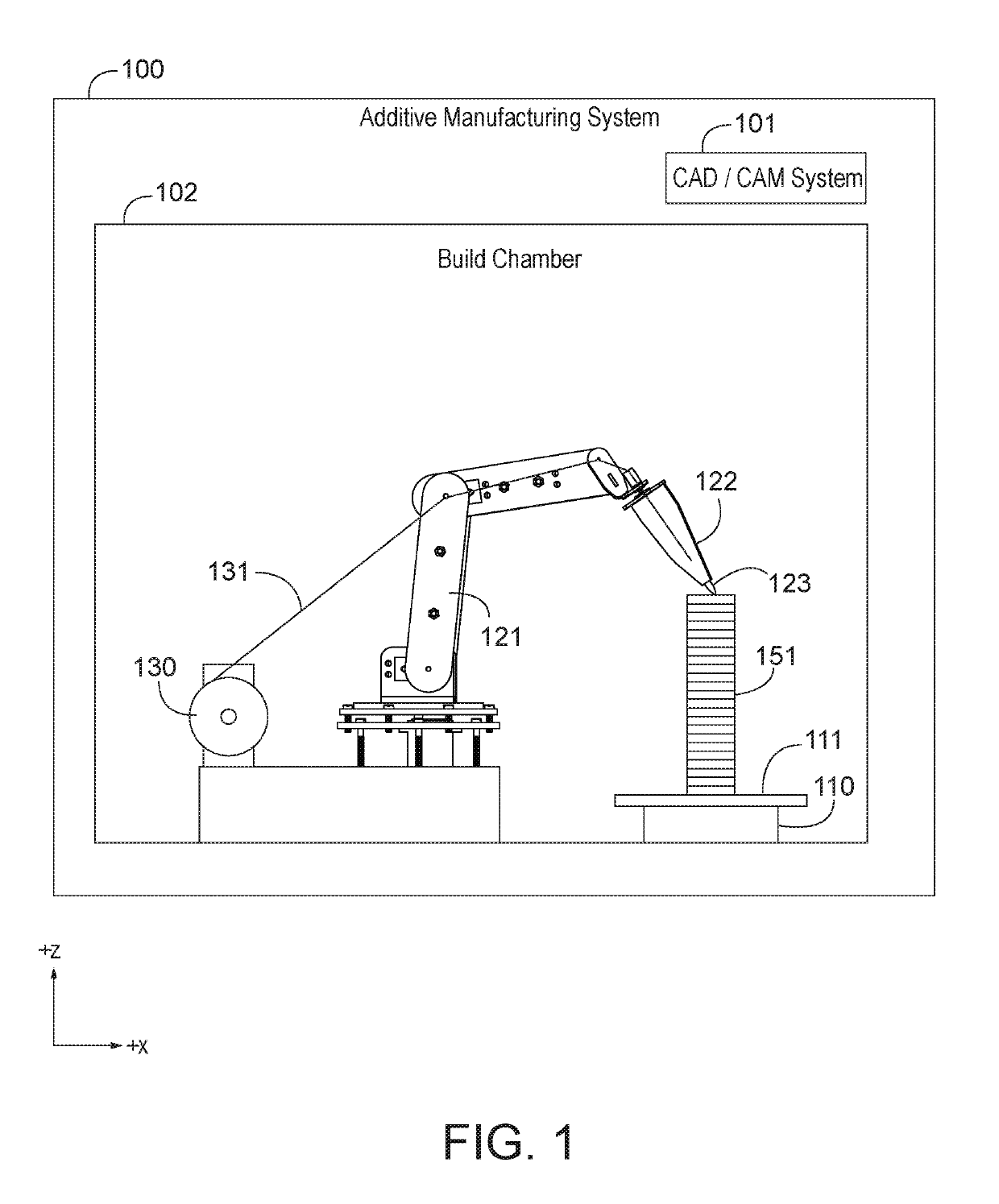
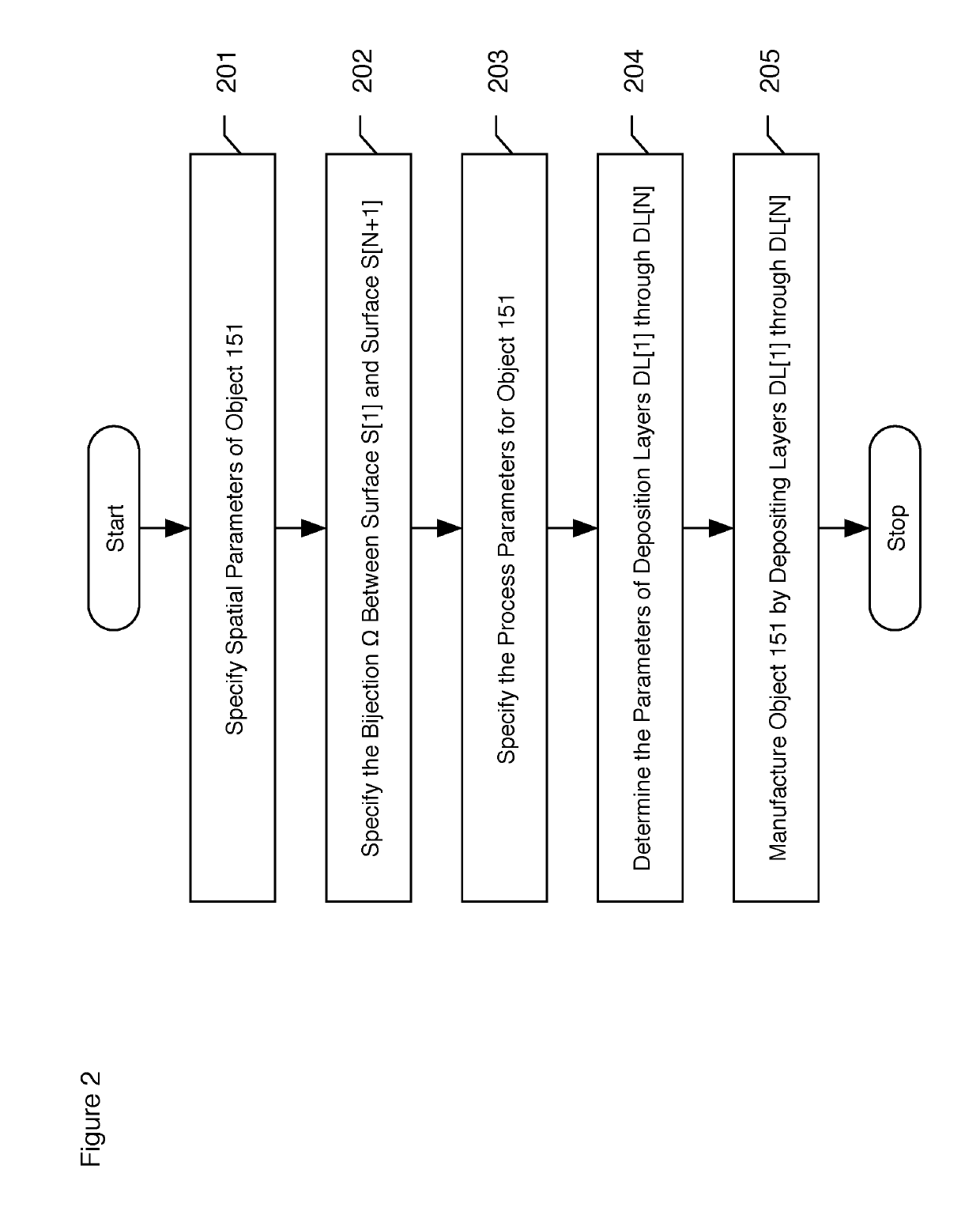
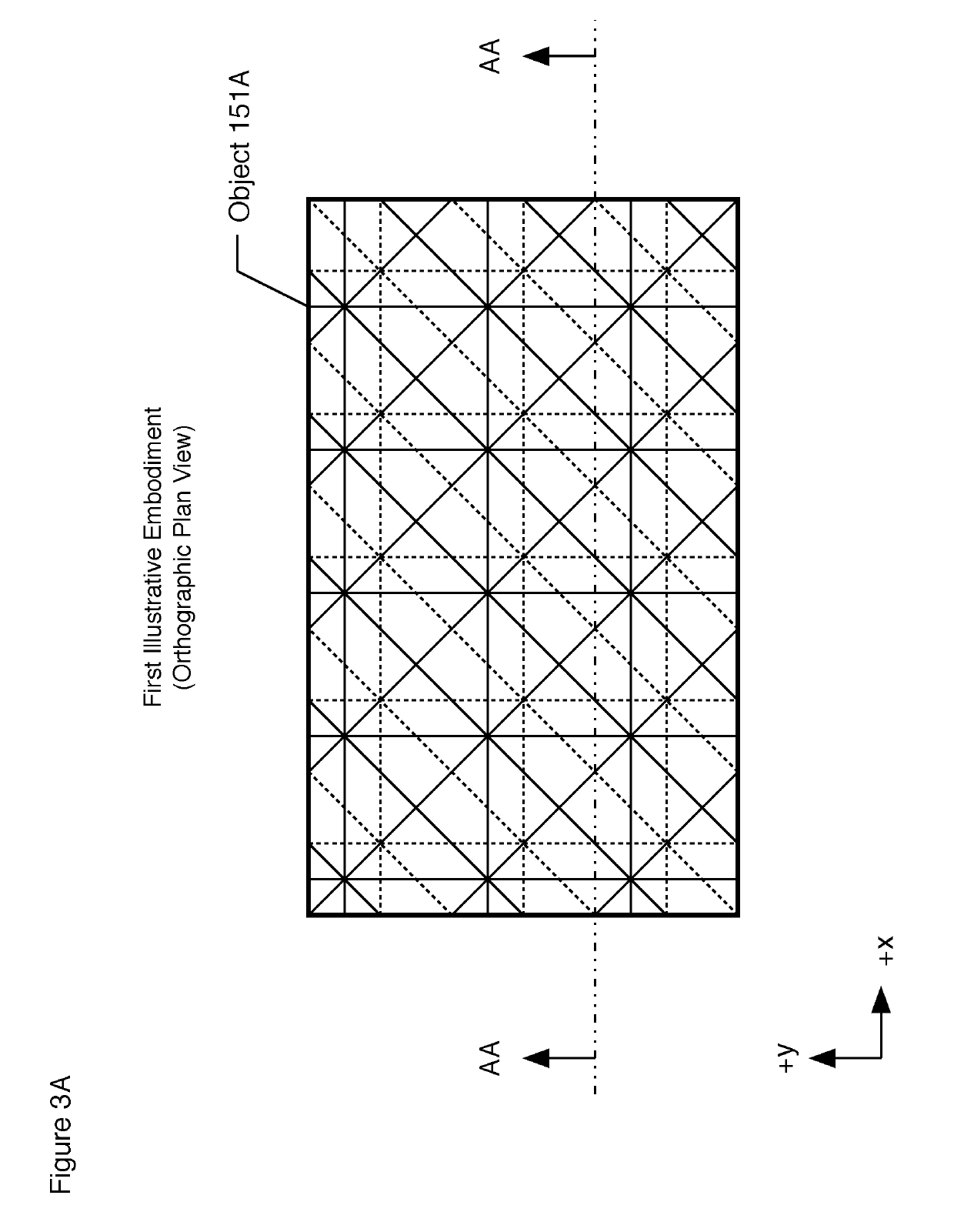
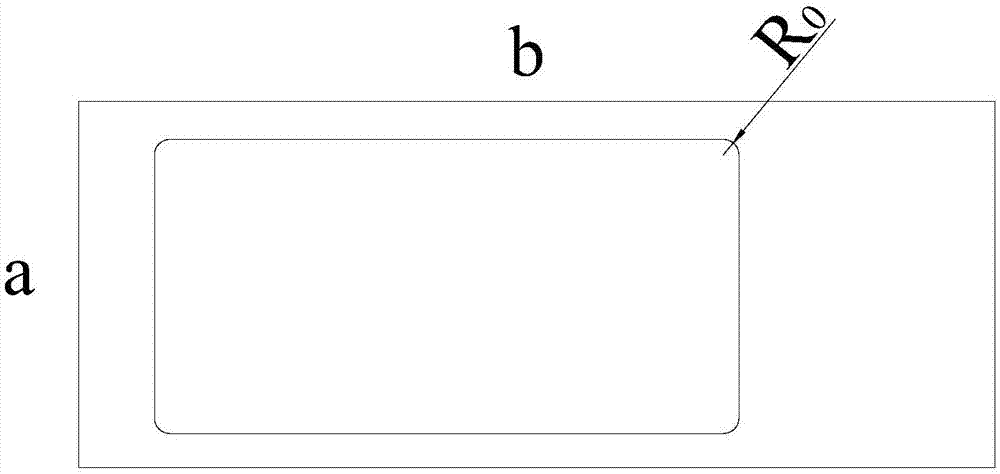
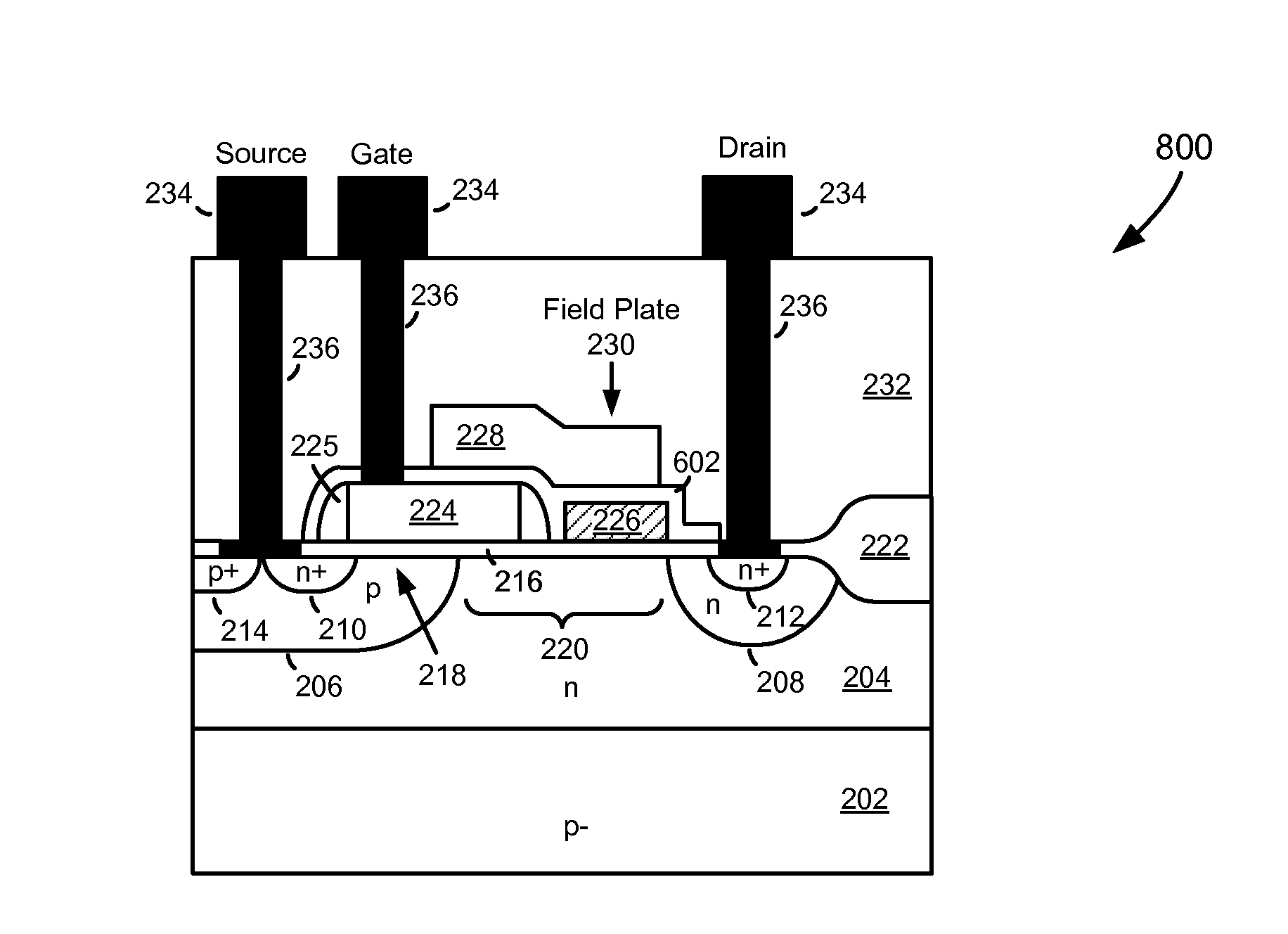
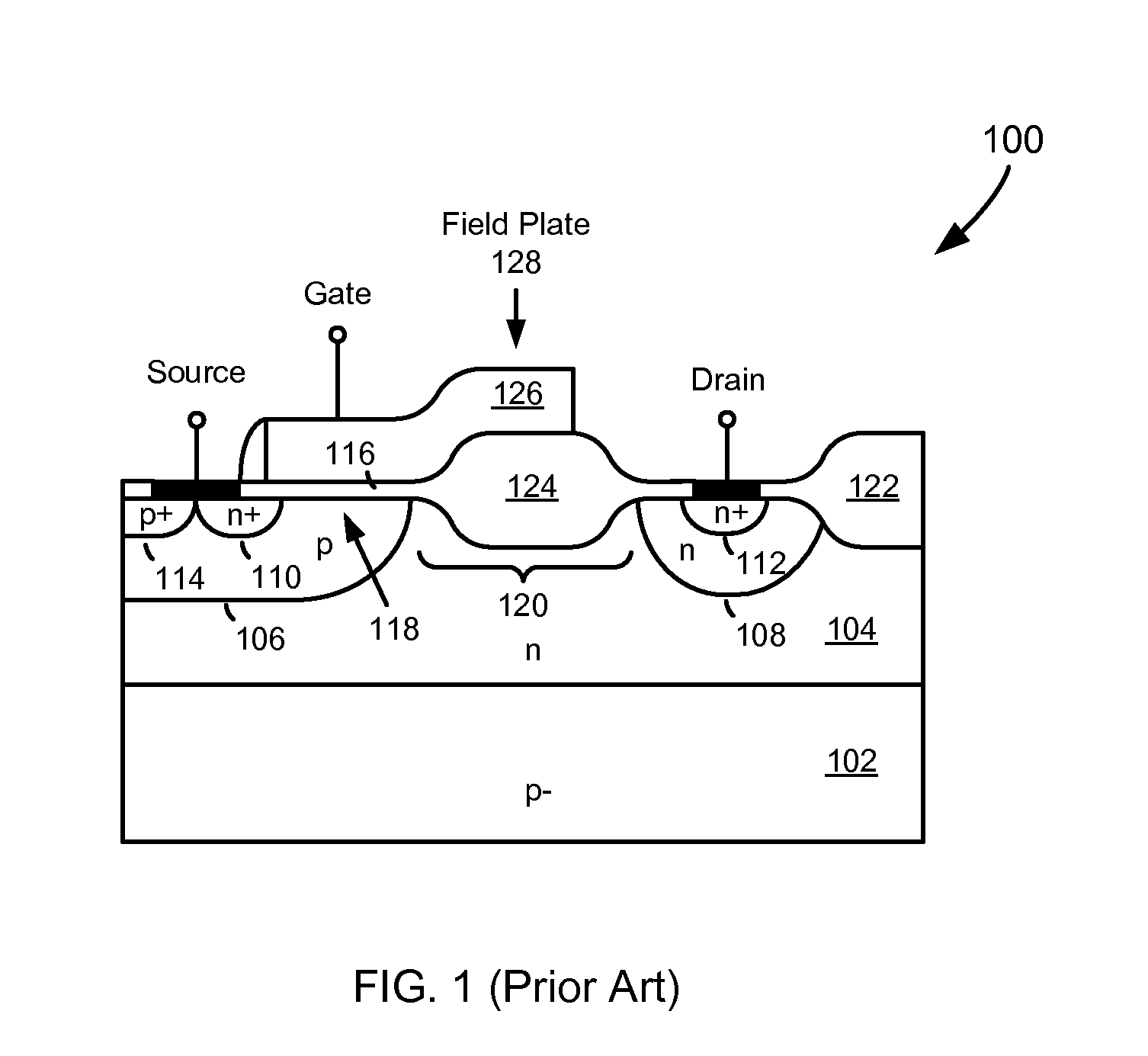
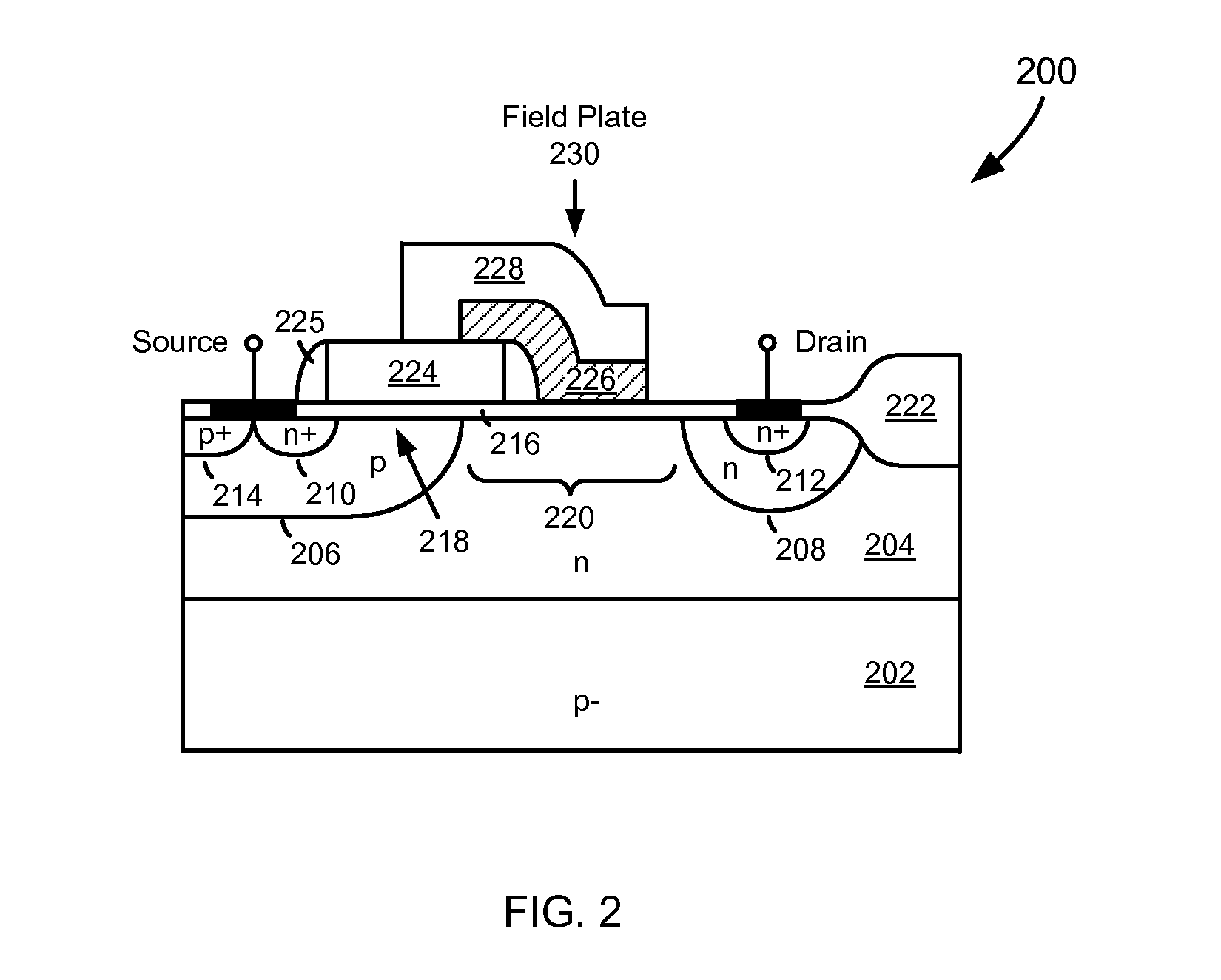
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3479results about How to "Control thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
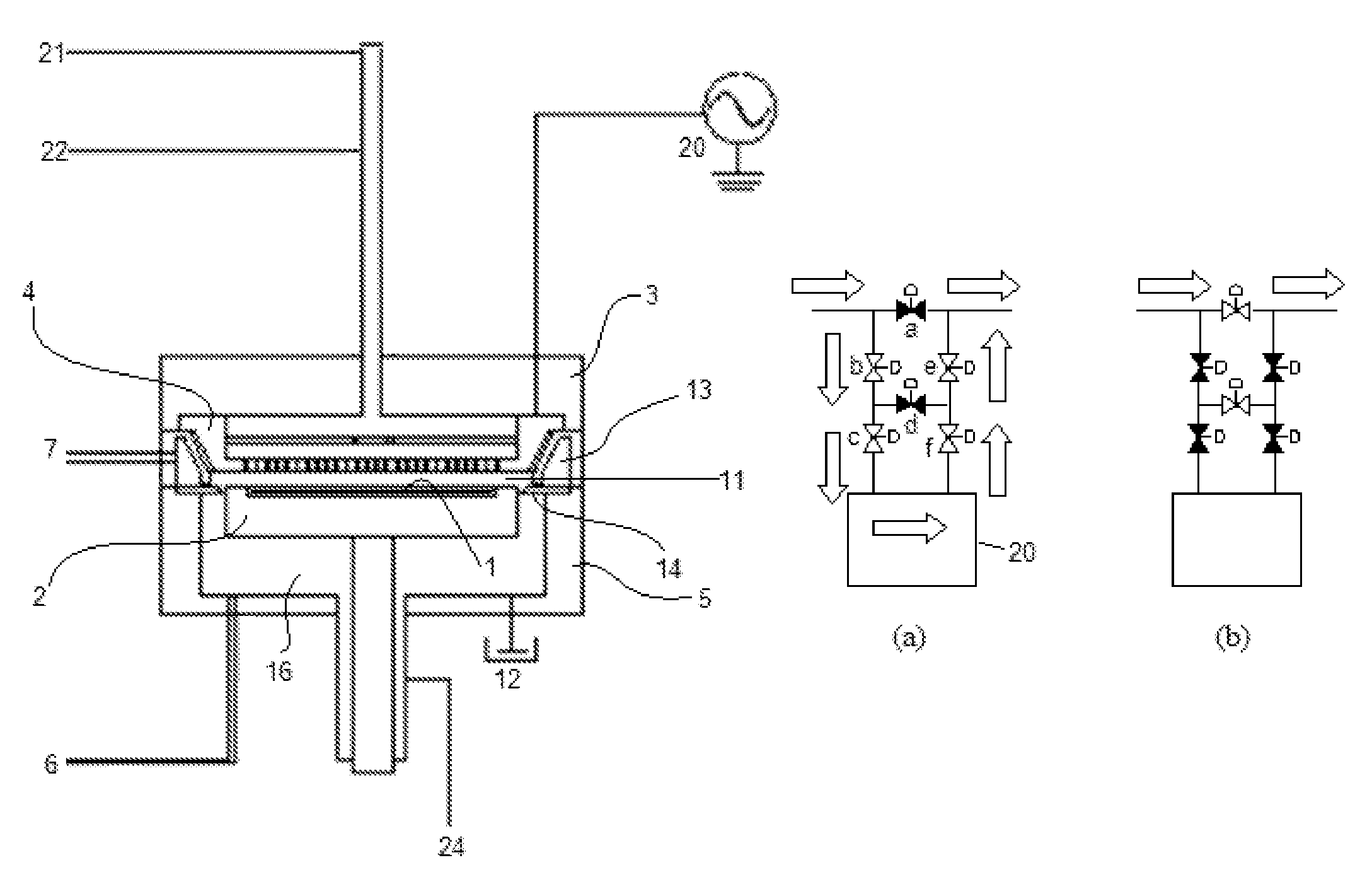
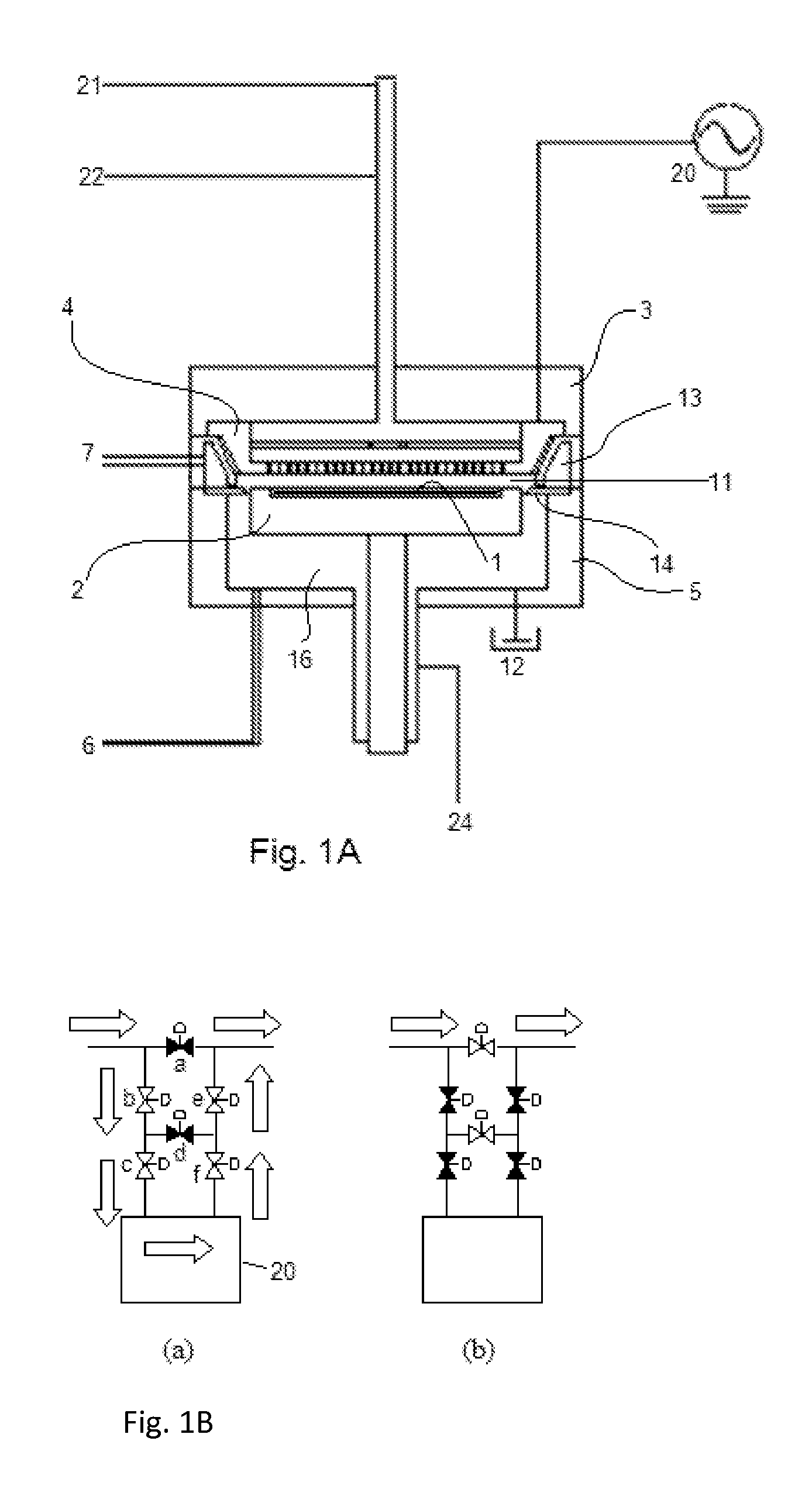
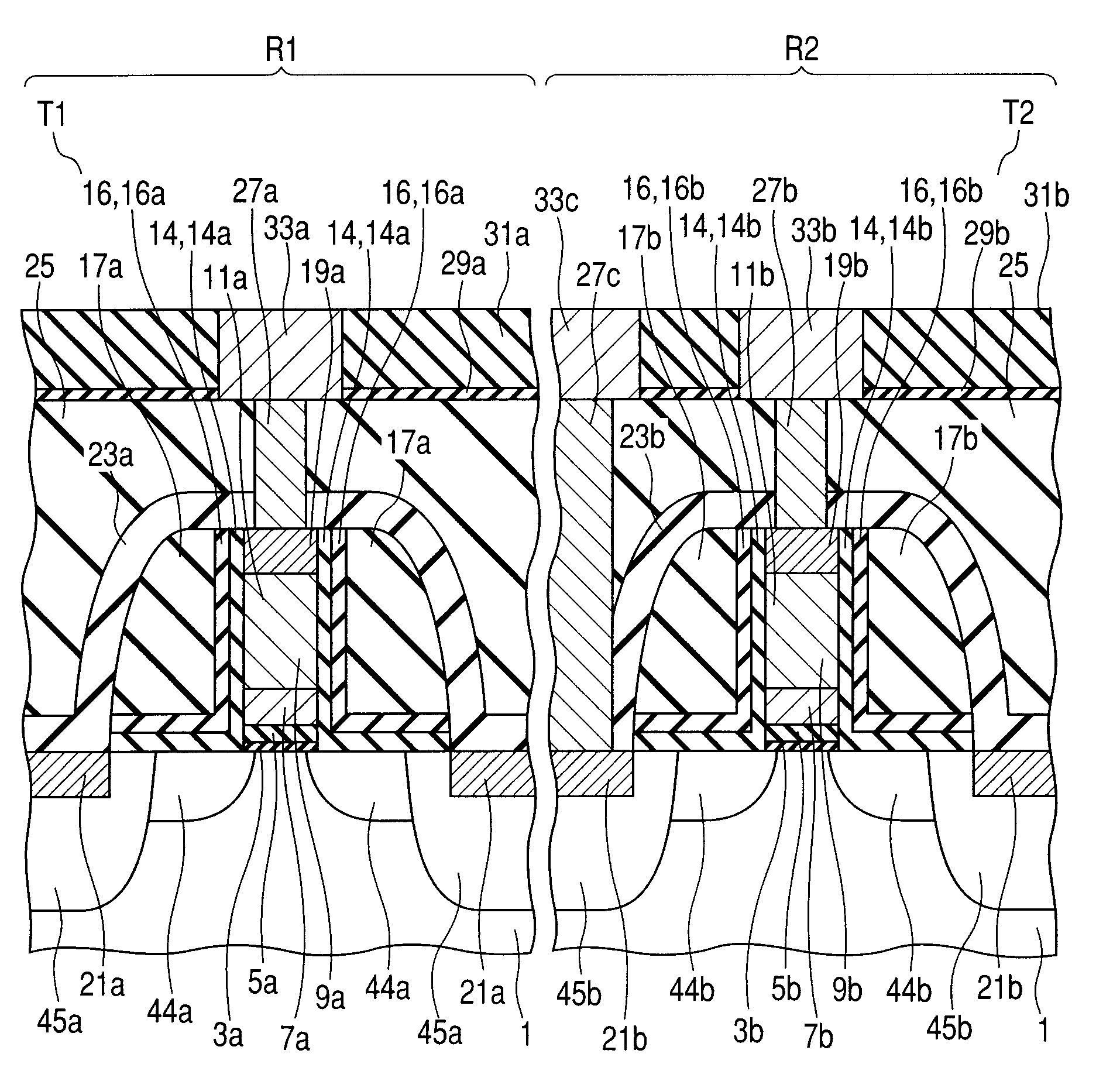
Method for forming dielectric film in trenches by PEALD using H-containing gas
ActiveUS9455138B1Increase deposition rateHigh film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsNoble gas
A method for forming a dielectric film in a trench on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) performs one or more process cycles, each process cycle including: (i) feeding a silicon-containing precursor in a pulse; (ii) supplying a hydrogen-containing reactant gas at a flow rate of more than about 30 sccm but less than about 800 sccm in the absence of nitrogen-containing gas; (iii) supplying a noble gas to the reaction space; and (iv) applying RF power in the presence of the reactant gas and the noble gas and in the absence of any precursor in the reaction space, to form a monolayer constituting a dielectric film on a substrate at a growth rate of less than one atomic layer thickness per cycle.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Linear aperture deposition apparatus and coating process
InactiveUS6202591B1High and stable rateEasy to useVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesSource material
A linear aperture deposition apparatus and process are provided for coating substrates with sublimed or evaporated coating materials. The apparatus and process are particularly suited for producing flexible films having an optical interference coating with a very high surface thickness uniformity and which is substantially free of defects from particulate ejection of a source material. The apparatus includes a source box containing a source material, a heating element to sublime or evaporate the source material, and a chimney to direct the source material vapor from the source box to a substrate. A flow restricting baffle having a plurality of holes is positioned between the source material and the substrate to confine and direct the vapor flow, and an optional floating baffle is positioned on the surface of the source material to further restrict the vapor flow, thereby substantially eliminating source material spatter.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
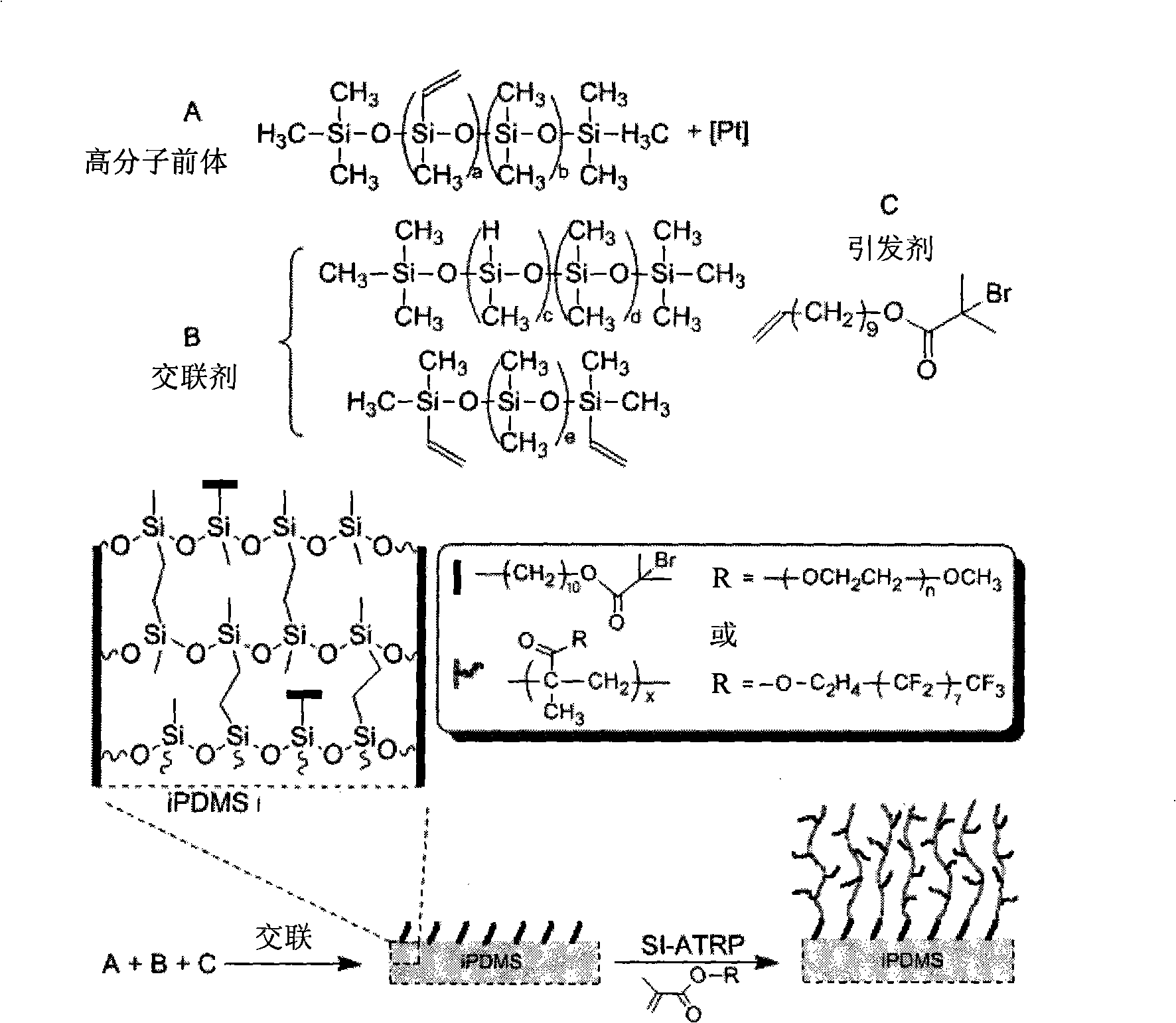
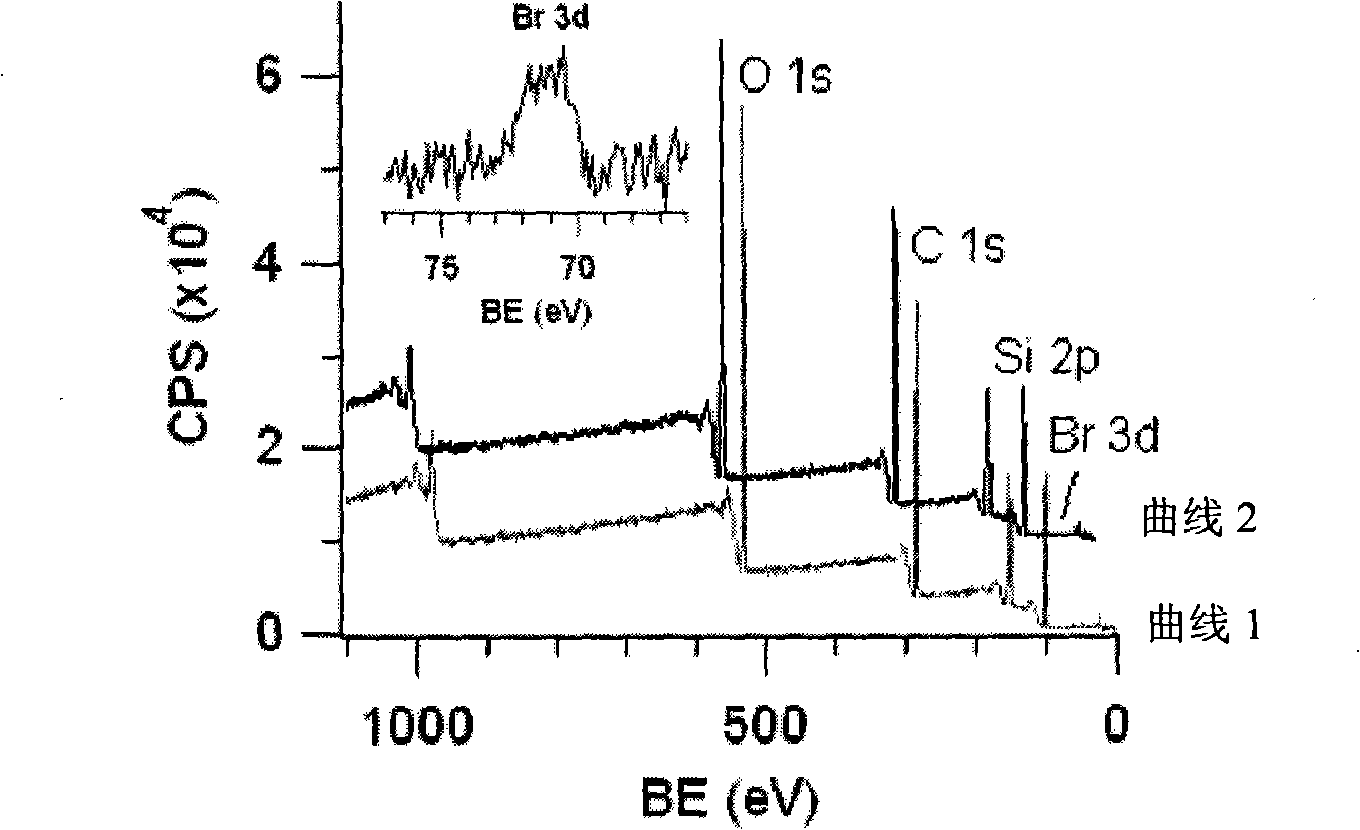
Polydimethylsiloxane with initiator on surface and its preparation method and use
The invention relates to polydimethylsiloxane which is provided with an initiator at the surface, and is the silicon-hydrogen bonding cross-linked polydimethylsiloxane, of which the surface contains 0.01 to 1At percent 2-bromine-2-methyl propioric acid 10-undecene ester. The material is formed by mixing a polymer precursor, a cross-liner and the initiator with olefinic end in the weight ratio of 10: 1: 4-0.01 and placing for 6 to 24 hours. The polydimethylsiloxane with the initiator at the surface which is provided by the invention further modifies a function layer on the surface by triggering the polymerization reaction on the surface, so the polydimethylsiloxane can be applied on biocompatible, organic solvent compatible and thermal sensitive materials. The invention uses the simple and convenient method to realize the universal, permanent, diverse and functional surface modified polydimethylsiloxane.
Owner:SUZHOU SIJU BIOMATERIALS
Back-gated fully depleted soi transistor
InactiveUS20110171792A1Prevent channelingControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOxideDopant
A fully depleted semiconductor-on-insulator (FDSOI) transistor structure includes a back gate electrode having a limited thickness and aligned to a front gate electrode. The back gate electrode is formed in a first substrate by ion implantation of dopants through a first oxide cap layer. Global alignment markers are formed in the first substrate to enable alignment of the front gate electrode to the back gate electrode. The global alignment markers enable preparation of a virtually flat substrate on the first substrate so that the first substrate can be bonded to a second substrate in a reliable manner.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
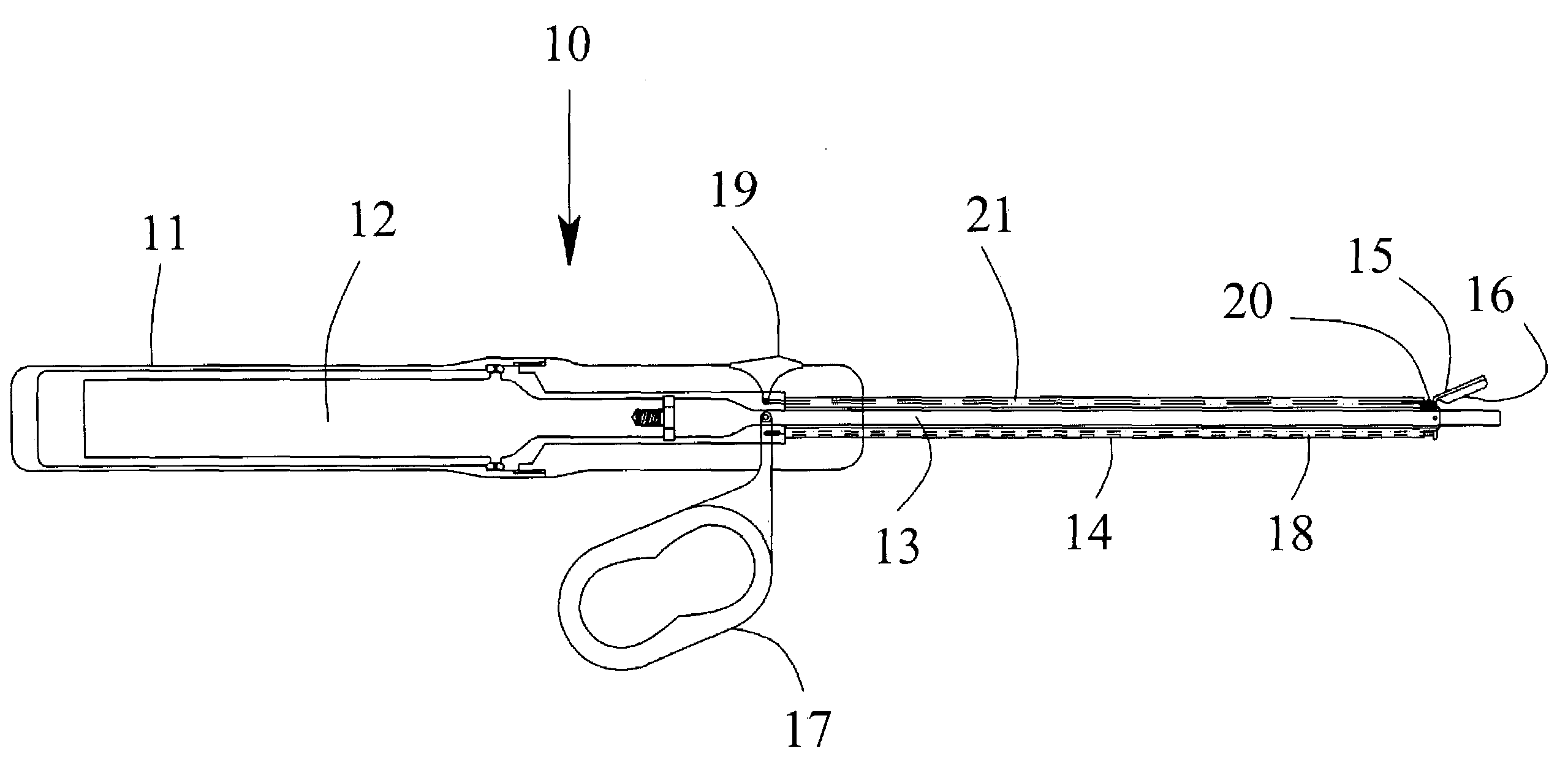
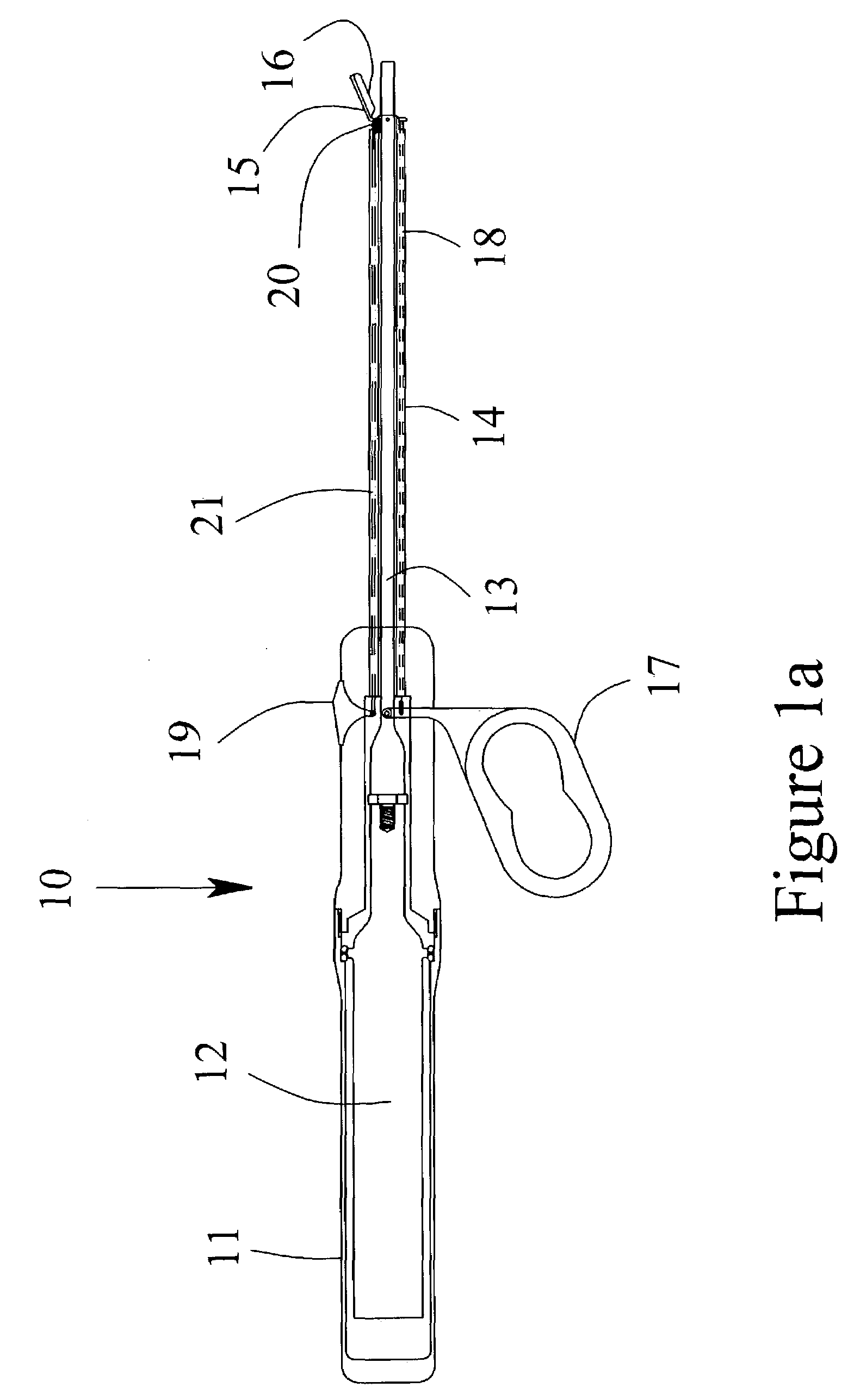
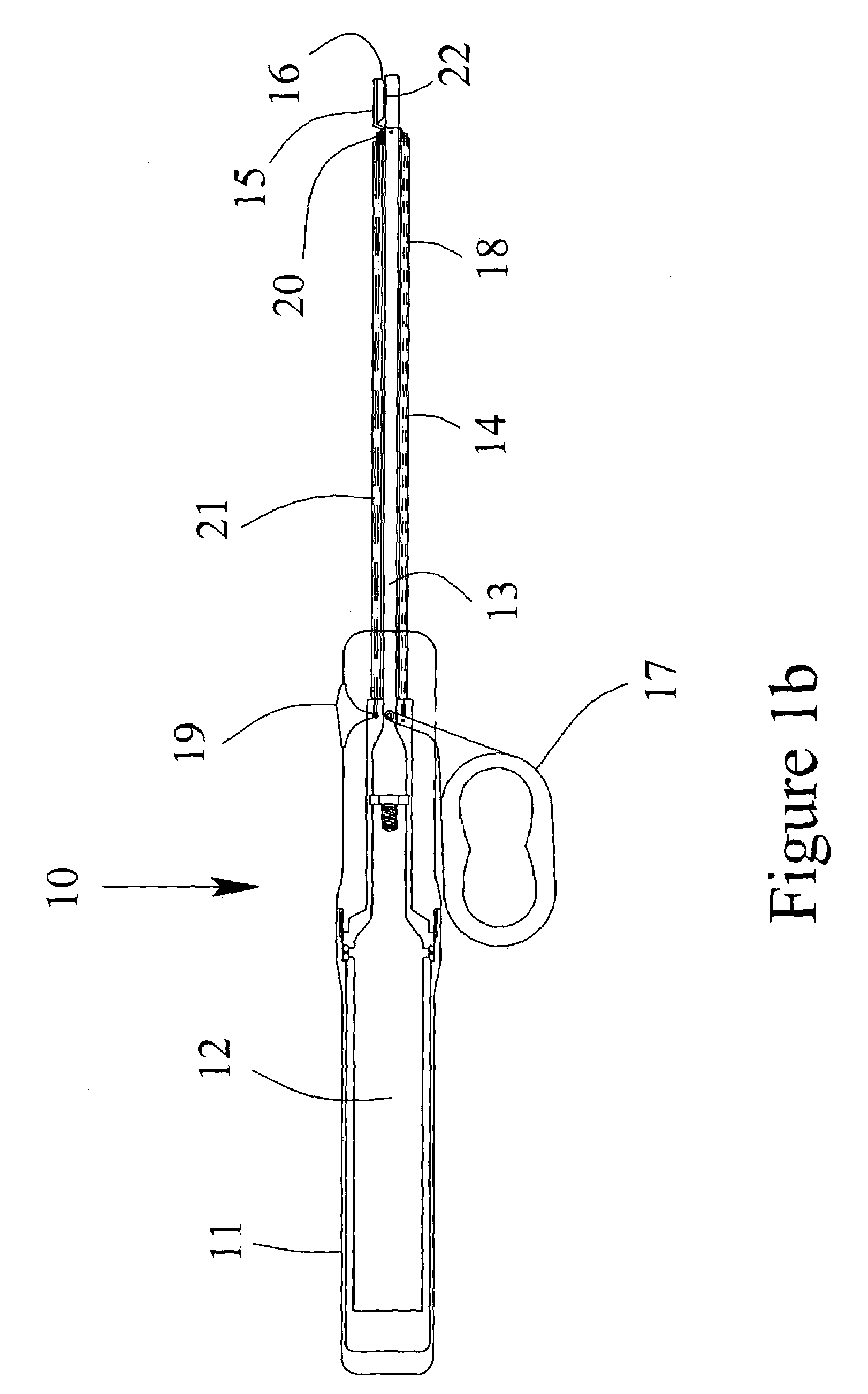
Ultrasonic device and method for tissue coagulation
ActiveUS7361172B2Good coagulationImprove the coagulation effectUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesDistal portionSurgical device
An ultrasonic surgical device for the coagulation of animal tissue having an ultrasonic applicator and a movable jaw with a jaw surface adjacent the distal portion of the ultrasonic applicator for movement toward the applicator to a closed position at a predefined clearance of between about 0.075 to about 1.9 millimeters from the applicator. The device may also include a mechanical cutting element that can be extended into the clearance to cut the tissue and means to vary the predefined clearance without removing the applicator from the patient. Tissue coagulating and cutting can be maximized and performed separately and can be easily monitored by the surgeon.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
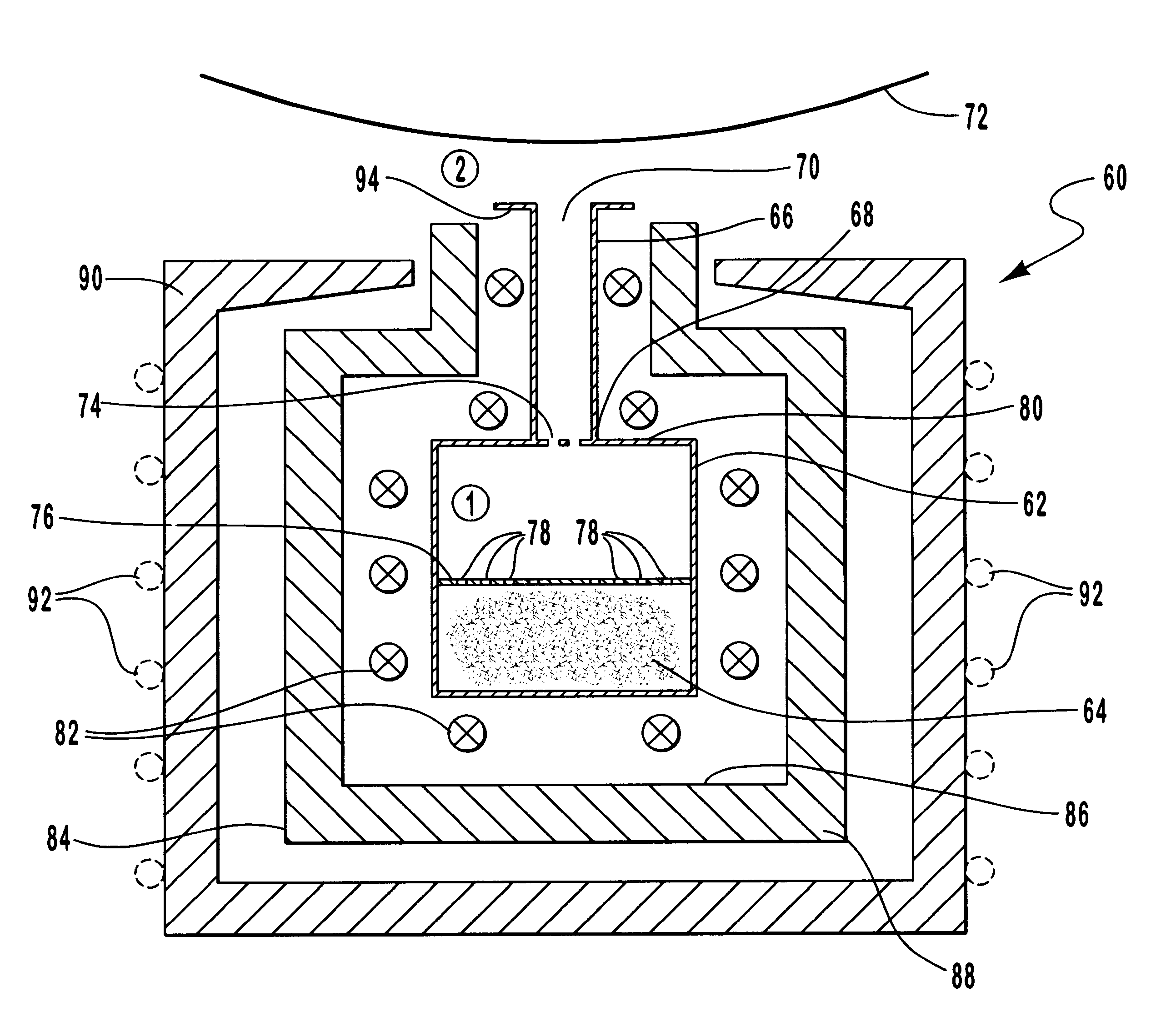
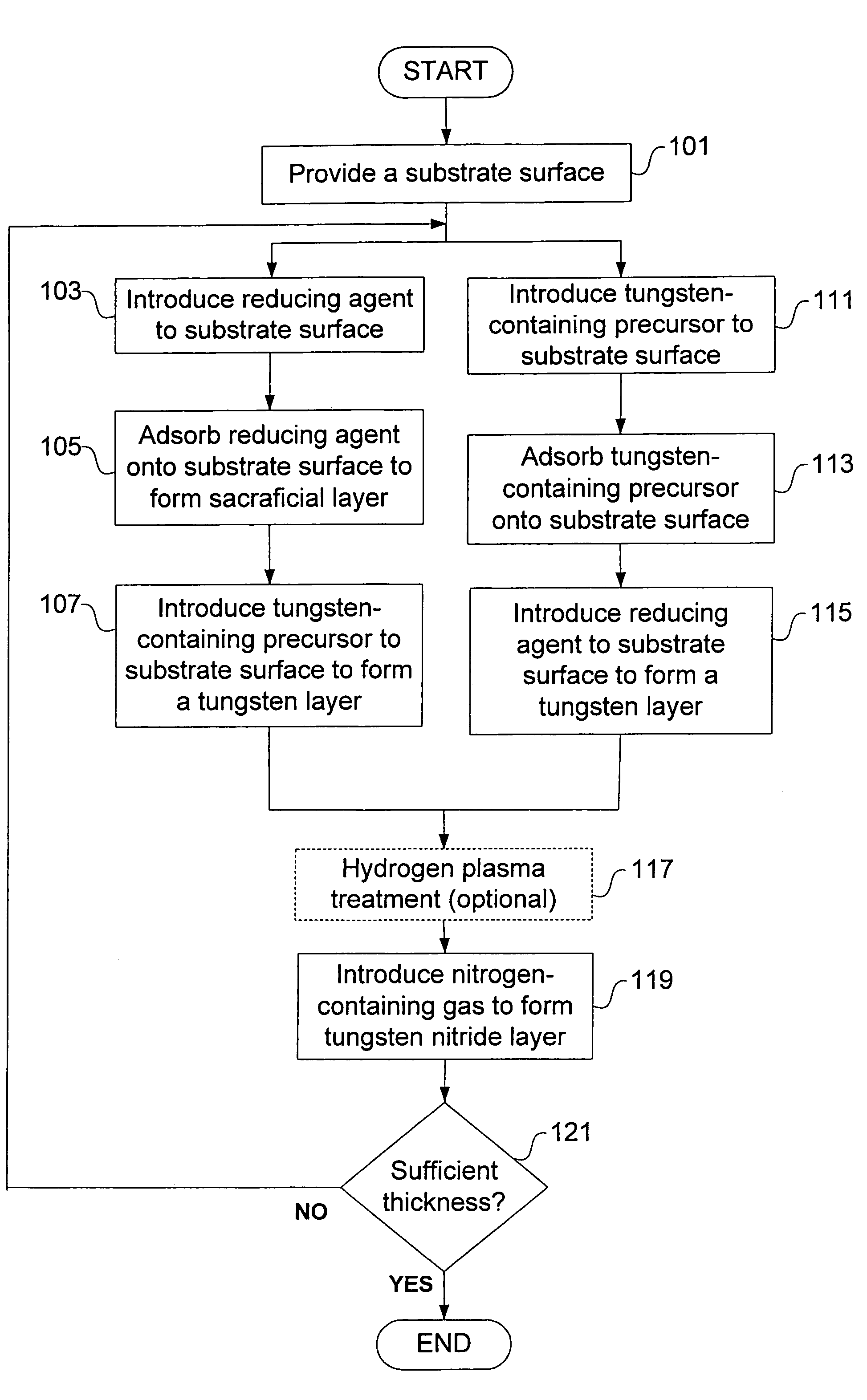
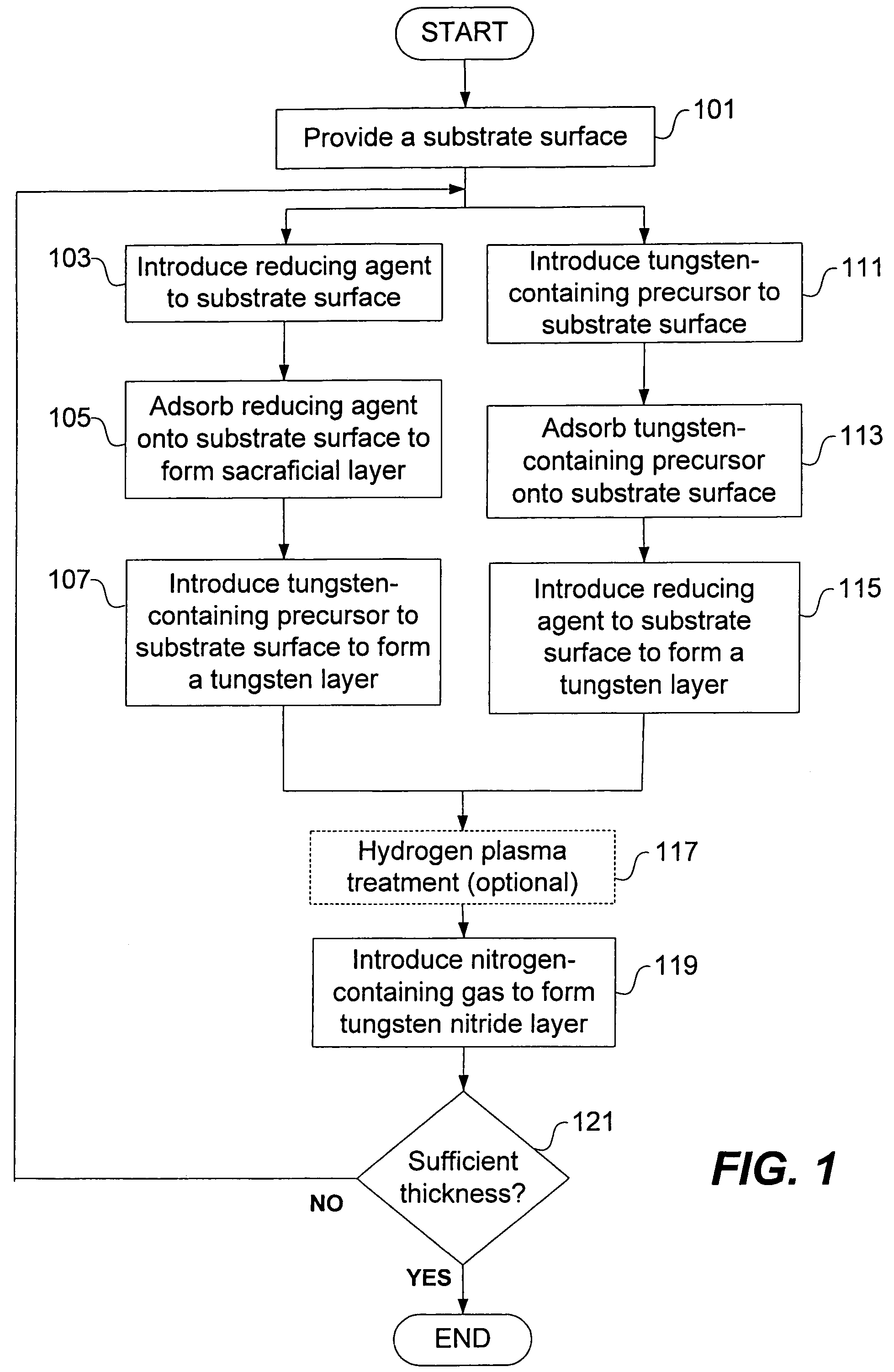
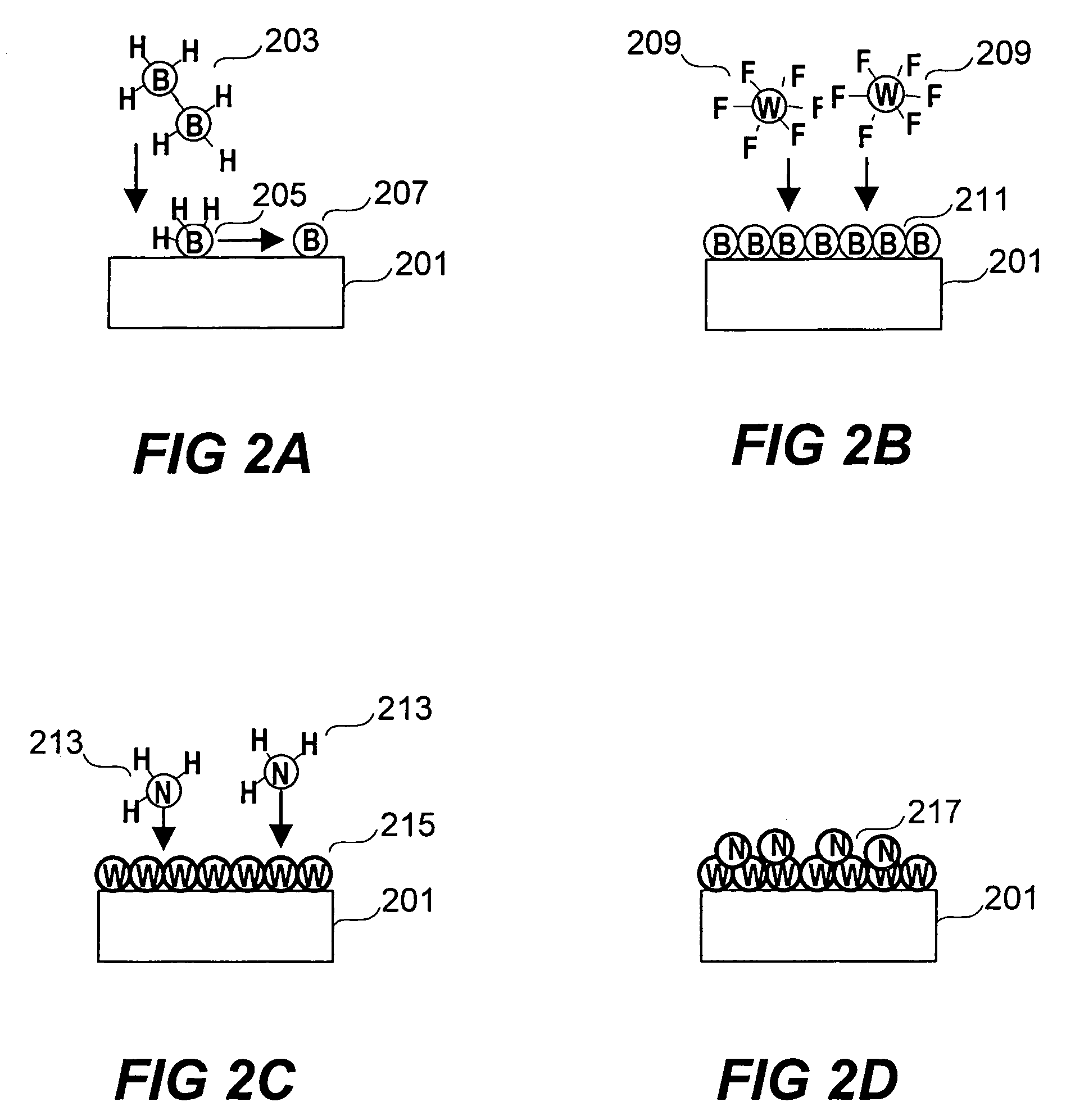
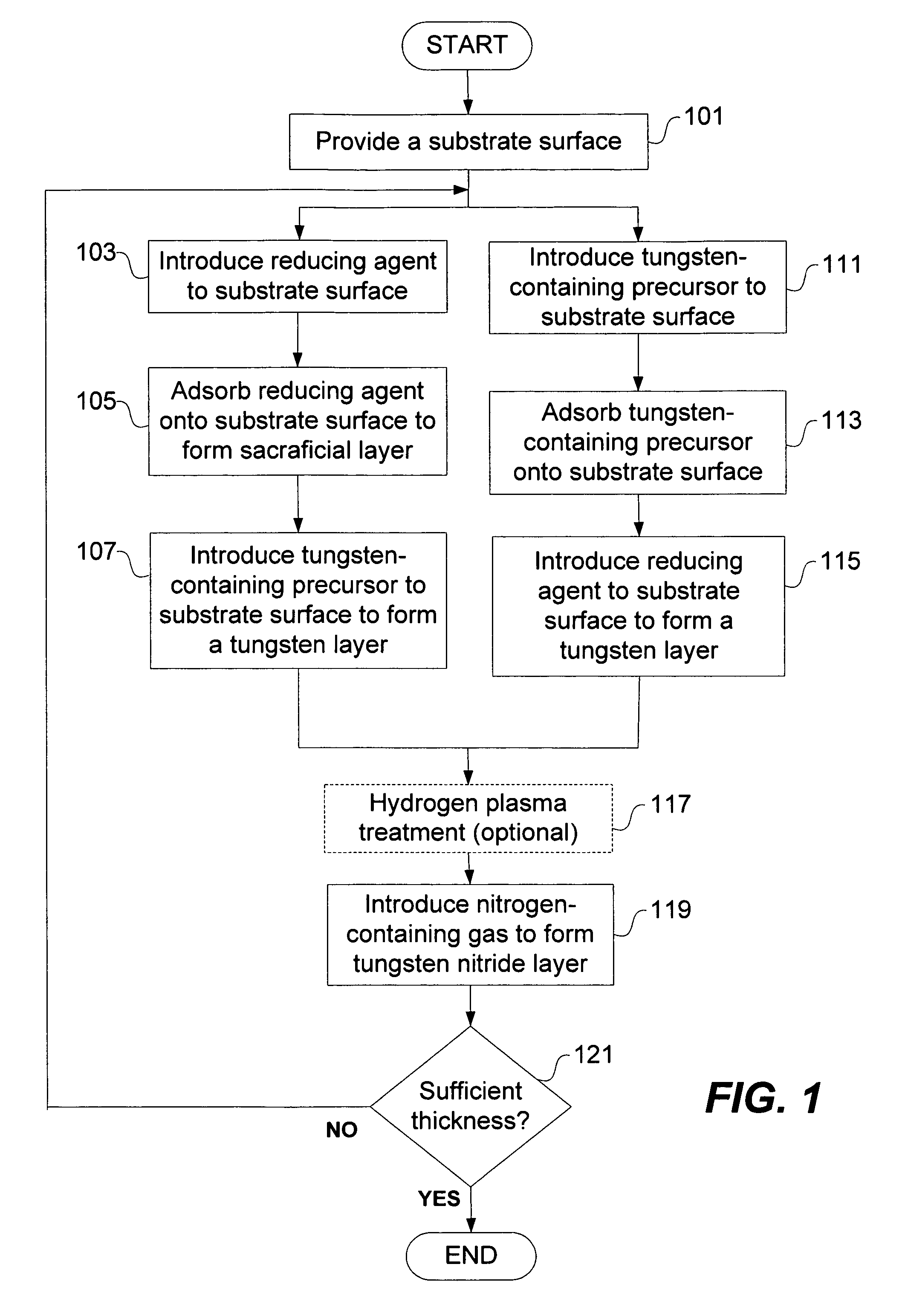
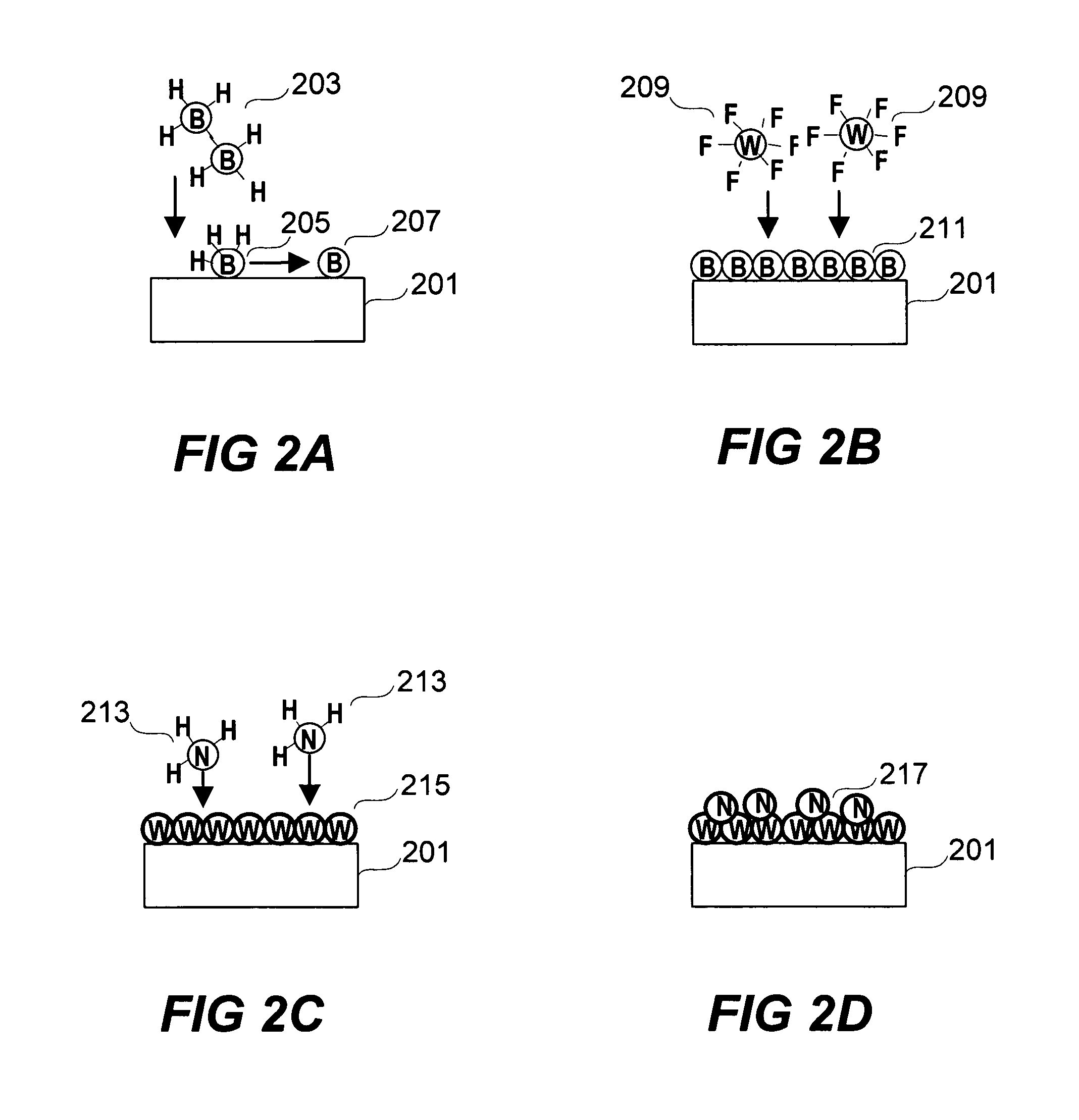
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS7005372B2Improve adhesionDeposition thickness is limitedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingArsineTungsten nitride
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
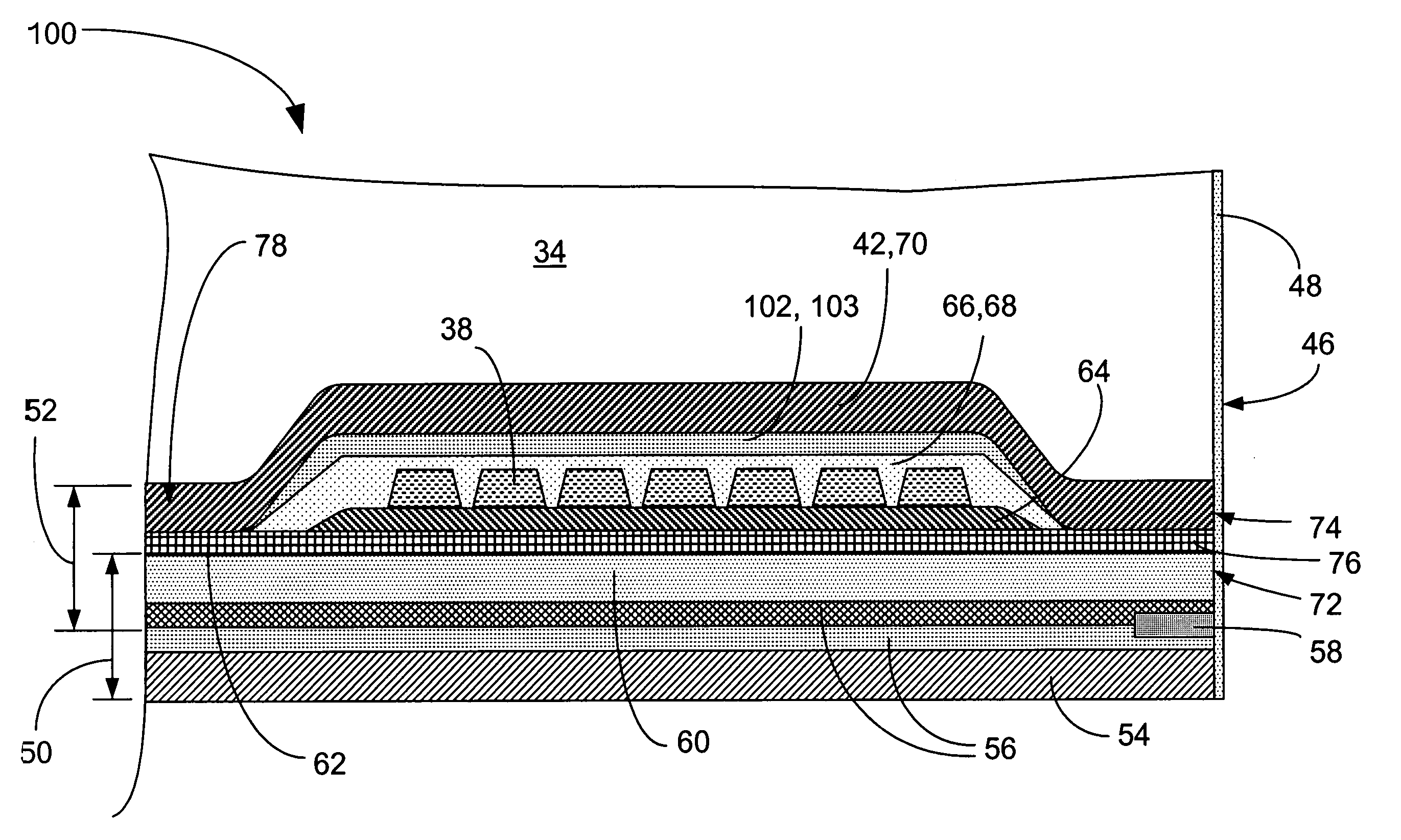
Insulation layer structure for inductive write heads and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6958885B1Avoid crackingImprove film propertiesConstruction of head windingsElectrical transducersResistInsulation layer
A computer disk drive (22) having a write head (52) which includes a coil (38), a photoresist insulation layer (66) formed on the coil (38), and an insulation shell layer (102) which is formed on the photoresist insulation layer (66). In the first preferred embodiment (100), the top pole (42) of the write head (52) is formed on the insulation shell layer (102).In the second preferred embodiment (200), the disk drive write gap (76) is formed on the insulation shell layer (102) and the top pole (42) of the write head (52) is formed on the write gap (76).The insulation shell layers (102) in both embodiments are preferably made of dielectric materials (103).Methods of fabrication for these embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method For Manufacturing Cable-Type Secondary Battery
ActiveUS20120009331A1Thickness of coating is limitedSuitable for manufactureFinal product manufactureVehicular energy storageElectrical batteryCurrent collector
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a cable-type secondary battery comprising an electrode that extends longitudinally in a parallel arrangement and that includes a current collector having a horizontal cross section of a predetermined shape and an active material layer formed on the current collector, and the electrode is formed by putting an electrode slurry including an active material, a polymer binder, and a solvent into an extruder, by extrusion-coating the electrode slurry on the current collector while continuously providing the current collector to the extruder, and by drying the current collector coated with the electrode slurry to form an active material layer.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Methods for growing low-resistivity tungsten film
InactiveUS7589017B2Low resistivityGood step coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron containingLayer thickness
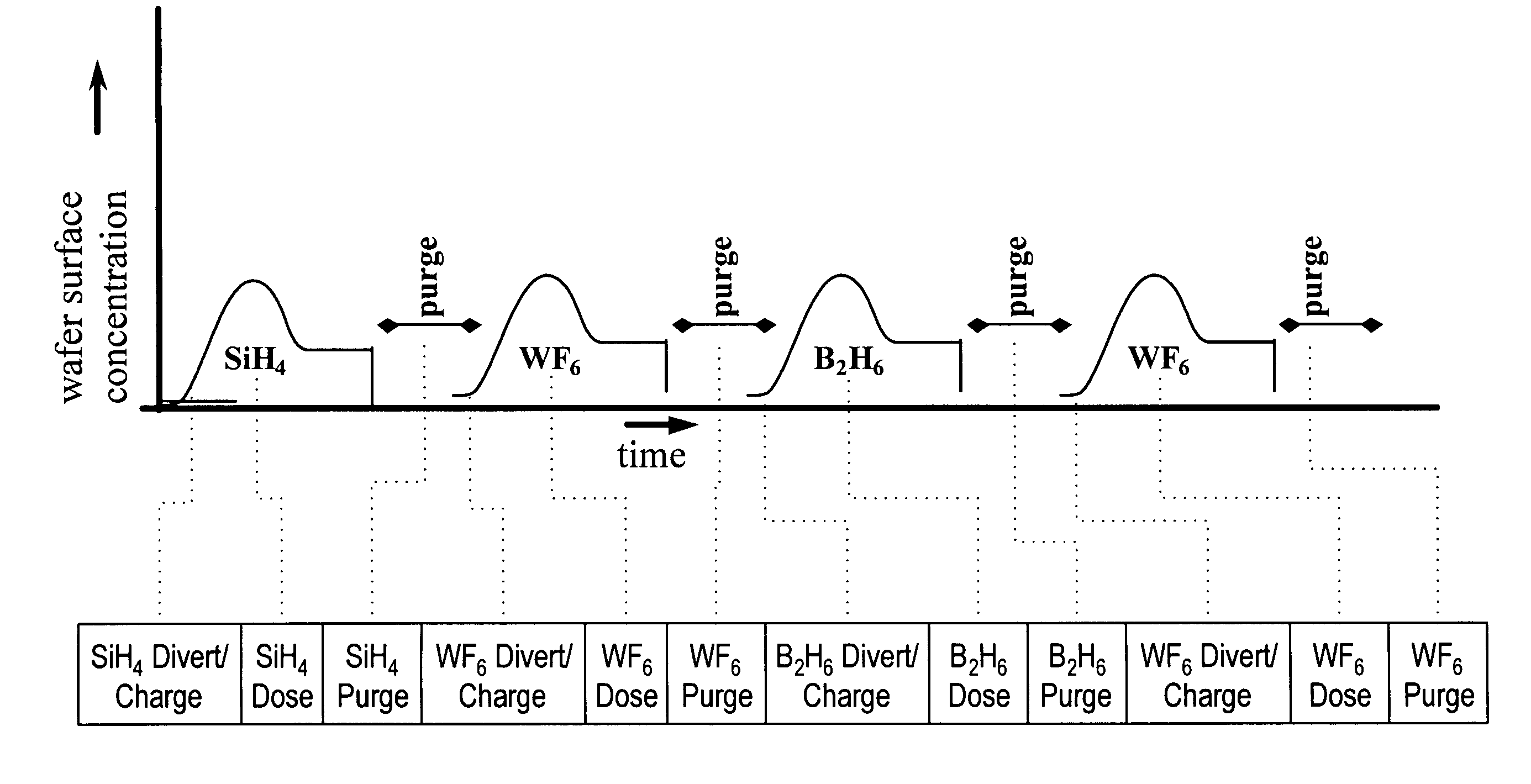
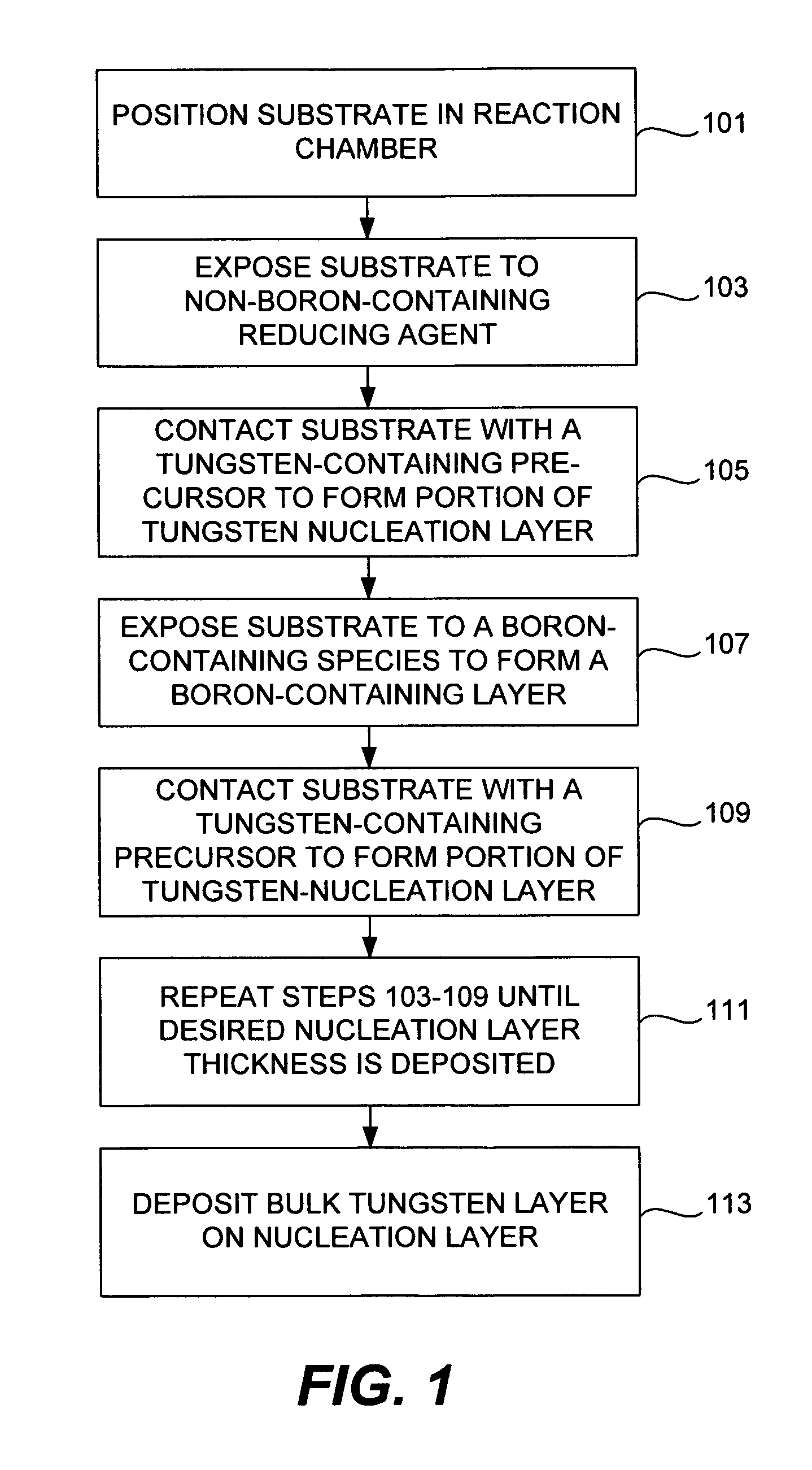
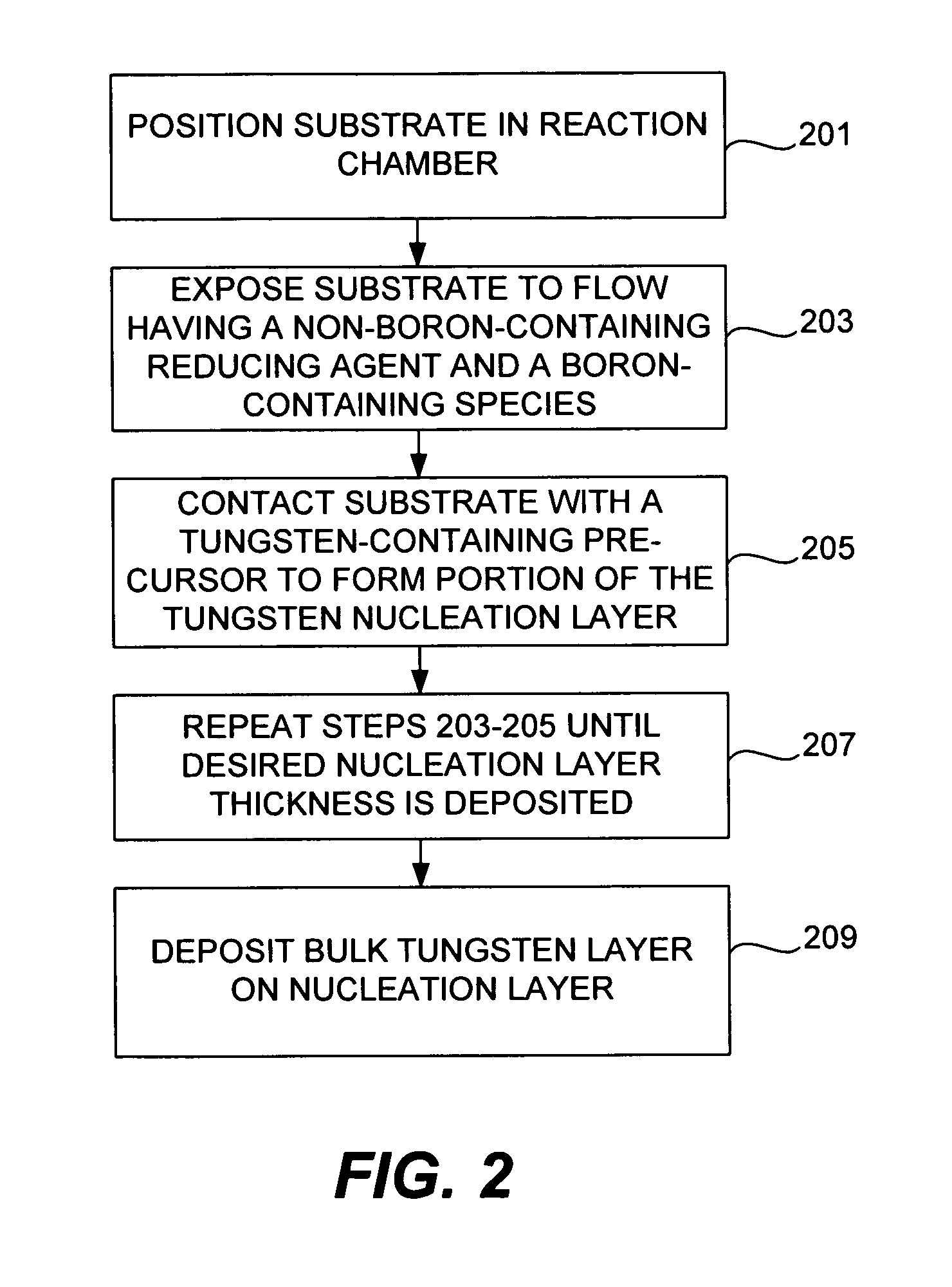
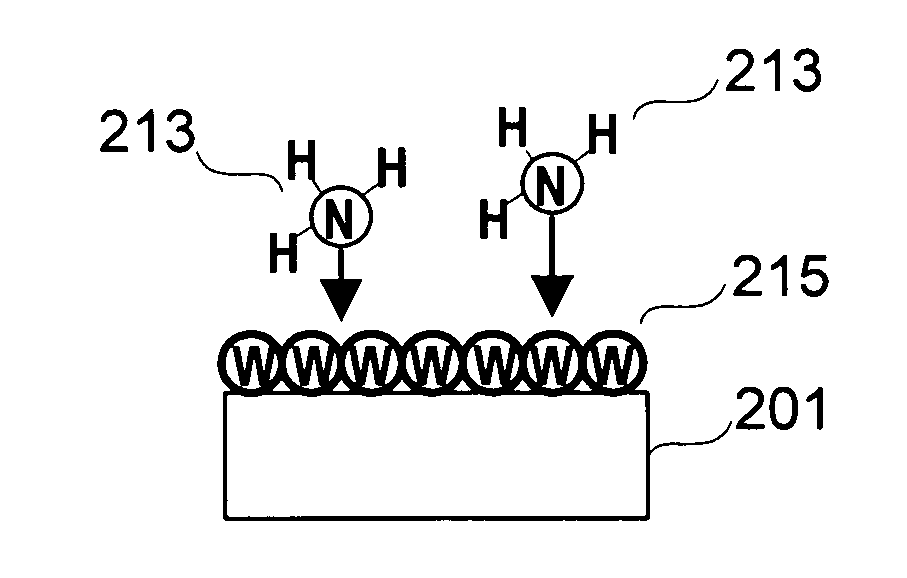
Improved methods for depositing low resistivity tungsten films are provided. The methods involve depositing a tungsten nucleation layer on a substrate and then depositing a tungsten bulk layer over the tungsten nucleation layer to form the tungsten film. The methods provide precise control of the nucleation layer thickness and improved step coverage. According to various embodiments, the methods involve controlling thickness and / or improving step coverage by exposing the substrate to pulse nucleation layer (PNL) cycles at low temperature. Also in some embodiments, the methods may improve resistivity by using a high temperature PNL cycle of a boron-containing species and a tungsten-containing precursor to finish forming the tungsten nucleation layer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS20060094238A1Improve adhesionControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantArsine
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveUS20030173671A1Improve production yieldImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, a first wiring line composed of a copper containing metal film is formed on or above a semiconductor substrate. A first interlayer insulating film is formed on a whole surface of the semiconductor substrate to cover the first wiring line. The first interlayer insulating film is selectively removed to form a connection hole reaching the first wiring line. A barrier metal film is formed to cover an inner surface of the connection hole and then a copper containing metal film is formed to fill the connection hole. The copper containing metal film formed outside the connection hole is removed. A second interlayer insulating film is formed on a whole surface of the semiconductor substrate to cover the copper containing metal film formed in the connection hole. The second interlayer insulating film is selectively removed to form a wiring line groove such that the copper containing metal film formed in the connection hole is exposed at a bottom. A barrier metal film is formed to cover an inside of the wiring line groove and then a copper containing metal film is formed to fill the wiring line groove. Then, the copper containing metal film outside the wiring line groove is removed to form a second wiring line.
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
Activated organic coatings on a fiber substrate
InactiveUS6517906B1Easy and less-expensive to manufactureImprove versatilityOther chemical processesFibre typesFiberDecomposition
A composite contains substrate fibers, and an activated organic coating, on the substrate fibers. The activated organic coating is formed at a low temperature, making possible the use of substrate fibers have a softening or decomposition temperature of at most 500° C.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Axially nested slide and lock expandable device
InactiveUS20090030501A1Reduce or minimize the device crossing profile and bulkReducing or eliminating the excess bulkStentsBlood vesselsVascular deviceUltimate tensile strength
The inventions relate generally to expandable medical implants for maintaining support of a body lumen and, in particular, to an axially nested, diametrically expandable, slide and lock vascular device for enlarging an occluded portion of a vessel. The axially nested vascular device desirably achieves both competitive crossing profiles while maintaining other key features, such as, for example, radial strength and luminal patency. The collapsed profile can also be made very thin without compromising radial strength. Thus, the vascular device can advantageously be deployed in small and difficult to reach areas or vessels. The axial nesting substantially eliminates radial overlap between mating structural elements thereby desirably allowing for a low, uniform profile.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
Axially nested slide and lock expandable device
InactiveUS20070032857A1Reduce or minimize the device crossing profile and bulkReducing or eliminating the excess bulkStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusVascular deviceUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates generally to expandable medical implants for maintaining support of a body lumen and, in particular, to an axially nested, diametrically expandable, slide and lock vascular device for enlarging an occluded portion of a vessel. The axially nested vascular device desirably achieves both competitive crossing profiles while maintaining other key features, such as, for example, radial strength and luminal patency. The collapsed profile can also be made very thin without compromising radial strength. Thus, the vascular device can advantageously be deployed in small and difficult to reach areas or vessels. The axial nesting substantially eliminates radial overlap between mating structural elements thereby desirably allowing for a low, uniform profile.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
Deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS7691749B2Improve adhesionControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingArsineTungsten nitride
Methods for depositing a tungsten nitride layer are described. The methods form a tungsten nitride layer using a carefully controlled deposition technique such as pulsed nucleation layer (PNL). Initially, a tungsten layer is formed on a substrate surface. The tungsten layer is then exposed to a nitriding agent to form a tungsten nitride layer. Methods of forming relatively thick layers of involve repeated cycles of contact with reducing agent, tungsten precursor and nitriding agent. In some cases, the cycle may also include contact with a dopant precursor such as phosphine or arsine.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
System and method for photocatalytic oxidation air filtration using a substrate with photocatalyst particles power coated thereon
ActiveUS20080286163A1Control thicknessControl UniformityPump componentsLighting and heating apparatusAir filtrationPhysical chemistry
The present invention relates to an air filtration system and a method for making a photocatalytic oxidation substrate by powder coating a photocatalyst onto a metal substrate.
Owner:SCI HEALTH DEV LTD
Highly luminescent nanostructures and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20150236195A1High quantum yieldControl thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsIndiumLuminescence quantum yield
Highly luminescent nanostructures, particularly highly luminescent quantum dots, are provided. The nanostructures have high photoluminescence quantum yields and in certain embodiments emit light at particular wavelengths and have a narrow size distribution. The nanostructures can comprise ligands, including C5-C8 carboxylic acid ligands employed during shell formation and / or dicarboxylic or polycarboxylic acid ligands provided after synthesis. Processes for producing such highly luminescent nanostructures are also provided, including methods for enriching nanostructure cores with indium and techniques for shell synthesis.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
Sub-micron-scale patterning method and system
InactiveUS20050084613A1Control thicknessGood film uniformityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLiquid layerMicron scale
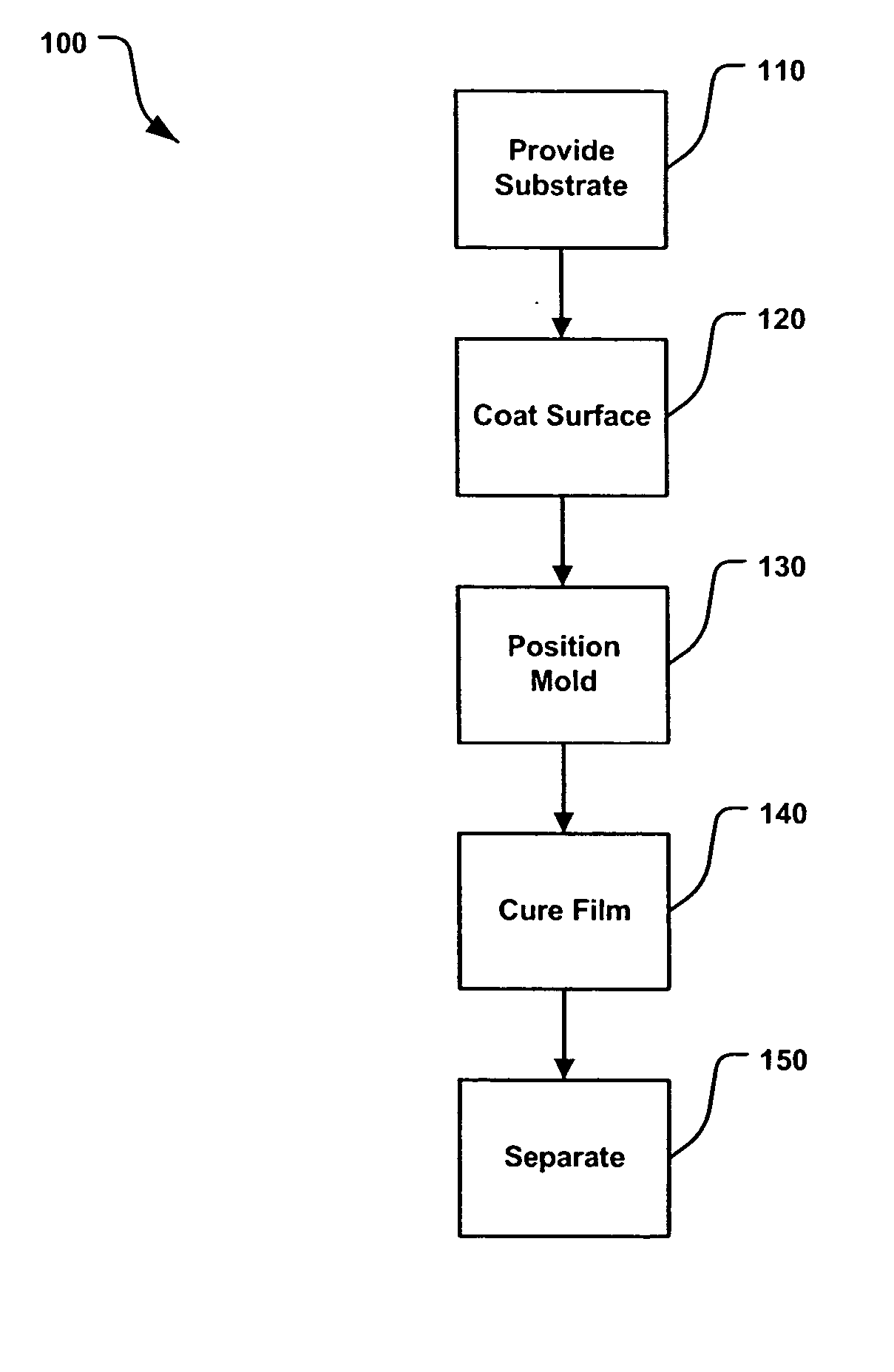
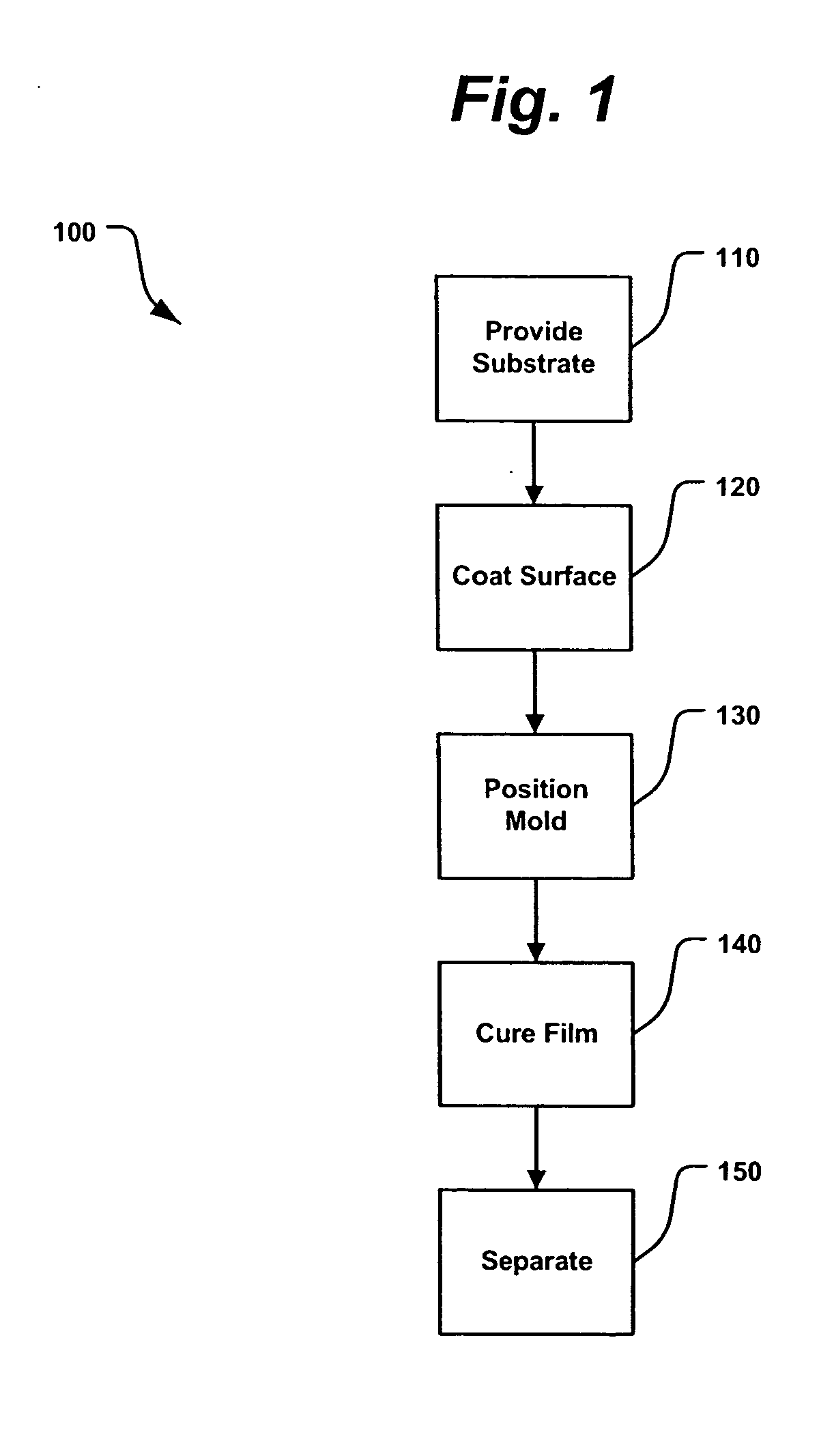
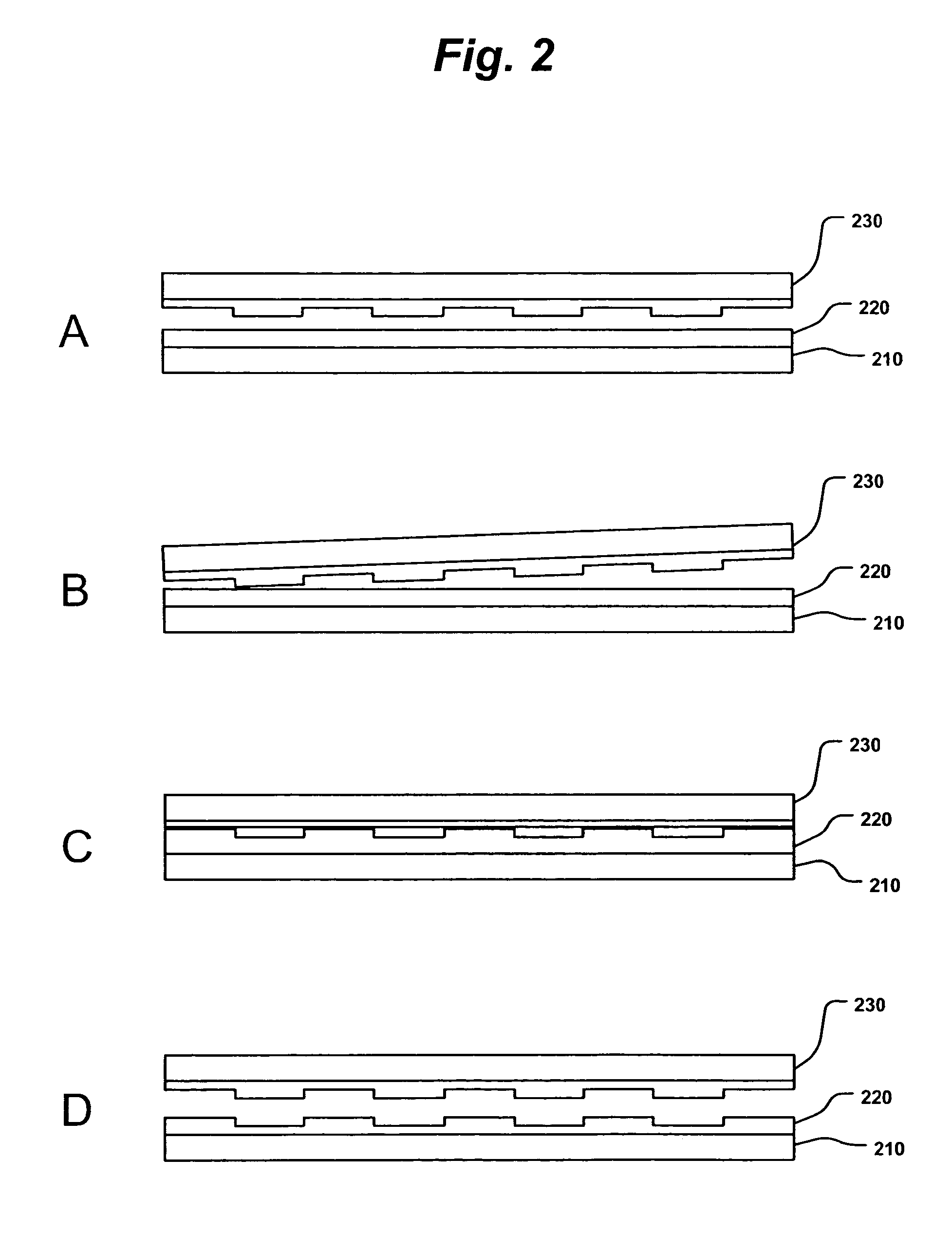
A method for replicating a nanopattern is disclosed. This method includes identifying a substrate; coating a surface of the substrate with a liquid layer; positioning a mold having a plurality of recesses defining a negative of the nanopattern in sufficient proximity with the coated liquid layer to cause the liquid layer to self-fill at least a portion of the plurality of recesses of the mold; and, chemically transforming the liquid layer to enable the transformed film to substantially retain the nanopattern.
Owner:WANG JIAN +2
Absorbent multilayer hydrogel wound dressings
ActiveUS20060200063A1Acceptable water uptake speedGood flexibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
The invention provides wound dressings comprising an absorbent (porous) hydrogel composition comprising a foam portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having an internal cellular structure, and a continuous portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having relatively continuous internal structure. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition includes apertures providing fluid flow communication through the continuous portion between an external surface of the continuous portion and the foam portion whereby the foam portion can take up external water or other fluid into the cellular structure through the apertures of the continuous portion. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition may be tacky to the skin, allowing its use as a bioadhesive.
Owner:KCI USA
Deposition of non-uniform non-overlapping curvilinear segments of anisotropic filament to form non-uniform layers
ActiveUS10391710B2Control thicknessEasy to manufactureAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresLine segmentAdditive layer manufacturing
A process of additive manufacturing in which a stack of non-planar layers of material are deposited for manufacturing an object. The non-planar layers can conform to the surface of the object or not. The non-planar layers can create structurally-advantageous interior structures in the object. The contours of the non-planar layers can be different or can be the same.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Packaging method for high-capacity polymer lithium ion cells
InactiveCN107394279AControl thicknessGuaranteed electrical performanceFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureLithiumBreakage rate
The invention discloses a packaging method for high-capacity polymer lithium ion cells. The packaging method comprises the following steps: (1) a bag is formed from at least one of two aluminum plastic films by stamping; when the thickness of a cell is smaller than 6 mm, one bag is formed from one aluminum plastic film by stamping, and when the thickness of a cell is larger than or equal to 6 mm, bags are formed from the two aluminum plastic films by stamping; (2) the cell is loaded into an opening of the bag formed from one aluminum plastic film by stamping, and the opening of the bag is correspondingly covered with the other aluminum plastic film; (3) three edges of the cell are sealed in a hot manner with seal heads. With adoption of the packaging method for the high-capacity polymer lithium ion cells, the breakage rate of the aluminum plastic films is reduced, the aluminum plastic film use efficiency is increased, and electrical performance of the high-capacity polymer lithium ion cells can be guaranteed effectively; the packaging method is simple to operate.
Owner:海口博澳国兴新能源科技有限公司
High-Voltage MOSFET with High Breakdown Voltage and Low On-Resistance and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20120228704A1Provide flexibilityAdditional freedomSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBody regionPhysics
A high-voltage transistor is formed in a deep well of a first conductivity type that has been formed in a semiconductor substrate or epitaxial layer of a second conductivity type. A body region of the second conductivity type is formed in the deep well, into which a source region of the first conductivity type is formed. A drain region of the first conductivity type is formed in the deep well and separated from the body region by a drift region in the deep well. A gate dielectric layer is formed over the body region, and a first polysilicon layer formed over the gate dielectric layer embodies the gate of the transistor. The field plate dielectric layer is formed over the drift region after the gate has been formed. Finally, the field plate dielectric is covered by a second polysilicon layer having a field plate positioned over the field plate dielectric layer in the drift region.
Owner:JU DONG HYUK
Film made from graphene-carbon nanotube composite material and preparation method of film
InactiveCN103725263AHave flexibilityGood flexibilityHeat-exchange elementsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsComposite filmLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a film made from a graphene-carbon nanotube composite material and a preparation method of film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing graphene and carbon nanotubes sufficiently and evenly via stirring and ultrasonic dispersion, reacting the graphene with the carbon nanotubes sufficiently via hydrothermal or solvothermal conditions, removing solvents after finishing the reaction to obtain the graphene-carbon nanotube composite materials which are preformed and tangled in a network structure, forming the film on the surfaces of various base materials via coating, spraying, spin-coating and filtering the obtained graphene-carbon nanotube composite materials to obtain the composite film made from the graphene-carbon nanotube composite materials and the base materials, and removing the base materials to obtain the film made from the graphene-carbon nanotube composite materials. According to the method, graphene-carbon nanotube composition is realized simply and effectively and dispersed in the solvents stably, and the two obtained films can be applied in the aspects of heat conduction and heat radiation systems of high calorific value electronic devices, LED (light-emitting diode) lamps and liquid crystal display products.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG KANGDE XIN OPTRONICS MATERIAL
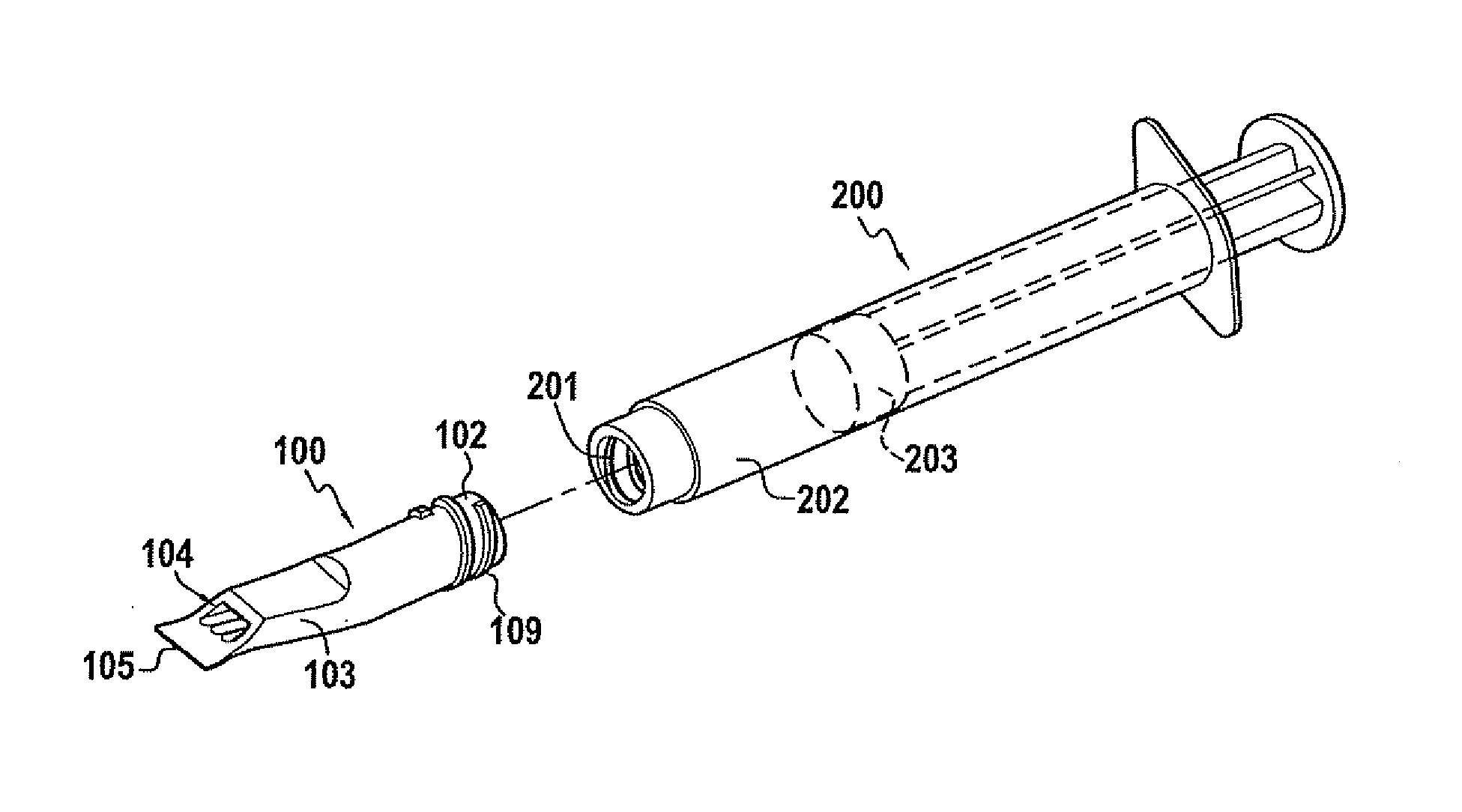
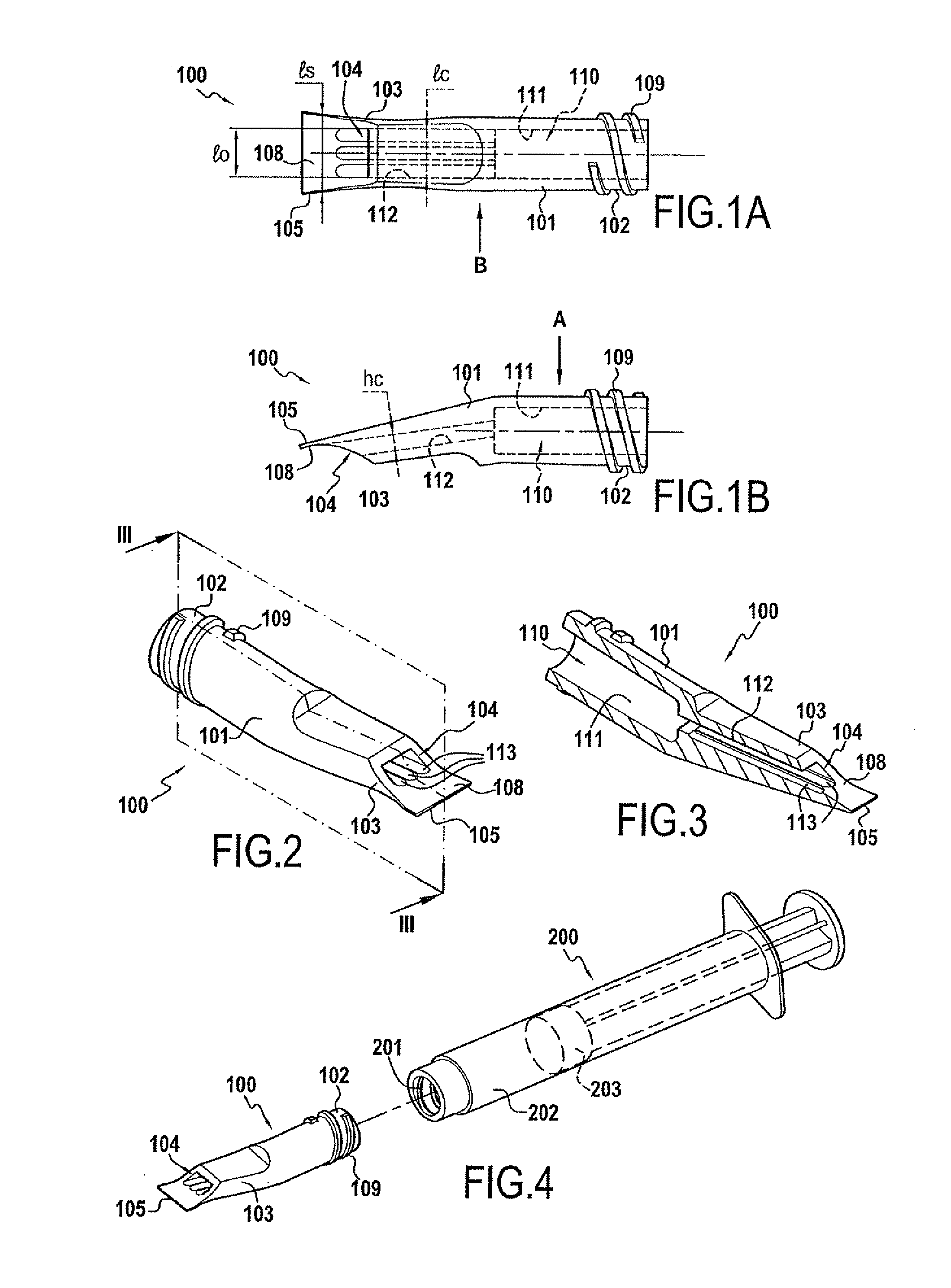
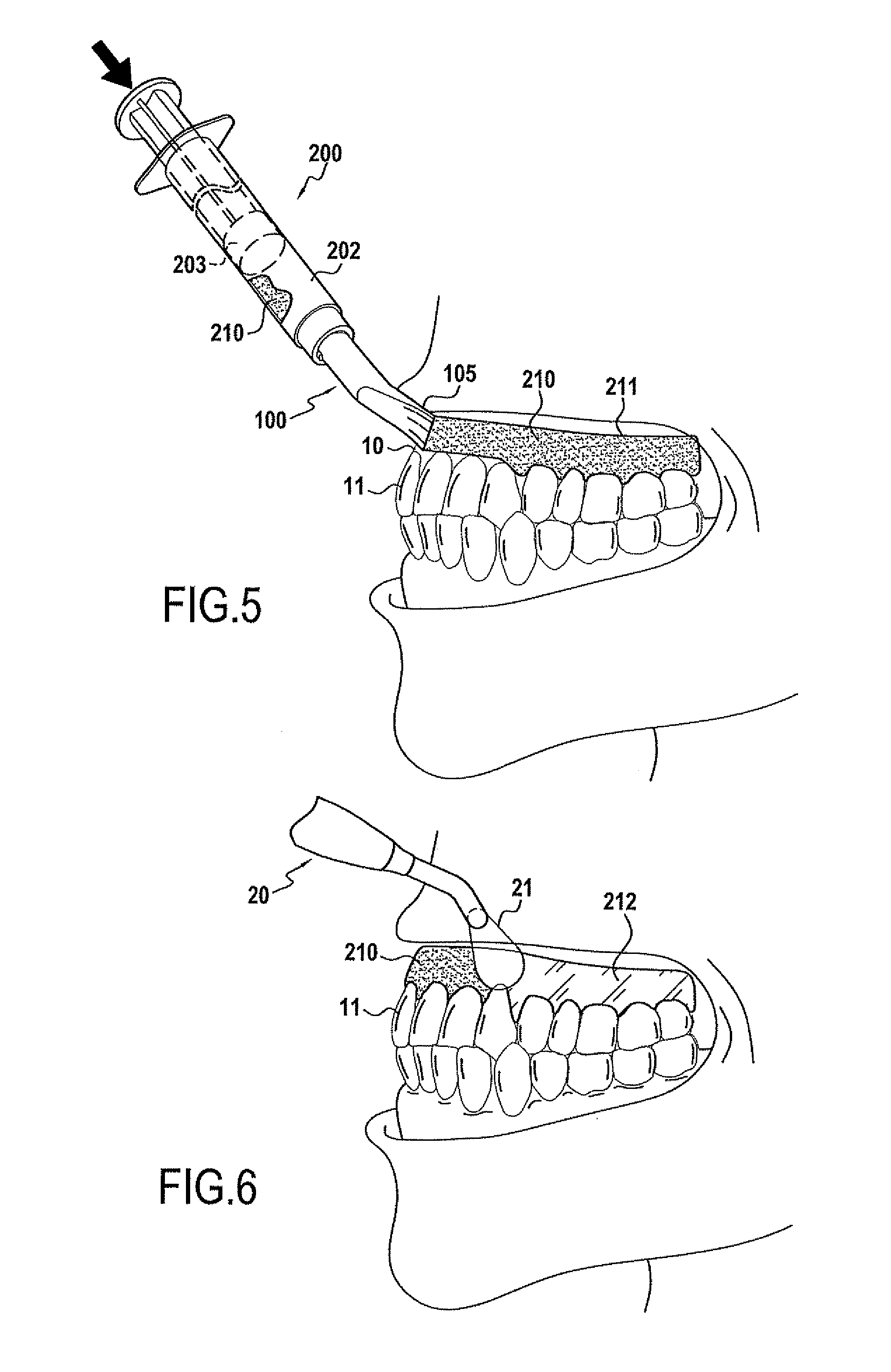
Application tip
InactiveUS20110027753A1Avoid risk of damageIncrease widthImpression capsLiquid surface applicatorsBiomedical engineering
Owner:MEDMIX SWITZERLAND AG
Multiribbon nanocellulose as a matrix for wound healing
InactiveUS20070053960A1Improve adaptabilityControl thicknessOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFiberWound healing
The present invention includes compositions and methods for the integration of a non-allergenic nanocellulose into a wound bed. The composition may be formed into a wide variety of implants, e.g., a suture, a sheet, a compress, a bandage, a band, a prosthesis, a fiber, a woven fiber, a bead, a strip, a clasp, a prosthesis, a catheter, a screw, a bone plate, a pin, a bandage or combinations thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Axially nested slide and lock expandable device
InactiveUS7914574B2Reduce or minimize the device crossing profile and bulkReducing or eliminating the excess bulkStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusVascular deviceUltimate tensile strength
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
Appliance for cooking by air flow
ActiveUS10117546B2Creates turbulenceAvoid creating dead zoneRoasters/grillsFrying pansEngineeringBreathing
Owner:SEB SA
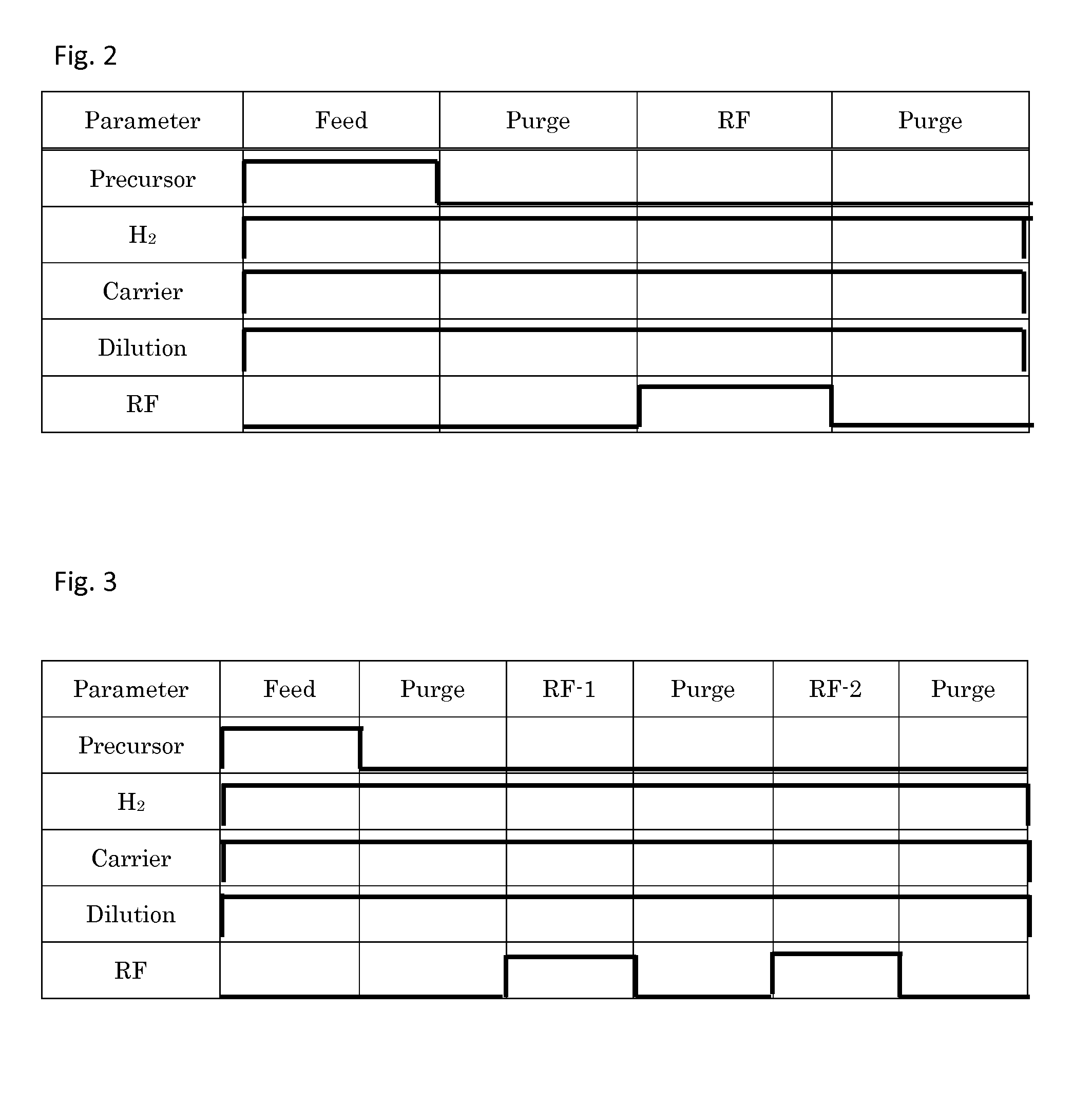
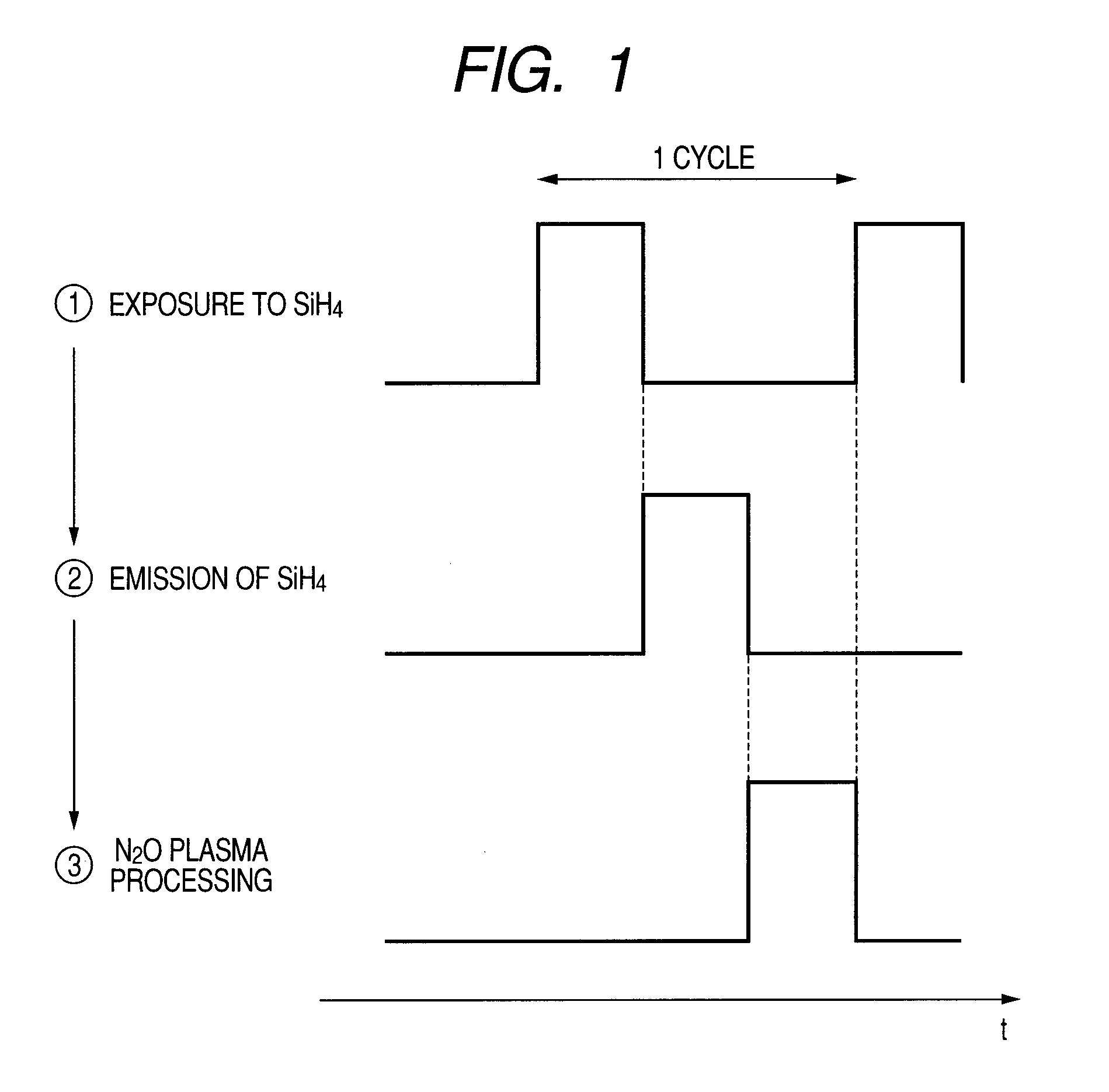
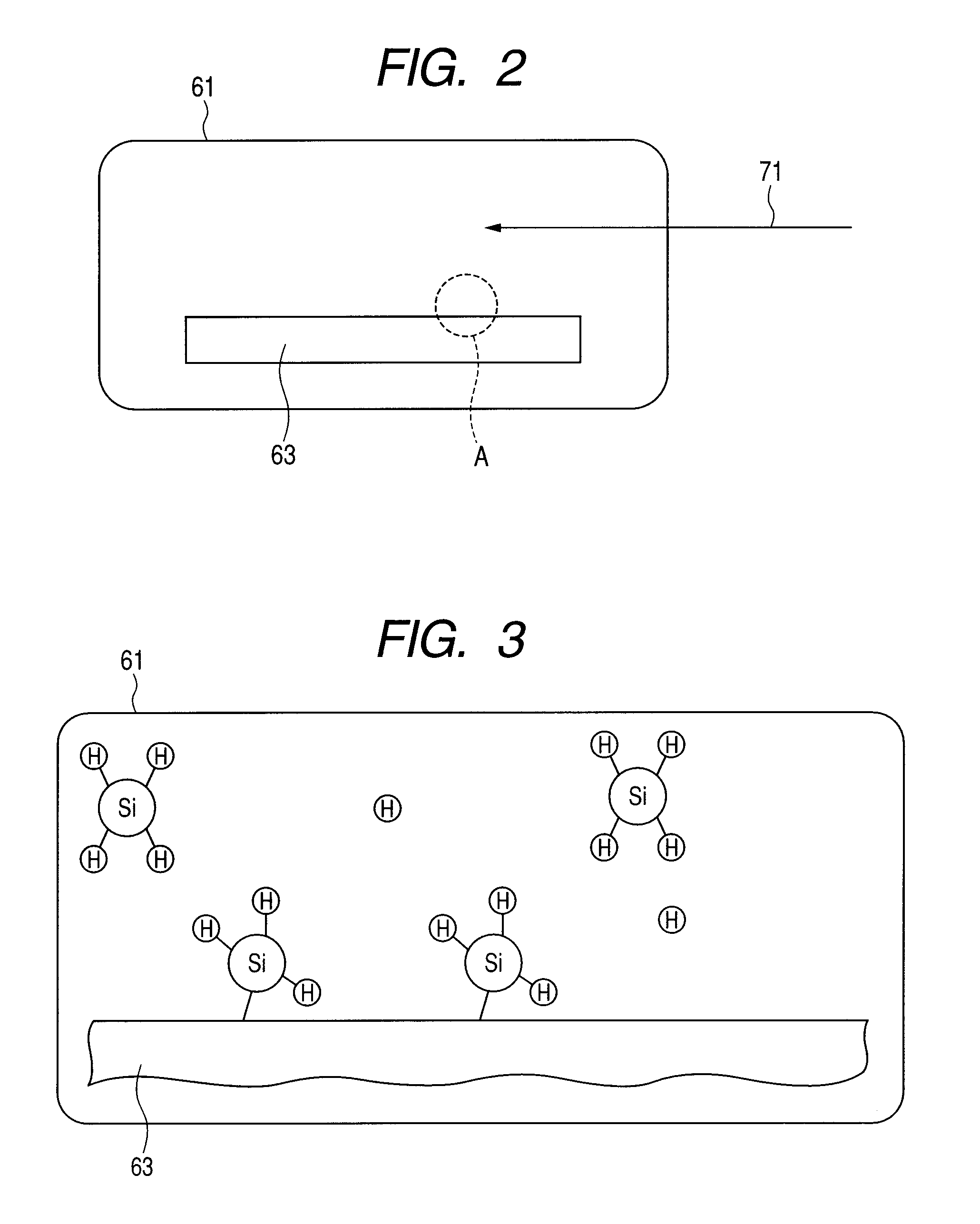
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110003445A1Good and thin silicon oxide filmUniformly formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideNitrous oxide
A manufacturing method of a semiconductor device is provided which can uniformly form a good and thin silicon oxide film or the like at a relatively low temperature. In step 1, a semiconductor substrate is exposed to monosilane (SiH4). Then, in step 2, the remaining monosilane (SiH4) is emitted. In step 3, the semiconductor substrate is exposed to nitrous oxide plasma. A desired silicon oxide film is formed by repeating one cycle including steps 1 to 3 until a necessary thickness of the film is obtained.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Photonic chip mounting in a recess for waveguide alignment and connection
InactiveUS6888989B1Control thicknessCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideIntegrated circuitLight wave
A coupling system for photonic integrated circuits and integrated optical waveguides is provided. A recess is formed in a substrate on which one or more integrated optical waveguides are disposed, the recess being located at the desired mounting location of the photonic integrated circuit. At least one end wall of the recess is inclined with respect to a normal to the substrate surface. At least one end face of a photonic integrated circuit is inclined to match the inclined end wall of the recess. The length, width, and depth of the recess are controlled so that inserting the photonic integrated circuit into the recess passively provides both lateral and vertical alignment of the photonic integrated circuit with the integrated optical waveguide(s).
Owner:HO SENG TIONG
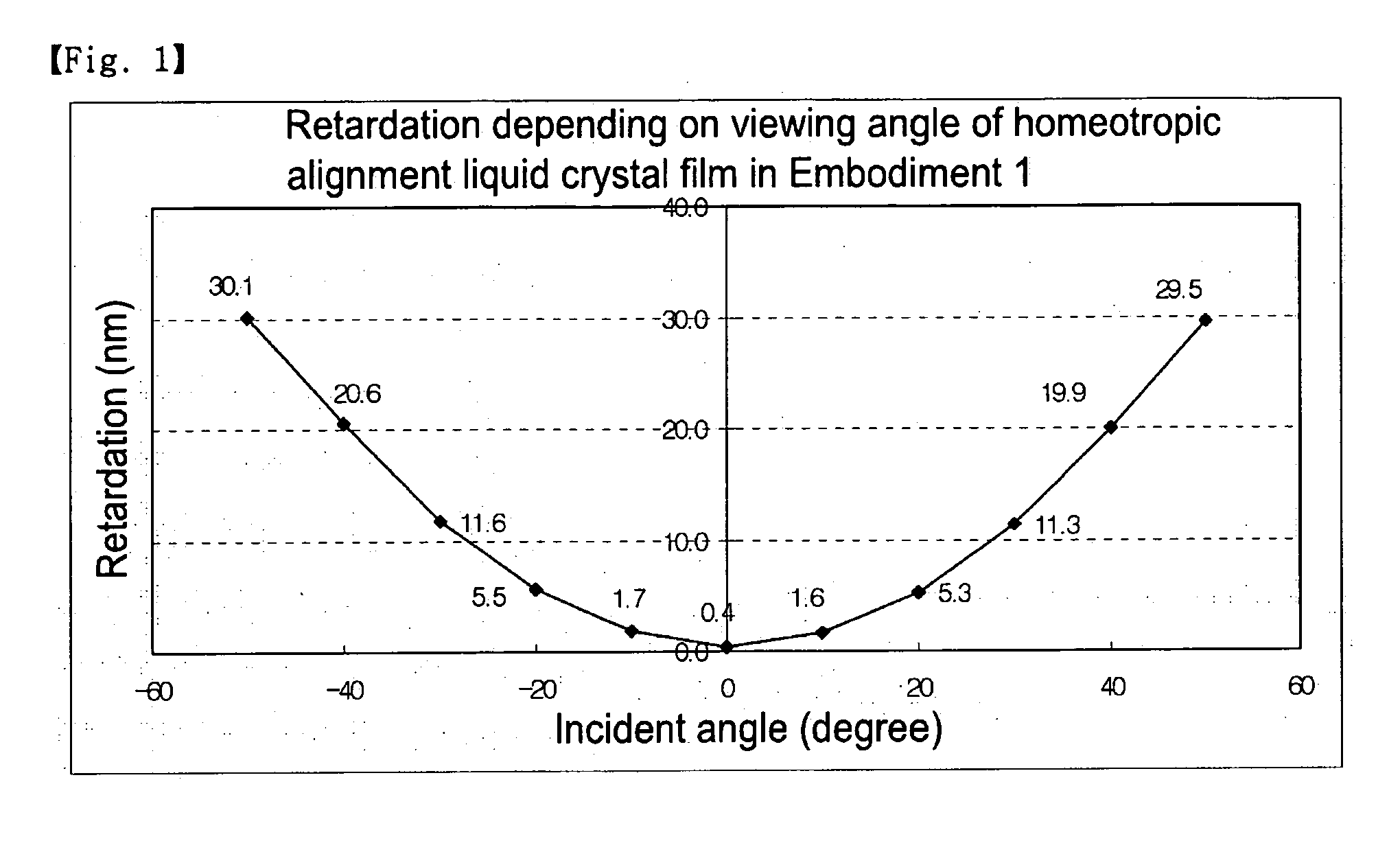
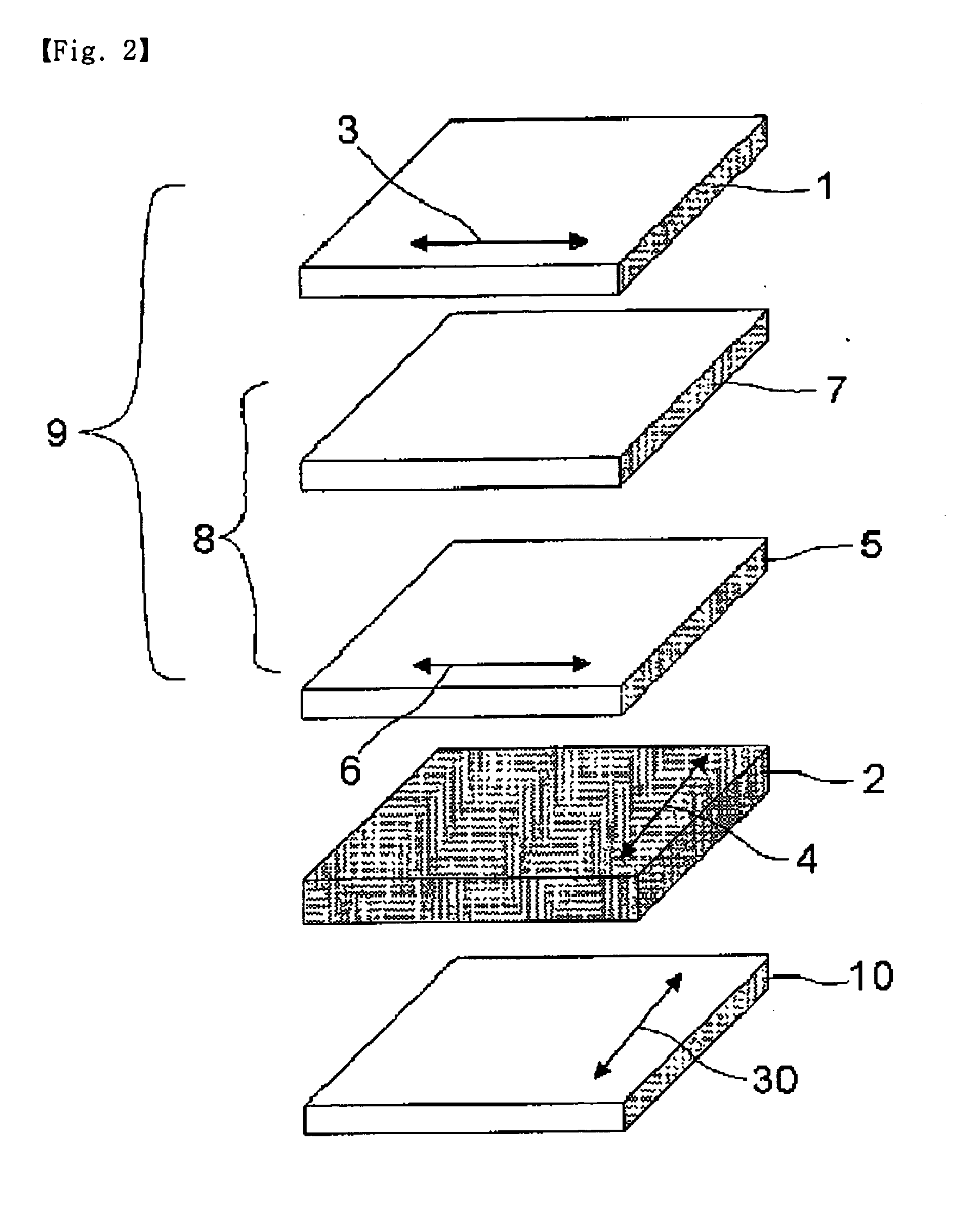
Retardation film having a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20060182900A1Reduce colorControl thicknessLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingChemistryHomeotropic alignment
The present invention relates to a retardation film having a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film, a polarizing film, an IPS (In-Plane Switching) mode liquid crystal display and a method for preparing the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film prepared from a liquid crystal mixed solution containing a polymerizable reactive liquid crystal monomer so as to improve a viewing angle characteristic of an ISP mode liquid crystal display and reduce a color shift; a retardation film prepared by integrating an oriented retardation film and a method for preparing the same; a polarizing film having the retardation film located between a polarizing element or plate and a liquid crystal cell and a method for preparing the same; and an IPS mode liquid crystal display having the polarizing film. There is an advantage in that since a homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film with a retardation of a thickness direction is prepared using a liquid crystal mixed solution containing a reactive liquid crystal monomer, a retardation film according to the present invention is not required for high-temperature heat treatment and cooling processes so that it can be applied to a high-speed continuous process. Further, there is an advantage in that a retardation film having an oriented retardation film integrated with the homeotropic alignment liquid crystal film is arranged between a polarizing element or polarizing plate of an IPS mod liquid crystal display and a liquid crystal cell so that a contrast ratio can be increased up to about 1520%, and a color shift characteristic can be also improved.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com