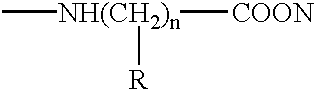Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "ErbB" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
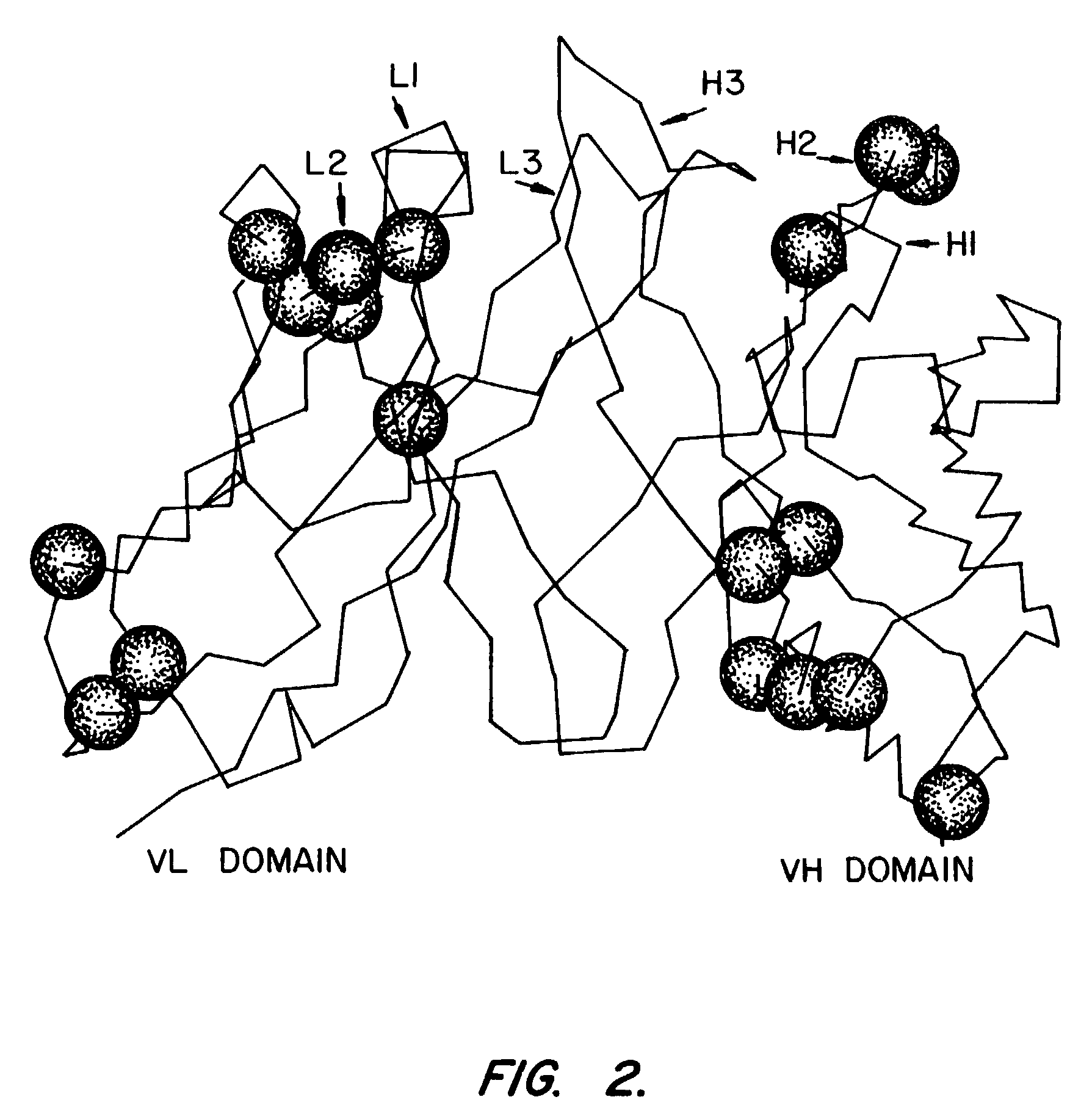
The ErbB family of proteins contains four receptor tyrosine kinases, structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), its first discovered member. In humans, the family includes Her1 (EGFR, ErbB1), Her2 (Neu, ErbB2), Her3 (ErbB3), and Her4 (ErbB4). The gene symbol, ErbB, is derived from the name of a viral oncogene to which these receptors are homologous: erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene. Insufficient ErbB signaling in humans is associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's Disease, while excessive ErbB signaling is associated with the development of a wide variety of types of solid tumor.
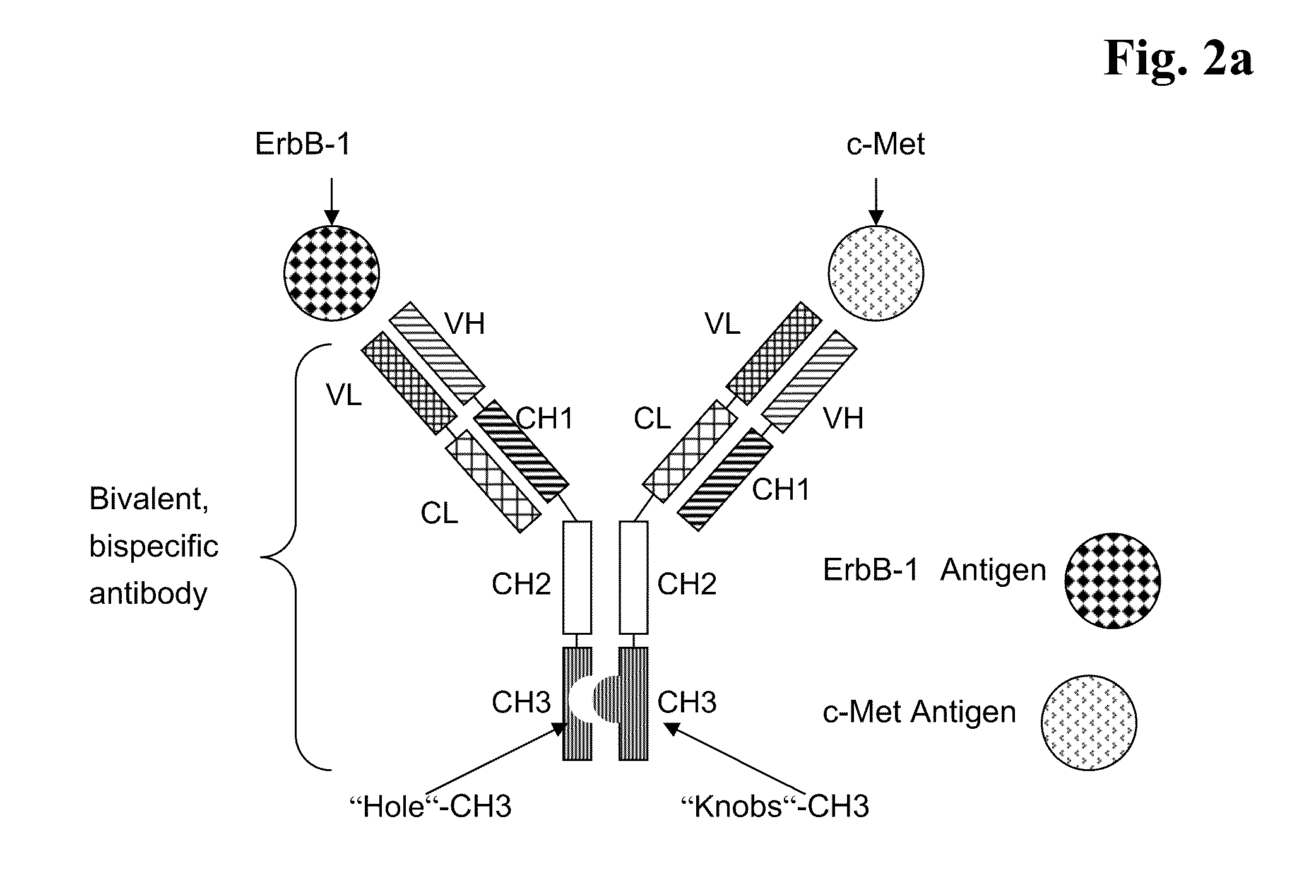
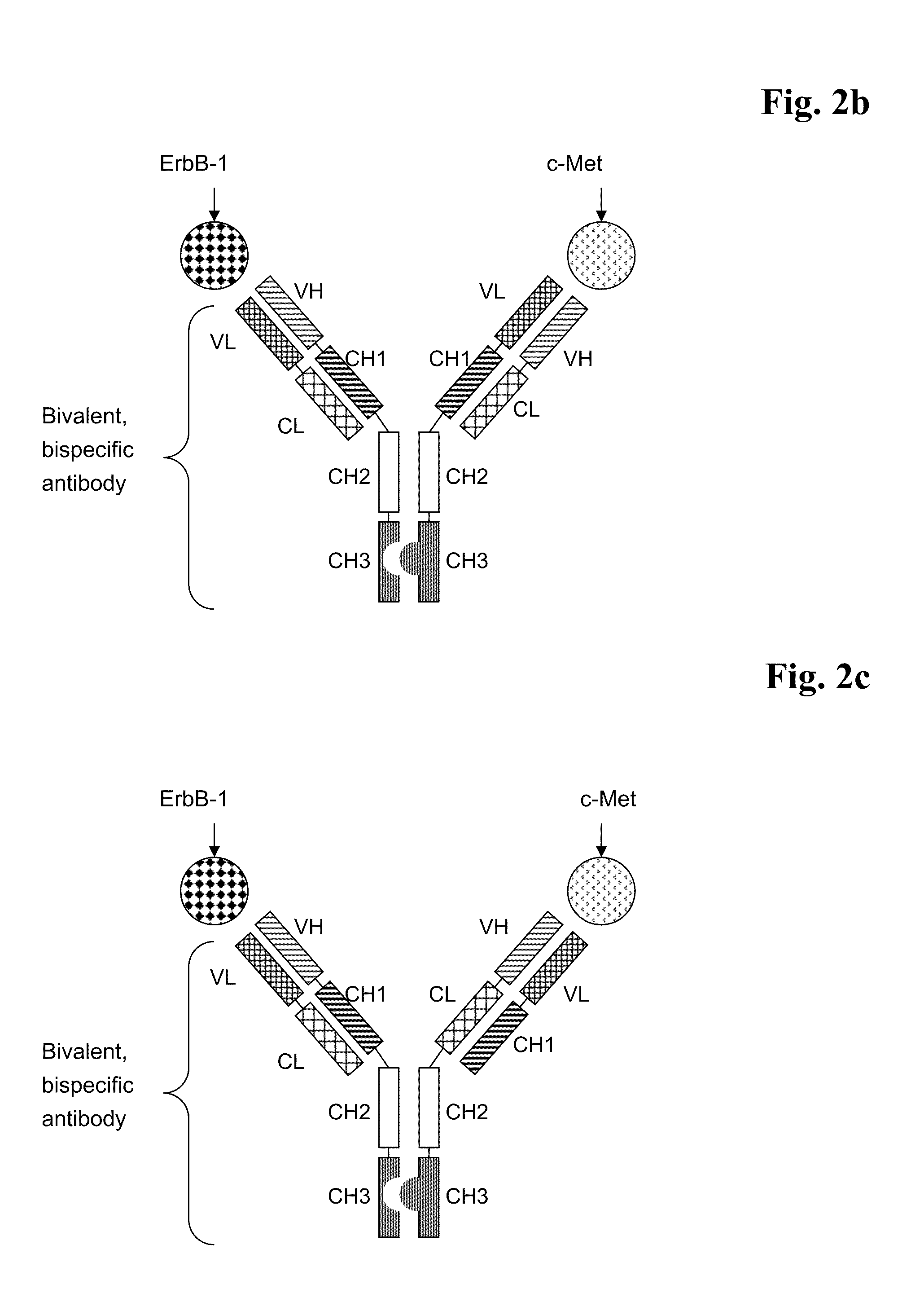
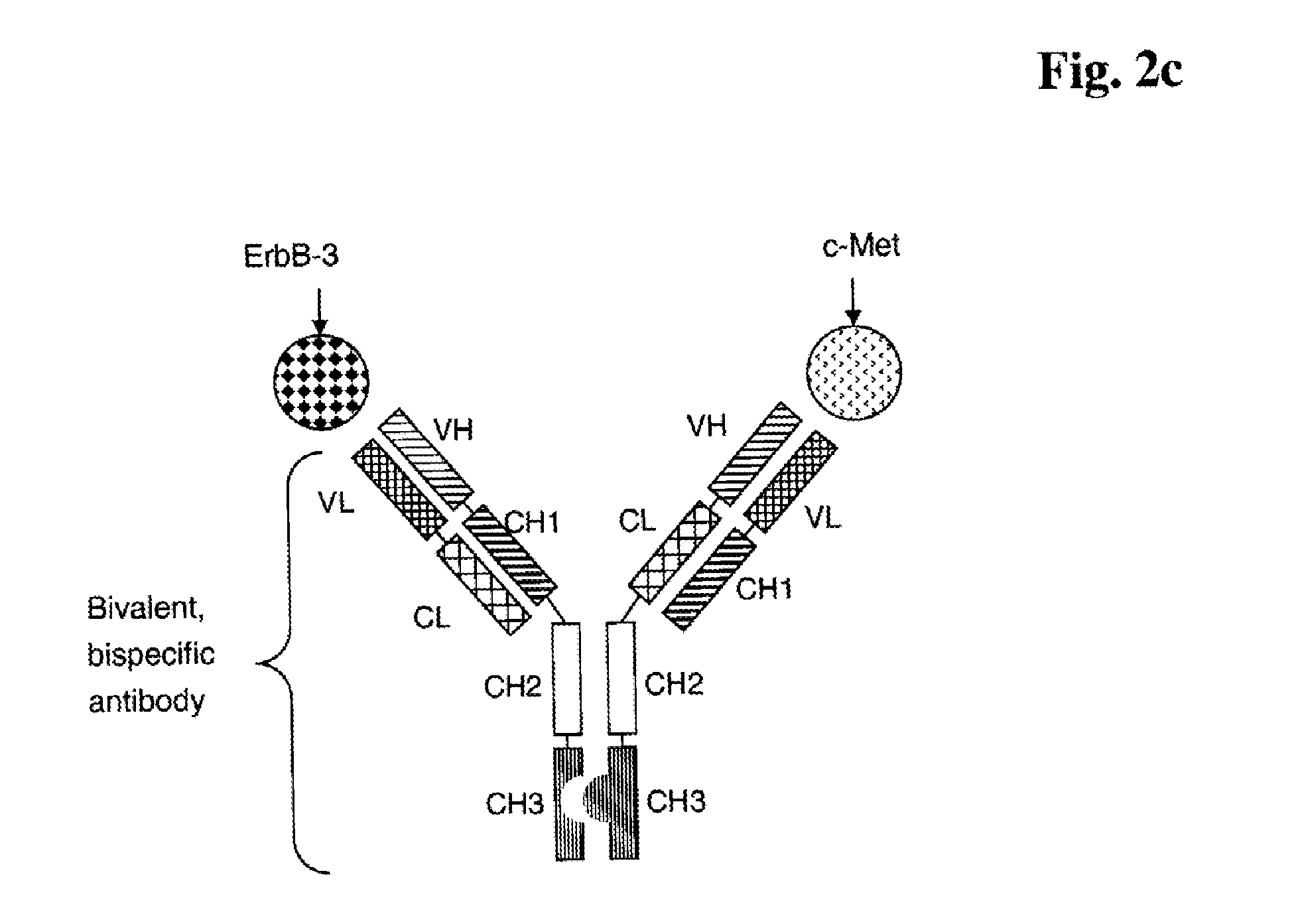
Bispecific Anti ErbB1 / Anti c Met Antibodies
InactiveUS20100254989A1Highly valuable propertyDecreased internalizationHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesC-MetErbB
The present invention relates to bispecific antibodies against human ErbB-1 and against human c-Met, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
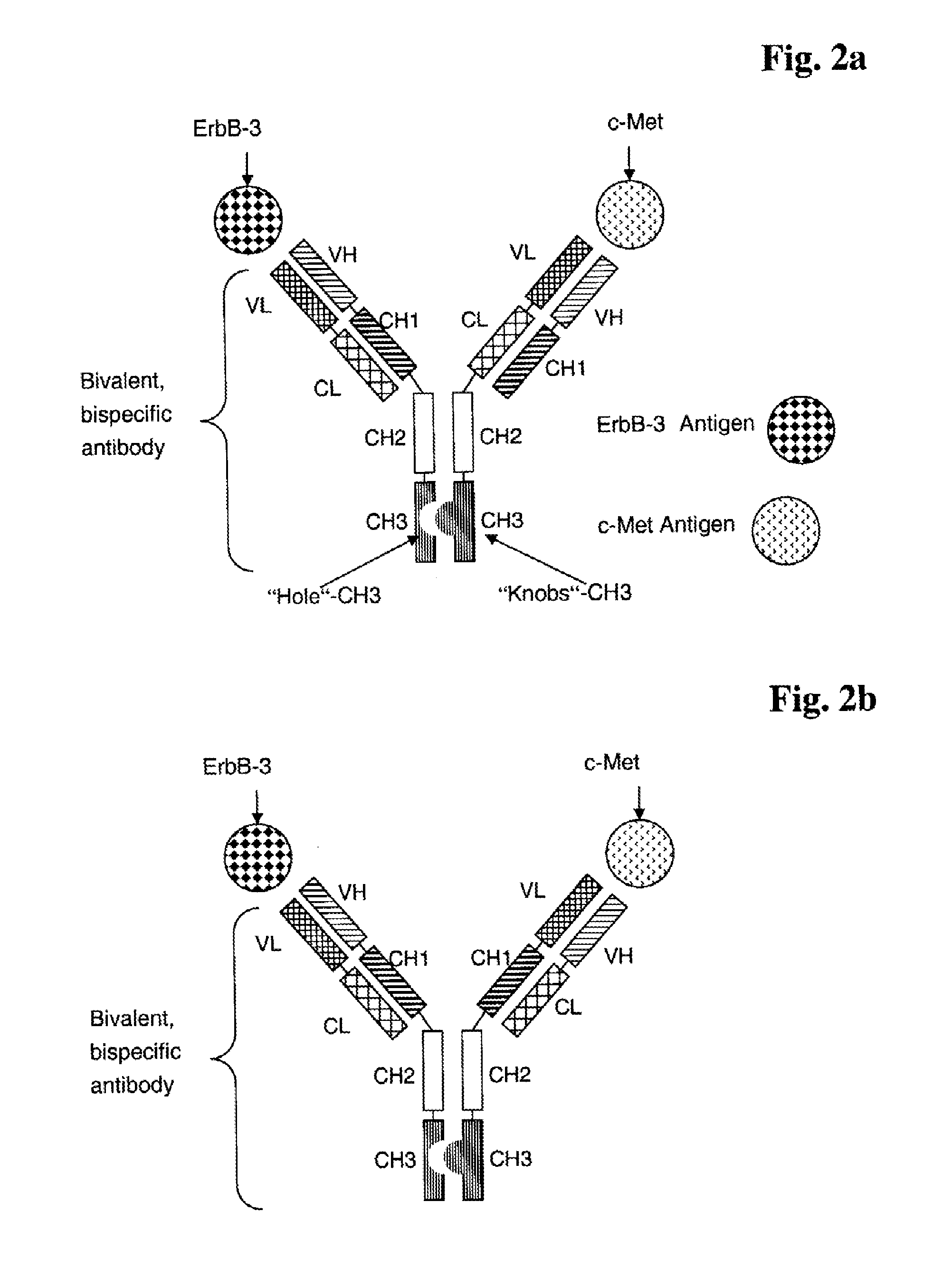
Bispecific Anti ErbB3 / Anti cMet Antibodies
InactiveUS20100256339A1Highly valuable propertyDecreased internalizationHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesC-MetBispecific antibody
The present invention relates to bispecific antibodies against human ErbB-3 and against human c-Met, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
ErbB antagonists for pain therapy
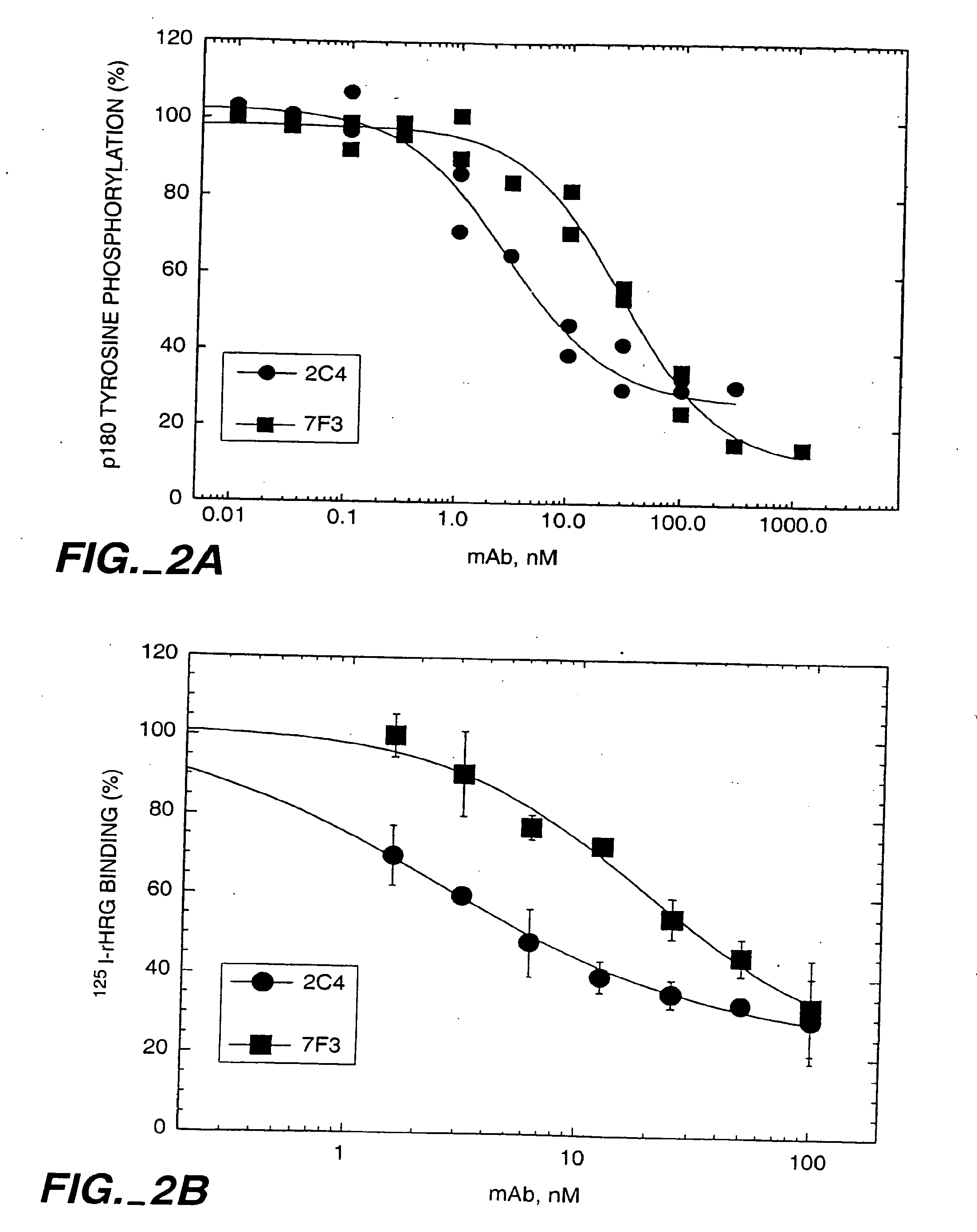
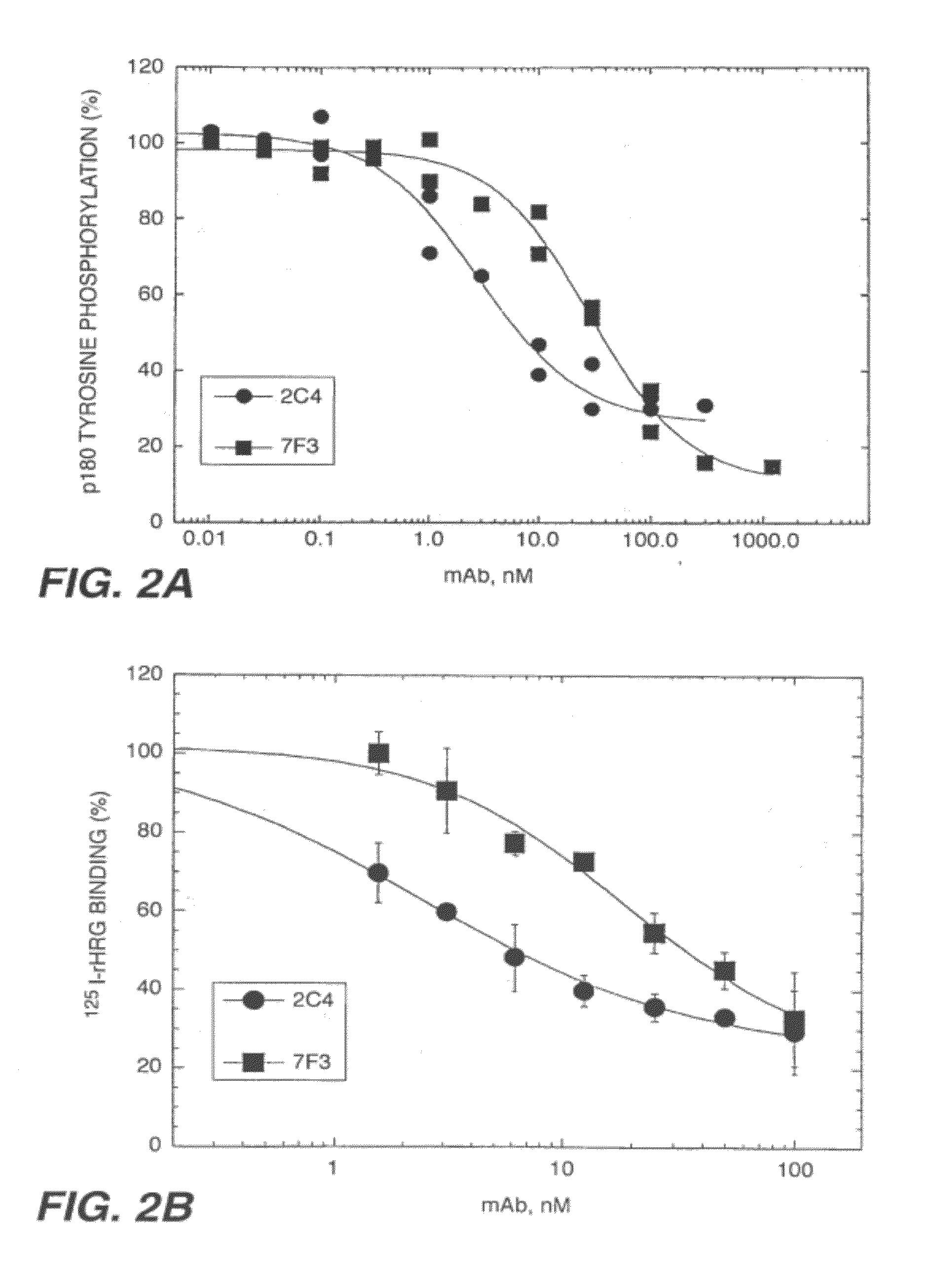
The present application describes the use of ErbB antagonist, especially ErbB2 antibodies such as rhuMAb 2C4, for treating pain.
Owner:AGUS DAVID
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176258A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesImmunodominant EpitopesMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein among other MN / CA IX-related inventions are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Subsets of the new antibodies are to either the proteoglycan-like (PG) domain or to the carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain of MN / CA IX, and methods are provided by which antibodies can be prepared to the other MN / CA IX domains. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
ErbB ANTAGONISTS FOR PAIN THERAPY
The present application describes the use of ErbB antagonist, especially ErbB2 antibodies such as rhuMAb 2C4, for treating pain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (S-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX'S coexpression with HER-2/NEU/C-ERBB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7816493B2Good curative effectSugar derivativesBiological material analysisKilodaltonC erbb 2
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) found in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Soluble CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer / cancer that detect or detect and quantitate s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 that provides potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer / cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer / precancer. Preferred are new antibodies, specific for non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, useful to detect soluble CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, preferably in combination with antibodies specific to immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
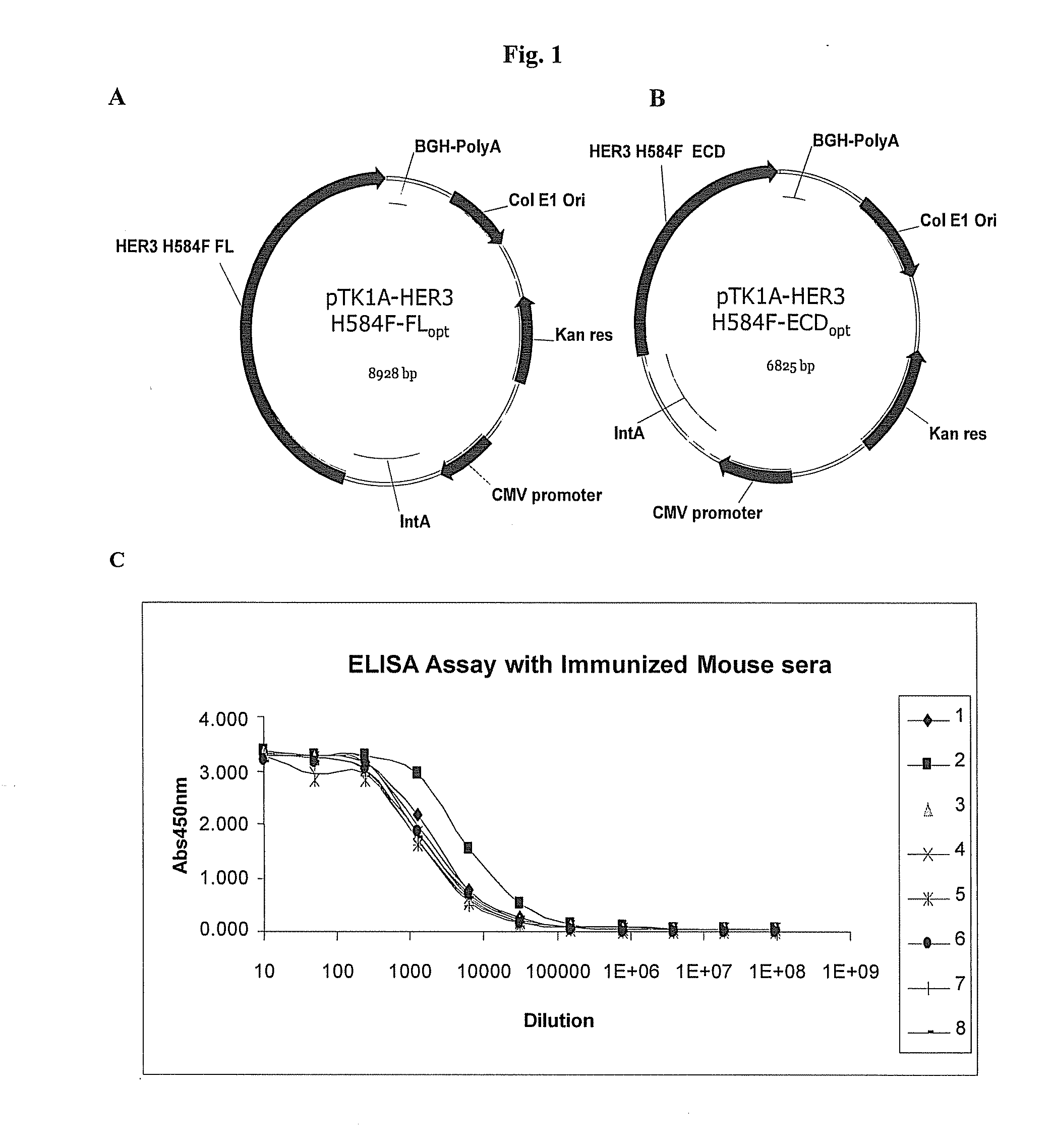
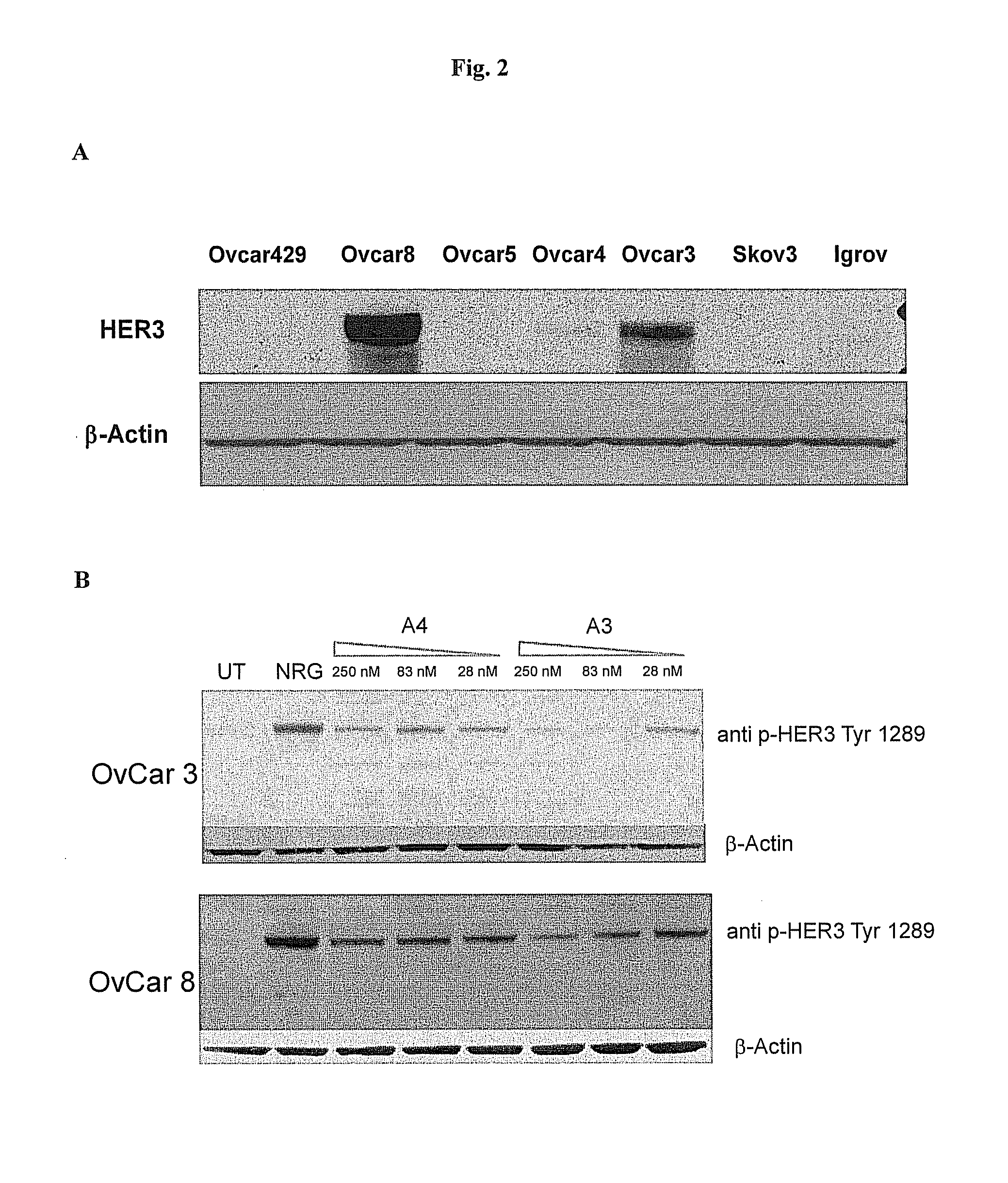
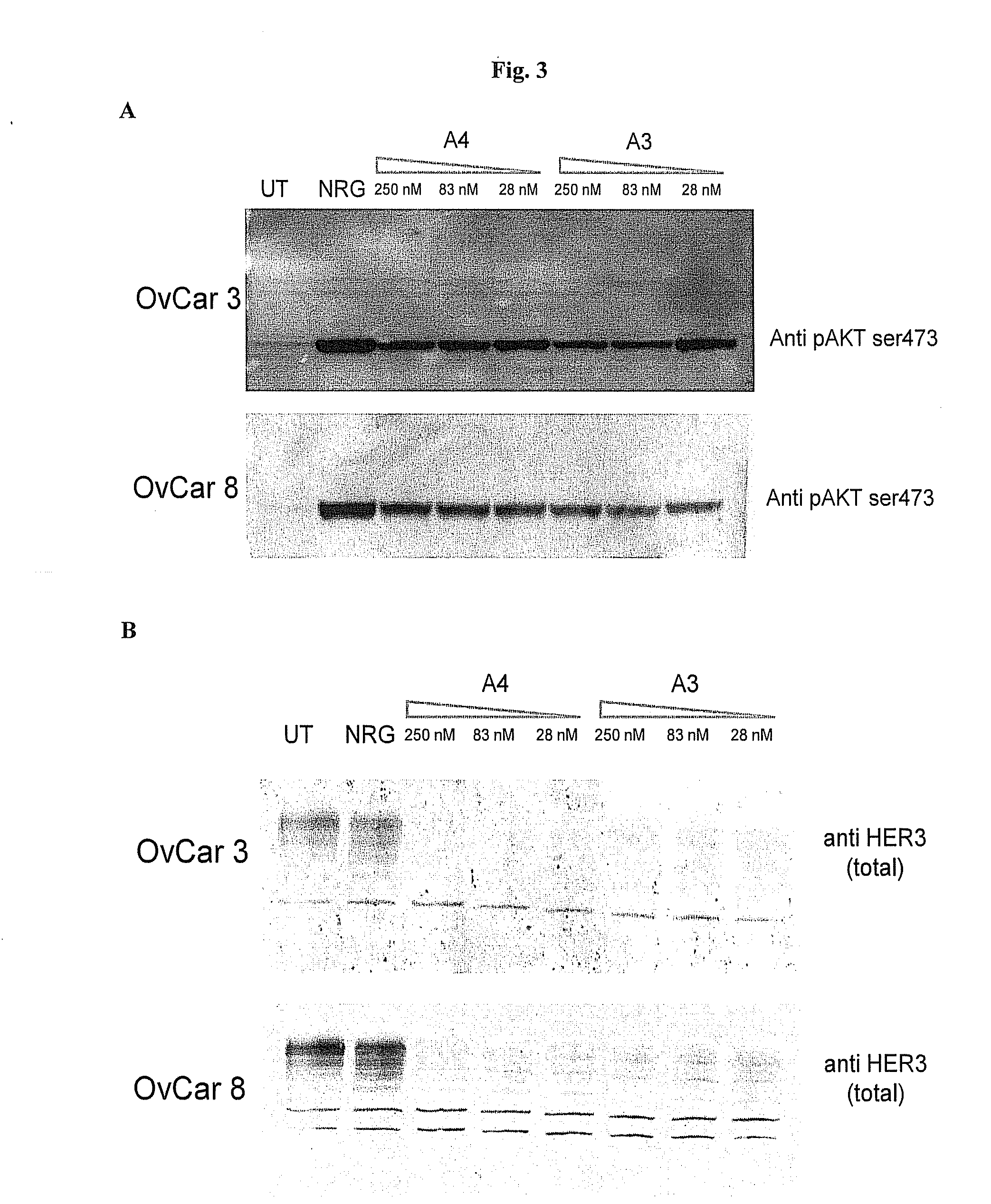
Erbb3 Based Methods and Compositions for Treating Neoplasms
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating neoplasms in mammals, particularly humans. More particularly, the present invention provides for methods for preventing, treating or delaying neoplasm in a mammal using an ErbB-3 protein, a nucleic acid encoding an ErbB-3 protein or a functional fragment thereof. The present invention also provides for isolated nucleic acids encoding an extracellular domain of the ErbB-3 protein, or a functional fragment thereof, substantially purified extracellular domain of the ErbB-3 protein, or a functional fragment thereof and antibodies that bind to an epitope in an extracellular domain of the ErbB-3 protein, or a functional fragment thereof. The present invention further provides for pharmaceutical compositions and / or vaccines comprising the extracellular domain of the ErbB-3 protein, or a functional fragment thereof, or nucleic acids encoding and antibodies binding to such extracellular domain or functional fragments thereof.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Gene detection assay for improving the likelhood of an effective response to an ErbB antagonist cancer therapy
InactiveUS20060228745A1Great likelihoodChoose accuratelyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFhit geneTumor cells
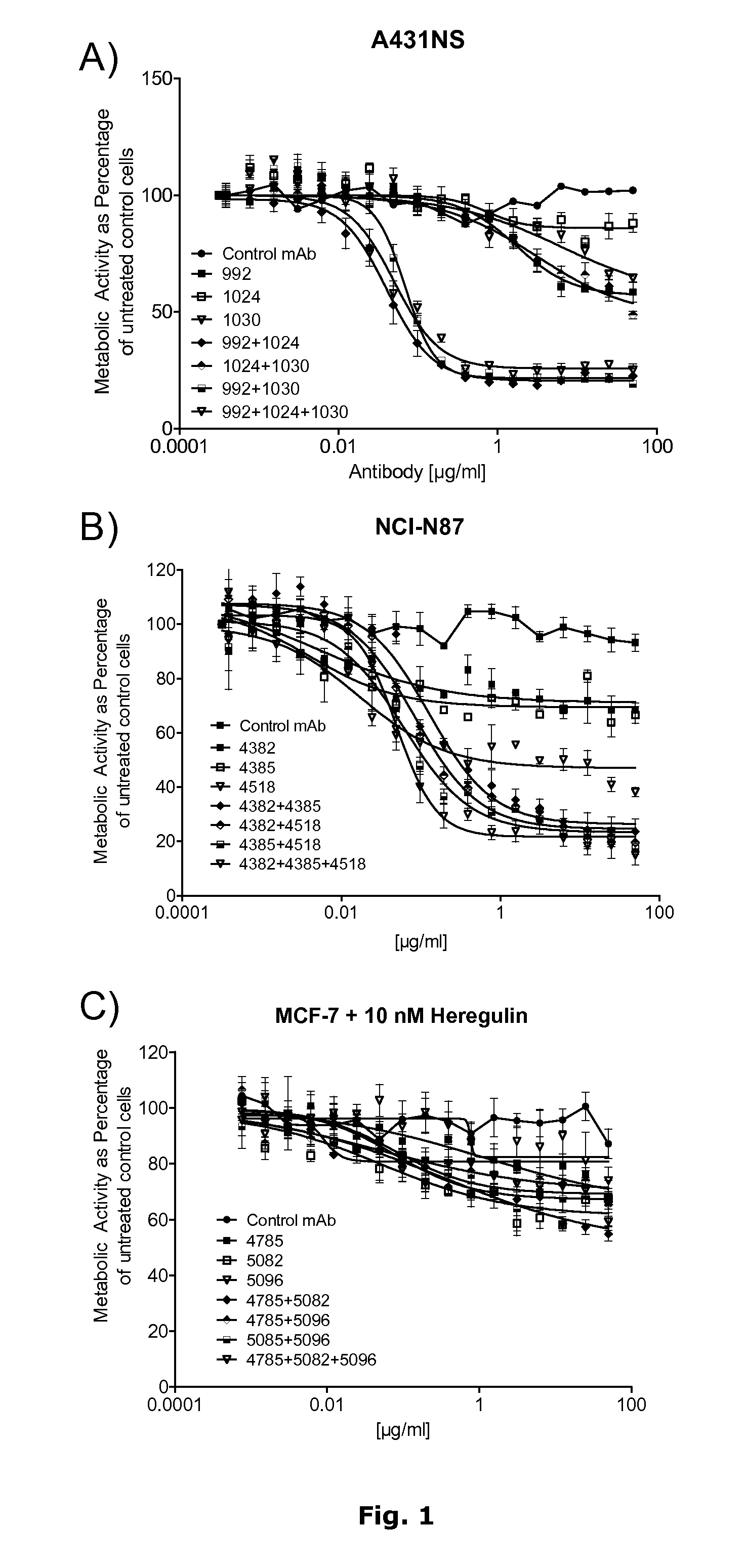
The invention provides a method for more effective treatment of patients susceptible to or diagnosed with tumors overexpressing ErbB, as determined by a gene amplification assay, with an ErbB antagonist. Such method comprises administering a cancer-treating dose of the ErbB antagonist, preferably in addition to chemotherapeutic agents, to a subject in whose tumor cells ErbB has been found to be amplified e.g., by fluorescent in situ hybridization. ErbB antagonists described include an anti-HER2 antibody. Pharmaceutical packaging for providing the components for such treatment is also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method of Treating Cancer Using a cMET and AXL Inhibitor and an ErbB Inhibitor
The present invention relates to a method of treating cancer in a patient comprising administering to the patient therapeutically effective amounts of:a) a compound of formula A:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1—R4, p, and q are as defined; and(b) an erbB inhibitor that inhibits erbB-1 or erbB-2 or erbB-3 receptor or a combination thereof. The method of the present invention addresses a need in the art with the discovery of a combination therapy that shows evidence of being a more effective therapy than previously disclosed therapies.
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
Pan-HER Antibody Composition
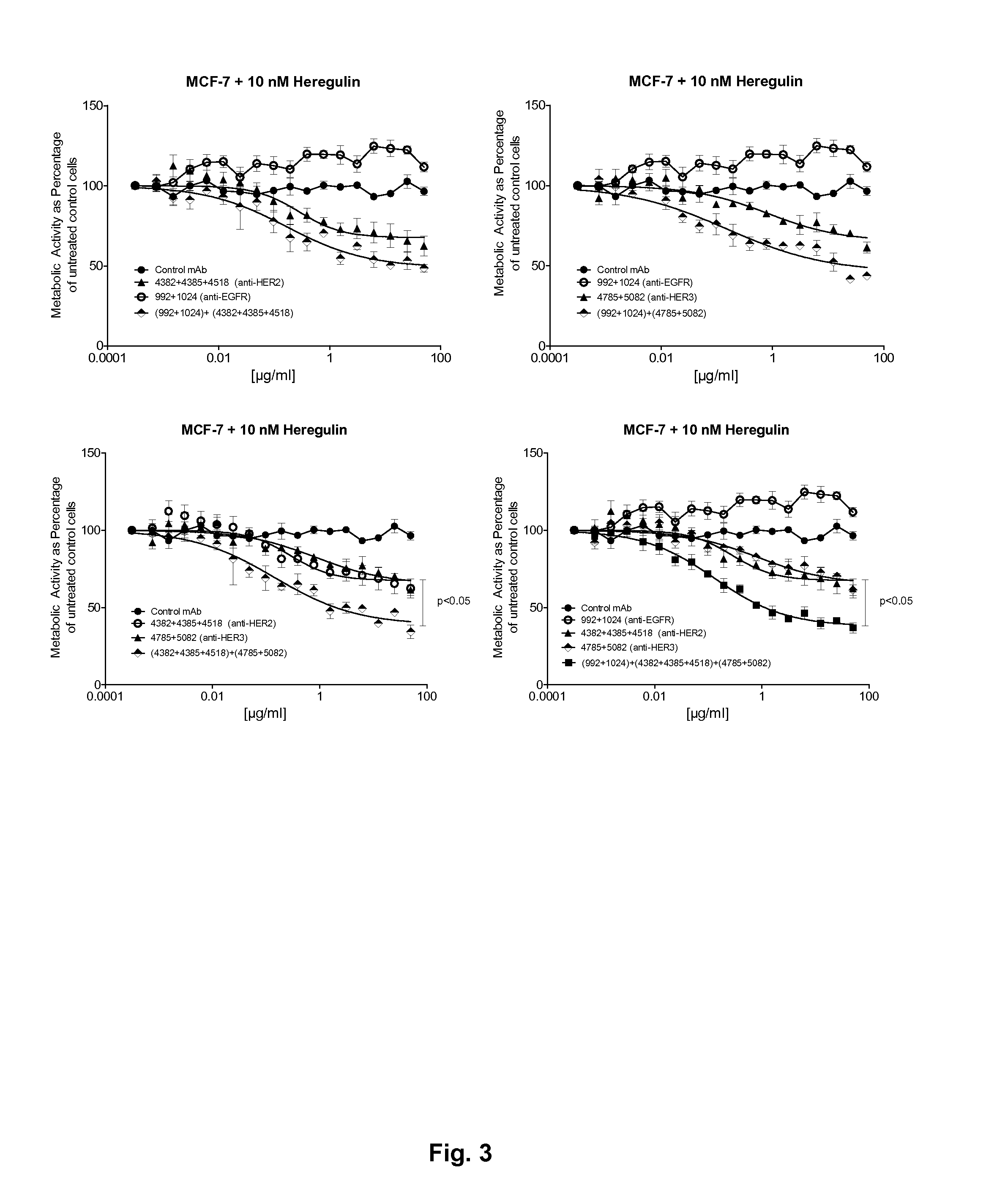
The present invention is directed to improved therapeutics against receptors within the EGFR / ErbB / HER family that more broadly interfere with multiple members of the HER family (pan-HER inhibition). More particularly, the invention is directed to the use of antibody compositions for human cancer therapy. In vitro studies have shown that the antibody compositions of the invention targeting multiple HER family receptors are superior to antibody compositions targeting only one HER family receptor.
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
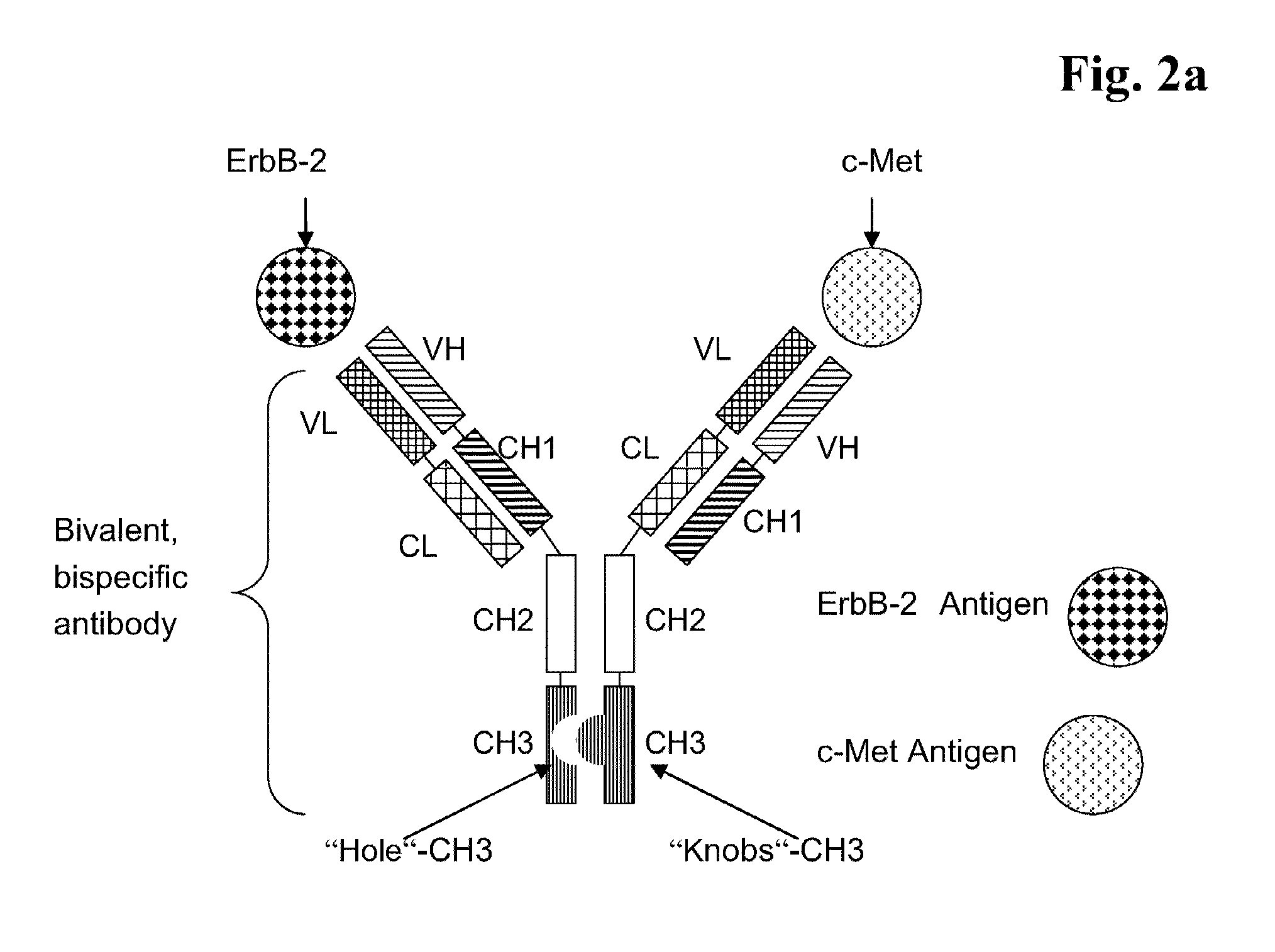
Bispecific Anti ErbB2 / Anti cMet Antibodies
InactiveUS20100254988A1Highly valuable propertyDecreased internalizationHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesC-MetErbB
The present invention relates to bispecific antibodies against human ErbB-2 and against human c-Met, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Combination of a purine-based cdk inhibitor with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and use thereof in the treatment of proliferative disorders
InactiveUS20100143350A1Low toxicityGood effectBiocideAntibody ingredientsErbBTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The present invention relates to combination comprising (i) an ErbB inhibitor; and (ii) a CDK inhibitor, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, selected from: (a) roscovitine; (b) 3-{9-isopropyl-6-[(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-9H-purin-2-ylamino}-2-methyl-pentan-2-ol; (c) 3-{9-isopropyl-6-[(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-9H-purin-2-ylamino}-pentan-2-ol; and (d) (2R,3S-3-(6-((4,6-dimethylpyridin-3-ylmethylamino)-9-isopropyl-9H-purin-2-ylamino)pentan-2-ol.Further aspects of the invention relate to pharmaceutical products and pharmaceutical compositions comprising combinations according to the invention, and methods of treatment using the same.
Owner:CYCLACEL
Bispecific Anti ErbB2/Anti cMet Antibodies
InactiveUS20130273054A1Increase heterodimerisationIncrease productionHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesC-MetErbB
The present invention relates to bispecific antibodies against human ErbB-2 and against human C-met, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Bispecific Anti ErbB1 / Anti cMet Antibodies
InactiveUS20130156772A1Increase heterodimerisationIncrease productionHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesMedicineC-Met
The present invention relates to bispecific antibodies against human ErbB-1 and against human c-Met, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Multispecific modular antibody
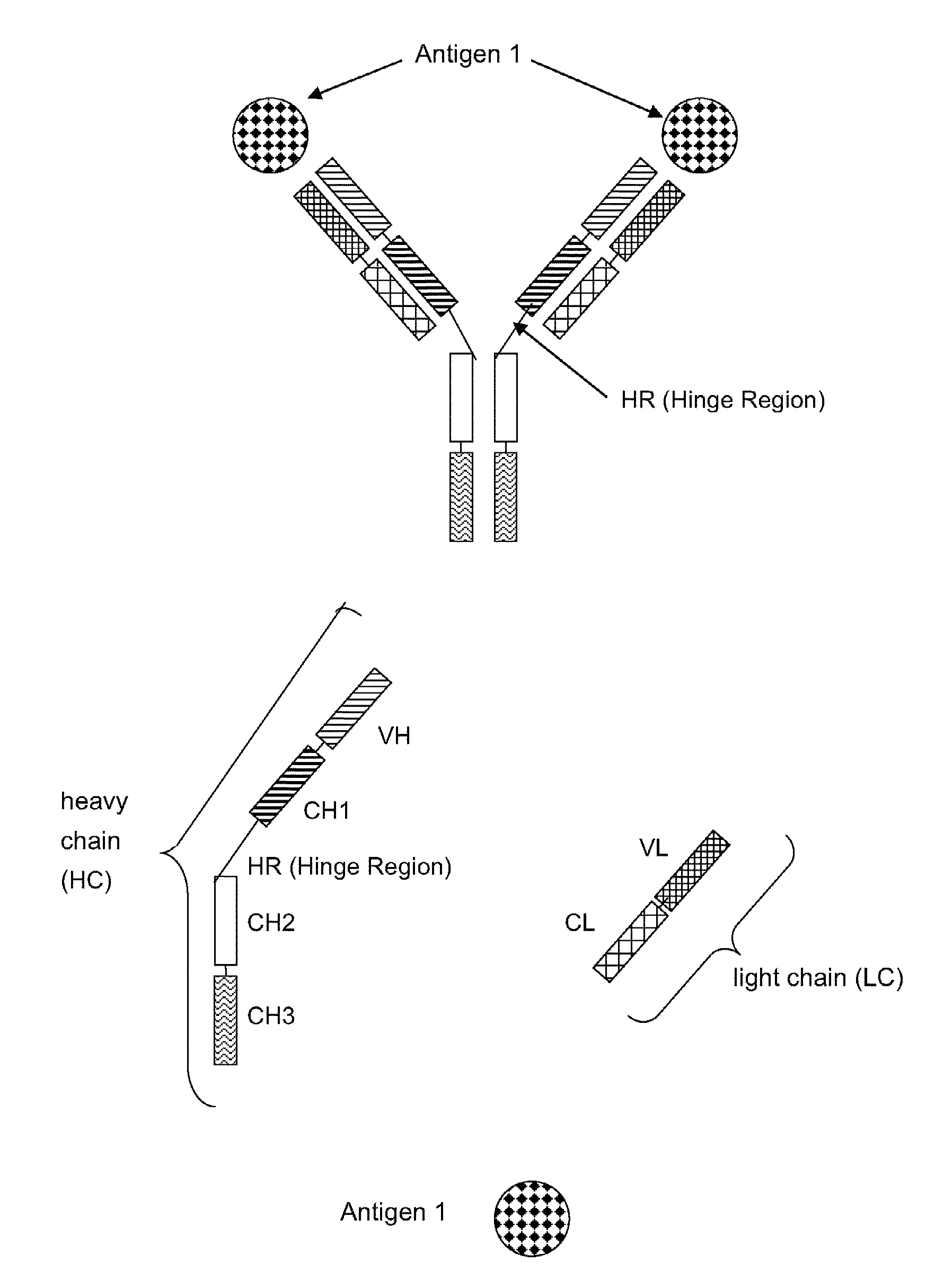
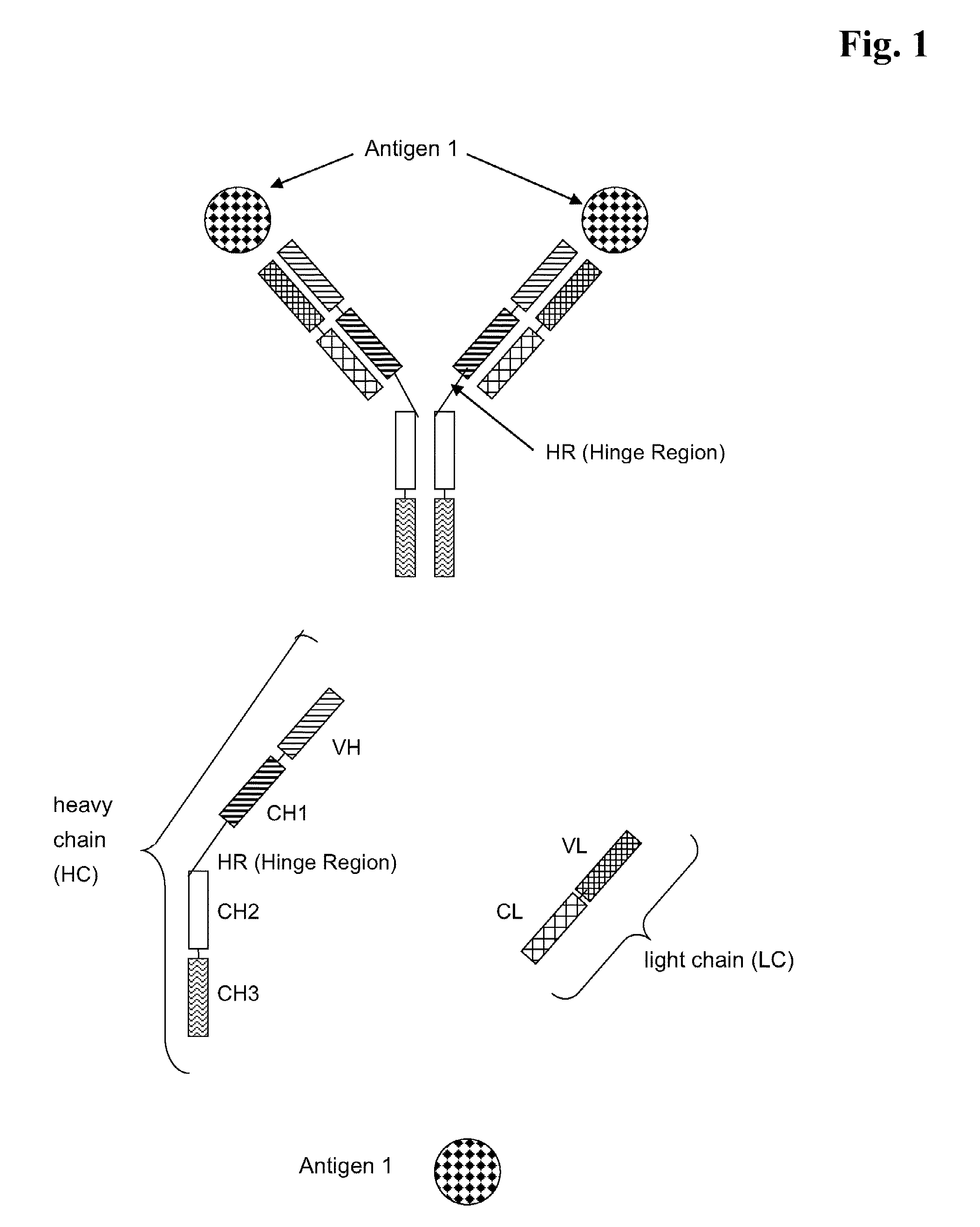
InactiveUS20120276104A1Synergistic effectLow killing activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsErbBEphA Receptors
The invention relates to an antibody having at least two specificities to bind a glycoepitope and a receptor of the erbB class on the surface of a tumor cell, thereby crosslinking the glycoepitope and the receptor, which antibody has apoptotic activity effecting cytolysis independent of NK cells, a method of producing such antibody and its use as a therapeutic.
Owner:F STAR BIOTECHNOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNGS & ENTWICKLUNGS GMBH
High affinity human antibodies to tumor antigens
This invention provides for novel human antibodies that specifically bind to c-erbB-2. The antibodies may be used alone or as components of chimeric molecules that specifically target and deliver effector molecules to cells overexpressing c-erbB-2.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
ErbB surface receptor complexes as biomarkers
InactiveUS20050130238A1Improve determinationIncrease laborDisease diagnosisBiological testingState dependentErbB
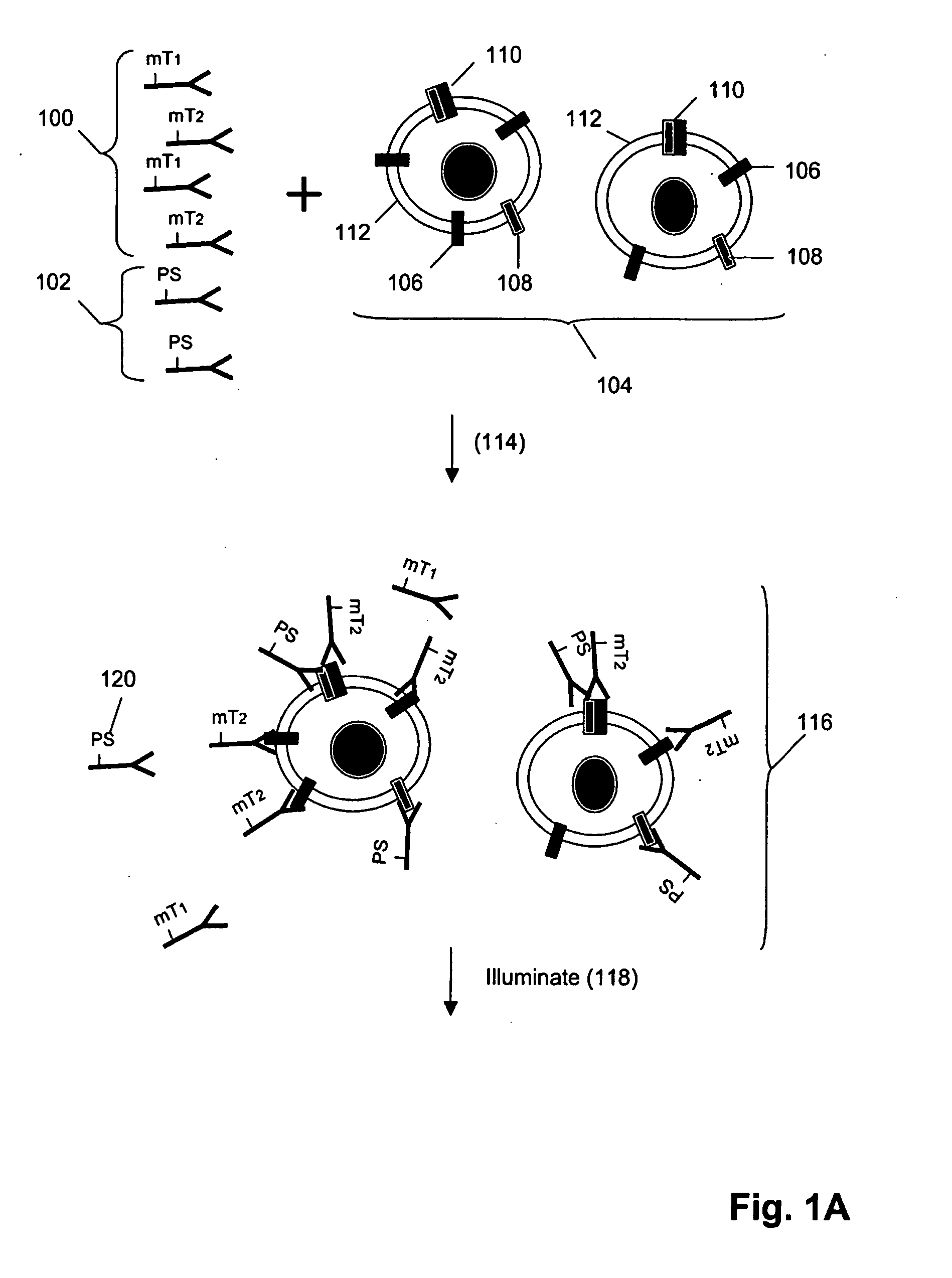
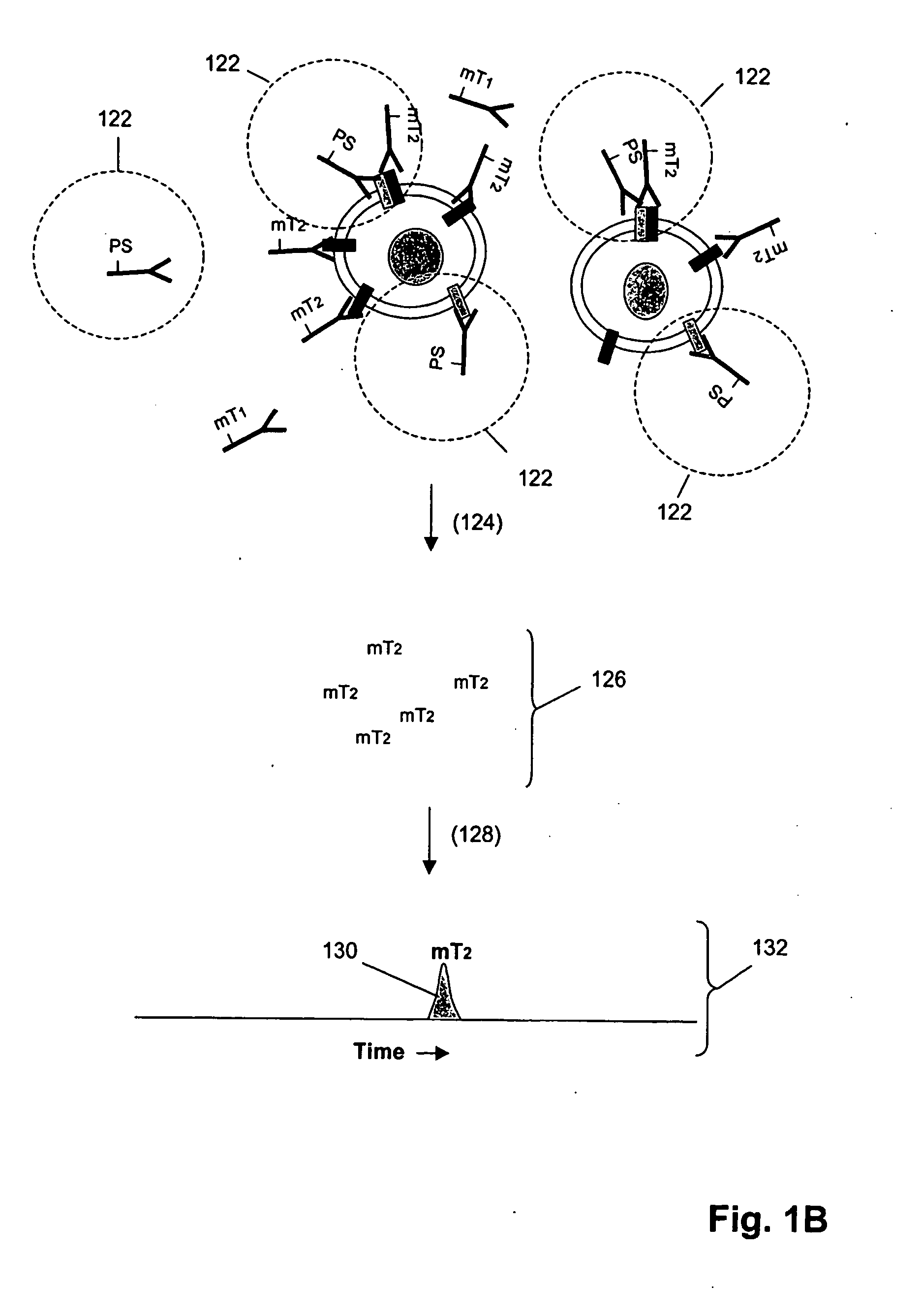
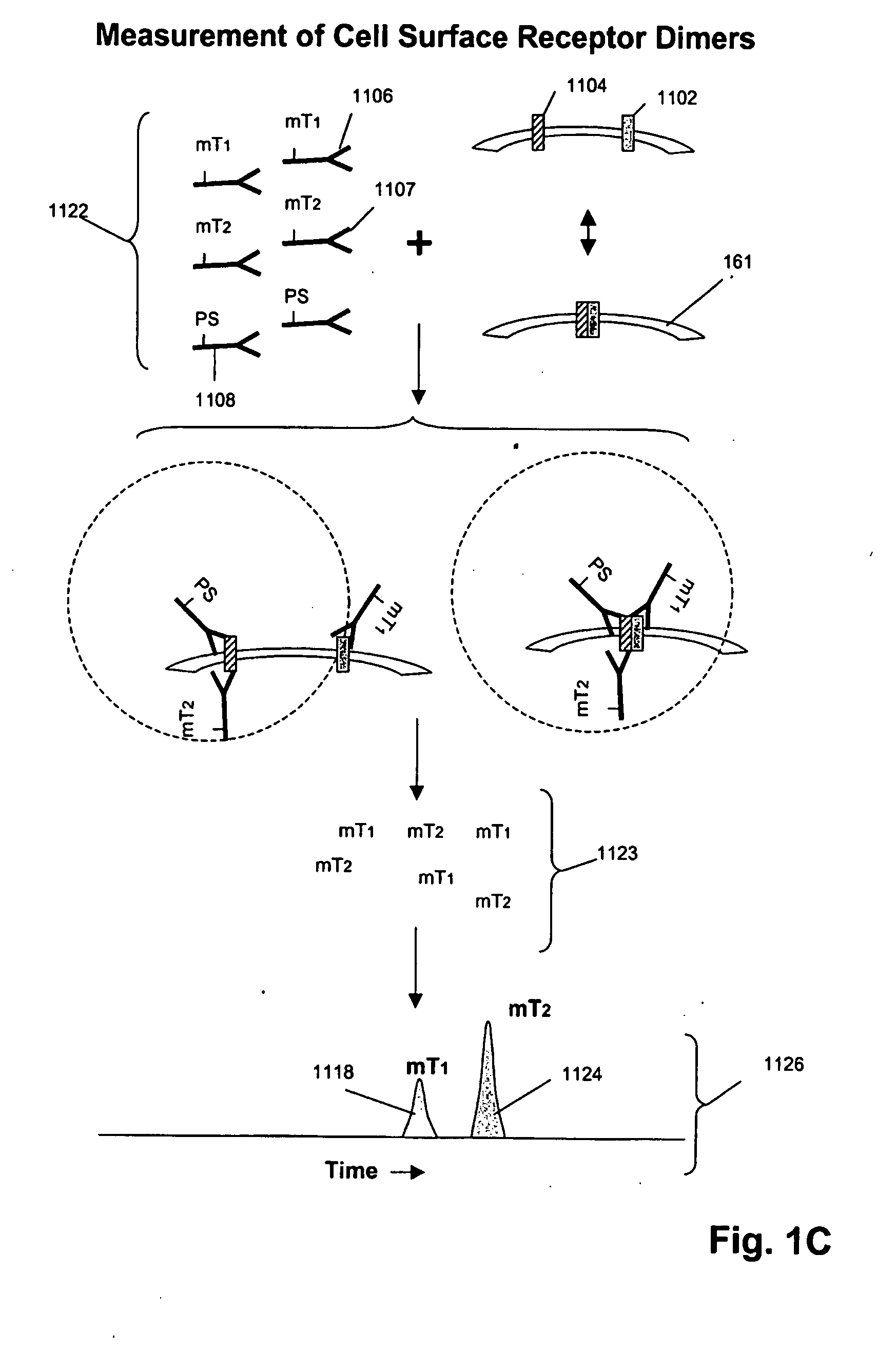
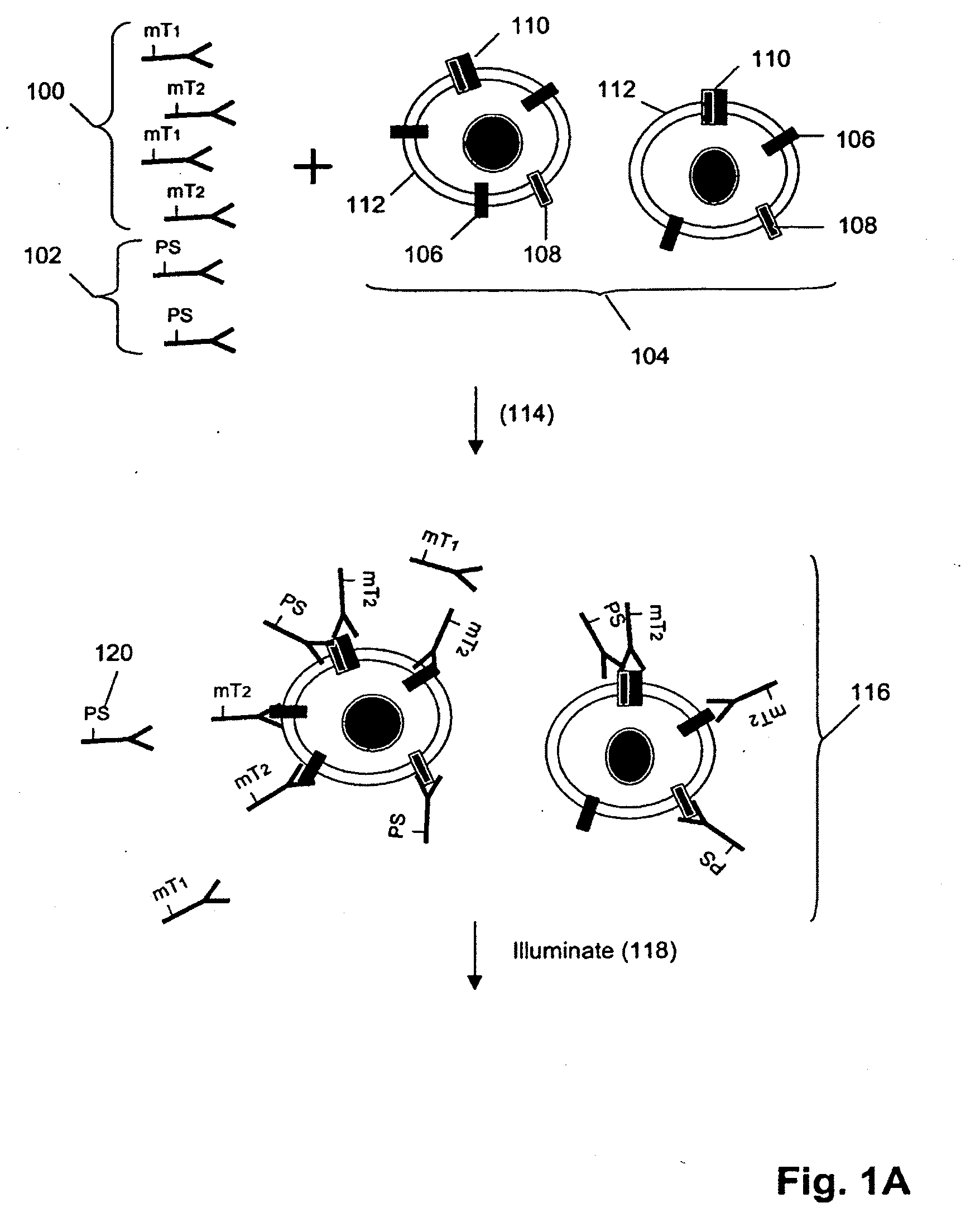
The invention is directed to a new class of biomarker in patient samples comprising dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors. In one aspect, the invention includes a method of determining the status of a disease or healthful condition by correlating such condition to amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors measured directly in a patient sample, in particular a fixed tissue sample. In another aspect, the invention includes a method of determining a status of a cancer in a specimen from an individual by correlating measurements of amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors in cells of the specimen to such status, including presence or absence of a pre-cancerous state, presence or absence of a cancerous state, prognosis of a cancer, or responsiveness to treatment. Preferably, methods of the invention are implemented by using sets of binding compounds having releasable molecular tags that are specific for multiple components of one or more types of receptor dimers. After binding, molecular tags are released and separated from the assay mixture for analysis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
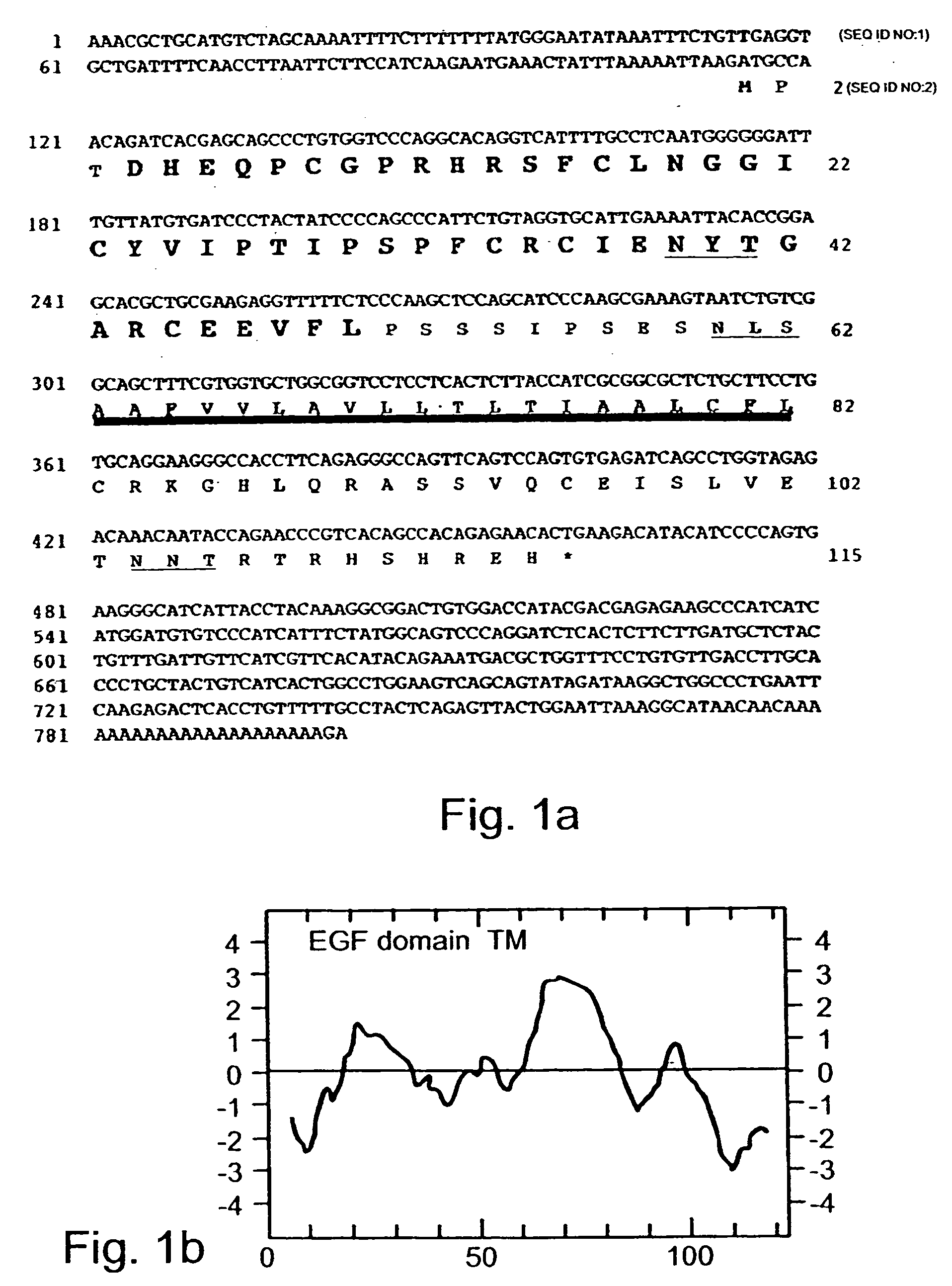
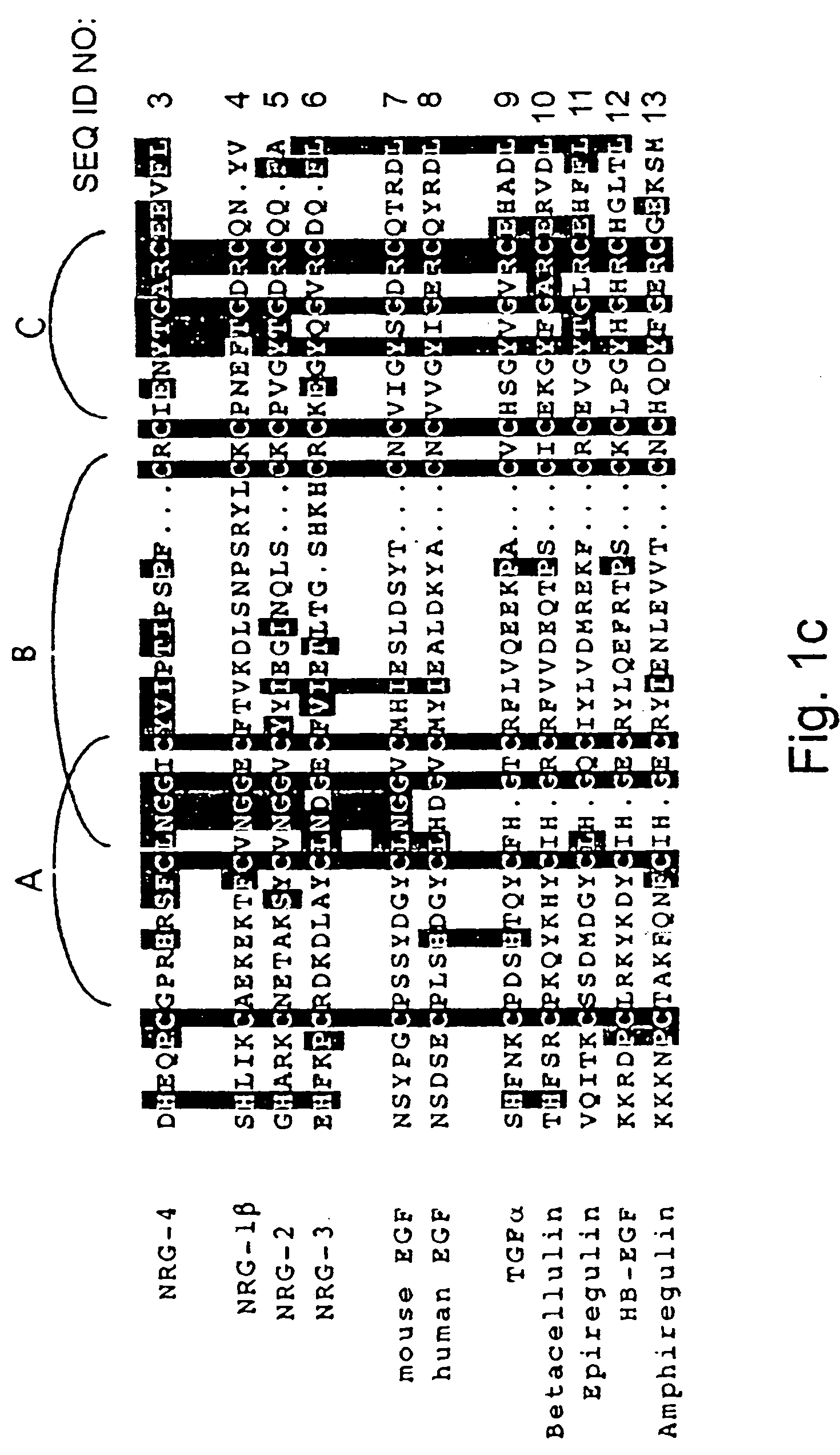
Growth factor which acts through erb b-4 rtk
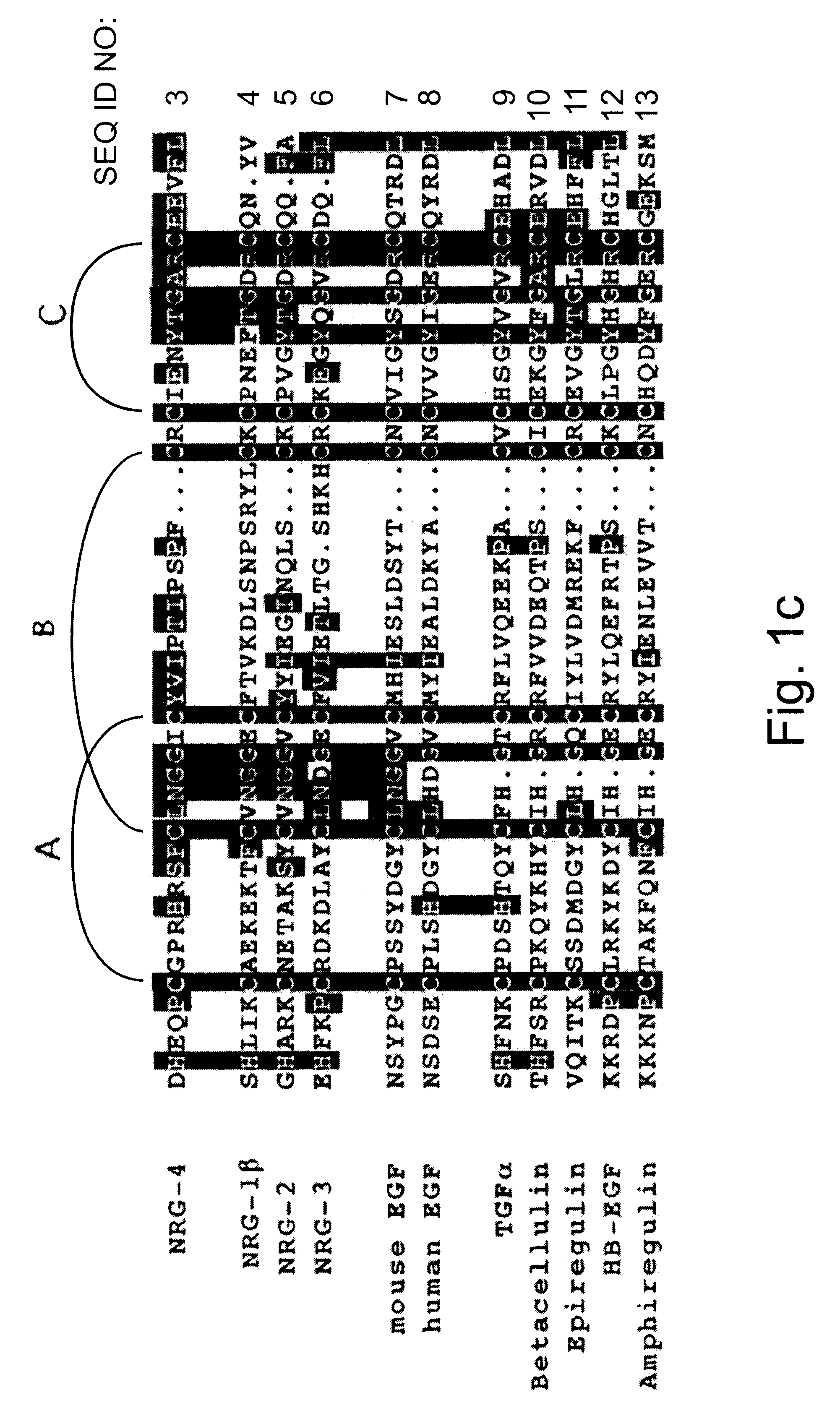
A novel ErbB-4 ligand, referred to herein as Neuregulin-4 (NRG-4) is disclosed as well as polynucleotide sequences encoding NRG-4, oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs derived from polynucleotide sequences, a display library displaying short peptides derived from NRG-4, antibodies recognizing NRG-4, peptides or peptide analogs derived from NRG-4, and pharmaceutical compositions and methods of employing peptides or peptide analogs, oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs, and / or polynucleotide sequences to up-regulate or down-regulate ErbB-4 receptor activity (signaling).
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Methods for Detecting Receptor Complexes Comprising PDGFR
InactiveUS20050170438A1Improve determinationIncrease laborDisease diagnosisBiological testingErbBTissue sample
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
ErbB antagonists for pain therapy
The present application describes the use of ErbB antagonist, especially ErbB2 antibodies such as rhuMAb 2C4, for treating pain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Polynucleotides encoding novel ErbB-2 polypeptides and kits and methods using same
InactiveUS20050123538A1High expressionSensitive and accurateReceptors for hormonesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsErbBPolynucleotide
Owner:COMPUGEN
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway biomarkers
InactiveUS20130189274A1Decrease in PTEN protein expressionInhibit bindingBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementTyrosine-kinase inhibitorErbB
Methods for treating breast cancer, specifically cancers resistant to treatment with one or more known breast cancer treatment drugs, and related patient selection strategies for predicting patient response to drug therapy, such strategies including detecting the presence or absence in a patient of one or more of PIK3CA gene amplification, a mutation in PIK3CA, and a decrease in PTEN protein expression, and treating a patient positive for the presence of one or more of same by administering to the subject a pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Owner:BERKENBLIT ANNA +5
Neuregulin mutant, screening method and use
The present invention provides a method of screening NRG mutant for activating ErbB acceptor specifically. The method includes the following steps: establishing 3D model of complex of NRG, ErbB3, ErbB4, NRG / ErbB3 and NRG / ErbB4 in a homogeneous model establishing process; molecular kinetically simulating conformation and stability of NRG / ErbB3 and NRG / ErbB4; MM / PBSA process of calculating the binding free energy between NRG and ErbB3 or ErbB4; scanning and calculating process based on alanine theory to determine the NRG and acceptor affinity change during the mutation from NRG residue to alanine and determining NRG mutant for activating ErbB acceptor specifically. The present invention also provides the NRG mutant and its application and preparation process.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
C-erbB-2 external domain: GP75
InactiveUS7282345B1Reduce chanceShortened time to relapseBiological testingImmunoassaysDiseaseProteinoid
Disclosed are methods and compositions for identifying malignant tumors that overexpress the c-erbB-2 oncogene. Assays useful for diagnosis and prognosis of neoplastic disease are provided which detect the external domain of c-erbB-2, the glycoprotein gp75 and quantitate the level of gp75 in the biological fluids of mammals carrying a tumor burden.Further disclosed are recombinant, synthetically and otherwise biologically produced novel proteins and polypeptides which are encoded by the external domain DNA sequence of the c-erbB-2 oncogene (the gp75 gene) or fragments thereof. Such gp75 proteins and polypeptides are useful as vaccines, therapeutically in the treatment of cancer either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic agents.Also disclosed are antibodies to such gp75 proteins and polypeptides which are useful diagnostically and therapeutically. Still further disclosed are test kits embodying the assays of this invention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
ErbB Surface Receptor Complexes as Biomarkers
The invention is directed to a new class of biomarker in patient samples comprising dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors. In one aspect, the invention includes a method of determining the status of a disease or healthful condition by correlating such condition to amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors measured directly in a patient sample, in particular a fixed tissue sample. In another aspect, the invention includes a method of determining a status of a cancer in a specimen from an individual by correlating measurements of amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors in cells of the specimen to such status, including presence or absence of a pre-cancerous state, presence or absence of a cancerous state, prognosis of a cancer, or responsiveness to treatment. Preferably, methods of the invention are implemented by using sets of binding compounds having releasable molecular tags that are specific for multiple components of one or more types of receptor dimers. After binding, molecular tags are released and separated from the assay mixture for analysis.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
Polynucleotides encoding a novel growth factor which acts through ErbB-4 kinase receptor tyrosine
A novel ErbB-4 ligand, referred to herein as Neuregulin-4 (NRG-4) is disclosed as well as polynucleotide sequences encoding NRG-4, oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs derived from polynucleotide sequences, a display library displaying short peptides derived from NRG-4, antibodies recognizing NRG-4, peptides or peptide analogs derived from NRG-4, and pharmaceutical compositions and methods of employing peptides or peptide analogs, oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs, and / or polynucleotide sequences to up-regulate or down-regulate ErbB-4 receptor activity (signaling).
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
N4-phenyl-quinazoline-4-amine derivatives and related compounds as erbb type i receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases
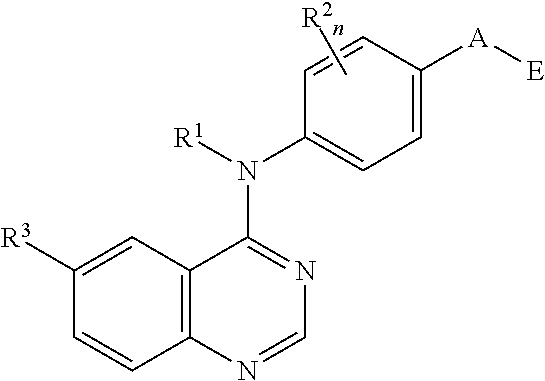
This invention provides compounds of Formula Iwherein B, G, A, E, R1, R2, R3, m and n are as defined herein, which are useful as type I receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and methods of use thereof in the treatment of hyperproliferative disorders in mammals.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA INC
Immunotherapy against erbb-3 receptor
ActiveUS20140017259A1EfficaciousHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellMonoclonal antibody
The present invention describes methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of cancer in mammals, more particularly in human subjects. More specifically, the invention concerns anti-tumor vaccines based upon plasmid DNA and / or genetic vectors carrying a codon-usage optimized sequence and coding for a mutant form of the ErbB-3 receptor. Furthermore, the invention refers to monoclonal antibodies directed against the ErbB-3 receptor, obtained using these methods and capable to block its activity in cancer cells.
Owner:TAKIS
Methods for Detecting Receptor Complexes Comprising PI3K
InactiveUS20050170439A1Improve determinationIncrease laborDisease diagnosisBiological testingErbBTissue sample
Abstract of the Disclosure The invention is directed to a new class of biomarker in patient samples comprising dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors. In one aspect, the invention includes a method of determining the status of a disease or healthful condition by correlating such condition to amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors measured directly in a patient sample, in particular a fixed tissue sample. In another aspect, the invention includes a method of determining a status of a cancer in a specimen from an individual by correlating measurements of amounts of one or more dimers of ErbB cell surface membrane receptors in cells of the specimen to such status, including presence or absence of a pre-cancerous state, presence or absence of a cancerous state, prognosis of a cancer, or responsiveness to treatment. Preferably, methods of the invention are implemented by using sets of binding compounds having releasable molecular tags that are specific for multiple components of one or more types of receptor dimers. After binding, molecular tags are released and separated from the assay mixture for analysis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Methods of and compositions for stimulation of glucose uptake into muscle cells and treatment of diseases
InactiveUS20070054851A1Promote cell survivalIncrease muscle massBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseGlucose uptake
The present invention relates to therapeutic uses of ErbB ligands, including betacellulin. The therapeutic uses include methods of using ErbB ligand family compounds alone, or in conjunction with other agents, for reducing blood glucose levels, treating Type I and Type II diabetes, obesity, muscle wasting diseases, and cardiotoxicity.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com