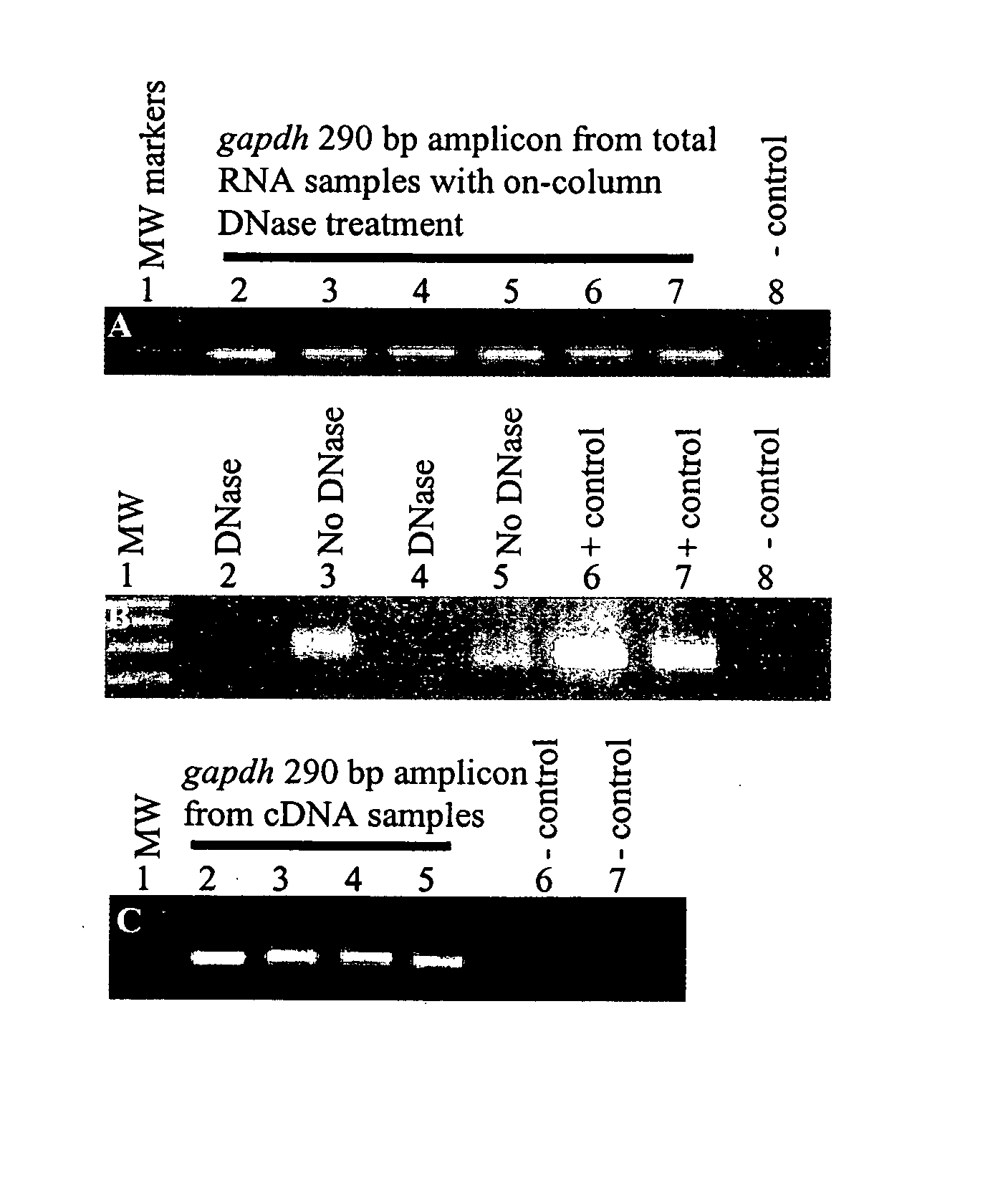
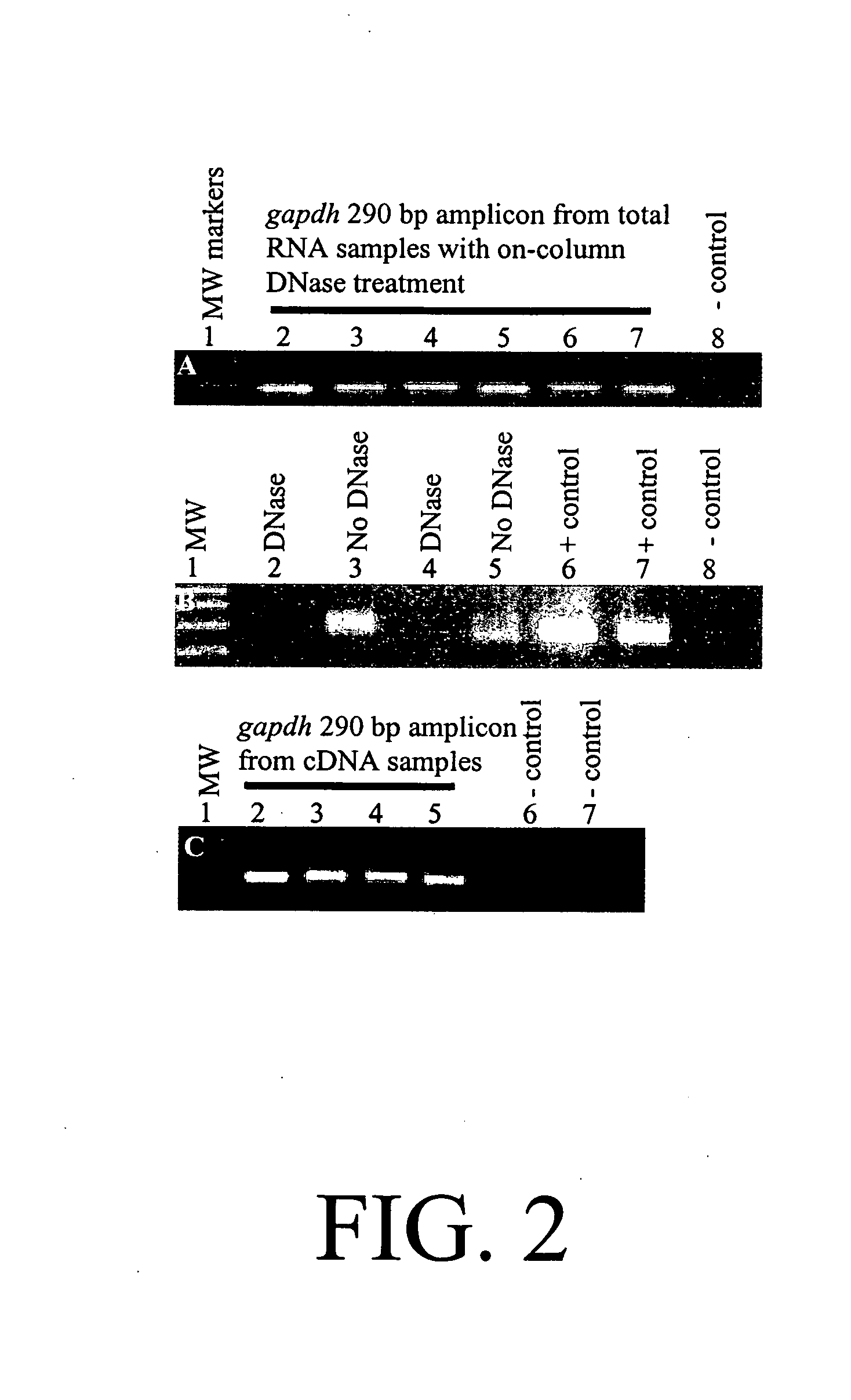
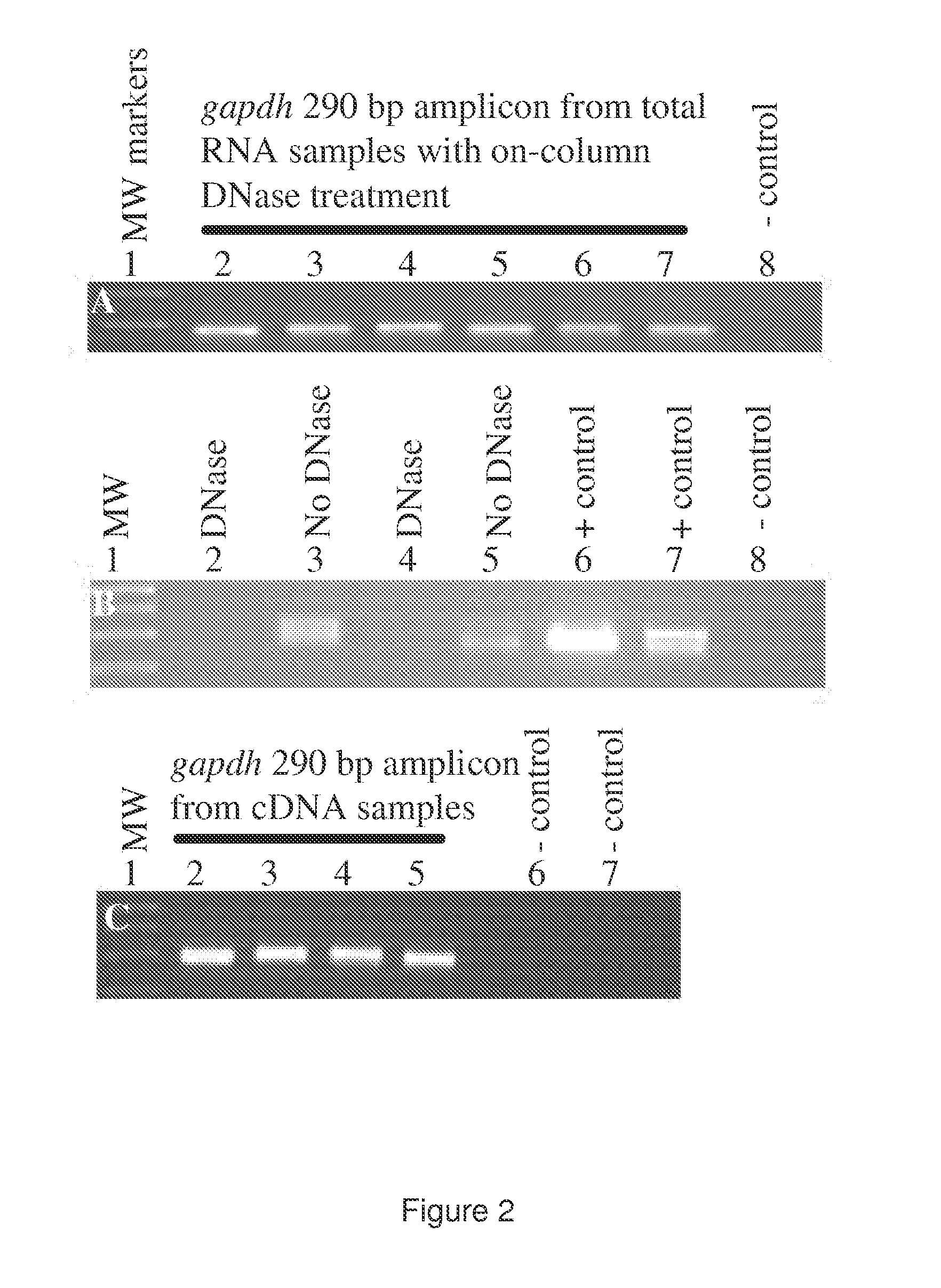
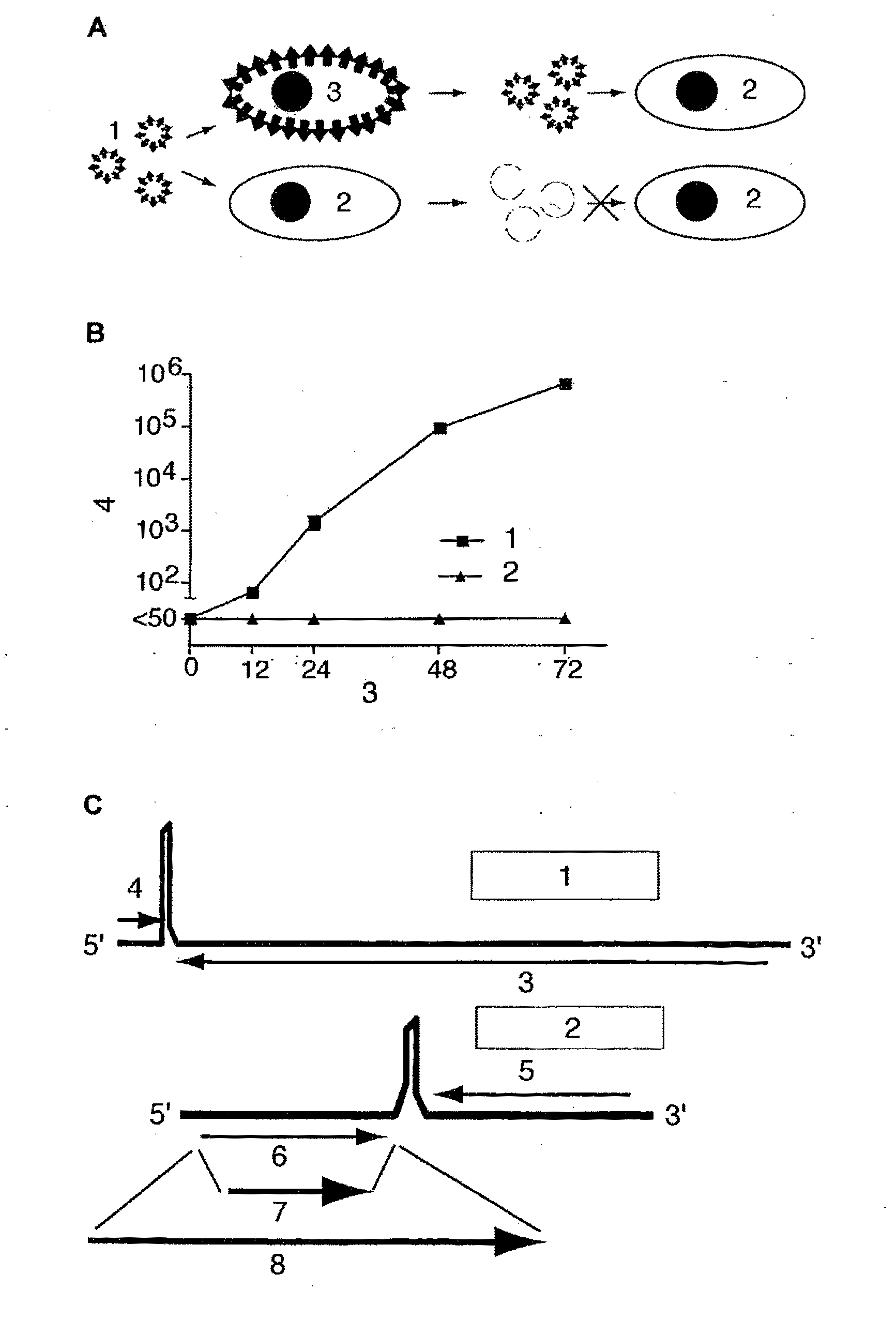
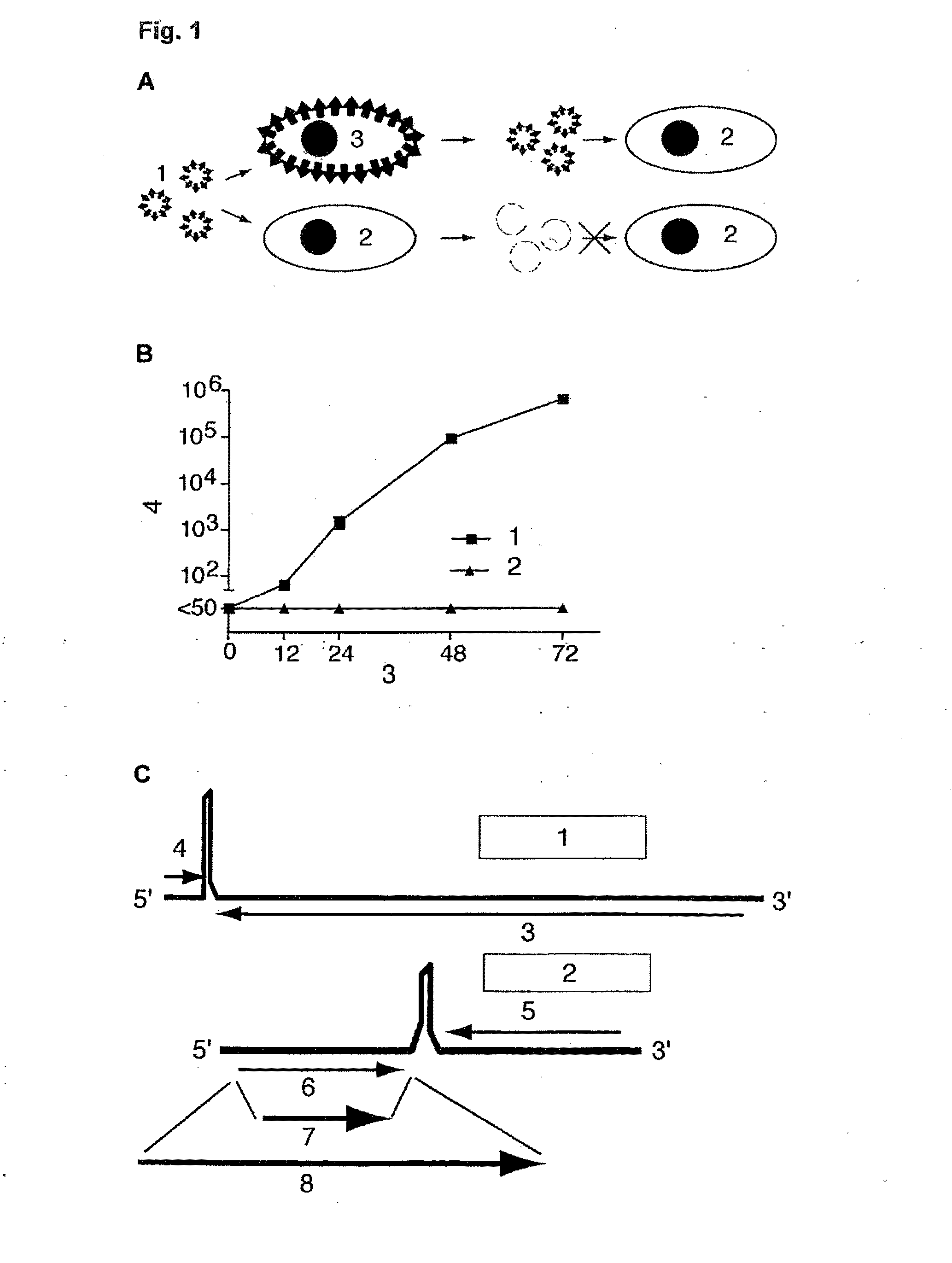
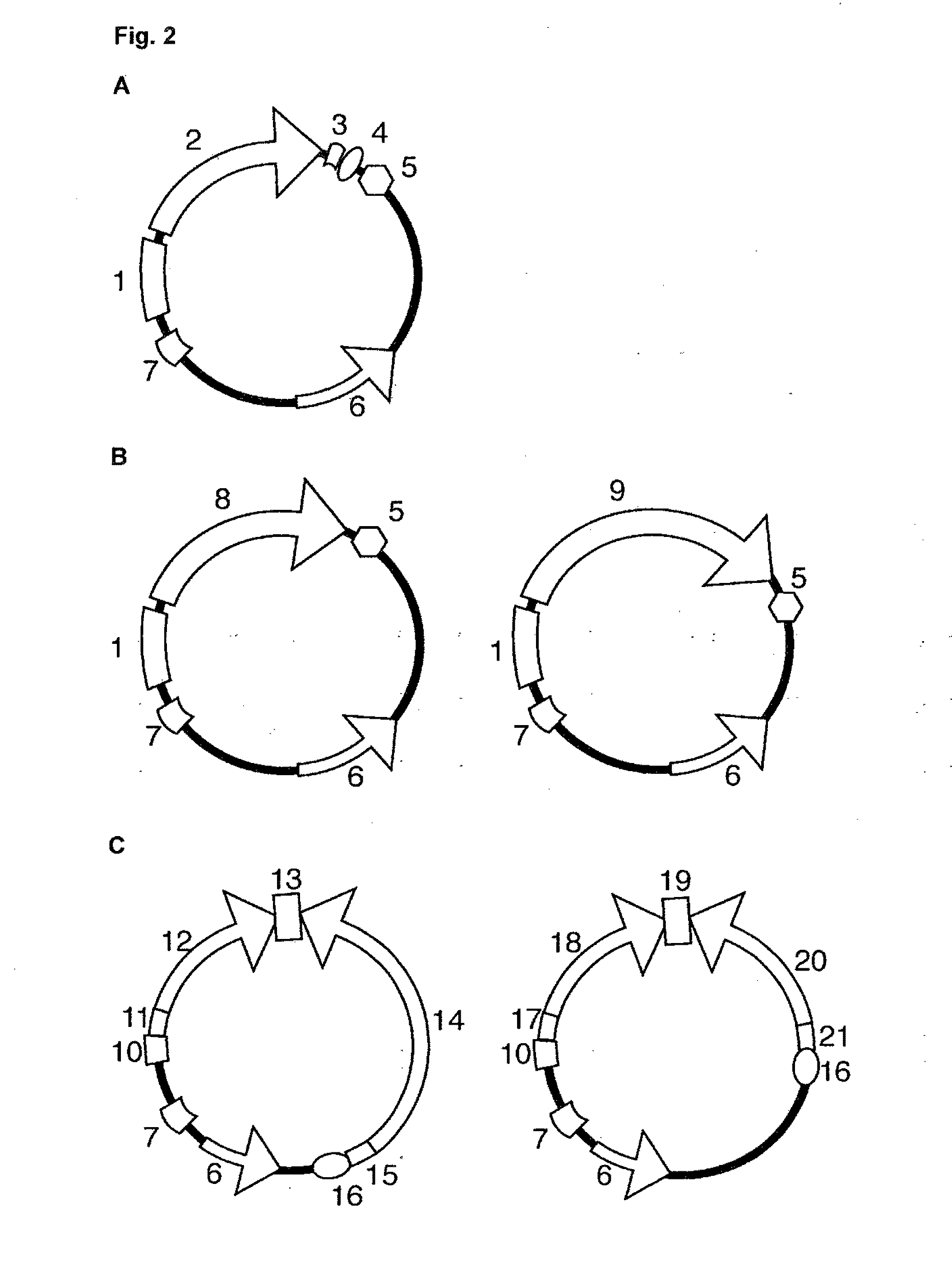
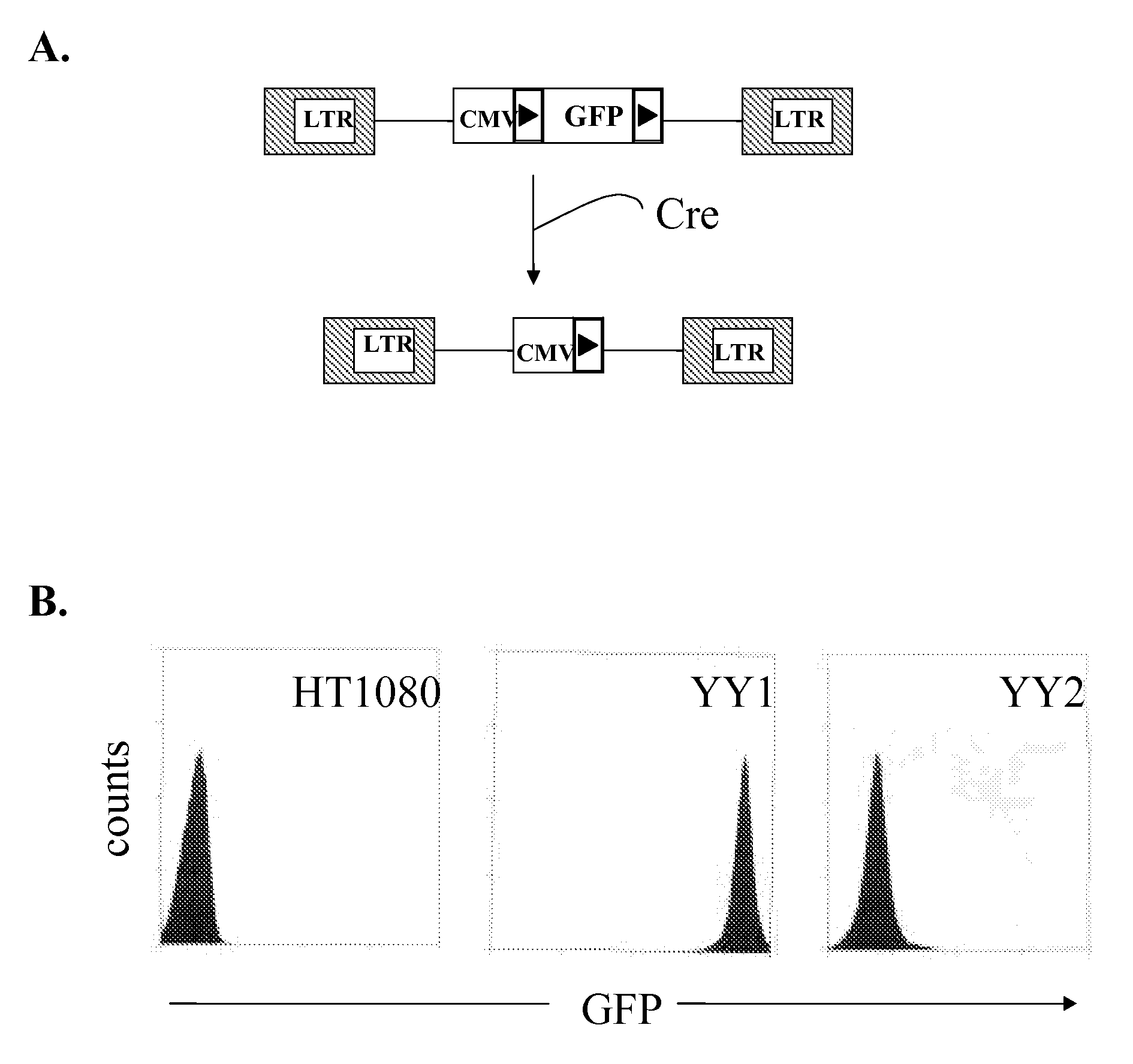
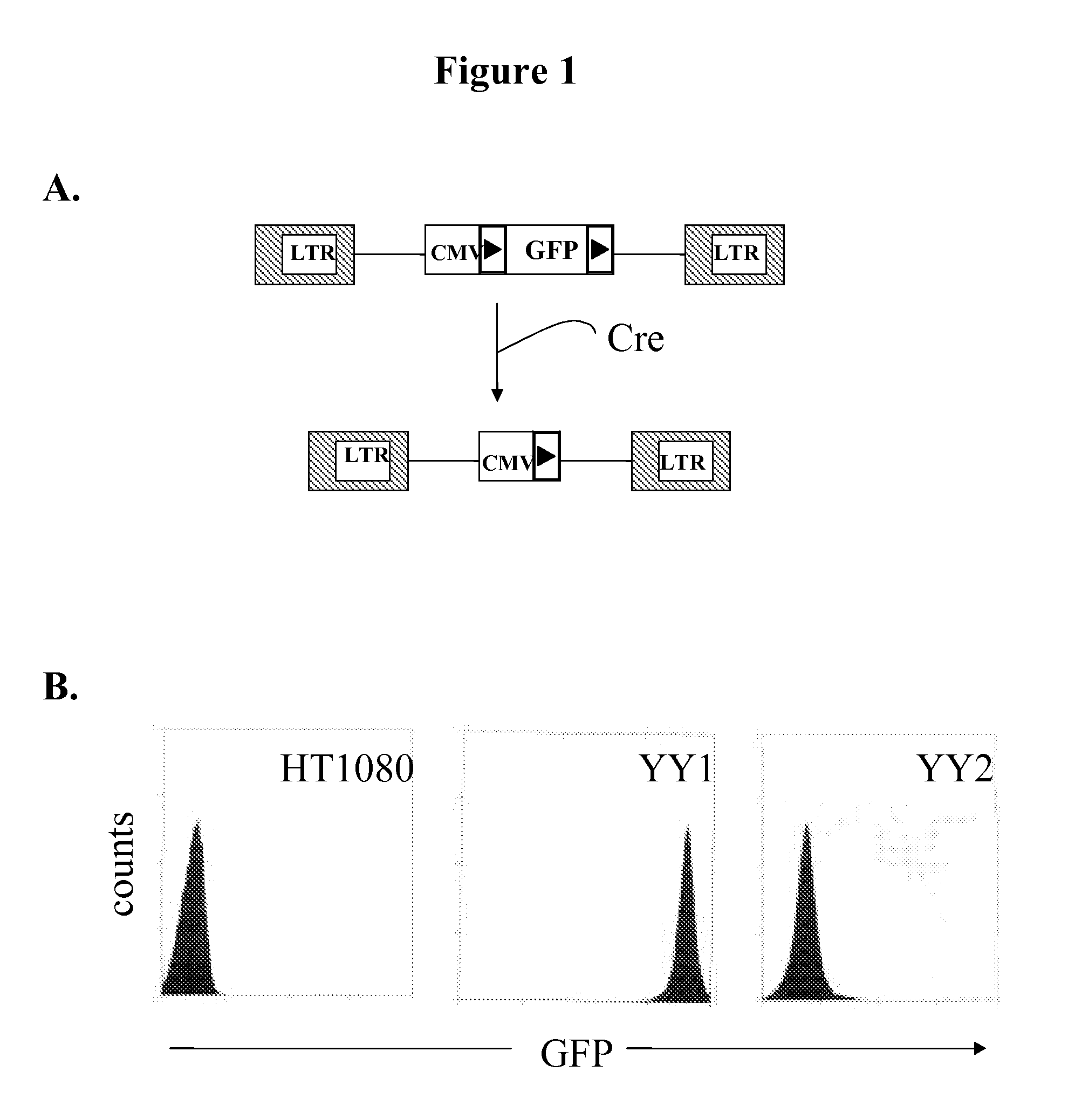
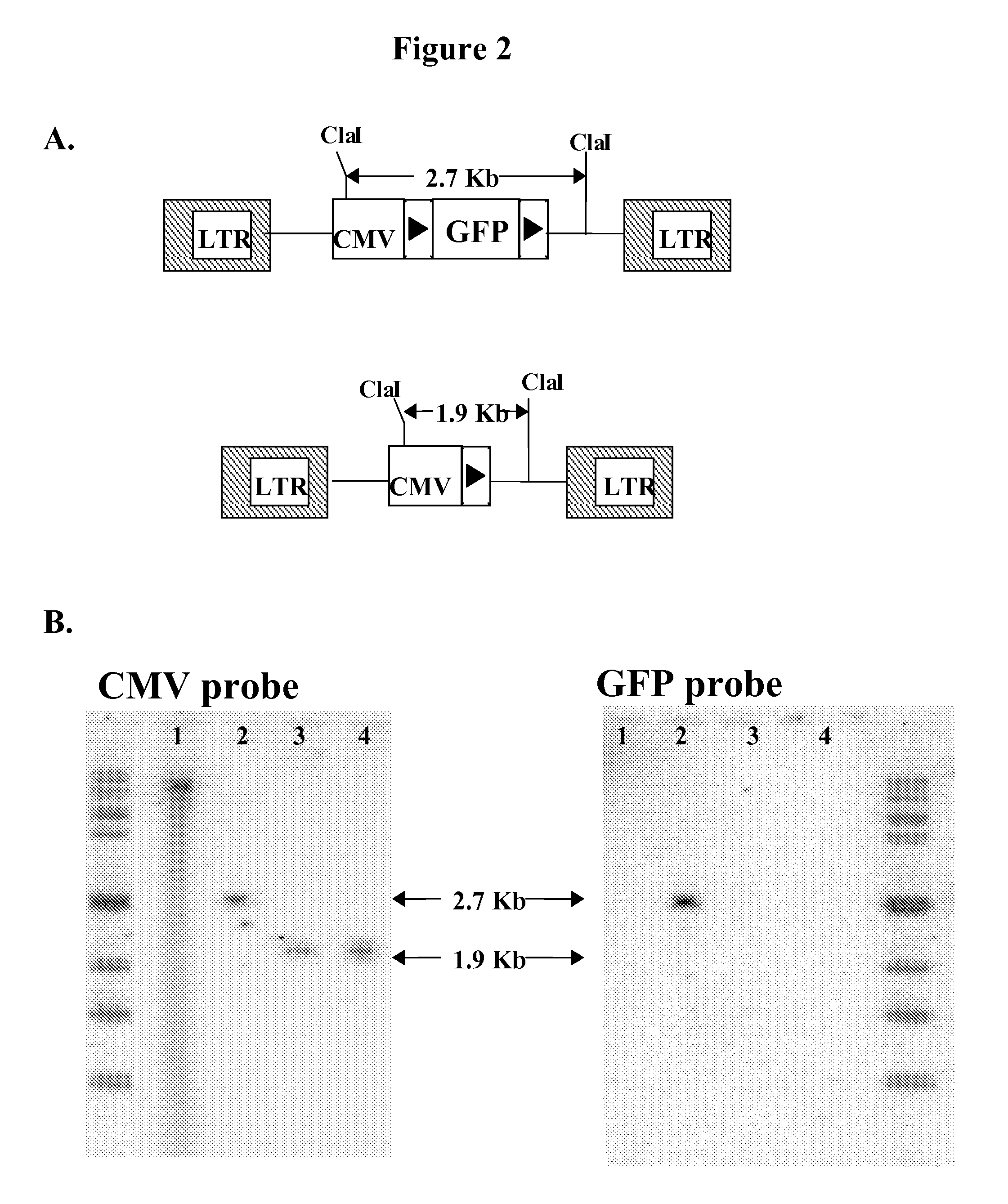
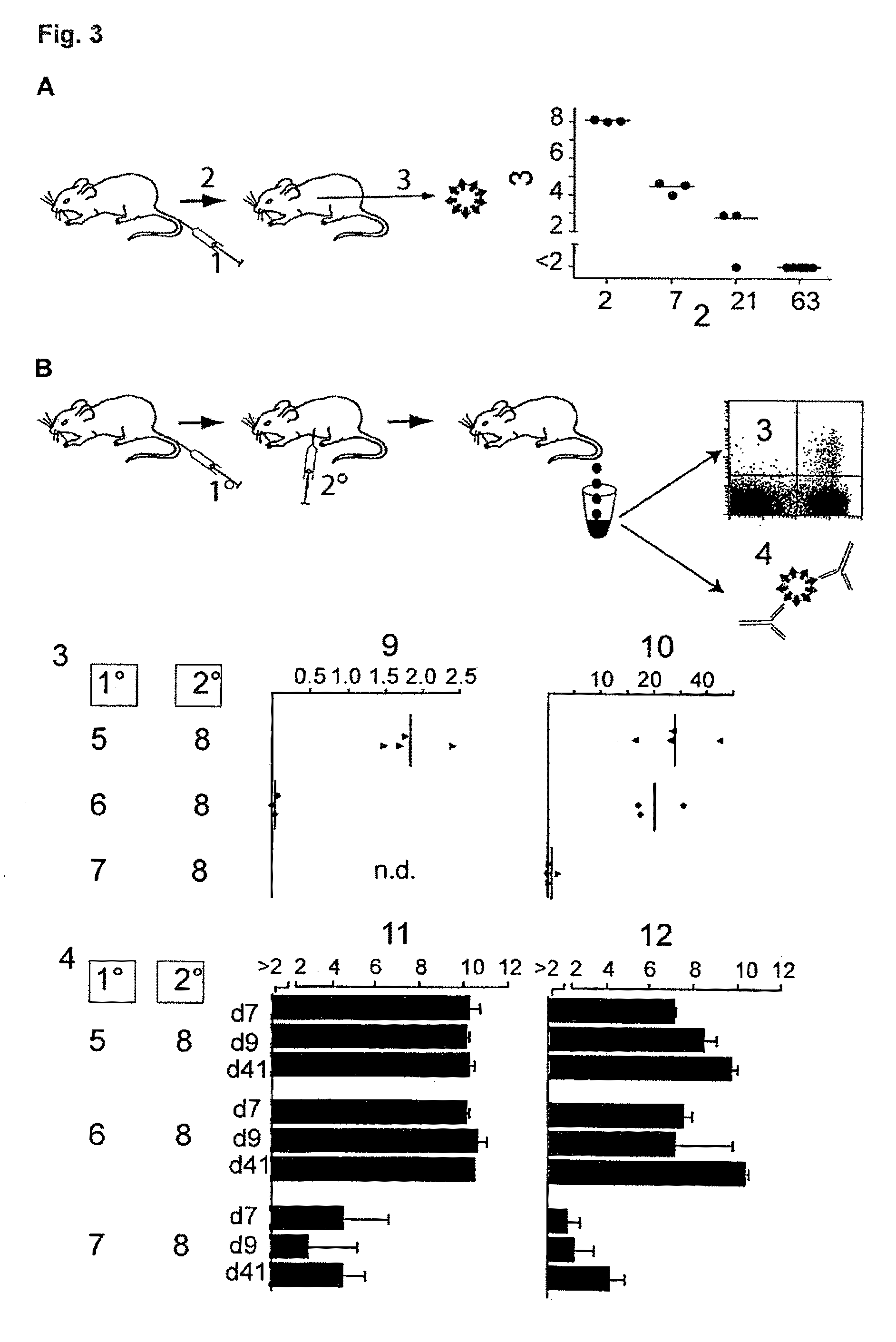
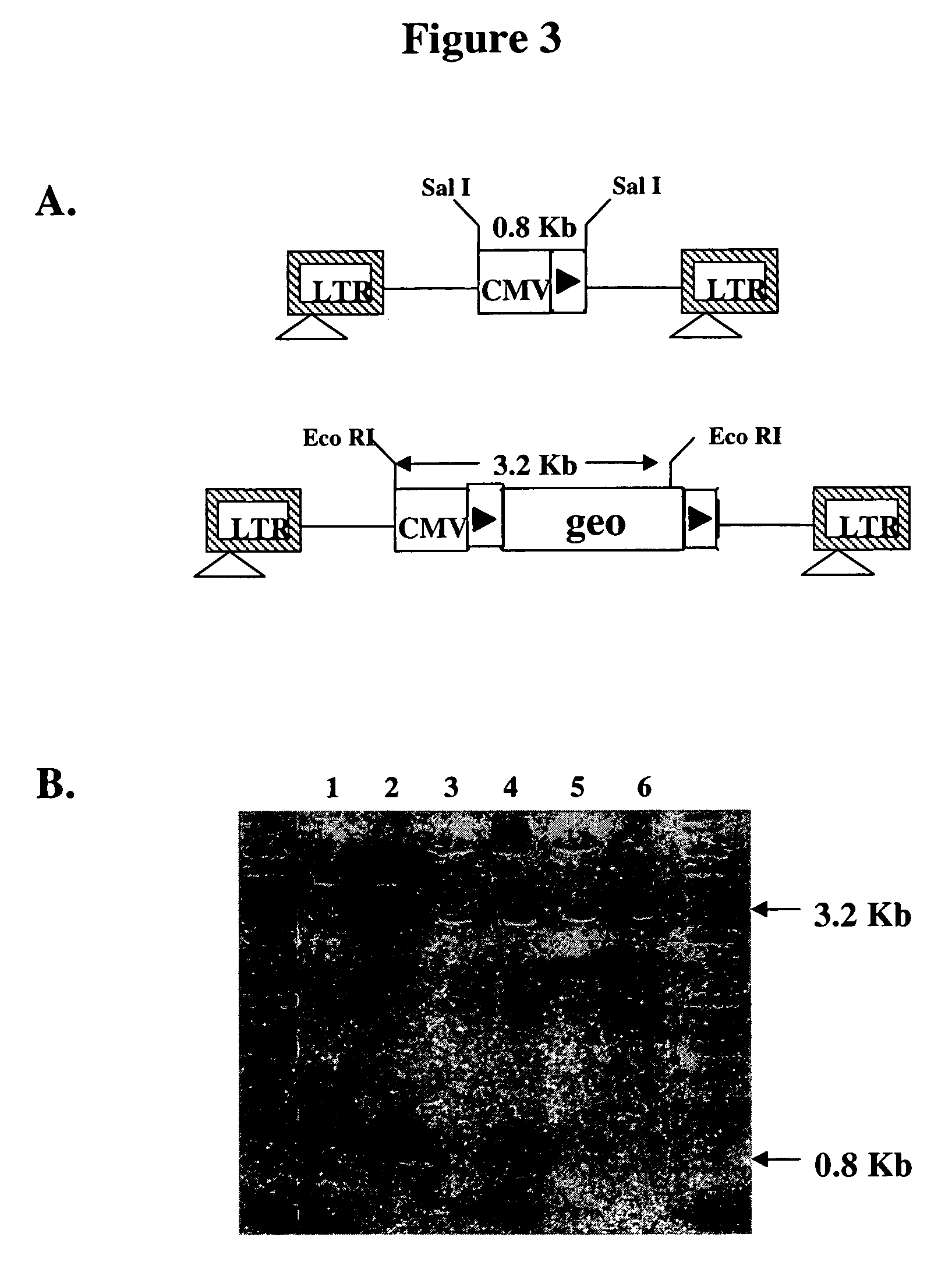
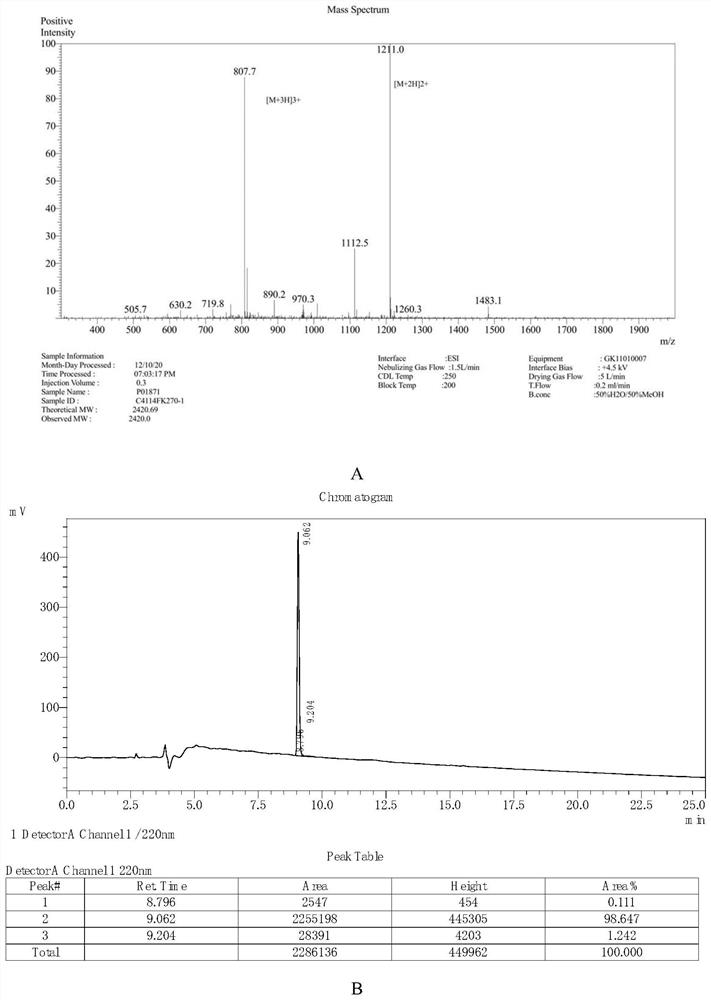
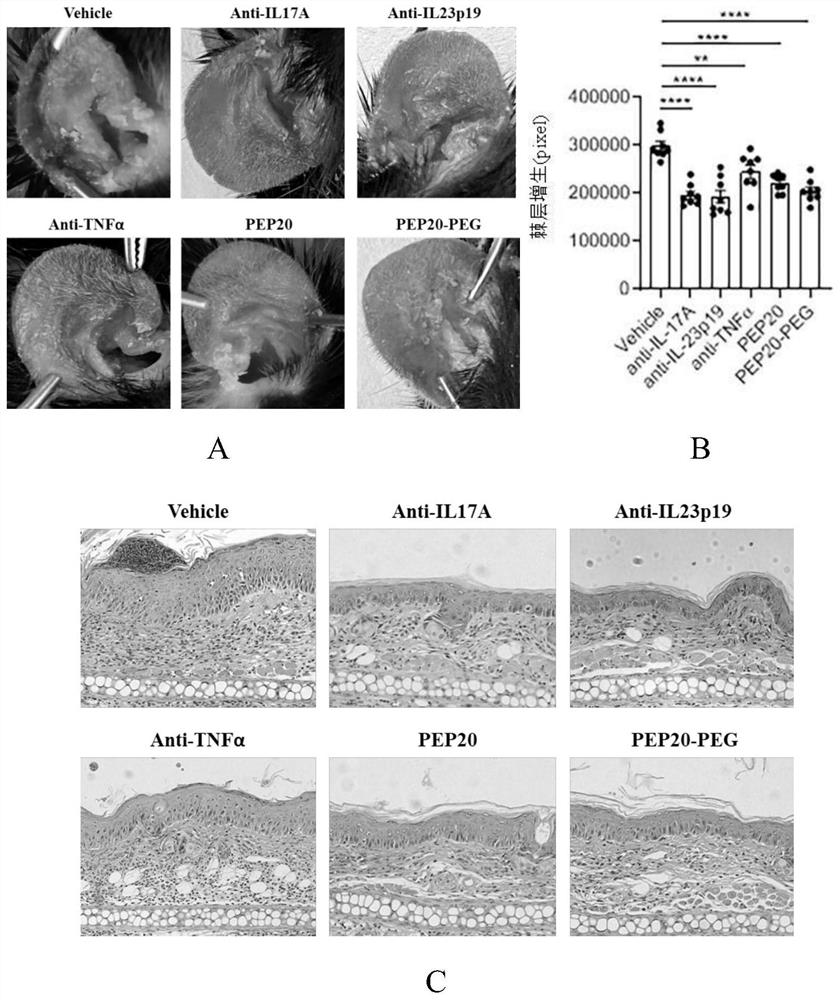
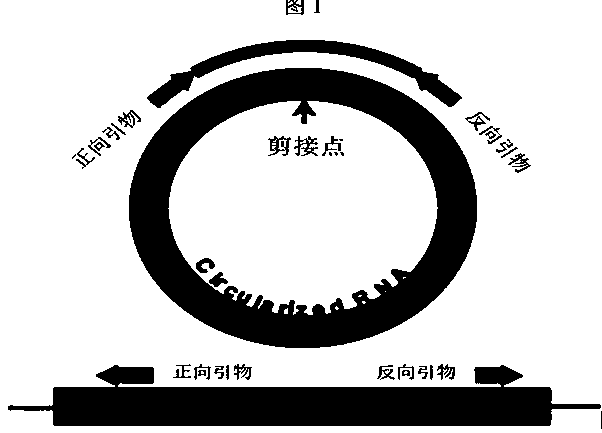
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Host gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In humans, the majority of snoRNA genes are located within highly expressed protein-coding or non-coding host genes, and more precisely in parts of the host genes called introns; elements of the host gene that are excluded during the synthesis of the mature RNA during the process of splicing.
Diagnosis and prognosis of infectious diseases clinical phenotypes and other physiologic states using host gene expression biomarkers in blood
InactiveUS20080020379A1High sensitivityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementWhite blood cellHost gene
The present invention provides a specific set of gene expression markers from peripheral blood leukocytes that are indicative of a host response to exposure, response, and recovery infectious pathogen infections. The present invention further provides methods for identifying the specific set of gene expression markers, methods of monitoring disease progression and treatment of infectious pathogen infections, methods of prognosing the onset of an infectious pathogen infection, and methods of diagnosing an infectious pathogen infection and identifying the pathogen involved.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Infectious Disease Clinical Phenotypes and other Physiologic States Using Host Gene Expression Biomarkers In Blood
InactiveUS20110183856A1High sensitivityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningWhite blood cellPhysiologic States
The present invention provides a specific set of gene expression markers from peripheral blood leukocytes that are indicative of a host response to exposure, response, and recovery infectious pathogen infections. The present invention further provides methods for identifying the specific set of gene expression markers, methods of monitoring disease progression and treatment of infectious pathogen infections, methods of prognosing the onset of an infectious pathogen infection, and methods of diagnosing an infectious pathogen infection and identifying the pathogen involved.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
ActiveUS20100297172A1Enhance protein expressionHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntigenDisease
The invention relates to an infectious arenavirus particle that is engineered to contain a genome with the ability to amplify and express its genetic information in infected cells but unable to produce further infectious progeny particles in normal, not genetically engineered cells. One or more of the four arenavirus open reading frames glycoprotein (GP), nucleoprotein (NP), matrix protein Z and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L are removed or mutated to prevent replication in normal cells but still allowing gene expression in arenavirus vector-infected cells, and foreign genes coding for an antigen or other protein of interest or nucleic acids modulating host gene expression are expressed under control of the arenavirus promoters, internal ribosome entry sites or under control of regulatory elements that can be read by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cellular RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. The modified arenaviruses are useful as vaccines and therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Novel lentiviral vectors for site-specific gene insertion
ActiveUS20080200663A1Easy to reorganizeSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryTherapy Trial
Murine leukemia virus (MLV) and lentivirus vectors have been used previously to deliver genes to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in human gene therapy trials. However, these vectors integrate randomly into the host genome, leading to disruption or inactivation of vital host genes. The present invention discloses a novel lentiviral vector system that overcomes this problem by integrating into a host genome in a site-specific manner.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Novel lentiviral vectors for site-specific gene insertion
ActiveUS20050266565A1Easy to reorganizeGenetic material ingredientsDepsipeptidesTherapy TrialVector system
Murine leukemia virus (MLV) and lentivirus vectors have been used previously to deliver genes to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in human gene therapy trials. However, these vectors integrate randomly into the host genome, leading to disruption or inactivation of vital host genes. The present invention discloses a novel lentiviral vector system that overcomes this problem by integrating into a host genome in a site-specific manner.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Method for identification and development of therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20060257865A1Slow onsetExcellent characteristicsHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell selectionAmino acid
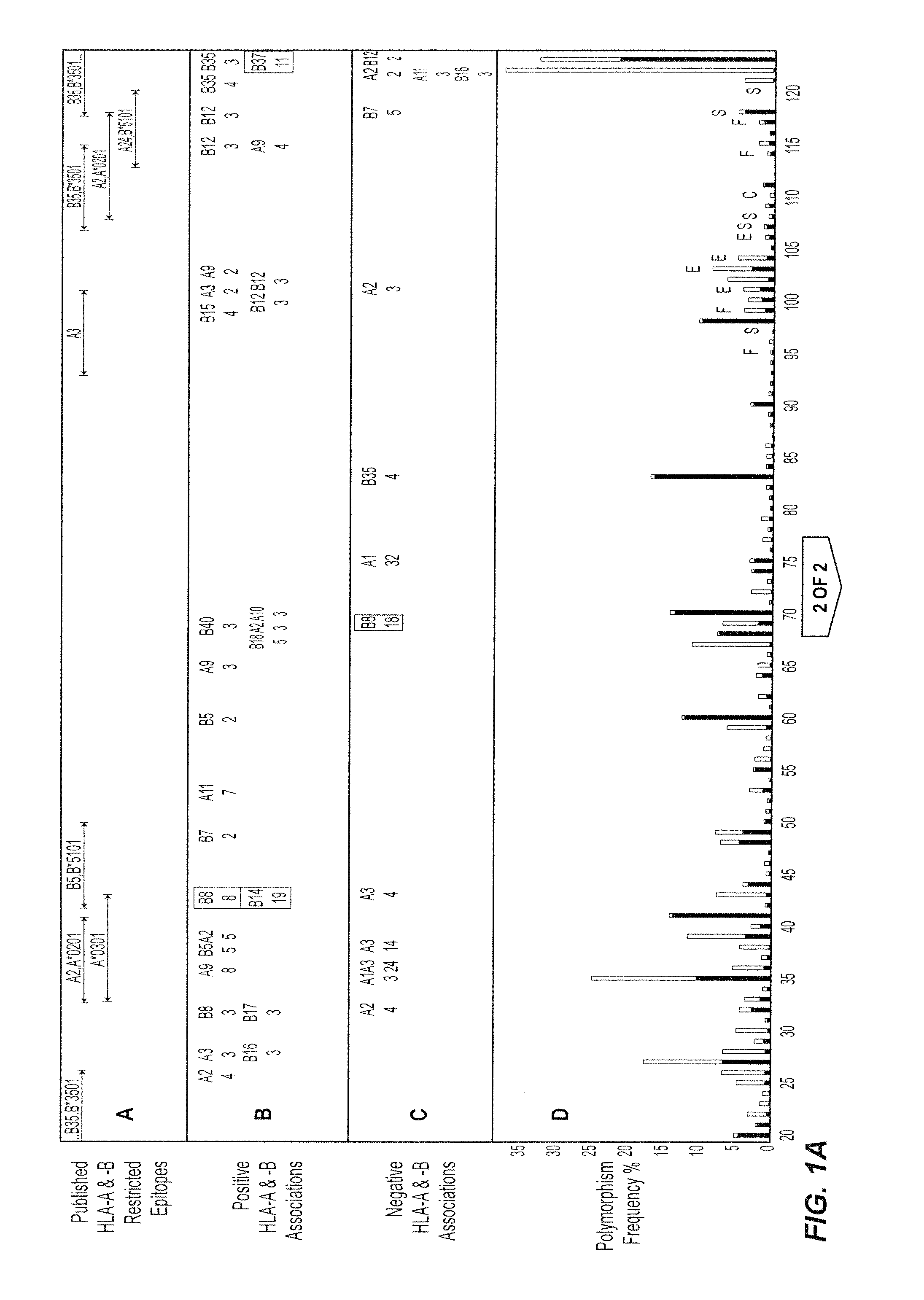
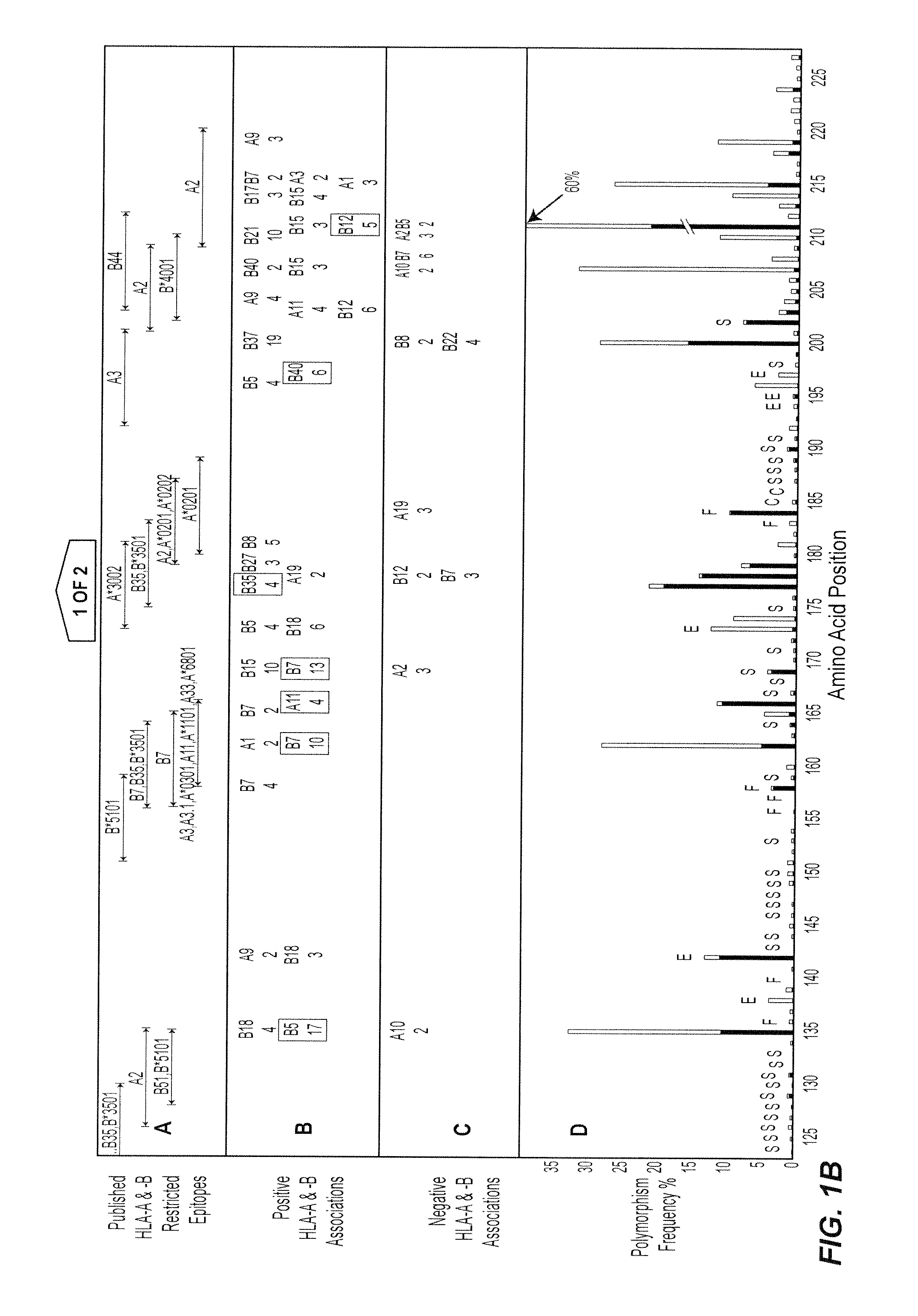
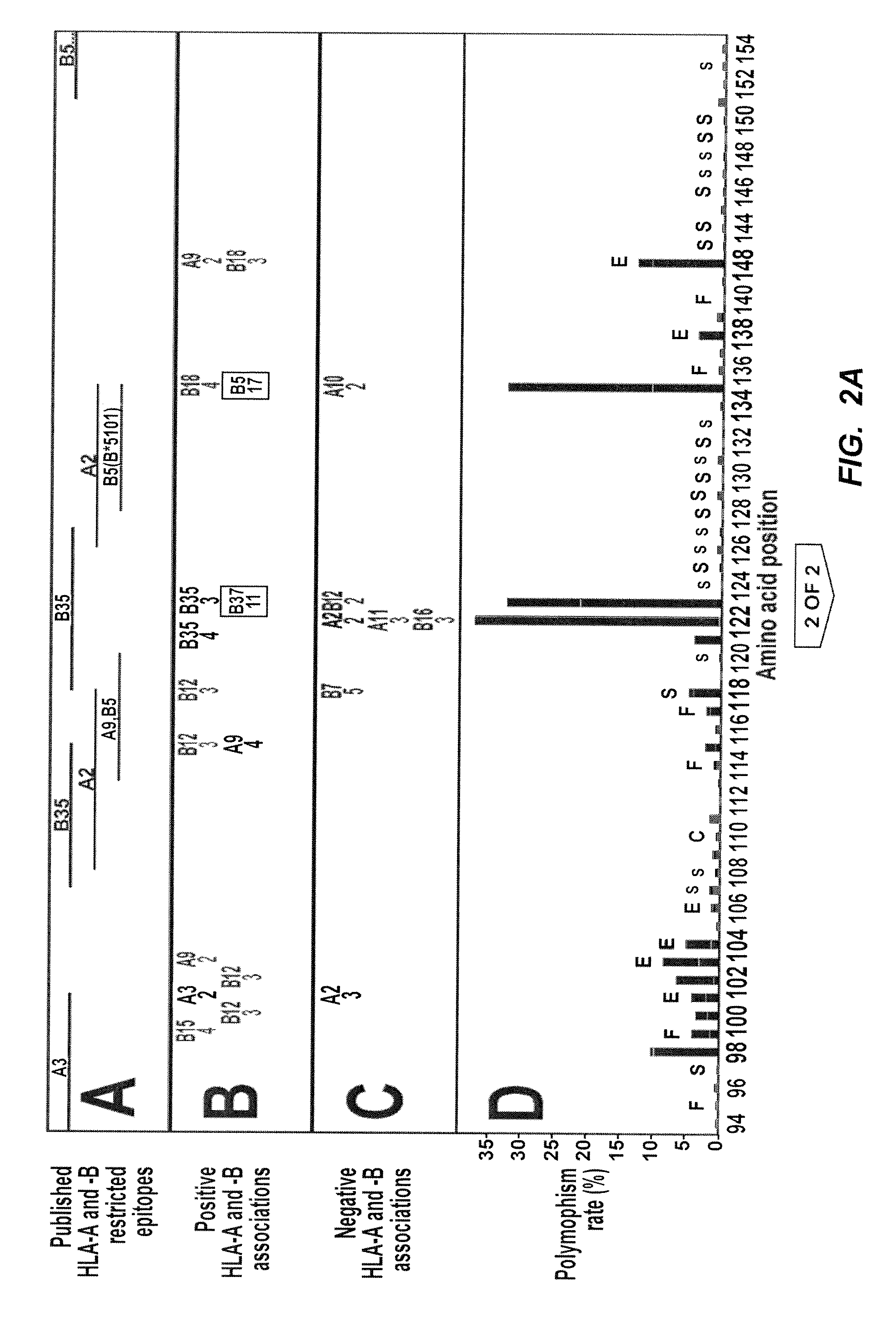
The present invention relates generally to the field of identification and determination of bioactive amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides method(s) for determining the influence of variation in host genes on selection of microorganisms with particular amino acid variants for the purpose of therapeutic drug or vaccine design or individualisation of such treatment. The invention also provides methods for identifying HLA allele-specific microorganism sequence polymorphisms that result from HLA restriction of antigen-specific cellular immune responses. It also provides diagnostic and therapeutic methodologies that may be used to measure or treat infection by a microorganism or to prevent infection by the microorganism.
Owner:EPIPOP
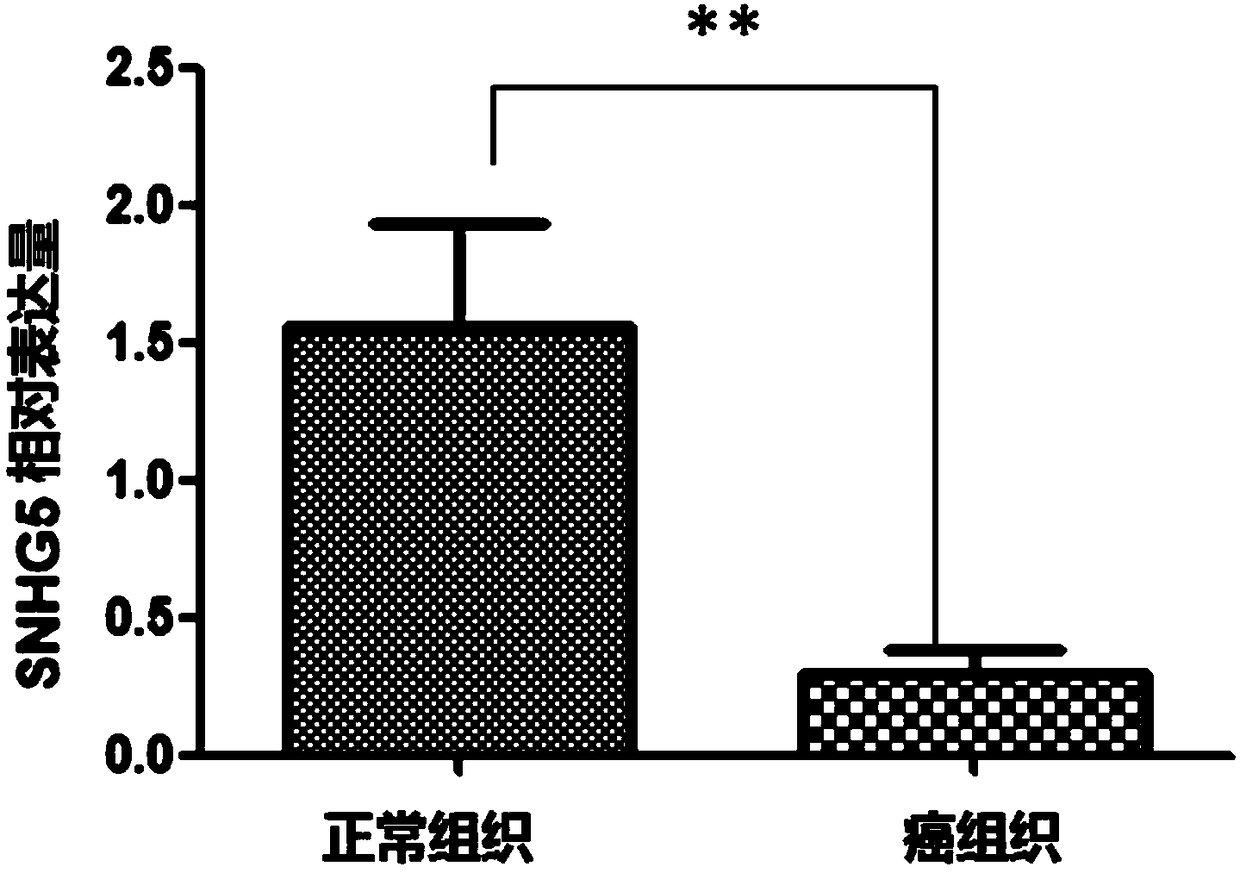
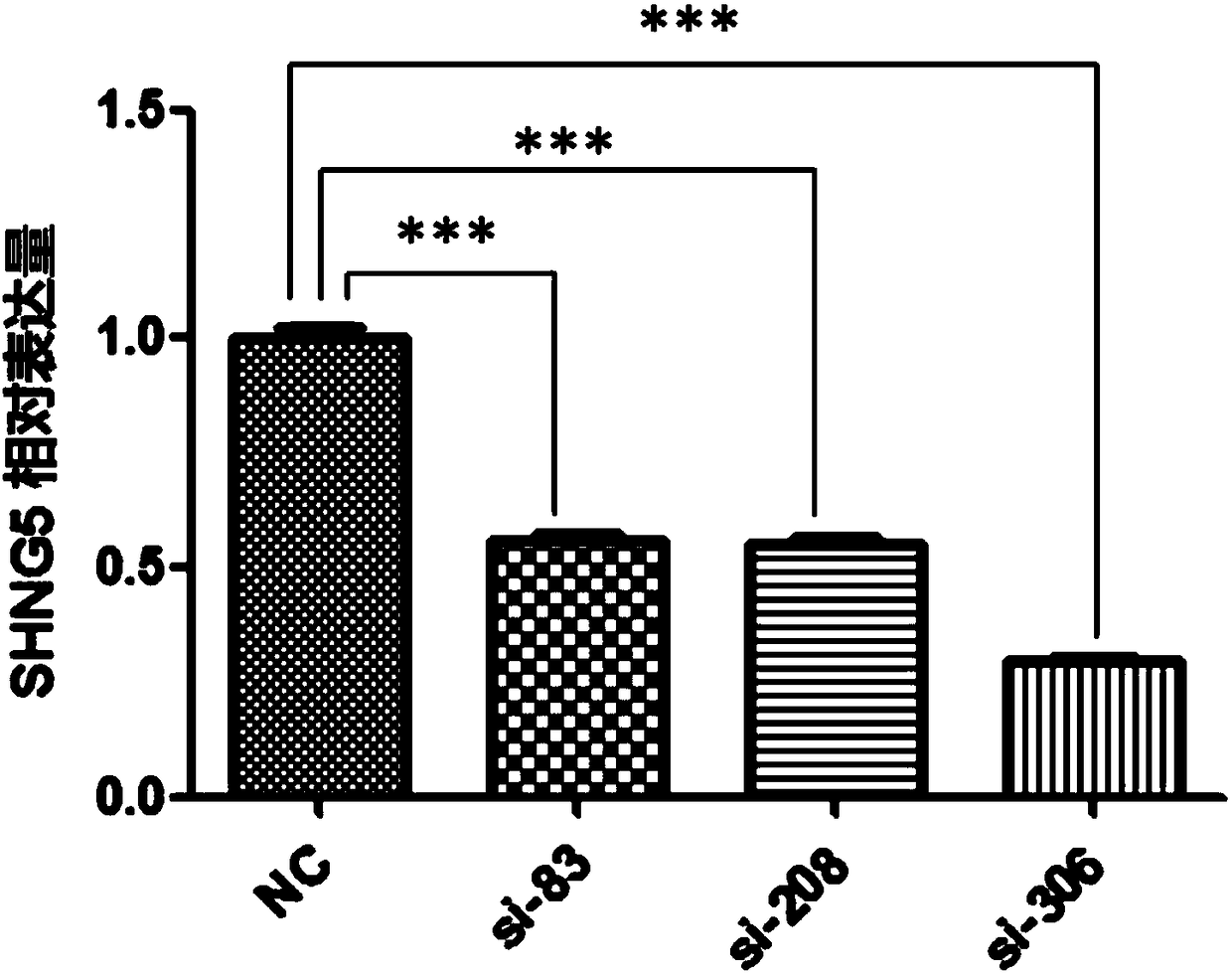
Application of SNHG5 (small nucleolar RNA host gene 5) in diagnosis, evaluation and efficacy prediction of breast cancer
InactiveCN108467891AHigh degree of malignancyMicrobiological testing/measurementApoptosisWilms' tumor
The invention discloses an application of SNHG5 (small nucleolar RNA host gene 5) in diagnosis, evaluation and efficacy prediction of breast cancer. It is found that lncRNA SNHG5 has significant low expression in breast cancer tissue and breast cancer cell lines, knockout of the lncRNA SNHG5 gene can enhance proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells and inhibit apoptosis, and thus, the expression level of long-chain non-coding RNA SNHG5 is closely related with diagnosis, transfer and relapse of tumor, patient prognosis and neoadjuvant chemotherapy effect are closely related, which indicates that the lncRNA SNHG5 gene can be used as a marker for diagnosis, prognosis evaluation or effect prediction. A breast cancer cell model which has low expression of SNHG5 and is established by transfecting breast cancer cell lines with small interference RNA can be used in a preparation method of a preparation for preventing relapse and transfer of breast cancer.
Owner:TONGDE HOSPITAL OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
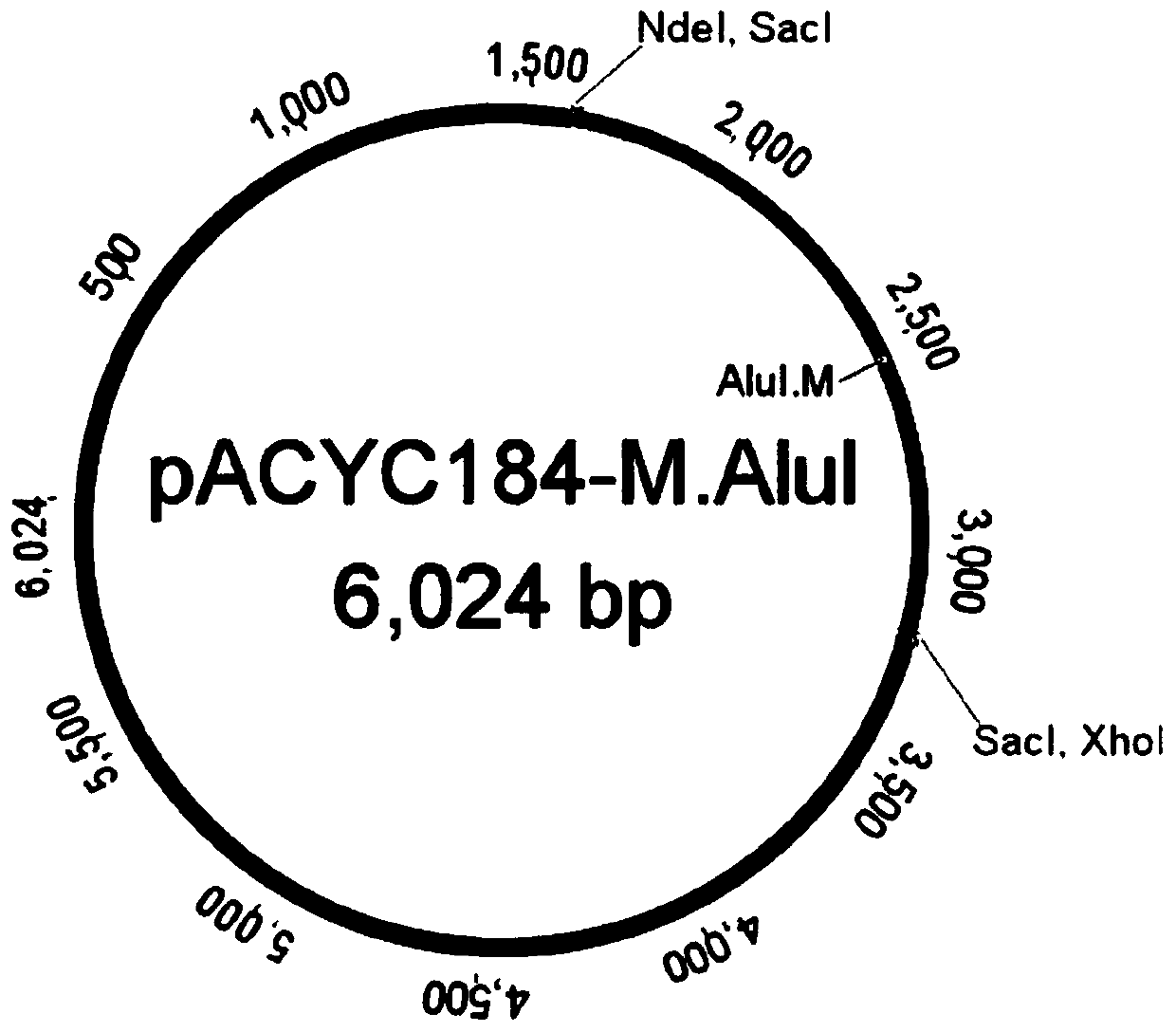
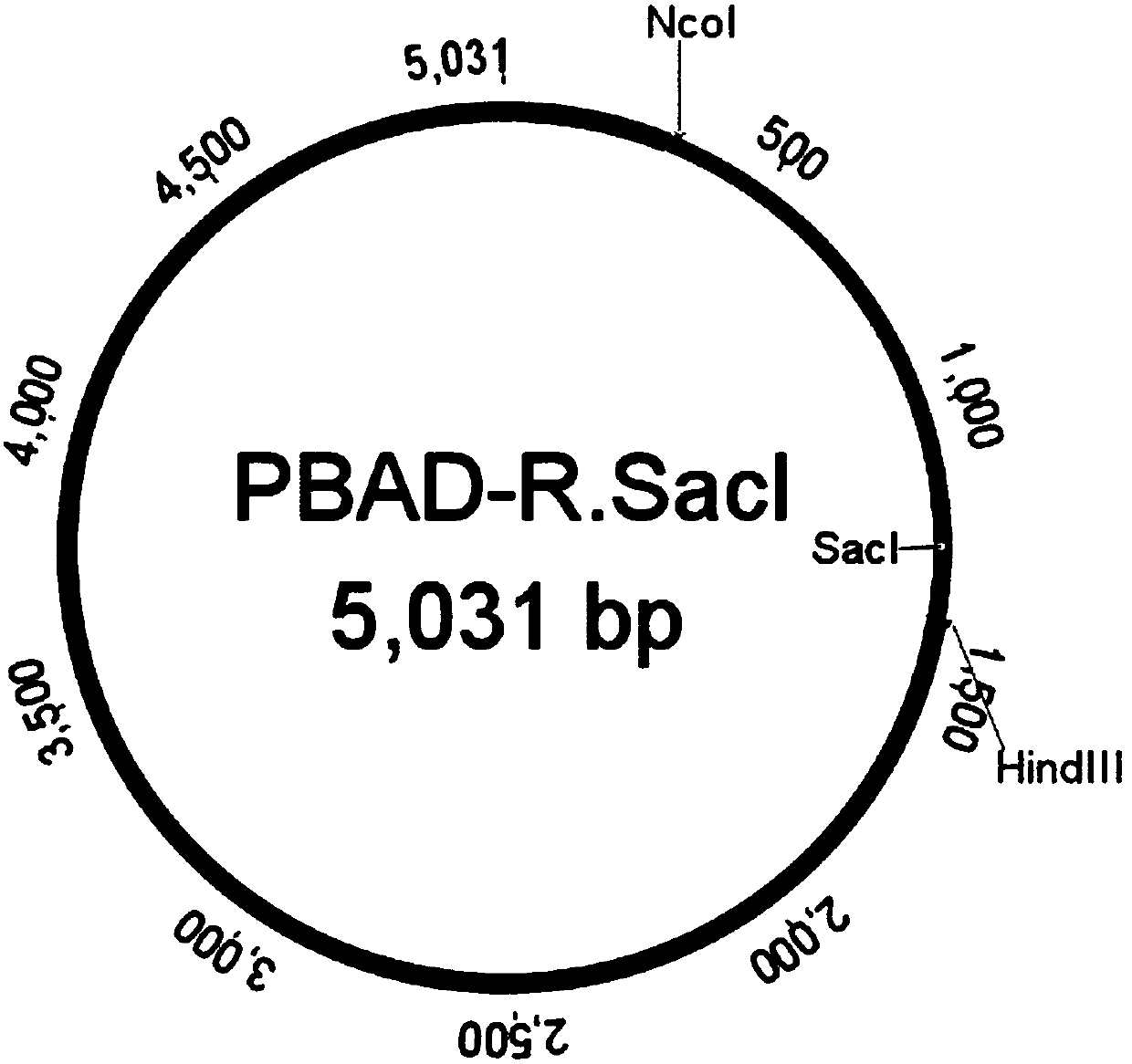
Screening method for methylated protective strain expressing restriction endonuclease SacI
InactiveCN107557372AEfficient recombinant expressionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHost geneOperon
The invention provides a screening method for methylated protective strain expressing restriction endonuclease SacI. The method comprises steps: screening and culturing recombinant expression plasmidpBAD-R. SacI transformed competence cells with correct sequencing to obtain a recombinant expression strain of restriction endonuclease SacI by establishment of recombinant expression strain of methyltransferase M. AluI, recombinant expression of restriction endonuclease SacI, and other steps; and performing enlarging cultivation on the strain, and inducing with arabinose to obtain the recombinantprotein of restriction endonuclease SacI. For the method disclosed by the invention, the efficient recombinant expression of the restriction endonuclease SacI can be achieved; the recombinant expression of the restriction endonuclease SacI is carried out by strict control of an arabinose operon expression system on background expression; the method is stable and efficient against digestion of therestriction endonuclease SacI on a host genome DNA; and an M. AluI methylated protection strain is also applicable to recombinant expression of other restriction endonucleases with similar recognition sites.
Owner:江苏愚公生命科技有限公司
A Method for Parallel Assembly of Multiple Segments of DNA
InactiveCN102296059AImprove efficiencyAvoid pollutionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiological bodyExtracellular
The invention relates to a method for parallel assembly of multi-segment DNA. Choose to insert the circular or linear unit vector into the circular host or linear host to form a gene carrier, and then recover the circular or linear vector to obtain the recombined DNA genetic material. Its characteristic is that it can realize parallel and simultaneous operation of multiple pieces of DNA, thereby improving the efficiency of DNA assembly to form a new DNA structure, and preventing DNA pollution and disproportionation, ensuring the quality of assembled DNA, so that it can achieve the design purpose. The time required to assemble multiple pieces of DNA is approximately proportional to log(N). The assembly operation is carried out outside or inside the cell, so that multiple DNA molecules can be spliced in any order to form a new DNA structure. It is suitable for application in the field of genetic engineering to obtain new organisms through genetic recombination.
Owner:石振宇
Method for high-flux screening of host genes essential for plant virus copying
InactiveCN108753815AShorten the timeSave experimental materialsVector-based foreign material introductionPlant virusMutant
The invention discloses a method for high-flux screening of host genes essential for plant virus copying, belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and aims to solve the problem that at present, an infective cloning construction method is low in virus infection efficiency and make gene expression difficult to control. The method for high-flux screening of host genes essential for plant virus copying specifically comprises the steps that an inducible promoter is utilized to establish inducible virus infection cloning, transgenic plants are used for constructing a mutant library throughagrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation plants, an inducer is utilized to induce virus infection after mutants germinate, the mutants are screened to obtain mutant plants which cannot be induced by viruses, and the host genes essential for plant virus copying are positioned and cloned by cooperating with a map-based cloning and whole genome sequencing method.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for Identification and Development of Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20100088037A1Excellent characteristicsIncreased longevityHydrolasesVirus peptidesImmunity responseTGE VACCINE
The present invention relates generally to the field of identification and determination of bioactive amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides method(s) for determining the influence of variation in host genes on selection of microorganisms with particular amino acid variants for the purpose of therapeutic drug or vaccine design or individualisation of such treatment. The invention also provides methods for identifying HLA allele-specific microorganism sequence polymorphisms that result from HLA restriction of antigen-specific cellular immune responses. It also provides diagnostic and therapeutic methodologies that may be used to measure or treat infection by a microorganism or to prevent infection by the microorganism.
Owner:EPIPOP
Metagenome extraction method for removing host genomic DNA based on CRISPR-Cas
InactiveCN110205318AStrong specificityImprove removal efficiencyHydrolasesDNA preparationGenomic sequencingBiotin-streptavidin complex
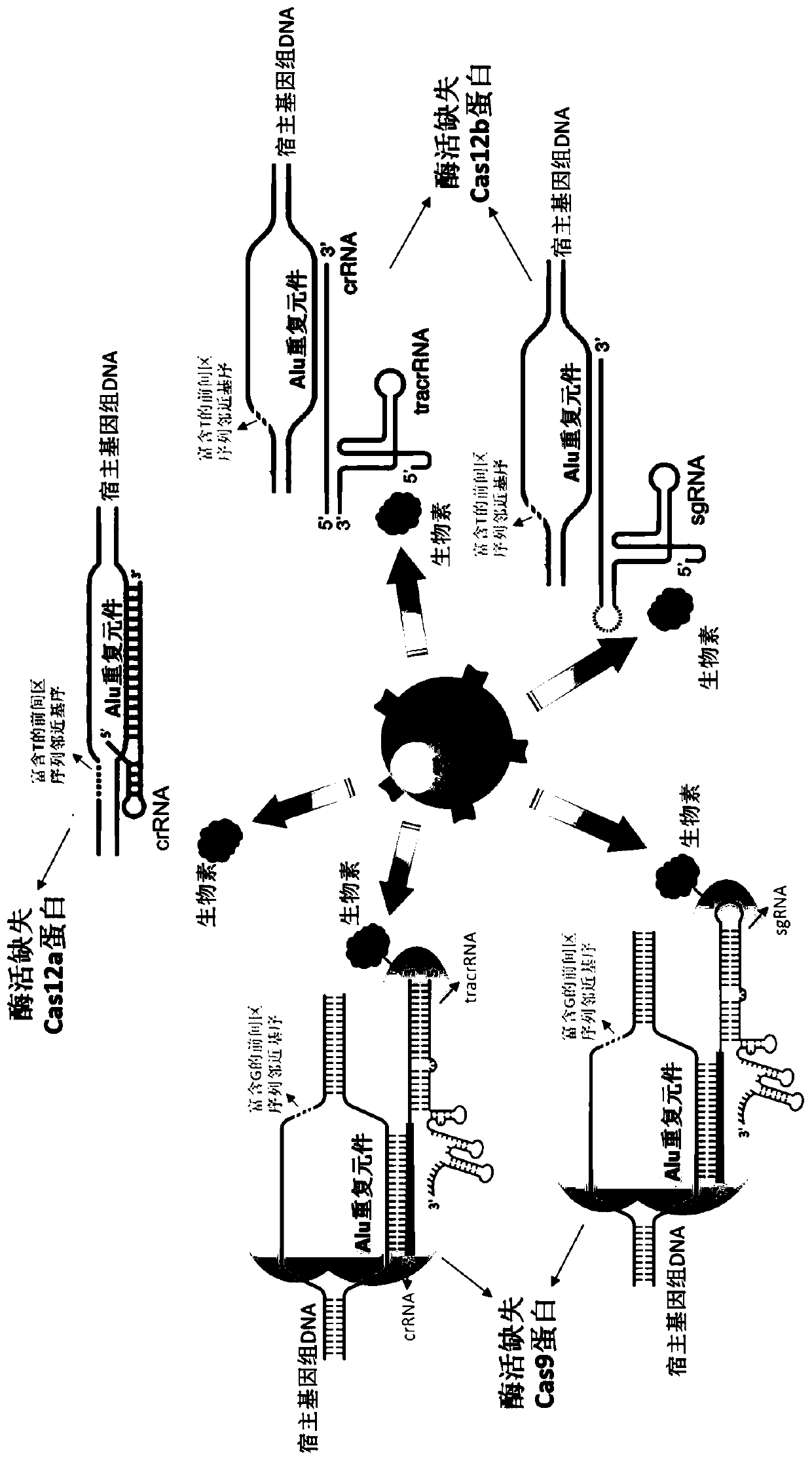
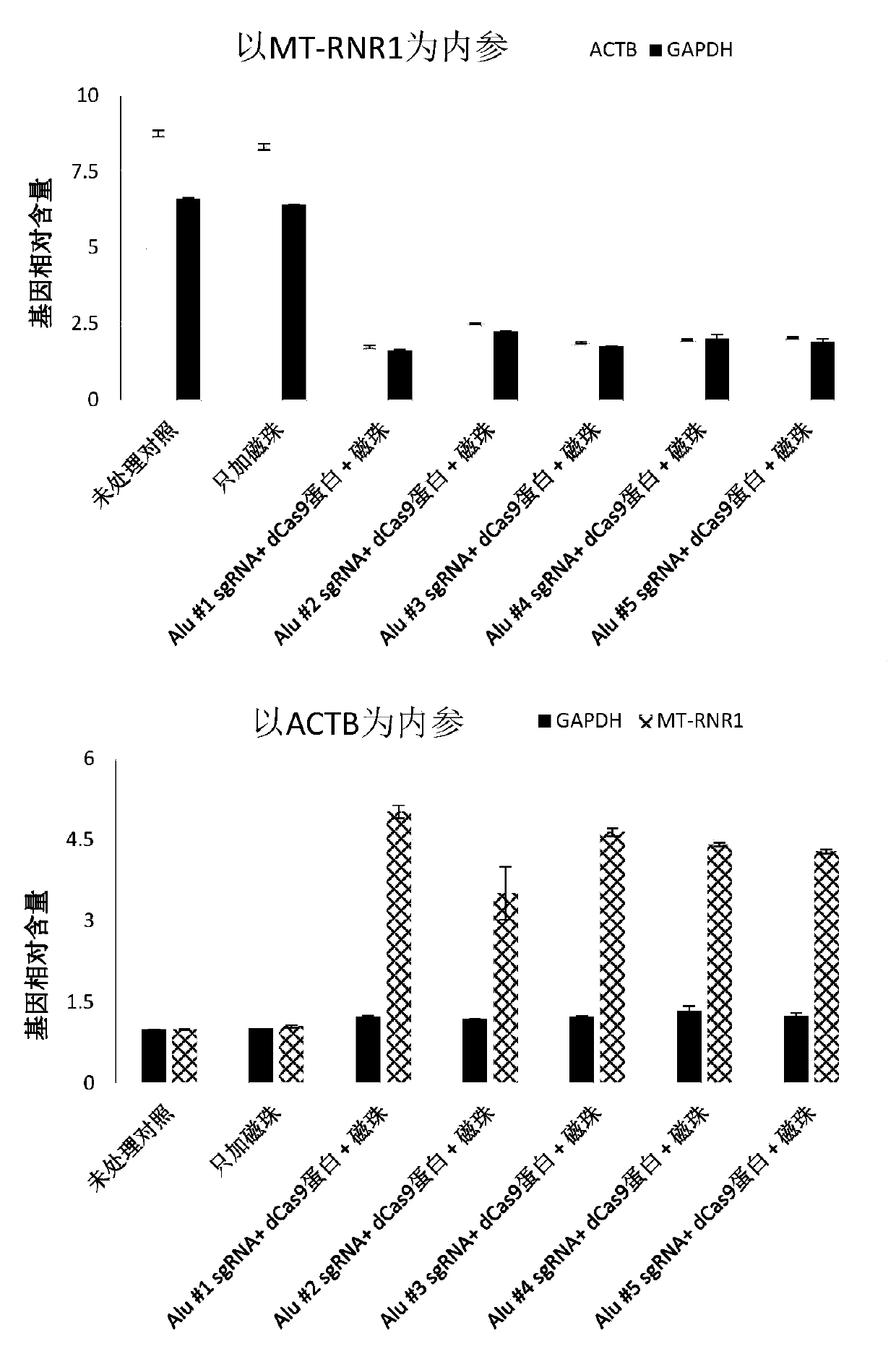
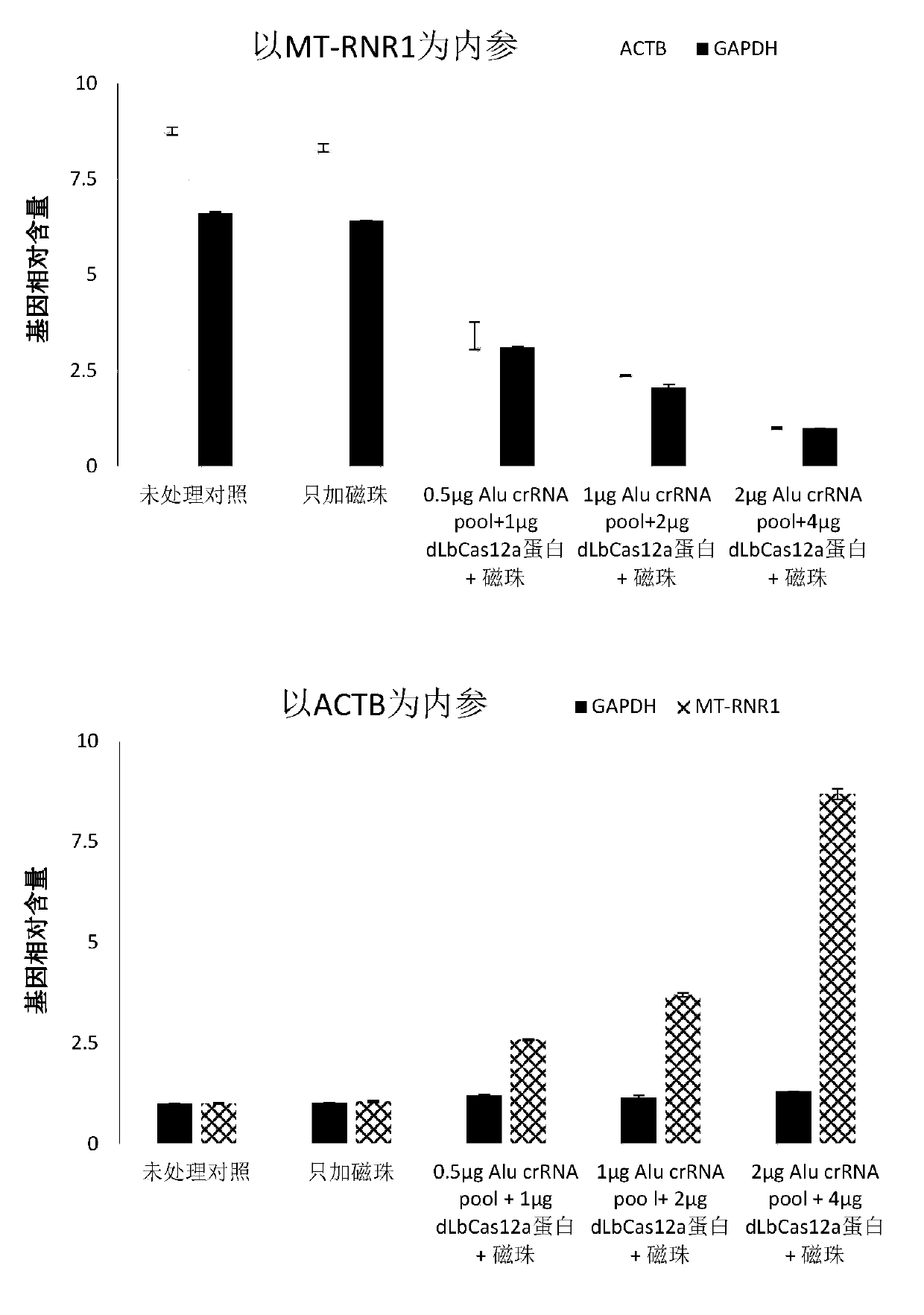
The invention discloses a metagenome extraction method for specifically reducing or removing a host genomic DNA based on a CRISPR-Cas system composition. The invention aims to provide a technique forreducing a host genomic DNA background in metagenome sequencing and improving effective sequencing data of other microorganisms. The CRSIPR-Cas system in the method comprises a plurality of crRNA or crRNA / tracrRNA derivatives, as well as a biotin-labeled Cas protein or variant protein with endonuclease activity deficiency. The sequence of the crRNA or crRNA / tracrRNA derivatives is complemented with a repetitive sequence Alu element region (target sequence) in the host genomic DNA, so that the binding of the Cas protein or the variant thereof with endonuclease activity deficiency is guided to be bonded on the host genomic DNA, the CRISPR-Cas system and the bonded host DNA are captured by adding magnetic beads coated with streptavidin, and thus the concentration of the host genomic DNA in asample solution is reduced and the abundance of nucleic acids of other non-host genomic DNA is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU MATRIDX BIOTECH CO LTD
Engineered oncolytic viruses containing hyper-binding sites to sequester and suppress activity of oncogenic transcription factors as a novel treatment for human cancer
ActiveUS20180099014A1Increase the number ofReduced activityUnknown materialsDsDNA virusesTranscription factor activityDecoy
In one or more embodiments, the present invention provides novel artificial, non-naturally-occurring double stranded DNA segments (and related methods) capable of acting as decoy binding sites for oncogenic transcription factors and a general method for suppressing aberrant activity of oncogenic transcription factors that promote cancer progression. In various embodiments, the present invention involves the sequestration of targeted oncogenic transcription factors at these artificial, non-naturally occurring engineered transcription factor binding sites, which have been introduced into the cells using oncolytic or other viruses that can be engineered to selectively target cancer cells. These artificial, non-naturally occurring engineered transcription factor binding sites act as decoys for binding so as to competitively sequester oncogenic transcription factors away from the host genomic DNA, thus abolishing or reducing oncogenic transcription factor activity and resulting in restored sensitivity to chemotherapy, increased apoptosis, and reduced cancer cell proliferation.
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERSITY
Application of short peptide to preparation of immunoregulation medicament
ActiveCN108690123ALow priceSmall molecular weightNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunologic disordersHost gene
The invention relates to application of a short peptide miPEP155 to preparation of an immunoregulation medicament. The short peptide is derived from a host gene of micro RNA155, and is named as miPEP155. The miPEP155 polypeptide can restrain the differentiation of Th17 cells, has an immunoregulation function, and can be used for preventing or treating autoimmune diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
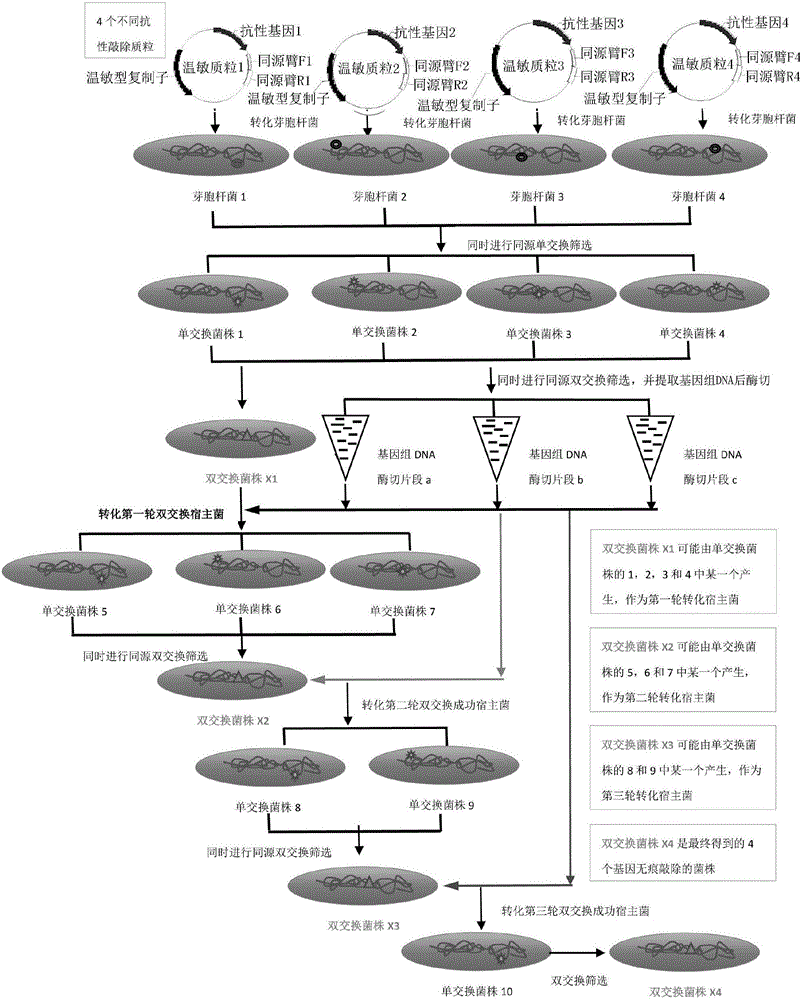
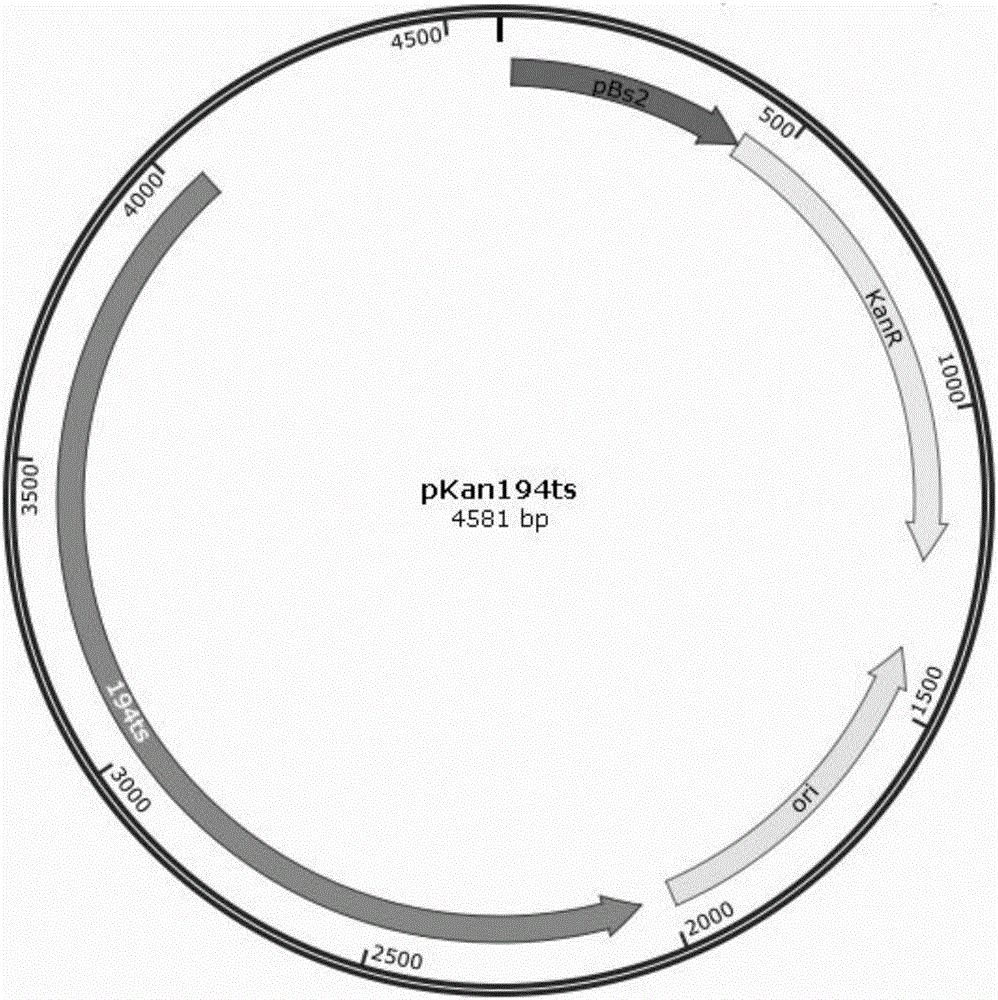
Multi-gene stacking knockout method for bacillus
ActiveCN106191092AImproving the efficiency of stacking knockoutsAchieve a traceless knockoutNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introduction3-deoxyriboseHost gene
The invention discloses a multi-gene stacking knockout method for bacillus. The multi-gene stacking knockout method includes: inserting homologous arm gene segments of upstream and downstream of multiple genes to be knocked out of the bacillus into thermo-sensitive type plasmids to convert the bacillus, forcing homologous single-crossover to happen to knockout plasmids in the bacillus and genome DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) of the knockout plasmids through high-temperature culture, and screening double-crossover bacterial strains through high-temperature subculture; extracting the genome DNAs of the multiple bacterial strains successful in gene single-crossover, performing double-crossover screening, stacking the bacterial strains successful in knockout as host strains for the nest round of stacking knockout, and sequentially stacking to finally realize multi-gene knockout of the bacillus. Traceless gene knockout of the bacillus is realized with the thermo-sensitive type plasmids, conversion efficiency can be improved by using the single-crossover hose genome DNAs to convert the bacillus, restoration of the knockout genes in the host strains can be effectively avoided, and multi-gene stacking knockout efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:WUHAN KANGFUDE BIOTECH CO LTD
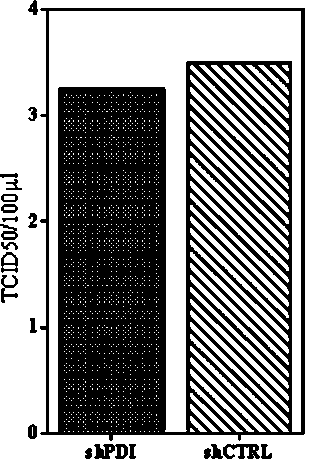
Small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) of targeted human protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) of targeted human protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) gene, of which the nucleotide sequence is selected from SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3. By using the protein coded gene sequence of the human PDI as the target gene, three 21nt target sequences are selected, and a complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence comprising all the target sequences and a nonsense interfering DNA chain are designed and synthesized; and after annealing, a pLVX-shRNA1 expression vector is inserted to construct three interfering plasmids for PDI. The experiment indicates that the RNA interfering expression vectors have very high inhibiting actions on the expression of the disulfide isomerase protein and can generate certain influence on replication of HCV (hepatitis C virus). The siRNA has huge application value and prospects in research and / or identification of gene functions, and preparation of gene drugs for resisting infections of HCV and other viruses by using the host gene as the target spot.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Viral Neoepitopes and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20170032103A1Verify and increase efficacyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsImmunotherapeutic agentHost gene
Contemplated antiviral / cancer treatments comprise analysis of neoepitopes from viral DNA that has integrated into the host genome, and design of immunotherapeutic agents against such neoepitopes.
Owner:NANTOMICS LLC
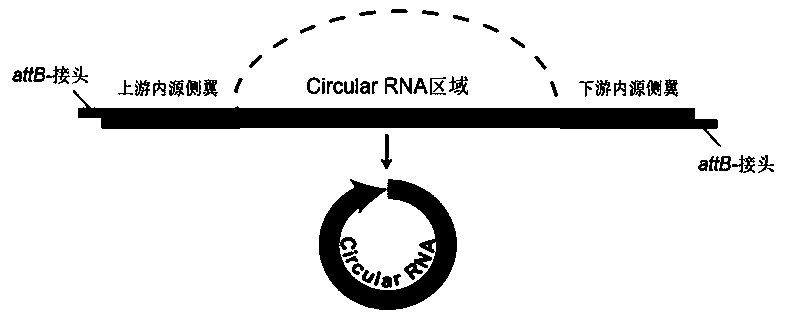
Construction method and application of annular RNA overexpression system of protoplast of moso bamboo
ActiveCN109486856AFast Transient ConversionStable transient conversionVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Host gene
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an annular RNA overexpression system of protoplast of moso bamboo and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The system constructs an annular RNA overexpression vector and converts the vector to the protoplast of moso bamboo. The construction method comprises the following steps: amplifying an annular RNA host genewith a high fidelity Taq enzyme and constructing an annular RNA overexpressed recombinant plasmid by a Gateway method by taking pUC19-35s-sGPF as a final vector; and extracting the recombinant plasmids massively and converting the plasmids to the protoplast of moso bamboo mediated by PEG to research the influence of annular RNA overexpression to transcription and post-transcription levels of thehost gene.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Double-sgRNA traceless gene editing plasmid as well as preparation method and application thereof
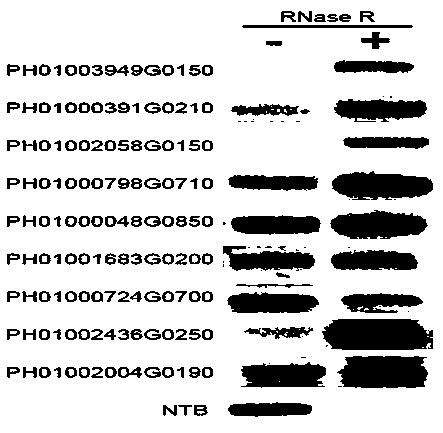
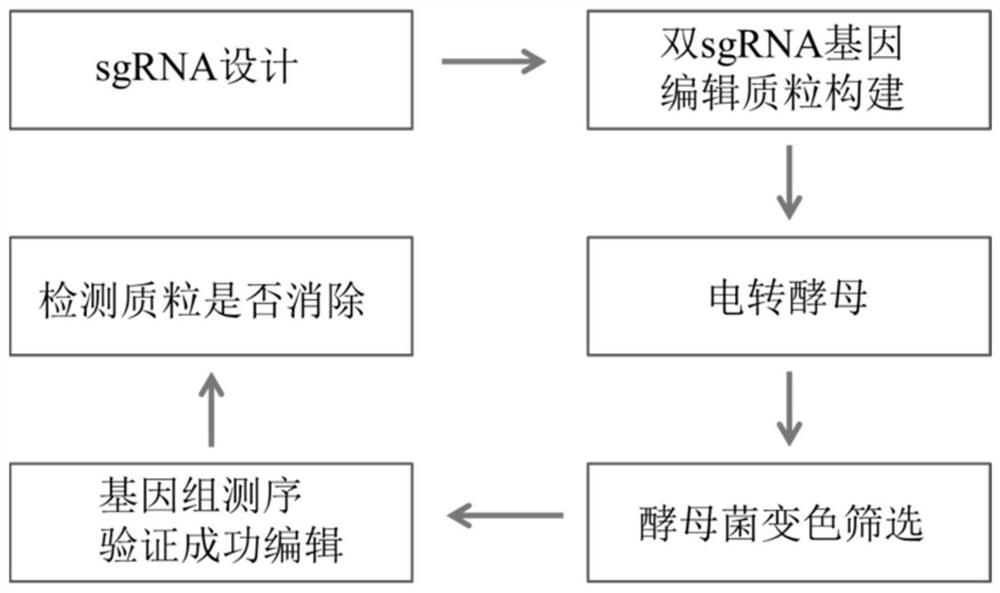
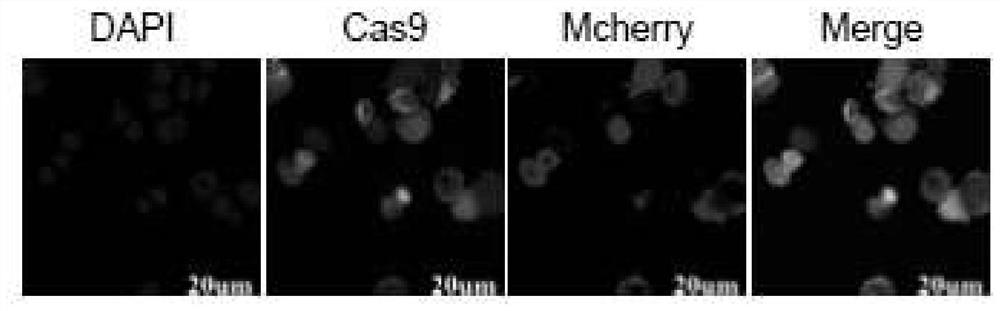
PendingCN111621512ASolve the problem of improving the off-target rateAddress issues that affect subsequent experimentsStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesHost geneGenetics
The invention provides a double-sgRNA traceless gene editing plasmid as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The plasmid comprises a Cas9 protein expression cassette and a double-sgRNA expression cassette, wherein the double-sgRNA expression cassette comprises host gene editing sgRNA and plasmid gene editing sgRNA. The plasmid containing the double-sgRNA is designed to perform gene editing on a host, one sgRNA of the double-sgRNA is used for performing gene editing on the host, and the other sgRNA is used for eliminating the plasmid, so that the aim of eliminating the gene editing plasmid while performing gene editing on the host is achieved, the off-target rate is not increased due to continuous expression of Cas9 protein, and subsequent experiments are not influenced. The plasmid is transformed into saccharomyces cerevisiae for gene editing, so that the traceless editing efficiency of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is obviously improved.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Cas9 system for efficiently editing bombyx mori genome and application of Cas9 system
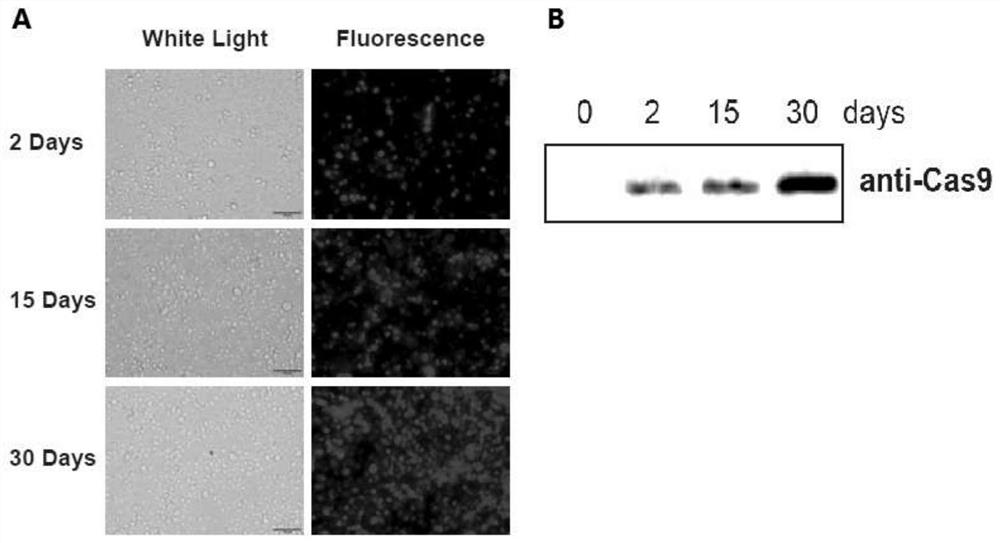
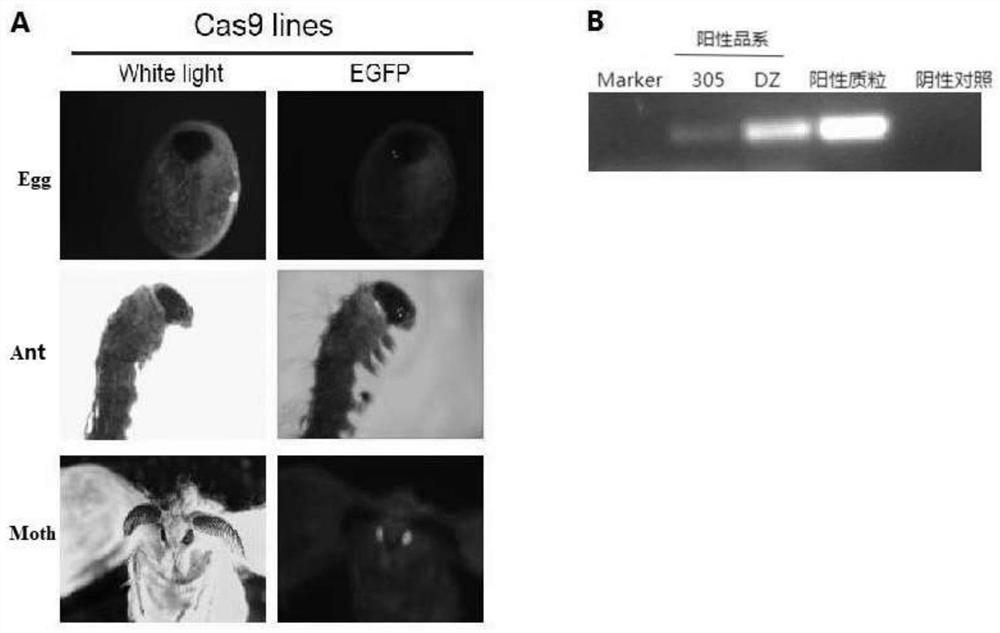
PendingCN112852871AImprove securityEfficient editingHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorPromoterRecombinant virus
The invention discloses a Cas9 system for efficiently editing a bombyx mori genome and an application of the Cas9 system. The system comprises a bombyx mori transgenic expression vector for expressing a Cas9 gene and bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus packaging virion containing an expression cassette U6-sgRNA expressed by a U6 promoter regulating sgRNA. A bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) genome is used as a vector, the U6-sgRNA expression cassette is recombined to the virus genome through Bac-to-Bac transposition, a recombinant virion is constructed, a Cas9 cell line or Cas9 bombyx mori is infected with the recombinant virus, and a target gene can be effectively edited. The established Cas9 system does not need a transfection process, is high in transfection efficiency and good in safety, can stably and efficiently edit a target gene, and can be suitable for research on functions of viral genes and related host genes, a baculovirus expression system and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Non-integration lentiviral vector system and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN101532031BEfficient gene transferLong-term gene expressionMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringVector systemHost gene
The invention discloses a non-integration slow virus vector system and the preparation and the application thereof. The non-integration slow virus vector system comprises a pLVTH vector, a pHelper1.0 vector, a pCMV-VSV-G vector and host cells. The pLVTH vector, the pHelper1.0 vector and the pCMV-VSV-G vector in the vector system are commonly transfected with the host cells to obtain the non-integration slow virus vector in the host cells by packing. The non-integration slow virus vector system of the invention can provide highly efficient gene transfer, longtime gene expression and wide host cells, cannot randomly integrate carried genes into host gene groups and provides a new method for the gene therapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JI KAI GENE TECH CO LTD
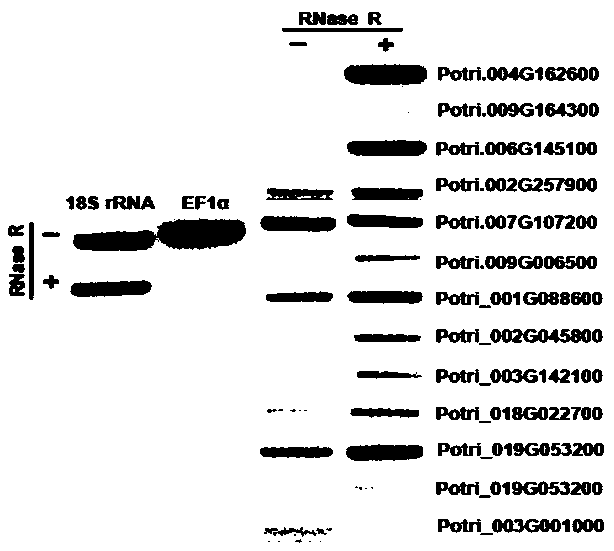
Primer for inhibiting sequence-specific amplification of 18S rDNA of shrimps and oysters and application thereof
ActiveCN108103059AGrowth inhibitionImprove scalabilityDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationProtozoa18s rdna
The invention discloses a primer for inhibiting sequence-specific amplification of 18S rDNA of shrimps and oysters. The primer mainly comprises base sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, five deoxyhypoxanthines inserted among the base sequences AG, and C3 spacers at the tail ends of the base sequences. The primer can effectively inhibit the amplification of host genes and enhance the amplification effect of 18S rDNA of other eukaryotes (such as protozoa, algae and fungi) in host bodies. The invention further discloses the application of the primer in preparing a reagent with the effect of inhibiting the sequence-specific amplification of 18S rDNA of the shrimps and oysters.
Owner:广州鸿真生物科技有限公司
Lentiviral vectors for site-specific gene insertion
ActiveUS7402436B2Easy to reorganizeGenetic material ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsTherapy TrialVector system
Murine leukemia virus (MLV) and lentivirus vectors have been used previously to deliver genes to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in human gene therapy trials. However, these vectors integrate randomly into the host genome, leading to disruption or inactivation of vital host genes. The present invention discloses a novel lentiviral vector system that overcomes this problem by integrating into a host genome in a site-specific manner.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Polypeptide and application thereof in preparation of immunomodulatory drugs
ActiveCN113501862ASmall molecular weightLow priceNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention provides a polypeptide and application thereof in preparation of an immunomodulatory drug. The functional polypeptide is a novel polypeptide PEP20 which is coded by a host gene of a long-chain non-coding RNA LINC01871; the polypeptide can specifically target CD8 < + > T cells in an inflammatory environment, inhibit differentiation of the CD8 < + > T cells to Tc17 cells, and inhibit over-differentiation and over-proliferation of the Tc17 cells and over-expression of IL-17A. The invention has an immune regulation function and can be used for preventing or treating autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. The PEP20 disclosed by the invention is small in molecular weight and can easily enter cells to play a role; the invention can be synthesized by a chemical method, is easy to prepare in a large scale, has good stability, and is lower in price and safer compared with the existing antibody for treating autoimmune inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Construction method and application of annular RNA overexpression system for protoplast of secondary xylem of poplar
ActiveCN109486855AImprove efficiencySimple and fast construction methodVector-based foreign material introductionHost geneGenetic engineering
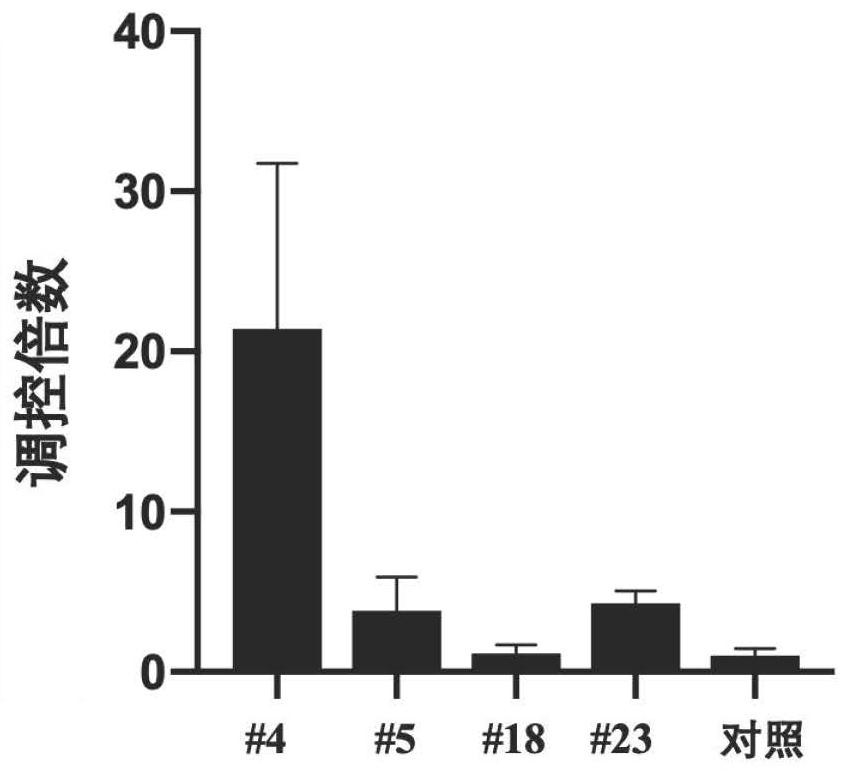
The invention discloses a construction method and application of an annular RNA overexpression system for a protoplast of a secondary xylem of a poplar, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The construction method comprises the following steps: carrying out molecular biological verification on annular RNA; constructing an overexpression recombinant plasmid of annular RNA; converting the protoplast of the poplar by virtue of a PEG-mediated recombinant plasmid; and carrying out molecular biological detection on the overexpression condition of annular RNA in the protoplast ofthe converted recombinant plasmid. The overexpression system can be applied to the regulation and control of the expression condition after the transcription of a host gene.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Screening method of influenza virus related host gene mutants
ActiveCN112553251AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMutantThelial cell
The invention discloses a screening method of influenza virus related host gene mutants, and belongs to the technical field of random mutation. In order to screen out host genes related to influenza viruses, the invention provides a screening method. The screening method comprises the following steps: 1) transfecting a human lung cancer cell strain with CAG-tTA plasmids to obtain a Tel-off cell strain of a transcription activator stably expressed and regulated by tetracycline; co-transfecting the Tel-off cell strain with a gene search vector and plasmids that effectively express transposase toobtain a whole-genome pulmonary epithelial cell gene mutation library; 2) infecting the mutation library obtained in the step 1) by using the H1N1-WSN influenza virus; and 3) extracting the genome DNA of the cell strain, resisting the H1N1-WSN influenza virus, obtained in the step 2), and carrying out sequencing by Splinkette PCR to obtain the influenza virus related host gene mutants. The screening method can be used for screening the influenza virus related host gene mutants.
Owner:THE THIRD MEDICAL CENT OF THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY GENERAL HOSPITAL
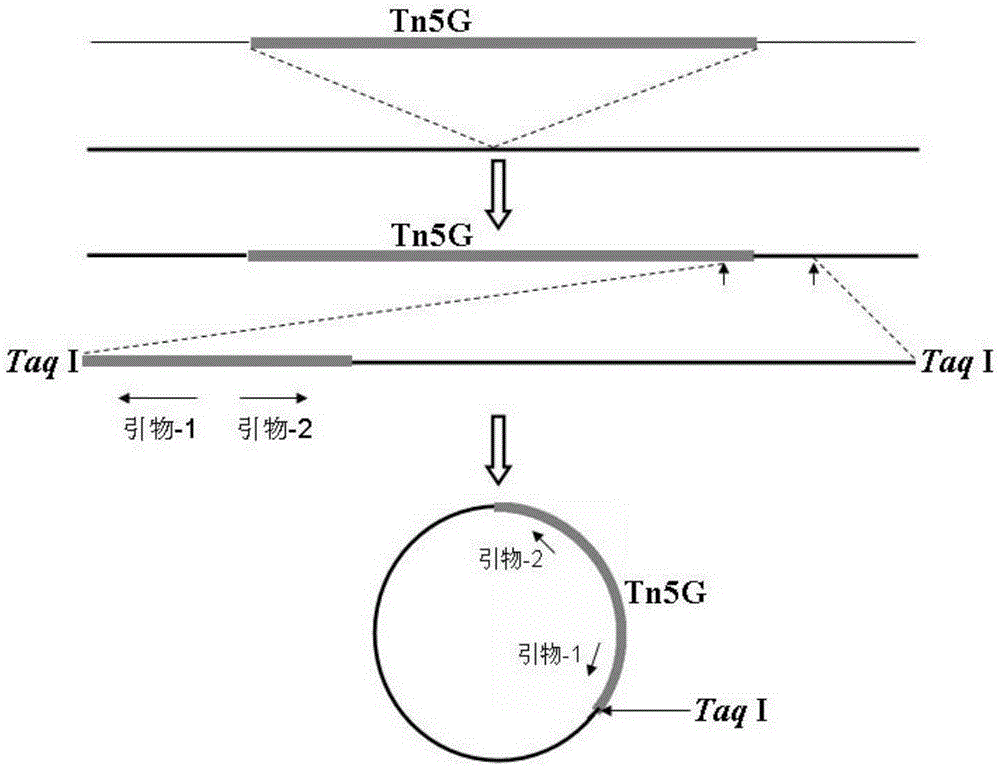
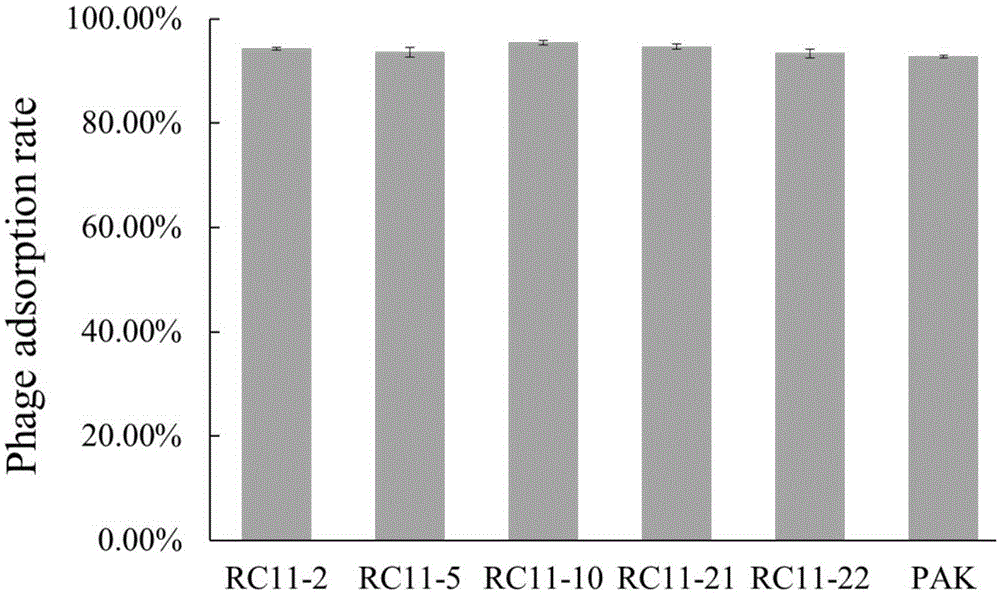
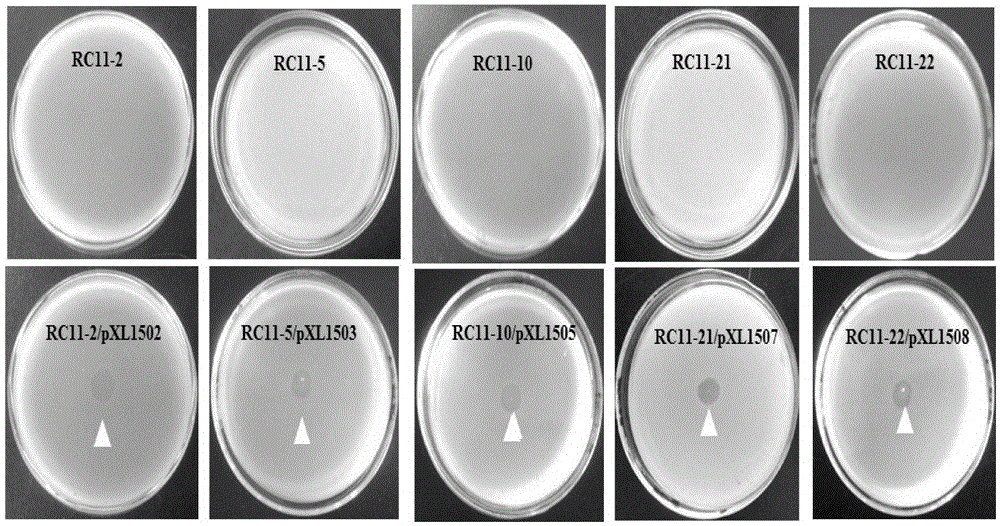
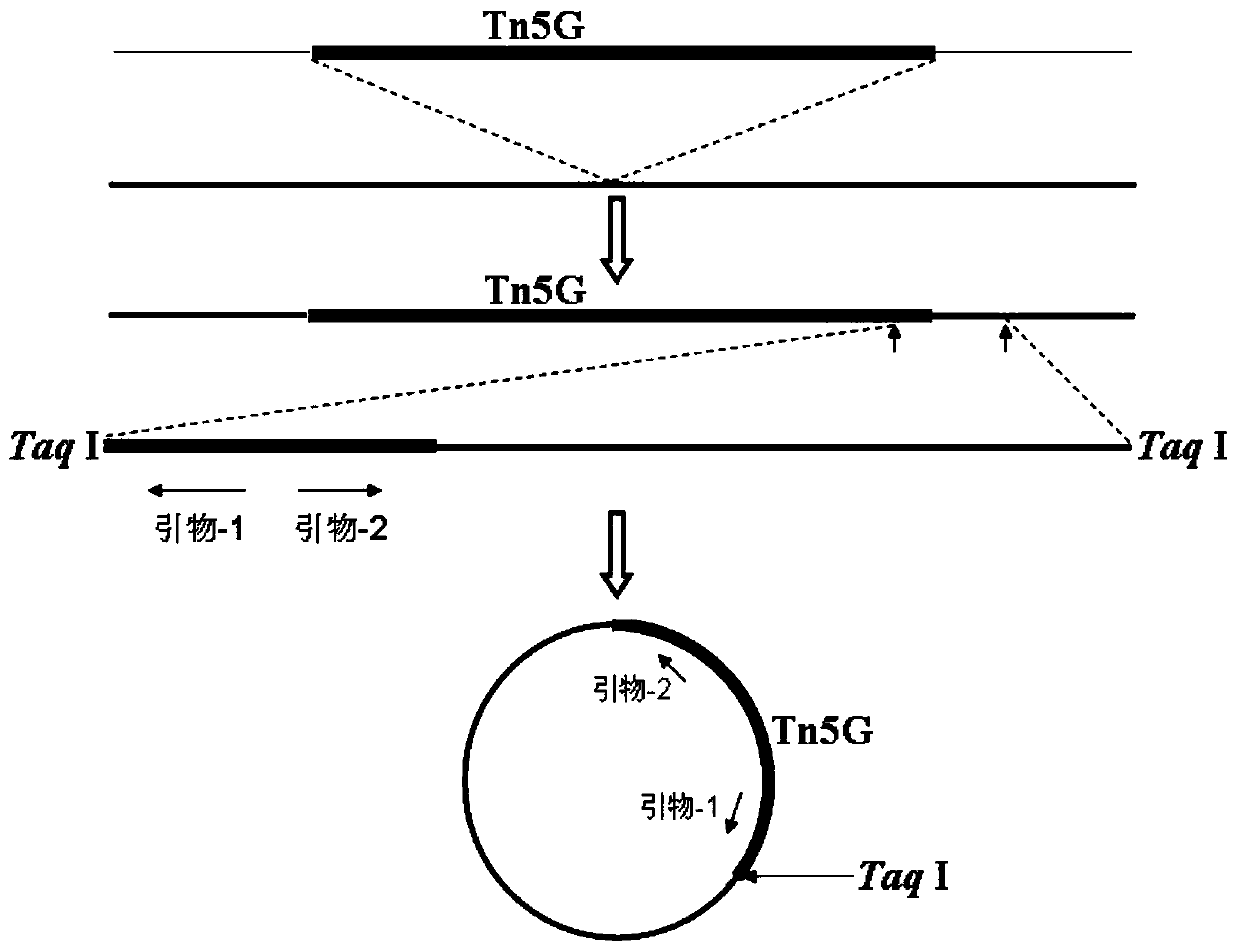
Genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa related to phage infection and application of genes
ActiveCN105400876AUnderstand molecular mechanismsTo achieve the effect of indirect treatment of viral infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnaplasma phagocytophilumAntiviral drug
The invention relates to functions of genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa and an application of the genes, wherein the gene BN889_05221, the gene PA0243, the gene PA3808, the gene PA1993 and the gene PA1115 of pseudomonas aeruginosa are the necessary host genes of phage infection, and are used for screening the relevant medicines for inhibiting the phage infection. According to the invention, through the study on the relevant host genes of phage infection, a molecular mechanism for the interaction between phage and host bacteria can be well understood, therefore, a theoretical basis is provided for the treatment on the phage, meanwhile, new target genes related to virus infection can be found, and assistance is provided for screening antiviral drugs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods and compositions for integration defective lentiviral vectors
The present invention provides an integration-defective lentiviral vector based on a parental lentivirus and related methods, the integration-defective lentiviral vector including one or more of the following: (a) a mutation, deletion or other modification of one or more binding sites for a host factor involved in gene silencing; (b) an addition of one or more binding sites for a transcription activator, which can be natural (such as but not limited to ubiquitous and / or tissue / cell type specific) including but not limited to SP1 NFkB, or synthetic including but not limited to binding sites for tetracycline regulated trans activators tTA, rtTA, tT65, and / or rtT65; (c) one or more nucleic acid sequences from a SV40 genome, wherein the one or more sequences are obtained from a region of the SV40 genome upstream to the SV40 poly-adenylation signal; (d) a shRNA expression cassette, which encodes a shRNA directed to a host gene involved in epigenetic silencing and / or in DNA repair pathways; or (e) any combination of (a), (b), (c) and (d), wherein as compared to the parental lentivirus, the integration-defective lentiviral vector resists gene silencing.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Genes related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and phage infection and their application
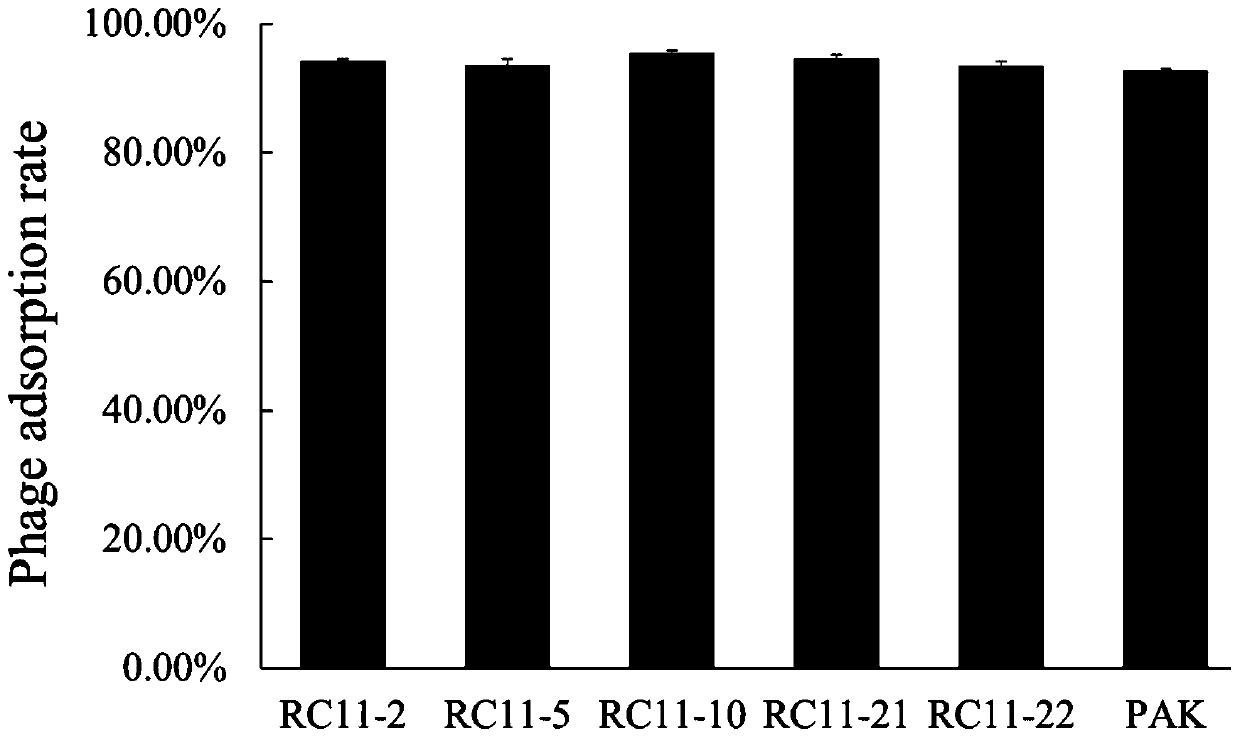
ActiveCN105400876BAdsorption has no effectUnderstanding the Molecular Mechanisms of InteractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnaplasma phagocytophilumAntiviral drug
The invention relates to functions of genes of pseudomonas aeruginosa and an application of the genes, wherein the gene BN889_05221, the gene PA0243, the gene PA3808, the gene PA1993 and the gene PA1115 of pseudomonas aeruginosa are the necessary host genes of phage infection, and are used for screening the relevant medicines for inhibiting the phage infection. According to the invention, through the study on the relevant host genes of phage infection, a molecular mechanism for the interaction between phage and host bacteria can be well understood, therefore, a theoretical basis is provided for the treatment on the phage, meanwhile, new target genes related to virus infection can be found, and assistance is provided for screening antiviral drugs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com