Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
273 results about "Homologous Sequences" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system on basis of CRISPR/Cas9, method for establishing exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system and application thereof
ActiveCN106191116ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionTarget geneIntegrated systems
The invention provides an exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system on the basis of CRISPR / Cas9, a method for establishing the exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system and application thereof. The exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system comprises vectors with report / donor functions and Cas9 expression vectors. Each report / donor vector comprises two target gent homologous arms and an exogenous sequence fragment positioned between the two target gene homologous arms; homologous sequences, which are positioned on a target gene, of the two target gene homologous arms of each report / donor vector are respectively positioned on two sides of a target sequence of the target gene and are connected with the target sequence of the target gene; the exogenous sequence fragments comprise promoters, resistant genes, shorn peptide sequences, report genes and polyA tails which are sequentially arrayed, two SSA repair homologous sequences of each resistant gene are inserted into the resistant gene, and the target sequence of each target gene is inserted in a space between the two corresponding SSA repair homologous sequences. The exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system, the method and the application have the advantages that exogenous genes can be integrated with endogenous gene sequences in an efficient site-directed and accurately targeted manner, and double-chromosome allelic gene double-knocking-in can be efficiently carried out.
Owner:成都中科奥格生物科技有限公司
Solid phase sequencing of biopolymers
InactiveUS20110172111A1Easy to determineMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBiopolymerSpectroscopy
This invention relates to methods for detecting and sequencing target nucleic acid sequences, to mass modified nucleic acid probes and arrays of probes useful in these methods, and to kits and systems which contain these probes. Useful methods involve hybridizing the nucleic acids or nucleic acids which represent complementary or homologous sequences of the target to an array of nucleic acid probes. These probes comprise a single-stranded portion, an optional double-stranded portion and a variable sequence within the single-stranded portion. The molecular weights of the hybridized nucleic acids of the set can be determined by mass spectroscopy, and the sequence of the target determined from the molecular weights of the fragments. Nucleic acids whose sequences can be determined include DNA or RNA in biological samples such as patient biopsies and environmental samples. Probes may be fixed to a solid support such as a hybridization chip to facilitate automated molecular weight analysis and identification of the target sequence.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
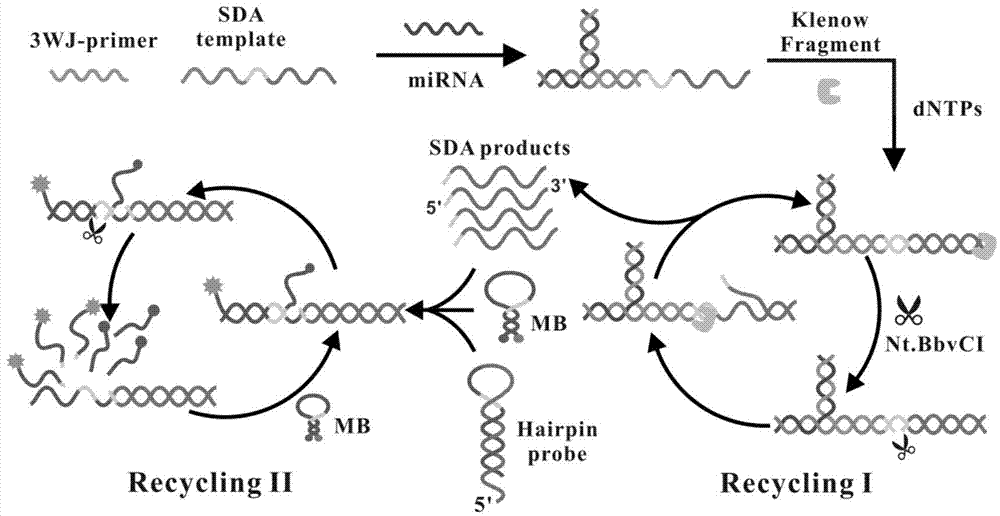
Cascading isothermal amplification based miRNA fluorescence detection kit and miRNA fluorescence detection method
InactiveCN103789435AEasy to distinguishHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDigestion
The invention discloses a cascading isothermal amplification based miRNA fluorescence detection kit and a miRNA fluorescence detection method. The target miRNA can specifically recognize and form a stable three-way crossing structure with a ternary probe through complementary hybridization of nucleic acids; a ternary primer in the three-way crossing structure performs strand displacement amplification (SDA) along a ternary template and generates a number of SDA template products; the SDA template product can open a difunctional hairpin probe to trigger nickase to perform signal amplification reaction finally; and a cyclophorase digestion molecular beacon can generate cascading amplified fluorescence signals. The kit can detect miRNA low to 100fM; and the detection method has superhigh specificity, can well distinguish highly homologous sequences at different mispairing positions and solves the difficult problem of false positive result caused by poor specificity in the existing detection method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof
InactiveCN105349537AImprove detection efficiencyImprove work efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceHomologous sequence
The invention discloses an upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof, and belongs to the field of upland cotton SNP marker development. The upland cotton SNP marker is obtained by developing a single-copy SNP marker of an upland cotton genome via chip hybridization and homologous sequence comparison, and picking out SNP markers in a linkage disequilibrium recession distance via linkage disequilibrium analysis. The SNP marker provided by the invention can be applied to analysis of genetic diversity and group structure, or to germplasm identification of upland cotton, is single-copy, and has no remarkable linkage disequilibrium among markers, so that the efficiency of detection, adopting the SNP marker, during analysis of genetic diversity, group structure or fingerprint identification can be greatly improved, and the work efficiency is higher.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
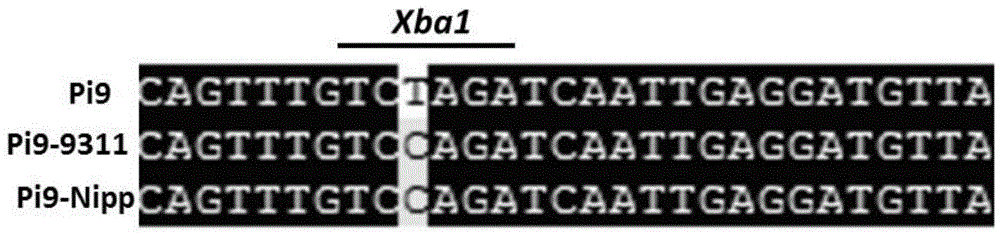
Anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps and application thereof
InactiveCN104630364ALimited applicabilityAccelerate the progress of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRice plantsHomologous sequence
The invention discloses an anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps and application thereof. The invention discloses a method for identifying or auxiliarily identifying whether rice contains anti-rice blast gene Pi9 and / or whether rice has rice blast resistance, which comprises the following steps: detecting 40804th nucleotide from the 5' terminal of 75-1-127BAC12.1 sequence or homologous sequence thereof in chromosome 6 of rice to be detected, and identifying according to the kind of the 40804th nucleotide the 5' terminal of the 75-1-127BAC12.1 sequence or homologous sequence thereof in chromosome 6 of rice. The anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps can accurately judge whether the selected rice plant contains the anti-rice blast gene Pi9, and thus, has important application meanings in accelerating the anti-rice blast rice species breeding progress.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources
ActiveCN105740650AOvercome the disadvantage of taking too longFully reflectProteomicsGenomicsInformaticsHomologous Sequences
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and accurately identifying high-throughput genome data pollution sources. The method comprises the steps that original genome sequencing data for denovo sequencing are firstly assembled to obtain assembly results, gene prediction is conducted on the assembly results, amino acid sequences of proteins corresponding to genes are obtained through translation, and blast comparison is conducted on assembled genomic sequences and the amino acid sequences respectively with an NT database and an NR database of the NCBI to obtain homologous sequences serving as original comparison databases; species information corresponding to the sequences is extracted from the original comparison databases and is sequenced, the species corresponding to the sequences are sequenced from most to least, and whether exogenous pollution exists or not is comprehensively judged by combining with gene data results and amino acid data results. The method can reduce high-throughput genome sequencing data pollution and subsequent bioinformatics analysis influence of exogenous pollution sources in a genome denovo project to the most degree and improve pollution source identifying speed and efficiency.
Owner:广西作物遗传改良生物技术重点开放实验室
Transgenic plants presenting a modified inulin producing profile
A method is disclosed for producing a transgenic plant with a modified inulin producing profile comprising in its genome a combination of one or more expressible 1-SST enzyme encoding genes and one or more expressible 1-FFT enzyme encoding genes, wherein either of these genes or both of them comprise one or more recombinant genes containing one or more 1-SST, respectively 1-FFT, enzyme encoding DNA sequences of plant origin or an expressible homologous sequence thereof. The invention also relates to a method for modifying and controlling the inulin profile of plants and to a method for producing inulin from said transgenic plants. Furthermore, a novel cDNA sequence of a 1-SST enzyme encoding gene of Helianthus tuberosus and a novel cDNA sequence of a 1-FFT enzyme encoding gene of Cichorium intybus are disclosed, novel recombinant DNA constructs and genes derived thereof, as well as novel combinations of expressible 1-SST and 1-FFT enzyme encoding genes. Moreover, the invention also relates to novel polypeptides, homologues thereof and fragments thereof, which have 1-SST activity of 1-FFT activity, and to antibodies capable of specifically binding one or more of them.
Owner:TIENSE SUIKERRAFINADERIJ +1
Mutant zymoprotein of D-amino acid oxidase and preparation method of mutant zymoprotein
The invention discloses a mutant zymoprotein of D-amino acid oxidase and preparation method of the mutant zymoprotein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: according to homologous sequence comparison result, respectively performing mutation on 115, 119 and 286 sites of D-amino acid oxidase in primary Arthrobacterprotophormiae (DSM15035) through site-specific mutagenesis technology to construct three-site mutation expression vector Pet-e115A / N119D / T286A; and carrying out prokaryotic expression and purification to obtain zymoprotein. An apparent secondary speed constant Kcat / Km of the obtained mutant protein to substrate D-Met is 1.39*10 to the power of 5s-1.M-1, is 5.03 times of wild type DAAO (D amino acid oxidase), and is 55.96 times of pKDAAO protein of pig kidney source. The detection efficiency of partial D-amino acid can be improved, and the good application value is realized.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Method for measuring short chain RNA by amplifying length polymorphism of DNA fragment
ActiveCN104120184AEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationA-DNAAmplified fragment length polymorphism
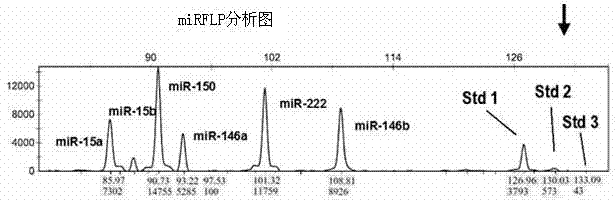
The invention discloses a method for measuring a short chain RNA by amplifying length polymorphism of a DNA fragment and belongs to the l field of molecular biological techniques. The method comprises the following steps: first, by using at least two synthesized small RNAs without natural homologous sequences as compared with the short chain RNA to be measured as an interior label of measurement, mixing the synthesized small RNAs in different numbers of molecules to form a dynamic small RNA standard molecular gradient; and then, mixing with the short chain RNA to be measured in equal amount according to the dynamic small RNA standard, and carrying out RNA inverse transcription, cDNA tailing, PCR synchronous amplification and fluorescent quantitative analysis on length polymorphism fragment of DNA of the PCR product to measure a relative proportion of the fluorescence intensity of the DNA fragment amplified by short chain RNA to be measured in the dynamic small RNA standard fluorescence intensity gradient. The method can absolutely quantify the short chain RNA, particularly miRNA, has high specificity, high sensitivity, objective result and good repeatability, can realize accurate quantification in a copy number range of 100-10<6> and is also suitable for RNA crude extracts.
Owner:CHENGDU NUOEN BIOLOGICAL TECH
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase gene in salvia root, and encoding protein and use thereof
The invention discloses a Red sage root Geranyl geraniol-based pyrophosphoric acid synthase gene and its encoded protein and the application thereof, which fills the blank of separating the Geranyl geraniol-based pyrophosphoric acid synthase gene from the traditional Chinese herb red sage root. The Geranyl geraniol-based pyrophosphoric acid synthase gene provided by the present invention has the nucleotide sequence No.73-1167 shown by the SEQ ID No.1; the encoded protein has amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2 or r homology sequence with one or a plurality of added, replaced, inserted or deleted nucleotide. The inventive Geranyl geraniol-based pyrophosphoric acid synthase gene can improve the terpenes active component tanshinone in the red sage root, which helps to improve the quality of red sage root herbs and has good application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
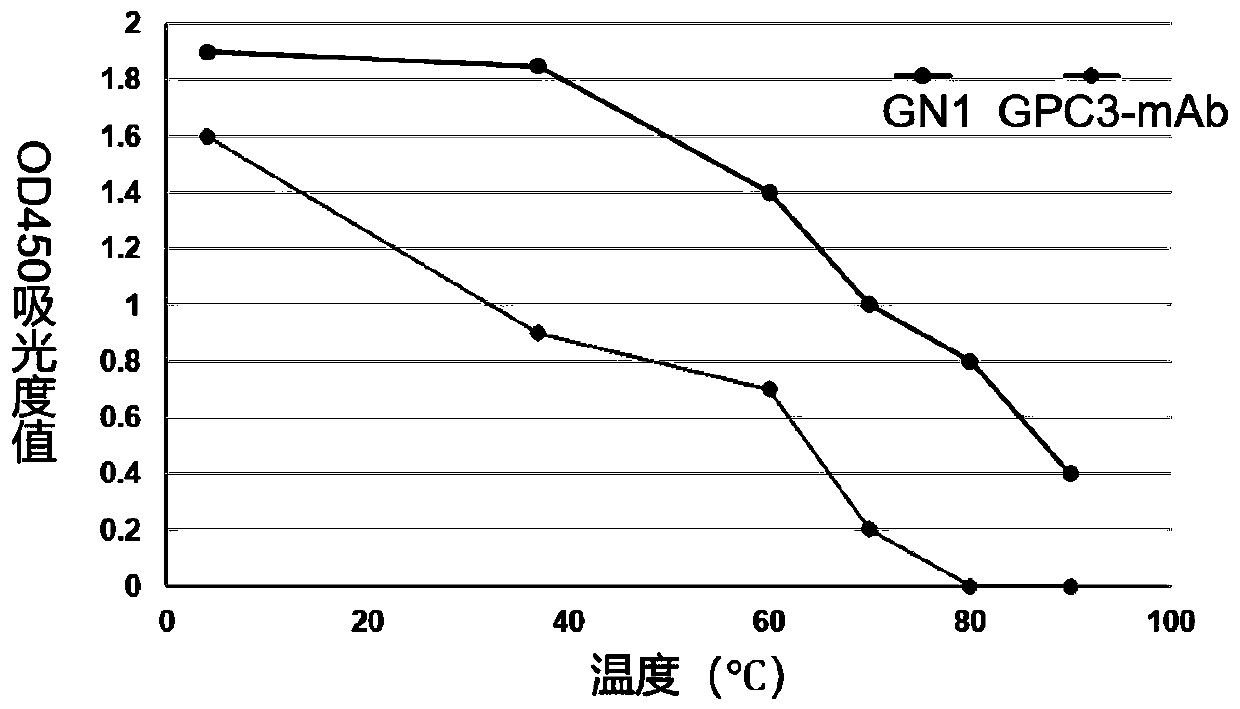
Nano-antibody GN1 specifically combined with GPC3 protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110872351ASmall molecular weightStable structureBacteriaImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAmino acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a nano-antibody GN1 specifically combined with a GPC3 protein. The nano-antibody GN1 is composed of a variable region of a heavy-chain antibody, the variable region of the heavy-chain antibody comprises an antigenic determinant complementary region and a skeleton region, the skeleton region is selected from the group consisting of FR1, FR2, FR3 and FR4 and homologous sequences thereof, the antigenic determinant complementary region is selected from the group consisting of CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 and homologous sequences thereof, the amino acid sequences of the CDR1 to the CDR3 are shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO. 3, the amino acid sequences of the FR1-4 are shown in formulas of SEQ ID NO. 4-7, the amino acid sequence of the antibody is shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.8, and the nucleotide sequence for encoding the amino acid is shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.9. The nano-antibody GN1 can be specifically combined with hepatoma carcinoma cells highly expressing the GPC3 protein to inhibit hepatoma carcinoma cell proliferation. The amino acid sequence of the nano-antibody GN1 or the nucleotidesequence of the nano-antibody GN1 or the recombinant plasmid containing the nucleotide sequence of the nano-antibody GN1 or the recombinant cell containing the recombinant plasmid containing the nucleotide sequence of the nano-antibody GN1 can be applied to research and development of diagnostic reagents and drugs for treating liver cancer.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Polypeptide Sequence Involved in the Modulation of the Immunosuppresive Effect of Viral Proteins
ActiveUS20080008683A1Stimulate immune responseReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsImmunosuppressive effectHomologous Sequences
The present invention relates to a polypeptide having a sequence of 7 to 20 amino acid residues, which is capable of modulating the immunosuppressive properties of a viral protein or a fragment thereof, against the host in which it is expressed (immunosuppression-modulatory sequence) when it substitutes the homologous sequence of the viral protein or fragment, the polypeptide including the minimum following consensus amino acid sequence: X1Y9Y10Y11CY12X2 wherein, X1 and X2 are selected to impact on the immunosuppressive properties, and Y9 to Y12 represent variable amino acid residues.
Owner:INSTITUT GUSTAVE ROUSSY +2
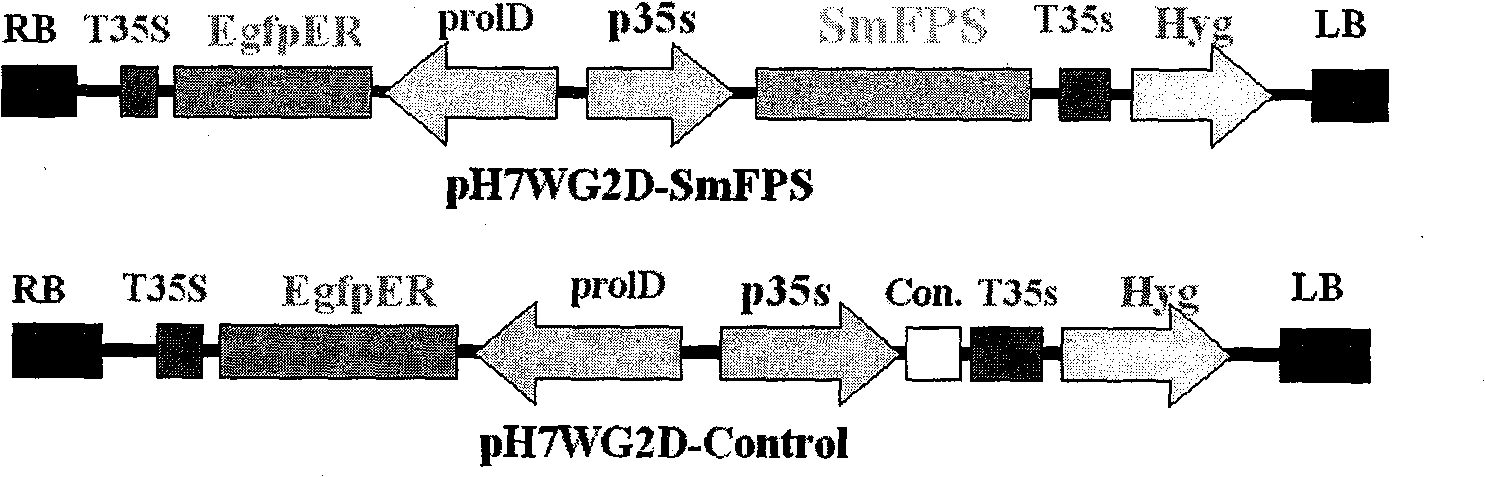
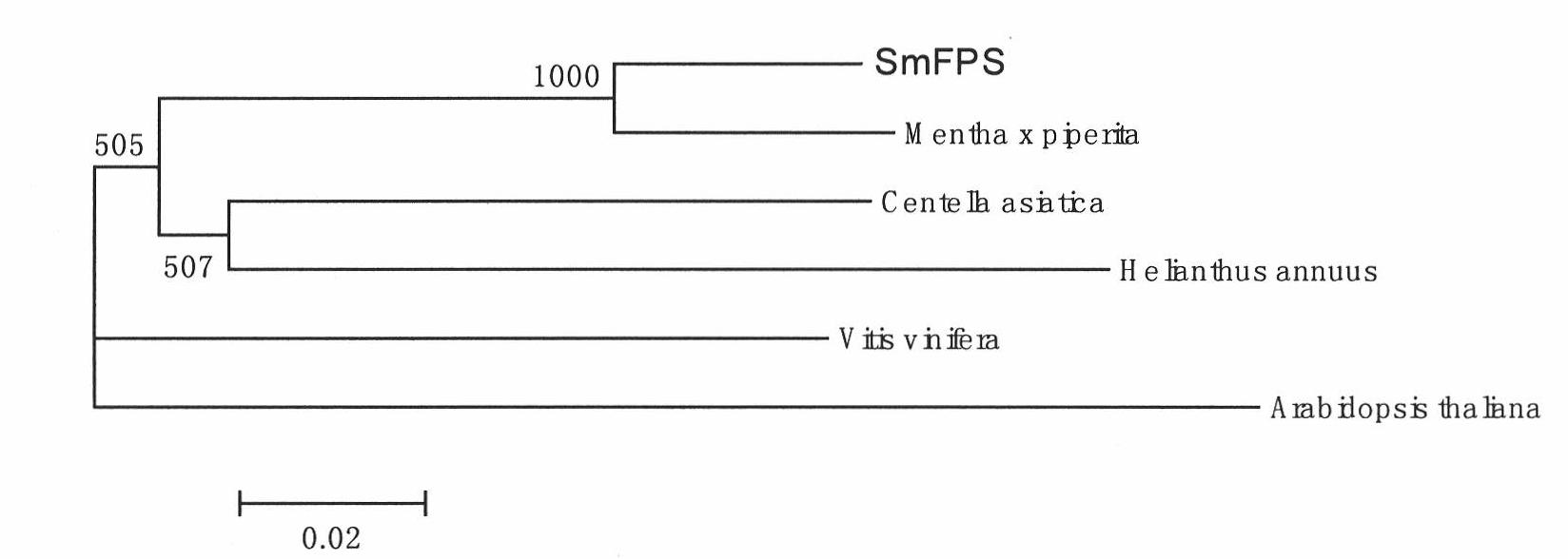
SmFPS (Salviamiltiorrhizabge Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase) gene as well as coded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101928716AIncrease contentRelieve severe plaque deficiencyTransferasesFermentationSalvia miltiorrhizaNucleotide
The invention discloses a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene as well as a coded protease and application thereof. The gene is obtained by clone from salviamiltiorrhizabge by utilizing a cDNA chip technology, which fills the blank of separating and cloning the farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene from a rare traditional Chinese medicine of salviamiltiorrhizabge. The farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more nucleotides or allelic genes and derived nucleotide sequence thereof. The protein coded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more amino acids. The farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene can improve the content of tanshinone which is diterpene active element in the salviamiltiorrhizabge by the biotechnology, is beneficial to the quality improvement of the salviamiltiorrhizabge medicine, can be used for the breeding selection and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
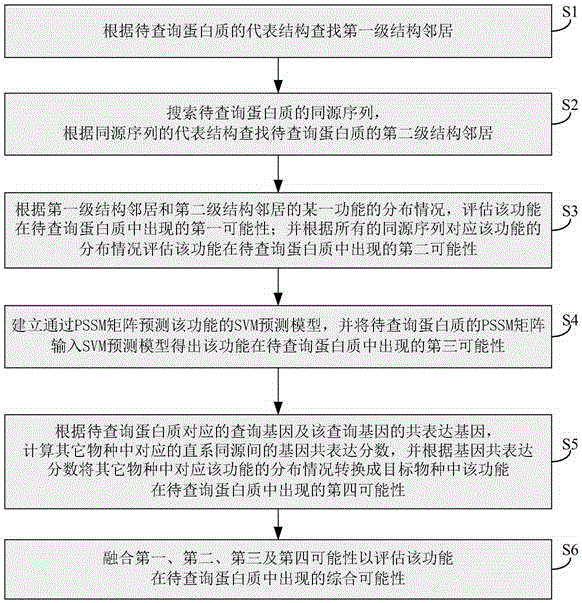
Marking method and system for protein functions
ActiveCN106599611AImprove labeling abilitySolve the costProteomicsGenomicsProtein insertionGene coexpression
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformation, and discloses a marking method and system for protein functions. Therefore, protein marking performance is improved, expensive cost of a bioexperiment method and poor efficiency are solved. The method comprises following steps: estimating the first possibility of a certain function in a to-be-inquired protein according to a first-stage structure neighborhood and a second-stage structure neighborhood; estimating the second possibility of the certain function in the to-be-inquired protein according to all homologous sequences; inputting a PSSM matrix of the to-be-inquired protein into an SVM prediction model to obtain the third possibility of the certain function in the to-be-inquired protein; converting the distribution of the function corresponding to other species according to the gene co-expression fraction into the fourth possibility of the function occurring in a target species in the to-be-inquired protein; and mixing the first possibility, the second possibility, the third possibility and the fourth possibility to estimate the comprehensive possibility of the function in the to-be-inquired protein.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Tobacco mosaic virus resistant N'au gene and cloning method and application thereof
The invention relates to isolation cloning and breeding application of a tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) resistant N'au gene. A nucleotide sequence of the TMV resistant N'au gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and amino acid of polypeptide coded by the TMV resistant N'au gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A non-transgenic TMV-resistant tobacco variety can be obtained by trans-breeding an N'au gene contained in germplasm resources into a TMV-sensitive main planting tobacco variety through a conventional breeding means. The N'au gene in the main planting tobacco variety has a homologous sequence high in nucleotide rate, so that short introgression fragment single plants carrying the N'au gene can be obtained easily through conventional breeding so as to obtain a TMV-resistant variety low in linkage drag. The gene can resist strains U1 and Cg of TMV at the same time. The novel antiviral gene N'au has great application prospect in cultivation of TMV-resistant tobacco.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Methods for generating genetic diversity by permutational mutagenesis
Methods for generating genetic diversity in a polynucleotide or polypeptide sequence are included. The methods include permutational mutagenesis strategies for introducing genetic diversity to alter or improve the function of the polynucleotide or polypeptide. The methods include aligning a set of homologous sequences and generating a consensus translation or a consensus sequence that encompasses the full diversity of the aligned sequences, and then incorporating that consensus translation or consensus sequence into a functional polypeptide or polynucleotide to test for altered or improved function.
Owner:ATHENIX
Nanobody GN2 composed of variable region of heavy chain antibody and preparation method and application of nanobody GN2
ActiveCN111320694ASmall molecular weightStable structureDigestive systemBiological material analysisEnzyme digestionEngineered genetic
The present invention relates to a nanobody GN2 composed of a variable region of a heavy chain antibody; and the variable region of the heavy chain antibody comprises an epitope complementary region selected from a group consisting of CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 and homologous sequences of the CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 and a skeleton region selected from a group consisting of FR1, FR2, FR3 and FR4 and homologous sequences of the FR1, FR2, FR3 and FR4. The present invention also relates to a preparation method and an application of the nanobody GN2. The nanobody GN2 can specifically bind to hepatocarcinoma cells that highly express GPC3 protein, inhibits hepatocarcinoma cell proliferation, and is small in molecular weight, stable in structure, good in heat resistance, high in affinity, easy for storage and transportation, weak in immunogenicity to human body, also strong in tumor tissue penetrating power, liable to express and genetically engineered, and particularly suitable for use as a diagnosticreagent or a therapeutic antibody. The method can retain more antigen epitopes, and is high in carrier quality, good in an enzyme digestion effect, high in connection efficiency, low in self-connection efficiency and also low in cost.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight character and preparation method and application
InactiveCN102703438ASpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaGrain weight
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to a specific molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight and a preparation method and an application. Hybridization is performed by using brassica napus L. A254 as a female parent and using brassica napus L. A177 as a male parent to construct a dihaploid colony (DH); data of the genotype and 1000-grain weight of the DH colony are analyzed to obtain QTLs loci of the grain weight character. MINI3 and TTG2 genes of A254 and A177 are cloned by a homologous sequencing method; specific molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different loci; the molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a are positioned on two grain weight QTLs loci of a A5 linkage group; related verification and application demonstrate that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a new genetic marker. The invention provides a new genetic marker for rape grain weight molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
L-alanine dehydrogenase mutant zymoprotein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103074309AIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesTurnover numberWild type
The present invention discloses L-alanine dehydrogenase mutant zymoprotein and a preparation method thereof. According to a homologous sequence secondary structure comparison result, site-specific mutagenesis of 73th lysine near an L-alanine dehydrogenase activity center of Bacilluspseudofirmus into alanine through PCR is performed to construct a mutant expression vector, and prokaryotic expression and Ni-NTA affinity chromatography purification are performed to obtain a mutant enzyme K73A, wherein specific activity of the obtained mutant enzyme K73A is 202% of specific activity the wild type, and other enzymatic properties are not changed. In addition, a turnover number Kcat on a substrate L-alanine by the mutant zymoprotein is 376.7 min<-1> and is 2.0 times the turnover number Kcat of the wild type, a turnover number Kcat on beta-NAD<+> by the mutant zymoprotein is 290.1 min<-1> and is 2.1 times the turnover number Kcat of the wild type, and the mutant zymoprotein can be applicable for production processes of production of pyruvic acid, L / D-alanine, and the like through improvement biology methods.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
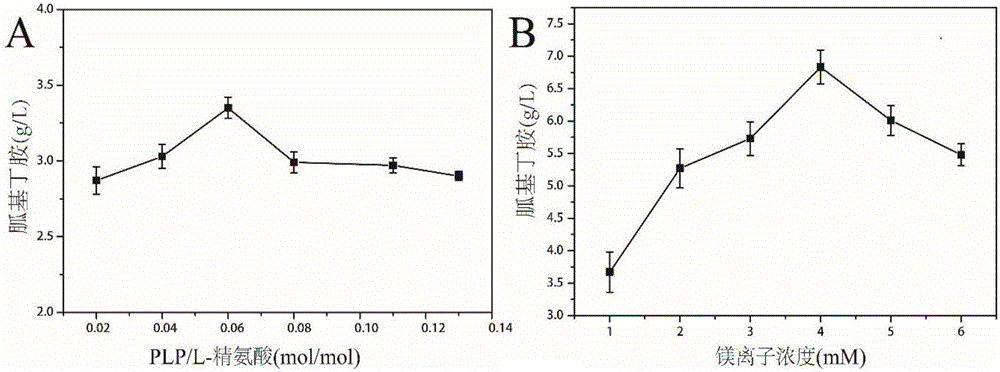
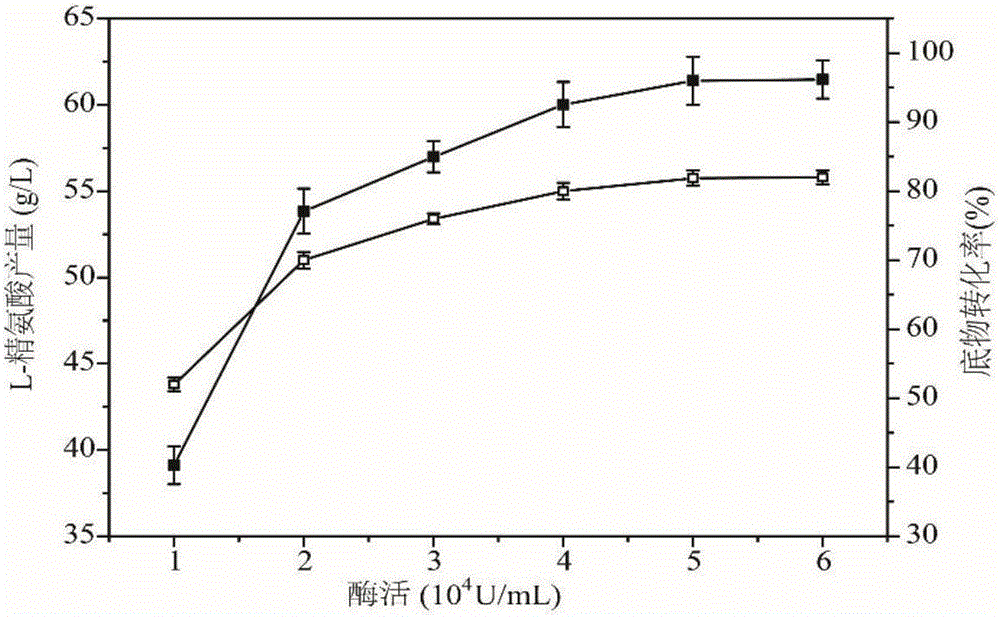
Arginine decarboxylase and application thereof
InactiveCN105861529AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionFermentationGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliArginine
The invention discloses arginine decarboxylase and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. Shewanella putrefaciens is cloned by adopting genome database mining and homologous sequence alignment and other virtual screening means and combining with a molecular biological means to obtain an arginine decarboxylase gene. The molecular biological means, process optimization and the like are adopted, the enzyme production capacity of arginine decarboxylase production strains is improved, and a platform for efficiently producing gamatine through biological catalysis is established by optimizing a catalytic system. Crude enzyme liquid obtained through fermentation is purified and then is converted, a reaction system is clear in composition, and extraction and purification of follow-up products are promoted. Under the condition of 37 DEG C, the decarboxylase has high activity, meanwhile is beneficial to the growth of escherichia coli of host cells, and at the temperature, the reaction speed is improved greatly, a conversion period should be 24 hours, the gamatine yield can be up to 61-71 g / L, and the conversion rate can be up to 68-82%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Short interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) for promoting scarless healing of skin wounds and application thereof
InactiveCN102031260AGenetic material ingredientsDermatological disorderSurgical operationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a short interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) molecule for promoting scarless healing of skin wounds, a cocktail combination of a plurality of siRNA molecules targeting a plurality of related genes of scarless healing of wounds, and a pharmaceutical composition taking the siRNA molecule or the cocktail combination thereof as an active ingredient. Proven by cell experiments and mouse and pig skin wound models, the pharmaceutical composition can promote scarless healing of skin wounds resulted from traumata, surgical operation, or diabetes skin ulcer and the like, wherein the siRNA molecule can target genes causing pathological repair of wounds or adverse reactions; the siRNA double chains have different lengths and different tail ends and can target a homologous sequence of the same gene of cells of human, mouse and pig; the plurality of siRNAs in the cocktail combination can simultaneously inhibit various related genes of wound inflammation and revascularization, and has more obvious drug effects; and pharmaceutical carriers such as histidine-lysine polymer, dendritic polymer or liposome and the like in the pharmaceutical composition in a nanoparticle form can enhance the siRNA to be introduced into the skin tissue.
Owner:SUZHOU SIRNAOMICS BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
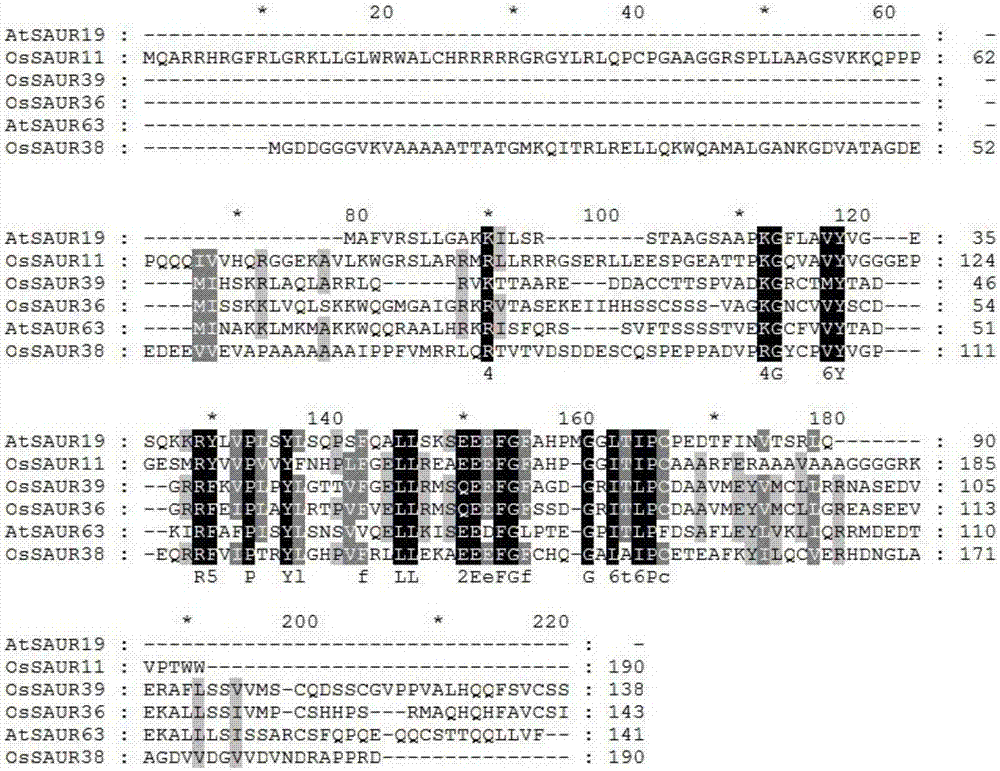
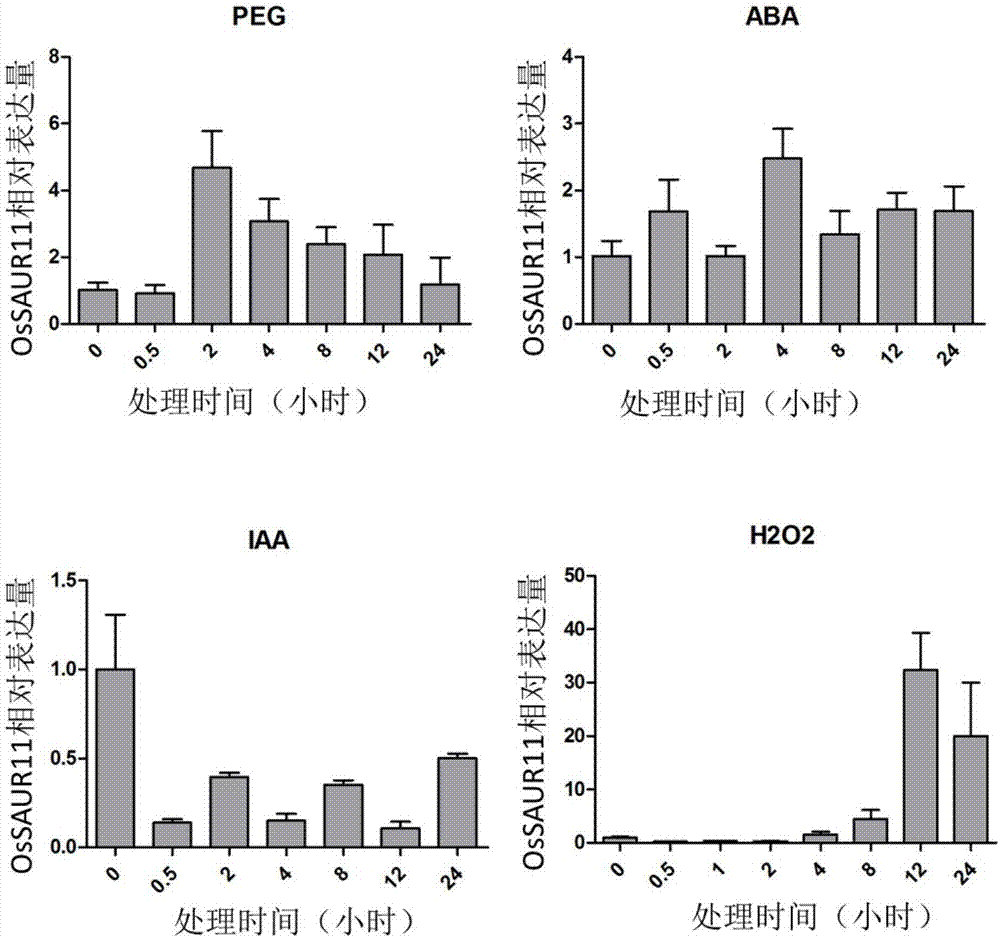
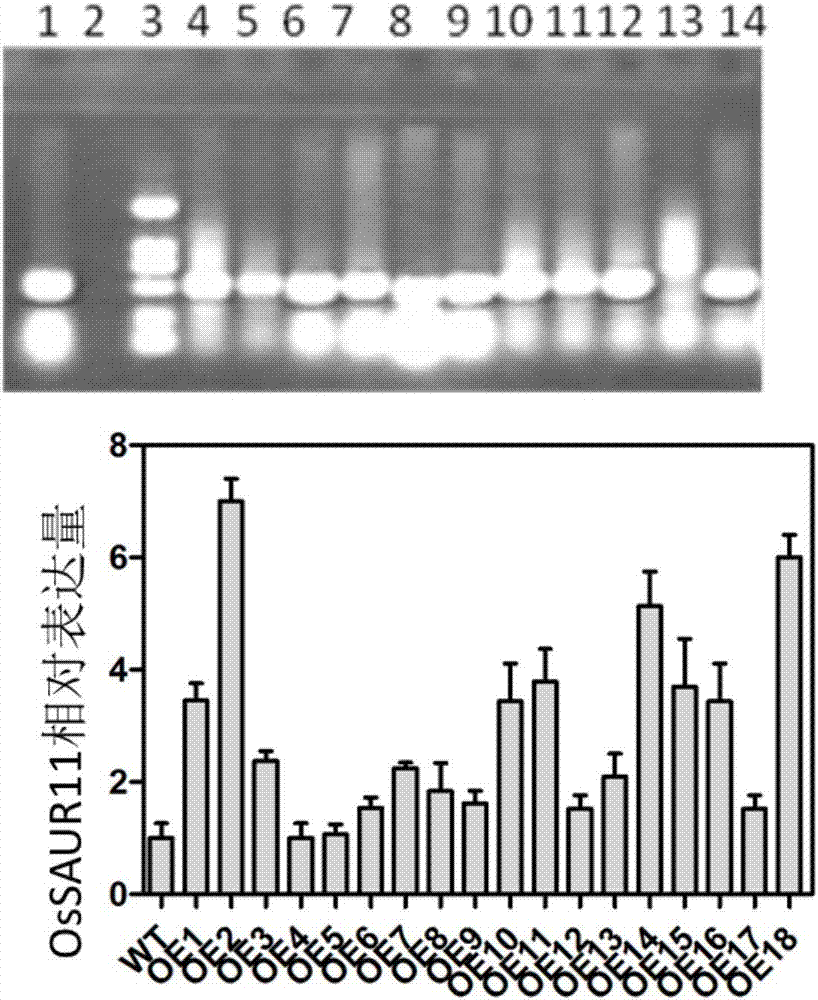
Rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes and encoding protein and application
The invention discloses rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes which are isolated and cloned from rice DNA fragments. Protein encoded by the genes contains SAUR family conserved structural domains. The rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes belong to the field of rice cloning genes. The sequence of the OsSAUR11 genes is as shown in followingsequences: a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, a DNA sequence at least 90% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 1 and a subfragment functionally equivalent to the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; the expression of the OsSAUR11 genes is the root development and stress resistance. The rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effectsthat the OsSAUR11 genes are in inducible expression of osmotic stress, abscisic acid and auxins, and overexpression of OsSAUR11 can enhance the deep root ratio of rice and enhance drought resistanceof the rice, is related to rice stress resistance, and has obvious response to adverse environments, thereby being applied to plant drought-resistance breeding, improving the root configuration and enhancing plant stress resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
Salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl A reductase gene and its coding protein and application
InactiveCN101250544AIncrease contentIncrease productionFungiBacteriaSalvia miltiorrhizaProtein insertion
The invention discloses a salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene, protein which is encoded by the salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene and the use thereof, which fills a gap that the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene is separated and cloned from salvia which is precious traditional Chinese medicine in China. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene which is provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence or a homologous sequence which adds, replaces, inserts or losses one or a plurality of nucleotides or allele thereof and the nucleotide sequence which is derived from the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene, which are displayed in the SED ID No.1. The protein which is encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence or the homologous sequence which adds, replaces, inserts or losses one or a plurality of amino acids, which is displayed in the SEQ ID No.2. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene which is provided by the invention can increase the content of tanshinone which is a terpenes active component in the salvia through the genetic engineering technology and can be used in research and industrialization for increasing the content of the tanshinone through utilizing the transgenic technology, which is helpful for improving the quality of salvia mi ltiorrhiza and has very good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Salviamiltiorrhizabge-cytochrome P450 (SmP450) gene as well as coded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101928715AIncrease contentRelieve severe plaque deficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationSalvia miltiorrhizaNucleotide
The invention discloses a cytochrome P450 (SmP450) gene as well as a coded protease and application thereof. The gene is obtained by clone from salviamiltiorrhizabge by utilizing a cDNA chip technology, which fills the blank of separating and cloning a structure-modification type functional gene which is cytochrome P450 (SmP450) gene from a rare traditional Chinese medicine of salviamiltiorrhizabge. The cytochrome P450 (SmP450) gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more nucleotides or allelic genes and derived nucleotide sequence thereof. The protein coded by the cytochrome P450 (SmP450) gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 or a homological sequence adding, substituting, inserting or lacking one or more amino acids. The cytochrome P450 (SmP450) can improve the content of tanshinone which is diterpene active element in the salviamiltiorrhizabge by the biotechnology, is beneficial to the quality improvement of the salviamiltiorrhizabge, can be used for the breeding selection and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood product, and application method thereof
InactiveCN104404131ALarge capacityReduce dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingPhylogenetic tree
The invention discloses a DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and an application method thereof. The technology is as below: constructing a high capacity database through a strategy by merging database of rosewood samples experiment data and a target plant; sequencing a DNA bar code sequence of the rosewood samples; merging the sequencing sequences with homologous sequences published in the Genbank database to construct a rosewood DNA bar code gene database with wide range of data sources; and establishing an algorithm and decision rules for the identification database by using matK+rbcL genes as the target DNA bar code gene for rosewood identification, and using a search tool method of a local alignment algorithm based on frequency, a genetic distance method based on Kimura-2-parameter probability and a phylogenetic tree method based on clustering analysis. The DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and the application method thereof establish an accurate and quick rosewood DNA bar code identification technology.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Beta-mannase gene and amino acid sequence of its coded product and preparation method
InactiveCN1807644AExpand genetic resourcesEnrich excellent candidate genesHydrolasesRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses an amino acid sequence of beta-mannase gene and coding making method in the biological domain, which is characterized by the following: extracting Armillariella tabescens main RNA of high activity by konjaku flour evoking; using consanguinity sequence of Genebank to design degenerate primer; carrying on PCR expanding to protectorate by primer; designing gene specificity primer to carry on 3'RACE and 5'RACE; cloning total long cDNA of beta-mannase gene; constructing eucaryon expressing carrier with pichia; building-up yeast gene engineering bacterial strain.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Calabash gourd anti-plague gene segment or gene marker and application
InactiveCN102703439AQuick assist selectionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideRapid identification
The invention mainly relates to a calabash gourd anti-plague gene segment or gene marker and application. Three calabash gourd anti-plague gene segments or gene markers are rapidly separated by adopting an anti-disease gene homologous sequence method, and by sequencing, the nucleotide lengths of the gene segments or gene markers are 510bp, 498bp and 501bp. According to the calabash gourd anti-plague gene segment or gene marker and application provided by the invention, the excavation period of the calabash gourd anti-plague gene is effectively shortened, and the rapid identification of plague gene is facilitated; the identified plague gene can be used for developing corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), SCAR (sequence-characterized amplified region) and the like), and can also be rapidly used for assisted selection of a molecule marker of the anti-plague gene, and the accuracy is high; development of multi-resistance breeding materials can be carried out by combining with other anti-disease gene molecule markers, the breeding time is shortened and the breeding efficiency is improved; and foundation is established for expounding the molecular mechanism of the anti-plague gene.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Promotor replacement method for improving volume of production of bacillus subtilis surfactin
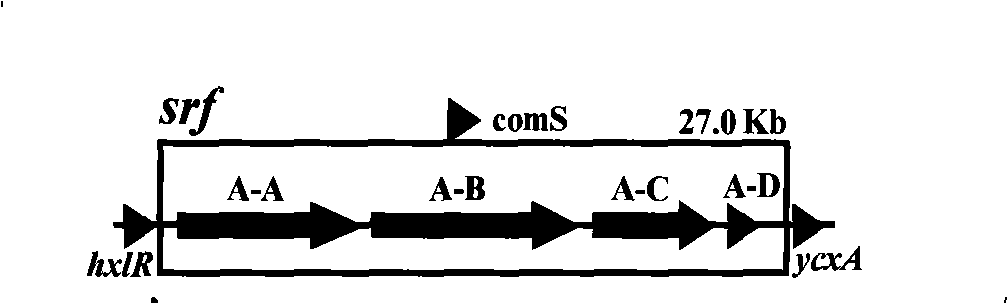
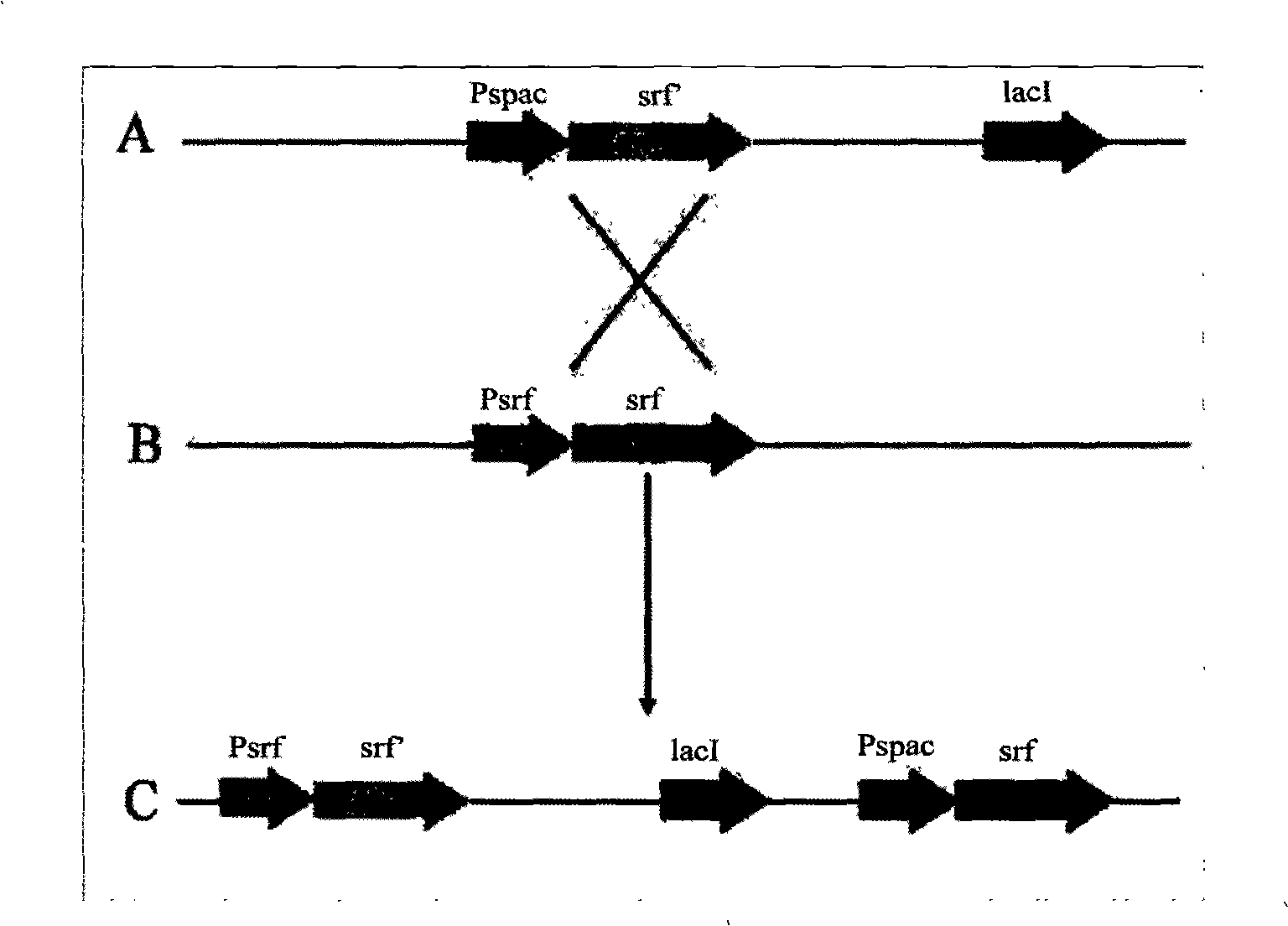
InactiveCN101402959AIncrease productionEasy to produceBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAntimikrobielle peptide
The invention relates to a promoter replacement method for improving the yield of Bacillus subtilis surfactin, belonging to the biotechnology field. The DNA homologous integration technology is adopted for allowing a promoter Pspac to replace the promoter of a Bacillus subtilis fmbR surfactin synthase gene. The homologous sequence of 1081bp is obtained by amplification from an fmbR strain genome through the PCR method and connected to HindIII and BamH I restriction enzyme cutting sites of a plasmid pMUTIN4, a well constructed vector is converted into wild Bacillus subtilis fmbR, thereby realizing the replacement through the screening by an antibiotic culture medium and the molecular biology method. The method can directly improve an antimicrobial peptide production strain on genetics, thereby having potential application value in industry. The yield of the strain surfactin is improved by about 4.85 times, and the yield of the surfactin can be improved by about 10 times under the IPTG induction.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Reverse detection for identification and/or quantification of nucleotide target sequences on biochips
InactiveUS20030157528A1Efficient discriminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotide sequencingHomologous Sequences
The present invention relates to a method for the identification and / or the quantification of one or more target nucleotide sequences (3) present homologous to each other and being possibly present in a sample and discrimination from possibly homologous sequences, by using two sets of nucleotide sequences (1 and 2), wherein a first set of nucleotide sequences possibly labelled (1) bind specifically to said target nucleotide sequences (3) in a first step and are detected and / or quantified through hybridisation with a second set of capture nucleotide sequences (2) having at least a part of sequence complementary to the possibly labelled nucleotide sequence (1) of the first set of nucleotide sequences, said capture nucleotide sequence (2) being immobilised upon the surface (4) of a solid support according to an array of at least 4 discrete regions / cm2, each of said discrete regions being bonded with one species of capture nucleotide sequences (2), and wherein the identification and quantification of the binding between the possibly labelled nucleotide sequence (1) and their corresponding capture nucleotide sequence (2) is correlated with the identification and the quantification of a target nucleotide sequence (3) present in the sample.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Polynucleotide for identifying male and female ginkgo strains and application thereof
ActiveCN110195068AThe result is stable and accurateGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPhysiologyNucleotide
The invention provides a polynucleotide for identifying male and female ginkgo strains. The polynucleotide comprises or consists of: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 5; or 2) a complement,degenerate or homologous sequence of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 5; or 3) a polynucleotide which hybridizes to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 under stringent conditions or a complement thereof; 4) a coding sequence of any of the sequences 1) to 3); or 5) a nucleotide sequence identical to a nucleotide of 10 bp or more in any of the sequences of sequences 1) to 4). The polynucleotide provided by the present invention is unique among male ginkgo plants, uses the same to identify male and female plants of ginkgo, has the advantages of stable and accurate results, good reproducibility and rapid detection, and provides a basis for the identification of male and female ginkgo by molecular markers.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com