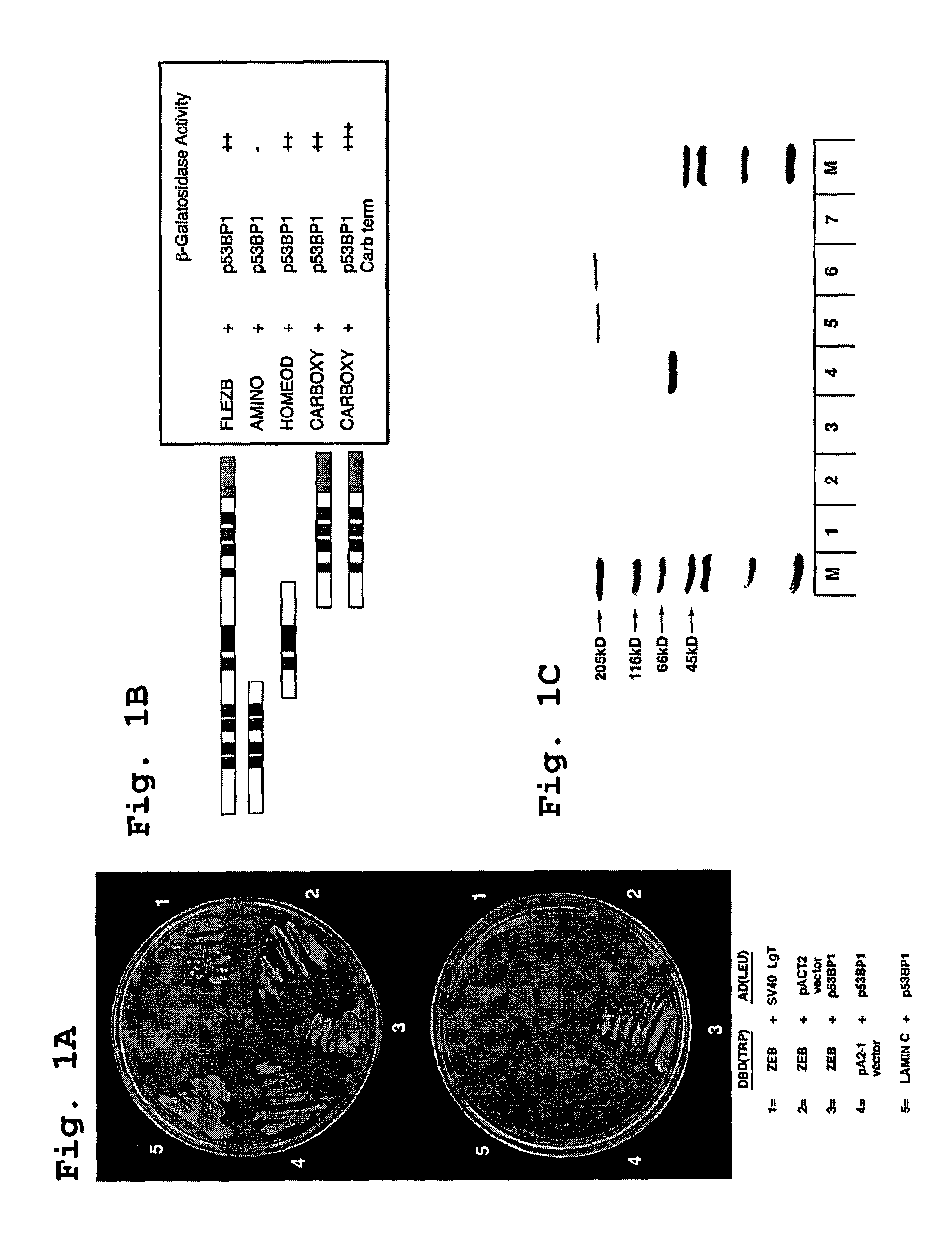
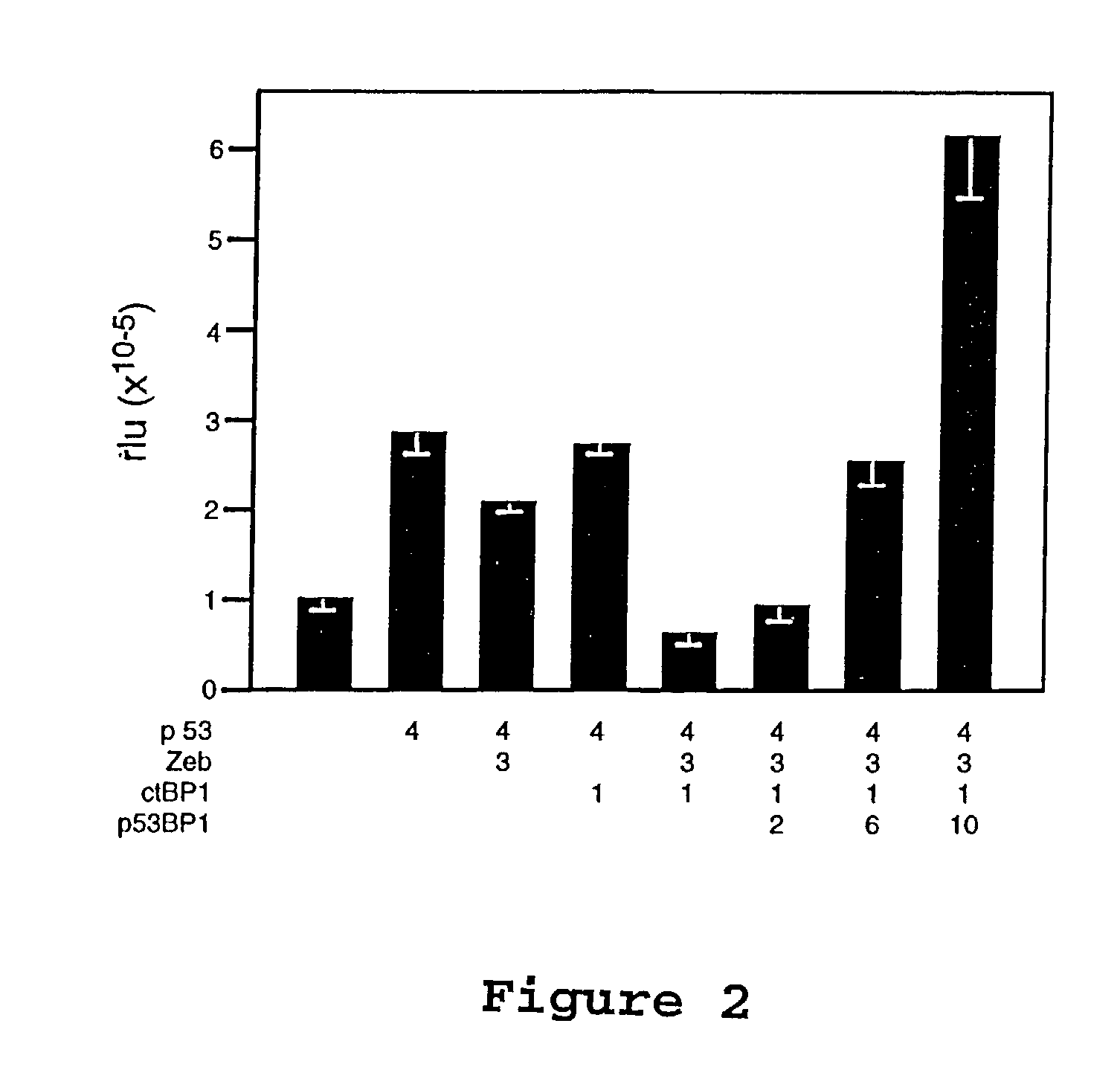
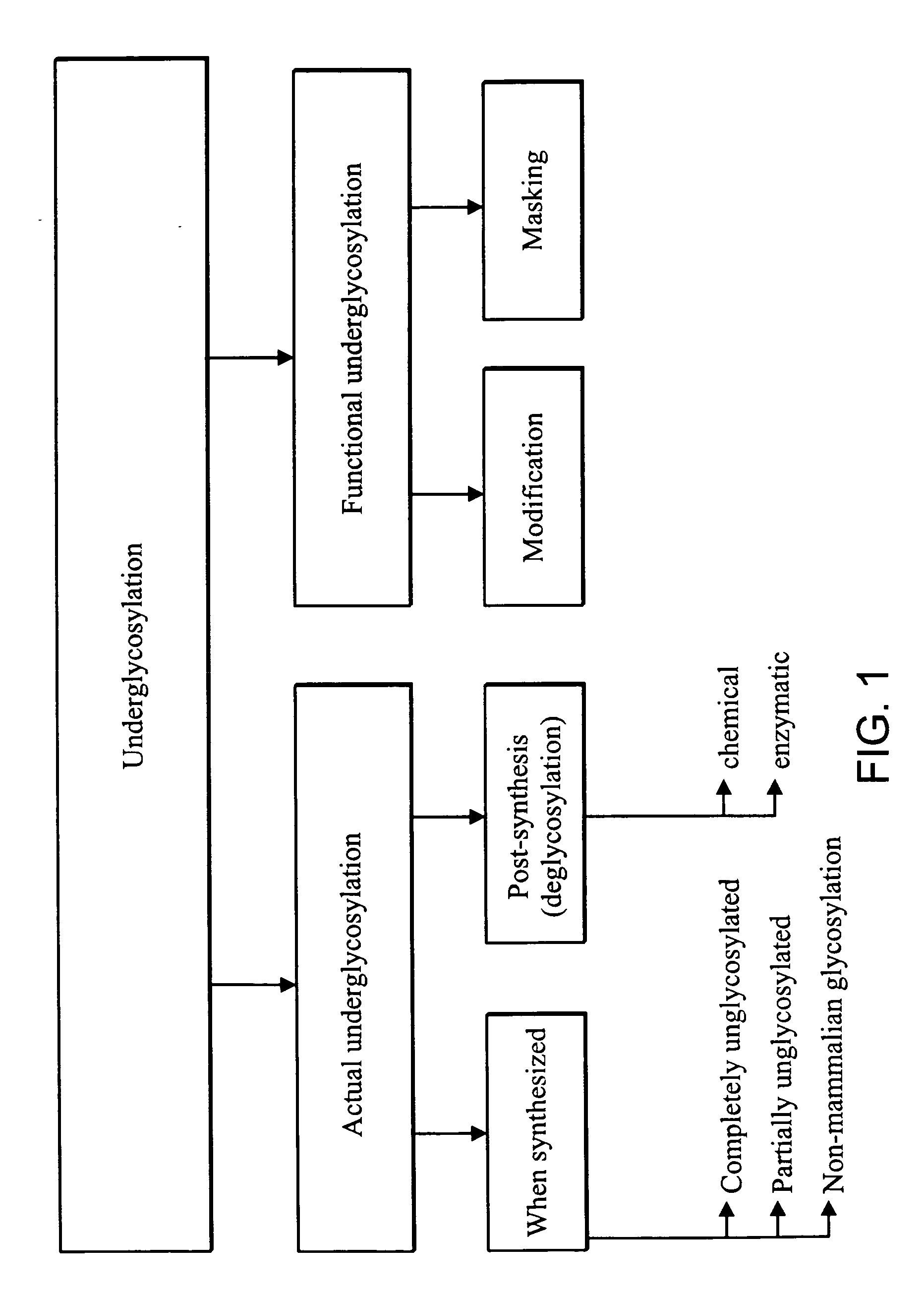
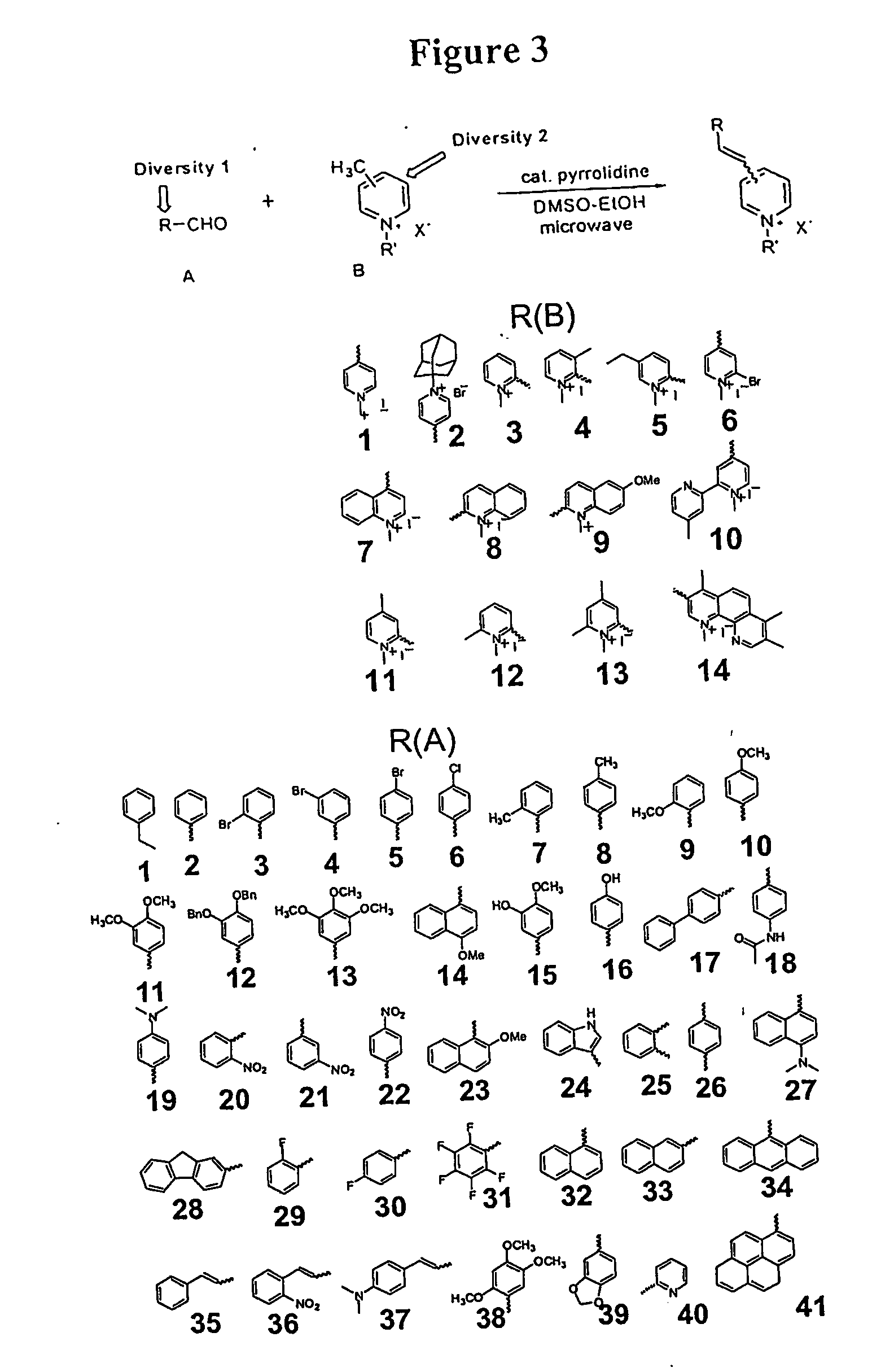
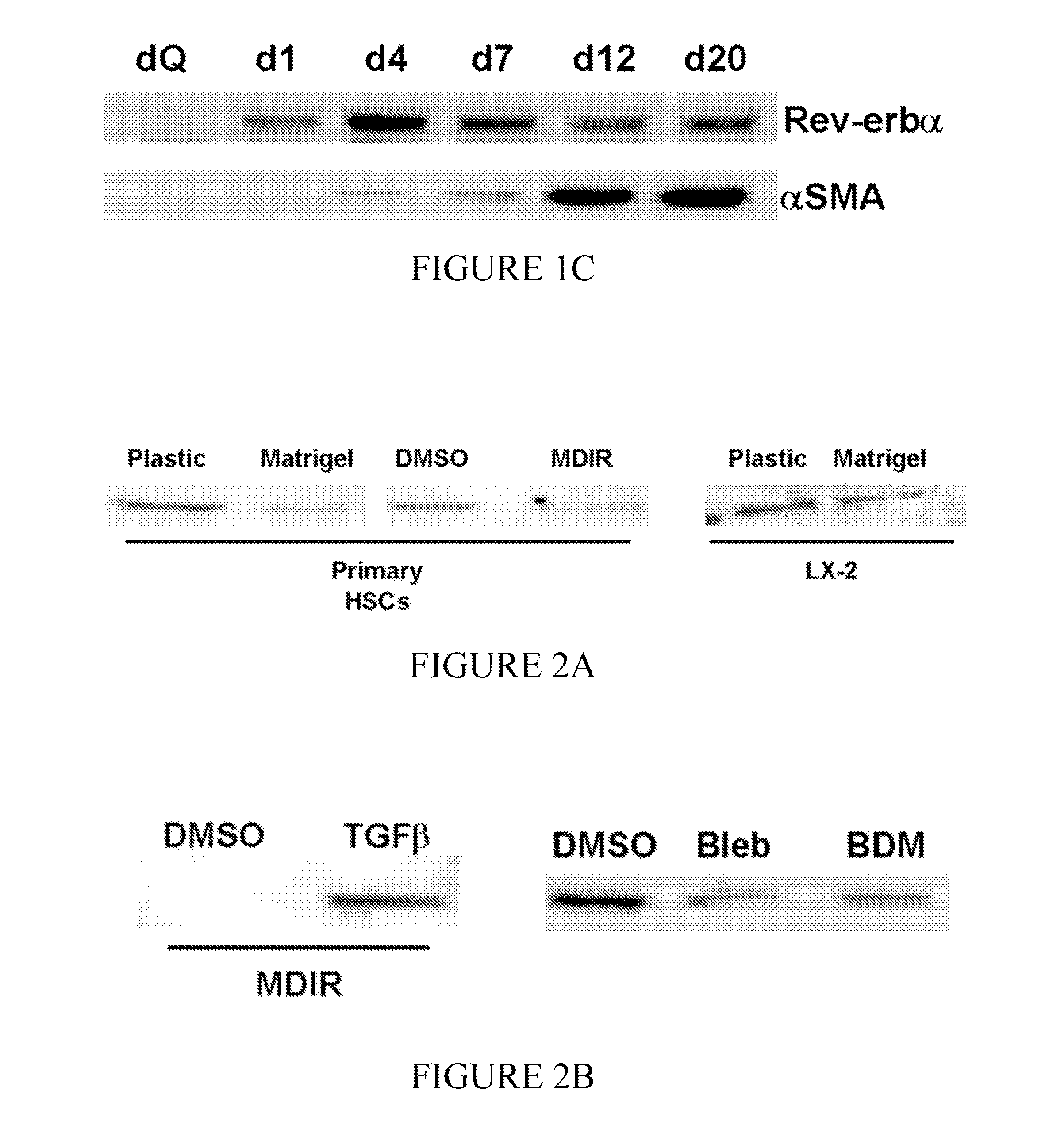
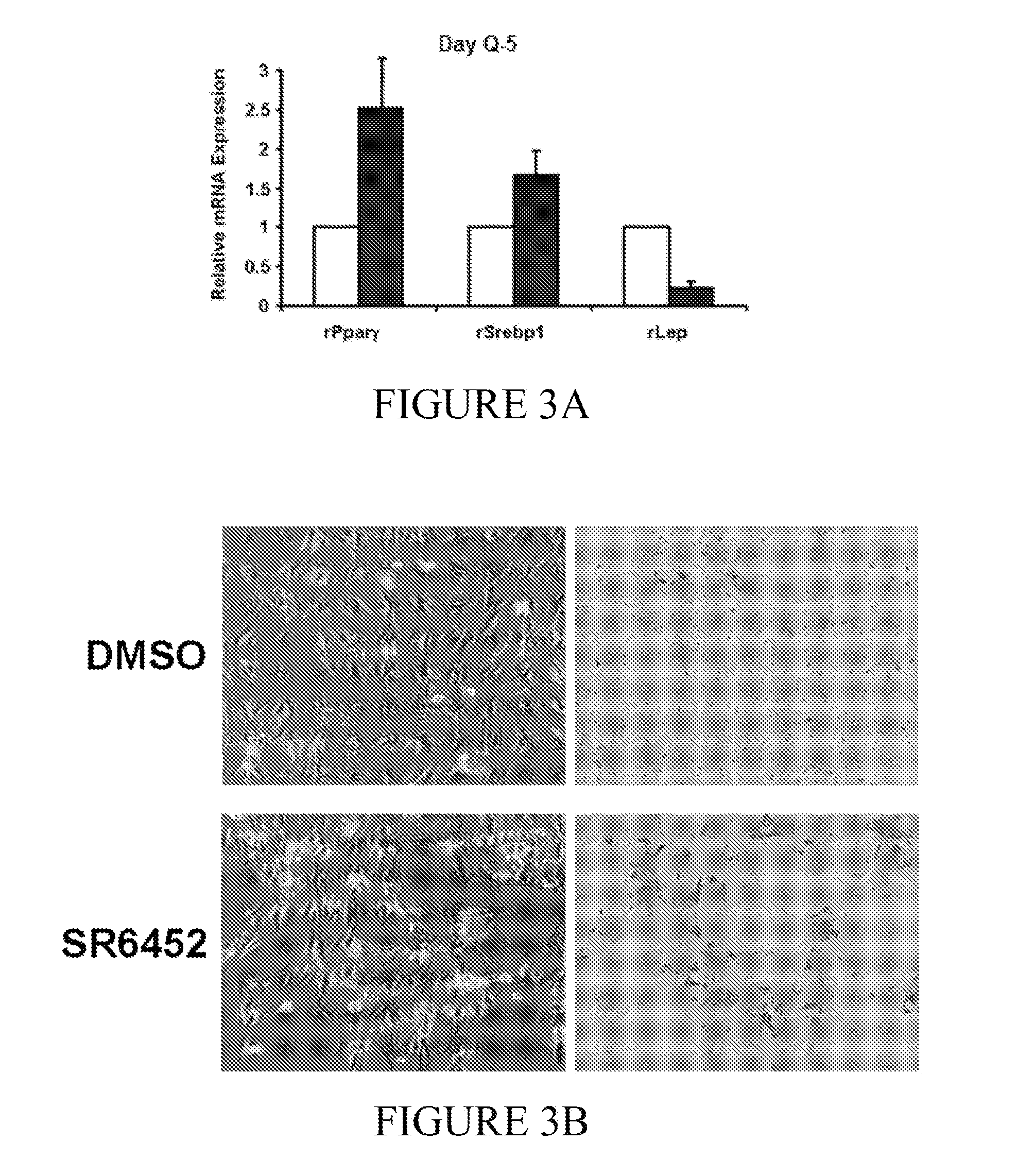
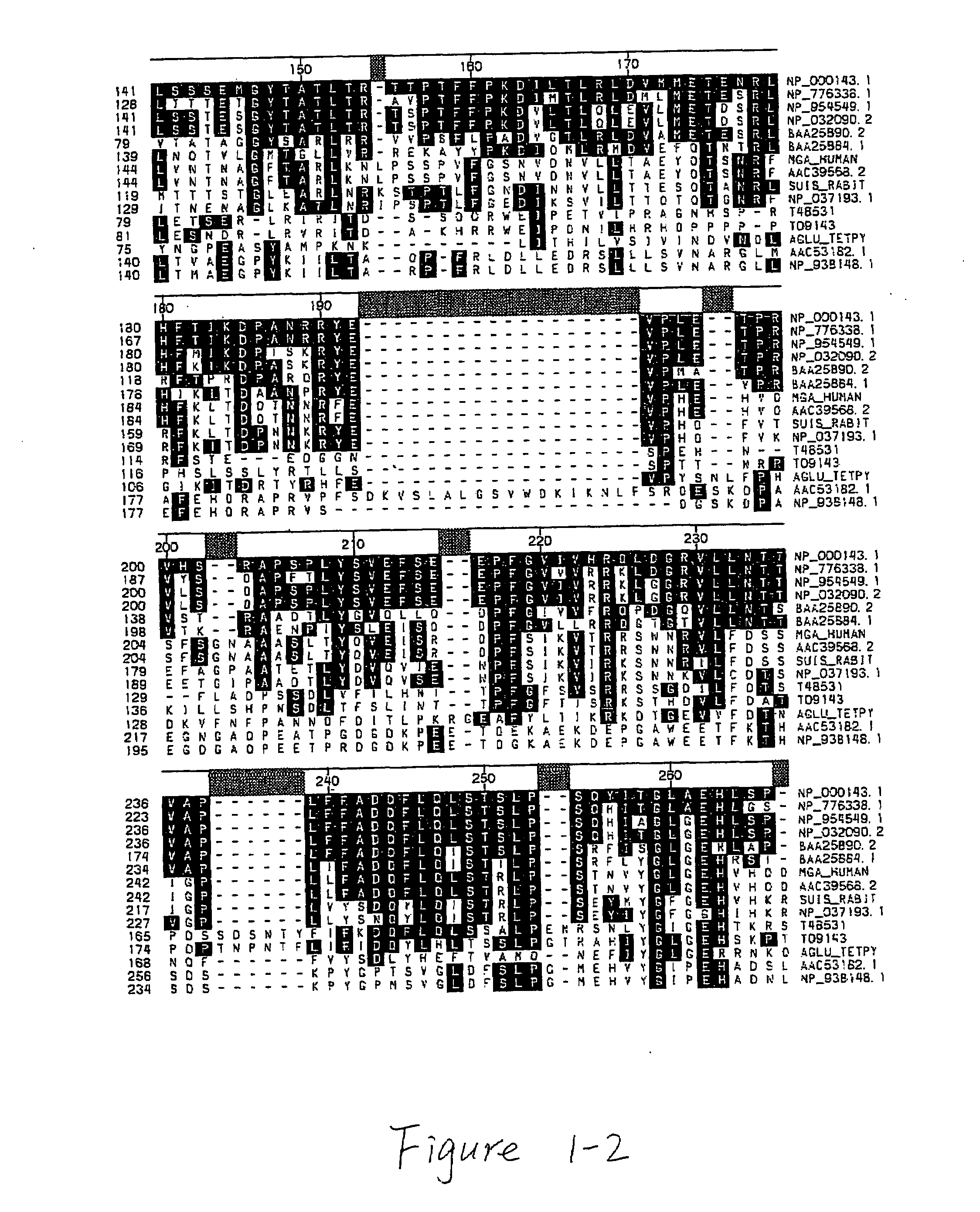
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
240 results about "Subcellular localization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cells of eukaryotic organisms are elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct membrane bound compartments. Some major constituents of eukaryotic cells are: extracellular space, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisome, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, nuclear matrix and ribosomes. Bacteria also have subcellular localizations that can be separated when the cell is fractionated. The most common localizations referred to include the cytoplasm, the cytoplasmic membrane, the cell wall and the extracellular environment. Most Gram-negative bacteria also contain an outer membrane and periplasmic space. Unlike eukaryotes, most bacteria contain no membrane-bound organelles, however there are some exceptions.
Methods and compositions useful for diagnosis, staging, and treatment of cancers and tumors
ActiveUS7078180B2Sugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthSpecific detection
Methods, compositions and kits which employ one or more ZEB specific detection reagents for detection and localization of ZEB associated molecules in tumor cells are disclosed. Also provided are methods for determining stage and progression of cancer in a mammal based on alterations in ZEB expression levels and subcellular localization. Also provided are methods for treating a cancer in a mammal by modulating ZEB expression levels and activity.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20050281805A1Extended half-lifeReduce the binding forcePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinLysosome
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
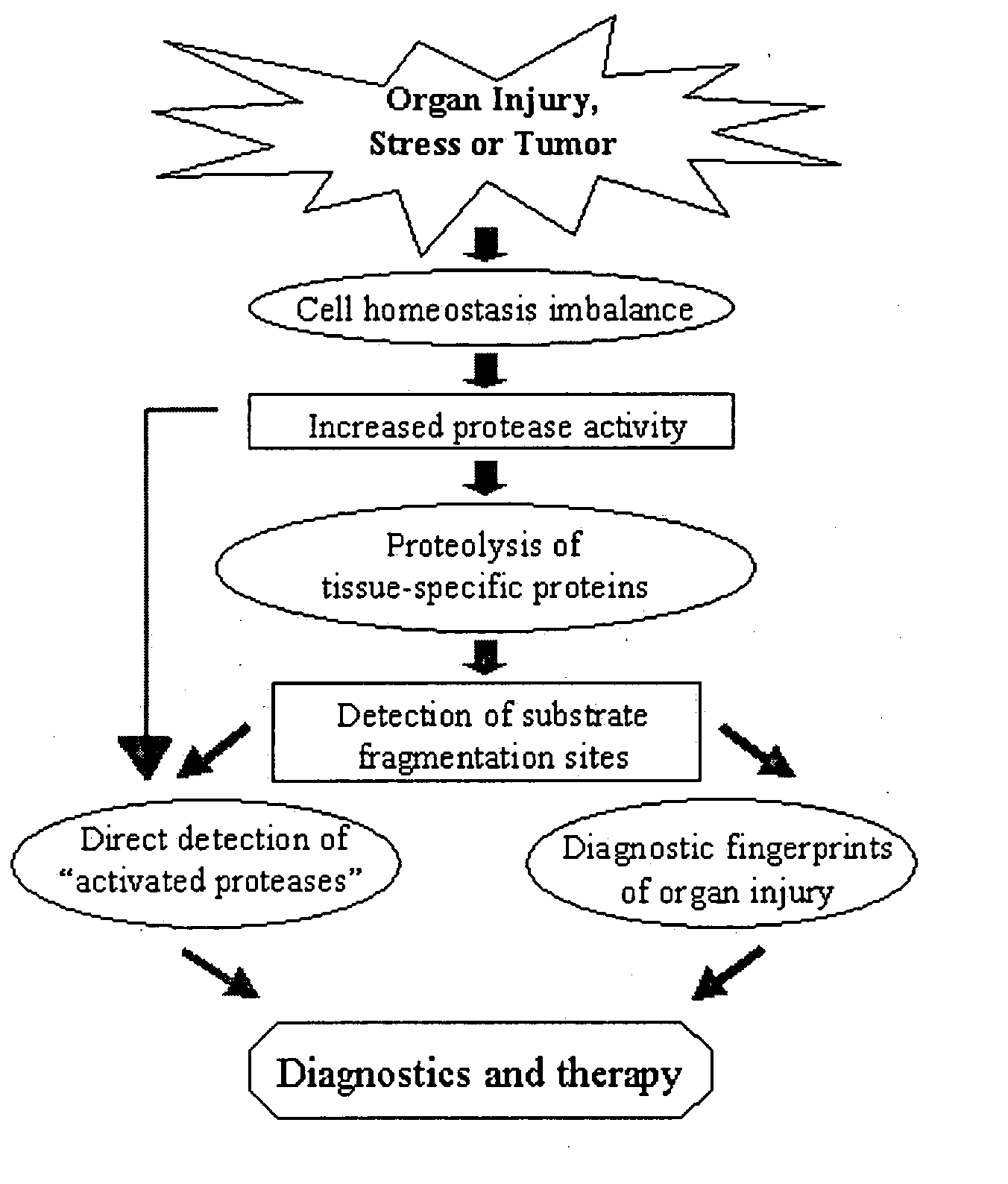
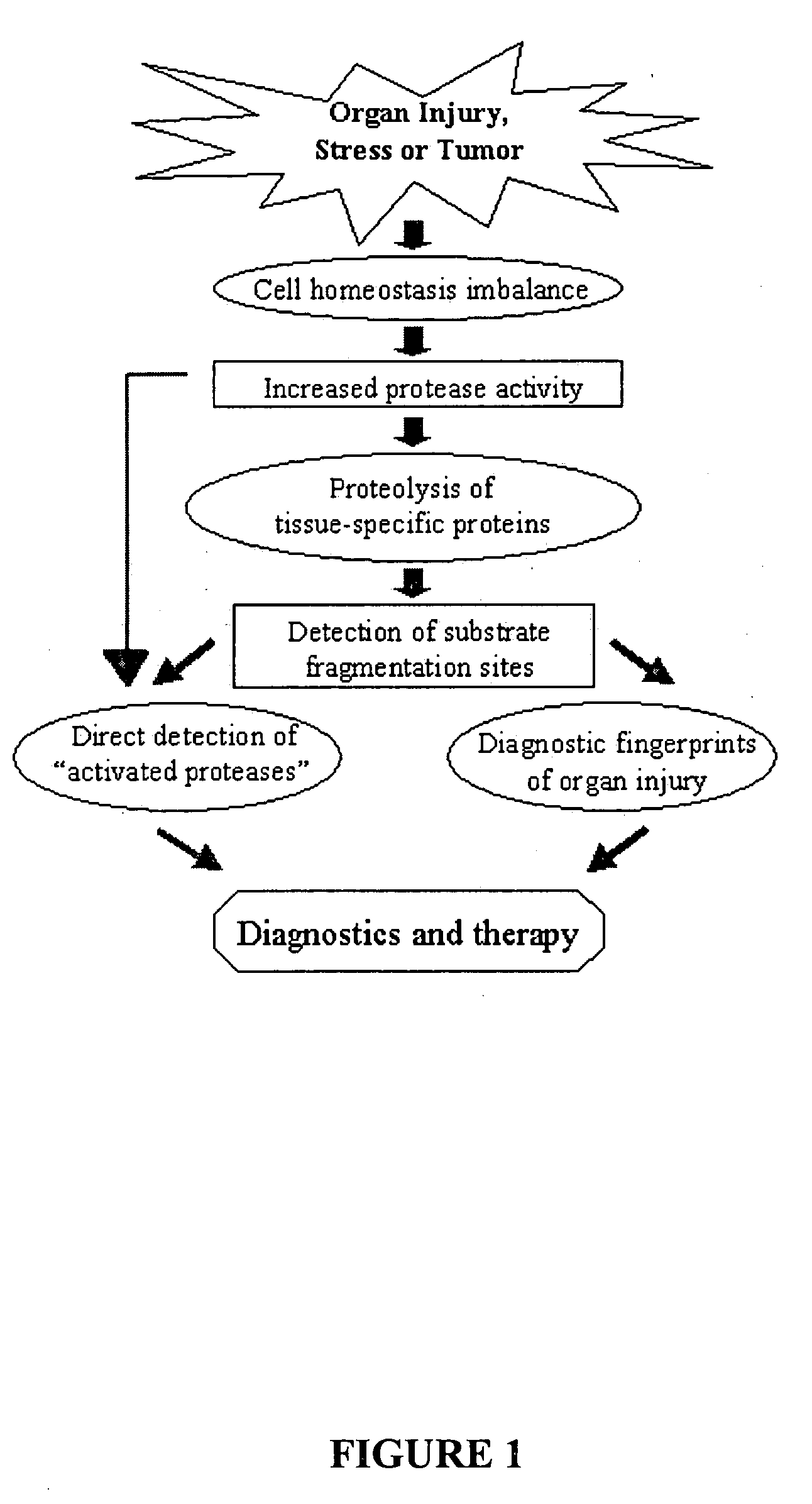
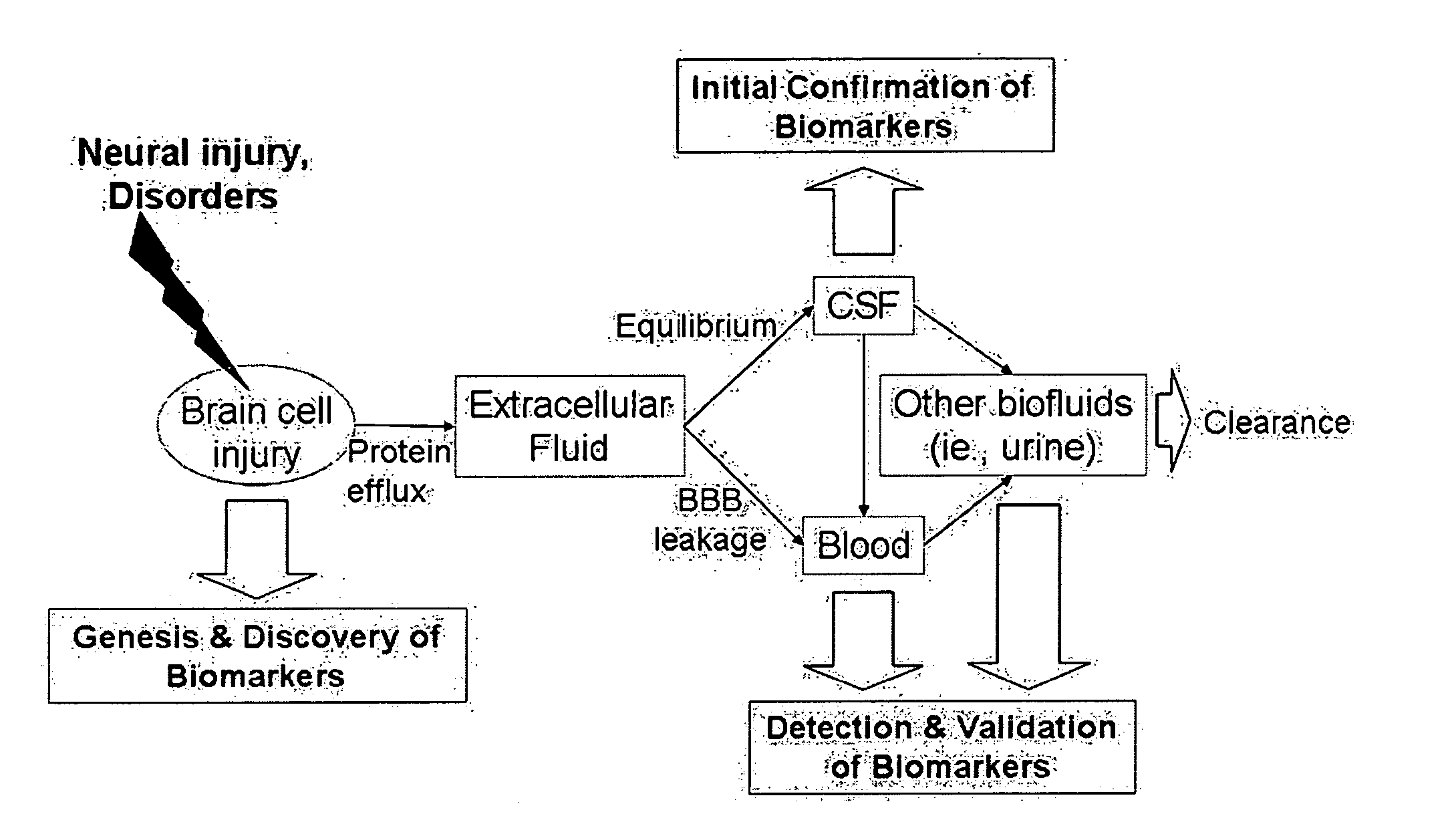
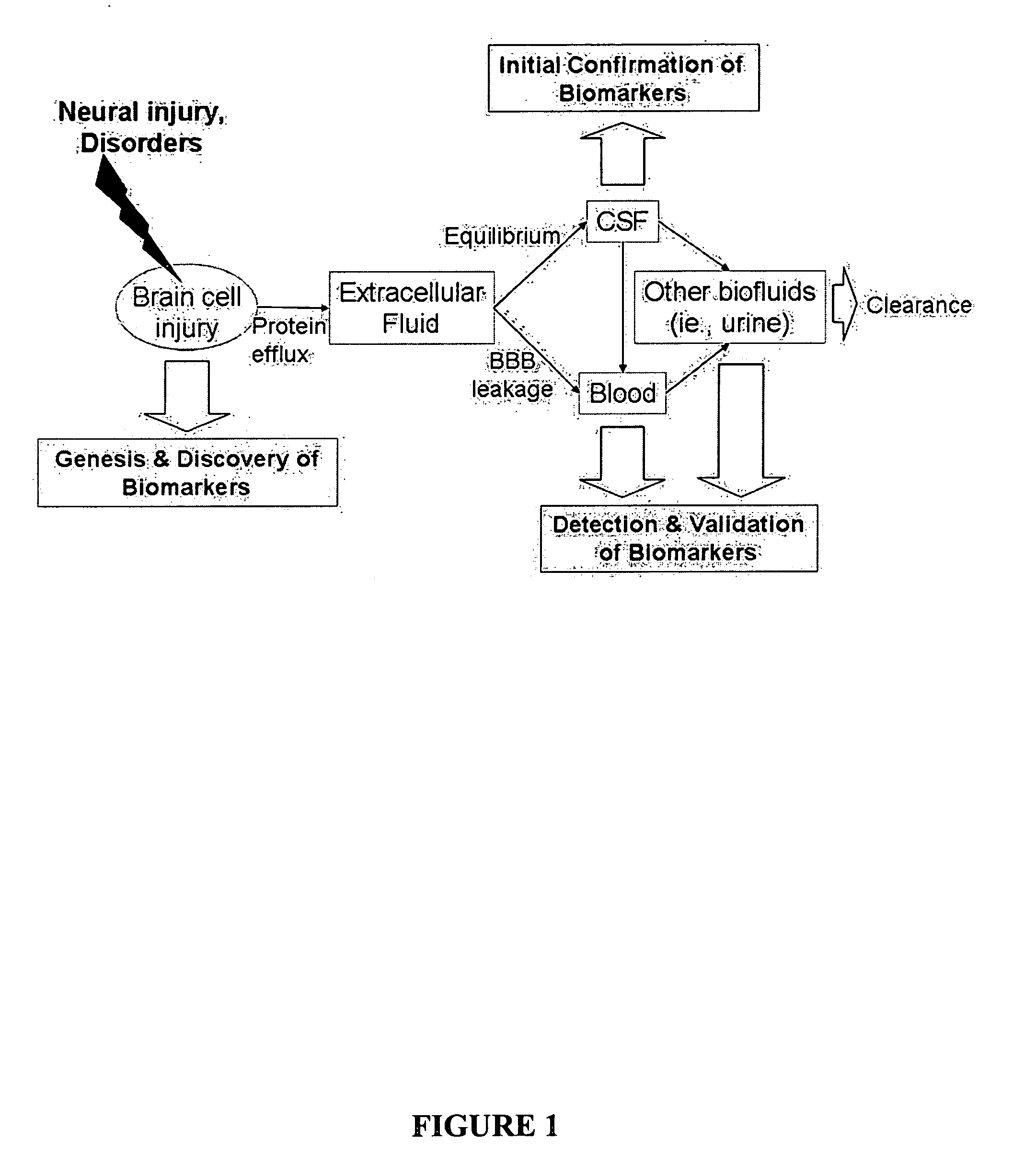
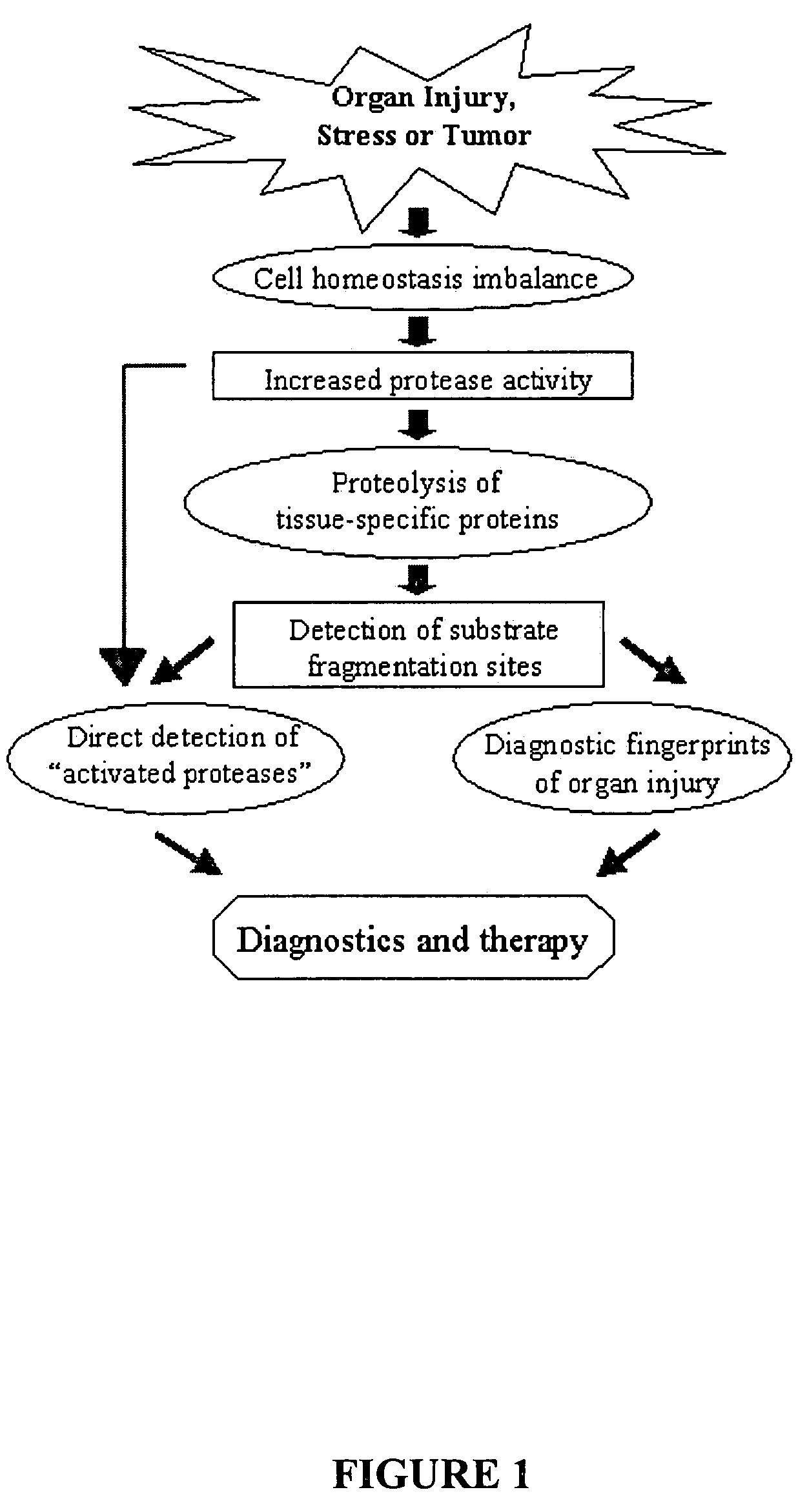
Proteolytic markers as diagnostic biomarkers for cancer, organ injury and muscle rehabilitation/exercise overtraining
ActiveUS20050260697A1Reliable detectionReliable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingOvertrainingMedicine
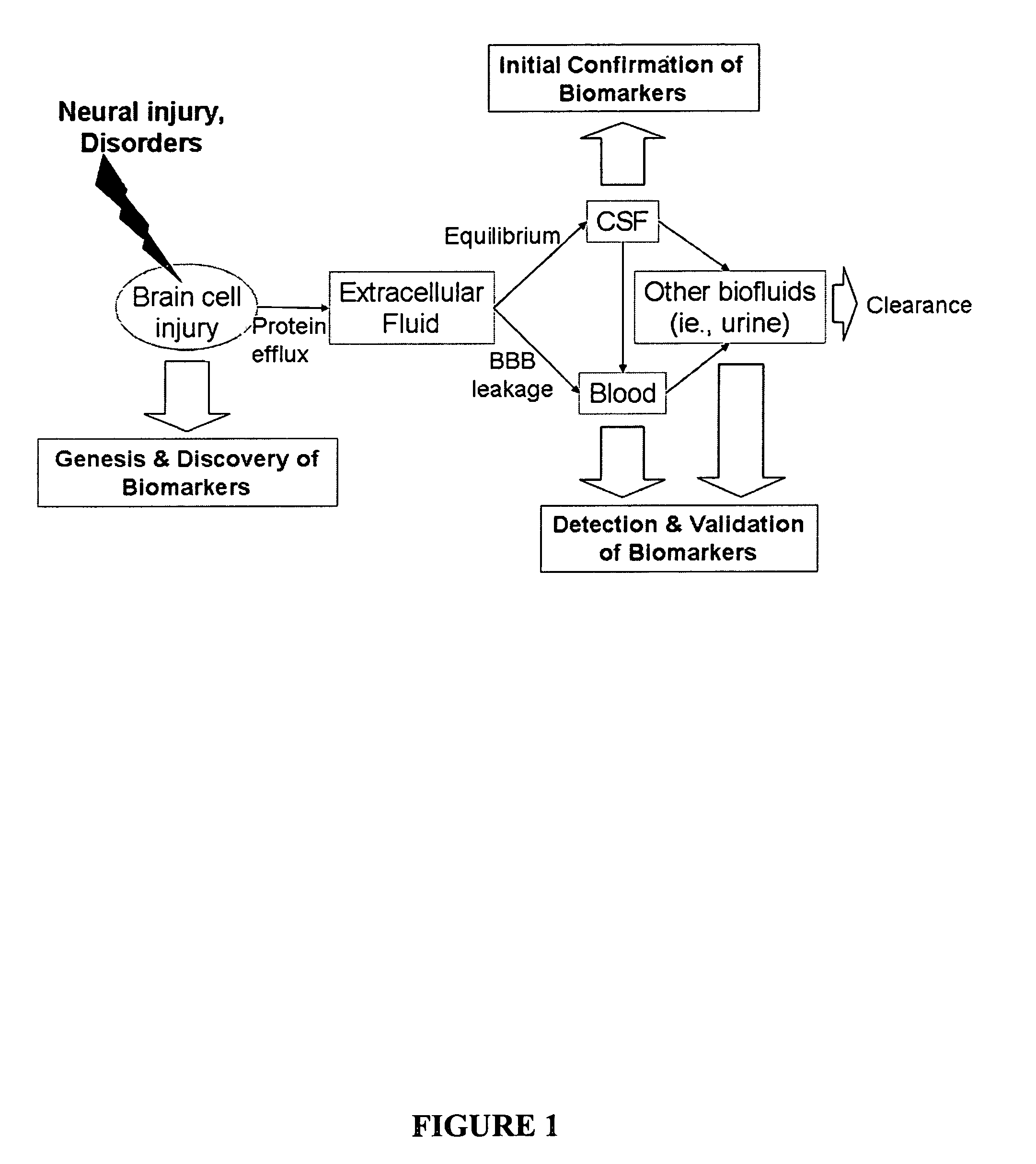
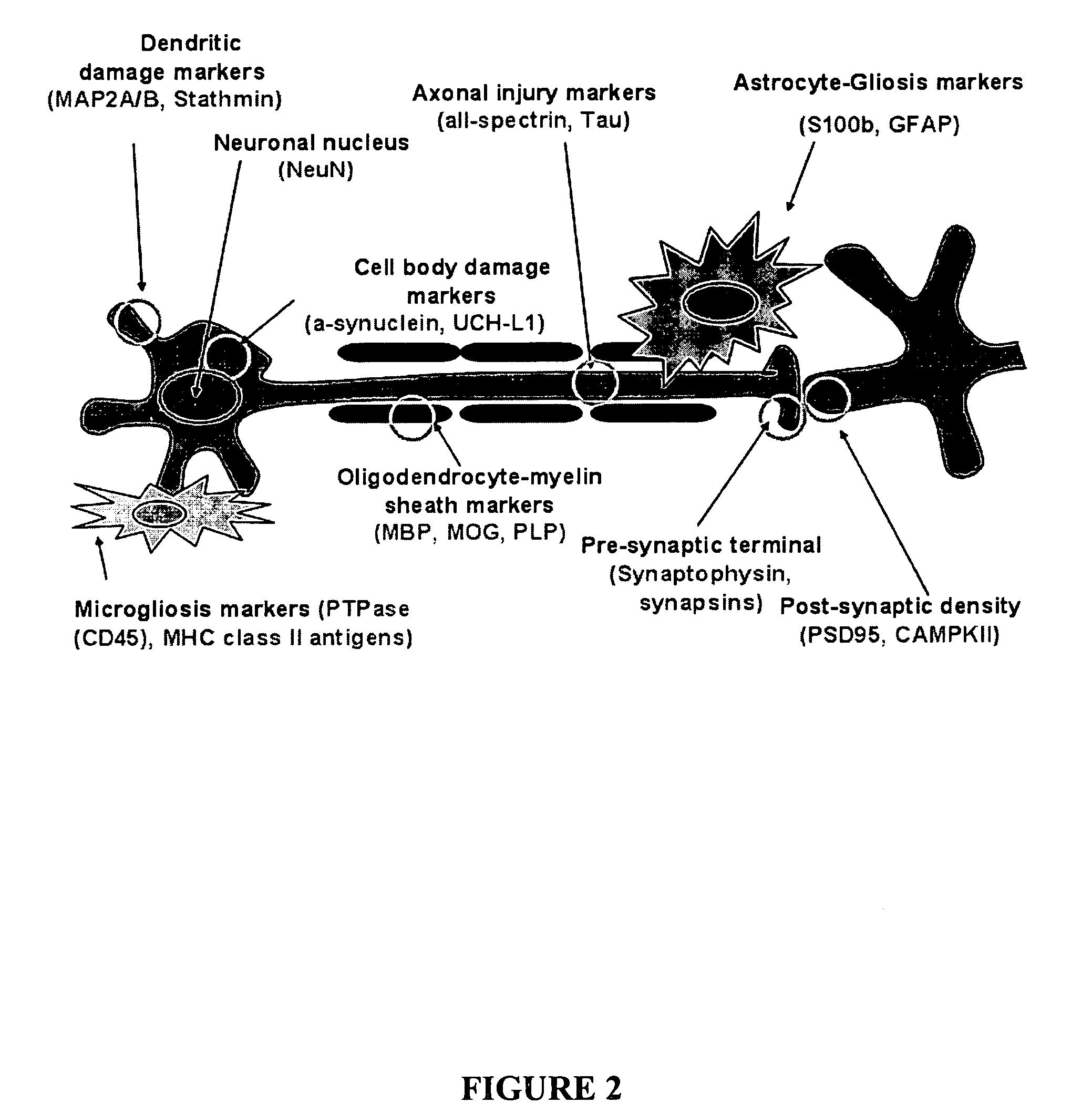
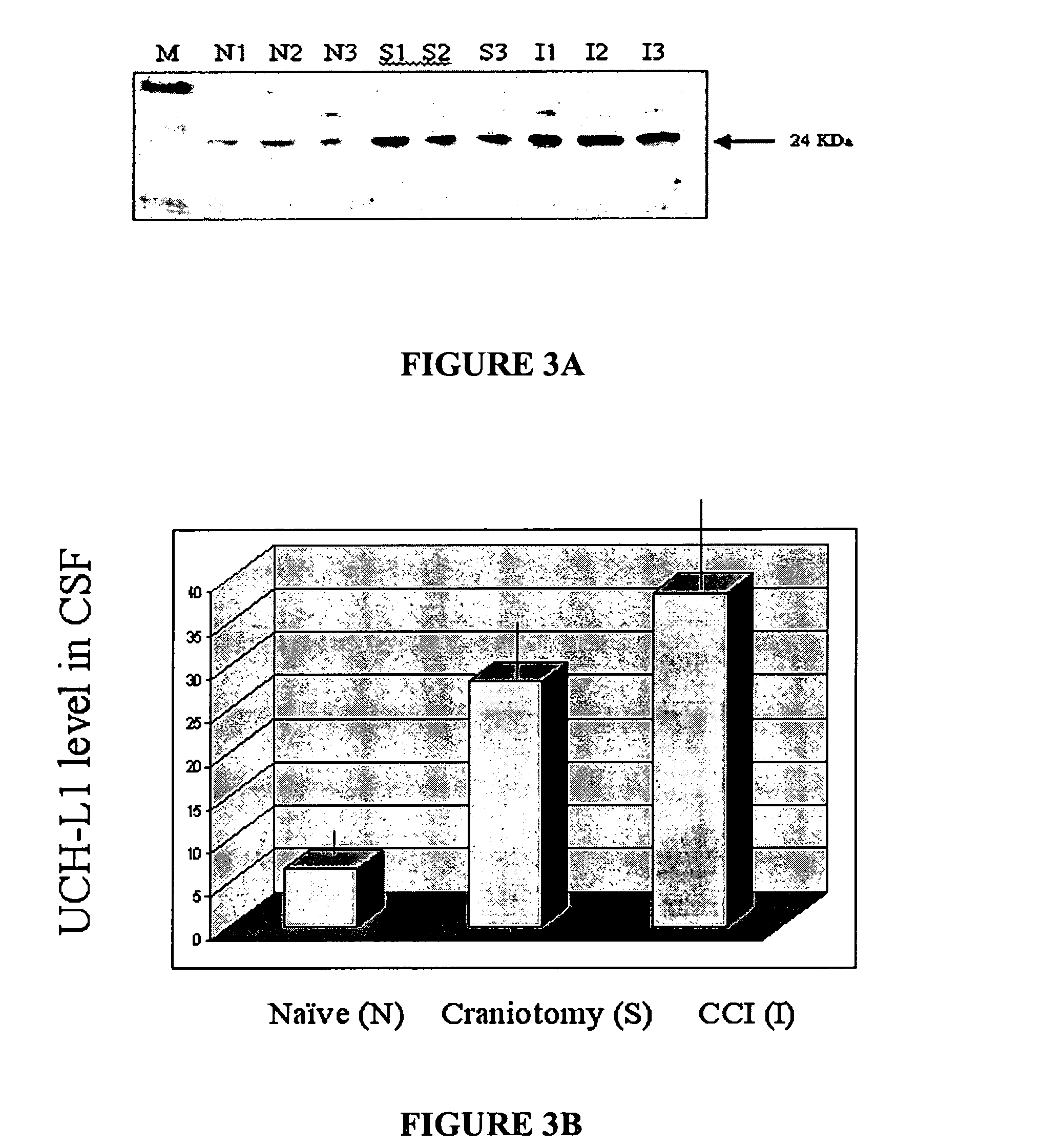
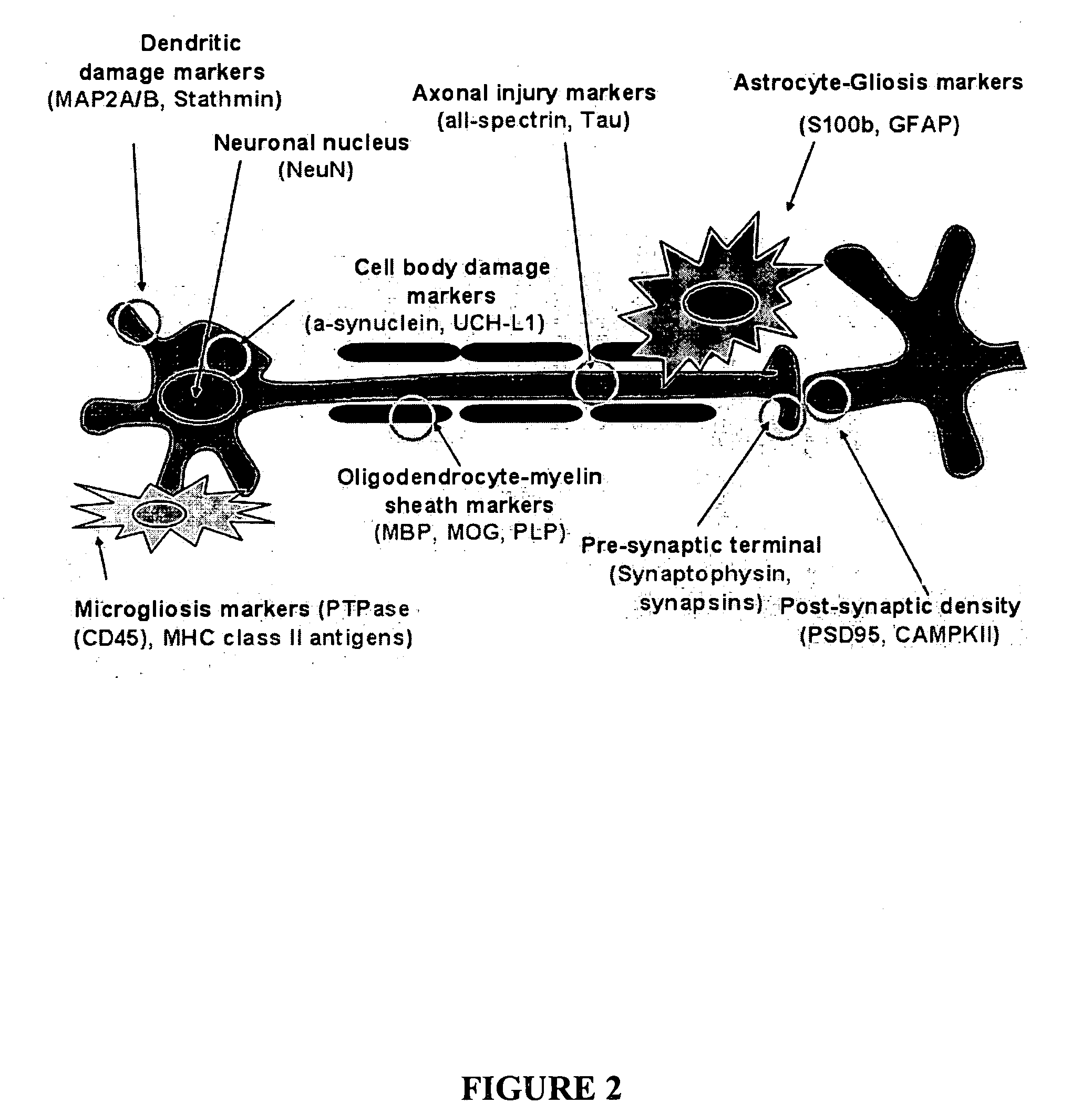
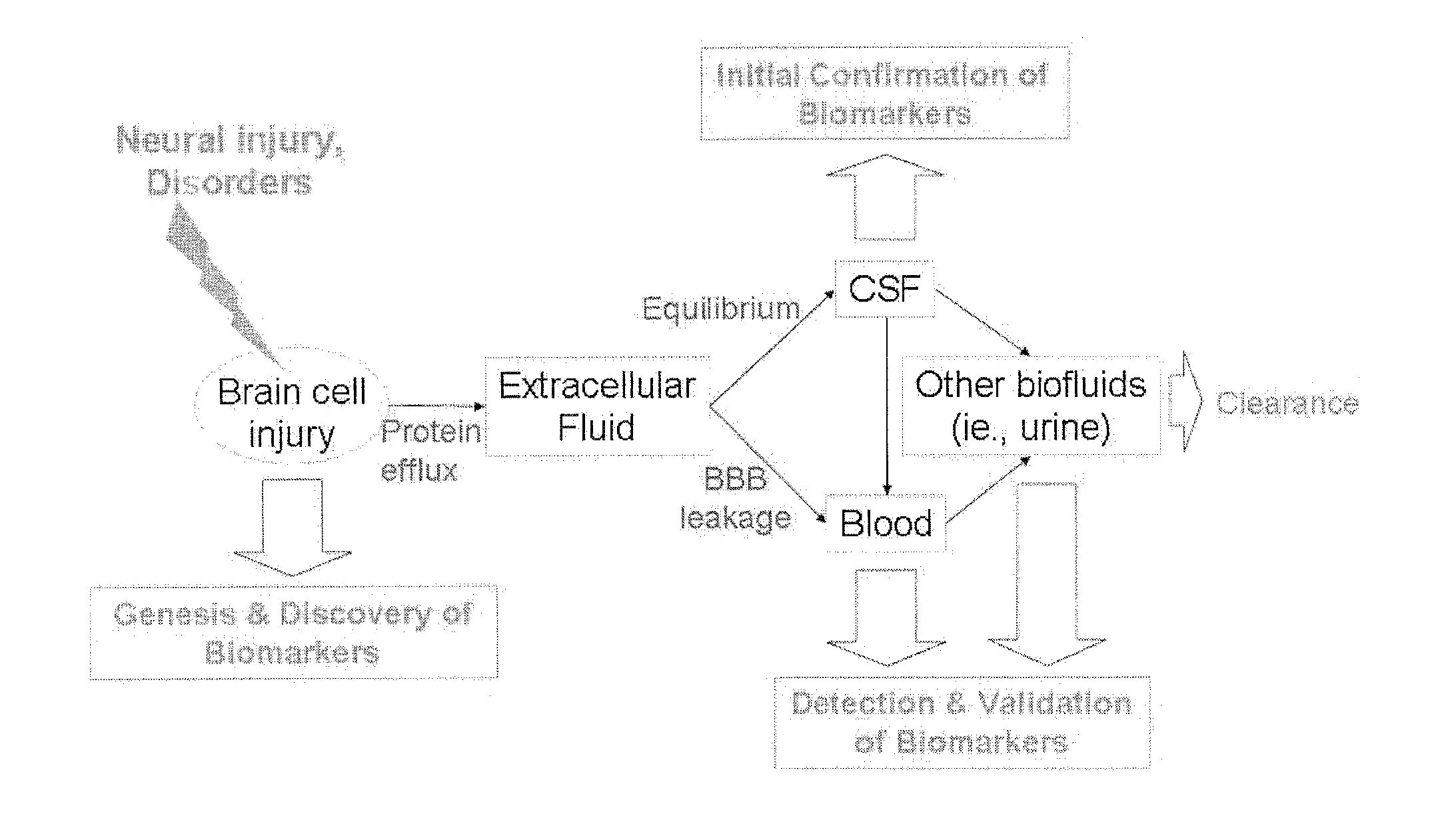
The present invention identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury, organ injury, and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Subcellular targeting of therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7396811B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
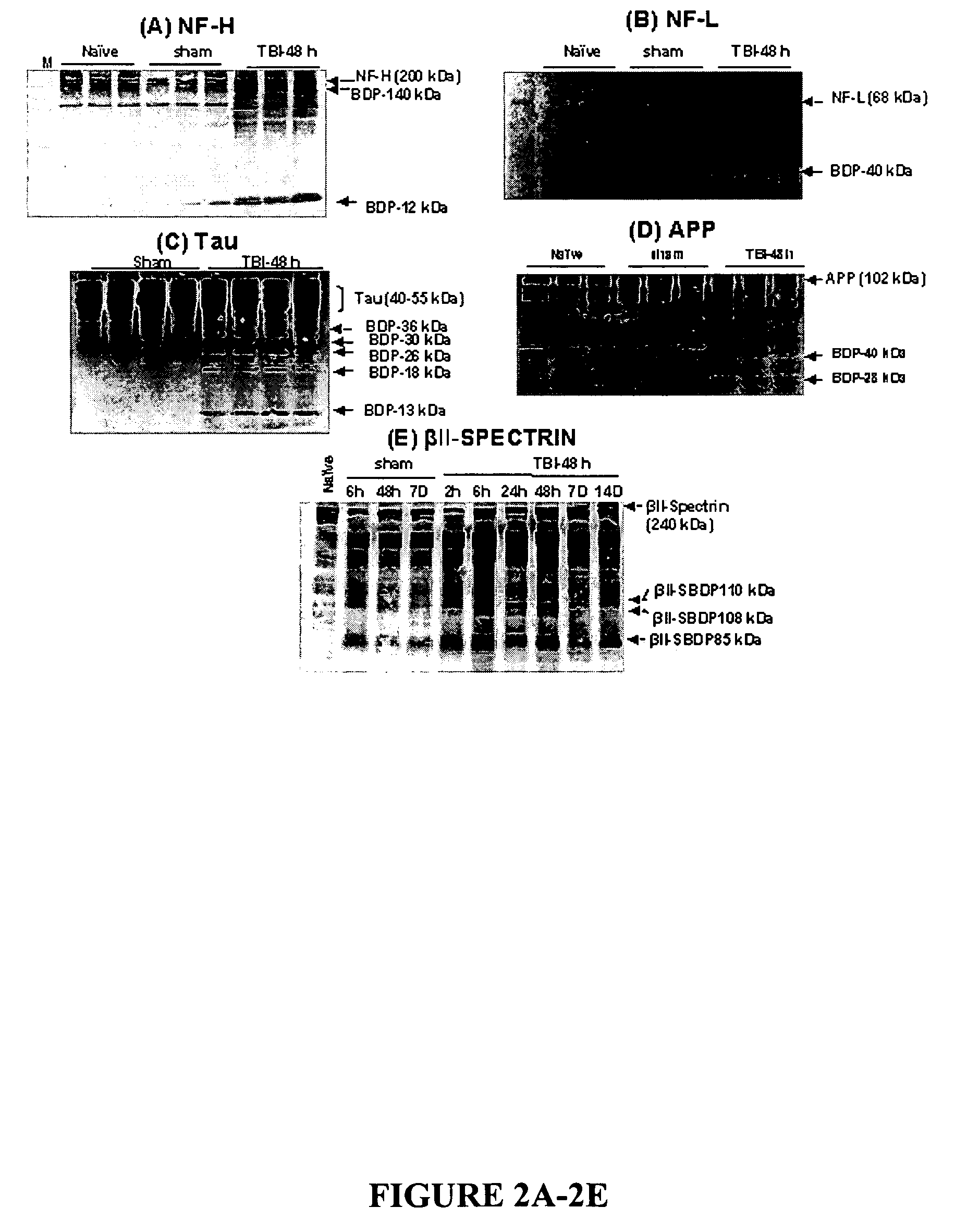
Neural proteins as biomarkers for traumatic brain injury
ActiveUS7396654B2Increase the amount of informationEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCell damageMedicine
The present invention identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7560424B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7629309B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinLysosome
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
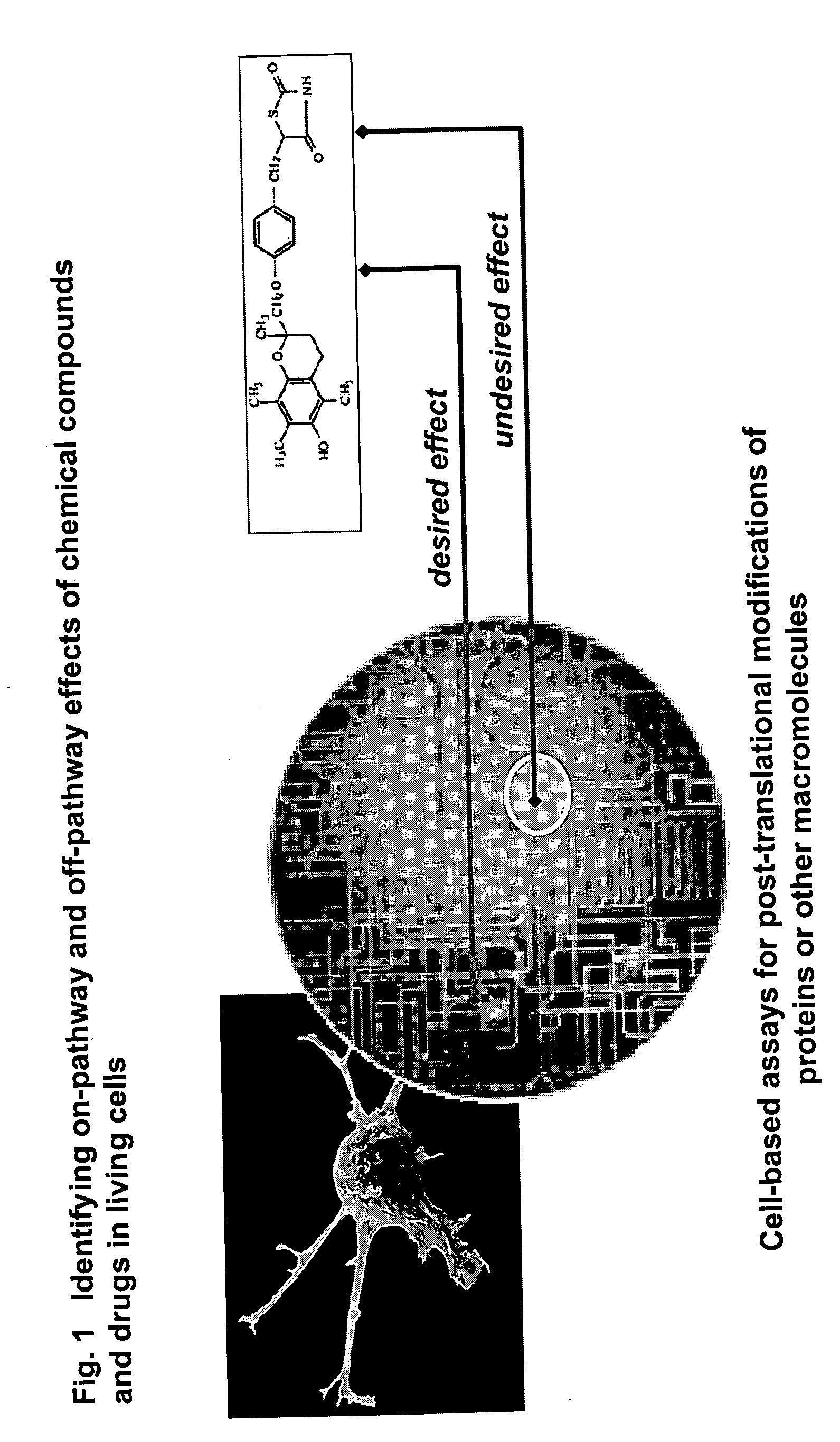
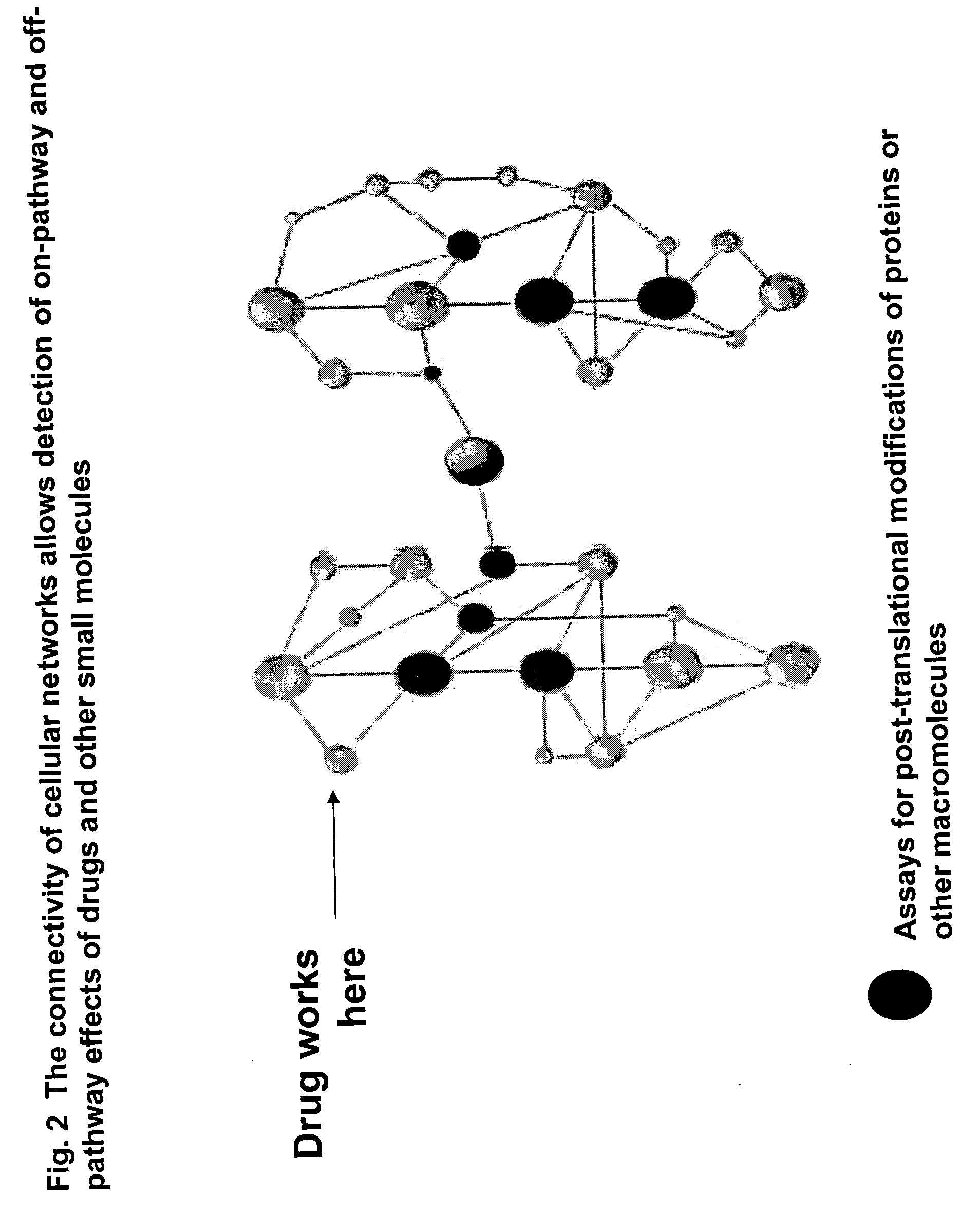
Pharmacological profiling of drugs with cell-based assays
InactiveUS20060040338A1Enable optimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningPost translationalAssay
The instant invention provides a method for establishing safety profiles for chemical compounds, as well as pharmacological profiling said method comprising (A) testing the effects of said chemical compounds on the amount and / or post-translational modifications of two or more macromolecules in intact cells; (B) constructing a pharmacological profile based on the results of said tests; and (C) comparing said profile to the profile(s) of drugs with established safety characteristics. Additionally, the invention is also directed to a composition comprising an assay panel, said panel comprising at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or post-translational modification of a protein and at least one high-content assay for the amount and / or subcellular location of a protein-protein interaction.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Neural proteins as biomarkers for nervous system injury and other neural disorders
ActiveUS20050260654A1Increase the amount of informationEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNervous systemMedicine
The present invention identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20090203575A1Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
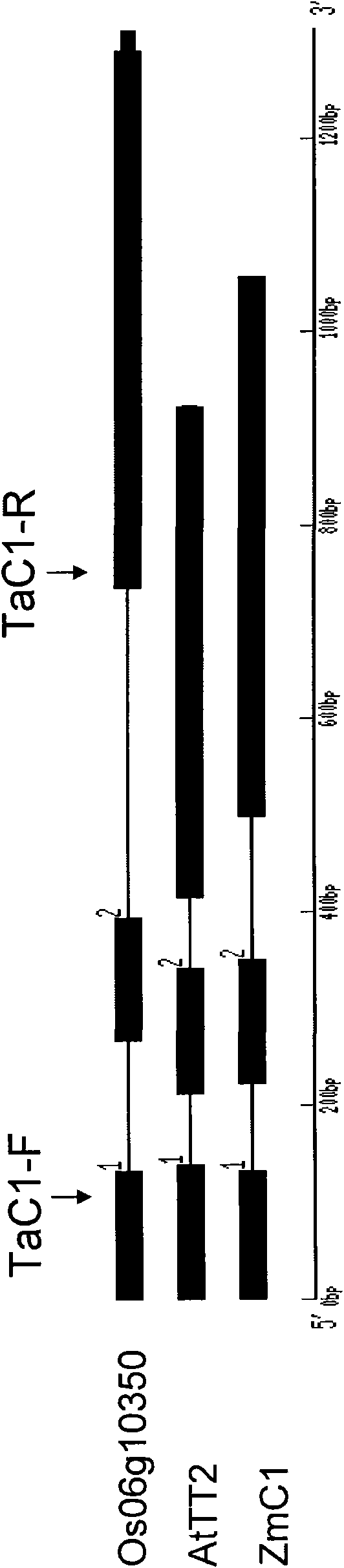
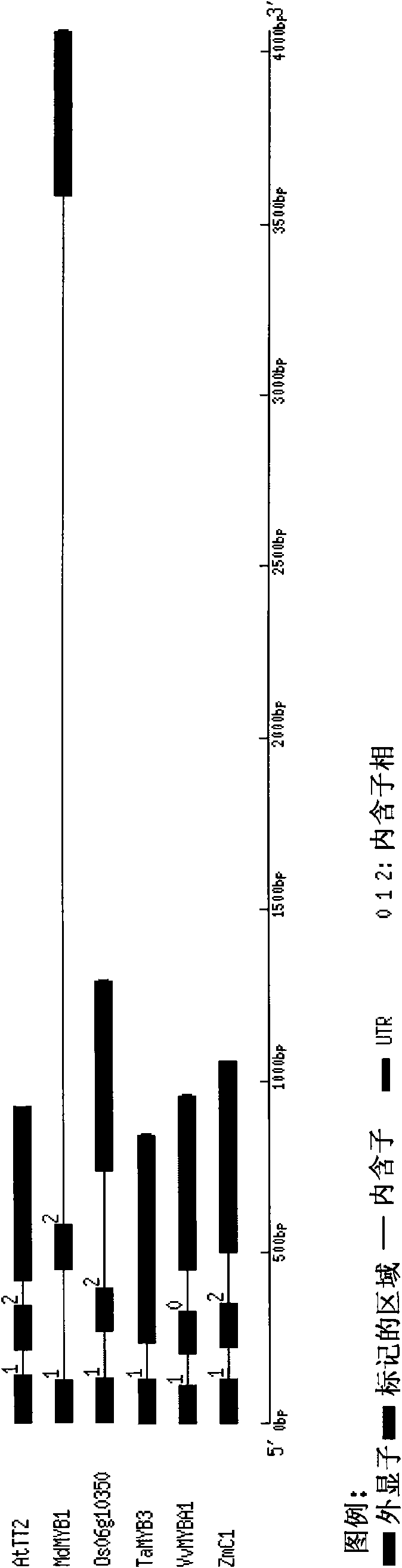
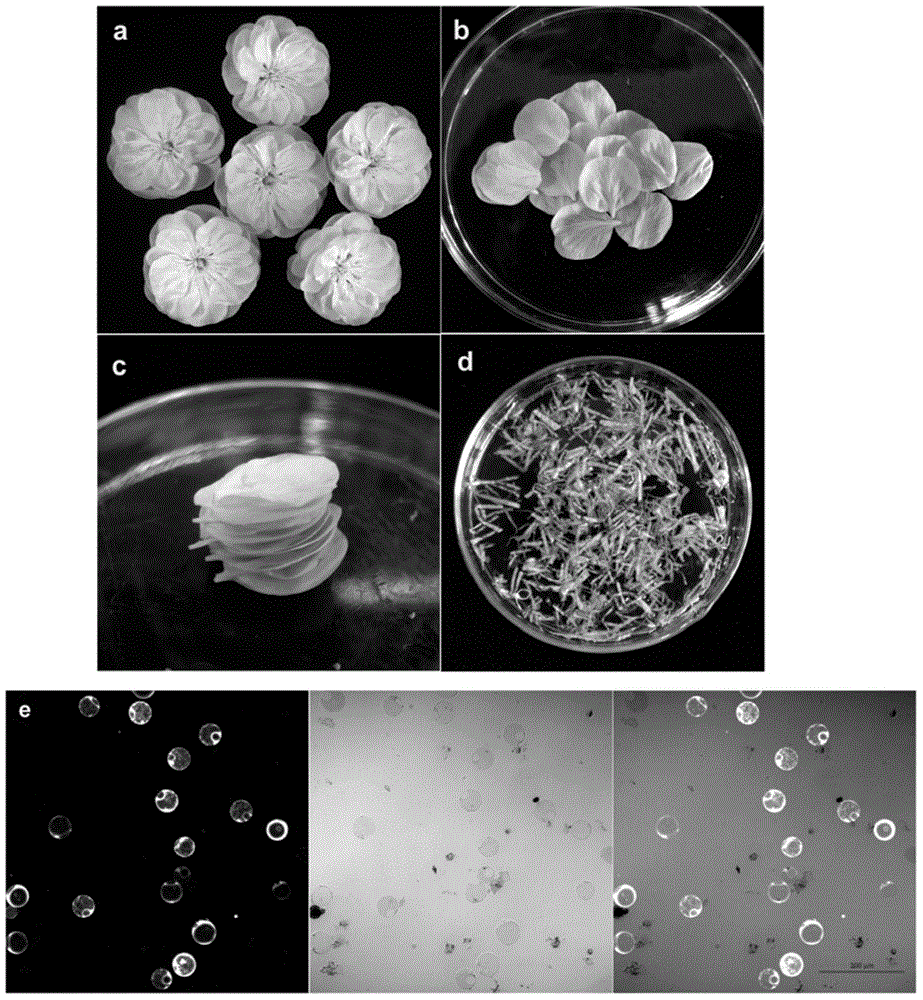
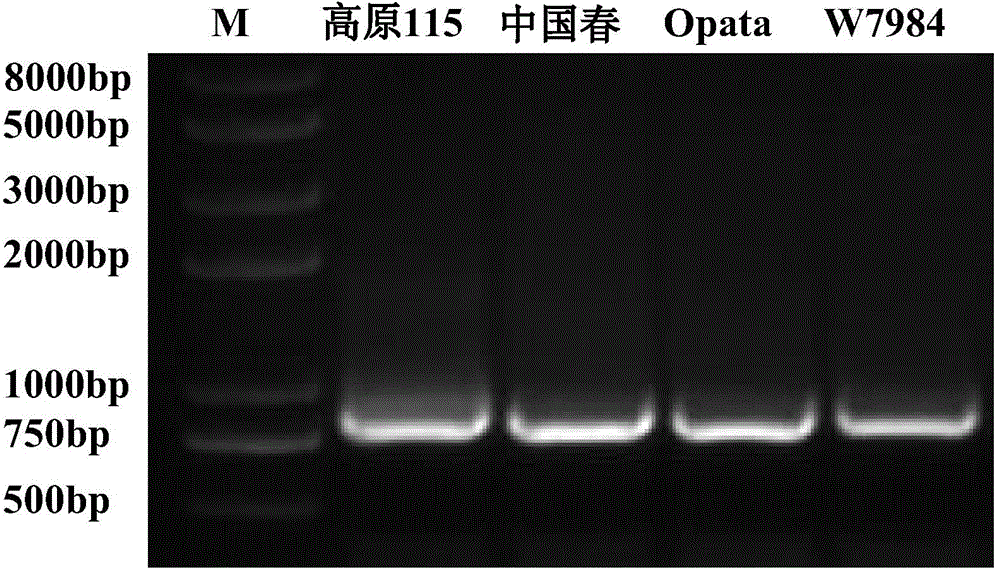
New wheat gene TaMYB3 for regulating synthetization and metabolization of anthocyanin
The invention provides a transcription factor TaMYB3 of a MYB class, which is separated from the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety and is used for regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. TaMYB3 is positioned between 0.62 and 0.95 of a long arm physical map of wheat 4B chromosome. The subcellular fraction of a protein product is positioned on a cell nucleus. Shown by a derived amino acid sequence, the TaMYB3 codes a MYB class transcription factor regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 of a purple kernel wheat variety increases under the induction of light. The TaMYB3 can promote skin cells of the plateau 115 kernels after dark treatment to synthetize anthocyanin under the existence of transcription factors ZmR of corns bHLH during transient expression. Single TaMYB3 genes and single ZmR genes can not induct the synthetization of anthocyani, which shows that the TaMYB3 genes have the transcriptional activity of regulating the synthetization and the metabolization of anthocyanin. barly strip mosaic virus (BSMV) mediates the expression quantity decrease of the TaMYB3 in the plateau 115 kernels, and reduces the quantity of anthocyanin in kernels. This shows that the TaMYB3 participates in the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in the plateau 115 kernels.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Proteolytic biomarkers for traumatic injury to the nervous system
The present invention identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury, organ injury, and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Complex formation for the stabilisation and purification of proteins of interest
InactiveUS20050059053A1Increase volumeReduce degradation rateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccinesAntigenPost translational
A method is described for altering the properties such as the accumulation, the stability and / or integrity, the subcellular localisation, the post-translational modifications, the ability to get purified, and the phase partitioning behaviour of natural or recombinant target proteins expressed in a host organism. The method involves the co-expression of natural or recombinant proteins along with a specific binding partner that sequesters the target recombinant protein into a complex. The binding partner is supplied as a separate protein allowing formation of intermolecular complexes or is fused to the protein of interest, allowing the formation of intramolecular complexes. The binding partner can also be used to alter the subcellular localisation without modifying the sequence or structure of the target protein itself. This can be achieved by either incorporating appropriate targeting signals into the binding ligand, which are then linked to the target protein through complex formation, or complex formation itself may alter the subcellular localisation. The same strategy can be used to provide an affinity tag to facilitate protein purification. The principle of the invention is demonstrated by the coexpression of an unstable antibody and its cognate antigen.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Methods of Treating Portal Hypertension
ActiveUS20150313871A1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationSubcellular localization
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Acid alpha-glucosidase and fragments thereof
ActiveUS20080299640A1Efficient deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesAcid alpha-glucosidaseLysosome
Targeted acid alpha-glucosidase therapeutics that localize to the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent, GAA, and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Method based on localization of Hsp90 to the centrosome
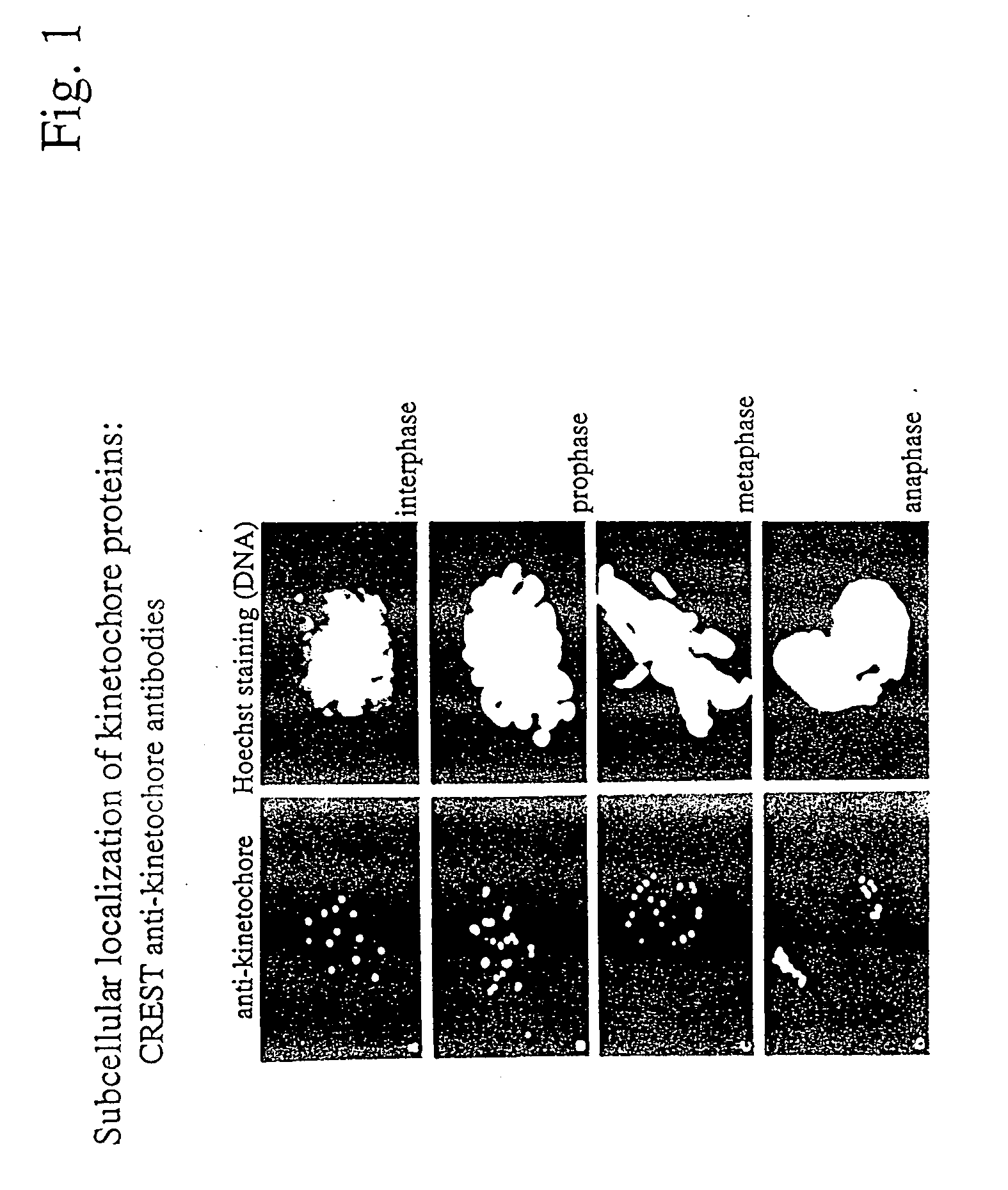
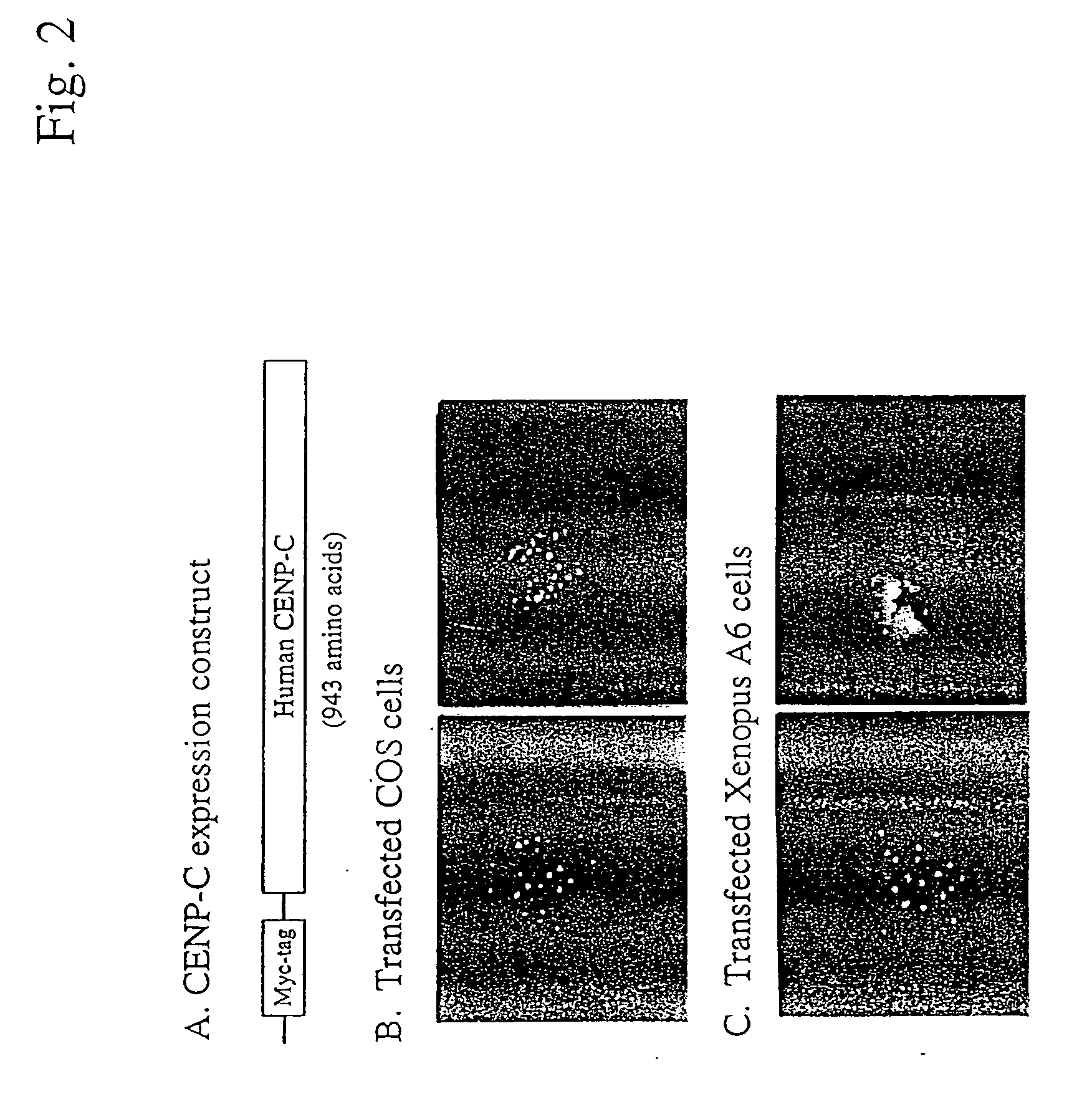
InactiveUS6335157B1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeHSP90 Heat-Shock Proteins
The present invention is directed to methods for screening for fragments, derivatives and analogs of Hsp90 that are altered in their subcellular localization, and thus, altered in their activity as compared to wild type Hsp90. The present invention is also directed to screening for modulators of Hsp90 activity as determined by assaying for altered subcellular localization of Hsp90. The present invention is further directed to diagnostic, prognostic and screening uses of Hsp90 / centrosome co-purification.
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
Neural proteins as biomarkers for nervous system injury and other neural disorders
ActiveUS20110177974A1Increase the amount of informationEasy diagnosisPeptide librariesNucleotide librariesNervous systemMedicine
The present invention identities biomarkers that are diagnostic of nerve cell injury and / or neuronal disorders. Detection of different biomarkers of the invention are also diagnostic of the degree of severity of nerve injury, the cell(s) involved in the injury, and the subcellular localization of the injury.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC +1
Compositions and methods for the identification of protein interactions in vertebrate cells
InactiveUS20050277116A1Short intracellular half-lifeShort lifeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiotechnologyChemical compound
The present invention relates to a two-hybrid system for studying protein-protein interactions in mammalian host cells. The invention provides methods, reagents and kits for carrying out the two-hybrid screen. Accordingly the invention provides a bait construct that is capable of targeting a bait protein to a specific subcellular locale within the host cell. The invention also provides a prey construct that contains a detection sequence fused to a prey protein. The bait and prey constructs are introduced into a host cell under conditions that promote expression of the bait and prey constructs. A positive bait / prey interaction can be detected by comparing the subcellular localization of the prey construct in relation to the bait construct. The invention also provides methods for screening for compounds capable of disrupting protein-protein interaction and methods for detecting interactions between proteins and small molecule compounds.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Preparation method and application of paddy rice green protoplast
InactiveCN102311937AIncrease vitalityGood growthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
According to the invention, the culture time of paddy rice is shortened by adjusting the growing conditions of paddy rice seedlings; a paddy rice green protoplast is prepared by an enzyme method; the preparation method is optimized, so vacuum pumping and the usage of a highly toxic reagent are avoided; and thus the preparation method of the paddy rice green protoplast is simpler and safer. The protoplast prepared by the method of the invention has a high cell survival rate, and a high transformation rate, is applicable to various analysis such as subcellular localization of target gene codingprotein, protein interaction, western blotting and the like, and is especially applicable to instantaneous expression research of light / chloroplast related gene.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
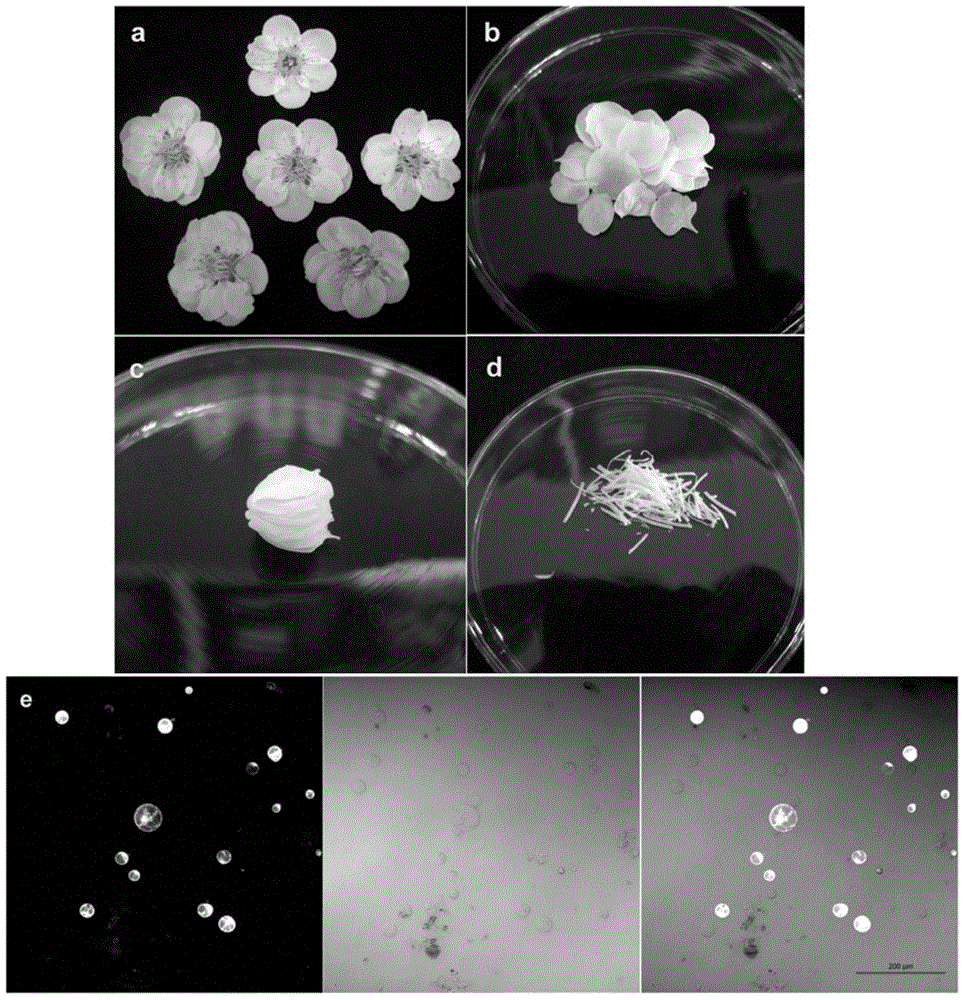
Method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast
The present invention relates to a method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast. The method comprises: (1) adopting plant petals as a material, and carrying out enzymolysis to obtain petal cell protoplast; (2) standing the petal cell protoplast for 20-40 min at a temperature of 2-8 DEG C; and (3) transforming plasmid into the protoplast by using a PEG and Ca<2+>-mediated method, and expressing the target protein. Compared with the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following beneficial effects that: the target protein can be expressed in a short time, the protoplast protein expression system can be used for research on target protein subcellular positioning and protein molecule interaction, the activity of the protoplast is normal, and the target protein expression detection results show that the method can be used for research on gene transcription level, protein expression level and substance metabolism level change in living cells and is the rapid and convenient target gene function research method.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
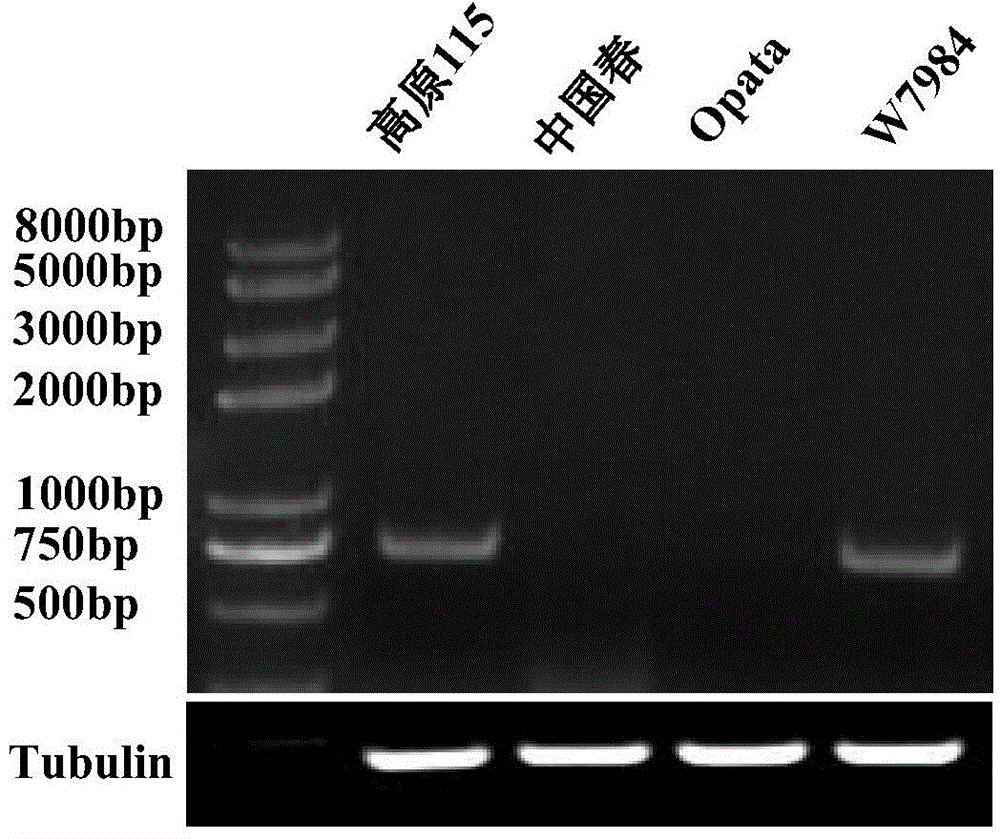
Novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling synthesis and metabolism of anthocyanin
InactiveCN104894142ARegulates transcriptional activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, wherein the novel wheat gene TaMYB7D is obtained through separation of the purple-grain wheat variety highland 115. The TaMYB7D is located on a wheat chromosome 7D, and a protein product subcell is located in a cell nucleus. A deduced amino acid sequence shows that TaMYB3 encodes an MYB transcription factor capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB7D in the coleoptiles of a purple wheat variety highland 115 grain can be increased under the induction of light. During transient expression, the TaMYB7D and the pericarpic cell of the highland 115 grain synthetize anthocyanin. Moreover, coseparation occurs between the color of the coleoptiles of the highland 115 grain and the expression of the TaMYB-7D, that is, the TaMYB7D has transcriptional activity used for adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and is the major gene of the purple coleoptiles of the TaMYB7D highland 115 grain.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Compositions and uses of motor protein-binding moieties
InactiveUS20050053591A1Enhancing cellular uptakeEnhancing transmembrane movementPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsSubcellular localizationMovement protein
The invention provides methods and reagents for efficient transport of macromolecules (such as drug therapeutics including nucleic acids and polypeptides) linked to motor protein-binding moieties (MPBM) intracellularly to a specific subcellular localization. One exemplary MPBP is dynein binding moiety (DBM). Drug therapeutics linked to DBM can be selectively, specifically, and actively transported intracellularly to the nucleus or peri-nuclear region, thus enhancing the uptake of such drug therapeutics into the target subcellular localization.
Owner:INSERT THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for increasing content of tanshinone in salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots
ActiveCN104894143AIncreased total tanshinone contentAlleviate shortagesFermentationGenetic engineeringSalvia miltiorrhizaFrame sequence
The invention provides a method for increasing content of tanshinone in salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots. According to the method, recombinant plant expression vectors are constructed with salvia miltiorrhiza bunge SmWRKY70 transcription factors, and SmWRKY70 gene modified salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots are obtained through genetic transformation of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge leaves. According to the method, 789 bp of a coding frame sequence of the SmWRKY70 transcription factors is isolated and cloned from salvia miltiorrhiza bunge, and 918 bp of a promoter sequence of the SmWRKY70 transcription factors is cloned; subcellular localization vectors of the SmWRKY70 transcription factors are constructed; overexpression vectors of SmWRKY70 genes are constructed, and overexpression salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots with the SmWRKY70 genes are obtained through genetic transformation of the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge leaves. The content of the tanshinone in the gene modified salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots obtained with the method is significantly increased, a novel high-quality drug resource is provided for production of the tanshinone with important clinical demands, and the active promotion effect on alleviating shortage of the tanshinone drug resource is realized, and the method has the important theoretical significance and the potential application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene and application
The invention discloses a rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the rhizoma gastrodiae glucosyltransferase gene is shown as SEQID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence asshown in SEQID NO:2 is coded. A glucosyltransferase gene sequence is screened out according to a CDS sequence provided by a rhizoma gastrodiae transcriptome, a nest type PCR primer is designed, and through amplification and splicing, an overall length sequence of the glucosyltransferase gene is obtained; a prokaryotic expression vector pGEX4T-UGT is constructed, proteins are obtained through expression and purification, a eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, subcellular localization is performed on expression of a UGT gene, glucosyltransferase is transferred into monokaryon honey mushroom mycelia by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infection method for the constructed eukaryotic expression vector pH2GW7.0 35S-UGT, transgene honey mushrooms are obtained, biosynthetic gastrodin is used,the rhizoma gastrodiae is artificially cultured by the transgene honey mushrooms, the content of gastrodin in the rhizoma gastrodiae is increased, and besides, the gastrodin can also be produced through culturing genetic engineering honey mushrooms.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for identifying key proteins based on cuckoo search algorithm
ActiveCN108319812AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityArtificial lifeProteomicsProtein-protein complexPredictive value
The invention discloses a method for identifying key proteins based on a cuckoo search algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of biological information. A protein interaction network is converted into an undirected graph, denoising processing is conducted on the protein interaction network to acquire gene expression data, subcellular localization information, standard protein complex information and GO annotation information corresponding to the protein, weighting processing is conducted on edges and nodes of the purified protein interaction network to generate a bird nest and cuckoos and update a bird nest adaptive value to generate the key proteins. The method can accurately identify the key proteins; simulation results show that the indexes such as sensitivity, specificity, F measure, a positive predictive value, a negative predictive value, correct rate and the like are superior; compared with other existing identification methods, the optimizing characteristics of the cuckoo search algorithm and topological characteristics of the protein interaction network are combined to identify the key proteins, and the recognition accuracy of the key proteins is improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Yunnan red pear PybMYB gene as well as prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN103146710AStrong specificityPrecise positioningImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesEscherichia coliImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses a Yunnan red pear PyMYB gene through pigment synthesis regulation and trichome development regulatory protein as well as a prokaryotic expression vector thereof and an application of the prokaryotic expression vector. The PyMYB gene is cloned from red fruit peel of Yunnan red pear NO.1 by using a RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technology, and then the gene is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by using the prokaryotic expression vector and is purified by a GST (Glutathione S-transferase) gel column purification method to obtain a Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein, wherein the Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein is used for the preparation of a PyMYB specific antibody and the application thereof in a PyMYB protein expression detection and immunoprecipitation, a chromatin co-immunoprecipitation and a fusion protein sedimentation experiment. The antibody prepared by the invention is strong in specificity, can accurately detect subcellular localization of the PyMYB protein, and is used for verifying protein interaction in the co-immunoprecipitation experiment, efficiently separating the protein and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment combined by the PyMYB protein and detecting the expression of the antibody in a transgenic plant.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cyclic RNA circBCBM1 and non-diagnostic fluorescent quantitative detection method
ActiveCN108796086ARing-formingImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceNormal cell
The invention discloses cyclic RNA circBCBM1 and a primer of the cyclic RNA circBCBM1 and the like in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification process. The cyclic RNA has high expression in a breast cancer brain metastasis cell and has moderate and low expression in other breast cancer cells and normal cells, and sub-cells are positioned in cell nucleuses; the cyclic RNA circBCBM1 disclosedby the invention appears in the lacking of breast cancer brain metastasis related cyclic RNA at present for the first time; the cyclic RNA circBCBM1 disclosed by the invention has a wide applicationspace in the aspects of breast cancer brain metastasis risk predication and a clinical diagnosis molecular marker, and a target spot of researching and developing a novel breast cancer brain metastasis medicine.
Owner:LIAOCHENG PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN102140131AAccording to Mendelian inheritanceIn line with the law of inheritancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideWild type
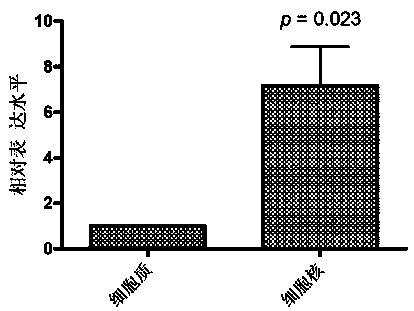
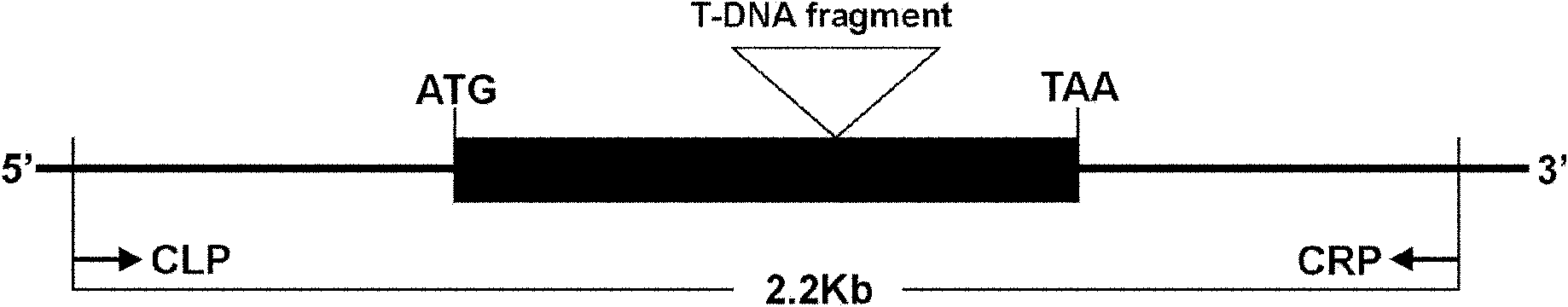
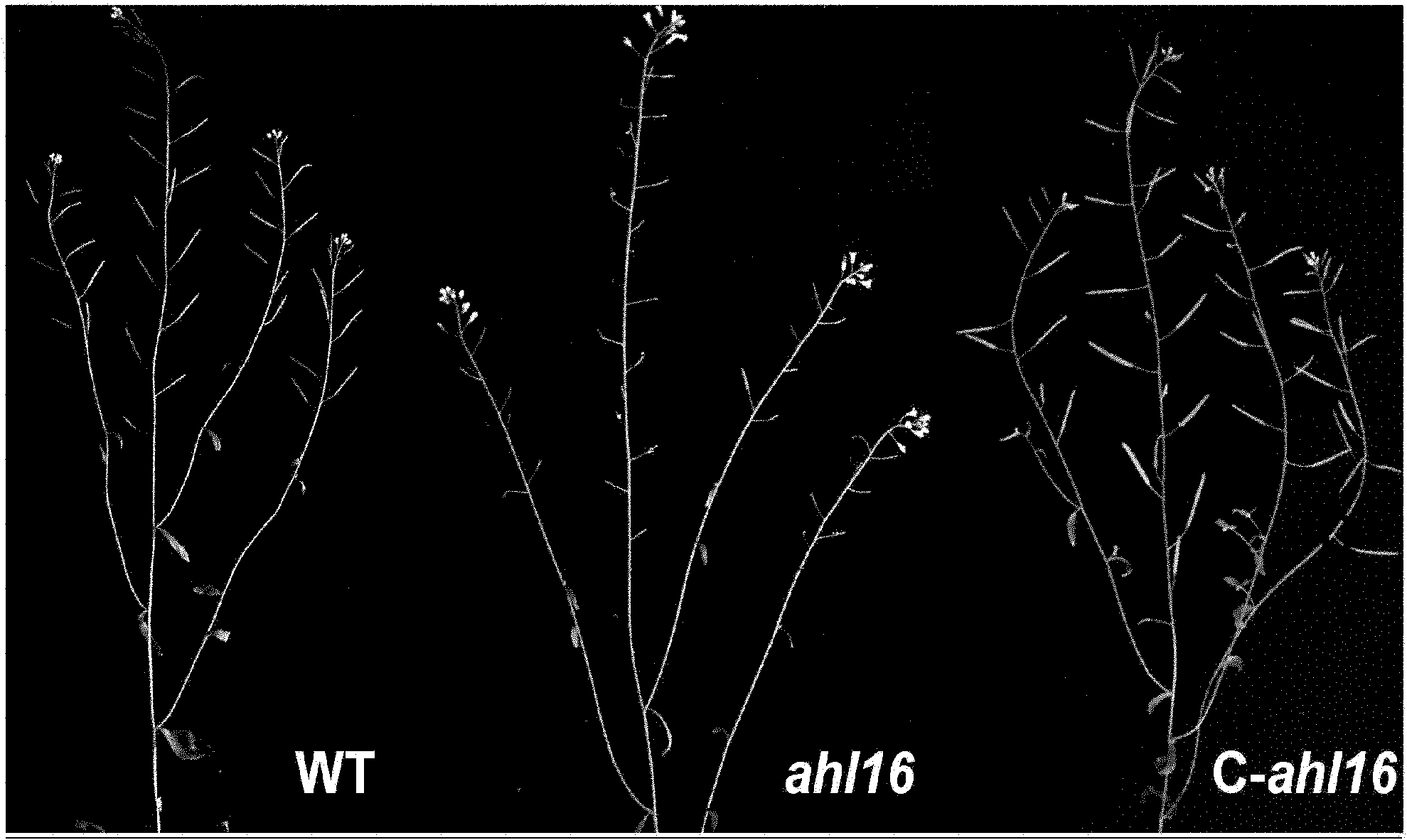
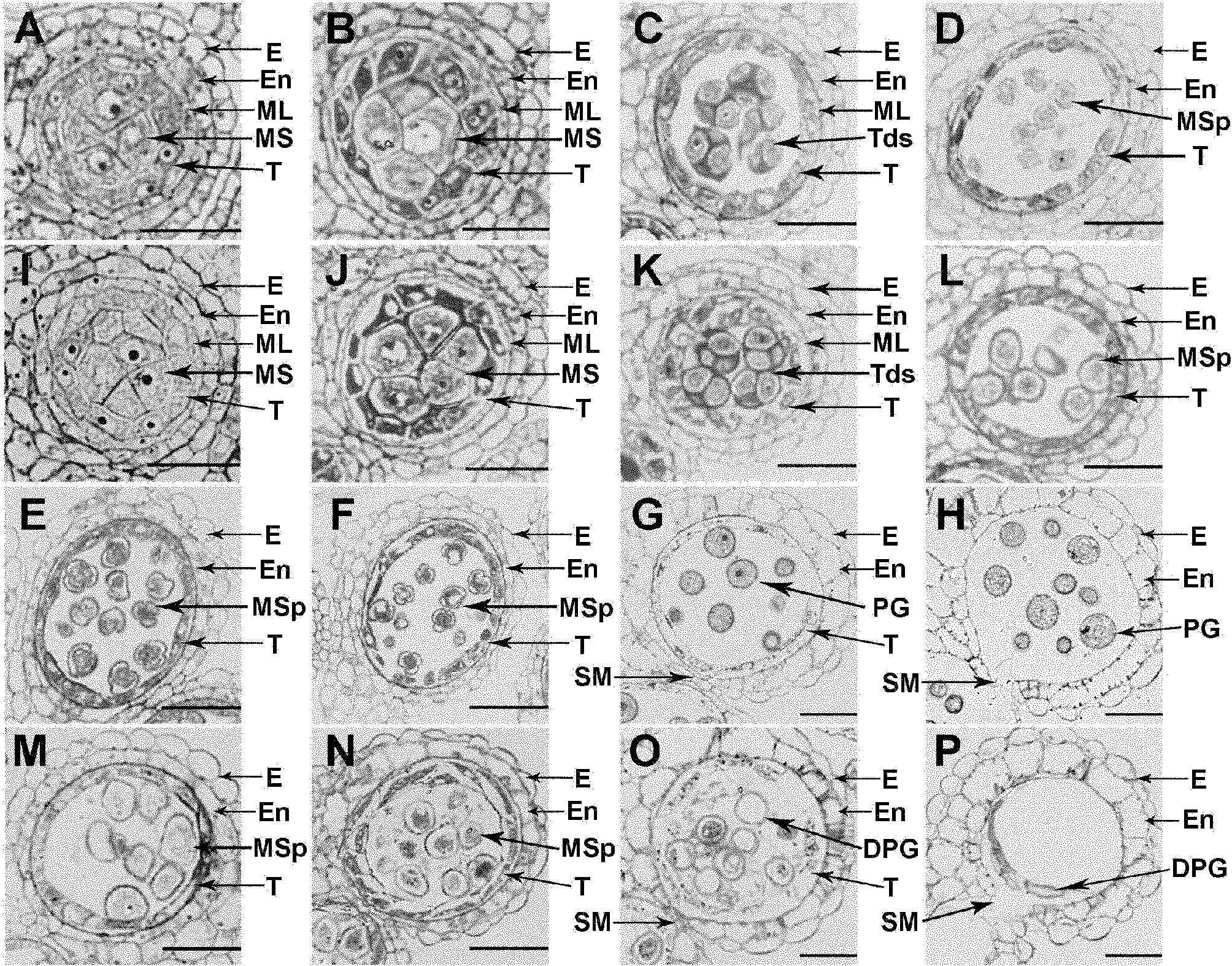
The invention relates to an anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. An Arabidopsis thaliana male sterile mutant ahl16 is screened out from T-DNA-inserted mutant population, a gene AHL16 controlling the fertility of Arabidopsis thaliana is cloned and identified, the nucleotide sequence of the gene AHL16 is represented by SEQ ID N0.1, and genetic complement experiments prove that the AHL16 gene in a wild type can restore the male sterile phenotype. Amino acid sequence analysis and subcellular localization experiments indicate that the AHL16 gene codes proteins of an AT-hookmotif nuclear localized protein family and is located in the nucleus. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the mutation of the gene leads to complete male sterility. The gene has a very important application value in aspects of explanation of influences of the growth of the inner layers of the outer walls of microspores and the structures of the inner walls on the fertility of plants and improvement on yield by hybrid seed production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of soybean MYB transcription factor gene in improvement of soybean isoflavone biosynthesis
InactiveCN106047889AIncreased isoflavone contentTo promote metabolismFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceEmbryo
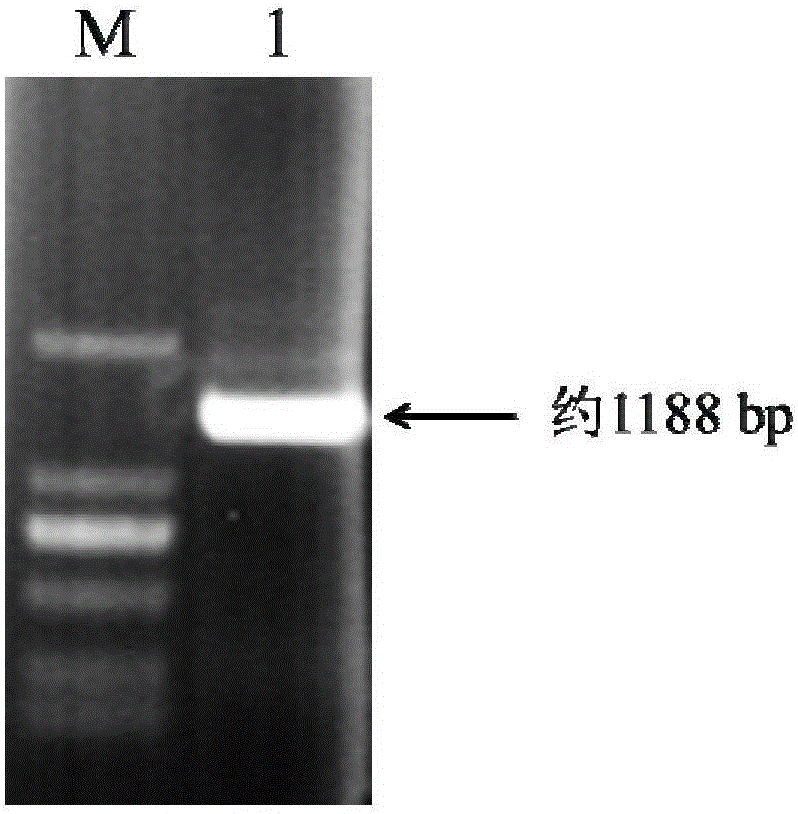
The invention relates to an application of a soybean MYB transcription factor gene in improvement of soybean isoflavone biosynthesis and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The GmMYB9 gene is 1188bp and encodes 395 amino acids; a yeast one-hybrid experiment result indicates that GmMYB9 has transcriptional activation activity, and a subcellular localization result proves that GmMYB9 is located in a cell nucleus; a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (polymerase chain reaction) result shows that expression tendency of GmMYB9 in a soybean development process from immature embryos to mature seeds is consistent with accumulation tendency of isoflavone, and the expression quantity of GmMYB9 in a variety with high isoflavone content is higher than that of GmMYB9 in a variety with low isoflavone content; the isoflavone content of seeds and leaves of T2-generation transgenic soybeans with the transformed GmMYB9 gene is increased, therefore, the GmMYB9 gene participates in regulation of the soybean isoflavone biosynthesis and has great significance in cultivation of the soybean varieties with high isoflavone content.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com