Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6695 results about "Surface tension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
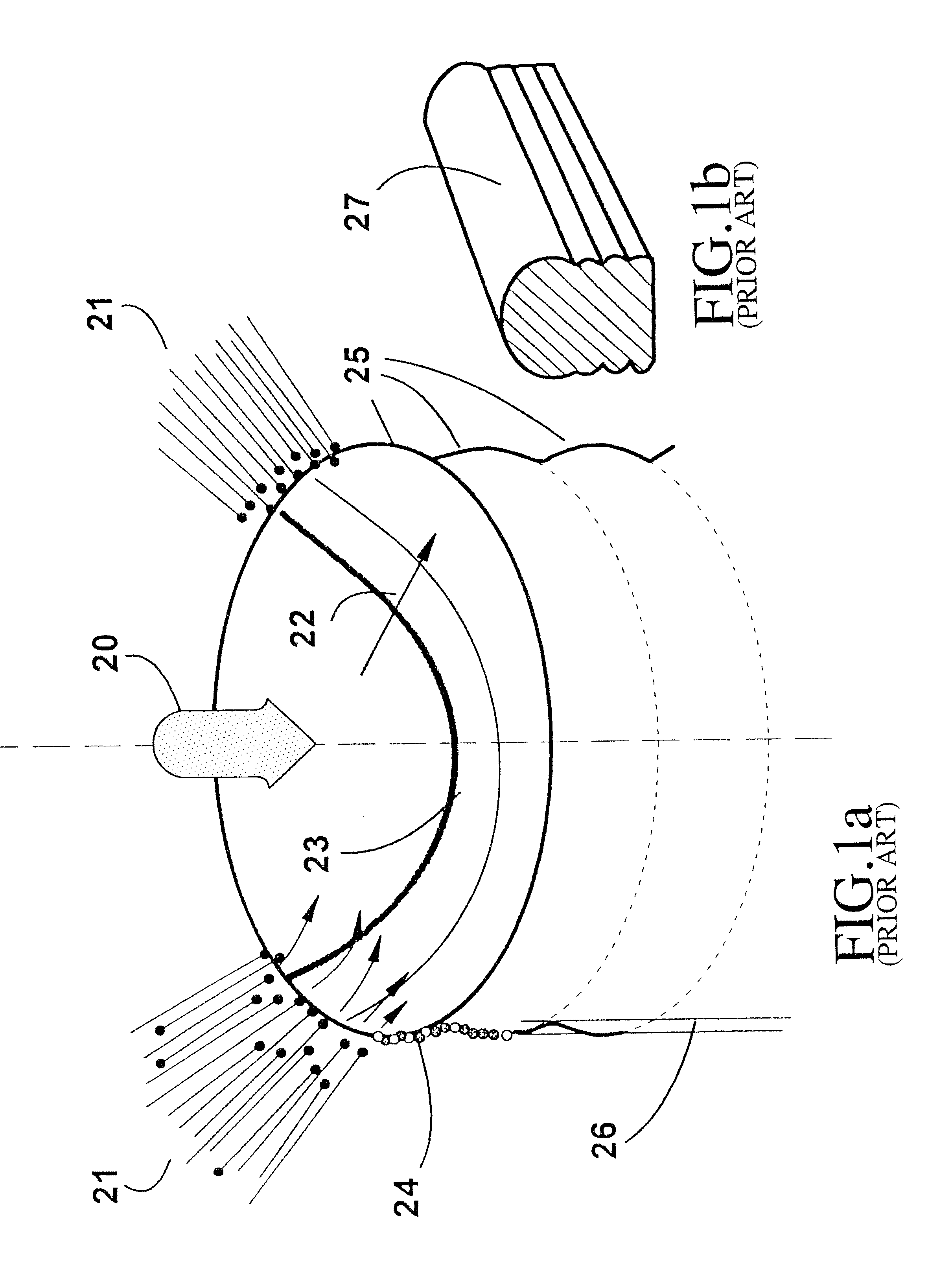
Surface tension is the tendency of fluid surfaces to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension allows insects (e.g. water striders), usually denser than water, to float and slide on a water surface.
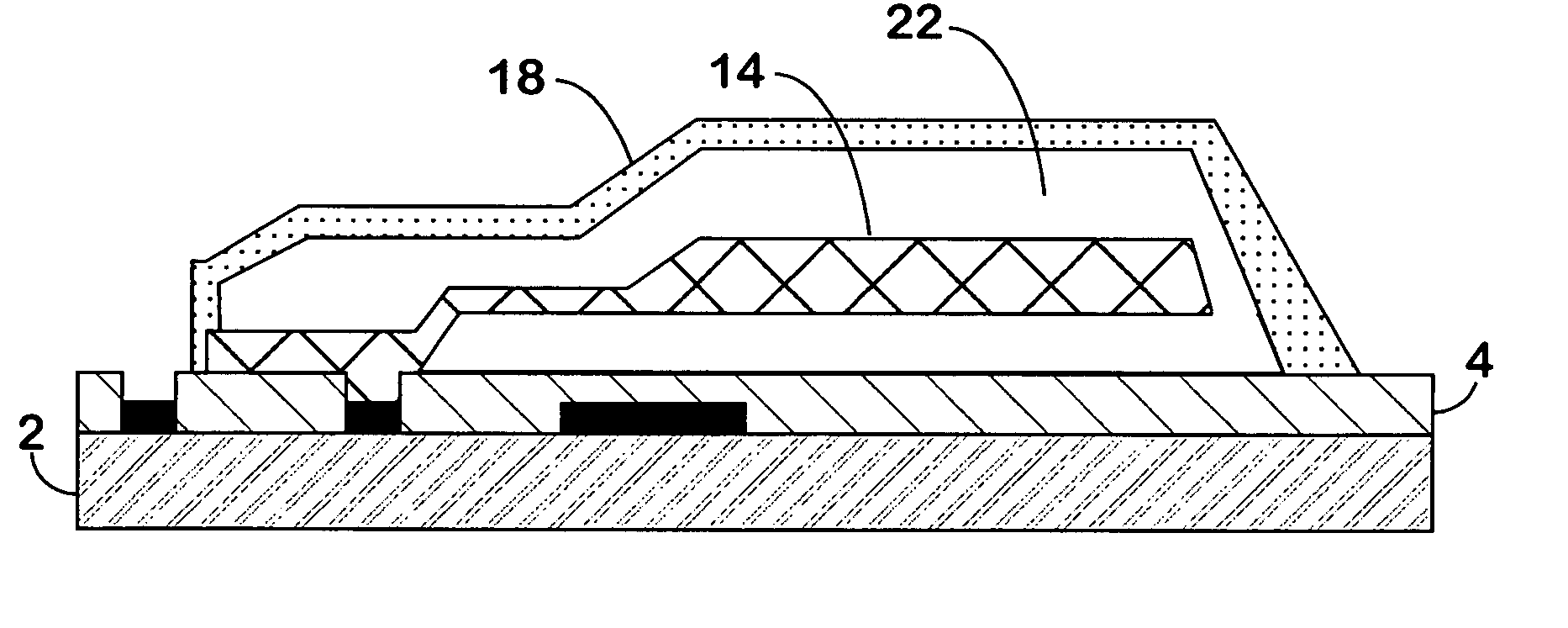
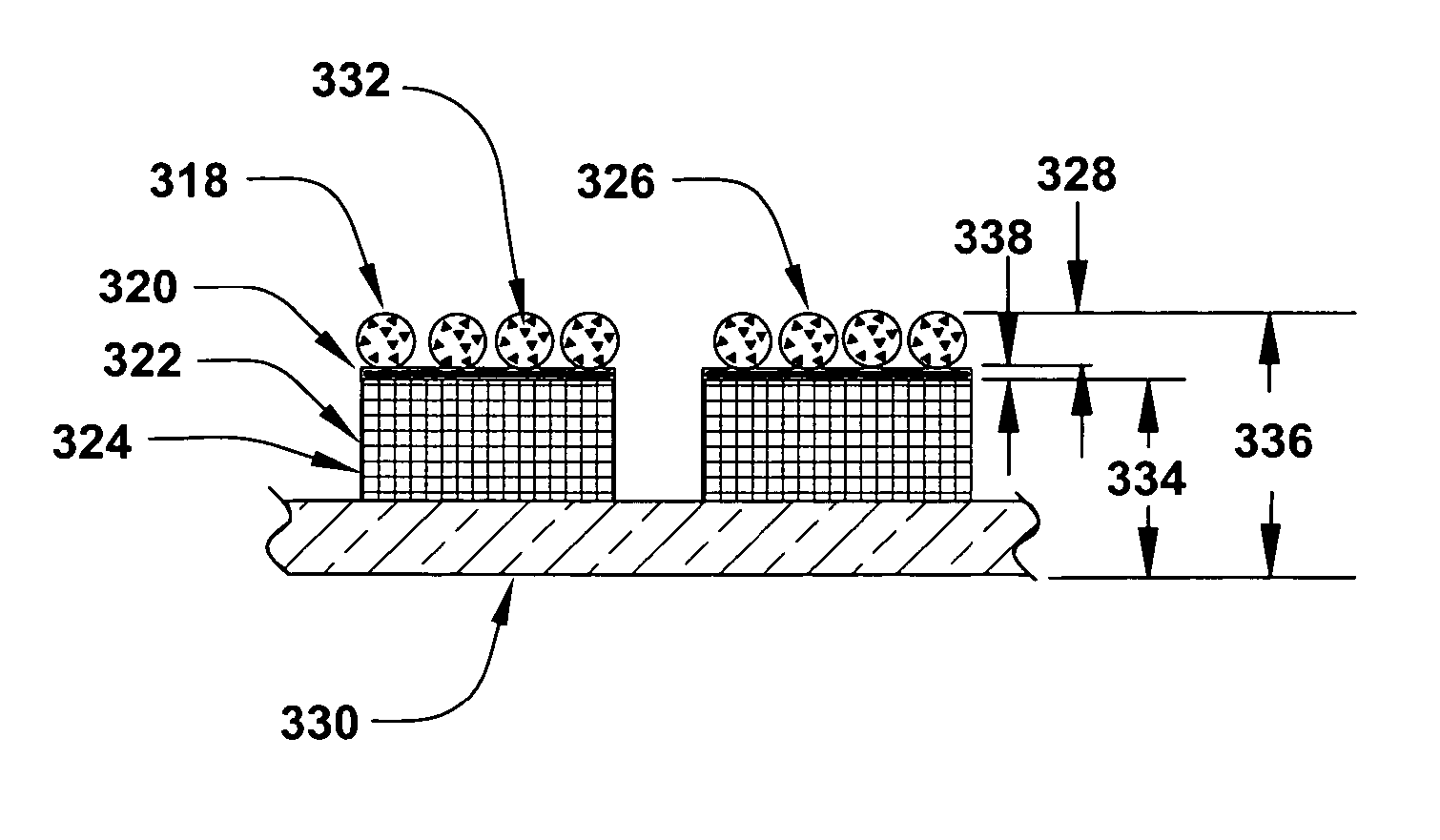
Shaped, fractured abrasive particle, abrasive article using same and method of making
ActiveUS20090169816A1Improve performanceLarge distributionPigmenting treatmentSpecial ornamental structuresPolymer chemistryAbrasive
Precursor alpha alumina abrasive particles in a mold are subjected to a drying process that cracks or fractures at least a majority of the precursor abrasive particles into at least two pieces thereby producing abrasive shards having a smaller size than the mold cavity from which they were made. The smaller abrasive shards, once formed, could be reassembled like jigsaw puzzle pieces to reproduce the original cavity shape of the mold from which they were made. The cracking or fracturing of the precursor abrasive particles is believed to occur by ensuring that the surface tension of the abrasive dispersion to the walls of the mold is greater than the internal attractive forces of the abrasive dispersion as the abrasive dispersion is dried within the mold cavity.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Cleaning solution for photoresist and method for forming pattern using the same
ActiveUS7238653B2Use cleanOrganic detergent compounding agentsTransportation and packagingResistAlcohol
Cleaning solutions for photoresist are disclosed which are useful for cleaning a semiconductor substrate in the last step of development when photoresist patterns are formed. Also, methods for forming photoresist patterns using the same are disclosed. The disclosed cleaning solution comprises H2O as a solution, a surfactant which is phosphate-alcoholamine salt represented by Formula 1, and an alcohol compound. The disclosed cleaning solution has lower surface tension than that of distilled water which has been used for conventional cleaning solutions, thereby improving resistance to photoresist pattern collapse and stabilizing the photoresist pattern formation.wherein R, x, y, z, a and b are as defined in the specification.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Manufacture of MEMS structures in sealed cavity using dry-release MEMS device encapsulation
InactiveUS7008812B1Eliminates undesirable liquid surface tensionIncrease etch rateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesMaterials sciencePlasma etching
The disclosed fabrication methodology addresses the problem of creating low-cost micro-electro-mechanical devices and systems, and, in particular, addresses the problem of delicate microstructures being damaged by the surface tension created as a wet etchant evaporates. This disclosure demonstrates a method for employing a dry plasma etch process to release encapsulated microelectromechanical components.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
Abrasive bead coated sheet and island articles
InactiveUS20050118939A1Simple processReduce investmentPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesWater basedSlurry
Flexible abrasive sheet articles having precision thickness flat-topped raised island structures that are coated with a monolayer of equal sized abrasive agglomerate are described. Methods of producing high quality equal-sized spherical shaped composite abrasive agglomerate beads containing small diamond abrasive particles are described. Beads are produced by level-filling fine mesh screens or perforated sheets with a water based metal oxide slurry containing abrasive particles and then using a fluid jet to eject the abrasive slurry lumps from the individual screen cells into a dehydrating environment. Surface tension forces form the ejected liquid lumps into spheres that are solidified and then heated in a furnace to form ceramic beads. These porous ceramic abrasive beads can be bonded directly onto the flat planar surface of a flexible backing material or they can be bonded onto raised island surfaces to form rectangular or disk abrasive sheet articles. Abrasive articles having equal sized abrasive beads are particularly suited for lapping and raised island articles are suited for high speed lapping. Non-abrasive equal-sized beads can also be formed using this simple bead manufacturing process, which requires only a very low capital investment.
Owner:DUESCHER WAYNE O
Method and reagent for producing narrow, homogenous reagent stripes
ActiveUS20050008537A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionReagent stripTest strips
The present invention concerns a reagent coating mass which can be used in slot-die-coating of flat support materials in the manufacturing processes of test strips. Advantageously, the reagent mass of the invention exhibits certain superior rheological properties such as viscosity, surface tension and thixotropy. The reagent mass is preferably used to coat thin, narrow and homogeneous stripes of reagent material onto flat web material.
Owner:ROCHE OPERATIONS +1
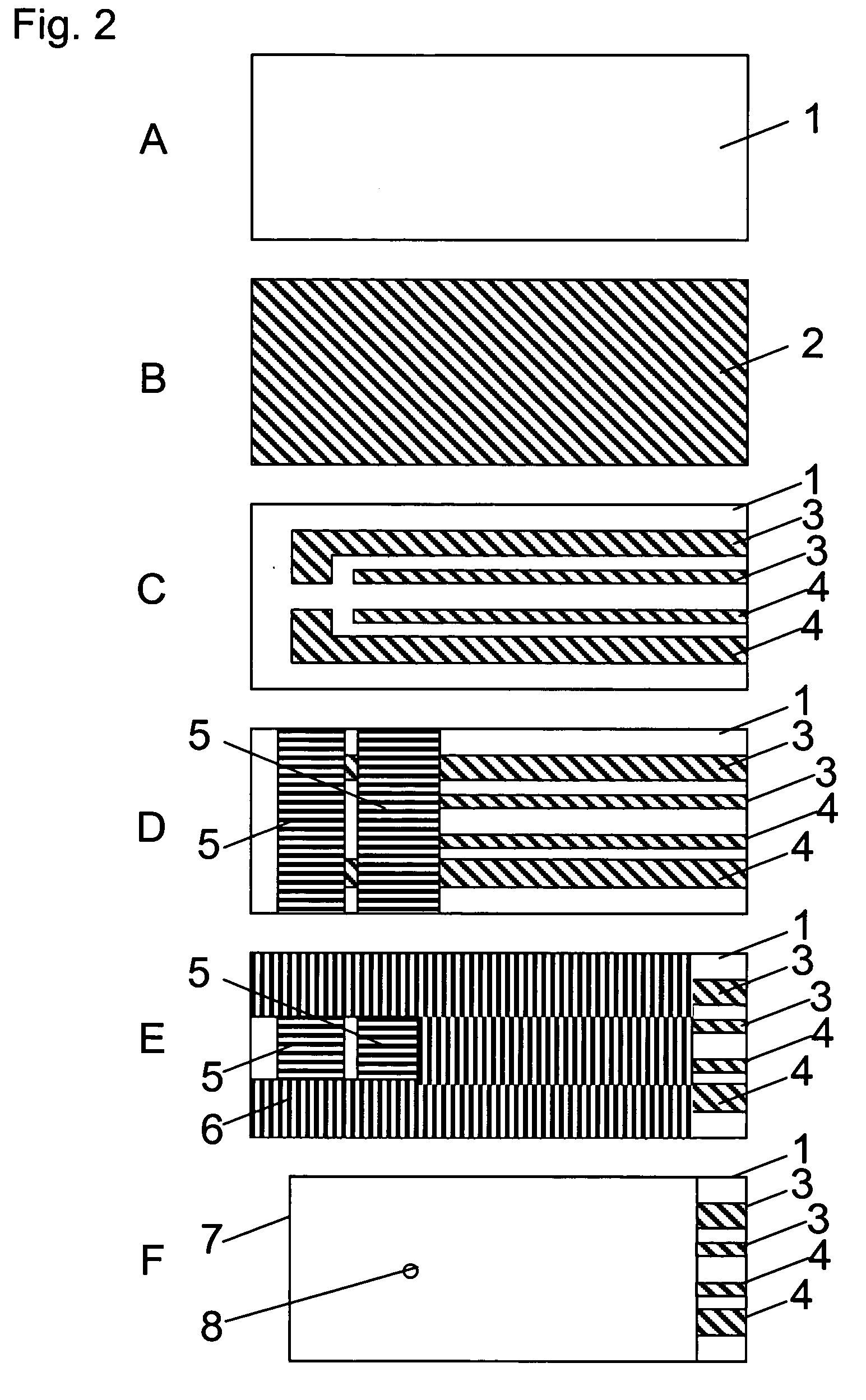
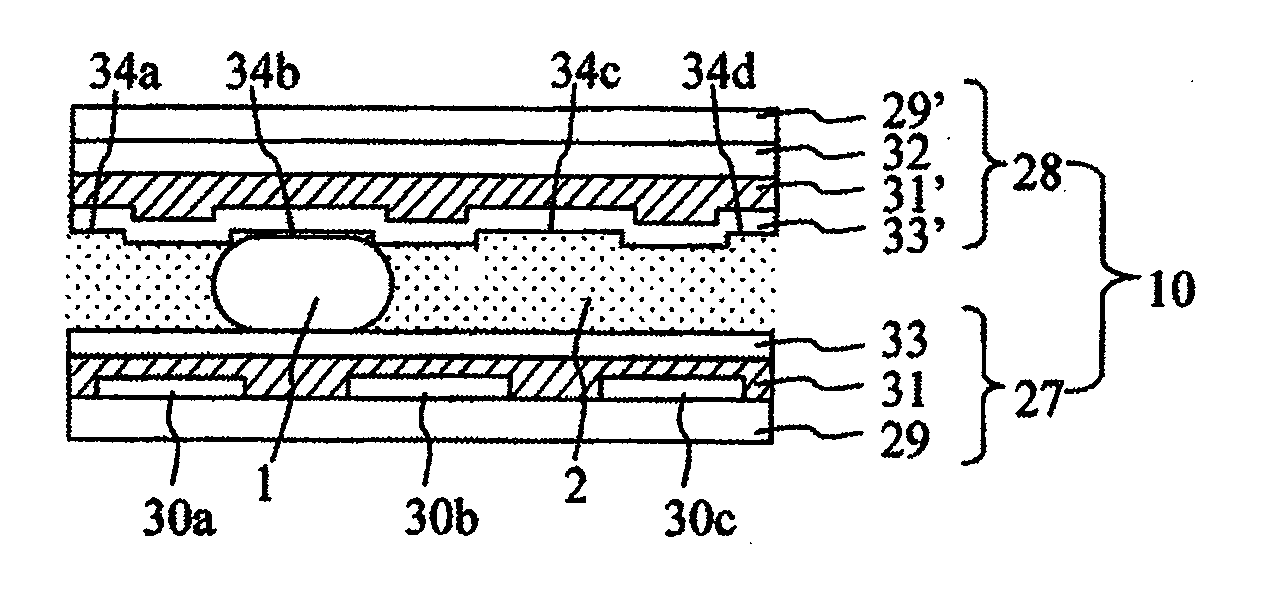
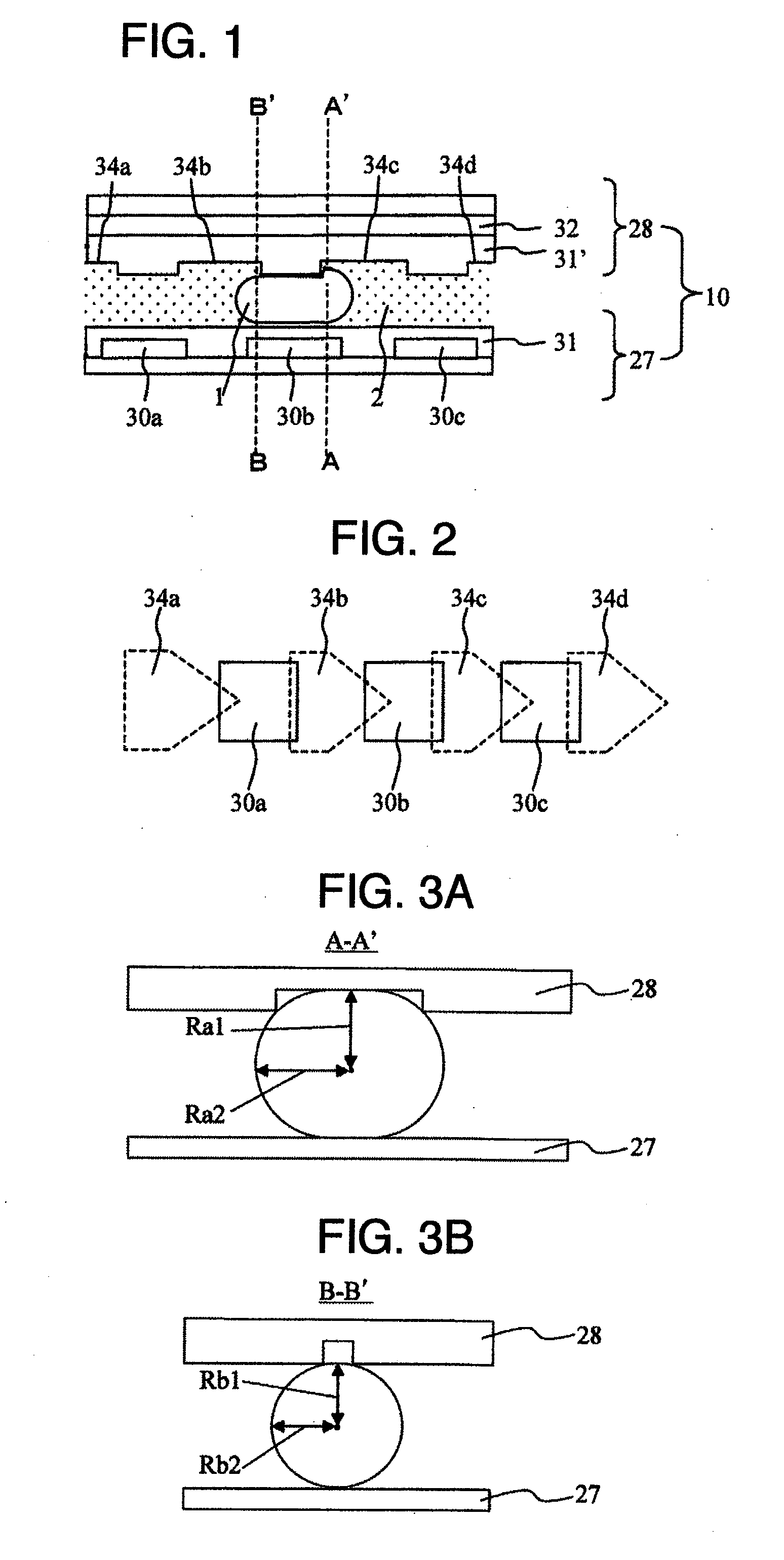
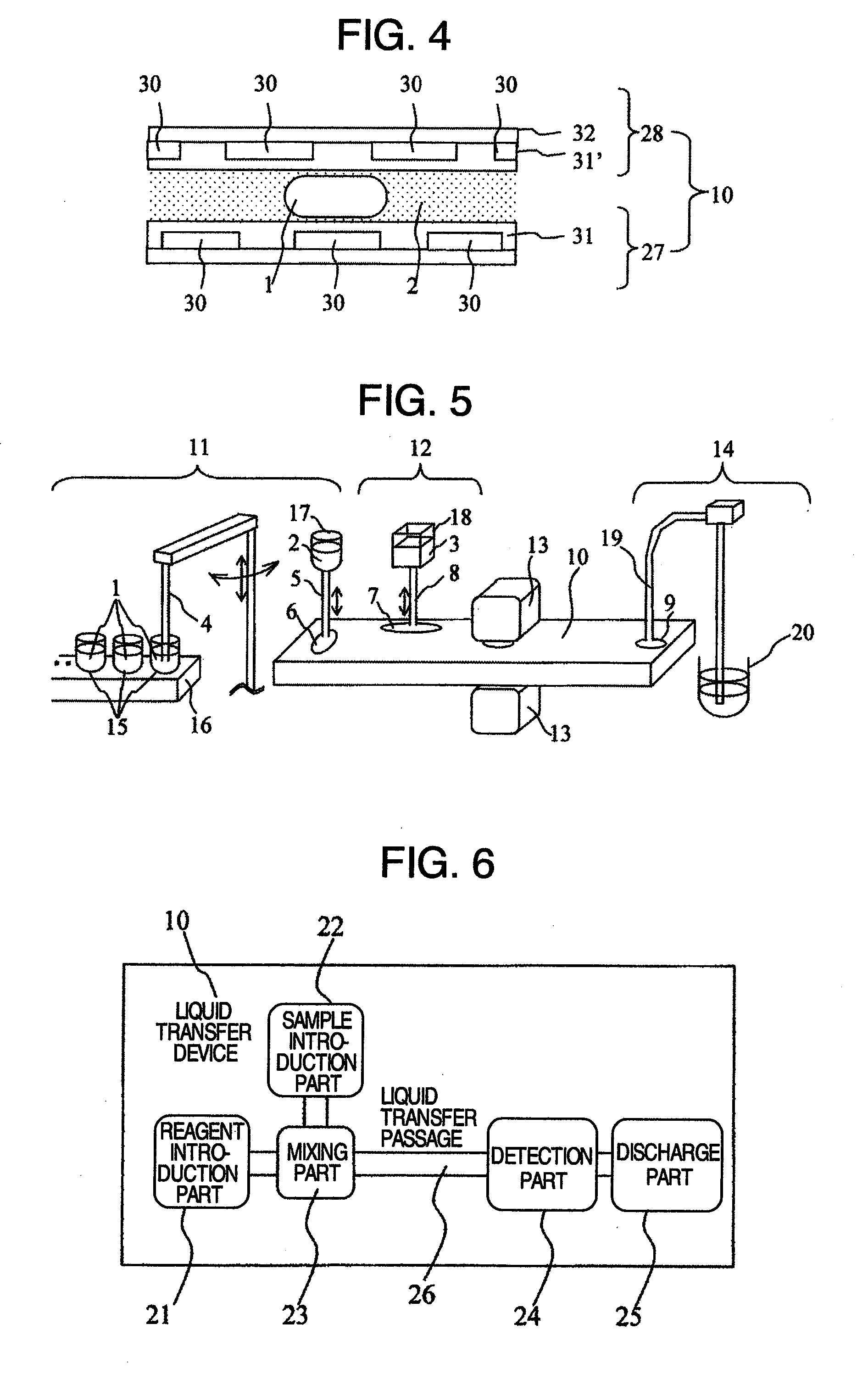
Liquid transfer device
InactiveUS20090321262A1Reduce in quantityEasy to controlSludge treatmentTransportation and packagingSpherical shapedEngineering
Provided is a liquid transfer device which controls electrically liquid position. The surface of the liquid transfer device is provided with unevenness in order to solve a problem of having a large number of electrodes for controlling voltage. The number of electrodes for controlling voltage can be halved by utilization of restoring force of liquid to a spherical shape by surface tension, in addition to electrical force.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Microfluidic control using dielectric pumping
InactiveUS6949176B2High-performance operationImprove reliabilityElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMiniaturizationEngineering
Devices and methods utilizing dielectric pumping and variable dielectric pumping to move fluids through microchannels. Two fluids having dissimilar dielectric constants form an interface that is positioned between two electrodes in order to move the interface and therefore the fluids. Dielectric pumping and variable dielectric pumping may be used to move fluids in miniaturized analytical packages containing microchannels in which forces created by surface tension predominate over the gravitational force.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
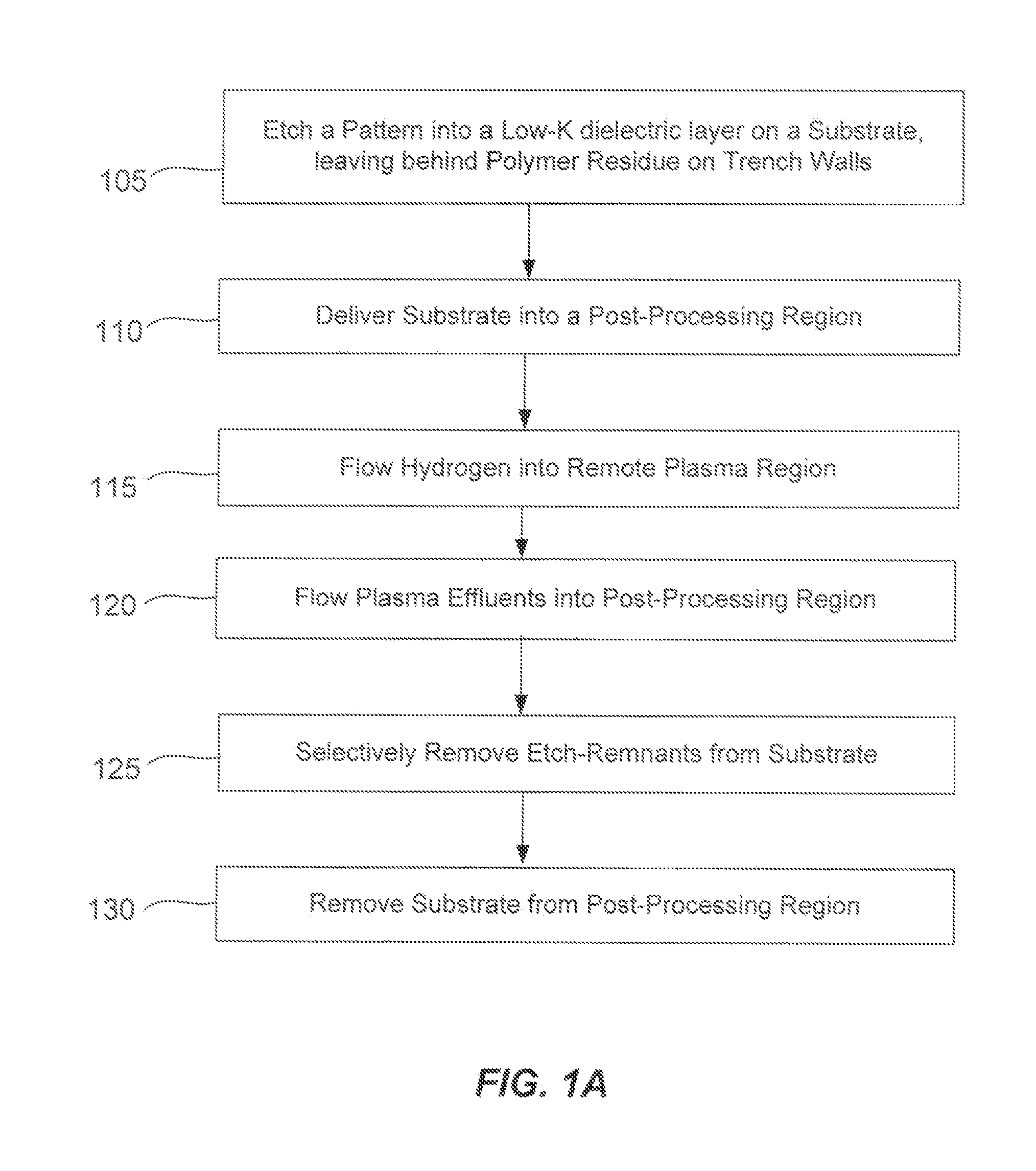
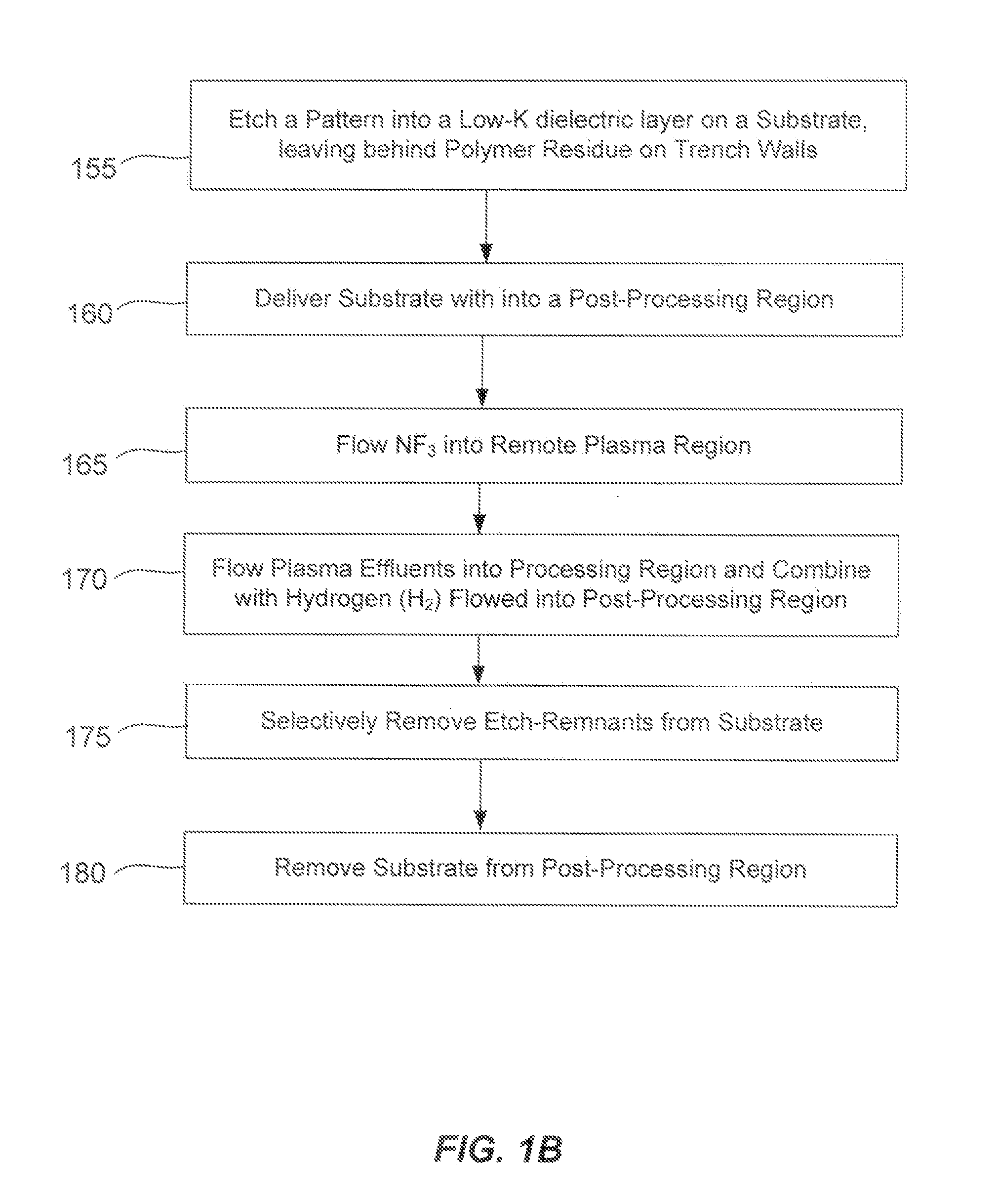
Etch remnant removal
InactiveUS20130298942A1Delicate featureLow dielectric constantElectric discharge tubesElectrostatic cleaningGas phaseDielectric layer
Methods of removing residual polymer from vertical walls of a patterned dielectric layer are described. The methods involve the use of a gas phase etch to remove the residual polymer without substantially disturbing the patterned dielectric layer. The gas phase etch may be used on a patterned low-k dielectric layer and may maintain the low dielectric constant of the patterned dielectric layer. The gas phase etch may further avoid stressing the patterned low-k dielectric layer by avoiding the use of liquid etchants whose surface tension can upset delicate low-K features. The gas phase etch may further avoid the formation of solid etch by-products which cars also deform the delicate features.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
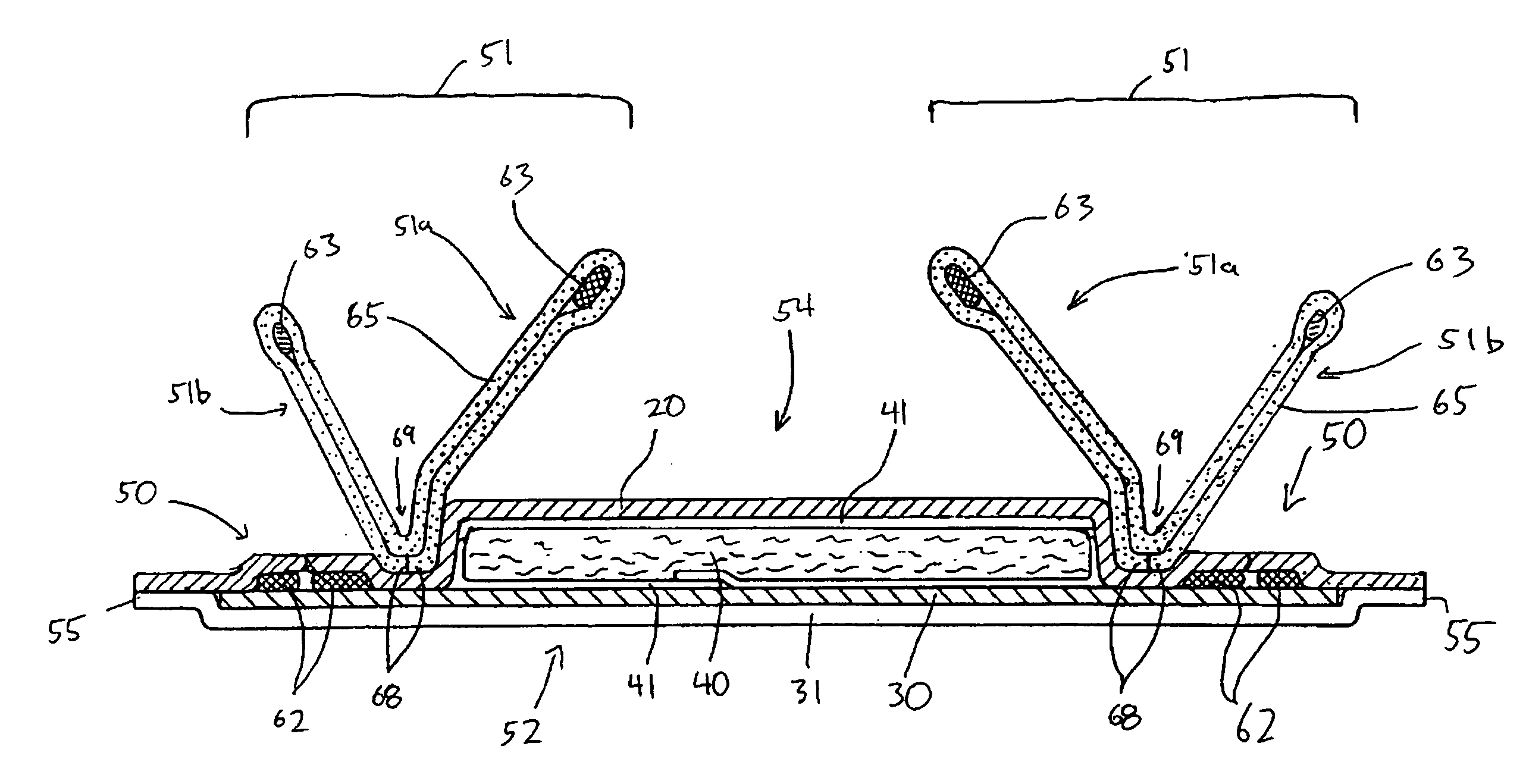
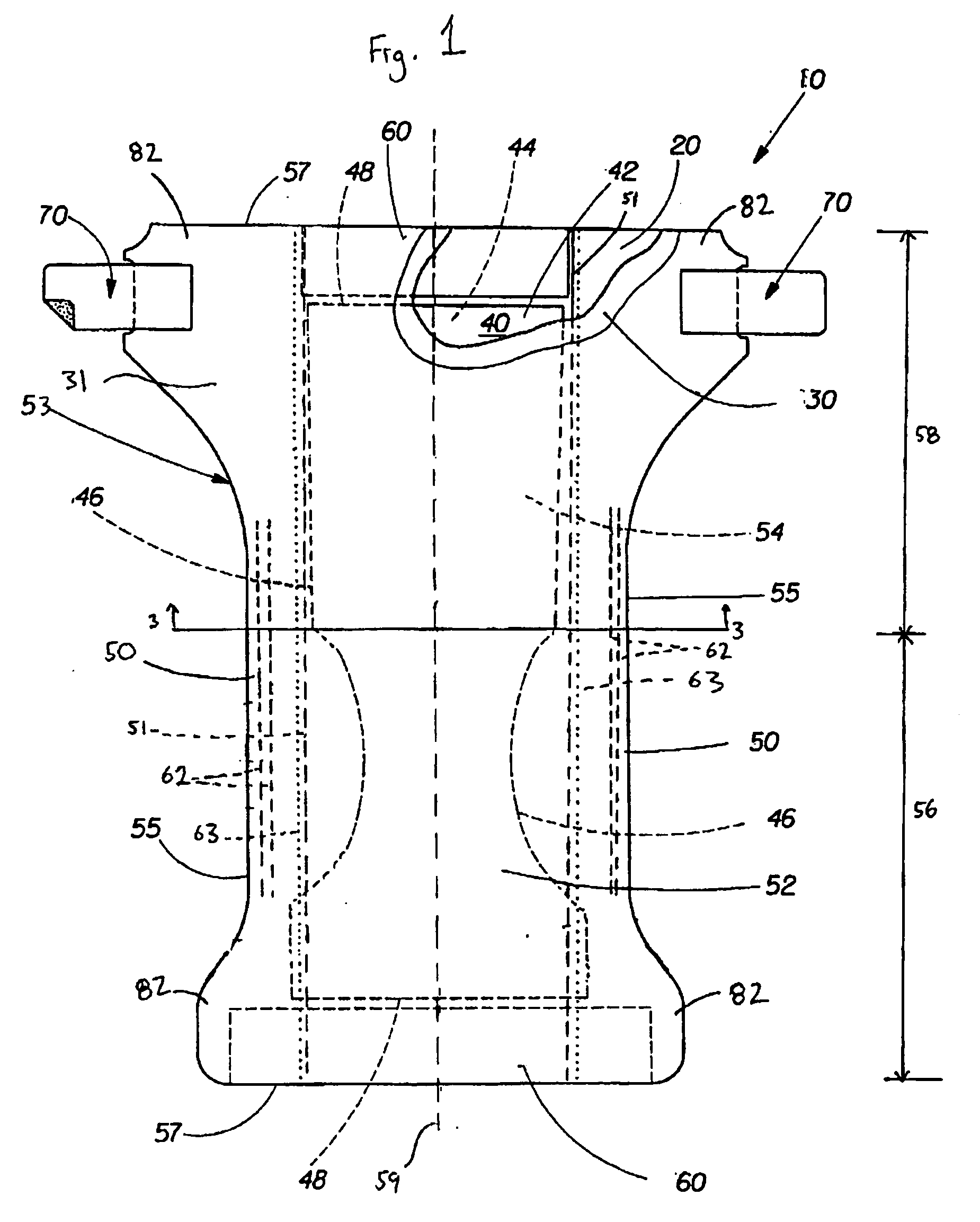
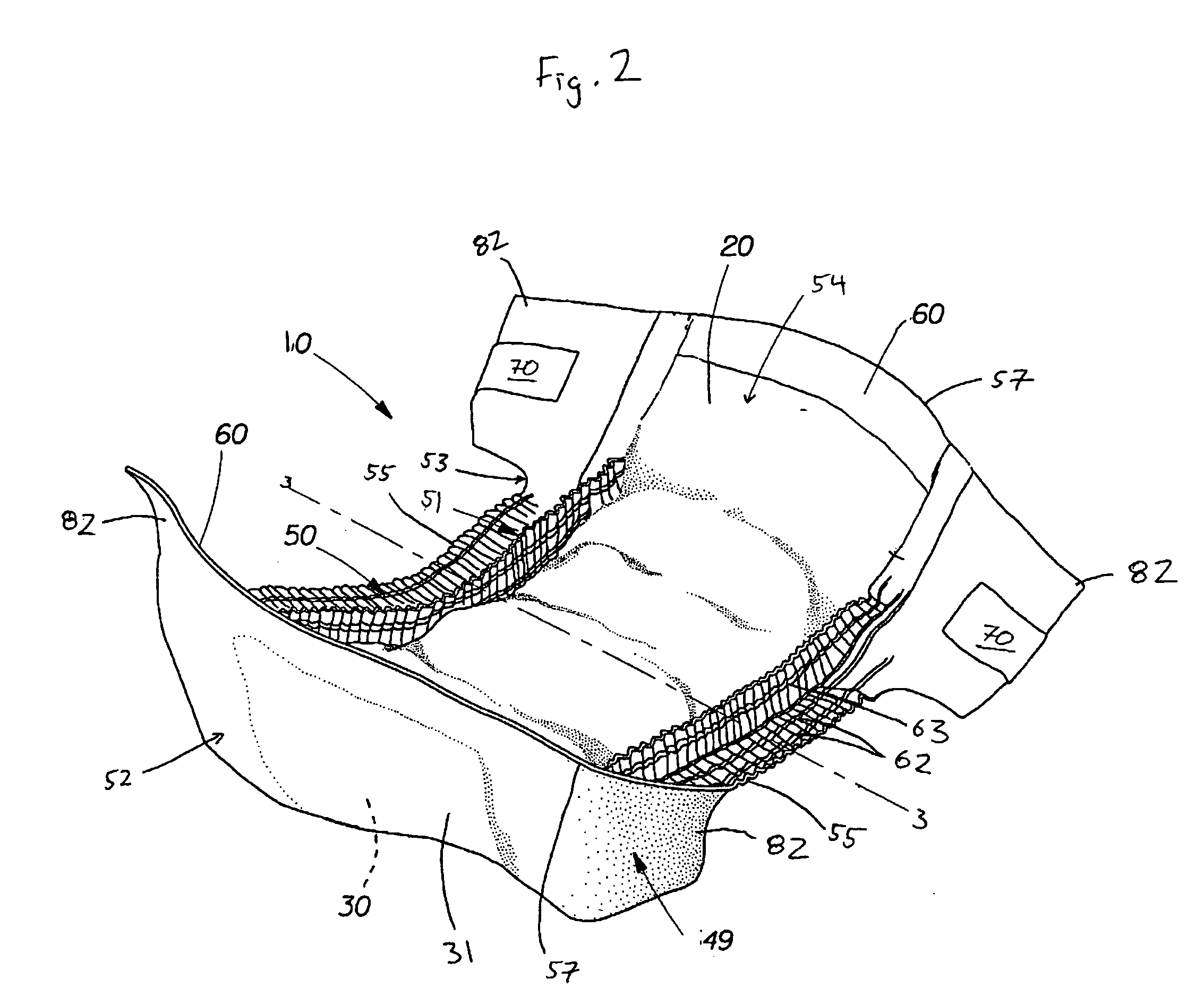
Hydrophobic surface coated absorbent articles and associated methods
The present invention relates to absorbent articles which include one or more components that have been treated with a hydrophobic surface coating intended to render such components impermeable to liquids having relatively low surface tensions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
Method and apparatus of spectrophotometry or the like on extremely small liquid samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably moved toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, the optical fibers go through a surface and are finished flush with its surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Hydrophobic surface coated light-weight nonwoven laminates for use in absorbent articles
The present invention relates to absorbent articles which include one or more barrier members comprising a light-weight nonwoven laminate that has been treated with a hydrophobic surface coating intended to render such components impermeable to liquids having relatively low surface tensions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Void-containing polyester shrink film
InactiveUS20050119359A1Improve performanceHigh opacitySynthetic resin layered productsLabelsPolyesterVolumetric Mass Density
Disclosed are polyester shrink films comprising a voiding agent dispersed within a continuous polyester phase. The voiding agent comprises at least one first polymer and at least one second polymer, in which the polymer components have selected physical properties such as glass transition temperature, melting point, tensile modulus, surface tension, and melt viscosity. The resulting shrink films have high opacity, a low coefficient of friction, lower density, low shrink force, and good printability. The films are useful for sleeve label and other shrink film applications, and their lower density allows them to be readily separated from soft drink bottles, food containers and the like during recycling operations. Also disclosed is a process for separating a void-containing polyester from a mixture of polymers.
Owner:SHELBY MARCUS DAVID +2
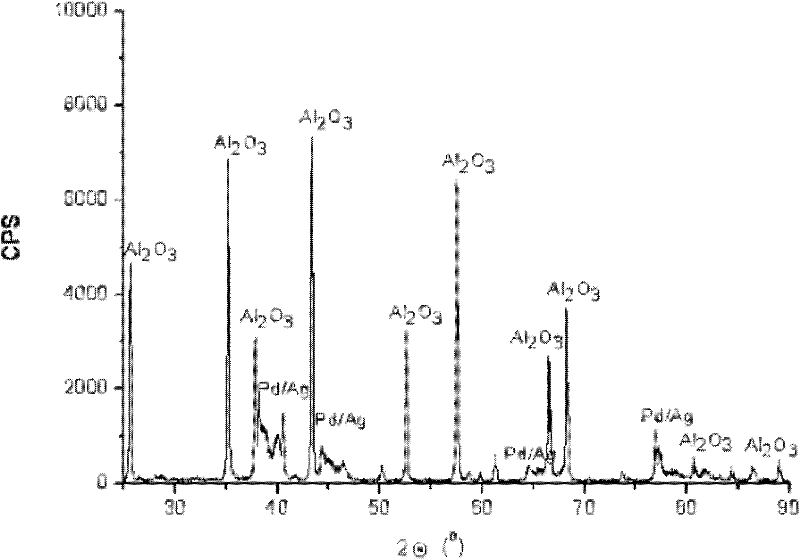
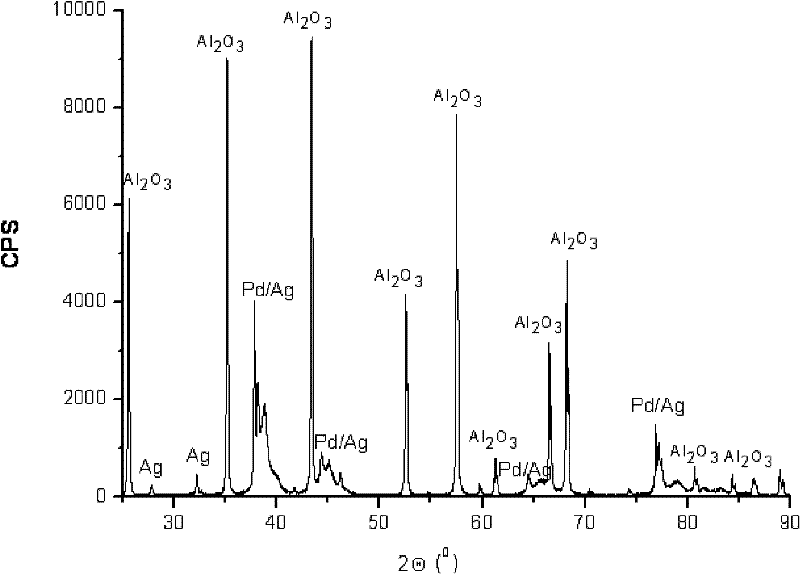
Palladium-silver bimetallic hydrogenation catalyst
ActiveCN102205243AGood choiceImprove hydrogenation activityHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsHydrogenation processSolvation
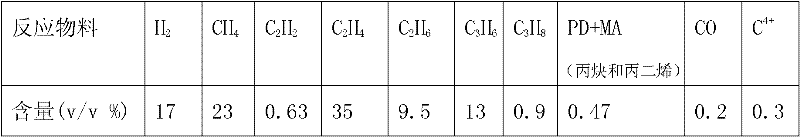
The invention relates to a palladium-silver bimetallic hydrogenation catalyst, a carrier of which mainly contains Al2O3 and which is characterized by comprising, based on 100% of the catalyst weight, 0.01-0.4% of Pd, 0.02-0.2% of Ag, and has a specific surface area of 1-100m<2> / g. The catalyst is obtained through three steps of: first, preparing a functionalized-high-molecular / Al2O3 precursor, then preparing a Pd-Ag-high-molecular / Al2O3 precursor, and lastly roasting the precursors at 380-550 DEG C for 2-6h. The preparation method overcomes the influences of dipping liquid surface tensionand solvation effect on palladium-silver disperseness, and the prepared catalyst has excellent selectivity. The catalyst of the invention can be applied to selective hydrogenation process of fractions such as C2 and C3, and has a good hydrogenation activity, excellent selectivity and good hydrogenation stability.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Quantum dot fluorescent inks
The present invention relates to inks and more particularly, to fluorescent ink formulations including quantum dots for various printing processes such as inkjet, flexographic, screen printing, thermal transfer, and pens. The inks include one or more populations of fluorescent quantum dots dispersed in polymeric material, having fluorescence emissions between about 450 nm and about 2500 nm; and a liquid or solid vehicle. The vehicle is present in a ratio to achieve an ink viscosity, surface tension effective, drying time and other printing parameters used for printing processes.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
Equal sized spherical beads
InactiveUS20080299875A1Other chemical processesMetal rolling stand detailsSpherical shapedMaterials science
A method of producing equal-sized spherical shaped beads of a wide range of materials is described. These beads are produced by forming the parent bead material into a liquid solution and by filling equal volume cells in a sheet with the liquid solution. The sheet cells establish the volumes of each of the cell mixture volumes which are then ejected from the cells by an impinging fluid. Surface tension forces acting on the ejected equal sized solution entities form them into spherical beads. The ejected beads are then subjected to a solidification environment which solidifies the spherical beads. The beads can be solid or porous or hollow and can also have bead coatings of multiple material layers.
Owner:DUESCHER WAYNE O
Laser consolidation methodology and apparatus for manufacturing precise structures
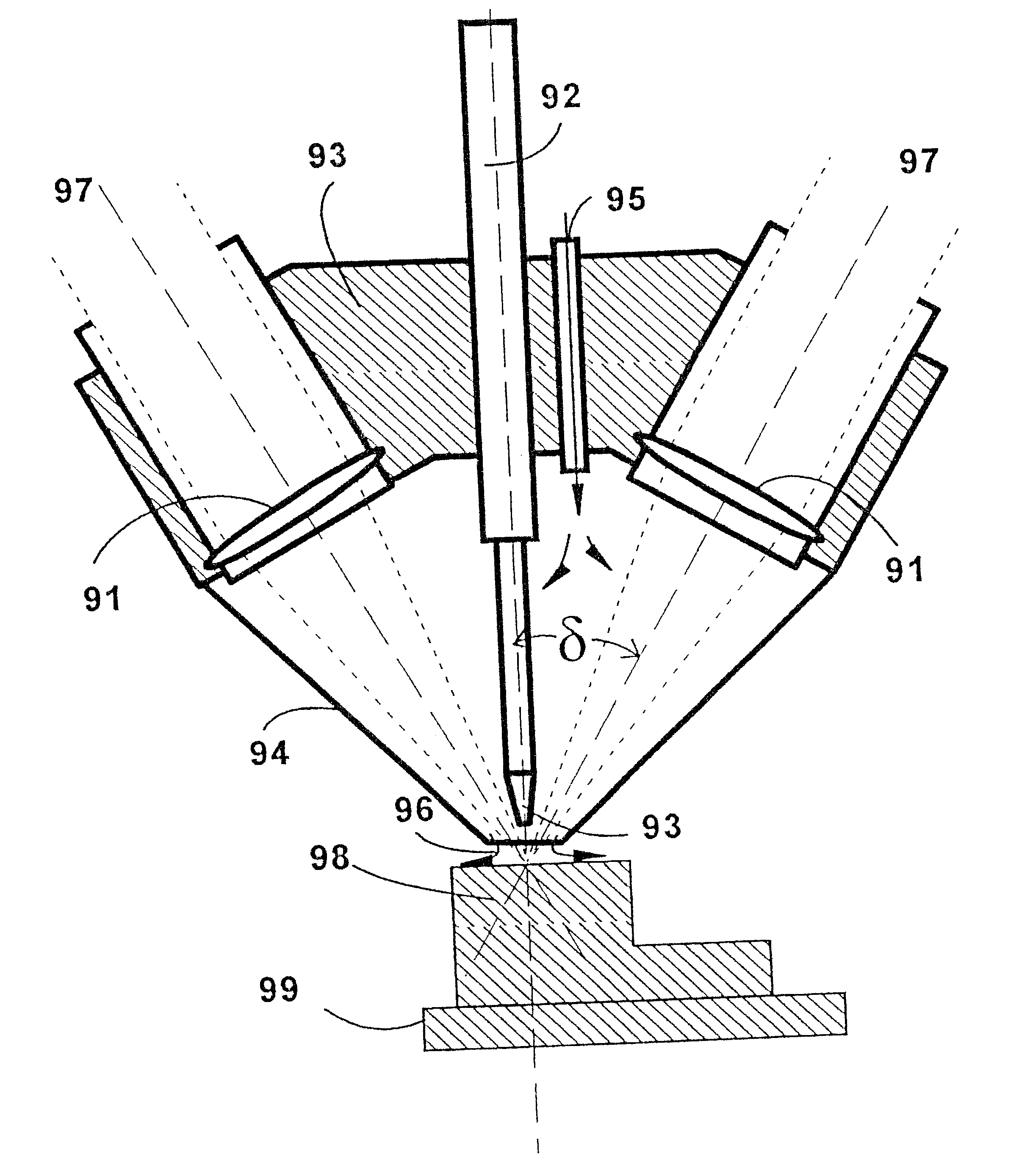
A laser consolidation methodology and apparatus for manufacturing precise three dimensional structures are disclosed. In the disclosed process, a plurality of beams of laser energy are arranged to impinge a circular area on a substrate, at an angle in the range of 25° to 30° to the normal to the substrate, melting a hemispherical region of the substrate. Powdered material is supplied to the melted region of the substrate in a direction substantially normal to the substrate. The rate of material feed is controlled so that the added material melts and forms together with underlying material a molten zone maintained spherical under the influence of surface tension. The substrate is moved relative to laser beams and material feed at a controlled rate so as to create a ridge of desired shape on the substrate, the top surface of which has a semicircular cross-section. Subsequent passes re-melt a thin layer of the ridge and further material is injected and melted so that the height of the ridge is increased by a precise amount, creating a uniform wall having smooth sides.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Dispenser and cosmetic or dermatological preparation comprising an auxiliary for use with dispenser
InactiveUS20050189377A1Improves haptic propertyReduce forceCosmetic preparationsPower operated devicesPolyolSURFACTANT BLEND
The present invention is a cosmetic or dermatological preparation for use with a dispenser that includes an auxiliary to keep the dispenser operating smoothly. The auxiliary is selected from the group consisting of (i) polyols having 2 to 6 carbon atoms and 2 to 6 hydroxyl or alkoxy groups and (ii) surfactants that reduce the surface tension of the preparation to less than 30 mN / m. The preparation is particularly suitable with a dispenser comprising a container and an inner container wall for housing a cosmetic or dermatological preparation; a follow-up plunger on a base side of the dispenser, which is capable of being slidably displaced on the inner container wall under the pressure of the ambient atmosphere; a head section on a top end of the dispenser that can be slidably displaced in relation to the container and that comprises a dispensing channel, the dispensing channel capable of being connected in a communicating manner to the container; a manually actuable delivery device comprising a variable-volume delivery chamber, a delivery element that can be displaced longitudinally in relation to the container and the head section, comprising a delivery plunger that can be slidably displaced within the delivery chamber and a delivery stem connected to the delivery plunger, and a delivery channel circumferentially enclosed by the delivery stem and comprising a delivery-channel inlet opening communicating with the delivery chamber and a delivery-channel outlet opening. The delivery channel outlet opening is capable of being moved into an open position relative to the dispensing channel by displacing the delivery element.
Owner:BEIERSDORF AG
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
InactiveUS6809826B2Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSmall sampleSpectroscopy
Method and apparatus of spectroscopy or the like on extremely small samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, optical fibers go through a surface and finish flush with the surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests. Means for determining wetted surface are provided.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
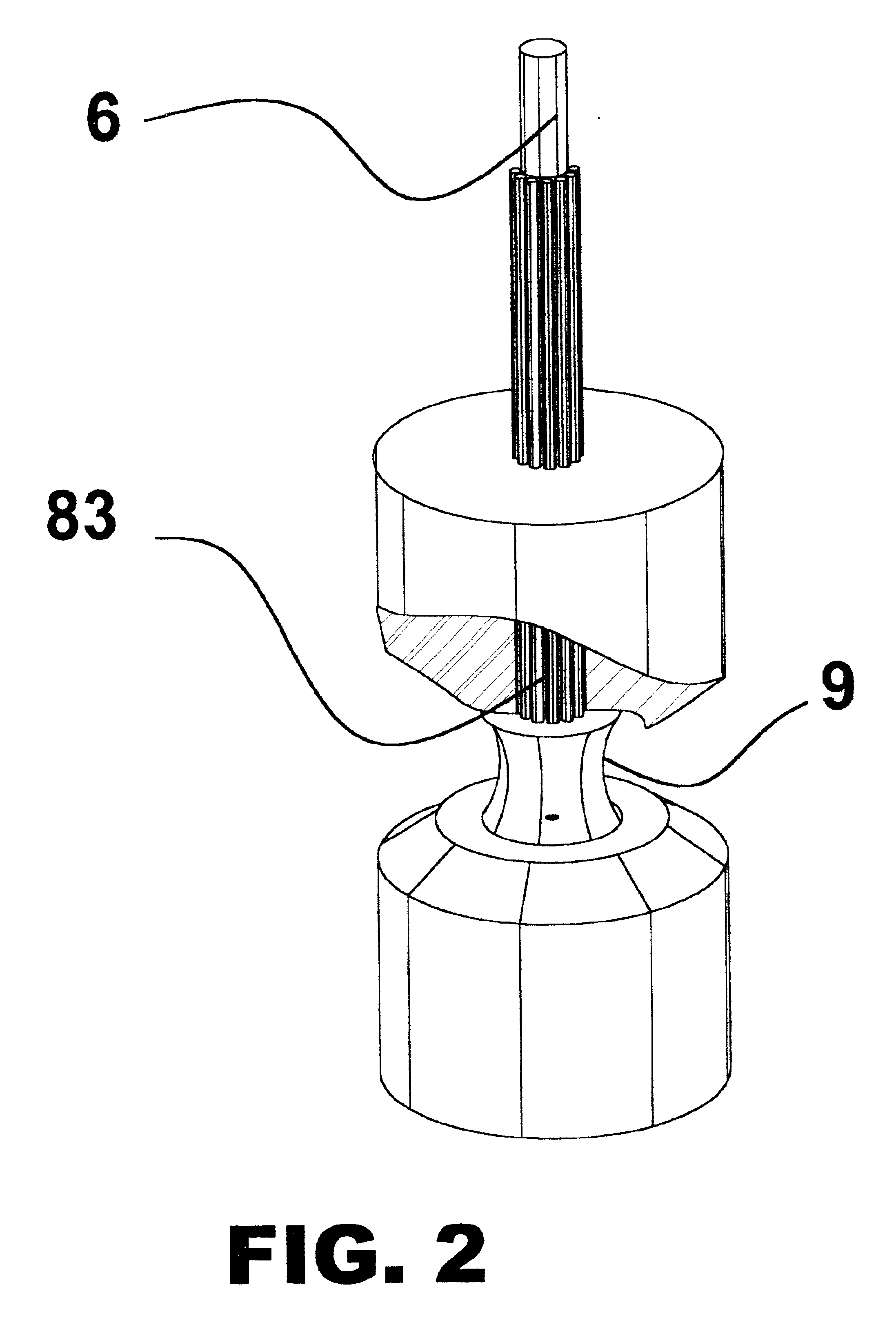
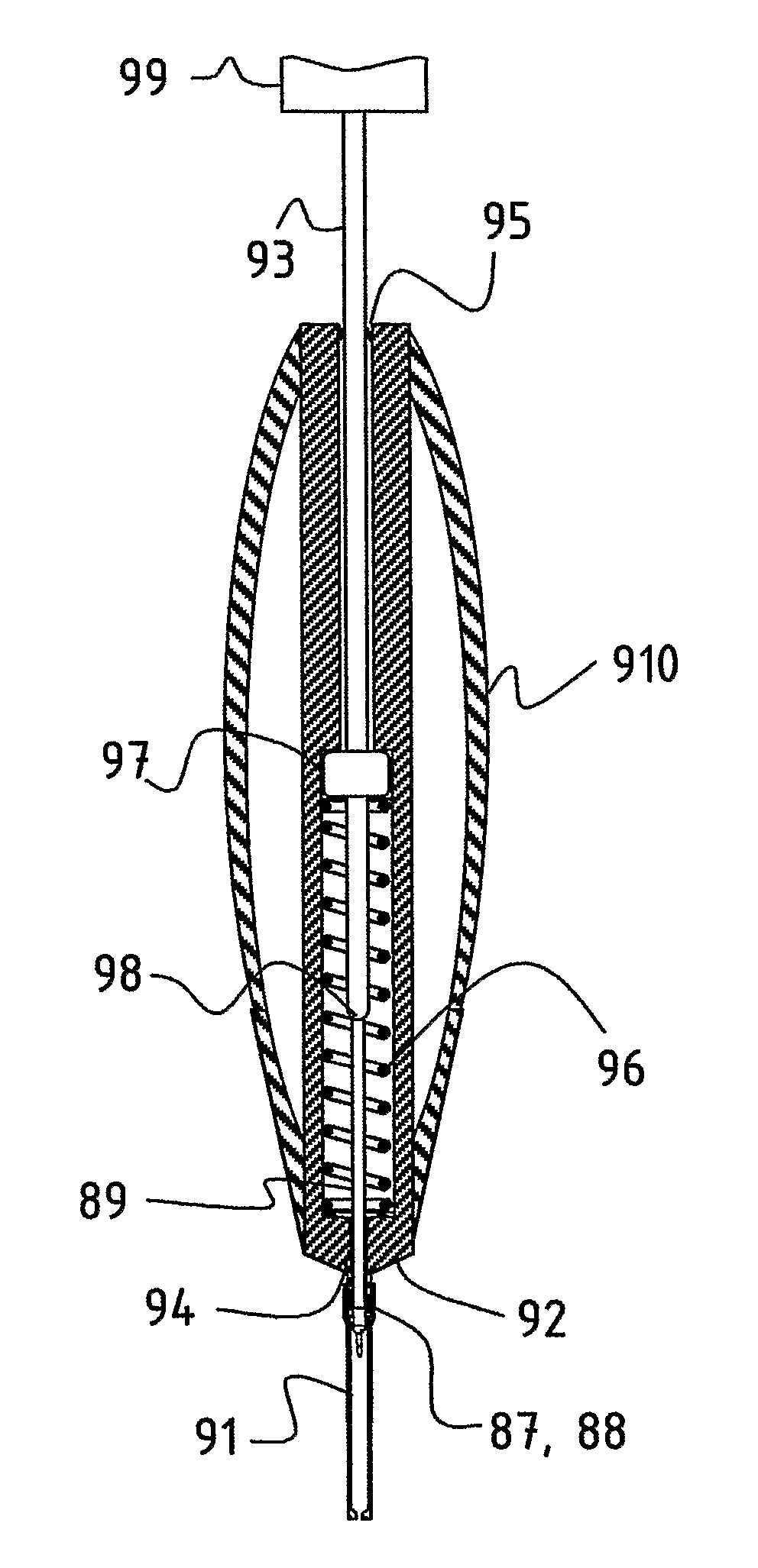
Method and Apparatus for Sampling and Analysis of Fluids
ActiveUS20070232956A1Eliminate needCatheterCharacter and pattern recognitionSuction stressEngineering
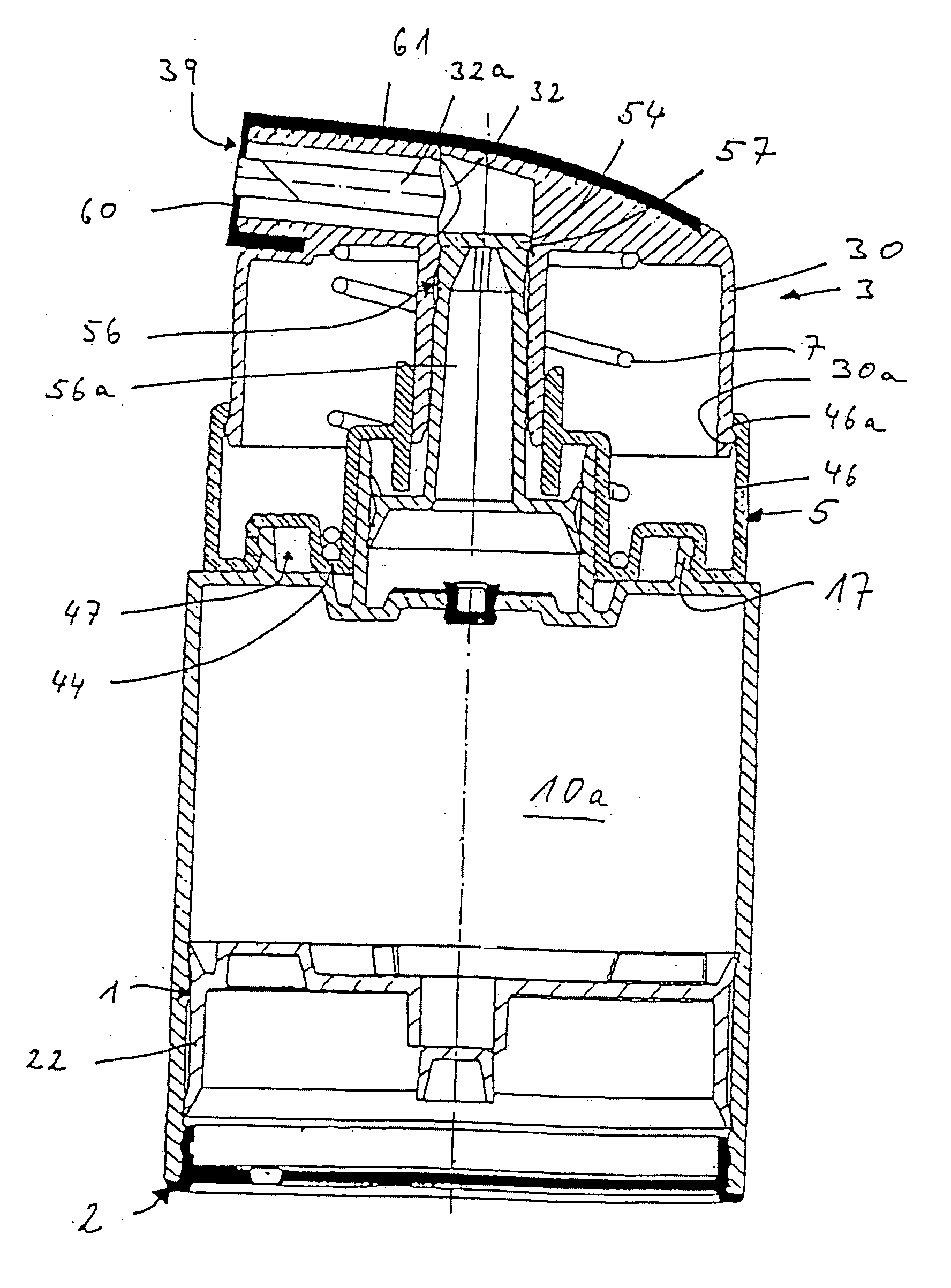
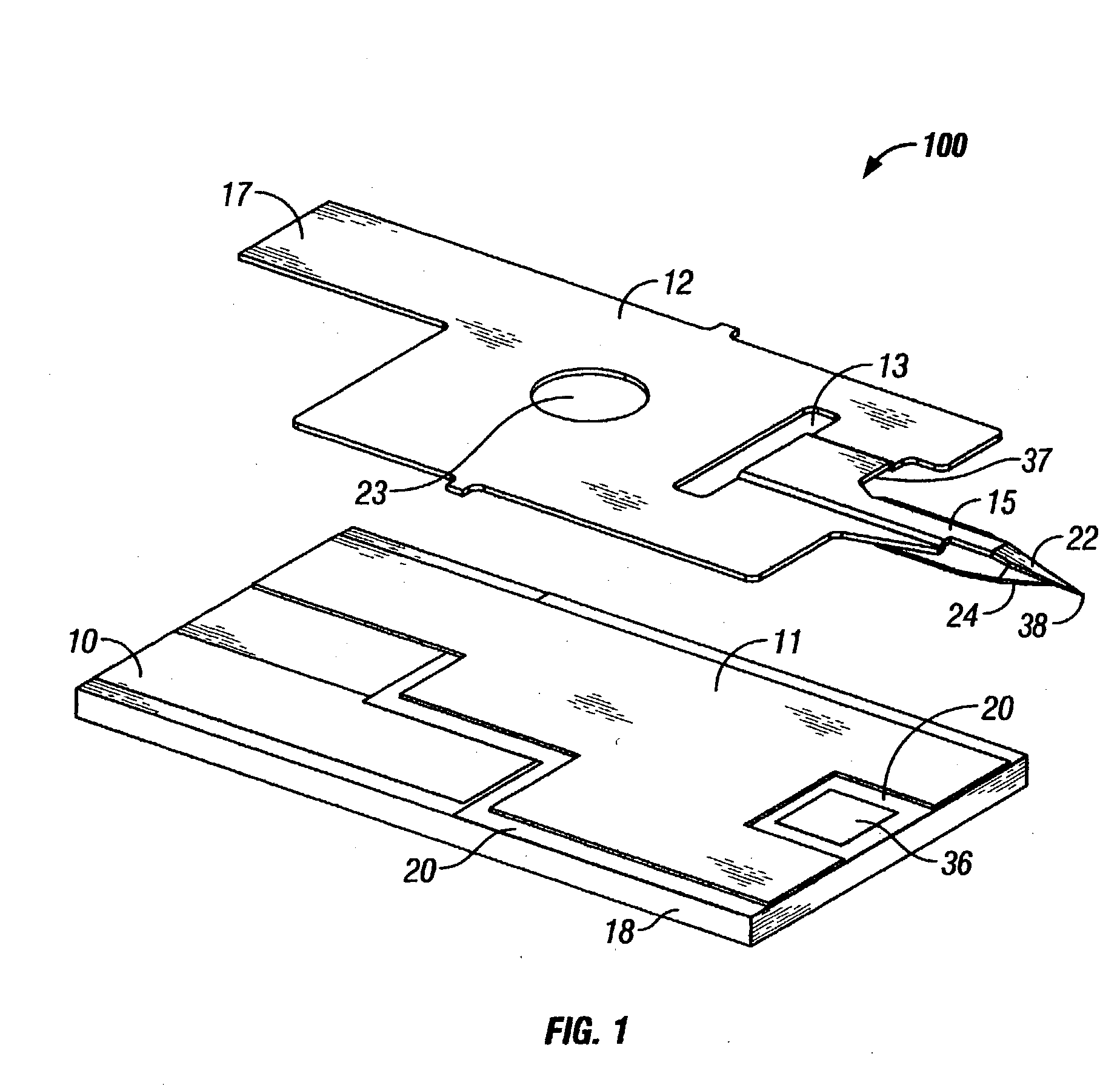
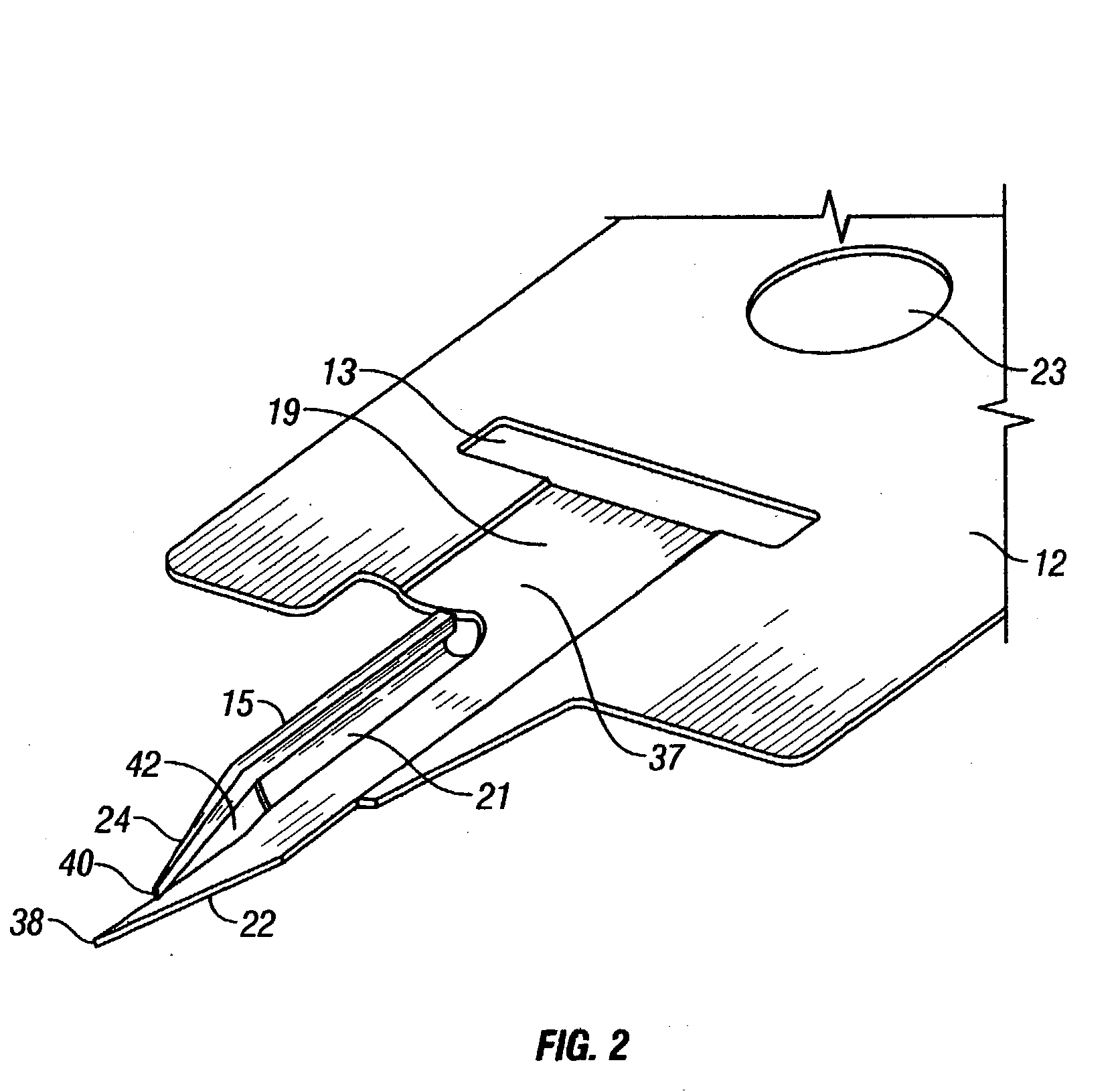
A medical device having a housing (2) with a bore (3) and a lancet (1) slidably fitting in the bore. The lancet operates as a positive displacement piston. In a retracted position, in which the lancet is rearwardly displaced along the bore to define a fluid-containing space in the bore forwardly on the lancet tip, the fluid-containing space has a cross-section dimension to allow fluid to be retained therein by surface tension. The device has a seal (6) operable substantially to prevent flow of fluid from the fluid-containing space past the seal means on movement of the lancet. Displacement of the lancet between the puncture and retracted positions provides suction for drawing fluid into and along the fluid-containing space from the forward end of the bore, and / or pressure for expelling fluid from the fluid-containing space via the forward end of the bore. Also disclosed are methods for operating the device.
Owner:MICROSAMPLE
Delivery system for dispensing volatiles
InactiveUS6378780B1Easy to carryMaintain consistencyMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesVena contracta diameterVolatiles
Disclosed herein is a piezoelectric liquid delivery system or atomizer for production of droplets of liquid or liquid suspensions by a battery operated dispenser utilizing an orifice plate in communication with a piezoelectric element. By control of the viscosity and surface tension of the liquid to be dispersed, an improved method of dispensing such liquid is achieved.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Light emitting diode package with positioning groove
InactiveUS20080029775A1Improve the problemPrecise positioningSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeDiode
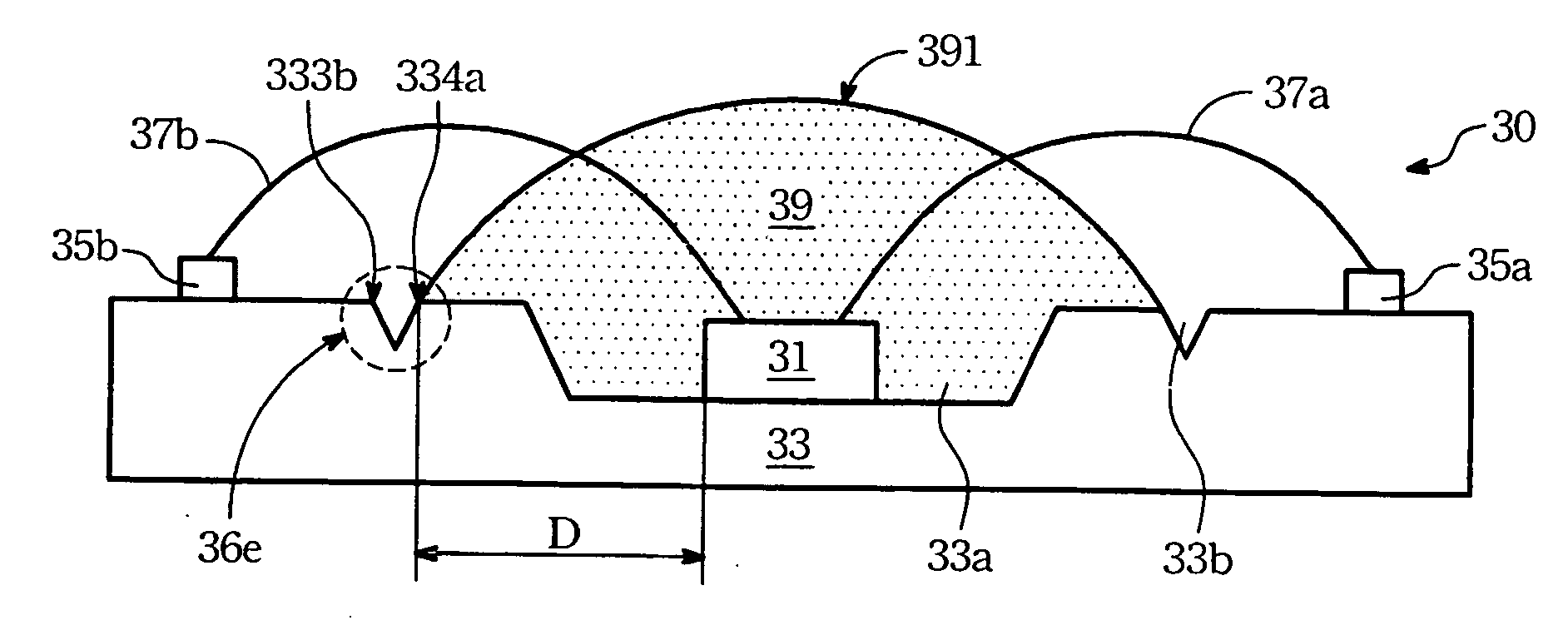
A light emitting diode package structure includes a light emitting diode, a substrate structure and at least one gel. A surface of the substrate structure has a concave and at least one groove. The concave is used for containing the light emitting diode. A predetermined distance (D) is between the groove and the light emitting diode. The groove is formed around the light emitting diode. The gel covers the light emitting diode and a portion of the surface of the substrate structure. The gel is limited to surface tension in the groove and is positioned in a predetermined region surrounded by the groove.
Owner:LUSTROUS TECH
Cation fluoride Gemini surface activator
InactiveCN1817431ALess quantityImprove stabilityTransportation and packagingMixingChemical structureCritical micelle concentration
A cationic fluoric surfactant Gemini and its chemical structure are disclosed. Its advantages are lower critical micell concentration, less consumption, and high dispersity, foam stability, penetrability and wettability.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Microfabricated rubber microscope using soft solid immersion lenses
Soft lithography with surface tension control is used to microfabricate extremely efficient solid immersion lenses (SILs) out of rubber elastomeric material for use in microscope type applications. In order to counteract the surface tension of the mold material in a negative mold that causes creep on a positive mold, material such as RTV is partially cured before use in order to allow the reticulation of polymer chains to change the viscosity of the uncured material in a controllable manner. In a specific embodiment, the techniques of soft lithography with surface tension control are used to make molded SILs out of the elastomer polydimethylsiloxane. The lenses achieve an NA in the range of 1.25. The principle of compound lens design is used to make the first compound solid immersion lens, which is corrected for higher light gathering ability and has a calculated NA=1.32. An important application of these lenses is integrated optics for microfluidic devices, specifically in a handheld rubber microscope for microfluidic flow cytometry.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for improving chamfer quality of disk edge surfaces with laser treatment
A carbon dioxide laser is used as a non-mechanical means for smoothing and polishing the as-cut chamfer surface at the edge of the disk. Applying laser radiation to the glass surface causes transient melting and resolidification. Due to surface tension effects, the glass resolidifies to produce a surface that is significantly smoother than it was before irradiation. If scratches or abrasive marks are present on the glass surface prior to irradiation, the irradiation process "polishes out" these defects as long as they are not too deep. At a wavelength near 10 mum, the penetration depth of the radiation into the glass is approximately 1 mum. Therefore, scratches and defects of this order of magnitude are eliminated. The quality of the resulting modified chamfer surface is far superior to the original mechanically ground and polished surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of producing recorded product (printed product) and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20080032072A1Quality improvementImprove transfer rateMeasurement apparatus componentsPrinting press partsSurface layerImage formation
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method of forming an image, which allows a high quality image to be formed on an intermediate transfer body including a surface layer with an ink-repelling property, and then to be transferred at a high transfer rate, and provides an image forming apparatus therefor. In the embodiment of the present invention, an ink image is formed on the intermediate transfer body, on the surface of which an oil and a water-soluble surfactant having surface tension in a range between more than 0 times and not more than 1.1 times of that of the oil are present. Subsequently, the formed ink image is transferred to a recording medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Integrated lance and strip for analyte measurement
The present invention relates, in general, to lancing elements for use in drawing bodily fluids out of a patient and, more particularly, to an improved lancing element including first and second elements positioned relative to each other such that an incision formed by the first element is held open by the second element and bodily fluids are pulled up the lancing element by surface tension on the first and second lancing elements.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Droplet ejector with oscillating tapered aperture
InactiveUS6926208B2Easy to operateLittle has been producedInking apparatusMovable spraying apparatusFluid injectionFluid supply
A fluid injection device for ejecting fluid droplets in response to electrical signals comprises an oscillating surface that has one or more tapered apertures, each aperture having a first and second opening. The first opening of each aperture is larger than the second opening. The first opening is in surface tension contact with the fluid to be ejected. The fluid interaction with the tapered aperture wall creates cycles of fluid compression and decompression inside the aperture, causing fluid to be drawn from the large opening and ejected out the small opening of the aperture. The device includes a fluid supply nozzle that transports fluid to the oscillating surface at the large opening of the apertures. A discharge valve controls the fluid supply. An electronic wave generator induces oscillation in the tapered aperture containing surface. The device is used to great advantage for fluid atomization and fluid spray.
Owner:NOVARTIS FARMA
Integrated lance and strip for analyte measurement
InactiveUS20040193202A1Cleaner lance woundIncrease in sizeIncision instrumentsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnalyteBody fluid
The present invention relates, in general, to lancing elements for use in drawing bodily fluids out of a patient and, more particularly, to an improved lancing element including first and second elements positioned relative to each other such that an incision formed by the first element is held open by the second element and bodily fluids are pulled up the lancing element by surface tension on the first and second lancing elements.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
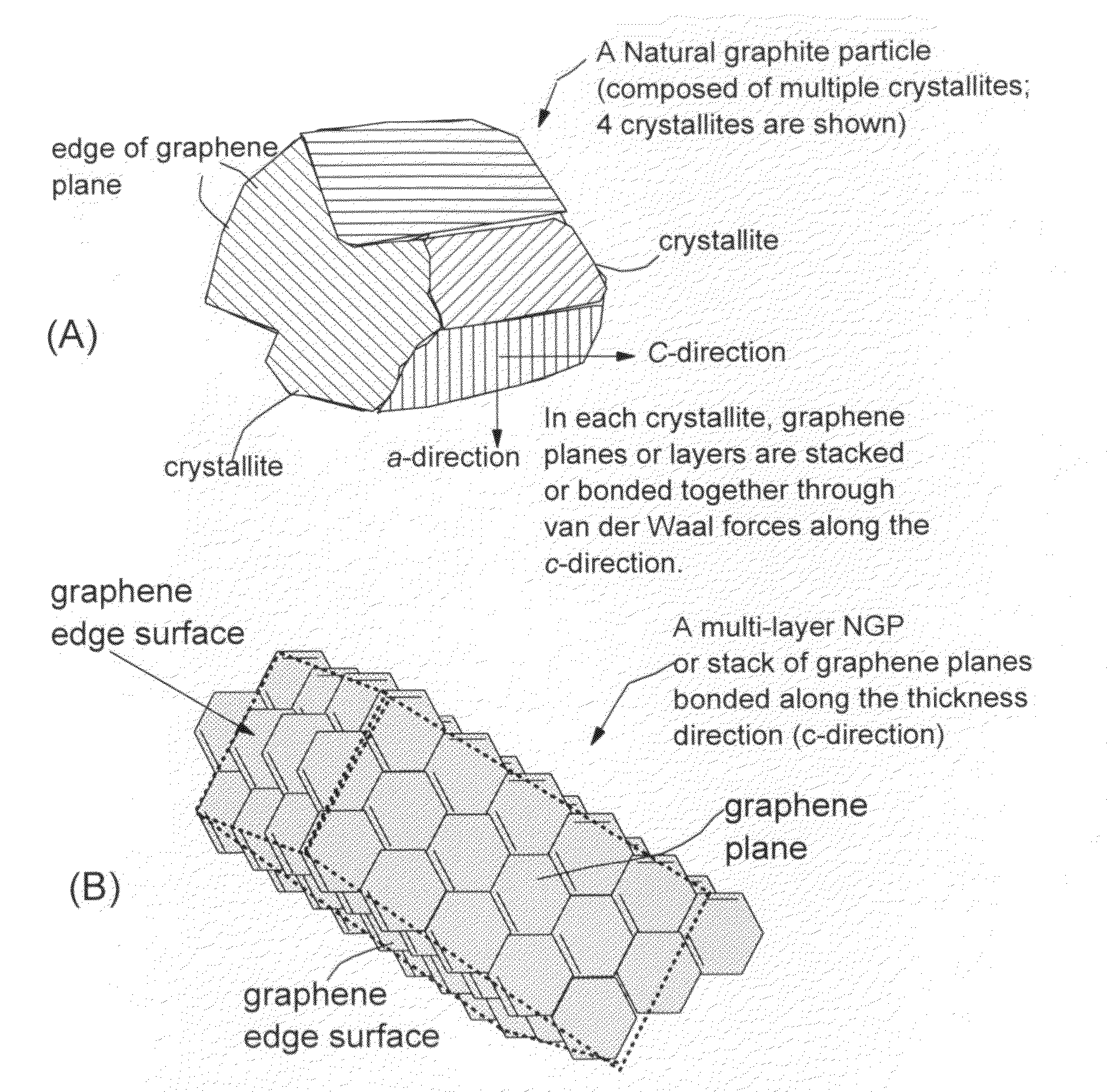
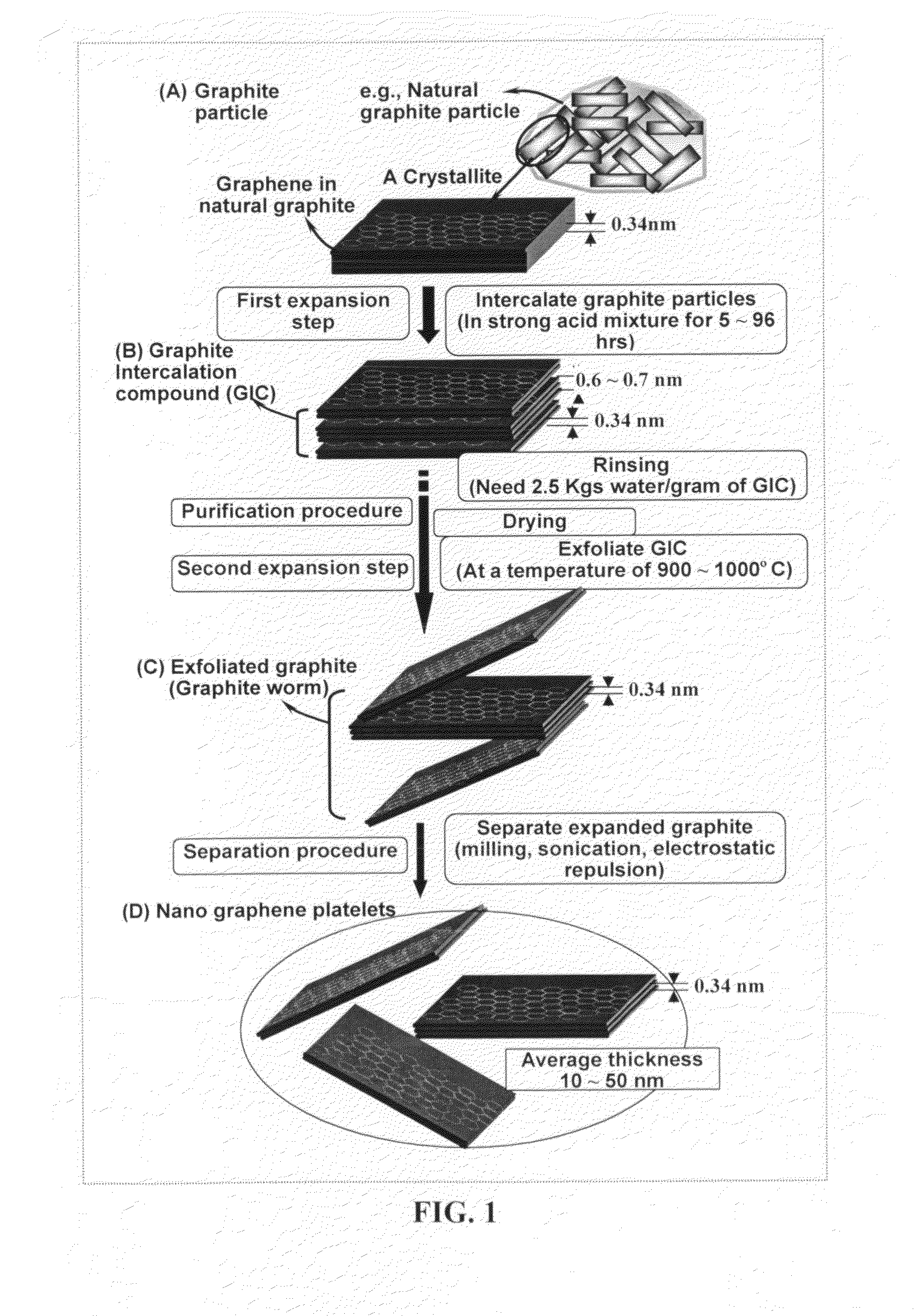
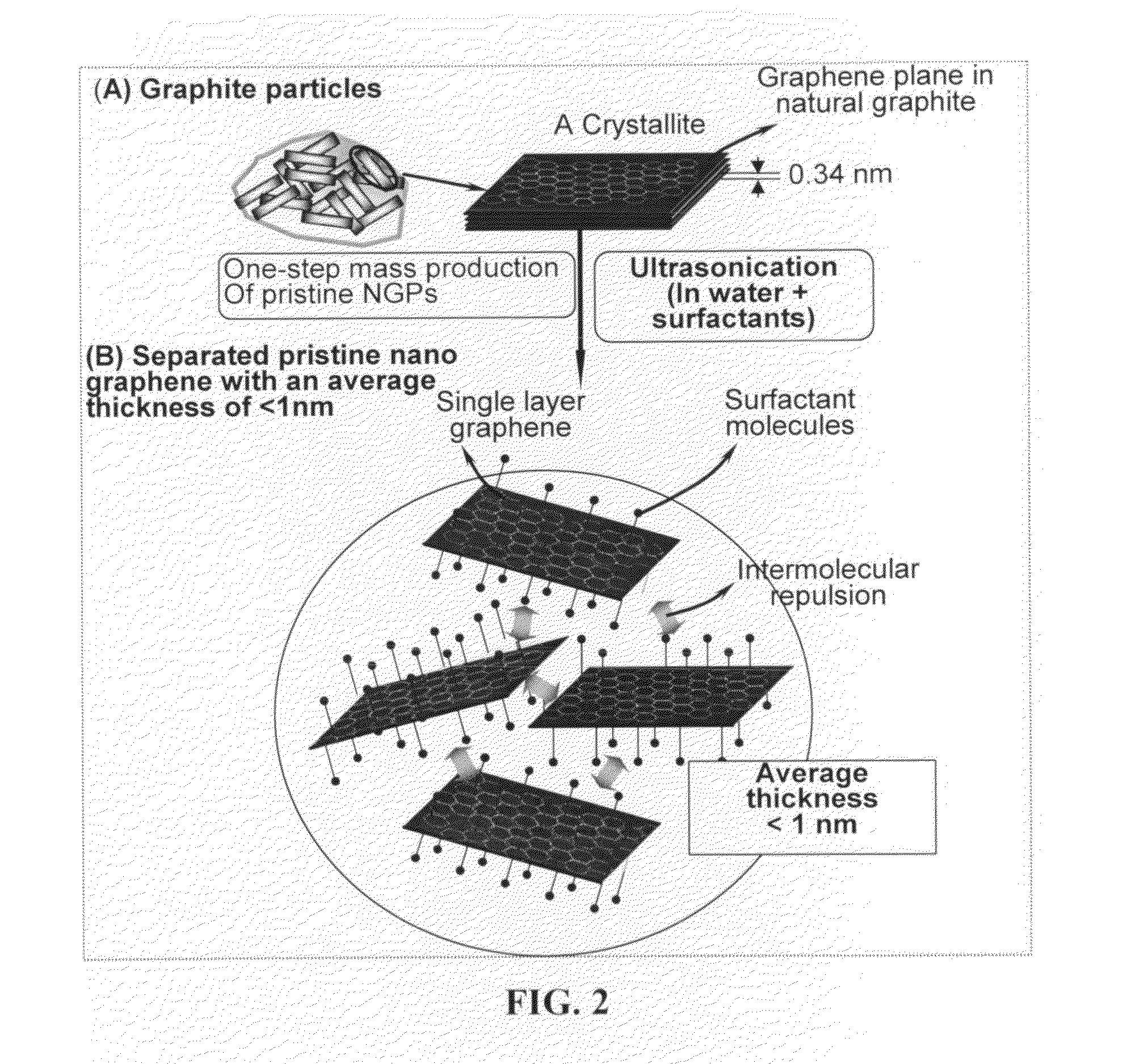
Mass production of pristine nano graphene materials
ActiveUS20110017585A1Reduce surface tensionImprove production yieldMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneLiquid mediumDisplay device
The present invention provides a method of producing pristine or non-oxidized nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are highly conductive. The method comprises: (a) providing a pristine graphitic material comprising at least a graphite crystallite having at least a graphene plane and an edge surface; (b) dispersing multiple particles of the pristine graphitic material in a liquid medium containing therein no surfactant to produce a suspension, wherein the multiple particles in the liquid have a concentration greater than 0.1 mg / mL and the liquid medium is characterized by having a surface tension that enables wetting of the liquid on a graphene plane exhibiting a contact angle less than 90 degrees; and (c) exposing the suspension to direct ultrasonication at a sufficient energy or intensity level for a sufficient length of time to produce the NGPs. Pristine NGPs can be used as a conductive additive in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays (e.g., to replace expensive indium-tin oxide), battery and supercapacitor electrodes, and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding, static charge dissipation, and fuel cell bipolar plate applications.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com