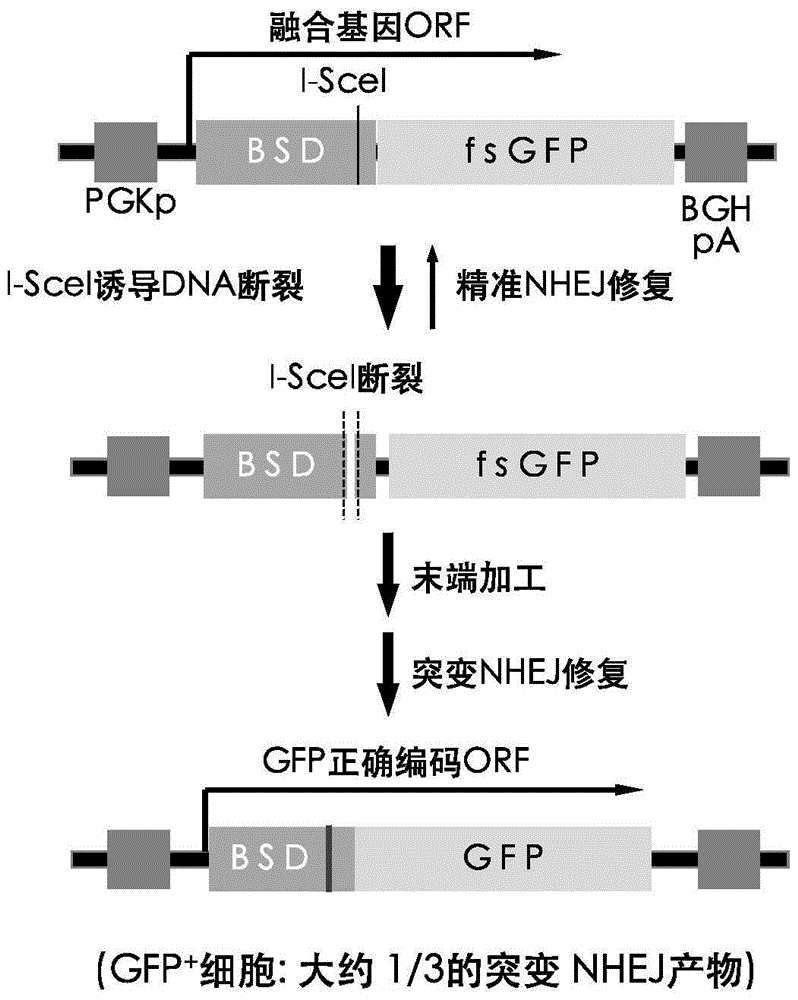
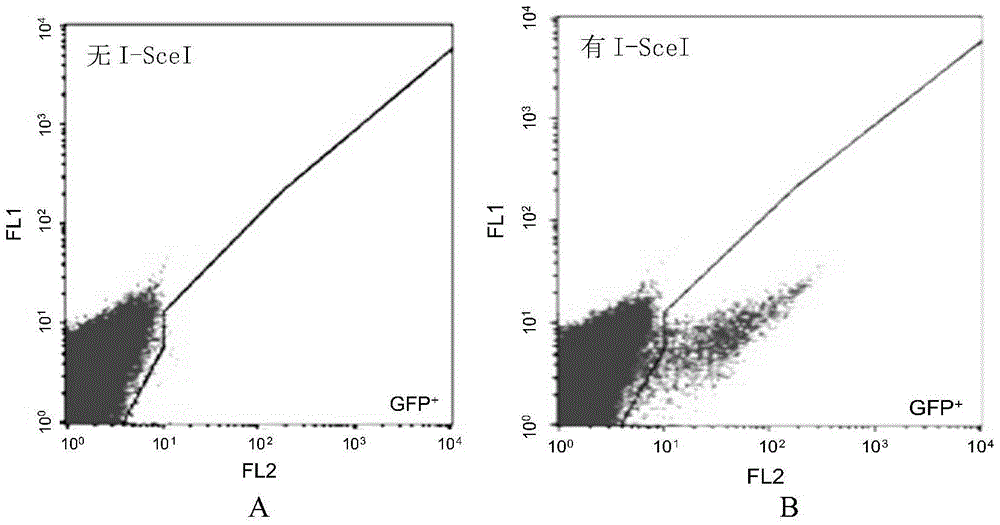
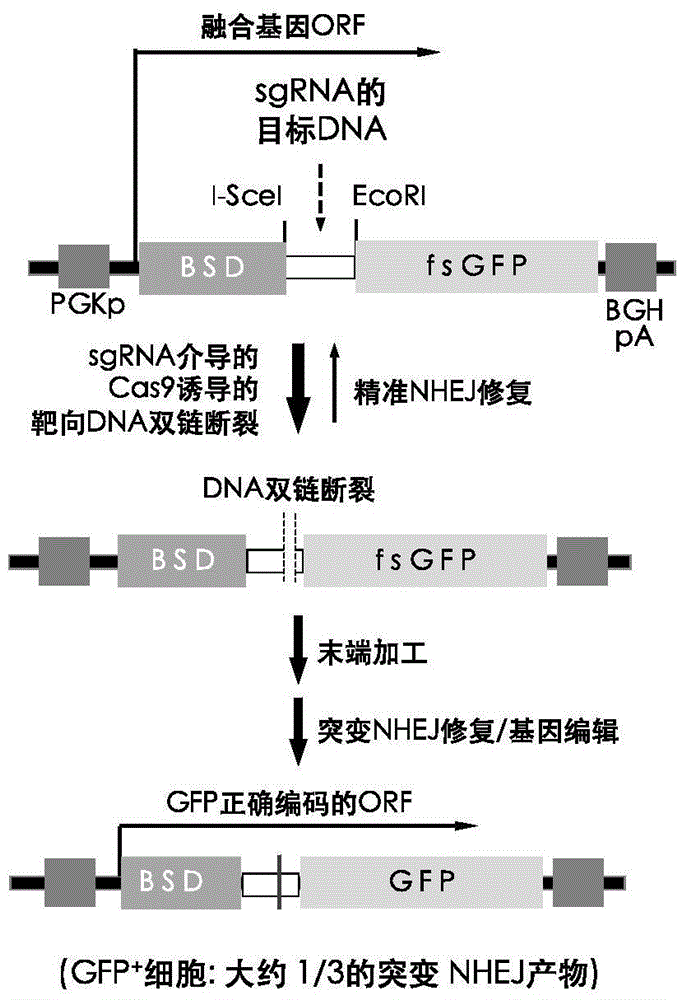
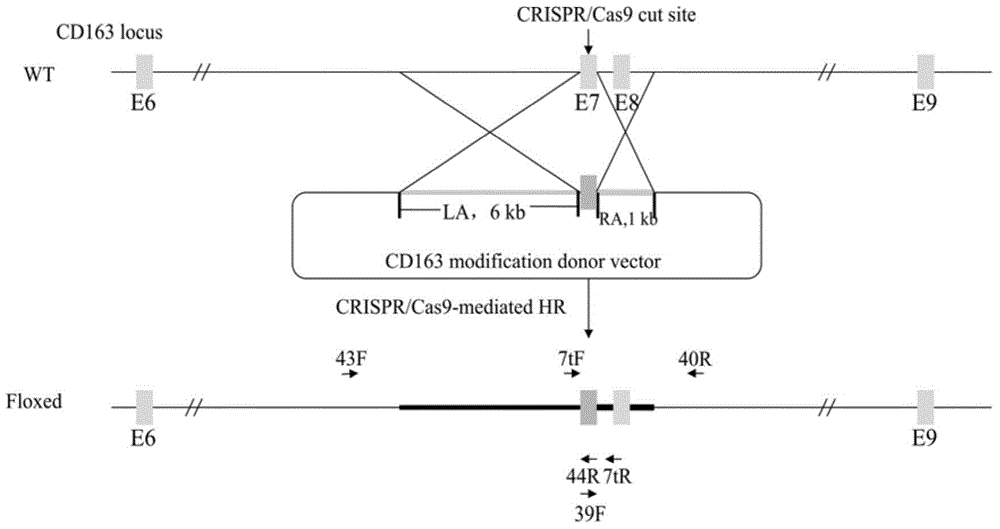
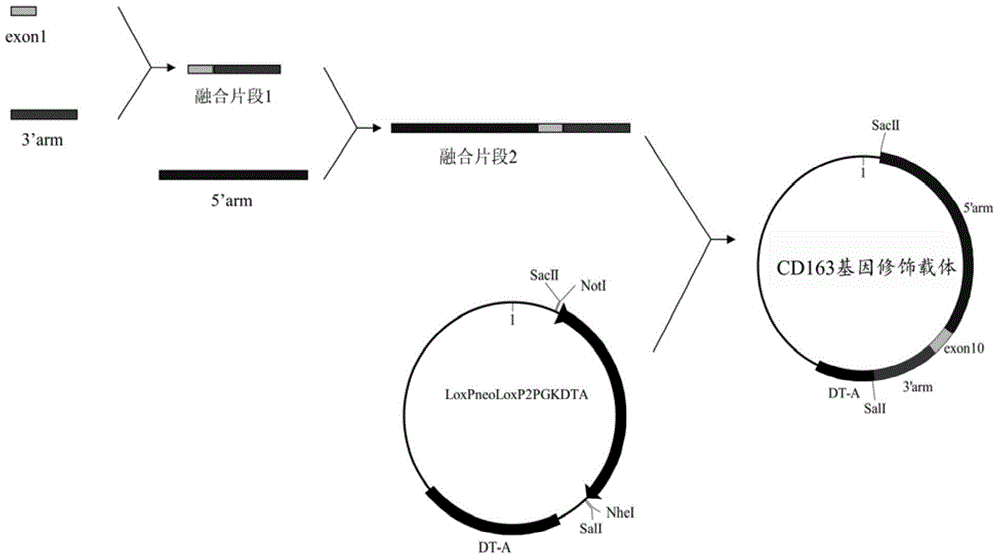
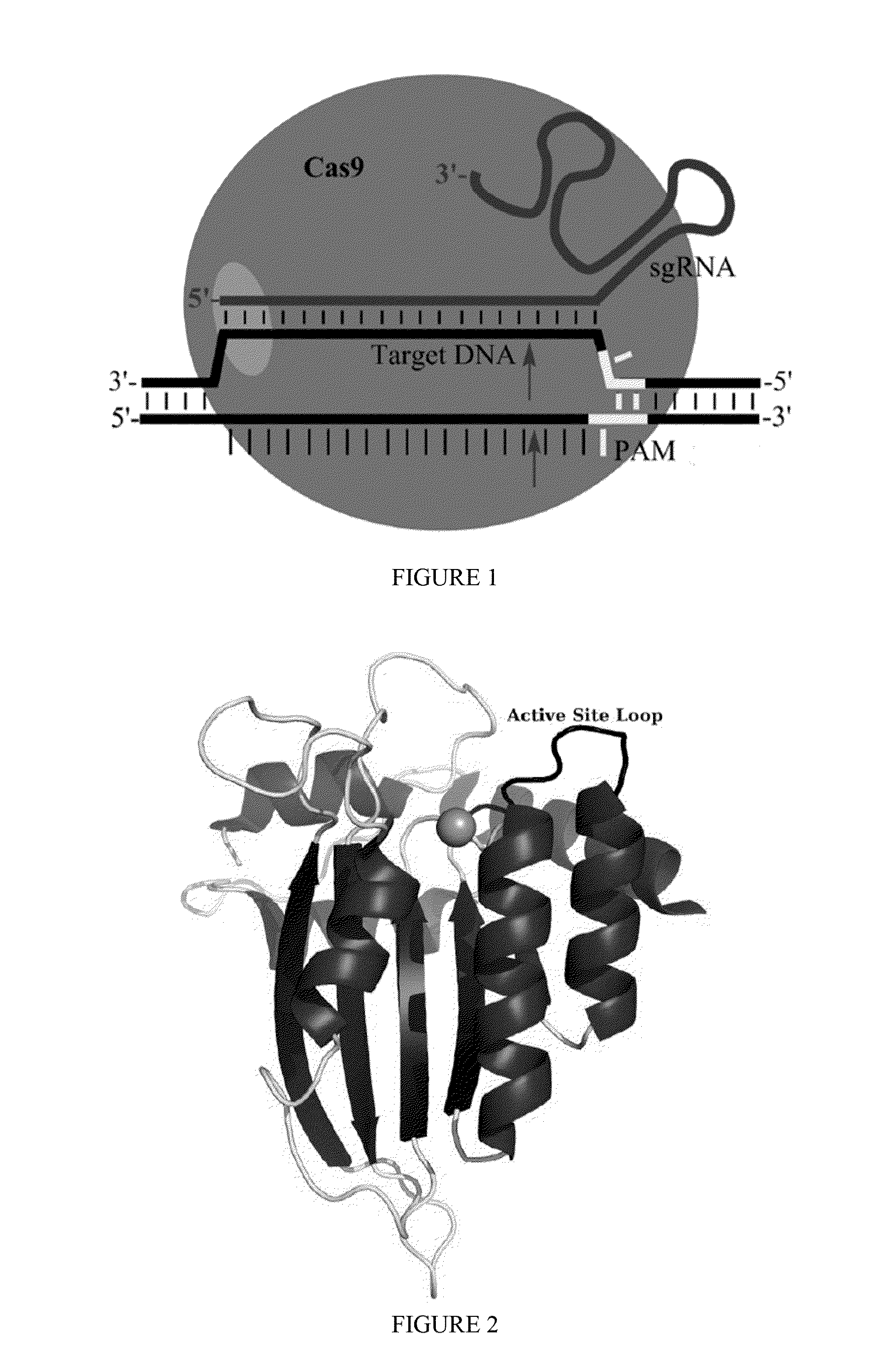
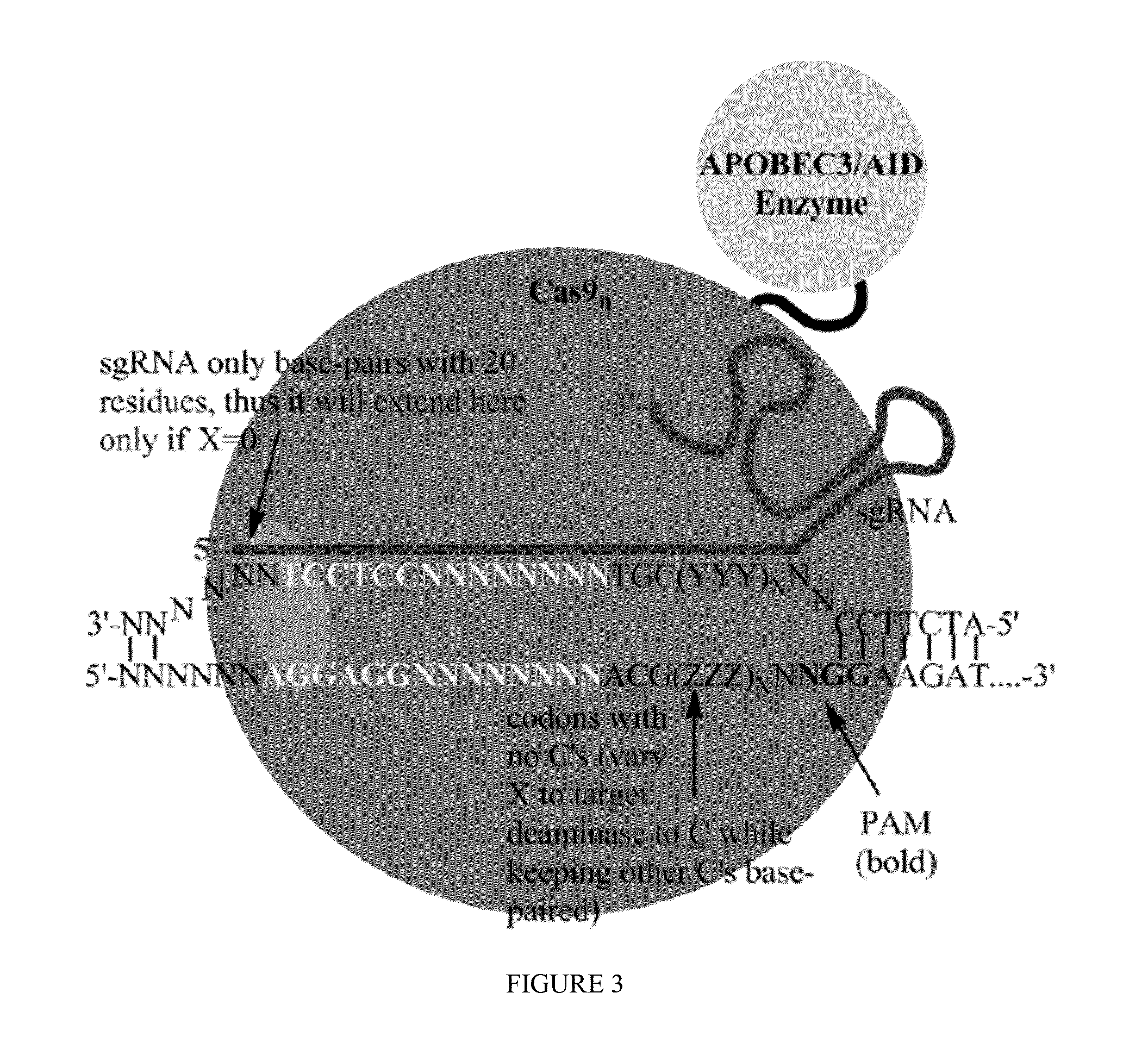
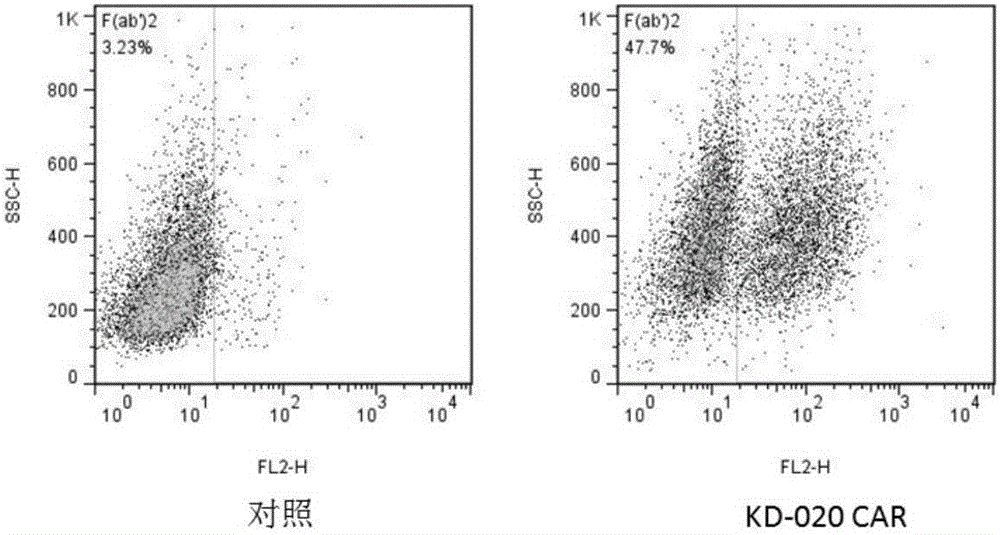
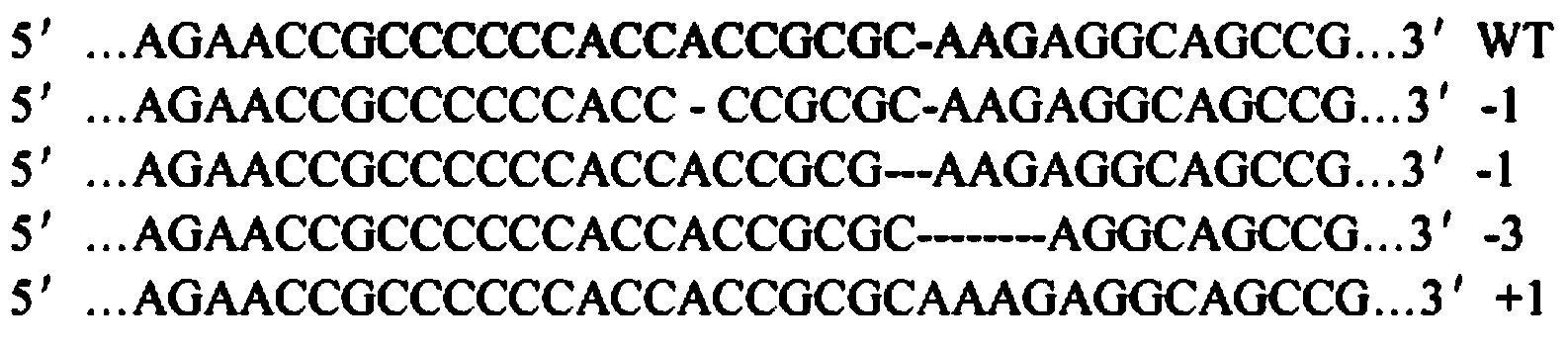Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2403 results about "Cas9" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
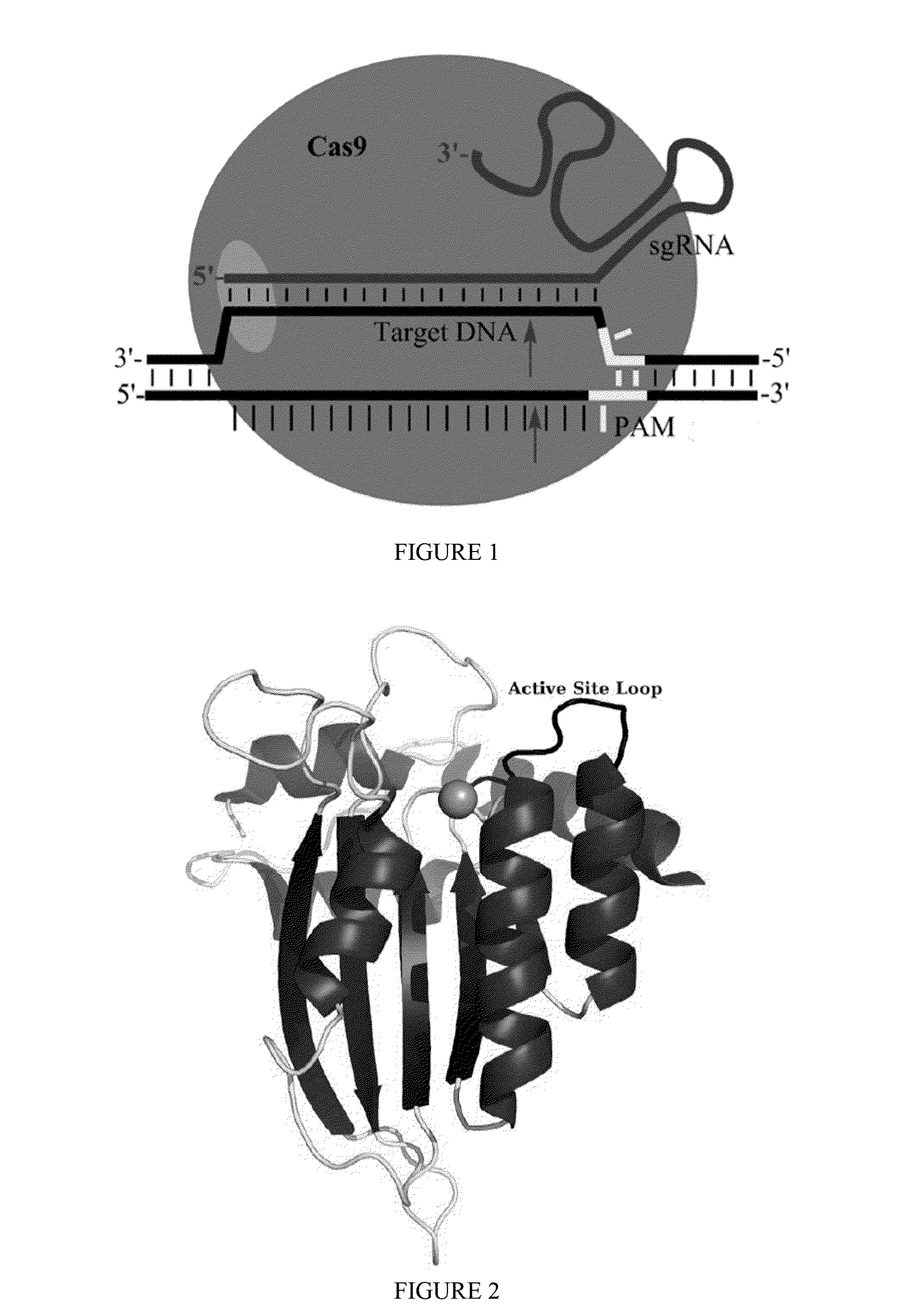
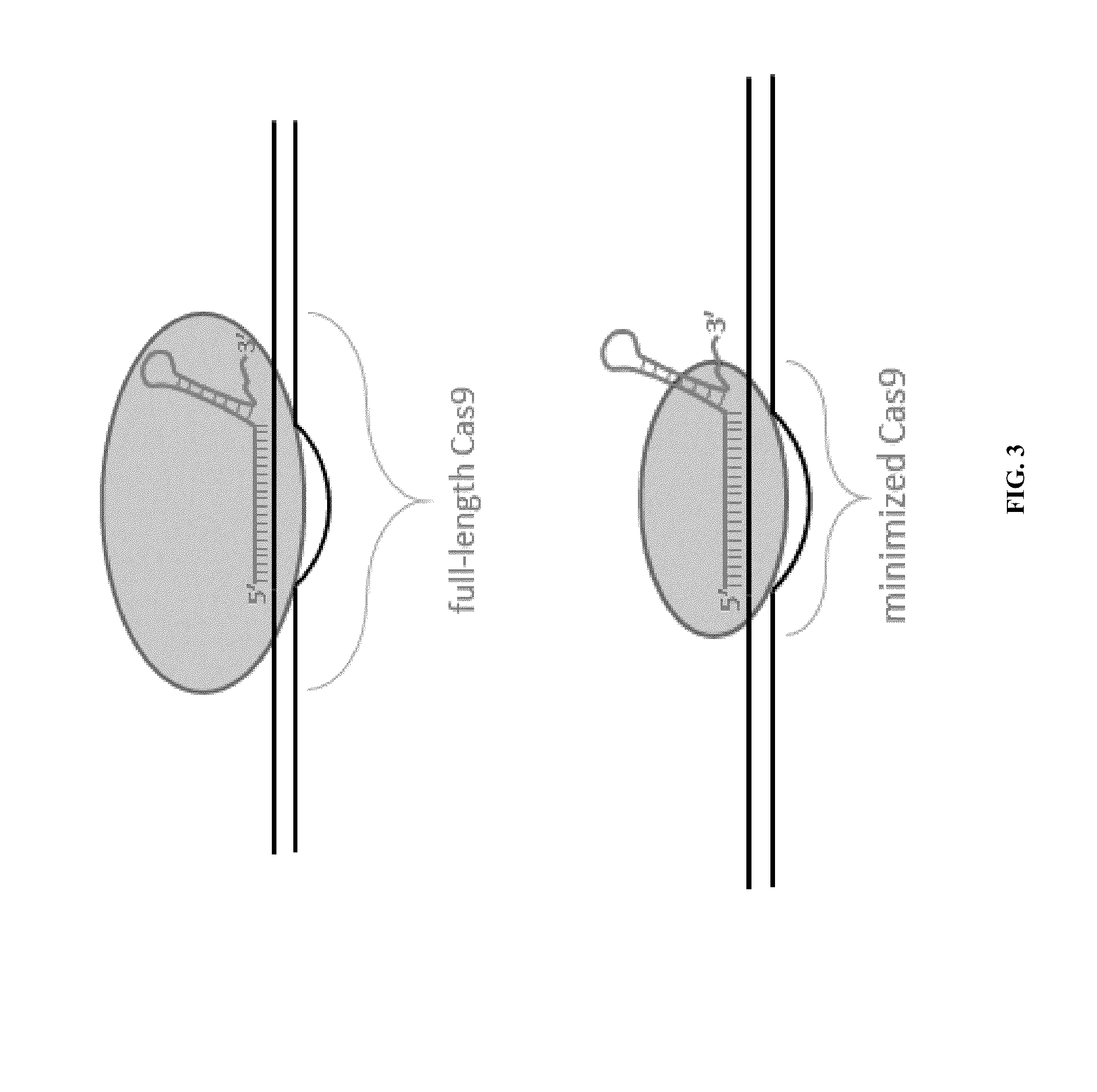
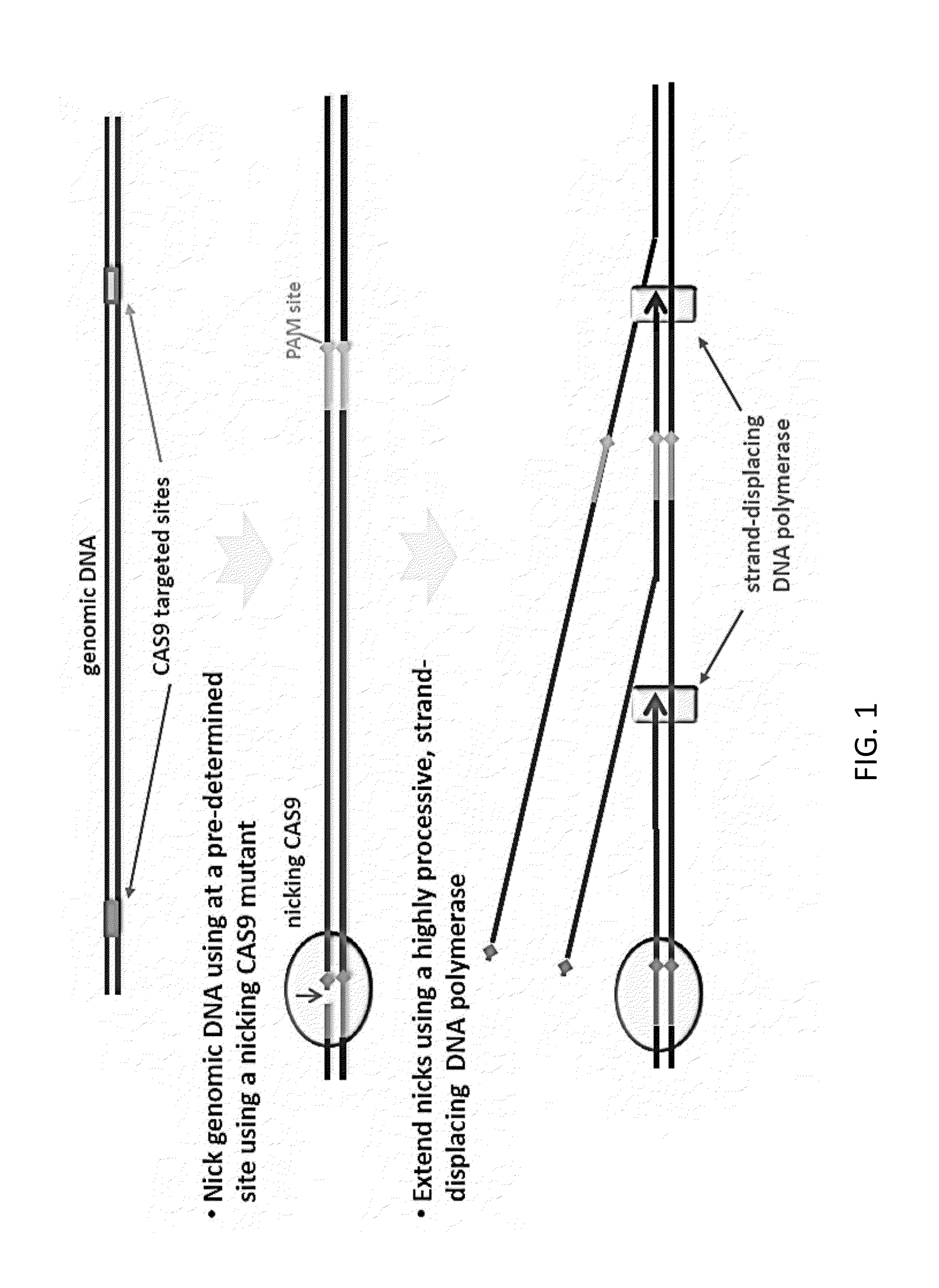
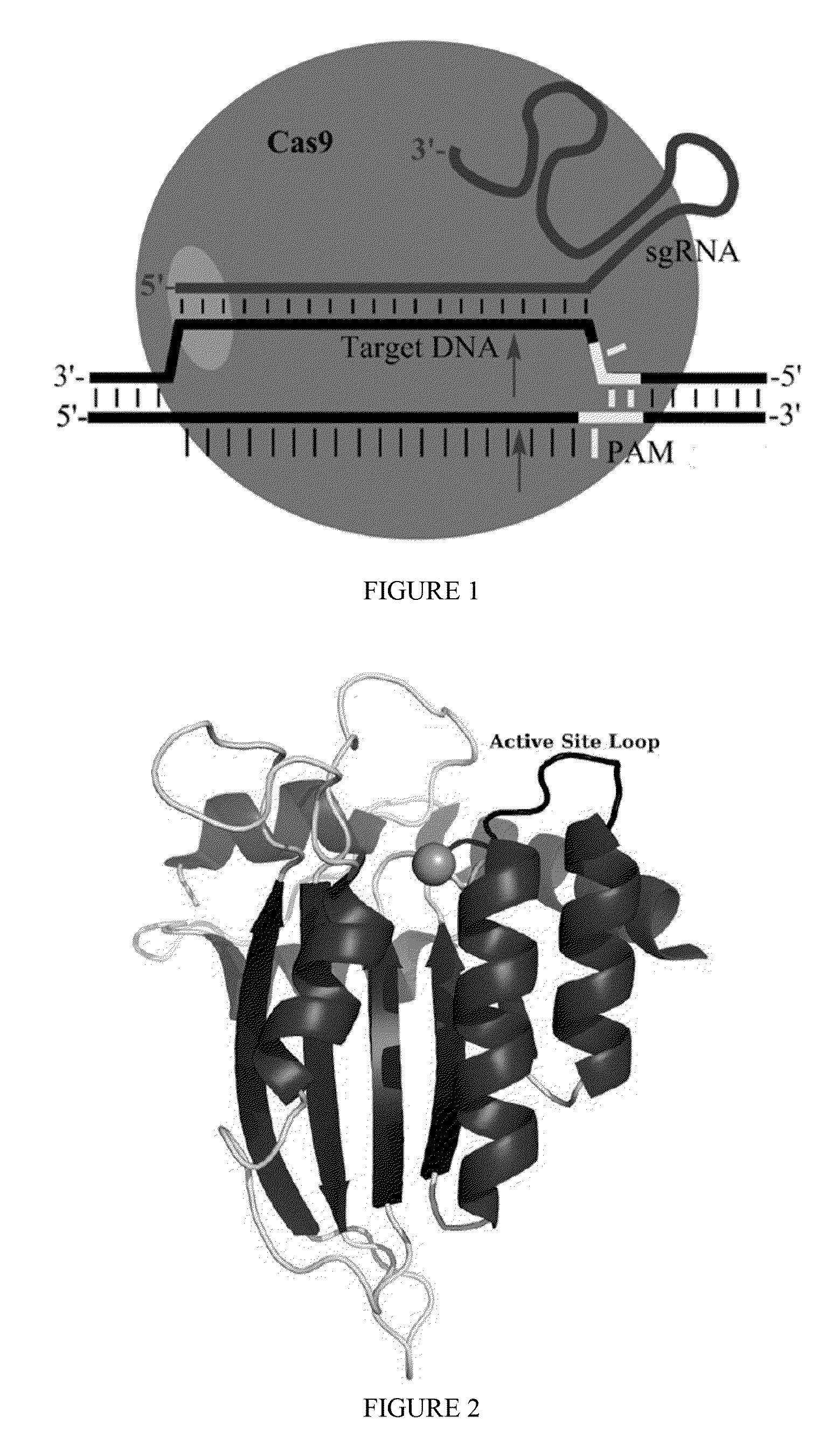
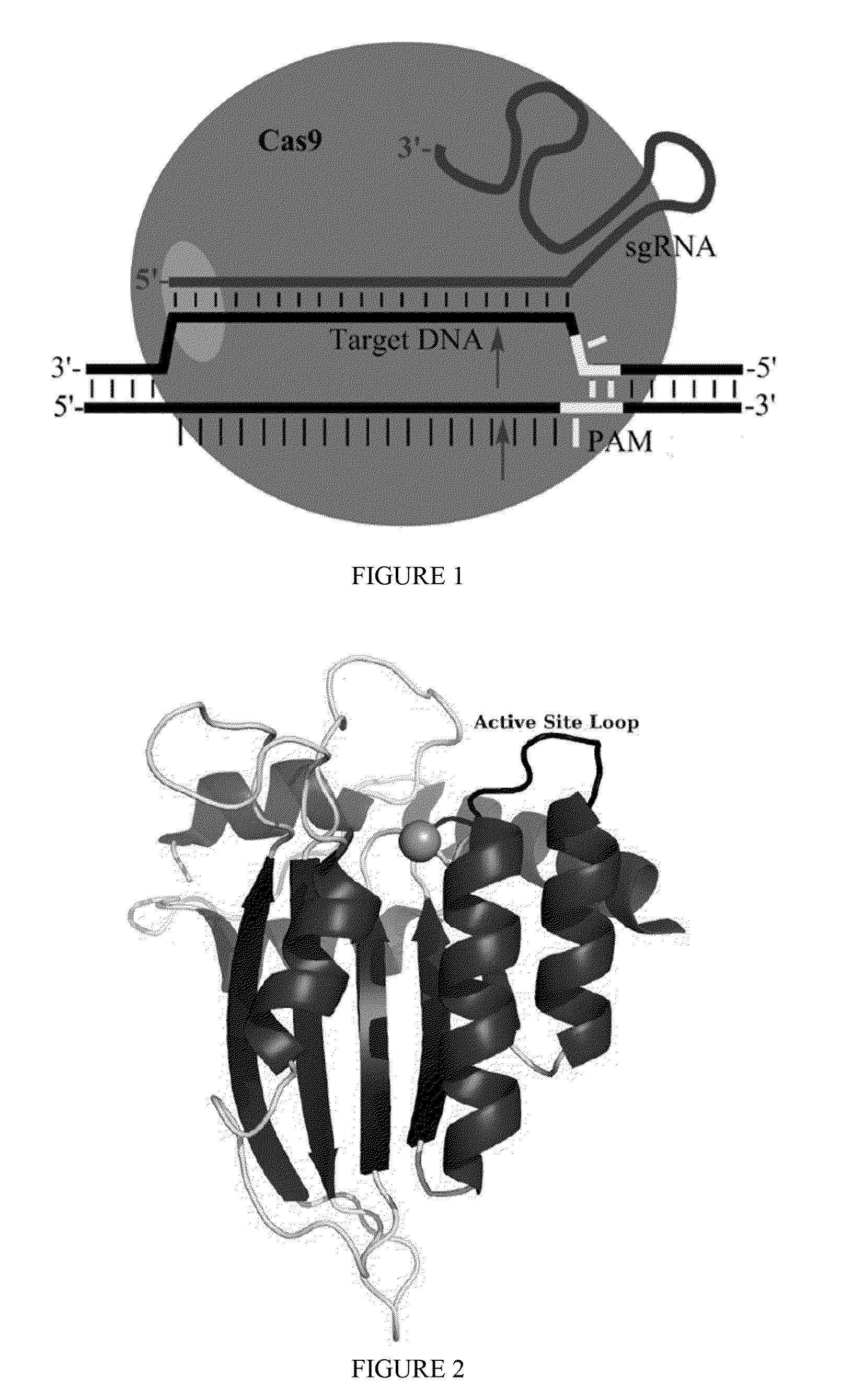
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9) is a protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses, and which is heavily utilized in genetic engineering applications. Its main function is to cut DNA and therefore it can alter a cell's genome.
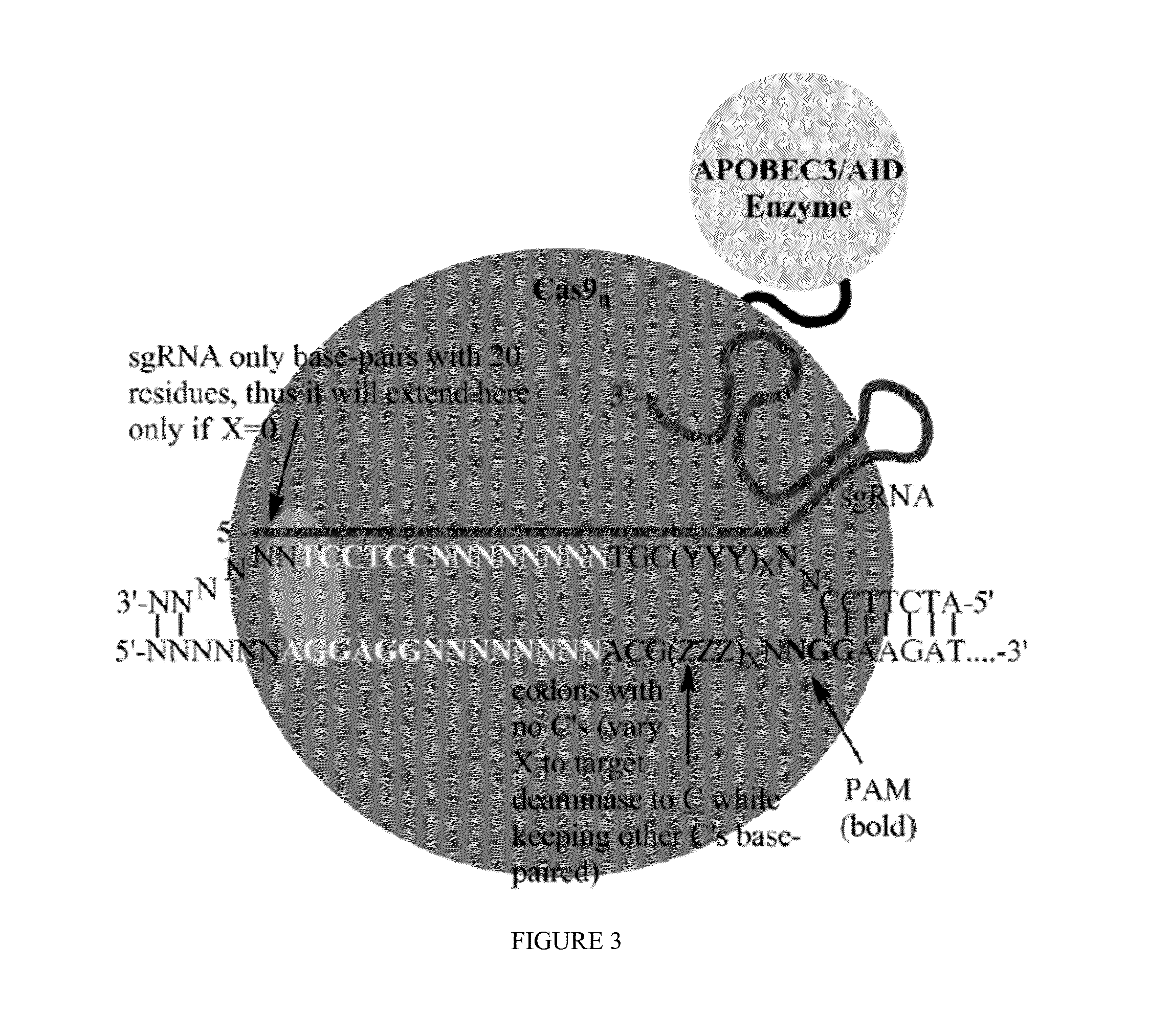
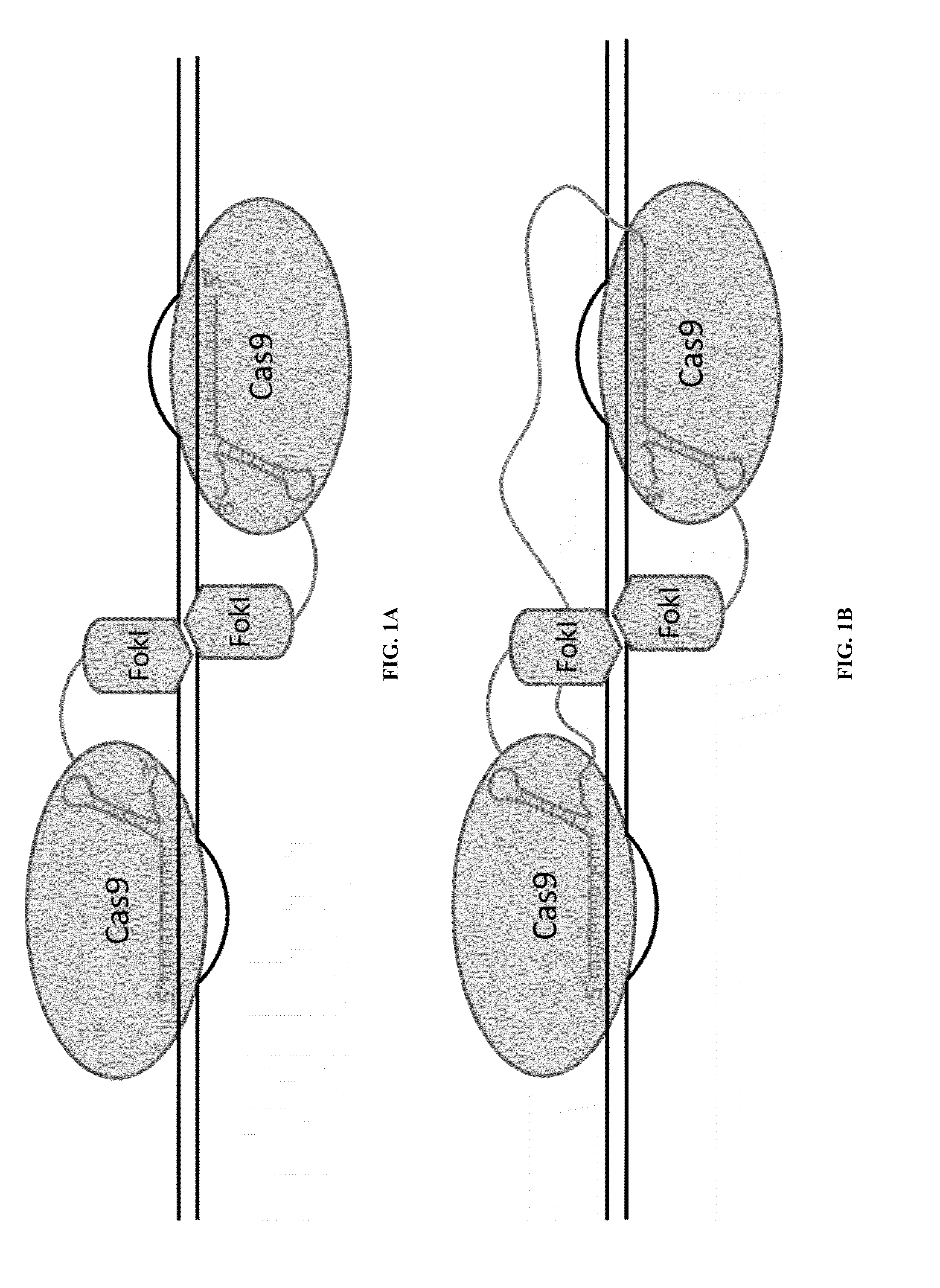
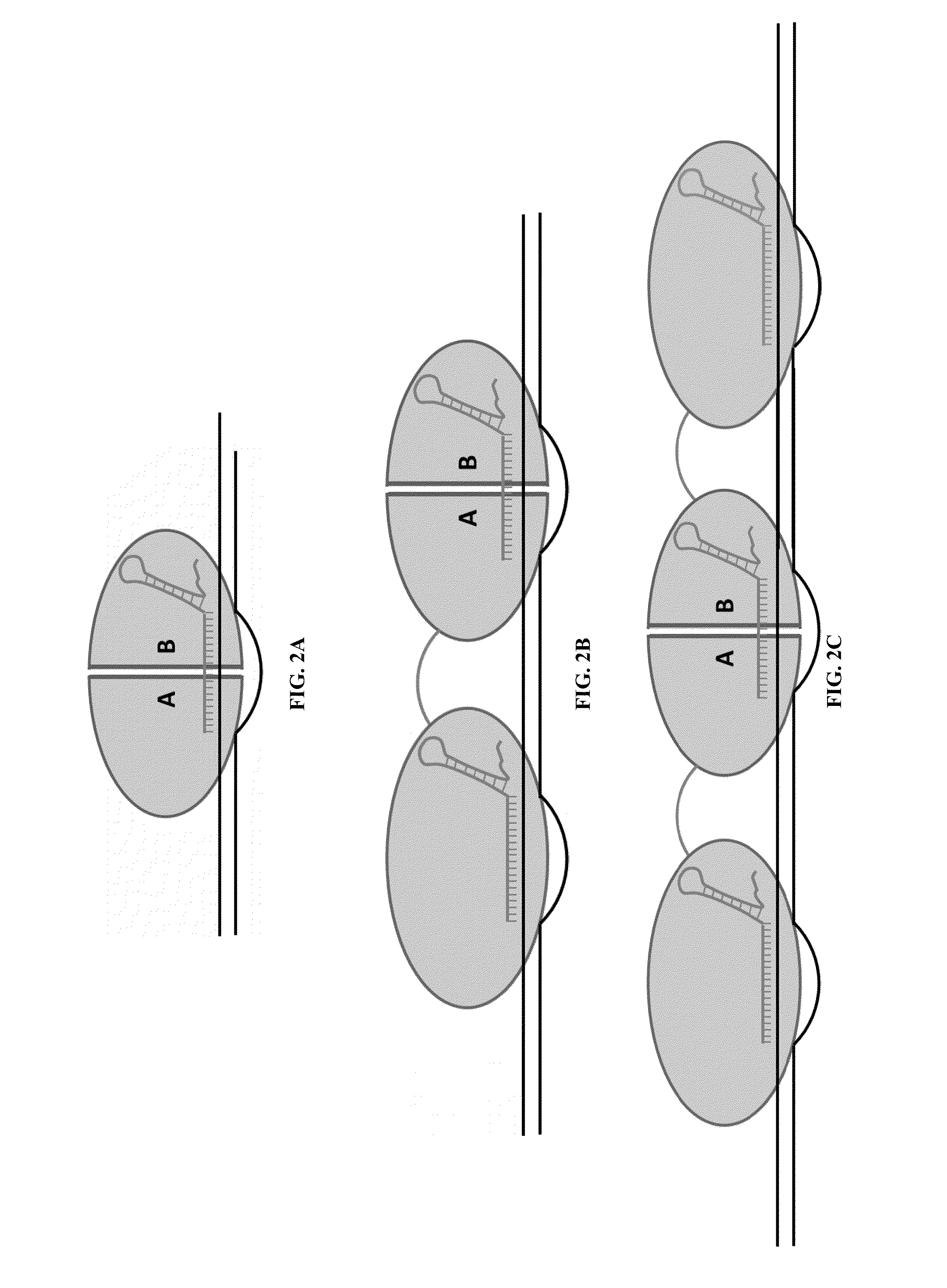
Fusions of cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains
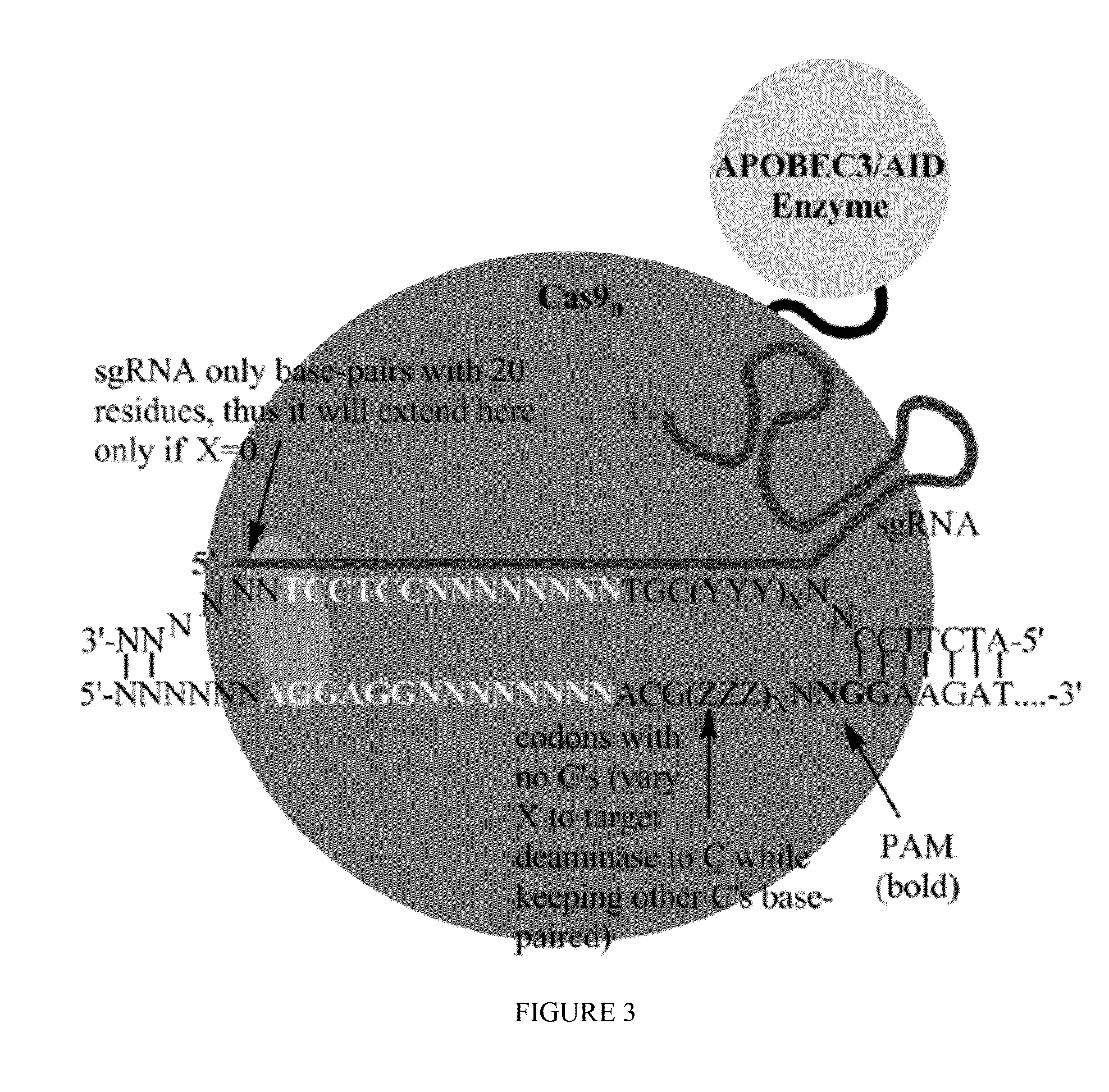
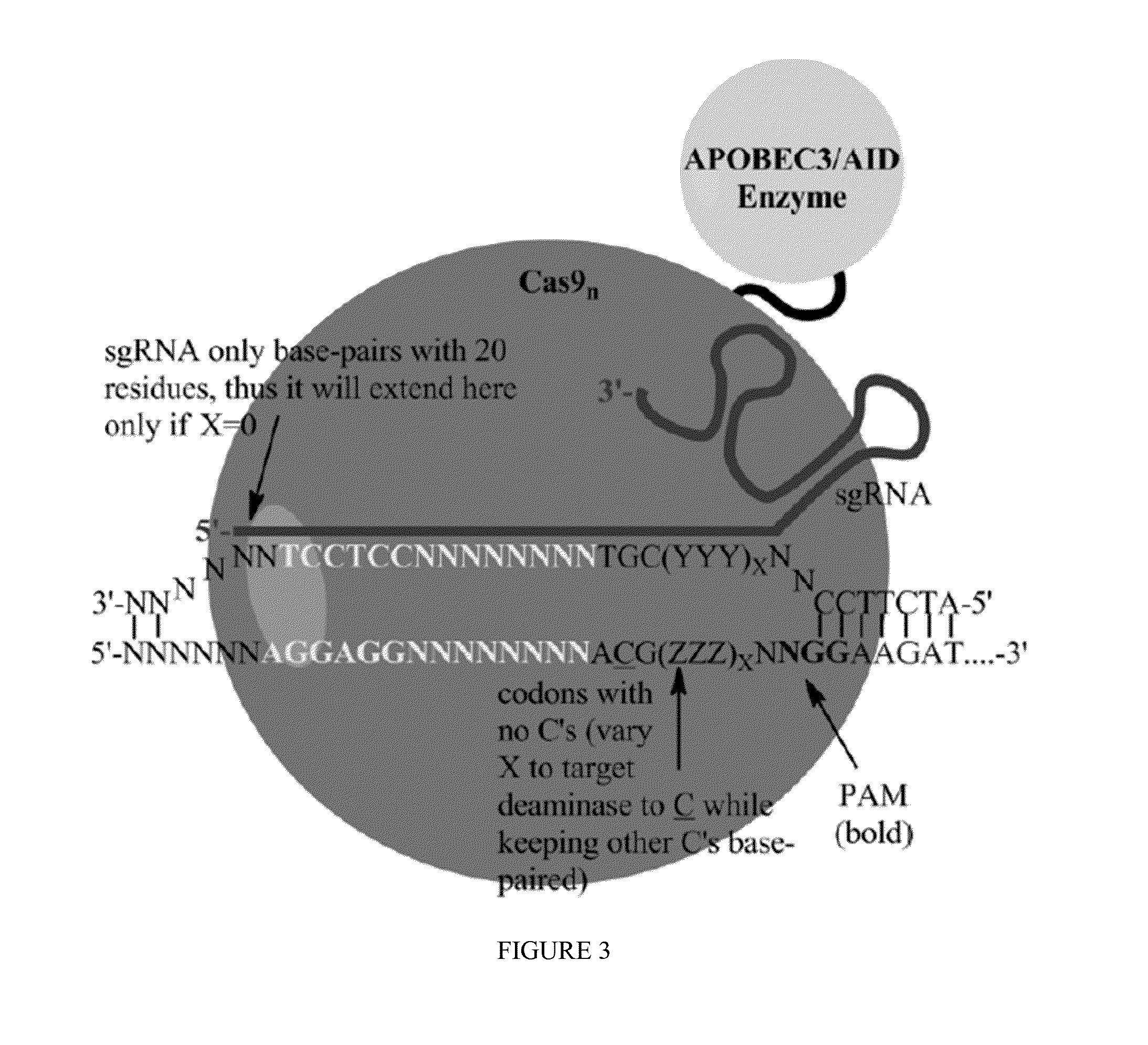
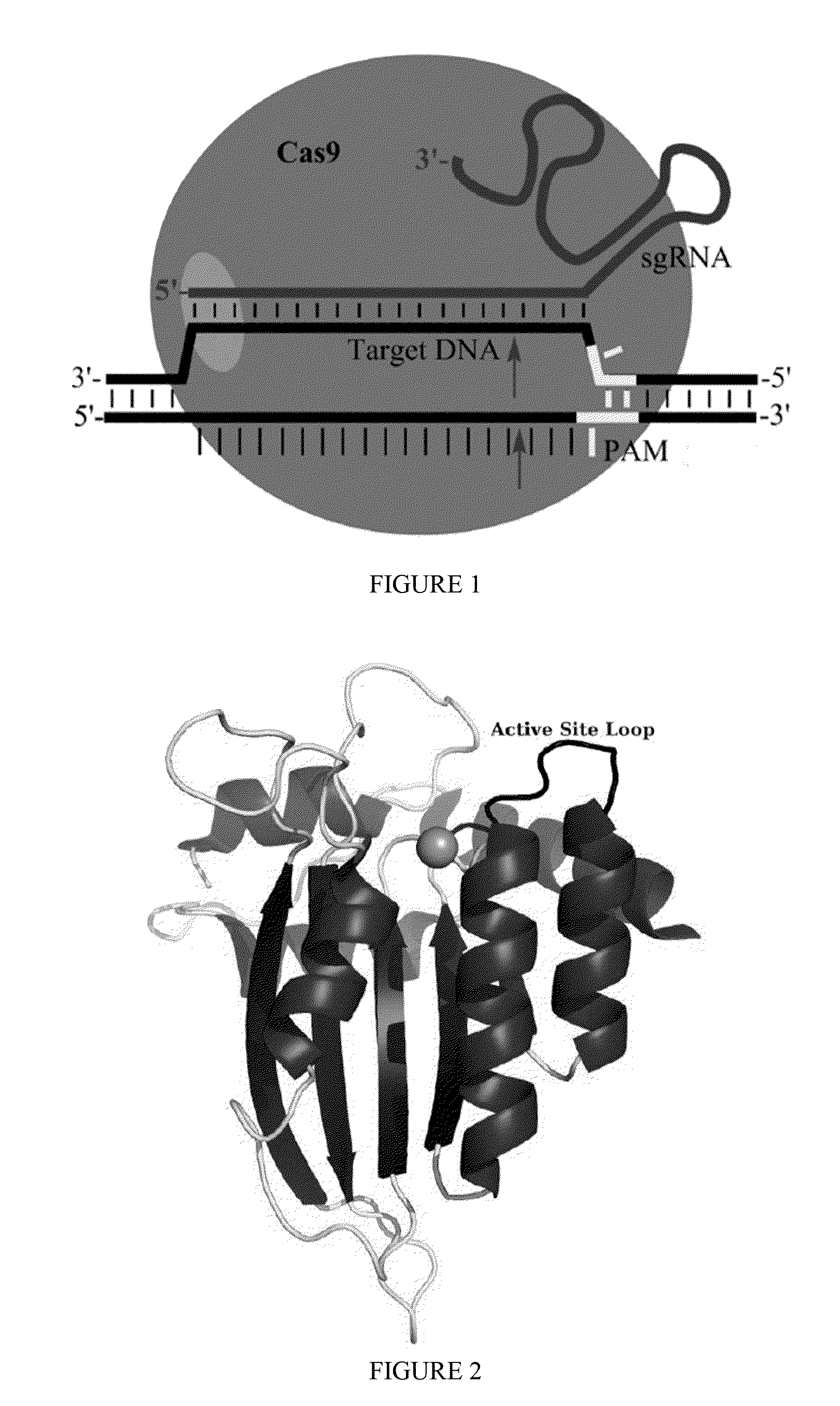
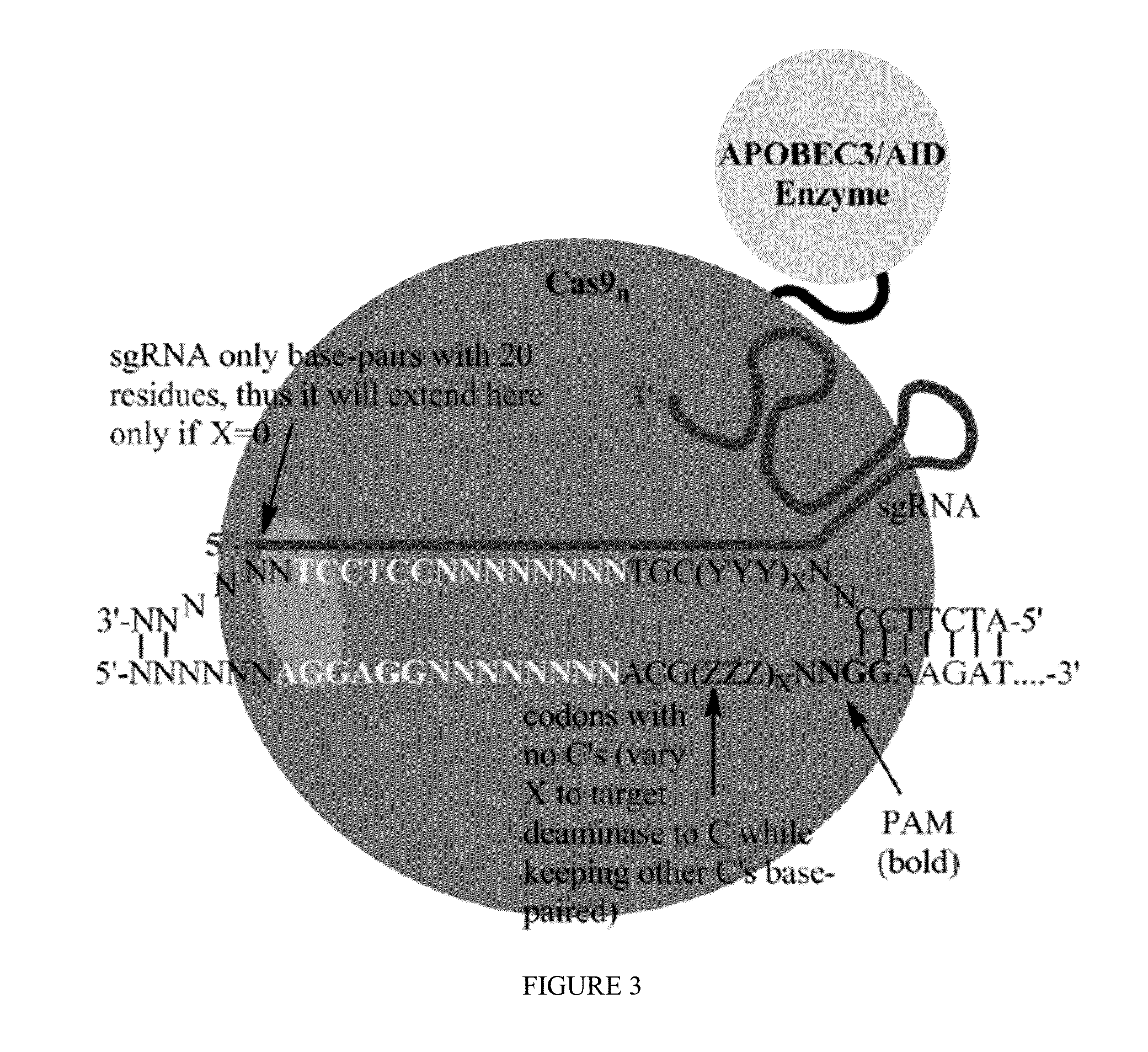
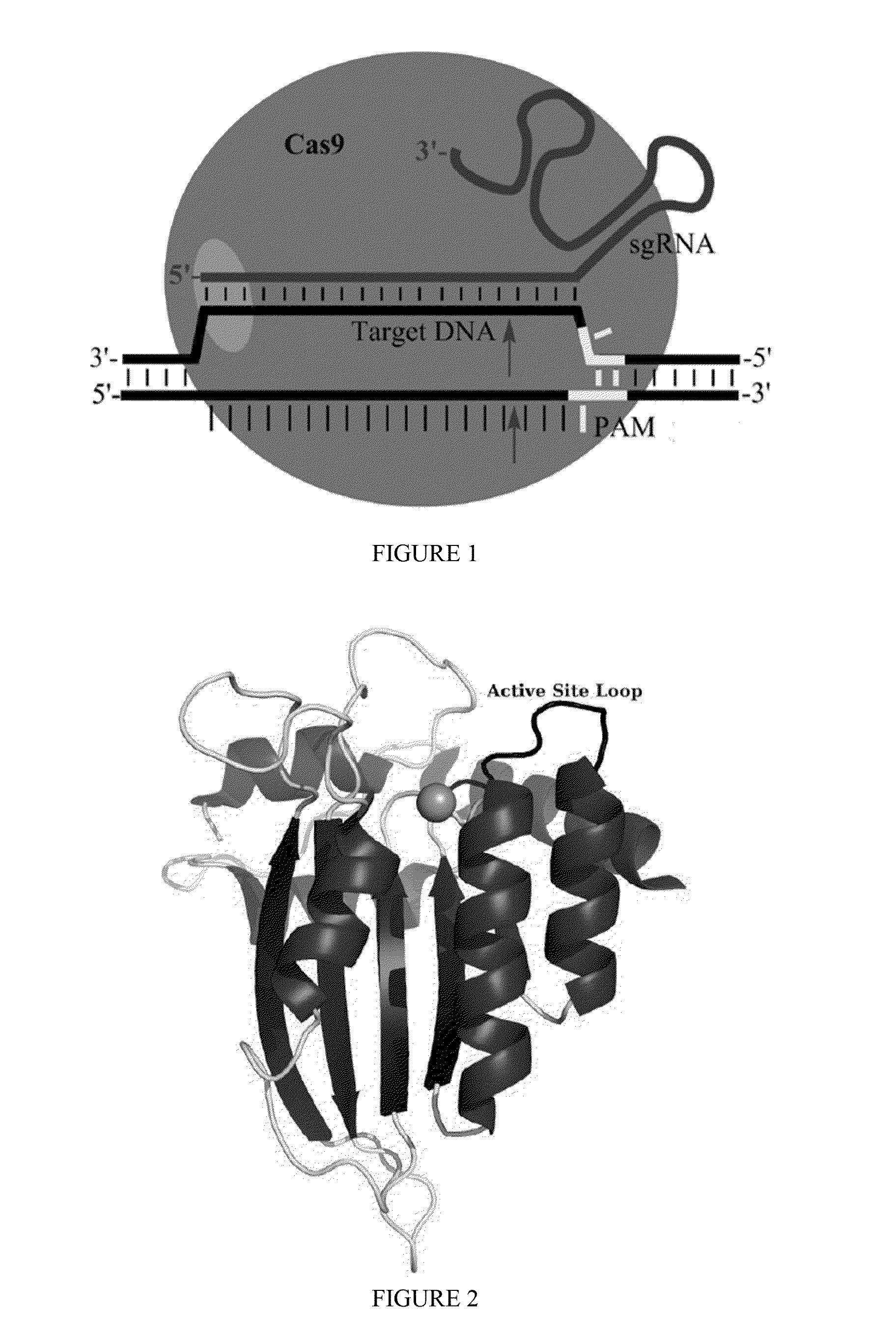
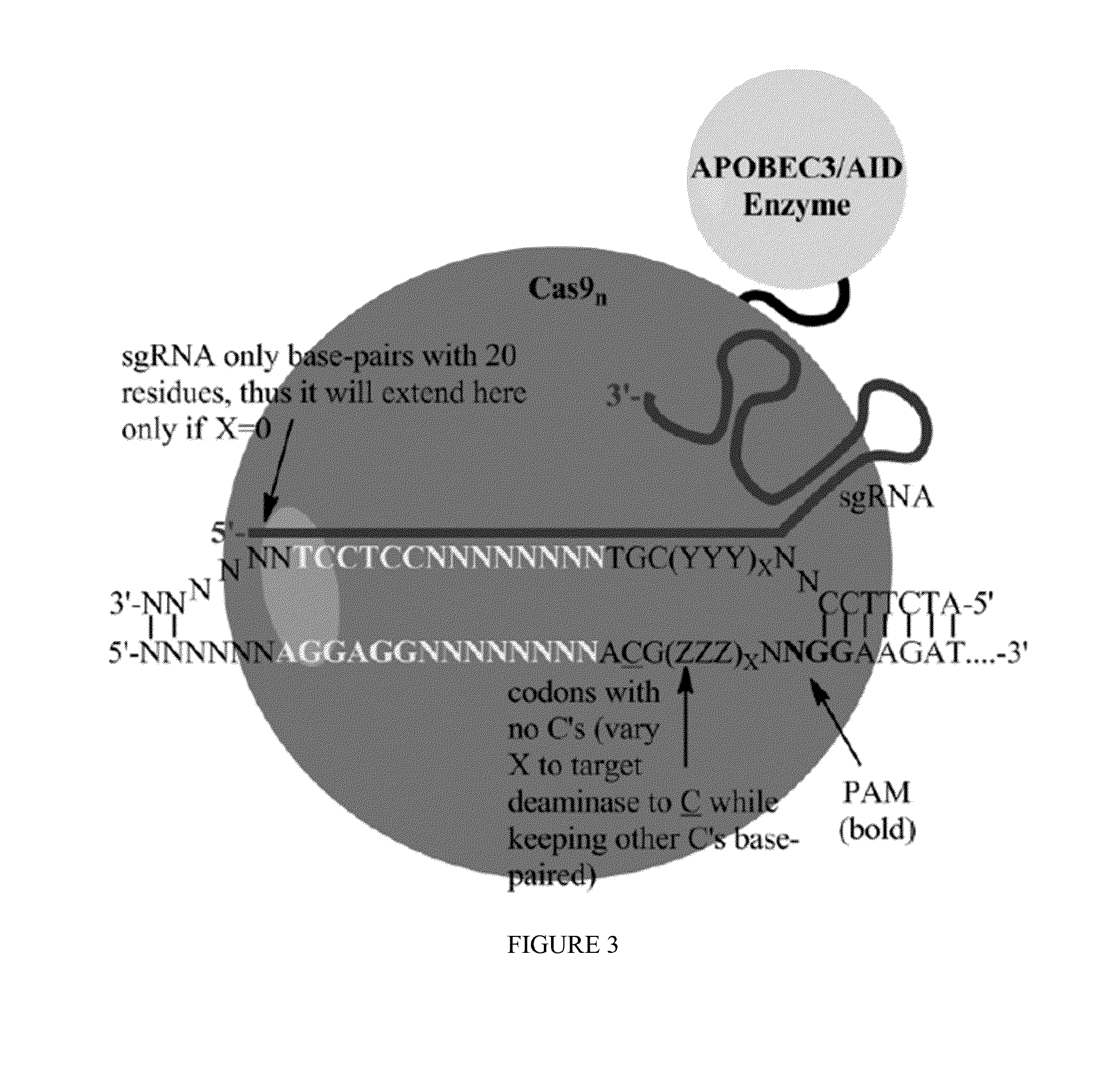
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150071898A1Strong specificityReduce the possibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaSite-specific recombinationResearch setting
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, and kits for improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. Also provided are variants of Cas9, e.g., Cas9 dimers and fusion proteins, engineered to have improved specificity for cleaving nucleic acid targets. Also provided are compositions, methods, and kits for site-specific recombination, using Cas9 fusion proteins (e.g., nuclease-inactivated Cas9 fused to a recombinase catalytic domain). Such Cas9 variants are useful in clinical and research settings involving site-specific modification of DNA, for example, genomic modifications.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
CAS9-based Isothermal Method of Detection of Specific DNA Sequence
ActiveUS20150211058A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionDNANucleic acid
The present invention relates to an isothermal method for detecting in a sample a target nucleic acid strand.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and helical-structure DNA sequence
ActiveCN103233028AUnable to cutImprove accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA repairEucoenogenes
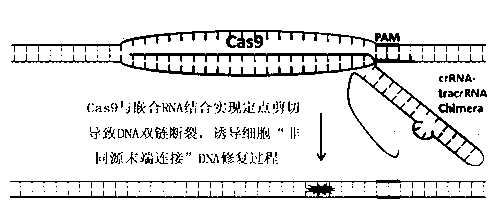
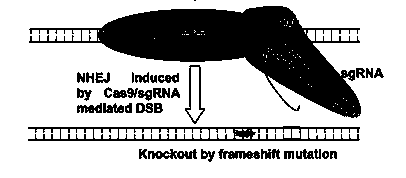
The invention discloses a specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and a helical-structure DNA sequence, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method comprises the following steps of 1, designing and constructing CRISPR / Cas9 and chimeric RNA, and 2, carrying out Cas9mRNA internal translation so that Cas9 nuclease and the chimeric RNA are bonded, carrying out fixed point clipping so that DNA double-chain cleavage is realized after the clipping, and introducing an exogenous DNA by induction of a natural DNA restoration process which is a non-homologous end bonding process of cells so that cell endogenous gene modification is realized. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method has simple processes, realizes flexible site recognition and has low energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING SYNC BIOTECH
Wheat genome site-specific modification method
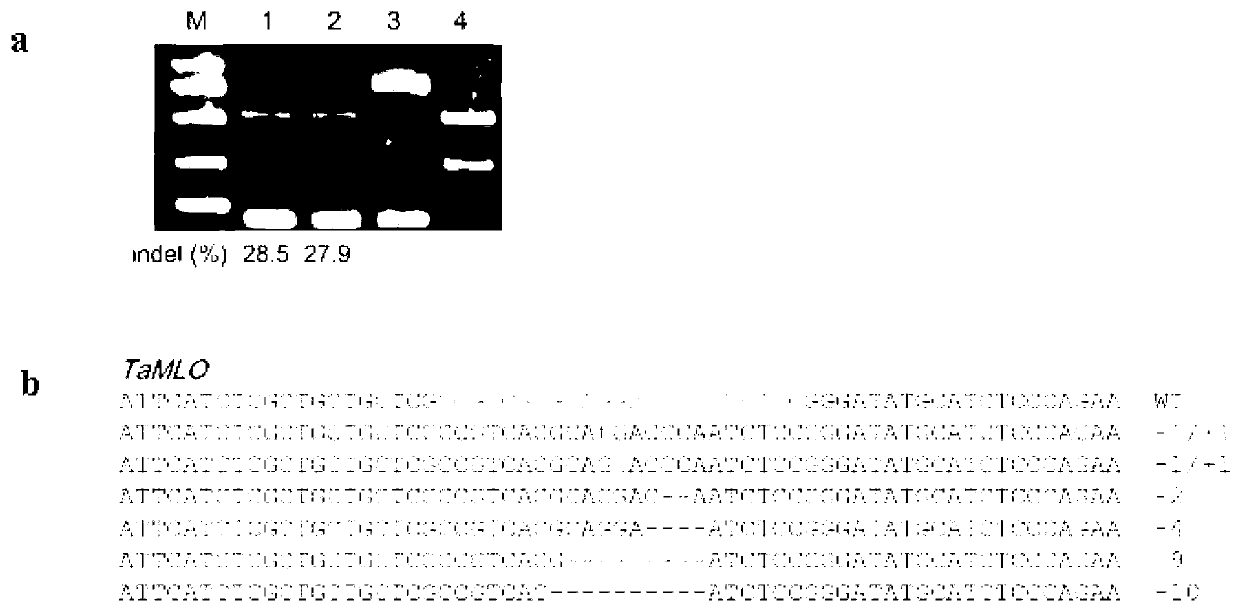
The invention discloses a wheat genome site-specific modification method which comprises the following steps: enabling wheat tissues to contain guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) and Cas9 nuclease; under the coaction of the guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease, cutting a double-chain target segment on the target gene; and by utilizing the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) restoration function of the wheat cells, finally implementing random insertion and / or random deletion on the target segment in the wheat target gene. The experiment proves that the method disclosed by the invention can successfully perform gene mutation on wheat.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Use of cationic lipids to deliver cas9
ActiveUS20150071903A1Prevent and delay onsetSlow onsetFusion with RNA-binding domainFusion with DNA-binding domainDiseaseLipid formation
Compositions, methods, strategies, kits, and systems for the supercharged protein-mediated delivery of functional effector proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro are provided. Compositions, methods, strategies, kits, and systems for delivery of functional effector proteins using cationic lipids and cationic polymers are also provided. Functional effector proteins include, without limitation, transcriptional modulators (e.g., repressors or activators), recombinases, nucleases (e.g., RNA-programmable nucleases, such as Cas9 proteins; TALE nuclease, and zinc finger nucleases), deaminases, and other gene modifying / editing enzymes. Functional effector proteins include TALE effector proteins, e.g., TALE transcriptional activators and repressors, as well as TALE nucleases. Compositions, methods, strategies, and systems for the delivery of functional effector proteins into cells is useful for therapeutic and research purposes, including, but not limited to, the targeted manipulation of a gene associated with disease, the modulation of the expression level of a gene associated with disease, and the programming of cell fate.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting caspase-9 point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant Caspase-9 protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with neuroblastoma. The methods provided are useful for correcting a Caspase-9 point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for constructing eukaryon gene knockout library by using CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)/Cas9 system
ActiveCN103668472AIncrease positive rateLow background valueNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGene expression
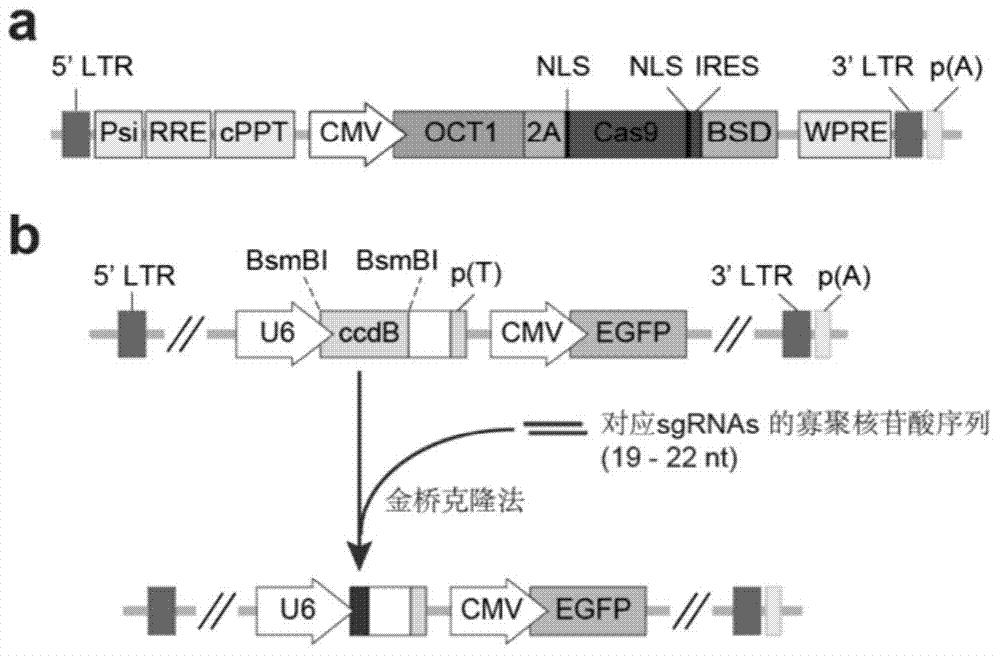
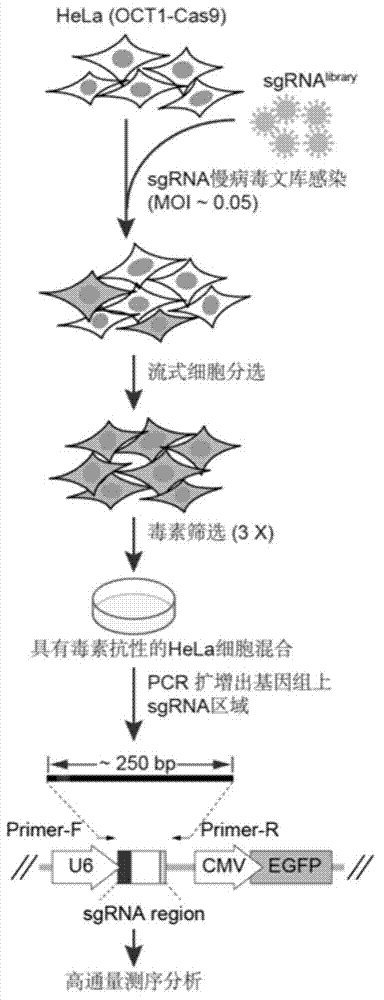
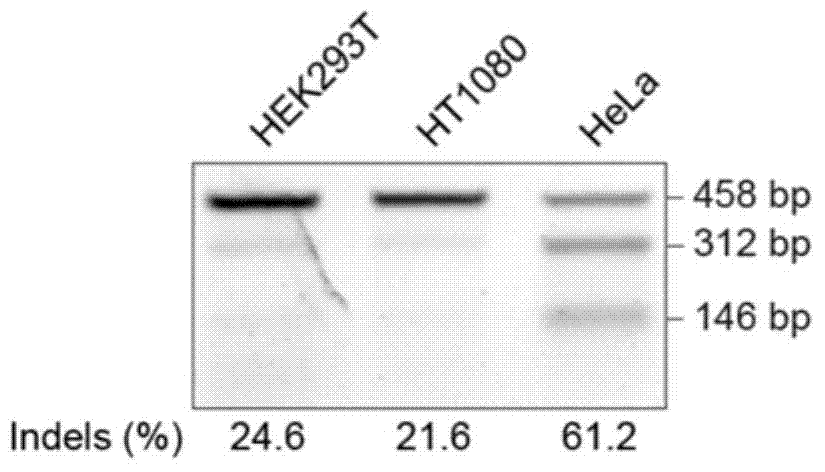
The invention provides a method for constructing a eukaryon gene knockout library by using a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: expressing genes encoded with Cas9 and OCT1 (Organic Cation Transporter 1) proteins into a eukaryon cell line; screening to obtain a cell line which stably expresses Cas9; and carrying out library construction and functional screening. The method has the greatest advantages that the method can be applied to most of eukaryon cell lines and is not limited by the specific cell line. Furthermore, the functional screening positive rate is high and the background value is low. According to a large-scale screening method, the cost is greatly reduced; the problems that the time is long and the labor cost is high due to the fact that a single gene knockout cell is prepared are solved.
Owner:EDIGENE BIOTECH INC
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting presenilin point mutations
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting pi3k point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant PI3KCA protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with a neoplastic disorder. The methods provided are useful for correcting a PI3KCA point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
CRISPR-Cas9 targeted knockout hepatitis b virus cccDNA and specific sgRNA thereof
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a method for specifically knocking out hepatitis b virus cccDNA by using CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting the hepatitis b virus cccDNA. The invention provides a method for specifically knocking out hepatitis b virus cccDNA by using CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA for specifically targeting the hepatitis b virus cccDNA. The sgRNA of specific targeted hepatitis b virus cccDNA prepared according to the invention can precisely target hepatitis b virus cccDNA and realize gene knockout. A preparation method is simple in steps and good in sgRNA targeting, and the knockout efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system is high.
Owner:AOMIAO BIOTECH GUANGZHOU CO LTD
CRISPR/Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector for human immunodeficiency virus gene therapy and lentivirus of CRISPR/Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector
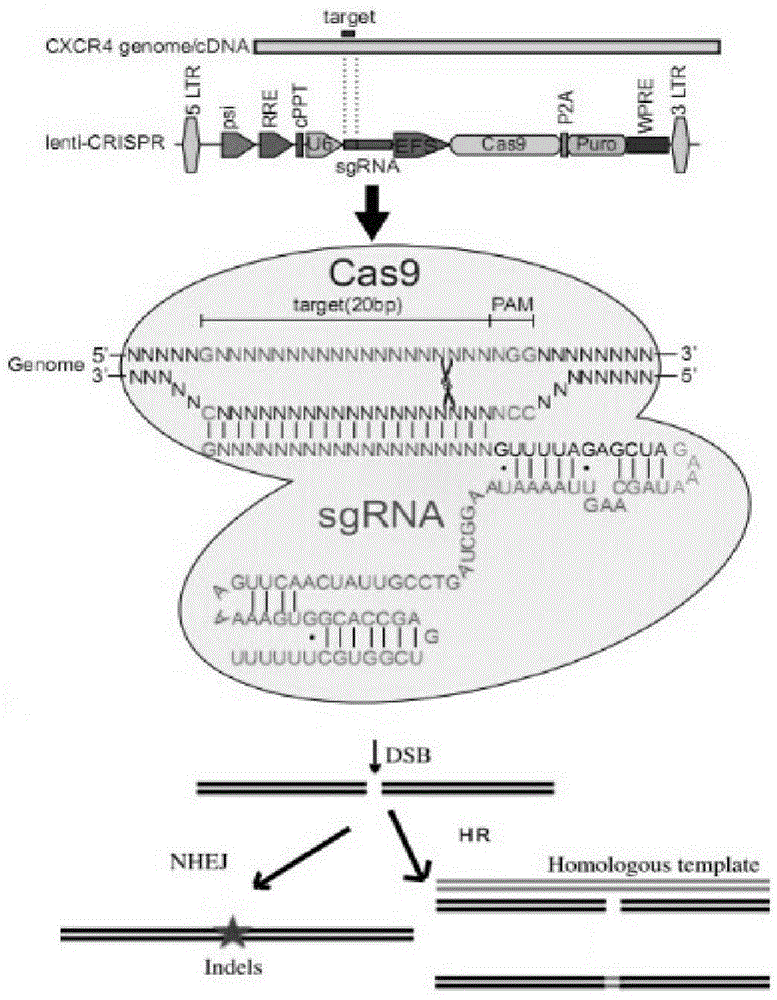
ActiveCN104480144AAvoid or delay intrusionInhibit the spread of infectionGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsEnzyme digestionCXCR4
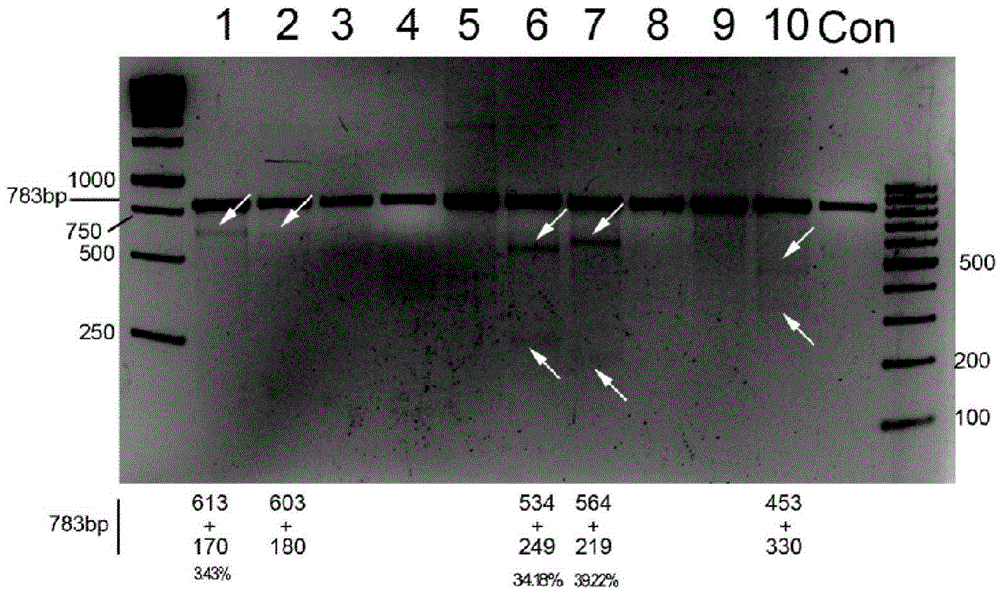
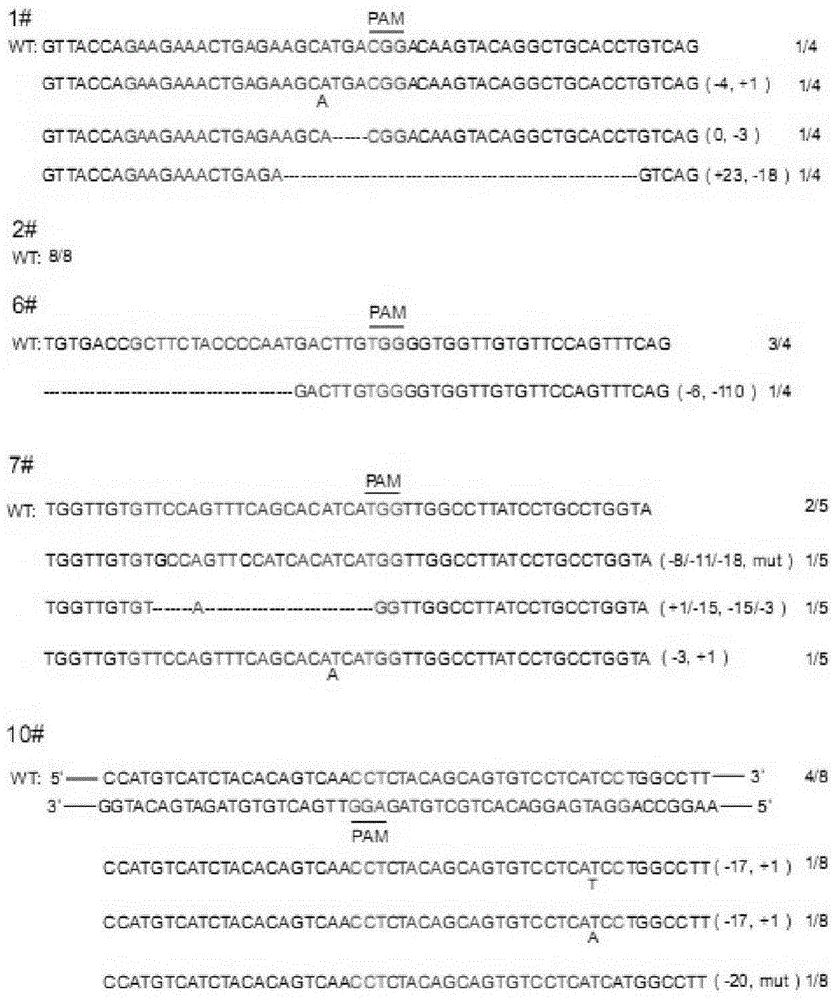
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical and biological engineering, and relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector for human immunodeficiency virus gene therapy and a lentivirus of the CRISPR / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector. The recombinant lentiviral vector is prepared by carrying out enzyme digestion on a lentiviral vectorlentiCRISPR by BsmBI and connecting into a BsmBI cohesive end-containing CXCR4 specific target sequence to recombine; the obtained CRISPR / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector is capable of mutating gene sequences at four different loci of ahuman immunodeficiency virusco-receptor CXCR4 and themutatuin rate is high and up to 25-75%. The cells transformed by the recombinant lentiviral vector cannot be infected by the human immunodeficiency virus. Compared with theRNAi-Knockdown, ZFN and TALEN technologies, the method has higher efficiency of suppressing the human immunodeficiency virus replication; the system is rapid to construct, simple and low in cost, is capable of preventing the invasion of the human immunodeficiency virus and is suitable for human immunodeficiency virus gene therapy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Breeding method for prolongation of rice fertility stage
ActiveCN104004782AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSelf-healingBiotechnology
The invention relates to a breeding method for prolongation of rice fertility stage, and the breeding method comprises the following steps: selecting a target fragment in a rice fertility stage determining gene Ehd3 exon region and constructing a plant CRISPR / Cas9 targeting recombinant vector, introducing into rice cells for regeneration to sprout; using an expression frame in the vector to realize shearing of Ehd3 exon region DNA in the rice cells so as to cause self healing of the rice cells; sequencing regeneration strain genome target fragments to obtain an afunction-mutational strain carrying two equipotential Ehd3 genes, and confirming the prolongation of the regeneration plant fertility stage by phenotypic identification. Experiments show that the method can quickly obtain fertility stage prolonged rice materials.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fast CRISPR-Cas9 working efficiency testing system and application thereof
InactiveCN105647968ATest accurateTested and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesEnzyme digestionRapid testing
The invention discloses a fast CRISPR-Cas9 working efficiency testing system and application thereof. The testing system comprises a plasmid used for expressing sg RNA, a plasmid used for expressing Cas9 and a reporting system used for testing the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing efficiency; the reporting system can splice the C-terminal of a nucleotide segment capable of coding effective protein and the N-terminal of a reporter gene and insert two restriction endonuclease enzyme digestion sites into the splicing position; before a special gene is edited (knocked out) through the CRISPR-Cas9 system, selection of a target sequence is vital, and the selection can influence the recognition efficiency of the sg RNA to target DNA, the binding efficiency of the sg RNA with the target DNA, the targeted cutting efficiency of the Cas9 and the NHEJ repairing efficiency. According to the system, the gene editing efficiency of different sgRNA-target DNA sequences can be quantitatively compared, the sgRNA with the best working effect can be determined within a short time, the actual knockout success rate is increased, therefore, the working cost can be lowered, the working efficiency can be improved, and the working progress can be promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of cloning reproductive and respiratory syndrome resisting pig
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods for correcting von willebrand factor point mutations
InactiveUS20150166985A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingFactor VIII vWF
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant von Willebrand Factor protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with von Willebrand disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting a vWF point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for knocking off animal FGF5 gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
ActiveCN104531704AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNAExon
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal FGF5 gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second FGF5 exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second FGF5 exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal FGF5 gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for knocking out PD-1 gene by utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 technology to construct MSLN-targeted novel CAR-T cell and application of method
PendingCN106480097ABlock escapeBlocking inhibitoryGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsT cellSolid tumor
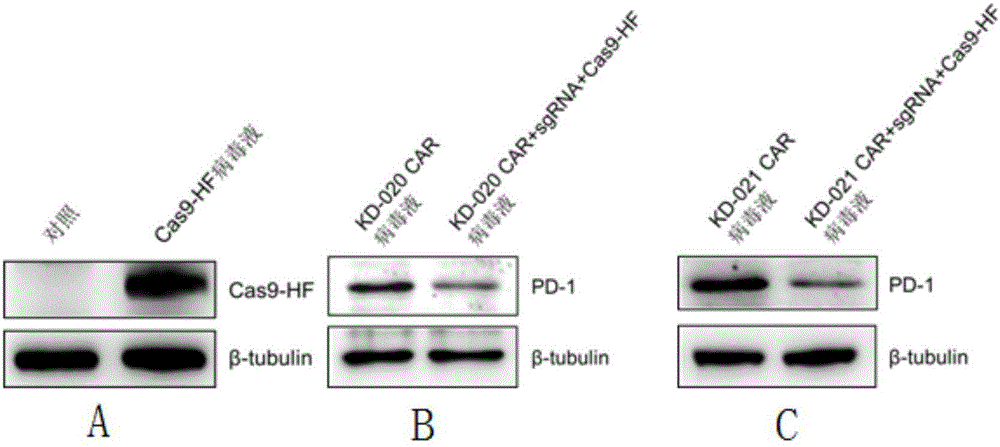
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a PD-1 gene by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology to construct an MSLN-targeted novel CAR-T cell. According to the method, a CAR-T cell is synchronously infected with a virus solution carrying sgRNA and Cas9-HF nuclease of a human PD-1 gene by utilizing the CRISPR / Cas9 technology to knock out the human PD-1 gene, so that the MSLN-targeted novel CAR-T cell is obtained. The novel CAR-T cell can be used for preparing a preparation used for treating solid tumors. A preparation method is simple in step, and the obtained CAR-T cell has high killing rate for solid tumor cells.
Owner:NANJING KAEDI BIOTECH INC
Methods for nucleic acid editing
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
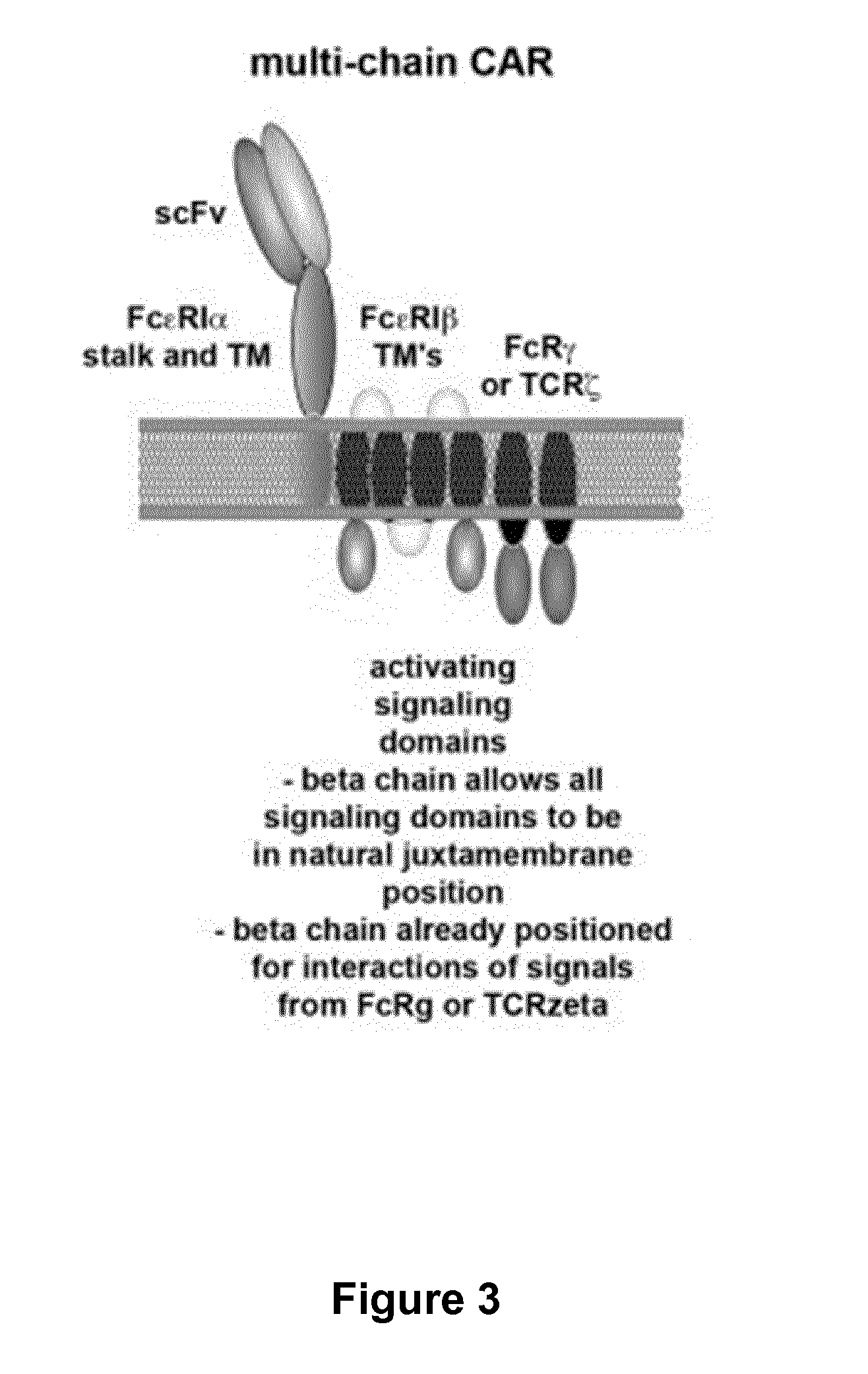
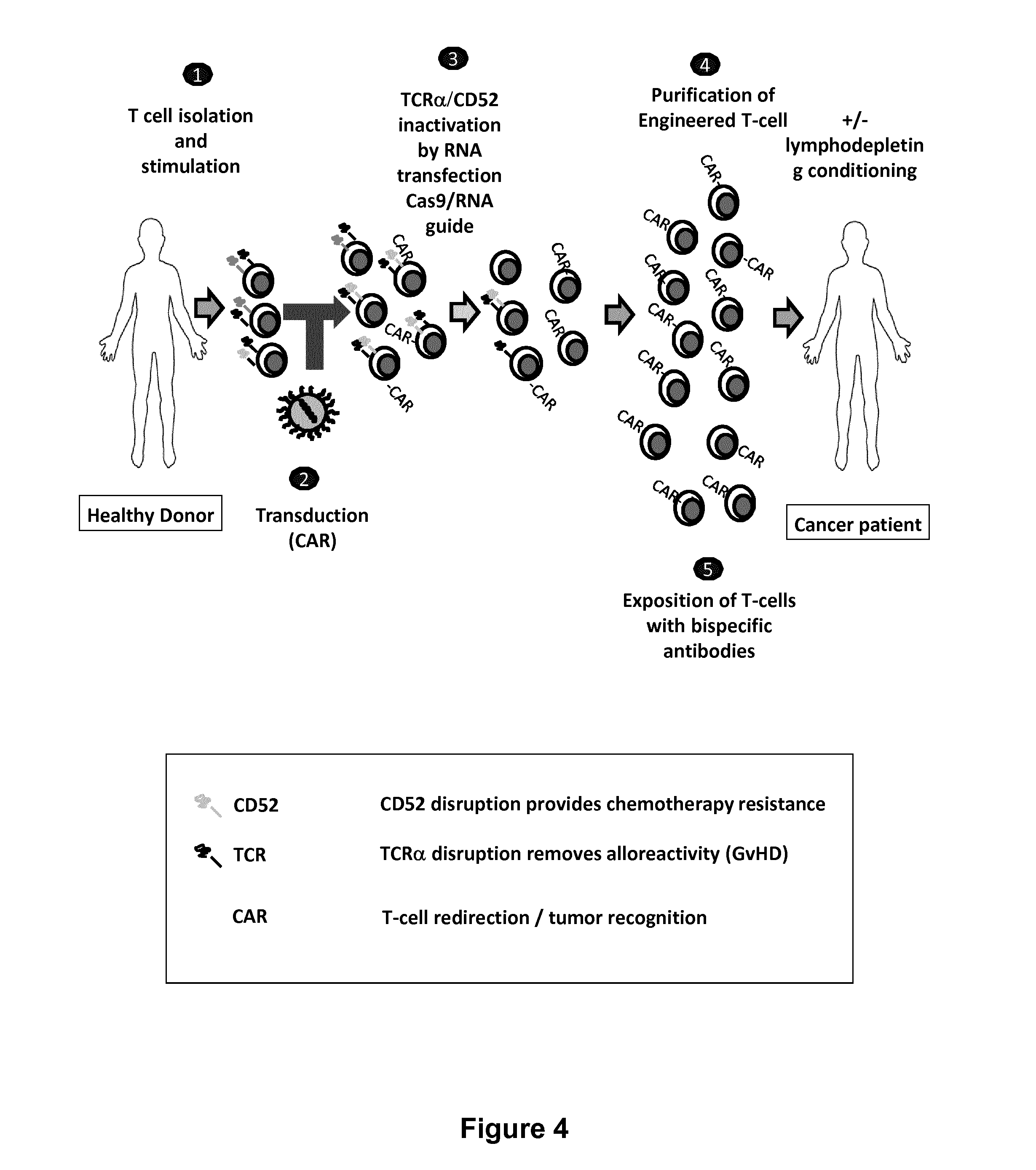
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160272999A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
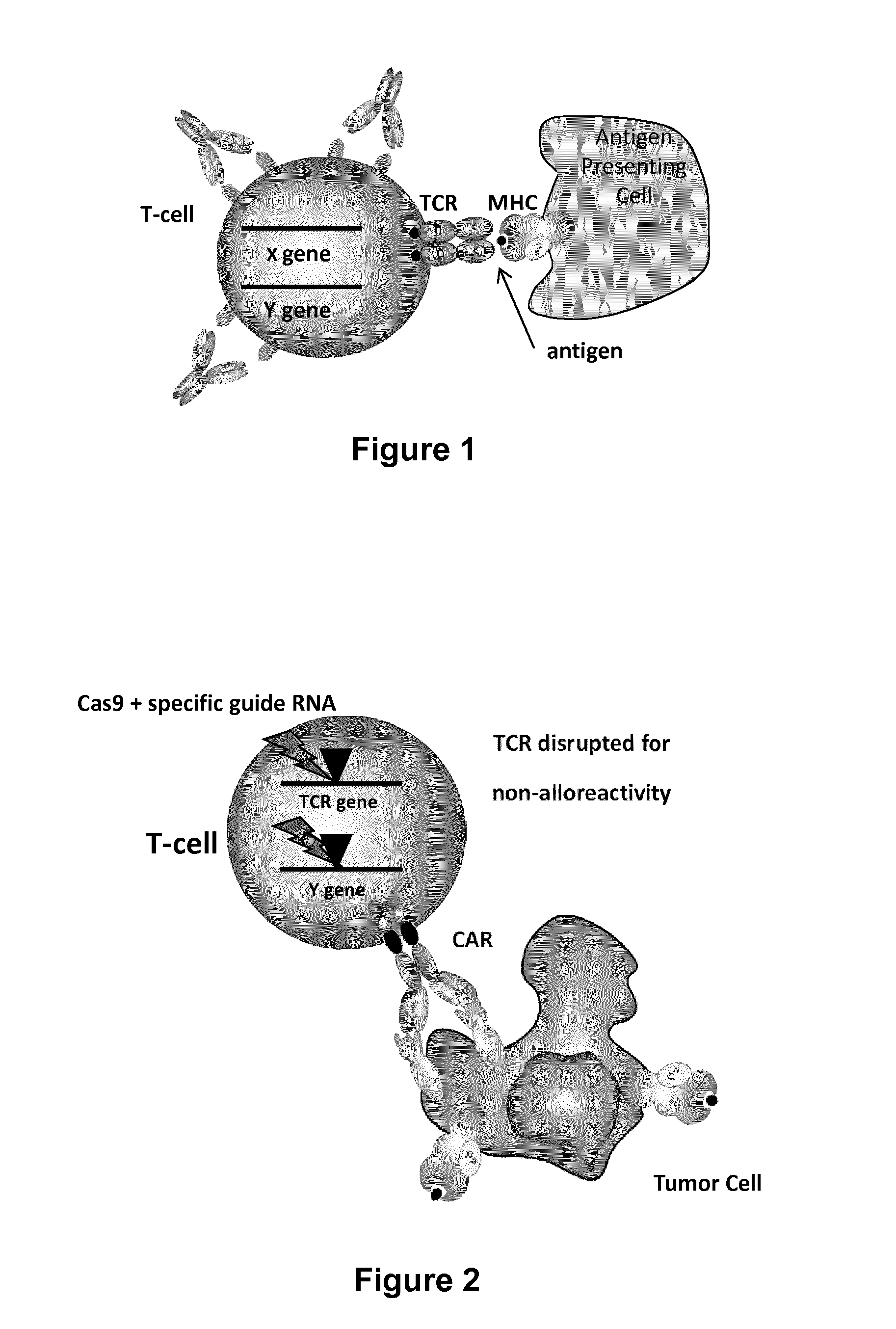
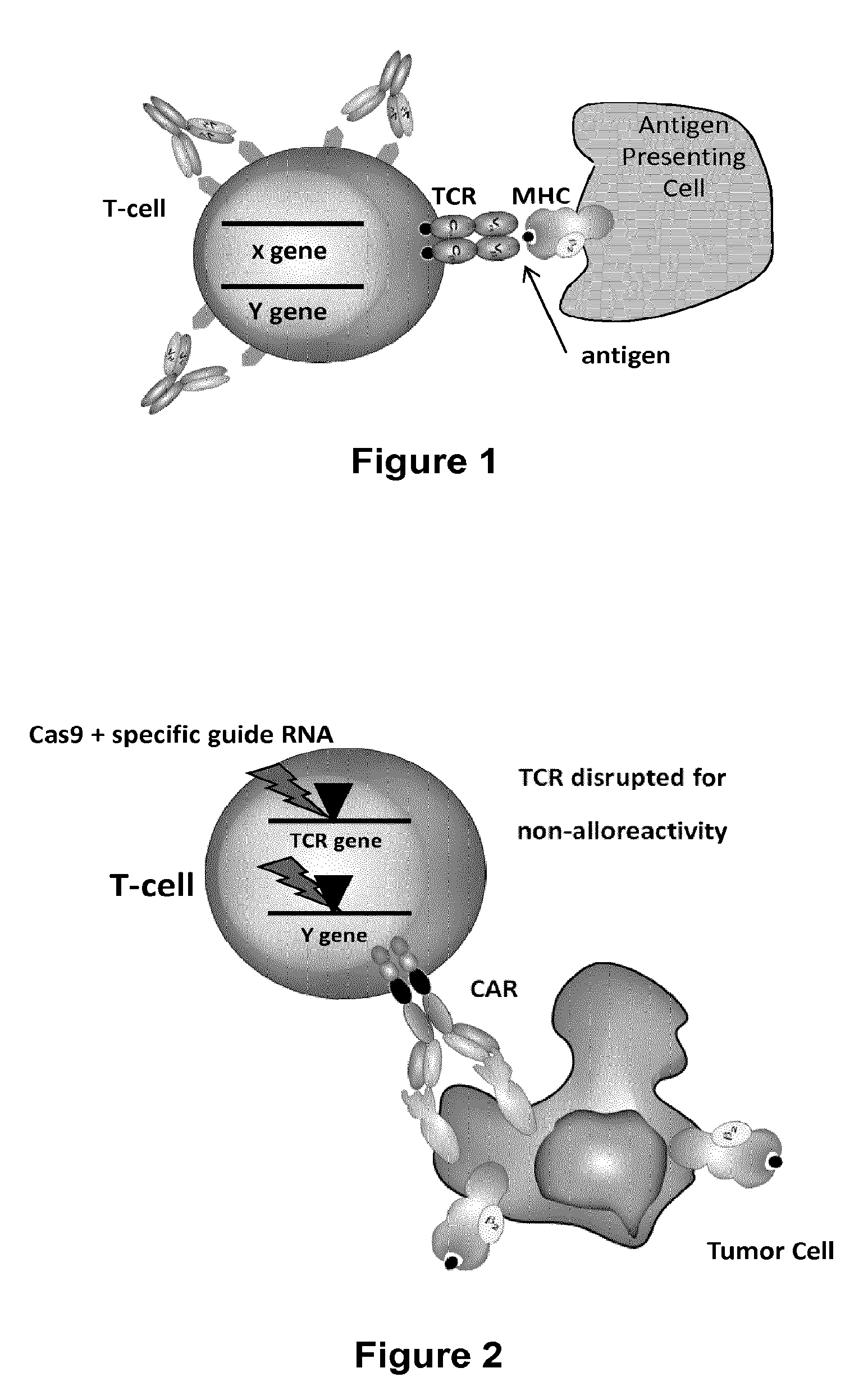
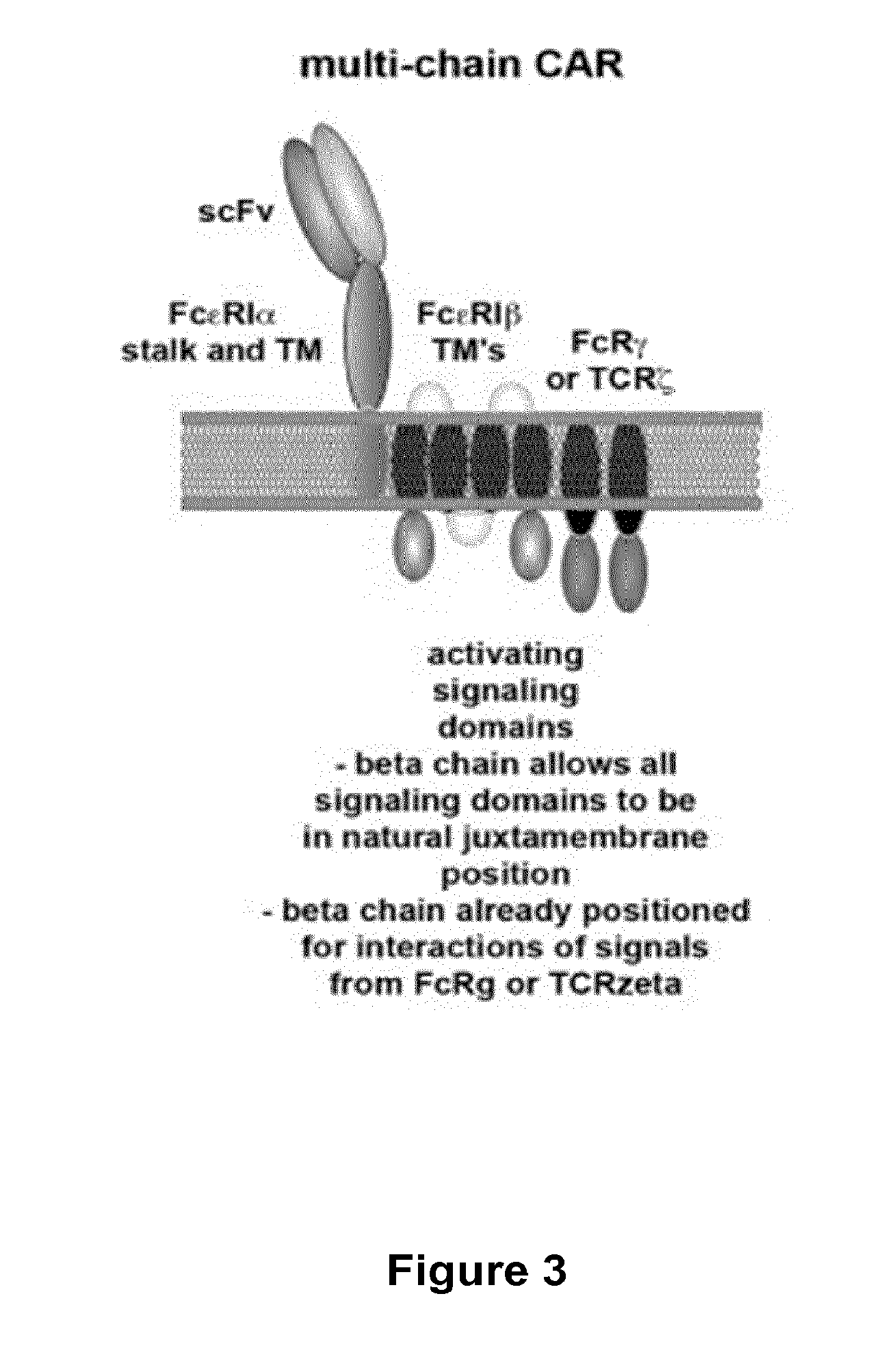
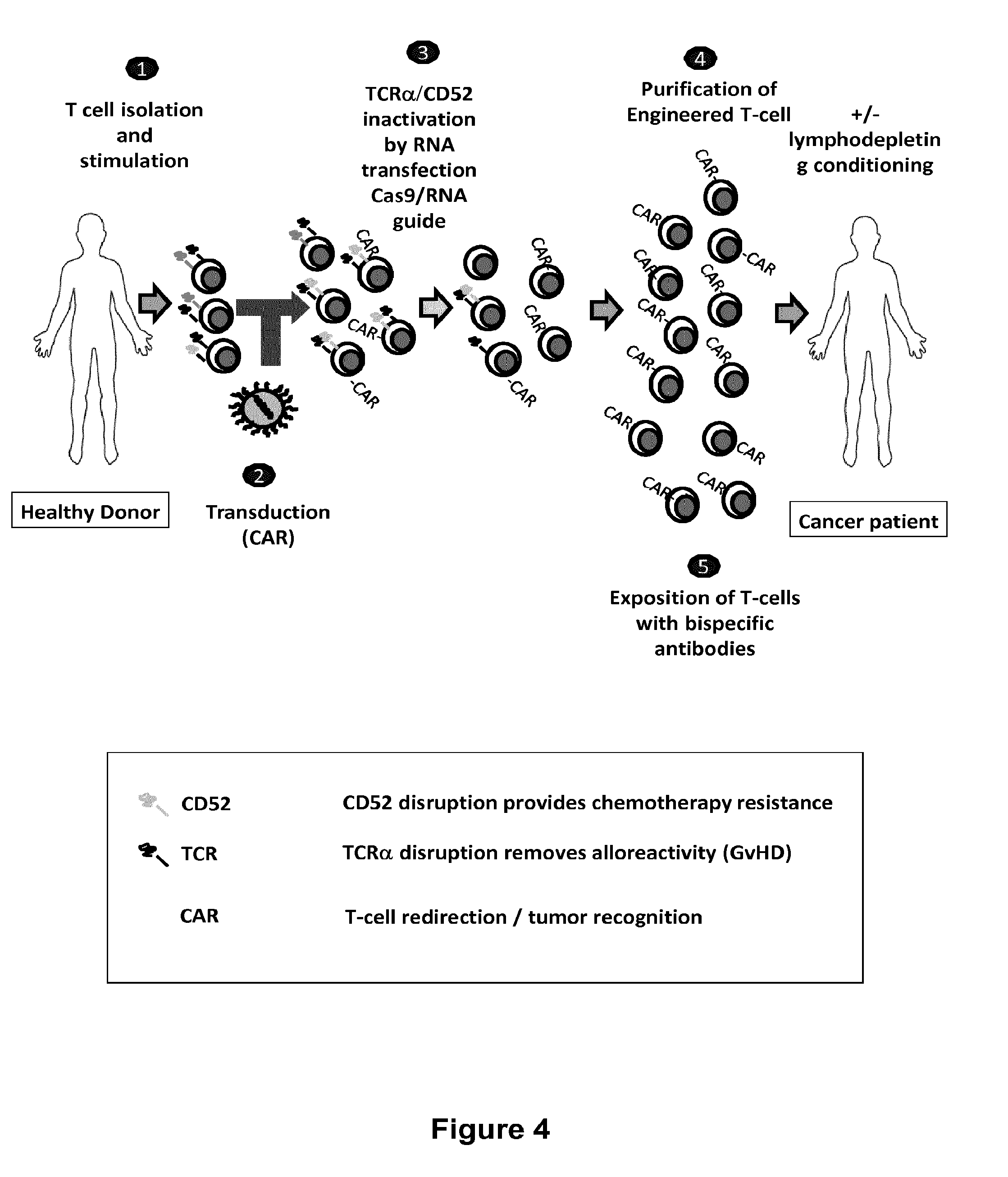
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
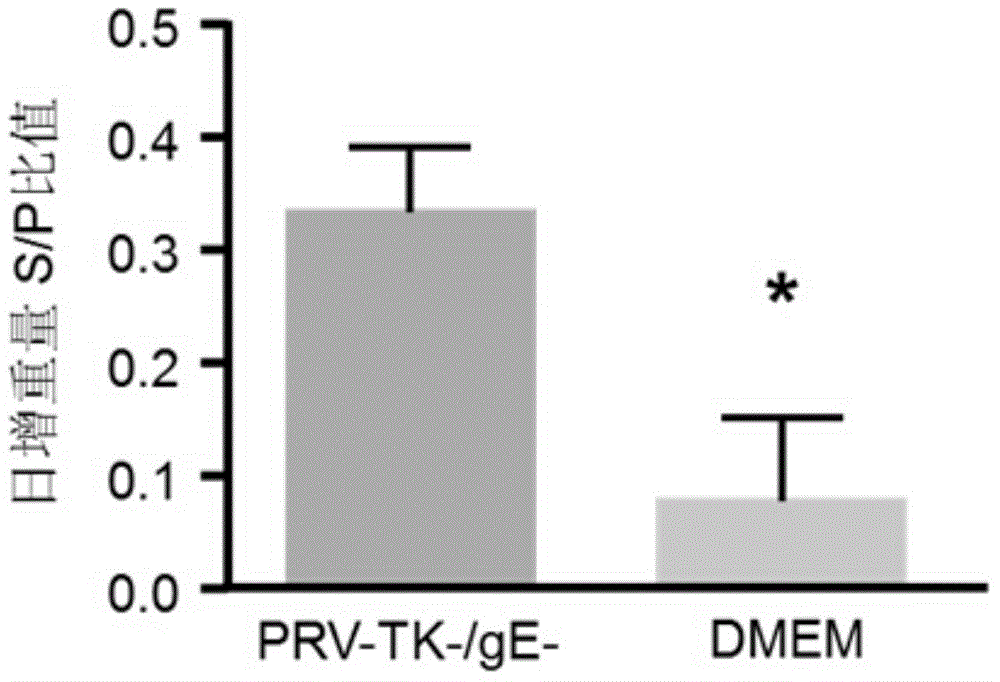
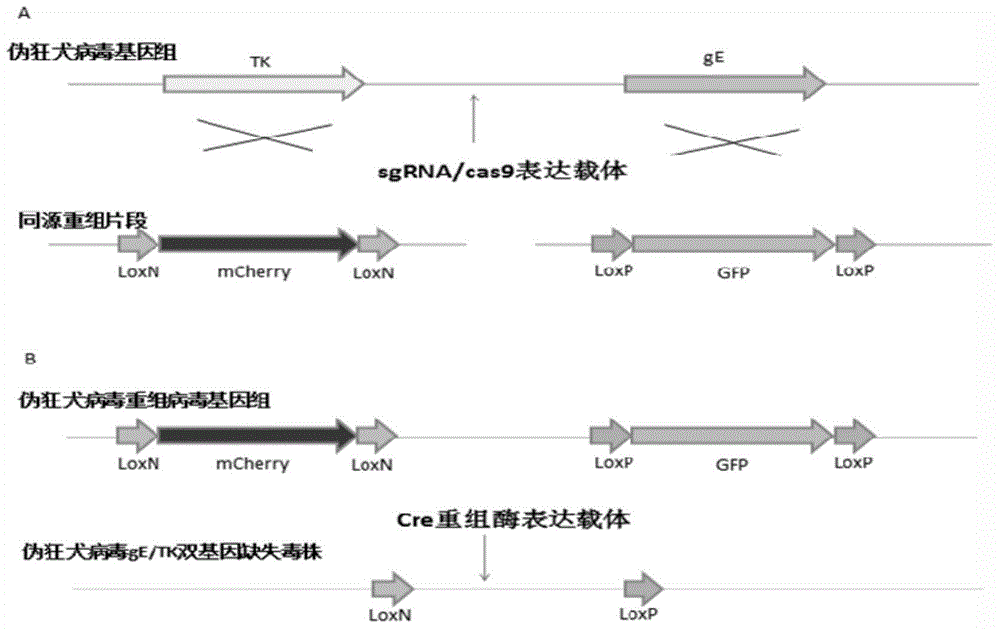
Method for preparing vaccine by editing pseudorabies virus genomes based on CRISPR/Cas9 and Cre/lox systems and application of method
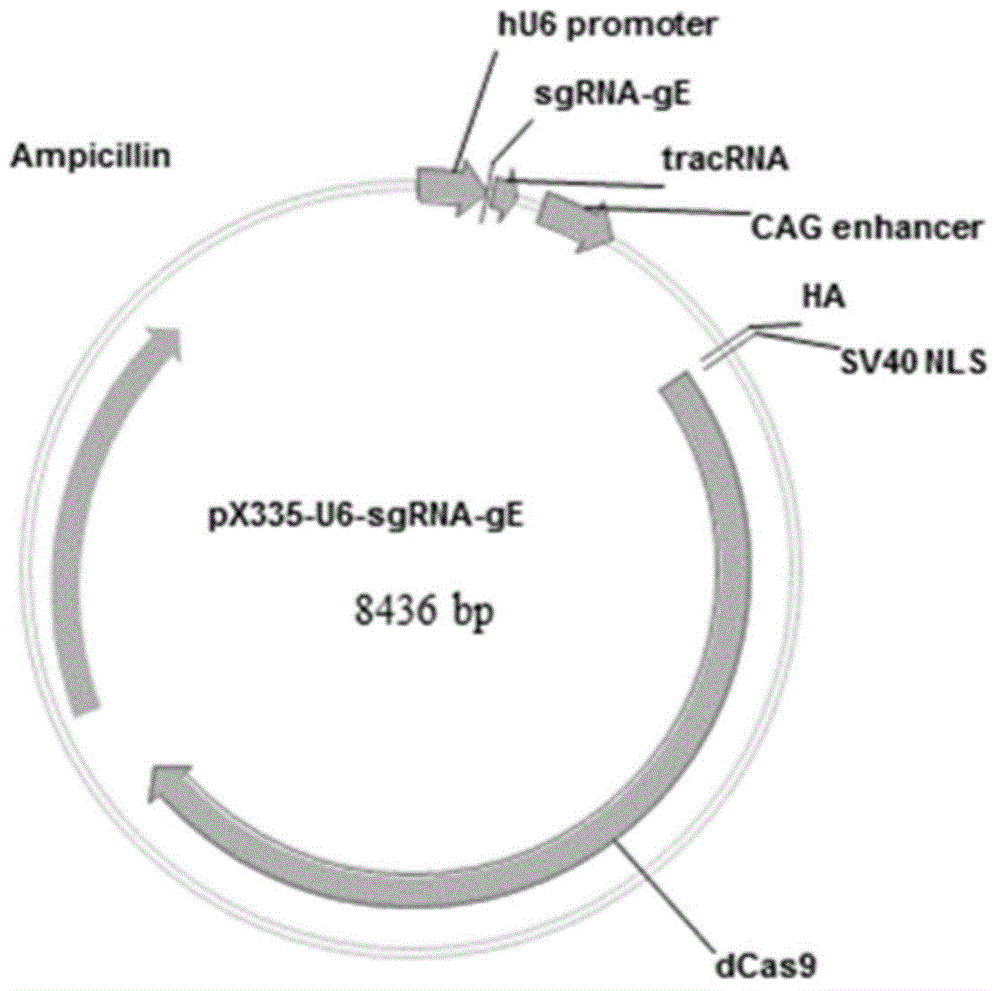
ActiveCN104894075AReduce disease lossEasy to operateAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesMCherry fluorescent proteinBiology
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing a vaccine by editing pseudorabies virus genomes based on a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system and a Cre / lox recombination system and an application of the method. According to the method, the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system is used for synchronously and efficiently recombining a GFP gene and a mCherry gene to a pseudorabies virus gE gene site and a TK gene site respectively to obtain conditional deletion strains of a gE gene and a TK gene; after purification, the Cre / lox system is used for cutting off extraneous GFP and mCherry genes in the pseudorabies virus recombinant virus genome so as to perform purification quickly to obtain a live pseudorabies virus vaccine lack of gE / TK genes; multiple genes are operated at the same time, so that multiple rounds of flows for knocking out multiple genes in the conventional method are reduced to one round; and meanwhile, the efficient edition of virus genes by using the CRISPR / Cas9 and Cre / lox systems simplifies about thirty generations of plaque purification processes into 3-4 generations, so that the preparation efficiency of the virus vaccine is greatly improved, and the method provides a strong guarantee for effectively preventing and controlling the larger-range popularization of variant pseudorabies viruses and reducing heavy economic losses.
Owner:武汉都为康生物科技有限公司
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160184362A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Method for knocking off animal myostatin gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN104531705AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal myostatin gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second myostatin exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second myostatin exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal myostatin gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
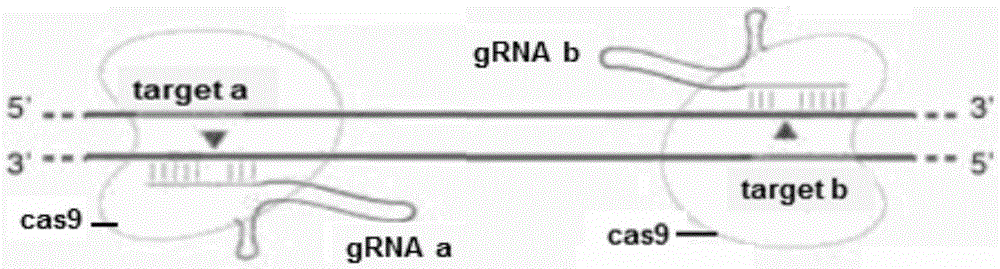
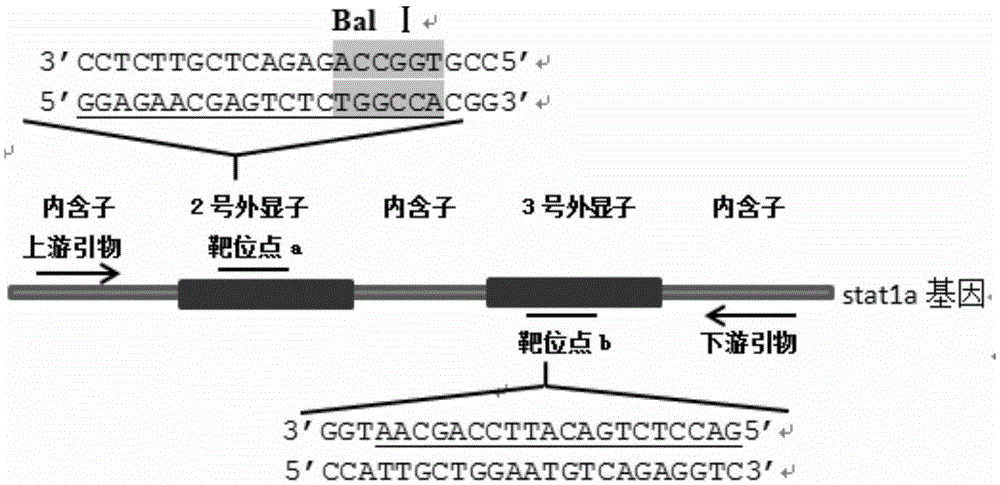
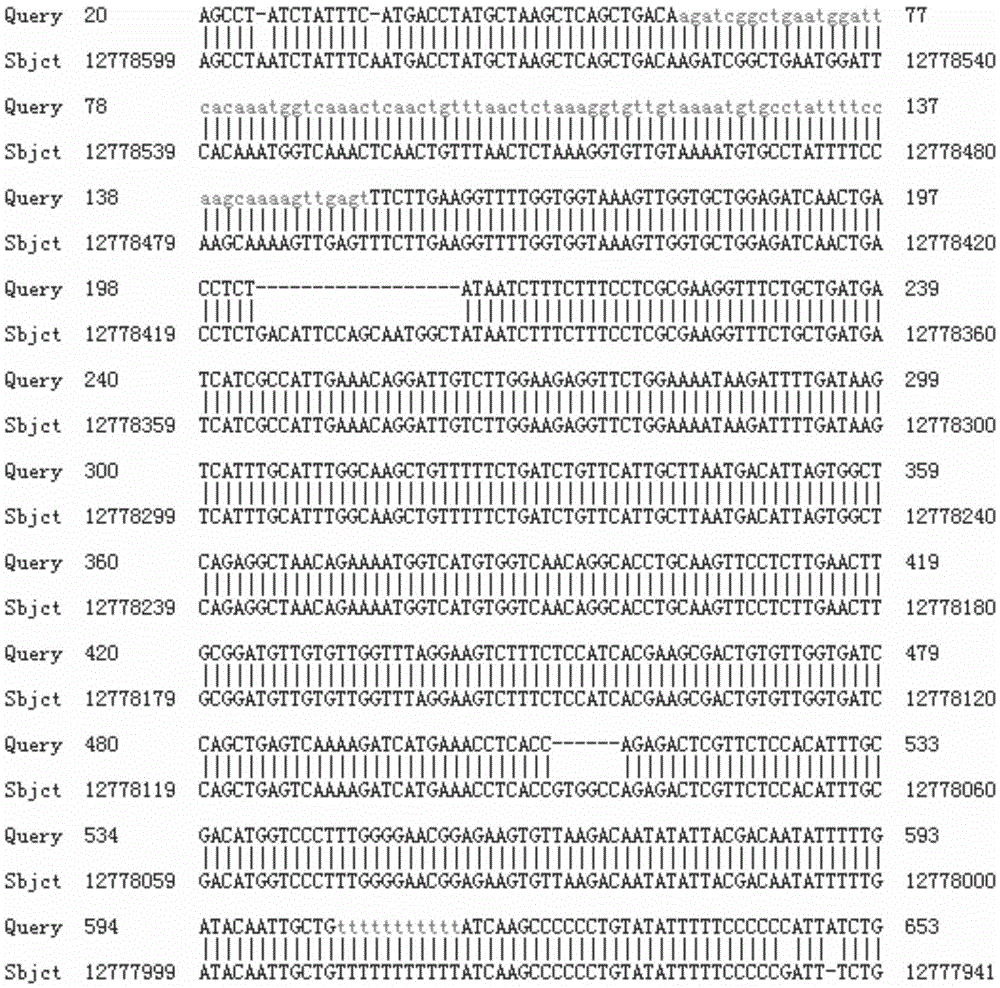
Method for breeding stat1a (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) gene-deleted zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN105647969AInefficient shooting techniqueLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesFish embryoEmbryo
A method for breeding stat1a (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) gene-deleted zebra fish through gene knockout comprises steps as follows: design of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout target site: a gRNA expression carrier is established and gRNA is synthesized in vitro; micro-injection of a zebra fish embryo; detection of effectiveness of the target site with a T7E1 method through Sanger sequencing; tail cutting identification according to the identification steps after two months of injection; TA cloning of a target sequence; Sanger sequencing of plasmids; obtaining of heritable F1 generation of a zebra fish mutant; obtaining of F2 generation homozygote of the zebra fish mutant, F3 generation pure line inheritance of the gene-deleted zebra fish with the above method, and obtaining of a new zebra fish strain.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
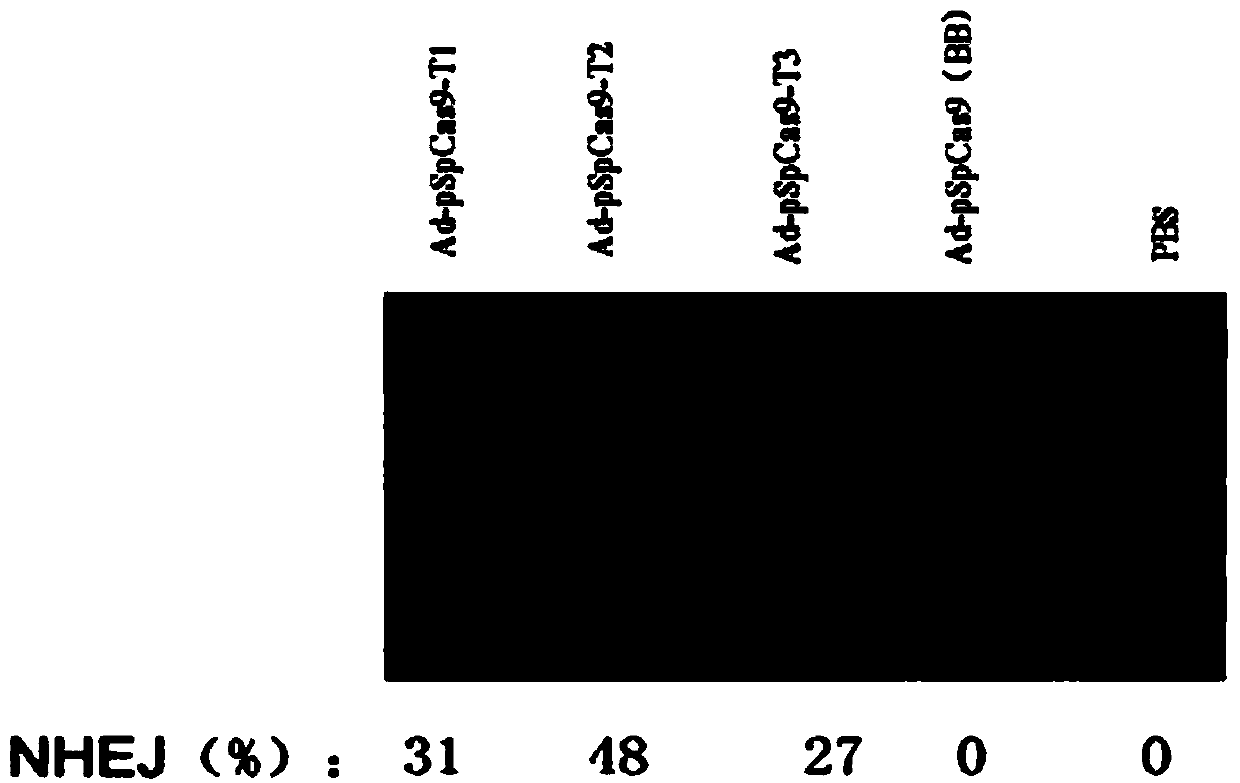
CRISPR/Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof
InactiveCN104004778AHigh knockout rateGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof. The targeted knockout vector is prepared through the following steps: after a pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid is subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using EcoRI and SacII, connecting the pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid with a pAdTrack-CMV plasmid subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using BstXI; after the obtained product is linearized by using BbsI, connecting the obtained product to a specific target sequence of a desired gene; and after the obtained object is linearized by using PmeI and dephosphorylated by using CIAP alkaline phosphatase, recombining the obtained product with a pAdEasy-1 plasmid. The targeted knockout vector can mutate gene sequences in target sequence areas, and the mutation rate is high, up to 30.6-45.8%, therefore, the targeted knockout vector can be used for gene site-directed mutation, and lays a foundation for gene therapy.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Molecular cloning method based on CRISPR/Cas9 and homologous recombination of saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous genes
ActiveCN105624146AStrong specificityEasy to fragmentFungiVector-based foreign material introductionTime transformationDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a novel molecular cloning method, and in particular to a method for obtaining recombinant vectors by modifying initial vectors through combined utilization of a CRISPR / Cas9 system and a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous gene homologous recombination system; only through one-time transformation and selection operations, the method can simultaneously complete insertion of ore or more target DNA fragments into the initial vectors, deletion of one or more DNA fragments from the initial vectors and / or substitution of one or more DNA fragments on the vectors for one or more target DNA fragments. The invention further relates to a reagent kit for conveniently and effectively applying the method provided by the invention.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
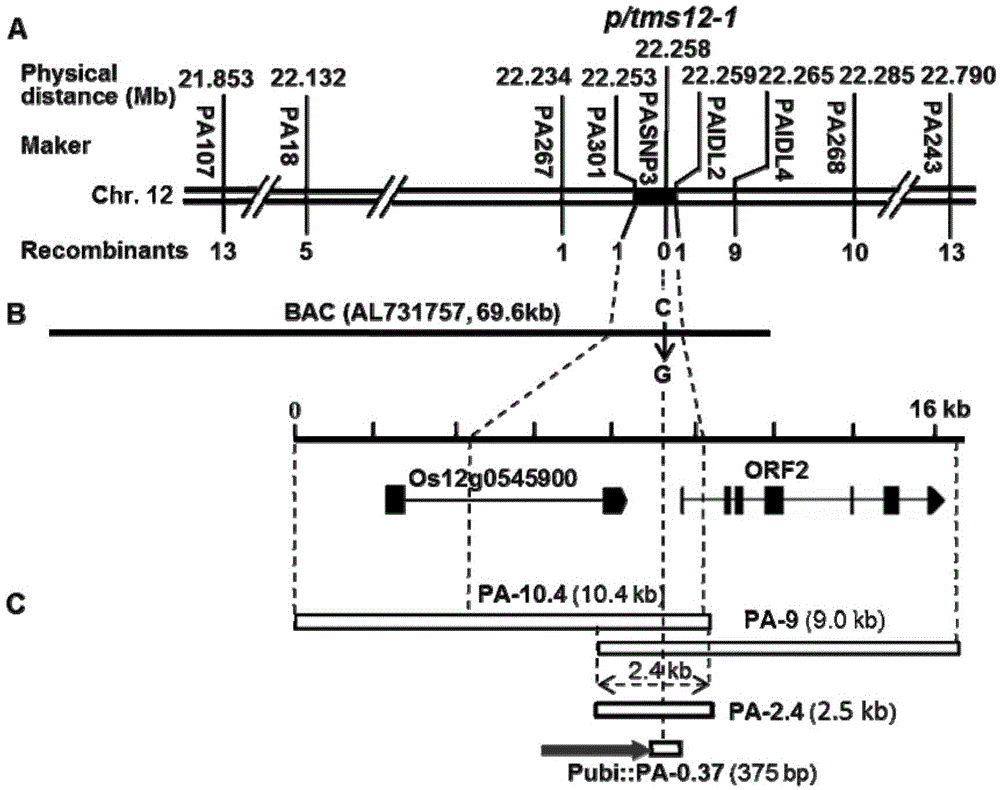
Method for obtaining temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P/TMS12-1 through CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/Cas9 system
ActiveCN104651392AAvoid possible risksAvoid damageVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceTransgenesis
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P / TMS12-1 through a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: cloning and controlling a Pei'ai 64S temperature-sensitive sterile major gene P / TMS12-1 fragment; designing a target sequence according to the P / TMS12-1 sequence; constructing a pU3-gRNA carrier of the target-containing sequence fragment; constructing a pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier; obtaining a positive transgenic seedling by utilizing the pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier containing the target sequence fragment; screening a mutant plant from the positive transgenic seeding; performing subculture planting on the mutant plant to obtain the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the CRISPR / Cas9 system is utilized to completely inactivate P / TMS12-1 non-coding RNA, and the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components is artificially cultivated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being strong in purposiveness, small in genome damages and capable of avoiding transgenic interference.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com