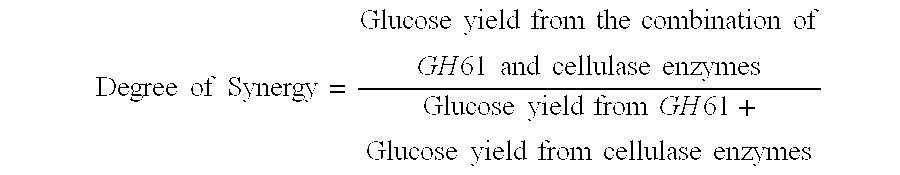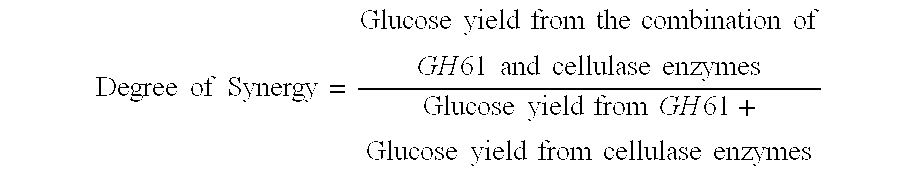Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Α glucosidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
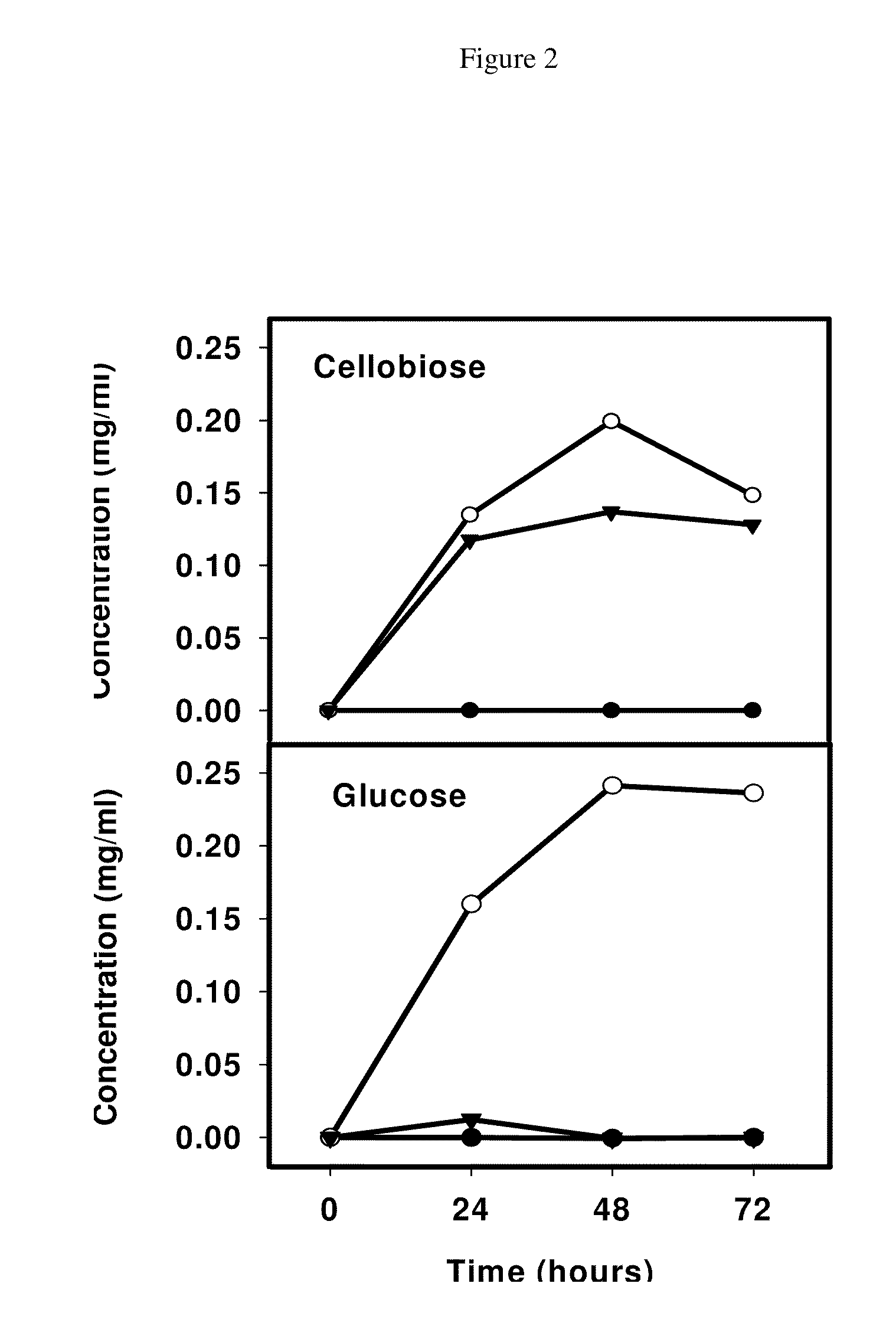
Procedure for the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass using a new heat-tolerant yeast
InactiveUS20050069998A1Low conversion rateReduce yieldFungiBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationSolid fraction
It includes the stages of grinding the lignocellulosic biomass to a size of 15-30 mm, subjecting the product obtained to steam explosion pre-treatment at a temperature of 190-230° C. for between 1 and 10 minutes in a reactor (2), collecting the pre-treated material in a cyclone (3) and separating the liquid and solid fractions by filtration in a filter press (9), introducing the solid fraction in a fermentation deposit (10), adding a cellulase at a concentration of 15 UFP per gram of cellulose and 12.6 International Units of β-glucosidase enzyme dissolved in citrate buffer pH 4.8, inoculating the fermentation deposit (10) with a culture of the heat-tolerant bacteria Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875, obtained by chemical mutagenesis from strain DER-26 of Kluyveromyces marxianus and shaking the mixture for 72 hours at 42° C.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACIONES ENERGETICAS MEDIO AMBIENTALLES Y TECNOLOGICAS (C I E M A T)
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
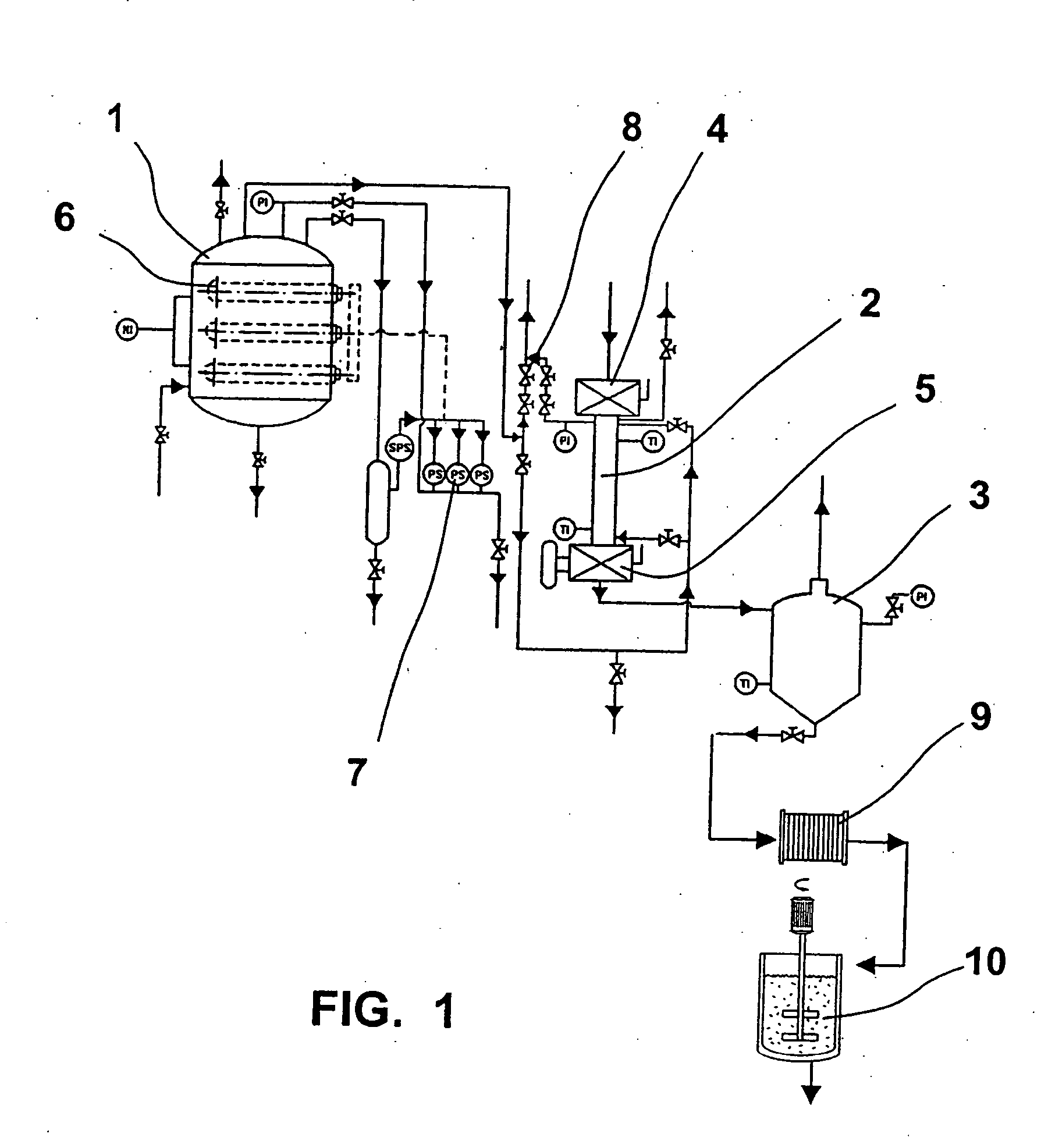
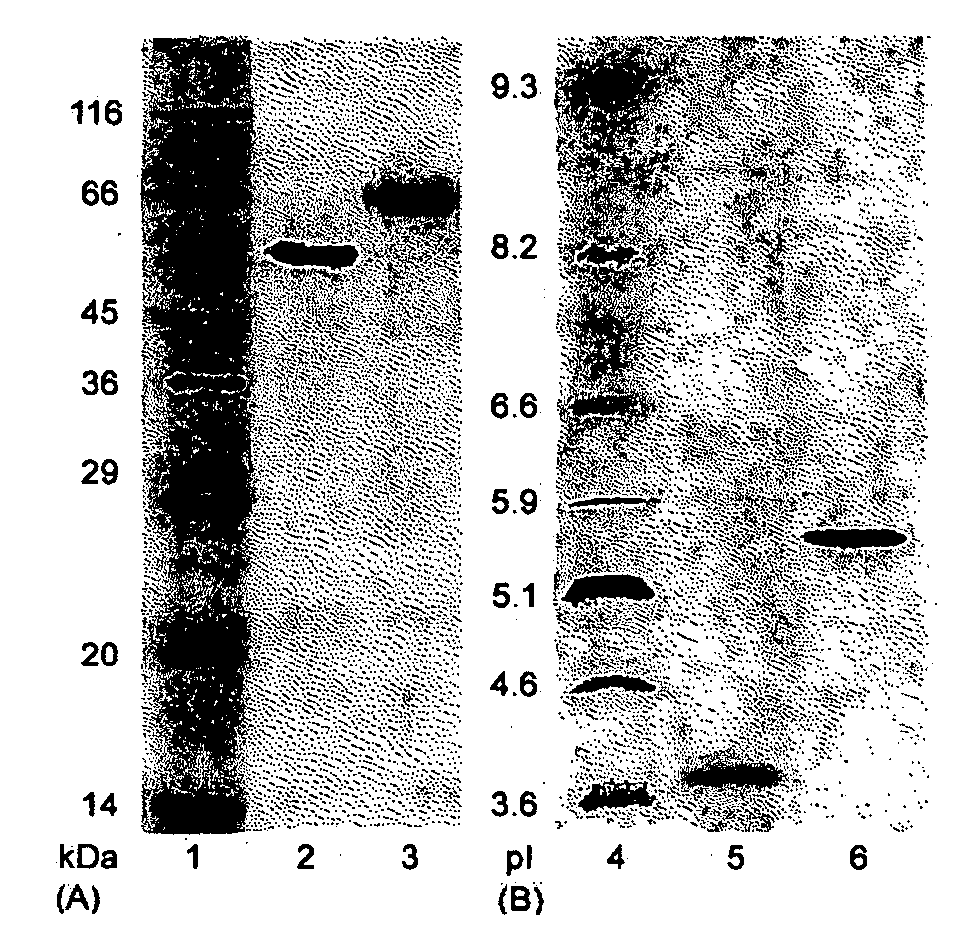
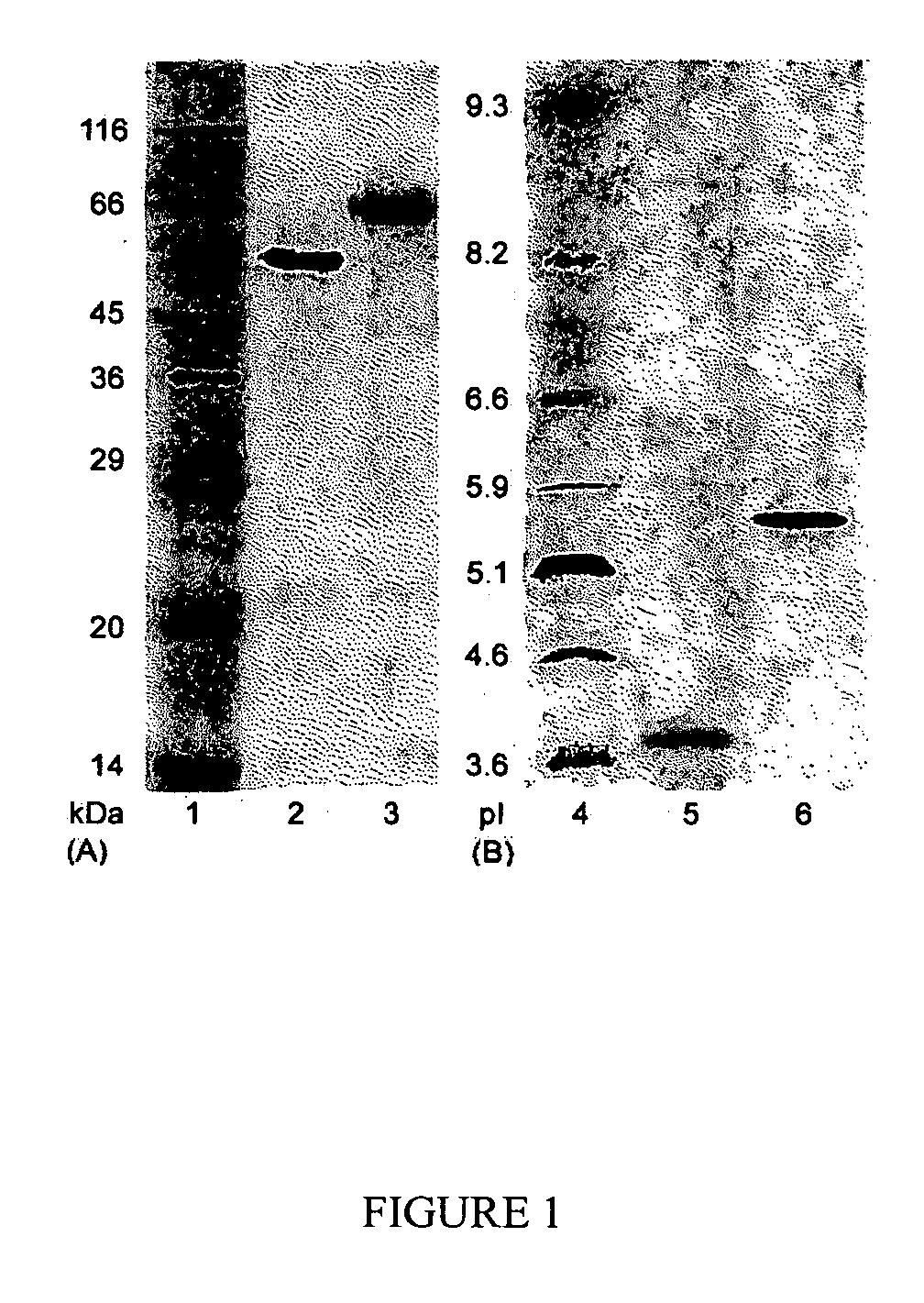
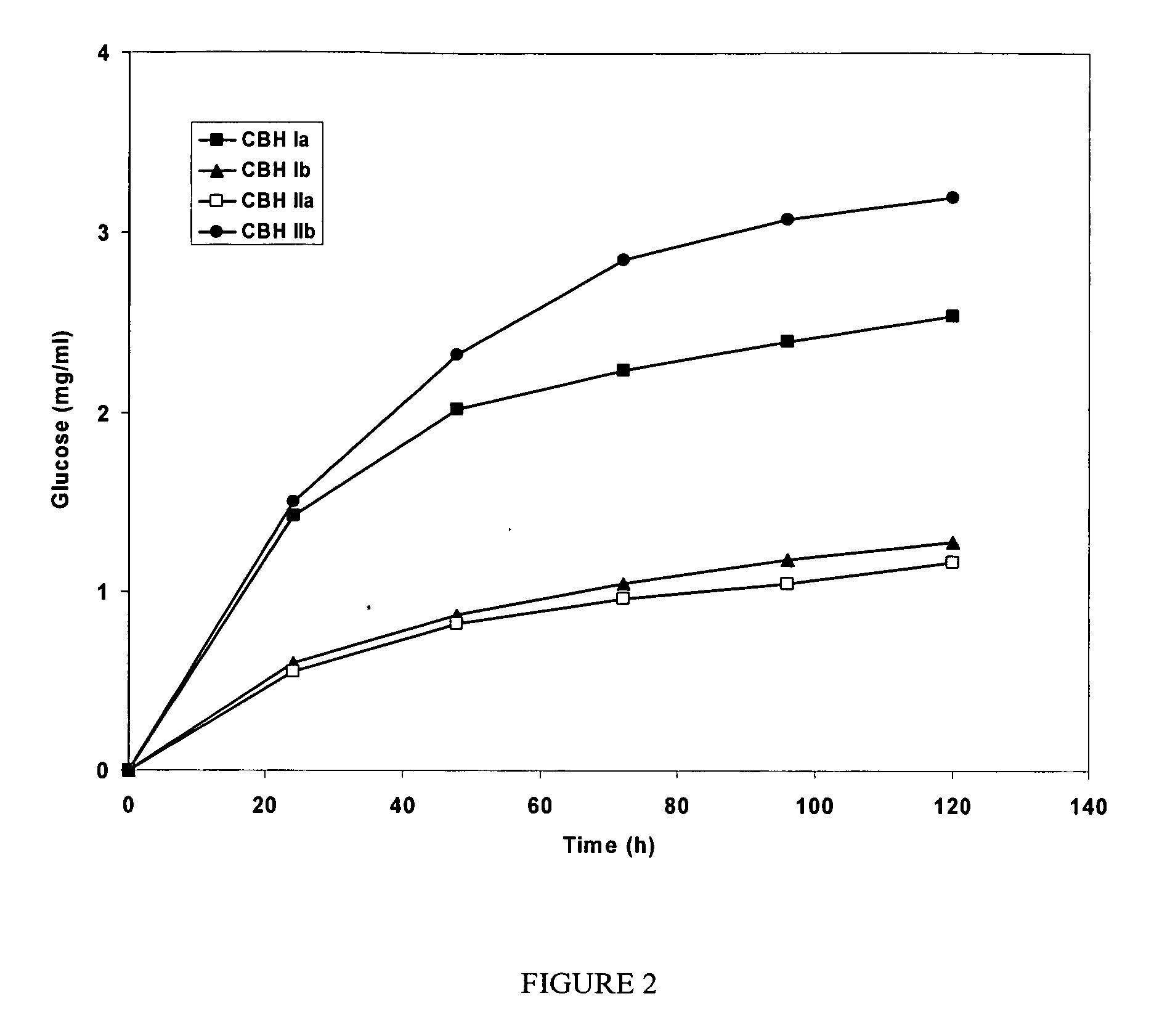
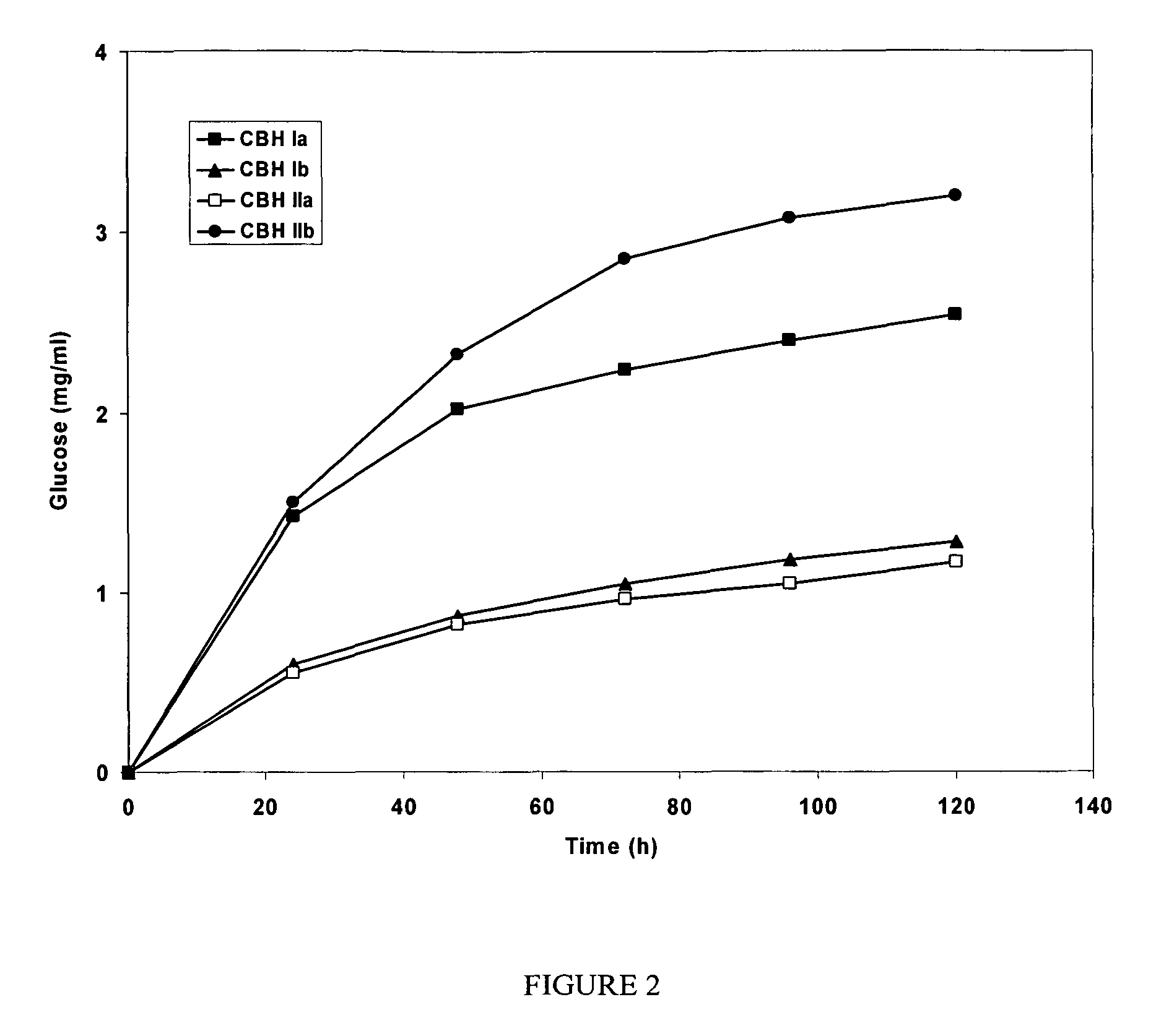
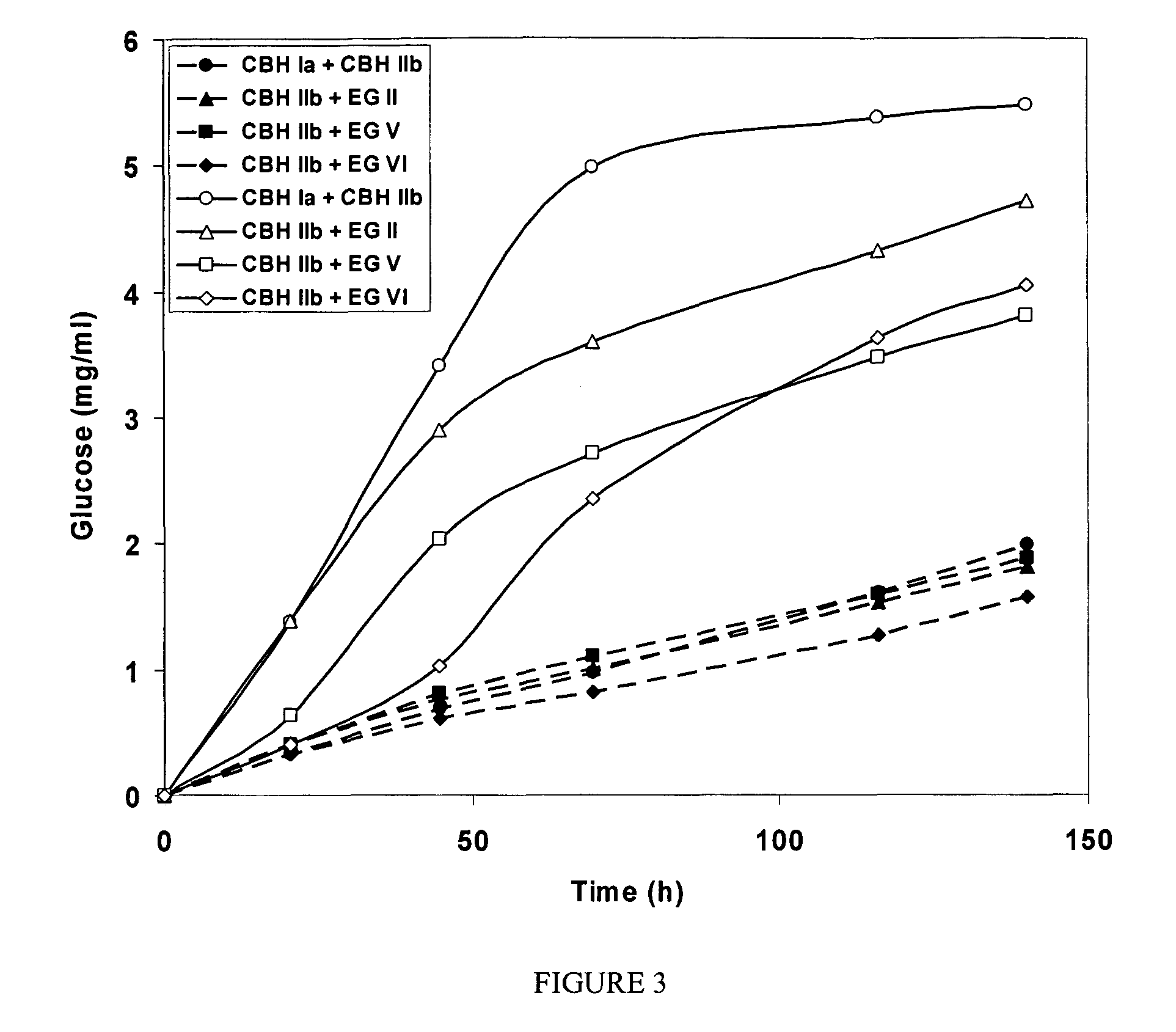
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Enzyme compositions for the improved enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and methods of using same
InactiveUS20090209009A1Extended reaction timeReduce probabilityBiofuelsChemical recyclingFiberEnzymatic hydrolysis
A process for the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose to produce a hydrolysis product comprising glucose from a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock and enzymes for use in the process are provided. The process comprises hydrolyzing an aqueous slurry of a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock with cellulase enzymes, one or more than one β-glucosidase enzyme and a binding agent for binding the β-glucosidase enzyme to fiber solids present in the aqueous slurry. During the hydrolysis, both the cellulase enzyme and β-glucosidase enzyme bind to the fiber solids. The hydrolysis is performed in a solids-retaining hydrolysis reactor so that unhydrolyzed fiber solids and bound enzyme are retained in the reactor longer than the aqueous phase of the slurry.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Construction of highly efficient cellulase compositions for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose
InactiveUS7883872B2High activityPronounced synergismBryophytesSugar derivativesCellulose bindingEnzymatic hydrolysis
This invention provides novel enzyme compositions using newly identified and isolated C. lucknowense enzymes, including CBH Ib CBH IIb, EG II, EG VI, β-glucosidase, and xylanase II in conjunction with previously identified enzymes CBH Ia, CBH IIa (previously described as Endo 43), and EG V. These enzyme compositions demonstrate an extremely high ability to convert lignocellulosic biomass (e.g., Avicel, cotton, Douglas fir wood pretreated by organosolv) to glucose. CBH Ia and IIb, which both have a cellulose-binding module (CBM) displayed a pronounced synergism with three major endoglucanases (EG II, EG V, EG VI) from the same fungus in hydrolysis of cotton as well as a strong synergy with each other. The enzyme compositions are effective in hydrolysis of the lignocellulosic biomass.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Plant extract, compositions containing same, method of extraction and uses thereof
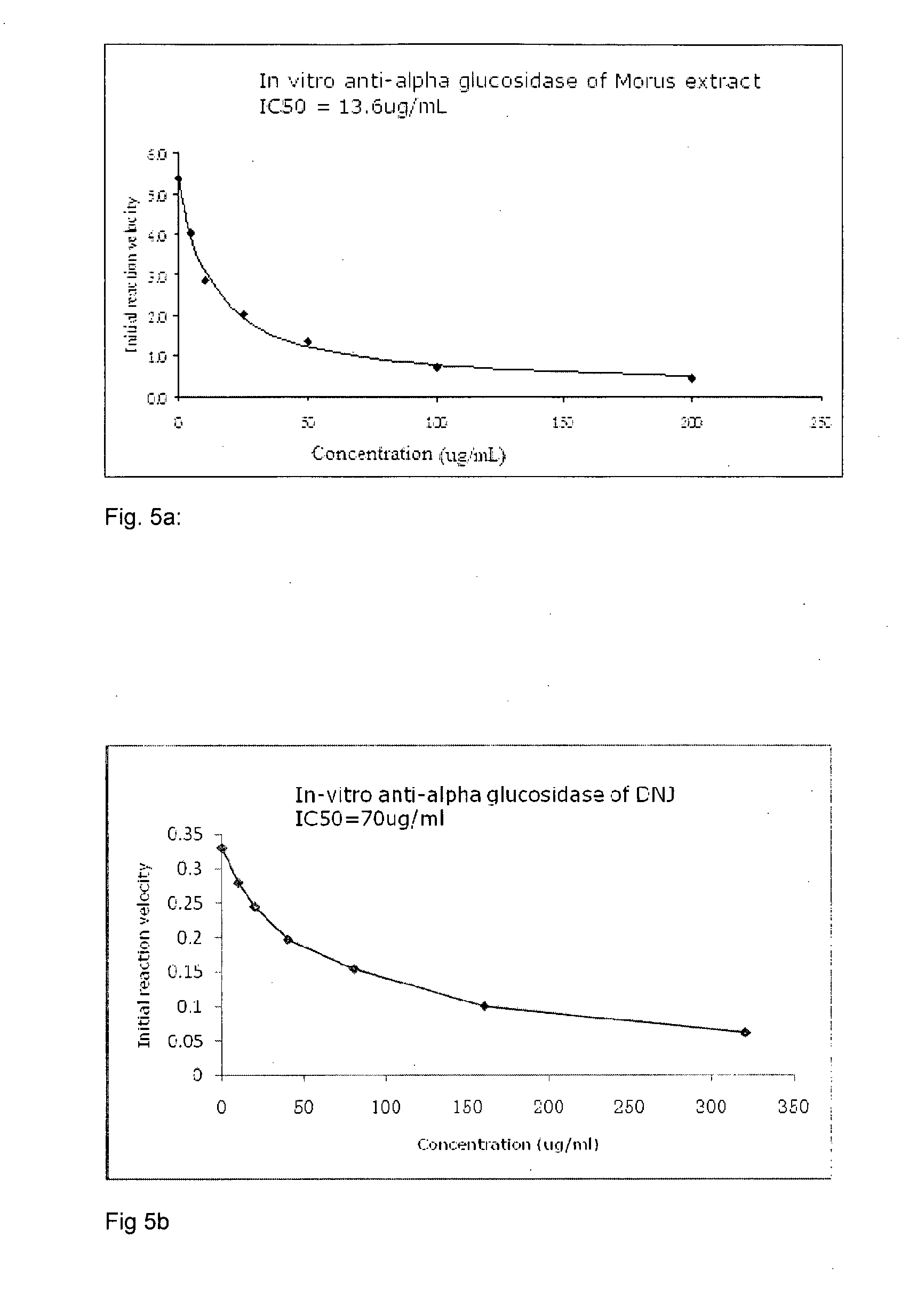
An extract from leaves of mulberry is disclosed. The extract has an IC50 value sufficient to inhibit α-glucosidase I. The extract may comprise 5-40% (w / w) total imino sugars and 20-70% (w / w) total amino acids. The extract may reduce the production of melanin for the treatment of such ailments or diseases caused by pigmentation as freckle, chloasma, striae gravidarum, sensile plaque and melanoma. The extract may also control blood glucose level.
Owner:BOTANIC CENTURY BEIJING
Modified barley α-glucosidase
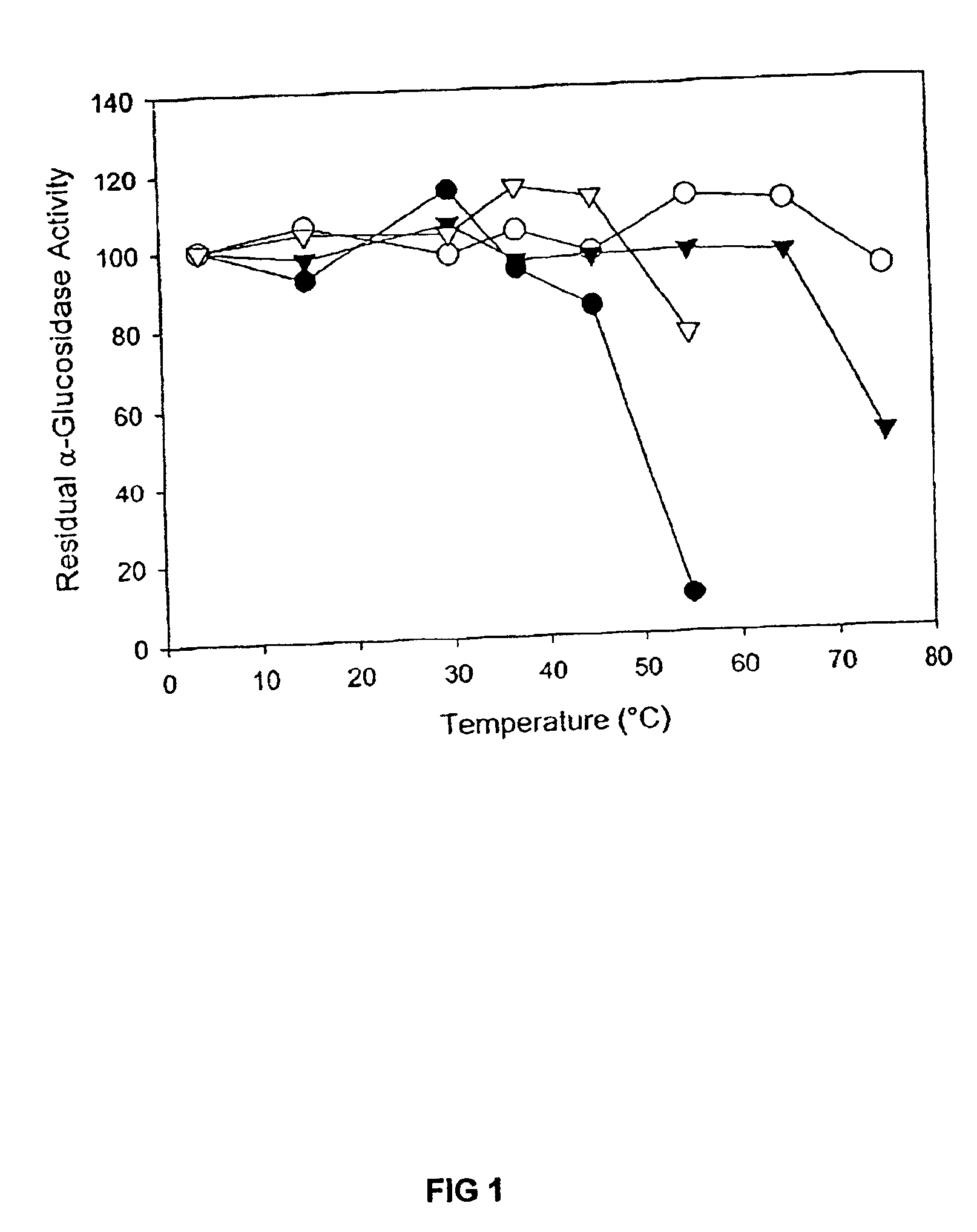
Barley α-glucosidase is an important enzyme in the conversion of barley starch to fermentable sugars during the industrial production of ethanol, as in brewing and fuel ethanol production. The enzyme is, however, relatively thermolabile, a disadvantage for an enzyme useful in industrial processes which are preferably conducted at elevated temperatures. Site directed mutagenesis has been conducted to make mutant forms of barley α-glucosidase which have improved thermostability. The sites for this site-directed mutagenesis were selected by sequence comparisons with the sequences of other α-glucosidase proteins which are more thermostable. The recombinant mutant enzymes thus produced have been demonstrated to improve the thermostability of the enzyme.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
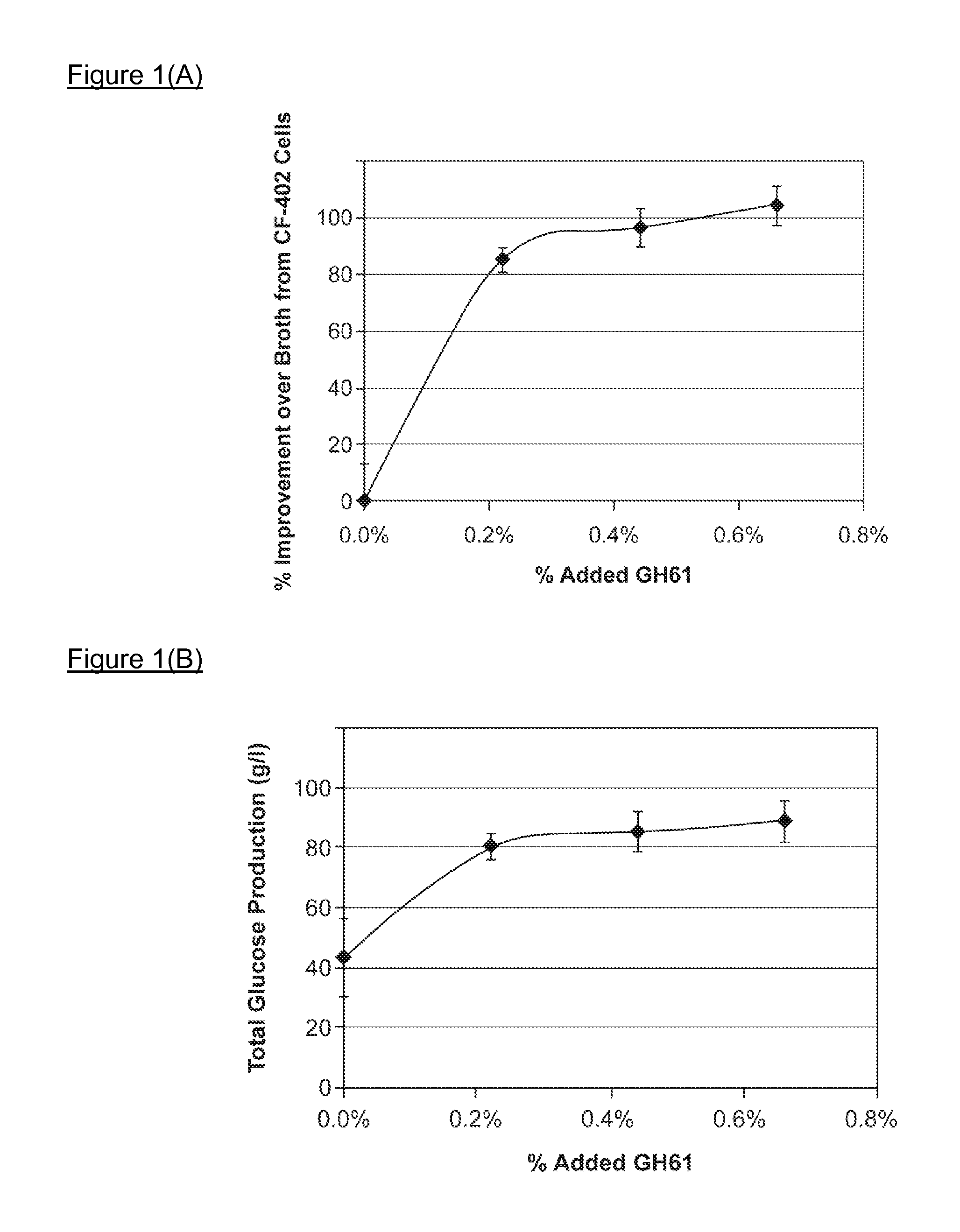
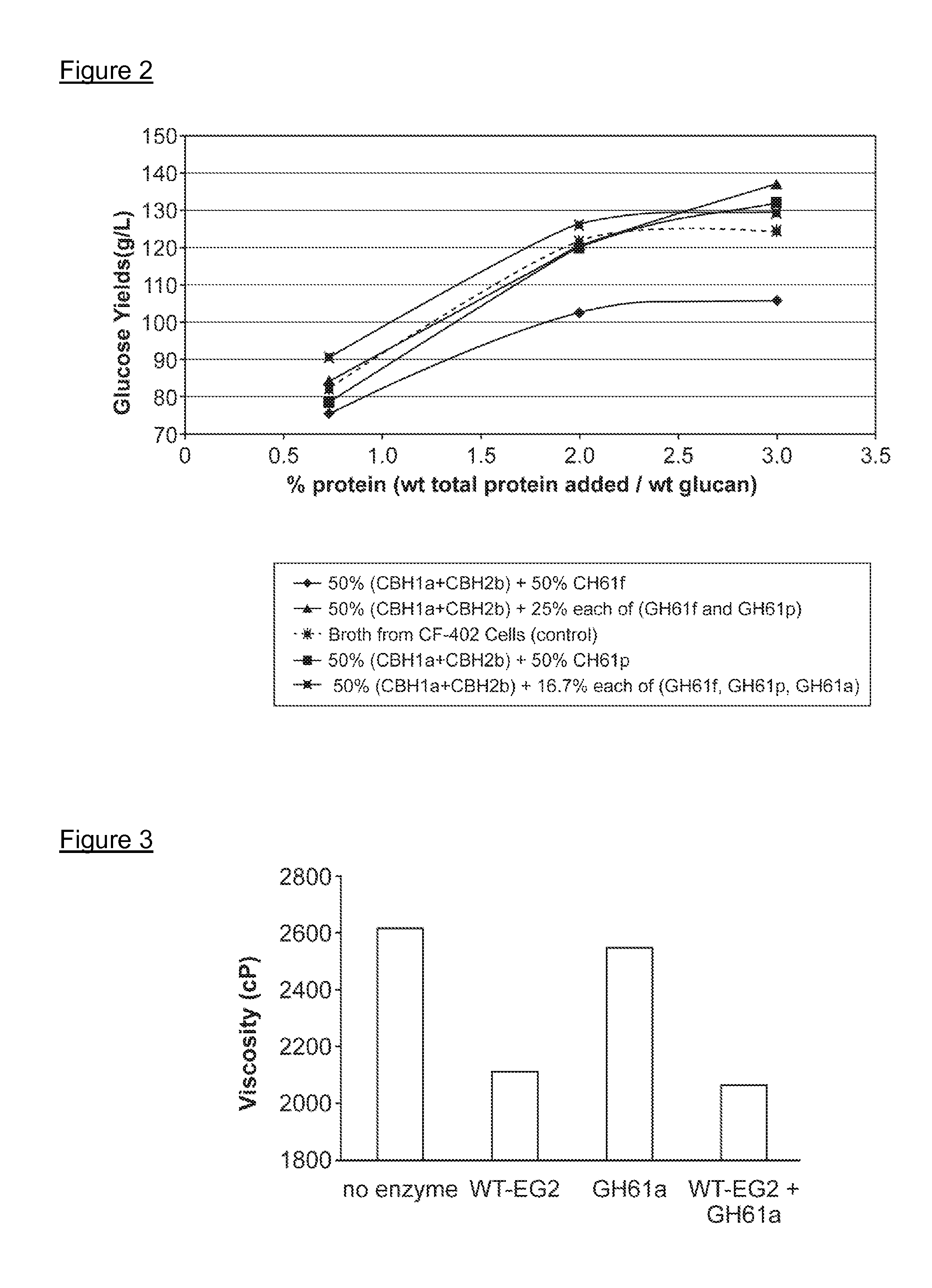
Use of Glycoside Hydrolase 61 Family Proteins in Processing of Cellulose
ActiveUS20120083019A1Increase productionImprove production yieldBiofuelsPeptide preparation methodsFermentable sugarCellulase
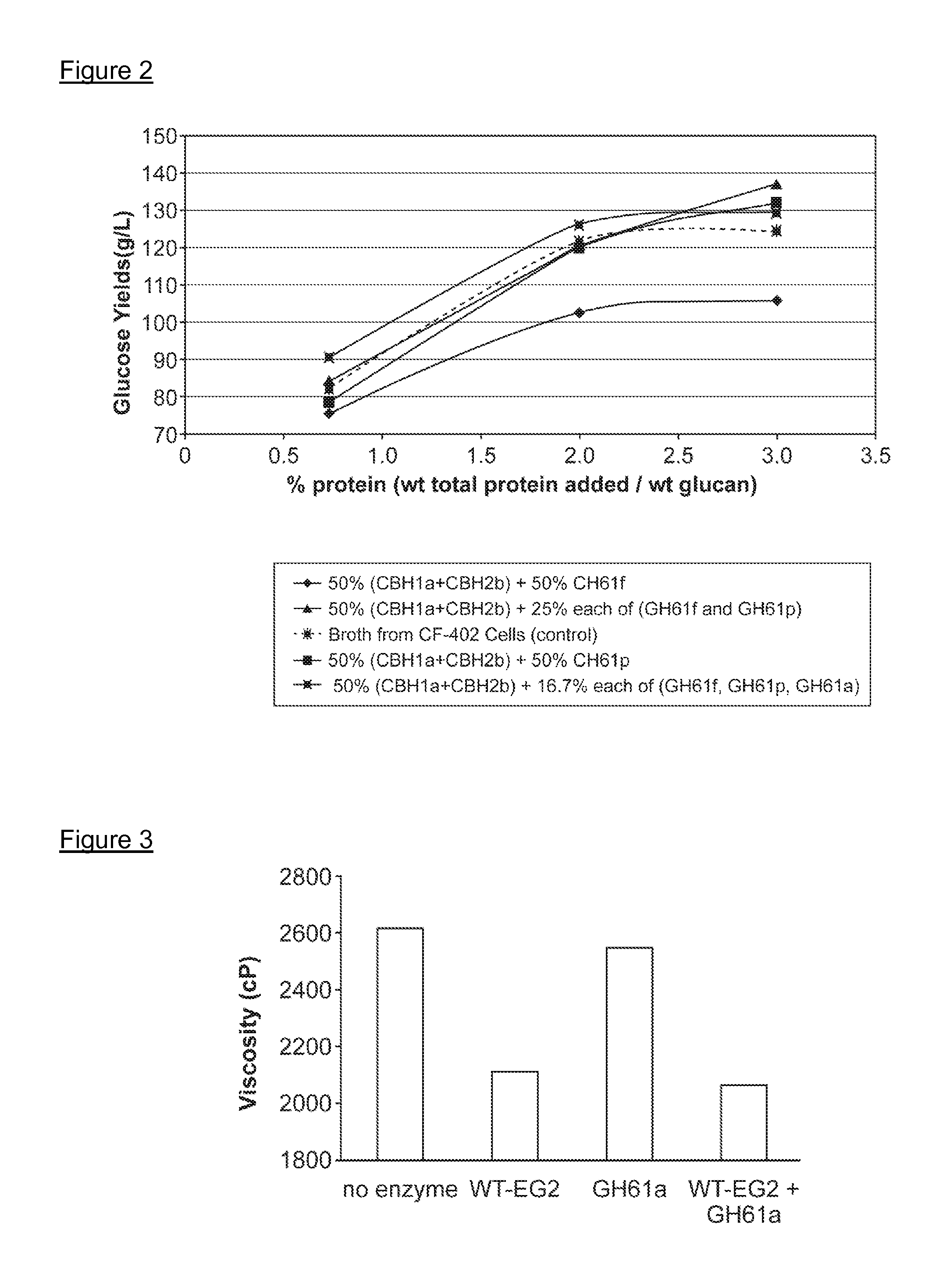
The invention provides recombinant GH61 proteins obtained from Myceliophtora thermophila, and nucleic acids that encode such proteins. The invention also provides protein fractions isolated from M. thermophila supernatant that have GH61 protein activity. These preparations can be used to increase yield of products from reactions in which a cellulose-containing substrate undergoes saccharification by one or more cellulase enzymes, such as endoglucanase, β-glucosidase, or cellobiohydrolase. Combinations of GH61 protein and cellulases can be used to break down cellulosic biomass into fermentable sugars in the production of ethanol.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
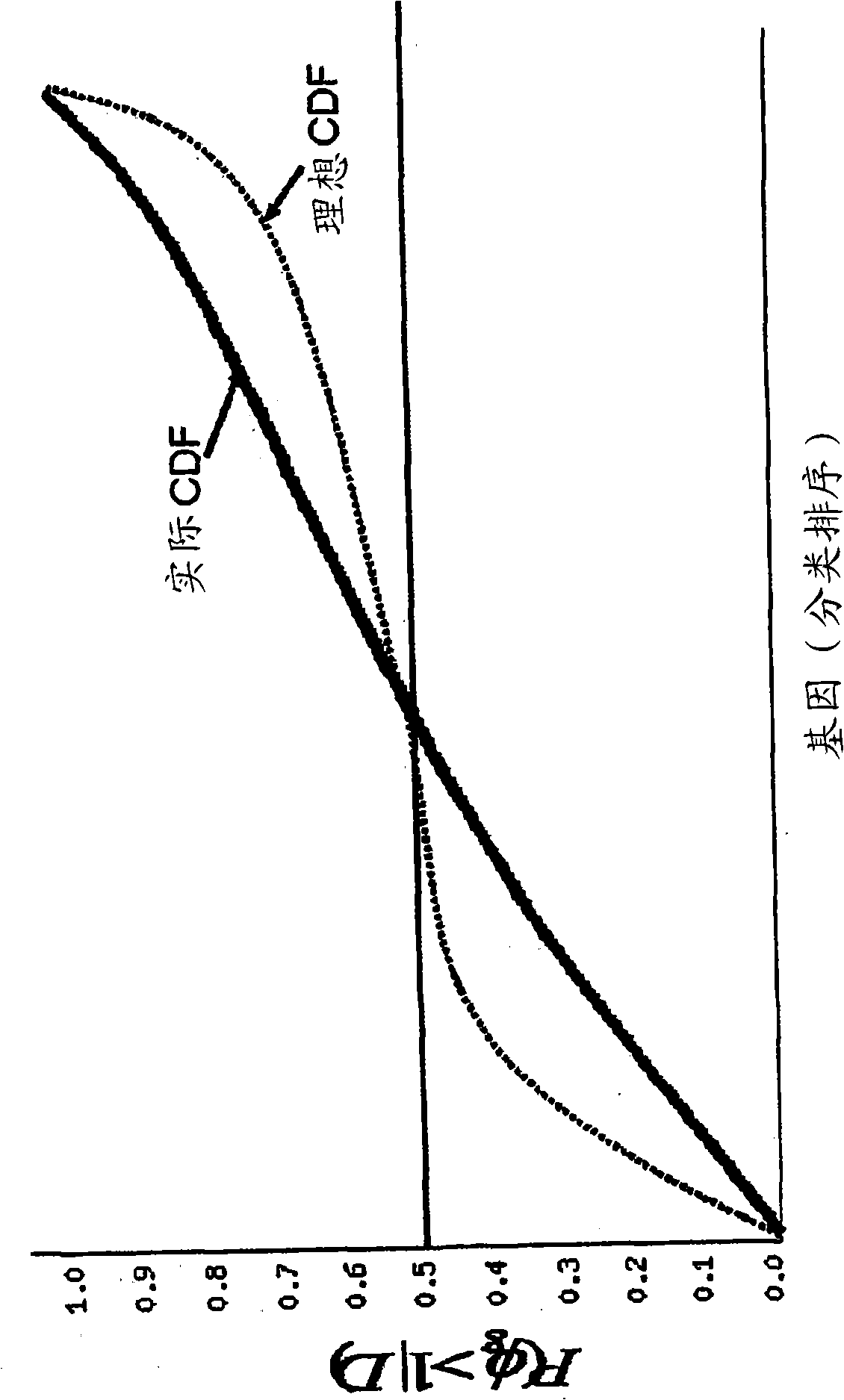
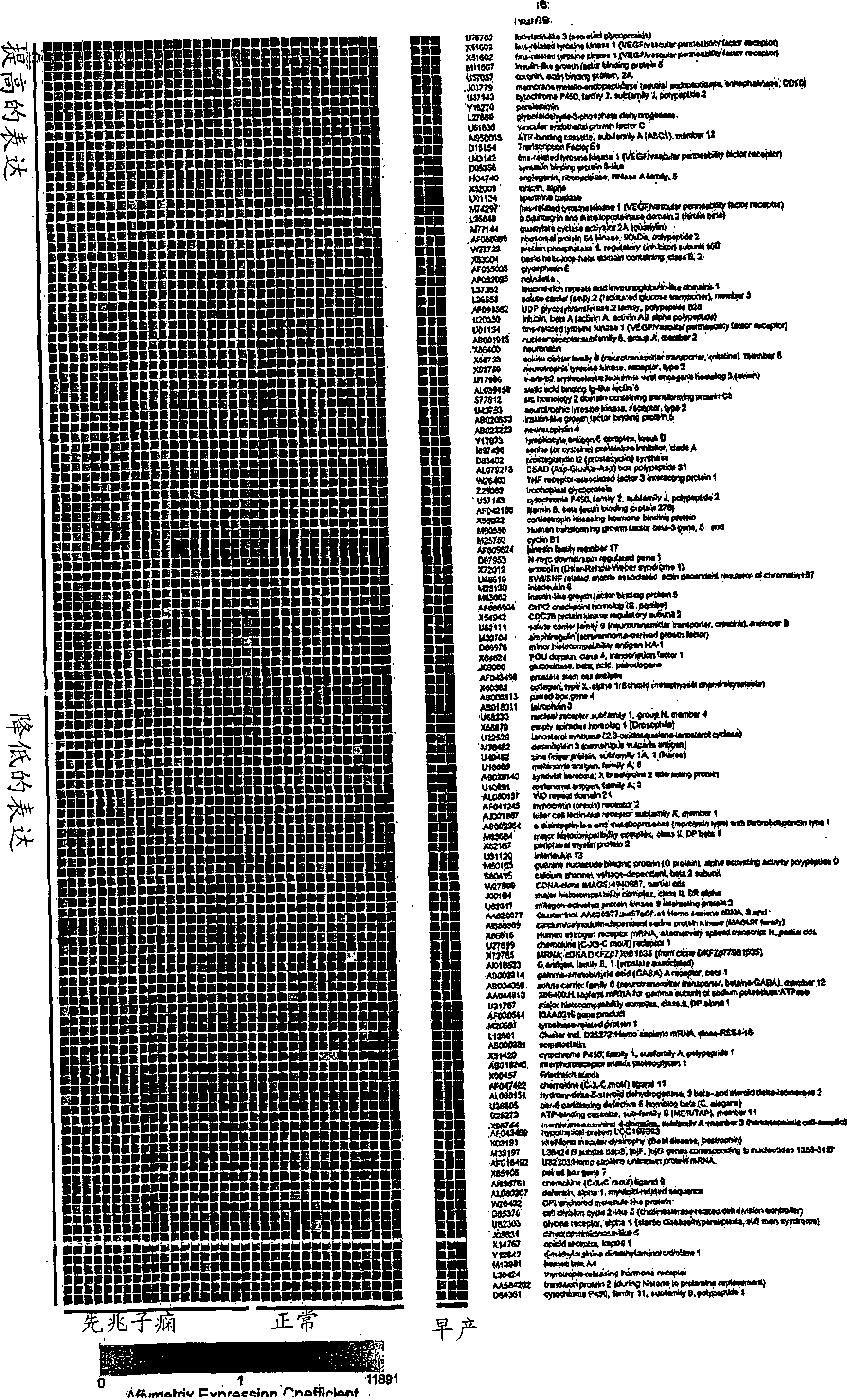
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
ActiveUS20060166277A1Diagnosing and effectively treatingSave maternalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPregnancyUdp glycosyltransferase
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1 anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
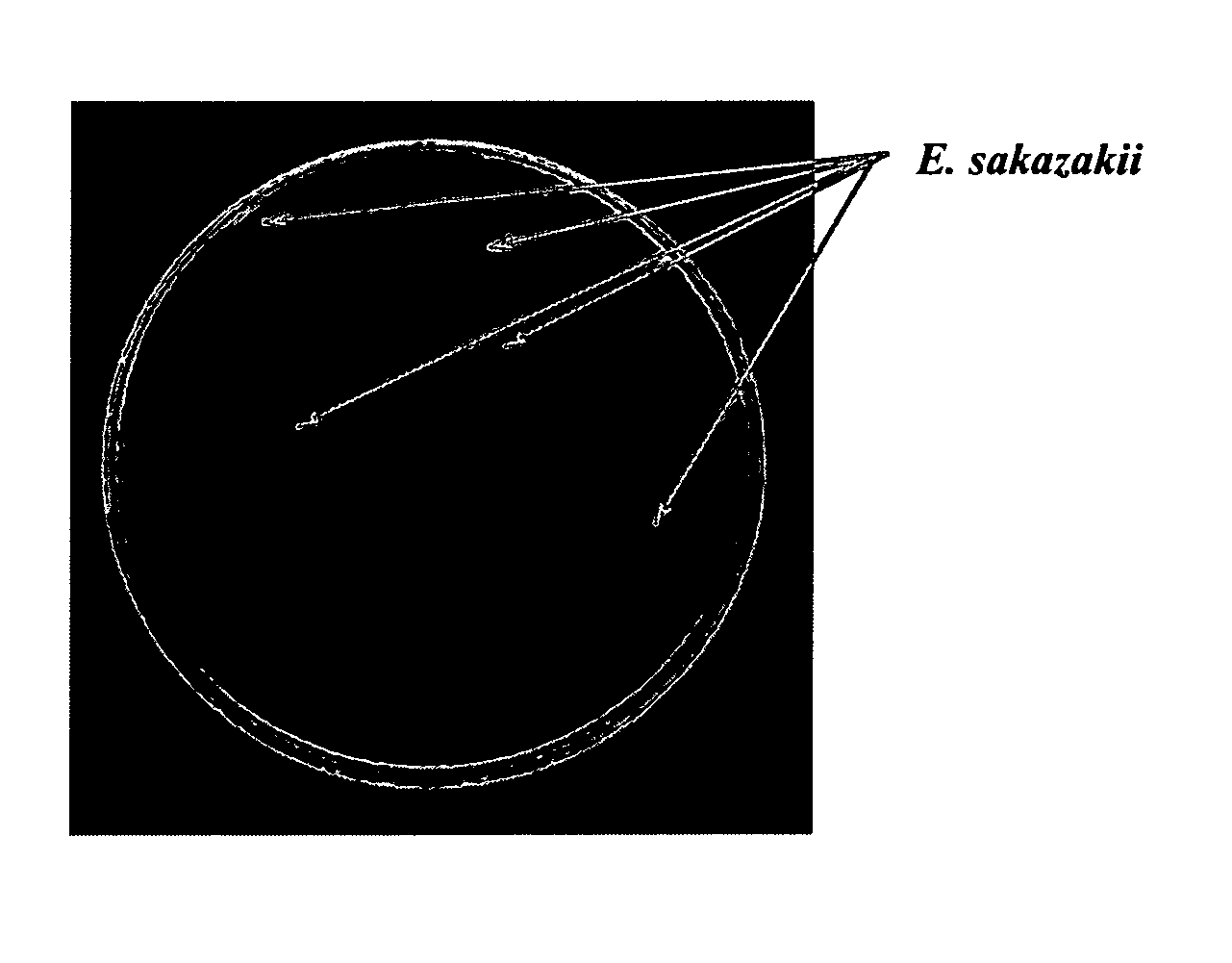
Fluorogenic selective and differential medium for isolation of Enterobacter sakazakii
Particular aspects provide novel compositions and methods useful for the growth, isolation and detection of microorganisms that have α-glucosidase activity (e.g., the bacterium E. sakazakii). Certain embodiments provide a novel growth and / or plating media, comprising a fluorogenic α-glucosidase substrate, which is both selective for and differential to E. sakazakii. In particular embodiments, the α-glucosidase substrate comprises 4-methylumbelliferyl-α-D-glucoside. Additional embodiments relate to a selection media. Further embodiments relate to a selective medium that is based on Tryptone Bile agar. Still further embodiments relate to OK media as defined herein. Other embodiments of the invention relate to methods for growing bacterial cultures on media that is selective for and differential to microorganisms that have α-glucosidase activity (e.g., the bacterium E. sakazakii).
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
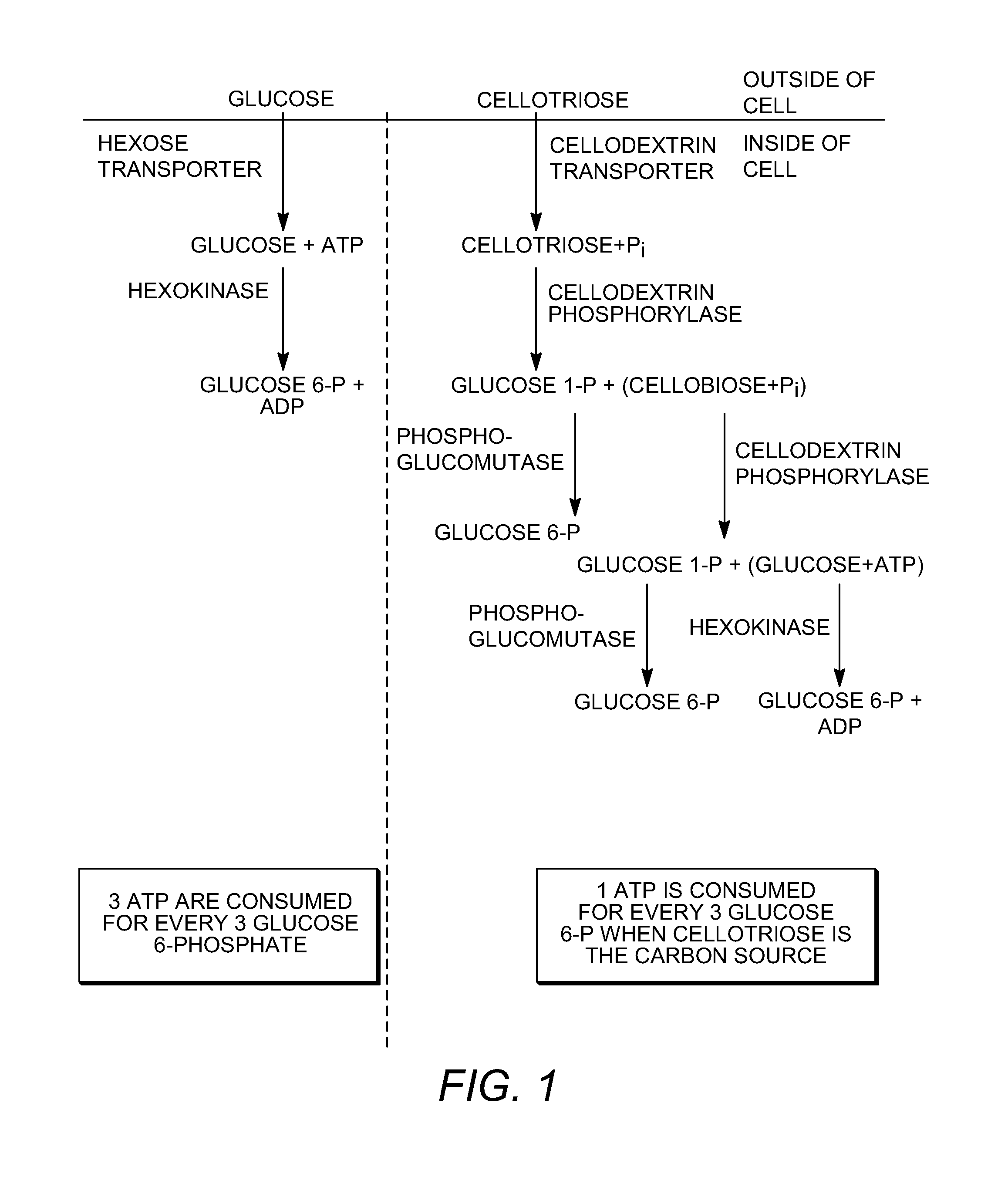
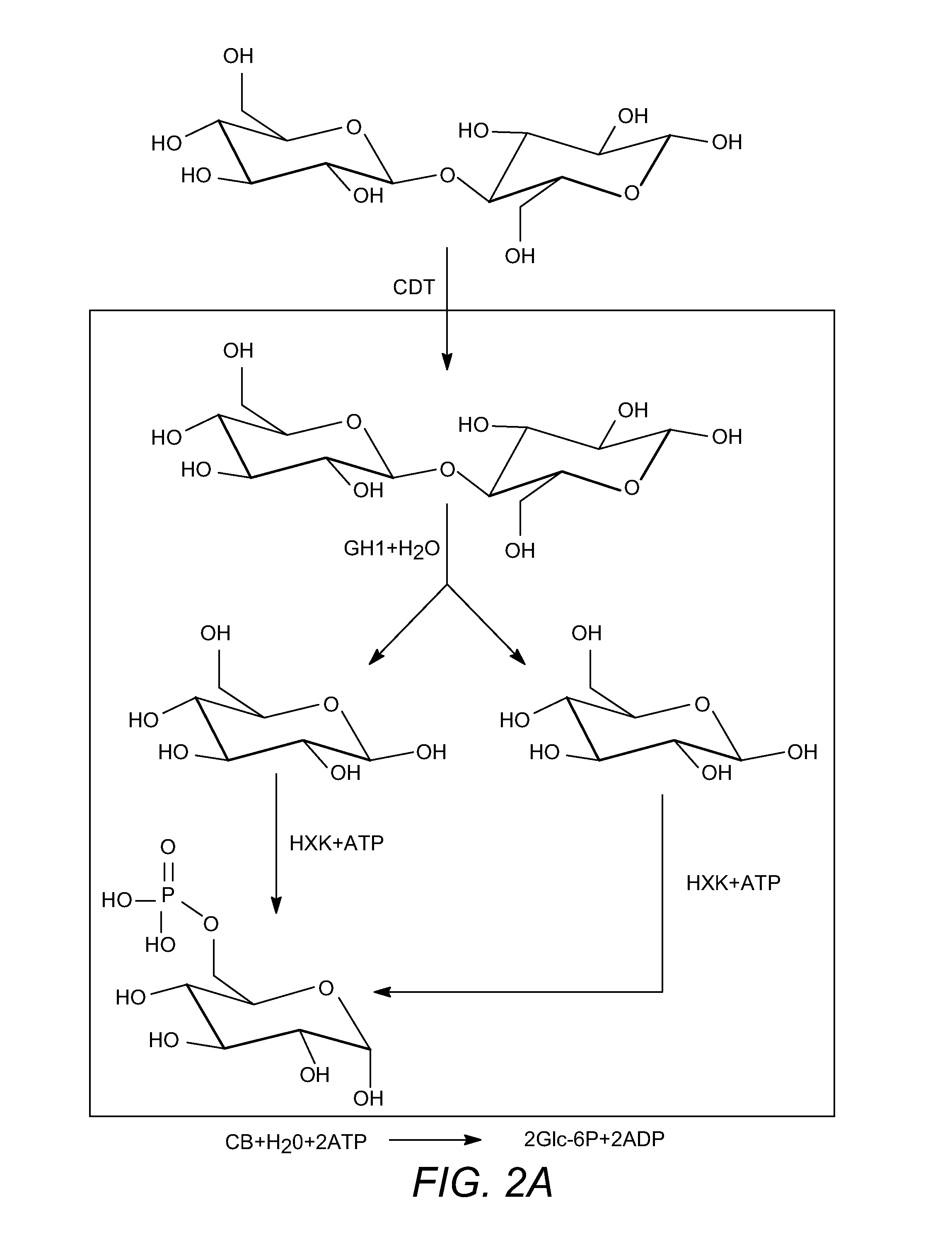
Enhanced cellodextrin metabolism
InactiveUS20140057323A1Reduce consumptionLess overall consumptionMicroorganismsBiofuelsGlucose utilizationHexokinase
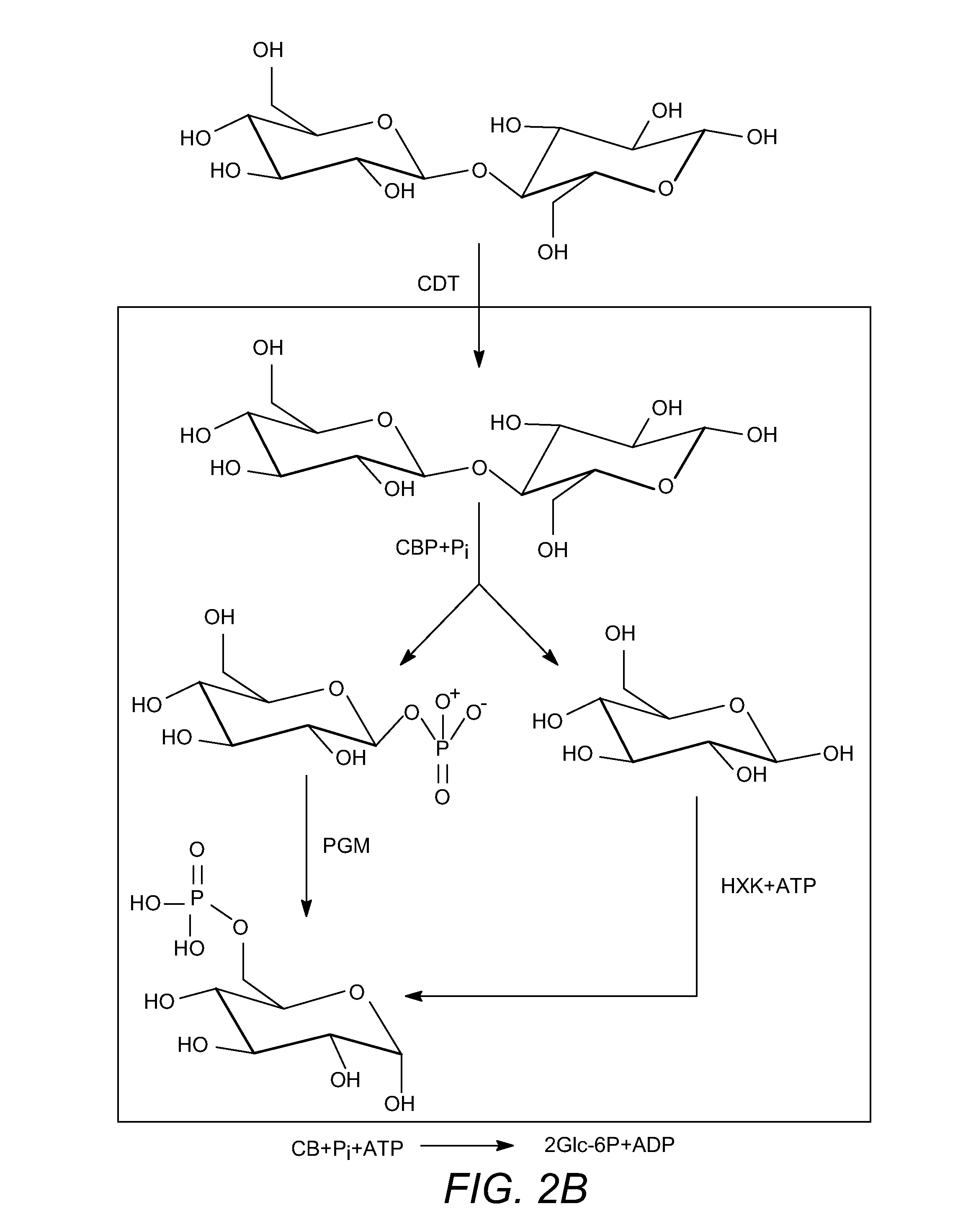
The present disclosure relates to host cells containing two or more of a recombinant cellodextrin transporter, a recombinant cellodextrin phosphorylase, a recombinant β-glucosidase, a recombinant phosphoglucomutase, or a recombinant hexokinase; and to methods of using such cells for degrading cellodextrin, for producing hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon derivatives from cellodextrin, and for reducing ATP consumption during glucose utilization.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Transgenic monocot plants encoding beta-glucosidase and xylanase
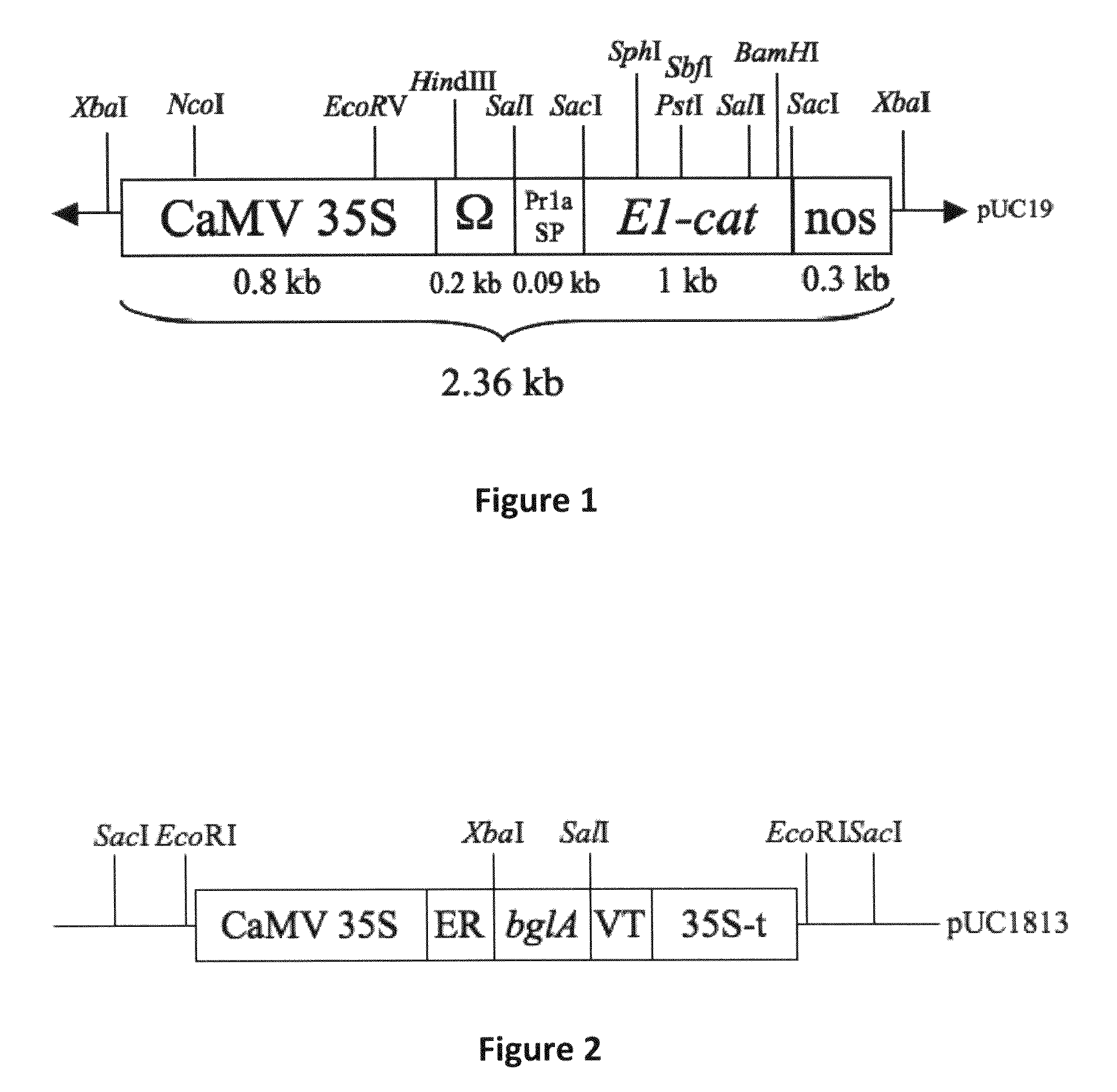
Plant proteins isolated from monocot plants from transformation of the monocot plant with DNA at least 80% homologous to the bglA gene encoding β-glucosidase from a rumen bacterium which is Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c and targeted to a subcellular compartment. The transformed plant is ground after the β-glucosidase has been accumulated, and the protein is extracted or used directly with the ground plant material to degrade cellobiose, in particular, to produce sugars used in fermentations, particularly to produce ethanol. Also, a gene at least 80% homologous to DNA XYL1 gene encoding a xylanase is also provided in a transformed plant and used to produce sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Fenugreek seed having reduced bitter taste and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100055241A1Poor appearanceReduce bitternessCocoaFood preparationAlgluceraseBeta-glucosidase
It is an object of the present invention to obtain fenugreek seeds having reduced bitter taste without causing significant changes in non-bitter components contained in fenugreek seeds.The present invention relates to a method for producing fenugreek seeds having reduced bitter taste, comprising allowing β-glucosidase to act on an eluate in which the components of fenugreek seeds have been eluted and then allowing the fenugreek seeds to absorb the eluate and β-glucosidase, and a food containing such fenugreek seeds.
Owner:HOUSE FOOD IND CO LTD
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Recombinant Yeast Strains Expressing Tethered Cellulase Enzymes
InactiveUS20100075363A1High binding affinityReduction in supernatant optical densityFungiSugar derivativesYeastBiotechnology
Recombinant yeast strains that saccharify, ferment and grow on insoluble and crystalline forms of cellulose are disclosed herein. The yeast strains express tethered cellulases including cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase and β-glucosidase. The recombinant organisms are particularly suited for consolidated bioprocessing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Process for recovering aroma from tea
Disclosed is a process for recovering volatile aroma compounds from a tea material. The process comprises the steps of: incubating the tea material in an aqueous medium; subjecting the incubated tea material to evaporation to obtain aroma-laden vapours; and condensing the aroma-laden vapours to recover an aroma condensate comprising volatile aroma compounds. The tea material is subjected to a step of extraction of soluble solids prior to step (a) and the aqueous medium in step (a) comprises an enzyme selected from cellulase, pectinase, β-glucosidase, primeverosidase or a mixture thereof.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER +1
Cloning, expression and application of a β-glucosidase gene
ActiveCN102268421AImprove securityThe follow-up processing process is convenientFungiMicroorganism based processesBeta-glucosidaseHigh activity
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a beta-glucosaccharase which can decompose lactose and has high activity under both high-temperature and low-temperature conditions, and a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently expressing secretion-type beta-glucosaccharase. The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase having an amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2, and constructs a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently secreting the beta-glucosaccharase. The gene engineering bacterium is collected in Common Microorganism Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the collection number is CGMCC No.4891. The beta-glucosaccharase produced by the method disclosed by the invention has high activity of galactosidase, and can be applied to dairy industry; and meanwhile, the beta-glucosaccharase has stable activity within wide pH value range and temperature range.
Owner:山西恩泽生物技术有限公司
Recombinant thermoascus aurantiacus beta-glucosidase variants for production of fermentable sugars from cellulosic biomass
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the expression of recombinant β-glucosidase variants, as well as their use in the production of fermentable sugars from cellulosic biomass.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Nutritional and safe soy milk making method of soy milk maker
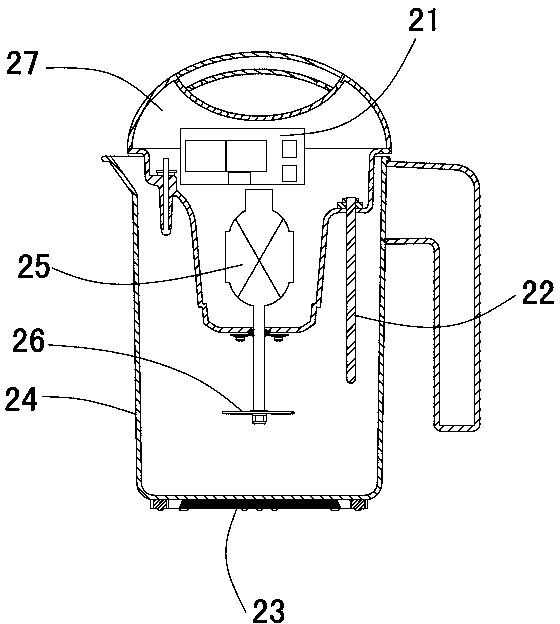
ActiveCN103719286AAdequate hydrolysis timeRelease fullyMilk substitutesFood scienceNutritive valuesAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a nutritional and safe soy milk making method of a soy milk maker, and aims at the problems that for a traditional view, water for soaking soybeans is not suitable for soy milk preparation, and dissolving-out condition of a functional component during soy milk making is almost ignored in the prior art. A main functional component soy isoflavone in soybeans plays an important role in the aspects of prevention and treatment for breast cancer and prostate cancer, improvement of climacteric syndrome and osteoporosis, protection for a cardiovascular system and the like. In order to change the misconception and obtain higher-content and high-activity isoflavone soybean milk to improve nutritive values of the soy milk, the soybeans are heated, sterilized and soaked for a long time before soy milk making, after the soybeans are soaked with the method, malignant bacteria in water can be effectively killed, and water for soaking the soybeans can be used for soy milk making; and besides, the activity of beta glucosaccharase in the soybeans can be maintained, glucosidic isoflavone hard to be absorbed by a human body is hydrolyzed into aglycone isoflavone, so that isoflavone in the soybeans are sufficiently released, and a better healthcare effect can be provided for consumers.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
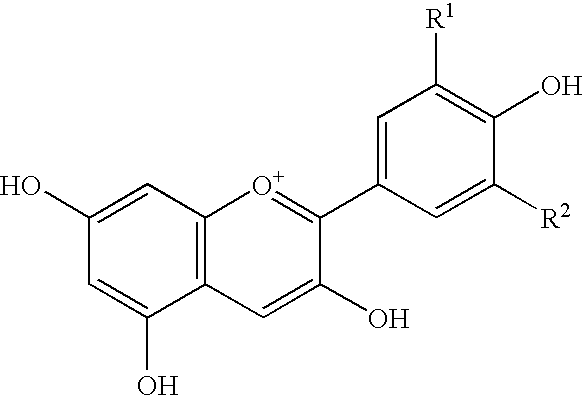
Process for producing purified anthocyanin and crystalline anthocyanin
Provided are a process for producing purified anthocyanidin glucoside in which a rhamnose end of anthocyanidin rutinoside is cleaved using rhamnosidase to convert the anthocyanidin rutinoside component into anthocyanidin glucoside, the anthocyanidin glucoside component being then purified and isolated; or a crystalline anthocyanidin glucoside salt obtained by further crystallizing the purified anthocyanidin glucoside and a process for producing the same.Also provided are a process for producing purified anthocyanidin rutinoside in which a glucose end of anthocyanidin glucoside is cleaved using β-glucosidase to degrade and remove the end, the anthocyanidin rutinoside component being then purified and isolated; or a crystalline anthocyanidin rutinoside salt obtained by further crystallizing the purified anthocyanidin rutinoside and a process for producing the same.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
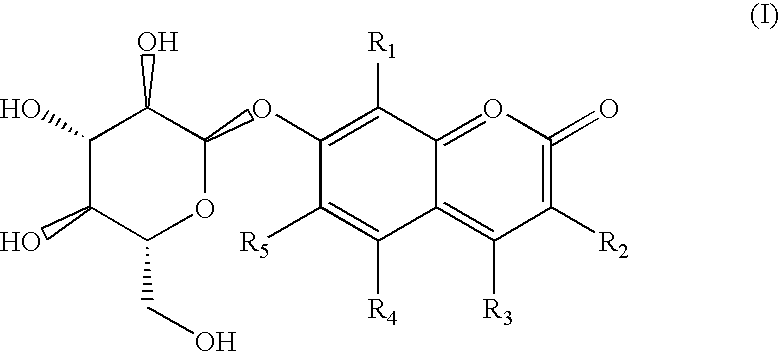
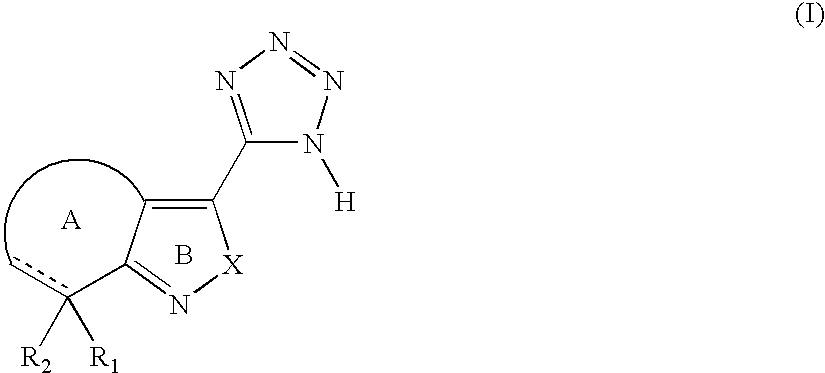
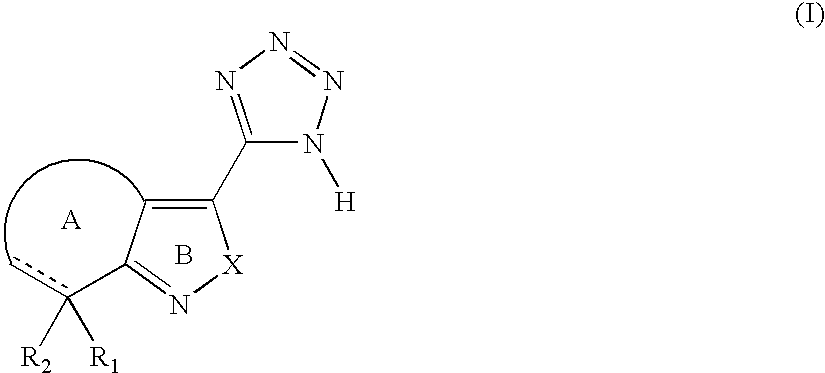
Tetrazole derivatives and methods of treatment of metabolic-related disorders thereof
The present invention relates to certain tetrazole derivatives of Formula (I), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, which exhibit useful pharmacological properties, for example, as agonists for the RUP25 receptor. Also provided by the present invention are pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the invention, and methods of using the compounds and compositions of the invention in the treatment of metabolic-related disorders, including dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, Syndrome-X and the like. In addition, the present invention also provides for the use of the compounds of the invention in combination with other active agents such as those belonging to the class of α-glucosidase inhibitors, aldose reductase inhibitors, biguanides, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, squalene synthesis inhibitors, fibrates, LDL catabolism enhancers, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, insulin secretion enhancers and the like.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA +1
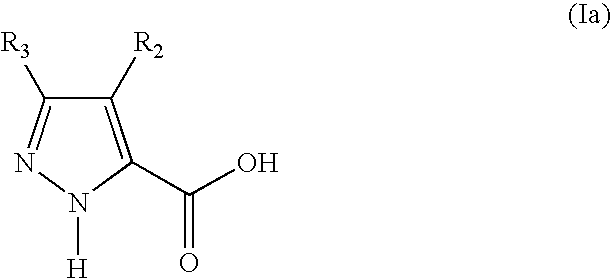
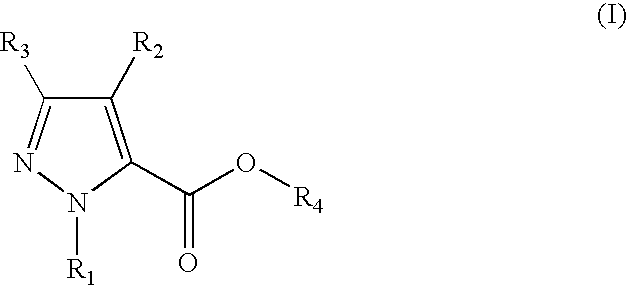
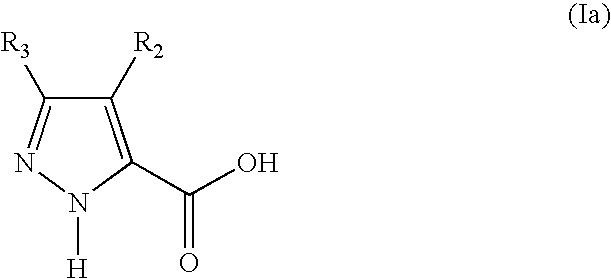
5-substituted 2h-pyrazone-3-carbixylic acid derivatives as antilipolytic agents for the treatment of metabolic-related disorders such as dyslipidemia
The present invention relates to certain pyrazole carboxylic acid derivatives of Formula (Ia), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as antilipolytic agents and against for the receptor RUP25, wherein: R2 is H, halogen, C1-12 alkyl or C1-12 haloalkyl; and R3 is C3-6 cycloalkyl, C1-12 alkyl, C1-12 haloalkyl, C3-6 cycloalkyl-C1-4-alkylene, aryl-C1-4-alkylene or heteroaryl-C1-4-alkylene, wherein said aryl-C1-4-alkylene and heteroaryl-C1-4-alkylene can be optionally substituted 1 to 5 substituents selected from the substituents listed in the claims. Also provided by the present invention are pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds of the invention, and methods of using the compounds and compositions of the invention in the treatment of metabolic-related disorders, including dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, Syndrome-X and the like. In addition, the present invention also provides for pharmaceutical compositions in combination with other active agents, for example, those agents belonging to the class of α-glucosidase inhibitors, aldose reductase inhibitors, biguanides, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, squalene synthesis inhibitors, fibrates, LDL catabolism enhancers, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, insulin secretion enhancers, thiazolidinedione and the like.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Nucleic acids and polypeptides useful for diagnosing and treating complications of pregnancy
InactiveCN101299962AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAlpha defensinInsulin-like growth factor-binding protein
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or treating pregnancy related hypertensive disorders that include the use of a polypeptide or a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide selected from the following: follistatin related protein, interleukin 8, inhibin A, VEGF-C, angiogenin, beta fertilin, hypothetical protein, leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor secreted protein, erythroid differentiation protein, adipogenesis inhibitory factor, corticotropin releasing factor binding protein, alpha-1- anti-chymotrypsin, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5, CD33L, cytokine receptor like factor 1, platelet derived endothelial growth factor, lysyl hydroxylase isoform 2, stanniocalcin precursor, secreted frizzled related protein, galectin-3, alpha defensin, ADAM-TS3, cholecystokinin precursor, interferon stimulated T-cell alpha chemoattractant precursor, azurocidin, sperminine oxidase, UDP glycosyltransferase 2 family polypeptide B28, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2, neutral endopeptidase, CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 2, beta glucosidase, lanosterol synthase, calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase, estrogen receptor-alternatively spliced transcript H, chemokine (CX3C motif) receptor 1, tyrosinase-related protein 1, hydoxy-delta-5-steroid dehyrogenase, dihydropyramidinase-like-4, and cytochrome P450-family 11.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
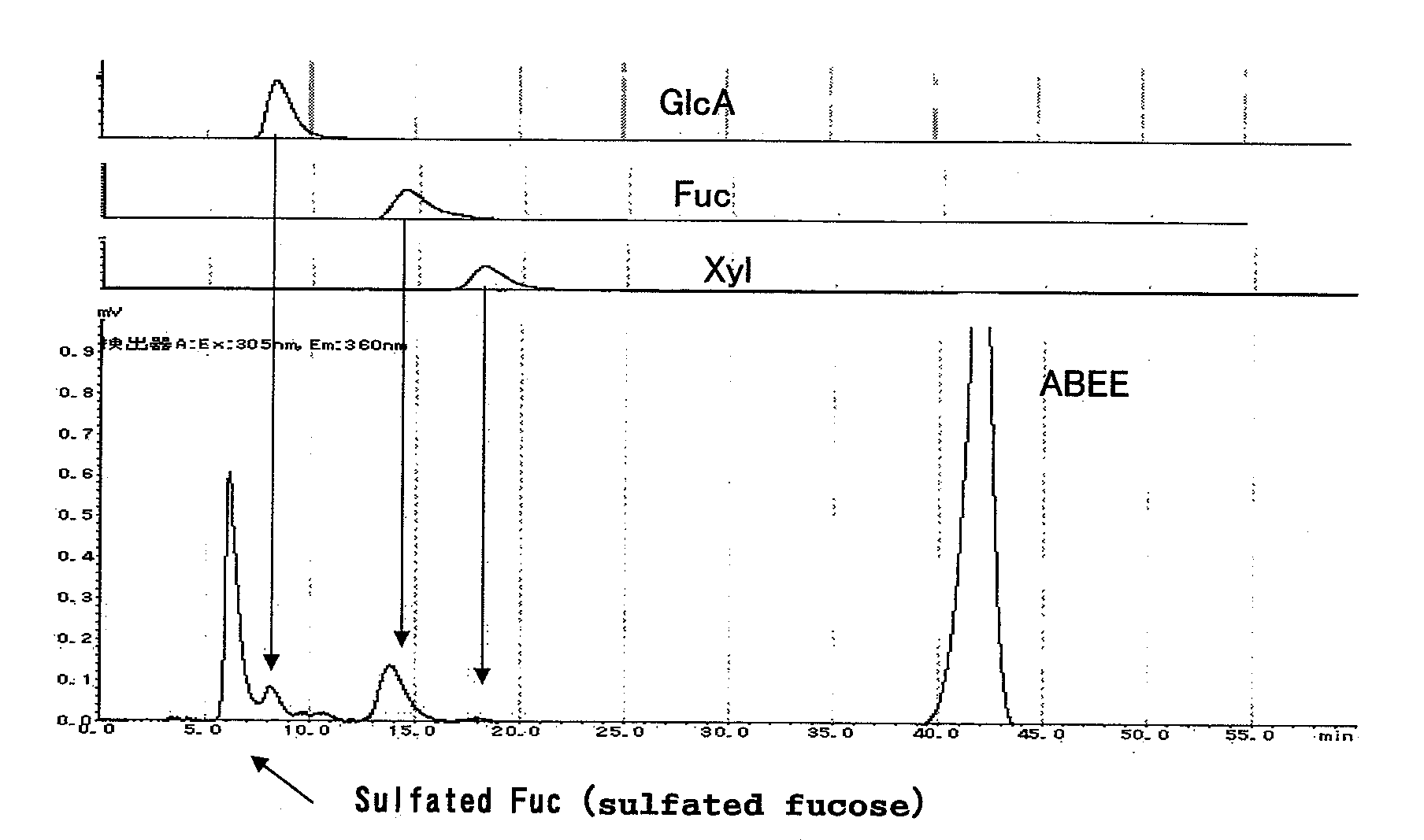
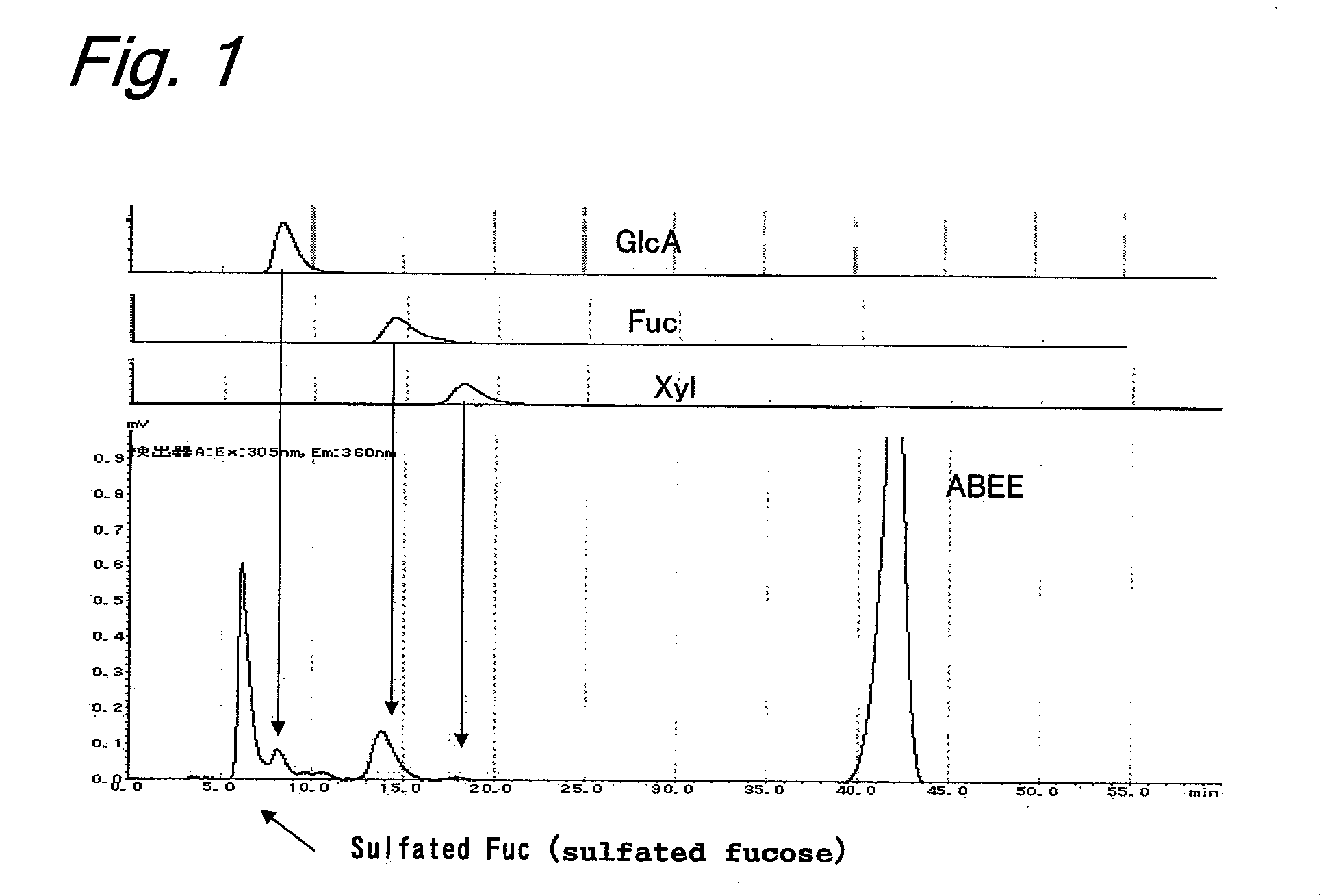
Oligosaccharides derived from fucoidan
The present invention provides a fucoidan-derived low molecular weight compound with a good quality of taste, which has a specified structure and function and is free from problems in absorption, antigenicity, uniformity, an anticoagulant activity and so on, which problems arise when developing fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide having an extremely large molecular weight, as drugs or health foods. As a result of analyzing low molecular weight compounds obtained by acid hydrolysis of fucoidan, the inventors have identified fucoidan oligosaccharides (I) to (XI). Further, these oligosaccharides have been found to have anti-obesity and / or blood glucose elevation suppressing effects through inhibition of carbohydrate and / or lipid absorption as a result of α-glucosidase inhibition and / or lipase inhibition.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD +1
Novel cellulase gene
ActiveUS20130023014A1Efficient productionLow costCellulosic pulp after-treatmentFungiGenomic DNAEndoglucanase Y
An object is to identify endoglucanase and β-glucosidase genes by isolating genomic DNA containing cellulase genes, which are classified into endoglucanases or β-glucosidases, from Acremonium cellulolyticus, and sequencing the nucleotide sequences thereof. The inventors intensively compared the amino acid sequences of known endoglucanases and β-glucosidases with each other to find conserved region of amino acid sequences in Acremonium cellulolyticus, and various primers were designed based on the information. PCR was carried out using the various primers thus designed and genomic DNA or cDNA as a template. As a result, gene fragments of endoglucanases and β-glucosidases were obtained. Primers were designed based on the gene fragments, and PCR was carried out to amplify nine genes of endoglucanases and β-glucosidases. The nucleotide sequences thereof were sequenced, and the present invention was completed.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA PHARMA CO LTD
Cellulase compositions and methods of using the same for improved conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into fermentable sugars
InactiveUS20140073017A1Improved saccharification efficacyImprove efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaFermentable sugarLignocellulosic biomass
The present invention relates to compositions that can be used in hydrolyzing biomass such as compositions comprising a polypeptide having β-glucosidase activity, methods for hydrolyzing biomass material, and methods for improving the stability and saccharification efficacy of a composition comprising such β-glucosidase polypeptides and / or activity.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Methods of saccharification of polysaccharides in plants
ActiveUS20110097786A1Speed up the processIncrease productionPulp by-products recoveryCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesBiotechnologyPlant tissue
Saccharification of polysaccharides of plants is provided, where release of fermentable sugars from cellulose is obtained by adding plant tissue composition. Production of glucose is obtained without the need to add additional β-glucosidase. Adding plant tissue composition to a process using a cellulose degrading composition to degrade cellulose results in an increase in the production of fermentable sugars compared to a process in which plant tissue composition is not added. Using plant tissue composition in a process using a cellulose degrading enzyme composition to degrade cellulose results in decrease in the amount of cellulose degrading enzyme composition or exogenously applied cellulase required to produce fermentable sugars.
Owner:APPLIED BIOTECH INST
Method and device for producing methane gas and lignin from straws
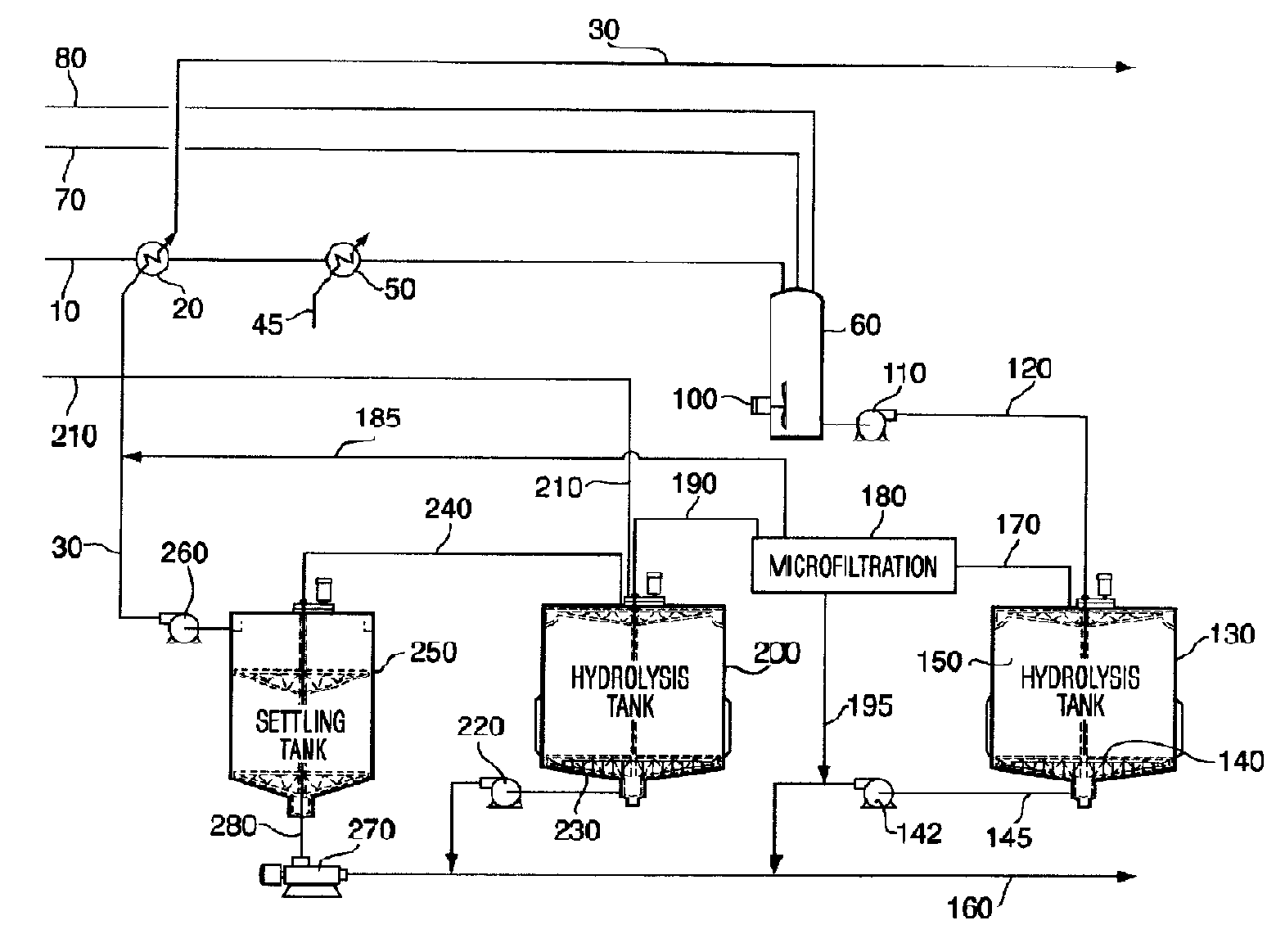
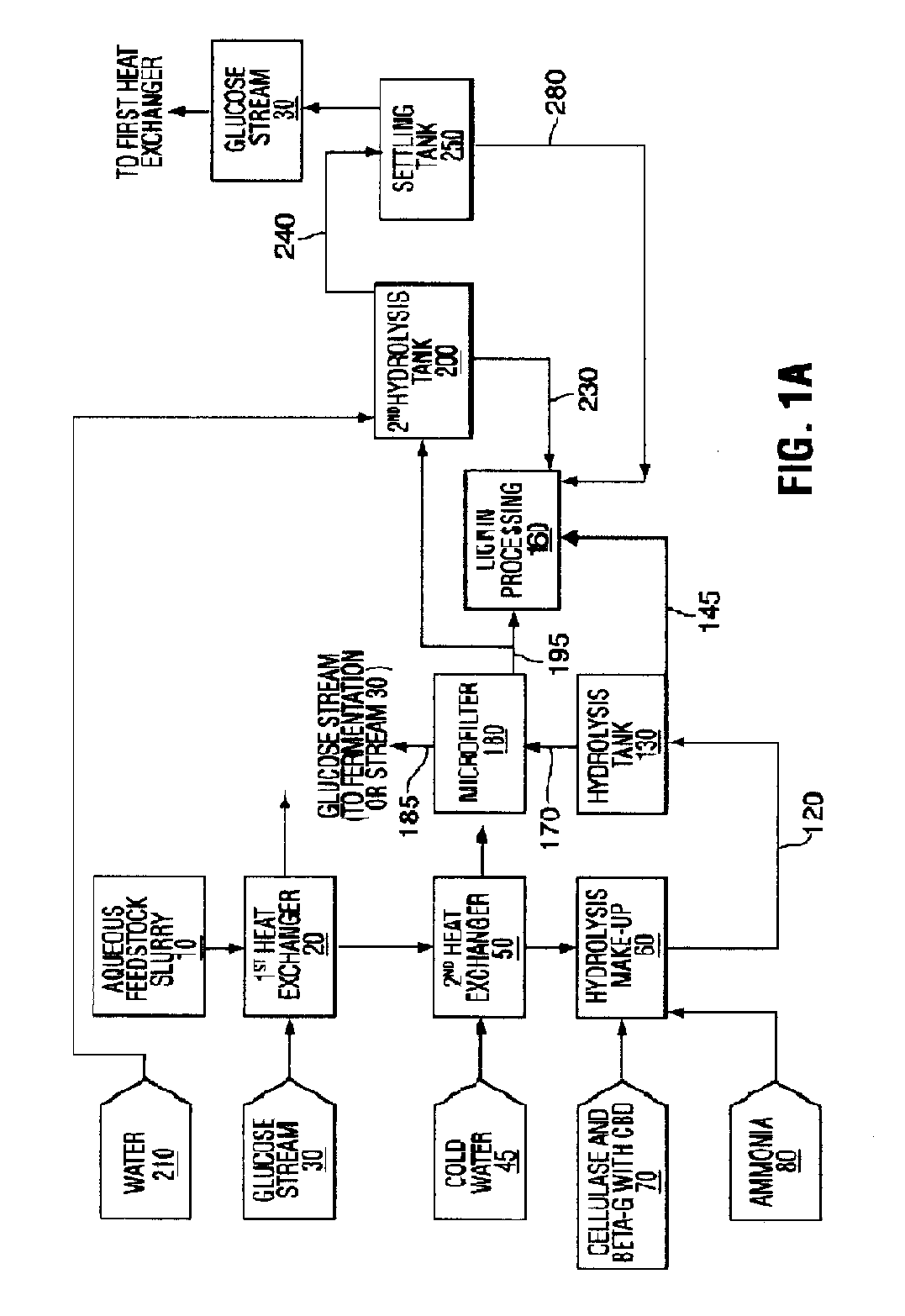
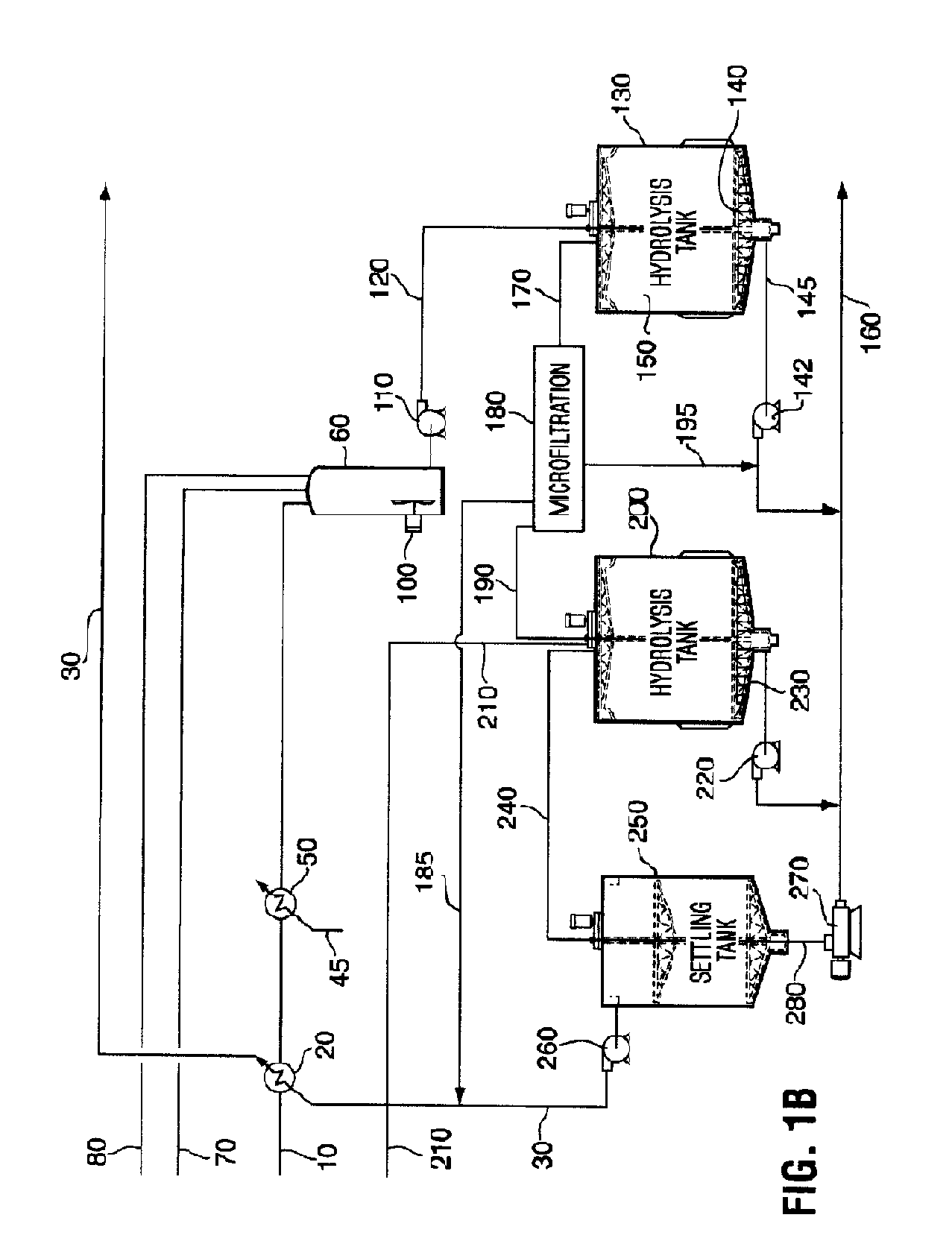
InactiveCN104818298AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyReduce inhibitionApparatus sterilizationGas production bioreactorsFiltrationHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method and device for producing methane gas and lignin from straws. The method comprises the following steps of removing impurities of straws, crushing the straws into straw powder, feeding the straw powder into a hydrolysis device, controlling a hydrolysis degree until all hemicelluloses is hydrolyzed and 20-100% of cellulose is hydrolyzed, feeding an upper hydrolysate into an anaerobic fermentation pool, carrying out fermentation to obtain crude methane gas, discharging lower lignin slurry, and carrying out filtration and drying to obtain lignin powder. Straw hydrolase comprises excision beta glucanase, incision beta glucanase, beta glucosidase and xylanase according to a mass ratio of 1: 1.2-10: 0.8-5: 1.5-8. The culture contains an inducer activator, and in use, the culture is added with a starter. The method and device used by the method fully utilize straws, produce methane gas and lignin, adjust a straw hydrolysis degree, produce marketable products and are suitable for different raw materials.
Owner:CATECH TECH
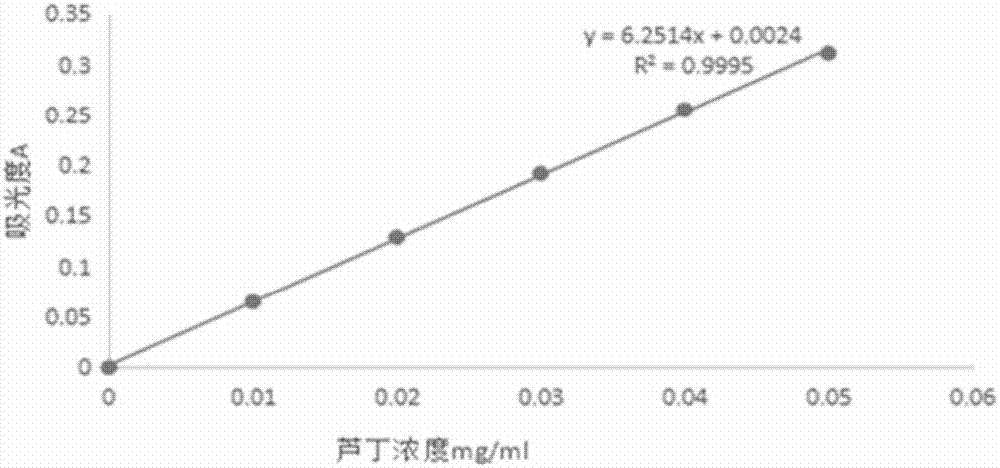
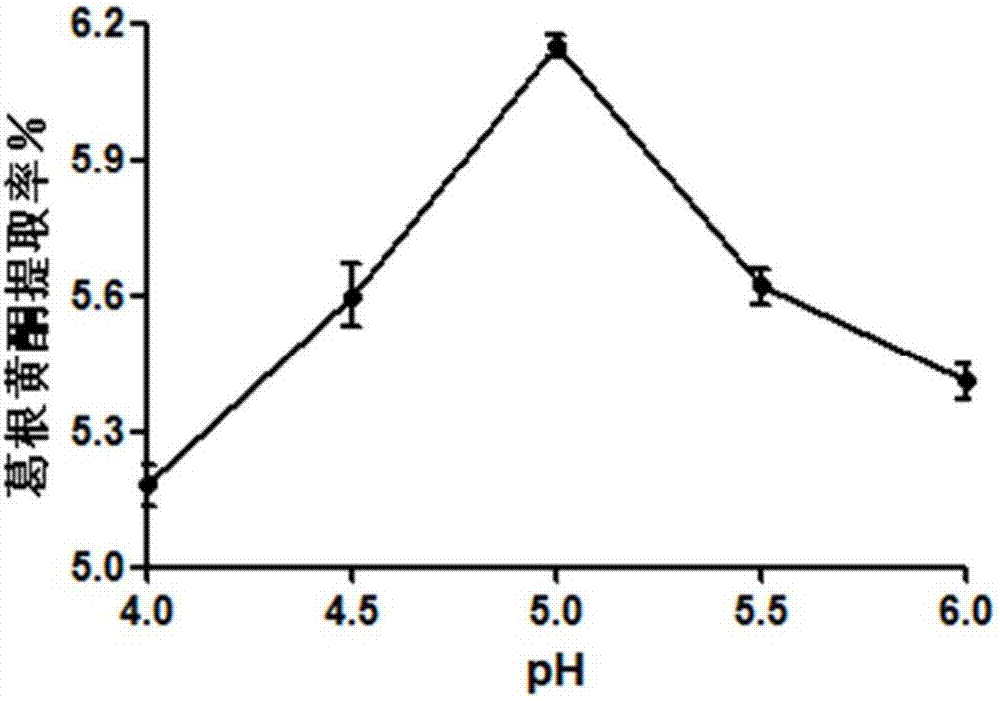
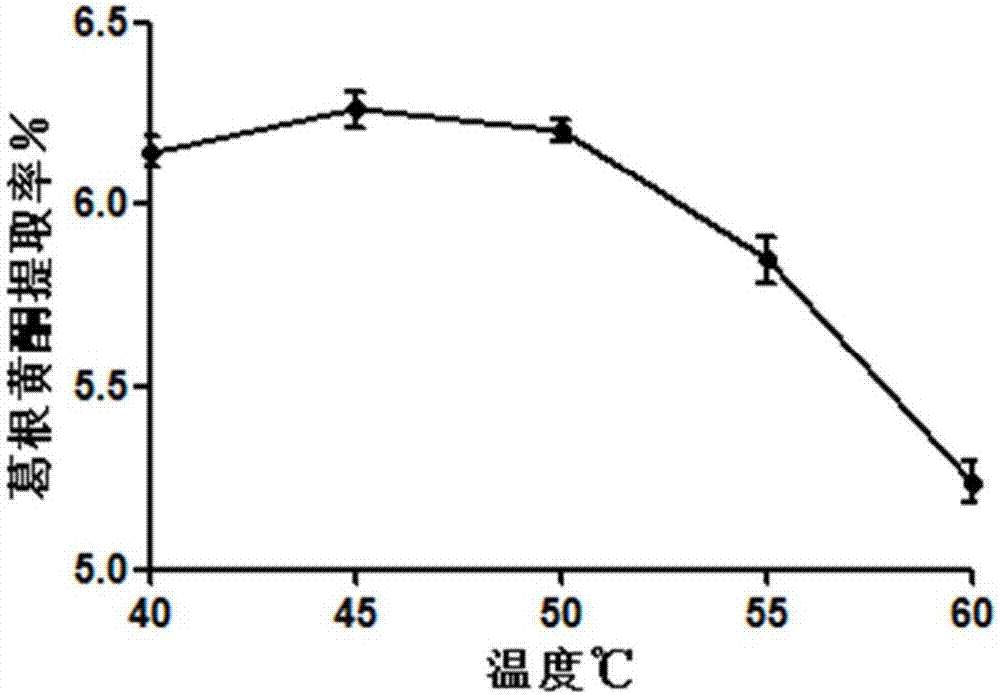
Compound enzyme used for extracting pueraria flavones, and method used for extraction with compound enzyme
InactiveCN107245483AHigh extraction rateNo pollution in the processOrganic chemistryGlycosylasesPectinaseAlglucerase
The invention discloses a compound enzyme used for extracting pueraria flavones, and a method used for extraction with the compound enzyme. The compound enzyme comprises pectase and beta-glucosidase; the total enzyme dosage of pectase and beta-glucosidase ranges from 150 to 400IU; the enzyme activity of beta-glucosidase accounts for 20 to 80% of the total enzyme dosage. The method comprises following steps: radix puerariae is weighed, smashed, and sieved; a disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution with a pH value ranging from 4.0 to 6.0 is added at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10-40:1; pectase and beta-glucosidase are added; reaction is carried out at 40 to 60 DEG C for 0.5 to 2.5h; and pumping filtering is carried out so as to obtain a finished product. The advantages are that: the compound enzyme can be used for extracting pueraria flavones, extraction efficiency can be increased effectively, the method is safe, and is friendly to the environment, no pollution is caused, the method is simple, and operation is convenient.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Hemicellulose-degrading enzymes
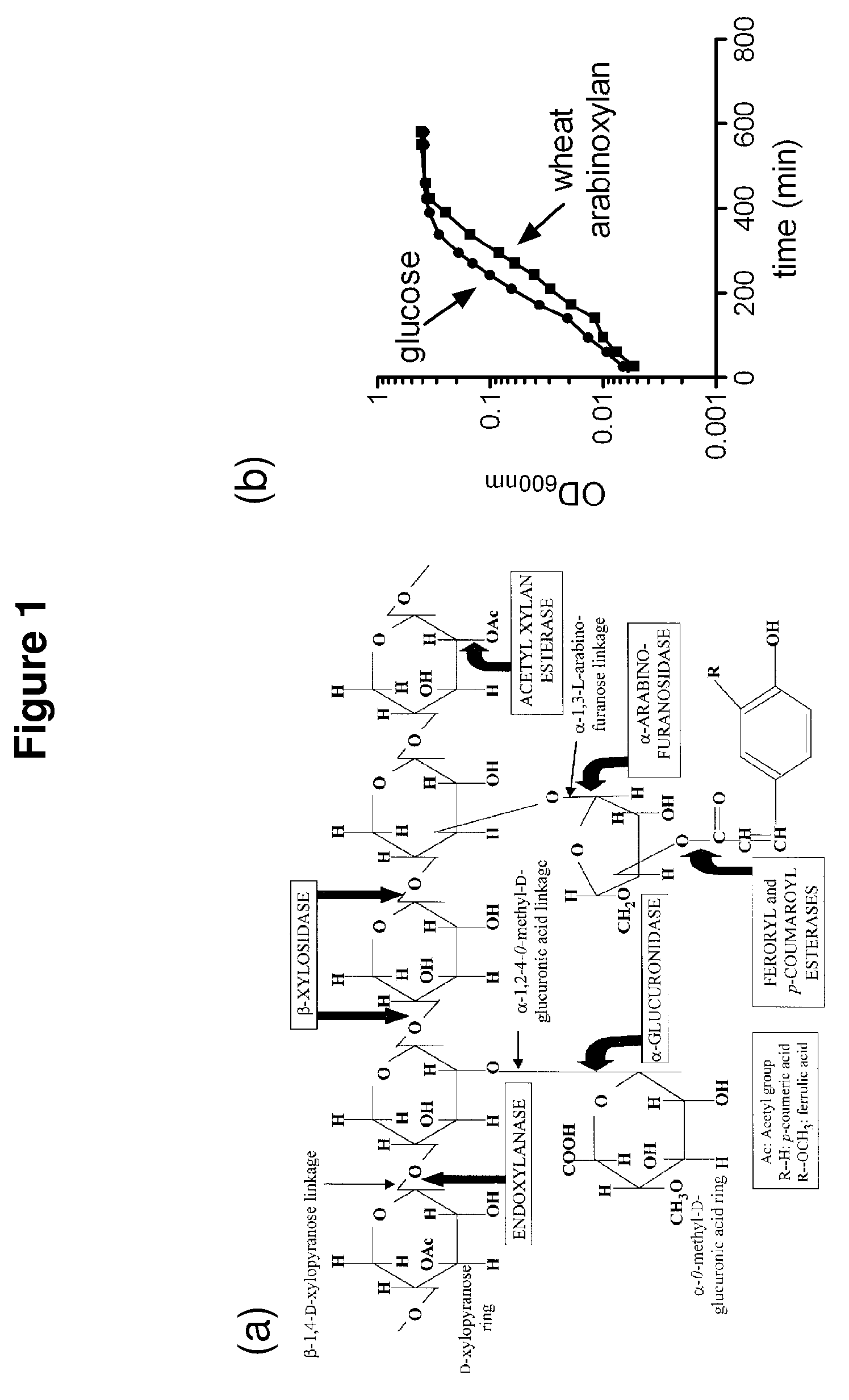
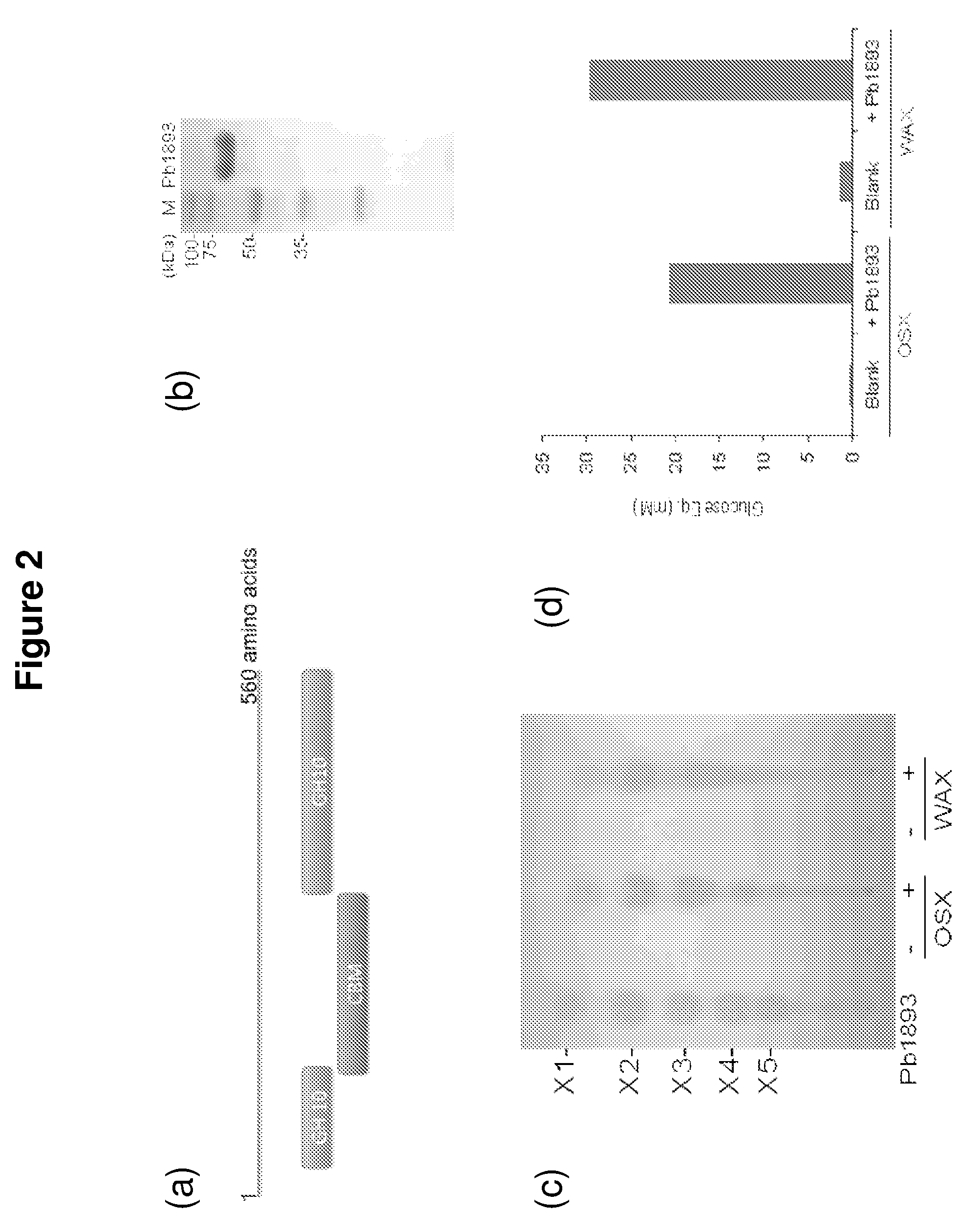
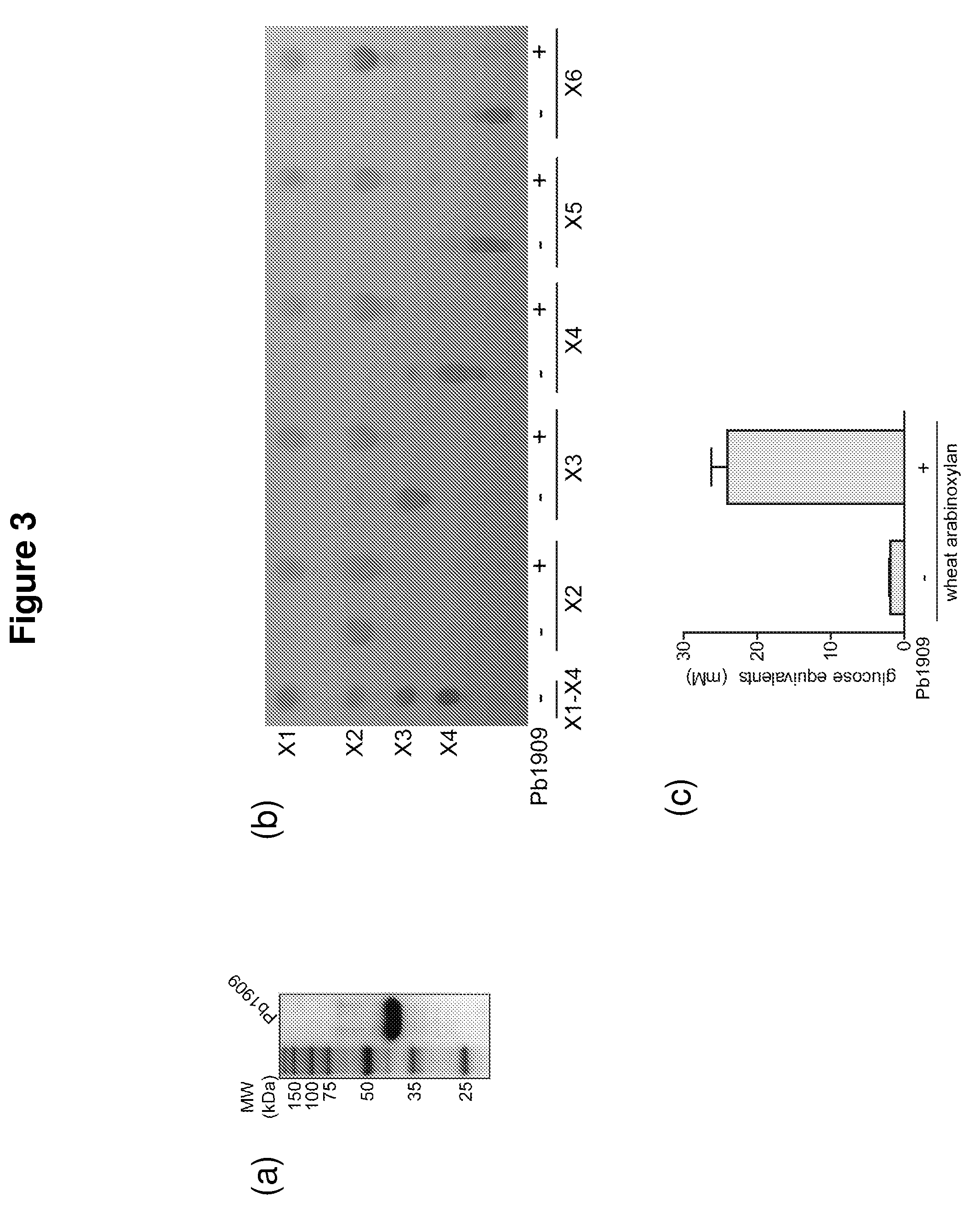
The present disclosure provides methods for the conversion of hemicellulose into fermentable sugars using enzymes isolated from Prevotella bryantii. Hemicellulose-degrading enzymes include an endoxylanase, a β-xylosidase, a bifunctional β-xylosidase and β-glucosidase, a bifunctional arabinofuranosidase and β-xylosidase, a glucuronidase, and an acetyl xylan esterase. The enzymes can be used to release sugars present in hemicellulose for subsequent fermentation to produce value-added products such as ethanol.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com