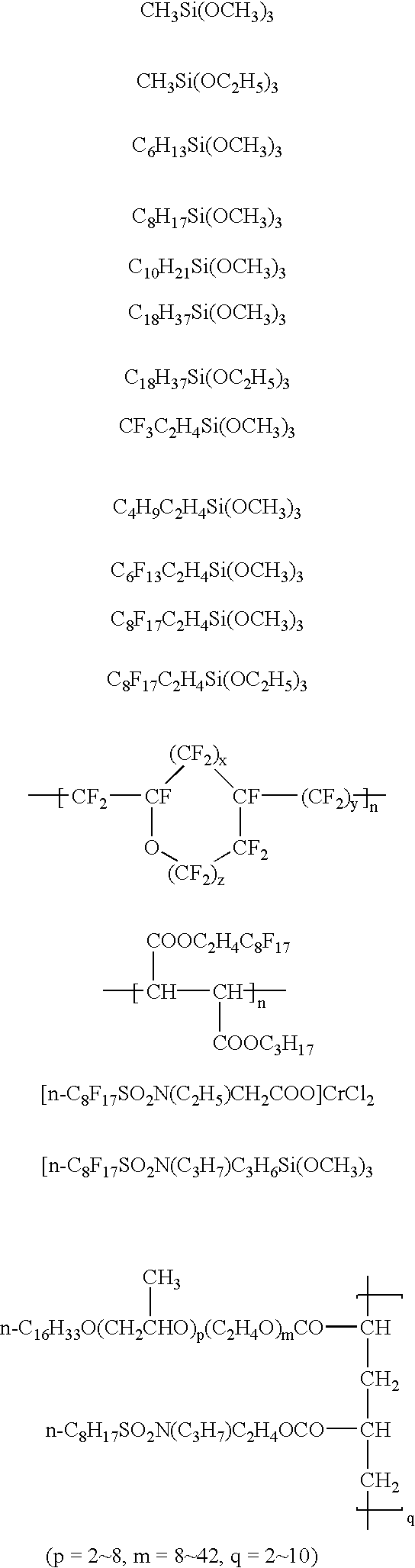
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition
InactiveUS20080014374A1Uniform thicknessPrevent productivity being deterioratedLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingSolution stateBisphenol
The invention is to provide such a polymerizable liquid crystal composition that is excellent in stability in a solution state, shows good coating property on a supporting substrate, and has uniform homeotropic alignment property. The polymerizable liquid crystal composition of the invention contains an acrylate compound and a bisphenol fluorene compound. The bisphenol fluorene compound is effective for controlling uniform homeotropic alignment of the polymerizable liquid crystal composition.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM +1
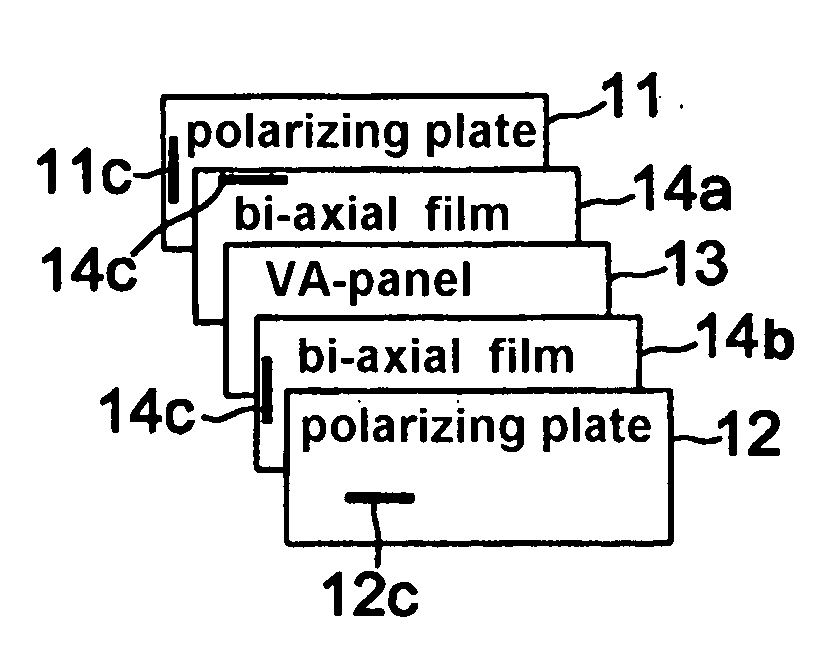
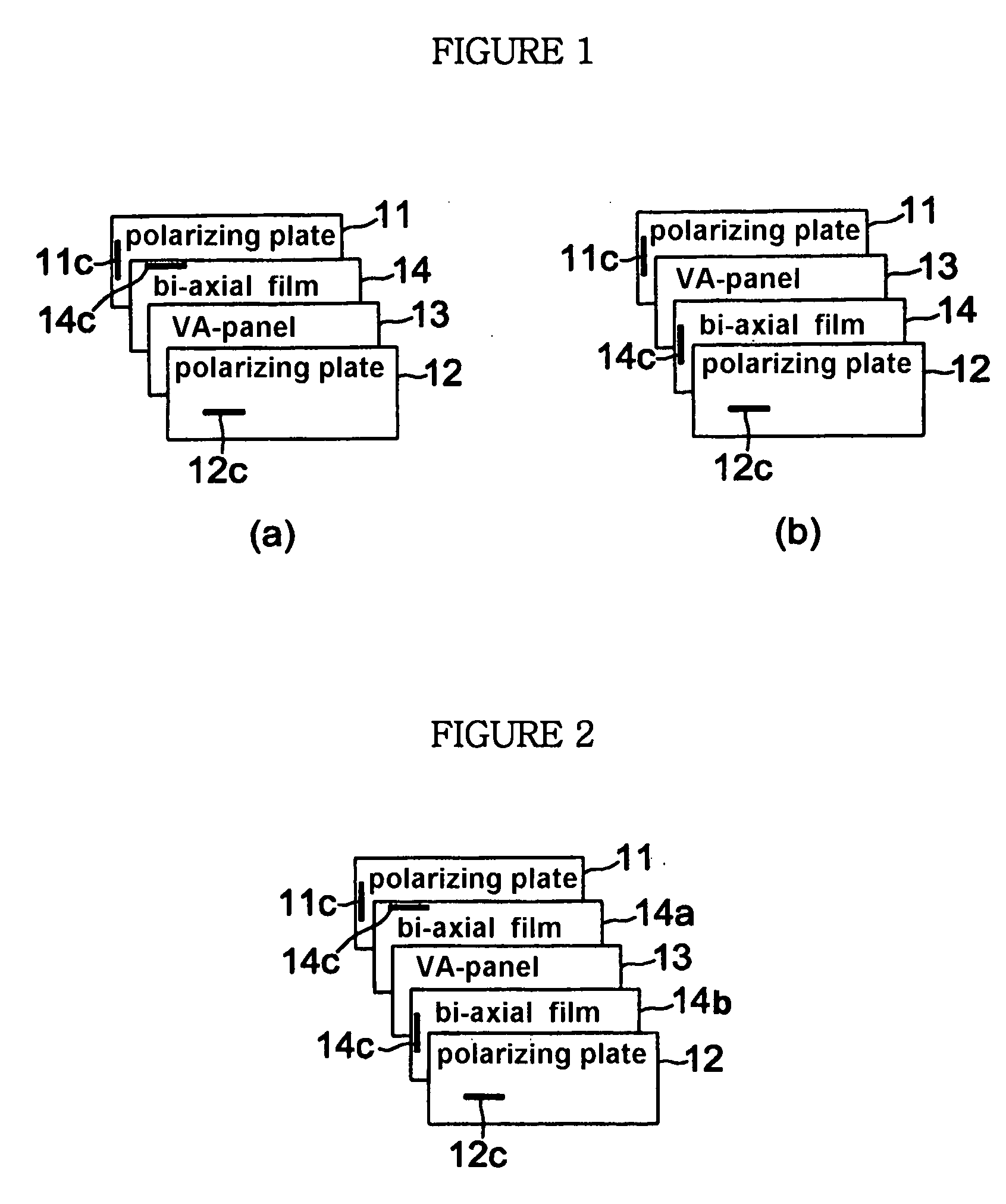
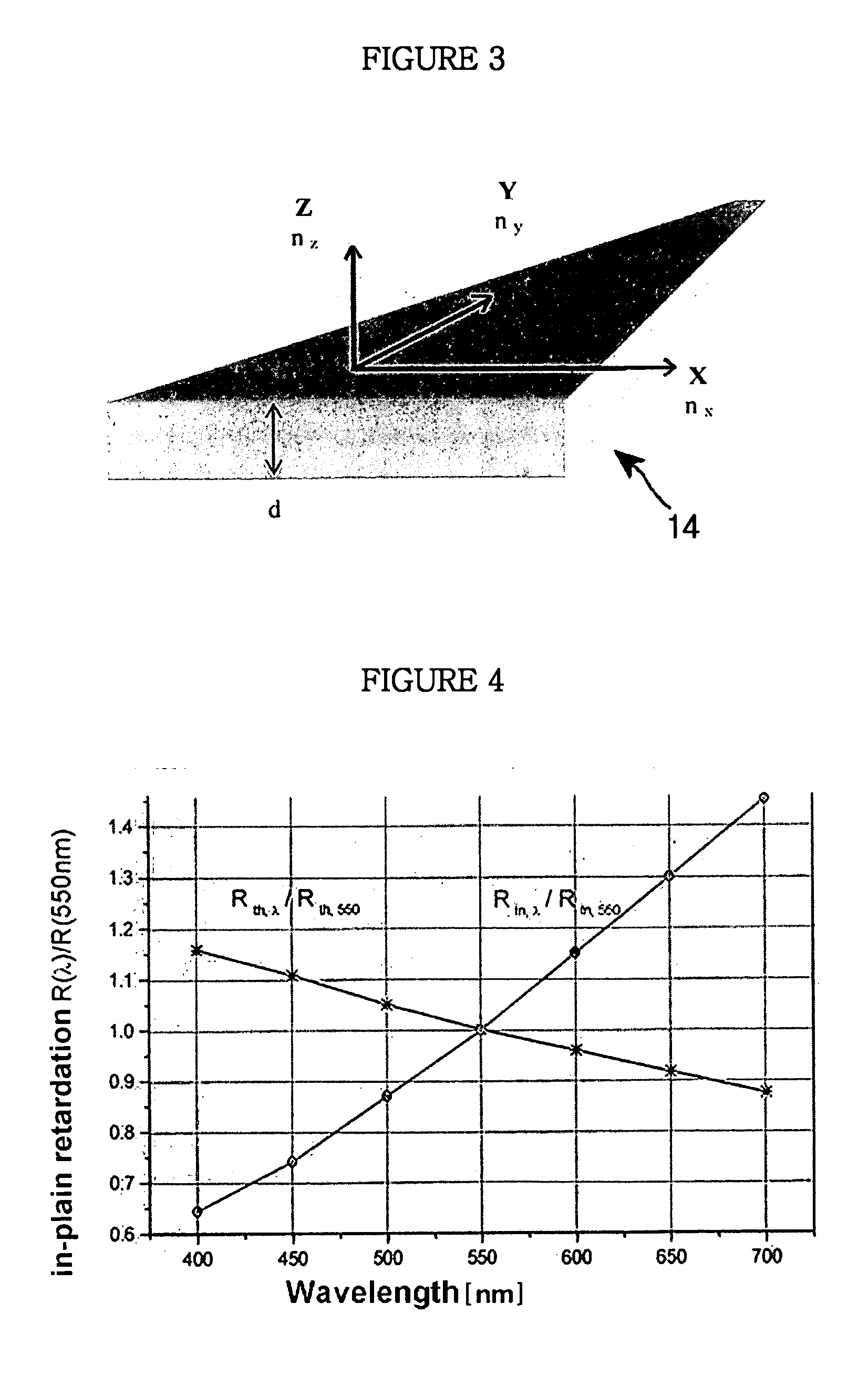
Bi-axial retardation compensation film and vertically aligned liquid crystal display using the same
ActiveUS20060132686A1Improve viewing angle characteristicsColoring at the tilt angle in a black state is minimizedNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayRefractive index
The present invention relates to a vertically aligned LCD (VA-LCD) employing a bi-axial retardation compensation film, in which an in-plain refractive index (nx, ny) and a thickness refractive index (nx) of the film is nx>ny>nz. The film has a reversed wavelength dispersion in which retardation is increased in proportion to the increase of a wavelength in the range of visible rays and has a normal wavelength dispersion in which an absolute value of the thickness retardation is decreased in proportion to the increase of a wavelength in the range of visible rays. The VA-LCD cell having a retardation compensation characteristic is comprised by arranging a bi-axial retardation compensation film between the vertically aligned panel and a upper and lower polarizing plate. The VA-LCD of the present invention improves contrast characteristics on a front surface and at a tilt angle and minimizes coloring in a black state according to the tilt angle.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Liquid crystal display panel capable of switching viewing angle and drive method thereof
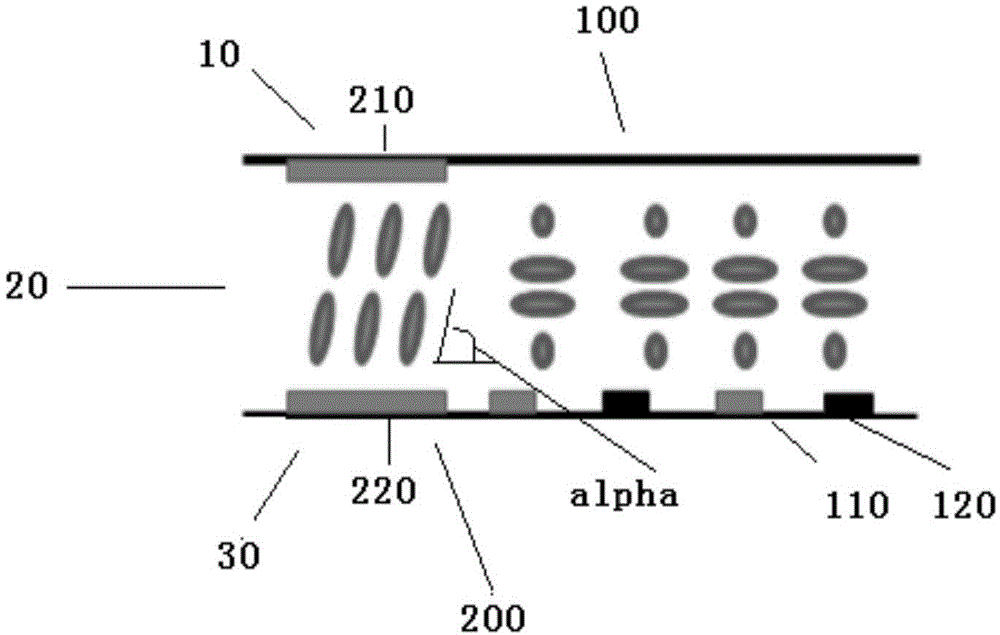
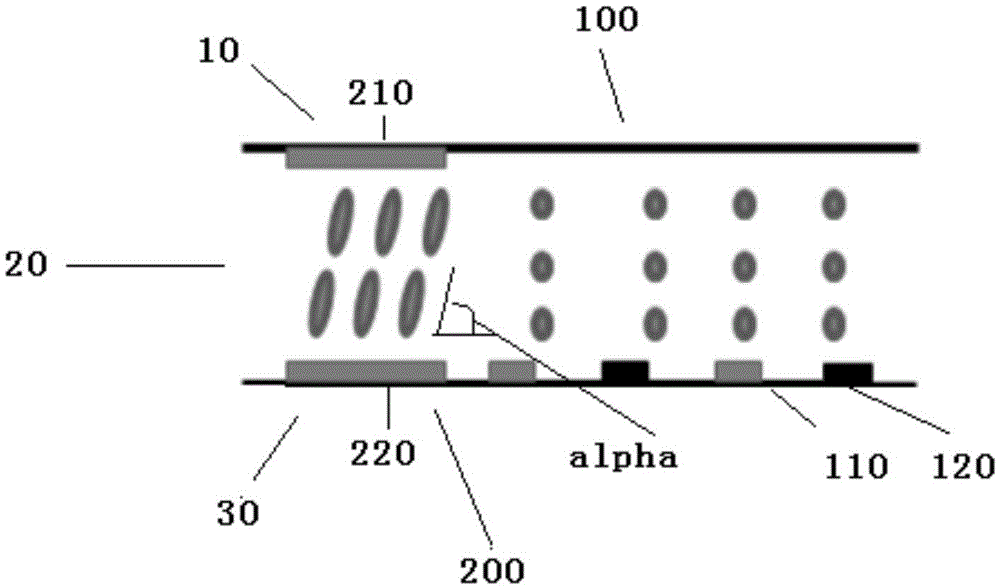
ActiveCN104460138AReduce thicknessEasy to operateStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsComputer scienceHomeotropic alignment
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display panel capable of switching the viewing angle and a drive method of the liquid crystal display panel. A pixel unit of a liquid crystal display panel display region comprises a primary pixel region and a secondary pixel region; the primary pixel region is homogeneous alignment and arranged in the primary pixel region, and a lower substrate is provided with pixel electrodes and public electrodes at intervals; the secondary pixel region is homeotropic alignment and arranged in the secondary pixel region, and an upper substrate and the lower substrate are correspondingly provided with an upper substrate electrode and a pixel electrode respectively. When no bias voltage is applied on the upper substrate electrode of the secondary pixel region, the liquid crystal molecules corresponding to the secondary pixel region do not defect, and the large viewing angle of the secondary pixel region leaks light, narrow viewing angle display is achieved; when the bias voltage is applied on the upper substrate electrode of the secondary pixel, the liquid crystal molecules corresponding to the secondary pixel region deflect to the plane-on state, the large viewing angle of the secondary pixel region does not leak the light any more, and wide-view-angle display is achieved.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Fast response liquid crystal mode
A novel nematic liquid crystal (LC) mode is based on the Fringing-Field-Switching of Vertically-Aligned liquid crystals. The VA-FFS mode is capable of generating very fast optical modulation without the use of very thin cell gap. IA major feature of this LC mode is that it has unusual fast relaxation time compared with the conventional nematic LC modes that require a thin cell gap. This fast relaxation occurs even at very low applied voltages and the operation is very stable. The fast-response mechanism of this LC mode involves the confinement of liquid crystal molecular switching within self-imposed thin LC layers. The present invention provides a novel approach to overcome the fundamental problem of the long relaxation time of the conventional nematic liquid crystal modes.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Liquid crystal display device having particular alignment controlling elements in transmissive and reflective pixel regions
ActiveUS7106405B2Wide viewing angleSuppress failureNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyDisplay device
To provide a transreflective liquid crystal display device that can produce a bright and high-contrast display with a wide viewing angle. A liquid crystal display device has a liquid crystal layer held between a pair of substrates and has a transmissive display region and a reflective display region in one dot region. The liquid crystal layer includes a liquid crystal being initially vertically aligned and having negative dielectric anisotropy. The pair of substrates have electrodes to drive the liquid crystal on sides facing the liquid crystal layer. The electrodes have openings and protrusions in the transmissive display region and the reflective display region, respectively. The opening areas of the openings and the in-plane occupying areas of the protrusions are larger in the reflective display region than in the transmissive display region.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition
ActiveUS20080241431A1Improve stabilityImprove adhesionLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingSolution stateOrganic chemistry
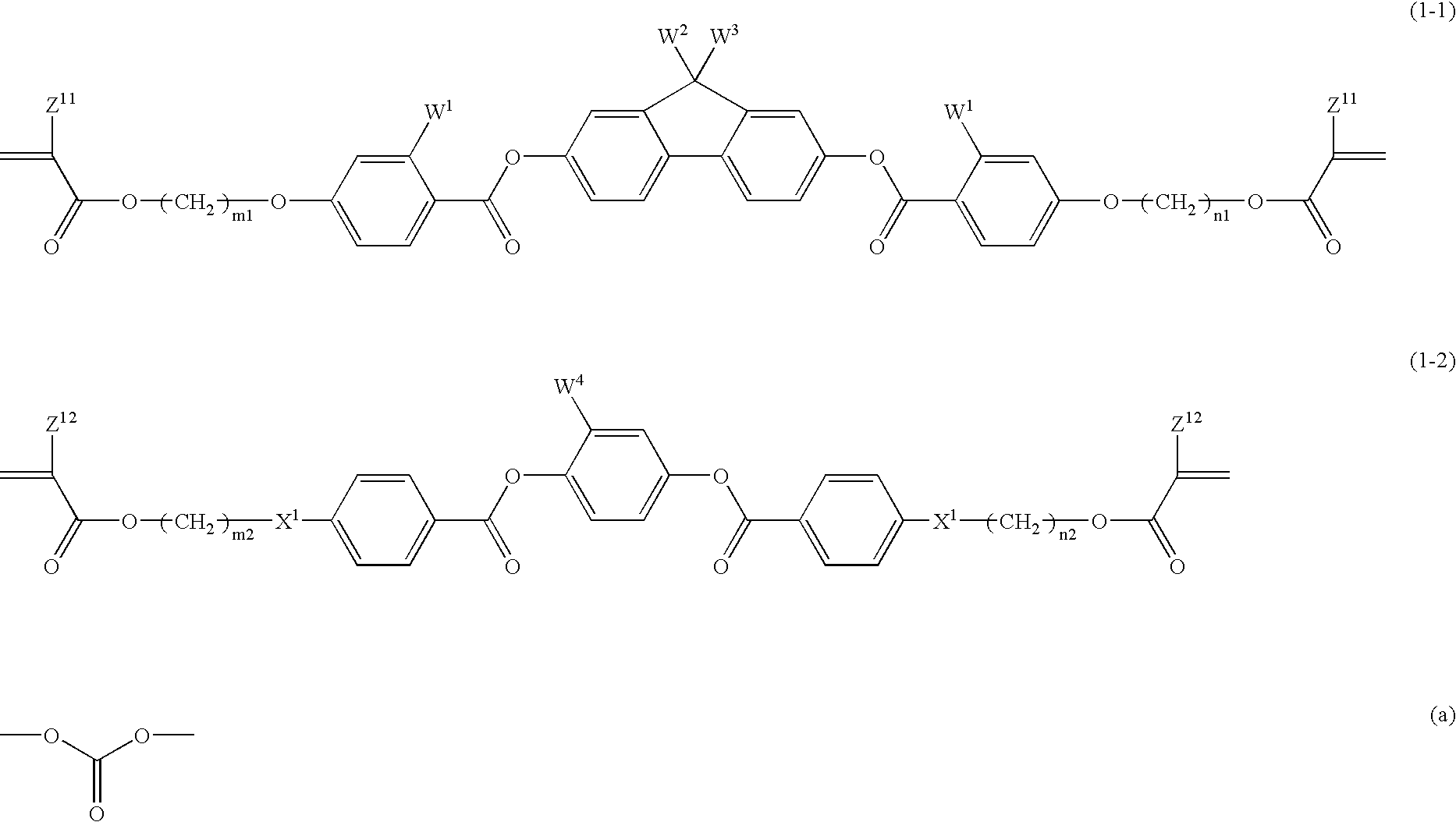
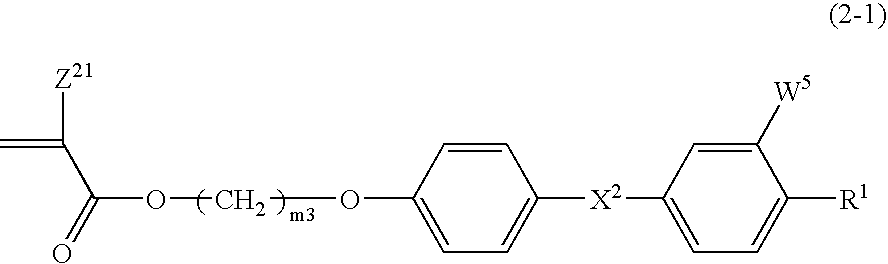
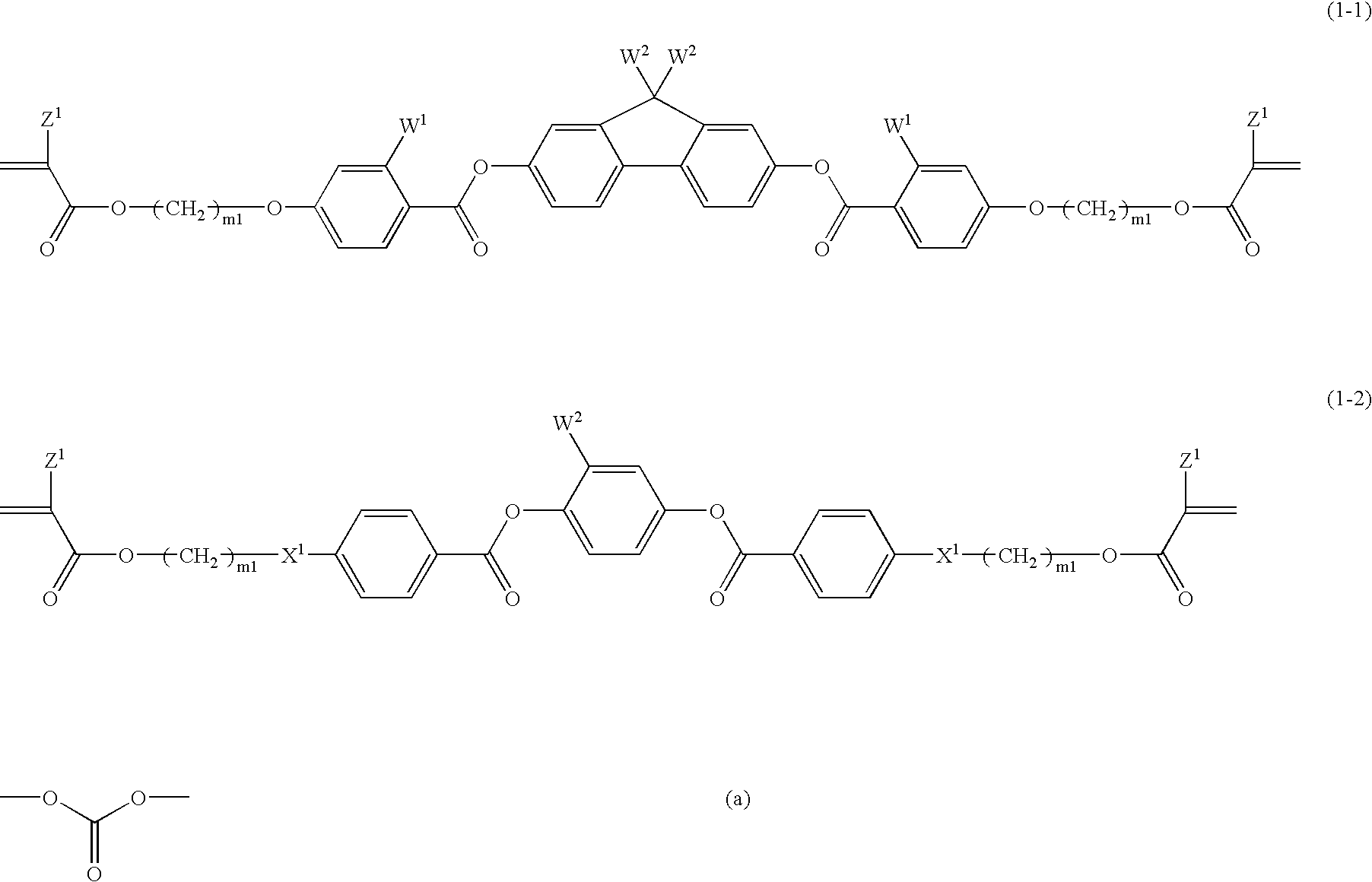
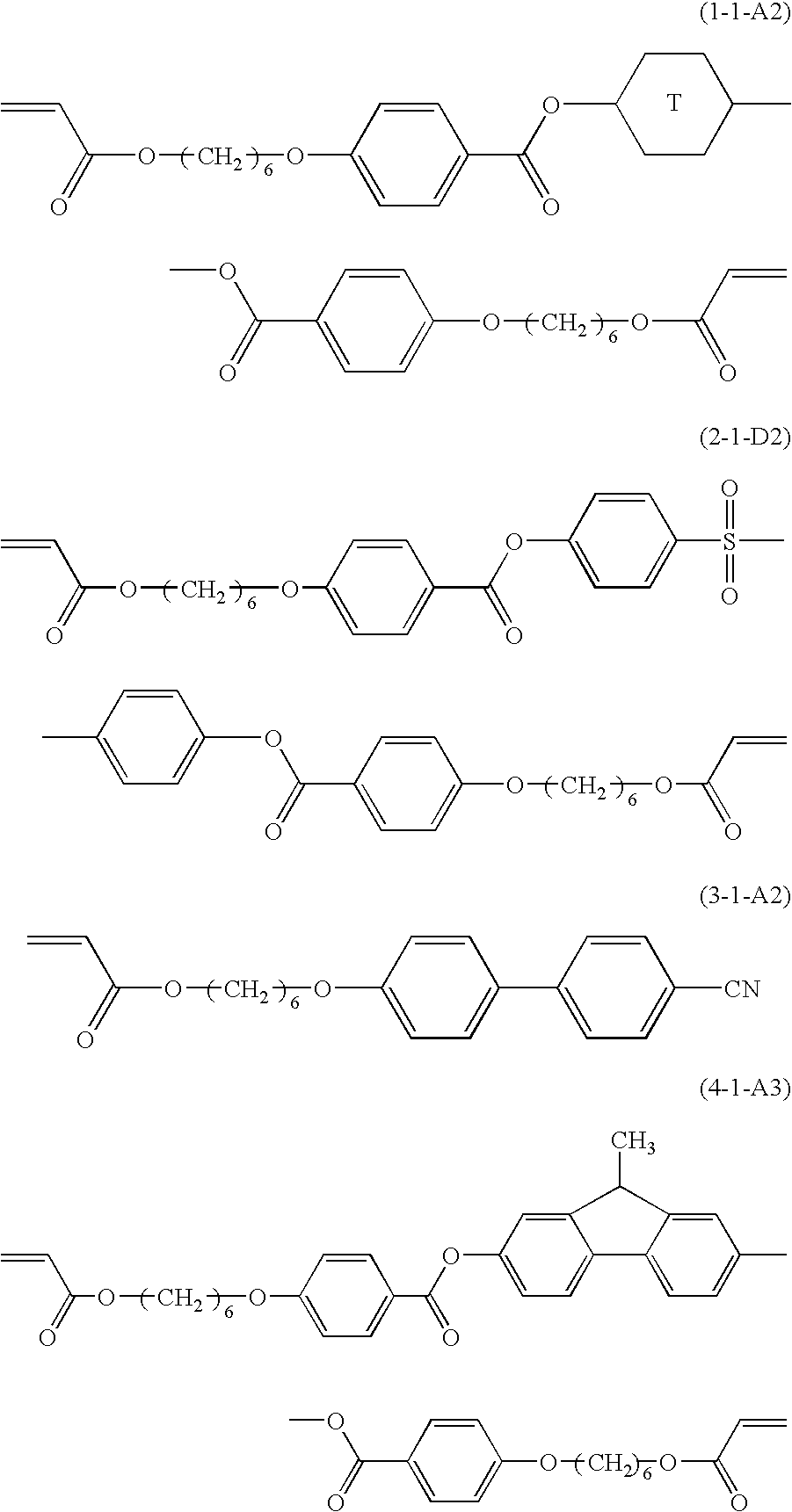
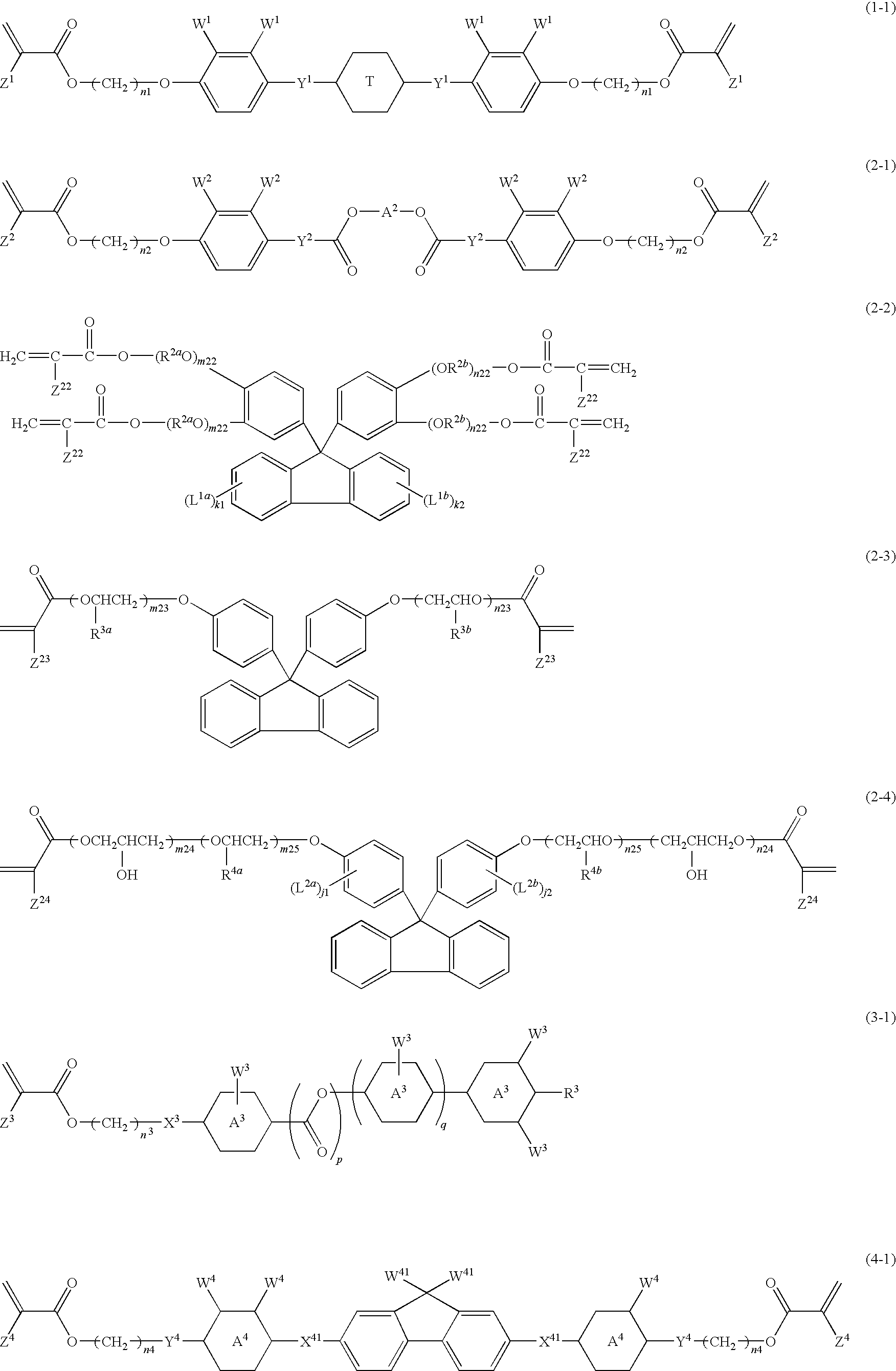
Such a polymerizable liquid crystal composition is to be provided that is excellent in stability in a solution state, shows good coating property on a supporting substrate, and has a uniform homeotropic alignment property. The polymerizable liquid crystal composition contains an acrylate compound, an epoxy compound and a bisphenol fluorene compound. The polymerizable liquid crystal composition contains a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by formulae (1-1) and (1-2) as a component (A), a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by formula (2) as a component (B), a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by formulae (3-1) to (3-3) as a component (C) and a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by formulae (4-1A), (4-1B), (4-2), (4-3), (4-4) and (4-5) as a component (D), and may optionally contain a compound selected from a group of compounds represented by formulae (5-1) and (5-2) as a component (E). The bisphenol fluorene compound is effective for controlling a uniform homeotropic alignment of the polymerizable liquid crystal composition.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
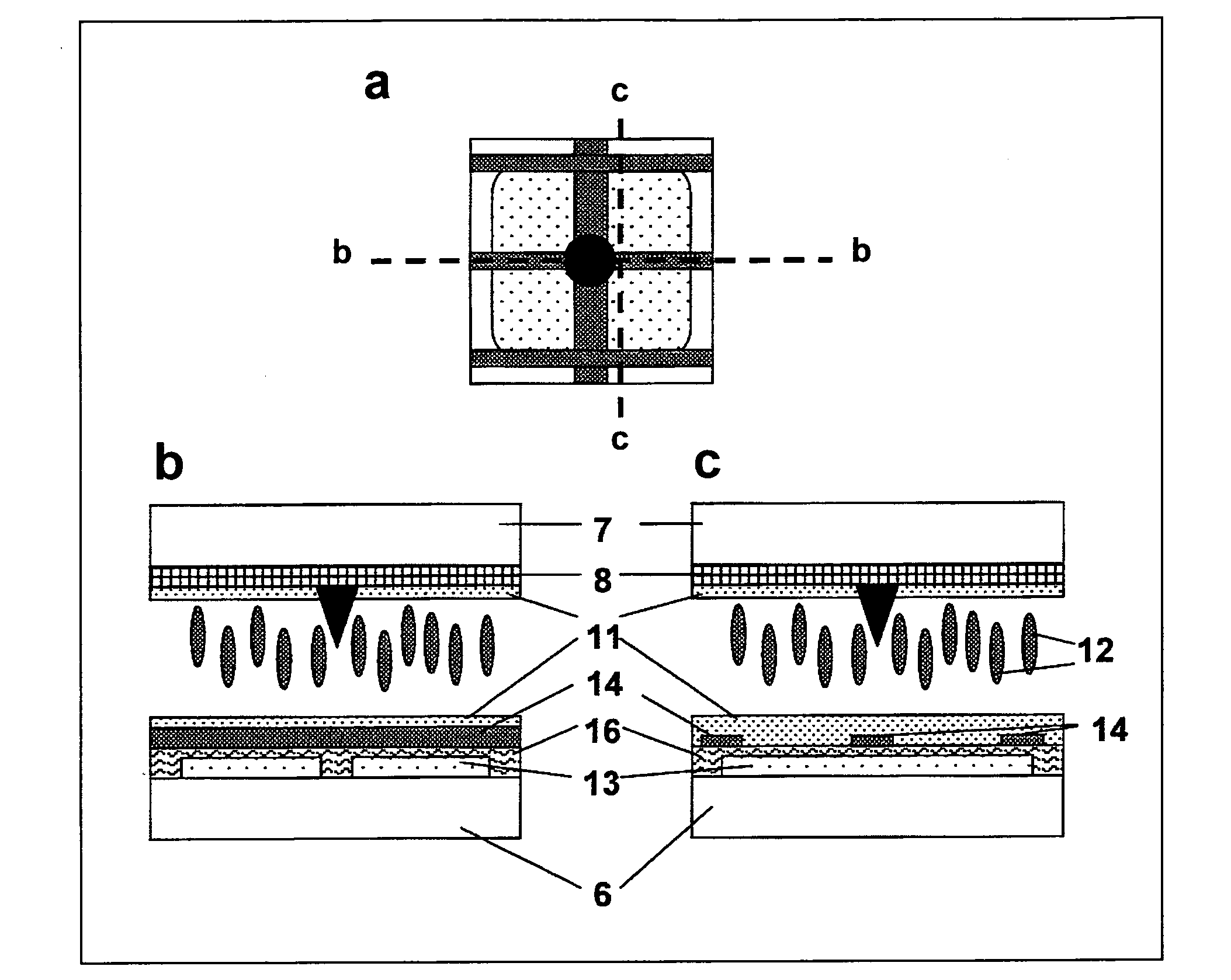
Liquid crystal device
ActiveUS20100220043A1Wider viewing angle propertyRange of view is limitedStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsActive matrixDisplay device
A liquid crystal device comprises an active matrix substrate (6) and a counter-substrate (7) provided with homeotropic alignment surfaces (11). A layer of nematic liquid crystal material is provided between the alignment surfaces (11) so as to form a vertically aligned nematic device. The substrates (6, 7) carry a pixel electrode arrangement and a counter-electrode arrangement which define a plurality of pixel regions. Each of least some of these regions has a pixel electrode (13), which may be split into two halves, and a counter-electrode (8) which are arranged to apply an electric field for controlling the liquid crystal director (12) out-of-plane tilt angle. A further electrode (14), for example in the form of a plurality of parallel fingers, cooperates with at least one of the other electrodes (8, 13) to apply a second electric field for controlling the director in-plane azimuth angle. Such a device may be used, for example, as a switchable public / private display.
Owner:SHARP KK
Polymerizable liquid crystal composition and homeotropically-aligned liquid crystal film
InactiveUS20100151154A1Reduced stabilityUniform homeotropic alignmentLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid-crystal displayOrganic chemistry
A polymerizable liquid crystal composition is provided that can contains a mixture of polymerizable compounds containing a compound represented by the formula (1-1), a compound represented by the formula (2), a compound represented by the formula (3-1) and a compound represented by the formula (4), and a amine silane coupling agent. The composition can form a polymerizable liquid crystal layer exhibiting a uniform homeotropic alignment by coating the composition on a supporting substrate, independently from the kind of the supporting substrate without a special alignment film. Examples of each of the components are shown below, in which ring T represents triptycen-1,4-diyl.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof] [liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/49f9e14e-252c-4879-946b-b99b8f2ac2d9/US20050088386A1-20050428-D00000.png)
![[liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof] [liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/49f9e14e-252c-4879-946b-b99b8f2ac2d9/US20050088386A1-20050428-D00001.png)
![[liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof] [liquid crystal display panel and driving circuit thereof]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/49f9e14e-252c-4879-946b-b99b8f2ac2d9/US20050088386A1-20050428-D00002.png)