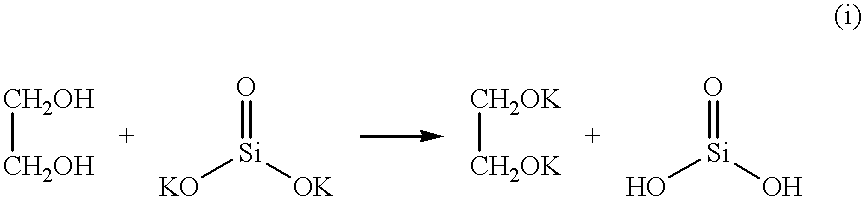
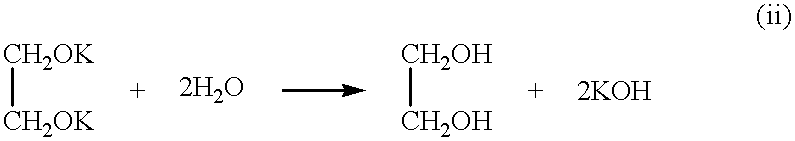
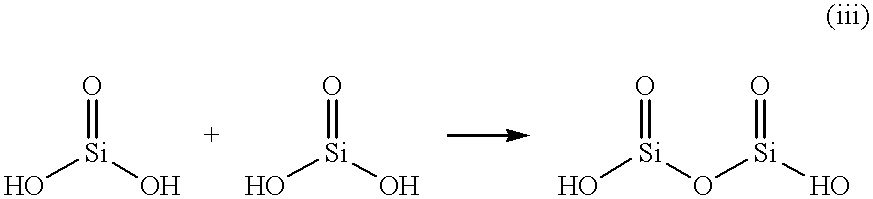
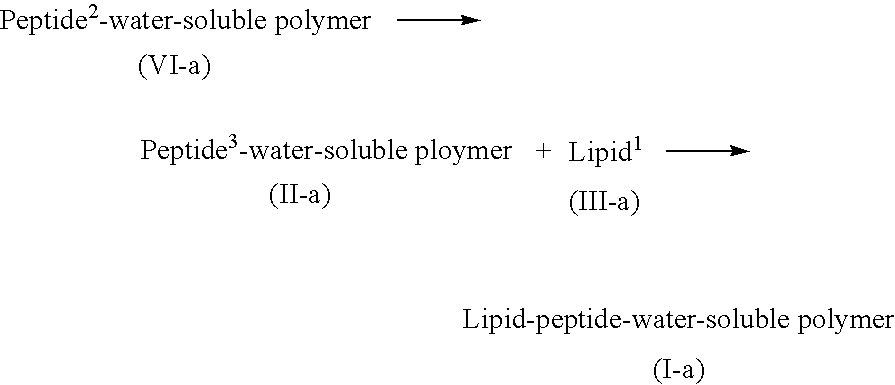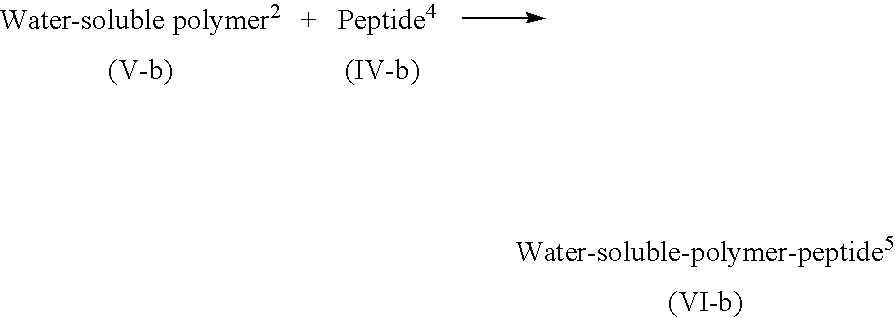Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
19390 results about "Colloid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a colloid is a mixture in which one substance of microscopically dispersed insoluble or soluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Sometimes the dispersed substance alone is called the colloid; the term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture (although a narrower sense of the word suspension is distinguished from colloids by larger particle size). Unlike a solution, whose solute and solvent constitute only one phase, a colloid has a dispersed phase (the suspended particles) and a continuous phase (the medium of suspension) that arise by phase separation. To qualify as a colloid, the mixture must be one that does not settle or would take a very long time to settle appreciably.
Coating composition for multiple hydrophilic applications
InactiveUS20030203991A1Tough and durable and printable surfaceImprove wettabilityOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsColloidWear resistance
A coating composition is disclosed which comprises an aqueous polymeric matrix, a hydrophilic polymer, a colloidal metal oxide and a crosslinker. The coating composition when applied on medical devices is hydrophilic, shows improved lubricity, abrasion resistance and substrate adhesion on metallic or plastic substrates. The coating also shows improved water sheeting thus providing the coated substrates with anti-fog properties. The coating absorbs aqueous dye or stain solutions making the substrate suitable for printing.
Owner:HYDROMER INC
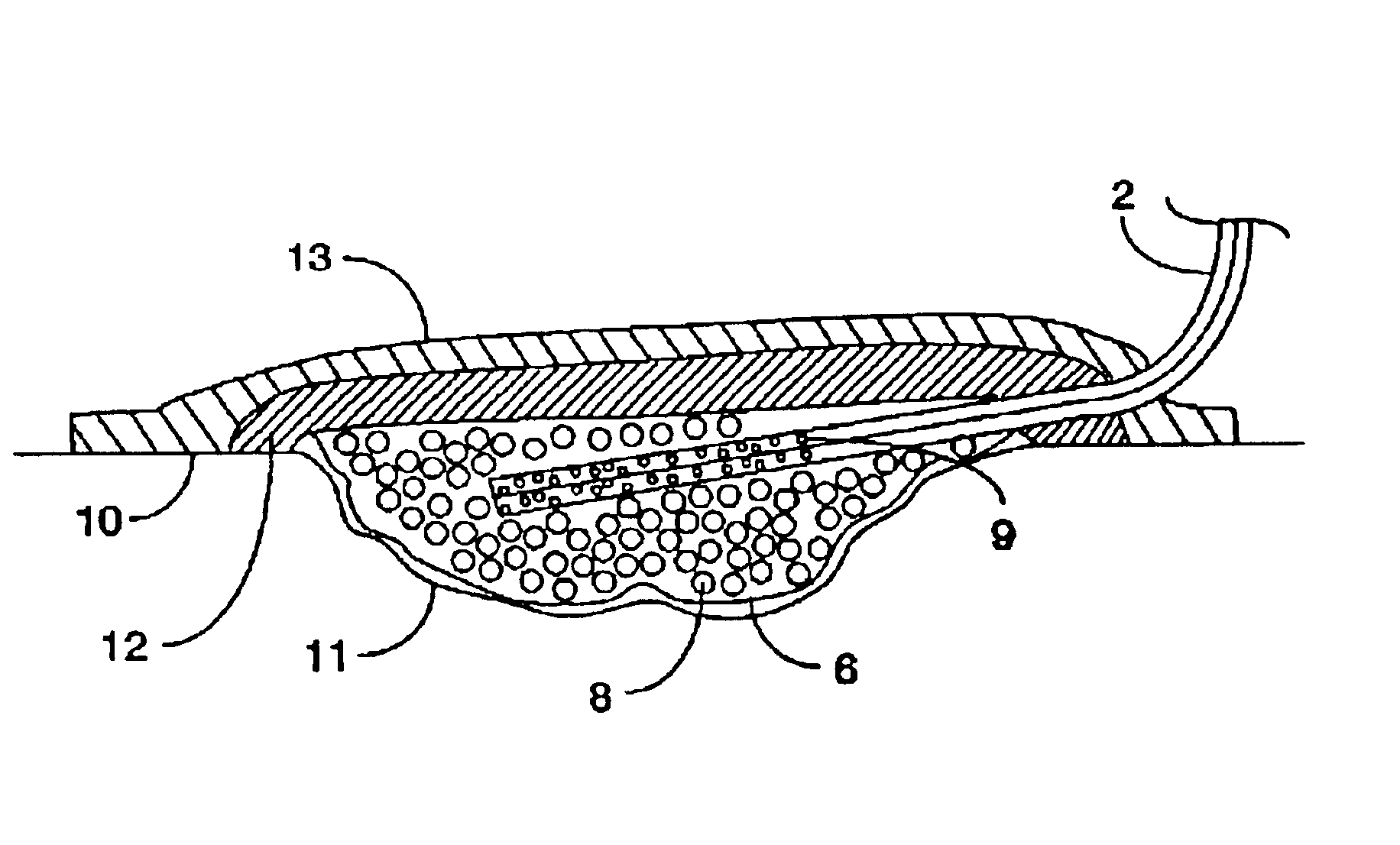
Closed wound drainage system
A portable closed wound drainage system that uses a pouch shaped dressing which is inserted into a wound. At least a portion of the outer surface of the pouch is porous to allow exudates to enter. Exudates are removed from the pouch by flexible tubing which is secured inside the pouch at one end, and secured at the other end to a portable drain / suction unit. The pouch contains porous material, and may optionally contain beads and fillers which are antibacterial in nature. The tubing can have a single or multi-lumen structure with perforations in the side walls of the end of the tube that is inserted in the pouch to allow body fluids to enter laterally. The portable drain / suction unit is preferably a portable battery powered device. The pouch and the tube are sealed by a flexible sealing material which is applied to the outer surface of the skin around the periphery of the pouch and the tubing as it exits the pouch. This sealing material is preferably a hydro-colloid, a silicone, or a lyogel, such as a hydrogel, which are easily deformable. A cosmetic cover sheet is attached to the patient's skin over the closed wound drainage system.
Owner:CONVATEC LTD
Water dispersible polypyrroles made with polymeric acid colloids for electronics applications
InactiveUS20050205860A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesWater dispersiblePolypyrrole
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of at least one polypyrrole and at least one colloid-forming polymeric acids at methods of making such compositions. The new compositions are useful in electronic devices including organic electronic devices such as organic light emitting diode displays, memory storage, electromagnetic shielding, electrochromic displays,and thin film transistors, field effect resistance devices.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Coating composition for multiple hydrophilic applications
InactiveUS7008979B2Improve adhesionImprove the lubrication effectSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsColloidWear resistance
Owner:HYDROMER INC
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
InactiveUS20050023710A1Improve bindingImpression capsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceFree form
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
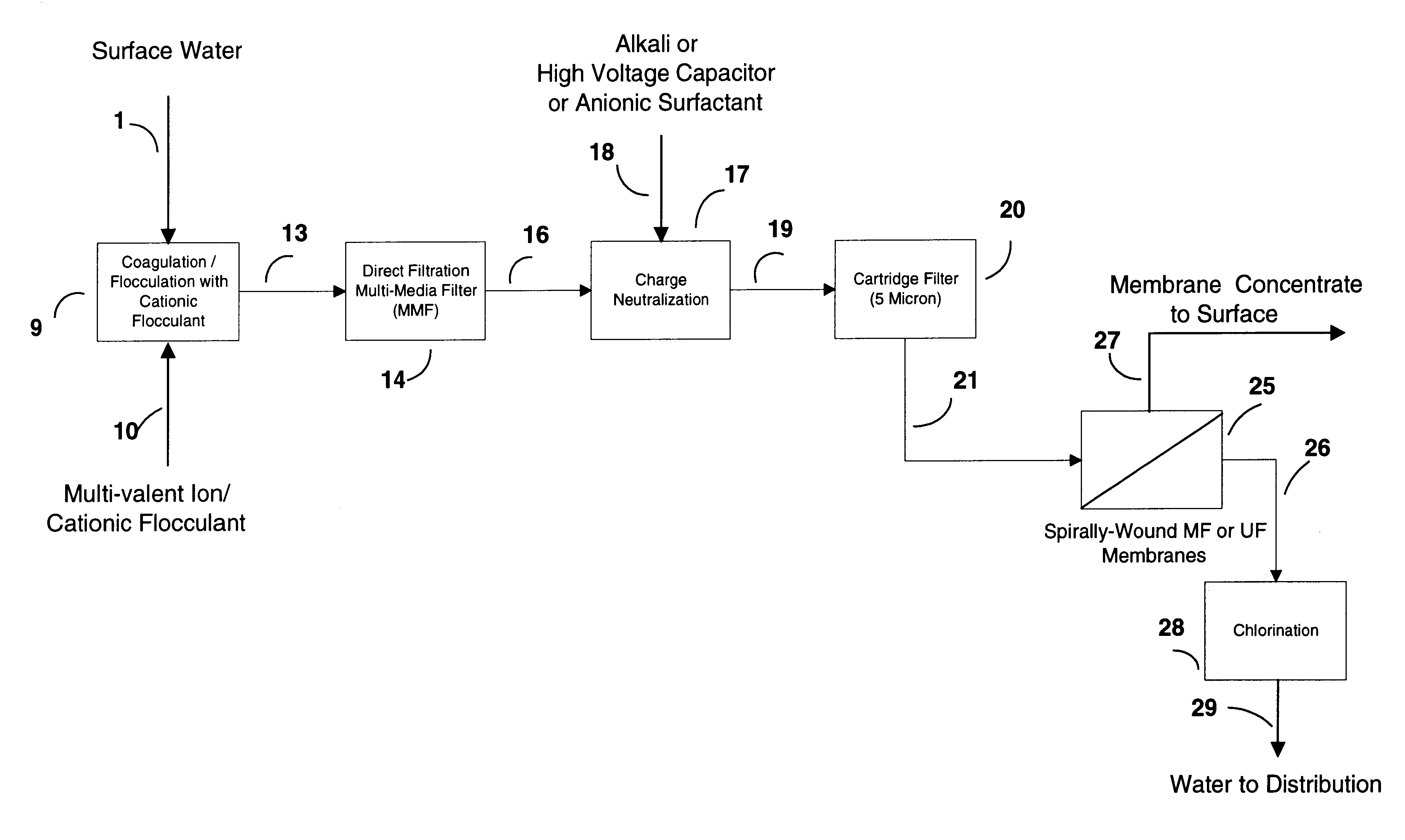
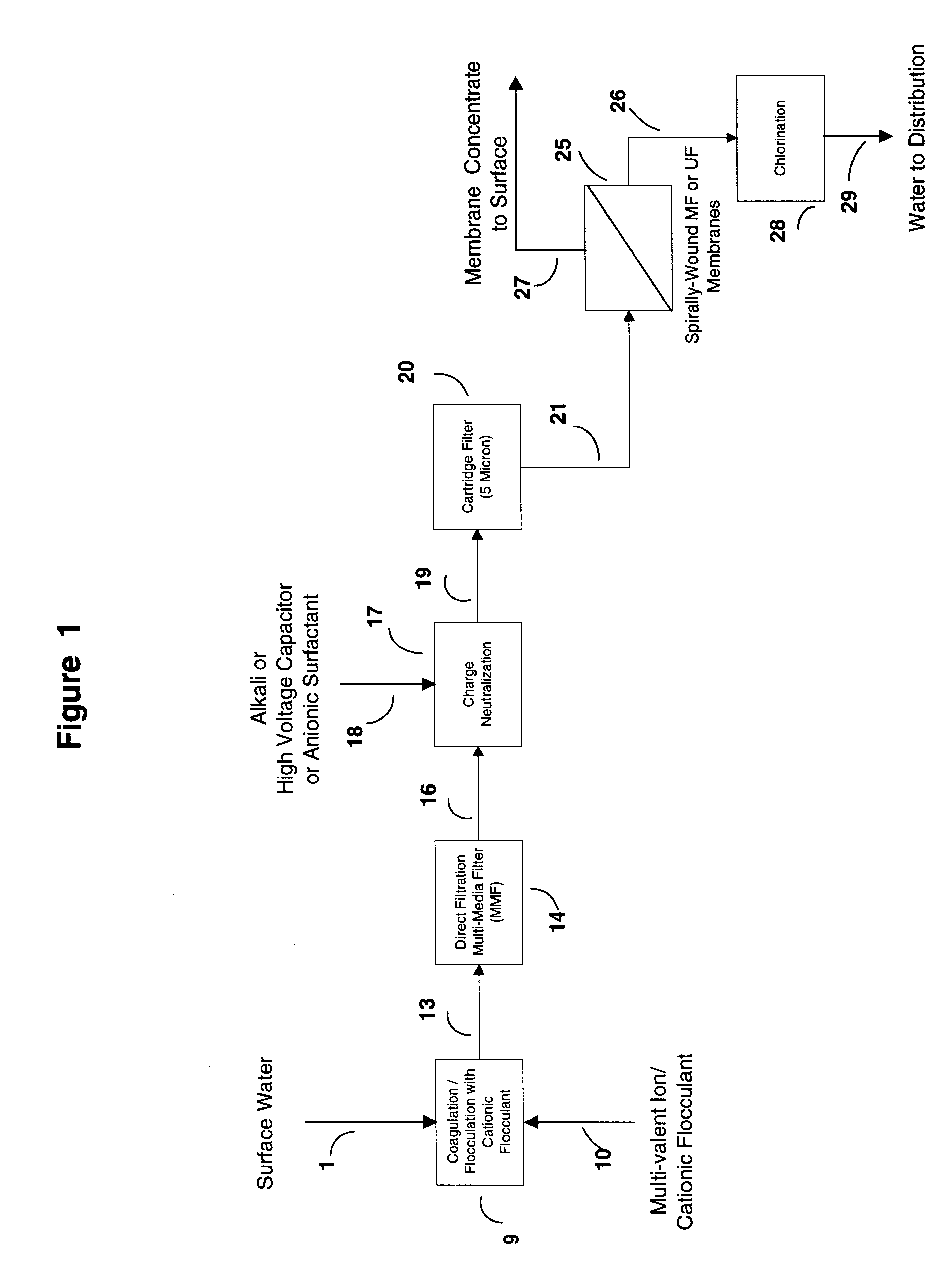
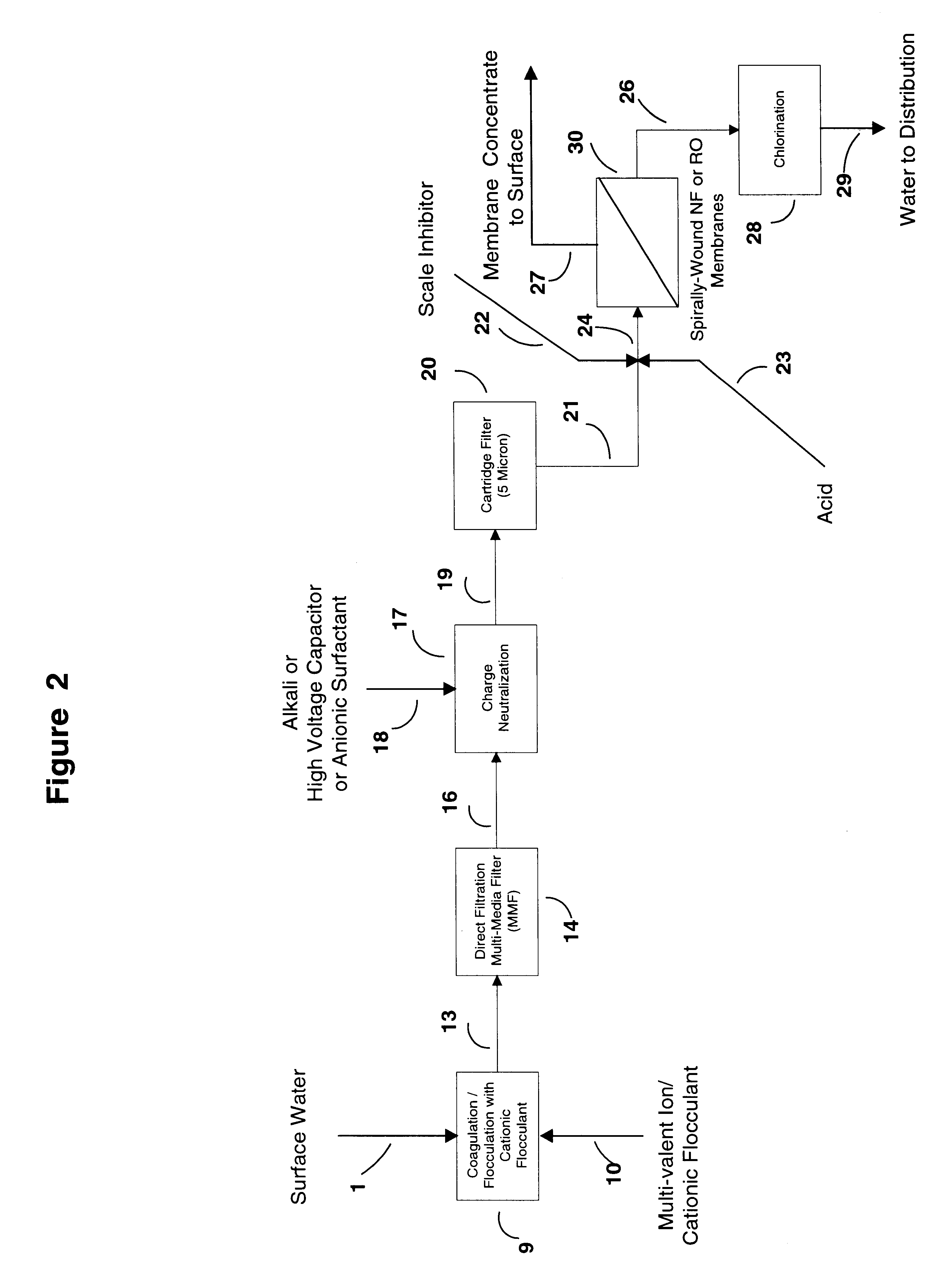
Water treatment process for membranes
InactiveUS6416668B1Effective and safe and reliable to produceCapital and operating costMembranesUltrafiltrationZeta potentialFiltration
This invention discloses a cost-effective process for separating contaminants and a wide-range of fouling material from surface water, ground water and from industrial effluents. Having undergone effective pre-treatment, the water can be purified further by using high-surface area spirally wound micro-filtration (MF), ultra-filtration (UF), nano-filtration (NF) or reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. High-quality potable water free from pathogen and other contaminants is thus produced at low-cost from the pre-treated surface water and ground-water. Conversely, pre-treated industrial effluents are further purified at a relatively low-cost using NF or RO membranes, thus producing water suitable for recycle or surface discharge. The process of this invention uses cationic inorganic and / or polymeric flocculants to coagulate and flocculate the water-borne colloidal matter (e.g. clays, iron hydroxides, naturally occurring matter (NOM's), etc.), followed by filtration using a multi-media filter, charge neutralization and reversal and final filtration using a 5-micron cartridge filter. These pre-treatment steps provides a good quality water having a low Silt Density Index and a significant negative zeta potential, thereby ensuring against irreversible chemical fouling of the spirally-wound membranes.
Owner:AL SAMADI RIAD A
Use of glucomannan hydrocolloid as filler material in prostheses
A prosthetic device for implantation into a mammalian body comprised of a non-absorbable biocompatible flexible material shell or sac filled with various biocompatible gel filler materials. The gel filler materials are comprised of biocompatible glucomannan obtained from konjac hydrocolloid flour and other biocompatible hydrocolloids, producing a natural look and feel for the prosthetic implants, especially reconstructive prostheses such as breast implants.
Owner:KONJAC TECH
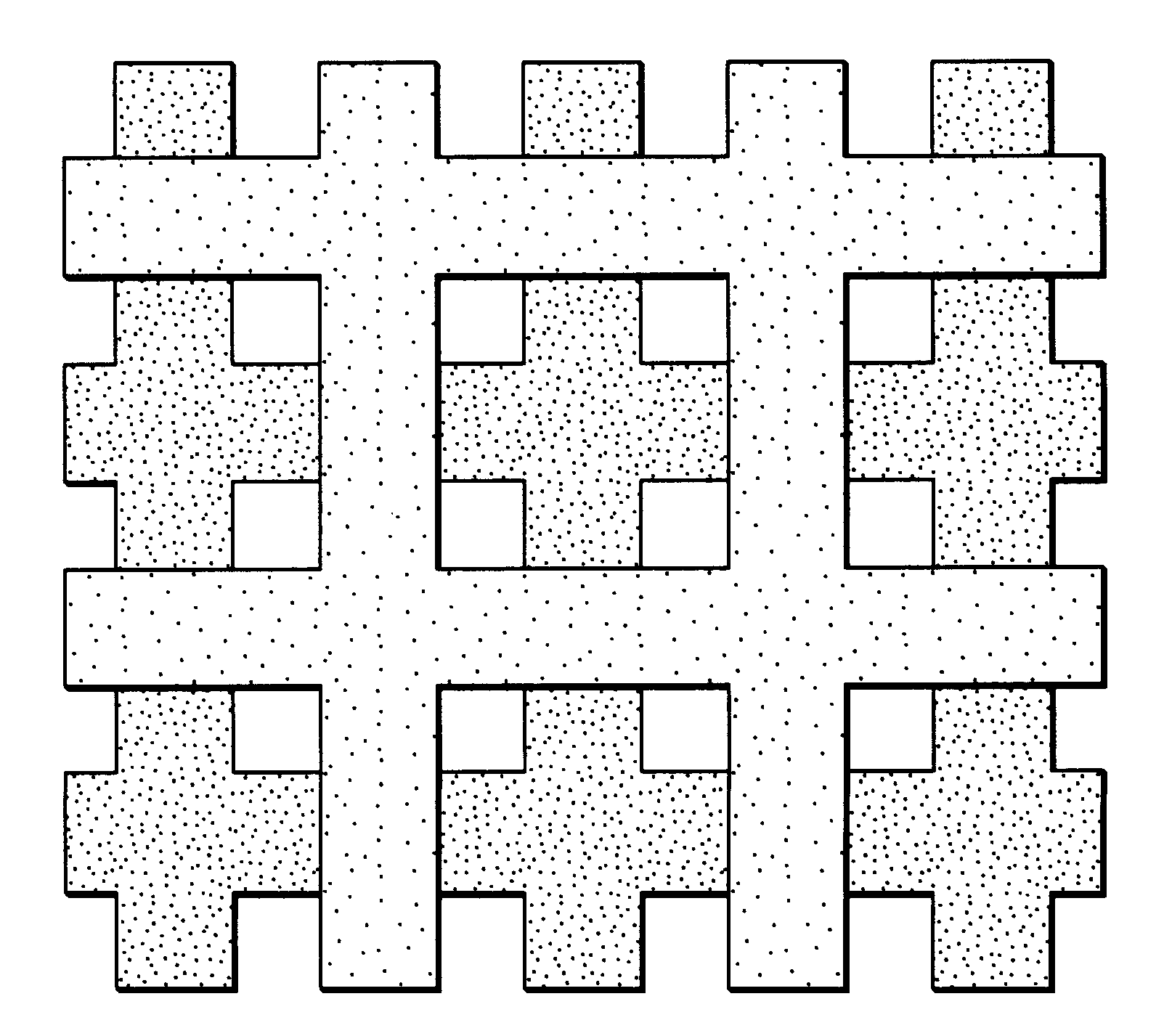
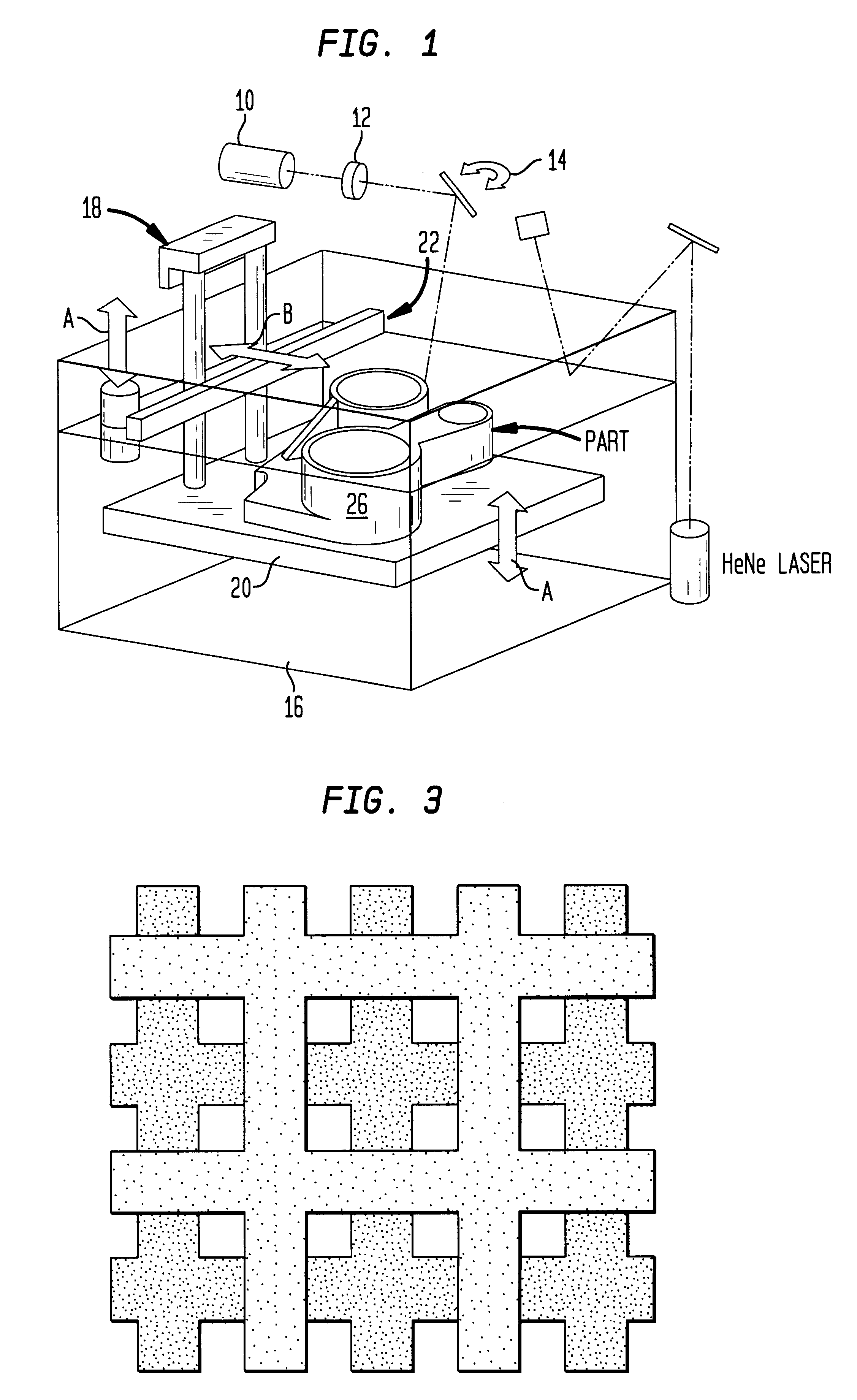
Controlled architecture ceramic composites by stereolithography
InactiveUS6283997B1Quality improvementFast preparationProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic compositeMetallurgy
A process for producing a ceramic composite having a porous network. The process includes providing a photocurable ceramic dispersion. The dispersion consists of a photocurable polymer and a ceramic composition. The surface of the dispersion is scanned with a laser to cure the photocurable polymer to produce a photocured polymer / ceramic composition. The photocured composition useful as a polymer / ceramic composite, or the polymer phase can be removed by heating to a first temperature that is sufficient to burn out the photocured polymer. It is then heated to a second temperature that is higher than the first temperature and is sufficient to sinter the ceramic composition to produce a purely ceramic composition having a porous network.Preferably and more specifically, the process uses a stereolithographic technique for laser scanning. The process can form a high quality orthopedic implant that dimensionally matches the bone structure of a patient. The technique relies upon laser photocuring a dense colloidal dispersion into a desired complex three-dimensional shape. The shape is obtained from a CAT scan file of a bone and is rendered into a CAD file that is readable by the stereolithography instrument. Or the shape is obtained directly from a CAD file that is readable by the stereolithography instrument.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP +2
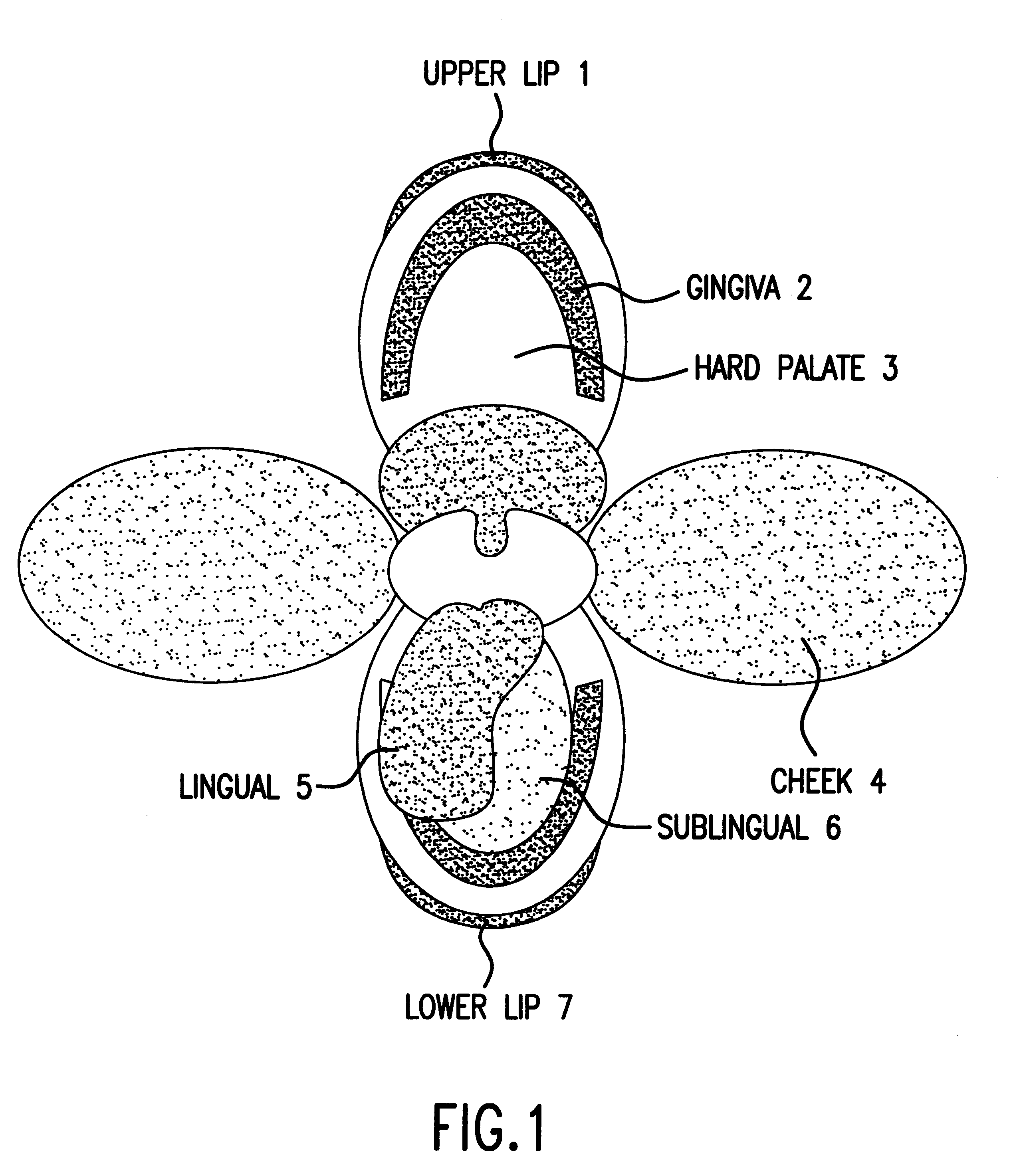
Compositions and methods for mucosal delivery
Mucosal surface-coat-forming film dosage units containing a water-soluble hydrocolloid, an effective dose of an active agent and a mucosal adhesion enhancer; wherein the active agent is encapsulated within a polymer which is chemically or physically distinct from the hydocolloid; wherein the mucosal adhesion enhancer is a starch graft copolymer; wherein the film exhibits a dry tack value of less than 3.5 g, a wet tack of greater than 35 g, a gelation temperature that is greater than 70° C. for a 2% polymer solution, a dry film thickness of less than 20 mil, a water content of 0.5 to 10%, a tensile strength greater than 1500 psi, a modulus in the range of 35,000 to 300,000 psi, a % elongation of less than 20%, a tear probagation resistance of 0.001 to 1 N, and a dissolution time in the range of 1 to 600 seconds upon application to an oral mucosal surface.
Owner:THALLIUM HLDG CO LLC
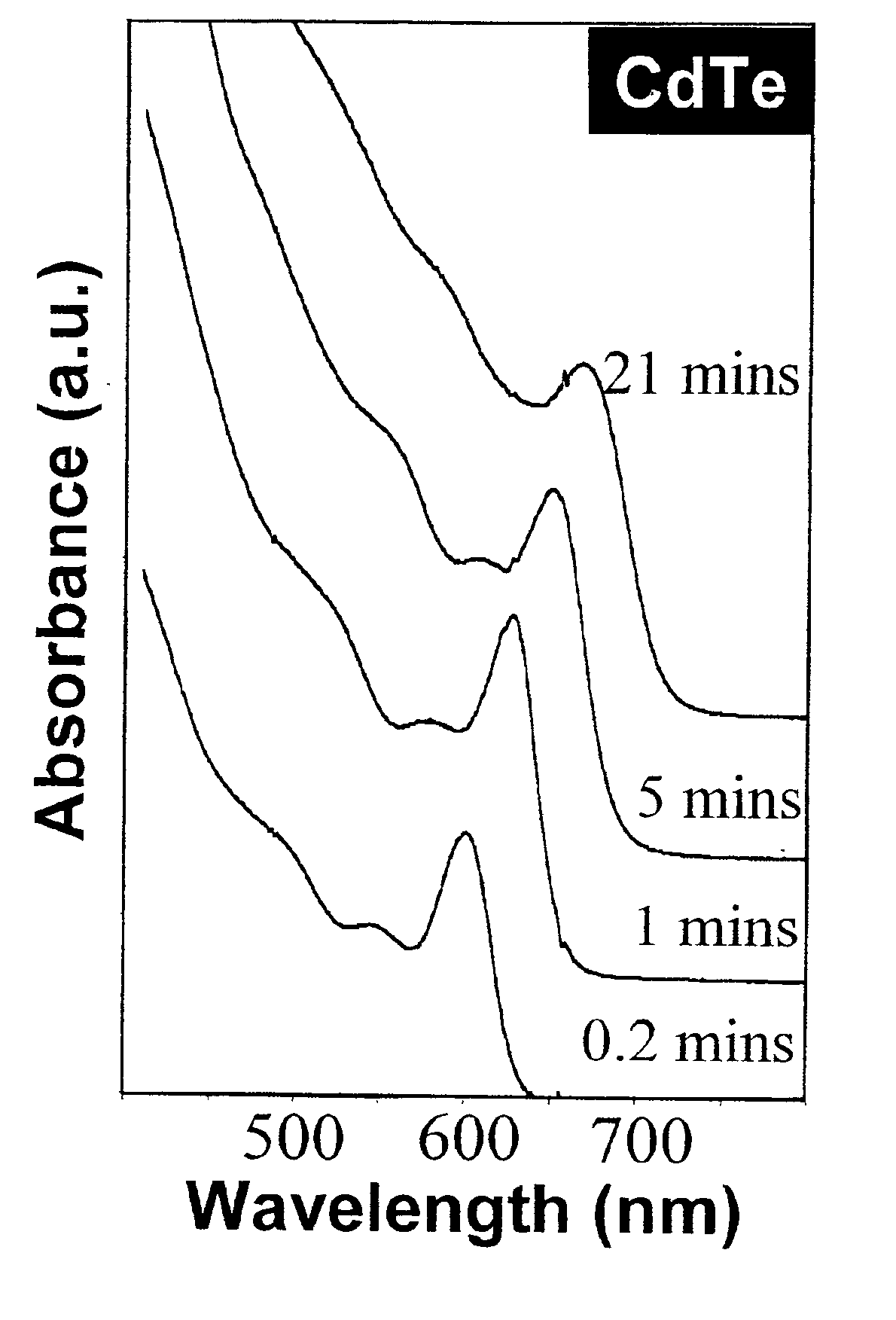
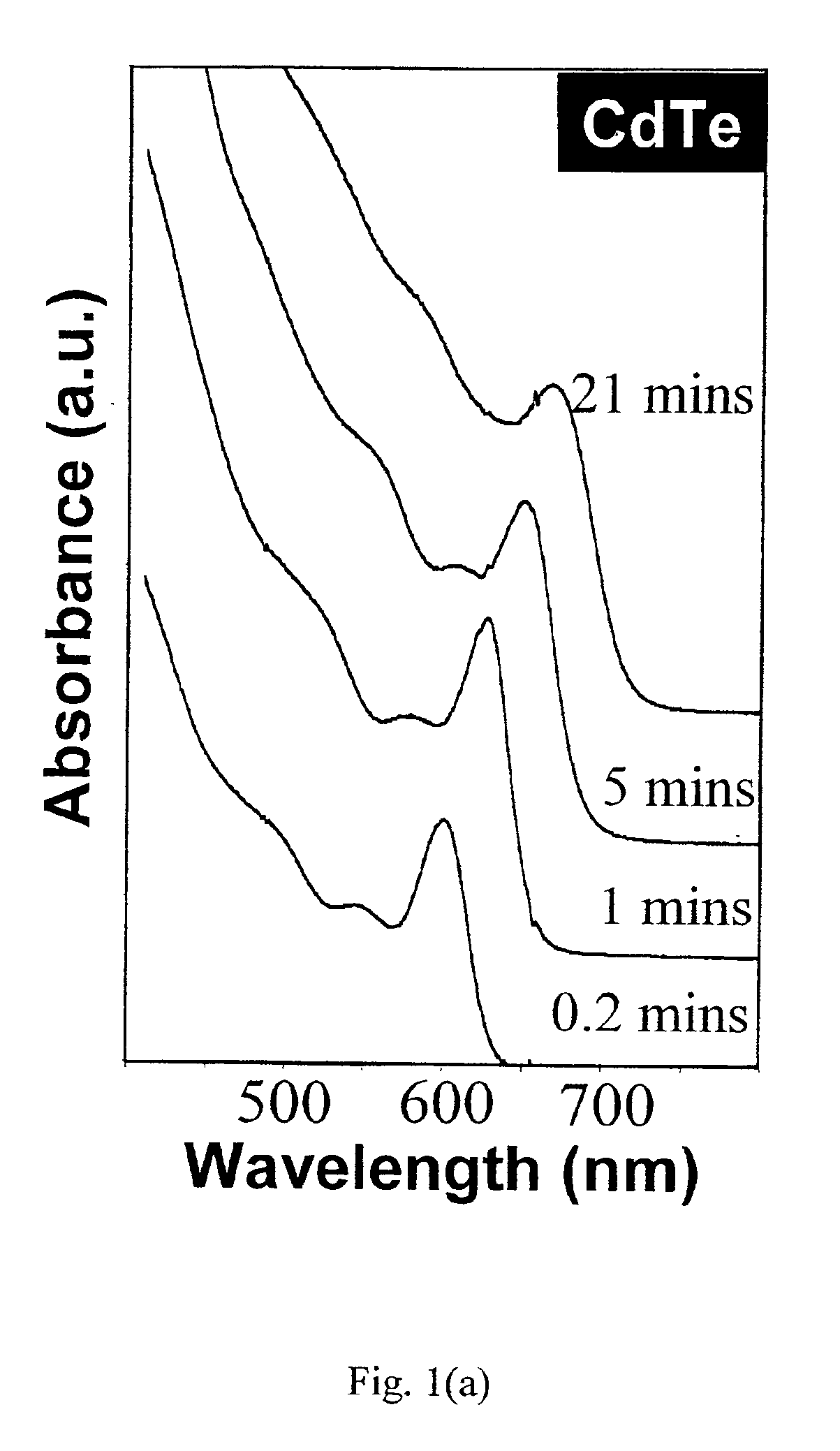
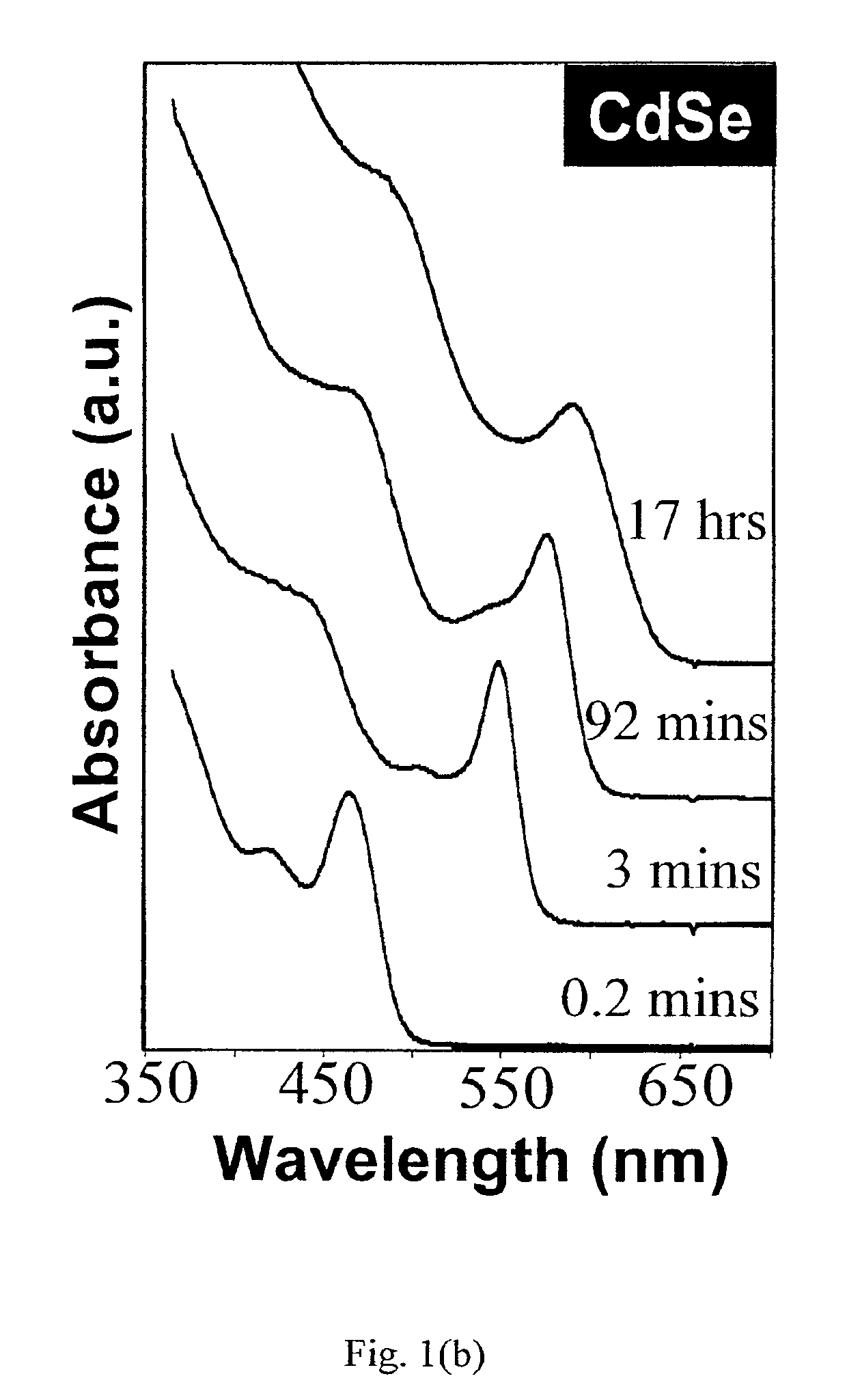
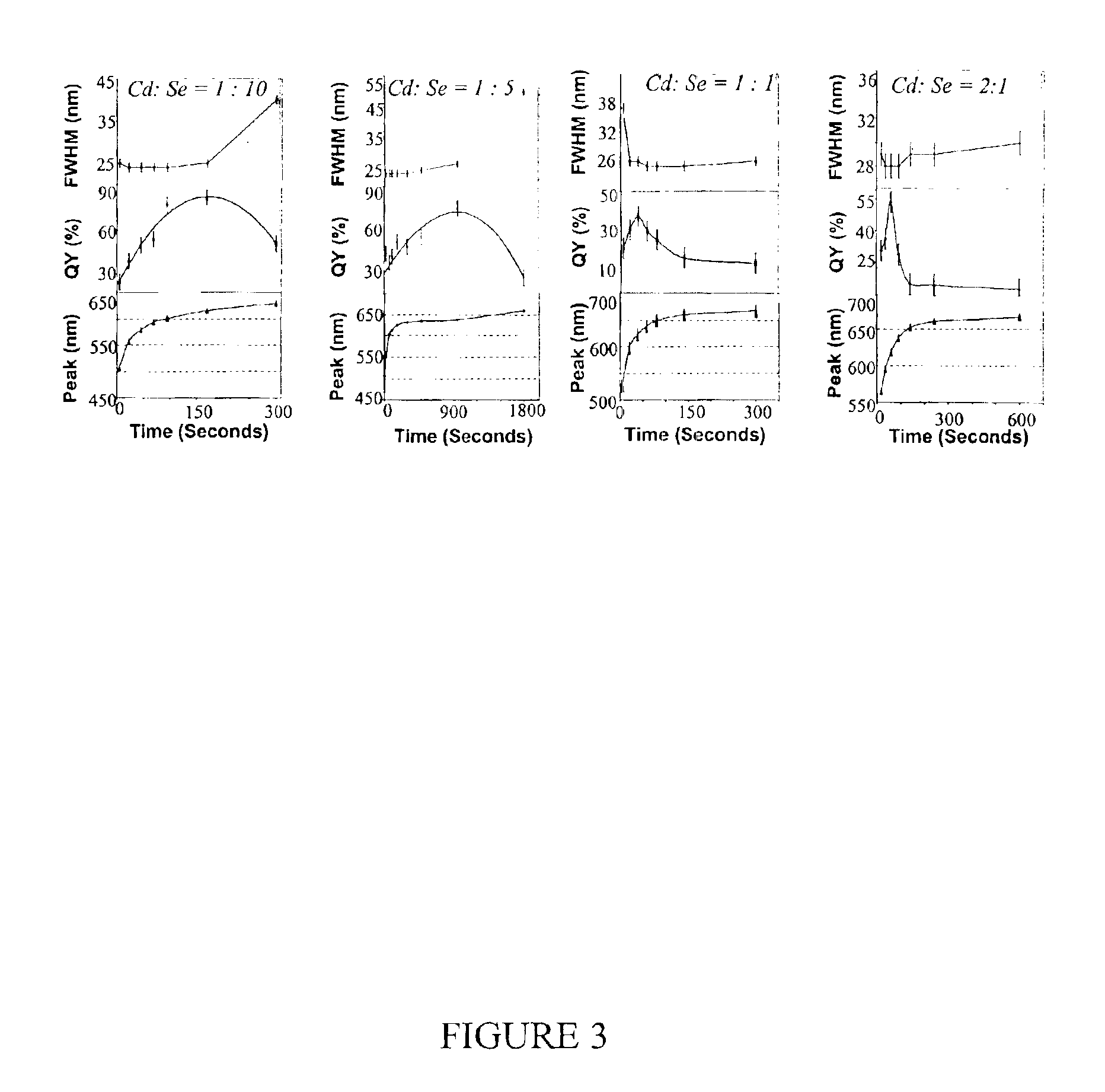
Synthesis of colloidal nanocrystals
InactiveUS6872249B2High crystallinityGood monodispersityFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologyPresent methodSulfur
A method of synthesizing colloidal nanocrystals is disclosed using metal oxides or metal salts as a precursor. The metal oxides or metal salts are combined with a ligand and then heated in combination with a coordinating solvent. Upon heating, the metal oxides or salts are converted to stable soluble metal complexes. The metal complexes are formed by cationic species combining with the ligands and / or with the coordinating solvent. Finally, an elemental chalcogenic precursor, for example, Se, Te, or S, is introduced into the soluble metal complex to complete the formation of the nanocrystals at a controllable rate. High-quality CdSe, CdTe, and CdS nanocrystals are produced when CdO is used as the cadmium precursor. With the present method, the size, size distribution, and shape (dots or rods) of the resulting nanocrystals can be controlled during growth. For example, the resulting nanocrystals are nearly monodisperse without any size separation. Further, the method represents a major step towards a green chemistry approach for synthesizing high-quality semiconductor nanocrystals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
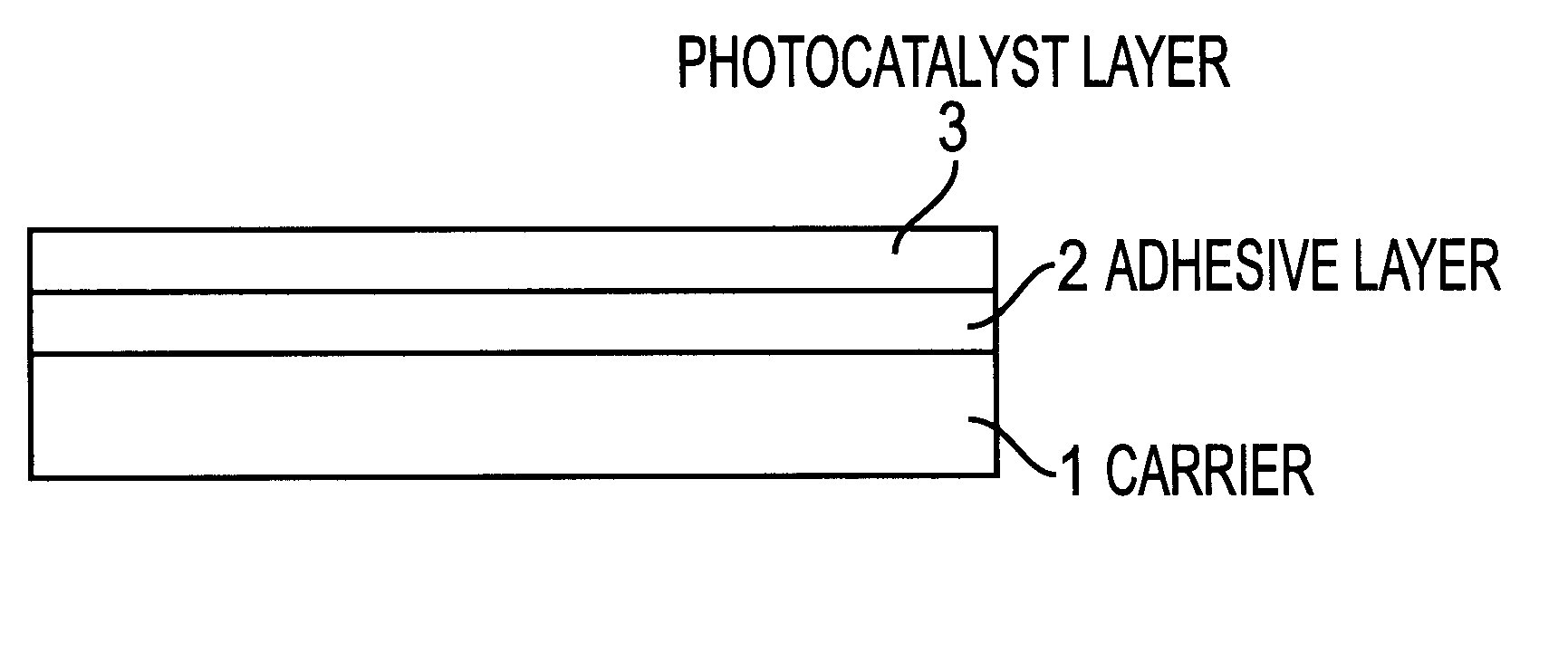
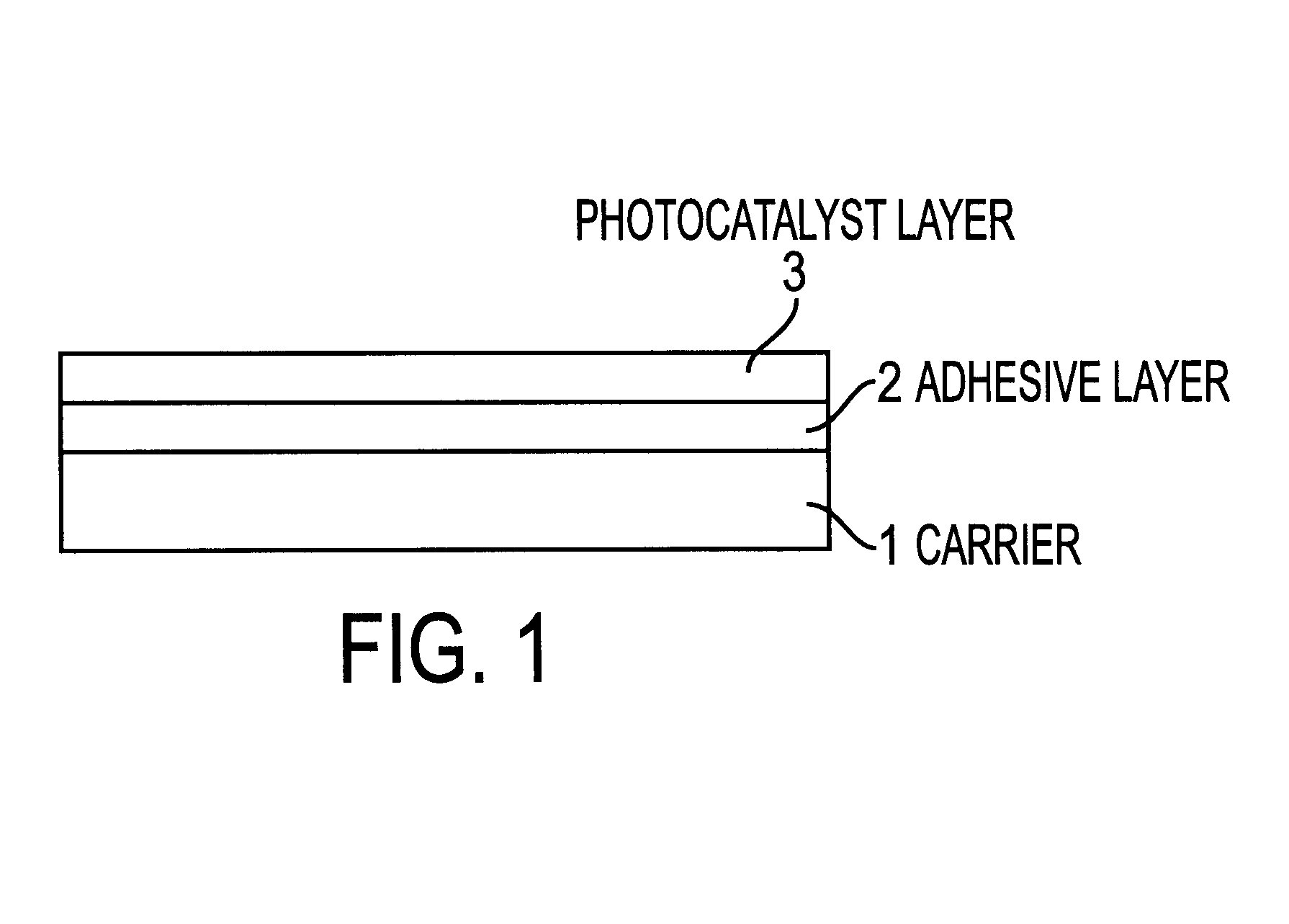
Photocatalyst-carrying structure and photocatalyst coating material
InactiveUS6228480B1Promote decompositionImprove adhesionGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsColloidal silicaColloid
The present invention provides a photocatalyst-carrying structure which has a structure, wherein an adhesive layer is provided in between a photocatalyst layer and a substrate, the adhesive layer is composed of silicon-modified resin, polysiloxane-containing resin or colloidal silica-containing resin, and for forming the photocatalyst layer a composition comprising a metal oxide gel or a metal hydroxide gel and a photocatalyst is used. Further, the present invention also provides a photocatalyst coating agent for producing a photocatalyst-carrying structure which contains silicon compound, at least one metal oxide sol or metal hydroxide sol, and at least one photocatalyst powder or sol.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
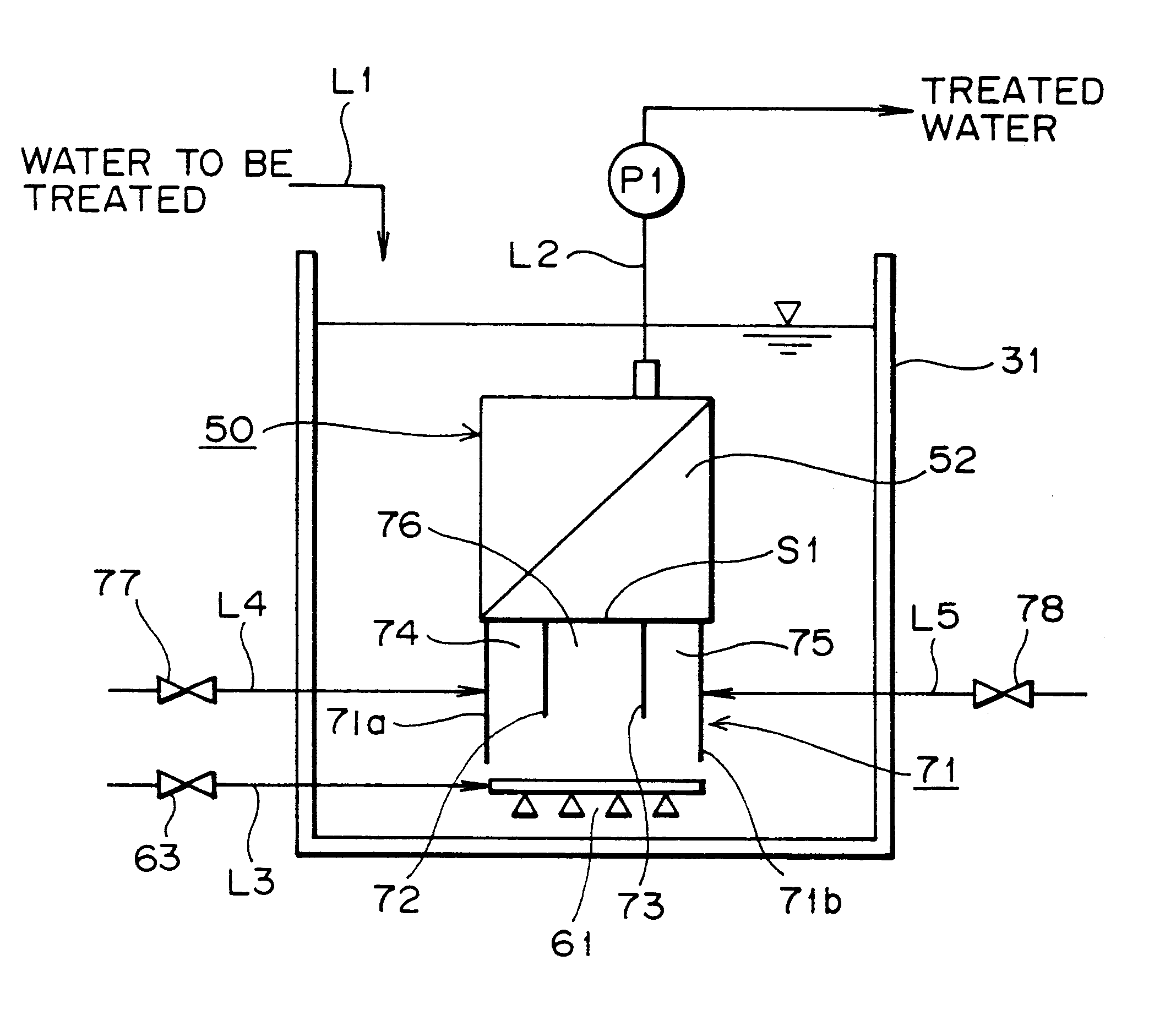
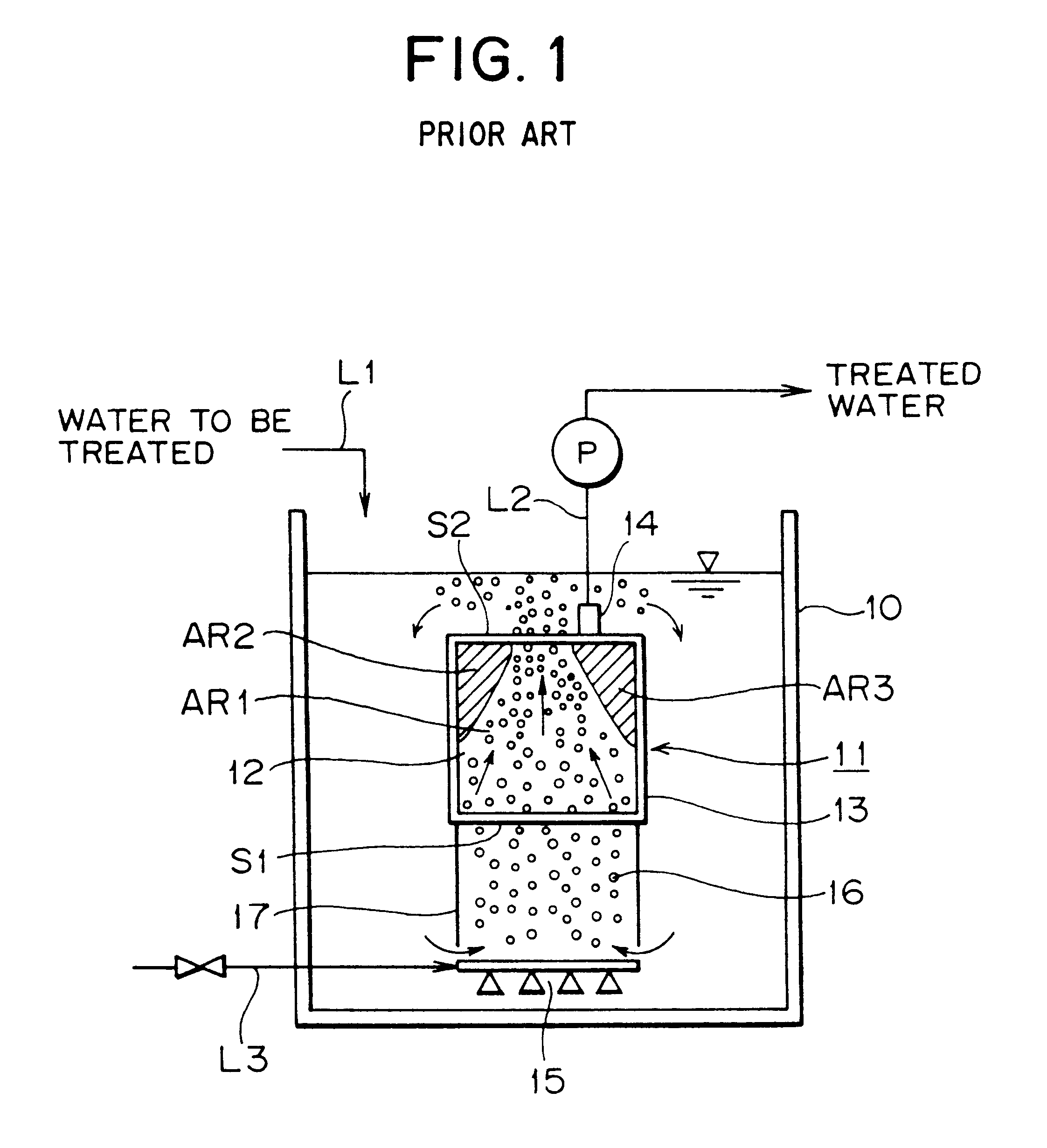
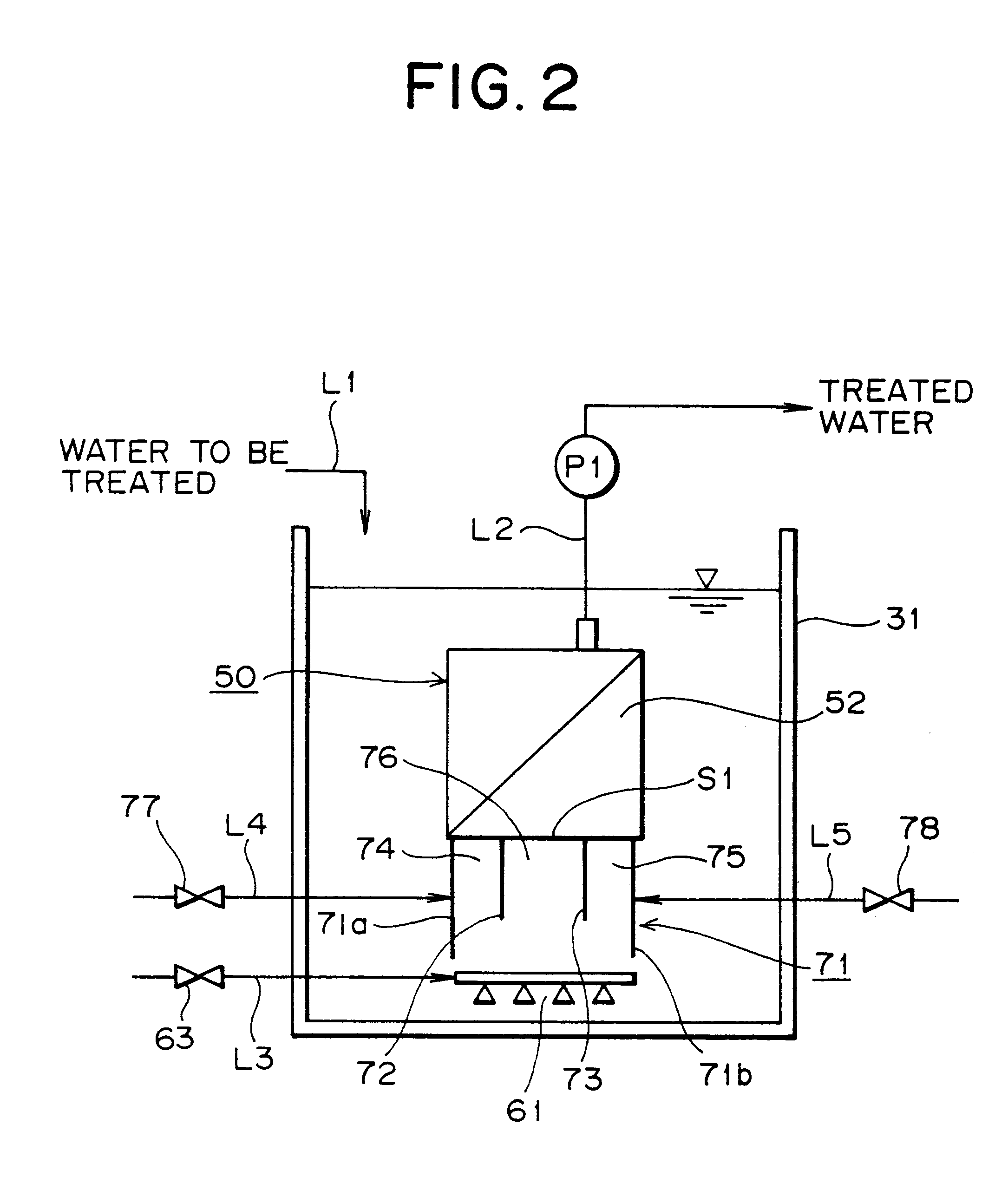
Membrane filter apparatus with gas discharge cleaning means
A membrane filter apparatus includes a membrane unit 50 composed of an array of membrane elements 51 disposed within a treatment tank 31. A skirt element 71 is disposed at a bottom portion of the membrane unit and an aerator 61 is disposed under the skirt. A partition is also disposed at the bottom of the membrane unit forming compartments within the skirt element. The gas bubbles discharged from the aerator increase their rising force upon entry into gaps between the membranes. Because of the arrangement of the partition within the skirt element the flow rate of bubbles along the opposite side edge portions of the membrane unit can be increased having the advantage of cleaning the entire surface of each membrane, thereby preventing clogging by sludge, SS, colloid, etc. within the gaps between the membranes. Therefore, filtration can be maintained over a longer period of time and the power required for filtration can be reduced, as well as, the frequency of manual periodic cleaning, chemical cleaning, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Compositions comprising lipophilic active compounds and method for their preparation
ActiveUS20090098200A1Quick releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryBiocideHydrophilic polymersCompound (substance)
Compositions are provided comprising a lipophilic active compound, e.g., a human or veterinary drug or a nutraceutical, interwoven with a polymeric matrix formed by two or more polymers, wherein one of the polymers is an amphiphilic polymer and the other polymer is either an amphiphilic polymer with a different hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance or a hydrophilic polymer, and the active lipophilic compound has modified physicochemical properties. The composition forms colloidal nanodispersion upon contact with aqueous media.
Owner:SOLUBEST
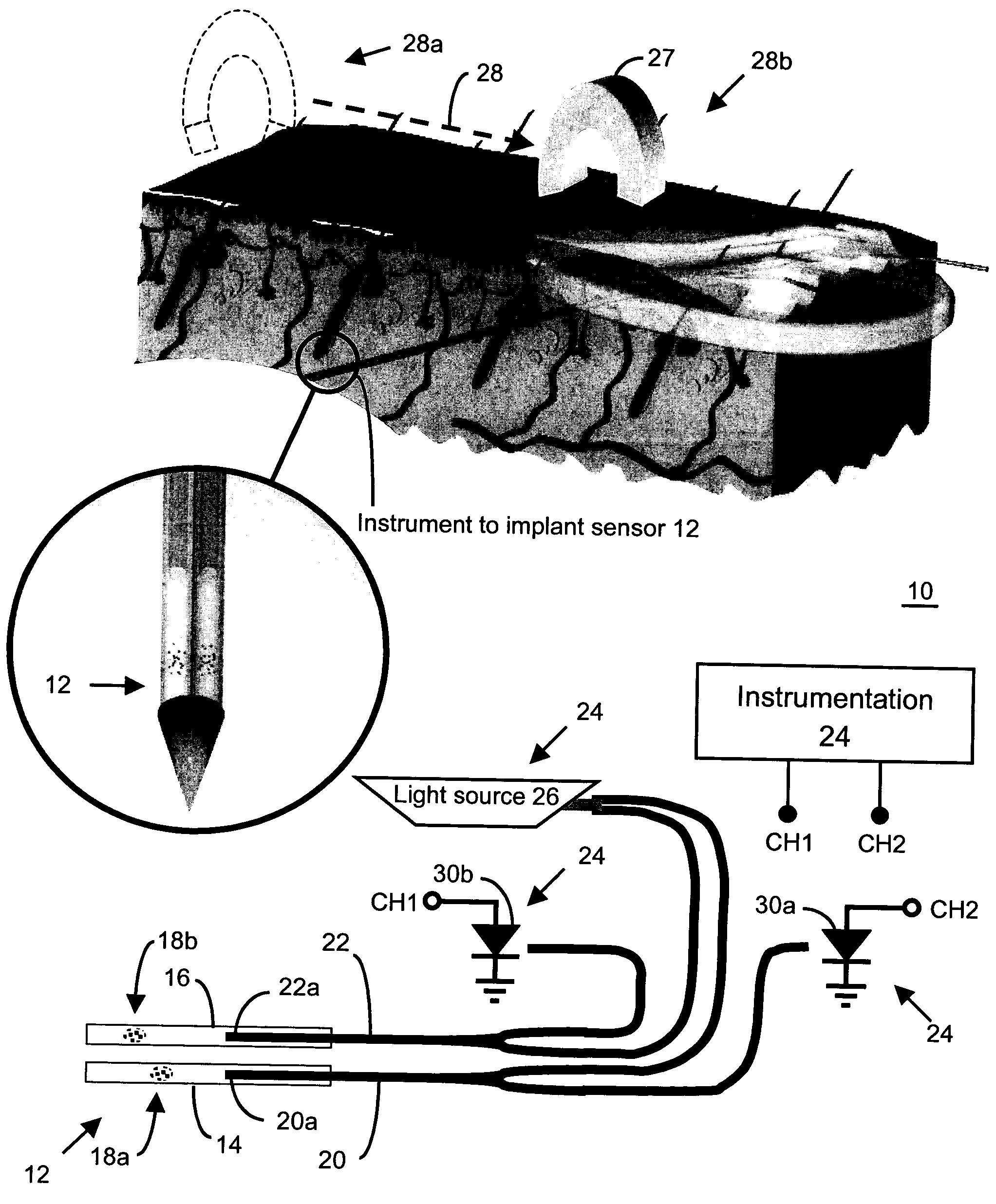
Method and apparatus for analyte sensing
InactiveUS7226414B2Reducing dispersion viscosityLow viscosityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringRare-earth elementEngineering
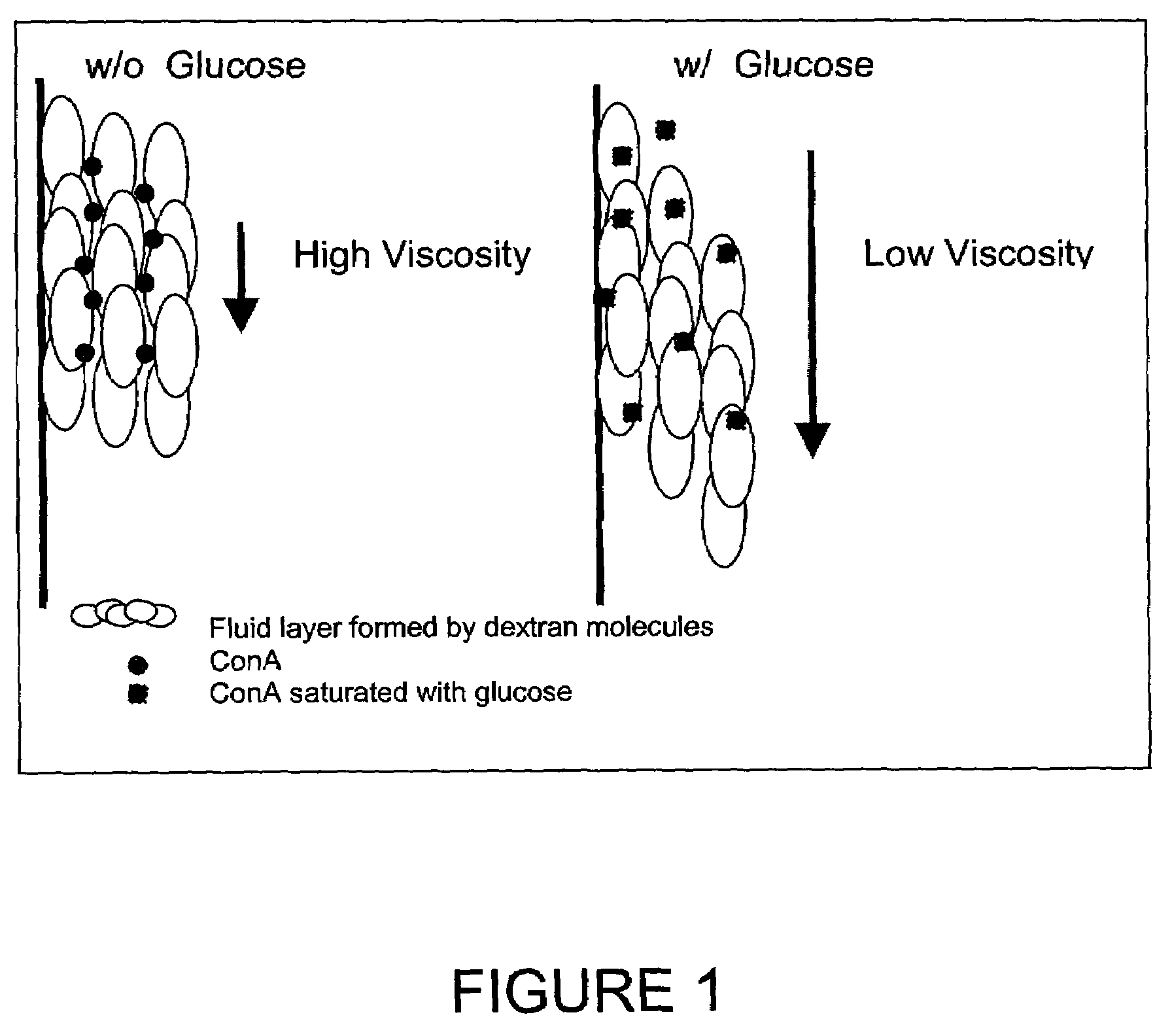
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a glucose sensing device for implantation within subcutaneous tissue of an animal body. In one embodiment, the glucose sensing device includes a first chamber containing first magnetic particles and a hydrocolloid solution (for example, ConA-dextran hydrocolloid) wherein the first magnetic particles are dispersed in the hydrocolloid solution. In operation, glucose within the animal may enter and exit the first chamber and the hydrocolloid solution changes in response to the presence or concentration of glucose within the first chamber. The sensing device also includes a reference chamber containing second magnetic particles and a reference solution wherein the second magnetic particles are dispersed in the reference solution. The reference solution (for example, oil or alcohol compounds) includes a known or fixed viscosity. The reference solution may also be a hydrocolloid solution (for example, ConA-dextran hydrocolloid). The first and / or second magnetic particles may include amine-terminated particles, at least one rare earth element (for example, neodymium or samarium), and / or a ferromagnetic material.
Owner:BIOTEX
Antimicrobial compositions containing colloids of oligodynamic metals
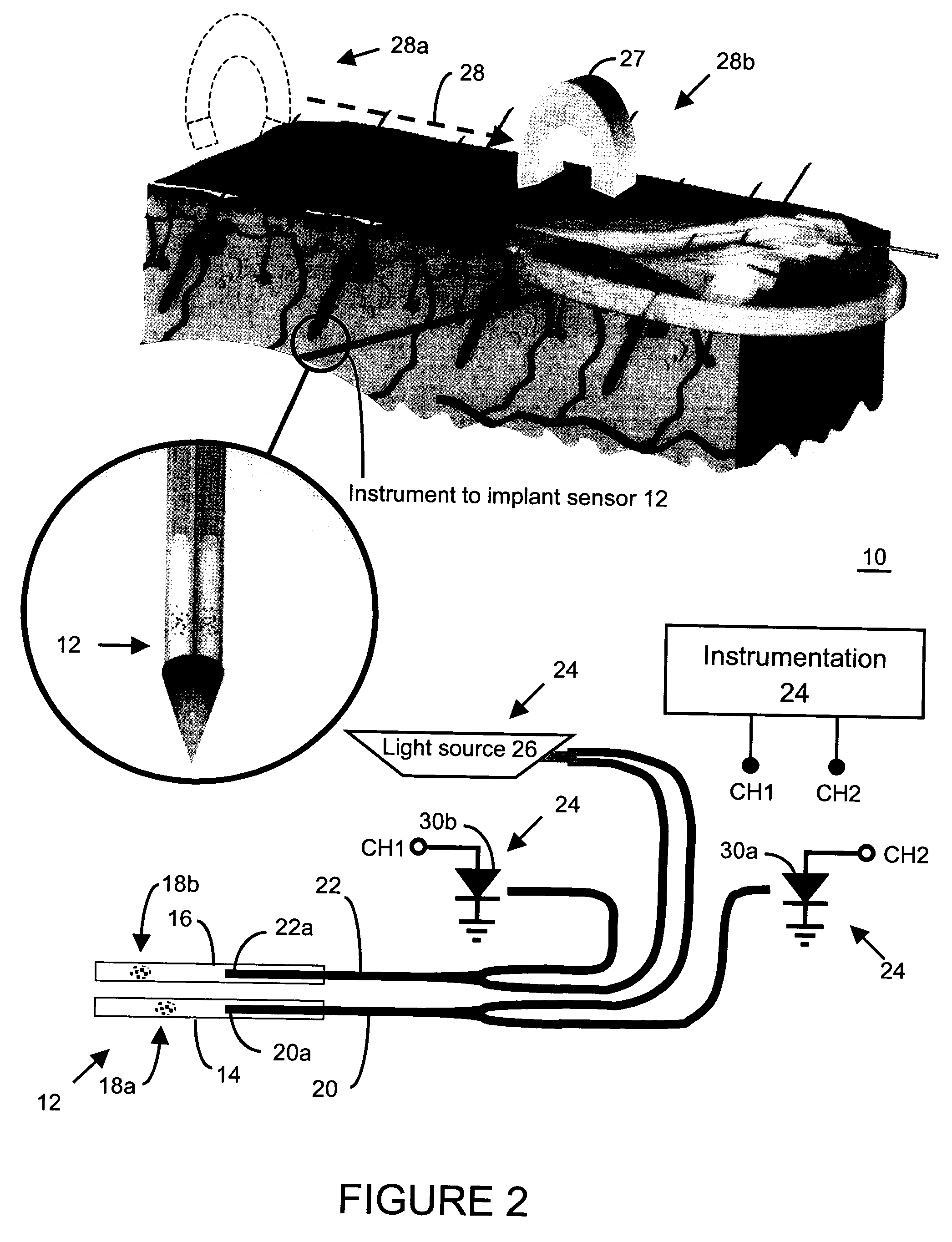
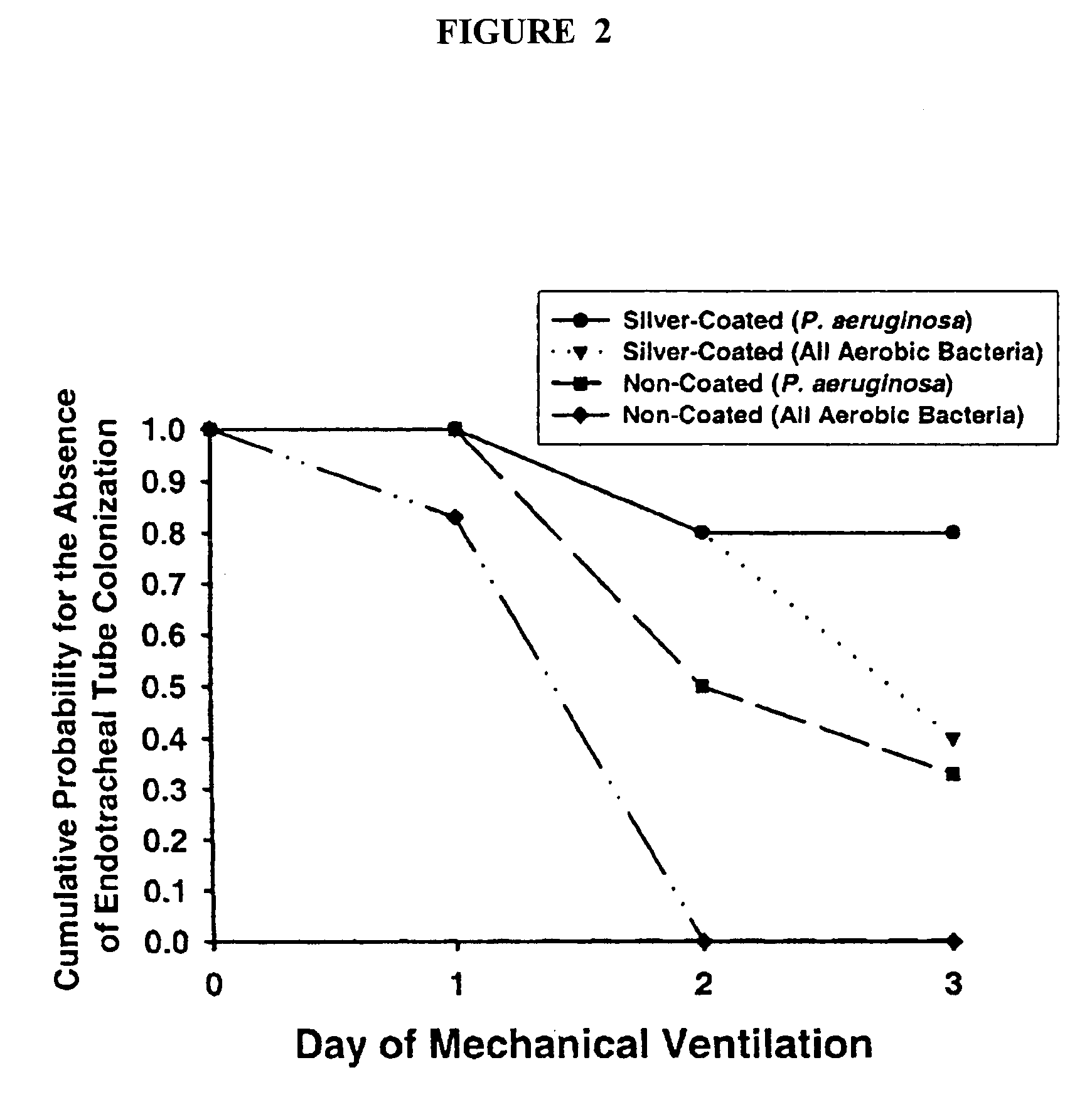
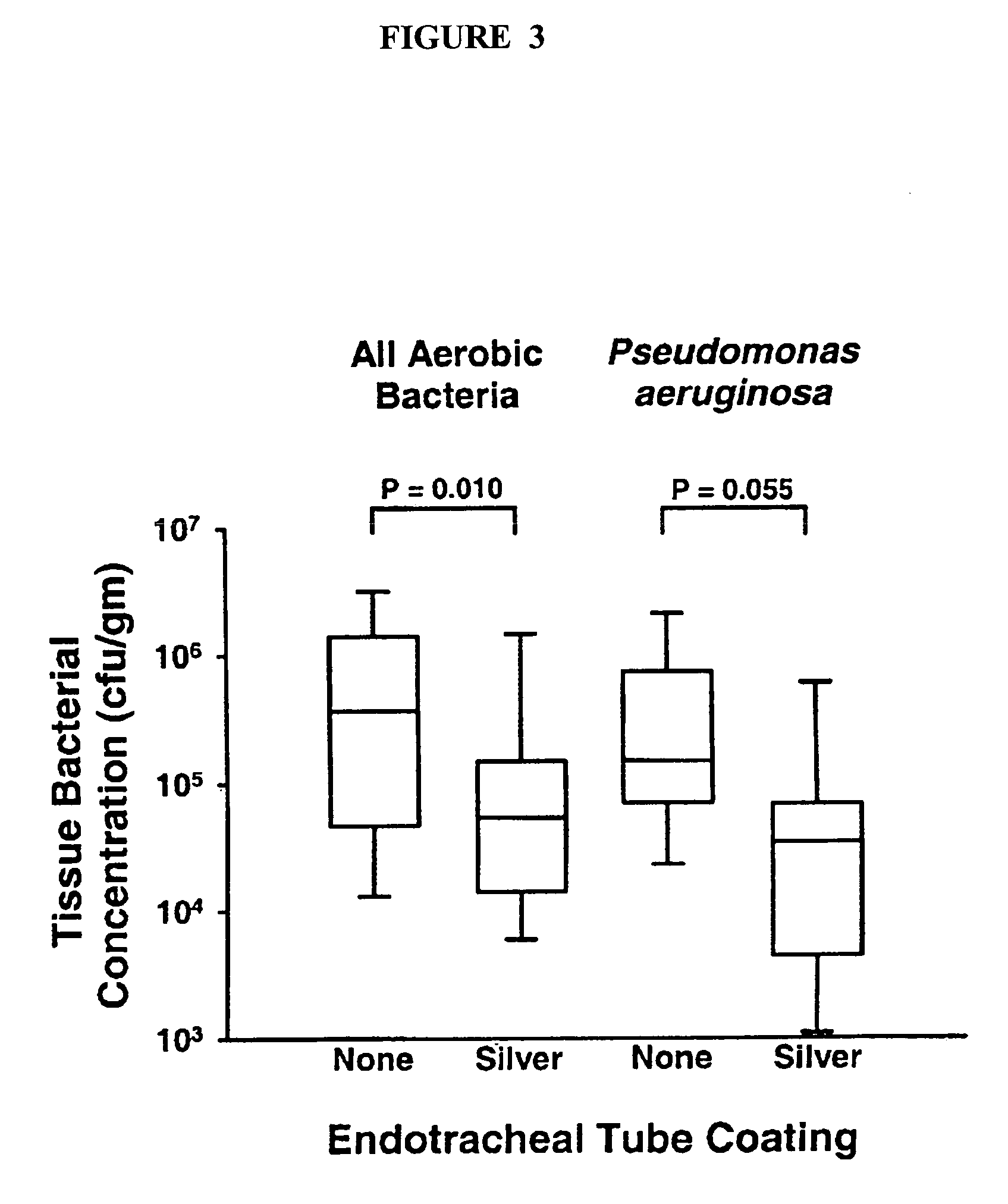
InactiveUS7179849B2Reduced settlingReduce agglomerationOrganic active ingredientsPretreated surfacesSolubilityCatheter
Owner:CR BARD INC
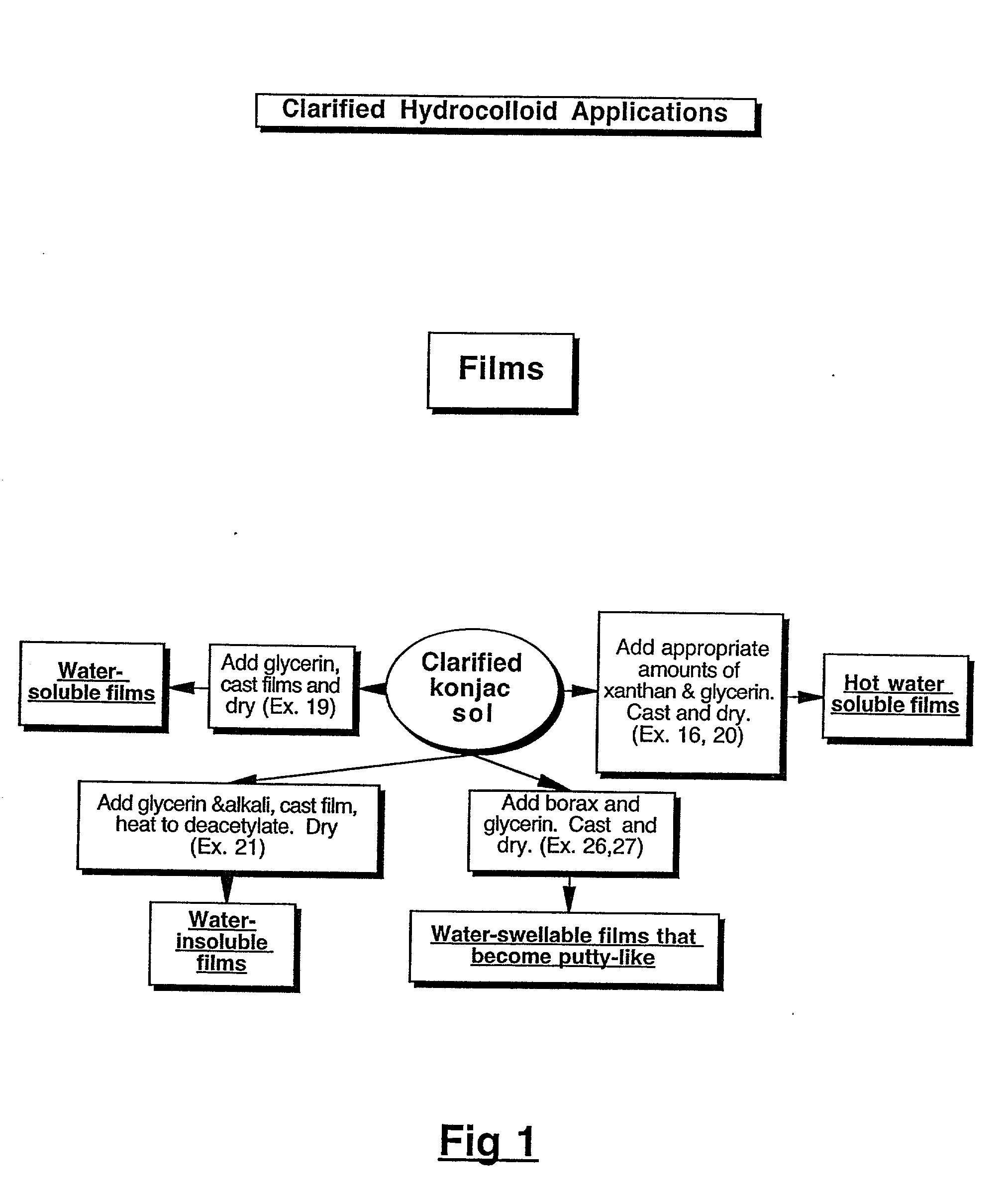
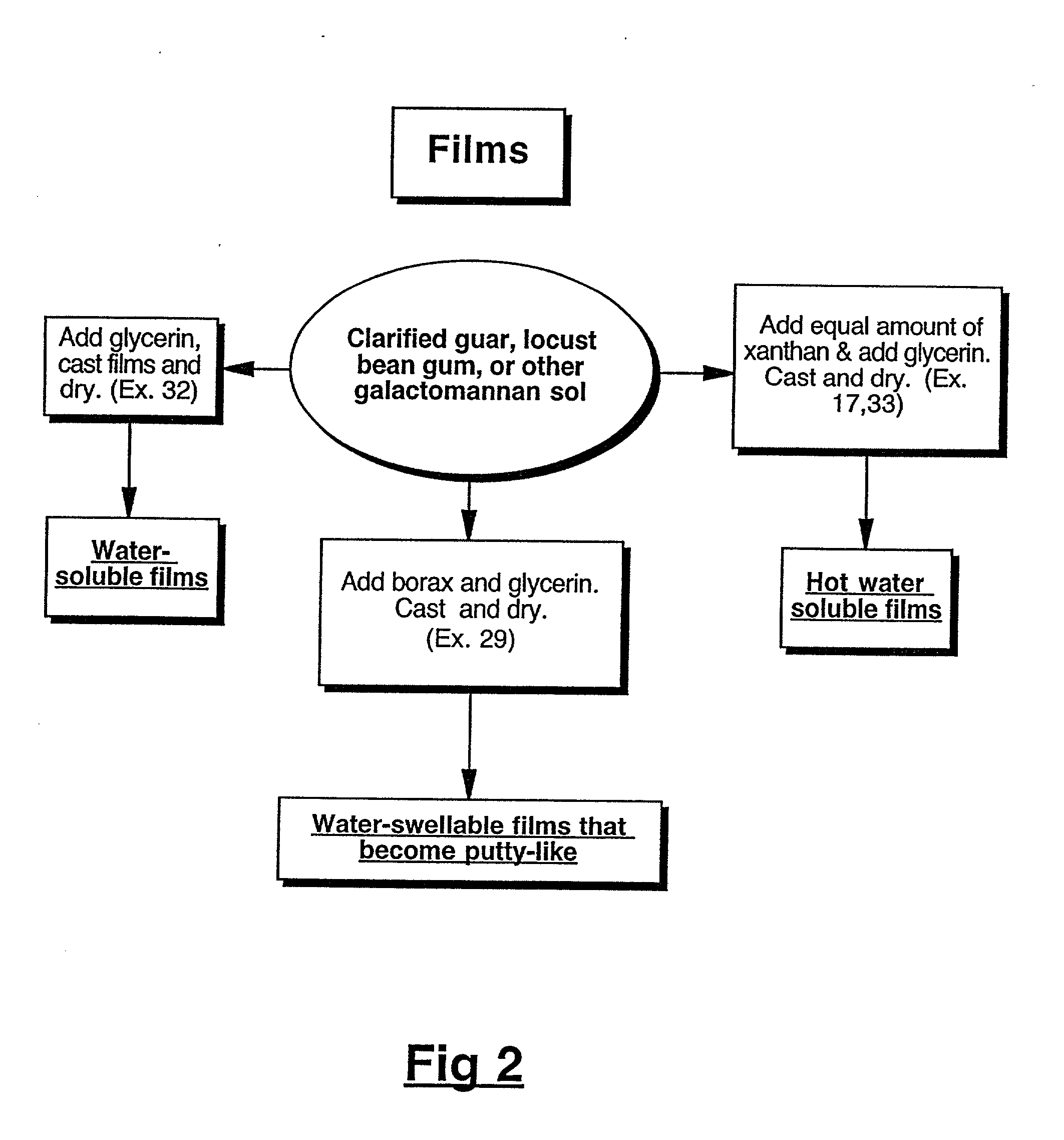
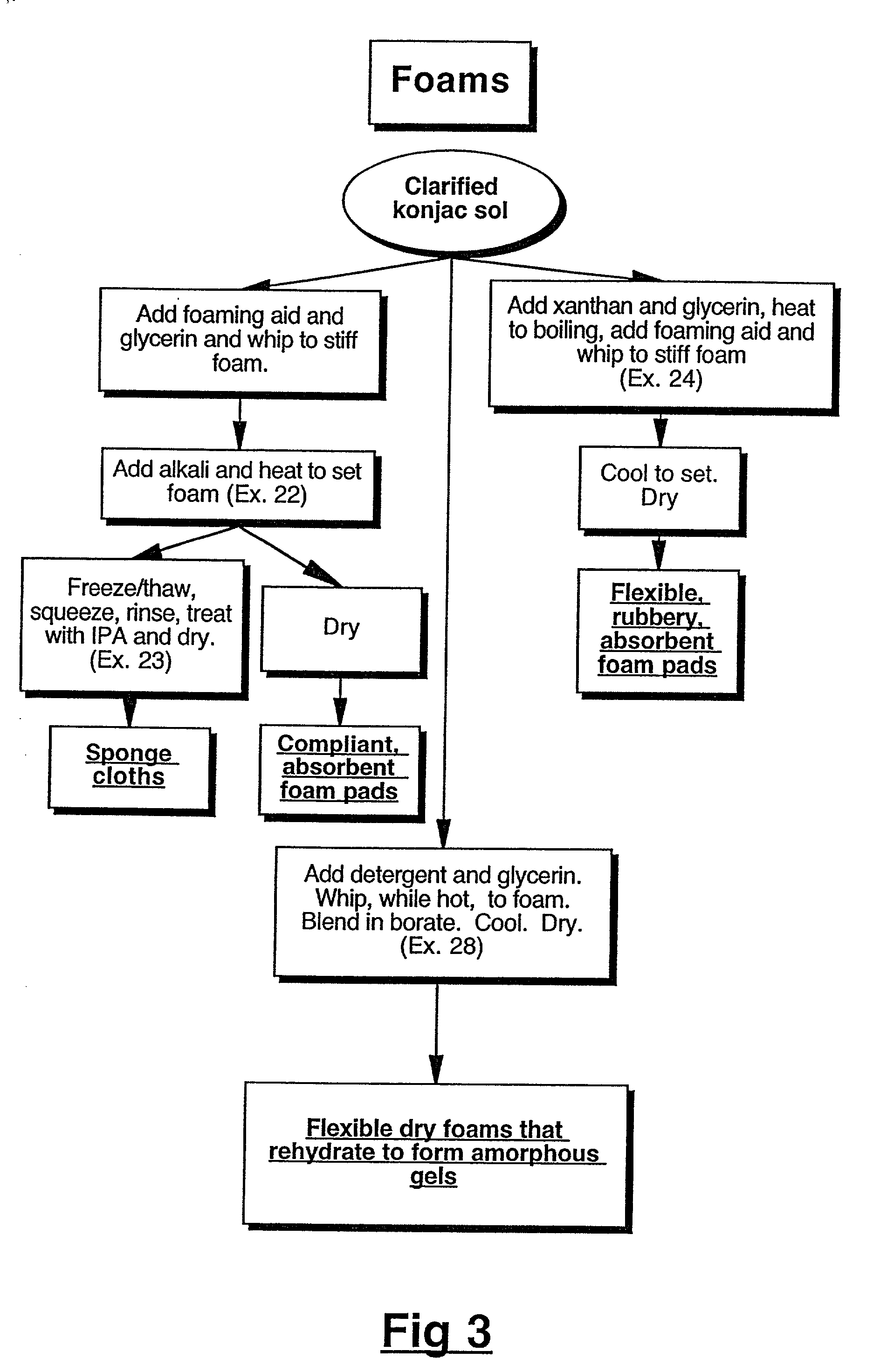
Physical forms of clarified hydrocolloids of undiminished properties and method of producing same
InactiveUS20020019447A1Good coagulationAssist dispersionOther chemical processesMixing methodsDiolPhysical form
This invention relates to novel forms of clarified hydrocolloids including gels, films, foams, capsules and sponges. The invention also pertains to novel processes for producing the various physical forms of the clarified hydrocolloids. The invention also includes clarified hydrocolloid composites; borated cis 1,2-diol containing hydrocolloids; and clarified hydrocolloids of low viscosity.
Owner:MARINE BIOPRODS INT
Non-gelatin capsule shell formulation
A film-forming hydrocolloid composition comprising kappa carrageenan, iota carrageenan, a bulking agent, plasticizer and water is described. The ratio of bulking agent to total carrageenan is from about 1:1 to 20:1. Kappa carrageenan is present in an amount of less than or equal to 50% by weight of total carrageenan present. To form the composition, all dry materials are mixed and added to a heated mixture of all liquid materials. The final mixture is heated until a composition free of particulate materials is formed. The formed composition can be cast or extruded into ribbons, films, sheets, tubes or the like, for encapsulating wet or dry materials including medicinal dosage forms, nutritional supplements, cosmetics, bath oils and gels, and paint balls.
Owner:PATHEON SOFTGELS INC
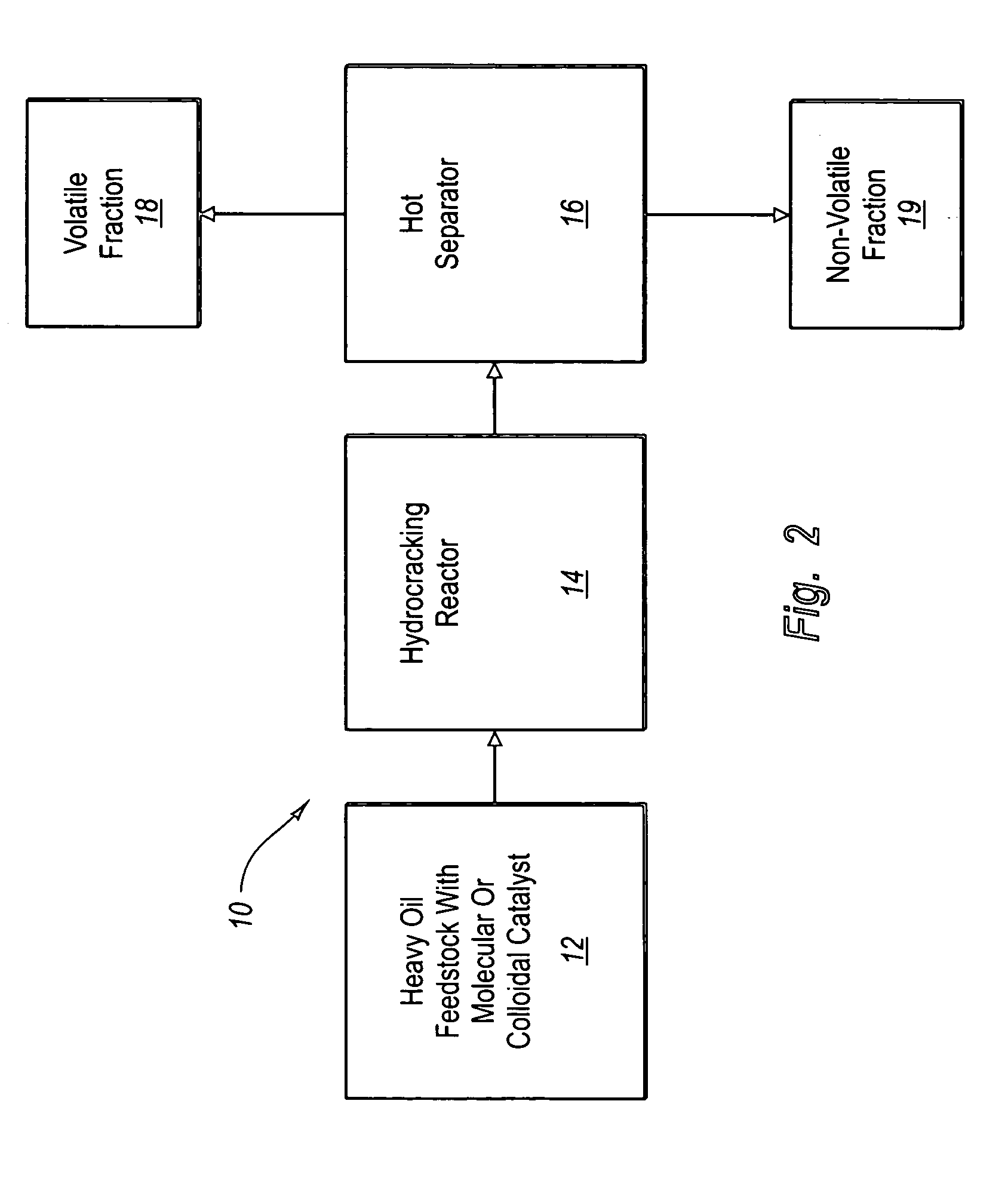
Hydroprocessing method and system for upgrading heavy oil using a colloidal or molecular catalyst
ActiveUS20050241993A1Inhibits eliminates formationEasy to useCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationColloidFuel oil
Methods and systems for hydroprocessing heavy oil feedstocks to form an upgraded material involve the use of a colloidal or molecular catalyst dispersed within a heavy oil feedstock, a hydrocracking reactor, and a hot separator. The colloidal or molecular catalyst promotes hydrocracking and other hydroprocessing reactions within the hydrocracking reactor. The catalyst is preferentially associated with asphaltenes within the heavy oil feedstock, which promotes upgrading reactions involving the asphaltenes rather than formation of coke precursors and sediment. The colloidal or molecular catalyst overcomes problems associated with porous supported catalysts in upgrading heavy oil feedstocks, particularly the inability of such catalysts to effectively process asphaltene molecules. The result is one or more of reduced equipment fouling, increased conversion level, and more efficient use of the supported catalyst if used in combination with the colloidal or molecular catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION LLC
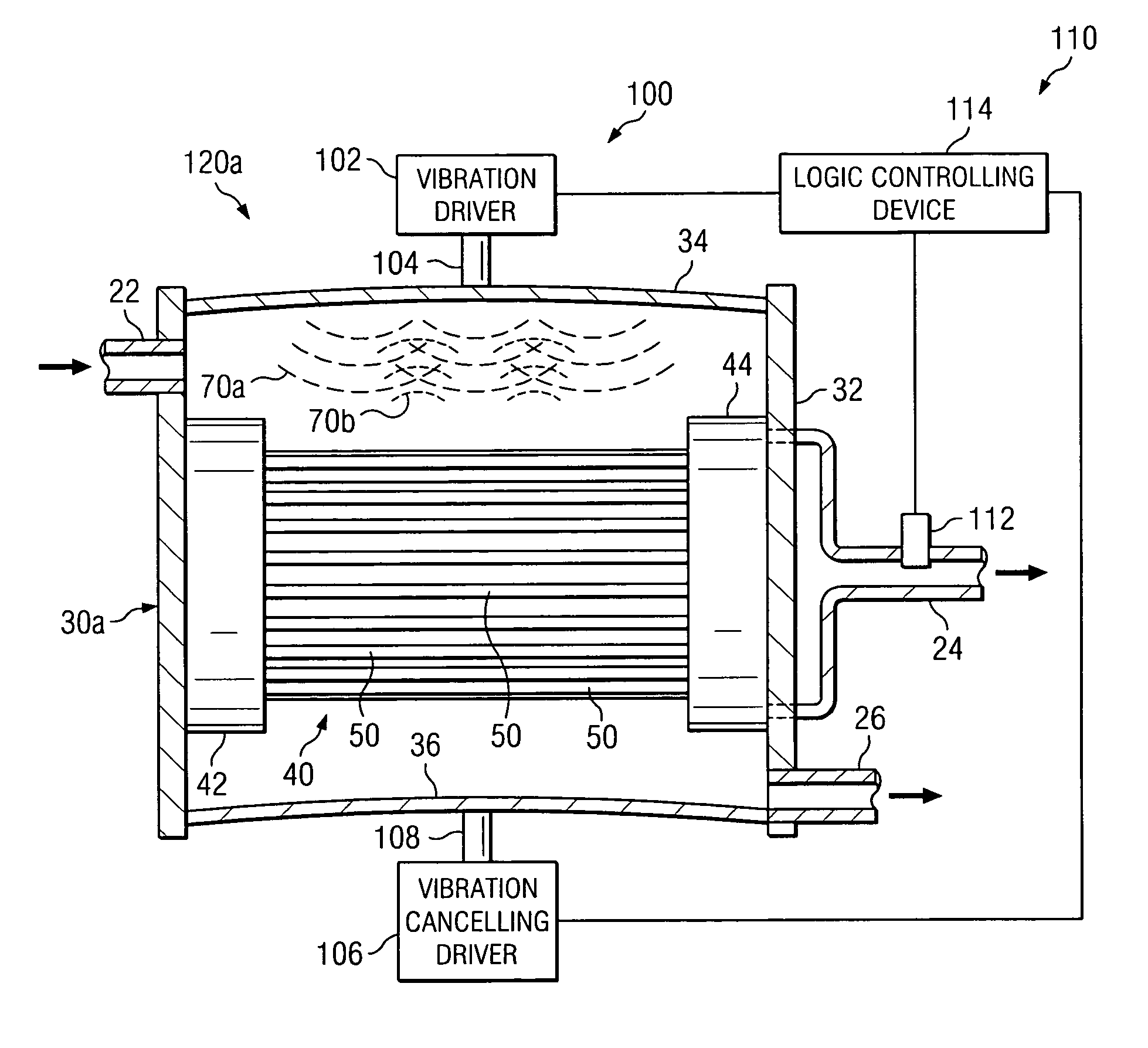
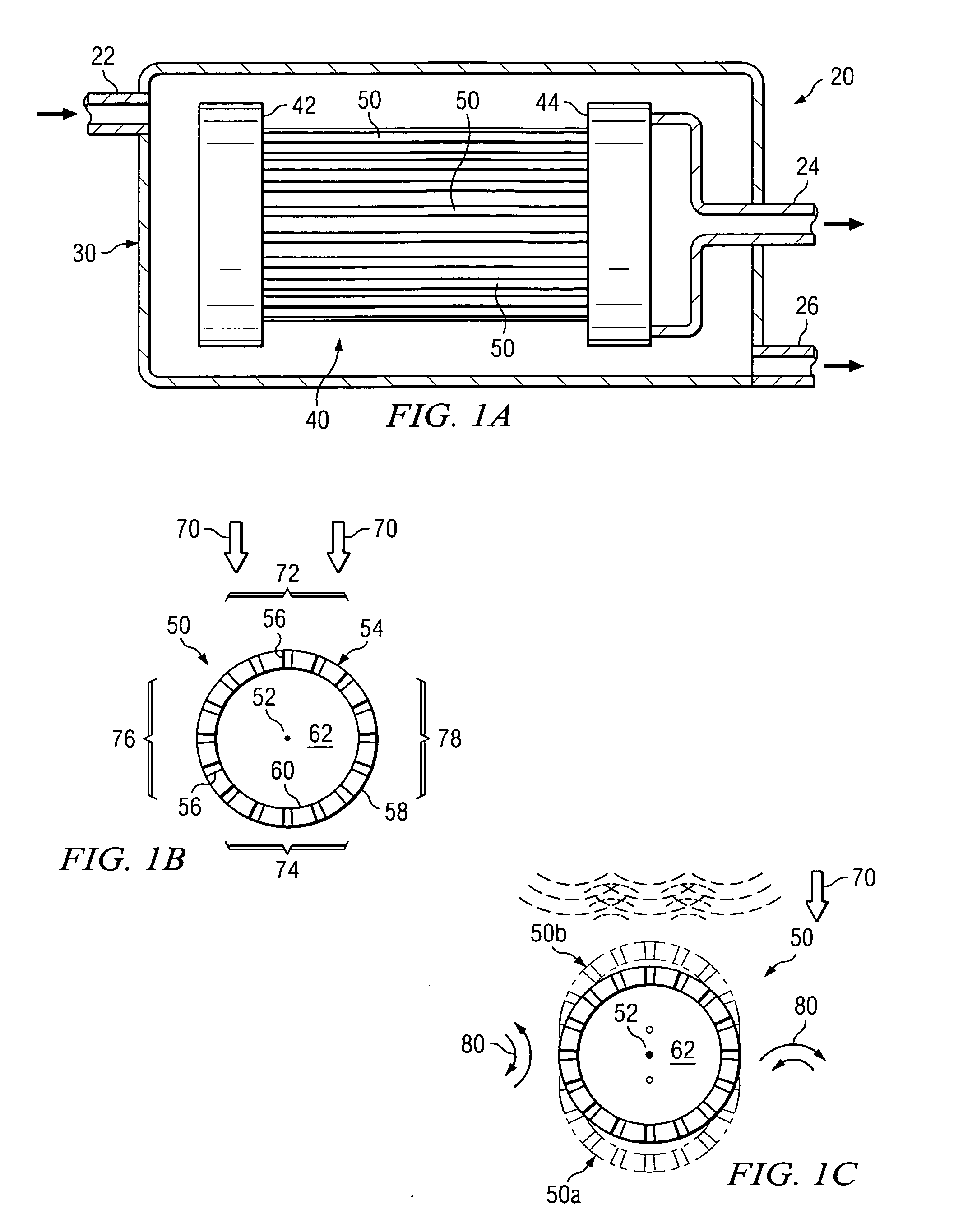
Cleaning hollow core membrane fibers using vibration
InactiveUS20050077227A1Minimize returnMinimize bounce backMembranesSpecific water treatment objectivesParticulatesFiber
A filtration system is provided with hollow membrane filter elements operable to remove solids, particulate and colloidal matter from a process fluid. Acoustic, vibration and ultrasonic energy may be used to clean exterior portions of the hollow membrane filter elements to allow substantially continuous filtration of process fluids. The filtration system may be satisfactorily used with process fluids having a relatively high concentrations of solids, particulate and colloidal matter.
Owner:PHASE
Foam and gel oat protein complex and method of use
InactiveUS6514487B1Smoothness and eleganceNormal skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientIrritation
A composition containing enhanced colloidal oatmeal which utilizes other avena sativa ingredients to neutralize the discomfort, irritation and inflammation of the skin, as well as maintaining normal skin, and can be used to treat many types of discomforts, including itching; due to poison ivy, oak and sumac, insect bites, sunburn, chicken pox, hives, prickly heat, chafing, and the like while maintaining the normal pH of the skin.
Owner:BARR TERESA LEIGH
Aqueous dispersions of polythienothiophenes with fluorinated ion exchange polymers as dopants
ActiveUS20060076557A1Solve problemsMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensCarbon nanotubeIon exchange
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of polythienothiophenes and colloid-forming polymeric acids. Films from invention compositions are useful as hole injection layers in organic electronic devices, including electroluminescent devices, such as, for example, organic light emitting diodes (OLED) displays, as hole extraction layers in organic optoelectronic devices, such as organic photovoltaic devices, and in combination with metal nanowires or carbon nanotubes in applications such as drain, source, or gate electrodes in thin film field effect transistors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Aqueous compositions, aqueous cutting fluid using the same, method for preparation thereof, and cutting method using the cutting fluid
InactiveUS6221814B1Promote degradationSimple treatmentOther chemical processesWork treatment devicesActivated sludgeLiquid waste
An aqueous cutting fluid which can reduce the impact on working environment and the global environment, and can achieve both preventing precipitates from becoming a hard cake and keeping high dispersibility for abrasive grains is provided. Such an aqueous cutting fluid is obtained by a method comprising dispersing abrasive grains (G) in an aqueous composition comprising a dispersion medium (M) containing a hydrophilic alcohol compound such as ethylene glycol, a lipophilic alcohol compound such as propylene glycol and water, and silica colloid particles dispersed stably in the medium. The dispersion medium (M) is odorless and not flammable. The abrasive grains (G) may settle out after a time, but they do not closely contact with one another, and therefore the resulting precipitates do not become a hard cake, which allows the re-dispersion and reuse of precipitated grains. The instant aqueous cutting fluid is inherently low viscous, and the reduction of viscosity owing to the contamination of water and the increase of viscosity owing to contamination of shavings are both moderate. As a result, the cutting fluid has a long life. And articles which have been cut using the cutting fluid can be washed with water. Further, as the dispersion medium (M) is a biodegradable low molecular weight organic compound, a waste liquid from a process using the cutting fluid can be disposed with an activated sludge.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD +1
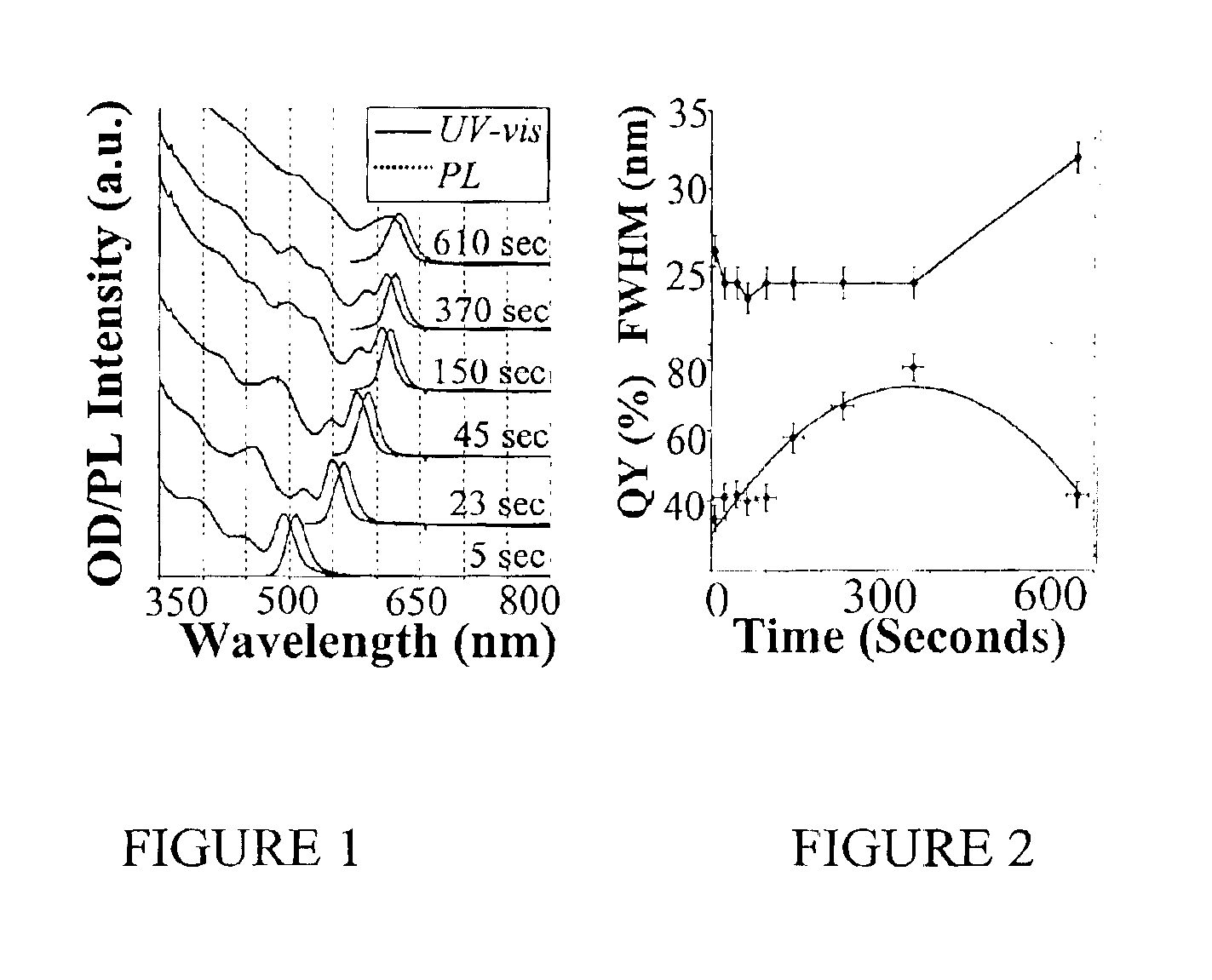
Colloidal nanocrystals with high photoluminescence quantum yields and methods of preparing the same
InactiveUS6869545B2Good monodispersityImprove launch performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsQuantum yieldPhotoluminescence
The present invention provides new compositions containing colloidal nanocrystals with high photoluminescence quantum yields, new synthetic methods for the preparation of highly luminescent colloidal nanocrystals, as well as methods to control the photoluminescent properties of colloidal nanocrystals. The new synthetic methods disclosed herein allow photoemission brightness (quantum yield) to be correlated with certain adjustable nanocrystal growth parameters associated with a given synthetic scheme.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method for preparing liquid colloidal dispersion of silver particles, liquid colloidal dispersion of silver particles, and silver conductive film
InactiveUS20060264518A1Good dispersionHighly conductive filmMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesScreen printingFiltration
A process for producing a fine silver particle colloidal dispersion which can simply form conductive silver layers and antimicrobial coatings by screen printing or the like. The process is characterized by having a reaction step of allowing an aqueous silver nitrate solution to react with a mixed solution of an aqueous iron(II) sulfate solution and an aqueous sodium citrate solution to form an agglomerate of fine silver particles, a filtration step of filtering the resultant agglomerate of fine silver particles to obtain a cake of the agglomerate of fine silver particles, a dispersion step of adding pure water to the cake to obtain a first fine silver particle colloidal dispersion of a water system in which dispersion the fine silver particles have been dispersed in the pure water, and a concentration and washing step of concentrating and washing the first fine silver particle colloidal dispersion of a water system.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
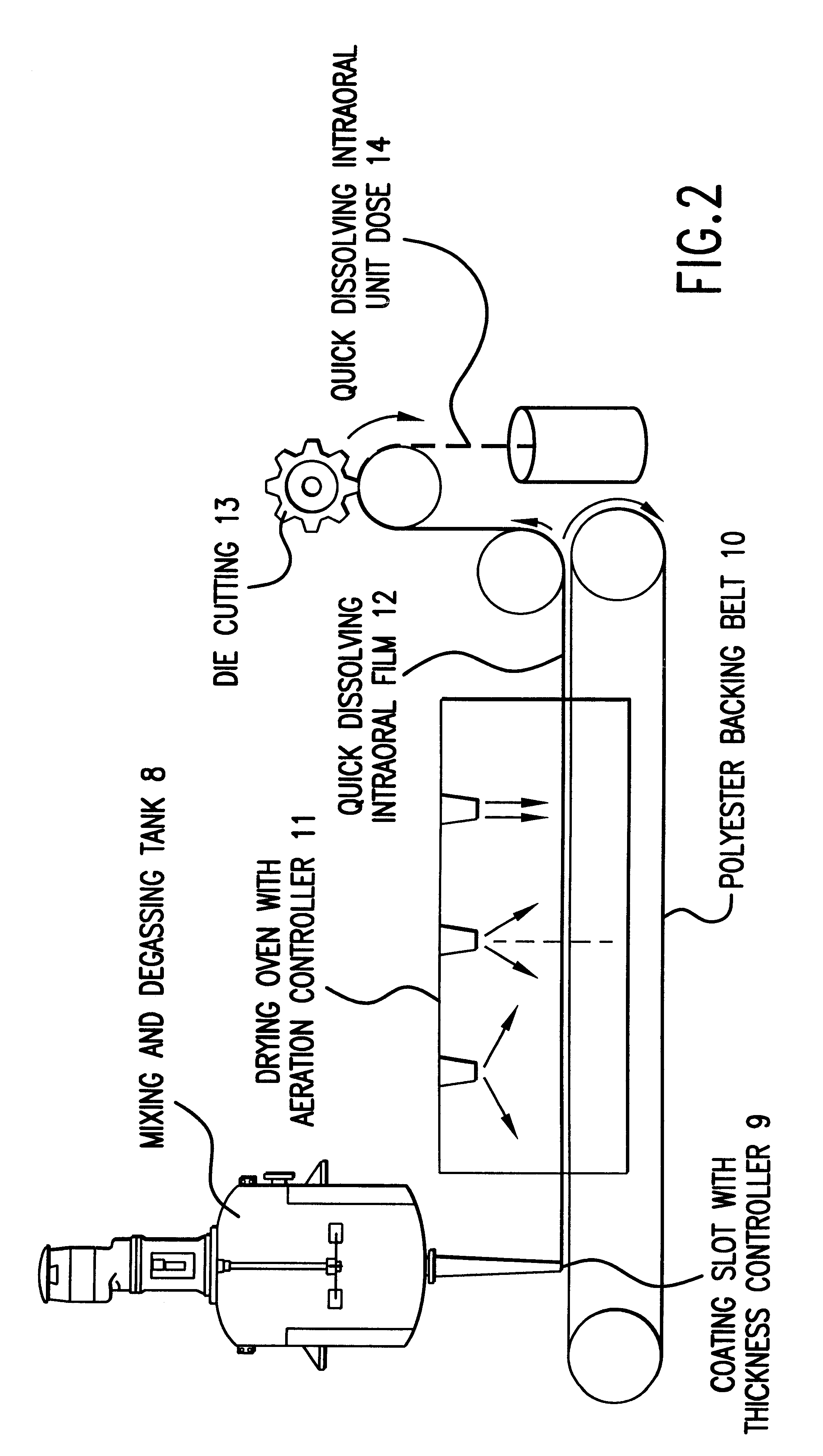
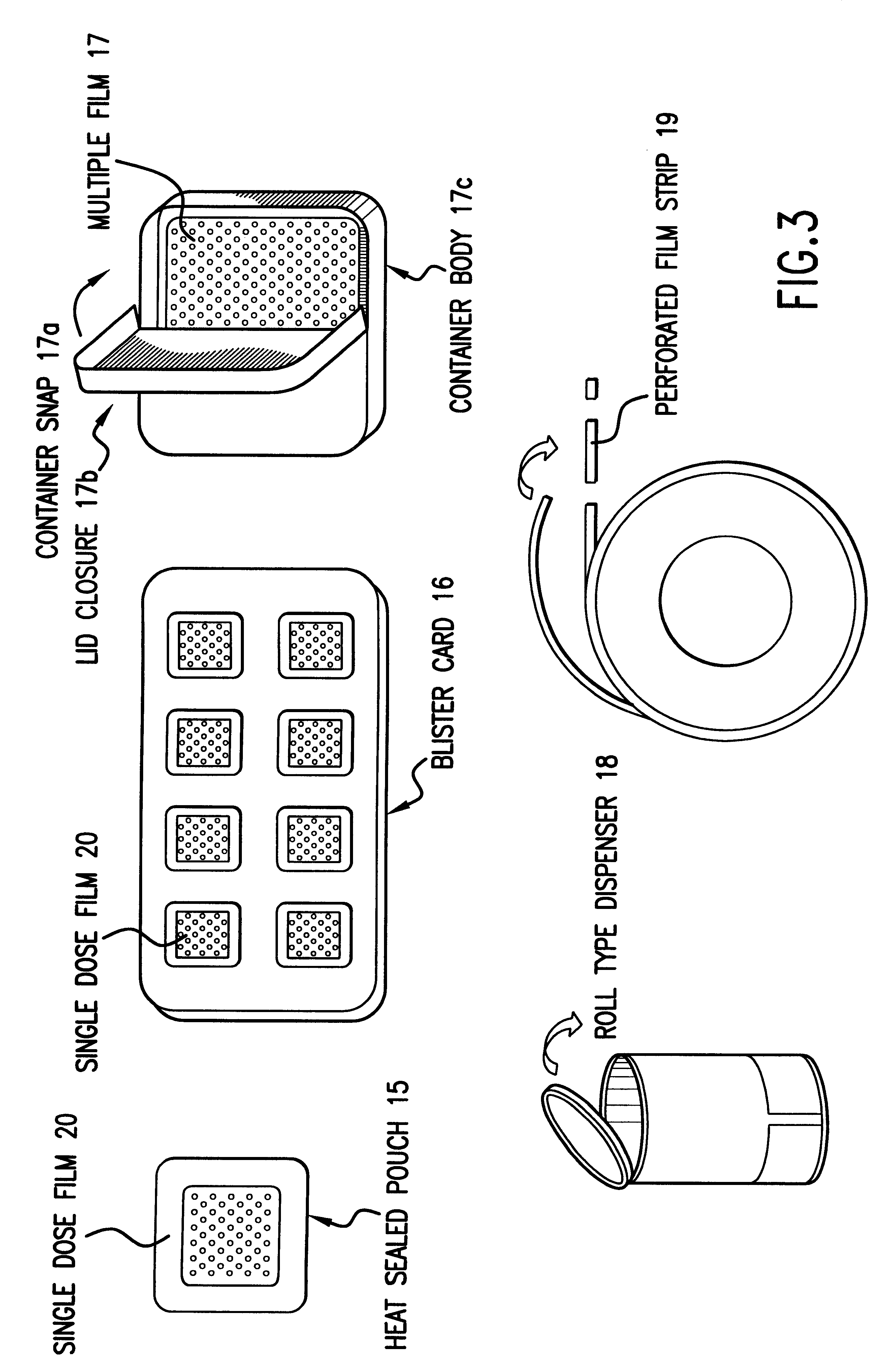
Edible film
InactiveUS20050089548A1Not easily friableEasy to handleMixingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineActive agent
An edible film that rapidly disintegrates when placed in the mouth to release an active agent, the film consisting of a hydrocolloid film-forming material and microparticles containing active agent
Owner:GIVAUDAN SA
Pharmaceutical excipient having improved compressibility
InactiveUS6103219AImprove compression performanceReduce the amount requiredCosmetic preparationsPowder deliverySilica particleColloid
A microcrystalline cellulose-based excipient having improved compressibility, whether utilized in direct compression, dry granulation or wet granulation formulations, is disclosed. The excipient is an agglomerate of microcrystalline cellulose particles and from about 0.1% to about 20% silicon dioxide particles, by weight of the microcrystalline cellulose, wherein the microcrystalline cellulose and silicon dioxide are in intimate association with each other. The silicon dioxide utilized in the novel excipient has a particle size from about 1 nanometer to about 100 microns. Most preferably, the silicon dioxide is a grade of colloidal silicon dioxide.
Owner:J RETTENMAIER & SOEHNE GMBH CO KG ROSENBERG
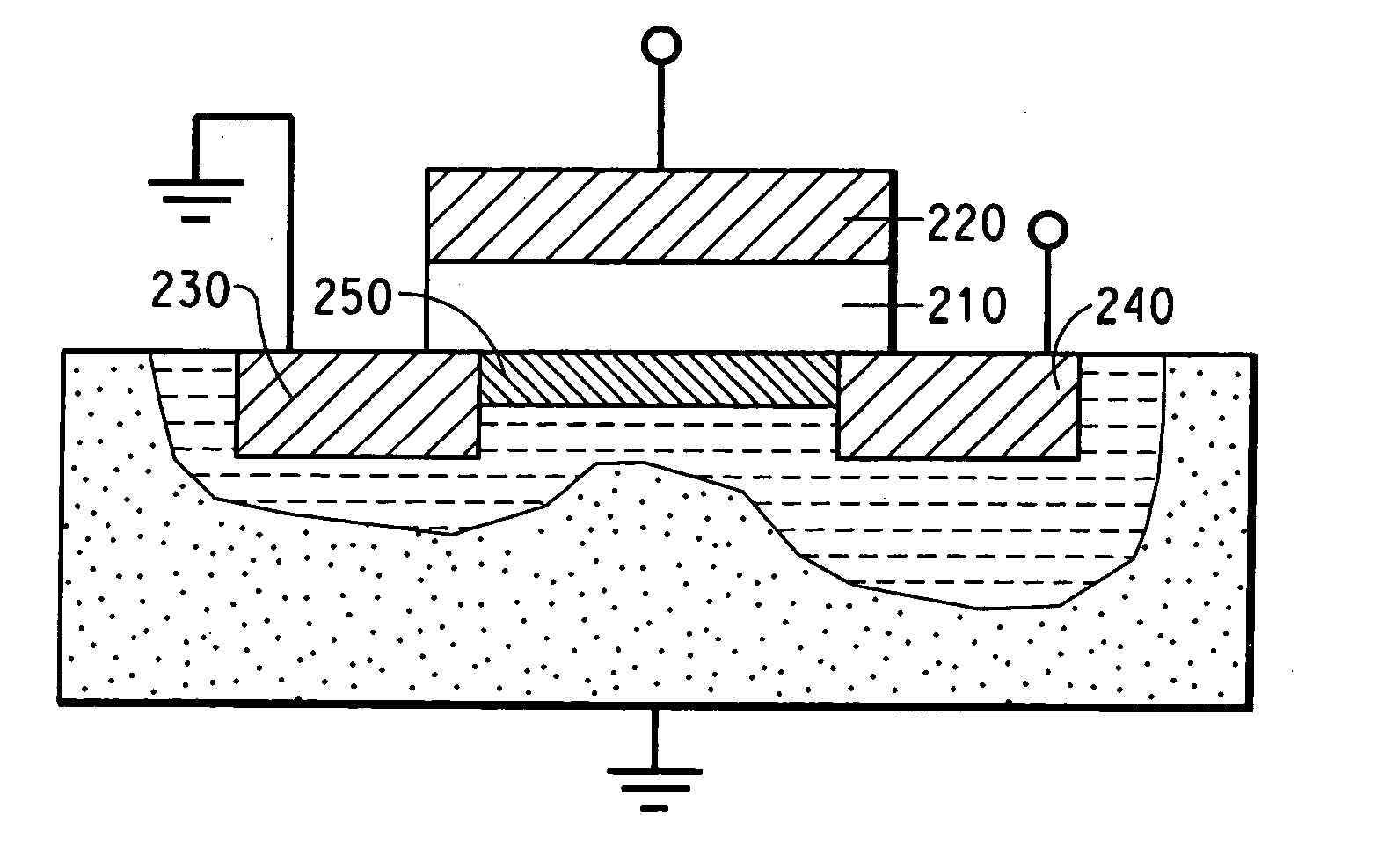
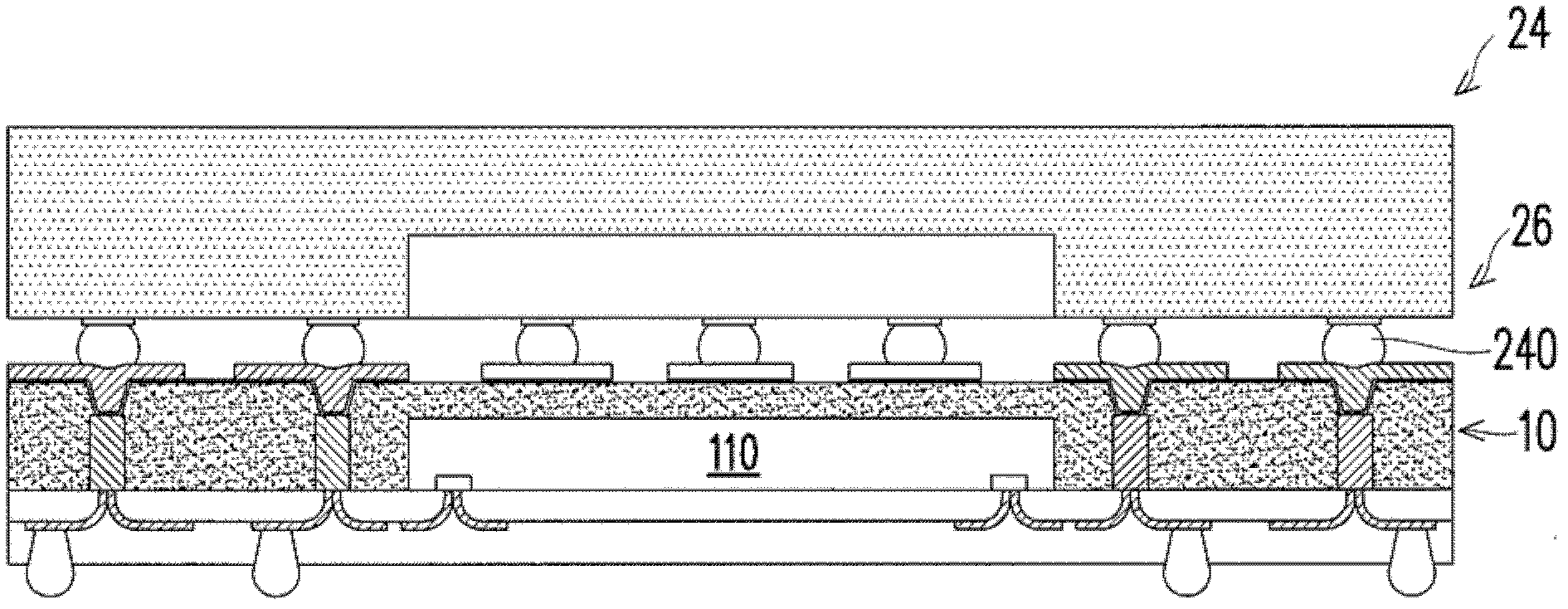
Semiconductor element packaging structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102324418ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionSemiconductor package
The invention discloses a semiconductor element packaging structure and a manufacturing method thereof. The semiconductor element packaging structure at least comprises a tube core, a rewiring layer and a plurality of electric conduction columns in electrical connections with the rewiring layer, wherein, the tube core and the electric conduction columns are wrapped by a packaging colloid, and a plurality of inner connection patterns on the packaging colloid are in electrical connections with the electric conduction columns and a stacked second semiconductor packaging.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Thermosensitive polymer carriers having a modifiable physical structure for biochemical analysis, diagnosis and therapy
The invention relates to thermosensitive polymers which contain magnetic and / or metallic colloids and whose physical structure can be altered through magnetic induction or through the supply of energy. The invention also relates to processes for the production of such thermosensitive polymers, and the use of such polymers for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:MAGNAMEDICS
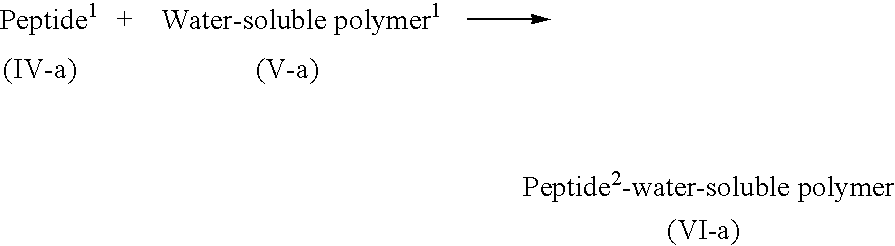
Lipid-peptide-polymer conjugates for long blood circulation and tumor specific drug delivery systems
The present invention relates to conjugates of a lipid, substrate peptide of an enzyme secreted from the cells of mammals, including humans, and a water-soluble polymer that can be used as colloidal carriers and the like of tissue-specific drug delivery systems, methods of producing these conjugates, peptide-water-soluble polymer conjugates optionally having protective groups that are useful as the intermediates of these conjugates, colloidal carriers made from these conjugates, and tissue-specific drug delivery systems that use these colloidal carriers.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com