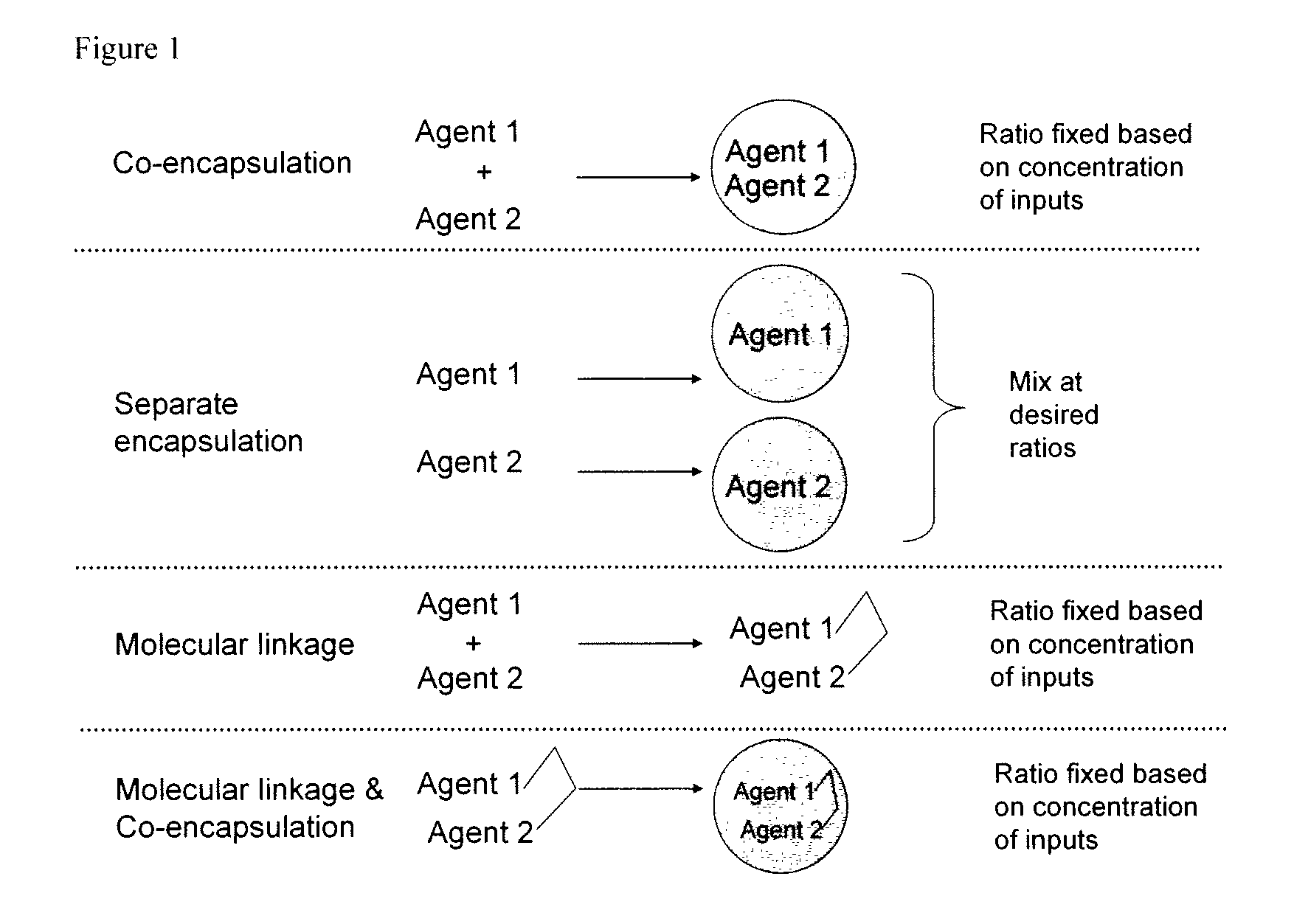
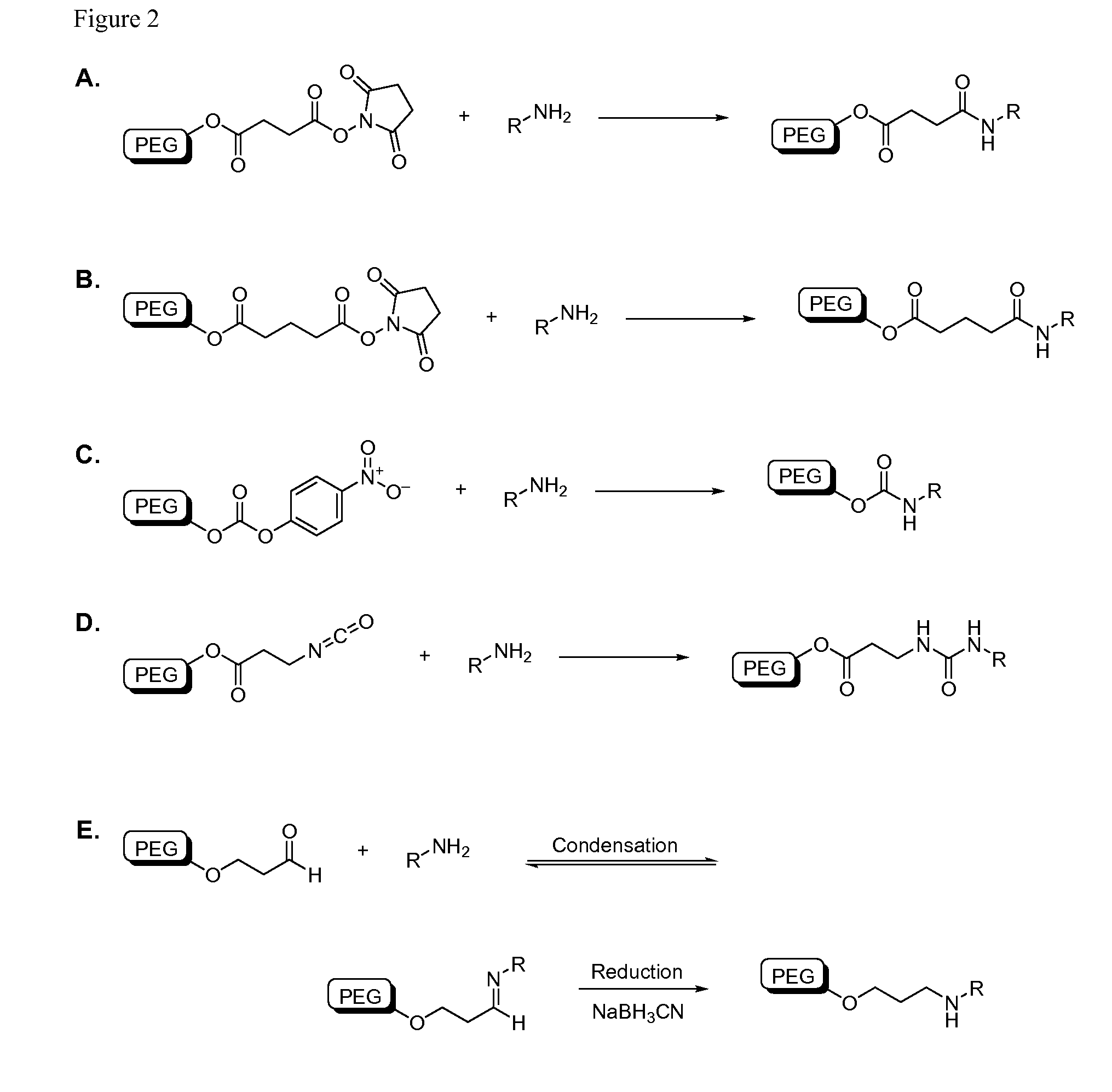
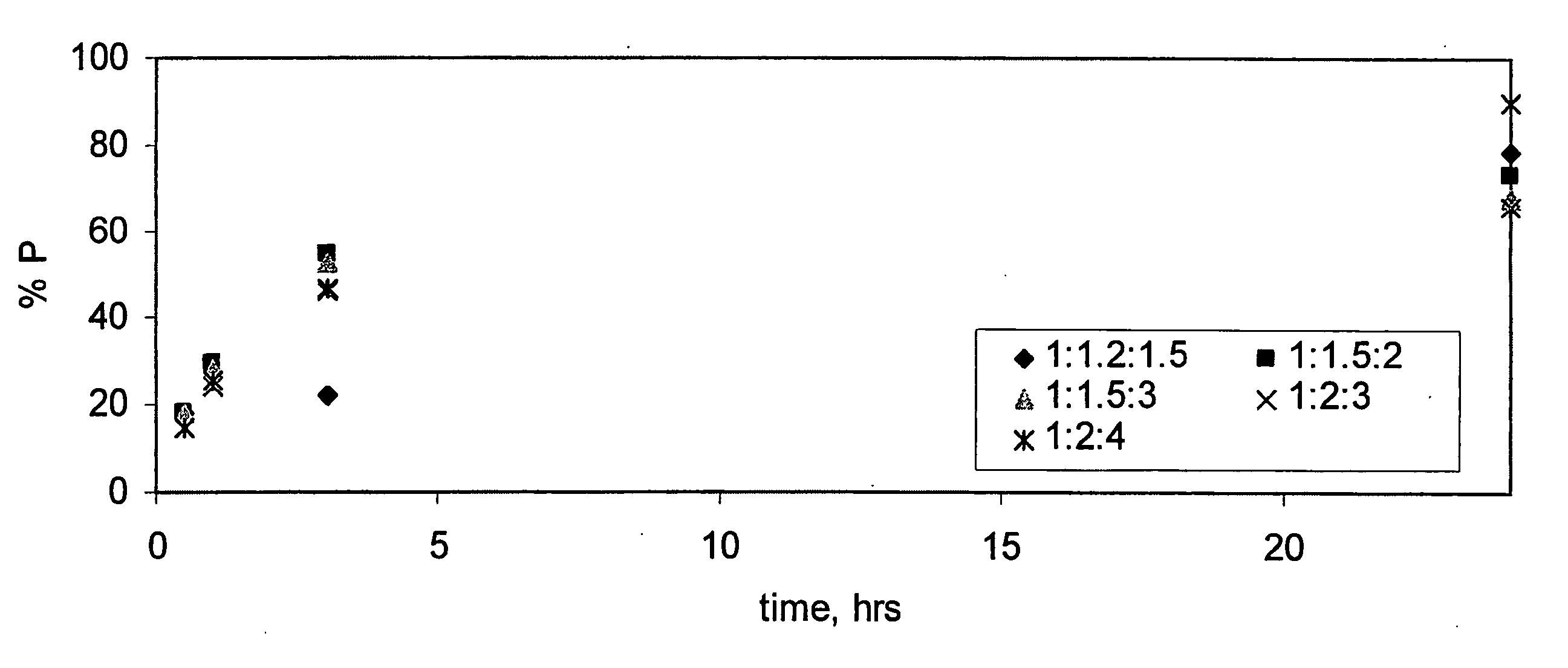
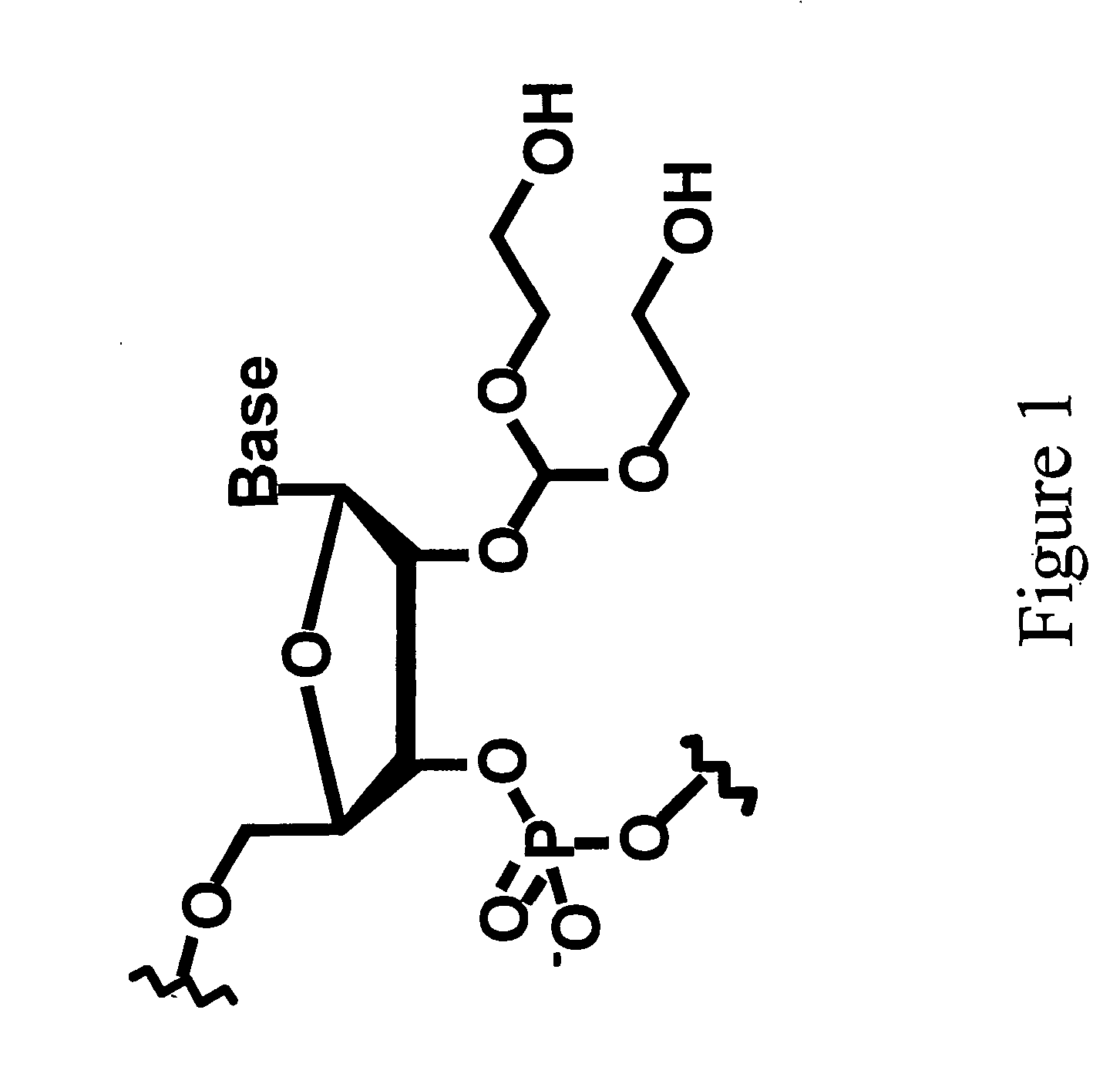
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
630 results about "Ribonucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
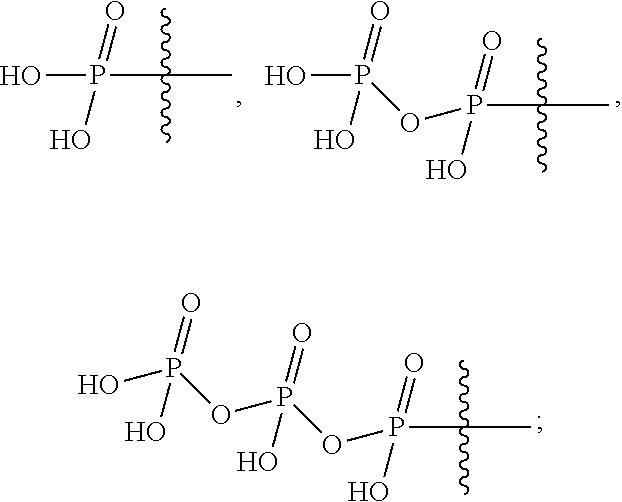
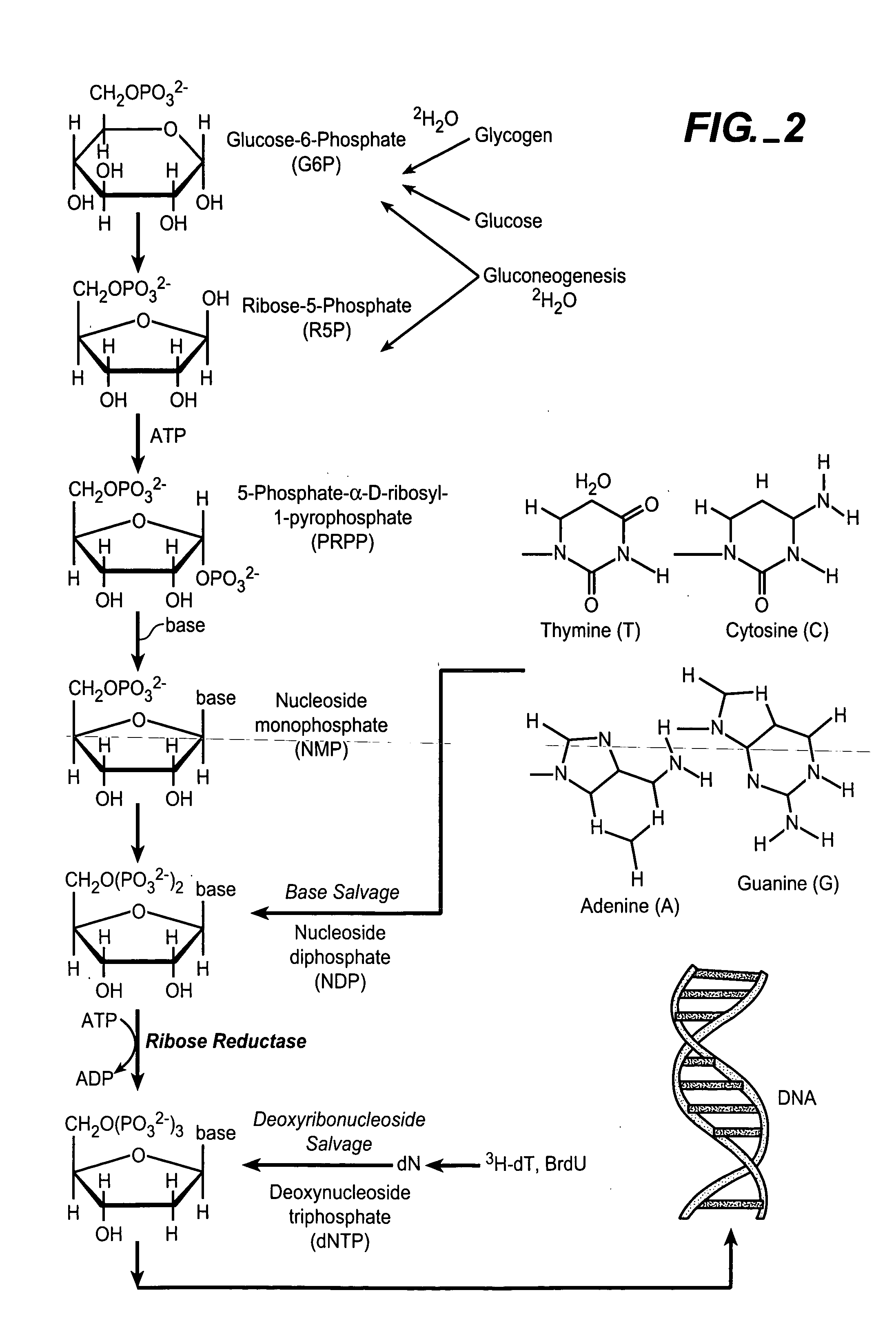
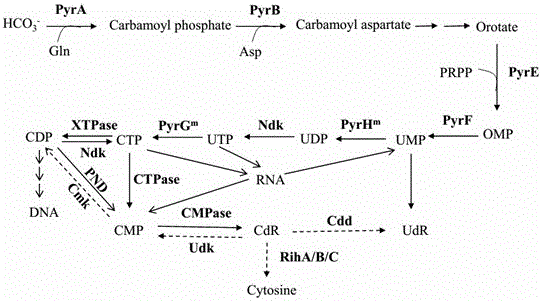
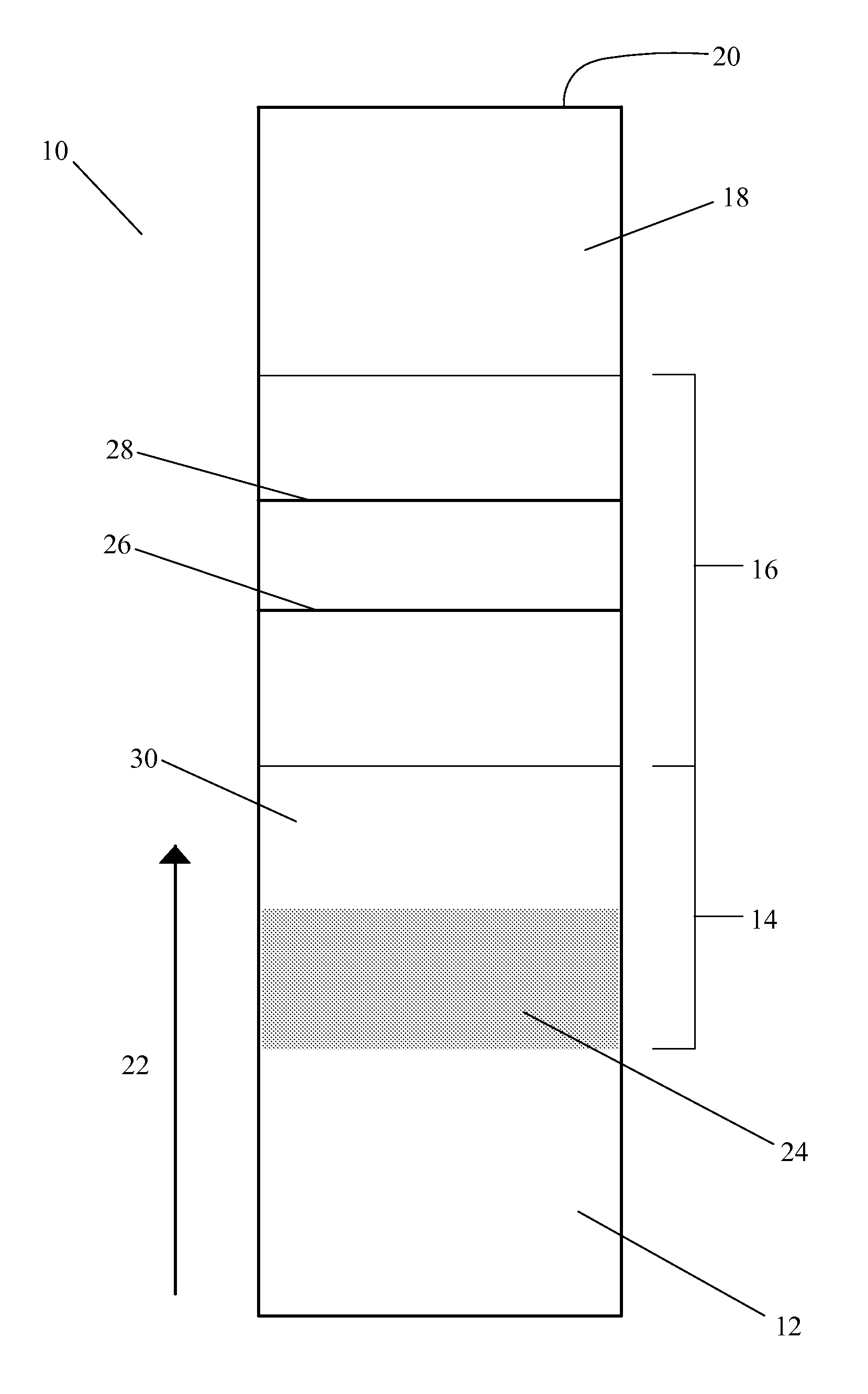
In biochemistry, a ribonucleotide is a nucleotide containing ribose as its pentose component. It is considered a molecular precursor of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. The monomer itself from ribonucleotides forms the basic building blocks for RNA. However, the reduction of ribonucleotide, by enzyme ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), forms deoxyribonucleotide, which is the essential building block for DNA. There are several differences between DNA deoxyribonucleotides and RNA ribonucleotides. Successive nucleotides are linked together via phosphodiester bonds by 3'-5'.
Oligoribonucleotides and methods of use thereof for treatment of alopecia, acute renal failure and other diseases
ActiveUS20060069056A1Increased riskImprove the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderOligoribonucleotidesARF - Acute renal failure
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
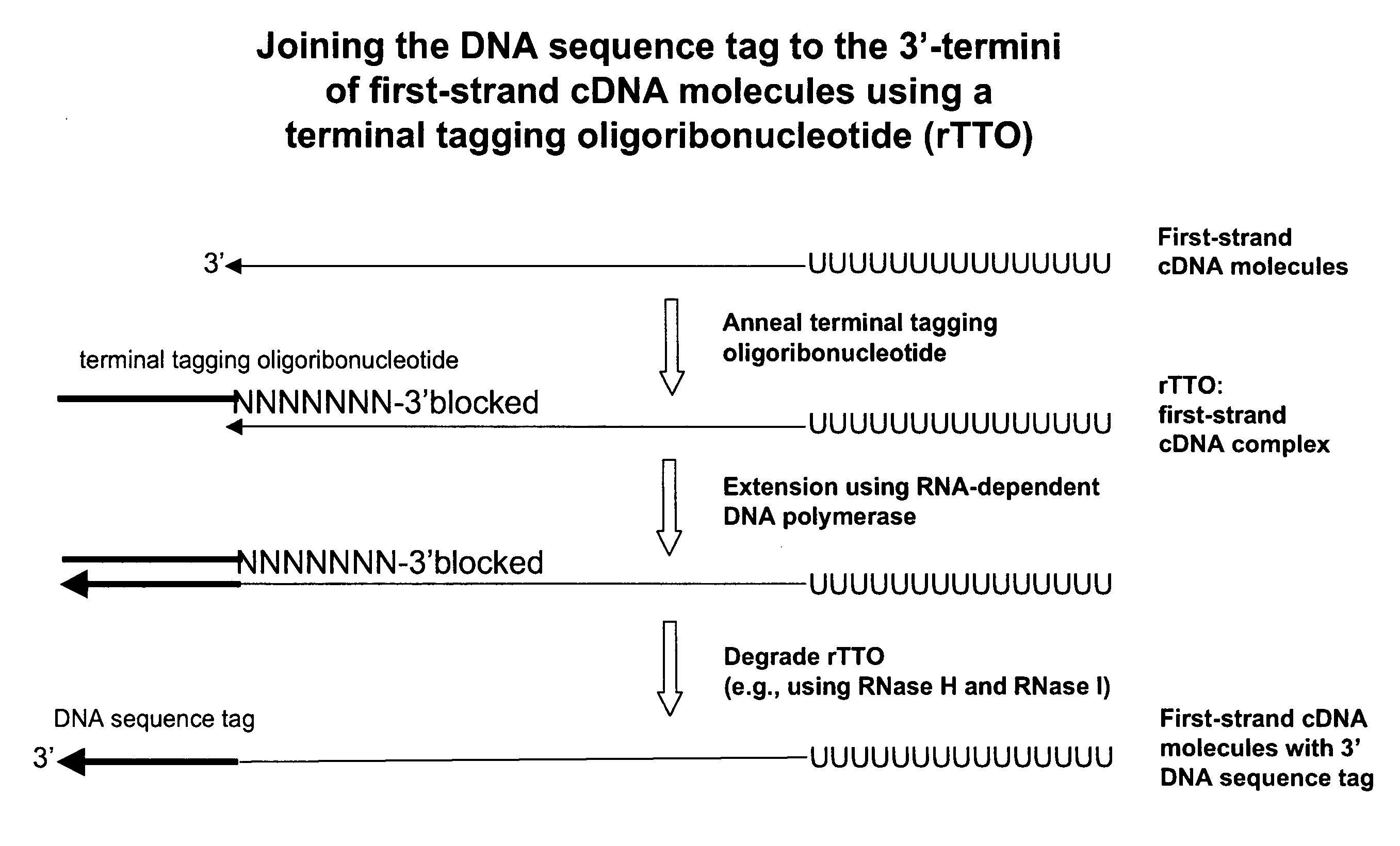
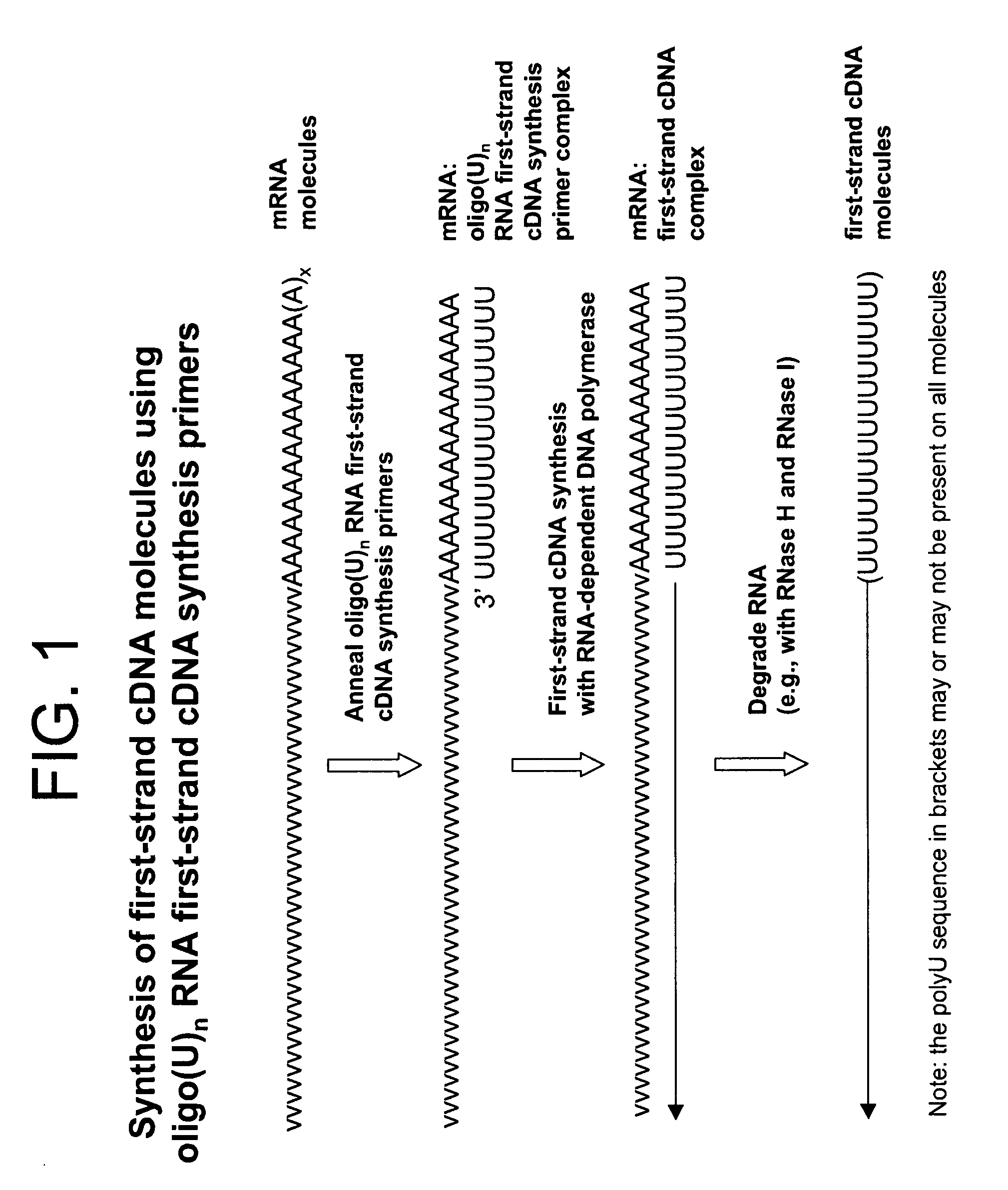
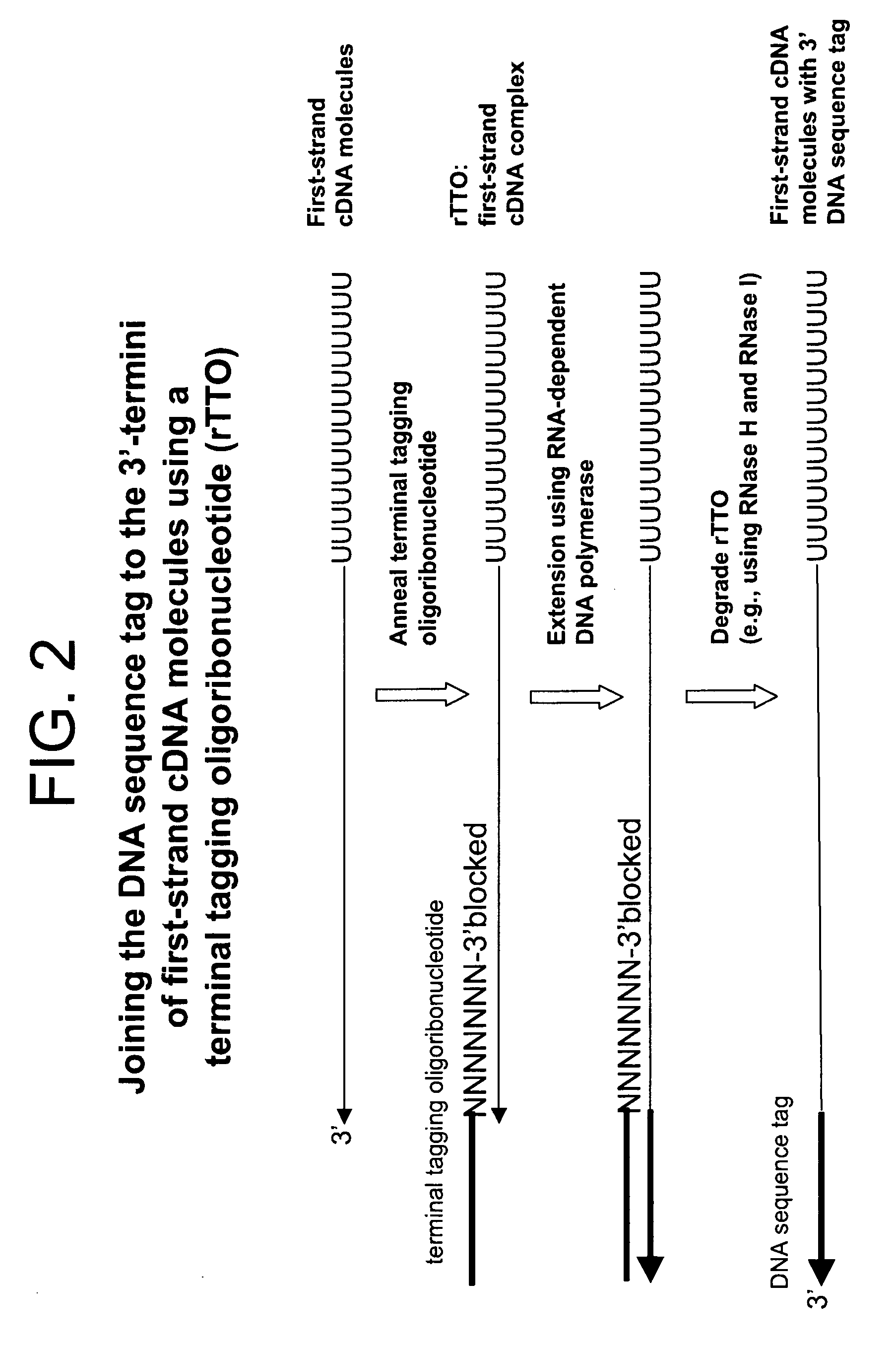
Synthesis of tagged nucleic acids
ActiveUS8039214B2Reduce in quantityGood removal effectMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesOligoribonucleotidesRibonucleotide synthesis
The present invention relates generally to methods, compositions and kits for synthesizing sense RNA molecules from one or more RNA molecules of interest in a sample. In exemplary embodiments, the methods use a terminal tagging oligoribonucleotide (rTTO) to join a DNA sequence tag to the 3′-termini of first-strand cDNA molecules. The use of an rTTO comprising ribonucleotides results in decreased oligonucleotide-derived background synthesis of RNA in the absence of sample RNA and, surprisingly and unexpectedly, also results in significantly increased yields of sense RNA molecules that exhibit sequences that are substantially identical to those of the RNA molecules of interest in the sample. The sense RNA molecules also have an RNA sequence tag on their 5′-termini that is useful for fixing the lengths of sense RNA molecules that are synthesized in a second or subsequent round.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR IMPROVED THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS WITH siRNA
InactiveUS20080311040A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove efficacyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectProtein
The present invention relates to chemically modified, linked double-stranded (ds)RNA compositions comprising two or more double-stranded (ds) oligoribonucleotides linked by at least one linking moiety and methods of formulating and delivering such compositions to modulate gene expression through target-specific RNA co-interference (RNAco-i). The compositions of the invention may optionally comprise a conjugation or a complex with one or more small molecule drugs, protein therapeutics, or other dsRNA molecules. The present invention is directed at the methods of production for, methods of use of, and therapeutic utilities for RNAi co-interference therapy utilizing the compositions of the invention.
Owner:FLAGSHIP VENTURES
Oligoribonucleotides and methods of use thereof for treatment of alopecia, acute renal failure and other diseases
ActiveUS20080287382A1Increased riskImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderRadical radiotherapyDisease cause
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribounucleotides
InactiveUS20050130201A1Ligate RNA moleculesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzymatic synthesisPolyribonucleotides
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis of polyribonucleotides using an RNA polymerizing enzyme. The invention provides ligating ribonucleotides comprising ligating a donor RNA molecule to an acceptor RNA molecule in the presence of RNA ligase and a splint, wherein the donor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety, the acceptor RNA molecule is comprised of at least one nucleotide and a ligation linker moiety and the splint is comprised of a polyribonucleotide. The invention also provides splints for use in splint-assisted enzymatic synthesis using an RNA polymerizing enzyme.
Owner:DHARMACON INC
Deprotection and purification of oligonucleotides and their derivatives
InactiveUS6989442B2Eliminate needLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleotide synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Chimeric primers for improved nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveUS20100291635A1Reduce formationLow efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Methods are provided for amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. The method use RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotides as primers. The primers have RNA residues scattered along their length and no two ribonucleotides in the prime are adjacent to one another. The methods are useful for reducing non-specific amplification products, such as primer dimers. The invention also provides kits comprising RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotide primers for practicing the amplification methods.
Owner:INFINIPLEX LTD
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
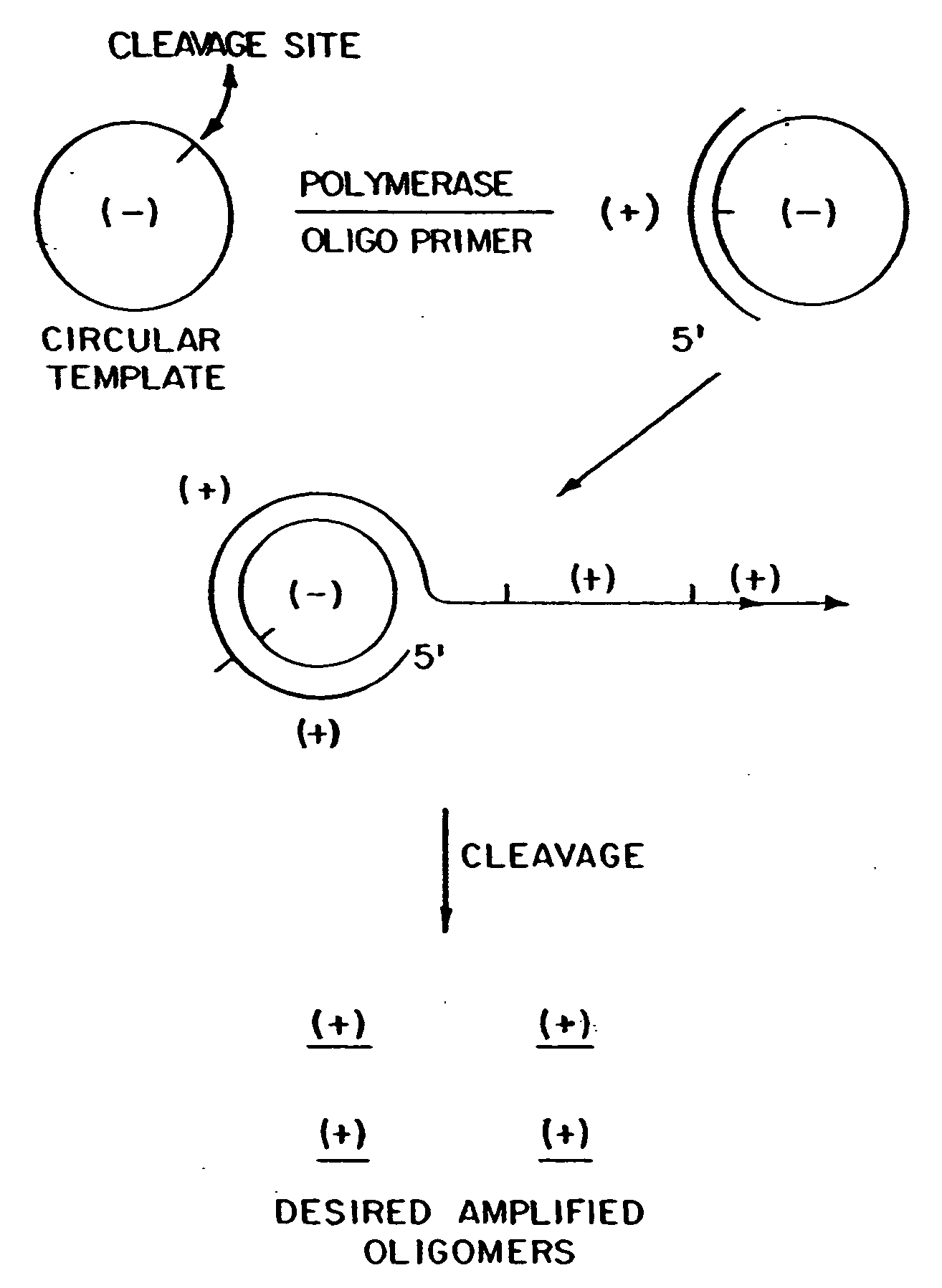
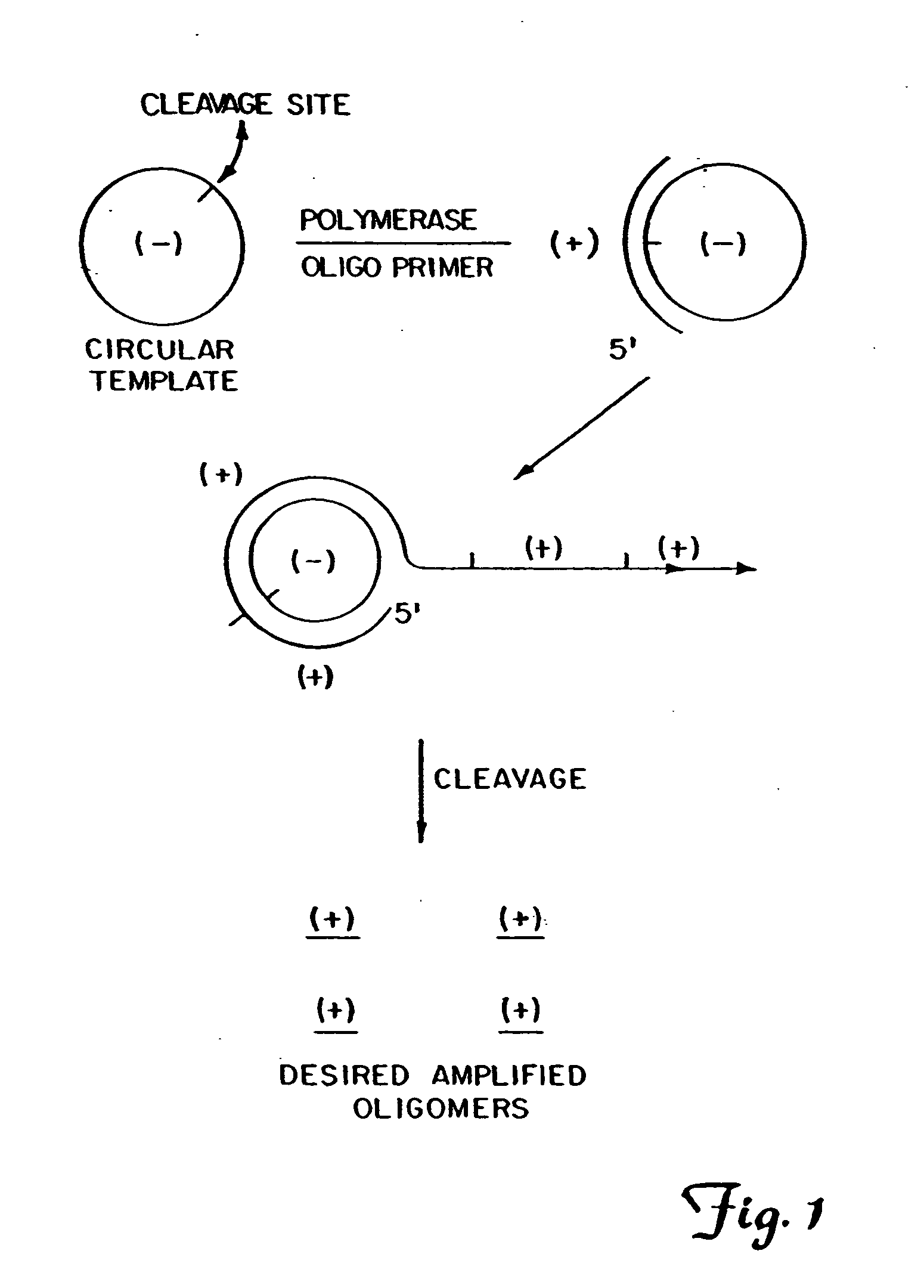
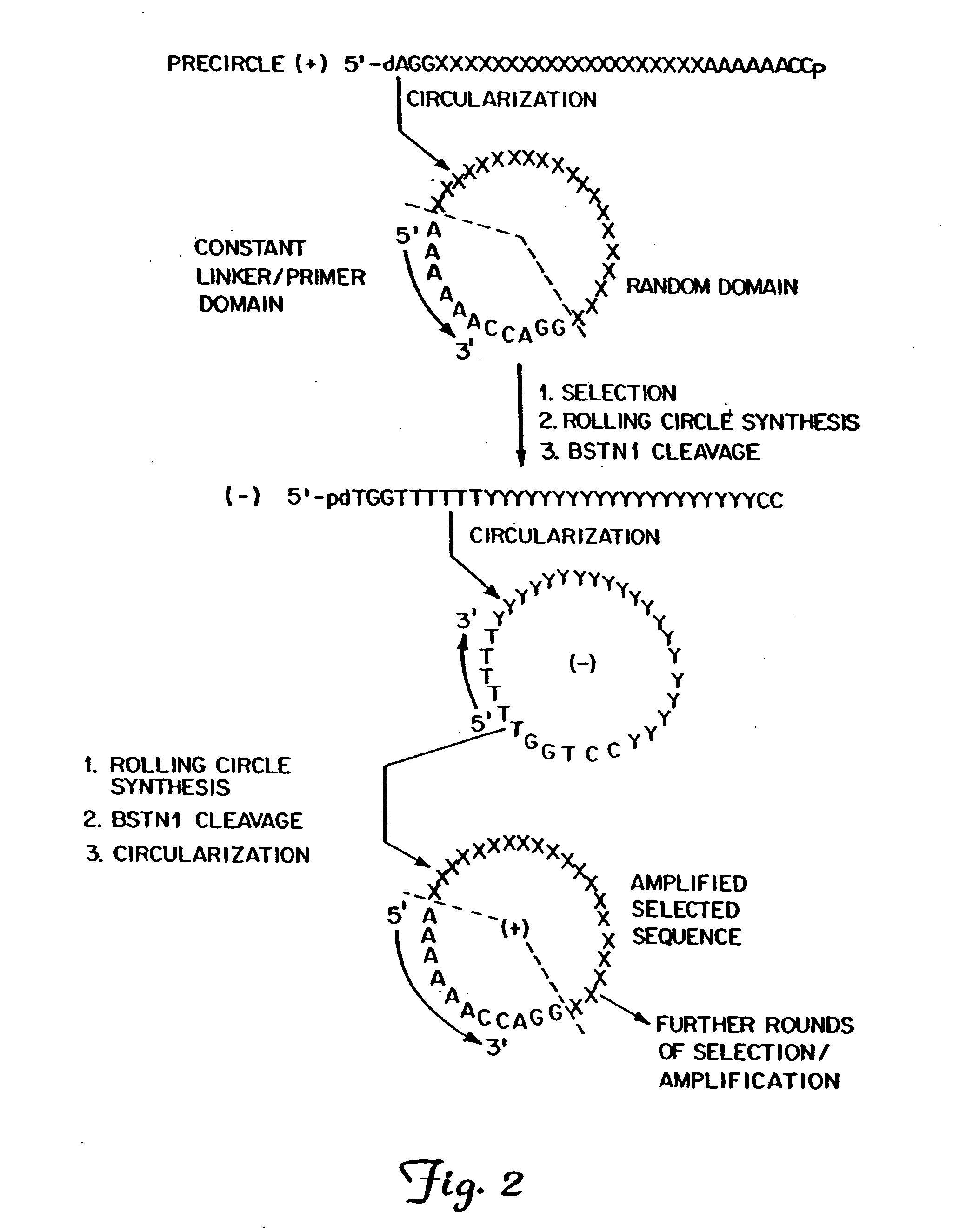
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules having ribothymidine
InactiveUS20060142230A1Improves ribonucleaseReduce off-target effectsPowder deliverySugar derivativesRibonucleotide synthesisDouble stranded
The invention relates to a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecule comprising between about 15 base pairs and about 40 base pairs, wherein at least one ribonucleotide of the dsRNA is a 5′-methyl-pyrimidine, and a method of using such modified dsRNA molecule to increase stability of RNA when in contact with a biological sample.
Owner:MDRNA
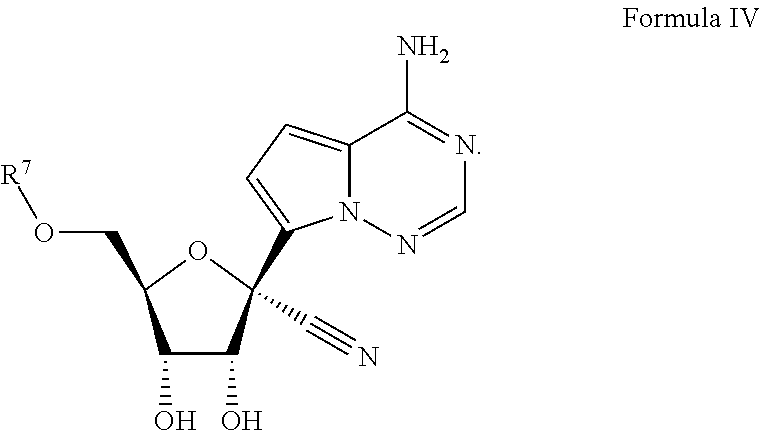
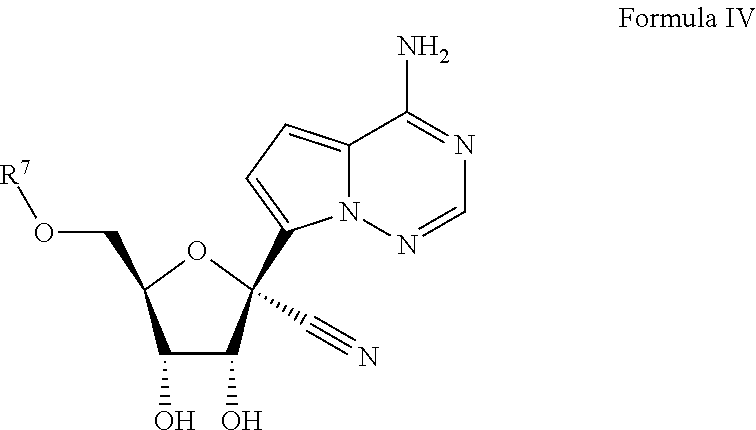
Methods for treating filoviridae virus infections
Provided are compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions for treating Filoviridae virus infections by administering ribosides, riboside phosphates and prodrugs thereof, of Formula IV:The compounds, compositions, and methods provided are particularly useful for the treatment of Marburg virus, Ebola virus and Cueva virus infections.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Compound mushroom flavoring and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a compound mushroom flavoring and a preparation method thereof. The main raw materials of the compound mushroom flavoring comprise meadow mushroom powder, straw mushroom powder, sodium glutamate, salt, sugar, maltodextrin, yeast extract, disodium 5'-ribonucleotide and yolk powder. The preparation method of the compound mushroom flavoring comprises the following steps: rinsing, boiling, pulverizing, pulping, homogenizing, concentrating and spray-drying fresh mushrooms, and then, obtaining mushroom powder; adding other raw materials; and carrying out the processes of mixing, granulating, drying and the like to obtain the compound mushroom flavoring. The compound mushroom flavoring has the flavor of the meadow mushroom and the straw mushroom simultaneously by organically mixing the sodium glutamate, the yeast extract, the disodium 5'-ribonucleotide and the mushroom powder, has strong functions of increasing freshness and increasing fragrance and has soft flavor. The cell walls of mushrooms can be broken by the homogenizing action to better release the substances in the cells of the mushrooms, thereby further improving the nutrient value of the product. The sugar is added in the concentration process, thereby further improving and increasing the flavor of the materials. The compound mushroom flavoring is granular and is convenient in use.
Owner:宜昌益农科技开发有限公司
Isothermal chimeric primer nucleic acid amplification methods using blocking oglionucleotide
InactiveUS7056671B2Improve targeting efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LRibonucleotide synthesis
Methods of amplifying a target nucleic acid whereby the target nucleic acid is amplified in the presence of a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate, a DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity, at least one chimeric oligonucleotide primer, at least one upstream block oligonucleotide and a RNase H; wherein the chimeric oligonucleotide primer contains a ribonucleotide positioned at the 3′-terminus; wherein the upstream block oligonucleotide is capable of annealing to a region 3′ to a portion in the nucleic acid as the template to which the chimeric oligonucleotide primer anneals; and compositions and kits thereof.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
5'-methylpyrimidine and 2'-O-methyl ribonucleotide modified double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20060122137A1Improves ribonuclease stabilityReduce off-target effectsPowder deliverySugar derivativesRibonucleotide synthesisDouble strand
The invention relates to a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecule comprising between about 15 base pairs and about 40 base pairs, at least one 5′-methyl-pyrimidine and at least one 2′—O-methyl ribonucleotide, and a methods of using such modified dsRNA molecule to increase stability of a siRNA molecule when in contact with a biological sample, to reduce off-target effects and to reduce interferon responsiveness (IFN) of the siRNA molecule.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
Bungarus fasciatus antibacterial peptide cathelicidin-BF, and genes and uses thereof
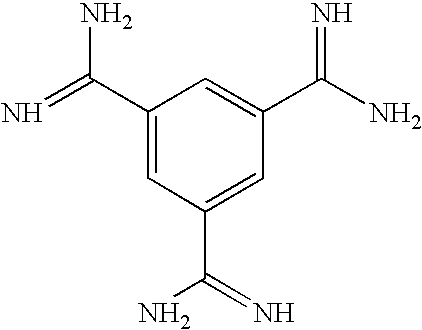
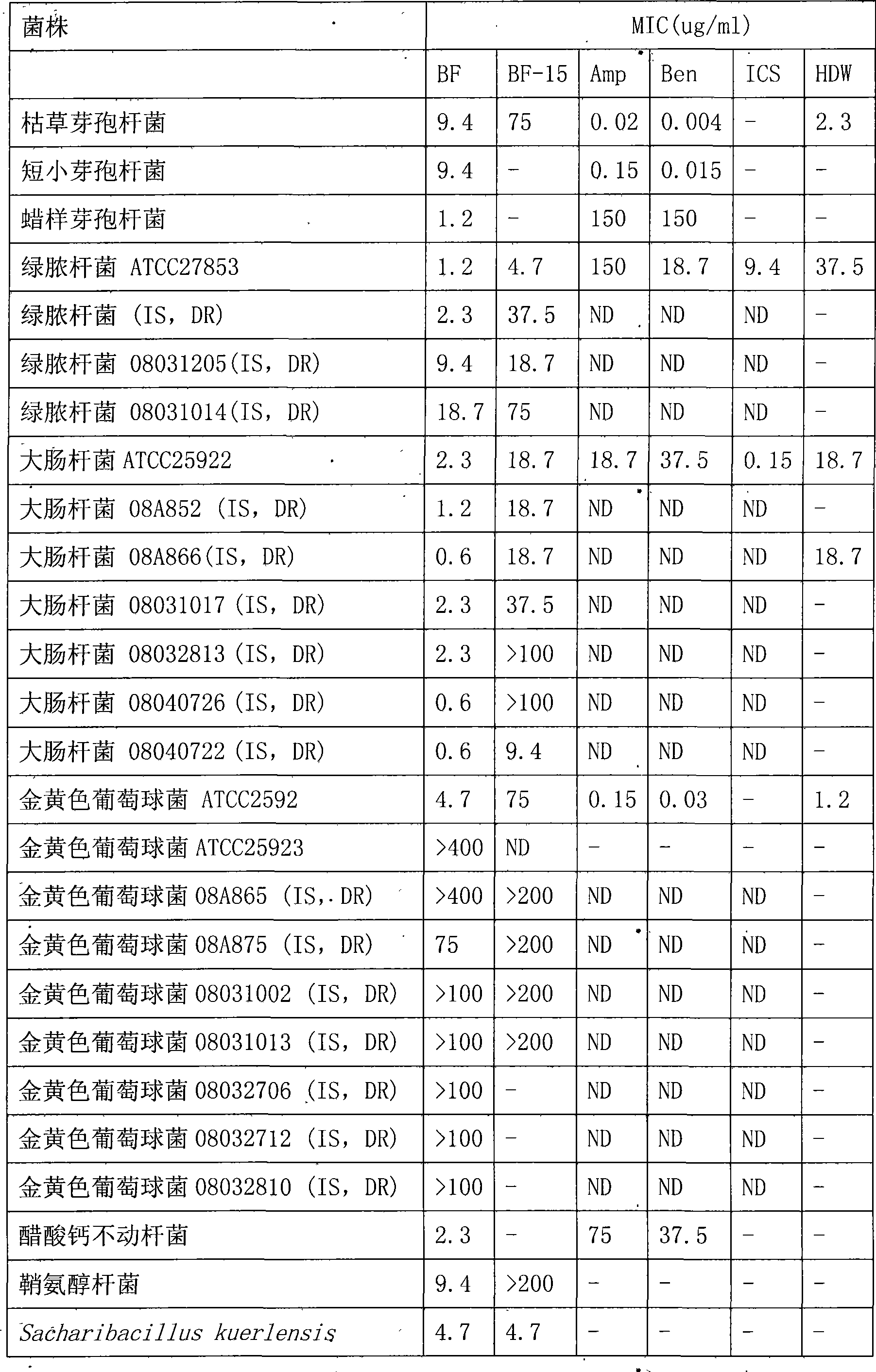
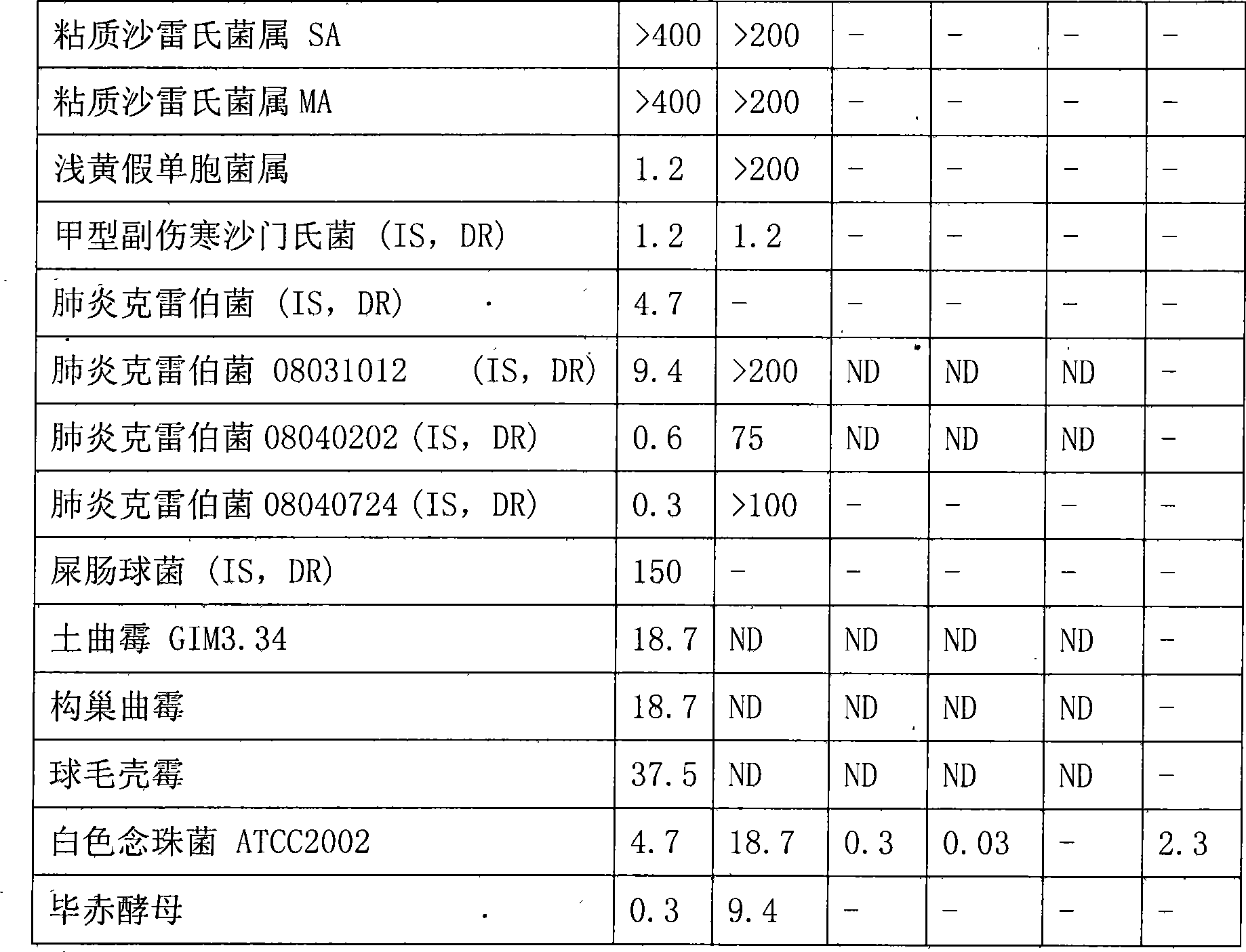
InactiveCN101412753ASmall molecular weightImprove the bactericidal effectFermentationAnimals/human peptidesArginineAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses cathelicidin-BF and a gene and application thereof, which belong to the field of biomedicine. The cathelicidin-BF is straight chain polypeptide and contains thirty amino acid residues, the molecular weight is 3,637.54Da, and the isoelectric point is 11.79. The complete sequence of the cathelicidin-BF is lysine-phenyl alanine-phenyl alanine-arginine-lysine-leucine- lysine-lysine-serine-valine-lysine-lysine-arginine-lactamine-lysine-glutamic acid-phenyl alanine- phenyl alanine-lysine-lysine-proline-arginine-valine-isoleucine-glycin-valine-serine-isoleucine- praline-phenyl alanine. The gene for encoding the cathelicidin-BF consists of 750 ribonucleotides, wherein 484th to 573rd ribonucleotides are used for encoding a mature peptide part. The cathelicidin-BF has small molecular weight, strong sterilization effect, and quick action time, and has quite strong killing function to a plurality of kinds of clinical drug-fast bacteria. In addition, the cathelicidin-BF also has the advantages of broad-spectrum antibiotics, salt independence and so on.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reagent for nucleic acid amplification and process for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS6261773B1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerPolymerase L
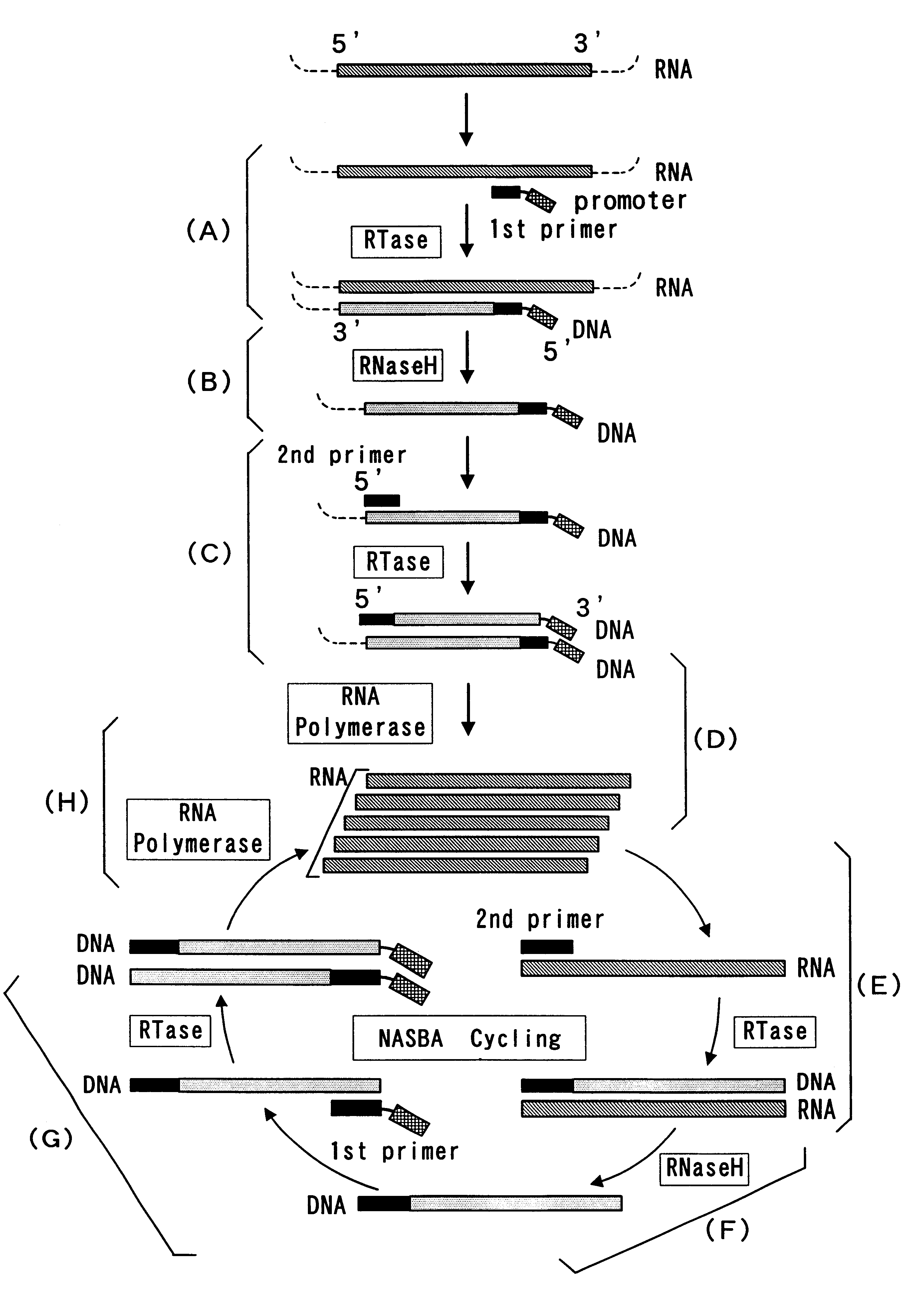
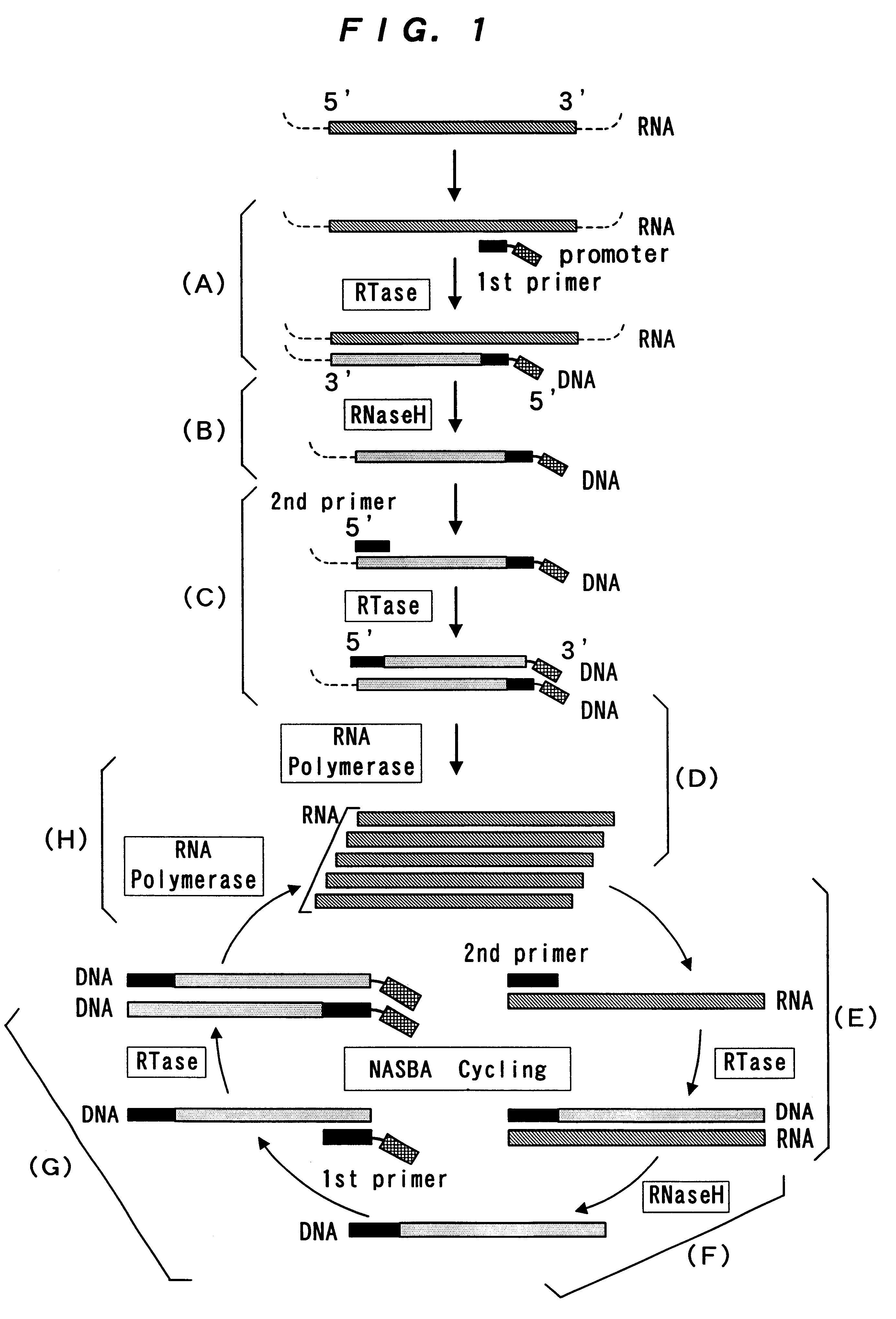
The present invention provide a process for sequence-specific nucleic acid amplification capable of improving the detection sensitivity and increasing the signal. In particular, the present invention provides a reagent for nucleic acid amplification containing at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts, specifically a reagent for nucleic acid amplification comprising, in addition to the at least one compound, a forward primer having a DNA sequence homologous to a sequence of a target RNA; a reverse primer having a DNA sequence complementary to a sequence of the target RNA and having a promoter for RNA polymerase attached to its 5' end; ribonucleotides; deoxyribonucleotides; a reverse transcriptase or RNA-directed DNA polymerase; a RNase H; a DNA polymerase or a reverse transcriptase having DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity; and a RNA polymerase. The present invention also provides a process for nucleic acid amplification characterized by carrying out a nucleic acid amplification reaction in the presence of at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Methods for evaluating ribonucleotide sequences
ActiveUS20090081643A1Easy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsRibonucleotide synthesisRibosome
Methods for identifying ribonucleotide sequences, in vitro, using the ribosome-mediated translation, are provided.
Owner:ANIMA CELL METROLOGY
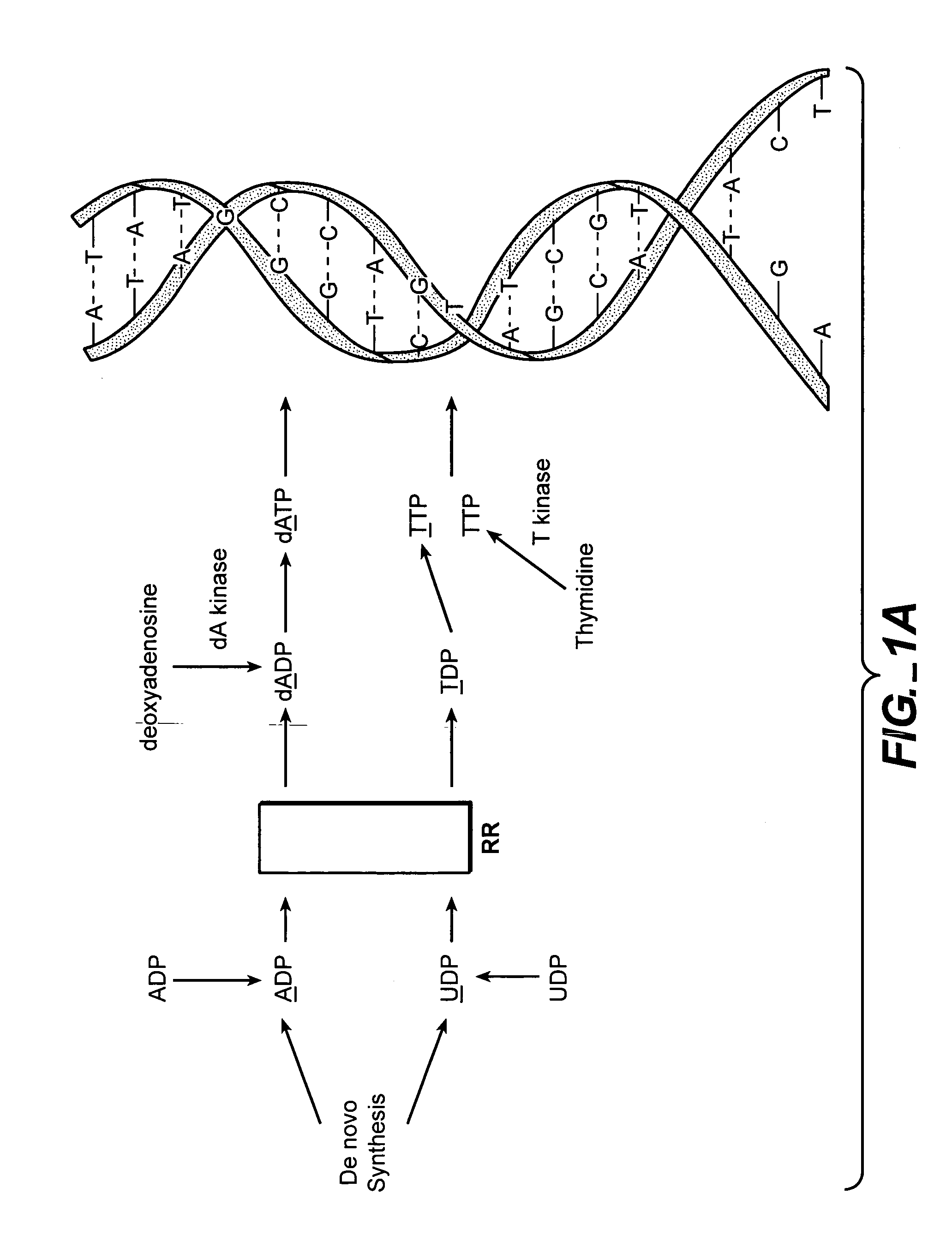
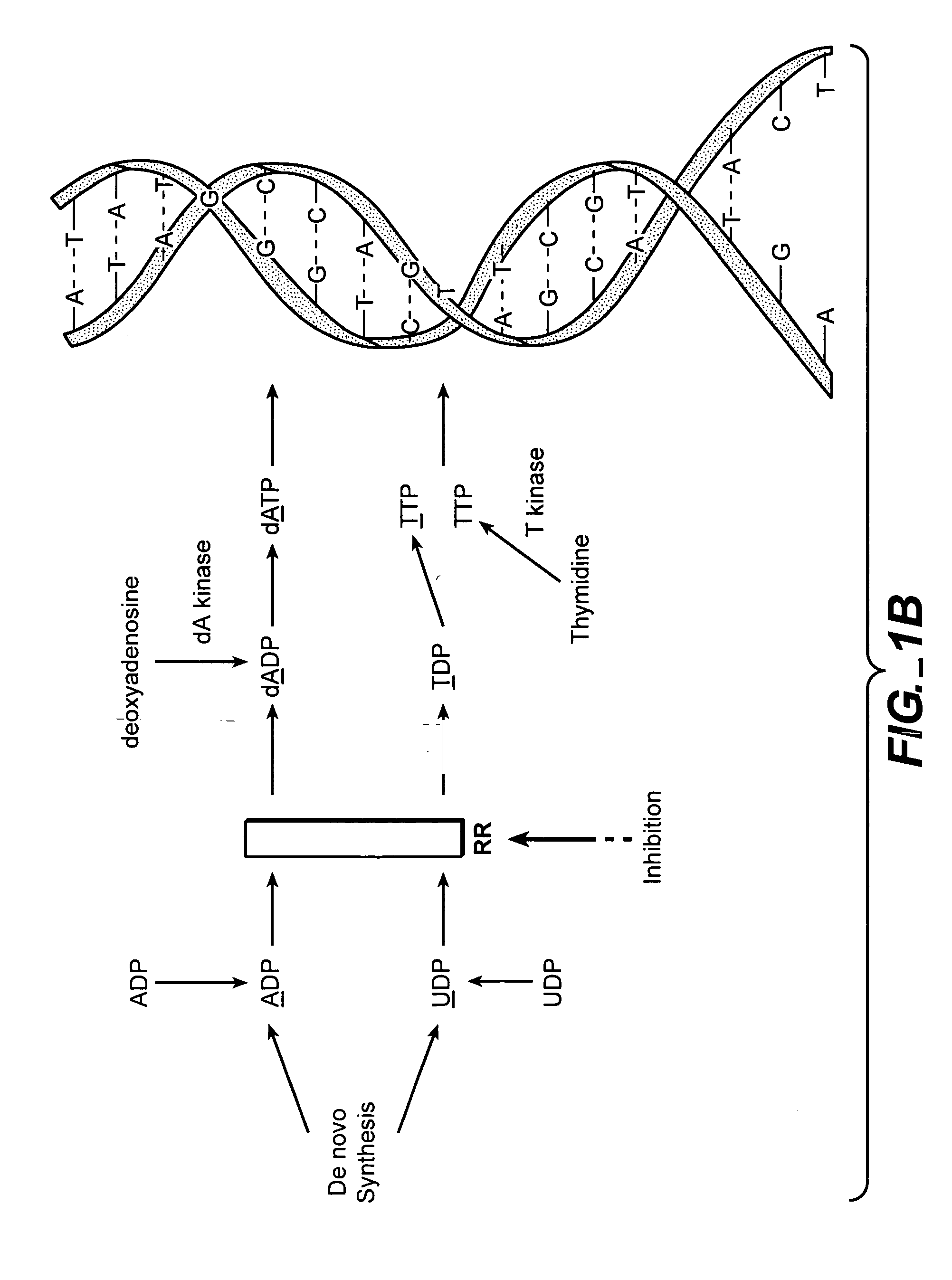
In vivo measurement of the relative fluxes through ribonucleotide reductase vs. deoxyribonucleoside pathways using isotopes
InactiveUS20050255509A1Increase salvageHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRate-determining stepDeoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis
The methods of the present invention allow for the measurement of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, an important enzyme in the de novo DNA synthesis pathway. Ribonucleotide reductase converts all four ribonucleotides to their deoxy form and is a rate-controlling step in this pathway. Biosynthetic pathways of deoxyribonucleotides (dN) have received considerable attention in the context of anti-proliferative chemotherapy. Inhibitors of various steps in dN biosynthesis, including inhibitors of RR are among the most useful chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, viral infections, and other therapeutic uses. DNA synthesis from the dN salvage pathway is also an important component to DNA replication. The relative contributions from RR vs. salvage pathways are critical to the actions and effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents that act on nucleoside metabolic pathways. Until now, however, it has not been possible to study these metabolic processes in vivo. Disclosed within are methods of measuring RR activity in vivo and in vitro which find use, among other things, in drug discovery, development, and approval.
Owner:KINEMED
Protective group for synthesis of RNA and derivative
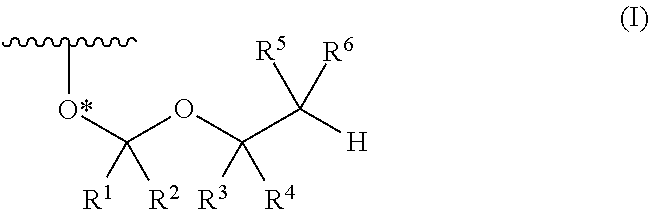
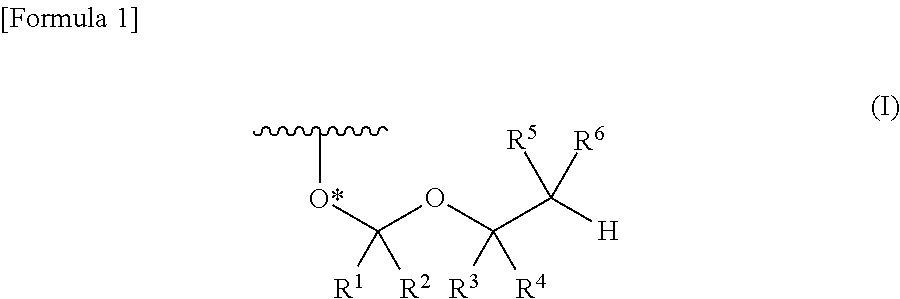
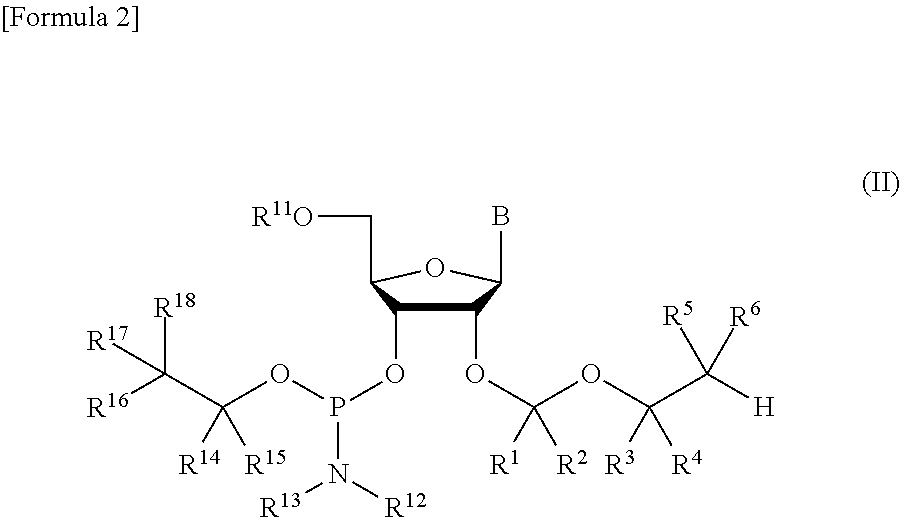
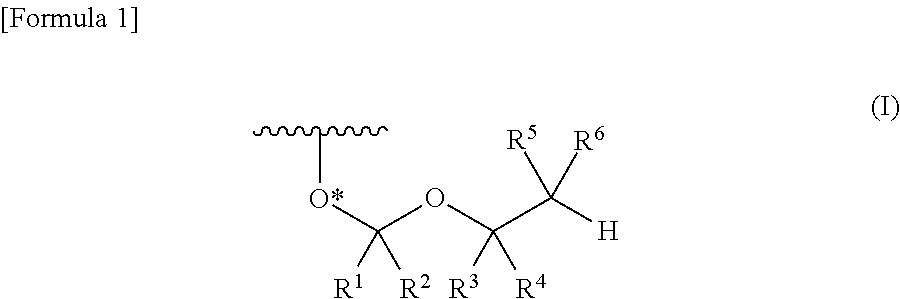
ActiveUS8470987B2Small hindranceEfficient removalSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsRibonucleosideRibose
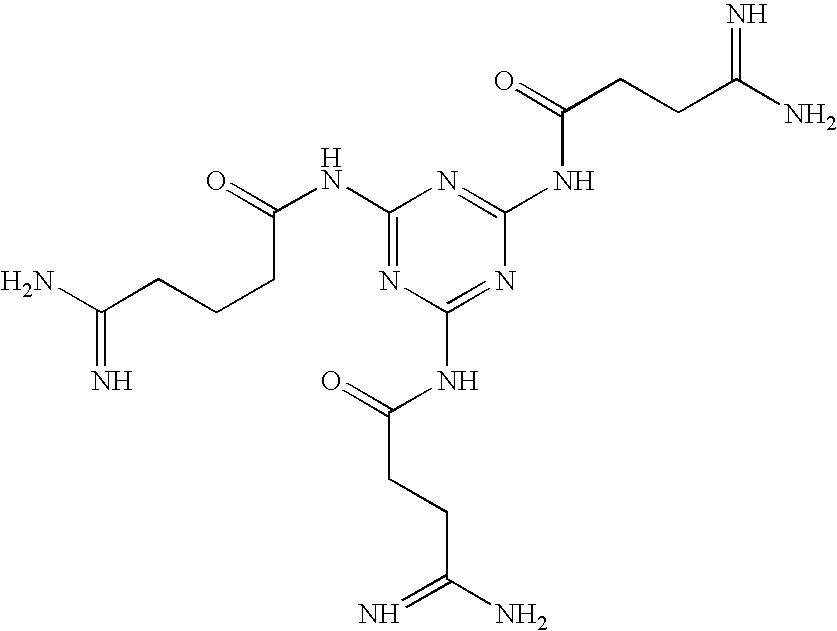
A protective group represented by the following general formula (I) (the oxygen atom attached with * represents oxygen atom of 2′-hydroxyl group of a ribonucleoside, a ribonucleotide or a derivative thereof; R1 and R2 both represent hydrogen atom, or represent a halogen atom, a C1-6 alkyl group, or a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group; R3 and R4 represent hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a C1-6 alkyl group, or a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group; and R5 and R6 represent a halogen atom, a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group, cyano group, nitro group, or the like), which is stable under the reaction conditions of the nucleic acid synthetic cycles and has little steric hindrance, and can be removed under mild conditions using fluoride ions as a base.
Owner:WAVE LIFE SCI LTD
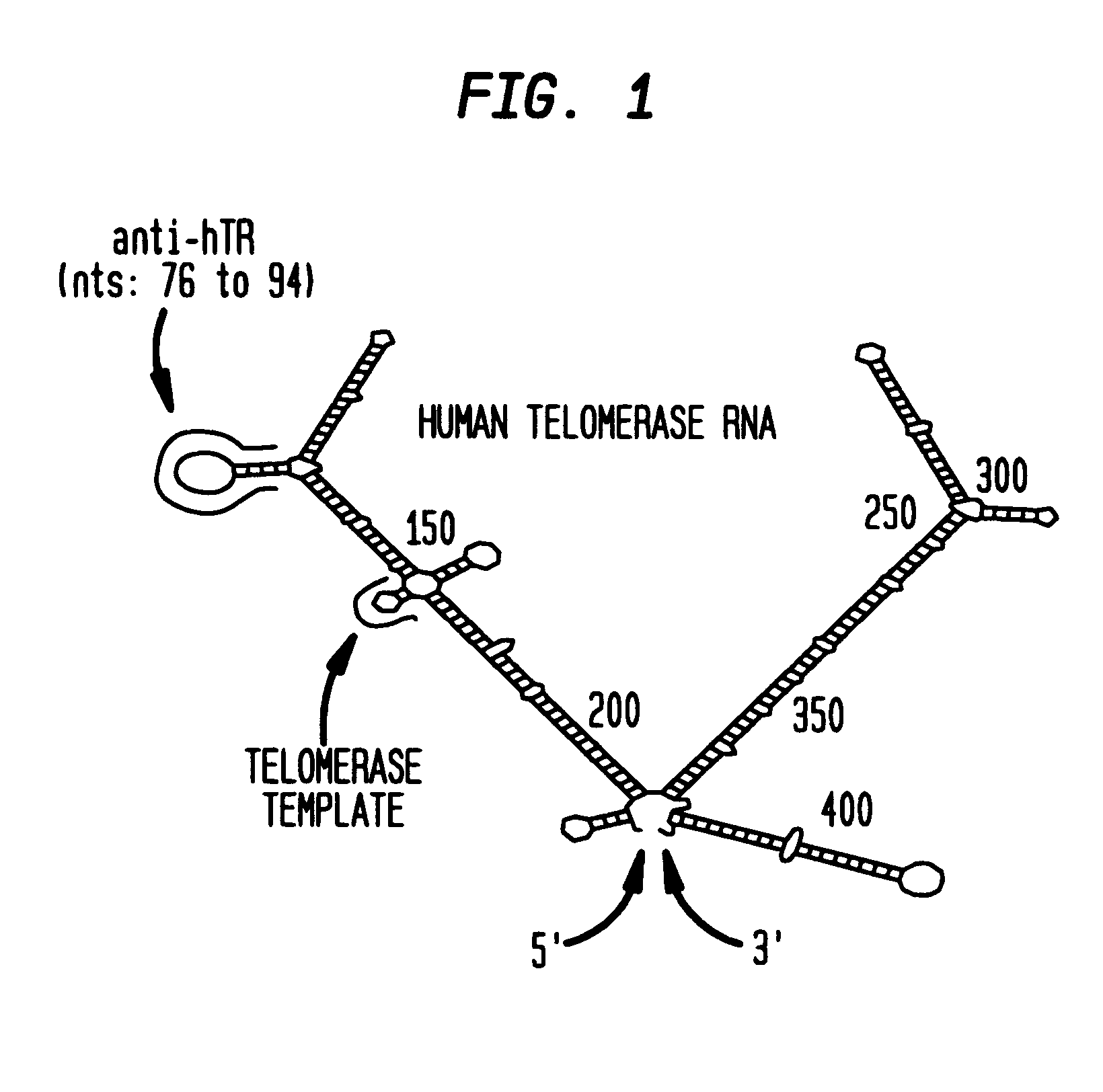
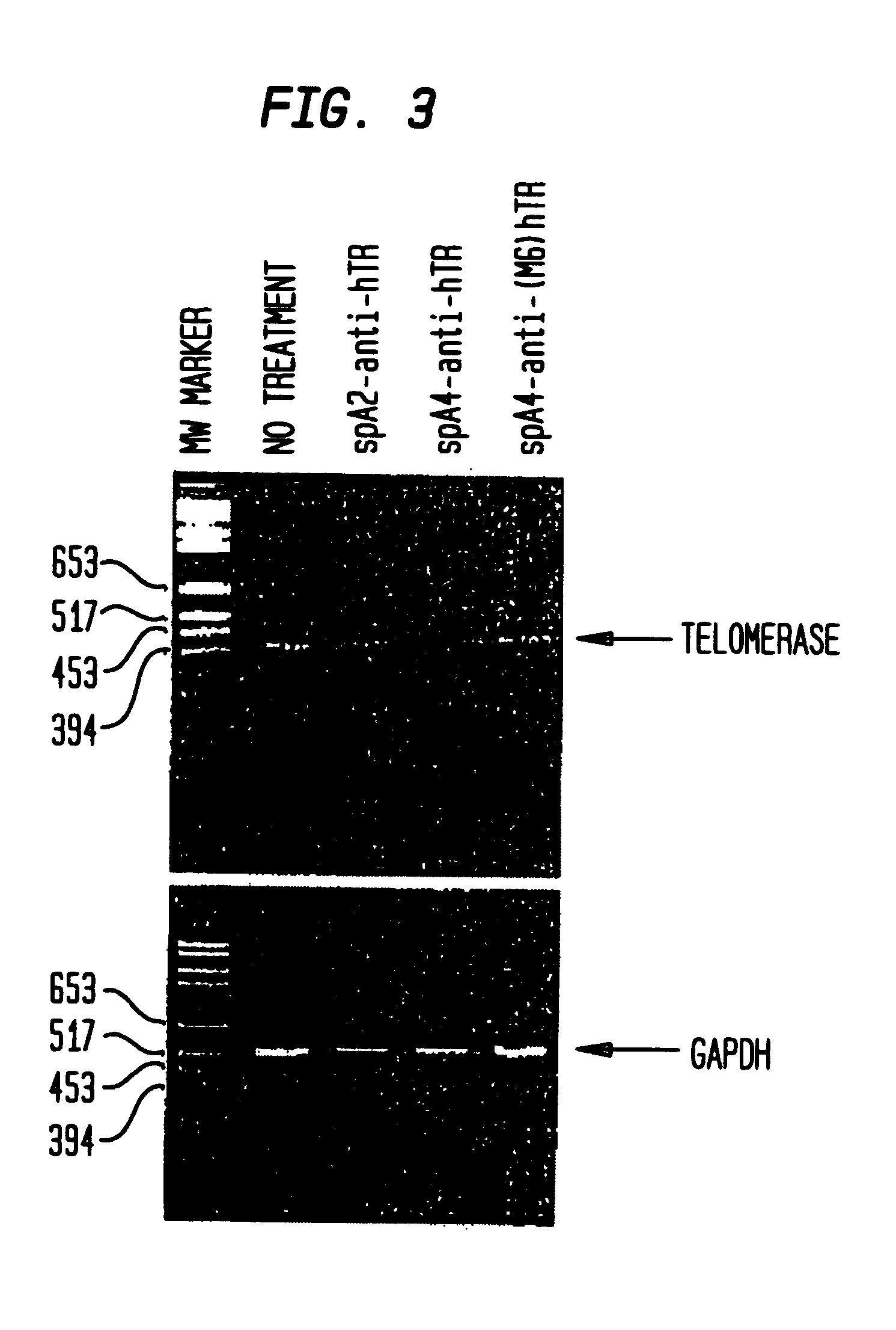
RNase L activators and antisense oligonucleotides effective to treat telomerase-expressing malignancies
InactiveUS6468983B2Facilitate cellular uptakeSuppressed growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTelomeraseDisease
The present invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising an oligonucleotide complementary to a region of the ribonucleotide component of telomerase attached to an activator of RNase L ("activator-antisense complex") which specifically cleaves the ribonucleotide portion of a telomerase enzyme. The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting telomerase enzymatic activity with activator-antisense complexes targeted to the RNA component of telomerase. The present invention further relates to methods of treating malignant neoplastic disease, wherein the malignant cells contain a telomerase activity that is necessary for the growth of the malignant cells.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Bone soup seasoning and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bone soup seasoning, which is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 45-50 parts of fresh bones, 6-10 parts of pigskins, a right amount of white sugar, a right amount of salt, a right amount of powdered monosodium glutamate, 2-4 parts of disodium 5'-ribonucleotide, 2-3 parts of mashed garlic, 4-5 parts of pitaya flowers, 3-4 parts of peach leaves, 2-3 parts of ginger, 10-15 parts of starches, 1-2 parts of Rhodiola rosea, 3-5 parts of agaricus blazei murill, 1-2 parts of bengal waterdropwort herbs, 2-3 parts of hericium, 3-5 parts of rhizoma ligustici wallichii and 0.08-0.12 part of xanthan gum. Through adding traditional Chinese medicinal materials such as pitaya flowers, peach leaves and rhodiola rosea, the seasoning disclosed by the invention not only has the characteristics that the seasoning is fresh, fragrant, delicious and rich in tastes, but also enhances the health care value, and further enhances the health-care benefits of the product.
Owner:FUYANG JIUZHEN FOOD
Hotpot condiment and preparation method
InactiveCN103393059AStrong spicy tasteHigh volatile oil contentFood preparationMonosodium glutamateCapsicum annuum
The invention discloses hotpot condiment and a preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: heating A grade rapeseed oil to 185-195 DEG C, adding dry red pepper powder, and stir-frying for 4 min at 175-185 DEG C; adding Pixian bean paste and fermented soya beans, and stir-frying for 3 min at 95-105 DEG C; adding ginger granules and garlic granules, and stir-frying for 4 min at 90-100 DEG C; adding pickled ginger and ciba pepper, and stir-frying for 2 min at 75-85 DEG C; adding compound spices and white granulated sugar, and stir-frying for 1 min at 80-90 DEG C; adding green pepper powder and red pepper powder, and stir-frying for 1.5 min at 75-85 DEG C; adding edible salt and monosodium glutamate, and stir-frying for 1 min at 80-90 DEG C; adding white spirit, millet wine, disodium 5'-ribonucleotide, yeast extract, edible essence, scallop powder, capsanthin and fermented glutinous rice, stir-frying for 1 min at 75-85 DEG C, and uniformly stirring the components. The hotpot is red in oil color, clear in soup color, spicy, fragrant, free of greasy feeling after eating for a long time and is led up to meaningful afterthoughts, thereby being well praised by consumers.
Owner:四川天味食品集团股份有限公司
Chimeric primers for improved nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveCN101842494AMicrobiological testing/measurementRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Methods are provided for amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. The method use RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotides as primers. The primers have RNA residues scattered along their length and no two ribonucleotides in the prime are adjacent to one another. The methods are useful for reducing non-specific amplification products, such as primer dimers. The invention also provides kits comprising RNA / DNA chimeric oligonucleotide primers for practicing the amplification methods.
Owner:INFINIPLEX LTD
Nitrite-substituted meat processing method
InactiveCN106071907AGood effectGood muscle toneFood ingredient as antioxidantFood ingredient as taste affecting agentBetaninEthyl maltol
The invention discloses a nitrite-substituted meat processing method, and belongs to the technical field of food processing. The nitrite-substituted meat processing method comprises the following steps: selecting raw materials, carrying out pickling treatment and processing a meat product, so that the final products of the meat product are prepared; and the nitrite is substituted by a nitrite substitute during the step of carrying out pickling treatment. The nitrite substitute comprises the following components in parts by weight: 4-5 parts of monascorubin, 0.7-1.3 parts of betanin, 4-6 parts of potassium sorbate, 2-3 parts of D-sodium isoascorbate, 1.5-2.5 parts of nisin, 9-11 parts of sodium lactate, 1-2 parts of natamycin, 5-6 parts of natural vitamin E, 1-2 parts of a rosemary extract, 0.5-1.5 parts of sage essential oil, 1-2 parts of tea polyphenols, 15-16 parts of L-sodium glutamate, 0.5-1.5 parts of flavoring 5'-disodium ribonucleotide, 40-43 parts of a yeast extract, 4-5 parts of sodium tripolyphosphate and 0.5-1.5 parts of ethyl maltol. The nitrite-substituted meat processing method disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to operate and free of nitrite addition; and the prepared meat products are very good in qualities, color, luster and taste.
Owner:邯郸市锦园食品有限公司
Recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and method for producing cytidine
ActiveCN106754602ARealize large-scale industrial productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaTransferasesRibonucleosideGenetic engineering
The invention provides a recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and a method for producing the cytidine from the recombinant microorganism. A degradation and use gene of the cytidine is knocked off, and the gene encodes cytidine ammonialyase, ribonucleotide hydrolase, cytidine / uridine kinase and nucleoside transporter. Meanwhile key enzymes in biological synthesis process of the cytidine are over-expressed, including degrading cytidine triphosphoric acid to cytidine triphosphoric acid pyrophosphorylase of the cytidine monohosphoric acid, and catalyzing the cytidine monohosphoric acid to cytidine monohosphoric acid phosphorylase of the cytidine. In addition, pyrimidine nucleoside process is subjected to genetic engineering reform, and feedback inhibition of the synthesis process is relieved. By using a biological fermentation method, the cytidine yield greater than 20g / L can be achieved for a recombinant strain in a fermentation tank of 5L, industrial on-scale production can be achieved, and meanwhile the recombinant microorganism is low in cytidine production cost, small in pollution, green and environmental-friendly and relatively high in popularization and application value.
Owner:BIOSYNTHETICA INC
Novel protective group for synthesis of RNA and derivative
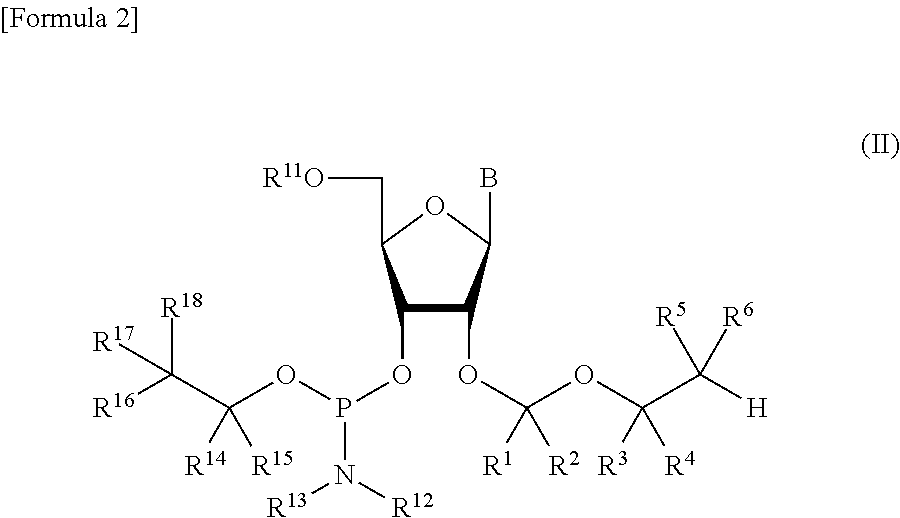
ActiveUS20110178284A1Small hindranceEfficient removalSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomRibonucleoside
A protective group represented by the following general formula (I) (the oxygen atom attached with * represents oxygen atom of 2′-hydroxyl group of a ribonucleoside, a ribonucleotide or a derivative thereof; R1 and R2 both represent hydrogen atom, or represent a halogen atom, a C1-6 alkyl group, or a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group; R3 and R4 represent hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a C1-6 alkyl group, or a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group; and R5 and R6 represent a halogen atom, a C1-6 halo-substituted alkyl group, cyano group, nitro group, or the like), which is stable under the reaction conditions of the nucleic acid synthetic cycles and has little steric hindrance, and can be removed under mild conditions using fluoride ions as a base.
Owner:WAVE LIFE SCI LTD
Lateral flow nucleic acid detector
InactiveUS20090305290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibonucleotide synthesisNucleic acid sequencing
Point-of-care binding assays include at least one target nucleic acid binding in a multiplex structure with at least one sequence in a partner nucleic acid associated with a label, due to complementary base pairings between at least one sequence in the target nucleic acid and at least one sequence in the partner nucleic acid. The assays overcome the inherent deficiencies of antibody-protein antigen assays. In a preferred embodiment, color tagged nucleic acid sequences are used to bind a complementary target nucleic acid. The tagged nucleic acid sequences are preferably made from deoxyribonucleotides, ribonucleotides, or peptide nucleotides.
Owner:RAPID PATHOGEN SCREENING INC
Amplification primer for PCR-mtDNA test of total chicken origin
InactiveCN101270392AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFowlPoultry disease
The invention mainly relates to detection of poultry-derived component, which mainly relates to detection of poultry-derived component by using PCR-mtDNA. A specific PCR-mtDNA amplification primers for detecting poultry-derived component is characterized by compring a upstream ribonucleotide with length of 18bp, a downstream ribonucleotide with length of 19bp, and the sequence of the upstream primer PF(18bp) is 5'-AGAACTACGAGCACAAAC-3', and the sequence of the downstream primer PR(19bp) is 5'-GCTATACCTTGACCTGTCT-3'. The detection of poultry-derived component by using PCR-mtDNA has the advantages that: the method is an accurate, rapid and reliable identification method and technology of poultry-derived component, and has the important practical significance of effective resistance on propagation and spread of bird flu and other poultry diseases. The research utilizes aseptic ultrapure water to dilute DNA template of poultry to cause the concentration to decrease to 12ng per Mul, 1.2 ng per Mul, 120 pg per Mul, 12 pg per Mul, 1.2 pg per Mul, 120 fg per Mul, 12 fg per Mul and 1.2 fg per Mul, and carries out PCR amplification. Known from the electrophoresis result of PCR product, the minimum concentration which can be detected is 120 pg per Mul, so the sensitivity of the primer is 120 pg per Mul.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Small interfering nucleic acid, composition and application
ActiveCN111139242AEnhanced inhibitory effectSignificant clinical significanceOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSense strandRibose
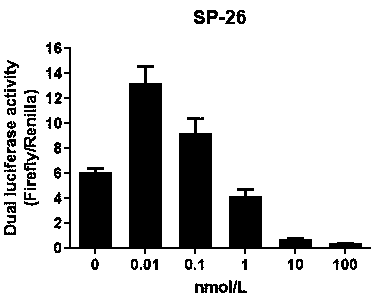
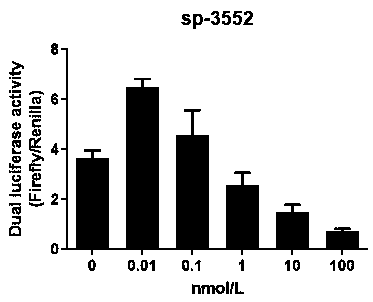
The invention discloses small interfering nucleic acid as well as a composition and application thereof. The invention claims to protect siRNA, which is PP-1758, PP-17660, PP-20091, PP-20163, SP-26, SP-179, SP-2013, SP-2867, SP-3169, SP-3552, MG-83, NP-208 or NP-241, wherein a part of nucleotides of the positive-sense strand are 2 '-O-methyl ribonucleotides, and a part of phosphate groups are thiophosphate groups. The invention provides brand new siRNA and a composition thereof. The brand new siRNA and the composition thereof can effectively prevent and / or treatment novel coronavirus.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA
Small interfering nucleic acid for inhibiting novel coronavirus, and composition and applications thereof
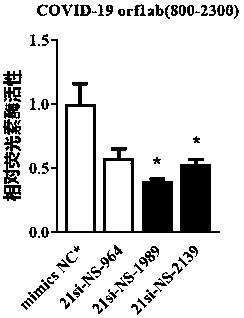
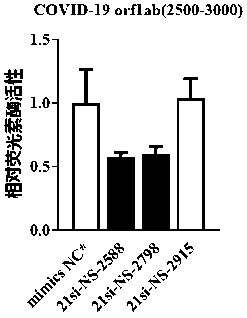
ActiveCN111139241AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSense strandRibonucleotide
The invention discloses small interfering nucleic acid for inhibiting novel coronavirus, and a composition and applications thereof. The siRNA contains a positive-sense strand and a antisense strand;the siRNA is 21-si-SP-2069, 21-si-SP-2289, 21-si-SP-3292, 21-si-P3-242, 21-si-P8-62, 21-si-P8-164, 21-si-P10B-158, 21-si-P14-19, 21-si-NP-722, 21-si-NP-1123, 21-si-NS-2139 or 21-si-NS-2798; and partial nucleotide of the positive-sense strand or the antisense strand is 2'-O-methyl ribonucleotide, and partial phosphate groups are phosphorothioate groups. The provided brand-new siRNA and the composition thereof can effectively prevent and / or treat novel coronavirus.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA +1
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
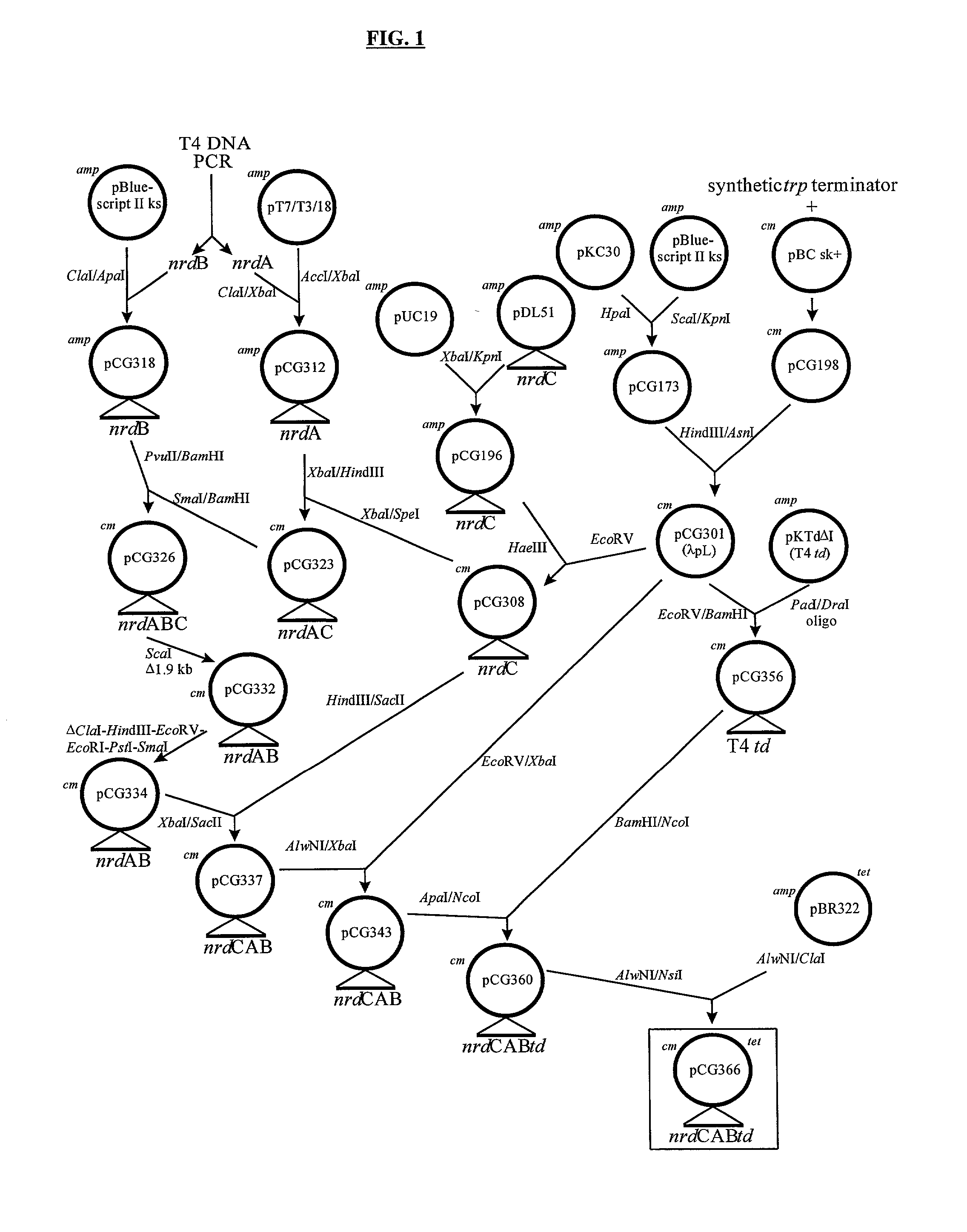
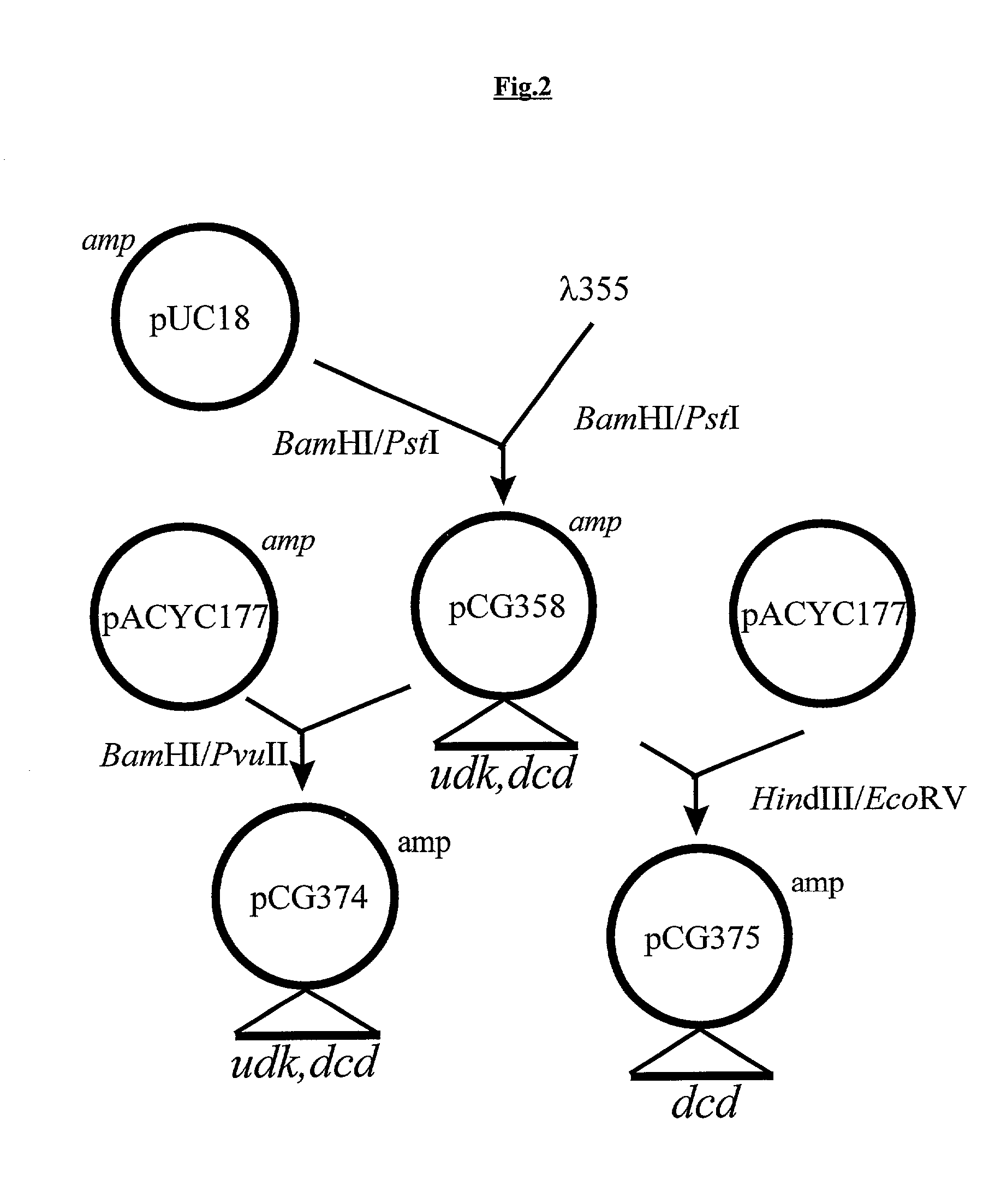
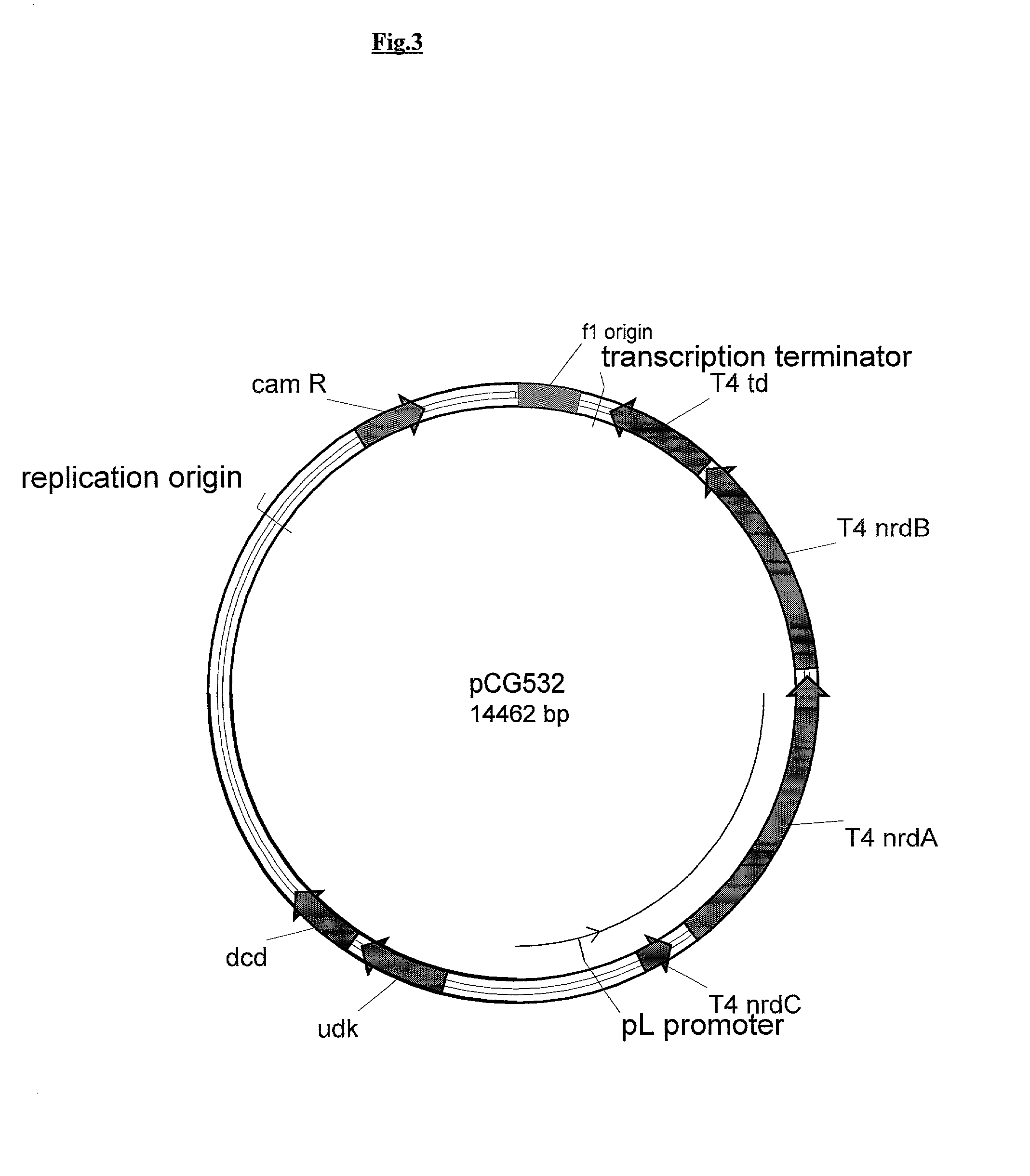
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com