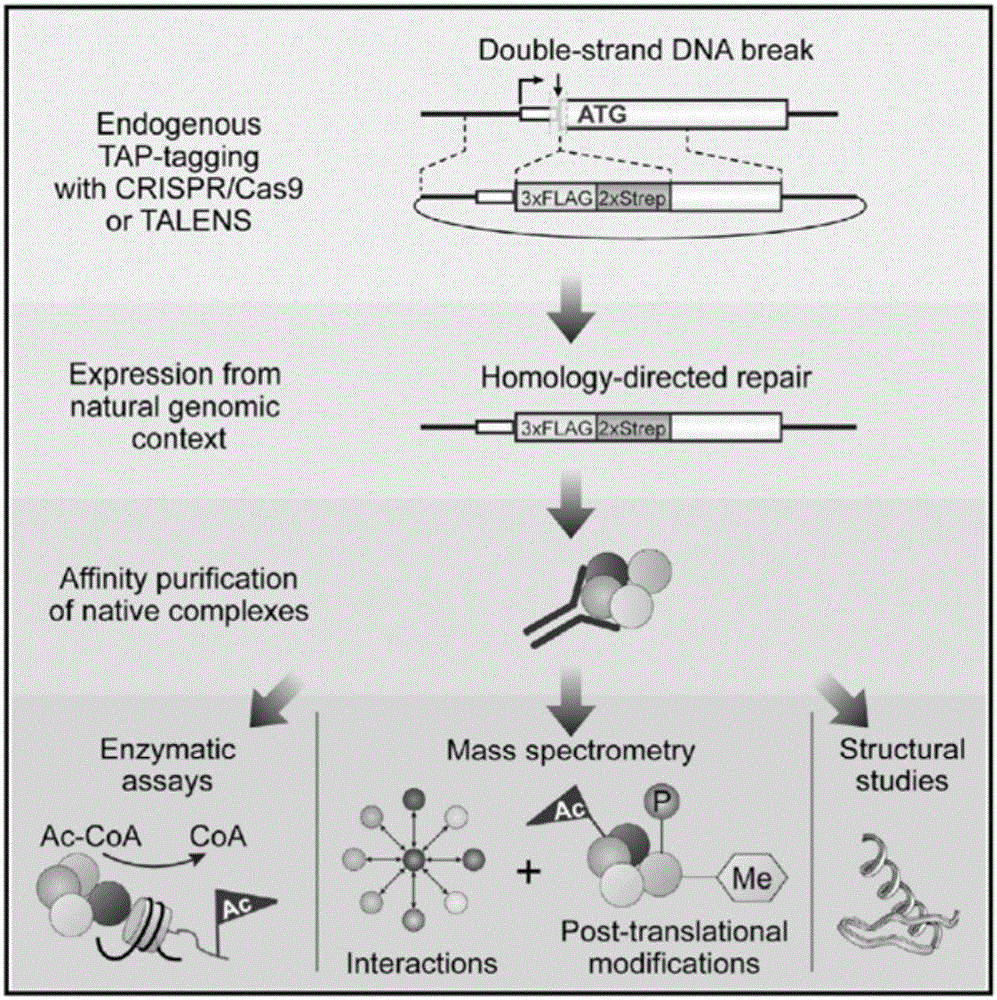
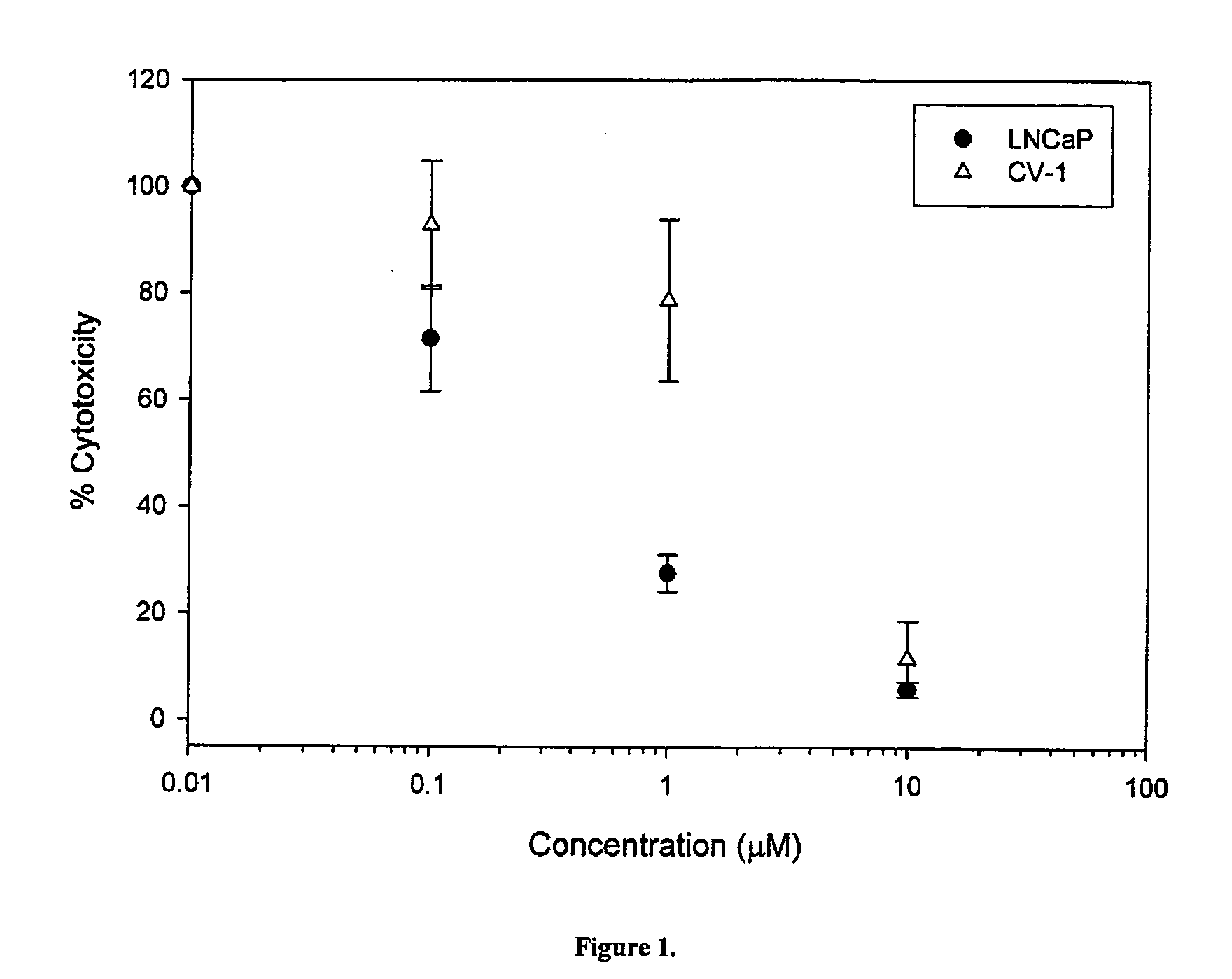
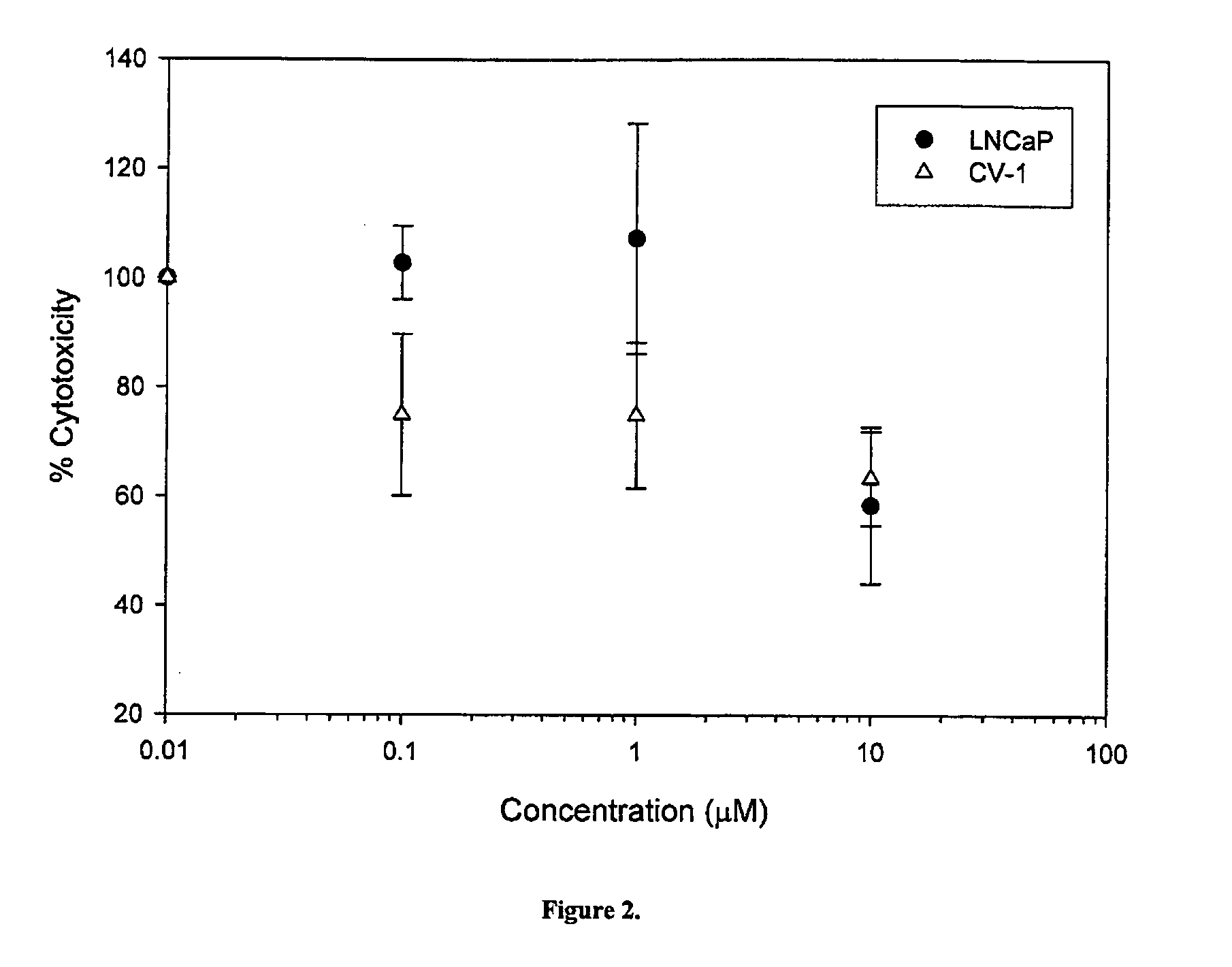
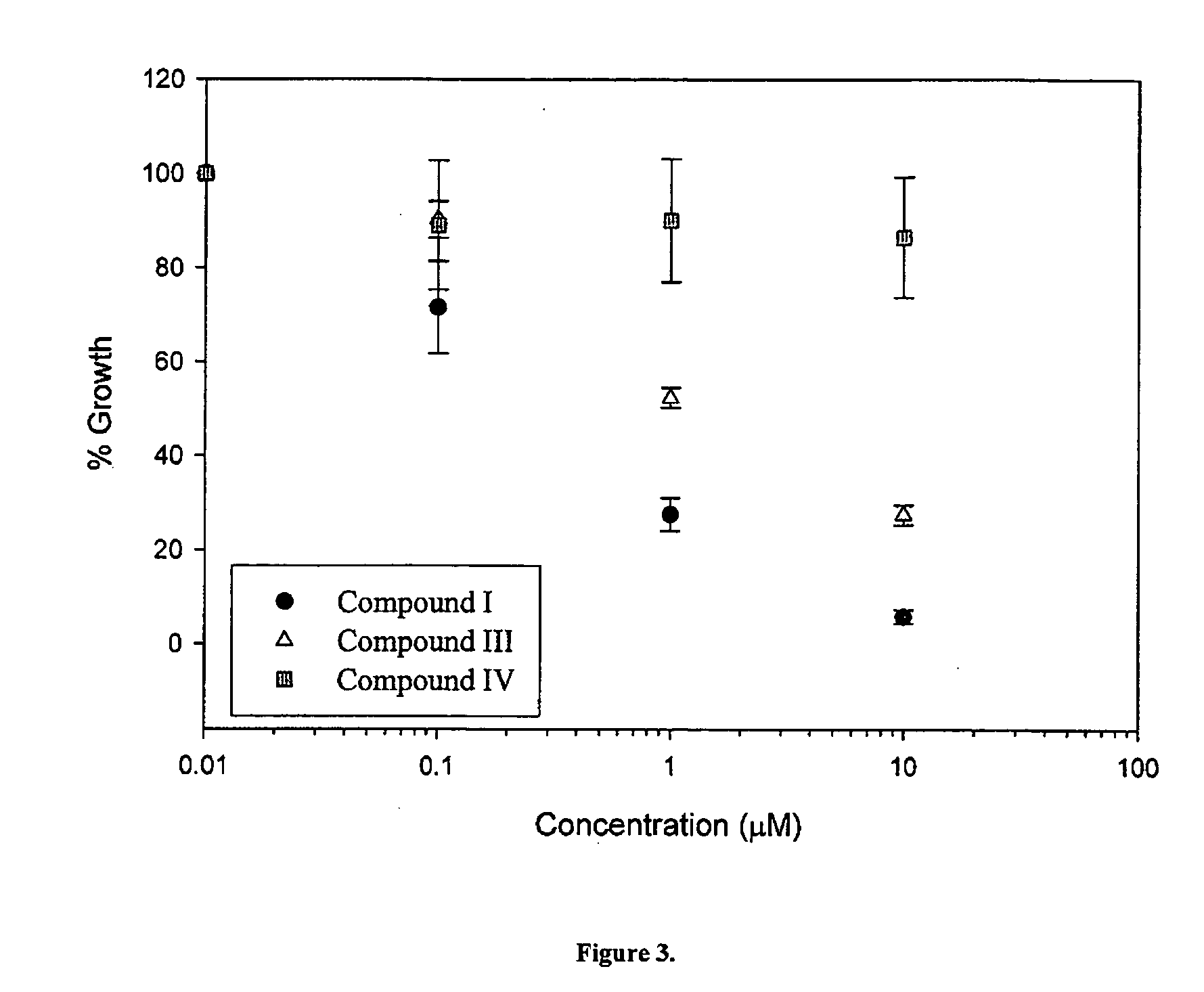
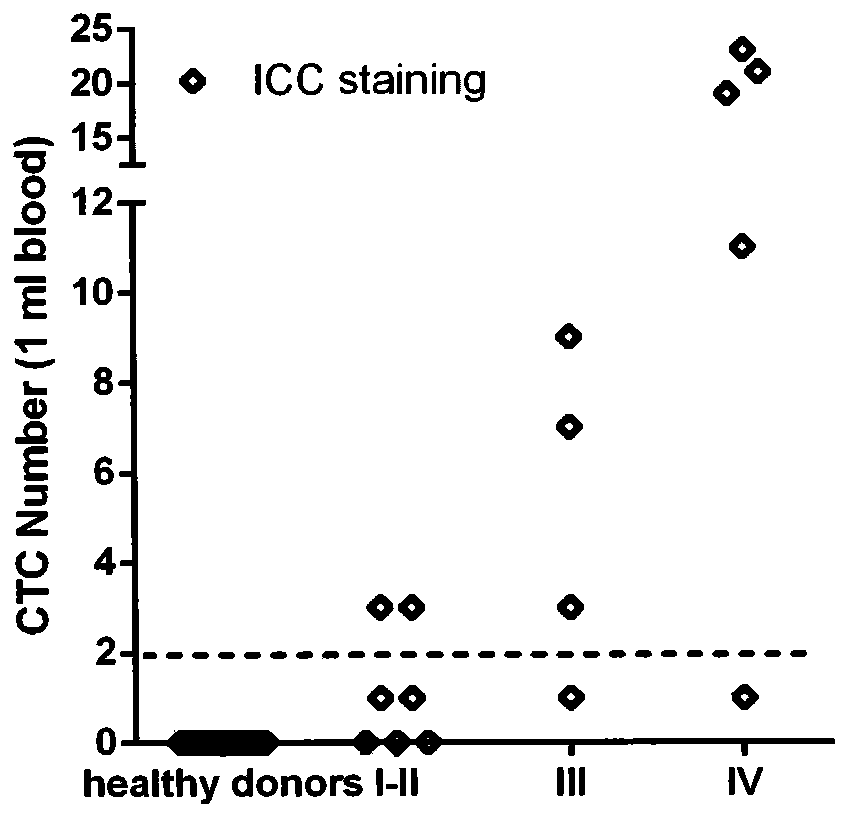
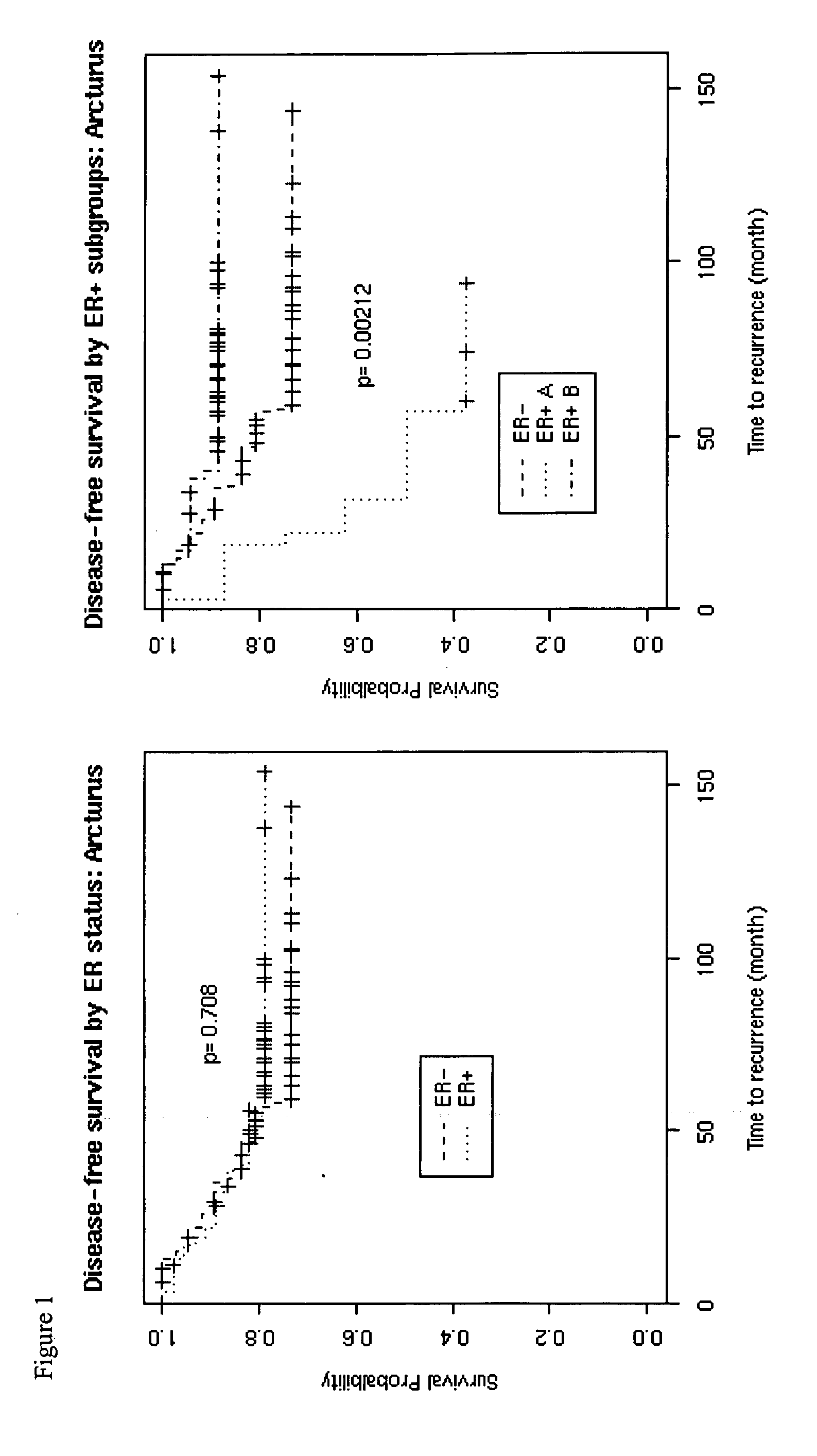
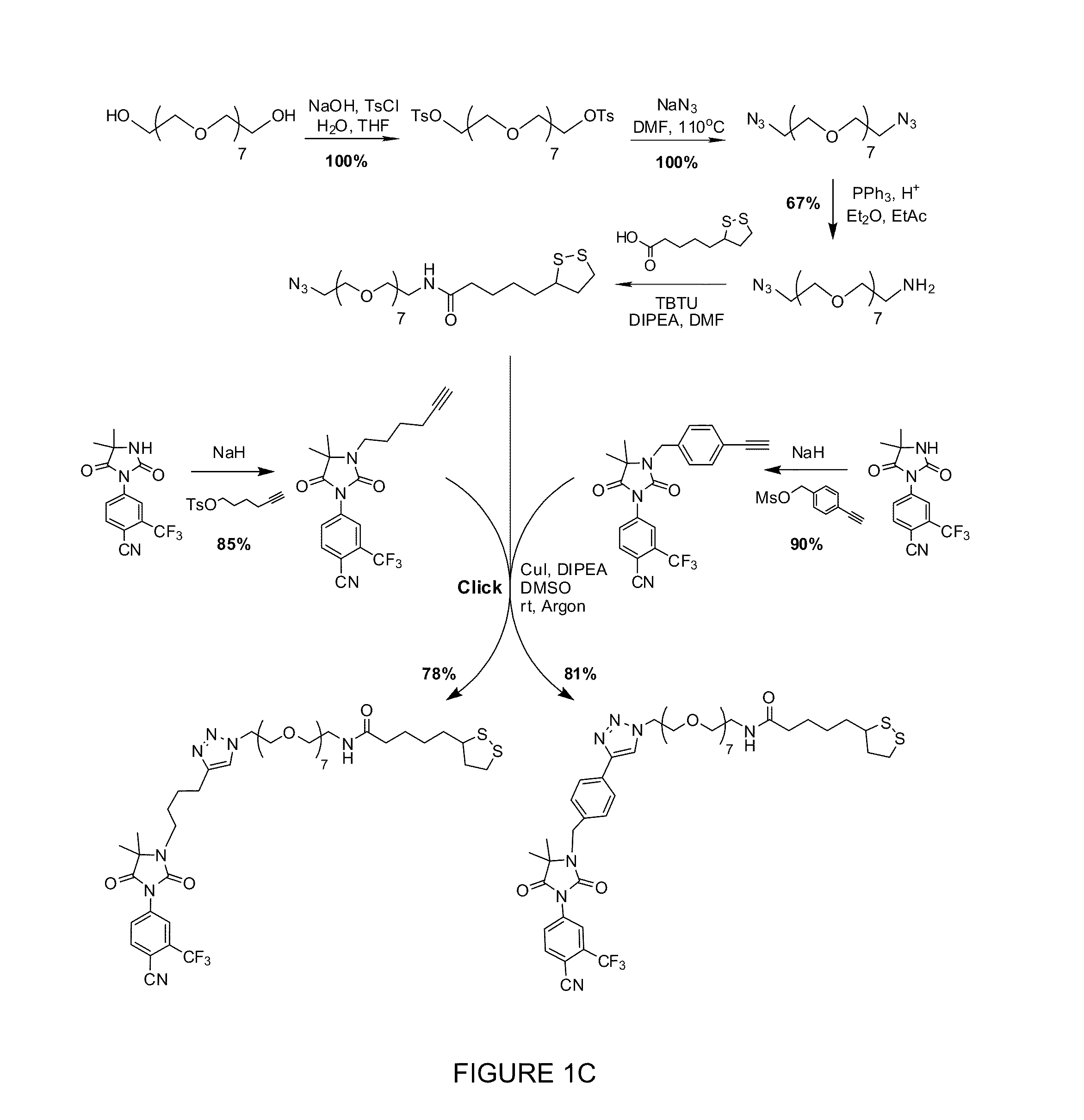
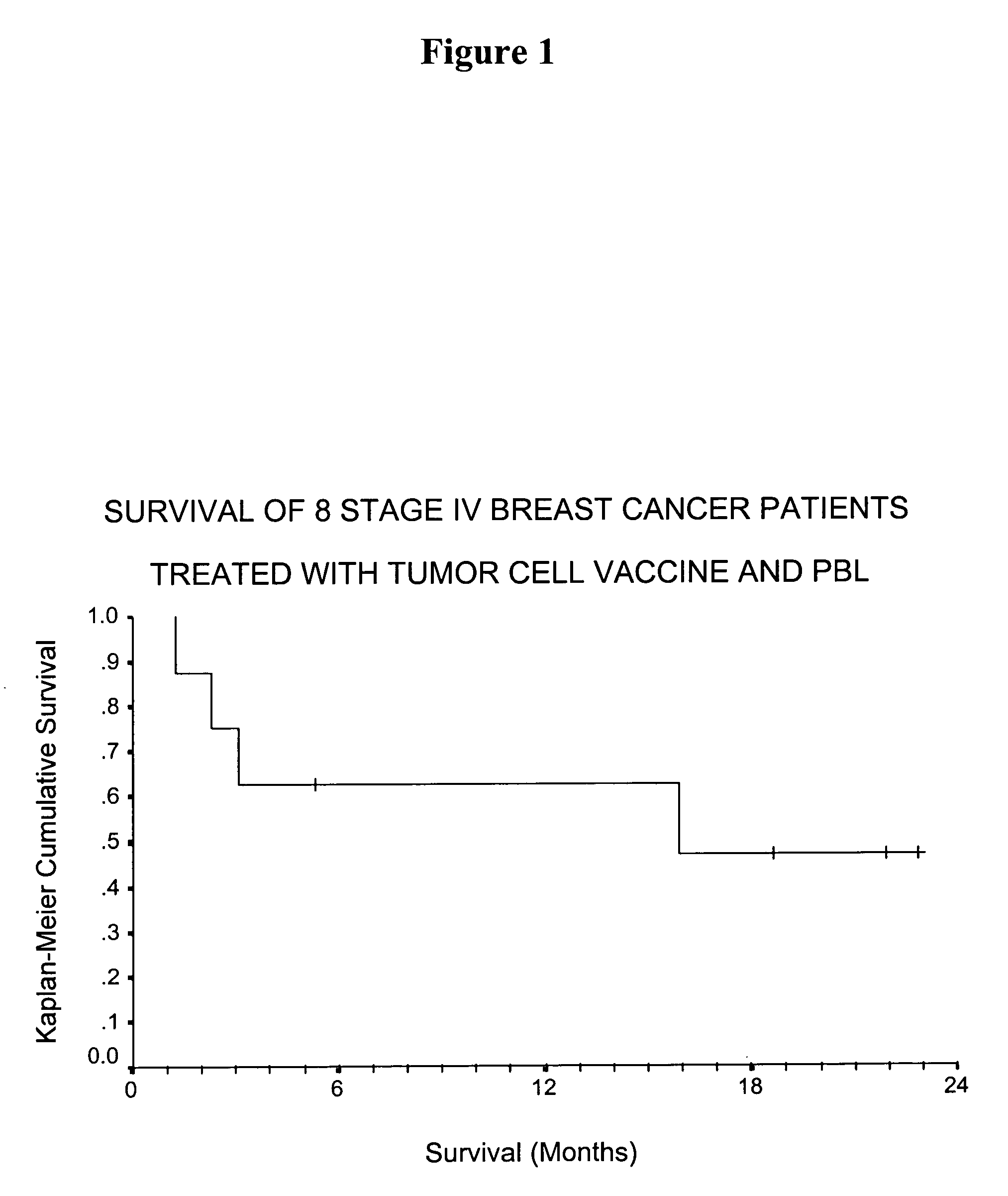
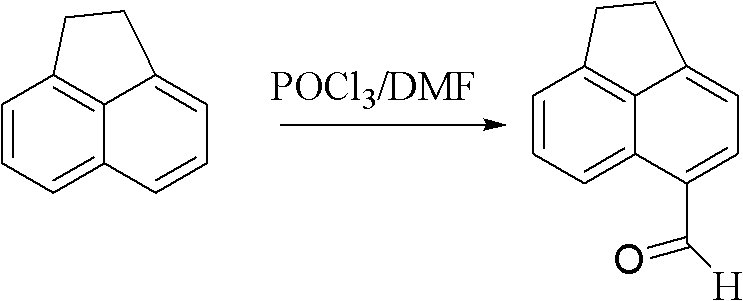Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1761 results about "Breast cancer cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
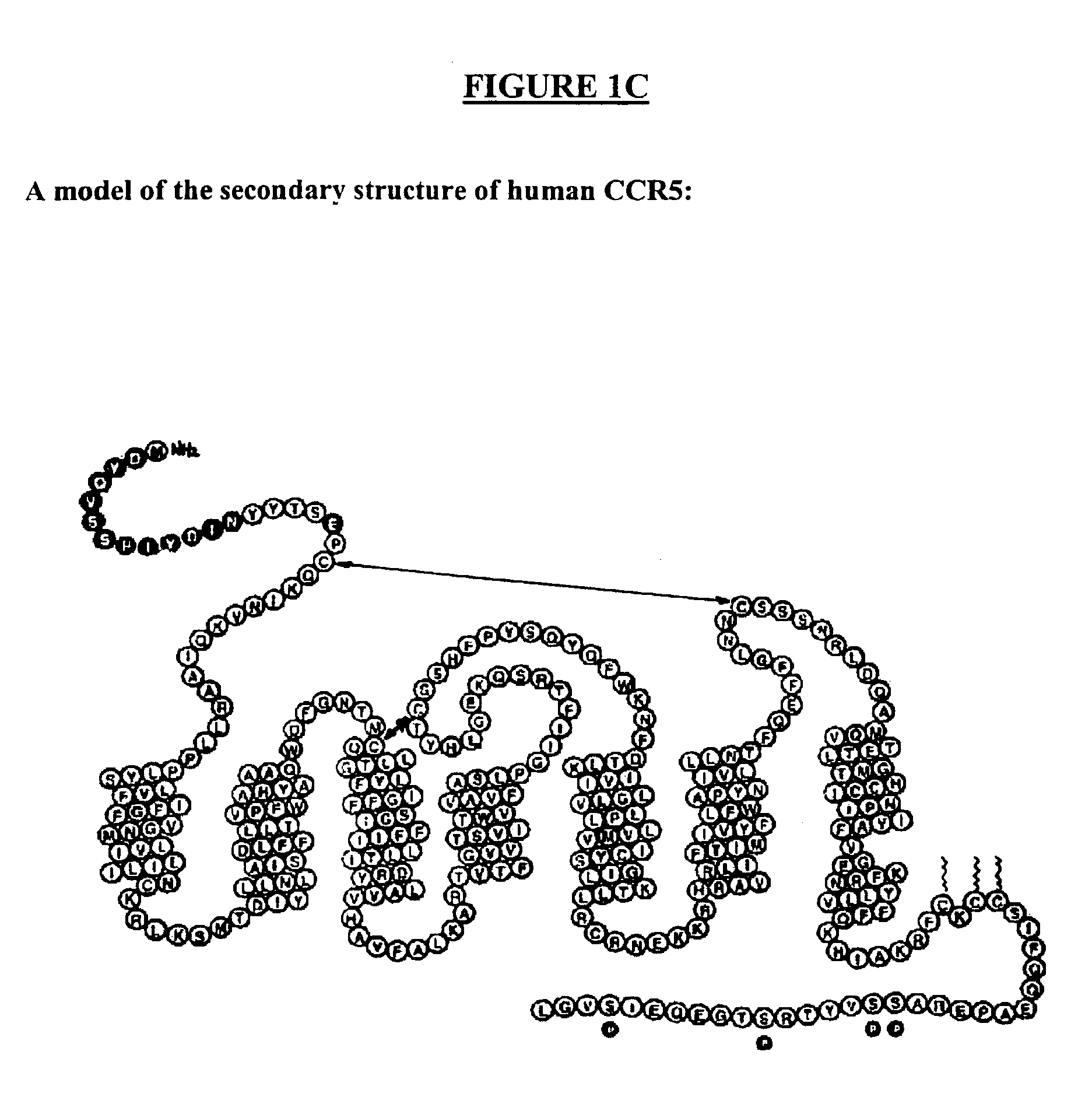
Human monoclonal antibodies against human CXCR4
Compositions are provided that comprise antibody against membrane proteins such as chemokine receptors. In particular, monoclonal human antibodies against human CXCR4 are provided that are capable of inhibiting HIV infection and chemotaxis in human breast cancer cells. The antibodies can be used as prophylactics or therapeutics to prevent and treat HIV infection and cancer, for screening drugs, and for diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with interactions with chemokine receptors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Compositions and methods for characterizing, regulating, diagnosing, and treating cancer
InactiveUS20050232927A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellOncology
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for characterizing, regulating, diagnosing, and treating cancer. For example, the present invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting tumorigenesis of certain classes of cancer cells, including breast cancer cells and preventing metastasis. The present invention also provides systems and methods for identifying compounds that regulate tumorigenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Prospective identification and characterization of breast cancer stem cells
InactiveUS20050089518A1Capacity loseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSurface marker
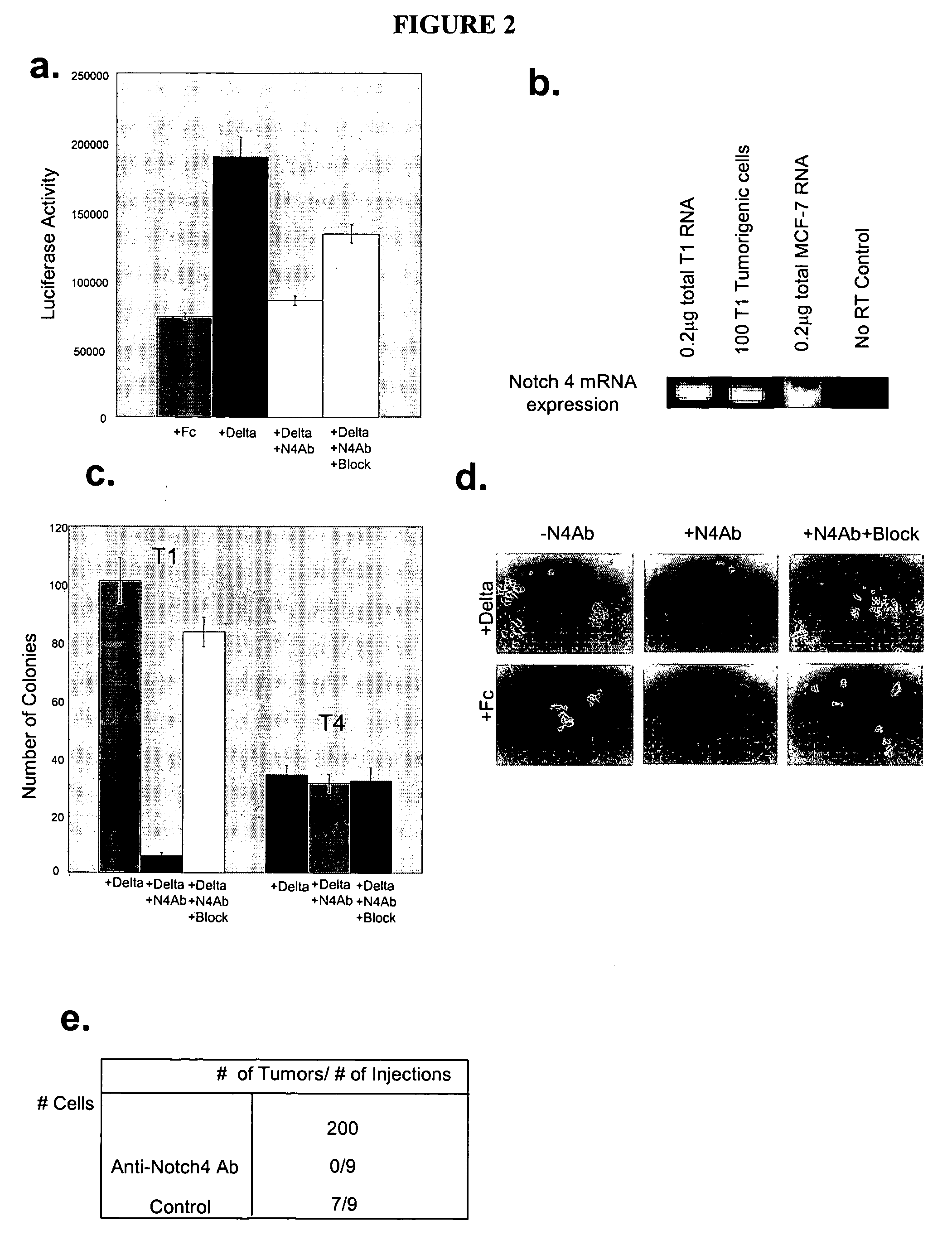
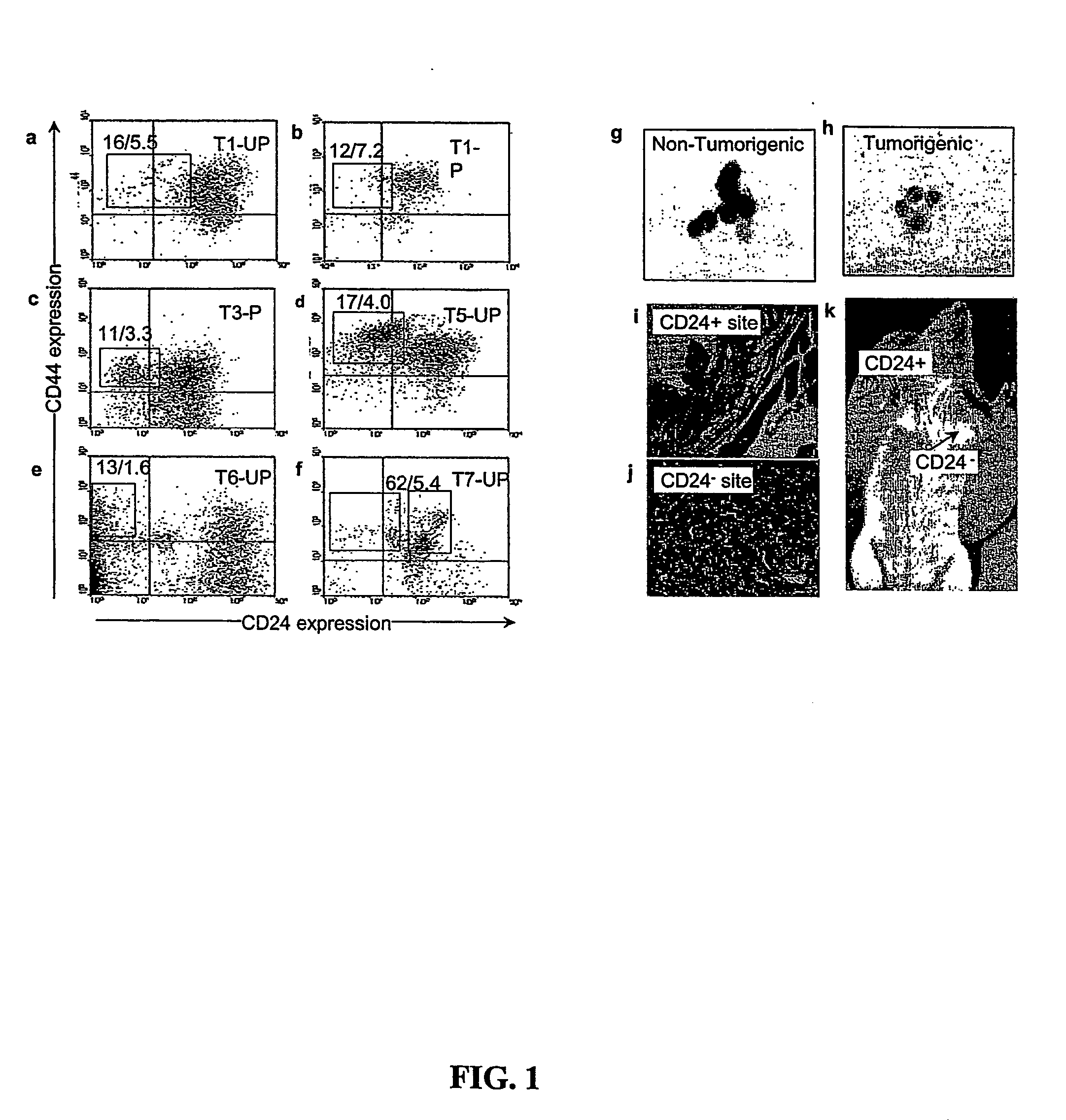
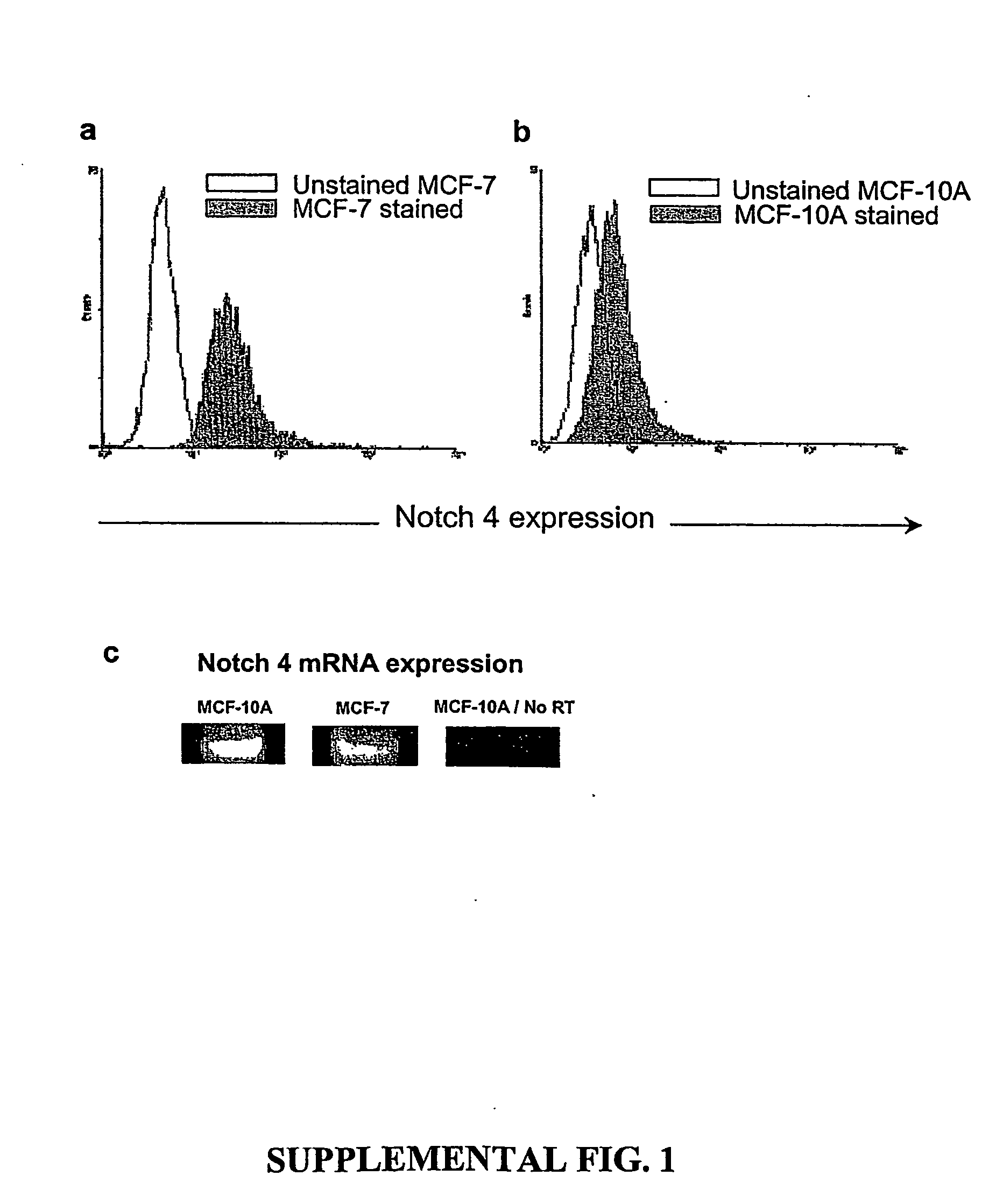
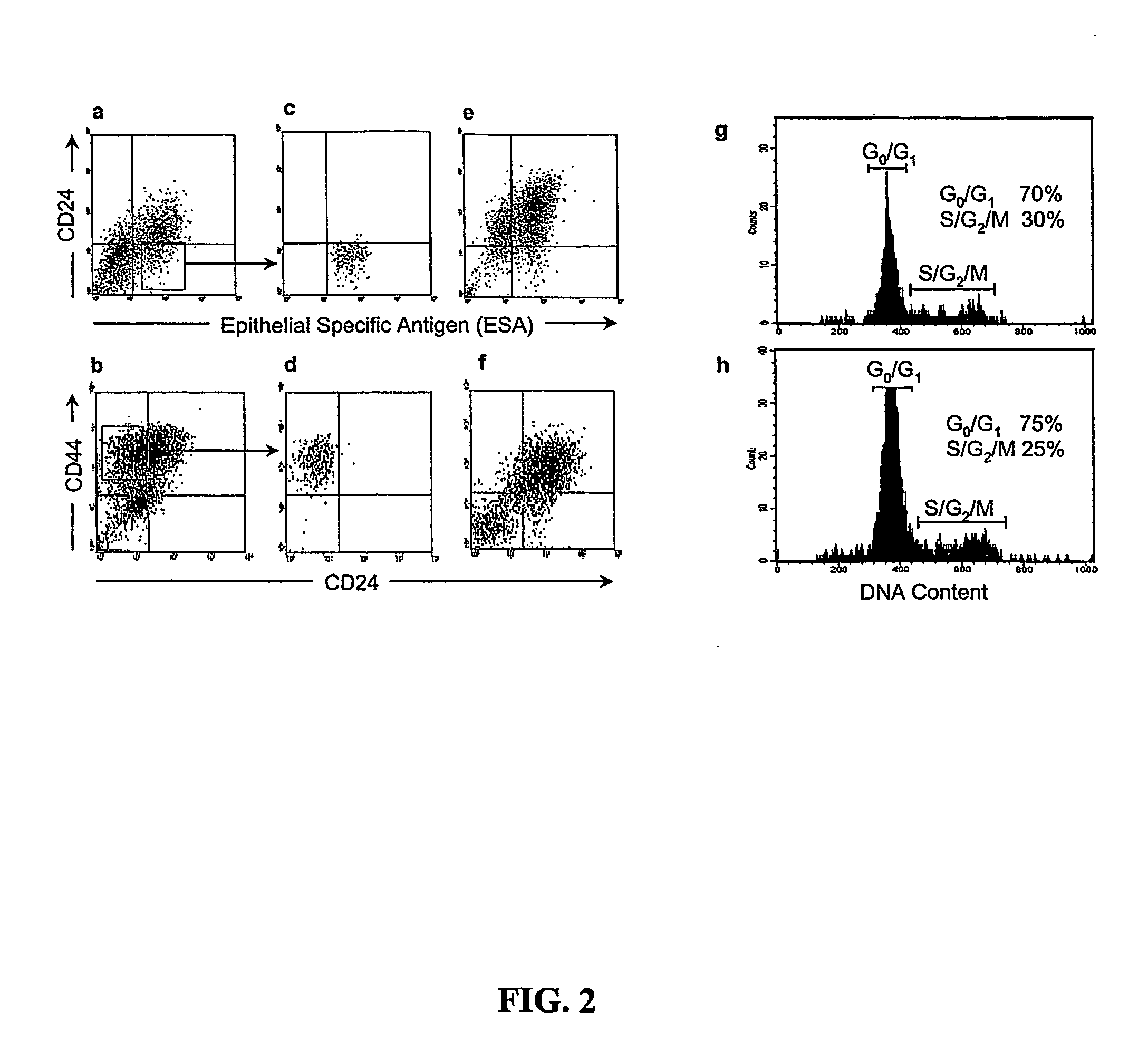
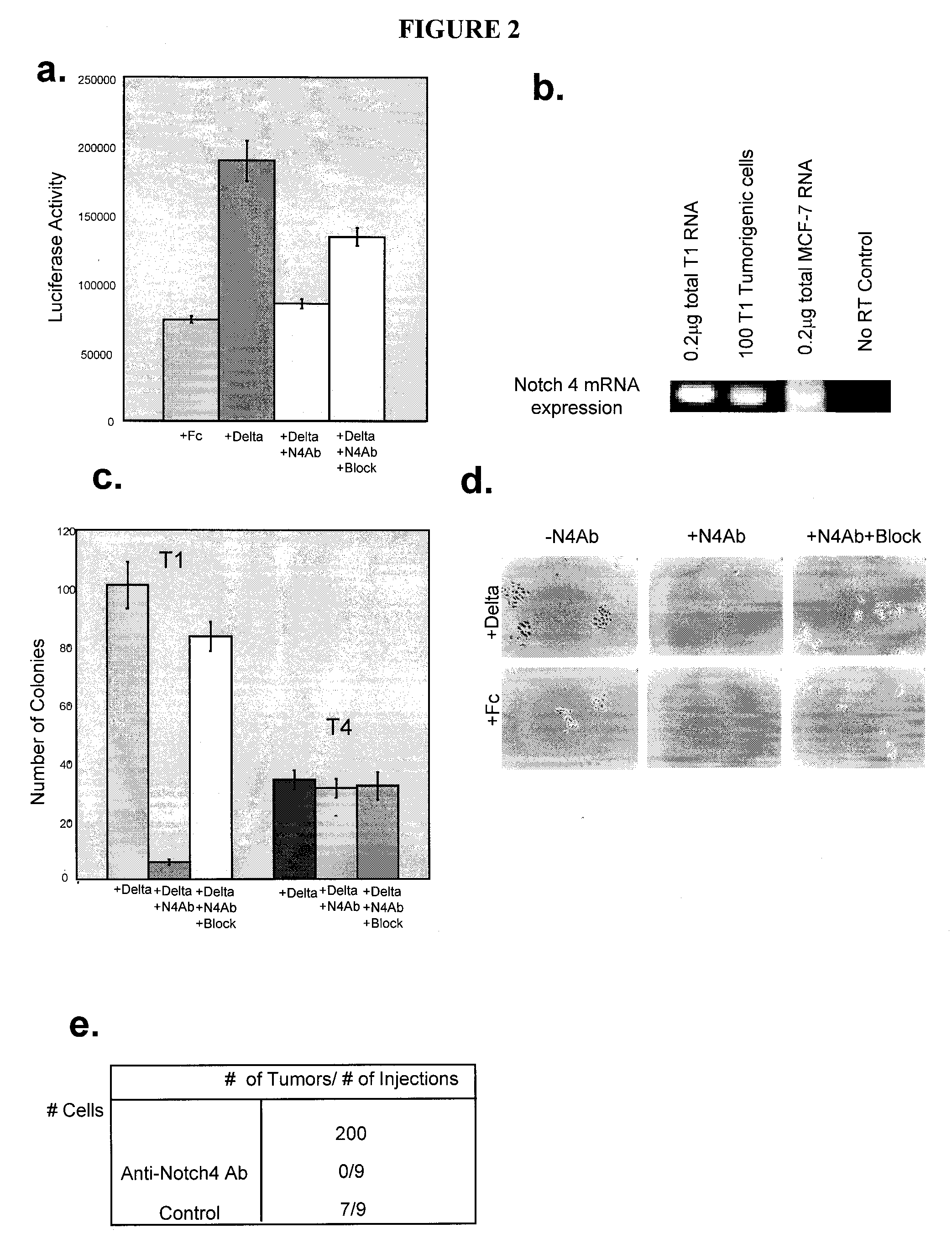
Human breast tumors contain hetrogeneous cancer cells. using an animal xenograft model in which human breast cancer cells were grown in immunocompromised mice we found that only a small minority of breast cancer cells had capacity to form new tumors. The ability to form new tumors was not a slochastic property, rather certain populations of cancer cells were depleted for the ability to form new tumors, while other populations were enriched for the ability to form new tumors. Tumorigenic cells could be distinguished from non-tumorigenic cancer cells based on surface marker expression. We prospectively identified and isolated the tumorigenic cells as CD4430CD24− / lowLINEAGE A few as 100 cells from this population were able to form tumors the animal xenograft model, while tens of thousands of cells from non-tumorigenic populations failed to form tumors. The tumorigenic cells could be serially passaged, each time generating new tumors containing and expanded numbers of CD44+CD24 Lineage tumorigenic cells as well as phenotypically mixed populations of non-tumorigenic cancer cells. This is reminiscent of the ability of normal stem cells to self-renew and differentiate. The expression of potential therapeutic targets also differed between the tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic populations. Notch activation promoted the survival of the tumorigenic cells, and a blocking antibody against Notch 4 induced tumorigenic breast cancer cells to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
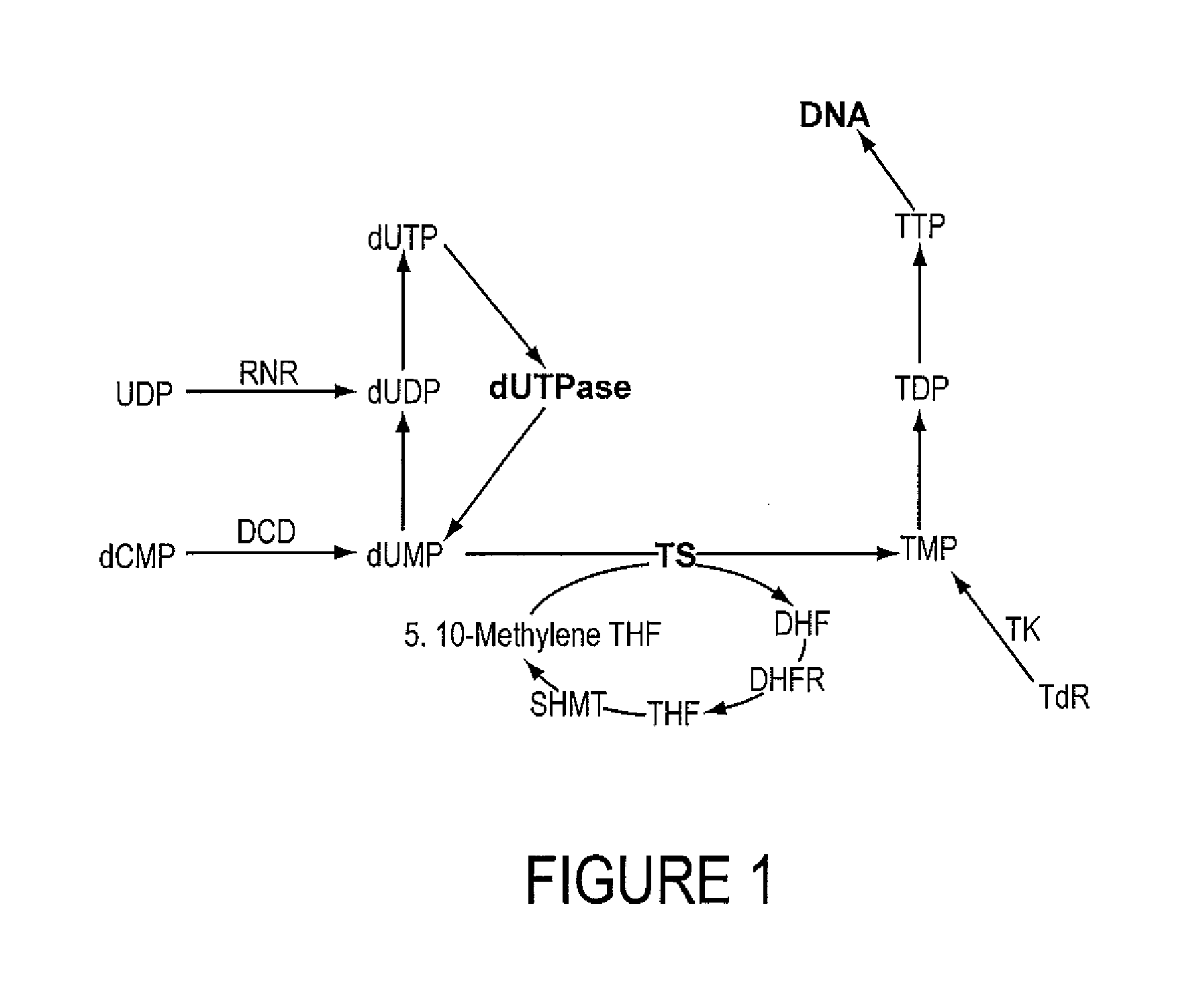
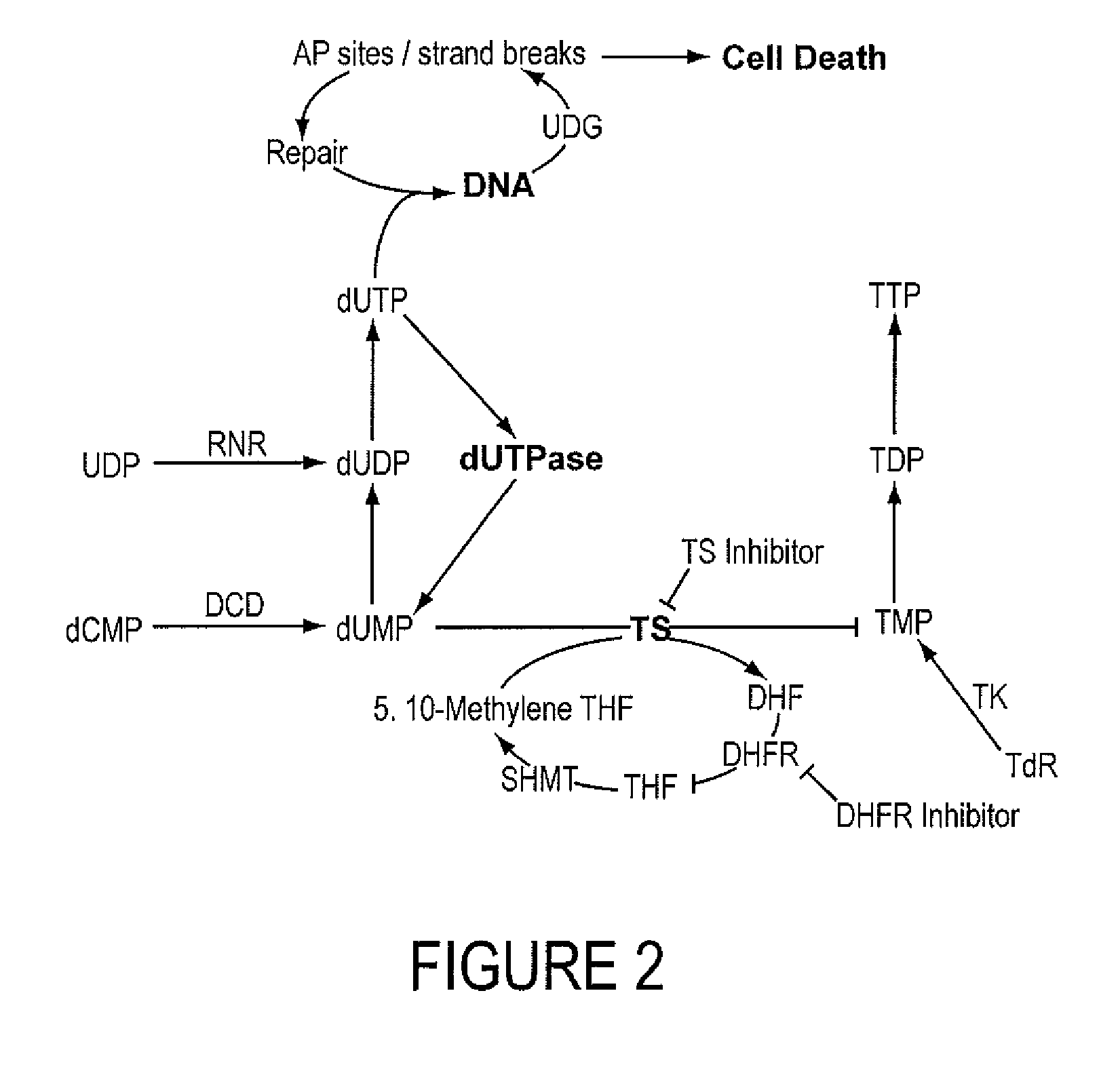
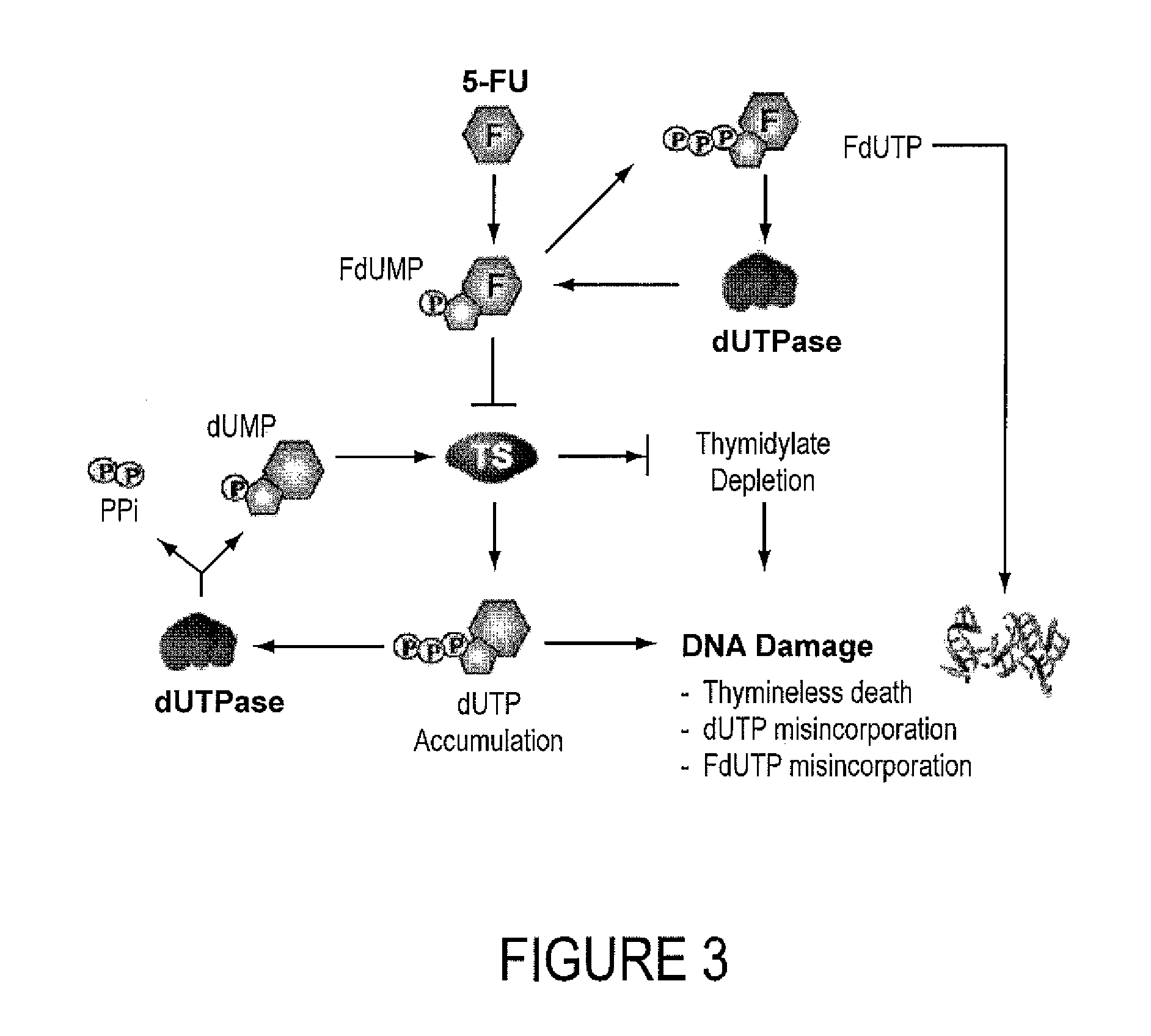
INHIBITORS OF dUTPase
InactiveUS20110212467A1Improve the immunitySuppresses dUTP poolOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryClinical efficacyUracil
Evidence demonstrating that elevated expression of dUTPase protects breast cancer cells from the expansion of the intracellular uracil pool, translating to reduced growth inhibition following treatment with 5-FU is provided. The implementation of in silica drug development techniques to identify and develop small molecule inhibitors of dUTPase are reported. As 5-FU and the oral 5-FU pro-drug capecitabine remain central agents in the treatment of a variety of malignancies, the clinical utility of a small molecule inhibitor to dUTPase represents a viable strategy to improve the clinical efficacy of these mainstay chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
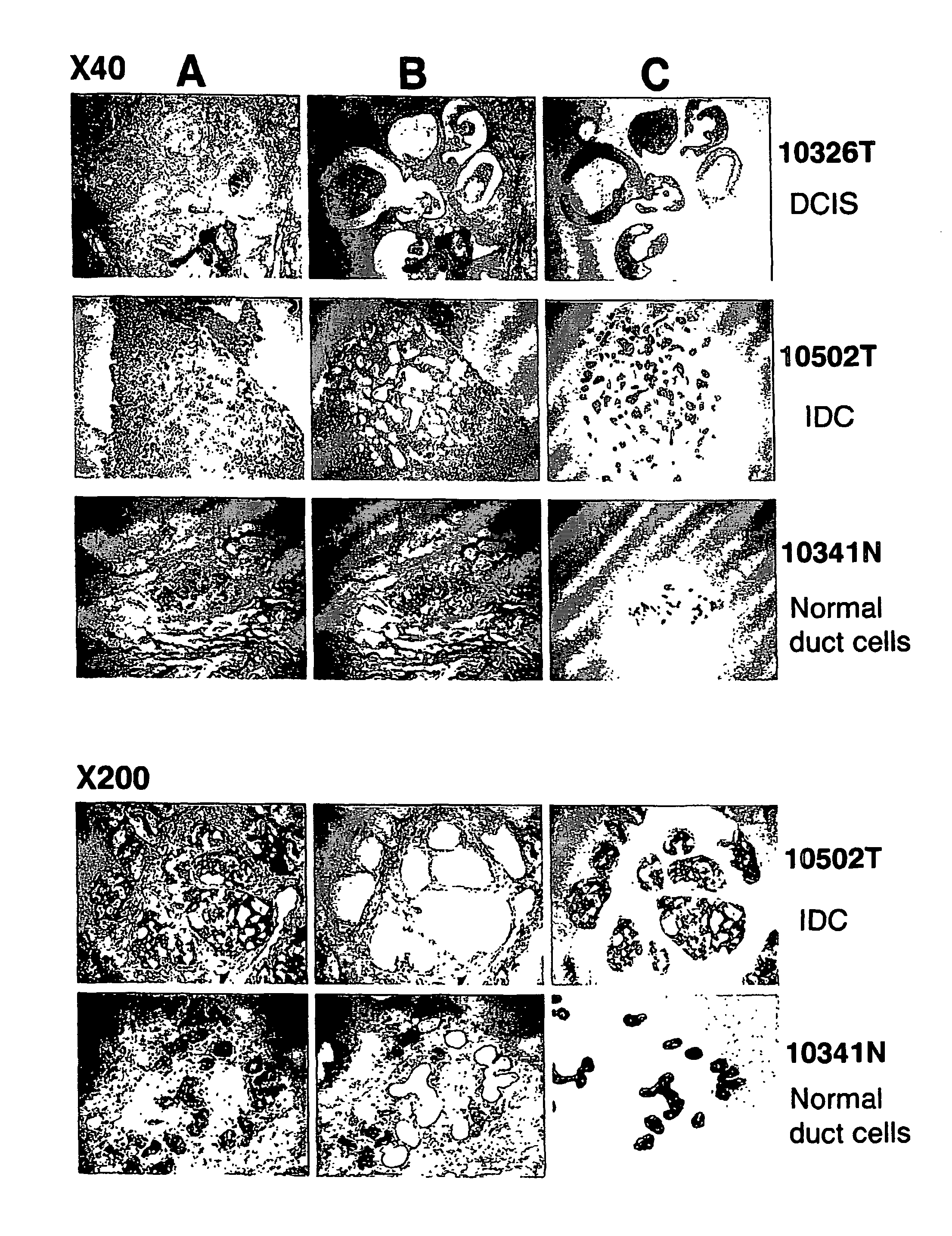
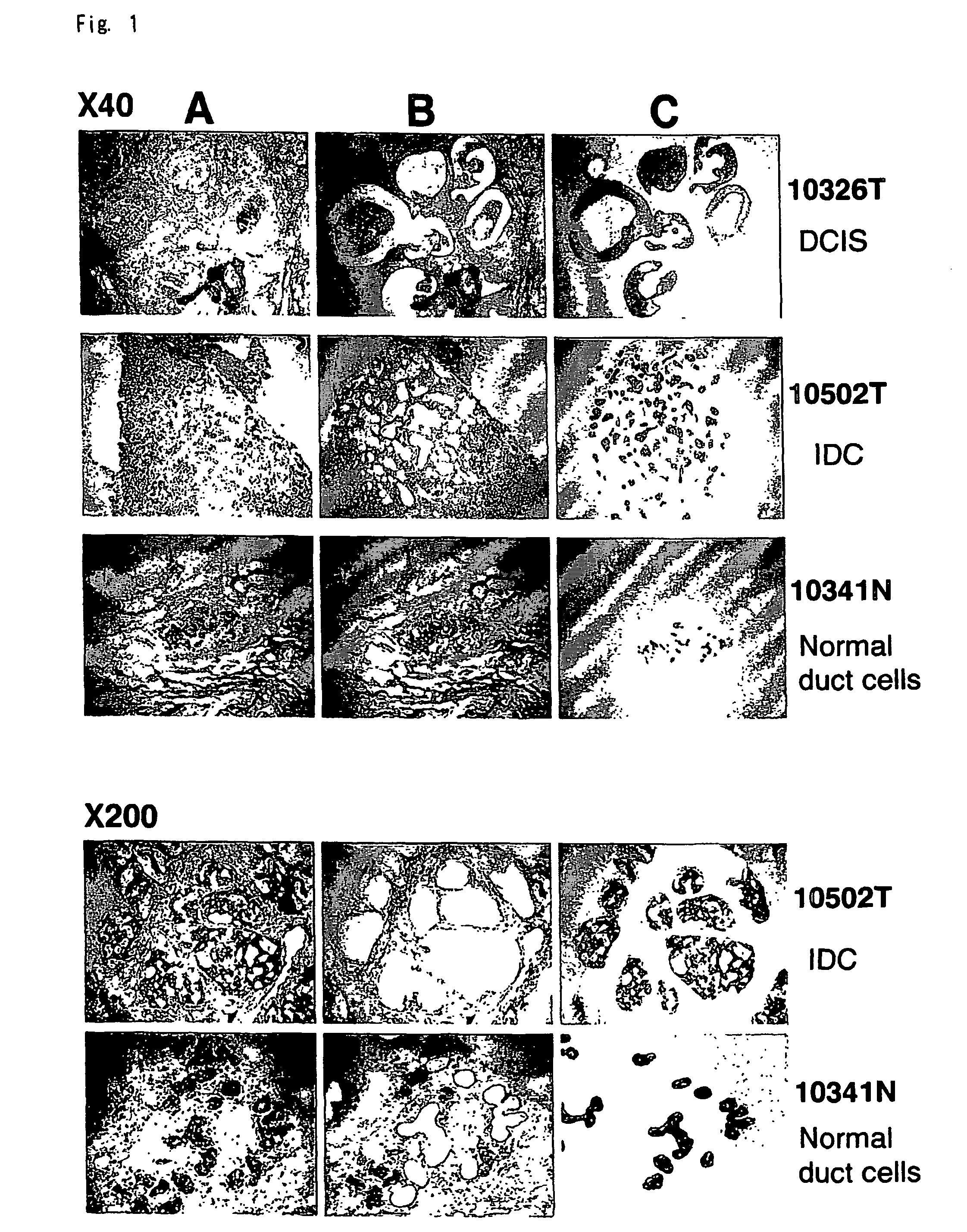
Method of Diagnosing Breast Cancer
InactiveUS20070269432A1Preventing metastasis of breast cancerMetastasis of breast cancer can be treated or preventedOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningBreast cancer metastasisNormal cell
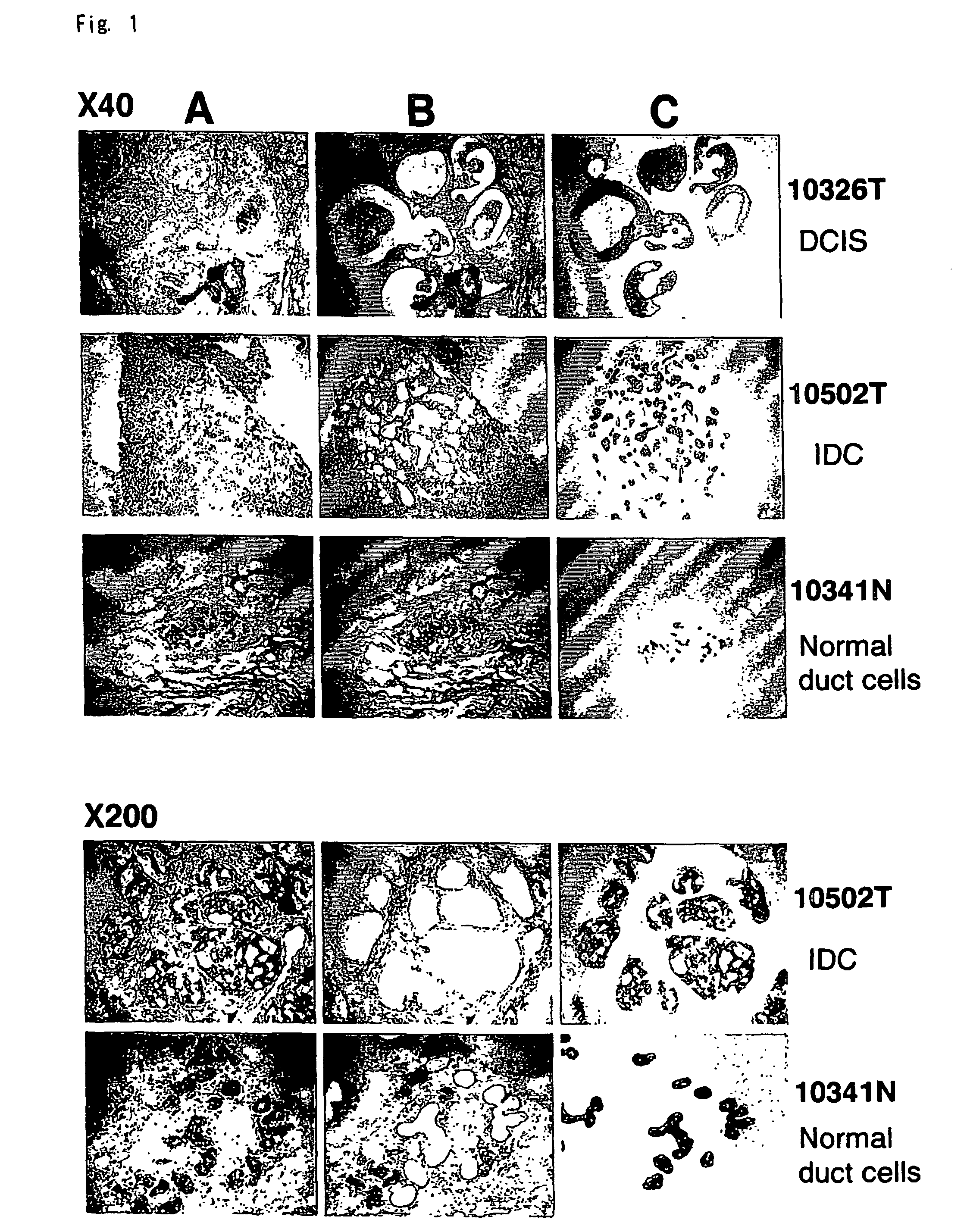
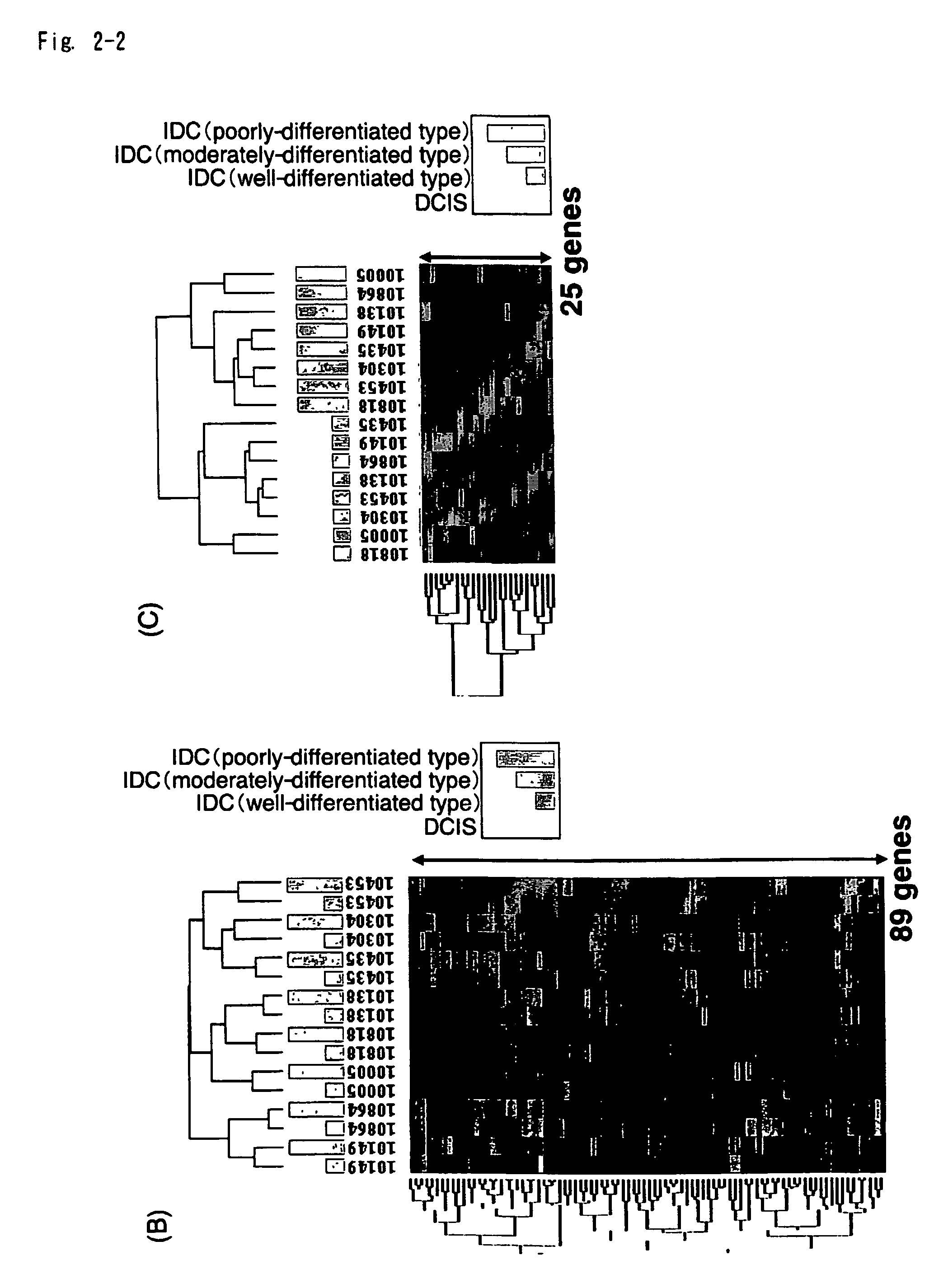
Objective methods for detecting and diagnosing breast cancer (BRC) are described herein. In one embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates between BRC cells and normal cells. In another embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates among BRC cells, between DCIS and IDC cells. The present invention further provides means for predicting and preventing breast cancer metastasis using BRC-associated genes having unique altered expression patterns in breast cancer cells with lymph-node metastasis. Finally, the present invention provides methods of screening for therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of breast cancer, methods of treating breast cancer and method for vaccinating a subject against breast cancer.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
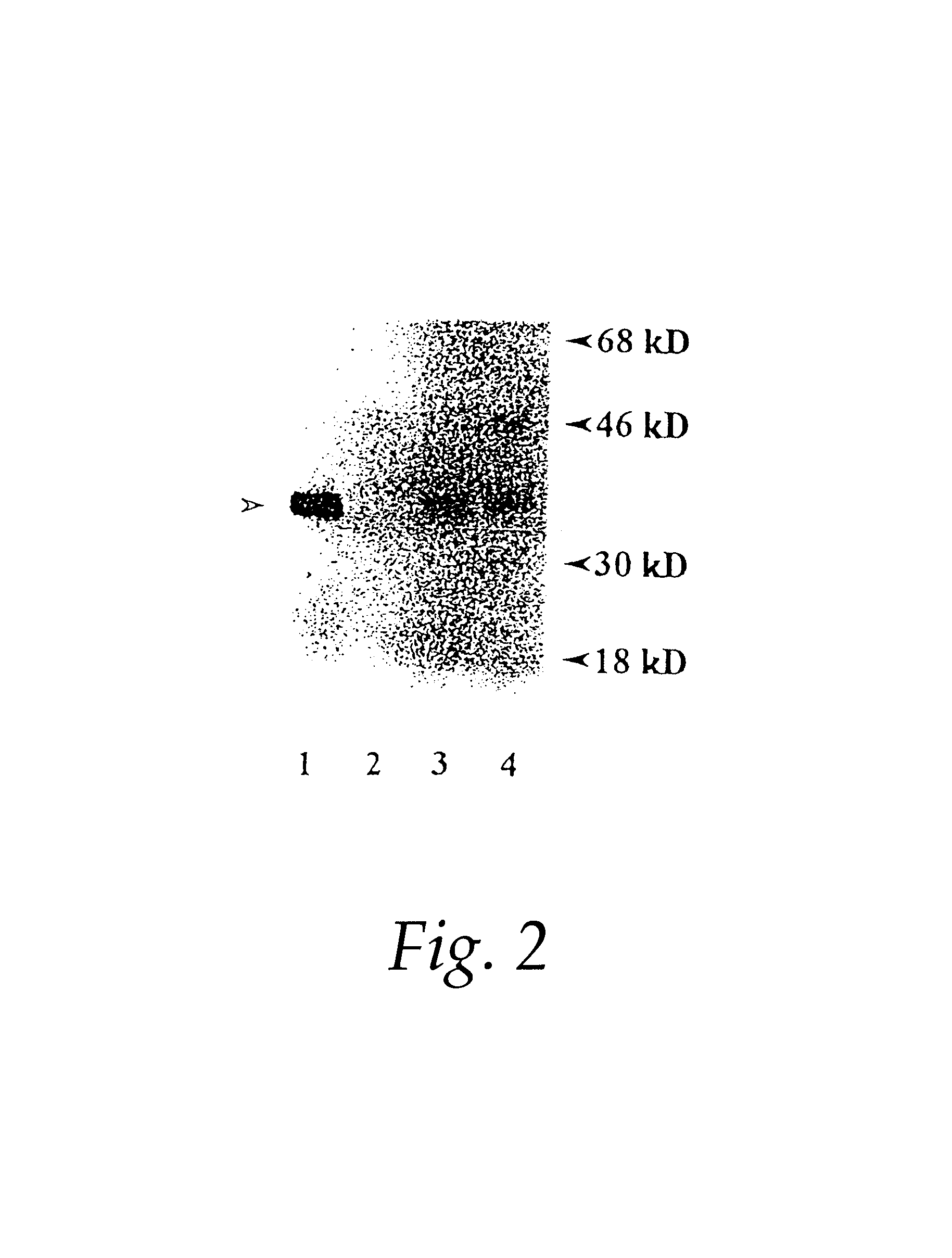
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
InactiveUS6399328B1Control metastatic potentialOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to a novel gene, Di12, that is differentially expressed as a 1.35 kb RNA in breast cancer tissues and cell lines, and in several normal tissues. The full length cDNA encodes a protein of 339 amino acids. Antibodies to the gene product were developed to investigate the expression of Di12 in breast cancer cell-lines and tumors. The Di12 protein was found in tissue sections of infiltrating ductal carcinomas (IDCs), but not in benign or normal breast specimens. Di12 wag also present in IDC-breast cancer patient sera, and its expression level increased markedly if IDC was accompanied by lymph node or distal metastases. As IDC constitutes ~70% of breast cancers seen clinically, the level of Di12 expression is useful for diseases diagnosis predicting disease progression and monitoring a therapeutic treatment.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Novel pathways in the etiology of cancer
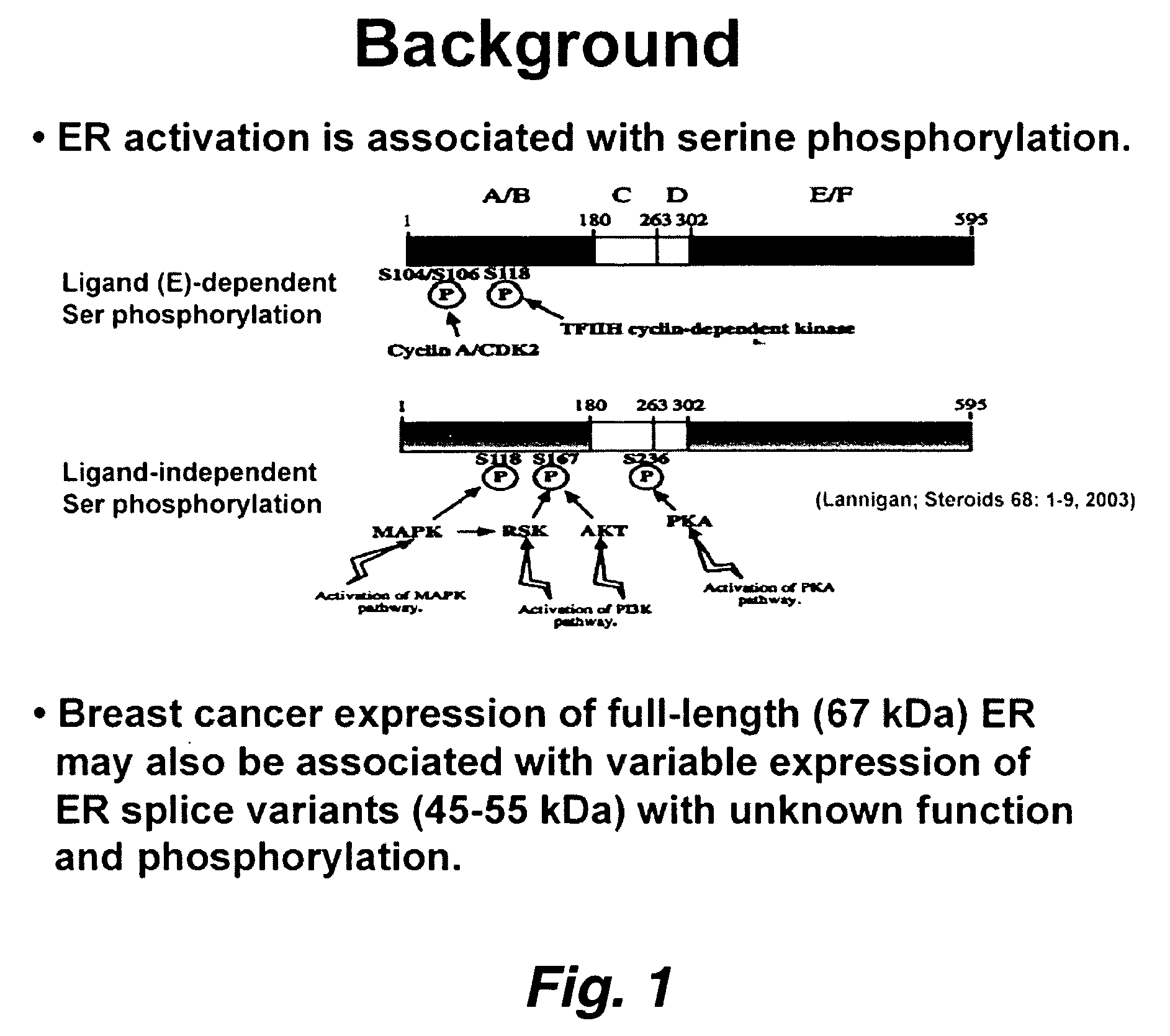
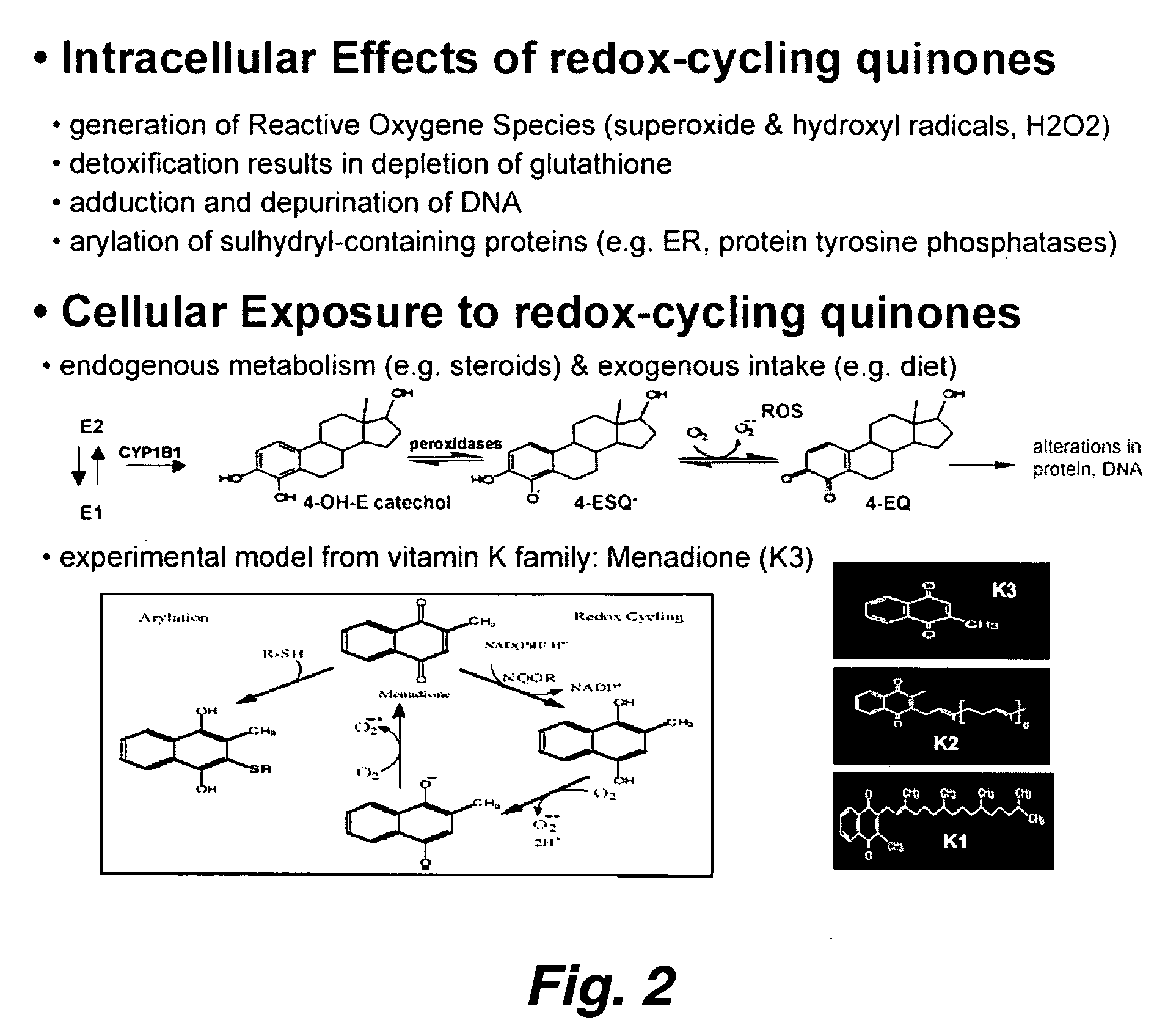
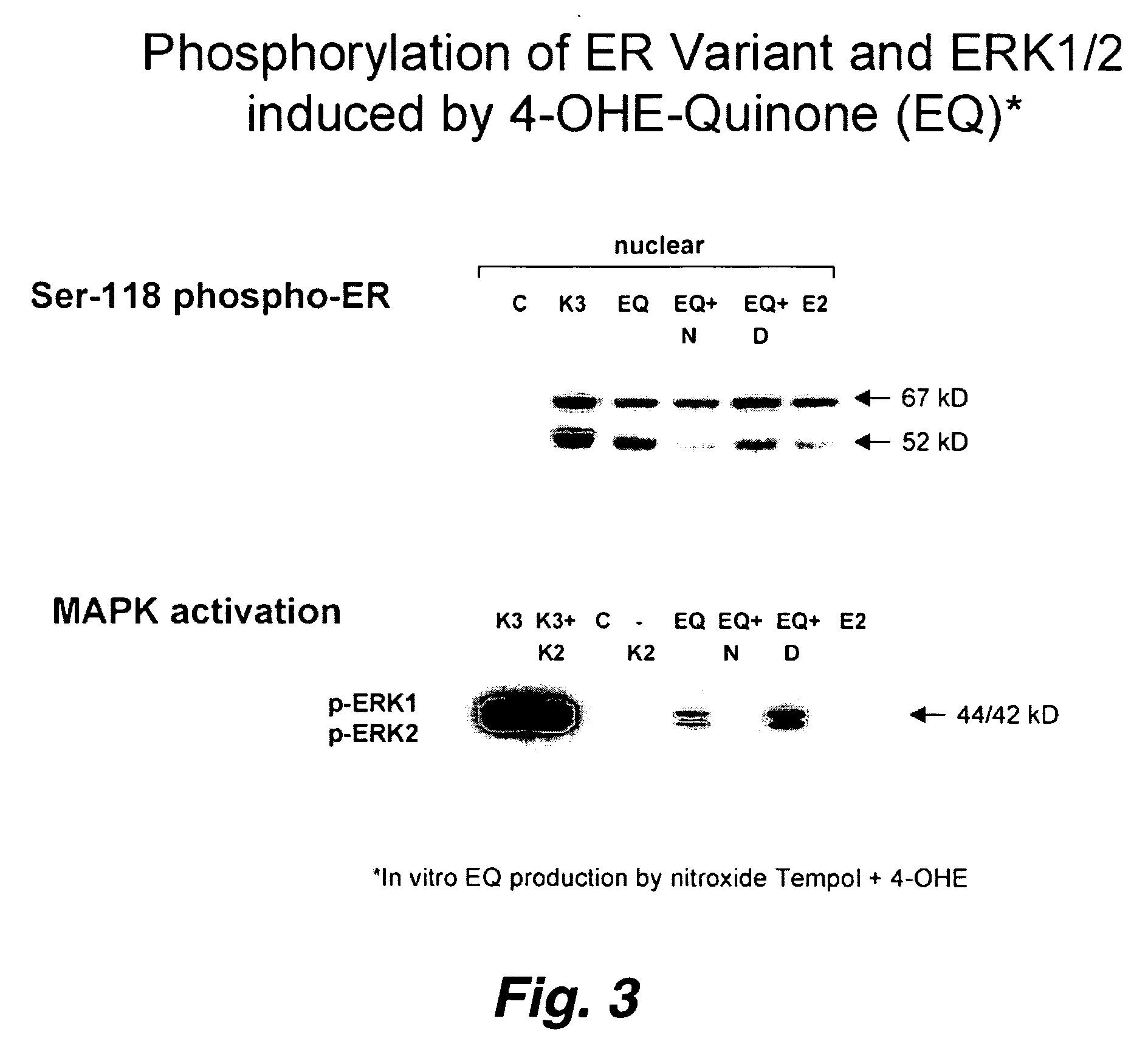
This invention pertains to the identification of two novel epithelial signaling pathways in ER-positive breast cancer s and the discovery that the cellular biology and (likely also the clinical outcome) of ER-positive breast cancer cells is unexpectedly altered when these signaling pathways are activated. The first pathway pertains to the discovery that NF-κB activation and / or DNA binding is implicated in the etiology of ER-positive breast (and other) cancers. The second pathway involves ligand-independent quinine-mediated ER activation by posphorylation (e.g. on SER-118 and SER-167 residues of ER) and nuclear translocation of full-length (67 kDA) ER as well as the phorphorylating activation of a truncated and nuclear-localized ER variant (˜52 kDa).
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Breast cancer cell characteristic analysis system based on deep learning
ActiveCN105447569AReduce overfittingImprove generalization abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsActivation functionFeature extraction
The invention discloses a breast cancer cell characteristic analysis system based on deep learning. Based on the deep learning, the system constructs a multilevel convolutional neural network to extract multilevel features, so higher analysis accuracy can be realized; an activation function of a model in the breast cancer cell characteristic analysis system disclosed by the invention is an unsaturated ReLU function, which has faster convergence properties; a pooling layer in the breast cancer cell characteristic analysis system disclosed by the invention adopts an overlapped pooling operation, it can be proved by cross validation that, compared with a traditional non-overlapped pooling layer, the overlapped pooling can further improve the analysis accuracy; and the breast cancer cell characteristic analysis system disclosed by the invention adopts a training mode of sparse autocoder pre-training and Dropout fine tuning to effectively reduce the over fitting of the model and enhance the generalization ability of the trained model, so that the analysis accuracy can be further improved.
Owner:BEIJING BAIHUI WEIKANG SCI & TECH CO LTD
Combinations of histone deacetylase inhibitors and either her2 inhibitors or pi3k inhibitors
ActiveUS20150099744A1Promote cell migrationReduce in quantityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHDAC inhibitorEndocrinology
The invention relates to combinations comprising an HDAC inhibitor and a Her2 inhibitor for the treatrent of breast cancer in a subject in need thereof. The invention also relates to combinations comprising an HDAC inhibitor and a PI3K inhibitor for the treatment of breast cancer in a subject in need thereof. Also provided herein are methods for treating breast cancer in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of one of the above combinations. Further provided are methods for inhibiting migration and / or invasion of a breast cancer cell in a subject by administering to the subject a HDAC6 specific inhibitor.
Owner:ACETYLON PHARMA
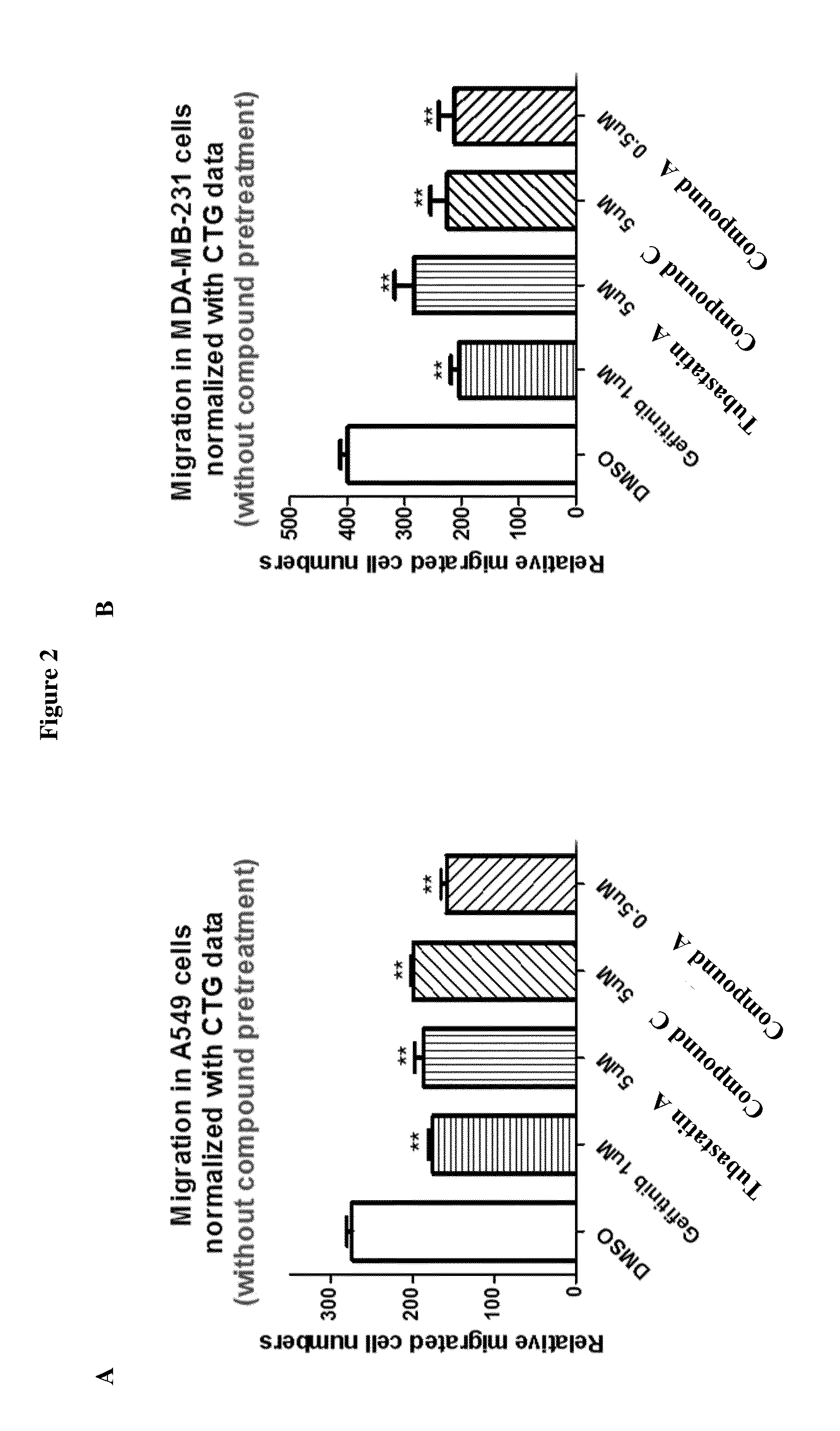
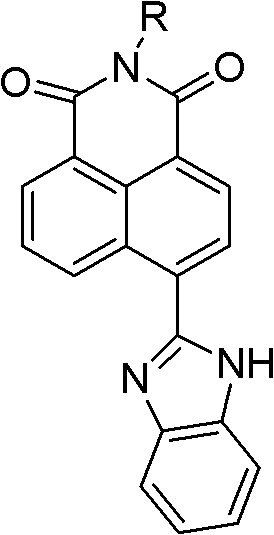
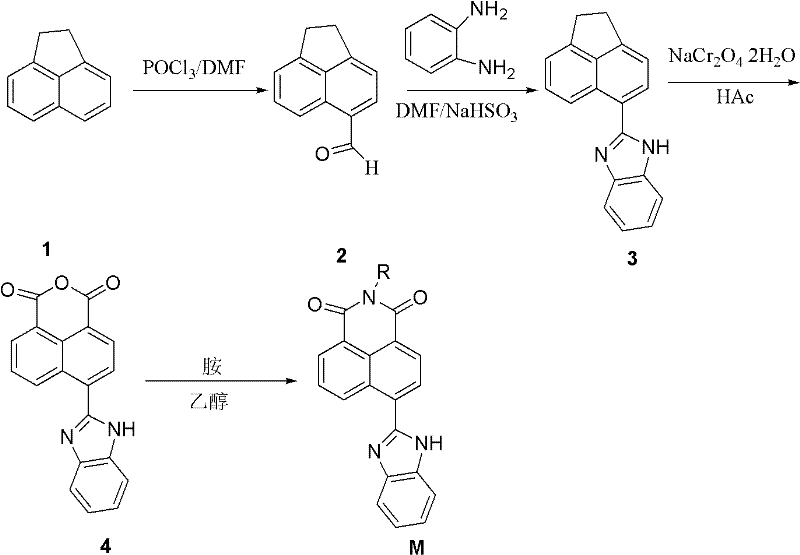
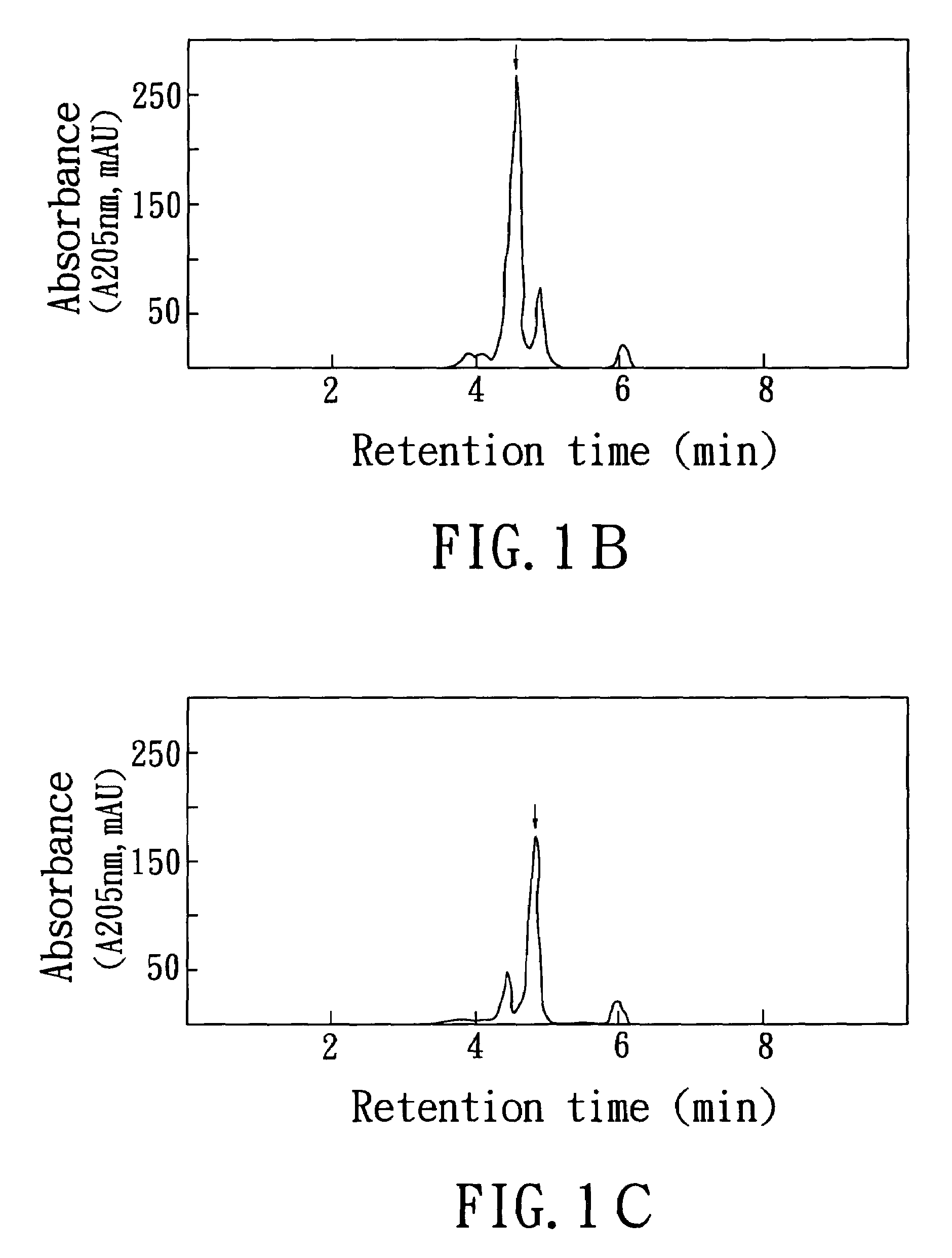
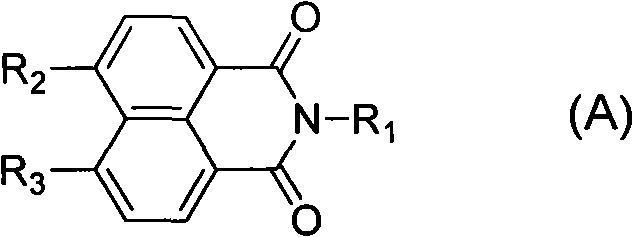
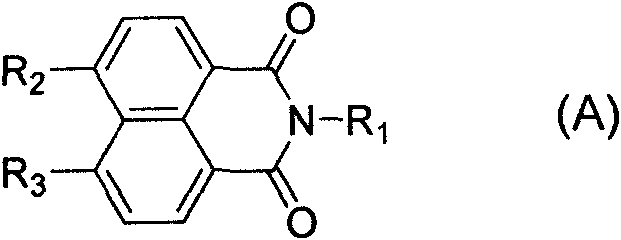
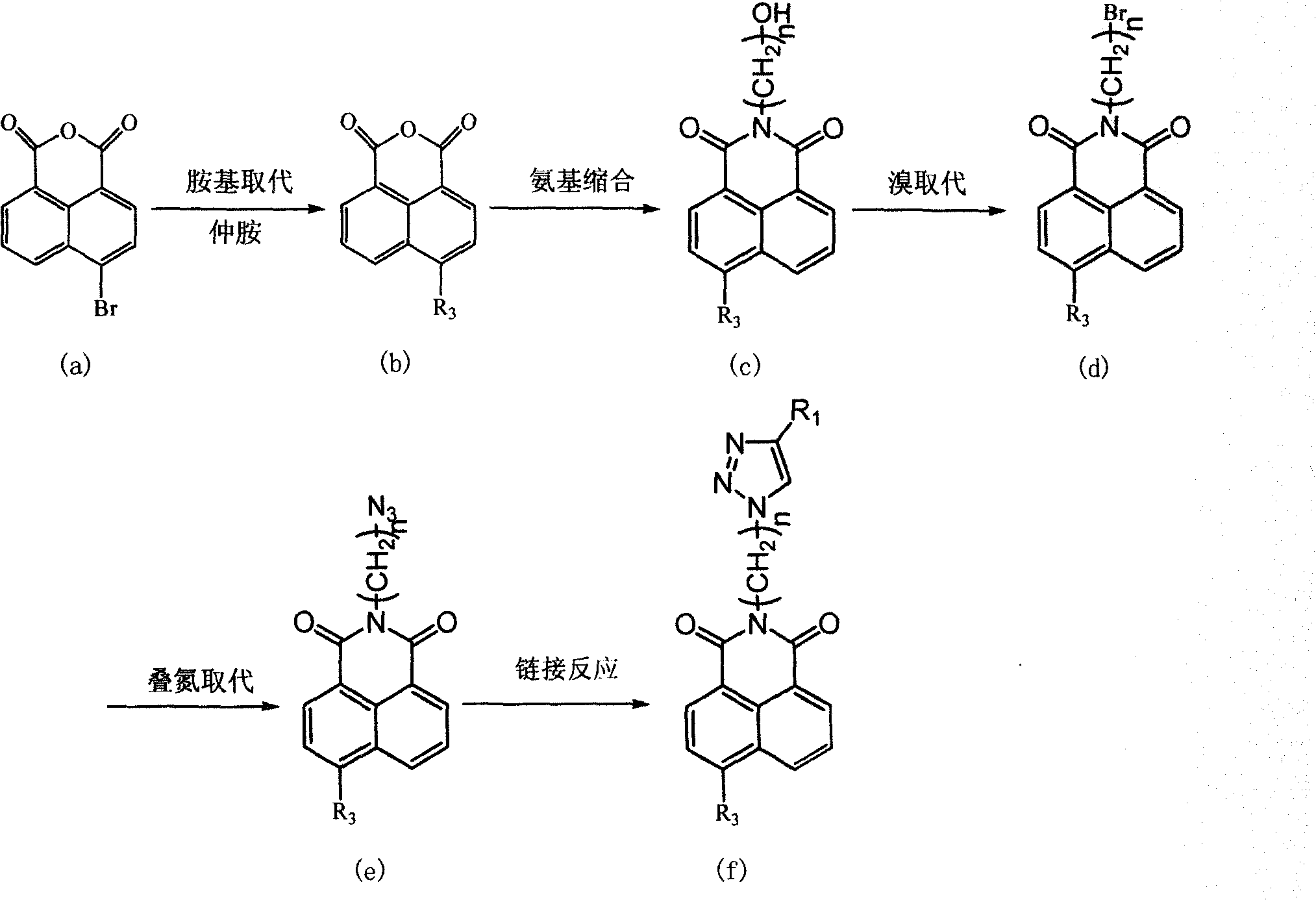
Synthesis of benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives and applications of benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives on cancer resistance
InactiveCN102206203AGood choiceGood tumor suppressor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPheochromocytomaOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to synthesis of benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives and applications of the benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives on cancer resistance, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis and pharmaceutical chemistry technology. The benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives are obtained through a method that a benzimidazole group is introduced into a fourth position of a naphthalene ring of naphthalimide. Experiments of proliferation inhibiting effects of the benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives on cancer cells adopt a microculture tetrozolium (MTT) reduction method and aim at MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, Hela human cervical cancer cells and PC12 rat adrenal medullary pheochromocytoma differentiated cells. Results of the experiments show that the benzimidazole-containing naphthalimide derivatives have the advantages of good inhibitory activity against cancer cells and good selectivity on cancer cells.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Endogenous protein marking method used for Chip-seq genome-wide binding spectrum
InactiveCN106399311AMeet the packaging ratioHigh infection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMaterial resourcesStable cell line
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Anti-cancer compounds and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050209320A1Shorten the progressDelay the progression of the cancerBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationProstate cancer cellCancer cell
The present invention relates to a novel class of anti-cancer compounds which selectively target androgen receptor (AR)-expressing cancer cells, such as prostate cancer cells and breast cancer cells. These agents comprise an androgen receptor (AR) binding moiety, which selectively targets the compounds to (AR)-expressing cancer cells, and a cytotoxic ablating moiety, such as a nitrogen mustard moiety. The inherent high density expression of the androgen receptor in certain cancers, such as prostate cancer and breast cancer, is thus used as a tool to selectively increase the intracellular concentration of cytotoxic compounds, such as alkylating agents, e.g. DNA alkylating agents, by selectively targeting the agents to the AR-expressing cancer cells. These agents, either alone or in a composition, are thus useful for treating, delaying the progression of, treating the recurrence of, suppressing, inhibiting or reducing the incidence of cancers characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells, such as prostate cancer. Accordingly, the present invention provides a) methods of selectively killing an (AR)-expressing cancer cell; b) methods of inducing apoptosis in an (AR)-expressing cancer cell; c) methods of treating a cancer characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells in a subject; d) methods of delaying the progression of a cancer characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells in a subject; e) methods of treating the recurrence of a cancer characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells in a subject; f) methods of suppressing, inhibiting or reducing the incidence of a cancer characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells in a subject; and g) methods of treating metastasis of a cancer characterized by the presence of AR-expressing cells in a subject; by administering to the subject or by contacting the cancer cells with a compound comprising an androgen receptor ligand moiety and an alkylating moiety, such as the novel compounds described herein.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED
Preparation method of nano sulfonated graphene and application of nano sulfonated graphene as gene transfer material
ActiveCN103641106ALow costReduce manufacturing costGenetic material ingredientsGrapheneSulfanilic acidHuman breast
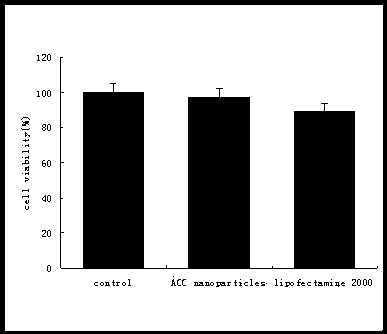
The invention relates to the technical field of gene transfer materials, particularly a preparation method of nano sulfonated graphene and application of nano sulfonated graphene as a gene transfer material. The preparation method of the nano sulfonated graphene comprises the following steps: 1. preparing graphene oxide; 2. preparing reduced graphene oxide; 3. preparing diazonium salt of sulfanilic acid; and 4. preparing the nano sulfonated graphene. The nano sulfonated graphene can be used as a gene transfer material since positive charges of ions on particle surfaces can be combined with green fluorescent proteins in a non-covalent mode to perform transfection; and when being used as a gene transfer material, the nano sulfonated graphene has the advantages of high transfection effect, favorable cell compatibility and high cell survival rate. The transfection efficiency of the nano sulfonated graphene in human breast cancer cells is up to 40% or so.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Human monoclonal antibodies against membrane proteins
Compositions are provided that comprise antibody against membrane proteins such as chemokine receptors. In particular, monoclonal human antibodies against human CXCR4 are provided that are capable of inhibiting HIV infection and chemotaxis in human breast cancer cells. The antibodies can be used as prophylactics or therapeutics to prevent and treat HIV infection and cancer, for screening drugs, and for diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with interactions with chemokine receptors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
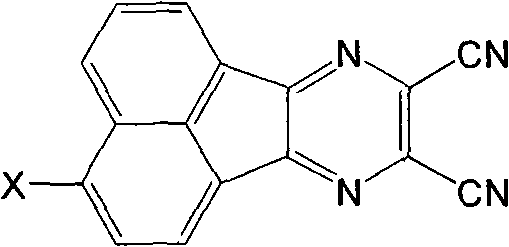
O-dicyano-acenaphtho pyrazine compound and anti-tumor application thereof
InactiveCN101723907AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryQuinonePyrazine
The invention relates to a DNA-targeted o-dicyano-acenaphtho pyrazine compound in the field of application of antineoplastic medicaments. The compound is prepared by taking acenaphthene quinone as a raw material and performing bromination, cyclization and aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction. The compound is characterized in that: one end takes an amino straight chain of a flexible side chain or an annular group as an electron-donating group, while the other end takes two cyanogen groups as electron-withdrawing groups; the two ends form an electron deficient large-plane conjugated system; and the structure accords with an ideal DNA intercalator. The compound shows obvious inhibitory activity to an in vitro test of MCF-7 (human mammary cancer cells).
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
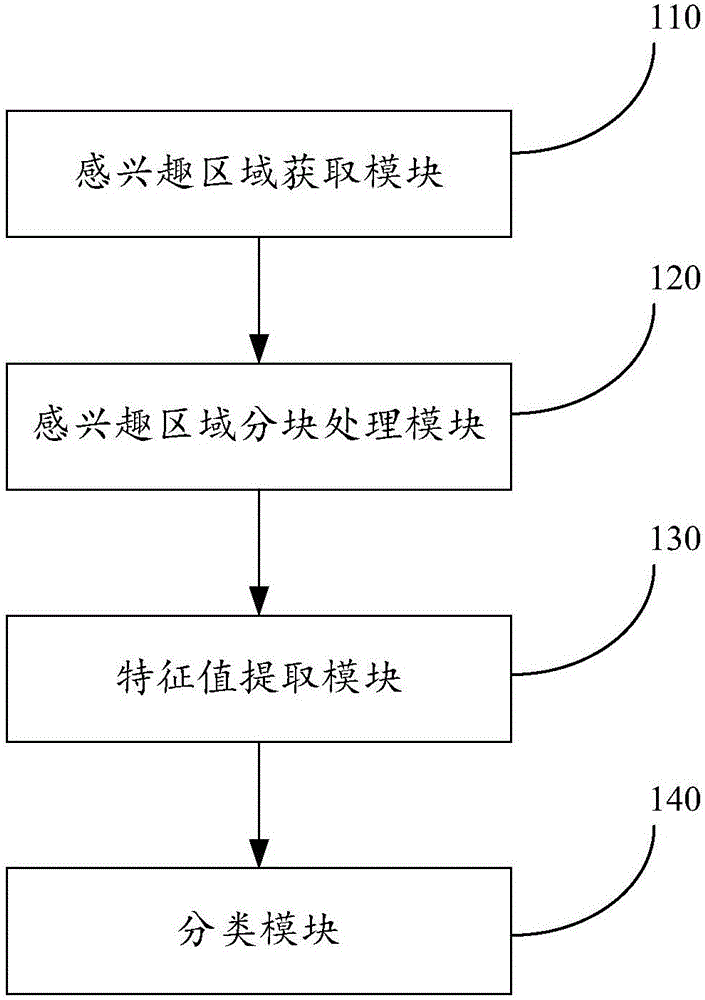
Classification method and system for cancer digital pathological cell image
ActiveCN106127255AOvercoming diversityOvercome irregularities and many other problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning machineClassification methods
The invention provides a classification method and a classification system for cancer digital pathological cell images. According to the classification method and the classification system, a suspected lesion region of interest is subjected to block processing, the suspected lesion region after block processing is subjected to feature extraction by utilizing partial matching pattern textural features, and the extracted features are classified and identified by adopting an extreme learning machine training method, so as to determine benign and malignant tumors and differentiate levels. The classification method and the classification system for the cancer digital pathological cell images utilize the partial matching pattern textural features for conducting feature extraction, analyze the textural features of cells from macroscopic and microscopic aspects, have the advantage of rotation invariance, effectively overcome the problems of diversity, irregularity and the like of cell morphology, provide reliable textural feature information for classification, apply an extreme learning machine to the classification of breast cancer cells, shorten the training time, accelerate the speed of classification and identification, and improve the accuracy of recognition.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Compositions and methods for characterizing, regulating, diagnosing, and treating cancer
InactiveUS20080260734A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadCancer cell
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for characterizing, regulating, diagnosing, and treating cancer. For example, the present invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting tumorigenesis of certain classes of cancer cells, including breast cancer cells and preventing metastasis. The present invention also provides systems and methods for identifying compounds that regulate tumorigenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of diagnosing breast cancer
InactiveUS7531300B2Preventing metastasis of breast cancerMetastasis of breast cancer can be treated or preventedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBreast cancer metastasisNormal cell
Objective methods for detecting and diagnosing breast cancer (BRC) are described herein. In one embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates between BRC cells and normal cells. In another embodiment, the diagnostic method involves determining the expression level of a BRC-associated gene that discriminates among BRC cells, between DCIS and IDC cells. The present invention further provides means for predicting and preventing breast cancer metastasis using BRC-associated genes having unique altered expression patterns in breast cancer cells with lymph-node metastasis. Finally, the present invention provides methods of screening for therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of breast cancer, methods of treating breast cancer and method for vaccinating a subject against breast cancer.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
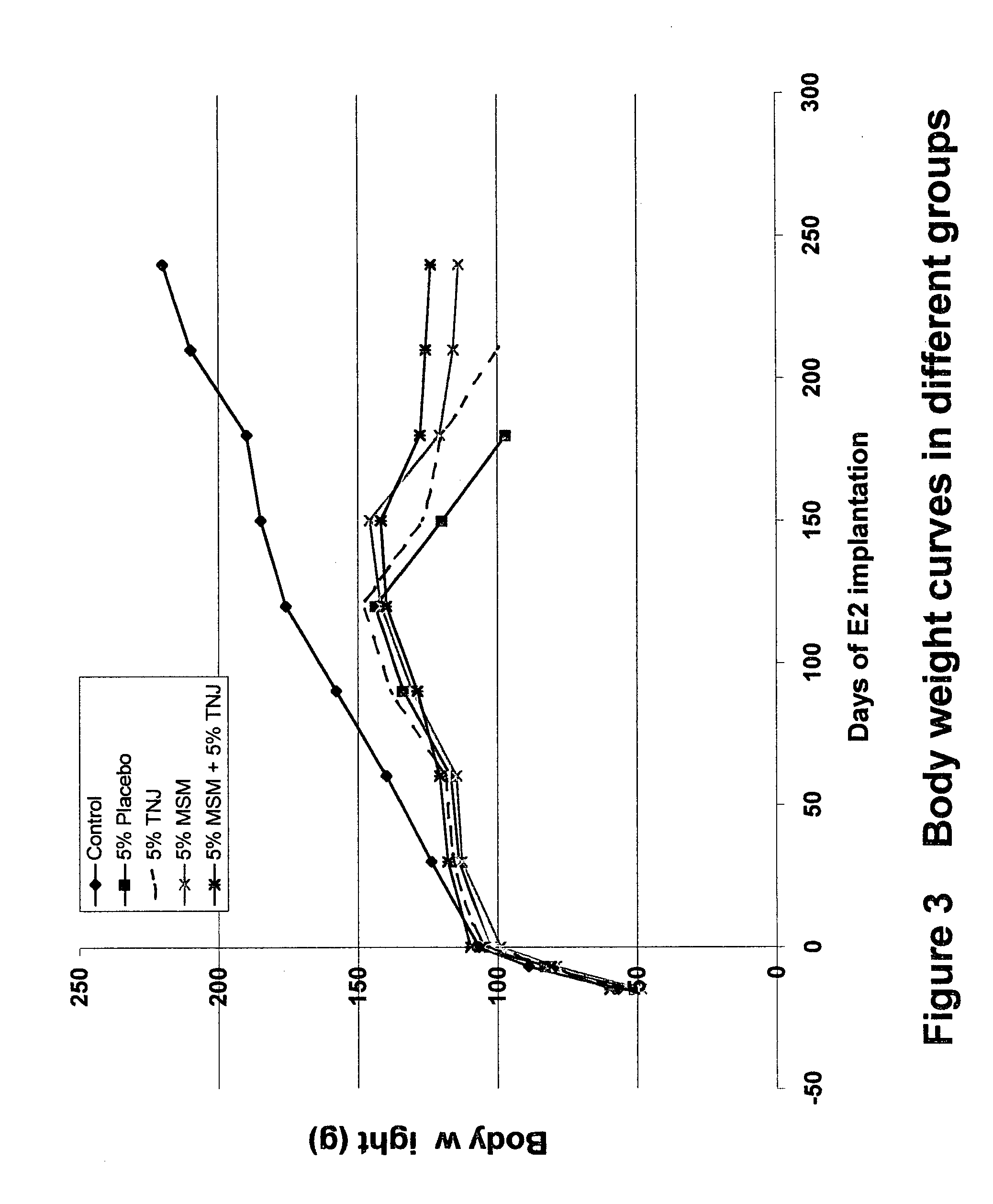
Preventative effects of morinda citrifolia on mammary breast cancer
InactiveUS20050037101A1Avoid conversionInhibit mammary tumor growthBiocideUnknown materialsCarcinogenLymphatic Spread
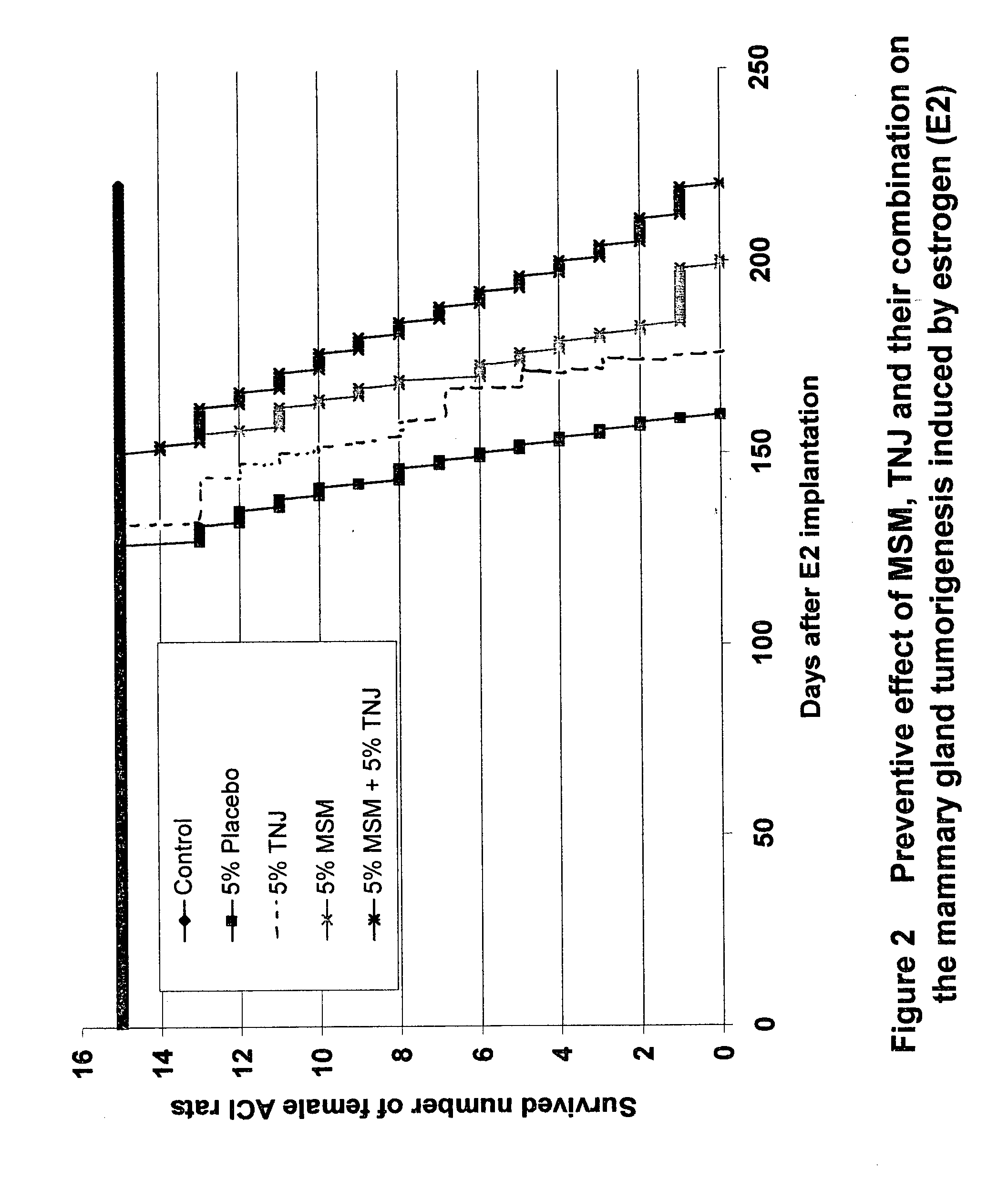
The present invention features a novel use of processed ingredients from the Indian mulberry plant. More specifically, the present invention features a novel use of processed Morinda citrifolia, namely Morinda citrifolia fruit juice, puree, or puree juice for treating breast cancer, and particularly for inhibiting and / or preventing the metastasis of carcinogenic cells within the mammary region of the breast, as well as destroying metastasized mammary or breast cancer cells. The present invention comprises the consumption of food products or medicinal products or compositions comprising processed Morinda citrifolia, in either puree or fruit juice form. The present invention also features a method of inhibiting carcinogen-mediated conversion of mammary cells and protecting DNA against carcinogen-mediated damage by administering a composition comprising water soluble Morinda citrifolia.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
Water soluble extract from plant of Solanum genus and the preparation process thereof, and pharmaceutical composition containing the water soluble extract
A water soluble extract from a plant of Solanum genus consists essentially of at least 60%–90% of solamargine and solasonine. A process for preparing the water soluble extract from the plant of Solanum genus involves the steps of hydrolysis with an acid, precipitation with a base, and separation treatments using chloroform, alcohol and water as extraction solvents. The water soluble extract prepared from the process can be directly dissolved in pure or neutral pH water to form a yellowish clear and transparent aqueous solution having a water solubility ranging from 2˜20 mg / ml or higher.The water soluble extract can be used as an active component in a pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting the growth of tumor / cancer cells, in particular liver cancer cells, lung cancer cells and breast cancer cells.
Owner:G&E HERBAL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Anti-tumor compound containing triazole heterocyclic structure and application thereof
InactiveCN101628912AGood antitumor activityHigh inhibition rateOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAbnormal tissue growthSide chain
The invention discloses a class of anti-tumor compounds containing a triazole heterocyclic structure and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of medicinal chemistry. The compounds containing the triazole heterocyclic structure introduce quintuple 1,2,3-triazole ring in the form of side chains through the amino condensation, bromination, nitrine substitution, link reaction and other reactions on the basis of naphthalimide parent structure, select tetrazolium salt reduction to test 7721 hepatocellular in the experiment of inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells, and also select sulfonyl rhodamine B protein staining method to test MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The experiment results show that the anti-tumor compounds have wide anti-tumor activity and good inhibition effect on the normal growth of tumor cells derived from different tissues of liver cancer, breast cancer and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
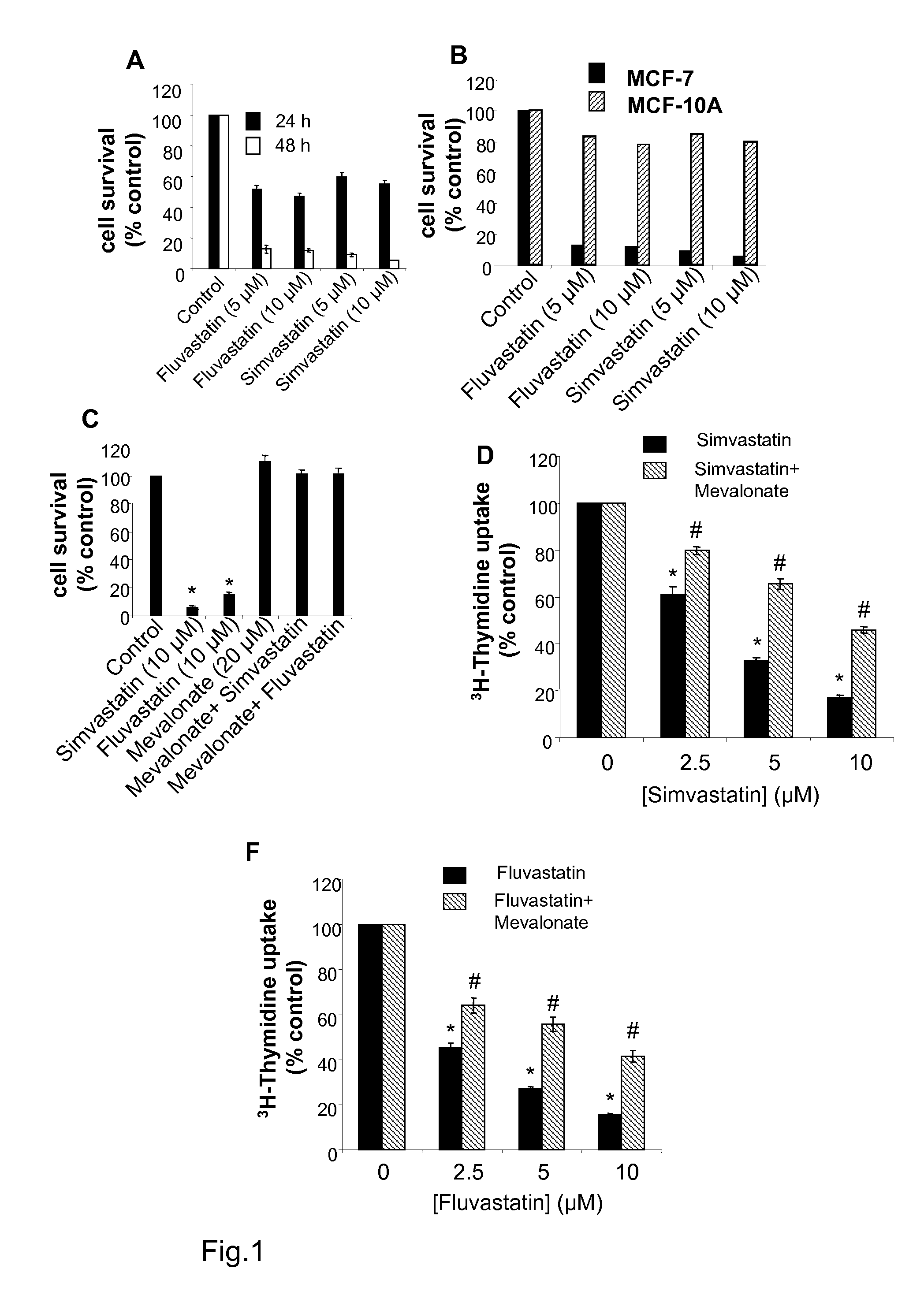
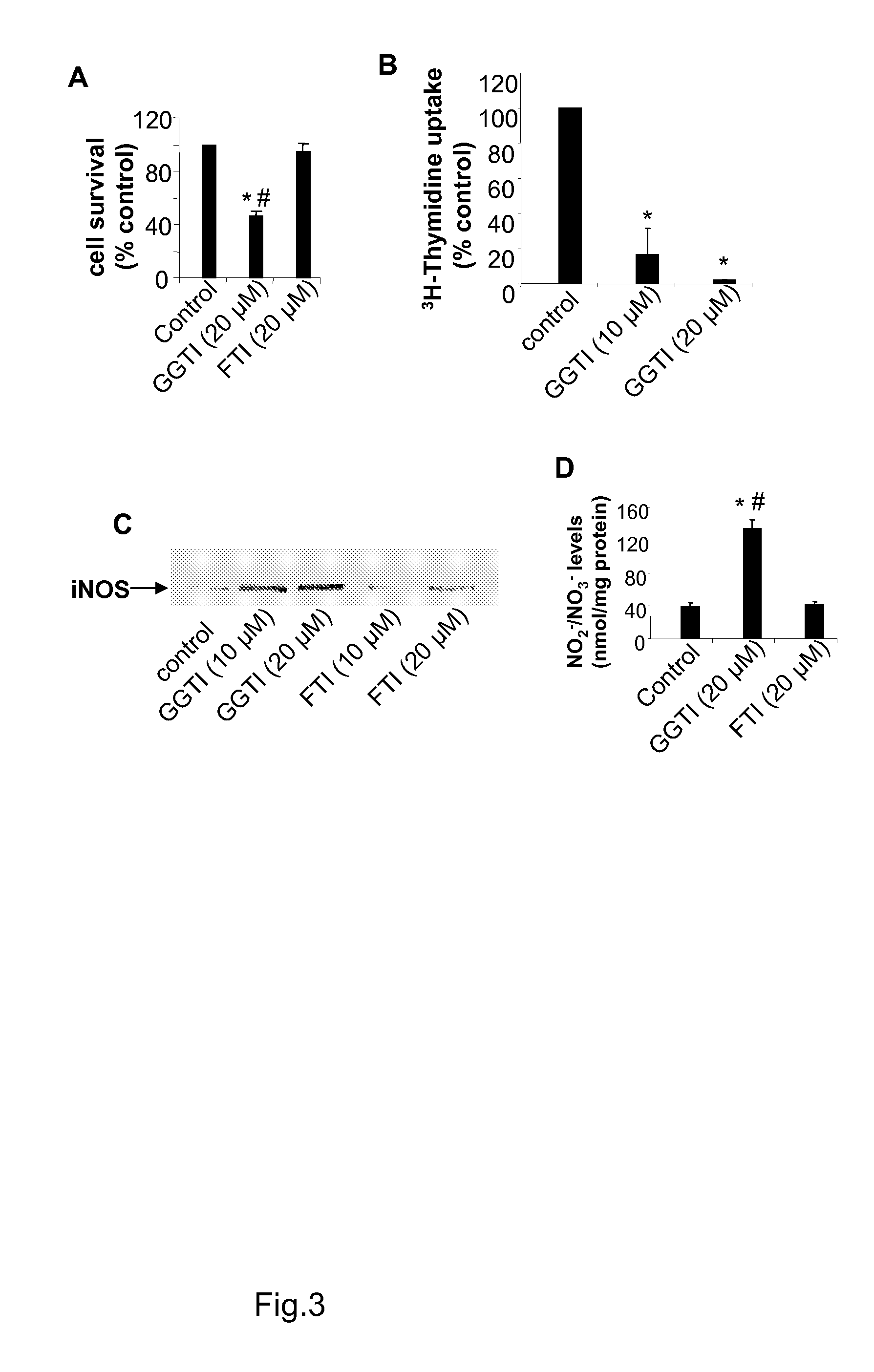
Methods for Treating Cancer
InactiveUS20070219208A1Cause deathInhibit proliferation causeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHMG-CoA reductaseNitric oxide formation
It is disclosed here that HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors inhibit the proliferation and cause the death of breast cancer cells by inducing the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) to promote intracellular nitric oxide formation, which the inventors found to be accomplished through the inhibition of protein geranylgeranylation. The disclosure here enables a new breast cancer treatment strategy that combines the inhibition HMG-CoA reductase or protein geranylgeranylation and the promotion of nitric oxide formation by iNOS.
Owner:MCW RES FOUND INC
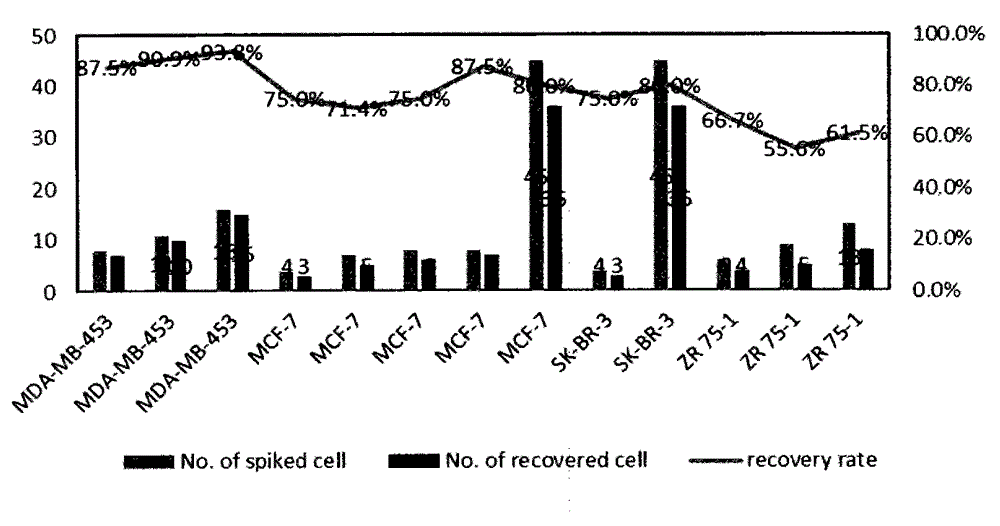
Method and kit for separating rare cells from peripheral blood
ActiveCN105891165AAvoid damageEnrich the connotation of stagingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceTumor cellsDensity gradient
The invention discloses a method for separating rare cells from peripheral blood and a kit using the same. The method integrates a negative enrichment technology and a density gradient centrifugation technology, has the advantages of high recovery rate, simpleness, and convenience, and generates little damage to rare cells in peripheral blood. By using the provided kit, tumor cells such as breast cancer cells can be separated from peripheral blood through the separation method. The kit and method can also be applied to early diagnosis, relapse monitoring, and drug effect evaluation, can be used to separate rare cells in body liquids such as pleural fluid, ascitic fluid, and the like, and have a wide application prospect.
Owner:郝淮杰
Breast cancer survival and recurrence
InactiveUS20050100933A1Accurate assessmentDetermining prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPatient survivalInvasive breast carcinoma
The invention provides for the identification and use of gene expression profiles, or patterns, with clinical relevance to breast cancer. In particular, the invention provides the identities of genes that are correlated with patient survival and breast cancer recurrence. The gene expression profiles may be embodied in nucleic acid expression, protein expression, or other expression formats and used to predict the survival of subjects afflicted with breast cancer and to predict breast cancer recurrence and. The profiles may also be used in the study and / or diagnosis of breast cancer cells and tissue, including the grading of invasive breast cancer, as well as for the study and / or determination of prognosis of a patient. When used for diagnosis or prognosis, the profiles may be used to determine the treatment of breast cancer based upon the likelihood of life expectancy and recurrence.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Targeted cellular delivery of nanoparticles
The various embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to compositions and methods for the targeted cellular delivery of nanoparticles. More particularly, the various embodiments of the present invention are directed to the cellular delivery of nanoparticles tethered to a ligand by way of a poly(ethylene glycol) linkage, wherein the ligand demonstrates a binding specificity for a cellular target. In an exemplary embodiment, the ligand is tamoxifen and the cellular target is the estrogen receptor, which is upregulated in many breast cancer cells.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Novel breast cancer cell lines and uses thereof
Owner:BRIACELL THERAPEUTICS
Nitrogenous heterocyclic compound, preparation method, intermediates, composition and application
ActiveCN107141293ASmall toxicityStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryNitrogenous heterocyclic compoundHuman gastric carcinoma
The invention discloses a nitrogenous heterocyclic compound, a preparation method, intermediates, a composition and application. The nitrogenous heterocyclic compound is as shown in the formula I, has high inhibitory activity to ErbB2 tyrosine kinase, has relatively good inhibitory activity to ErbB2 high-expression human breast cancer cells BT-474, human gastric carcinoma cells NCI-N87 and the like, meanwhile, has relatively weak inhibitory activity to EGFR kinase, is a small-molecule inhibitor with good selectivity to ErbB2 target spots, therefore, is high in safety and can effectively enlarge the safety window in the medicine administration process.
Owner:SHANGAI PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions of diaryl-isoxazole derivatives for the prevention and treatment of cancers
InactiveUS7250432B2Excellent activity of inhibiting cancer cell migrationHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryLymphatic SpreadAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and the treatment of cancers containing diaryl-isoxazole derivatives as an effective ingredient. Diaryl-isoxazole derivatives of the present invention inhibit metastasis of breast cancer cell lines and angiogenesis, so that they can be produced as a metastasis inhibitor and further as a pharmaceutical composition for the prevention and the treatment of angiogenesis related diseases including cancers, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or angiogenesis diseases caused in eyeball, etc.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Lipoic-acid-modified nanometer polypeptide carrier and preparation method and application thereof
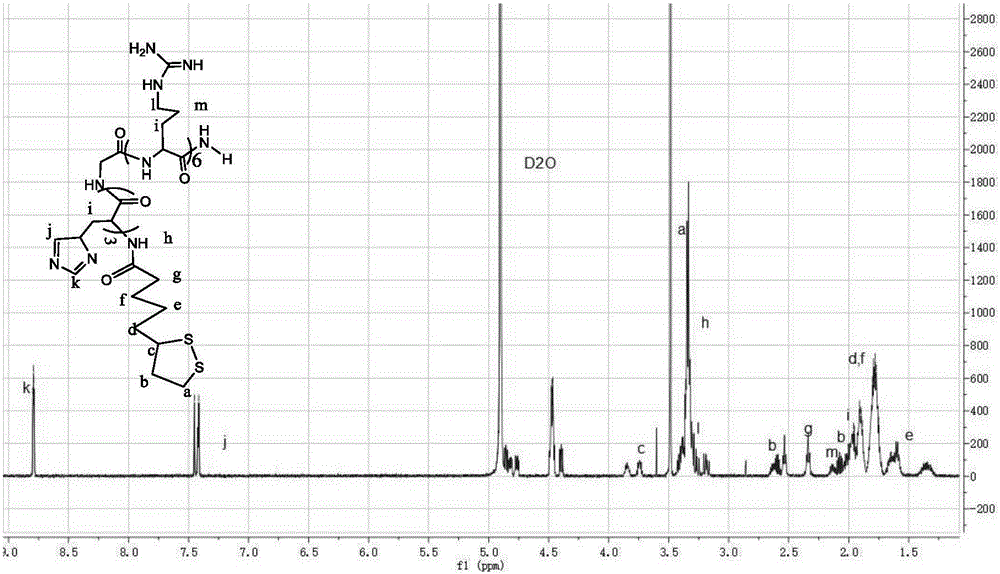
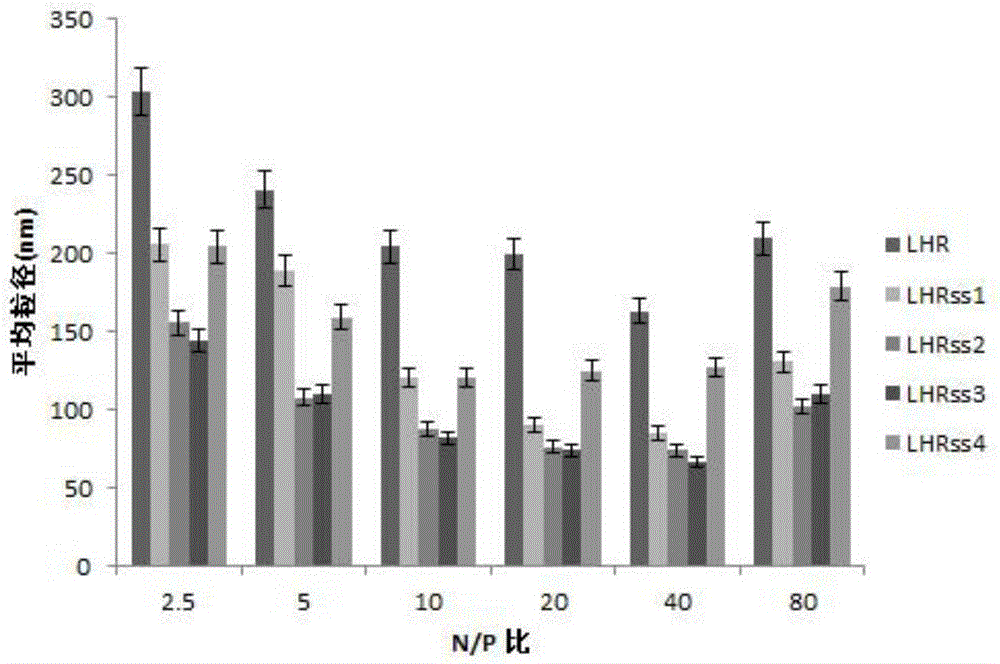
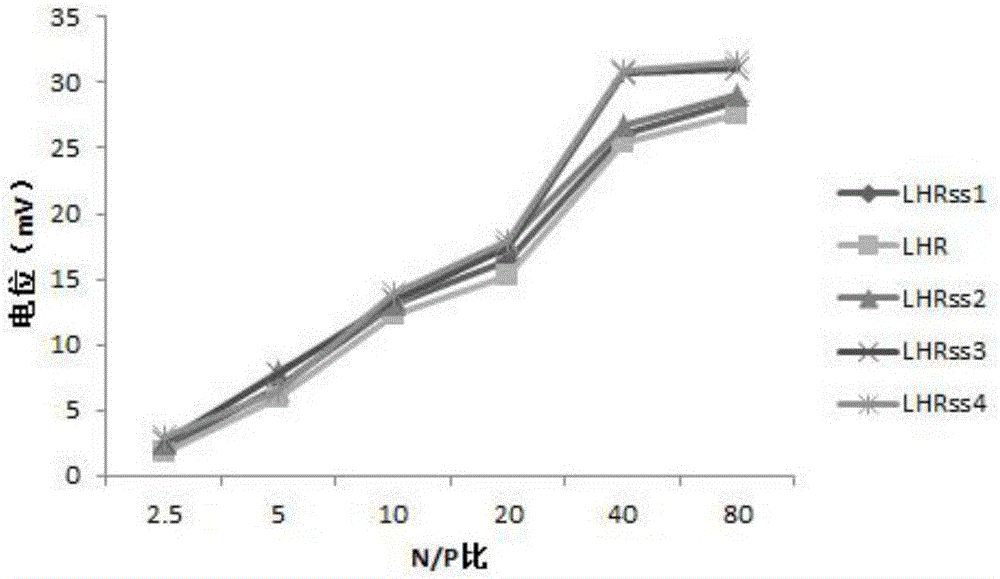
ActiveCN105727307ALow cytotoxicityPromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSide effectArginine
The invention relates to the field of medical technologies, in particular to a lipoic-acid-modified nanometer polypeptide carrier and a preparation method and application thereof.The lipoic-acid-modified nanometer polypeptide carrier is composed of arginine, histidine, lipoic acid and cysteine.A disulfide bond contained in lipoic acid is adopted for cross-linking, a formed polypeptide polymer can be rapidly degraded in cells and will not accumulate in the cells, and arginine and cysteine in polypeptide are in-vivo amino acid and are free of toxic and side effects to the human body.A CCK-8 cell proliferation test shows that the prepared nanometer carrier has low cell toxicity and meanwhile has good capacity of co-delivery of a gene and chemotherapy drugs; the nanometer carrier can specifically enhance the sensitivity of drug-resistant cells to the chemotherapy drugs in breast cancer drug-resistant treatment and promote apoptosis of breast cancer cells, and therefore becomes a targeted, efficient and low-toxicity nanoscale delivery system in breast cancer drug-resistant treatment.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Products and preparation method of double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells
InactiveCN105950561AMammal material medical ingredientsNGF-receptor/TNF-receptor superfamilySingle-Chain AntibodiesCytotoxicity
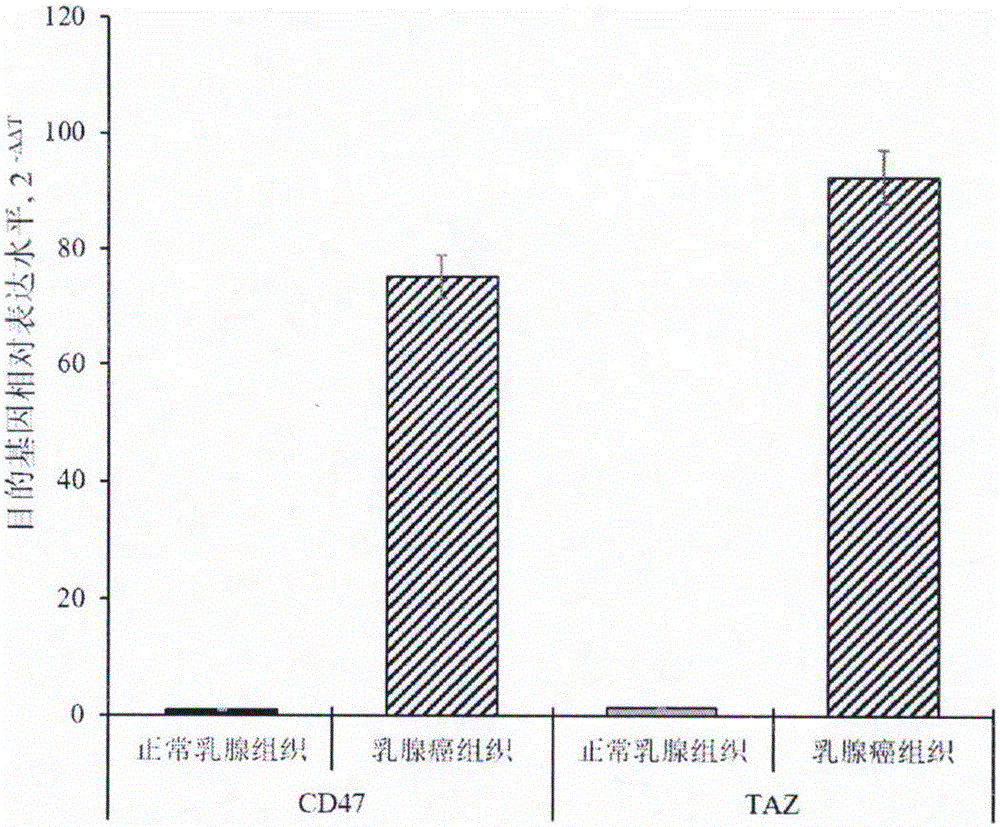
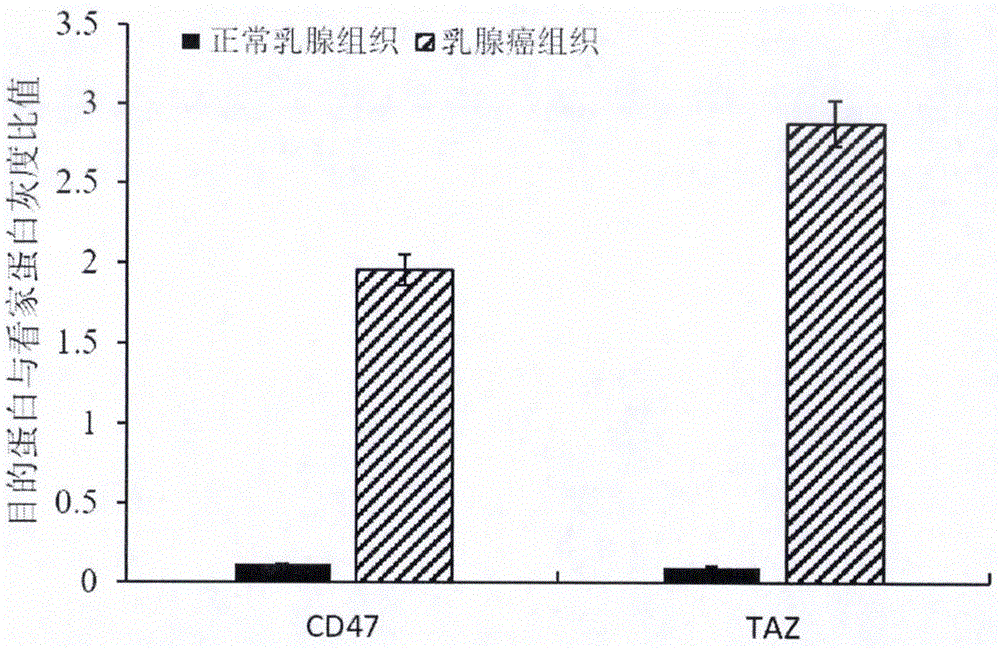
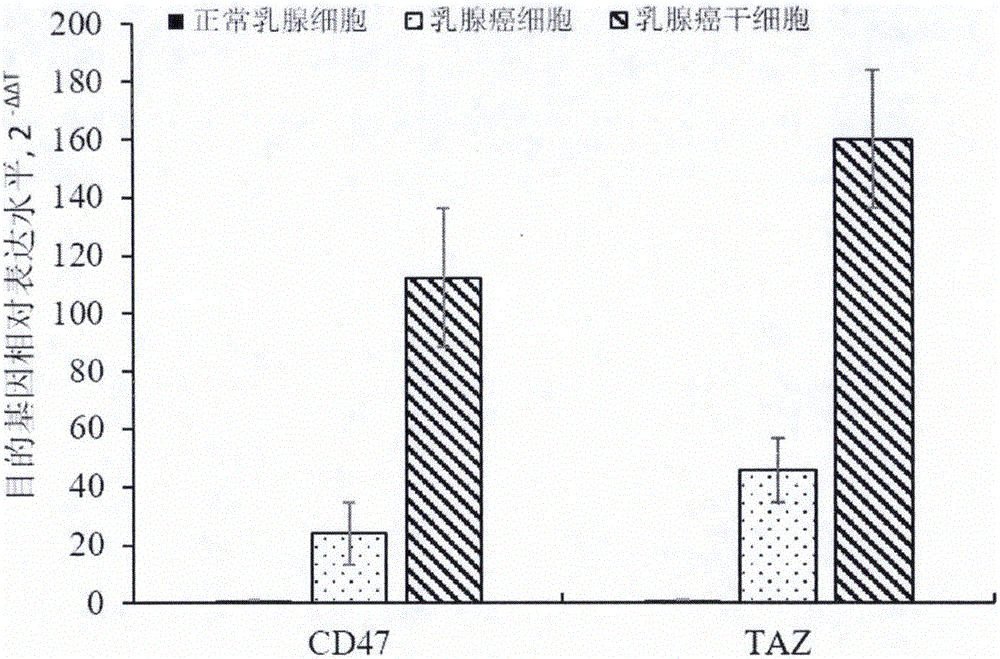
The invention provides a preparation method of a double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells. The preparation method is characterized in that integrin-associated protein (CD47) and transcriptional coactivator (TAZ) are both highly expressed in breast cancer tissues, especially in the breast cancer stem cells; by established CD47 and TAZ over-expressed breast cancer cells, higher proliferation and metastasis capacity and cancer stem cell features are shown. Extracellular domain of the two breast cancer stem cell antigens CD47 and TAZ are targeted to generate monoclonal strains in specific binding under immunity action, and single-chain antibodies in specific binding with the CD47 and TAZ by genetic recombination are obtained to construct a human CD47 and TAZ containing double chimeric antigen receptor gene recombined to a virus vector to transfect human T lymphocyte. By high expression of the double chimeric antigen receptor gene in specific binding with human CD47 and TAZ expressing breast cancer stem cells, a first signal and a costimulatory signal can be activated to trigger anti-breast-cancer cytotoxicity, and high cytotoxicity in in-vivo and in-vitro anti-cancer experiments is achieved.
Owner:泰州市数康生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com