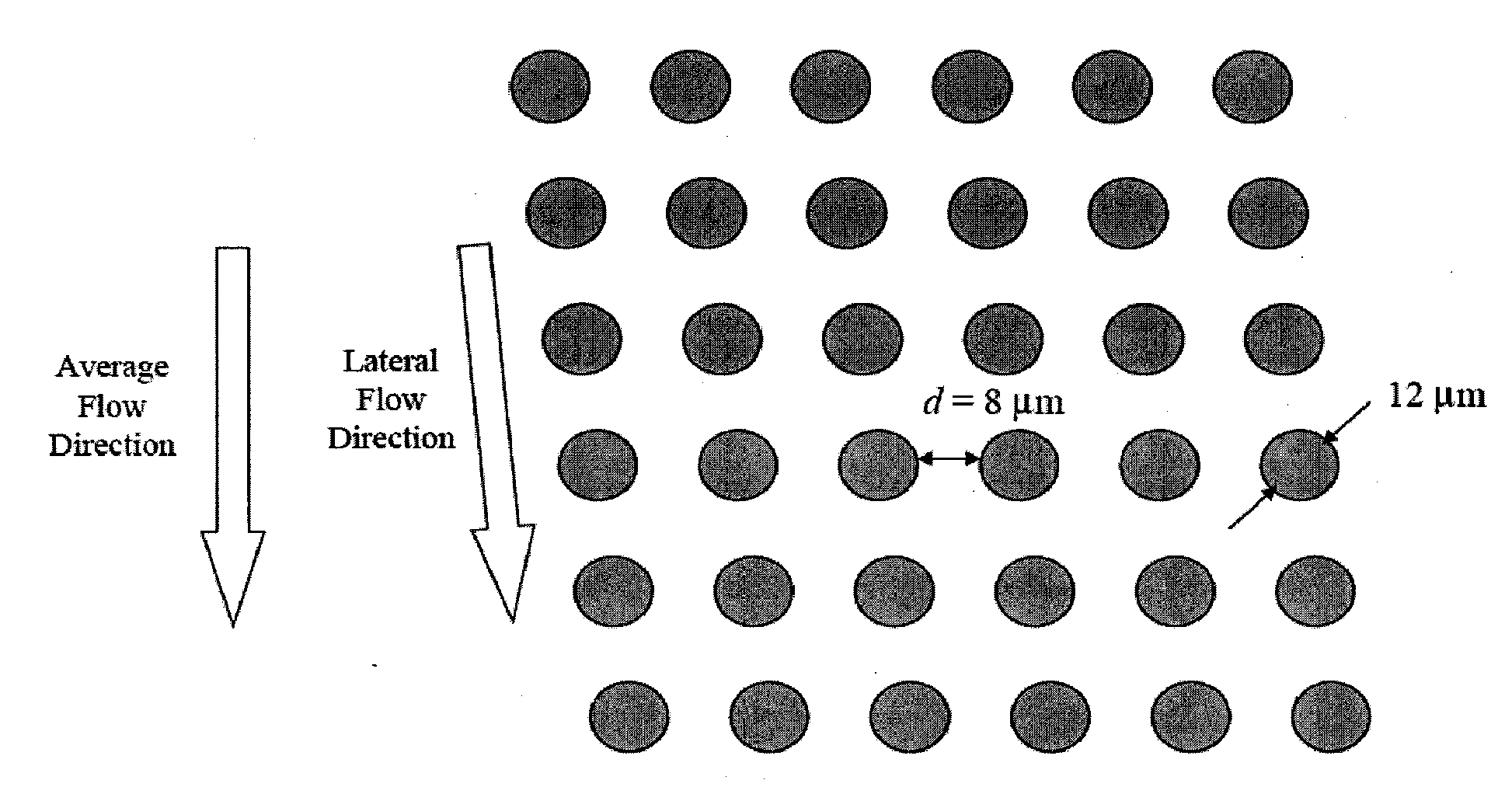
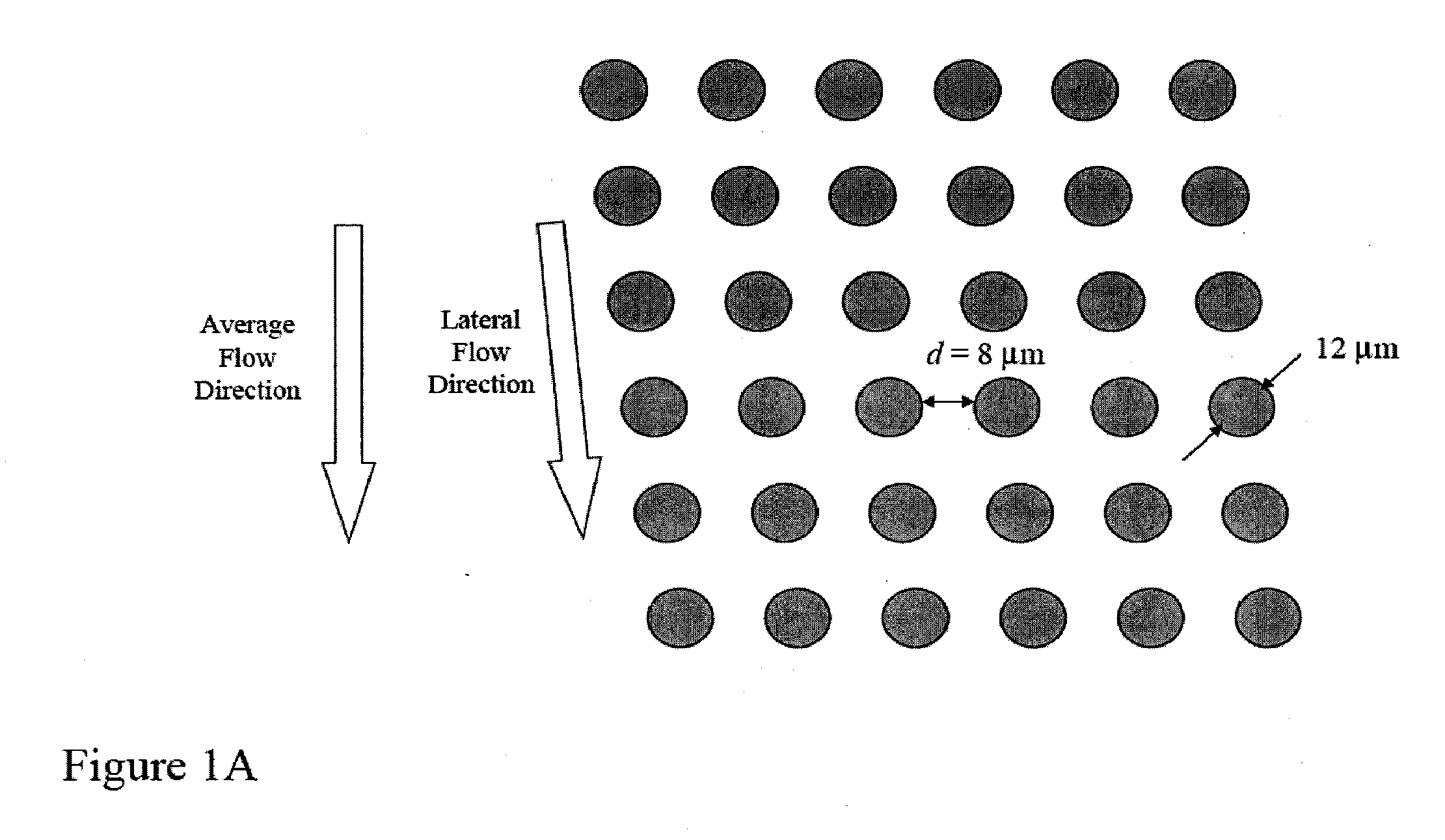
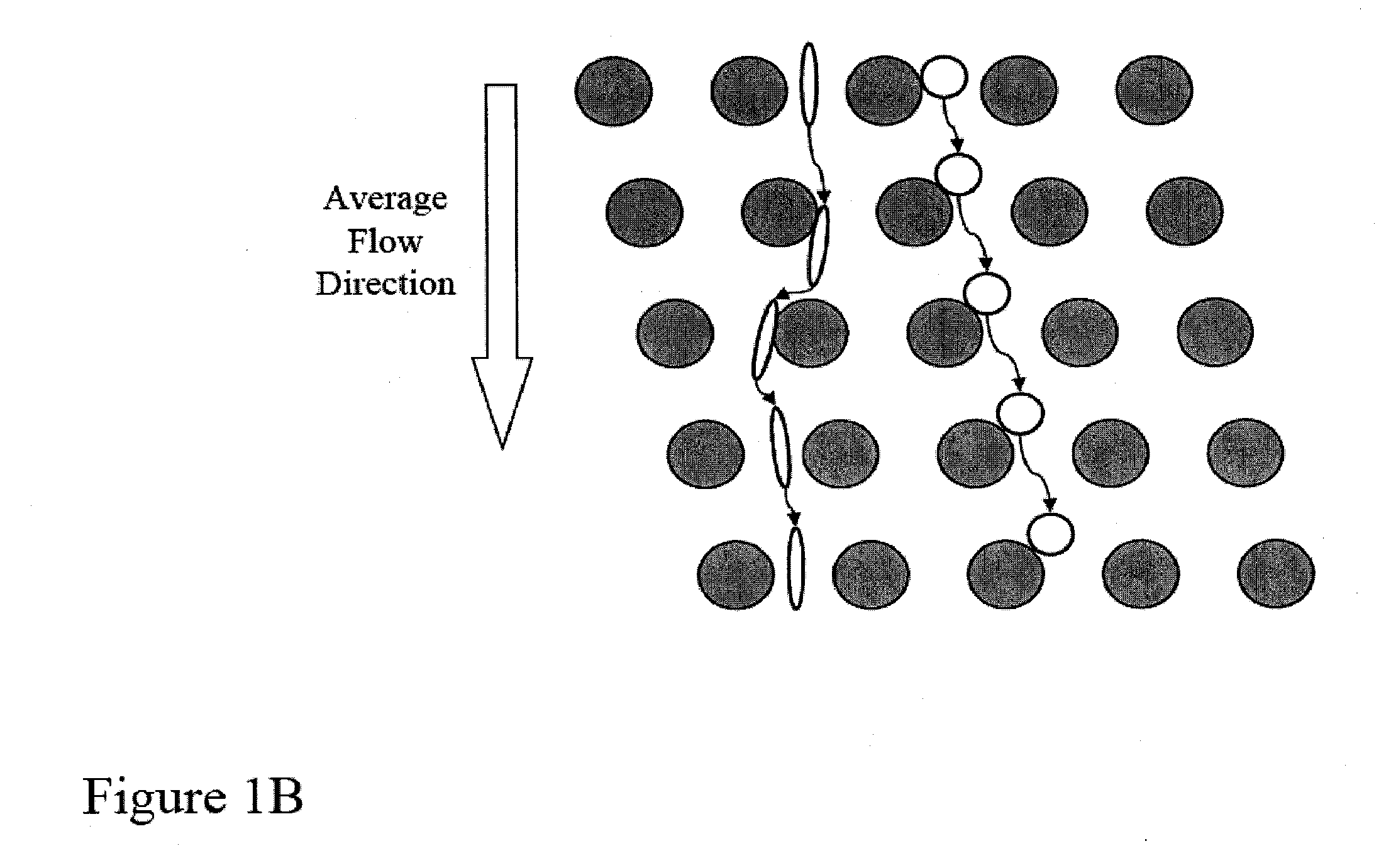
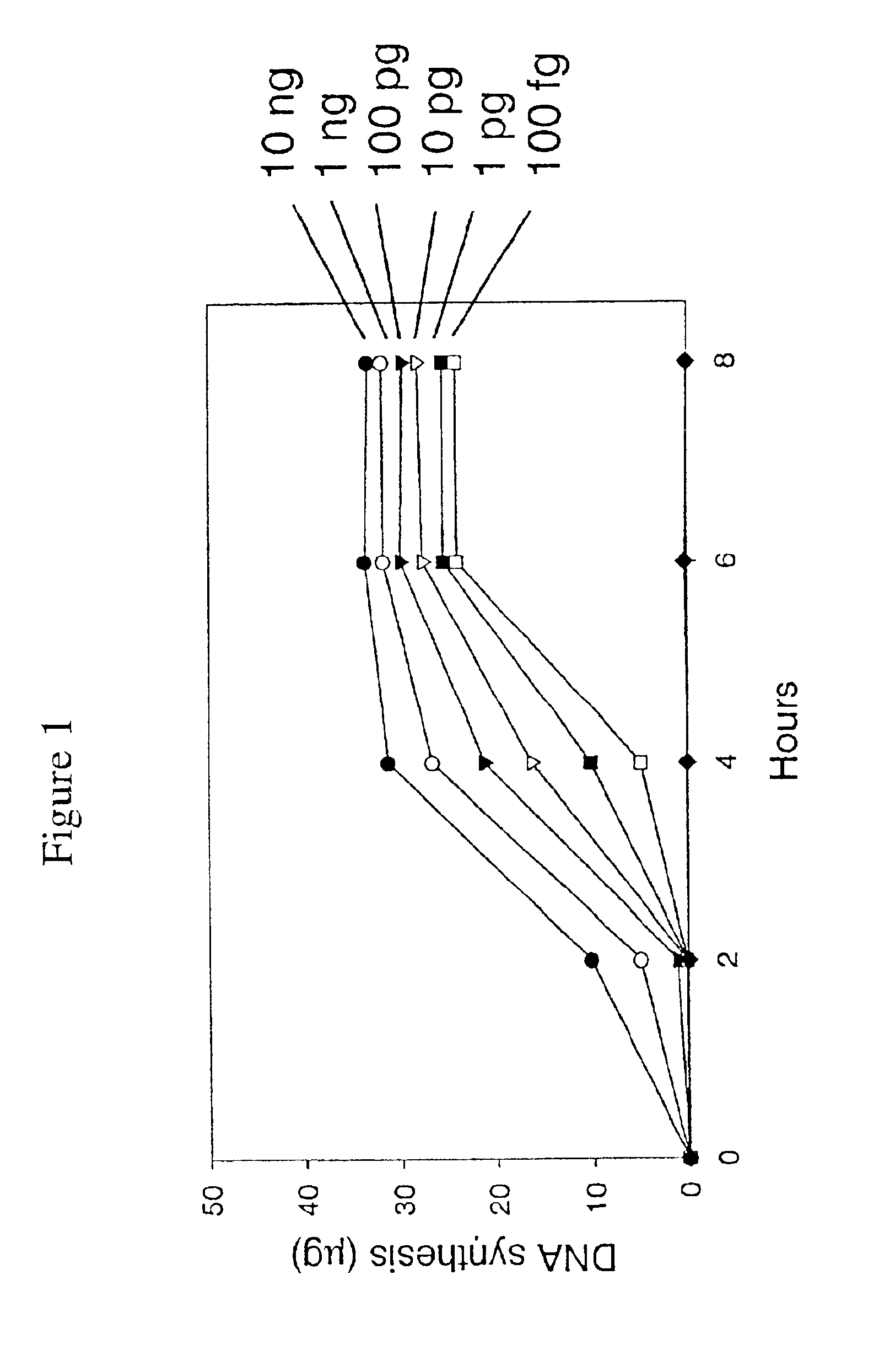
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2848 results about "Genomic DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid is chromosomal DNA, in contrast to extra-chromosomal DNAs like plasmids. It is also then abbreviated as gDNA. Most organisms have the same genomic DNA in every cell; however, only certain genes are active in each cell to allow for cell function and differentiation within the body.
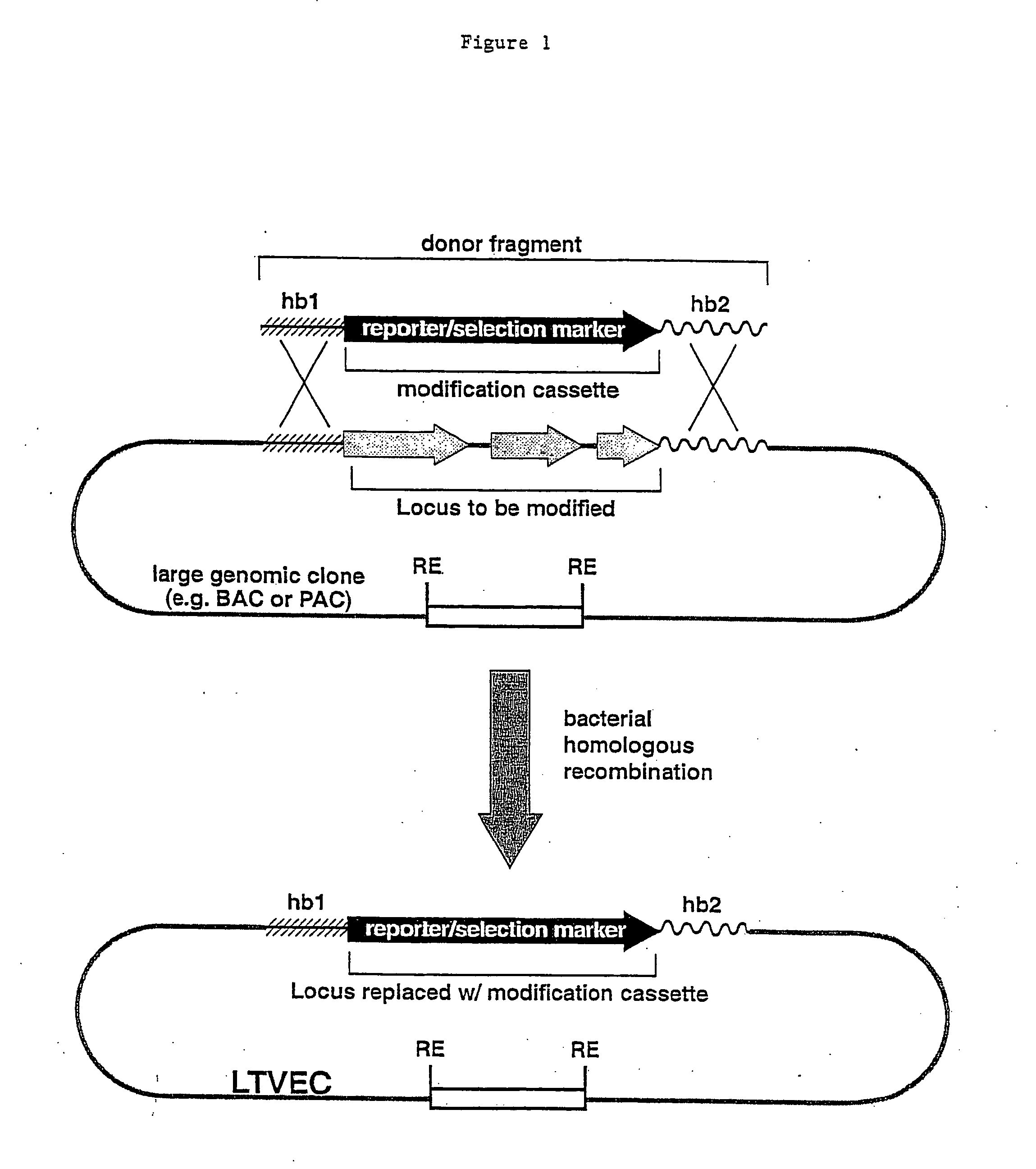
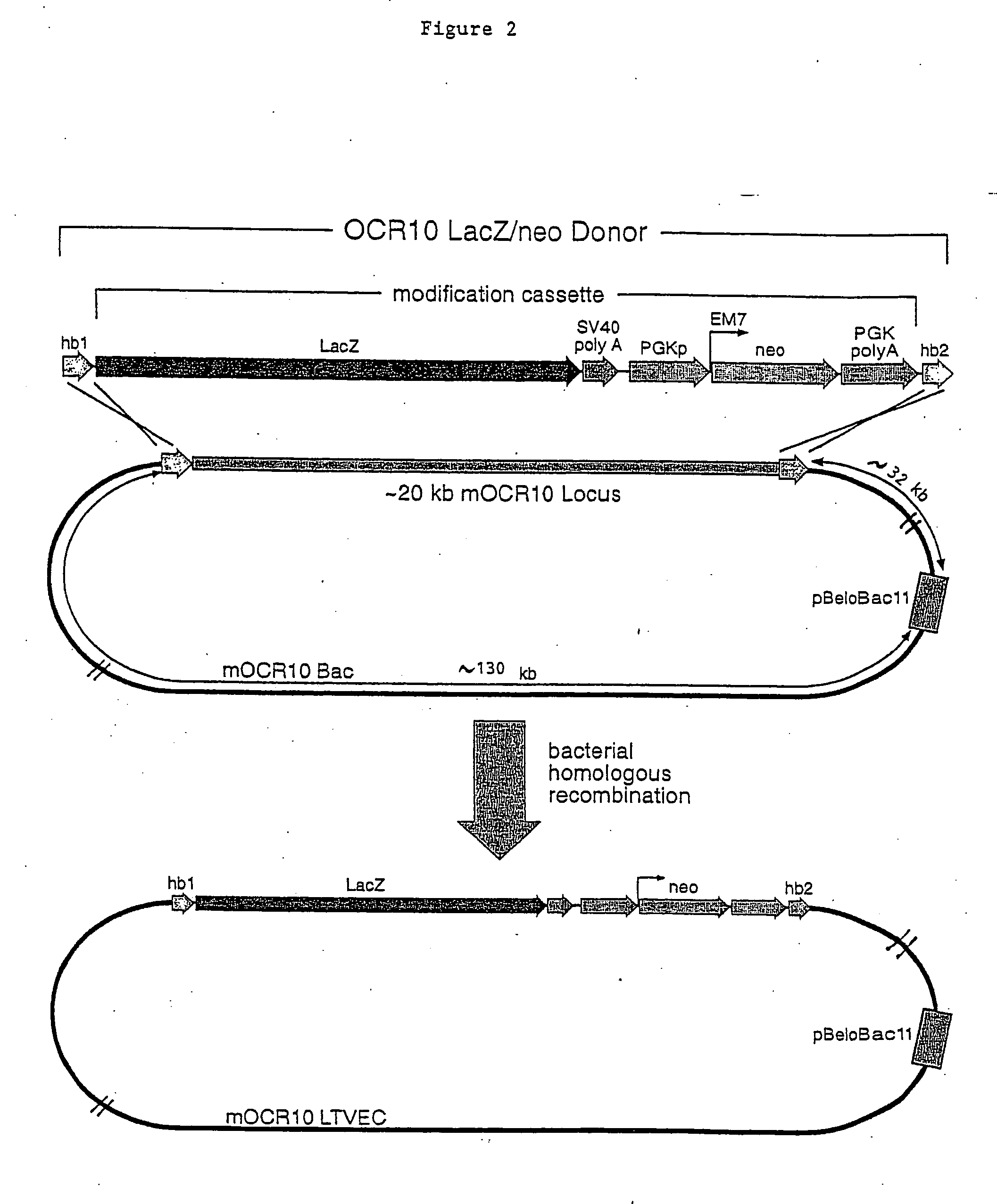
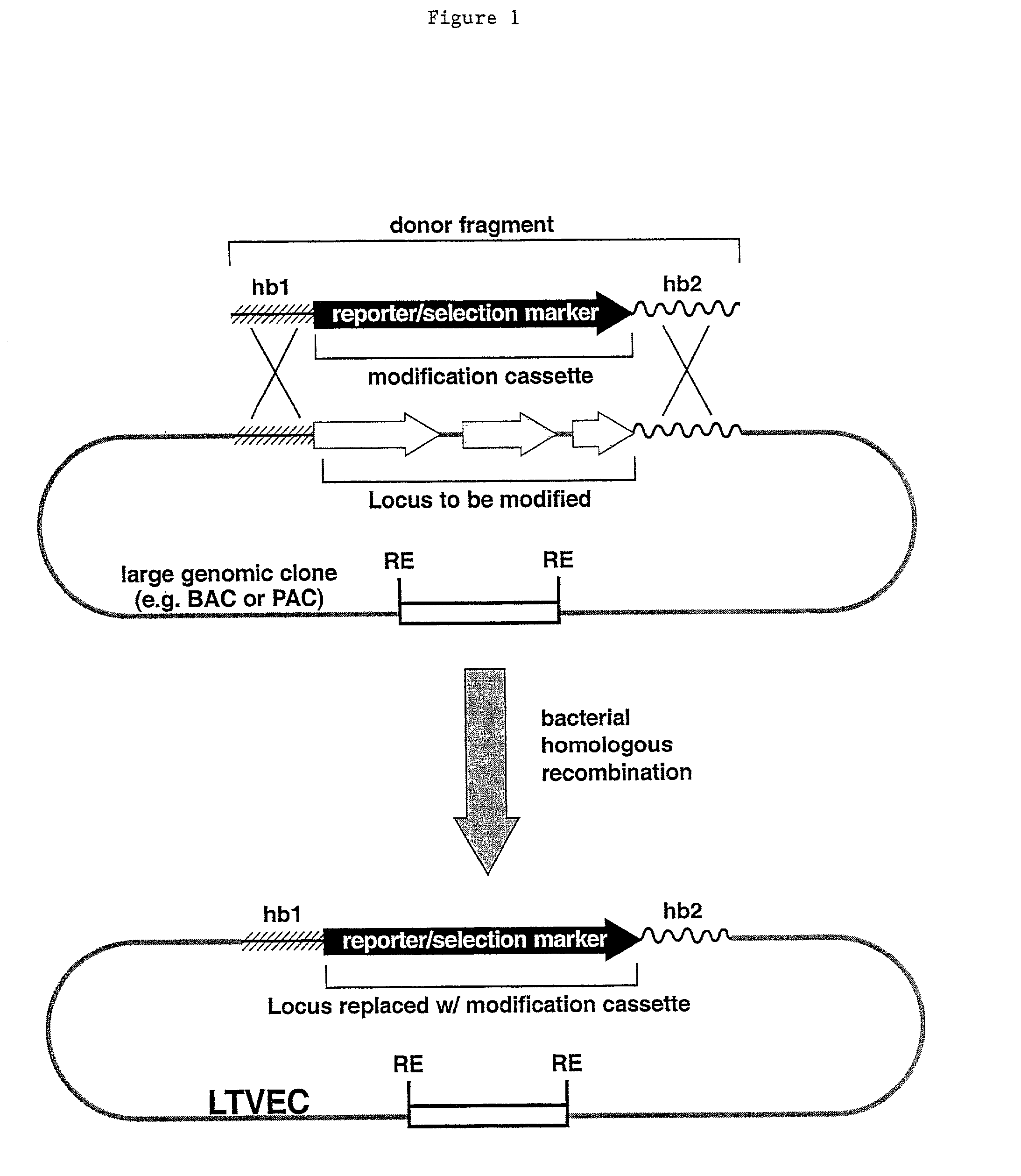
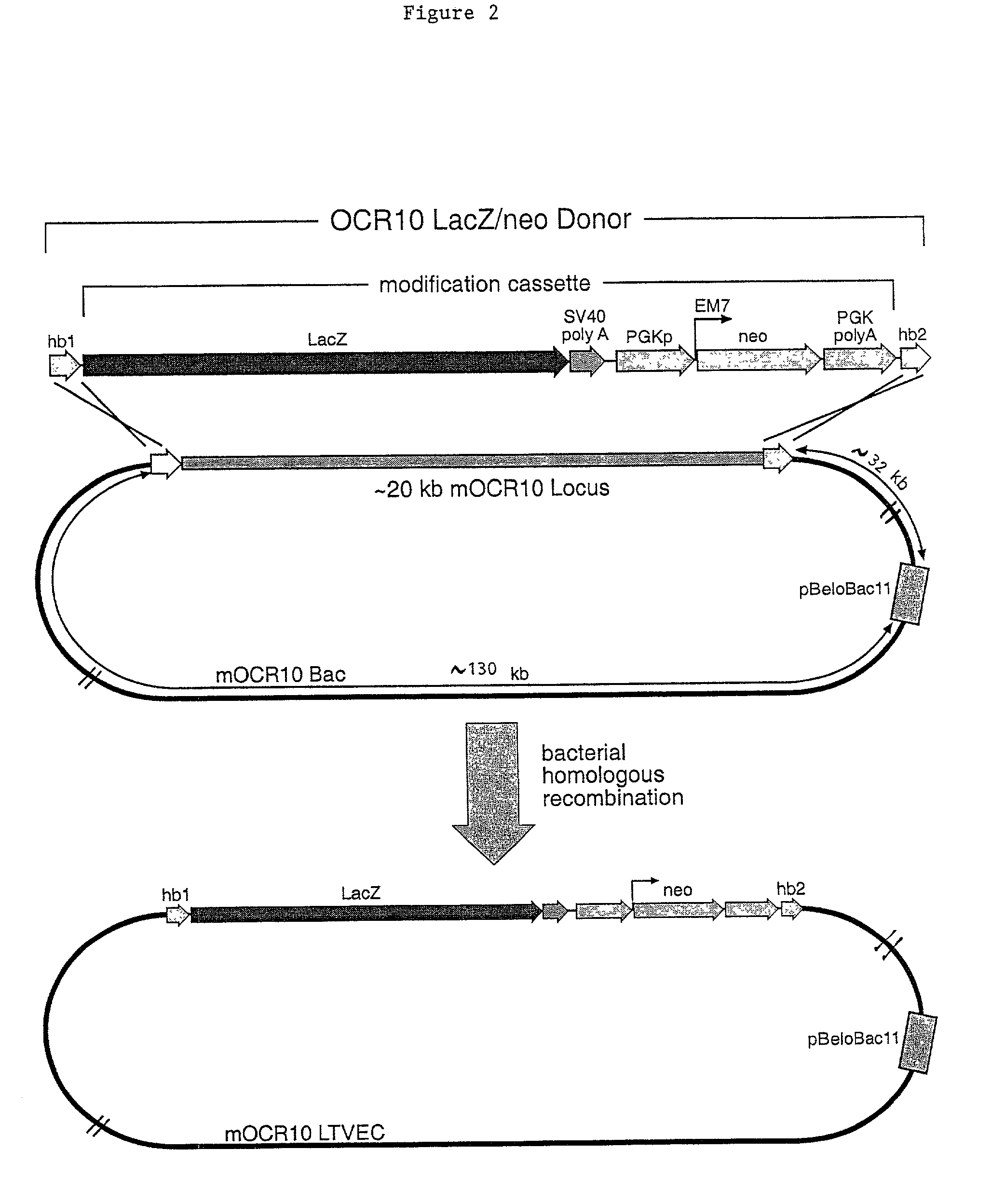
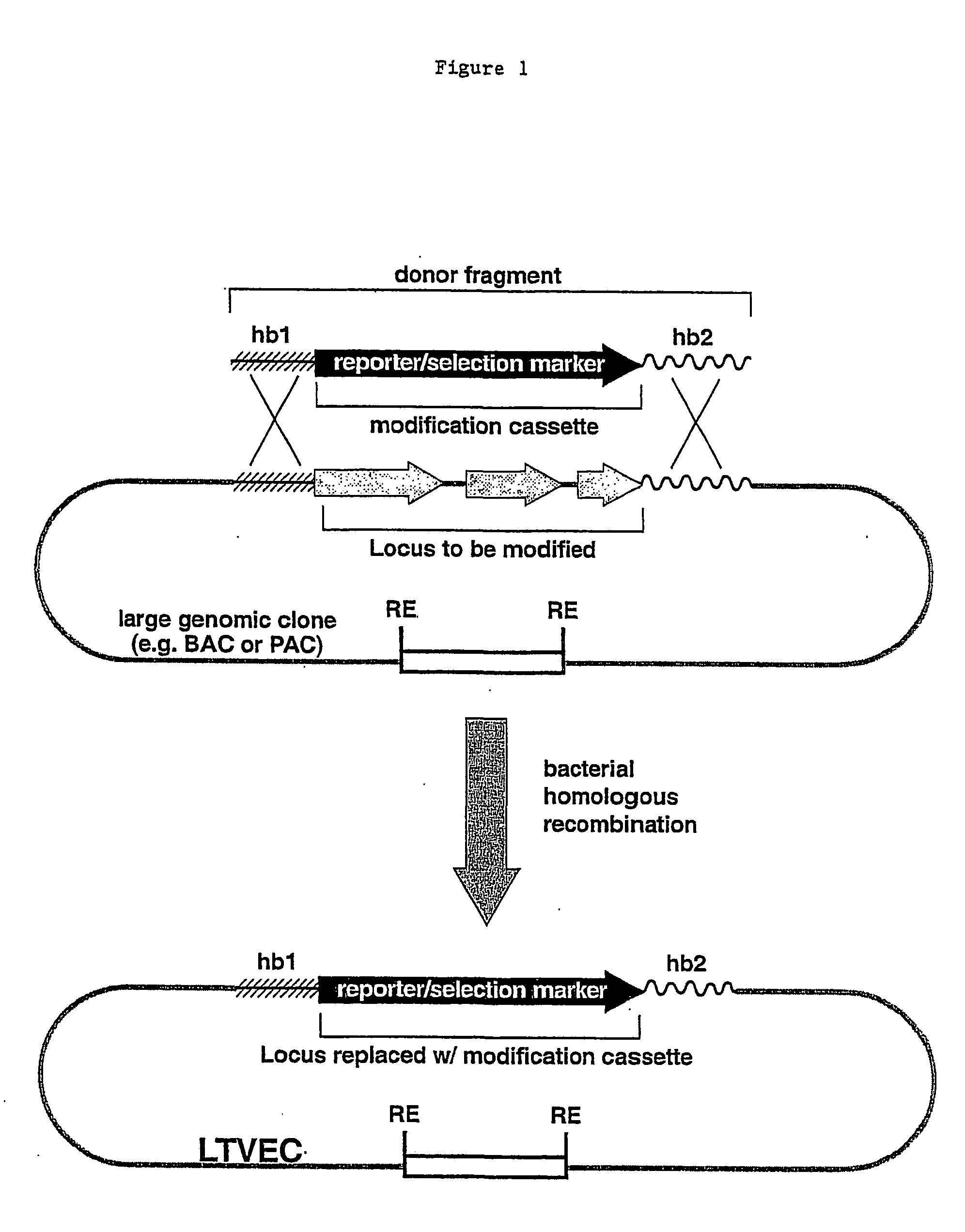
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
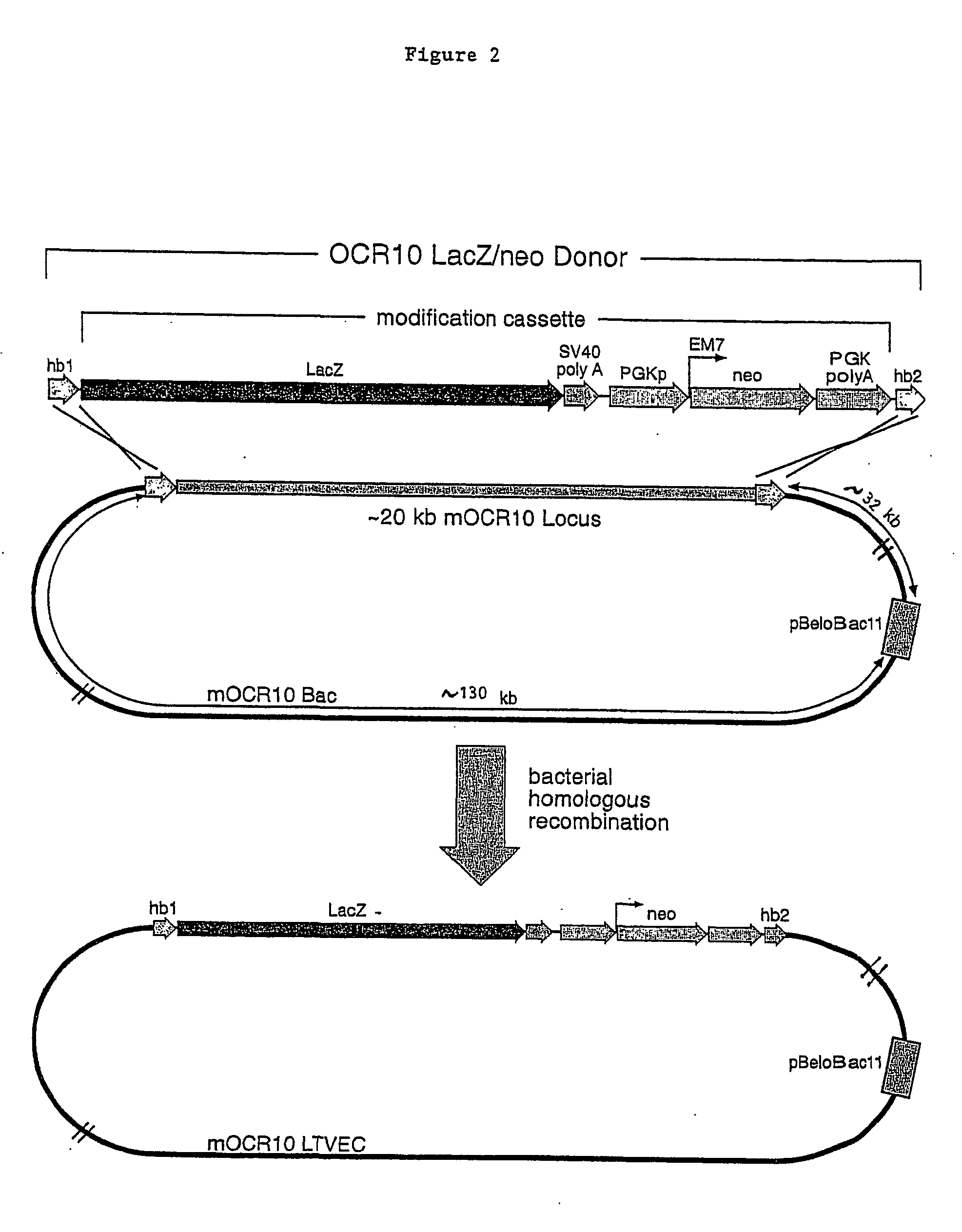
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
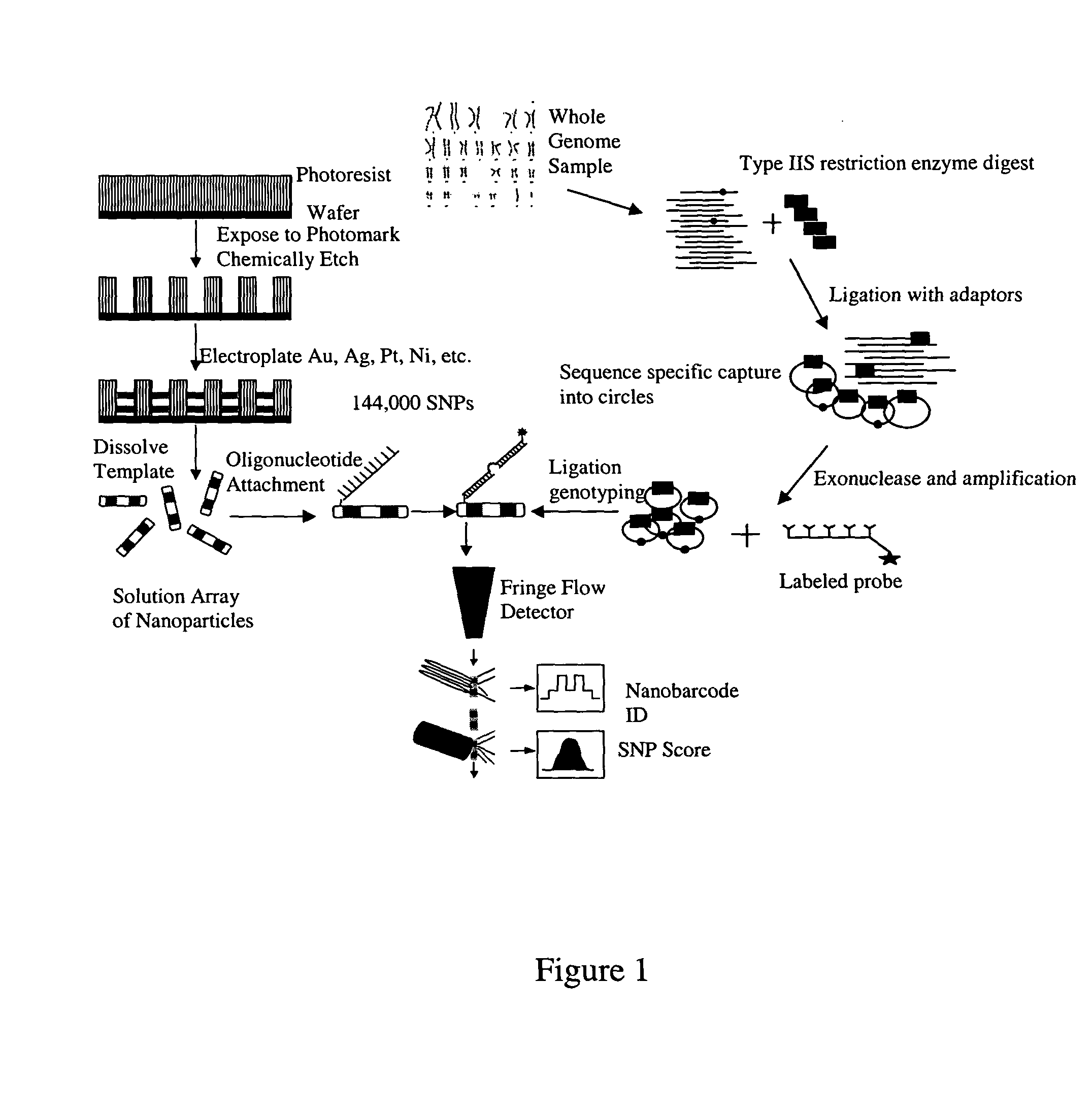
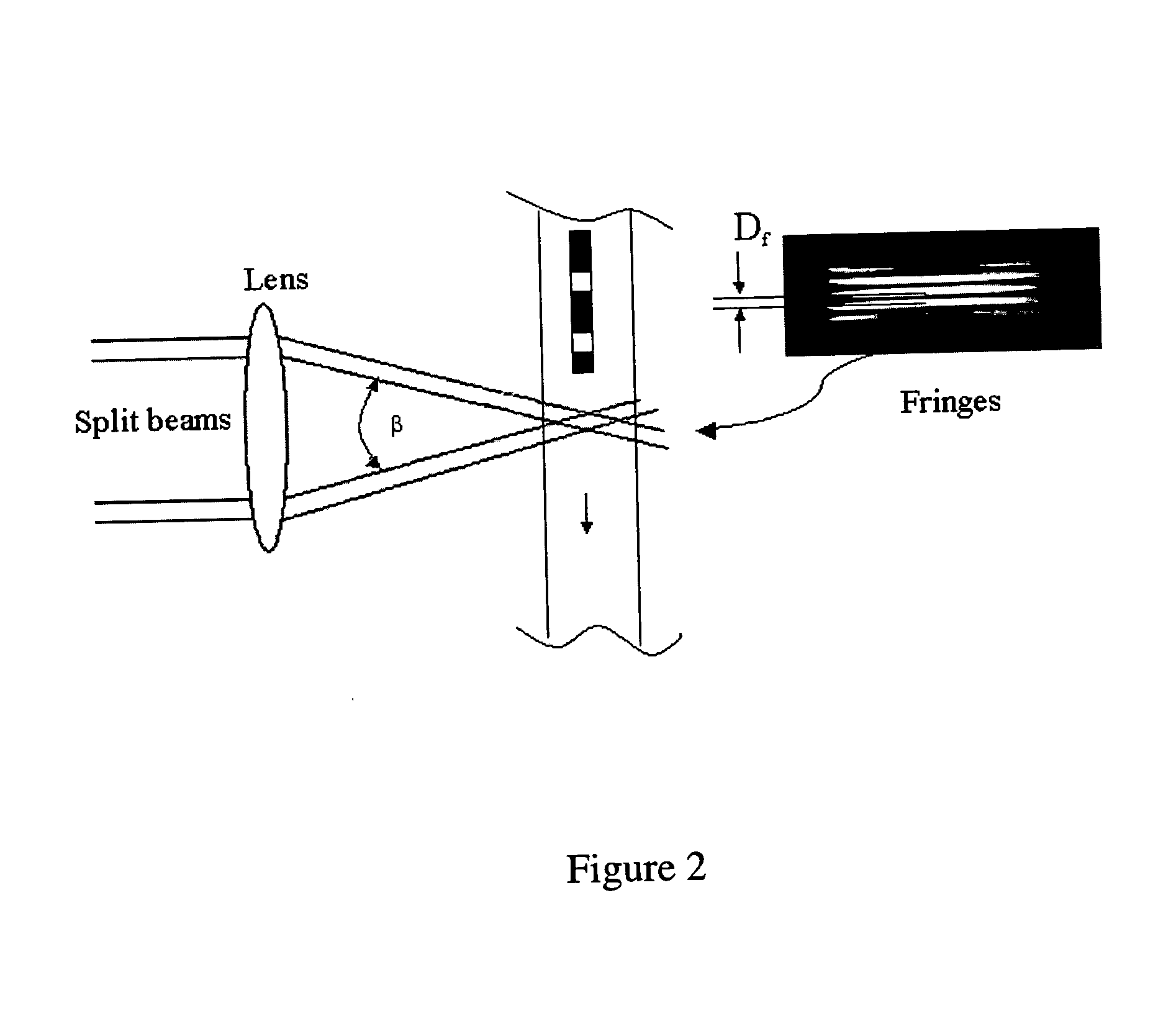
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
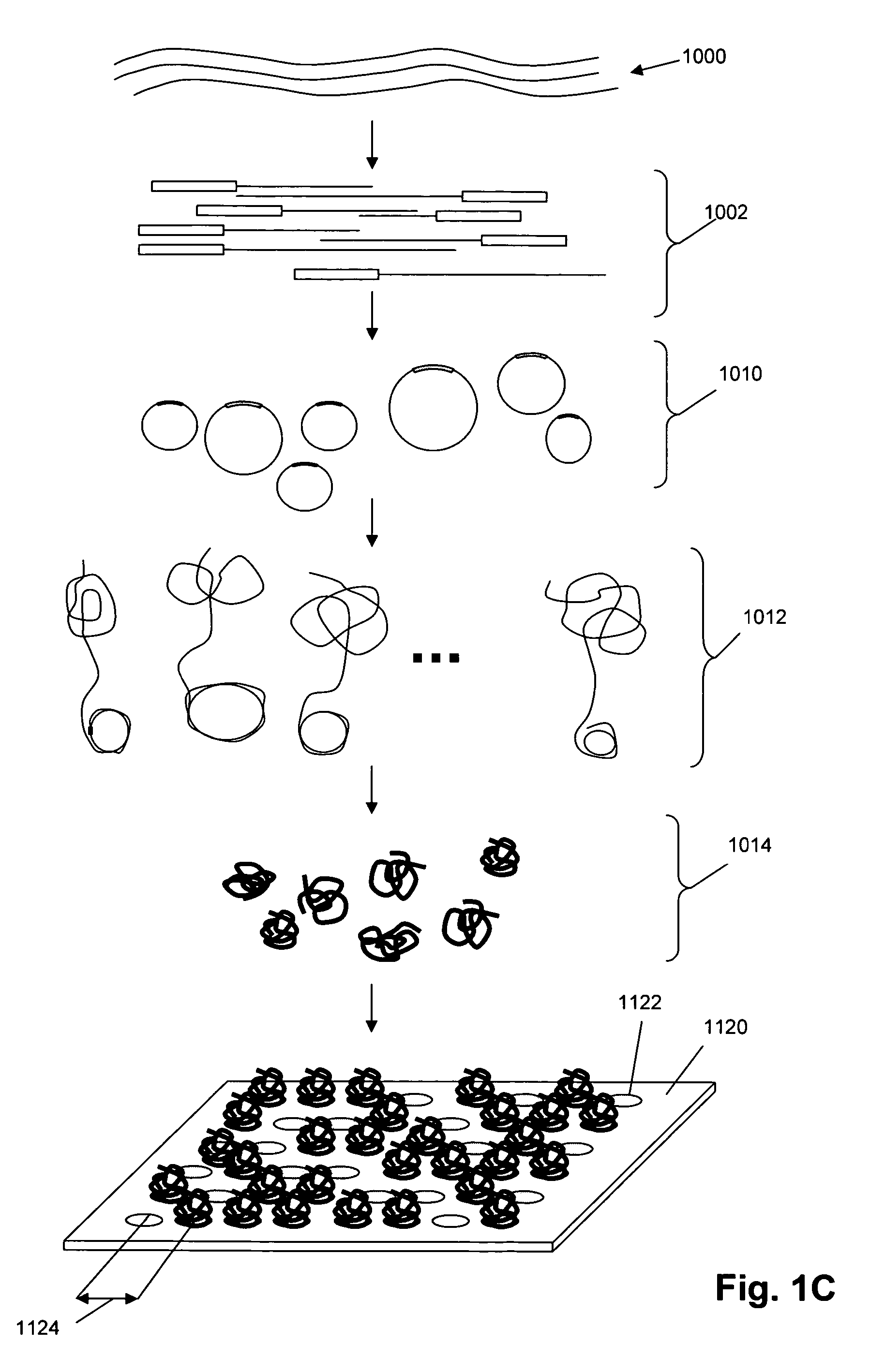
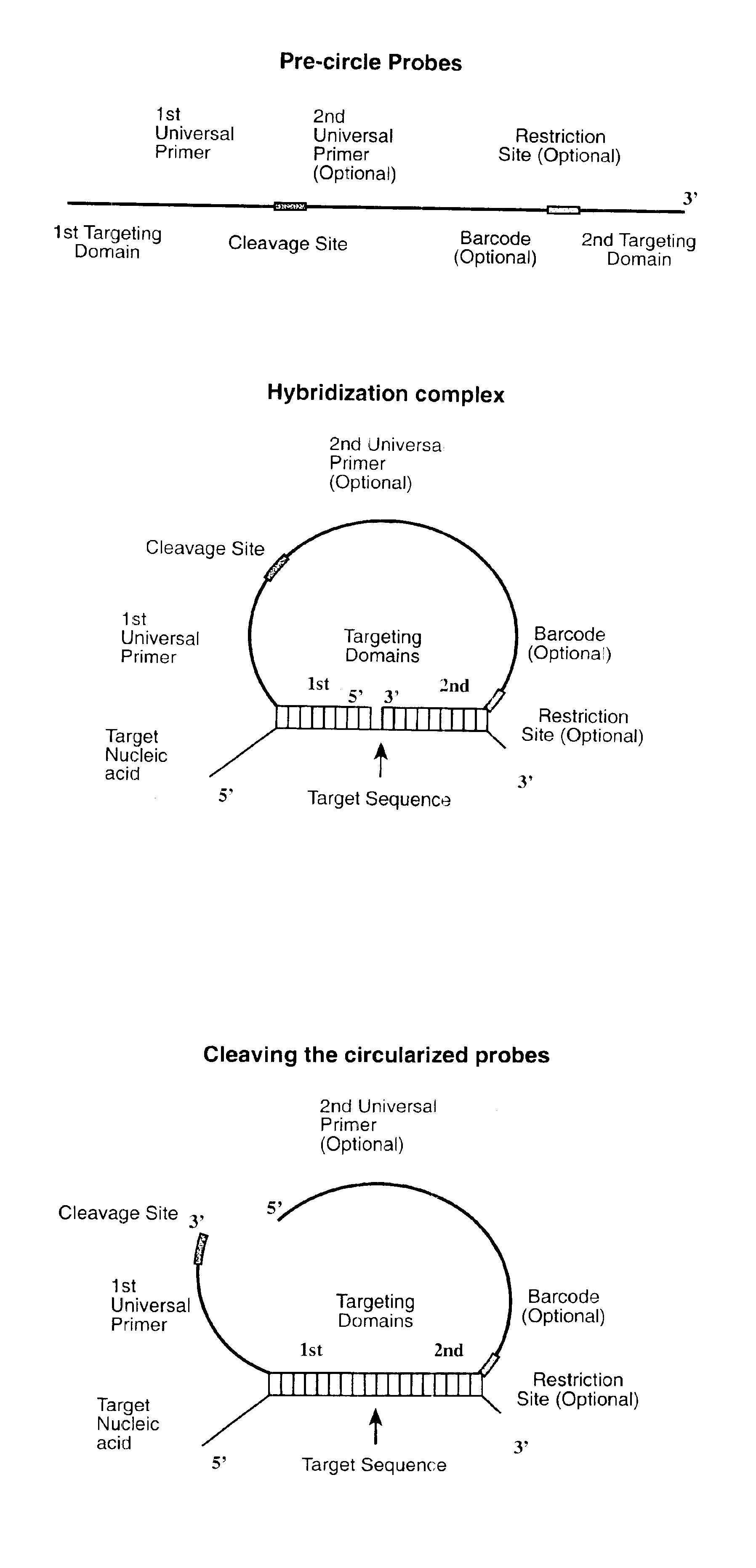
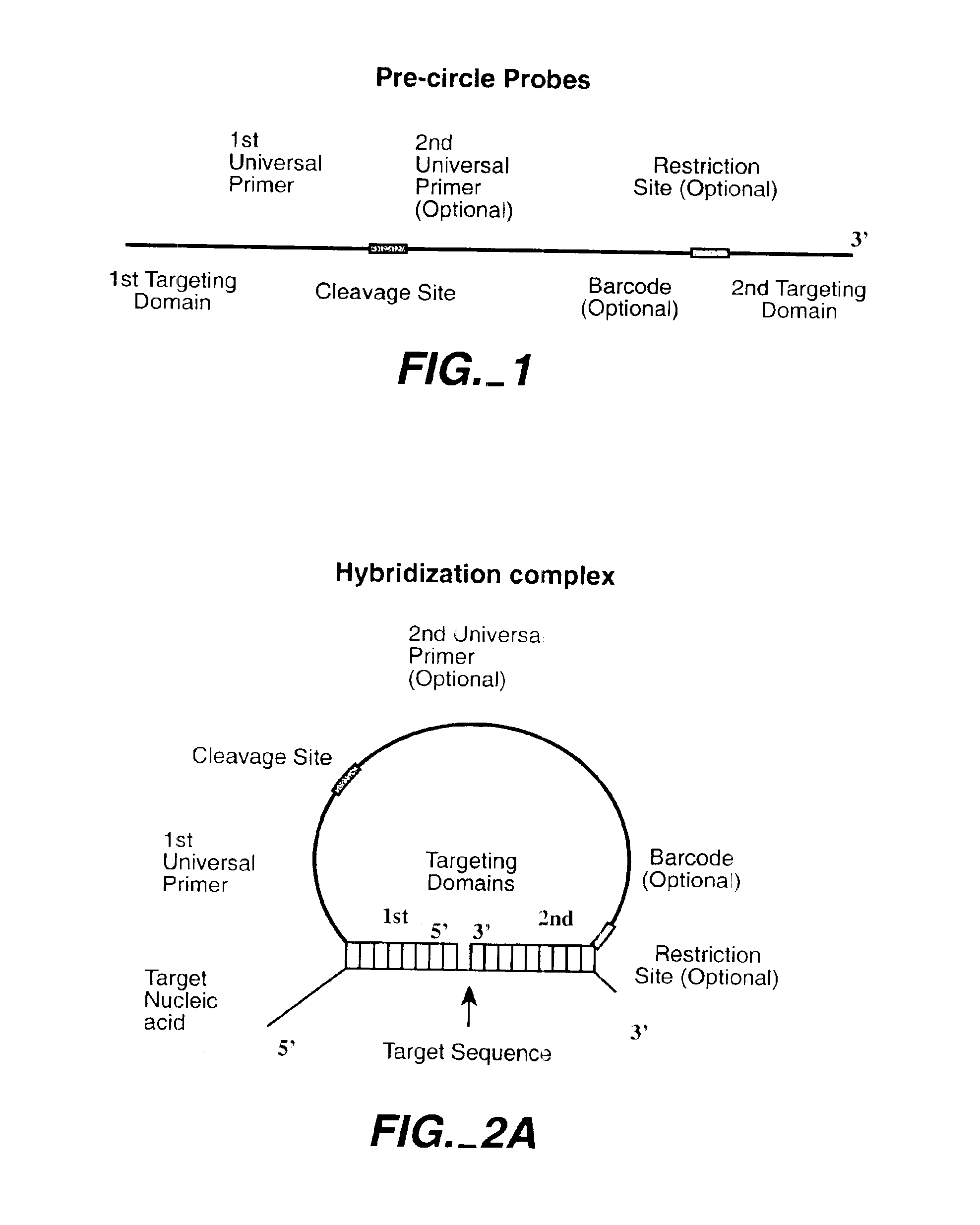
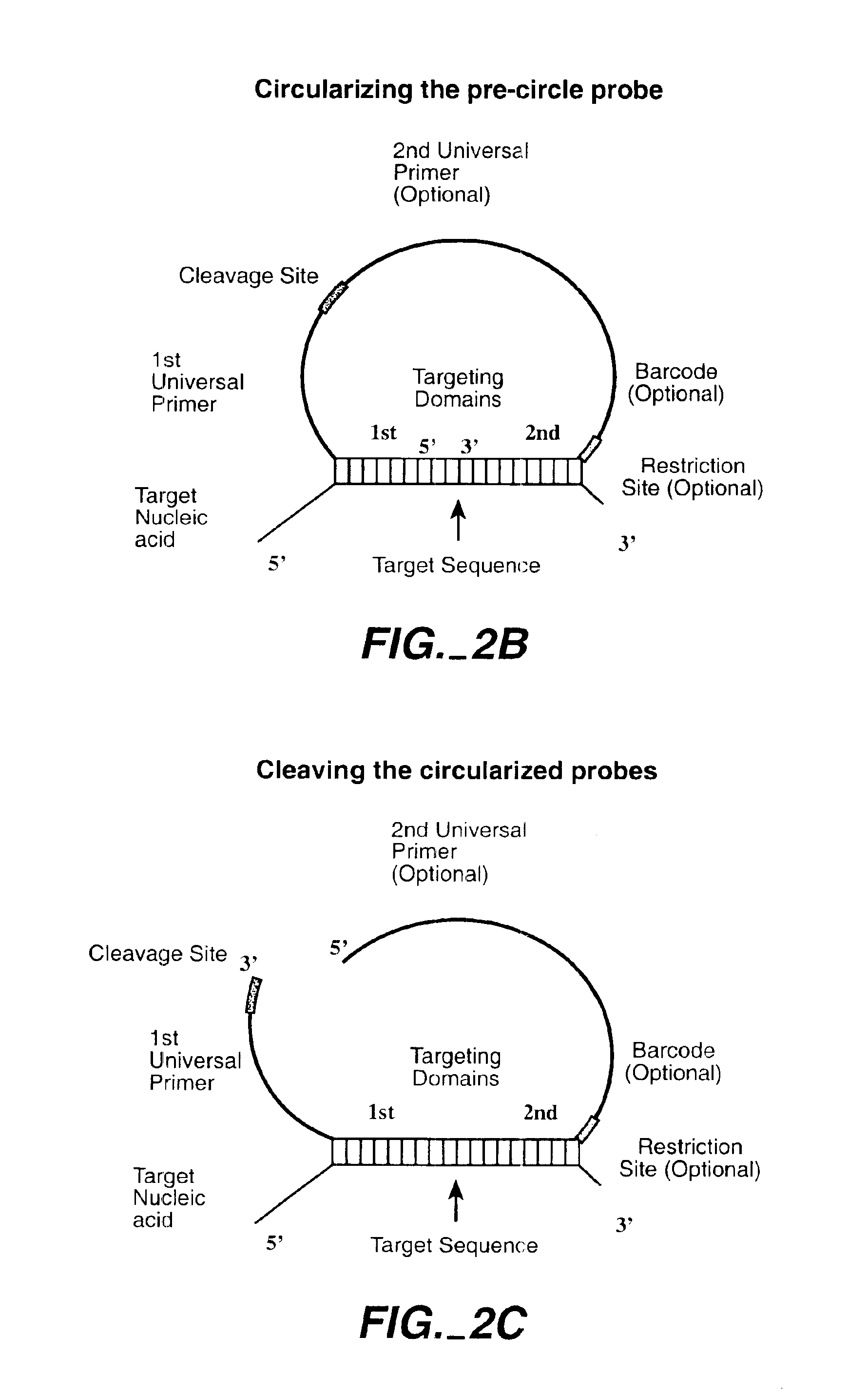
Direct multiplex characterization of genomic DNA
The invention is directed to novel methods of multiplexing nucleic acid reactions, including amplification, detection and genotyping. The invention relies on the use of precircle probes that are circularized in the presence of the corresponding target nucleic acids, cleaved, and then amplified.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
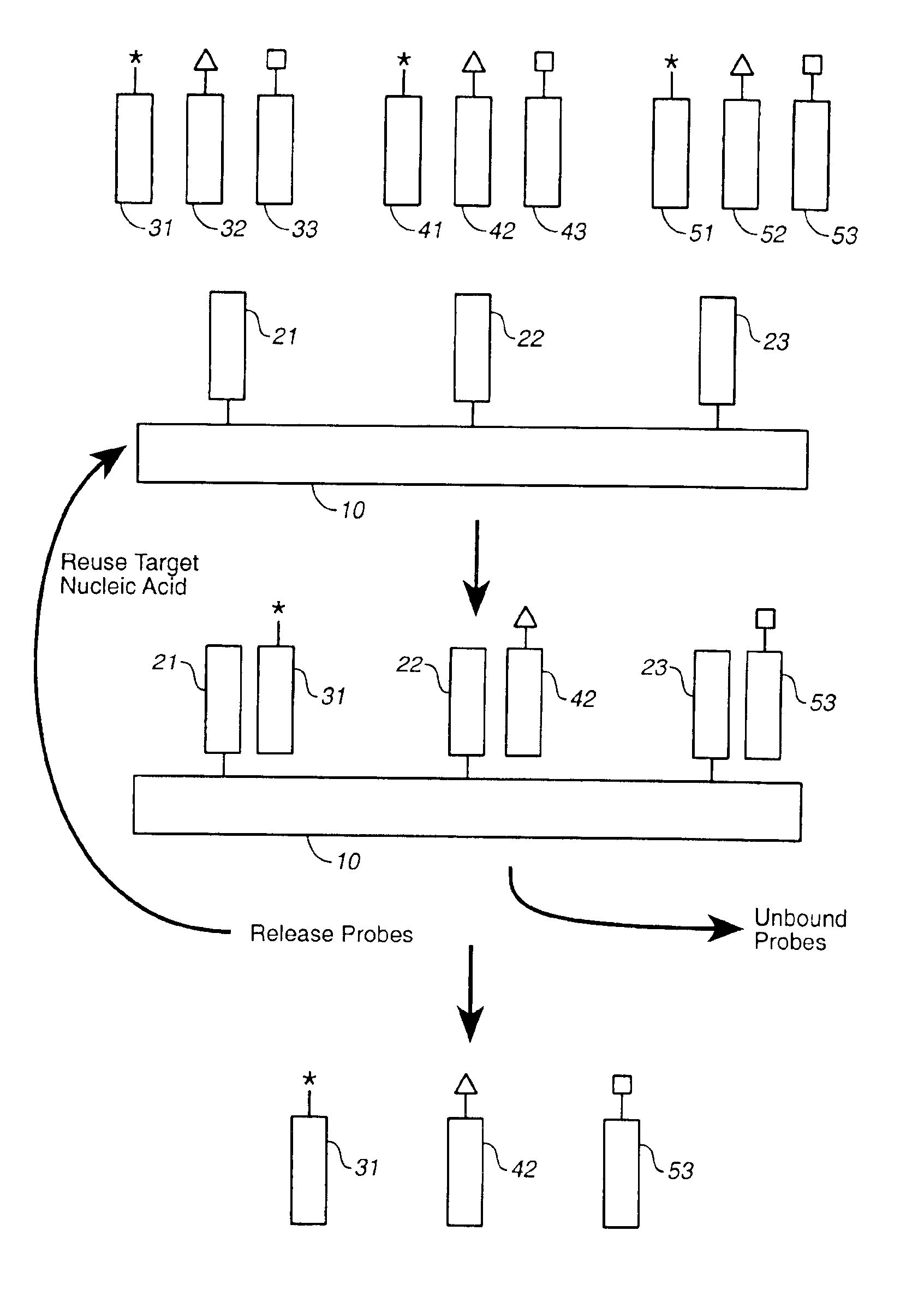
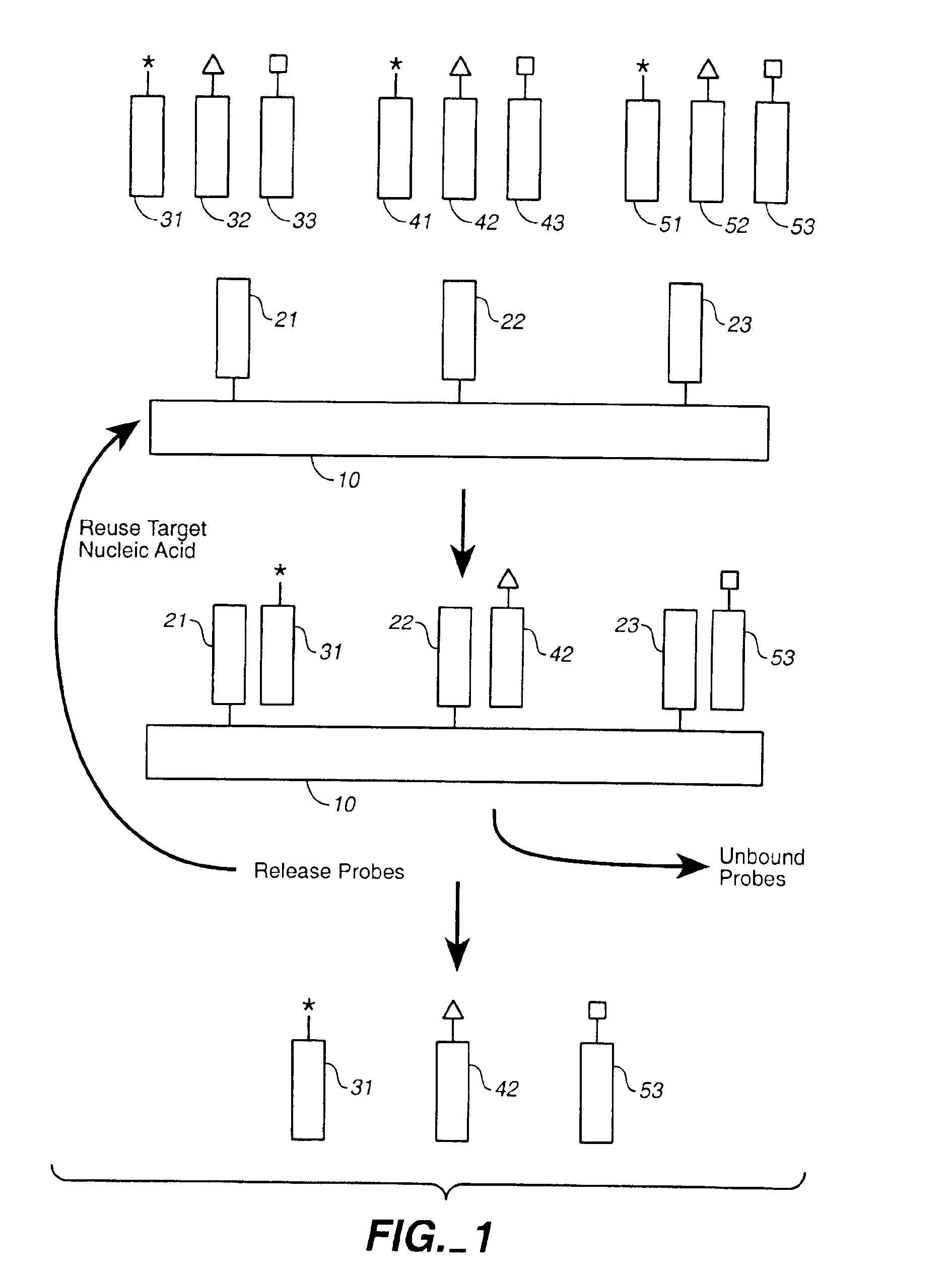
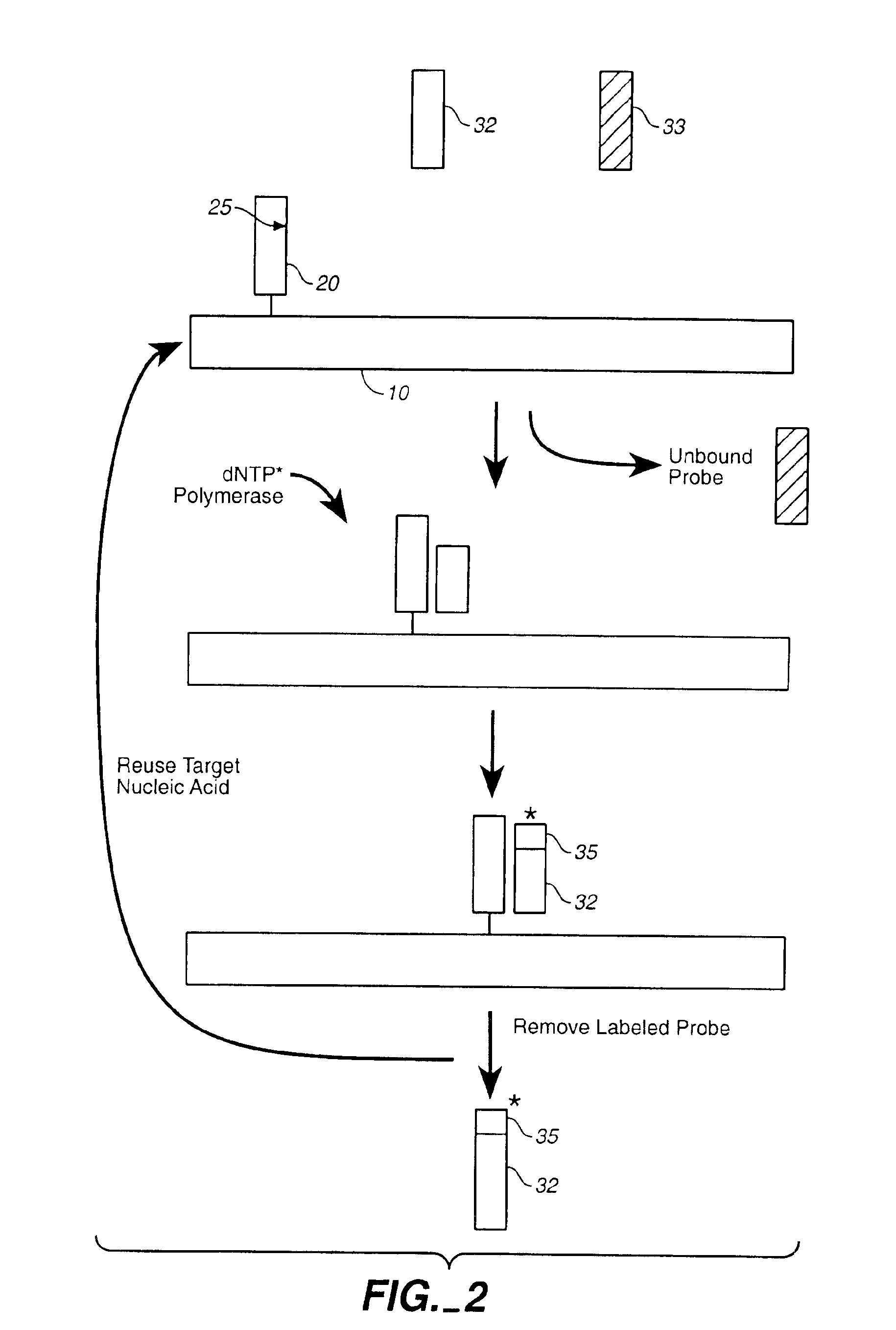
Compositions and methods for repetitive use of genomic DNA
The present invention relates to detection or genotyping (or other sample analysis) of target nucleic acids following immobilization of the target nucleic acids onto a surface. The target nucleic acids can be re-used multiple times, thus conserving sample materials and simplifying sample preparation.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
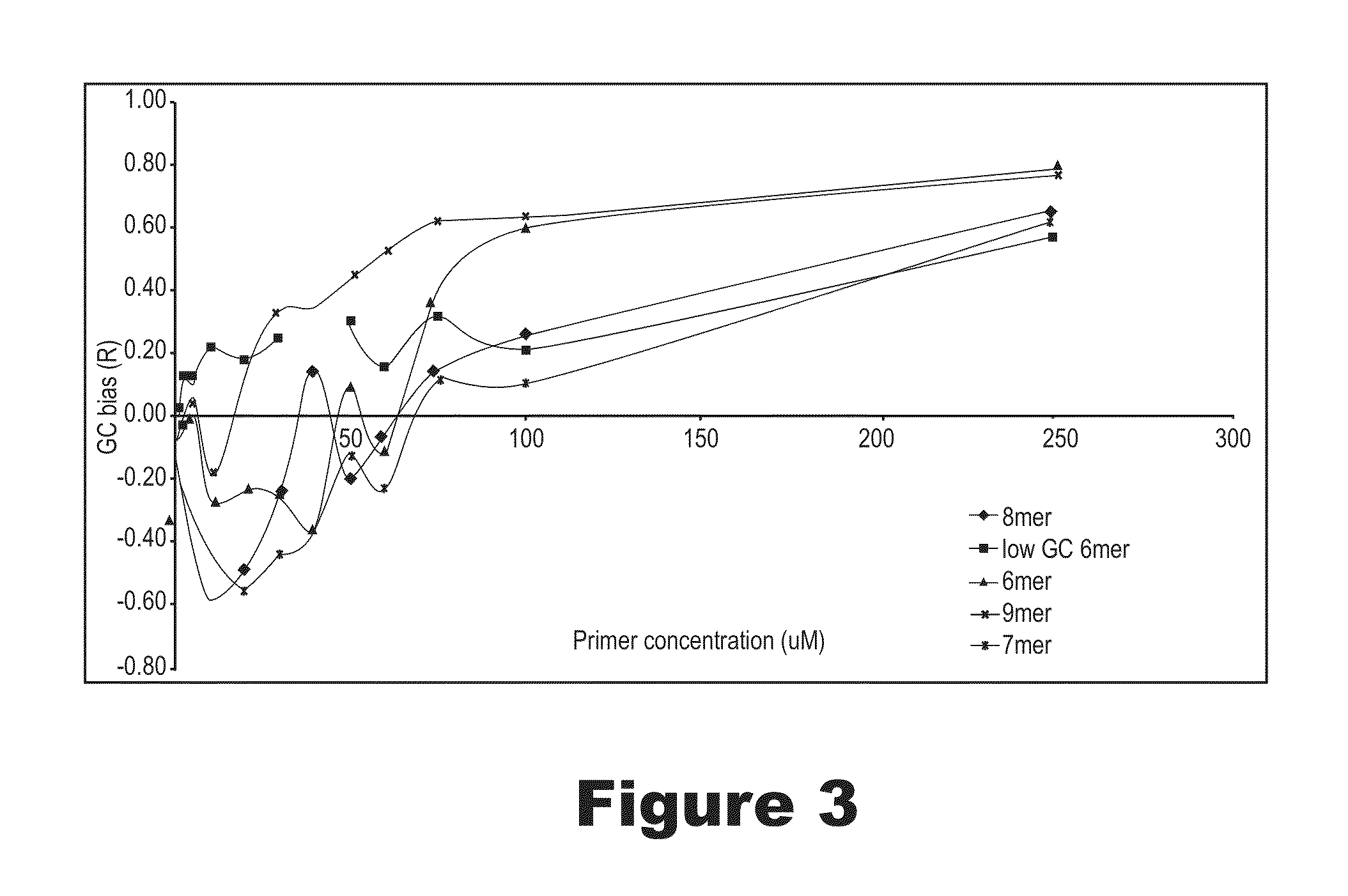
Methods and compositions for long fragment read sequencing
ActiveUS20110033854A1Less coverageLess GC biasSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAComputational biology
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for long fragment read sequencing. The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for preparing long fragments of genomic DNA, for processing genomic DNA for long fragment read sequencing methods, as well as software and algorithms for processing and analyzing sequence data.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Method of sequencing genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6018041ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
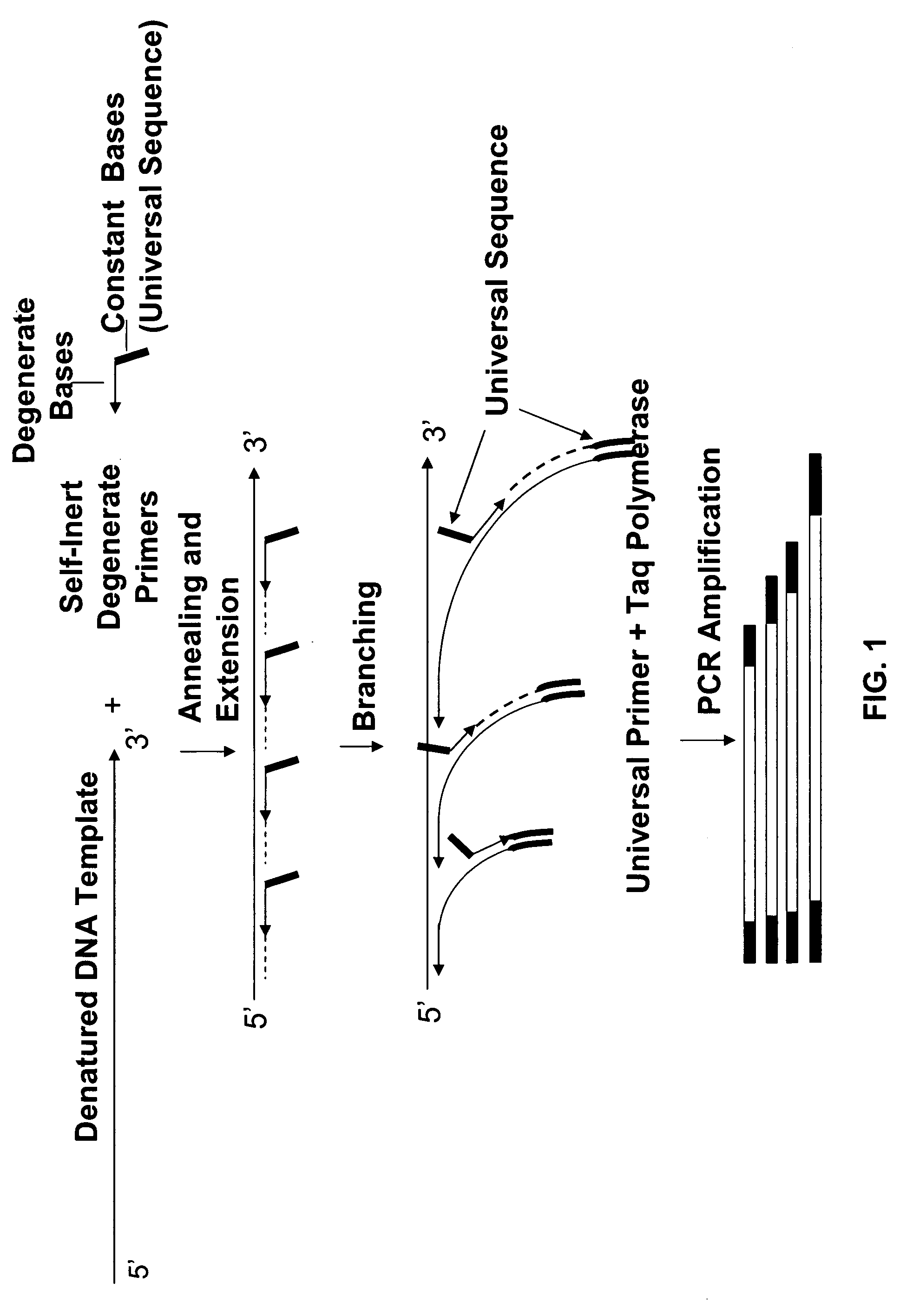
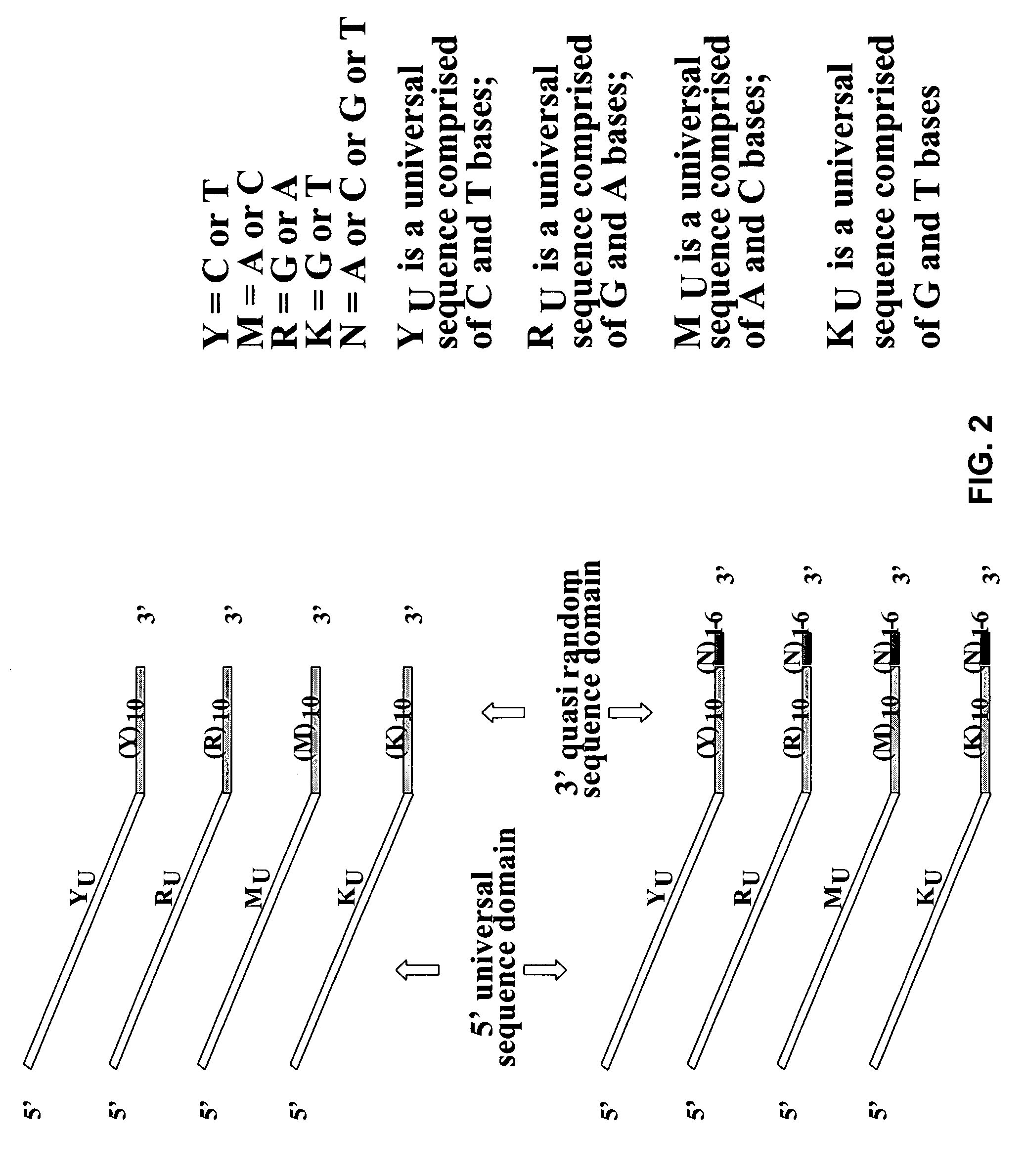
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:HYSEQ
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
Described herein are methods to diagnose or prognose cancer in a subject by enriching, detecting, and analyzing individual rare cells, e.g., epithelial cells, in a sample from the subject. Also described are methods for labeling regions of genomic DNA in individual cells in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the method includes detecting the presence of gene mutations in individual rare cells in a subsample.
Owner:GPB SCI +2
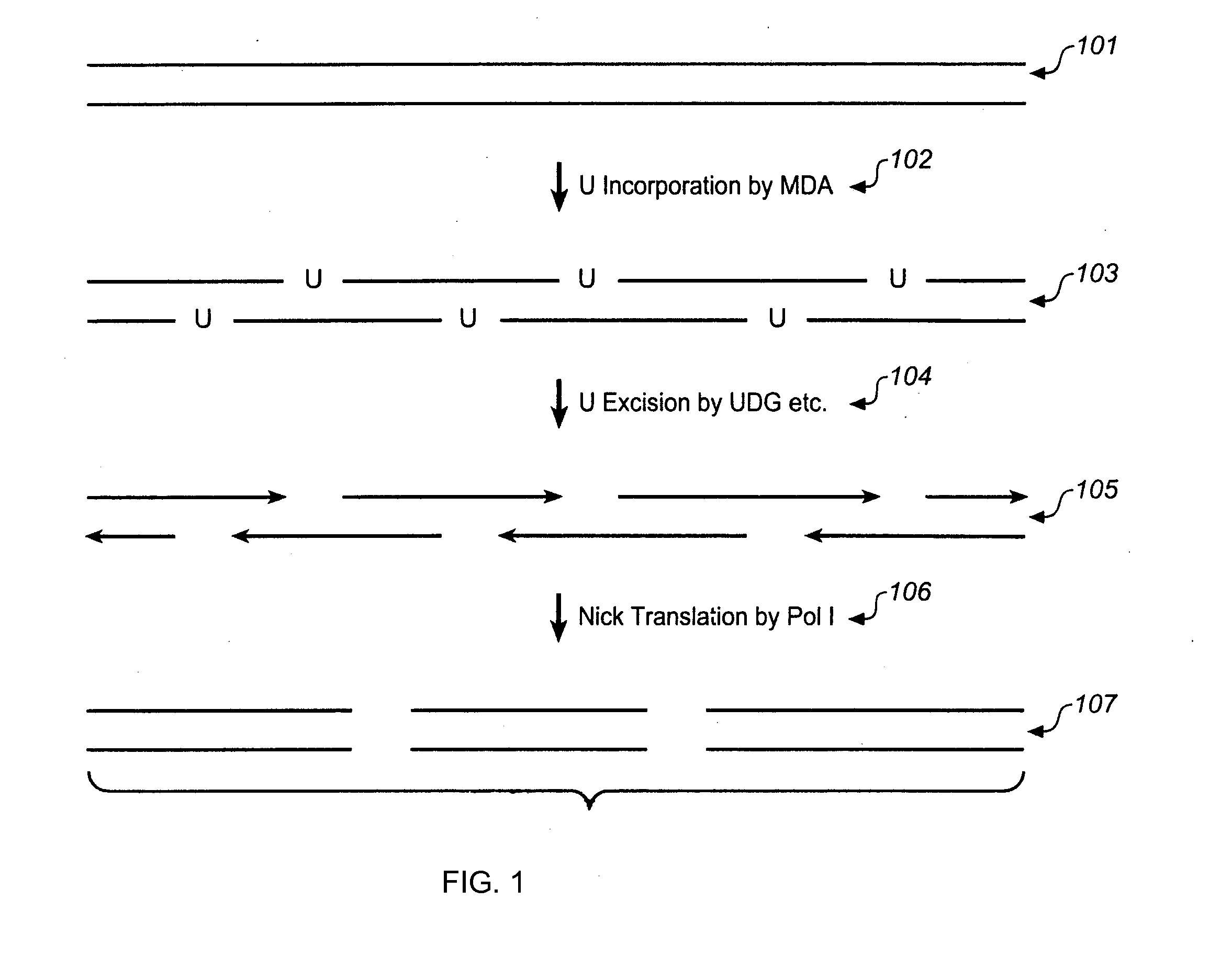
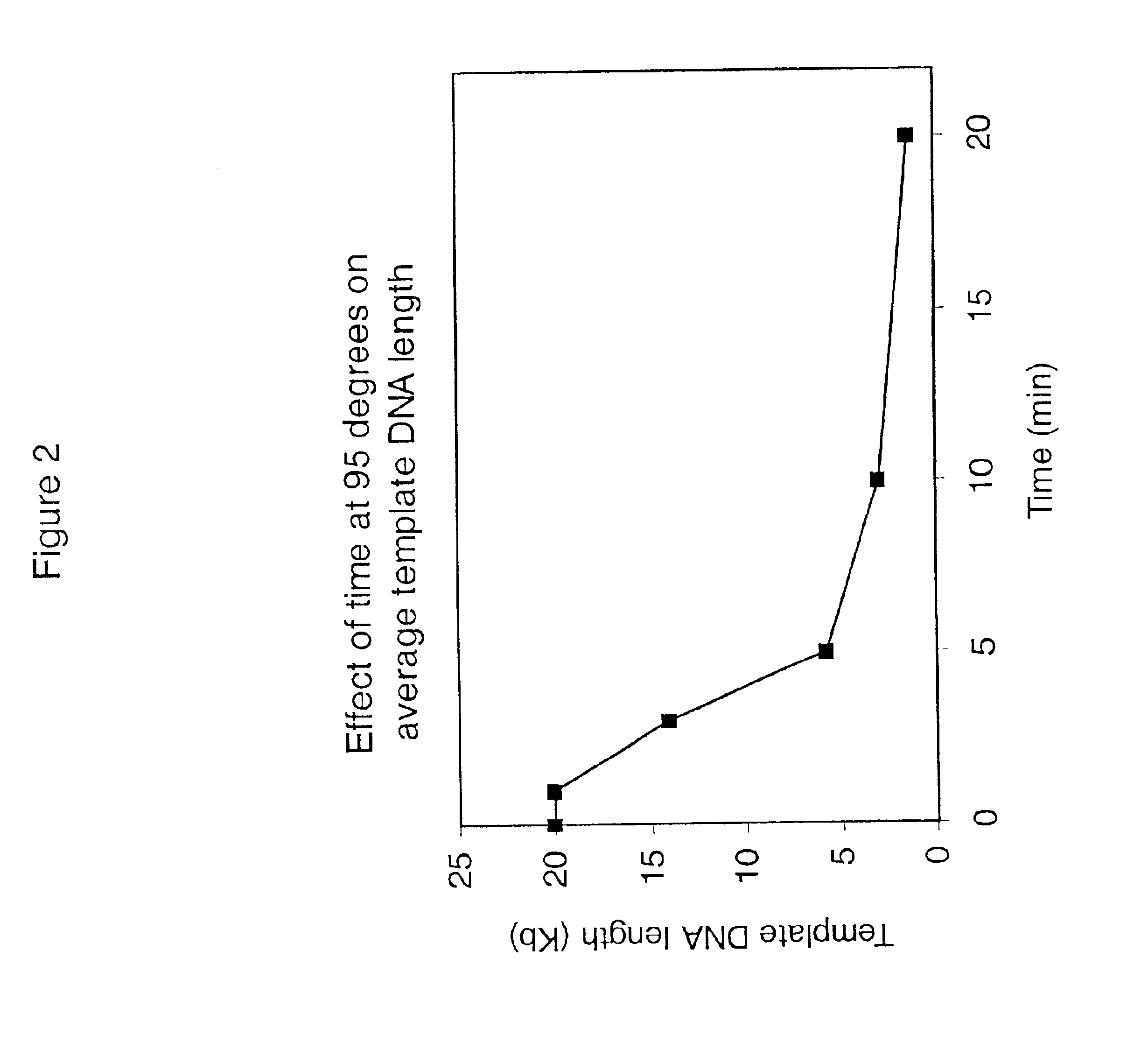
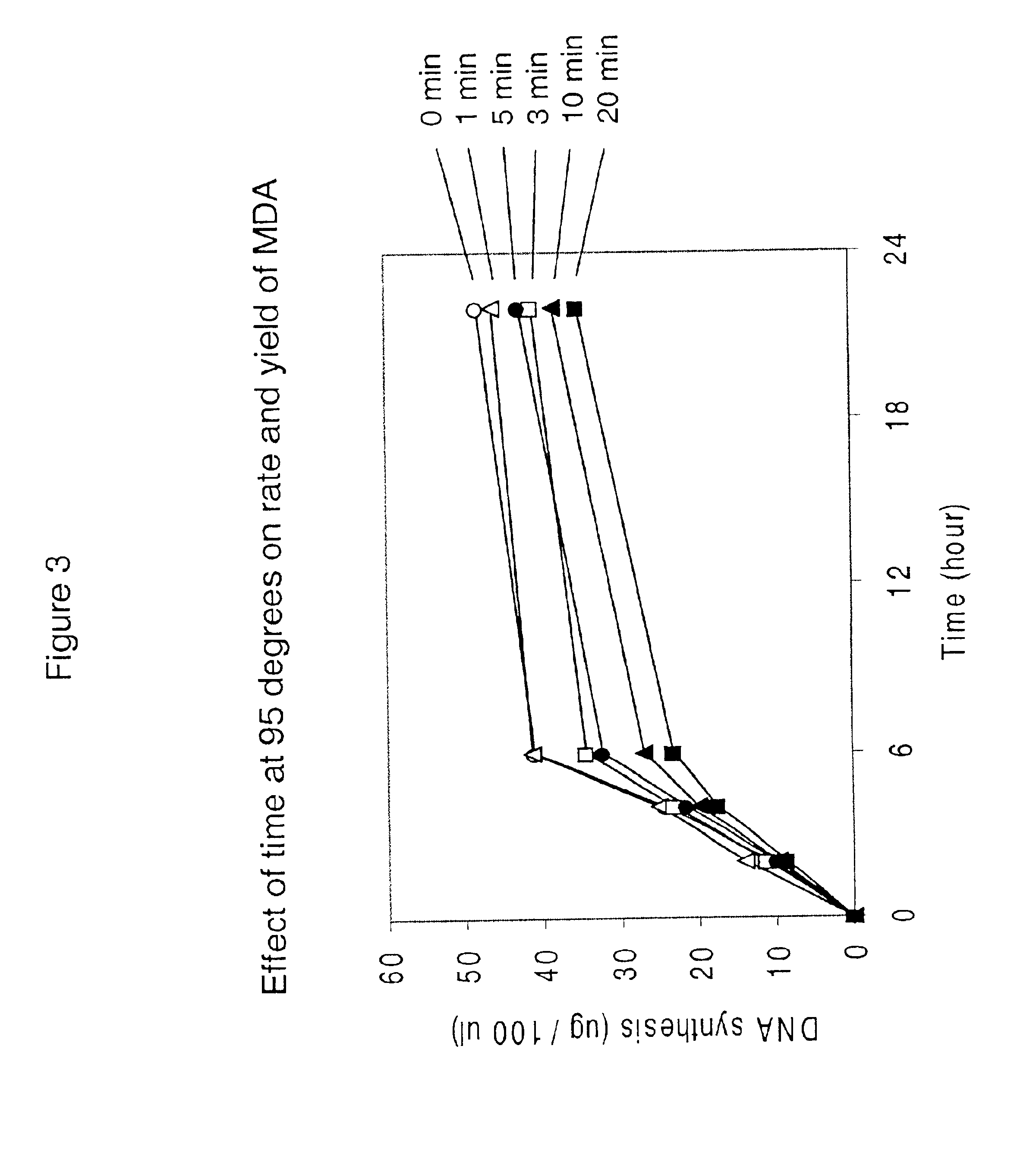
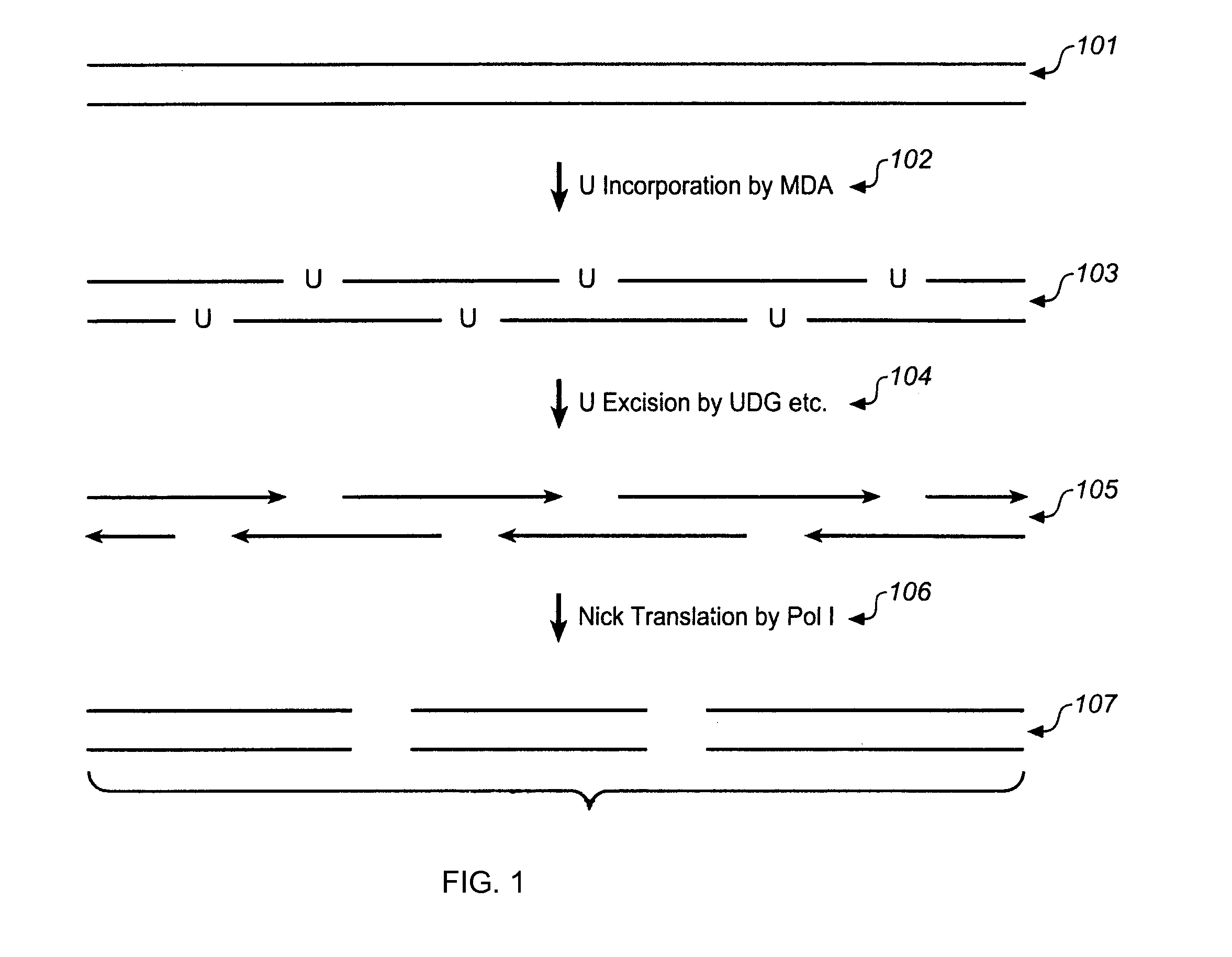
Multiple displacement amplification
InactiveUS6977148B2Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideGenomic DNA
Disclosed are compositions and a method for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest. The disclosed method generally involves replication of a target sequence such that, during replication, the replicated strands are displaced from the target sequence by strand displacement replication of another replicated strand. In one form of the disclosed method, the target sample is not subjected to denaturing conditions. It was discovered that the target nucleic acids, genomic DNA, for example, need not be denatured for efficient multiple displacement amplification. The primers used can be hexamer primers. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the primers are nuclease resistant. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the melting temperature of the primer is altered relative to a primer of the same sequence without the modified nucleotide(s). The DNA polymerase can be φ29 DNA polymerase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Universal selective genome amplification and universal genotyping system
InactiveUS20050019776A1Enriches SNPsImprove reuseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSmall fragmentGenomic DNA
The invention relates to methods for isolating and amplifying small fragments of genomic DNA for genotyping polymorphisms in human populations.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
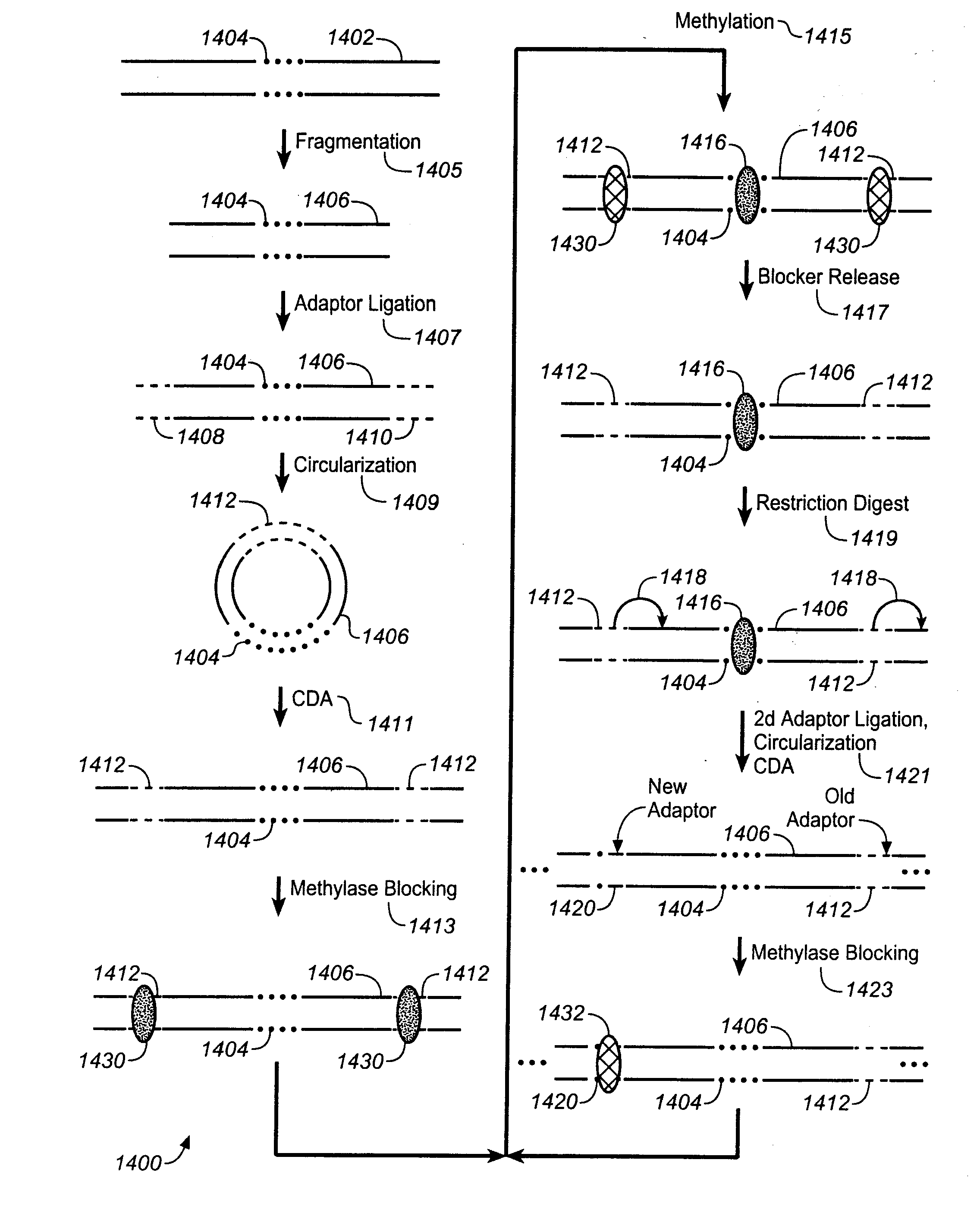
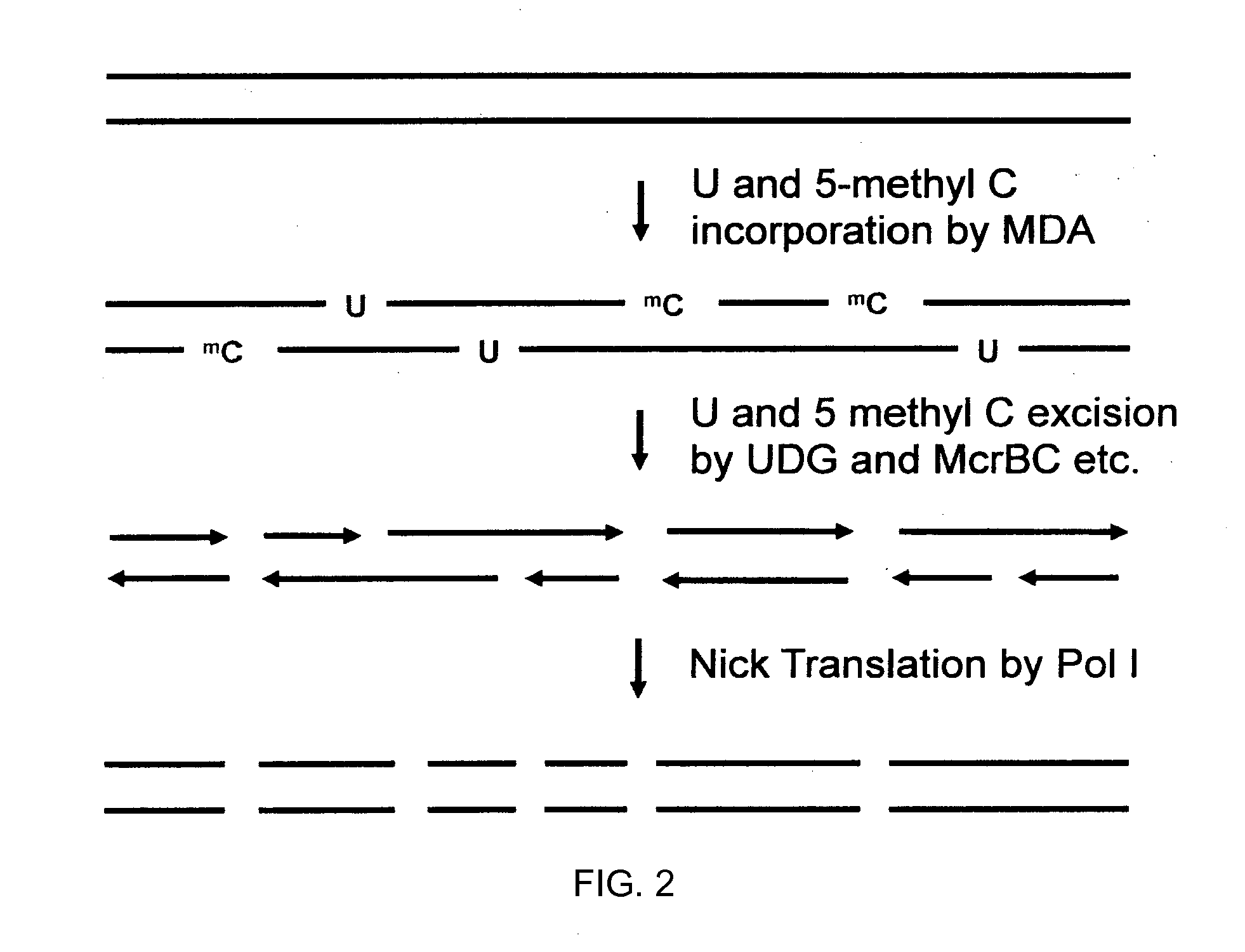
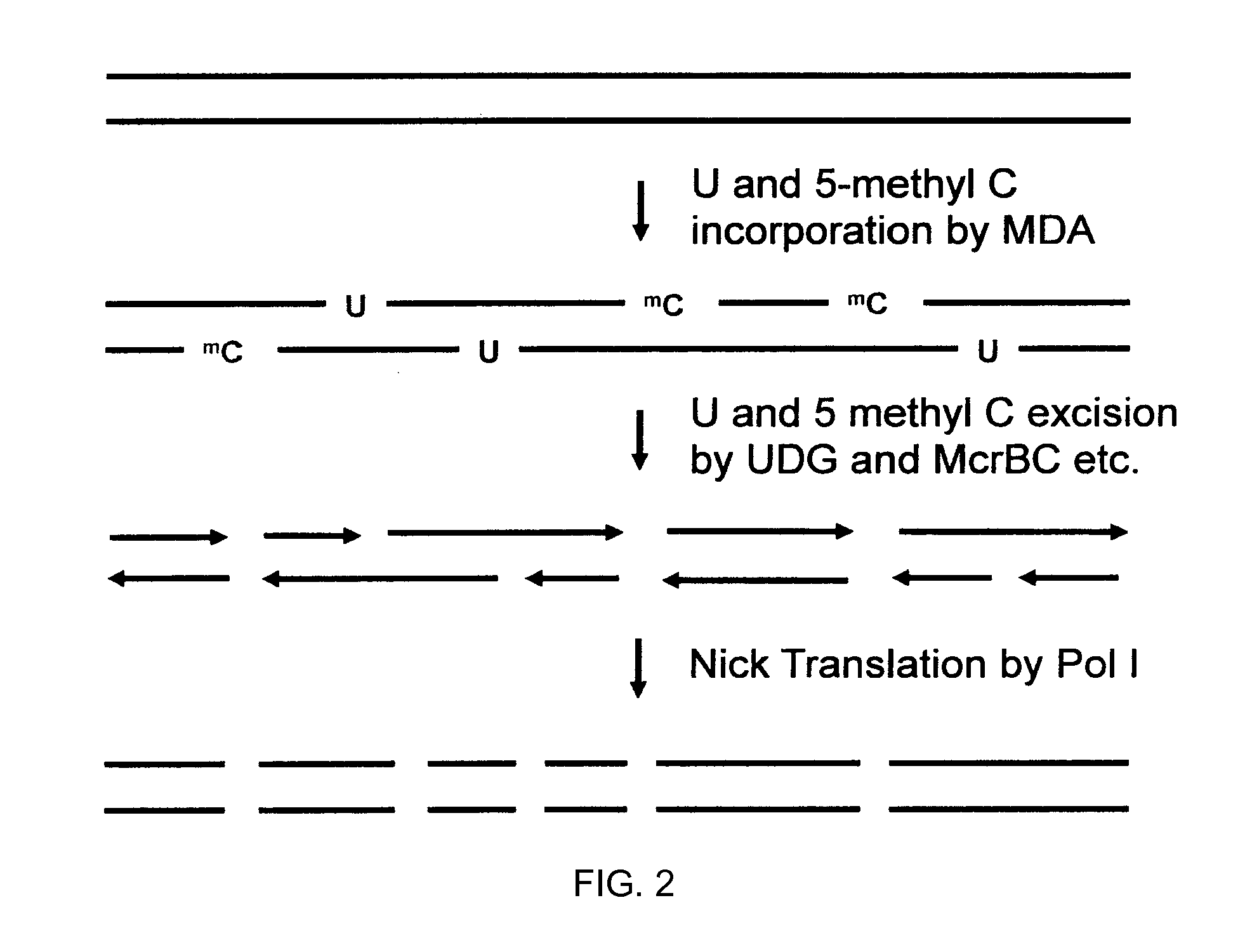
Method for producing complex DNA methylation fingerprints
InactiveUS6214556B1Accurately determineSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFingerprintGenomic DNA
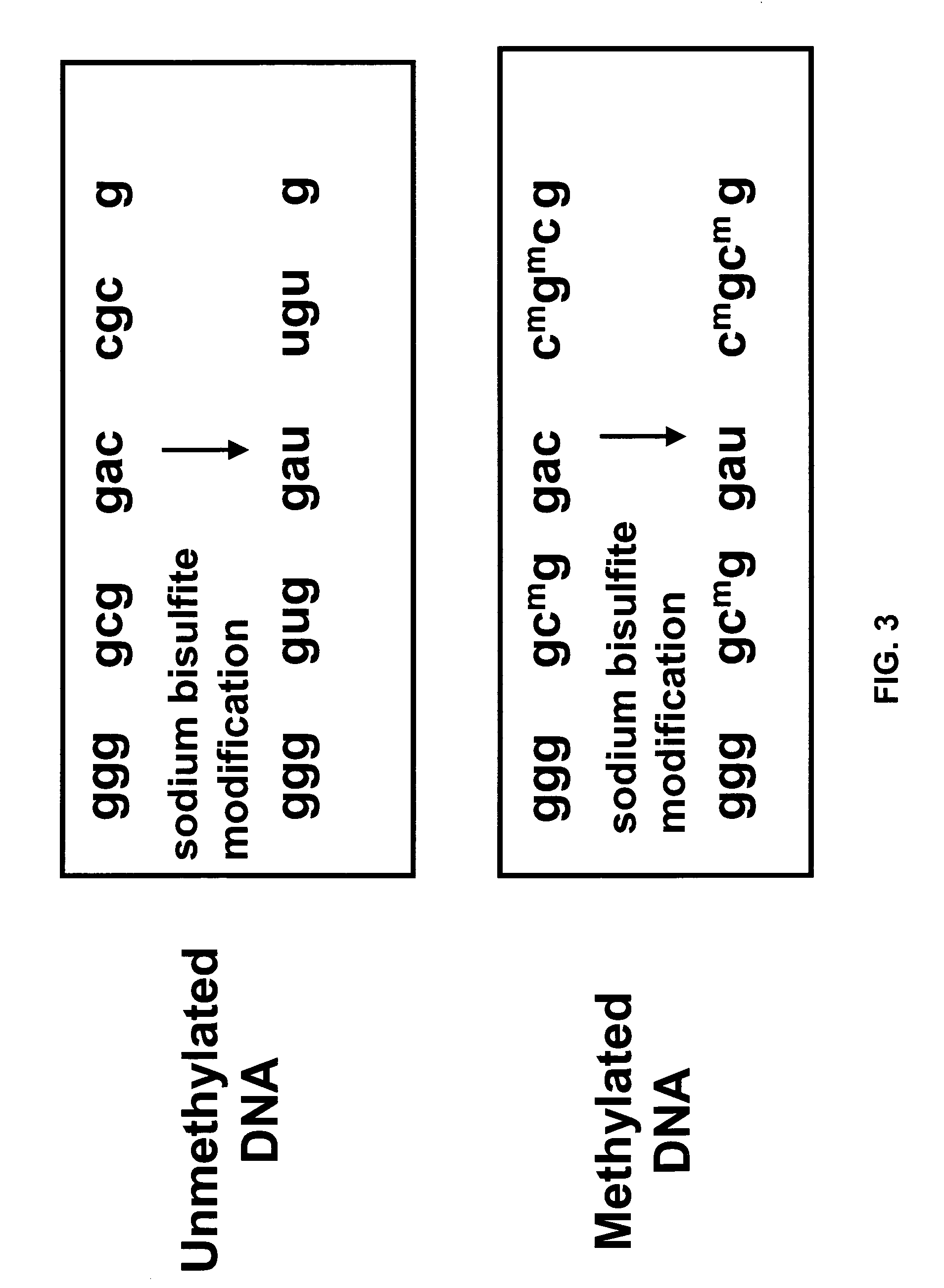
Method for characterizing, classifying and differentiating tissues and cell types, for predicting the behavior of tissues and groups of cells, and for identifying genes with changed expression. The method involves obtaining genomic DNA from a tissue sample, the genomic DNA subsequently being subjected to shearing, cleaved by means of a restriction endonuclease or not treated by either one of these methods. The base cytosine, but not 5-methylcytosine, from the thus-obtained genomic DNA is then converted into uracil by treatment with a bisulfite solution. Fractions of the thus-treated genomic DNA are then amplified using either very short or degenerated oligonucleotides or oligonuclcotides which are complementary to adaptor oligonucleotides that have been ligated to the ends of the cleaved DNA. The quantity of the remaining cytosines on the guanine-rich DNA strand and / or the quantity of guanines on the cytosine-rich DNA strand from the amplified fractions are then detected by hybridization or polymerase reaction, which quantities are such that the data generated thereby and automatically applied to a processing algorithm allow the drawing of conclusions concerning the phenotype of the sample material.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Rare cell analysis using sample splitting and DNA tags
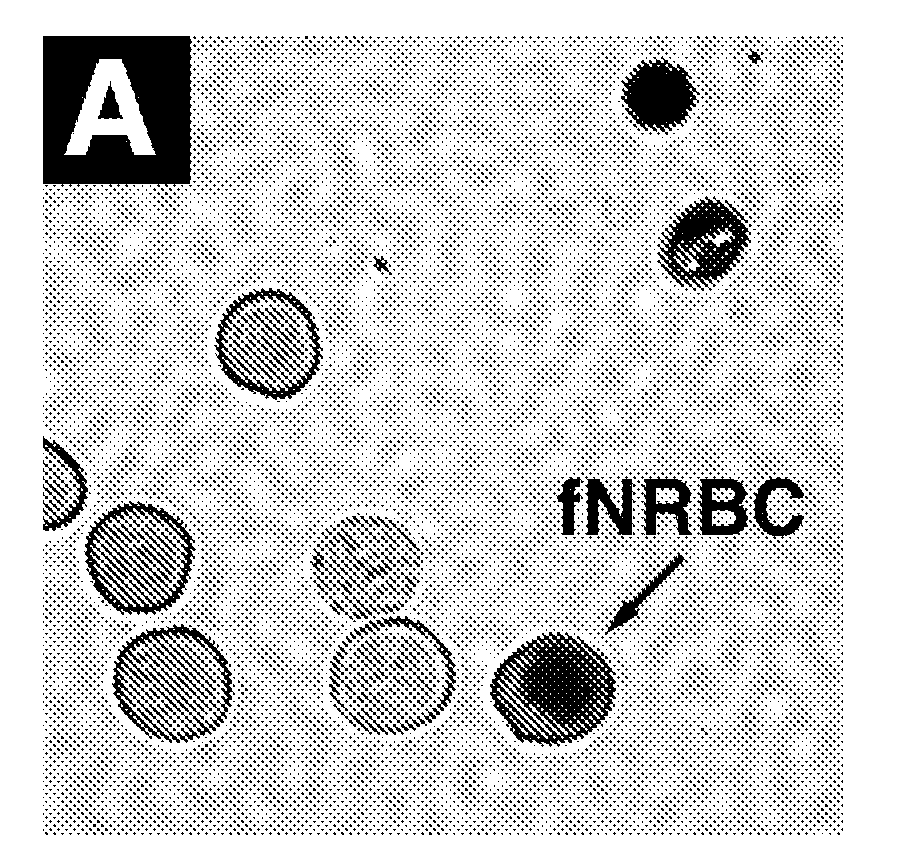
ActiveUS20080220422A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFetal abnormalityRare cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, e.g. aneuploidy. The present invention involves labeling regions of genomic DNA in each cell in said mixed sample with different labels wherein each label is specific to each cell and quantifying the labeled regions of genomic DNA from each cell in the mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying labeled DNA polymorphisms from each cell in the mixed sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC +2
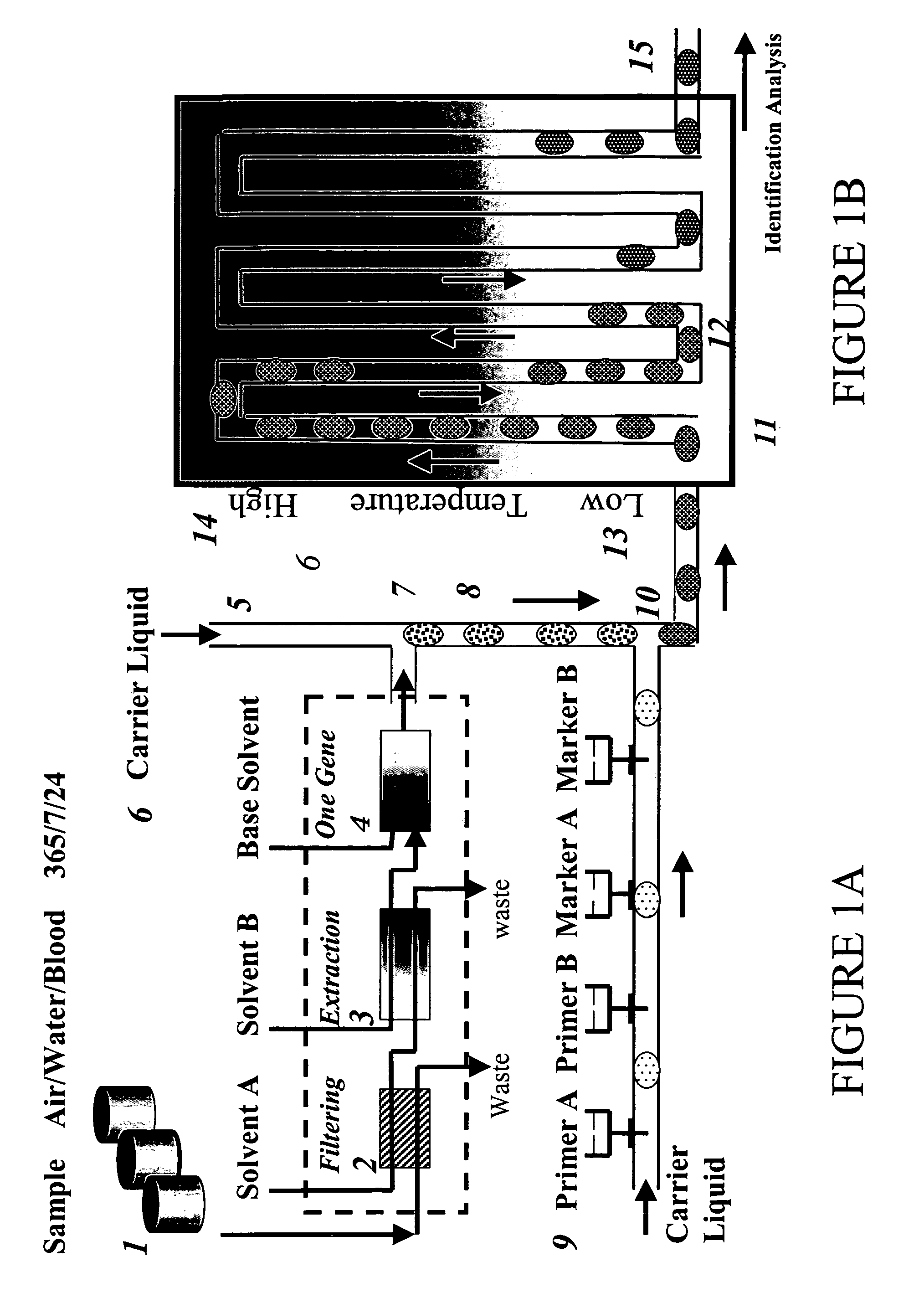
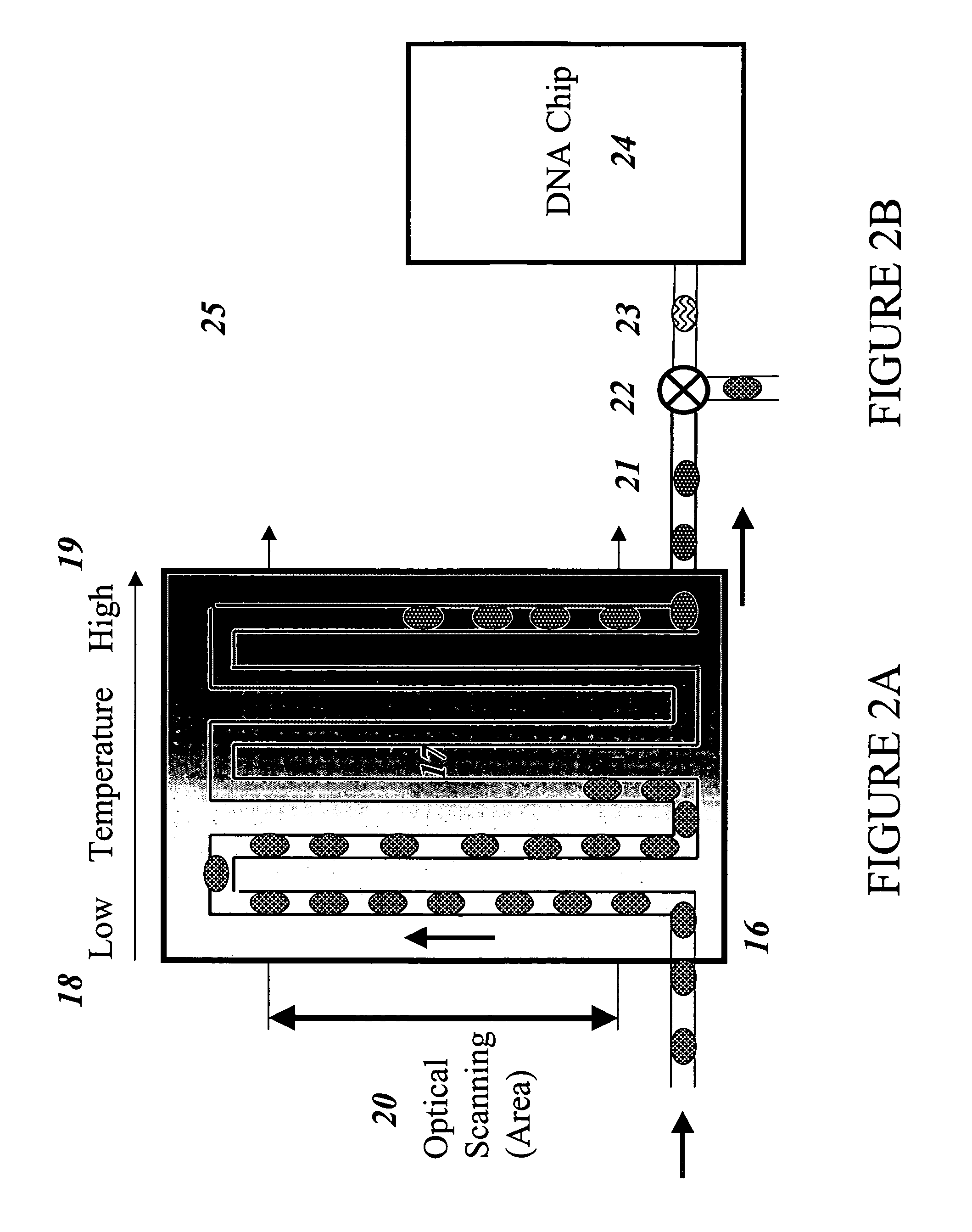
Devices and methods for monitoring genomic DNA of organisms
InactiveUS7604938B2Low costAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNADna amplification
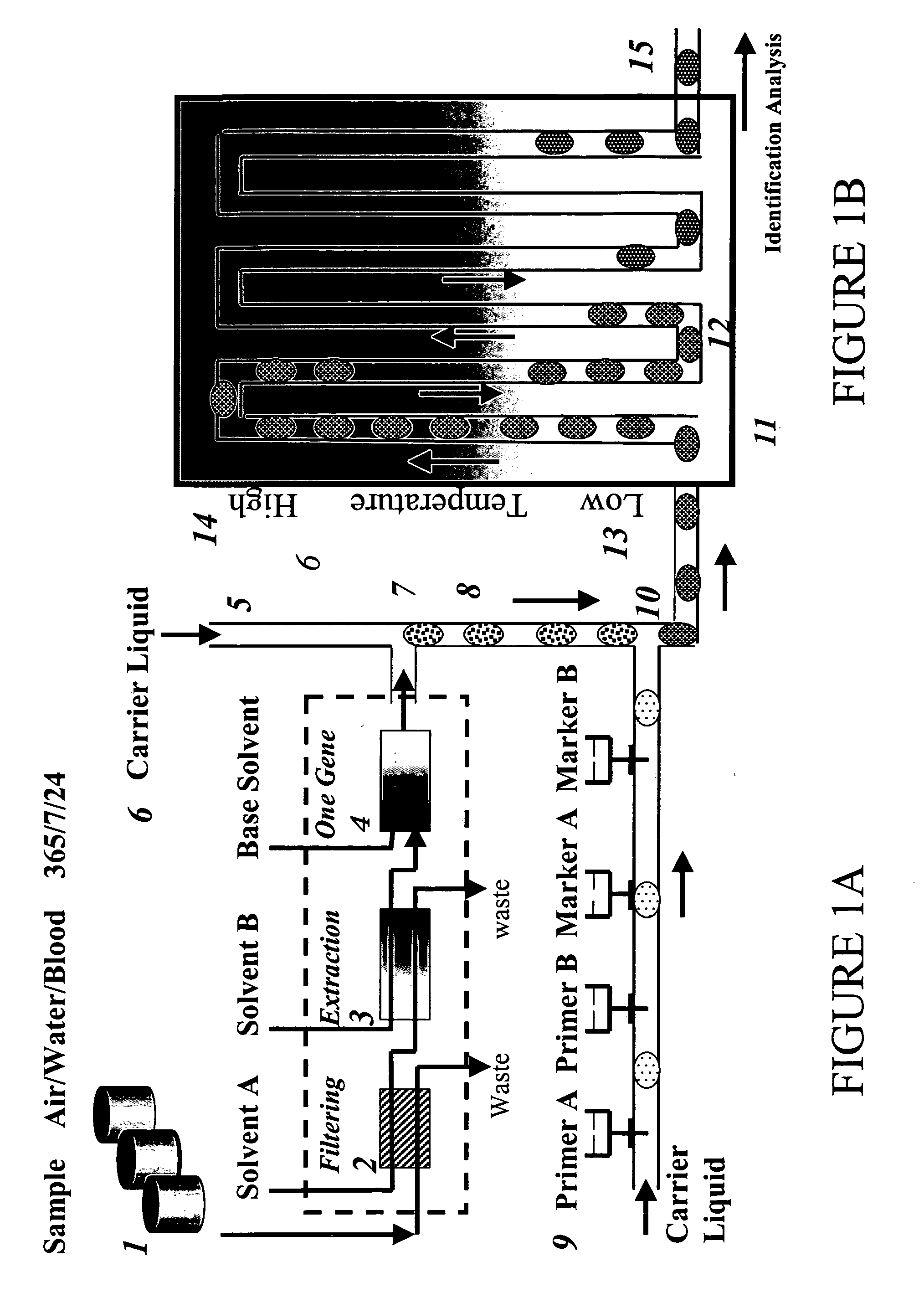
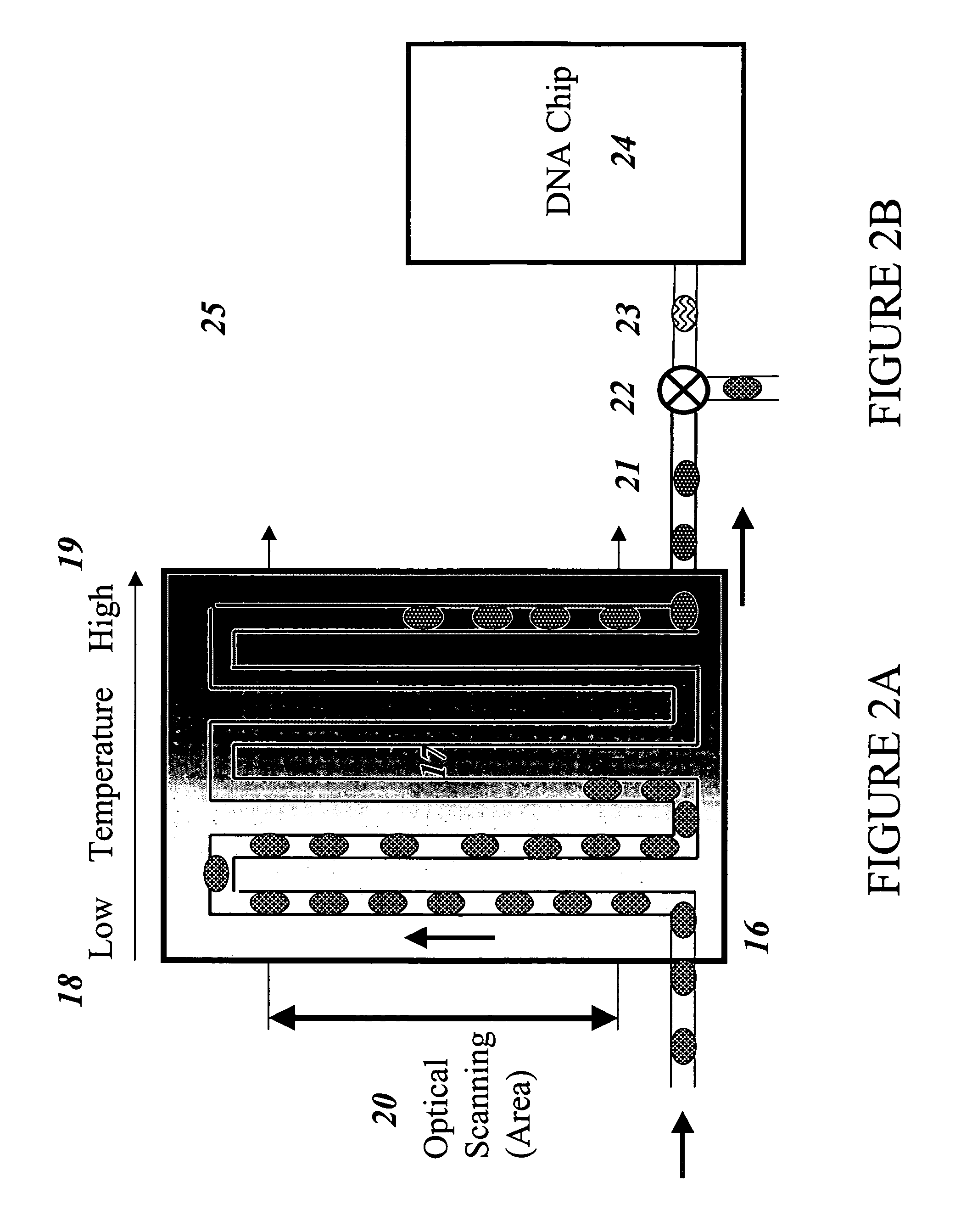
The invention provides an apparatus that can be used in methods of preparing, amplifying, detecting, and / or optionally selecting for further analysis the genomic material from an organism for the rapid detection and / or classification of an organism in a sample (e.g., screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or optionally further analyzing, e.g., sequencing, the genomic material of the organism). The invention further provides methods of using the apparatus, e.g., in combination with novel SGP primers for improved use in waveform-profiling methods of DNA amplification. It is an object of the invention to provide an apparatus for fully automated analysis of genomic material, and multiple methods of using the apparatus that are beneficial to society, e.g., the apparatus may be used in methods of screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or selecting genomic material for further analysis (e.g., sequencing) in relation to monitoring a source for the presence of contaminating organisms.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Oligonucleotides for genotyping thymidylate synthase gene
ActiveUS20070031829A1Sensitive and convenient detectionEasy to aimSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenomic DNA
Oligonucleotides for genotyping the thymidylate synthase gene are provided. The number of tandem repeats in the promoter region of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the hybridization of an oligonucleotide of the invention to the genomic DNA of a subject. Therefore, the genotype of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the number of tandem repeats. The genotype relates to the responsiveness of a subject towards an antitumor agent.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Devices and methods for monitoring genomic DNA of organisms
InactiveUS20060257893A1Low costAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNADna amplification
The invention provides an apparatus that can be used in methods of preparing, amplifying, detecting, and / or optionally selecting for further analysis the genomic material from an organism for the rapid detection and / or classification of an organism in a sample (e.g., screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or optionally further analyzing, e.g., sequencing, the genomic material of the organism). The invention further provides methods of using the apparatus, e.g., in combination with novel SGP primers for improved use in waveform-profiling methods of DNA amplification. It is an object of the invention to provide an apparatus for fully automated analysis of genomic material, and multiple methods of using the apparatus that are beneficial to society, e.g., the apparatus may be used in methods of screening for, identifying, quantifying, and / or selecting genomic material for further analysis (e.g., sequencing) in relation to monitoring a source for the presence of contaminating organisms.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
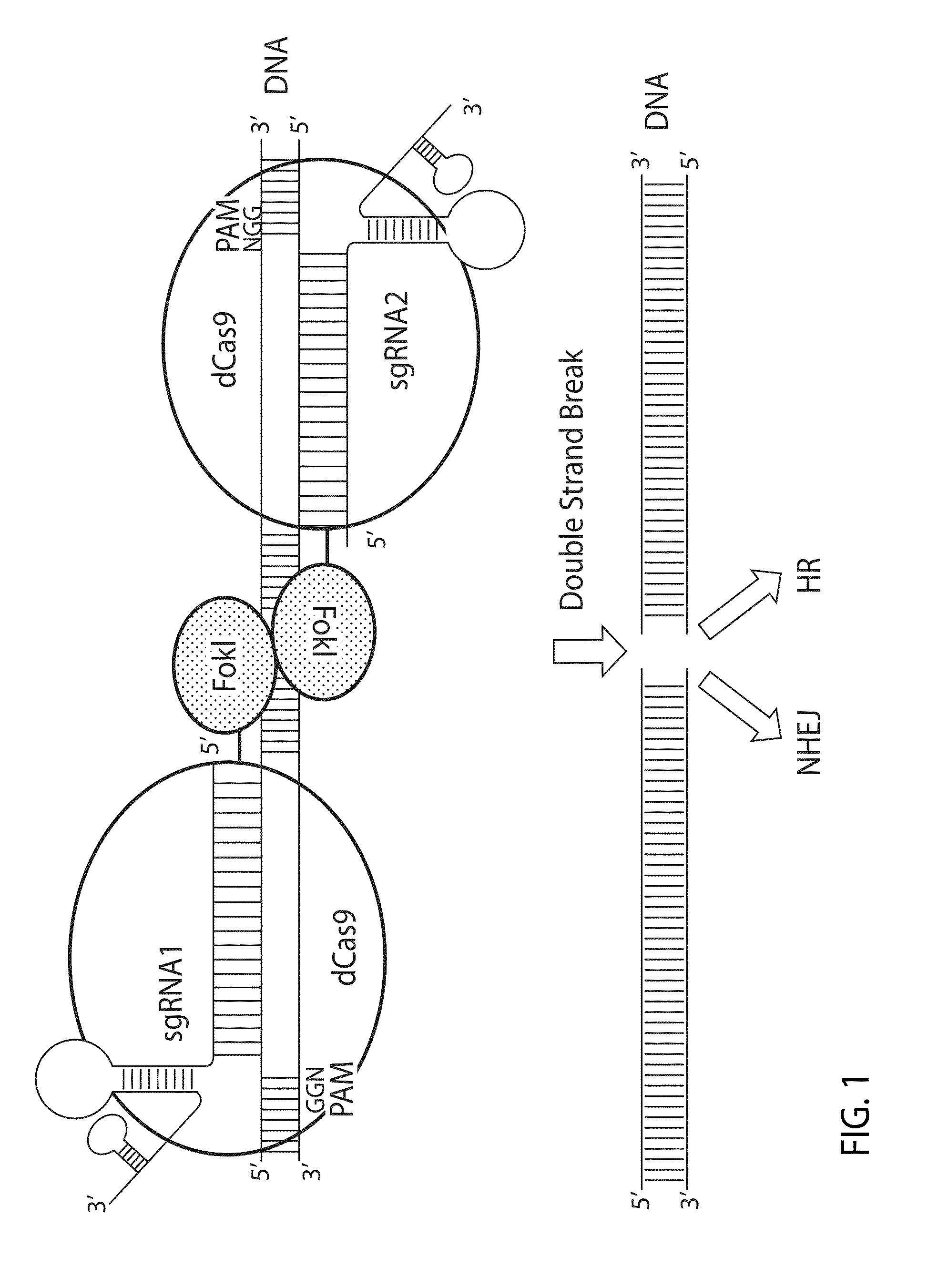
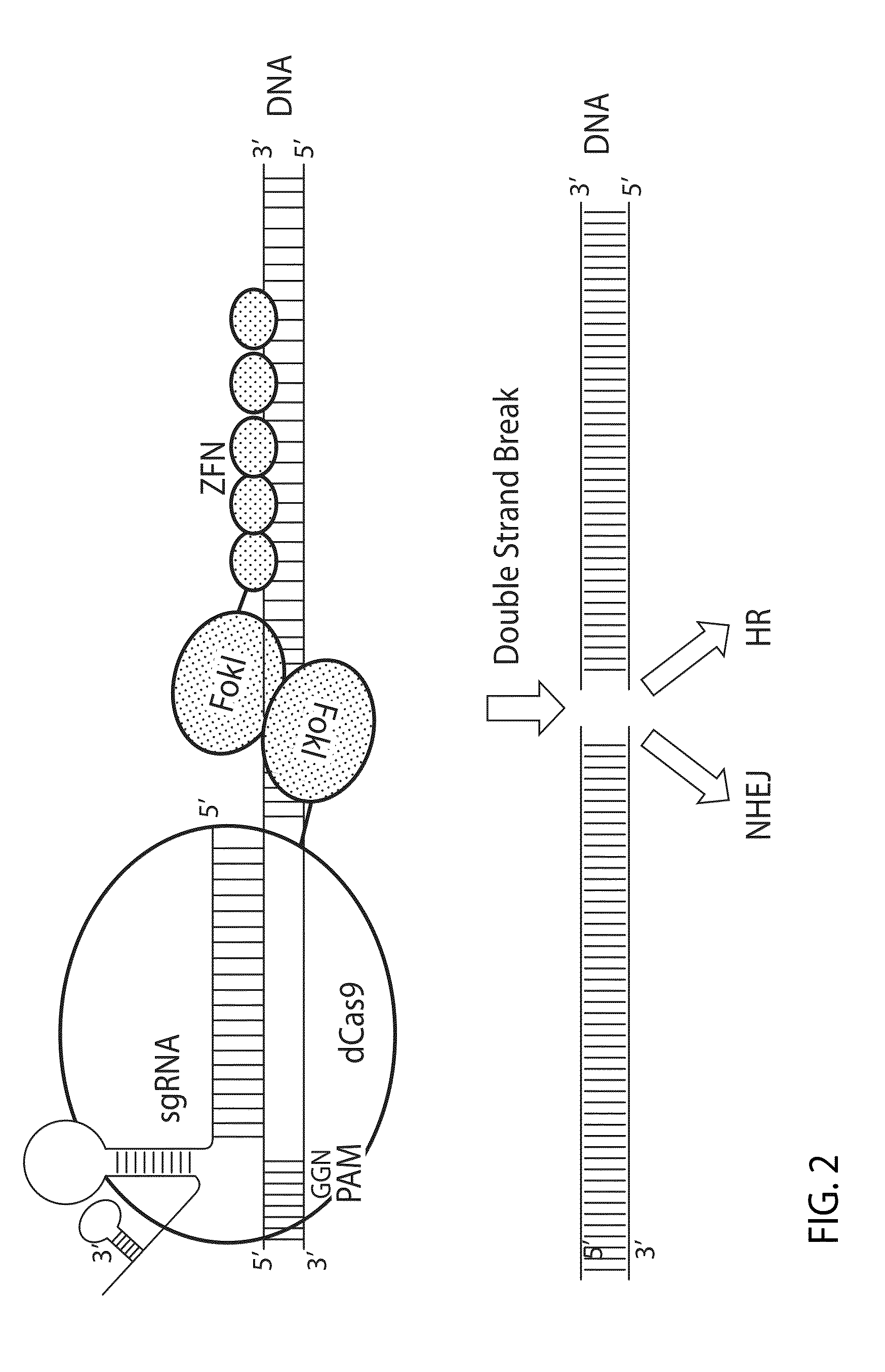
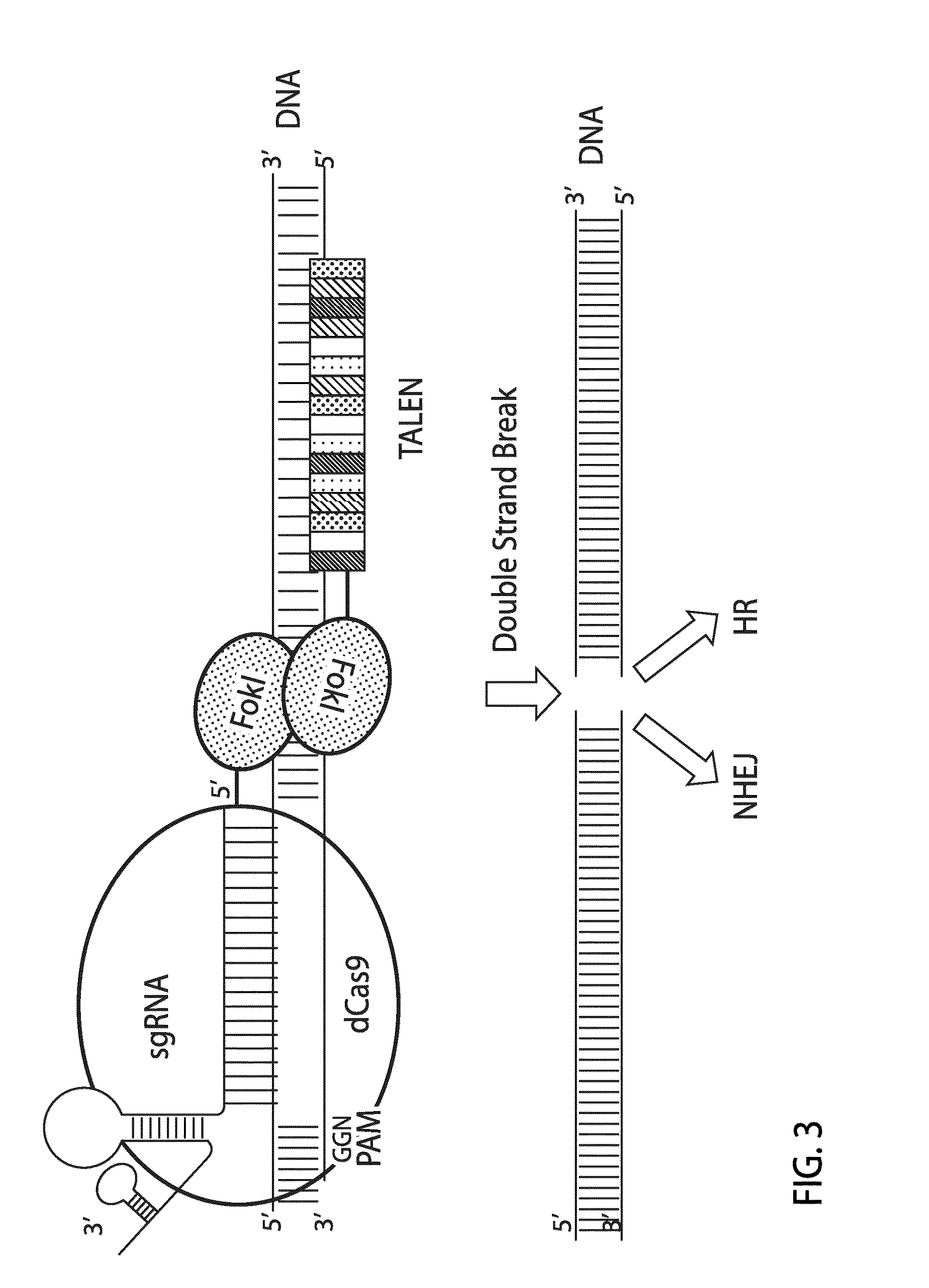
Crispr/cas system-based novel fusion protein and its applications in genome editing
An inactive CRISPR / Cas system-based fusion protein and its applications in gene editing are disclosed. More particularly, chimeric fusion proteins including an inCas fused to a DNA modifying enzyme and methods of using the chimeric fusion proteins in gene editing are disclosed. The methods can be used to induce double-strand breaks and single-strand nicks in target DNAs, to generate gene disruptions, deletions, point mutations, gene replacements, insertions, inversions and other modifications of a genomic DNA within cells and organisms.
Owner:SAGE LABS
Apparatus for and method of processing biological samples
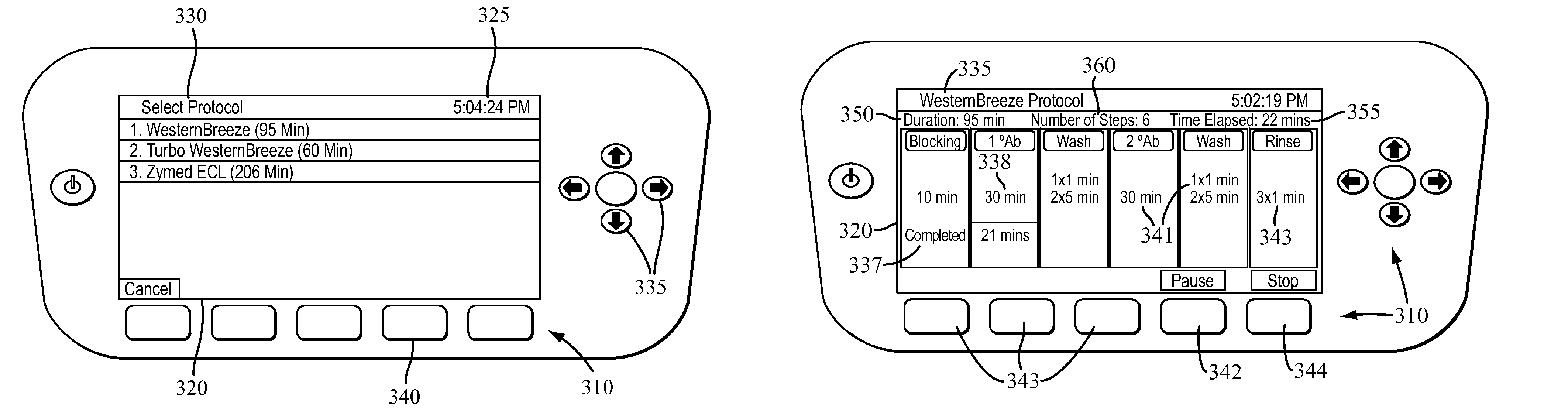
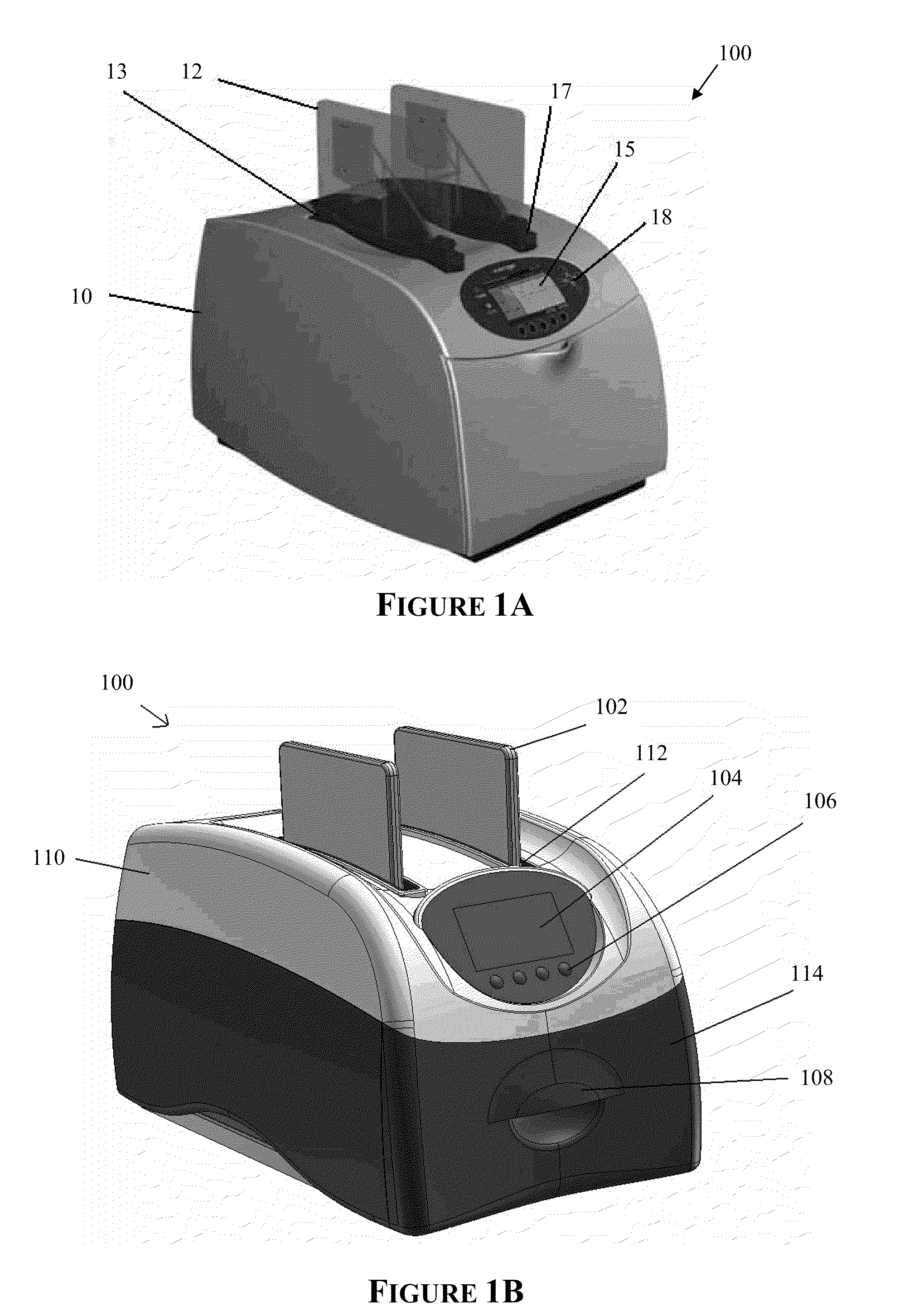
The present invention provides systems, devices, apparatuses and methods for automated bioprocessing. Examples of protocols and bioprocessing procedures suitable for the present invention include but are not limited to: immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, recombinant protein isolation, nucleic acid separation and isolation, protein labeling, separation and isolation, cell separation and isolation, food safety analysis and automatic bead based separation. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods of western blot processing. Other embodiments include automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for separation, preparation and purification of nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA or fragments thereof, including plasmid DNA, genomic DNA, bacterial DNA, viral DNA and any other DNA, and for automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for processing, separation and purification of proteins, peptides and the like.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods and compositions for long fragment read sequencing
ActiveUS8592150B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAComputational biology
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for long fragment read sequencing. The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for preparing long fragments of genomic DNA, for processing genomic DNA for long fragment read sequencing methods, as well as software and algorithms for processing and analyzing sequence data.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
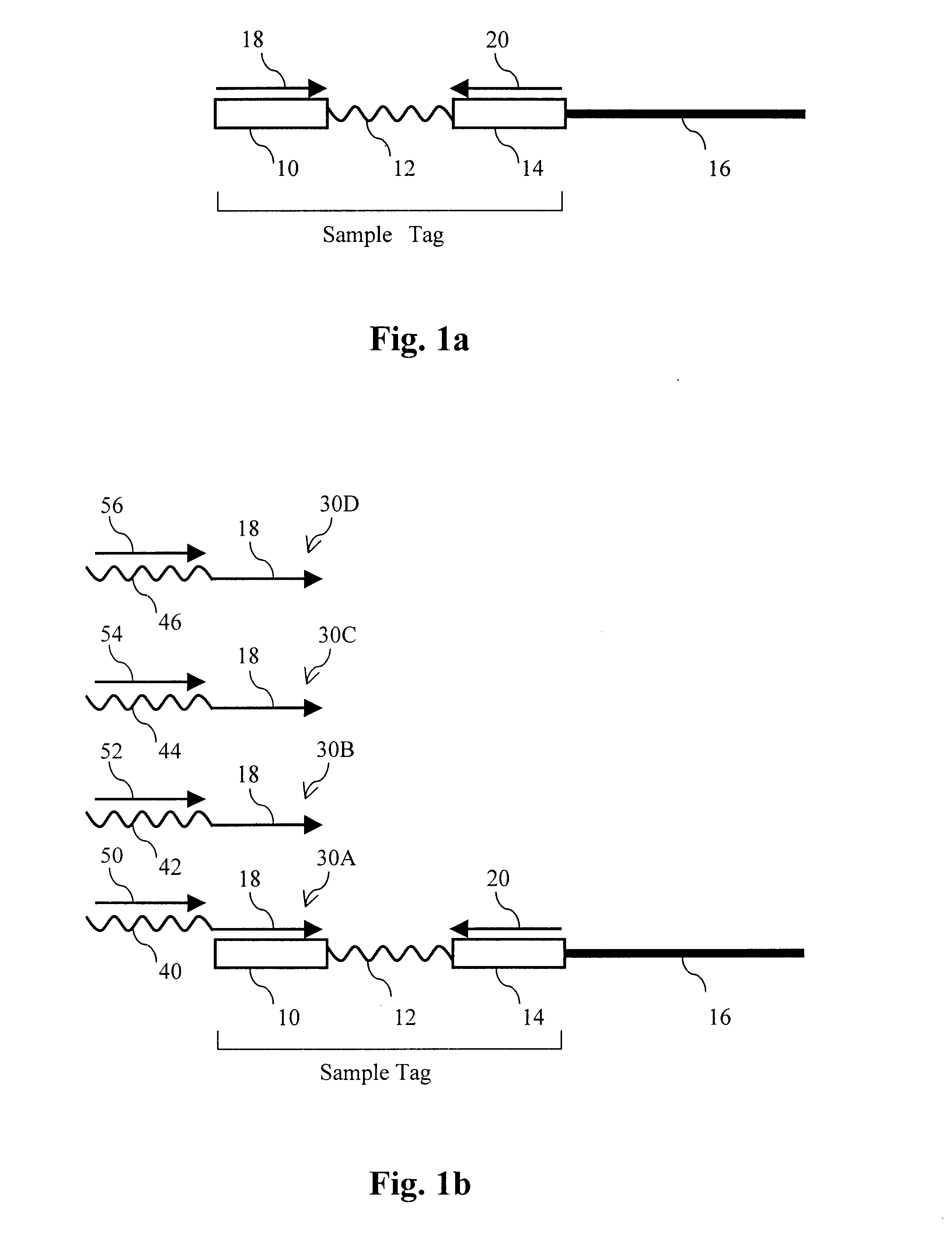
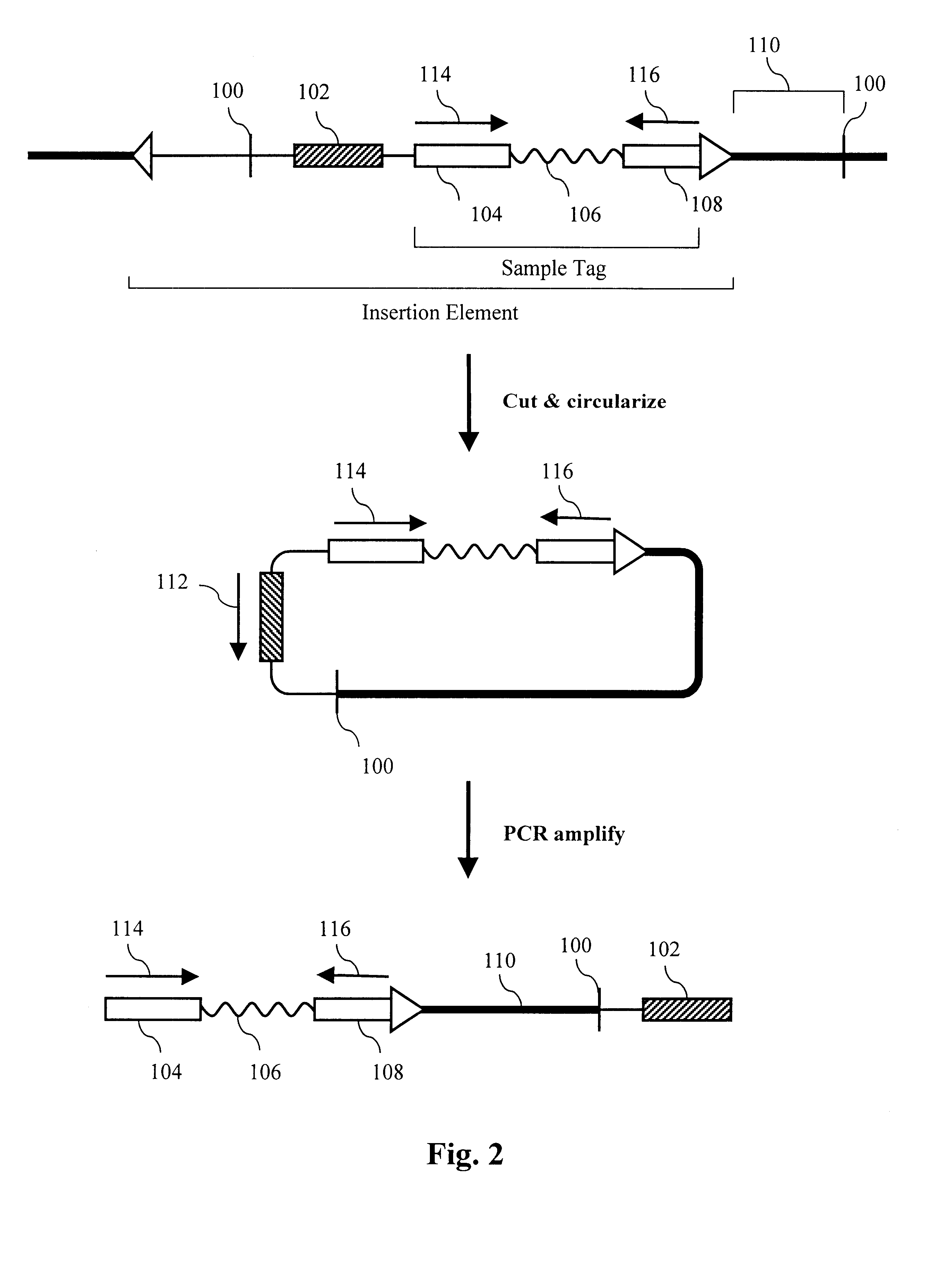
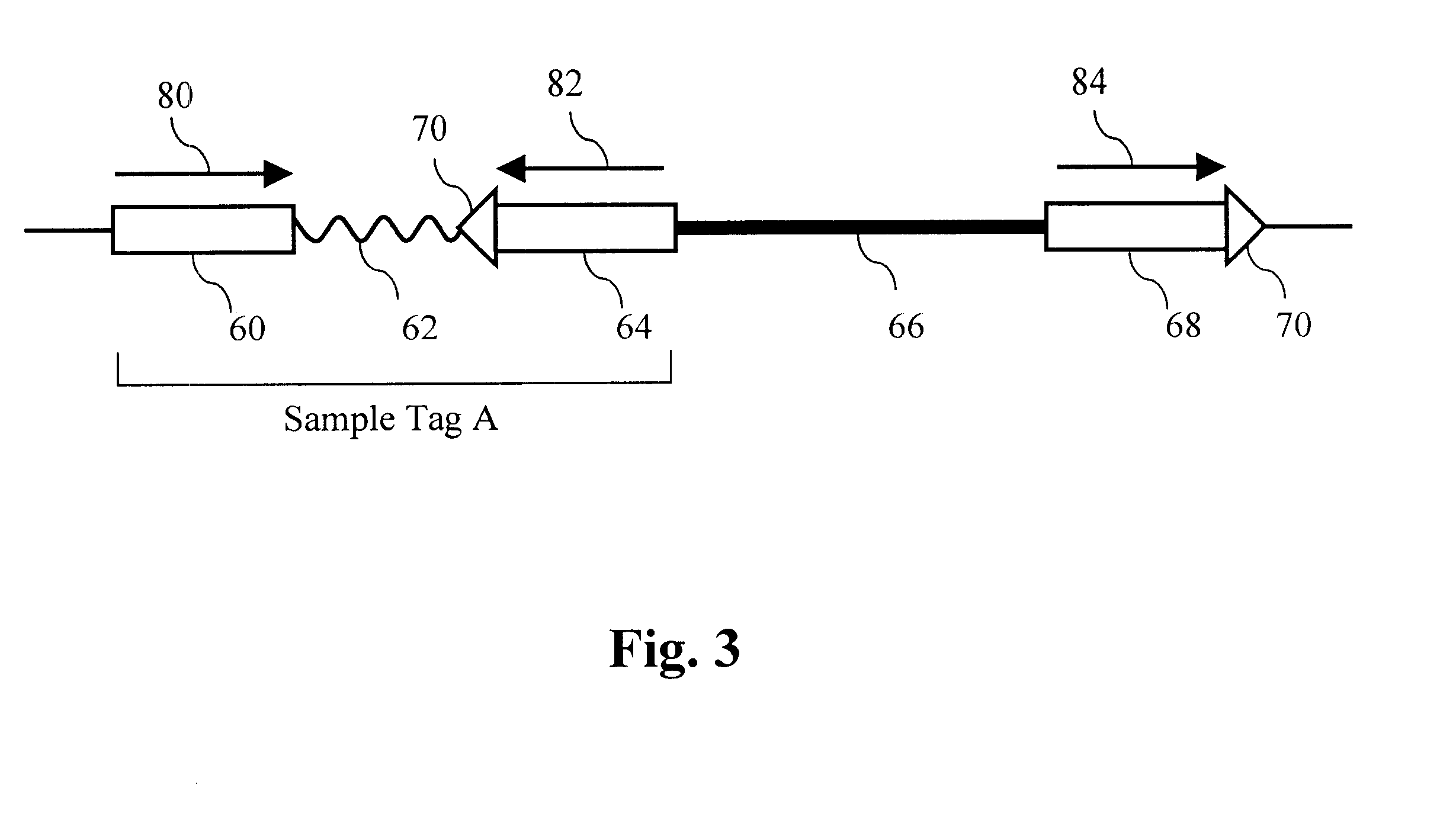
Parallel methods for genomic analysis
The present invention provides parallel methods for determining nucleotide sequences and physical maps of polynucleotides associated with sample tags. This information can be used to determine the chromosomal locations of sample-tagged polynucleotides. In one embodiment, the polynucleotides are derived from genomic DNA coupled to insertion elements. As a result, the invention also provides parallel methods for locating the integration sites of insertion elements in the genome.
Owner:STRATHMANN MICHAEL P
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
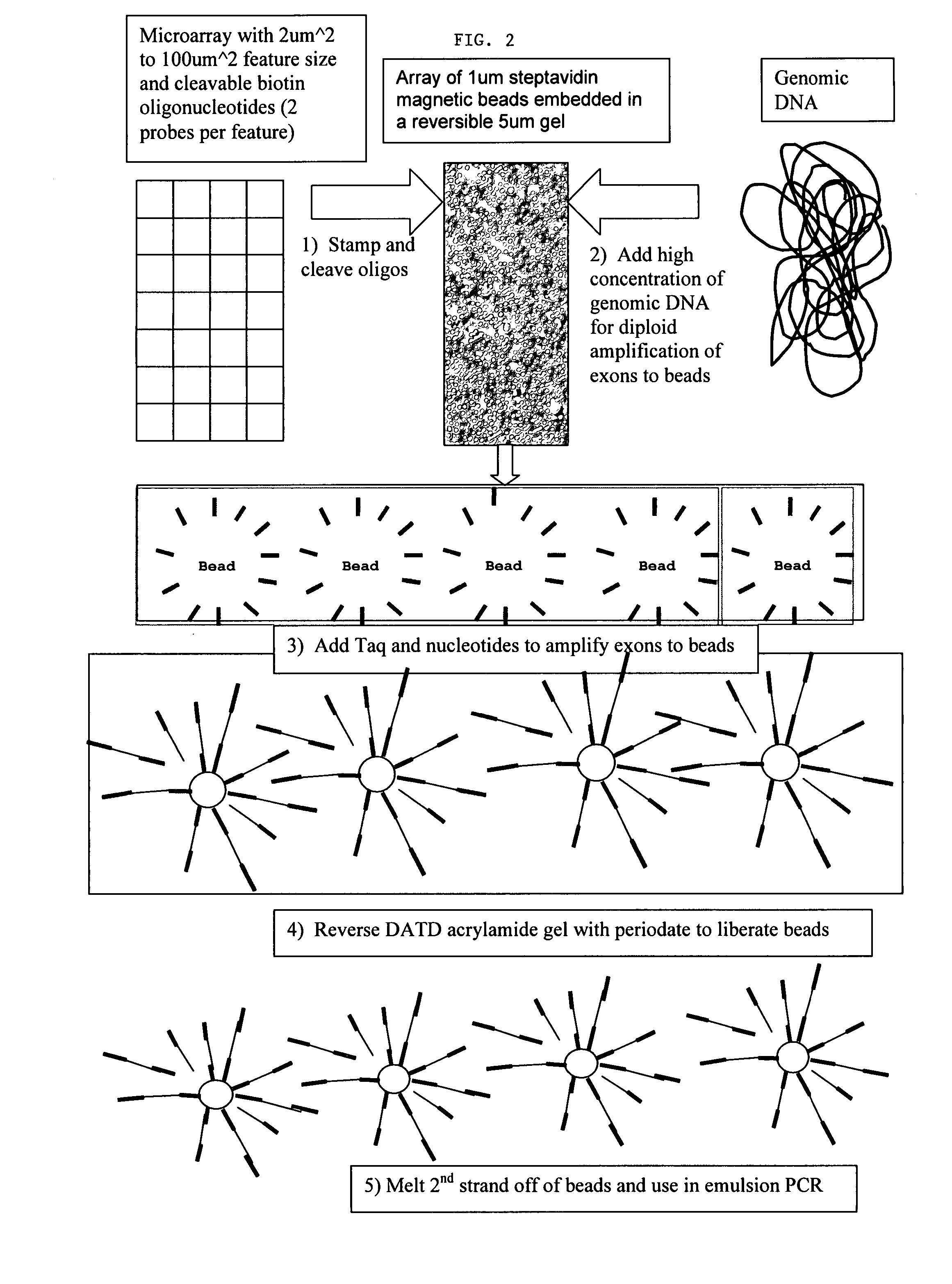
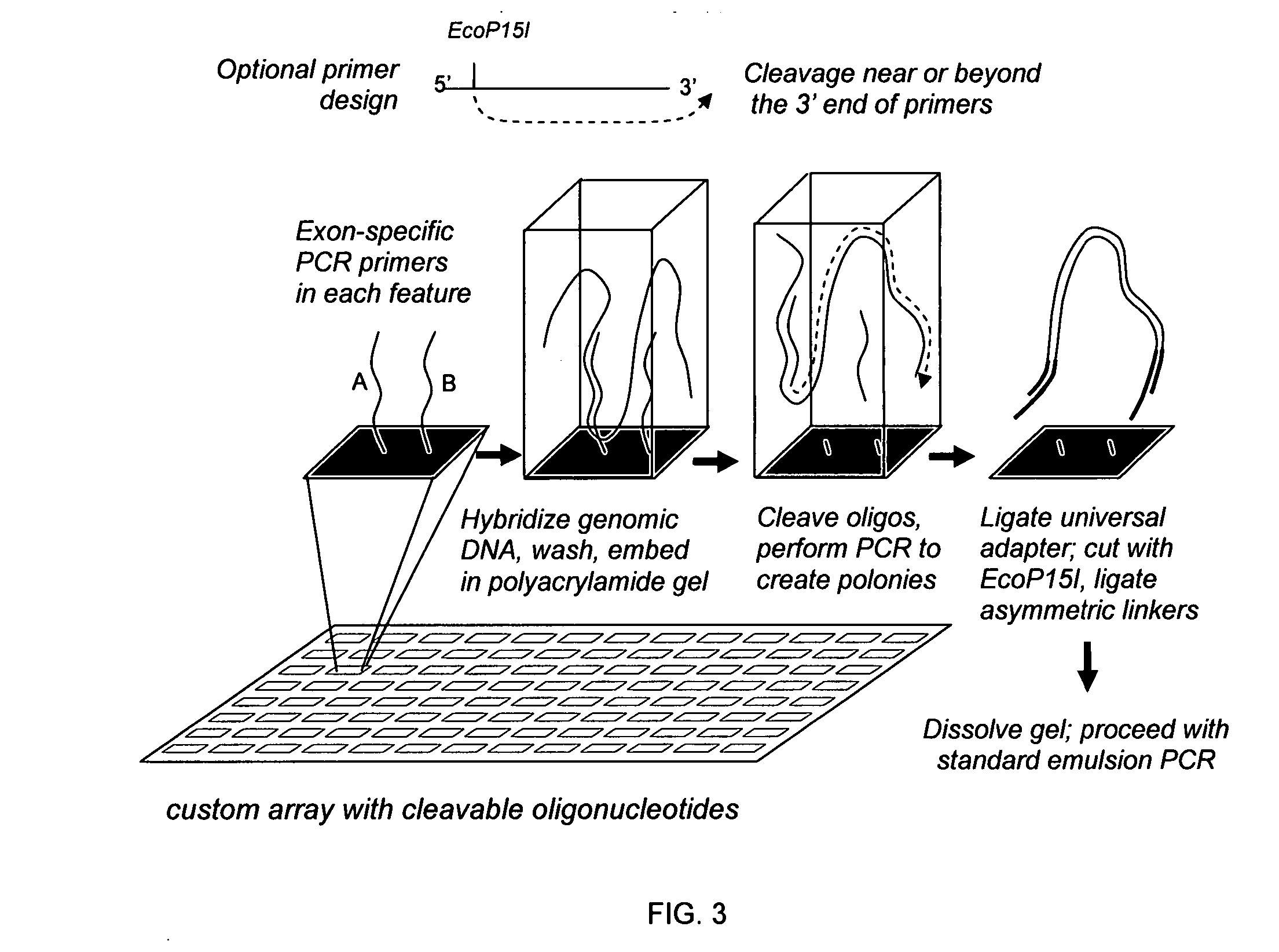
Directed enrichment of genomic DNA for high-throughput sequencing
InactiveUS20070231823A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNANucleotide
The present invention provides microarrays of oligonucleotide primer pairs, and in particular, microarrays of primers that comprise at least one cleavable linkage. Also provided are methods to capture oligonucleotide primer pairs from one or more microarrays, and methods to use the captured oligonucleotide primer pairs, such as for amplification of a target polynucleotide sequence. In addition, methods of using a microarray to isolate, purify and / or amplify a target polynucleotide are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED GENETIC ANALYSIS CORP
Methods and compositions for generating and amplifying DNA libraries for sensitive detection and analysis of DNA methylation
InactiveUS20050202490A1Reduce stepsReduce stretchMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA methylationCell free
The present invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for obtaining epigenetic information, such as DNA methylation patterns, through the preparation, amplification and analysis of Methylome libraries. In several aspects of the present invention, there are methods based on methylation-dependent enrichment or depletion of genomic DNA isolated from cellular and cell-free sources. In additional embodiments, there are methods and compositions for single-step high throughput preparations of Methylome libraries.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Methods for the isolation of nucleic acids and for quantitative DNA extraction and detection for leukocyte evaluation in blood products
InactiveUS6958392B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole blood productWhite blood cell
A method for isolating nucleic acid which comprises:(a) applying a sample comprising cells containing nucleic acid to a filter, whereby the cells are retained as a retentate and contaminants are removed;(b) lysing the retentate from step (a) while the retentate is retained by the filter to form a cell lysate containing the nucleic acid;(c) filtering the cell lysate with the filter to retain the nucleic acid and remove remaining cell lysate;(d) optionally washing the nucleic acid retained by the filter; and(e) eluting the nucleic acid, wherein the filter composition and dimensions are selected so that the filter is capable of retaining the cells and the nucleic acid.Additionally, there is provided a substrate for lysing cells and purifying nucleic acid having a matrix and a coating and an integrity maintainer for maintaining the purified nucleic acid. Also provided is a method of purifying nucleic acid by applying a nucleic acid sample to a substrate having an anionic detergent affixed to a matrix, the substrate physically capturing the nucleic acid, bonding the nucleic acid to a substrate and generating a signal when the nucleic acid bonds to the substrate indicating the presence of the nucleic acid. A kit for purifying nucleic acid containing a coated matrix and an integrity maintenance provider for preserving the matrix and purifying nucleic acid is also provided. Further, there is provided a method for quantifying DNA, such as double-stranded or genomic DNA, isolated from cells, such as leukocytes to determine the numbers of leukocytes in a sample of leukoreduced blood.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
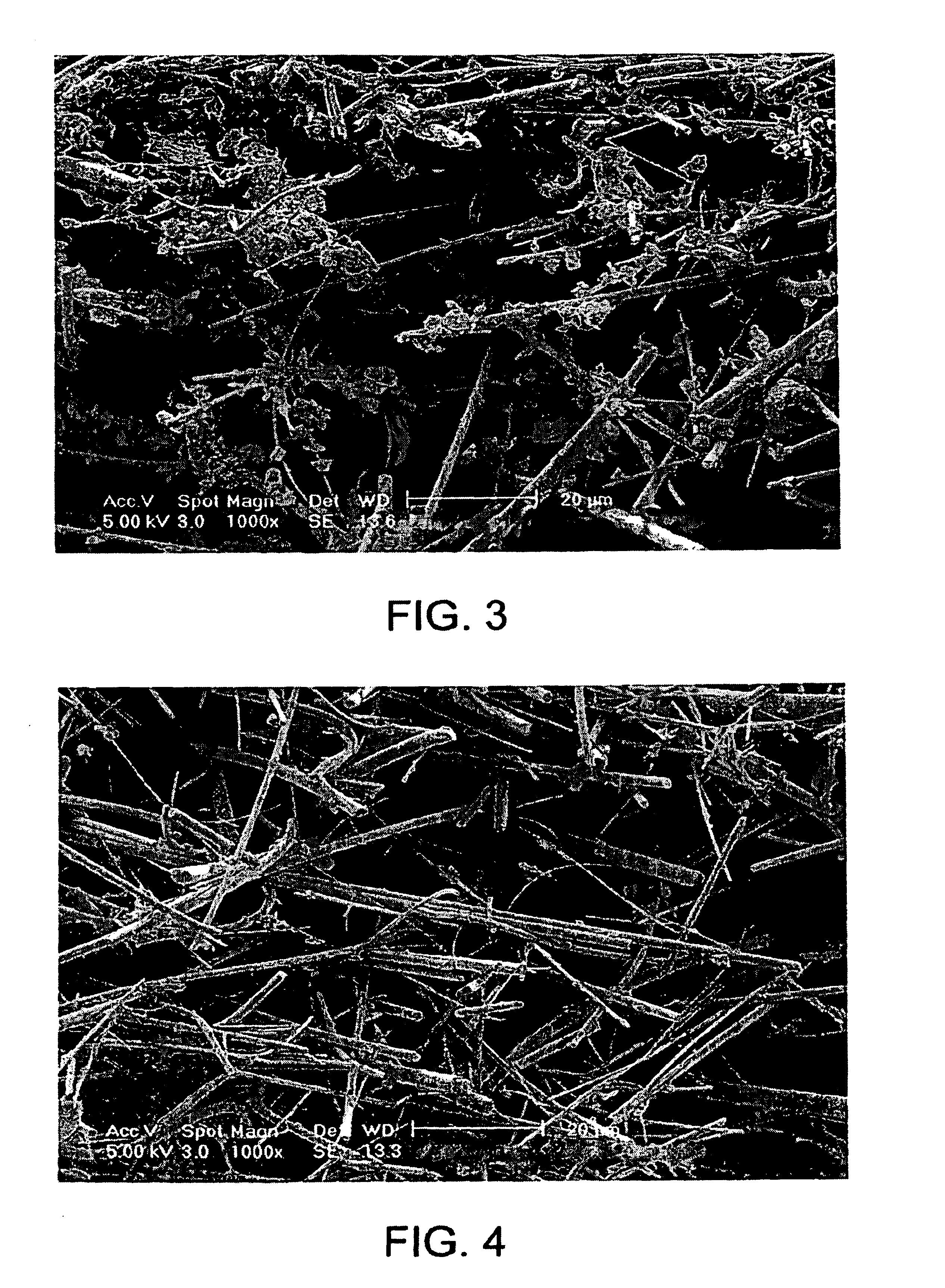
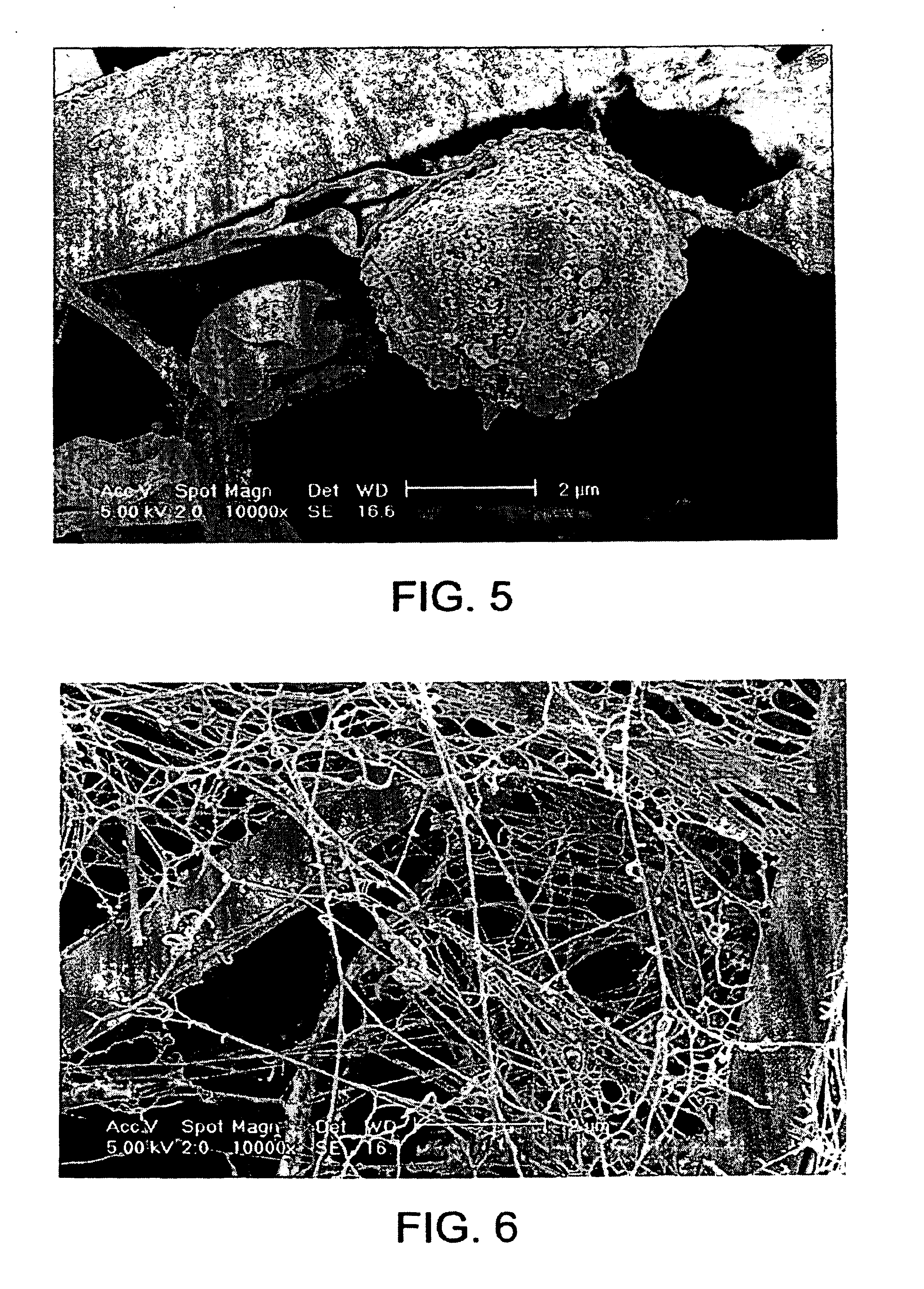
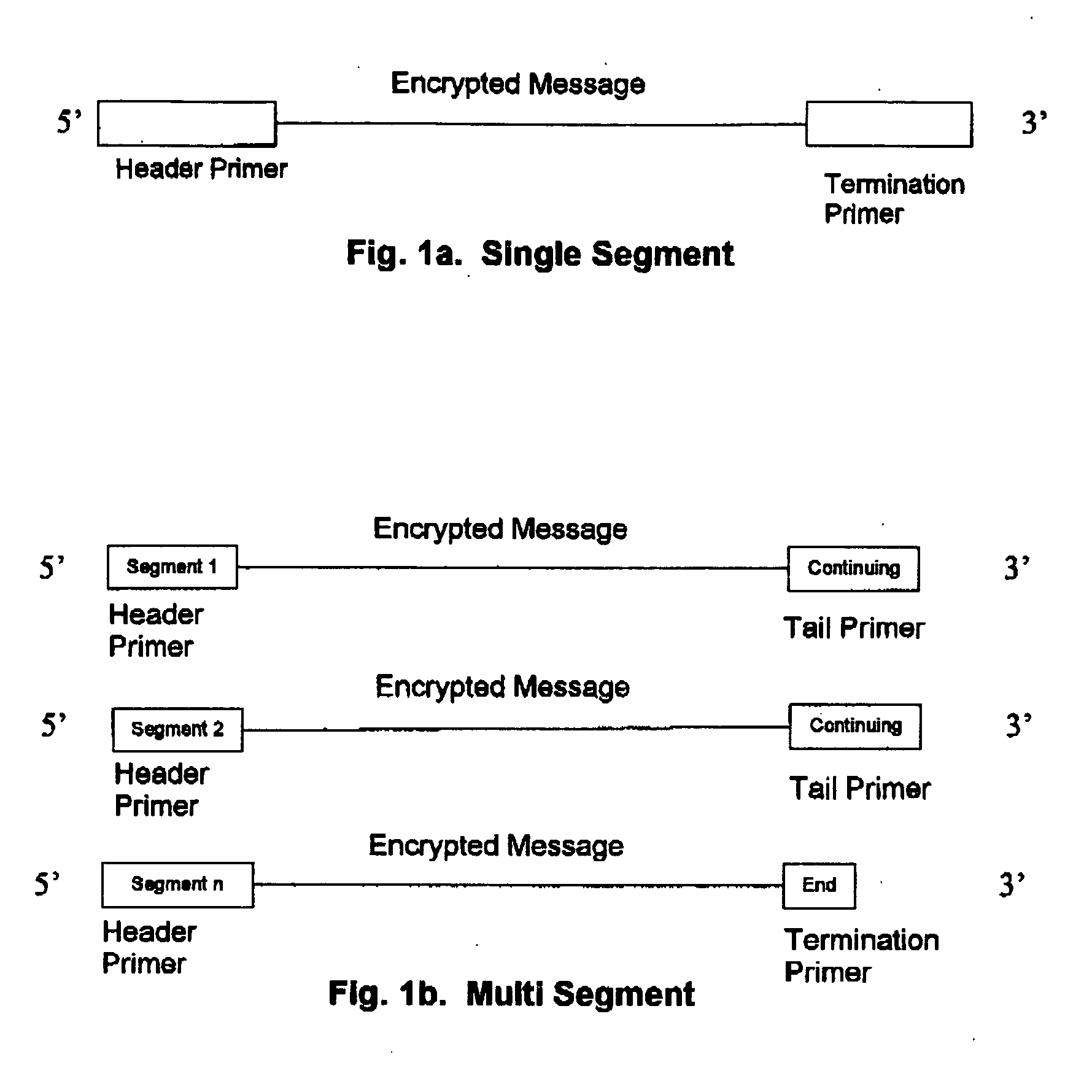
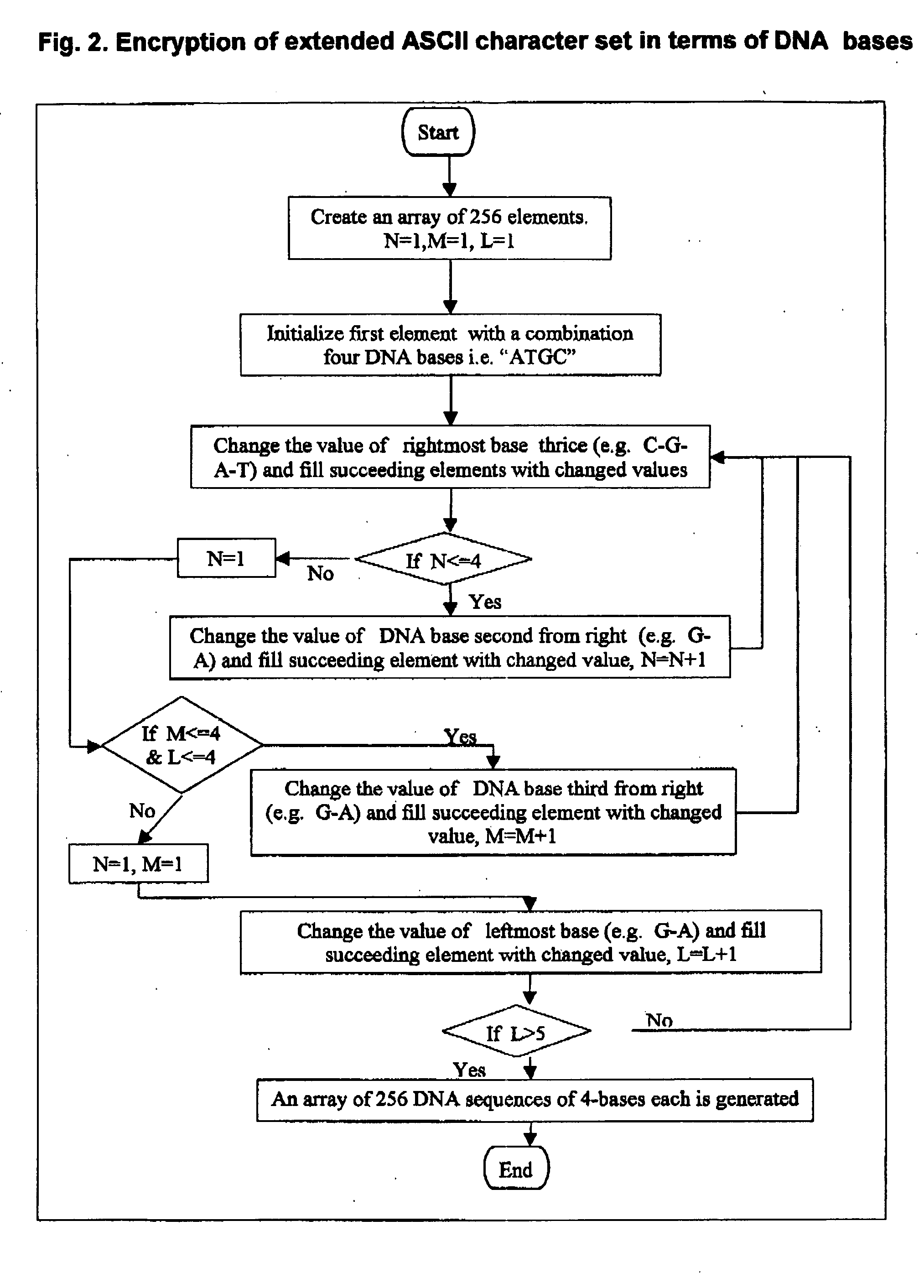
Method for storing information in DNA
InactiveUS20050053968A1Microbiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHuman DNA sequencingPresent method
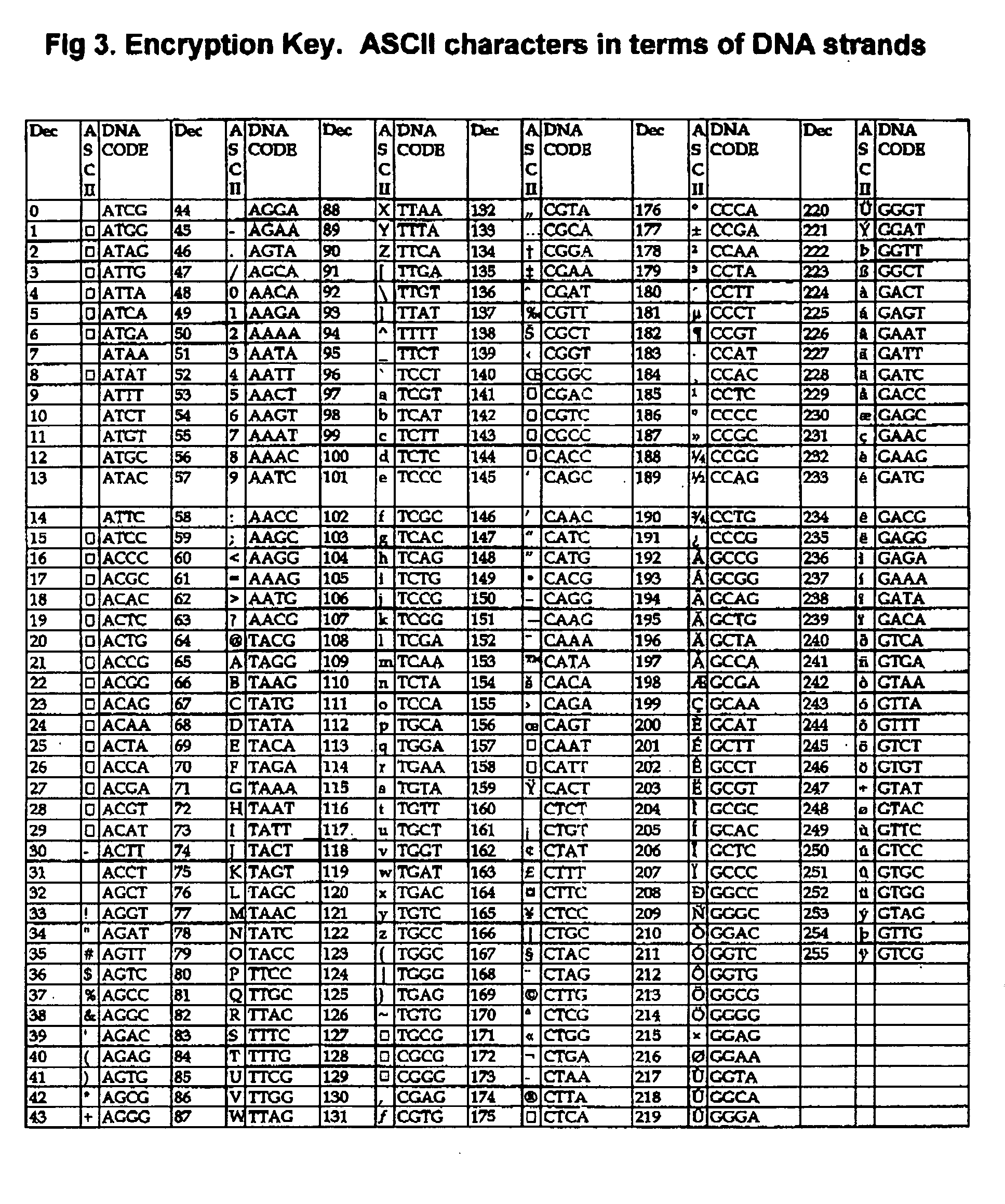
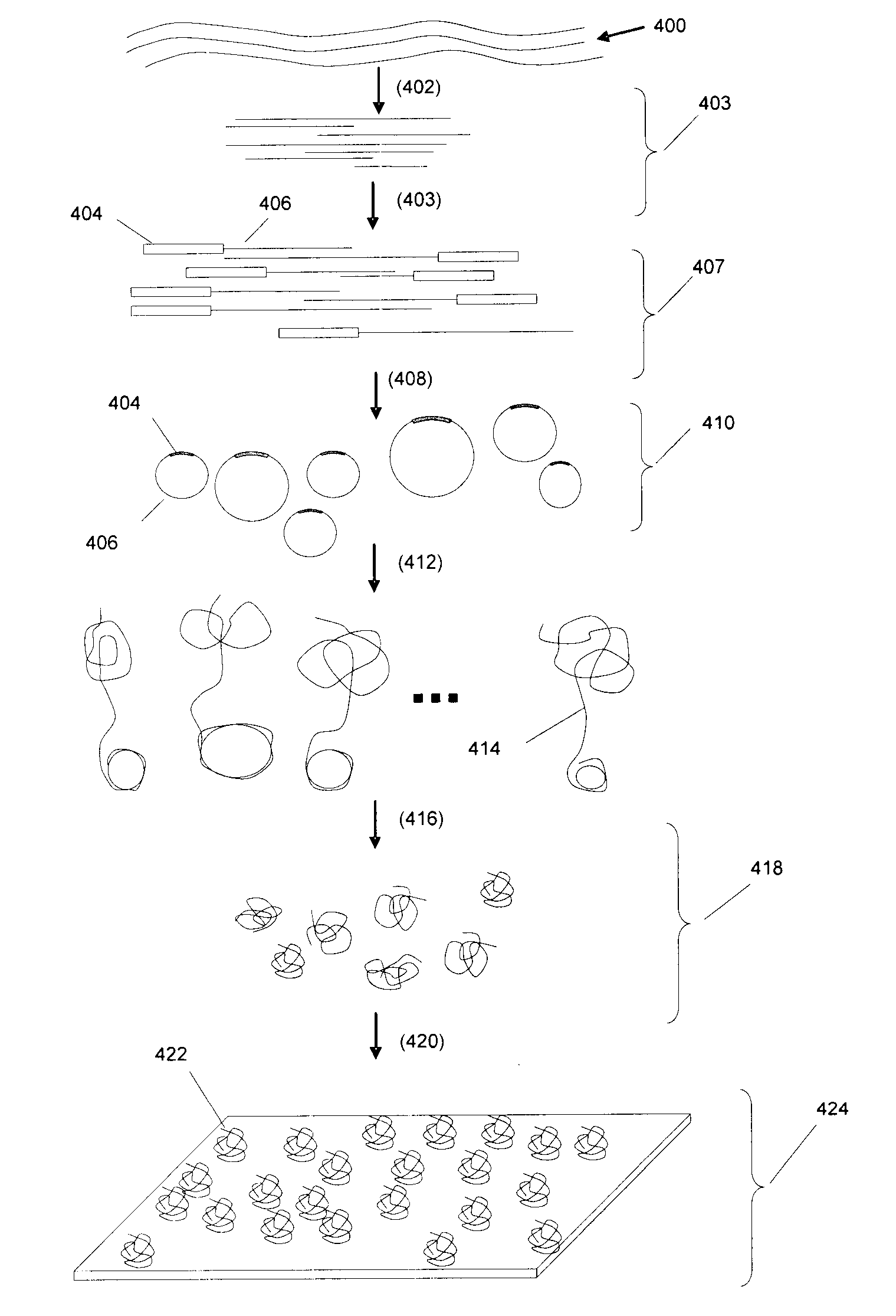
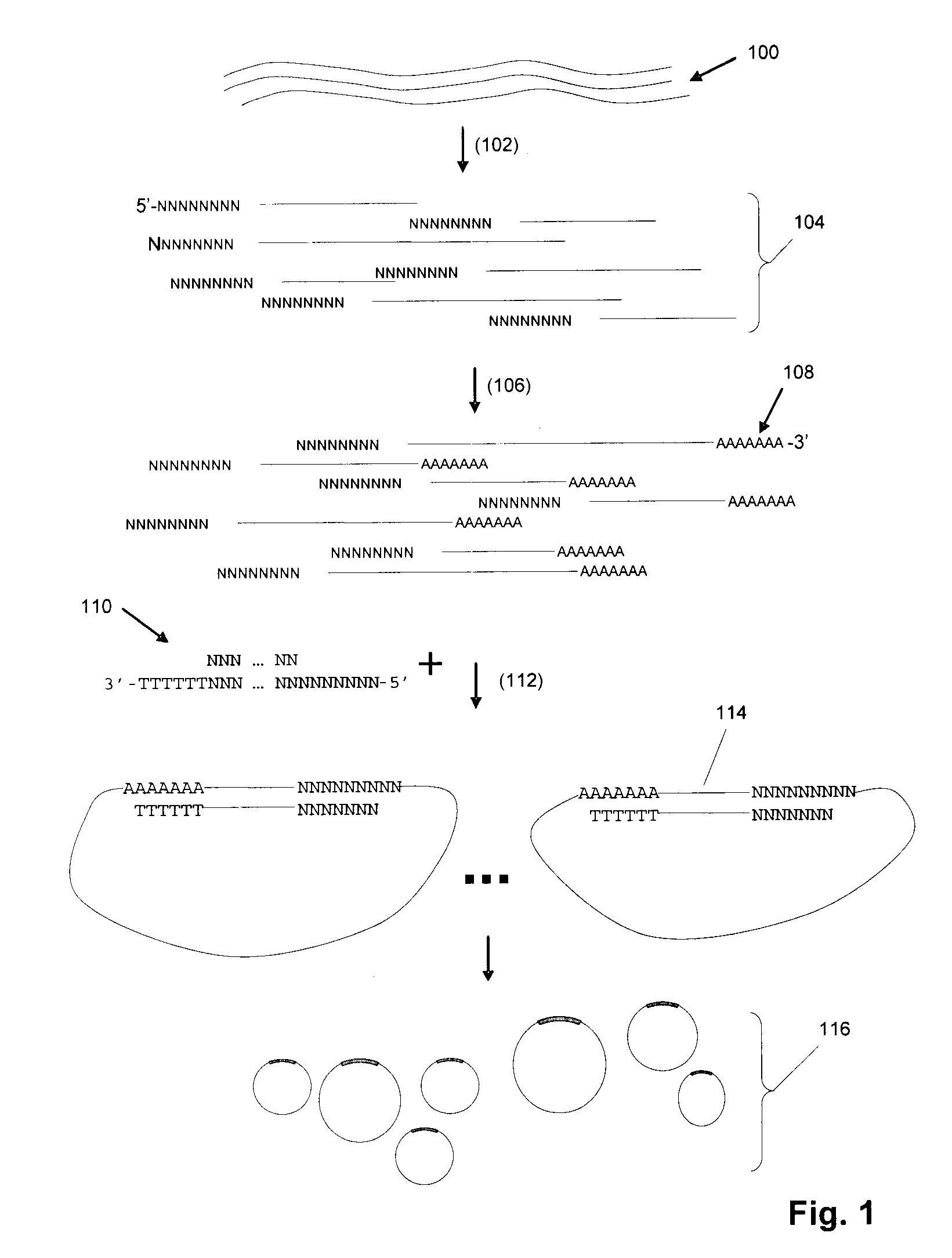
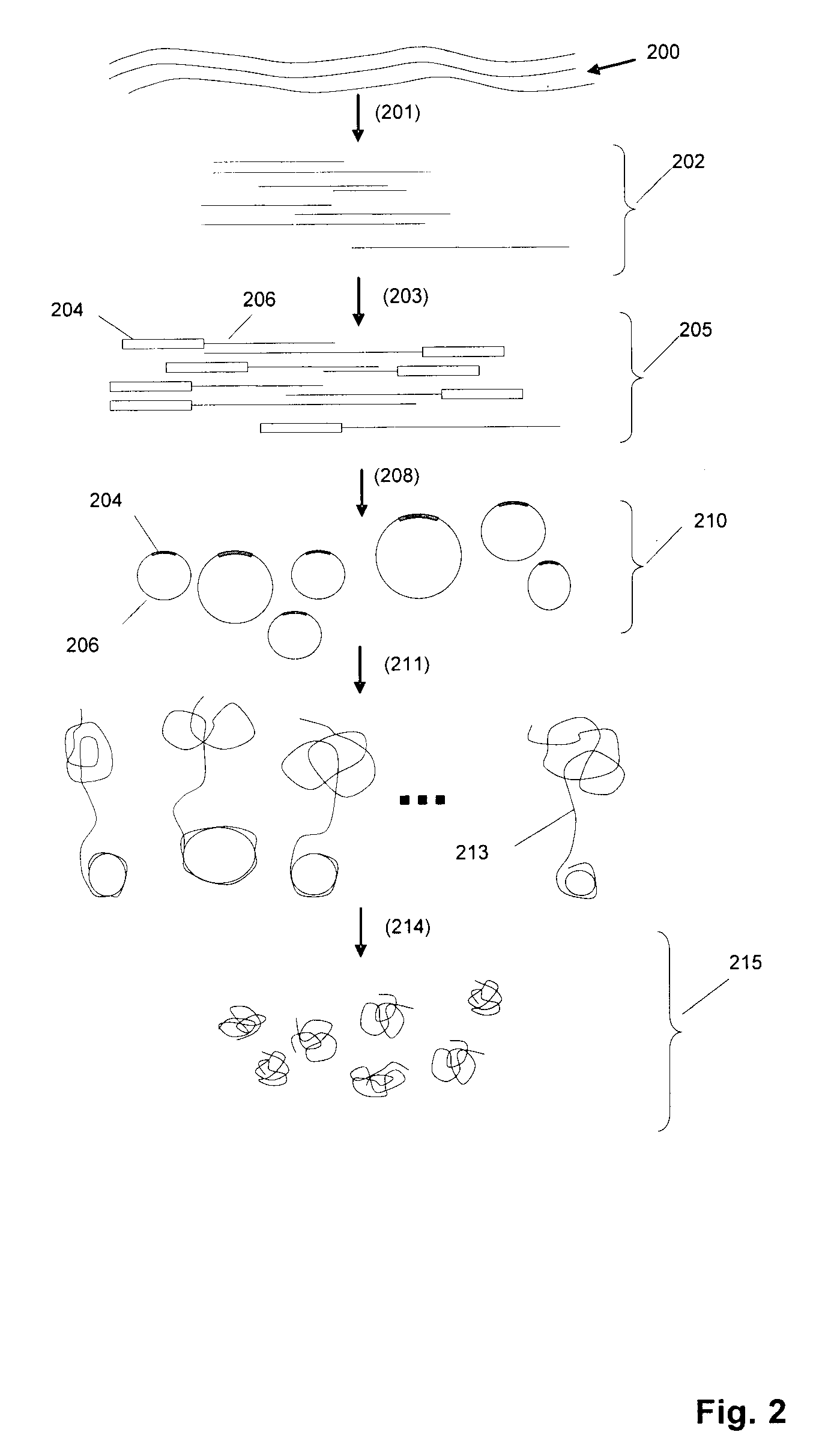
DNA is a natural molecular level storage device. Molecular storage devices use each molecule or part of it for storing a character. Thus it is possible to store information million of times than presently used storage devices. For example a JPEG image (i.e. flag of India) having file size of 1981 Bytes can be encrypted using 7924 DNA bases which occupies about 2694.16 nanometers In other words flag of India can be encrypted 8.07×105 times in human genome which comprises 6.4×109 DNA bases and occupy a tiny volume of about 0.02 μm3. A method for storing information in DNA has been developed which includes software and a set of schemes to encrypt, store and decrypt information in terms of DNA bases. The main advantages of the present method over exiting art is that it addresses complete set of extended ASCII characters set and thereby, encryption of all kind of digital information (text, image, audio etc.). First of all, information is, encrypted along with carefully designed sequences known as header and tail primers at both the ends of actual encrypted information. This encrypted sequence is then synthesized and mixed up with the enormous complex denatured DNA strands of genomic DNA of human or other organism.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Detection of chromosomal disorders
InactiveUS20050250111A1Improve accuracyFast and accurate and simple and inexpensive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseGenomic DNA
Methods for detecting in a single assay any one of multiple chromosomal disorders that result from aneuploidy or certain mutations, particularly microdeletions, and kits for use therein. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is carried out to amplify eukaryotic genomic DNA using a plurality of primer oligonucleotide pairs wherein one primer of each pair has a detectable label attached 5′ thereto. A plurality of the primer pairs are targeted to DNA segments of different chromosomes of interest which are indicative of potential chromosomal disorders, and one pair is targeted for a control gene. The amplified PCR products are purified, and single-stranded DNA having the detectable labels is obtained therefrom and hybridized with spots on a microarray that each contain DNA oligonucleotide probes having nucleotide sequences complementary to a nucleotide sequence of one strand of each segment. The microarray is imaged for presence of labels on its respective spots, and the absence or presence of chromosomal disorders as indicated by one or more of the targeted DNA segments of interest is diagnosed by first comparing the imaging results to the imaging of spots specific to the control gene and then to results obtained from imaging normal DNA.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Efficient arrays of amplified polynucleotides
ActiveUS20080318796A1Well formedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAPolynucleotide
The present invention is related generally to analysis of polynucleotides, particularly polynucleotides derived from genomic DNA. The invention provides methods, compositions and systems for such analysis. Encompassed by the invention are arrays of polynucleotides in which the polynucleotides have undergone multiple rounds of amplification in order to increase the strength of signals associated with single polynucleotide molecules.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
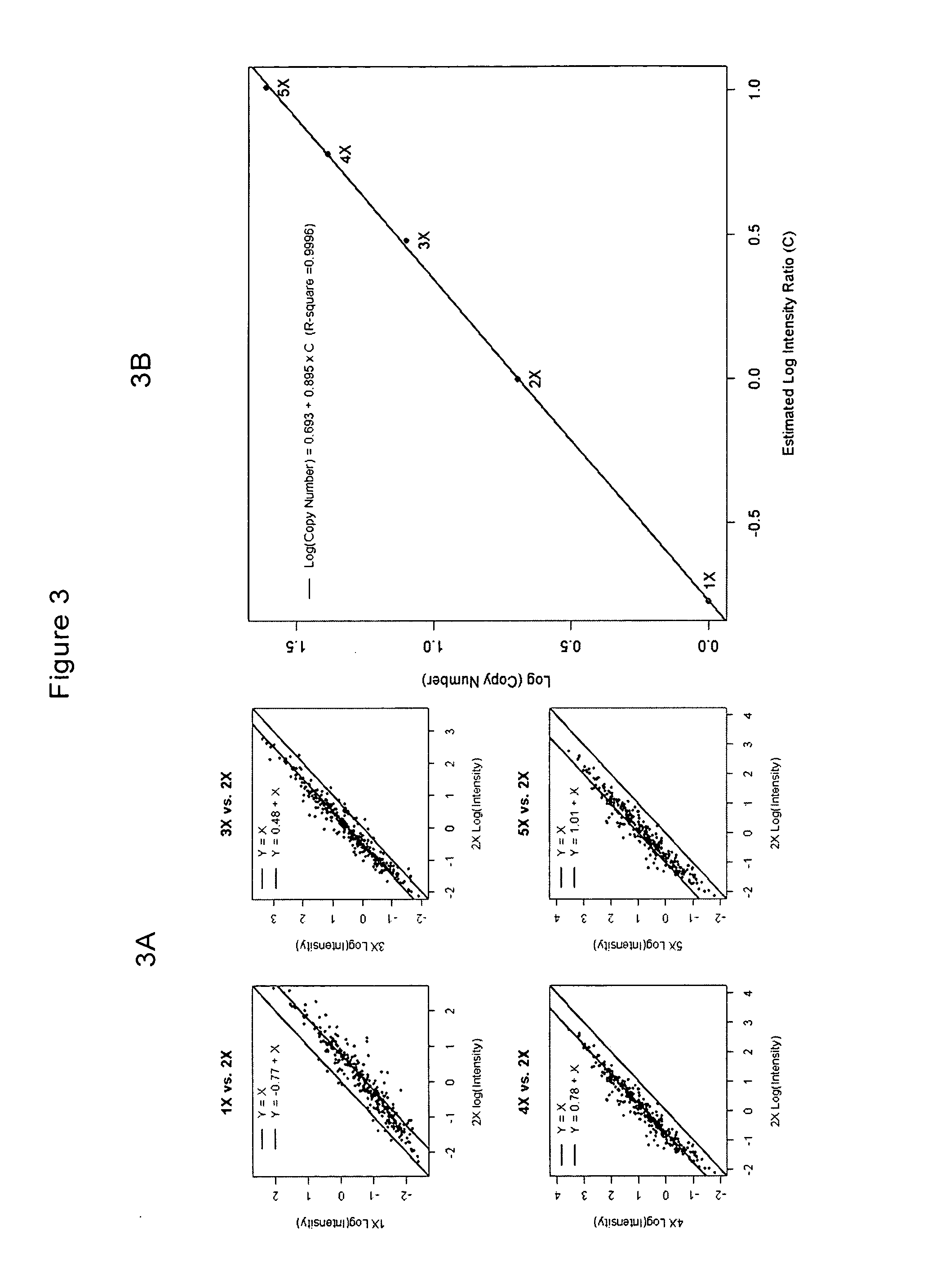
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
InactiveUS20050064476A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic DNANormal tissue
Methods of identifying changes in genomic DNA copy number are disclosed. Methods for identifying homozygous deletions and genetic amplifications are disclosed. An array of probes designed to detect presence or absence of a plurality of different sequences is also disclosed. The probes are designed to hybridize to sequences that are predicted to be present in a reduced complexity sample. The methods may be used to detect copy number changes in cancerous tissue compared to normal tissue. The methods may be used to diagnose cancer and other diseases associated with chromosomal anomalies.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com