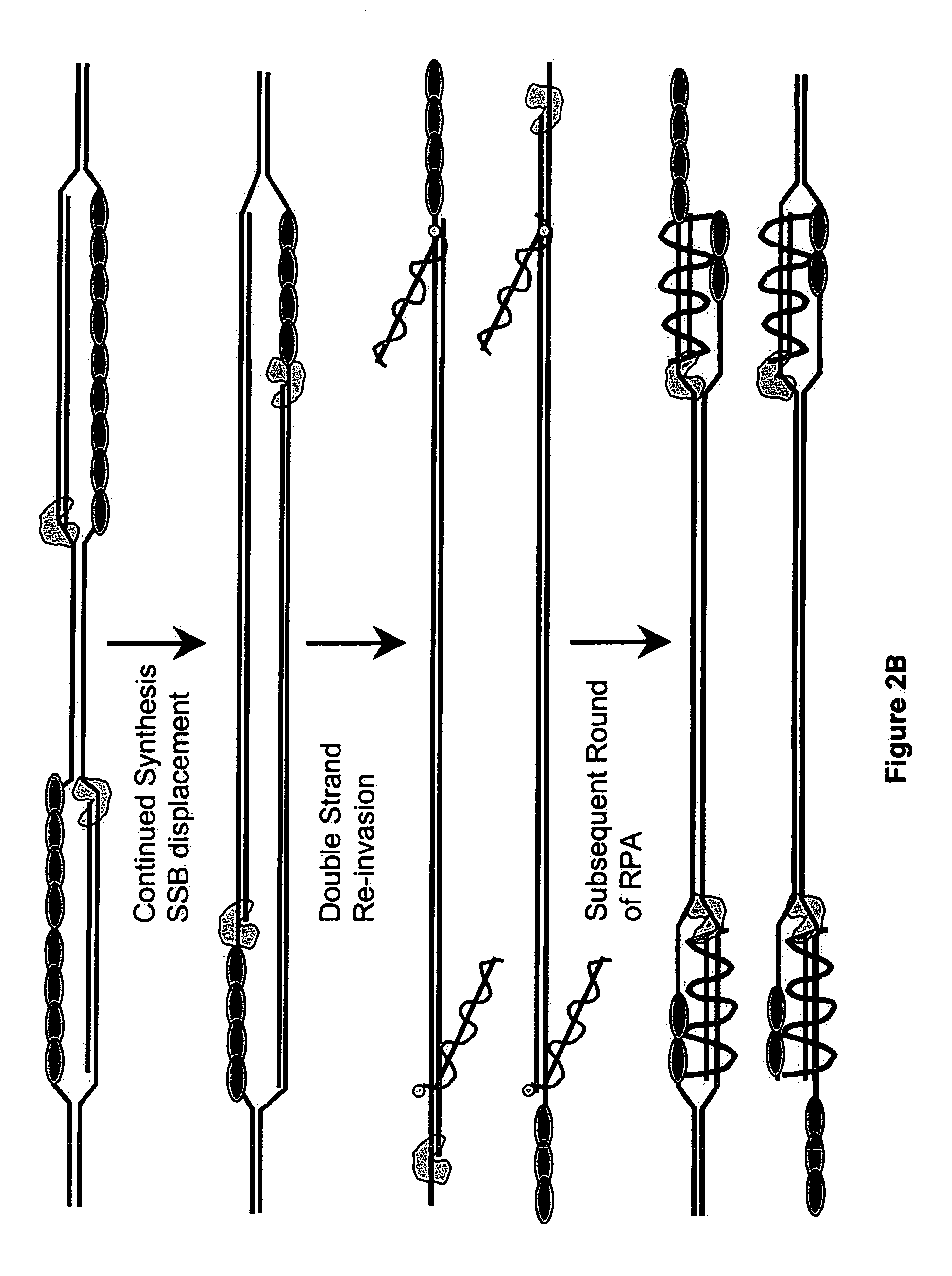
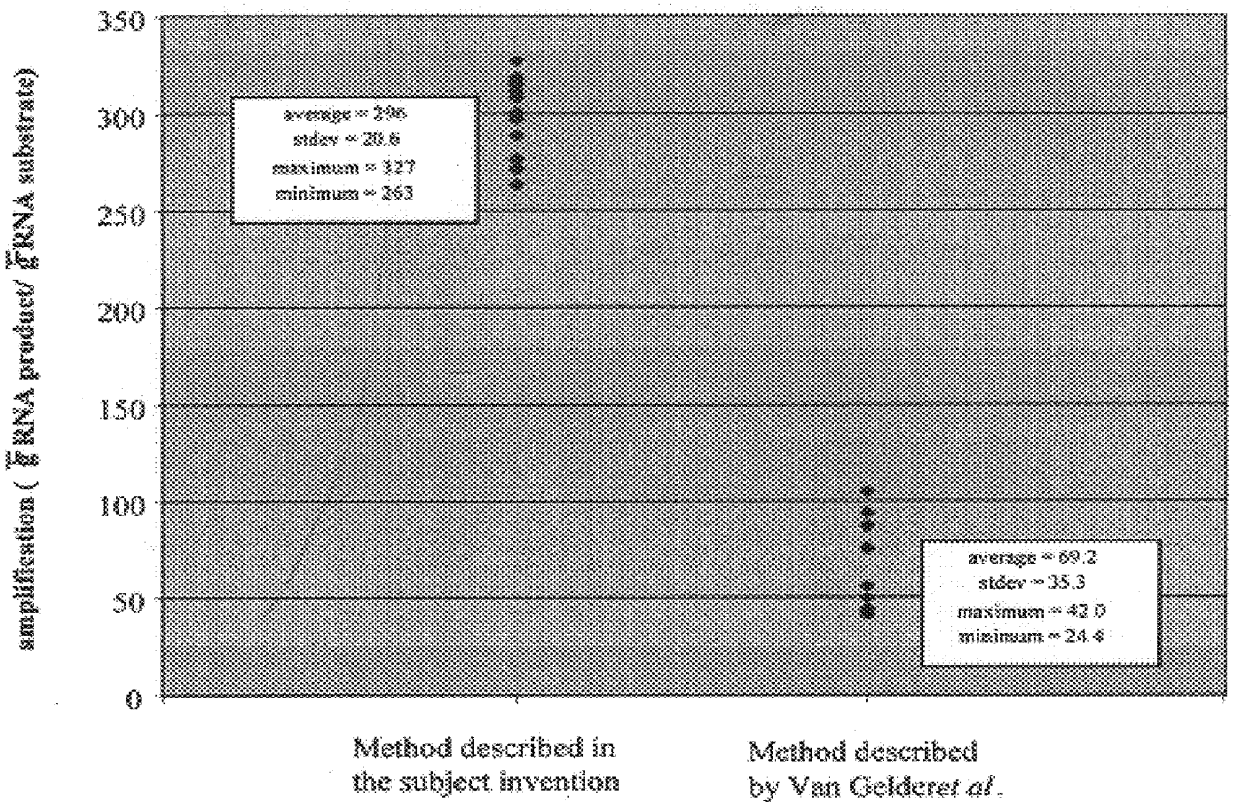
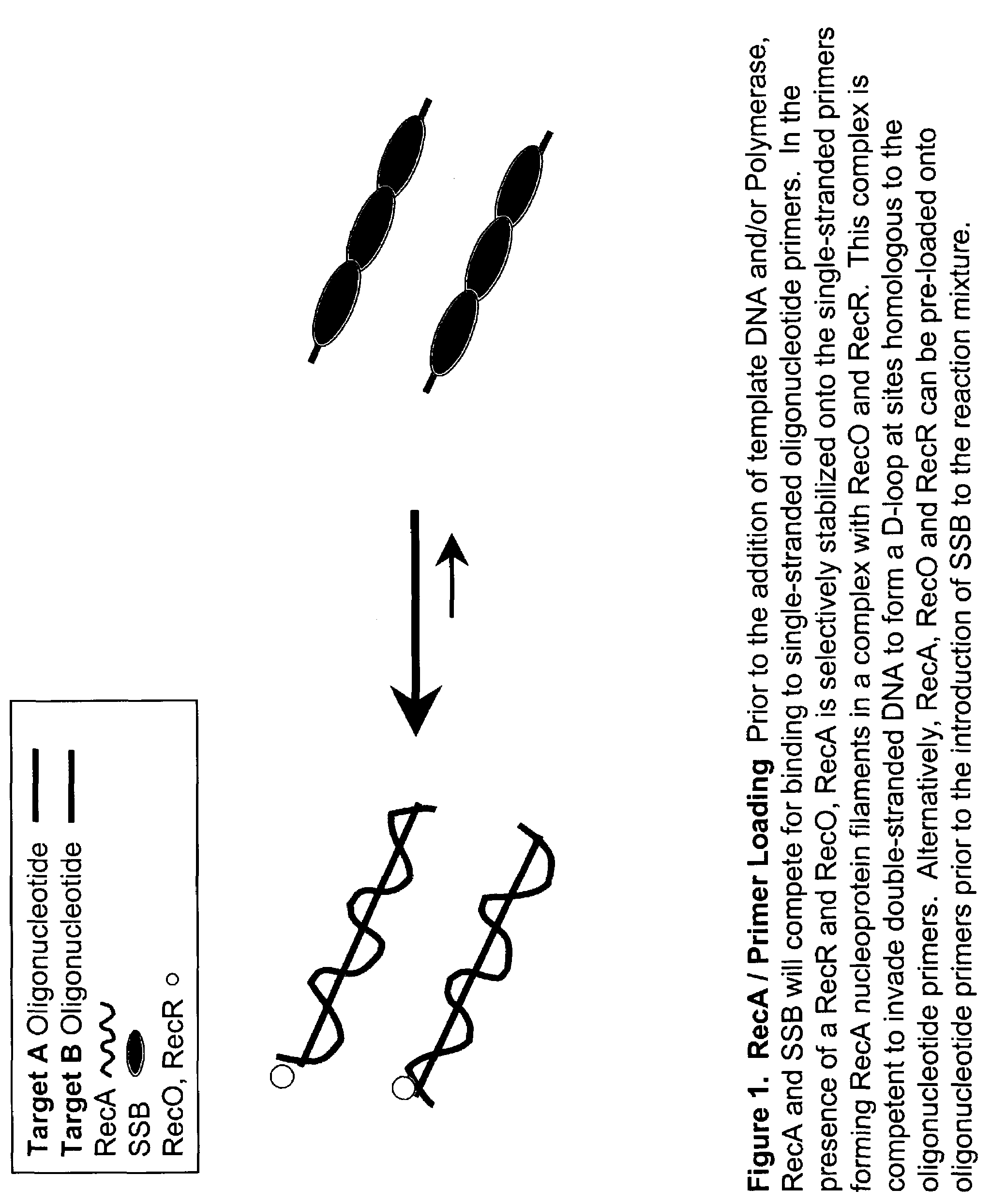
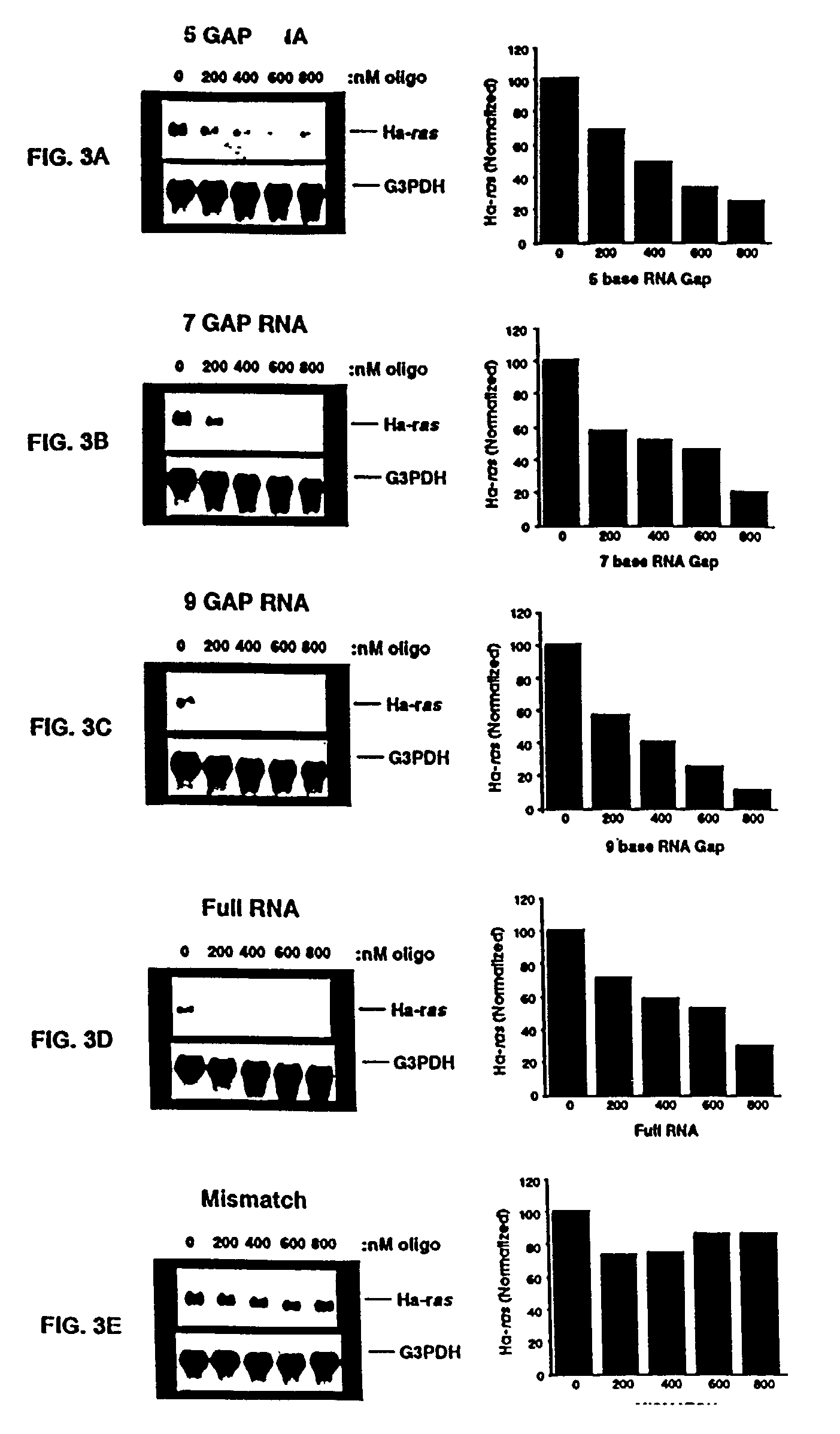
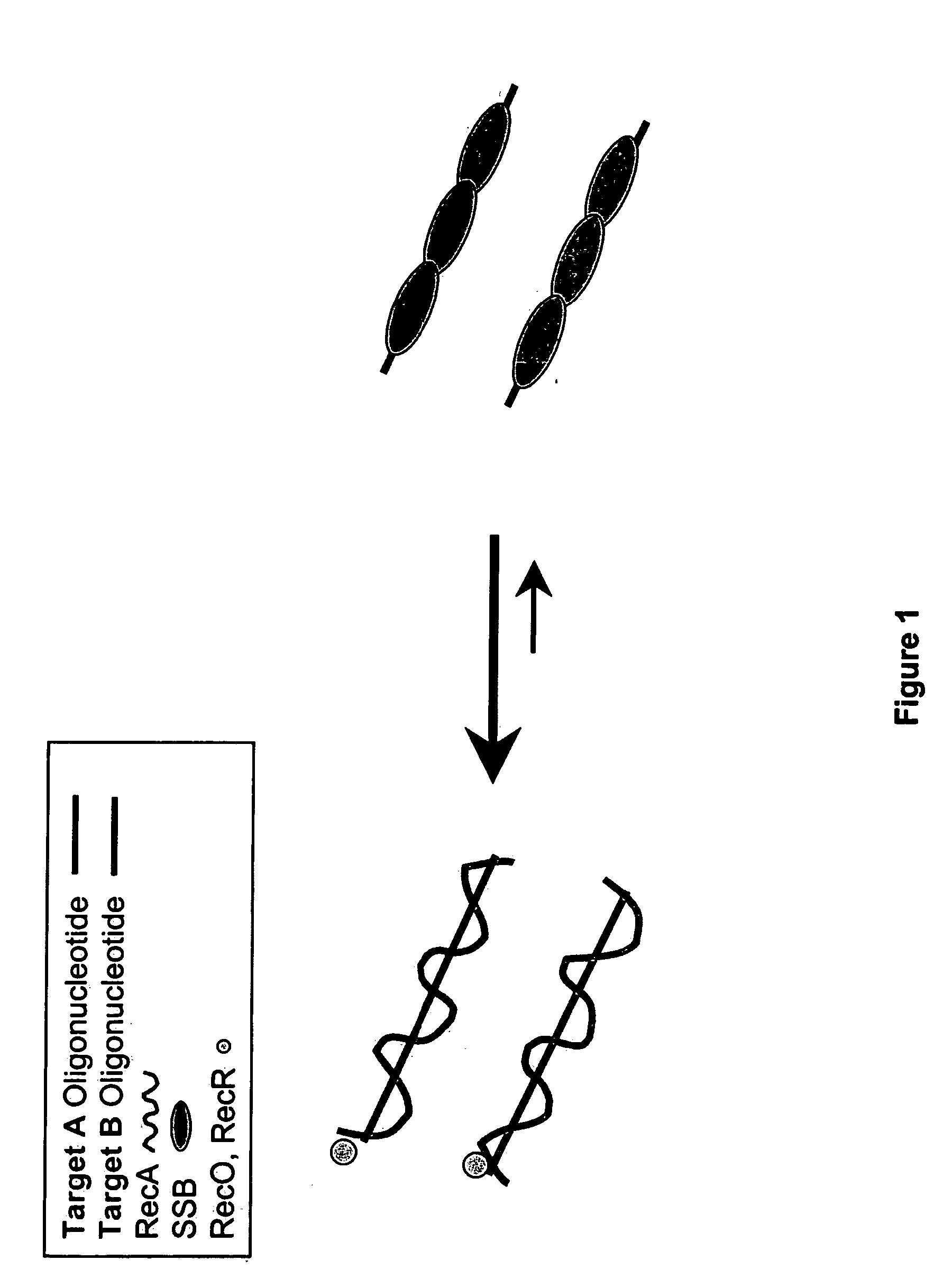
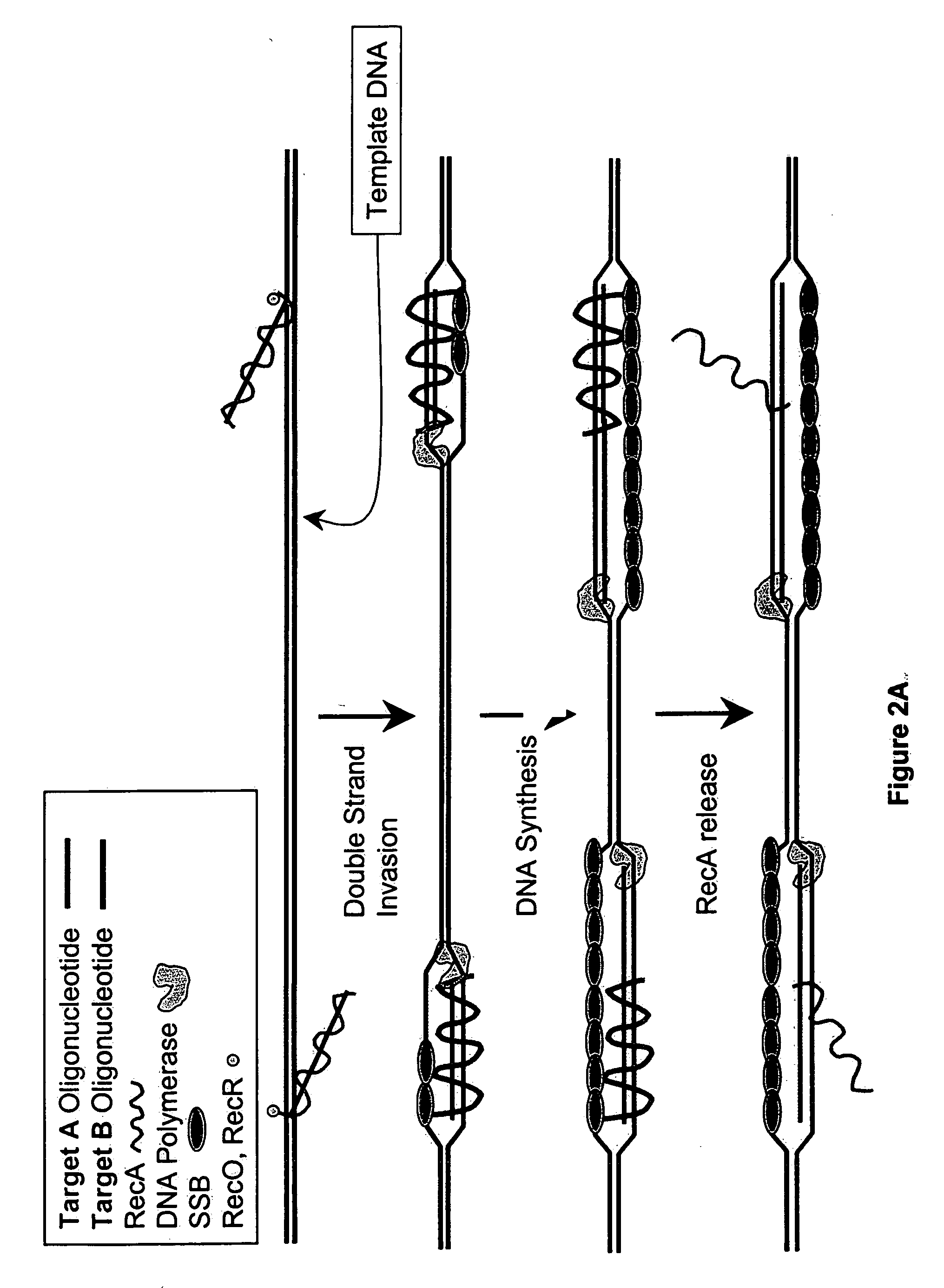
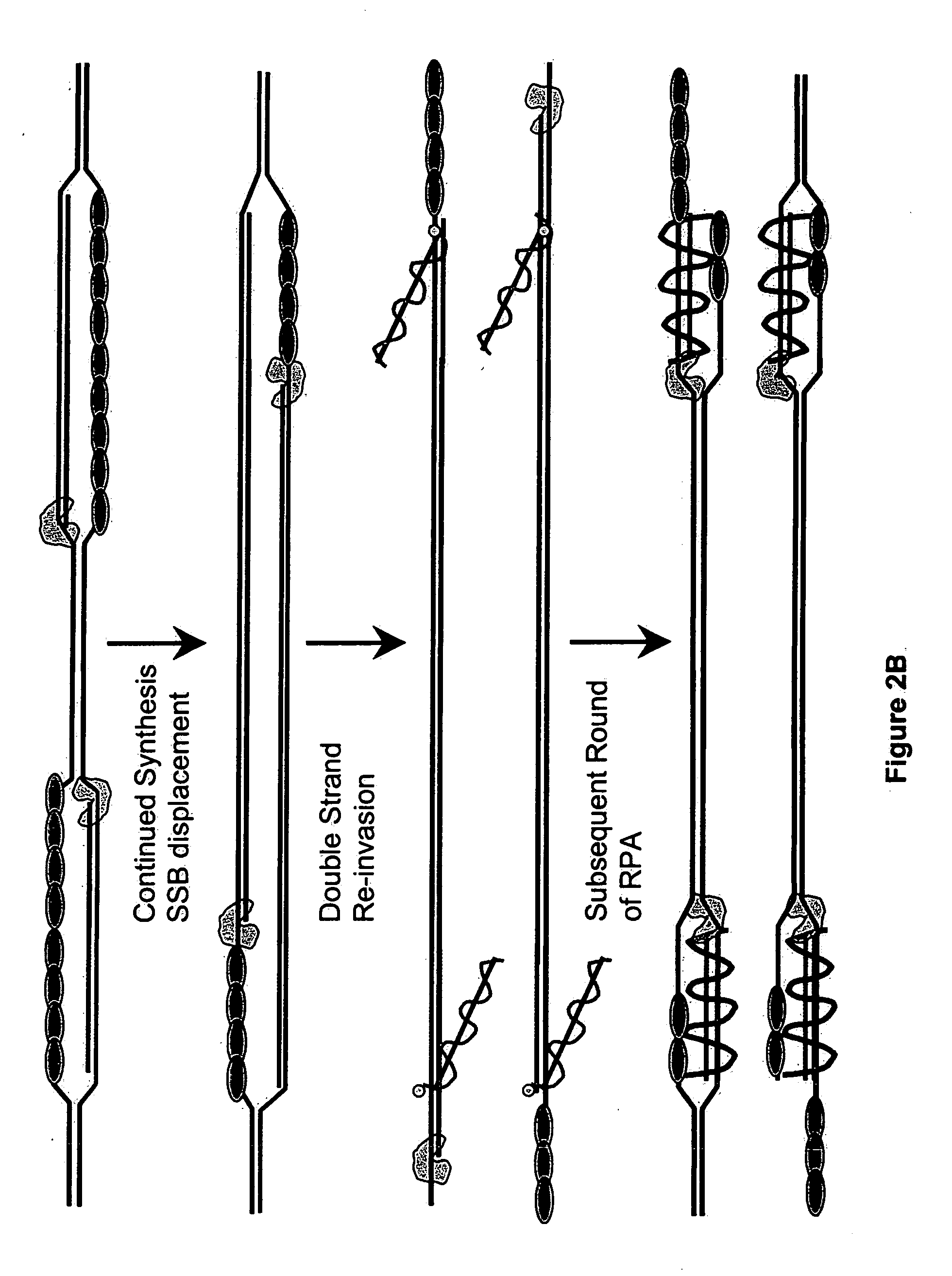
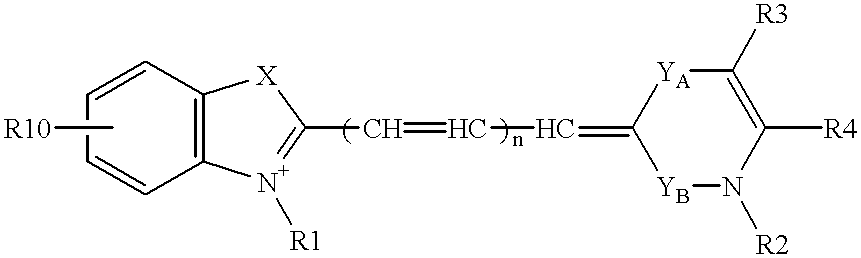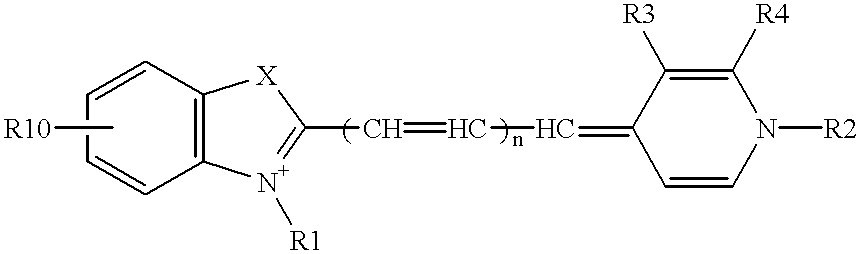Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1745 results about "Double stranded" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
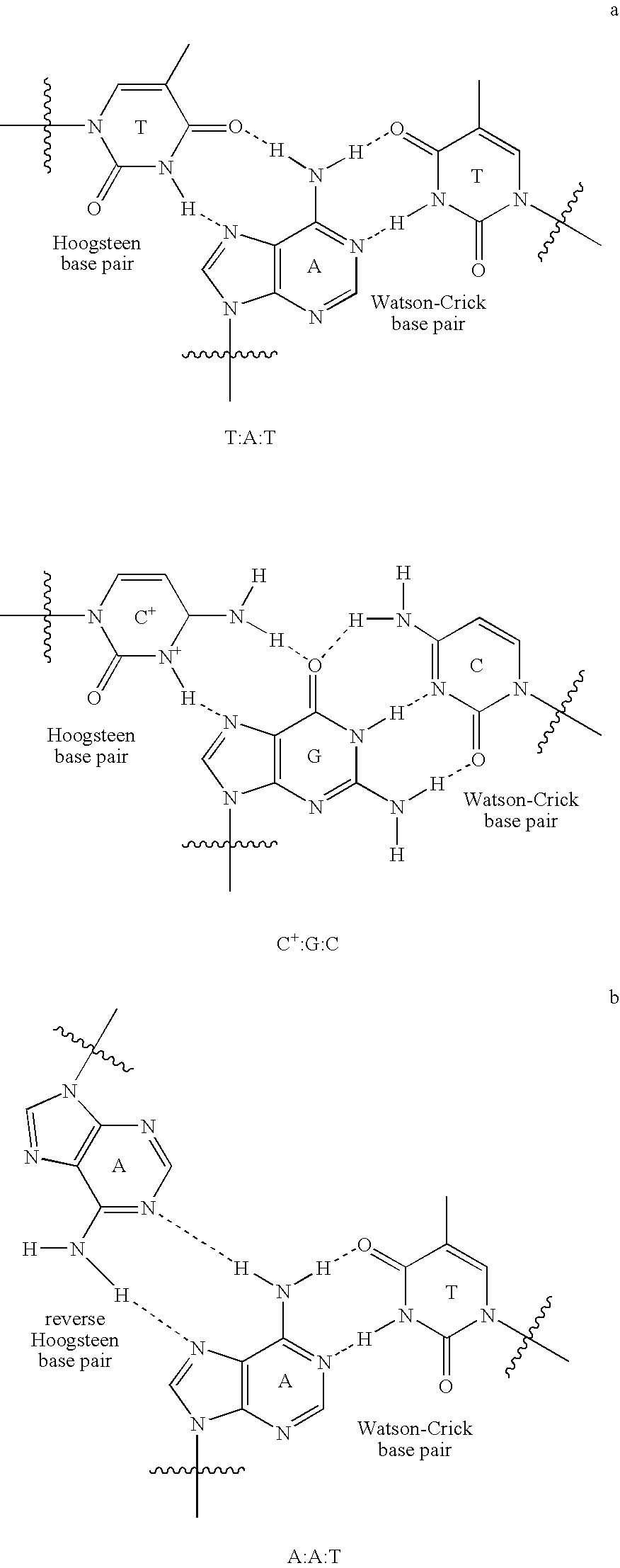
Double stranded double stranded two adjacent strands. Double stranded RNA (dsRNA): In eukaryotes, it is an accidental byproduct of transcriptional process. It may occur as the genome of certain viruses (such as reovirus) or may be produced during viral replication as a general marker for viral infection.
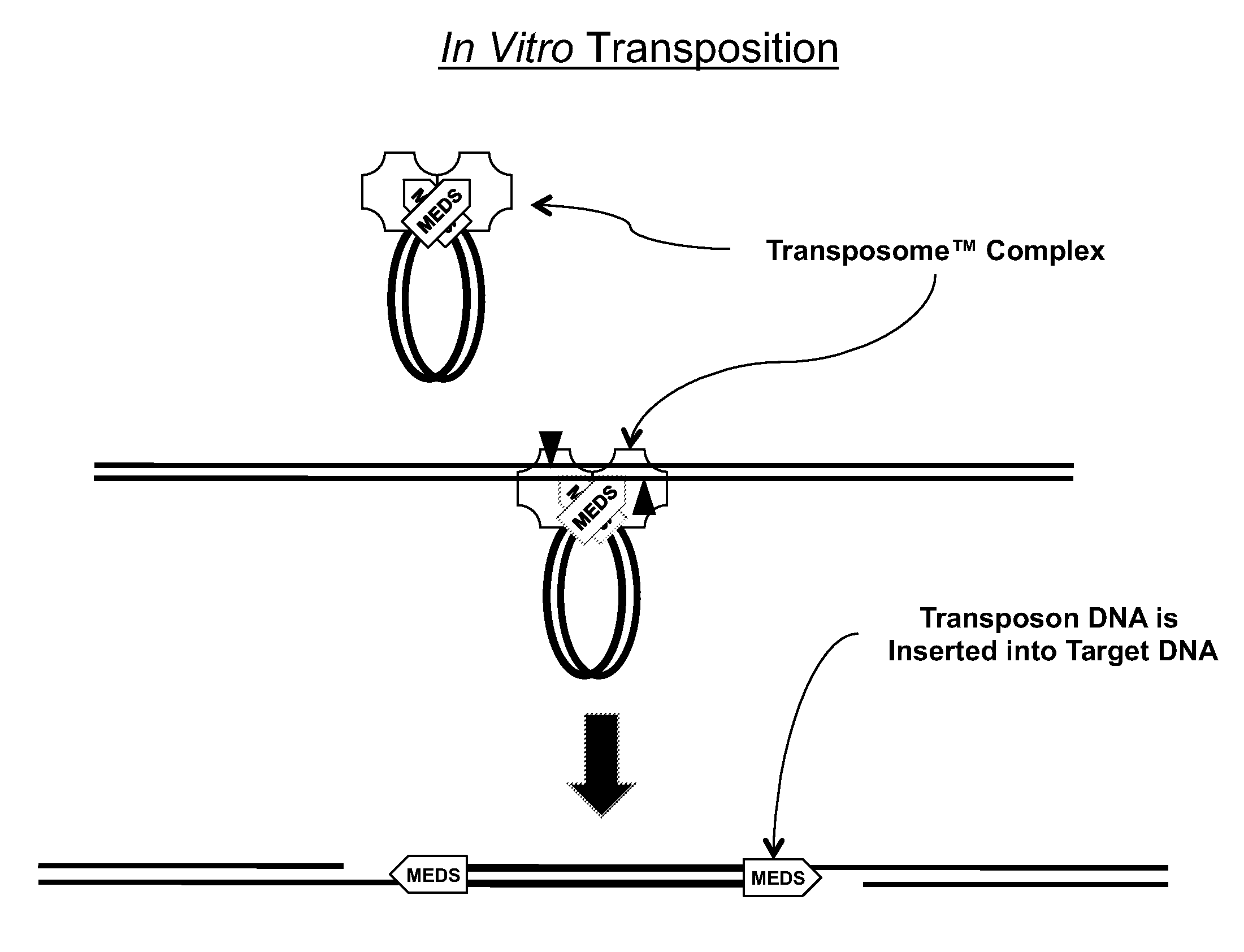
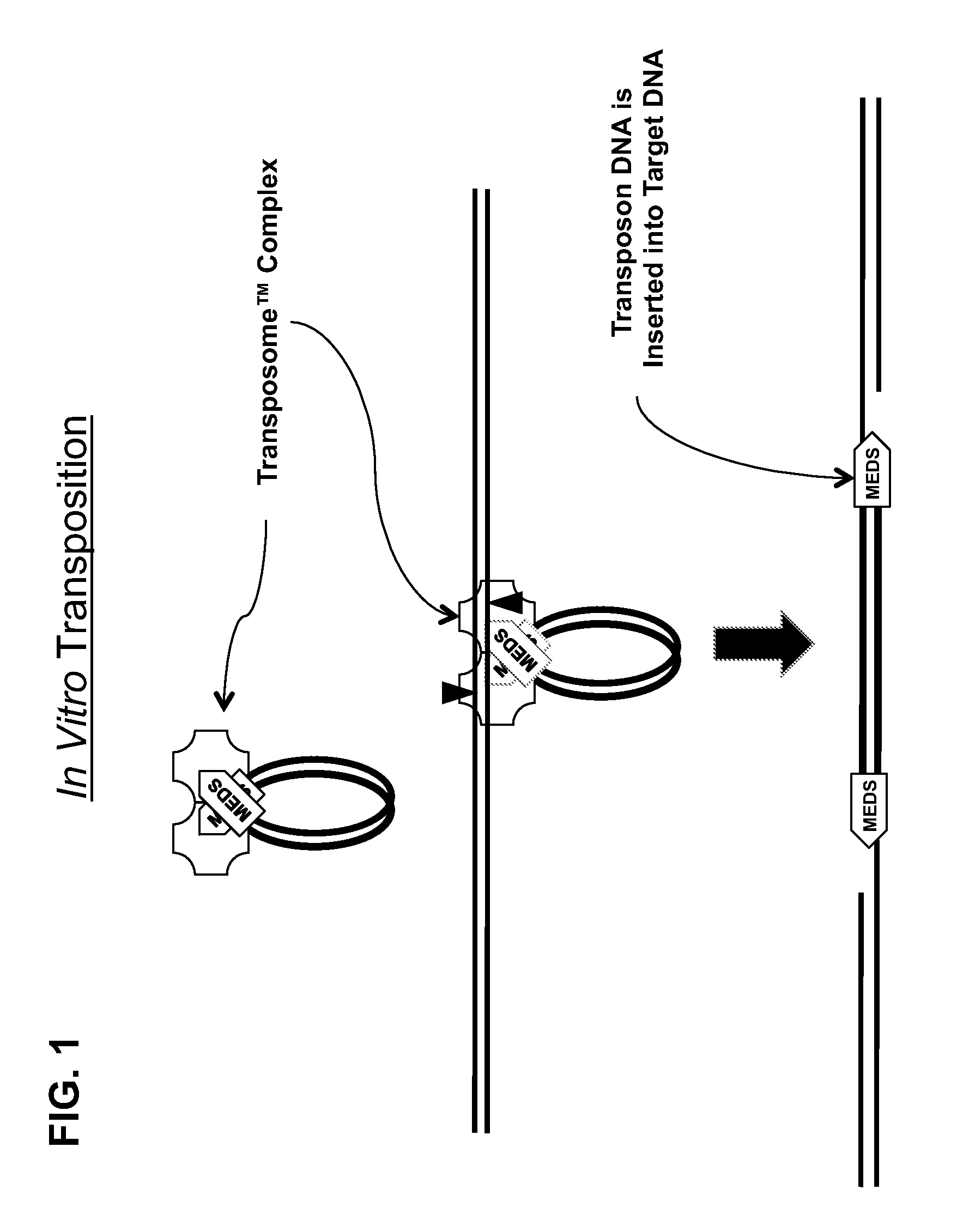
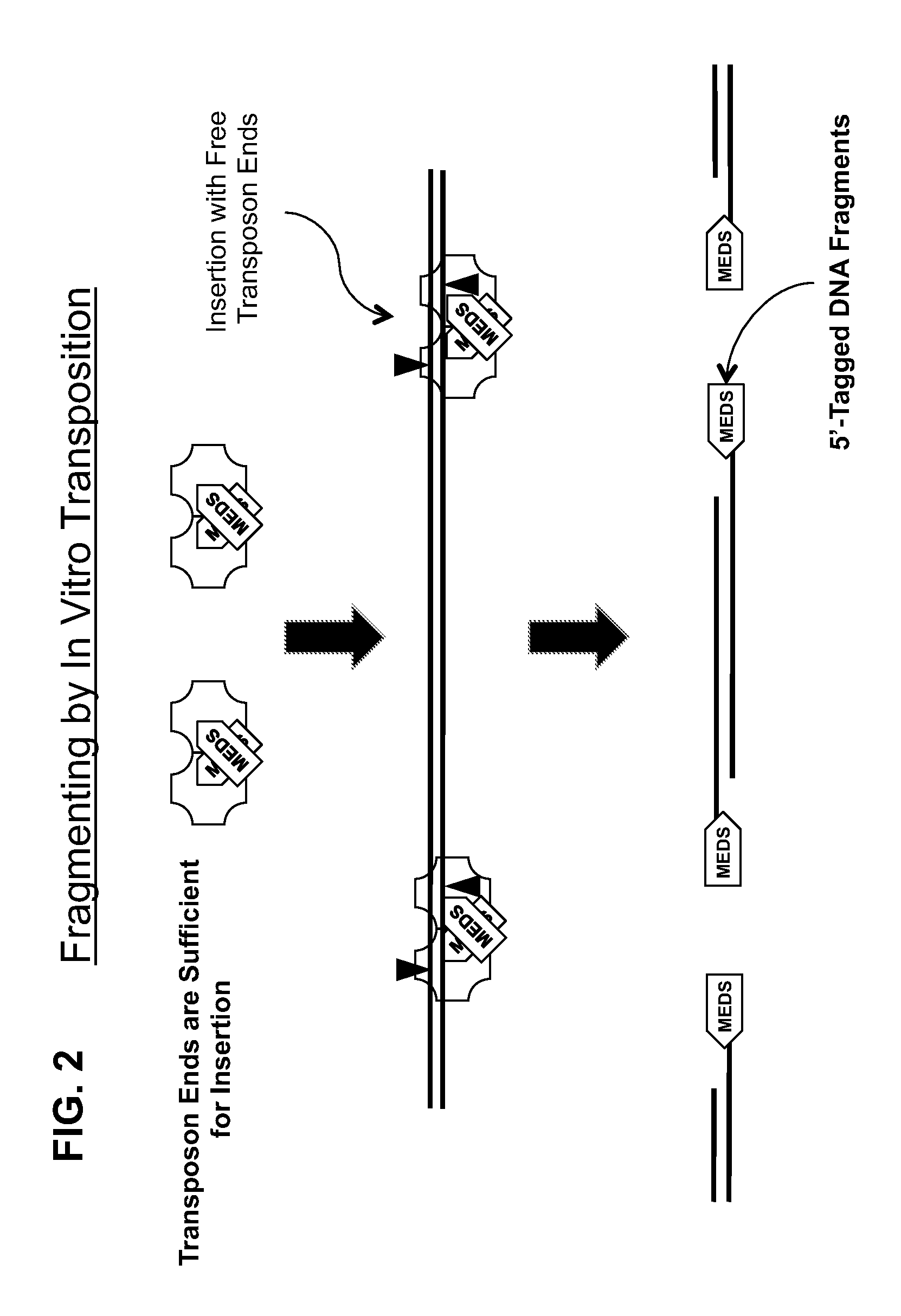
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Molecular encoding of nucleic acid templates for PCR and other forms of sequence analysis
InactiveUS20070020640A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingOligonucleotideDouble stranded
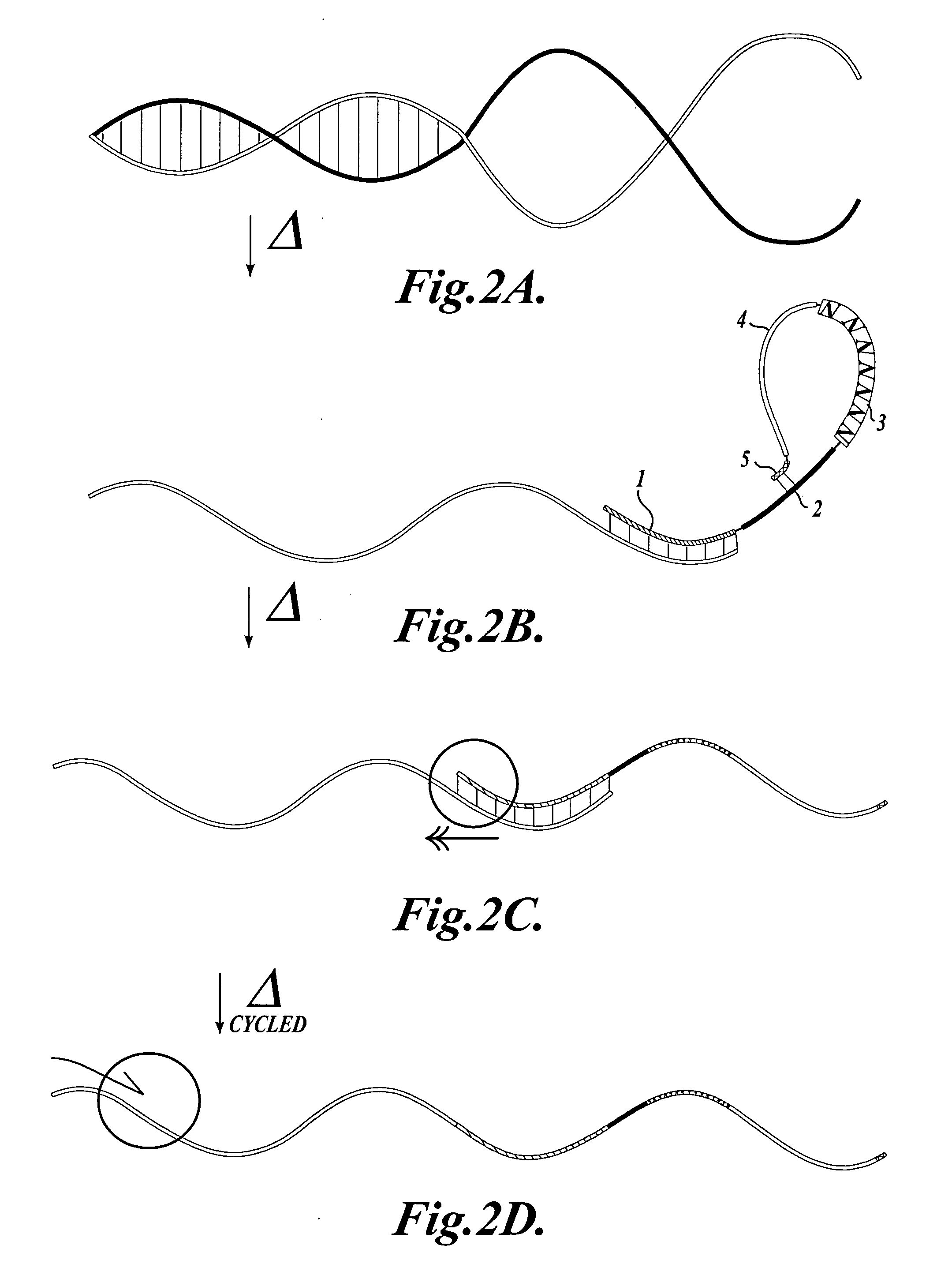
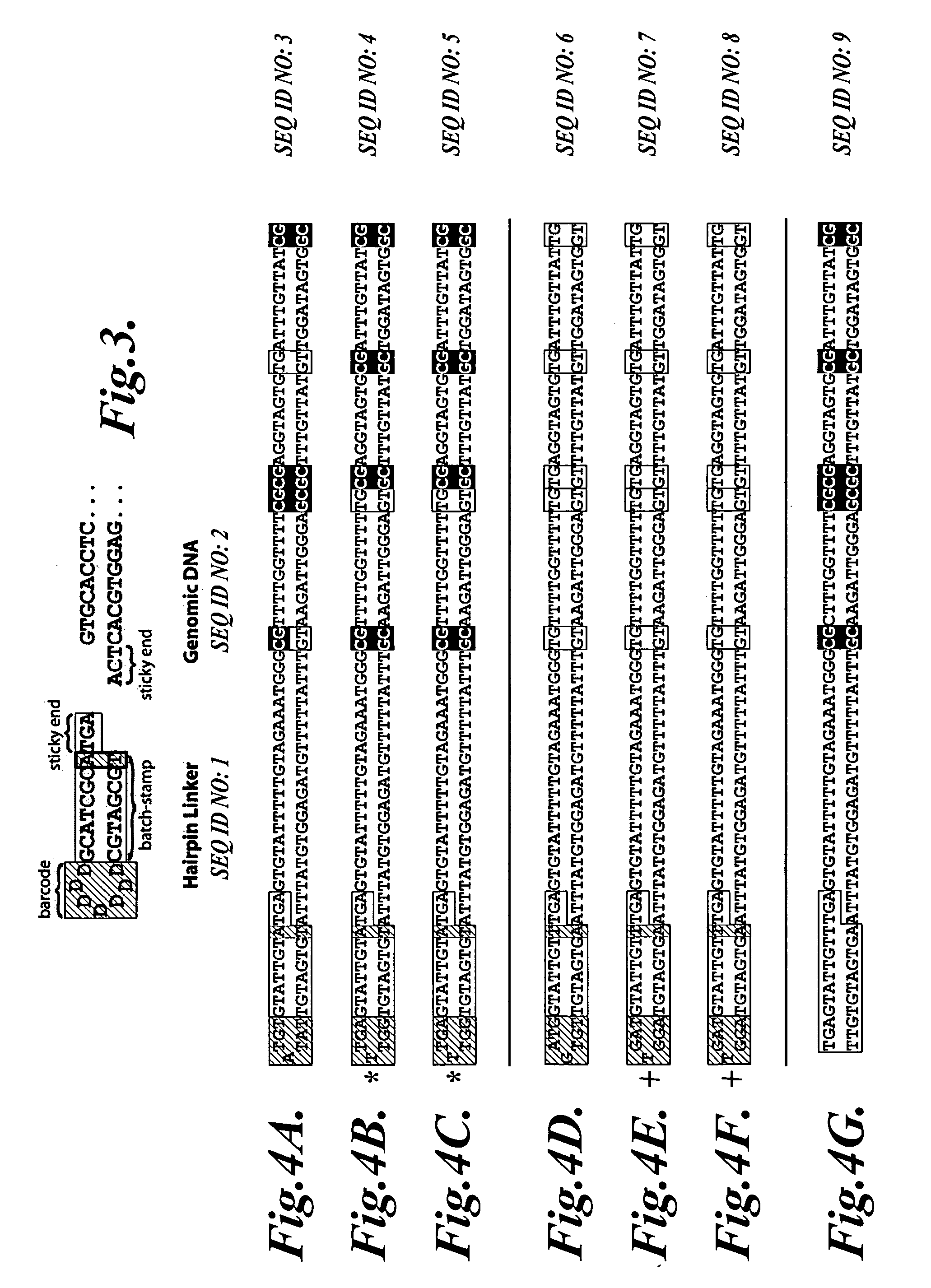
In a first aspect, the present invention provides methods for authenticating a nucleic acid molecule and its sequence with a molecular barcode and batch-stamp. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for authenticating a nucleic acid amplification product. In a further aspect, the present invention provides compositions for encoding both single-stranded and double-stranded target nucleic acids with coded oligonucleotides. The compositions are useful in the practice of the methods of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
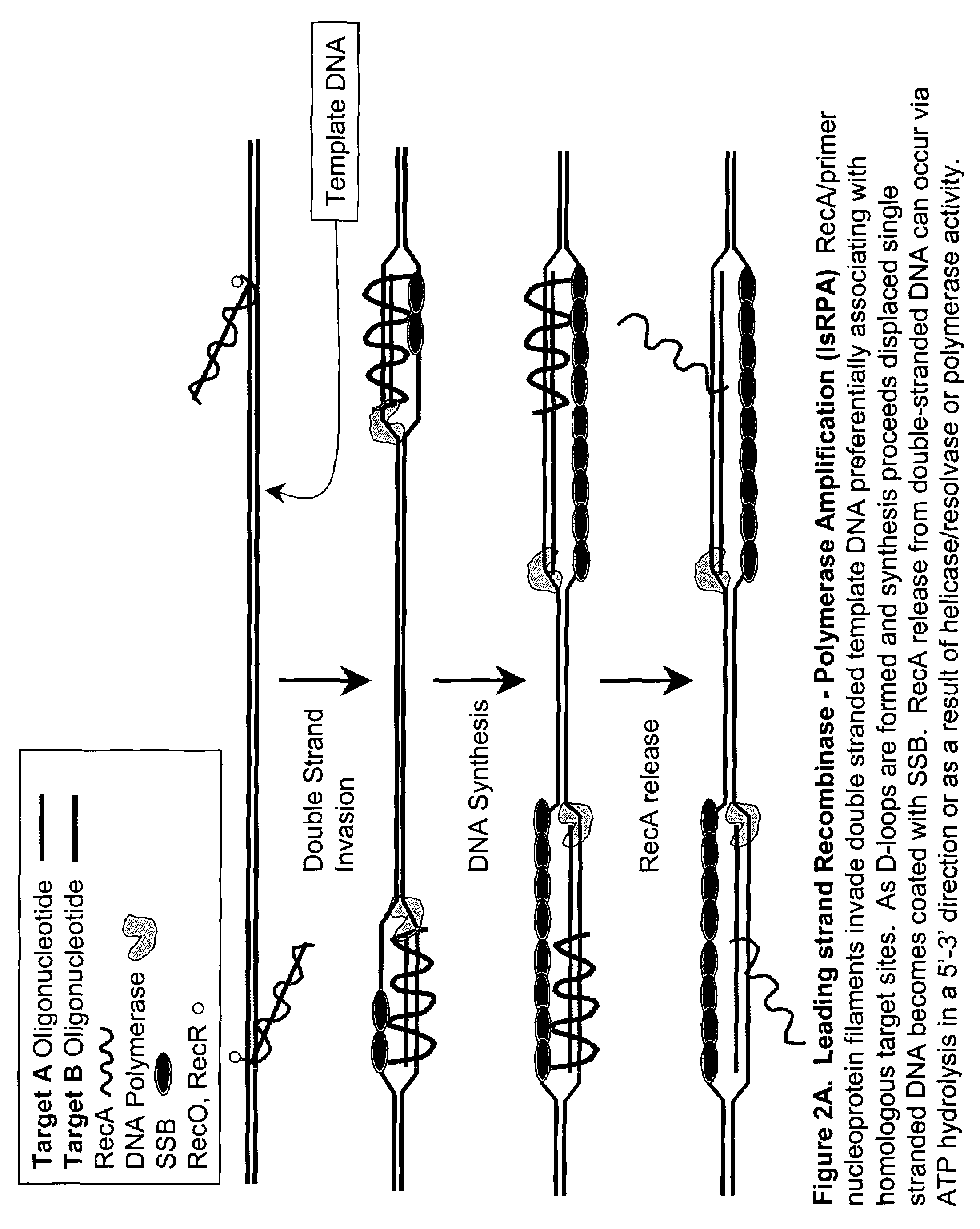
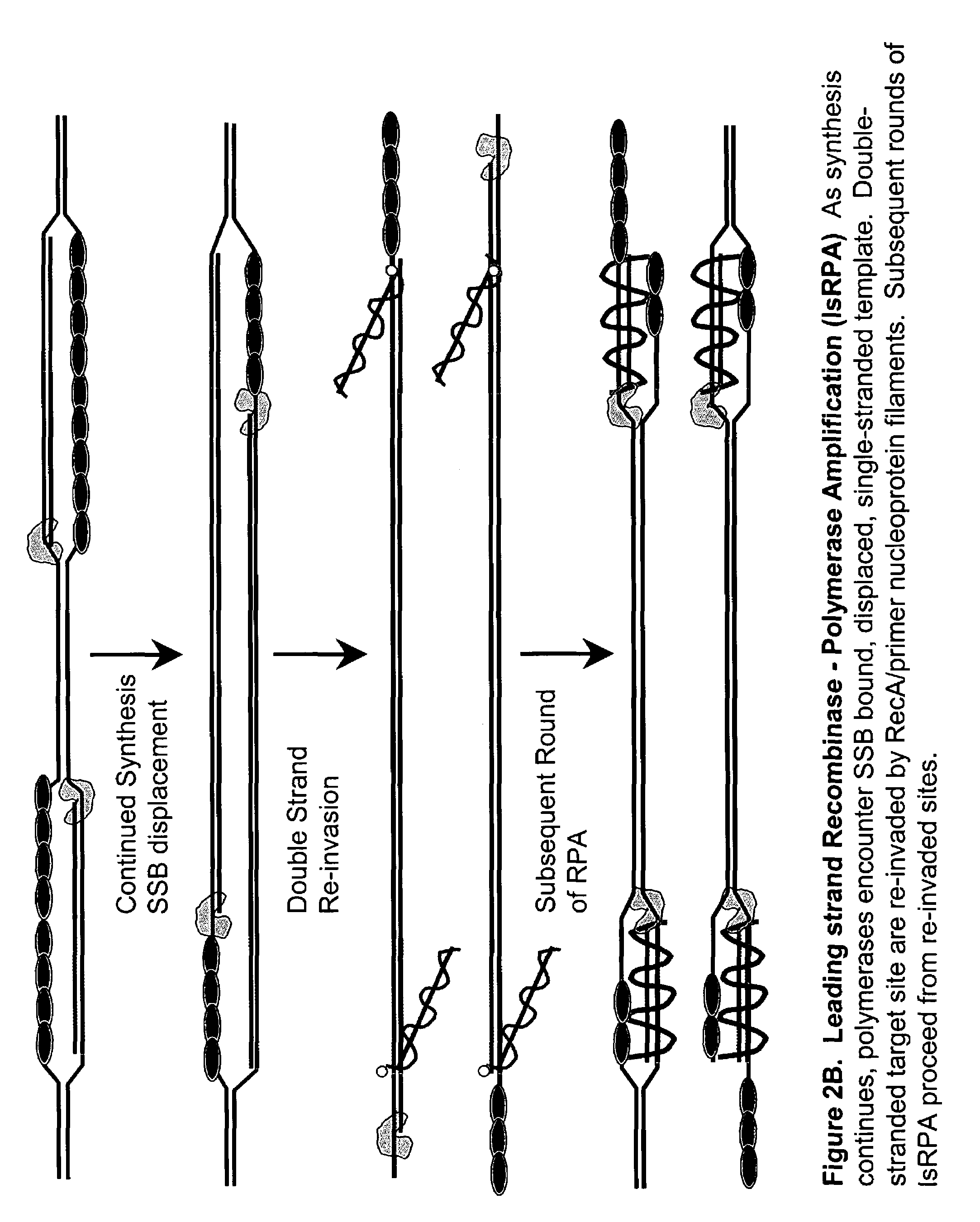
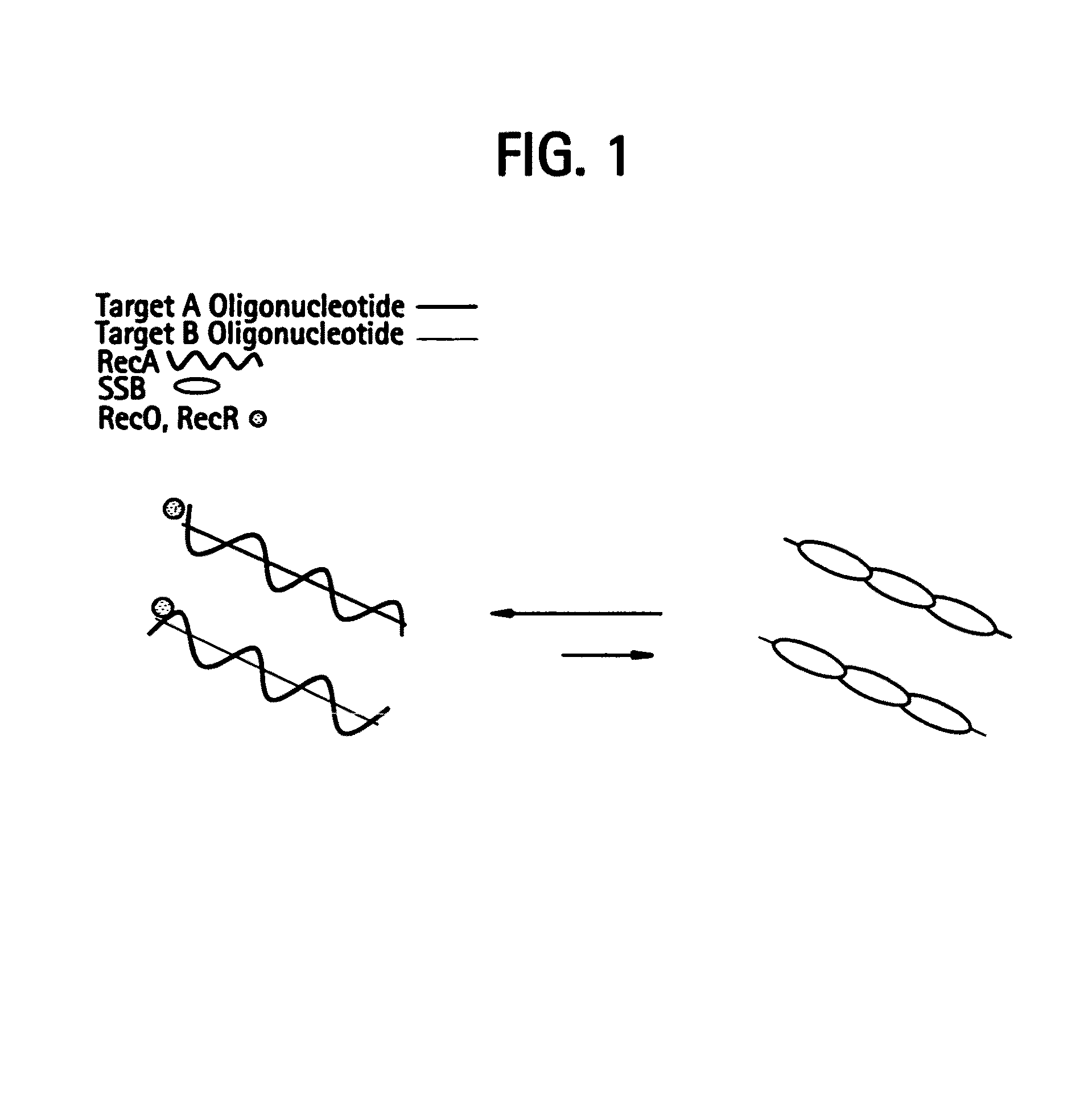
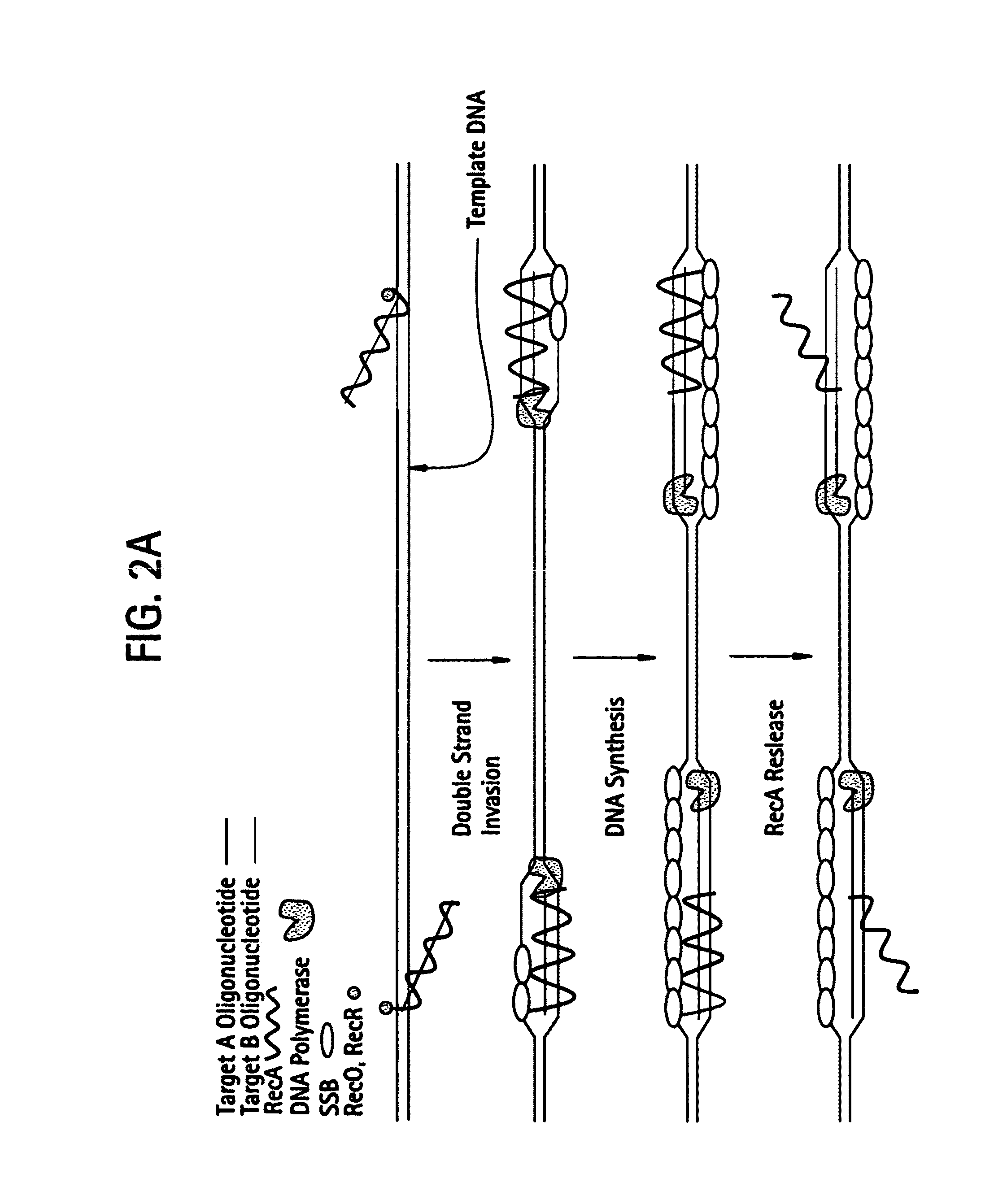
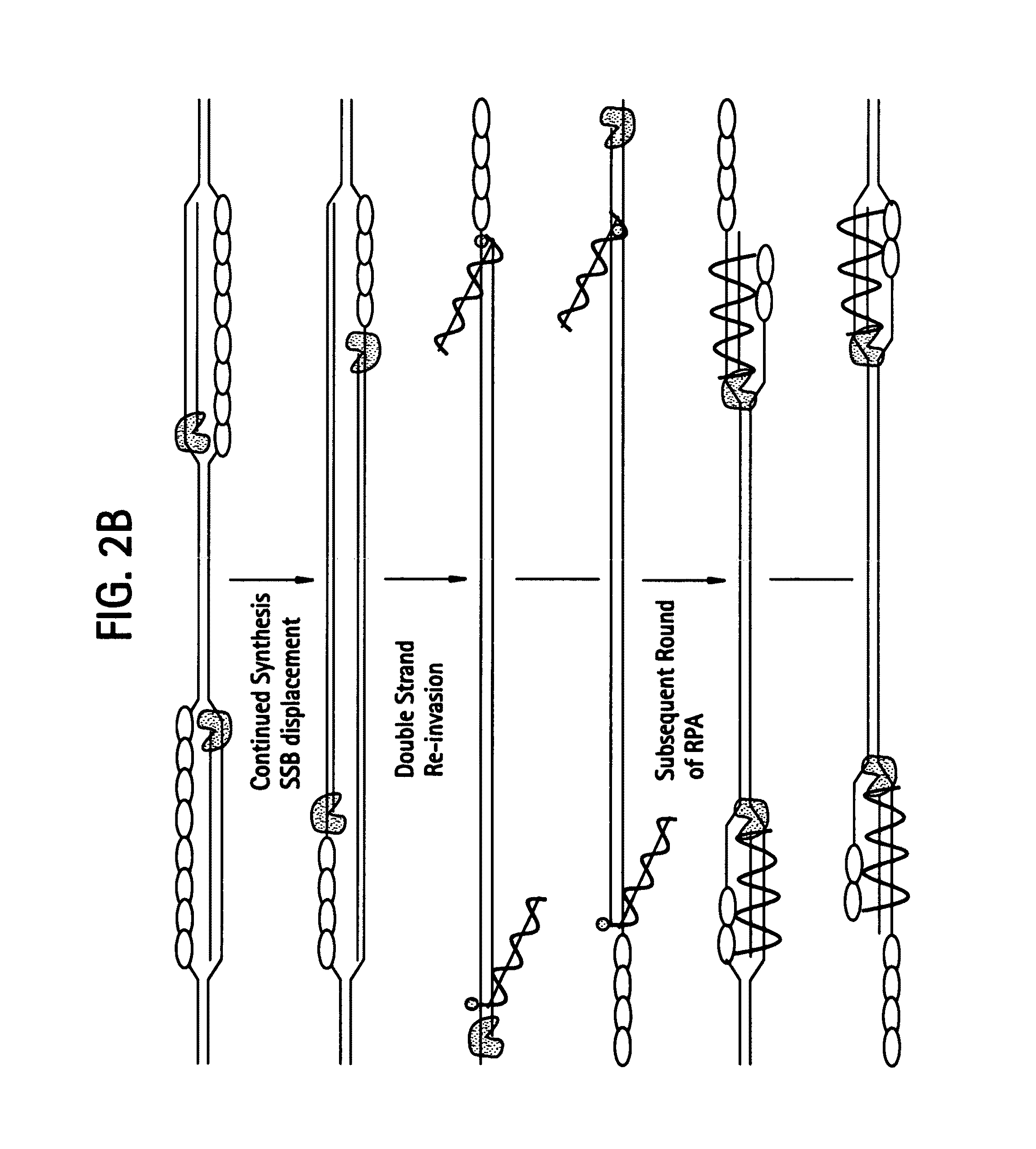
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS7399590B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinase Polymerase AmplificationSingle strand
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
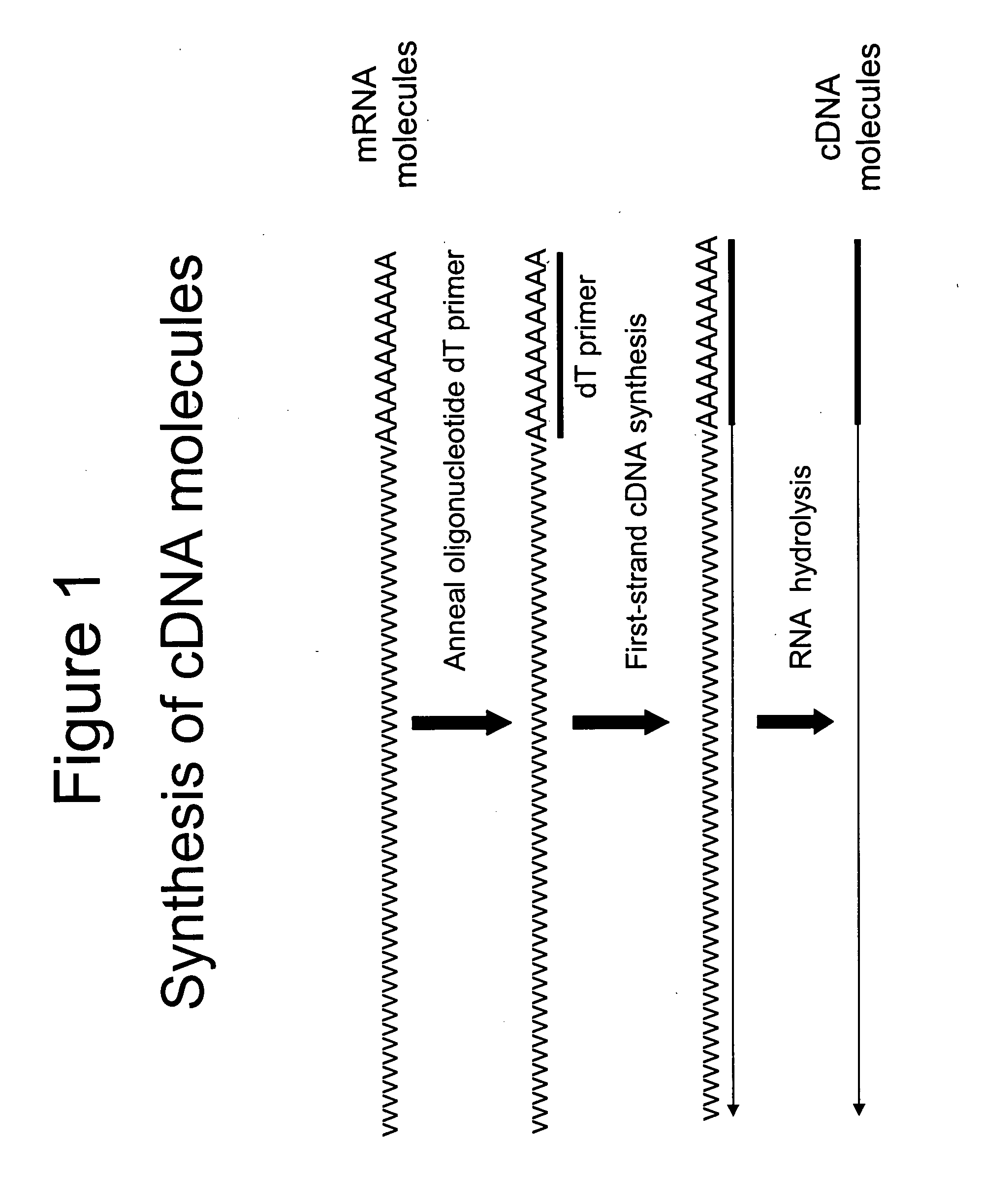
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6132997ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
Methods for linearly amplifying mRNA to produce antisense RNA are provided. In the subject methods, mRNA is converted to double-stranded cDNA using a promoter-primer having a poly-dT primer site linked to a promoter sequence so that the resulting double-stranded cDNA is recognized by an RNA polymerase. The resultant double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into antisense RNA in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods find use a variety of different applications in which the preparation of linearly amplified amounts of antisense RNA is desired. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
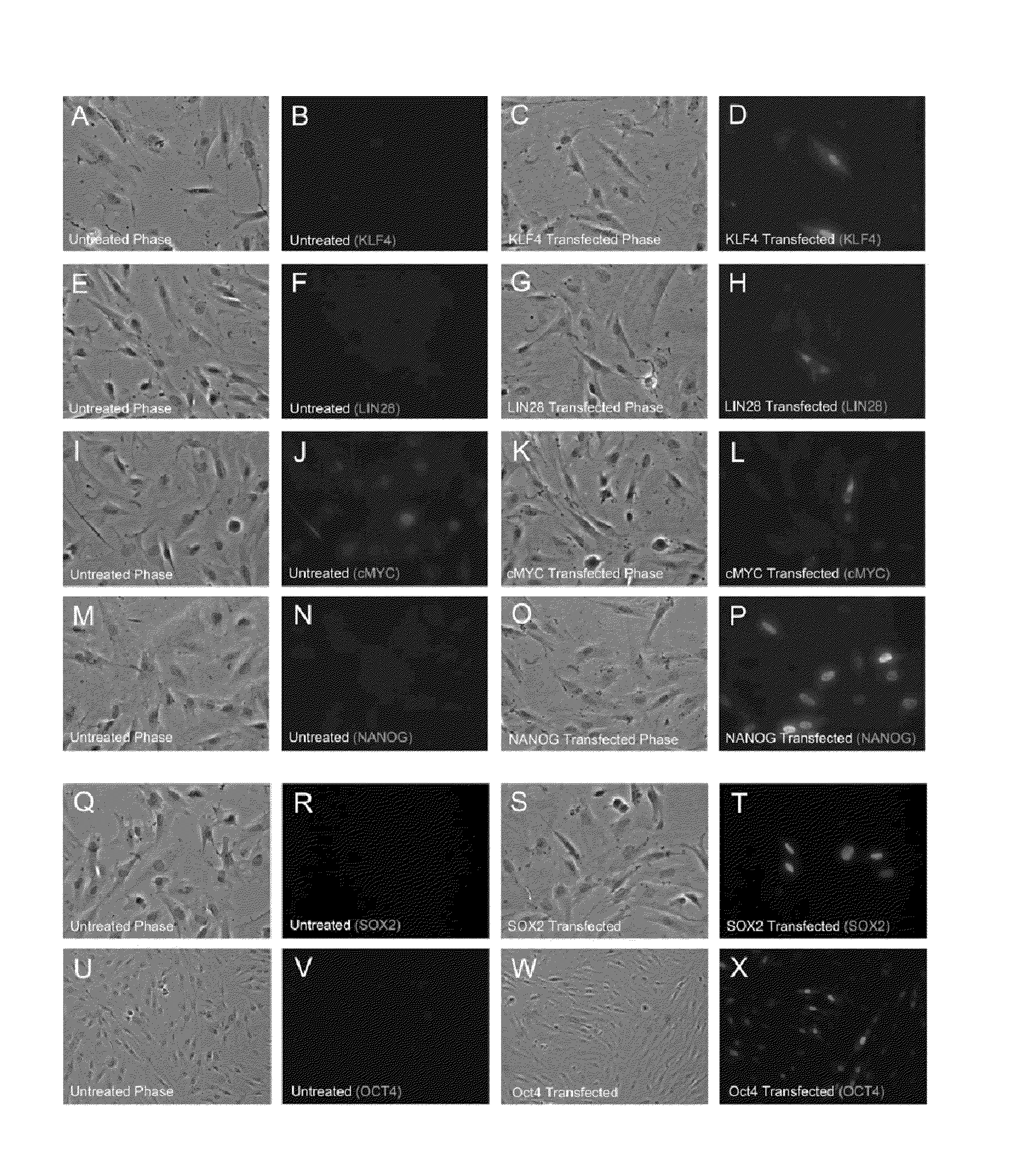
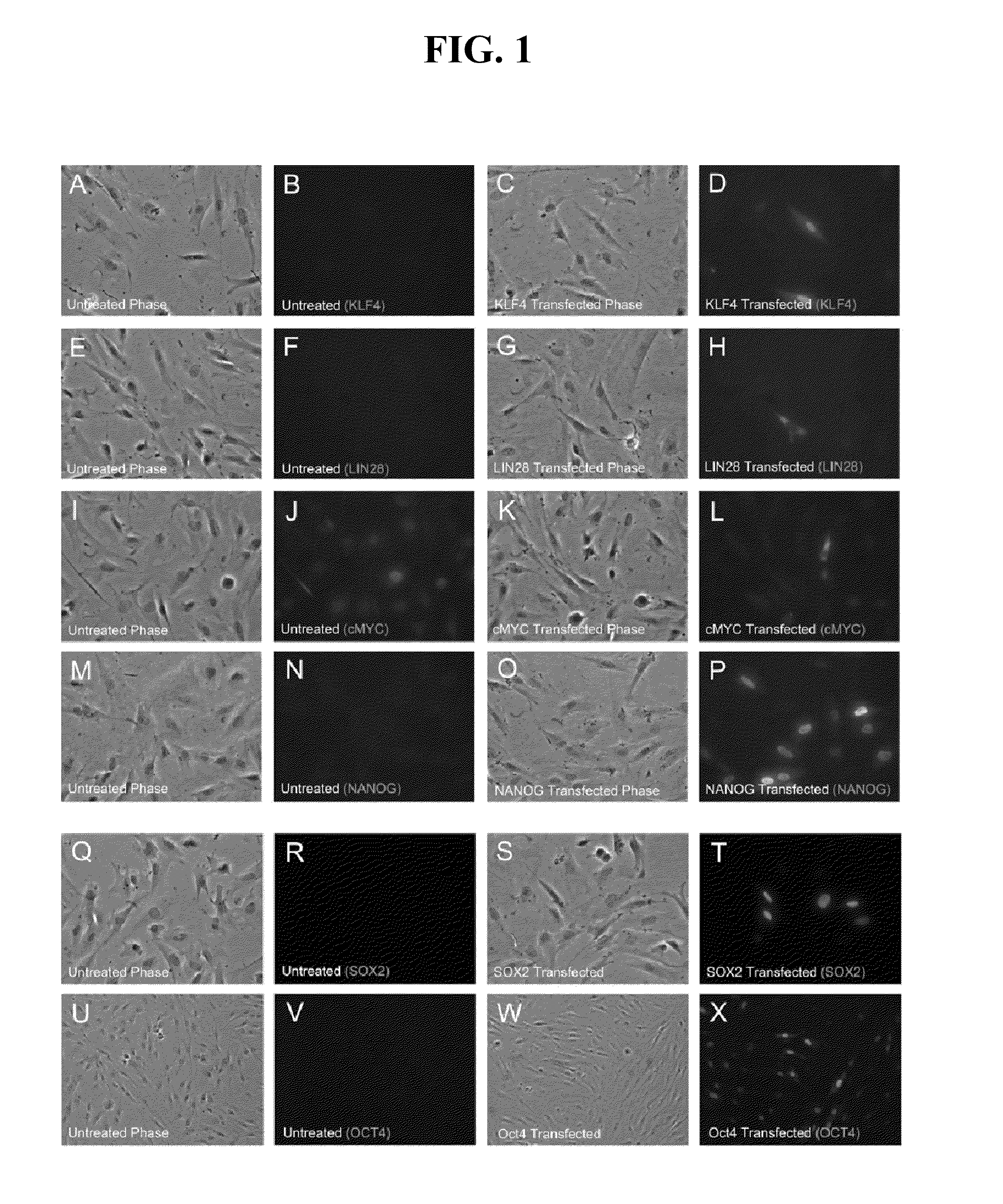
RNA preparations comprising purified modified RNA for reprogramming cells
ActiveUS20110143397A1Promote growthArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsSingle strandSomatic cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for reprogramming somatic cells using purified RNA preparations comprising single-strand mRNA encoding an iPS cell induction factor. The purified RNA preparations are preferably substantially free of RNA contaminant molecules that: i) would activate an immune response in the somatic cells, ii) would decrease expression of the single-stranded mRNA in the somatic cells, and / or iii) active RNA sensors in the somatic cells. In certain embodiments, the purified RNA preparations are substantially free of partial mRNAs, double-stranded RNAs, un-capped RNA molecules, and / or single-stranded run-on mRNAs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS7270981B2Web data indexingMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandRecombinase Polymerase Amplification
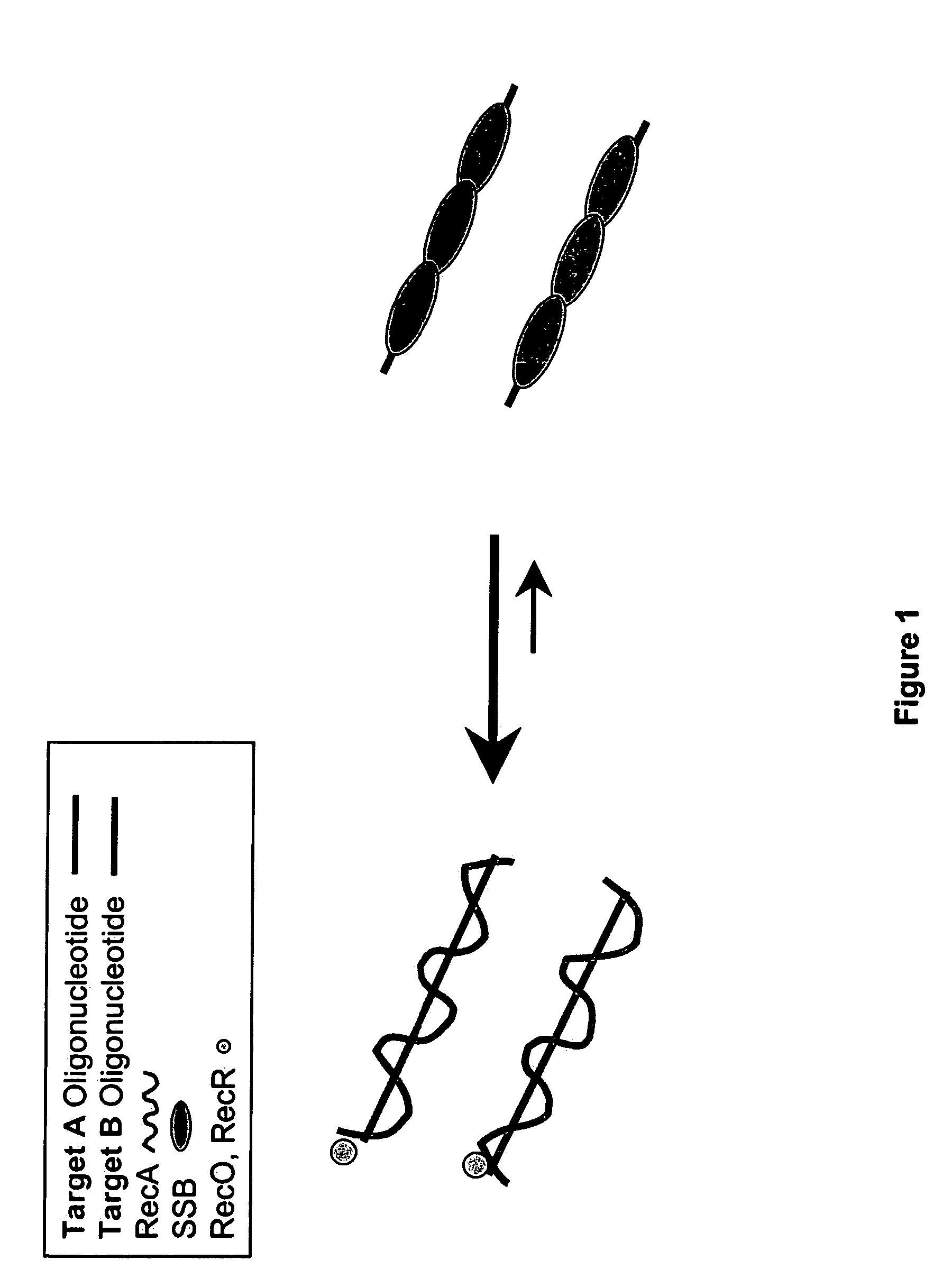
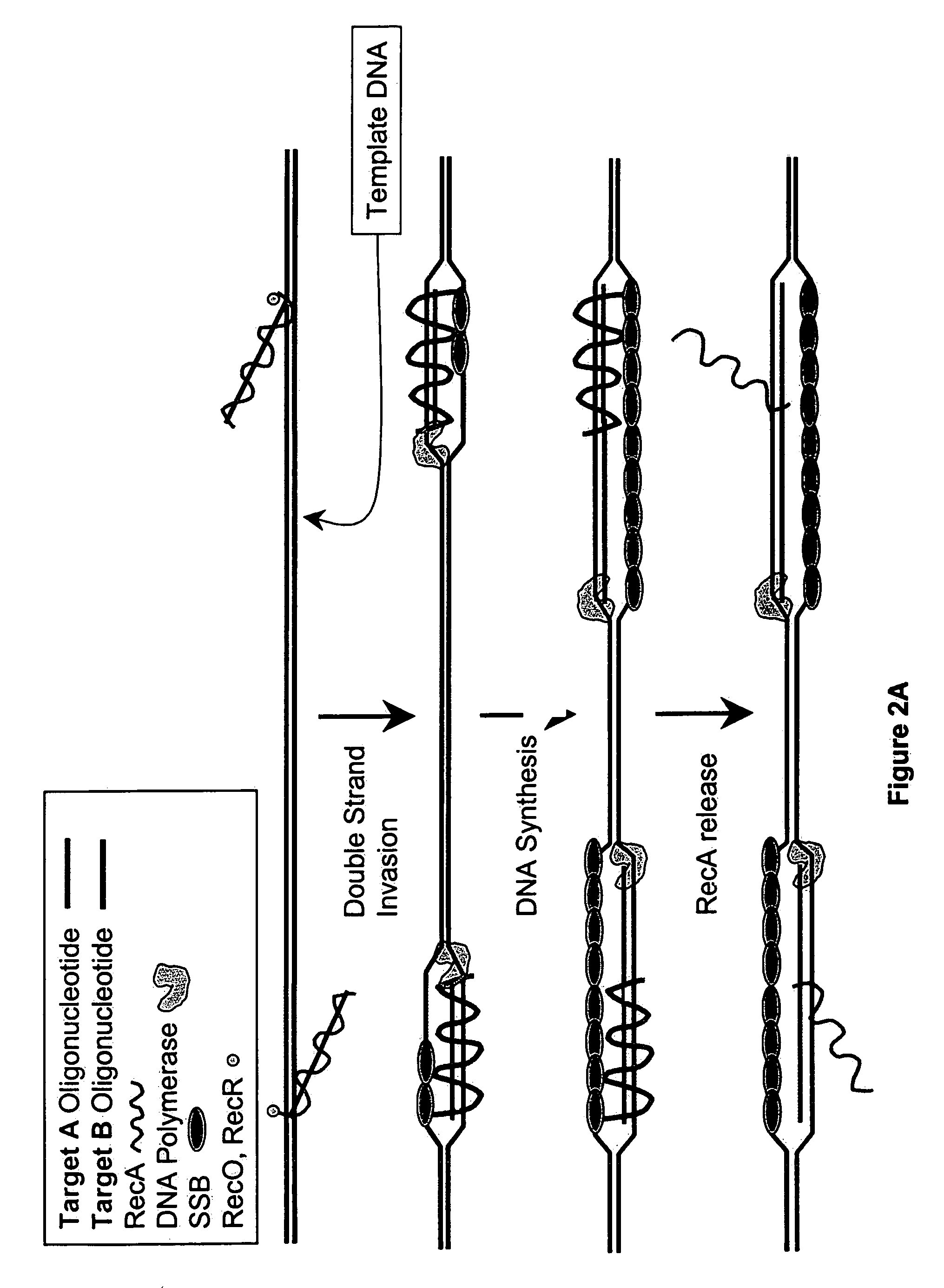
This disclosure describe three related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of the bacterial RecA and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods has the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes. Further, the improved processivity of the disclosed methods allow amplification of DNA up to hundreds of megabases in length.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS20050112631A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinase Polymerase AmplificationSingle strand
This disclosure describe three related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes. Further, the improved processivity of the disclosed methods may allow amplification of DNA up to hundreds of megabases in length.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
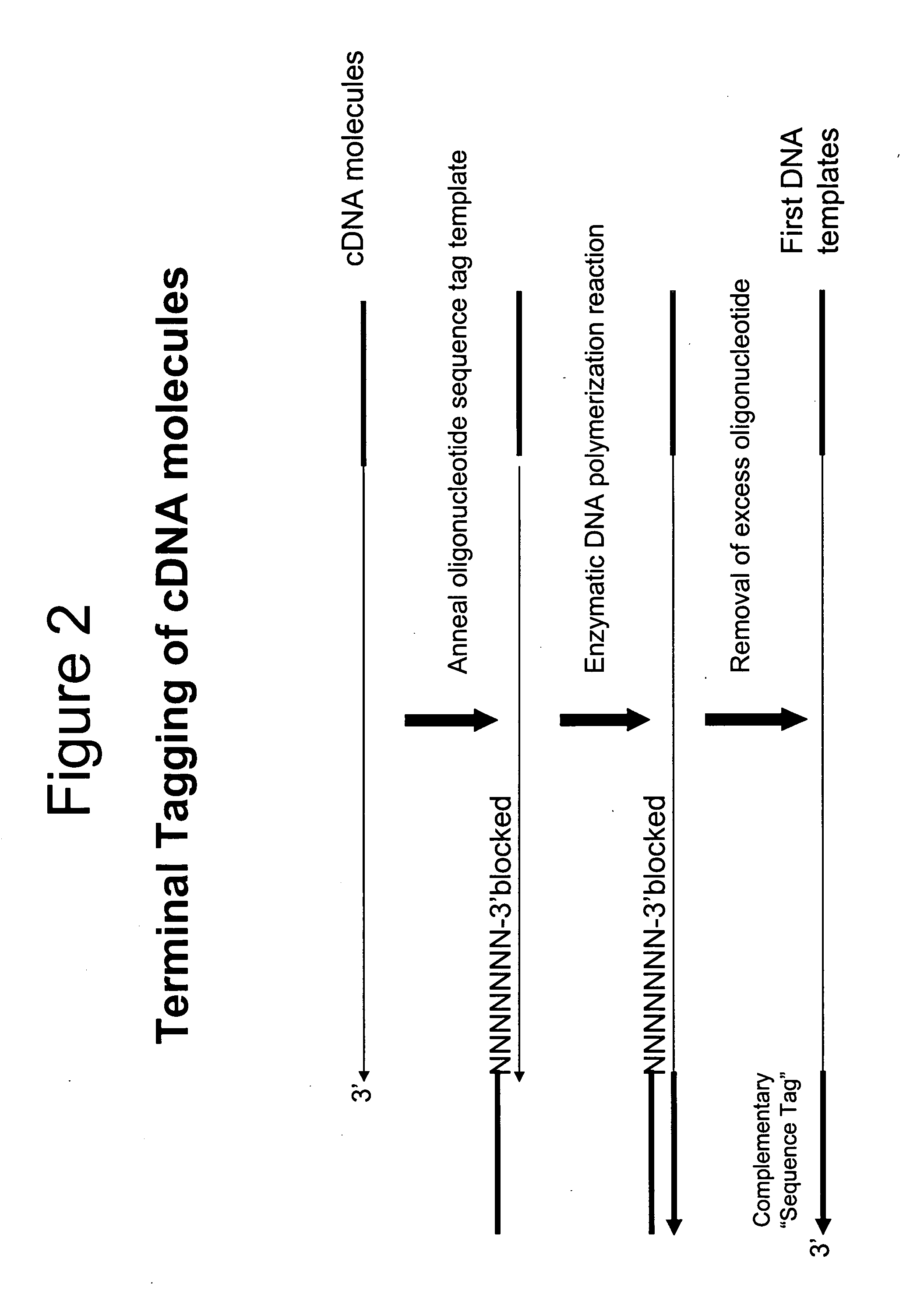
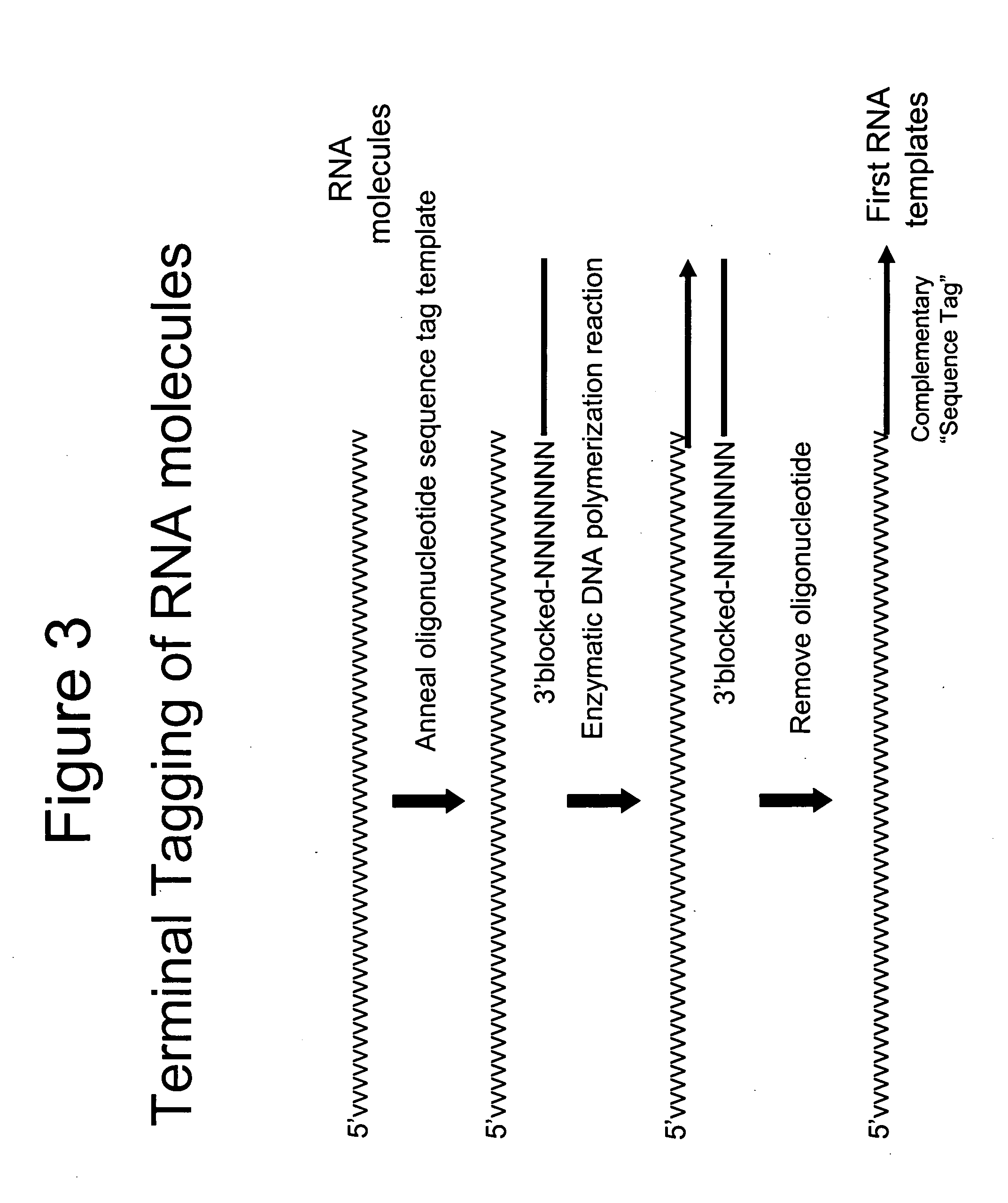
Selective terminal tagging of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050153333A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationDouble stranded
A method is provided for adding a terminal sequence tag to nucleic acid molecules for use in RNA or DNA amplification. The method involves contacting with a mixture of oligonucleotides, each having a sequence tag template, a random sequence and a blocked 3′ terminus, under conditions such that, the random sequence anneals with the nucleic acid molecules and the nucleic acid molecules are extended using the sequence tag template as template. For synthesis of RNA from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates having a double stranded promoter sequence and synthesizing RNA from the DNA templates. For amplification of sequences from DNA molecules having terminal sequence tags, the method includes forming DNA templates by extension of one primer having a sequence that is complementary to the terminal sequence tag and another primer having a sequence that is derived form one of the DNA molecules.
Owner:EPICENT BIOTECH
Methods and compositions for the specific inhibition of gene expression by double-stranded RNA
Owner:CITY OF HOPE +1
Single-stranded and double-stranded oligonucleotides comprising a 2-arylpropyl moiety
ActiveUS20060008822A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderNucleotidePhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. The aralkyl ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
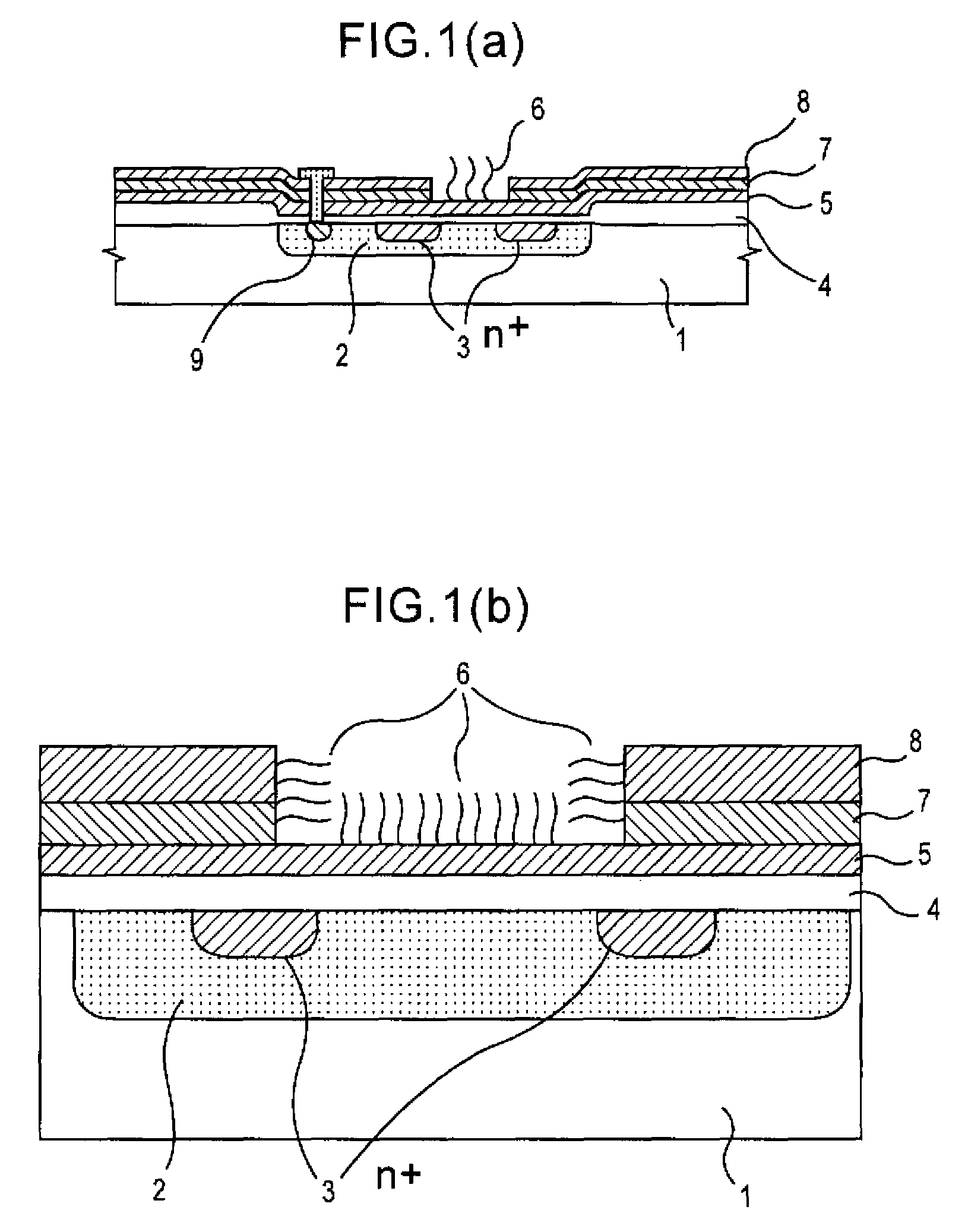
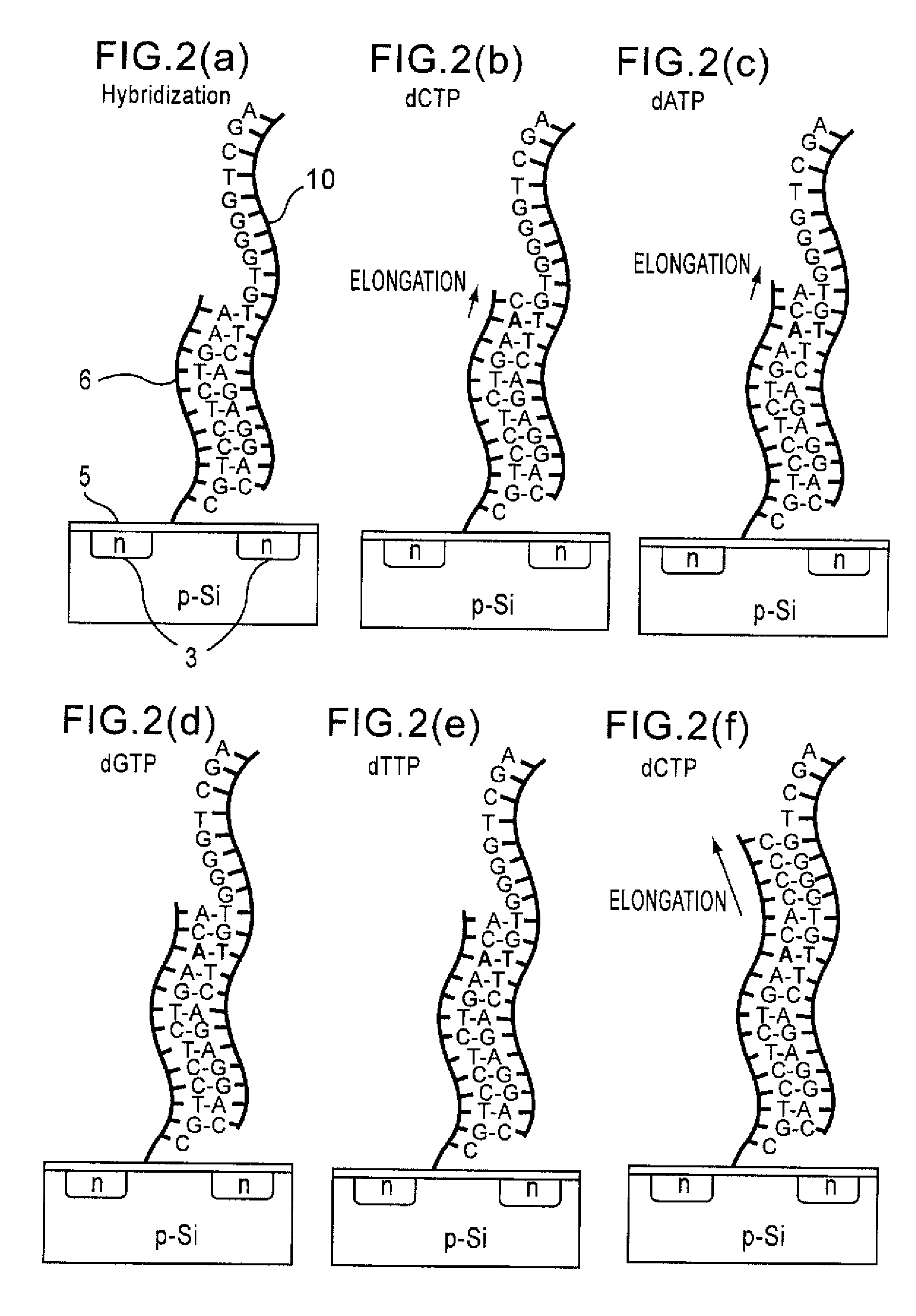
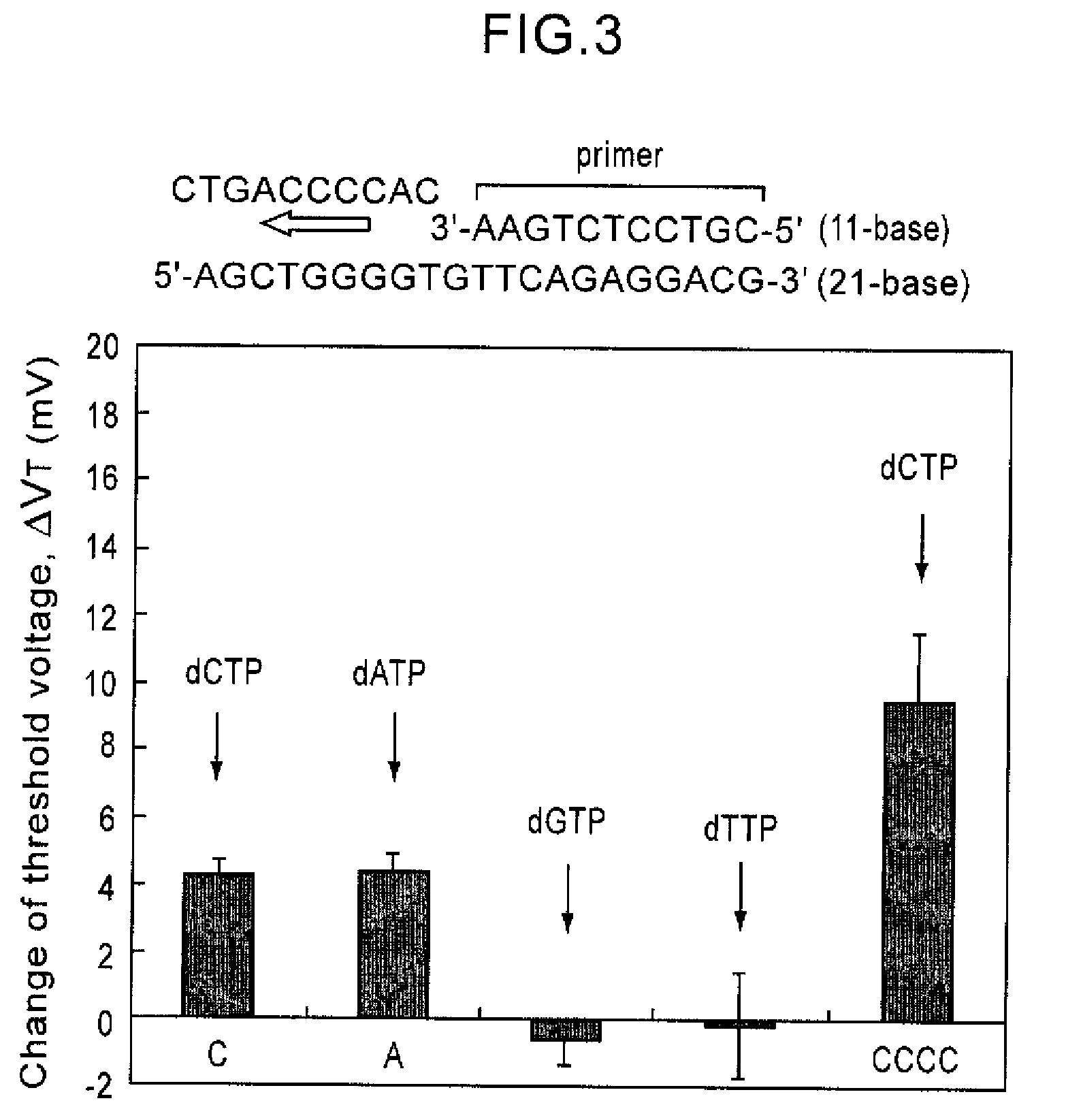
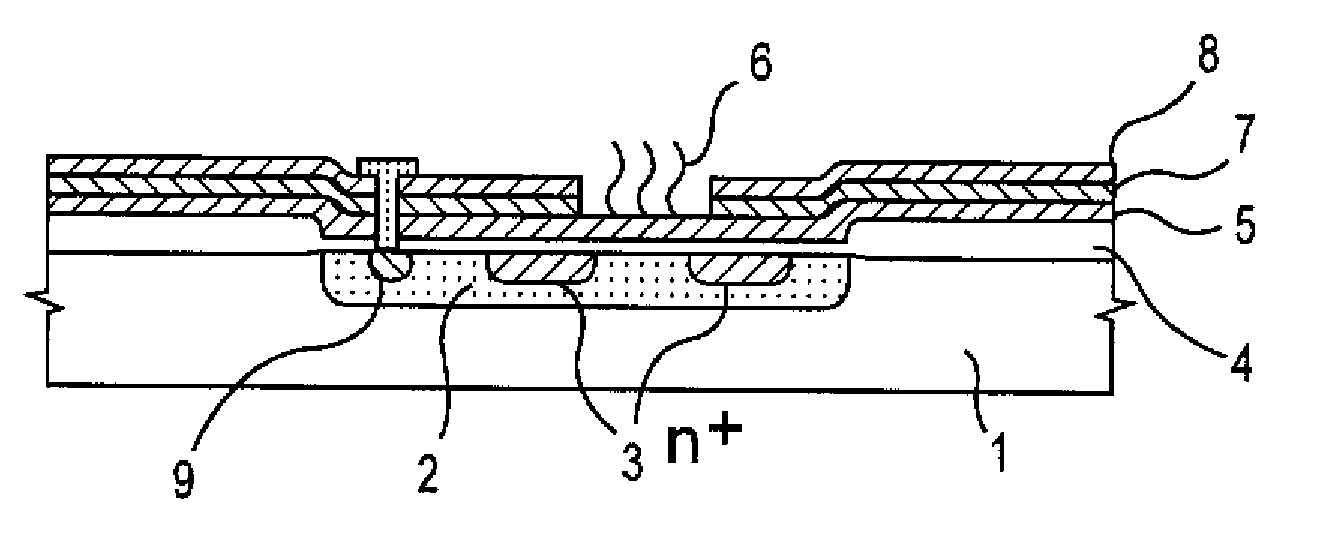
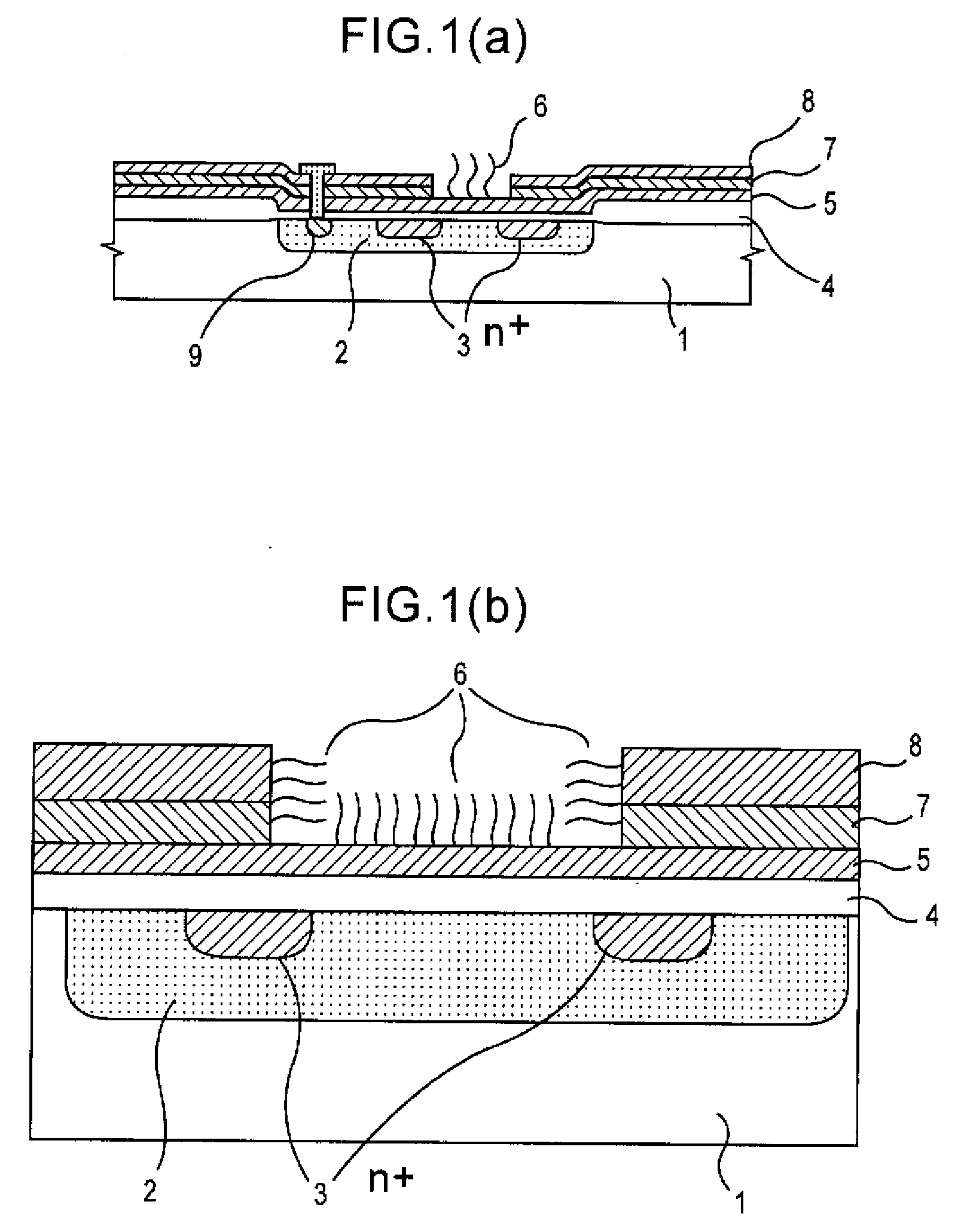
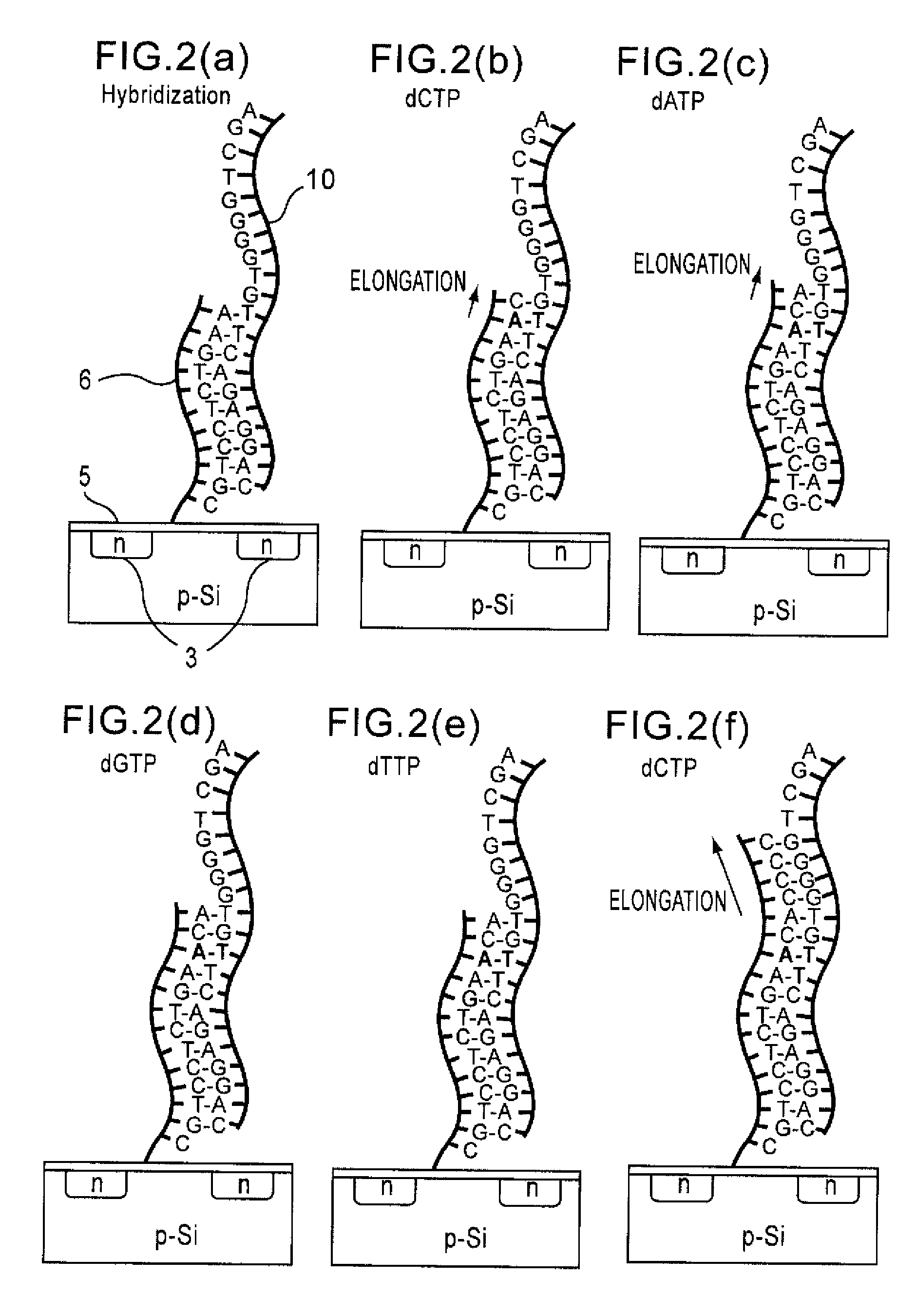
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
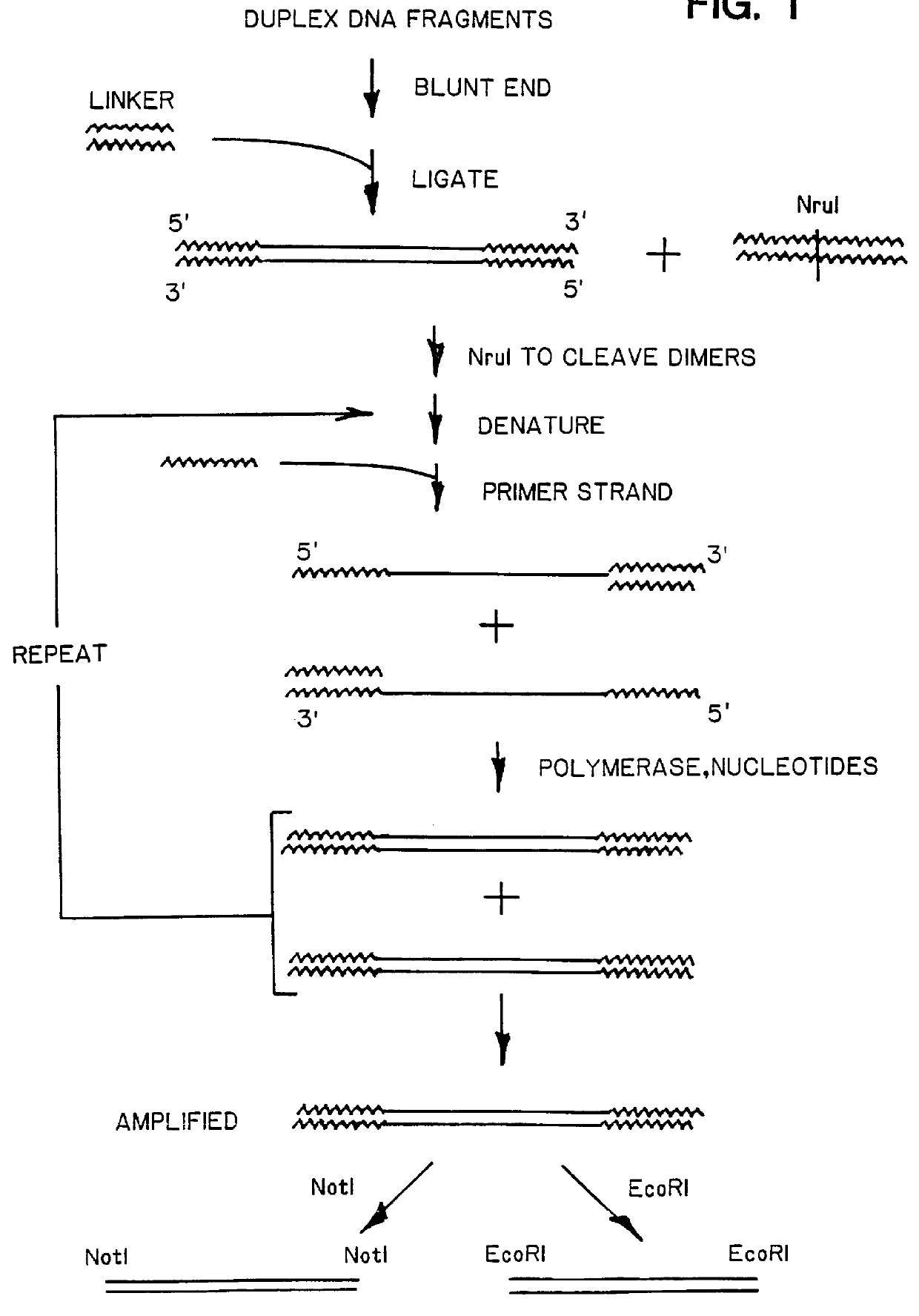
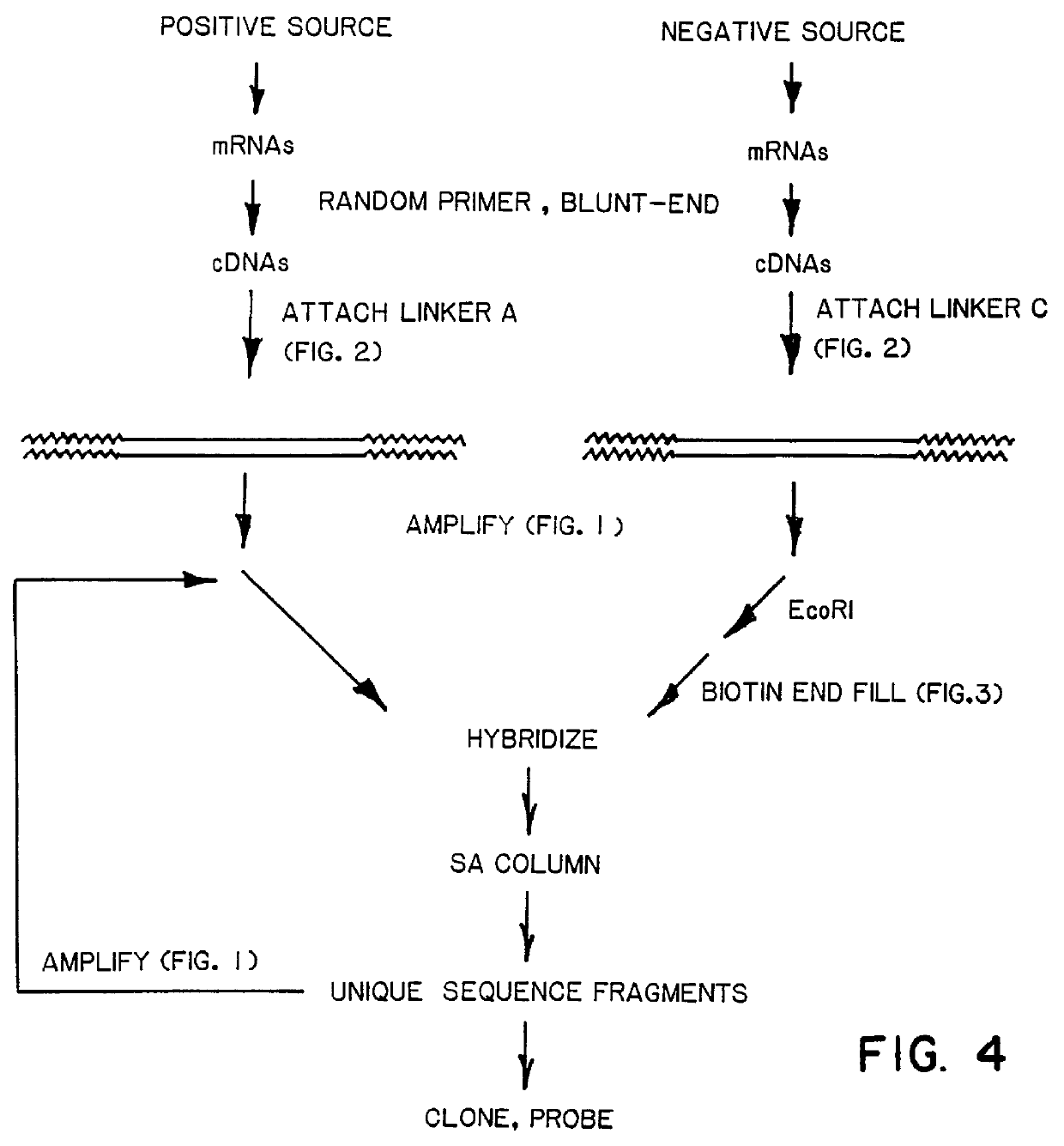
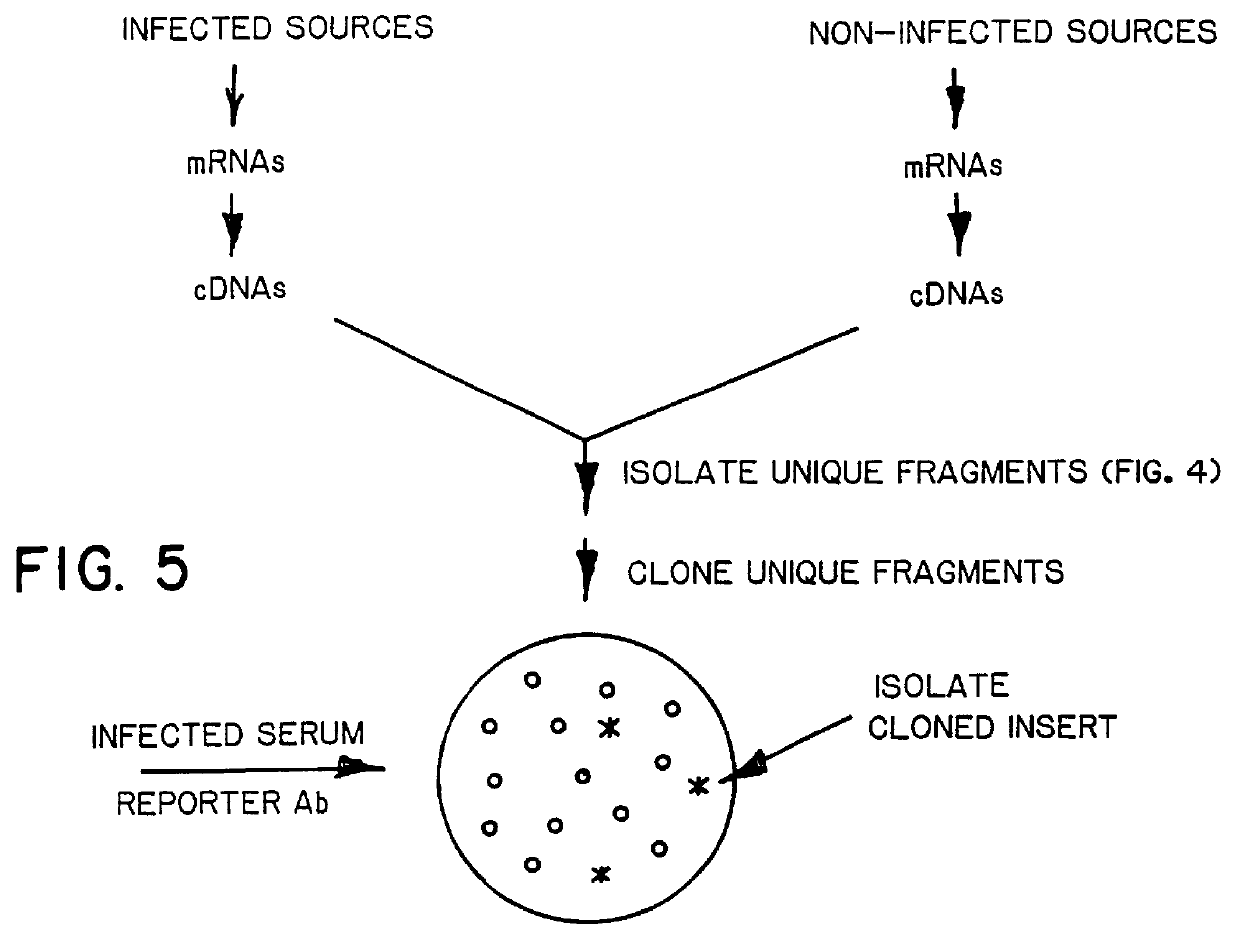
DNA amplification and subtraction techniques
InactiveUS6107023AImprove concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid speciesDna amplification
A method of isolating genomic or RNA-derived duplex fragments which are unique to one of two fragment mixtures. The fragments in positive-source and negative-source mixtures are separately equipped with end linkers, and each mixture is amplified by successive primed-strand replications, using a single primer which is homologous to the associated linker. The second-source linker is biotinylated, and the fragments in this mixture are hybridized in molar excess with the fragments in the positive-source mixture. DNA species which are not hybridized with the biotinylated species, i.e., species that are unique to the positive-source mixture, are isolated after removal of hybridized species by affinity chromatography. Also disclosed is a method of amplifying a mixture of DNA fragments by repeated linker / primer replication.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC +1
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432249B2High affinityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsOrganism
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Method for the generation of compact tale-nucleases and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130117869A1Simple processSimple and efficient vectorizationFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesDNA-binding domainNuclease
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of compact Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) that can efficiently target and process double-stranded DNA. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for the creation of TALENs that consist of a single TALE DNA binding domain fused to at least one catalytic domain such that the active entity is composed of a single polypeptide chain for simple and efficient vectorization and does not require dimerization to target a specific single double-stranded DNA target sequence of interest and process DNA nearby said DNA target sequence. The present invention also relates to compact TALENs, vectors, compositions and kits used to implement the method.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for the isolation of nucleic acids and for quantitative DNA extraction and detection for leukocyte evaluation in blood products
InactiveUS6958392B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole blood productWhite blood cell
A method for isolating nucleic acid which comprises:(a) applying a sample comprising cells containing nucleic acid to a filter, whereby the cells are retained as a retentate and contaminants are removed;(b) lysing the retentate from step (a) while the retentate is retained by the filter to form a cell lysate containing the nucleic acid;(c) filtering the cell lysate with the filter to retain the nucleic acid and remove remaining cell lysate;(d) optionally washing the nucleic acid retained by the filter; and(e) eluting the nucleic acid, wherein the filter composition and dimensions are selected so that the filter is capable of retaining the cells and the nucleic acid.Additionally, there is provided a substrate for lysing cells and purifying nucleic acid having a matrix and a coating and an integrity maintainer for maintaining the purified nucleic acid. Also provided is a method of purifying nucleic acid by applying a nucleic acid sample to a substrate having an anionic detergent affixed to a matrix, the substrate physically capturing the nucleic acid, bonding the nucleic acid to a substrate and generating a signal when the nucleic acid bonds to the substrate indicating the presence of the nucleic acid. A kit for purifying nucleic acid containing a coated matrix and an integrity maintenance provider for preserving the matrix and purifying nucleic acid is also provided. Further, there is provided a method for quantifying DNA, such as double-stranded or genomic DNA, isolated from cells, such as leukocytes to determine the numbers of leukocytes in a sample of leukoreduced blood.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Sample preparation on a solid support
ActiveUS20140194324A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid massDNA fragmentation
Presented are methods and compositions for using immobilized transposase and a transposon end for generating an immobilized library of 5′-tagged double-stranded target DNA on a surface. The methods are useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including massively parallel DNA sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Oligoribonucleotides and methods of use thereof for treatment of alopecia, acute renal failure and other diseases
ActiveUS20060069056A1Increased riskImprove the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderOligoribonucleotidesARF - Acute renal failure
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of a target gene
ActiveUS7829693B2Inhibit expression of target geneOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseNucleotide
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) having a nucleotide sequence which is substantially identical to at least a part of a target gene and which is no more than 49, preferably less than 25, nucleotides in length, and which comprises a complementary (antisense) RNA strand having a 1 to 4 nucleotide overhang at the 3′-end and a blunt 5′-end. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene, at low dosages (i.e., less than 5 milligrams, preferably less than 25 micrograms, per kg body weight per day). The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Method of Analyzing Dna Sequence Using Field-Effect Device, and Base Sequence Analyzer
ActiveUS20080286767A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
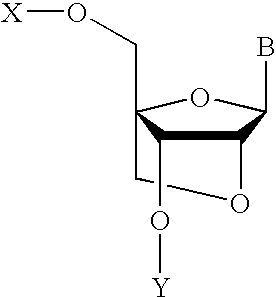
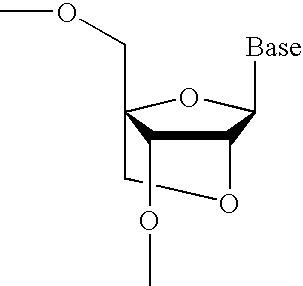
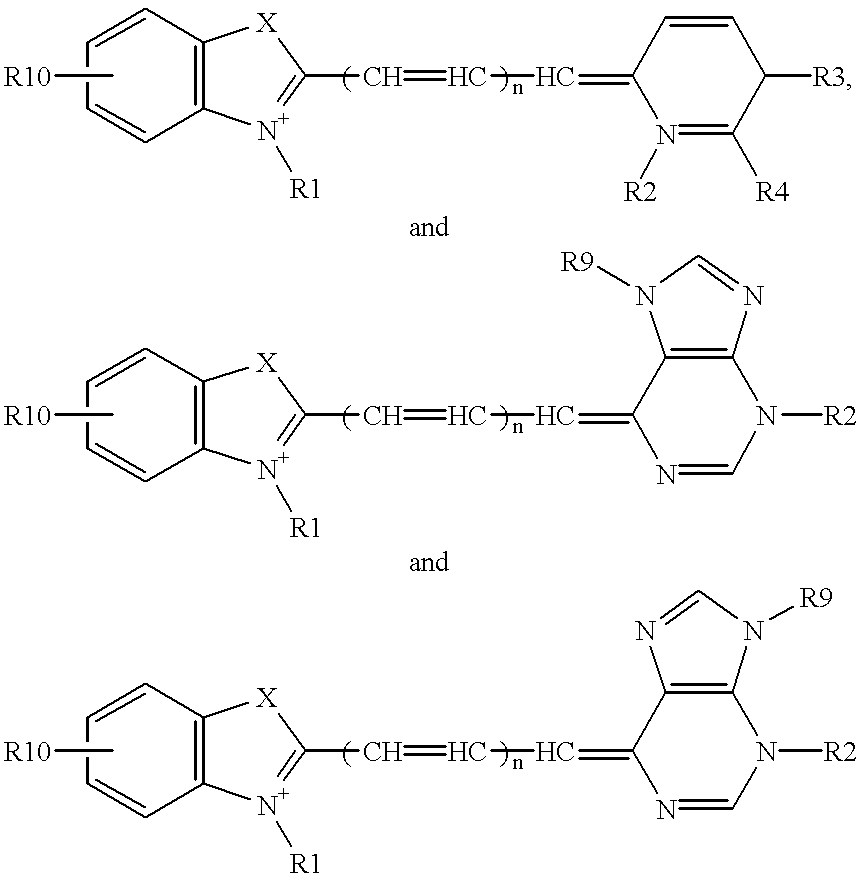
Nucleoside analogs and oligonucleotide derivatives containing these analogs
Nucleoside analogues expressed by the following general formula where B represents an aromatic base having carbonyl oxygen at the 2-position, or a 2-hydroxyphenyl group, or oligonucleotide derivatives containing one or more of the nucleoside analogues are provided.The oligonucleotide derivatives are triplex-forming oligonucleotide derivatives which bind specifically to target double-stranded DNA with high affinity in the antigene method to form triplexes, and can thereby control and inhibit the expression of relevant genes efficiently, and which show high resistance to nucleases.
Owner:IMANISHI TAKESHI
Recombinase polymerase amplification
This disclosure describes related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes, thus offering easy and affordable implementation and portability relative to other amplification methods. Further RPA reactions using light and otherwise, methods to determine the nature of amplified species without a need for gel electrophoresis, methods to improve and optimize signal to noise ratios in RPA reactions, methods to optimize oligonucleotide primer function, methods to control carry-over contamination, and methods to employ sequence-specific third ‘specificity’ probes. Further described are novel properties and approaches for use of probes monitored by light in dynamic recombination environments.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Probe for analysis of target nucleic acids
The invention is a probe for detecting nucleic acids having a particular sequence. It is composed of two joint units. One unit is chemically different from natural nucleic acids, but has the ability to recognize a particular sequence of bases or base pairs in single or double-stranded DNA of RNA. The other unit is a compound whose detectable properties are altered upon binding to nucleic acids.
Owner:LIGHTUP TECH
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
Detection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS9273349B2Enhanced hybridizationConfidenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue sampleSingle strand
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods, cells & organisms
InactiveUS20150079680A1Reduce chanceGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNABiological bodyDNA fragmentation
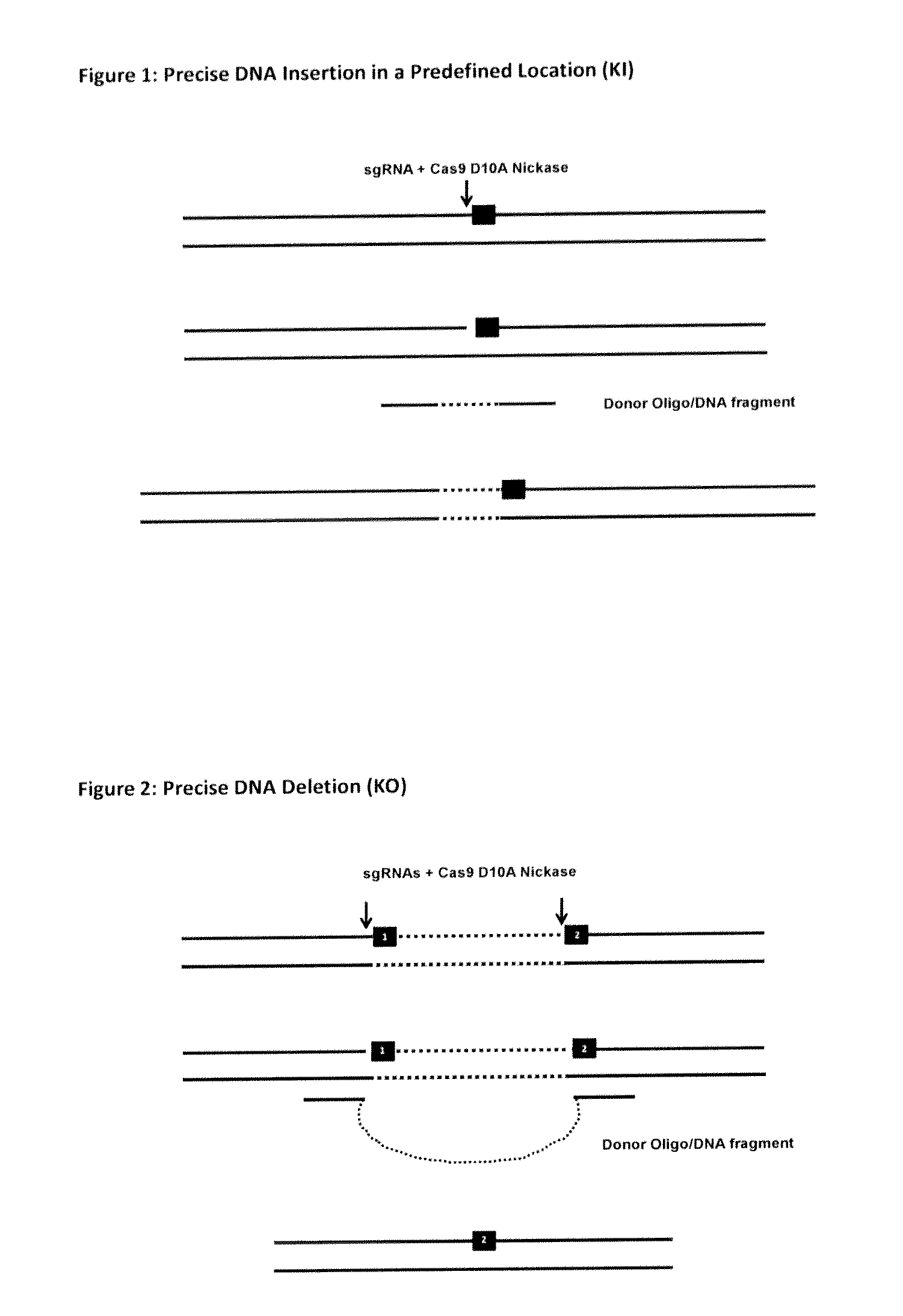
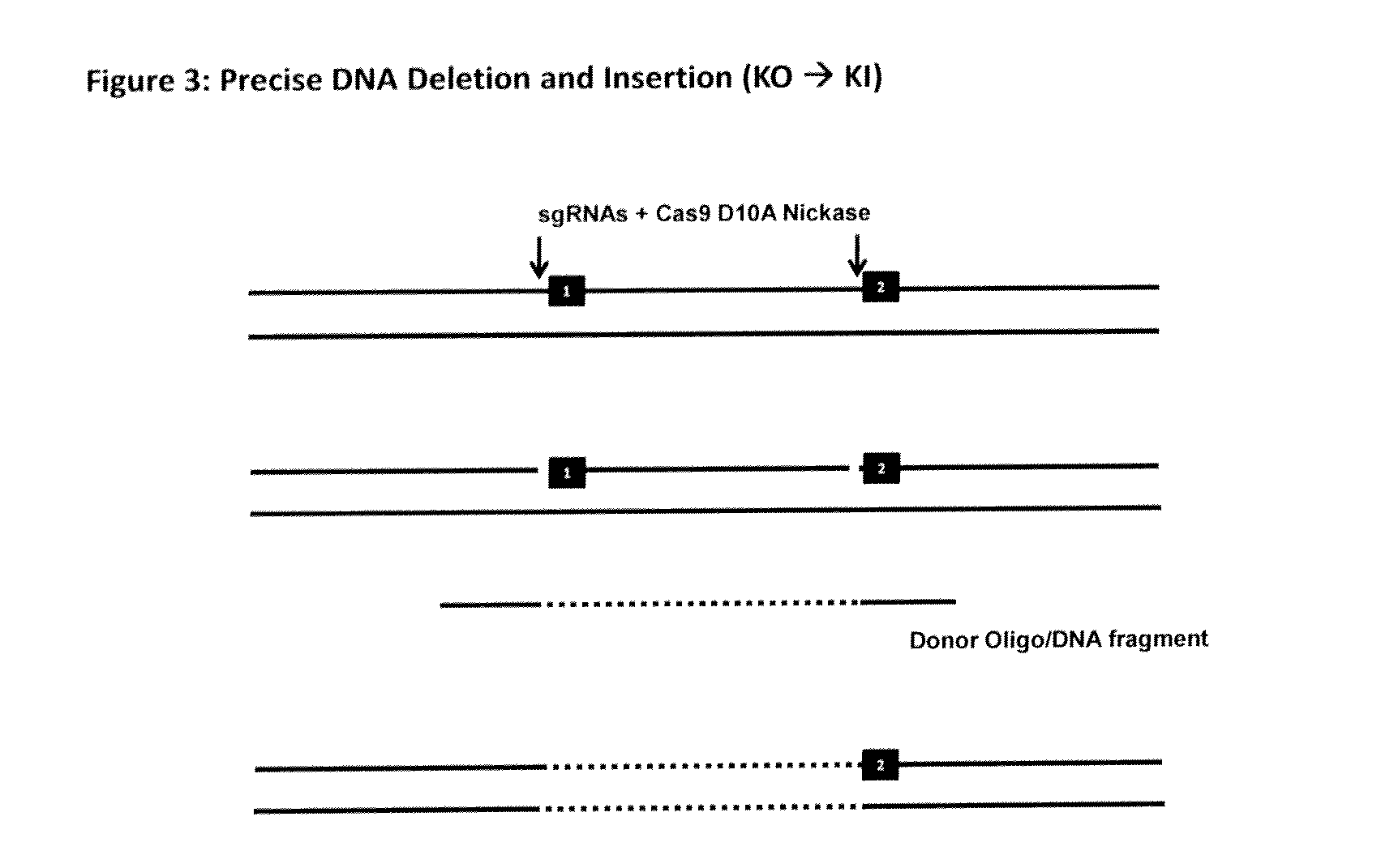
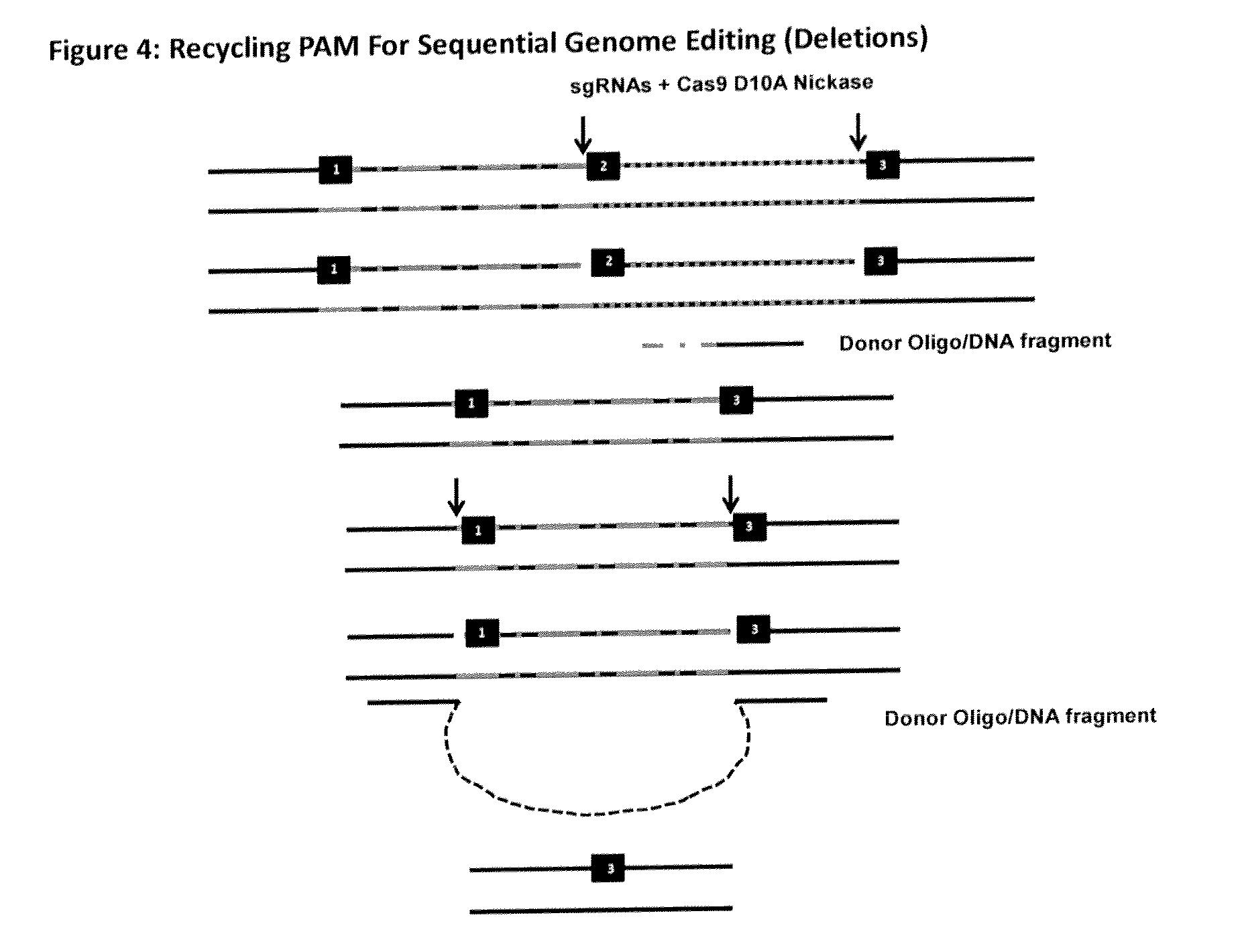
The invention relates to an approach for introducing one or more desired insertions and / or deletions of known sizes into one or more predefined locations in a nucleic acid (eg, in a cell or organism genome). They developed techniques to do this either in a sequential fashion or by inserting a discrete DNA fragment of defined size into the genome precisely in a predefined location or carrying out a discrete deletion of a defined size at a precise location. The technique is based on the observation that DNA single-stranded breaks are preferentially repaired through the HDR pathway, and this reduces the chances of indels (eg, produced by NHEJ) in the present invention and thus is more efficient than prior art techniques. The invention also provides sequential insertion and / or deletions using single- or double-stranded DNA cutting.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
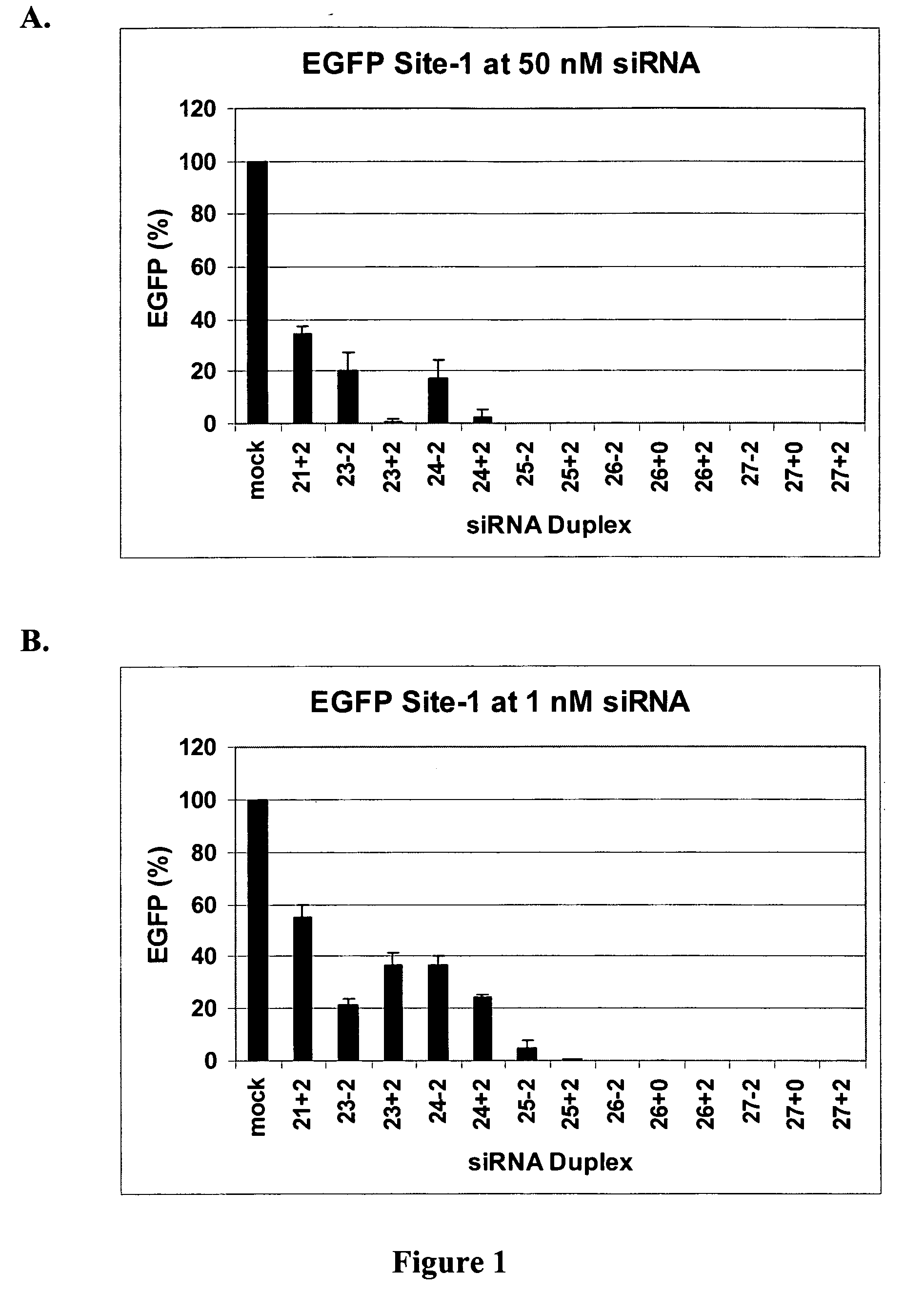
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR IMPROVED THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS WITH siRNA
InactiveUS20080311040A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove efficacyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectProtein
The present invention relates to chemically modified, linked double-stranded (ds)RNA compositions comprising two or more double-stranded (ds) oligoribonucleotides linked by at least one linking moiety and methods of formulating and delivering such compositions to modulate gene expression through target-specific RNA co-interference (RNAco-i). The compositions of the invention may optionally comprise a conjugation or a complex with one or more small molecule drugs, protein therapeutics, or other dsRNA molecules. The present invention is directed at the methods of production for, methods of use of, and therapeutic utilities for RNAi co-interference therapy utilizing the compositions of the invention.
Owner:FLAGSHIP VENTURES
Method of inhibiting gene expression
InactiveUS20050004064A1Improve stabilityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The present invention relates to a method for inhibiting expression of a target gene, which comprises transfecting a cell, tissue, or individual organism with a double-stranded polynucleotide comprising DNA and RNA having a substantially identical nucleotide sequence with at least a partial nucleotide sequence of the target gene.
Owner:ALPHAGEN +1
In vitro recombination method
ActiveUS20070037197A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand DNA-binding proteinSequence identity
The present invention relates, e.g., to in vitro method, using isolated protein reagents, for joining two double stranded (ds) DNA molecules of interest, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule share a region of sequence identity, comprising contacting the two DNA molecules in a reaction mixture with (a) a non-processive 5′ exonculease; (b) a single stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) which accelerates nucleic acid annealing; (c) a non strand-displacing DNA polymerase; and (d) a ligase, under conditions effective to join the two DNA molecules to form an intact double stranded DNA molecule, in which a single copy of the region of sequence identity is retained. The method allows the joining of a number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Double-stranded and single-stranded RNA molecules with 5 ' triphosphates and their use for inducing interferon
InactiveUS20060178334A1Strong responseInhibits and prevents viral infectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsSingle-Stranded RNADouble stranded
Double-stranded and single-stranded RNA molecules, and their use in methods for inducing interferon are provided. The interferon induction provides anti-viral and other medically useful effects, such as anti-cancer effects. Also provided are methods for reducing or inhibiting interferon induction exhibited by such molecules, particularly siRNA and shRNA molecules produced in vitro.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com