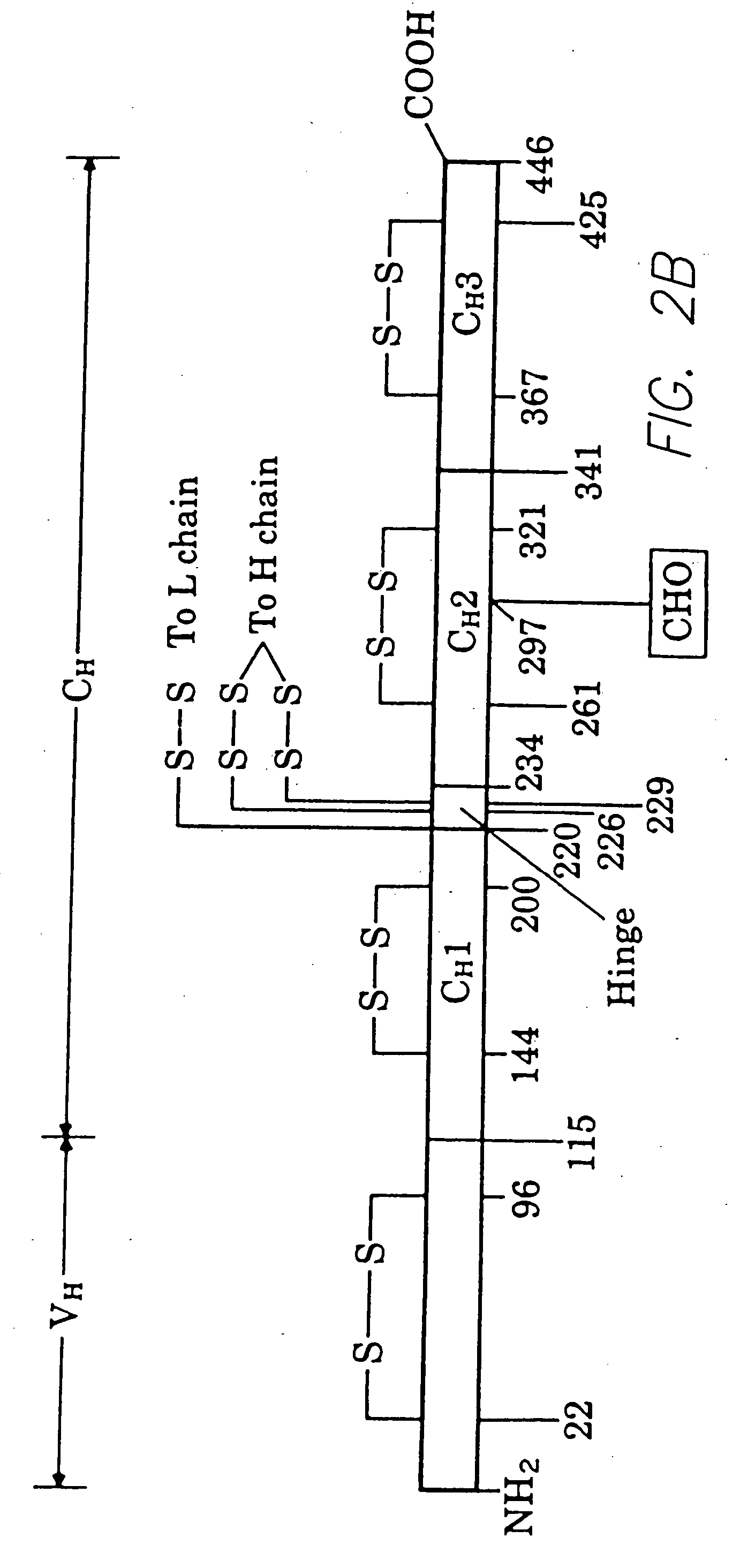
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1215 results about "Gene code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
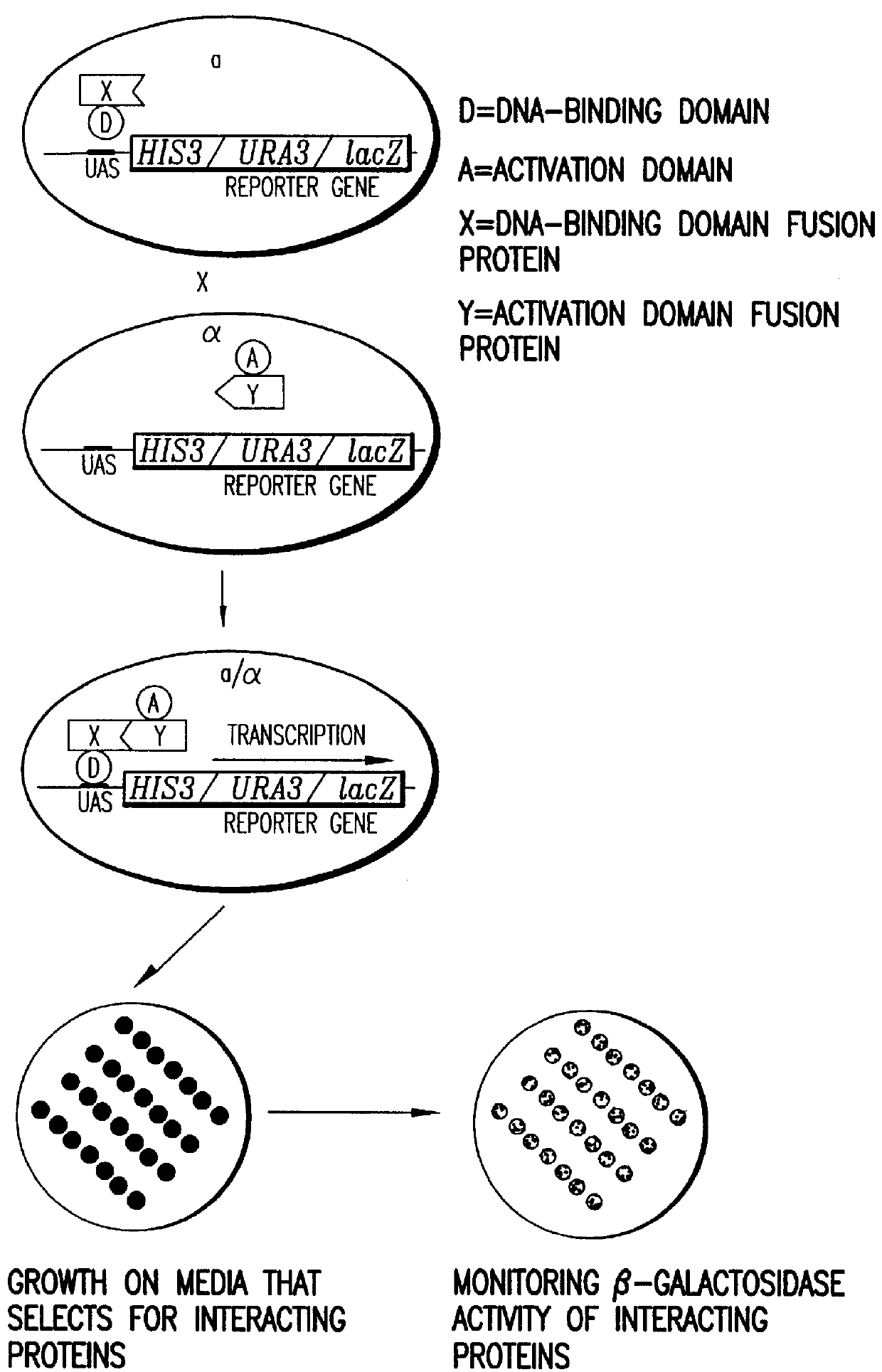
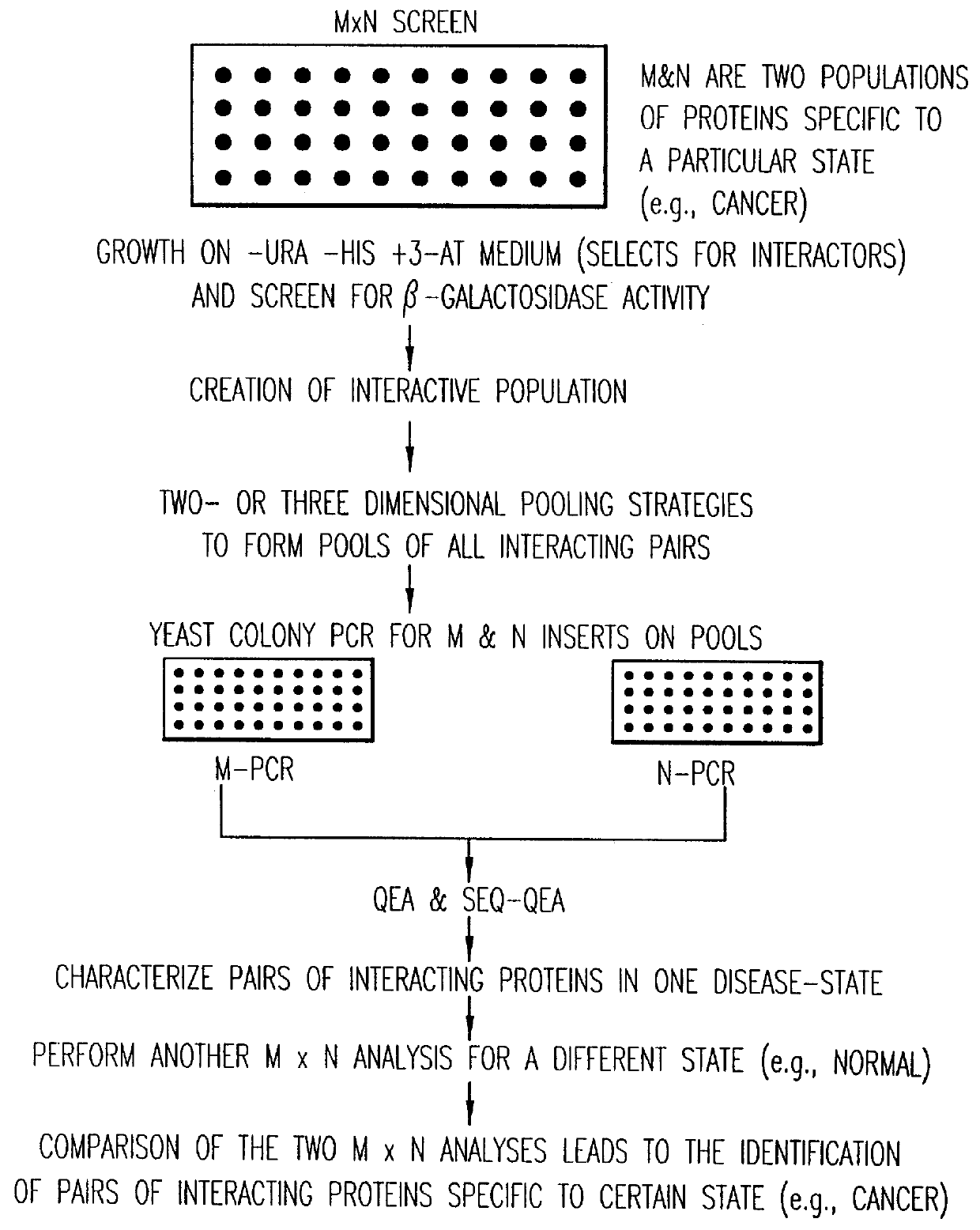
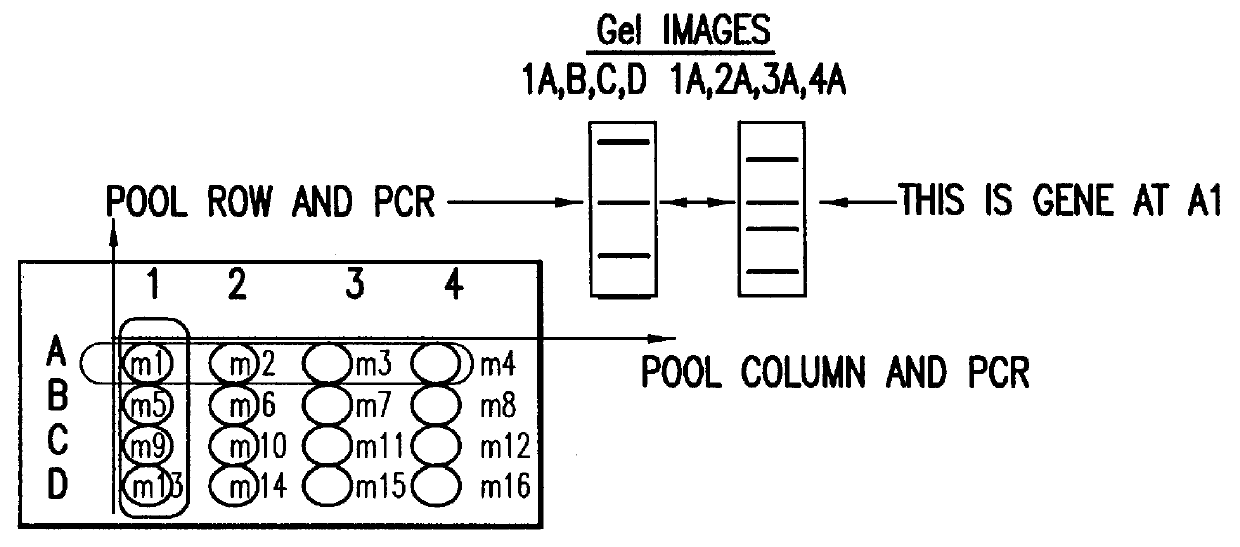
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
L-cysteine producing microorganism and method for producing L-cysteine
InactiveUS20050221453A1High expressionBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyMicroorganismCysteine thiolate
L-Cysteine is produced by culturing a microorganism having an ability to produce L-cysteine and modified so that expression of emrAB, emrKY, yojIH, acrEF, bcr, or cusA gene should be enhanced in a medium to produce and accumulate L-cysteine in the medium and collecting the L-cysteine from the medium. Genes coding for novel L-cysteine-excreting proteins are identified, and utilized for breeding of L-cysteine-producing microorganism to provide a novel method of producing L-cysteine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof
ActiveCN105154473AAvoid risks caused by random insertionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransposon integrationInsertion site
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to an efficient and safe transposable element integration system and application thereof and further relates to a nucleic acid construction body and application thereof. The nucleic acid construction body concretely and sequentially comprises the following elements of a transposable element 5' terminal repetition sequence, a polyclone insertion site, a poly A tailing signal sequence, a transposable element 3' terminal repetition sequence, a transposase coding sequence and a promoter controlling the expression of transposase. The polyclone insertion site is used for inserting an exogenous gene coding sequence and a selective promoter for controlling the expression of exogenous genes in an operability mode. The poly A tailing signal sequence has a poly A tailing signal function in the forward and reverse directions, and the direction of an expression cassette of transposase is reverse to that of an exogenous gene expression cassette. The nucleic acid construction body can be used for efficiently and safely expressing mediated exogenous genes in host cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +1
Arginine repressor deficient strain of coryneform bacterium and method for producing L-arginine
InactiveUS20020045223A1Produced in advanceSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
L-Arginine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which an arginine repressor involved in L-arginine biosynthesis is deleted by disrupting a gene coding for the repressor, and which has L-arginine producing ability in a medium to produce and accumulate L-arginine in the medium, and collecting the L-arginine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Production of D-lactic acid with yeast
InactiveUS20070031950A1Increase productivityHigh yieldFungiOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyLactate dehydrogenase
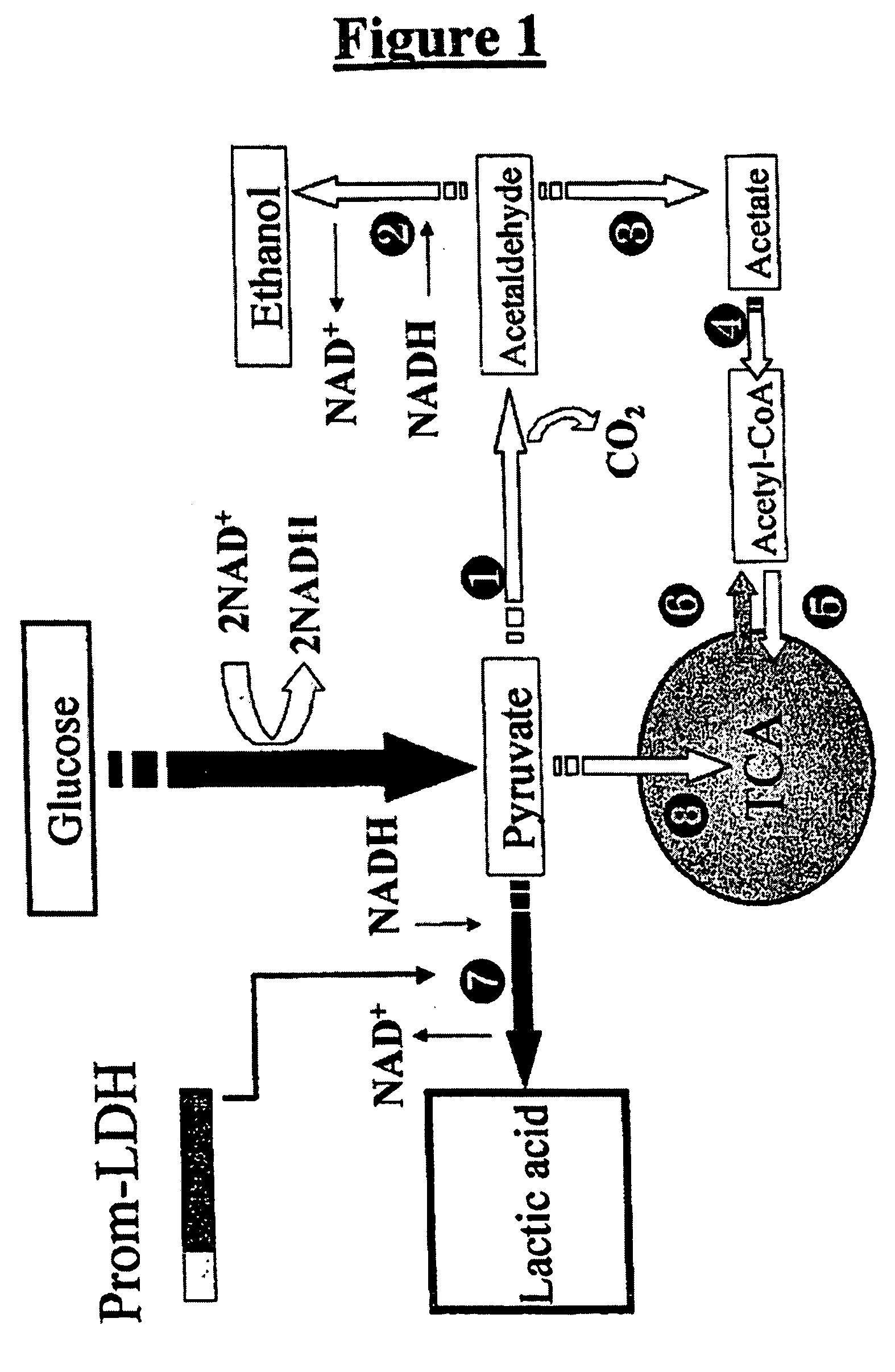
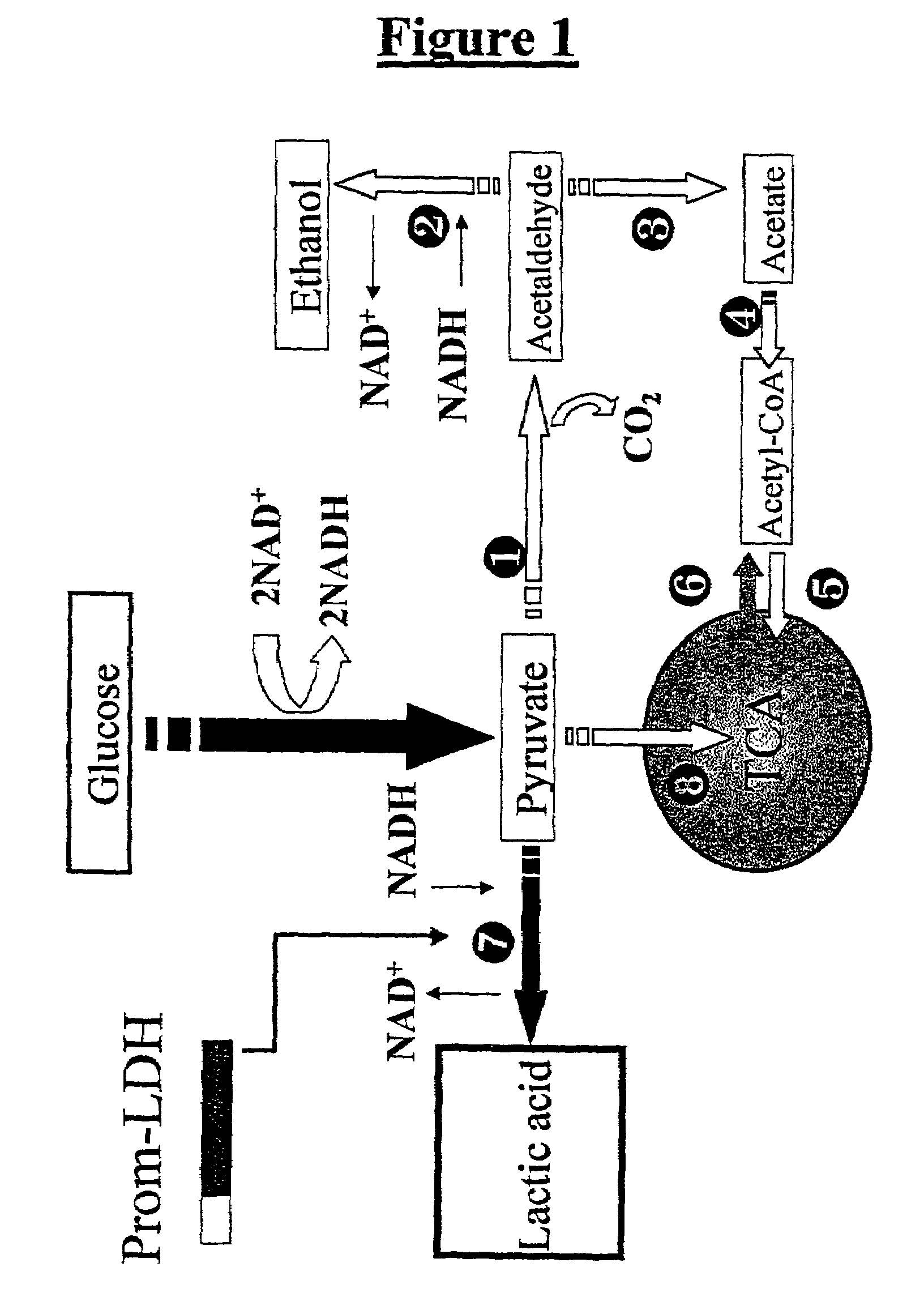
A yeast strain, wherein the yeast strain is transformed with at least one copy of a gene coding for <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactate dehydrogenase functionally linked to a promoter sequence allowing the expression of the gene in the yeast strain and the yeast strain has undergone disruption of one or more pyruvate decarboxylase genes or pyruvate dehydrogenase genes. Also, a method of producing <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid including culturing such a yeast strain in a medium and recovering <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Inhibitor oligonucleotides and their use for specific repression of a gene
A method of treating a disease resulting from the expression of a harmful gene is described. The method includes the step of administering a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition having at least one double stranded oligonucleotide including two complementary oligonucleotide sequences forming a hybrid. Each oligonucleotide sequence comprises at one of their 3′ or 5′ ends one to five unpaired nucleotides forming single-strand ends extending beyond the hybrid. One of the oligonucleotide sequences is substantially complementary to a target sequence belonging to a DNA or messenger RNA molecule of a gene coding a mutated or nonmutated androgen receptor.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Method for tapping the immunological repertoire
InactiveUS6969586B1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsGene repertoireCatalytic receptors
The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Dideoxynucleotide-triphosphate utilization by the hyper-thermophilic DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS6333183B1High sensitivityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBinding site
Polymerases from the Pol I family which are able to efficiently use ddNTPs have demonstrated a much improved performance when used to sequence DNA. A number of mutations have been made to the gene coding for the Pol II family DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus with the aim of improving ddNTP utilisation. "Rational" alterations to amino acids likely to be near the dNTP binding site (based on sequence homologies and structural information) did not yield the desired level of selectivity for ddNTPs. However, alteration at four positions (Q472, A486, L490 and Y497) gave rise to variants which incorporated ddNTPs better than the wild type, allowing sequencing reactions to be carried out at lowered ddNTP:dNTP ratios. Wild type Pfu-Pol required a ddNTP:dNTP ratio of 30:1; values of 5:1 (Q472H), 1:3 (L490Y), 1:5 (A486Y) and 5:1 (Y497A) were found with the four mutants; A486Y representing a 150-fold improvement over the wild type. A486, L490 and Y407 are on an alpha-helix that lines the dNTP binding groove, but the side chains of the three amino acids point away from this groove; Q472 is in a loop that connects this alpha-helix to a second long helix. None of the four amino acids can contact the dNTP directly. Therefore, the increased selectivity for ddNTPs is likely to arise from two factors: 1) Small overall changes in conformation that subtly alter the nucleotide triphosphate binding site such that ddNTPs become favoured; 2) interference with a conformational change that may be critical both for the polymerisation step and discrimination between different nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Oligonucleotide compositions and methods for treating disease including inflammatory conditions
InactiveUS20050153919A1Reduced activityReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPhosphodiesteraseAllograft rejection
The invention relates to therapeutic antisense oligonucleotides directed against genes coding for phosphodiesterase (PDEs) and the use of these in combination. These antisense oligonucleotides may be used as analytical tools and / or as therapeutic agents in the treatment of disease associated with reduced cellular cAMP in a patient, such as inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract including, for example, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute respiratory distress syndrome, bronchitis, chronic bronchitis, silicosis, pulmonary fibrosis, lung allograft rejection, allergic rhinitis and chronic sinusitis as well as other conditions in which an increase in cyclic AMP or a decrease in PDE levels is beneficial.
Owner:TOPIGEN PHARMA
Method for tapping the immunological repertoire
InactiveUS20060019260A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene repertoireCatalytic receptors
The present invention relates to a method for isolating from the immunological gene repertoire a gene coding for a receptor having the ability to bind a preselected ligand. Receptors produced by the gene isolated by the method, particularly catalytic receptors, are also contemplated.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
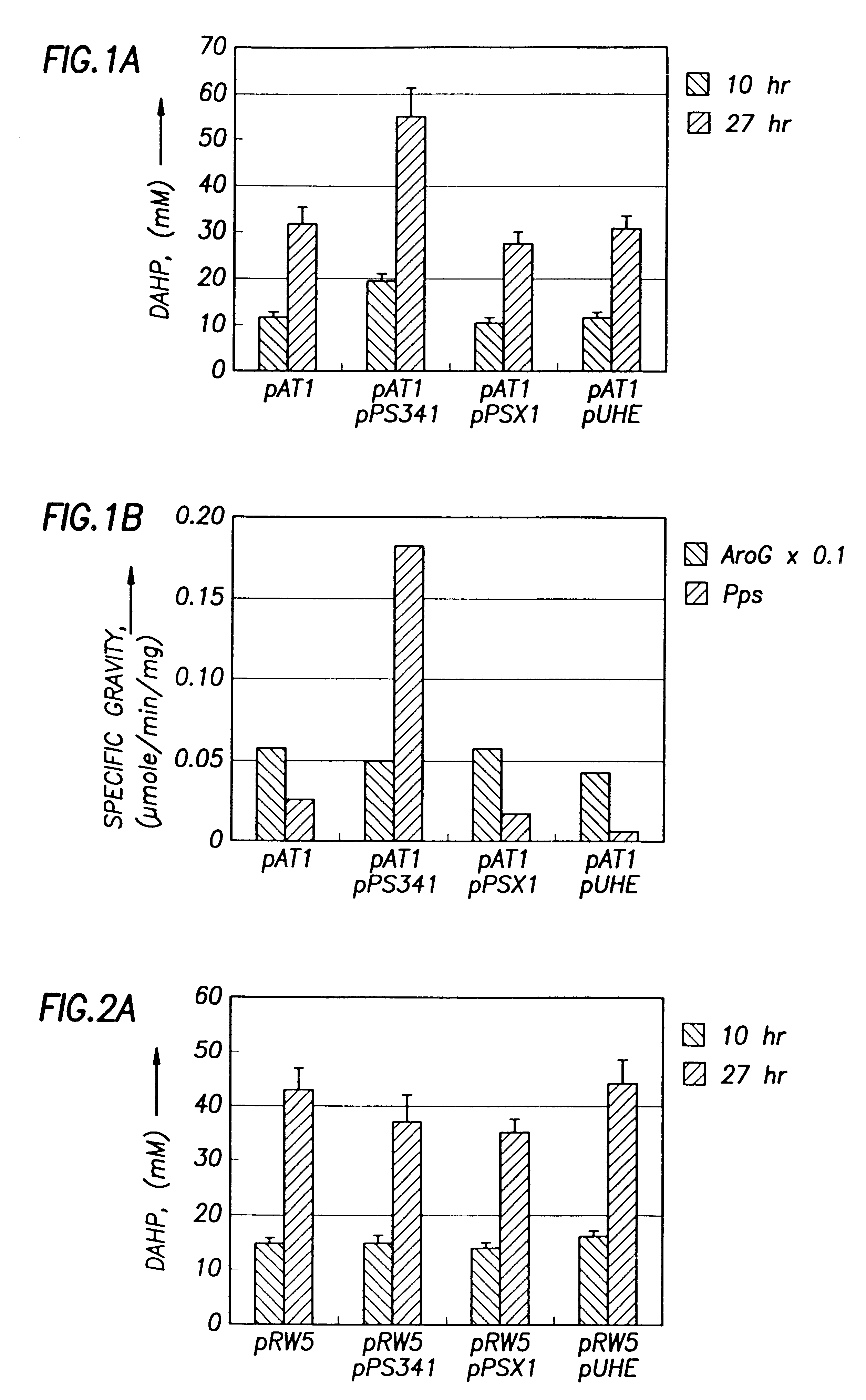
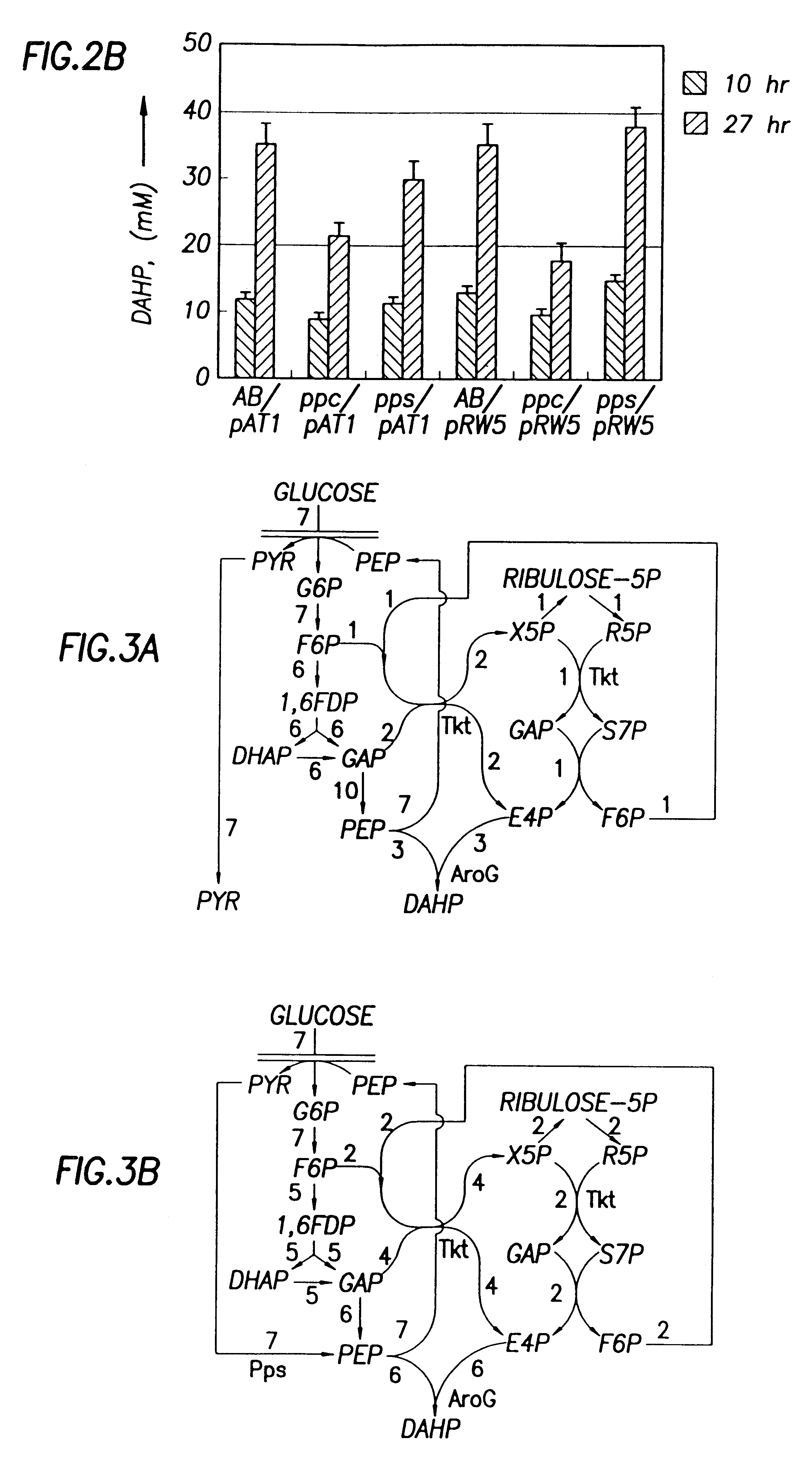
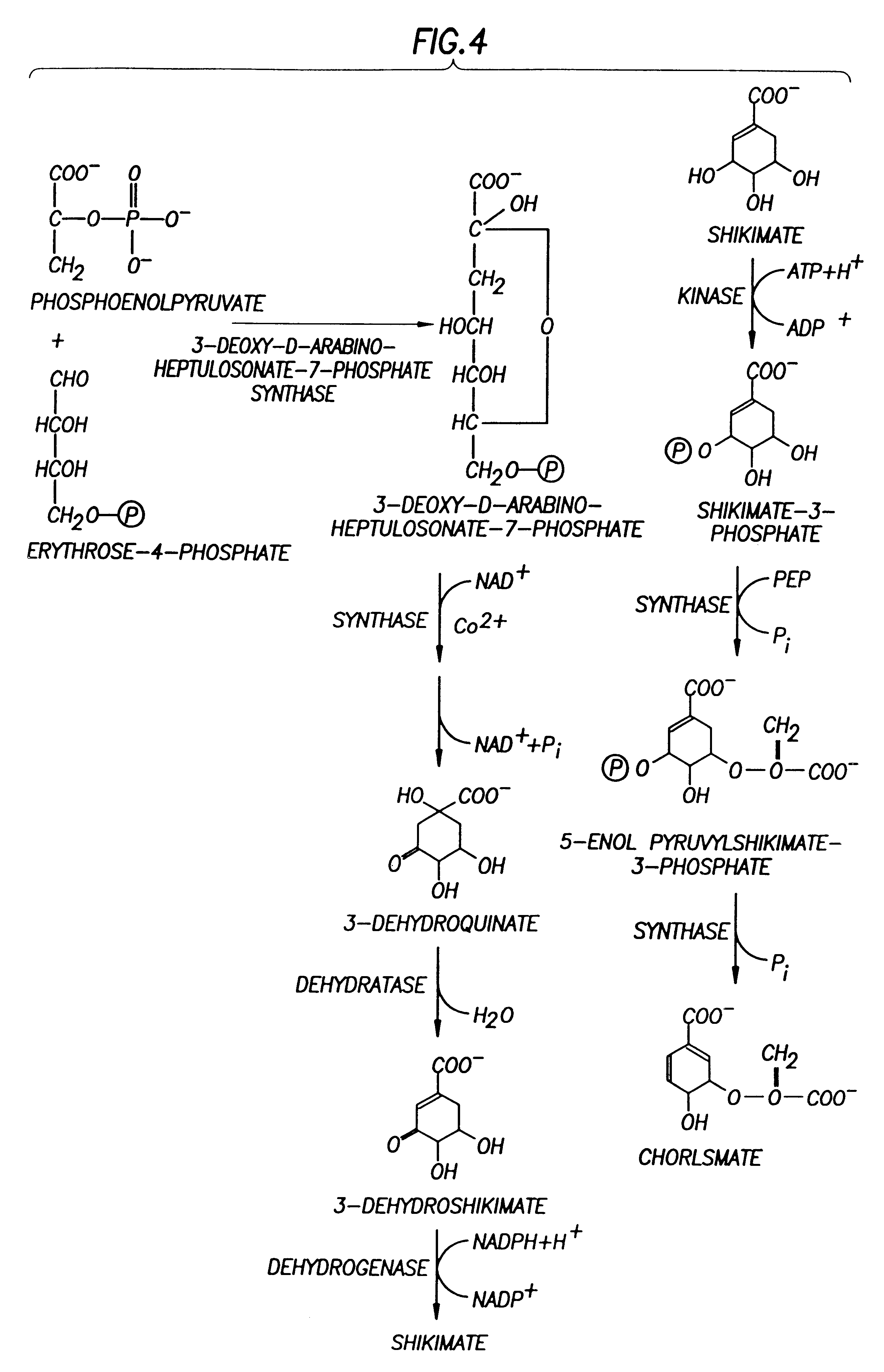
Microorganisms and methods for overproduction of DAHP by cloned PPS gene
InactiveUS6489100B1Decreasing DAHP productionWide rangeSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismPyruvate synthase
Genetic elements comprising expression vectors and a gene coding for phosphoenol pyruvate synthase is utilized to enhance diversion of carbon resources into the common aromatic pathway and pathways branching therefrom. The overexpression of phosphoenol pyruvate synthase increases DAHP production to near theoretical yields.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
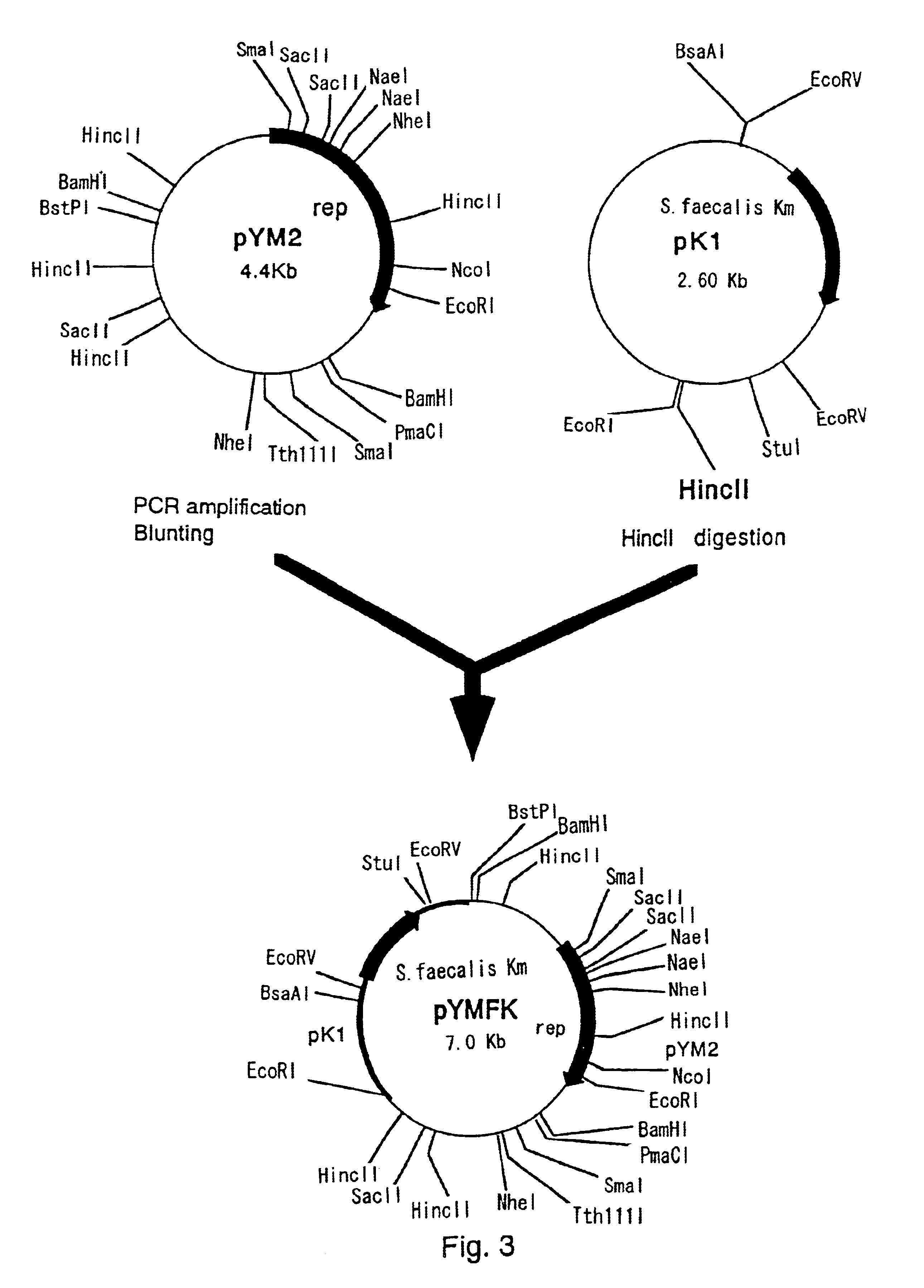
Plasmid autonomously replicable in coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS6905819B1Easy to optimizeImproving a coryneform bacteriumBacteriaSugar derivativesCorynebacterium amycolatumAmino acid
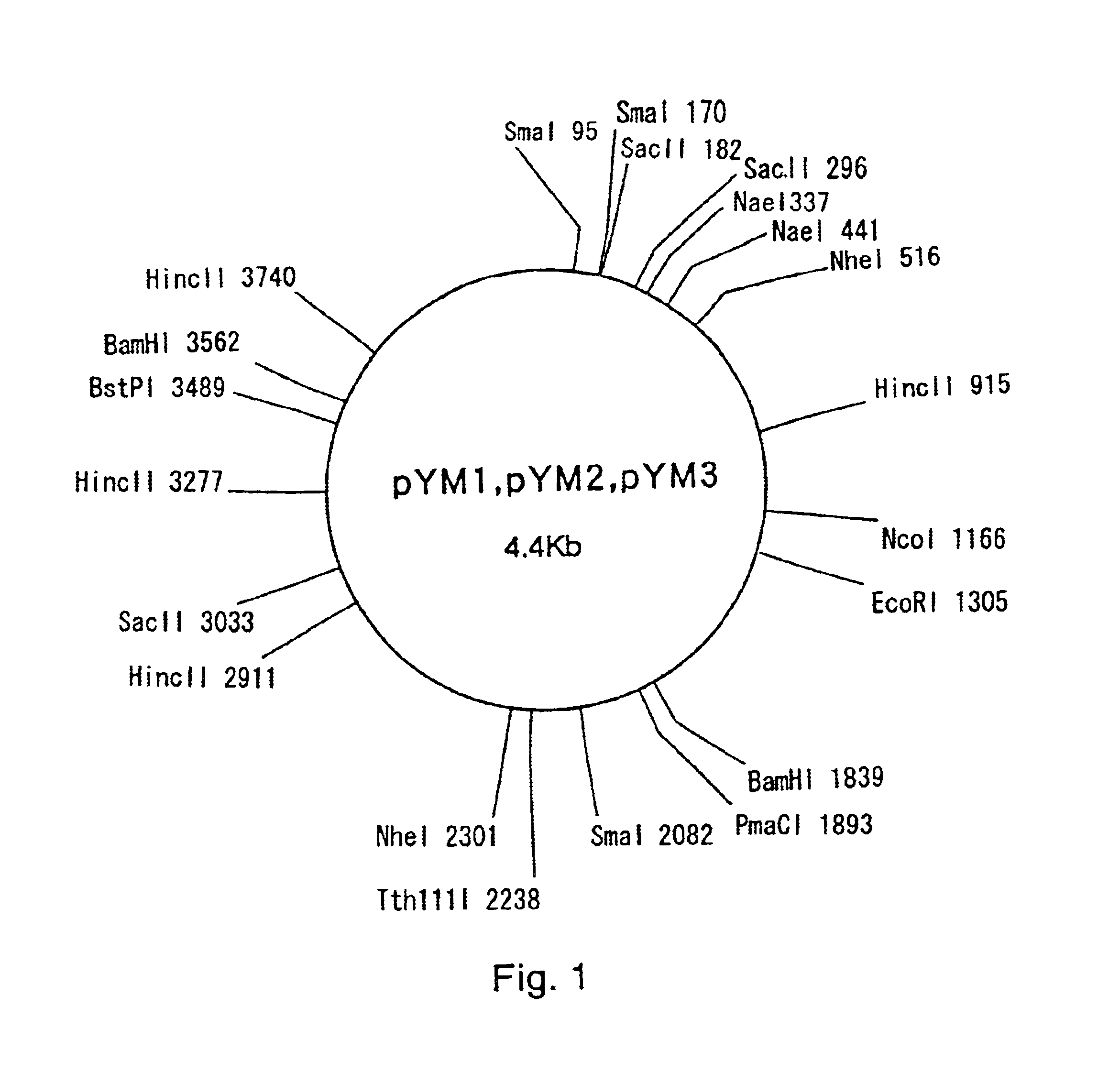
A plasmid which is able to be isolated from Corynebacterium thermoaminogenes, and which comprises a gene coding for a Rep protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence having homology of 90% or more to the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. and has a size of about 4.4 kb or about 6 kb, or a derivative thereof.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Cod uracil-DNA glycosylase, gene coding therefore, recombinant DNA containing said gene or operative parts thereof, a method for preparing said protein and the use of said protein or said operative parts thereof in monitoring or controlling PCR
InactiveUS20020155573A1Efficient productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyUracil-DNA glycosylase
It is disclosed a novel enzyme present in cod liver, a DNA sequence encoding the enzyme or operative parts or biologically functional parts thereof, a novel recombinant DNA comprising the gene or tho operative or biologically functional parts thereof, a method of preparing the enzyme from cod liver and from bacteria carrying the gene, the bacteria carrying the gene per se, and the use of the protein in monitoring and / or controlling PCR or related reaction systems.
Owner:BIOTEC PHARMACON
Process for the fermentative production of proteins
InactiveUS20080254511A1High-yieldPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBiotechnologyHeterologous
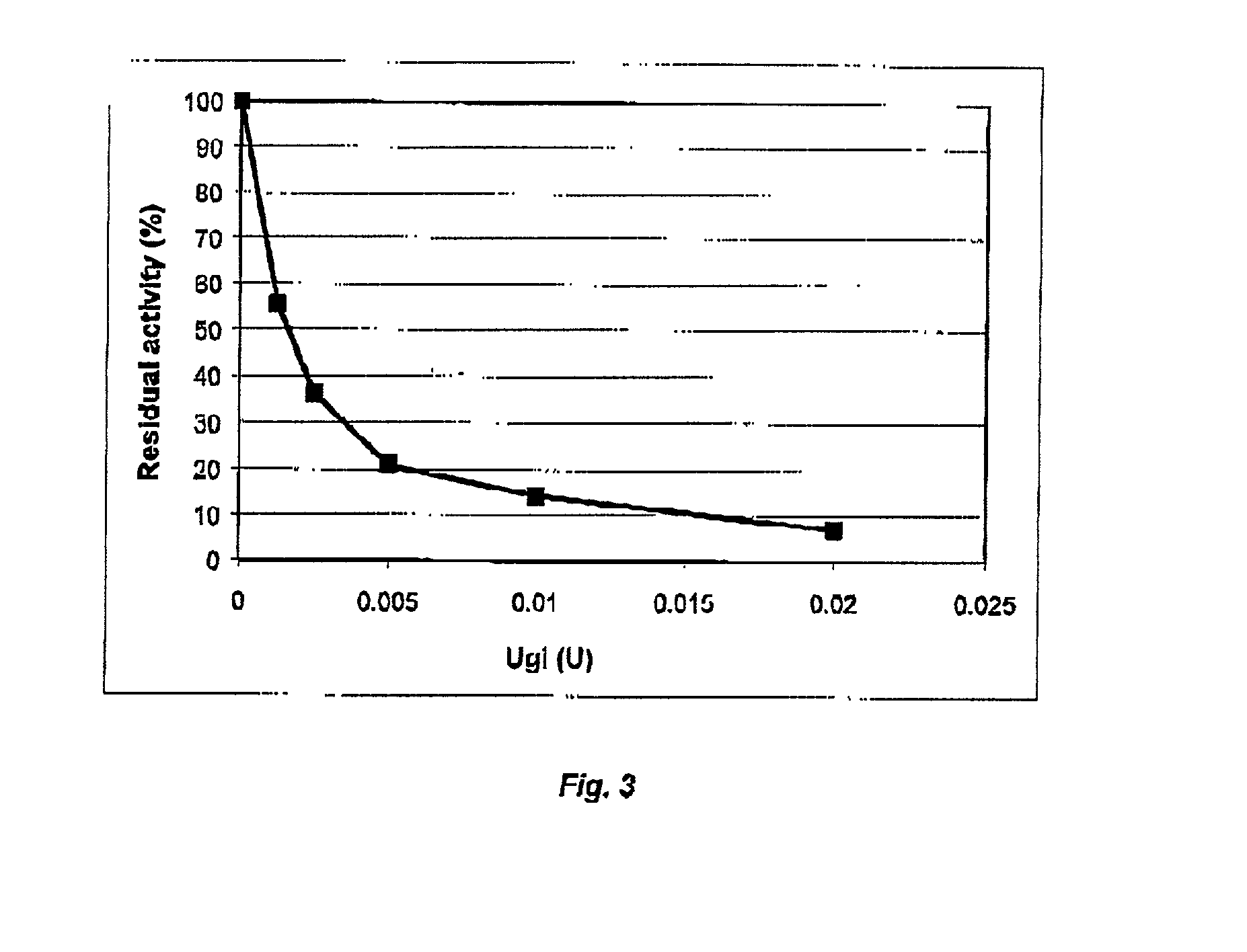
The present invention relates to a process for producing a heterologous protein by means of an E. coli strain in a fermentation medium. The process comprises fermenting an E. coli strain in a fermentation medium. The E. coli strain has a mutation in the lpp gene or in the promoter region of the lpp gene, and contains a gene coding for a heterologous protein which is functionally linked to a signal sequence coding for a signal peptide. The fermentation medium includes Ca2+ ions in a concentration above 4 mg / l or Mg2+ ions in a concentration above 48 mg / l. The E. coli strain secretes the heterologous protein into the fermentation medium. The protein is removed from the fermentation medium.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Processes for producing lactic acid using yeast transformed with a gene encoding lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
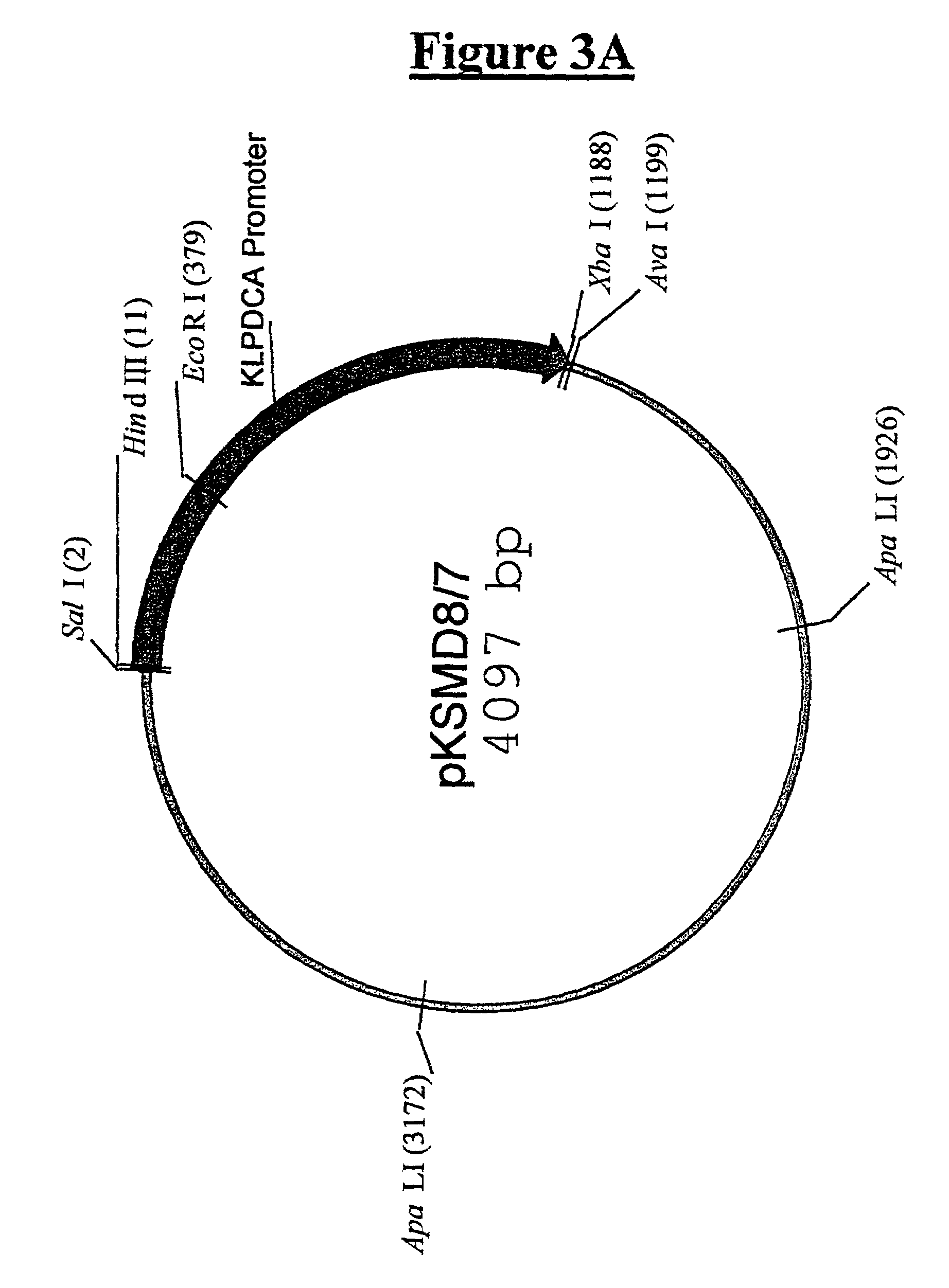
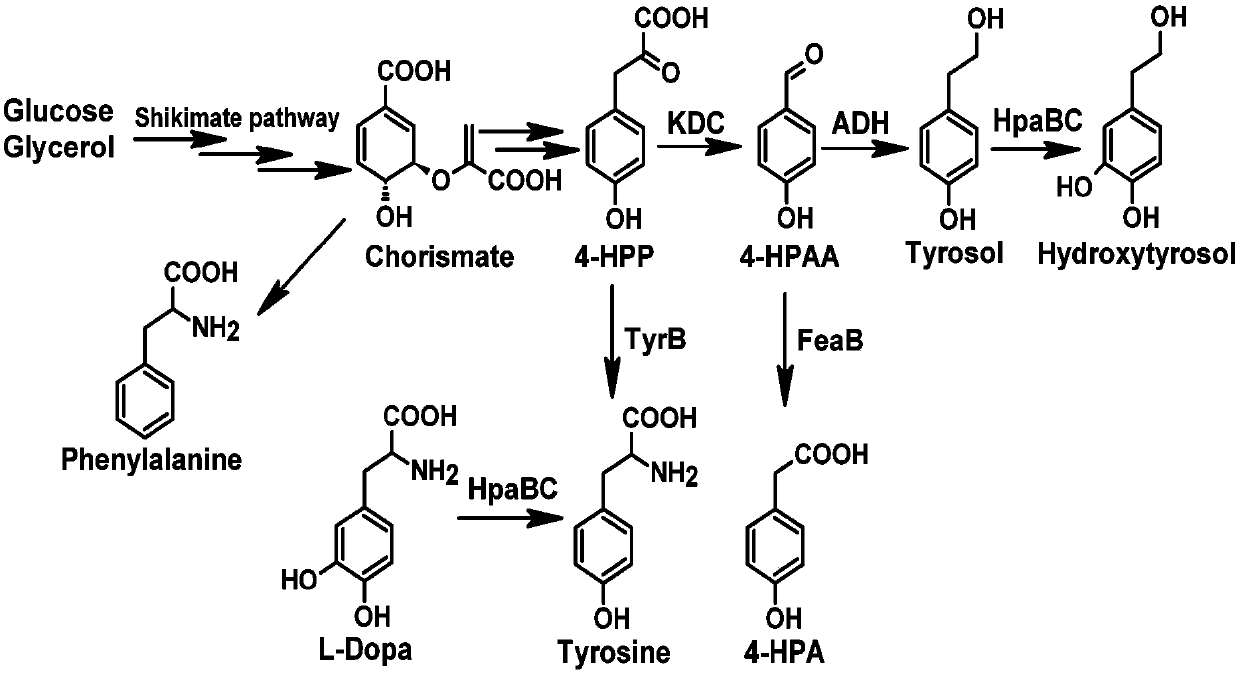
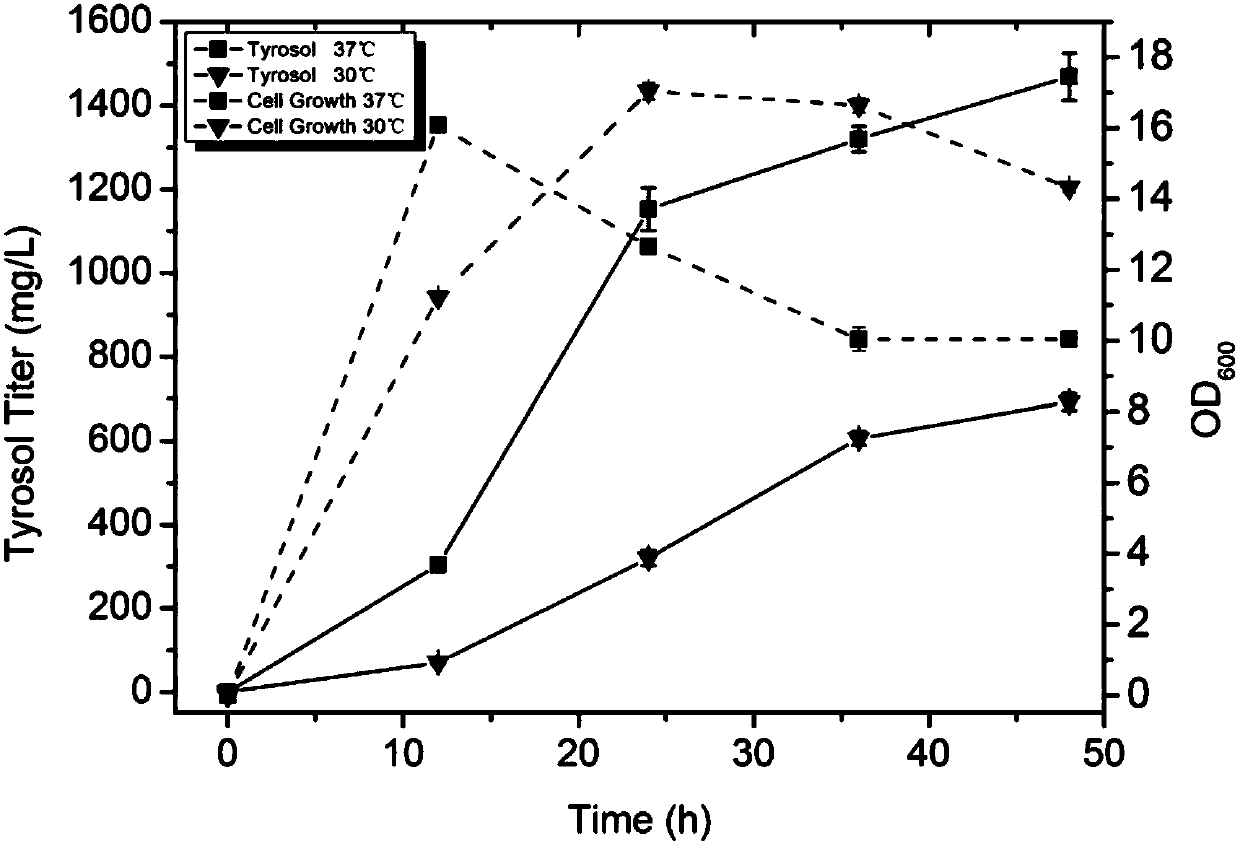
Method for producing tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol through heterologous metabolic pathways
ActiveCN107586794AEfficient extractionEfficient productionFermentationAlcohol dehydrogenaseGene code
The invention discloses a method for producing tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol through heterologous metabolic pathways, wherein metabolic pathways for producing hydroxytyrosol are introduced into hosts forproducing the hydroxytyrosol; more specifically, the method comprises the following steps: producing tyrosol by efficiently expressing aminotransferase, ketoacid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase in the hosts, then introducing 4-hydroxyphenylacetate hydroxylase to produce the hydroxytyrosol. Genes coded by the enzymes are constructed on an expression plasmid or integrated to a genome. Through the method, production hosts capable of producing the hydroxytyrosol by using glucose, glycerinum and tyrosine can be prepared by introducing the genes coded by the enzymes to the hosts; meanwhile,the invention also discloses a biphasic cultivation method, so that the production of the hydroxytyrosol is more efficient.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
ActiveUS20100297172A1Enhance protein expressionHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntigenDisease
The invention relates to an infectious arenavirus particle that is engineered to contain a genome with the ability to amplify and express its genetic information in infected cells but unable to produce further infectious progeny particles in normal, not genetically engineered cells. One or more of the four arenavirus open reading frames glycoprotein (GP), nucleoprotein (NP), matrix protein Z and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L are removed or mutated to prevent replication in normal cells but still allowing gene expression in arenavirus vector-infected cells, and foreign genes coding for an antigen or other protein of interest or nucleic acids modulating host gene expression are expressed under control of the arenavirus promoters, internal ribosome entry sites or under control of regulatory elements that can be read by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cellular RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. The modified arenaviruses are useful as vaccines and therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
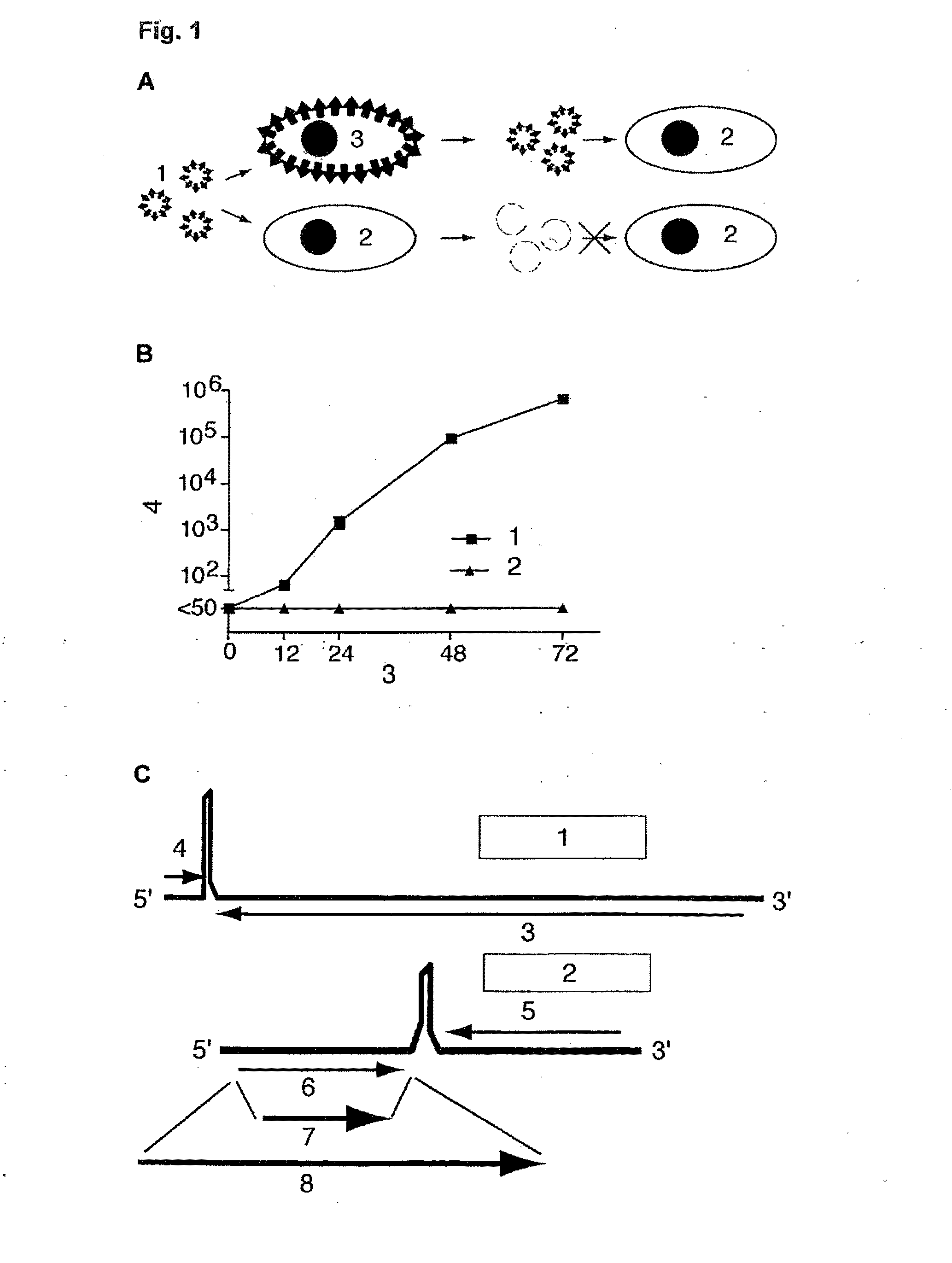
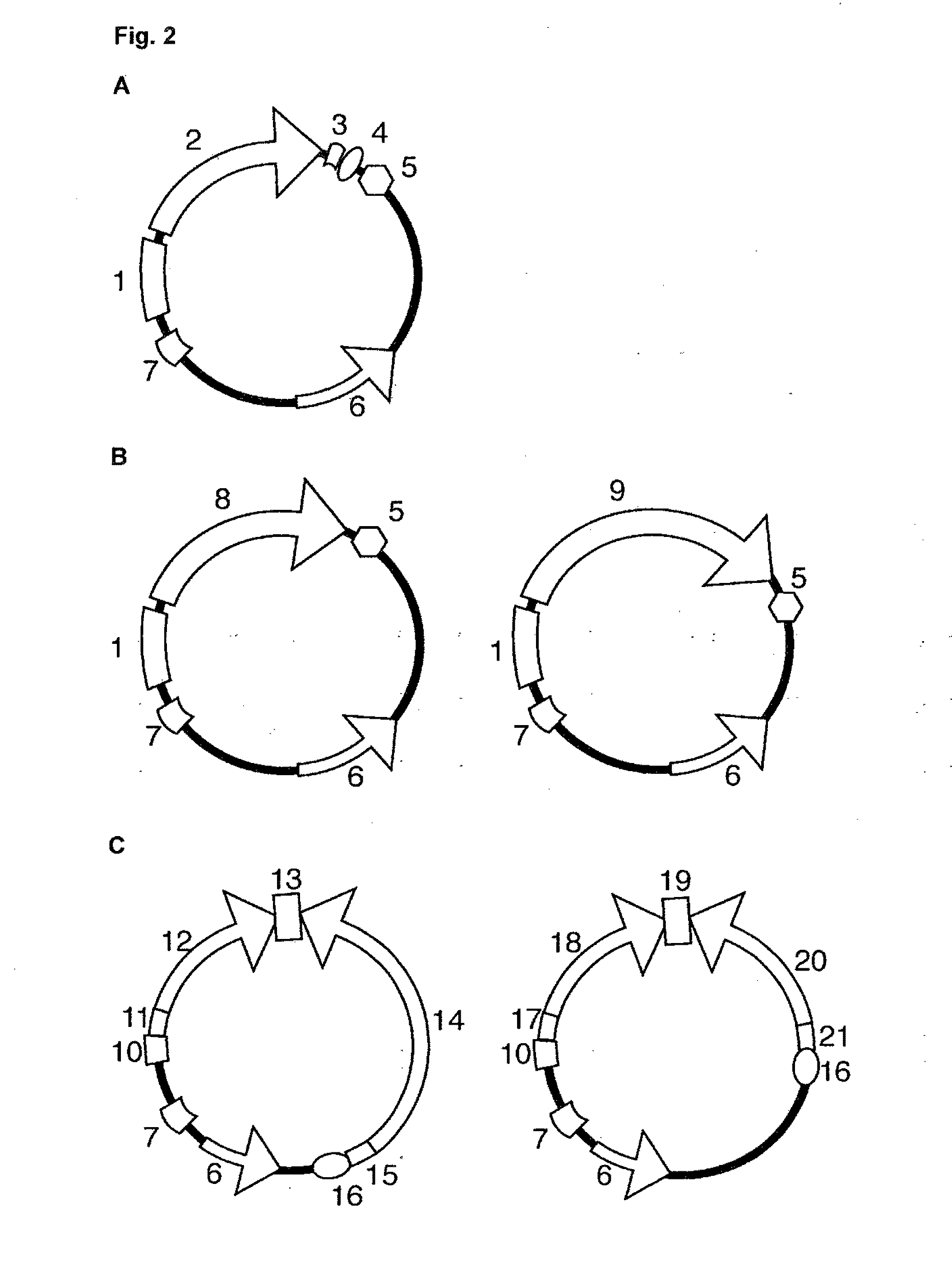
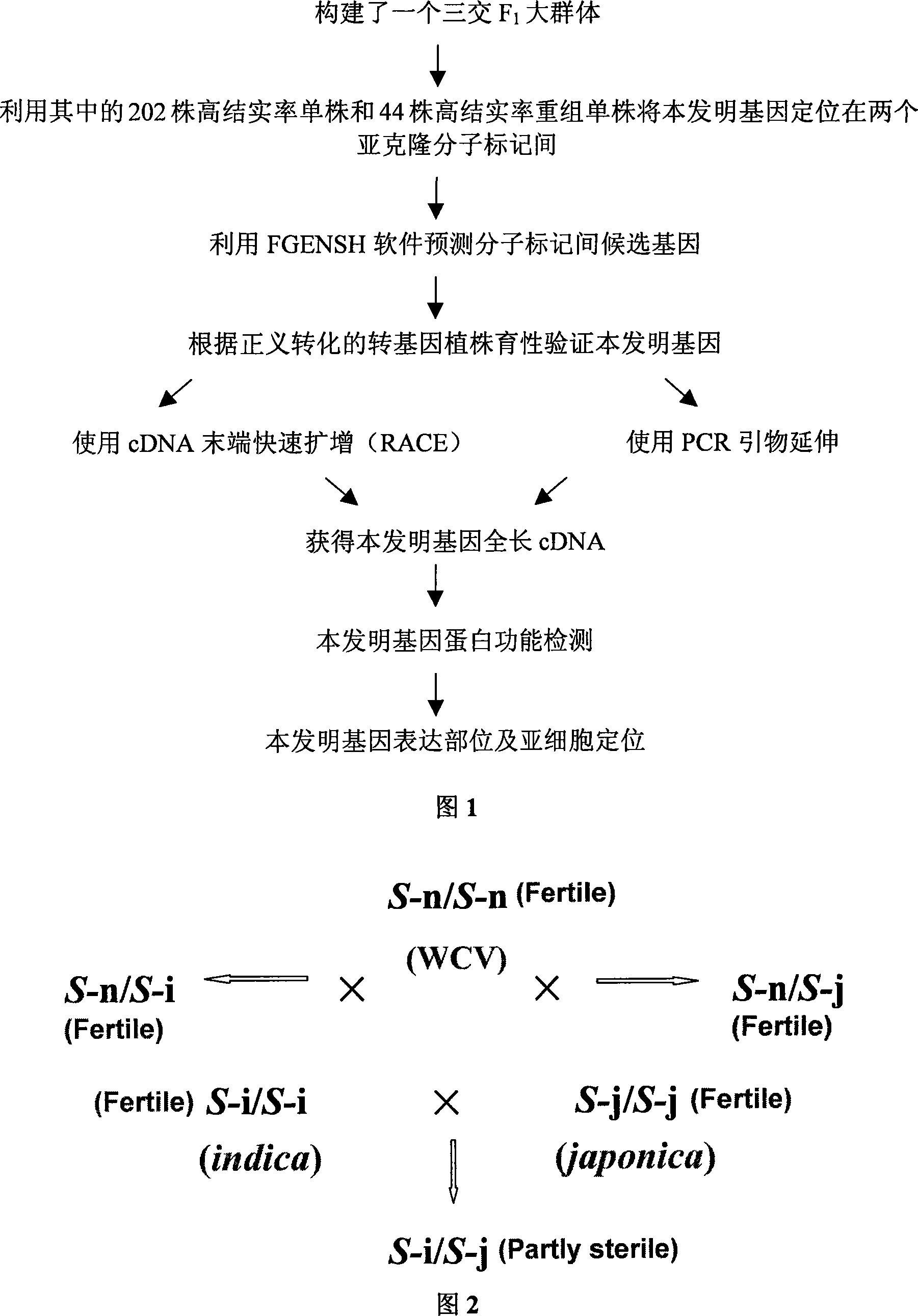
Separating clone of rice wide compatibility gene S5 and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering and concretely relates to the separation clone of paddy wide compatibility gene S5, a function validation and an application thereof for improving the paddy. The segment of the gene contains paddy wide compatibility gene coding aspartic proteinase. Subspecific Indica-Japonica paddy has strong hybrid advantage than varietal paddy, but the sterility of the subspecific Indica-Japonica hybrid restricts using the hybrid advantage thereof. The wide compatibility gene cloned by the present invention can conquer the sterility of the subspecific Indica-Japonica hybrid of the paddy and accordingly uses the strong hybrid advantage of the subspecific Indica-Japonica to further improve the output of the paddy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
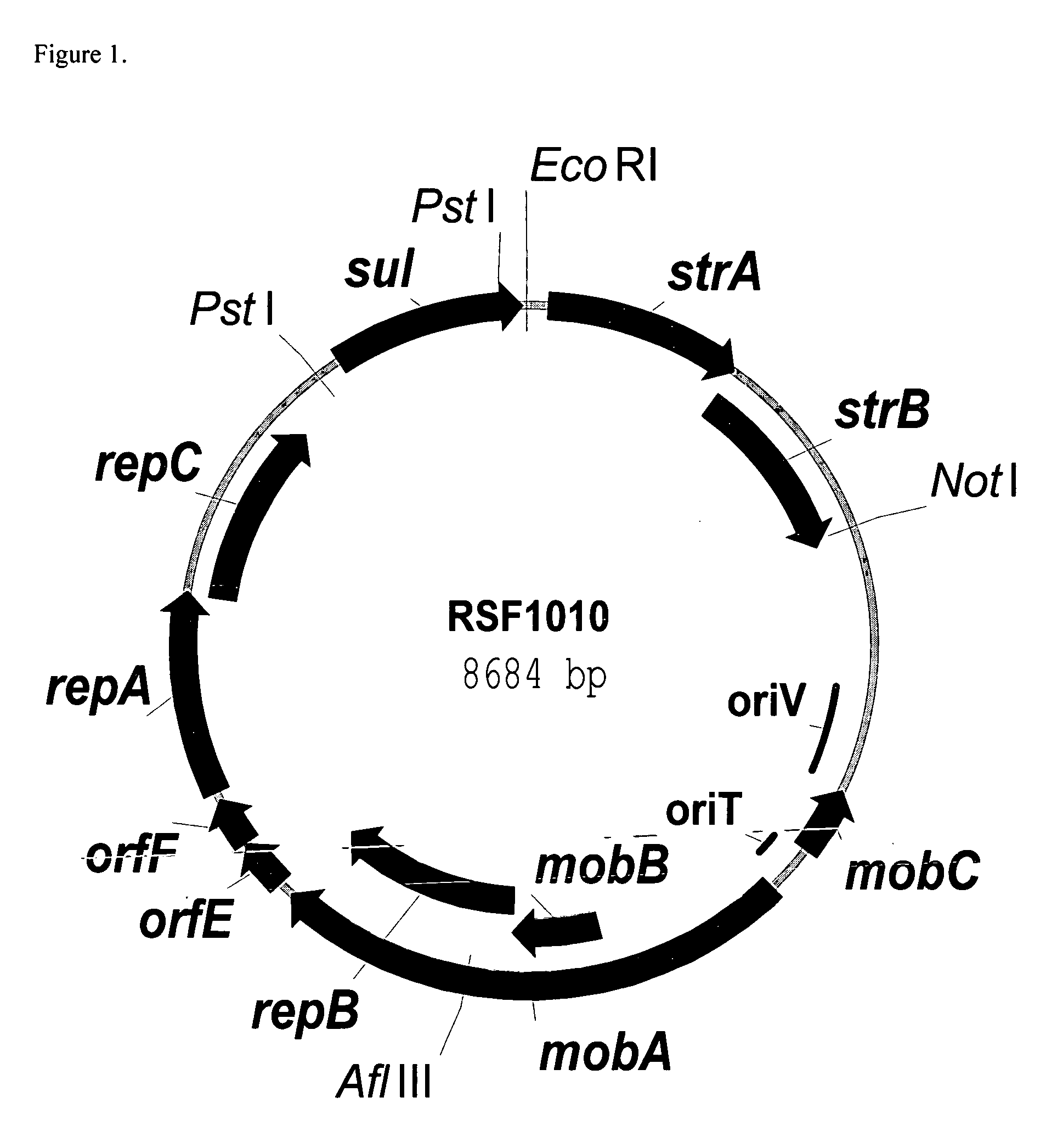
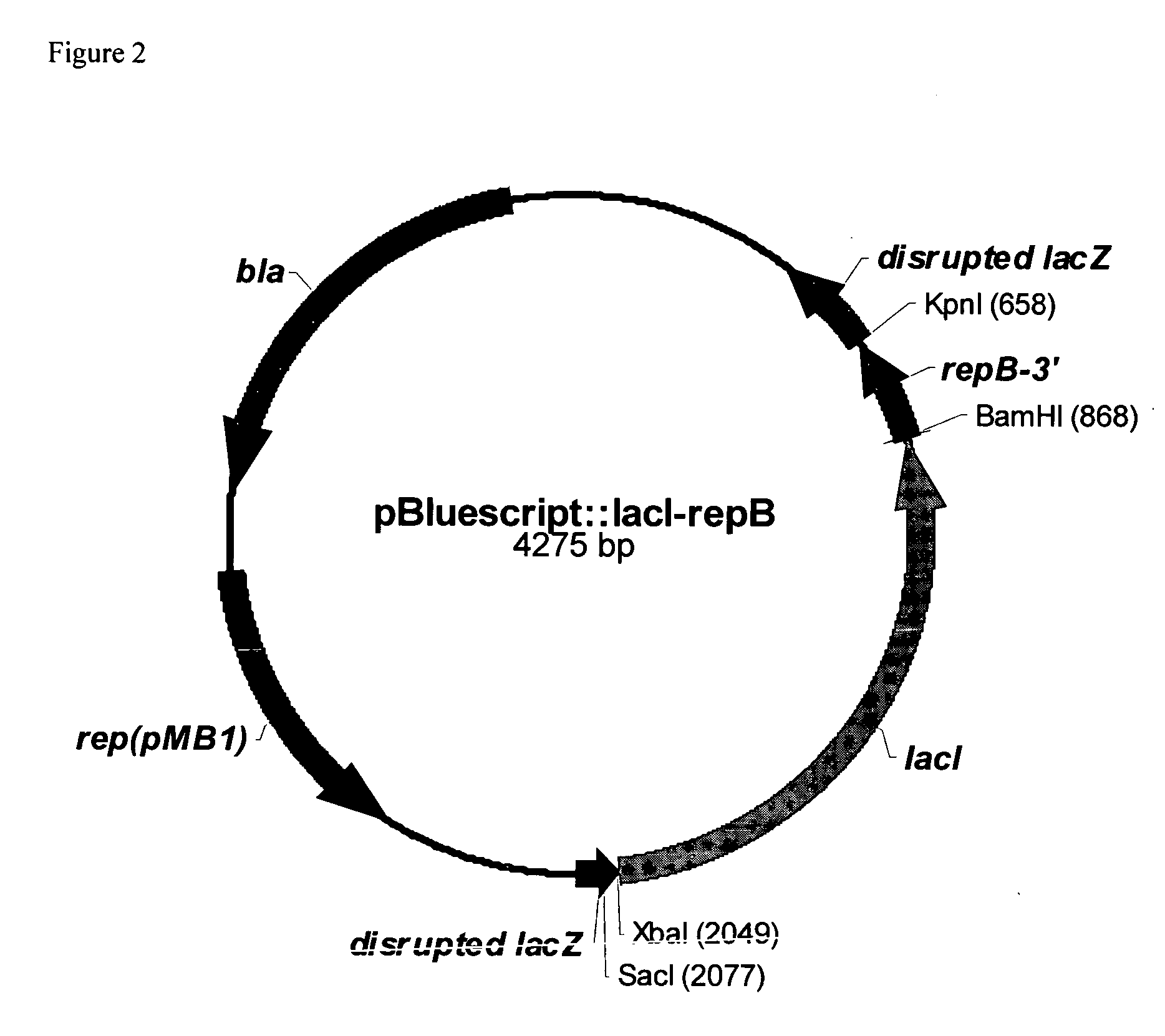
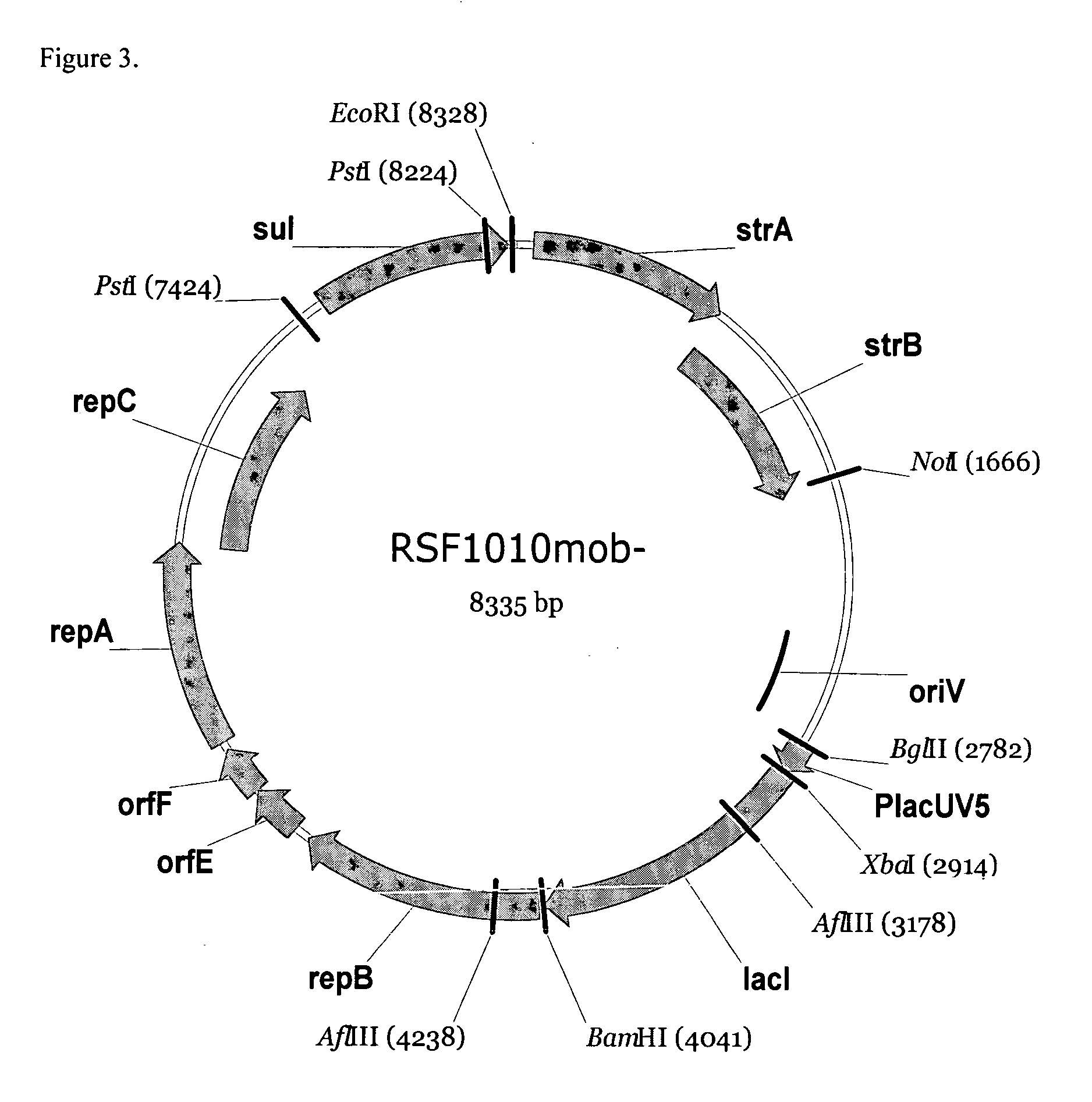
RSF1010 derivative Mob' plasmid containing no antibiotic resistance gene, bacterium comprising the plasmid and method for producing useful metabolites
A Mob− plasmid having a RSF1010 replicon, comprising a gene coding for Rep protein and said plasmid has been modified to inactivate gene related to mobilization ability. The present invention also describes a bacterium having an ability to produce useful metabolites, comprising the plasmid and said bacterium lack active thymidylate synthase coded by thyA gene and thymidine kinase coded by tdk gene, and a method for producing useful metabolites, such as native or recombinant proteins, enzymes, L-amino acids, nucleosides and nucleotides, vitamins, using the bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant human plasminogen kringle5, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a mutant human plasminogen kringle5 gene mK5 and an amplification primer of the mK5 gene, the mutant human plasminogen kringle5 gene modified by adding glutathione-S-transferase before the gene mK5, and a method for preparing protein mK5 recombinant protein of two gene codes, glutathioneS transferase (GST)-mK5 fusion protein and two proteins, wherein the mK5 gene and the GST-mK 5 gene can be applied to preparing medicaments for treating angiogenesis diseases. By the invention, the number of exogenous amino acid in the recombinant K5 protein molecules obtained by a gene engineering method is remarkably reduced, the K5 bioactivity of the obtained mK5 is improved, while the mK5 activity of the GST-mK5 fusion protein is maintained, the stability and water solubility of the protein are improved, the purification steps of an expressed product are simplified, and the purity of the product is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) marker and its application
InactiveCN102321760AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoGenetic recombination
Belonging to the field of biotechnology, the invention discloses a non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) marker, which is STAT3, and also can include CEA, CA125 and CYFRA21-1. The invention confirms the high expression of STAT3 in peripheral blood and serum, and discloses application of STAT3 in preparation of NSCLC diagnostic reagents by the inventor. Specifically, by making use of a genetic recombination technology and targeting at the gene coding region of STAT3, an eukaryotic expression vector PSUPER-STAT3 able to transcribe in vivo and generate small interference RNA (siRNA) is constructed successfully, and is transfected into an eukaryotic cell, thus laying a foundation for a further experimental study on lung cancer RNAi (RNA interference) and antitumor gene therapy. Utilization of the RNAi technology can effectively inhibit the gene expression of STAT3, induce cell apoptosis, and establish the base for molecular mechanism research and gene therapy of lung cancer, thus providing application of the marker provided in the invention in preparing related targeted medicines.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
InactiveCN101275144AAvoid pollutionSimple purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
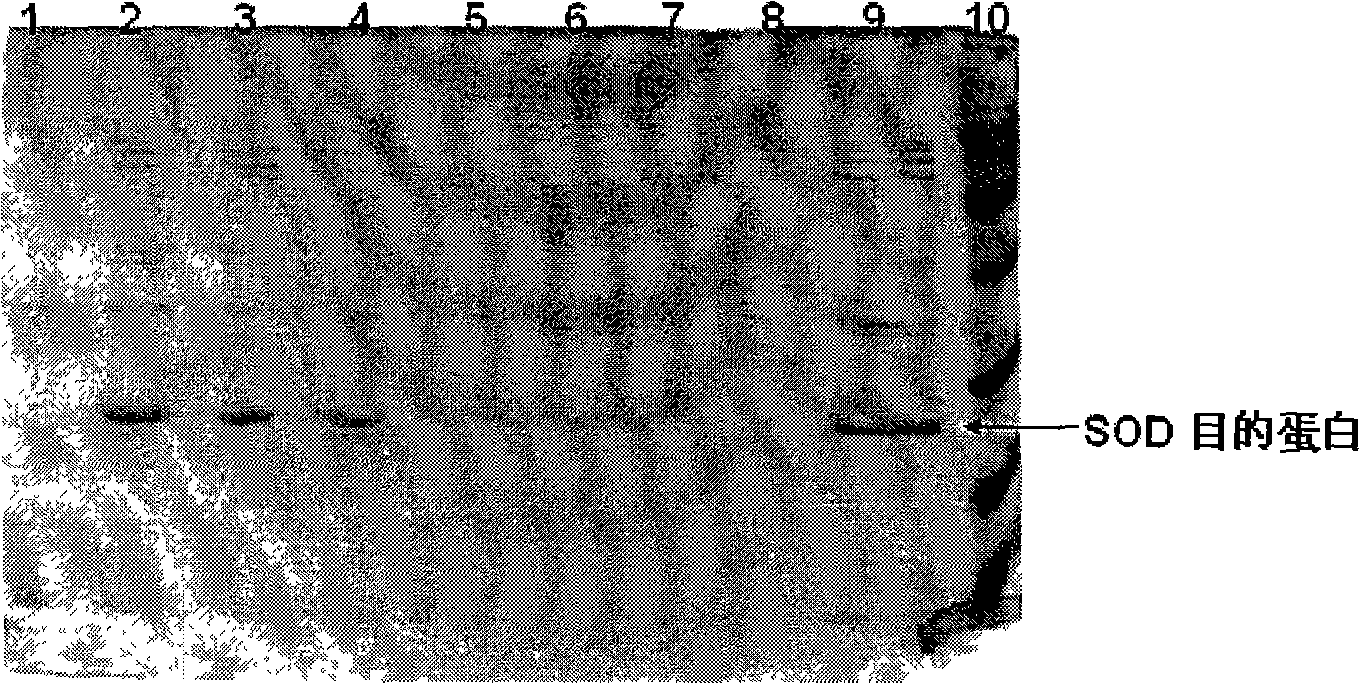
The present invention provides a high density fermentation and a purification process of a recombination high temperature resistance superoxide dismutase, the construction method of the invention includes: using gene coded for SOD in a thermophilic bacteria as a template, designing specific primer amplification target gene having restriction enzyme sites, after double digestion, connecting to plasmid vector pET28a after the same double digestion, constructing a recombinant plasmid, named for pSOD, transforming plasmid pSOD to competence escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by chemical transformation method, obtaining strain having high SOD yield after screening, completing the construction of SOD engineering bacteria; the fermentation process includes four steps of first order seed culture, secondary order feed culture, batch fermentation and induced expression, fermentation product SOD is finally obtained; the fermentation process realizes high level expression of SOD, the expression of the target protein is more than 60% of the bacterial protein total; SOD has excellent thermal stability and heat resistance, the expression product accounts for more than 60% of the whole proteins, and fully soluble protein, avoiding any trouble in the course of inclusion body renaturation; the purification process is simple, having high yield, lower cost, the final product SOD has high purification, high activity and strength stability.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG +1
In Vivo Delivery of Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20160040161A1Reduce deliveryEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderProtozoaBacteroides
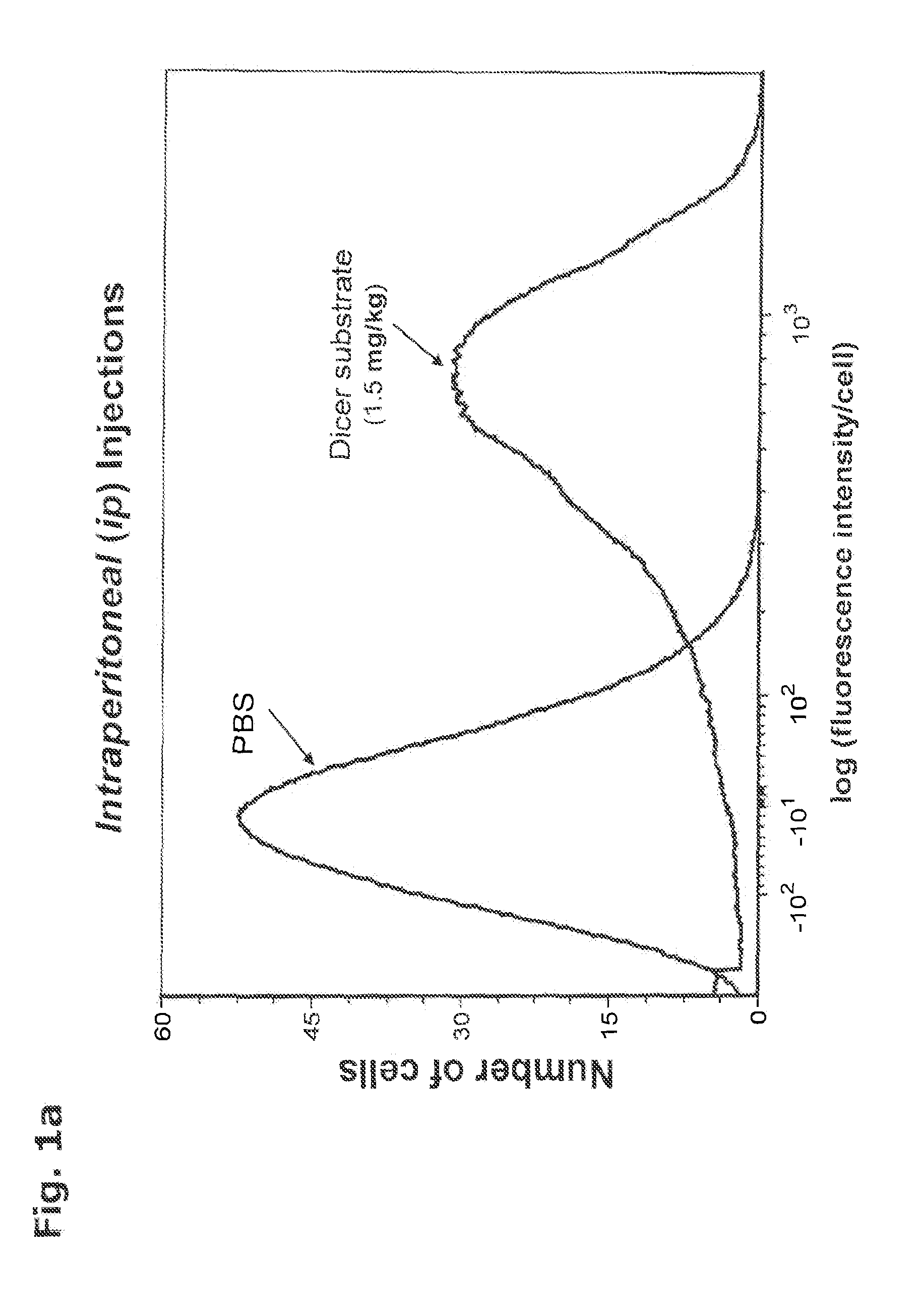
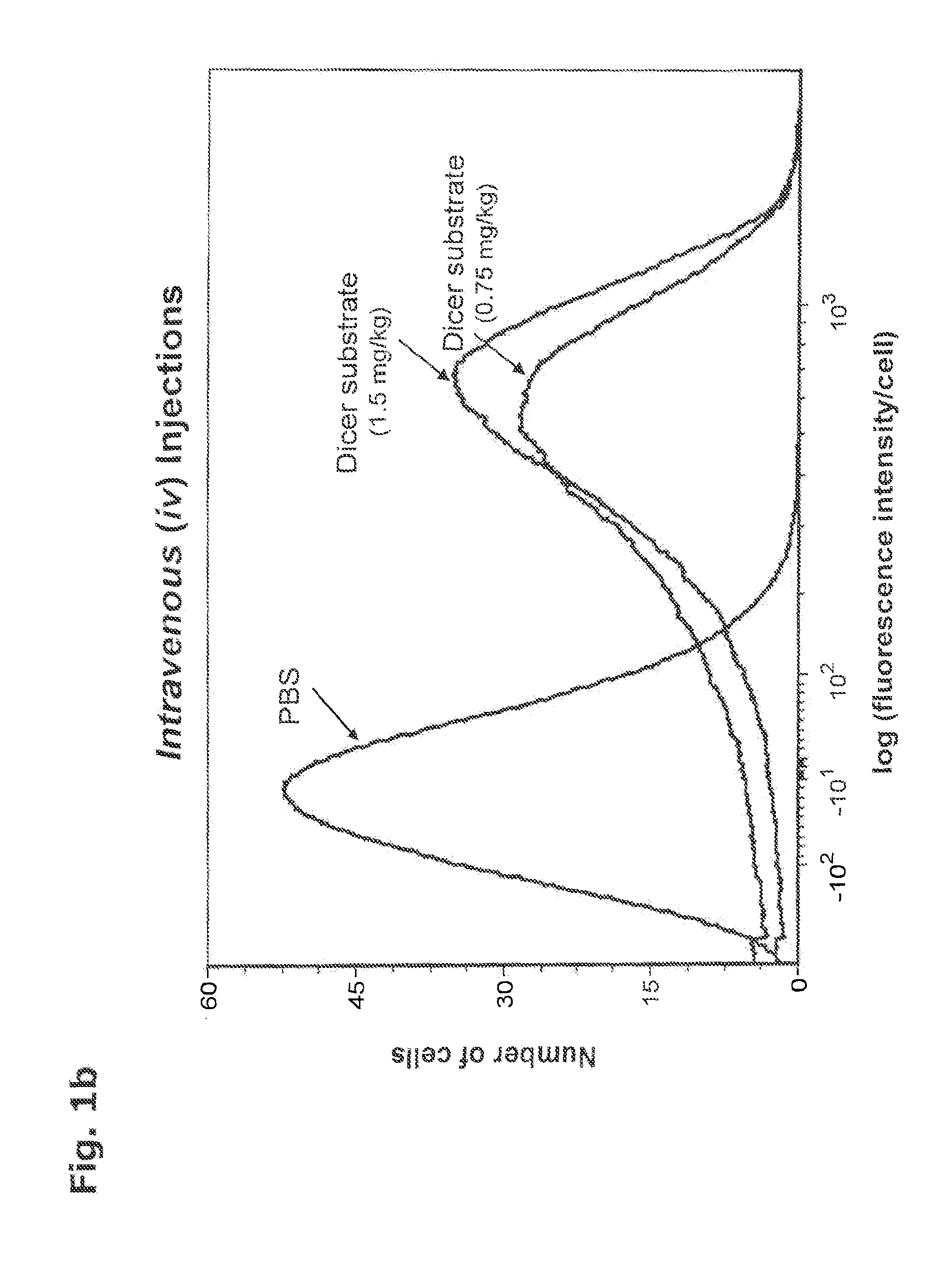
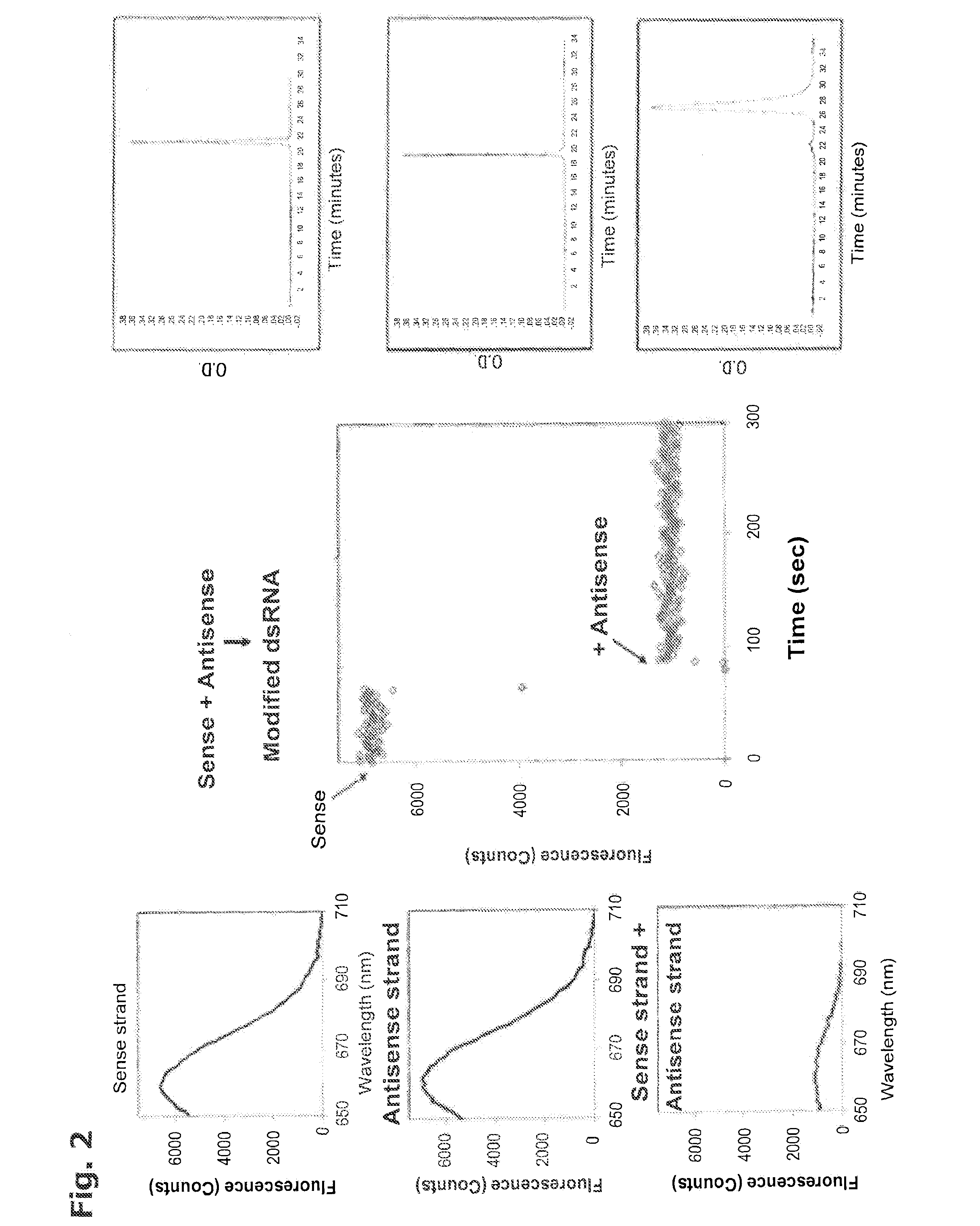
This invention provides a method for the in vivo delivery of oligonucleotides. The invention utilizes the presence of one or plurality of HES linked to an oligonucleotide to deliver a nucleic acid sequence of interest into the cytoplasm of cells and tissues of live organisms. The delivery vehicle is nontoxic to cells and organisms. Since delivery is sequence-independent and crosses membranes in a receptor-independent manner, the delivered oligonucleotide can target complementary sequences in the cytoplasm as well as in the nucleus of live cells. Sequences of bacterial or viral origin can also be targeted. The method can be used for delivery of genes coding for expression of specific proteins, antisense oligonucleotides, siRNAs, shRNAs, Dicer substrates, miRNAs, anti-miRNAs or any nucleic acid sequence in a living organism. The latter include mammals, plants, and microorganisms such as bacteria, protozoa, and viruses.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Lipase, its gene, yalulipolytic geast for producing said enzyme and its application
ActiveCN1948470AWide substrate adaptabilityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesFungiConservative mutationAmino acid
This invention relates to a preparation of a kind of lipase and the method of using the lipase to compound ester. Exactly is that amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO:1 or its lipase of conservative mutation sequence, it also relates to the gene coding this lipase, Yarrowia lipolytica generating this lipase.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
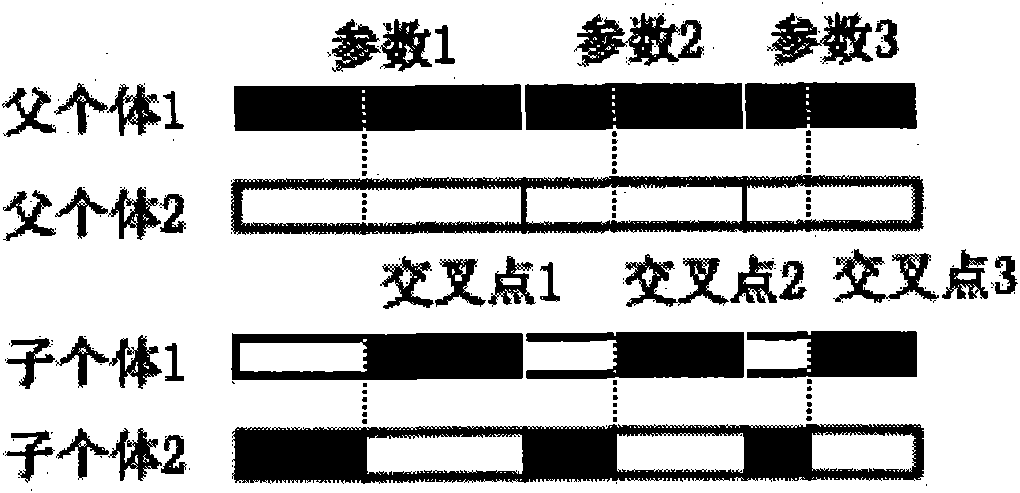
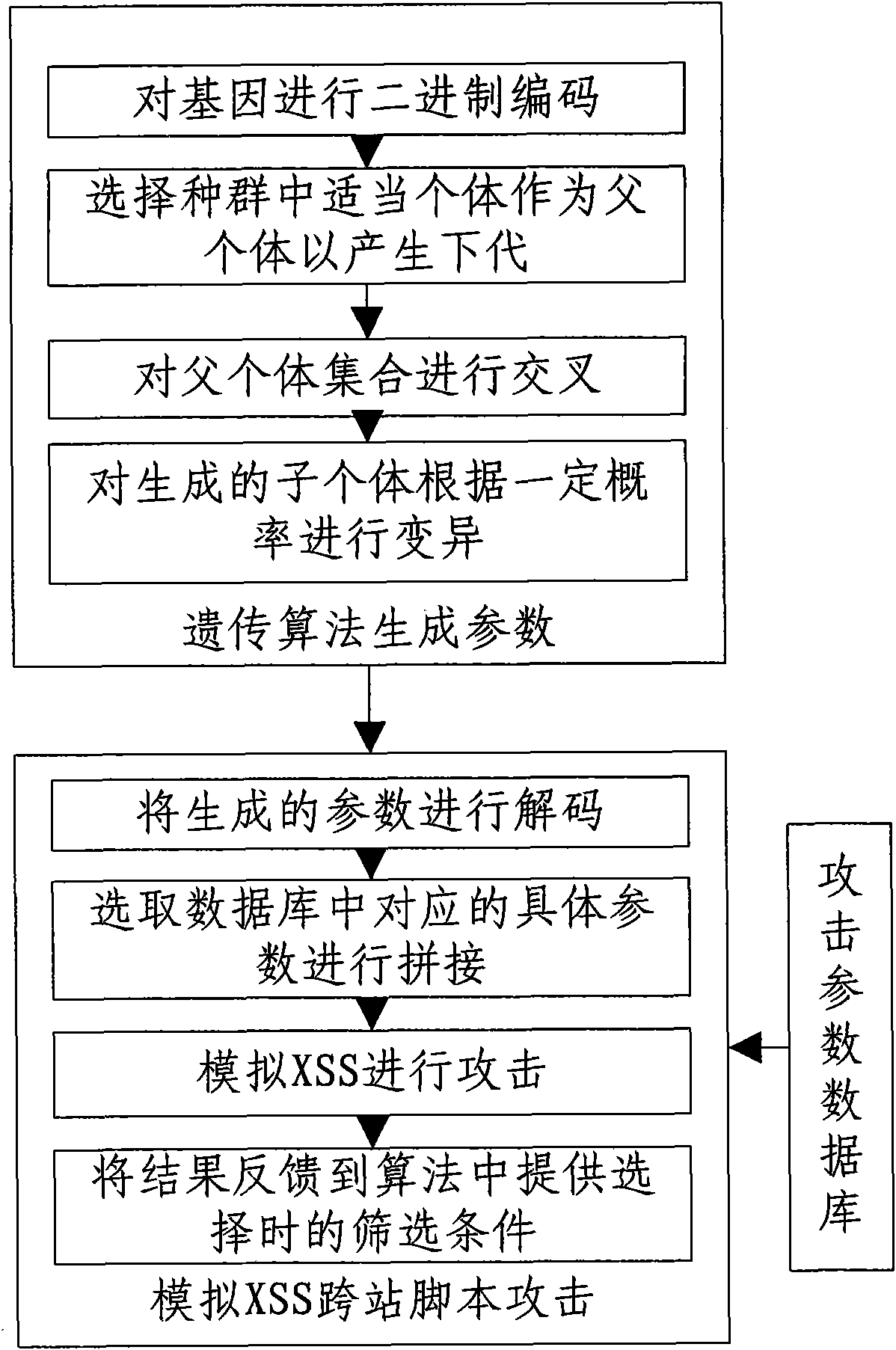
Method for automatically generating cross site script (XSS) vulnerability detection parameter by using genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101894237AQuick buildWide coverageGenetic modelsPlatform integrity maintainanceAlgorithmGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a method for automatically generating a cross site script (XSS) vulnerability detection parameter by using a genetic algorithm. The method realizes the algorithm according to the parameter rules of XSS vulnerabilities and the principle of the genetic algorithm by designing a set of detection parameter set, coding / decoding strategy and attack parameter database, using crossing, variation and selection operations of the genetic algorithm and designing a simulated attack operation. New parents and offspring are continuously generated through the feedback result of the simulated attack operation and the gene coding strategy, and the algorithm is circularly executed till reaching an expected algebra. The method for automatically generating the XSS vulnerability detection parameter by using the genetic algorithm is reliable and complete, has wide coverage and high execution speed, and can be applied to the field of automatically generating the XSS vulnerability detection parameter.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
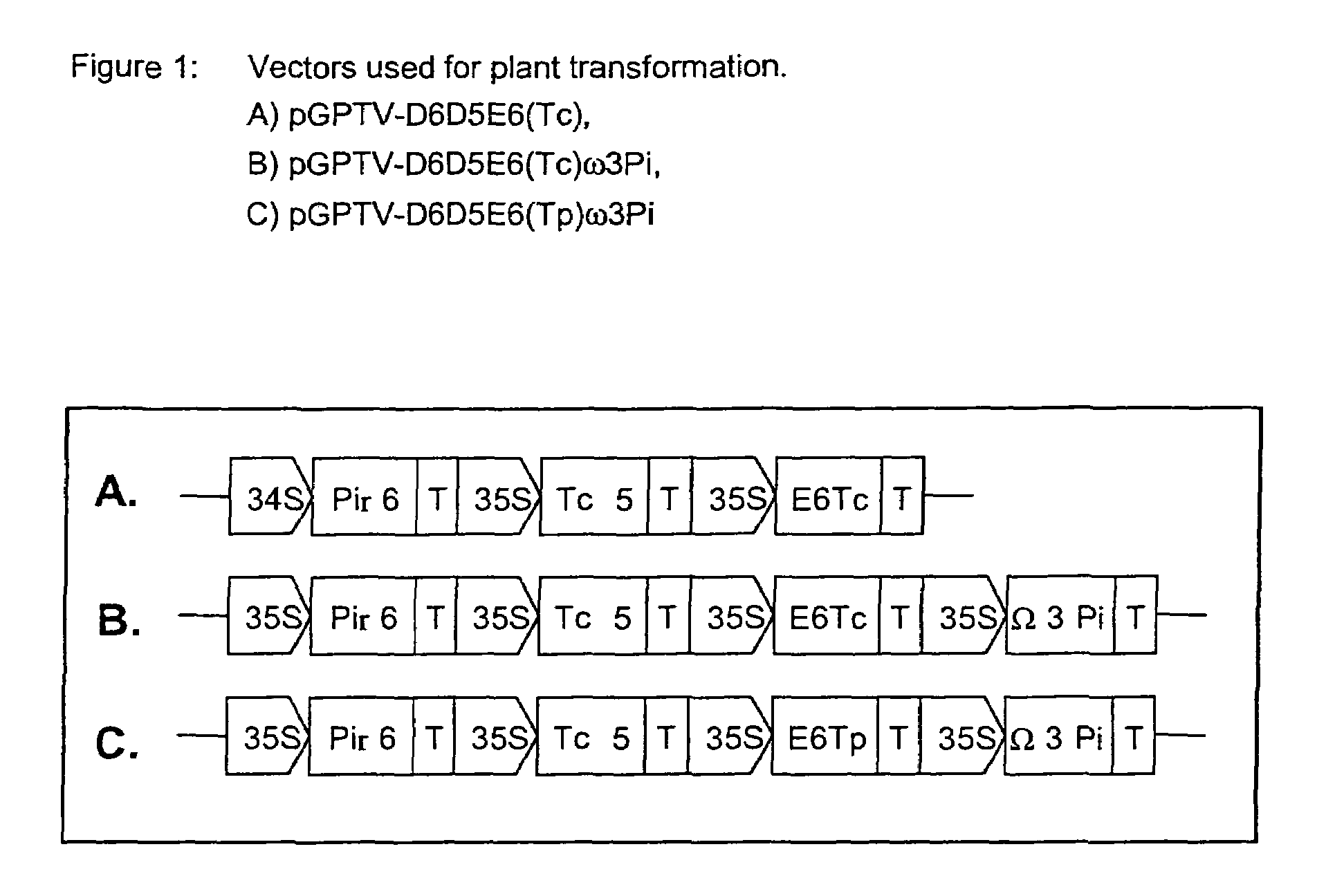
Method for producing arachidonic acid and/or eicosapentaenoic acid in useful transgenic plants
InactiveUS8134046B2Simple and inexpensive and economicalHigh nutritional valueCosmetic preparationsBiocideBiotechnologyTransgene
The present invention relates to a process for producing arachidonic acid and / or eicosapentaenoic acid in transgenic useful plants by introducing into the plant nucleic acids coding for polypeptides having Δ6-desaturase, Δ6-elongase or Δ5-desaturase activity. Furthermore, a gene coding for an ω3-desaturase is advantageously expressed in said useful plants. In another advantageous embodiment of the process, further nucleic acid sequences coding for polypeptides of fatty acid or lipid metabolism biosynthesis may be expressed in the plants. Particularly advantageous nucleic acid sequences here are those coding for a Δ8-desaturase, Δ12-desaturase, Δ15-desaturase, Δ4-desaturase, Δ9-elongase and / or Δ5-elongase activity.The invention further relates to the use of the oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced in the process according to the invention in feedstuffs or foodstuffs, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
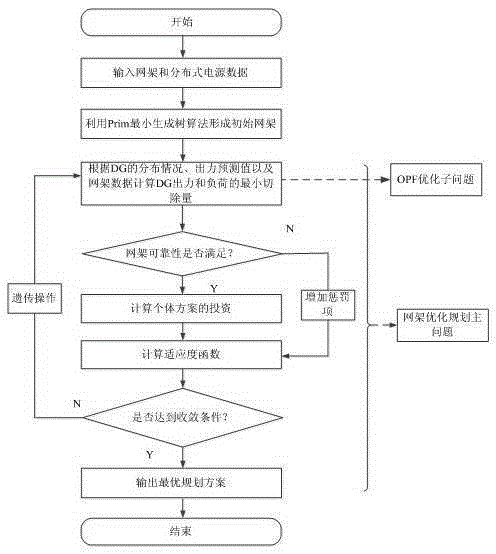
Active power distribution network frame planning method on the basis of bi-level planning
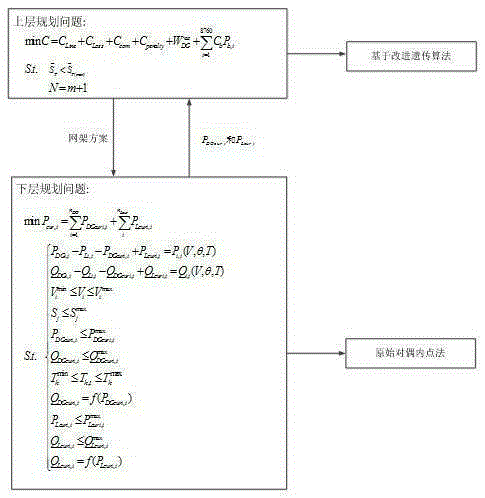
InactiveCN105279615AReduce the amount of resectionResourcesSystems intergating technologiesControl engineeringGenetics algorithms
The present invention discloses an active power distribution network frame planning method on the basis of a bi-level planning. The active power distribution network frame planning method on the basis of the bi-level planning comprises the following steps: the first step, bi-level planning model constitution; the second step, gene code; the third step, formation of an original scheme; the fourth step, individual good and bad evaluation; the fifth step, genetic operation; and the sixth step, selection of an optimal scheme. According to the invention, a model is established about an active power distribution network frame planning problem on the basis of a bi-level planning concept, and an improved genetic algorithm is used for solution. Compared with a traditional active power distribution network frame planning method, the bi-level planning concept and the improved genetic algorithm are led in the active power distribution network frame planning method on the basis of a bi-level planning to solve problems. In respect of modeling, the bi-level planning model adopted by the invention is converted to a bi-level planning problem, namely an upper layer planning problem is the construction of a line and the lower layer planning problem is minimum active power output excised amount of distributed generation under the network frame.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO
Transferase and amylase, process for producing the enzymes, use thereof, and gene coding for the same
The invention provides a novel transferase that acts on a saccharide, as a substrate, composed of at least three sugar units wherein at least three glucose residues on the reducing end are linked alpha-1,4 so as to transfer the alpha-1,4 lingages to a alpha-1,alpha-1 linkages; a process for producing the transferase; a gene coding for the same; and a process for producing an oligosaccharide by using the same. Also provided are a novel amylase that has a principal activity of acting on a saccharide, as a substrate, composed of at least three sugar units wherein at least three sugar units on the reducing end side are glucose units and the linkage between the first and the second glucose units is alpha-1,alpha-1 while the linkage between the second and the third glucose units is alpha-1,4 so as to liberate alpha,alpha-trehalose by hydrolyzing the alpha-1,4 linkage and another activity of hydrolyzing the alpha-1,4 linkage within the molecular chain of the substrate and that liberates disaccharides and / or monosaccharides as the principal final products; a process for producing the amylase; a gene coding for the same; and a process for producing alpha,alpha-trehalose by using a combination of the transferase and the amylase.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20090098621A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesGemella
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com