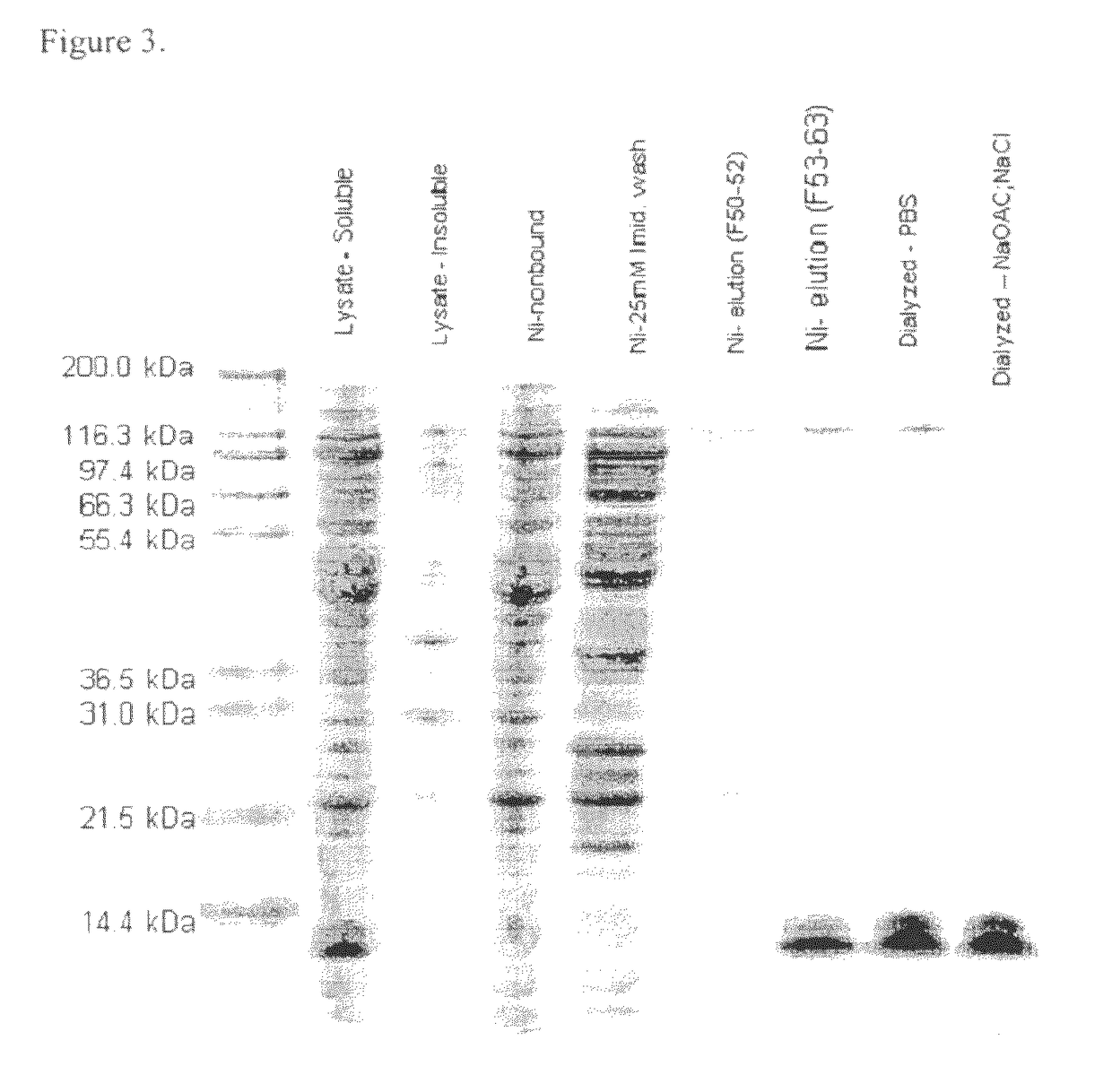
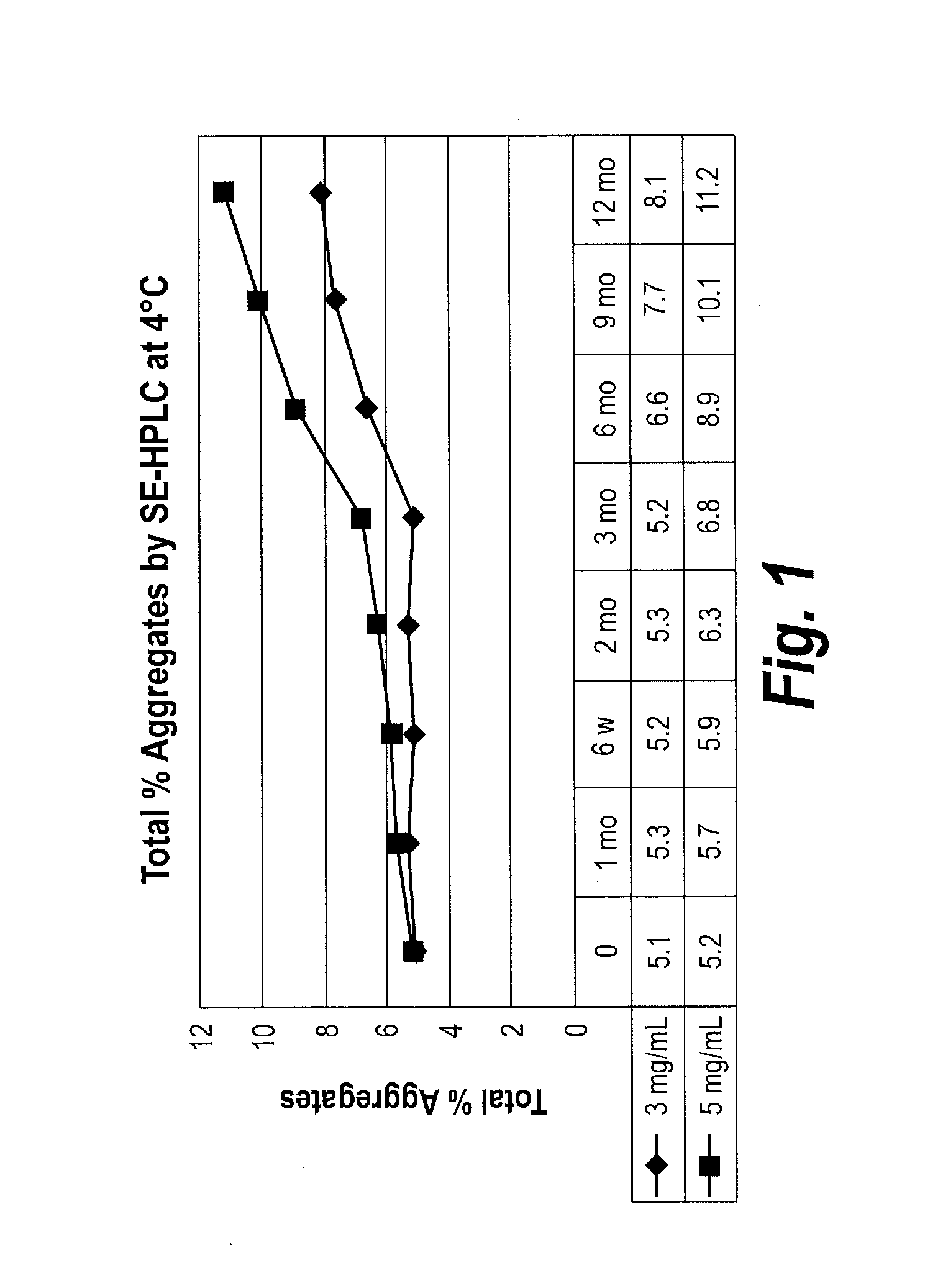
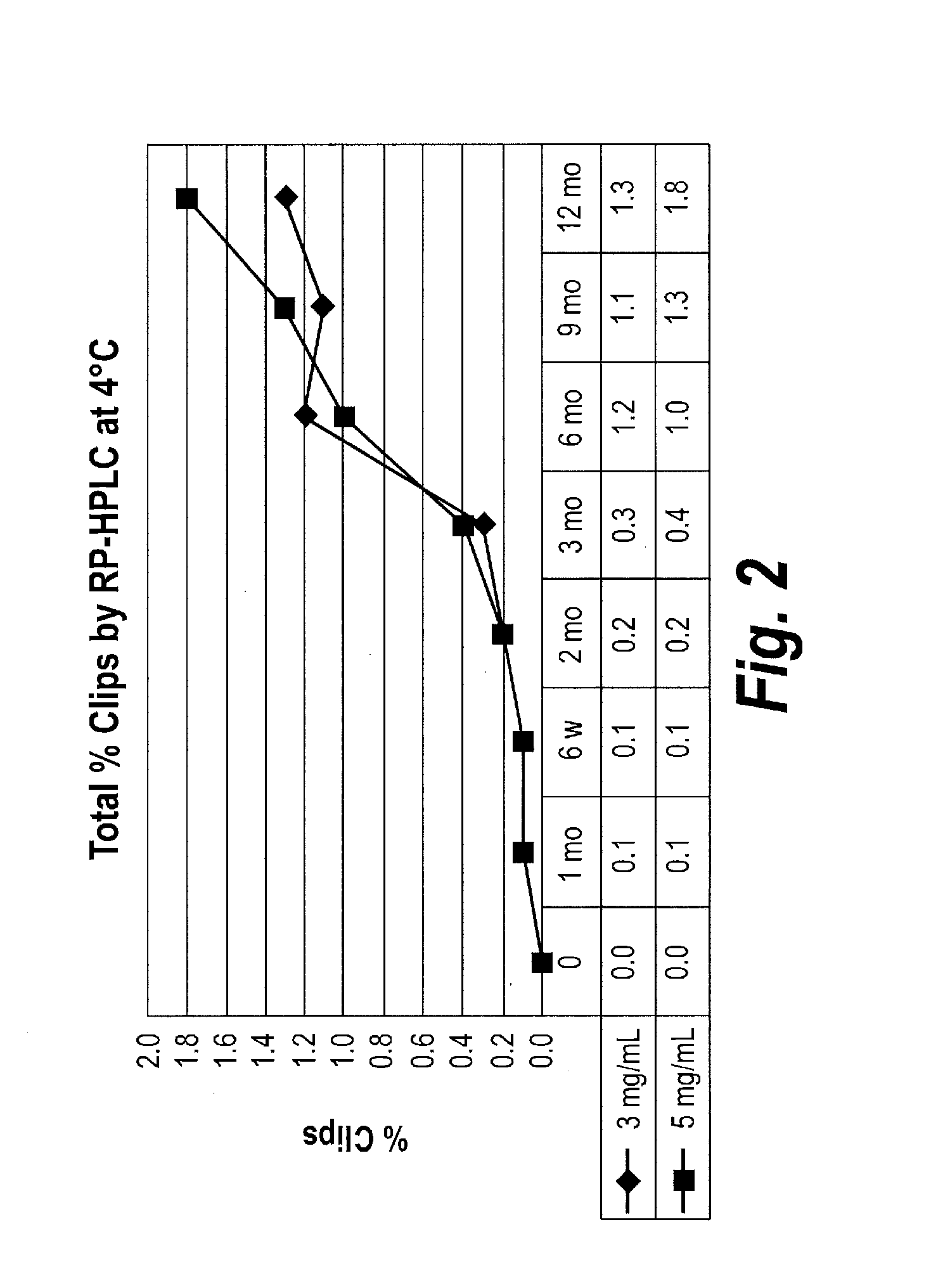
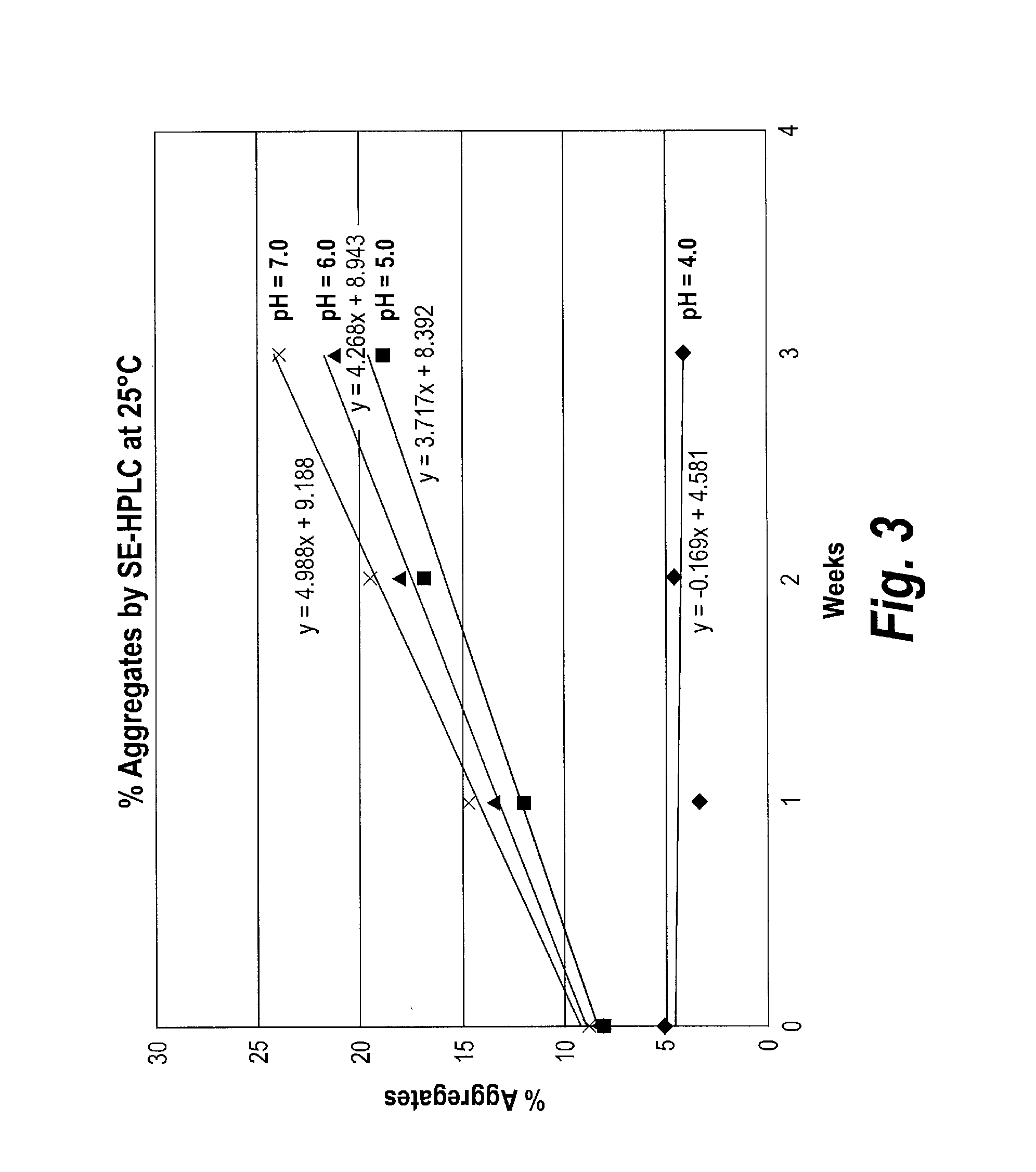
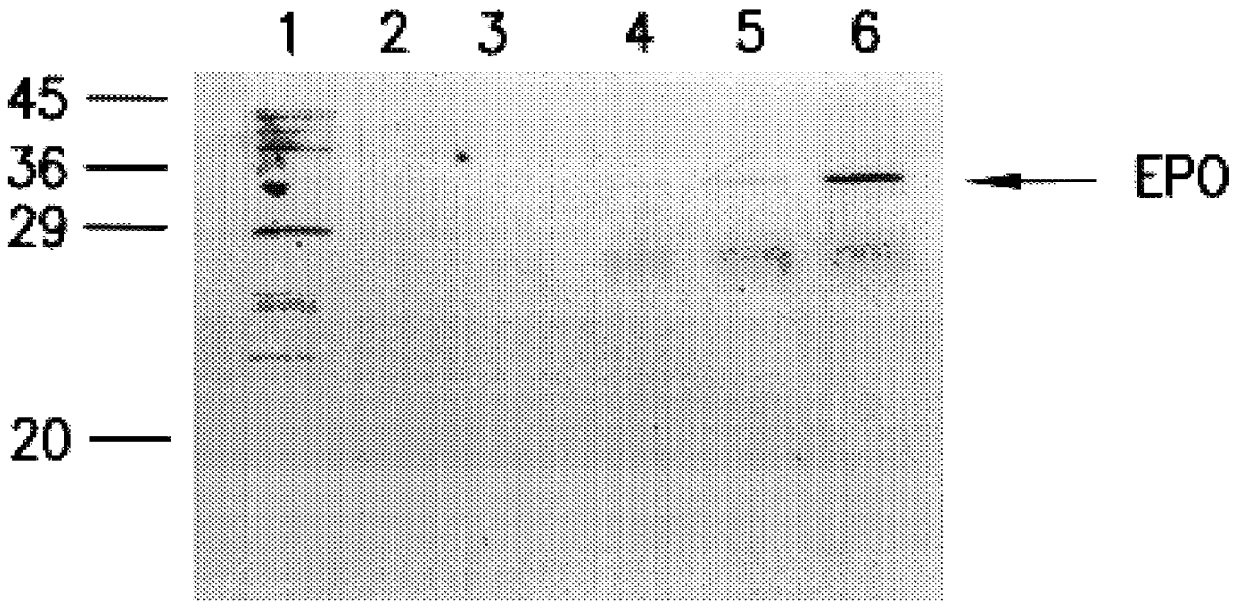
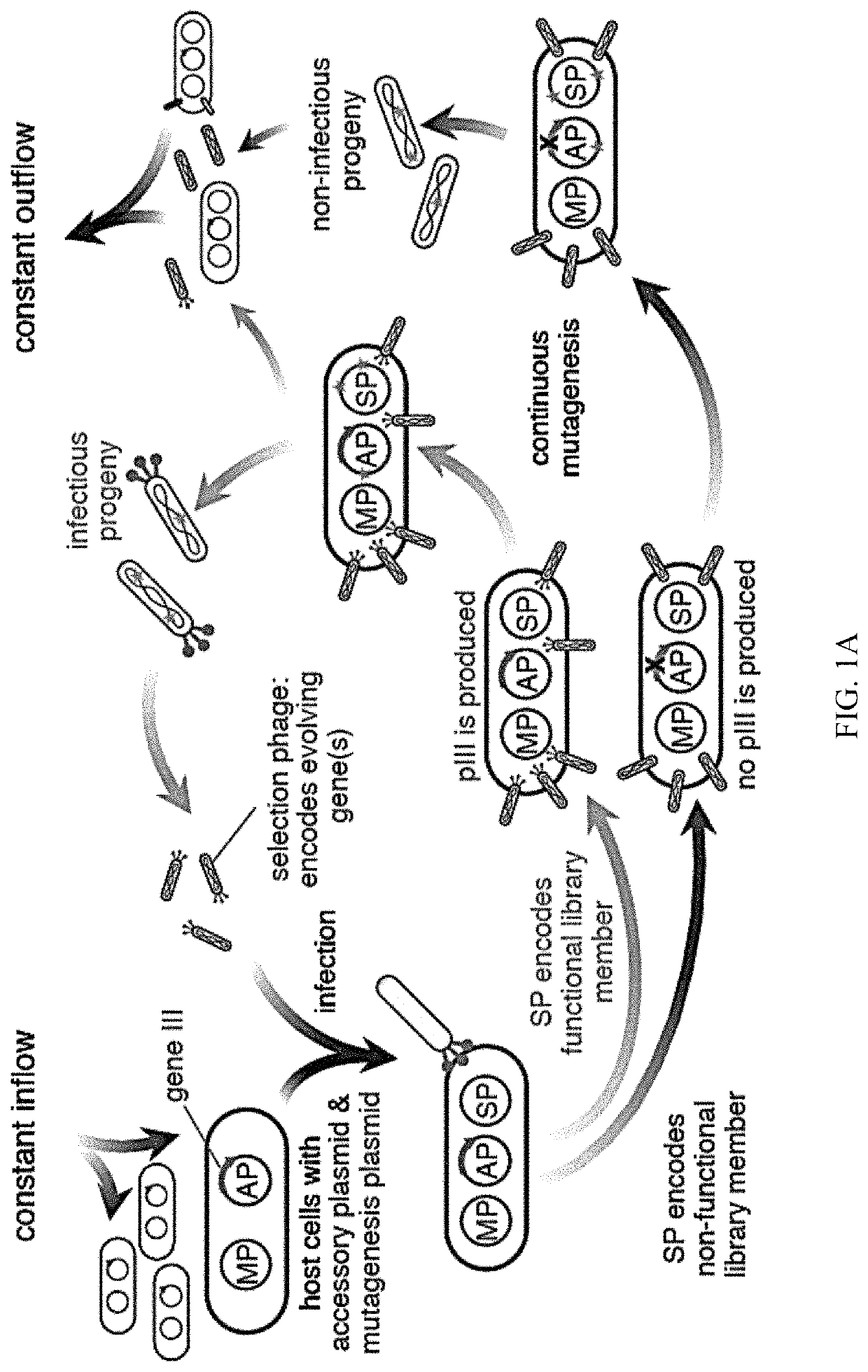
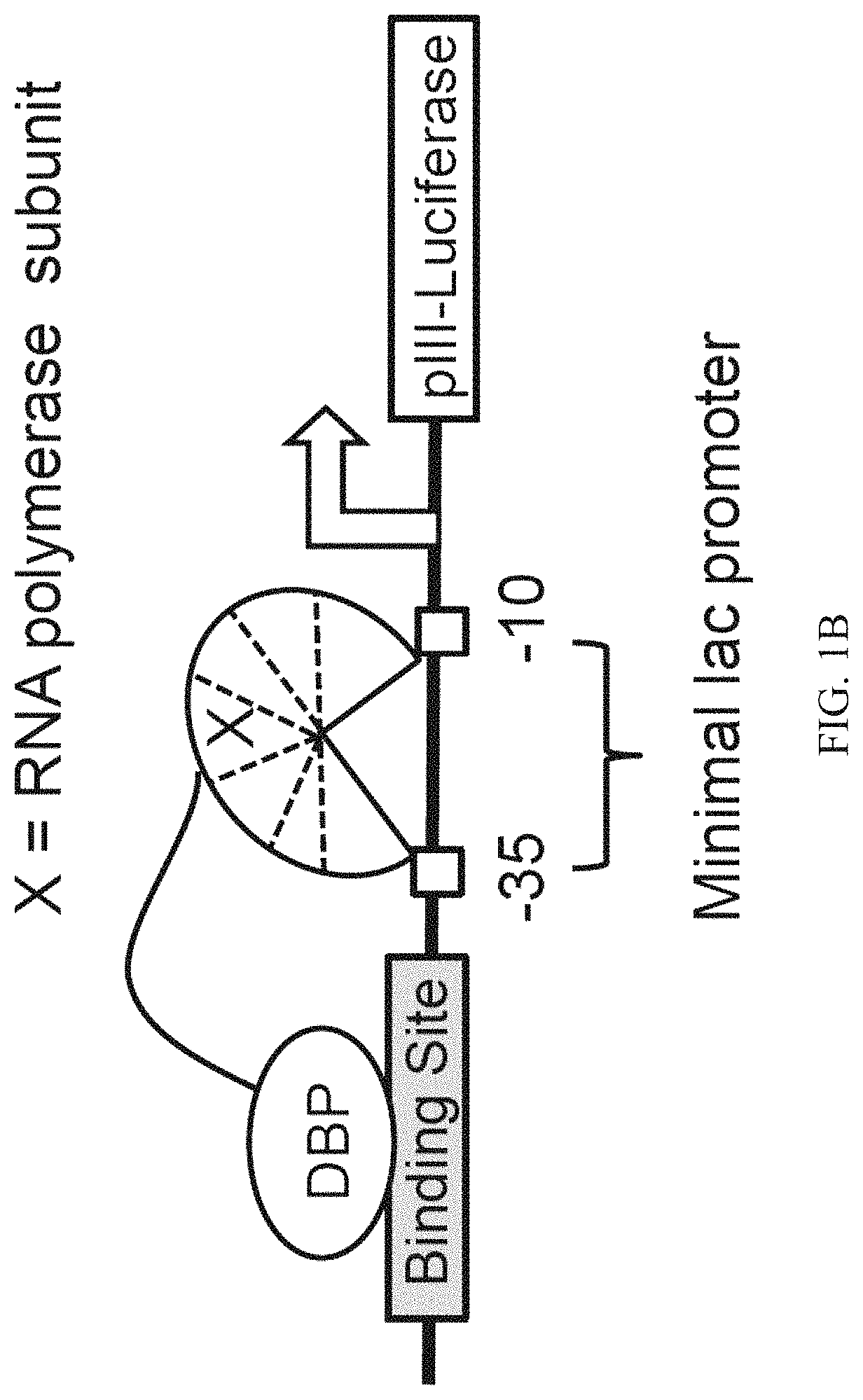
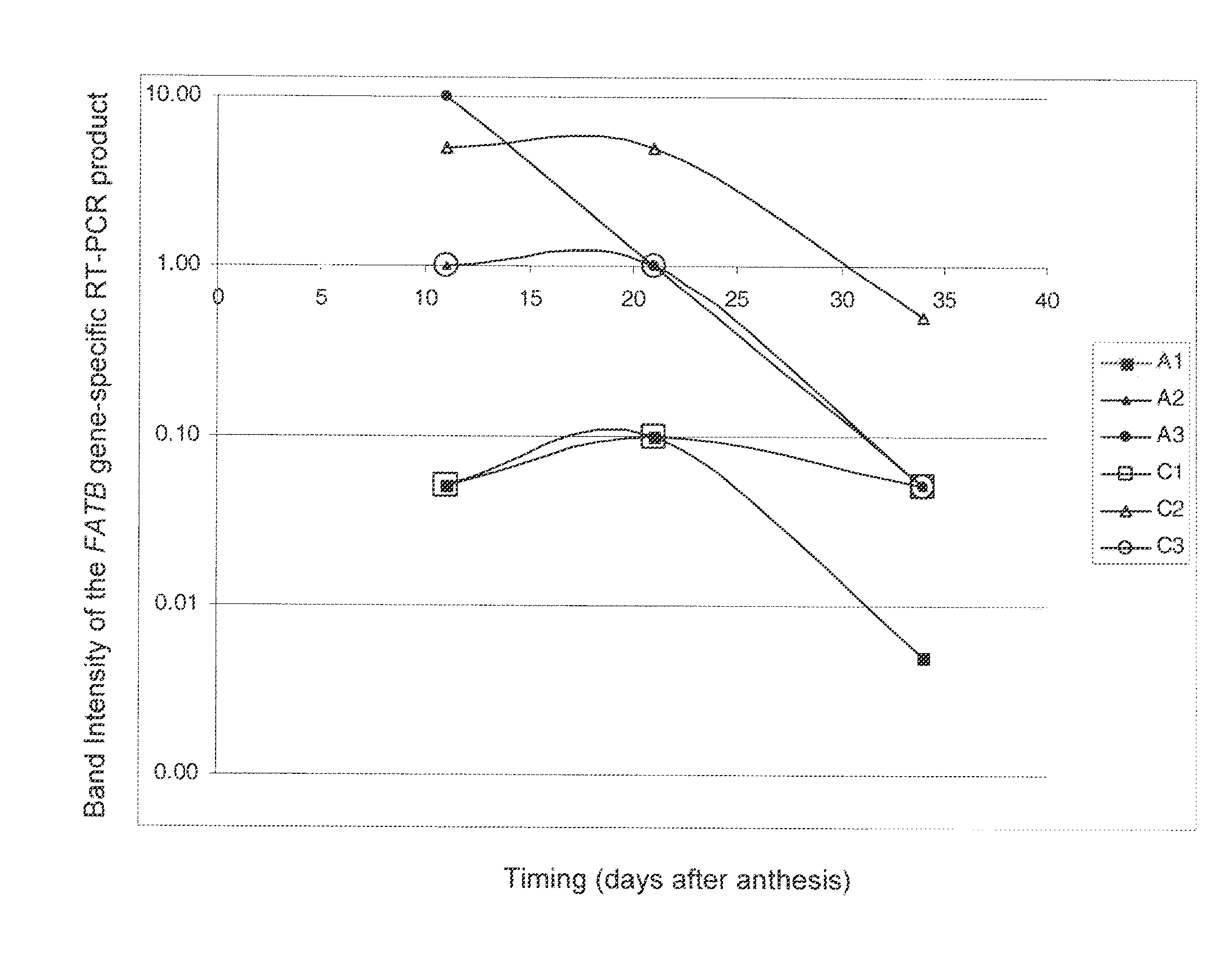Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
404 results about "Proteinoid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proteinoids, or thermal proteins, are protein-like, often cross-linked molecules formed abiotically from amino acids. Sidney W. Fox initially proposed that they may have been precursors to the first living cells (protocells). The term was also in the 1960s to describe peptides that are shorter than twenty amino acids found in hydrolysed protein, but this term is no longer commonly used.
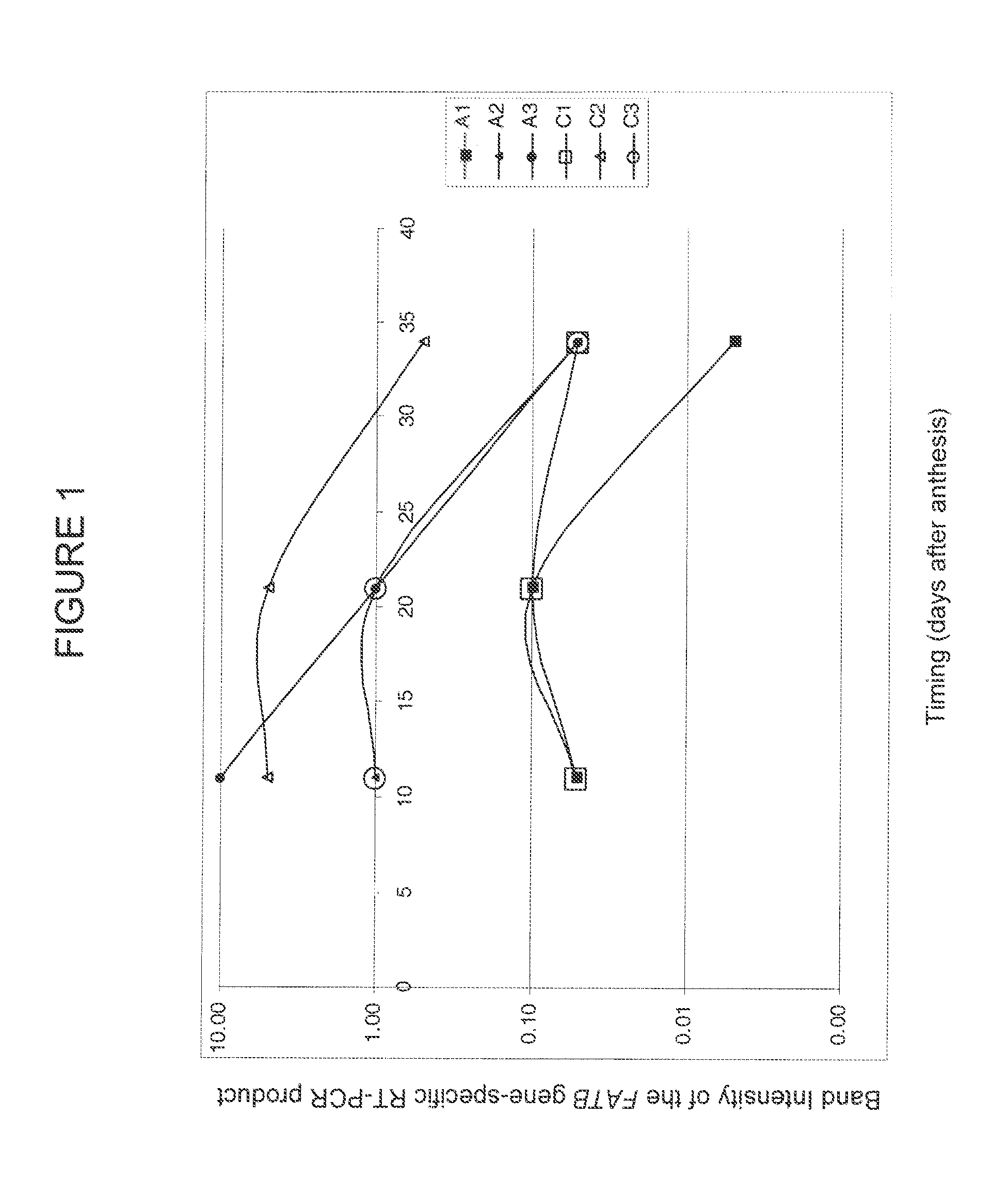
Brassica plant comprising mutant fatty acyl-acp thioesterase alleles
ActiveUS20110145944A1Reduce the amount requiredMinimal level of functional FATB proteinHydrolasesImmunoglobulinsAcyl carrier proteinWild type
The invention relates to crop plants comprising novel seed lipid compositions. Provided are both wild type and mutant nucleic acid molecules encoding Brassica fatty acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesterase B proteins (FATB) and the proteins as such. Also provided are Brassica plants, tissue and seeds comprising at least three mutant fatB alleles in their genome, whereby the seed oil fatty acid composition or profile is significantly altered.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
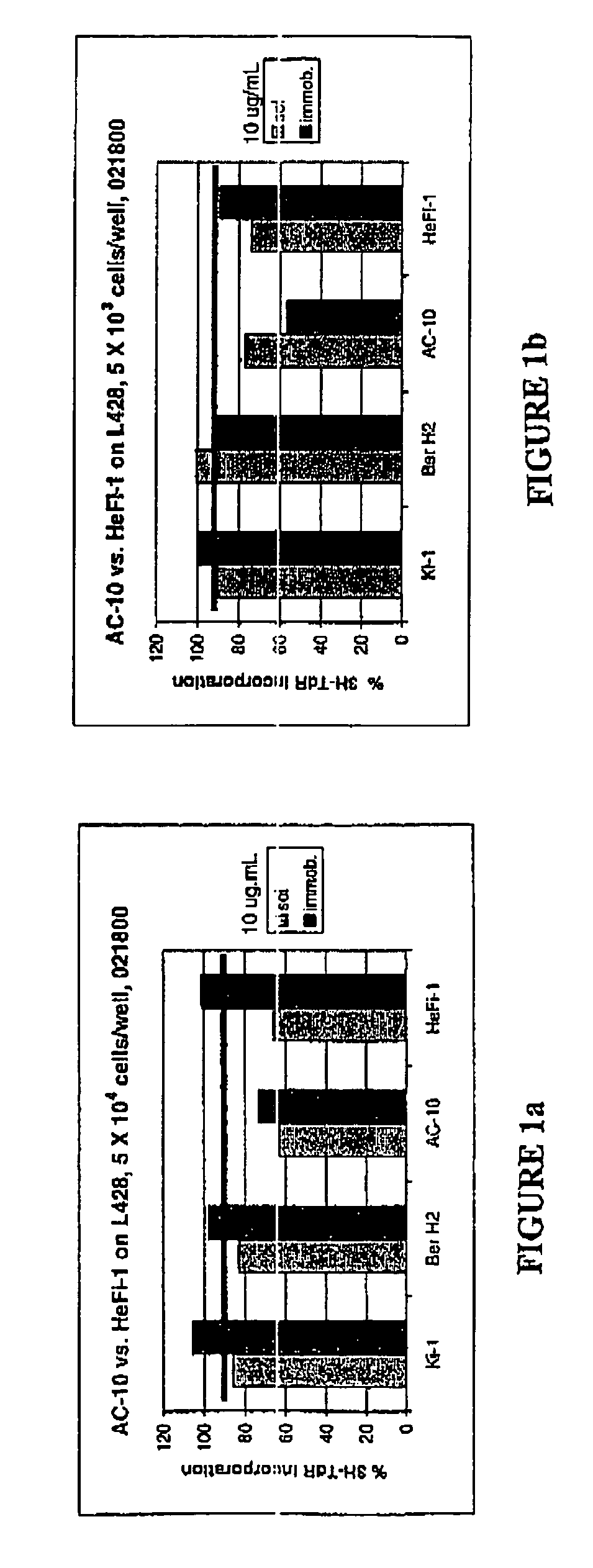
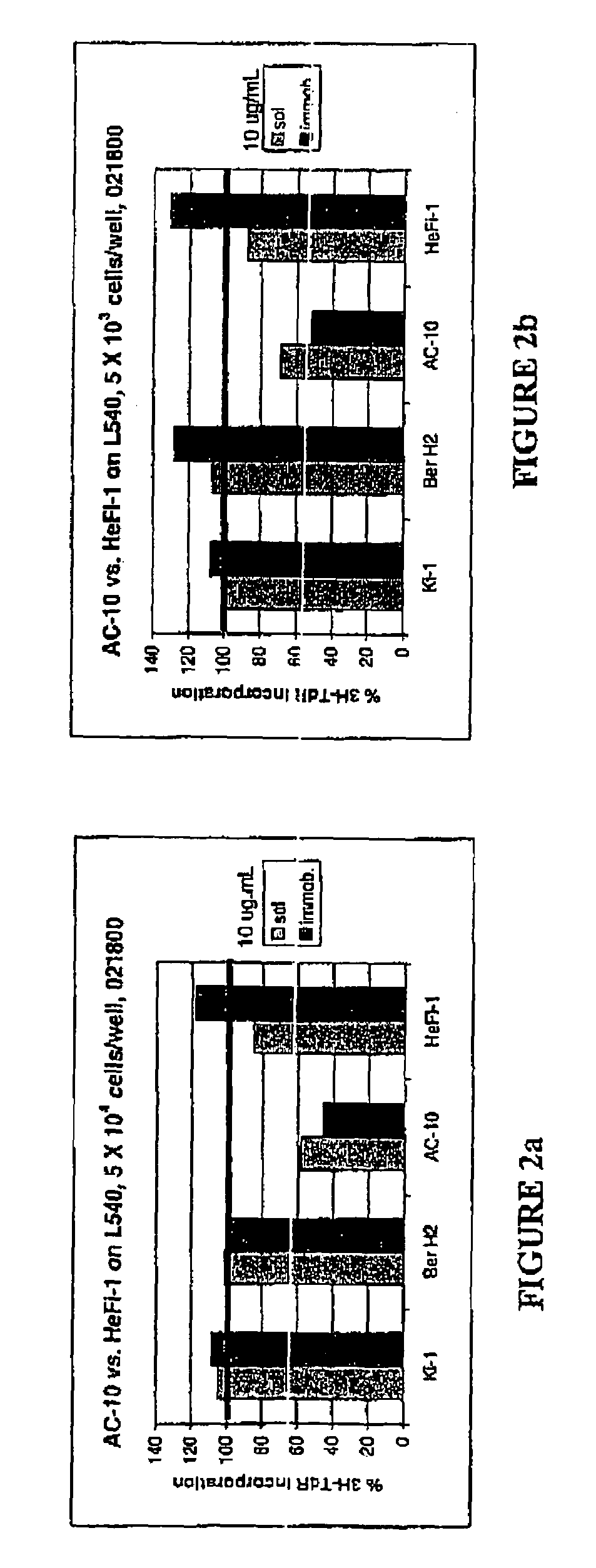
Recombinant anti-CD30 antibodies and uses thereof
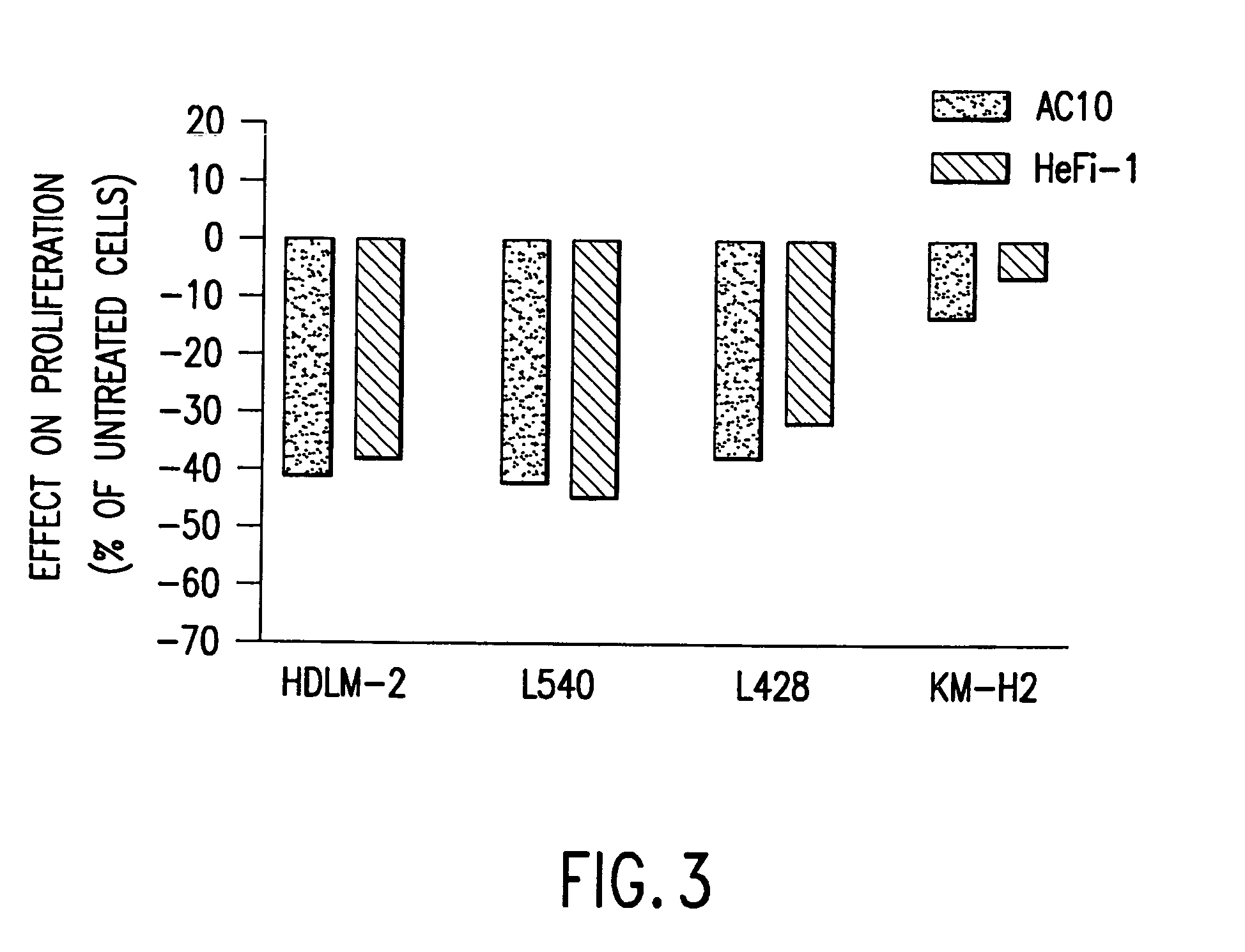
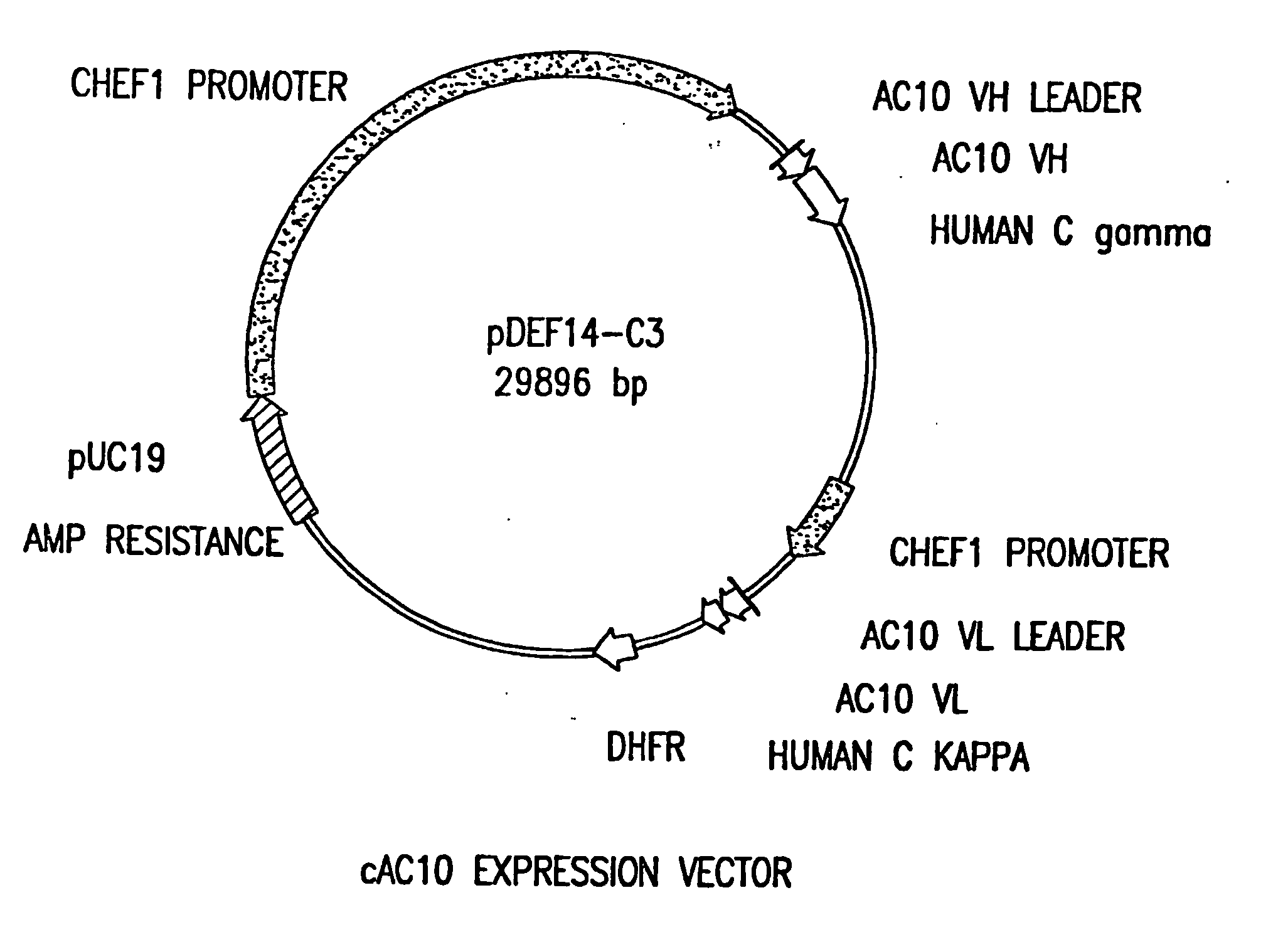
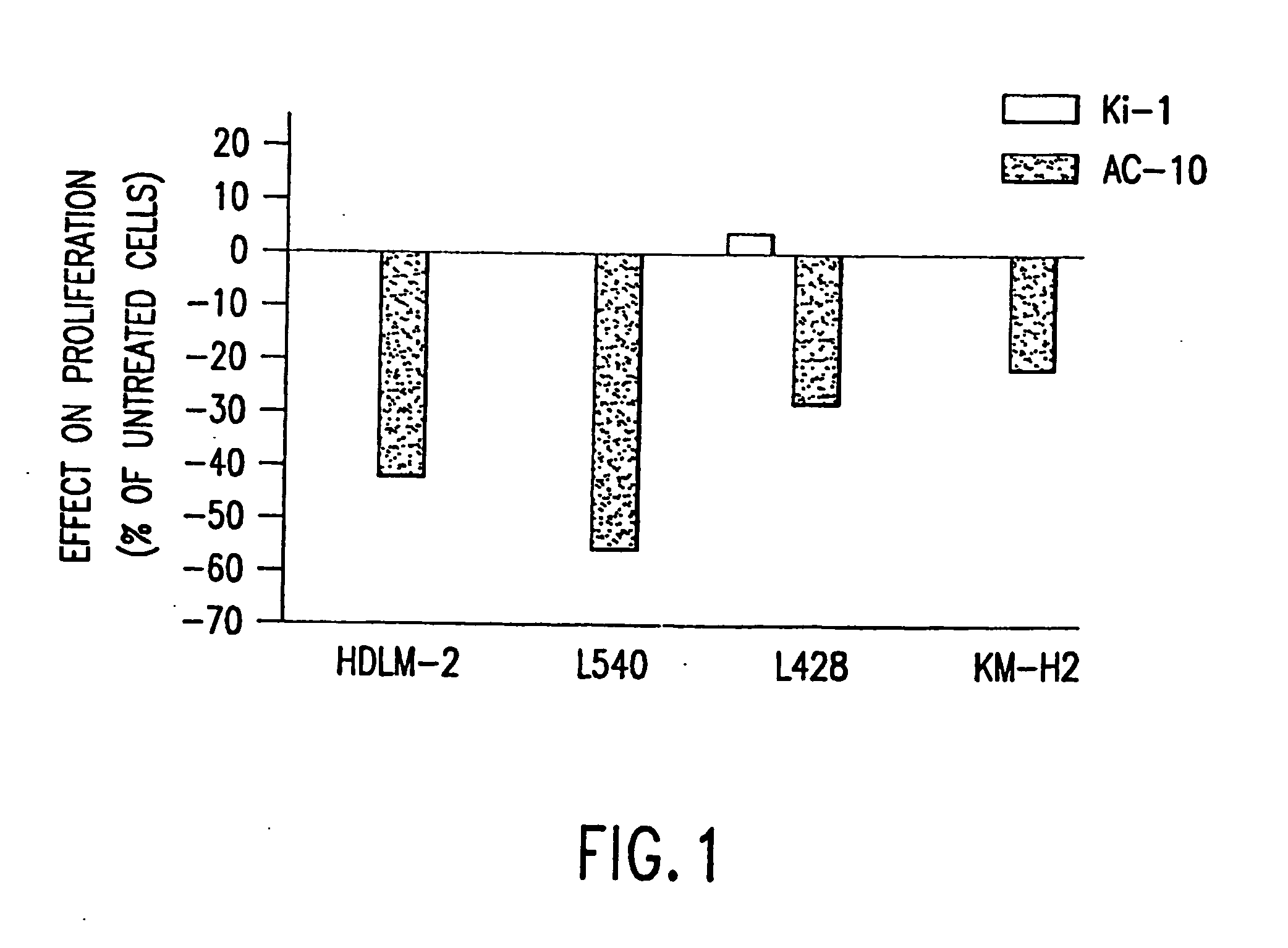
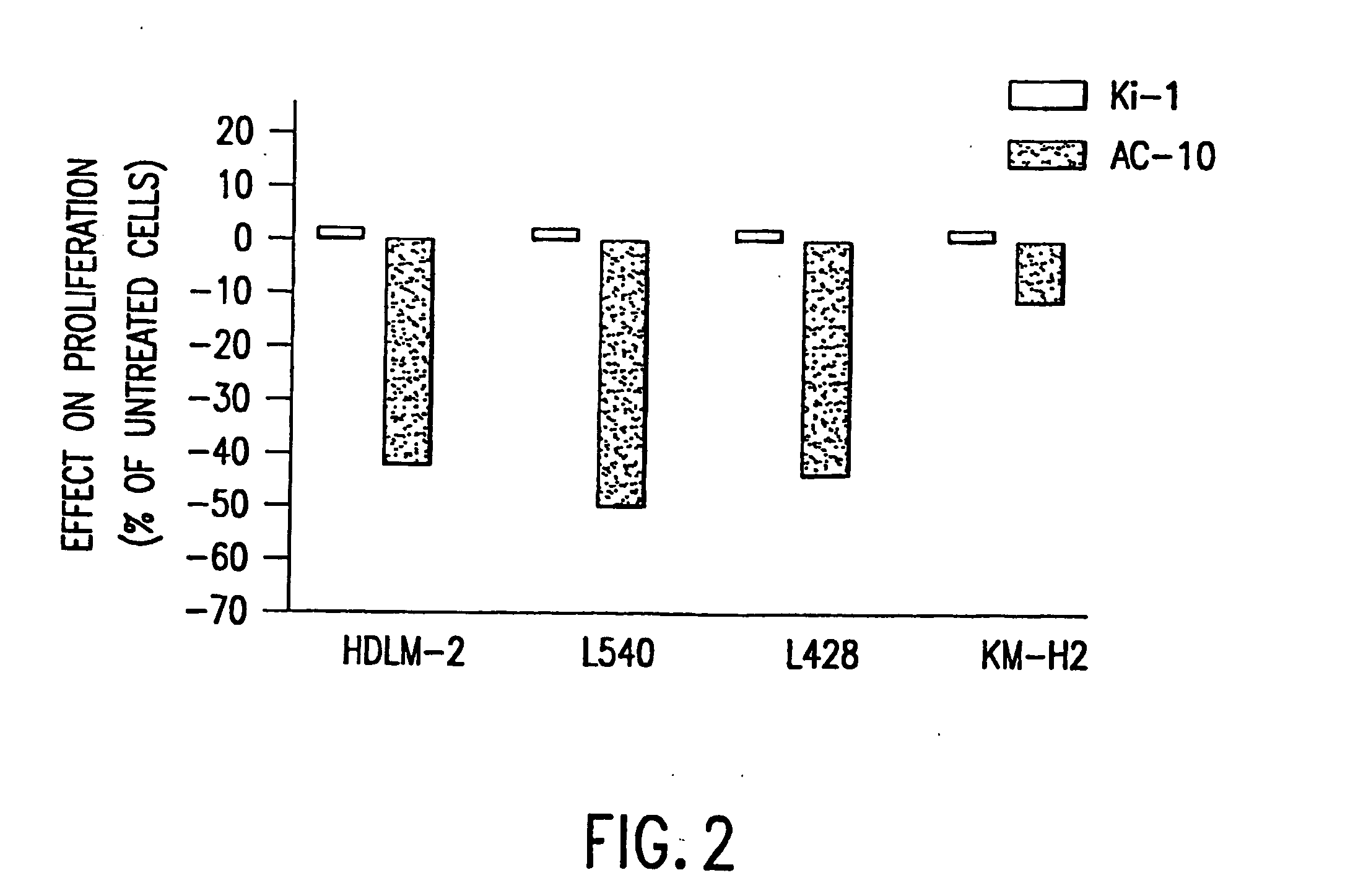
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Hodgkin's Disease, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30, or compete with monoclonal antibodies AC10 or HeFi-1 for binding to CD30, and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on Hodgkin's Disease cells. Such proteins include derivatives of monoclonal antibodies AC10 and HeFi-1. The proteins of the invention can be human, humanized, or chimeric antibodies; further, they can be conjugated to cytotoxic agents such as chemotherapeutic drugs. The invention further relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins of the invention. The invention yet further relates to a method for identifying an anti-CD30 antibody useful for the treatment or prevention of Hodgkin's Disease.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS20050255548A1Easy to foldImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsWAS PROTEINAntibody
Disclosed herein are proteins that include a fibronectin type III domain having at least one randomized loop. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Recombinant Anti-Cd30 Antibodies and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of Hodgkin's Disease, comprising administering proteins characterized by their ability to bind to CD30, or compete with monoclonal antibodies AC10 or HeFi-1 for binding to CD30, and exert a cytostatic or cytotoxic effect on Hodgkin's disease cells in the absence of effector cells or complement. Such proteins include derivatives of monoclonal antibodies AC10 and HeFi-1. The proteins of the invention can be human, humanized, or chimeric antibodies; further, they can be conjugated to cytotoxic agents such as chemotherapeutic drugs. The invention further relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins of the invention. The invention yet further relates to a method for identifying an anti-CD30 antibody useful for the treatment or prevention of Hodgkin's Disease.
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC
Organ-specific proteins and methods of their use
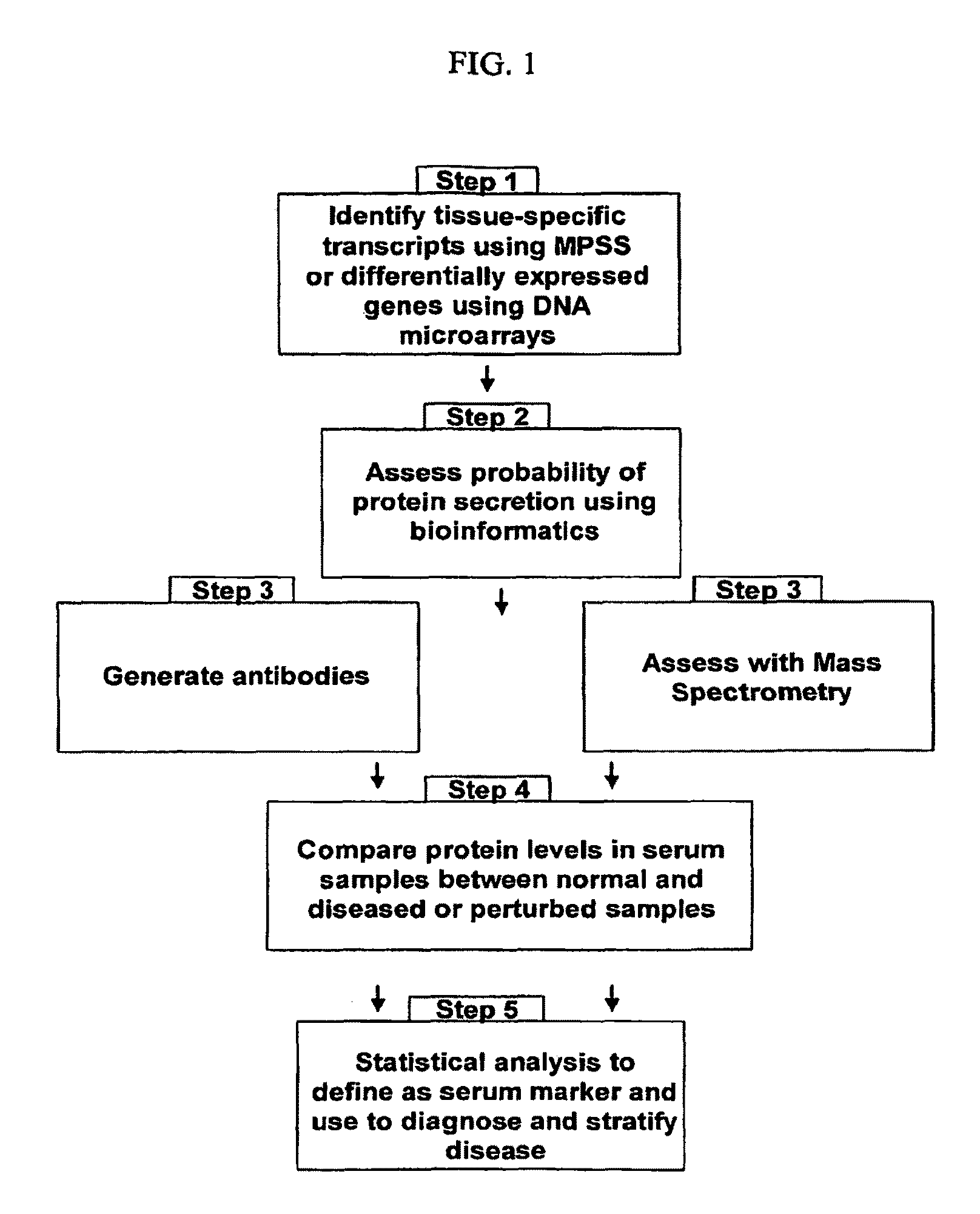
The present invention relates generally to methods for identifying and using organ-specific proteins and transcripts. The present invention further provides compositions comprising organ-specific proteins and transcripts encoding the same, detection reagents for detecting such proteins and transcripts, and diagnostic panels, kits and arrays for measuring organ-specific proteins / transcripts in blood, biological tissue or other biological fluid.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY +1
Organ-specific proteins and methods of their use
The present invention relates generally to methods for identifying and using organ-specific proteins and transcripts. The present invention further provides compositions comprising organ-specific proteins and transcripts encoding the same, detection reagents for detecting such proteins and transcripts, and diagnostic panels, kits and arrays for measuring organ-specific proteins / transcripts in blood, biological tissue or other biological fluid.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY +1
Pharmaceutically acceptable FN3 polypeptides for human treatments
InactiveUS20060246059A1Optimal folding and stability and solubilityImproved biophysical propertyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsWAS PROTEINBiology
Disclosed herein are proteins that include an immunoglobulin fold and that can be used as scaffolds. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
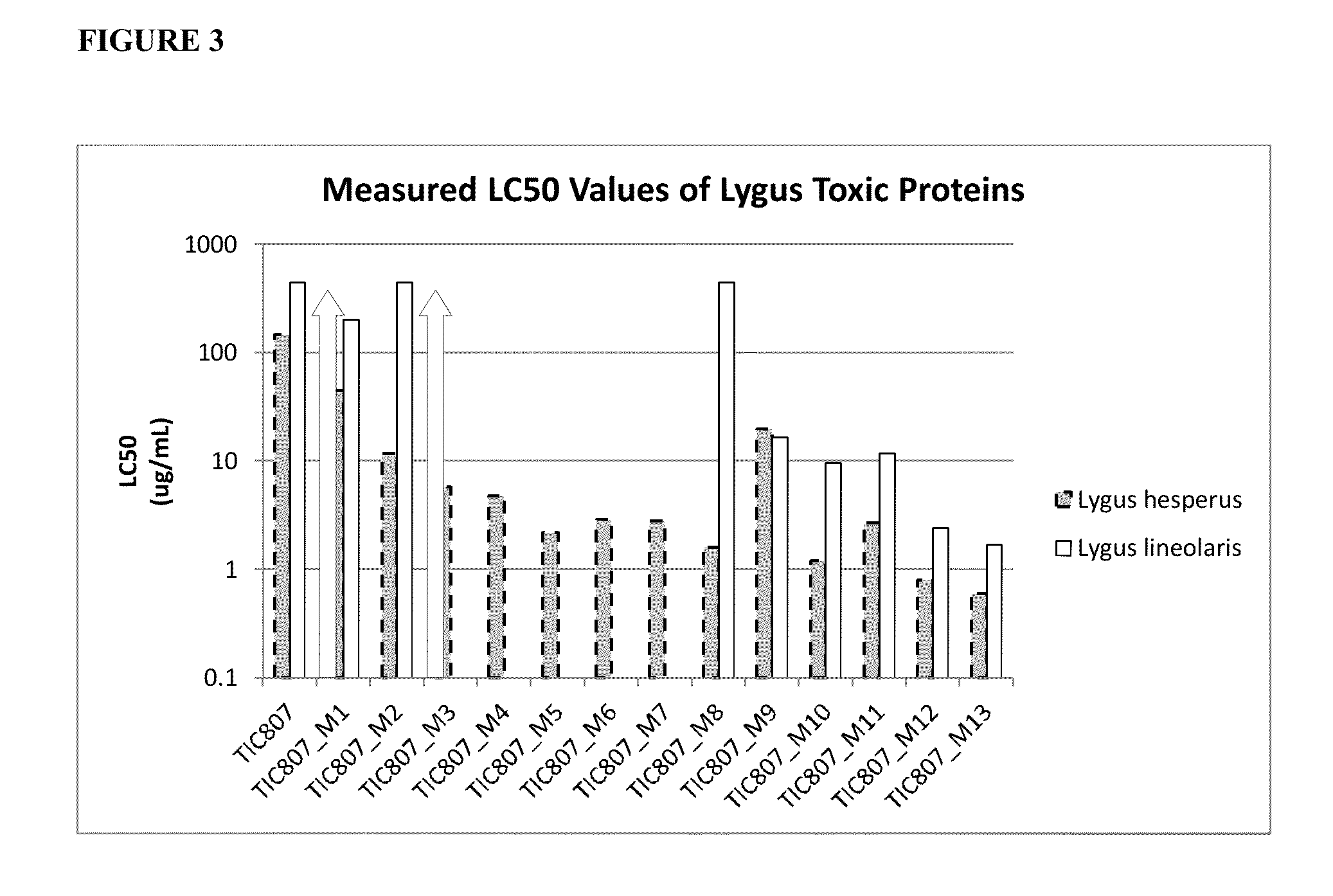
Proteins Toxic To Hemipteran Insect Species
The present invention discloses Hemipteran insect inhibitory proteins, methods of using such proteins, nucleotide sequences encoding such proteins, methods of detecting and isolating such proteins, and their use in agricultural systems.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for treating acromegaly and giantism with growth hormone antagonists
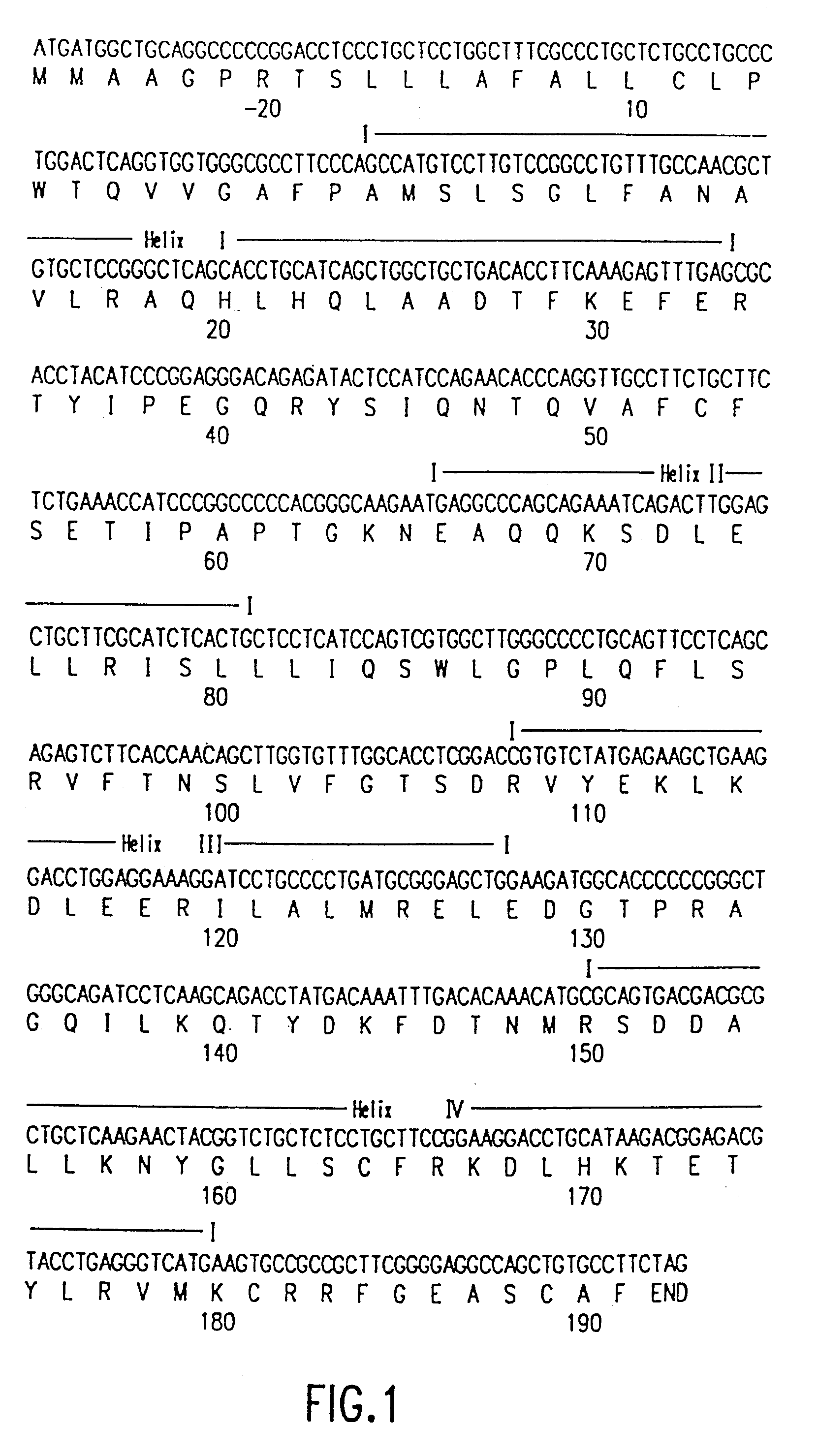
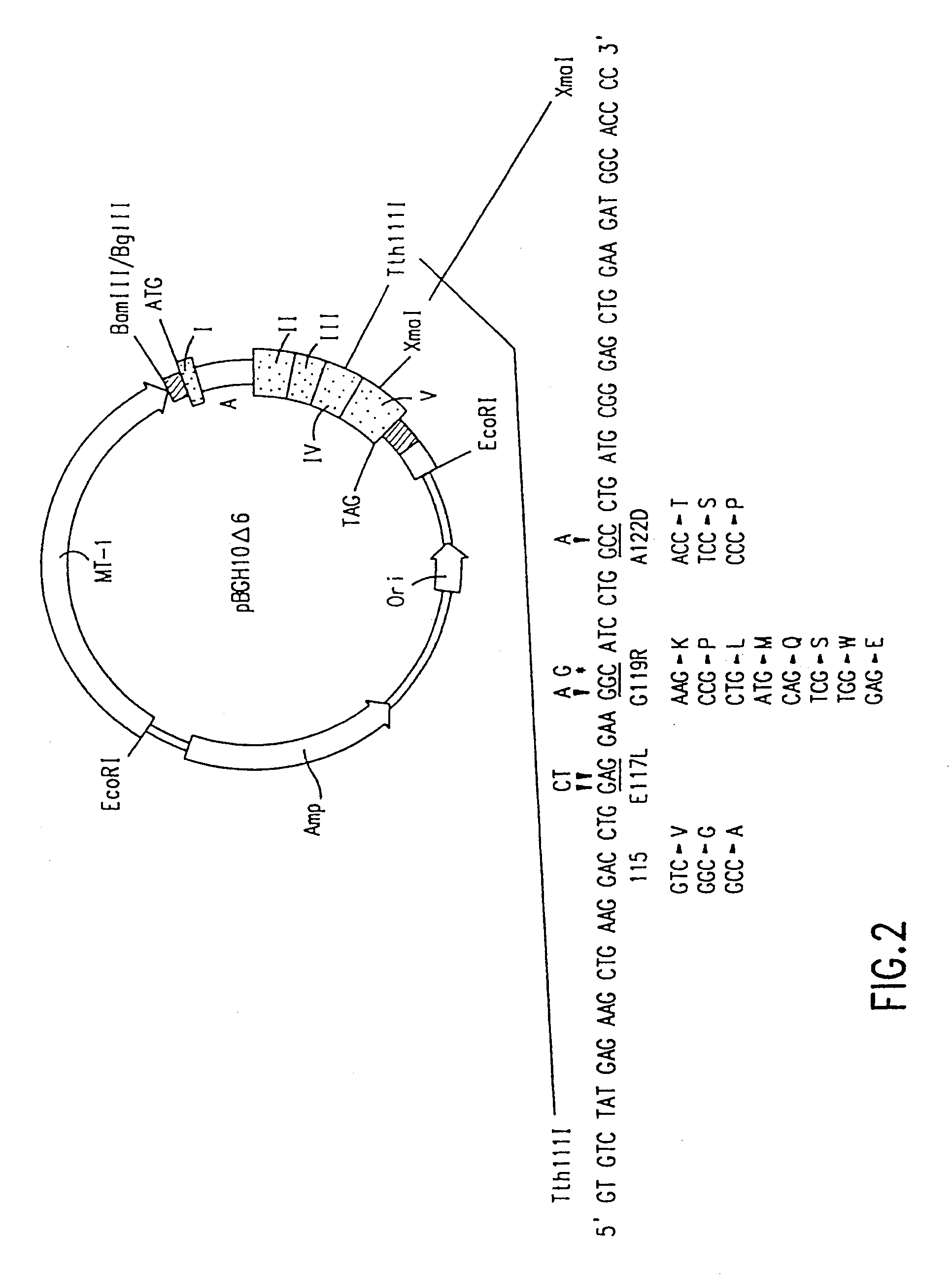
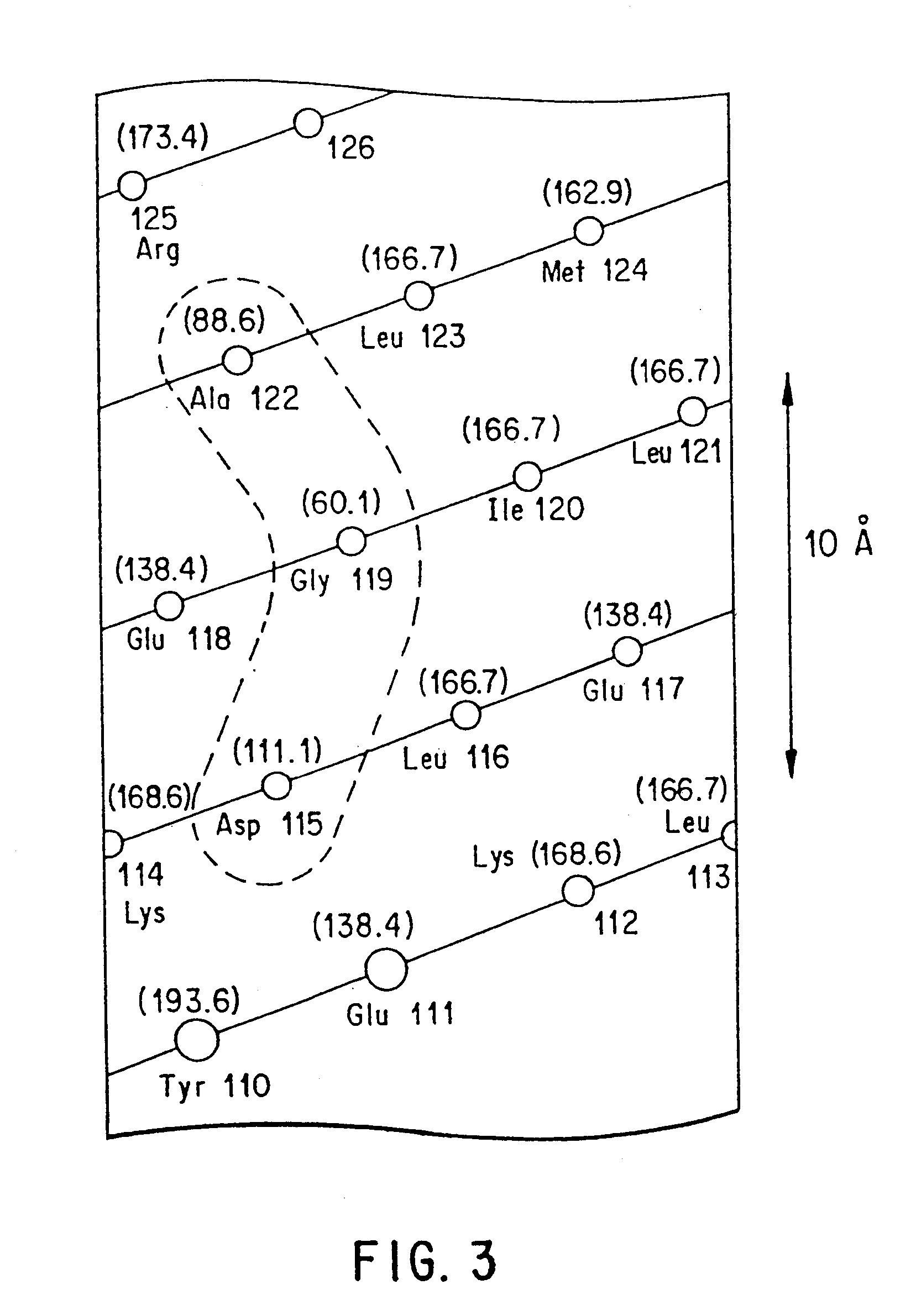
The present invention relates to antagonists of vertebrate growth hormones obtained by mutation of the third alpha helix of such proteins (especially bovine or human GHs). These mutants-have growth-inhibitory or other GH-antagonizing effects. These novel hormones may be administered exogenously to animals, or transgenic animals may be made that express the antagonist. Animals have been made which exhibited a reduced growth phenotype. The invention also describes methods of treating acromegaly, gigantism, cancer, diabetes, vascular eye diseases (diabetic retinopathy, retinopathy of prematurity, age-related macular degeneration, retinopathy of sickle-cell anemia, etc.) as well as nephropathy and other diseases, by administering an effective amount of a growth hormone antagonist. The invention also provides pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more growth hormone antagonists.
Owner:OHIO UNIV EDISON ANIMAL BIOTECH INST
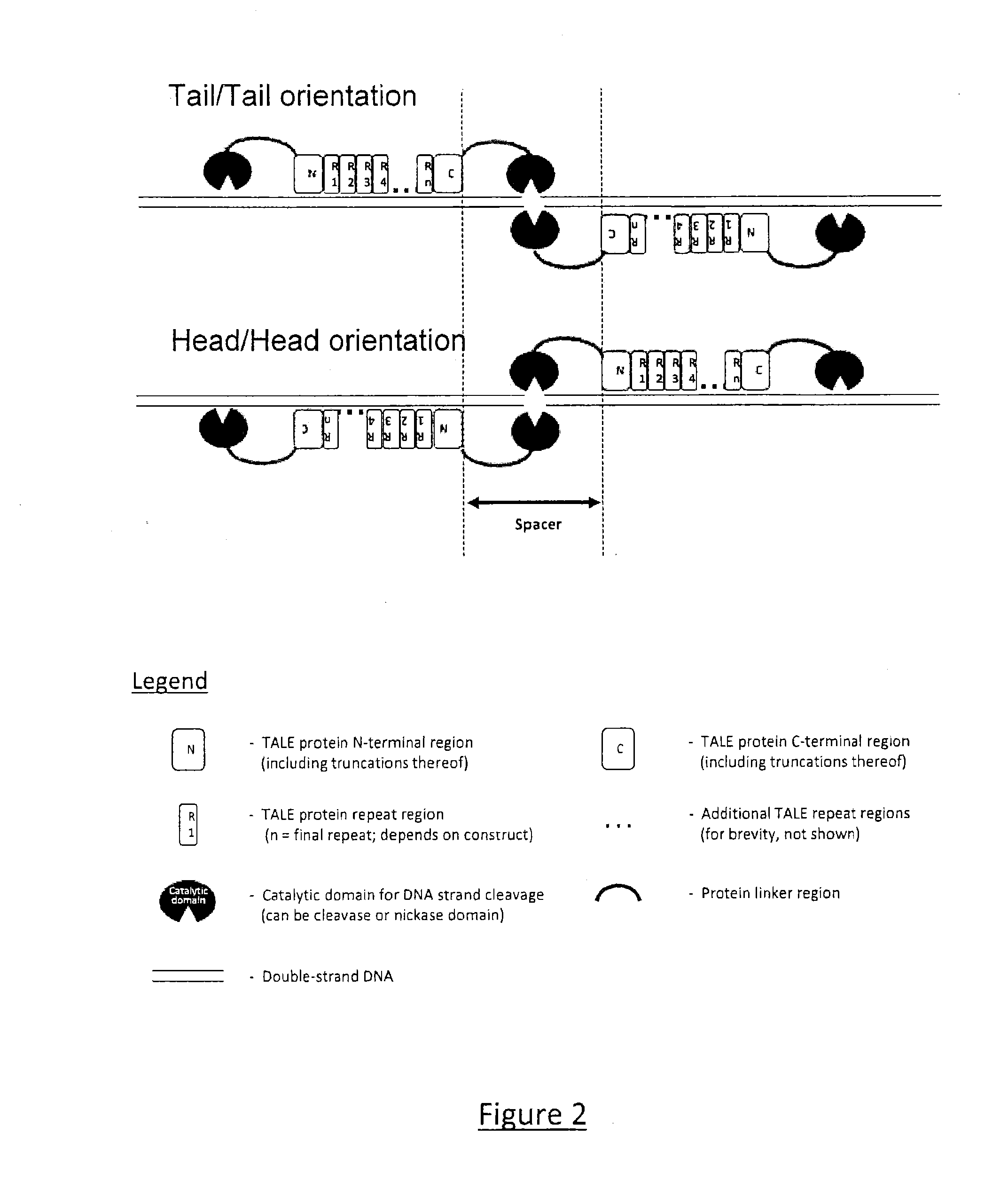
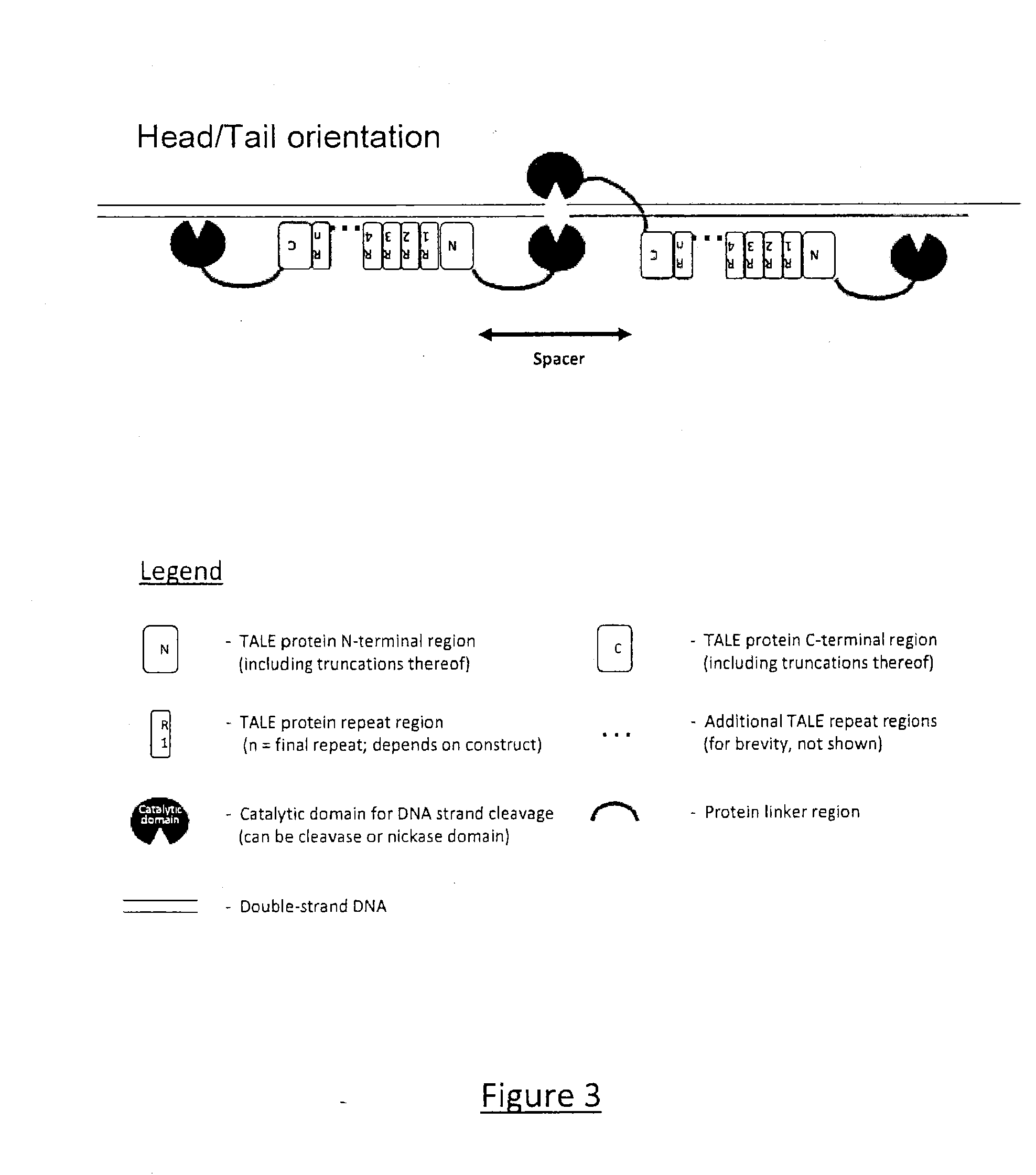
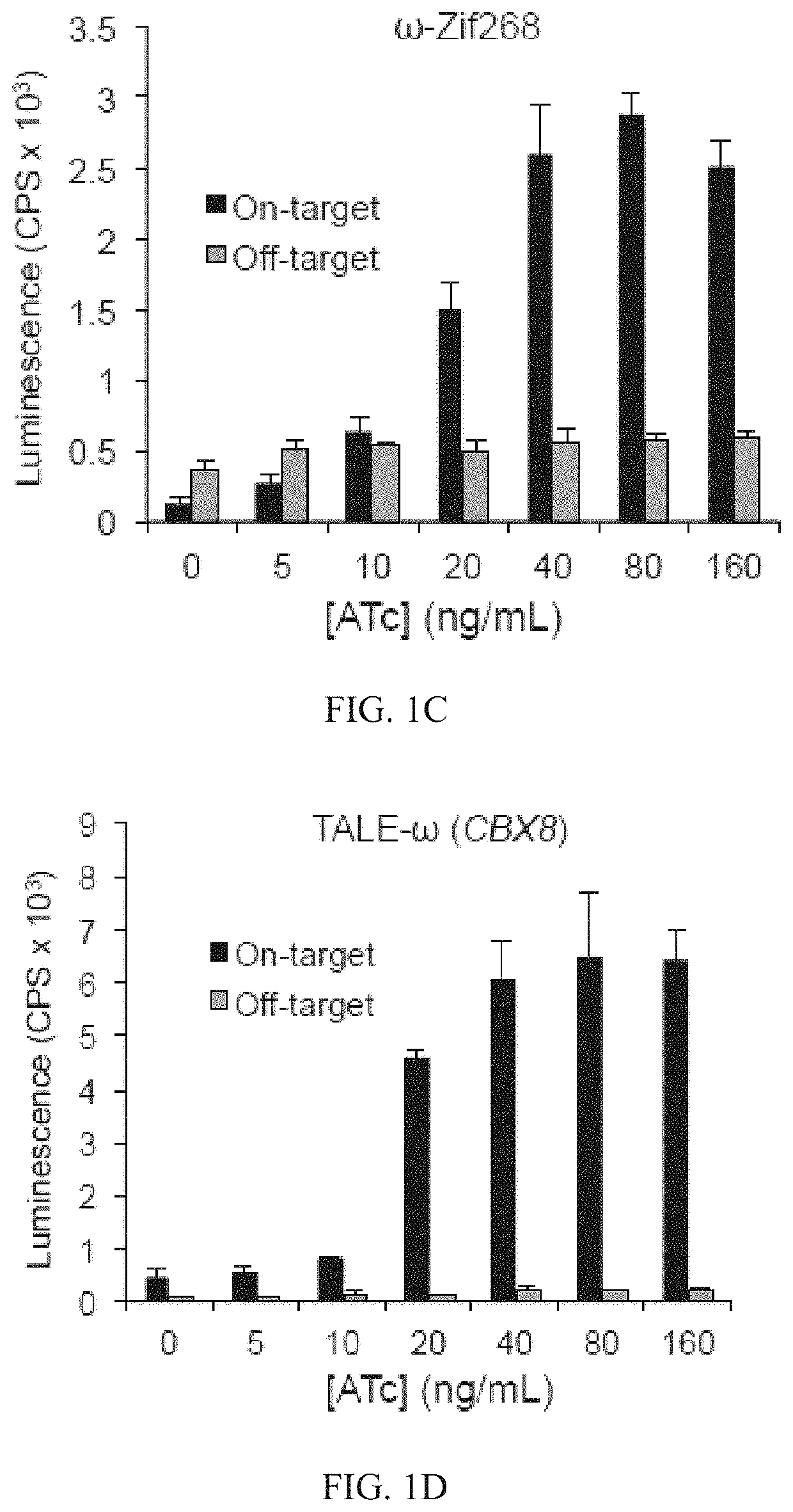
Transcription Activator-Like Effector (TALE) Fusion Protein
ActiveUS20150203871A1EfficientlyFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesDouble strandedNuclease
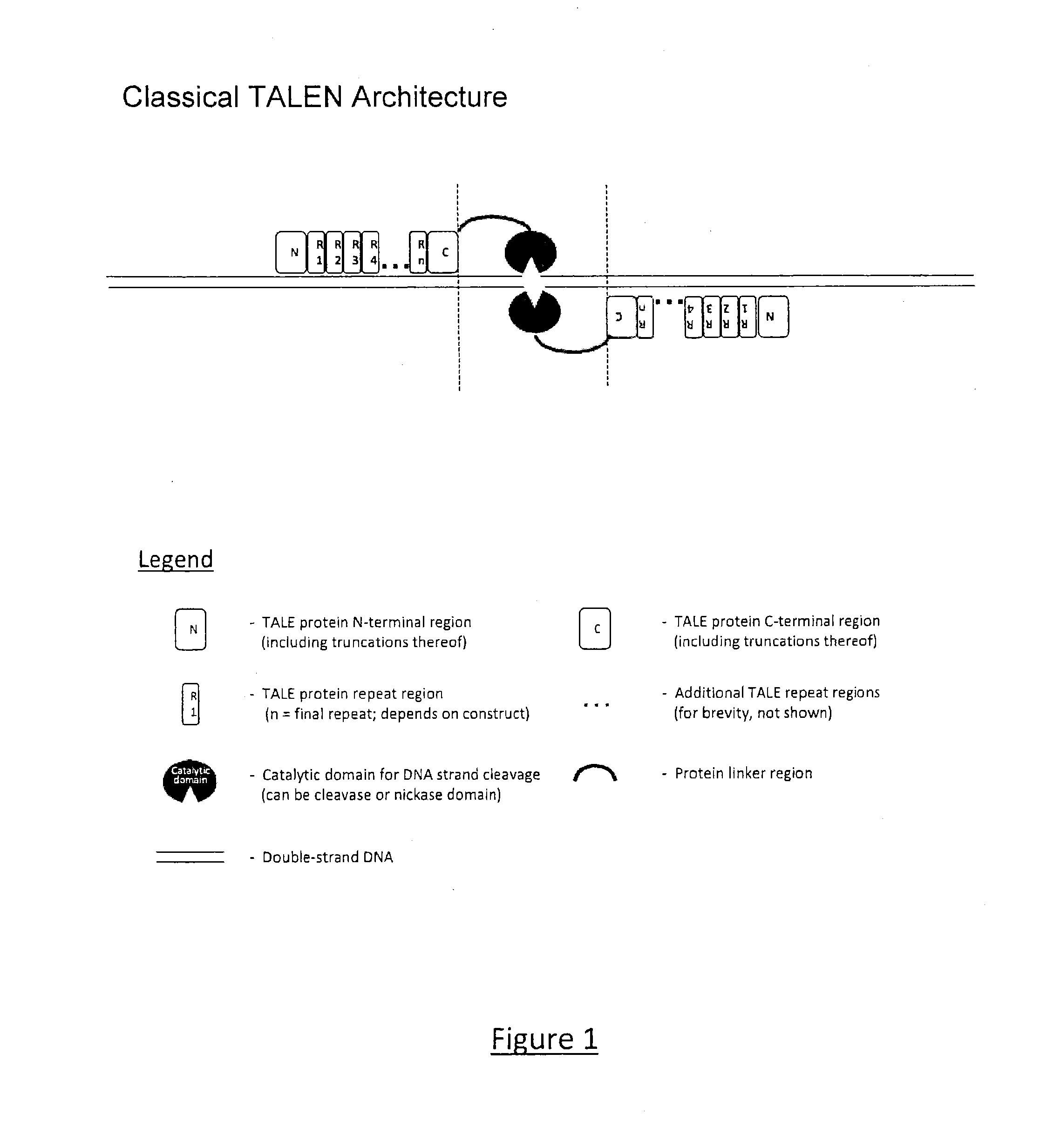
The present invention relates to Transcription Activator-Like Effector (TALE) derived proteins that allow to efficiently target and / or process double stranded nucleic acid sequences. The proteins of the invention are typically chimeric protein monomers composed of a core scaffold comprising Repeat Variable Dipeptide regions (RVDs) having binding specificity to a DNA target sequence, to which is fused a catalytic domain to its N-terminal. This later catalytic domain, which can be a monomer of a nuclease, is placed at this position to possibly interact with another catalytic domain fused to another TAL monomer, such that, when said monomers are binding to their respective target DNA sequences, both catalytic domains form a catalytic entity likely to process DNA in the proximity of these target sequences. This new TAL architecture makes it possible to target only one DNA strand, which is not the case, for instance, with classical TALEN architectures. The present invention also relates to vectors encoding such proteins and compositions or kits in which Transcription Activator-Like Effector (TALE) proteins of the present invention are used.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
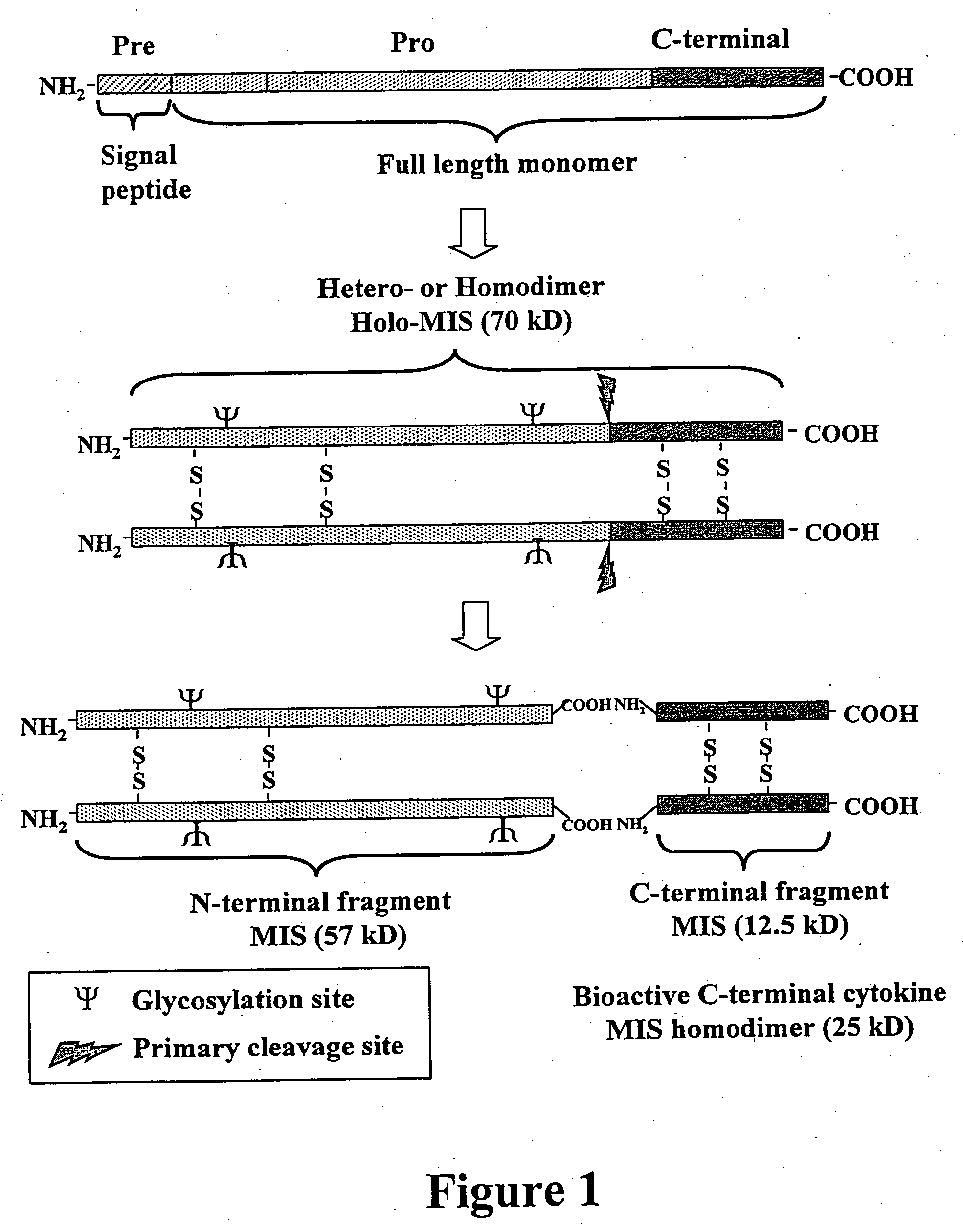
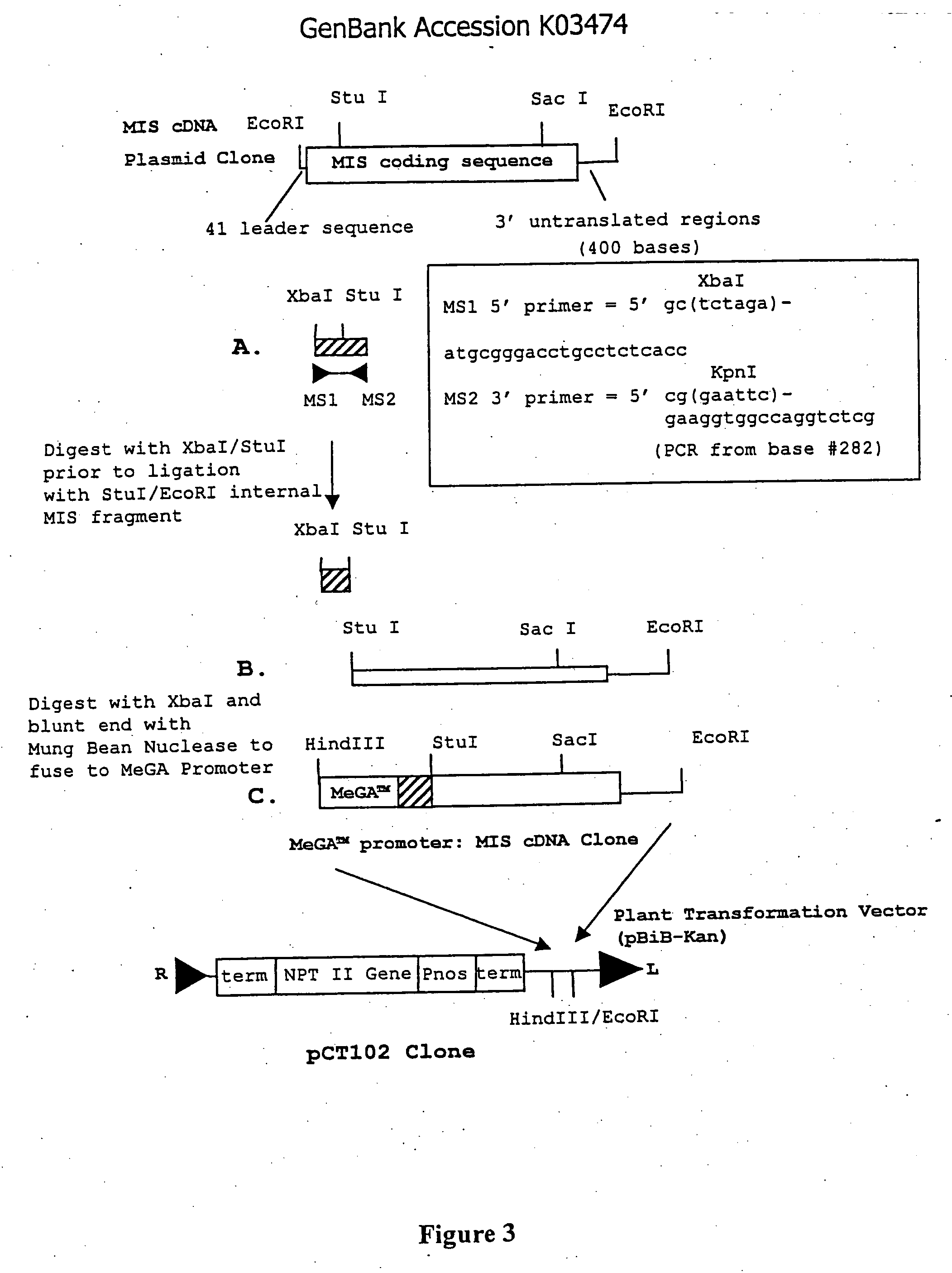
Gene expression and production of TGF-beta proteins including bioactive mullerian inhibiting substance from plants
InactiveUS20060248616A1Reduce eliminatePromote accumulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyGreek letter beta
This invention describes a novel method of producing bioactive recombinant proteins from plants. General methods of designing and engineering plants for expression and production of such proteins are also disclosed. Methods for the expression of Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) proteins, such as Müllerian Inhibiting Substance (MIS), in plants, and methods of producing recombinant proteins from plants are specifically disclosed. Furthermore, the present invention provides methodology for the direct expression and production of a bioactive C-terminal fragment of a TGF-β protein, such as C-terminal MIS. The new method is more cost-effective than other large-scale expression systems, by eliminating the need for costly cell culture and fermentation manufacturing facilities.
Owner:RADIN DAVID N +1
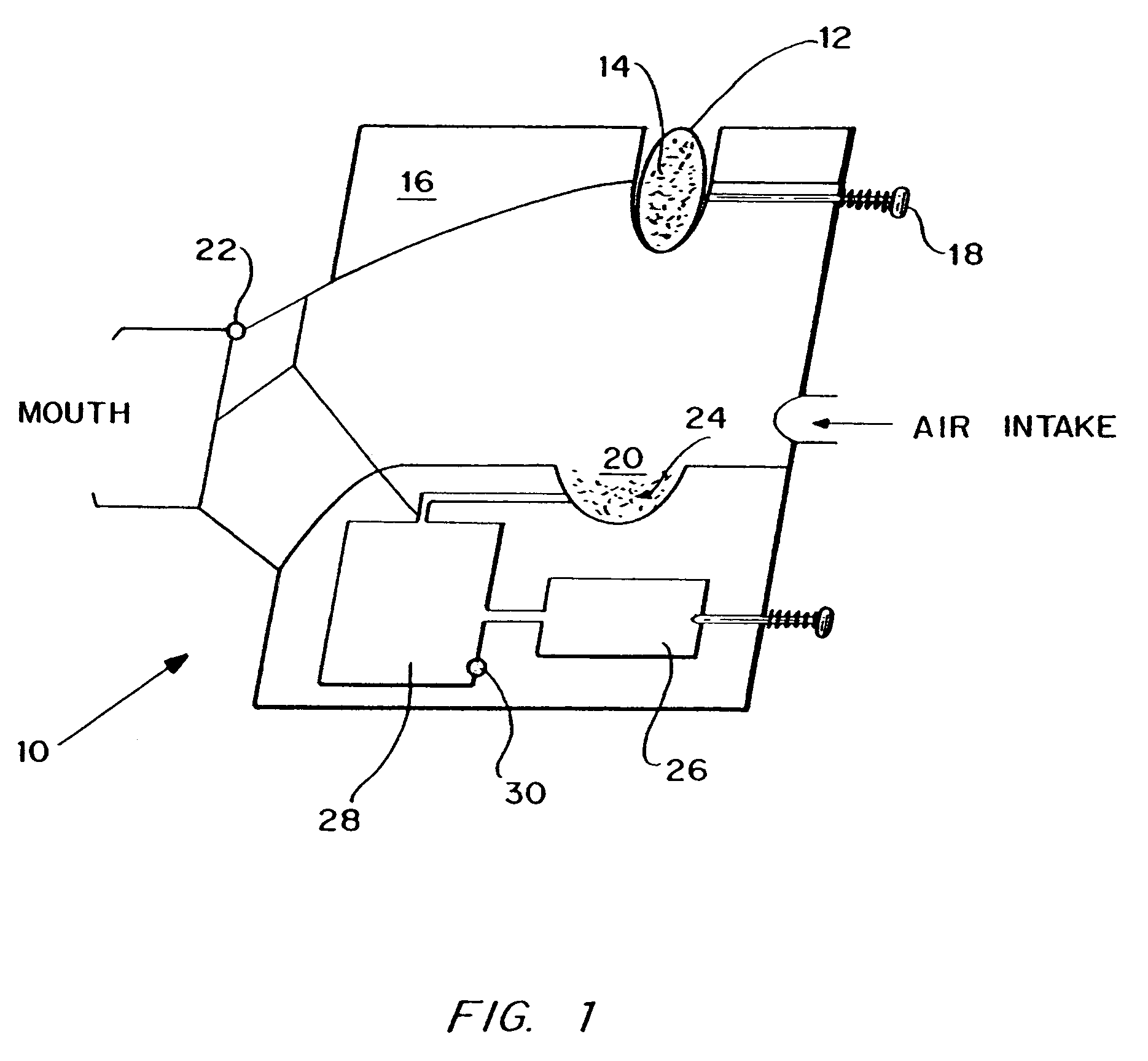
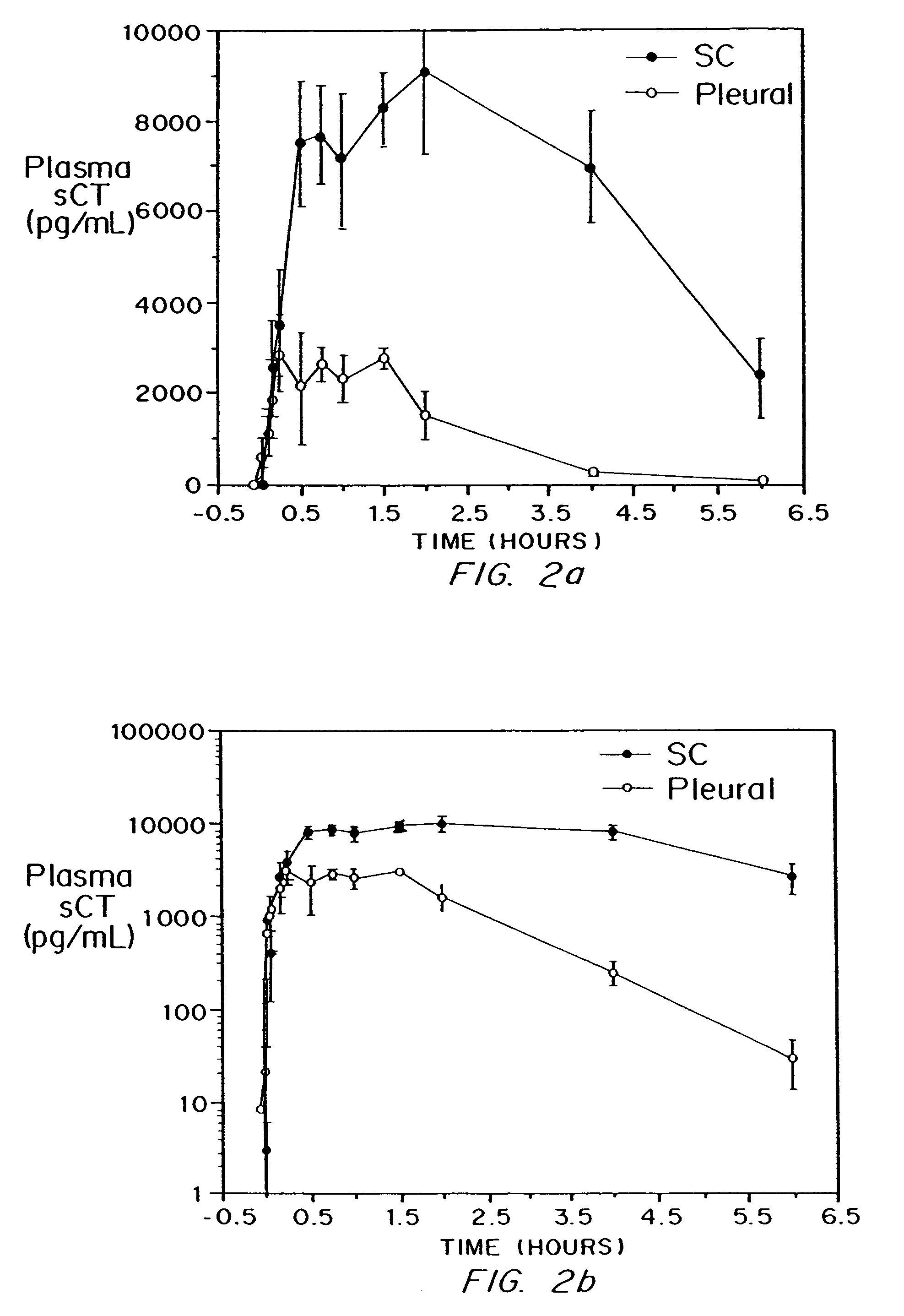
Method for drug delivery to the pulmonary system
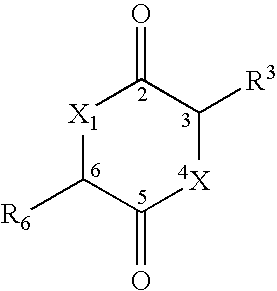
Drug delivery to the pulmonary system has been achieved by encapsulation of the drug to be delivered in microparticles having a size range between 0.5 and ten microns, preferably in the range of two to five microns, formed of a material releasing drug at a pH of greater than 6.4. In a preferred embodiment, the drug delivery system is based on the formation of diketopiperazine microparticles which are stable at a pH of 6.4 or less and unstable at pH of greater than 6.4, or which are stable at both acidic and basic pH, but which are unstable at pH between about 6.4 and 8. Other types of materials can also be used, including biodegradable natural and synthetic polymers, such as proteins, polymers of mixed amino acids (proteinoids), alginate, and poly(hydroxy acids). In another embodiment, the microparticles have been modified to effect targeting to specific cell types and to effect release only after reaching the targeted cells.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
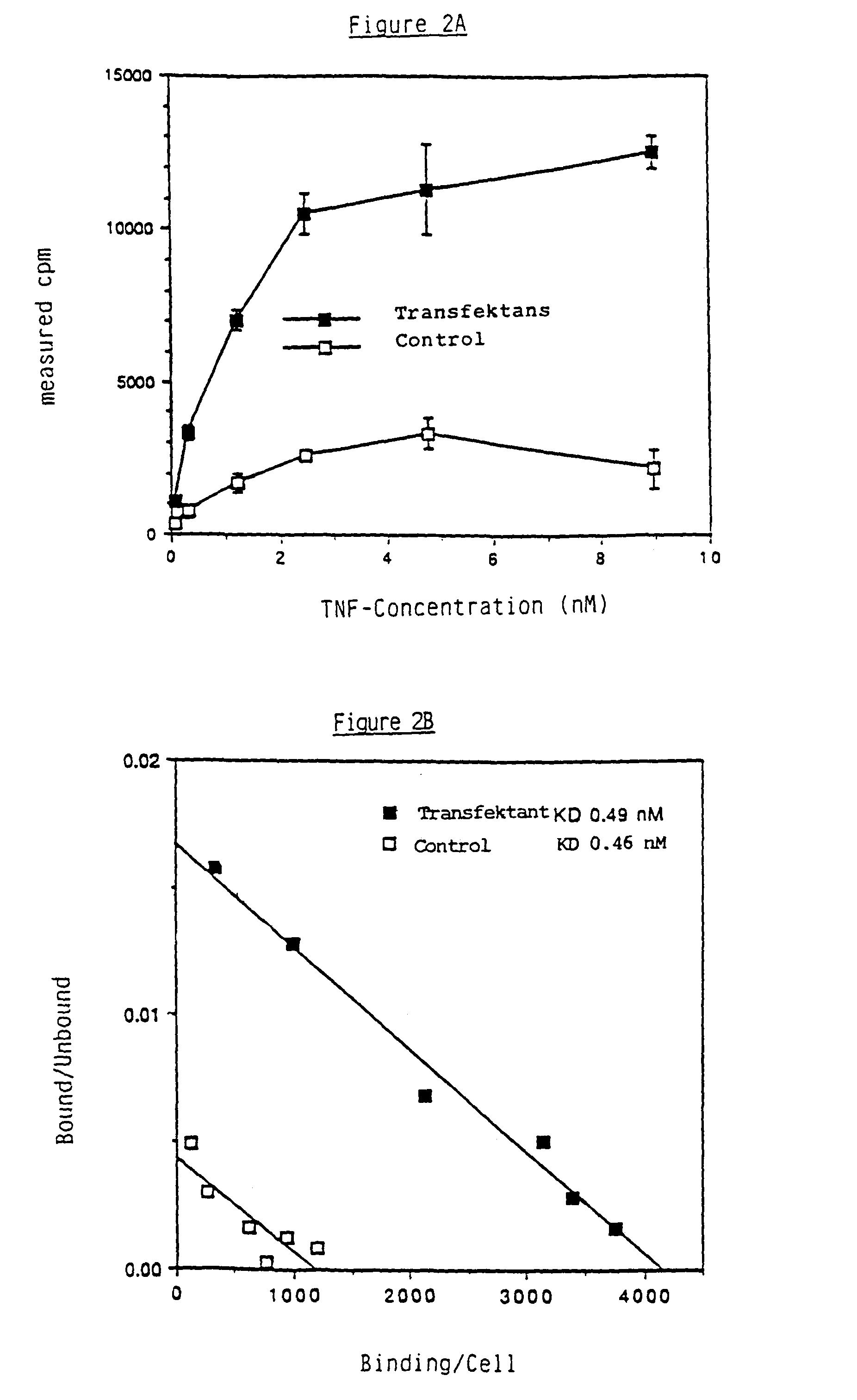
Human TNF receptor fusion protein
The present invention is concerned with non-soluble proteins and soluble or insoluble fragments thereof, which bind TNF, in homogeneous form, as well as their physiologically compatible salts, especially those proteins having a molecular weight of about 55 or 75 kD (non-reducing SDS-PAGE conditions), a process for the isolation of such proteins, antibodies against such proteins, DNA sequences which code for non-soluble proteins and soluble or non-soluble fragments thereof, which bind TNF, as well as those which code for proteins comprising partly of a soluble fragment, which binds TNF, and partly of all domains except the first of the constant region of the heavy chain of human immunoglobulins and the recombinant proteins coded thereby as well as a process for their manufacture using transformed pro- and eukaryotic host cells.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Production of high-quality protein isolates from defatted meals of Brassica seeds
The present invention provides a method for processing defatted oil seeds, comprising the steps of: (a) solubilizing at least a portion of the protein contained in the oil seeds to produce suspended residual solids and a first solution comprising protein, phenolic-protein complexes, and free phenolic compounds; (b) separating at least a portion of the free phenolic compounds from the first solution and recovering a free phenolic reduced solution; and (c) treating the free phenolic reduced solution to precipitate at least a portion of the protein as a precipitated protein isolate and recovering a treated solution containing a soluble protein isolate. Novel protein products are also disclosed. Food and drink products containing the novel protein products are also disclosed.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
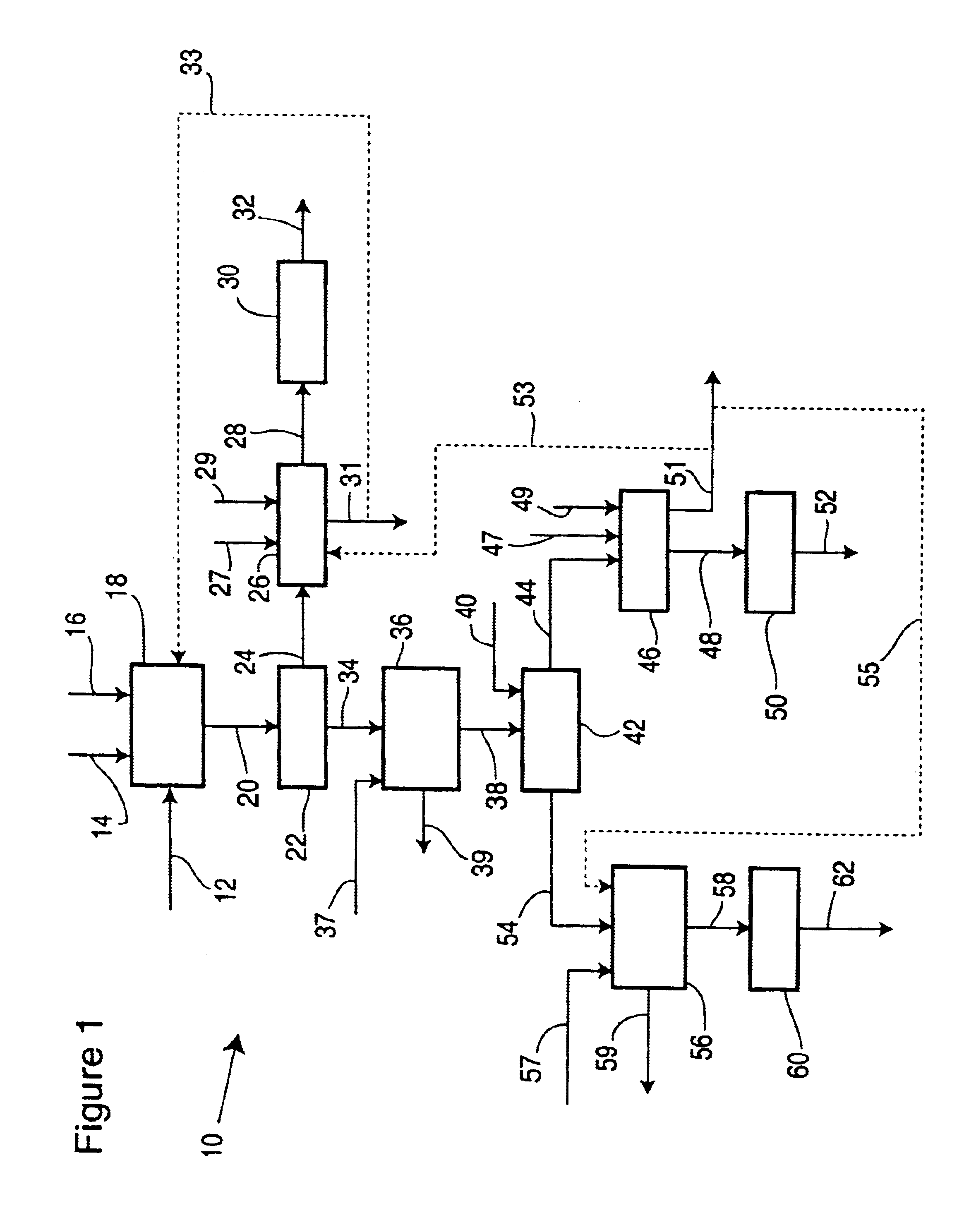
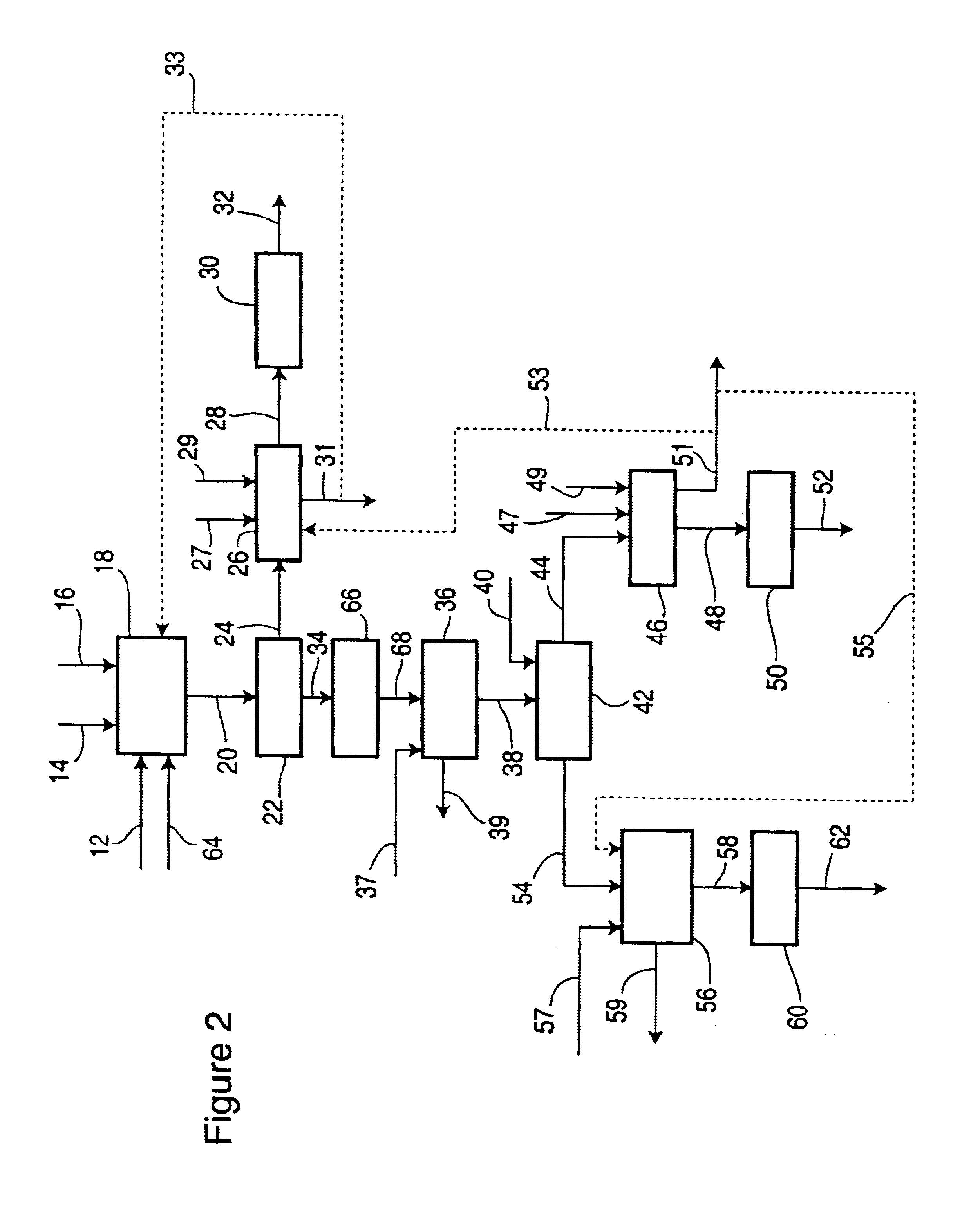
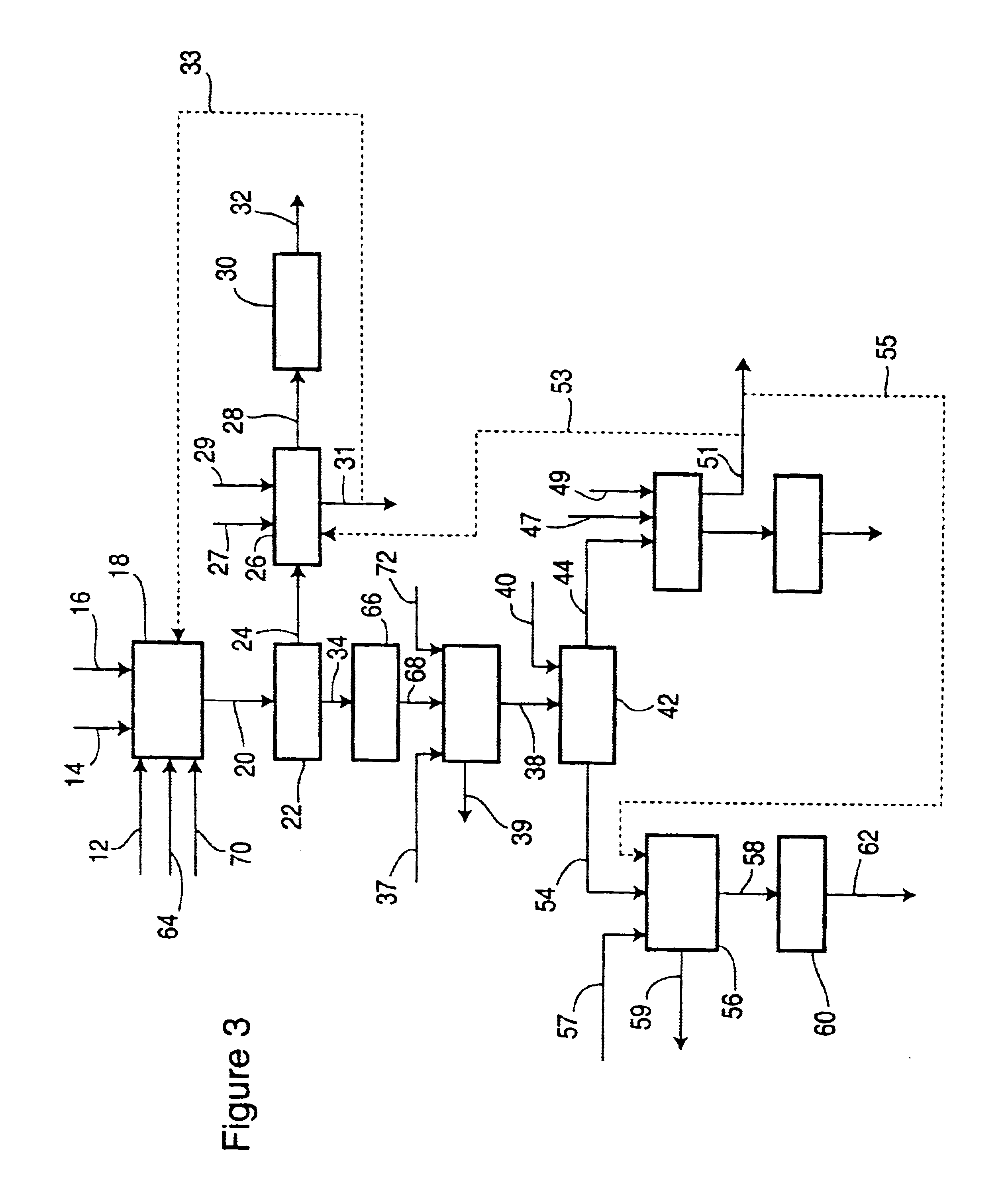
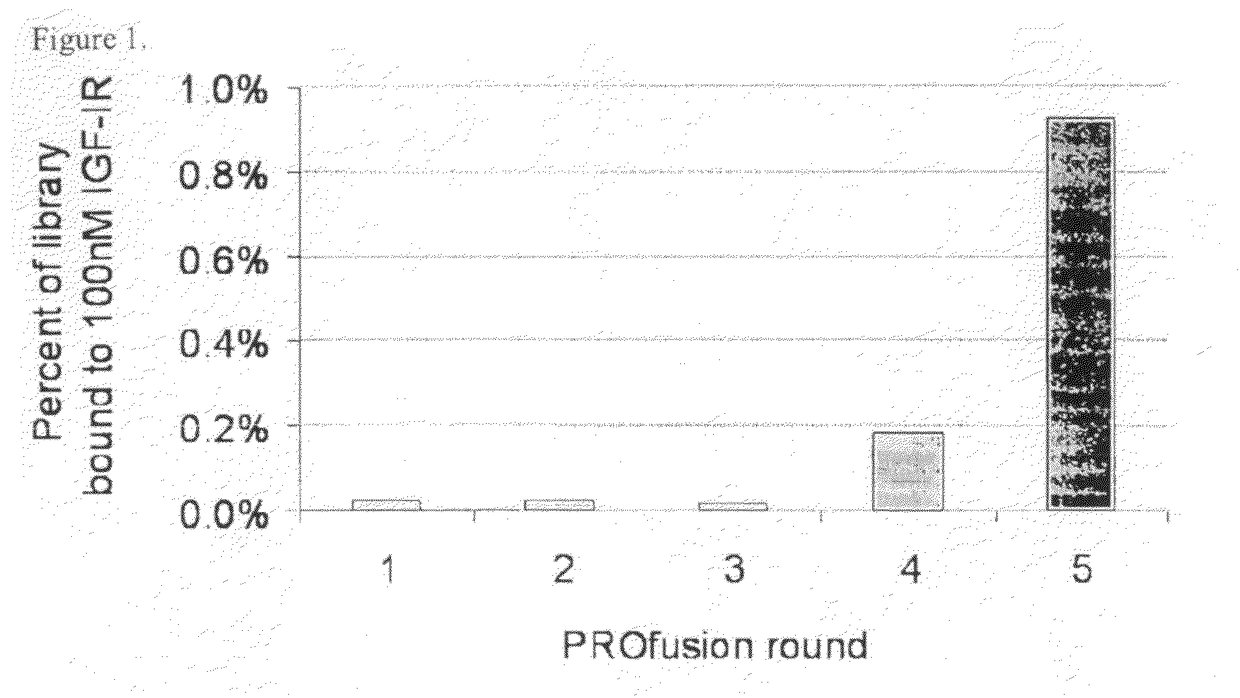
Targeted therapeutics based on engineered proteins for tyrosine kinases receptors, including IGF-IR
ActiveUS8470332B2Reduce activationDistribution morePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReceptorTyrosine
The present invention provides innovative proteins that bind to insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR), as well as other important proteins. The invention also provides innovative proteins in pharmaceutical preparations and derivatives of such proteins and the uses of same in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The invention further provides cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotide encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the innovative proteins.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Fibronectin based scaffold proteins having improved stability
ActiveUS20130184212A1Improve stabilityReduce fragmentationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsScaffold proteinProteinoid
The present application provides fibronectin based scaffold proteins associated with improved stability. The application also relates to stable formulations of fibronectin based scaffold proteins and the use thereof in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The application further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotides encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and to vectors comprising such polynucleotides.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
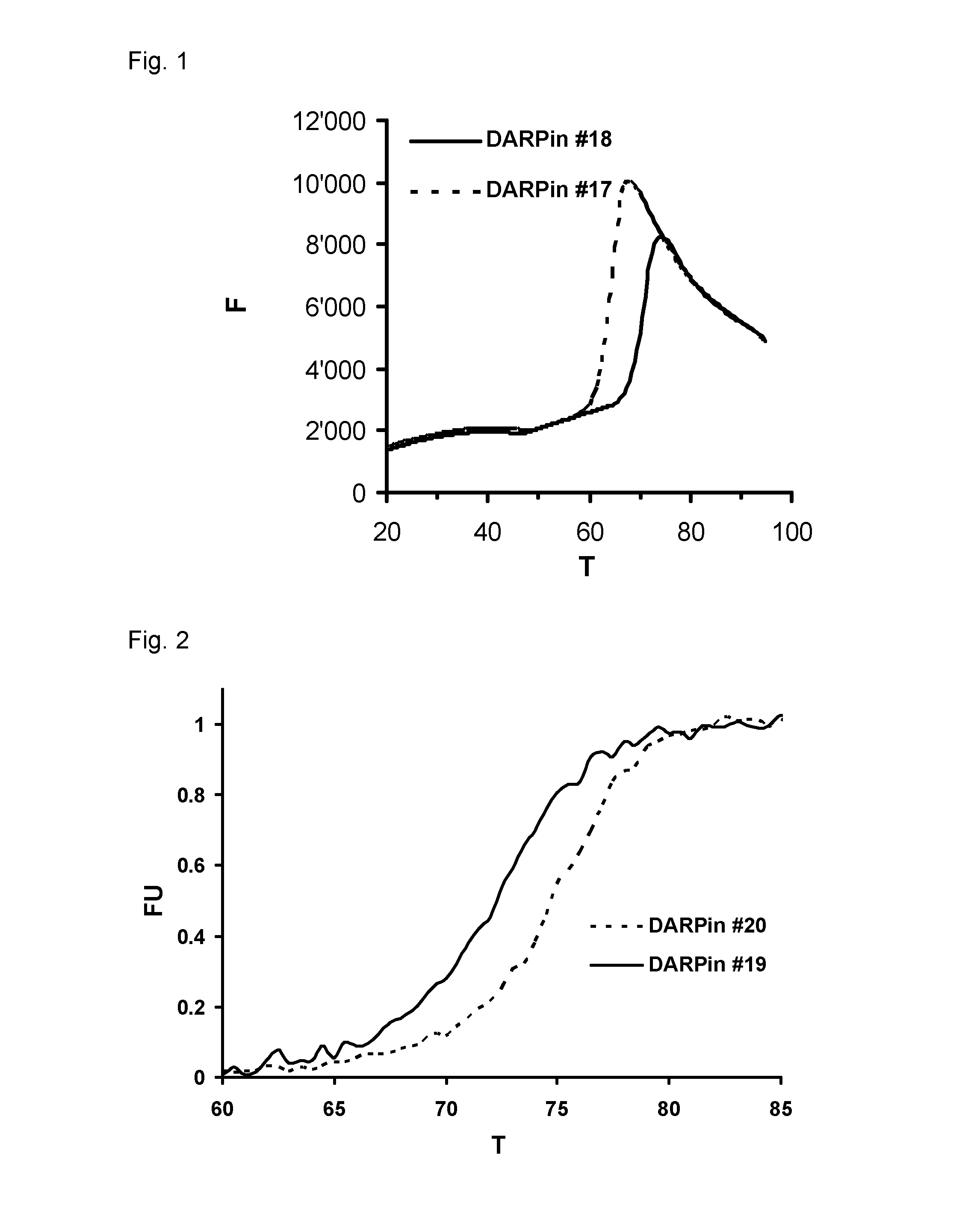
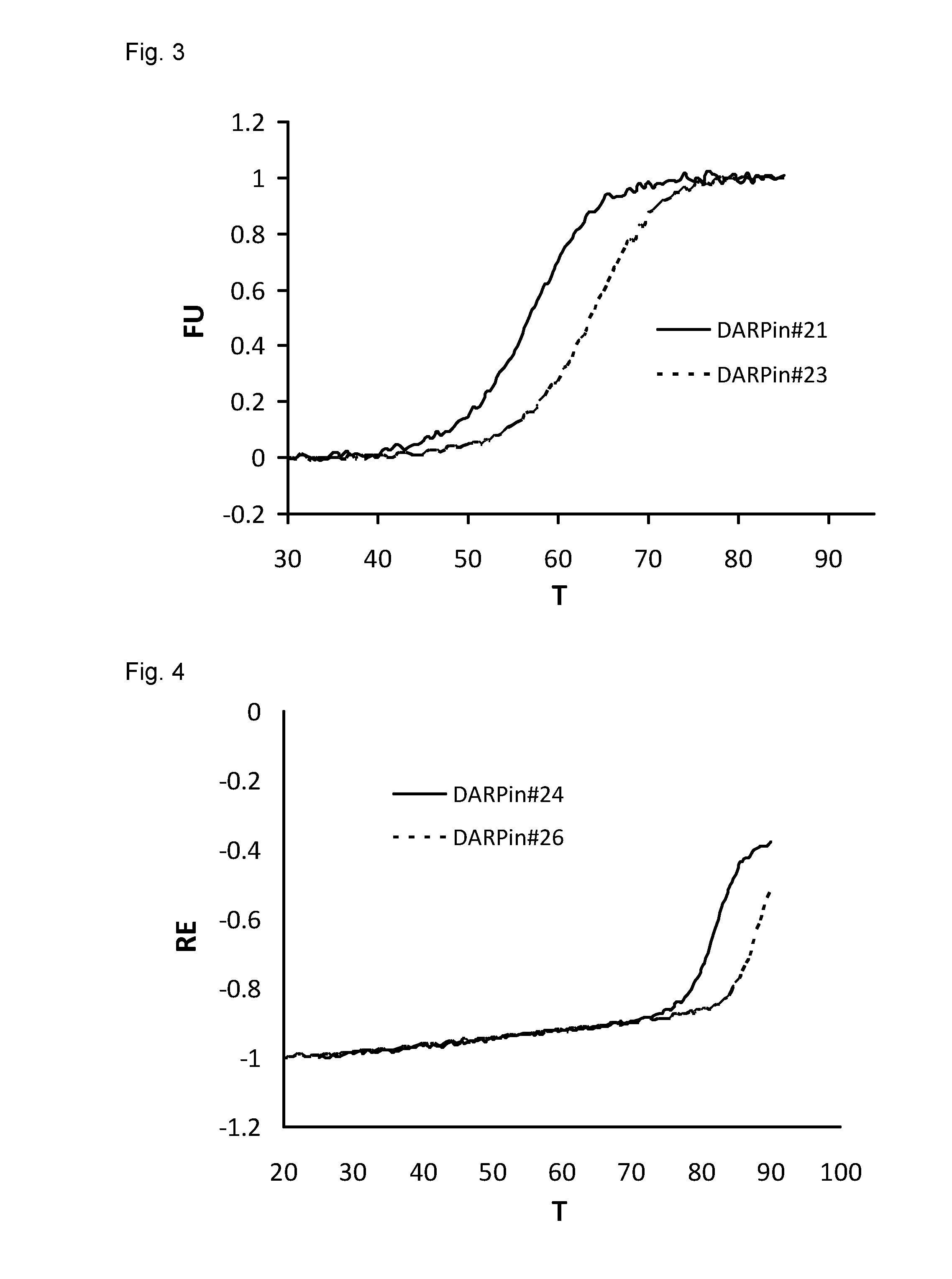
Improved capping modules for designed ankyrin repeat proteins
ActiveUS20130296221A1Improve thermal stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyDisease
Improved N-terminal capping modules for designed ankyrin repeat proteins (DARPins) conferring improved thermal stability to the DARPins are described, as well as nucleic acids encoding such proteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such proteins and the use of such proteins in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:MOLECULAR PARTNERS AG
Consumer products
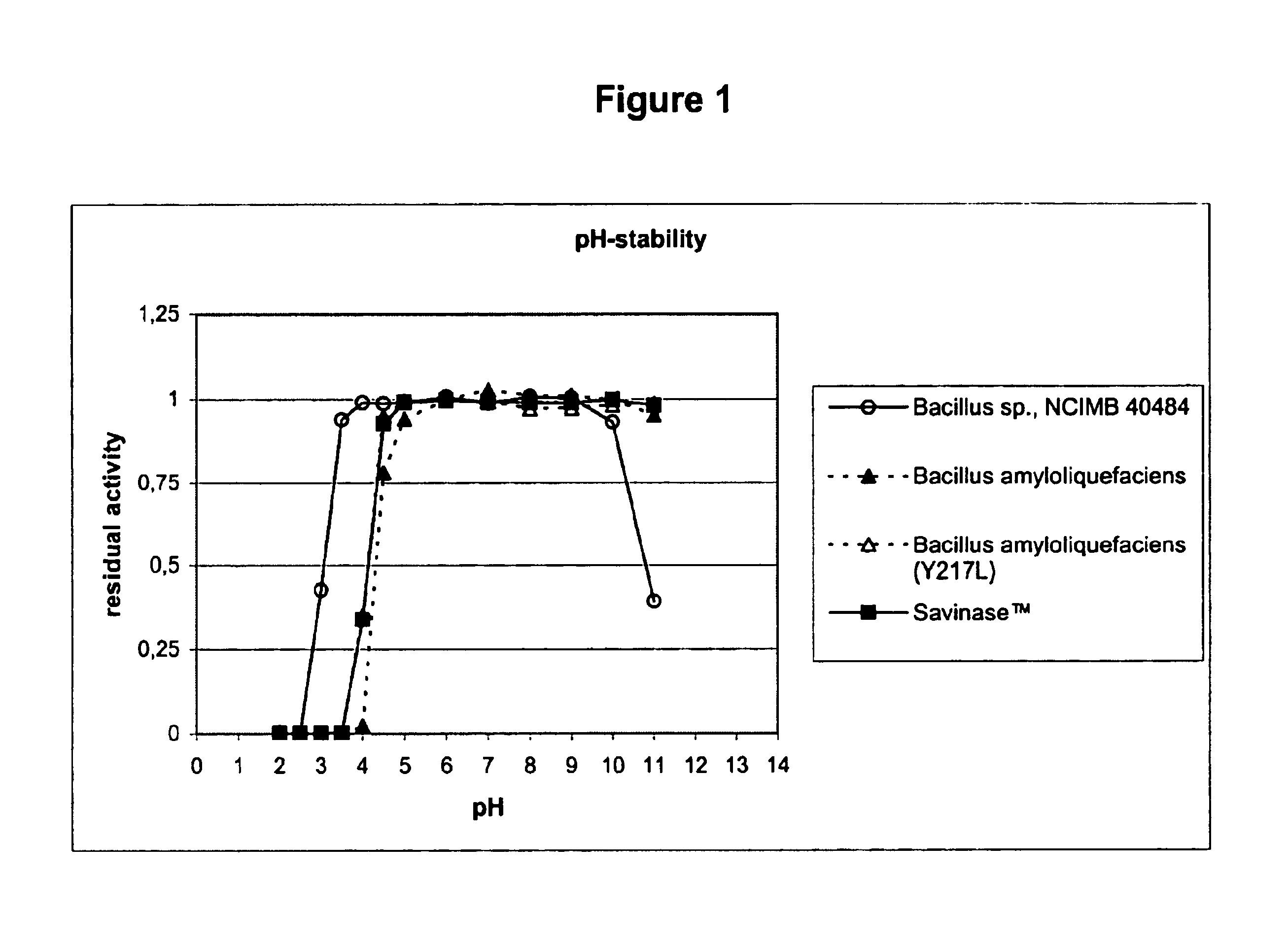
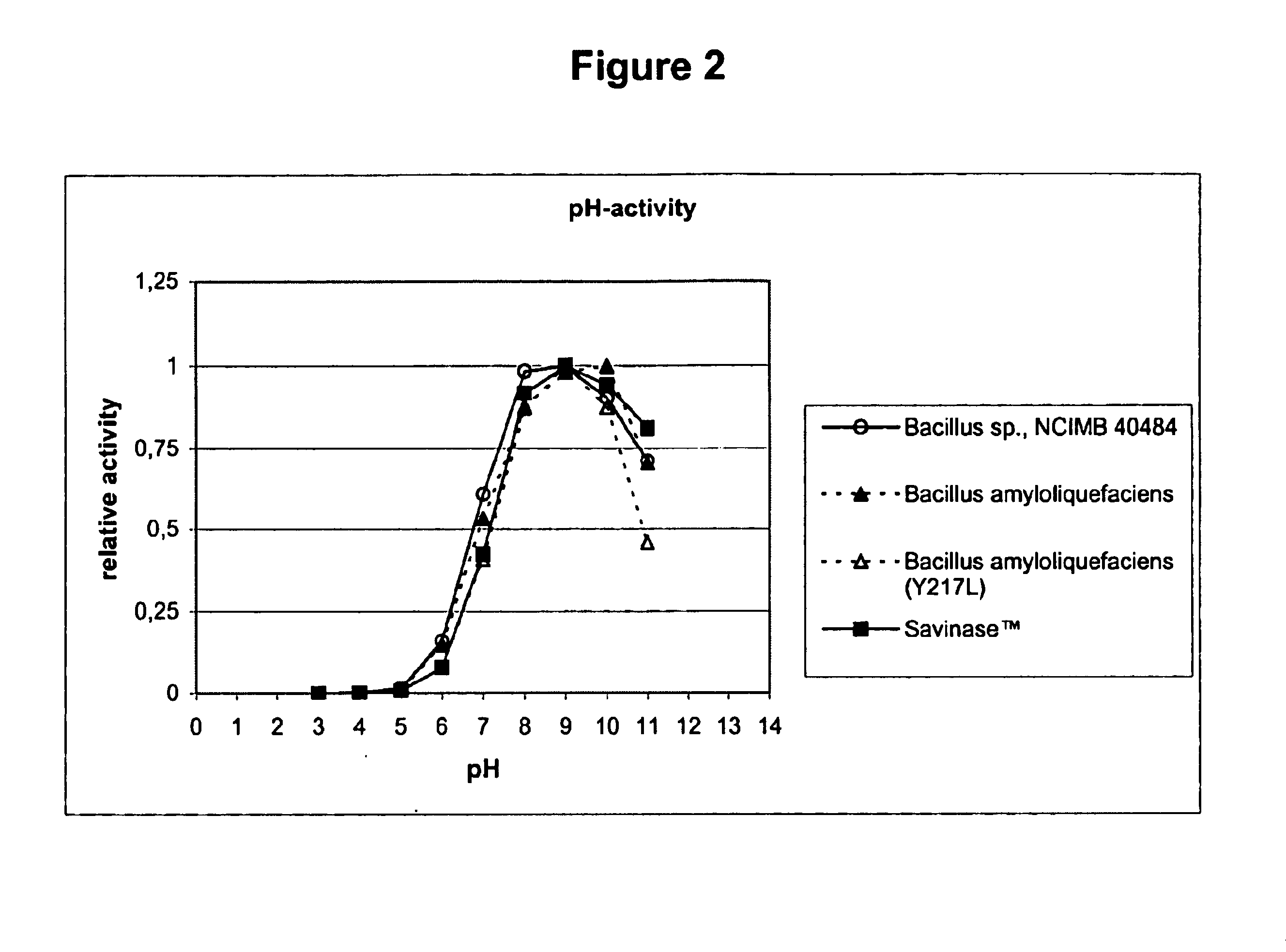
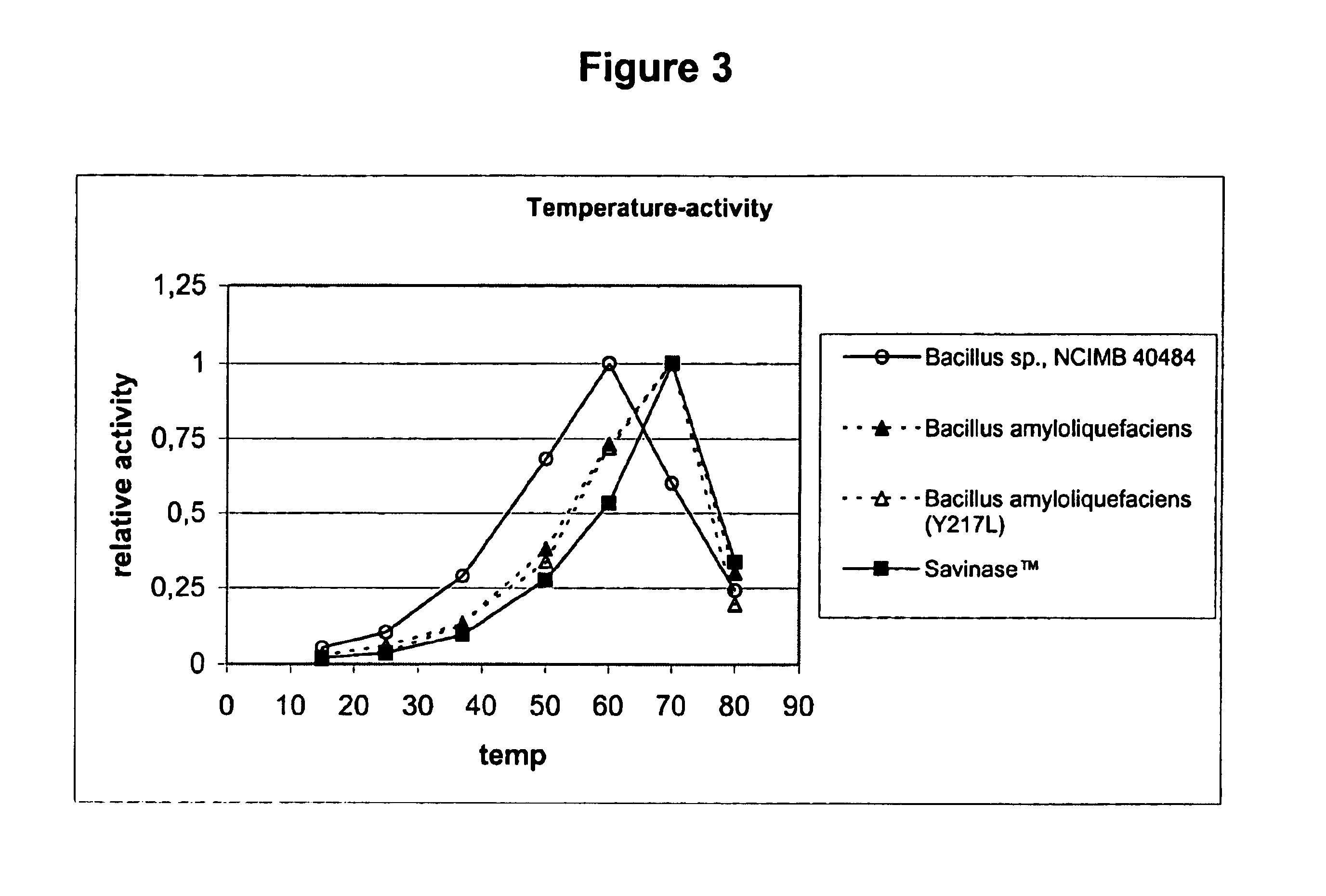
InactiveUS20130123162A1Non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent materialsBacillus lentusProteinoid
This invention relates to consumer products comprising proteases, particularly cold water proteases and processes for making and using such products. Such consumer products provide improved cleaning, whiteness and / or freshness. Such proteases are derived from a parent enzyme, for example Bacillus lentus, by substitution, insertion and / or deletion of one or more of the parent enzymes' amino acids.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
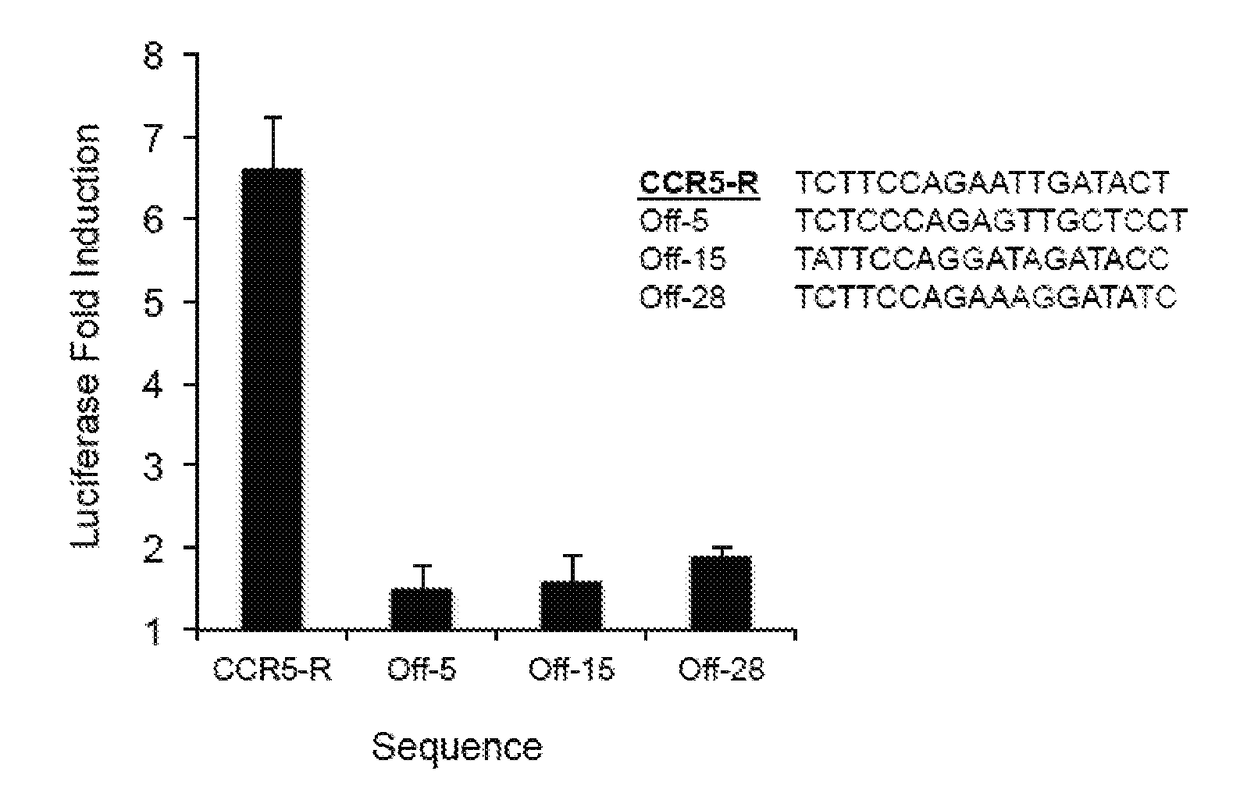
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20200277587A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. Another drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
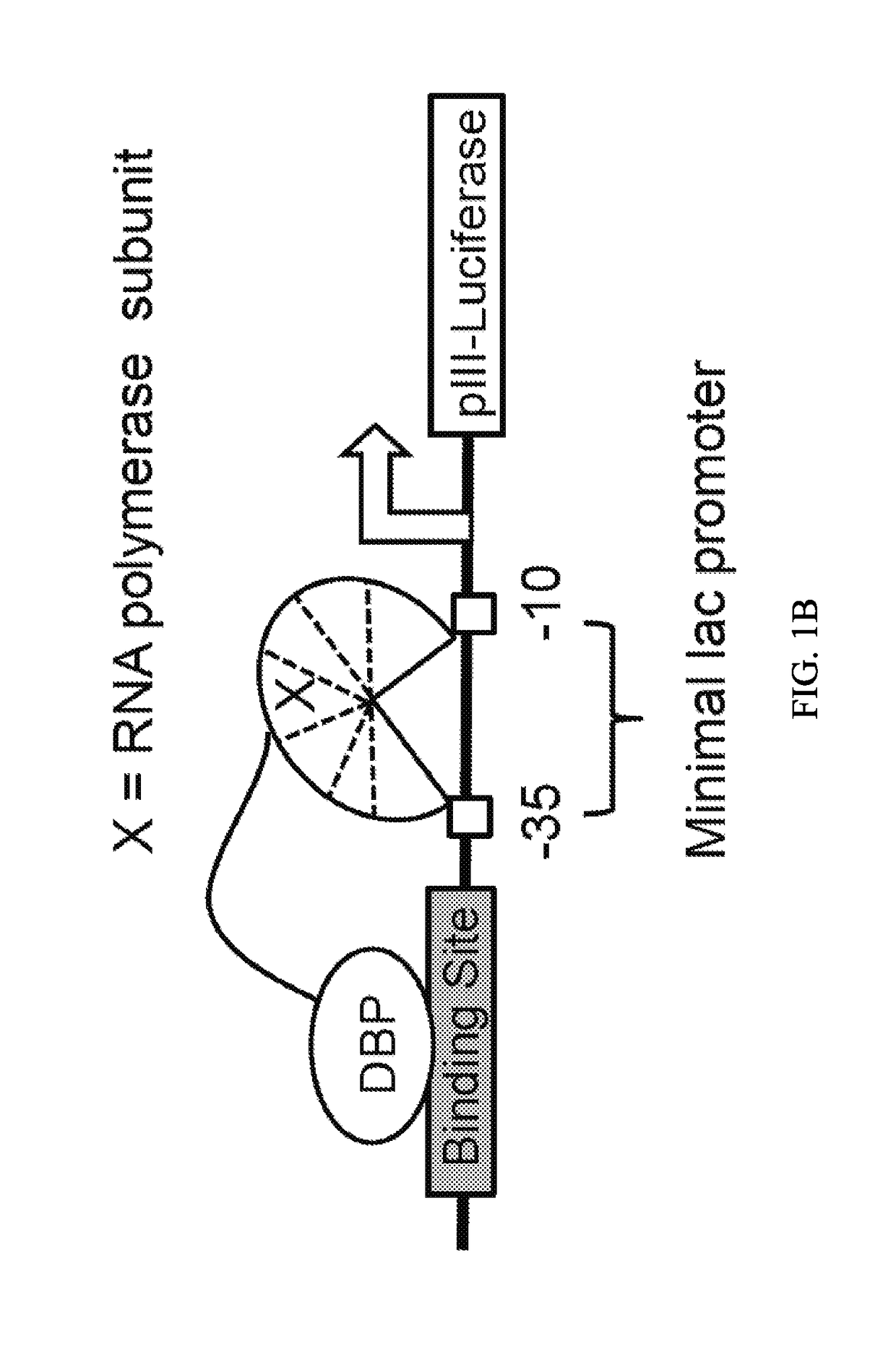
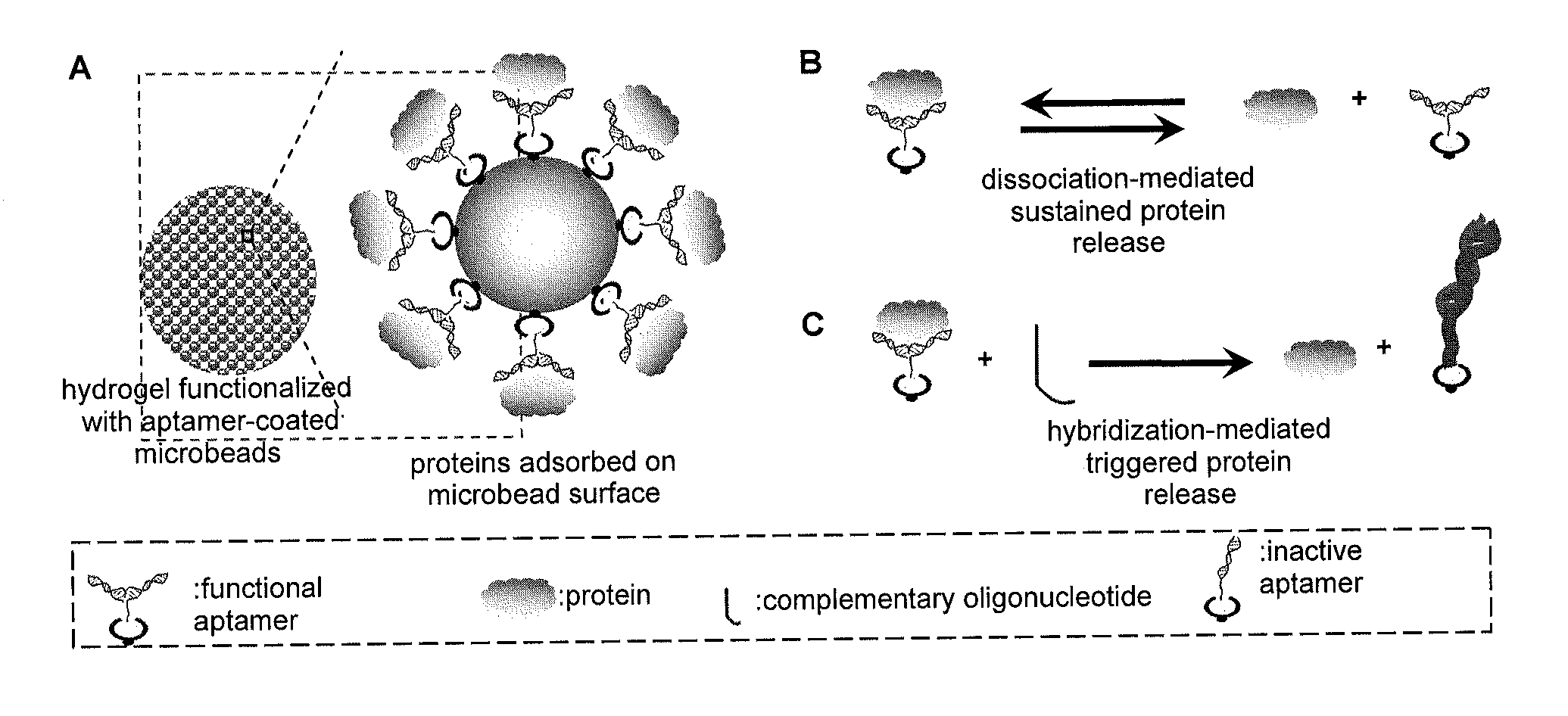
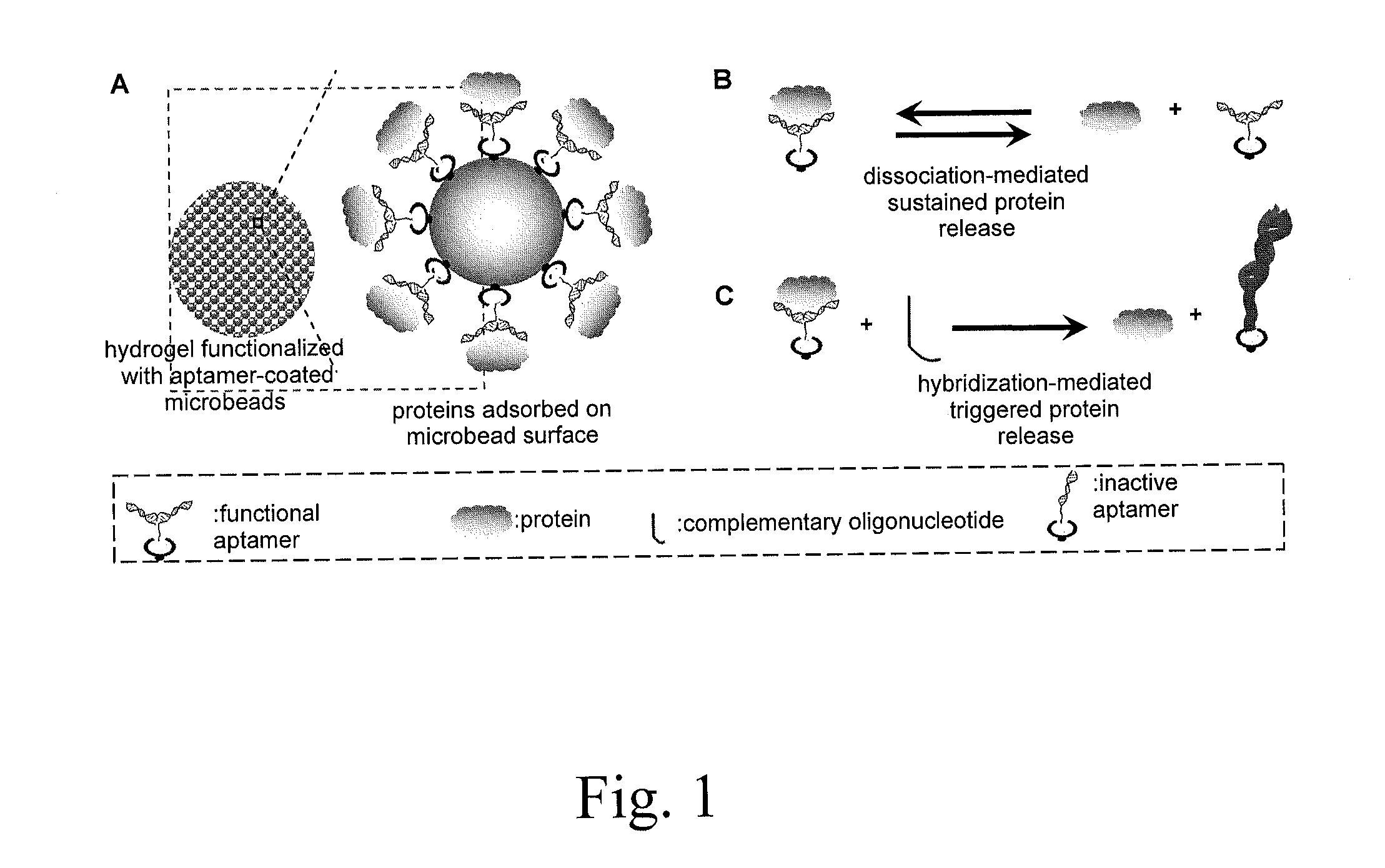
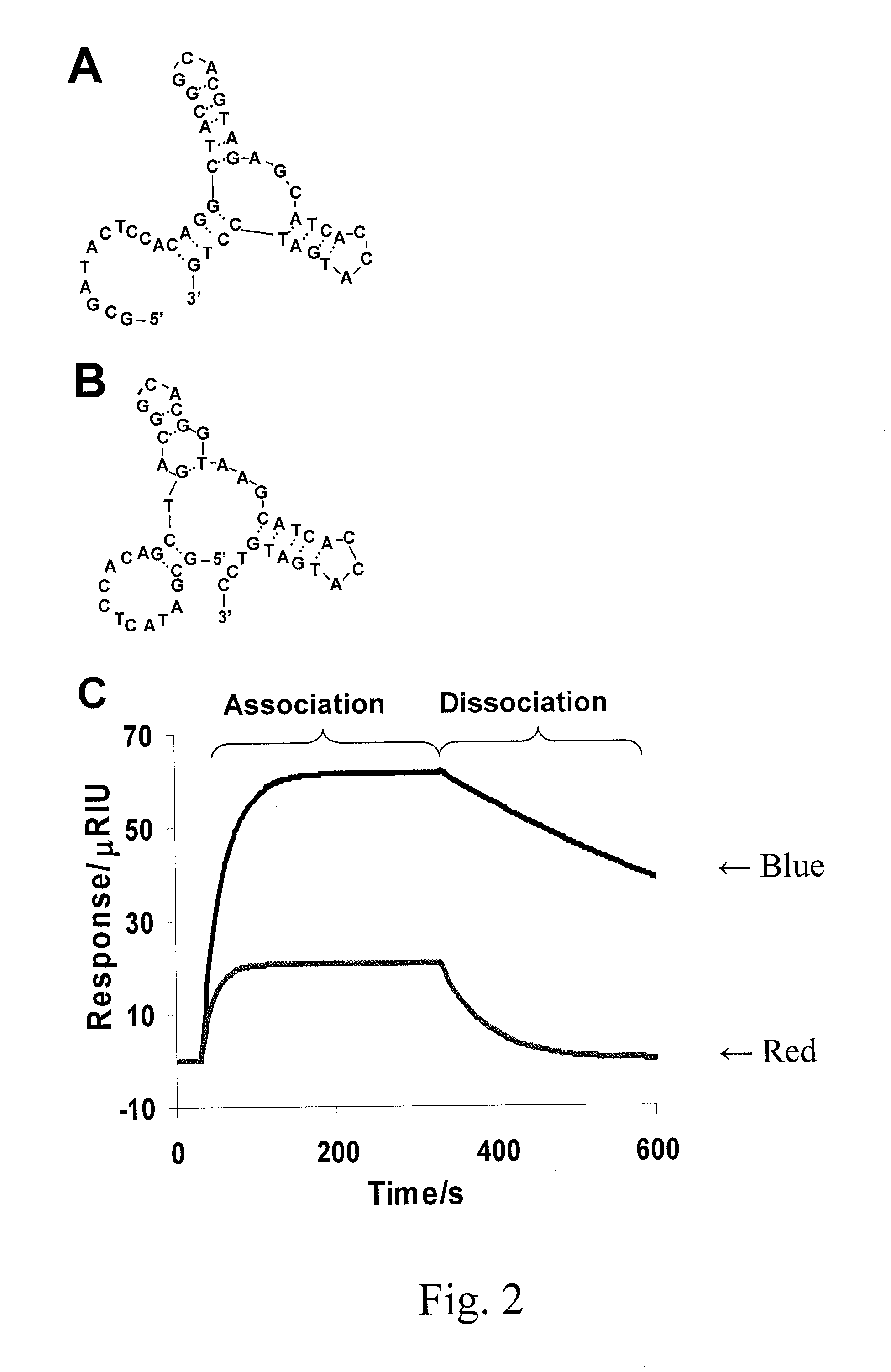
Affinity hydrogels for controlled protein release
InactiveUS20130196915A1High binding affinityStrong specificityPowder deliverySaccharide peptide ingredientsDiseaseControl release
The present invention relates to novel porous matrix composites and formulations for controlled protein delivery and the uses therefor. The present invention also provides methods of synthesizing such protein delivery systems. The composites comprise affinity sites embedded in the matrix where the affinity sites are functionalized with nucleic acid aptamers having high affinity for proteins to be released. The aptamers function as binding affinity sites for the proteins to be released. In certain embodiments, release rates are controlled by tuning the binding affinity of the nucleic acid aptamers to the proteins at a desired level. In yet other embodiments, complementary oligonucleotides that hybridize with the aptamers are employed to trigger accelerated release of the proteins when desired. Various in situ injectable hydro gels functionalized with aptamers are provided for treating a condition and disease in a subject in need of a therapeutic protein.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Nucleic acid and corresponding protein entitled 161P2F10B useful in treatment and detection of cancer
InactiveUS20030165505A1Quick filterOvercome difficultiesHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsSpecific proteinDisease
A protein obtainable from a non pathogenic microorganism, said protein having mucosa binding promoting activity and a molecular weight of 20-40 kD is disclosed. Application of such a protein or a peptide derived therefrom in a method of screening non pathogenic microorganisms for a microorganism capable of specifically binding mucosa, said method comprising detection in a manner known per se of the presence of a particular protein on or in a microorganism or in a culture of microorganisms, said particular protein being the already defined protein. Kits suitable for such a screening method are also disclosed. Use of a component selected from the group of components comprising a protein or peptide as defined an expression vector comprising nucleic acid encoding such protein or peptide a recombinant microorganism or a part of said microorganism expressing such protein or peptide, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity a non pathogenic microorganism capable of expressing such protein or peptide or a part of said microorganism, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity as pharmaceutically active component in a pharmaceutical composition for prophylaxis and / or treatment of disease or illness associated with a mucosa colonising pathogenic microorganism. Use of such components as food additive and compositions comprising such components are described.
Owner:AGENSYS
Expression cloning processes for the discovery characterization, and isolation of genes encoding polypeptides with a predetermined property
InactiveUS6197502B1Protein production is suppressedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteRapid identification
The present invention is directed to a method for detection, characterization and isolation of nucleic acids encoding proteins of a desired property, such as a particular cellular localization. The invention further provides for rapid expression of such proteins or glycoproteins in mammalian cells and for facilitated purification of the novel secreted proteins or glycoproteins. Further, the invention provides for radioactive labelling of the novel proteins or glycoproteins, for rapid identification of sites of binding including animals and for rapid production of infective viral vectors for use in gene transfer.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
Evolution of TALENs
ActiveUS10612011B2Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Designed ankyrin repeat proteins binding to platelet-derived growth factor
New designed ankyrin repeat proteins with binding specificity for PDGF-BB are described, as well as nucleic acids encoding such PDGF binding proteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such proteins and the use of such proteins in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:MOLECULAR PARTNERS AG
Use of acid-stable subtilisin proteases in animal feed
Acid-stable proteases of the subtilisin family, their use in animal feed, feed-additives and feed compositions containing such proteases, and methods for the treatment of vegetable proteins using such proteases.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Adherence factors of non pathogenic microorganisms and applications thereof for screening microorganisms for specific probiotic properties; novel pharmaceutical compositions and food additives comprising such microorganisms and adherence factors
A protein obtainable from a non pathgenic microorgansim, said protein having mucosa binding promoting activity and a molecular weight of 20-40 kD is disclosed. Application of such a protein or a peptide derived therefrom in a method of screening non pathogenic microorganisms for a microorganism capable of specifically binding mucosa, said method comprising detection in a manner known per se of the presence of a particular protein on or in a microorganism or in a culture of microorganisms, said particular protein being the already defined protein. Kits suitable for such a screening method are also disclosed. Use of a component selected from the group of components comprising a protein or peptide as defined; an expression vector comprising nucleic acid encoding such protein or peptide; a recombinant microorganism or a part of said microorganism expressing such protein or peptide, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity; a non pathogenic microorganism capable of expressing such protein or peptide or a part of said microorganism, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity as pharmaceutically active component in a pharmaceutical composition for prophylaxis and / or treatment of disease or illness associated with a mucosa colonizing pathogenic microorganism. Use of such components as food additive and compositions comprising such components are described.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Anchovy enzymolysis protein flavouring liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101385526AEasy to operateDelicious and richAnimal proteins working-upFood preparationBiotechnologyNutritive values
The present invention relates to an anchovy enzymatic protein seasoning liquid and a preparation method thereof. Fresh or frozen and unfrozen anchovy is used as a raw material. Papain, compound protease and flavor enzyme are combined as compound enzyme to be hydrolyzed as short peptide protein liquid. After anchovy protein enzymatic hydrolysate is processed for killing enzyme, residue and liquid are separated to obtain hydrolysate solution; active carbon with the weight of 1 percent to 3 percent of the weight of the hydrolysate solution is added for filtering; 0.5 percent to 1 percent of beta-cyclic dextrin is added for debitterizing; the solution is condensed to 1 / 2 to 1 / 3 of the original volume after centrifugal filtration; colorant with the weight of 0.05 percent to 0.2 percent of the weight of the condensed anchovy protein enzymatic hydrolysate, 0.05 percent to 0.2 percent of emulsifier and 5 percent to 25 percent of seasoning are added for homogenizing and seasoning. The seasoning liquid preserves all nutrient contents and functional factors of anchovy, has high nutrient value and fresh and dense taste, is easy for digesting and absorbing and has the health care efficacies on reducing cholesterol, eliminating fatigue, improving body immunity, etc. The preparation method has reasonable technology, simple operation and strong operability and is easy for realizing the industrialized production.
Owner:SHANDONG HOMEY AQUATIC DEV +1
Cysteine variants of interleukin-11 and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070111240A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementInterleukin 11Cysteine thiolate
Disclosed are cysteine variants of interleukin-11 (IL-11) and methods of making and using such proteins in therapeutic applications.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
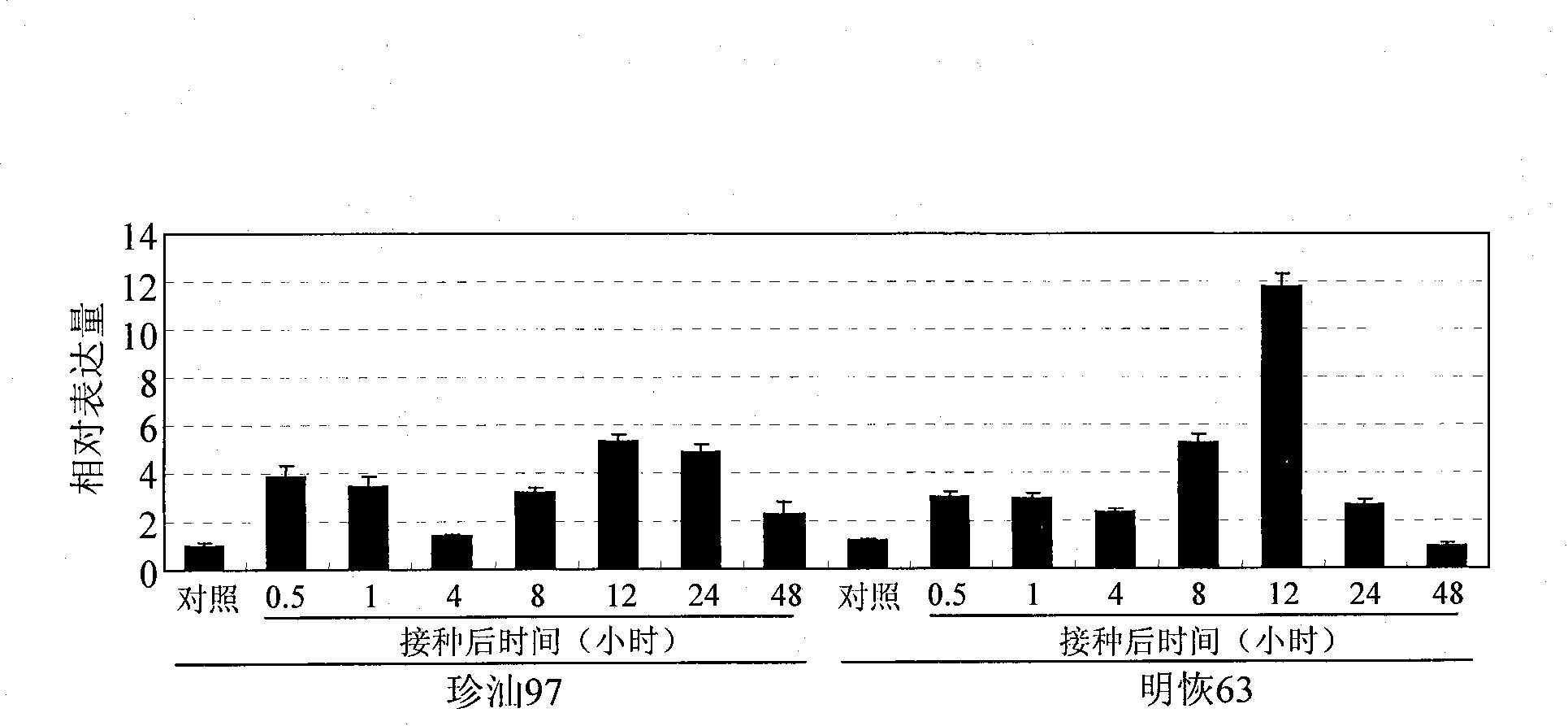
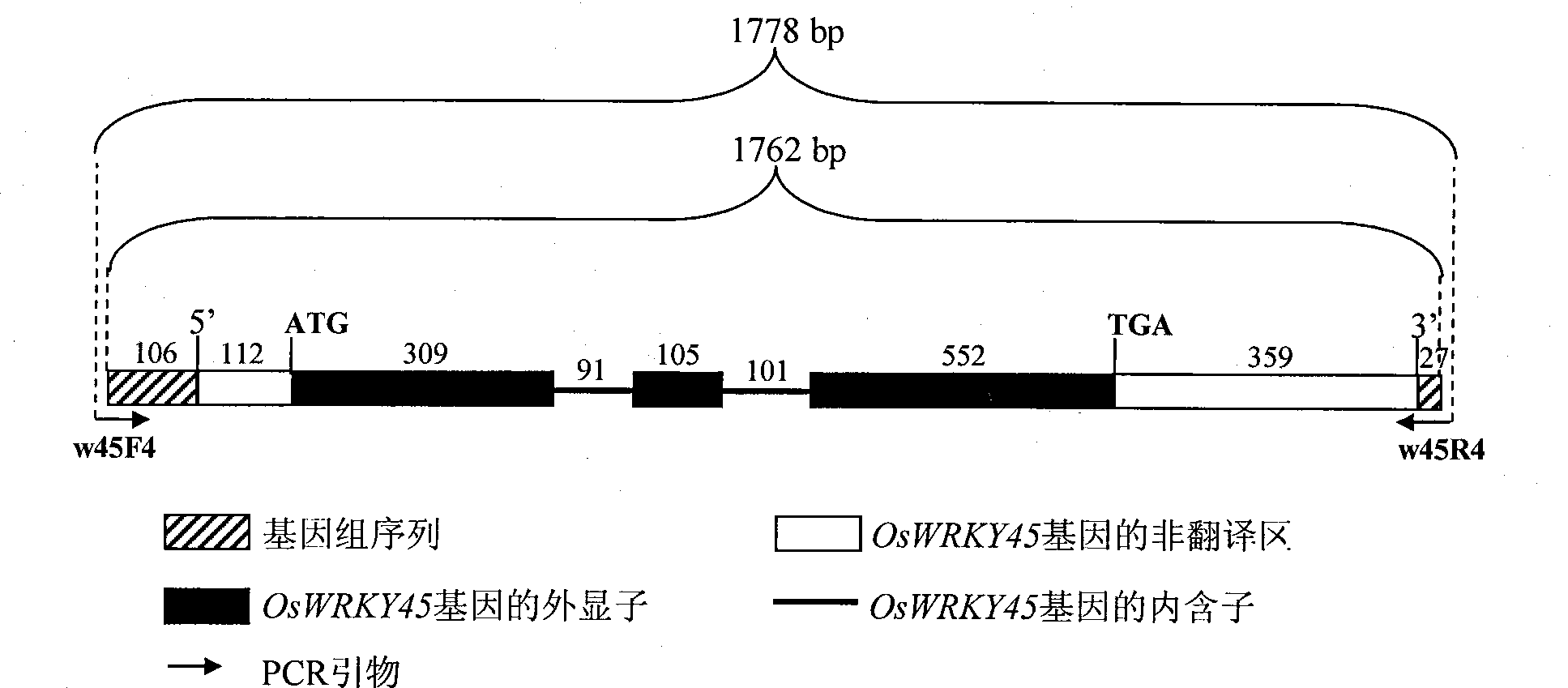
Rice disease resistance relevant gene OsWRKY45-2 and application thereof in improving rice disease resistance
InactiveCN101386856AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular relates to isolating clone and functional verification of a DAN fragment containing a gene OsWRKY45-2 related to rice disease resistance. The gene OsWRKY45-2 codes WRKY proteinoids and can endow rice with resistance to the diseases caused by bacterial pathogenic bacteria, namely the leaf blight bacteria (Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae) and fungal pathogenic bacteria, namely the rice blast bacteria (Magnaporthe grisea). The fragment and the exogenous regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred into rice, thus the resistance capability of transgenic rice with over-expression OsWRKY45-2 against bacterial blight in and rice blast is improved remarkably.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com