Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
290 results about "Maximum dimension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
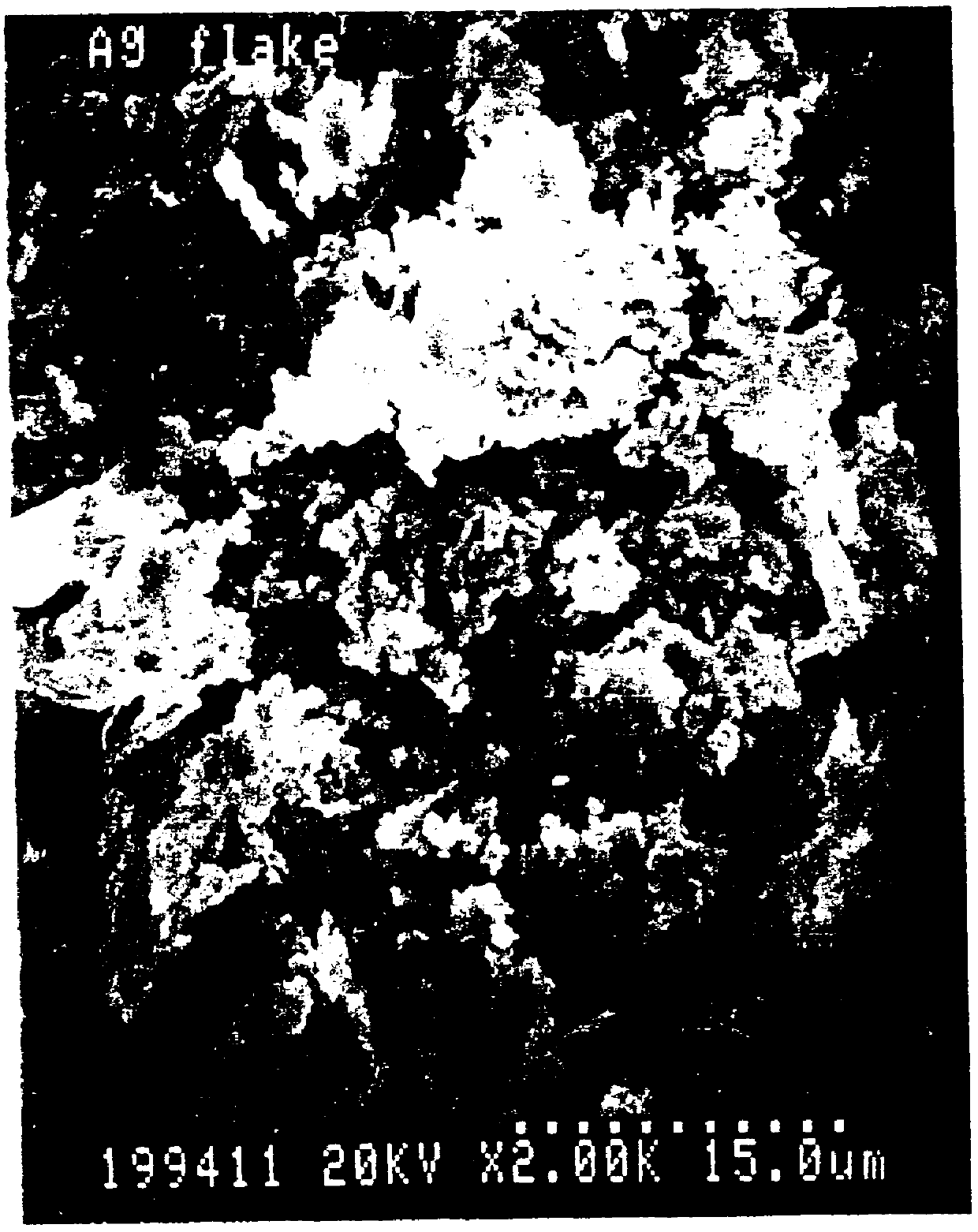
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
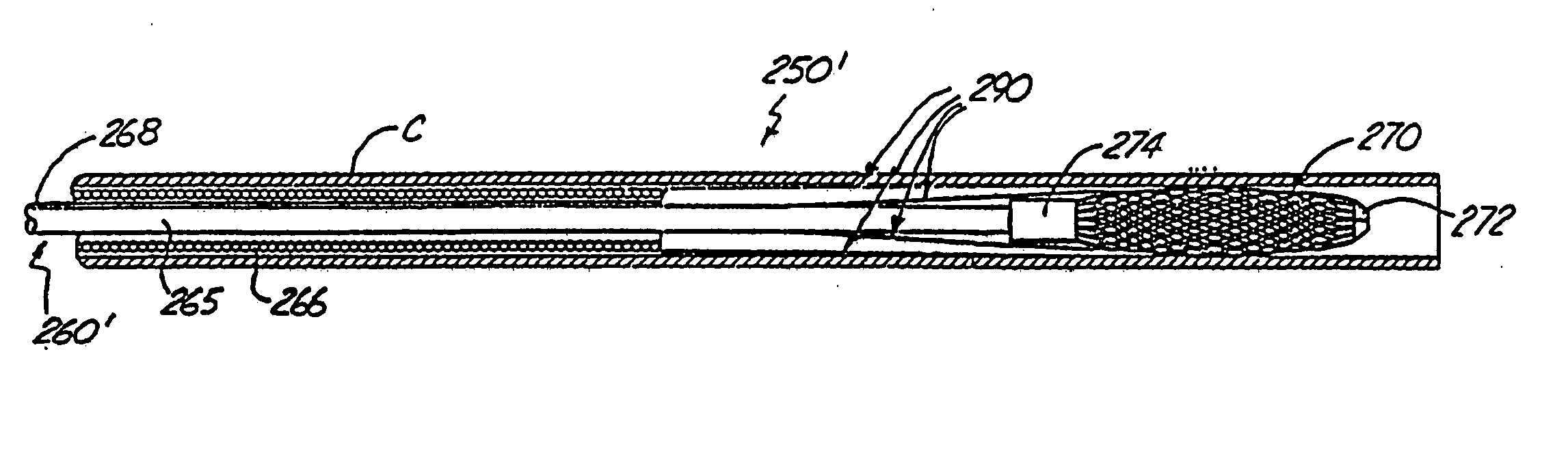
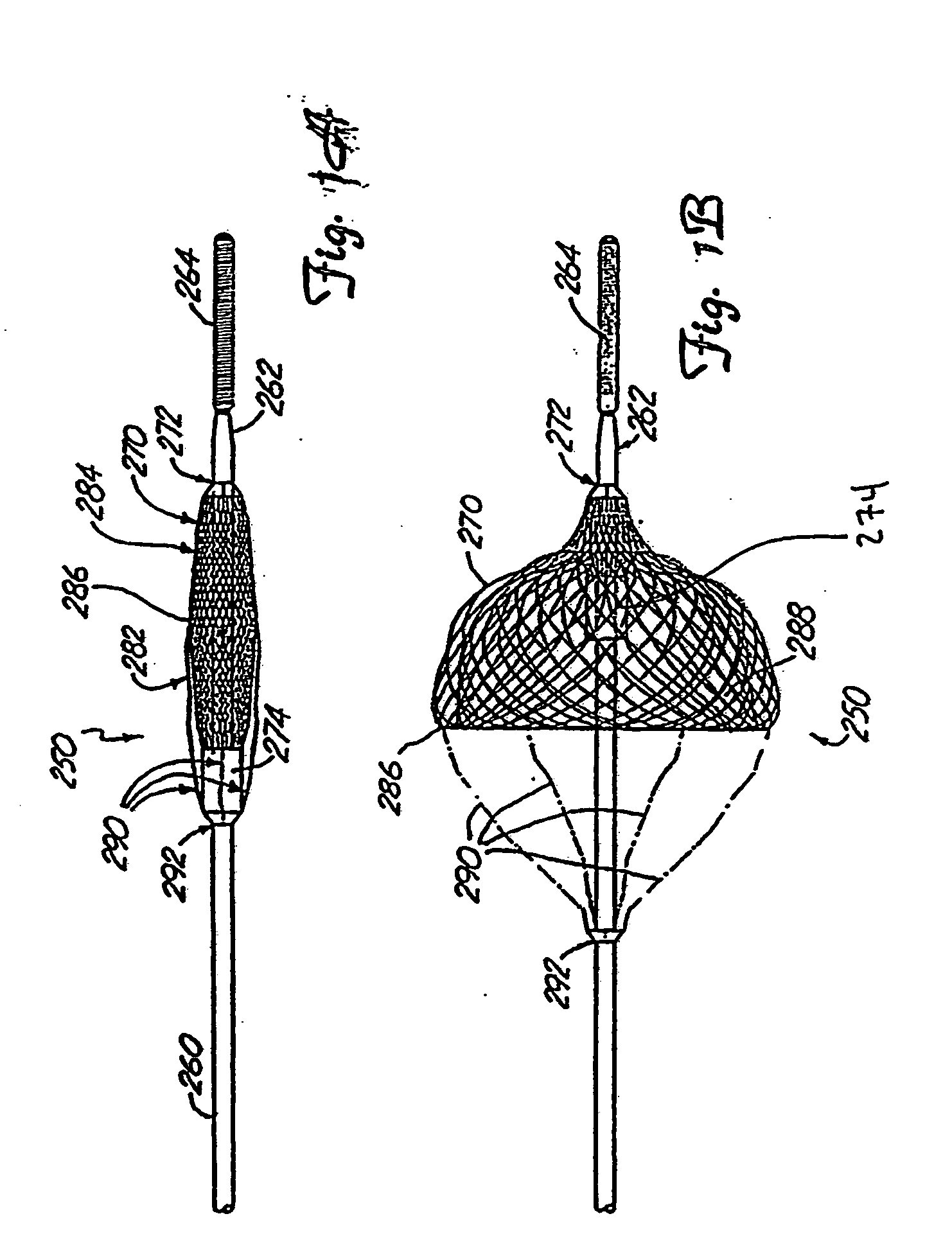
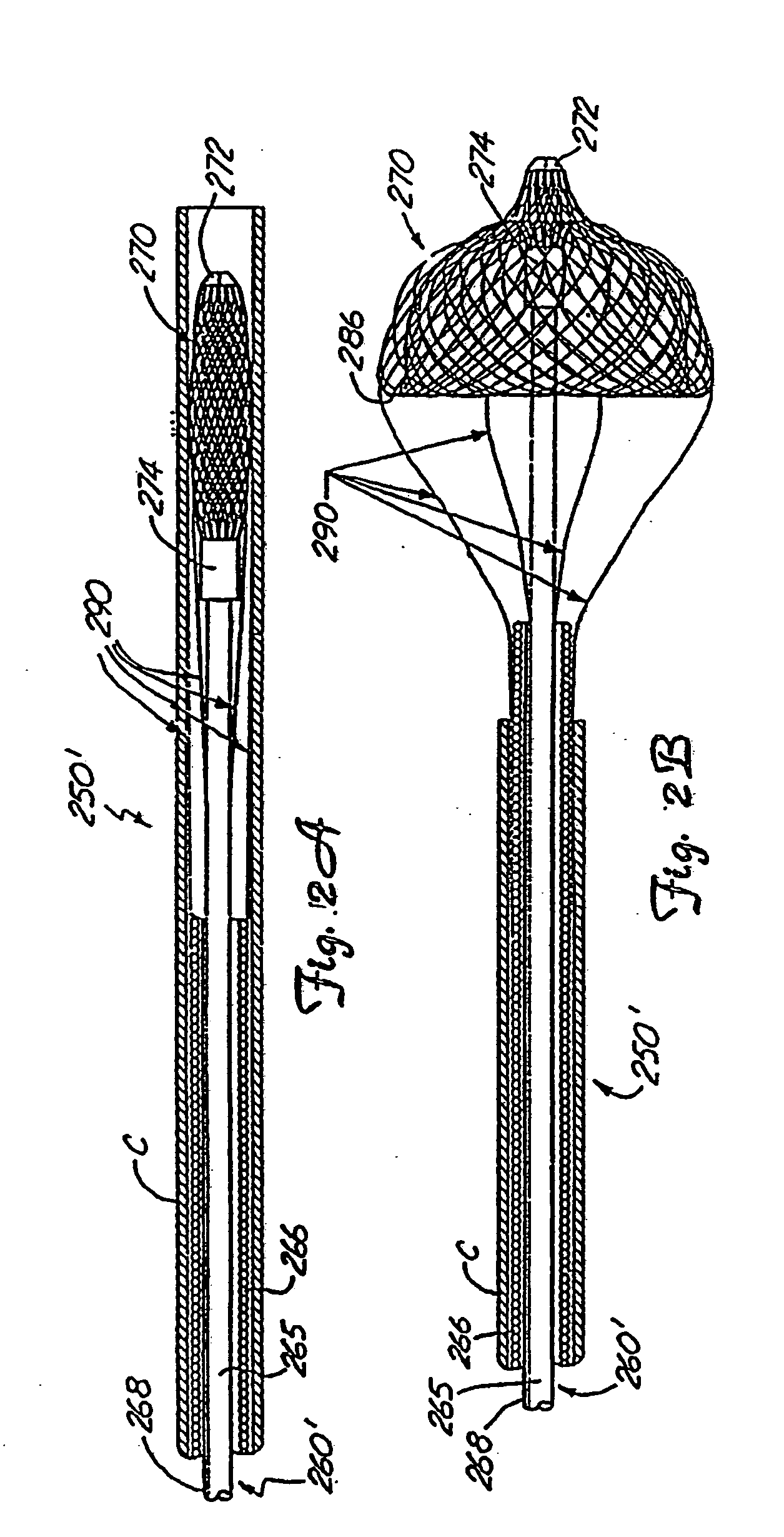
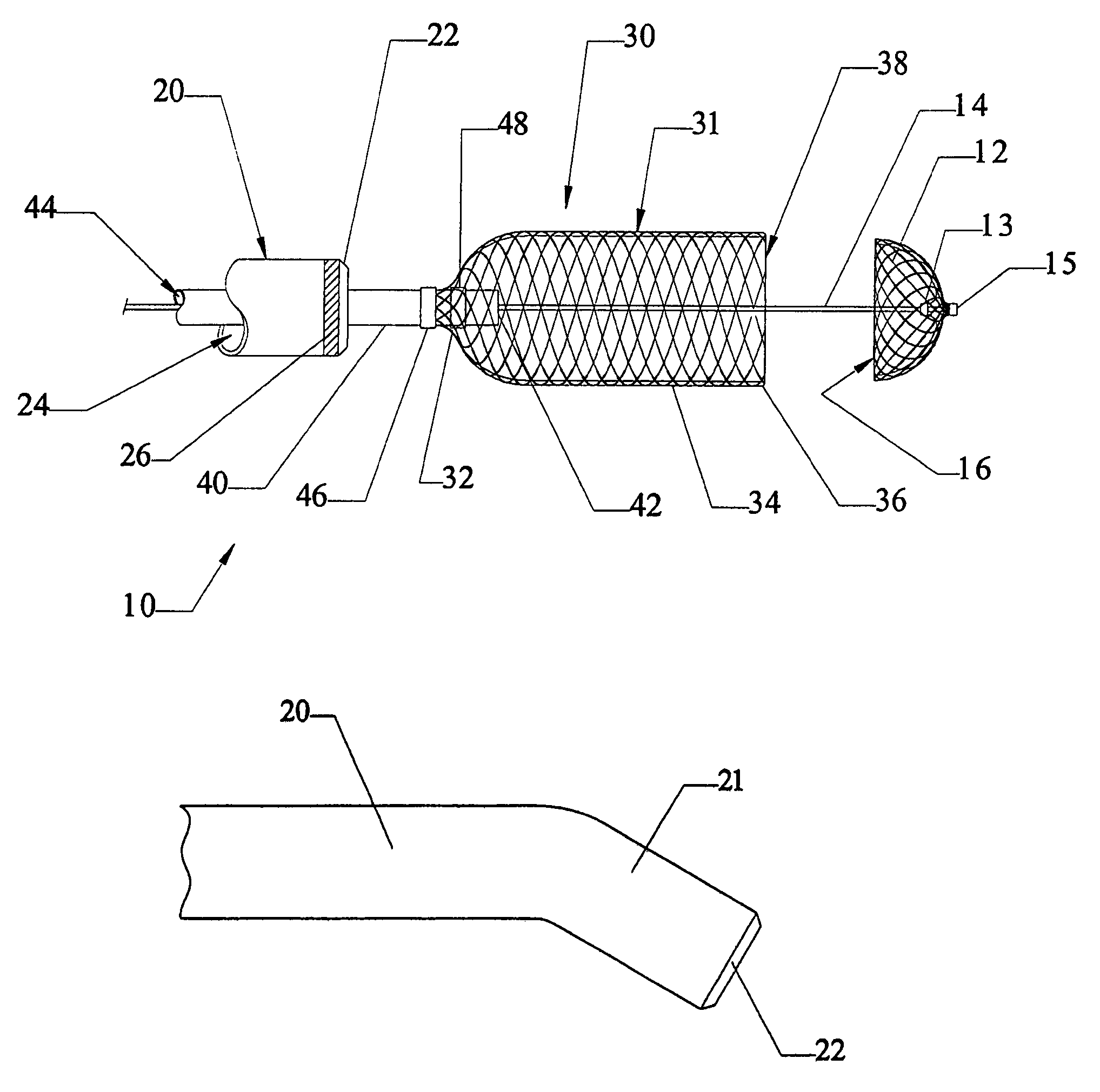
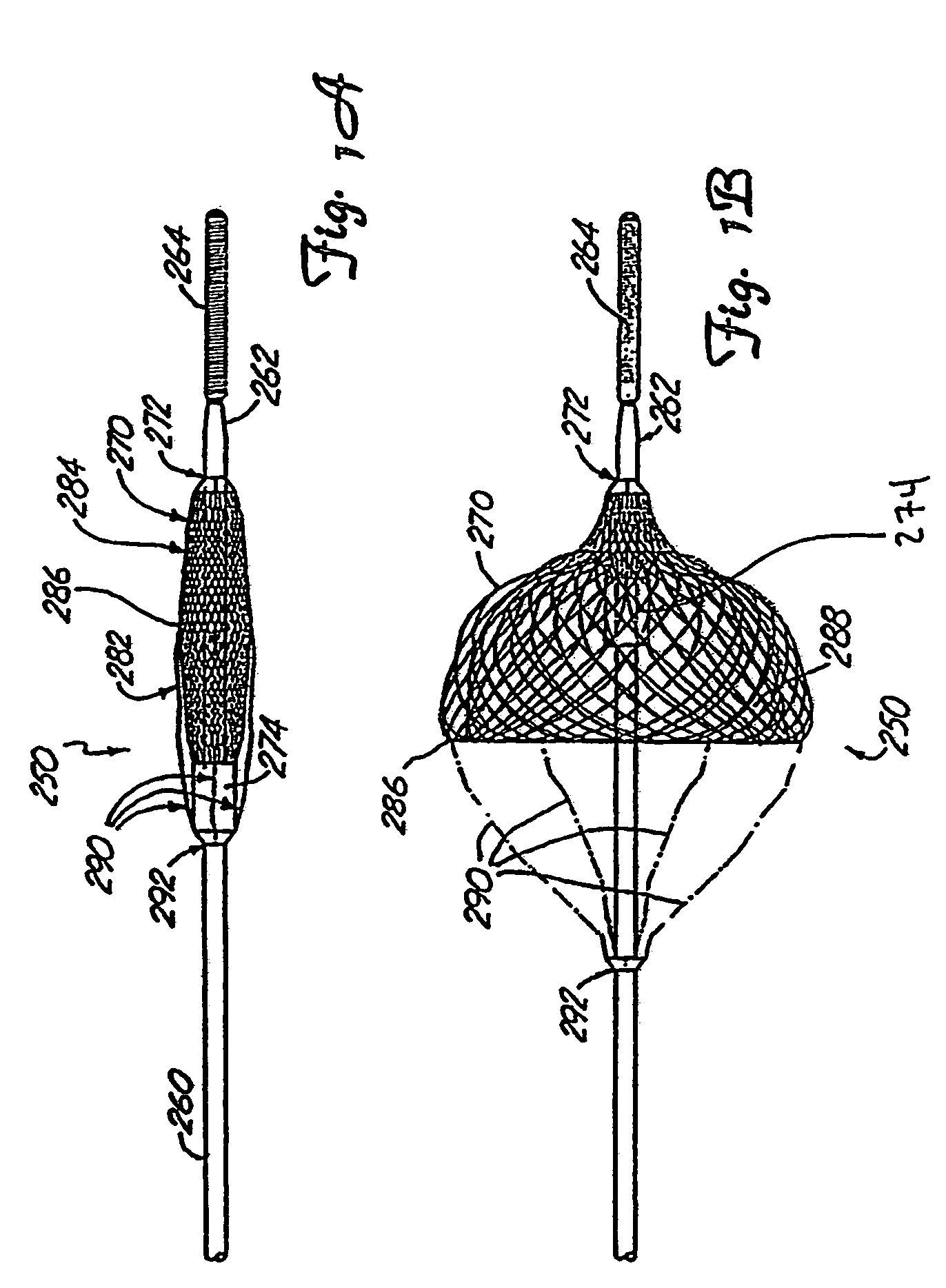
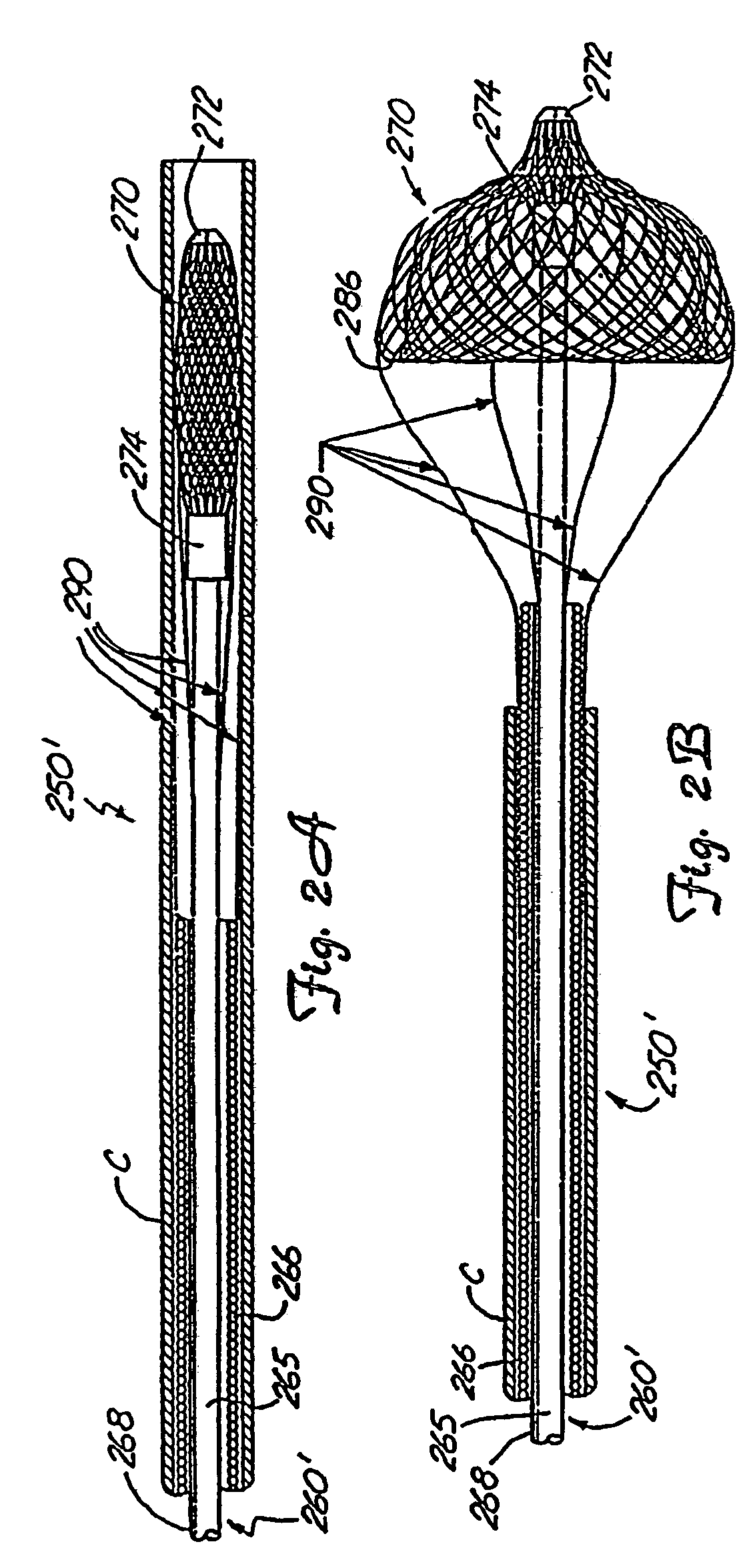
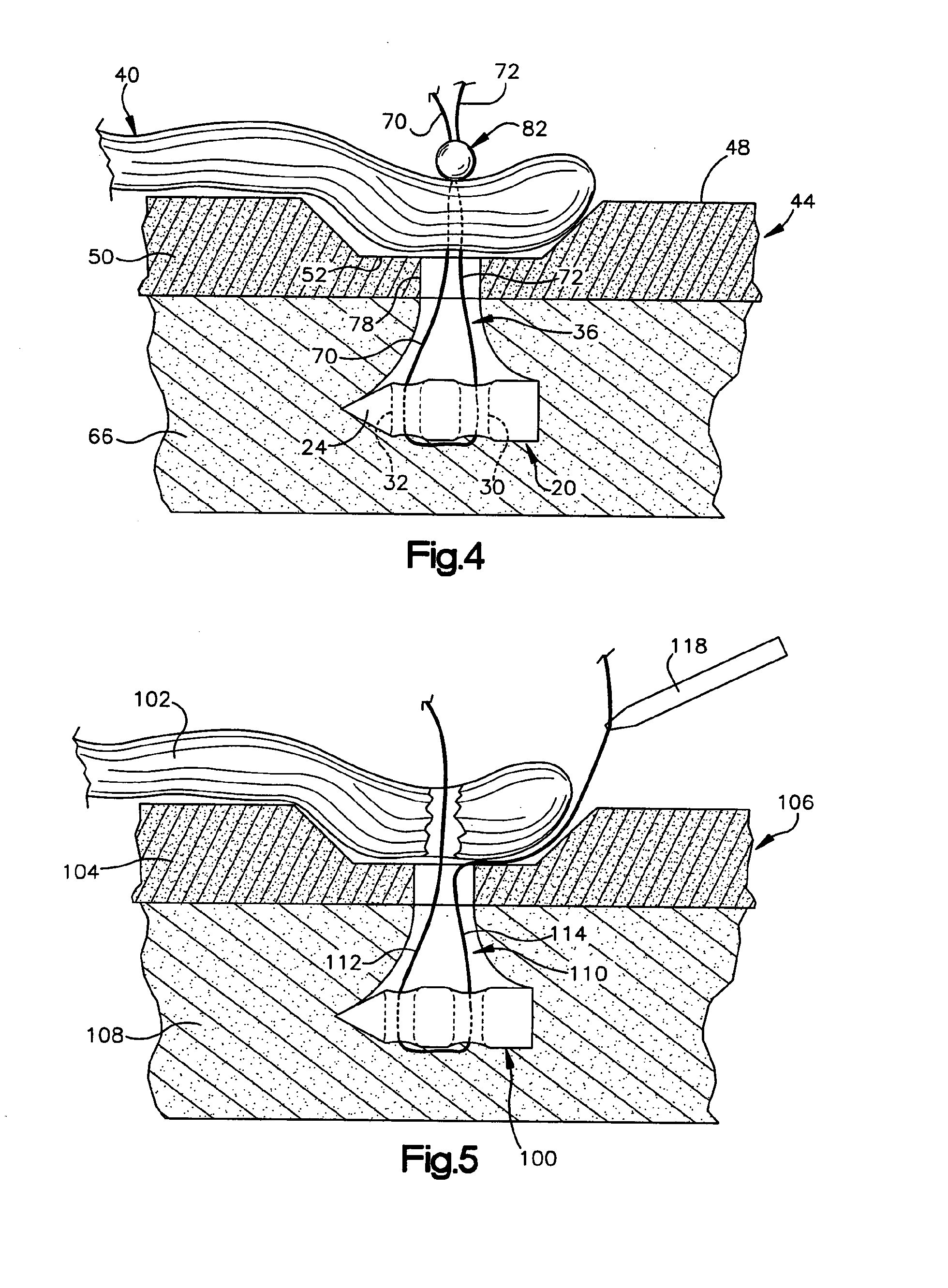
Minimally invasive medical device deployment and retrieval system
The present invention provides a medical device retrieval system comprising a working element carried by a flexible, elongate shaft, the working element having a proximal profile and the shaft extending proximally from the working element and a retrieval cover slidable carried along the shaft of the medical device, the cover having a deployed configuration and being capable of being compressed into a compressed configuration for deployment, yet resiliently substantially return to the deployed configuration; the cover in its deployed configuration having a radially reduced proximal portion, a distally open distal end defining a distal opening having a maximum dimension at least as great as the maximum dimension of the proximal profile of the working element of the medical device, and an elongate internal recess defined between the proximal portion and the distal end.
Owner:EV3
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS6610351B2Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsMaximum dimensionActive component
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
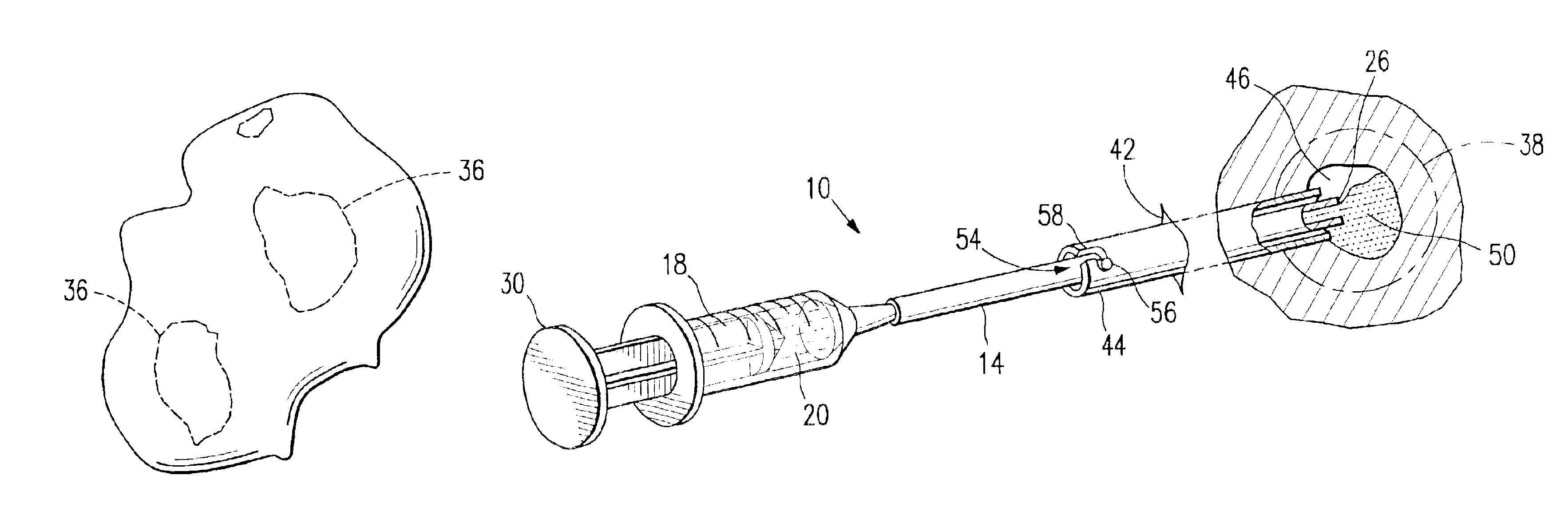
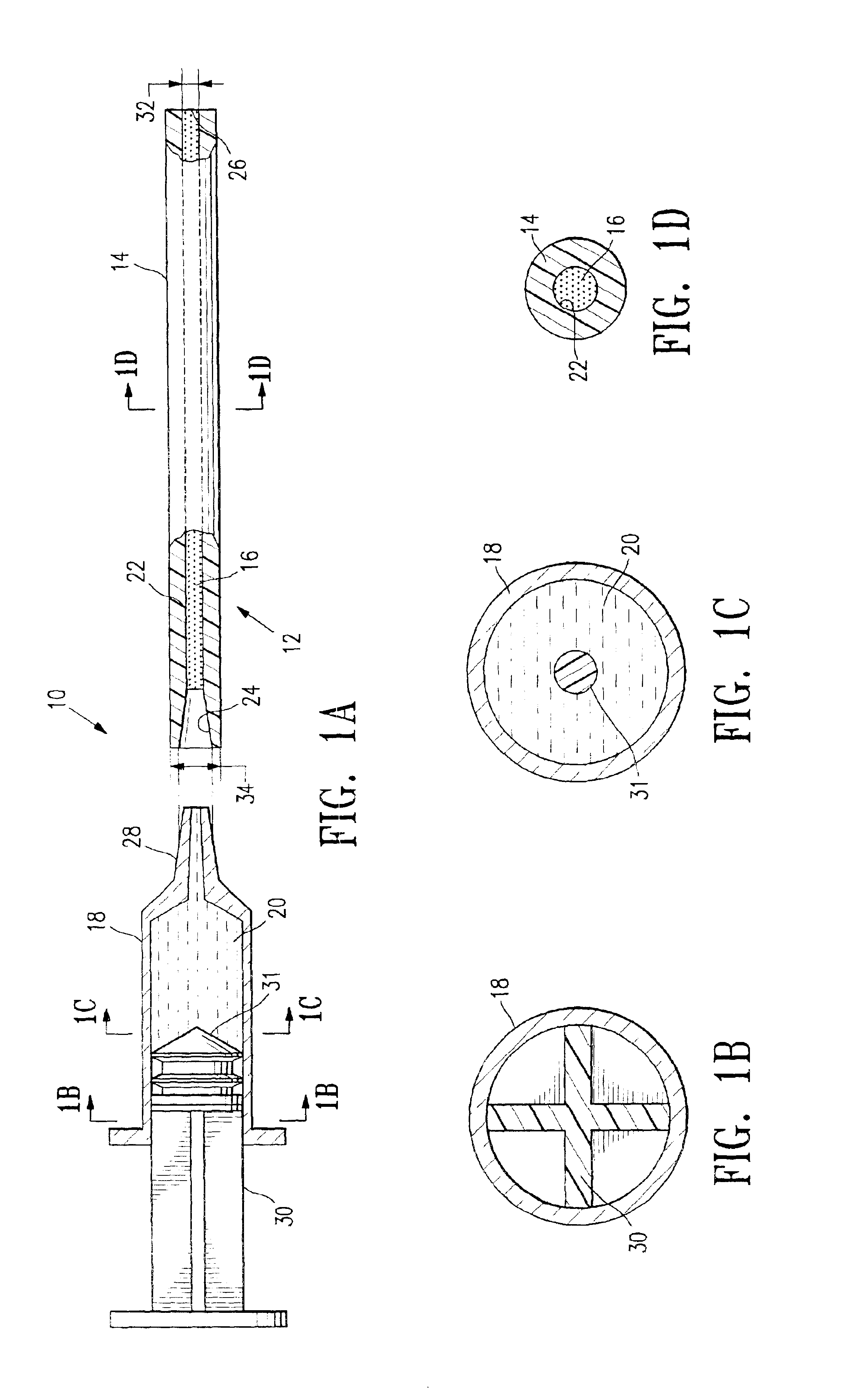
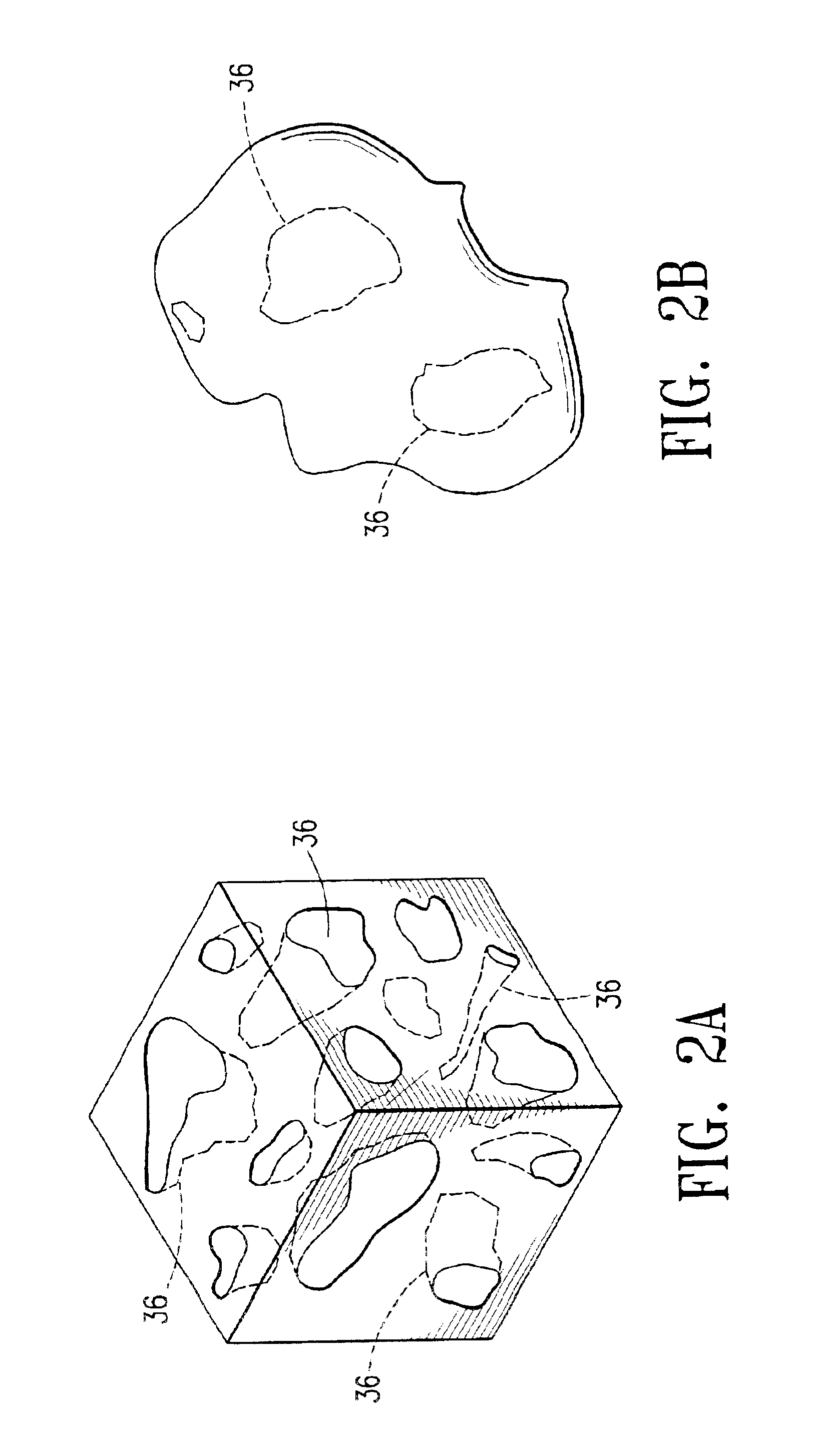
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS6862470B2Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS20020025490A1Easy to useQuality improvementOptical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyLaser lightLasing wavelength
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
Raman-active taggants and thier recognition
InactiveUS20040058058A1Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryLasing wavelengthLaser light
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:SHCHEGOLIKHIN ALEXANDER NIKITOVICH +4
Capacitor based force sensor
ActiveUS7148882B2Difference can be detectedTransmission systemsForce measurementCapacitanceMaximum dimension
The invention provides a novel capacitive device configured to detect differences in an applied force over a continuous range of applied force that includes zero force. The device includes first and second electrodes that are spaced apart a predetermined distance from each other in a rest position. A measurable capacitance exists between the first and second electrodes. Structured elements having a predetermined maximum dimension are positioned in the device to control the predetermined distance between the first and second electrodes. An applied force to the device causes a change in the distance between the first and second electrodes and a related change in the capacitance that can be measured to determine information related to the applied force.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
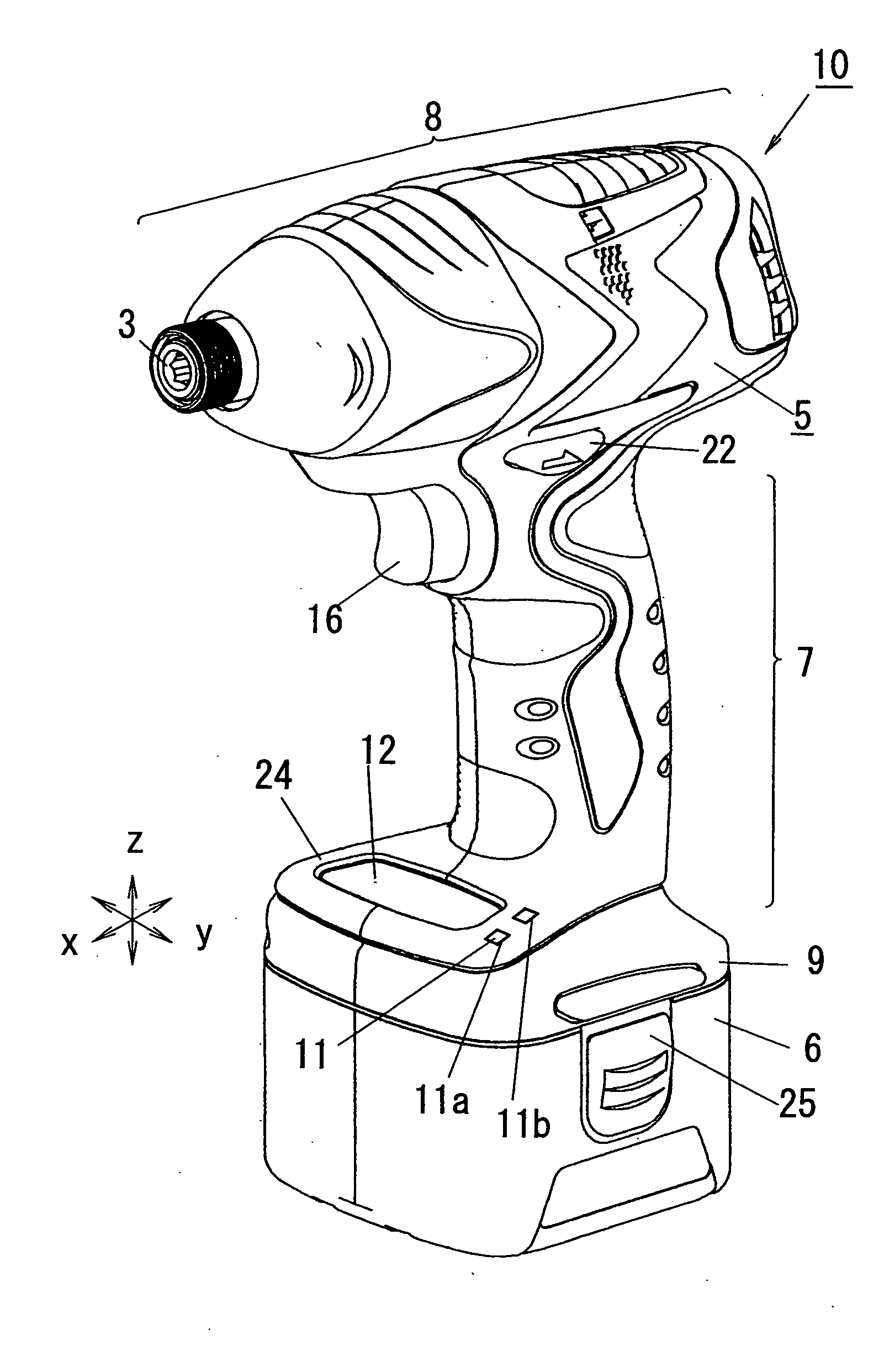
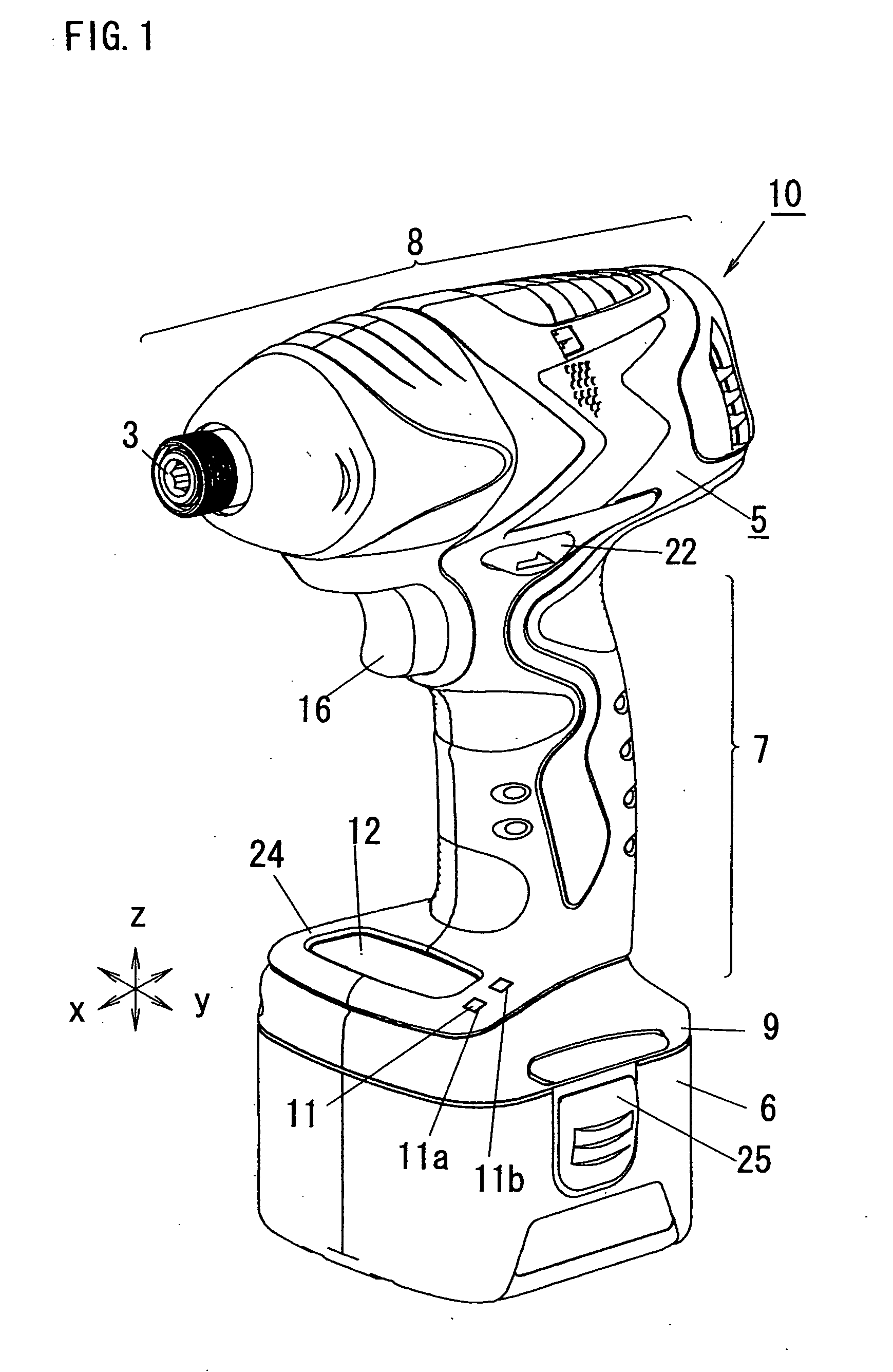
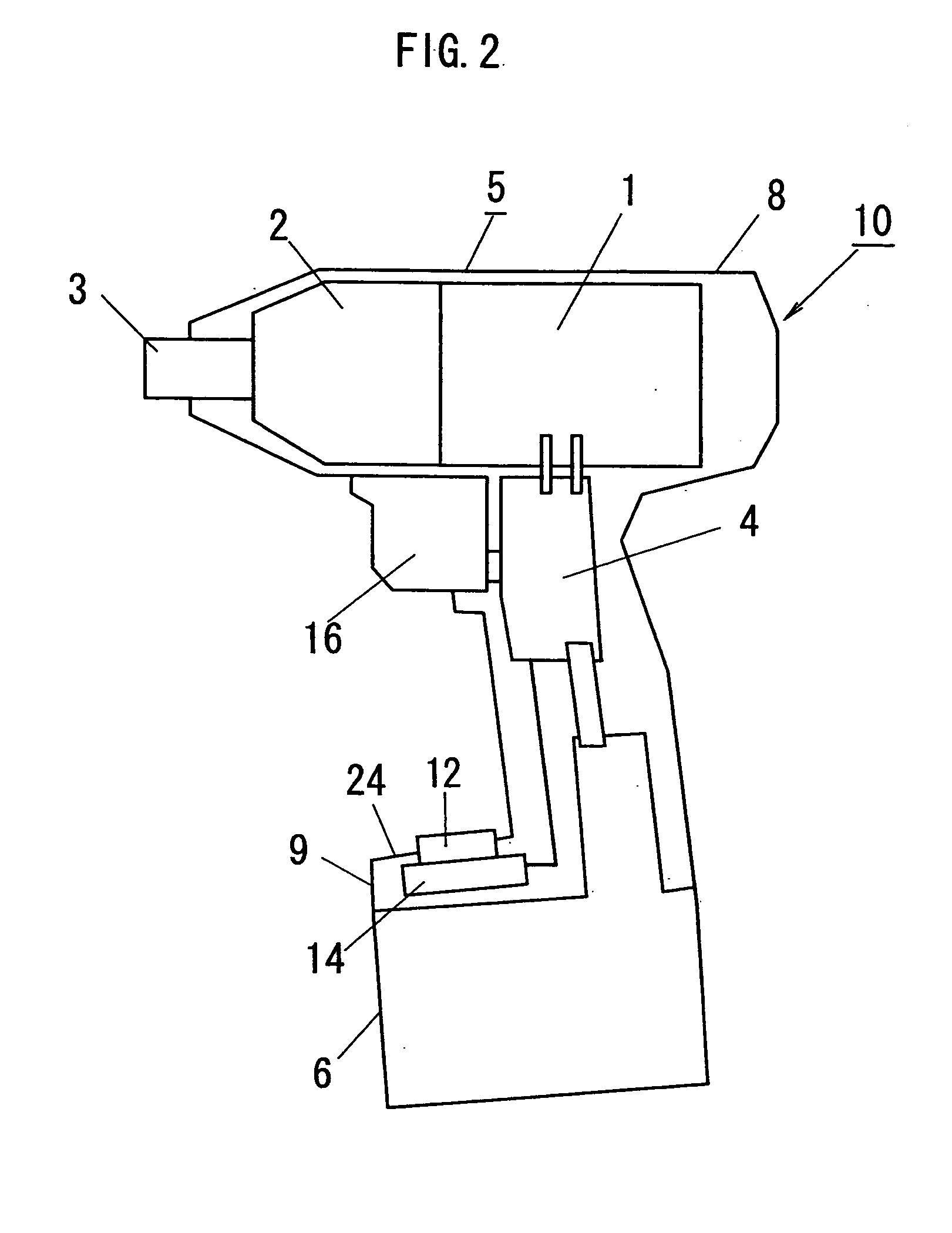
Transportable power tool
InactiveUS20050121209A1Low costEasy to useDrilling rodsConstructionsMaximum dimensionReduction drive
A transportable power tool such as an impact driver has a power unit in which a motor and a reducer-transmitter are contained, a grip and a coupler unit with which a battery pack is coupled. Maximum dimensions of the power unit and maximum dimensions of the battery pack in a direction perpendicular to both of center axes of the power unit and the grip and in a direction parallel to the center axis of the power unit are larger than those of the grip in the same directions. Operation members used for selecting an operation mode of the motor and a display device are provided at positions near to the grip from a line binding contacting portions of the power unit and the battery pack when the power unit and the battery pack are simultaneously contacted with the same plane in each state.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
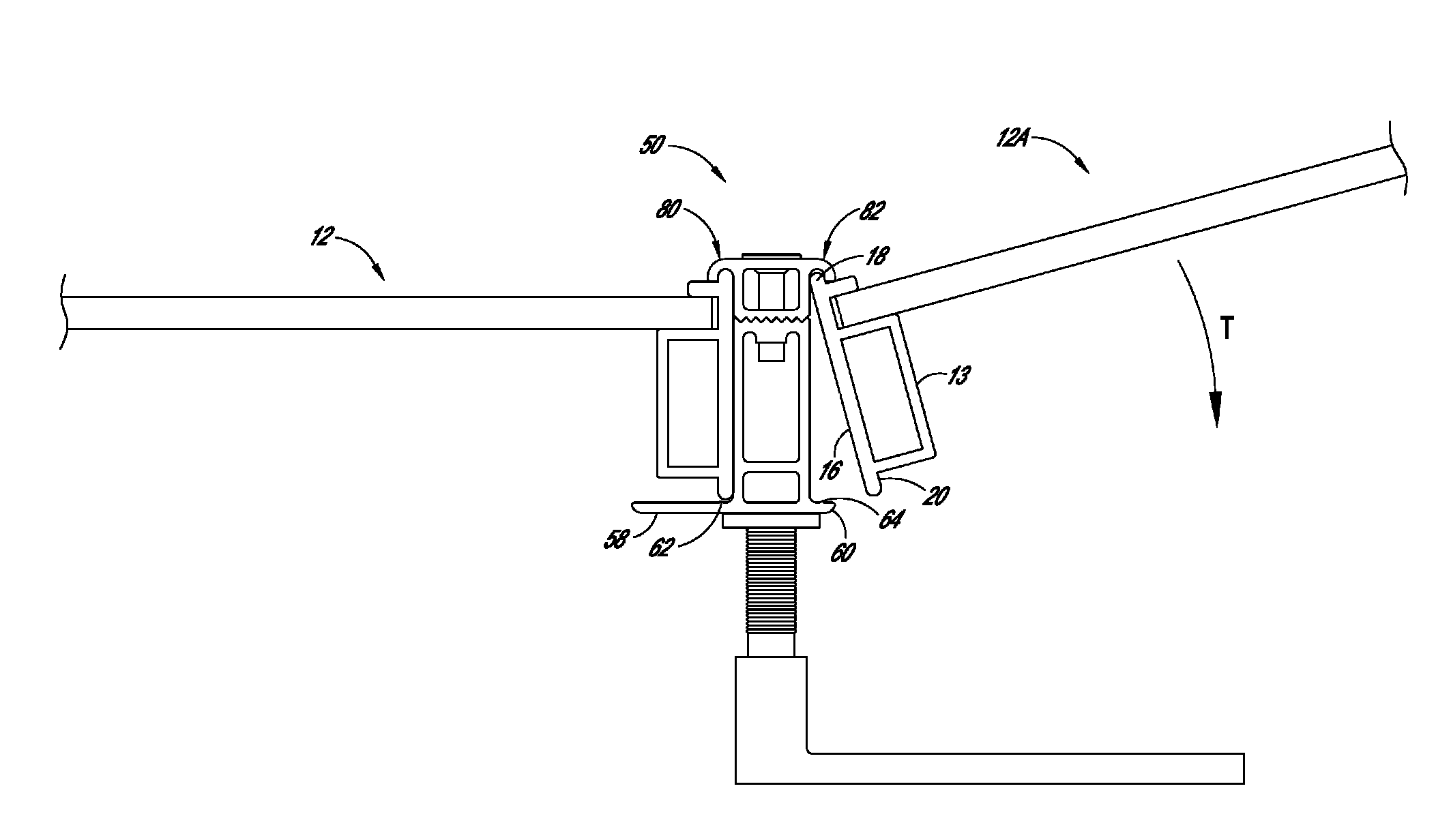
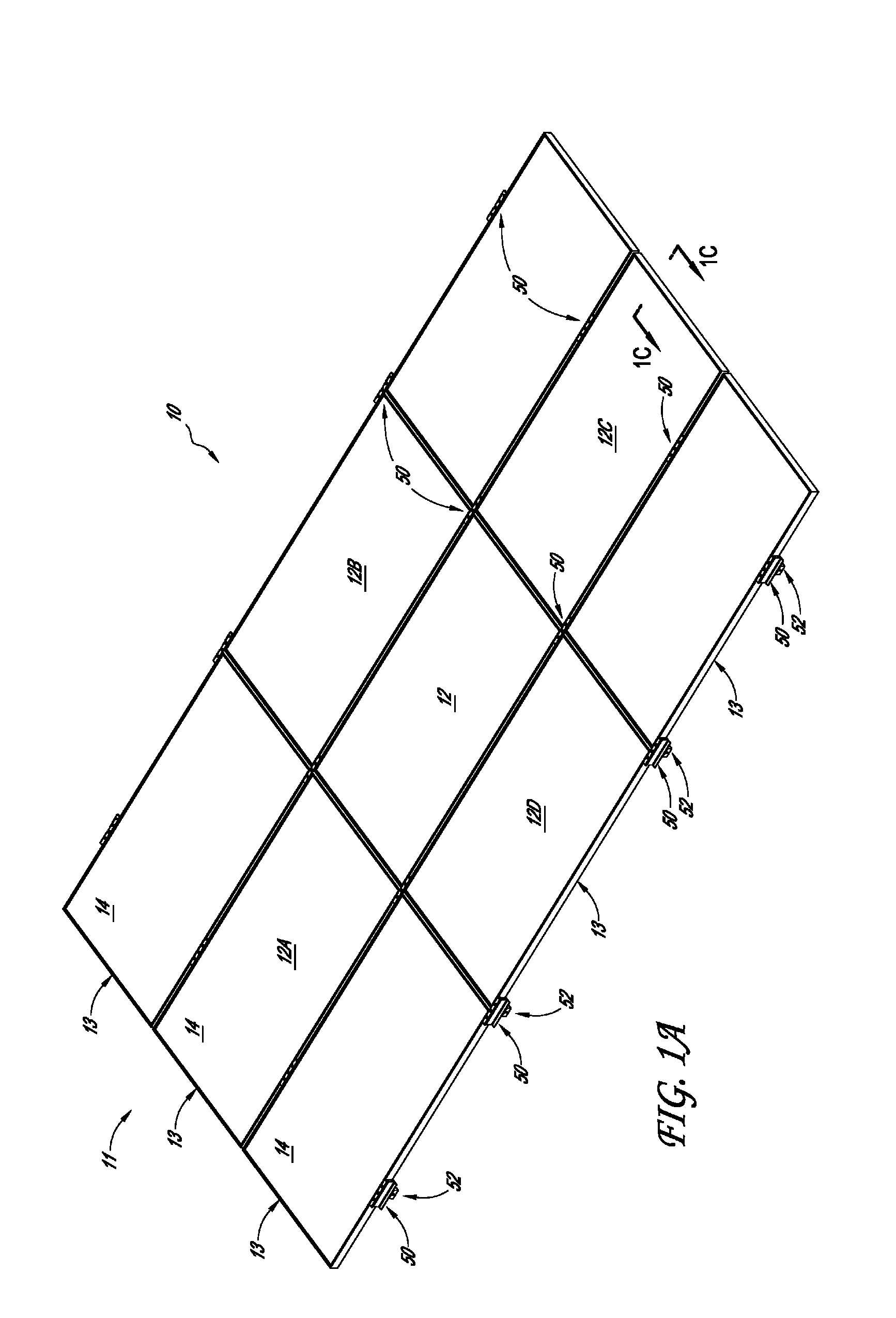
Mounting system for solar module array
ActiveUS8683761B2Significant laborPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyMaximum dimensionComputer module
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Micro-porous mesh stent with hybrid structure
Owner:ENDOTEX INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Display devices
InactiveUS20050088404A1Static indicating devicesPicture reproducers using projection devicesMaximum dimensionOptoelectronics
Apparatus including: a substrate, having a substrate surface, at least a portion of which is transparent or apertured; and an array of objects each having a maximum dimension smaller than 1 mm attached to the substrate and having an axis about which the object can rotate, wherein the object has two stable positions, a first stable position at which the object covers a transparent or apertured portion of the substrate and a second stable position at which the transparent portion is at least partially uncovered.
Owner:FLIXEL LTD
Hydrodynamic seal with improved extrusion abrasion and twist resistance
A hydrodynamically lubricating seal has a generally circular seal body defining a static sealing surface and having a dynamic sealing lip projecting from the seal body and defining a dynamic sealing surface, a non-hydrodynamic edge and a non-circular angulated flank having a flank angle. The flank angle and the dynamic sealing surface have theoretical intersection being positioned from the non-hydrodynamic edge by a variable distance having a minimum dimension being greater than {fraction (1 / 16)} inch and also having a maximum dimension. The circular seal body defines a theoretical center-line and, when viewed in a longitudinal cross-section taken along the theoretical center-line, a hydrodynamic inlet curve is shown that blends the theoretical intersection between the flank angle and the dynamic sealing surface. This hydrodynamic inlet curve is tangent to the dynamic sealing surface at a location of tangency and has a rate of curvature less than the rate of curvature of a ⅛ inch radius.
Owner:KALSI ENG
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS20050143656A1Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Data centre
ActiveUS8514572B2Facilitating correct positioningImprove efficiencyDomestic cooling apparatusTemperatue controlMaximum dimensionAir cycle
A data center (100) includes at least one rack room (in for example module 140) having a floor and a plurality of rack storage areas on the floor, each rack storage area being arranged to accommodate a plurality of racks (143) in which a plurality of rack-mountable electronic components may be housed, one or more controllable air circulation systems (in for example module 122), one or more cold aisles (144) in the rack room, each cold aisle being adjacent to a rack storage area, and one or more hot aisles (145) in the rack room, each hot aisle being adjacent to a rack storage area. There may be a large air duct, in the form of a personnel corridor (123), for transporting, under the control of the one or more air circulation systems, cooling air, above the floor, to the one or more cold aisles. The air supply corridor / duct (123) may have a height greater than 1.5 m above the floor and a cross-sectional area of at least 2 m2 and a maximum dimension in the plane of the cross-section of less than 3 m.
Owner:BRIPCO
Planetary transmission
A planetary gear set lubricating unit which supplies oil from inside a component adjacent the planetary gear set, via a radial bore and an oil catcher, axially through a bore of a planetary gear bolt to planetary gear bearings. The oil catcher forms a ring-shaped chamber, which can be filled with lubricant, and is arranged beside the planetary carrier approximately over the reference diameter of the planetary bolt. The oil catcher has outlet pipes extending axially to direct oil in the chamber. The oil catcher has ovular radial protrusions arranged such that a maximum radial dimension is close to the bolts and a minimum radial dimension is arranged between adjacent planetary bolts. The radially inner edge of the axial bore of the planetary bolts is radially located between the minimum and maximum dimensions of the protrusions. The chamber is delimited by a cover plate and a gasket.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Cable assembly for mobile media devices
InactiveUS7918685B1Communication cablesElectric connection structural associationsElectricityDocking station
Disclosed herein is a mobile media device cable assembly for connecting a mobile media device with an accessory device, e.g., a docking station, audio system (stereo) or video system (television). The cable assembly provides multi-pin connections while the device is in a case or cover. The assembly comprises a flexible cable having a plurality of wires for transmitting audio, video, data, and power signals. The plurality of wires are in communication with respective pins of multi-pin female and male connectors on either terminus of the flexible cable. A first ground return comprising a flexible wire shield encapsulates the plurality of wires, and a second ground return comprising a flexible wire shield is surrounded by the first ground return. The second ground return encapsulates and electrically isolates the wires a subset of the plurality of wires, i.e., the wires that transmit audio and video signals, to prevent electric signal crossover. In one embodiment, at least two pins of each of the female and male connectors are electrically associated with the second ground return. In another embodiment, the multi-pin male connector comprises a first printed circuit board, where one end of the board is soldered to the plurality of wires and has a maximum dimension of 16 mm, and a housing associated with the multi-pin male connector has a maximum dimension of 27 mm.
Owner:CABLEJIVE
RF-Enablement of Products and Receptacles Therefor
InactiveUS20060232417A1Hand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsMaximum dimensionElectrical battery
An RFID tag in a receptacle is active and includes a microprocessor, a data storage device operable to store a selected code (e.g. an ID code to identify said object or said product), the object including a display for displaying the aforesaid selected code upon a signal from the microprocessor and an energy storage device (e.g. a lithium ion battery), operable to energize the microprocessor, the display, and the transmitter. The tag has an antenna having a dimension thereof that is substantially as large as to a maximum dimension of receptacle.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
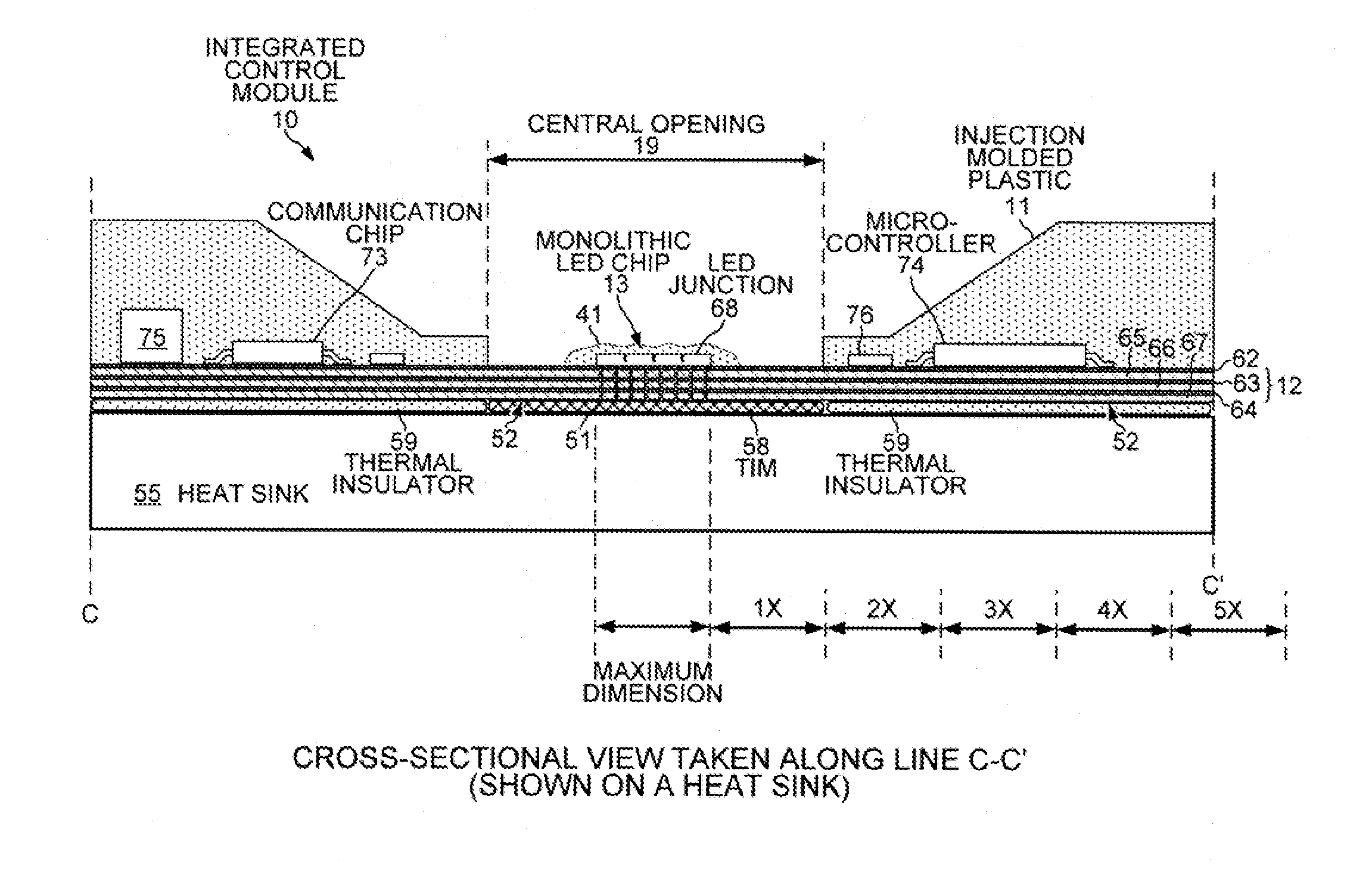
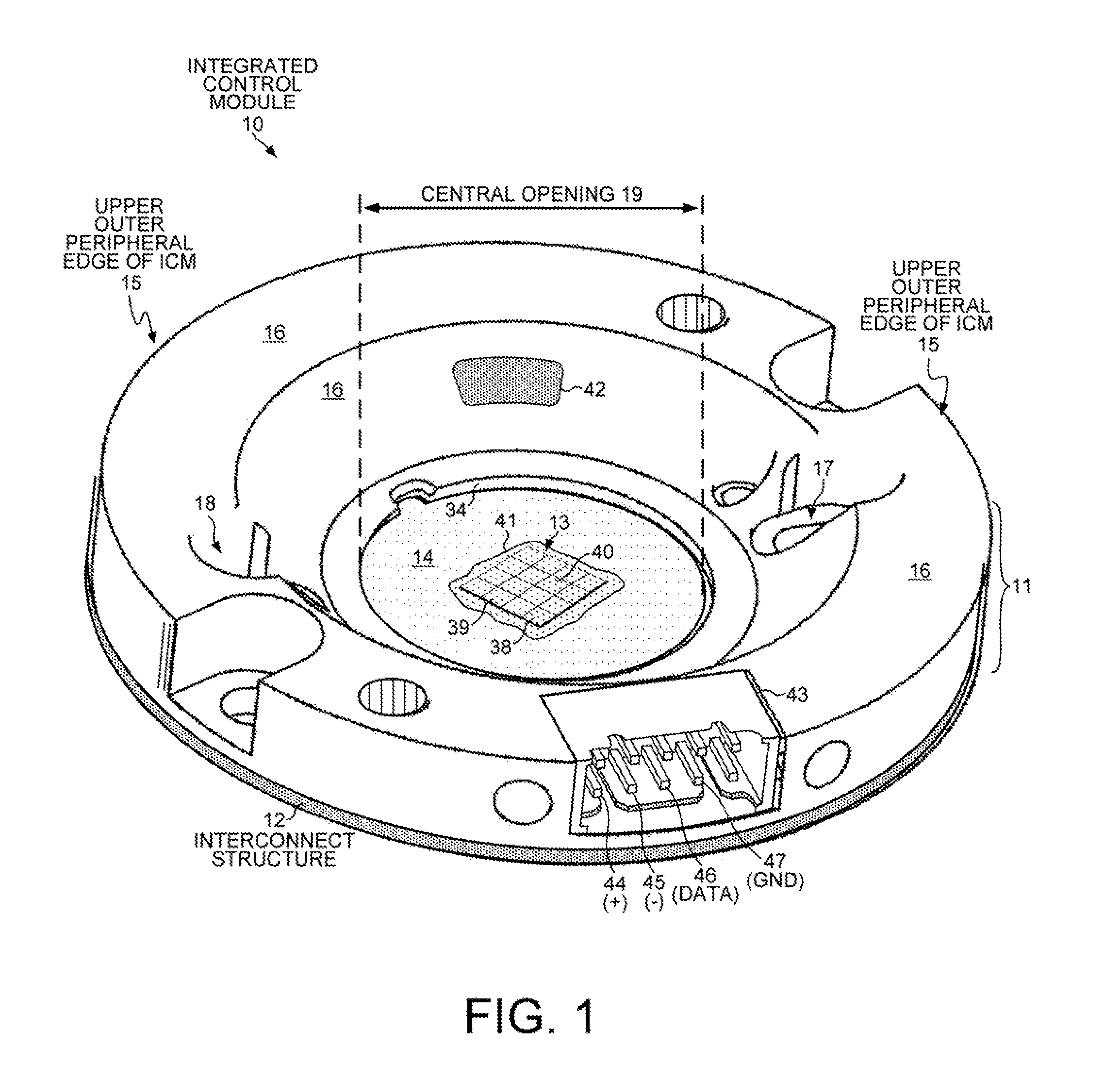
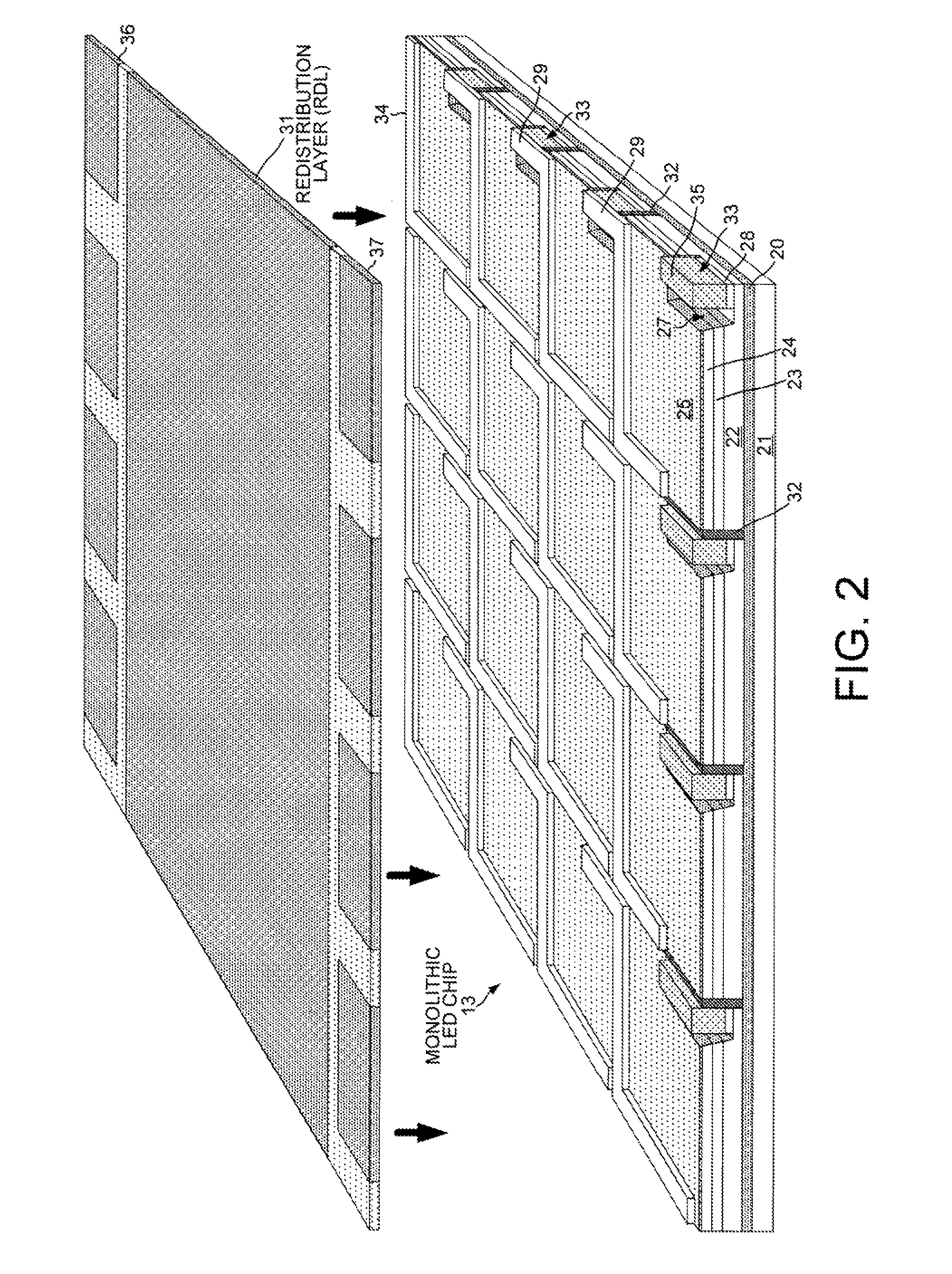
Monolithic LED chip in an integrated control module with active circuitry
ActiveUS9277618B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDriving currentMaximum dimension
A lighting device includes a monolithic LED chip flip-chip mounted onto an interconnect structure. The monolithic chip includes LED junctions formed from a single LED junction. An active electronic component is also mounted onto the interconnect structure at a distance from the monolithic chip that is less than five times the maximum dimension of the monolithic chip. The active electronic component controls LED drive currents independently supplied to the LED junctions. Different types of phosphor are disposed laterally above the various LED junctions. A color sensor measures the light emitted from the lighting device when drive currents are supplied to first and second LED junctions. The active electronic component then supplies more drive current to the first LED junction than to the second LED junction in response to the color sensor measuring the light emitted when the prior LED drive currents are supplied to the first and second LED junctions.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
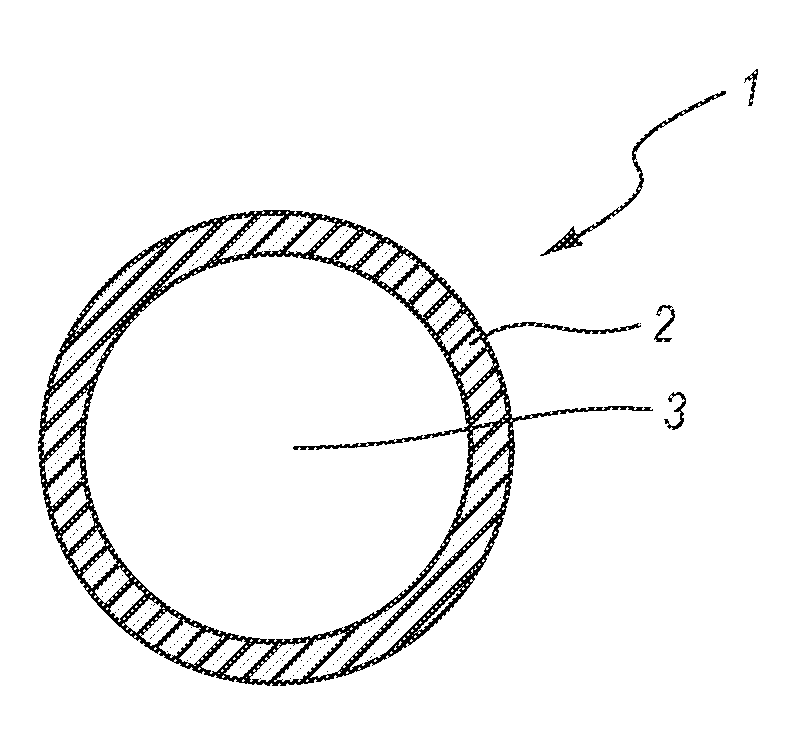
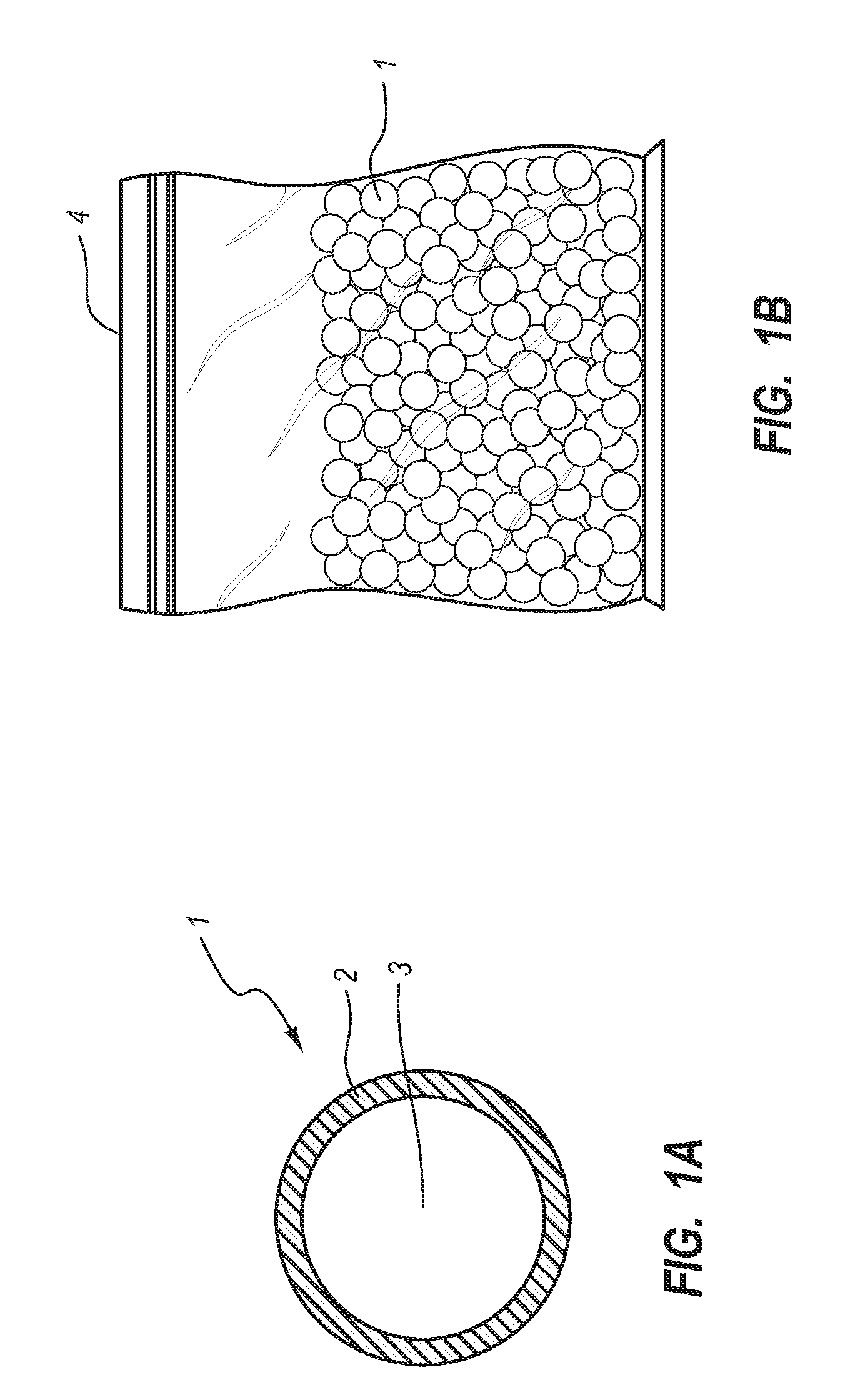
Magnetically shielded conductor
A magnetically shielded conductor assembly containing a conductor disposed within an insulating matrix, and nanomagentic material and nanoelectrical material disposed around the conductor. The conductor has a resistivity at 20 degrees Centigrade of from about 1 to about 100 microohm-centimeters. The insulating matrix is composed of nano-sized particles having a maximum dimension of from about 10 to about 100 nanometers. The insulating matrix has a resistivity of from about 1,000,000,000 to about 10,000,000,000,000 ohm-centimeter. The nanomagnetic material has an average particle size of less than about 100 nanometers. The nanomagnetic material has a saturation magnetization of from about 200 to about 26,000 Gauss. The magnetically shielded conductor assembly is flexible, having a bend radius of less than 2 centimeters.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
Coated fibrous nodules and insulation product
Coated fibrous nodules suitable for forming an insulation product are provided, comprising fibrous nodules formed from inorganic fibers, wherein a majority of the fibrous nodules has a maximum dimension of about one-half inch, and wherein the fibrous nodules are coated with a solution comprising water and a water soluble binder. Also provided is an insulation product formed from the coated fibrous nodules.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Rubberized asphalt pellets
A storage-stable rubberized asphalt paving pellet can include fines in the core. The core can be an asphalt-based binder at about 70% to about 95% by weight of the core. The asphalt-based binder can include: ground tire rubber from about 15% to about 30% by weight of the asphalt-based binder, and pavement grade asphalt from about 85% to about 70% by weight of the asphalt based binder. The core can include fines at about 30% to about 1% by weight of the core. The shell coating the core can provide the pellet with a maximum dimension of about 1 / 16 inch to about 2 inches. The shell can include a water-resistant polymer or wax, or a coating of fines. In one aspect, the fines are lime fines or ground asphalt pavement fines. Optionally, the fines can be mineral or rock fines as described herein.
Owner:BILLIAN I P
Polarization-selectively blazed, diffractive optical element
InactiveUS20060039072A1Good effectBlaze efficiency of one polarization condition is considerably greaterPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsMaximum dimensionElectromagnetic radiation
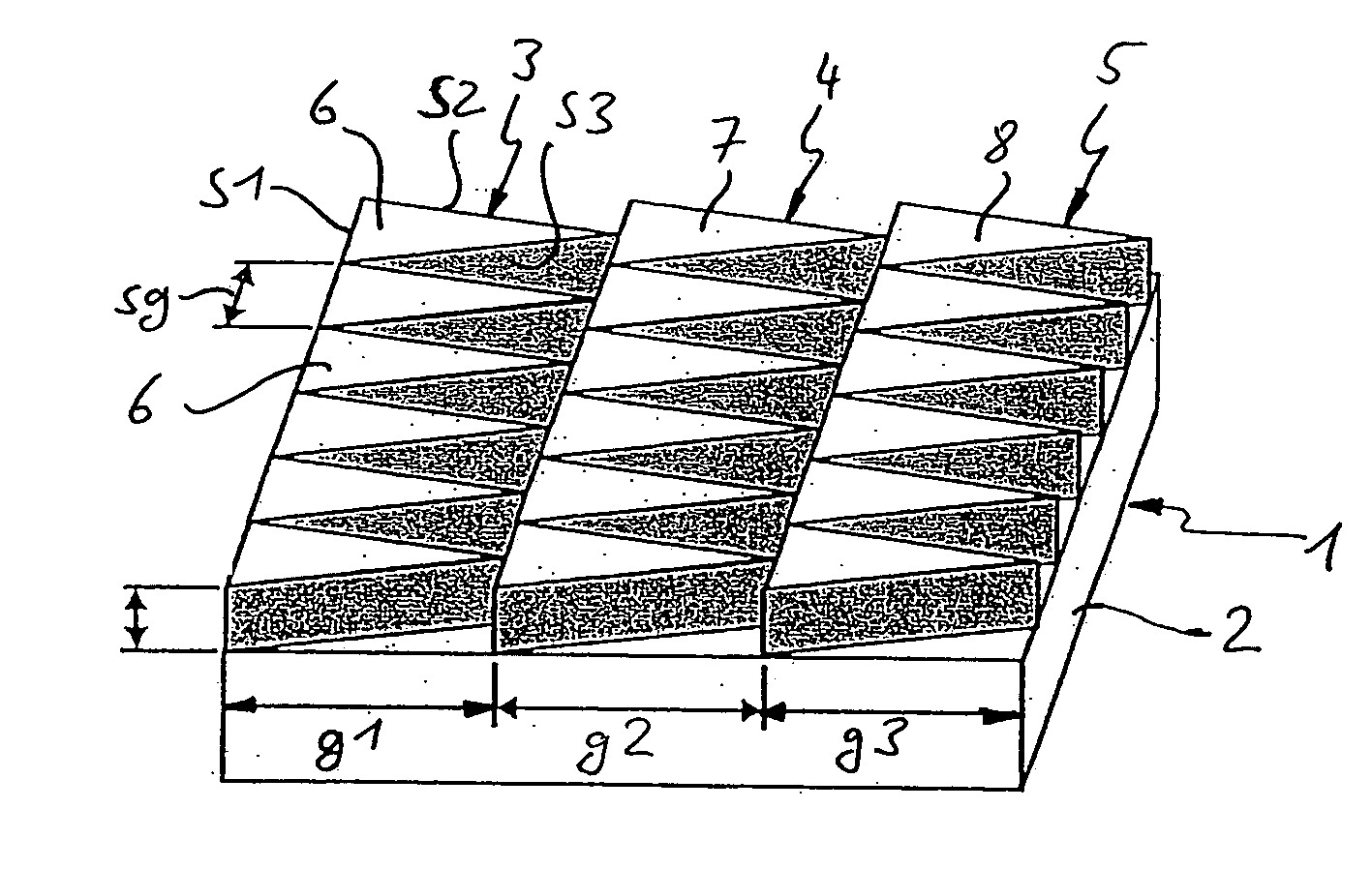
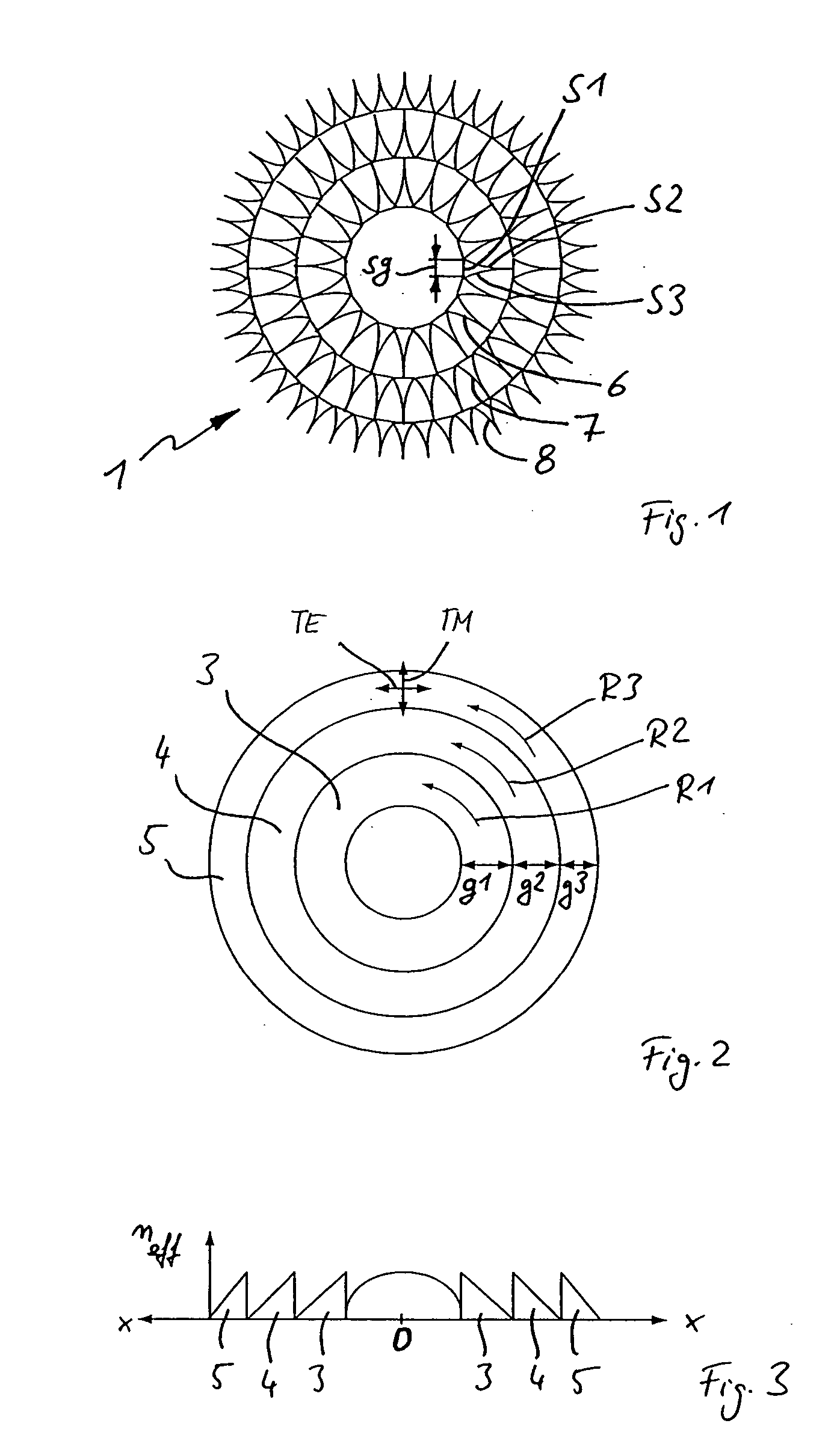
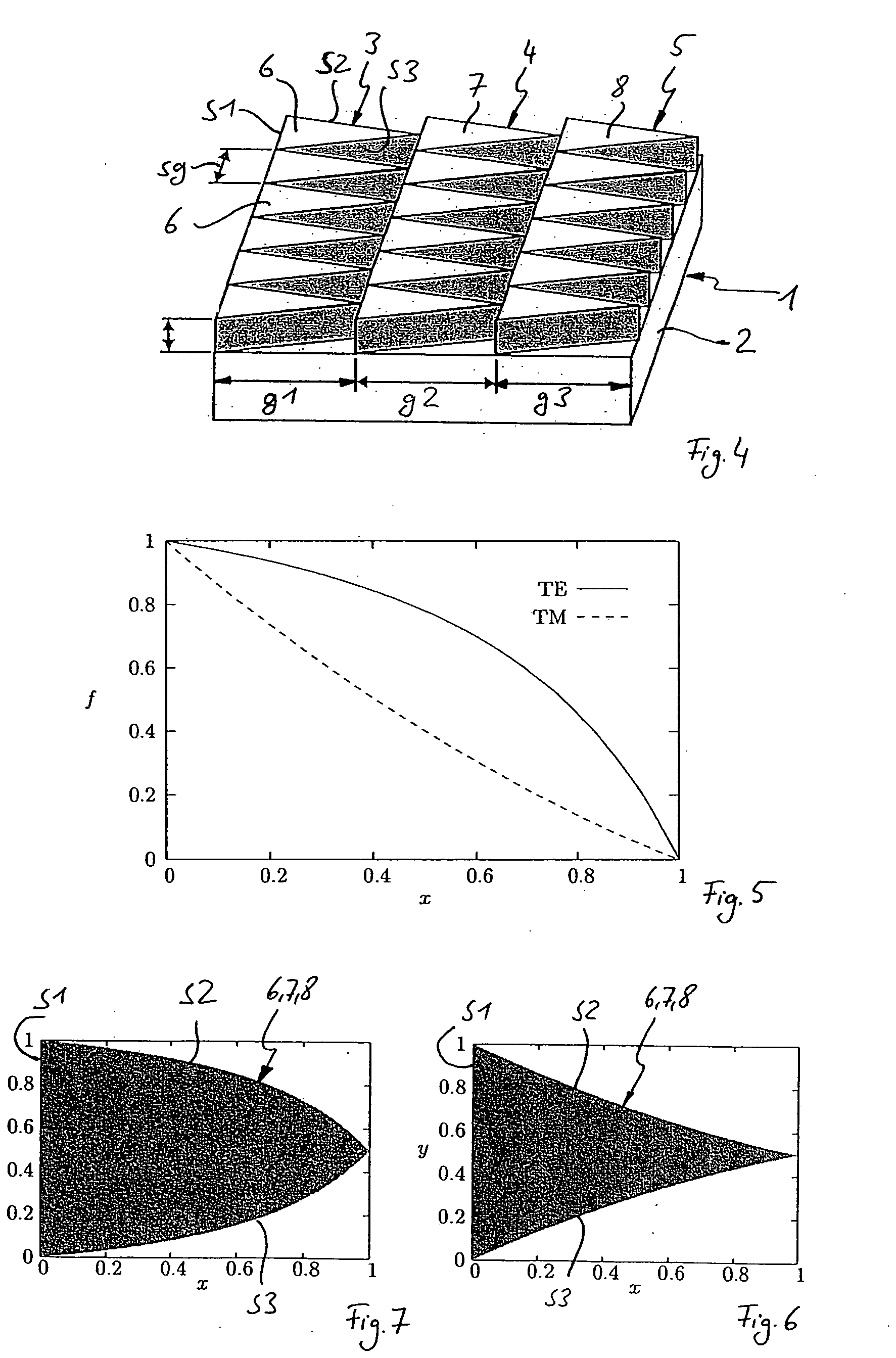
A polarization-selectively blazed, diffractive optical element is provided, comprising a plurality of contiguous blaze structures, which extend along a given geometrical path and each have a width (g1, g2, g3) perpendicular to their direction of extension (R1, R2, R3), said width being greater than the wavelength (X) of the electromagnetic radiation for which the diffractive optical element is designed, and each of said blaze structures comprising a plurality of individual substructures, which are arranged next to each other in the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3) according to a predetermined period (sg), said substructures providing the blaze effect and each having the shape, when viewed from above, of a closed geometrical surface whose dimension parallel to the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3) varies perpendicular to the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3), but is always smaller than the wavelength (X) of the electromagnetic radiation, and whose maximum dimension perpendicular to the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3) is greater than the wavelength (X) of the electromagnetic radiation, wherein the filling ratio (f) of the individual substructures in the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3) relative to the period (sg) is selected such, as a function of the position perpendicular to the direction of extension (R1, R2, R3), that the blaze effect is optimized for one of two mutually orthogonal polarization conditions of the electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Device for mixing and/or injecting cements
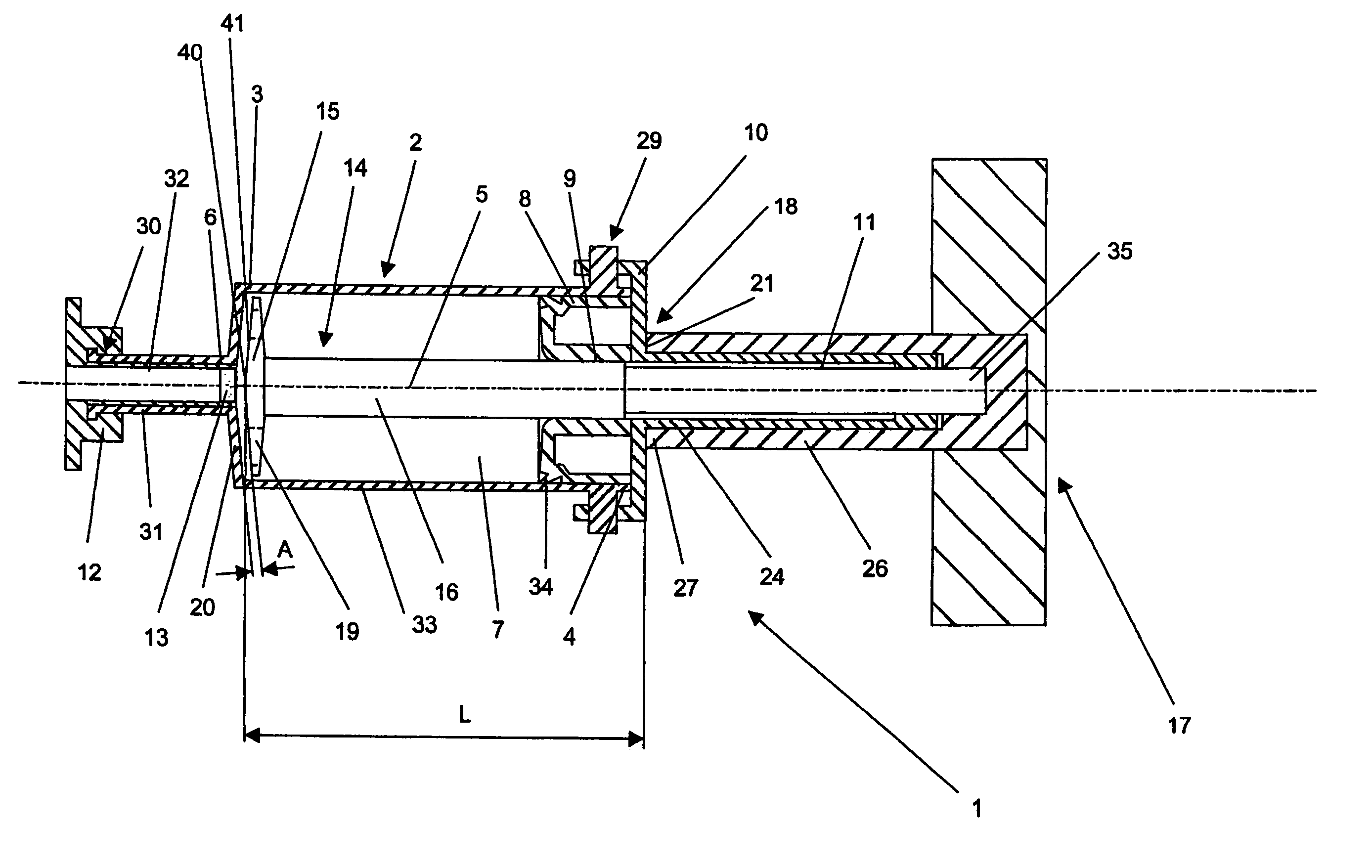
InactiveUS6974247B2Reduce wearMinimum distanceCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMaximum dimensionLocking mechanism
The present invention relates to a device for storing and / or mixing and / or injecting cements, especially bone cements. The device includes a tube having a longitudinal axis, a front end with an outlet opening, a rear end; and an internal cylindrical cavity having a first end and a second end; a locking mechanism detachably connected to the front end of the tube so that the outlet opening can be sealed; and a lid detachably connected to the rear end of the tube; the lid having a borehole extending therethrough. The device also includes: a mixer having a mixing shaft sized and configured to extend through the borehole formed in the lid and a mixing tool at one end thereof, the mixer being axially and rotationally moveable inside of the cavity; a driving mechanism connected to the mixer shaft so that the mixer can be axially and rotationally moved with respect to the tube; and a first restraining mechanism for limiting the axial movement of the mixer with respect to the tube so that the a minimum distance A remains between the front face of the mixing tool and the front wall of the cavity; wherein the cylindrical cavity has a diameter D and the mixing tool has a maximum dimension X such that X is less than D.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Metal-sealing material-feedthrough and utilization of the metal-sealing material feedthrough with an airbag, a belt tensioning device, and an ignition device
ActiveUS20070187934A1Improve solderabilityImprove corrosion resistanceBlasting cartridgesPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMaximum dimensionAirbag
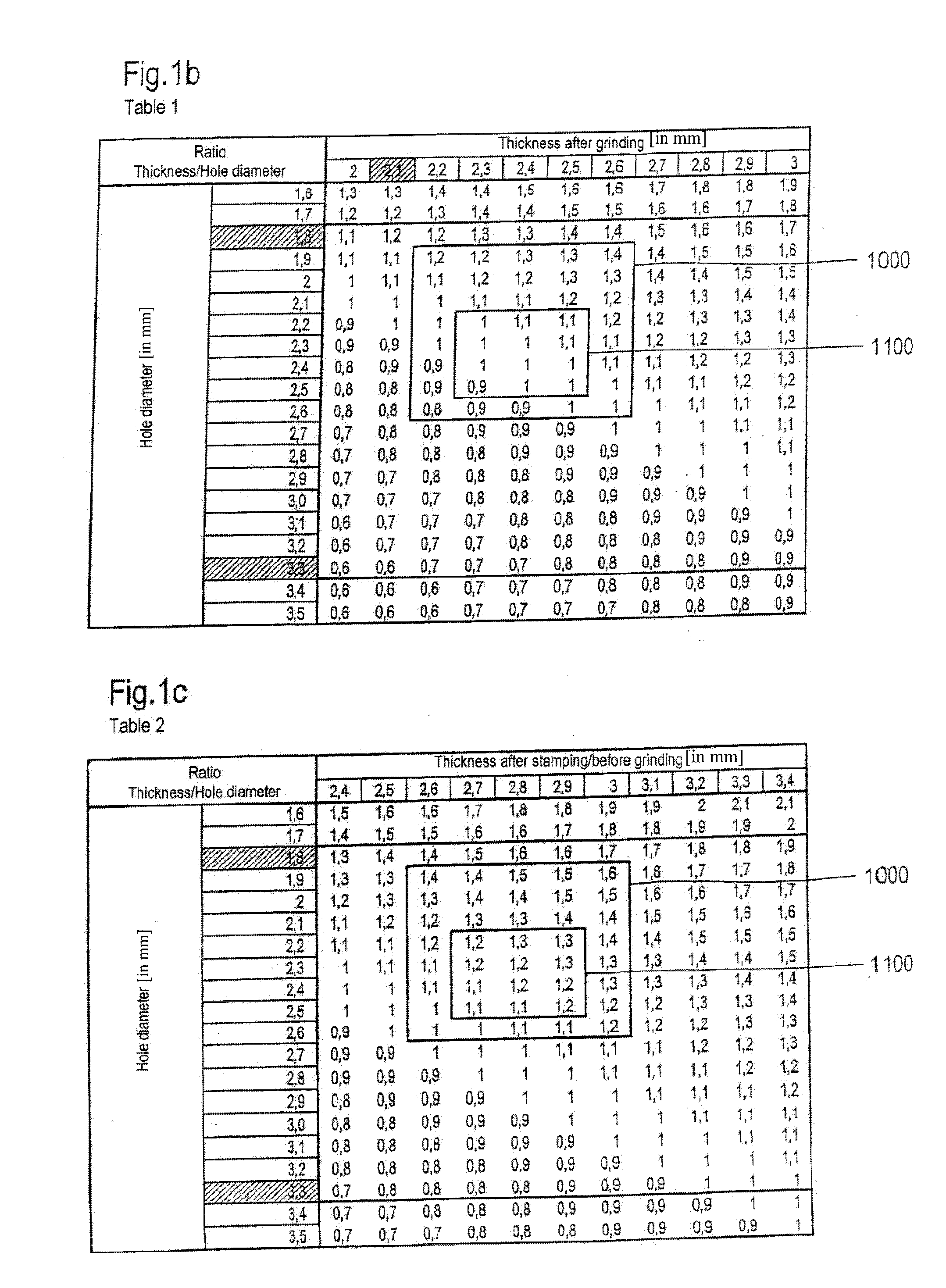
The present invention relates to a metal-sealing material-feedthrough for igniters of airbags or belt tensioning devices, especially glass-metal-feedthrough, including at least one metal pin which is located in a feedthrough opening in the base body in a sealing material, wherein the base body has a front side and a back side. Structure is provided between the front and the back side in order to avoid a relative movement of sealing material in the direction toward the back relative to the inside circumference of the feedthrough opening. At least the feedthrough opening is punched out of the base body. The base body is configured so that the ratio of thickness (D) of the base body to the maximum dimension of the feedthrough opening vertical to the axis direction of the feedthrough opening is in the range of between and including 0.9 to 1.6.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Shot, devices, and installations for ultrasonic peening, and parts treated thereby
InactiveUS20060021410A1Easy and quick to treatShorten treatment timeVibratory devicesMaximum dimensionMetallurgy
Shot for use in a peening installation, the shot having: hardness greater than or equal to 800 HV; density greater than or equal to 8 g / cm3; and pieces having a maximum dimension less than or equal to 1.5 mm.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Current diverter strip and methods
ActiveUS20050041362A1Minimal impactSensitive to damageAircraft lighting protectorsEmergency protective arrangement detailsDielectricMaximum dimension
A current diverter strip is provided having a dielectric (22) located above a plurality of conductive segments (24). An insulator (30) is also provided among said conductive segments (24) and below said dielectric (22). When RF transparency is required, the conductive segments (24) can have a maximum dimension that is approximately 1 / 6th of a wavelength of the highest operating frequency of an antenna that may be communicating through the current diverter strip. The dielectric (22) may be colored to match the color of the structure to which it is implemented. Upon exposure to a strong electric field, the current diverter strip (20) forms an ionized channel above the dielectric (22). In various implementations, the current diverter strip may be radio frequency transparent, environmentally and chemically resistant, color matched to its surroundings, and / or can withstand repeated uses.
Owner:HALL ALLEN L
Encapsulated particles
The disclosed technology relates generally to material systems which include a plurality of particles and methods of making the same. The particles have a core and a shell which encapsulates the core and has at least one atomic element not included in the core. The cores of the particles have a median maximum dimension that is less than 10 microns and a median of at least one axial dimension that is between 10 nm and 500 nm. The shells of the particles have a median thickness that is less than 100 nm, a silicon concentration that is between 10% and 50% on the basis of the weight of the shells, and an aluminum concentration that is between 0.01% and 5% on the basis of the weight of the shells.
Owner:NANOCOMPOSIX LLC
Method of connecting body tissue to a bone
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS
Methods of bonding two aluminum-comprising masses to one another
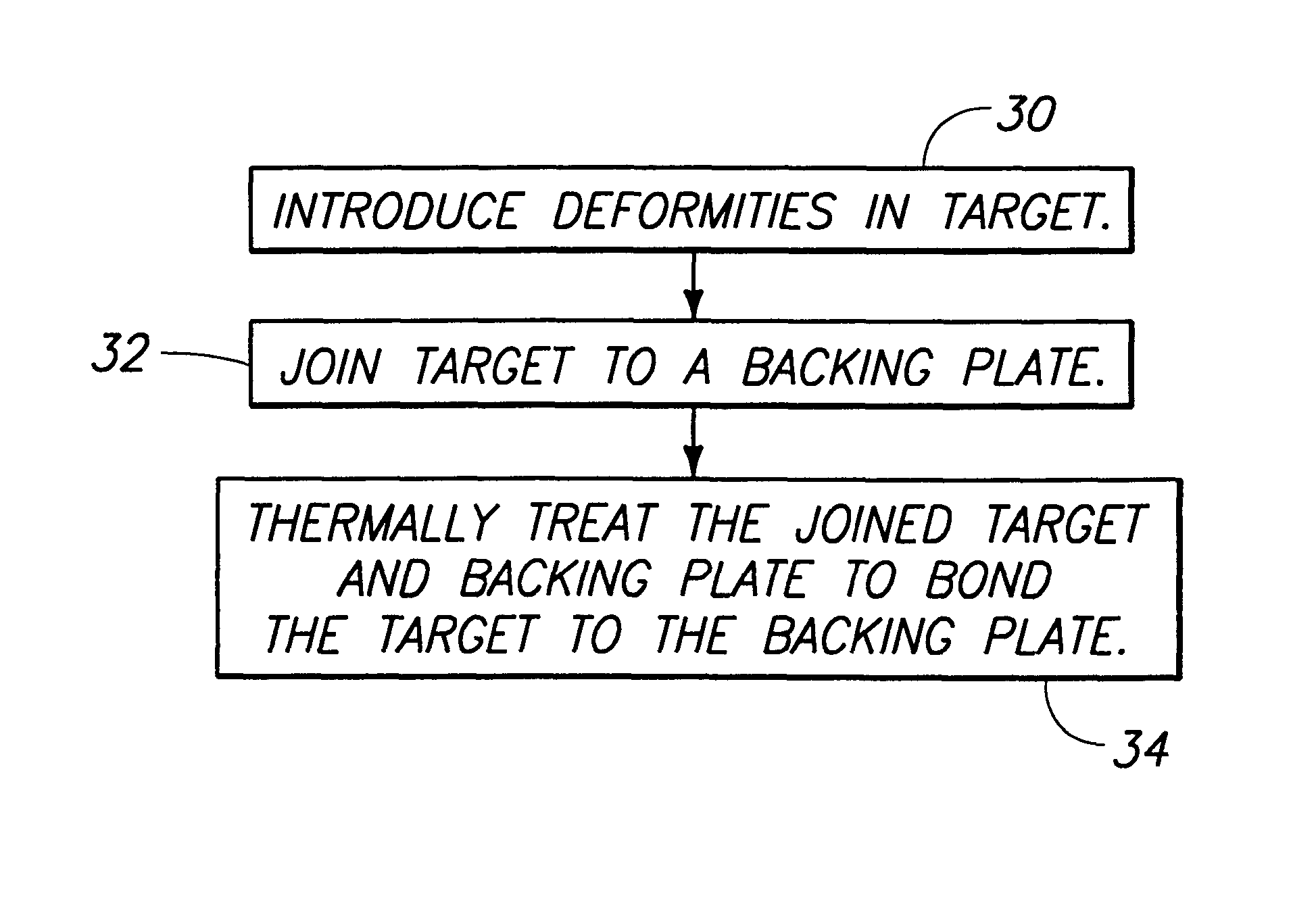
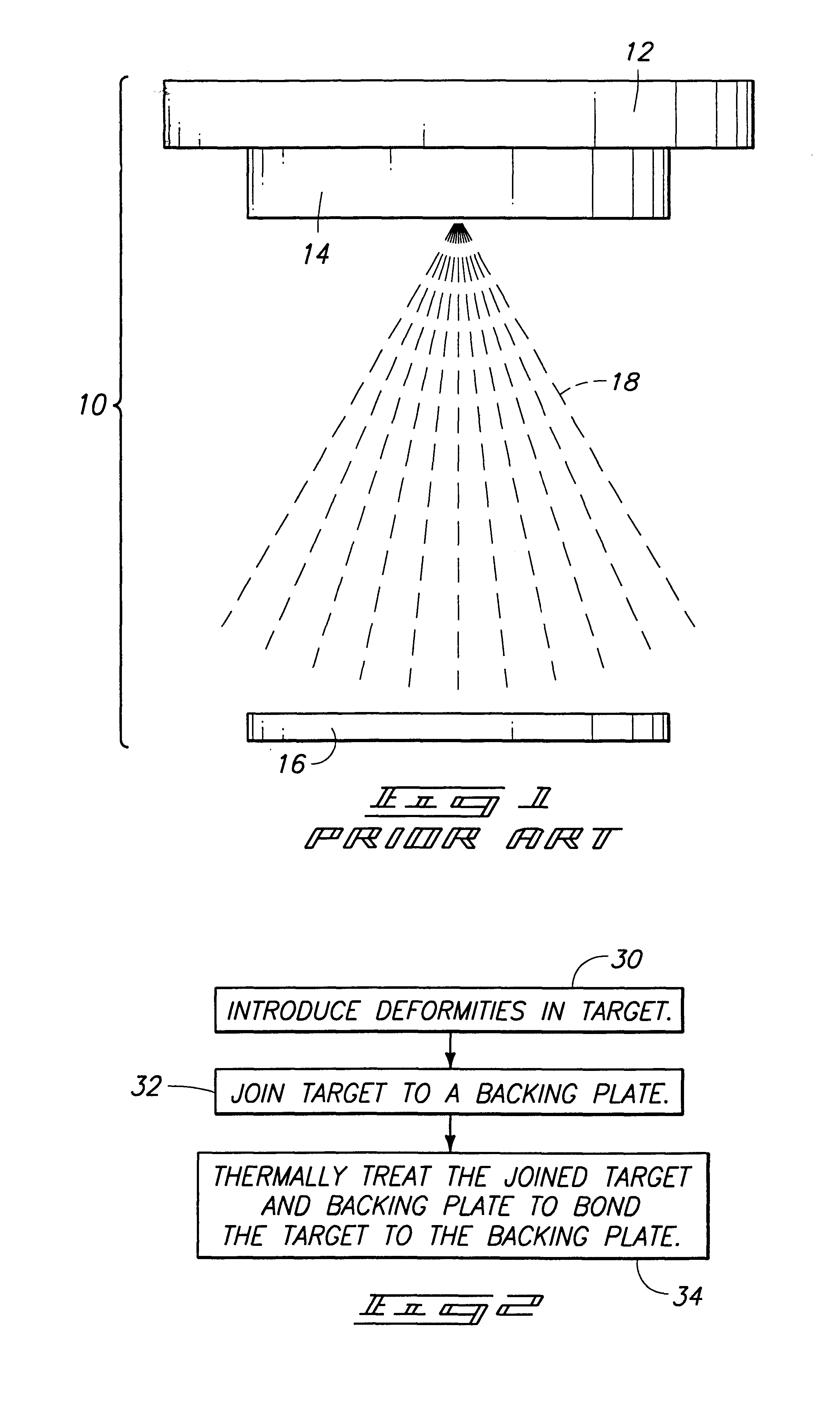
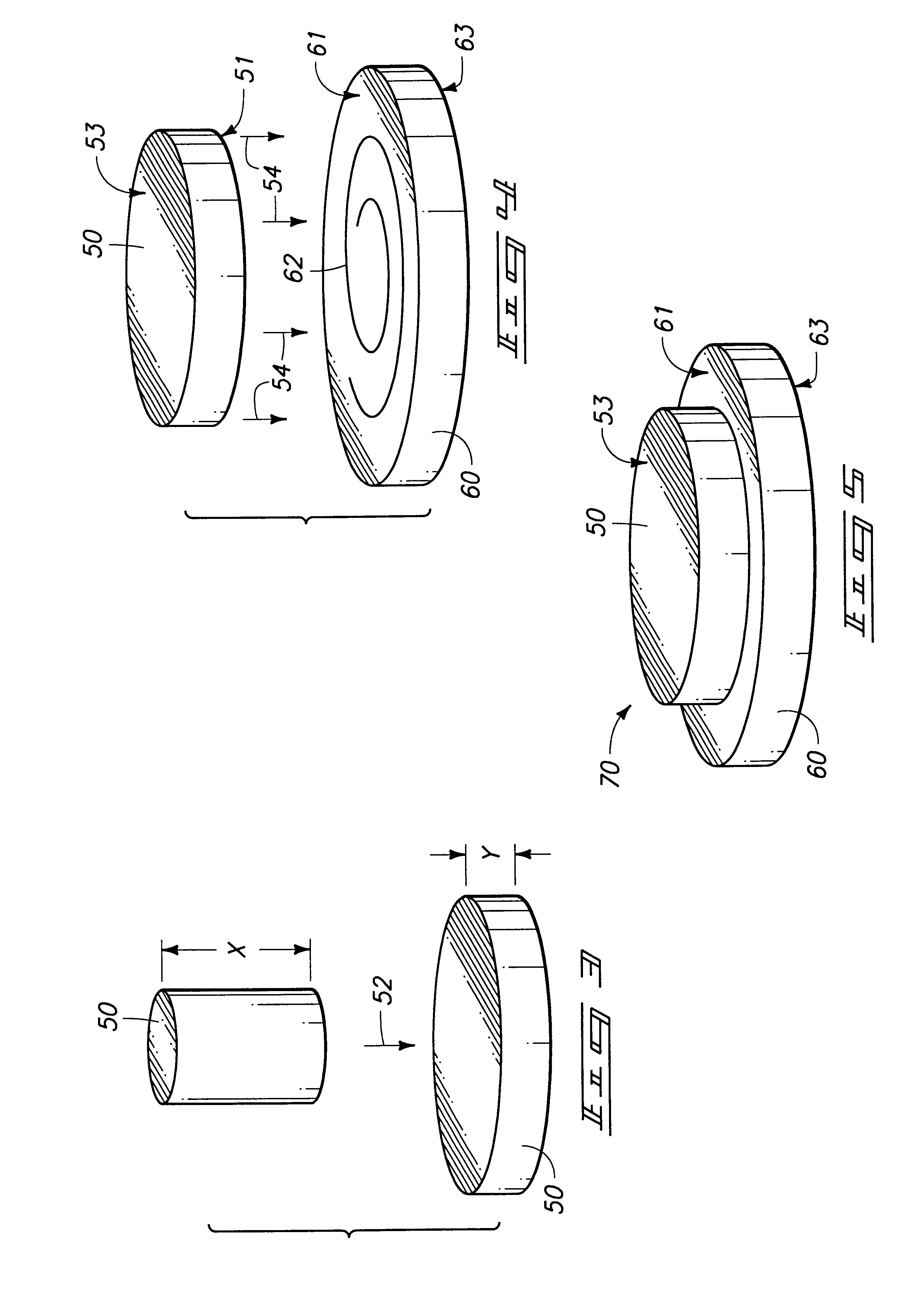
The invention encompasses a method of bonding a first mass to a second mass. A first mass of first material and a second mass of second material are provided and joined in physical contact with one another. The first and second masses are then diffusion bonded to one another simultaneously with the development of grains of the second material in the second mass. The diffusion bonding comprises solid state diffusion between the first mass and the second mass. A predominate portion of the developed grains in the second material have a maximum dimension of less than 100 microns. The invention also encompasses methods of forming a physical vapor deposition target bonded to a backing plate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com