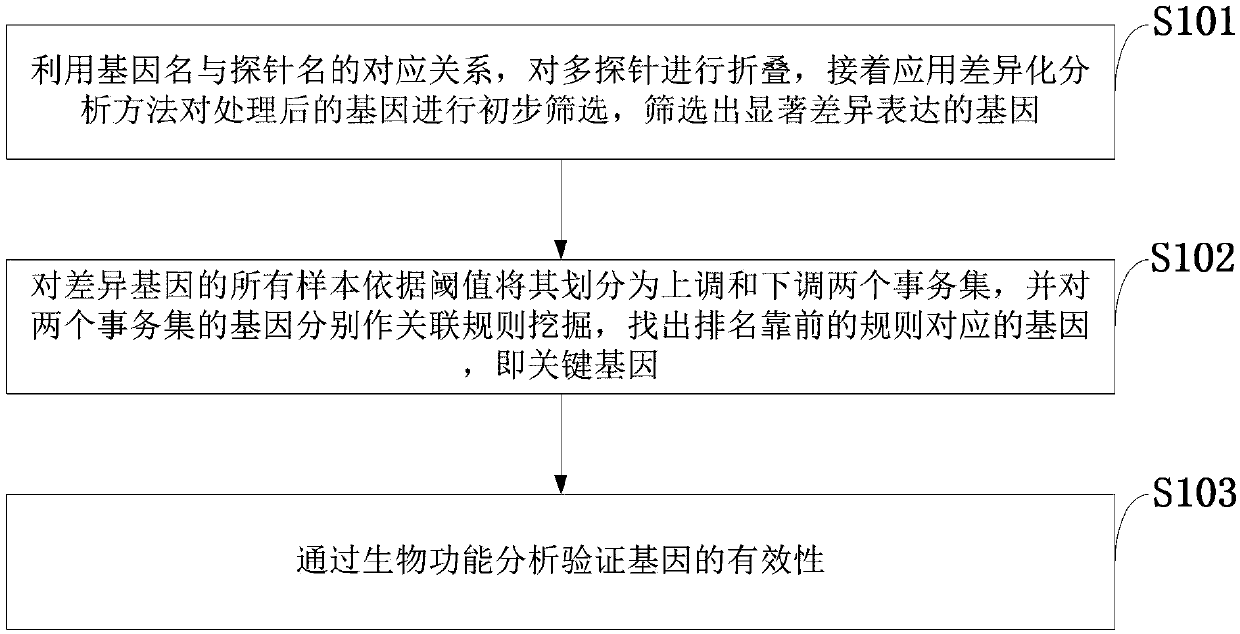
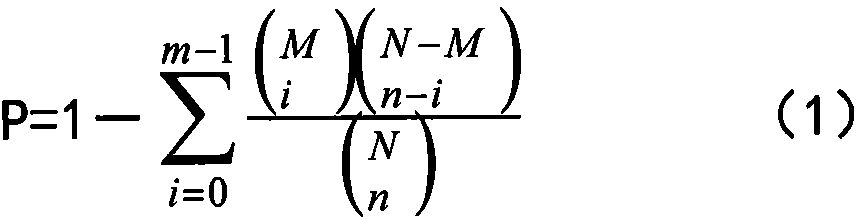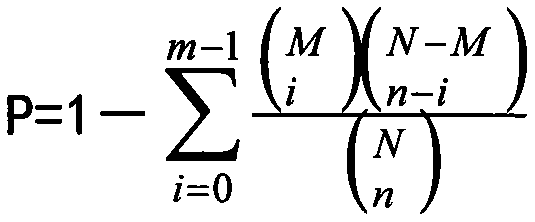Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
496 results about "Key genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
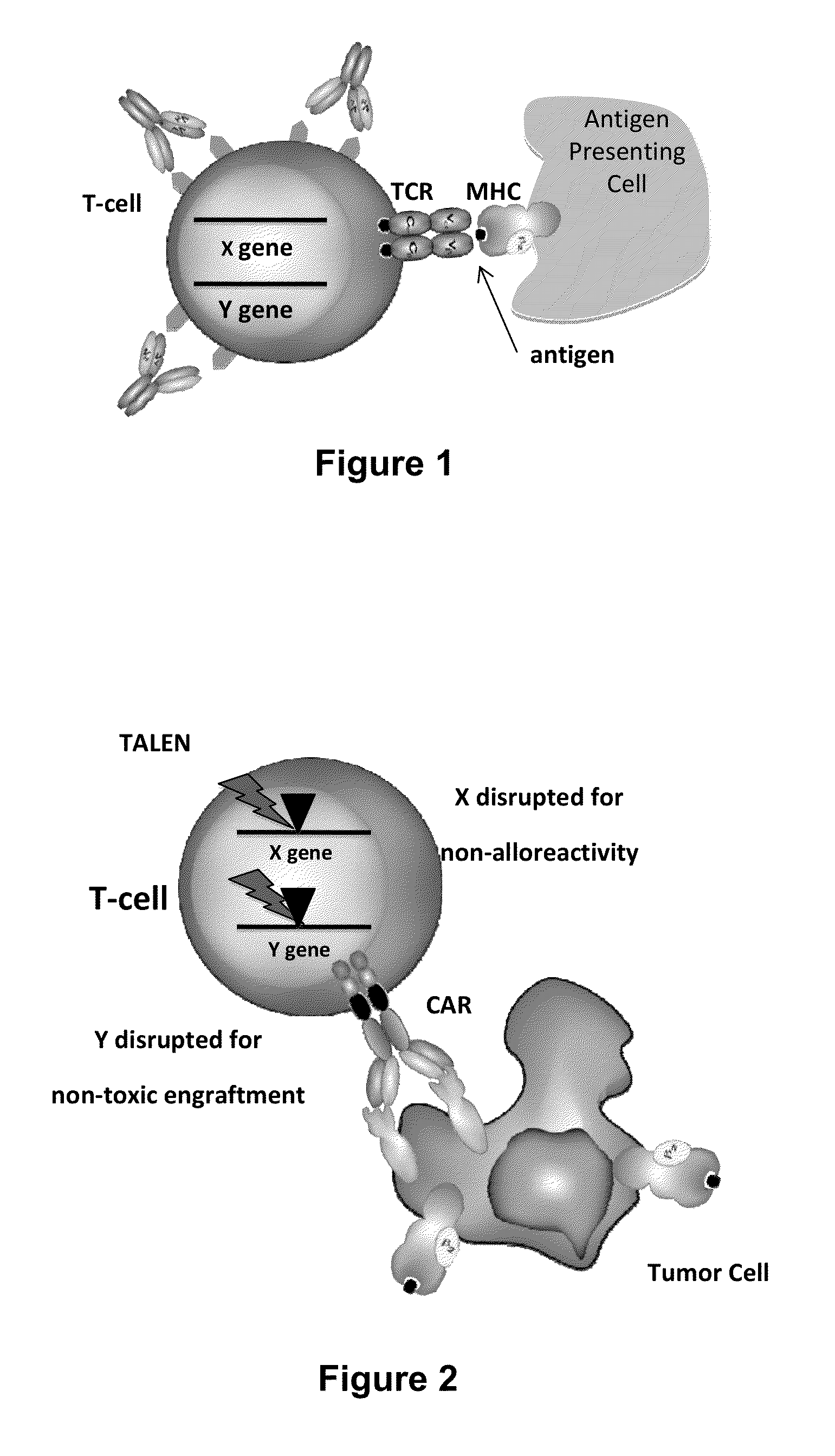
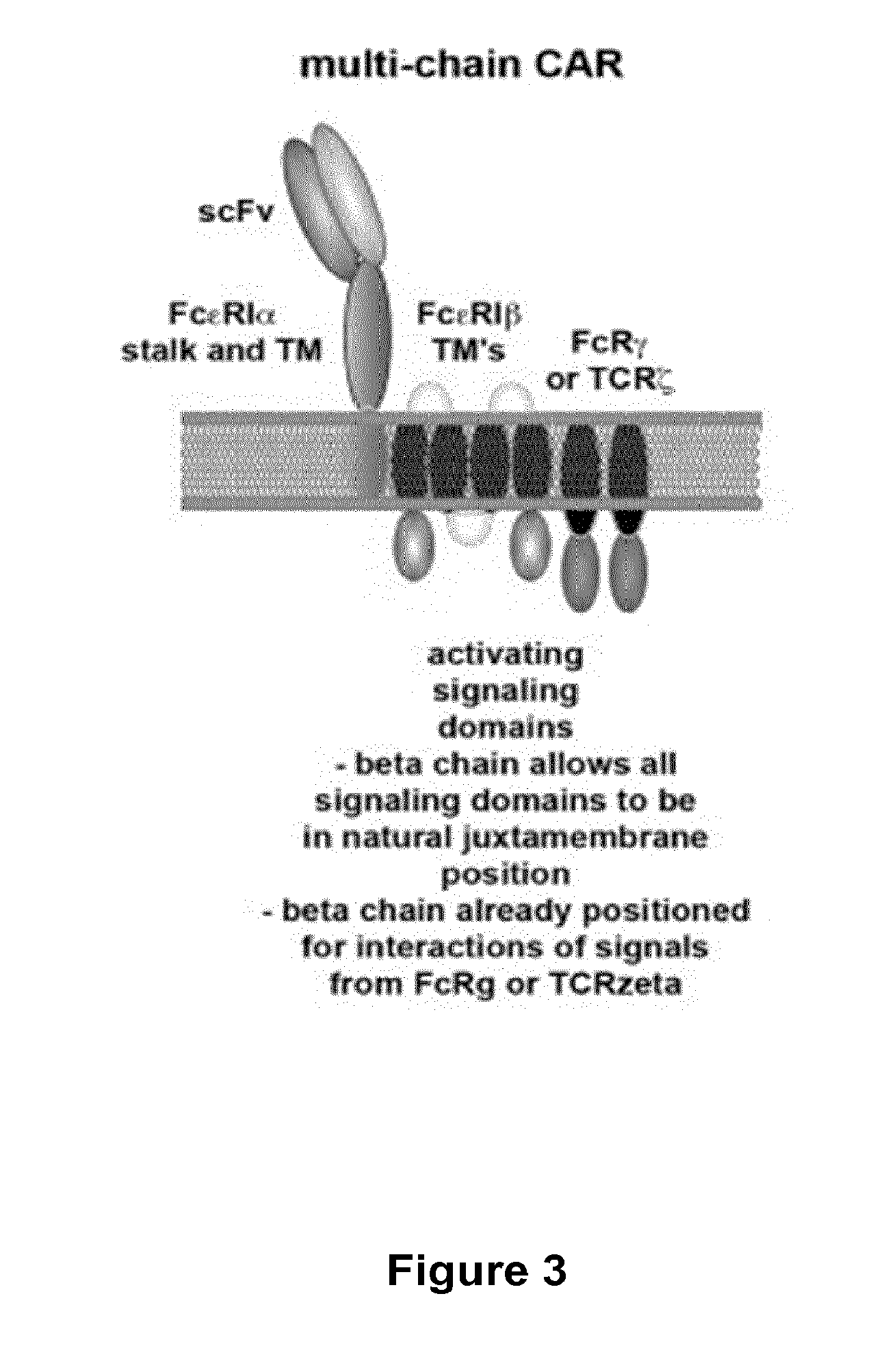
KEY WORDS GENETICS GENOTYPE The genetic makeup of an organism It describes the organism in terms of the alleles it contains, usually in the context of a particular characteristic An organism with two identical alleles for a gene is homozygous. An organism with two different alleles for the same gene are heterozygotes.
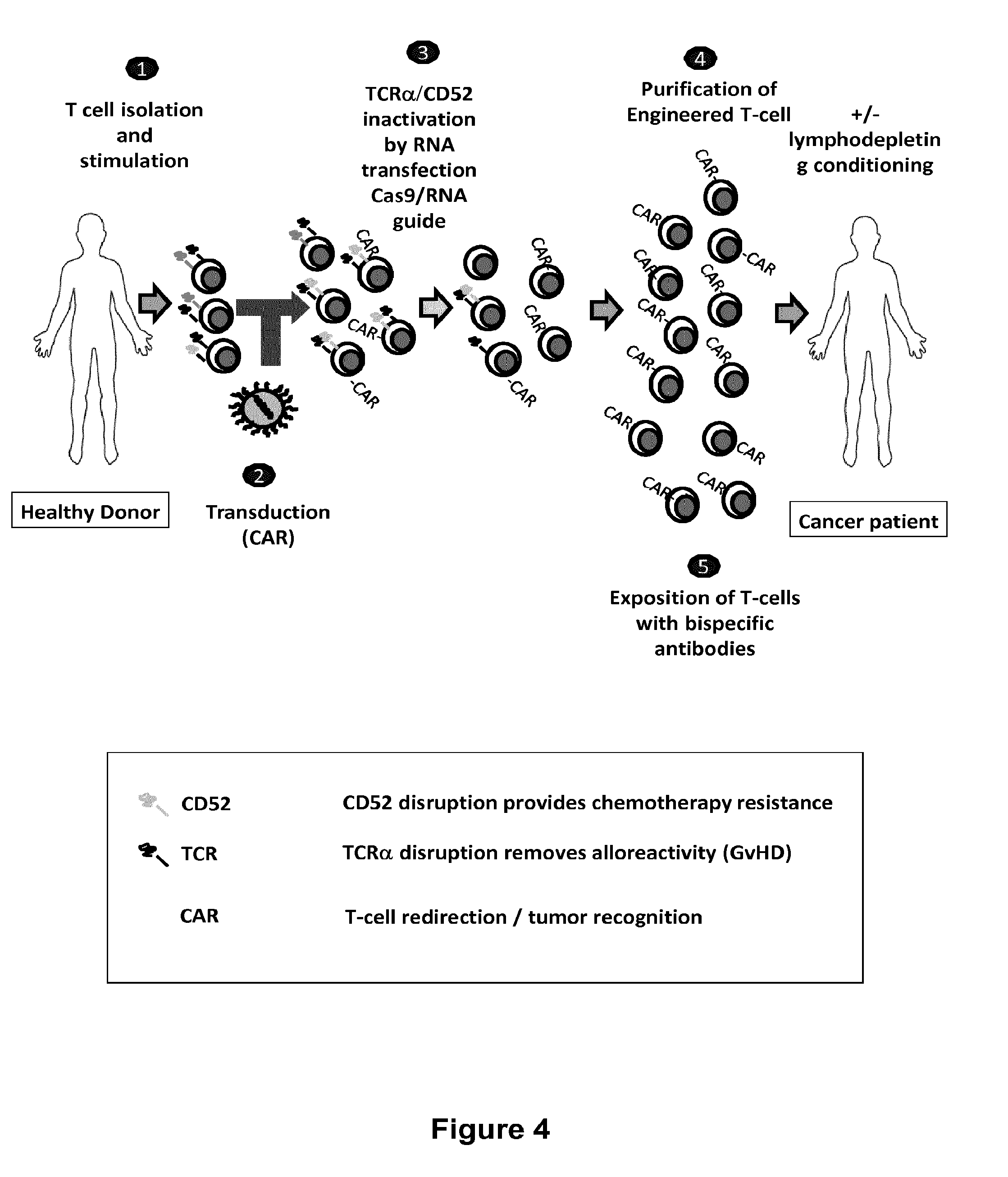
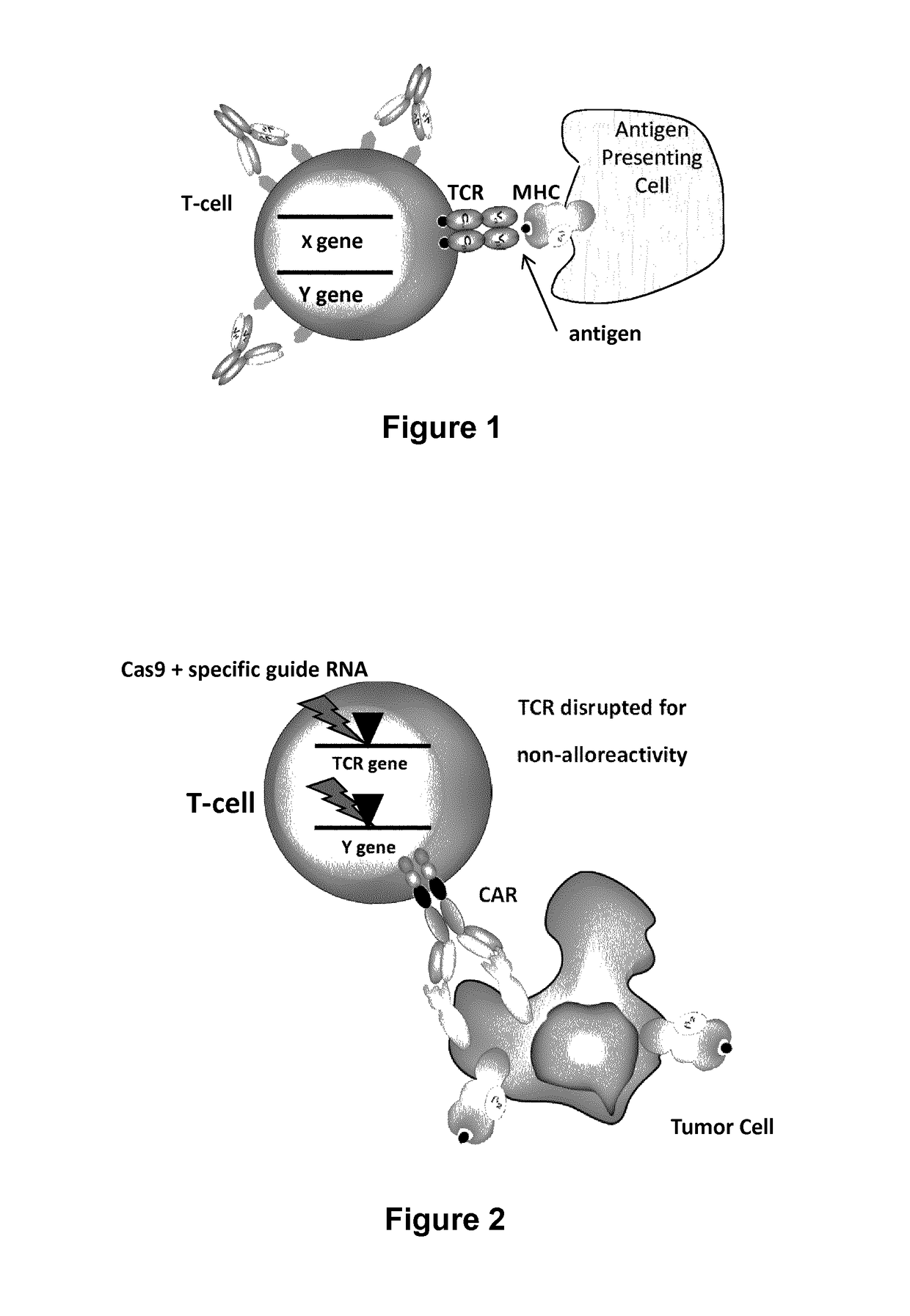
Methods for engineering allogeneic and immunosuppressive resistant t cell for immunotherapy
ActiveUS20130315884A1Precise positioningPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunosuppressive drugPrimary cell
Methods for developing engineered T-cells for immunotherapy that are both non-alloreactive and resistant to immunosuppressive drugs. The present invention relates to methods for modifying T-cells by inactivating both genes encoding target for an immunosuppressive agent and T-cell receptor, in particular genes encoding CD52 and TCR. This method involves the use of specific rare cutting endonucleases, in particular TALE-nucleases (TAL effector endonuclease) and polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides, to precisely target a selection of key genes in T-cells, which are available from donors or from culture of primary cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
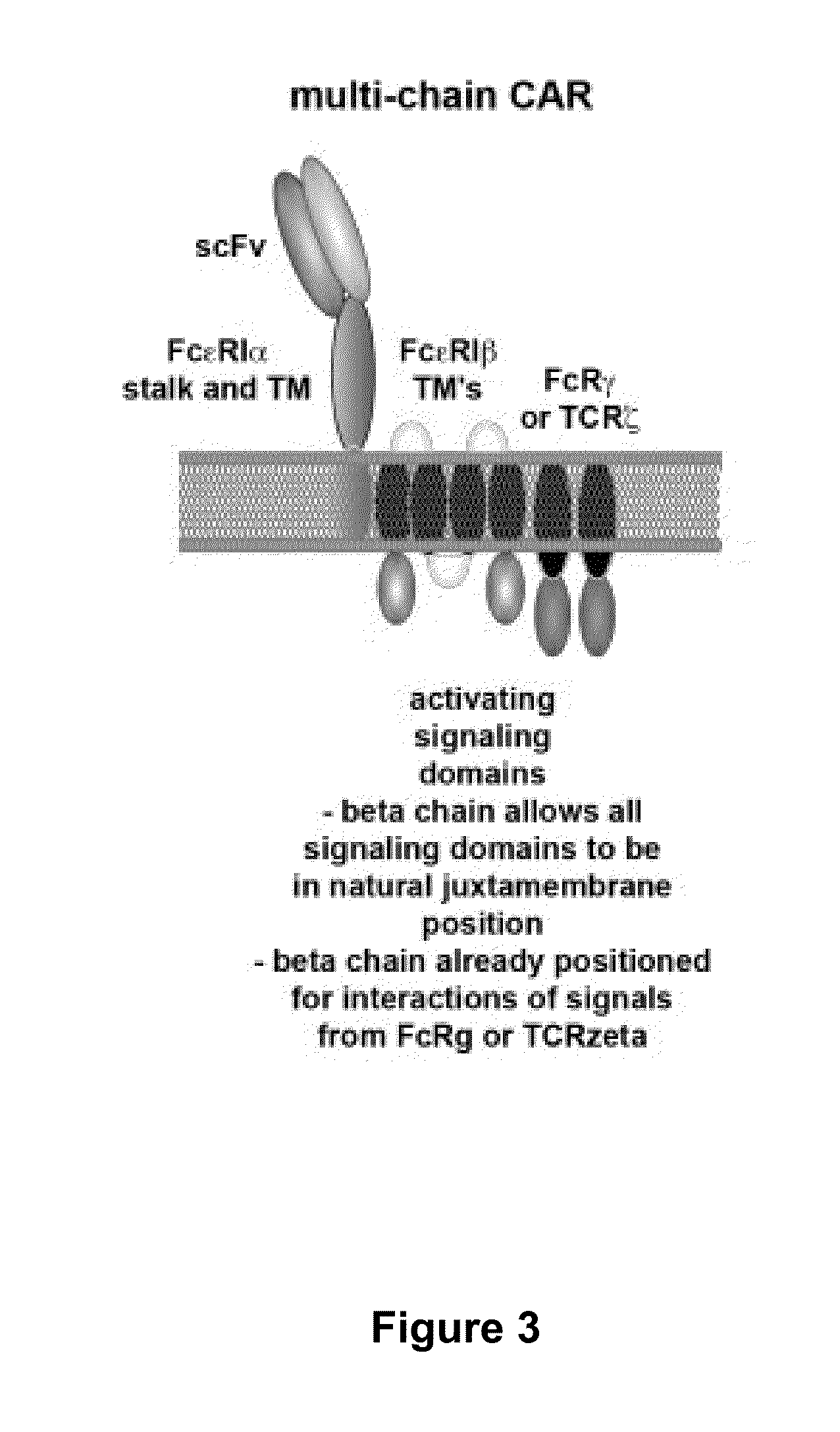
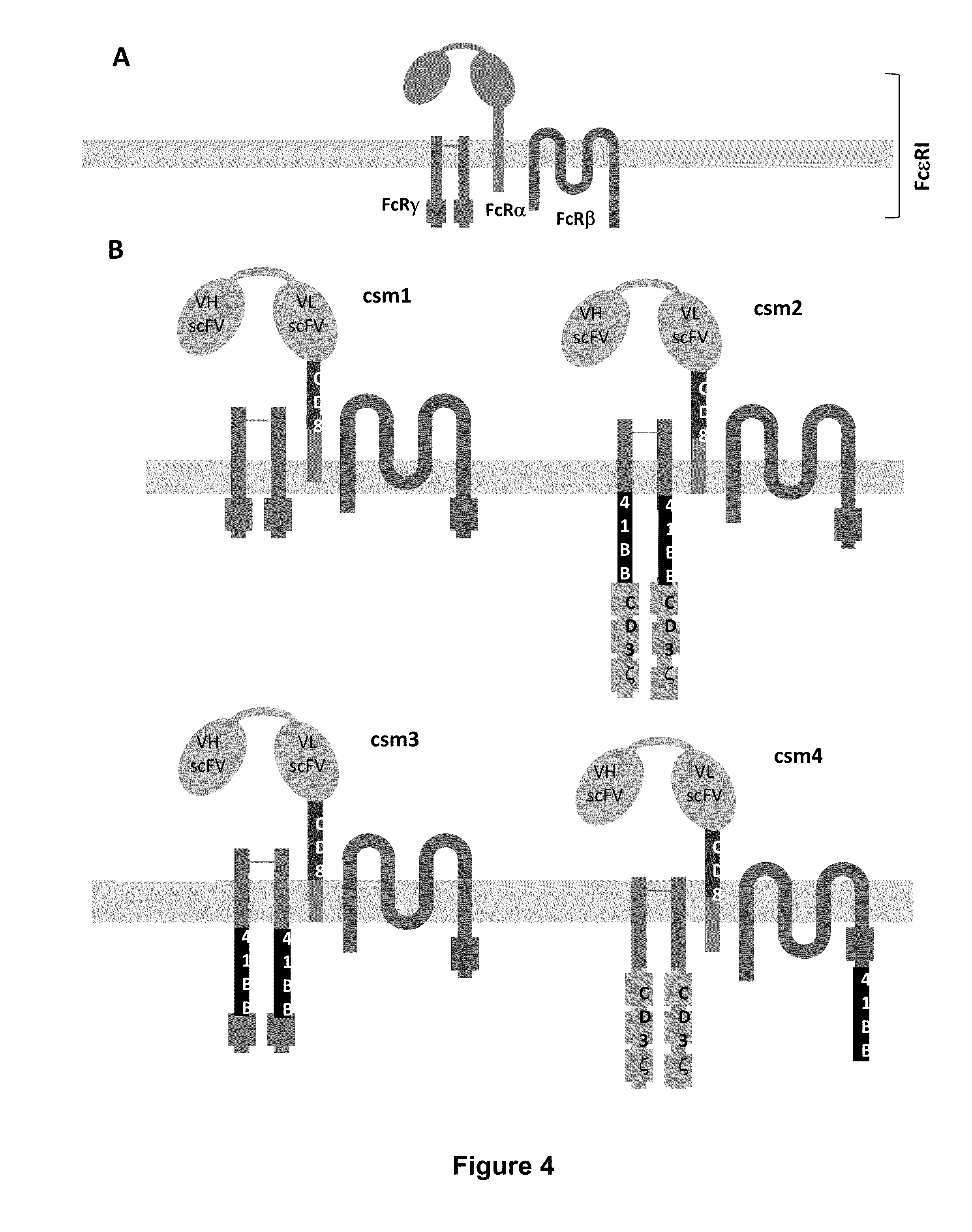
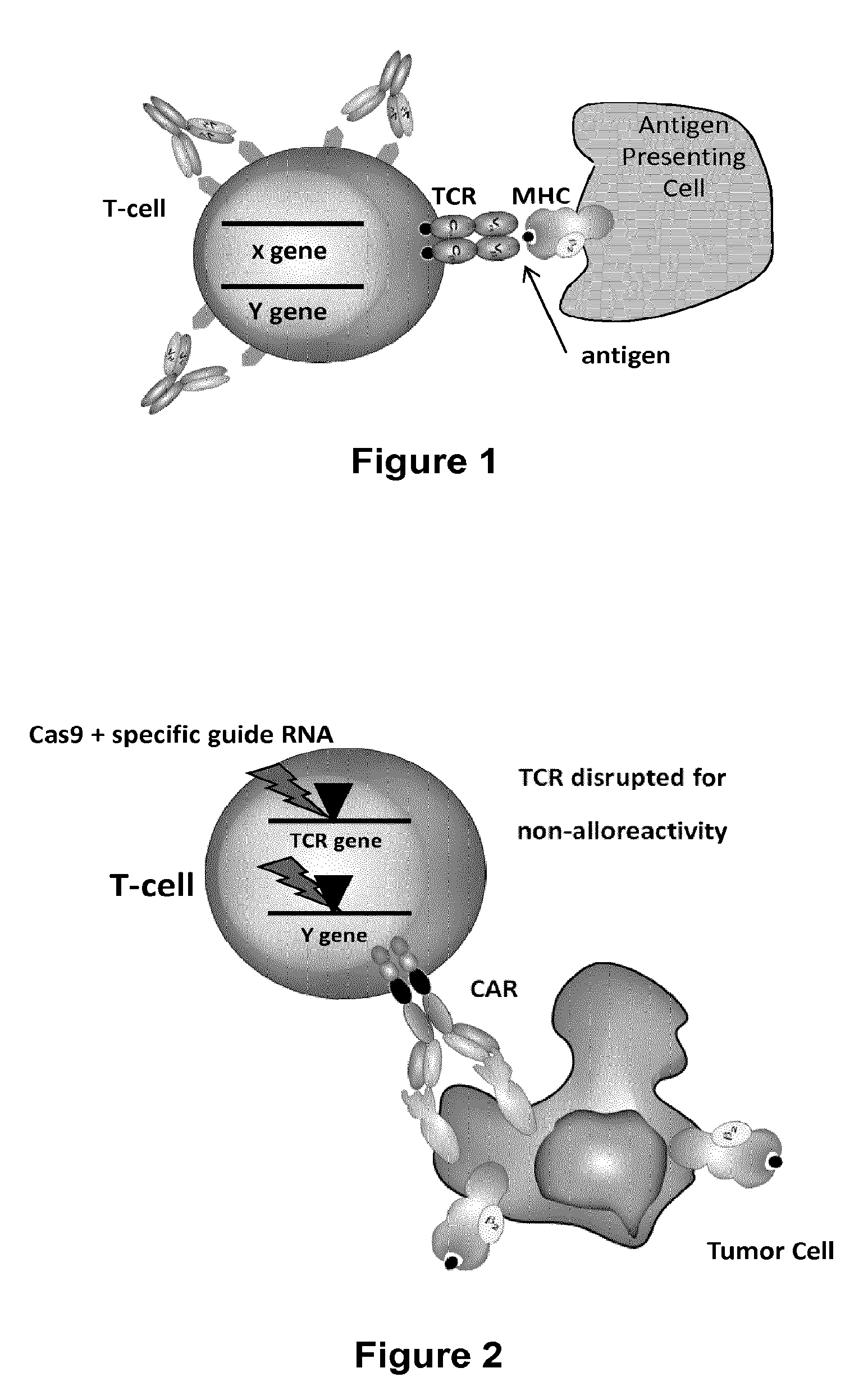
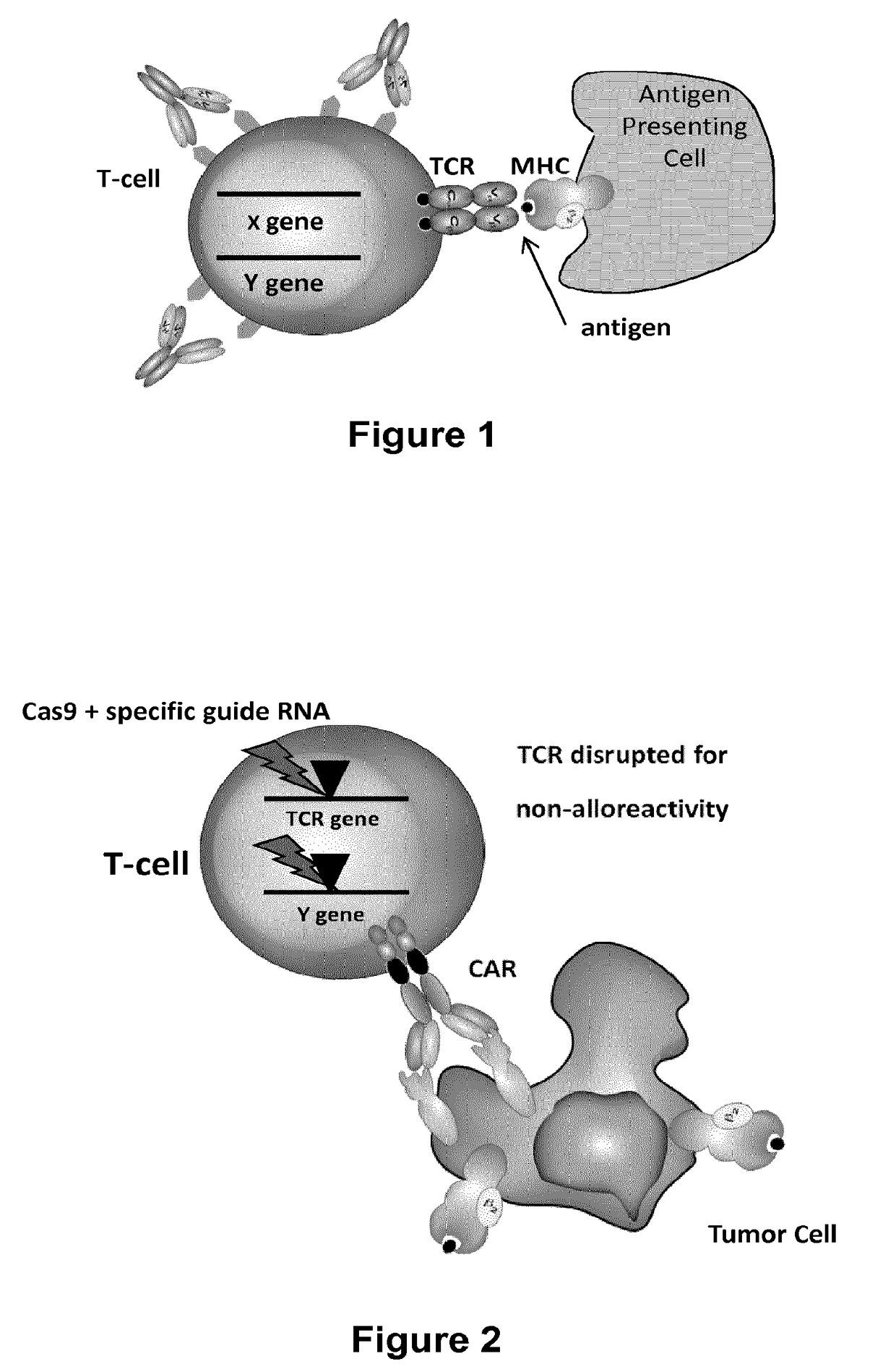
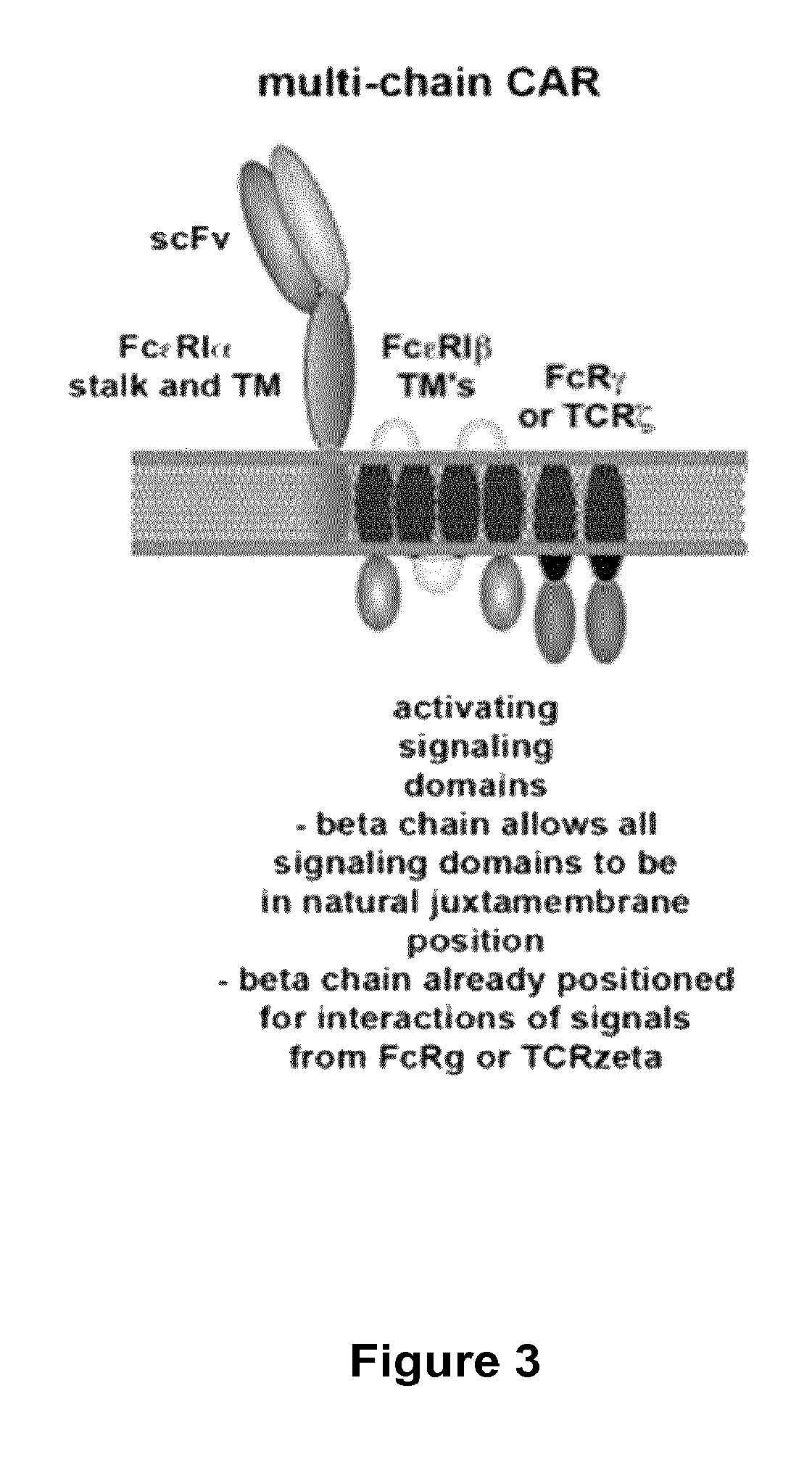
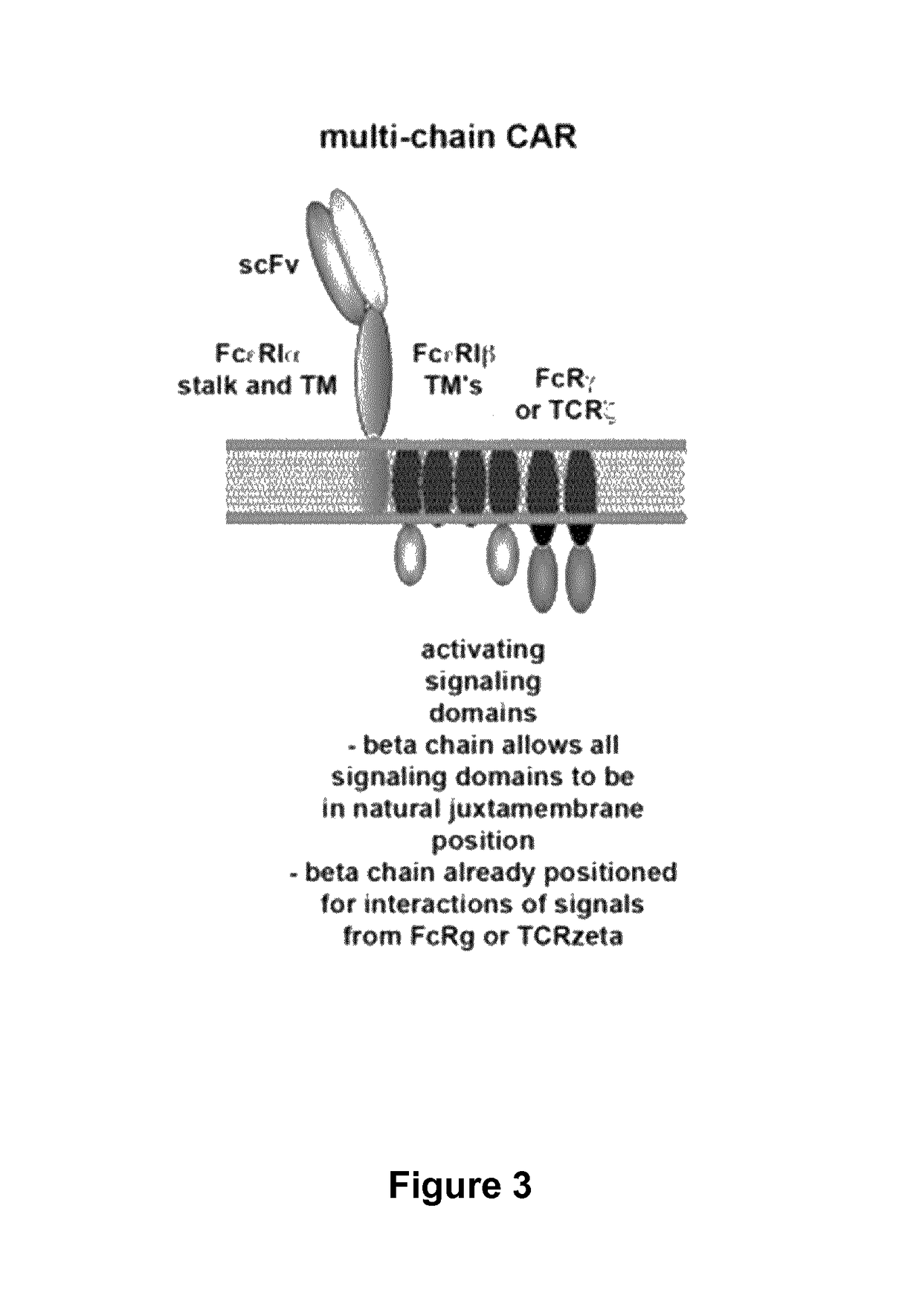
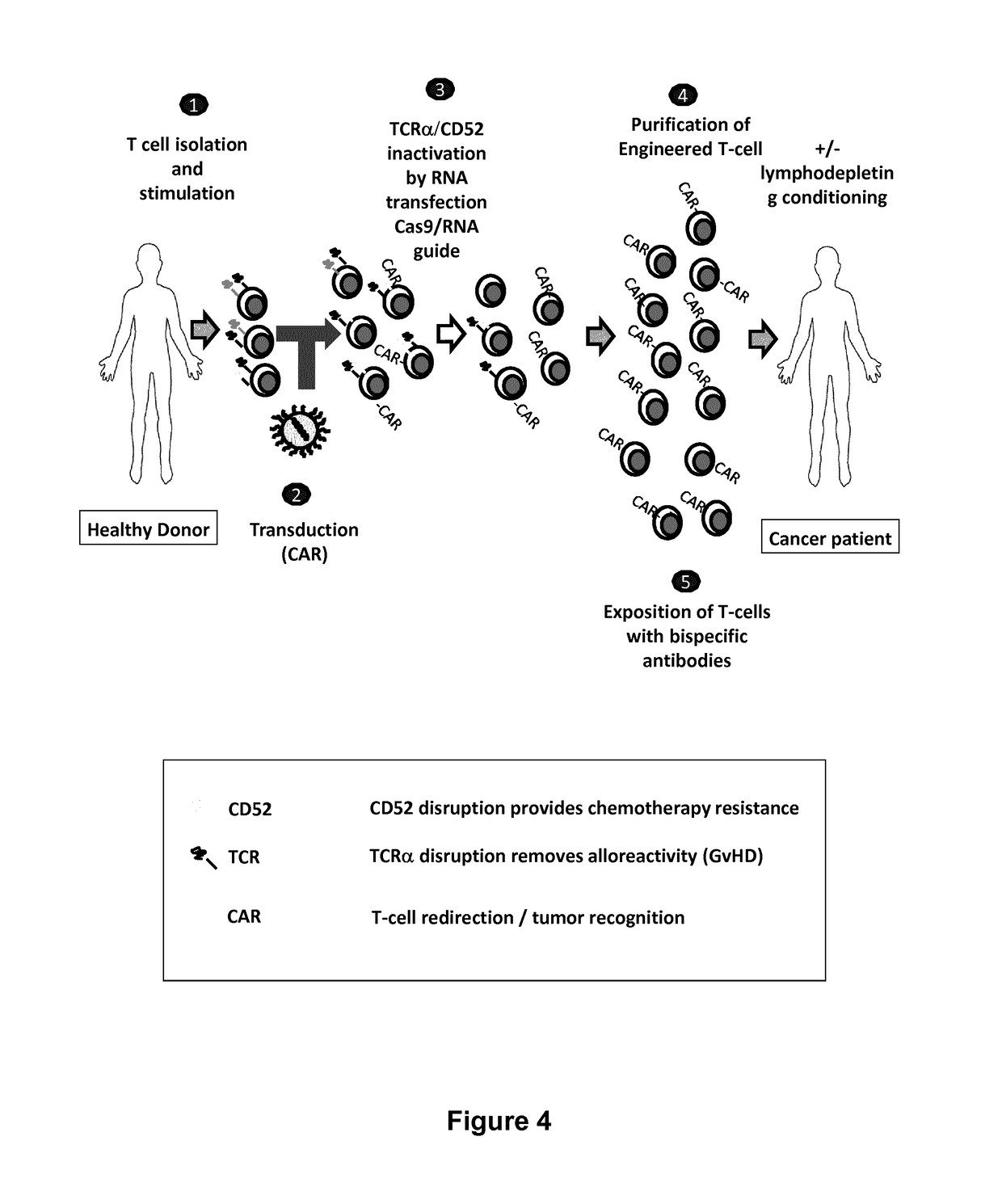
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160184362A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for engineering T cells for immunotherapy by using RNA-guided CAS nuclease system
ActiveUS9855297B2Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
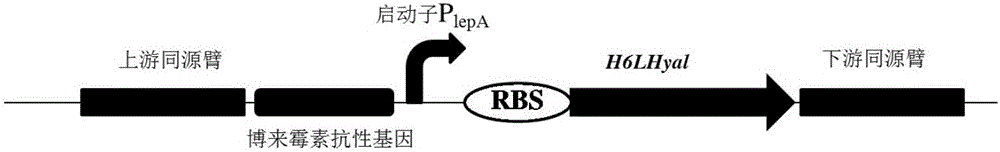
Construction method of recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of generating hyaluronic acid with specific molecular weight
ActiveCN105087456AIncrease productionReduce viscosityBacteriaTransferasesStreptococcus zooepidemicusHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a construction method of recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of generating hyaluronic acid with specific molecular weight, belonging to the field of the bioengineering technology. According to the method, the production of hyaluronic acid is realized through integration of hyaluronic synthase (hasA) with streptococcus zooepidemicus source to bacillus subtilis; meanwhile, overexpression is realized on key genes of the synthetic route of HA, so that the high yield of bacillus subtilis is realized; on the basis, the hyaluronidase with the leech source is integrated to the genome of the bacillus subtilis, then mutant library construction is realized on ribosome bind sites (RBS) from the genetic expression translational level, and thus a series of mutants with different expression levels of hyaluronidases are obtained through high throughput screening; the yield of the hyaluronic acid achieves 19.38g / L, the molecular weight ranges from 103-106 Dalton, certain basis is laid for efficiently preparing micromolecule hyaluronic acids, and the construction method is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Culturing method of auxilliary bud less tobacco after topping
The present invention discloses a tobacco cultivation method. Said method is characterized by that it adopts a molecular biological technique to identify key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth after the tip is pruned, then uses nocuity inducible promoter to drive antisense RNA and make it promptly express after the tip is pruned so as to inhibit the expression of said key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth and make the axillary bud can not be germinated or grown.
Owner:贾朝钧
Methods for engineering T cells for immunotherapy by using RNA-guided CAS nuclease system
ActiveUS9890393B2Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102994439AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliShikimate kinase
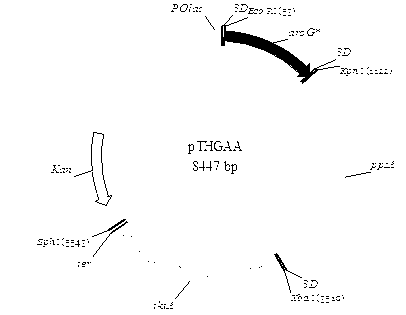
An Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and a construction method and application thereof belong to the technical field of microbial gene engineering. The invention firstly utilizes a molecular biology technique to delete shikimic acid kinase I gene (aroK) and shikimic acid kinase II gene (aroL) of Escherichia coli CICIMB0013, and a gene (ptsG) of a key protein EIIBC<Glc> and a quinin acid / shikimic acid dehydrogenase gene (ydiB) of a glucose phosphotransferase system to obtain an Escherichia coli mutant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 (delta aroK, delta aroL, delta ptsG, delta ydiB). The invention also constructs a recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA containing key genes comprising aroG*,ppsA and tktA in a metabolic pathway of shikimic acid; and the recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA is transferred into the recombinant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 to obtain a recombinant Escherichia coli B0013 (SA4 / pTHGAA) capable of producing shikimic acid efficiently. The Escherichia coli recombinant strain provided by the invention can realize efficient accumulation of shikimic acid in a fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
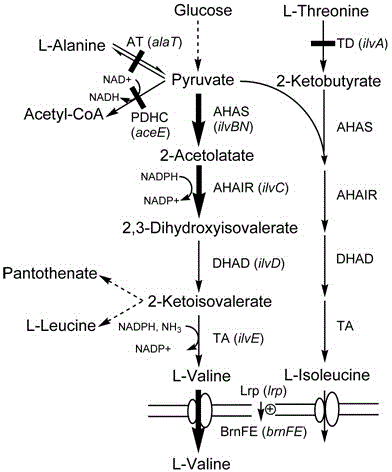
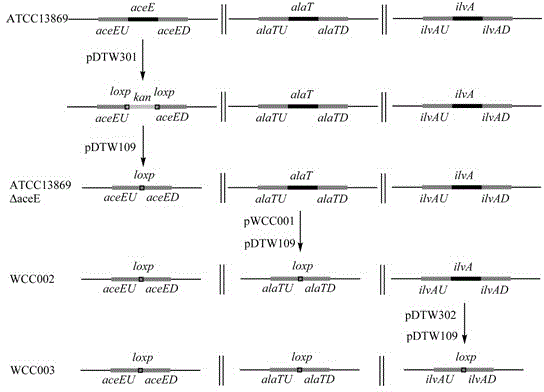
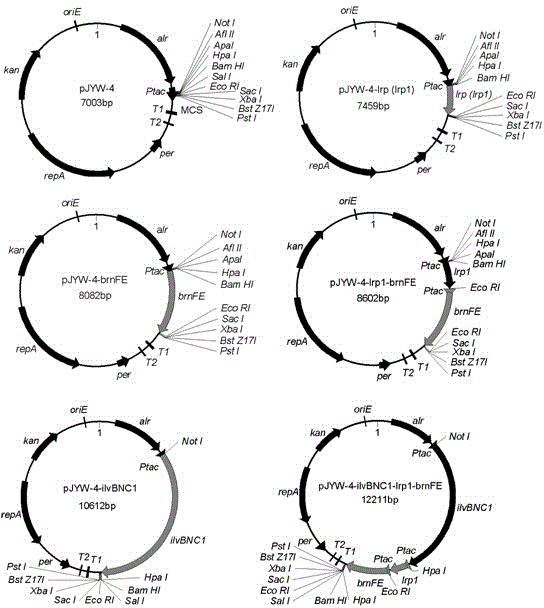
Construction of corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria for high-yielding production of L-valine and method for fermentation production of L-valine
The invention discloses construction of a strain of corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria for high-yielding production of L-valine and a method for fermentation production of L-valine, and belongs to the technical field of food biological engineering. Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13869 is used as an original bacterial strain, knockout combination of genes of aceE, alaT and ilvA is carried out, and an ATCC13869[delta]aceE[delta]alaT[delta]ilvA mutant bacterial strain is obtained and named as WCC003; expression combination of genes of lrp1, brnFE and ilvBNC1 is carried out on the WCC003, and expression-combined engineering bacteria WCC003 / pJYW-4-(ilvBNC1)-lrp1-brnFE are obtained and preserved in China center for type culture collection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2014149; the expression-combined engineering bacteria are used for fermentation production of L-valine. The corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria based on the expression regulating protein Lrp, the transfer protein BrnFE and the L-valine synthetic route key gene ilvBNC1 and used for high-yielding production of L-valine are provided, advantageous mutation Arg39Trp of Lrp in corynebacterium glutamicum is clear and definite for the first time, a fact that Lrp and BrnFE are used for fermentation production of L-valine is also reported for the first time, and the study on the expression combination of the genes of lrp1, brnFE and ilvBNC1 is also created for the first time.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
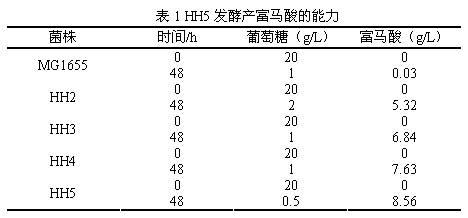
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering strain for producing fumaric acid as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102031227AEasy to buildEasy to useFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering strain for producing fumaric acid as well as a construction method and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The construction method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: cloning key genes containing dehydrogenase genes (RoMDH) and fumarase genes (RoFUM1) in the accumulation path of the fumaric acid from the Rhizopus oryzae NRRL1526 capable of accumulating a large amount of fumaric acid, and converting the Saccharomyces cerevisiae BMA64 by connecting to the plasmid pY26TEF / GPD capable of realizing high-copy two-way expression in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering strain for producing fumaric acid. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering strain disclosed by the invention can accumulate the fumaric acid in the cytoplasm, the fermentation method is simple, the yield can reach 26.2mg / L, and the invention establishes a basis for industrialization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing fumaric acid in metabolic engineering construction.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for establishing pancreatic cancer miRNA prognosis model and screening targeted gene
PendingCN112391470AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPancreas CancersTreatment targets
The invention discloses a method for establishing a pancreatic cancer miRNA prognosis model and screening a targeted gene. The model comprises hsa-mir-424, hsa-mir-126, hsa-mir-3613 and hsa-mir-4772,nine key genes are identified, and the nine key genes comprise MMP14, ITGA2, THBS2, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL11A1, COL6A3, COL12A1 and COL5A2. According to the method for establishing the pancreatic cancermiRNA prognosis model, by means of TCGA and GEO databases, data is subjected to multi-step analysis through a plurality of R language installation packages and combines with clinical information, a Cox proportional risk regression model is established to search for prognosis biomarkers, the targeted gene of miRNA is predicted, the key genes related to pancreatic cancer are found out by utilizing Cytoscape, and related molecular functions and action mechanisms of the key genes are predicted through KEGG and GO analysis so as to search for new treatment targets and prognosis markers of pancreatic cancer patients.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV +1
Method for screening cattle high altitude hypoxia adaptation molecular markers and application thereof
ActiveCN109994153AEfficient and accurate screeningPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHigh altitude hypoxiaGenome evolution
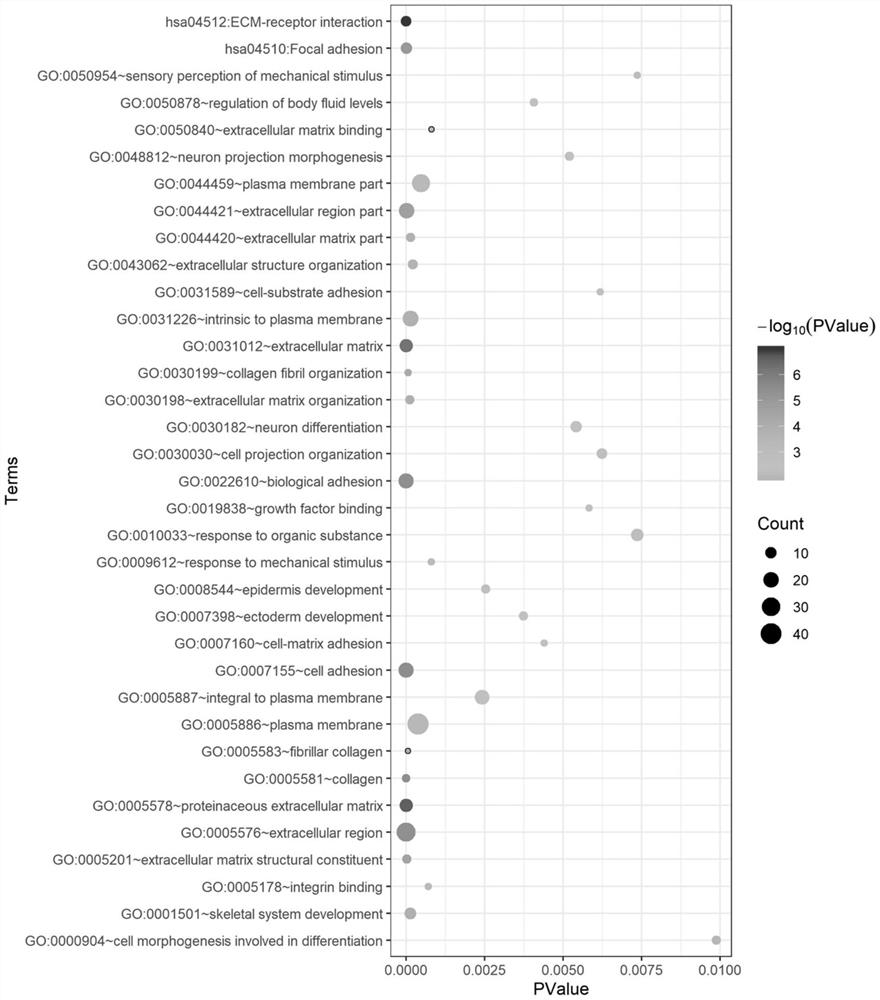
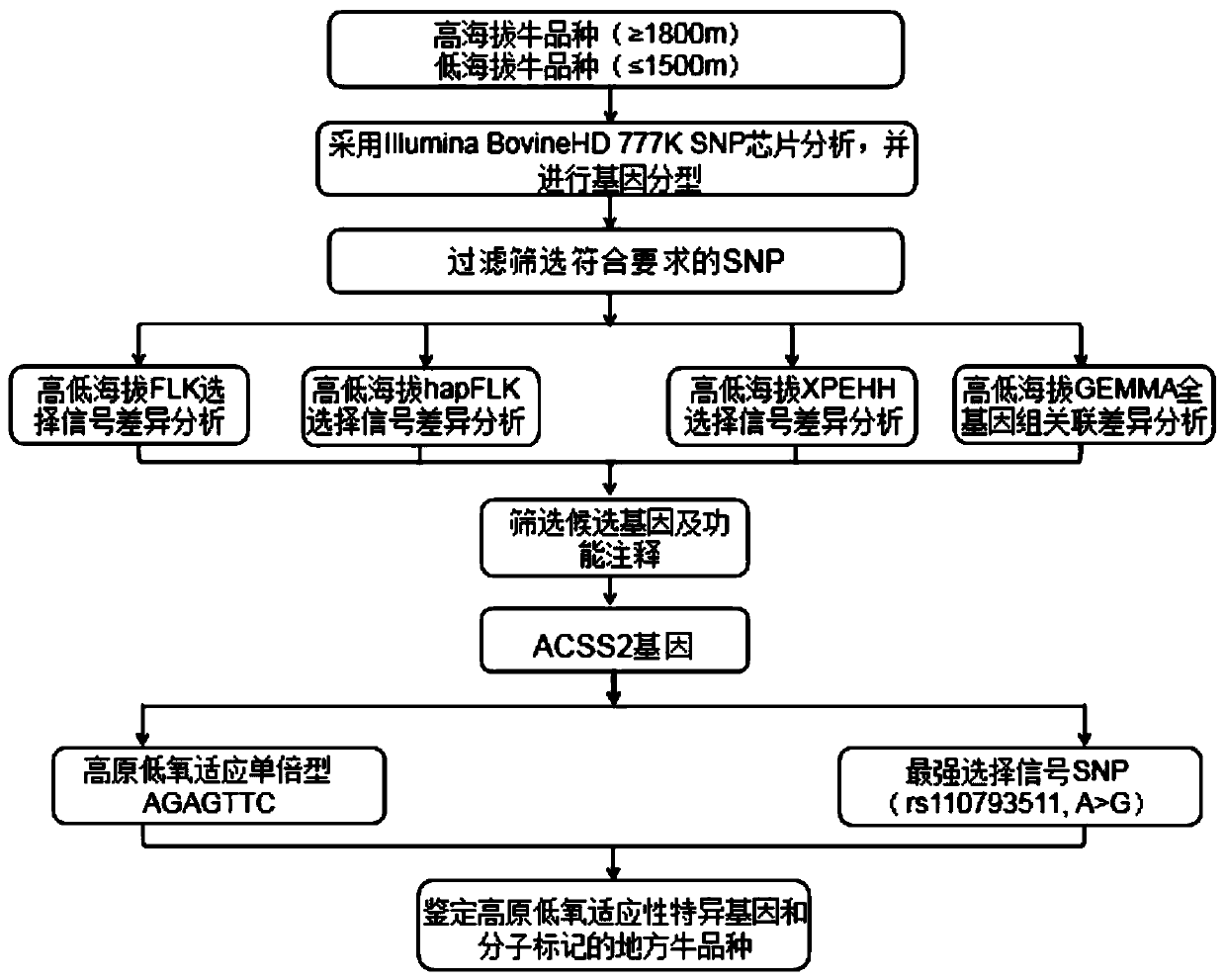
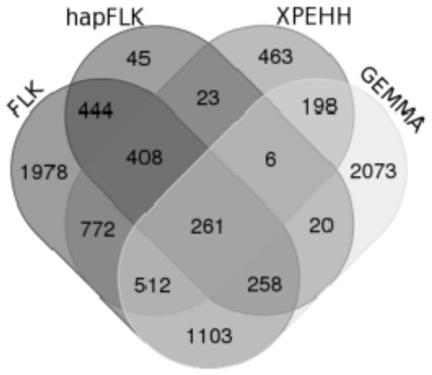
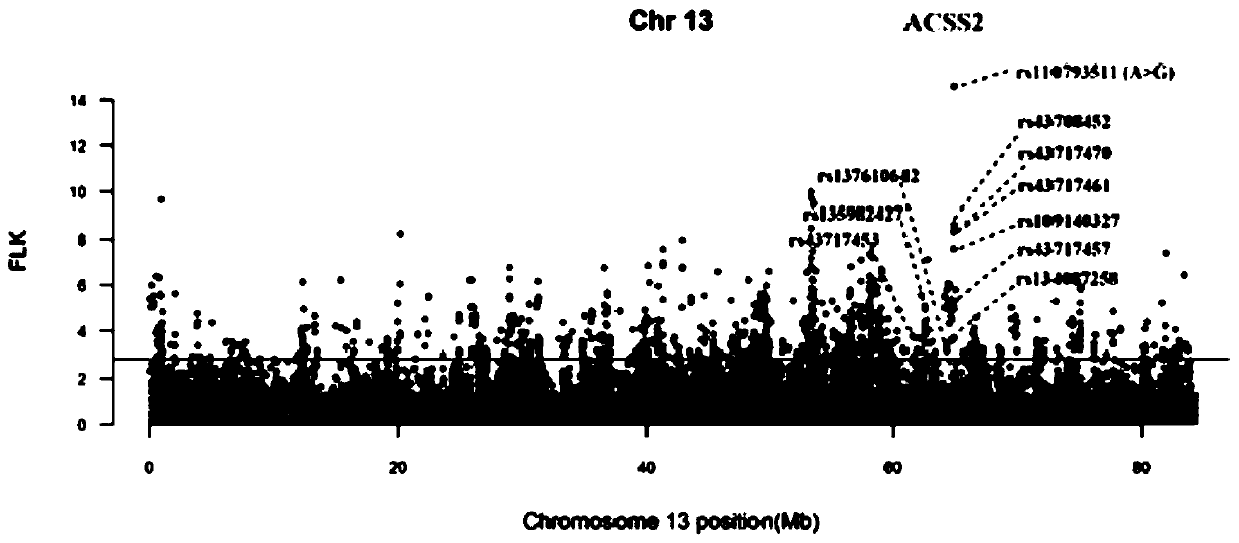
The invention provides a method for screening cattle high altitude hypoxia adaptation specific molecular marker, and furthermore a cattle kind or individual which is suitable for high altitude hypoxiasurvival is screened through the specific marker. The method aims at a high altitude hypoxia adaptation heredity characteristic of a kettle kind, and selects local cattle kinds which are distributedin high altitude regions at aspects of genome evolution, selecting and adapting. Multiple genome selecting signals, a full-genome association analysis method and a strategy are combined. Key genes andmolecular makers which are suitable for high altitude hypoxia are efficiently and accurately screened. Reasonable method designed is realized. The detecting method according to the key gene and marker designing has advantages of high accuracy, and convenient application operation. According to the method of the invention, through analyzing different altitude cattle kinds, a gene ACSS2 which is related with high altitude hypoxia adaptation and a haplotype thereof are found; and furthermore a specific SNP which bears a strongest selecting signal is positioned; and the method realizes an important meaning and a high practicability value for cattle molecule breeding operation.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid
InactiveCN102618570ARealize accumulationCumulative acid production effect is idealBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFumarase
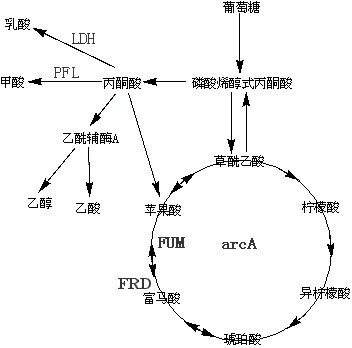
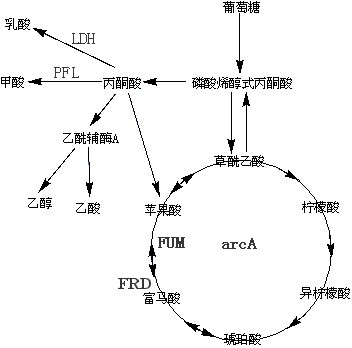
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for constructing escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria for producing fumaric acid. The method for constructing the escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria mainly comprises the following steps of: inactivating or knocking fumarase serving as key enzyme for converting fumaric acid into malic acid in a tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle out, and knocking a key gene arcA for inhibiting the TCA cycle out. Further, key enzyme genes in paths of succinic acid, lactic acid and formic acid can also be knocked out, so the fumaric acid can be accumulated under the anaerobic condition.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
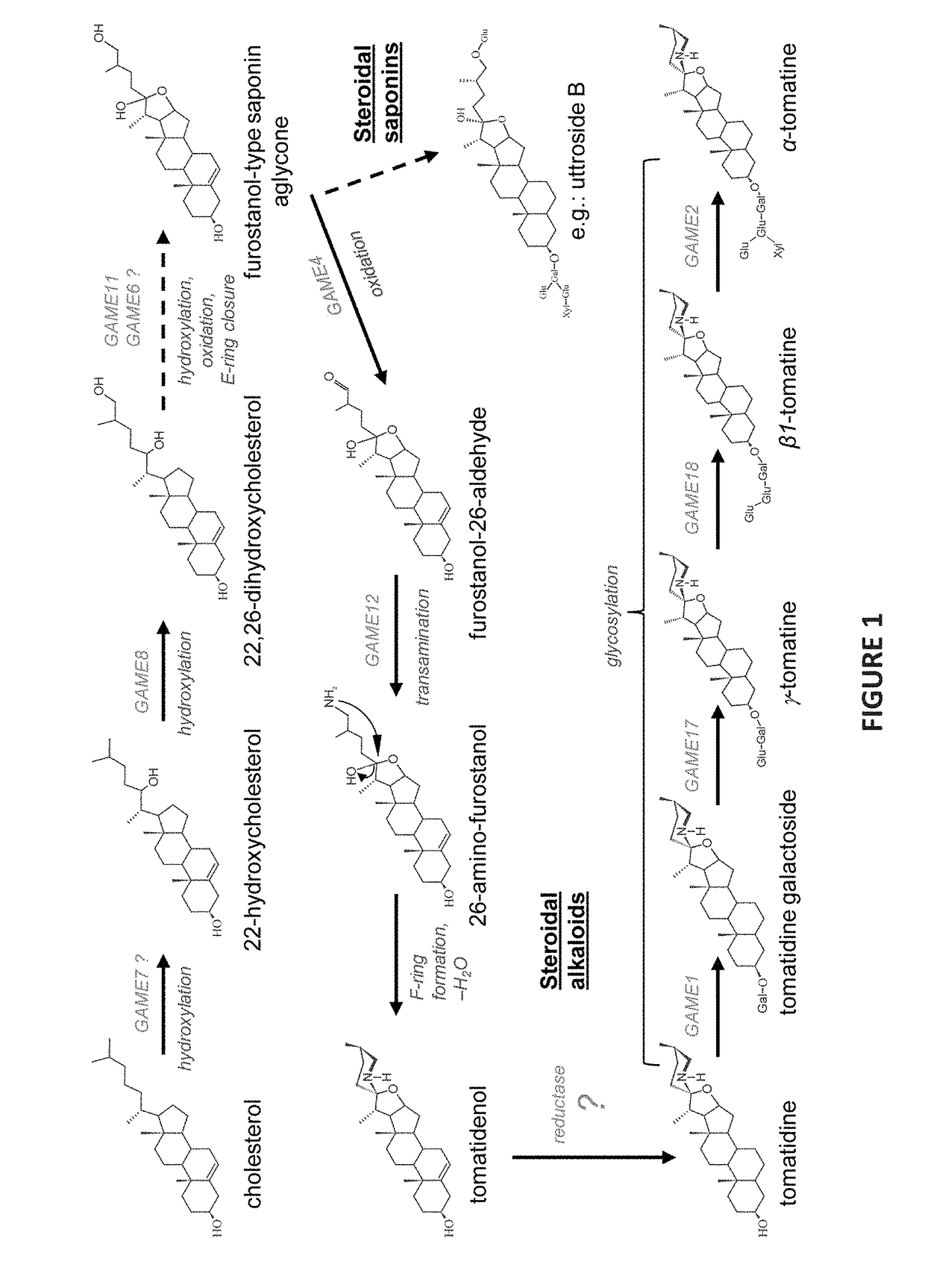
Plant with altered content of steroidal alkaloids
ActiveUS20190059314A1Elevation/reduction in contentLower Level RequirementsEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionCholesterolSteroidal alkaloid
The present invention relates to key genes in the biosynthesis of steroidal alkaloids and saponins, including regulatory genes and enzyme-encoding genes, and to use thereof for altering the content of steroidal (glyco)alkaloids or phytosterols in plants. The present invention provides genetically modified plants or gene edited plants with altered content of steroidal (glyco)alkaloids, particularly to Solanaceous crop plants with reduced content of antinutritional steroidal glycoalkaloids and to the increase in phytosterols, including cholesterol or cholestanol in these plants. The present invention also provides methods of altering gene expression.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
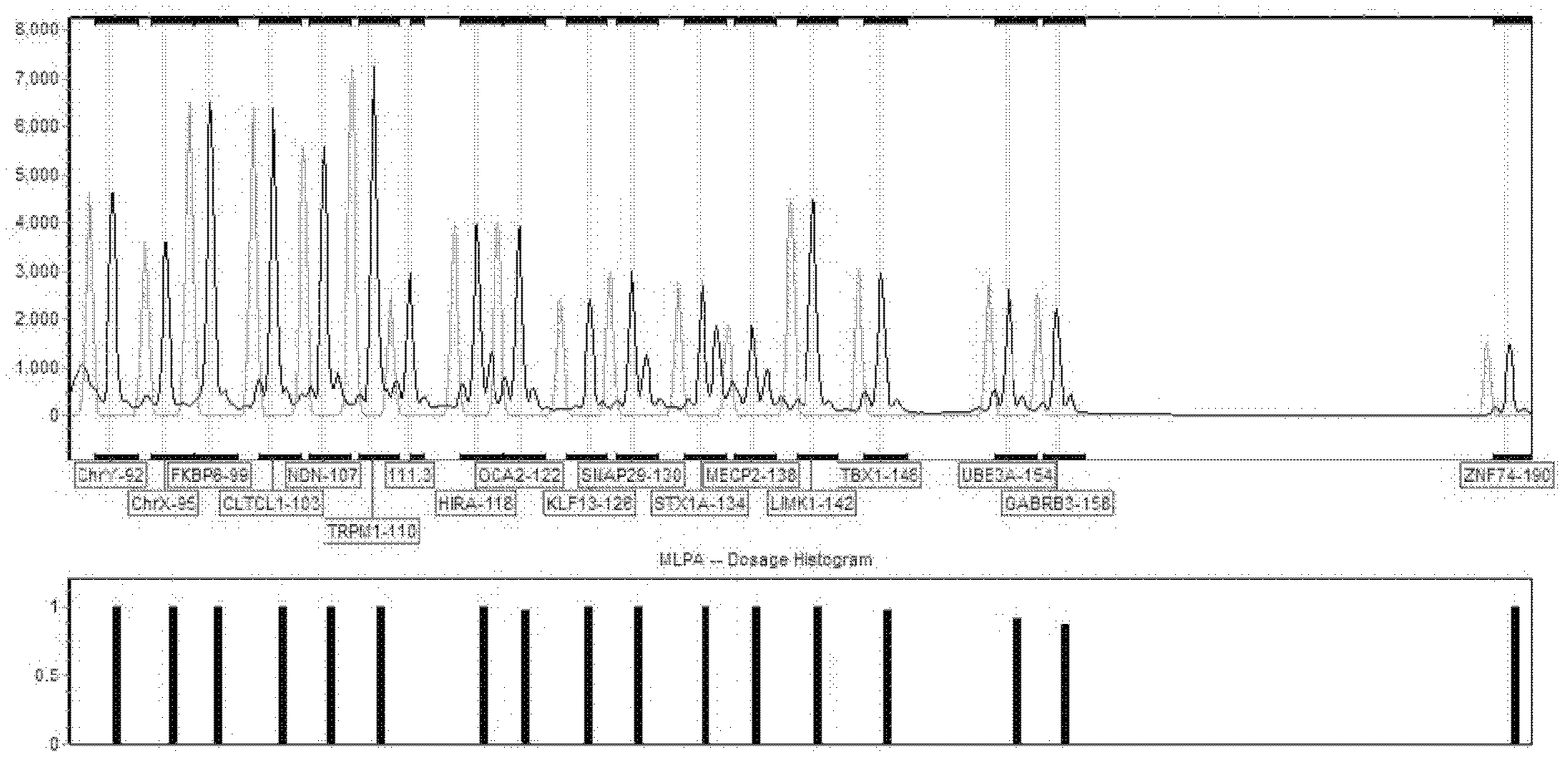
Molecular combination probe for diagnosing and screening chromosome microdeletion syndrome
InactiveCN103014142AEconomic screeningQuick screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPhosphorylation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a molecular combination probe for diagnosing and screening chromosome microdeletion syndrome. The molecular combination probe is used for selecting the key gene of the Williams syndrome, the 22q11 microdeletion syndrome, the Prader-Willi syndrome, the Angelman syndrome, the 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome and the Rett syndrome, or the gene within a critical area, or the gens arranged at two ends within a duplication / deletion fragment, selecting the sequence which meets a corresponding condition as a probe sequence according to the sequence of the gene, and adding a general primer sequence and adding a phosphorylation mark to the 5'end of a probe left-half sequence and the 3'end of a right-half probe to prepare the combination probe for the multiple continuous probe amplification technology. According to the combination probe provided by the invention, the defects of the fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) can be overcome, a plurality of sequences can be analyzed for once, and the molecular combination probe is higher in resolution ratio, sensitivity and repeatability. The probe can be used for the clinical molecular diagnosing and screening of the six-chromosome microdeletion syndrome.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria and application of genetically engineered bacteria in production of 1,5-pentanediamine
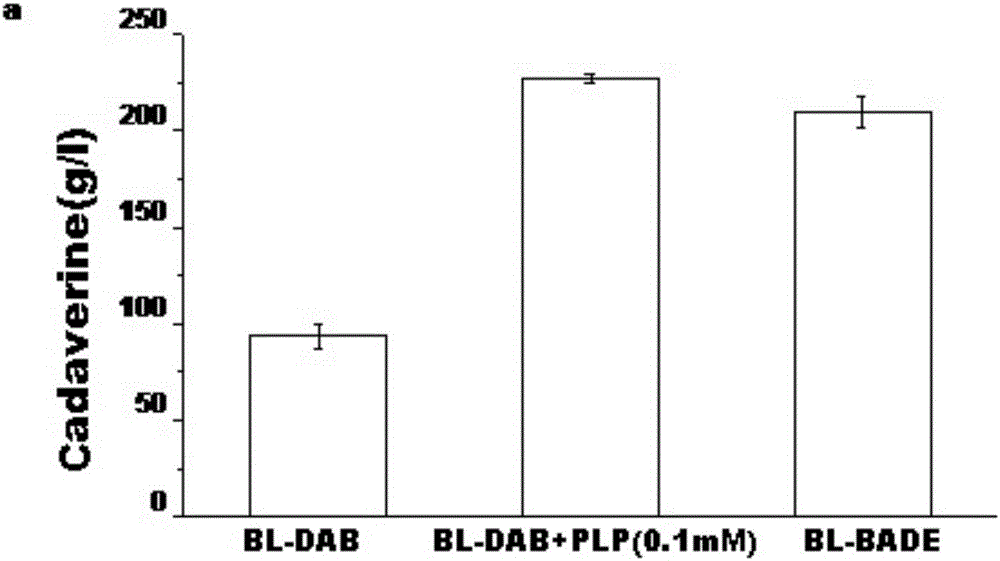
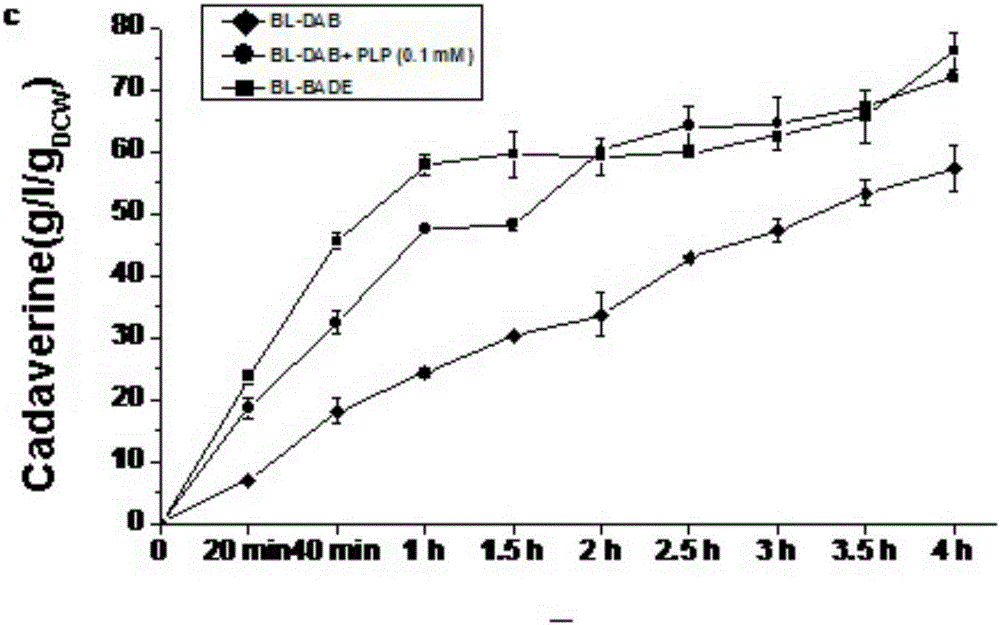
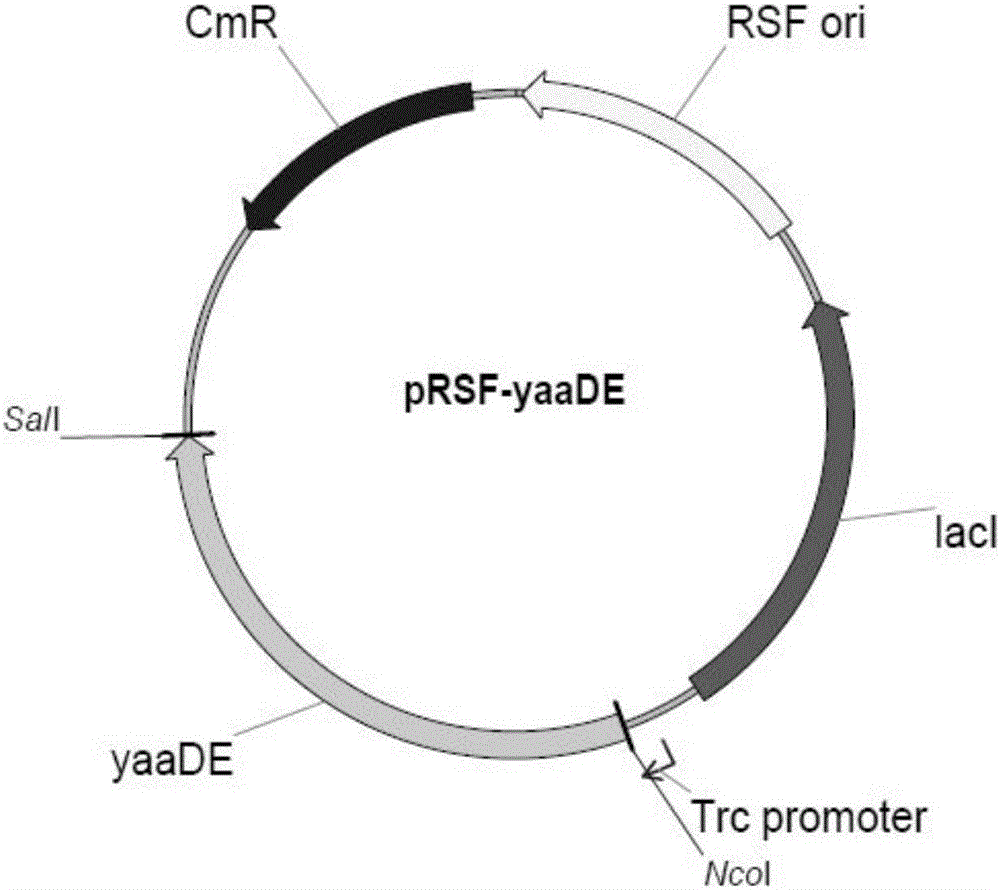
InactiveCN106148373AEfficient Transformation ProductionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBiotechnology
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to genetically engineered bacteria for increasing synthesis of PLP (pyridoxal phosphate) in escherichia coli mycetocyte and a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine from the genetically engineered bacteria. A gene engineering technique is utilized, a key gene for synthesis of PLP through ribose-5-phosphate is subjected to heterologous expression in escherichia coli, and an efficient conversion production strain of 1,5-pentanediamine is established. Under the condition that PLP is not externally added, the genetically engineered bacteria can be converted within 4 h, and the content of produced 1,5-pentanediamine reaches 250 g / l and is far higher than that reported in the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Low-phosphorus-resisting key gene GmPHR25 in plant phosphorus signal network and applications of low-phosphorus-resisting key gene GmPHR25
ActiveCN107435047AImproved Stress Resistance GeneticsGenetic improvementPlant peptidesFermentationDynamic balanceSignaling network
The invention discloses cloning and applications of a key regulation gene GmPHR25 in a plant phosphorus signal network. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of coded protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The research shows that overexpression of GmPHR25 can increase the concentrations of soluble phosphorus and total phosphorus of soybean isolated hairy roots and compound plants under treatment of high and low phosphorus, the biomass is improved under the condition of low phosphorus, the biomass of the isolated hairy roots and the compound plants is reduced under the condition of high phosphorus, therefore, GmPHR25 can regulate the growth of transgenic soybeans and the dynamic balance of phosphorus in the body of gene soybeans, and plays an important role in adapting to low-phosphorus stress of plants; GmPHR25 can regulate the adaptation of plants to low-phosphorus stress in soil through a transgenic technology, and also can be used for genetic improvement of leguminous crops for adapting to acid soil, thus having a very important market prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Protein and gene for adjusting and controlling low temperature saccharification of potato as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102634497AReduce the degree of lusterImprove the ability to resist low temperature saccharificationBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
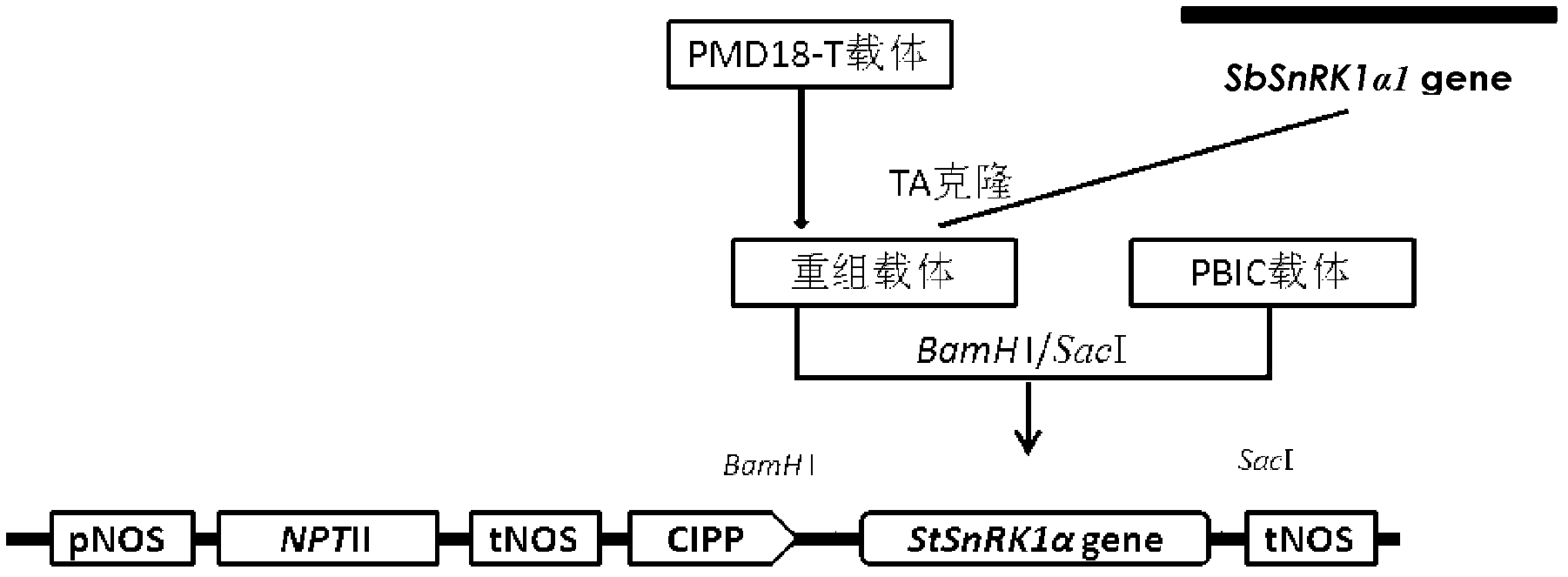
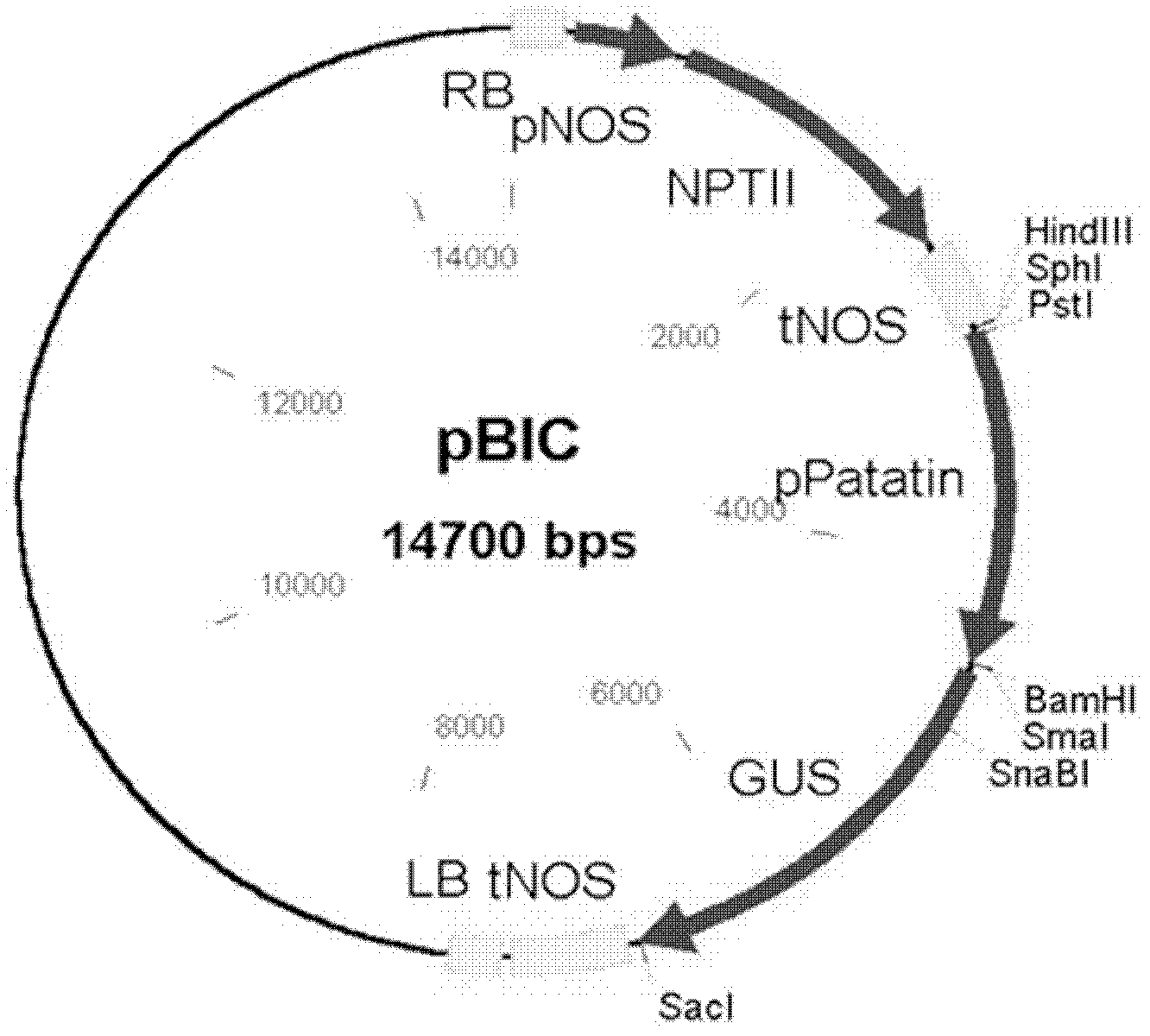
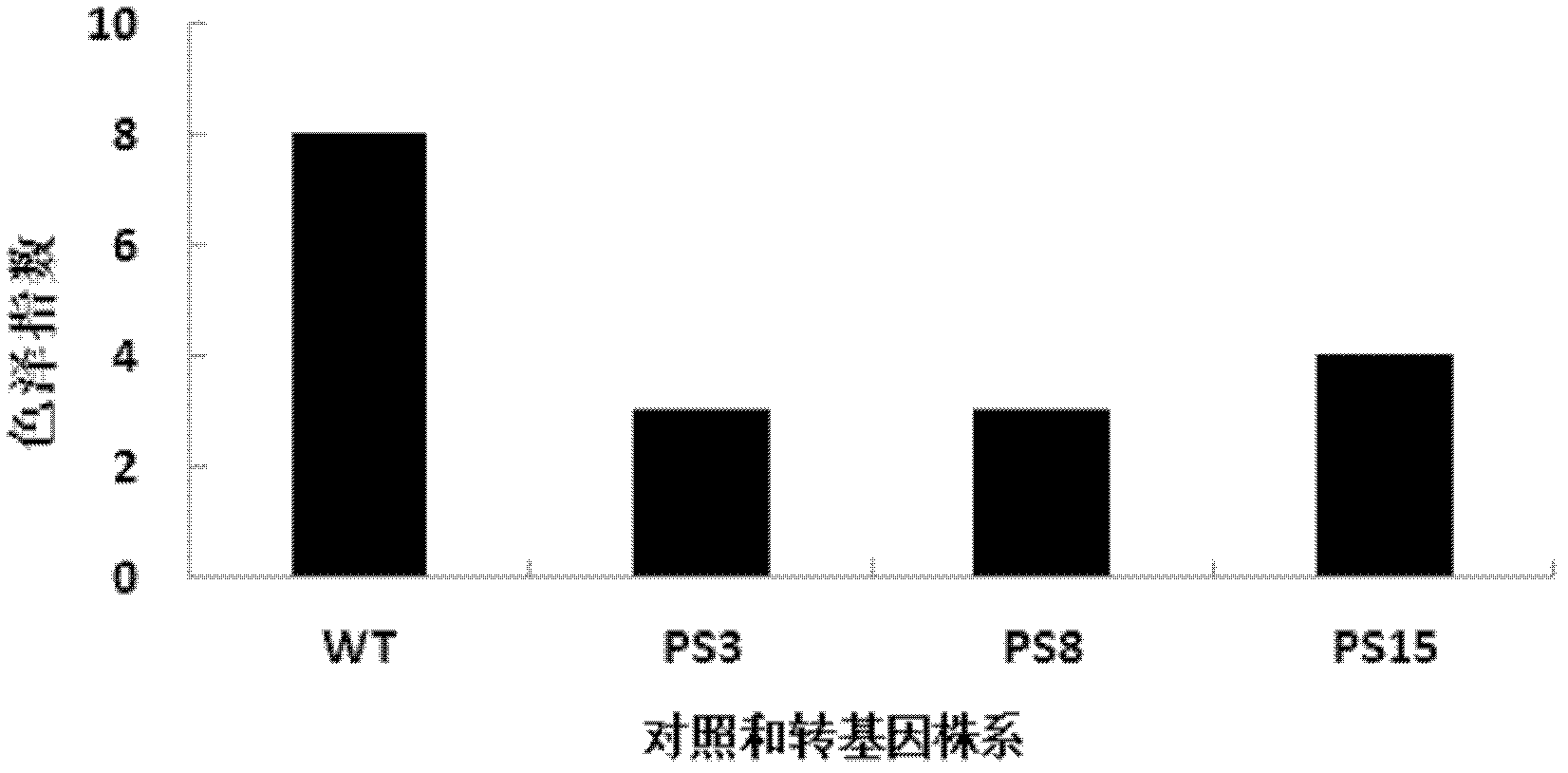
The invention belongs to the technical field of the plant gene engineering, and relates to a key gene StSnSnRK1a for adjusting and controlling low temperature saccharification of potatoes and application thereof. A gene StSnSnRK1, which is obviously relative to the low temperature saccharification of potatoes, is cloned, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as the sequence table SEQIDNO:1, and an amino acid sequence is shown as the sequence table SEQIDNO:2. The biological function tests and transgenic strain phenotype approve that the gene StSnSnRK1a in the invention has obvious effects on preventing the low temperature saccharification of the potatoes, and provides a novel efficient path for the mechanism research in preventing the low temperature saccharification of the potatoes and the improvement of the existing varieties.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
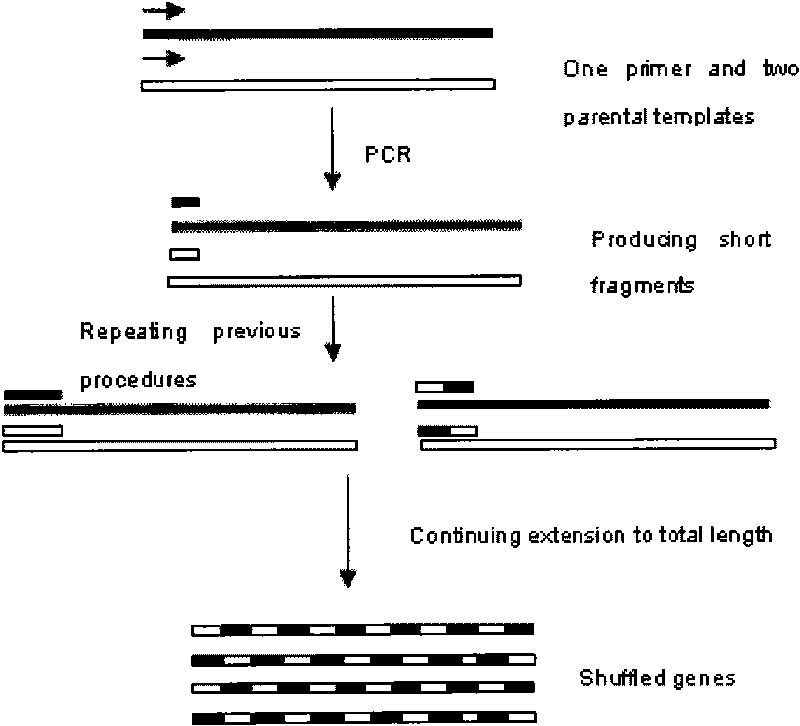
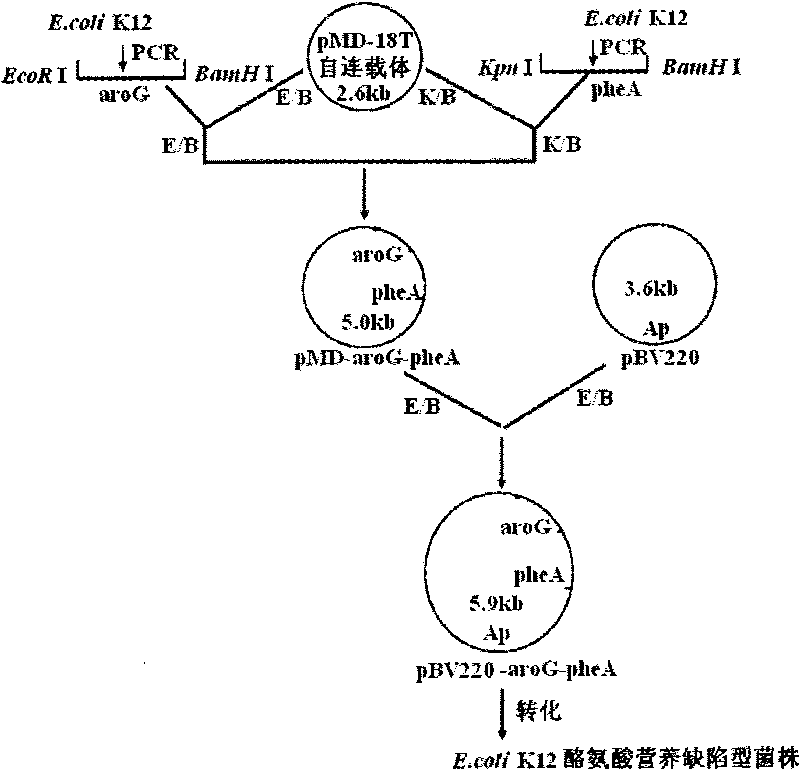
In-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains
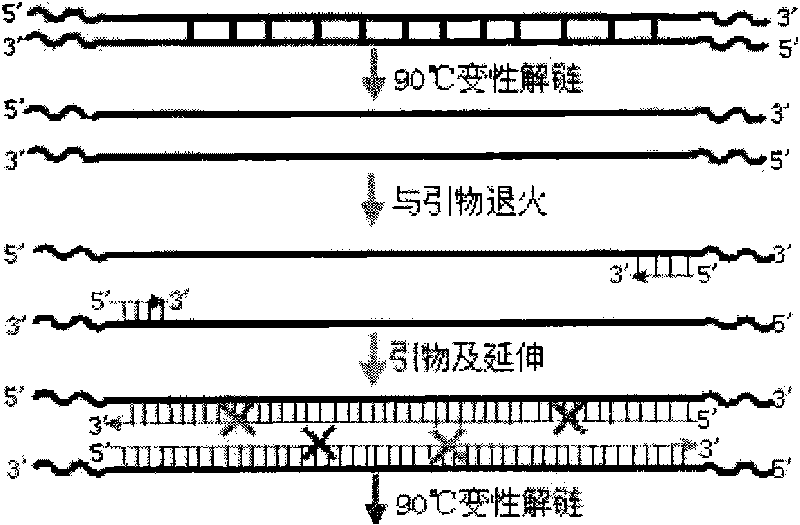
InactiveCN101698853ASpeed up evolutionHigh catalytic activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhenylalanineMetabolic balance
The invention relates to an in-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains, which is realized in a way that: using genes aroG and pheA on an L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain constructed in the room as a whole; carrying out the in-vitro directed coevolution modification by using an error-prone PCR technology and a recombinant DNA technology; and screening to obtain a mutant strain, of which the yield of L-phenylalanine is increased by 114%. In the invention, by modifying the gene formed by coupling and connecting aroG and pheA in series, the key genes aroG and pheA in the metaboly process of the L-phenylalanine are used as a whole to carry out the directed modification, thereby obtaining a new metabolic balance, so that the expressed enzyme has high-efficiency catalytic activity and can resist the feedback inhibition of the L-phenylalanine, thereby obtaining the new modified high-yield L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain by screening. The method can provide an example for modifying the acid production rate of any amino acid gene engineering strain.
Owner:MAIDAN BIOLOGICAL GROUP FUJIAN
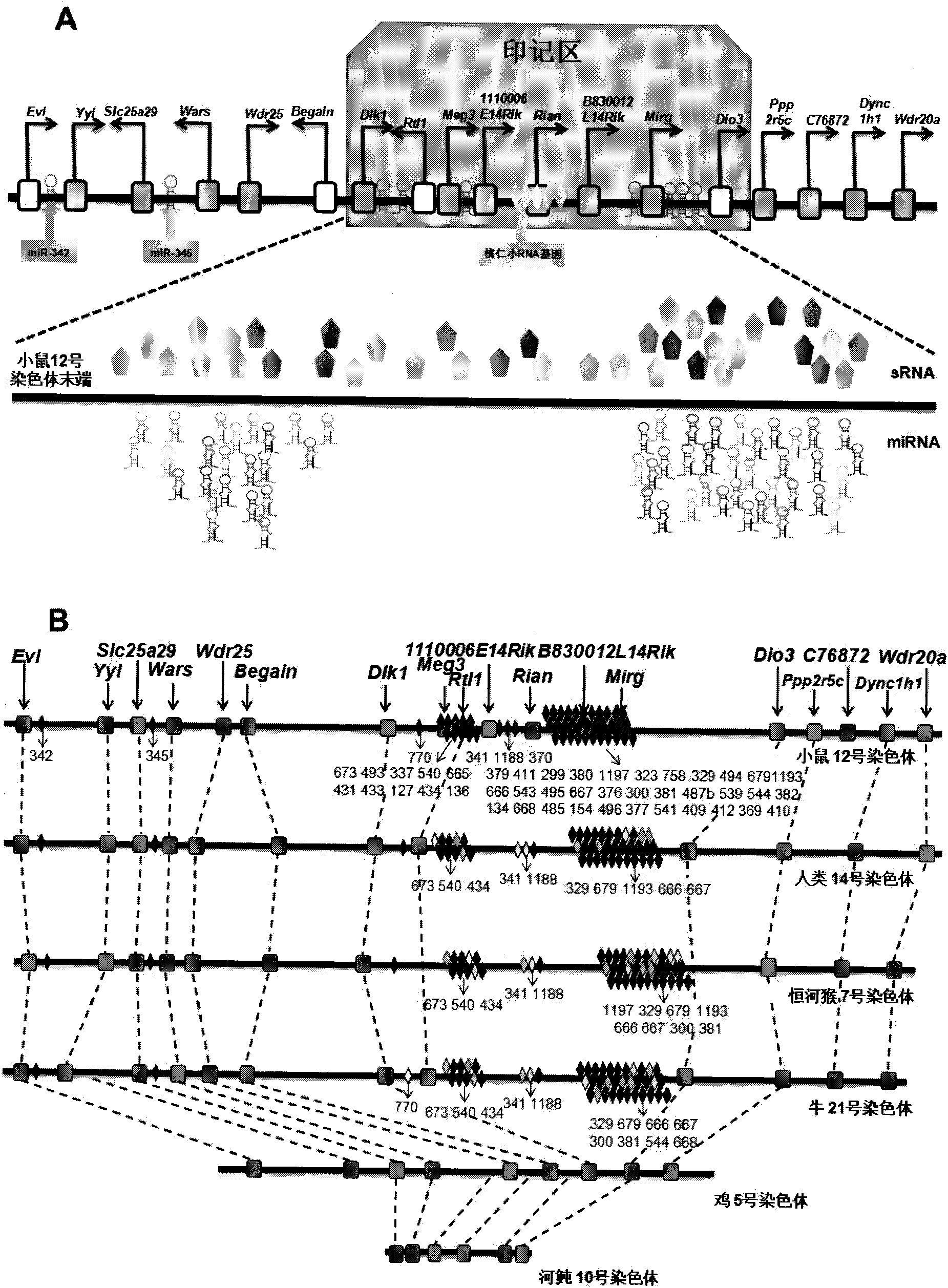
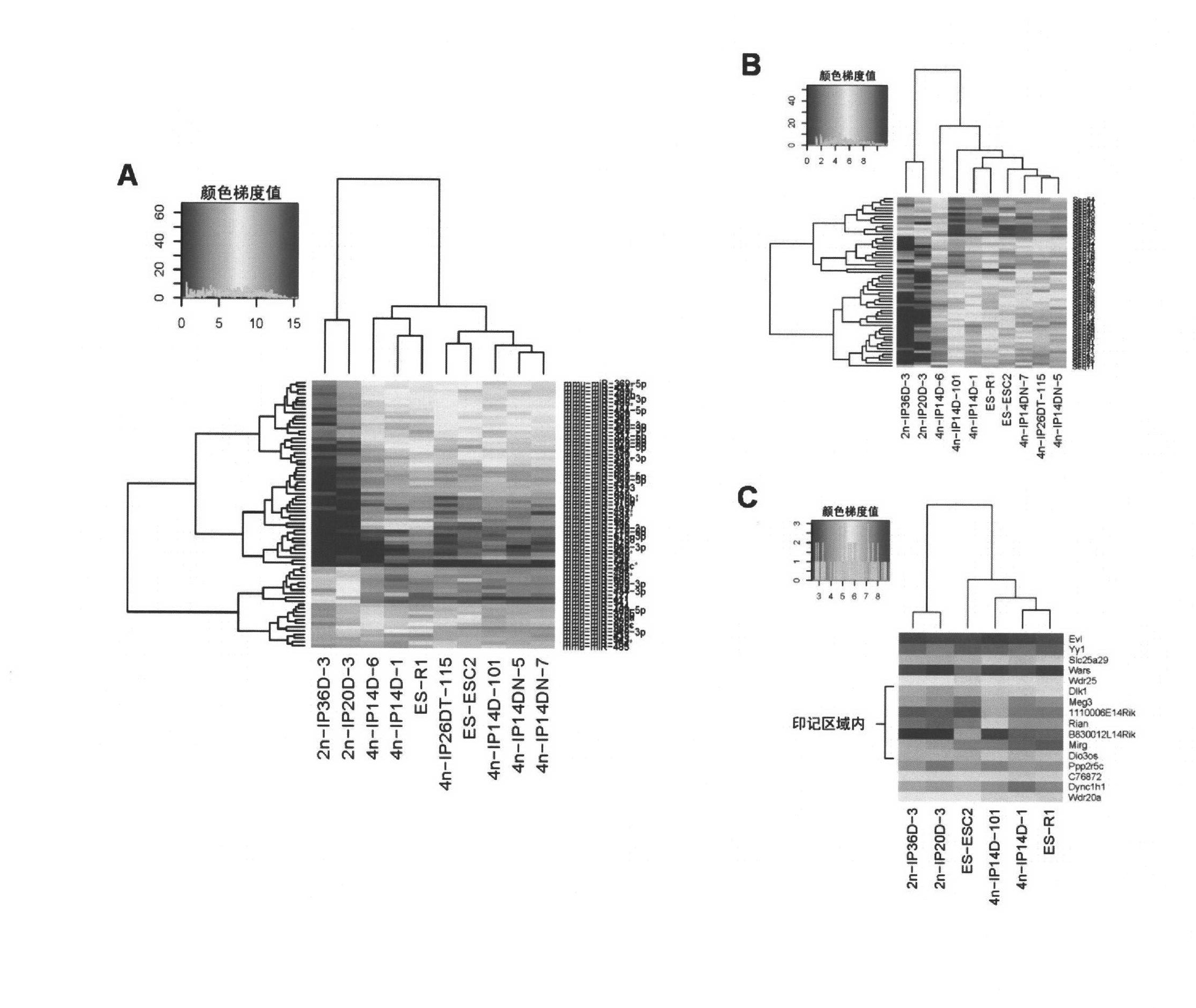
Key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs or combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency
The invention relates to key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or a combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency. The invention is characterized in that the key genes, microRNAs, other non-coding RNAs or a combination is highly expressed in the stem cell with complete pluripotency and the expression is obviously repressed or silent in the stem cell without complete pluripotency. The genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs are the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs positioned in the chromosome imprinting region named as Dlk1-Dio3 on the long arm of mouse chromosome 12 and the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in the genome collinearity regions of other mammals, which have 70%-100% of homology. The invention also relates to applications of the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or the combination thereof used for identifying the pluripotency of the stem cell and regulating cell pluripotency, applications in stem cell typing, applications for regulating the cell pluripotency and the pluripotency state and level of the cell, applications in disease treatment, and applications in the drug target development of tumor treatment or the development of antitumor drugs.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for screening and annotating of longissimus dorsi differential expression genes of pigs of different varieties
InactiveCN104636638ADeepen understandingSpecial data processing applicationsLongissimus dorsiLongissimus
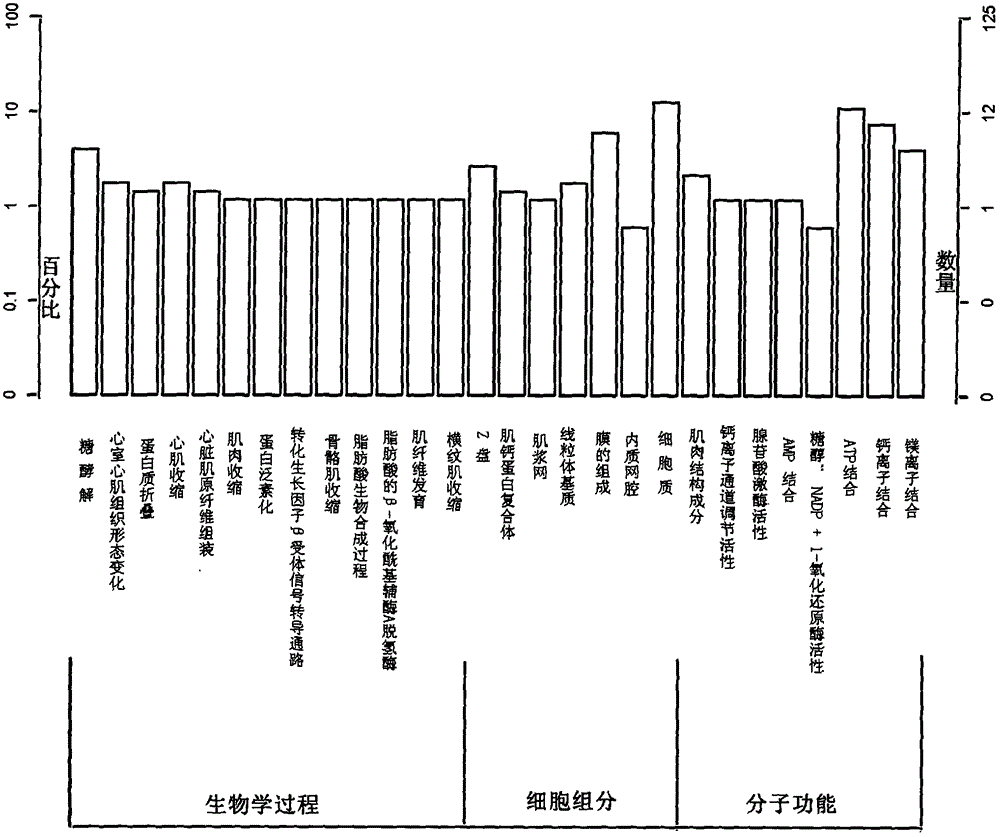
The invention discloses a method for screening and annotating of longissimus dorsi differential expression genes of pigs of different varieties. The method comprises the following steps that 1, sampling and sequencing are conducted; 2, original data are processed; 3, differential genes are screened; 4, function significance enrichment analysis is conducted; 5, Pathway significance enrichment analysis is conducted. According to the method, a high throughout transcriptome sequencing technology is adopted, the gene expression profiles of longissimus dorsi tissue of the pigs of different varieties are established, the differential expression genes are obtained, the differential expression genes are selected through GO analysis and pathway analysis, the key gene of controlling the meat quality trait is determined, control over muscle growth and development and fat metabolism can be better understood, and the molecular biology evidence is provided for the following research of the molecular mechanism forming the difference of the meat quality and the growth trait of domestic and oversea varieties.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
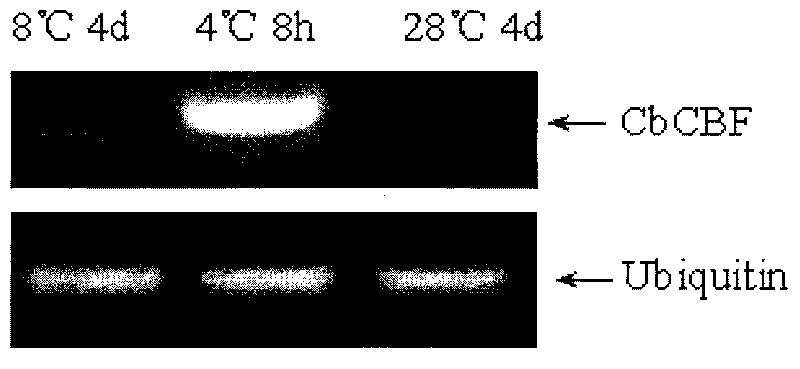
Promoter of shepherd spurse CBF path key gene CbCBF and applications thereof
InactiveCN101693891AImprove cold resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotidePlant genetic engineering
The invention pertains to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a promoter CBFP of a key gene CbCBF of a shepherd spurse CBF path and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is showed as SEQ ID NO:1, wherein CbCBF gene and the promoter thereof contain the nucleotide sequence of the 2283rd basic group in the sequence showed in the sequence table of SEQ ID NO:1, and the nucleotide sequence encodes a transcription factor which is induced by low temperature and can regulate and control a cold-inductive gene. The promoter area contains two ABRE cis-acting elements which are serially arranged, thus being capable of specifically playing a response reaction to low temperature and ABA; and the promoter area contains three MYCRE cis-acting elements CANNTG, thus being capable of being combined with an upstream control element (ICE) (inducer of CBF expression). An inductive expression carrier structured by using the genetic promoter can powerfully induces the expression of a target gene when the plant is stressed by low temperature. The invention also provides the applications of the promoter in cultivating cold-resistant plants, which realizes the breed improvement of crops.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
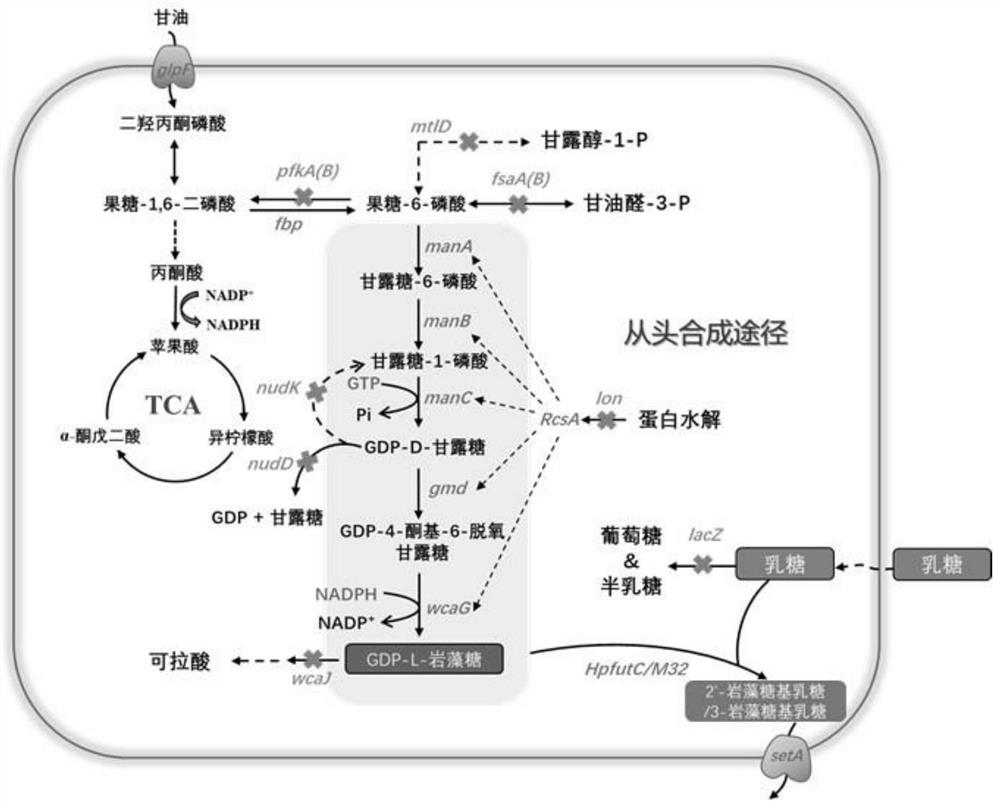
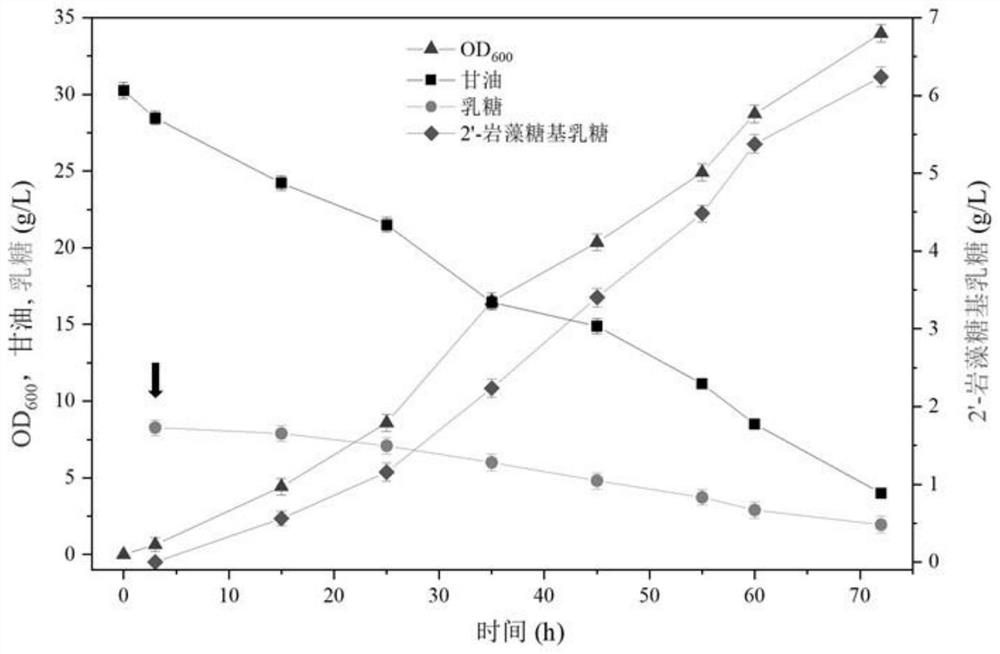
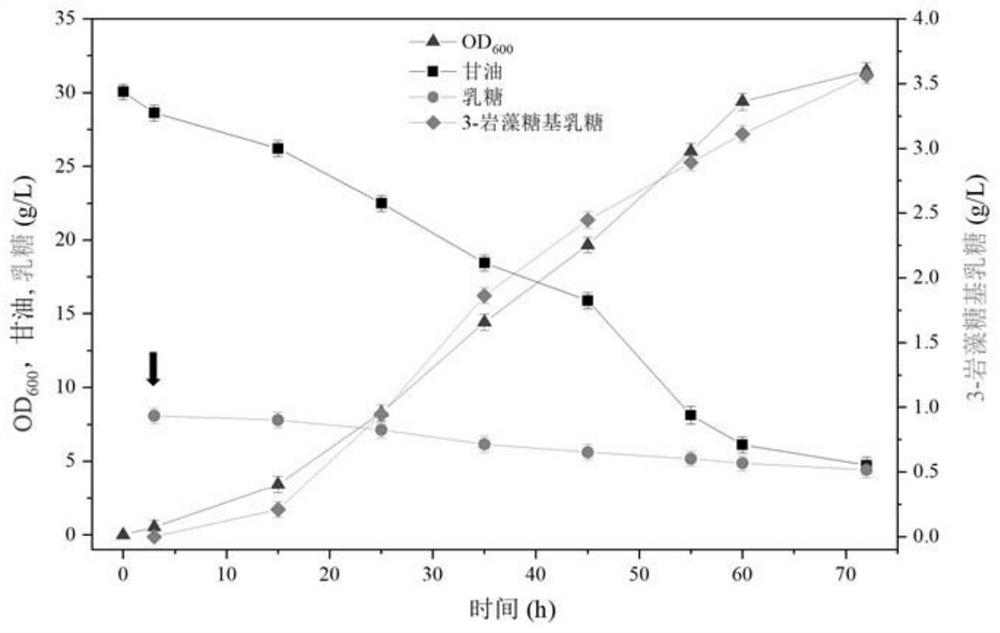
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and production method
PendingCN114480240AGrow fastImprove expression levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell factory
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and a production method of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to metabolic engineering and food fermentation technologies. According to the invention, a synthetic biological means is utilized, an escherichia coli cell factory of fucosyllactose is constructed based on a de novo synthetic route, bypass related genes lacZ, wcaJ, nudD, pfkA and lon in host cells are knocked out by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, and genes manB, manC, gmd and wcaG are assembled through a multi-plasmid expression system, so that the fucosyllactose is obtained. Constructing expression vectors with different copy numbers to increase the expression level of key genes; fucosyltransferase from different sources is screened, so that the activity of rate-limiting enzyme is improved. The constructed recombinant escherichia coli can be used for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose by utilizing glycerol, is stable in heredity and high in expression level, and has obvious industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Multiple target points miRNA antisense nucleic acid technique
ActiveCN101121934ASignificant effect and effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidNucleotide
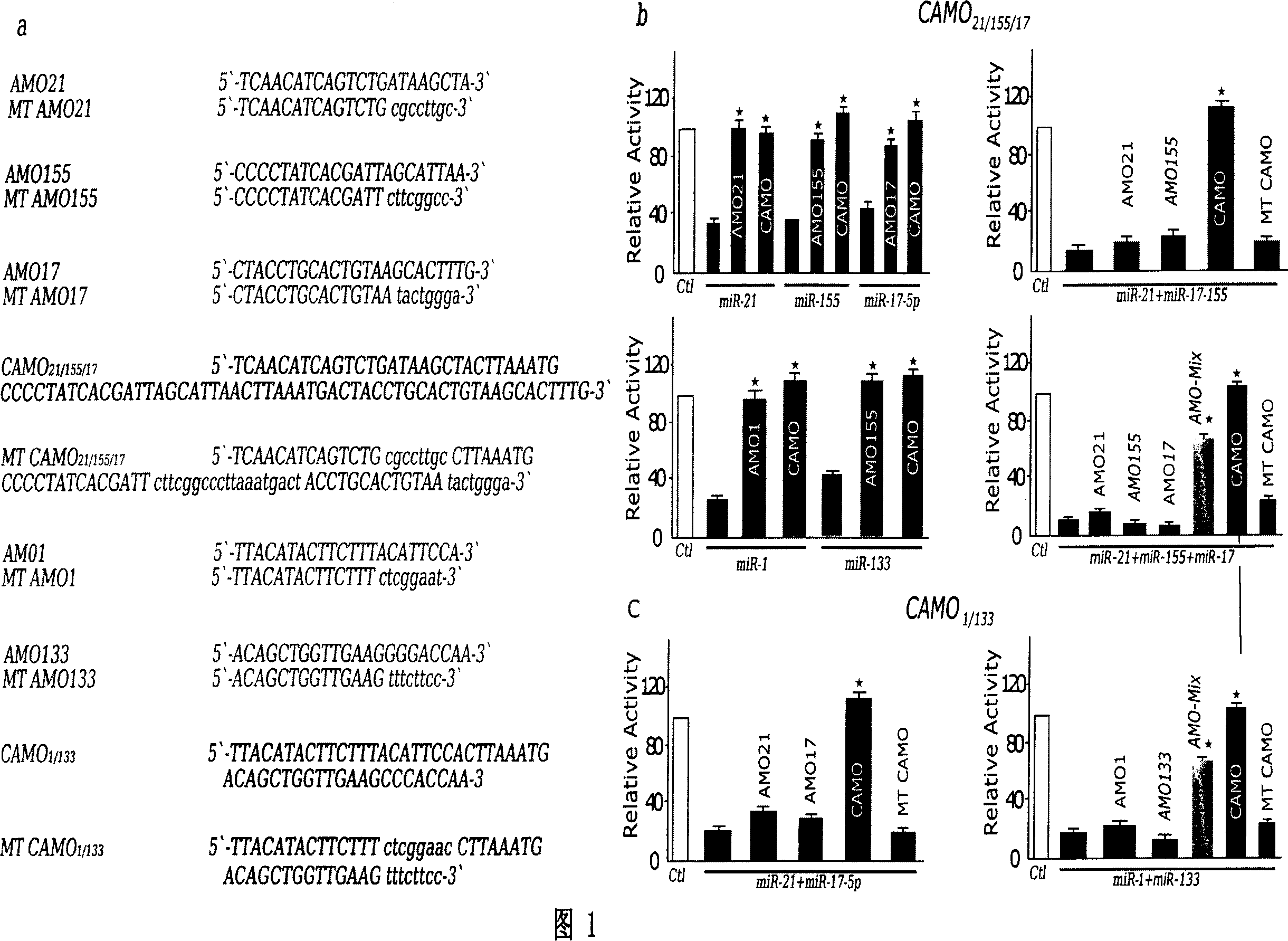
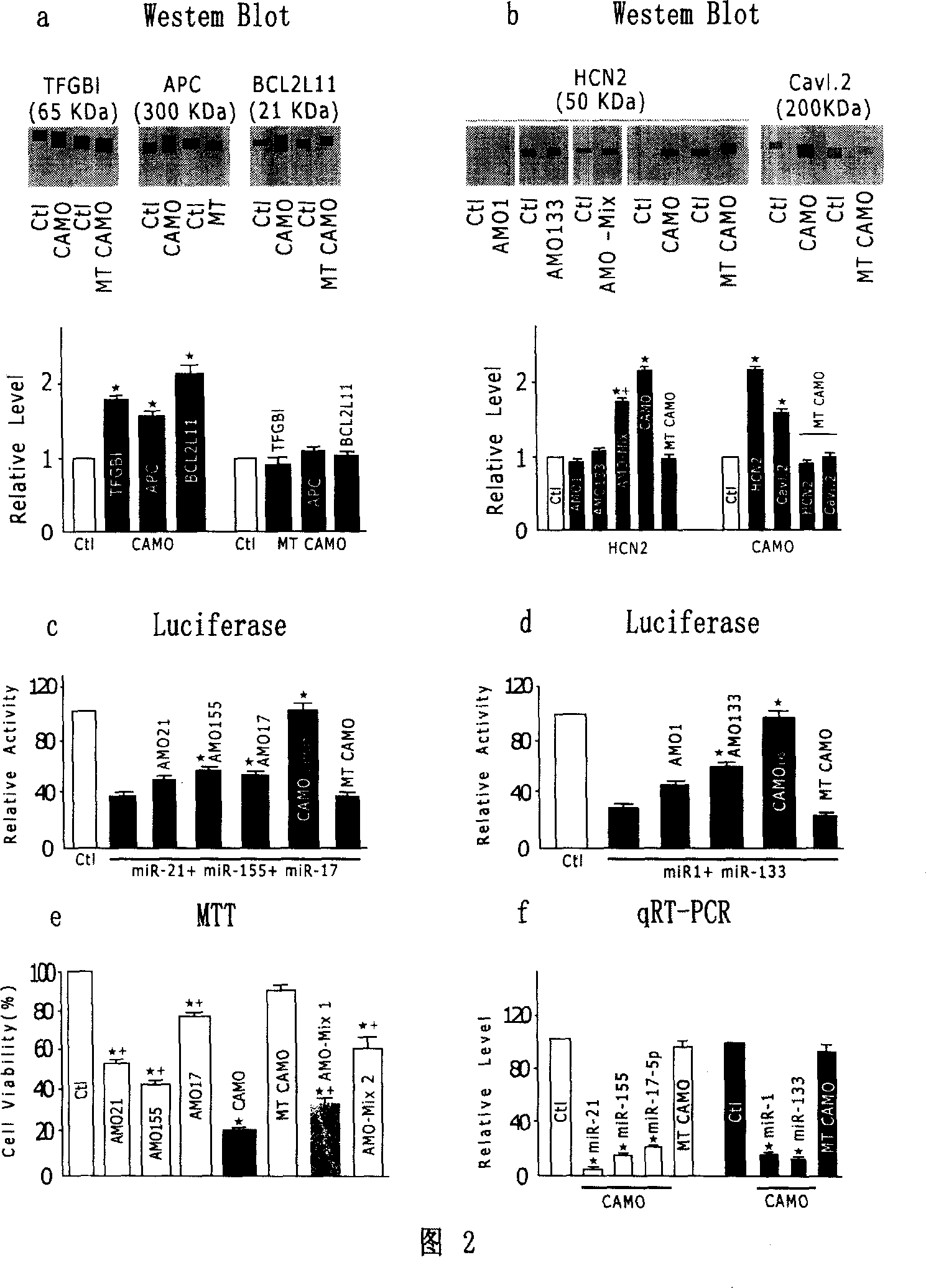
The invention discloses a technology of multi-target miRNA antisense nucleotide, relating to an antisense nucleotide technology. The invention is capable to solve the problems of existing method for silencing miRNAs, e.g. single target and poor action efficacy. The technology of multi-target miRNA antisense nucleotide is achieved by the following procedures: 1. miRNA that capable to regulate the key gene (i.e. pathogenic gene) is found through gene chip screening or provision of documentation; 2. a plurality of antisense miRNA antisense nucleotides are designed into a single-nucleotide sequence that can silence a plurality of multi-target miRNAs, i.e. the technology of multi-target miRNA antisense nucleotide is achieved. The invention can be used as a simple and direct method to conduct study on the bioprocess containing various miRNAs and genes. Compared with existing methods, the greatest advantage of CAMO method lies in that one drug molecule is capable to regulate multi-target genes and the action efficacy is stronger. The invention can well settle the problems of existing methods, i.e. single target and poor action efficacy.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
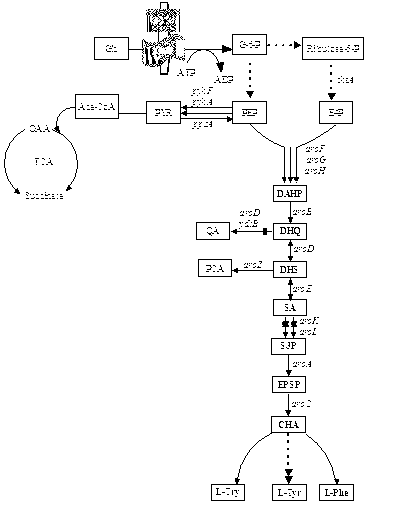
Shikimic acid prepared bacterial strain and constructing method
InactiveCN101139566AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShikimic acidMicrobiology
The invention discloses a shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain and a constructing method for the bacterial strain. First, bacterial strain W3110 (delta aroL delta aroK) with gene aroL and aroK knocked out is constructed, and a recombination expression plasmid pSUFEBPT containing key gene aroF, aroE, aroB, ppsa and tktA in the metabolism of shikimic acid is constructured, then the recombination expression plasmid is transferred into the bacterial strain W3110 (delta aroL delta aroK) with gene aroL and aroK knocked out, so as to get the shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain. The shikimic-acid-producing bacterial strain in the invention can achieve the effective accumulation of shikimic acid in fermentation, and lay a foundation for the industrialization of shikimic-acid production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
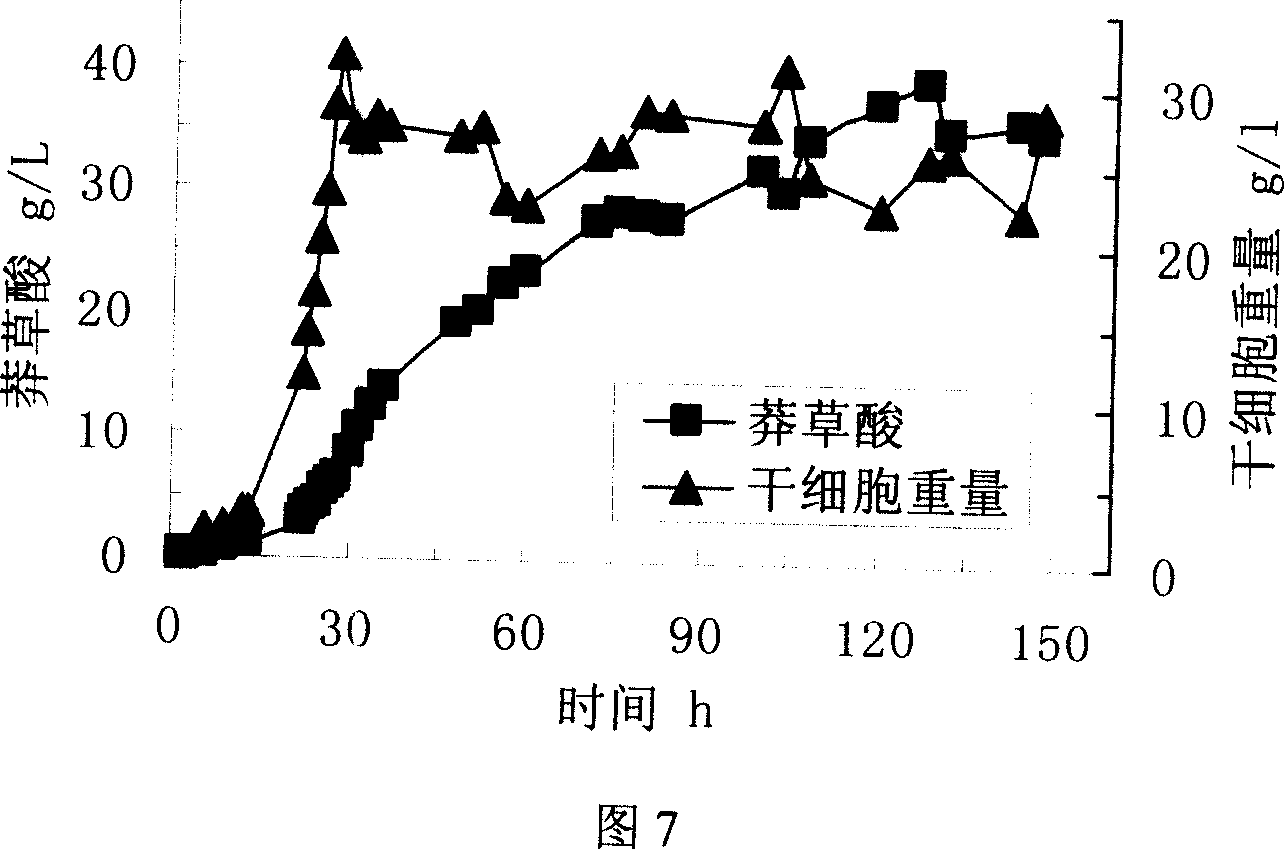
Key gene PeWOX11b for adventitious root development of poplar and application of key gene PeWOX11b
The invention discloses a key gene PeWOX11b for adventitious root development of poplar. The nucleotide sequence of the key gene PeWOX11b is shown by SEQNO1. According to the key gene PeWOX11b and the application thereof disclosed by the invention, the PeWOX11b gene is transferred into the poplar, so that the number of adventitious roots of transgenic poplar for over-expression of the PeWOX11b gene is increased, adventitious roots grow on stems and new plants can also grow on the adventitious roots at different positions, the result shows that the PeWOX11b gene is a key factor for controlling the generation and the development of the adventitious roots of the poplar and has an important application value in the fields of forest genetic engineering and vegetative forestry.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Key gene for regulating and controlling chlorophyll degradation in the senescence process of plant and application thereof
InactiveCN101831450AExtend the life of the priceExtended postharvest green periodFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNutrition
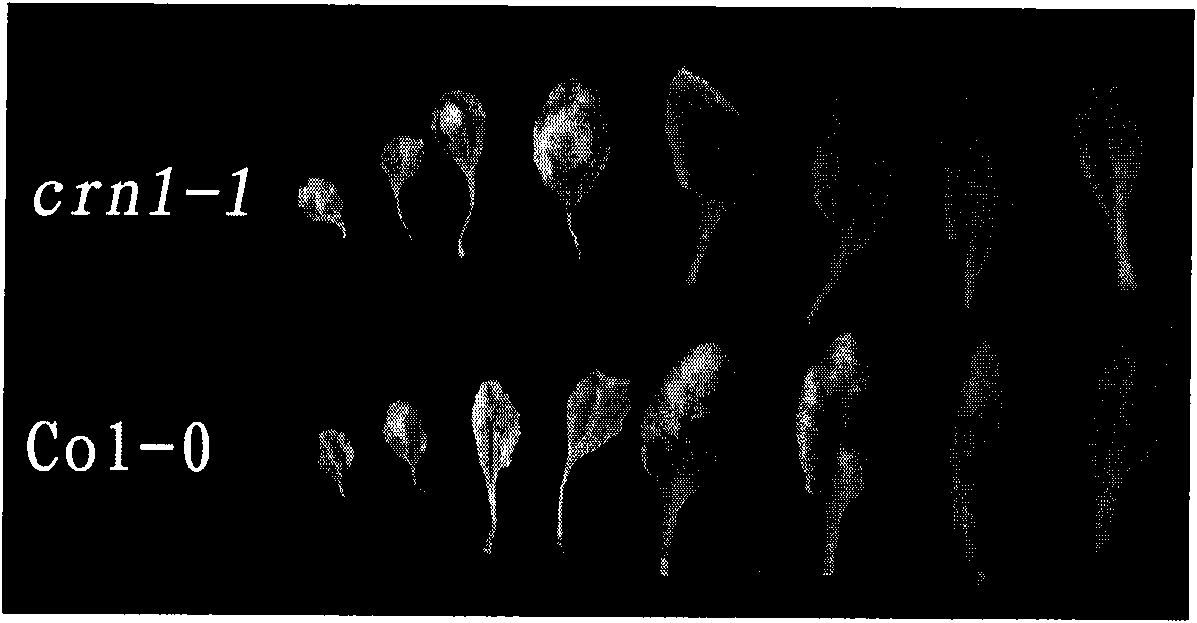
The invention relates to a new key gene participating in the regulation and the control of chlorophyll degradation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of plant gene engineering. Stay-green traits can prolong the commodity price service life of green leafy vegetables and the postharvest green period of fodder crops so as to increase the content of main nutrition constituents, i.e. chlorophylls and proteins; and the stay-green traits can also outstandingly improve the green period and the landscape effect of lawn plants. The invention provides the key gene AtCRN1 for regulating and controlling the chlorophyll degradation and metabolism of plants. An amino acid coding sequence of the key gene AtCRN1 is characterized by being SEQ ID No: 2. The invention also provides a method for establishing a stay-green plant strain, comprising the following steps of: inducing the gene AtCRN1 of a target plant to generate mutation through chemical or physical factors; and destroying or reducing the expression of the gene AtCRN1. Besides, detecting whether the gene AtCRN1 with overall length is contained in a plant genome or not can also be used as a molecular auxiliary breeding method for screening / identifying the stay-green plant strain.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN113817658AIncrease production intensityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid through xylose induction. Escherichia coli is used as a starting strain, an N-acetylglucosamine synthesis pathway is integrated on a genome, an N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene neuB from collar algae are introduced, an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis pathway is constructed, and a key gene nano ATEK of a catabolism pathway of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic pathways of precursor substances required by synthesis of the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multi-copy reinforcement, part of bypass metabolic pathways are knocked out, key enzyme genes for producing GlcNAc and Neu5Ac are optimized according to different copy numbers, the optimal proportion of the key enzyme genes is finally determined, and the high-yield strain of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is obtained. The highest yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 28g / L, the highest production intensity can reach 0.67 g / (L*h) which is the highest value reported at present, and the N-acetylneuraminic acid has important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium, and applications thereof in preparation of L-phosphinothricin
ActiveCN108795835AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium, and applications thereof in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The genetically engineered bacterium comprises Escherichia coli and recombinant plasmids transferred into Escherichia coli; the recombinant plasmids contain transaminase gene and pyridoxal phosphate synthetic route enzyme gene; the nucleotide sequence of the transaminase geneis represented by SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the pyridoxal phosphate synthetic route enzyme gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.2-5. According to the applications, genetic engineering technology is adopted to express ribose-5-phosphate pathway synthesis key gene PdxST in Escherichia coli, or enhance Escherichia coli self PLP synthesis pathway key gene epd, pdxJ, and dxs expression; preparation of the coenzyme reinforced transaminase genetically engineered bacterium through construction is capable of increasing intracellular coenzyme PLP content obviously, avoiding adding of externally-sourced PLP in production of L-phosphinothricin using the genetically engineered bacterium, increasing transaminase enzyme activity and stability obviously, prolonging transaminase half life, reducing production cost, and increasing L-phosphinothricin production efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
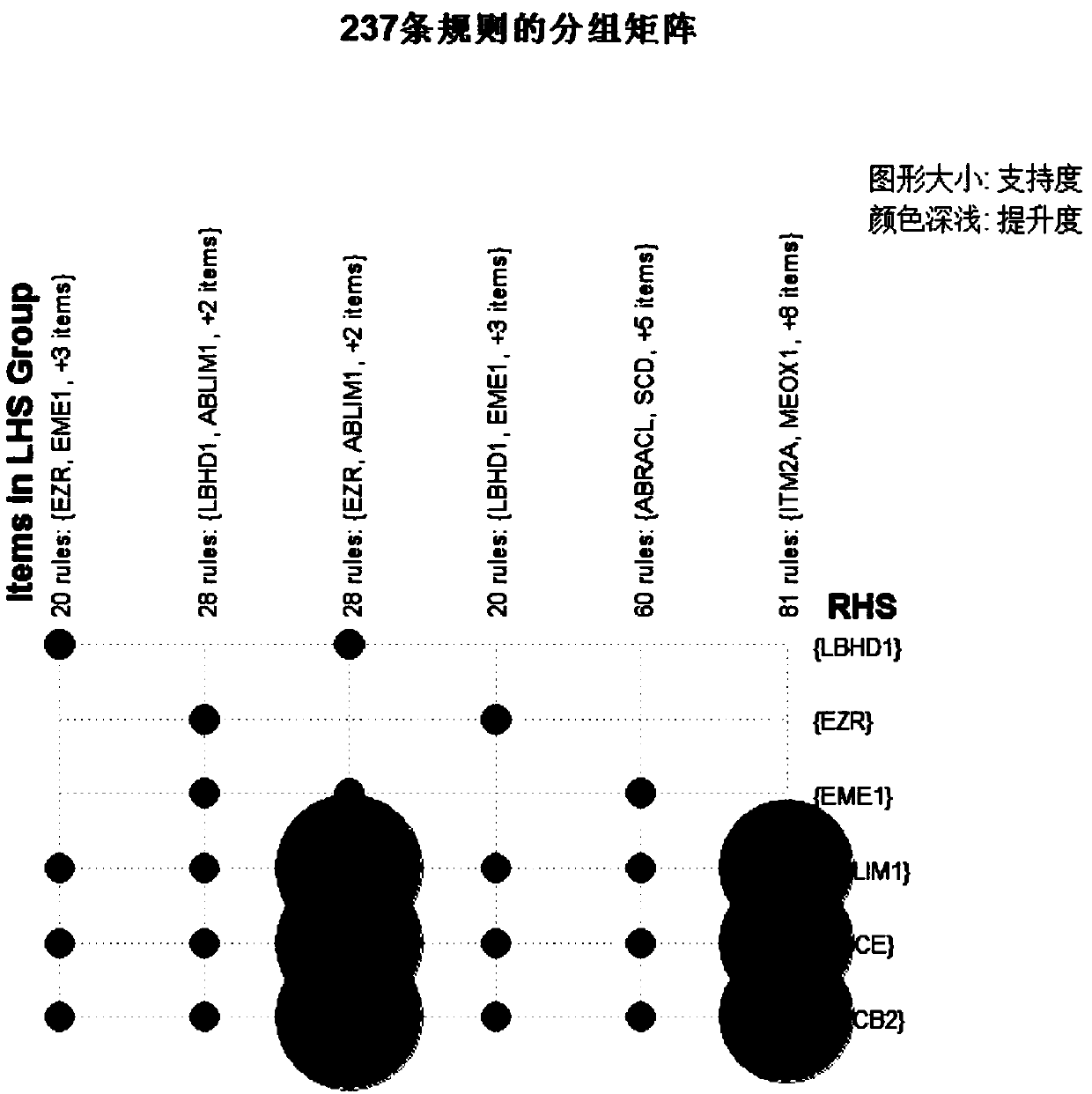
Method for mining whole genome key genes by differentiation and association rules
ActiveCN108038352AEasy to identifyEasy to handleBiostatisticsProteomicsGenome wide expressionCvd risk
The invention belongs to the technical field of data processing, and discloses a method for mining whole genome key genes by differentiation and association rules. The method comprises the following steps: folding multiple pores by using a corresponding relationship between a gene name and a probe name, and then preliminarily screening treated genes by using an application differentiation method to obtain genes with remarkable differential expression; dividing all samples of differential genes into an up-regulation transaction set and a down-regulation transaction set according to threshold values, separately mining genes of the two transaction sets by the association rules, and finding out genes which correspond to top-ranked rules, namely the key genes; and finally, verifying the effectiveness of the genes by biological function analysis. Association between samples and association between genes are considered comprehensively, whole genome expression data can be processed, the key genes with outstanding expression are found out, and the method has important significance on disease risk prediction, research on pathogenesis of complicated diseases, biological pharmacy technologiesand the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com