Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10648 results about "Screen printing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
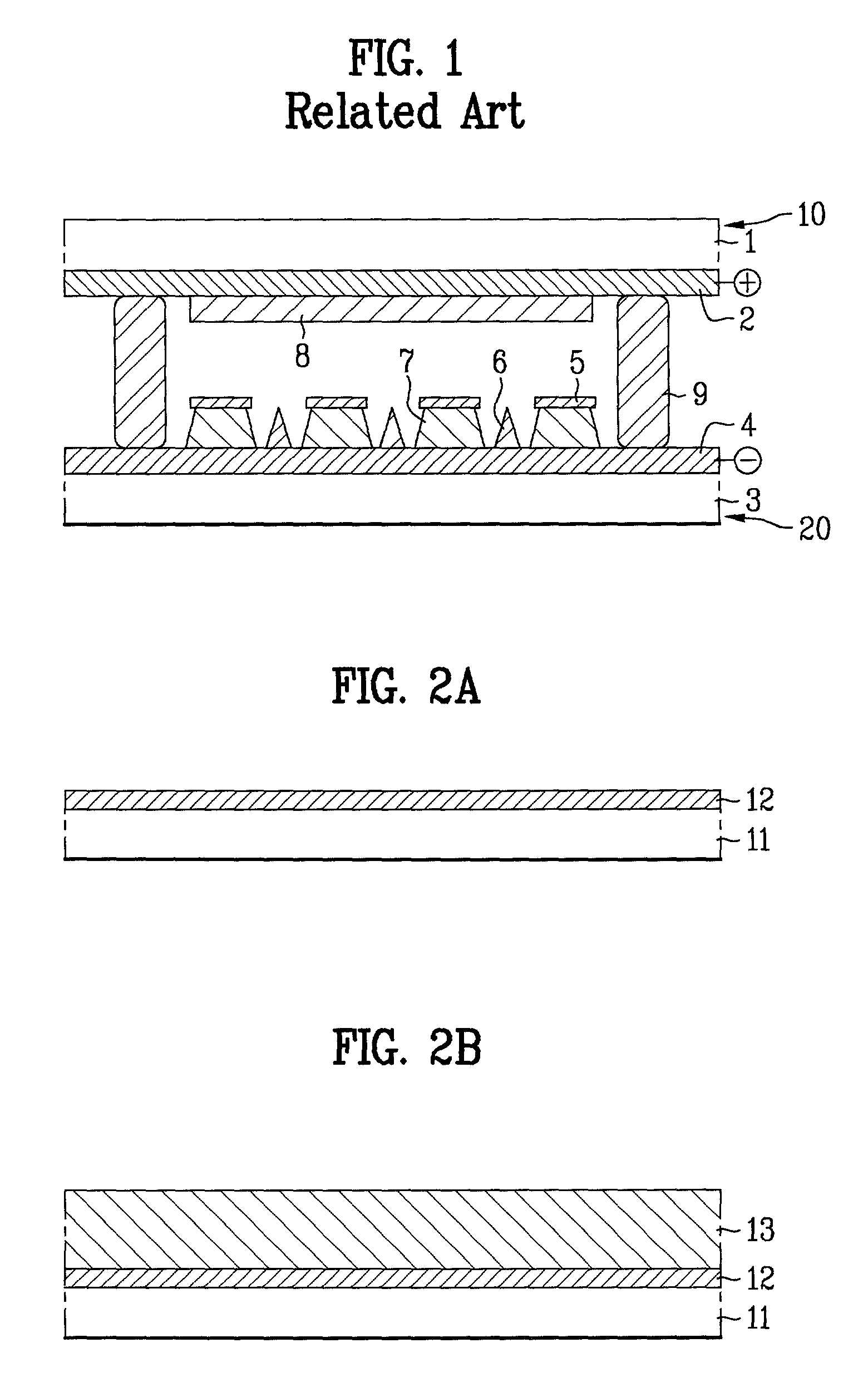
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One color is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multicoloured image or design.
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
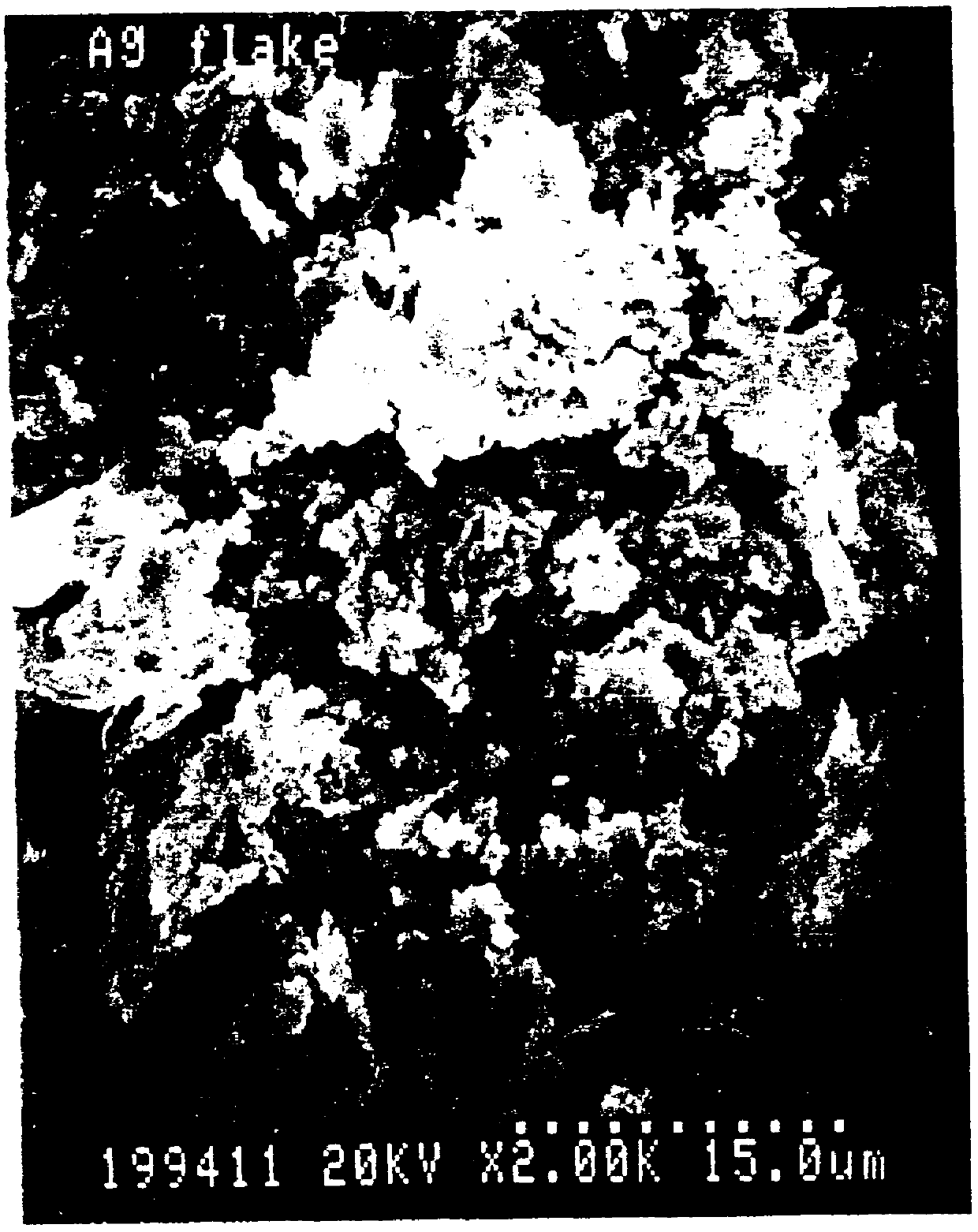
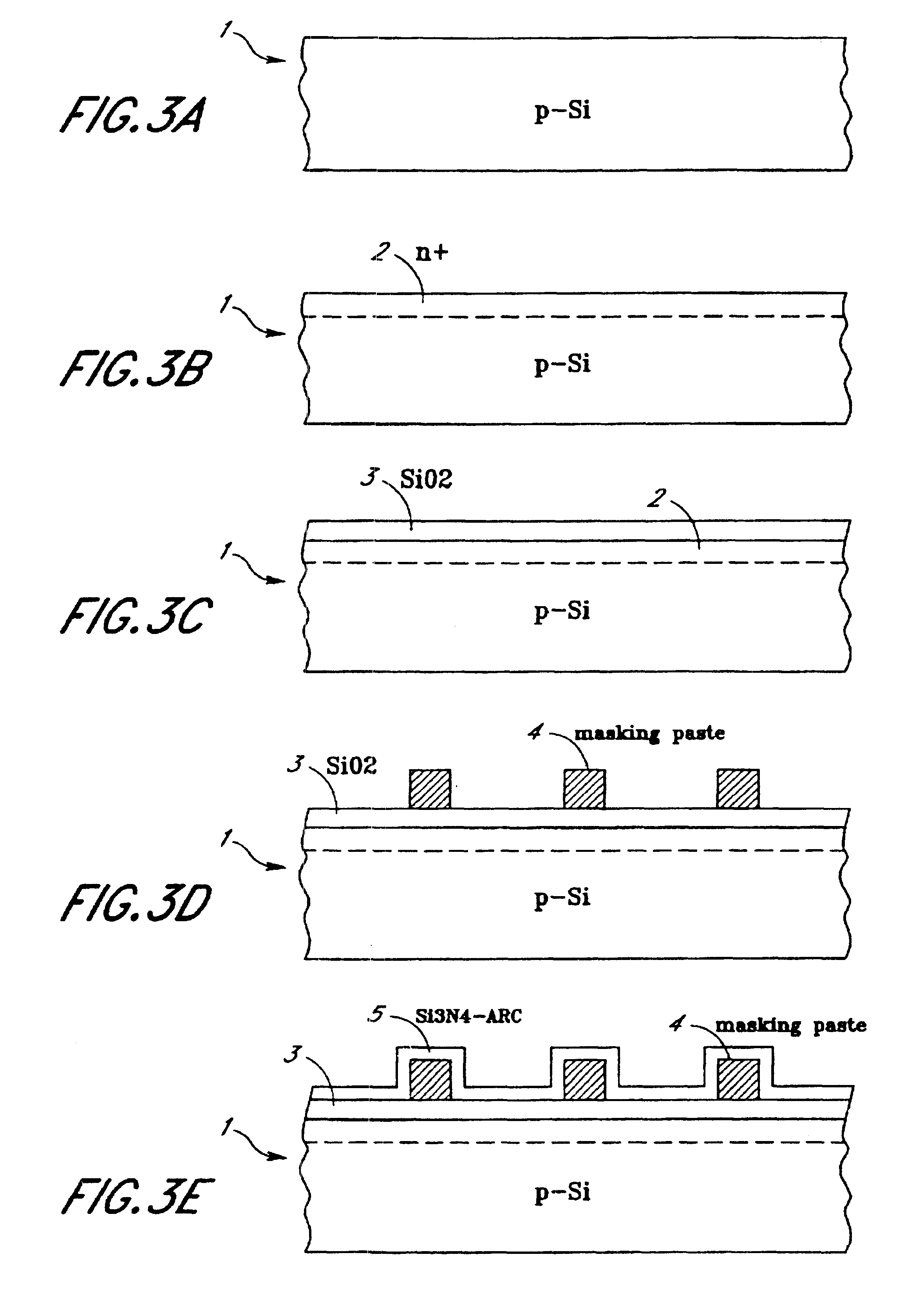
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
Highly catalytic screen-printing ink
ActiveUS7018568B2Easy to produceConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialConductive polymerPrinting ink
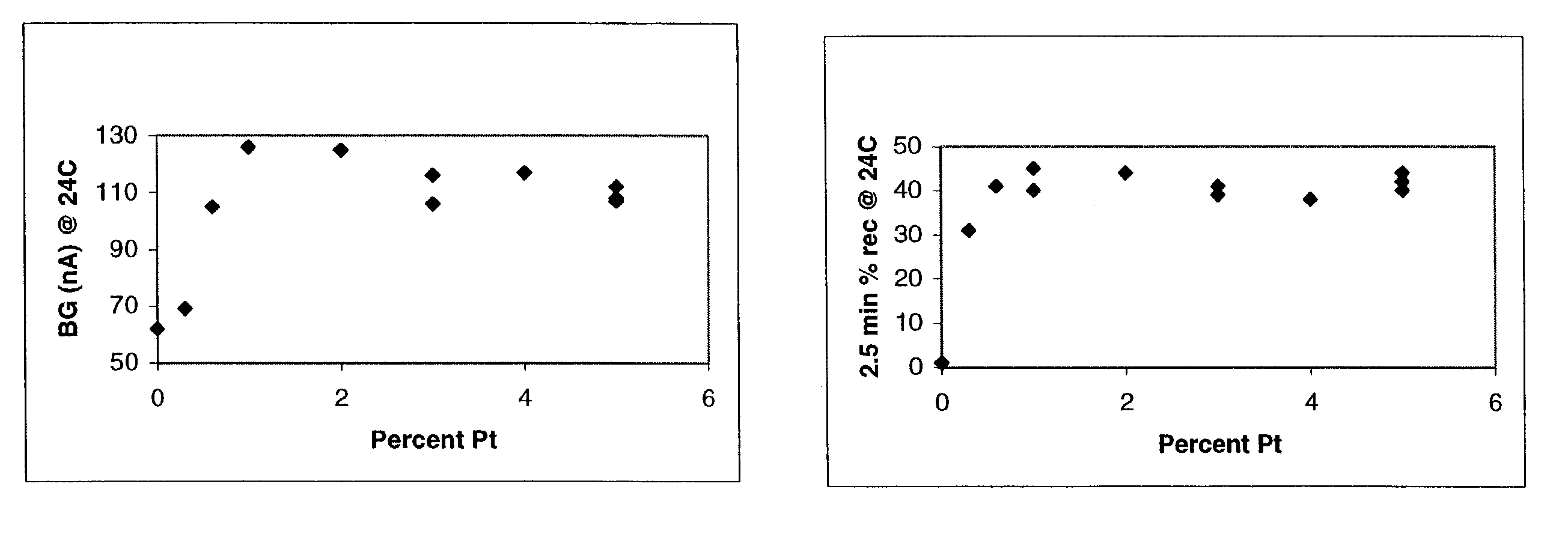
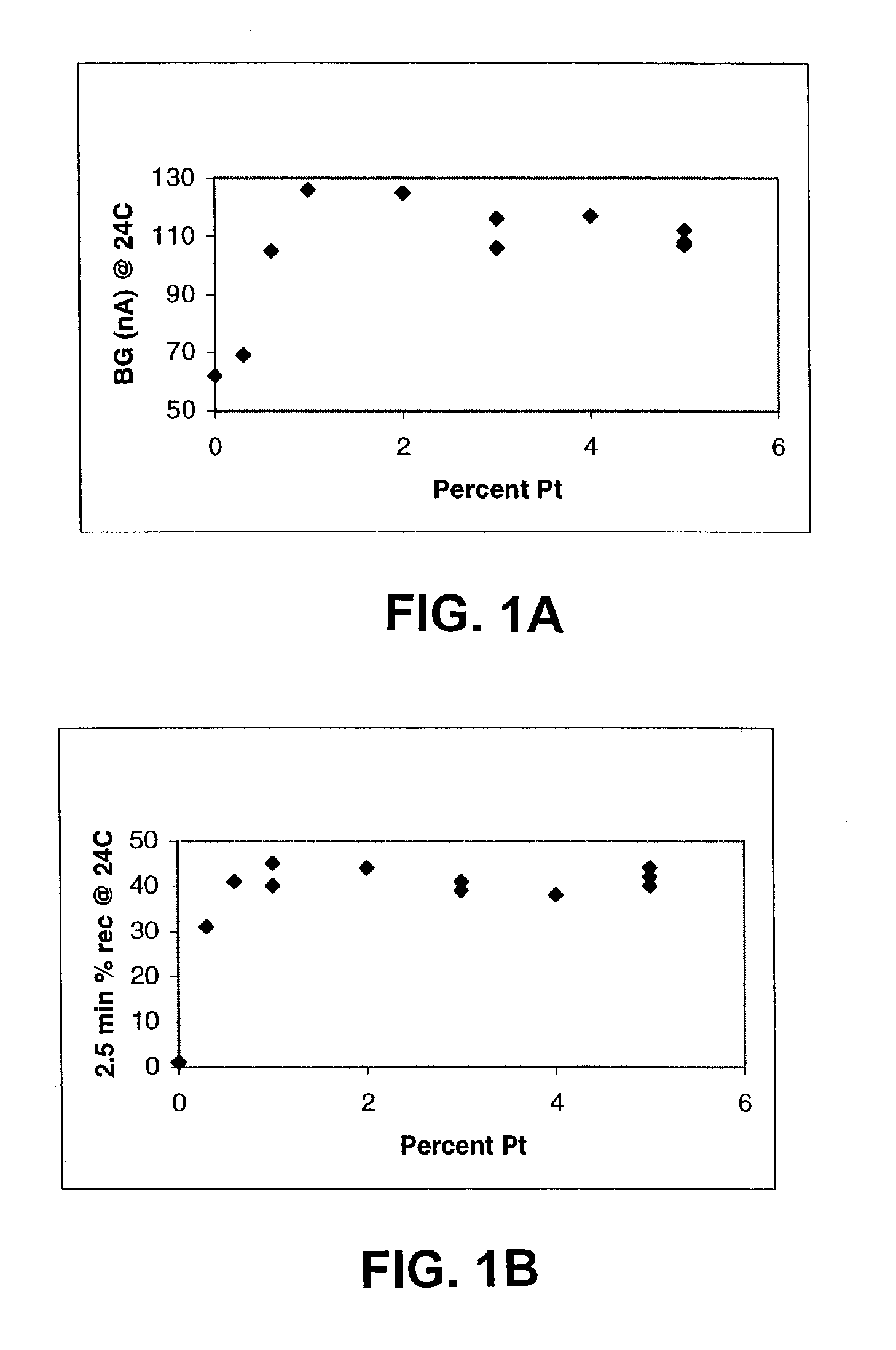
The invention is directed to conductive polymer compositions, catalytic ink compositions (e.g., for use in screen-printing), electrodes produced by deposition of an ink composition, methods of making, and methods of using thereof. An exemplary ink material comprises platinum black and / or platinum-on-carbon as the catalyst, graphite as a conducting material, a polymer binding material, and an organic solvent. The polymer binding material is typically a copolymer of hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers. The conductive polymer compositions of the present invention can be used, for example, to make electrochemical sensors. Such sensors can be used in a variety of analyte monitoring devices to monitor analyte amount or concentrations in subjects, for example, glucose monitoring devices to monitor glucose levels in subjects with diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
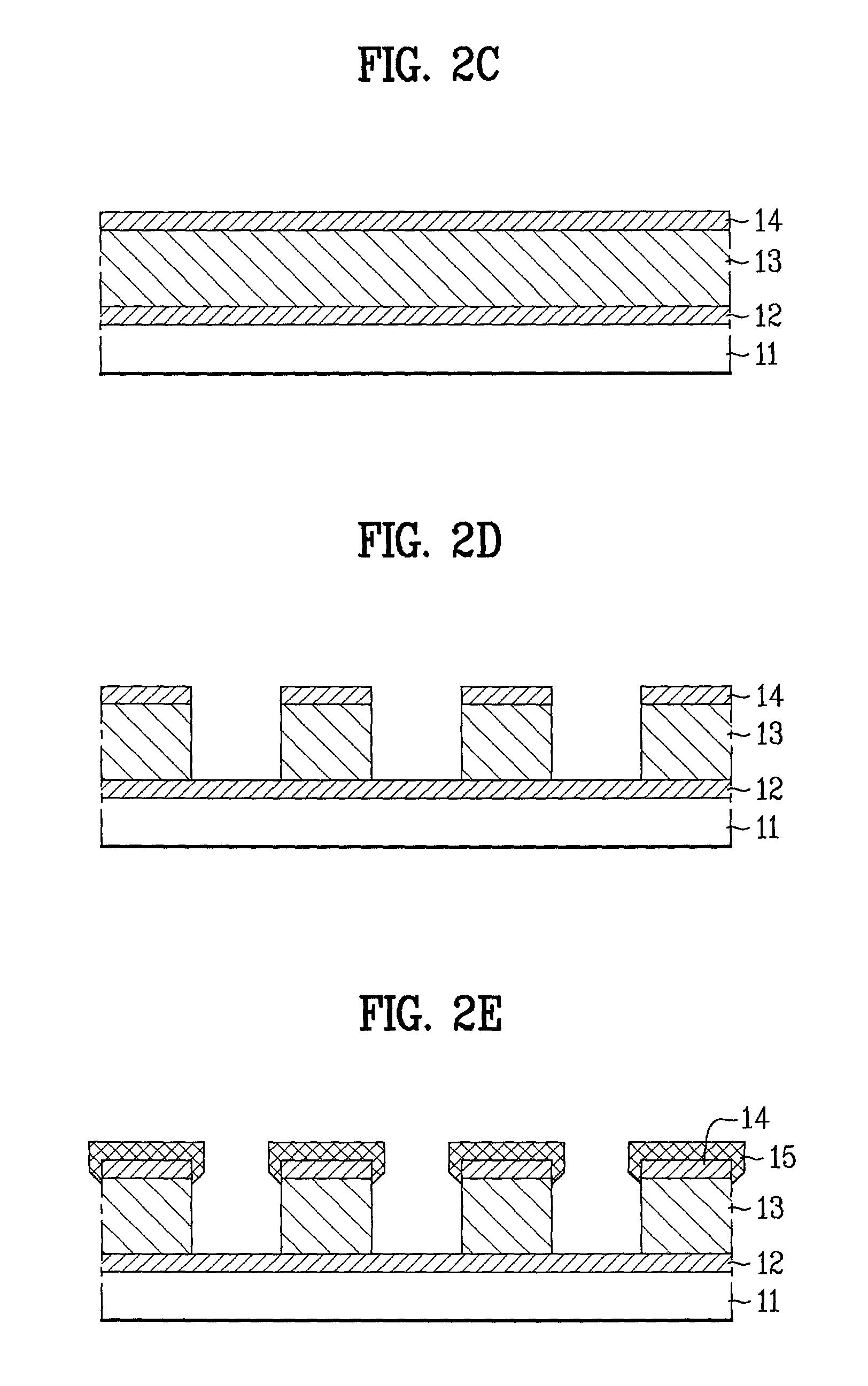
Screen printing shaped articles
Shaped ceramic articles can be obtained by screen printing the desired shapes from a dimensionally stable dispersion of a precursor of the ceramic onto a surface, drying the screen printed shapes so obtained and firing them to generate the shaped ceramic articles.
Owner:SAINT GOBAINNORTON INDAL CERAMICS
Methods for achieving improved color in microencapsulated electrophoretic devices
InactiveUS7667684B2Efficiently cheaply manufactureCheap to makeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesScreen printingComputer graphics (images)
A method for manufacturing a full color, reflective display includes the steps of depositing a first plurality of electrophoretic display elements in substantial registration with a first electrode and a second plurality of electrophoretic display elements in substantial registration with a second electrode. The electrophoretic display elements include a capsule containing a species of particles dispersed in a suspending fluid. The selective deposition of the display elements can be achieved by ink-jet printing methods, screen printing methods or other printing methods. In some embodiments the electrodes are printed onto the substrate before selective deposition of the display elements, while in other embodiments the substrate is provided having the electrodes already disposed on it. In still other embodiments, the sequence of printing of electrodes and electrophoretic display elements can be varied.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Luminescent ink for printing of organic luminescent devices
InactiveUS6372154B1Improve efficiencyEasy transitionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolventOrganic compound
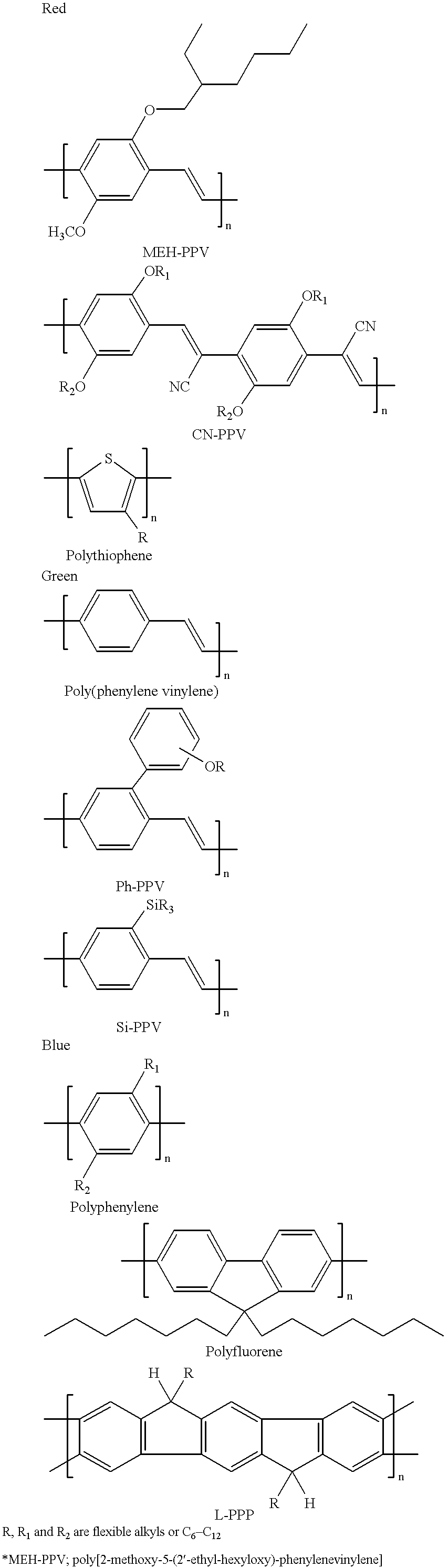
Organic luminescent ink (L-ink) is disclosed for use in printing thin films of organic luminescent material. The L-ink is particularly useful in fabricating organic optoelectronic devices, e.g. organic luminescent devices. The L-ink contains at least one organic luminescent material mixed with a solvent and other functional additives to provide the necessary optical, electronic and morphological properties for light-emitting devices (LEDs). The additives play an important role either for enhanced thin film printing or for better performance of the optoelectronic device. The functional additives may be chemically bound to the luminescent compounds or polymers. Luminescent organic compounds, oligomers, or polymers with relatively low solution viscosity, good thin film formability, and good charge transporting properties, are preferred. The L-inks can be cross-linked under certain conditions to enhance thin film properties. The L-ink can be used in various printing methods, such as screen printing, stamp printing, and preferably ink-jet printing (including bubble-jet printing).
Owner:CANON KK
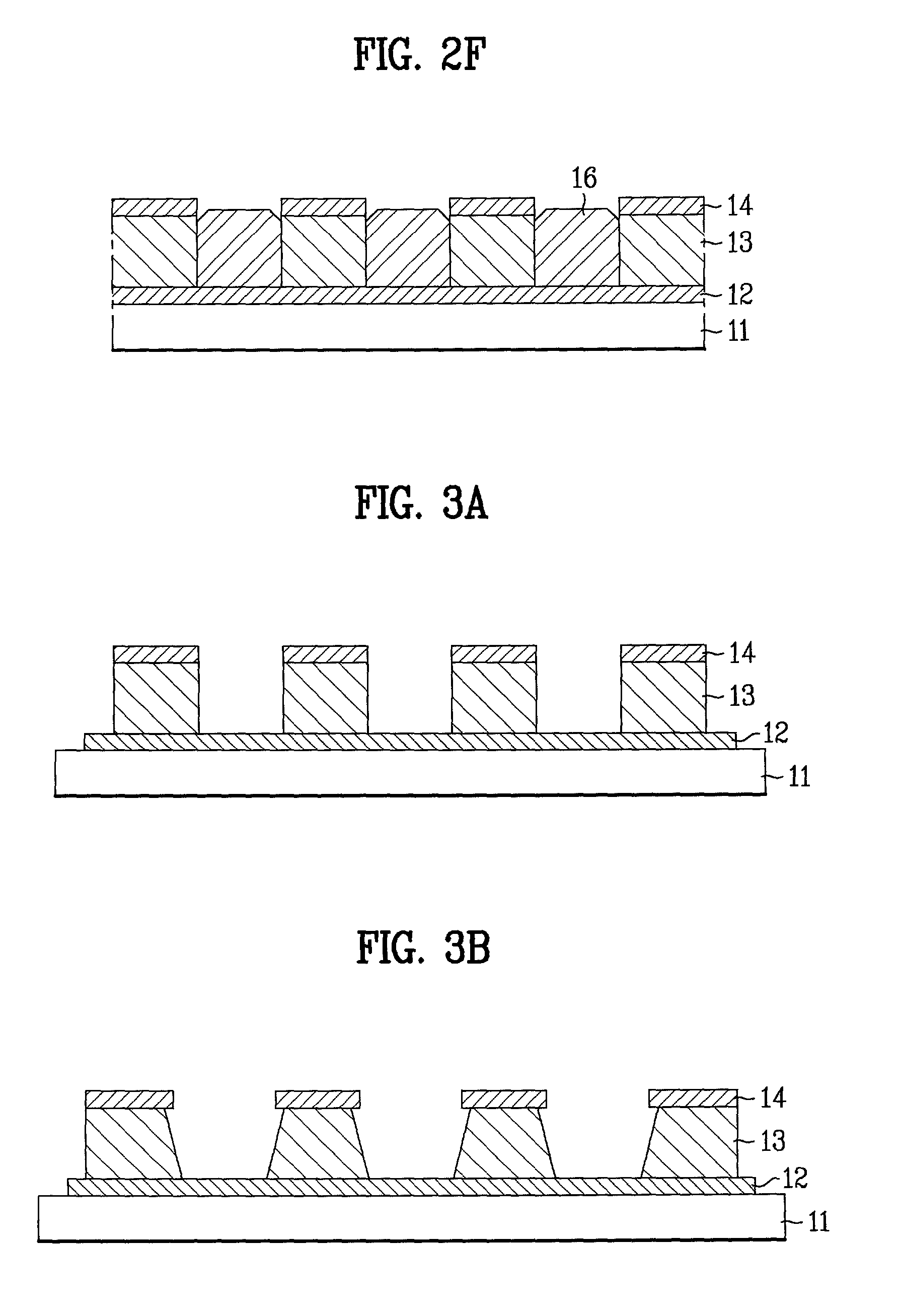
Integrated circuit substrate having laser-embedded conductive patterns and method therefor
InactiveUS6930256B1Printed electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsScreen printingHigh density
An integrated circuit substrate having laser-embedded conductive patterns provides a high-density mounting and interconnect structure for integrated circuits. Conductive patterns within channels on the substrate provide interconnects that are isolated by the channel sides. A dielectric material is injection-molded or laminated over a metal layer that is punched or etched. The metal layer can provide one or more power planes within the substrate. A laser is used to ablate channels on the surfaces of the outer dielectric layer for the conductive patterns. The conductive patterns are electroplated or paste screen-printed and an etchant-resistive material is applied. Finally, a plating material can be added to exposed surfaces of the conductive patterns. An integrated circuit die and external terminals can then be attached to the substrate, providing an integrated circuit having a high-density interconnect.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Light emitting device with silicone resin layer formed by screen printing
ActiveUS7745818B2Improve heat resistanceConvenient lightingDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsScreen printingPolystyrene
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20010004979A1Stable driving voltageUniform characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLow voltageCarbon nanotube
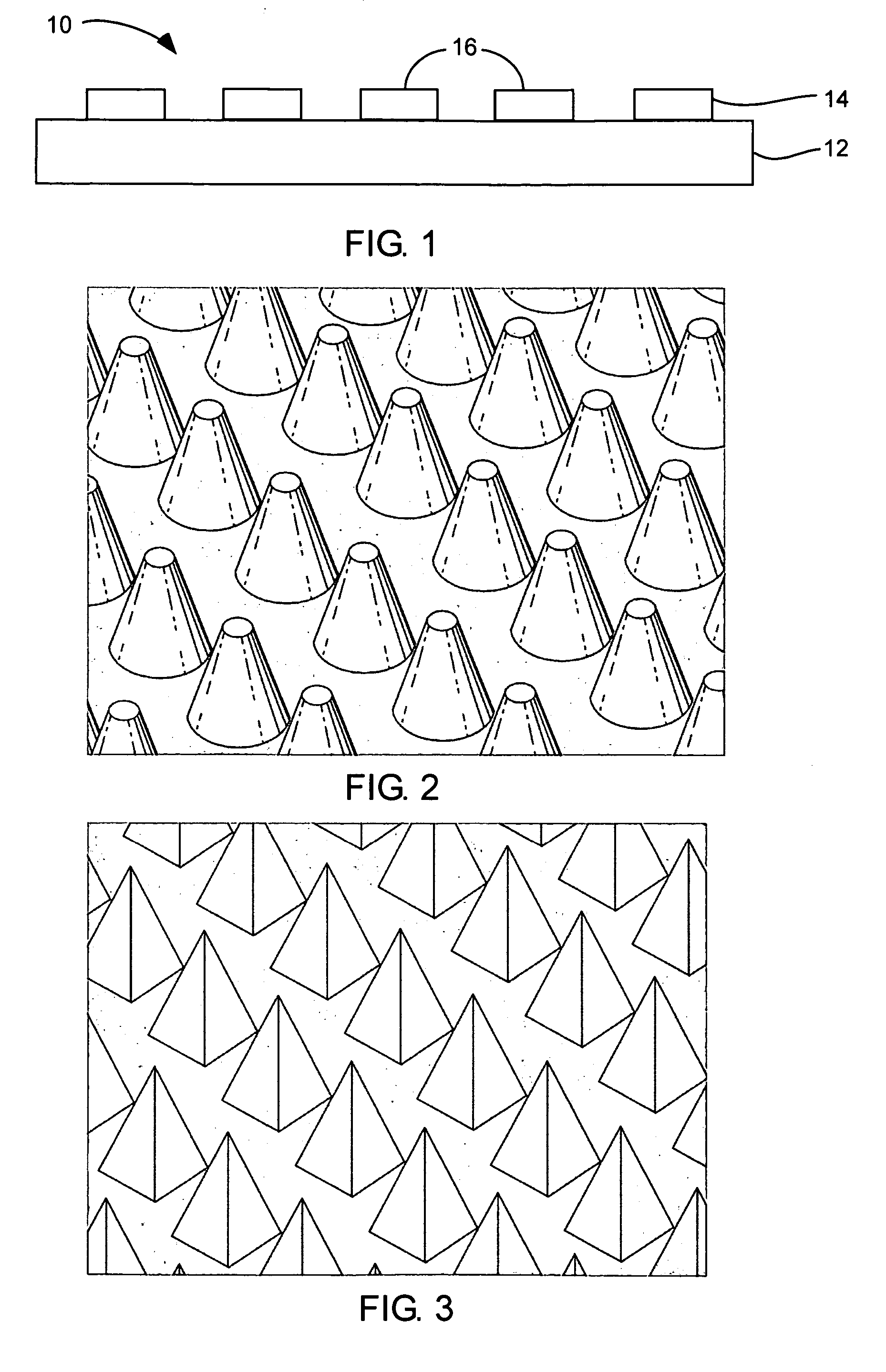
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same, the field emission display including a cathode array having a cathode electrode formed on a substrate, insulating layers and carbon nanotube films for use as emitter electrodes formed alternately on the cathode electrode, and a gate electrode formed on the insulating layer, thereby permitting fabrication of a large sized cathode plate at a low cost because the film is formed by screen printing and exposure, which can reduce the cumbersome steps in fabrication of the related art Spindt emitter tip, and both a low voltage and a high voltage FEDs because the carbon nanotube film used as the emitter has a low work function, with an easy and stable electron emission capability.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Fixed abrasive tools and associated methods
InactiveUS20050227590A1Easy to remove debrisAdequate material removal rateAbrasion apparatusPlane surface grinding machinesScreen printingMostly True
A fixed abrasive tool incorporating nanodiamond particles is described and disclosed. A fixed abrasive tool can include a polishing layer on a substrate. The polishing layer can include an organic matrix with nanodiamond particles therein. The polishing layer can be formed in a wide variety of configurations, depending on the specific polishing application. Most often, the polishing layer can include a plurality of projections which can have a wide variety of configurations in order to achieve a particular polishing performance. Nanodiamond particles used in the present invention can have a particle size from about 1 nm to about 50 nm, and preferably about 2 nm to about 10 nm. Optionally, the nanodiamond particles can include a carbonaceous coating. Such fixed abrasive tools can be formed by screen printing of a slurry of nanodiamond particles and an organic binder to form a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. Other methods can also be used to form the disclosed nanodiamond fixed abrasive tools. These fixed abrasive tools are particularly suitable for polishing expensive workpieces such as silicon wafers, integrated circuitry, gemstones, and hard drive platters.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
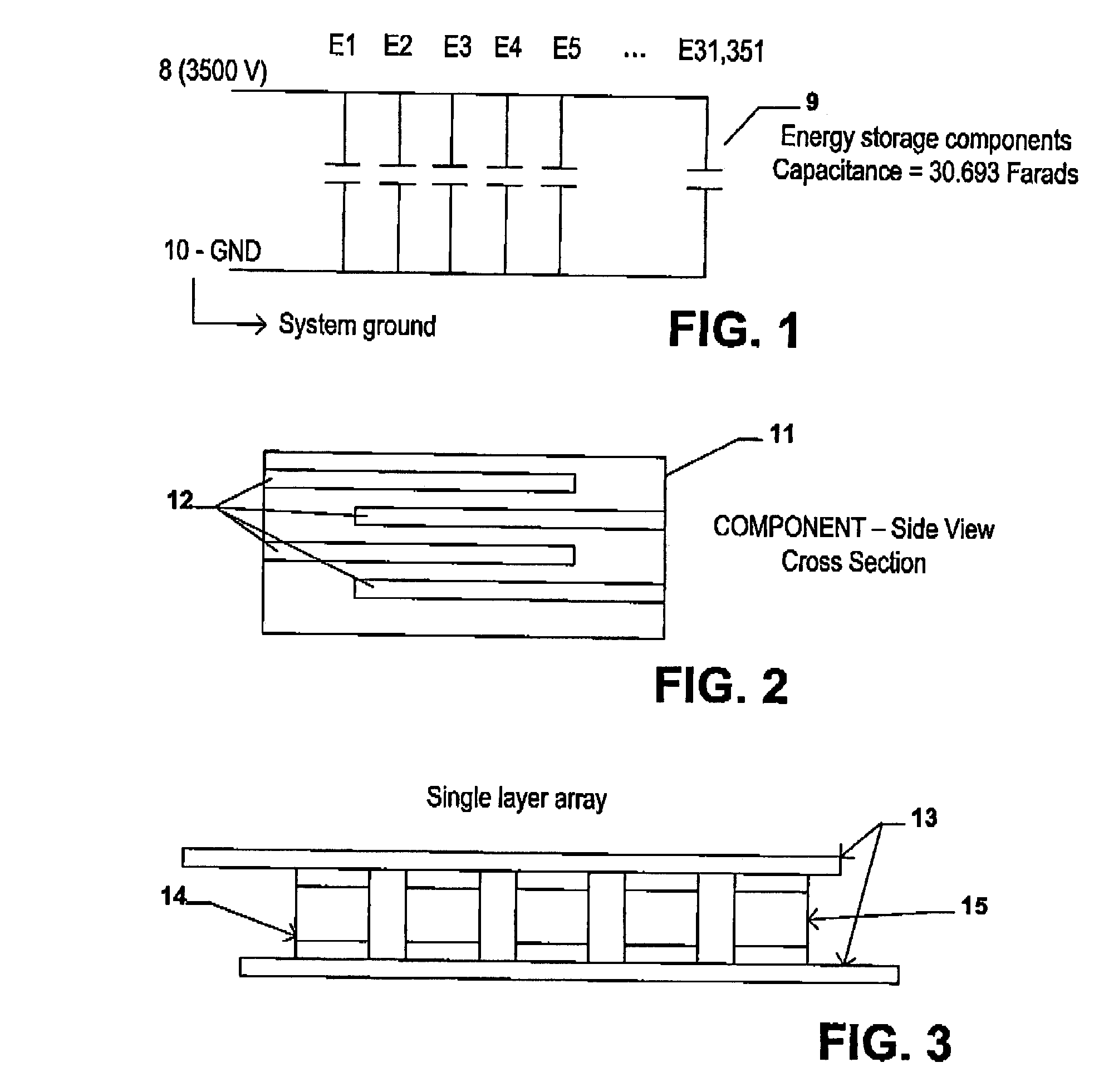
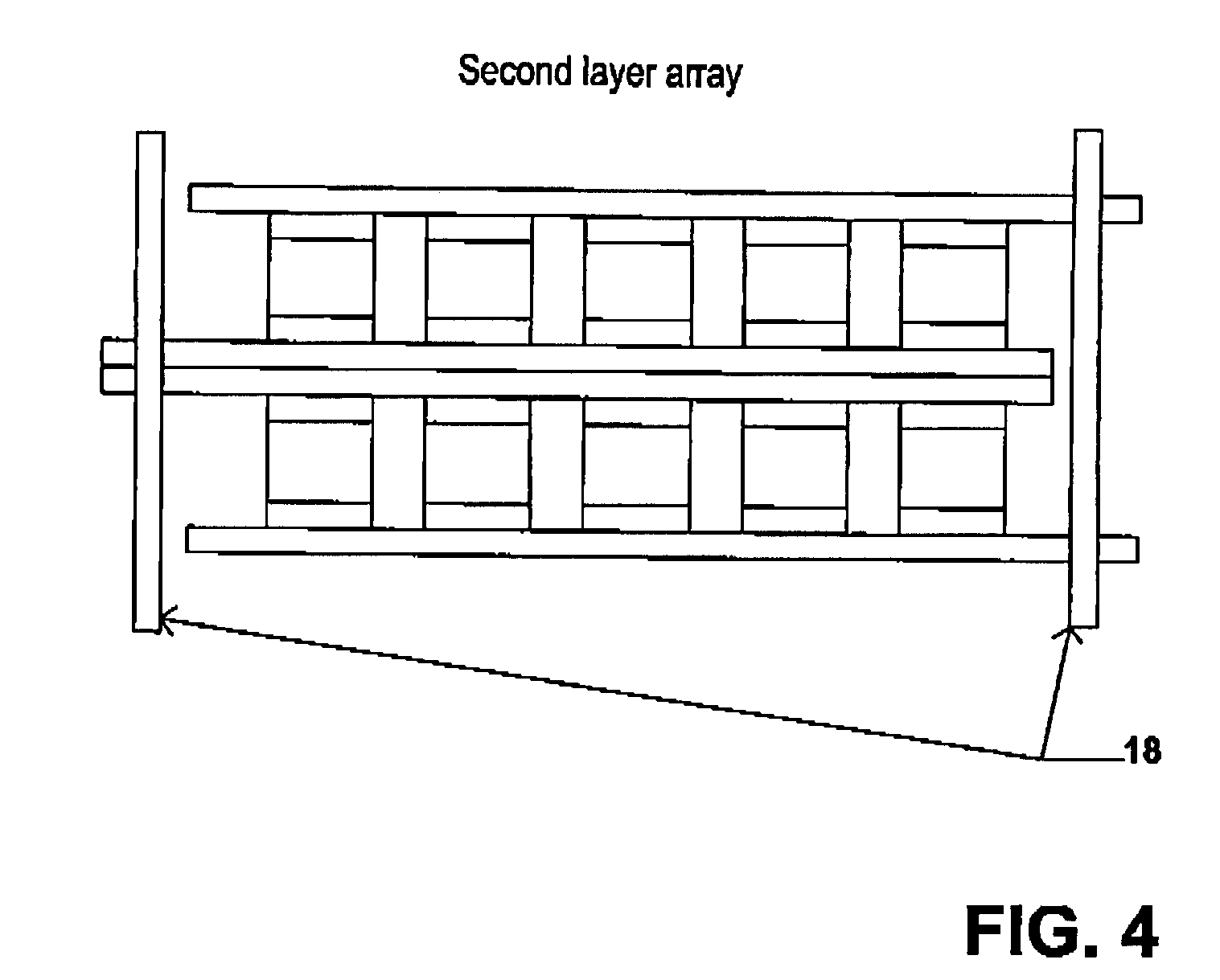
InactiveUS7033406B2Reduce sinteringLowering hot-isostatic-pressing temperatureElectrical storage systemFixed capacitor electrodesBarium titanatePermittivity
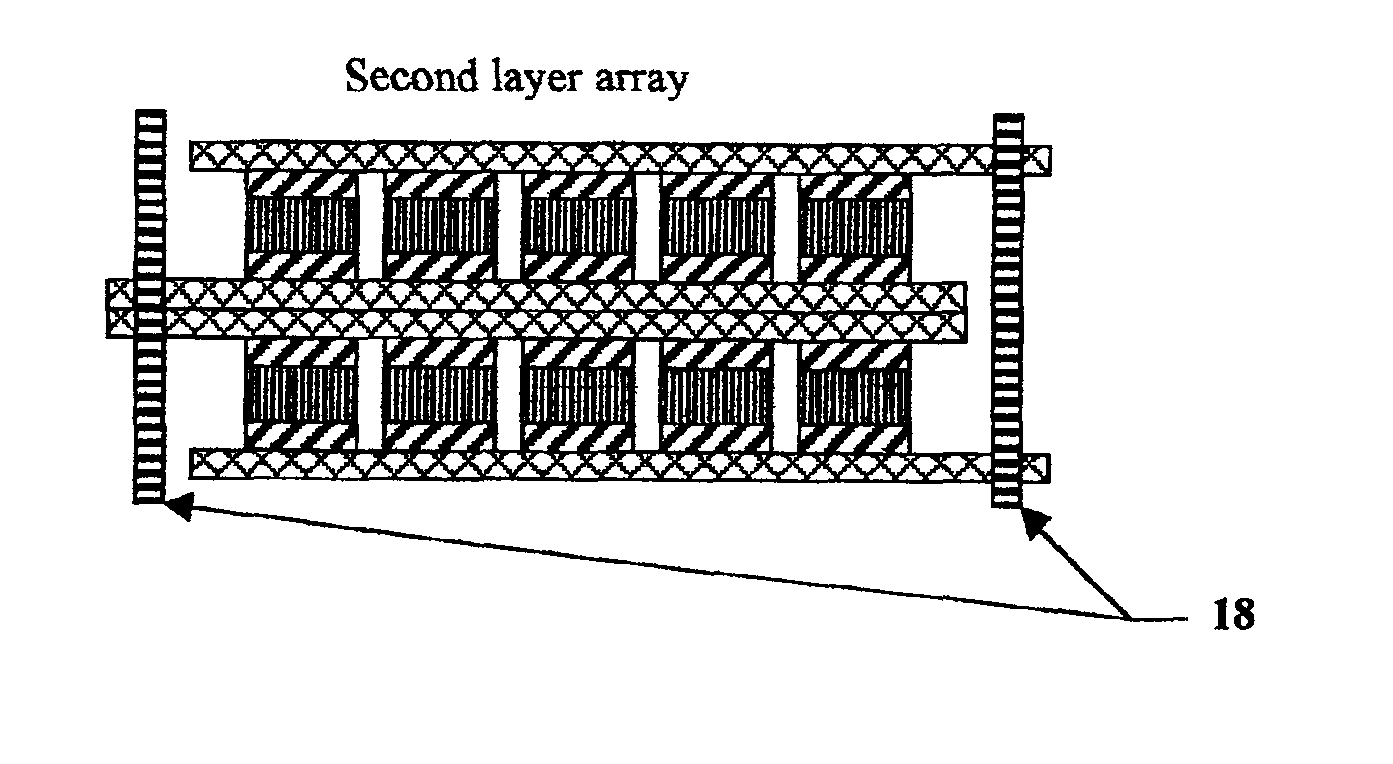
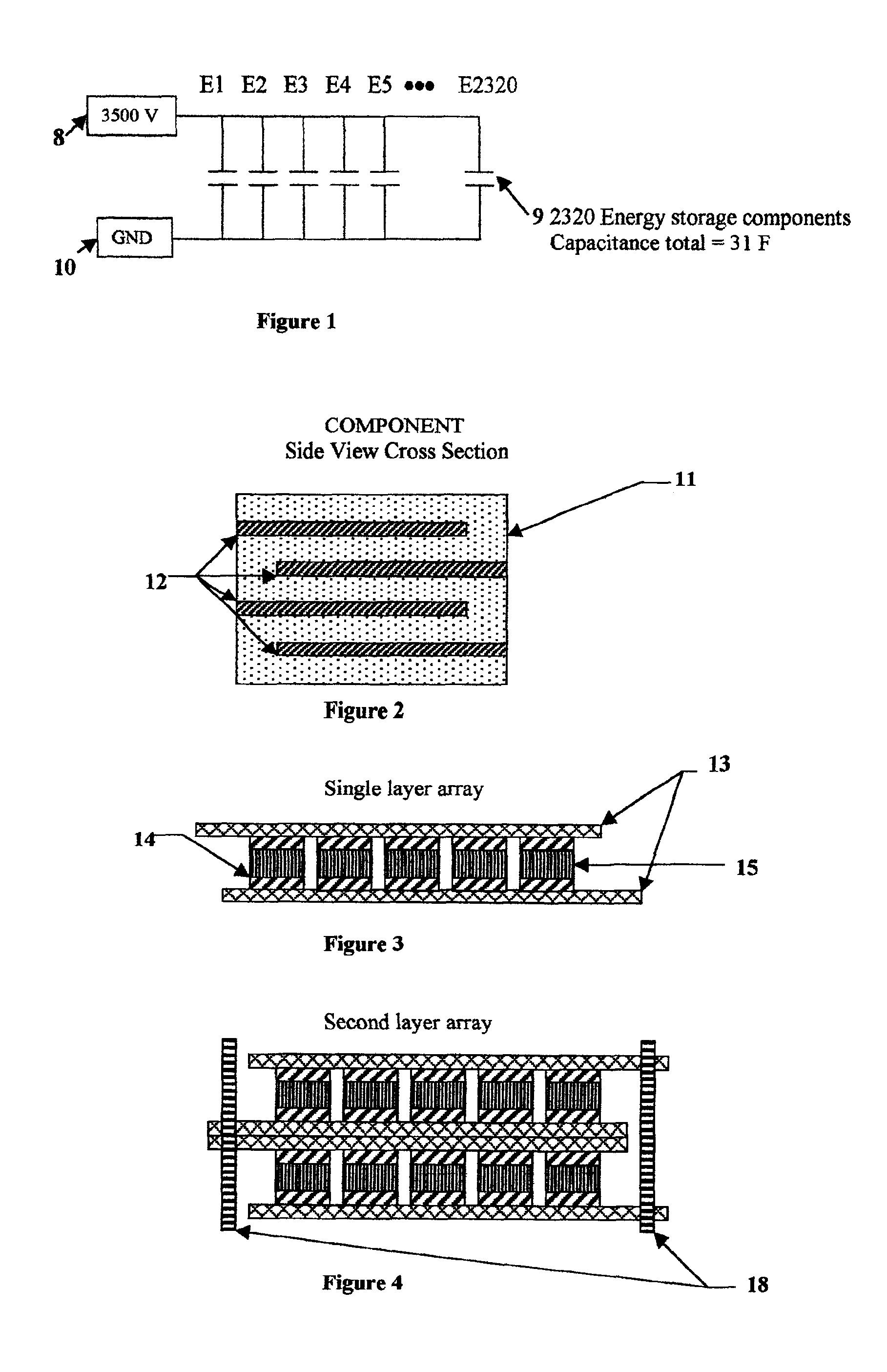
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
Method of preparing solar cell front contacts
InactiveUSRE37512E1Reduce carrier recombination lossImprove barrier propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationScreen printingOhmic contact
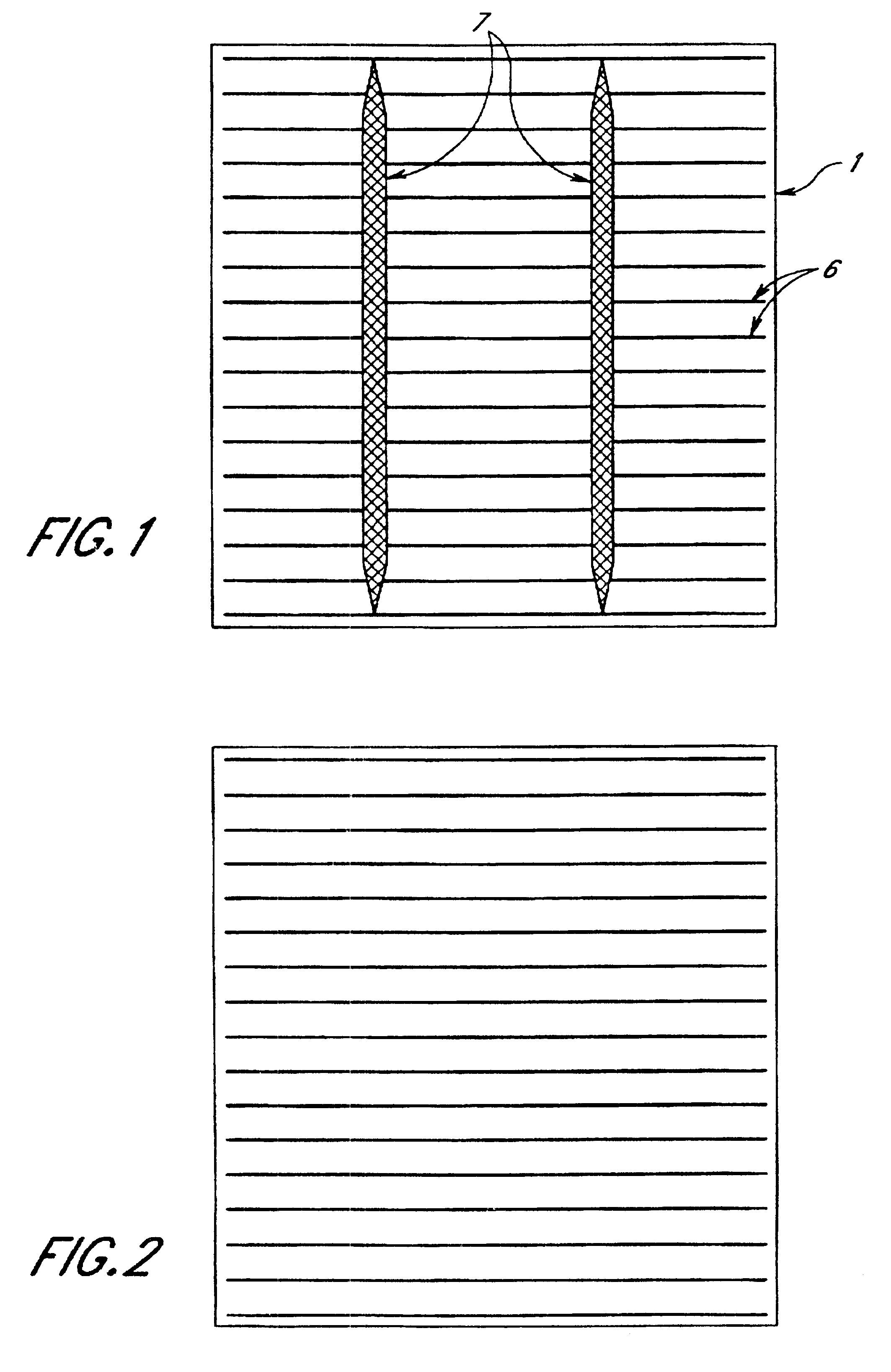
Method of preparing on a solar cell the top contact pattern which consists of a set of parallel narrow finger lines and wide collector lines deposited essentially at right angles to the finger lines on the semiconductor substrate, characterized in that it comprises at least the following steps:(a) screen printing and drying the set of contact finger lines;(b) printing and drying the wide collector lines on the top of the set of finger lines in a subsequent step;(c) firing both finger lines and collector lines in a single final step in order to form an ohmic contact between the finger lines and the semiconductor substrate and between the finger lines and the wide collector lines.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
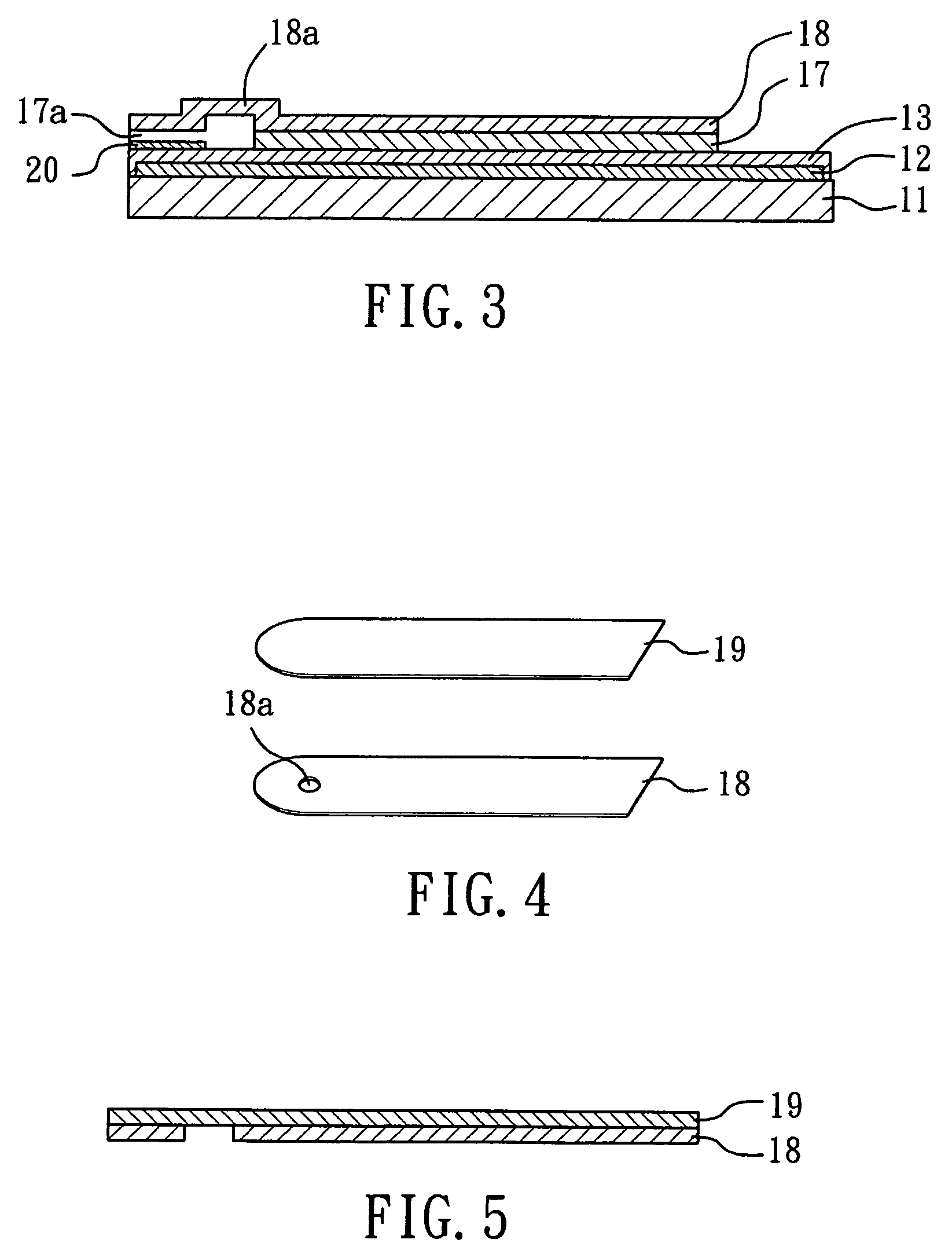
Electrochemical biosensor by screen printing and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS7138041B2Rapid sample inflowSmall volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerSiphon
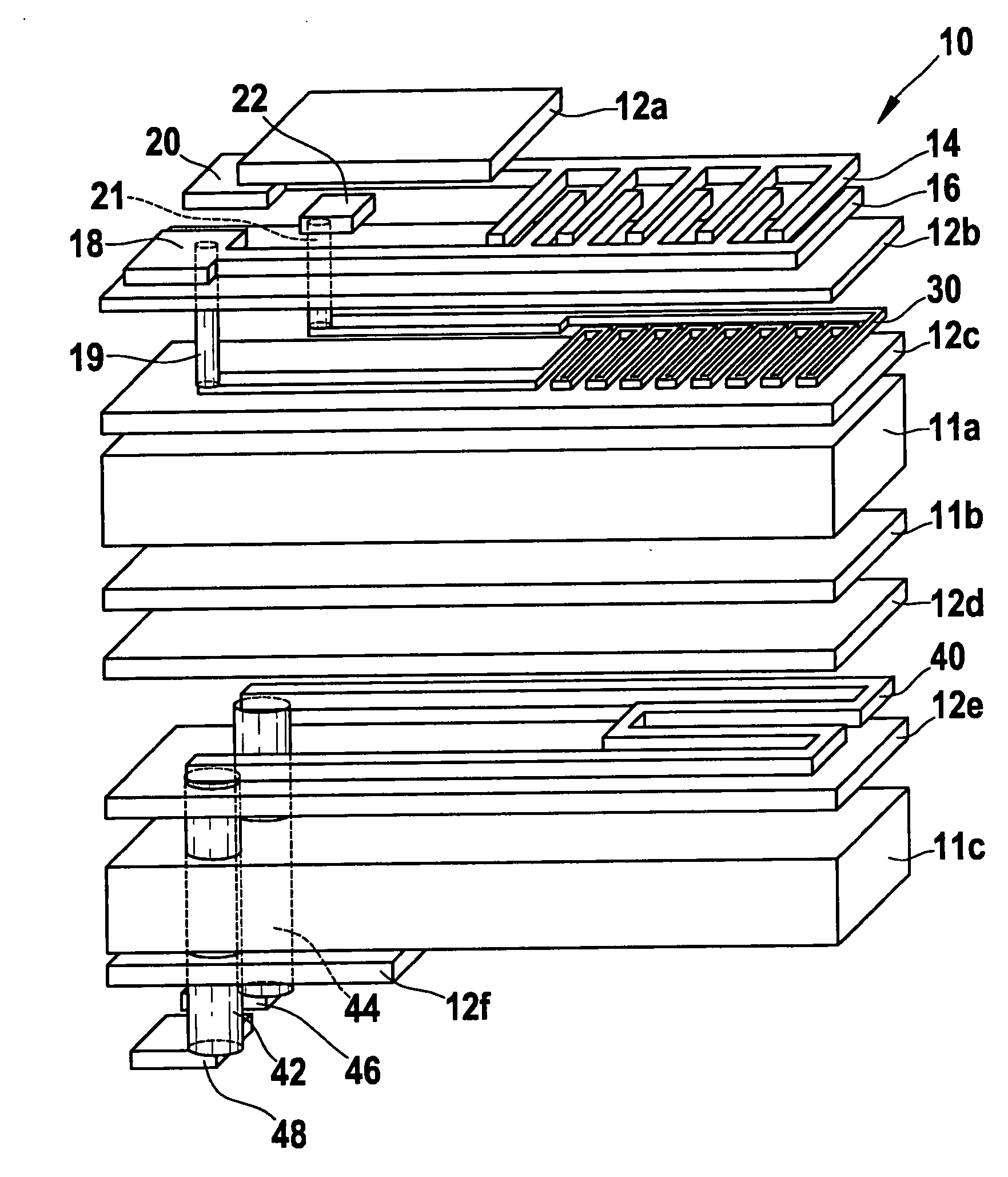
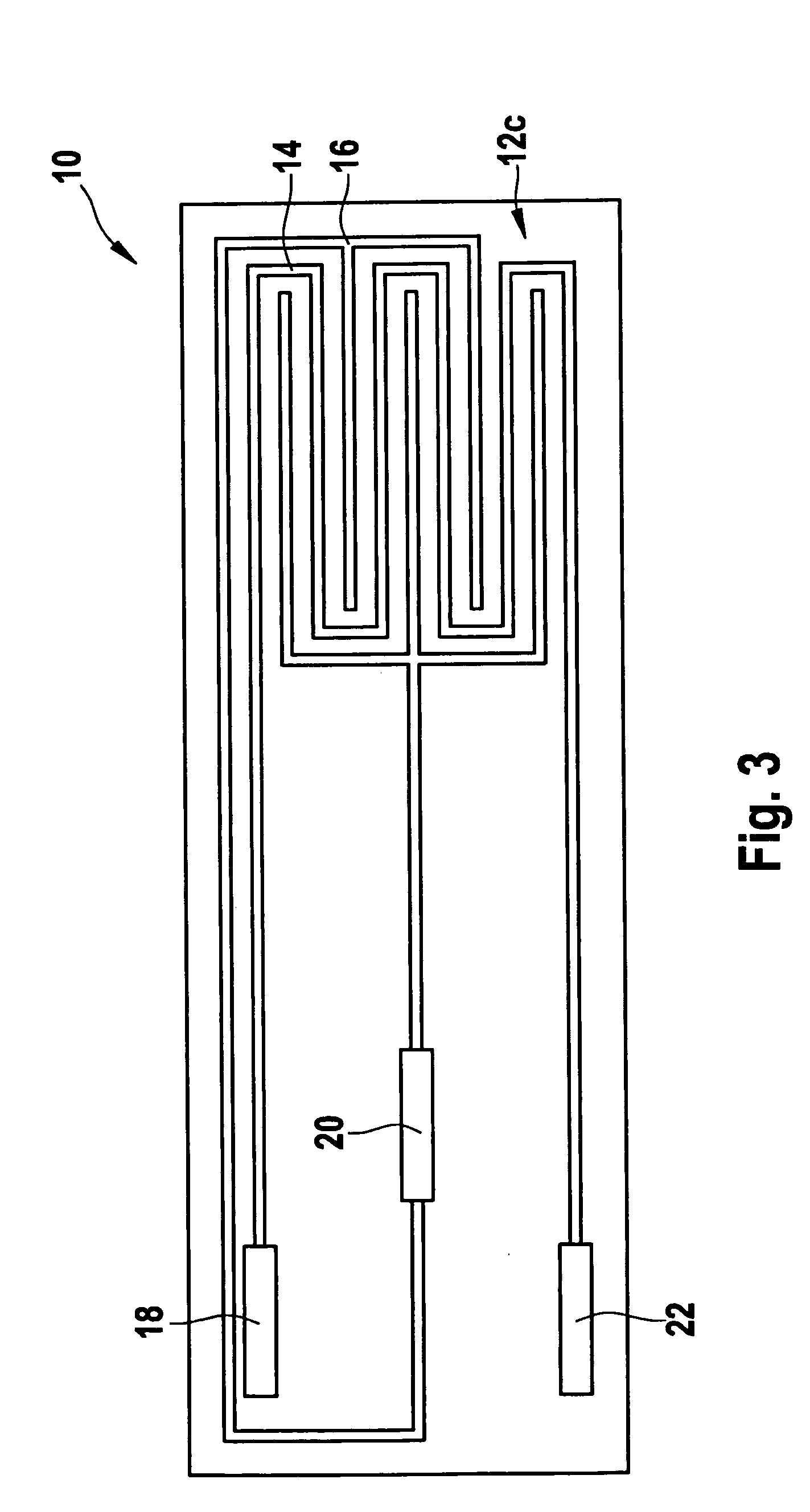
An electrochemical biosensor formed by screen printing and method of fabricating such biosensor is disclosed in the present invention. The biosensor can quickly absorb a sample to be measured therein, effectively control volume of the sample fed and “fill-and-position” the sample therein. The biosensor includes an electrode layer (electrode area) comprising two or three electrodes, which are a working electrode, a reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode (tri-electrode) on an insulating substrate. An active reaction layer containing reactant, reaction catalyst, mediator, wetting agent and surfactant is spread on the surface of the electrode layer. A sample inflow area is formed above the electrode area by adding an upper cover on top of a middle insulating layer with a U-shaped opening formed therein. Sample solution with a minute amount about 0.8 to 1 μl can be rapidly introduced into the electrode area and the active reaction layer via the inflow area by siphon or capillary, where the ingredient of the sample can be analysed by measuring reaction between the sample, reaction catalyst and mediator in the reaction layer using electrochemical potentiometric or amperometric method. An upwardly extended closed space formed within the upper cover above the electrode area adjacent to the front of conductive wires can be effectively used to control sample volume and “fill-and-position” the sample.
Owner:GENERAL LIFE BIOTECHNOLGOY
Quantum dot fluorescent inks
The present invention relates to inks and more particularly, to fluorescent ink formulations including quantum dots for various printing processes such as inkjet, flexographic, screen printing, thermal transfer, and pens. The inks include one or more populations of fluorescent quantum dots dispersed in polymeric material, having fluorescence emissions between about 450 nm and about 2500 nm; and a liquid or solid vehicle. The vehicle is present in a ratio to achieve an ink viscosity, surface tension effective, drying time and other printing parameters used for printing processes.
Owner:EVIDENT TECH
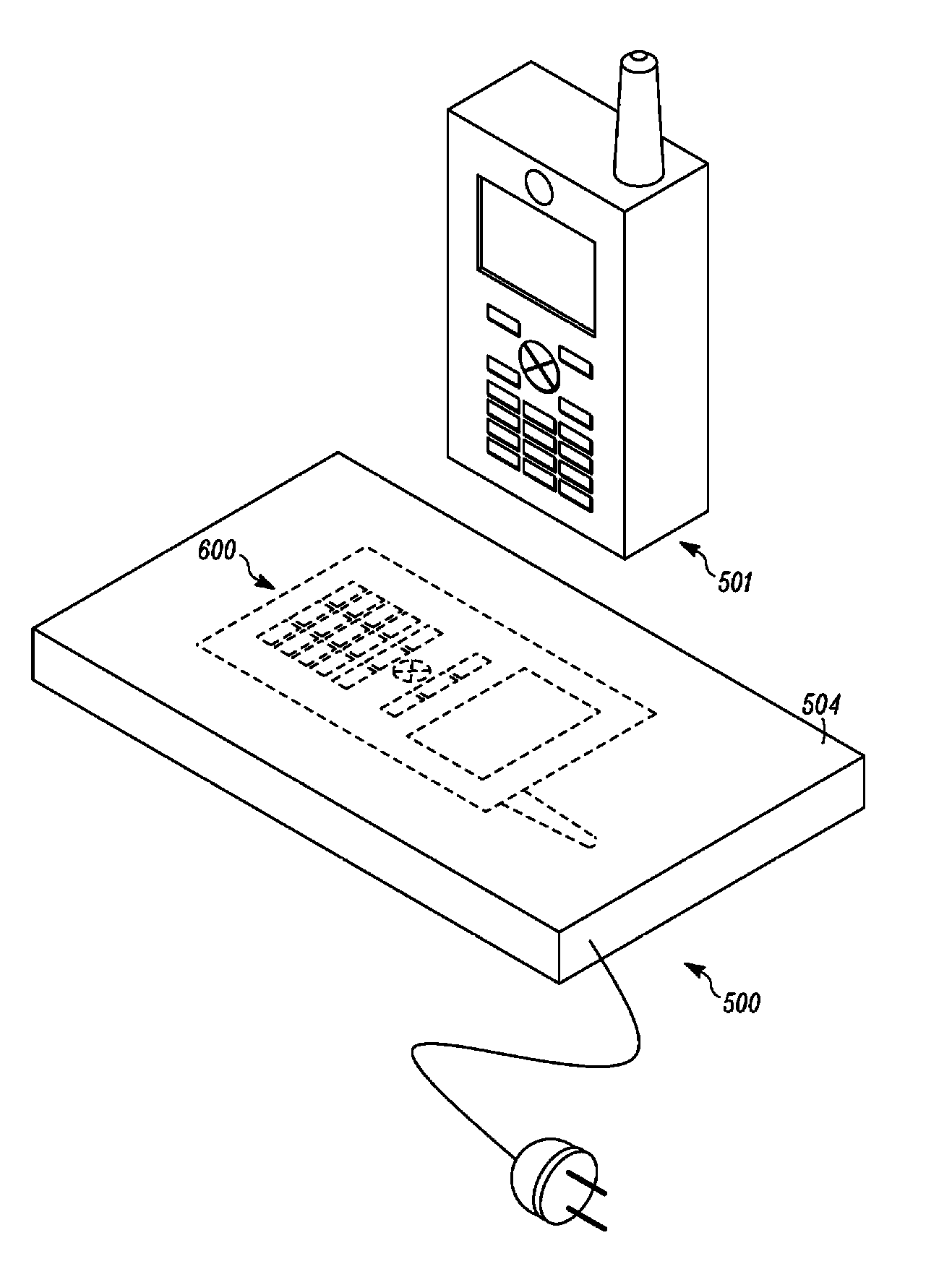
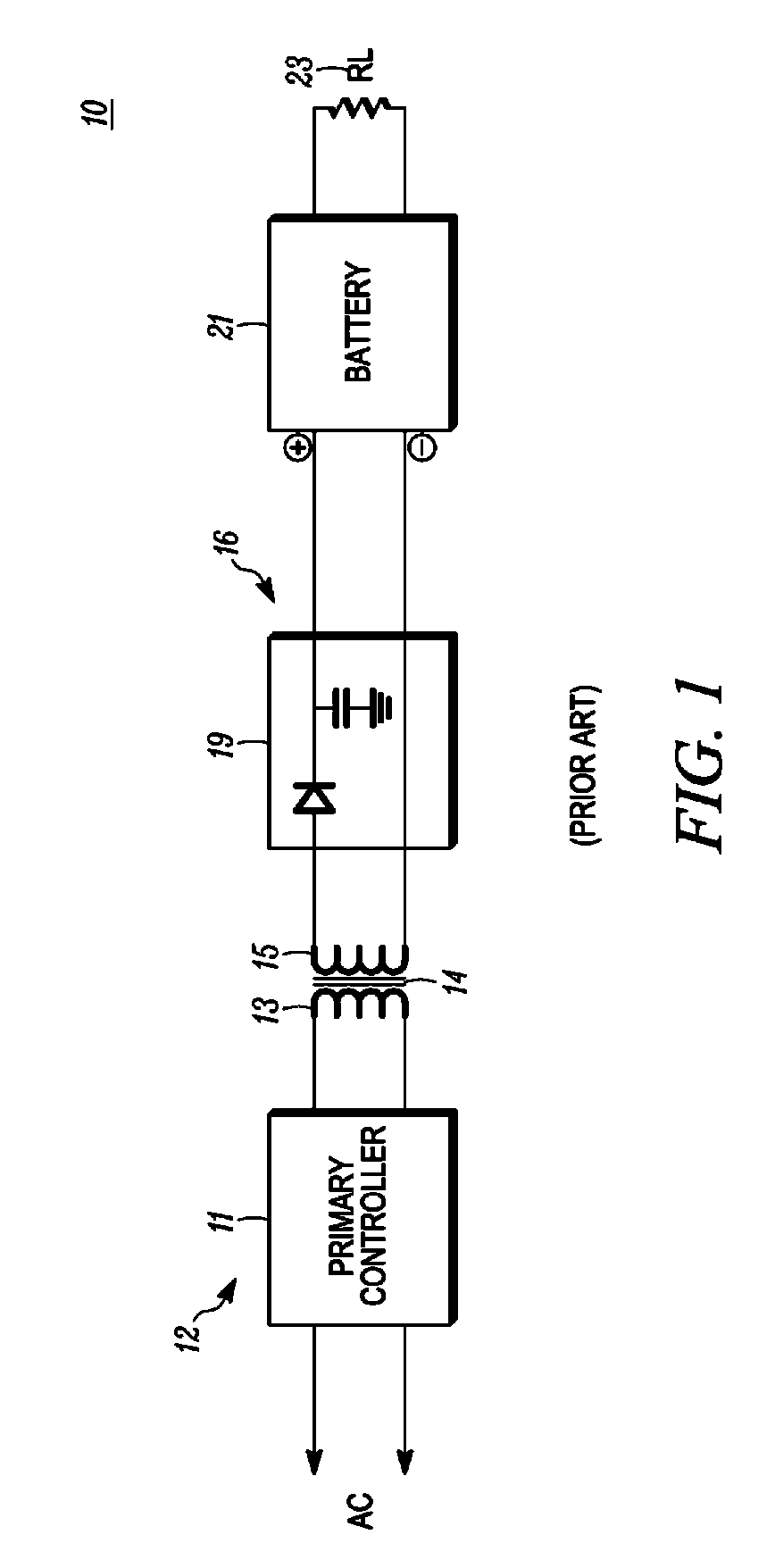
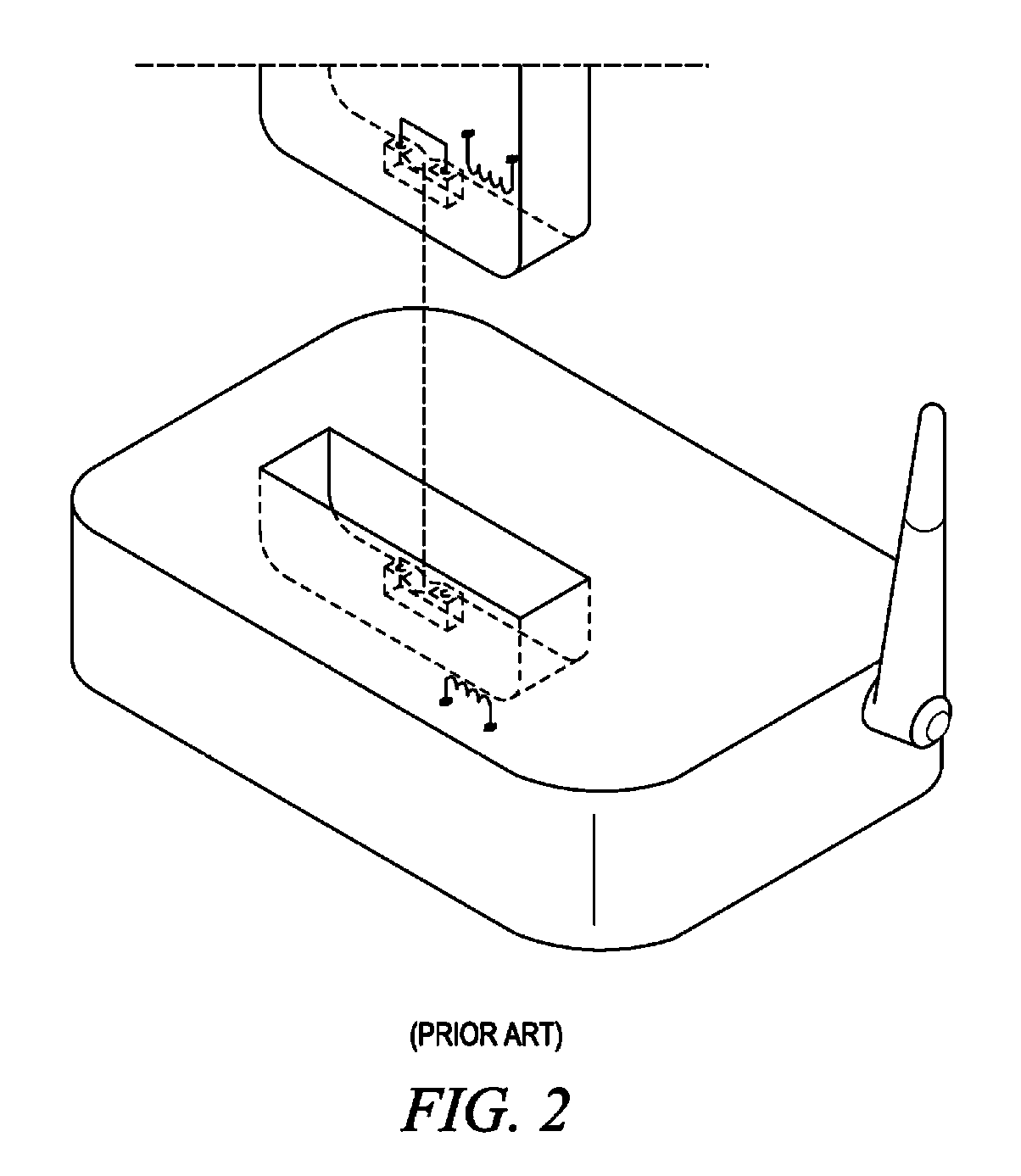
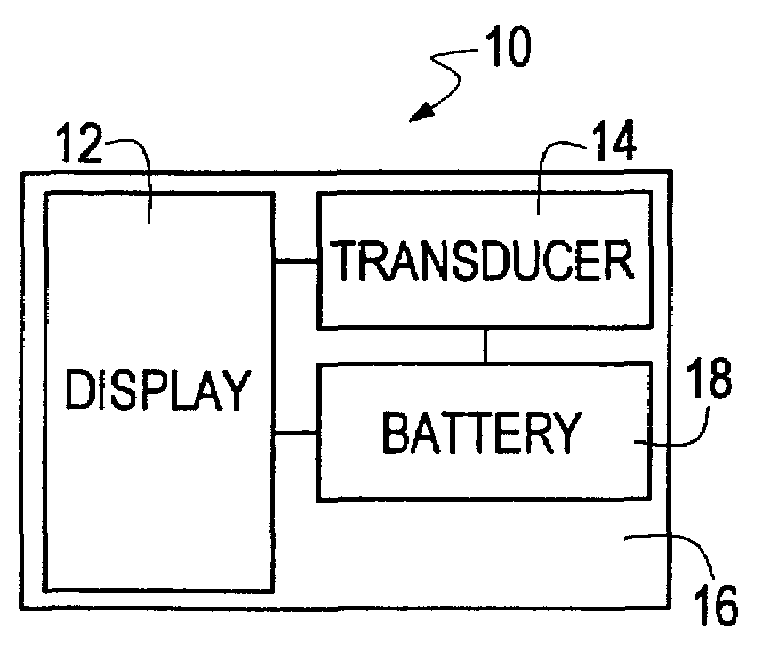
Contact less charger with alignment indicator
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Adhesive backed displays
InactiveUS7728811B2Consumes littleIncrease flexibilityStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesScreen printingElectrical battery
A process for creating an electronically addressable display includes multiple printing operations, similar to a multi-color process in conventional screen printing. In some of the process steps, electrically non-active inks are printed onto areas of the receiving substrate, and in other steps, electrically active inks are printed onto different areas of the substrate. The printed display can be used in a variety of applications. This display can be used as an indicator by changing state of the display after a certain time has elapsed, or when a certain pressure, thermal, radiative, moisture, acoustic, inclination, pH, or other threshold is passed. In one embodiment, the display is incorporated into a battery indicator. A sticker display is described. The sticker is adhesive backed and may then be applied to a surface to create a functional information display unit. This invention also features a display that is both powered and controlled using radio frequencies. It describes a complete system for controlling, addressing, and powering a display. The system includes an antenna or antennae, passive charging circuitry, and active control system, a display, and an energy storage unit. There is also a separate transmitter that provides the remote power for the display. The system is meant to be used anywhere it is useful to provide intermittent updates of information such as in a store, on a highway, or in an airport. A tile-based display allowing a modular system for large area display is created using a printable display material.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Manufacturing method of plasma display panel that includes adielectric glass layer having small particle sizes
InactiveUS6439943B1Alternating current plasma display panelsVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureScreen printingMetallurgy
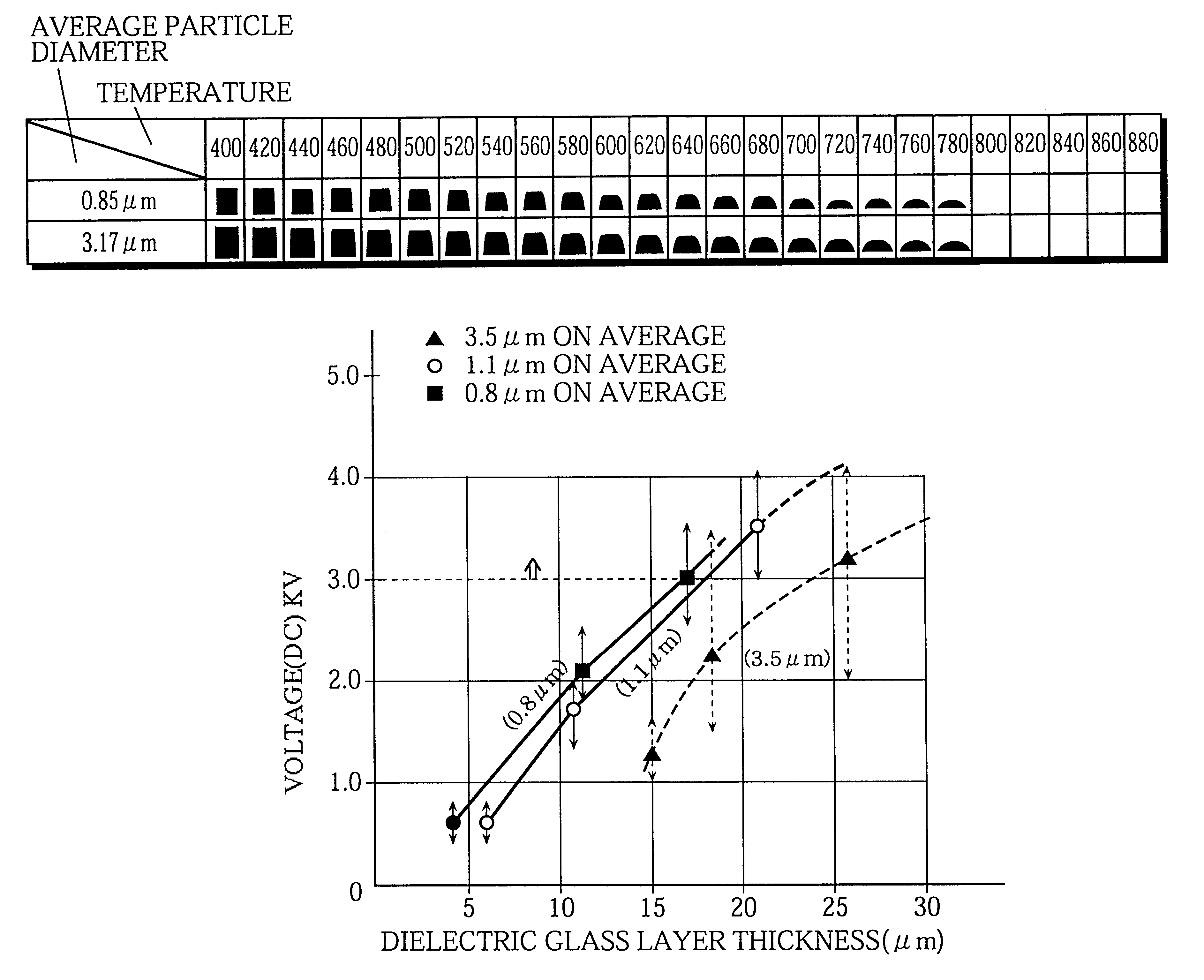
The object of the present invention is to provide a high-intensity, reliable plasma display panel even when the cell structure is fine by resolving the problems such as a low visible light transmittance and low voltage endurance of a dielectric glass layer. The object is realized by forming the dielectric glass layer in the manner given below. A glass paste including a glass powder is applied on the front glass substrate or the back glass substrate, according to a screen printing method, a die coating method, a spray coating method, a spin coating method, or a blade coating method, on each of which electrodes have been formed, and the glass powder in the applied glass paste is fired. The average particle diameter of the glass powder is 0.1 to 1.5 mum and the maximum particle diameter is equal to or smaller than three times the average particle diameter.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of metallizing a solar cell substrate
InactiveUS20080128019A1Photovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceScreen printing
Embodiments of the invention contemplate the formation of a low cost solar cell using a novel high speed electroplating method and apparatus to form a metal contact structure having selectively formed metal lines using an electrochemical plating process. The apparatus and methods described herein remove the need to perform one or more high temperature screen printing processes to form conductive features on the surface of a solar cell substrate. The resistance of interconnects formed in a solar cell device greatly affects the efficiency of the solar cell. It is thus desirable to form a solar cell device that has a low resistance connection that is reliable and cost effective. Therefore, one or more embodiments of the invention described herein are adapted to form a low cost and reliable interconnecting layer using an electrochemical plating process containing a common metal, such as copper.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Three-dimentional components prepared by thick film technology and method of producing thereof
Object of the present invention are components with three dimensional structure prepared by thick film technology by print, where between the printed layers is inserted at least one membrane. The membrane is according to the present to invention at least in a part of the final product. The membrane can be provided with holes which are necessary for next technological steps. The inserted membranes can have pores of the size of 50˜tm to 10 nm and a thickness of 1 to 200˜tm. Method of producing of components with three-dimensional structure by thick film printing technology according to the invention lies in that between some of the printed layers is inserted a suitable membrane, which allows to lay on next layers without influence to previous layers. The printing can be done by screen-printing.
Owner:ING ILJA KREJCI ENG
Photoluminescence color wheels
InactiveUS20120201030A1Increase the areaSimplify capture of lightPoint-like light sourceProjectorsScreen printingPhosphor
A color wheel comprises: a rotatable disc having a light reflective face and a region of photoluminescence material deposited on the light reflective face. The region of photoluminescence material comprises a substantially uniform thickness layer of a mixture of particles of the photoluminescence material that is deposited on the light reflective face of the disc by screen printing. The photoluminescence materials can comprise blue light or UV excitable photoluminescence materials such as phosphor materials or quantum dots. Color modulated light sources and a method of manufacturing a color wheel are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Method for preparing liquid colloidal dispersion of silver particles, liquid colloidal dispersion of silver particles, and silver conductive film
InactiveUS20060264518A1Good dispersionHighly conductive filmMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesScreen printingFiltration
A process for producing a fine silver particle colloidal dispersion which can simply form conductive silver layers and antimicrobial coatings by screen printing or the like. The process is characterized by having a reaction step of allowing an aqueous silver nitrate solution to react with a mixed solution of an aqueous iron(II) sulfate solution and an aqueous sodium citrate solution to form an agglomerate of fine silver particles, a filtration step of filtering the resultant agglomerate of fine silver particles to obtain a cake of the agglomerate of fine silver particles, a dispersion step of adding pure water to the cake to obtain a first fine silver particle colloidal dispersion of a water system in which dispersion the fine silver particles have been dispersed in the pure water, and a concentration and washing step of concentrating and washing the first fine silver particle colloidal dispersion of a water system.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Methods for achieving improved color in microencapsulated electrophoretic devices
InactiveUS20100103502A1Efficiently and cheaply manufactureCheap to makeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScreen printingComputer graphics (images)
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Integrated Filter Feedthrough Assemblies Made From Low Temperature Co-Fired (LTCC) Tape
InactiveUS20070217121A1Prevent leakageAvoid spreadingAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyScreen printingState of art
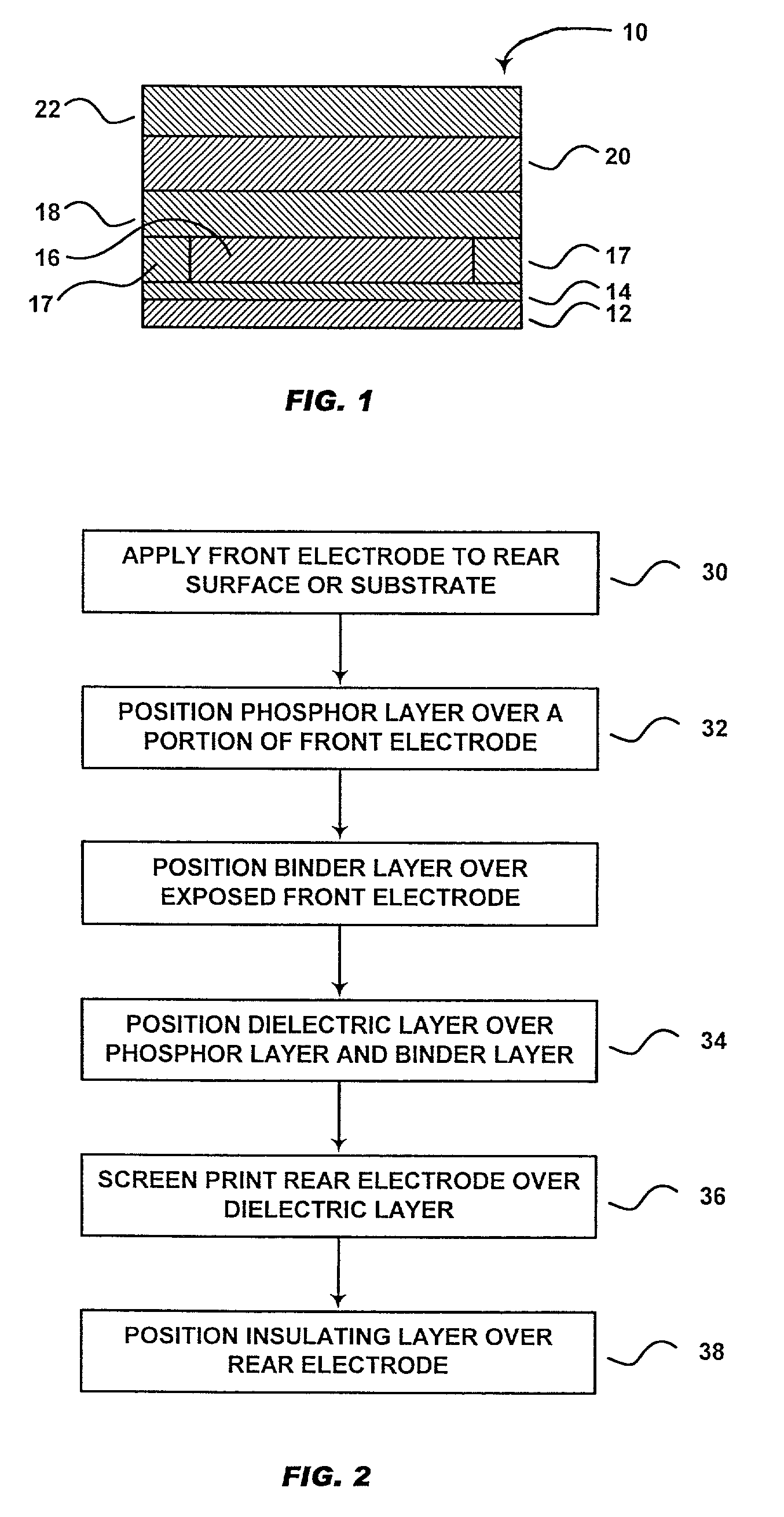
A filter capacitor comprising a substrate of at least one layer of a low temperature co-fires ceramic (LTCC) tape supporting alternating active and ground electrode layers segregated by a dielectric layer is described. The substrate is preferably a laminate of three LTCC tapes pieces that are heated under pressure and at a relatively low temperature to become a laminate that maintains its shape and structure dimensions even after undergoing numerous sintering steps. Consequently, relatively thin active and ground electrode layers along with the intermediate dielectric layer can be laid down or deposited on the LTCC substrate by a screen-printing technique. A second laminate of LTCC tapes is positioned on top of the active / dielectric / ground layers to finish the capacitor. Consequently, a significant amount of space is saved in comparison to a comparably rated capacitor or, a capacitor of a higher rating can be provided in the same size as a conventional prior art capacitor.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Etch patterning of nanostructure transparent conductors
Owner:CHAMP GREAT INTL
Method for producing topographical pattern on papermachine fabric by rotary screen printing of polymeric material
ActiveUS7799382B2Keep the distanceExact matchMachine wet endLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingScreen printingEngineering
A method for producing a topographical pattern on or in a papermachine fabric. The method for creating the pattern on or in an fabric, includes producing a topographical polymer pattern on or in a papermachine fabric using a rotary screen. The instant abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
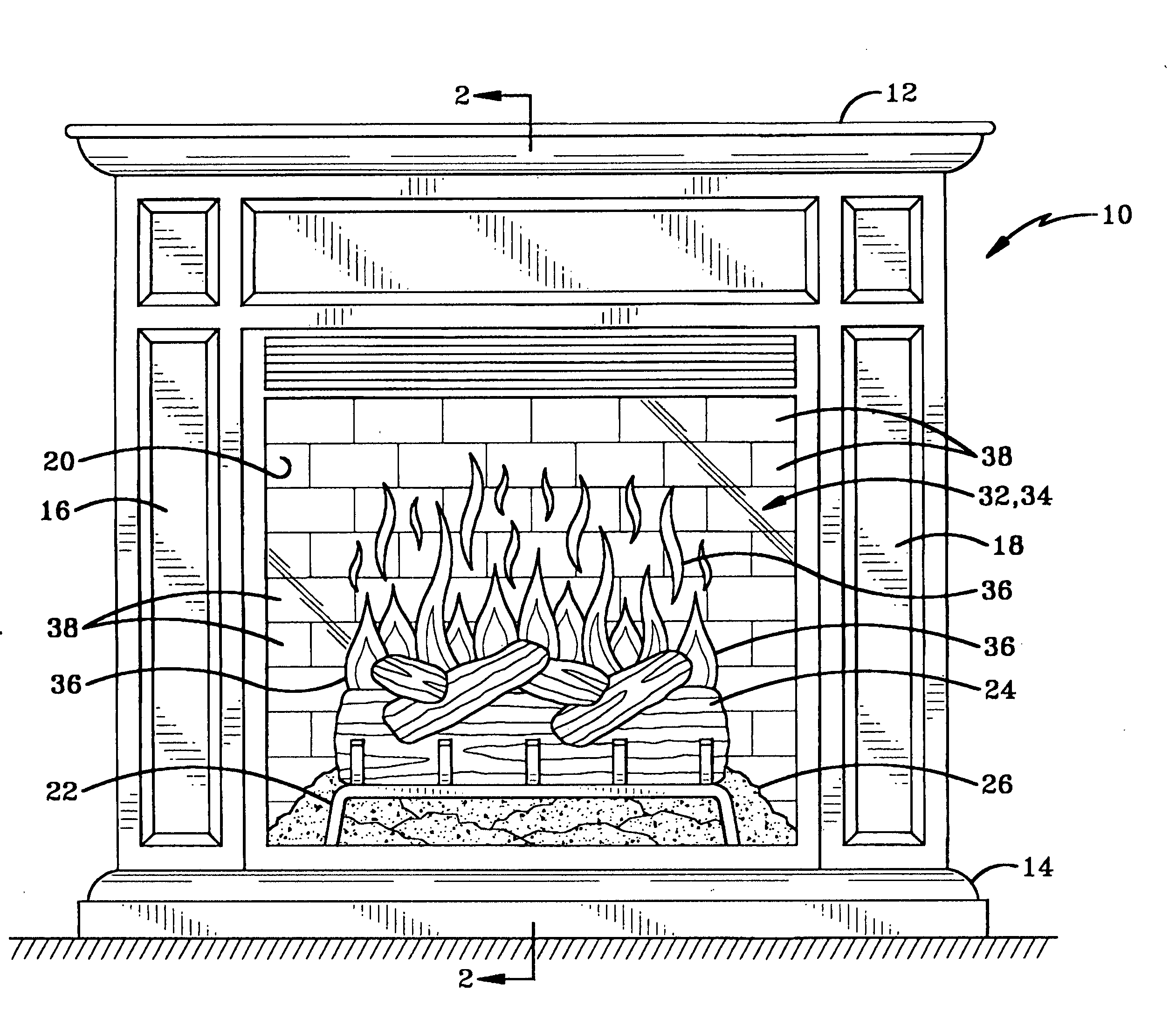
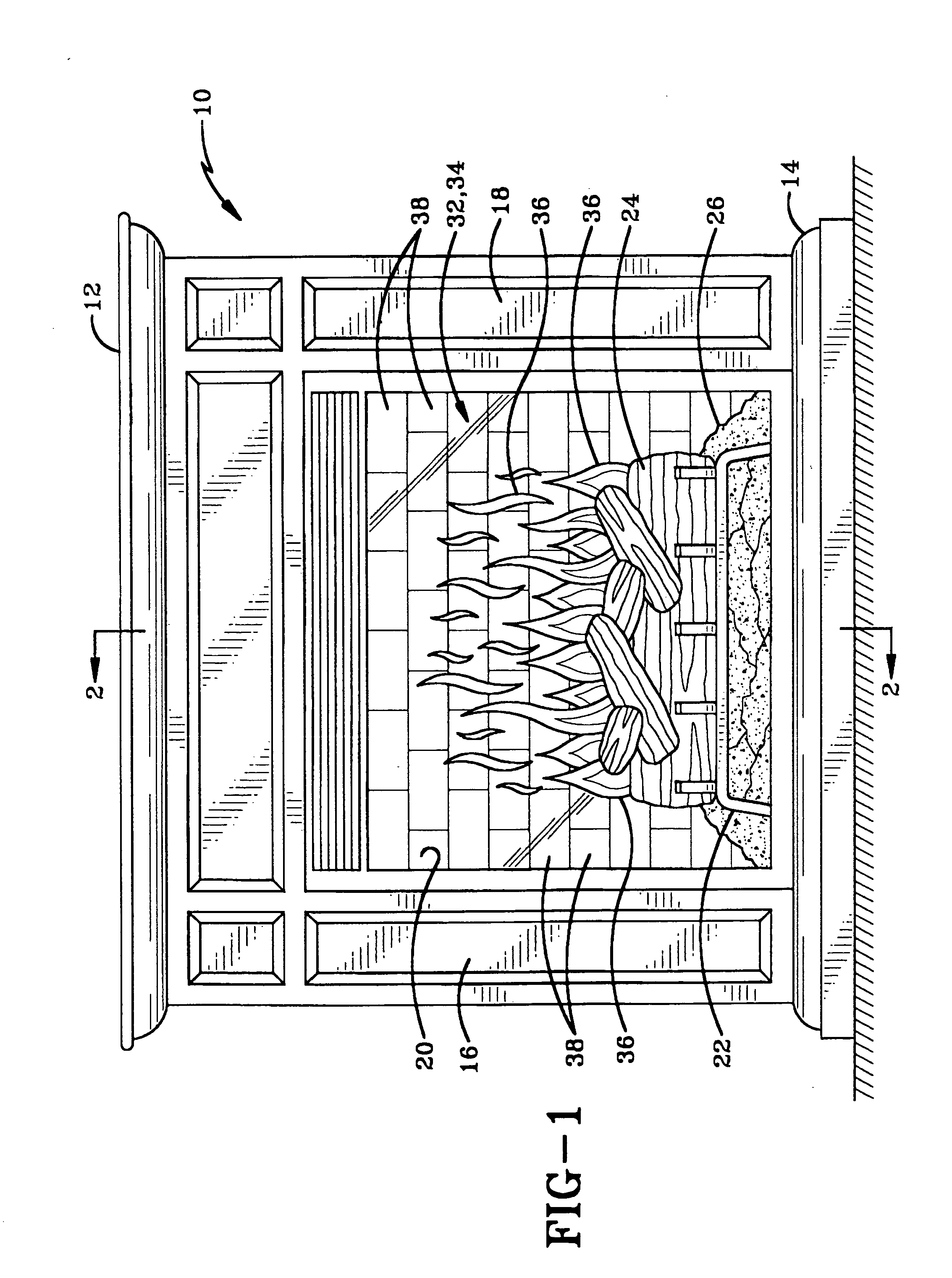
Panel for use in electric fireplace and fireplace incorporating the same
A panel for simulating a firebox for use in an electric fireplace and an electric fireplace incorporating the same. The electric fireplace includes housing with a grate, a plurality of artificial firelogs positioned on the grate and an ember bed positioned under the grate. A light source is positioned to transmit light through a plurality of apertures in a rotatable cylinder that is disposed rearwardly of the firelogs. The panel is a planar member that is positioned in the housing between the cylinder and the firelogs. The panel includes a pattern thereon which represents a firebox of a wood-burning fireplace. The pattern is formed by silk-screening, painting or etching a pattern of a flat wall of firebricks, a recessed wall of firebricks, stones, logs or any other markings that represent a firebox found in a fireplace. The light source preferably transmits light through flame-shaped apertures in the rotatable cylinder, thereby projecting flame-shaped images onto the panel or onto a screen that is positioned forwardly of the panel.
Owner:REFRACTORY SPECIALTIES
Sensor Element for Gas Sensors and Method for Operating Same
ActiveUS20090217737A1Simple structureCost-effectiveInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceScreen printing
A sensor element is provided for gas sensors, in particular to determine particles in gas mixtures, the sensor element including at least one electrochemical measuring element exposed to the gas mixture to be determined, and at least one temperature-measuring element integrated into the sensor element. The temperature-measuring element includes a resistor track, which has an electric resistance of less than 180 Ohm at 0° C. The resistor track may thus be produced by thin-foil technology, such as screen printing, for example.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Utilization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) plastic and composition-modified barium titanate powders in a matrix that allows polarization and the use of integrated-circuit technologies for the production of lightweight ultrahigh electrical energy storage units (EESU)
InactiveUS7466536B1Low costLower sintering temperatureCell electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricManufacturing technologyBarium titanate
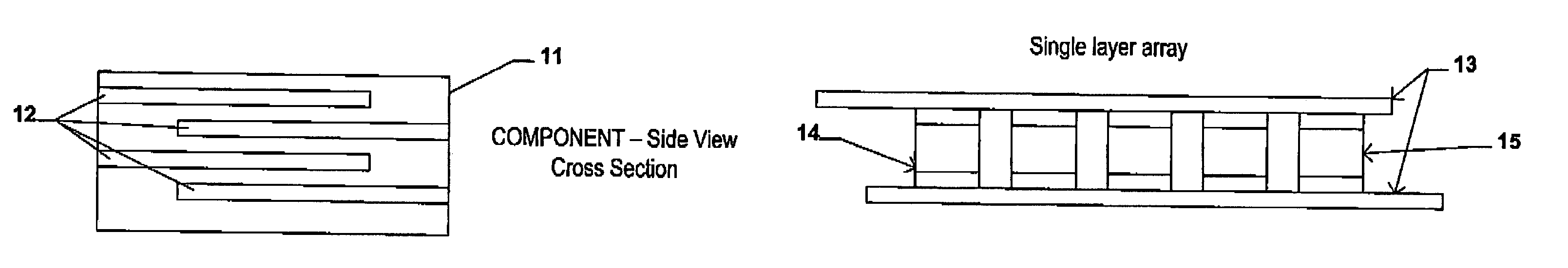
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is single coated with aluminum oxide and then immersed in a matrix of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) plastic for use in screen-printing systems. The ink that is used to process the powders via screen-printing is based on a nitrocellulose resin that provide a binder burnout, sintering, and hot isostatic pressing temperatures that are allowed by the PET plastic. These lower temperatures that are in the range of 40° C. to 150° C. also allows aluminum powder to be used for the electrode material. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of conventional ceramic and plastic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of aluminum electrodes and high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The 31,351 components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store at least 52.22 kW·h of electrical energy. The total weight of an EESU with this amount of electrical energy storage is 281.56 pounds including the box, connectors, and associated hardware.
Owner:EESTOR
Electroluminescent sign
Owner:LUMIMOVE
Glucose extraction patch and its manufacturing process
InactiveUS20060235284A1Easy constructionEasy to manufactureElectrotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityScreen printing
Glucose extraction patch and its manufacturing process are provided. The patch comprises two gel discs containing enzymes that react with glucose to produce hydrogen peroxide, a frame for having two holes for accommodating the discs, a supporter for holding the discs, and a flexible printed circuit. The printed circuit includes electrodes for contacts with the gel discs, terminals for electrical connection with a measuring device, and circuits for electrical connection between the electrodes and the terminals. The electrodes are formed on the printed circuit by silk screening. Preprocessing may be applied to the electrodes after they are formed on the printed circuit.
Owner:KMH
Liquid sensor and ice detector
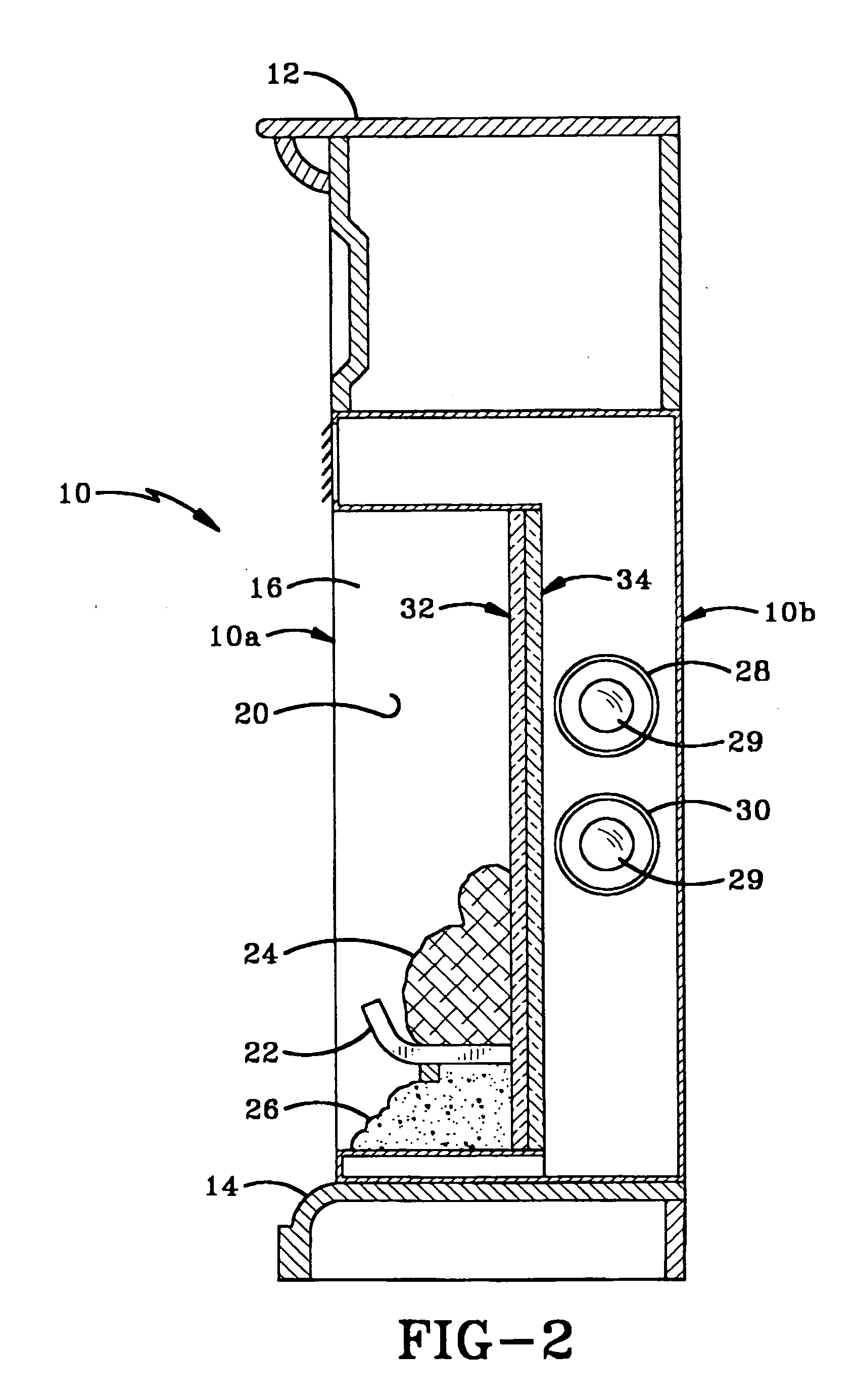
InactiveUS20050126282A1Difference in efficiencyRemove heat moreMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesScreen printingLiquid temperature
An improved apparatus and a method of measuring and interpreting reliably, simply and accurately the information on continuous liquid level, liquid temperature and other liquid properties within a vessel. The apparatus could be made of a powered heater element and temperature sensors can be screen-printed, vacuum deposited, etched, welded, soldered or plated on one or both sides of a single rigid or a flexible substrate. The geometry of the heater determines the curve shape, such as steepness or shallowness of a temperature profile along a heater. Various parallel and serial configurations of thermocouples or temperature sensors can be used to measure the temperature along a heater. Simultaneous measurements from all the temperature sensors, before and after heat is applied, are used to generate accurate temperature profiles for the entire heater. Different features of the temperature profiles will determine accurately the liquid level, liquid temperature and other liquid properties. Apparatus of the invention may also be used to detect ice formation.
Owner:MAATUK JOSEF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com