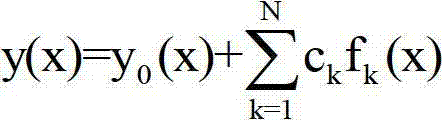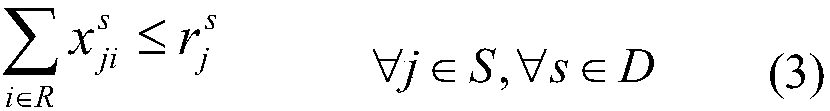Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
509 results about "Crossover" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
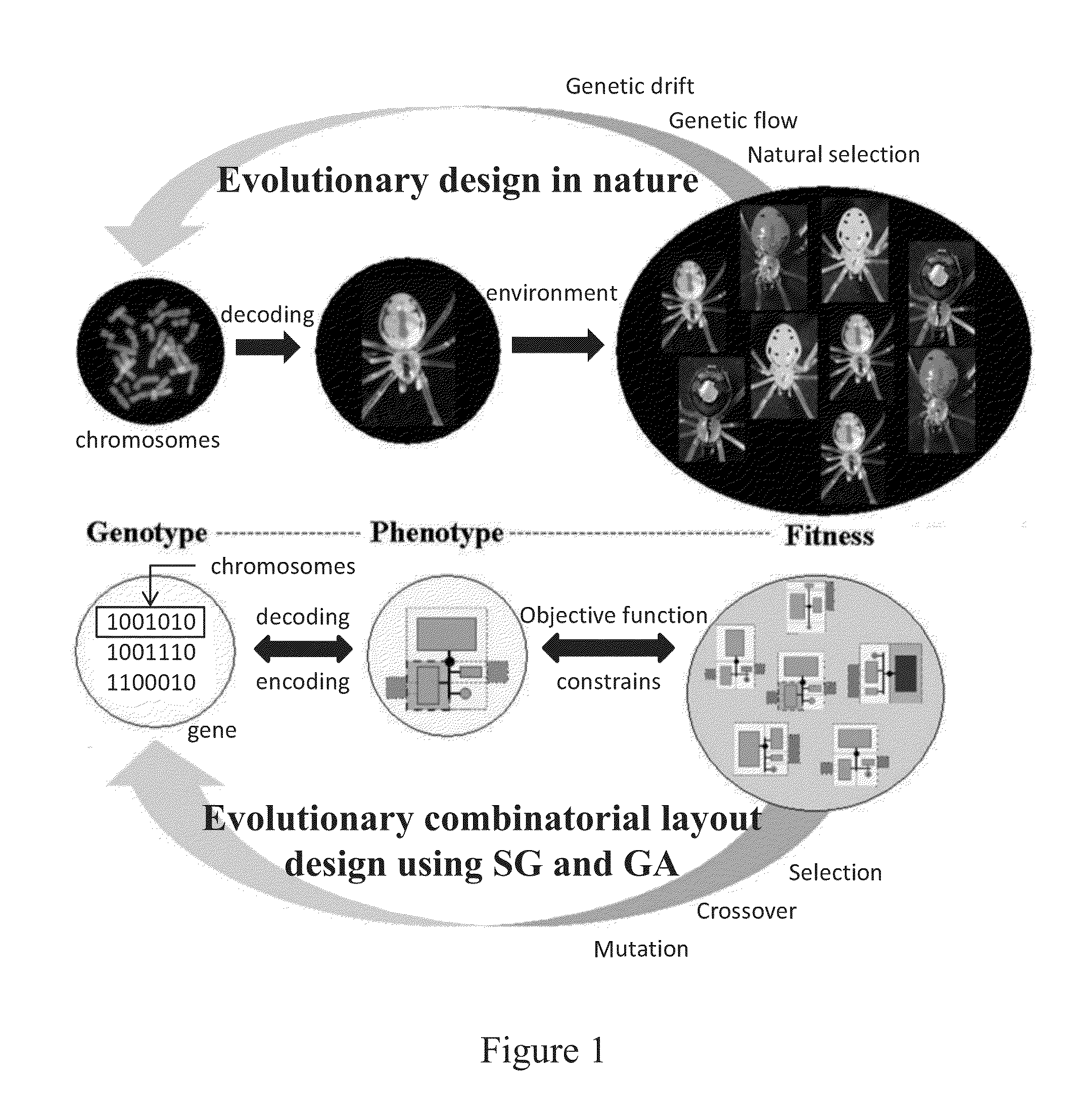
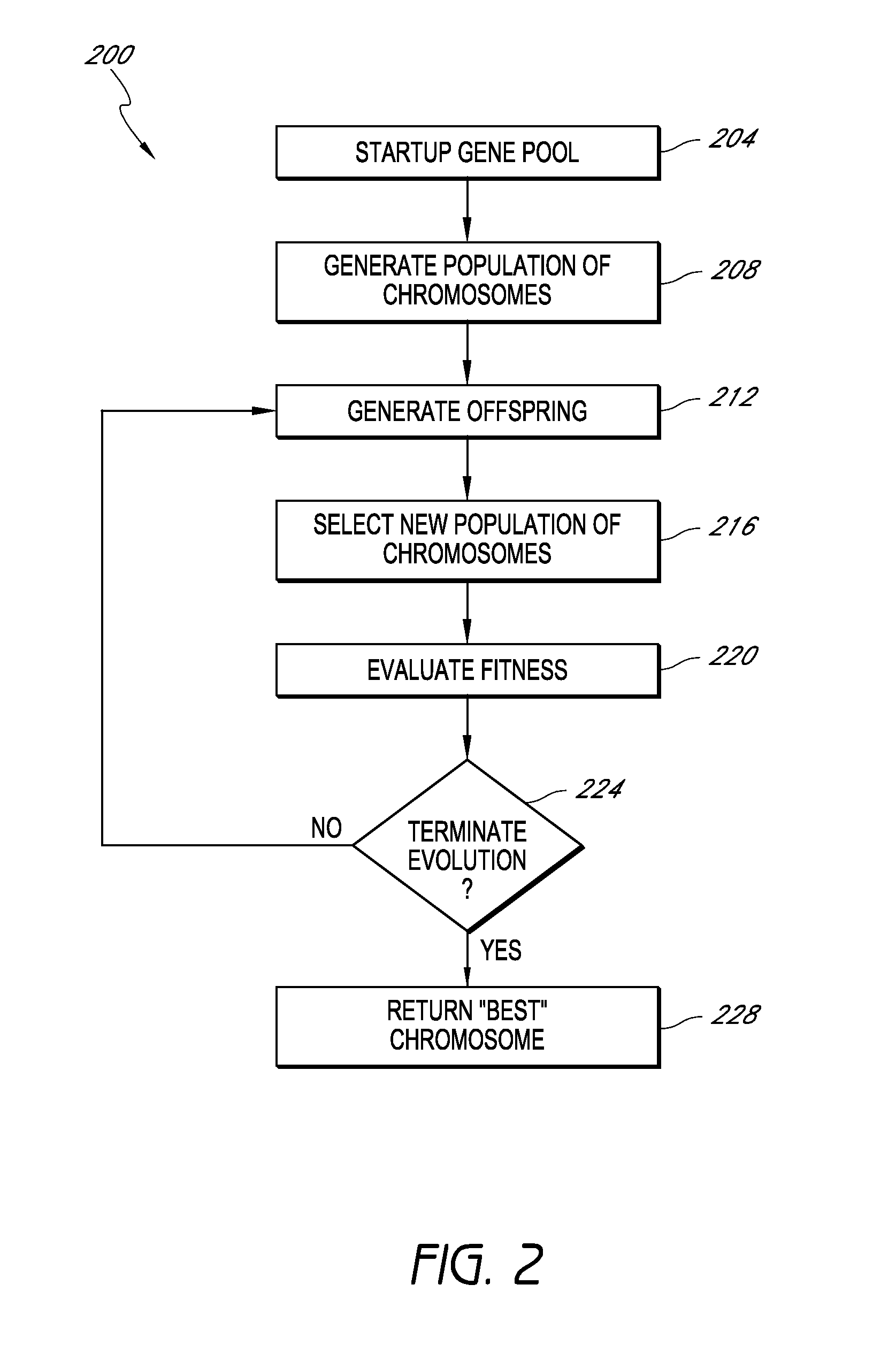
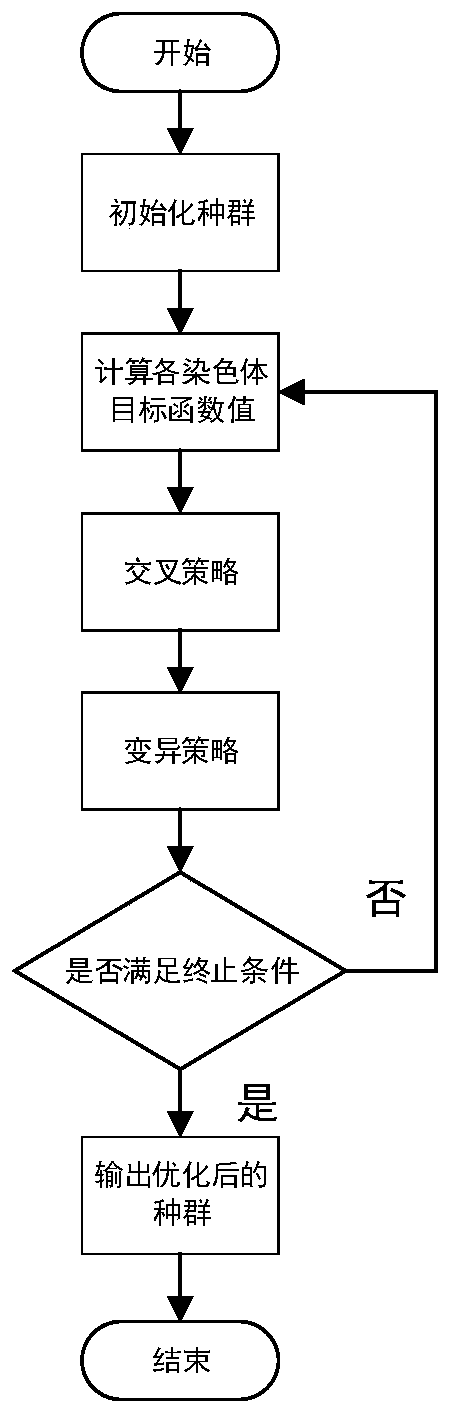
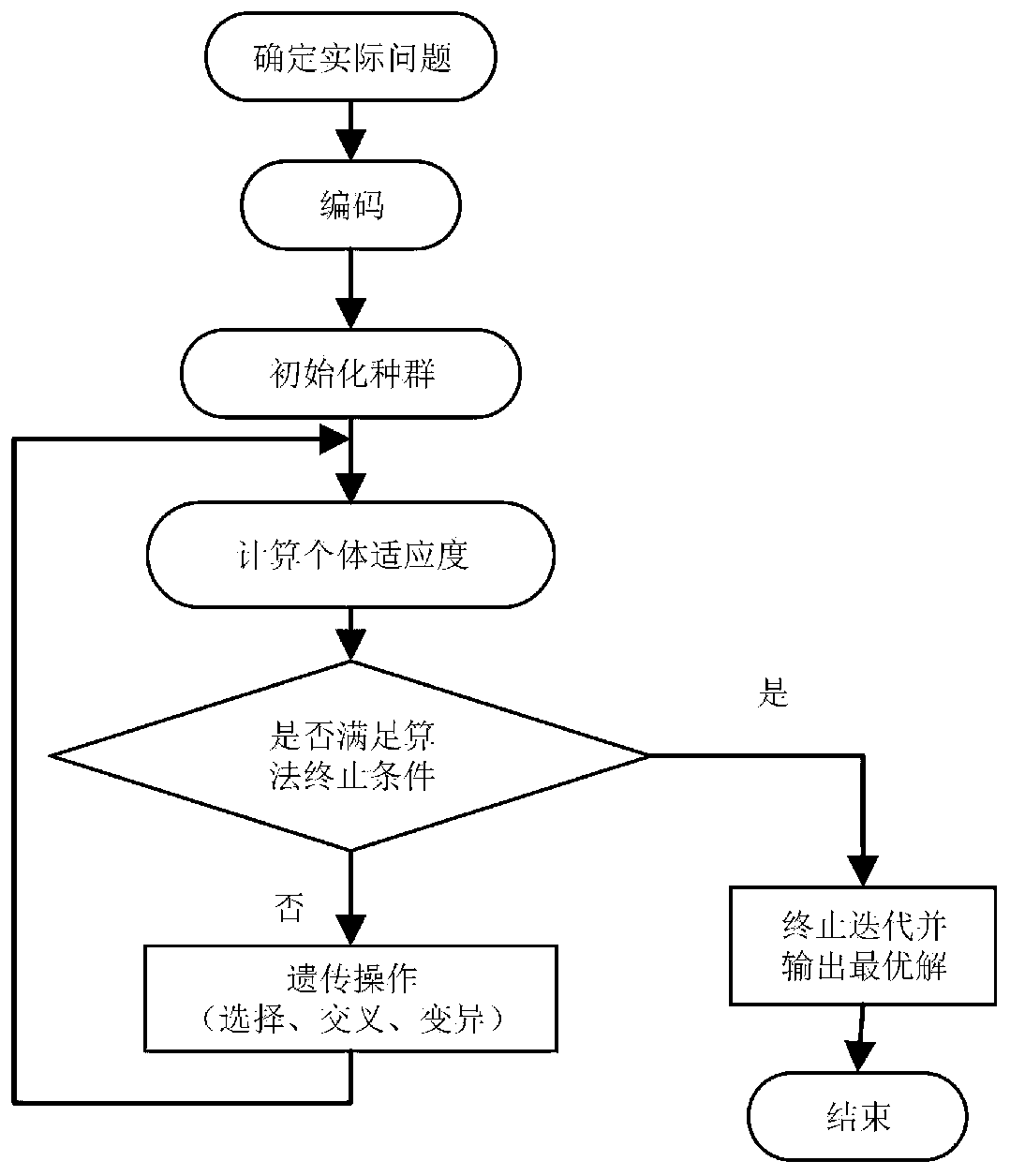
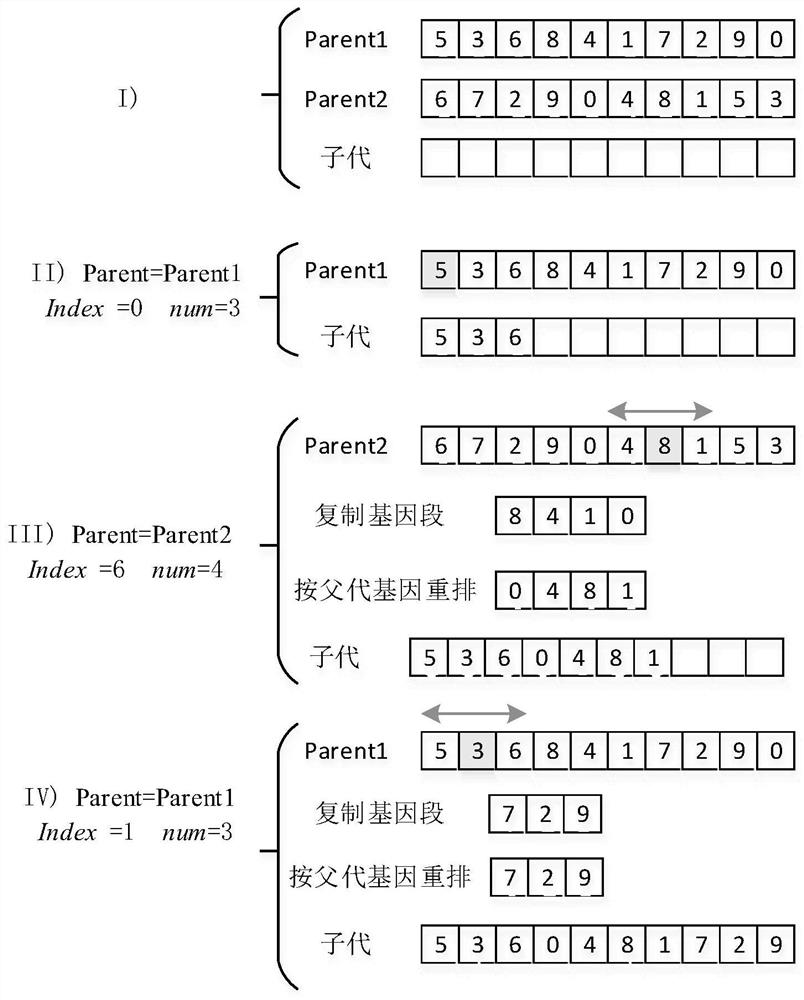
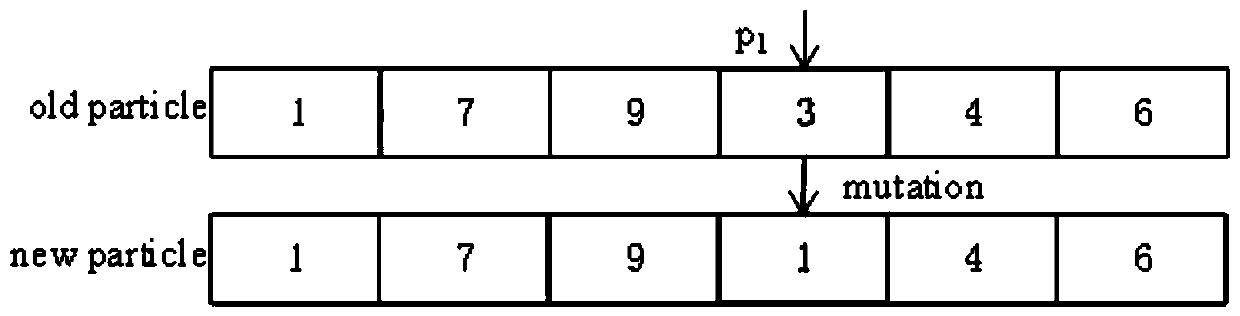
In genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation, crossover, also called recombination, is a genetic operator used to combine the genetic information of two parents to generate new offspring. It is one way to stochastically generate new solutions from an existing population, and analogous to the crossover that happens during sexual reproduction in biology. Solutions can also be generated by cloning an existing solution, which is analogous to asexual reproduction. Newly generated solutions are typically mutated before being added to the population.
Intelligent layout method used for rectangular part
InactiveCN103500255AMeet the process requirementsEfficient searchSpecial data processing applicationsRelevant informationAlgorithm
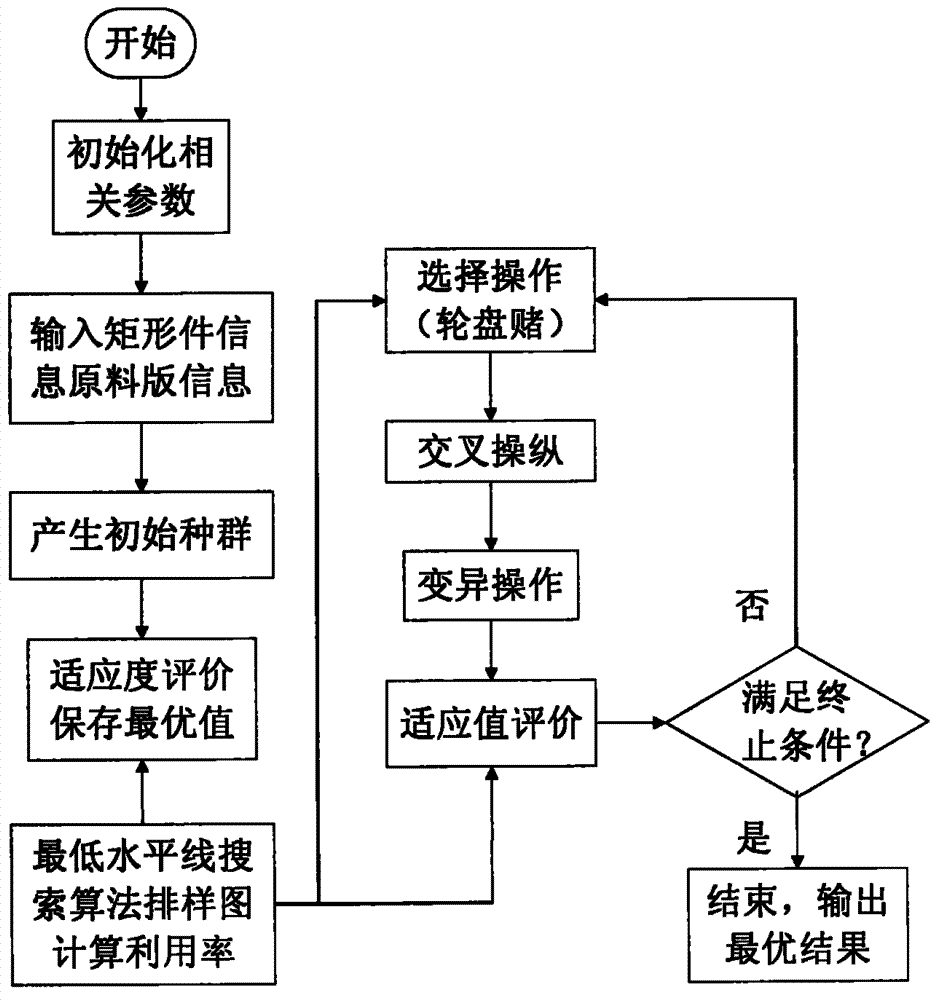
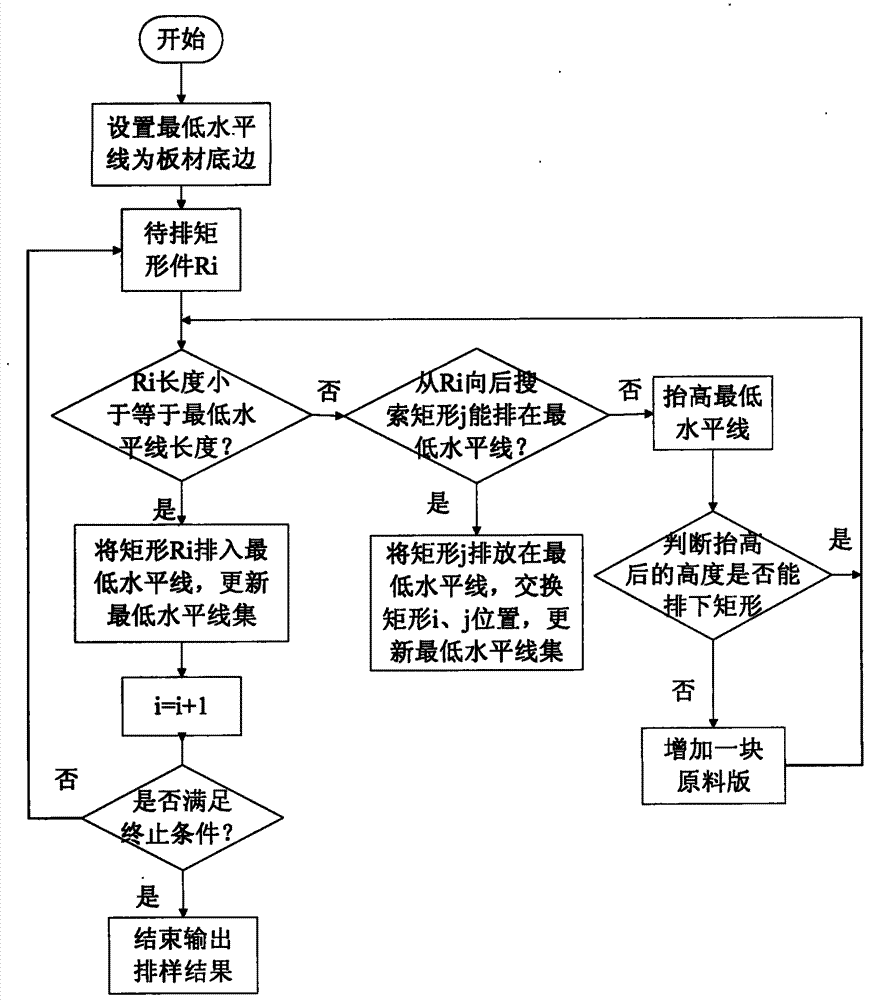
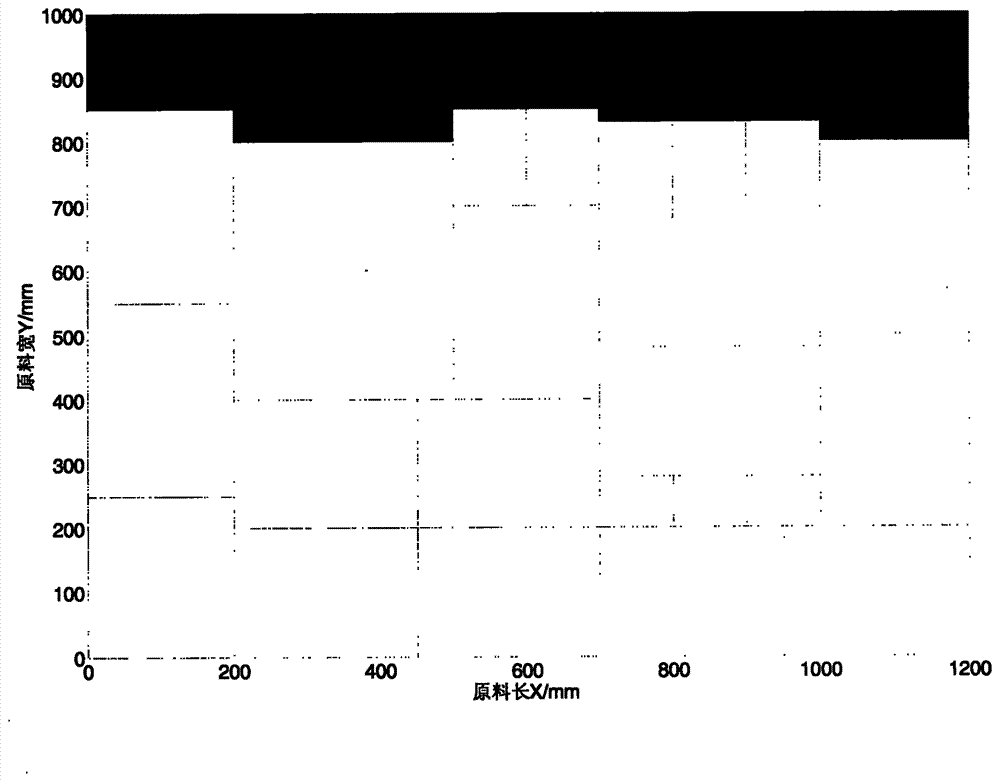
The invention discloses an intelligent layout method used for a rectangular part. The method comprises the steps that S1 relative parameters of the genetic algorithm are initialized; S2 relative information of the rectangular part is extracted from a rectangular part bank to be laid out; S3 relative information of raw material boards is extracted from a board tank; S4 the obtained information is coded, and primary species are generated randomly; S5 one-by-one decoding is conducted on the primary species by means of the lowest horizontal line search algorithm to obtain solution using efficiency; S6 selection, crossover and mutation operation is conducted according to the genetic algorithm until iteration is finished, and the optimal layout scheme is output. According to the intelligent layout method, the process requirement of the rectangular part can be met well, the intelligent algorithm and the heuristic algorithm are combined, one optimizing scheme can be found rapidly and efficiently, and therefore the material using rate of an enterprise is greatly improved, layout time can be obviously shortened, and layout efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional encasement novel genetic algorithm model under multi-constrain condition
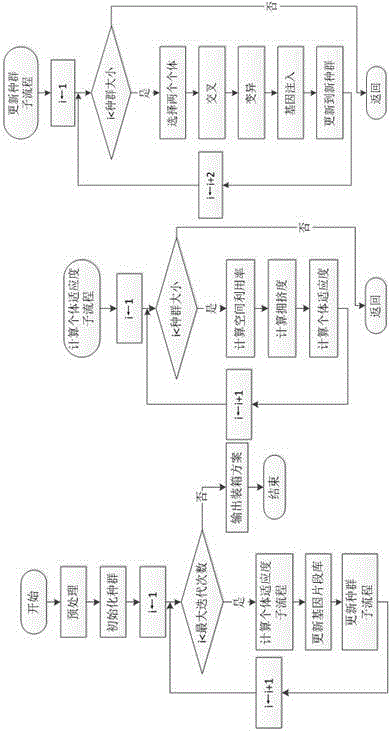
The invention relates to a three-dimensional encasement novel genetic algorithm model under a multi-constrain condition. At present, the logistics transportation industry rapidly develops, but encasement plan decision models are not perfect; particularly, a three-dimensional encasement model under the multi-constrain condition has the following typical problems: 1, the time complexity is higher; 2, the space utilization ratio is lower; 3, a encasement plan cannot be perfect. The design considers the constraint conditions such as the space utilization ratio, the centre-of-gravity position and the load bearing in the encasement problem, combines an improved genetic algorithm with a Monte Carlo method, a gene injection algorithm and a non-dominated sorting algorithm, aims at improving the space utilization ratio of the encasement plan and reducing the time complexity of the algorithms under the multi-constrain condition, and belongs to the field of intelligent arithmetic optimization. The three-dimensional encasement novel genetic algorithm model is mainly characterized in that population is initialized through the Monte Carlo method based on normal distribution; the gene injection algorithm is used in the encasement decision mode; the probability of crossover, mutation and gene injection operators is fitness functions; an online space combining method is used.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
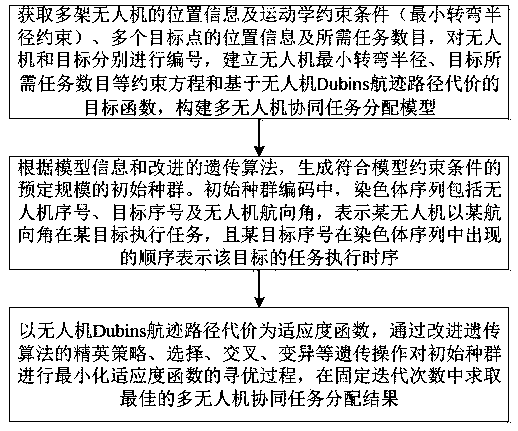
Multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task allocation method based on improved genetic algorithm
InactiveCN110766254AImprove collaborationSolving the Problem of Efficient Resource AllocationResourcesPosition/course control in three dimensionsSimulationGenetics algorithms
The invention provides a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task allocation method based on an improved genetic algorithm. The method comprises the following three steps: establishing constraint equations such as the minimum turning radius of an unmanned aerial vehicle and the number of tasks required by a target, and a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task allocation model based on Dubins flight path cost; generating an initial population of a predetermined scale conforming to model constraint conditions; taking the Dubins track path cost of the unmanned aerial vehicle as a fitness function, and iteratively updating the initial population by using genetic operations such as elite strategy, selection, crossover, variation and the like of an improved genetic algorithm to generate a feasible solution which minimizes the target function in fixed iteration times, and taking the feasible solution as a result of multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task allocation and route planning. The method has wide application value in multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task combat, is beneficial to implementation of multi-unmanned aerial vehicle multi-target cooperativetask execution, and improves the task completion efficiency. The method has important significance in the field of multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative control.
Owner:深圳市白麓嵩天科技有限责任公司
An optimization algorithm based on multi-objective resource-constrained project scheduling model
The invention provides an optimization algorithm based on multi-objective resource-constrained project scheduling model. The scheduling model requires scheduling the start time of each activity to achieve the optimal goal under the condition of satisfying the relevant constraints. Based on the RCPSP model, the invention introduces the optimal resource balance as the objective, and expands the model to a multi-objective model. The solution of RCPSP is mainly based on the heuristic algorithm. When the task list is used to encode chromosomes in the heuristic algorithm, the task list initialized randomly may not satisfy the constraint relation between the top and bottom. The invention provides an individual generation mode based on control relation, which presents a new crossover operator andmutation operator based on the NSGA-II algorithm. The invention can greatly reduce the time complexity of the algorithm, realize the balanced allocation of resources, improve the production efficiencyand save the production cost while ensuring the solution precision of the algorithm, thereby improving the economic benefit of the resource scheduling production process.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
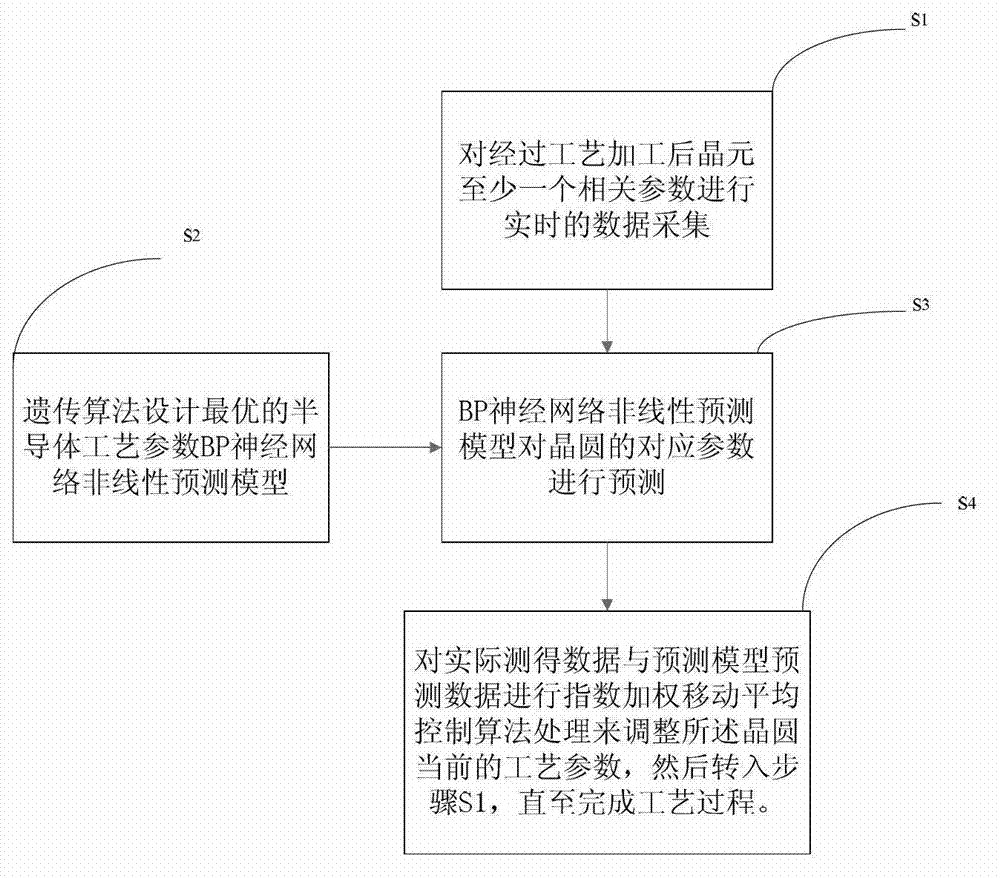
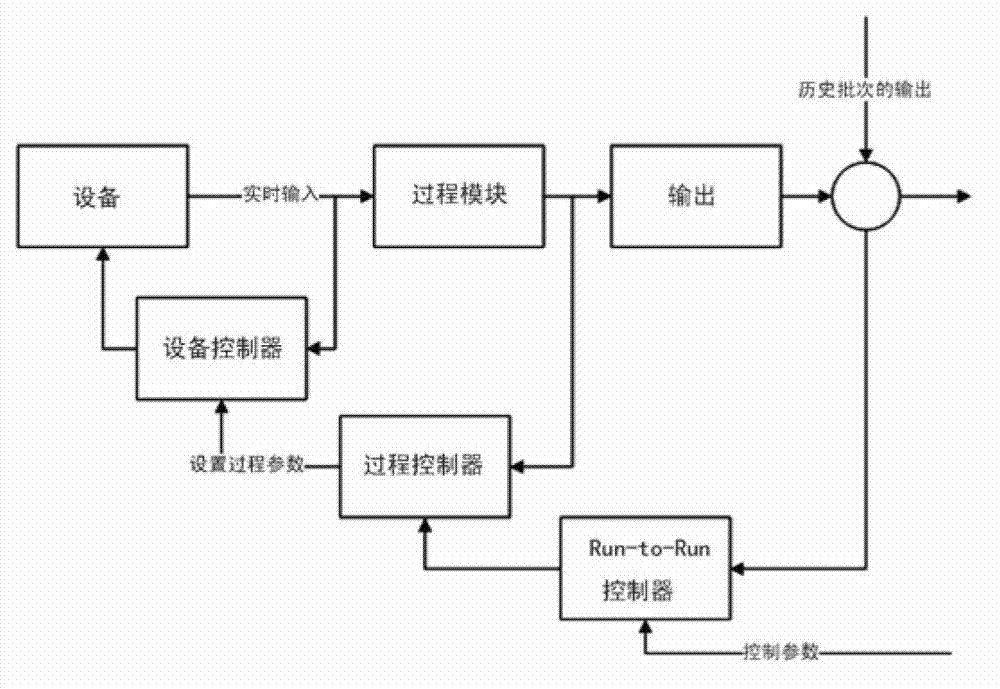
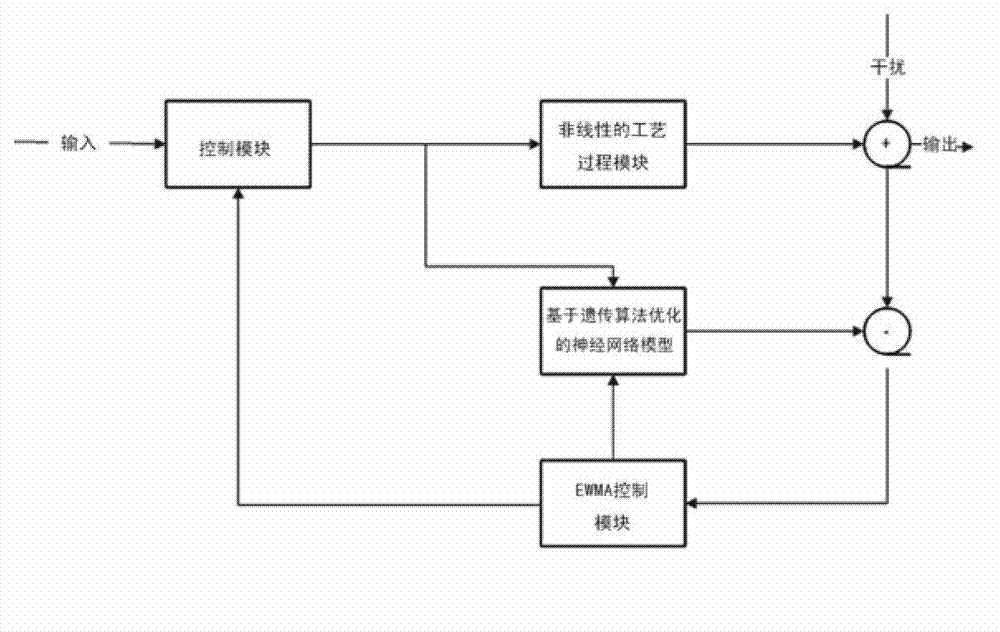
Parameter optimization control method of semiconductor advance process control
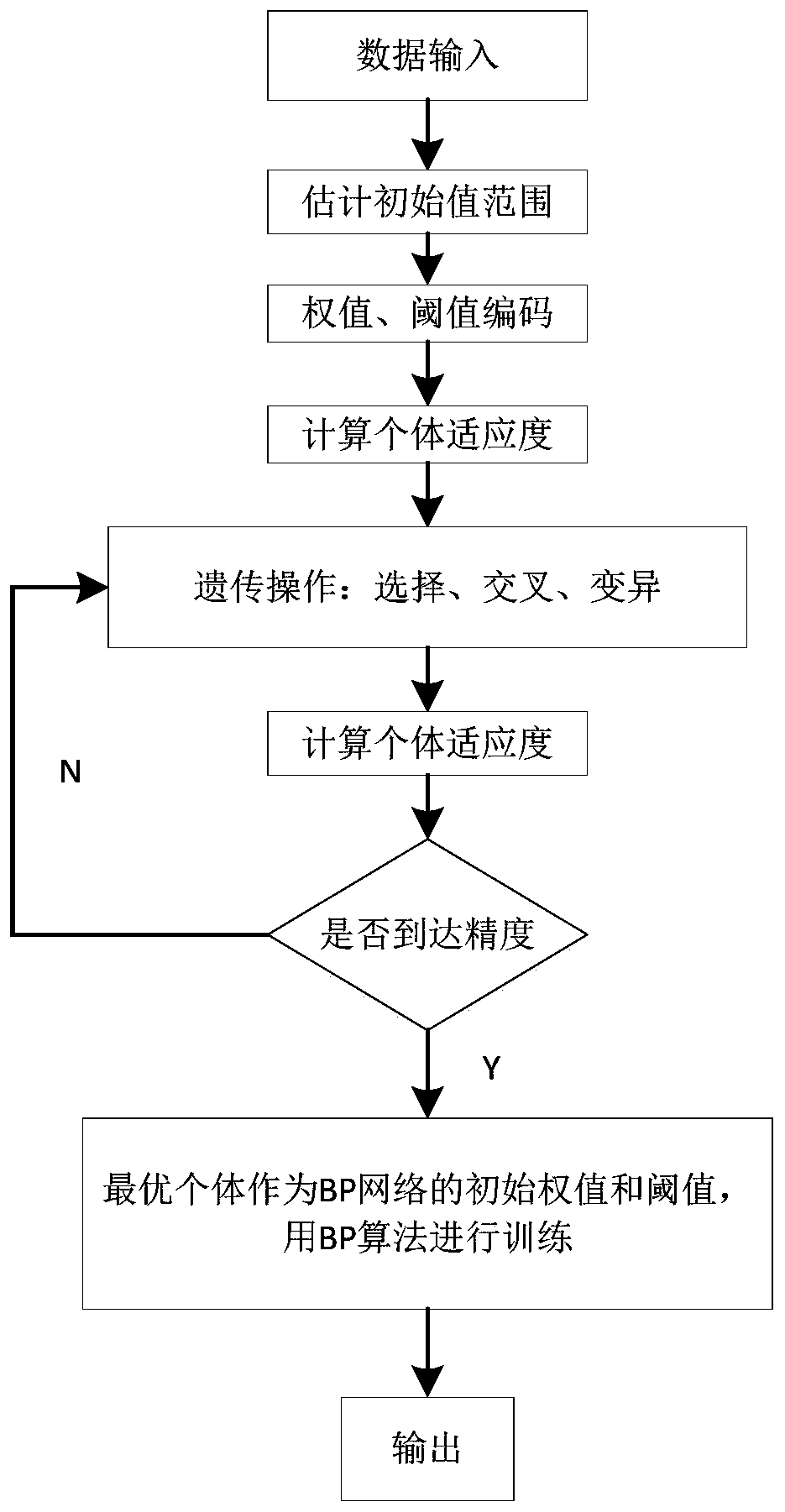
The invention discloses a parameter optimization control method of semiconductor advance process control (APC). In semiconductor technological process, a traditional method uses a linear prediction model for the optimization control method of batch process. The parameter optimization control method of the semiconductor advance process control uses an optimized back propagation (BP) neural network prediction model based on genetic algorithm, optimizes the initial weight values and threshold values of the neural network through the genetic algorithm, uses selecting operation, probability crossover and mutation operation and the like according to the fitness function F corresponding to each chromosome, and outputs the optimum solution finally to determine the optimum initial weight value and the threshold value of the BP neural network. The performance of the BP neural network is improved with an additional momentum method and variable learning rate learning algorithm being used, so that the BP neural network after being trained can predict the non-linear model well. The genetic algorithm in the method has good global searching ability, a global optimal solution or a second-best solution with good performance is easy to obtain, and the genetic algorithm well promotes the improvement of modeling ability of the neural network.
Owner:苏科斯(江苏)半导体设备科技有限公司
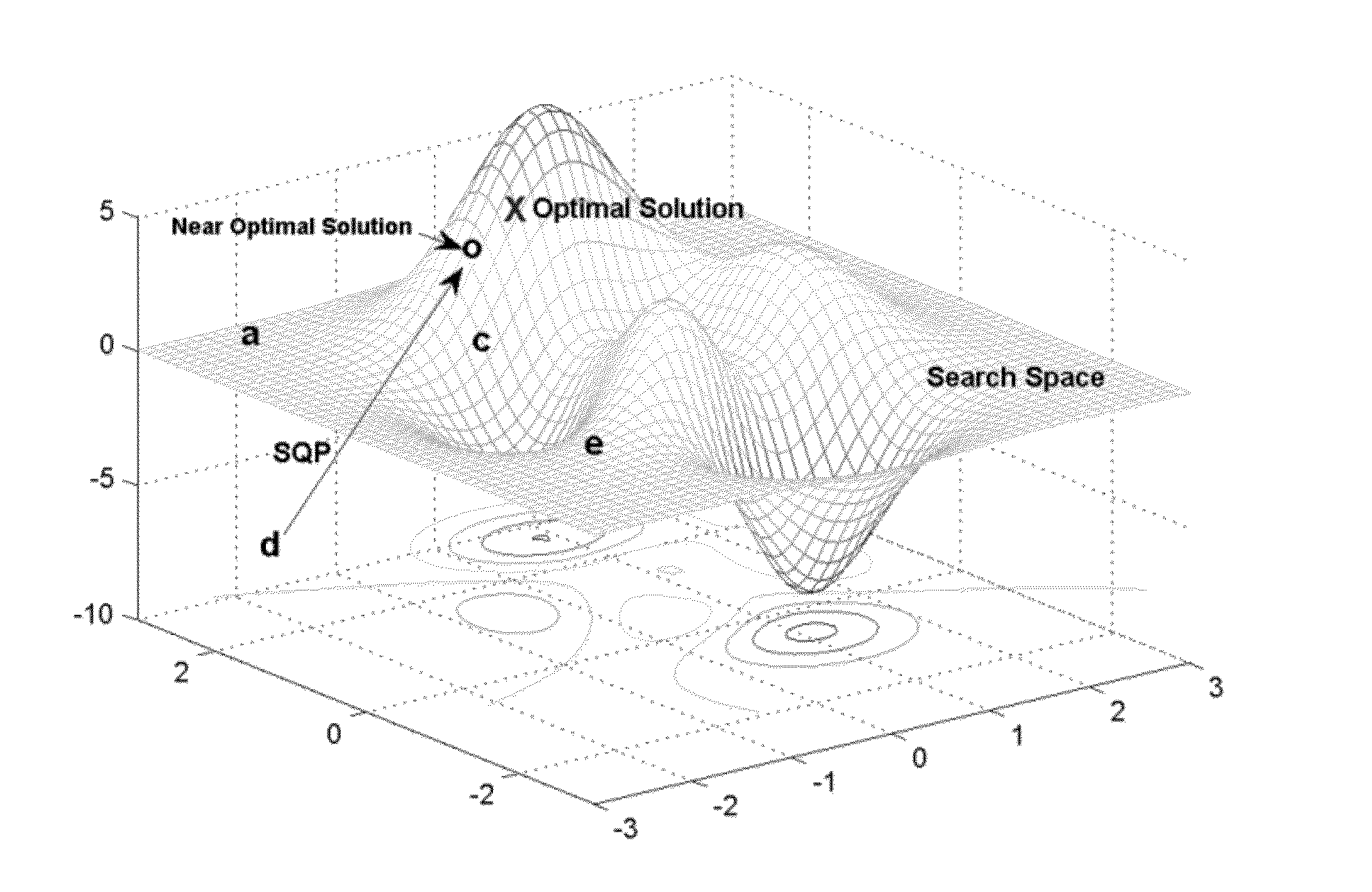
Computational device implemented method of solving constrained optimization problems
InactiveUS20130110751A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingAlgorithmGenetic algorithm
A computational device implemented method utilizes a genetic algorithm and modifies the offspring of the genetic algorithm that fall outside of the feasible search space after crossover so that the offspring will be within the feasible search space. To place the offspring in the feasible search space, NFC and HSQPC mechanisms are used.
Owner:TAIF UNIV
Customer classification method and device based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
InactiveCN110930182AAvoid the disadvantage of being prone to falling into local extremumImprove search accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeLocal optimumFeature Dimension
The embodiment of the invention provides a customer classification method and device based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: initializing a particle speed and a particle position according to a classification number and a feature dimension, and setting an initial value, so as to build an initial population of a particle swarm; performing iterative updating operation on the inertia weight, the particle speed and the particle position of the population according to a preset fitness function including the customer characteristic data until apreset iteration frequency is reached; after the number of iterations is preset, respectively carrying out selection operation, crossover operation and mutation operation on the particle swarm according to a genetic algorithm after each update for next iteration update until the iteration update reaches the total number of iterations or meets a convergence condition; and obtaining a clustering center according to the particle swarm reaching the total number of iterations or meeting the convergence condition, and classifying the customers. According to the method, through organic fusion of thegenetic algorithm, falling into a local optimal solution can be avoided, the later convergence speed is increased, and the search precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
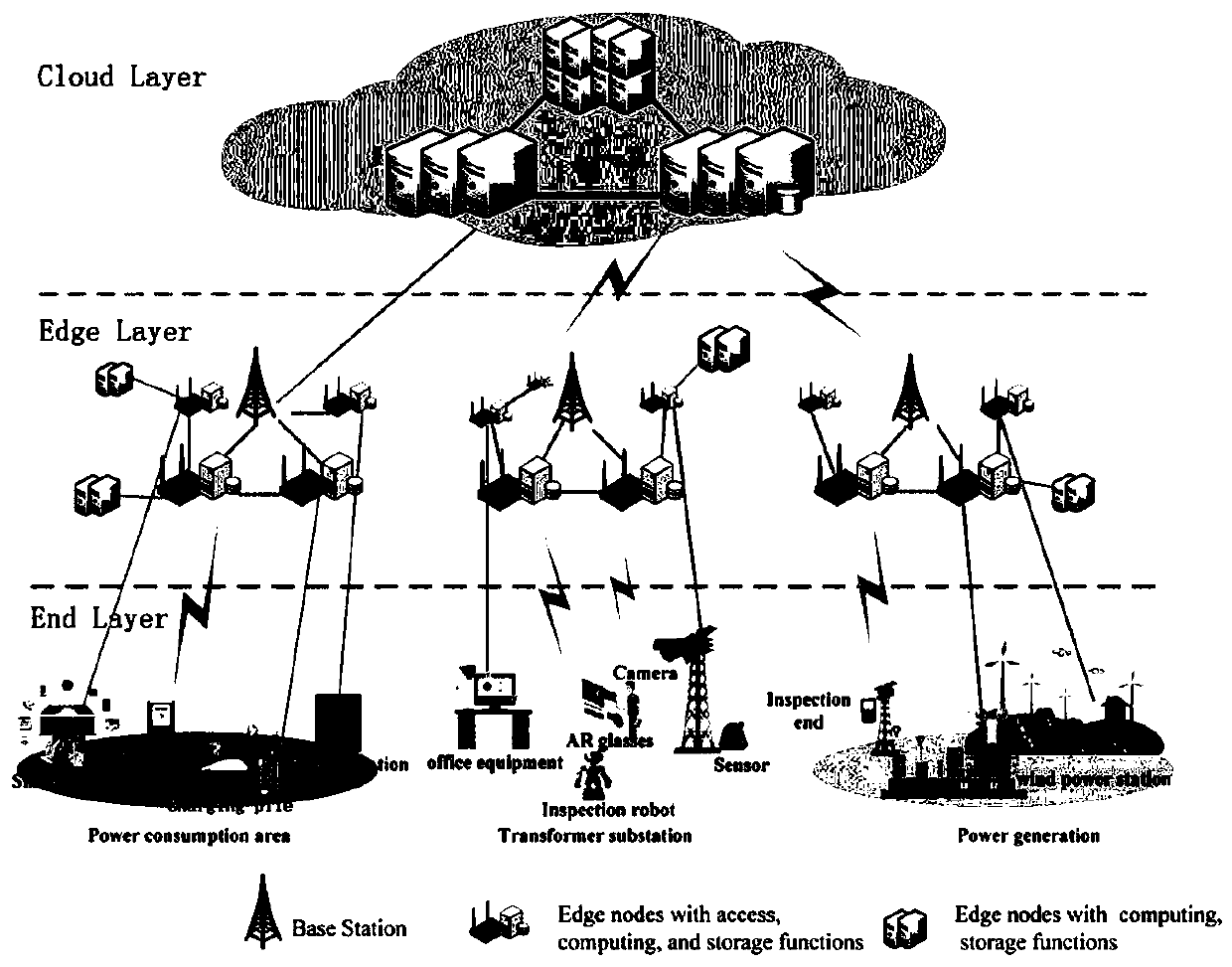
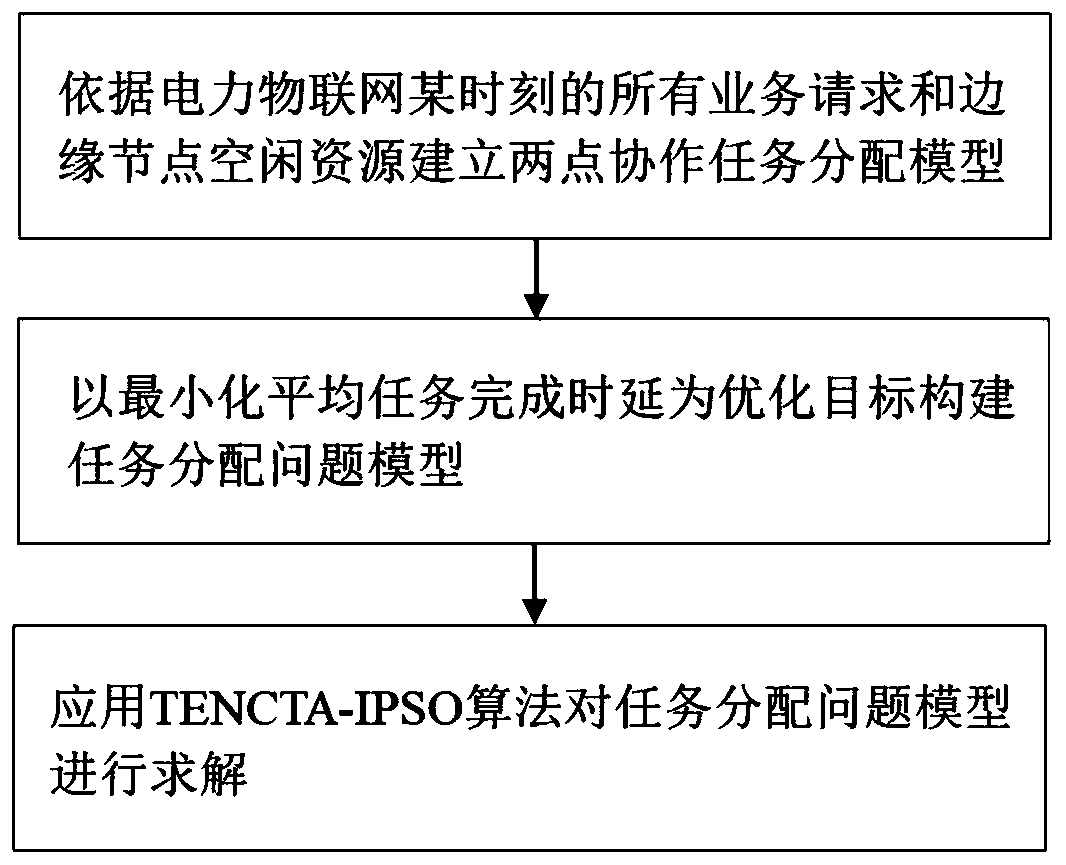
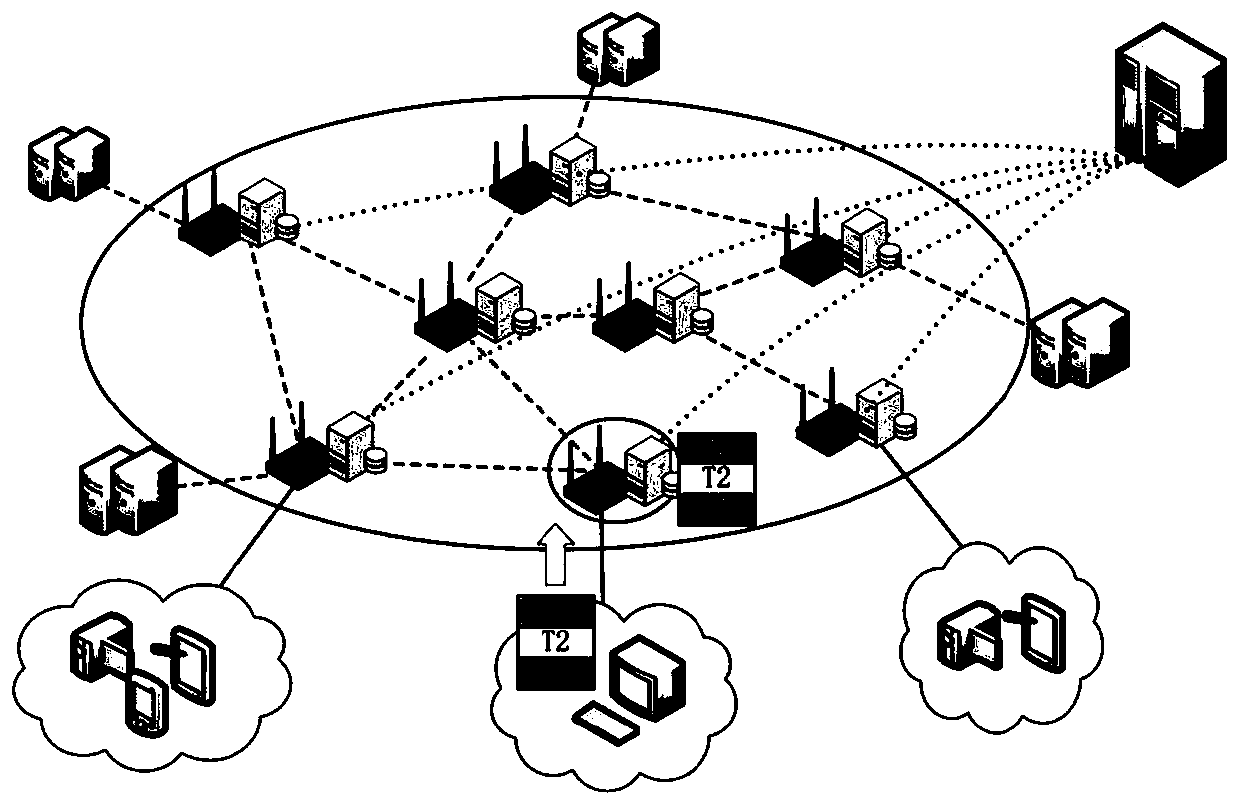
Electric power Internet of Things task allocation method based on edge cooperation
ActiveCN111445111AReduce task completion delayIncrease diversityResourcesTask completionLocal optimum
The invention discloses an electric power Internet of Things task allocation method based on edge cooperation. The method comprises the steps that a two-point cooperation task allocation model is established according to all service requests and EN idle resources of the electric power Internet of Things at a certain moment; a task allocation problem model is constructed by taking the minimized average task completion delay as an optimization target; and the task allocation problem model is solved by applying a TENCTA-IPSO algorithm. According to the method, the task completion time delay of the power grid service is effectively reduced. According to the TENCTA-IPSO algorithm, a particle updating strategy in a particle swarm algorithm is improved by utilizing crossover and mutation operations of a genetic algorithm; the particle swarm diversity is improved while the self-learning ability of the particles is kept, premature is prevented from falling into local optimum, and the calculatedtask allocation scheme shortens the average task completion delay to the maximum extent.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
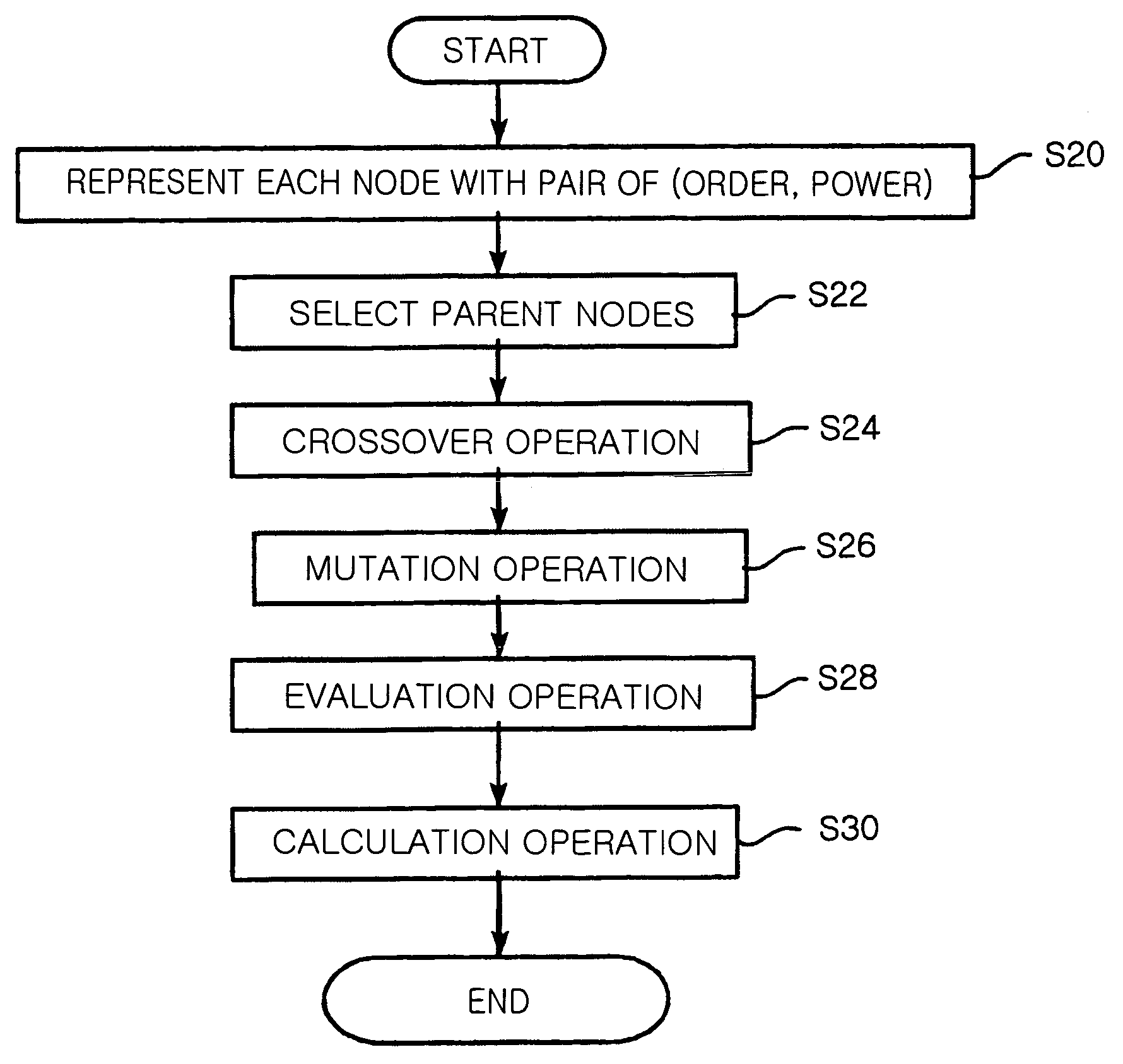
Method for selecting broadcast routing path using genetic algorithm in Ad-hoc network
ActiveUS20070133504A1Minimize the numberMinimize power consumptionPower managementNetwork topologiesGenetic algorithmDistributed computing
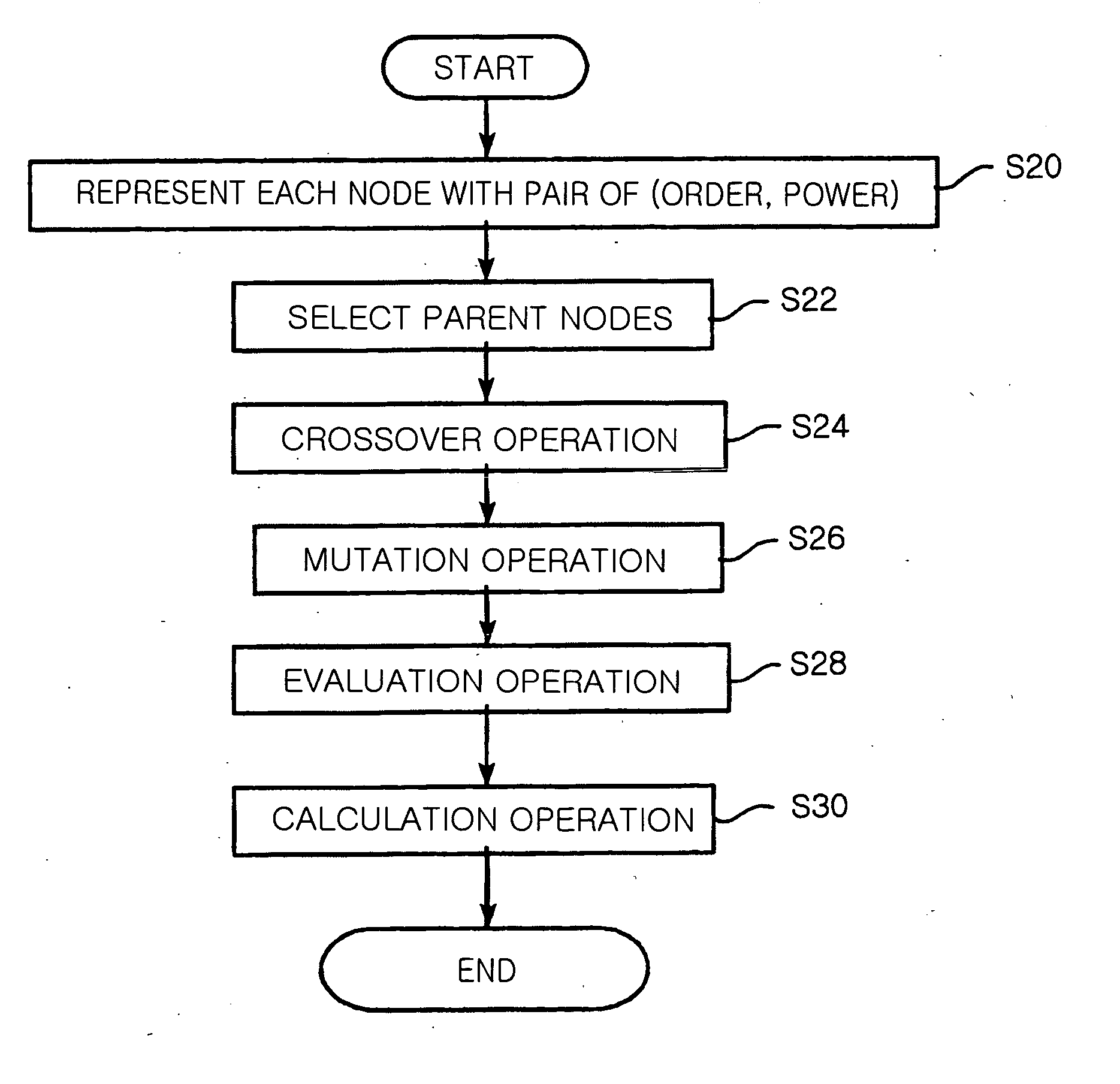
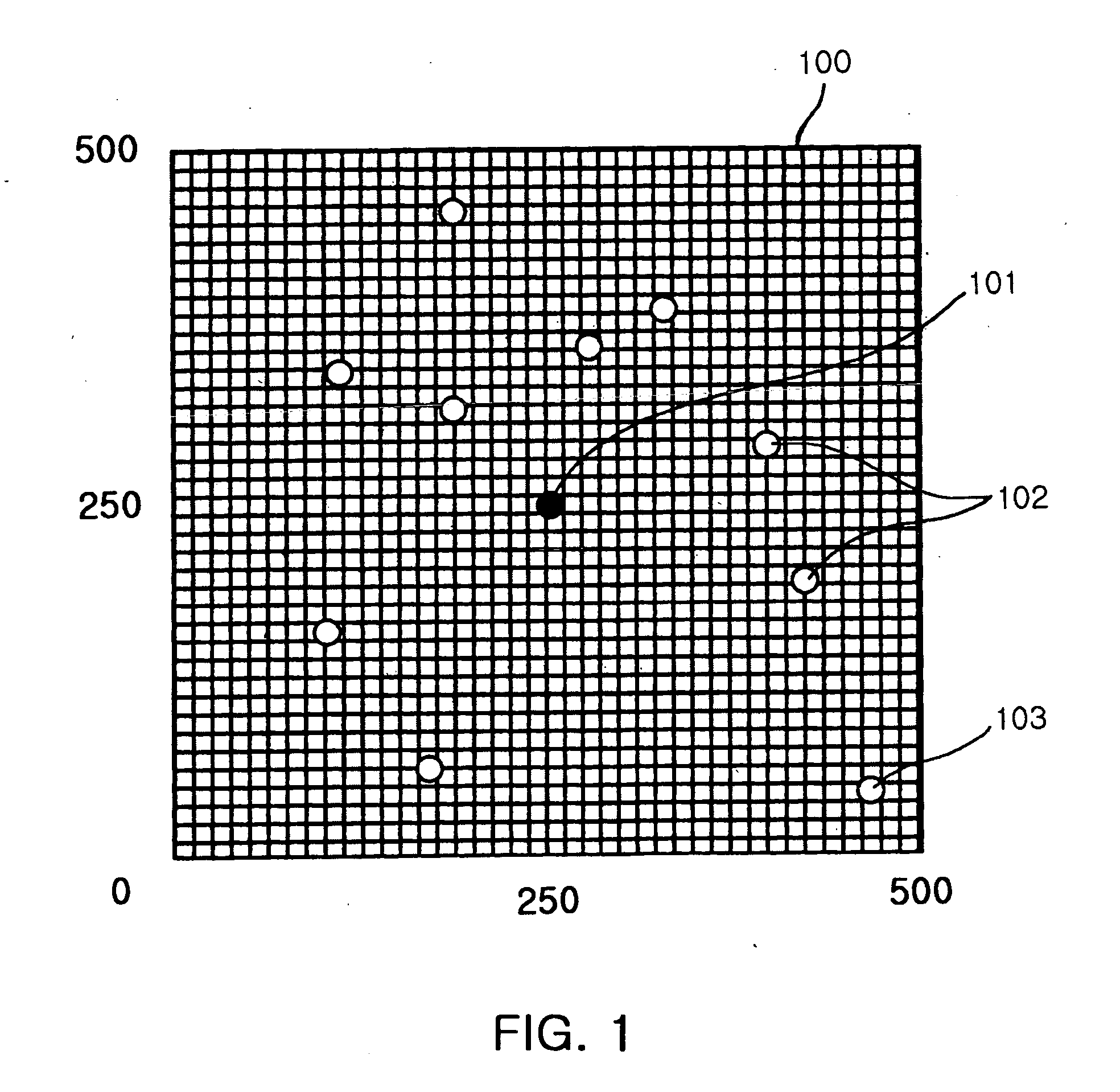
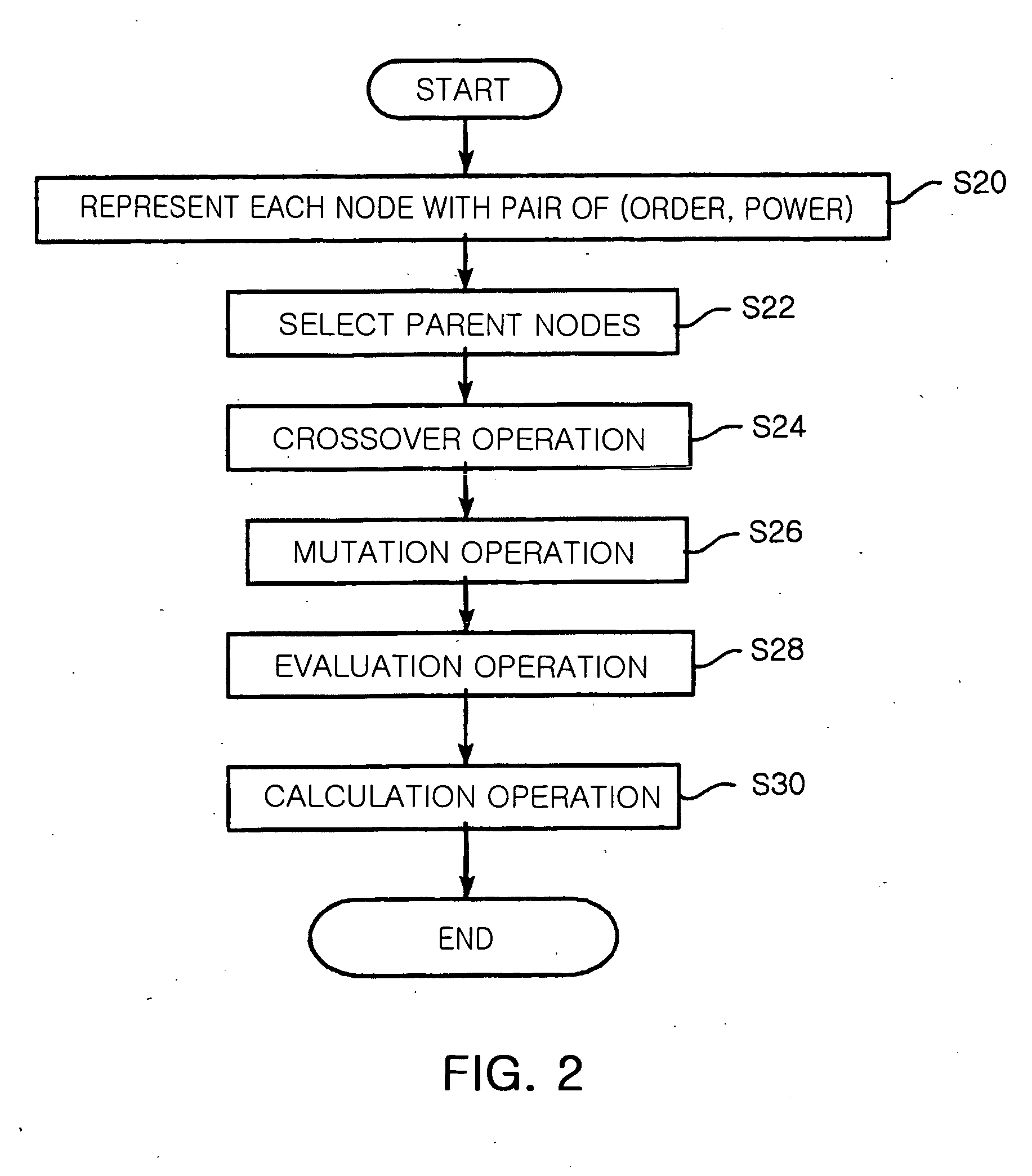
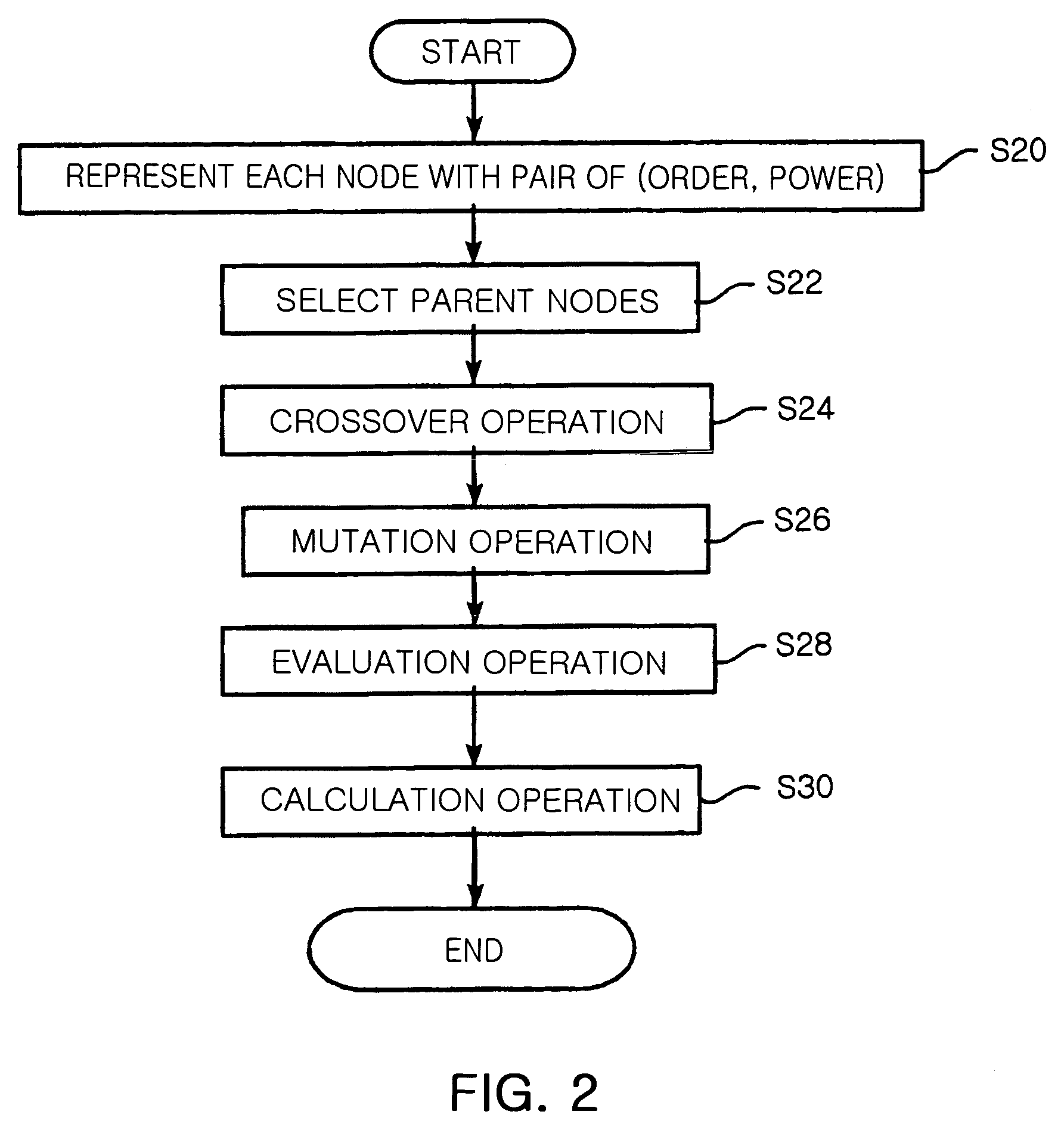
Provided is a method for selecting a broadcast routing path using a genetic algorithm in an Ad-hoc network. In the method, a plurality of nodes of the Ad-hoc network is defined as one chromosome, and the chromosome is represented with pairs of {order, power} in each node. Child nodes are created by performing an order based crossover and a power based crossover with respect to parent nodes neighboring to a source node. A mutation operation is performed with respect to the parent nodes and the child nodes. Relay nodes are determined by converting order and power information of each node of the chromosome into routing tree information. Power of the relay nodes is determined. A broadcast routing path is selected using the number and power of the relay nodes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
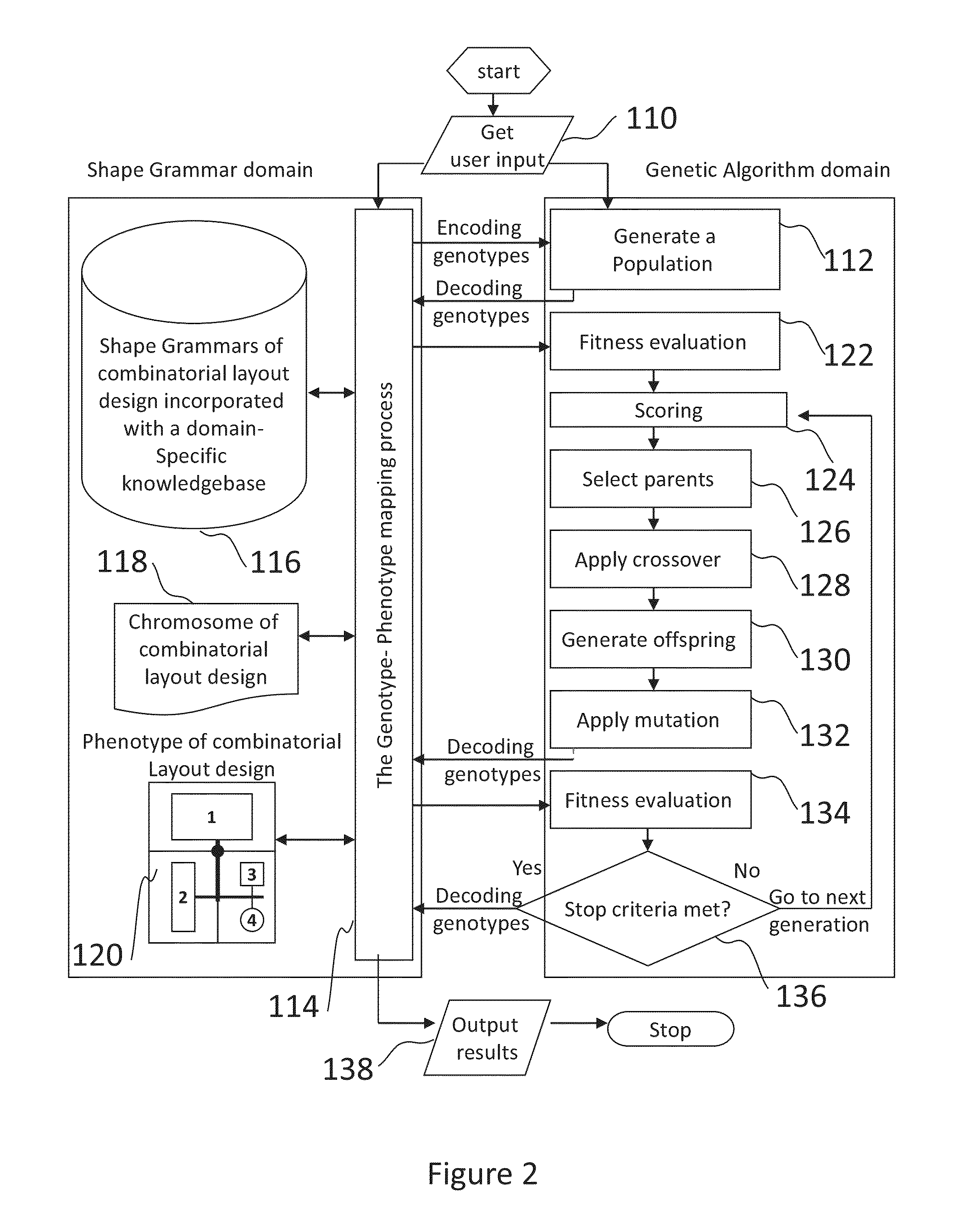
Method and system for combinatorial layout design
InactiveUS9317626B2Quality improvementShorten the timeMulti-objective optimisationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmGenetics algorithms
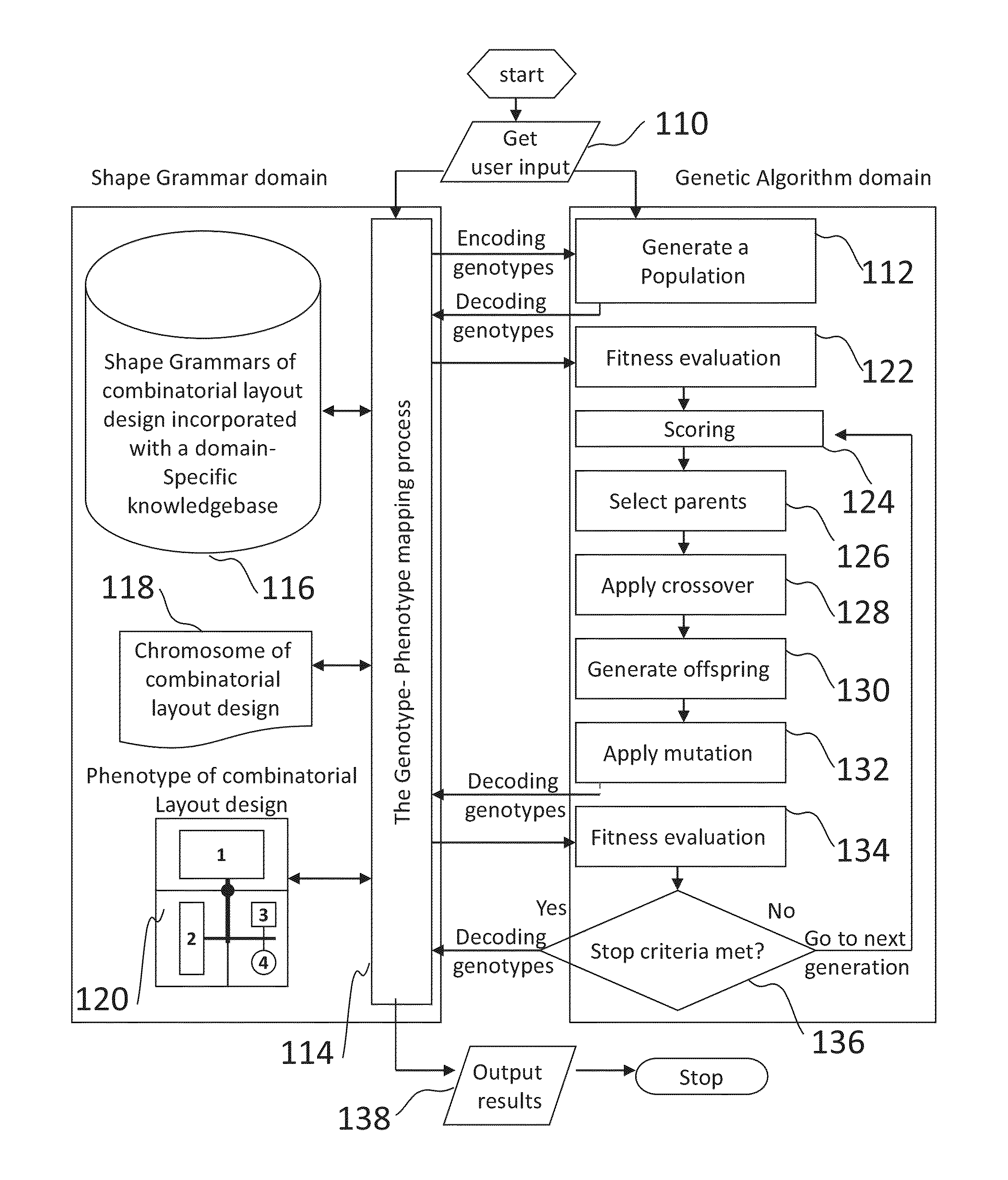
The present invention discloses a method for combinatorial layout design, in particular family mold layout design, using a computer. The method starts with receiving design specific parameters and information about molding parts from user. A Genetic Algorithm module is then invoked to generate a population of layout designs which satisfies the design specific parameters. The Genetic Algorithm module first automatically generates a population of specially designed chromosome with three interdependent sessions. Crossover, mutation and replacement operation are applied on the population subsequently to evolve such towards a more optimal population over successive generations. In each generation step, a Genotype-Phenotype mapping module is utilized to decode the chromosome to corresponding layout design for fitness evaluation. A system for combinatorial layout design automation and optimization using this evolutionary design approach is also disclosed in the present invention.
Owner:CHAN WAI MAN
Method for selecting broadcast routing path using genetic algorithm in Ad-hoc network
ActiveUS7613165B2Minimize consumptionMinimize the numberPower managementInformation formatAlgorithmGenetics algorithms
Provided is a method for selecting a broadcast routing path using a genetic algorithm in an Ad-hoc network. In the method, a plurality of nodes of the Ad-hoc network is defined as one chromosome, and the chromosome is represented with pairs of {order, power} in each node. Child nodes are created by performing an order based crossover and a power based crossover with respect to parent nodes neighboring to a source node. A mutation operation is performed with respect to the parent nodes and the child nodes. Relay nodes are determined by converting order and power information of each node of the chromosome into routing tree information. Power of the relay nodes is determined. A broadcast routing path is selected using the number and power of the relay nodes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Self-crossover genetic algorithm for solving flexible job-shop scheduling problem
InactiveCN106610653ADiversity guaranteedExcellent genesProgramme total factory controlAlgorithmJob shop scheduling
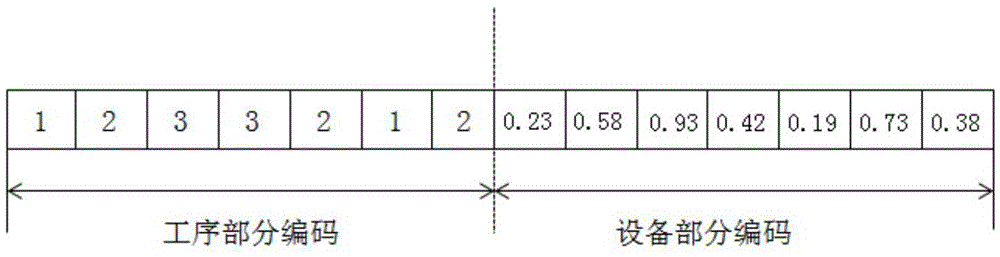
The invention provides a self-crossover genetic algorithm for solving a flexible job-shop scheduling problem. The algorithm relates to the field of job-shop scheduling, and particularly relates to the field of flexible job-shop scheduling. The existing genetic algorithms are mostly amphilepsis, the coding mode is complex, crossover and variation are caused to be complex, and a non-feasible solution is easy to acquire. The invention provides monolepsis-based self-crossover whose coding, crossover and variation are performed on a uniparental chromosome. The coding uniparental chromosome is divided into a working procedure portion and an equipment portion, wherein the working procedure portion is coded based on the workpiece number, and the equipment portion represents selected equipment by using the probability. Self-crossover is performed on the working procedure portion, and the equipment portion also performs the same crossover transform along with the working procedure portion. Two types of variation operators are adopted, exchange type variation is adopted for the working procedure portion, and insertion type variation is adopted for the equipment portion. The self-crossover genetic algorithm provided by the invention has the characteristics of high practicability and wide application range.
Owner:SICHUAN YONGLIAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
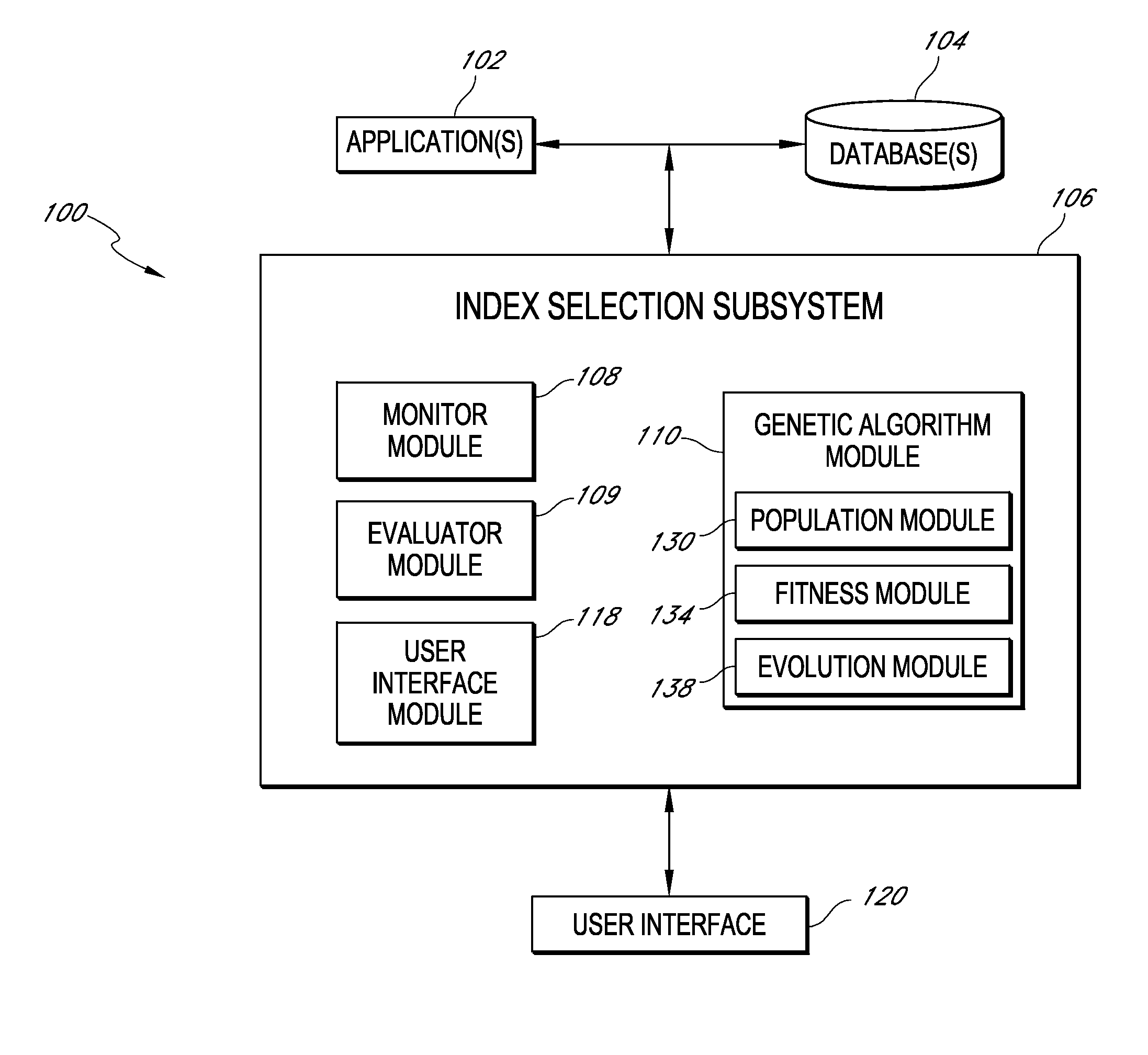
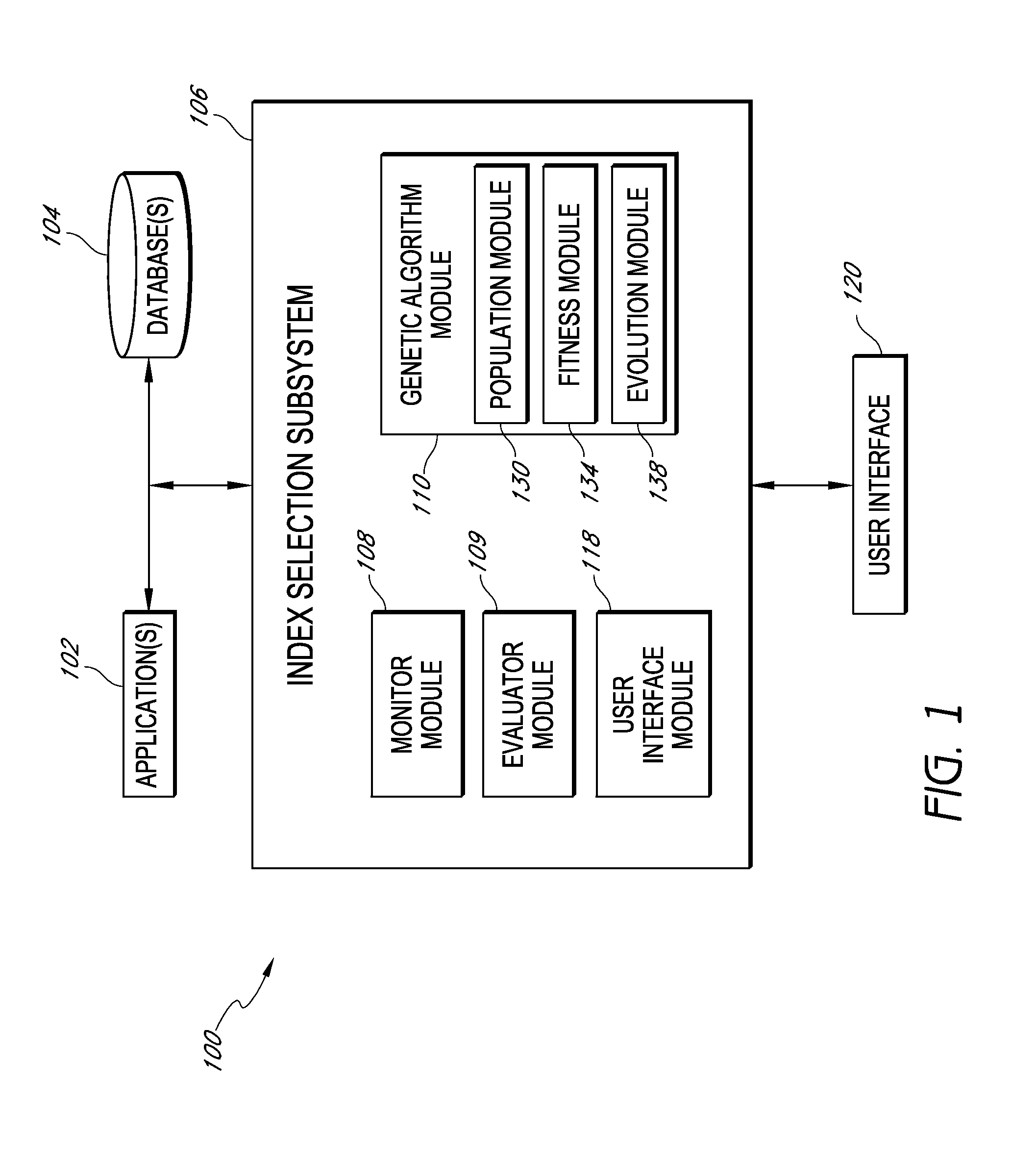
Systems and methods for index selection in collections of data
ActiveUS8499001B1Improve performanceShorten the timeDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesData set
Systems and methods are disclosed that utilize a genetic algorithm to search for an index configuration for a collection of data such as, e.g., a database. Genetic algorithms can include stochastic search heuristics that mimic processes of natural evolution including inheritance, mutation, crossover, and selection. A population of chromosomes representing candidate index configurations can evolve to increase or optimize the fitness of the population and to identify the best (e.g., most fit) index configuration. Fitness of a chromosome may be measured based at least in part on the cost of computer resources used for executing Structured Query Language (SQL) statements in the indexed database. In various implementations, virtual indexing may be used to simulate building an index, chromosomes may be encoded using non-bitmapped representations of index configurations, chromosomes may include genes representing a column in a table in a database, dropping an index from a table in a database, or a composite index for a database, and / or a participation pool may be used to select fitter genes for an initial population of chromosomes.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
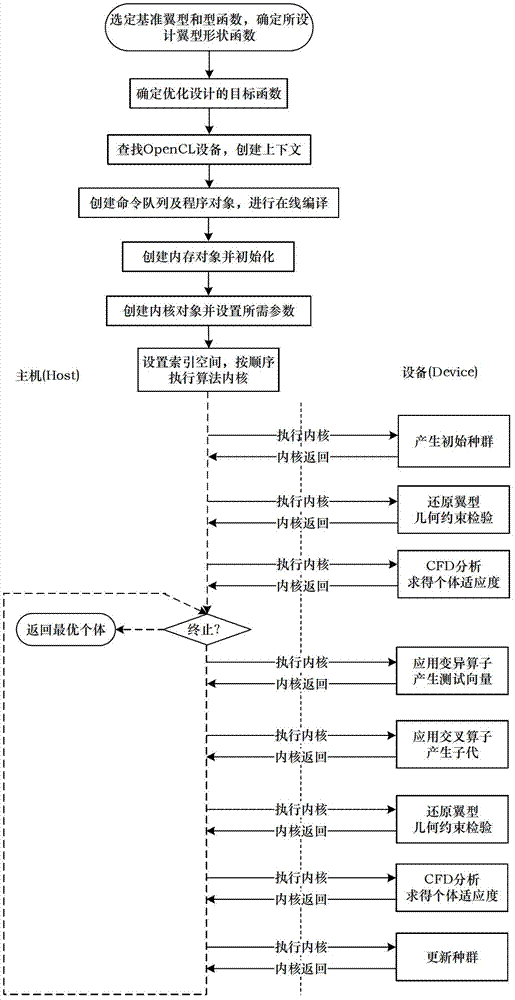
Wing profile optimal design method of parallel difference evolutionary algorithm based on open computing language (Open CL)
InactiveCN102779207AImprove design efficiencyReduce computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsMutation operatorParallel processing
The invention provides a wing profile optimal design method of a parallel difference evolutionary algorithm based on open computing language (Open CL). The wing profile optimal design method is used for wing profile design. A standard wing profile function and a profile function are selected, the profile function serves as a design variable, an optimization objective function is determined, steps of the difference evolutionary algorithm are divided into different stages according to processed data, and all stages are packaged in different cores for operating based on Open CL. In population updating, mutation operators are used for generating test vectors and crossover operators are used for generating descendants; individuals in a population are restored to the wing profile shape and tested whether to meet geometric constraint; computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis is used for obtaining fitness of the individuals and seeking the optimum individual, and whether the optimum individual meets performance constraint is tested; and finally iteration is finished and the optimum result is copied back into a host internal storage. The wing profile optimal design method achieves parallel processing of a wing profile design process, performs sufficient search in effective space, shortens design period, achieves cross-platform wing profile optimal design, and improves design efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
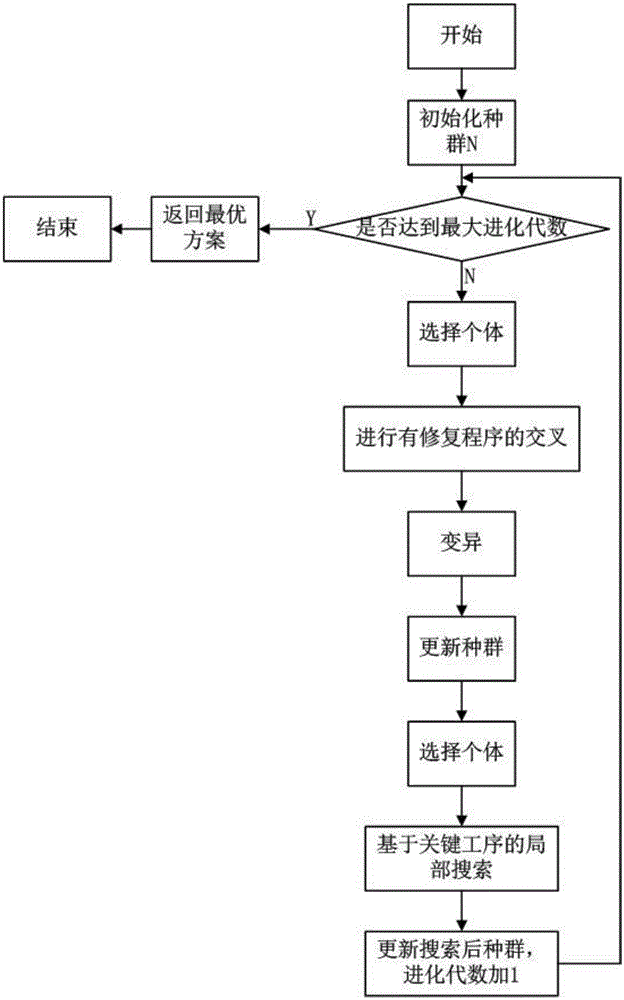
Critical process-combined genetic local search algorithm for solving flexible job-shop scheduling
InactiveCN106611230AGuaranteed feasible solutionTotal completion time is smallForecastingResourcesPopulationGenetic algorithm
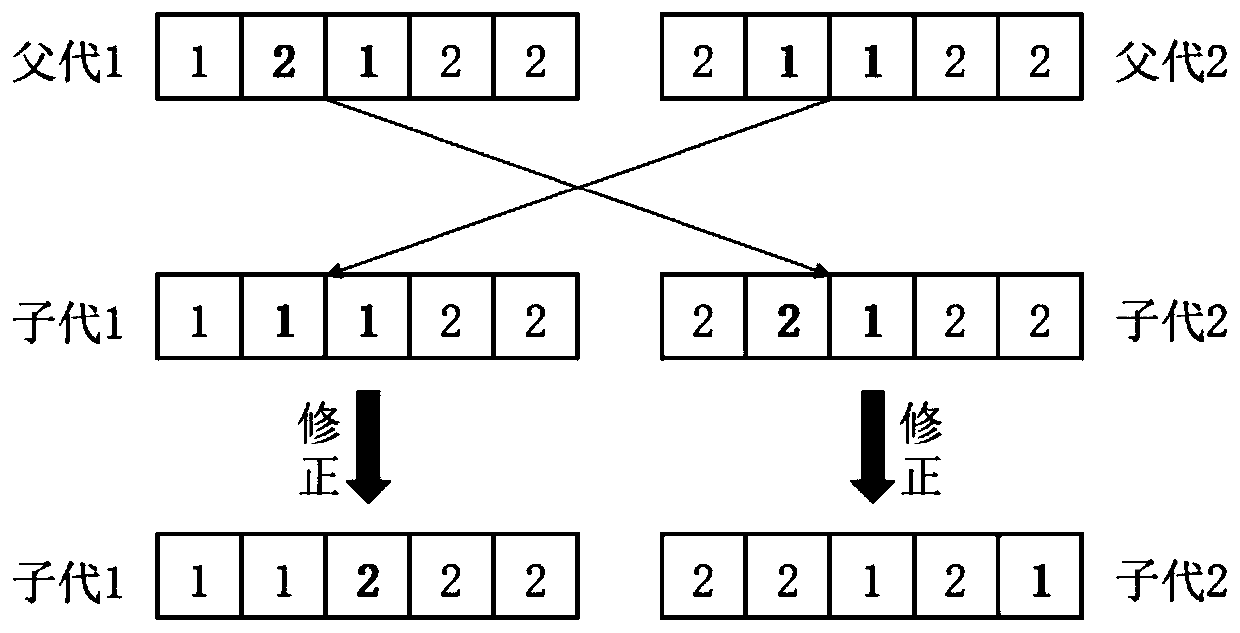
The invention provides a critical process-combined genetic local search algorithm for solving flexible job-shop scheduling and aims at solving the problems that an infeasible solution can be generated by a genetic algorithm in an operation and the solving result is unstable to cause insufficient local search capability due to the randomness of local search in the prior art. The disadvantages are overcome by combining the methods of a cross repairing procedure, a critical process-based local search method and the like. According to the genetic local search algorithm, a novel vector-based encoding mode is adopted when populations are initialized, a gene repairing procedure is carried out during crossover operation of the genetic algorithm and the search range is controlled by adopting critical process-based search. The flexible job-shop scheduling problem can be solved, and the genetic local search algorithm has the characteristic of high practicability.
Owner:SICHUAN YONGLIAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
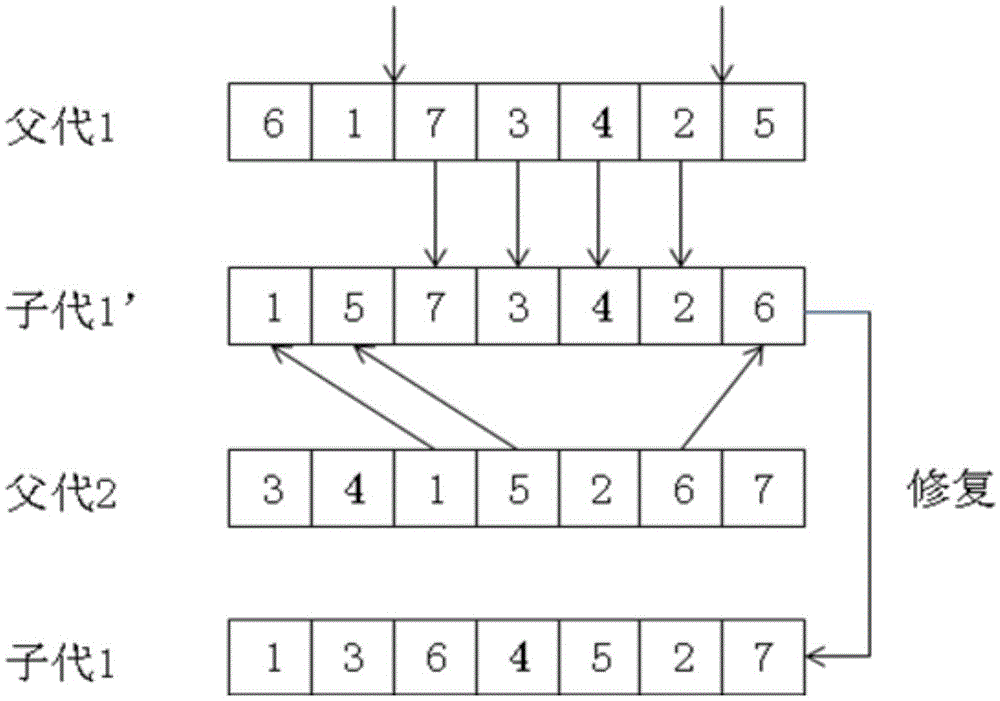
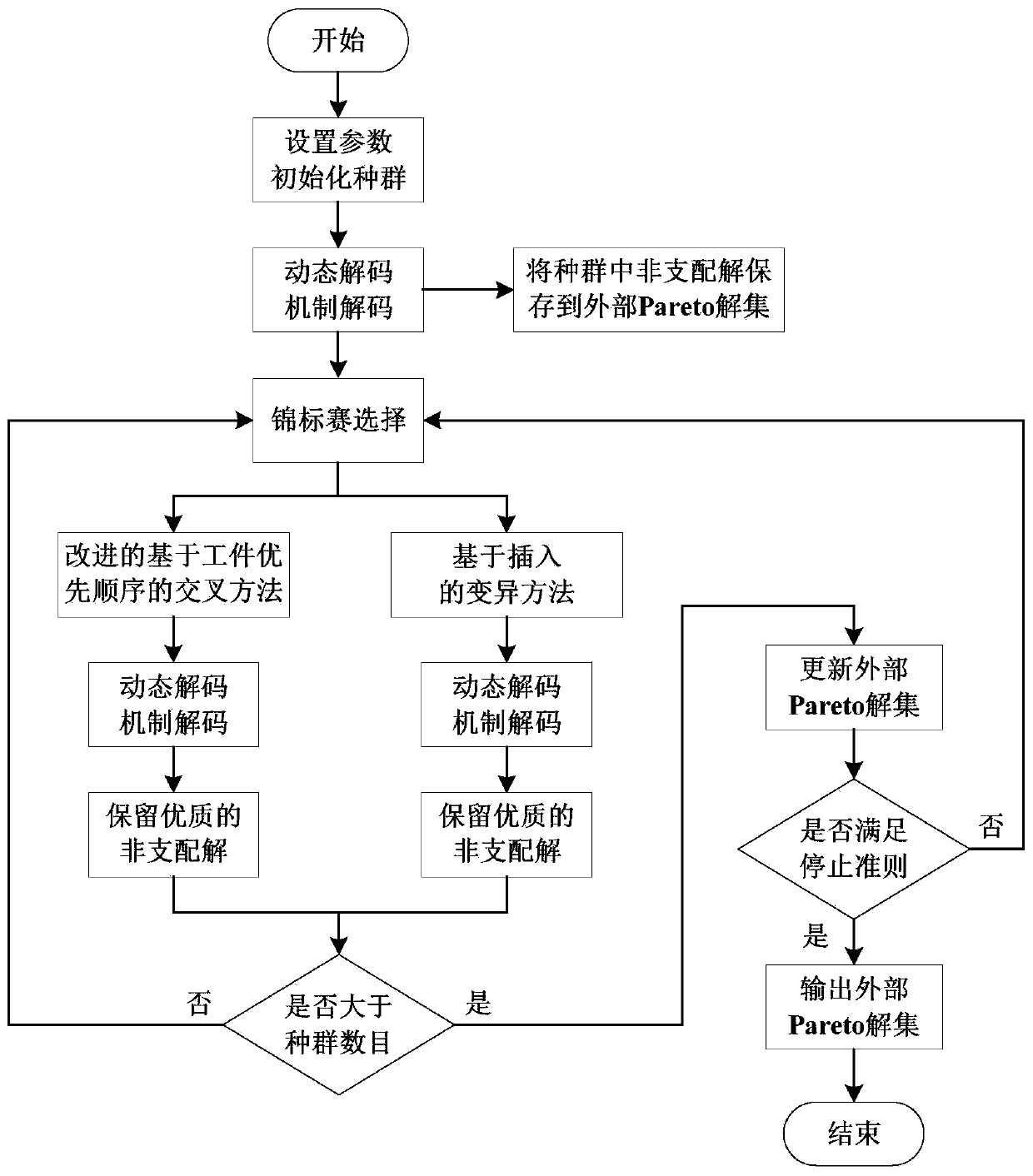
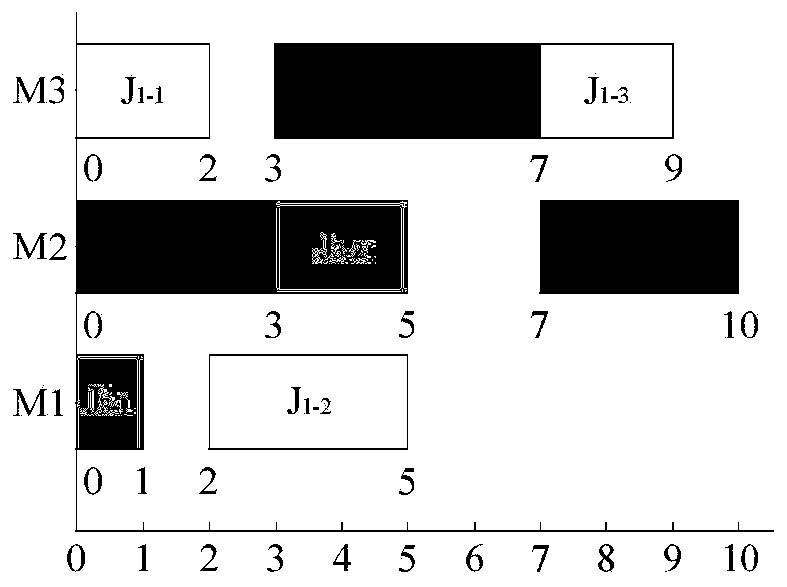
Flexible job shop scheduling method based on dynamic decoding mechanism
PendingCN110796355ARich non-dominated solutionDesign optimisation/simulationResourcesJob shop schedulingImproved algorithm
The invention discloses a flexible job shop scheduling method based on a dynamic decoding mechanism. The invention relates to the technical field of flexible job shop scheduling. According to the flexible job shop scheduling method based on the dynamic decoding mechanism, improved MOGA is adopted for solving, and an improved workpart-priority-based crossover method, an insertion variation method and an initialized population strategy are integrated, so that optimal design of multi-target flexible job shop scheduling is completed. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: 1) modeling; the method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a dynamic decoding mechanism, (2) initializing a population, (3) carrying out genetic manipulation, and (4) updating an external Pareto solution set, and proving that after the dynamic decoding mechanism is applied, an improved algorithm can obtain richer non-dominated solutions and higher-quality non-dominated solutions,and then the optimal design of multi-target flexible job shop scheduling is completed.
Owner:JIANGSU JINLING INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG CO LTD
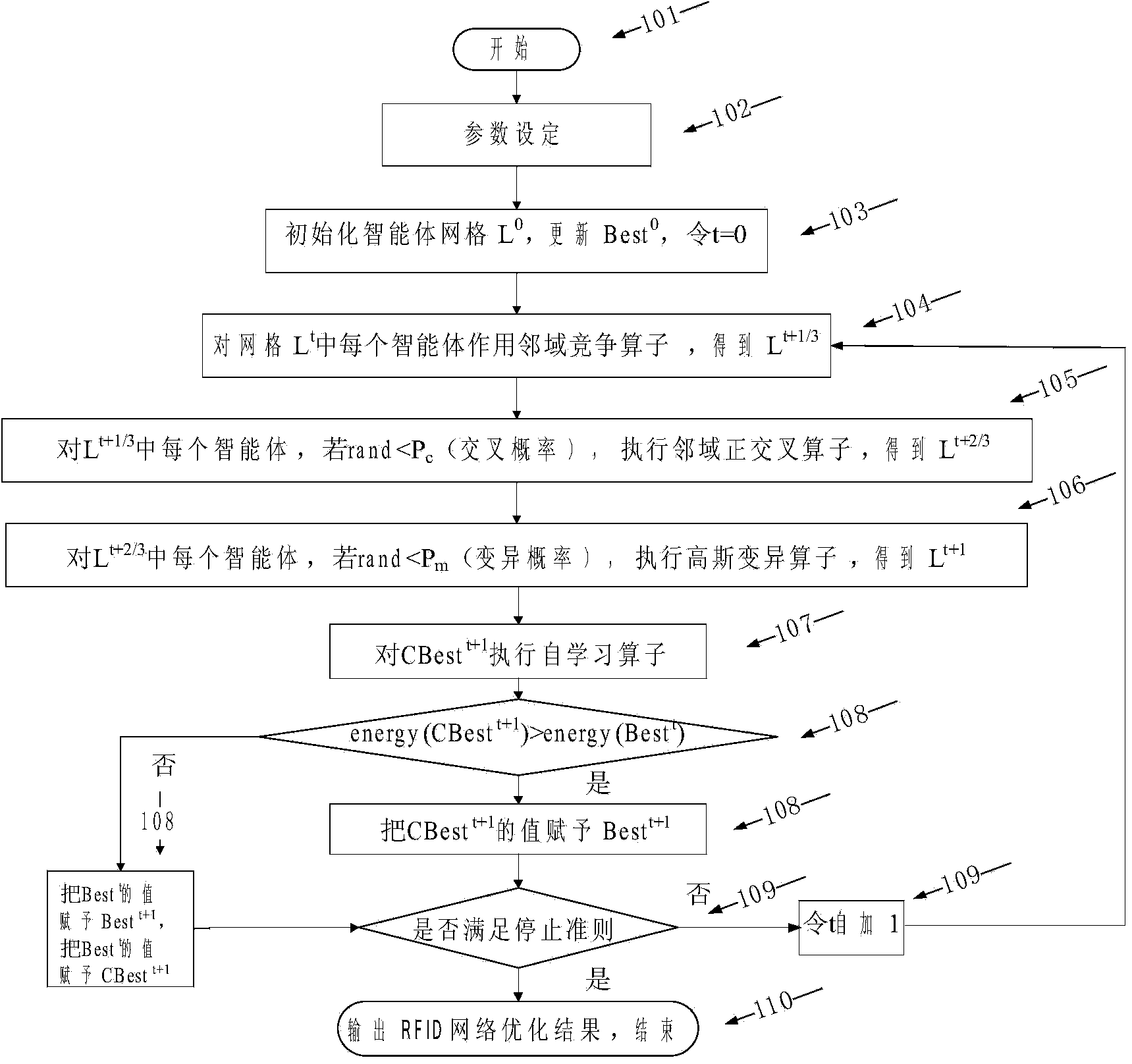
RFID network topology method based on multi-agent evolutionary algorithm
ActiveCN103729680ASmall population sizeFast stabilityGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAutomatic controlMutation operator
The invention discloses an RFID network topology method based on the multi-agent evolutionary algorithm and belongs to the field of automatic control and information technology. The method combines a multi-agent system with evolutionary computation to solve the RFID network topology problem. The method is characterized in that each agent in an agent grid is initialized according to two algorithms, and then a neighborhood competition operator, a neighborhood right-angled crossover operator, a mutation operator and a self-learning operation are designed to optimize the agents. Verification results show that the method has great advantages in terms of solving the maximum coverage rate of reader-writers, the minimum number of the reader-writers and the minimum interference rate of the reader-writers when used for evaluating and solving the RFID network topology problem and is an effective method for solving the RFID network topology problem.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for predicting subsidence of soil outside pit based on differential evolution support vector machine
InactiveCN103198215AAvoid disasterSpecial data processing applicationsCurve fittingSafety monitoring
The invention discloses a method for predicting subsidence of soil outside a pit based on a differential evolution support vector machine. The method comprises collection of the subsidence of on-site soil outside the pit, determination of a rough change rule of data to be a tangent curve, tangent fitting on subsidence data through differential evolution (DE), reasonable selection method of a scaling factor F and a crossover probability Cr of the DE, determination of a decision function of the support vector machine (SVM), simulation of generation of the subsidence data, evaluation and the like. The method comprises the following steps: through the DE, determining the basic form of a subsidence function for the soil outside the pit according to the subsidence data, and then performing parametric inversion; taking an obtained analytic function as the decision function of the SVM, and performing kernel function conversion on the decision function by the SVM; and finally, performing fitting prediction through the SVM, and detecting data conformity. Through the subsidence data of the on-site soil and the subsidence prediction simulation, curve fitting of the SVM is quicker and the prediction is more accurate; and the method can be widely applied to safety monitoring on foundation pit construction.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for optimizing multi-grade light-splitting passive optical network of distribution communication network
ActiveCN104618134AGood effectCommunication construction costs are minimizedMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksComputation complexityMathematical model
The invention relates to a method for optimizing a multi-grade light-splitting passive optical network of a distribution communication network. The method is that the network at the current grade bears the gene optimization result of the network at the previous grade through the cascading genetic algorithm. The method specifically comprises the steps of designing a gene code; creating constraint conditions for the gene code, and selecting adaptability functions; performing crossover and variation operation for the gene code on the premise that the constraint conditions for the gene code are met; performing multi-generation iterative crossover and variation operation to obtain the optimal gene code of the PON network at the current level; returning to step (1) to bear the gene code of previous level when the number of the network layers of the multi-grade light-slitting passive optical network is less than n, and updating the adaptability function; finishing the optimization when the number of the network layers of the multi-grade light-slitting passive optical network is more than 1. According to the method, the optimal light splitter and relatively high network star topology in the network are selected from the optimized multi-grade light-splitting network, and therefore, the network communication construction cost is saved; the network planning is constructed into a mathematical model, thus the expandability is improved, and the calculation complexity is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
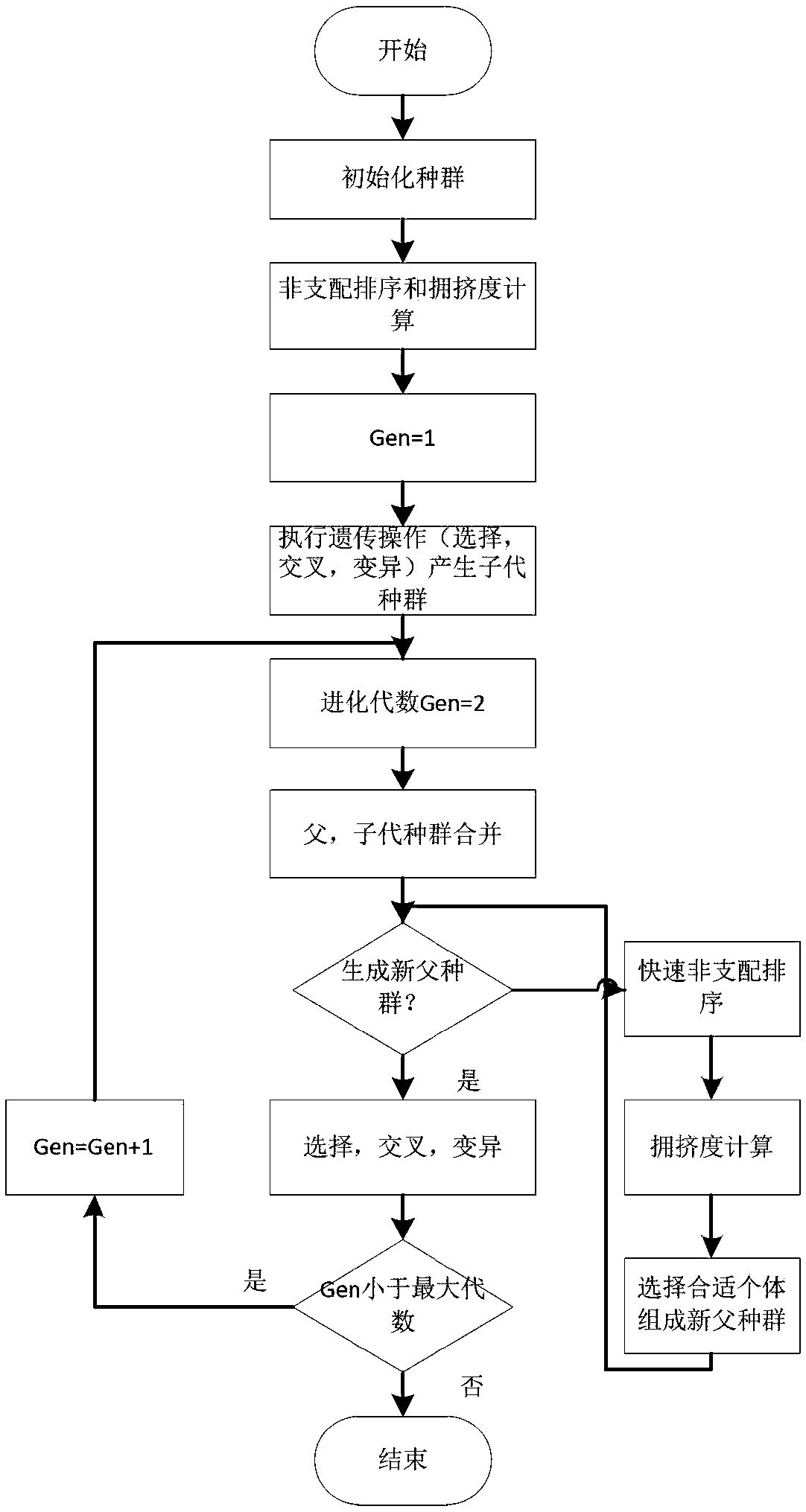
Improved NSGA-II algorithm-based modular scheduling method of emergency response materials
ActiveCN107730056AImprove completenessImprove the distribution effectForecastingArtificial lifeModularityChild population
The invention discloses an improved NSGA-II algorithm-based modular scheduling method of emergency response materials. The method includes: 1, generating an initial population and genetic variables thereof according to constraint conditions; 2, carrying out crossover and heredity on the population to generate a child population; 3, merging the parent population and the child population, and carrying out fast non-dominated sorting on a merged population; 4, calculating a chromosome neighborhood set, and adopting an elimination mechanisms to select a new parent population; 5, repeating the step2, the step 3 and the step 4 until maximum iteration frequency is reached; and 6, selecting all non-dominated solutions of a population to use the same as optimal scheduling schemes. According to themethod, the optimal schemes of modular scheduling of the rescue materials can be obtained, thus rescue costs can be reduced, rescue efficiency can be improved, and timely effective developing of rescue work can be guaranteed.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Multi-target flexible job shop scheduling method based on double-layer genetic algorithm
ActiveCN111242503AExcellent non-dominated solution setOptimizing Crossover StrategiesResourcesManufacturing computing systemsAlgorithmGenetics algorithms
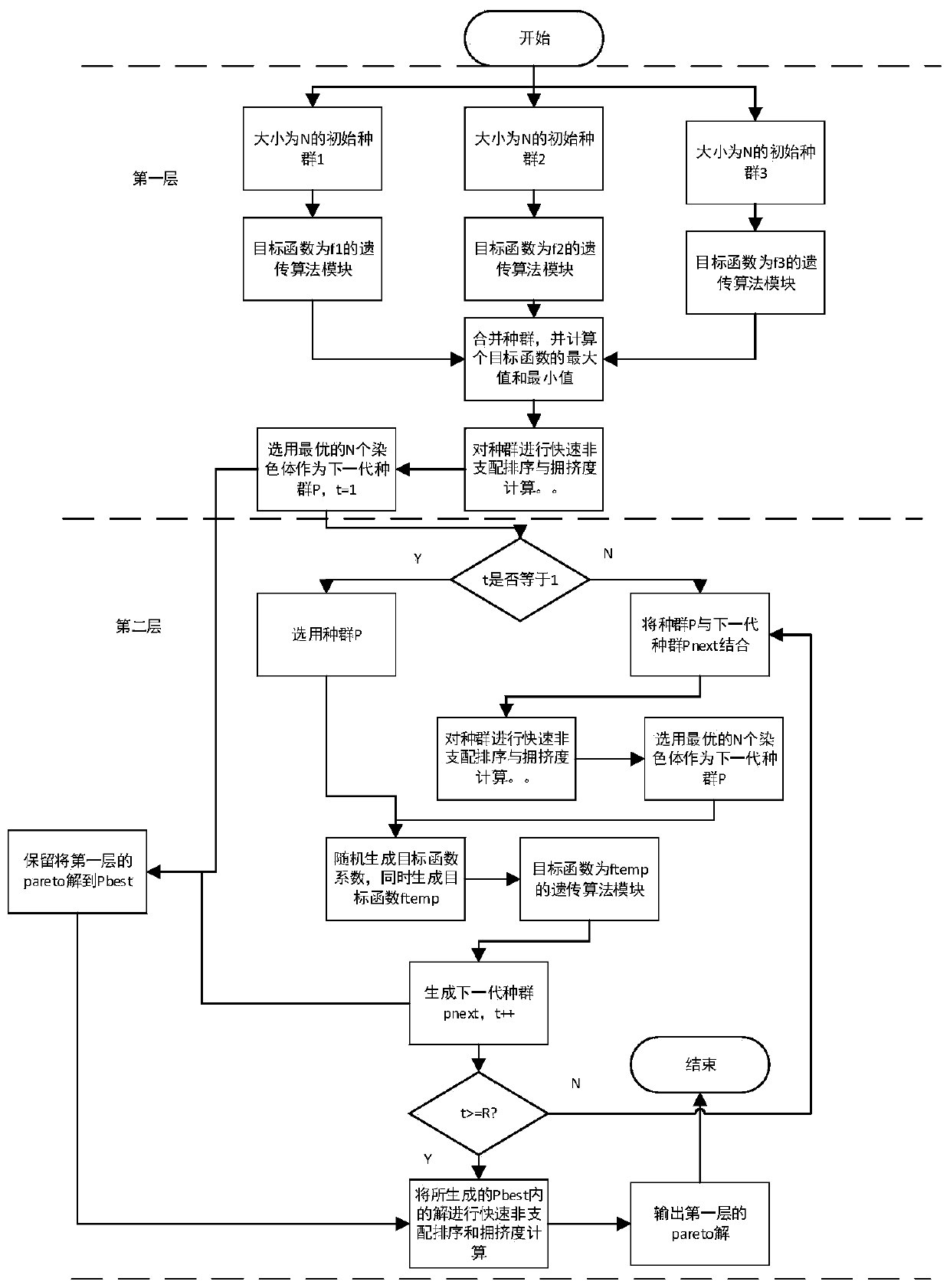
A multi-target flexible job shop scheduling method based on a double-layer genetic algorithm is characterized in that a traditional genetic algorithm is improved, so that a population optimized by thegenetic algorithm within limited time has high quality; meanwhile, the solving mode of the traditional genetic algorithm for the multi-target problem is changed, a double-layer solving framework is provided, and compared with the traditional genetic algorithm, the solving quality is obviously improved. According to the method, the crossover strategy and the mutation strategy are optimized, and the selection operator is deleted. The improved genetic algorithm is combined with a rapid non-dominated sorting and congestion degree calculation module, a special process framework is designed for theimproved genetic algorithm, and the improved genetic algorithm is called as a double-layer genetic algorithm. According to the algorithm, an excellent non-dominated solution set can be obtained within limited time, and the algorithm has good practicability and can be well applied to actual workshop scheduling.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
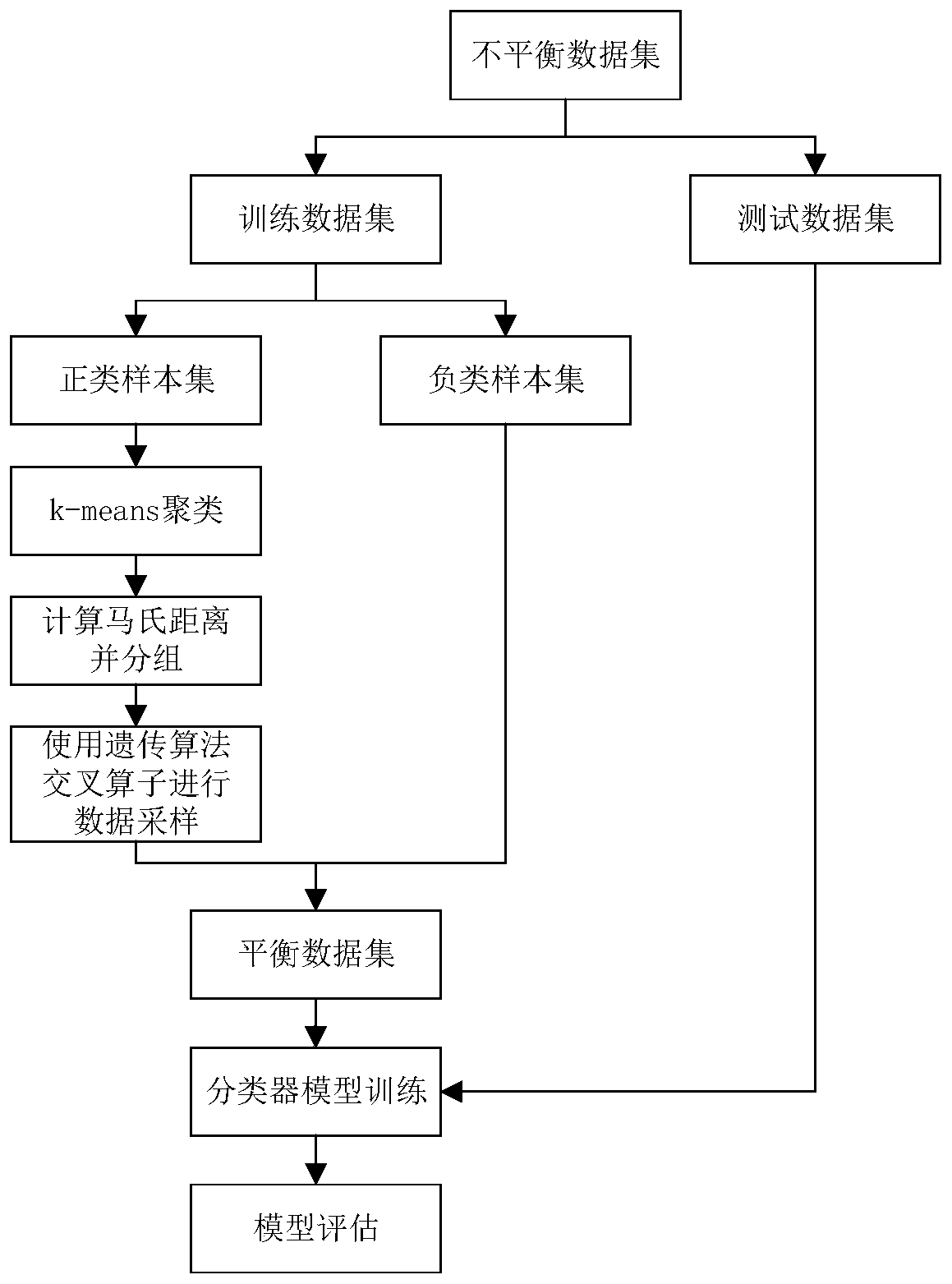
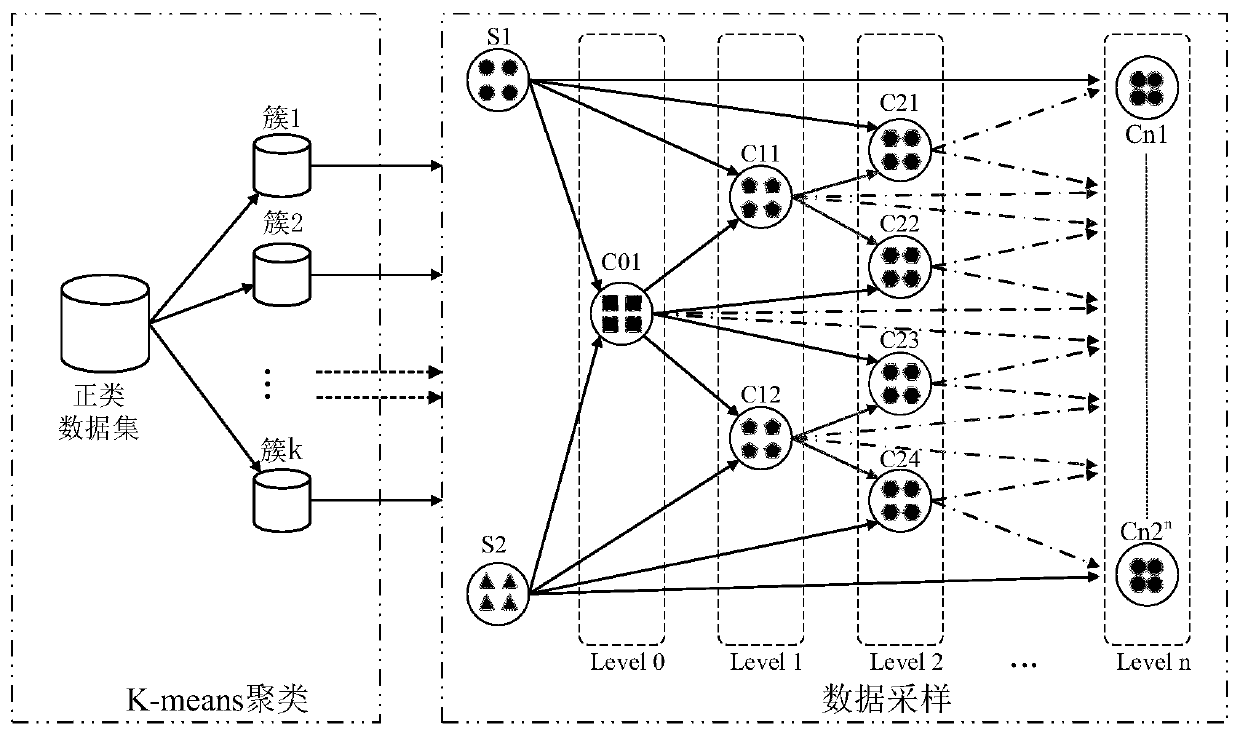
Unbalanced data set oversampling method based on genetic algorithm and k-means clustering
PendingCN110674846AImprove recognition rateAvoid the impact of dimensions between different attributesCharacter and pattern recognitionGenetic algorithmsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses an unbalanced data set oversampling method based on a genetic algorithm and k-means clustering, and the method comprises the following steps: inputting an original unbalanced data set, and dividing the unbalanced data set into a training data set and a testing data set; dividing the training data set into a positive class sample set and a negative class sample set; clustering the positive class sample set by using a k-means clustering algorithm to obtain a plurality of different clusters; allocating corresponding sampling weights to the number of samples in each cluster; calculating the Mahalanobis distance of the sample data in each cluster, and dividing the sample data into two groups of parent class sample data sets according to the Mahalanobis distance; according to a crossover operator in the genetic algorithm, forming a new positive class sample by by utilizing the parent class sample data set; combining the newly synthesized positive class sample and theoriginal training data set into a balanced data set; training a classifier model by utilizing the balance data set; and evaluating the performance of the classifier model by utilizing the test data set. According to the method, the classification accuracy of the classifier model on the positive samples in the unbalanced data set can be effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cloud task scheduling method based on phagocytic particle swarm genetic hybrid algorithm
ActiveCN110851272ADiversity guaranteedExpand your searchProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationCompletion timeAlgorithm
The invention discloses a cloud task scheduling method based on a phagocytic particle swarm genetic hybrid algorithm. The method includes: in order to solve the task scheduling problem in the cloud environment, changing a position and speed updating mode in a standard particle swarm algorithm, respectively carrying out primary division and secondary division on each generation of individuals of the particle swarm by utilizing a fitness function and a load balancing standard deviation, and respectively carrying out phagocytic variation and crossover variation operations on different finally divided particle sub-populations to obtain a cloud task scheduling scheme. Through simulation experiments, the cloud task scheduling method provided by the invention is compared with other several existing cloud task scheduling methods; the result shows that the method provided by the invention obviously shortens the overall completion time of the cloud task, has higher convergence precision, and proves the effectiveness of the cloud task scheduling method based on the phagocytosis particle swarm genetic hybrid algorithm.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Batch scheduling optimization method based on deep reinforcement learning and genetic algorithm
ActiveCN112488315AQuality improvementImprove generalization abilityForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmBatch machine
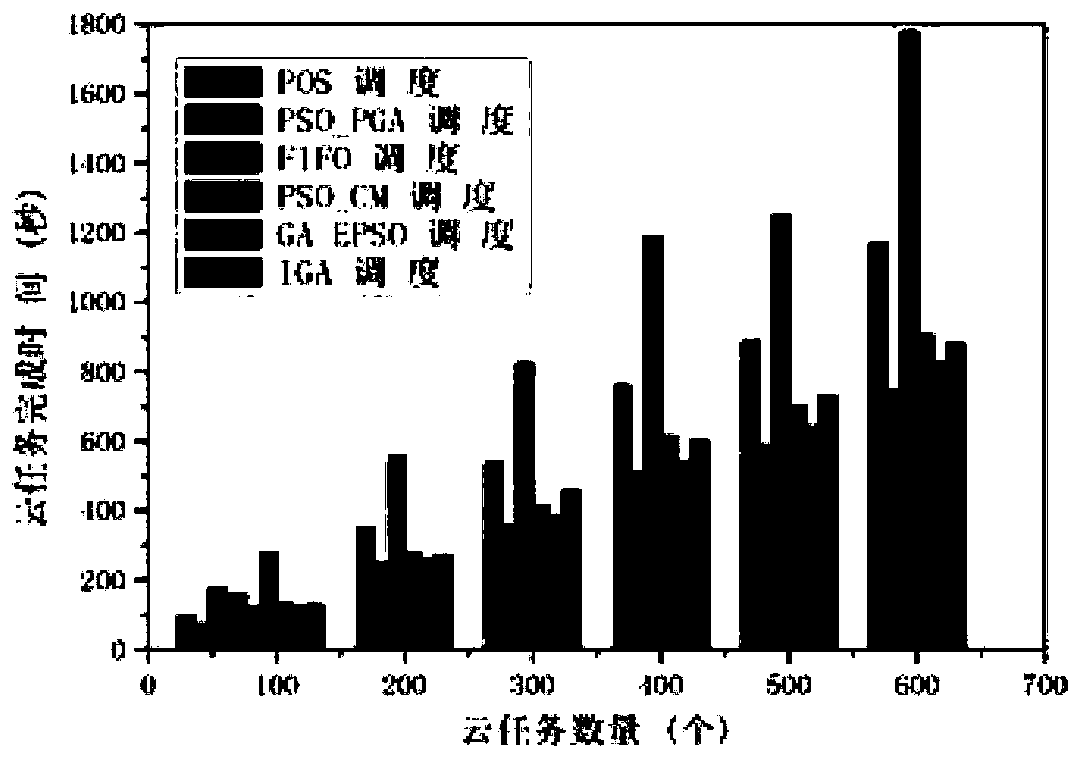
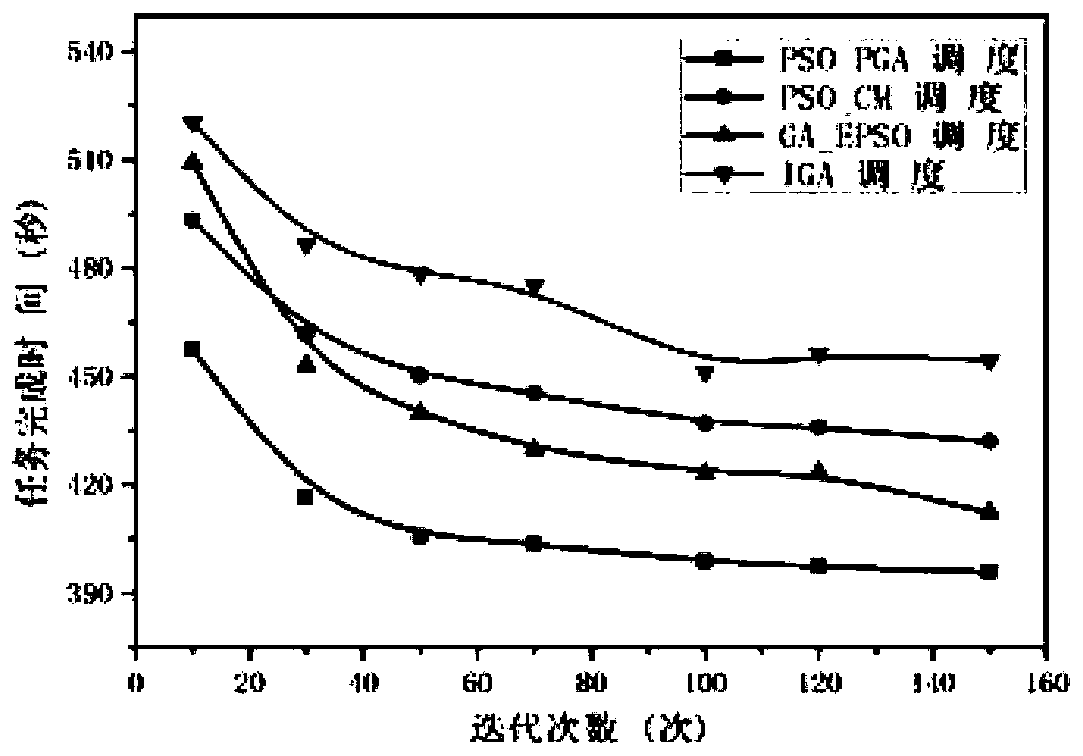
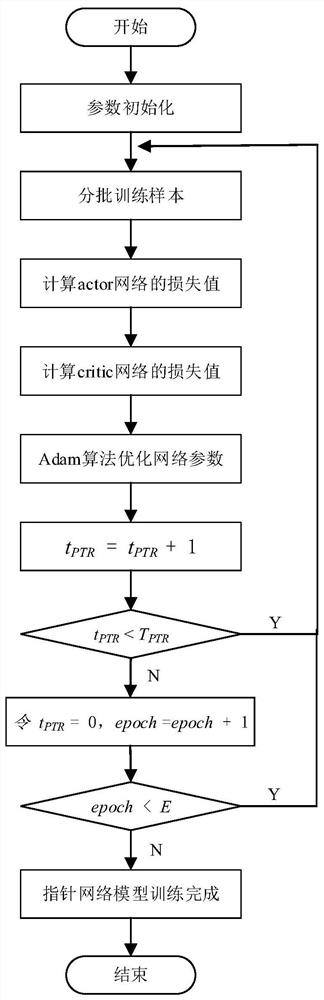
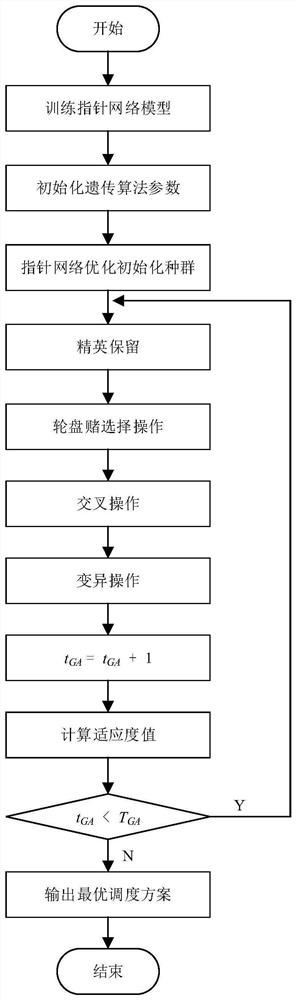
The invention belongs to the field of production and manufacturing scheduling, and discloses a batch scheduling optimization method based on deep reinforcement learning and a genetic algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: building a mathematic model of a difference workpiece batch scheduling problem; establishing a strategy model of the problem by adopting a pointer network; training a pointer network model by using an actor-critic algorithm; defining and initializing parameters of a genetic algorithm; optimizing the initial population of the genetic algorithm by using the trained pointer network; further optimizing the scheduling scheme by adopting a genetic algorithm; and the optimal scheme obtained by the genetic algorithm being used as a production scheme for processing workpieces by the batch processor. Compared with a traditional heuristic algorithm, the pointer network can obtain a better solution; in addition, in the crossover operation of the genetic algorithm, a novelcrossover mode is provided, and the performance of the scheme can be further improved by improving the optimization capability of the genetic algorithm on the basis of the scheduling scheme obtainedby the pointer network.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
BP neural network wind speed prediction method based on genetic algorithm optimization
PendingCN111160520ASolve difficult-to-converge phenomenaImprove computing efficiencyForecastingNeural architecturesSimulationEngineering
The invention discloses a BP neural network wind speed prediction method based on genetic algorithm optimization. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting wind speed data of a wind power plant, establishing a BP neural network prediction model, and estimating an initial value range; then, performing real number coding on the weight and the threshold of the neural network, randomly generating a group of initial individuals to form an initial population, and each initial individual represents an initial solution of a problem; calculating the fitness of each individual in thepopulation, performing selection, crossover and mutation operations to form a next generation of population, evaluating the fitness of the individuals in the new population, judging convergence conditions, selecting an optimal individual, and taking the optimal individual as an initial weight and a threshold of the neural network; and finally, training by utilizing matlab to obtain a wind speed prediction value. According to the method, the wind speed prediction efficiency and accuracy of the BP neural network are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-target flexible job shop scheduling method based on improved ecological niche genetic algorithm
ActiveCN111222642AImplement schedulingSolve fitResourcesManufacturing computing systemsAlgorithmGenetics algorithms
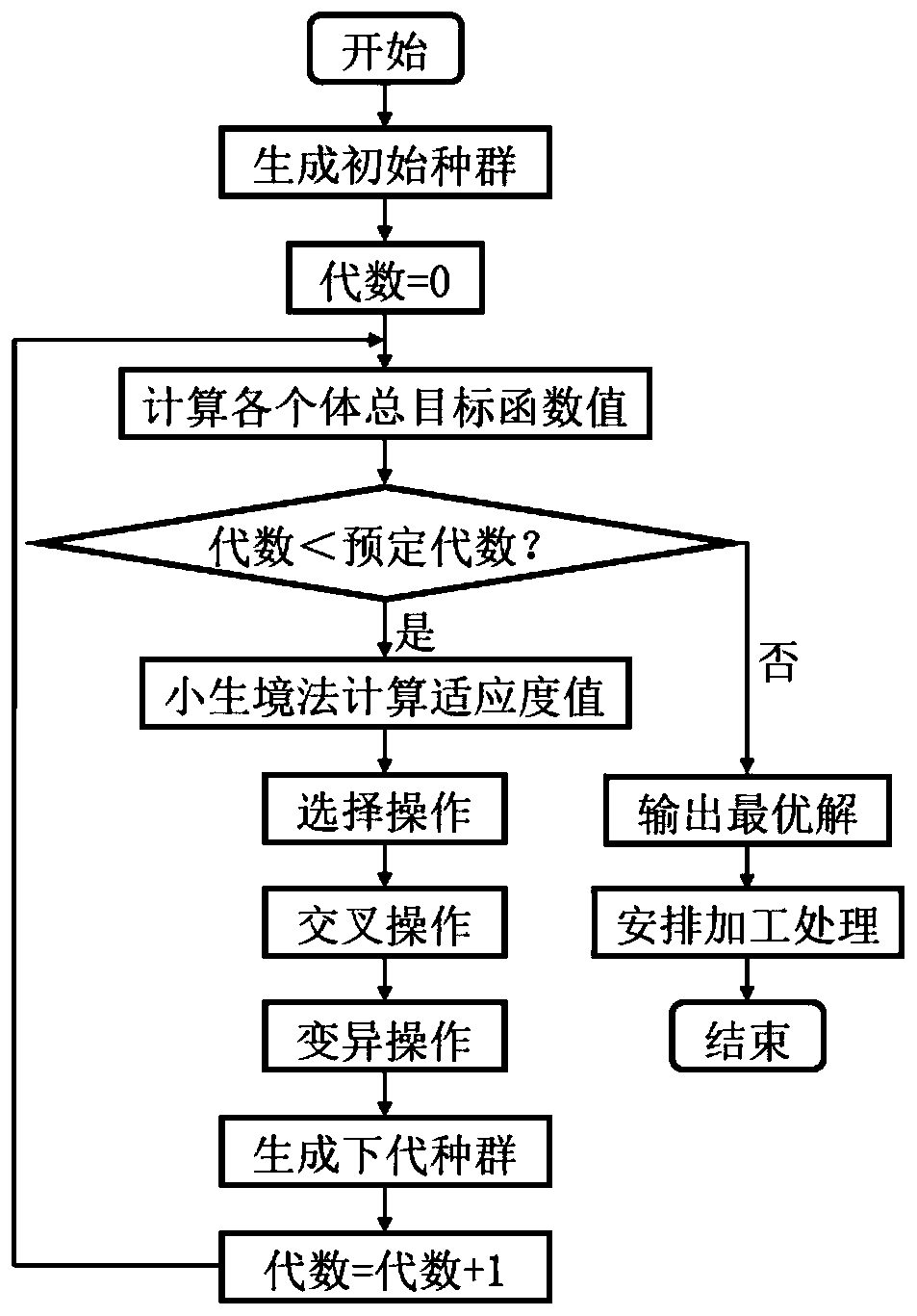
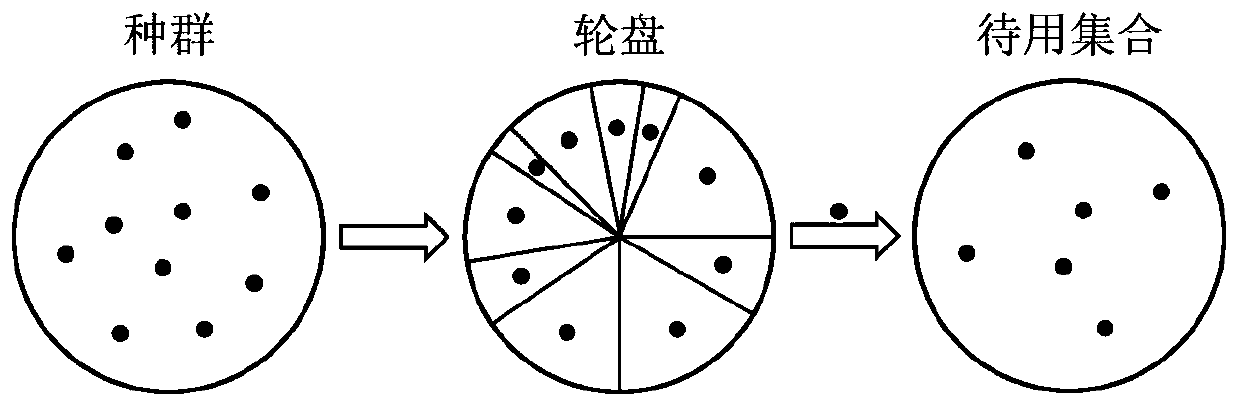
The invention discloses a multi-target flexible job shop scheduling method based on an improved niche genetic algorithm. Constructing a production scheduling sequence according to the process data ofall the workpieces in the multi-target flexible job shop, taking the production scheduling sequence as an individual, and generating a primary population; calculating a total objective function valueof the individual, and calculating a fitness value of the individual by using an improved niche method; selecting an individual set in a roulette mode according to the fitness value; implementing crossover operation and mutation operation of the genetic algorithm; forming a new population by the obtained individuals and the individuals with the highest fitness value in the generation population; repeating the steps until a termination condition is met, outputting an optimal individual in the last generation population, and arranging processing treatment by adopting a scheduling sequence of theoptimal individual, so as to realize multi-target flexible job shop scheduling. The improved ecological niche genetic algorithm is adopted to solve the scheduling problem in the production process, ahigh-quality scheduling result can be stably obtained, workshop resource allocation is optimized, and therefore the production efficiency of a workshop is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Construction project multi-objective optimization method
InactiveCN111062119AResolve ambiguityImprove engineering applicabilityDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationMulti objective optimization algorithmAlgorithm
The invention provides a construction project multi-objective optimization method. The construction project multi-objective optimization method comprises the following steps: determining a mathematical model and genetic algorithm parameters of multi-objective optimization; establishing a population with feasible constraints and a population target function matrix; calculating an objective weight of the target function by adopting an entropy weight method according to the target function matrix, and synthesizing a hybrid dynamic weight of the target function; sorting the population by adoptinga method based on dynamic weight to obtain a Pareto temporary solution set; attaching virtual fitness values to individuals according to population individual sorting, and selecting a filial generation population by adopting a proportional selection operator and a roulette method; performing crossover operation on the filial generation population; performing mutation operation on the filial generation population after the crossover operation; combining the Pareto temporary solution set with the filial generation population after mutation operation to generate a new population; and if the algorithm termination condition is met, terminating the algorithm, otherwise, returning. According to the method, the problem of ambiguity between an original multi-objective optimization algorithm and engineering application is well solved, and the method has better engineering applicability.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV +2
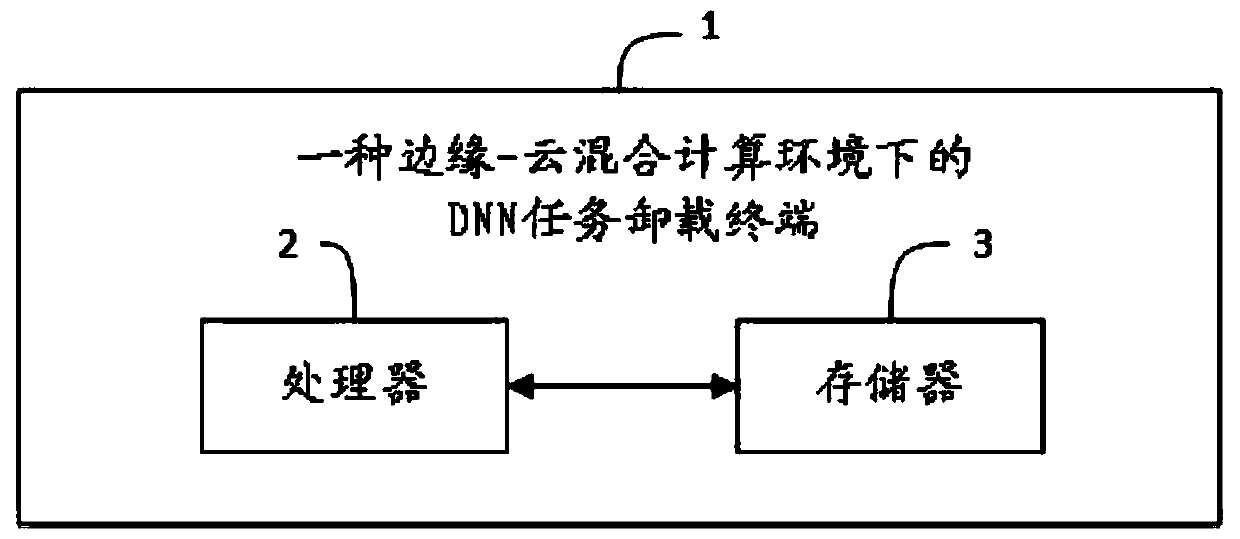
DNN task unloading method and terminal in edge-cloud hybrid computing environment
ActiveCN111399933AAccurately estimate costsLow costProgram loading/initiatingNeural architecturesLocal optimumAlgorithm
The invention provides a DNN task unloading method in an edge-cloud hybrid computing environment and a terminal. According to the types and the number of computing nodes, the number of DNN tasks to be unloaded and the number of layers of each DNN task to be unloaded, calculating the number of the DNN tasks to be unloaded; establishing a target function based on total cost minimization; determining a corresponding constraint condition. The influences of conditions such as computing power and time delay constraints of different types of nodes are considered, the feasibility of the obtained optimal solution is guaranteed, when the optimal solution is solved, crossover operation and mutation operation in the genetic algorithm are introduced into the particle swarm algorithm, a specific algorithm is given, and the problem that the particle swarm algorithm is prone to falling into local optimum in the optimal solution solving process is effectively solved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Calculation unloading method based on hybrid genetic algorithm in mobile edge calculation
PendingCN112181655AImprove search abilityResource allocationArtificial lifeTheoretical computer scienceGlobal optimal
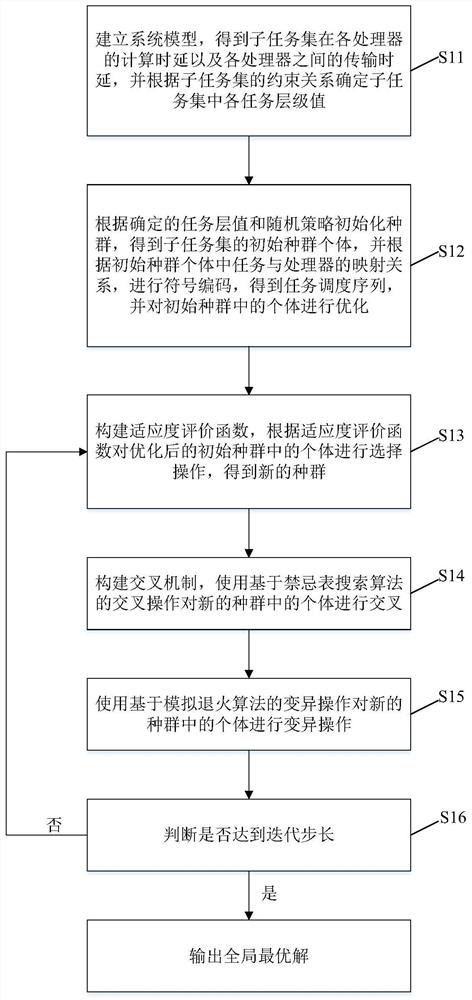
The invention discloses a hybrid genetic algorithm-based calculation unloading method in mobile edge calculation, which comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a system model to obtain calculation time delay of a sub-task set in each processor and transmission time delay among the processors, and determining each task layer value in the sub-task set according to a constraint relationship of the sub-task set; S2, initializing a population according to the determined task layer value and a random strategy to obtain initial population individuals of the sub-task set, performing symbol coding to obtain a task scheduling sequence, and optimizing the individuals in the initial population; S3, constructing a fitness evaluation function, and performing selection operation on individuals inthe optimized initial population; S4, constructing a crossover mechanism, and crossover individuals in the new population by using crossover operation based on a tabu table search algorithm; S5, performing mutation operation on individuals in the new population by using mutation operation based on a simulated annealing algorithm; and S6, judging whether the iteration step length is reached or not, and if not, repeating the step S3-S5; and if so, outputting a globally optimal solution.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Differential-evolution protein-structure head-beginning prediction method based on multistage sub-population coevolution strategy
ActiveCN106503486AIncrease diversityHigh precisionProteomicsGenomicsPredictive methodsSub populations
The invention discloses a differential-evolution protein-structure head-beginning prediction method based on the multistage subpopulation coevolution strategy. The differential-evolution protein-structure head-beginning prediction method includes the following steps that under a differential-evolution algorithm framework, the conformational space dimensionality is reduced through a Rosetta Score3 coarse-granularity knowledge energy model; an evolution population is divided into a plurality of subpopulations according to the similarity, coevolution is carried out on the subpopulations, and the individual diversity of the population can be improved; the evolutionary process is divided into three stages, different variation crossover strategies are adopted at different stages, and the premature convergence problem can be solved; the conformational space can be effectively sampled in cooperation with the high global searching ability of the differential-evolution algorithm, and the high-accuracy conformation close to the natural state is obtained through searching. Based on the differential-evolution algorithm, the differential-evolution protein-structure head-beginning prediction method based on the multistage subpopulation coevolution strategy is low in conformational space searching dimension and high in convergence speed and prediction accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com