Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Anthocyanin biosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
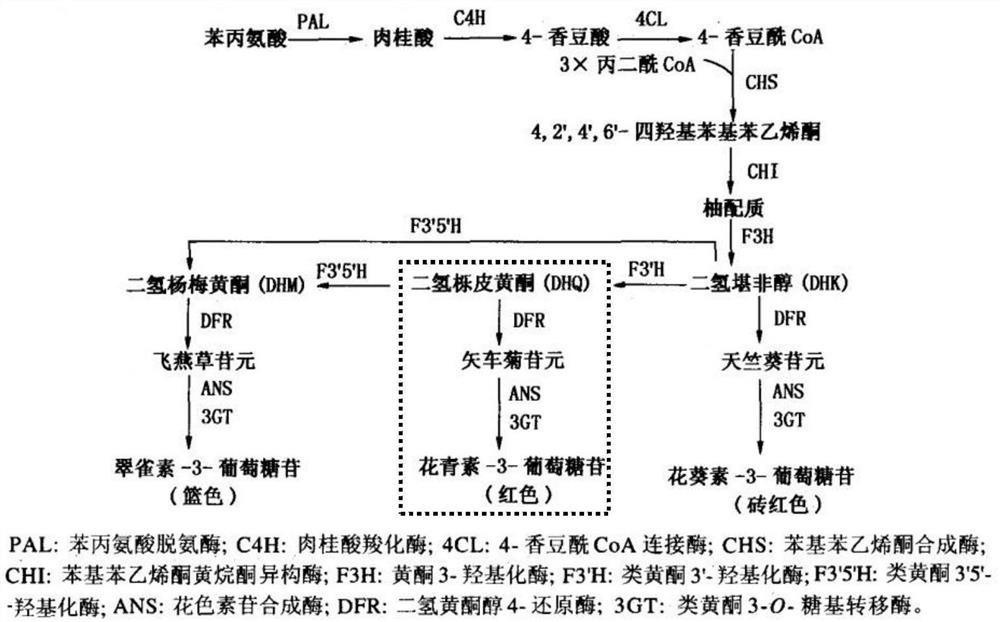
Anthocyanins biosynthesis is one of the most studied secondary metabolite pathway in plants. It is well-known now that anthocyanins biosynthesis is regulated by several metabolic factors, majority of which are similar across various plant species.
New wheat gene TaMYB3 for regulating synthetization and metabolization of anthocyanin
The invention provides a transcription factor TaMYB3 of a MYB class, which is separated from the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety and is used for regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. TaMYB3 is positioned between 0.62 and 0.95 of a long arm physical map of wheat 4B chromosome. The subcellular fraction of a protein product is positioned on a cell nucleus. Shown by a derived amino acid sequence, the TaMYB3 codes a MYB class transcription factor regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety increases under the induction of light. The TaMYB3 can promote skin cells of the plateau 115 kernels after dark treatment to synthetize anthocyanin under the existence of transcription factors ZmR of corns bHLH during transient expression. Single TaMYB3 genes and single ZmR genes can not induct the synthetization of anthocyani, which shows that the TaMYB3 genes have the transcriptional activity of regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. barly strip mosaic virus (BSMV) mediates the expression quantity decrease of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 kernels, and reduces the quantity of anthocyanin in kernels. This shows that the TaMYB3 participates in the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plateau 115 kernels.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
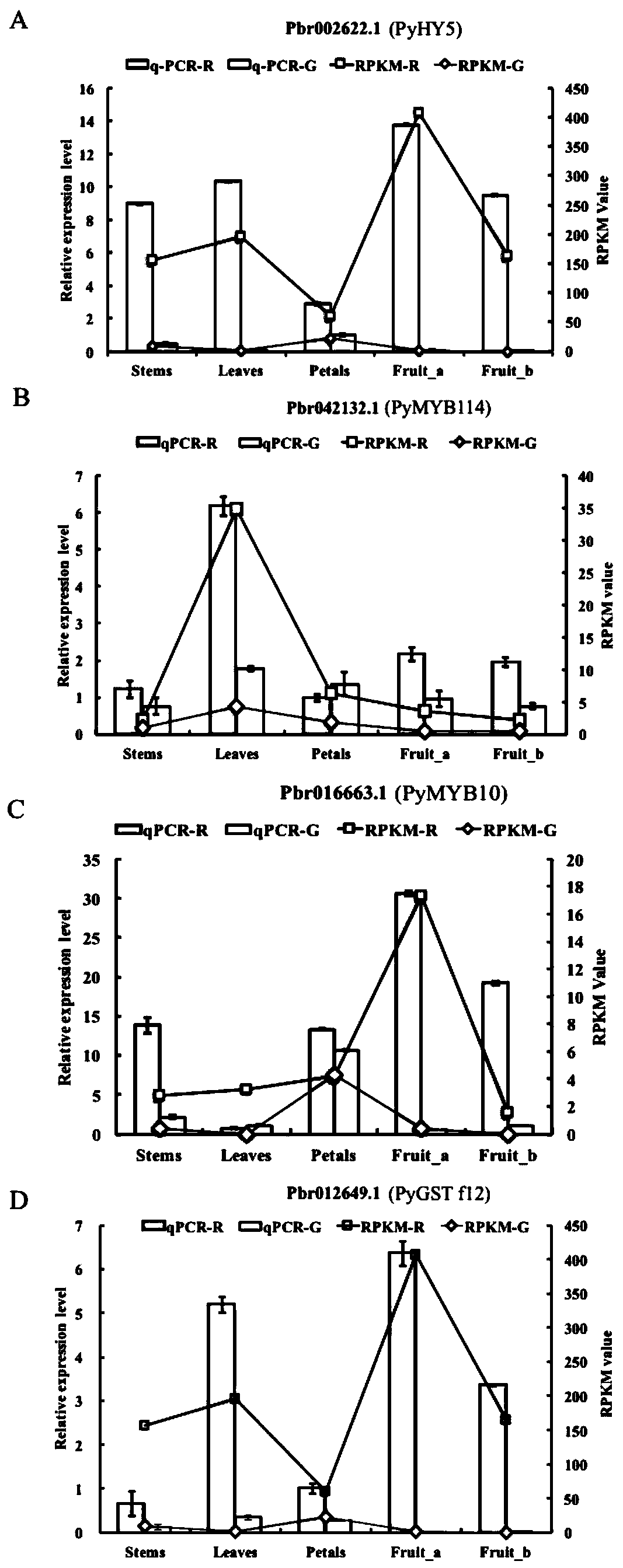
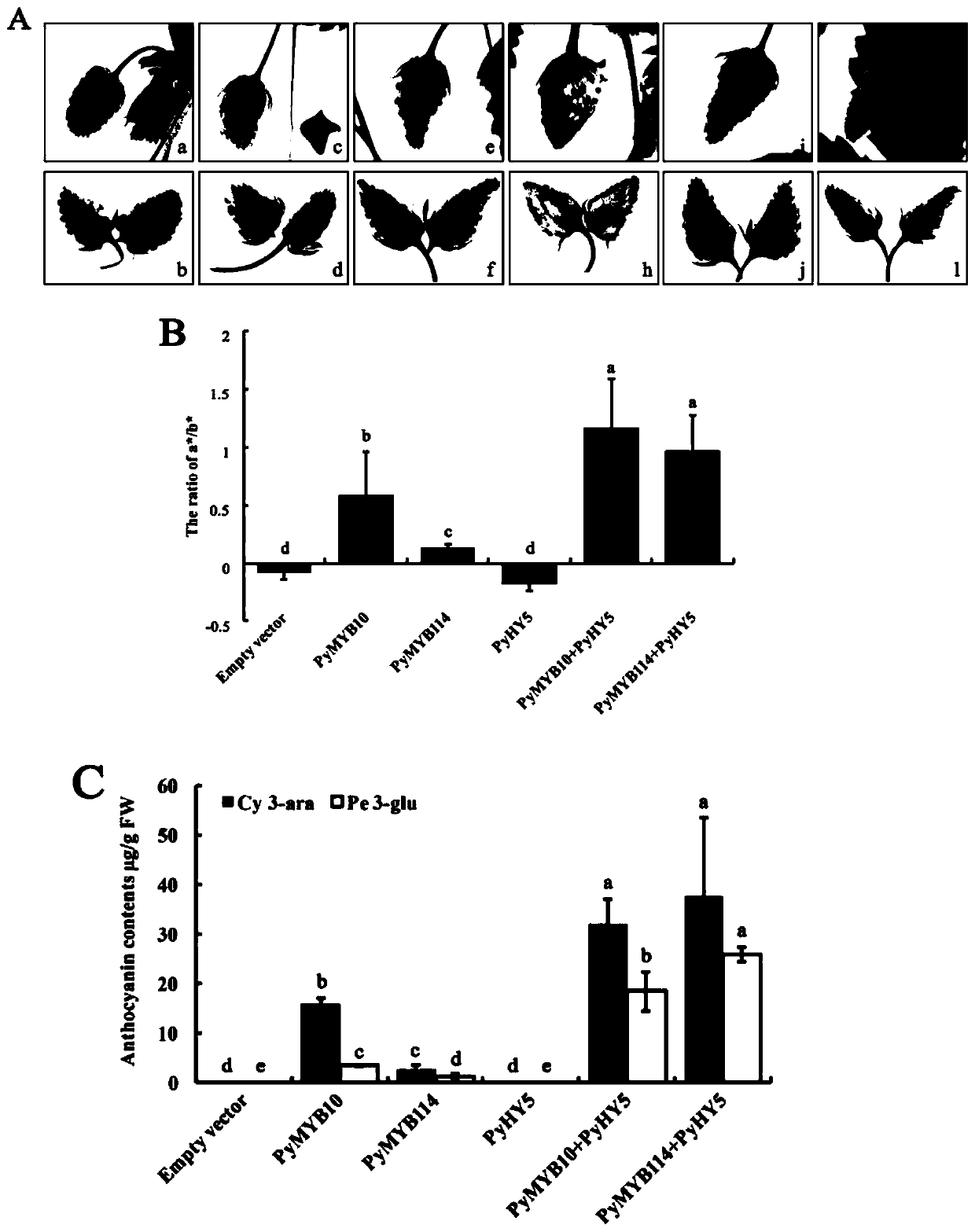
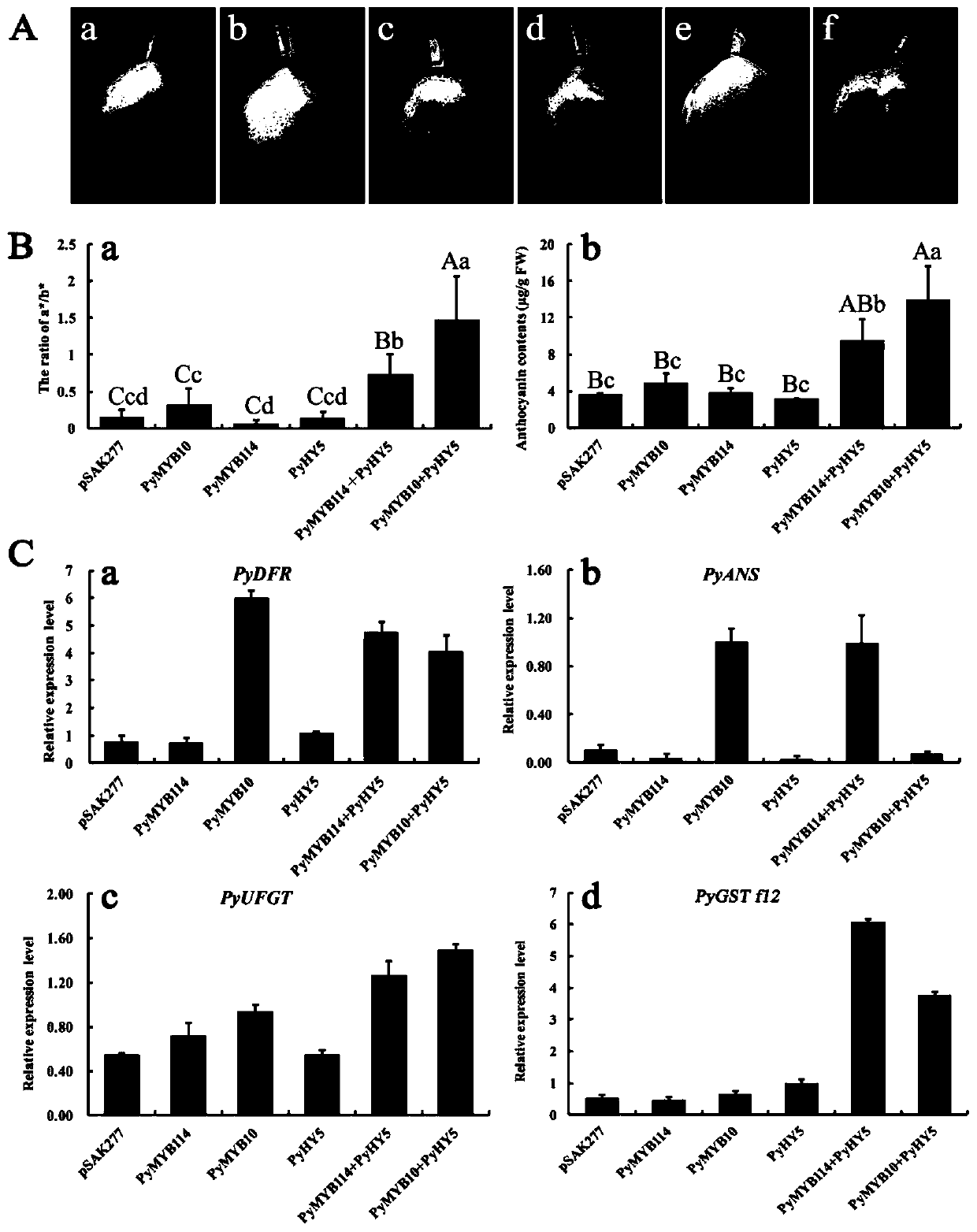
Pear transcription factor PyHY5, and recombinant expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PyHY5 and application of a recombinant expression vector of the pear transcription factor PyHY5. The nucleotide sequence of a transcription factor PyHY5 gene which is separated from 'Red Zaosu' pears and has a function of promoting anthocyanin biosynthesis of pear peels is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the encoded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor PyHY5 gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. Transcription factors PyHY5 and PyMYB114 are co-transformed into strawberry and pear fruits by an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method;according to biological function verification, the cloned PyHY5 gene and a cofactor PyMYB114 thereof interact to promote the transport function of anthocyanin in the pear peels; through discovery of new functions of the PyHY5, new genetic resources are provided for molecular breeding that promotes accumulation of the anthocyanin in the pear peels, and new genetic resources are provided for the implementation of green agriculture; the development and utilization of the genetic resources is beneficial to agricultural cost reduction and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110066326AEasy to synthesizeImprove antioxidant capacityPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, and particularly relates to a thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis and an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the thellungiella salsuginea transcription factor EsMYB41 for controlling plant anthocyanin synthesis is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Byconstructing an EsMyb41 containing over expression vector, tobacco and arabidopsis are transferred, and EsMYB41 transgenic tobacco and arabidopsis are obtained; results find that the transgenic planthas the almost whole-plant claret-colored phenotype; the anthocyanin content of different tissues of transgenic plants and the expression of the anthocyanin synthesis structure gene are both remarkably higher than the wild type, and meanwhile under the salt stress, the anti-oxidase capability of the transgenic plant is improved remarkably.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
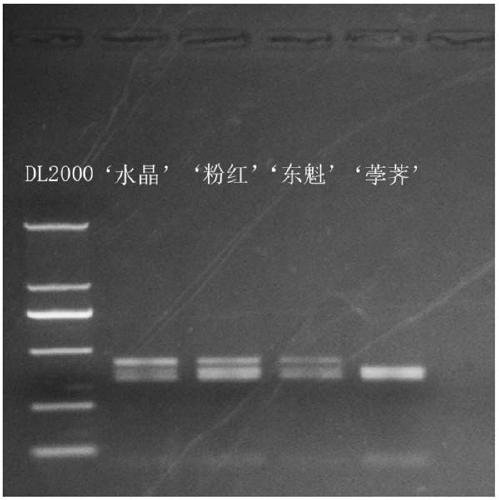
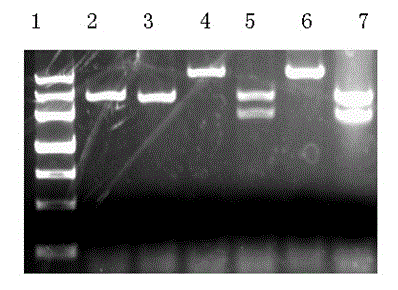
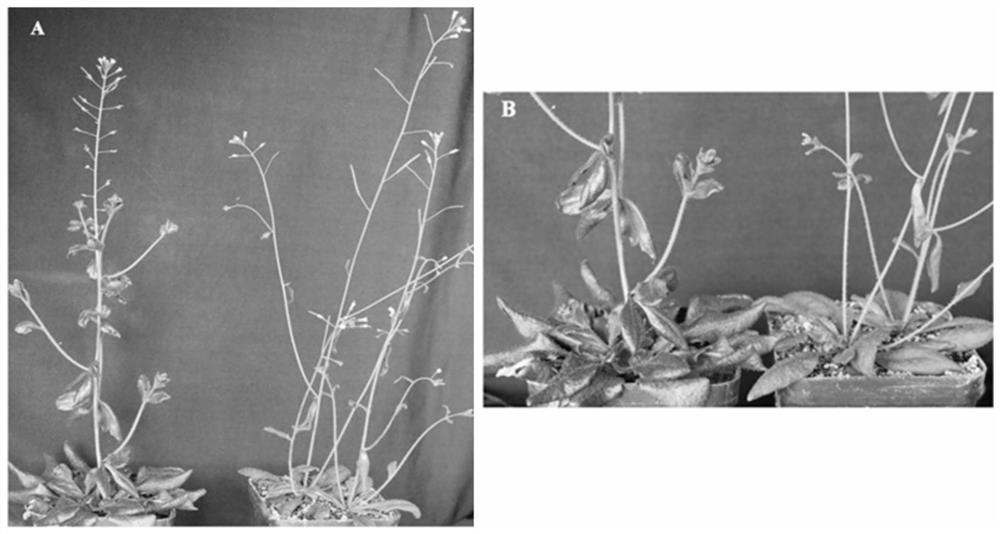
Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
The present invention discloses a biological synthesis of a Yunnan red pear anthocyanidin and a specific segment [delta]PybHLH of a trichome generating developmental regulation protein PybHLH gene and a prokaryotic expression vector thereof. By cloning the specific fragment [delta]PybHLH from Yunnan red pears through RT-PCR technology, and constructing a prokaryotic expression vector thereof and expressing in escherichia coli, a Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH purified protein is obtained. The Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH purified protein is applied to the preparation of a PybHLH specific antibody which can be used for a PybHLH expression detection, immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunization coprecipitation. The antibody has a strong specificity, can accurately detect subcellular positioning of the PybHLH protein, efficiently conduct the purification of the PybHLH protein, separate proteins and DNA fragments combined by the PybHLH protein and detect expressing condition thereof in transgenic plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of a bayberry CAPS marker in detection of allo-related MrMYB1 Alleles in Chinese Bayberry
PendingCN109182579AEasy to identifyAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeAllele
The invention provides application of a bayberry CAPS marker in detection of allo-related MrMYB1 Alleles in Chinese Bayberry, wherein the CAPS marker is a set of primer pairs and a restriction enzyme,the primer pair sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1-2, that restriction endonuclease is HhaI. The invention can easily, accurately and efficiently identify the alleles MrMYB1 and MrMYB1d of the transcription factor MrMYB1 gene of Myrica rubra regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis and different genotypes of Myrica rubra. The molecular marker can be used to predict the coloring ability of Myrica rubra fruits and molecular assisted selection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Yunnan red pear PybHLH gene as well as prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN103146709AStrong specificityReduce non-specific bandsImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a Yunnan red pear PybHLH gene through anthocyanin biosynthesis, trichome development and a salt stress regulatory protein and a prokaryotic expression vector thereof. The PybHLH gene is cloned from red fruit peel of Yunnan red pear NO.1 by using a RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technology, then the prokaryotic expression vector pGEX-4T-PybHLH is constructed, PybHLH protein is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by pGEX-4T-PybHLH vector and then is purified, and Yunnan red pear PybHLH purified protein is obtained; the prokaryotic expression vector of the PybHLH gene is applied to preparing a pybHLH specific antibody, and the obtained pybHLH specific antibody is also used for researching the interaction of the protein and protein as well as the protein and DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) and the detection to PybHLH transgenic plant. The obtained pybHLH specific antibody contains glutathione S transferase (GST) and is applied to researching the interaction of the protein through Far Western blotting and co-immunoprecipitation and accurately separating and obtaining the protein and DNA segment which are interacted with PybHLH.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
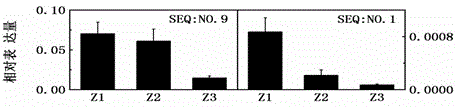
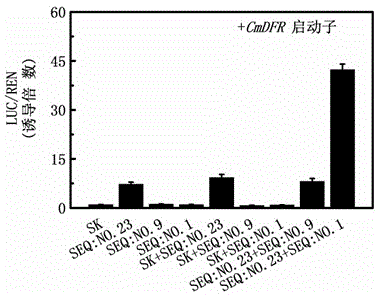
Chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation
The invention provides a chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor (CmbHLH2) involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation. A nucleotide sequence of the chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor is shown as SEQ: NO.1. When the CmbHLH2 and a CmMYB6 coordinate to perform instantaneous over-expression in tobacco leaves, anthocyanin accumulation can be strongly induced to change the original green color of the leaves into a red color. Therefore, by means of transgenosis, over-expression of the CmbHLH2 in a plant is achieved or expression of the CmbHLH2 in the chrysanthemum plant is inhibited so that anthocyanin synthesis enhanced and inhibited transgenic plants can be obtained respectively, and the colors and luster of the transgenic plants can change with anthocyanin synthesis change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant vector for rapidly obtaining non-GMO genome editing plants and method for using same
ActiveCN109234310AShorten flowering timeShorten the timeVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenome editingNucleotide
Provided are a recombinant vector for rapidly obtaining non-GMO genome editing plants and a method for using the same. The recombinant vector comprises an expression element containing PAP1 and NtFT;The original vector is a vector of CRISPR / Cas9 for plant gene editing containing sgRNA gene, Cas9 gene and screening tag gene; The NtFT expression element produces proteins that promote early flowering and the PAP1 expression element produces proteins that promote anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants. The invention can greatly shorten the time for obtaining the gene editing mutation offspring, and screens the offspring plants by plant color, thus not only retaining the offspring of the target gene mutation, but also ensuring that the mutation offspring does not contain the transgenic fragment, and simultaneously can significantly improve the gene editing efficiency. The invention can be used for preparing the gene editing mutation offspring, and can greatly shorten the time for obtaining thegene editing mutation offspring. The method of the invention is simple, fast, cheap and efficient.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
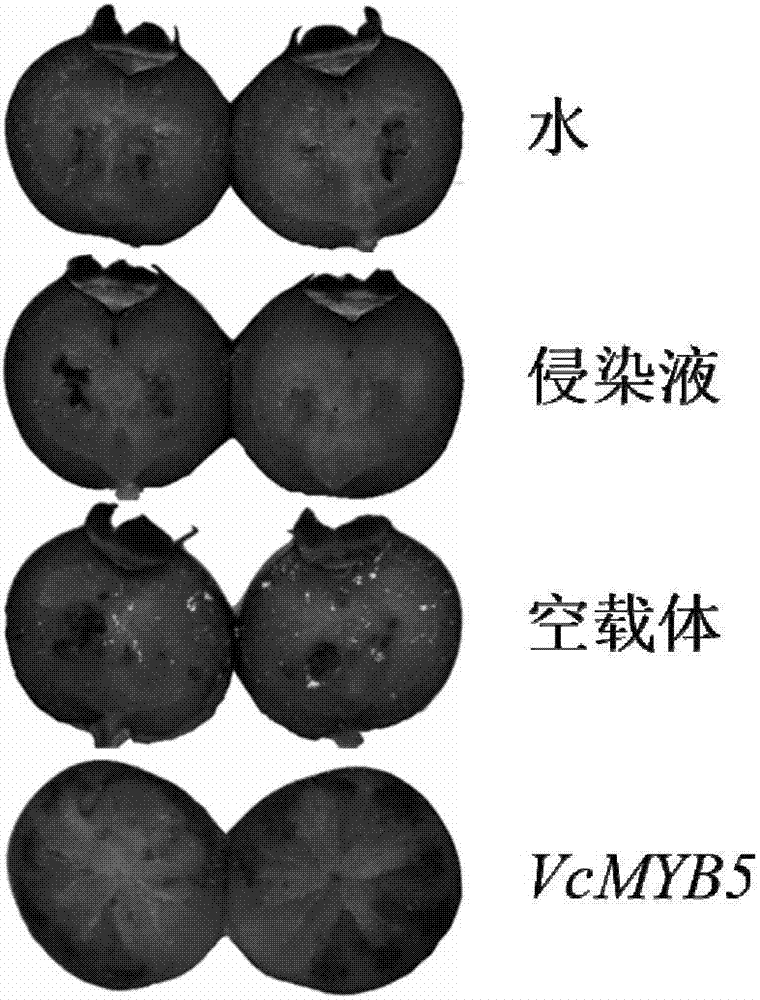
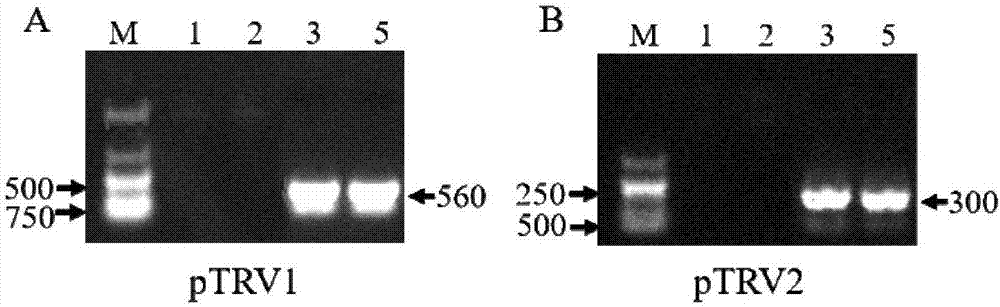
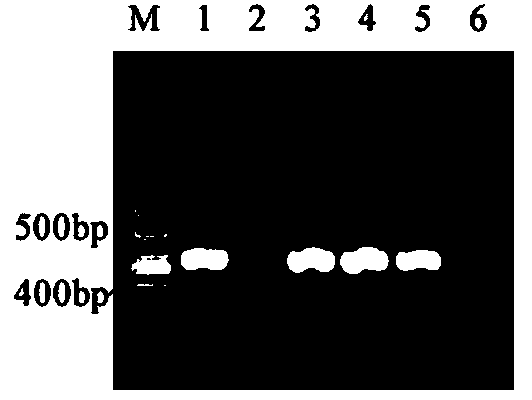
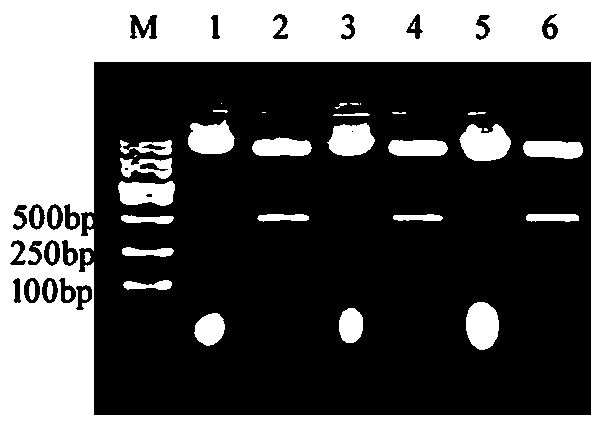
Protein capable of regulating and controlling content of anthocyanin in blueberry fruit as well as encoding gene and application of protein
The invention discloses a protein capable of regulating and controlling the content of anthocyanin in a blueberry fruit as well as an encoding gene and application of the protein. The protein provided by the invention is any one of the following proteins: (a) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 1, (b) a protein which is obtained via performing substitution and / or deletion and / or adding of one or several amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 1, comes from blueberries, is relevant to the content of anthocyanin in a plant product and is derived from the sequence 1, and (c) a protein which is homologous with the amino acid sequence defined by (a) or (b) by 99 percent or above, 95 percent or above, 90 percent or above, 85 percent or above or 80 percent or above, comes from the blueberries and is relevant to the content of the anthocyanin in the plant product. The protein and the encoding gene thereof which are provided by the invention are used for regulating and controlling biological synthesis of the anthocyanin in the blueberry fruit. The protein has important significance for cultivation of a new blueberry variety with higher anthocyanin content.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Plant expression vector based on Arabidopsis thaliana (At)-pri-miR828 gene and construction and application thereof
InactiveCN103614412ARegulation of biosynthesisImprove qualityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a plant expression vector pC2300-pOT2-At-pri-miR828 based on an Arabidopsis thaliana (At)-pri-miR828 gene and construction and application thereof. The plant expression vector pC2300-pOT2-At-pri-miR828 contains the At-pri-miR828 gene and a pOT2 cloning vector CaMV35s promoter, and has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 5. After plants are subjected to transfection by the plant expression vector disclosed by the invention, plants with high expression of the At-pri-miR828 gene can be obtained, and the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plants is regulated and controlled.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
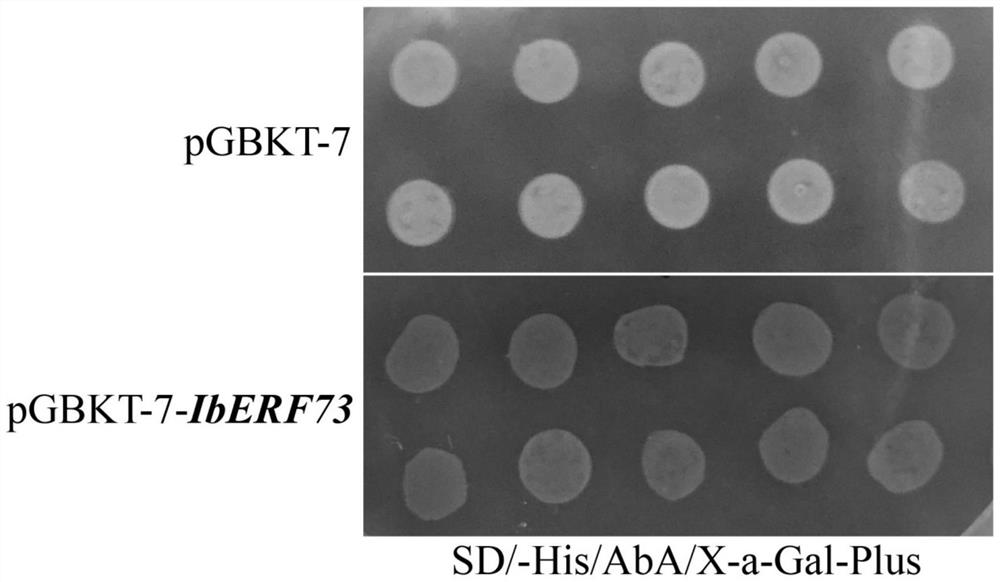
Upstream regulatory factor IbERF73 and application thereof in regulation of expression of purple sweet potato IbWD40
ActiveCN113929759AHigh pigment contentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesYeastSubcellular localization
The invention discloses an upstream regulatory factor IbERF73 and application thereof in regulation of expression of purple sweet potato IbWD40. According to the invention, a purple sweet potato strain A5 is used as an experimental material, a promoter sequence of IbWD40 is cloned, and the upstream regulatory factor IbERF73 of an IbWD40 gene is successfully obtained through a yeast one-crossing library screening experiment. A yeast single-crossing rotary experiment and a dual-luciferase report system are used for detection to confirm that interaction exists between an IbWD40 promoter and the upstream regulatory factor IbERF73. A subcellular localization result shows that the IbERF73 is localized in a cell nucleus. A self-activation activity experiment result shows that the IbERF73 has self-activation activity. A basic theory of molecular regulation and control of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis can be enriched and deepened theoretically, and meanwhile, new thoughts and clues are expected to be provided for cultivation measures for improving the content of pigments in tuberous roots of purple sweet potatoes.
Owner:广东省科学院南繁种业研究所
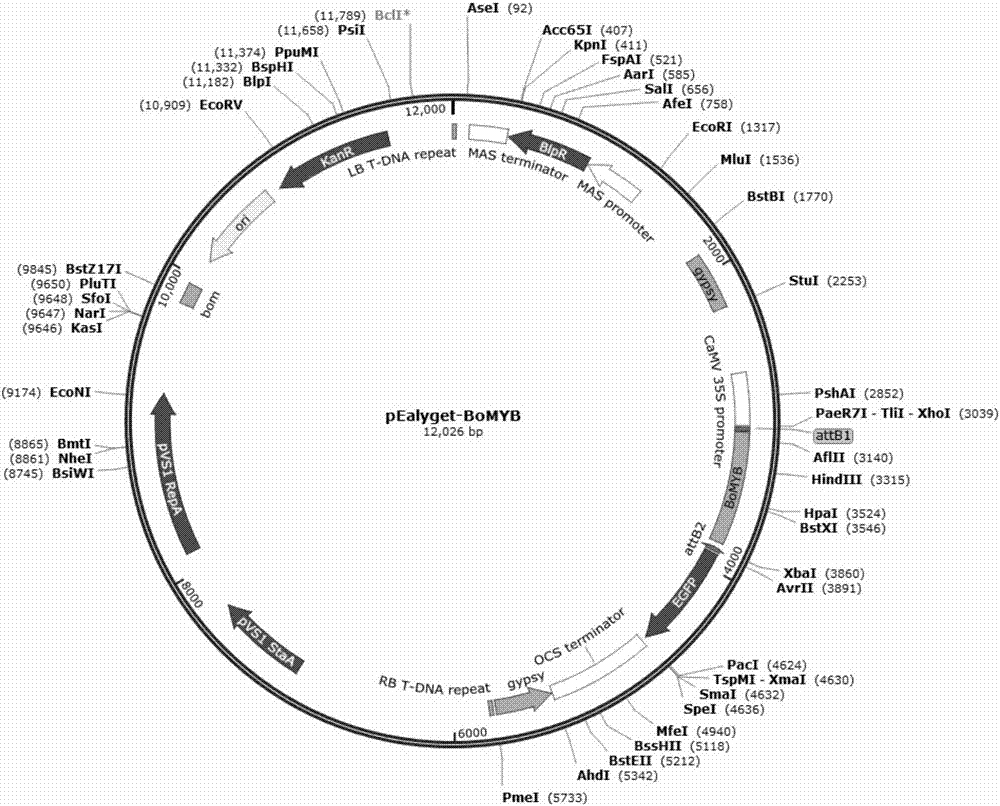
Ornamental collard anthocyanin relevant R2R3-MYB gene BoMYB and expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses an ornamental collard anthocyanin relevant R2R3-MYB gene BoMYB and an expression vector and application thereof. The cDNA sequence of the BoMYB gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The BoMYB gene can be used for regulating and controlling the biosynthesis of the anthocyanin. The collard anthocyanin purple leaf property regulating and control gene BoMYB is obtained by a homologouscloning method; a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method is used for studying the expression mode of the BoMYB gene in different tissues; analysis results show that the tissue specificity is realized in the BoMYB expression; the gene expression quantity is relevant to the anthocyanin content in each tissue. The heterologous expression verification in arabidopsis proves that the accumulationof the anthocyanin in the transgenic arabidopsis plants can be increased through the BoMYB overexpression.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
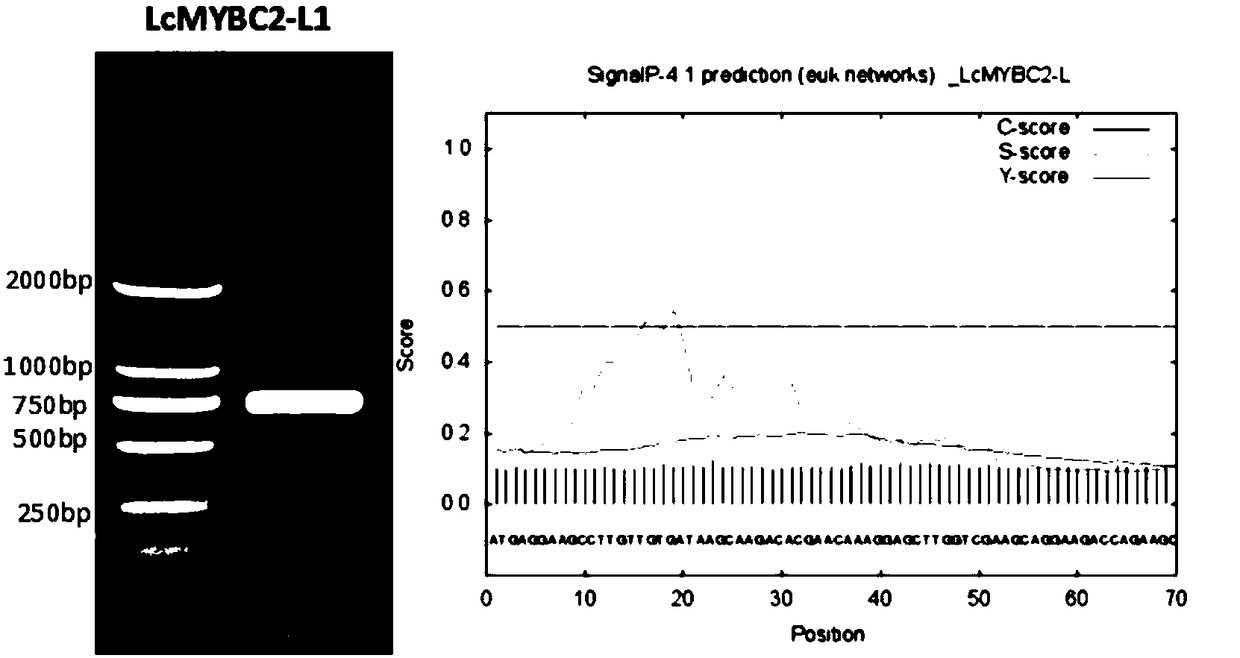
Litchi anthocyanin biosynthesis negative regulation gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108976293AInhibit biosynthesisImproving Color Genetic EngineeringPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumColor changes
The invention relates to a litchi anthocyanin biosynthesis negative regulation gene and application thereof. According to the invention, a litchi anthocyanin biosynthesis negative regulation gene is cloned (named LcMYBC2) for the first time, which is a MYB gene with a length of 708 bp and a number of encoded amino acids of 235. Through the plant transformation technology such as tobacco, the largeamount of expression of the negative regulation gene can inhibit the biosynthesis of tobacco anthocyanins and change the color of flowers. Therefore, the gene has broad application prospects in genetic engineering such as litchi coloring change and horticultural crop color gene in production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
VbMYB gene and encoding protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of plant molecular biology, and particularly relates to a vaccinium bracteatum thunb myb transcription factor VbMYB gene and an encoding protein and application thereof. The invention provides a vaccinium bracteatum thunb myb transcription factor VbMYB. The nucleotide sequence of the VbMYB is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. The expression of the vaccinium bracteatum thunb myb transcription factor VbMYB gene and the accumulation of anthocyanin in vaccinium bracteatum thunb peel are positively correlated, and tobacco leaves can be strongly induced toaccumulate anthocyanin. It shows that the VbMYB can be used for effectively inducing plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and is an anthocyanin synthesis positive regulation factor. The vaccinium bracteatumthunb myb transcription factor VbMYB has a transcriptional regulation effect on anthocyanin biosynthesis, can be applied to gene engineering and breeding of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis, and changes the color of tissue such as plant fruits.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Anthocyanin biosynthesis in carrot plants
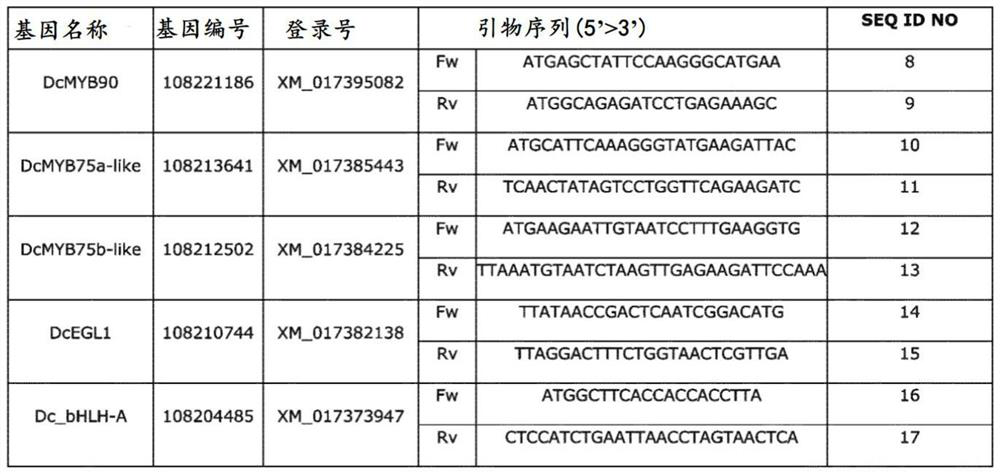
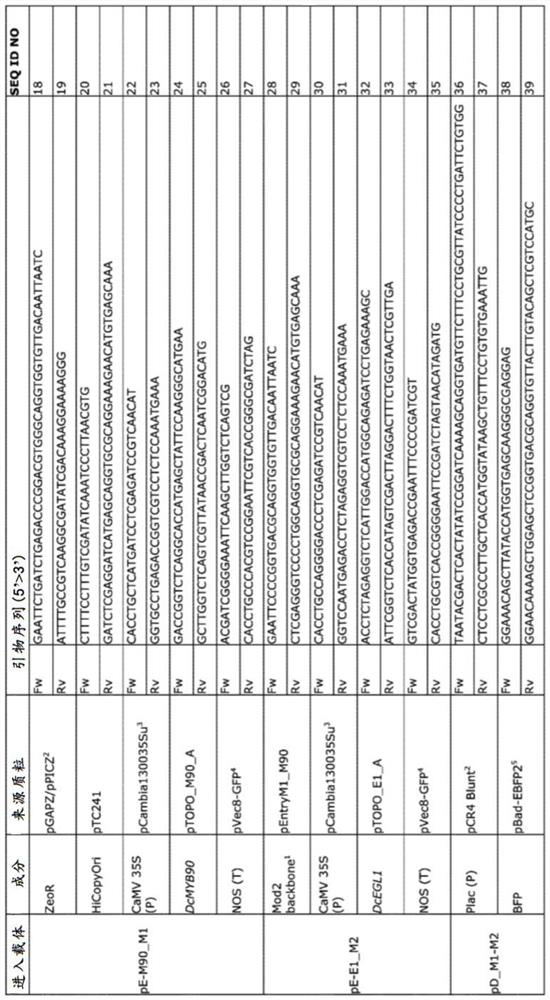
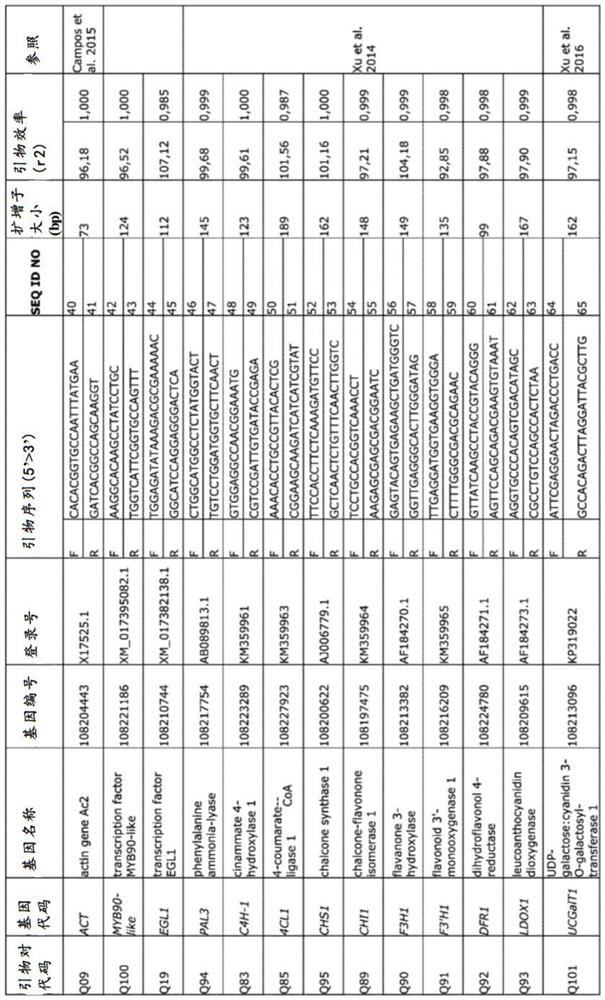
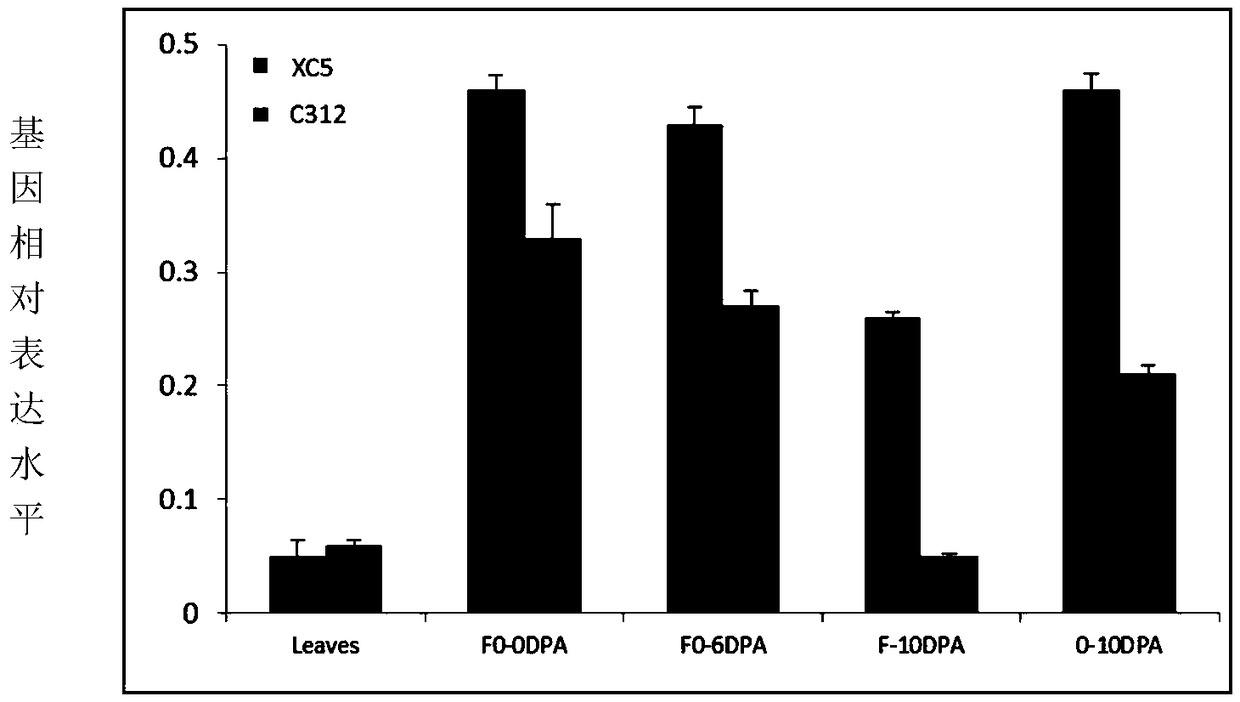
The present invention provides transgenic carrot plants comprising at least one heterologous DNA sequence encoding: (a) a promoter of a transcription factor gene; or (b) a transcription factor geneoperably linked to a promoter; wherein the heterologous DNA sequence increases the expression of at least one gene encoding a sinapic acid glucosyltransferase (USAGT). The transcription factor gene is preferably DcMYB90 (SEQ ID NO:1) or DcEGL1 (SEQ ID NO:2) or a sequence having at least 80% identity to the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 or at least 80% identity to the sequence of SEQ ID NO:2, wherein the sequence encodes a transcription factor protein increasing the expression of sinapic acid glucosyltransferase (USAGT) having the sequence of SEQ ID NO:4.
Owner:OTERRA AS +1
Method for improving cotton characters
ActiveCN109234305AChange compositionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceAnthocyanin metabolism
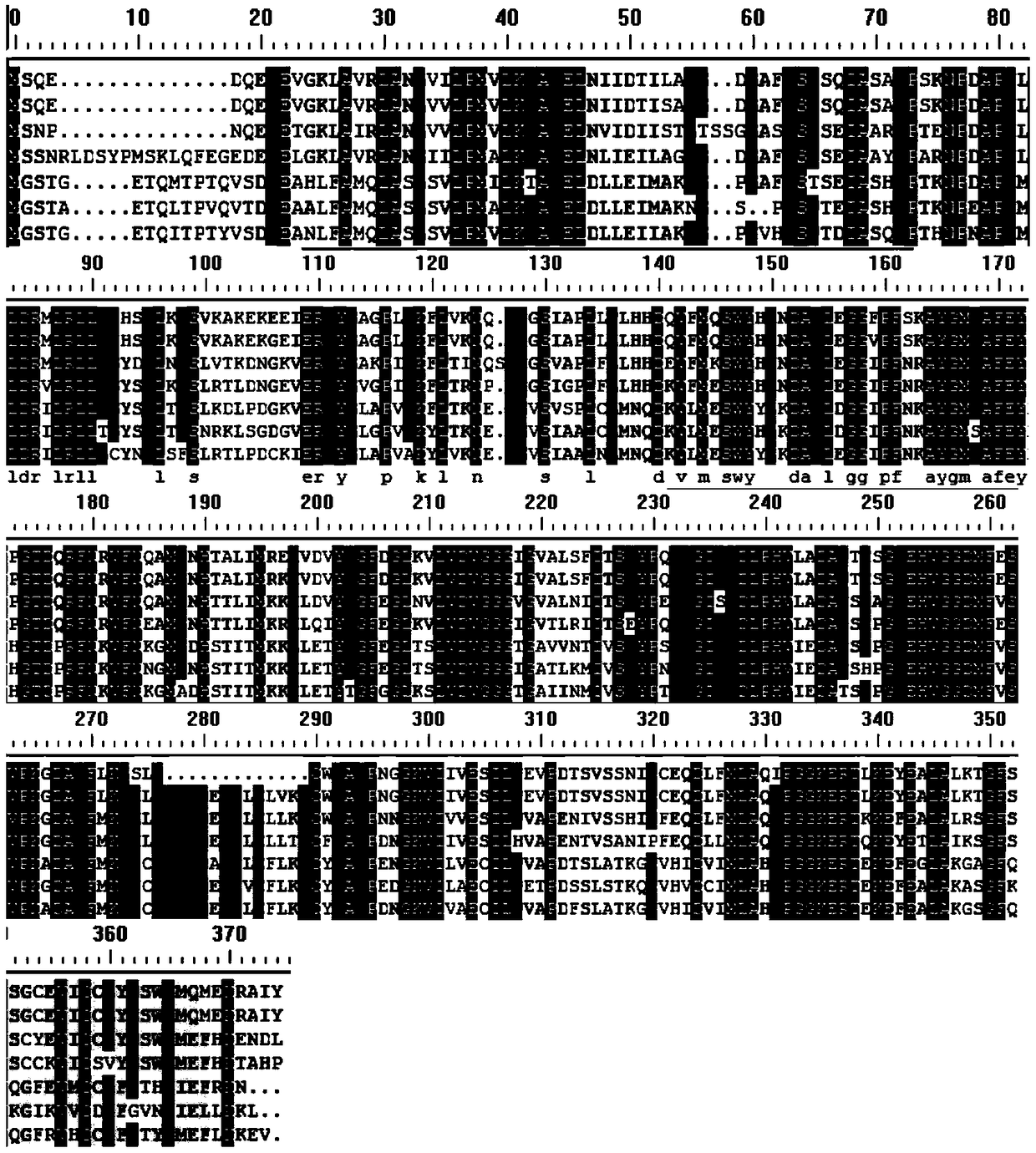
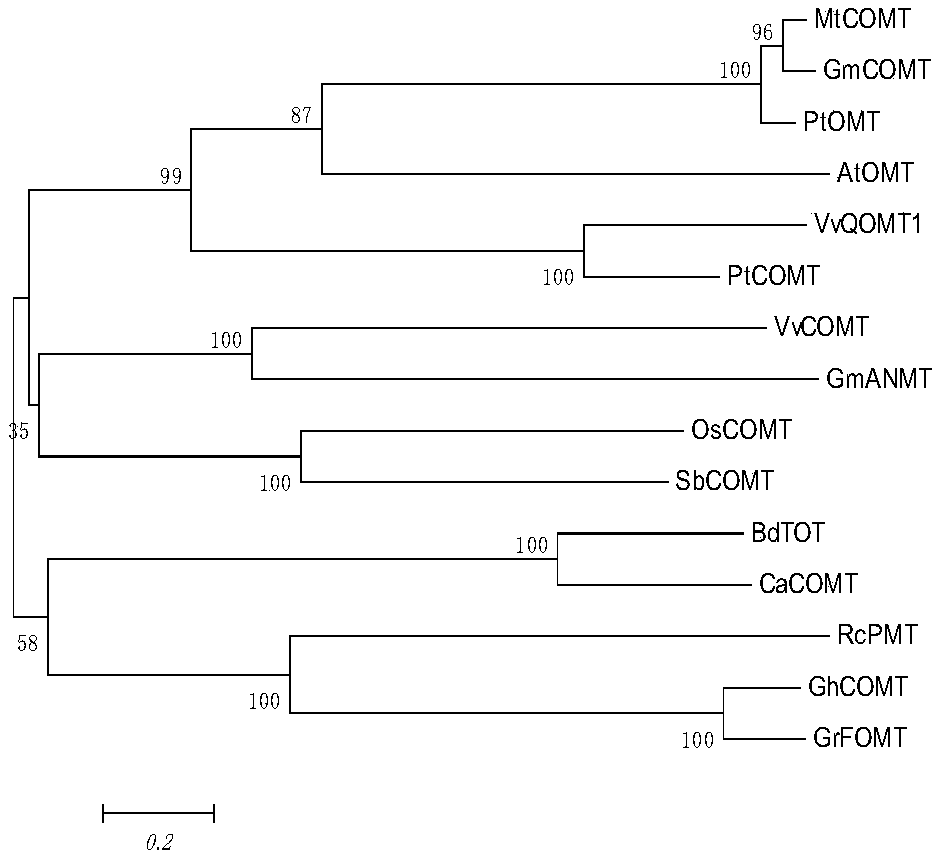
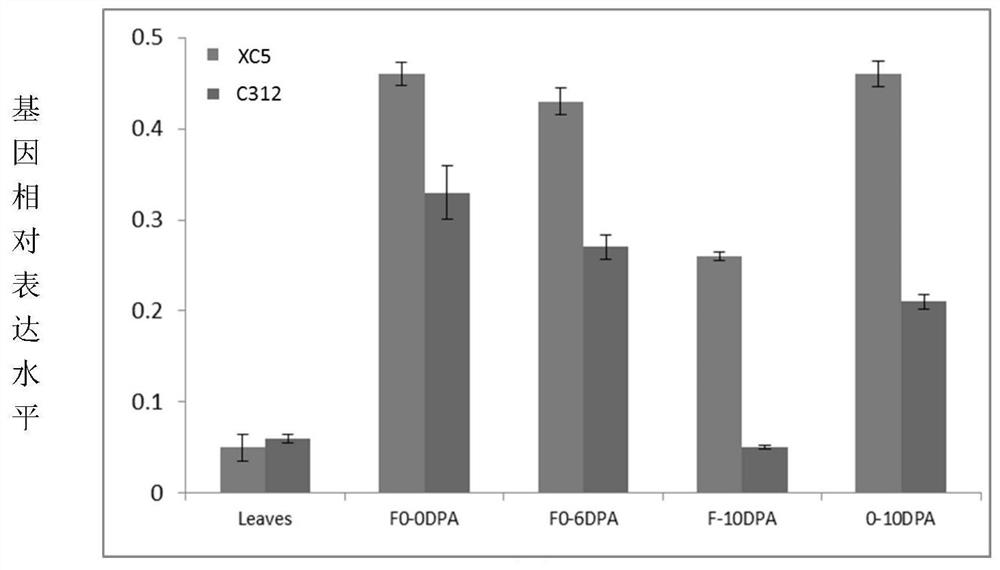
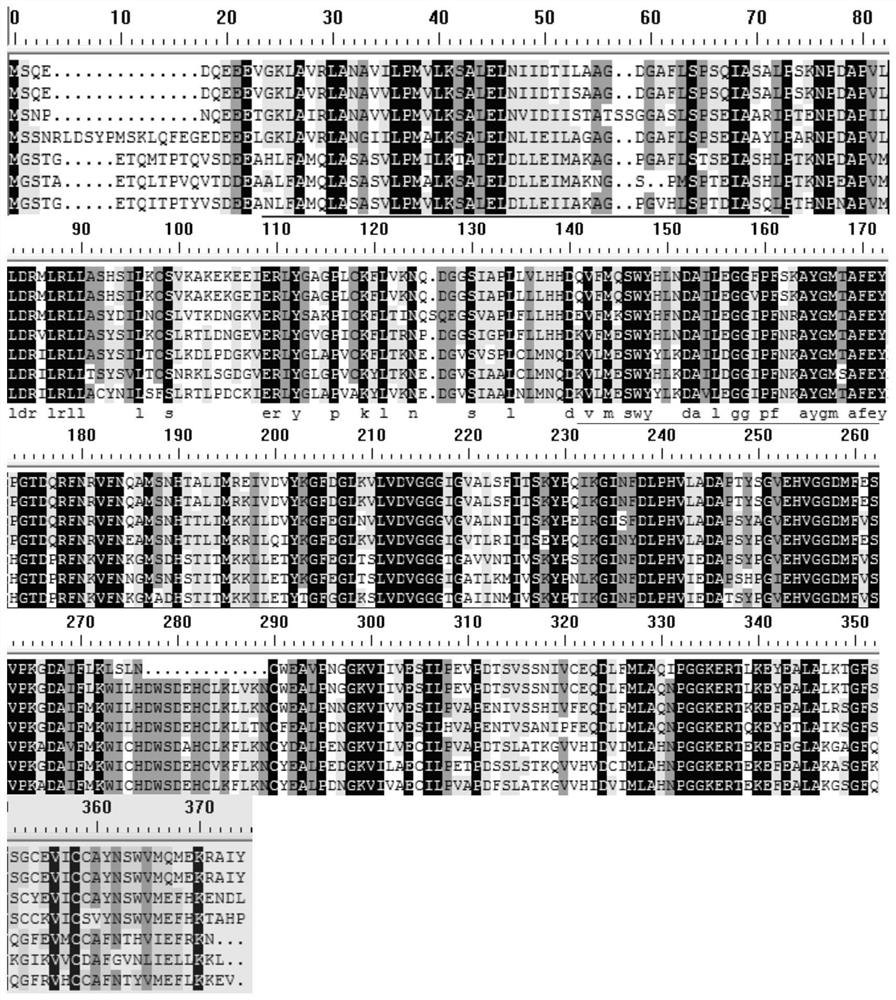
The invention discloses a method for improving cotton characters, which inhibits or knocks out cotton anthocyanin methylation modifying gene GhOMT1. A change in cotton properties according to the present invention, By regulating the expression of anthocyanin modifying genes in the anthocyanin metabolic pathway, cells can not synthesize anthocyanin or anthocyanin, change the composition and contentof anthocyanin monomer, feedback activate anthocyanin biosynthesis, cause a large amount of anthocyanin or intermediate product accumulation, make plants appear purple, and anti-senescence, anti-freeze traits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
A method for improving cotton properties
ActiveCN109234305BChange compositionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAnthocyanin metabolismOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses a method for improving cotton traits, which is to inhibit or knock out the cotton anthocyanin methylation modification gene GhOMT1. The change of the cotton character of the present invention, by regulating the expression of the anthocyanin modification gene in the anthocyanin metabolic pathway, leads to the inability to synthesize the specific anthocyanin or anthocyanin that the cell needs, and changes the composition and content of the anthocyanin monomer , the feedback activates anthocyanin biosynthesis, resulting in the accumulation of a large amount of anthocyanins or intermediates, making the plant appear purple, and has anti-aging and anti-freezing properties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Application of peony PsMYB1 gene in changing color and flower color of plant mottles
ActiveCN114836431ALighten the colorTotal anthocyanin content decreasedMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesNicotiana tabacumGermplasm
The invention discloses application of a peony PsMYB1 gene in changing color and flower color of plant mottles. A constructed PsMYB1 gene silencing vector is transformed into peony petals for expression, after the petals grow for 7 days, the phenotype of PsMYB1 transgenic peony flower spots is observed, and it is found that the color of the flower spots is obviously light, the total anthocyanin content in the flower spots is obviously reduced compared with a wild type, and the expression level of anthocyanin biosynthesis related genes in the flower spots is obviously reduced; and a new peony germplasm with light-color piebald is created. A constructed PsMYB1 gene overexpression vector is transformed into tobacco for expression, after the plant blooms, the petal phenotype of the PsMYB1 transgenic tobacco is observed, and it is found that the color of petals is obviously red, the total anthocyanin content in the petals is obviously increased compared with that of wild type petals, and the expression level of anthocyanin biosynthesis related genes in the petals is obviously increased; and a new tobacco germplasm with bright petals is created.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
New wheat gene TaMYB3 for regulating synthetization and metabolization of anthocyanin
The invention provides a transcription factor TaMYB3 of a MYB class, which is separated from the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety and is used for regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. TaMYB3 is positioned between 0.62 and 0.95 of a long arm physical map of wheat 4B chromosome. The subcellular fraction of a protein product is positioned on a cell nucleus.Shown by a derived amino acid sequence, the TaMYB3 codes a MYB class transcription factor regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB3 inthe plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety increases under the induction of light. The TaMYB3 can promote skin cells of the plateau 115 kernels after dark treatment to synthetize anthocyanin under the existence of transcription factors ZmR of corns bHLH during transient expression. Single TaMYB3 genes and single ZmR genes can not induct the synthetization of anthocyani, which shows that theTaMYB3 genes have the transcriptional activity of regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. barly strip mosaic virus (BSMV) mediates the expression quantity decrease of theTaMYB3 in the plateau 115 kernels, and reduces the quantity of anthocyanin in kernels. This shows that the TaMYB3 participates in the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plateau 115 kernels.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
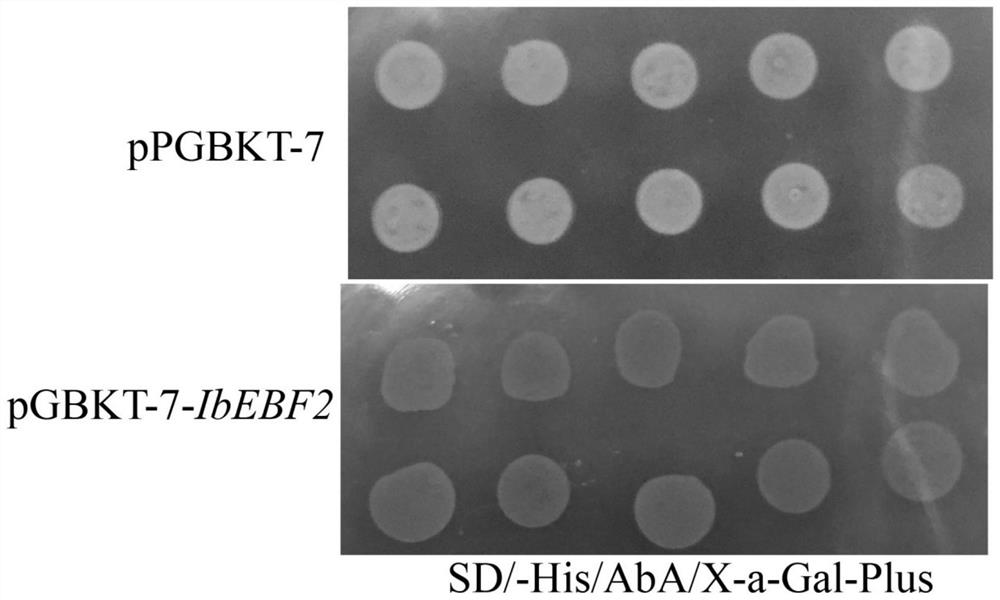
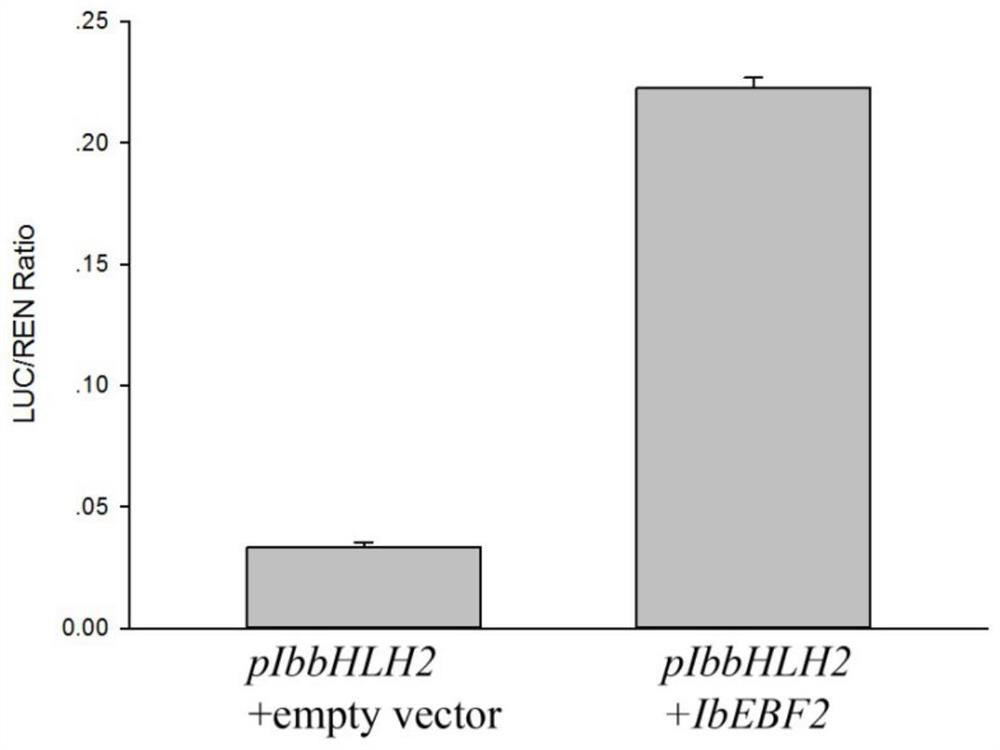
Upstream regulatory factor IbEBF2 and application thereof in regulating IbbHLH2 expression of purple sweet potatoes
The invention discloses an upstream regulatory factor IbEBF2 and application thereof in regulating IbbHLH2 expression of purple sweet potatoes. According to the invention, a purple sweet potato strain A5 is used as an experimental material, a promoter sequence of IbbHLH2 is cloned, and an upstream regulatory factor IbEBF2 of an IbbHLH2 gene is successfully obtained through a yeast one-hybrid library screening experiment. A yeast one-hybrid rotary experiment and a dual-luciferase report system are used for detection to confirm that the IbbHLH2 promoter interacts with an upstream regulatory factor IbEBF2. A subcellular localization result shows that IbEBF2 is localized in a cell nucleus. A self-activation activity experiment result shows that the IbEBF2 has self-activation activity. The basic theory of molecular regulation and control of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis can be enriched and deepened theoretically, and meanwhile, new thoughts and clues are expected to be provided for cultivation measures for improving the content of pigments in purple sweet potato tuberous roots.
Owner:广东省科学院南繁种业研究所
Key glycosyl transferase for piebald formation and coloring as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses key glycosyltransferase for piebald formation and coloring as well as a coding gene and application of the key glycosyltransferase. The glycosyl transferase provided by the invention is a protein as shown in a) or b): a) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and b) a protein which is formed by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table, has mottle formation and coloring glycosyl transferase activity and is derived from a). The glycosyl transferase PhUGT78A22 provided by the invention can be used for accurately catalyzing the conversion of glycosylated anthocyanin in spots or non-spots, so that the difference between petal spots and non-spot anthocyanin in'harmony 'is caused. A new perspective is provided for molecular regulation and control of anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation, a new thought is provided for flower color breeding for improving the ornamental value, and reference is provided for deeply knowing a molecular regulation and control mechanism of anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
BHLH transcription factor for promoting anthocyanin synthesis in lotus and application thereof
Owner:金天国际医疗科技有限公司 +1
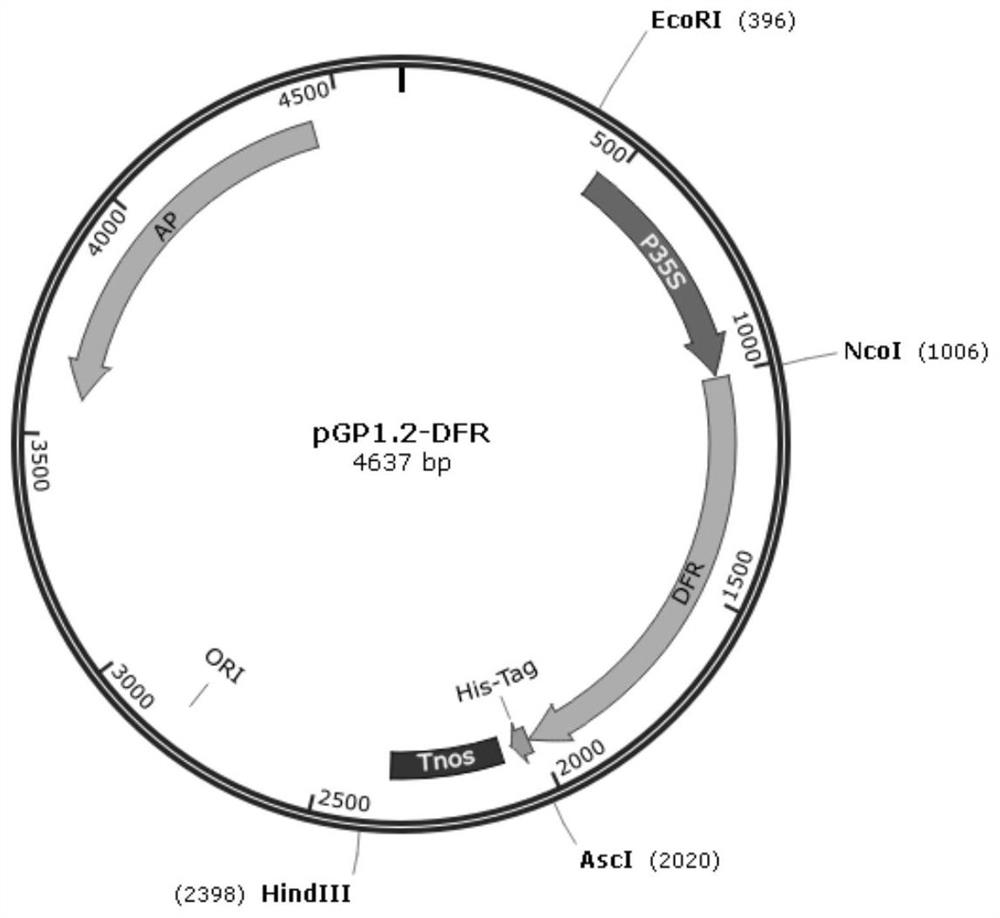
Composition and method for biosynthesis of anthocyanins
The invention discloses a composition and method for biosynthesis of anthocyanins. According to the composition and the method, enzyme genes DFR, LDOX and UFGT in a plant anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway are utilized to construct a vector for the biosynthesis of the anthocyanins and a host cell containing the vector, the vector and the host cell are applied to the biosynthesis of the anthocyanins, and a different anthocyanin biosynthesis method is provided for the prior art. Further, through addition of different substrates for the DFR, technicians in the field can obtain the anthocyanins with different colors.
Owner:HANGZHOU ADVANCED BIOSCIENCE CO LTD +1
A kind of cultivation method of colored cotton
ActiveCN109234304BIncreased fiber lengthHigh strengthTransferasesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a method for cultivating colored cotton. The method is one of the following: (1) using cotton purple mutant HS2 as a parent to cross with different varieties of cotton to obtain colored cotton; (2) knocking out and editing , interfere or overexpress key enzyme genes in cotton anthocyanin biosynthesis and metabolism pathway to obtain colored cotton; the key enzyme genes include PAL, C4H, 4CL-8, CHS, CHI, F3H, F3'H, F3'5 'H, DFR, LAR, LDOX, ANR, OMT or GST.
Owner:孙玉强
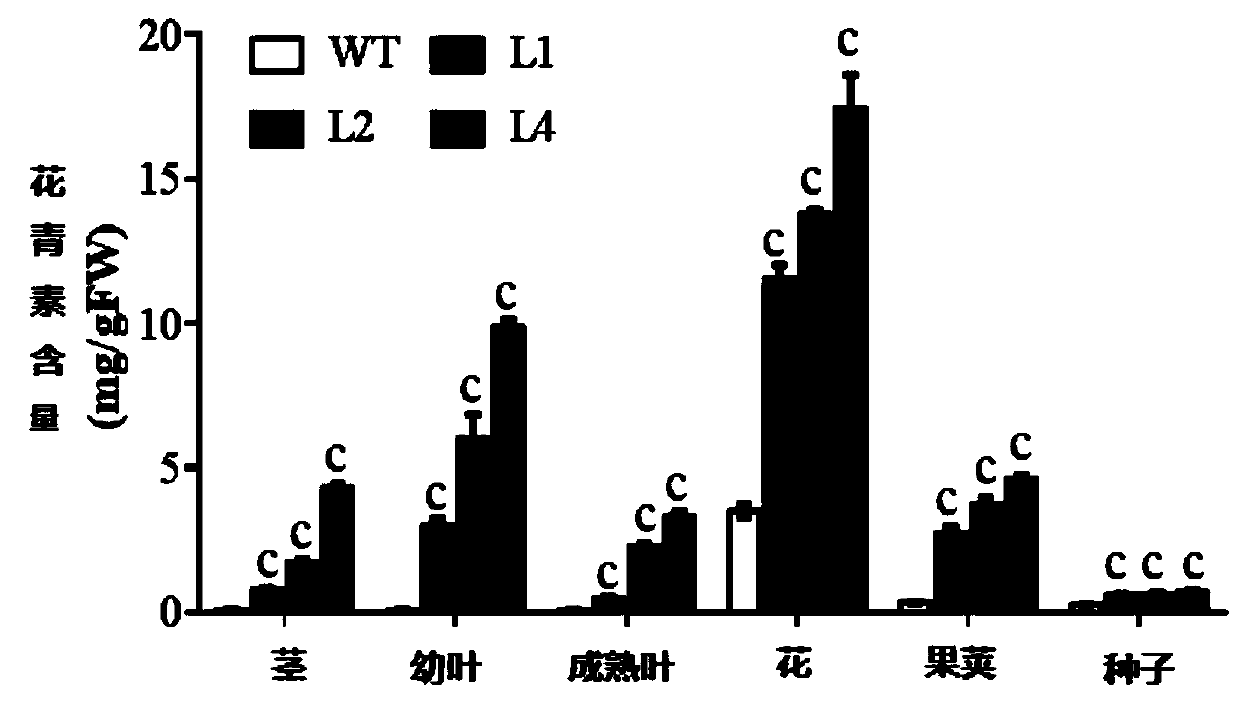
Application of purple cabbage anthocyanin biosynthesis regulatory gene BrTT8 to photoinduction type purple tomatoes cultivation and method
InactiveCN105505947AIncrease anthocyanin contentActively explorePlant peptidesFermentationAdditive ingredientPetal
The invention discloses application of a purple cabbage anthocyanin biosynthesis regulatory gene BrTT8 to photoinduction type purple tomatoes cultivation and a method. The nucleotide sequence of the purple cabbage anthocyanin biosynthesis regulatory gene BrTT8 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 3. The gene is constructed to be a recombinant expression vector, and converted into tomato leaves through an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method, finally transgenic tomato plants are obtained, and when the transgenic tomato plants are irradiated by strong light, stems, leaves, petals and upper ends of fruits of transgenic tomatoes are purple, the content of anthocyanin and the content of flvonol in the fruits are improved remarkably; synthesis of anthocyanin does not exist in tissue of transgenic tomatoes cultivated under weak light irradiation, the risks of diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular can be reduced by eating food rich in ingredients such as anthocyanin and flavone regularly, the obtained transgenic tomatoes have important application value, and the purple transgenic tomatoes have certain ornamental value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Chrysanthemum bhlh transcription factor involved in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis
The invention provides a chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor (CmbHLH2) involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation. A nucleotide sequence of the chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor is shown as SEQ: NO.1. When the CmbHLH2 and a CmMYB6 coordinate to perform instantaneous over-expression in tobacco leaves, anthocyanin accumulation can be strongly induced to change the original green color of the leaves into a red color. Therefore, by means of transgenosis, over-expression of the CmbHLH2 in a plant is achieved or expression of the CmbHLH2 in the chrysanthemum plant is inhibited so that anthocyanin synthesis enhanced and inhibited transgenic plants can be obtained respectively, and the colors and luster of the transgenic plants can change with anthocyanin synthesis change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
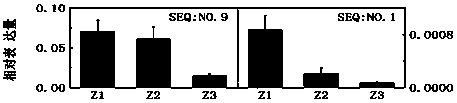
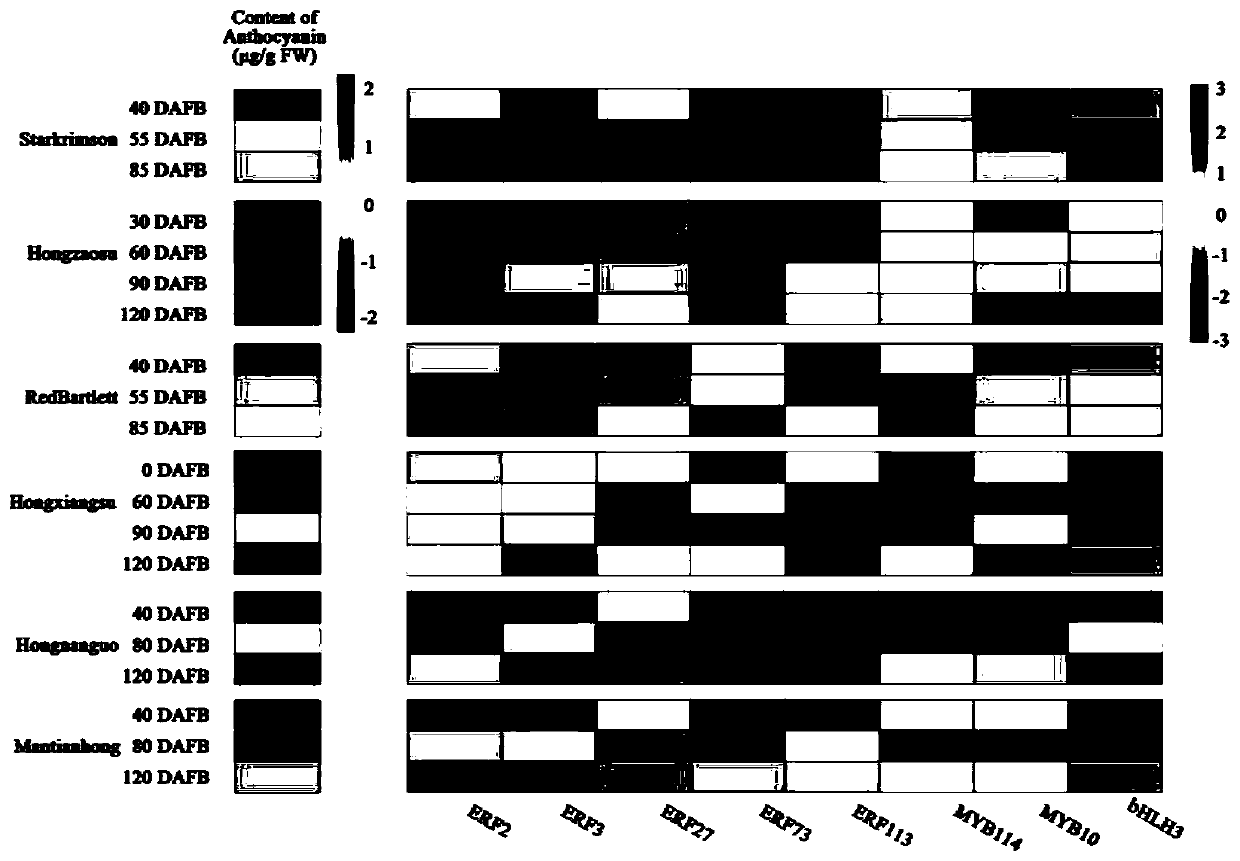
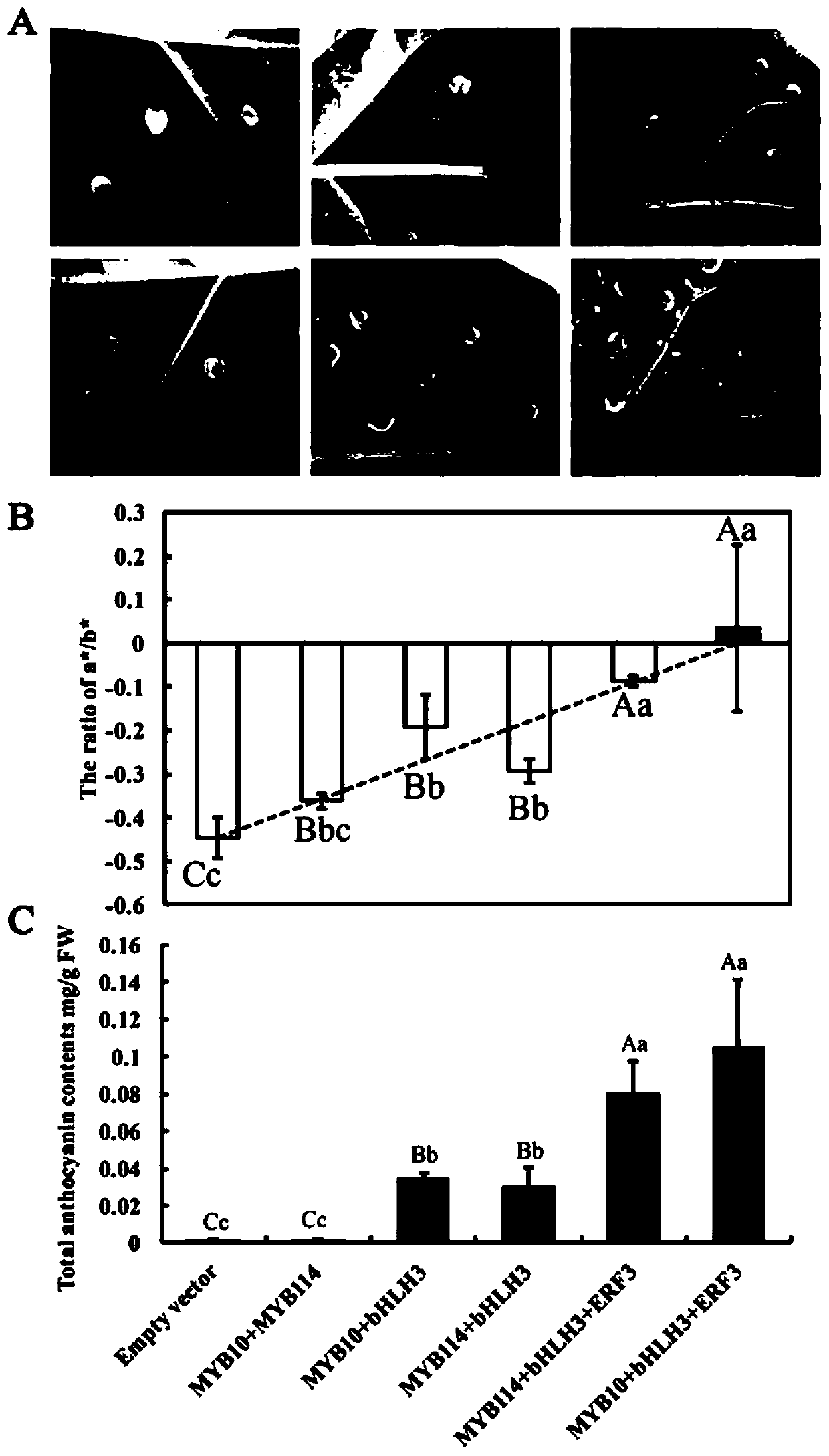
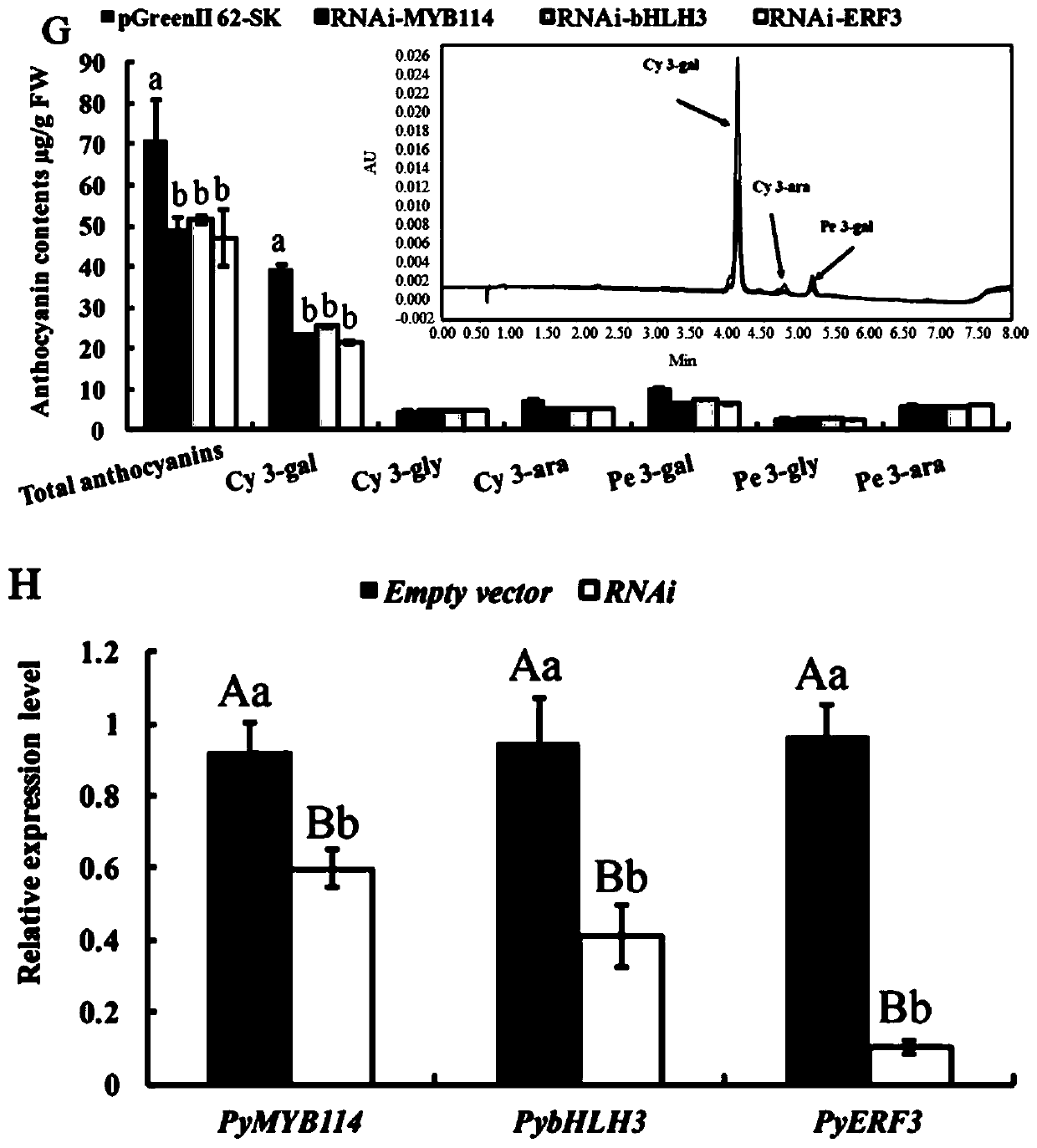
Pear transcription factor pyerf3 and its recombinant expression vector and application
ActiveCN107686840BPromote biosynthesisAchieve friendlyPlant peptidesFermentationFragariaNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a pyrus transcription factor PyERF3 as well as a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. A transcription factor PyERF3 gene which is separated from 'Starkrimson'pyrus and has an effect of promoting pyrus peel anthocyanin biosynthesis has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and a coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table. The transcription factor is subjected to instantaneous conversion in tobacco, strawberry and pear fruits by virtue of an agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation method. Biological function verification proves that the PyERF3 gene cloned in the invention and other transcription factors PyMYB114 and PybHLH3 form transcriptional control complex so as to promote the biosynthesis of the pyrus peelanthocyanin. Discovery of the gene PyERF3 provides novel gene resources for promoting molecular breeding of pyrus peel anthocyanin synthesis and provides novel genetic resources for implementing green agriculture. Development and utilization of the genetic resources contribute to reduction of the agricultural cost and realization of environment friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rice anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation gene OsTTG1 and application thereof
PendingCN113265407AReduce anthocyanin contentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPlant stem
The invention provides a rice anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation gene OsTTG1 and an application thereof, and the rice anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation gene OsTTG1 comprises a rice anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation gene OsTTG1, and the nucleotide sequence of the rice anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation gene OsTTG1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention relates to a biological material containing a gene OsTTG1. The invention also discloses the application of the gene OsTTG1 or the biological material in regulating and controlling the anthocyanin content of the plant and a method for reducing or increasing the anthocyanin content of the plant. The experiments prove that the content of anthocyanin in plant stems can be reduced by knocking out the OsTTG1, the content of the anthocyanin in the plants can be increased by increasing illumination or reducing temperature to increase the expression level of the OsTTG1, and a foundation is laid for researching postgraduate growth of rice rich in anthocyanin.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plant expression vector based on Arabidopsis pri-mir828 gene and its construction and application
InactiveCN103614412BImprove qualityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a plant expression vector pC2300-pOT2-At-pri-miR828 based on an Arabidopsis thaliana (At)-pri-miR828 gene and construction and application thereof. The plant expression vector pC2300-pOT2-At-pri-miR828 contains the At-pri-miR828 gene and a pOT2 cloning vector CaMV35s promoter, and has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 5. After plants are subjected to transfection by the plant expression vector disclosed by the invention, plants with high expression of the At-pri-miR828 gene can be obtained, and the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plants is regulated and controlled.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150934.PNG)
![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150937.PNG)
![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150940.PNG)