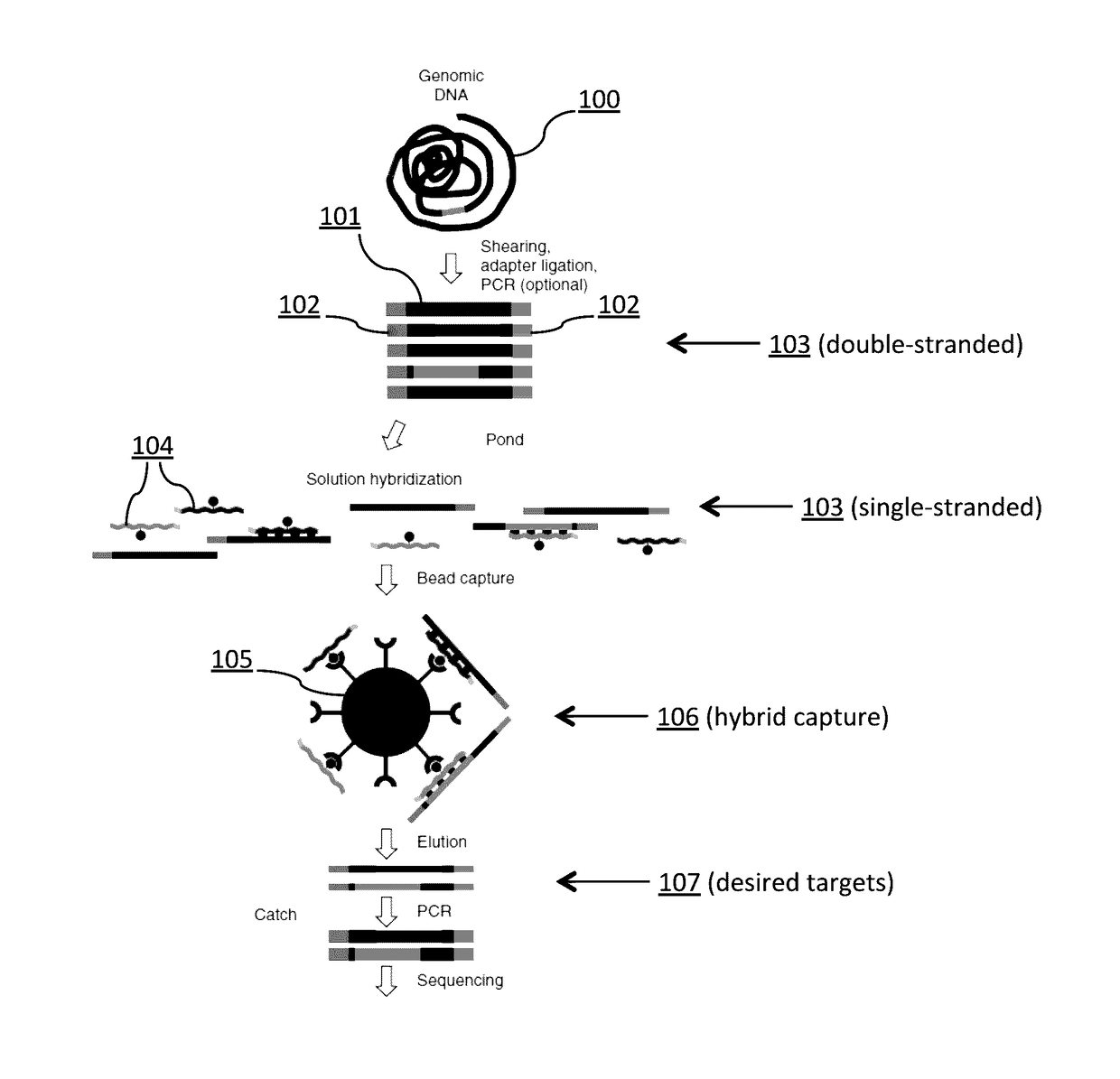
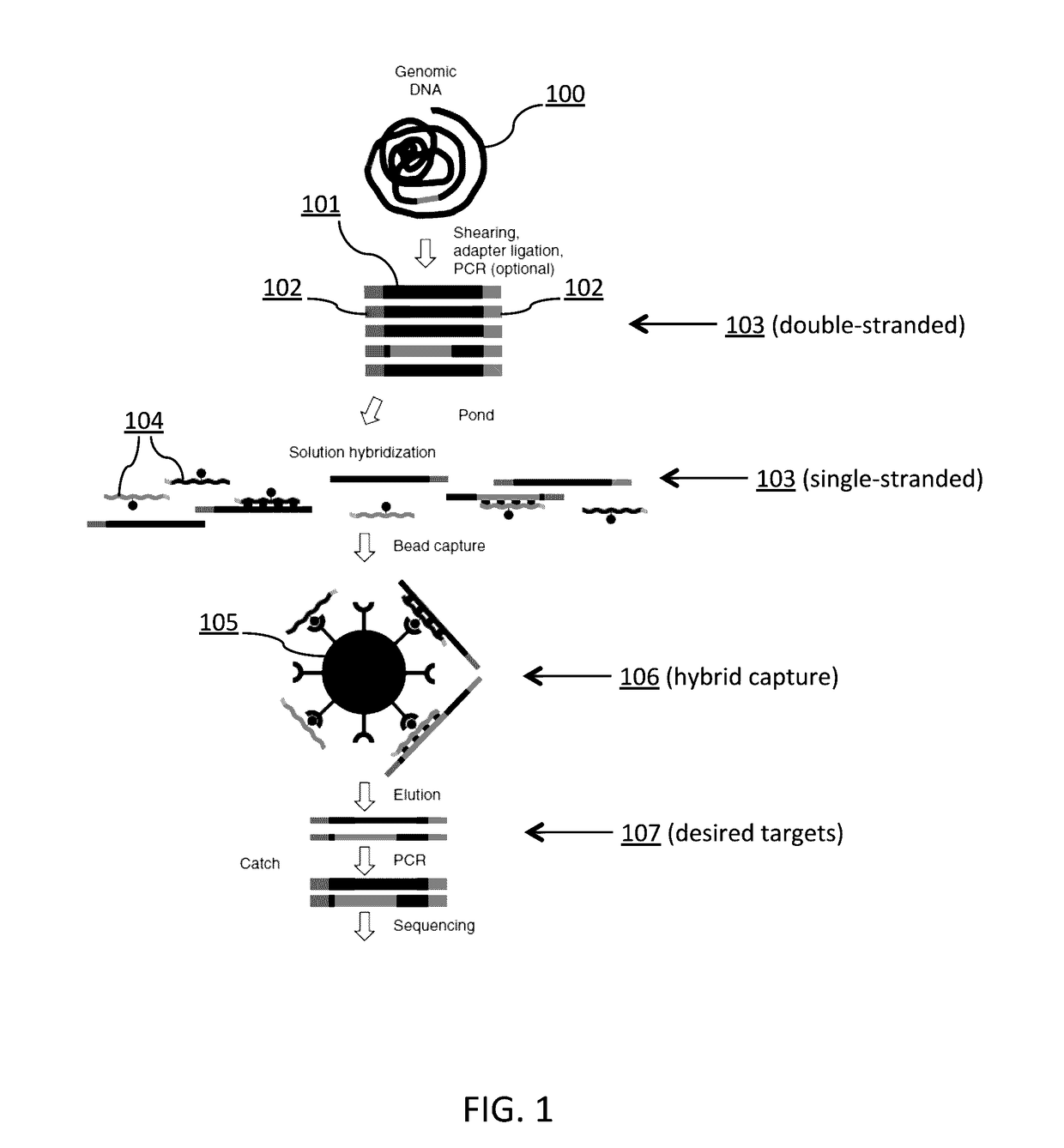
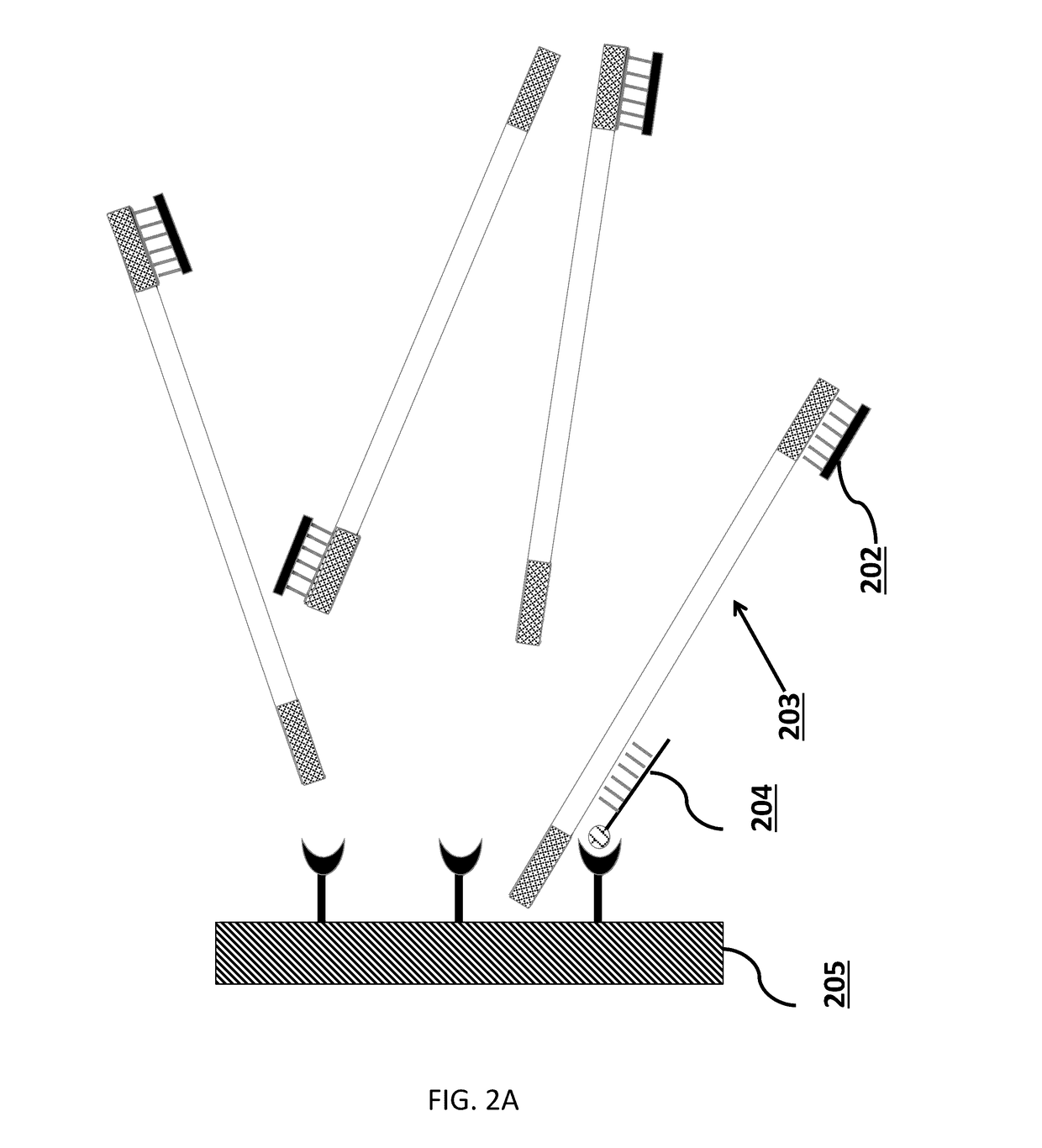
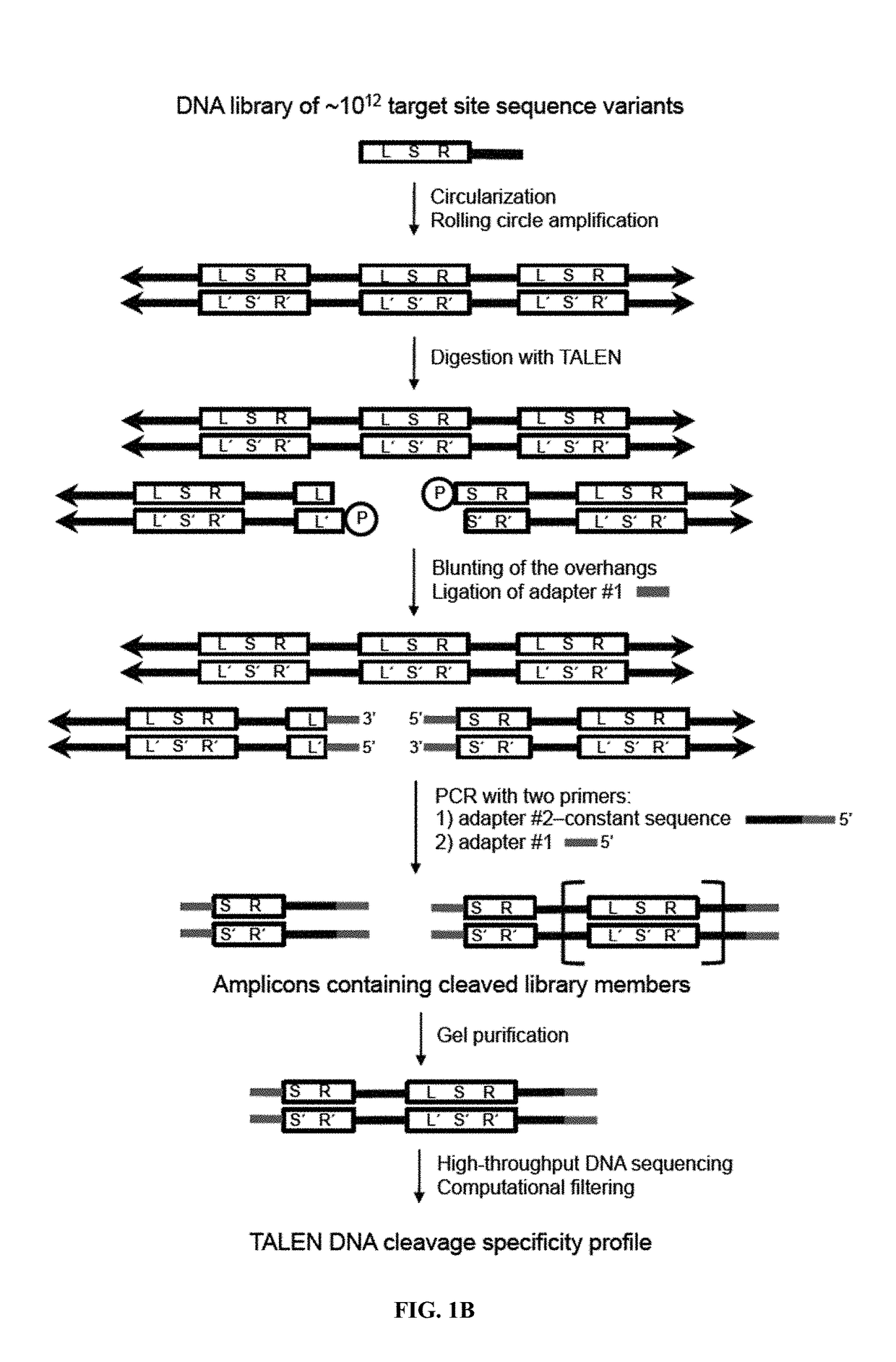
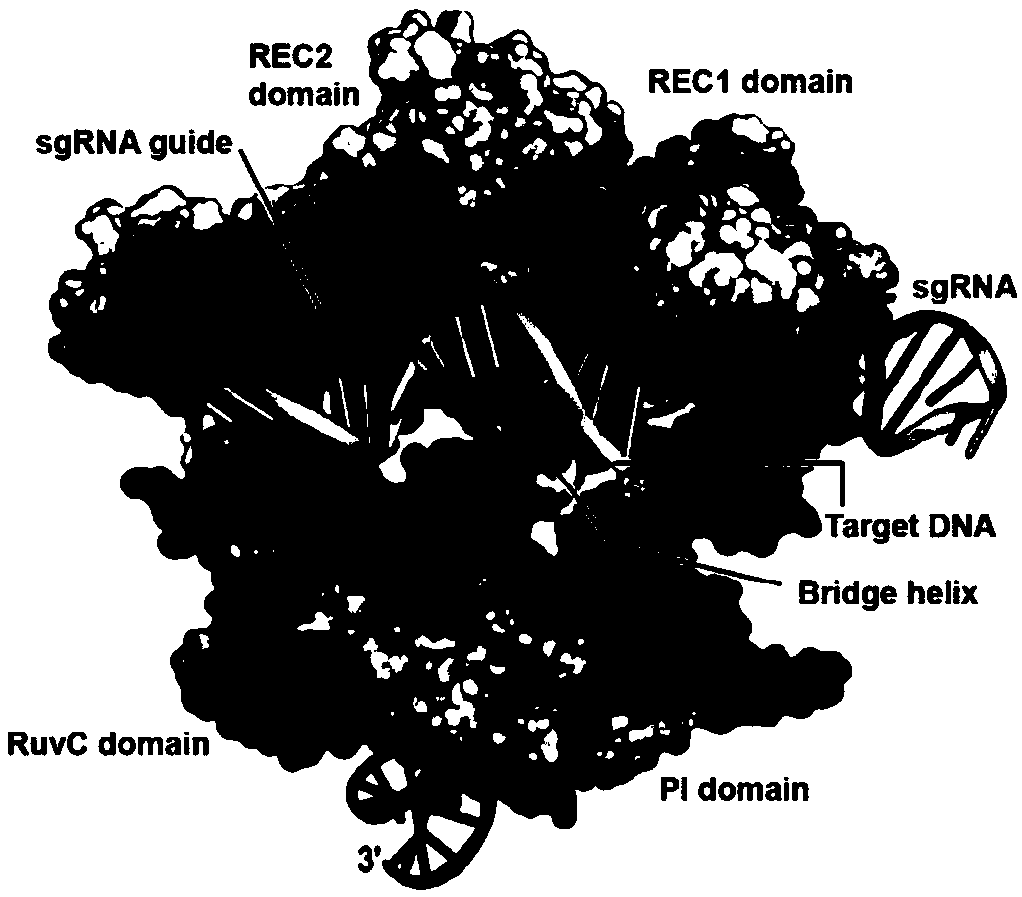
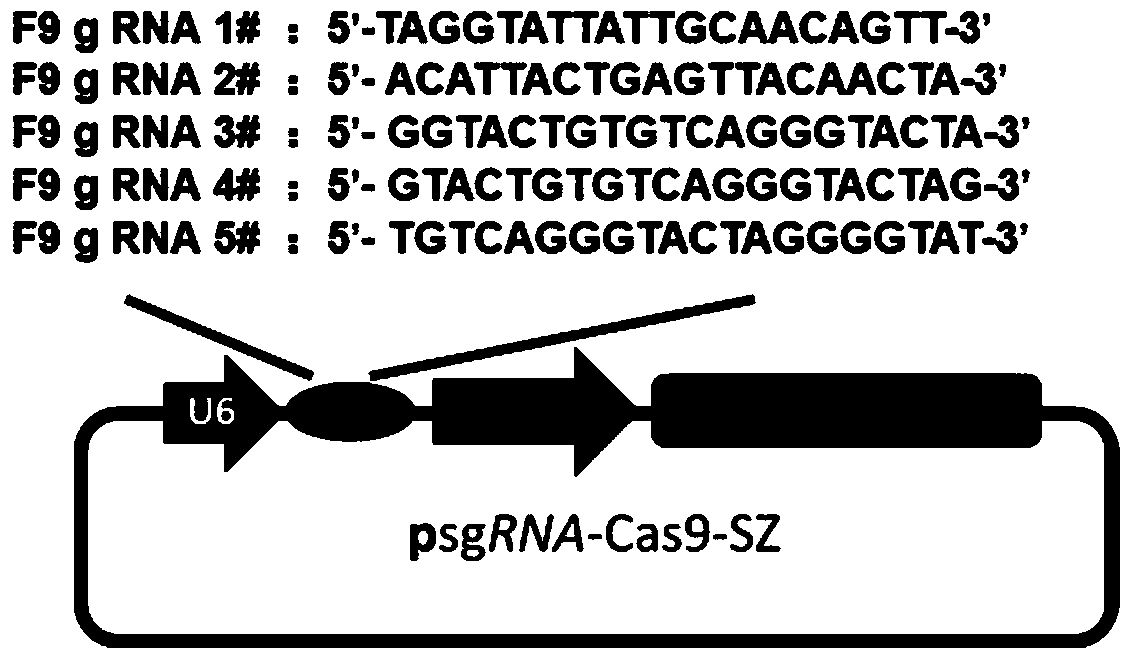
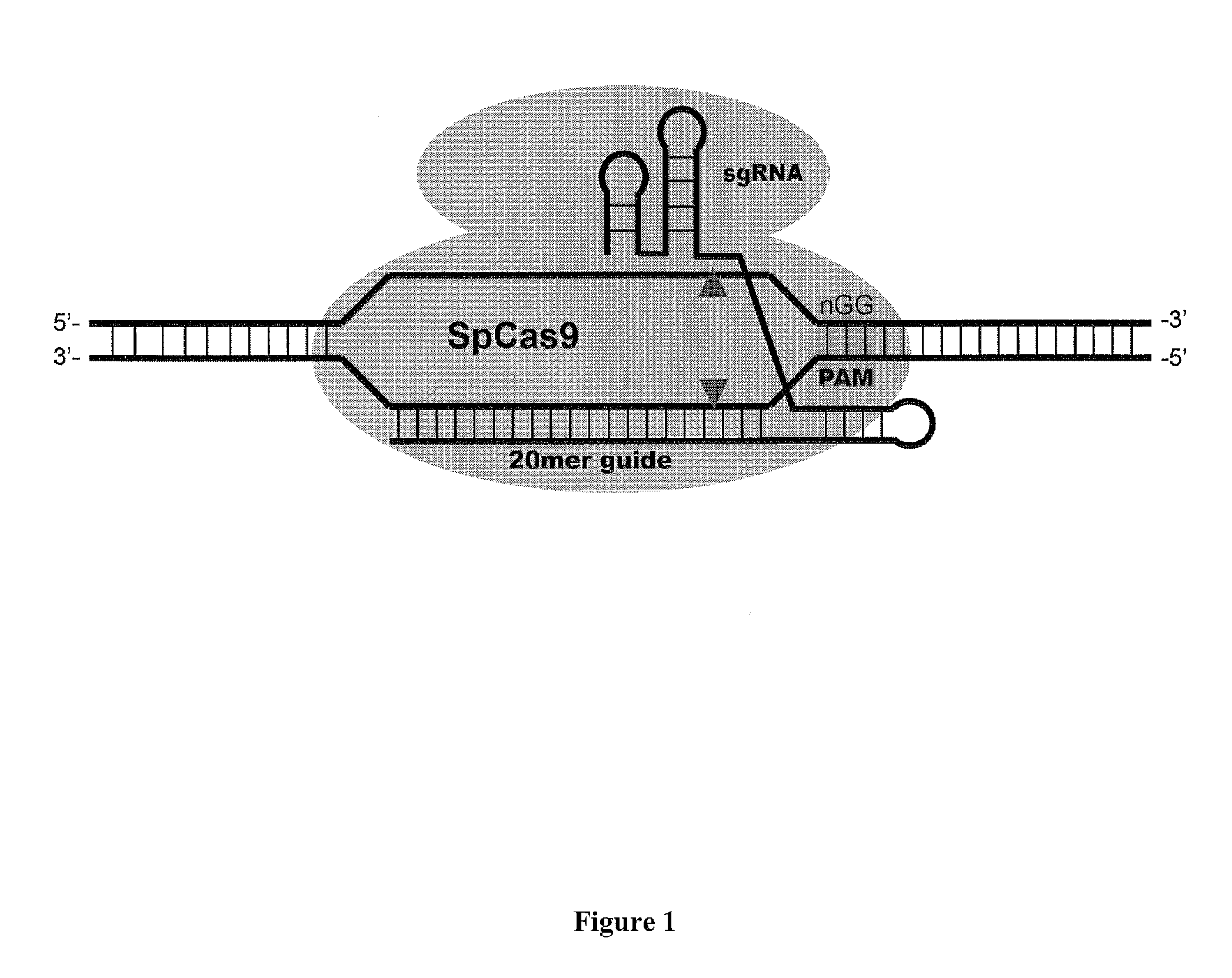
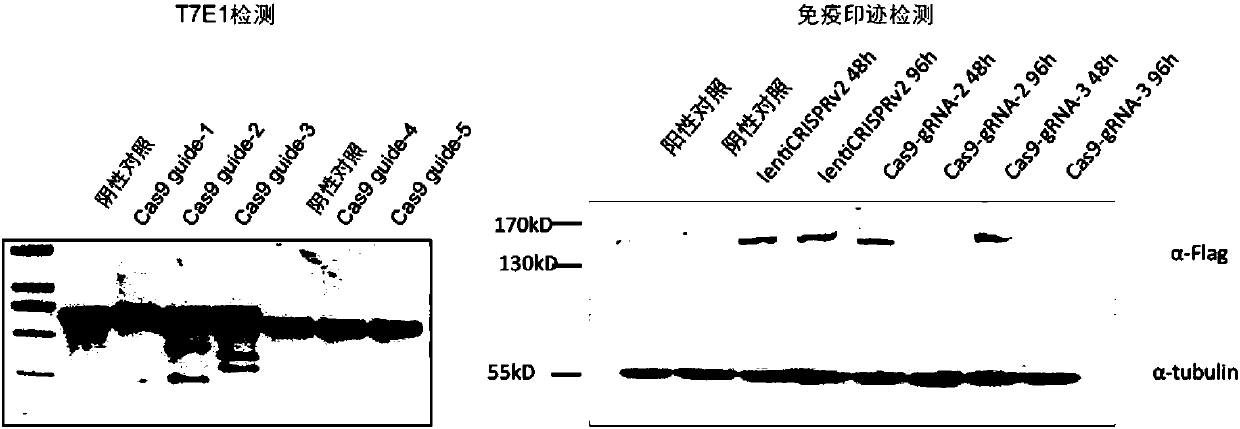
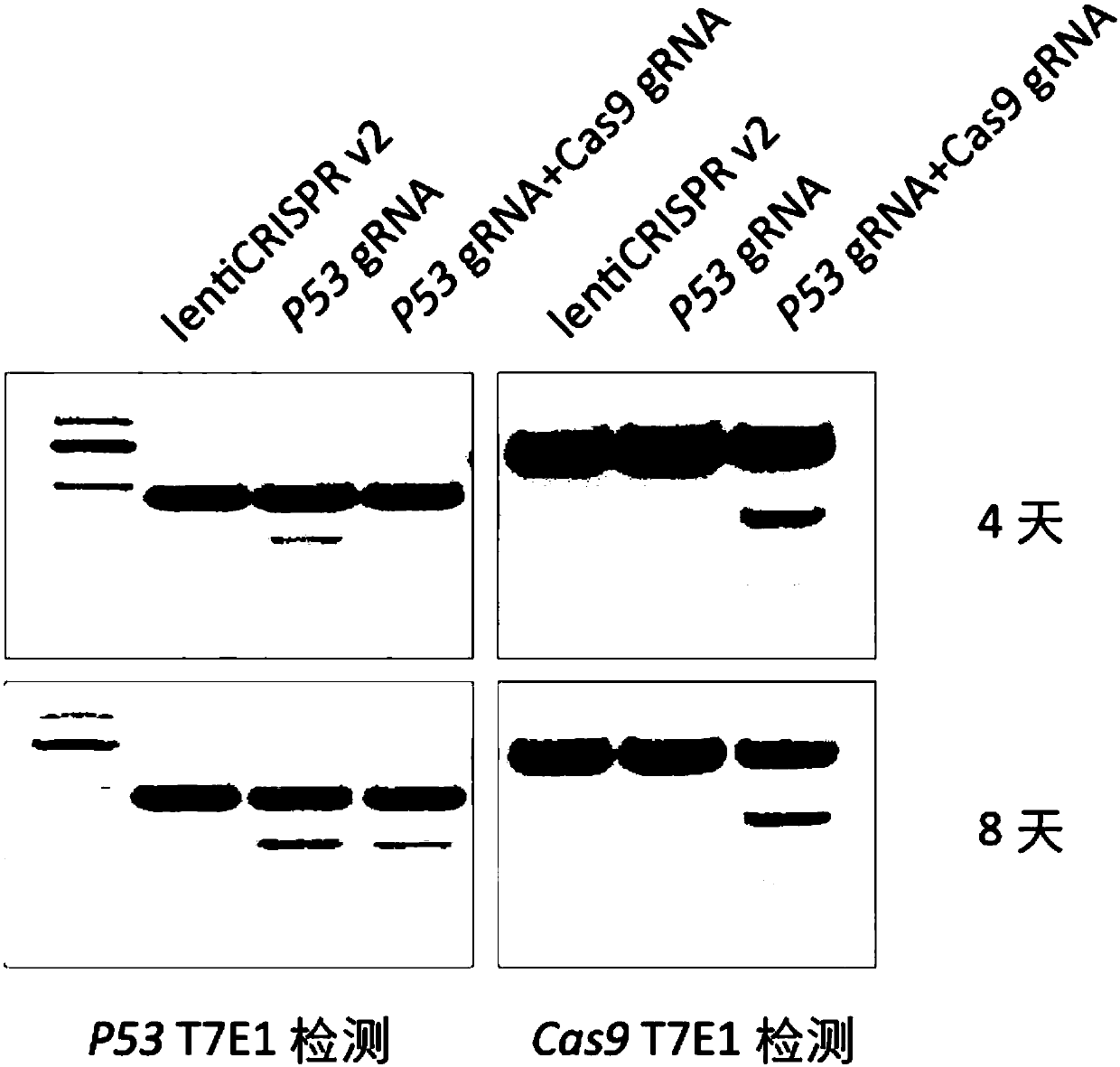
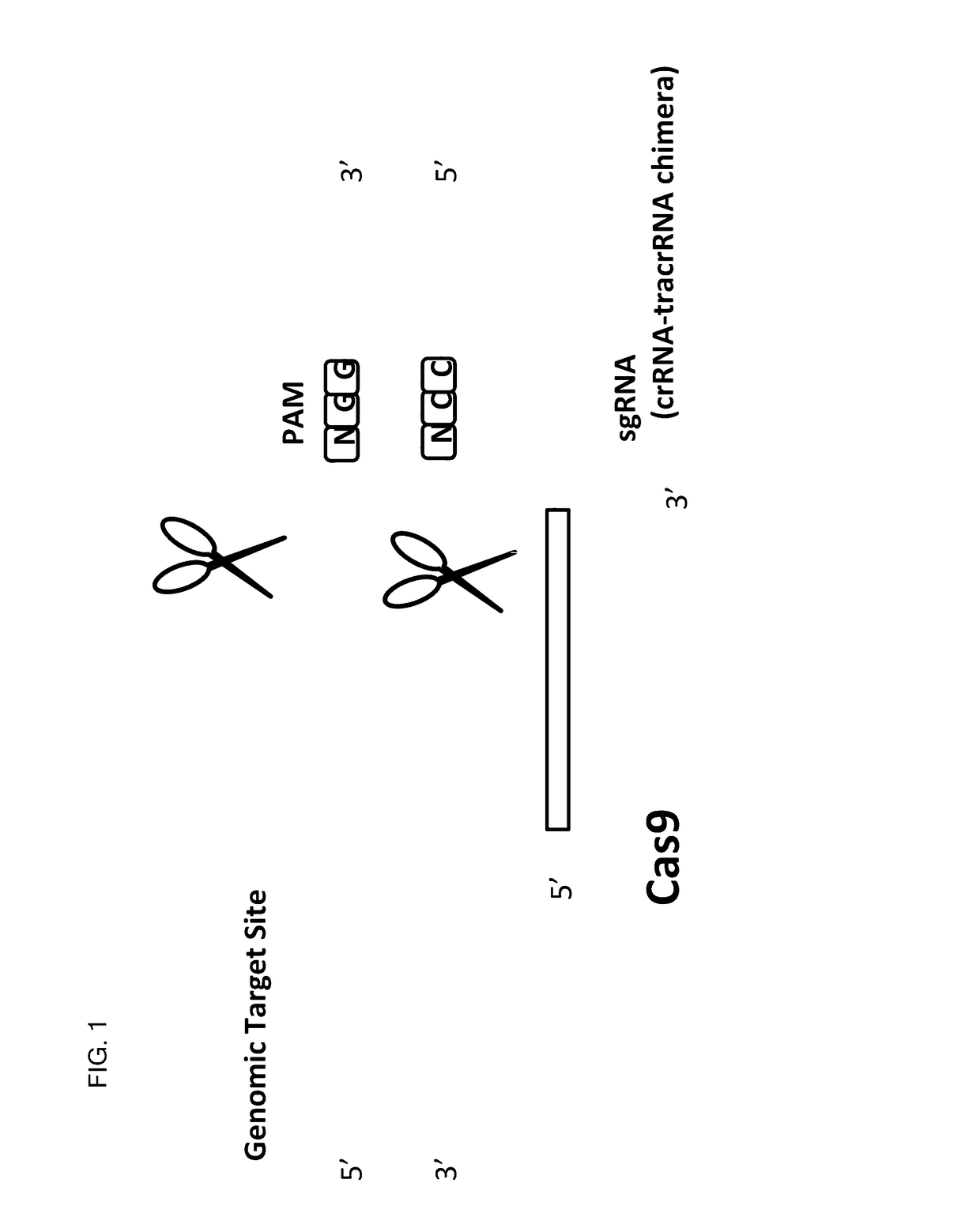
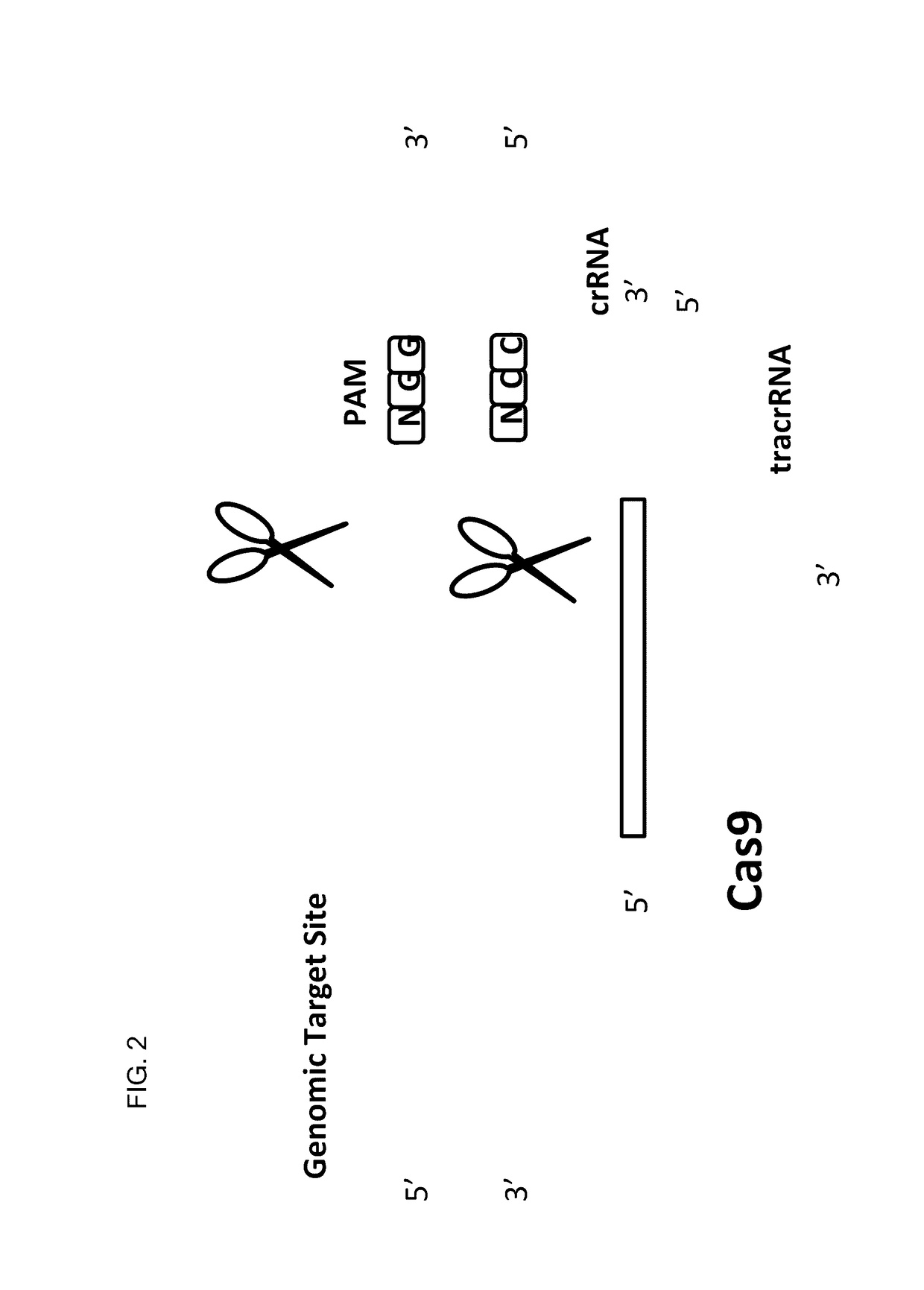
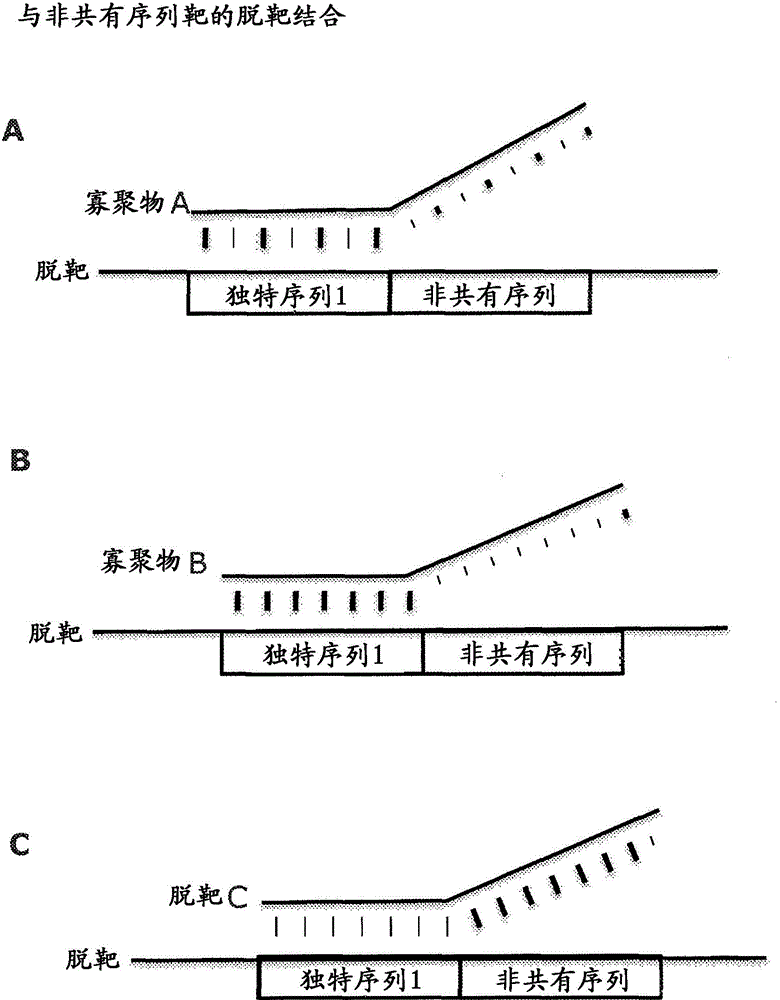
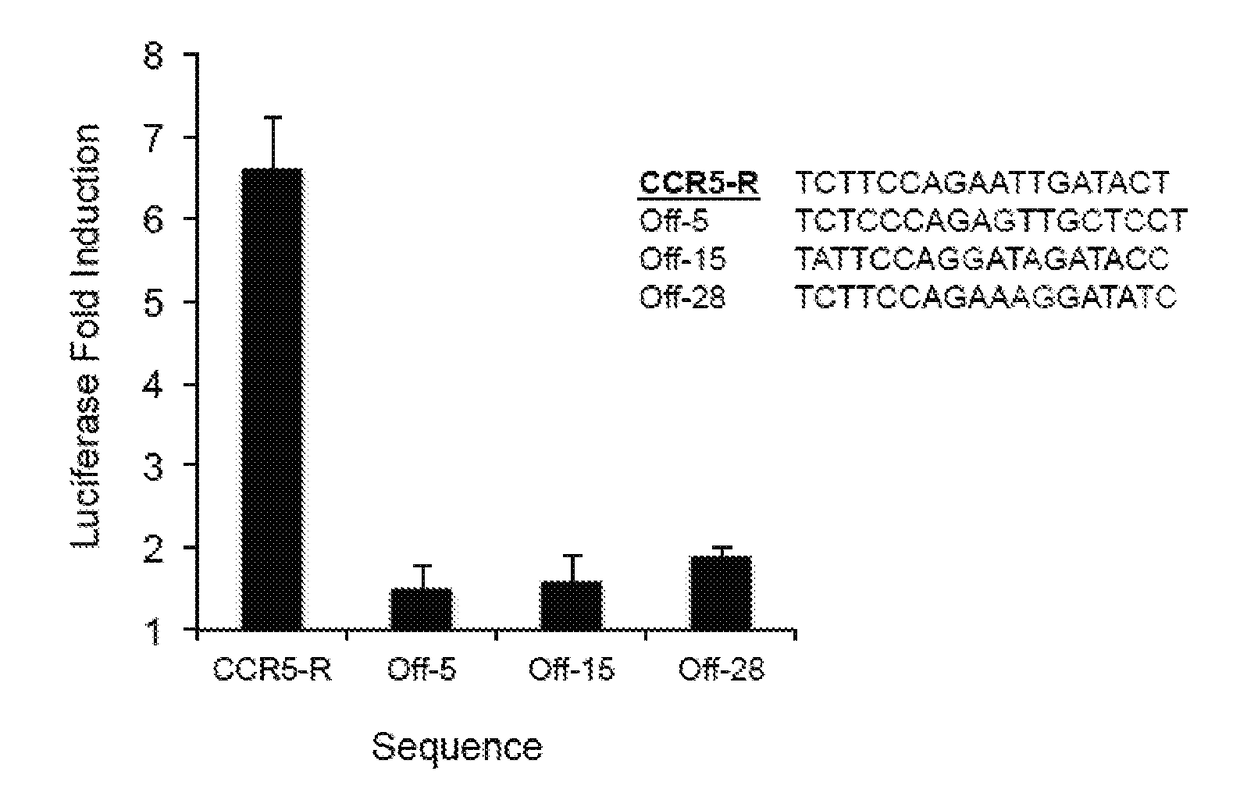
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
195 results about "Off targets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
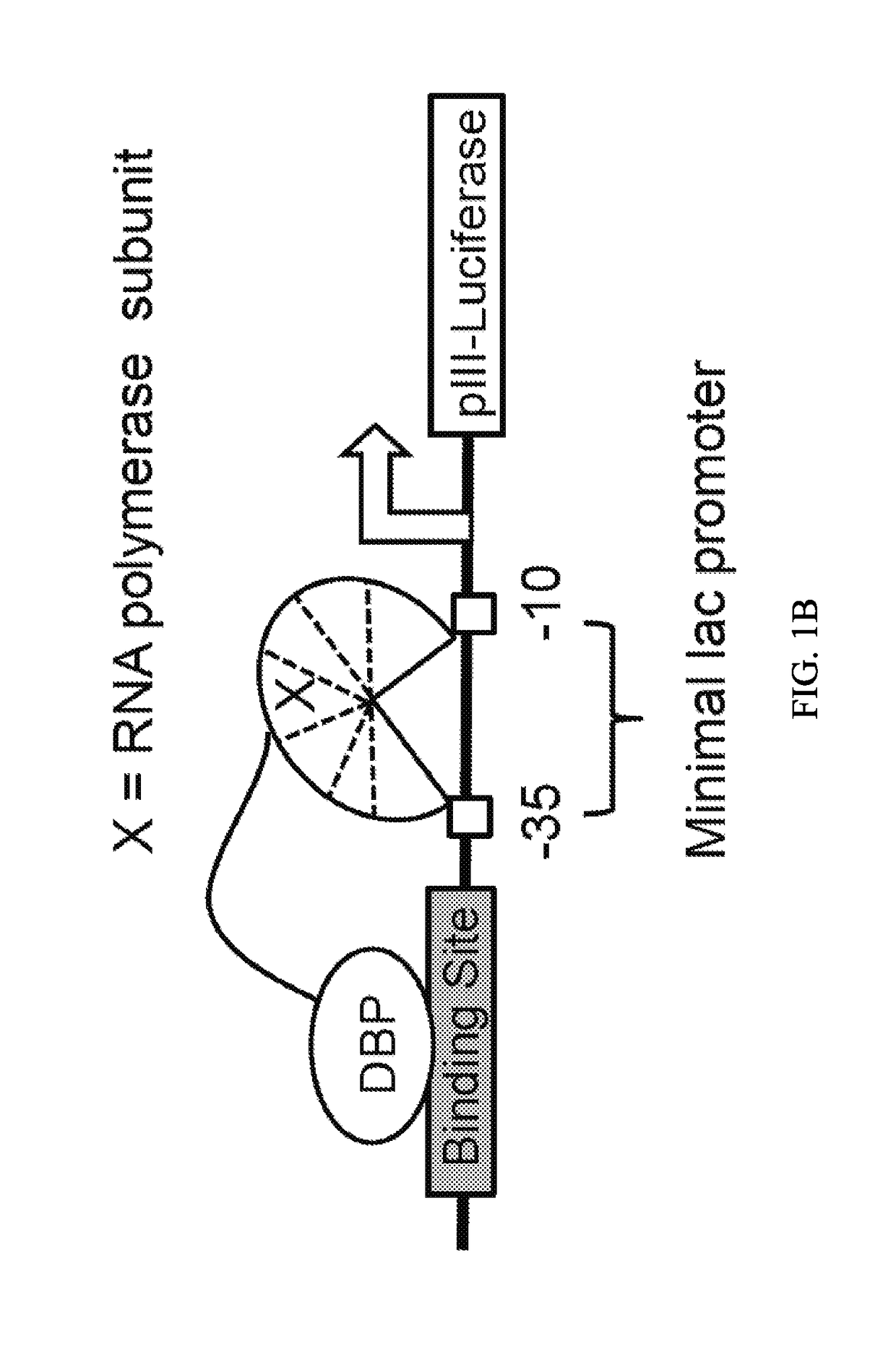
Methods for determining therapeutic index from gene expression profiles
InactiveUS6222093B1Low therapeutic indexLow indexChemical property predictionSugar derivativesDrug specific IgEMedicine
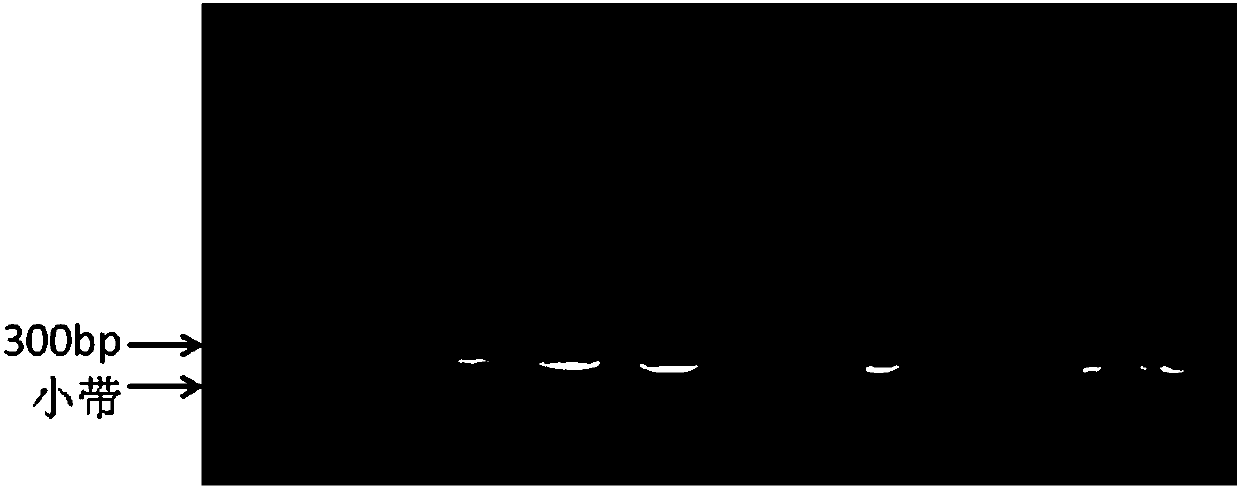
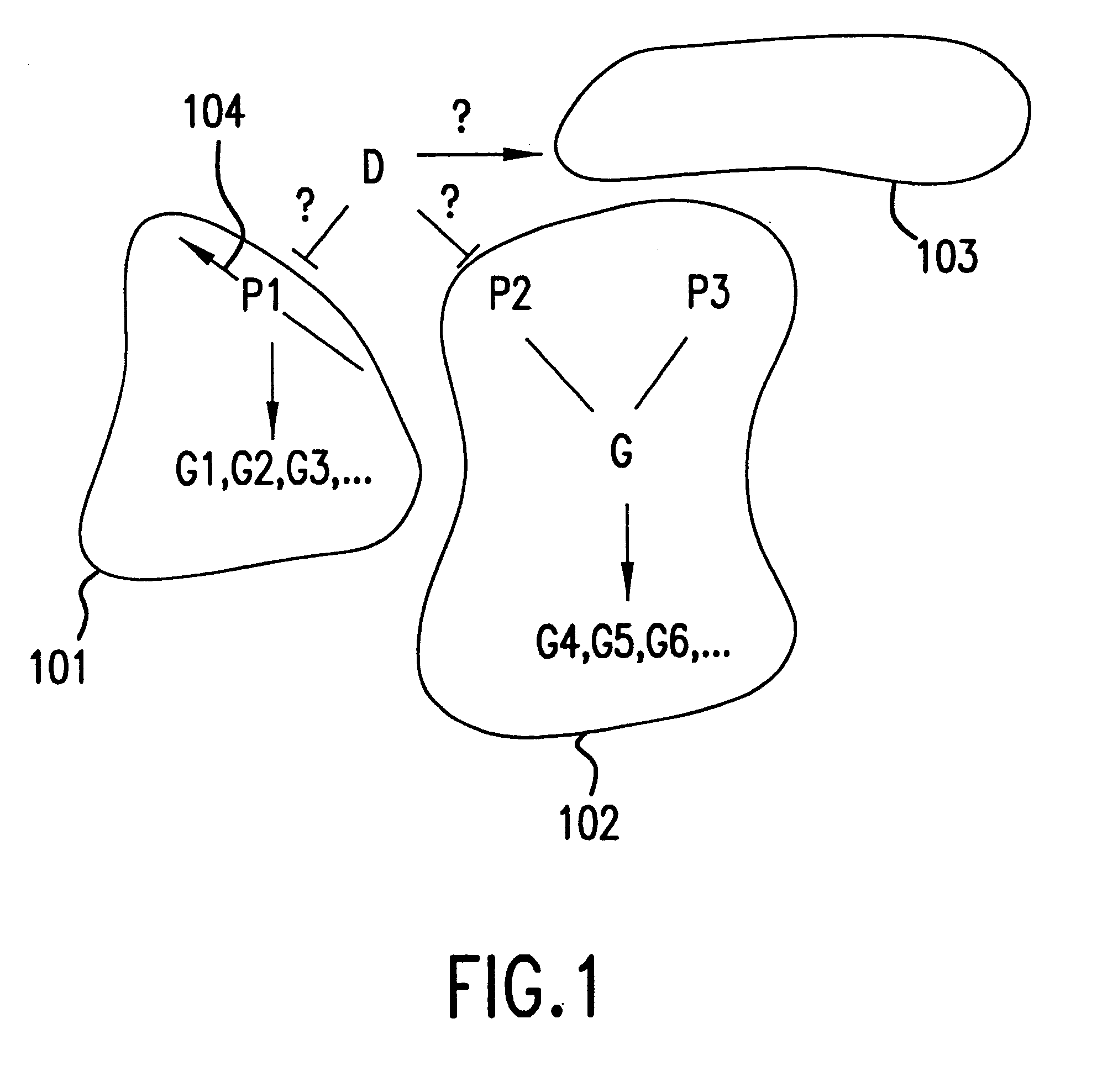
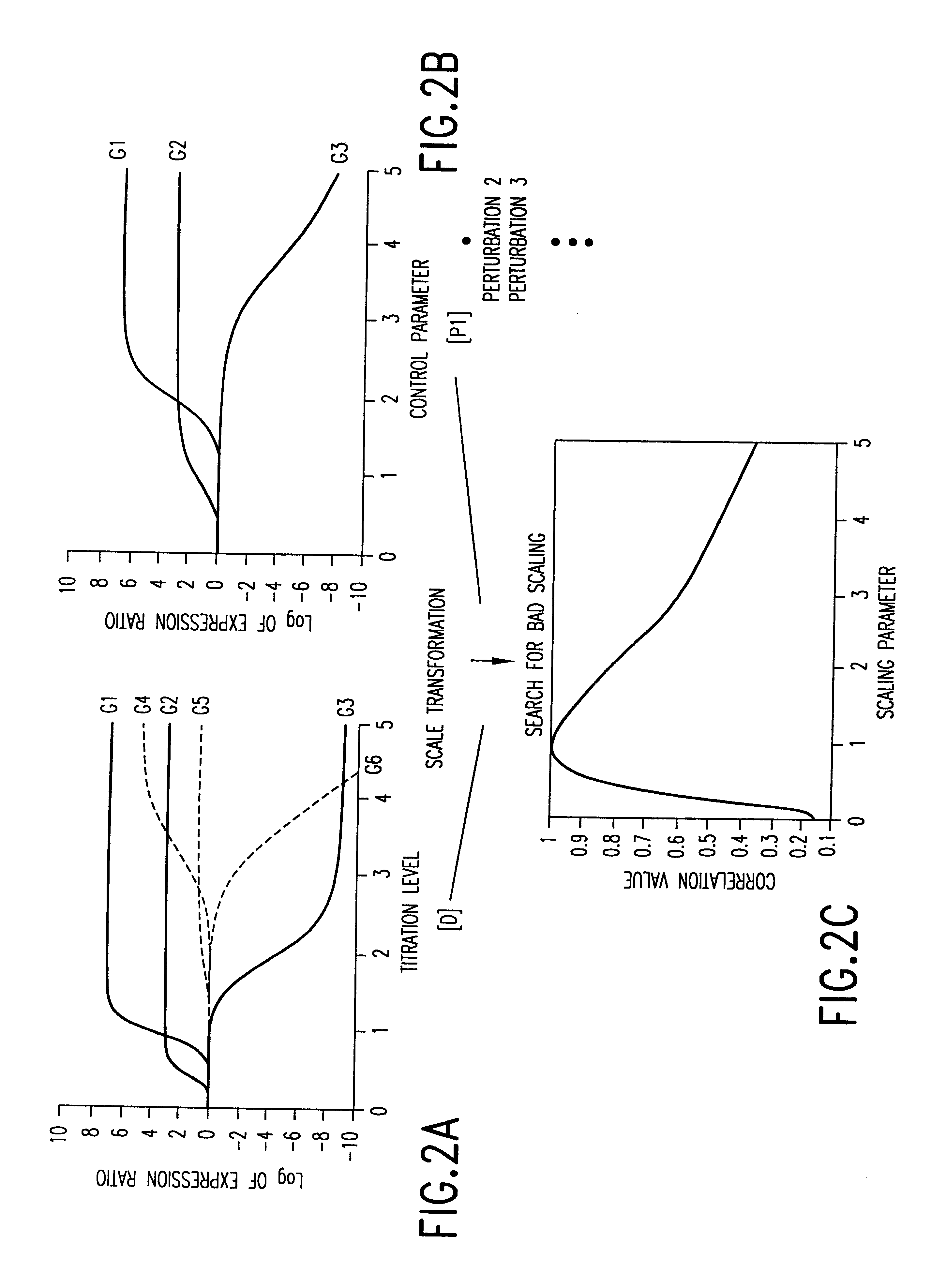
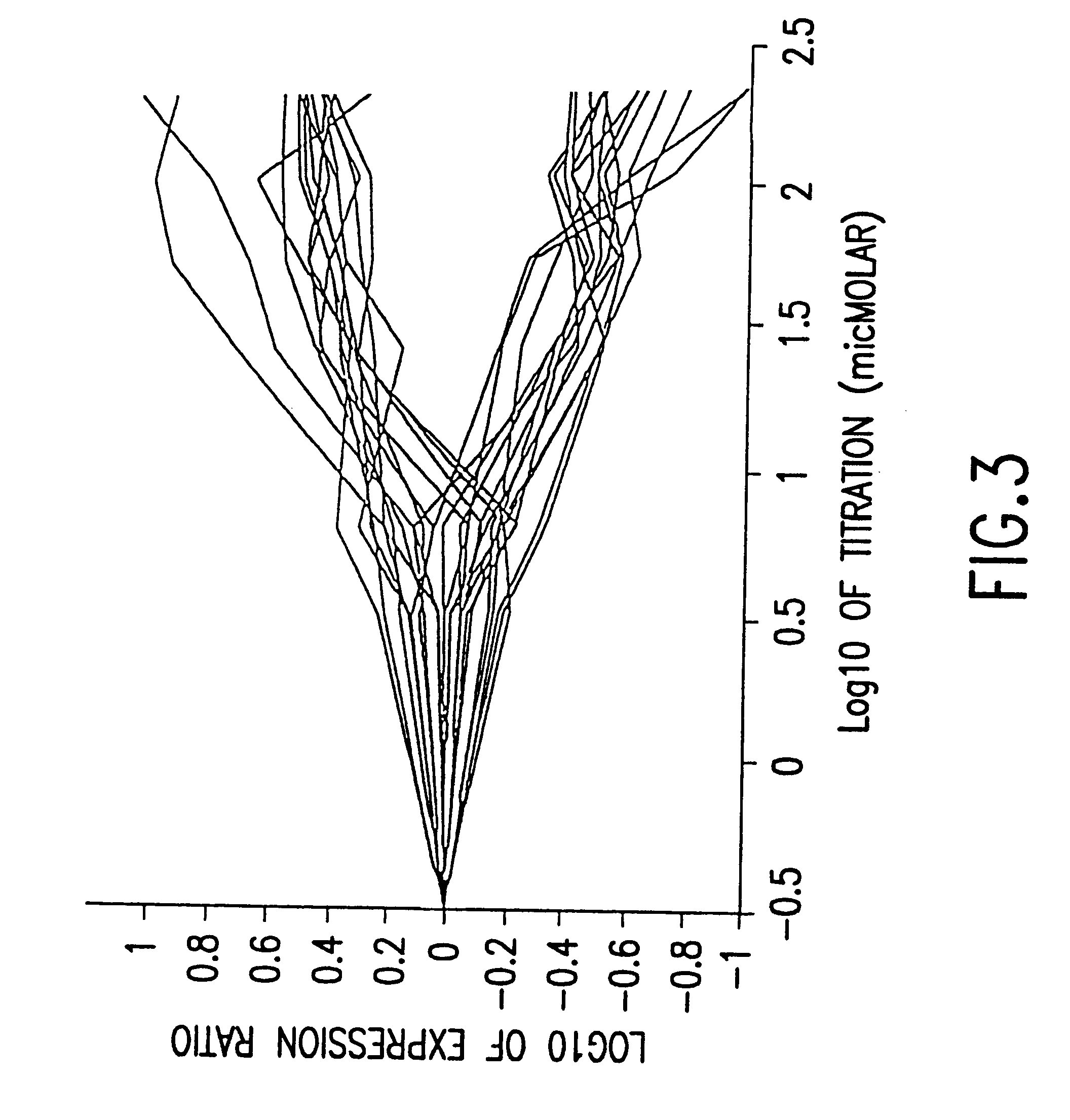
This invention provides methods for determining drug specificity, therapeutic index and effective doses for individual patients. According to the methods of the invention, graded levels of drug are applied to a biological sample or a patient. A plurality of cellular constituents are measured to determine the activity of the drug on a target pathway and at least one off-target pathway. A drug specificity is determined by comparing the target and off target activities of the drug. A therapeutic concentration (or dose) is defined as a concentration (or dose) of the drug that induces certain response in the target pathway. A toxic concentration (or dose) is defined as a concentration (or dose) of the drug that induces certain response in the off target pathway. Therapeutic index is the ratio of the toxic concentration over therapeutic concentration. Methods are also provided to determine an effective dose of a drug for a patient by measuring the activity of the drug on the particular patient.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
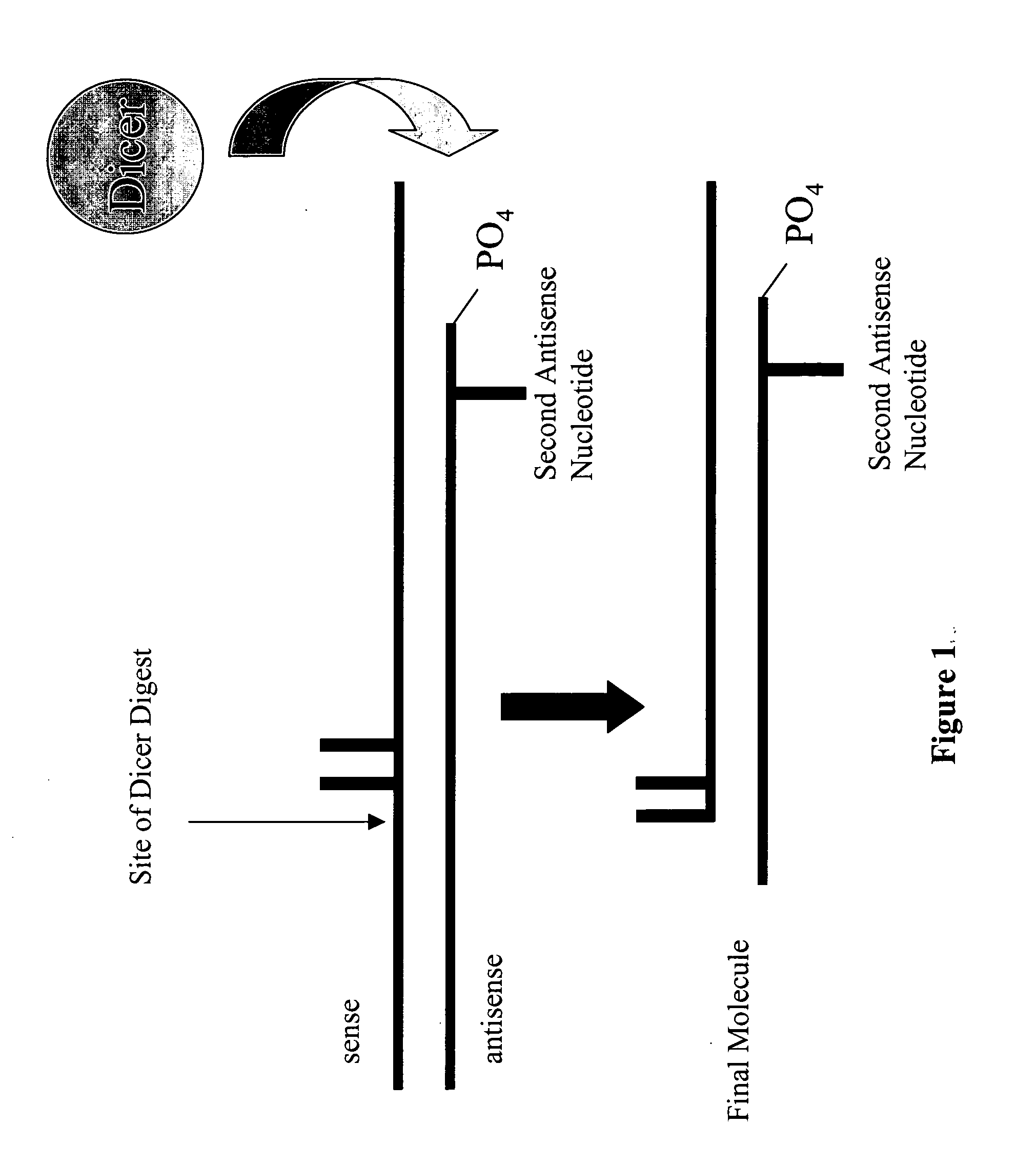
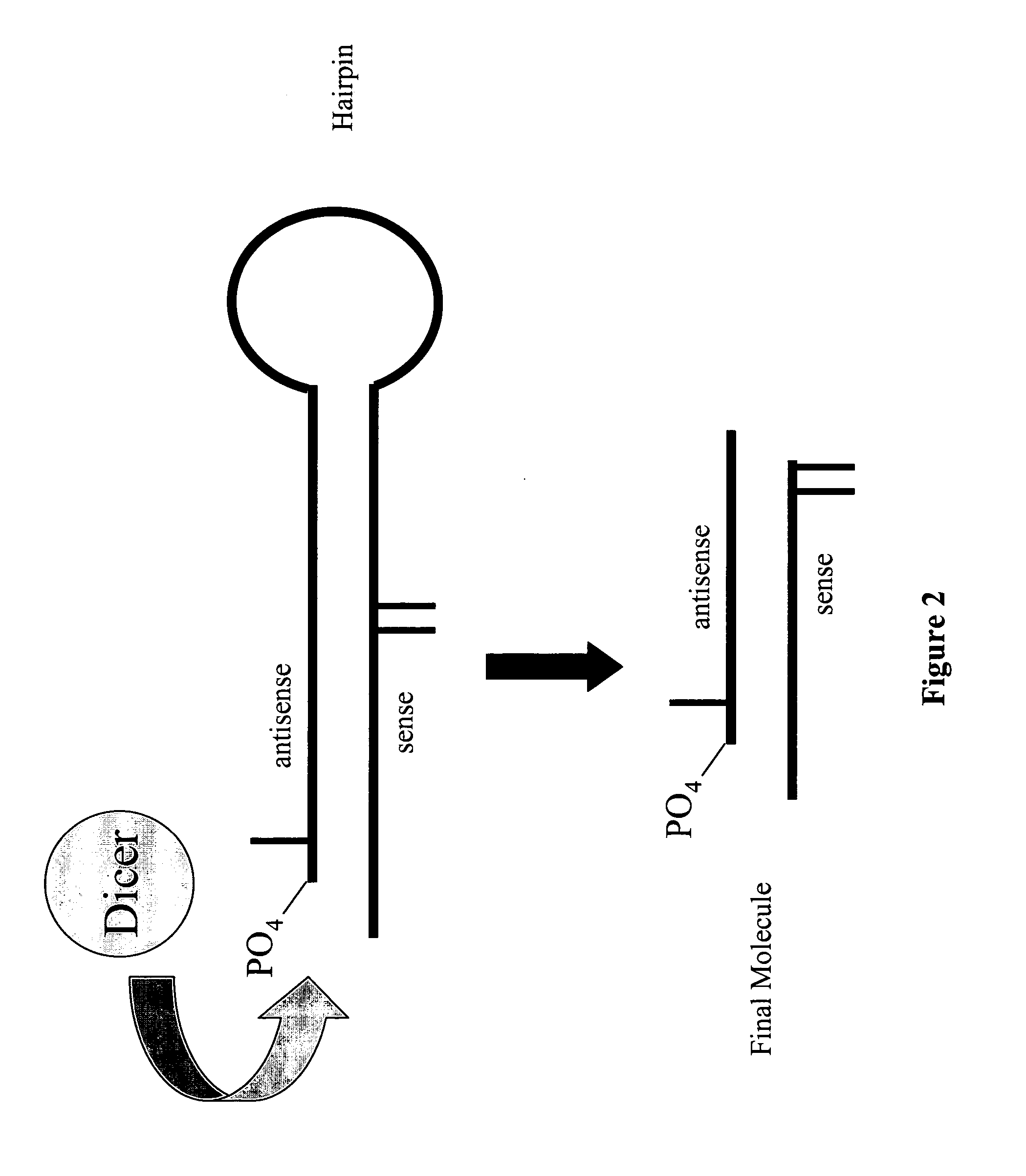
Modified polynucleotides for reducing off-target effects in RNA interference
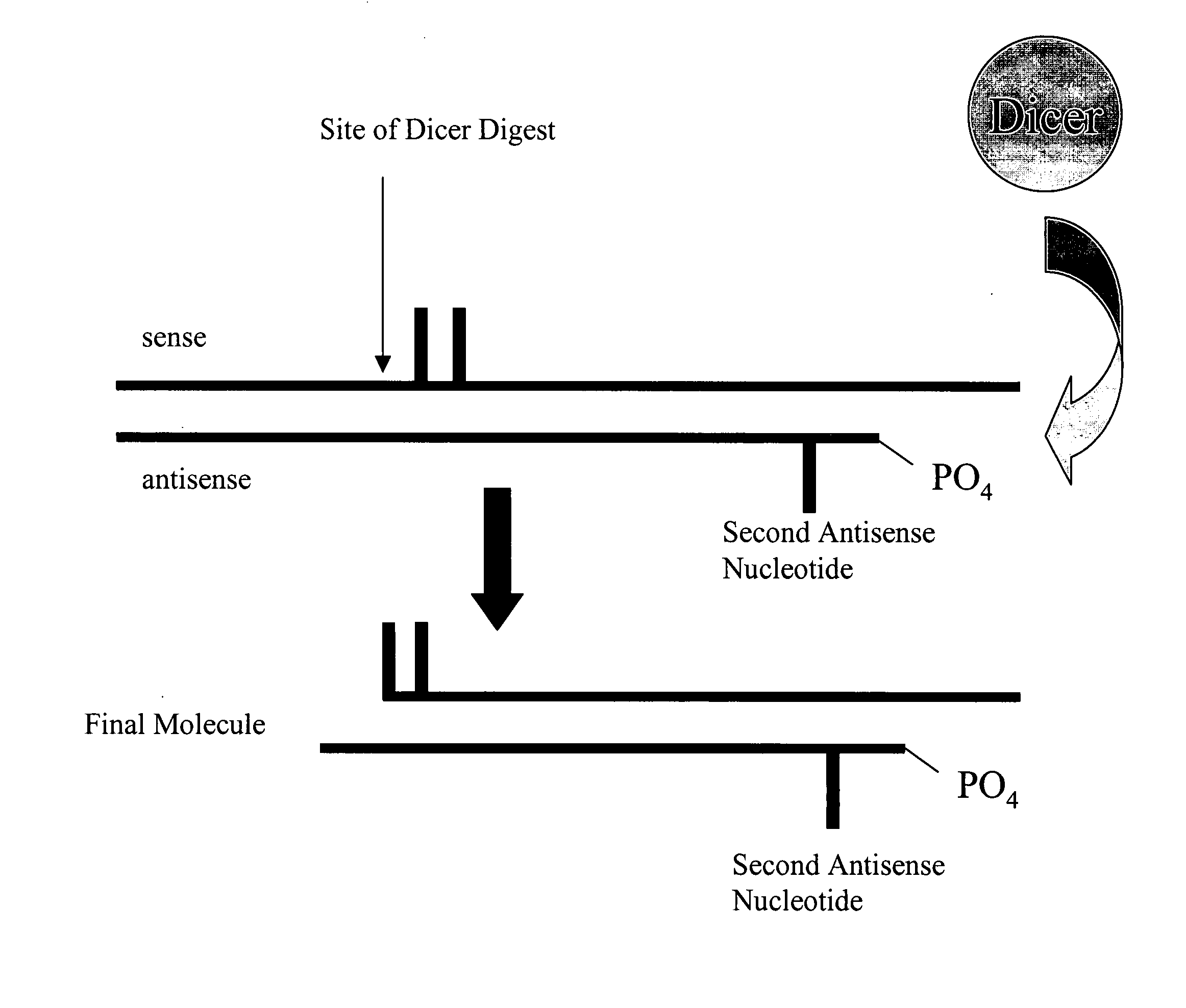
ActiveUS20050223427A1Easy to retouchBroaden applicationSugar derivativesHydrolasesGene silencingPolynucleotide
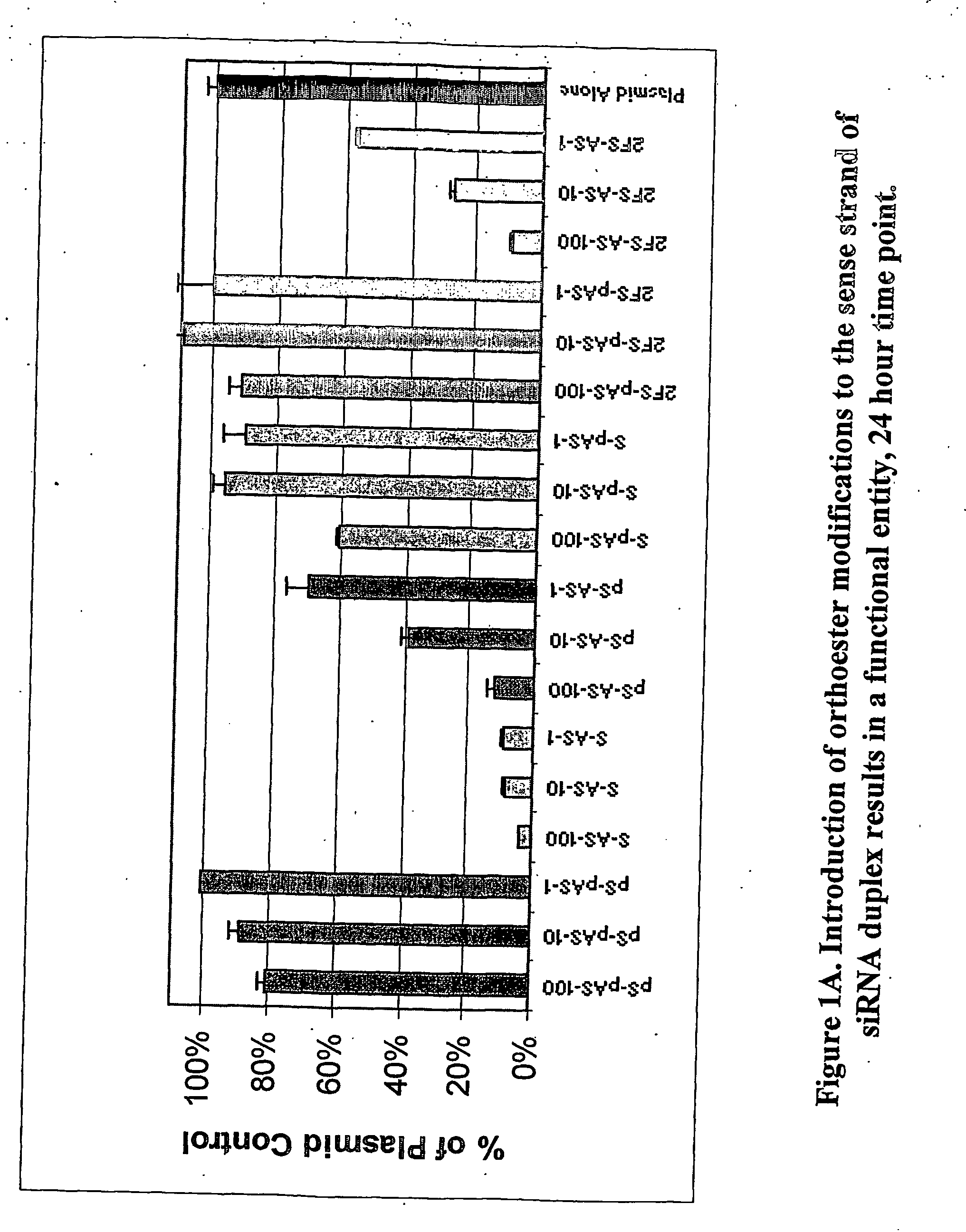
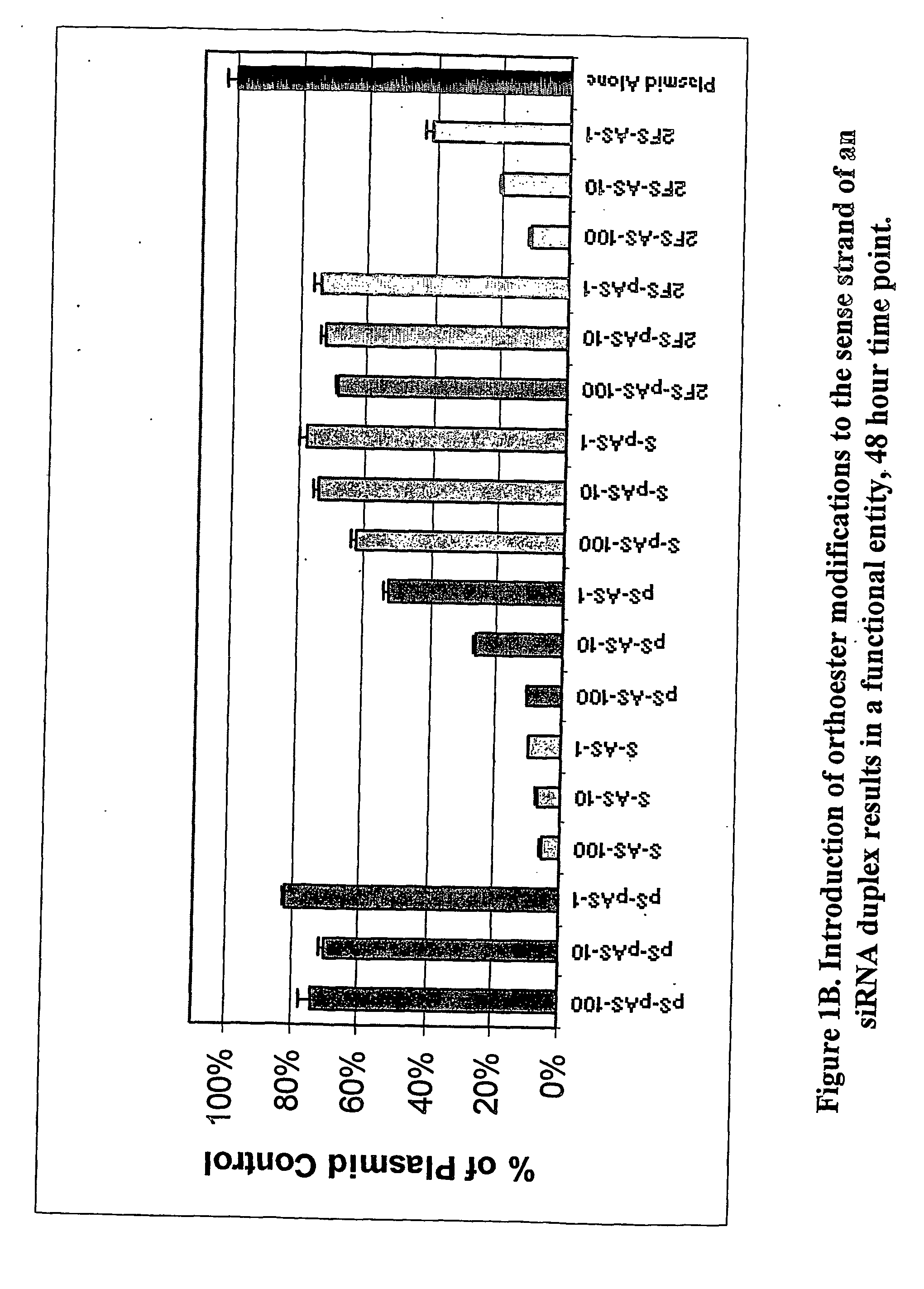
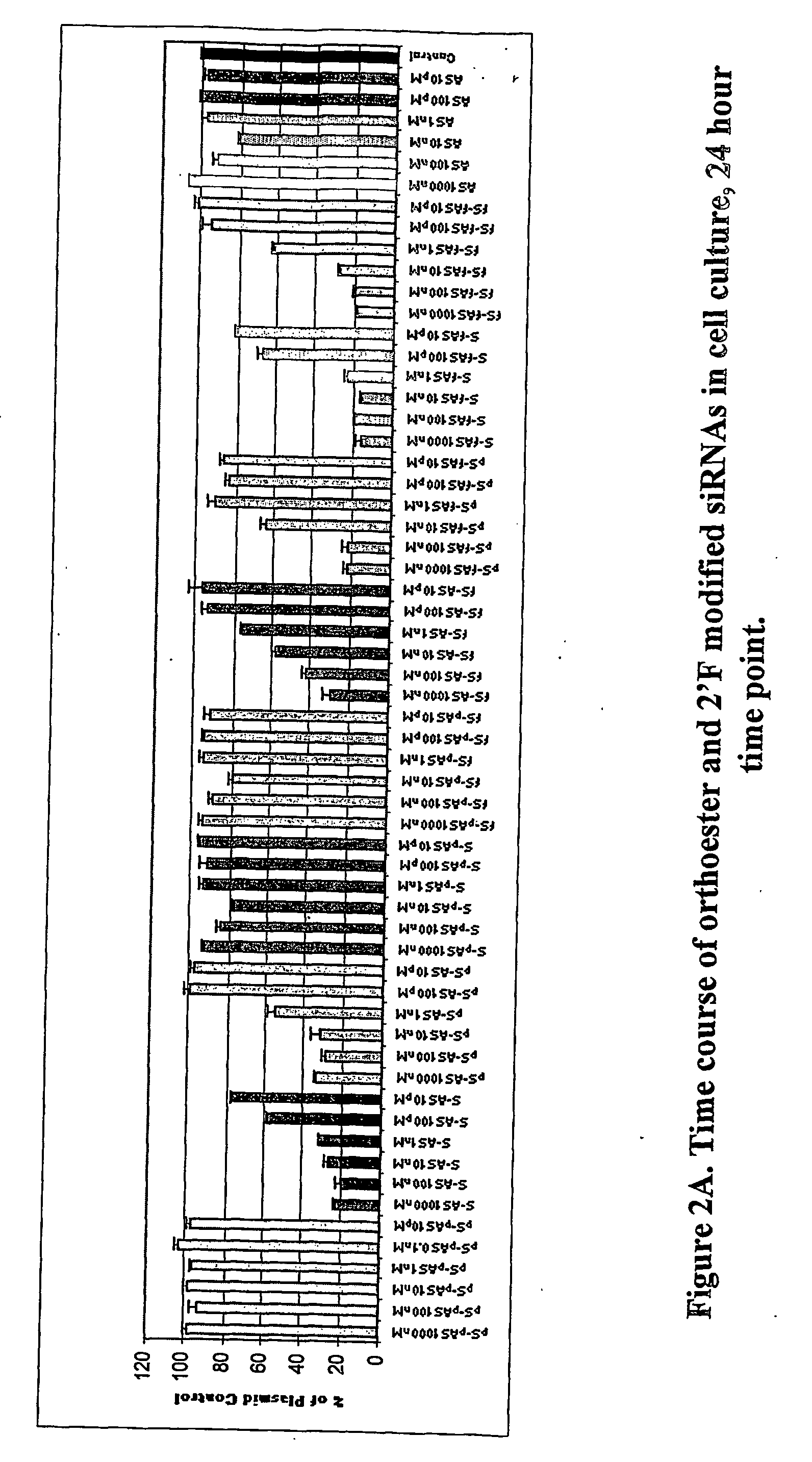
Methods and compositions for performing RNA interference with decreased off-target effects are provided The methods and compositions permit effective and efficient applications of RNA interference to applications such as diagnostics and therapeutics through the use of modifications to the siRNA. Uniquely modified siRNAs have been developed that reduce off-target effects incurred in gene-silencing. The modifications comprise 2′-O-alkyl or mismatch modification(s) at specific positions on the sense and / or antisense strands.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC +1
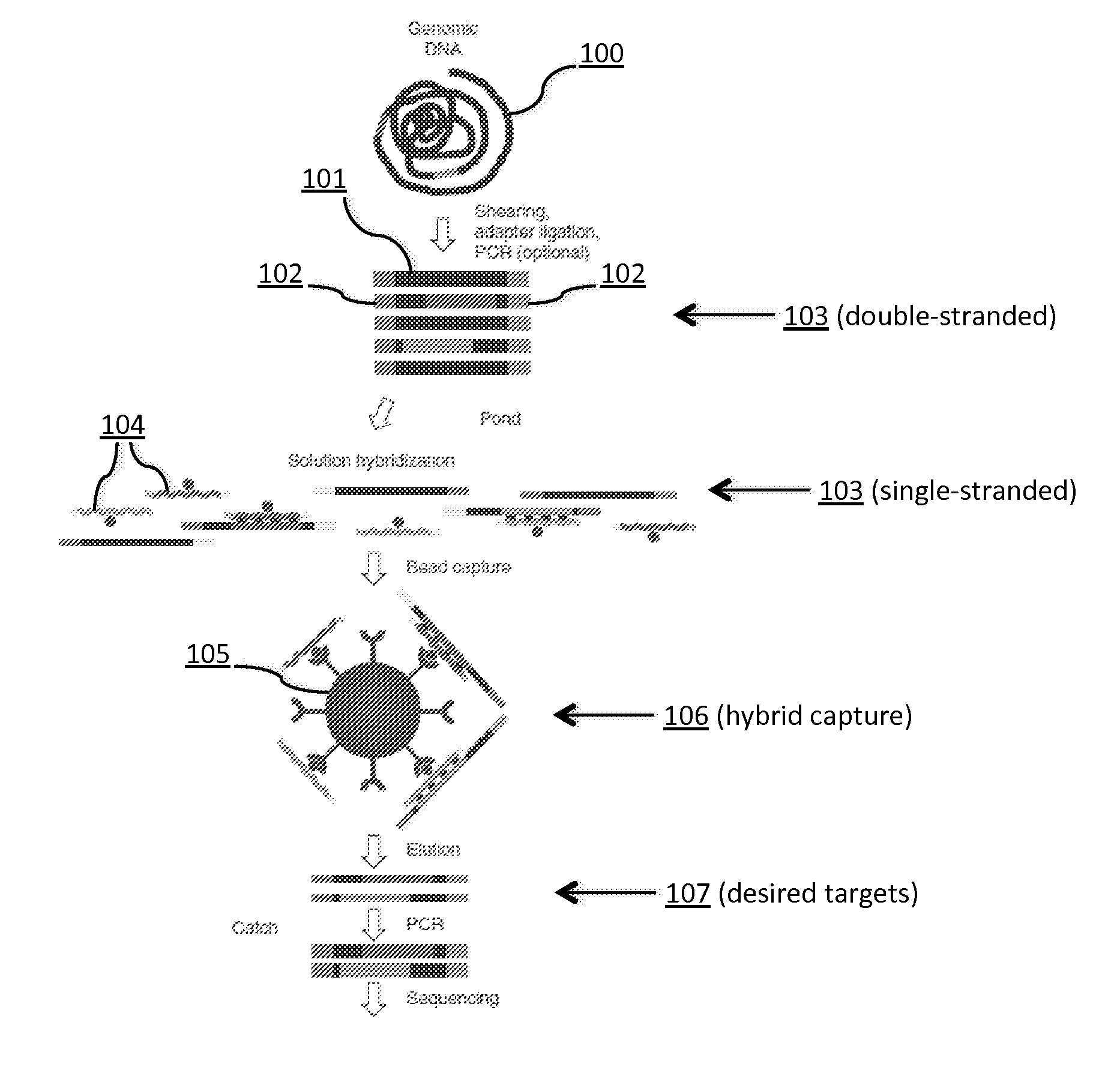
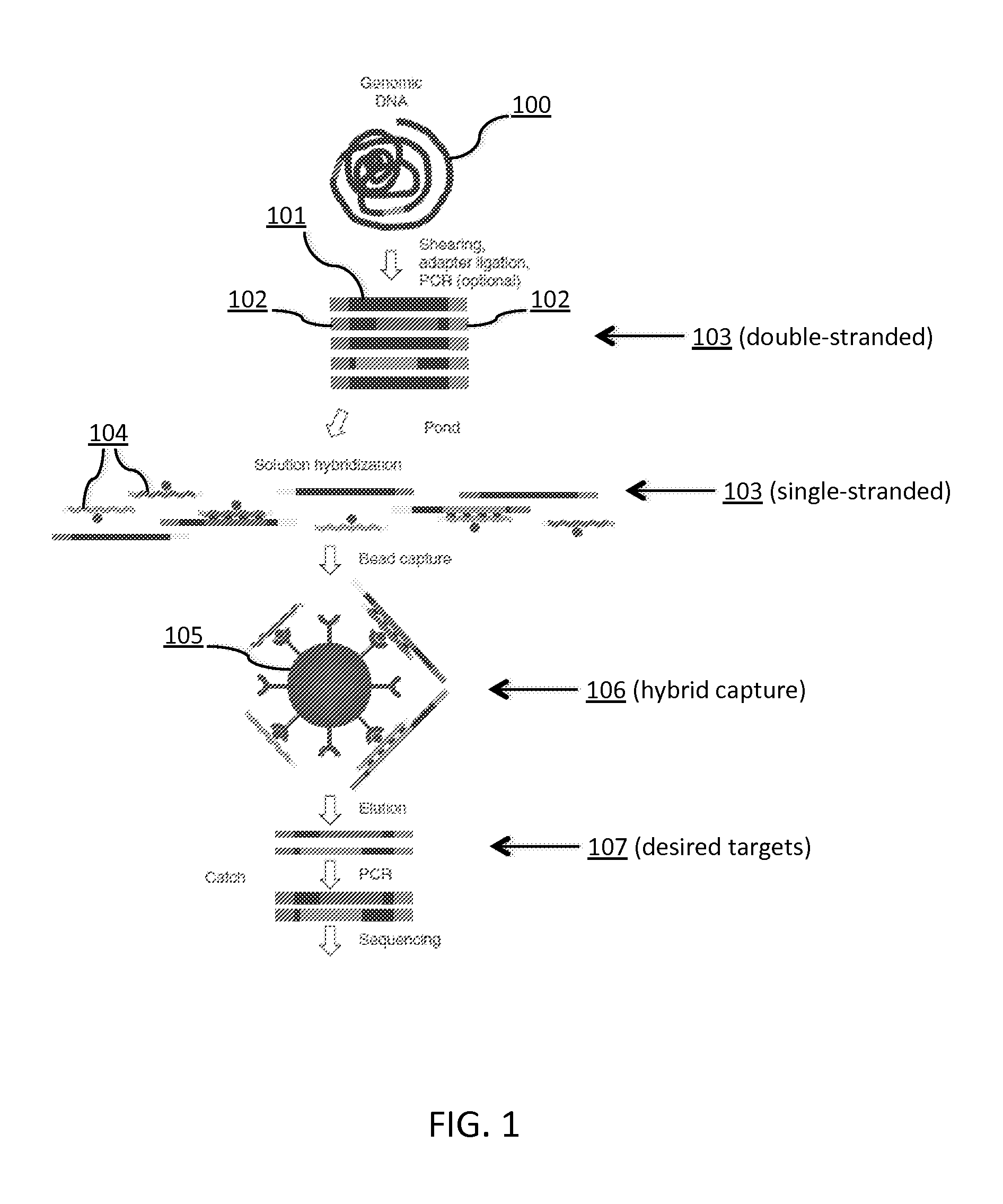
Tm-enhanced blocking oligonucleotides and baits for improved target enrichment and reduced off-target selection
ActiveUS20140031240A1Capture efficiency decreaseLow overall depthSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesDecoyTarget enrichment
The invention is directed to modified oligonucleotide compositions and methods for selectively reducing unwanted nucleic acid contaminants and enriching for desired nucleic acid targets from complex genomic nucleic acid mixtures for sequencing applications. The modified oligonucleotide compositions include one or more modified groups that increase the Tm of the resultant oligonucleotide composition.
Owner:FOUND MEDICINE INC +1
Modified polynucleotides for use in rna interference
InactiveUS20070167384A1Inhibit expressionImprove stabilityBiocideHydrolasesPhosphorylationOrthoester
Owner:DHARMACON INC
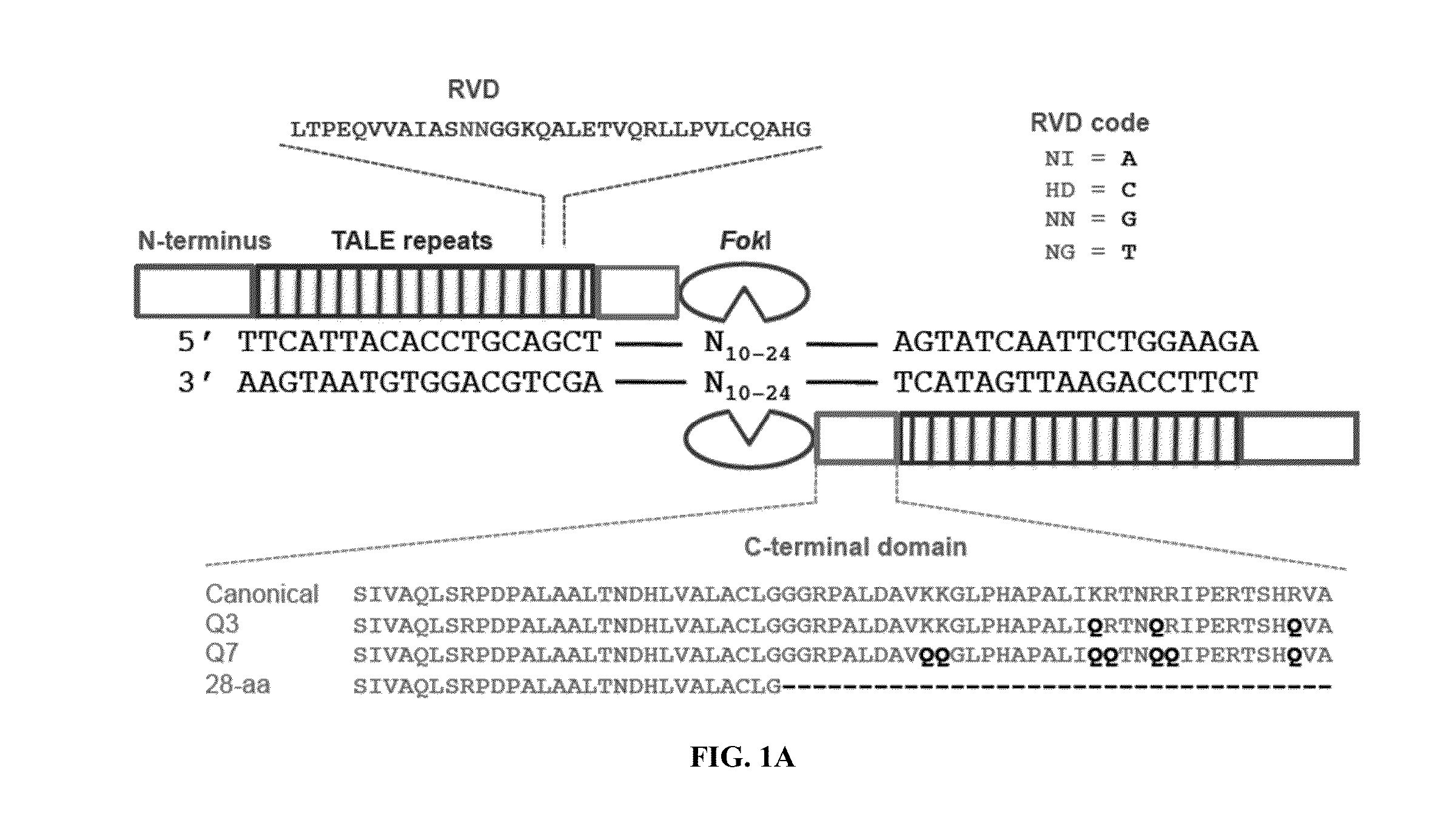
Engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE) domains and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150056177A1Increased on-target cleavage efficiencyReducing unspecific bindingFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleaseGenome
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with improved specificity and methods for generating and using such TALEs.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
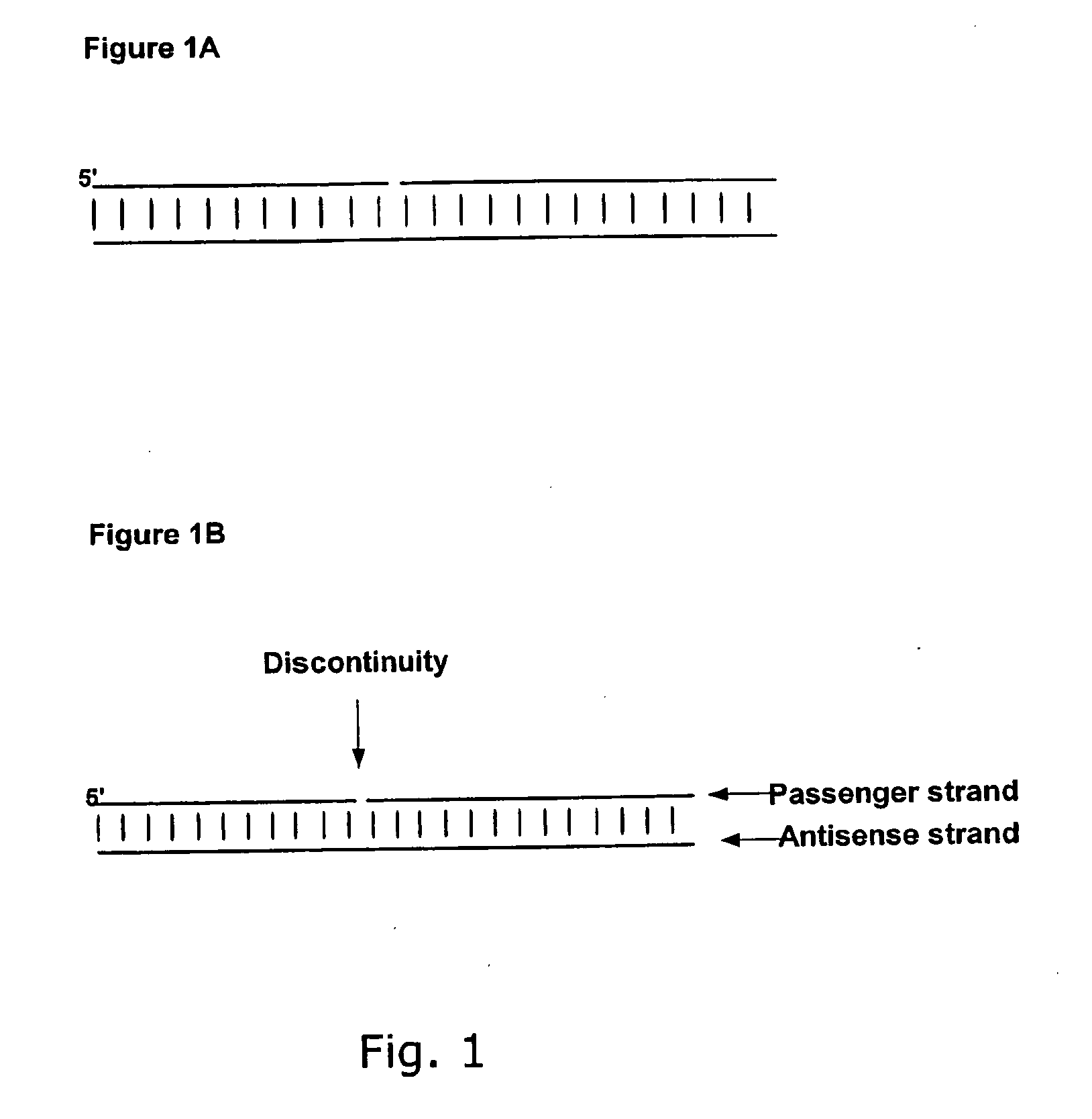
Small Internally Segmented Interfering RNA
ActiveUS20090182136A1Increase serum stabilityProlongs target knock downSugar derivativesActivity regulationPharmaceutical drugRegulator gene
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical and therapeutic compositions which comprise RNA complexes comprising an antisense strand and a discontinued passenger strand capable of regulating gene expression. The use of a discontinued passenger strand reduces off target effects of the RNA complexes and also has other advantages.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence for pig gene editing and screening method thereof
ActiveCN105886616AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome editingScreening method
The invention discloses an efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence for pig gene editing and a screening method thereof. The screening method includes: screening functional genes, performing ORF analysis, predicting a functional gene sgRNA recognition site guide sequence, detecting whole-genome off-target sites, grading predicted target sites according to off-target information and target site positions, sequencing, screening and statistically counting results, optimizing algorithms and developing software. The efficient specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence and the screening method thereof have the advantages that the pig specific sgRNA recognition site guide sequence is obtained through strict screening and inspection and includes the sgRNA recognition site guide sequences, for CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, of all pig protein encoding genes; the authenticating, grading and inspecting algorithms for specific sgRNA recognition and software corresponding to the algorithms and used for predicting and evaluating the pig functional gene sgRNA recognition site guide sequence are widely applicable to the sgRNA specific site prediction of non-model species with whole-genome sequences.
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
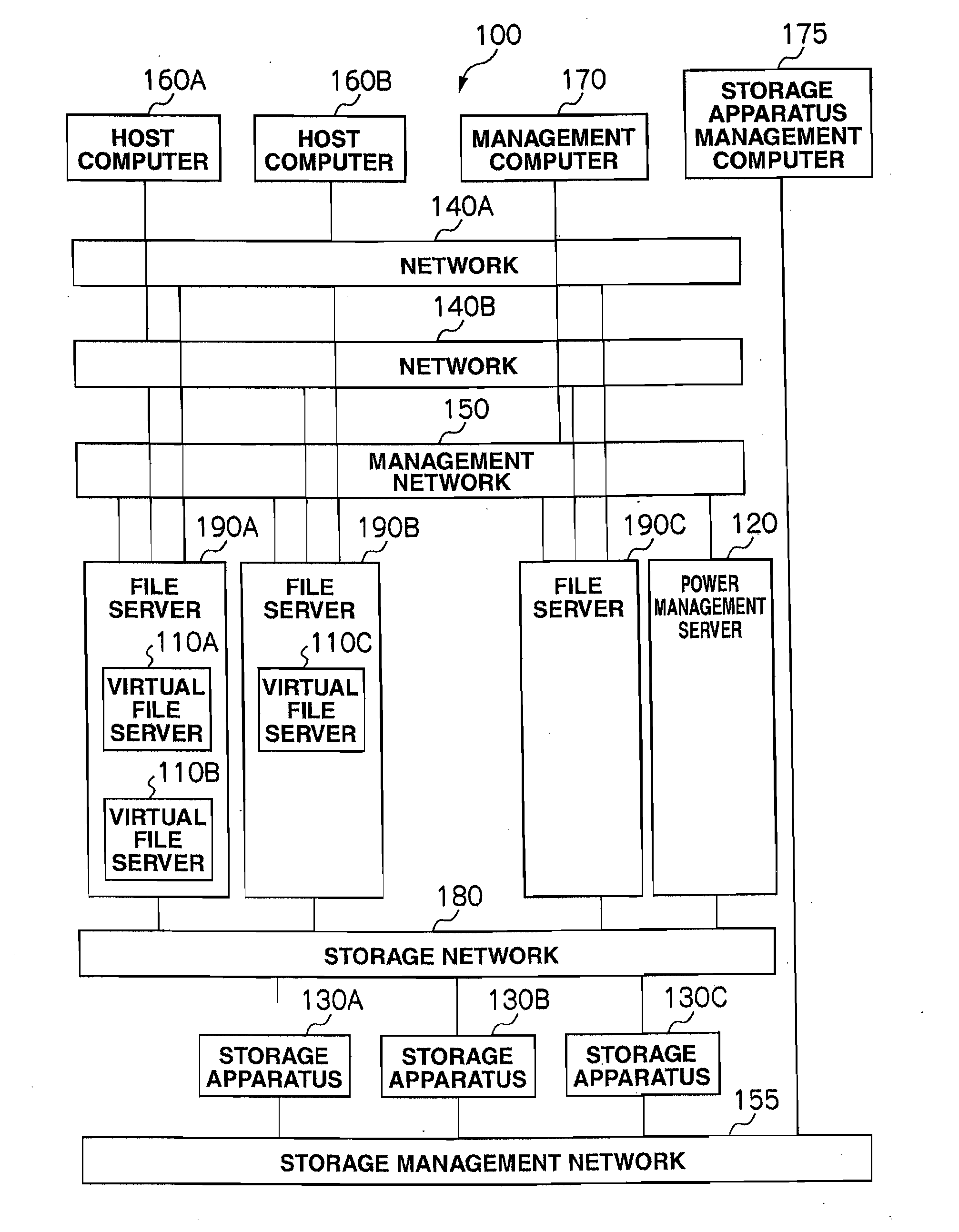
Storage system and power consumption reduction method for the same
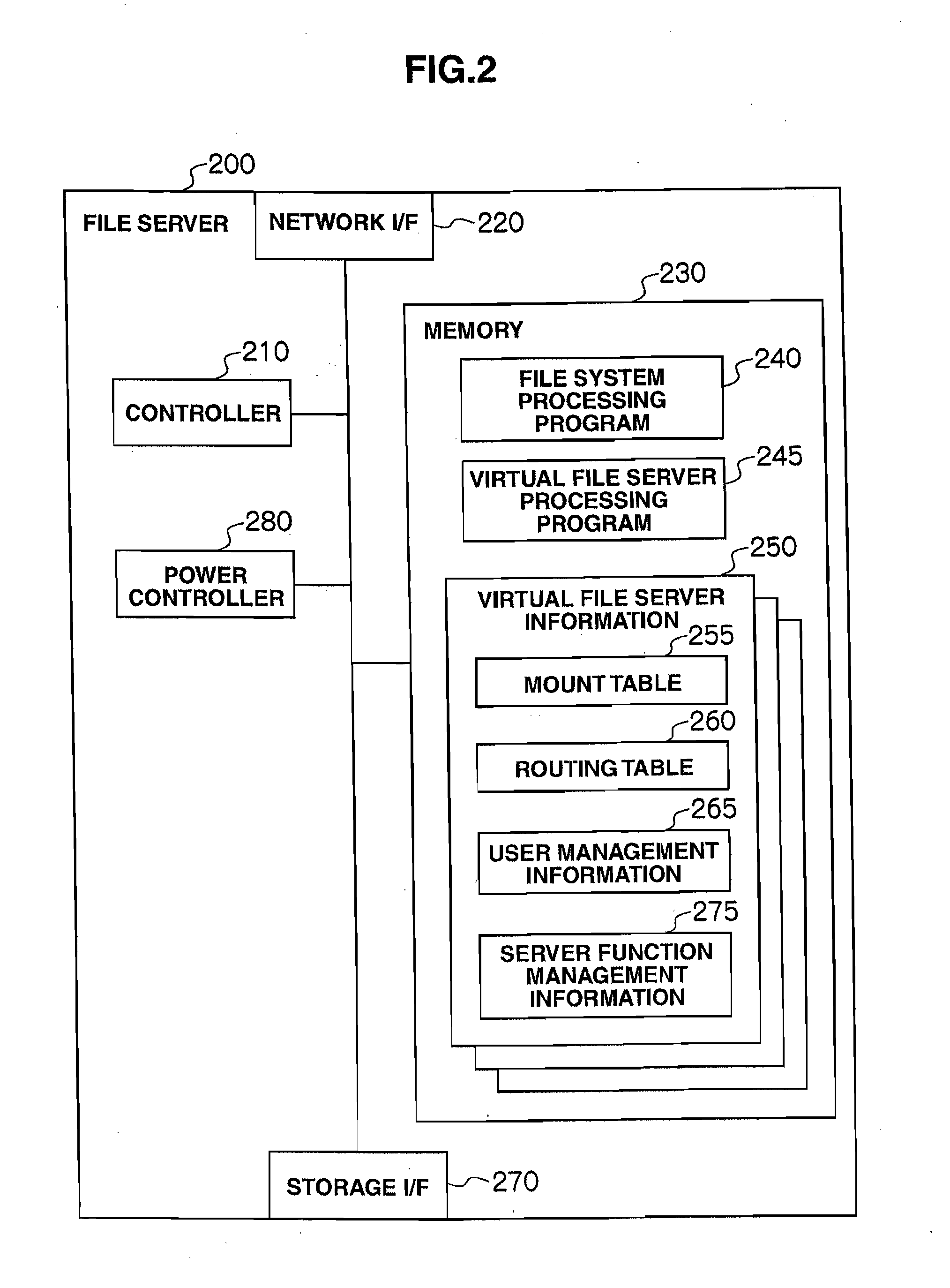
ActiveUS20110307729A1Reduce power consumptionAverage power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionFile serverOff targets
In a storage system that includes two or more file servers each including an arbitrary number of operating virtual file servers, a management server: holds a load information table regarding a load on each virtual file server for each time period and redundancy information table for the storage system; judges, with reference to the load information table and redundancy information table, whether or not the loads on the virtual file servers can be handled by a smaller number of file servers than the number of currently-operating file servers; selects, if the judgment result is positive, a power-off target file server and makes another file server fail over a virtual file server in the power-off target file server; and turns off the power-off target file server.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN108018316AEasy to makeLow miss rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMeiotic nuclear divisionEmbryo
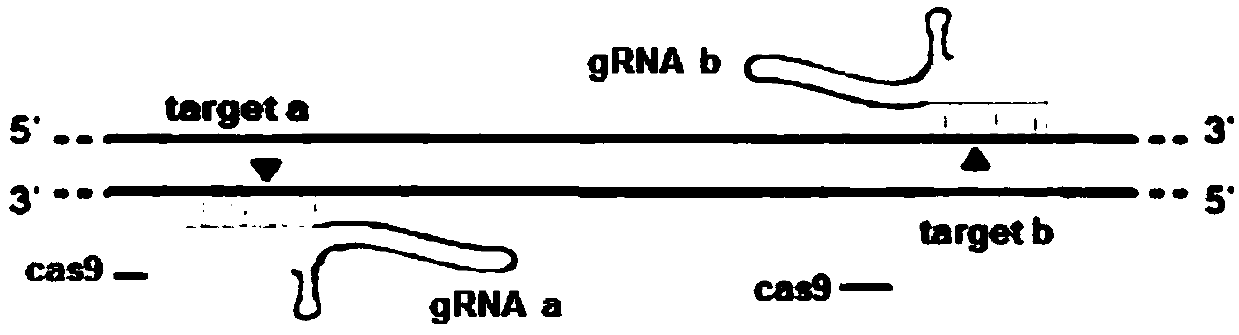
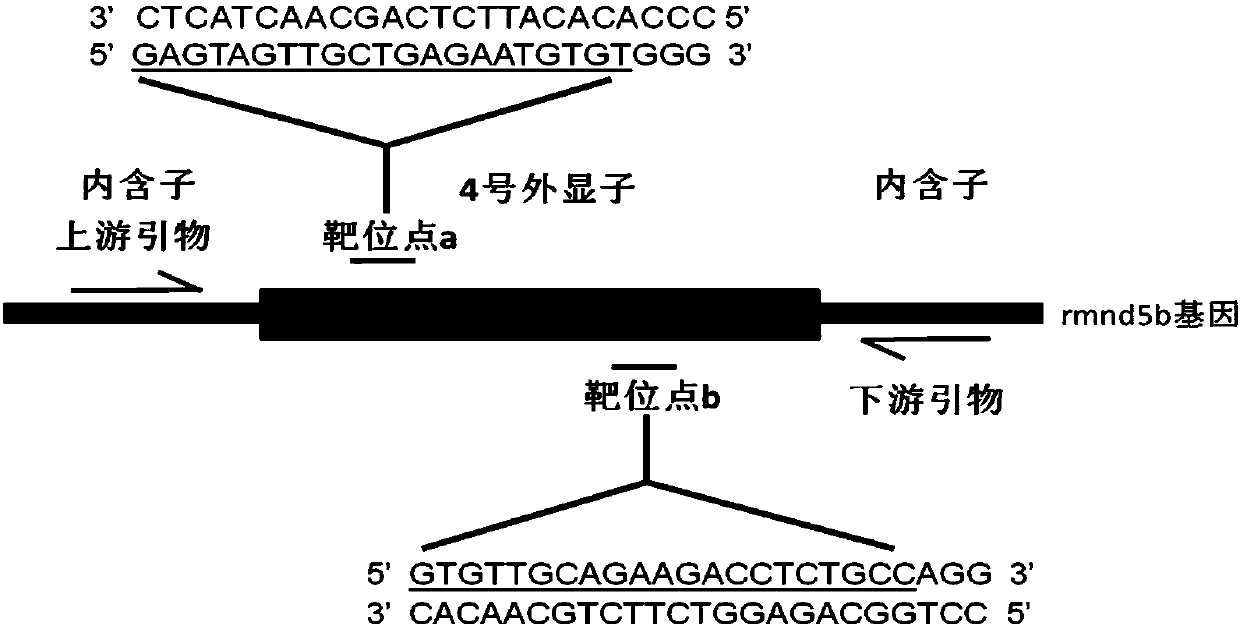
The invention discloses a method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout and belongs to the field of gene knockout. According to the method, construction of a gRNA expression vector and gRNA in-vitro synthesis are performed through design of a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated 9) gene knockout target site, micro-injection is performed on an embryo of the zebra fish, the effectiveness of the target site is detected, tail cutting identification is performed, TA cloning is performed on a target sequence, plasmids are subjected to Sanger sequencing, an F1 generation of heritable zebra fish mutants is obtained, the same mutant female fish and male fish are picked from mutants of the F1 generation, hybridization is performed, an F2 generation of the zebra fish mutants is obtained, F2 generation homozygote is picked from the F2 generation of the zebra fishmutants, F3 generation pure-line inheritance is performed, and an rmnd5b gene deletion type zebra fish strain is obtained. The method is lower in off-target rate and has good medical research value inresearch of the correlation between rmnd5b gene deletion and development of other organs.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Tm-ENHANCED BLOCKING OLIGONUCLEOTIDES AND BAITS FOR IMPROVED TARGET ENRICHMENT AND REDUCED OFF-TARGET SELECTION
ActiveUS20170096706A1Minimizing off-target selectionConducive to survivalMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDecoyTarget enrichment
Owner:FOUNDATION MEDICINE INC +1
Engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE) domains and uses thereof
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with improved specificity and methods for generating and using such TALEs.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for breeding tcf25 gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN107988268AEfficient and More Precise SilenceEasy to makeHydrolasesMicroinjection basedDiseaseGenotype Analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of gene knockout, and particularly discloses a method for breeding a tcf25 gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout. The method comprises the steps of through a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, designing an appropriate targeting gene locus on a tcf25 gene of the zebra fish, synthesizing in vitro to obtain specific sgRNA and Cas9-mRNA, microinjecting into a cell of the zebra fish, and after culturing an embryo for 60h, selecting the embryo for carrying out genotyping, so that the effectiveness of the selected locus is verified. The method provided by the invention is lower in off-target rate, removes the tcf25 gene through interference, is beneficial to further revealing the whole process of cardiac morphogenesis and a molecular mechanism regulating the process through researching functions through a genetics means, and is of great importance on understanding a cardiac disease pathology and researching and developing a new therapeutic schedule medically.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
5'-methylpyrimidine and 2'-O-methyl ribonucleotide modified double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20060122137A1Improves ribonuclease stabilityReduce off-target effectsPowder deliverySugar derivativesRibonucleotide synthesisDouble strand
The invention relates to a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecule comprising between about 15 base pairs and about 40 base pairs, at least one 5′-methyl-pyrimidine and at least one 2′—O-methyl ribonucleotide, and a methods of using such modified dsRNA molecule to increase stability of a siRNA molecule when in contact with a biological sample, to reduce off-target effects and to reduce interferon responsiveness (IFN) of the siRNA molecule.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
Getting-off targeted reminding method and device
ActiveCN107599971AAvoid missingSave manpower and material resourcesSignalling/lighting devicesAlarmsTransport engineeringOff targets
The embodiment of the present invention provides a getting-off targeted reminding method and device. The method comprises the following steps: receiving at least one piece of vehicle usage informationof a passenger, wherein the vehicle usage information includes identification (ID) information and / or route information of the passenger, and the ID information includes the account, the mobile phonenumber, the photograph and / or the name of the passenger; detecting the vehicle environment and information of the boarding passenger, including detecting the seat position information of the passenger and detecting the luggage position information, and determining whether the passenger carries luggage or not; a calculation processing module receiving the detected data and matching the data with the vehicle usage information to determine whether to remind the passenger or not according to needs; and reminding the passenger getting off, reminding the passenger not getting off, or reminding thepassenger missing the luggage or taking the wrong luggage according to an instruction of the calculation processing module. According to the invention, the seat, the luggage position and the ID of thepassenger are bond, thereby being capable of reminding the passenger getting off when the passenger needs to get off.
Owner:UISEE SHANGHAI AUTOMOTIVE TECH LTD
Safe and efficient CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology
InactiveCN108795902AImprove editing targetingImprove editing efficiencyHydrolasesDNA preparationA-DNASite-directed mutagenesis
The invention aims at the technical defects of off-target effects of an existing CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology to carry out site-directed mutation of an amino acid site on a site combined with a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of Cas9 protein to obtain the Cas9 protein with low off-target efficiency,so as to realize a gene editing unction with higher targeting performance and higher efficiency. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a method for carrying out HEK293T cell gene editing by adopting a gene editing method.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHANGENE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Cas9-DNA Targeting Unit Chimeras
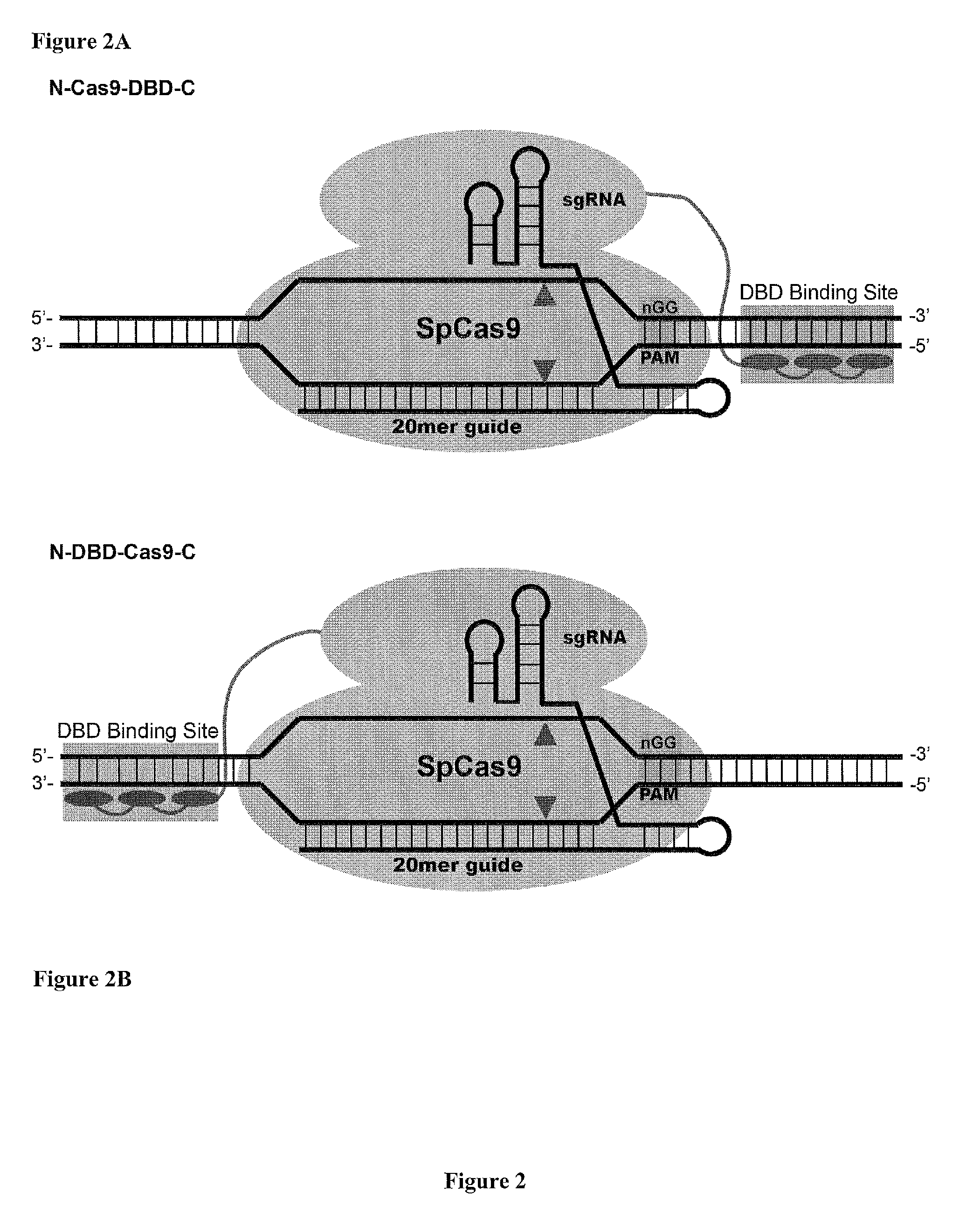
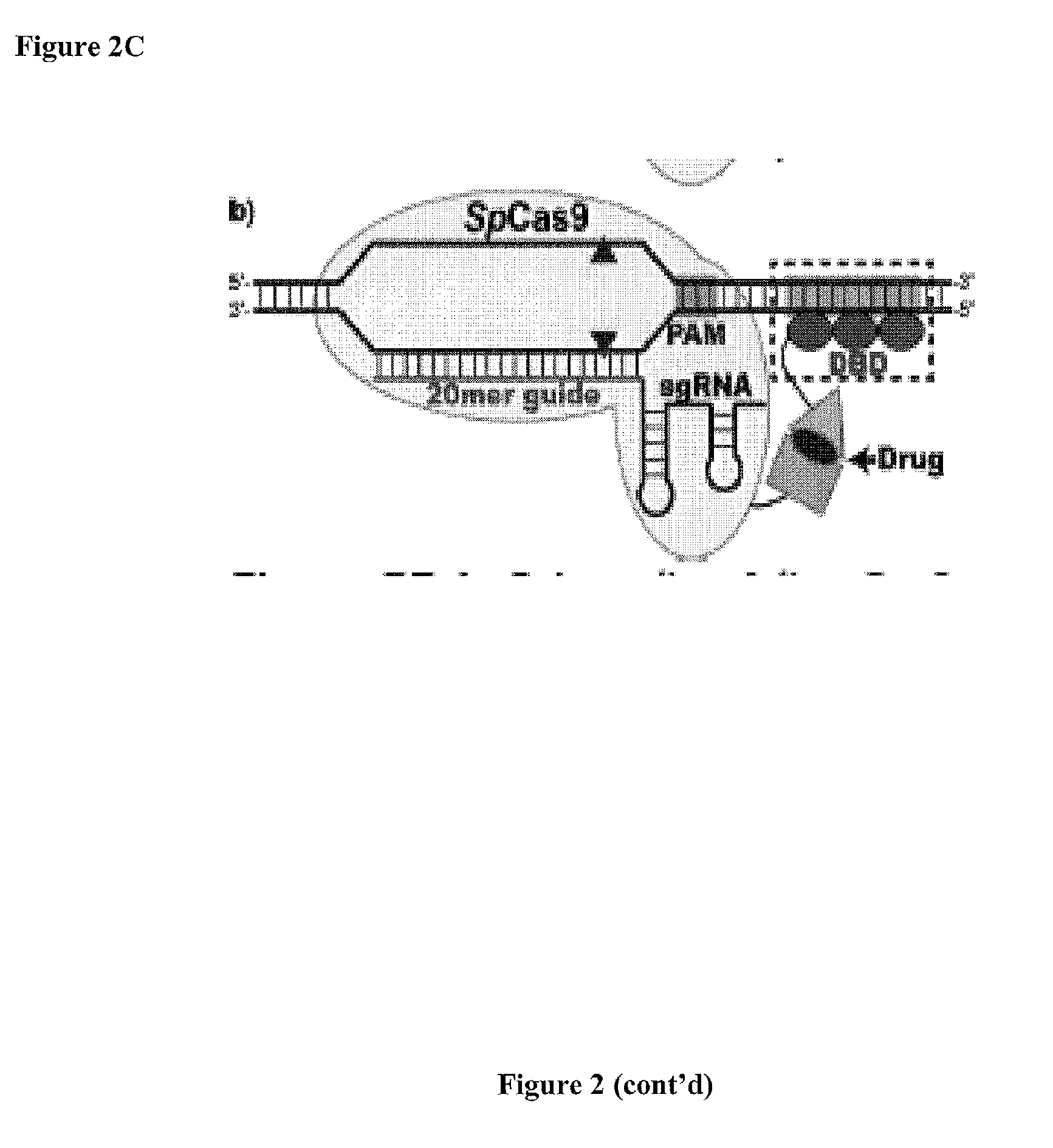
ActiveUS20160177278A1High precisionIncrease diversityFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesHuman DNA sequencingDna targeting
The present invention provides a Cas9 platform to facilitate single-site nuclease gene editing precision within a human genome. For example, a Cas9 nuclease / DNA-targeting unit (Cas9-DTU) fusion protein precisely delivers a Cas9 / sgRNA complex to a specific target site within the genome for subsequent sgRNA-dependent cleavage of an adjacent target sequence. Alternatively, attenuating Cas9 binding using mutations to the a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) recognition domain makes Cas9 target site recognition dependent on the associated DTU, all while retaining Cas9's sgRNA-mediated DNA cleavage fidelity. Cas9-DTU fusion proteins have improved target site binding precision, greater nuclease activity, and a broader sequence targeting range than standard Cas9 systems. Existing Cas9 or sgRNA variants (e.g., truncated sgRNAs (tru-gRNAs), nickases and FokI fusions) are compatible with these improvements to further reduce off-target cleavage. A robust, broadly applicable strategy is disclosed to impart Cas9 genome-editing systems with the single-genomic-site accuracy needed for safe, effective clinical application.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
CRISPR/Cas9 technology-based monocotyledon gene knockout vector and application thereof
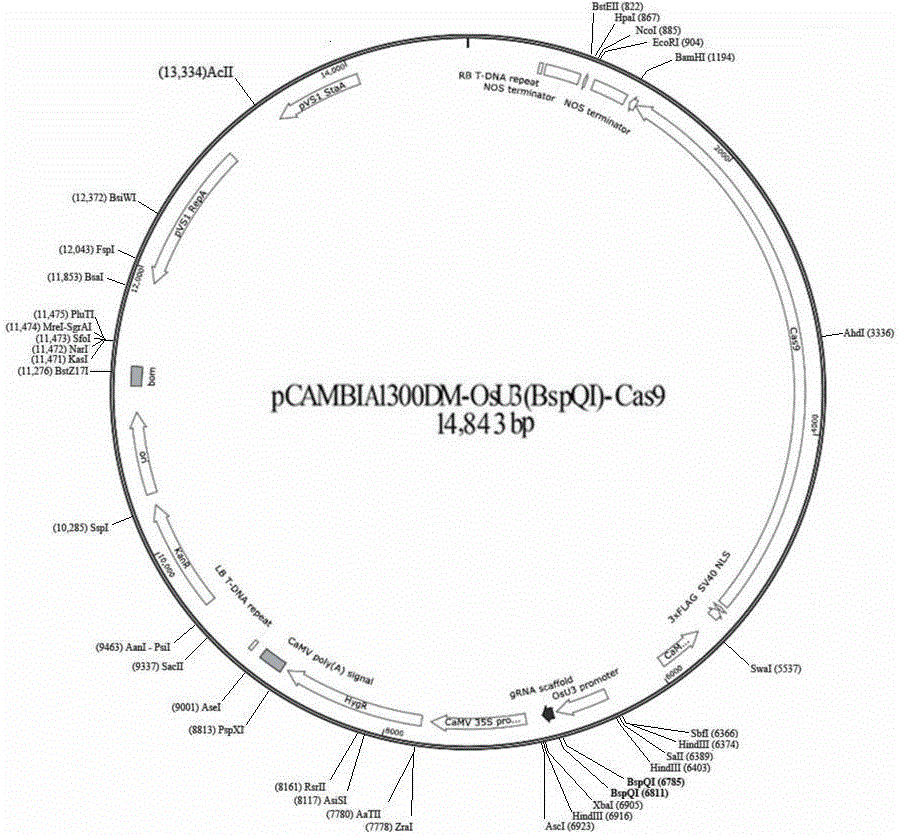
InactiveCN106434737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionInsertion siteOff targets
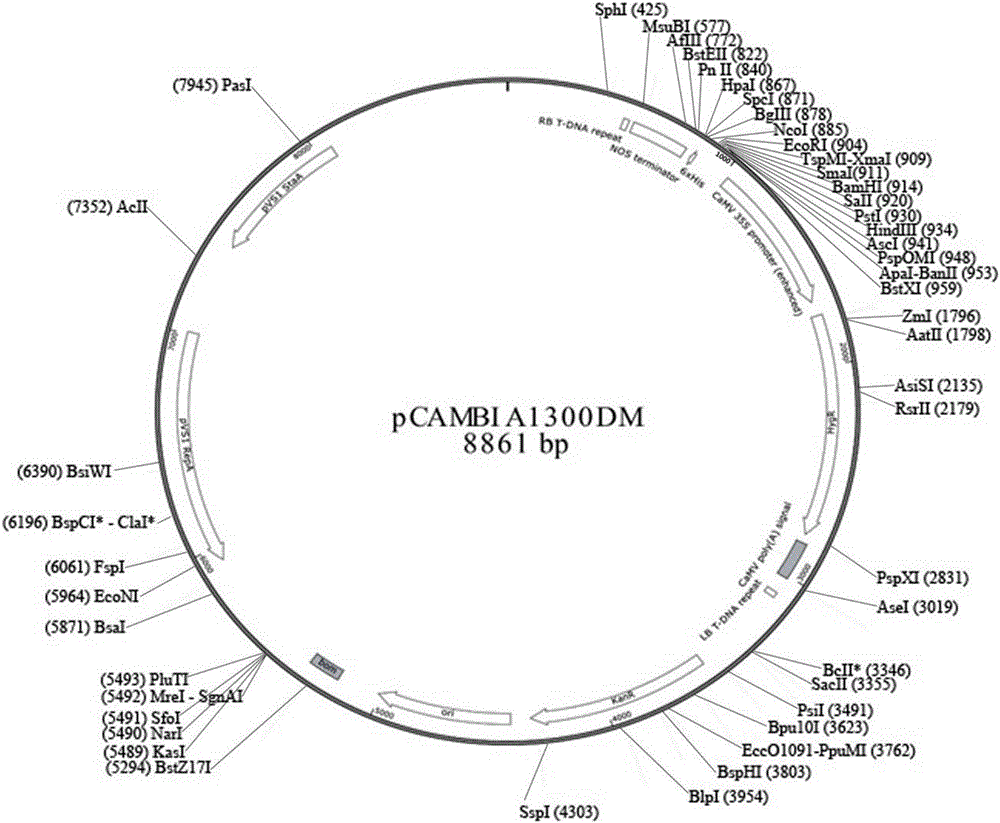
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 technology-based plant gene knockout vector and an application thereof. The plant gene knockout vector is monocotyledon CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9, and contains a BspQ I insertion site. The CRISPR / Cas9 plant knockout binary vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9 commonly constructed by an sgRNA-OsU3 sequence composed of the BspQ I insertion site and a 2x35s-hSpCas9-ter sequence can realize high-efficiency rapid construction of the monocotyledon gene knockout vector through a one-step restriction and ligation method; and the CRISPR / Cas9 knockout vector pCAMBIA1300DM-OsU3(BspQ I)-Cas9 has the characteristics of high targeting efficiency and low off-target efficiency, and can be applied to plant target gene knockout or applied to plant gene editing in a kit form.
Owner:内蒙古中科正标生物科技有限责任公司
Novel sirna structure for minimizing off-target effects and relaxing saturation of rnai machinery and the use thereof
InactiveUS20120238017A1Enhanced gene silencing effectsSolve the real problemSugar derivativesActivity regulationNucleotideSense strand
The present invention relates to a novel siRNA structure and the use thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to a double-stranded small interfering RNA molecule (siRNA molecule) comprising a 19-21 nucleotide (nt) antisense strand and a 15-19 nt sense strand having a sequence complementary to the antisense sequence, wherein the 5′ end of the antisense strand has a blunt end and the 3′ end of the antisense strand has an overhang, and to a method for silencing the expression of a target gene using the siRNA molecule.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Methods and compositions for blocking off-target nucleic acids from cleavage by crispr proteins
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
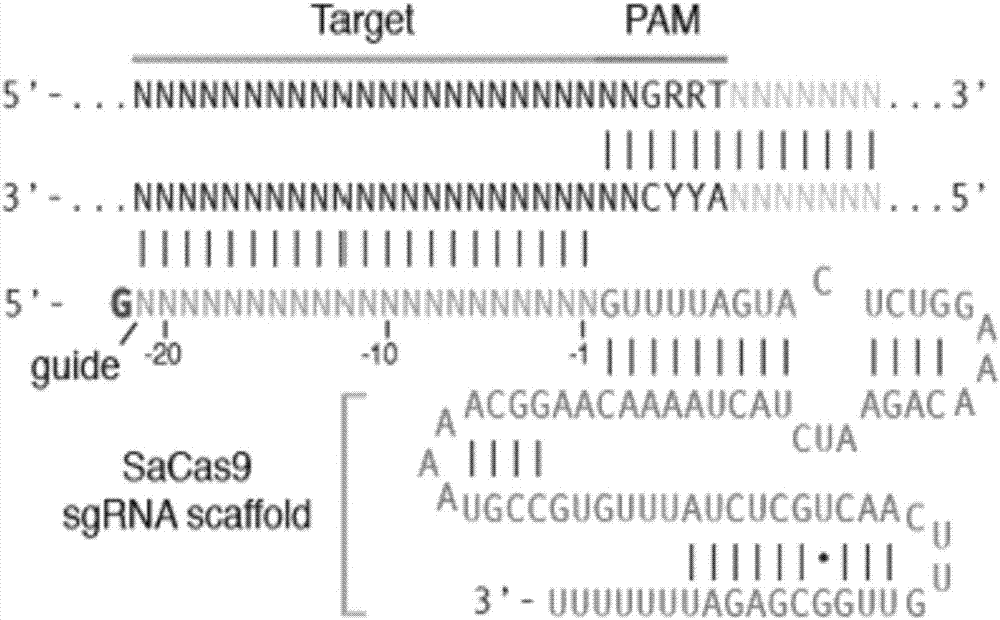
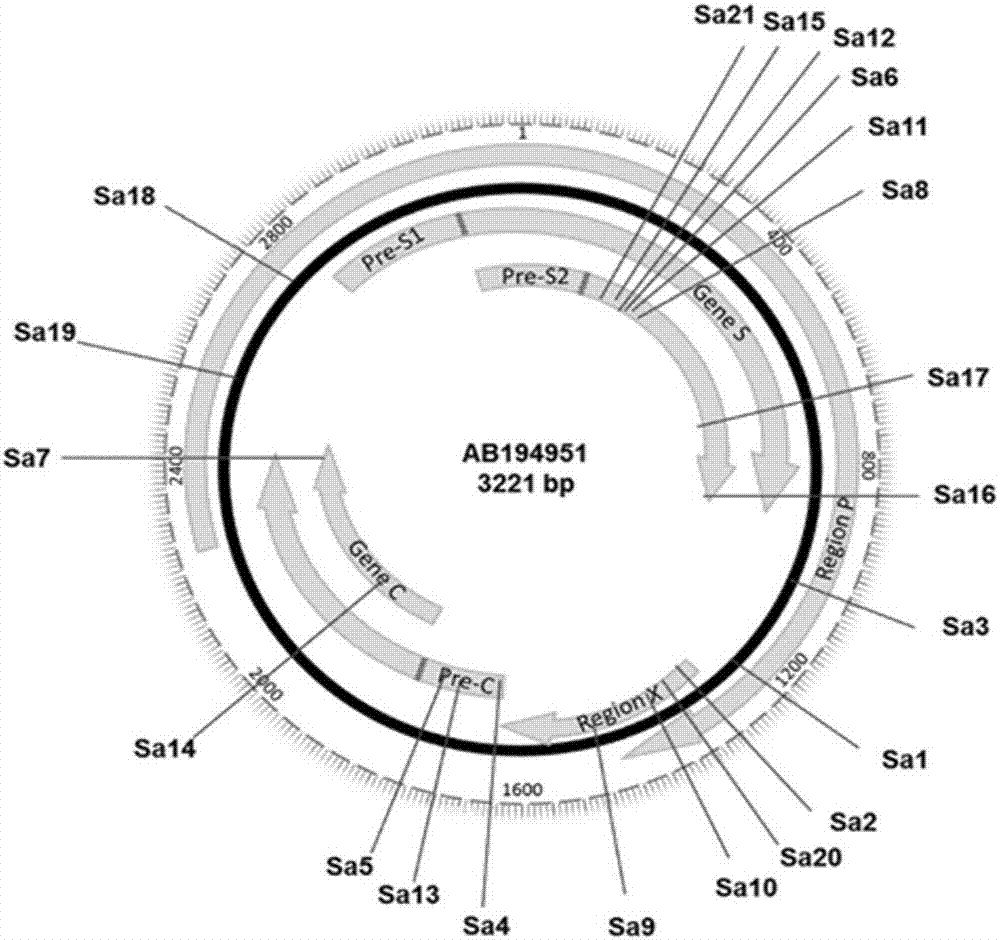
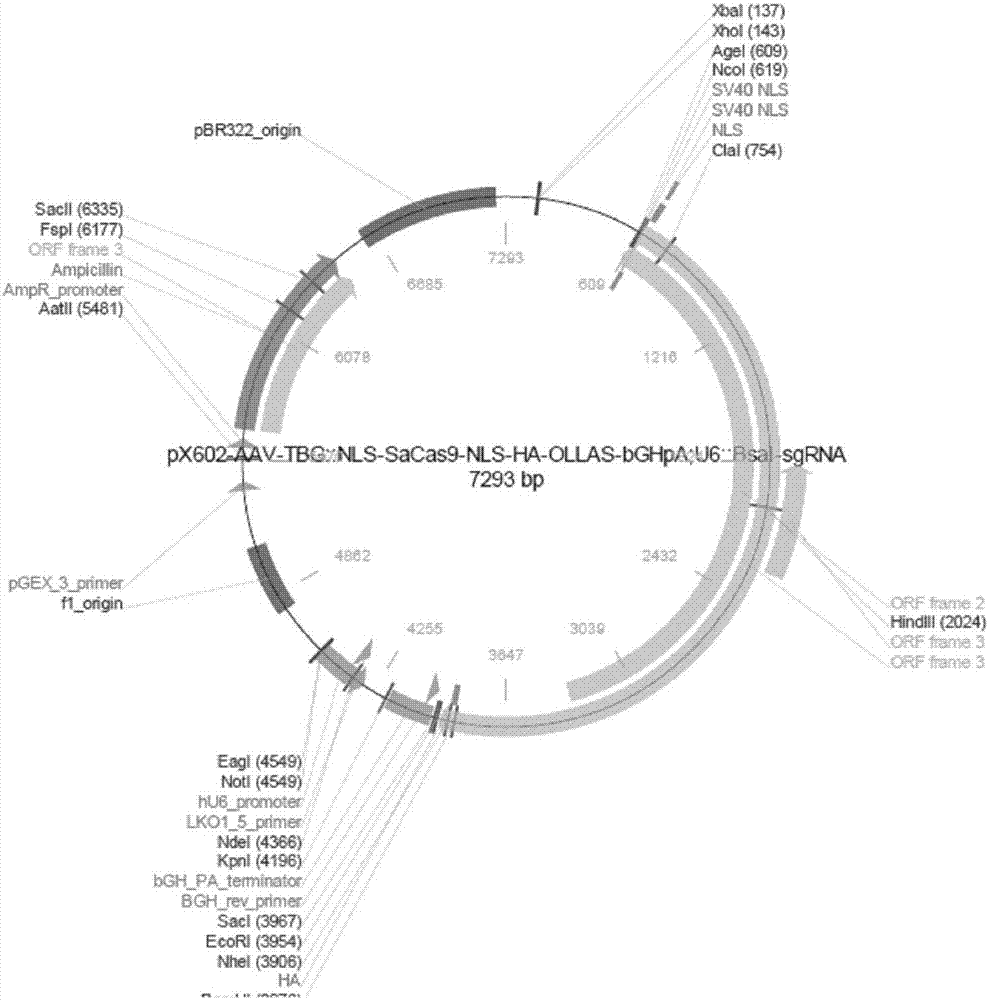
rAAV8-CRISPR-SaCas9 system and application of system in preparing hepatitis B therapeutics
The invention discloses a gRNA sequence. The sequence is capable of editing a DNA sequence in the manner of taking a hepatitis B viral genome specific locus as a target sequence. The invention also discloses a CRISPR-SaCas9 system containing the gRNA sequence and a recombinant adeno-associated virus packaged with the system. The system and the packaging virus show higher HBV scavenging activity in cells and in transgenic mice body. On the 38th day after twice continuous high dose injection, the contents of HBsAg and HBeAg in experimental group mice serum, compared with the control group, are respectively reduced by 62.96+ / -7.59% and 65.18+ / -3.08%; the HBV DNA content in the serum, compared with the control group, is reduced by 92.82+ / -3.67%; the liver and other visceral organs of the experimental mice are all free from any pathologic change, the off-target effect is also not detected and the application prospects of the gRNA sequence and the corresponding CRISPR-SaCas9 system provided by the invention in preparing the hepatitis B therapeutics are shown.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
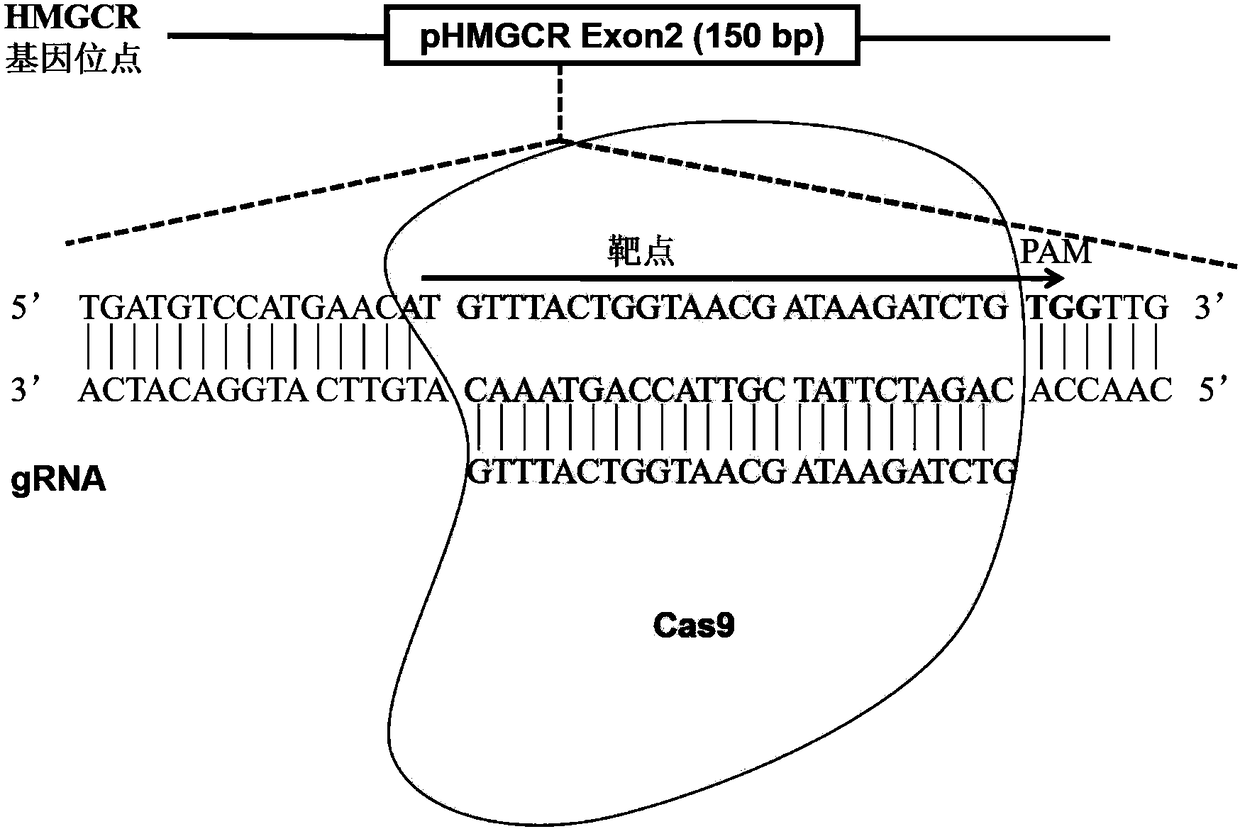
Method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology
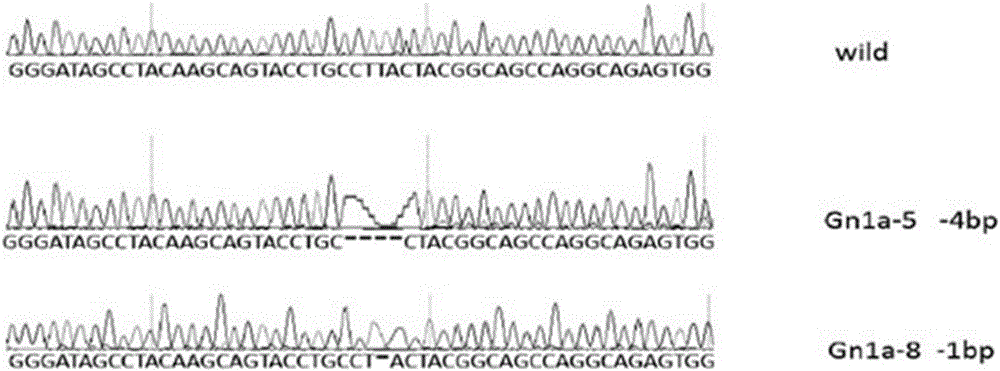
The invention relates to a method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on the CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The method is characterized in that two CRISPR / Cas9 target sequence aiming at the HMGCR gene isdesigned, a gRNA single chain is synthesized in vitro, annealing is performed to obtain two gRNA double-chain DNA target insertion fragments, the insertion fragments are inserted into PX459 (pSpCas9(BB)-2A-Puro)V2.0 vectors to obtain the two different-locus plasmids of the target HMGCR gene; the two plasmids are transfected into PK15 cells, puromycin is used to process the cells, the processed cell genome DNA is extracted to perform PCR amplification, the PCR product is denatured, annealing is performed, and then T7E1 is used to perform HMGCR gene knockout identification. The method has the advantages that method can be used for analyzing the expression conditions of sequence and mRNA after the HMGCR gene knockout, whether an off-target phenomenon exists or not can be verified by using amethod combining PCR and T7E1 enzyme treatment, and accordingly the specificity based on target sequence HMGCR-gRNA can be determined; the method is applicable to cell and animal models to achieve fixed-point HMGCR gene knockout, has a reference value to the knockout of other genes, and is good in effect, simple, economical, short in time and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
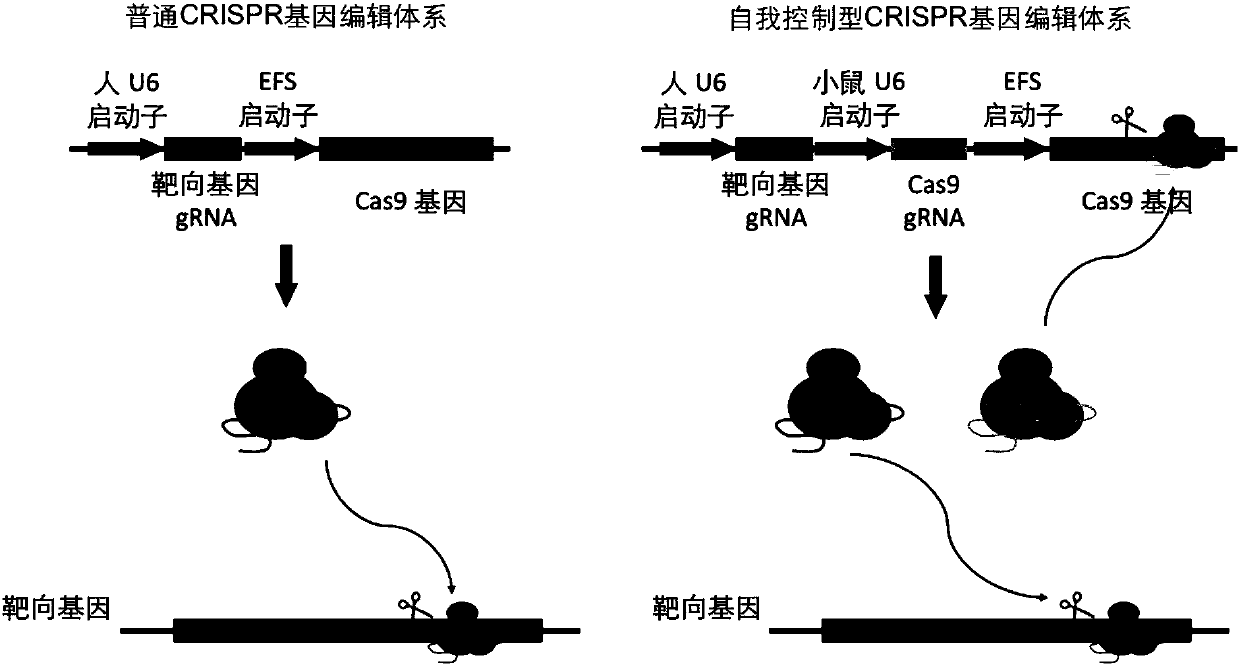
Highly specific CRISPR genome editing system
The invention provides a highly specific CRISPR genome editing system. The gRNA of a target Cas9 gene is introduced into a CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing system, when (or after) target cell genome editingis performing, the gRNA of the target Cas9 gene can mediate the cutting of Cas9 gene, thus the expression time of the Cas9 gene is prominently reduced, the off-target effect caused by long term expression of Cas9 in a CRISPR system is reduced, and the targeting specificity is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Allele selective gene editing and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170080107A1Improve efficiencyHigh frequencySenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseGene selection
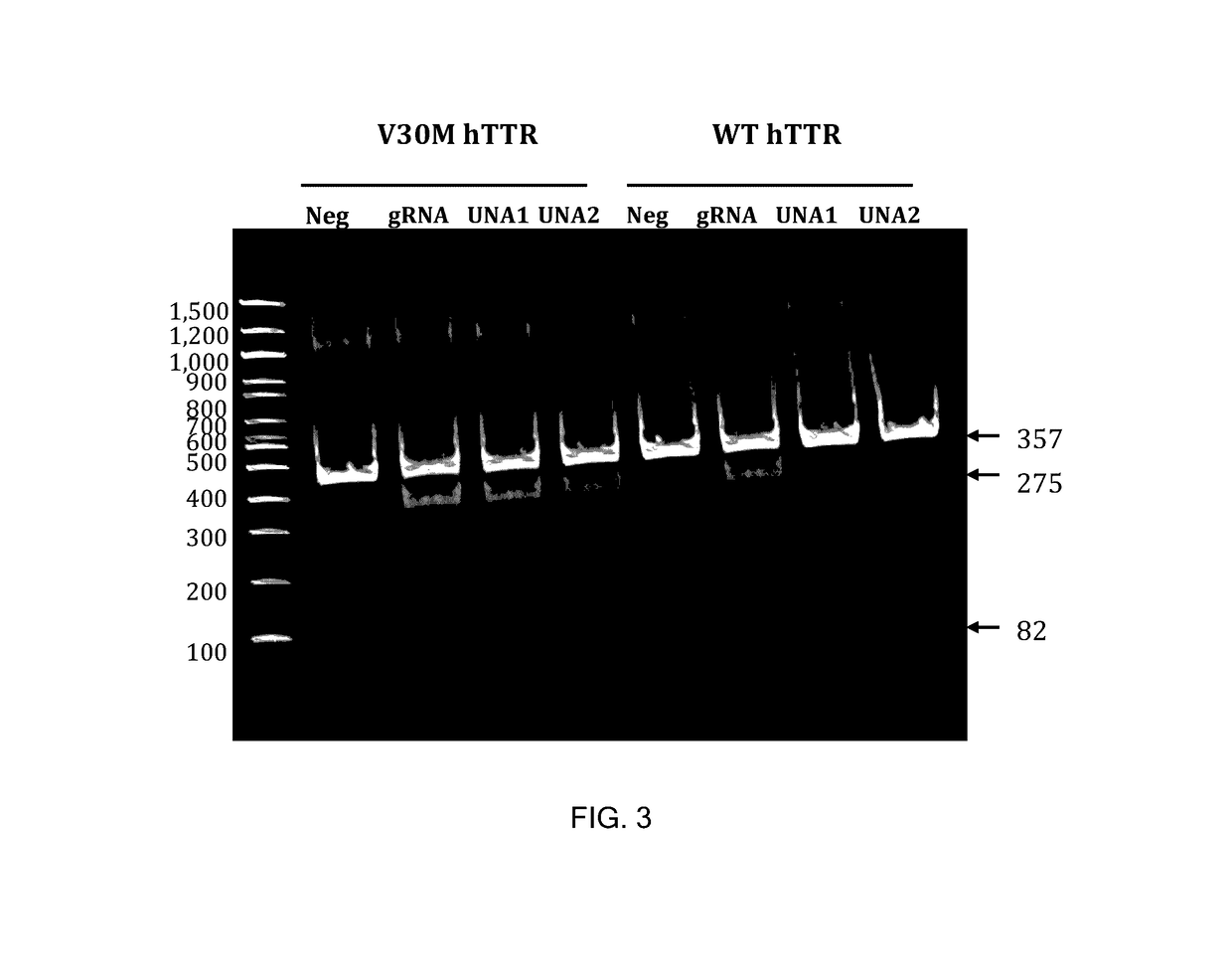
This invention encompasses compounds, structures, compositions and methods for therapeutic guide molecules that direct CRISPR gene editing. A guide molecule for directing gene editing can be allele selective, or disease allele selective, and can exhibit reduced off target activity. A guide molecule can be composed of monomers, including UNA monomers, nucleic acid monomers, and modified nucleotides, wherein the compound is targeted to a genomic DNA. The guide molecules of this invention can be used as active ingredients for editing or disrupting a gene in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
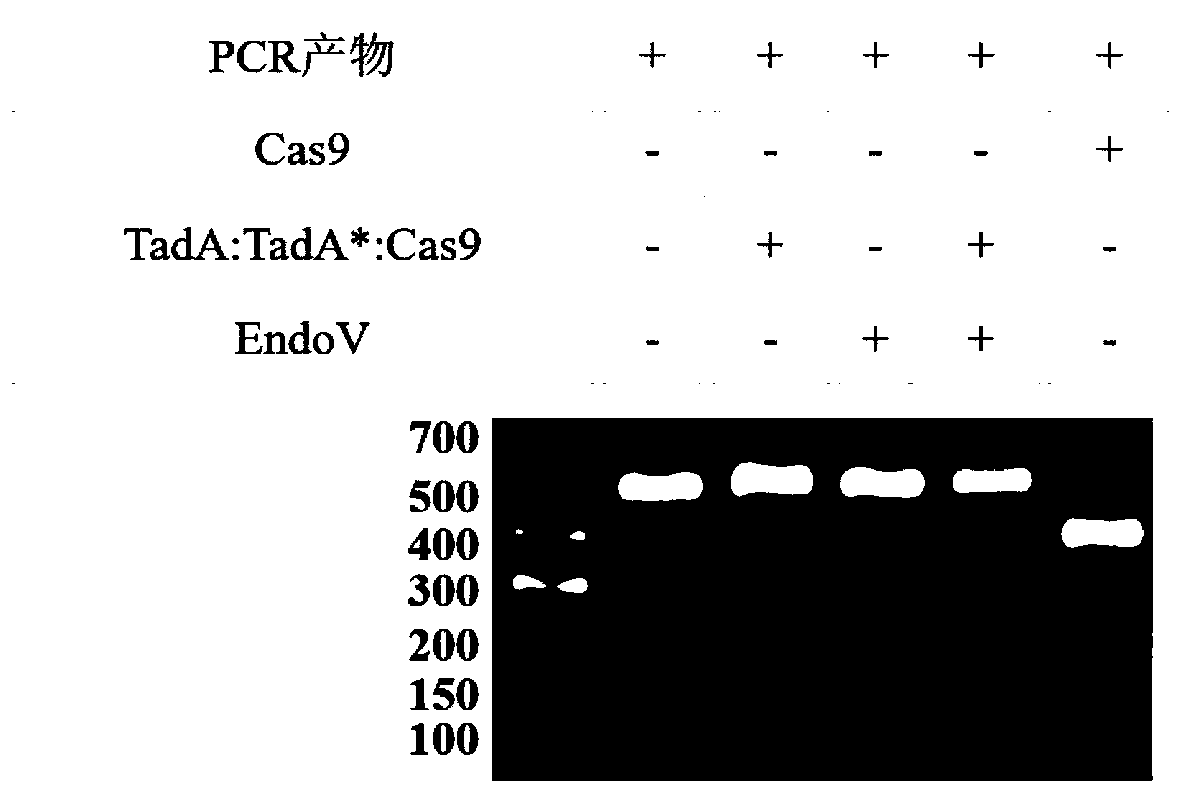
Method for detecting off-target effect of adenine base editor system based on whole genome sequencing, and its application in gene editing
PendingCN109295186AAccelerate cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesGenome editingWhole genome sequencing
The invention provides a method for detecting the off-target effect of an adenine base editor system based on whole genome sequencing, and its application in gene editing, The adenine base editor system comprises a TadA:TadA*:Cas9 fusion gene and gRNA. The system can catalyze the efficient replacement of adenine (A) at a target site with guanine (G), and has a broad application prospect in human disease gene editing therapy and disease model construction. The first method for detecting the off-target effect of the ABE system in a whole genome range, called EndoV-seq method for short, is developed in the invention. The EndoV-seq method provided by the invention has a broad application prospect in the field of gene editing, especially gene editing therapy.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Oligomers with improved off-target profile
ActiveCN104955950AOff-target binding is not easySugar derivativesActivity regulationLow affinityOligomer
Owner:GUANGDONG MAIJINJIA BIOTECH CO LTD
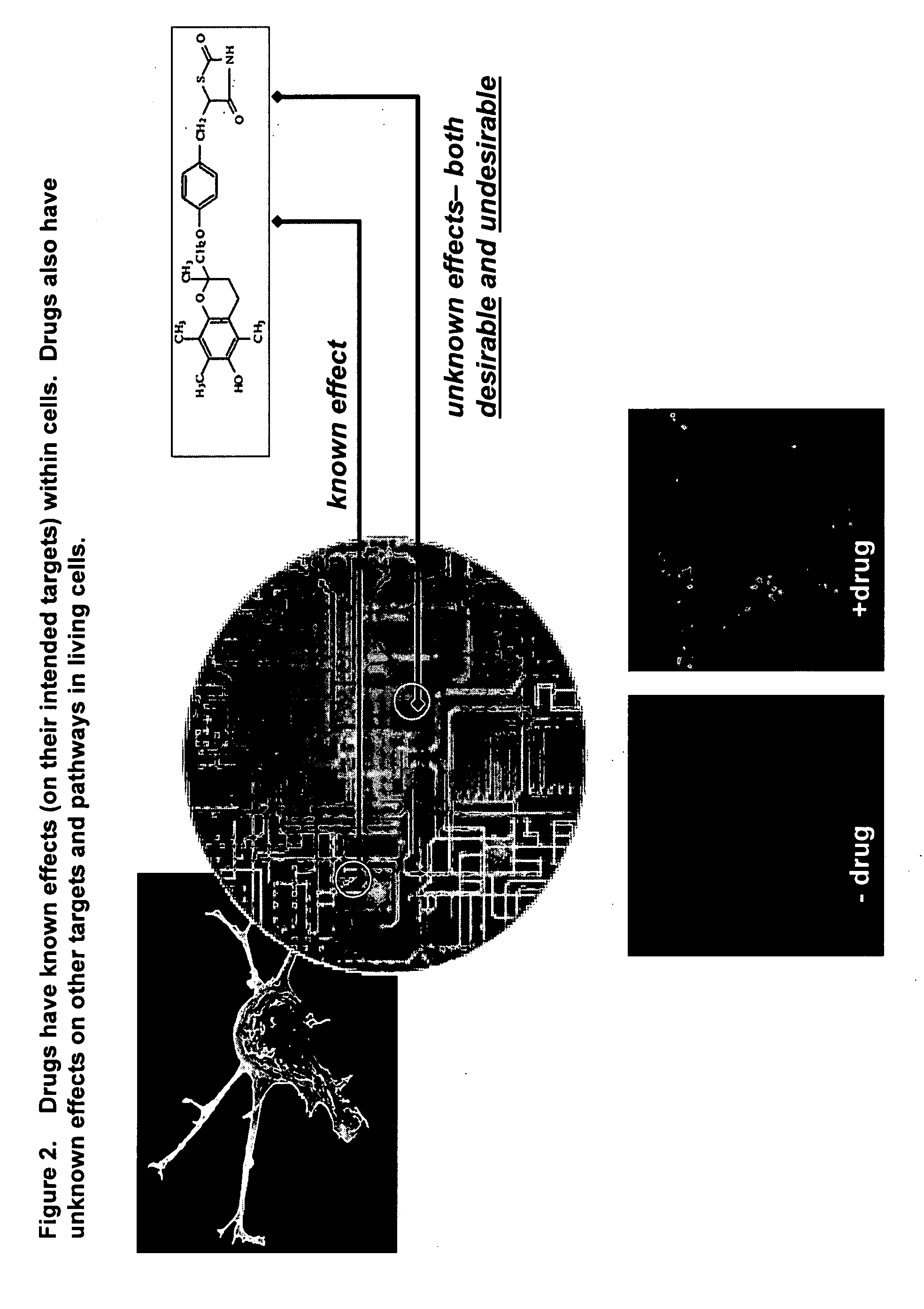
Identifying off-target effects and hidden phenotypes of drugs in human cells
InactiveUS20070212677A1Enable optimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHuman bodyToxicant
This invention provides principles, methods and compositions for ascertaining the mechanism of action of pharmacologically important compounds in the context of network biology, across the entire scope of the complex pathways of living cells. Importantly, the principles, methods and compositions provided allow a rapid assessment of the on-pathway and off-pathway effects of lead compounds and drug candidates in living cells, and comparisons of lead compounds with well-characterized drugs and toxicants to identify patterns associated with efficacy and toxicity. The invention will be useful in improving the drug discovery process, in particular by identifying drug leads with desired safety and efficacy and in effecting early attrition of compounds with potential adverse effects in man.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
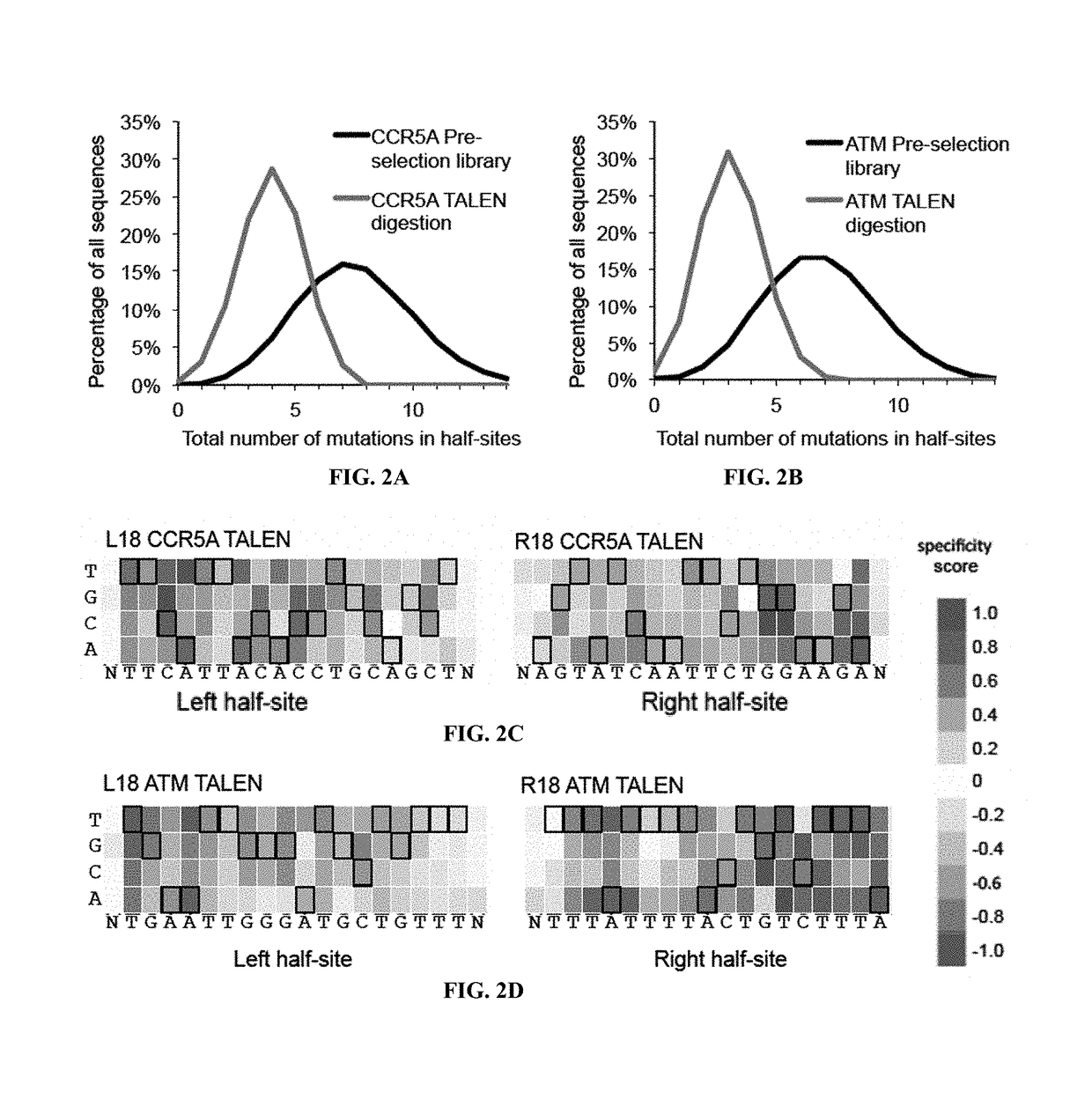
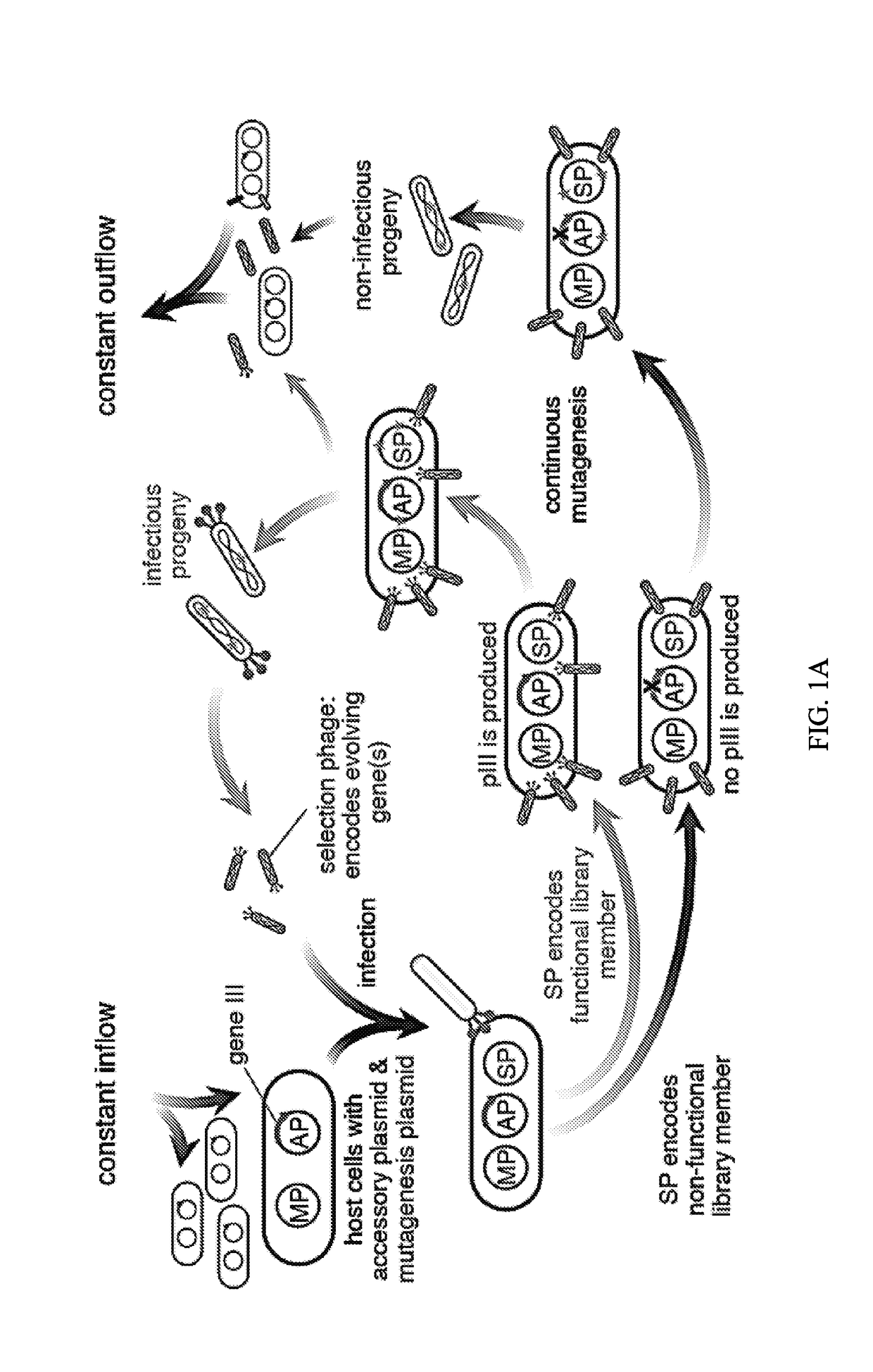
Evolution of talens
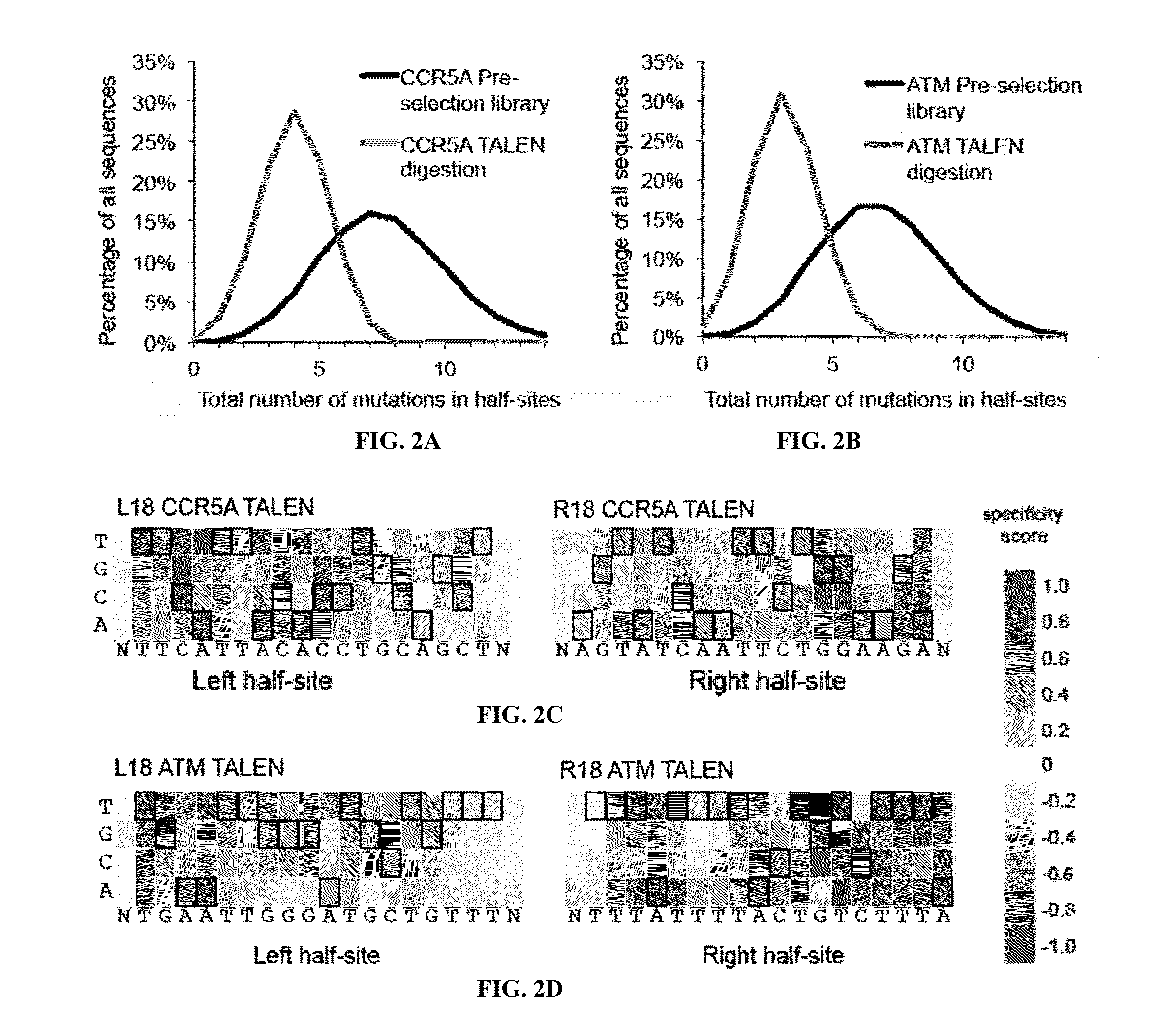
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
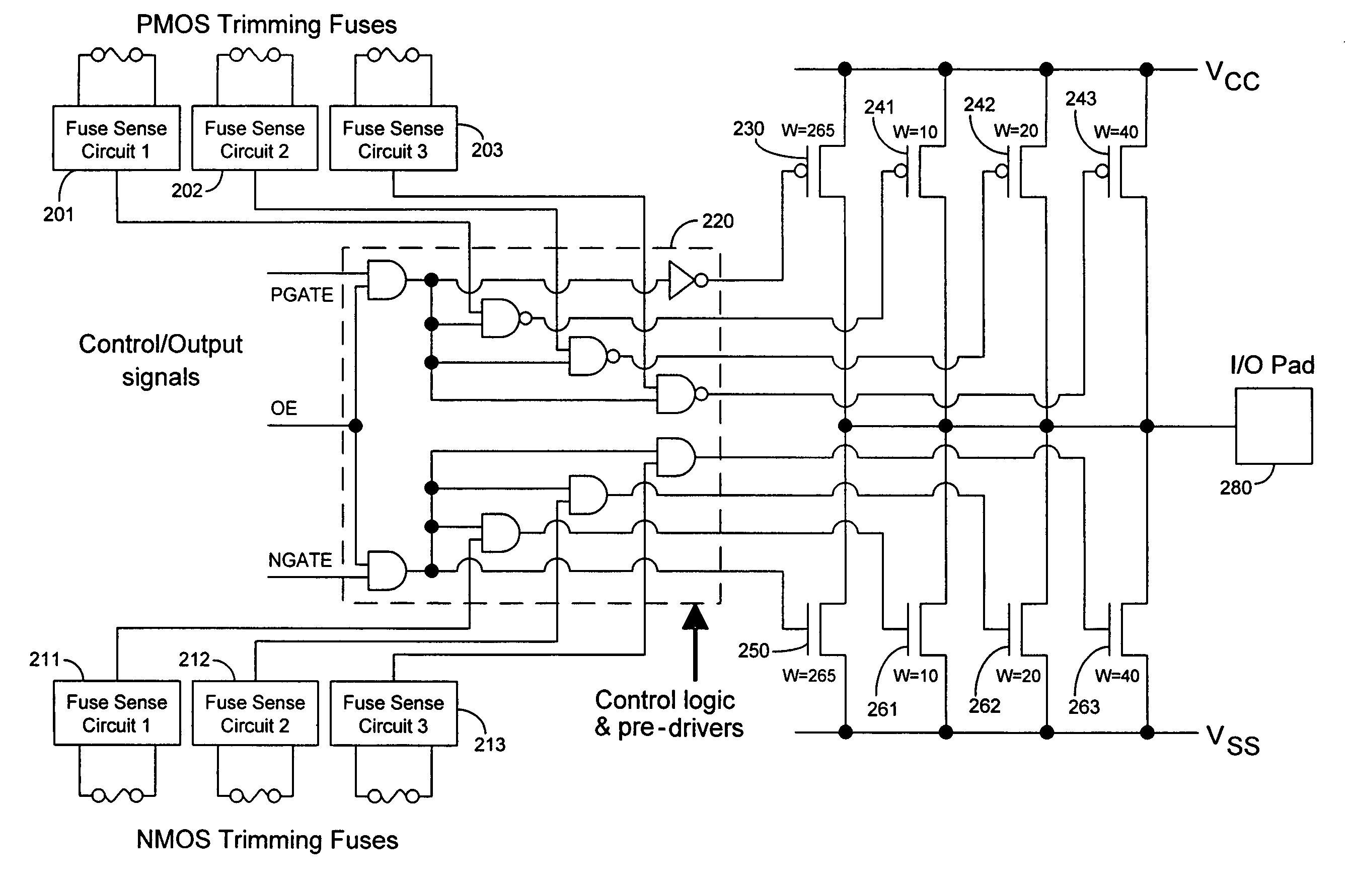
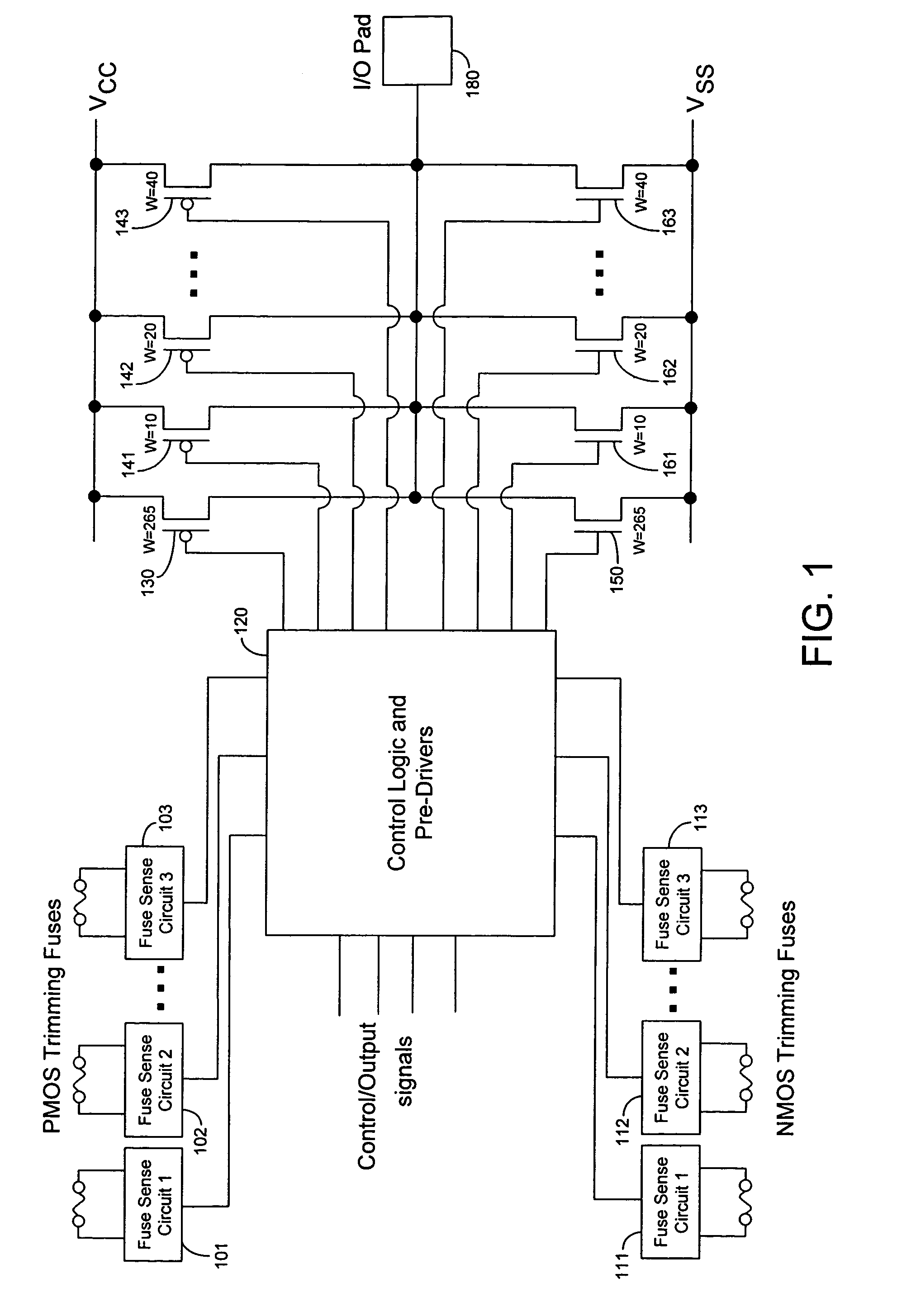
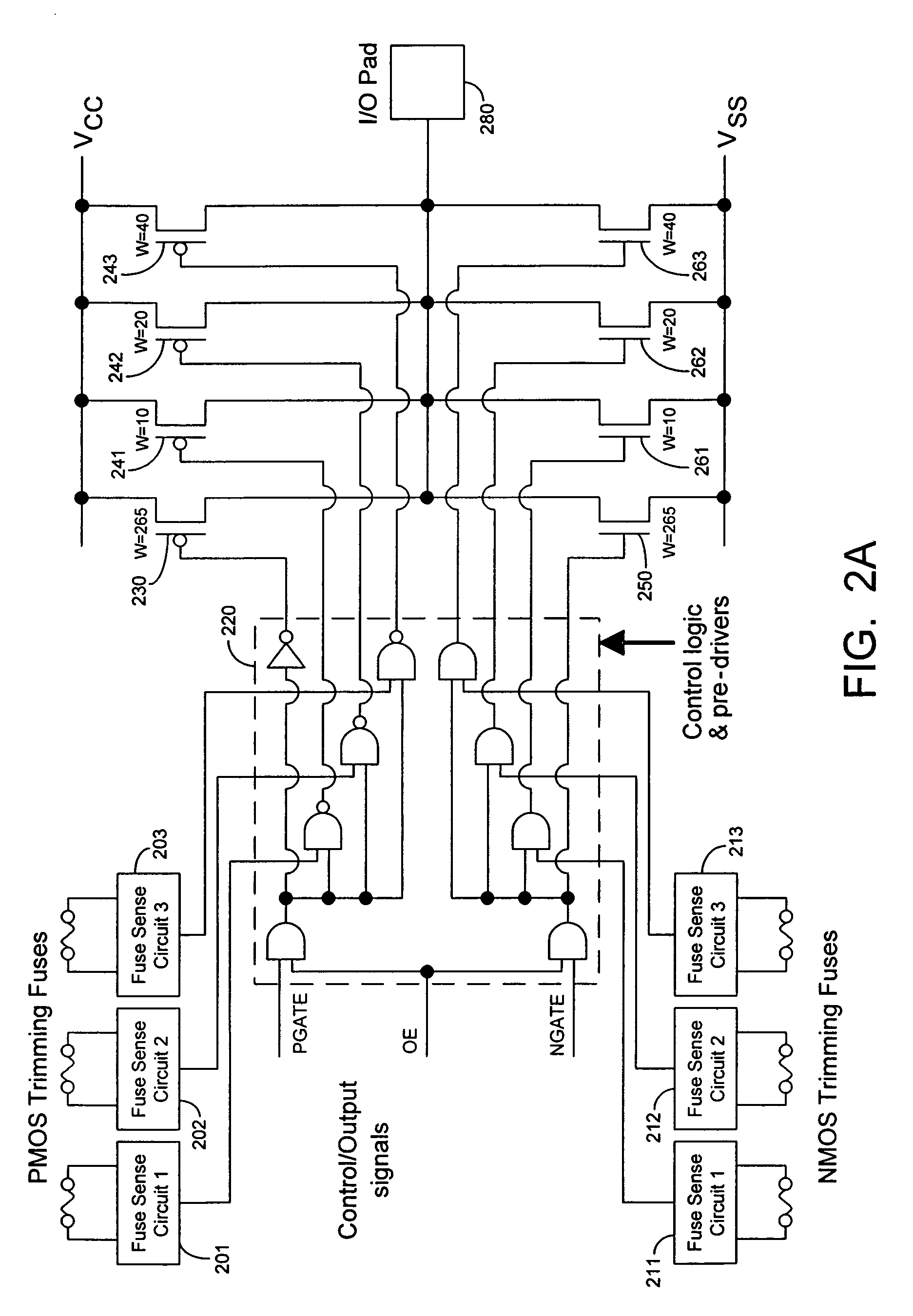
Techniques for trimming drive current in output drivers
InactiveUS7355453B2Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDriving currentOff targets
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Development of a Protein-Based Biotherapeutic Agent That Penetrates Cell-Membrane and Induces Anti-Tumor Effect in Solid Tumors - Improved Cell-Permeable Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (iCP-SOCS3) Proteins, Polynucleotides Encoding the Same, and Anti-Tumor Compositions Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20160060314A1Improve anti-tumor effectImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotherapeutic agentOff targets
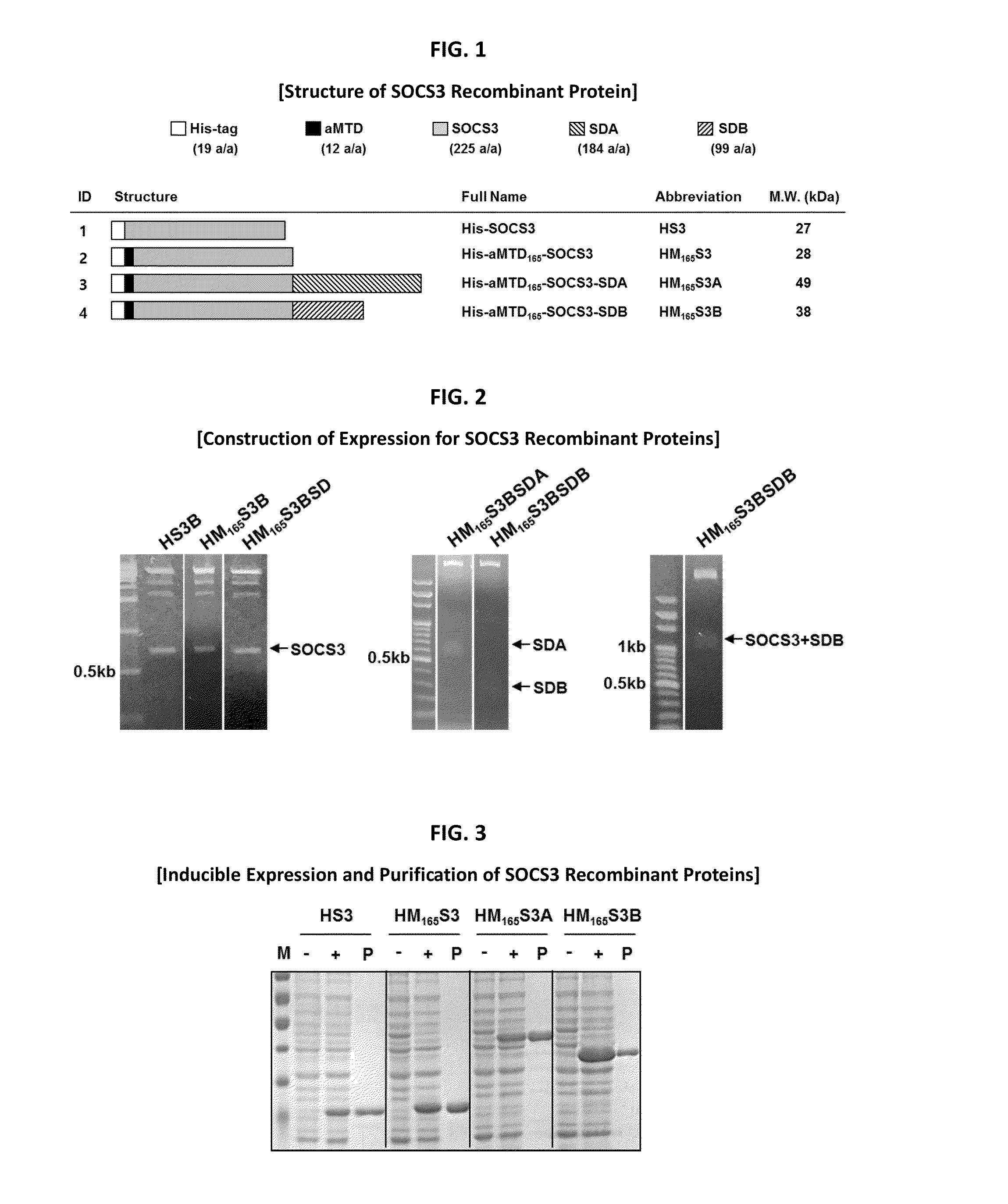
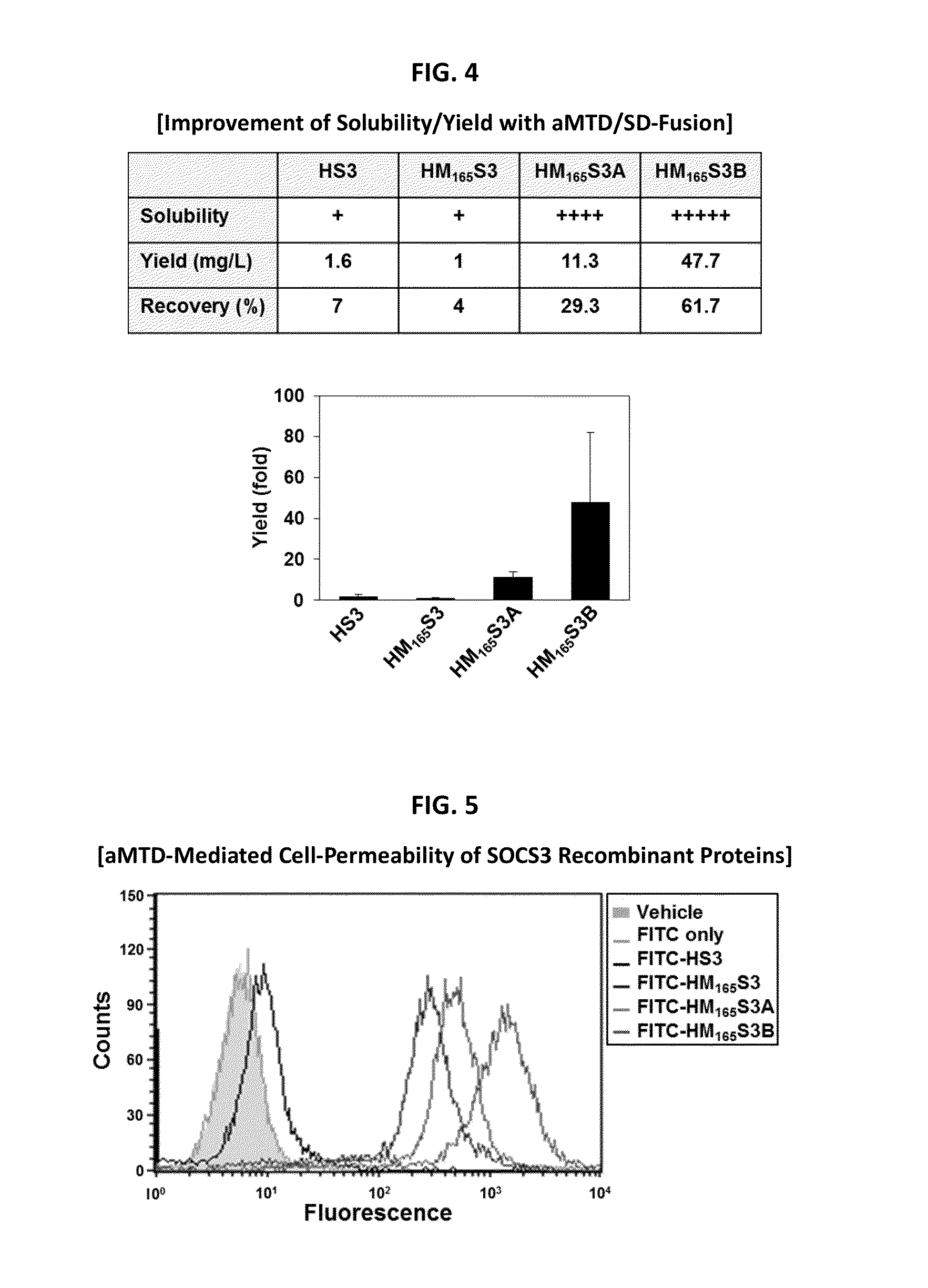
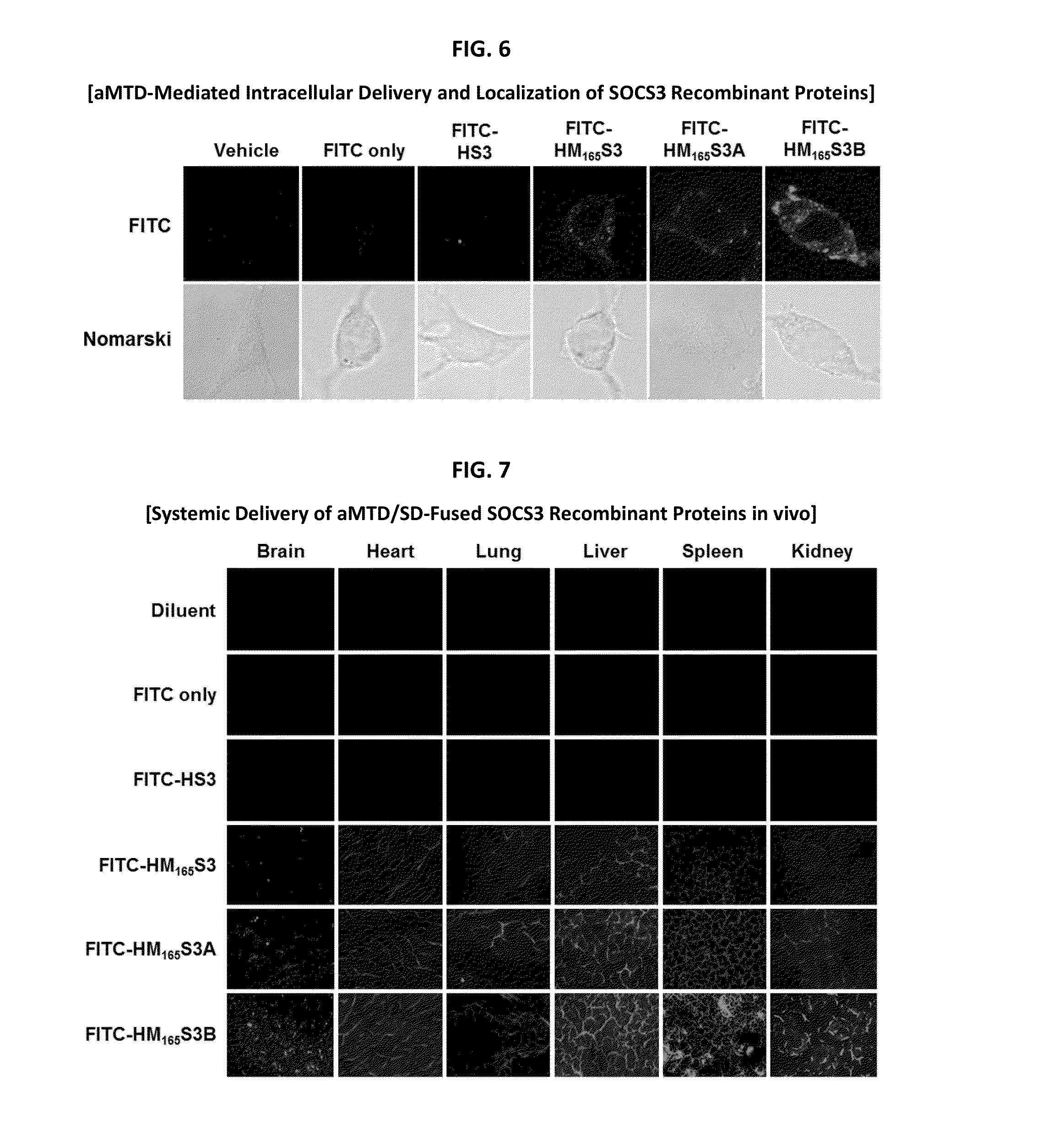
In principle, protein-based biotherapeutics offers a way to control biochemical processes in living cells under non-steady state conditions and with fewer off-target effects than conventional small molecule therapeutics. However, systemic protein delivery in vivo has been proven difficult due to poor tissue penetration and rapid clearance. Protein transduction exploits the ability of some cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) sequences to enhance the uptake of proteins and other macromolecules by mammalian cells. Previously developed hydrophobic CPPs, named membrane translocating sequence (MTS), membrane translocating motif (MTM) and macromolecule transduction domain (MTD), are able to deliver biologically active proteins into a variety of cells and tissues. Various cargo proteins fused to these CPPs have been used to test the functional and / or therapeutic efficacy of protein transduction. The recombinant proteins consisting of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (CP-SOCS3) protein fused to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 4-derived MTM were developed to inhibit inflammation and apoptosis. However, CP-SOCS3 fusion proteins expressed in bacteria cells were hard to be purified in soluble form. To address these critical limitations, CPP sequences called advanced MTDs (aMTDs) have been developed in this art. This is accomplished by (i) analyzing previous developed hydrophobic CPP sequences to identify specific critical factors (CFs) that affect intracellular delivery potential and (ii) constructing artificial aMTD sequences satisfied for each critical factor. In addition, solubilization domains (SDs) have been incorporated into the aMTD-fused SOCS3 recombinant proteins to enhance solubility with corresponding increases in protein yield and cell- / tissue-permeability. These recombinant SOCS3 proteins fused to aMTD / SD having much higher solubility / yield and cell- / tissue-permeability have been named as improved cell-permeable SOCS3 (iCP-SOCS3) proteins. Previously developed CP-SOCS3 proteins fused to MTM were only tested or used as anti-inflammatory agents to treat acute liver injury. In the present art, iCP-SOCS3 proteins have been tested for use as anti-cancer agents in the treatment of various cancers likes gastric, colorectal and breast cancer, and glioblastoma. Since SOCS3 is frequently deleted in and loss of SOCS3 in tumors promotes resistance to apoptosis and proliferation, we reasoned that iCP-SOCS3 could be used as a protein-based intracellular replacement therapy for the treatment of various cancers. The results demonstrated in this art support the reasoning: treatment of cancer cells with iCP-SOCS3 results in reduced cancer cell viability, enhanced apoptosis of solid tumors including gastric, colorectal and breast cancer, and glioblastoma and loss of cell migration / invasion potential. Furthermore, iCP-SOCS3 inhibits the growth of gastric and colorectal tumors in a subcutaneous xenografts model. In the present invention with iCP-SOCS3, where SOCS3 is fused to an empirically determined combination of newly developed aMTD and customized SD, macromolecule intracellular transduction technology (MITT) enabled by the advanced MTDs may provide novel protein therapy against various tumors such as gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, glioblastoma, and breast cancer.
Owner:JO DAEWOONG +1
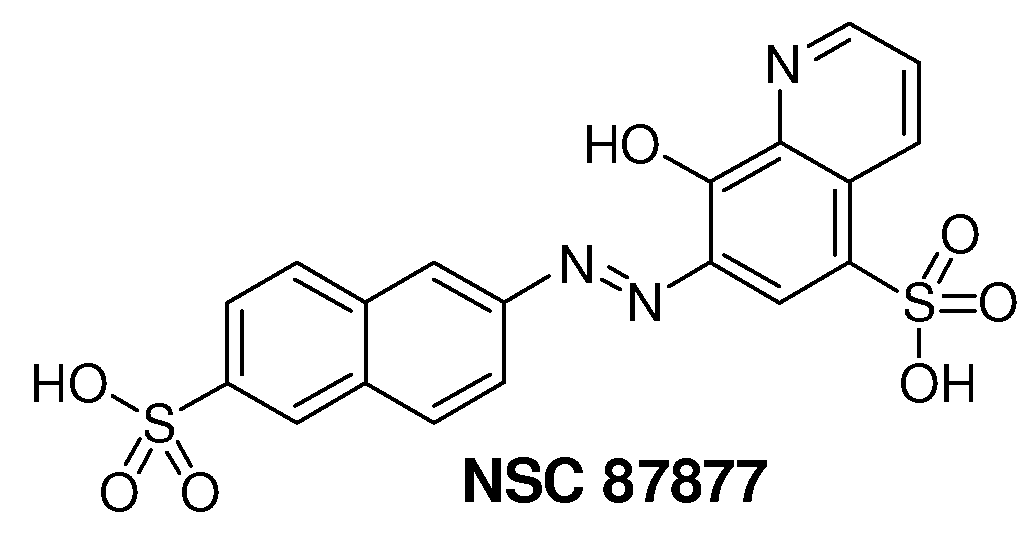
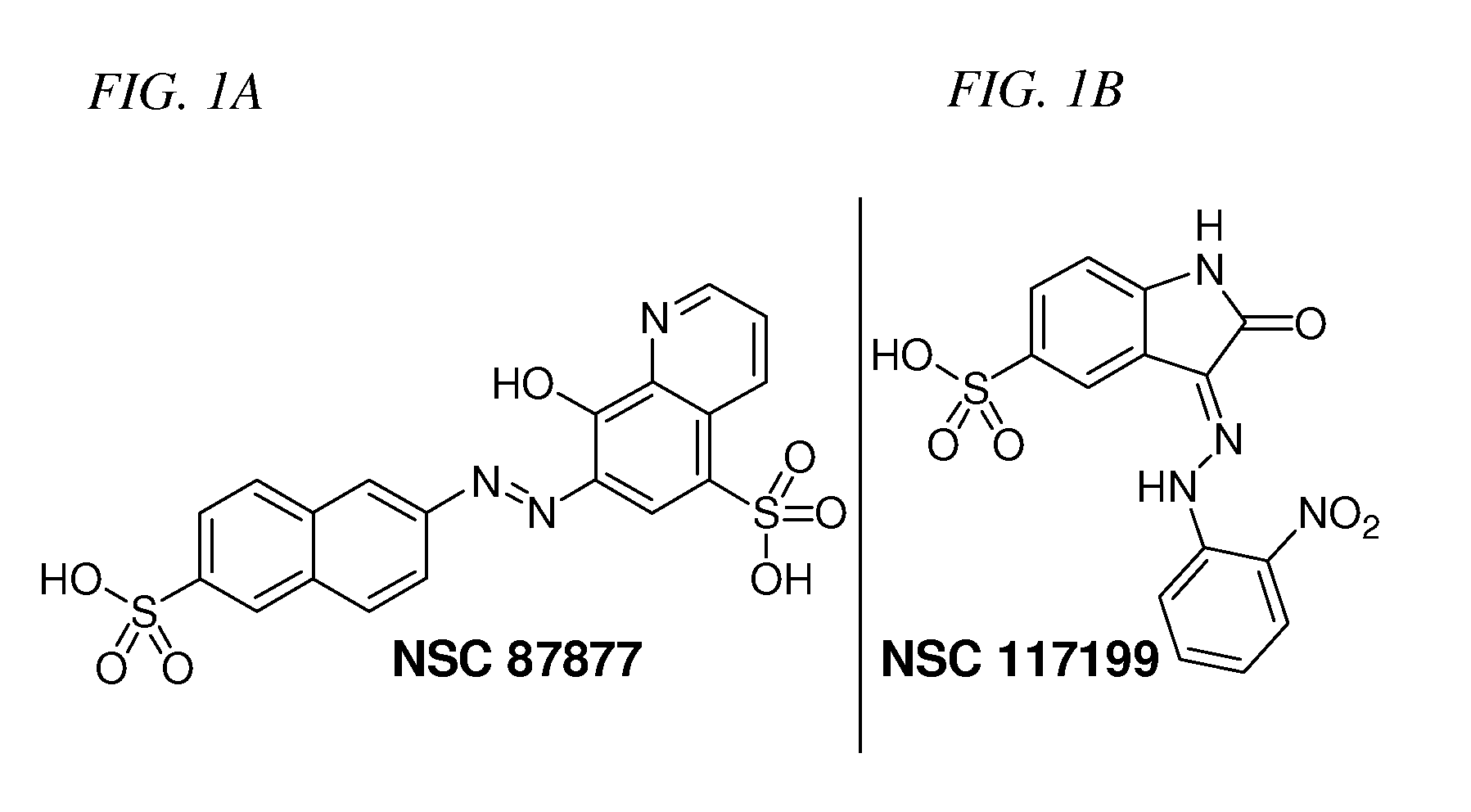
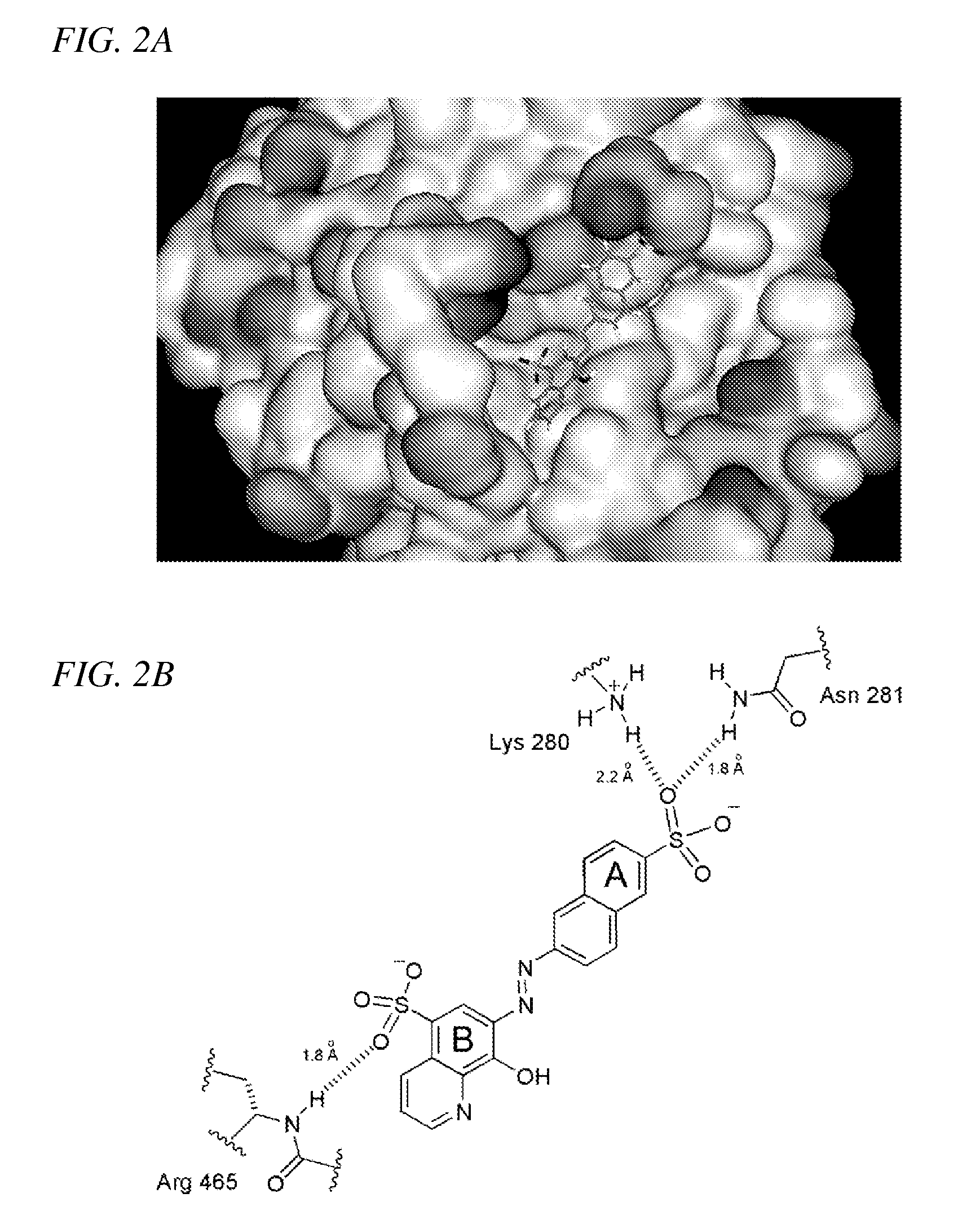
Inhibition of Shp2/PTPN11 Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase by NSC-87877, NSC-117199 and Their Analogs
Compounds and associated methods for inhibiting a protein tyrosine phosphatase. By a combination of experimental and virtual screenings of the NCI Diversity Set chemical library, NSC-87877 and NSC-117199 have been identified as Shp2 PTP inhibitors. Significantly, NSC-87877 is active in cell-based assays and has no detectable off-target effects in the EGF-stimulated Erk1 / 2 activation pathway. Additionally, a number of analogs of NSC-117199 have been produced. These analogs exhibit enhanced protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition and are found to be potent and / or selective inhibitors of Shp1 and / or Shp2 protein tyrosine phosphatases.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com