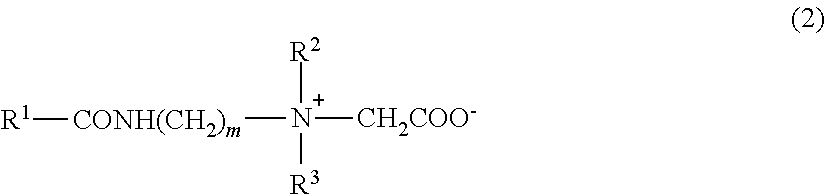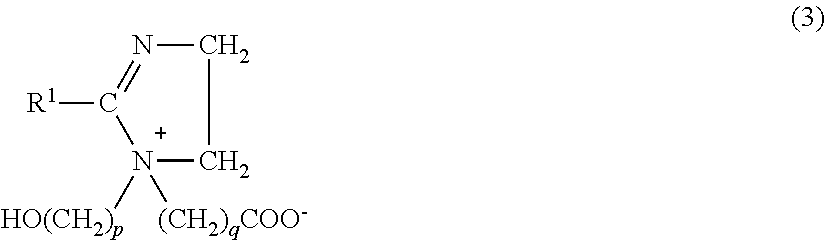Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Total degree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
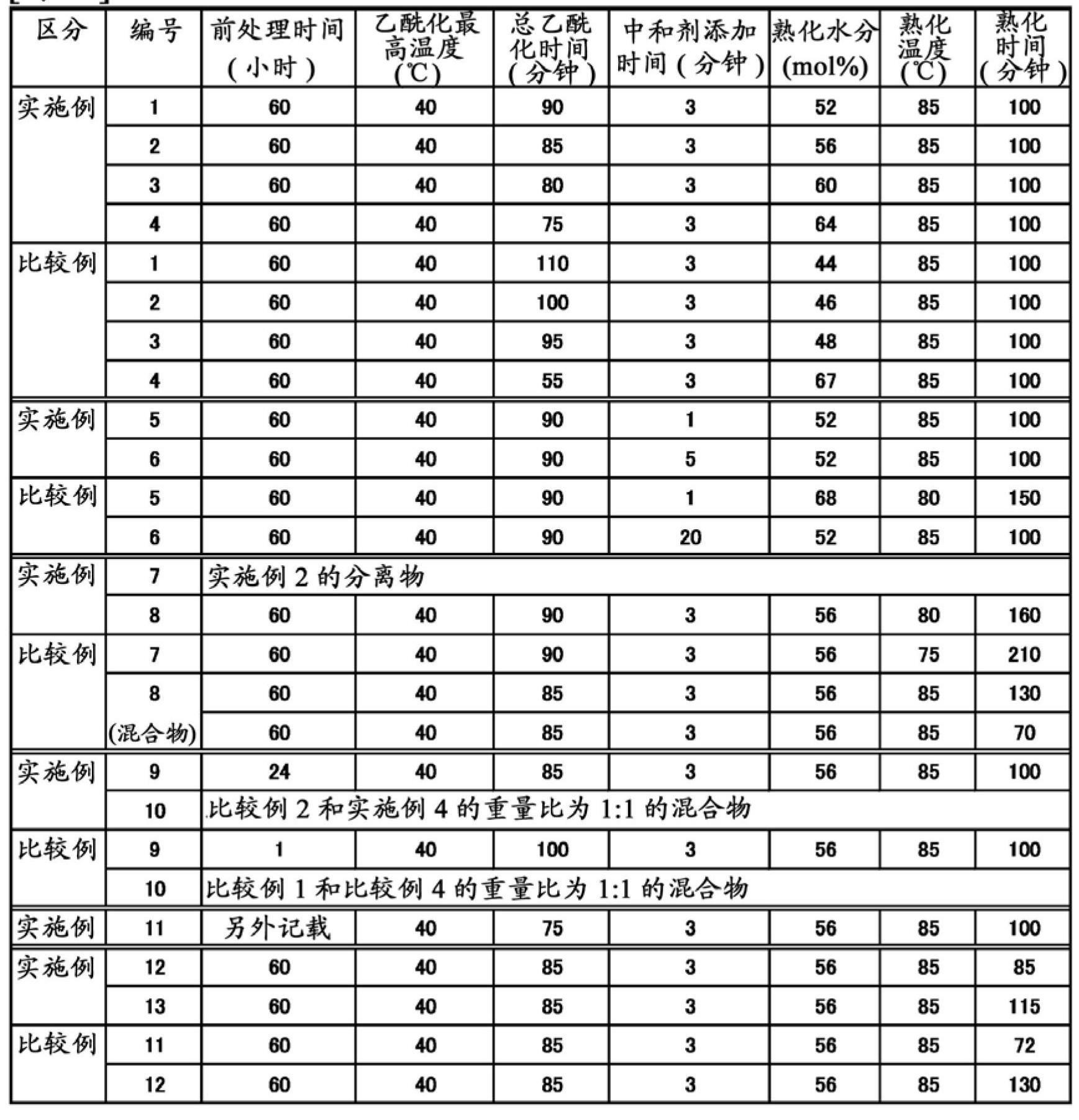
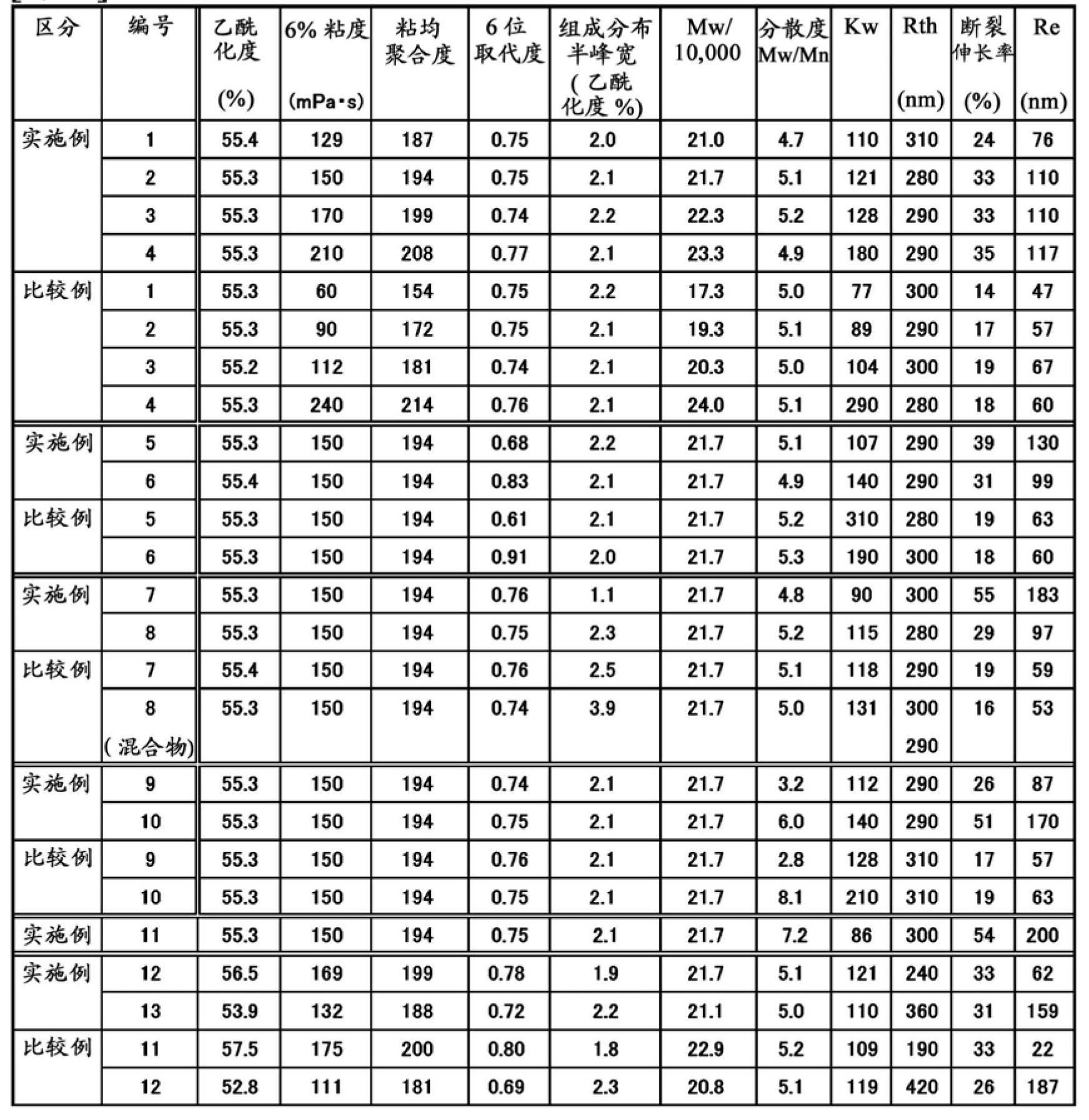
The degree of total leverage can be explained or calculated simply as: Degree of total leverage = Degree of operating leverage x Degree of financial leverage =. The degree of operating leverage is equivalent to: Contribution margin (Total sales – Variable costs) / Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)
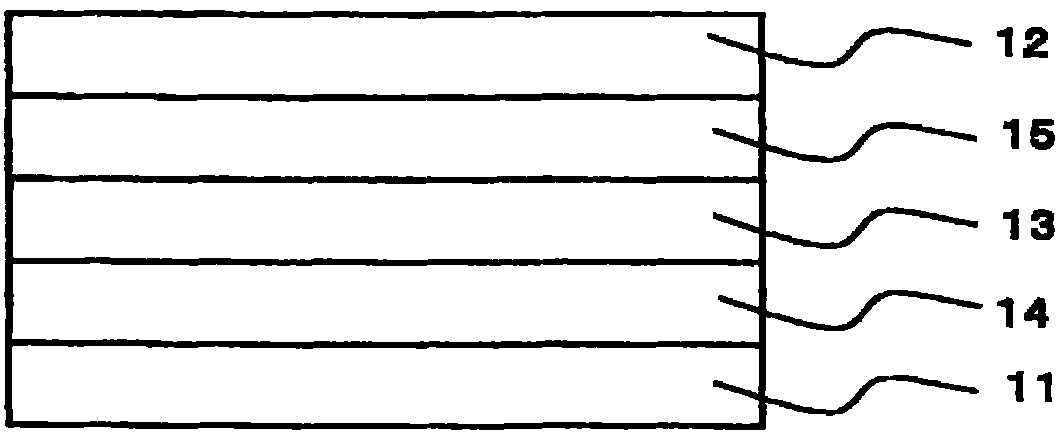
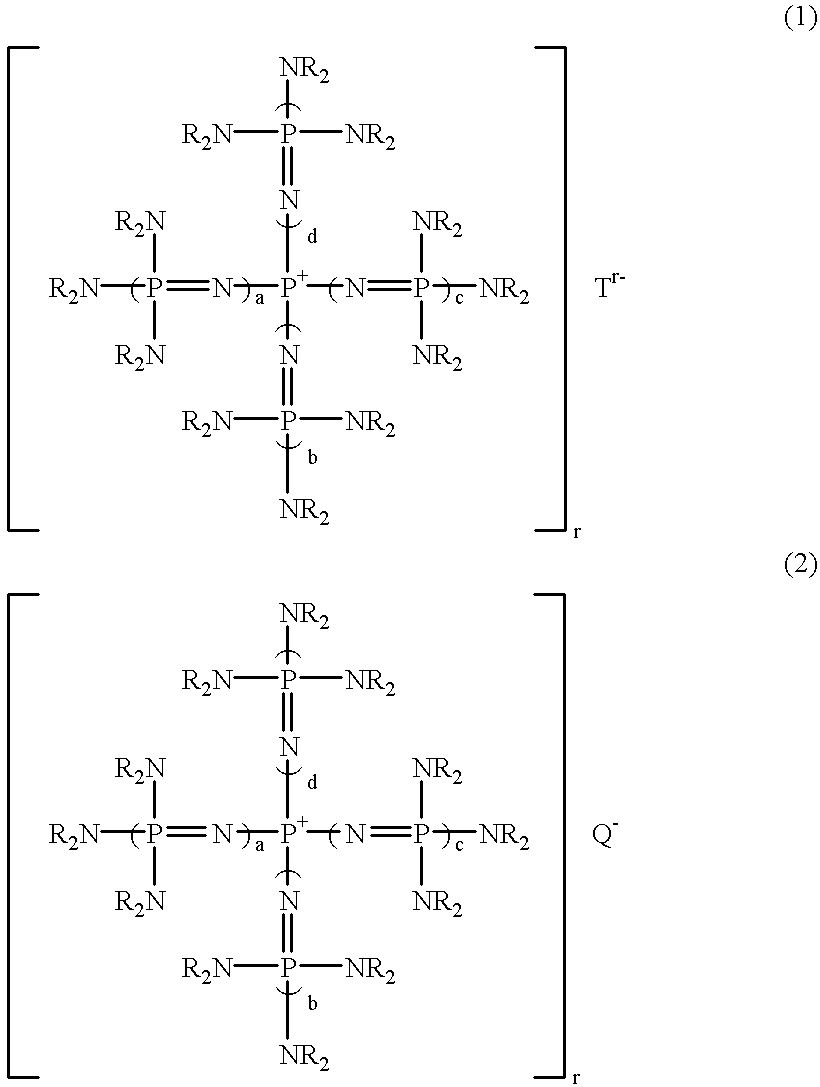
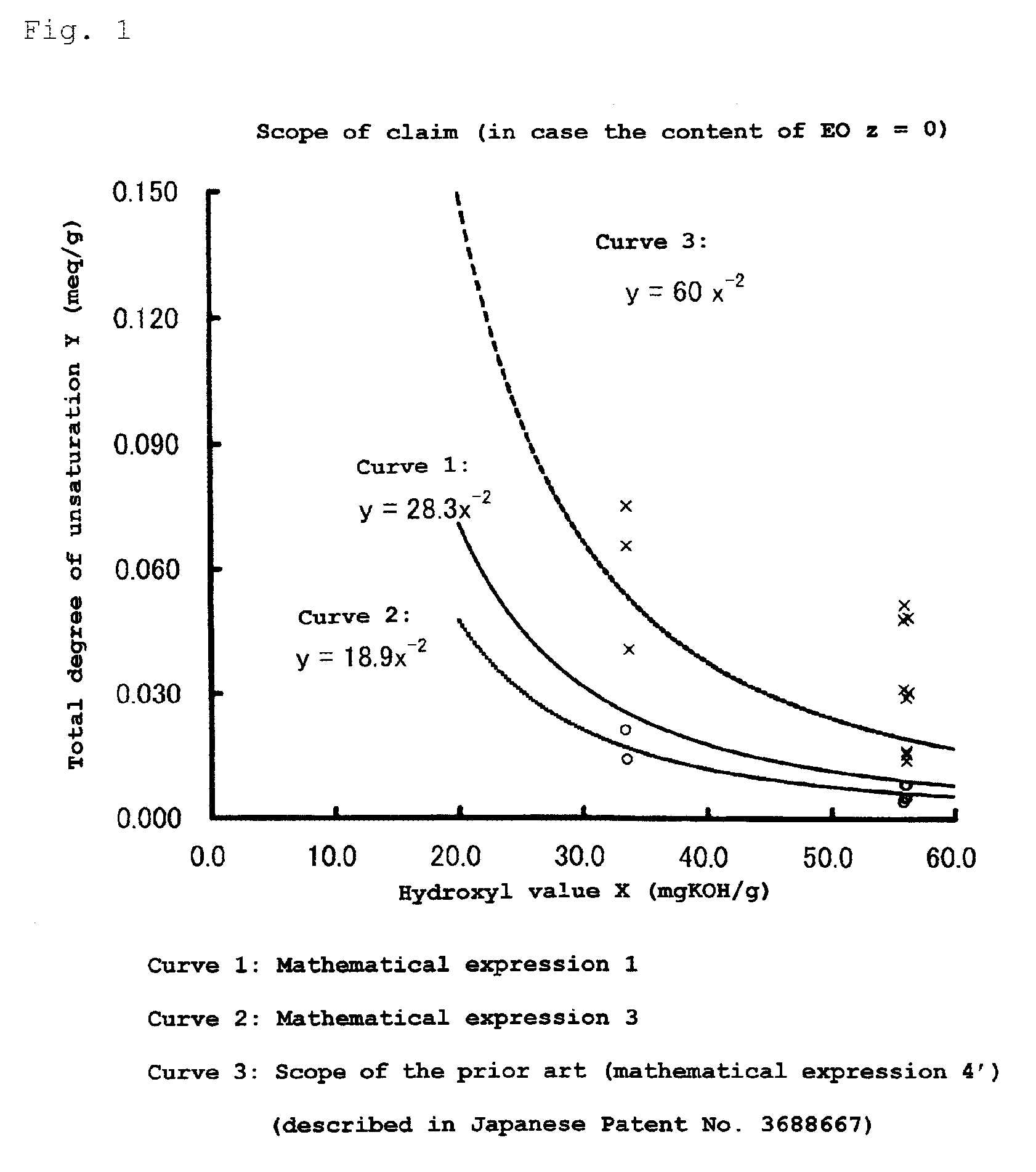
Polyoxyalkylene polyols, derivatives thereof, and process for producing the polyoxyalkylene polyols
The present invention is a polyoxyalkylene polyol, its manufacture method, and derivatives, wherein: it is obtained using a phosphazenium compound as a catalyst; the hydroxyl value is 2~200 mgKOH / g; total degree of unsaturation is 0.0001~0.07 meq. / g; the head-to-tail bond selectivity of the polyoxyalkylene polyol is 95 mole %; and when the maximum height of the peak of GPC elution curve is set to be 100%, W20 is defined as the peak width at the 20% peak height, and W80 is defined as the peak width at 80% peak height, the ratio of W20 / W80 is 1.5 or greater, and less than 3.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM & SKC POLYURETHANES INC
Device for comminuting dry ice granules, and dry ice dispensing arrangement having such a device
The invention relates to a device for comminuting dry ice granules, comprising a housing having a flow channel for dry ice granules which can be applied, by means of compressed gas, to a surface to be cleaned, and also comprising a first comminution member for comminuting the dry ice granules which are to be dispensed. In order to provide a device of this kind with which different degrees of comminution of dry ice granules can be achieved in a simple manner, it is proposed according to the invention that the device has at least one second comminution member which can be disposed in the housing in a position in which a total degree of comminution, which is greater than the individual degree of comminution which can be achieved solely by the first comminution member, can be achieved in combination with the first comminution member. A dry ice dispensing arrangement for dispensing a mixture of compressed gas and dry ice granules is also proposed, having a device of the above kind.
Owner:ALFRED KARCHER GMBH & CO KG
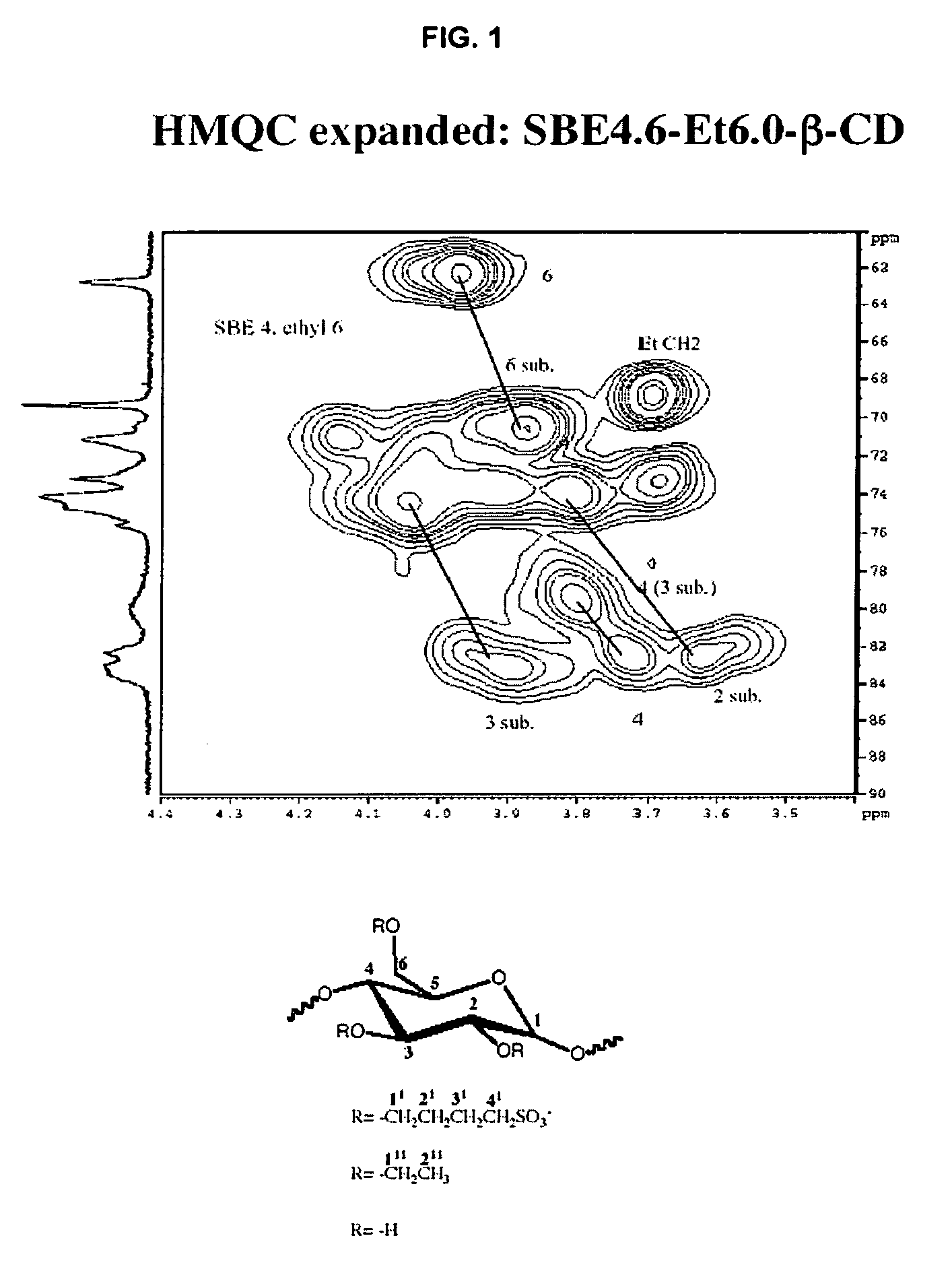
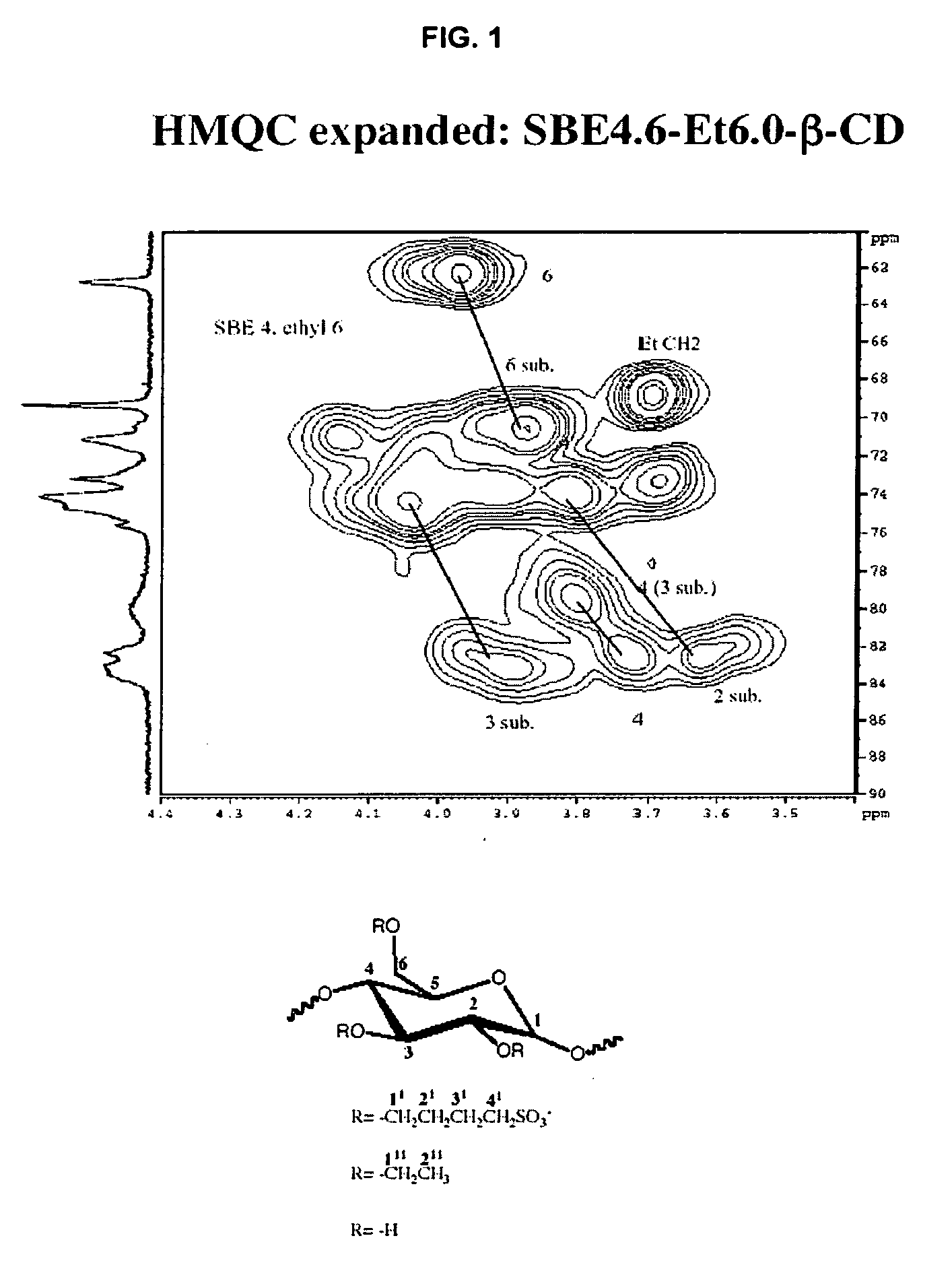
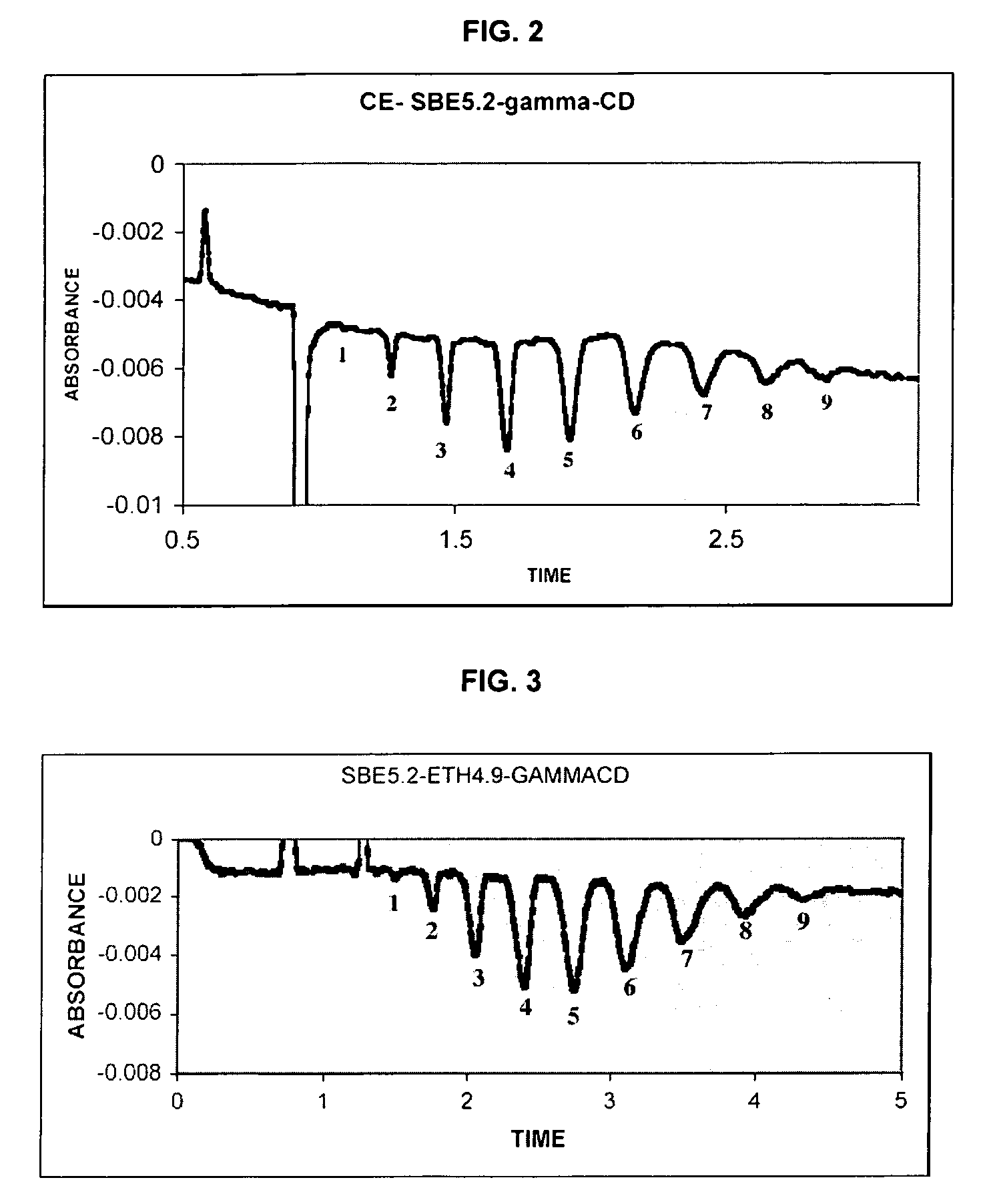
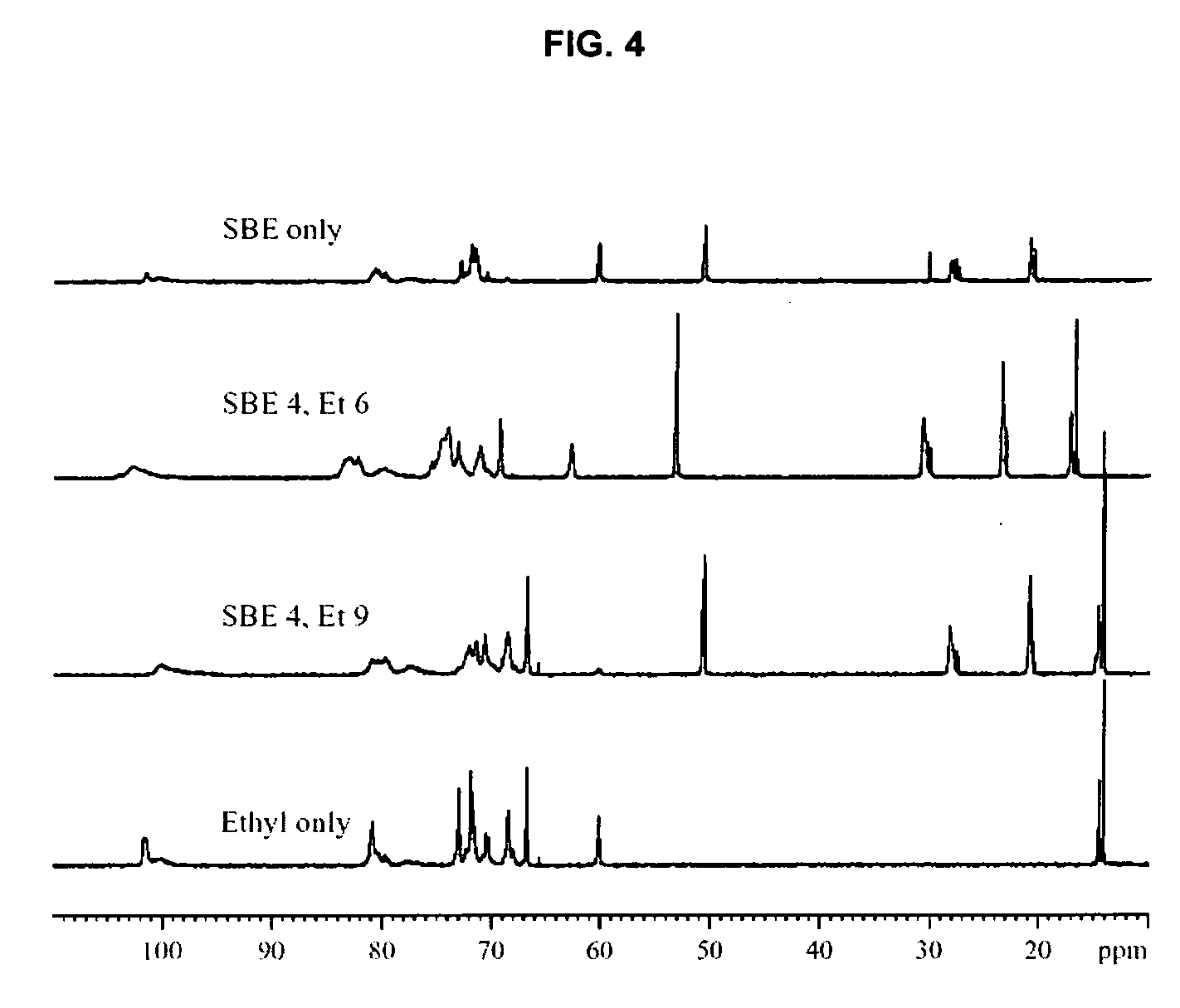
Sulfoalkyl ether-alkyl ether cyclodextrin derivatives
ActiveUS7625878B2Improve propertiesHigh degree of substitutionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityCyclodextrin derivative
A sulfoalkyl ether-alkyl ether cyclodextrin (SAE-AE-CD) derivative is provided. The SAE-AE-CD possesses advantages over known SAE-CD and AE-CD derivatives as well as over the parent cyclodextrin by being more water soluble and less membrane disturbing. The SAE-AE-CD includes at least one sulfoalkyl ether group and at least one alkyl ether group even though the degree of substitution for the functional groups can be different. The SAE functional group can be present in molar excess over the AE functional group and vice versa. The total degree of substitution of the cyclodextrin, with respect to both functional groups, can be varied such that a minority or a majority of the hydroxyl moieties of the CD are derivatized. The SAE-AE-CD derivative can be used to solubilize compounds with insufficient water solubility. In some cases, they also stabilize compounds in solution against degradation or to solubilize degradation products formed during degradation. In addition, SAE-AE-CD can also be used for other purposes such as osmotic agents, agents used to mask the taste of problematic drugs. Surprisingly, while AE-CDs are known to be toxic by being membrane disturbing, SAE-AE-CDs are less membrane disturbing and therefore have greater safety.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Sulfoalkyl ether-alkyl ether cyclodextrin derivatives
ActiveUS20060258537A1Improve propertiesHigh degree of substitutionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSolubilityCyclodextrin Derivatives
A sulfoalkyl ether-alkyl ether cyclodextrin (SAE-AE-CD) derivative is provided. The SAE-AE-CD possesses advantages over known SAE-CD and AE-CD derivatives as well as over the parent cyclodextrin by being more water soluble and less membrane disturbing. The SAE-AE-CD includes at least one sulfoalkyl ether group and at least one alkyl ether group even though the degree of substitution for the functional groups can be different. The SAE functional group can be present in molar excess over the AE functional group and vice versa. The total degree of substitution of the cyclodextrin, with respect to both functional groups, can be varied such that a minority or a majority of the hydroxyl moieties of the CD are derivatized. The SAE-AE-CD derivative can be used to solubilize compounds with insufficient water solubility. In some cases, they also stabilize compounds in solution against degradation or to solubilize degradation products formed during degradation. In addition, SAE-AE-CD can also be used for other purposes such as osmotic agents, agents used to mask the taste of problematic drugs. Surprisingly, while AE-CDs are known to be toxic by being membrane disturbing, SAE-AE-CDs are less membrane disturbing and therefore have greater safety.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Cellulose acylate and solution thereof
InactiveUS6984730B2Improve stabilityLow viscositySugar derivativesPhotosensitive materialsCellulosePolymer
A cellulose acylate which is a polymer obtained by substituting cellulose with acyl groups in 2-, 3-, 6-positions. The total degree of acyl substitution in the 2- and 3-positions is regulated to from 1.70 to 1.90. The degree of 6-position acyl substitution is regulated to 0.88 or higher.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Cellulose acylate and solution thereof
InactiveUS20040059106A1Improve stabilityLow viscositySugar derivativesPhotosensitive materialsCellulosePolymer
A cellulose acylate which is a polymer obtained by substituting cellulose with acyl groups in 2-, 3-, 6-positions. The total degree of acyl substitution in the 2- and 3-positions is regulated to from 1.70 to 1.90. The degree of 6-position acyl substitution is regulated to 0.88 or higher.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool and polyurethane resin
ActiveUS9388271B2Satisfactory mechanical property and moisture resistanceSufficient reactivityOrganic chemistryArylHalogen
There is provided a polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool (S) represented by formula (2). In the formula (2), R2 represents an m-valent group in which m active hydrogens are removed from the active hydrogen-containing compound (H); Z is an alkylene group or a cycloalkylene group, and these groups are unsubstituted or substituted with a halogen atom or an aryl group. A hydroxyl value x, total degree of unsaturation y and the content of ethylene oxide z satisfy mathematical expression (3). In mathematical expression (3), x represents 5 to 280 mgKOH / g, y represents total degree of unsaturation represented by a unit meq / g, and z is from 0 to 50.R2—[—(ZO)p-(AO)q-(CH2CH2O)r-H] (2)y≦18.9×x−2×(100−z) / 100 (3)
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Cellulose ester film, polarizer and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090317567A1Improve stabilityHigh RthLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCellulose ester membranePolymer science
A cellulose ester film with Rth>0 nm comprising a cellulose ester having a total degree of substitution of at least 2.3 and a polymer X with a weight-average molecular weight of 500-100000 satisfying 30%≦A≦100%, wherein A indicates the polymerization ratio of a monomer whose homopolymer has a negative birefringence, is excellent in humidity stability and wet heat durability.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
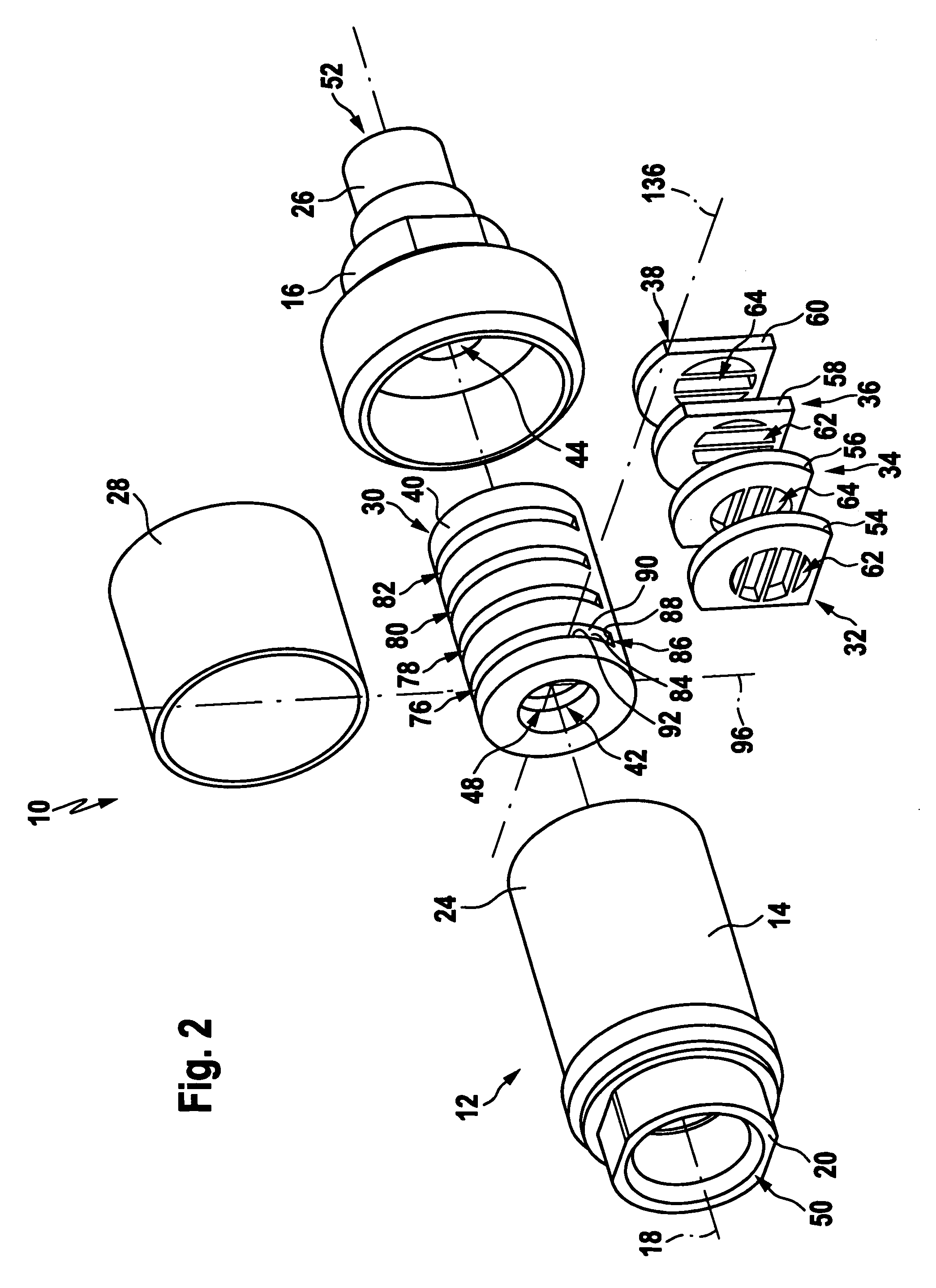
Apparatus and method for steering a vehicle
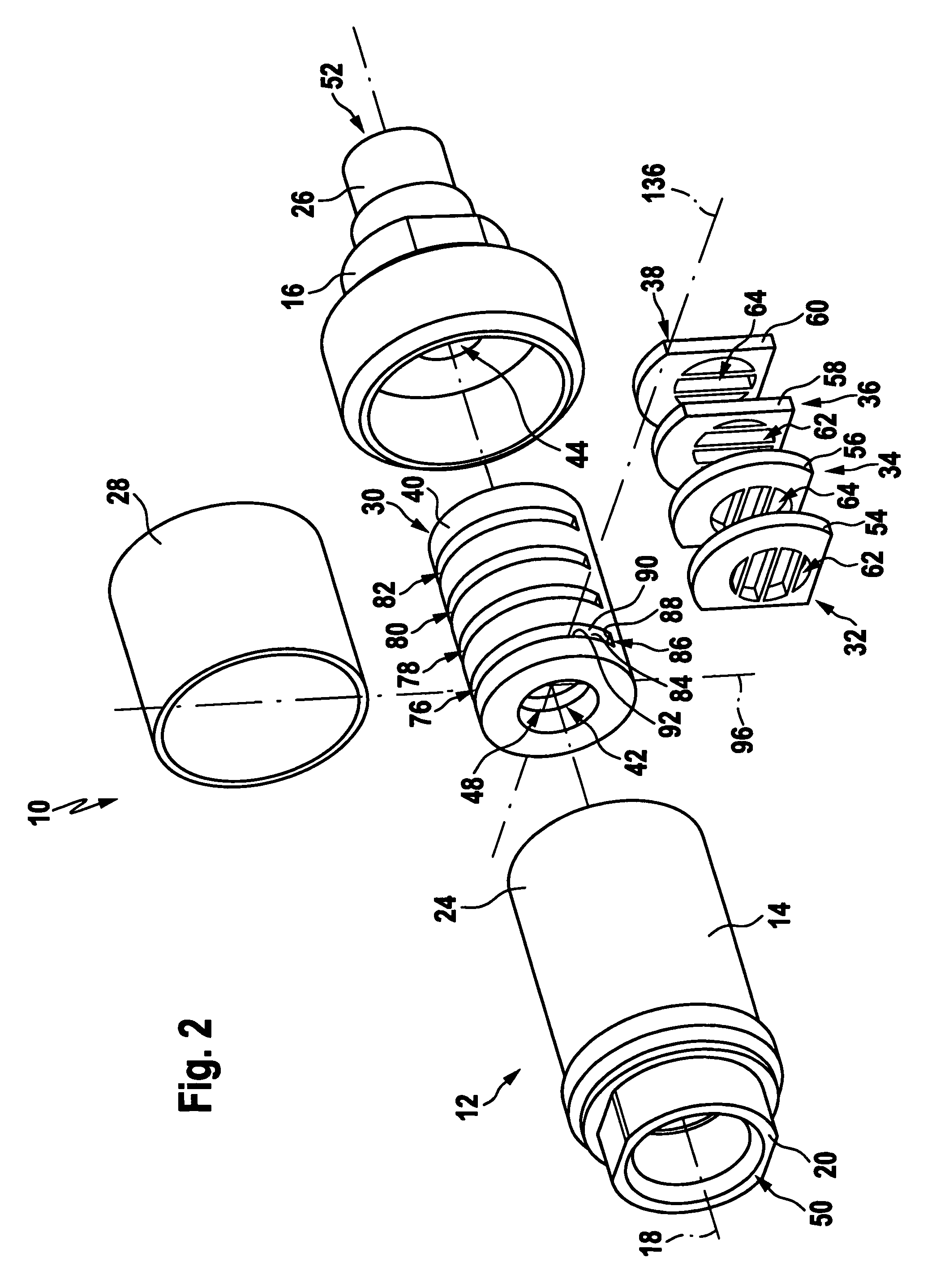
A steering system for a vehicle may include a load displacement system allowing transient loads of the steering mechanism to be displaced. The steering system may also include a first coupling mechanism coupling an electric motor to a rack housing, and a second coupling mechanism coupling a ball nut to a rack. A method for providing an actuation force to a rack of a vehicle includes isolating non-axial loads from an electric motor of a steering system and isolating non-axial loads from a linearly actuatable member of a rotary-to-linear conversion device in the steering system. An actuator for a steering system may include a rotary to linear actuator, a movable linear section, and an interface between the rotary to linear actuator and the linear section. The interface may include one or more cylindrical joints, revolute joints, compliant members, or a block on a plane wherein the total degrees of freedom for the system including the rotary to linear actuator, rack, and interface may be one, while the interface may be limited to three degrees of freedom.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Apparatus and method for steering a vehicle
A steering system for a vehicle may include a load displacement system allowing transient loads of the steering mechanism to be displaced. The steering system may also include a first coupling mechanism coupling an electric motor to a rack housing, and a second coupling mechanism coupling a ball nut to a rack. A method for providing an actuation force to a rack of a vehicle includes isolating non-axial loads from an electric motor of a steering system and isolating non-axial loads from a linearly actuatable member of a rotary-to-linear conversion device in the steering system. An actuator for a steering system may include a rotary to linear actuator, a movable linear section, and an interface between the rotary to linear actuator and the linear section. The interface may include one or more cylindrical joints, revolute joints, compliant members, or a block on a plane wherein the total degrees of freedom for the system including the rotary to linear actuator, rack, and interface may be one, while the interface may be limited to three degrees of freedom.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
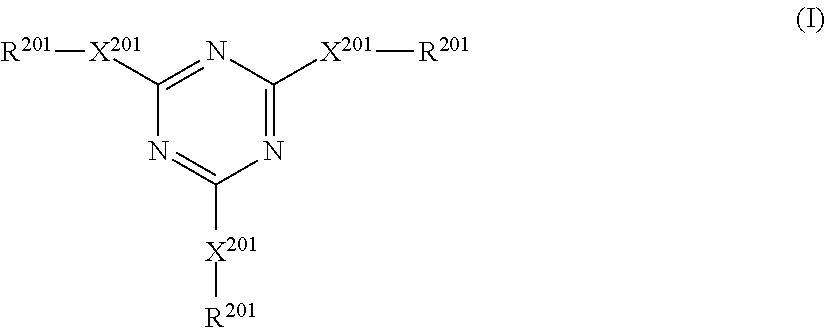
Cellulose derivatives for inhibiting crystallization of poorly water-soluble drugs
InactiveUS20150004237A1Improve bioavailabilityImprove solubilityPowder deliveryBiocideHydrogen atomWater soluble drug
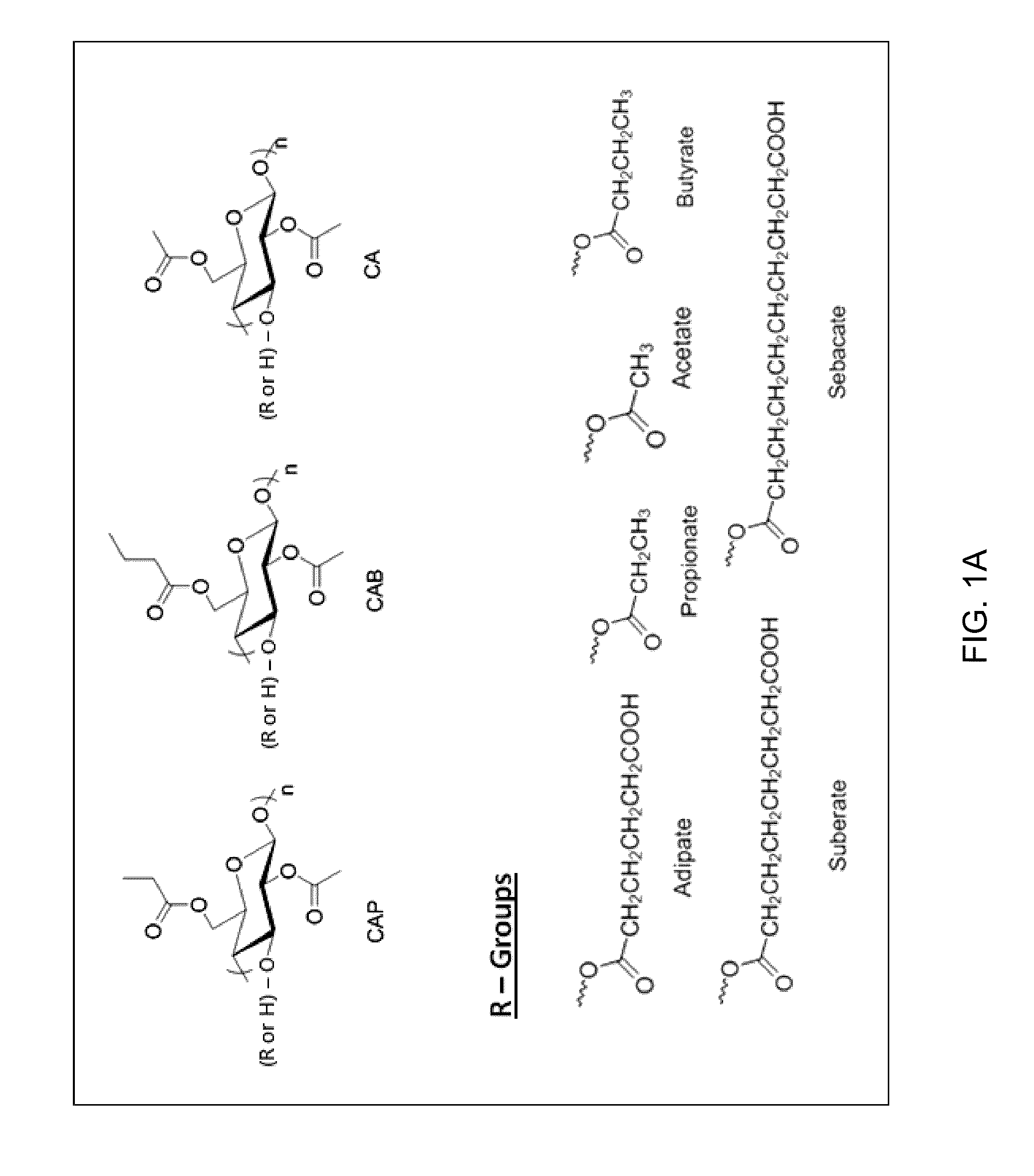
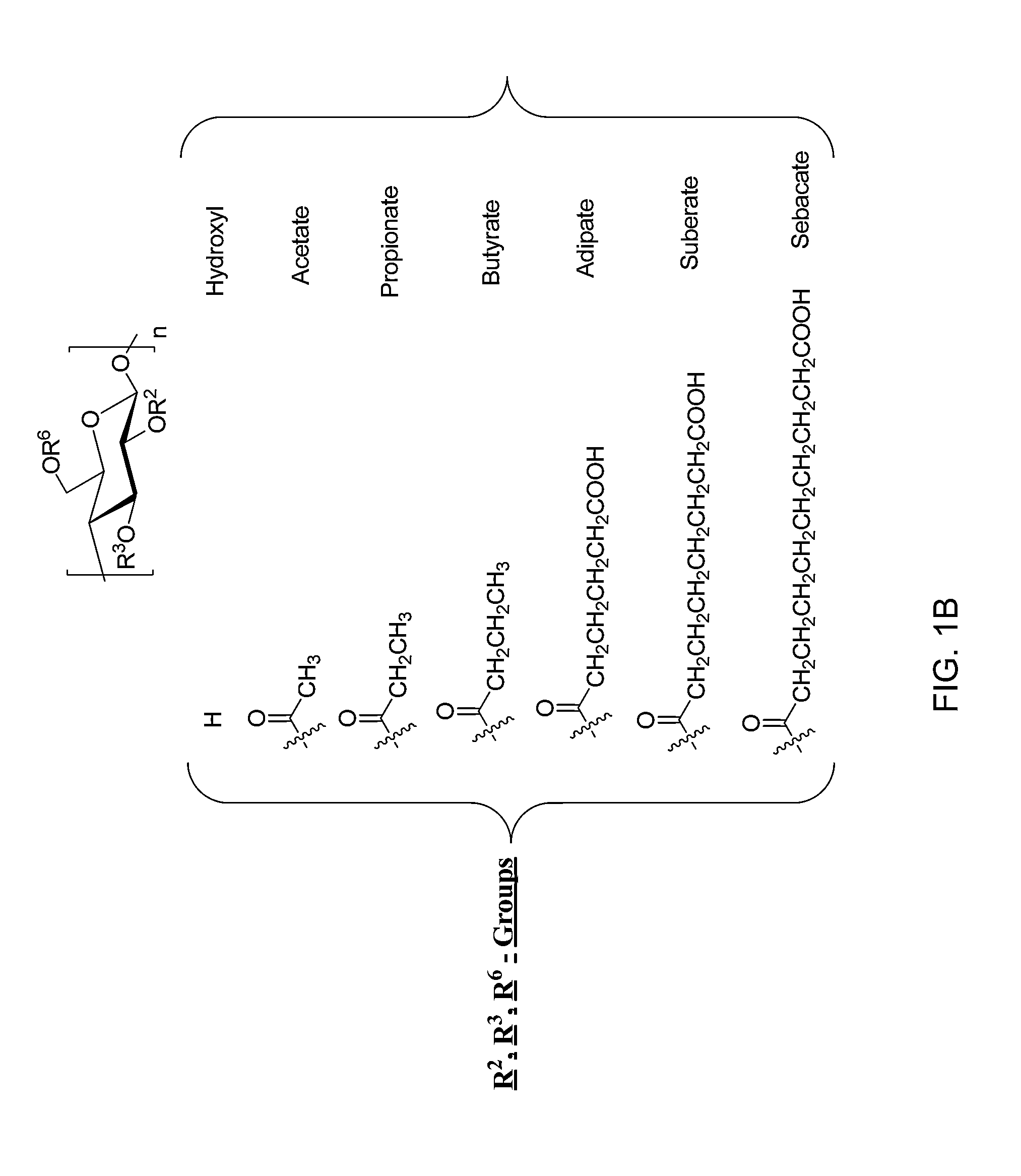
Provided are cellulose esters useful for inhibiting solution crystallization of drugs. Specific polymers include cellulose esters of formula I:wherein n of the ω-carboxyalkanoyl group,is 3, 4, 6, or 8 to provide a ω-carboxyalkanoyl group chosen from succinoyl, glutaroyl, adipoyl, sebacyl, and suberyl groups; and wherein R is chosen from: a hydrogen atom; and an alkanoyl group chosen from acetyl, propionyl, butyryl, valeroyl, hexanoyl, nonanoyl, decanoyl, lauroyl, palmitoyl, and stearoyl groups; wherein there is a total degree of substitution of the alkanoyl group and the ω-carboxyalkanoyl group of at least 2.0; and wherein the polymer comprises m repeating units where n=1 to 1,000,000, or 10 to 100,000, or 100 to 1,000, such as 1 to 6,000. Embodiments further include compositions comprising cellulose esters and poorly water-soluble drugs, which compositions exhibit greater solubility and stability in solution as compared to the drugs alone.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
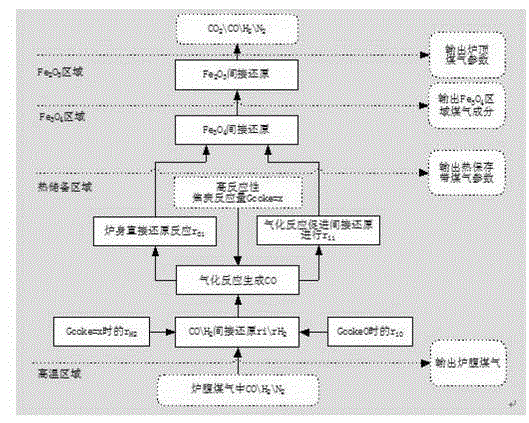
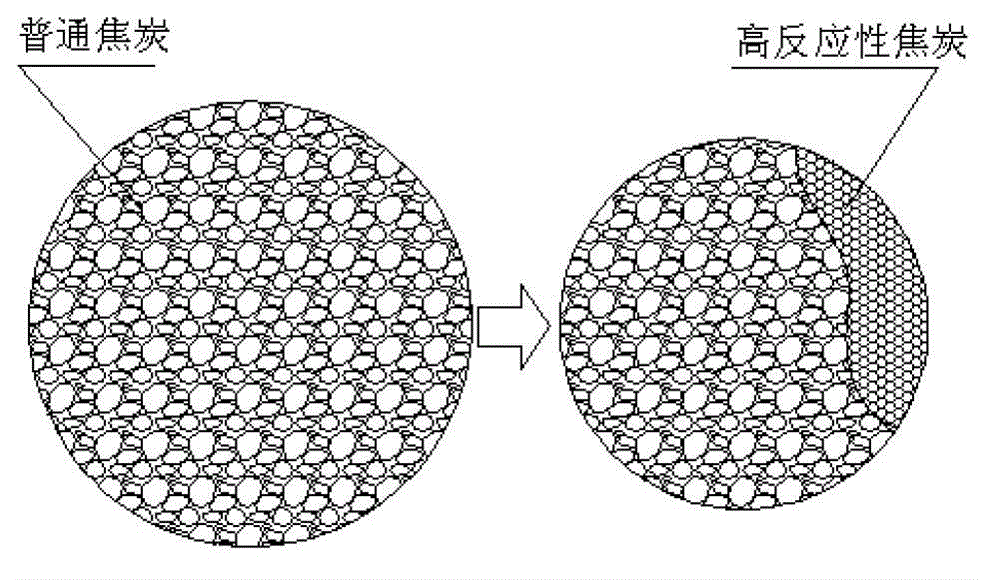
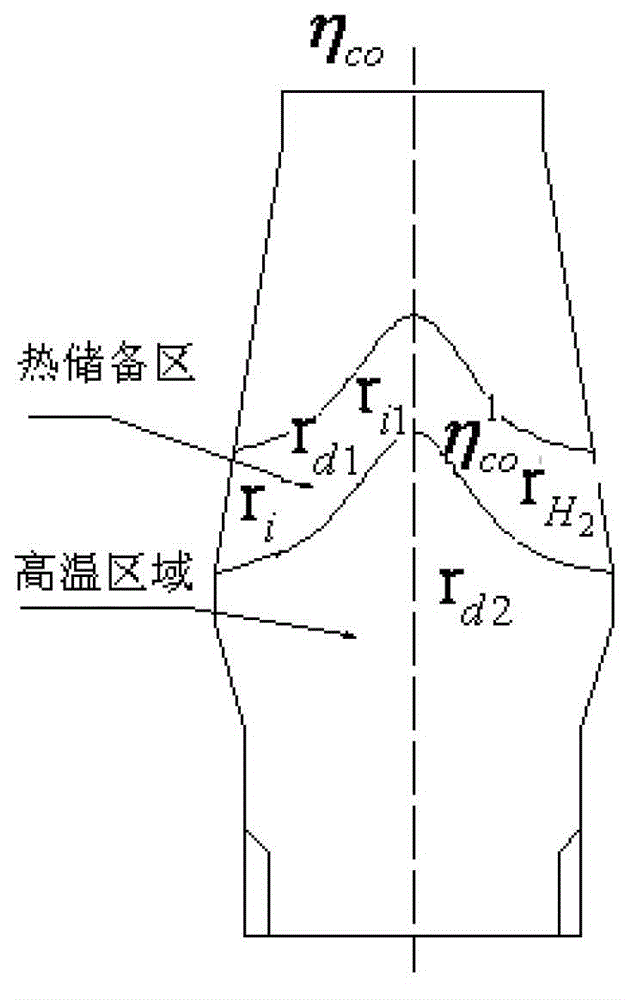
Method for computing degree of direct reduction and gas utilization rate of blast furnace under condition of high-reactivity coke
InactiveCN102876823ABlast furnace detailsSpecial data processing applicationsMetallurgical cokeCalculation methods
The invention belongs to the field of blast furnace iron making, and relates to a method for computing the gas utilization efficiency of a blast furnace under the condition that high-reactivity coke is added into the blast furnace. The method further can be used for respectively computing degrees of direct reduction and degrees of indirect reaction of a high-temperature region and a heat storage region of the blast furnace under the condition that the high-reactivity coke is added into the blast furnace. The total degree of direct reduction of the blast furnace is r<d>, and the gas utilization rate of the blast furnace is eta<co>. By the method, the degree of direct reduction of the blast furnace for smelting and the gas utilization of the blast furnace can be accurately computed under raw material conditions, production of the blast furnace can be guided, and the method is also applicable to the traditional blast furnace under the condition of using metallurgical coke.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
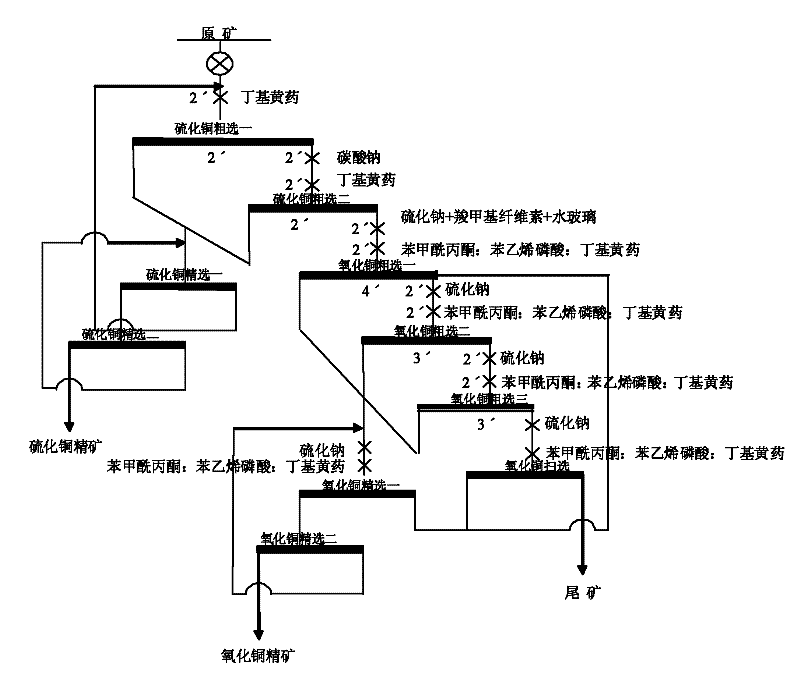
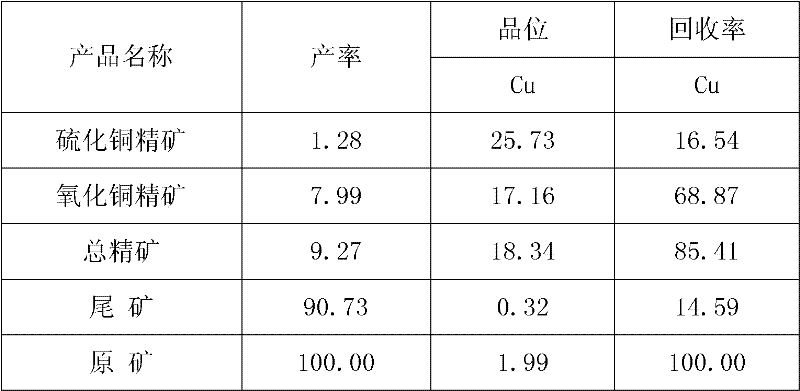
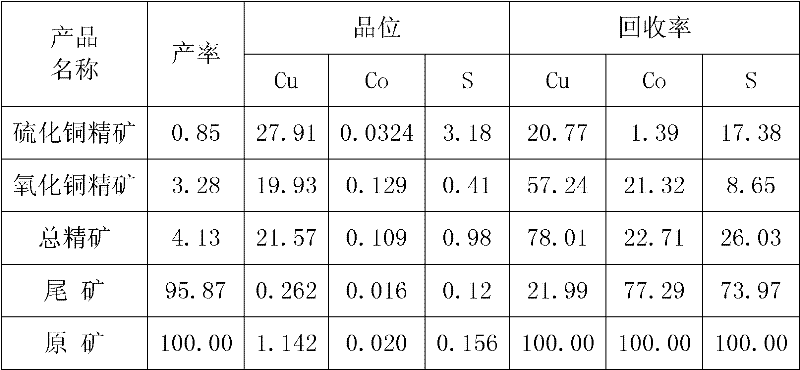
Efficient copper-cobalt oxide ore combination collecting agent and copper oxide ore beneficiation method
The invention discloses an efficient copper-cobalt oxide ore combination collecting agent and a copper oxide ore beneficiation method. The combination collecting agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 50-120 parts of benzoyl acetone, 150-360 parts of phosphoric acid styrene and 150-360 parts of butyl xanthate. The beneficiation method has the following steps: classifying theraw ore in advance, thus products with the total degree of fineness less than 0.074mm take up 65-75% finally; carrying out floatation on products together, carrying out floatation on sulfide ore firstly, carrying out floatation on ore oxide then; adding a regulating agent and an inhibiting agent for size mixing in advance, thus the ore pump concentration is 20-25% under the condition of alkalescency; and then adding the combination collecting agent, and carrying out floatation after stirring for two minutes, thus copper oxide concentrate products are obtained. The combination collecting agentand the method have the characteristics of good selectivity, less medicament dosage and high recovery rate.
Owner:HUNAN HUAXIONG NEW MATERIALS
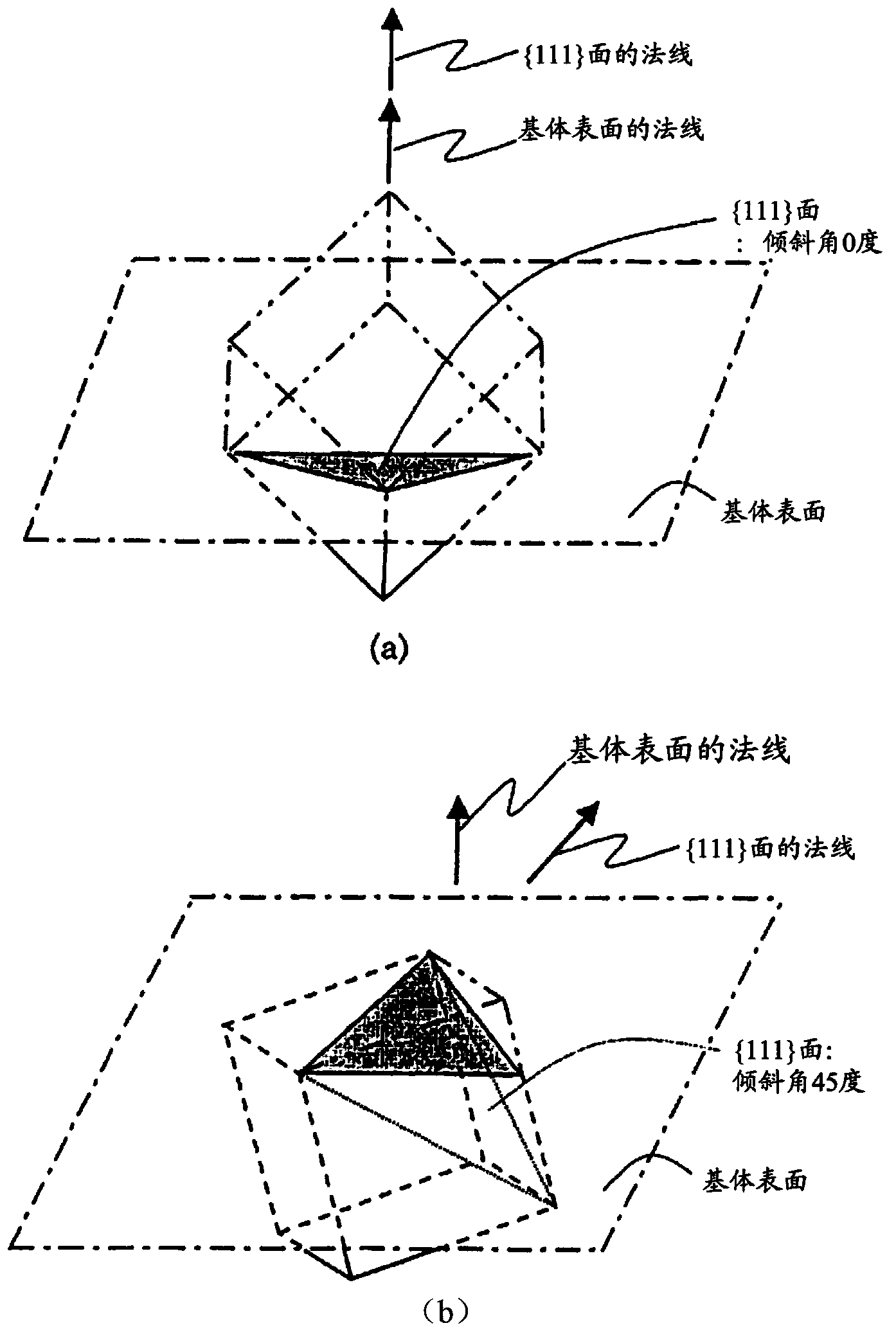
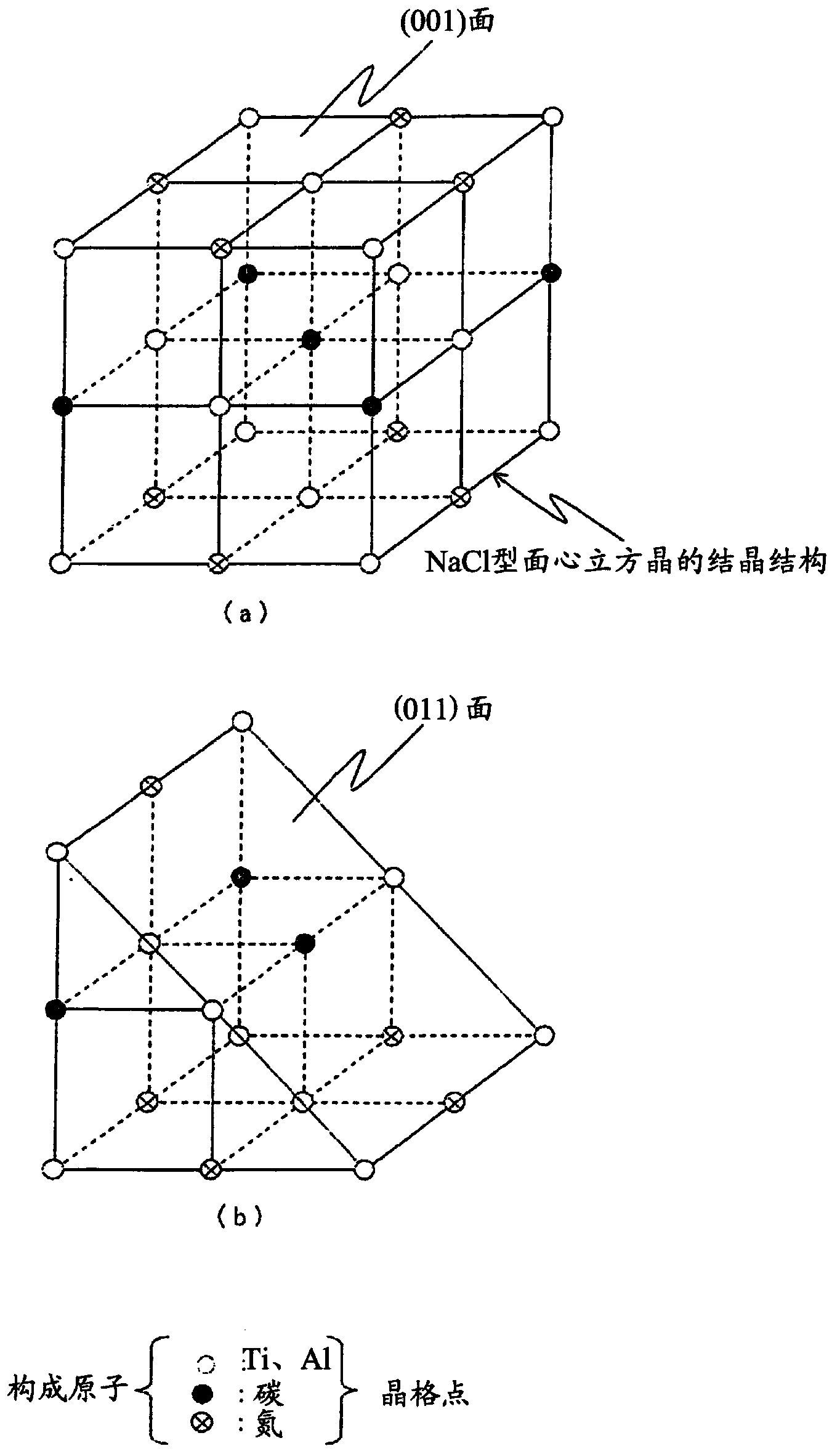
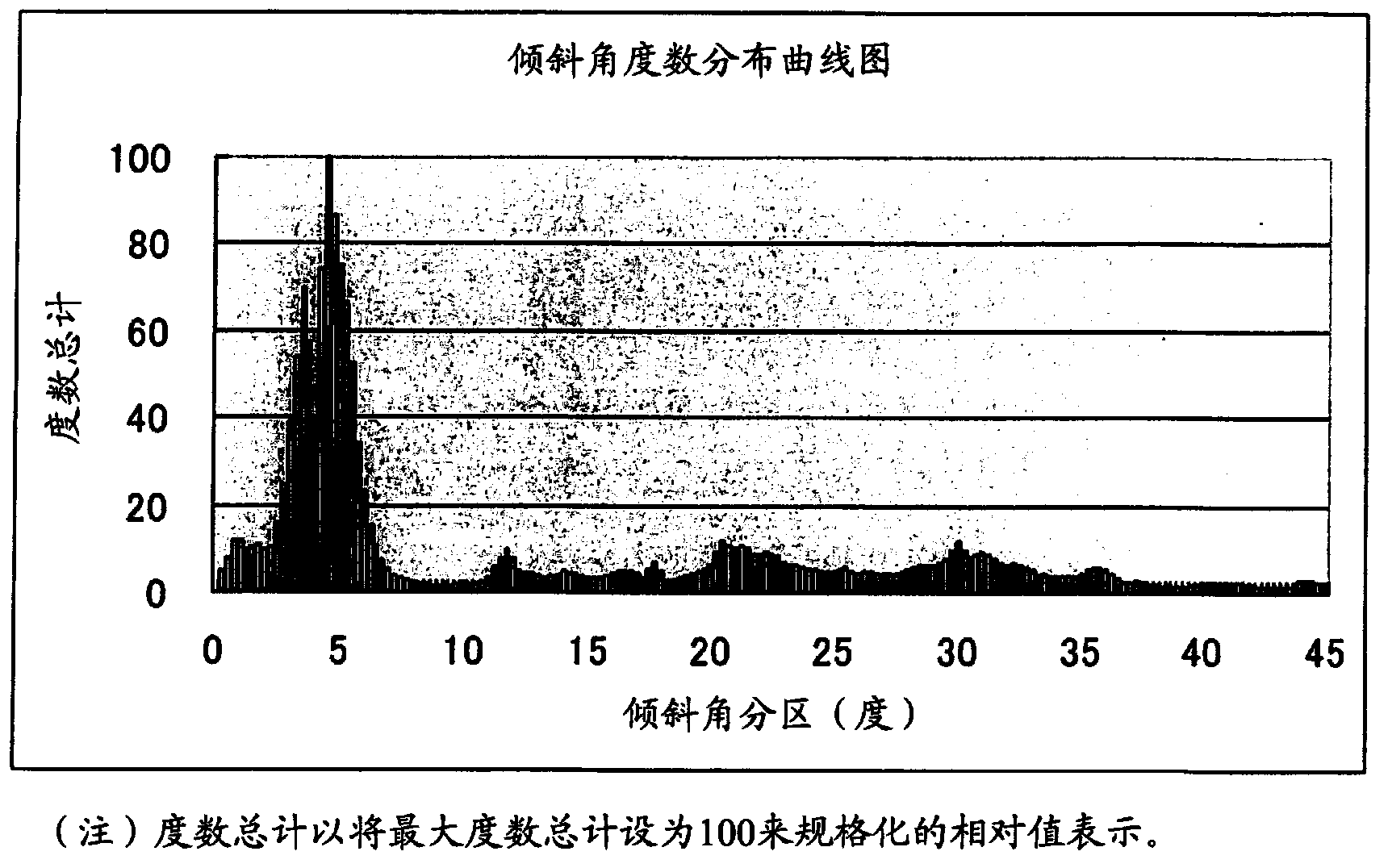
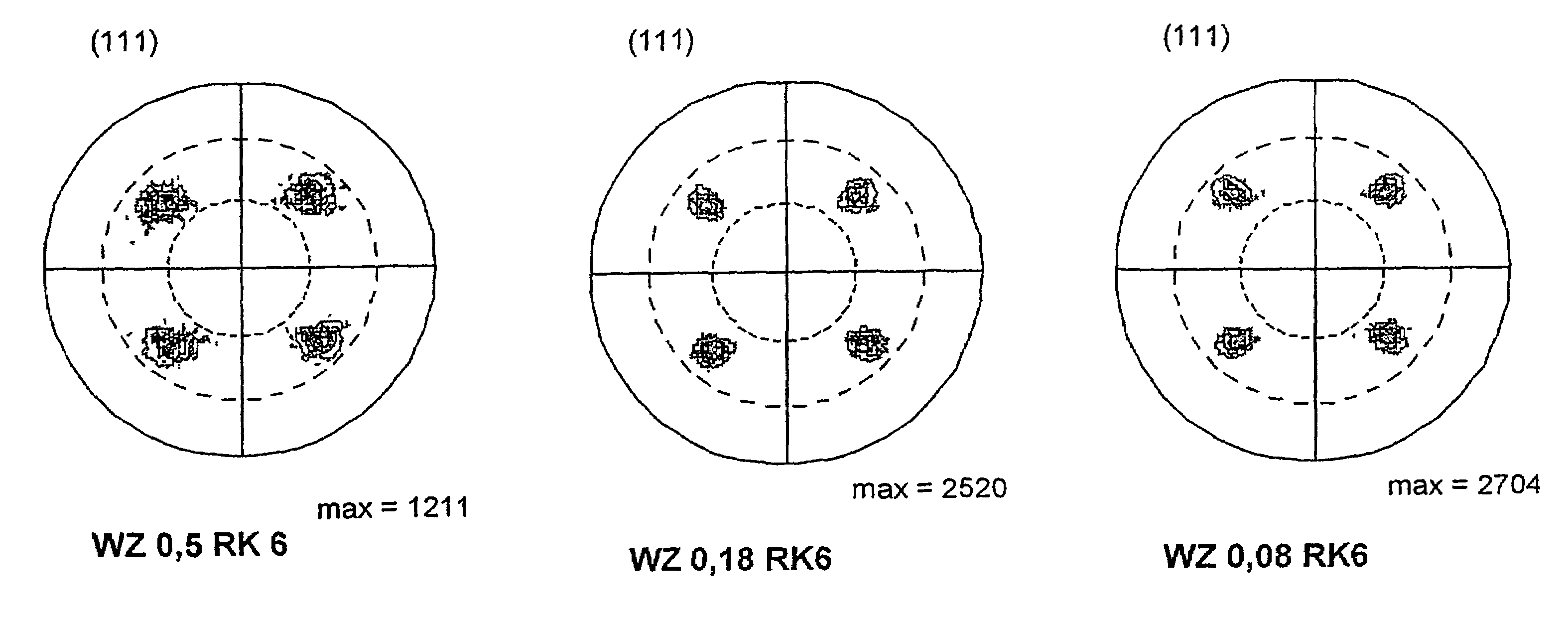
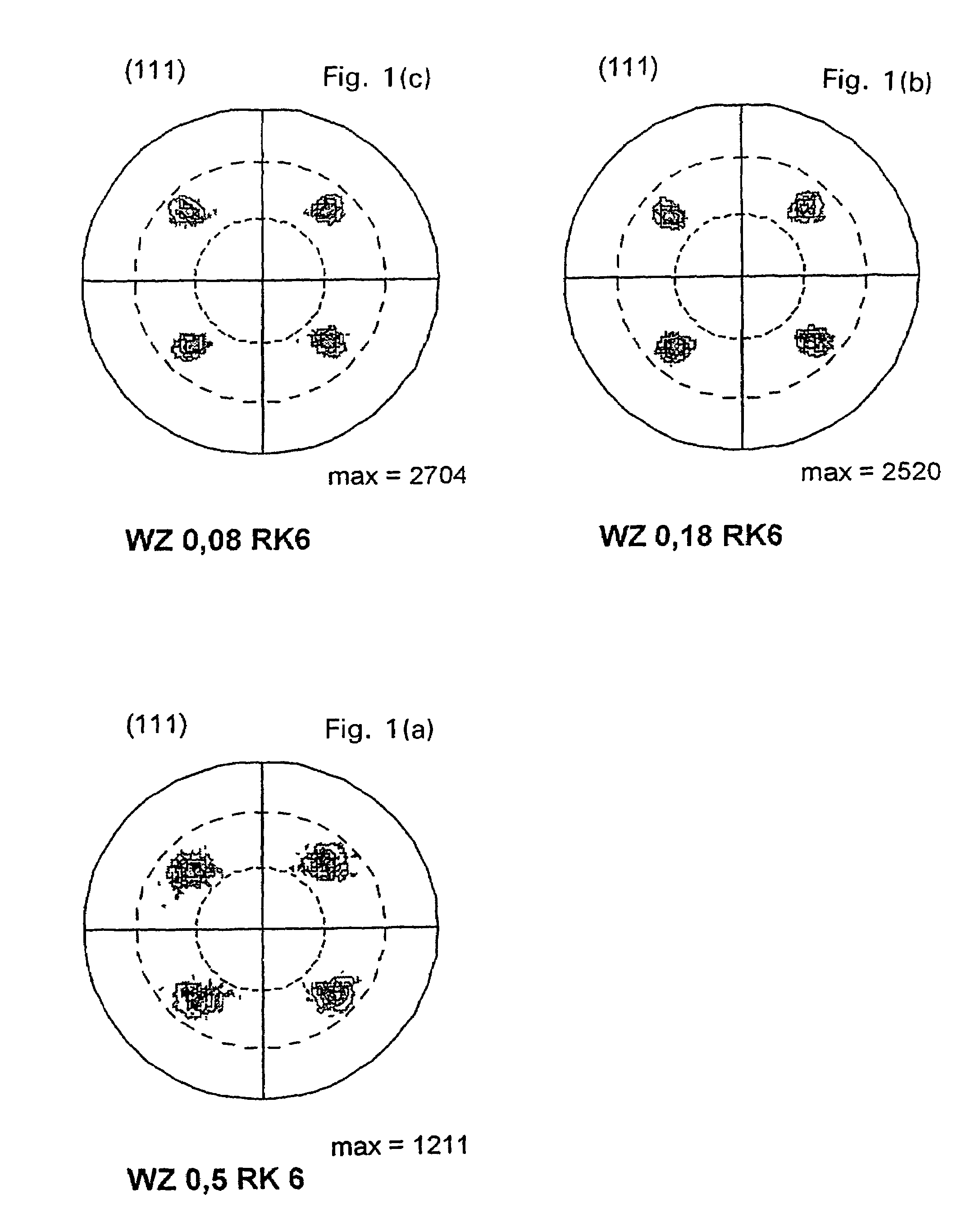
Surface coating cutting tool
ActiveCN103572250ASuppresses chippingSuppression defectChemical vapor deposition coatingCrystal structureChemical vapor deposition
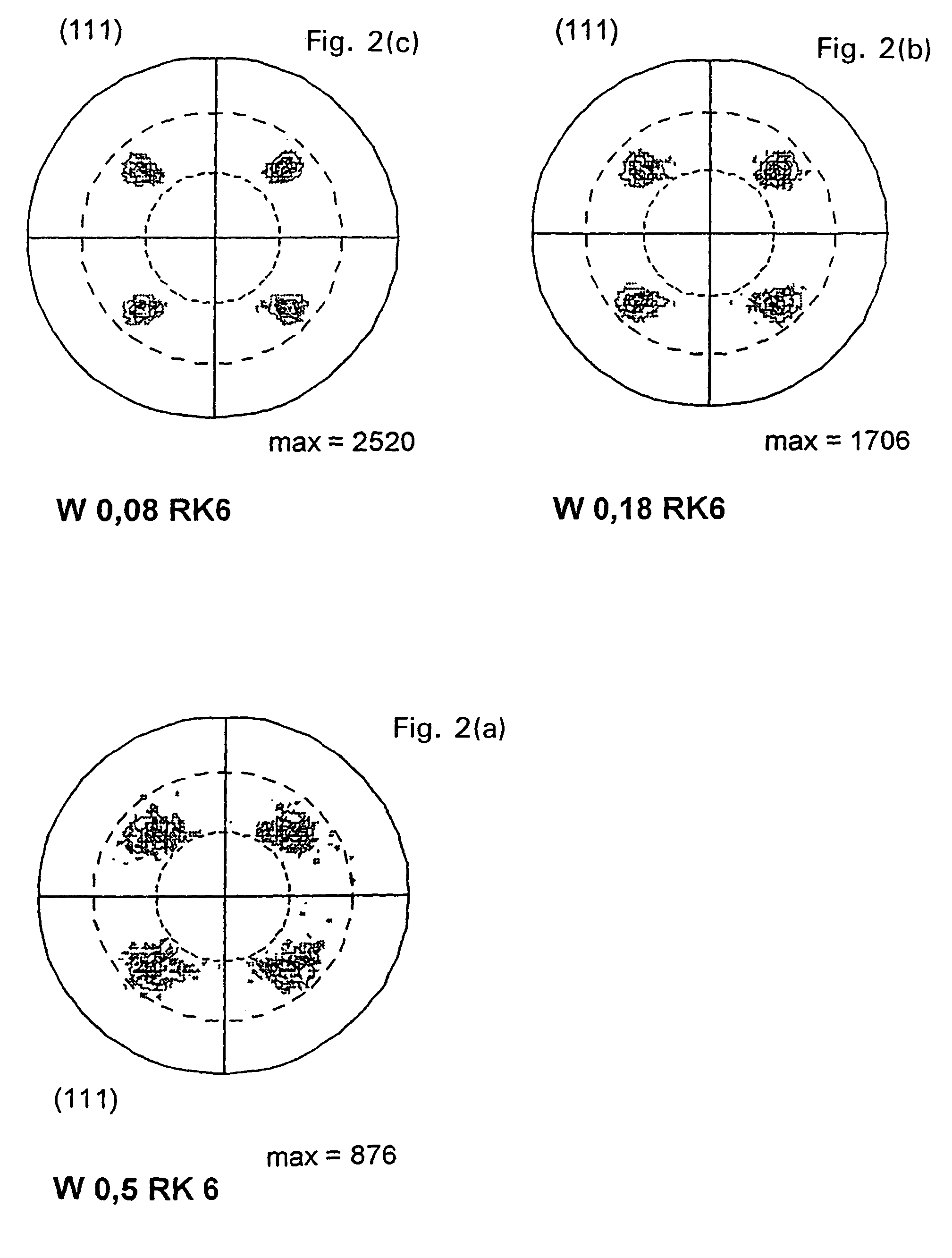
The present invention provides a surface coating cutting tool with a hard coating layer, wherein the hard coating layer plays an excellent flaking-proof role in the high-speed intermittent cutting machining operation on alloy steel materials and the like. According to the technical scheme of the surface coating cutting tool, the surface of a substrate is coated with a hard coating layer which is a (Ti1-XAlX) (CYN1-Y) layer of a cubic crystal structure and evaporated through the chemical vapor deposition process with Al(CH3)3 as one component of reaction gases, wherein the atomic ratios of X and Y are as follows: 0.55 <= X <= 0.95, and 0.0005 <= Y <= 0.005. In the hard coating layer, among the inclined angle degree distribution of the inclined angles formed by relative relationship between the normal of the {111} surface of a measured crystal particle and the normal direction of the surface of the substrate, degrees in the range of 2-12 is more than 45% of the total degree, and moreover, in the shared lattice point distribution curve graph of the component atom of the hard coating layer, the distribution proportion of Sigma 3 at the side of the surface of the substrate is less than 20%, on the other hand, Sigma 3 at the side of the surface of the coating layer has the highest peak valve and the distribution proportion of Sigma 3 is more than 50%.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Cellulose diacetate for retardation film
ActiveCN102597824ATaking into account the visibilityConsider filterabilityPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolymer scienceOptical property
Disclosed is a cellulose acetate that enables a cellulose acetate optical film, which expresses optical properties when stretched, to achieve excellent stretchability and excellent optical properties after being stretched. Specifically disclosed is a cellulose diacetate for a retardation film, which has a total degree of substitution of acetyl groups of 2.27-2.56. The cellulose diacetate for a retardation film is characterized by having a degree of dispersion (Mw / Mn) of more than 3.0 but 7.5 or less, a degree of substitution at the 6-position of 0.65-0.85, a half width of the distribution of the degree of acetylation of 1.0-2.3 and a viscosity average degree of polymerization of 182-213 (inclusive). It is preferable for the cellulose diacetate for a retardation film to have a 6% viscosity of 120-230 mPas and a weight average molecular weight (Mw) of 205,000-235,000 (inclusive).
Owner:DAICEL CORP
Golf ball resin composition and golf ball
ActiveUS20140031145A1Increase flexibilityEnhance resilienceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarboxylic acidCopolymer
The invention provides a resin composition for golf balls having excellent resilience, flexibility and fluidity, and golf balls having excellent resilience and shot feel. The resin composition comprises: (A) at least one selected from the group consisting of (a-1) a binary copolymer of an olefin and a C3-8 α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid, (a-2) a metal ion-neutralized product of a binary copolymer of an olefin and a C3-8 α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid, (a-3) a ternary copolymer of an olefin, a C3-8 α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid, and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester, and (a-4) a metal ion-neutralized product of a ternary copolymer of an olefin, a C3-8 α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid, and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester; (B) a compound containing a hydrocarbon chain, a cationic moiety, and an anionic moiety in its molecule; and (C) a nonionic surfactant, wherein a total degree of neutralization expressed by the following equation is 50-300 mol %:Totaldegreeofneutralization(%)=∑(numberofmolesofcationcomponentinresincompositionvalenceofcationcomponent×)∑(numberofmolesofanioncomponentinresincompositionvalenceofanioncomponent×)×100
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
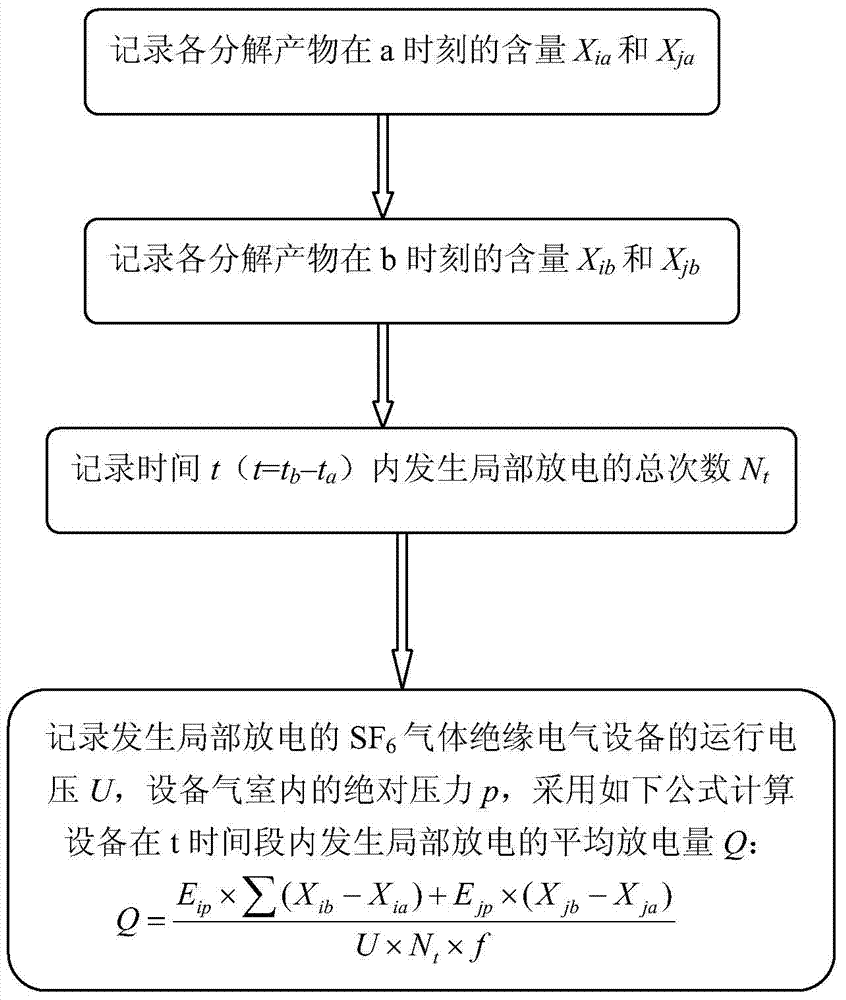
Method for calculating running electrical equipment partial discharge quantity through SF6 decomposition product content
ActiveCN104749506ASolve the problem that the partial discharge in the equipment cannot be quantitatively detectedTesting dielectric strengthDecompositionSulfur hexafluoride
The invention provides a method for calculating running electric equipment partial discharge quantity through SF6 decomposition product content. The method includes: S1, recording the content of decomposition products at the time of a; S2, recording the content of the decomposition products at the time of b; S3, recording total degree Nt of partial discharge occurring in the time of t; S4, calculating average discharge quantity Q of the partial discharge, occurring in the time of t, of equipment. Partial discharge level in the equipment is calculated through SF6 gas decomposition product content, the problem that the partial discharge quantity in the equipment cannot be quantitatively detected when the partial discharge occurs under the running condition of existing sulfur hexafluoride gas-insulated equipment is solved, and very important data support can be provided for the running state or fault degree evaluation of the sulfur hexafluoride gas-insulated equipment.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Thermosetting polyurethane elastomer composition, polyurethane elastomer and method for its production
Provided is a polyurethane elastomer with a low hardness, a high strength and a high elongation. The polyurethane elastomer is obtained by reacting and curing an isocyanate-terminated prepolymer (i) obtained by reacting a polyoxyalkylene polyol having an average number of hydroxyl groups of over 2, a total degree of unsaturation of less than 0.05 meq / g and a number-average molecular weight of from 4000 to 20000, with a polyisocyanate compound, and a curing agent (ii) containing as curing components a polyoxytetramethylene polyol (a) and a chain extender (b) having two active-hydrogen-containing groups and having a number-average molecular weight of not more than 500.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Composition for polyurethane foam, polyurethane foam obtained from the composition, and use thereof
A composition for polyurethane foams which comprises: one or more polyols and / or one or more polymer-containing polyols which are polyols containing, dispersed therein, fine polymer particles obtained by polymerizing a compound having an unsaturated bond; water; a catalyst; a foam stabilizer; and a polyisocyanate. The polyols comprise (A) a plant-derived polyol produced from a raw material obtained from a plant and (B) a low-monool-content polyol having a total degree of unsaturation of 0.050 meq / g or lower. Also provided is a polyurethane foam obtained by foaming the composition for polyurethane foams. The polyurethane foam contributes to a reduction in environmental burden and gives a cushioning material having a well-balanced combination of moderate hardness, moderate resilience, and excellent durability.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM & SKC POLYURETHANES INC
Illumination system for a microlithography projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20060126049A1Small degreePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLighting systemPlane of incidence
An illumination system for a microlithography projection exposure apparatus is designed for illuminating an illumination field with an illumination radiation with a predeterminable degree of coherence σ, it being possible to adjust the degree of coherence within a degree of coherence range extending into the range of very small degrees of coherence of significantly less than σ=0.2. The illumination system may have a first optical system for generating a predeterminable light distribution in an entrance plane of a light mixing device, and also a light mixing device for homogenizing the impinging radiation. The first optical system and the light mixing device can in each case be changed over between a plurality of configurations corresponding to different degree of coherence ranges. The degree of coherence ranges overlap and are dimensioned such that the resulting total degree of coherence range is larger than the individual degree of coherence ranges.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
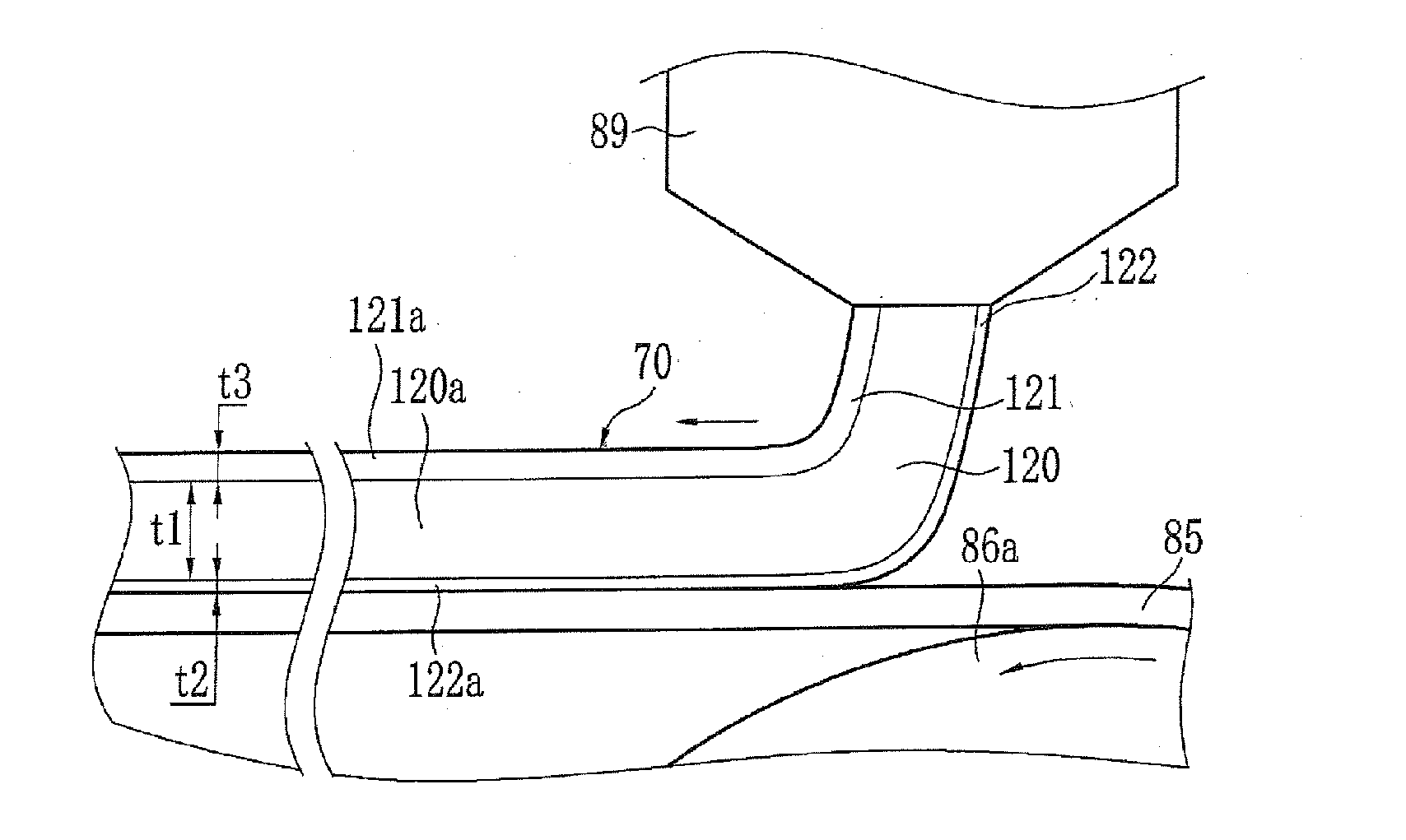
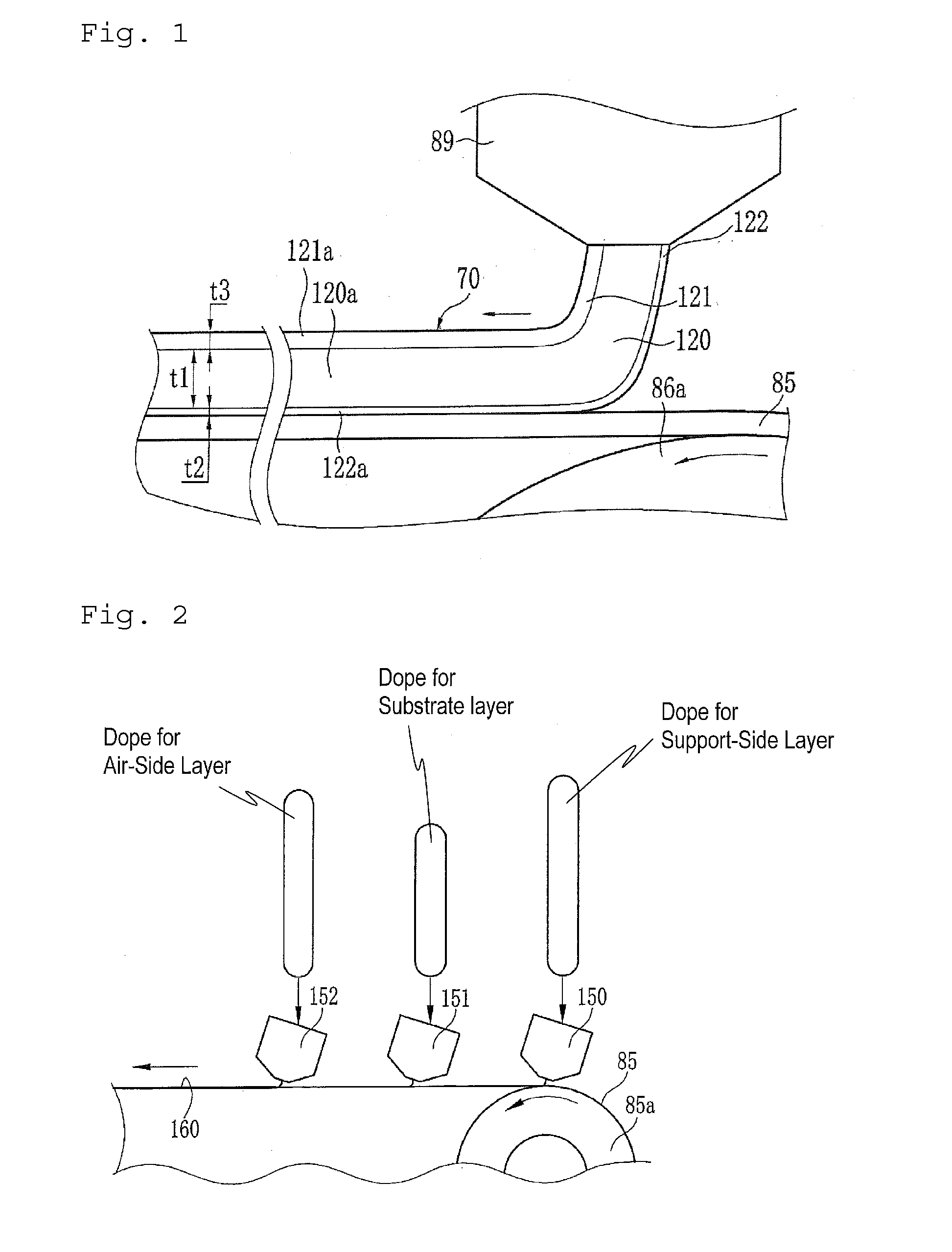
Cellulose acylate laminate film, method for producing cellulose acylate laminate film, polarizer and liquid crystal display device
InactiveCN101875252ALow hazeImproved wavelength dispersion performanceSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCelluloseLiquid-crystal display
A cellulose acylate laminate film, which comprises a low-substitution layer comprising a non-phosphate compound and a cellulose acylate having a total degree of acyl substitution of more than 2.0 and less than 2.7 and a high-substitution layer comprising a cellulose acylate having a total degree of acyl substitution of more than 2.7<Z2, wherein Re at a wavelength of 550 nm is the same as or larger than Re at a wavelength of 440 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Cellulose diacetate for retardation film
ActiveUS20120172585A1Satisfactory stretchabilityImprove filtering effectPolarising elementsAcetic acidPolymer science
To provide a cellulose acetate which gives a cellulose acetate optical film exhibiting optical properties as a result of stretching, in which the film shows excellent stretchability and gives a stretched film having excellent optical properties.Disclosed is a cellulose diacetate for a retardation film, having a total degree of acetyl substitution of from 2.27 to 2.56, in which the cellulose diacetate has a polydispersity Mw / Mn of more than 3.0 and 7.5 or less, a degree of substitution at the 6-position of from 0.65 to 0.85, a half height width of acetylation distribution of from 1.0 to 2.3, and a viscosity-average degree of polymerization of 182 or more and 213 or less. The cellulose diacetate for a retardation film preferably has a 6-percent viscosity of from 120 to 230 mPa·s and preferably has a weight-average molecular weight Mw of 205,000 or more and 235,000 or less.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
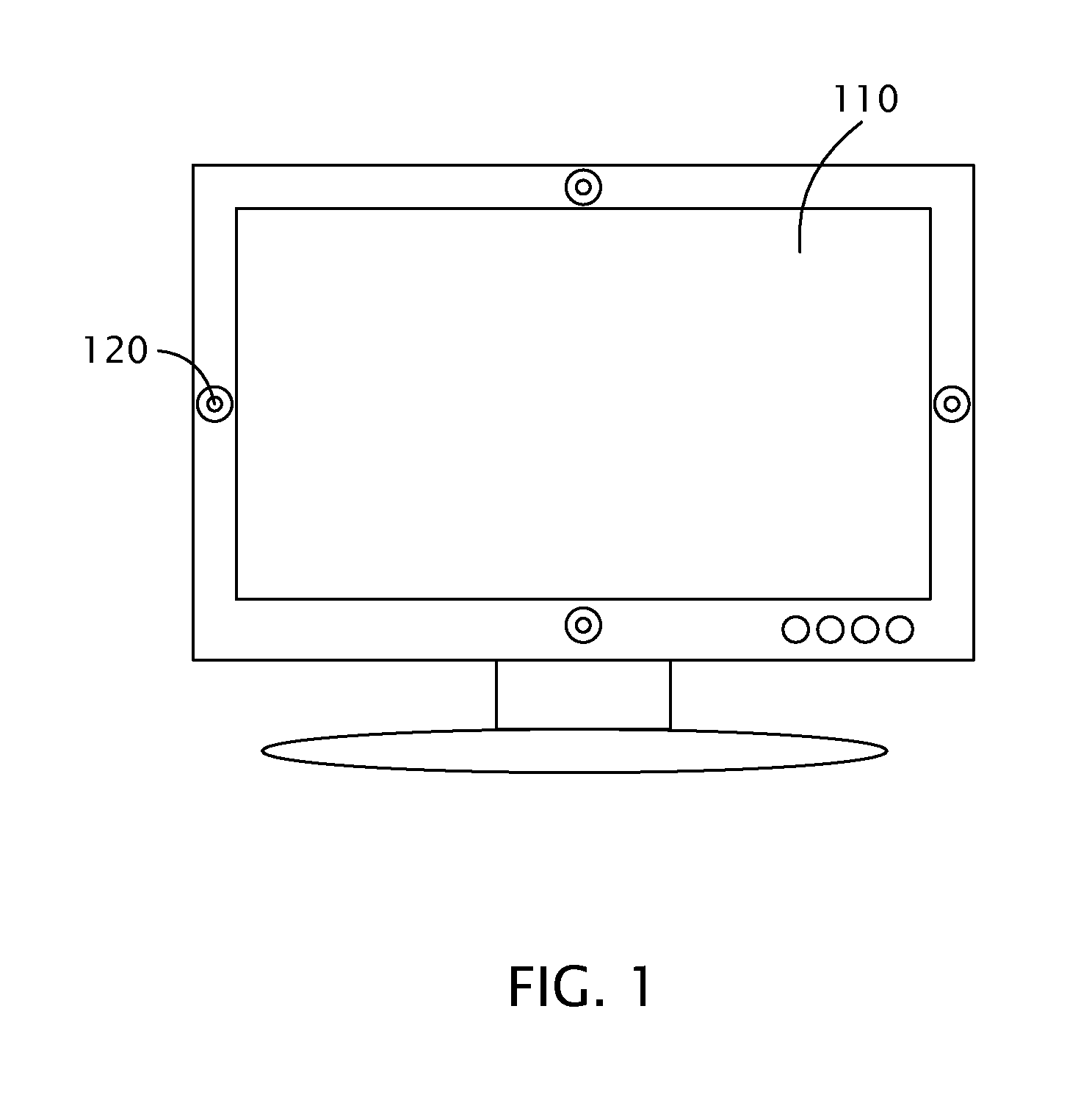
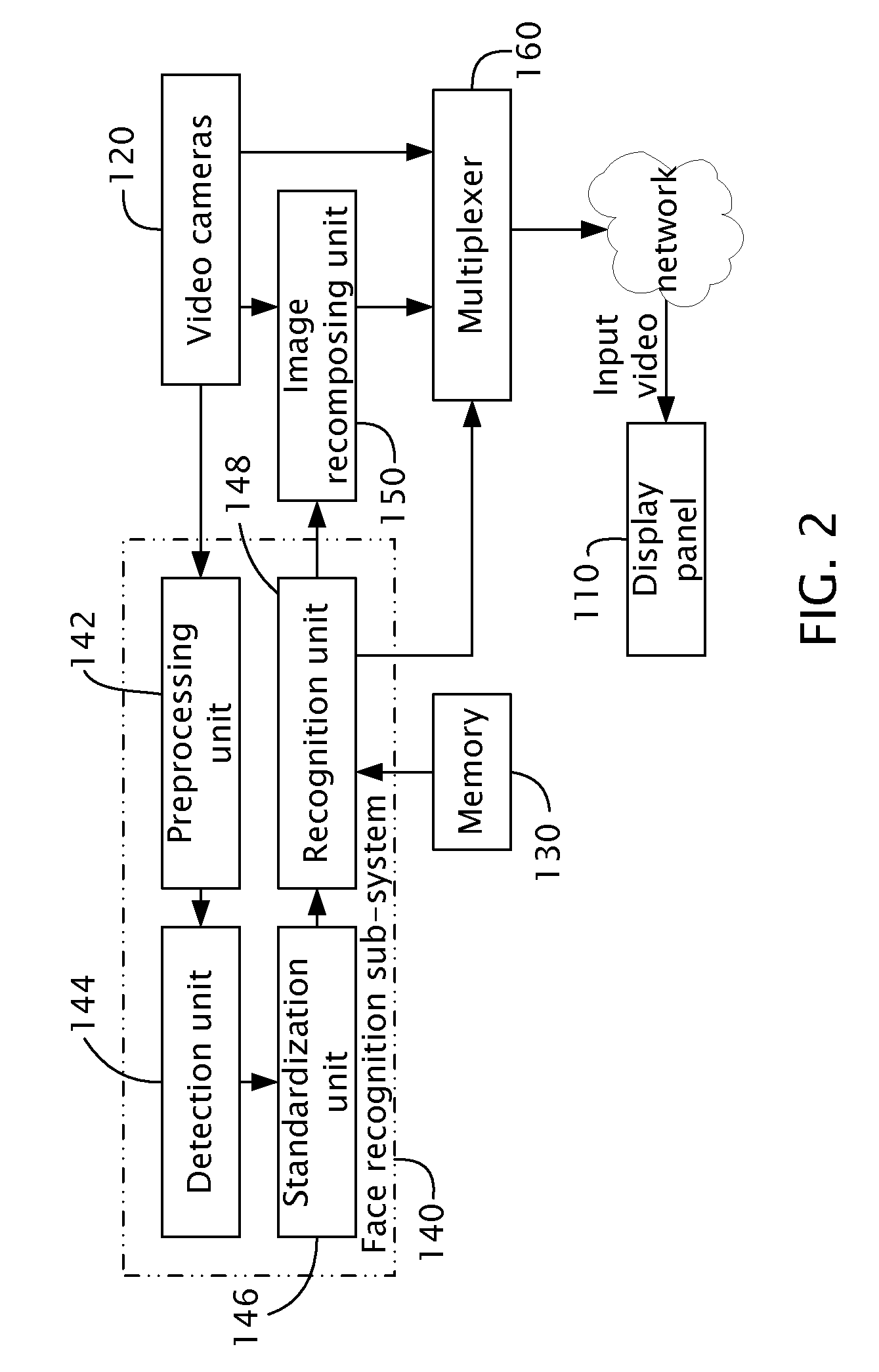
Video instant messaging system and method thereof
InactiveUS20090167840A1High similarityMultiplex communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorComputer graphics (images)
A video instant messaging method includes: picking up information in front of a display panel from different directions to capture a number of facial images; extracting a number of groups of characteristic vectors from the facial images respectively; measuring a number of degrees of similarity each associated with a extracted characteristic vector using a group of reference characteristic vector; calculating a number of total degrees of similarity each associated with a facial image using the measured degrees of similarity; and transmitting the facial image having the highest total degree of similarity.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method for producing metallic strips
InactiveUS7285174B2Reduce thicknessSave energySuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentCopperTotal degree
A method for producing metallic strips having a high-grade cube texture based on nickel, copper, aluminum, silver or alloys of these metals including austenitic iron-nickel alloys makes it possible to obtain, during a subsequent annealing process and with lower total degrees of forming, a recrystallization cube layer of a quality equal to that of one obtained using customary roll forming and produces a better quality cube texture with comparable total degrees of forming. To this end, a forming method is provided during which the materials are formed by cold drawing before their recrystallization annealing thereby rendering them high-grade. The tools used for this include: a) non-driven roll devices with an axially parallel flat pair of rolls or turk's head arrangements with two pairs of rolls or; b) fixed drawing jaws that are slanted toward one another. The strips produced according to the invention can be used, for example, as a coating support for producing strip-shaped high-temperature superconductors.
Owner:INST FUER FESTKOERPER & WERKSTOFFORSCHUNG DRESDEN EV
Method for establishing egg shaped digestion tank simplified model
InactiveCN101211380AReduce the number of degrees of freedomFully functionalSustainable biological treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsPolygonal lineInteraction problem
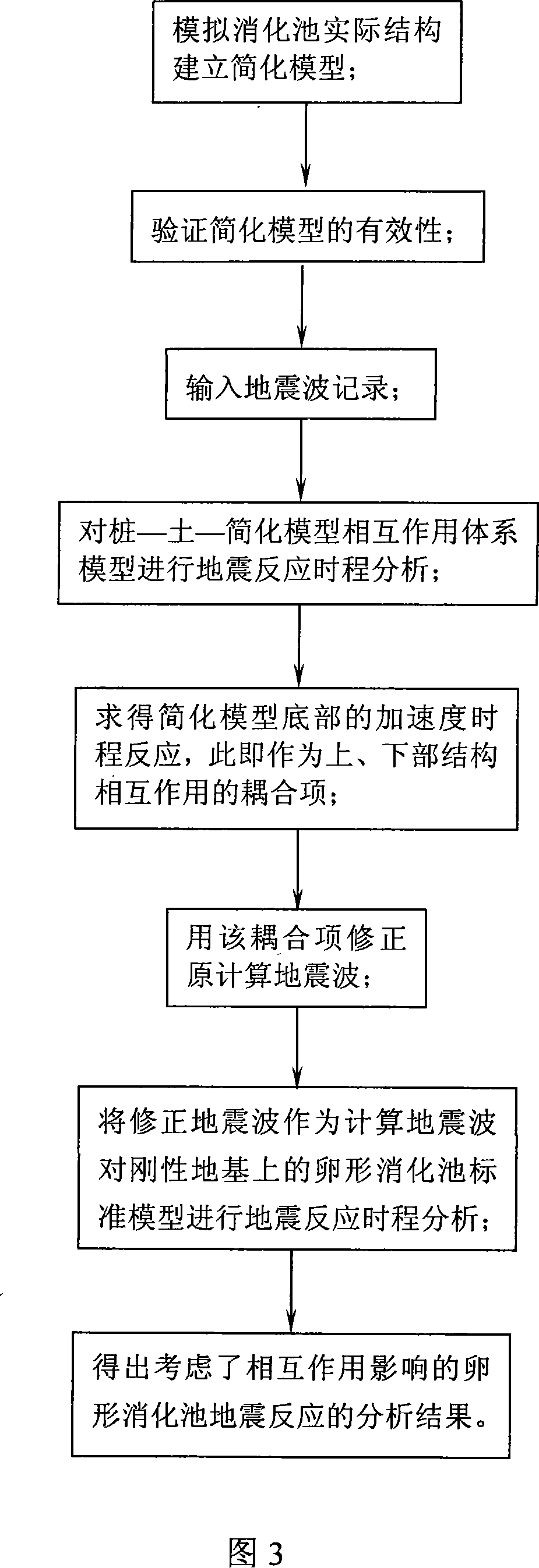
The invention discloses a method for establishing a simplified module for egg-shaped digestion tanks; the method uses a branched modalities plus two-step analysis method, so as to establish simplified the module based on the standard module of an egg-shaped digestion tank; the steps are as follows: Establish a simplified module for the egg-shaped digestion tank body: Separate one part of the pile cap in the overall arc direction of the tank wall, so as to form the extension part of the tank wall housing and, therefore, create an intact hollow egg-shaped housing; establish the simplified module for the pile cap of the egg-shaped digestion tank: Simplify the step folding line of the pile cap into straight lines, and simplify the slope on both sides of the pile cap roof surface into a horizontal position, so as to form a V-shaped profile with a straight edge; verify the validity of the simplified module. The simplified modeling method of the invention can not only considerably reduce the total degree of freedom of the structure and improve the operation speed, but also sufficiently expand functions of all kinds of programs themselves, so as to bring forth uttermost convenience for solving complicated interaction problems in actual engineering design with prior programs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
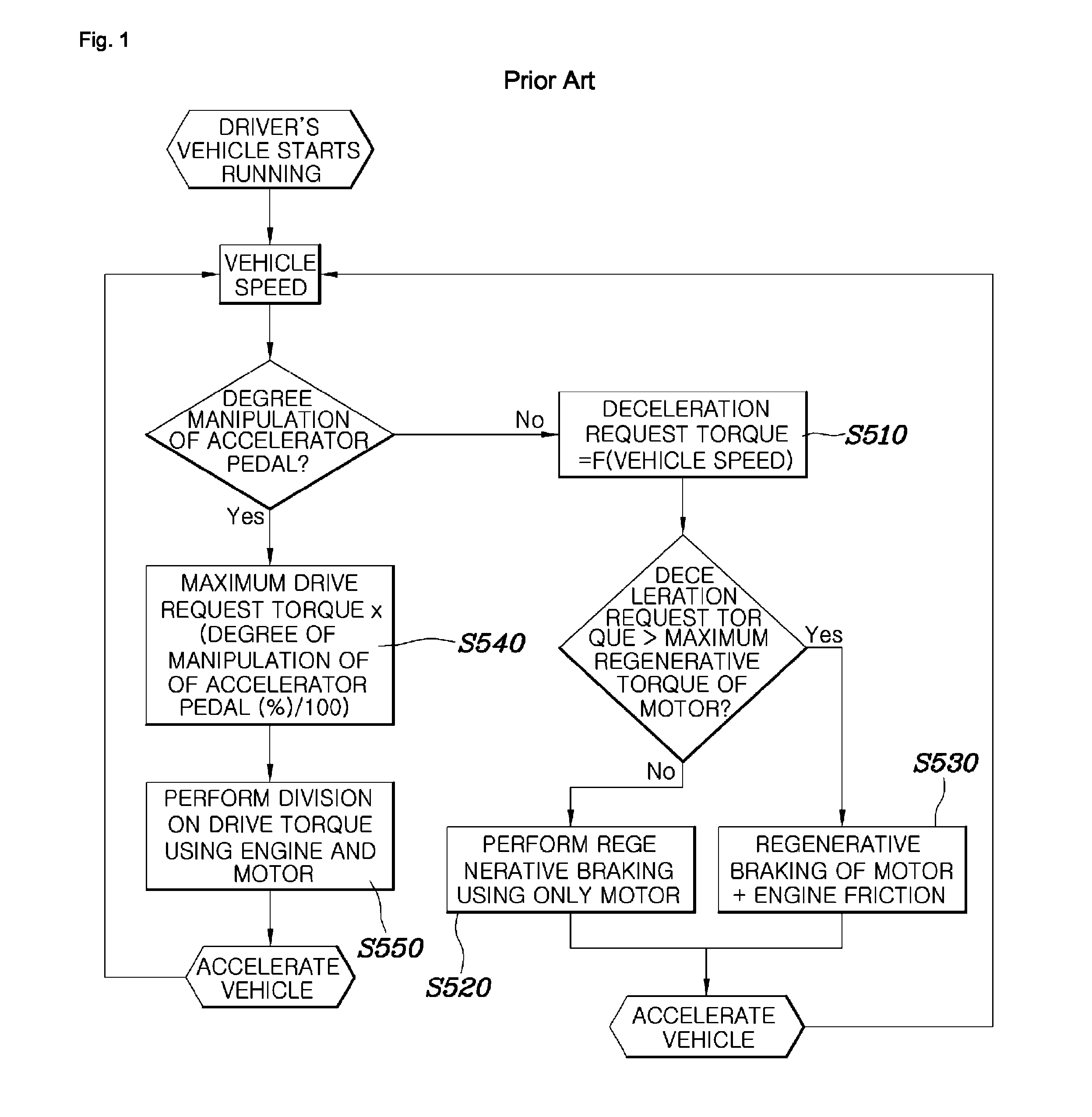
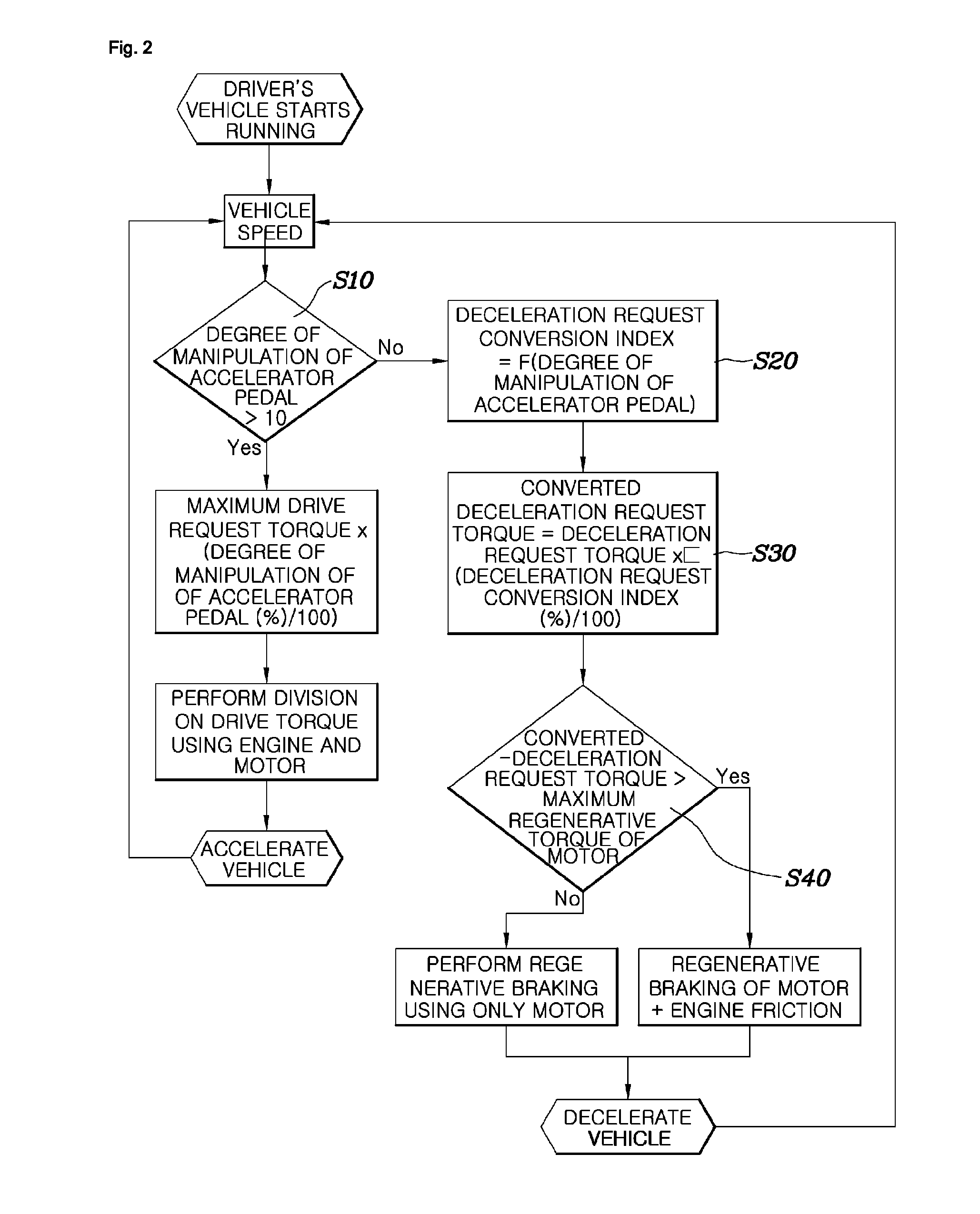
System and method for controlling coasting of hybrid vehicle equipped with automated manual transmission
ActiveUS8706379B2Amount of regenerative braking of a vehicle is appropriately variedPrevent durabilityHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsRegenerative brakeExecution control
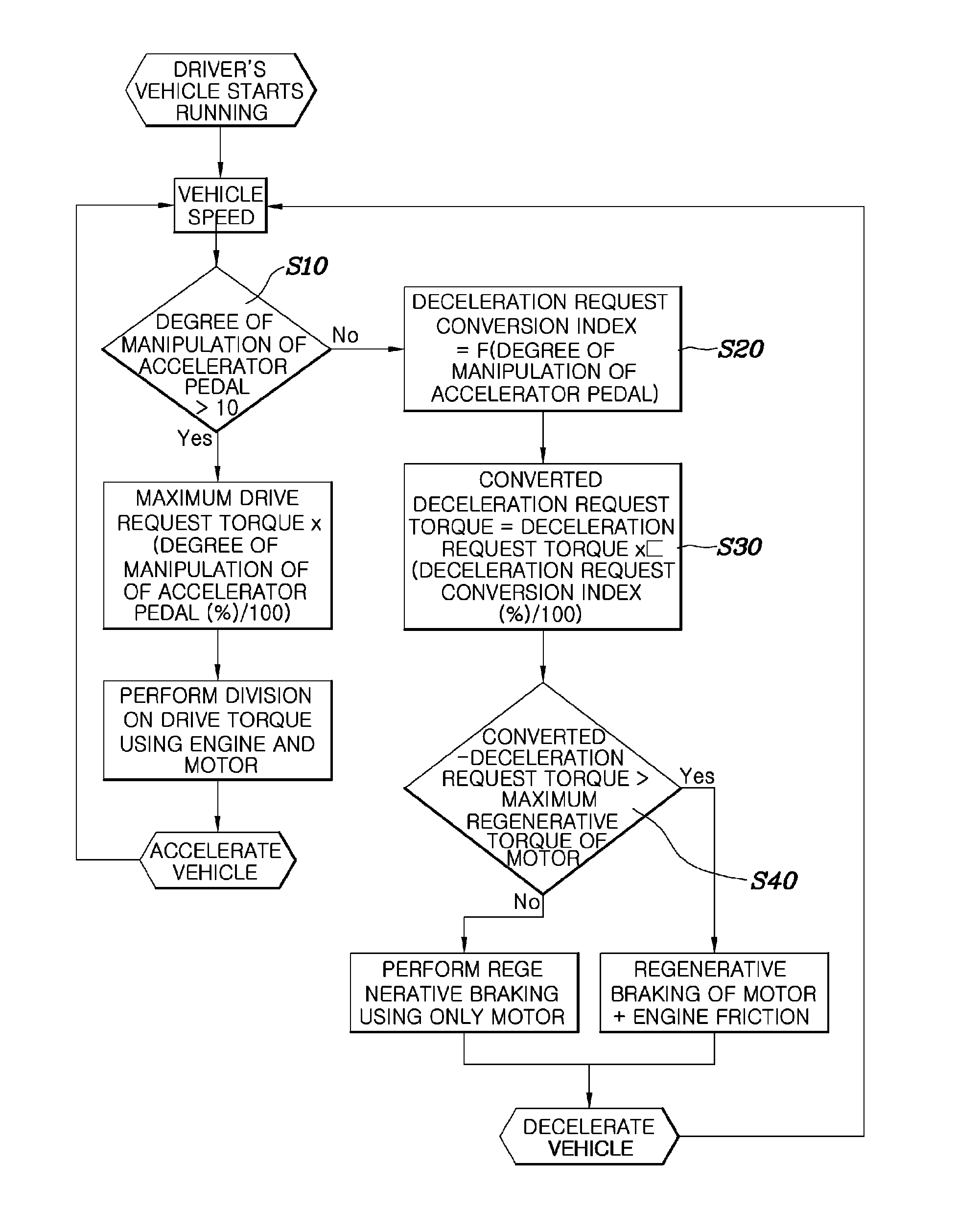
A technique for controlling coasting of a hybrid vehicle equipped with an Automated Manual Transmission (AMT) is disclosed herein. First, the amount of regenerative braking is varied based on the degree of manipulation of an accelerator pedal within the predetermined control range of a total degree of manipulation of the accelerator pedal from when the accelerator pedal is not being manipulated. The amount of regenerative braking decreases as the degree of manipulation of the accelerator pedal increases. The control range is used to perform control in such a way as to vary the amount of regenerative braking according to the amount of manipulation of the accelerator pedal. Further, the control range is set to within a range of initial 5 to 20% of the total degree of manipulation of the accelerator pedal.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Device for comminuting dry ice granules, and dry ice dispensing arrangement having such a device
The invention relates to a device for comminuting dry ice granules, comprising a housing having a flow channel for dry ice granules which can be applied, by means of compressed gas, to a surface to be cleaned, and also comprising a first comminution member for comminuting the dry ice granules which are to be dispensed. In order to provide a device of this kind with which different degrees of comminution of dry ice granules can be achieved in a simple manner, it is proposed according to the invention that the device has at least one second comminution member which can be disposed in the housing in a position in which a total degree of comminution, which is greater than the individual degree of comminution which can be achieved solely by the first comminution member, can be achieved in combination with the first comminution member. A dry ice dispensing arrangement for dispensing a mixture of compressed gas and dry ice granules is also proposed, having a device of the above kind.
Owner:ALFRED KARCHER GMBH & CO KG
High-density elastic polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) fabric and method for producing same
InactiveCN101748548AHeating/cooling textile fabricsWoven fabricsPolytetramethylene terephthalateHigh density
The invention discloses high-density elastic polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) fabric and a method for producing the same. Warp yarn or / and weft yarn for weaving the PBT high-density elastic fabric is / are composite PBT yarn. One part of the composite PBT yarn is S-twisted, and the other part is Z-twisted. The total degree twist of the composite PBT yarn is 0-10T / M. The method for producing the PBT high-density elastic fabric comprises the following steps: producing composite PBT yarn, weaving the composite PBT yarn into fabric and post-processing the fabric. The composite PBT yarn is produced after two parts of original yarn are false twisted in opposite directions with the false twisting process and then are combined and interlaced. The stiff soft thick elastic PBT fabric is produced by processing, weaving and dying the composite PBT yarn.
Owner:TORAY FIBER RES INST(CHINA) CO LTD
Cellulose acylate laminate film and its production method, polarizer and liquid-crystal display device
InactiveUS20130083274A1Excellent peelabilityHigh front contrastCellulosic plastic layered productsPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayCellulose acetate
A cellulose acylate laminate film containing a skin B layer that contains a cellulose acetate satisfying 2.50≦Z2<3.00 (Z2 means a total degree of acyl substitution) and a core layer that is thicker than the skin B layer and contains a cellulose acylate satisfying 2.00<Z1≦2.50 (Z1 means a total degree of acyl substitution), wherein the core layer and the skin B layer contain a retardation-controlling agent having refractive index anisotropy and the difference between the refractive index anisotropy measured on one surface of the film and the refractive index anisotropy measured on the other surface thereof is at most 0.0005.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid absorption fiber
The invention aims to provide a liquid absorption fiber. The fiber comprises a polymer represented by the following structural form shown in the description, wherein R is at least one selected from a group consisting of -NH2, -OCH2CH2OH, -OCH2CH2CH2OH, -OH, -ONa, -OK and -OCa; m, n and p respectively represent the quantity percentages of corresponding repeating units in a polymer molecule, and meet the following relational expression: m+n+p=1, p / (m+n+p)=0.05 to 0.30; when the degree of substitution D is defined to be m / (m+n+p): the total degree of substitution of the fiber Ds is 0.09 to 0.8, and the value of the degree of substitution Do of the polymer at the center point of the cross section of the fiber / the degree of substitution Dx of the polymer on the edge of the cross section of the fiber is 0 to 0.98. By the use of a simple process, the antibacterial performance, the liquid absorption property and the like of the fiber are improved by controlling the proportions of the repeating units with different substituent groups in the polymer contained in the fiber and enabling the degree of substitution of the outer side (edge) of the fiber to be greater than that of the inside (center) of the fiber; the fiber suitable for clinical application, particularly applicable in the aspects such as hemostasis, burns and chronic wound treatment, is provided.
Owner:JIANGSU NEWVALUE MEDICAL PROD CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com