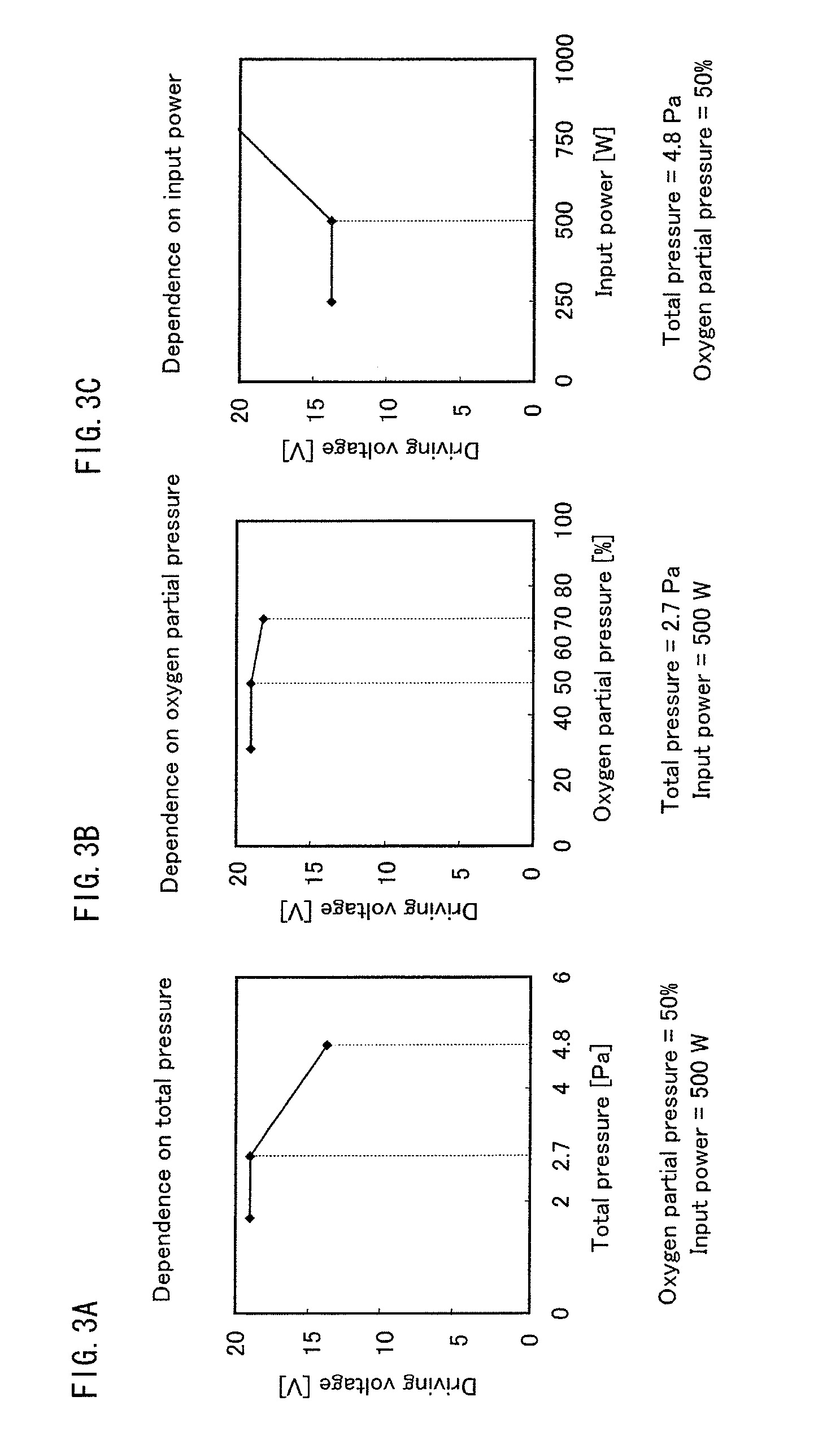
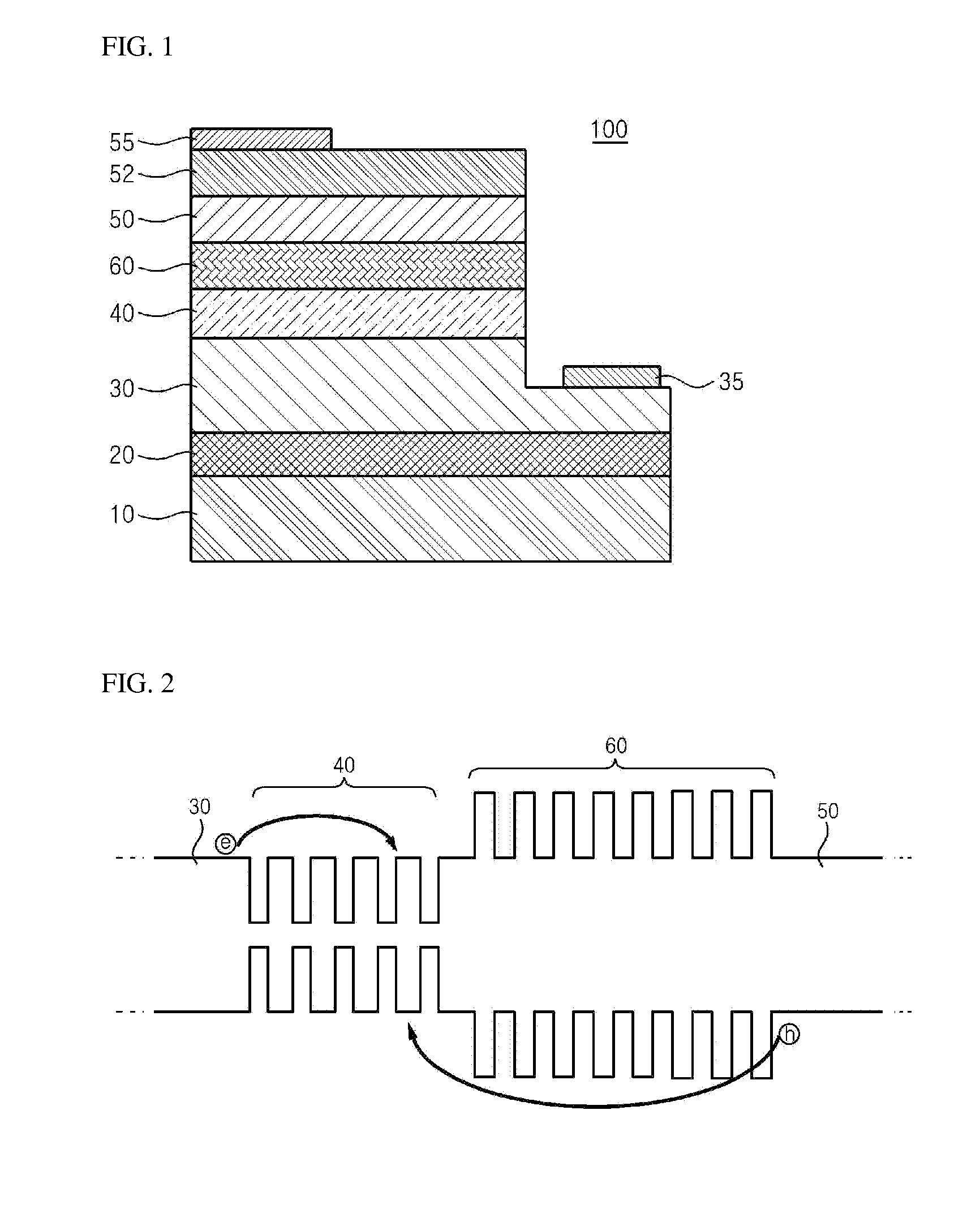
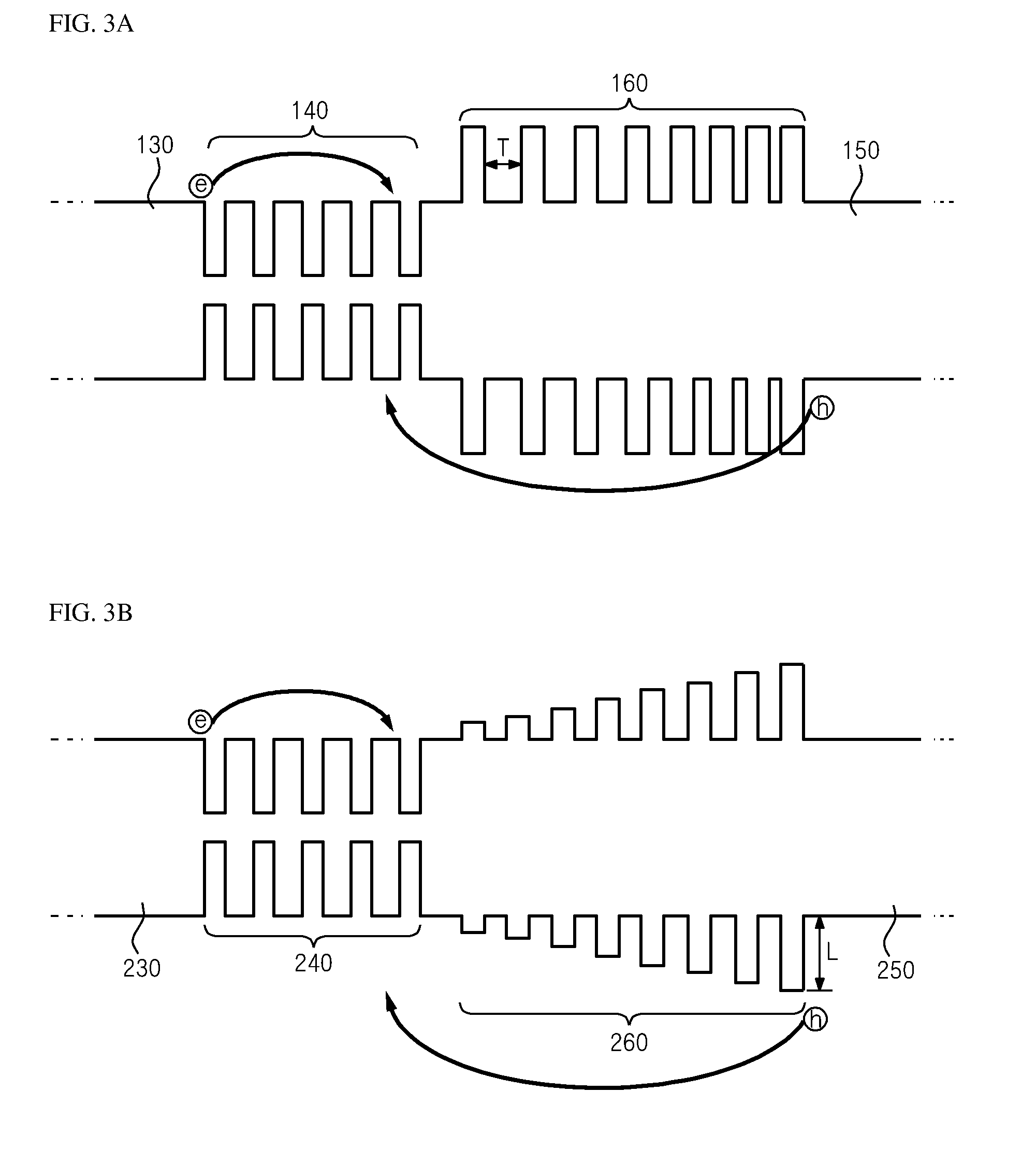
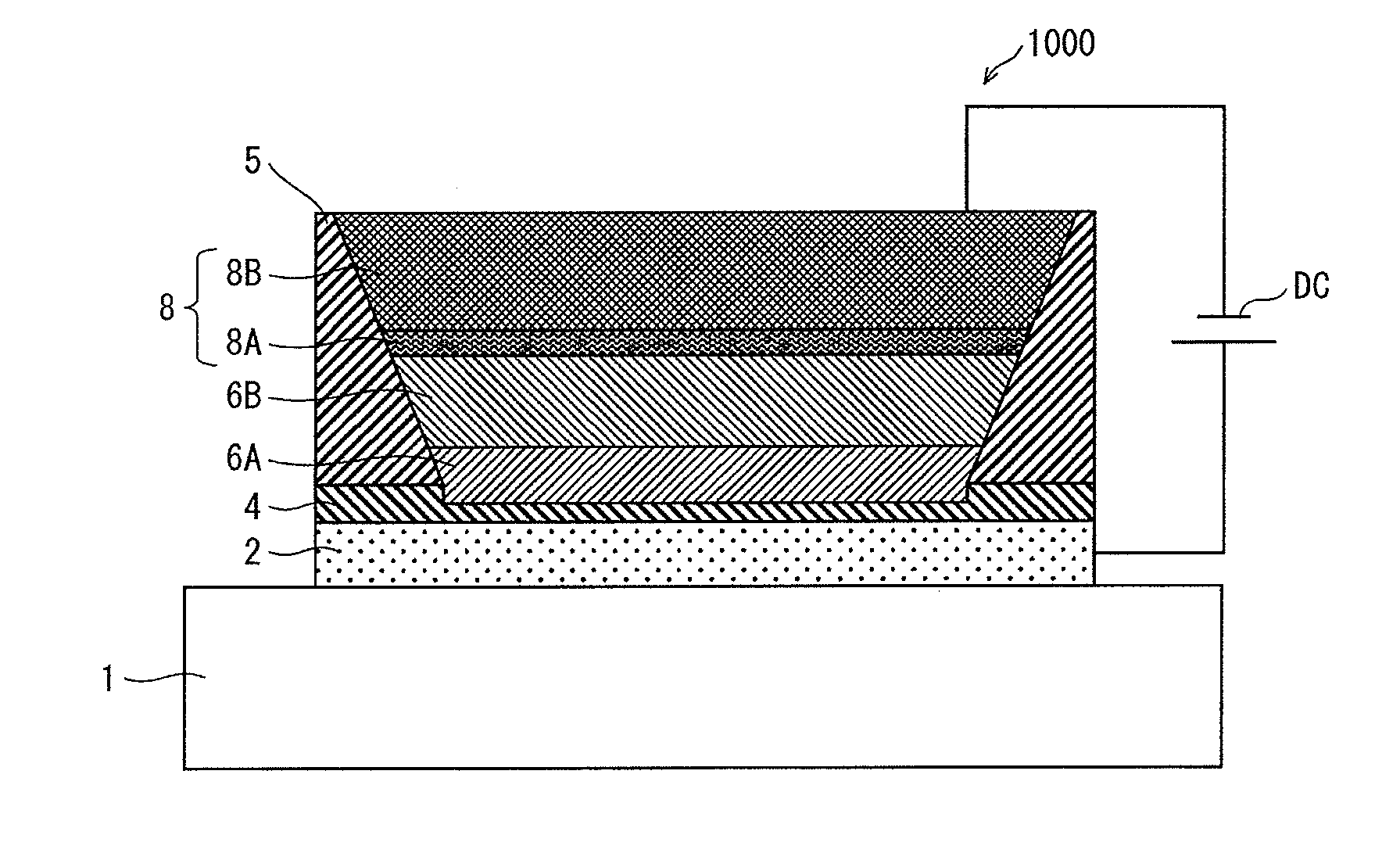
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
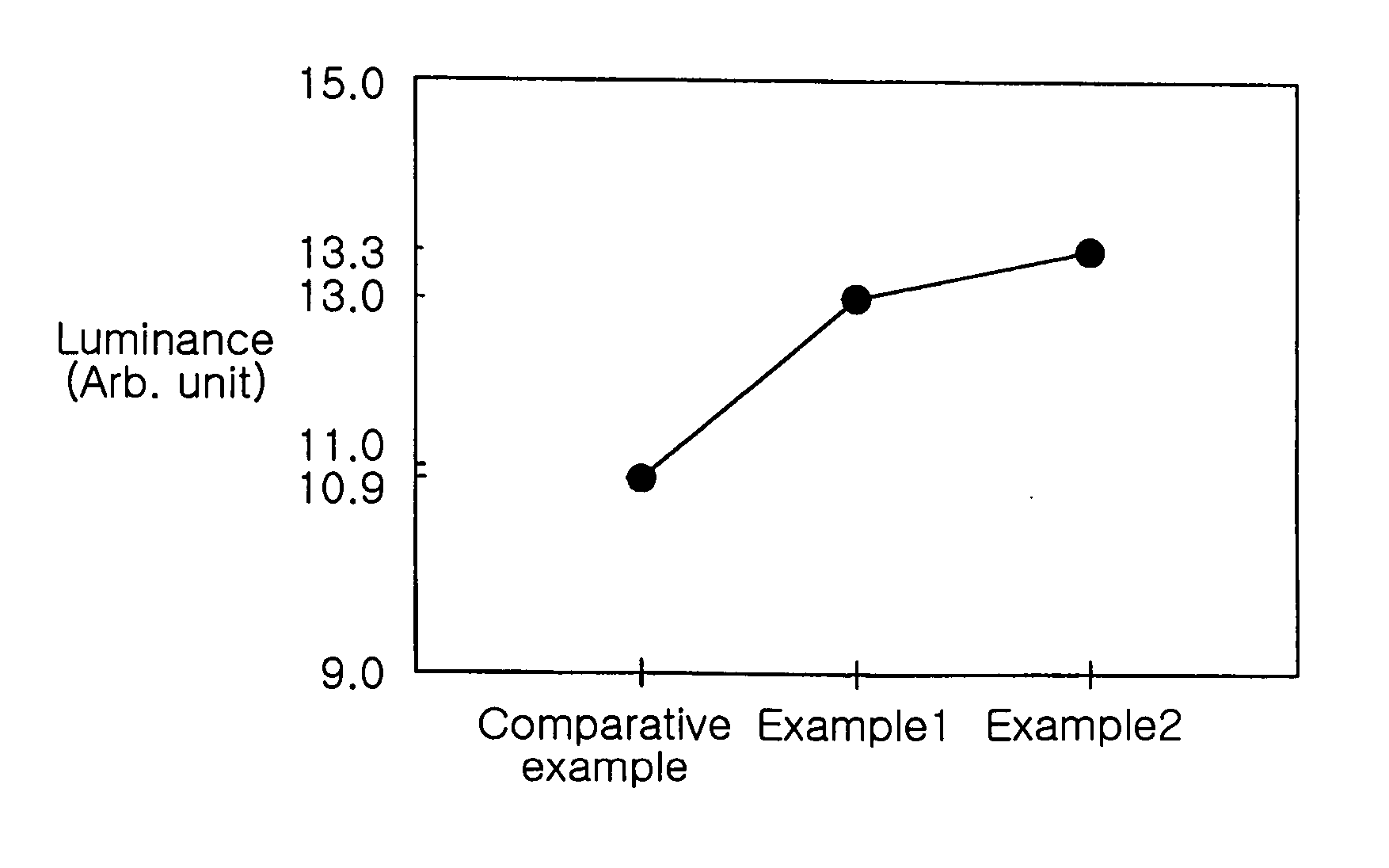
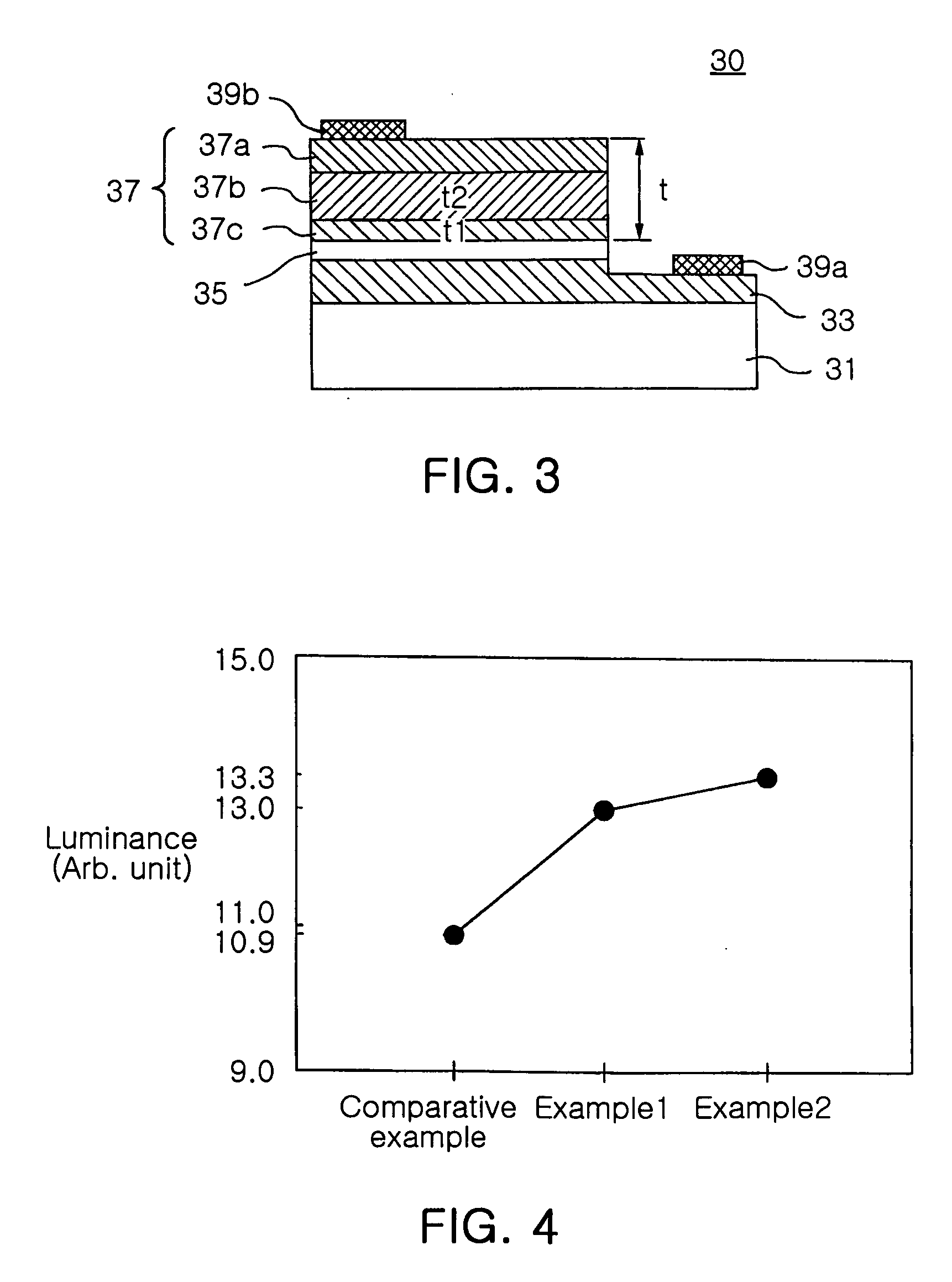
119results about How to "Improve hole injection efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
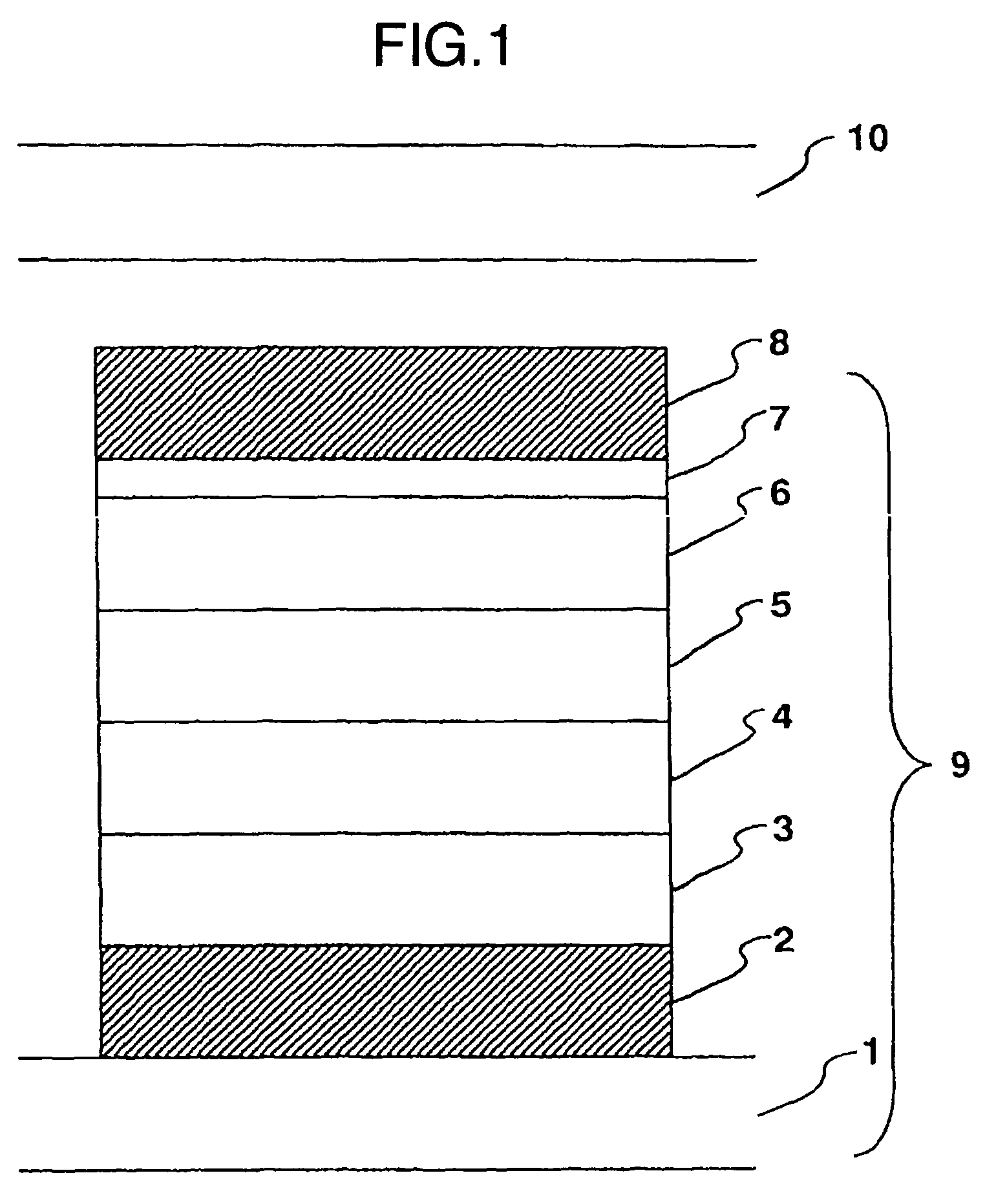
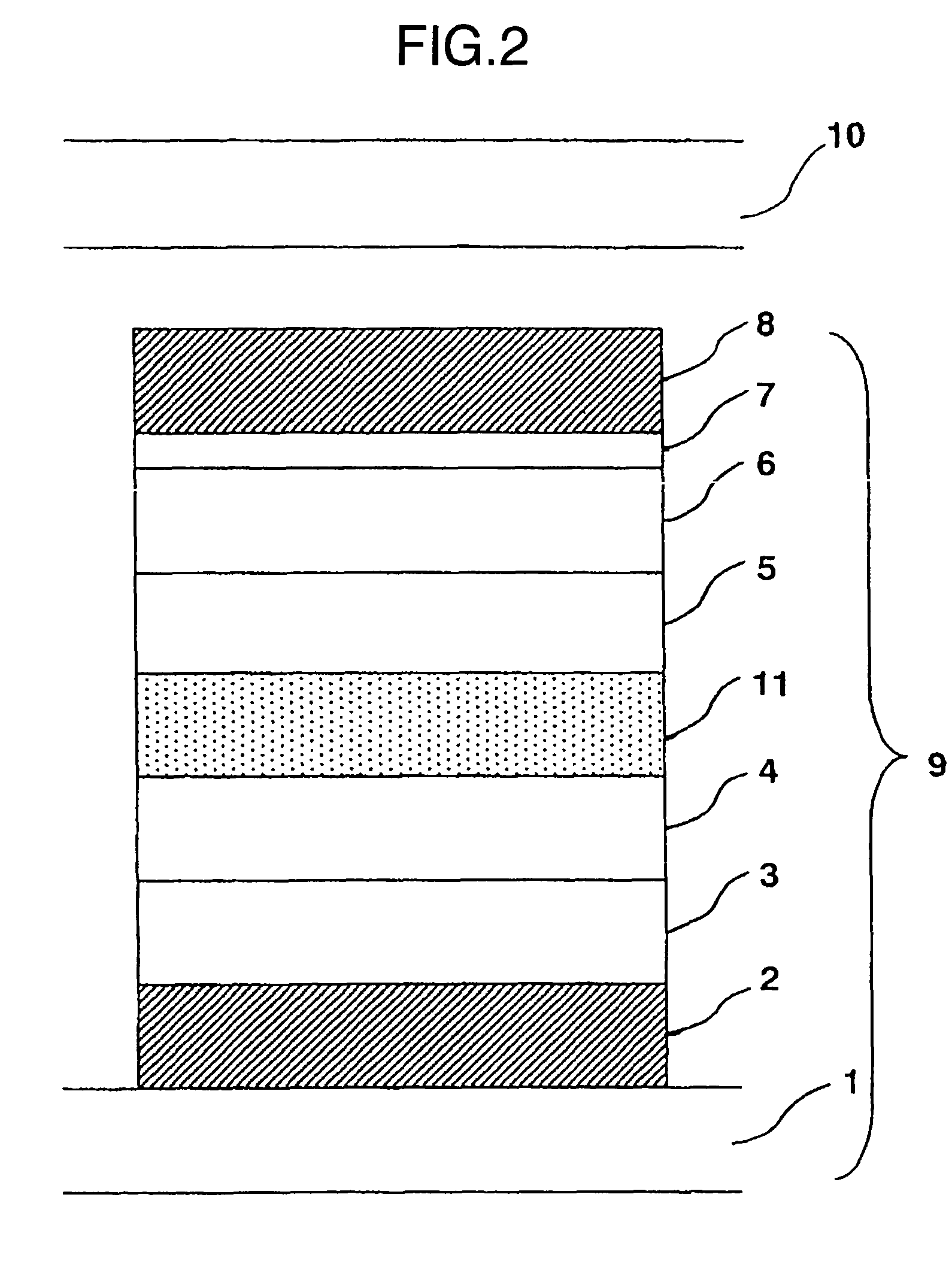
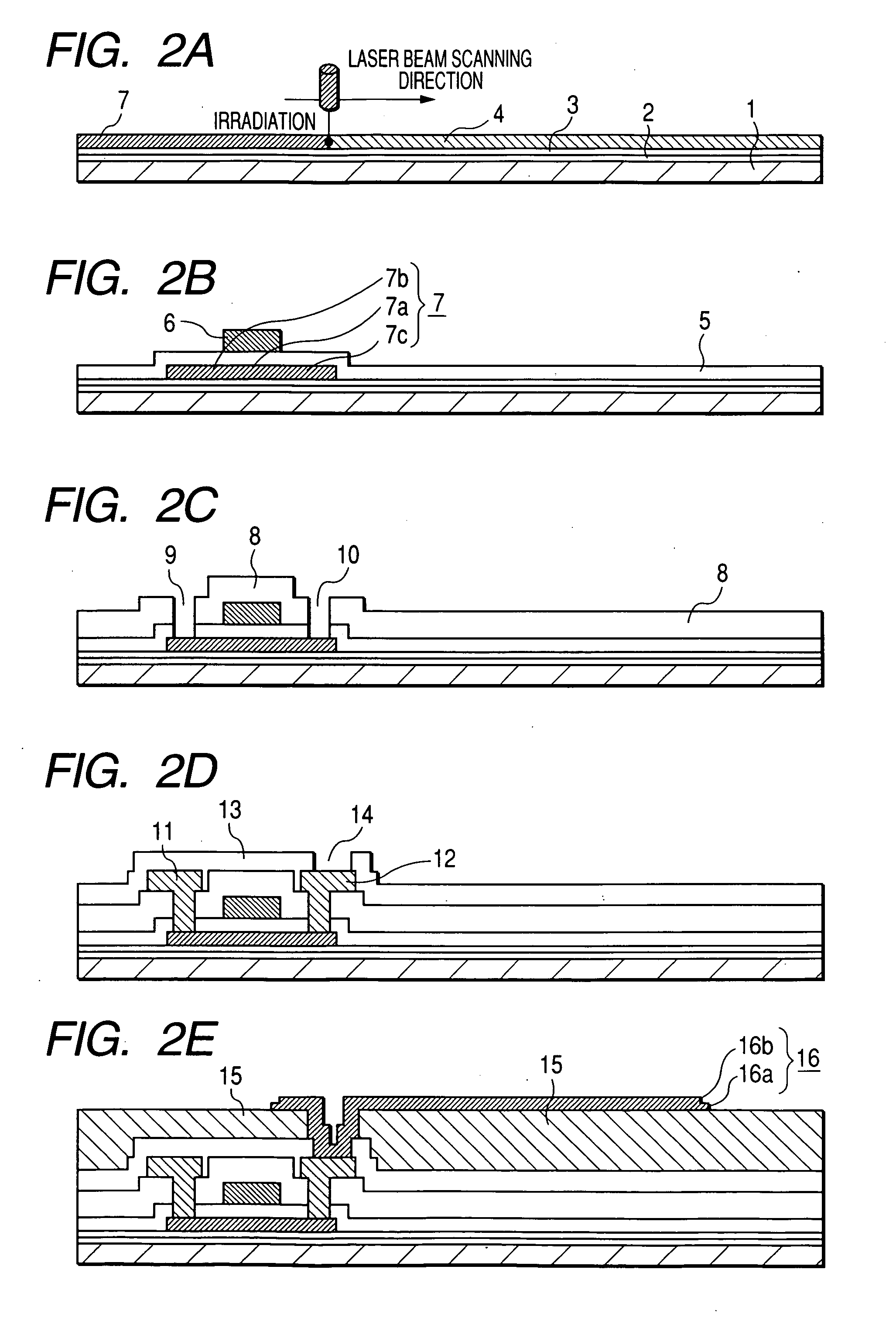
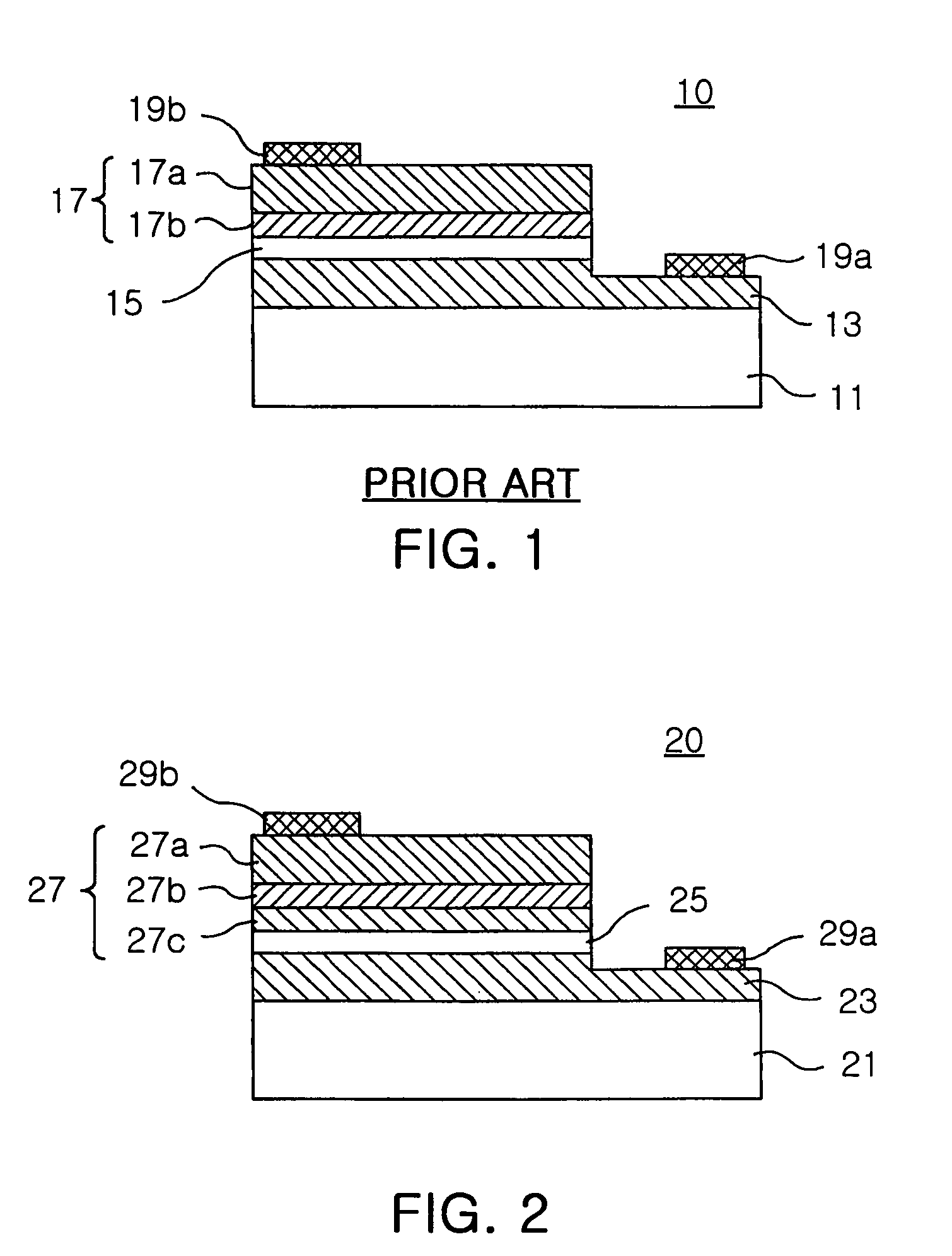
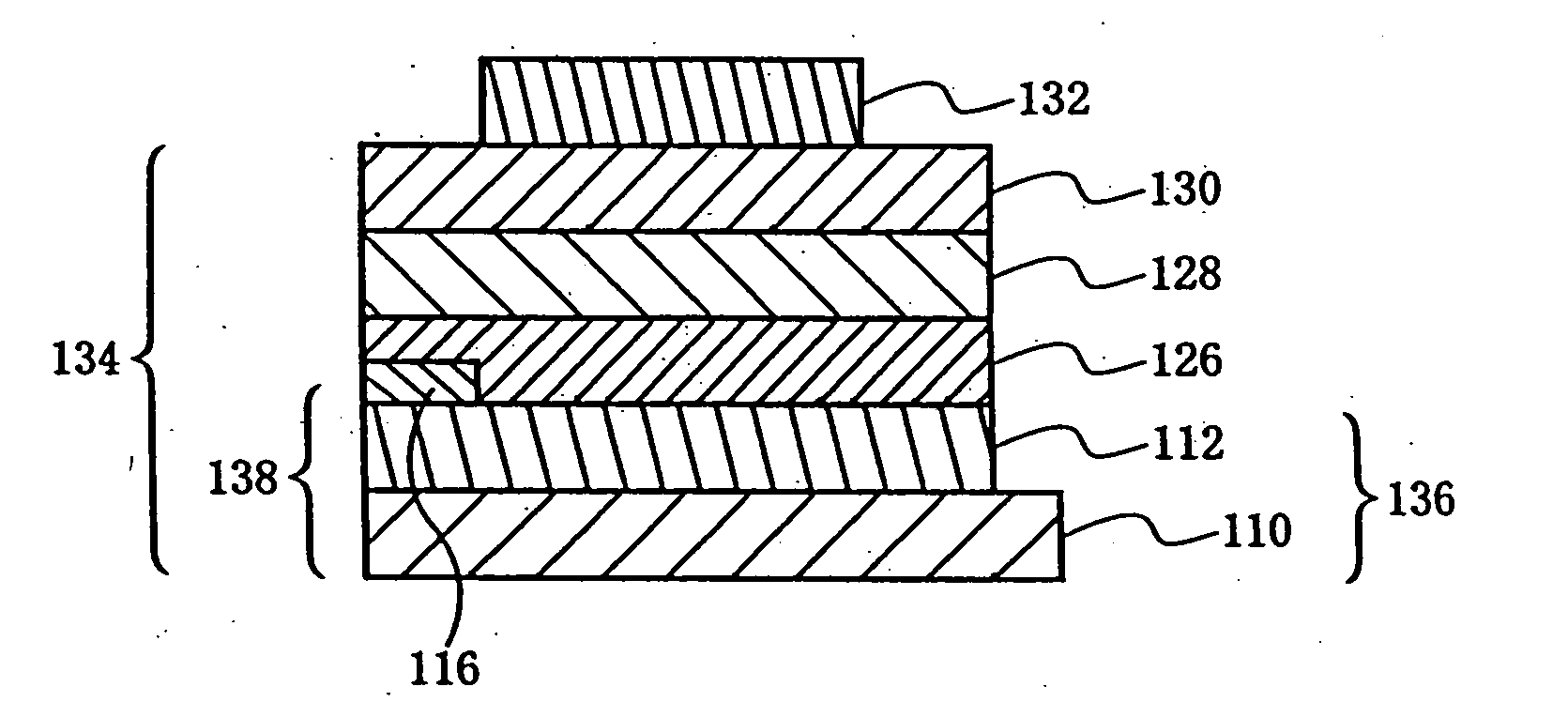
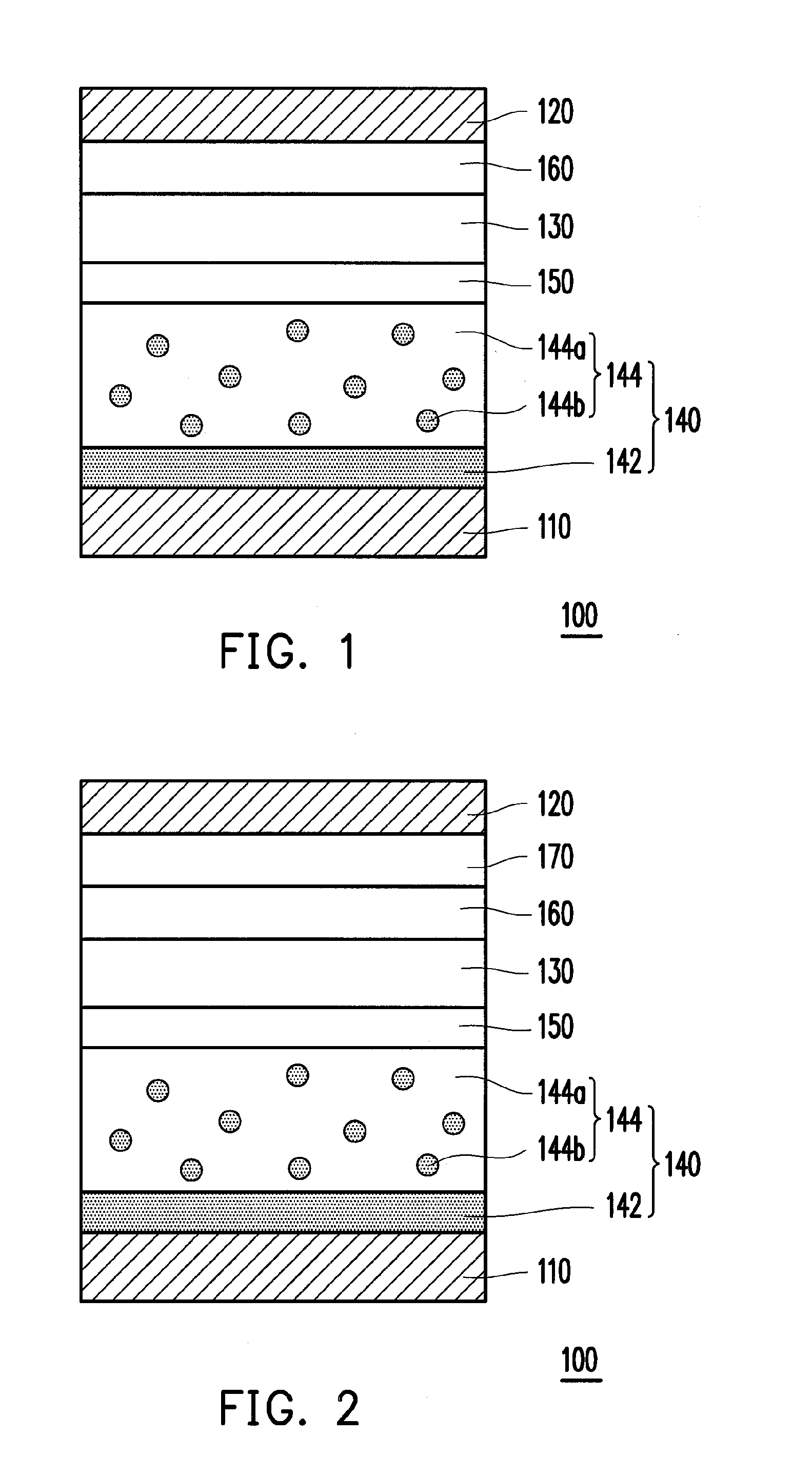
Organic light-emitting element, image display device and production method thereof
ActiveUS20050221121A1High structural reliabilityLight interference effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantElectron
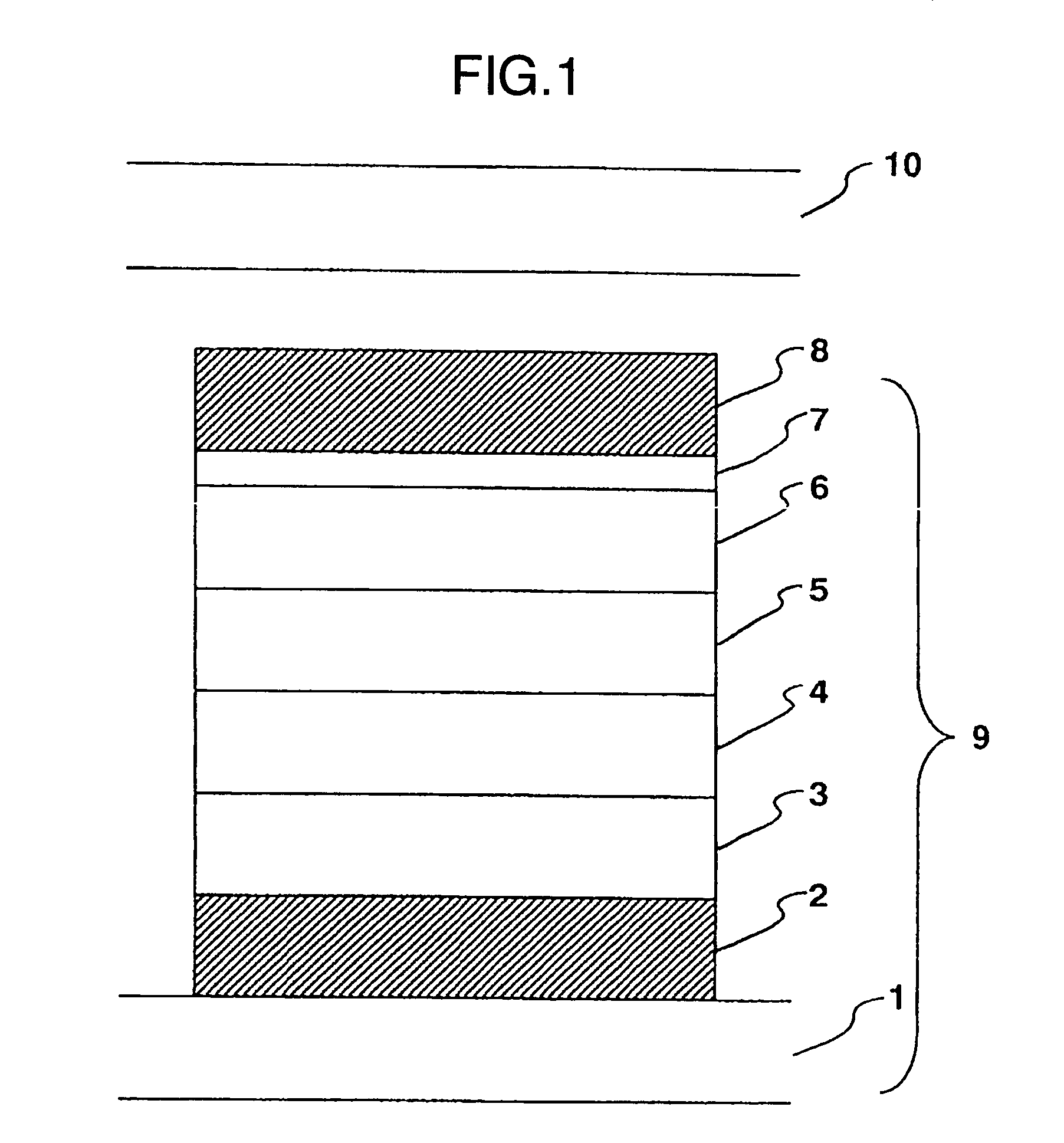
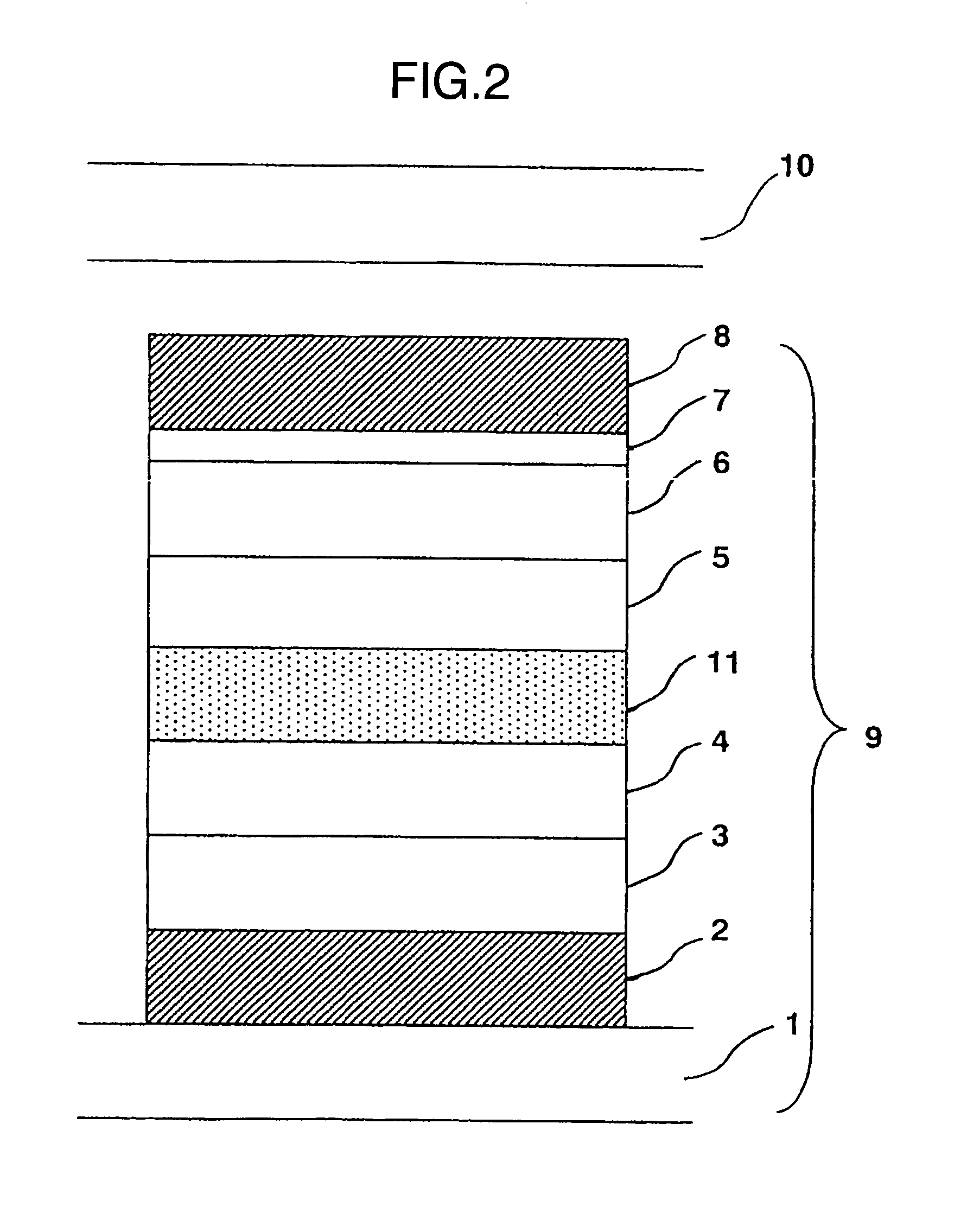
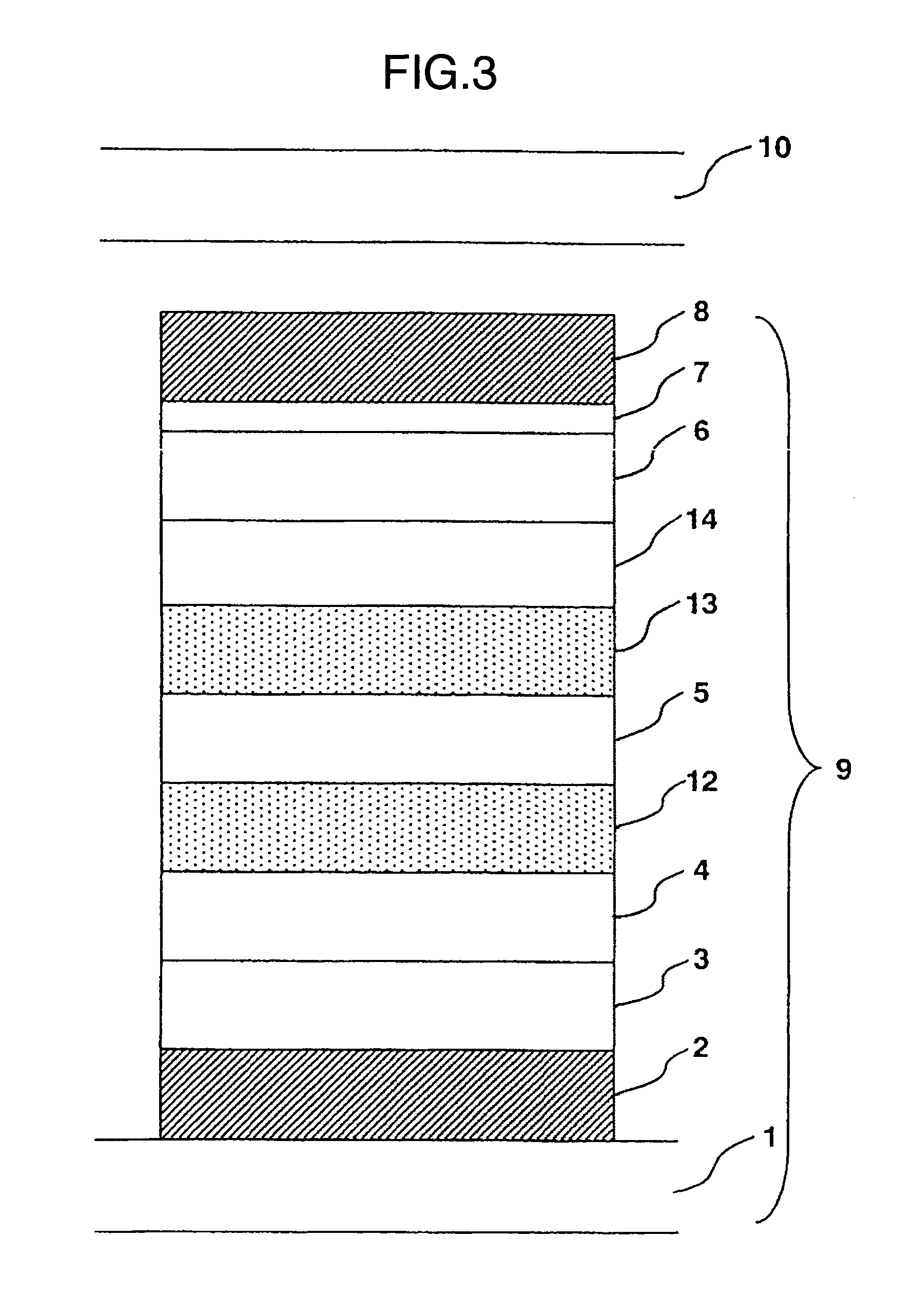
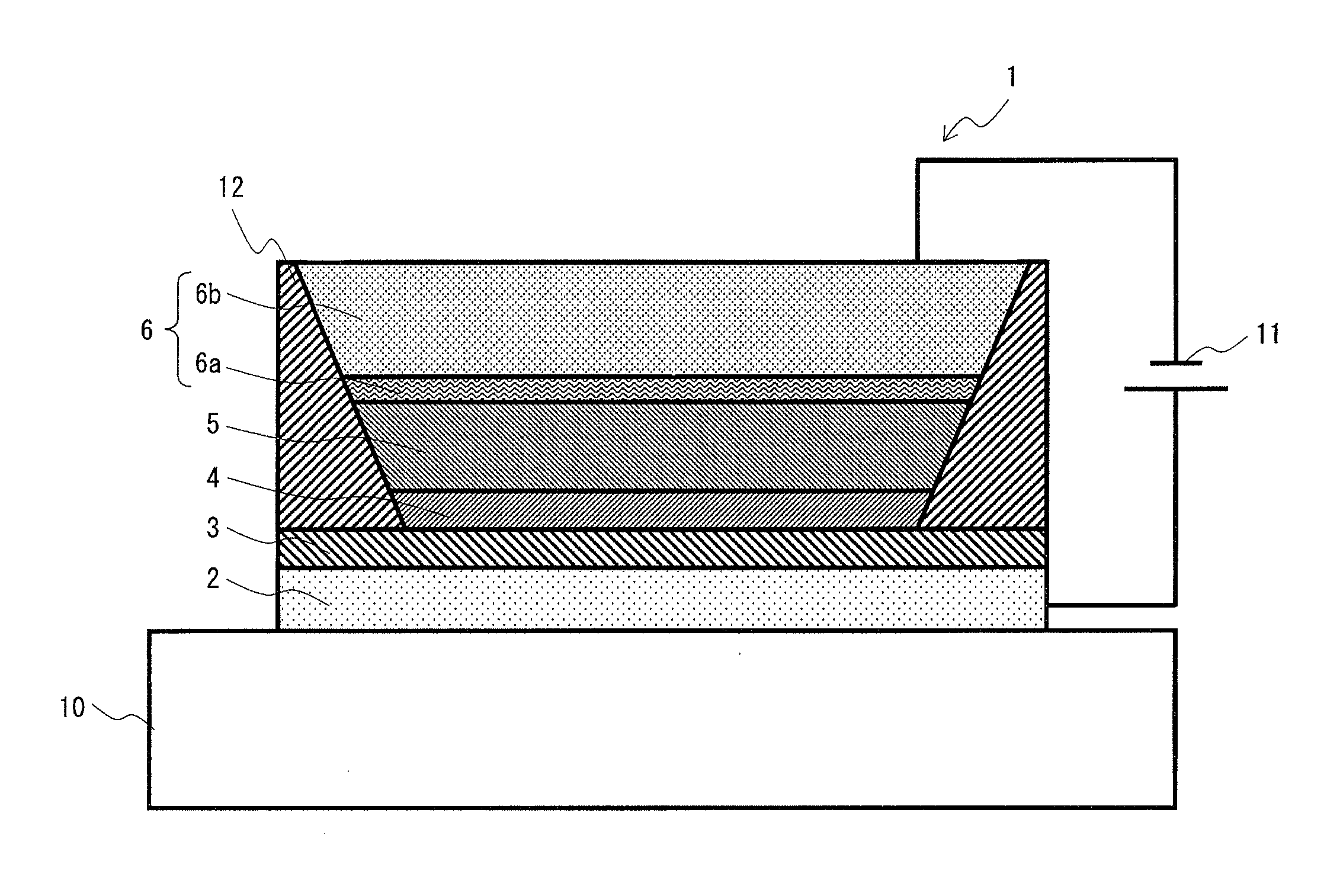
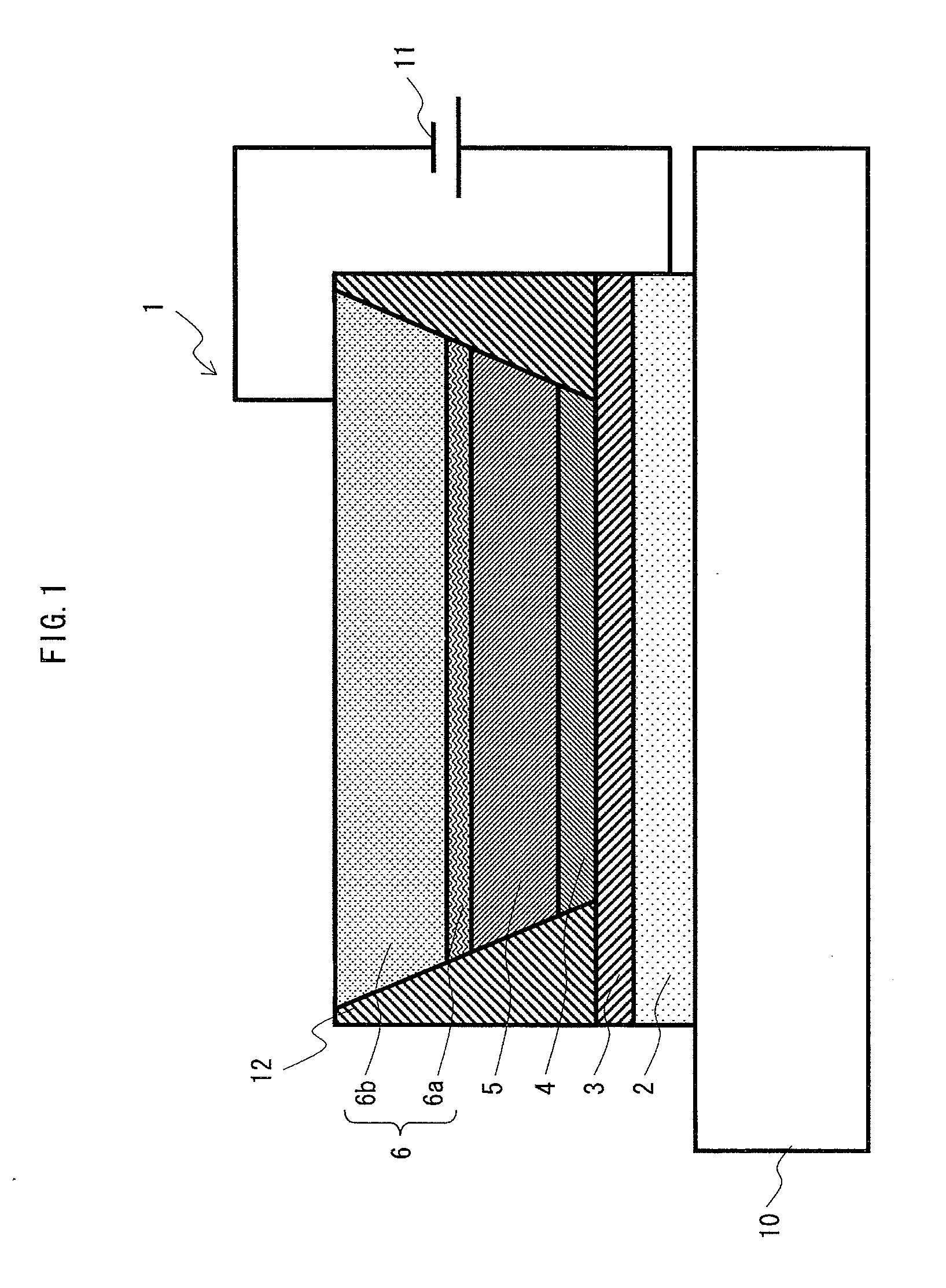
It is an object to provide an organic light-emitting element having two or more light-emitting layers, wherein degradation of each constituent material for the light-emitting layer is reduced to improve reliability of the element. The present invention provides an organic light-emitting element having a laminated structure with a first mixed light-emitting layer 4 composed of a hole transport material, an electron transport material and a dopant which determines a color of an emitted light, and a second mixed light-emitting layer 5 composed of a hole transport material, an electron transport material and a dopant which determines a color of an emitted light, and also provides an image display device which uses the organic light-emitting element.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Organic electroluminescent elements
InactiveUS6344283B1Improve film propertiesImprove hole injection efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLayered productsArylOrganic electroluminescence
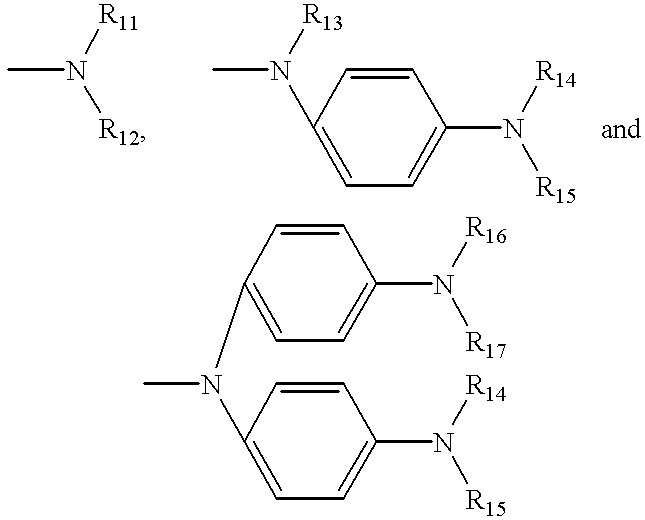
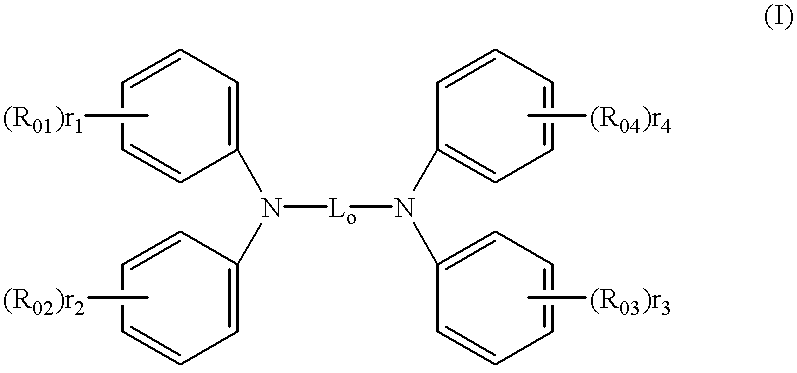
An organic EL device comprising a cathode, an anode, and at least one organic compound layer containing an organic compound represented by formula (I):where L0 is any one of o-, p-, and m-phenylene groups which have two, three or four rings and which have a substituent with the proviso that when L0 is a phenylene group having four rings, the phenylene group may have an unsubstituted or substituted aminophenyl group somewhere therein, and at least one of R01, R02, R03 and R04 is any one of the following groups:where R1, R12, R13, R14, R15, R16 and R17 are each a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, and r1, r2, r3 and r4 are each an integer of 0 to 5 with the proviso that r1+r2+r3+r4>=1.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Light emitting element including a barrier layer and a manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7291967B2Improve stabilityExcellent luminous propertiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHole injection layerSilicon oxide
According to the invention, an insulating or semi-insulating barrier layer which has a thickness where a tunnel current can flow through is provided between a hole injection electrode and an organic compound layer with hole transport characteristics (a hole injection layer or a hole transport layer). Specifically, a thin insulating or semi-insulating barrier layer which contains silicon or silicon oxide; silicon or silicon oxide and a light transmitting conductive oxide material; or silicon or silicon oxide, a light transmitting conductive oxide material, and carbon may be provided between a light transmitting conductive oxide film formed of a light transmitting conductive oxide material, such as ITO and a hole injection layer containing an organic compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic el element
ActiveUS20120061656A1Improve hole injection efficiencyImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandElectron hole
An organic light-emitting element includes an anode, a functional layer, and a hole injection layer between the anode and the functional layer. The functional layer contains an organic material. The hole injection layer injects holes to the functional layer. The hole injection layer comprises tungsten oxide and includes an occupied energy level that is approximately 1.8 electron volts to approximately 3.6 electron volts lower than a lowest energy level of a valence band of the hole injection layer in terms of binding energy.
Owner:JOLED INC
Organic light-emitting element, image display device and production method thereof
ActiveUS8026662B2High structural reliabilityLight interference effectDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantElectron
It is an object to provide an organic light-emitting element having two or more light-emitting layers, wherein degradation of each constituent material for the light-emitting layer is reduced to improve reliability of the element. The present invention provides an organic light-emitting element having a laminated structure with a first mixed light-emitting layer 4 composed of a hole transport material, an electron transport material and a dopant which determines a color of an emitted light, and a second mixed light-emitting layer 5 composed of a hole transport material, an electron transport material and a dopant which determines a color of an emitted light, and also provides an image display device which uses the organic light-emitting element.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
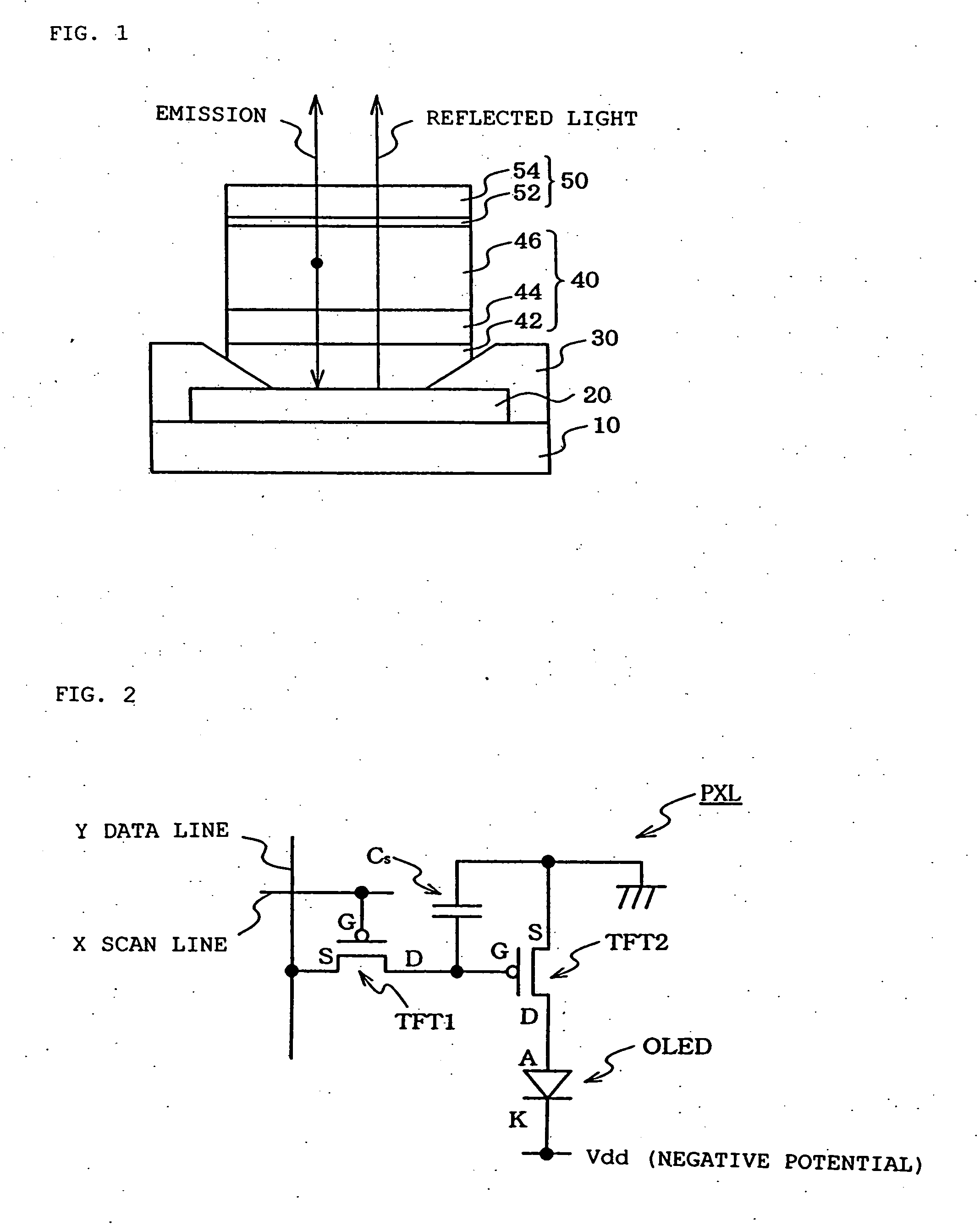
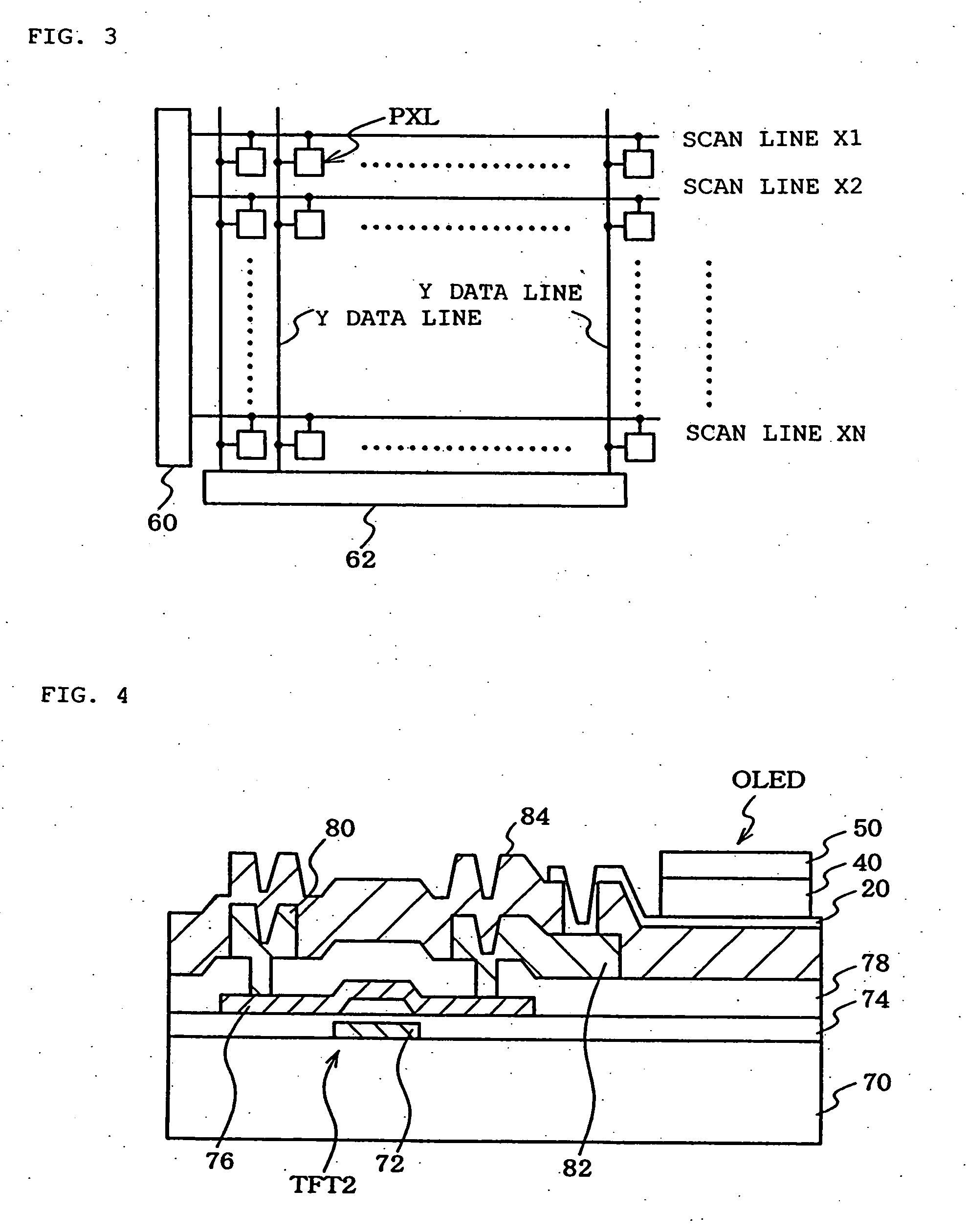
Organic electroluminescence type display apparatus
InactiveUS20060192481A1Brighter imageHigh light efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensRoad vehicles traffic controlOrganic electroluminescenceImpurity
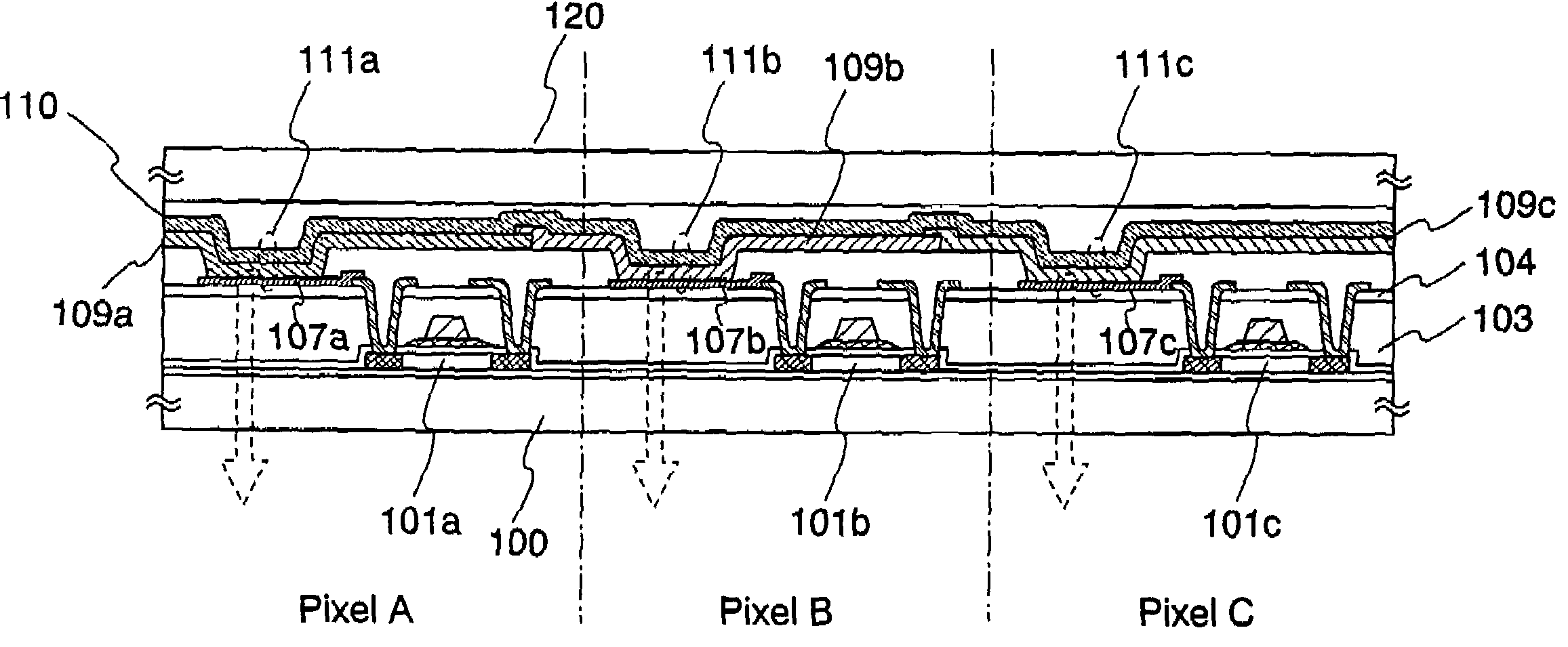
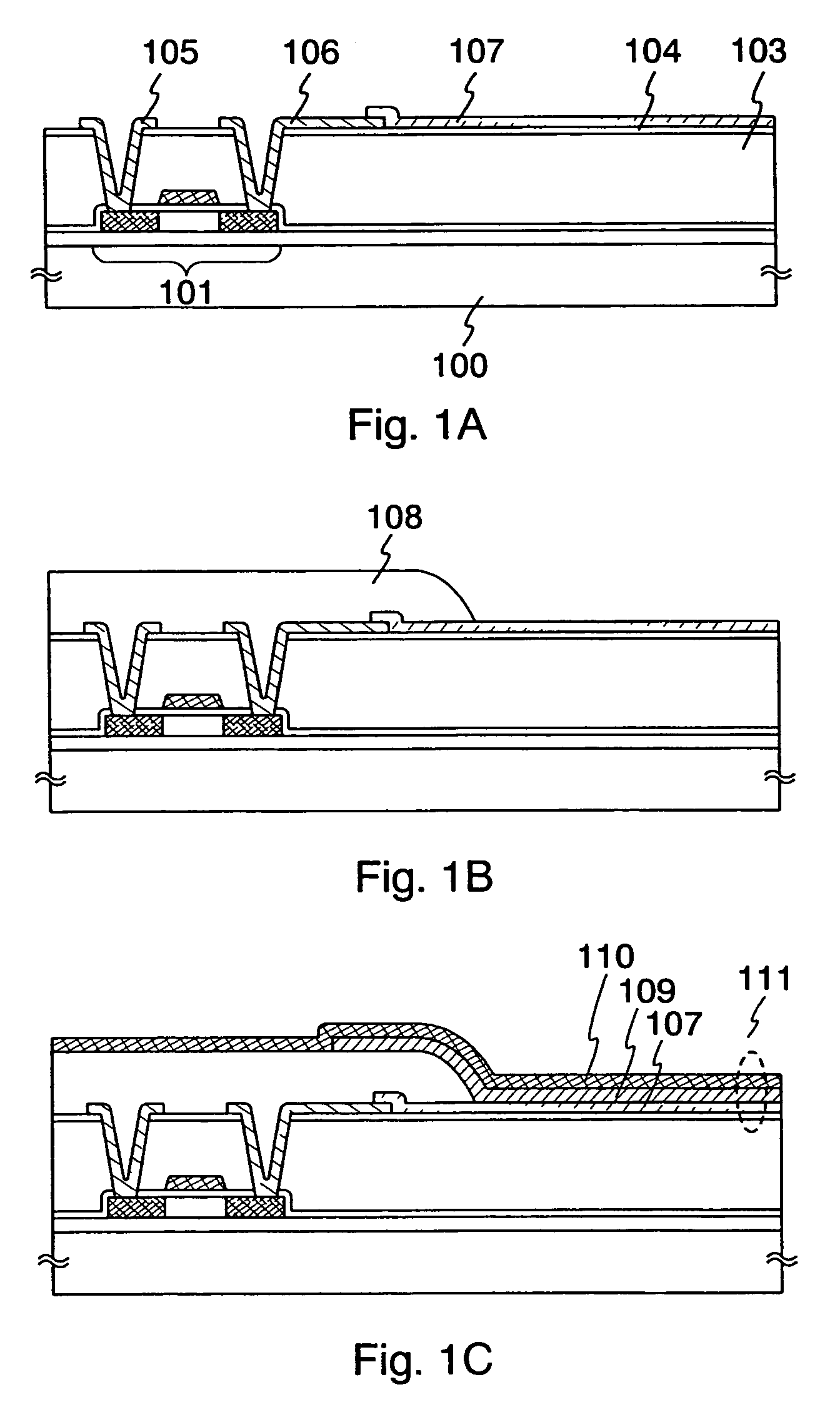
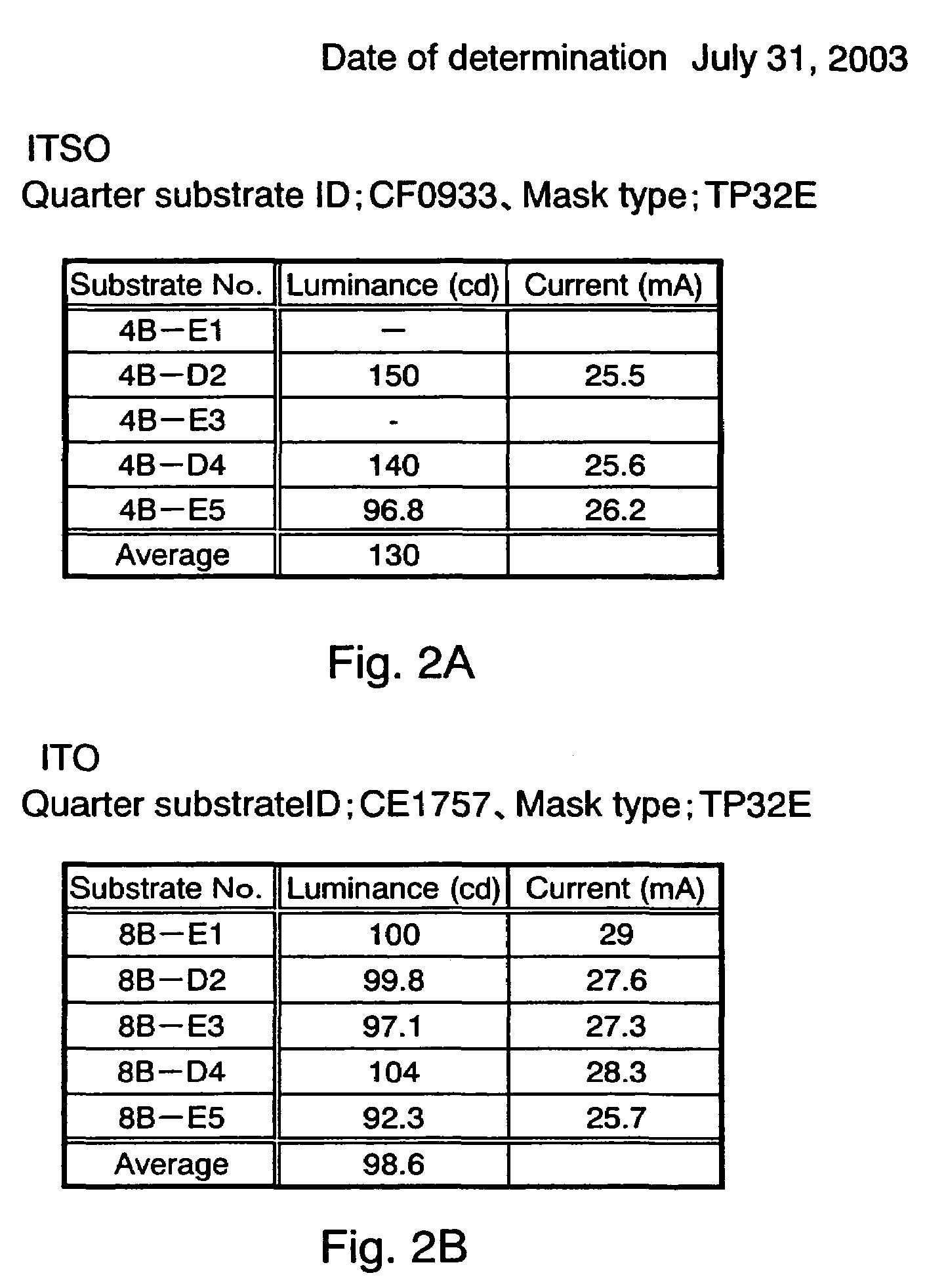
An organic electroluminescence type display apparatus of top emission type, in which a thin film transistor (TFT), a flattening film made of organic resin and an organic EL element, in which at least an anode, an electroluminescence layer and a cathode are laminated on the flattening film in this order, are formed in each picture element in a display region on a substrate. The anode is composed of at least two layer film including an aluminum (Al) alloy film containing as a impurity at least one of transition metals of the eighth group of 3d into Al and including a light transmitting conductive oxide film laminated on the Al alloy film.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Nitride based semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20050179027A1Improve hole injection efficiencyImprove injection efficiencyNanoopticsPackagingGalliumActive layer
Disclosed herein is a nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device. The nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device comprises an n-type clad layer made of n-type Alx1Iny1Ga(1−x1−y1)N (where 0≦x1≦1, 0≦y1≦1, and 0≦x1+y1≦1), a multiple quantum well-structured active layer made of undoped InAGa1−AN (where 0<A<1) formed on the n-type clad layer, and a p-type clad layer formed on the active layer wherein the p-type clad layer includes at least a first layer made of p-type Iny2Ga1−y2N (where 0≦y2<1) formed on the active layer and a second layer made of p-type Alx3Iny3Ga(1−x3−y3)N (where 0<x3≦1, 0≦y3≦1, and 0<x3+y3≦1) formed on the first layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Display device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090042326A1Improve luminous performanceReduce power consumptionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceSilicon oxide
According to one aspect of the present invention, a laminated structure of conductive transparent oxide layers containing silicon or silicon oxide is applied as an electrode on the side of injecting a hole (a hole injection electrode; an anode) instead of the conventional conductive transparent oxide layer such as ITO. In addition, according to another aspect of the invention, a laminated structure of conductive transparent oxide layers containing silicon or silicon oxide, each of which content is different, is applied as a hole injection electrode. Preferably, silicon or a silicon oxide concentration of the conductive layer on the side where it is connected to a TFT ranges from 1 atomic % to 6 atomic % and a silicon or silicon oxide concentration on the side of a layer containing an organic compound ranges from 7 atomic % to 15 atomic %.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Green nitride light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxial wafer and growth method thereof
InactiveCN102969417AEase the separationPromote excitationSemiconductor devicesLuminous fluxLight-emitting diode
The invention relates to a green nitride LED epitaxial wafer and a growth method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor photo-electricity. The method is characterized in that an InGaN material layer with a low content of In components is grown between a quantum barrier and a quantum well in each quantum well active area when a plurality of quantum well active areas are grown; a quantum barrier is grown on a cap layer in a last quantum well active area, a hole injection layer is grown on the quantum well, and a p-AlGaN electronic blocking layer is grown on the hole injection layer. According to the green nitride LED epitaxial wafer and the growth method thereof, the process is reasonable, and the production is facilitated; LED chips are manufactured through a standard chip process, so that the internal quantum efficiency is improved, and the hole injection efficiency is improved greatly; and manufactured chips are high in luminous flux after being packaged, the inverse antistatic capacity reaches more than ten thousand volts, the electricity is not leaked under 8-volt inverse voltage measurement, and the working voltage is smaller than 3.1 volts under a 15 mA forward current.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGKE SEMICON LIGHTING
Organic electroluminescence device, conductive laminate and display
InactiveUS20070103055A1Improve efficiencyFunction increaseConductive layers on insulating-supportsDischarge tube luminescnet screensNiobiumCerium
An organic electroluminescent device including a cathode 50, an anode 20, and an emitting layer interposed between the cathode 50 and the anode 20, at least a part of the anode 20 in contact with the emitting layer 40 containing at least one element selected from lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, samarium, and europium, and at least one element selected from chromium, tungsten, tantalum, niobium, silver, palladium, copper, nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, platinum, and silicon. Since holes are efficiently injected into the emitting layer from the anode, the drive voltage of the organic EL device can be decreased, whereby the lifetime of the organic EL device can be increased.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS9029843B2Excellent characteristicsConvenient lightingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandBinding energy
Owner:JOLED INC
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20140319454A1Improve lighting efficiencyIncrease hole injectionSemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumSuperlattice
The present invention discloses a nitride semiconductor light emitting device with improved light efficiency. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device includes a n-type nitride layer and p-type nitride layer, an active layer disposed between the n-type and p-type nitride layers and with a multiple quantum well structure wherein a plurality of quantum well layers and a plurality of quantum barrier layers are stacked alternatively in the active layer, and a superlattice layer between the active layer and the p-type nitride layer with asymmetric structure. Herein, a thickness of a well layers gradually increases from the p-type nitride layer to the active layer and the height of the barrier layers gradually increases from the active layer to the p-type nitride layer and therefore, an injection efficiency of a hole supplied from p-type nitride layer to an active layer is increased.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence element
ActiveUS20130134403A1Injection of hole be improveEnhanced level of longevitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsOrganic electroluminescence
An organic light-emitting element comprising: an anode; a cathode; banks; a functional layer between the anode and the cathode; and a hole injection layer between the anode and the functional layer. The functional layer includes one or more sublayers including a light-emitting sublayer defined by the banks and that contains an organic material. The hole injection layer comprises tungsten oxide, includes an occupied energy level that is approximately 1.8 electron volts to approximately 3.6 electron volts lower than a lowest energy level of a valence band of the hole injection layer in terms of a binding energy, has a surface facing the functional layer, and has a recessed structure such that a portion of the surface overlapping with the light-emitting sublayer is located closer to the anode than other portions. The recessed structure has a recessed portion whose inner surface is in contact with the functional layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
Semiconductor light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140374700A1Increase hole concentrationImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellElectron blocking layer
A semiconductor light-emitting diode, including: an n-GaN layer, a quantum well layer, an electron blocking layer, and a p-GaN layer, which are sequentially stacked on a substrate. The electron blocking layer includes at least one first AlGaN layer and at least one second AlGaN layer. The first AlGaN layer and the second AlGaN layer are alternately stacked. The adjacent first and second AlGaN layers have different Al component.
Owner:HC SEMITEK CORP
Organic electroluminescence type display apparatus
InactiveCN1825622AImprove reflection efficiencyImprove luminous efficiencyRoad vehicles traffic controlElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceImpurity
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Emitting organic laser thin film device equipped with gold nanoparticle enhanced light pumped surface and application and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106936059AEnhanced emission ratioImprove laser characteristicsLaser detailsElectricityOrganic laser
The invention discloses an emitting organic laser thin film device equipped with a gold nanoparticle enhanced light pumped surface and an application and a preparation method thereof. The device is based on the gold nanoparticle local surface plasmon resonance effect and scattering effect so that the properties of surface emitting laser can be effectively improved, including enhancement of emitting intensity, reduction of threshold and enhancement of quality factor. The device is characterized in that the device is composed of a glass substrate, gold nanoparticles, a spacing layer and a gain medium. The laser gain medium is composed of doped small organic molecule host and guest materials. The spacing layer and the gain medium are identical in the host materials. The laser structure is used as a color conversion layer to be applied to an organic electro-diode, and an organic dye thin film layer can be excited to emit light in the combined device by using light emitted by the light-emitting layer so that an effective scheme can be provided for realizing a simple structure electrically pumped organic laser device. The structure is prepared by a vacuum vapor plating method so as to be easy and fast.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
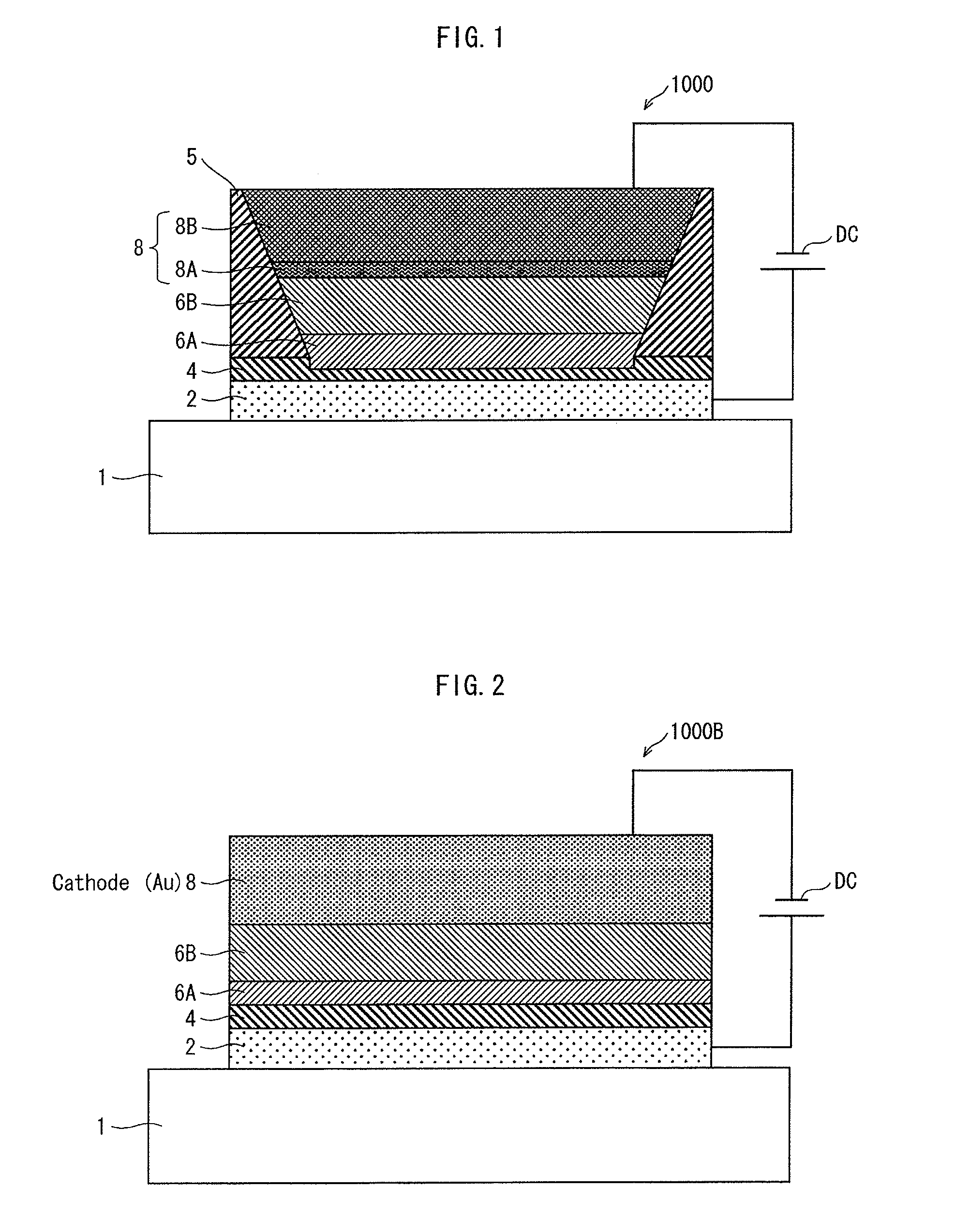
Organic electroluminescent device with high resistance inorganic hole injecting layer
InactiveUS6373186B1Improve hole injection efficiencyImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh resistanceHole injection layer
To realize an organic EL device having an excellent hole injection efficiency, improved luminous efficiency, low operating voltage, and low cost, the invention provides an organic EL device comprising a hole injecting electrode, an electron injecting electrode, and at least one organic layer between the electrodes, at least one of the organic layer having a light emitting function. The device further has a high resistance inorganic hole injecting layer between the hole injecting electrode and the organic layer. The high resistance inorganic hole injecting layer is capable of blocking electrons and has conduction paths for carrying holes.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
AlGa-based semiconductor ultraviolet device for improving luminous efficiency and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108231960AHigh light efficiencyReduce contentSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyQuantum well
The present invention provides an AlGa-based semiconductor ultraviolet device for improving luminous efficiency and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of semiconductors.The epitaxial structure of the device comprises a substrate, an AlN buffer layer, an n-type AlGaN layer, an AlxGa1-xN / AlyGa1-yN luminescence active region, the last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer, ap-type AlGaN electron blocking layer, a p-type AlGaN layer and a contact layer, wherein 0.01<=x and y<=1. The luminescence active region comprises a plurality of quantum well layers and a plurality ofquantum barrier layers, the quantum well layers and the quantum barrier layers are alternately arranged, and the last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer is an aluminium ingredient gradient layer. The last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer of aluminium ingredient gradient is introduced in the ultraviolet device to optimize the energy band structure of the device, effectively improve the electron restriction effect and enhance the cavity injection efficiency so as to improve the quantum efficiency and the luminescence efficiency of the semiconductor ultraviolet device.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF SEMICON IND TECH
Semiconductor white light light-emitting diode
ActiveCN108598227AImprove hole injection efficiencyPrevent leakageSemiconductor devicesQuantum dotNon doped
The invention discloses a semiconductor white light light-emitting diode. The semiconductor white light light-emitting diode is characterized in that V-pits comprise first V-pits and second V-pits; the first V-pits comprise non-doped ZnO quantum dots and CdS<y>Se<1-y> / ZnO core-shell structured nanometer columns to give out red light; the second V-pits comprise non-doped ZnO quantum dots and ZnS<z>Se<1-z> / ZnO core-shell structured nanometer columns to give out green light; multiple quantum wells between the first V-pits and the second V-pits give out blue light; and therefore, the white light light-emitting diode mixed by the red light, the green light and the blue light is formed.
Owner:LIMING VOCATIONAL UNIV
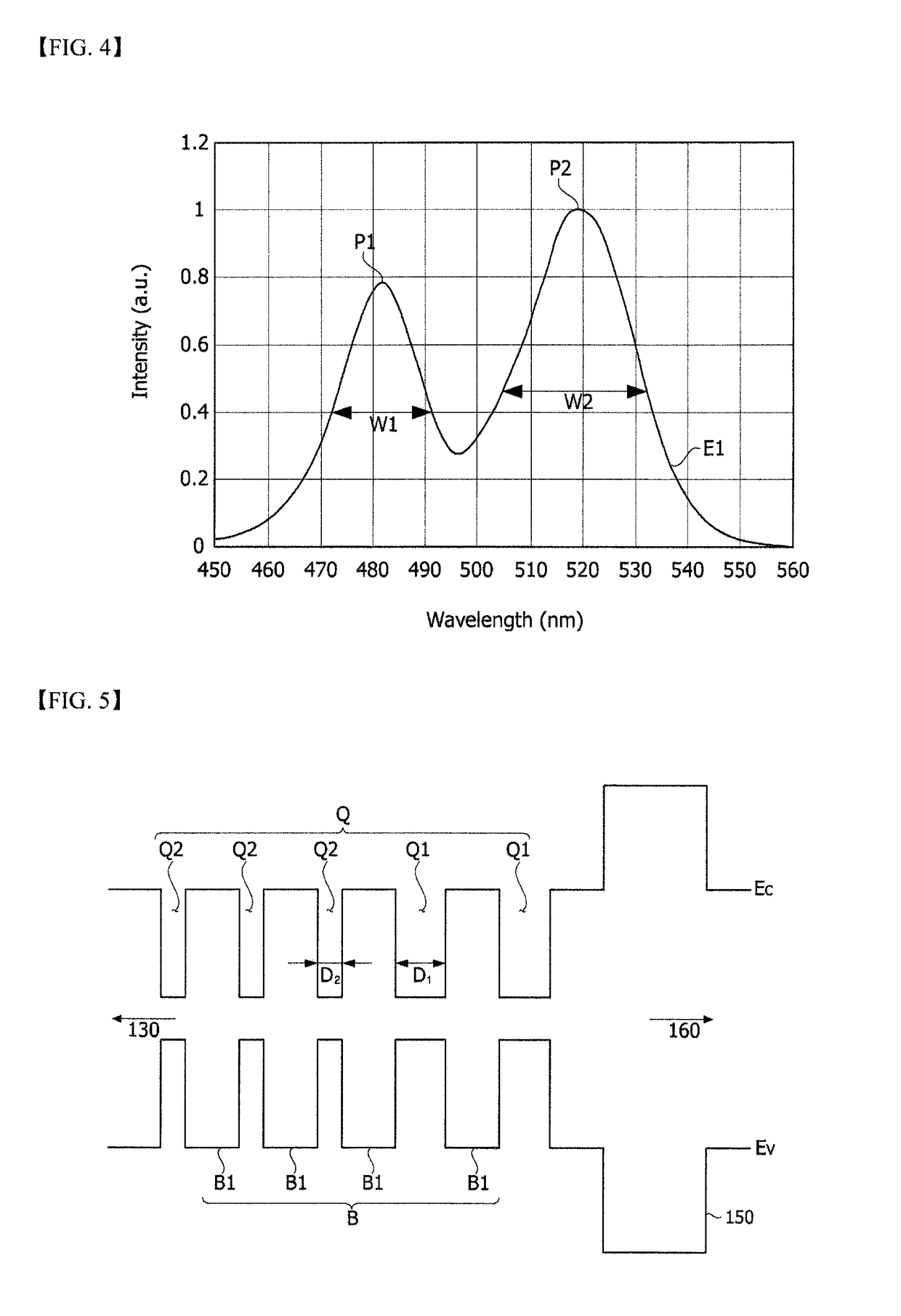
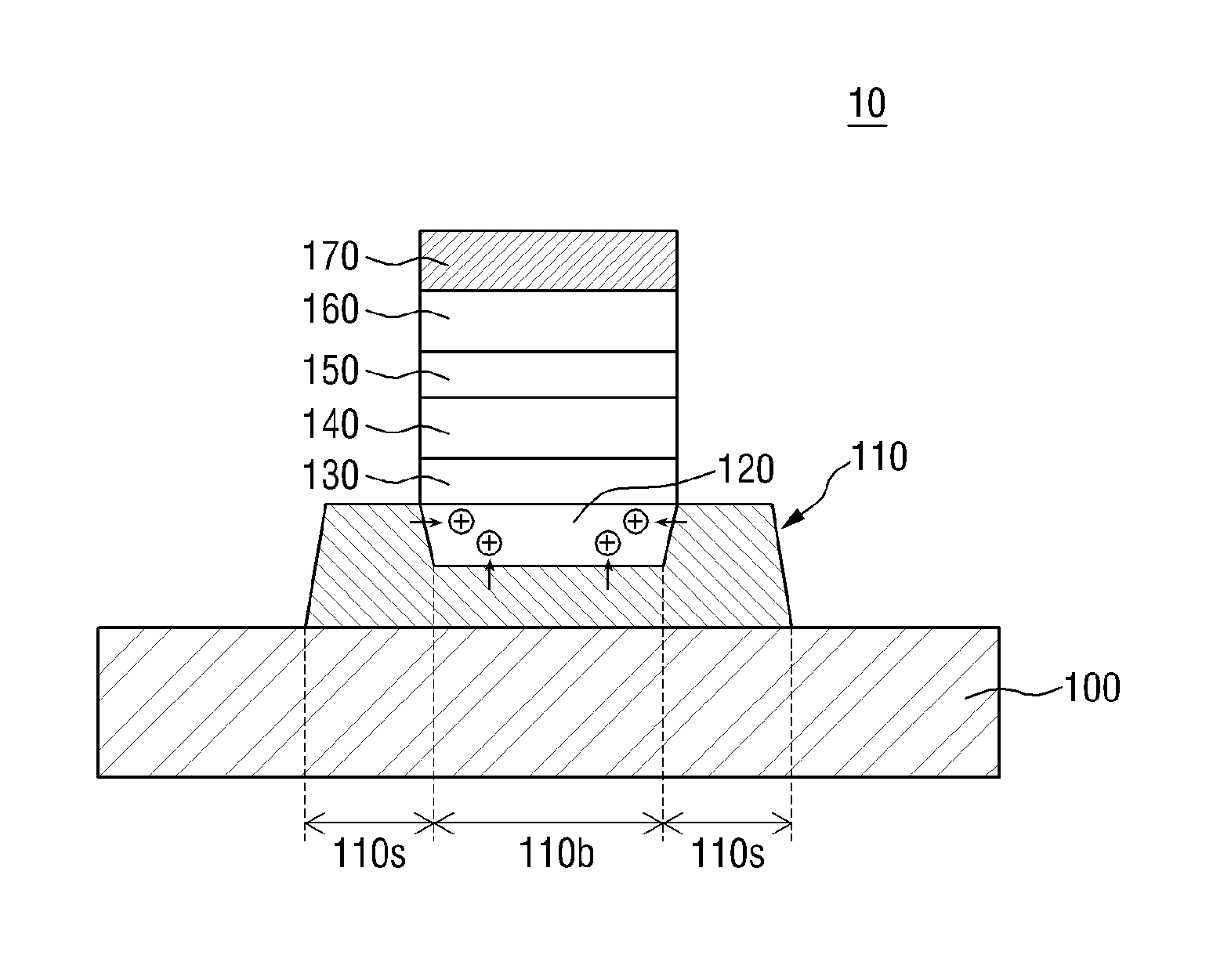
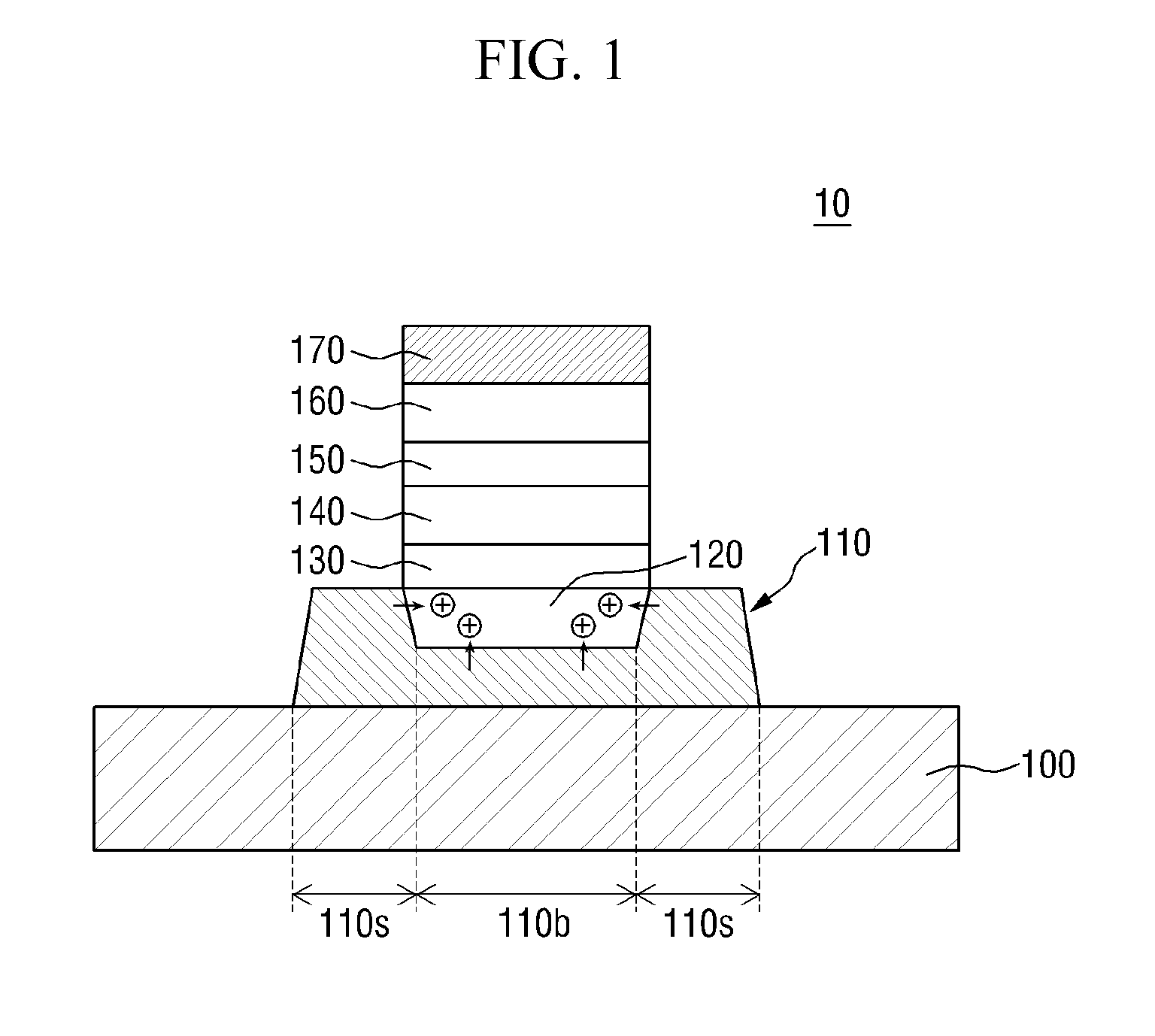
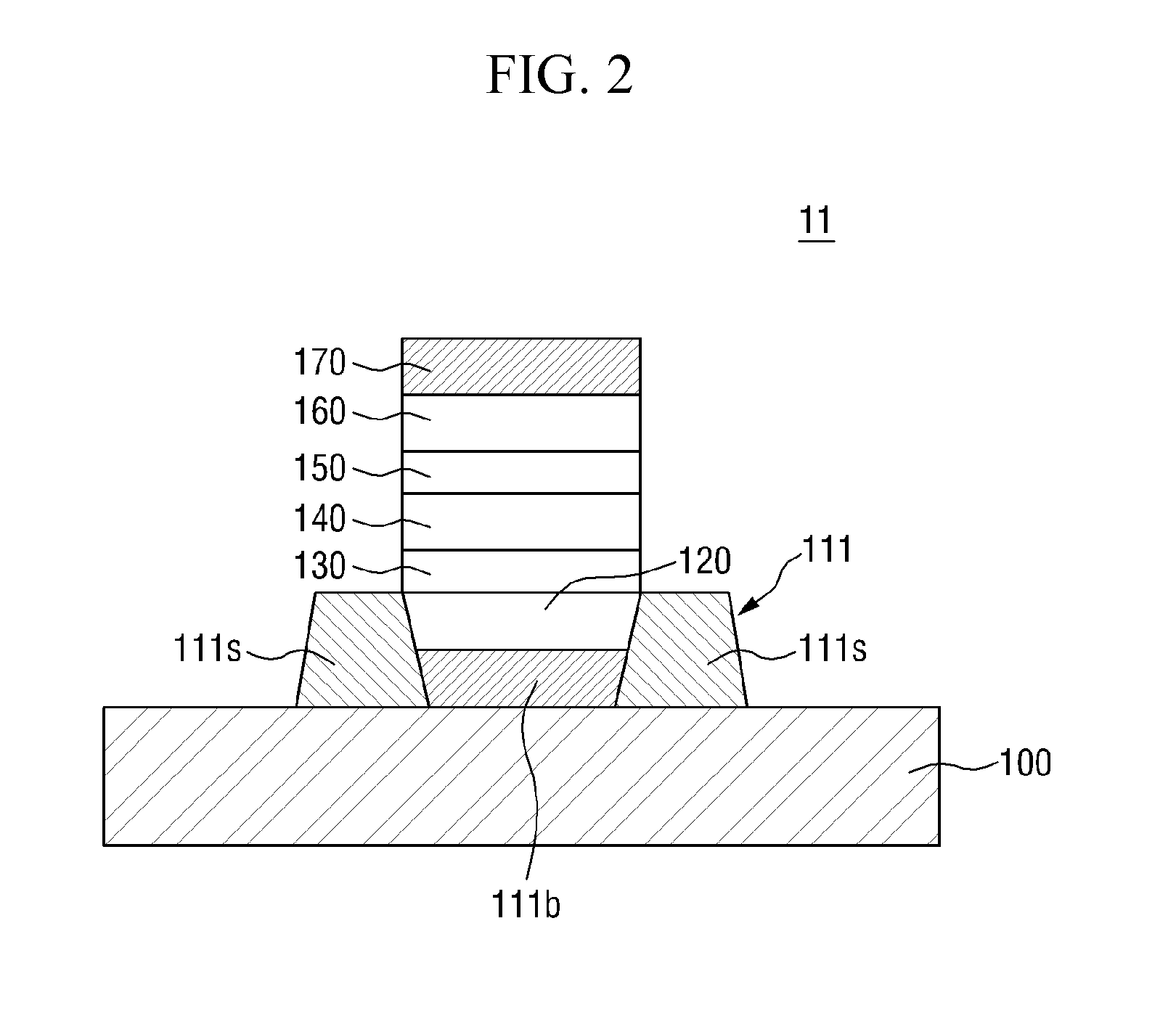
Light-emitting device and lighting device including the same
Disclosed in one embodiment is a light-emitting device comprising: a first conductive semiconductor layer; an active layer arranged on the first conductive semiconductor layer, and including a plurality of first recesses; an EBL arranged on the active layer, and including a plurality of second recesses arranged on the first recesses; and a second conductive semiconductor layer arranged on the EBL, wherein the ratio of a first area doping concentration and a second recess doping concentration is from 1:0.8 to 1:1, the active layer emits first light and second light, the first light has a peak in a wavelength of 450 nm to 499 nm, and the second light has a peak in a wavelength of 500 nm to 550 nm.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
SOI LIGBT with controllable collector trough
ActiveCN107342321AImprove hole injection efficiencyEliminate the snapback phenomenonSemiconductor devicesHigh densityVoltage drop
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, and specifically relates to an SOI LIGBT with a controllable collector trough. Compared with a conventional structure, the LIGBT mainly introduces a controllable collector trough structure to a collector end and introduces a plurality of trough grid structures to the collector. During the forwarding conduction, the bias voltage of a trough collector relative to the collector is negative, and a side wall of the collector trough forms a high-density P-type reflection layer so as to increase the hole implantation. The segmented trough grid structures serve as the blocking layers of hole extraction. Therefore, the increase of the hole / electron concentration in a drift region facilitates the obtaining of a lower forwarding conduction voltage drop. Meanwhile, because an N+ collector region is located on the upper surface of a P+ collector region and does not make contact with an N-type drift region, a new device does not has a voltage turning-back effect. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the LIGBT, compared with a conventional short-circuit anode-LIGBT structure, is higher in switching-off speed and lower in forwarding conduction voltage drop, and does not have the voltage turning-back effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
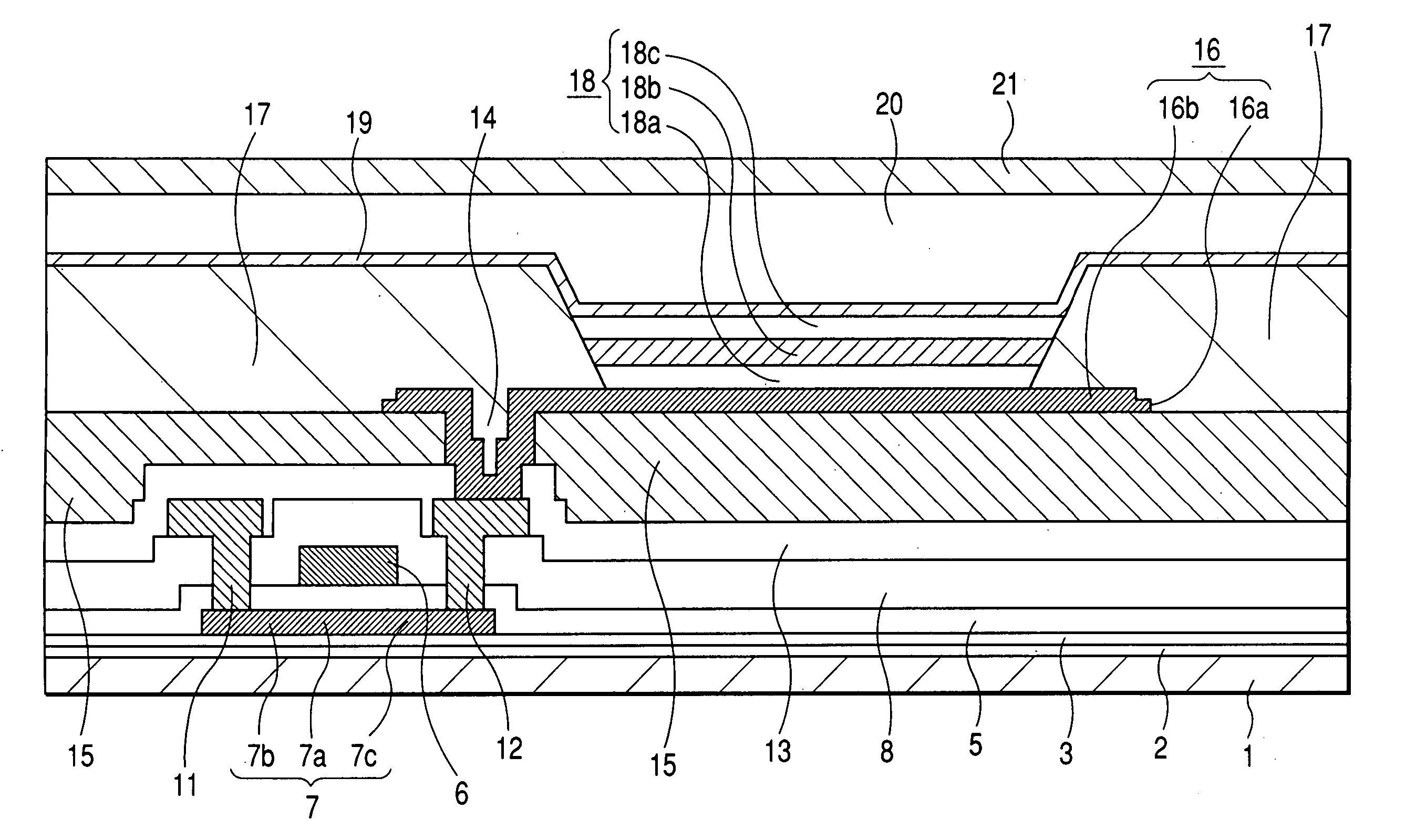
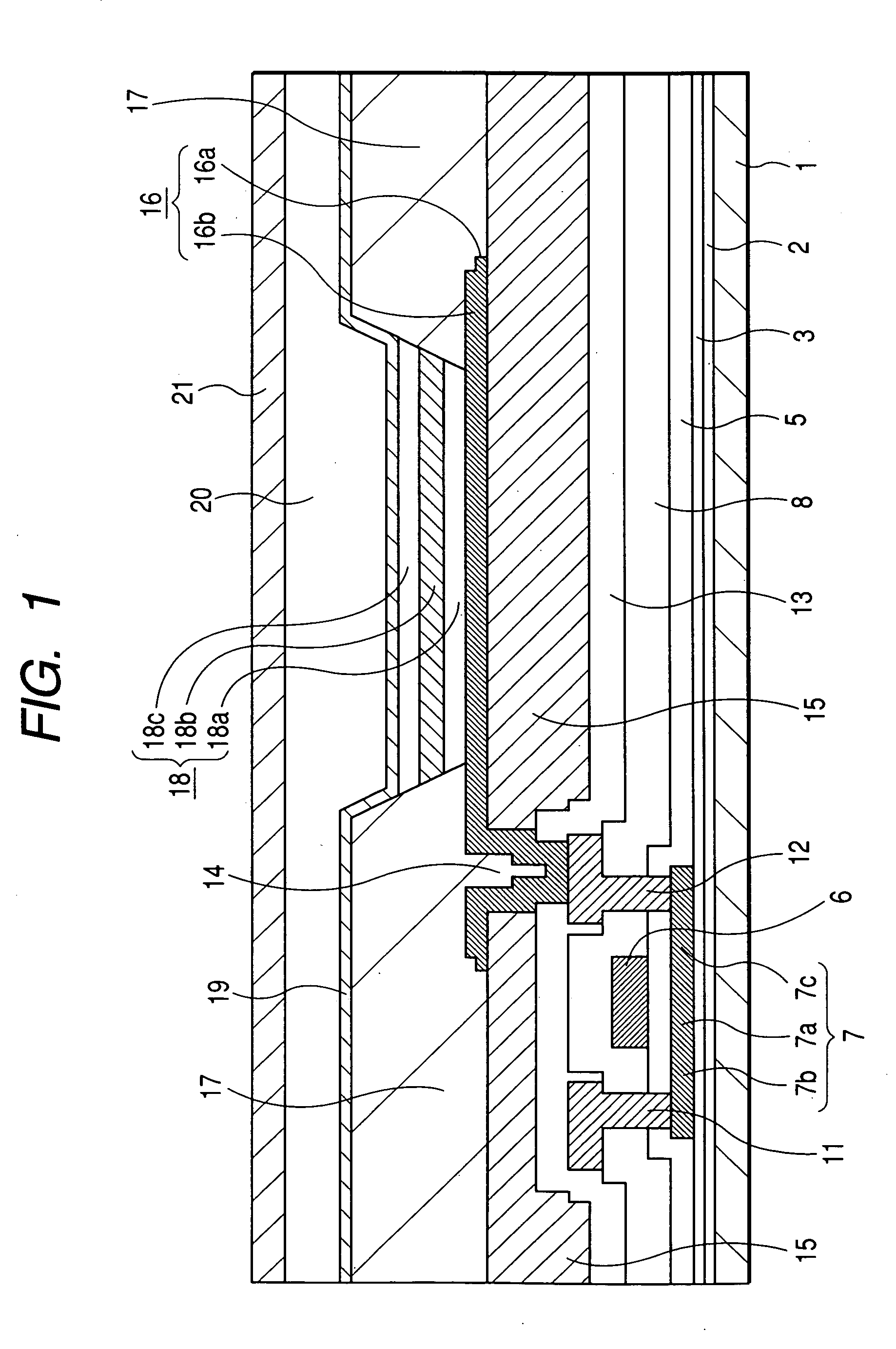
Organic light-emitting diode display and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20150014634A1Improve hole injection efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerDisplay device
An organic light-emitting diode display includes a substrate, a first electrode which is disposed on the substrate, a trench defined in a top surface of the first electrode, and a hole injection layer which is disposed in the trench.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
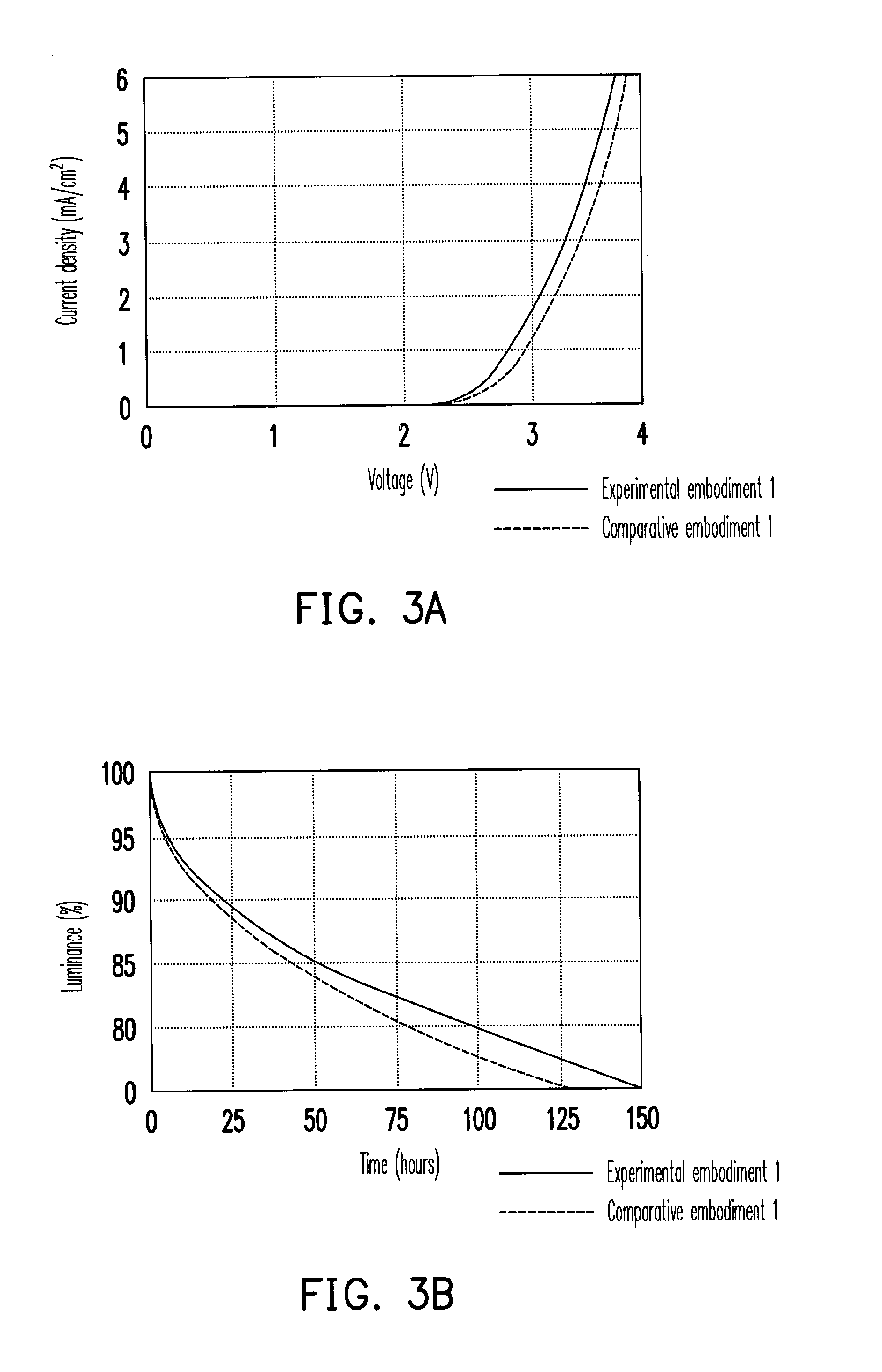
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20120168725A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduce the driving voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescent device including a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, a light emitting layer and a hole injection layer is provided. The light emitting layer is disposed between the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer. The hole injection layer is disposed between the first electrode layer and the light emitting layer, wherein the hole injection layer includes a first material layer and a second material layer. The second material layer is disposed on the first material layer and includes a main material and a doping material, wherein the doping material of the second material layer and a material of the first material layer are substantially the same.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9269852B2Improve quantum efficiencyImprove hole injection efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellElectron blocking layer
A semiconductor light-emitting diode, including: an n-GaN layer, a quantum well layer, an electron blocking layer, and a p-GaN layer, which are sequentially stacked on a substrate. The electron blocking layer includes at least one first AlGaN layer and at least one second AlGaN layer. The first AlGaN layer and the second AlGaN layer are alternately stacked. The adjacent first and second AlGaN layers have different Al component.
Owner:HC SEMITEK CORP
Method for producing and epitaxial substrate for compound semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS7459326B2Highly efficient injection of holeImprove protectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact layerLight emission
In order to improve light-emission efficiency without degrading protection performance of a light-emitting layer structure a three p-type layer structure composed of first to third layers is provided in contact with a light-emitting layer structure. The first layer is an n-type AlGaN layer that serves as a protective layer, the third layer is a GaN:Mg layer that serves as a contact layer and the second layer is an AlGaN:Mg layer formed between these layers as an intermediate layer. The provision of the intermediate layer enables an InGaN layer to be thoroughly protected from heat during growth of layers above even if the n-type AlGaN layer is made thin, whereby the GaN:Mg layer can be brought near the light-emitting layer structure to enhance the efficiency of hole injection into the light-emitting layer structure and thus increase the light-emission efficiency.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Light emitting diode with electron blocking layer in resonant tunneling structure
ActiveCN107195746AImprove the blocking effectIncreased efficiency of injection into the active regionSemiconductor devicesPotential wellOhmic contact
The invention discloses a light emitting diode with an electron blocking layer in a resonant tunneling structure. The light emitting diode comprises a substrate, an n-type nitride layer, a multiple quantum well layer, the electron blocking layer, a p-type nitride layer and a p-type nitride ohmic contact layer, an n-type electrode which is arranged on the n-type nitride layer, and a p-type electrode which is arranged on the p-type nitride layer, wherein the substrate, the n-type nitride layer, the multiple quantum well layer, the electron blocking layer, the p-type nitride layer and the p-type nitride ohmic contact layer are arranged in order from the bottom up. The electron blocking layer is composed of a p-type doped nitride barrier layer, a non-doped nitride potential well layer, and a non-doped barrier layer which increases the hole transmittance through a resonance tunneling effect, wherein the p-type doped nitride barrier layer, the non-doped nitride potential well layer and the non-doped barrier layer are arranged in order from bottom to top. The light emitting diode provided by the invention has the advantages that electrons are effectively prevented from passing through an active region into a p-type region, which increases the injection efficiency of a hole into the active region through the electron blocking layer; a good electronic blocking effect is realized through a simple growth mode and less layer structures; and the hole injection efficiency significantly higher than a traditional electronic blocking layer structure is acquired.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Nitride based semiconductor light-emitting device
ActiveUS20080001138A1Improve hole injection efficiencyImprove injection efficiencySolid-state devicesNanoopticsGalliumActive layer
Disclosed herein is a nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device. The nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device comprises an n-type clad layer made of n-type Alx1Iny1Ga(1-x1-y1)N (where 0≦x1≦1, 0≦y1≦1, and 0≦x1+y1≦1), a multiple quantum well-structured active layer made of undoped InAGa1-AN (where 0<A<1) formed on the n-type clad layer, and a p-type clad layer formed on the active layer wherein the p-type clad layer includes at least a first layer made of p-type Iny2Ga1-y2N (where 0≦y2<1) formed on the active layer and a second layer made of p-type Alx3Iny3Ga(1-x3-y3)N (where 0<x3≦1, 0≦y3≦1, and 0<x3+y3≦1) formed on the first layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optoelectronic device
ActiveUS20150041787A1Reduce conductivityEliminate gap effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerSemiconductor
This invention generally relates to an optoelectronic device and a method of fabricating such a device, and more particularly to an optoelectronic device comprising an anode layer, a semiconductive layer provided over the anode layer, and a cathode layer provided over the semiconductive layer, the anode layer comprising a plurality of electrically conductive tracks connected together and spaced apart from one another with gaps therebetween, the device further comprising a first and one or more further hole injection layers provided between the anode layer and the semiconductive layer and extending across said gaps, wherein the first hole injection layer has a conductivity greater than the conductivity of the one or more further hole injection layers.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
LED epitaxial structure and making method thereof
ActiveCN105355741AIncrease hole injection areaImprove hole injection efficiencySemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumElectrically conductive
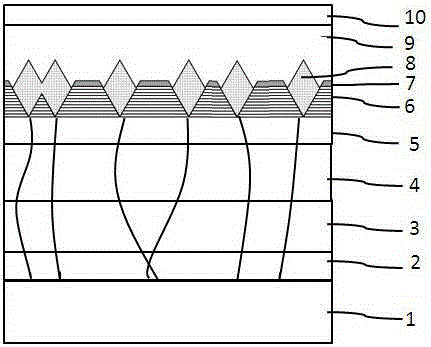
The invention provides an LED epitaxial structure and a making method thereof. The LED epitaxial structure sequentially comprises, from bottom to top, a substrate, a first conductivity type semiconductor layer, a superlattice, a multiple-quantum well layer with V-shaped pits, a hole injection layer, and a second conductivity type semiconductor layer, and is characterized in that the hole injection layer is shaped as a double-hexagonal pyramid, fills the V-shaped pits, and is embedded into the second conductivity type semiconductor layer.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
LED epitaxial structure based on h-BN tunnel junction as hole injection layer
ActiveCN107293624AIncrease chance of tunnelingEnhanced electric fieldSemiconductor devicesDielectricSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to an LED epitaxial structure based on an h-BN tunnel junction as a hole injection layer. The invention is characterized in that the epitaxial structure comprises a substrate, an n-type semiconductor material layer, a multi-quantum well layer, a p-type electronic blocking layer, a p-type semiconductor material layer, a p-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer, an h-BN layer and an n-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer, the relative dielectric constant of the n-BN layer is 3-5.1, the relative dielectric constant is less than the relative dielectric constant of the p-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer and the n-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer, the thickness of the h-BN layer is 1nm-5nm; and the p-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer, the h-BN layer and the n-type heavily doped semiconductor material layer constitute a tunnel junction together. The LED epitaxial structure has a tunnel junction structure capable of improving the hole injection efficiency of an LED device, thereby increasing the tunneling probability of carriers, improving the current expansion effect, and significantly improving the quantum efficiency and light output power in the LED.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com