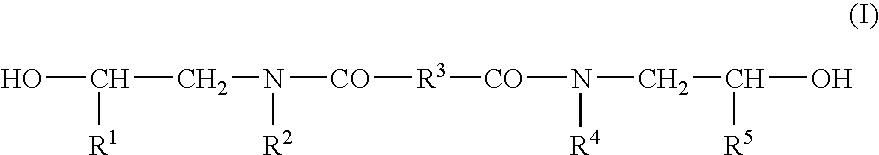Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
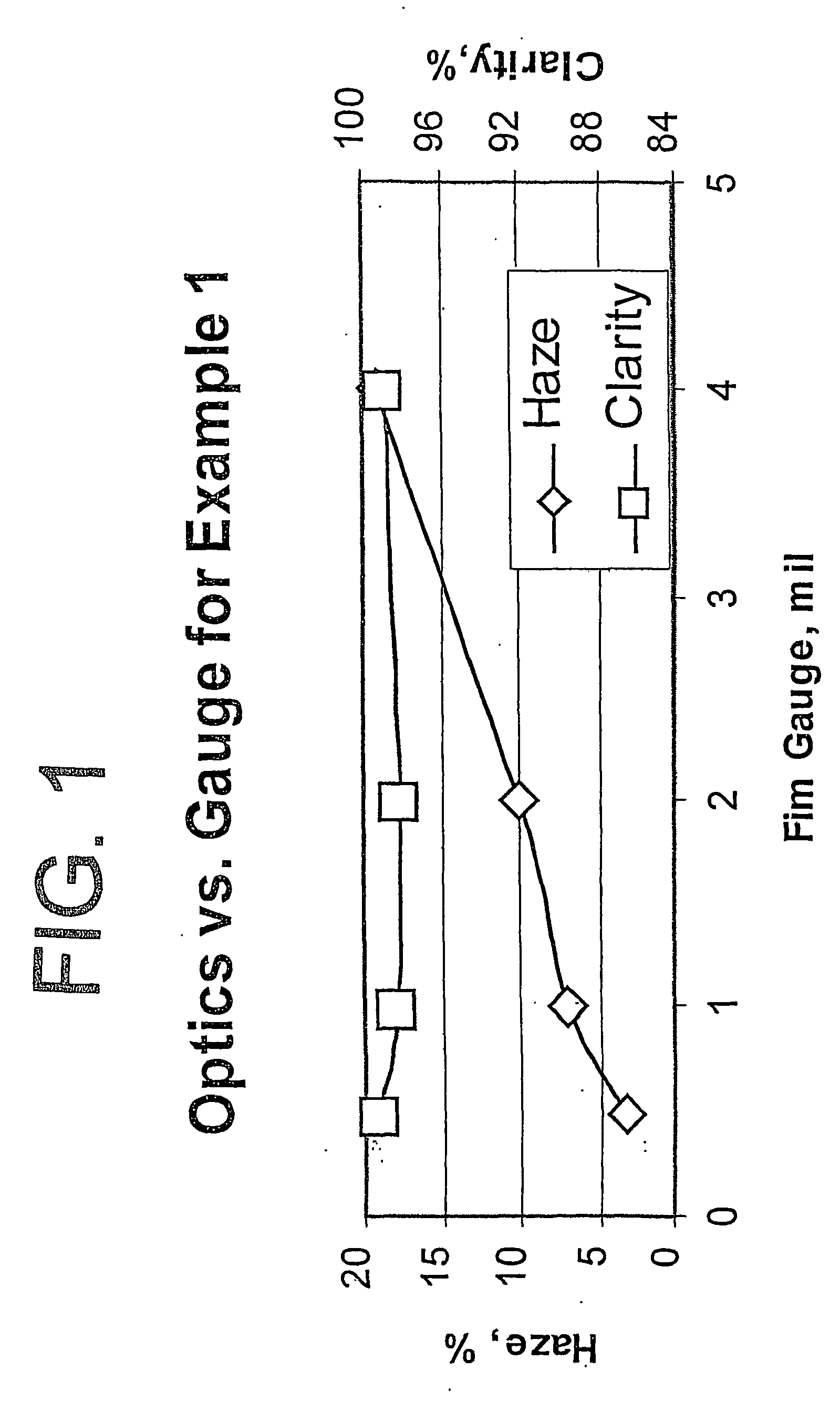
255results about How to "Improve film properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
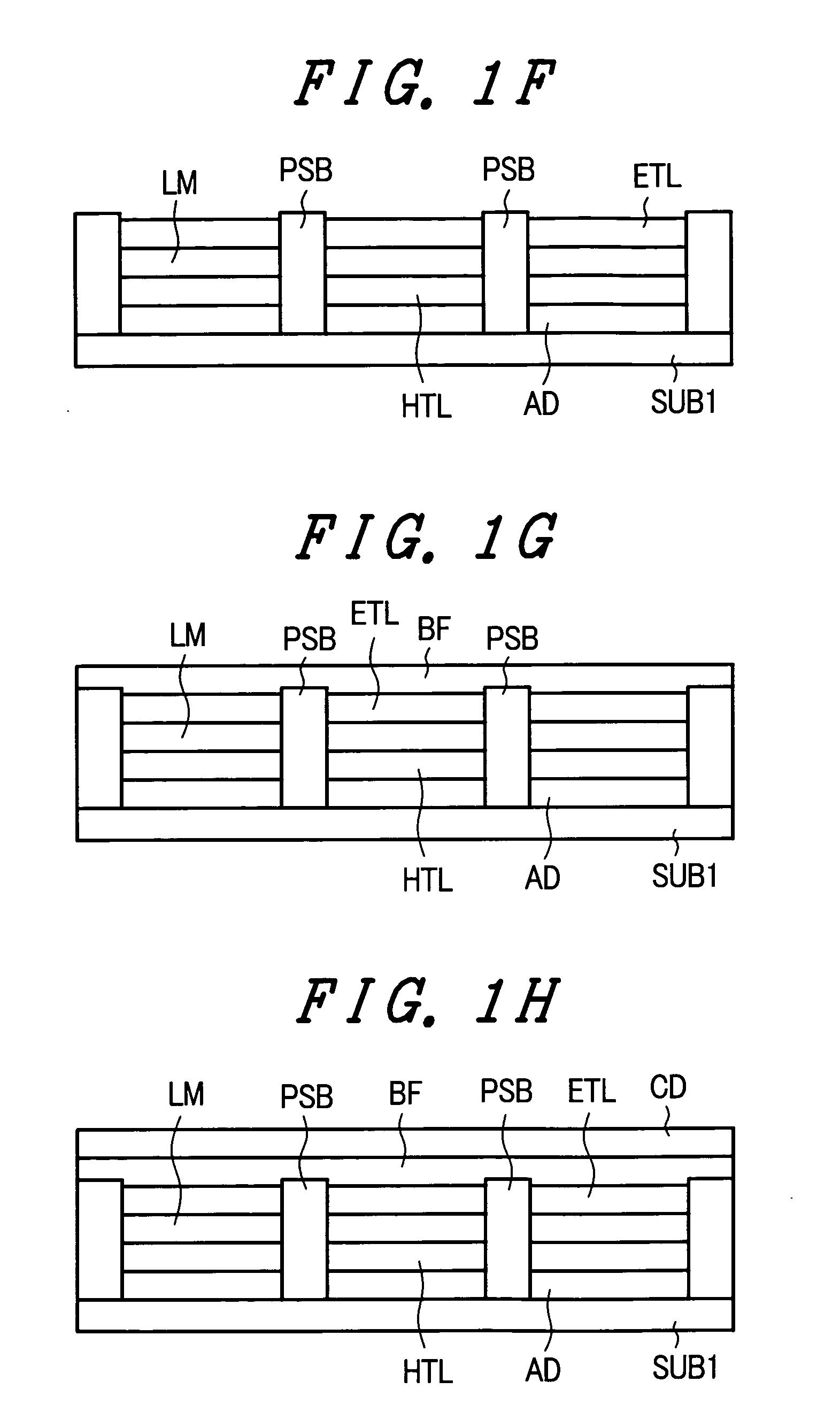
Method for vapor deposition of a metal compound film
InactiveUS20020172768A1Improve film propertiesEfficiently stackedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLanthanideNitrogen
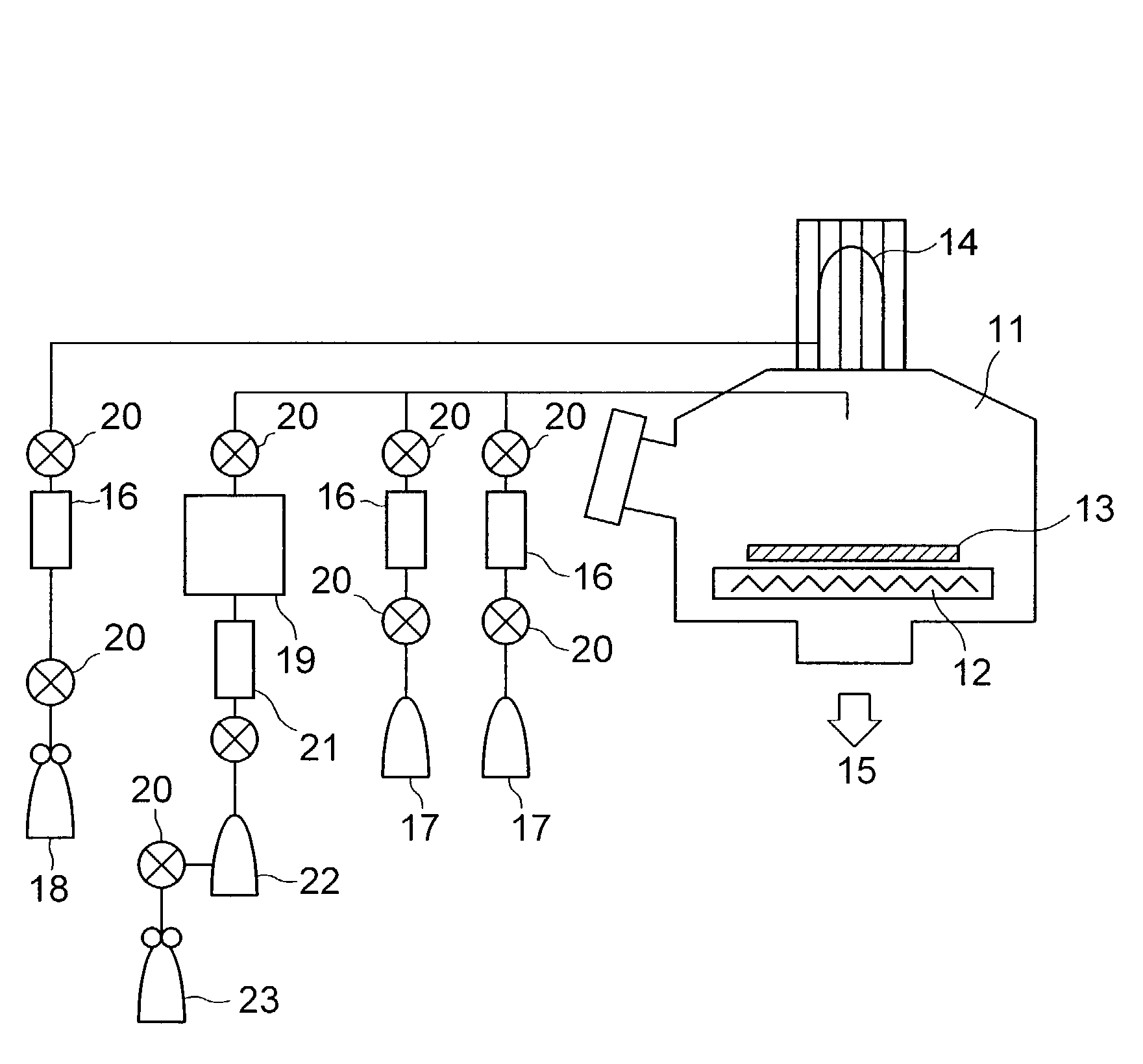
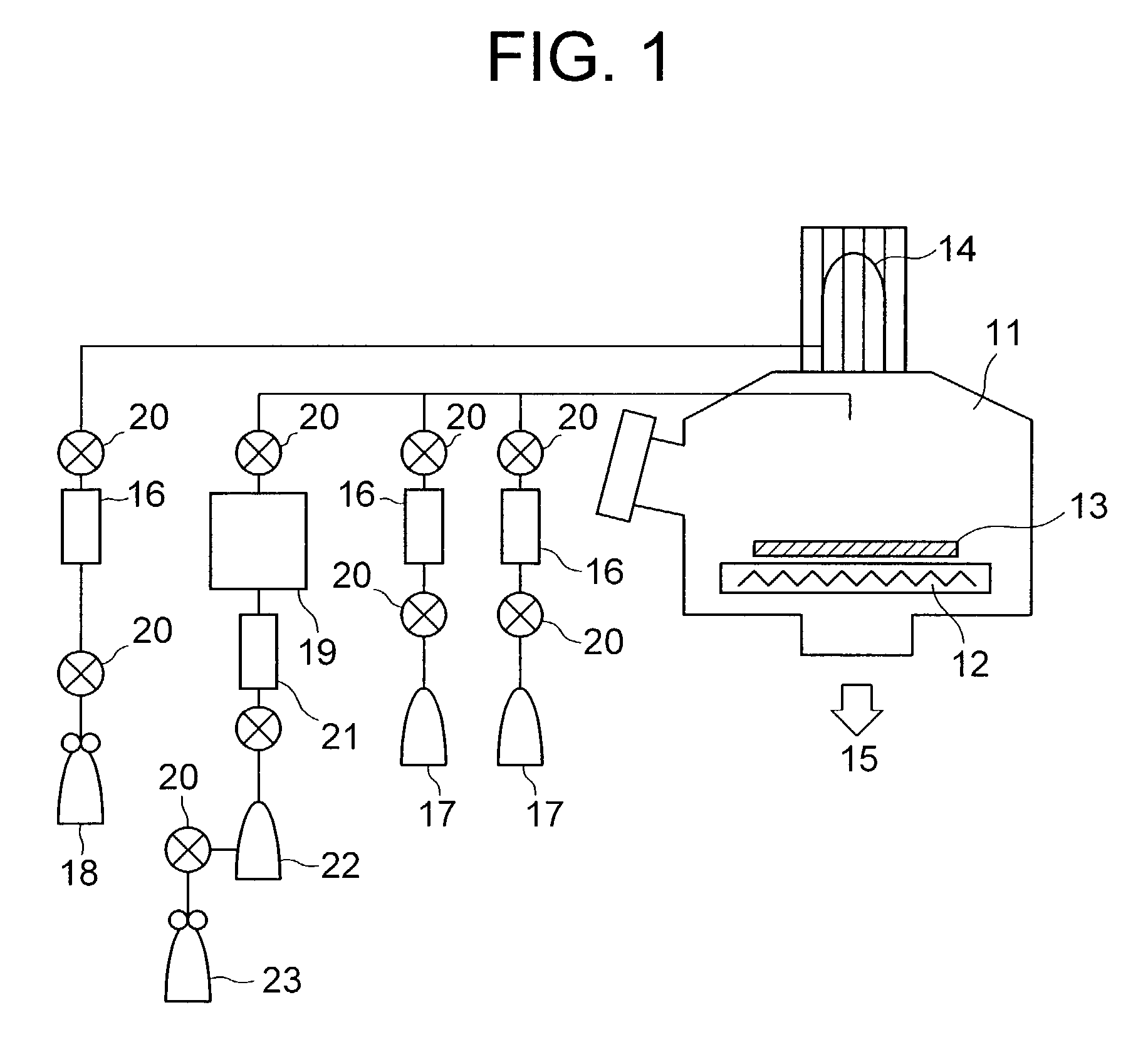
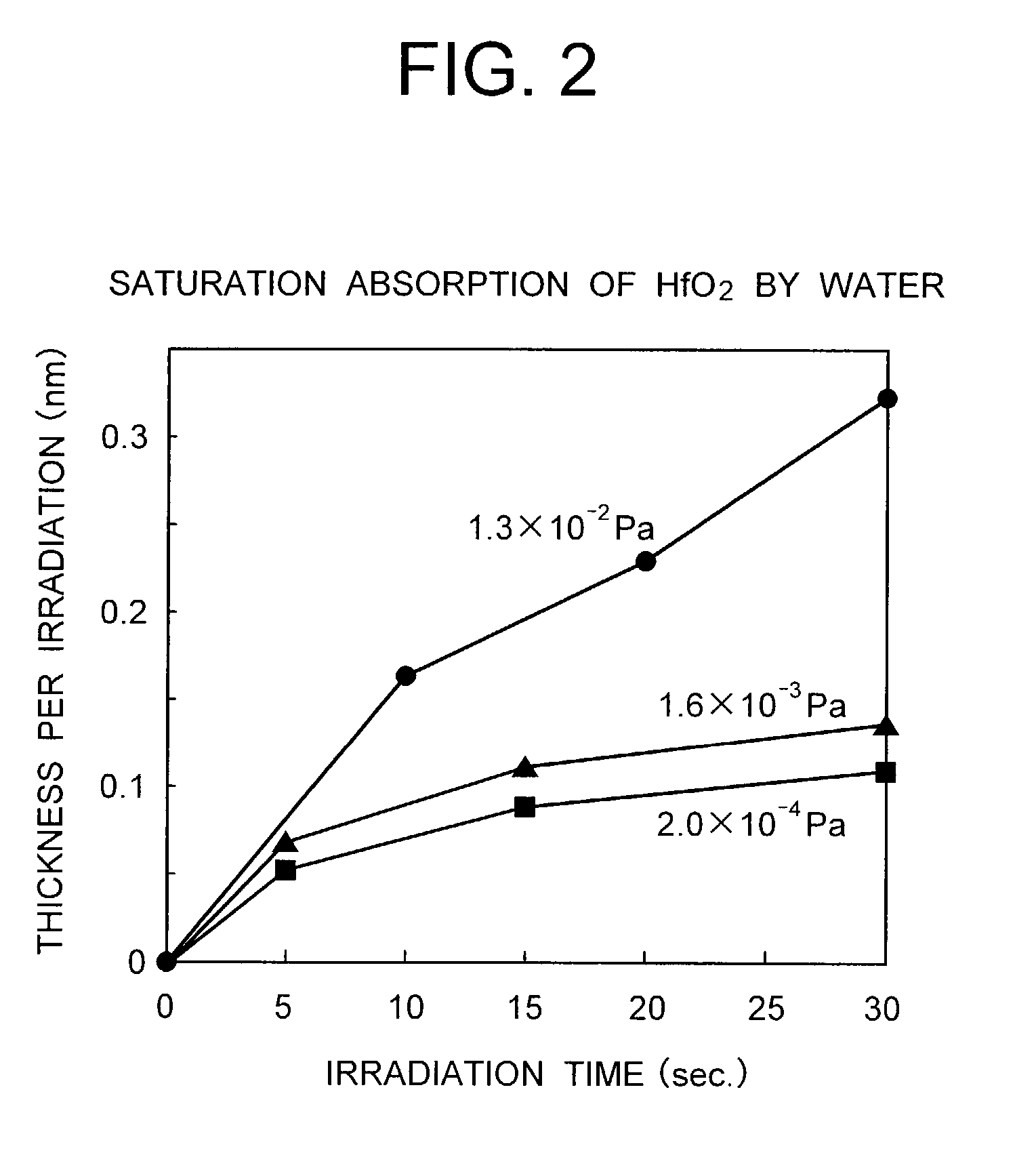
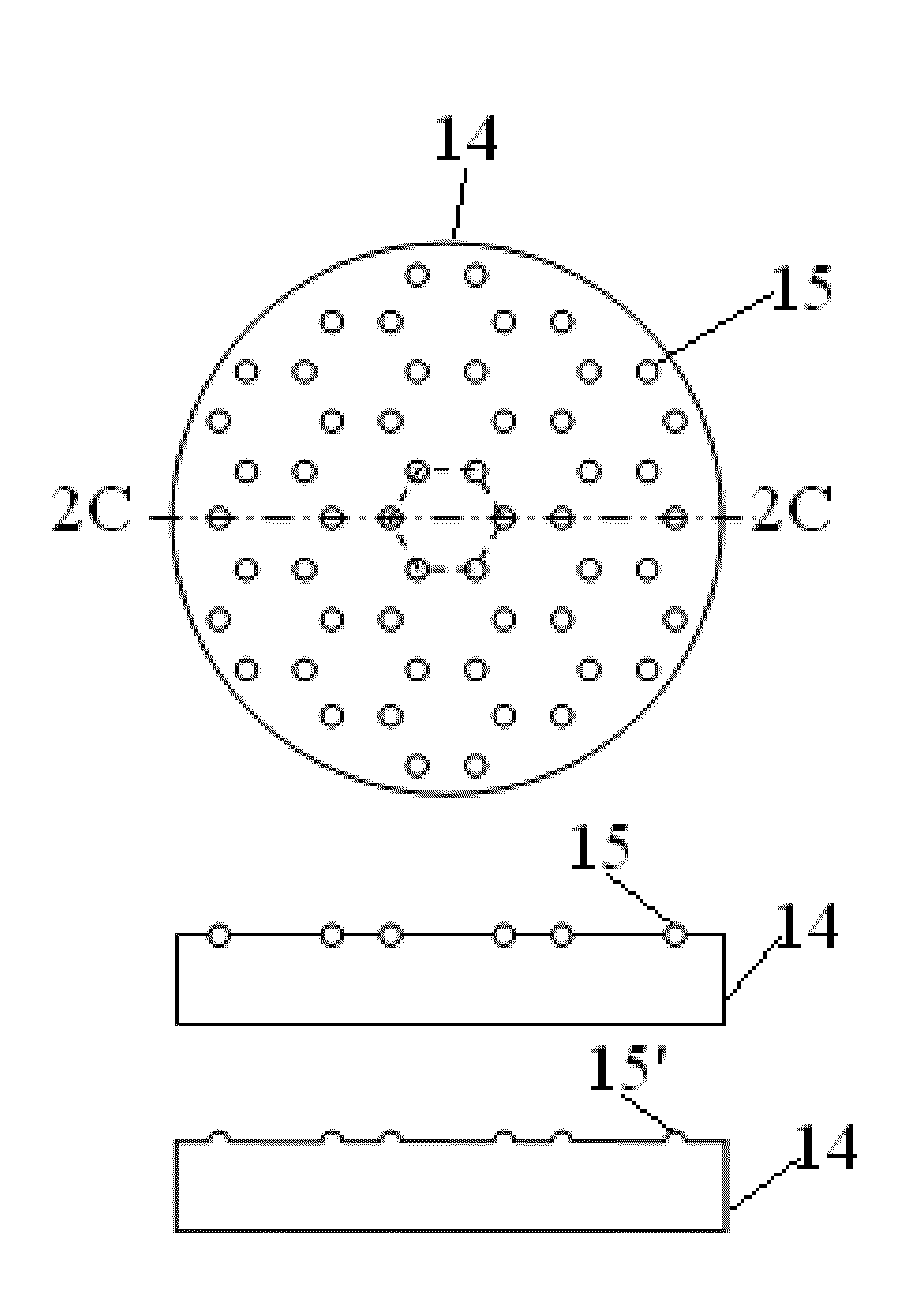
A method for forming a metal compound film includes alternate irradiation of an organometal compound and oxygen or nitrogen radicals to deposit monoatomic layers of the metal compound. The organometal compound includes zirconium, hafnium, lanthanide compounds. The resultant film includes little residual carbon and has excellent film characteristic with respect to leakage current.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Wafer-Supporting Device and Method for Producing Same
ActiveUS20130014896A1Improve uniformity of film thickness and film propertyReduce contact areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesEngineeringSemiconductor
A wafer-supporting device for supporting a wafer thereon adapted to be installed in a semiconductor-processing apparatus includes: a base surface; and protrusions protruding from the base surface and having rounded tips for supporting a wafer thereon. The rounded tips are such that a reverse side of a wafer is supported entirely by the rounded tips by point contact. The protrusions are disposed substantially uniformly on an area of the base surface over which a wafer is placed, wherein the number (N) and the height (H [μm]) of the protrusions as determined in use satisfy the following inequities per area for a 300-mm wafer:(−0.5N+40)≦H≦53; 5≦N<100.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
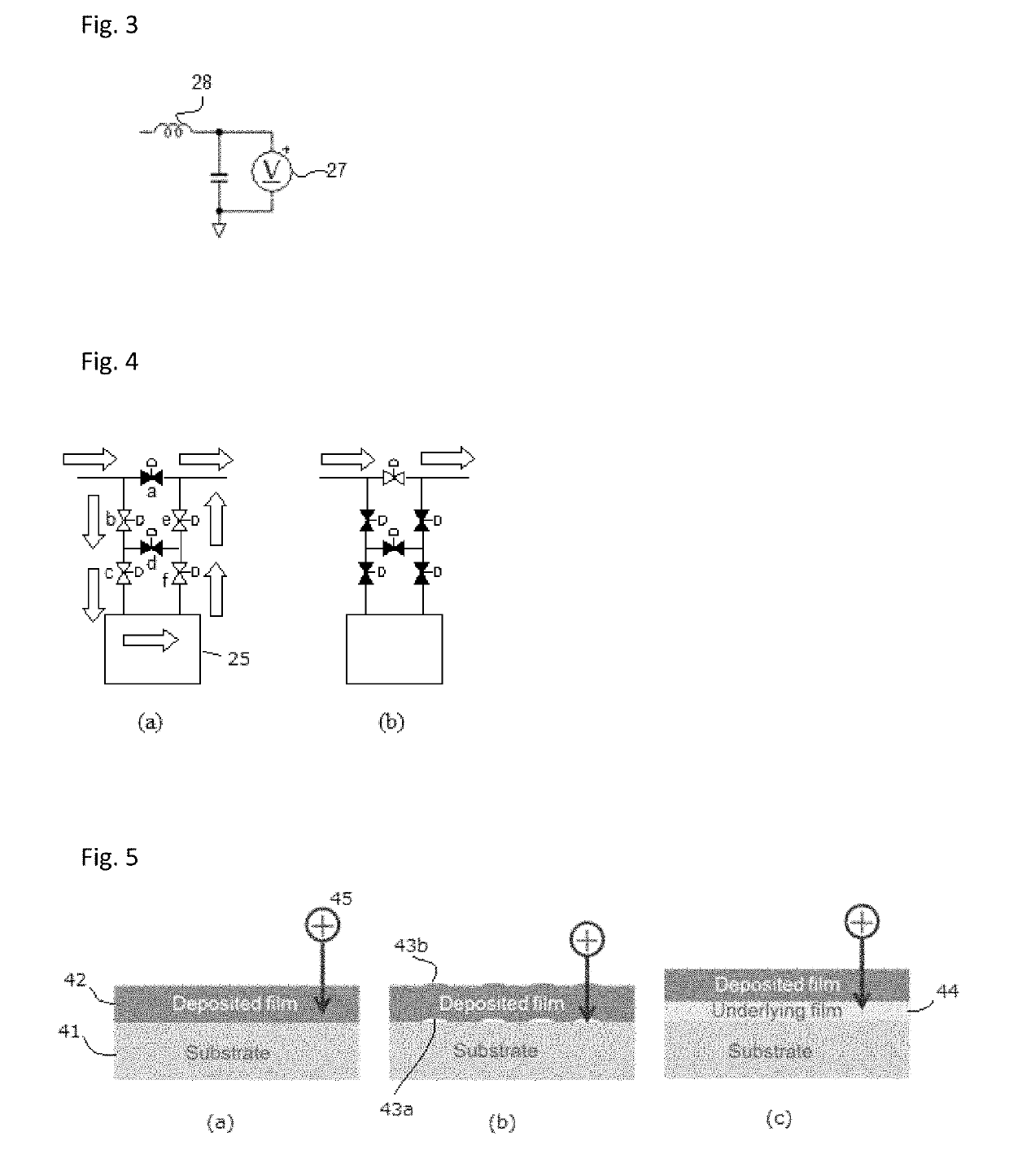
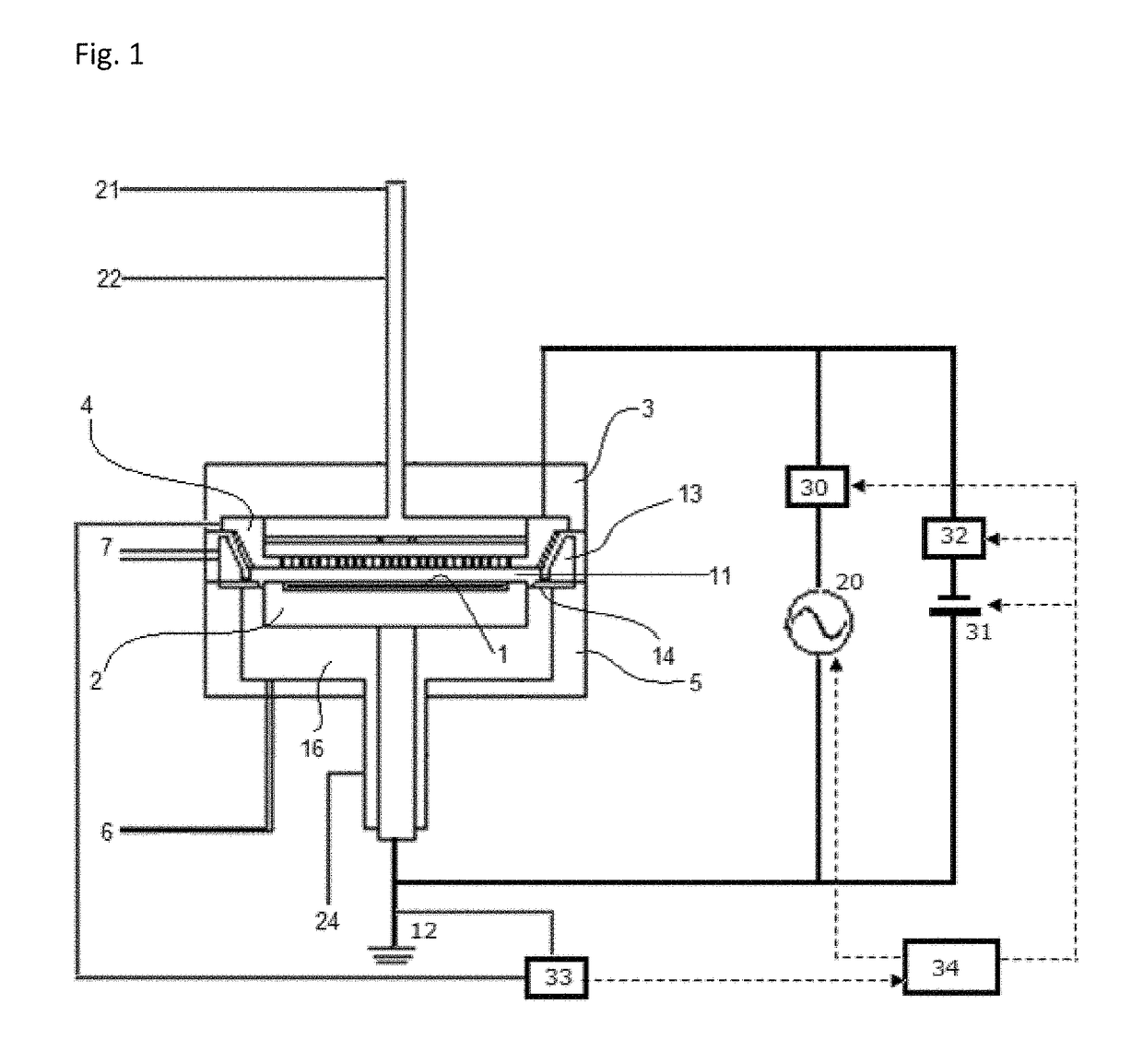
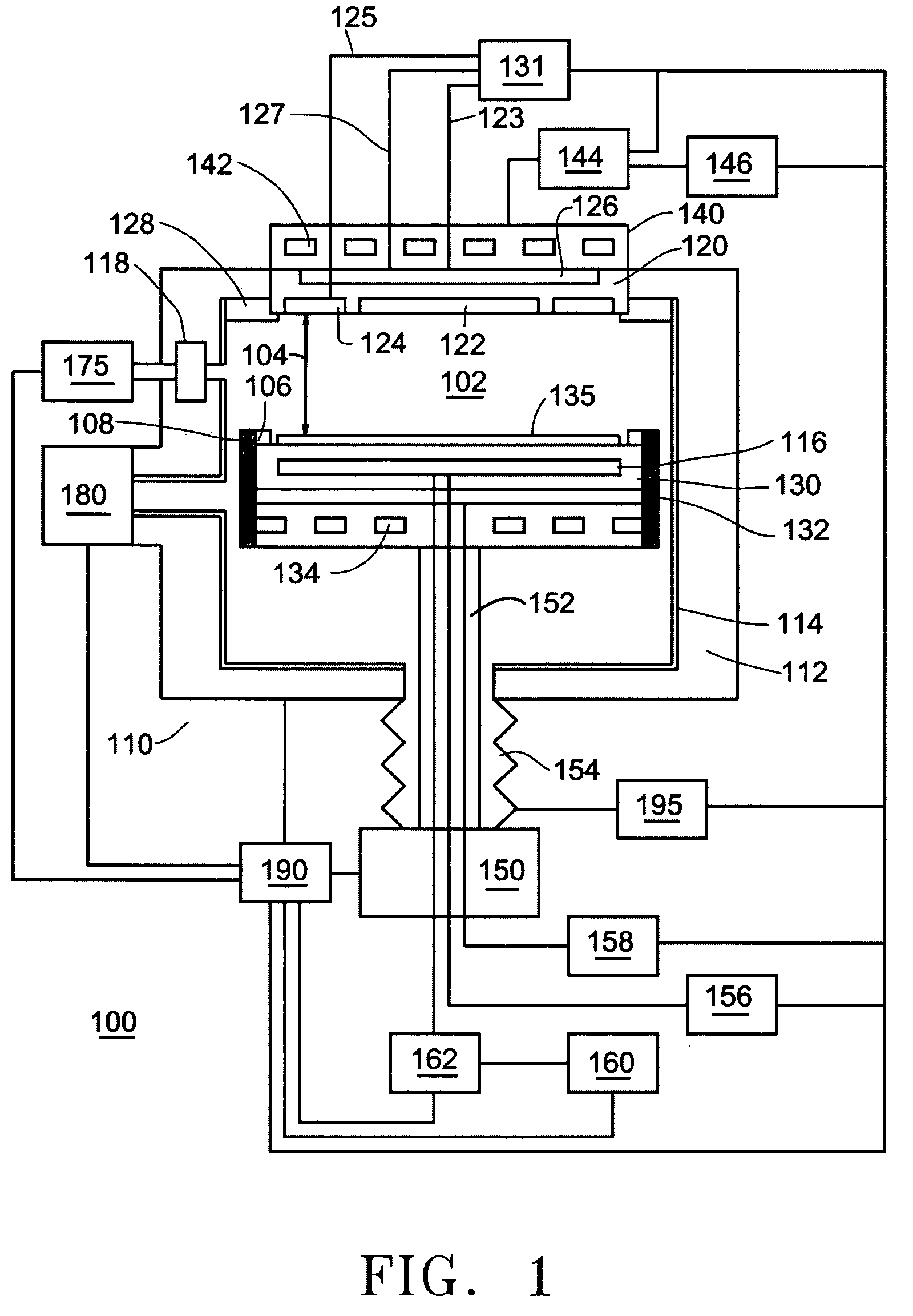
Method of depositing film by PEALD using negative bias
ActiveUS10312055B2Less particle generationLower average energyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
A method of forming a film on a substrate by PEALD includes deposition cycles, each including (i) feeding a precursor in a pulse to a reaction space to adsorb a precursor on a surface of a substrate; (ii) after step (i), applying RF power to a second electrode to generate in the reaction space a plasma to which the precursor-adsorbed surface is exposed, thereby forming a sublayer on the surface; and (iii) applying a bias voltage to the second electrode while applying RF power in step (ii), which bias voltage is negative with reference to a potential on a surface of the first electrode, wherein the cycle is repeated to deposit multiple sublayers until a film constituted by the sublayers has a desired thickness.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of depositing film by peald using negative bias
ActiveUS20190035605A1Low ion energyHigh throughputElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNegative bias
A method of forming a film on a substrate by PEALD includes deposition cycles, each including (i) feeding a precursor in a pulse to a reaction space to adsorb a precursor on a surface of a substrate; (ii) after step (i), applying RF power to a second electrode to generate in the reaction space a plasma to which the precursor-adsorbed surface is exposed, thereby forming a sublayer on the surface; and (iii) applying a bias voltage to the second electrode while applying RF power in step (ii), which bias voltage is negative with reference to a potential on a surface of the first electrode, wherein the cycle is repeated to deposit multiple sublayers until a film constituted by the sublayers has a desired thickness.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
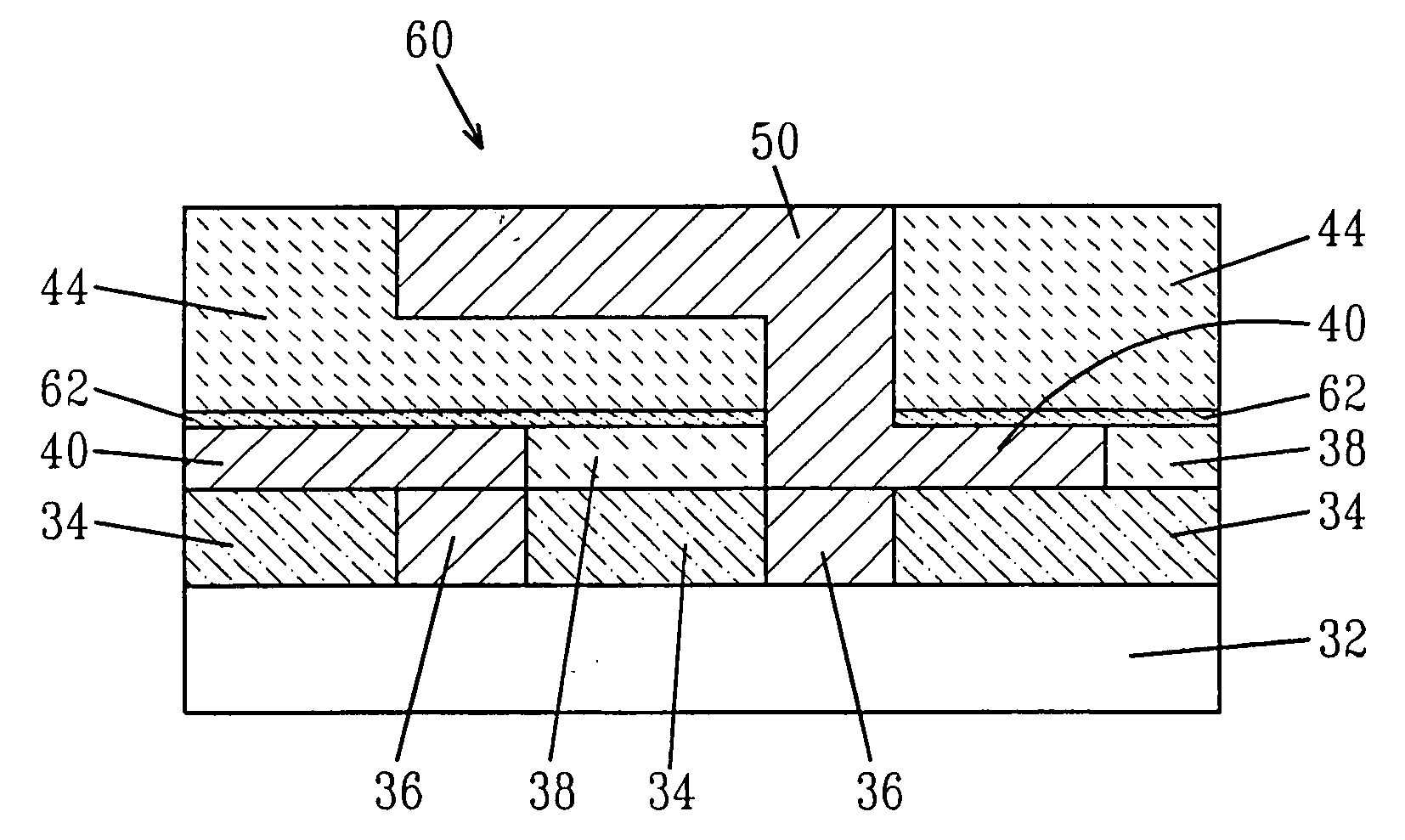
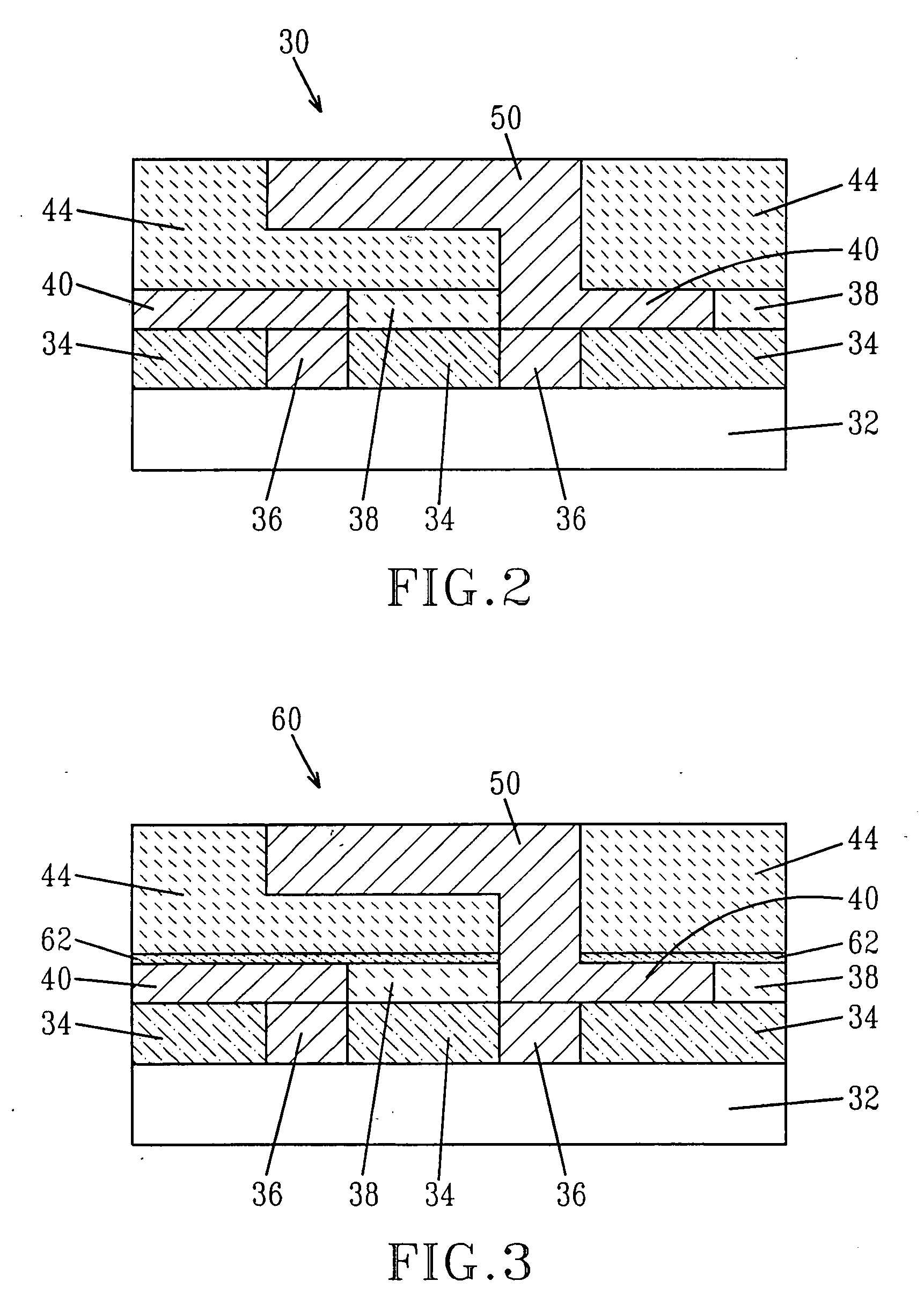
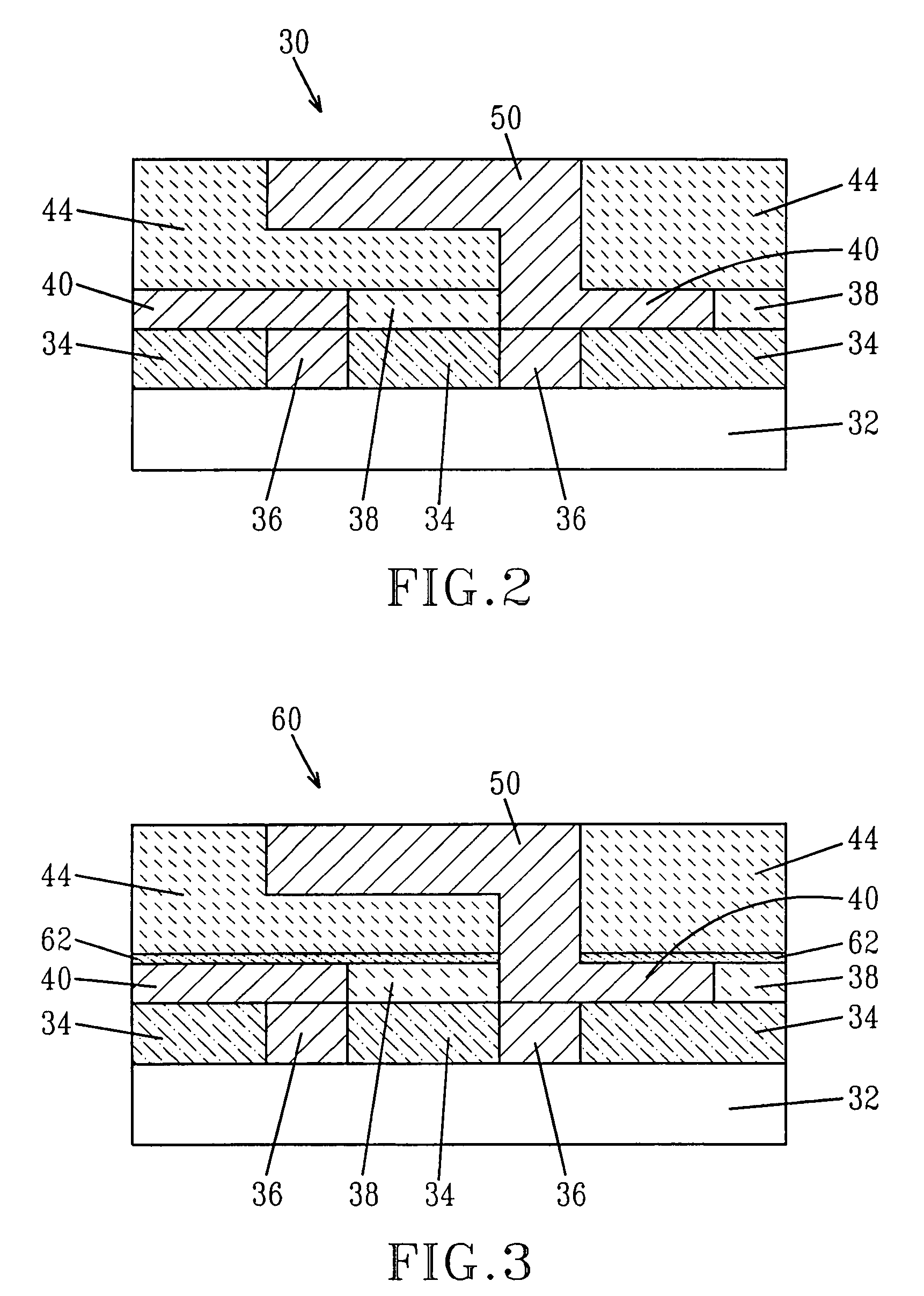
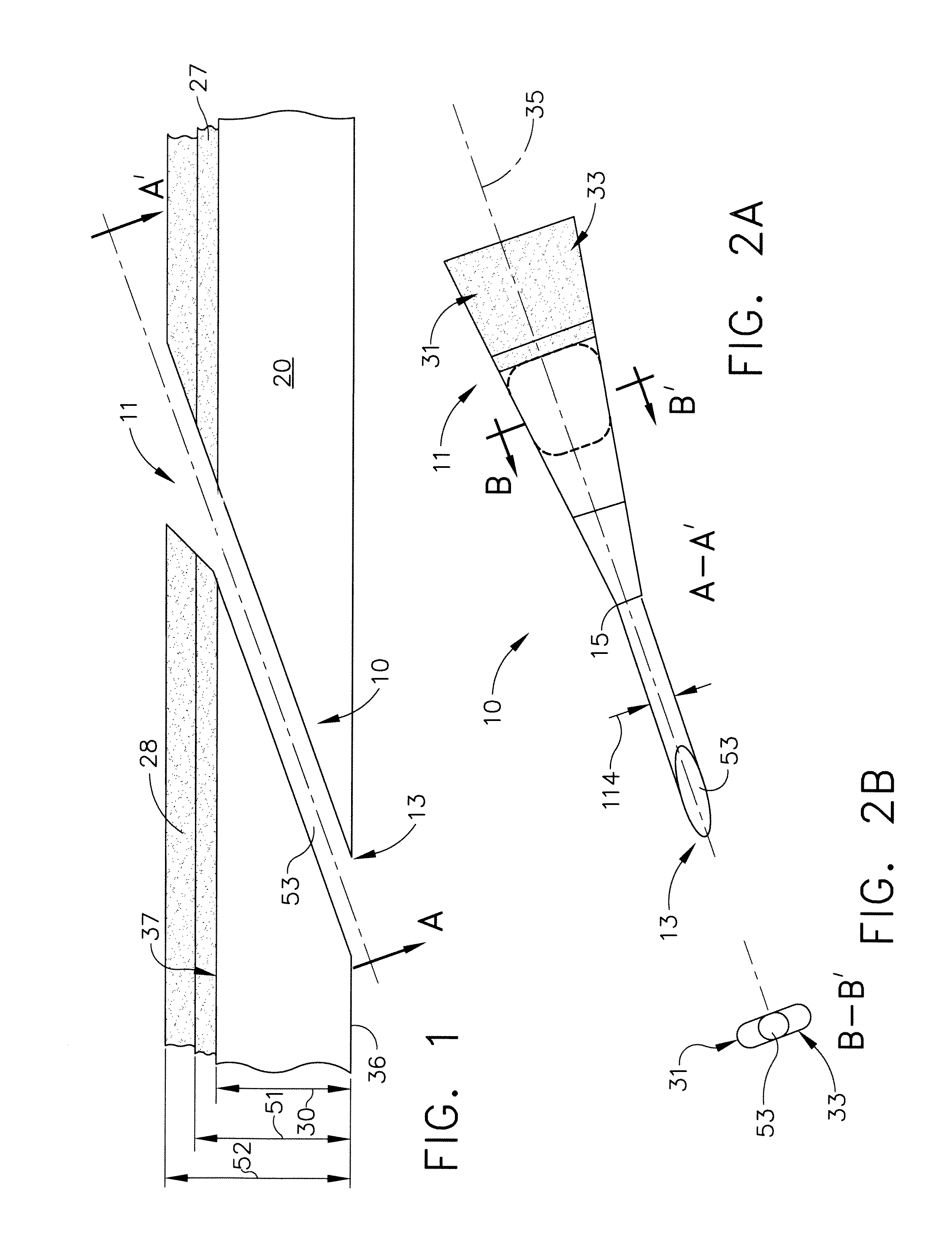
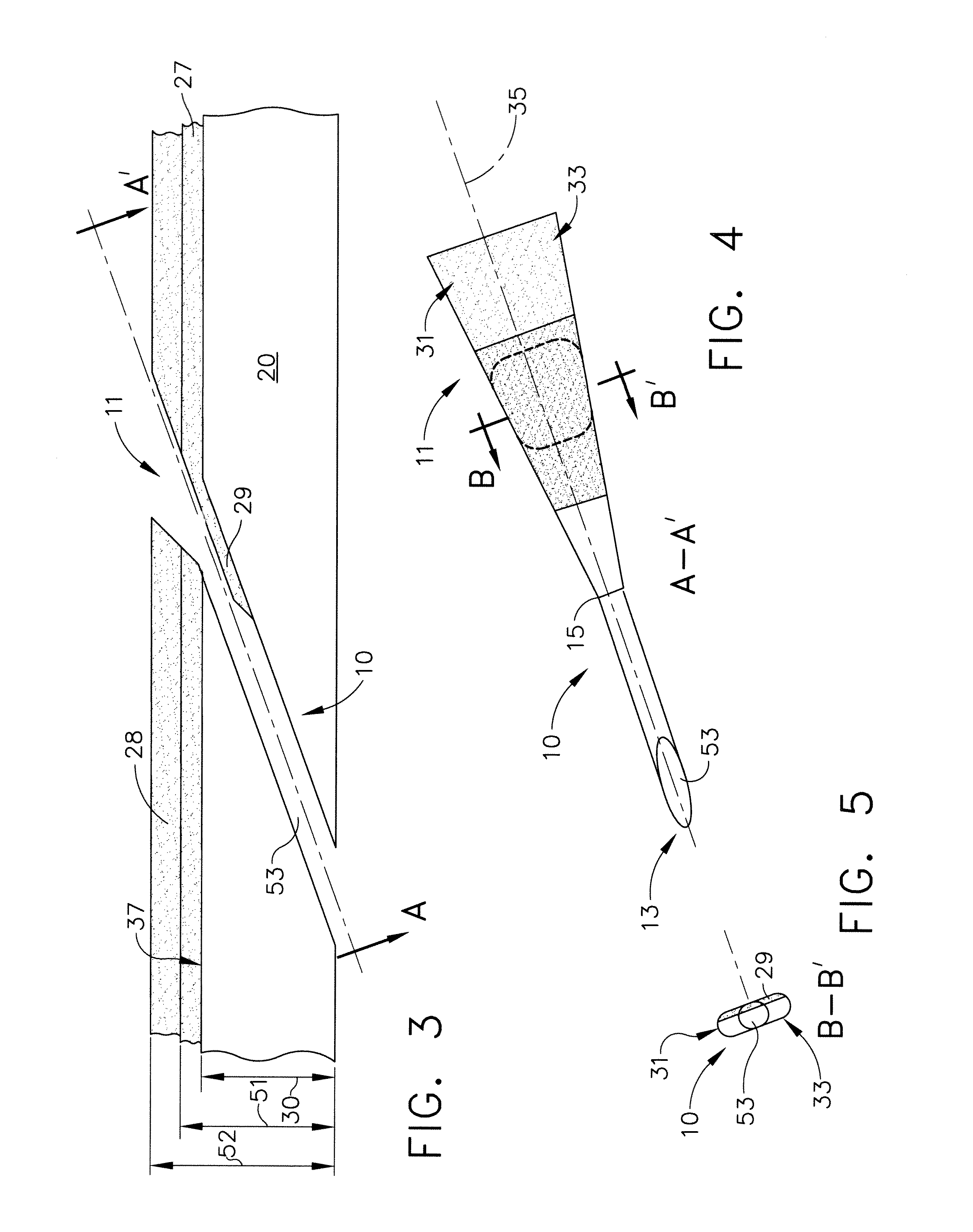
Insulation layer structure for inductive write heads and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6958885B1Avoid crackingImprove film propertiesConstruction of head windingsElectrical transducersResistInsulation layer
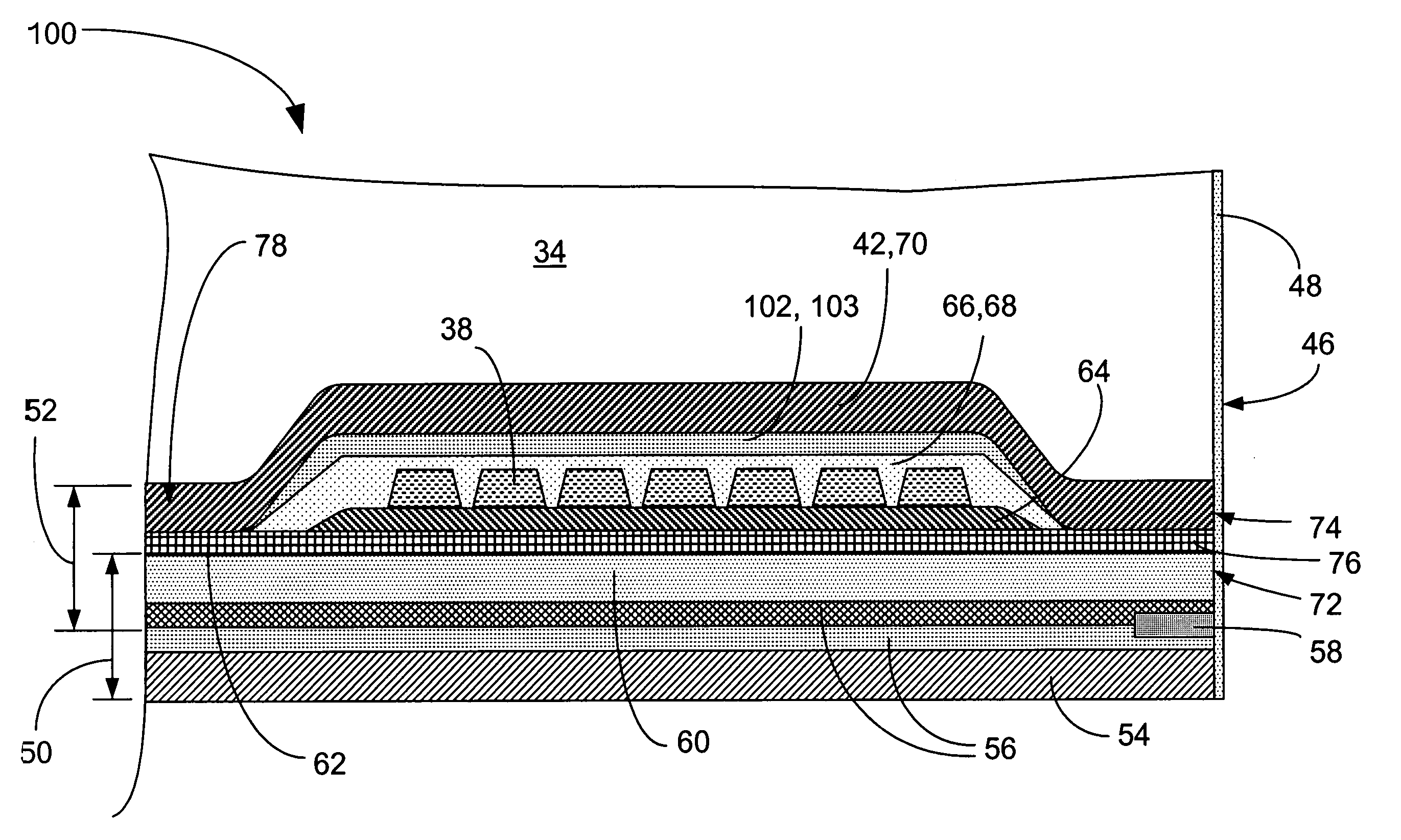
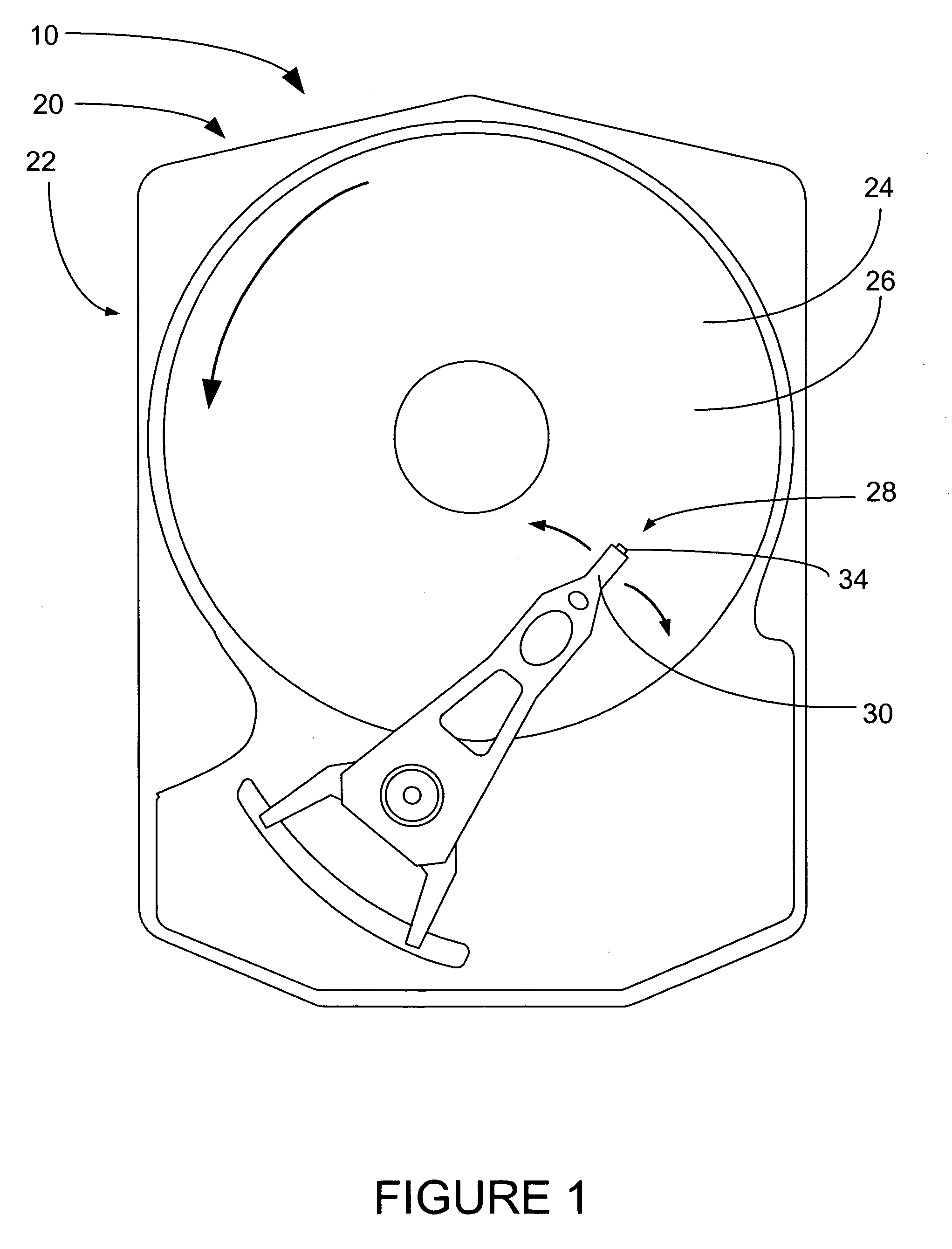
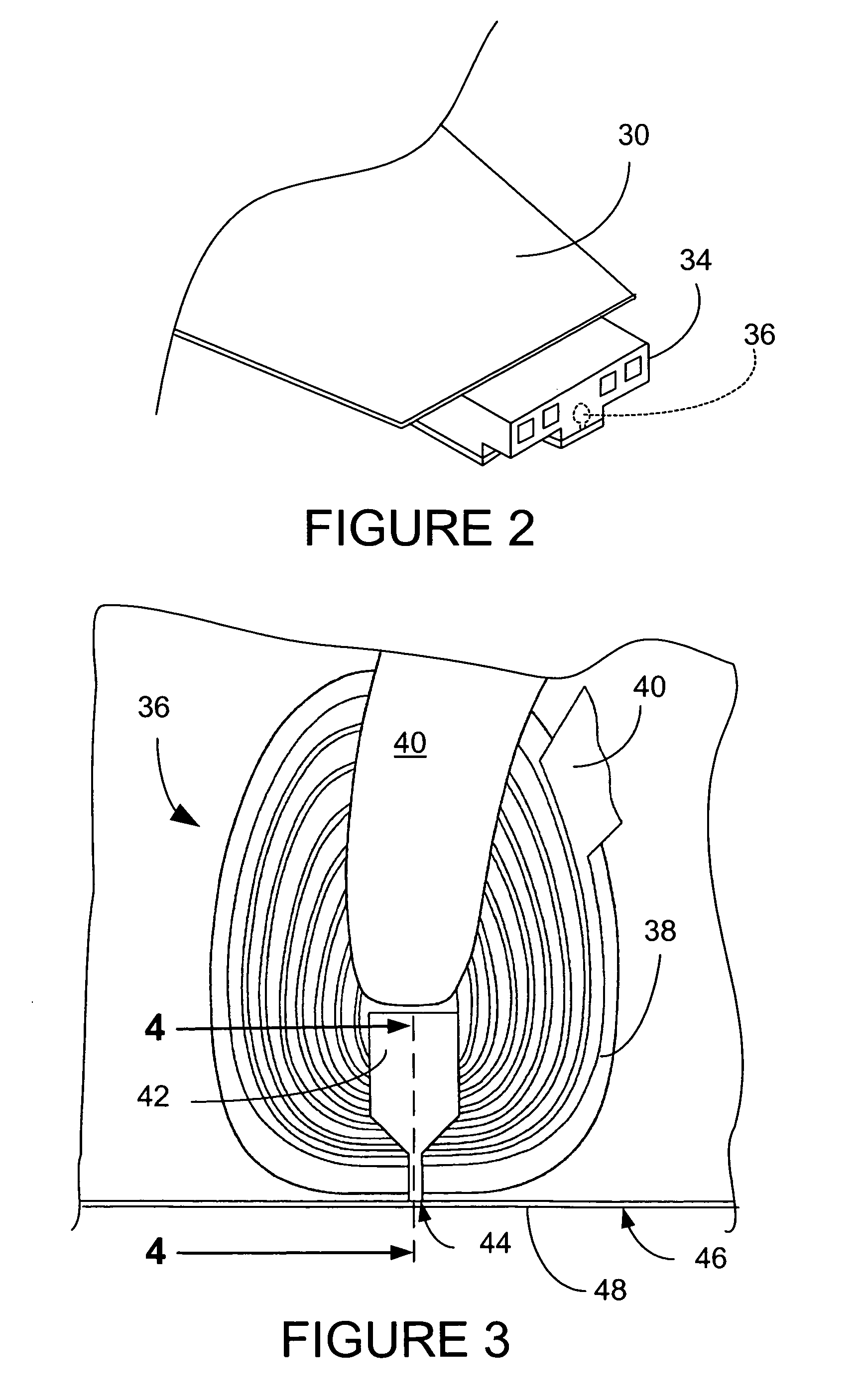
A computer disk drive (22) having a write head (52) which includes a coil (38), a photoresist insulation layer (66) formed on the coil (38), and an insulation shell layer (102) which is formed on the photoresist insulation layer (66). In the first preferred embodiment (100), the top pole (42) of the write head (52) is formed on the insulation shell layer (102).In the second preferred embodiment (200), the disk drive write gap (76) is formed on the insulation shell layer (102) and the top pole (42) of the write head (52) is formed on the write gap (76).The insulation shell layers (102) in both embodiments are preferably made of dielectric materials (103).Methods of fabrication for these embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
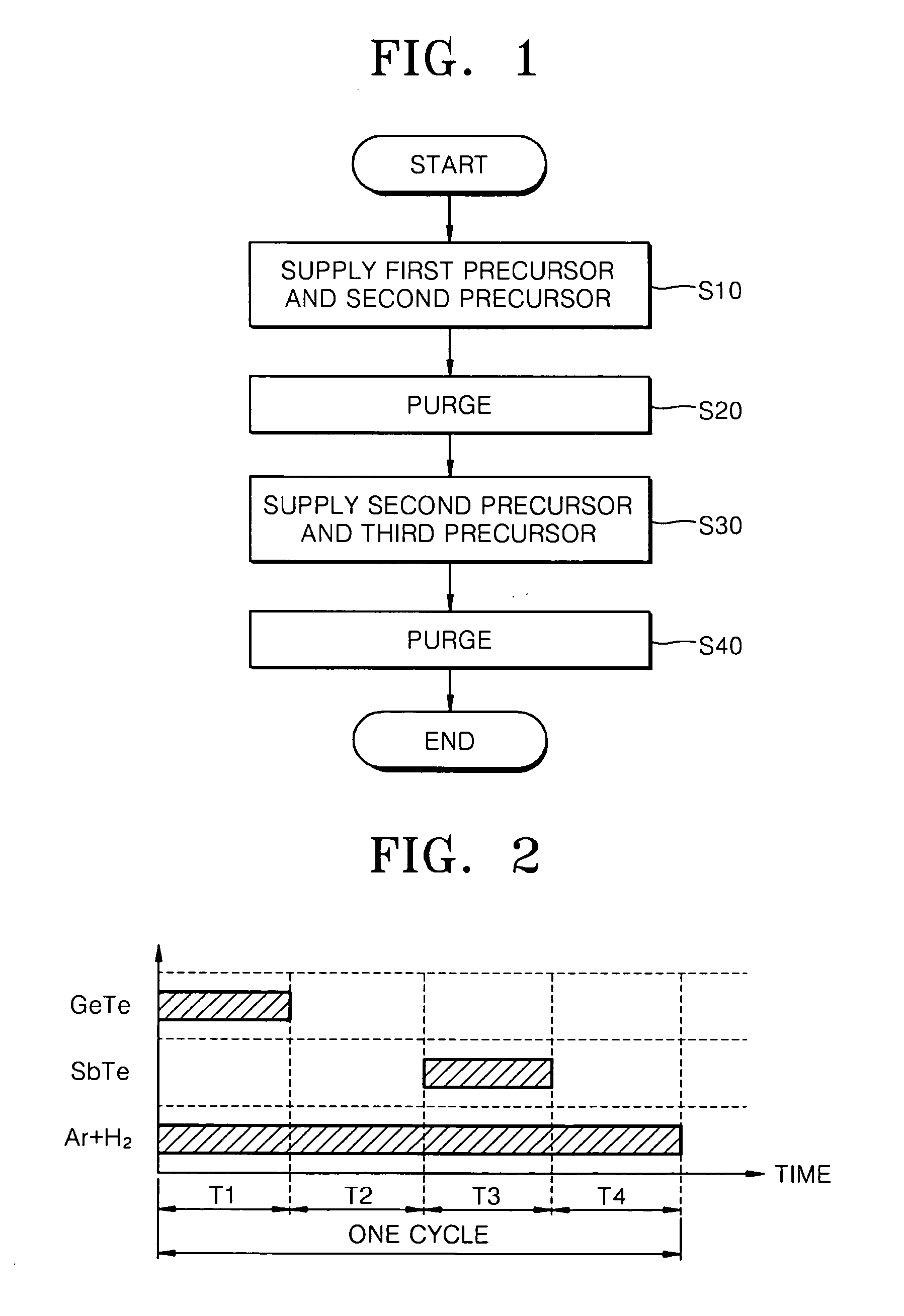
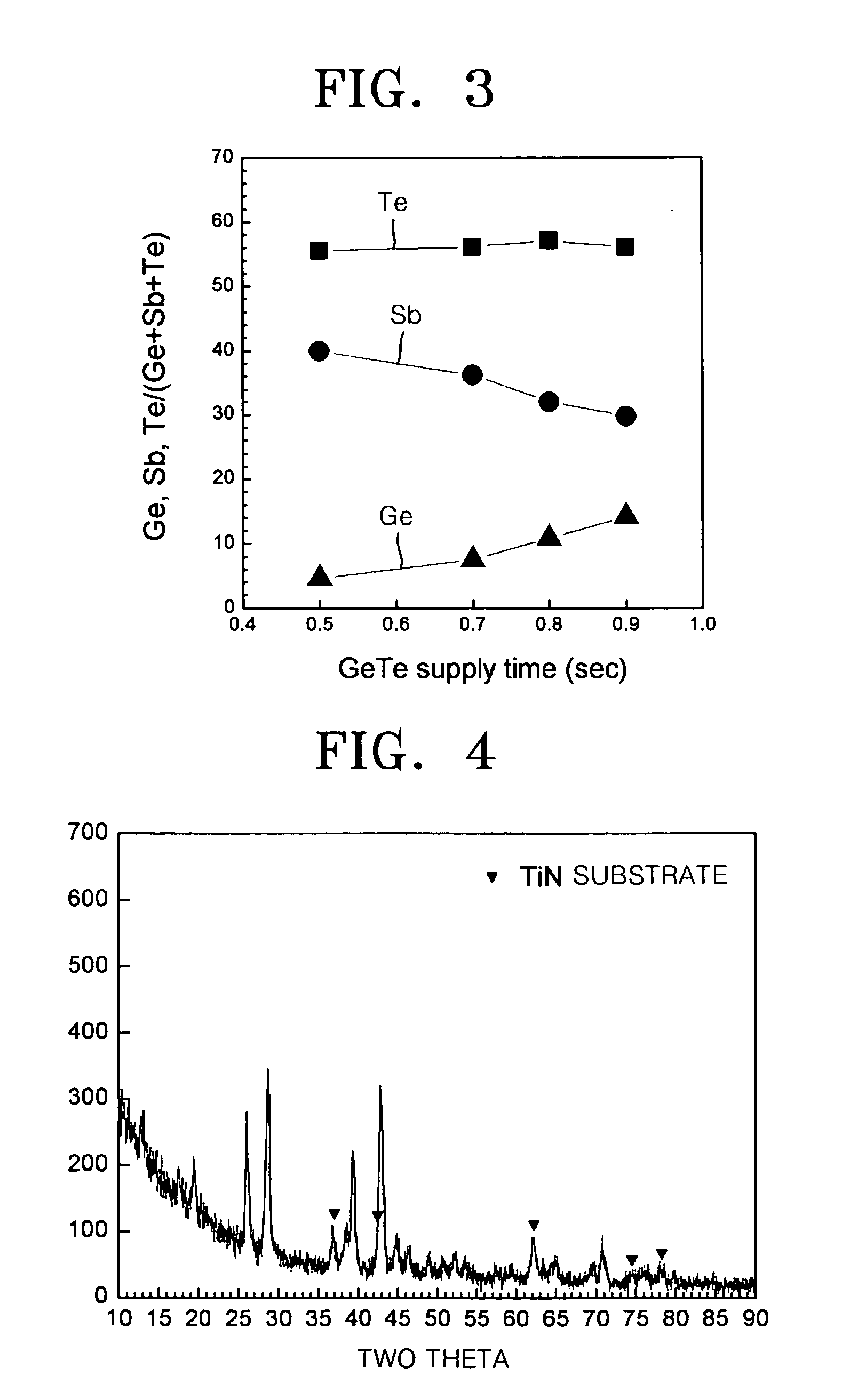
Methods of forming phase change material thin films and methods of manufacturing phase change memory devices using the same
InactiveUS20070160760A1Improve film propertiesSolid-state devicesChemical vapor deposition coatingPhase-change materialPhase-change memory
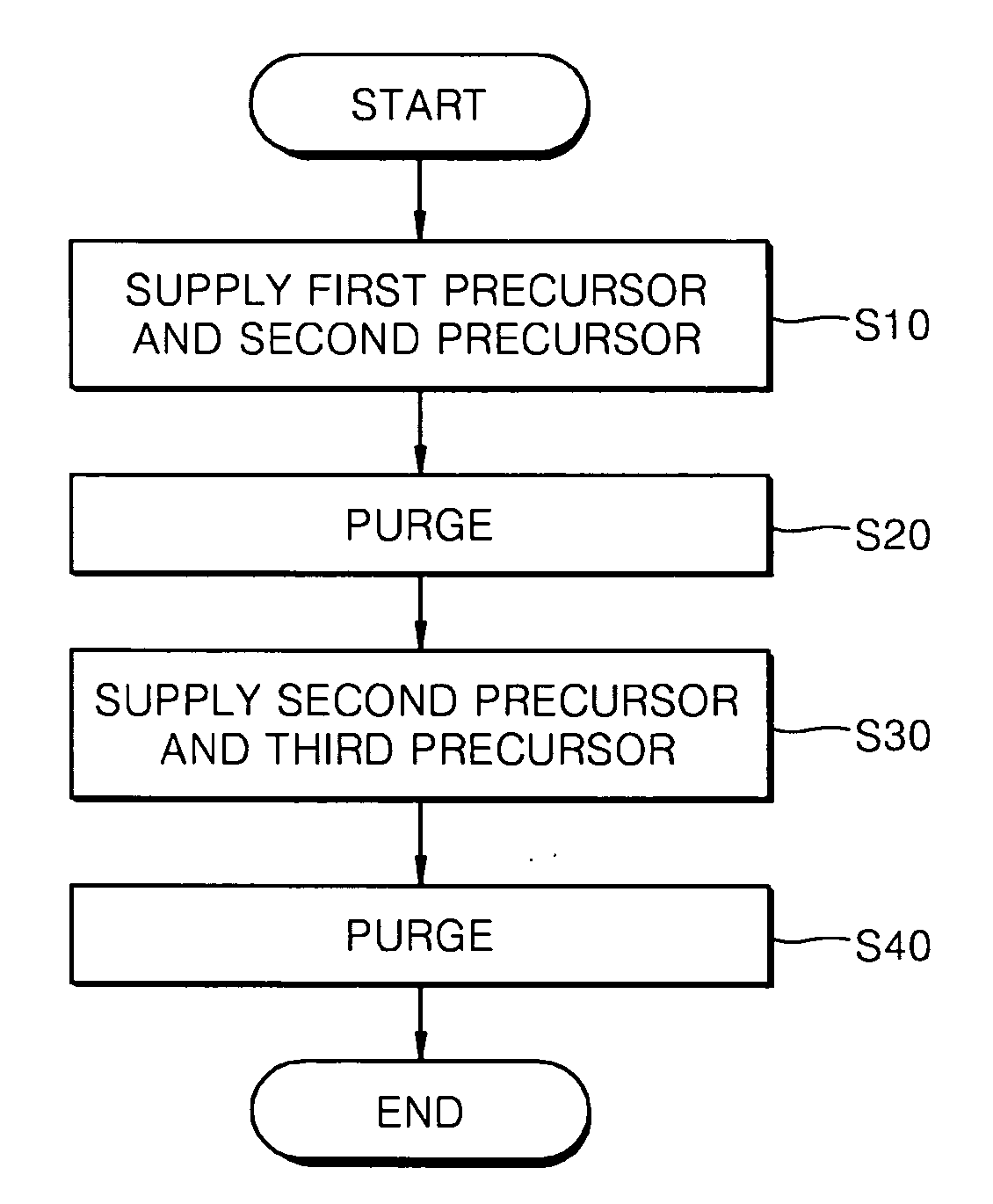
A method of forming a phase change material thin film comprises supplying a first precursor including Ge and a second precursor including Te into a reaction chamber concurrently to form a GeTe thin film on a substrate. A second precursor including Te and a third precursor including Sb are concurrently supplied into the reaction chamber and onto the GeTe thin film to form a SbTe thin film. The supplying of the first and second precursors and the supplying of the second and third precursors to form a GeSbTe thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof, semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof, and manufacturing method of insulating film
InactiveUS7955995B2Improve film propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron temperatureOxygen
An object is to provide a technique to manufacture an insulating film having excellent film characteristics. In particular, an object is to provide a technique to manufacture a dense insulating film with a high withstand voltage. Moreover, an object is to provide a technique to manufacture an insulating film with few electron traps. An insulating film including oxygen is subjected to plasma treatment using a high frequency under the conditions where the electron density is 1×1011 cm−3 or more and the electron temperature is 1.5 eV or less in an atmosphere including oxygen.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
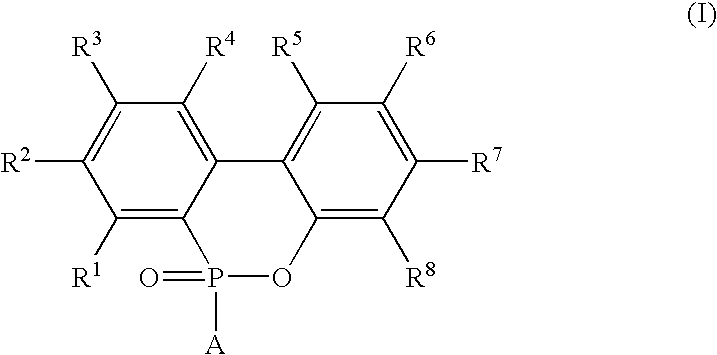
Organic electroluminescent elements
InactiveUS6344283B1Improve film propertiesImprove hole injection efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLayered productsArylOrganic electroluminescence
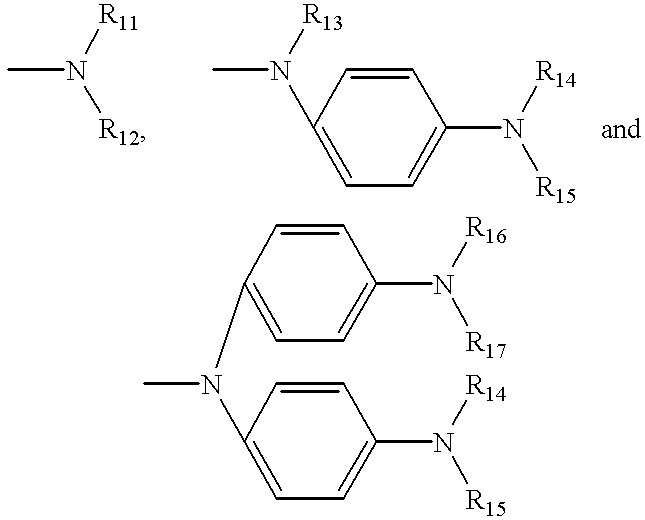
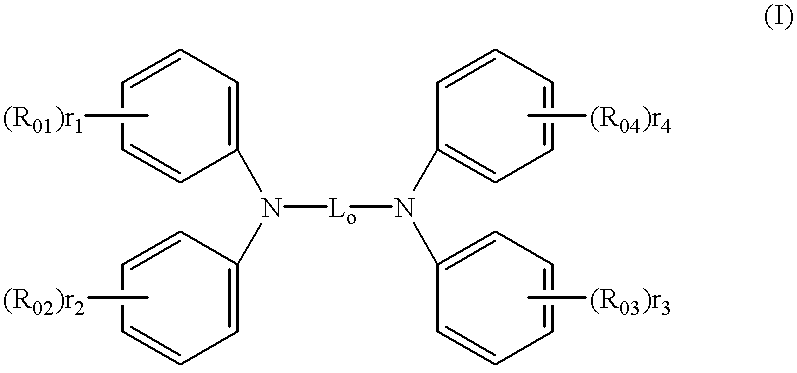
An organic EL device comprising a cathode, an anode, and at least one organic compound layer containing an organic compound represented by formula (I):where L0 is any one of o-, p-, and m-phenylene groups which have two, three or four rings and which have a substituent with the proviso that when L0 is a phenylene group having four rings, the phenylene group may have an unsubstituted or substituted aminophenyl group somewhere therein, and at least one of R01, R02, R03 and R04 is any one of the following groups:where R1, R12, R13, R14, R15, R16 and R17 are each a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, and r1, r2, r3 and r4 are each an integer of 0 to 5 with the proviso that r1+r2+r3+r4>=1.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Ultra low k plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition processes using a single bifunctional precursor containing both a SiCOH matrix functionality and organic porogen functionality
InactiveUS20060079099A1Easy to controlImprove film thickness uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDisiloxaneEpoxy
A method for fabricating a SiCOH dielectric material comprising Si, C, O and H atoms from a single organosilicon precursor with a built-in organic porogen is provided. The single organosilicon precursor with a built-in organic porogen is selected from silane (SiH4) derivatives having the molecular formula SiRR1R2R3, disiloxane derivatives having the molecular formula R4R5R6—Si—O—Si—R7R8R9, and trisiloxane derivatives having the molecular formula R10R11R12—Si—O—Si—R13R14—O—Si—R15R16R17 where R and R1-17 may or may not be identical and are selected from H, alkyl, alkoxy, epoxy, phenyl, vinyl, allyl, alkenyl or alkynyl groups that may be linear, branched, cyclic, polycyclic and may be functionalized with oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine containing substituents. In addition to the method, the present application also provides SiCOH dielectrics made from the inventive method as well as electronic structures that contain the same.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Cellulose acylate laminate film, method for producing same, polarizer and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20100055356A1High degree of substitutionExcellent releasabilityLiquid crystal compositionsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolarizerLiquid-crystal display
A stretched cellulose acylate laminate film having a skin layer containing a cellulose acylate with a total degree of acyl substitution of more than 2.7 and a core layer containing a cellulose acylate with a total degree of acyl substitution of 2.0-2.7 wherein the core layer is thicker than the skin B layer and at least one of these layers contains a retardation-controlling agent, is excellent in high expressibility, little optical unevenness and good releasability from a support.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Packaging film
A film of biodegradable polylactic acid polymers and copolymers is produced by coextrusion which displays improved winding and manufacturability and end use performance. The film is coextruded from polylactic acid (PLA) polymers and copolymers and biaxially oriented. The surface layer(s) of the film is modified with a particle and displays improved COF, blocking resistance, reduced static generation, improved winding and improved package formation on packaging machines.
Owner:BIAX INT
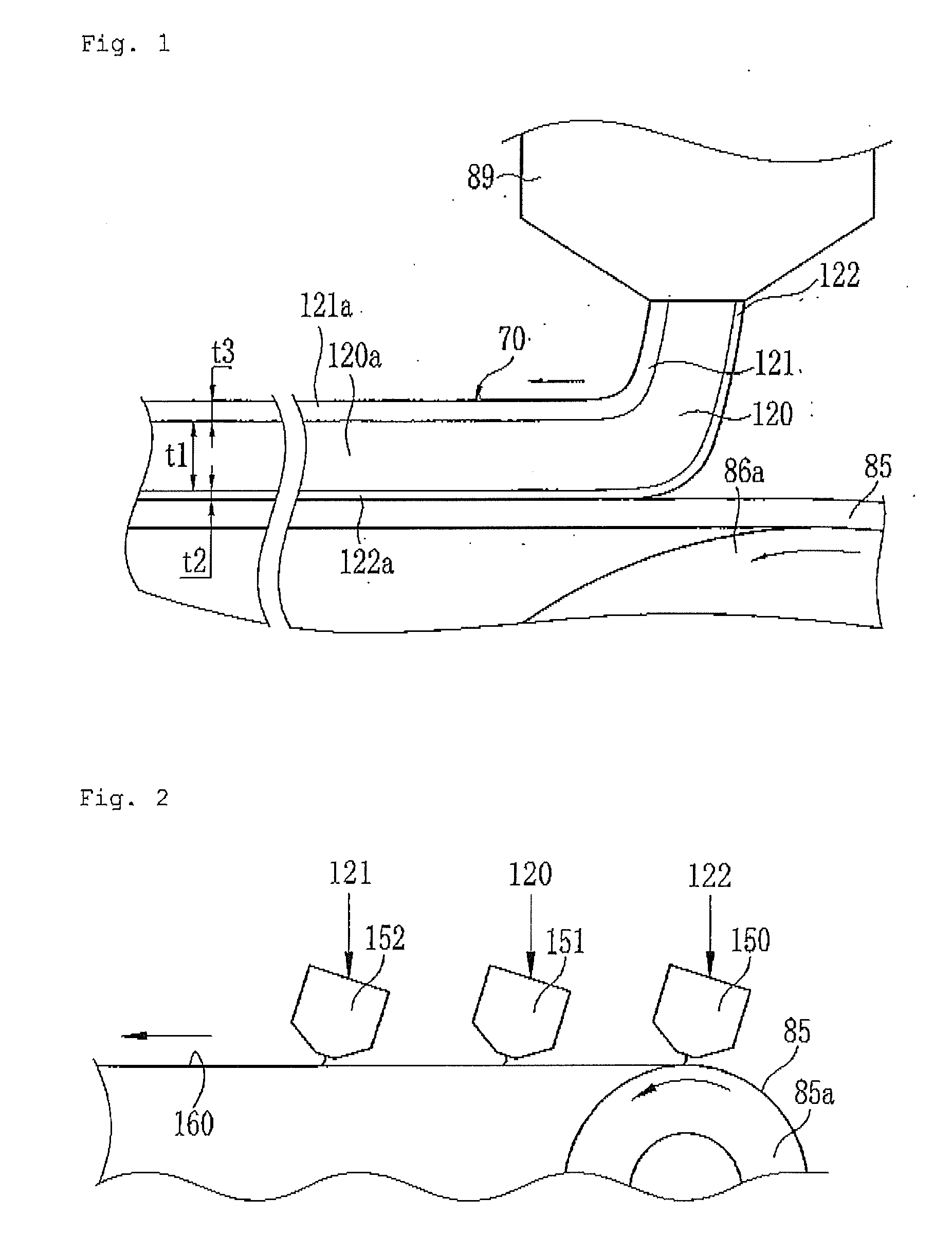
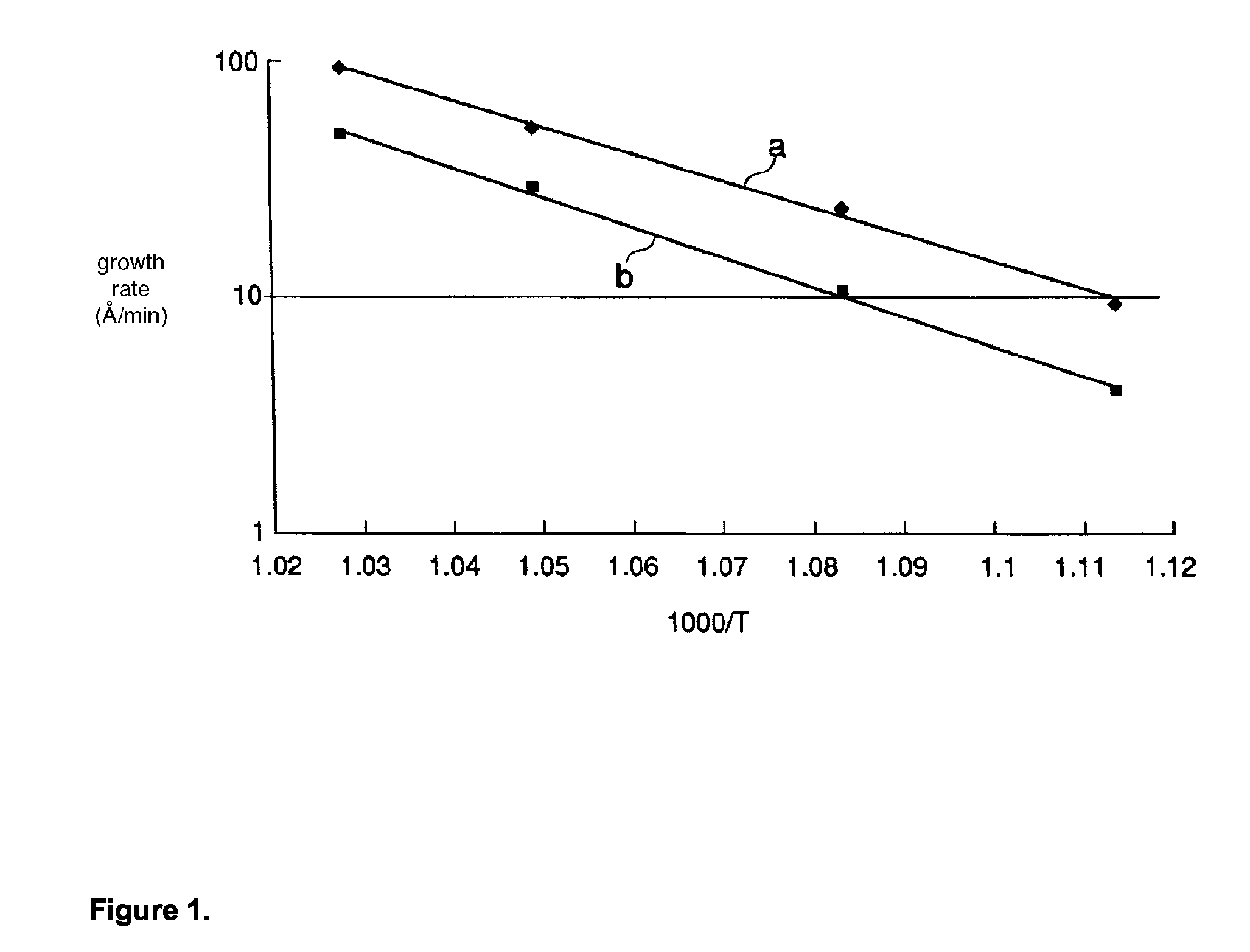
Method for Producing Silicon Nitride Films
ActiveUS20080260969A1Excellent film propertyHigh resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTrisilylamineSilicon nitride
(Problem) To provide a method for producing silicon nitride films by vapor deposition that, while employing trisilylamine as precursor, can produce silicon nitride films that exhibit excellent film properties and can do so at relatively low temperatures and relatively high growth rates. (Solution) Method for producing silicon nitride film, said method being characterized by feeding gaseous trisilylamine and gaseous nitrogen source comprising at least two amine-type compounds selected from amine-type compounds with formula (1) NR1R2R3 (R1, R2, and R3 are each independently selected from hydrogen and C1-6 hydrocarbyl) into a reaction chamber that holds at least one substrate and forming silicon nitride film on said at least one substrate by reacting the trisilylamine and said nitrogen source.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Aqueous dispersion
ActiveUS20040097600A1Effective and stableShorten drying timeMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSilica particleSilane compounds
The invention relates to a method of producing an aqueous dispersion comprising mixing at least one silane compound and colloidal silica particles to form silanized colloidal silica particles, mixing said silanized colloidal silica particles with an organic binder to form the dispersion. The invention also relates to a dispersion obtainable by the method, and the use thereof.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
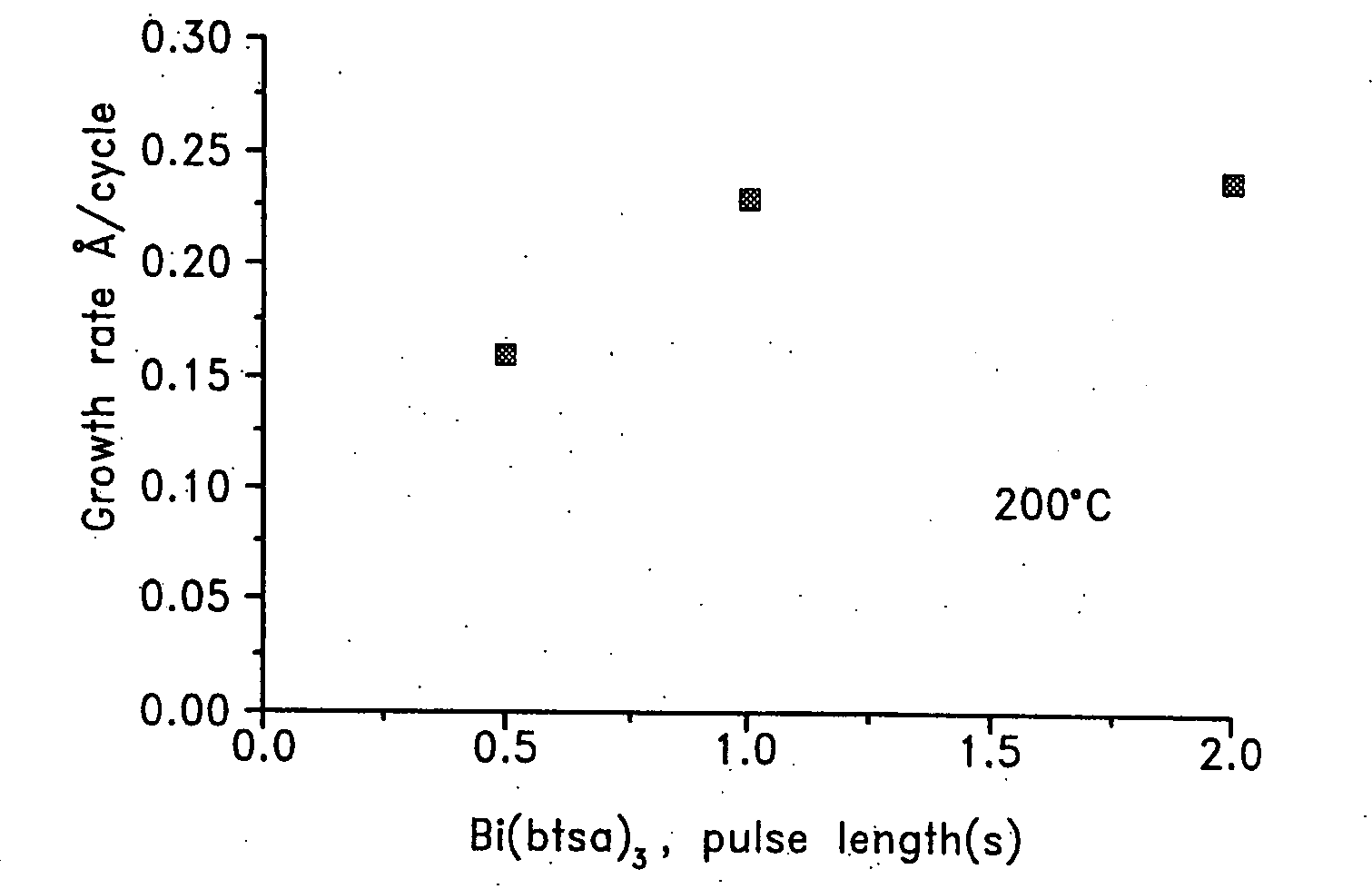
Process for producing oxide films
ActiveUS20050089632A1Reduce decreaseImprove film propertiesCeramicsSolid-state devicesSilyleneBismuth compound
A process for producing bismuth-containing oxide thin films by Atomic Layer Deposition, including using an organic bismuth compound having at least one silylamido ligand as a source material for the bismuth oxide. Bismuth-containing oxide thin films produced by the preferred embodiments can be used, for example, as ferroelectric or dielectric material in integrated circuits and / or as superconductor materials.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method for controlling properties of conformal silica nanolaminates formed by rapid vapor deposition
ActiveUS7297608B1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove film propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityGas phase
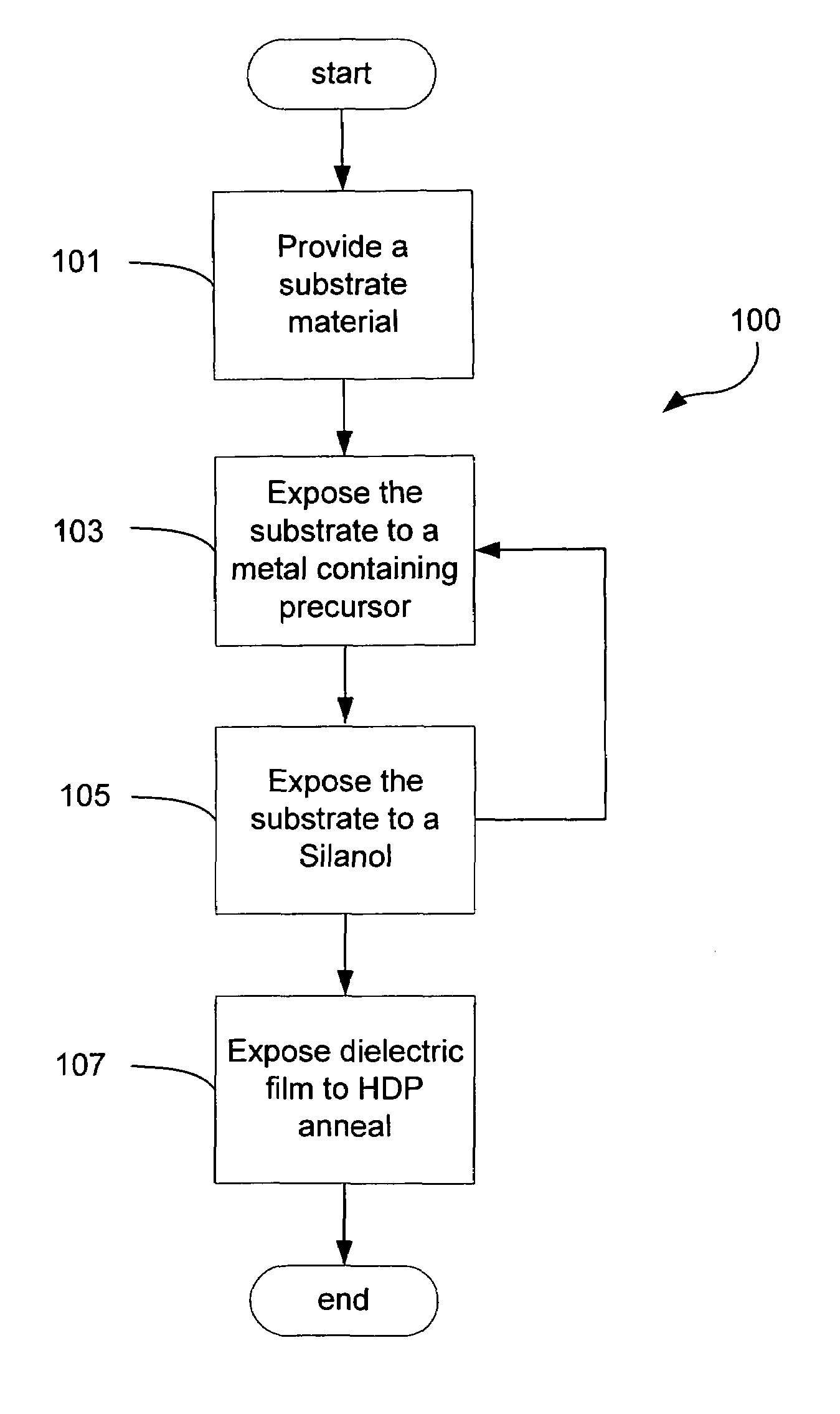
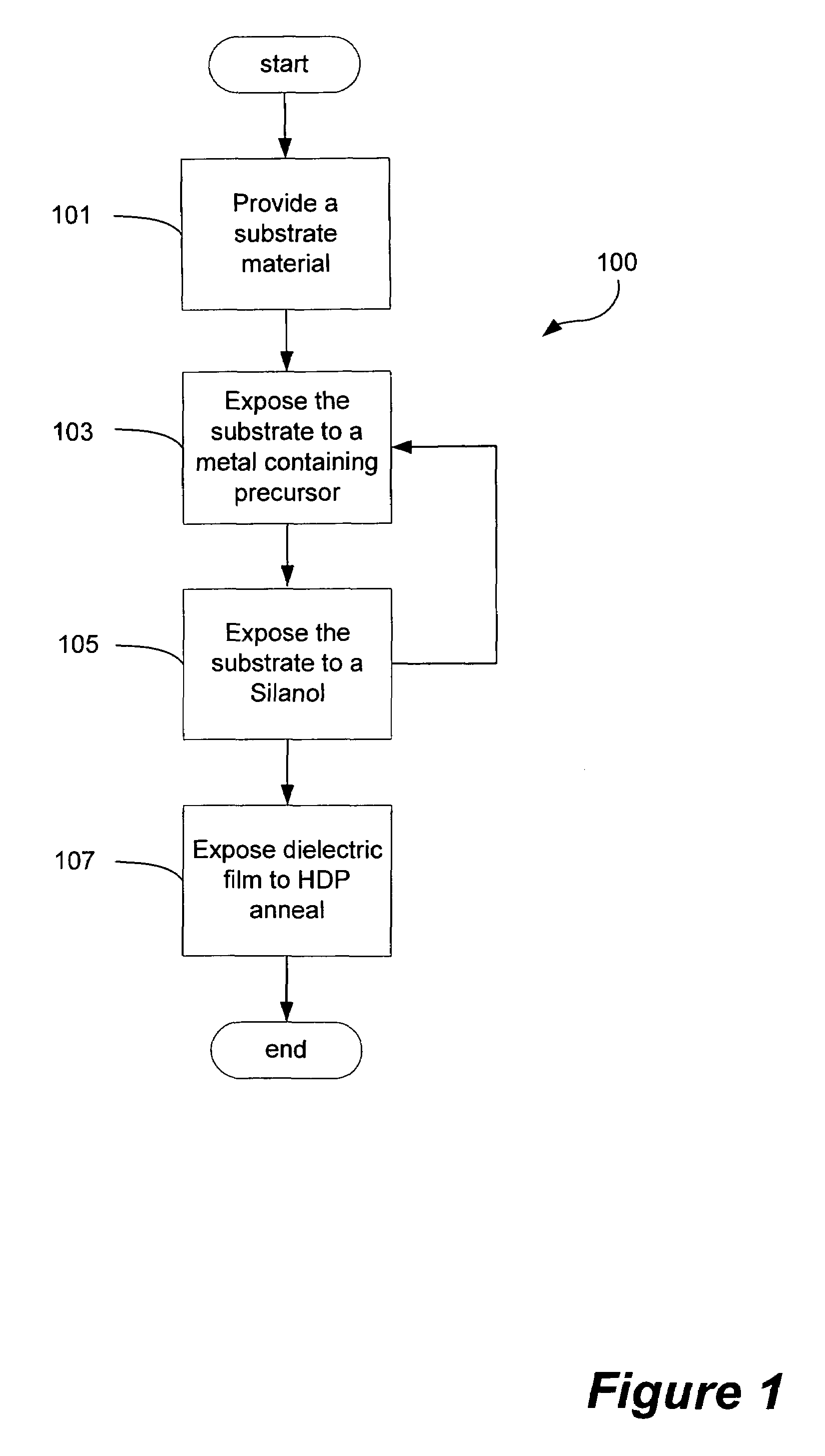
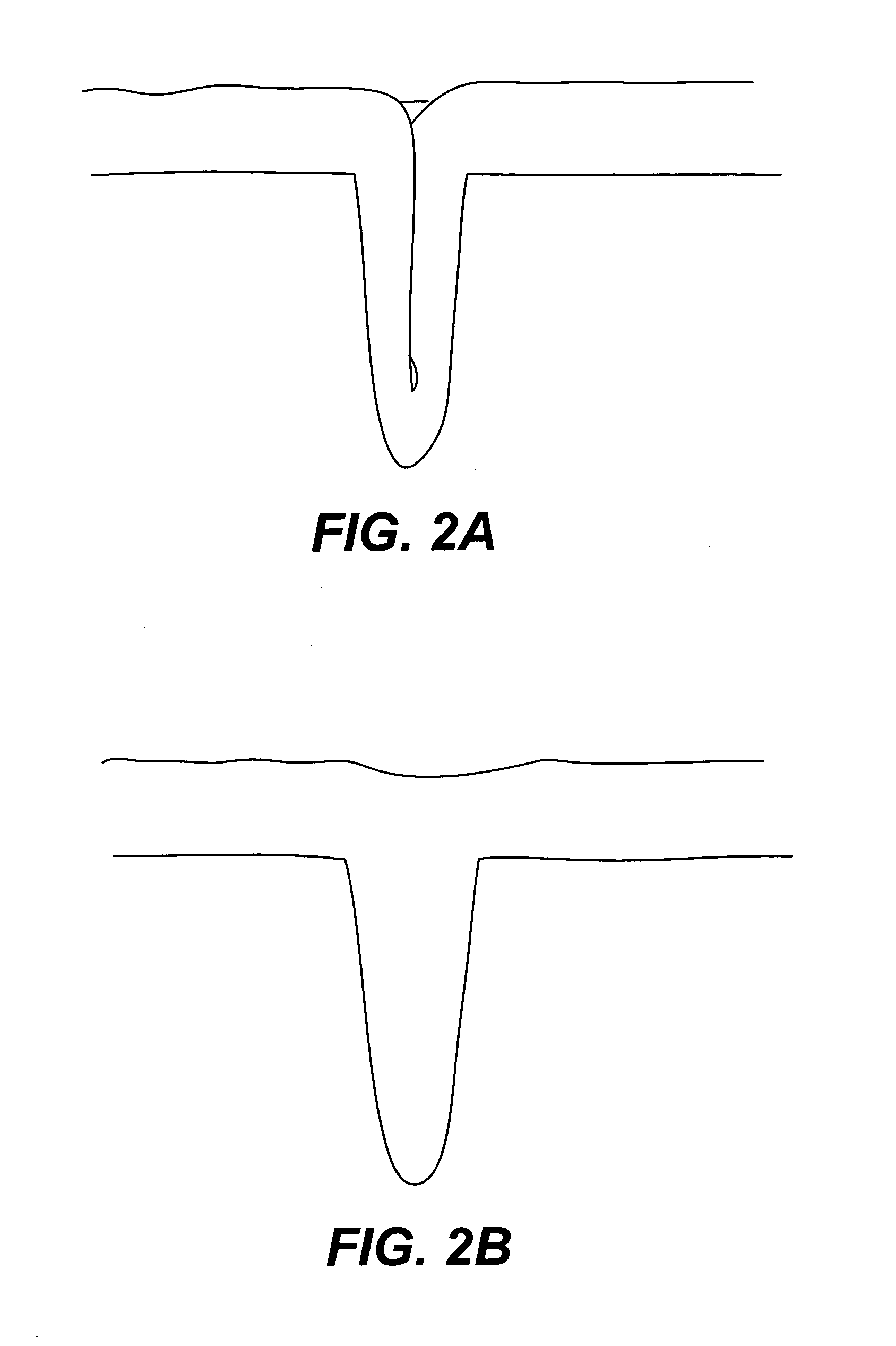
A method employing atomic layer deposition rapid vapor deposition (RVD) conformally deposits a dielectric material on small features of a substrate surface. The resulting dielectric film is then annealed using a high density plasma (HDP) at a temperature under 500° C. in an oxidizing environment. The method includes the following three principal operations: exposing a substrate surface to an aluminum-containing precursor gas to form a substantially saturated layer of aluminum-containing precursor on the substrate surface; exposing the substrate surface to a silicon-containing precursor gas to form the dielectric film; and annealing the dielectric film in a low temperature oxygen-containing high density plasma. The resulting film has improved mechanical properties, including minimized seams, improved WERR, and low intrinsic stress, comparable to a high temperature annealing process (˜800° C.), but without exceeding the thermal budget limitations of advanced devices.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Curing Dielectric Films Under A Reducing Atmosphere
InactiveUS20070299239A1Lessen timeEfficiently removeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical speciesReducing atmosphere
The present invention provides a process for forming a porous dielectric film, the process comprising: forming onto at least a portion of a substrate a composite film comprising Si, C, O, H and Si—CH3 groups, wherein the composite film comprises at least one silicon-containing structure-forming material and at least one carbon-containing pore-forming material; and exposing the composite film to an activated chemical species to at least partially modify the carbon-containing pore-forming material, wherein at least 90% of Si—CH3 species in the as deposited film remains in the film after the exposing step as determined by FTIR.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Ultra low k plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition processes using a single bifunctional precursor containing both a SiCOH matrix functionality and organic porogen functionality
InactiveUS7491658B2Improve film propertiesEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricEpoxy
A method for fabricating a SiCOH dielectric material comprising Si, C, O and H atoms from a single organosilicon precursor with a built-in organic porogen is provided. The single organosilicon precursor with a built-in organic porogen is selected from silane (SiH4) derivatives having the molecular formula SiRR1R2R3, disiloxane derivatives having the molecular formula R4R5R6—Si—O—Si—R7R8R9, and trisiloxane derivatives having the molecular formula R10R11R12—Si—O—Si—R13R14—O—Si—R15R16R17 where R and R1-17 may or may not be identical and are selected from H, alkyl, alkoxy, epoxy, phenyl, vinyl, allyl, alkenyl or alkynyl groups that may be linear, branched, cyclic, polycyclic and may be functionalized with oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine containing substituents. In addition to the method, the present application also provides SiCOH dielectrics made from the inventive method as well as electronic structures that contain the same.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Soft de-chucking sequence
InactiveUS20060046506A1Improve propertiesImprove film propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
A method and apparatus for improving the properties of a deposited film. The method includes depositing a low-k dielectric on a substrate using a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition process and performing a soft de-chucking sequence after depositing the low-k dielectric film using a soft plasma process. The apparatus includes a chamber having an upper electrode coupled to a first RF source and a substrate holder coupled to a second RF source; and a showerhead for providing multiple precursors and process gasses.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Composition for forming layer to be plated, method of producing metal pattern material, metal pattern material
ActiveUS20100080964A1Improve film propertiesImprove propertiesLayered productsDecorative surface effectsElectrical polarityPolymer
A composition including a polymer, the polymer having a non-dissociative functional group that interacts with a plating catalyst or a precursor thereof, a radical polymerizable group, and an ionic polar group; a method of producing a metal pattern material using the same: and a metal pattern material produced by the method.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for forming thin film and method for fabricating liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS7011981B2Simple processImprove surface uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDiffusion barrier
A method for forming a thin film and a method for fabricating a liquid crystal display device using the same are provided. The method provides a process that is simplified. Uniform thin film characteristics can be obtained. The method for forming a thin film includes the steps of forming a diffusion barrier film on a substrate, forming a metal seed layer on the diffusion barrier film, removing a metal oxide film formed on a surface of the metal seed layer using an electric plating method, and depositing metal on the metal seed layer in which the metal oxide film is removed.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method of manufacturing electron device and organic electroluminescent display and ink for organic amorphous film
InactiveUS20060045959A1Improve efficiencyImprove throughputTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesSolubilityDistillation
The present invention provides a method which can form a uniform amorphous film using an organic low molecular weight material which is refined by distillation or sublimation. The viscosity of ink is regulated by mixing two kinds of solvents so as to increase a surface tension of the ink and the solubility of the organic material in a drying step whereby an amorphous film made of an organic material is selectively formed in a recessed region defined by a partition wall layer using an ink jet method.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Composite Powder Coating Material, Process for Production Thereof and Method for the Color Matching of Powder Coating Material Technical Field
InactiveUS20070299196A1Improve film propertiesHighly uniform hueLiquid surface applicatorsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsSolventMaterials science
The present invention provides a composite powder coating composition obtained by granulating, with a liquid binder, a plurality of starting powder coating materials that are different from each other in hue and / or kind of base resin, and drying the granules, the liquid binder being a solution or dispersion of a binder compound having a softening temperature of 30 to 200° C. and containing a self-crosslinkable functional group or groups and / or a functional group or groups that complementarily react with functional groups of the starting powder coating materials, in a solvent that does not dissolve the starting powder coating materials; production process therefor; and a method for color-matching a composite powder coating composition, the method comprising the steps of dry blending, for color matching, a plurality of starting powder coating materials having different hues, granulating the resulting blend by adding the above-mentioned liquid binder, and drying the granules.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Ion assisted deposition source
InactiveUS6238537B1Minimize damageReduce gas flowCellsElectric discharge tubesElectronAtomic physics
In accordance with one specific embodiment of the present invention, the ion assisted deposition source for thin films comprises an axially symmetric discharge region into which an ionizable gas is introduced, a sputter target at one end of that region, an axially symmetric magnetic field within and extending out the opposite and open end of that region, an anode around the circumference of that region, and an electron emitting cathode located near the open end of that region. Particles are sputtered from the sputter target, pass through the discharge region, and are deposited on a deposition substrate located exterior of both the discharge region and the deposition source. A beam of energetic ions from the discharge region bombards the film being deposited to improve the adhesion, density, and other properties of that film. The density of the plasma can be controlled with the emission from the cathode, the emission of sputtered particles from the sputter target can be controlled with the negative potential of that target, while the energy of the ions used to assist in the deposition can be controlled with the positive potential of the anode. The deposition source thus simultaneously generates a flux of sputtered material with which to deposit a film on a substrate and a beam of energetic ions to assist in that deposition, and does so with a simple and economical apparatus.
Owner:KAUFMAN & ROBINSON
Substrate with shaped cooling holes and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20120102959A1Improve film propertiesContinuous combustion chamberLayered productsCombustorEffusion
A substrate having one or more shaped effusion cooling holes formed therein. Each shaped cooling hole has a bore angled relative to an exit surface of the combustor liner. One end of the bore is an inlet formed in an inlet surface of the combustor liner. The other end of the bore is an outlet formed in the exit surface of the combustor liner. The outlet has a shaped portion that expands in only one dimension. Also methods for making the shaped cooling holes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Water-soluble flame-retardant polyester resin, resin composition containing the resin, and fiber product treated with the resin composition
InactiveUS7358323B2Improve flame retardant performanceEliminate the problemSynthetic resin layered productsHeat resistant fibresSolubilityFiber
A water-soluble, flame retardant polyester resin is obtained by a condensation reaction or a polycondensation reaction of a dicarboxylic-acid component, a glycol component, a water-solubility imparting component and a reactive phosphorus-containing compound such that a ratio of the water-solubility imparting component in a total of the dicarboxylic-acid component and the water-solubility imparting component is in a range of 1 to 60 mol %. Since this polyester resin can be dissolved in a solvent by allowing a halogen-free, phosphorus-containing polyester with excellent flame resistance to have water solubility, it is possible to improve applicability and eliminate problems of working environment and environmental destruction resulting from organic solvents. In addition, even when treating substrates such as fibers and PET films with the polyester resin, there is no deterioration of these substrates.
Owner:GOO CHEM IND
Polypropylene films with enhanced moisture barrier properties, process for making and composition thereof
InactiveUS20080286547A1Improve film propertiesLow water vapor transmission rateFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsWater vaporMoisture barrier
Multi-layer films particularly suited for packaging applications, including a core layer, the core layer having at least one nucleating agent and at least one water vapor transmission inhibitor are provided. Optionally, the multi-layer film may have at least one skin layer and at least one tie layer located intermediate the core layer and the at least one skin layer. Embodiments may have the advantage of superior barrier properties and very low water vapor transmission rates.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Polypropylene composition for air quenched blown films
InactiveUS20070054997A1High barrier propertiesHigh stiffnessSpecial tyresGranular deliveryCrystallization temperatureCrystallinity
The invention is directed to a polypropylene resin, which is suitable for manufacturing an air quenched blown film. The resin has a melt flow rate of greater than 5 g / 10 min, less than 2% xylene solubles, a pentad isotacticity of greater than 95%, an isotactic pentad / triad ratio of greater than 95%, a crystallinity of at least 65%, and a crystallization temperature of at least 127° The polypropylene resin contains from 500 ppm to 2500 ppm of a nucleator / clarifier additive. A quenched blown film made from resin exhibits a crystallization onset temperature of at least 116° C. and a crystallization half-life time of less 4.1 seconds or less when tested using fast DSC analysis with a scan rate of 200° C. / minute.
Owner:BRASKEM AMERICA
Polyimide-based polymers, copolymers thereof and positive type photoresist compositions comprising the same
ActiveUS8257901B2High resolutionImprove film propertiesRadiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusResistPositive type
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Conductive substance-adsorbing resin film, method for producing conductive substance-adsorbing resin film, metal layer-coated resin film using the same, and method for producing metal layer-coated resin film
ActiveUS20100113264A1Improve adhesionReduce unevennessLamination ancillary operationsOther chemical processesHigh definitionMetal
The invention provides a conductive substance-adsorbing resin film on which a conductive layer being excellent in adhesion to the resin film and having less unevenness at the interface with the resin film can easily be formed, a method for producing the same, a metal layer-coated resin film on which a high definition wiring excellent in adhesion to the insulating resin film can easily be formed, which is obtained by using the conductive substance-adsorbing resin film of the invention, and a method for producing a metal layer-coated resin film that is a material capable of easily producing a printed-wiring board having a high definition wiring. The invention also provides a conductive substance-adsorbing resin film including at least two resin layers, wherein at least one of the resin layers is an adsorbing resin layer having a property of adsorbing a conductive substance or a metal. This conductive substance-adsorbing resin film is allowed to adsorb a metal and subjected to plating, whereby a metal layer-coated resin film can be obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for coating metallic surfaces with a composition that is rich in silane
ActiveCN1777699AAesthetic quality unchangedEfficient use ofEfficient propulsion technologiesAnti-corrosive paintsOrganic filmPolymer science
Pre-coating of a metal surface prior to further coating or other treatment uses an aqueous composition wholly or mainly free of chromium (VI) compounds and is such that (a) the composition contains (i) an at least partially hydrolyzable silane and (ii) a metal chelate; and (b) the cleaned, etched or pretreated metal is contacted with the composition and the formed film is dried (and optionally hardened) to a thickness of 0.01-10 mu . Independent claims are also included for (1) the process in which the aqueous composition also contains (iii) an organic film-former comprising a water-soluble or -dispersible (co)polymer of acid number 3-250 and (iv) a long-chain alcohol film-forming aid.; and (2) compositions containing (i) and (ii) at 0.1-10 : 1 ratio and optionally also (iii) and (iv) .
Owner:CHEMETALLGMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com